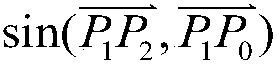Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
96 results about "Look-ahead" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In backtracking algorithms, look ahead is the generic term for a subprocedure that attempts to foresee the effects of choosing a branching variable to evaluate one of its values. The two main aims of look-ahead are to choose a variable to evaluate next and the order of values to assign to it.
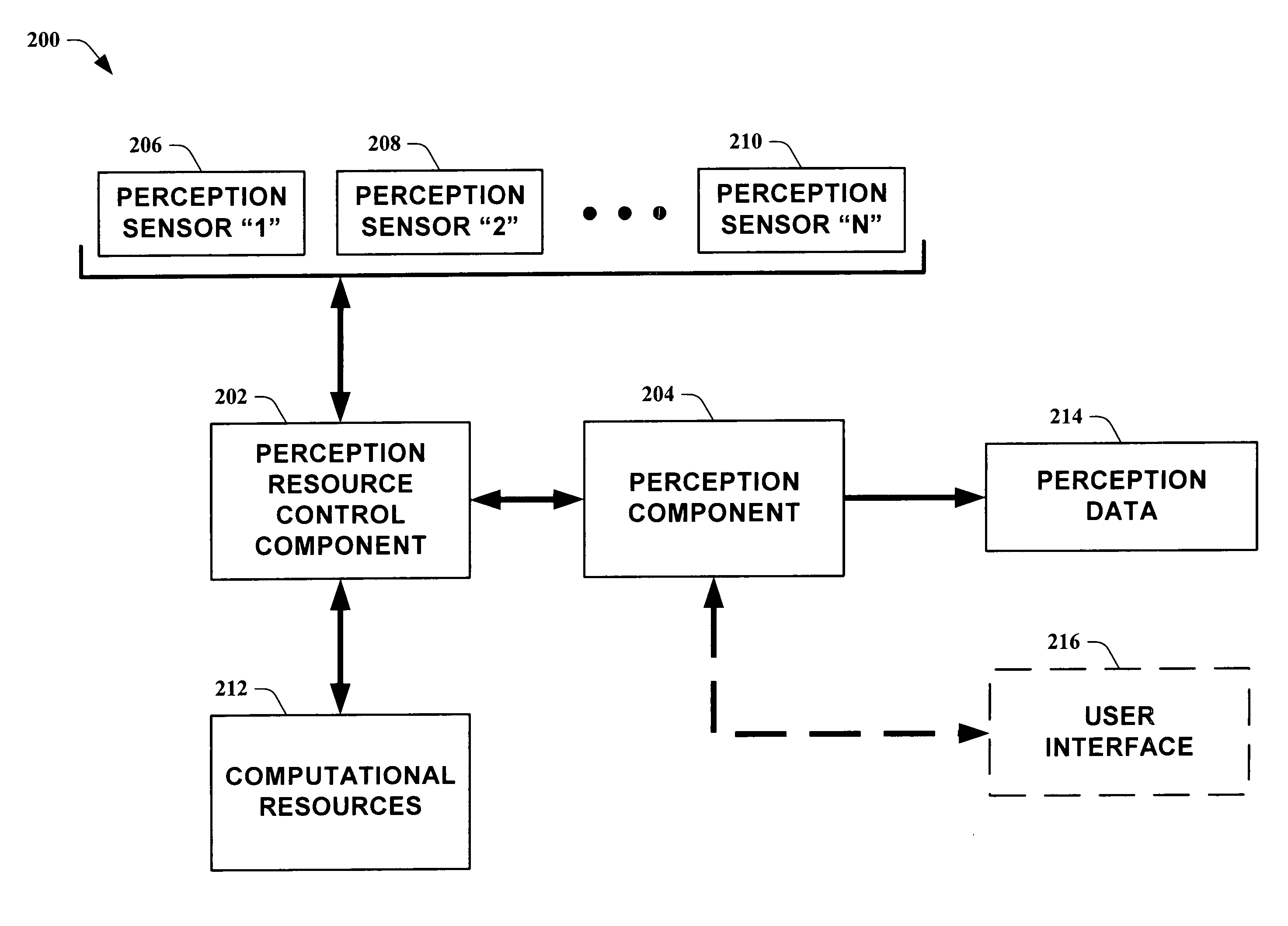
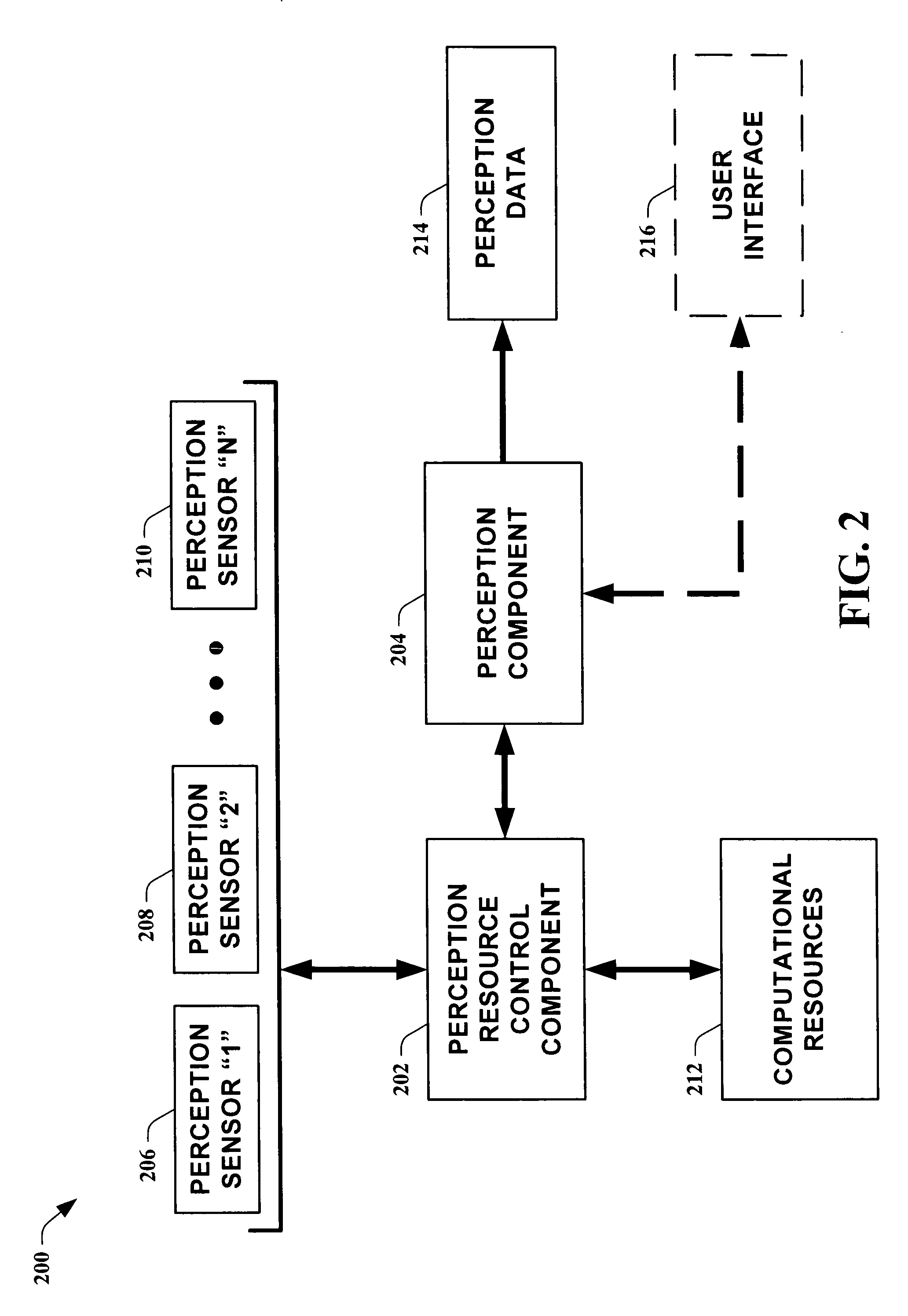
Systems and methods for guiding allocation of computational resources in automated perceptual systems
ActiveUS20050132378A1Facilitate in inferring human-centric notion of contextReducing computational resource burdenDigital computer detailsBiological neural network modelsPattern perceptionInformation Harvesting
The present invention leverages analysis methods, such as expected value of information techniques, rate-based techniques, and random selection technique, to provide a fusion of low-level streams of input data (e.g., raw data) from multiple sources to facilitate in inferring human-centric notions of context while reducing computational resource burdens. In one instance of the present invention, the method utilizes real-time computations of expected value of information in a greedy, one-step look ahead approach to compute a next best set of observations to make at each step, producing “EVI based-perception.” By utilizing dynamically determined input data, the present invention provides utility-directed information gathering to enable a significant reduction in system resources. Thus, of the possible input combinations, the EVI-based system can automatically determine which sources are required for real-time computation relating to a particular context.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
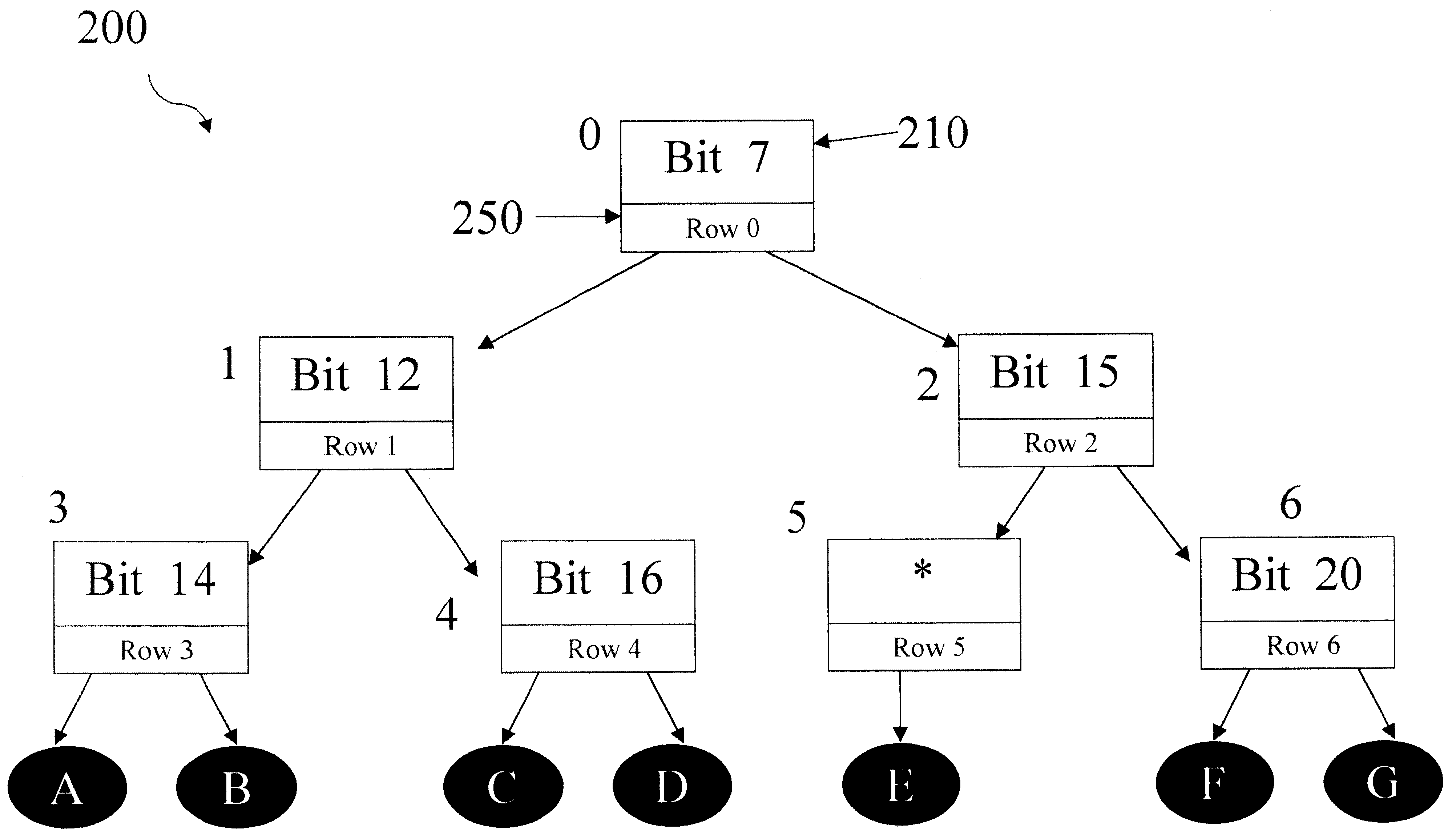
Look-ahead tree structure
InactiveUS6532457B1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalTheoretical computer scienceData store
A method and system for storing and retrieving data using a radix-search tree is disclosed. The method encorporates: (a) storing a plurality of nodes, each of the nodes having node-attributes, in a radix-search tree, and (b) retrieving the node-attributes of the plurality of nodes in single memory access. The system encorporates: (a) a data storage module for storing a plurality of sub-trees containing a plurality of nodes having node attributes, wherein the node attributes of at least one of the sub-trees are stored in a contiguous memory block, and (b) a processor that is operative to perform operations including: (i) transferring the node attributes of at least one of the sub-trees to the data storage module, and (ii) retrieving the node attributes of at least one of the sub-tree s from the data storage module.
Owner:GOLDEN GATE BRIDGE FUND LP +1
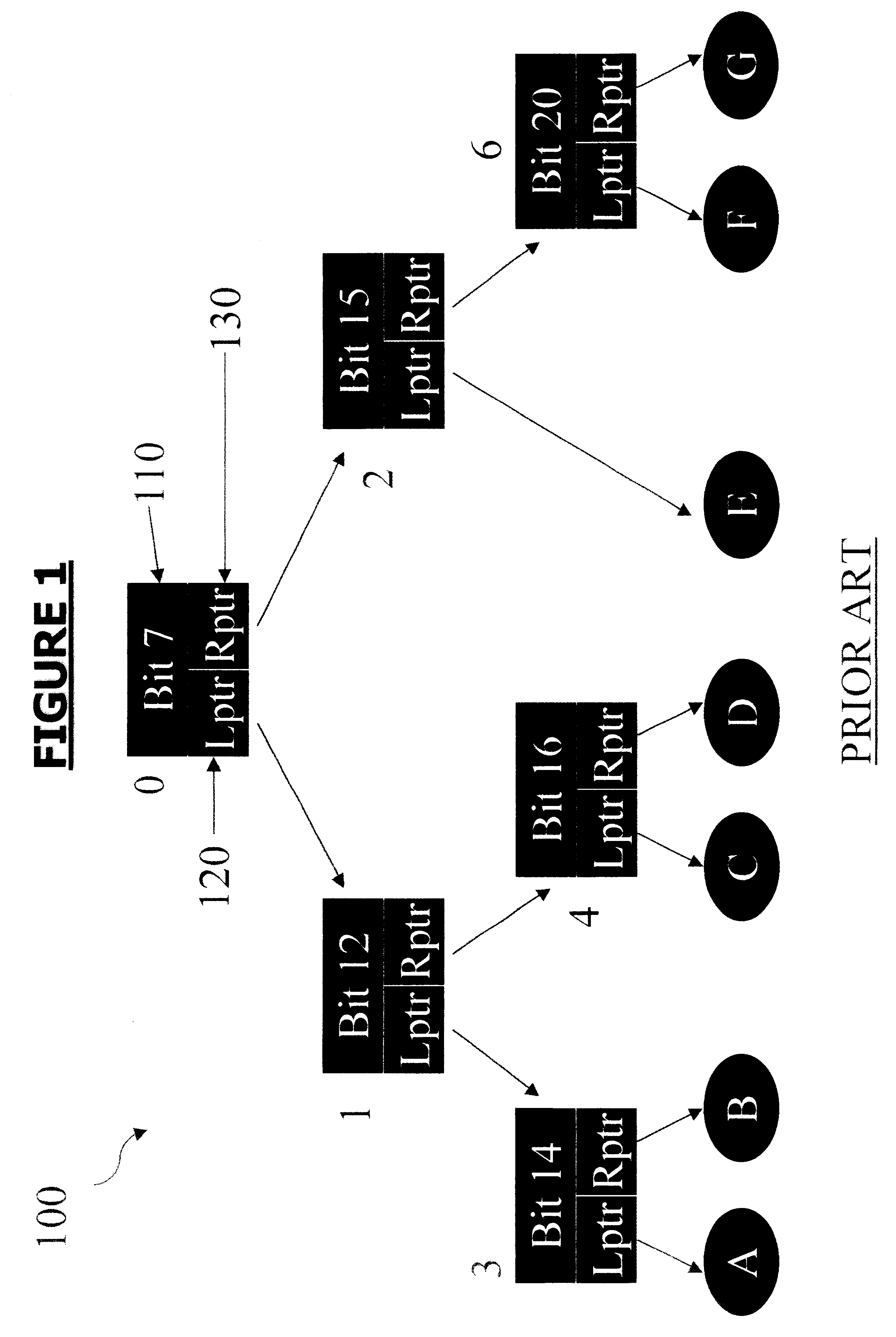
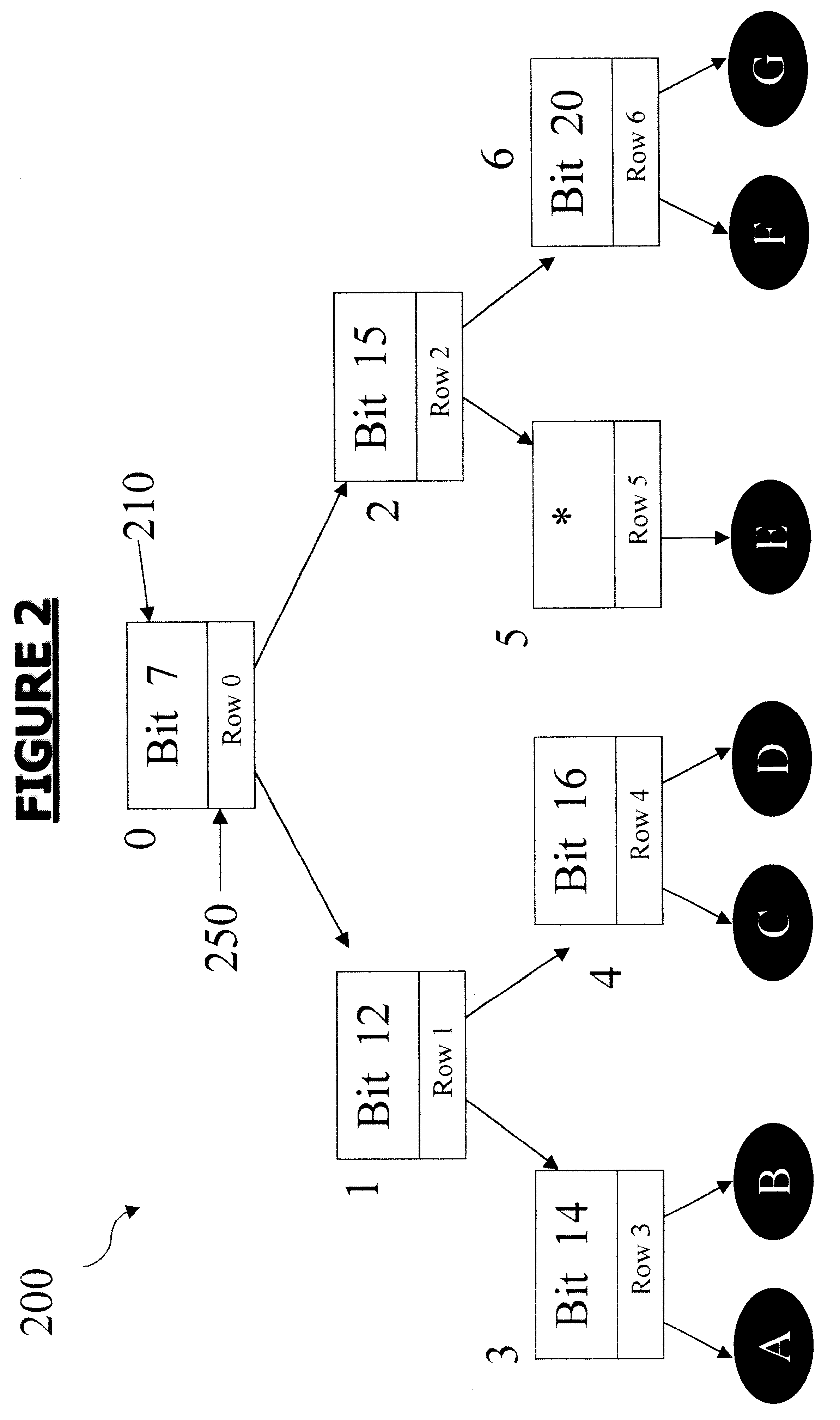
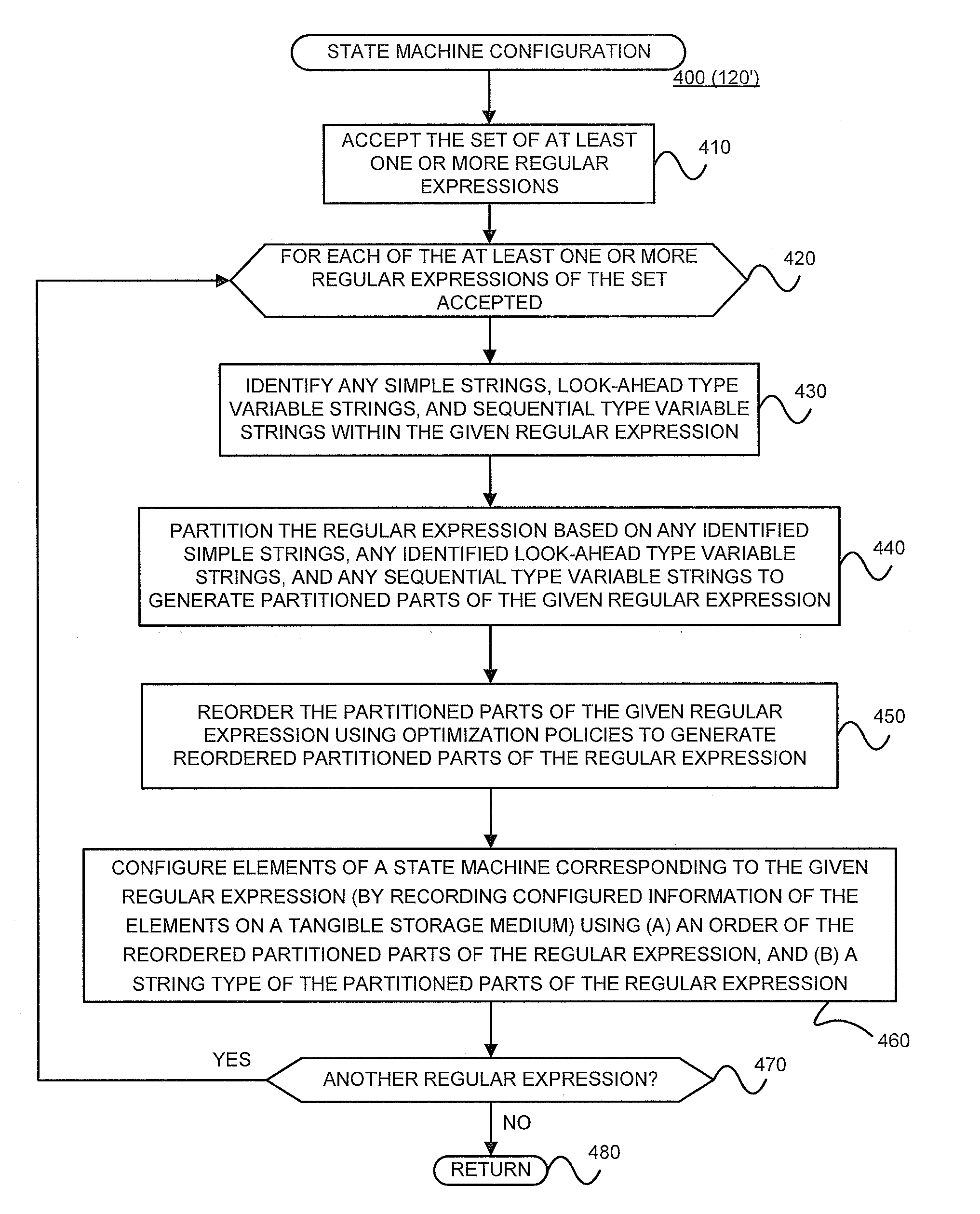
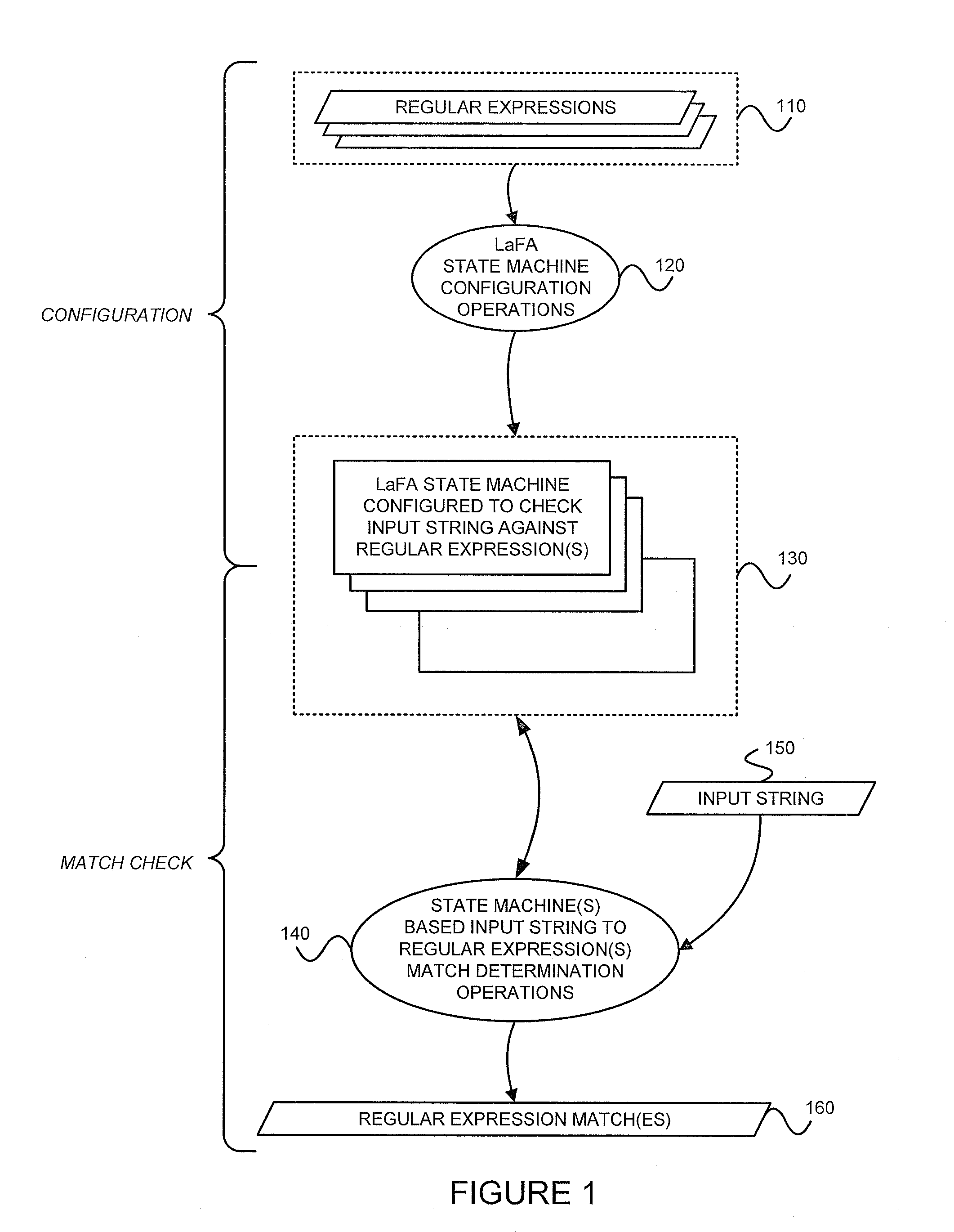
Configuring state machines used to order and select matching operations for determining whether an input string matches any of at least one regular expression using lookahead finite automata based regular expression detection
InactiveUS20110093484A1Less memorySmall memory requirementDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsNODALAutomaton
State machines used to order and select matching operations for determining whether an input string matches any of at least one regular expression are configured by (1) accepting the set of regular expression(s), and (2) for each of the regular expression(s) of the set accepted, (A) identifying any look-ahead type strings within the given regular expression, (B) identifying any sequential type strings within the given regular expression, (C) partitioning the regular expression based on any identified simple strings, any identified look-ahead type variable strings, and any sequential type variable strings to generate partitioned parts of the given regular expression, (D) reordering the partitioned parts of the given regular expression using optimization policies to generate reordered partitioned parts of the regular expression, and (E) configuring nodes of a state machine corresponding to the given regular expression, by recording configured information of the nodes on a tangible storage medium, using (i) an order of the reordered partitioned parts of the regular expression, and (ii) a string type of the partitioned parts of the regular expression. Once configured, the state machines may accept an input string, and for each of the regular expression(s), check for a match between the input string accepted and the given regular expression using the configured nodes of the state machine corresponding to the given regular expression. Checking for a match between the input string accepted and the given regular expression using configured nodes of a state machine corresponding to the given regular expression by using the configured nodes of the state machine may include (1) checking detection events from a simple string detector, (2) submitting queries to identified modules of a variable string detector, and (3) receiving detection events from the identified modules of the variable string detector.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
