Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
72 results about "Linear stage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A linear stage or translation stage is a component of a precise motion system used to restrict an object to a single axis of motion. The term linear slide is often used interchangeably with "linear stage", though technically "linear slide" refers to a linear motion bearing, which is only a component of a linear stage. All linear stages consist of a platform and a base, joined by some form of guide or linear bearing in such a way that the platform is restricted to linear motion with respect to the base. In common usage, the term linear stage may or may not also include the mechanism by which the position of the platform is controlled relative to the base.
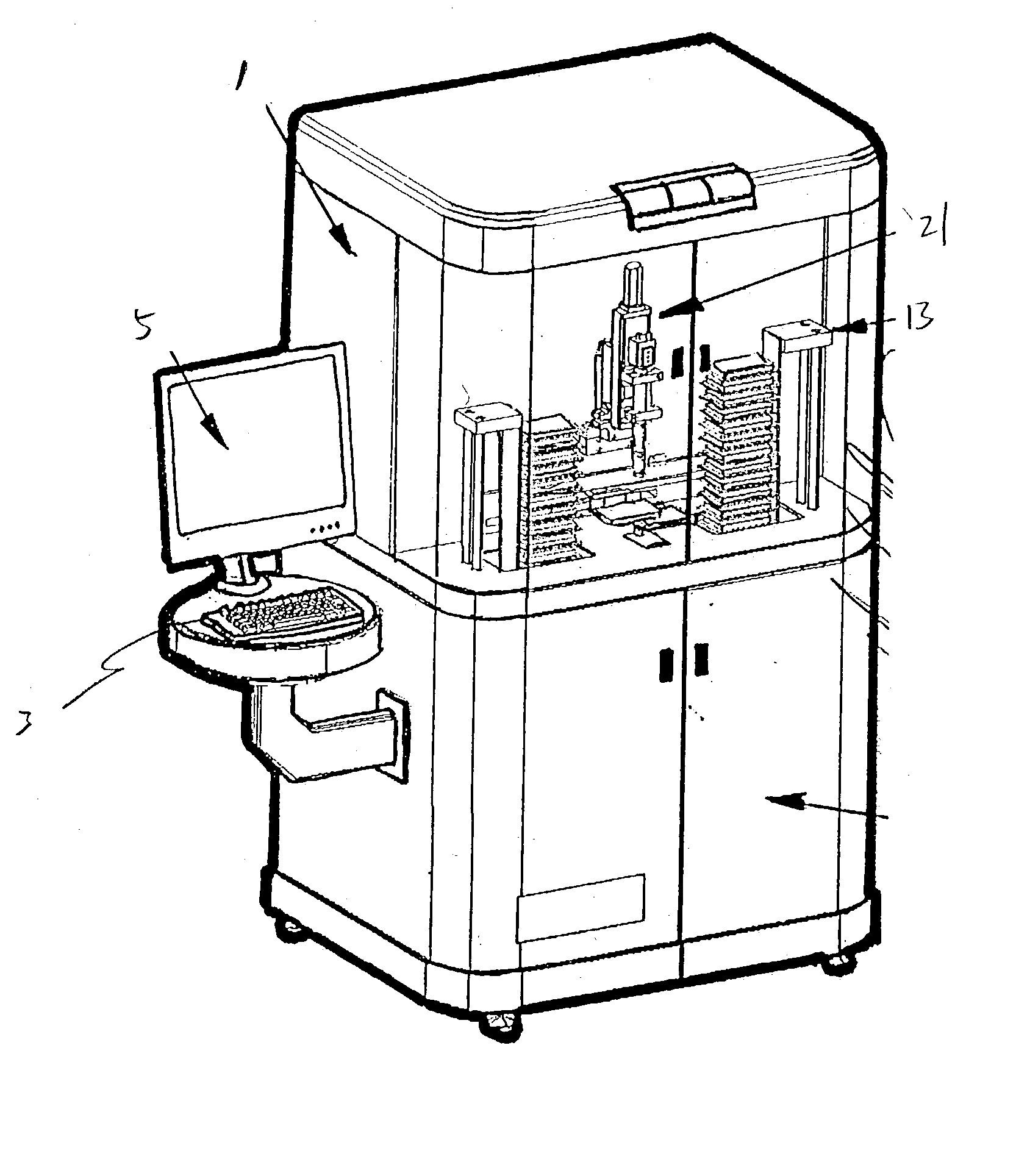
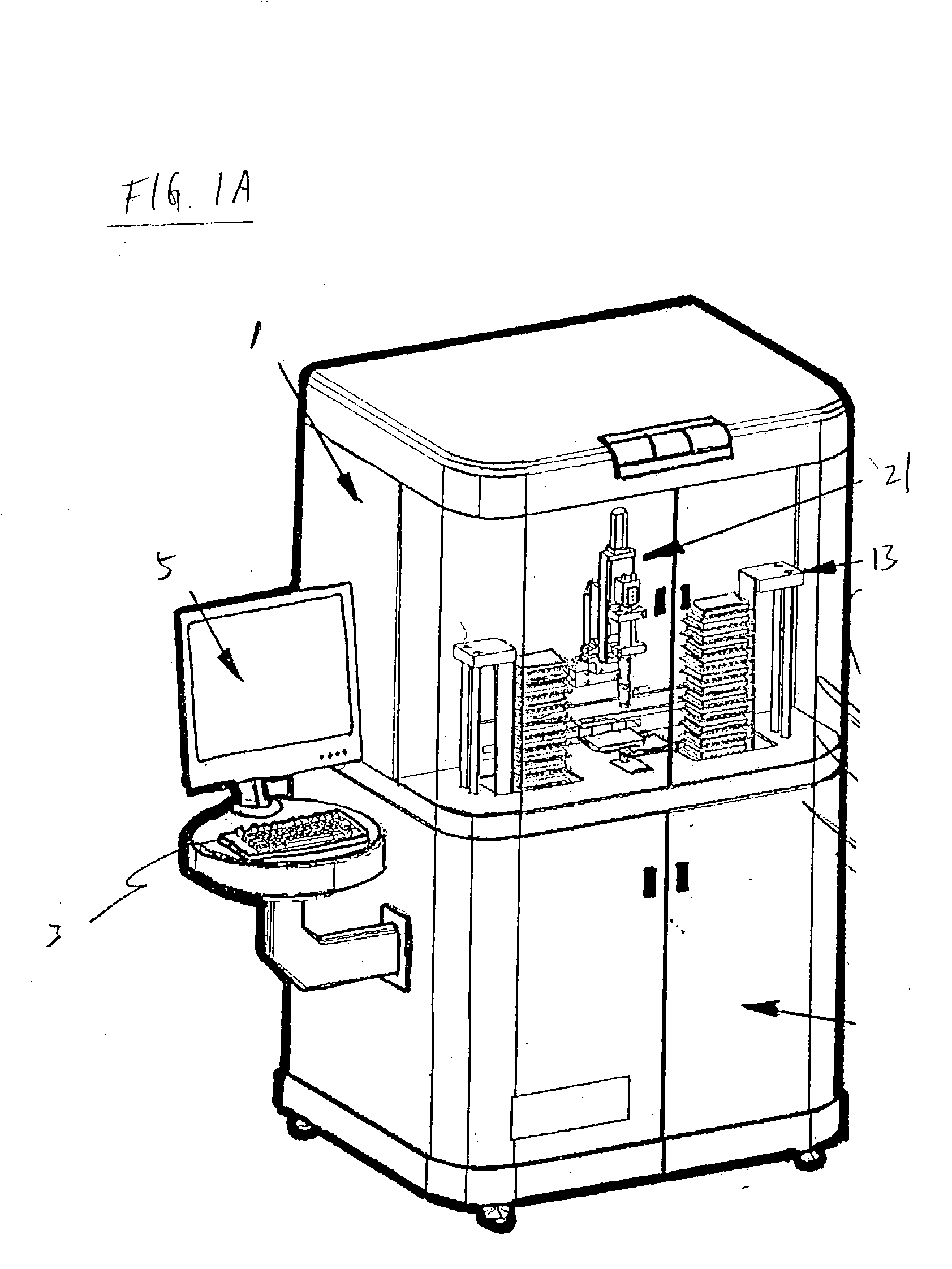