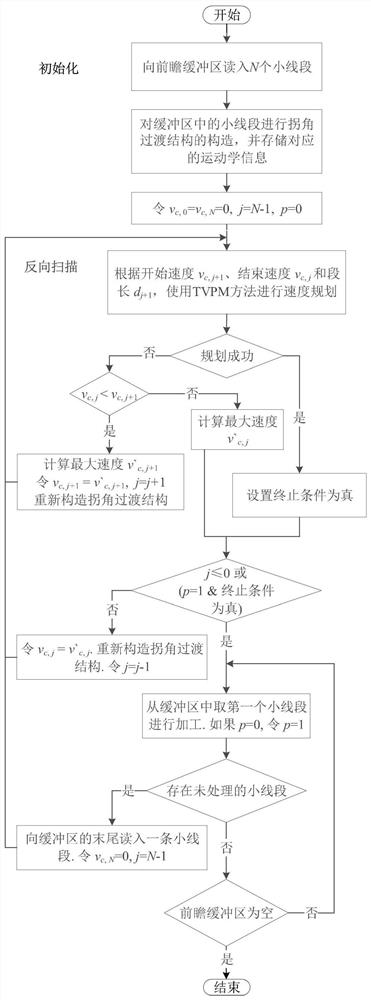
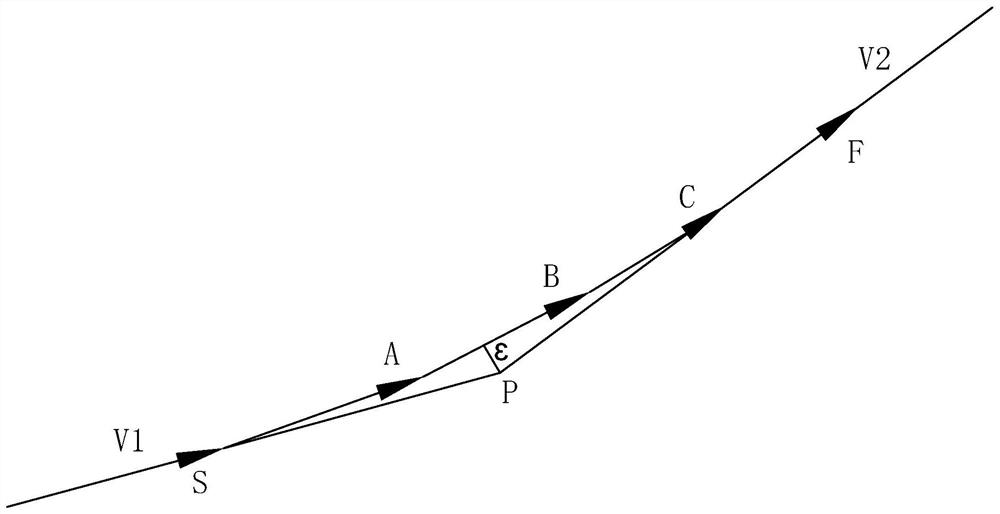
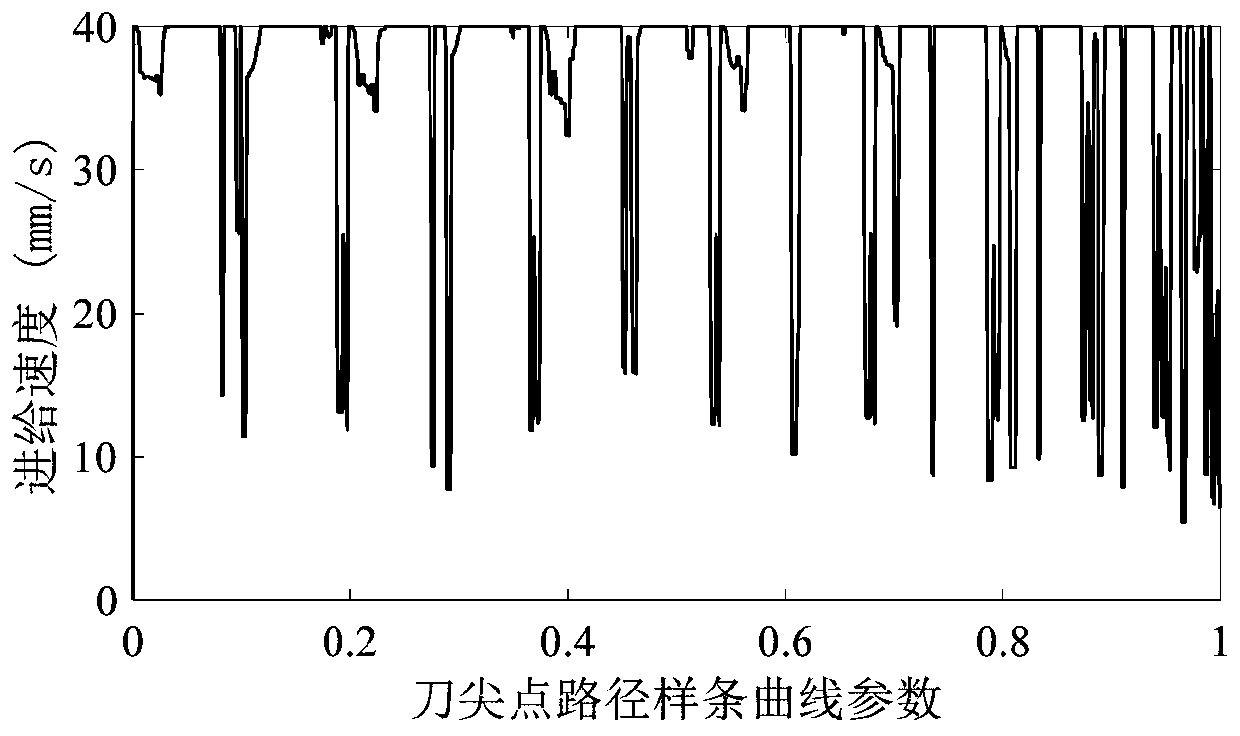
Dynamic adaptive speed look-ahead control method of continuous small line segment trajectories
The invention discloses a dynamic adaptive speed look-ahead control method of continuous small line segment trajectories. The method comprises the steps that S1 the maximum speed of connecting points is calculated and the speed look-ahead number of segments is determined; S2 entering a deceleration area or not is judged, and the process jumps to the step S3 if the judgment result is no; S3 initial speed and end speed are compared; and the process jumps to the step S4 if the initial speed is greater than the end speed; S4 whether the deceleration distance constraint condition is met is judged; and the process jumps to the step S7 if the judgment result is yes, or the process jumps to the step S5; S5 whether the deceleration distance in which the initial speed reduces to the end speed is less than the current line segment displacement length is judged, and the process jumps to the step S7 if the judgment result is yes, or the process jumps to the step S6; S6 the maximum initial speed of the current segment displacement length constraint is searched and cycling is performed until tracing back to the look-ahead start point; S7 the non-look-ahead path is updated and whether the segment of the current line segment is less than the look-ahead number of segments is judged, and the process jumps to the step S2 if the judgment result is yes, or the process jumps to the step S8; and S8 speed look-ahead control is ended. High-speed connection of transition speed between the continuous trajectories can be effectively realized so that the processing time can be greatly shortened and the processing efficiency can be enhanced.
Owner:深圳市旗众智能科技有限公司
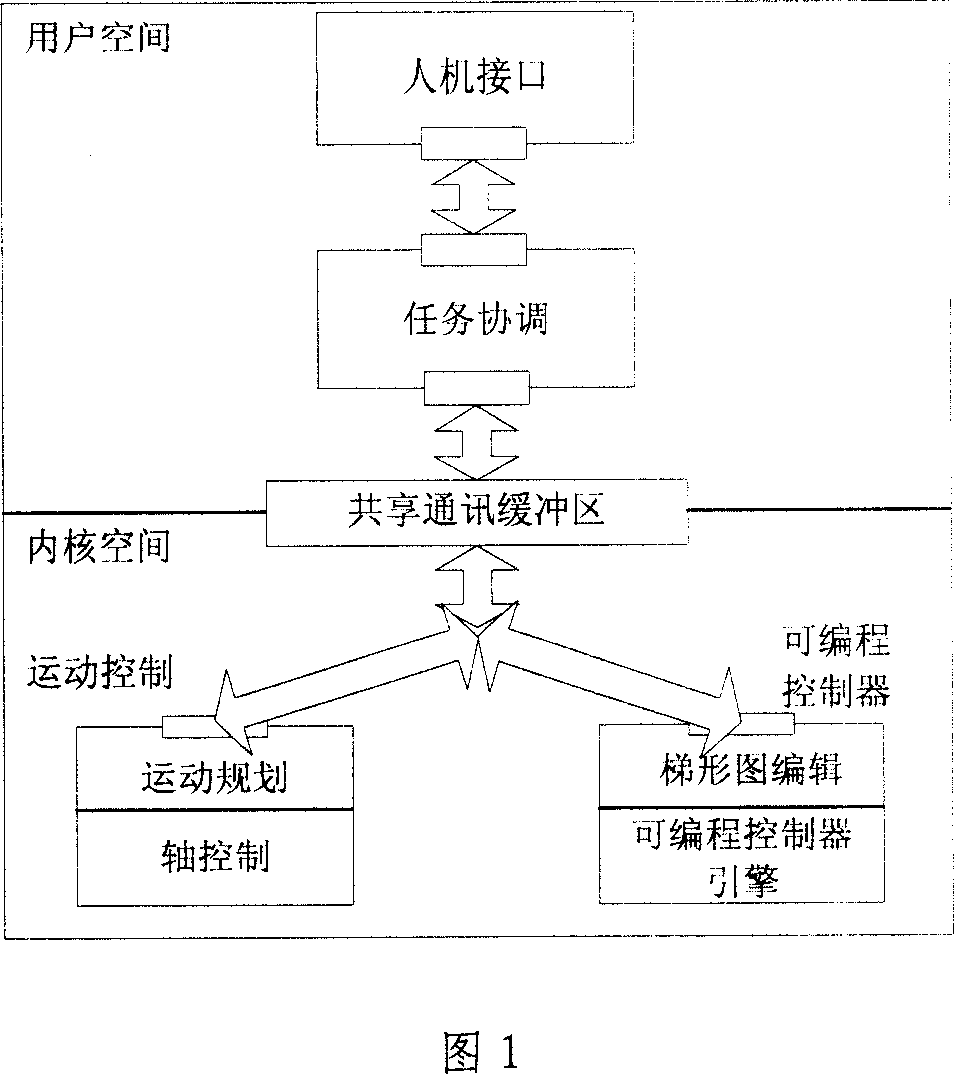
Dynamic forward-looking processing method of small program segment and implementing device
ActiveCN1967421AImplement Velocity PlanningAdaptableAutomatic control devicesComputer controlProgram segmentHuman–machine interface
The invention discloses the dynamic forward-looking method and implementation equipment for small program pieces, which uses human-machine interface, task coordination, movement control and programmable controller. It loads the movement control and the programmable controller in the system kernel space, and loads the human-machine interface and the task coordination in the system user space, and communicates with each other through the system sharing communications buffer; the movement control includes two parts of movement planning and axis control; its characteristics are: the movement planning uses dynamic forward-looking method to process the speed planning to the small program pieces interpreted by the task coordination part, and forms the speed set value in processing, and implements the machine servo axis smooth movement by the axis control in the processing. The invention can effectively addresses the speed smooth problem and the pointed transition problem in the small segment processing, thereby improving the surface machining quality of the workpiece.
Owner:SHENYANG GOLDING NC & INTELLIGENCE TECH CO LTD
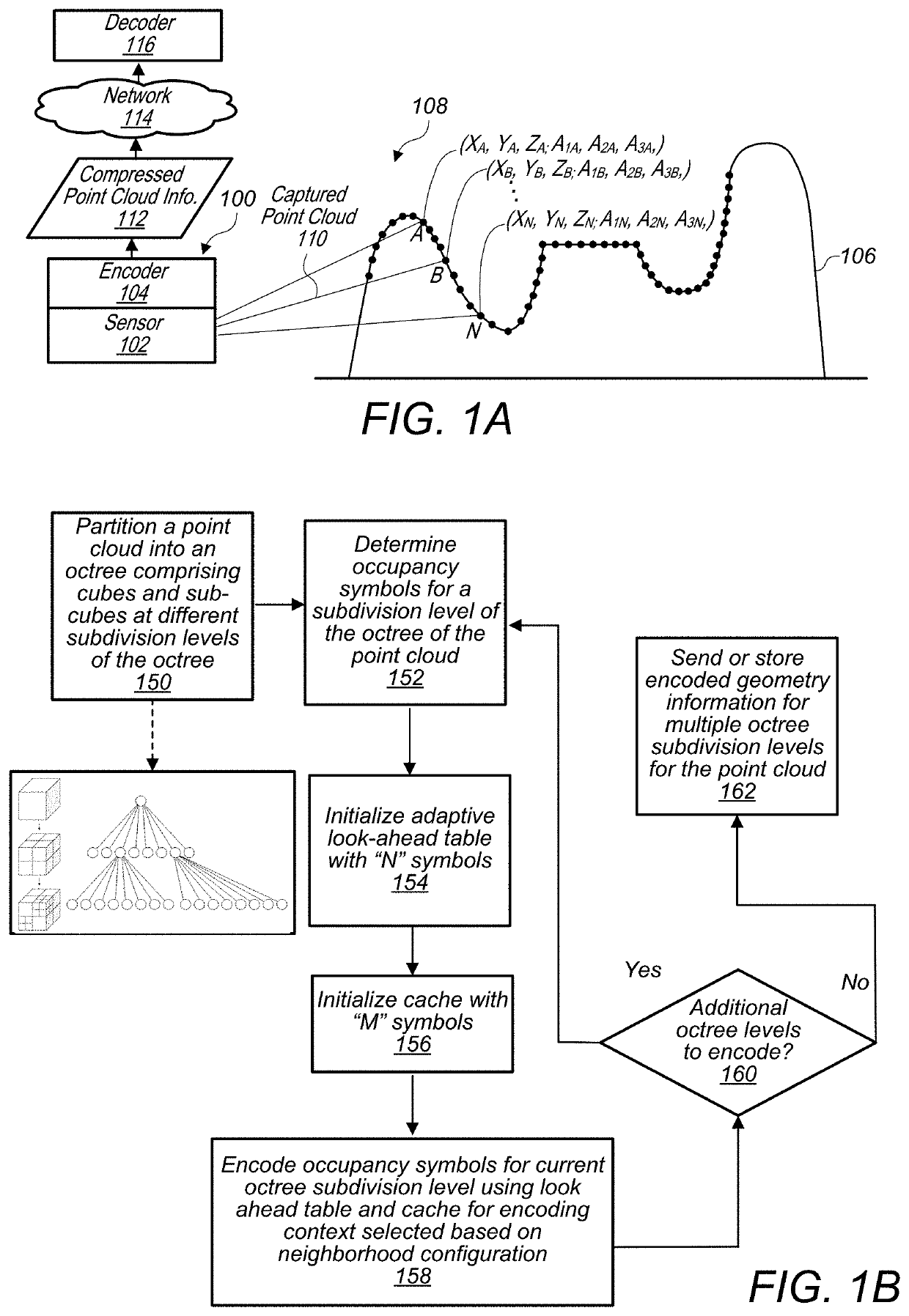
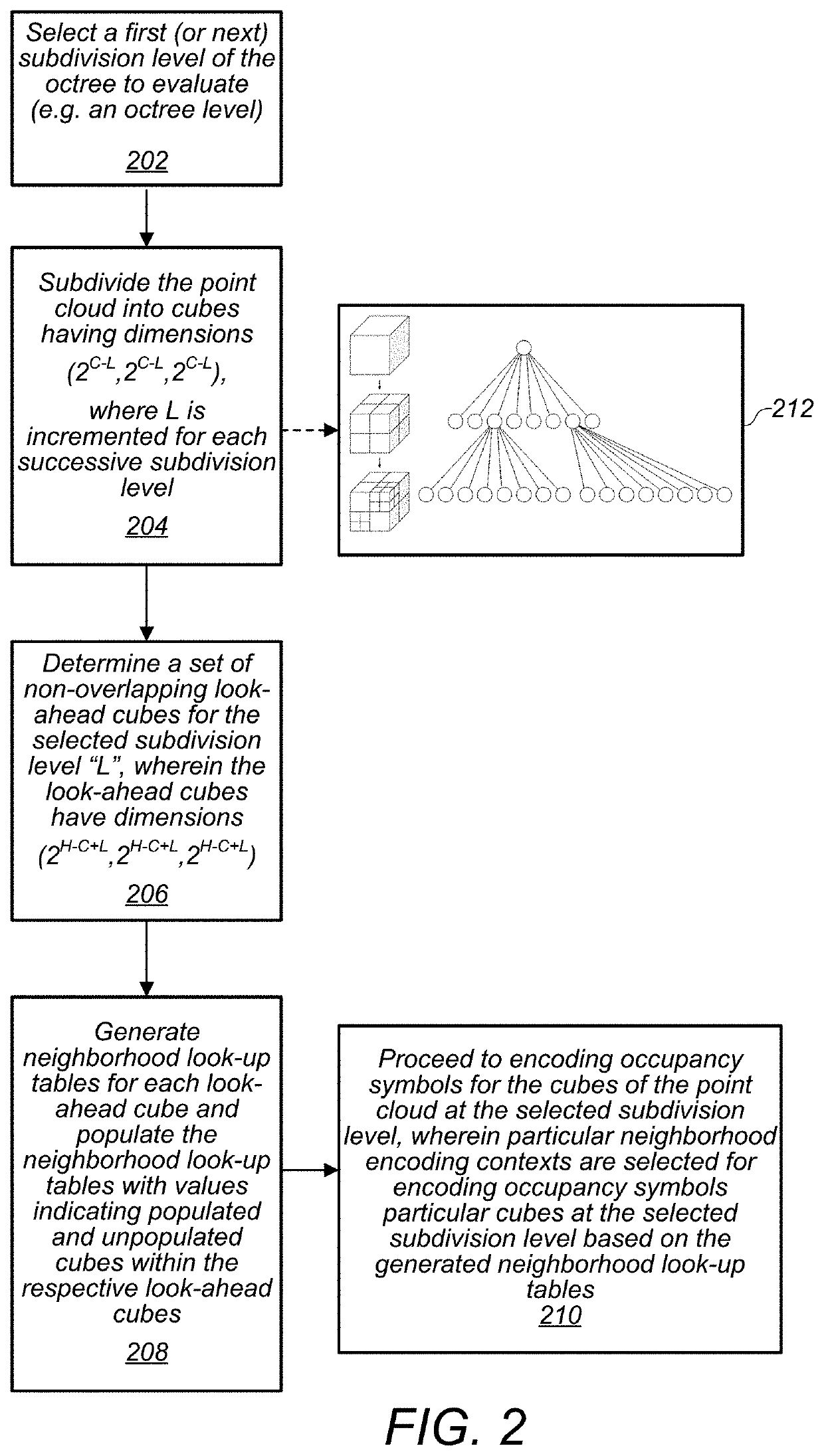
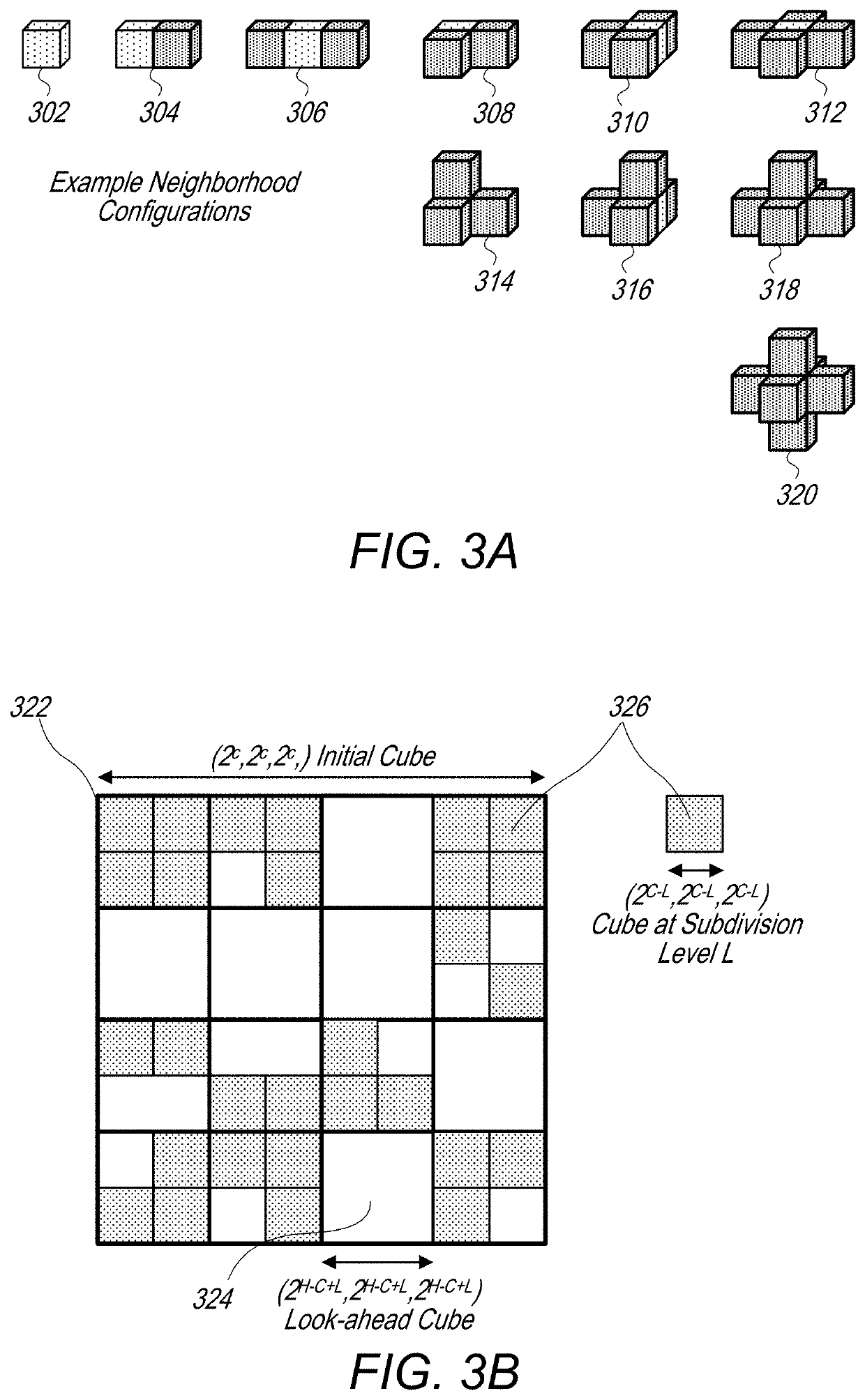
Point cloud geometry compression using octrees and binary arithmetic encoding with adaptive look-up tables
An encoder is configured to compress point cloud geometry information using an octree geometric compression technique that utilizes a binary arithmetic encoder, a look-ahead table, a cache, and a context selection process, wherein encoding contexts are selected based, at least in part, on neighborhood configurations. In a similar manner, a decoder is configured to decode compressed point cloud geometry information utilizing a binary arithmetic encoder, a look-ahead table, a cache, and a context selection process.
Owner:APPLE INC
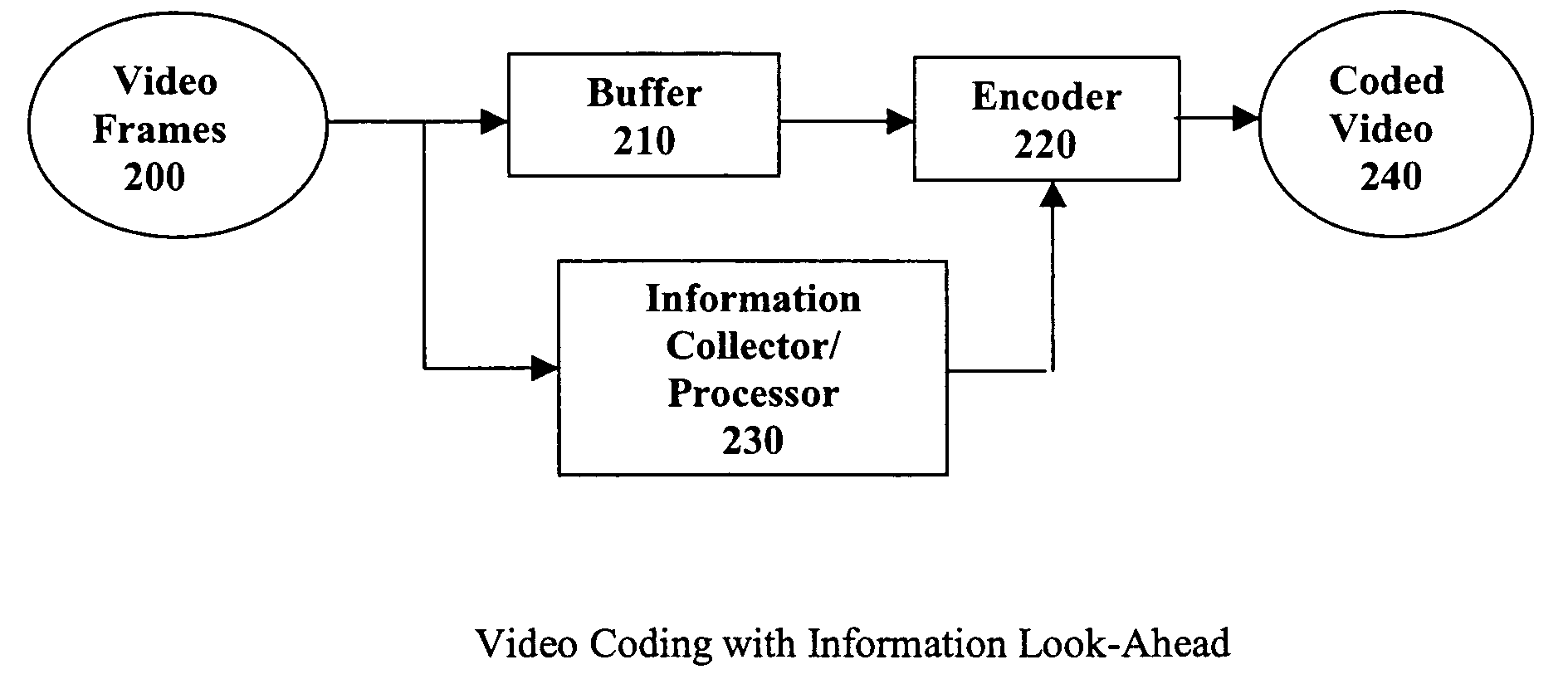
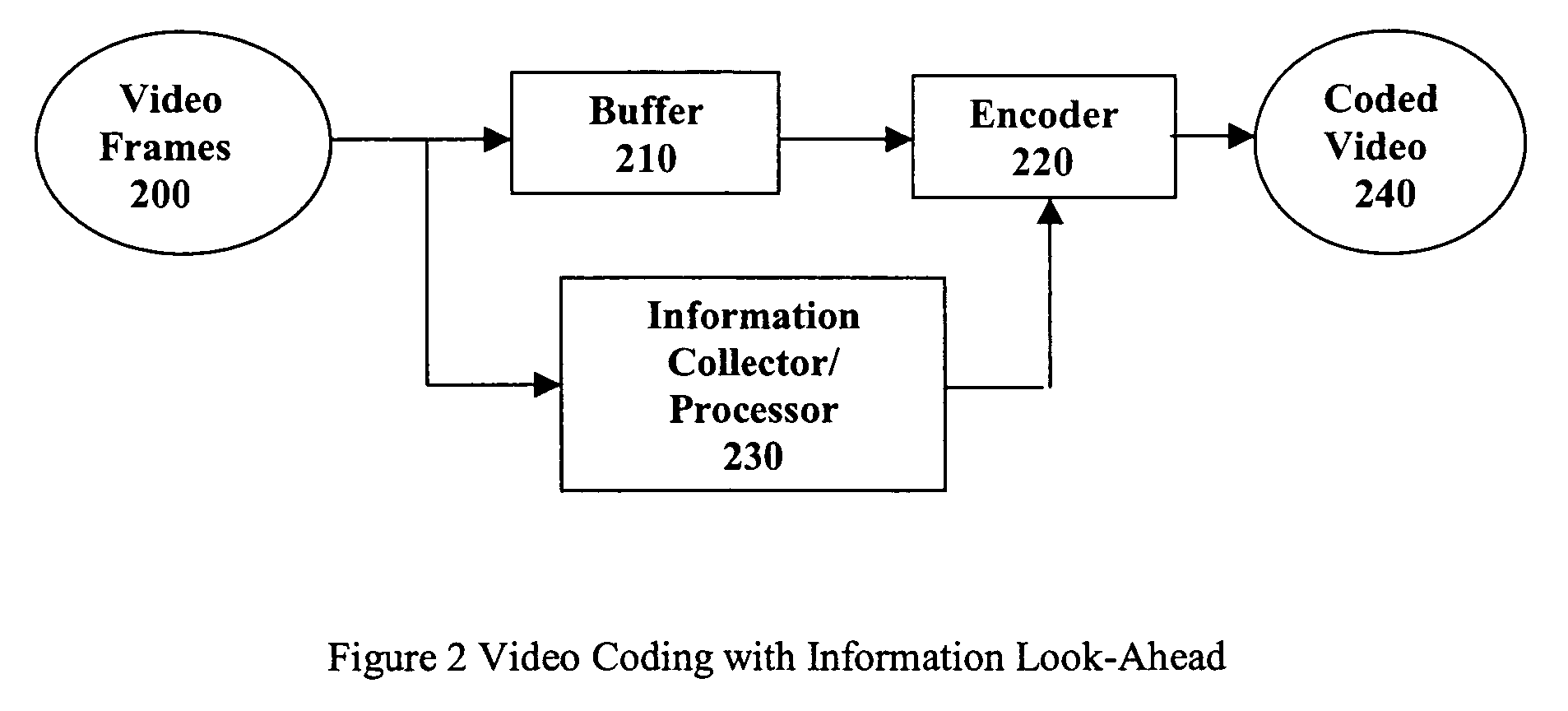
Method and system for multiple pass video coding
InactiveUS20050058200A1Efficient algorithmColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo encodingInformation processor
A real-time MPEG video coding system with information look-ahead for constant bit rate (CBR) applications, such as, for example, Video-on-Demand (VoD) over ADSL. This scheme employs two MPEG encoders. The second encoder has a buffer to delay the input by an amount of time relative to the first encoder to create a look-ahead window. In encoding, the first encoder collects the information of statistics and rate-quality characteristics. An on-line information processor then uses the collected information to derive the best coding strategy for the second encoder to encode the incoming frames in the look-ahead window. The second encoder uses the encoding parameters from the processor as the coding guide to execute the coding strategy and generate the final bitstream.
Owner:IBM CORP
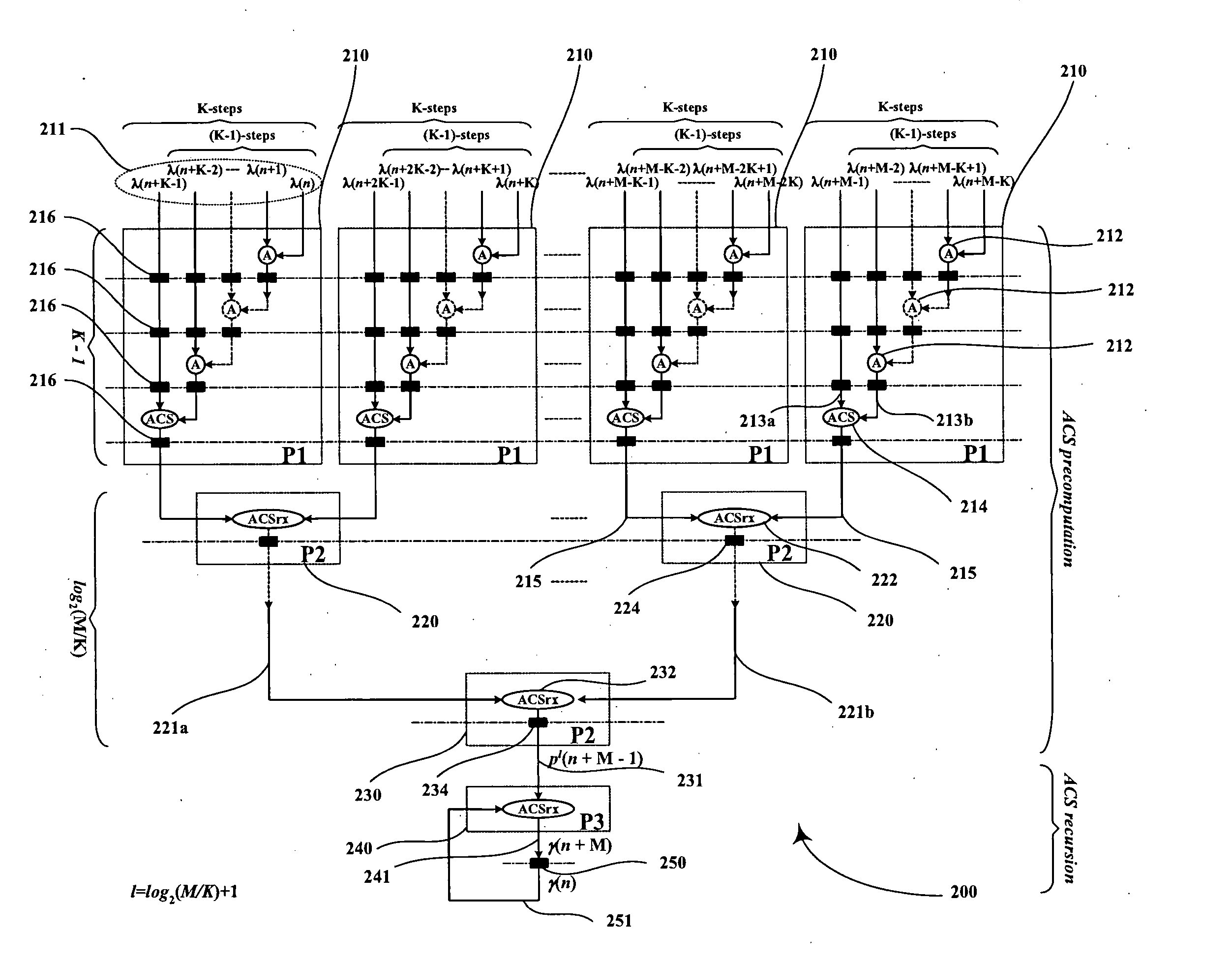
Low-latency architectures for high-throughput viterbi decoders
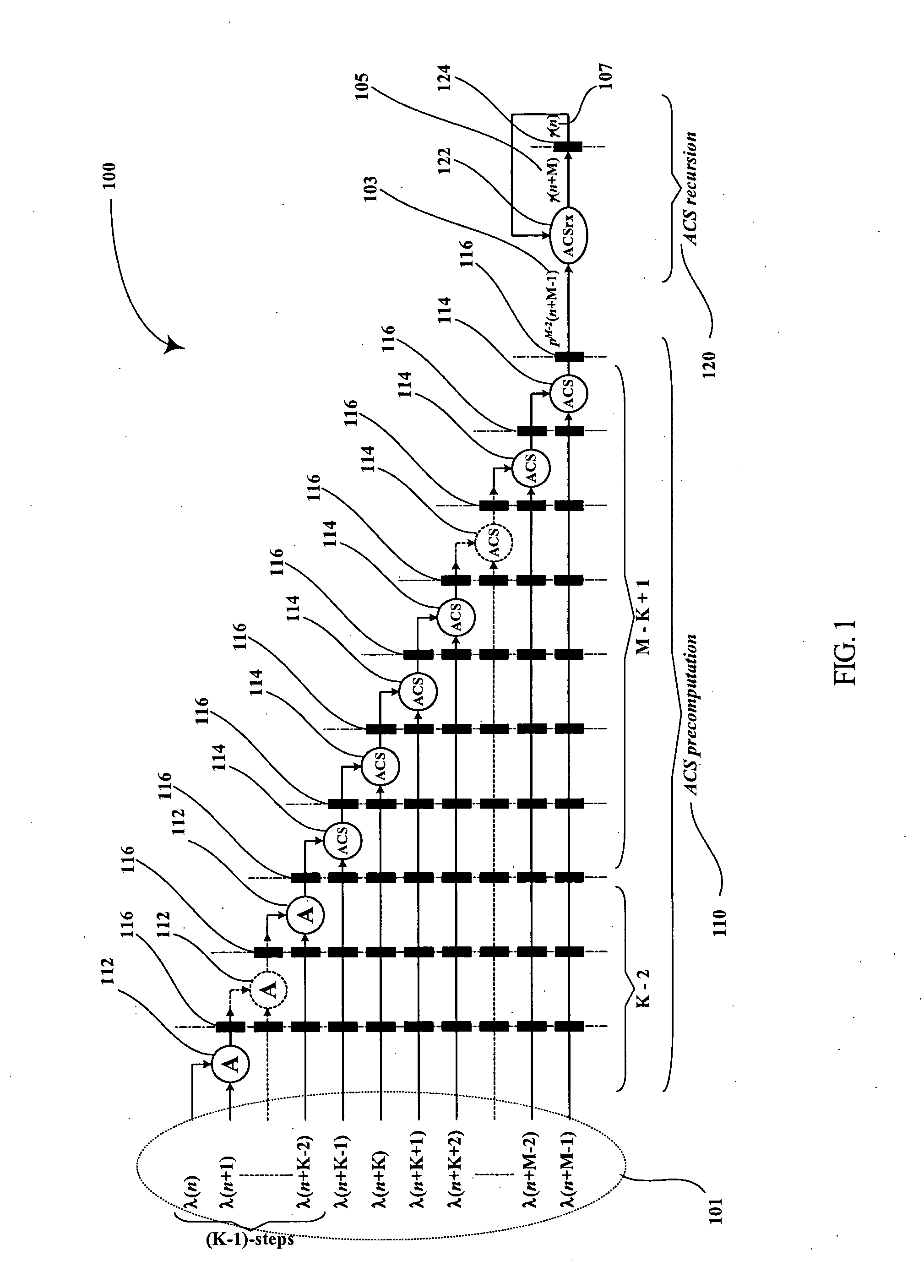
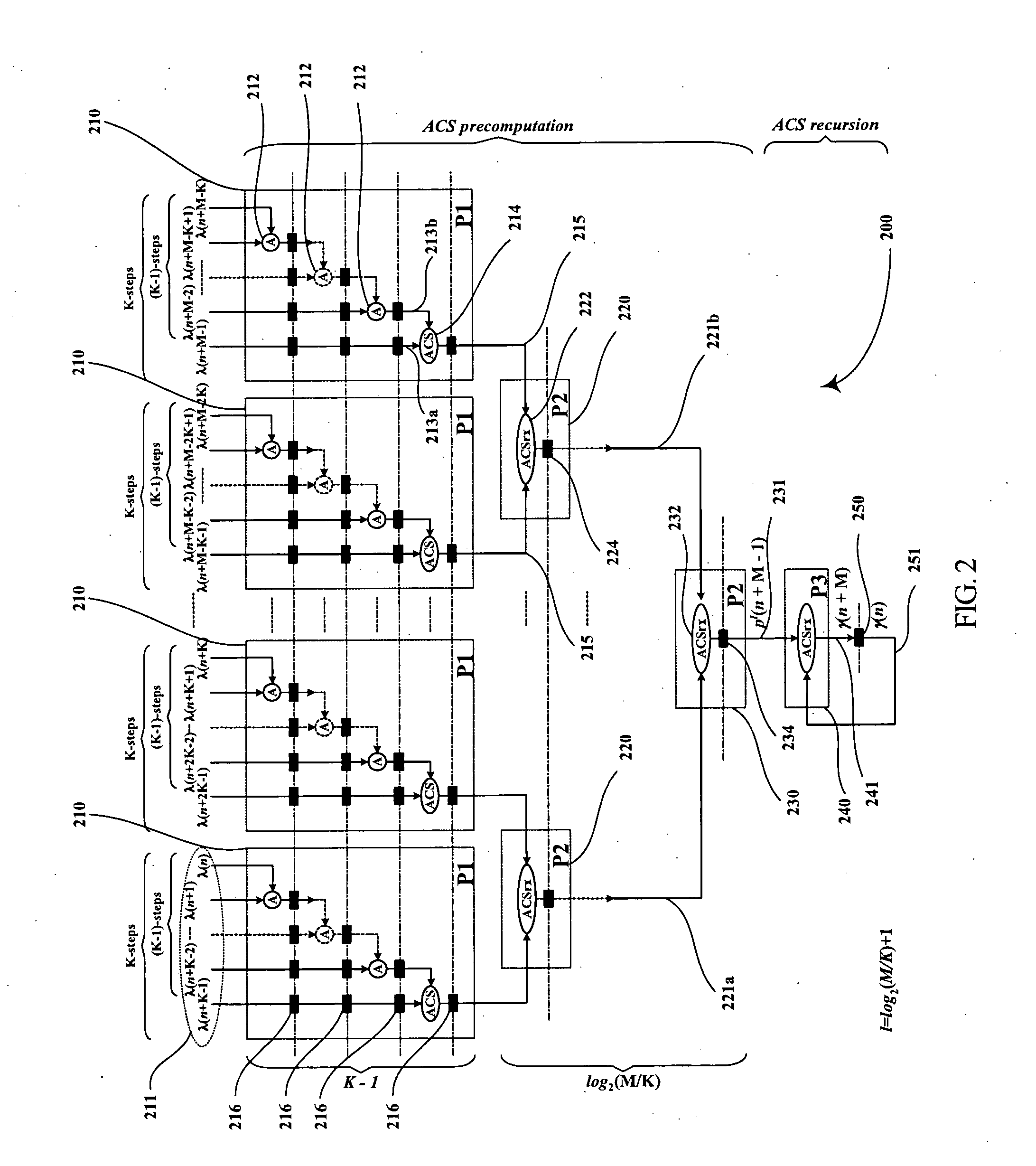
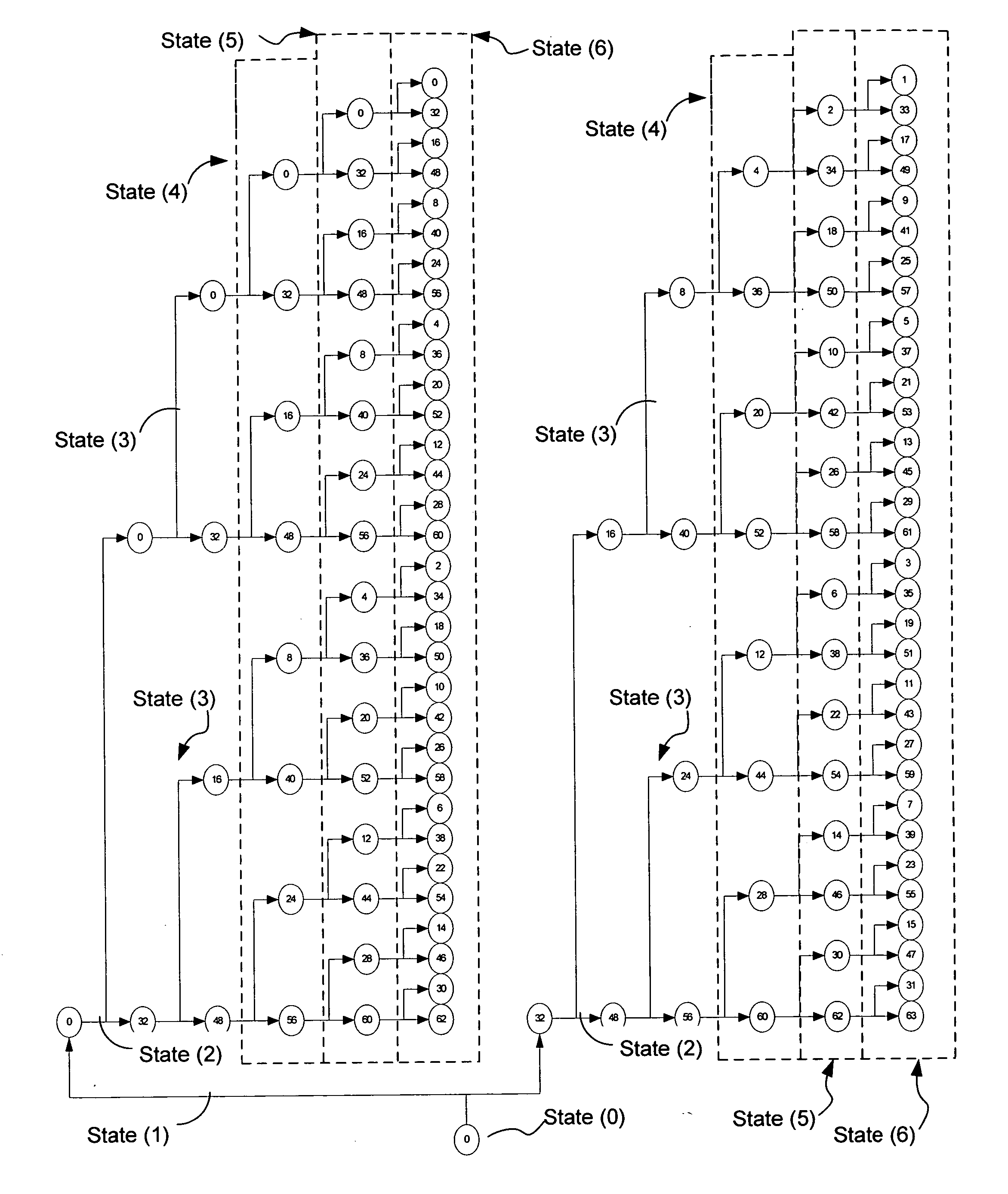
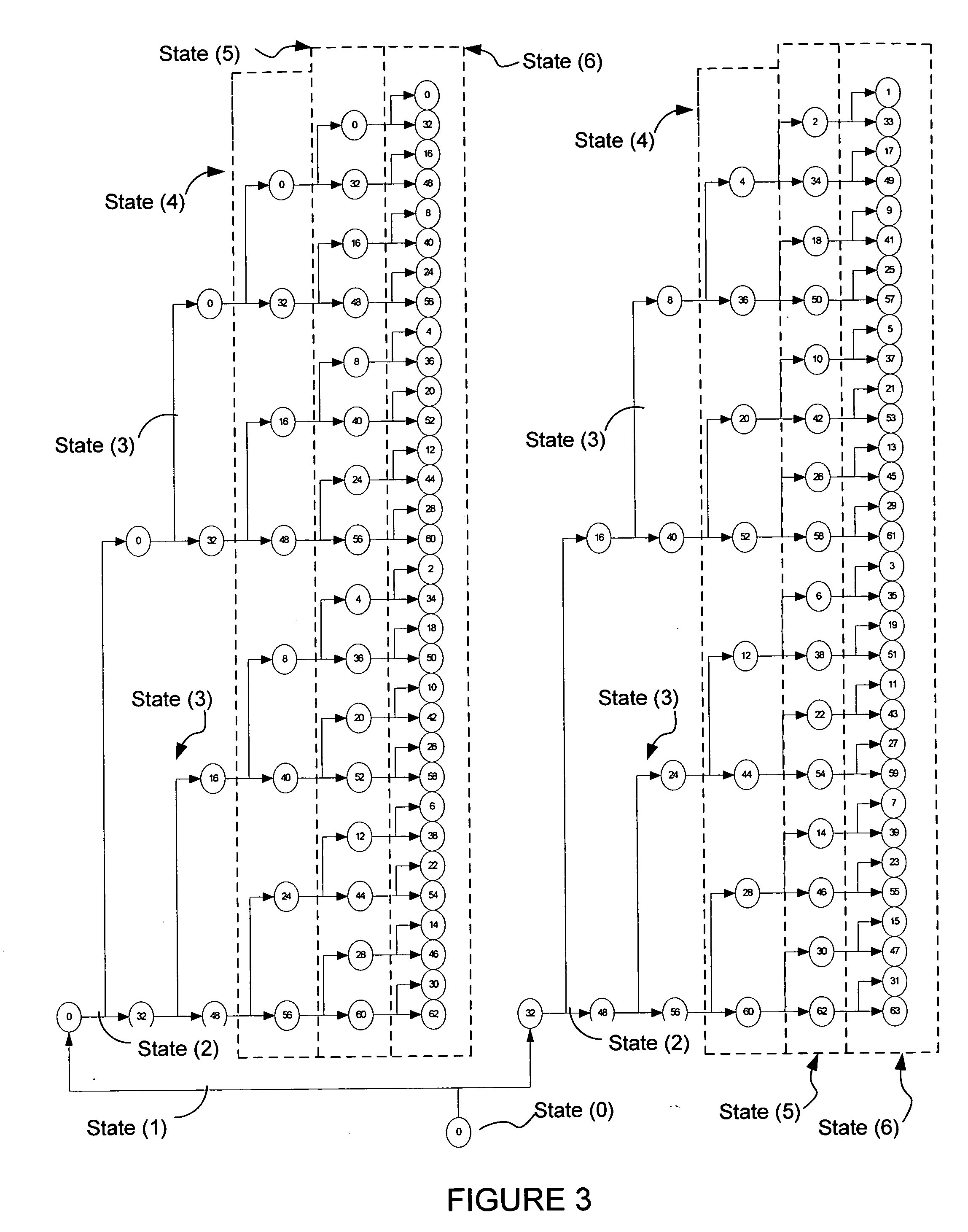
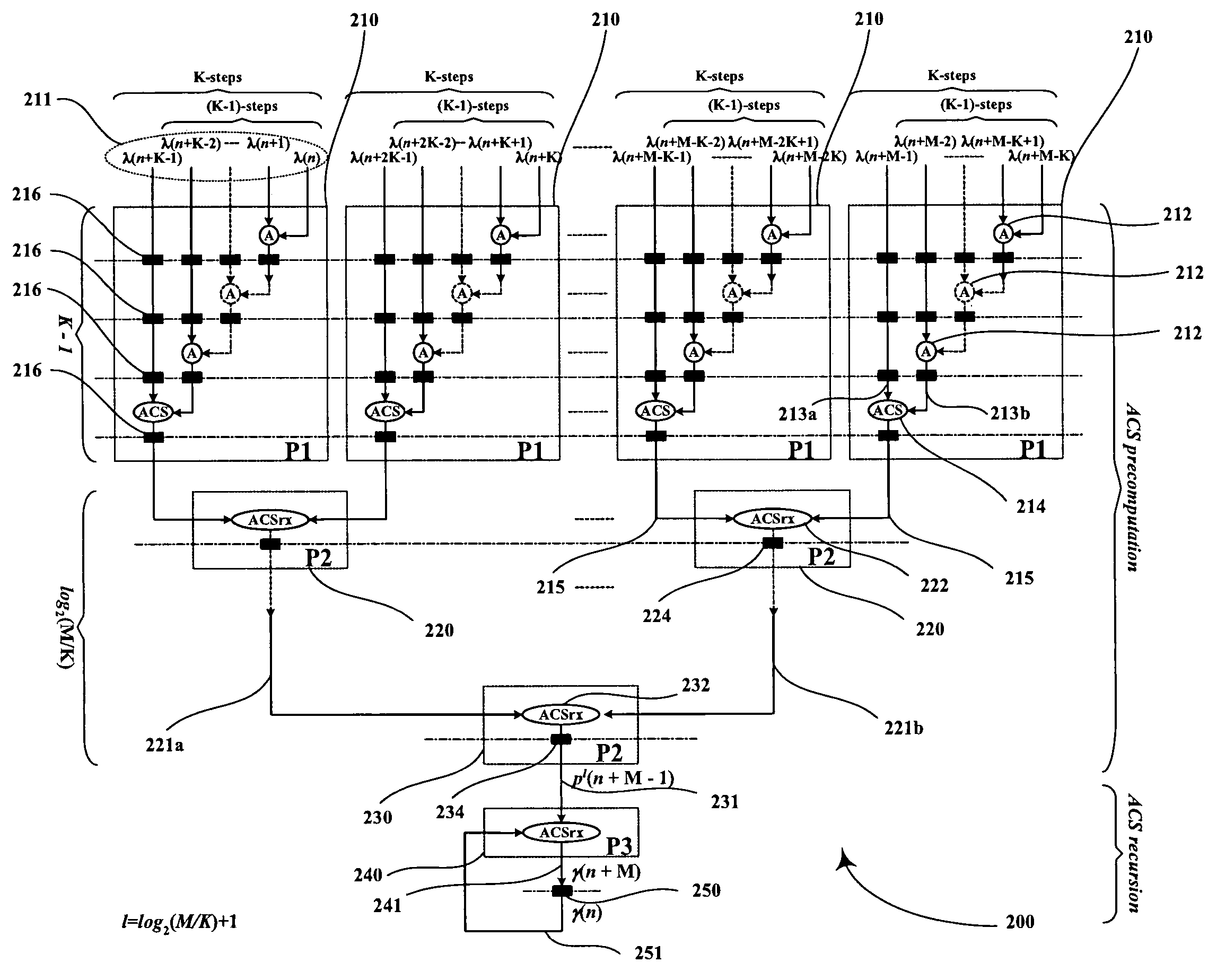
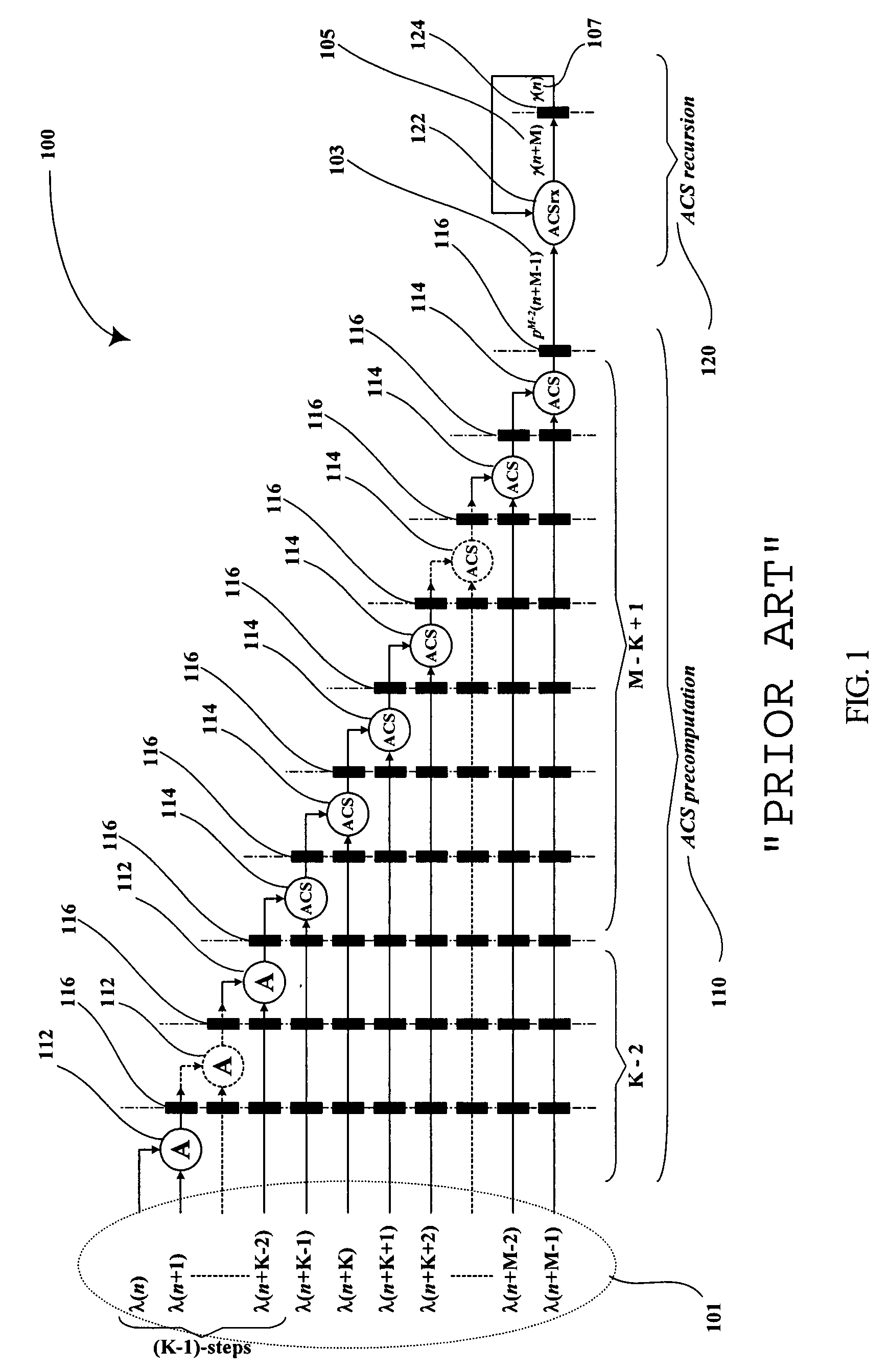
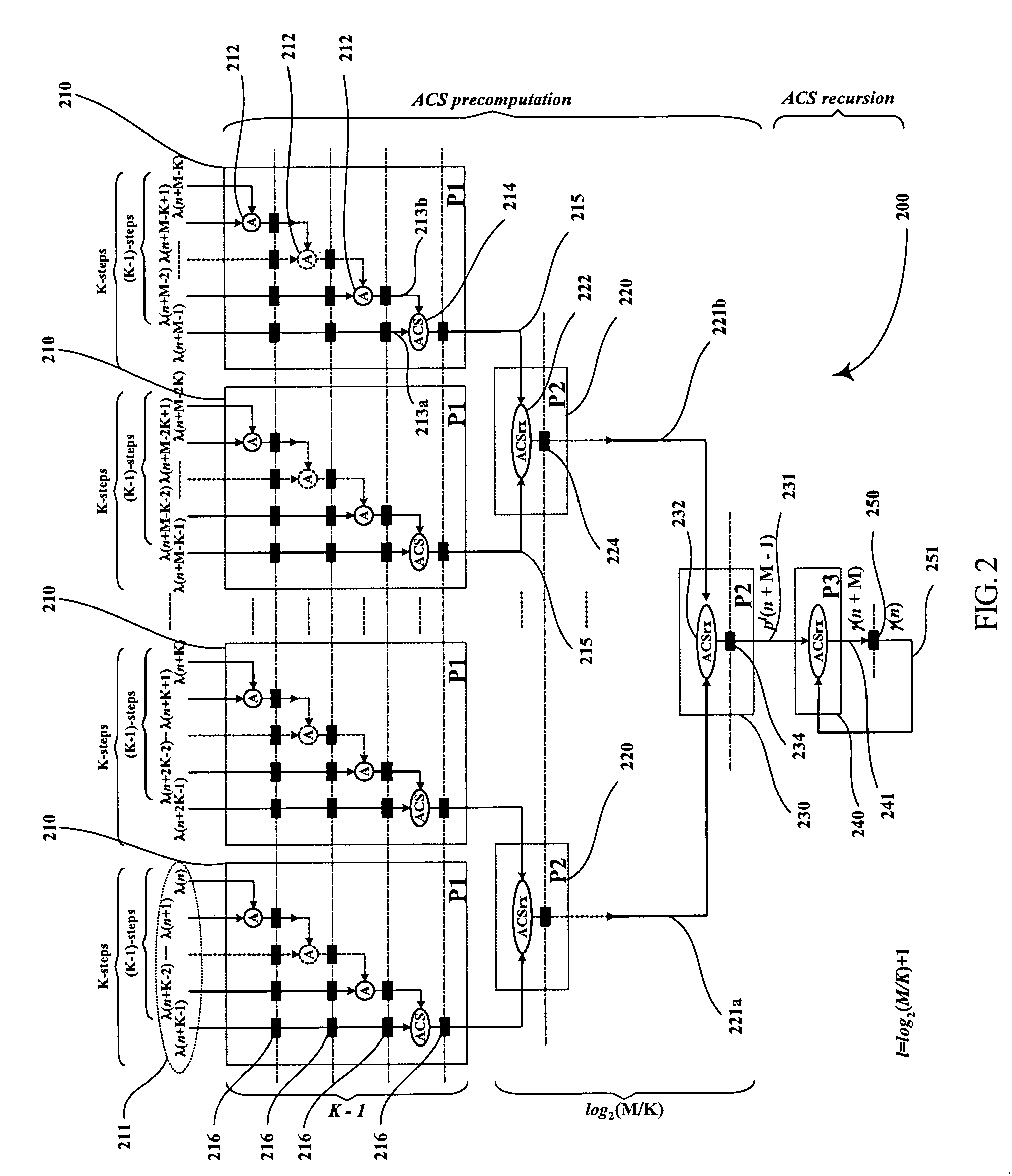
InactiveUS20050060633A1Lower latencyImprove throughputTelevision system detailsData representation error detection/correctionPrecomputationLatency (engineering)
Digital circuits and methods for designing digital circuits are presented. More particularly, the present invention relates to error correction circuits and methods in communications and other systems. In the present invention, a novel K-nested layered look-ahead method and its corresponding architecture, which combine K-trellis steps into one trellis step (where K is the encoder constraint length), are proposed for implementing low-latency high through-put rate Viterbi decoder circuits. The main idea of the present invention involves combining K-trellis steps as a pipeline structure and then combining the resulting look-ahead branch metrics as a tree structure in a layered manner to decrease the ACS precomputation latency of look-ahead Viterbi decoder circuits. The proposed method guarantees parallel paths between any two trellis states in the look-ahead trellises and distributes the add-compare-select (ACS) computations to all trellis layers. It leads to regular and simple architecture for the Viterbi decoding algorithm. The look-ahead ACS computation latency of the proposed method increases logarithmically with respect to the look-ahead step (M) divided by the encoder constraint length (K) as opposed to linearly as in prior work. The main advantage of this invention is that it has the least latency among all known look-ahead Viterbi decoder circuits for a given level of parallelism.
Owner:PARHI KESHAB K
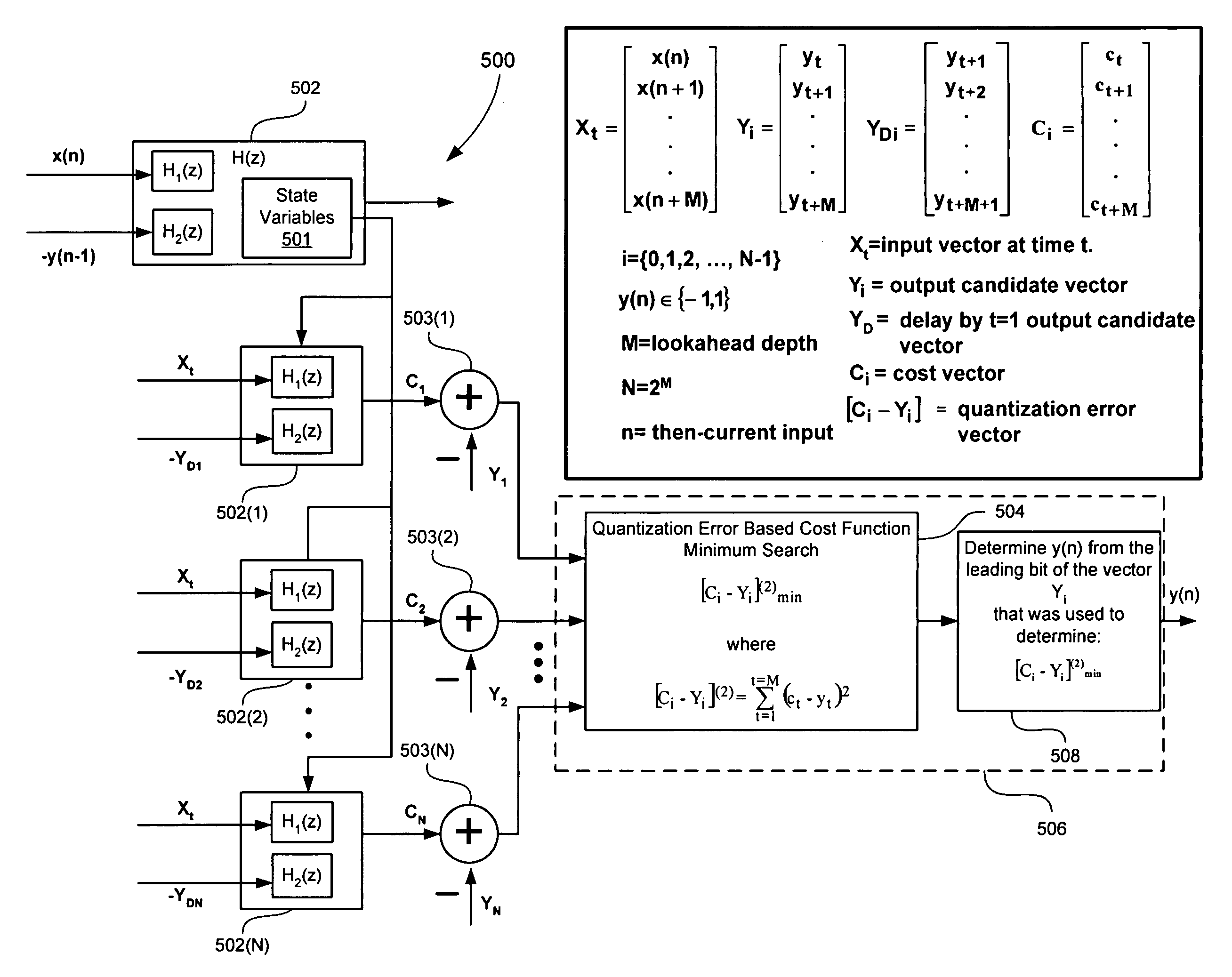
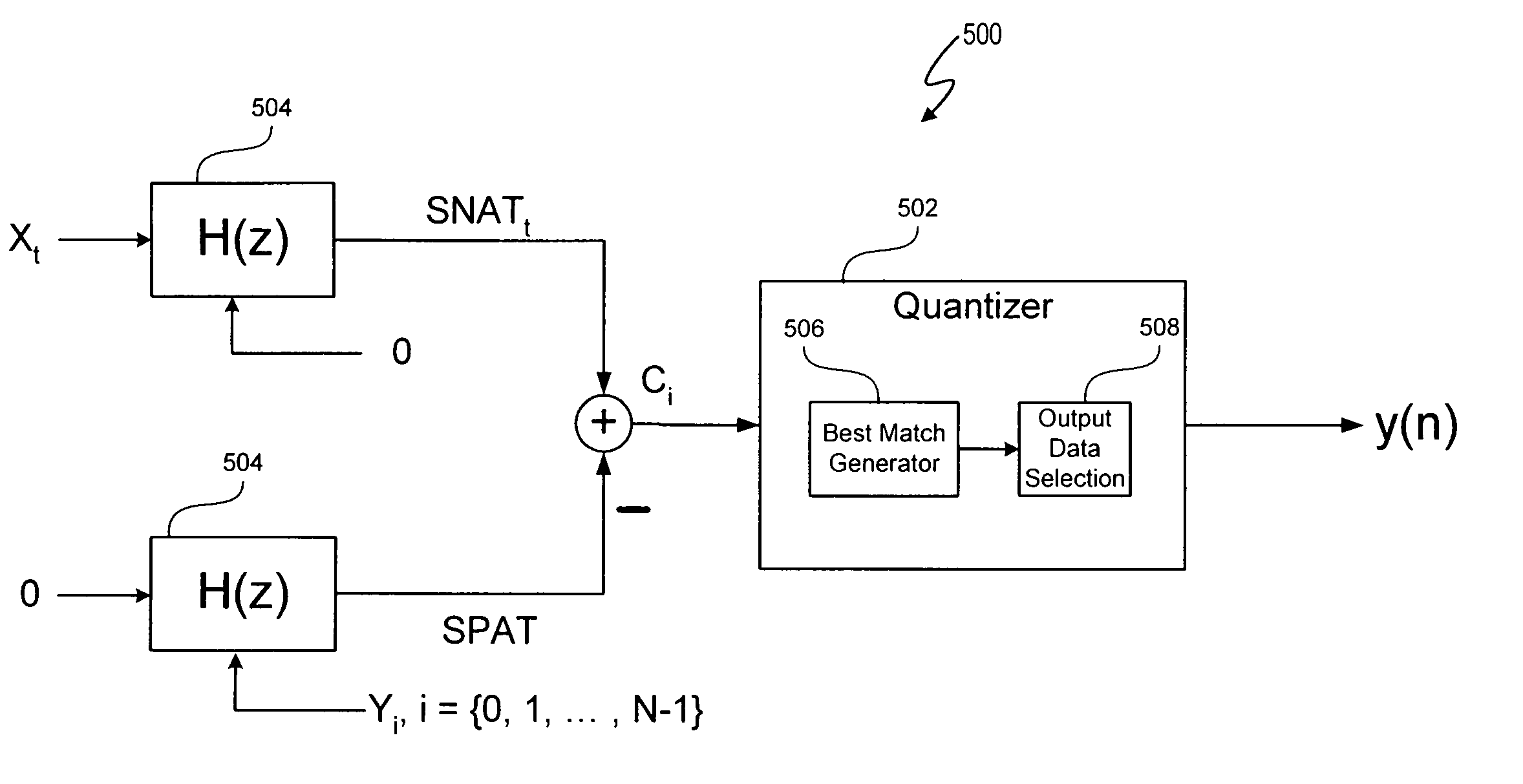
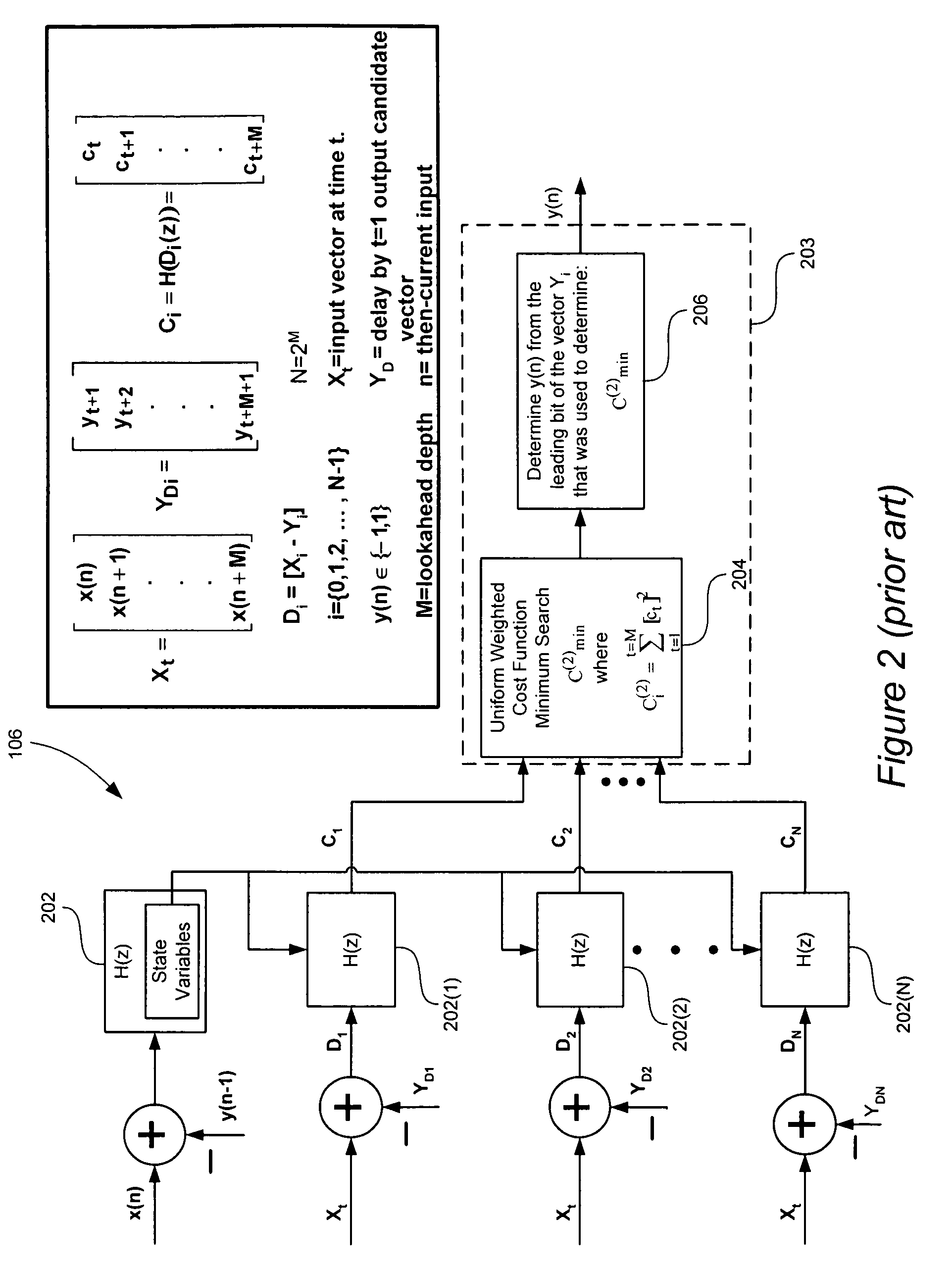
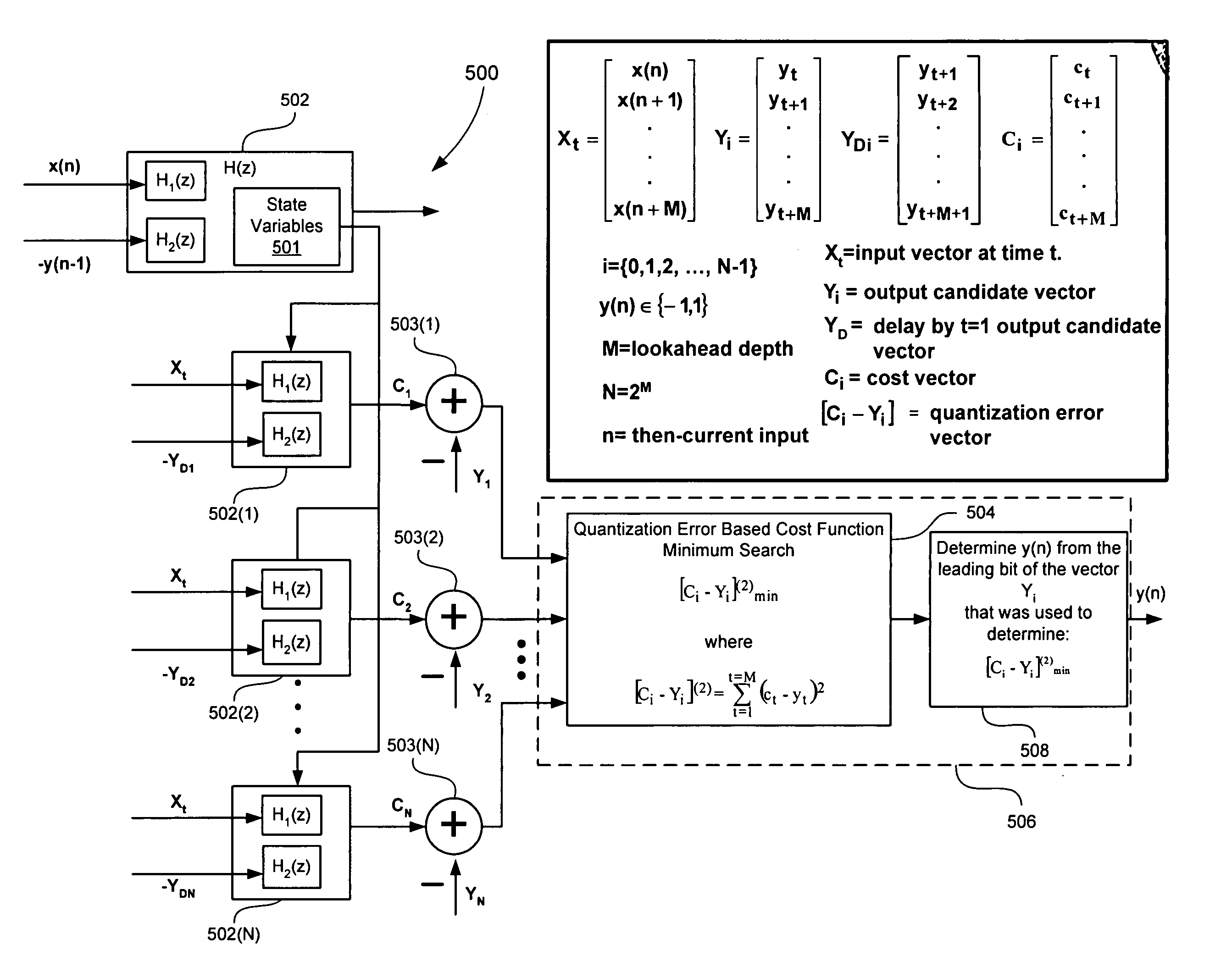
Signal processing with look-ahead modulator noise quantization minimization
ActiveUS7196647B2Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionEngineeringQuantization (signal processing)
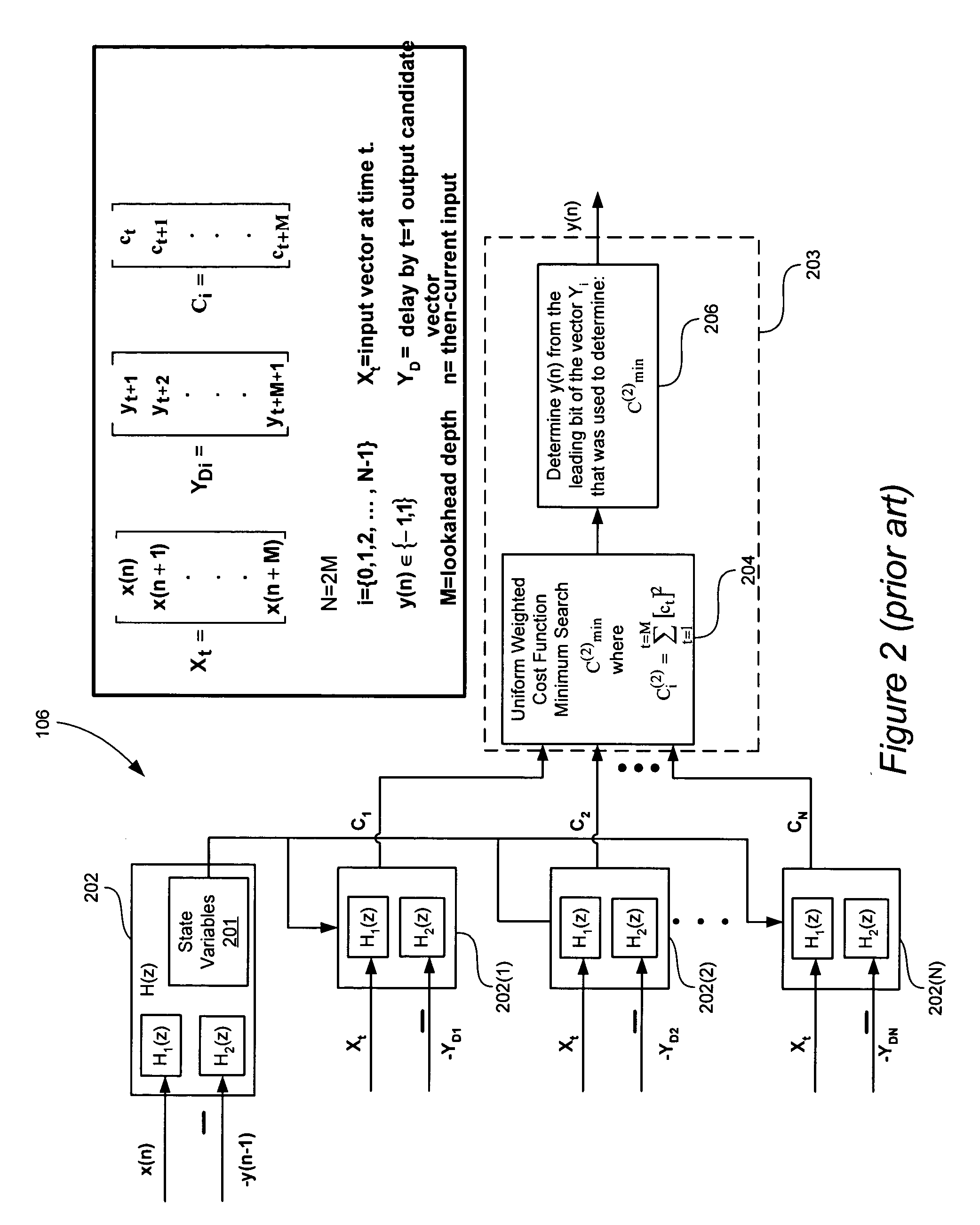
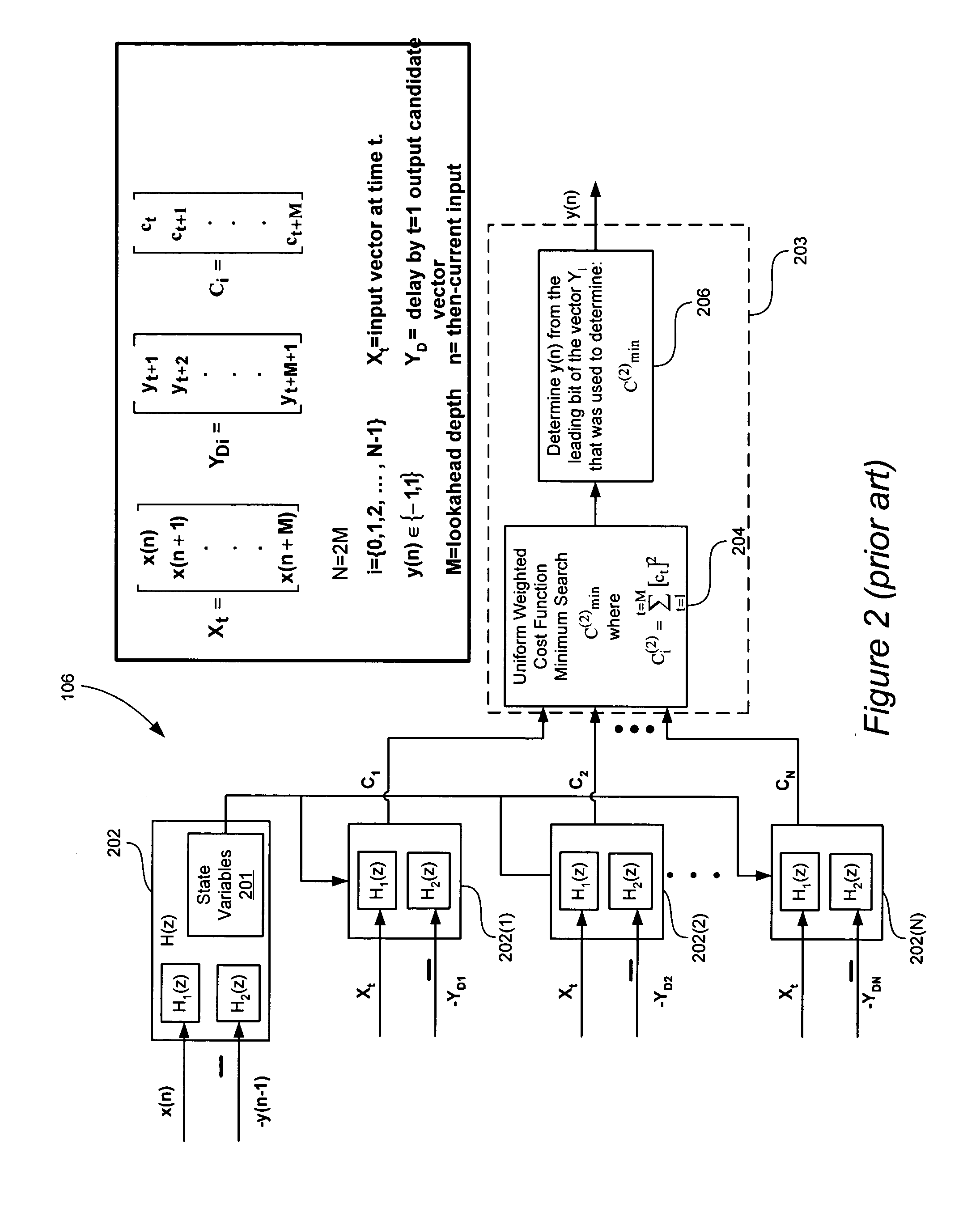
A signal processing system includes a look-ahead delta-sigma modulator that processes multiple output candidate vectors and an input vector to determine a quantization error vector for each output candidate vector. In one embodiment, the quantization error vector represents a difference between a cost value vector and an input candidate vector. Look-ahead delta-sigma modulator output values are selected using the quantization error vectors by, for example, determining the minimum power quantization error vector for each input vector X and selecting the output value from the input candidate vector associated with the minimum power quantization error vector. Quantization error vectors can also be weighted using a non-uniform weighting vector.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Look-ahead functionality tuning for independent sections
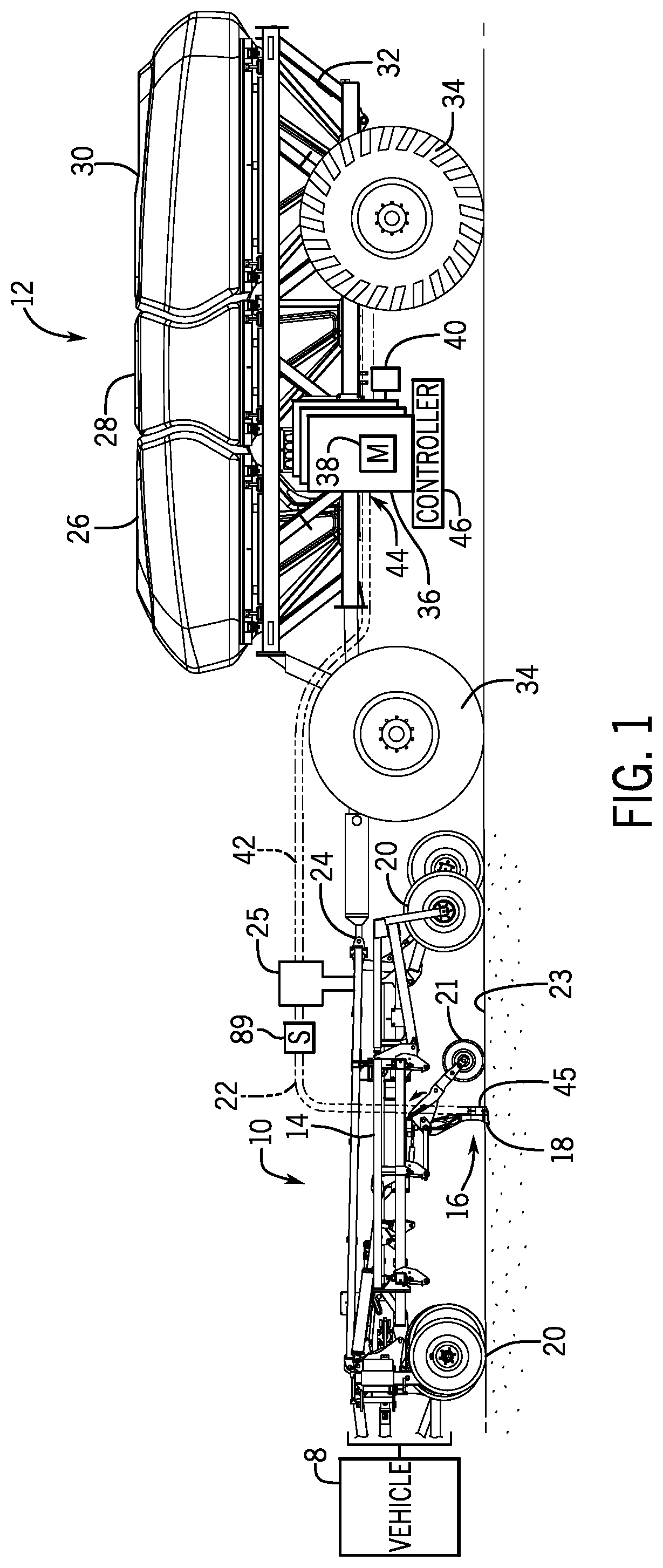
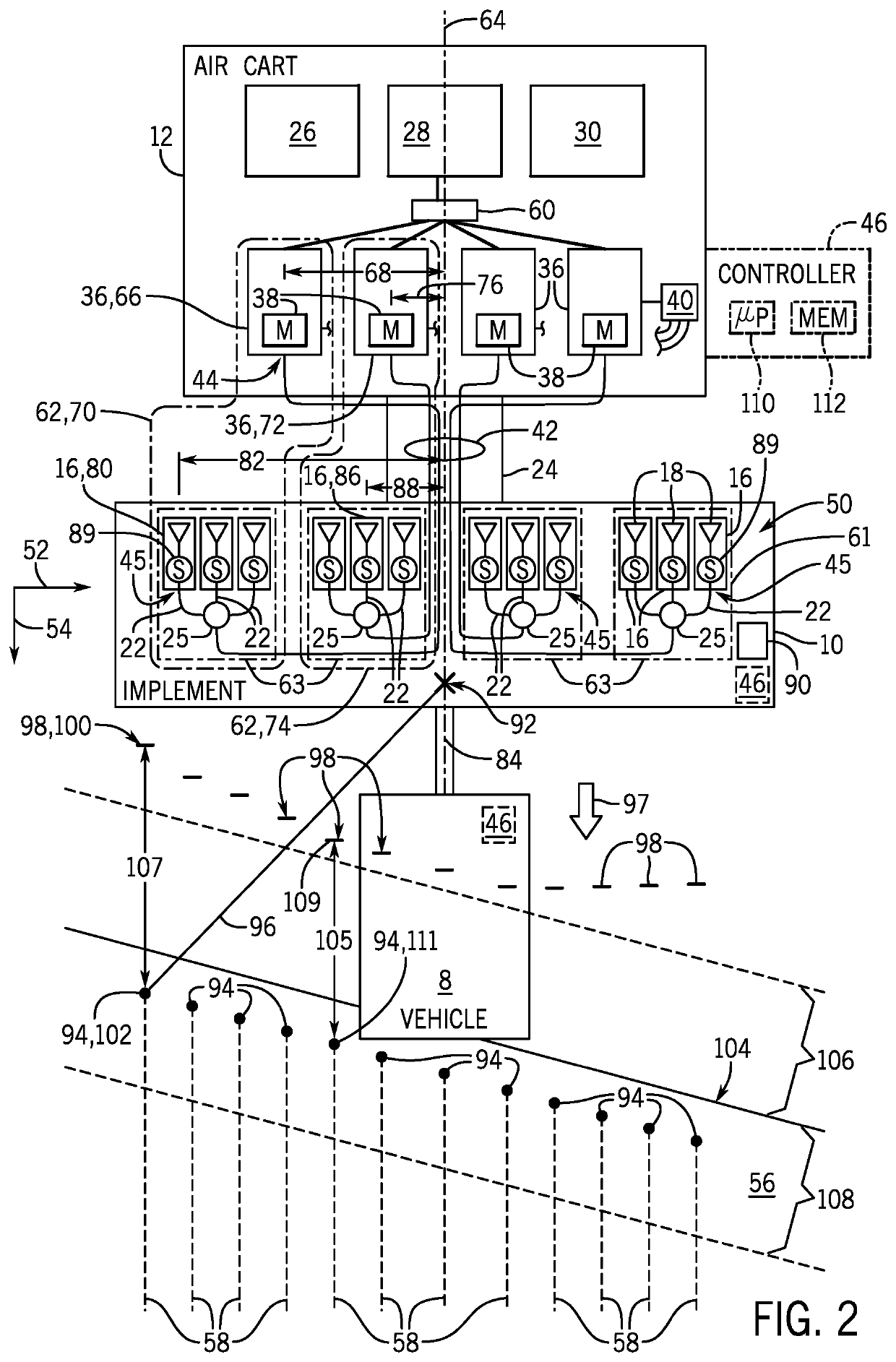
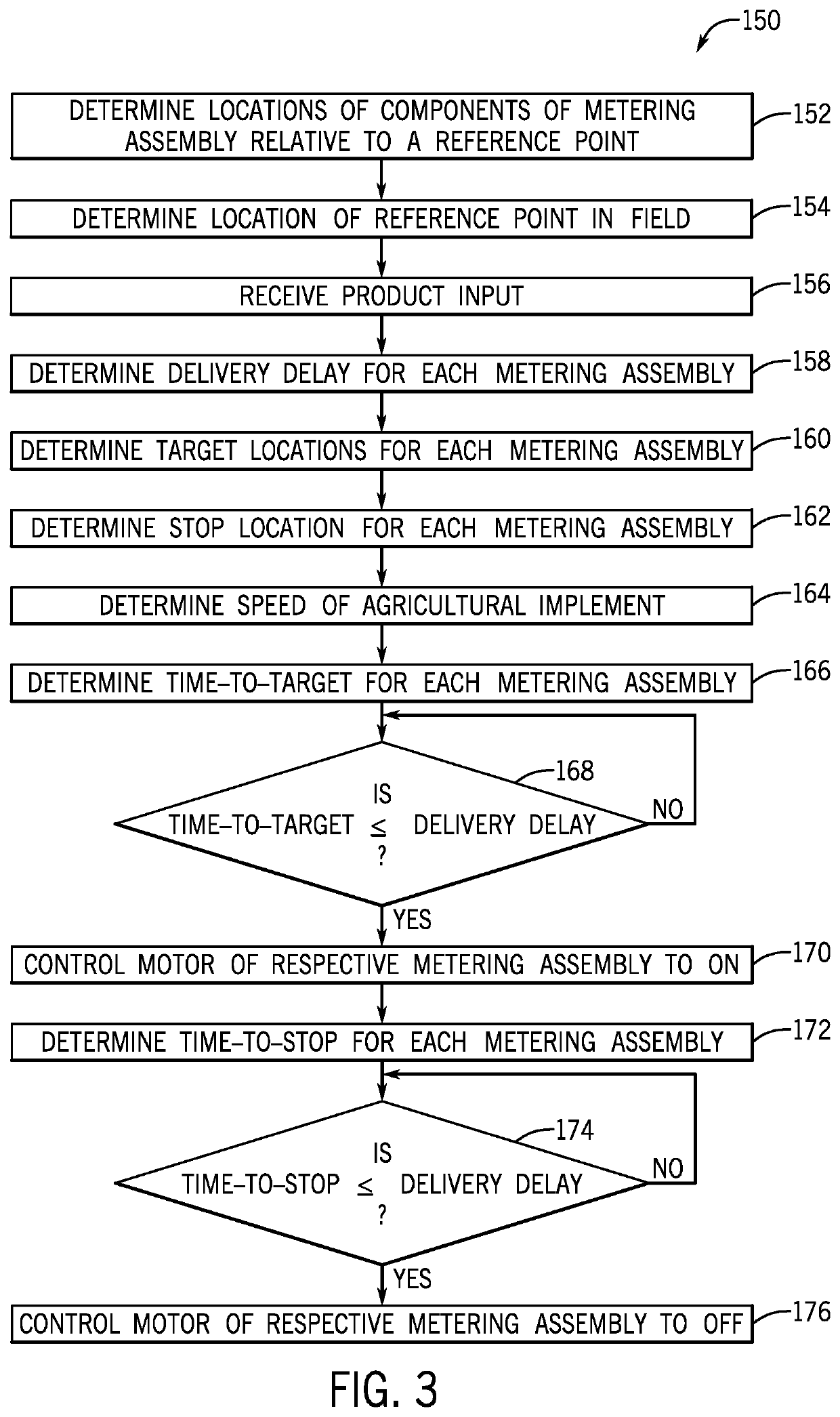
ActiveUS20200260637A1Fertiliser distributersFlow control using electric meansAgricultural scienceControl engineering
An agricultural product delivery system having a controller with a non-transitory computer readable medium configured to store instructions and a processor configured to execute the instructions. The instructions may include instructions to determine a first time-to-target of a first metering section of an agricultural implement in a field, determine a second time-to-target of a second metering section of the agricultural implement in the field, control a first motor coupled to the first metering section to an ON state when the first time-to-target is less than or equal to a first delivery delay of the first metering section, and control a second motor coupled to the second metering section to the ON state when the second time-to-target is less than or equal to a second delivery delay of the second metering section.
Owner:CNH IND CANADA
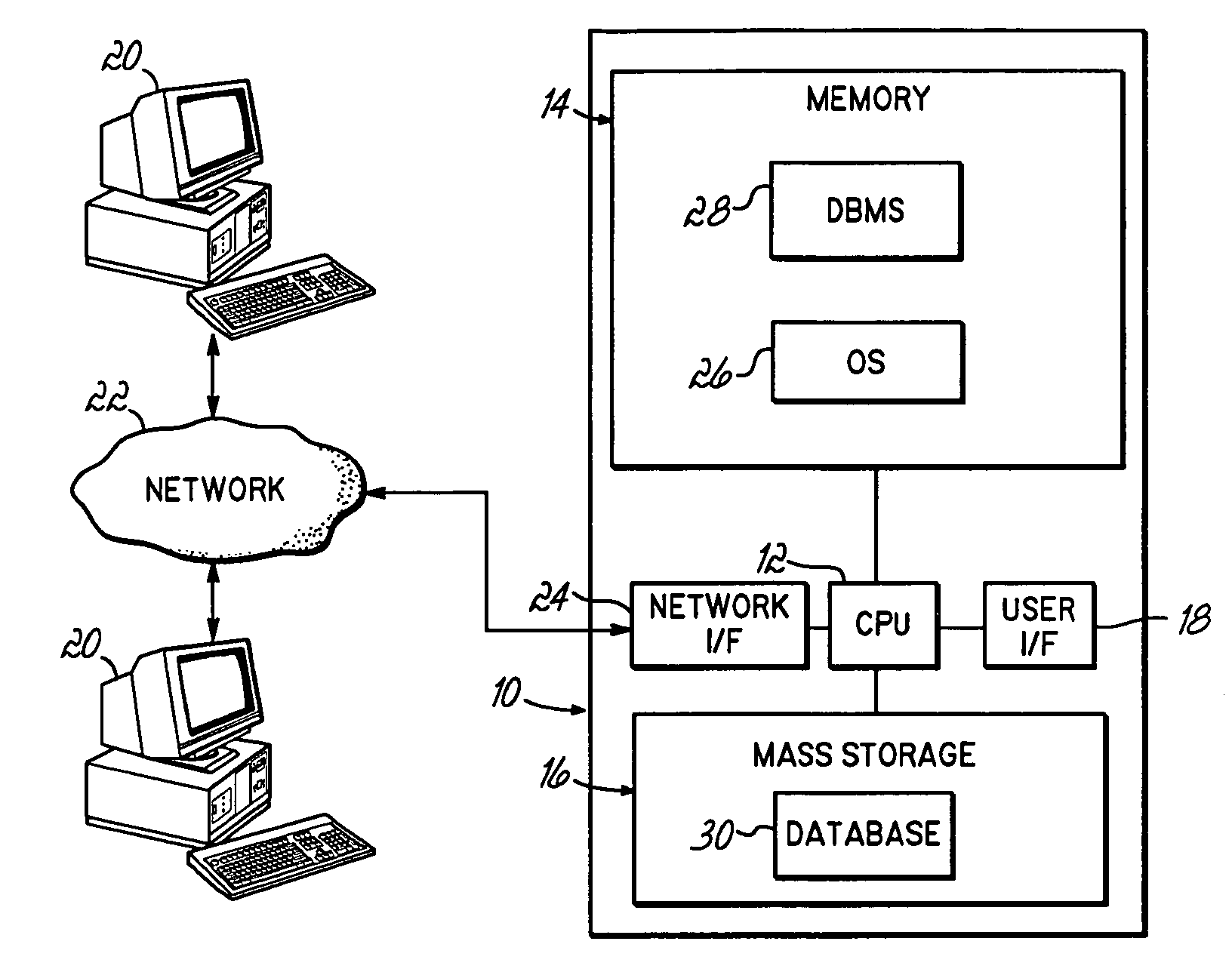
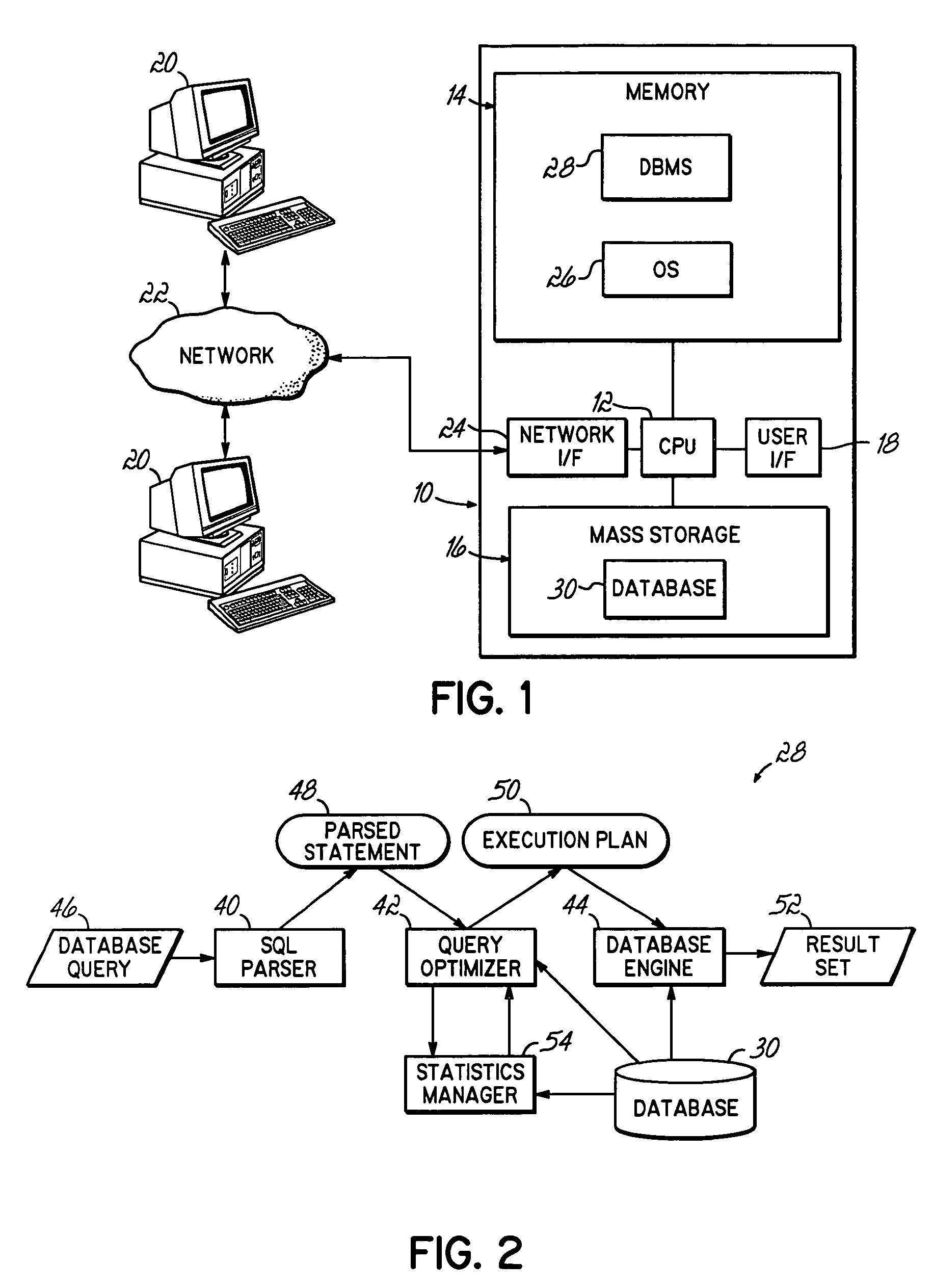
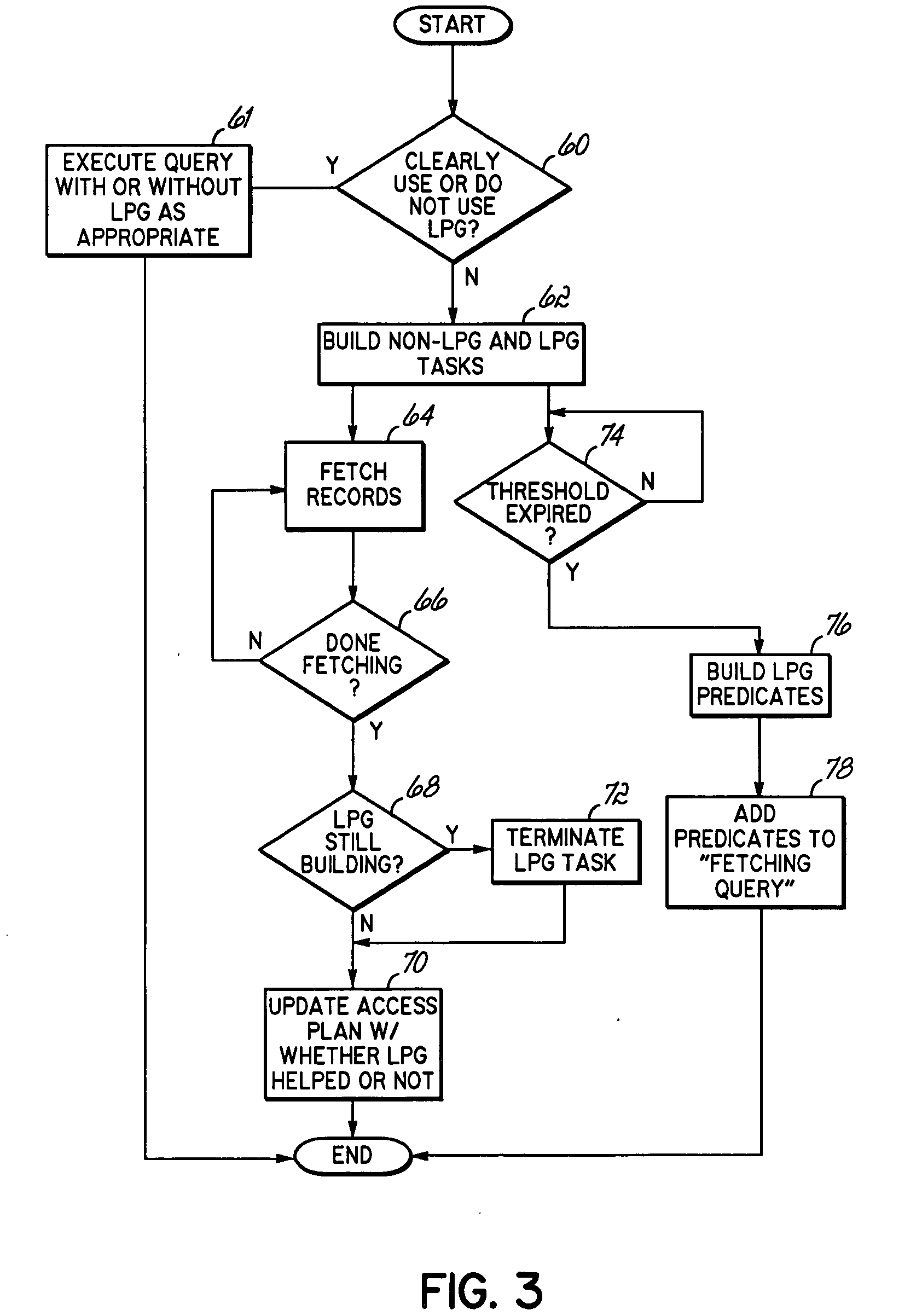
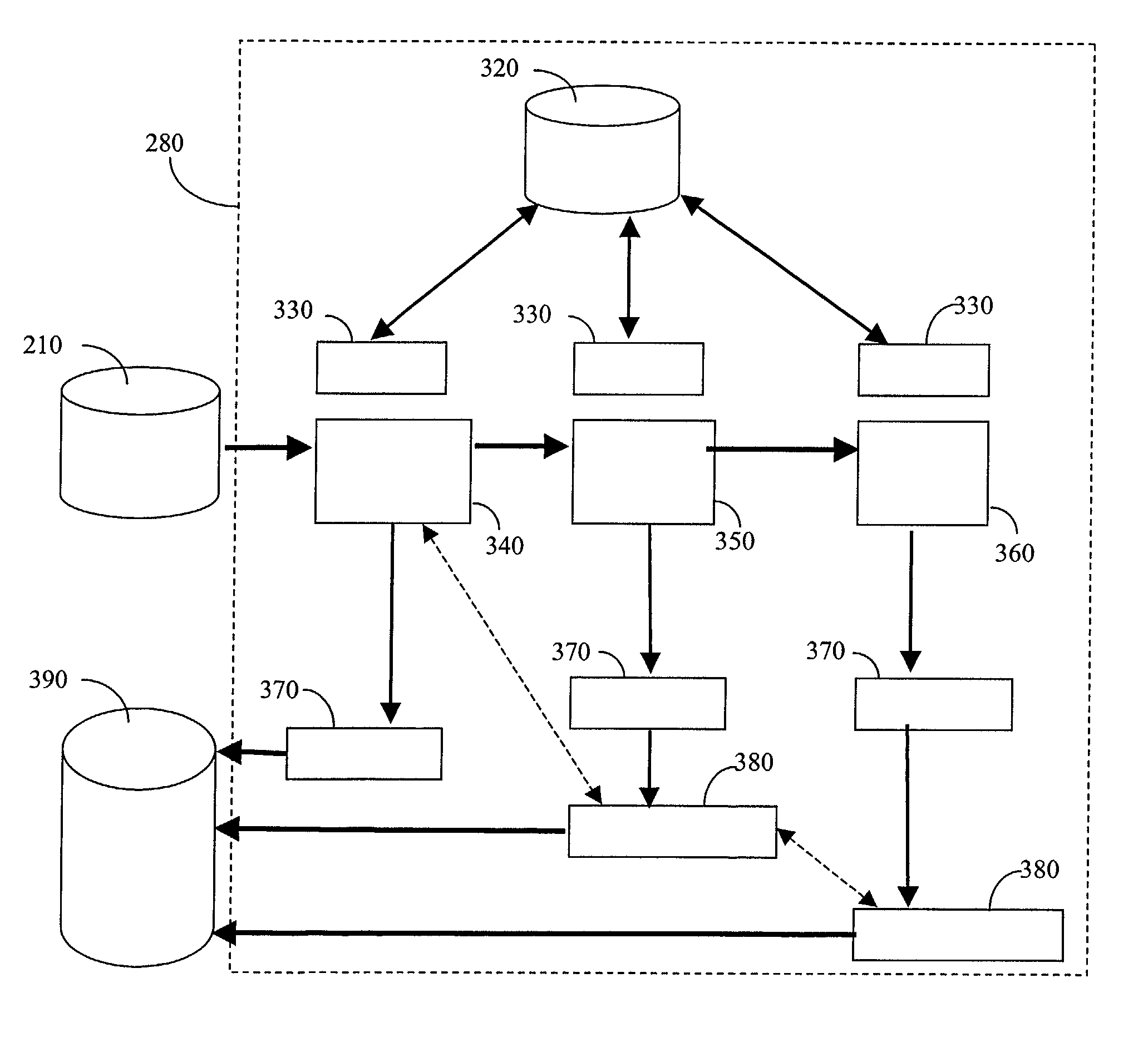
Dynamic look ahead predicate generation
InactiveUS20060218129A1Efficiently determinedImprove query performanceData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalOptimal decisionProgram planning
An apparatus, program product and method that employ a dynamic use of Look Ahead Predicate Generation that will enable the database, database engine, and / or query optimizer to alter the processing of a query, and react to sub-optimal access plan selection and additional factors arising after processing has begun, to heal many poor performing queries. Conventional use of LPG requires the query optimizer to decide whether or not to use LPG before the processing of a query begins. As a result, the query optimizer may not only make sub-optimal decisions, but the query optimizer may not consider additional factors that may arise as the query is processing. However, the dynamic use of LPG allows predicates to be built after processing of the query has started and the ability to alter the query's processing to improve query performance.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatus and method for handling of multi-level circuit design data
ActiveUS6993733B2CAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationProcessor registerEngineering
A system and method for implementation of look-ahead design methodology. Efficient debugging of a design is accomplished by evaluating the high level register transfer level (RTL) representation of a device being designed by quickly simulating the downstream implementation of that device to expose potential implementation problems that would otherwise be found much later in the design or manufacturing cycle.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
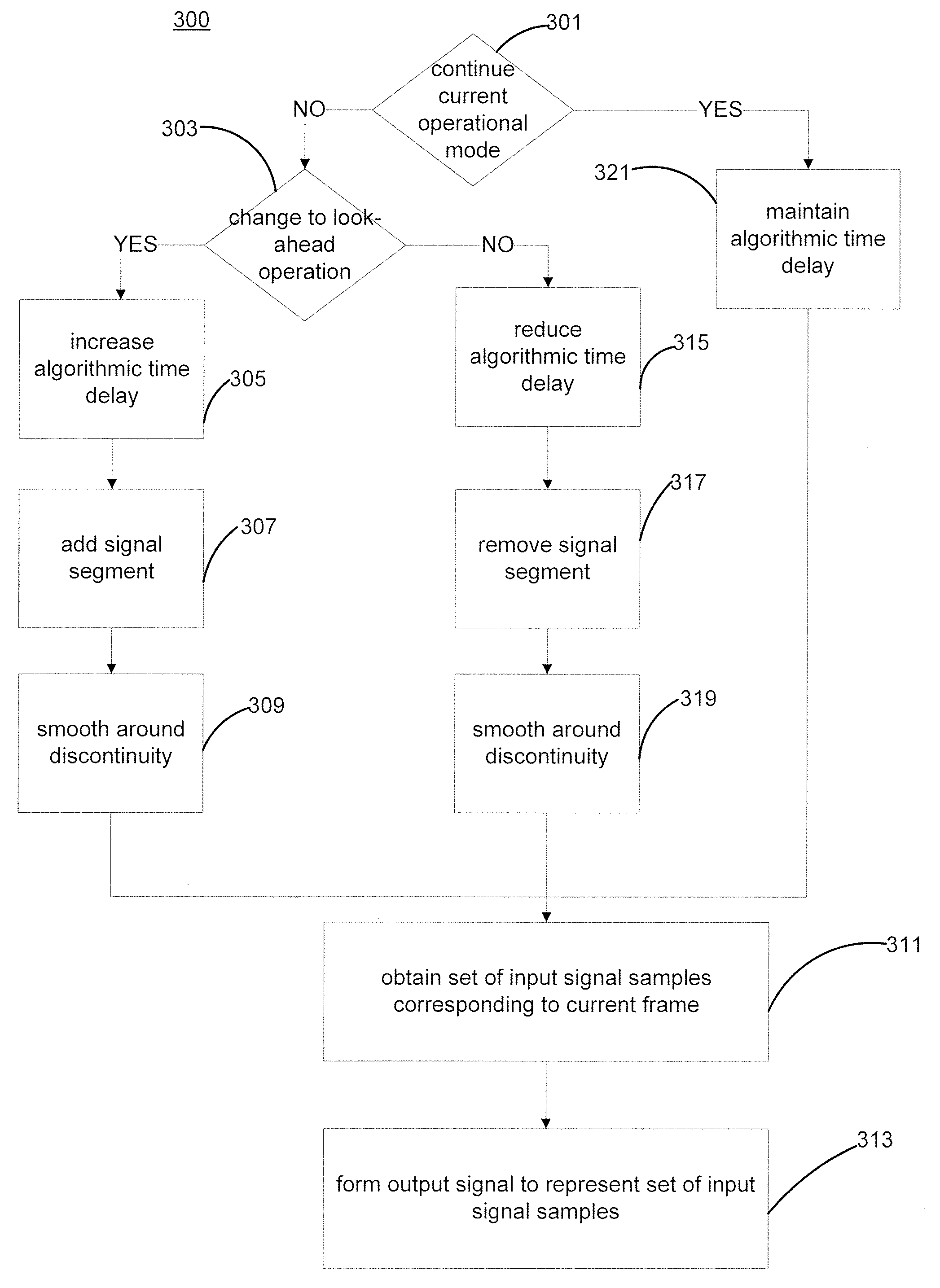
Encoder Delay Adjustment
The present invention provides methods and apparatus for adjusting an algorithmic time delay of a signal encoder. An input signal is sampled at a predetermined sampling rate. When look-ahead operation is initiated, the algorithmic time delay is increased by the look-ahead time duration. When look-ahead operation is terminated, the algorithmic time delay is decreased by the look-ahead time duration. A set of input signal samples is aligned in accordance with the algorithmic time delay, and an output signal that is representative of the set of signal samples is formed. A first signal segment is added to an input signal waveform when the look-ahead operation is initiated, and a second signal segment is removed from the input signal waveform when the look-ahead operation is terminated. Pointers that point to a beginning of the current frame and to new input signal samples are adjusted when the operational mode changes.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Methods for optimal multi-channel assignments in vehicular ad-hoc networks
InactiveUS20080279141A1Reduce the amount of calculationExpand selectionNetwork topologiesConnection managementComputer networkDepth-first search
A communications path is established among an ordered sequence of moving nodes, representing vehicles. Available channels may differ from one node to the next node and a node cannot use the same channel for both receiving and transmitting information. Three methods are described that provide an optimal sequence of channel assignments between the nodes. A sequence of channel assignments is called optimal if it establishes a communications path from the first node in the sequence to the last node in the sequence, or, if such a path does not exist, from the first node to the farthest node possible in the sequence. The first method uses a depth-first search starting from the first node in the sequence. The second method uses a “look ahead” scheme in the depth-first search method. The third method requires only a single pass through the sequence of nodes by identifying optimal channel assignments in subsequences of nodes without a need for backtracking.
Owner:TOYOTA INFORTECH CENT U S A +2
Look-ahead delta sigma modulator having an infinite impulse response filter with multiple look-ahead outputs
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
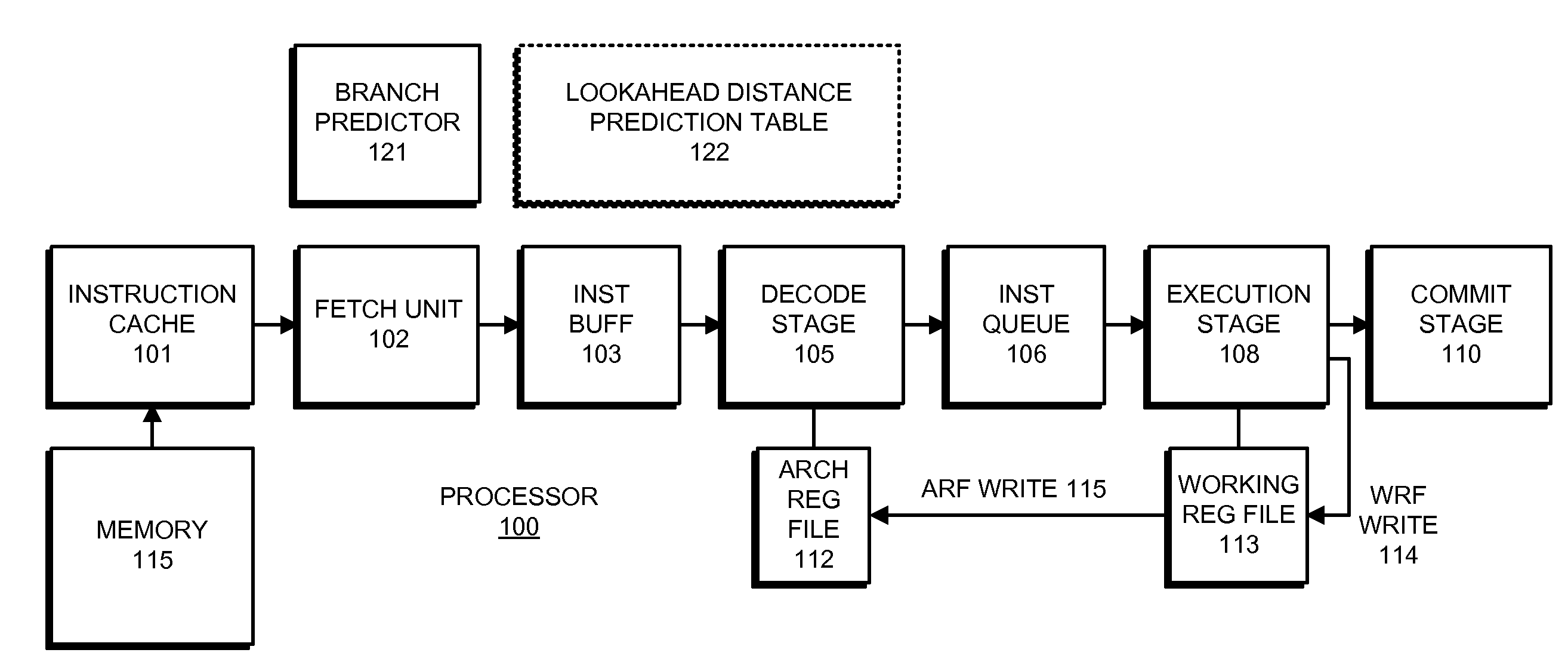
Reducing hardware costs for supporting miss lookahead
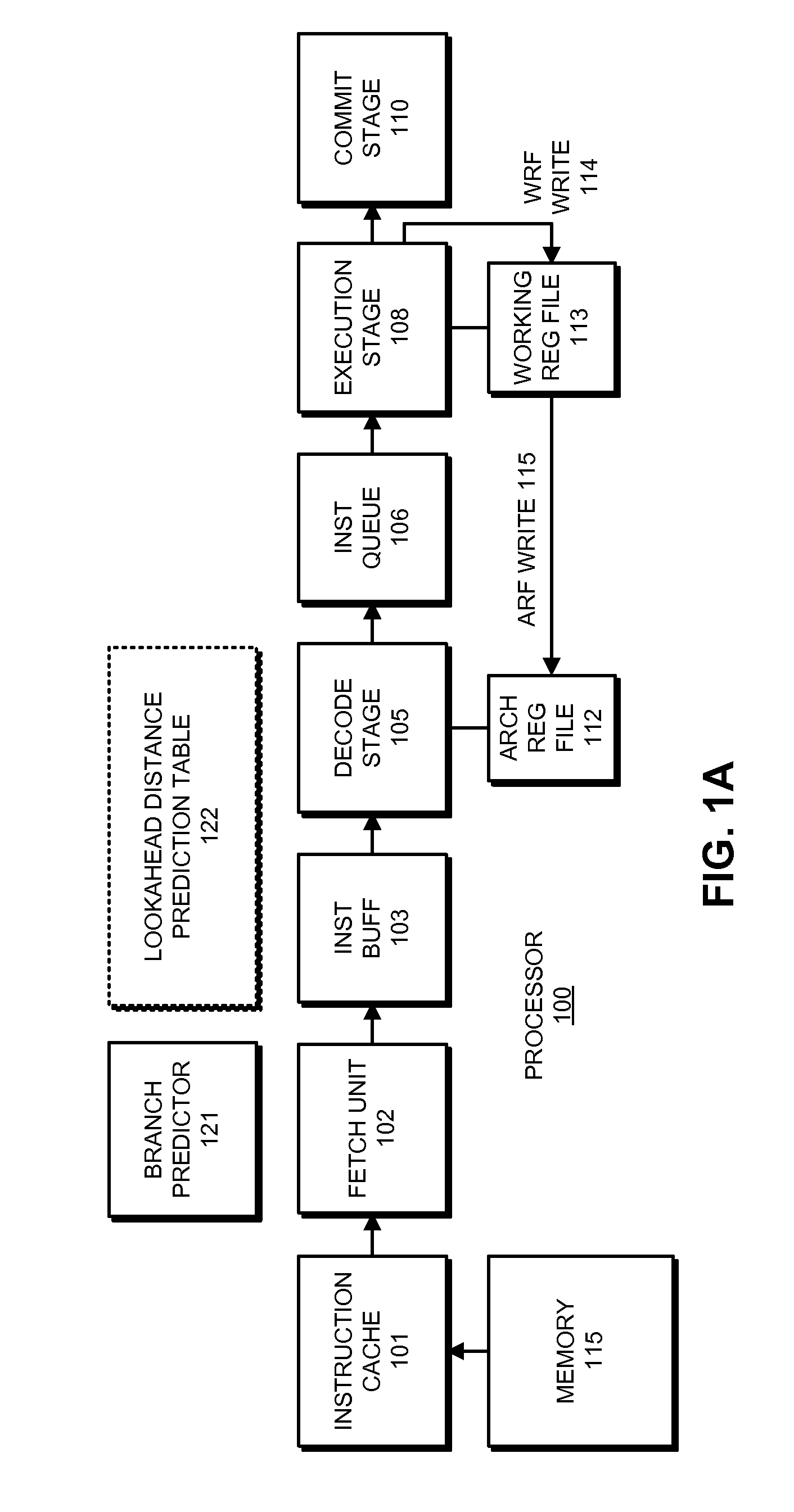
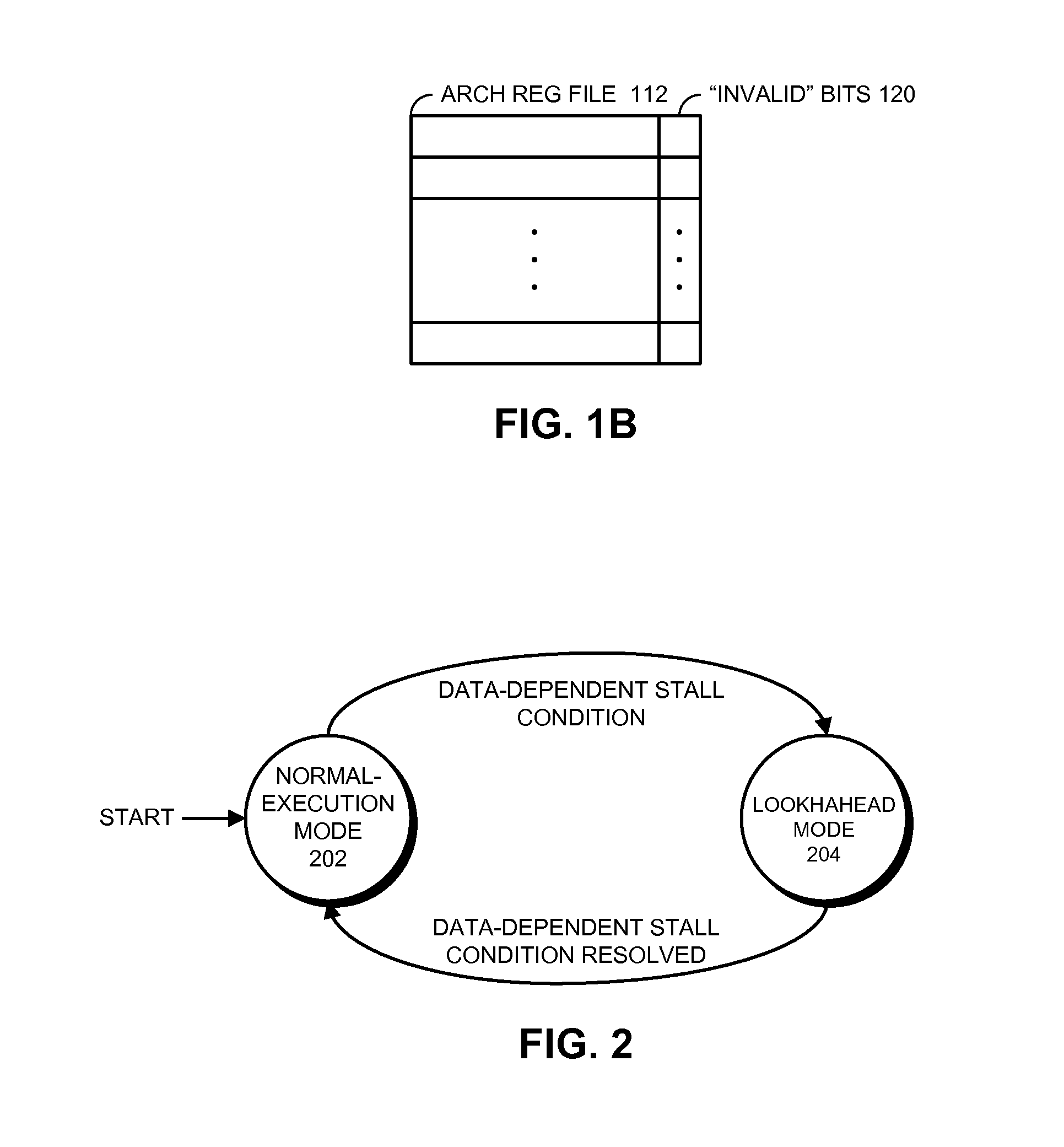
ActiveUS20130124828A1Eliminate needDigital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionProgram instructionData dependency
The disclosed embodiments relate to a system that executes program instructions on a processor. During a normal-execution mode, the system issues instructions for execution in program order. Upon encountering an unresolved data dependency during execution of an instruction, the system speculatively executes subsequent instructions in a lookahead mode to prefetch future loads. When an instruction retires during the lookahead mode, a working register which serves as a destination register for the instruction is not copied to a corresponding architectural register. Instead the architectural register is marked as invalid. Note that by not updating architectural registers during lookahead mode, the system eliminates the need to checkpoint the architectural registers prior to entering lookahead mode.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Systems and methods for providing a fine to coarse look ahead in connection with parametrization metrics in a graphics system
InactiveUS20050253844A1Improve textureMinimizes metricCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingImage resolutionGraphics
Systems and methods are provided for providing a fine-to-coarse look ahead in connection with parametrization in a graphics system. The use of a variety of parametrization metrics may be supplemented and improved by the fine-to-coarse look ahead techniques of the invention. First, the metric of a parametrization is minimized using a coarse-to-fine hierarchical solver, and then accelerated with a fine-to-coarse propagation. The resulting parametrizations have increased texture resolution in surface regions with greater signal detail at all levels of detail in the progressive mesh sequence.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Numerical control system, device with storage function and NURBS curve interpolation method
The invention discloses a numerical control system, a device with a storage function and a NURBS curve interpolation method. The NURBS curve interpolation method comprises: establishing a look-ahead buffer and storing buffer node data in the look-ahead buffer; and acquiring current insertion according to buffer node data and confirming the interpolation speed of a current interpolation cycle and performing NURBS curve interpolation through the interpolation point; determining whether an NURBS curve is finished interpolation or not, entering a next interpolation cycle if not. The invention notonly reduces the acquisition amount of an algorithm, but also reduces the acquisition amount of the algorithm by establishing a look-ahead buffer, thereby saving the curvature limit speed and the backward limit speed of the arc length interval by the forward buffer, and maintaining the look-ahead buffer according to the look-ahead buffer update method. The time overhead of each interpolation cyclealso ensures the real-time nature of the interpolation.
Owner:SHENZHEN A&E INTELLIGENT TECH INST CO LTD
Viterbi decoder with survivor bits stored to support look-ahead addressing
ActiveUS20050182999A1Improve throughputRule out the possibilityError correction/detection using convolutional codesOther decoding techniquesViterbi decoderData integrity
In accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, a Viterbi decoder is described that operates on convolutional error correcting codes. The decoder allows for a pipelined architecture and a unique partitioning of survivor memory to maintain data integrity. Throughput rate is improved and stalling minimized by accessing memory words using a look-ahead function to fill the pipeline.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Corner transition smoothing method for smoothing axial jerk
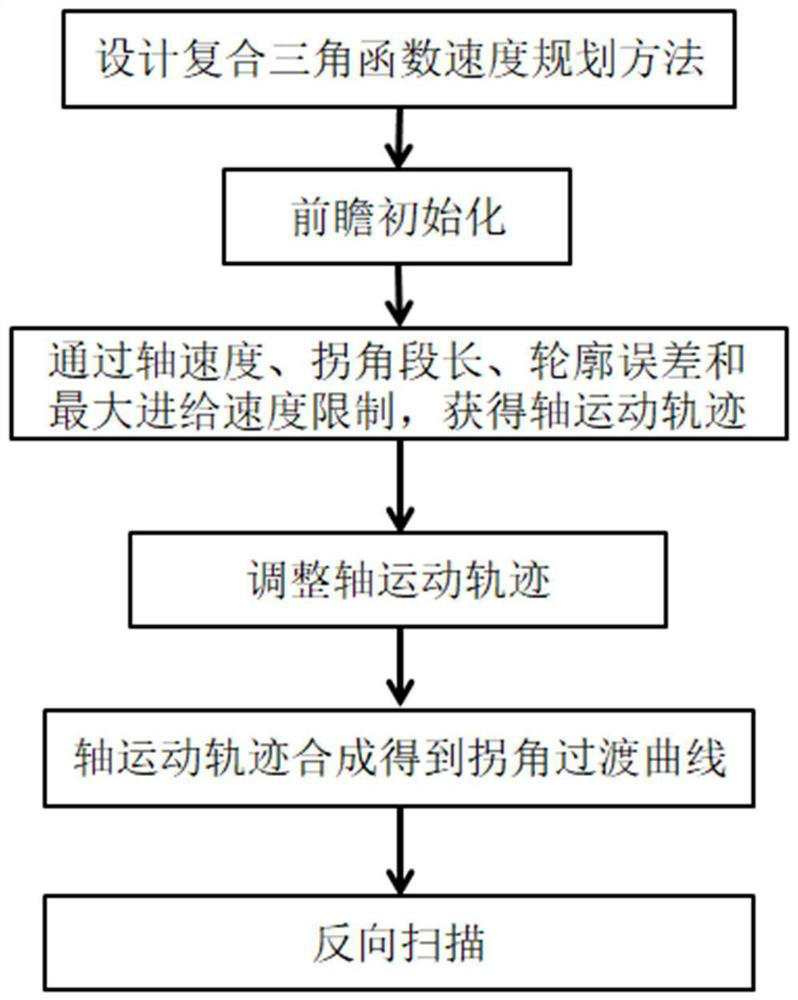
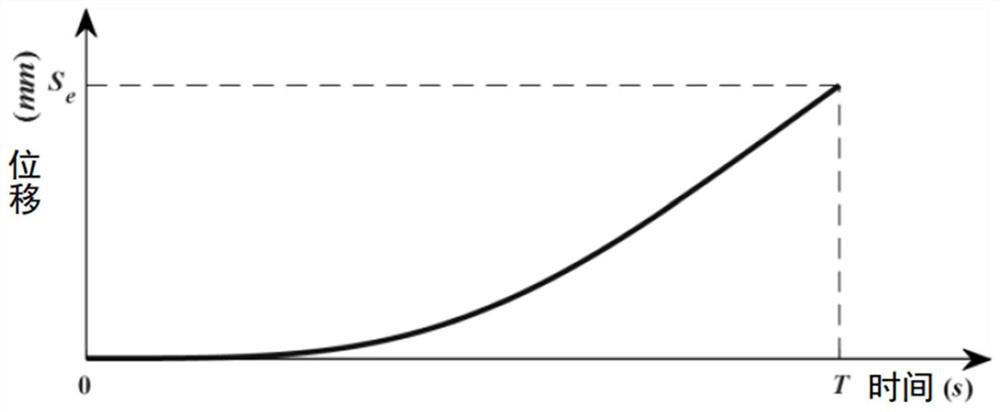
The invention discloses a corner transition smoothing method for smoothing axial jerk. The corner transition smoothing method comprises the following steps: designing a composite trigonometric function speed planning method; carrying out look-ahead initialization; constructing a corner transition curve, calculating axial kinematics trajectories on coordinate axes under axial speed limitation, corner section length limitation, contour error limitation, maximum feeding speed limitation and maximum axial acceleration limitation, and synthesizing the axial kinematics trajectories on the two coordinate axes to obtain the corner transition curve; and performing reverse scanning, and performing composite trigonometric function speed planning on all interpolation line segments forwards in sequencefrom the last small line segment. According to the method, a composite trigonometric function speed planning method is utilized, corner transition curve construction and uniaxial speed planning are completed at the same time within one step, the processing time consumed by motion trail control is remarkably shortened, smooth axial speed, axial acceleration and axial jerk control is achieved, andthe machining efficiency and the machining quality of the numerical control machine tool are improved.
Owner:NANJING INST OF TECH
Signal processing with look-ahead modulator noise quantization minimization
ActiveUS20050156766A1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionSignal processingComputer science
A signal processing system includes a look-ahead delta-sigma modulator that processes multiple output candidate vectors and an input vector to determine a quantization error vector for each output candidate vector. In one embodiment, the quantization error vector represents a difference between a cost value vector and an input candidate vector. Look-ahead delta-sigma modulator output values are selected using the quantization error vectors by, for example, determining the minimum power quantization error vector for each input vector X and selecting the output value from the input candidate vector associated with the minimum power quantization error vector. Quantization error vectors can also be weighted using a non-uniform weighting vector.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Continuous micro-line segment look-ahead control interpolation algorithm
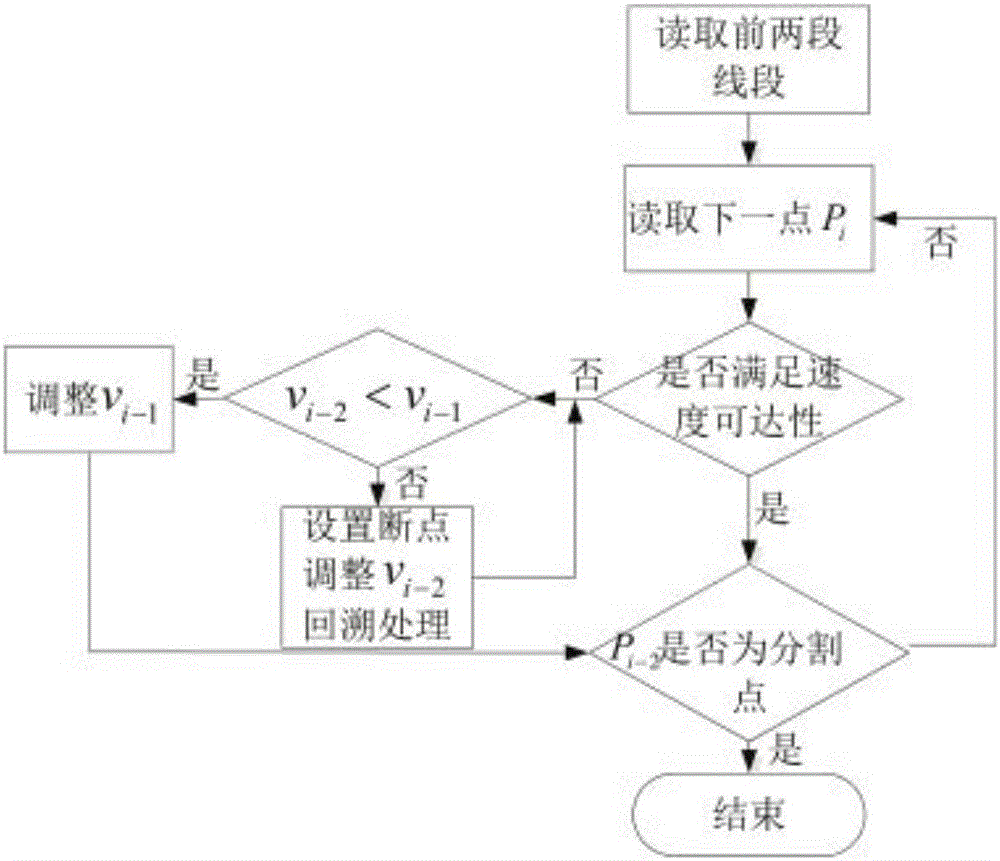
InactiveCN106802627AImprove work efficiencyImprove working precisionProgramme controlComputer controlReachabilityComputer science
The invention provides a continuous micro-line segment look-ahead control interpolation algorithm. The algorithm includes the following steps: calculating an actual interpolation distance s1 of a first micro-line segment; calculating an actual interpolation distance si-2 of a previous micro-line segment; through speed reachability determination of prospect optimization analysis, analyzing speed reachability between corresponding switch speeds of two ends (Pi-2 and Pi-1) of a (i-2) line segment; determining a speed segmenting point: if [alpha]i-3<[alpha]i-2 and [alpha]i-2=[alpha]i-1, needing to calculate the switch angle of the next point and conducting analysis, and if [alpha]i-2<[alpha]i-3, indicating that Pi-2 is not the speed segmenting point; if the speed segmenting point is not found, repeating the above 2-4 steps, and if the speed segmenting point is found, ending the look-ahead, and carrying out a look-ahead speed plan with the previous speed segmenting point being a starting point during the next look-ahead. According to the invention, the machining speed changes steadily, and the machining efficiency is greatly increased.
Owner:苏州达尔普工业控制有限公司
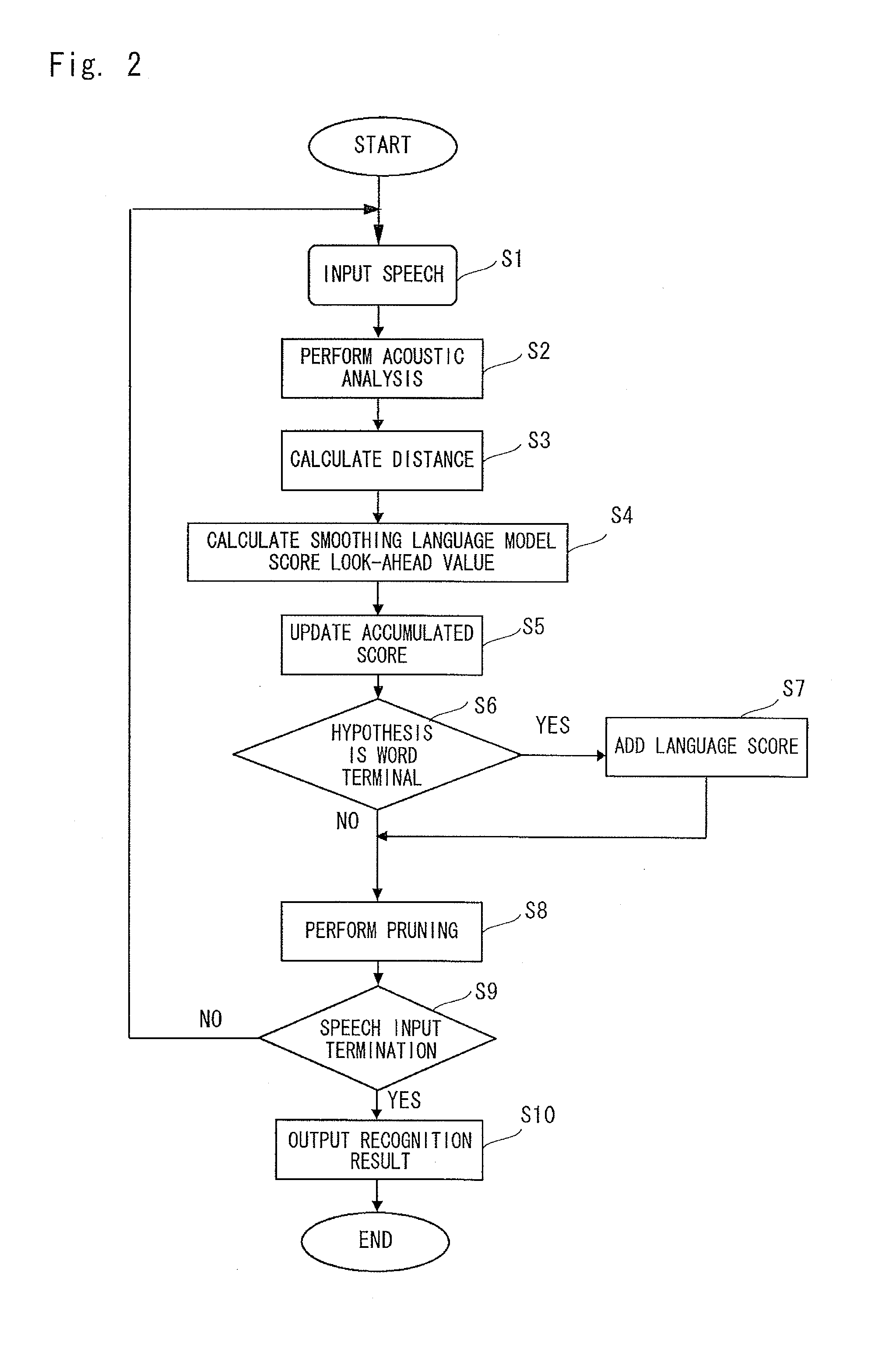
Language model score look-ahead value imparting device, language model score look-ahead value imparting method, and program storage medium
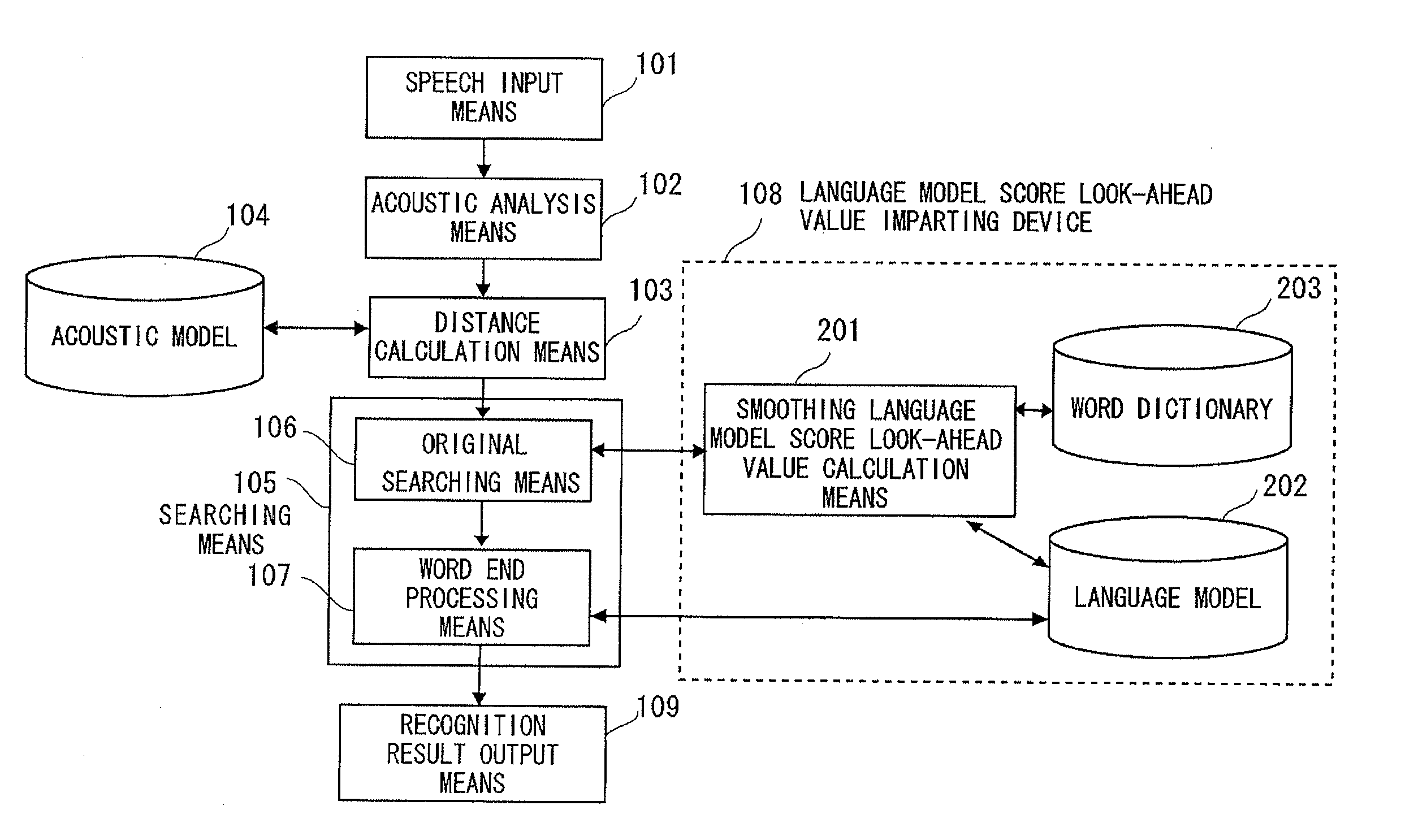
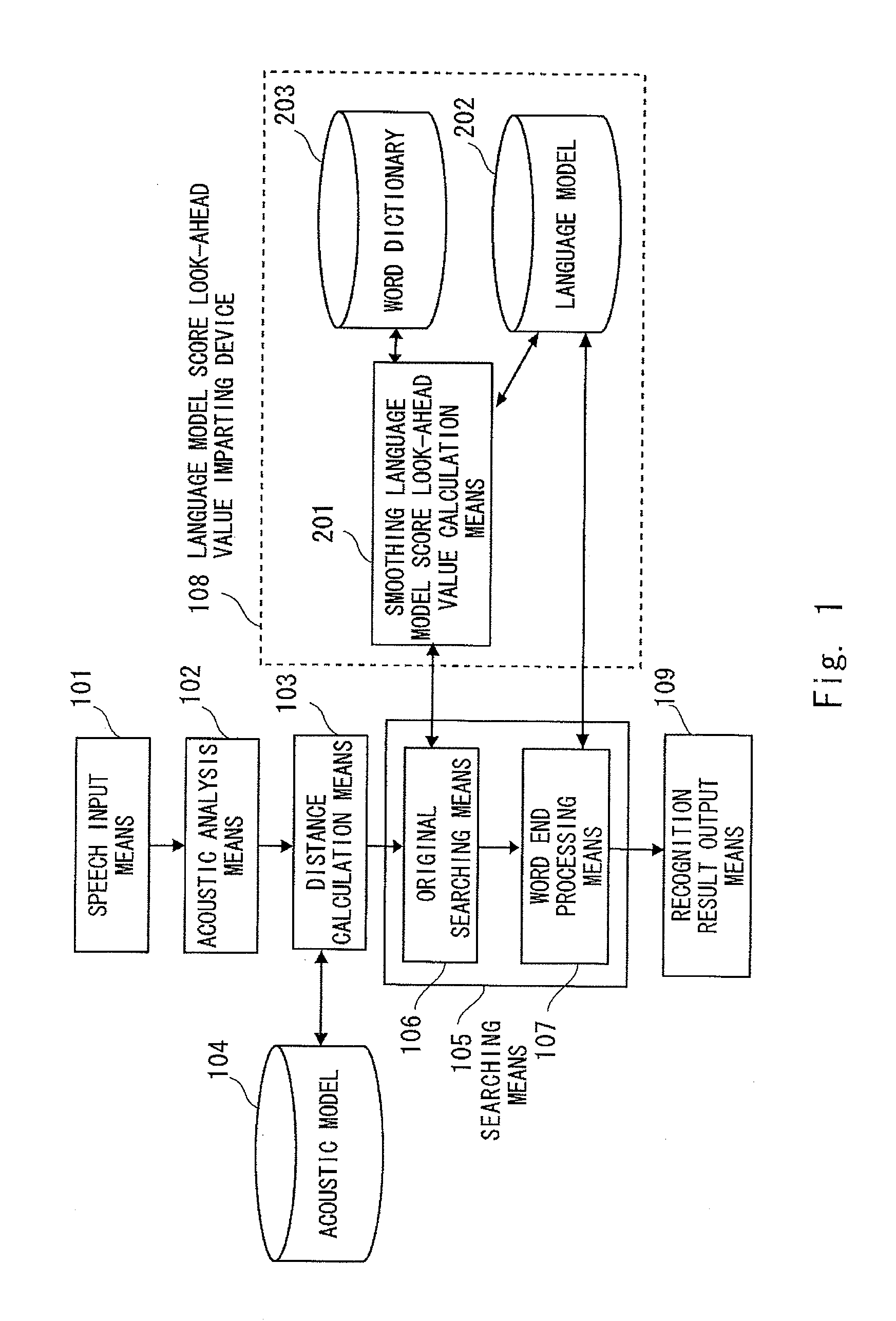
InactiveUS20110191100A1Increase the number ofAvoid concentrationSpeech recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsNatural language processingBeam search
A speech recognition apparatus that performs frame synchronous beam search by using a language model score look-ahead value prevents the pruning of a correct answer hypothesis while suppressing an increase in the number of hypotheses. A language model score look-ahead value imparting device 108 is provided with a word dictionary 203 that defines a phoneme string of a word, a language model 202 that imparts a score of appearance easiness of a word, and a smoothing language model score look-ahead value calculation means 201. The smoothing language model score look-ahead value calculation means 201 obtains a language model score look-ahead value at each phoneme in the word from the phoneme string of the word defined by the word dictionary 203 and the language model score defined by the language model 202 so that the language model score look-ahead values are prevented from concentrating on the beginning of the word.
Owner:NEC CORP
Low-latency architectures for high-throughput Viterbi decoders
InactiveUS7308640B2Lower latencyImprove throughputTelevision system detailsData representation error detection/correctionPrecomputationLatency (engineering)
Digital circuits and methods for designing digital circuits are presented. More particularly, the present invention relates to error correction circuits and methods in communications and other systems. In the present invention, a novel K-nested layered look-ahead method and its corresponding architecture, which combine K-trellis steps into one trellis step (where K is the encoder constraint length), are proposed for implementing low-latency high-throughput rate Viterbi decoder circuits. The main idea of the present invention involves combining K-trellis steps as a pipeline structure and then combining the resulting look-ahead branch metrics as a tree structure in a layered manner to decrease the ACS precomputation latency of look-ahead Viterbi decoder circuits. The proposed method guarantees parallel paths between any two trellis states in the look-ahead trellises and distributes the add-compare-select (ACS) computations to all trellis layers. It leads to regular and simple architecture for the Viterbi decoding algorithm. The look-ahead ACS computation latency of the proposed method increases logarithmically with respect to the look-ahead step (M) divided by the encoder constraint length (K) as opposed to linearly as in prior work. The main advantage of this invention is that it has the least latency among all known look-ahead Viterbi decoder circuits for a given level of parallelism.
Owner:PARHI KESHAB K
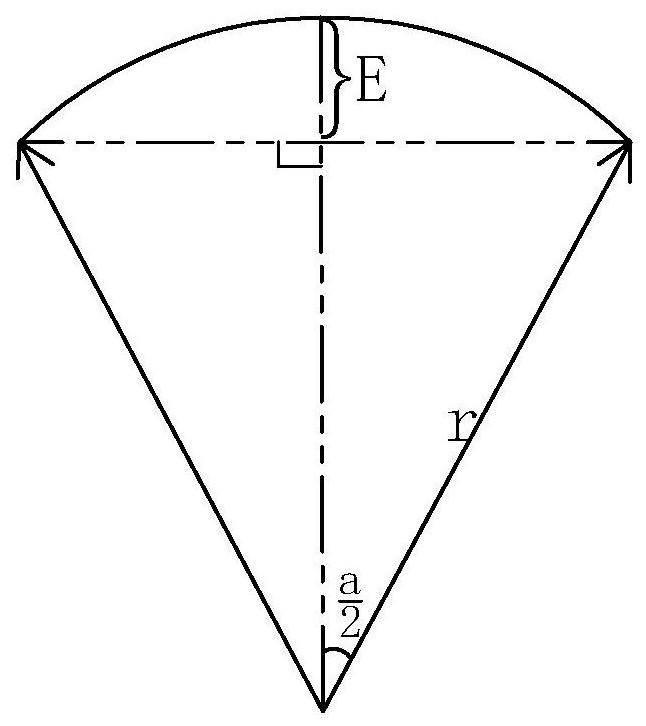
Multi-cycle optimal corner interpolation method based on straight line segments and arc paths
The invention relates to a multi-cycle optimal corner interpolation method based on straight line segments and arc paths. The method comprises the following operation steps: (1) discretizing arcs in amachining path into straight line segments based on a specified processing error E; (2) determining corner transition time, corner speed, corner distance and corner acceleration a of each corner according to the maximum acceleration of each driving shaft of a numerical control machine tool, the corner machining precision, the geometrical parameters of the corner of the machining path and the optimization target of realizing the maximum sum of the speed before the corner and the speed after the corner; and (3) carrying out look-ahead processing: adjusting the optimal interpolation parameter ofeach corner to enable the machining speeds of the two ends of each straight line section meet the accessibility requirement. According to the method, the maximum acceleration capacity of each drivingshaft of the numerical control machine tool is fully utilized, the arcs in the machining path are dispersed into the straight line sections meeting the error requirement, the change in the speed direction at the corners is transited by adopting a plurality of interpolation periods, and a more efficient look-ahead processing method is adopted, so that the machining speed of a product is greatly increased.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Redundant mechanical arm real-time look-ahead trajectory planning method based on NURBS curve interpolation algorithm
PendingCN114131612AInterpolation speed increasedDoes not change the end interpolation speed directionProgramme-controlled manipulatorTotal factory controlTrajectory planningControl theory
The invention discloses a redundant mechanical arm real-time look-ahead trajectory planning method based on an NURBS curve interpolation algorithm, and relates to the field of redundant mechanical arm application. According to the method, a tail end planning interpolation speed is obtained by giving a tail end target path point of the mechanical arm, constructing an NURBS parameter curve as a tail end expected path and adopting an acceleration and deceleration control algorithm, mechanical arm tail end path errors caused by interpolation are considered in a Cartesian space, the interpolation speed is limited according to bow height errors, a look-ahead algorithm is introduced, and the end planning interpolation speed is obtained. The interpolation speed is scaled by considering the joint speed and acceleration constraint of the mechanical arm, meanwhile, prediction of a deceleration point is achieved, NURBS curve interpolation is achieved through a pre-estimation correction method to obtain a tail end expected track, joint variables are solved through inverse kinematics, and joint limiting is achieved through redundancy characteristics and a gradient projection method. Real-time trajectory planning meeting the kinematics constraint condition of the mechanical arm is achieved, and the tail end trajectory tracking precision is guaranteed on the premise that the physical limit of the mechanical arm is not exceeded.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
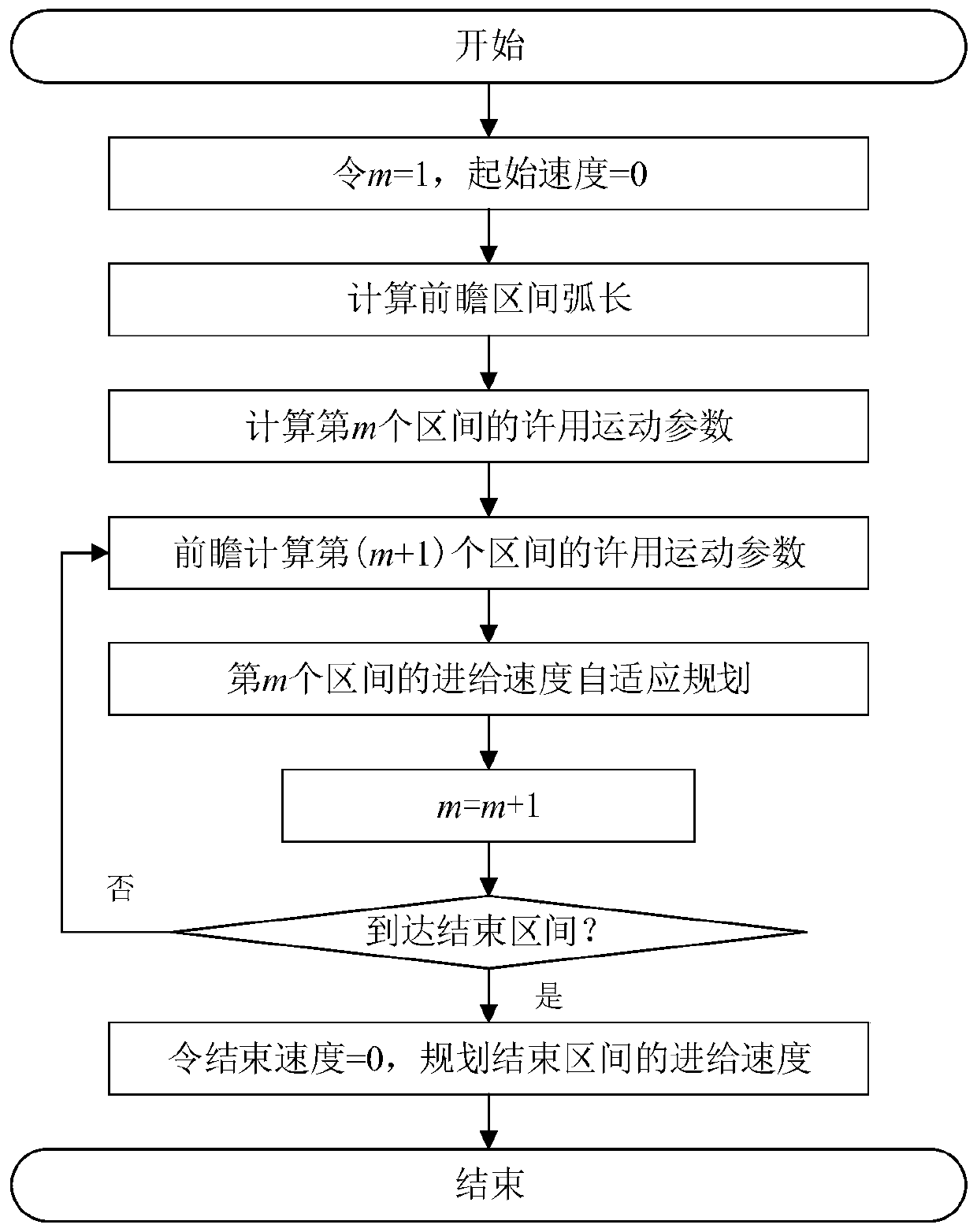
Interval adaptive planning method for five-axis machining feed speed
ActiveCN110989504ARealize forward planning by regionGet the most out of performanceNumerical controlNumerical controlControl engineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of robots and high-grade numerical control machine tools, and particularly relates to an interval adaptive planning method for five-axis machining feed speed. Based on application of a look-ahead window, the influence of the out-of-window curve morphology on the current interval feed speed planning is cut off; allowable feed parameters of a current interval and a look-ahead interval are calculated based on a differential principle; and the feed speed profile of the current interval is planned according to the allowable feed parameters of the previous interval, the current interval and the look-ahead interval, so that regional look-ahead planning of the overall feed speed of the long spline curve path is achieved. The calculation efficiency is high, and the machine tool performance can be fully utilized on the premise that feed shaft driving capacity constraints are met.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
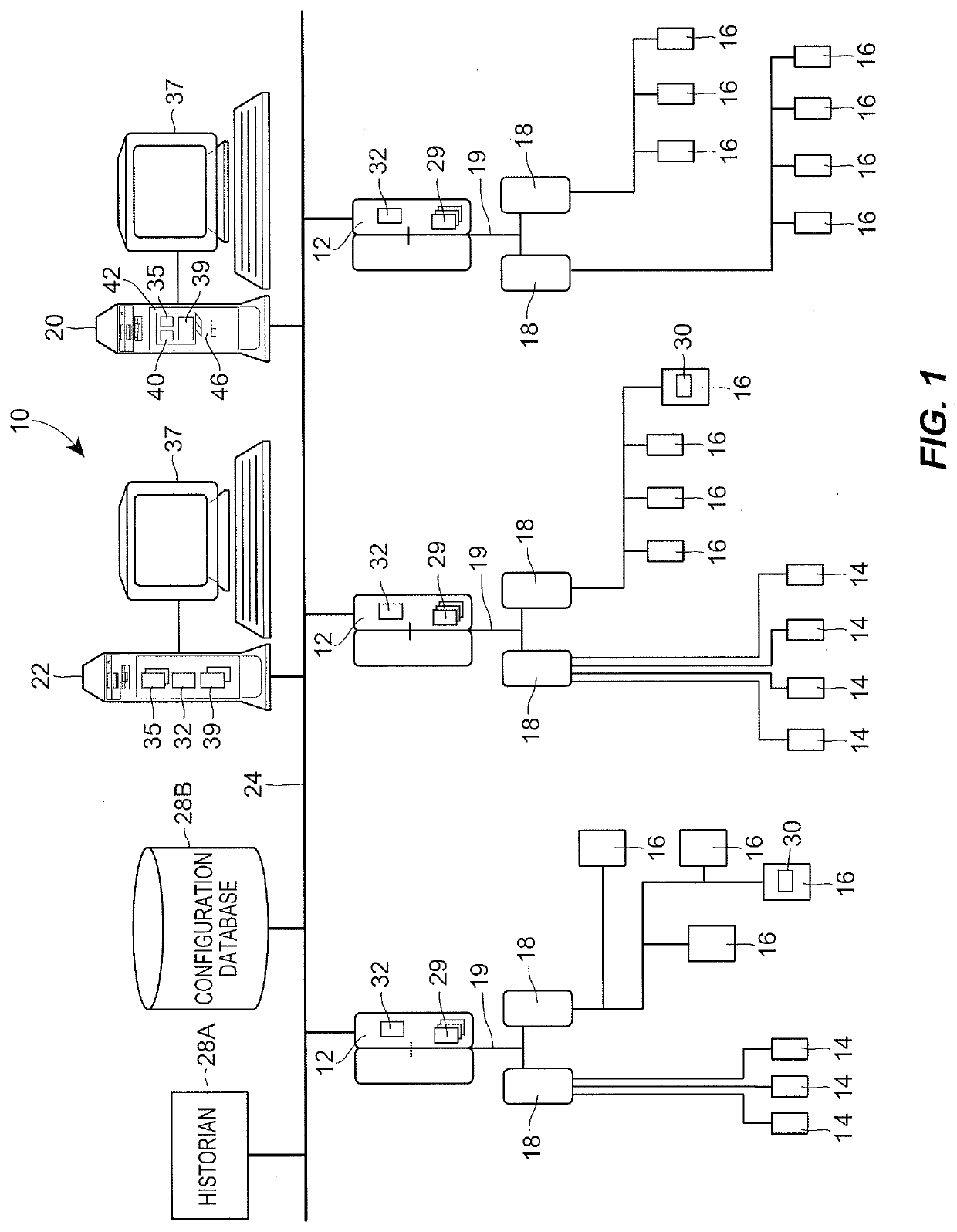
Real-Time Control Using Directed Predictive Simulation Within a Control System of a Process Plant
ActiveUS20210011466A1Improve the level ofLikelihood of of controlSimulator controlTesting/monitoring control systemsReal-time Control SystemTime control
A real-time control system includes a simulation system to implement a predictive, look-ahead function that provides an operator with information that enables a higher level of situational awareness of the expected transitional events of future steps within the control program or sequence logic. The simulation system enables future steps and transitions to be monitored before they actually occur, which enables the operator to recognize and potentially take action, in a current time step, to alleviate the underlying cause of the problem, thus reducing the likelihood of or preventing a sequence stall of the control program.
Owner:EMERSON PROCESS MANAGEMENT POWER & WATER SOLUTIONS
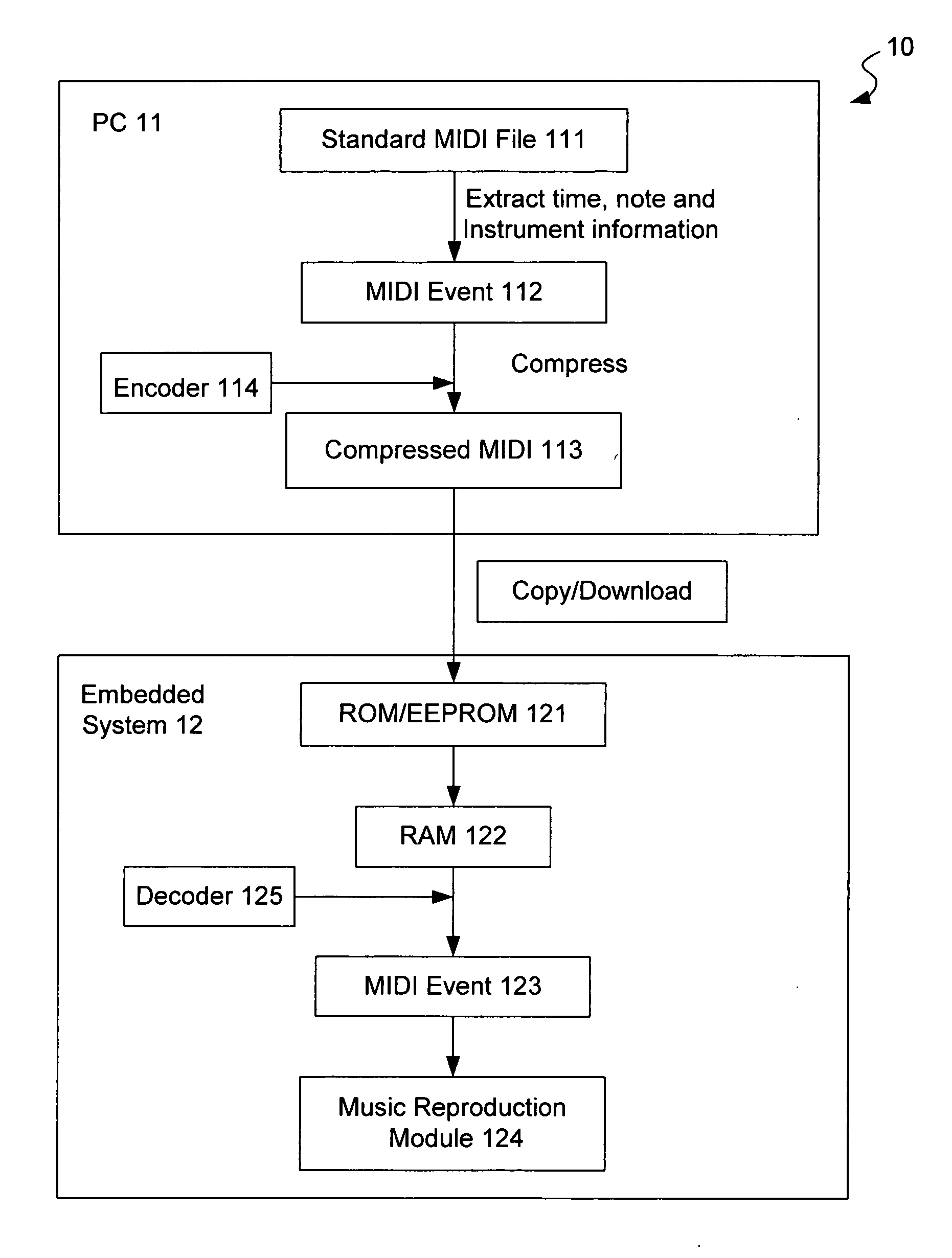
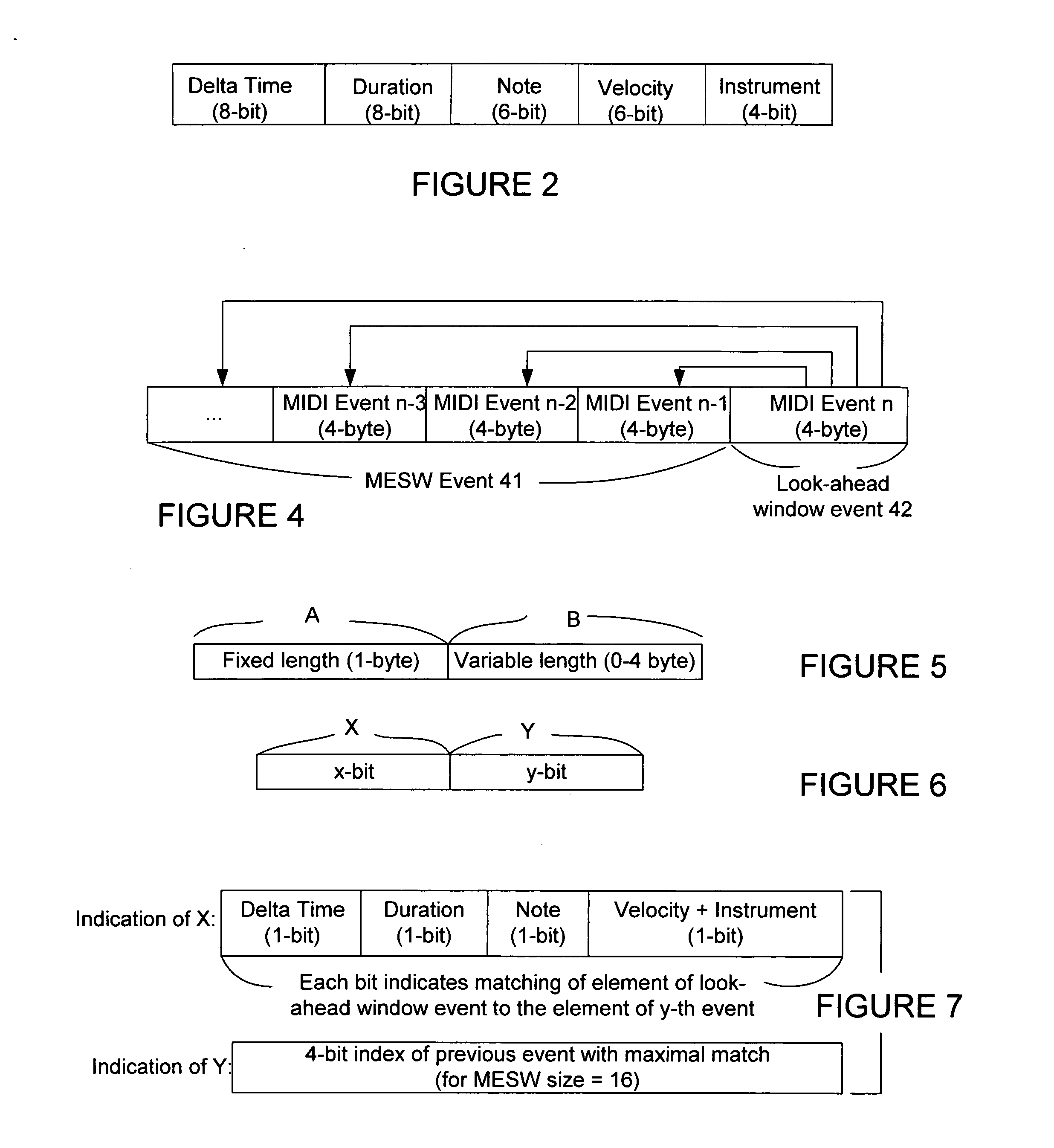
Method for fast compressing and decompressing music data and system for executing the same
MIDI compression and decompression methods that reduce the size of a standard MIDI file and maintains information to play the MIDI music. The exemplary method of the invention makes use of the high correlation and repetitions between a look-ahead MIDI event and previous set of MIDI events. An adjustable size Lempel-Ziv-like MIDI Event Search Window (MESW) is created during the compression and decompression process to allow searching of matched events or event elements in previous window size of MIDI events. Further reduction of the MIDI events can be made by discarding the matched events in the event search window. Therefore, with 4-bit of MIDI event search window, the number of MIDI events stored in the window can be more than 16.
Owner:VTECH TELECOMM
Method and apparatus for pipelined joint equalization and decoding for gigabit communications
InactiveUS20060020877A1Reduced state sequence estimationImprove throughputData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionGigabitPrecomputation
A method and apparatus for the implementation of reduced state sequence estimation is disclosed, with an increased throughput using precomputation (look-ahead), with only a linear increase in hardware complexity with respect to the look-ahead depth. The present invention limits the increase in hardware complexity by taking advantage of past decisions (or survivor symbols). The critical path of a conventional RSSE implementation is broken up into at least two smaller critical paths using pipeline registers. Various reduced state sequence estimation implementations are disclosed that employ one-step or multiple-step look-ahead techniques to process a signal received from a dispersive channel having a channel memory.
Owner:TAYCO PANELINK +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com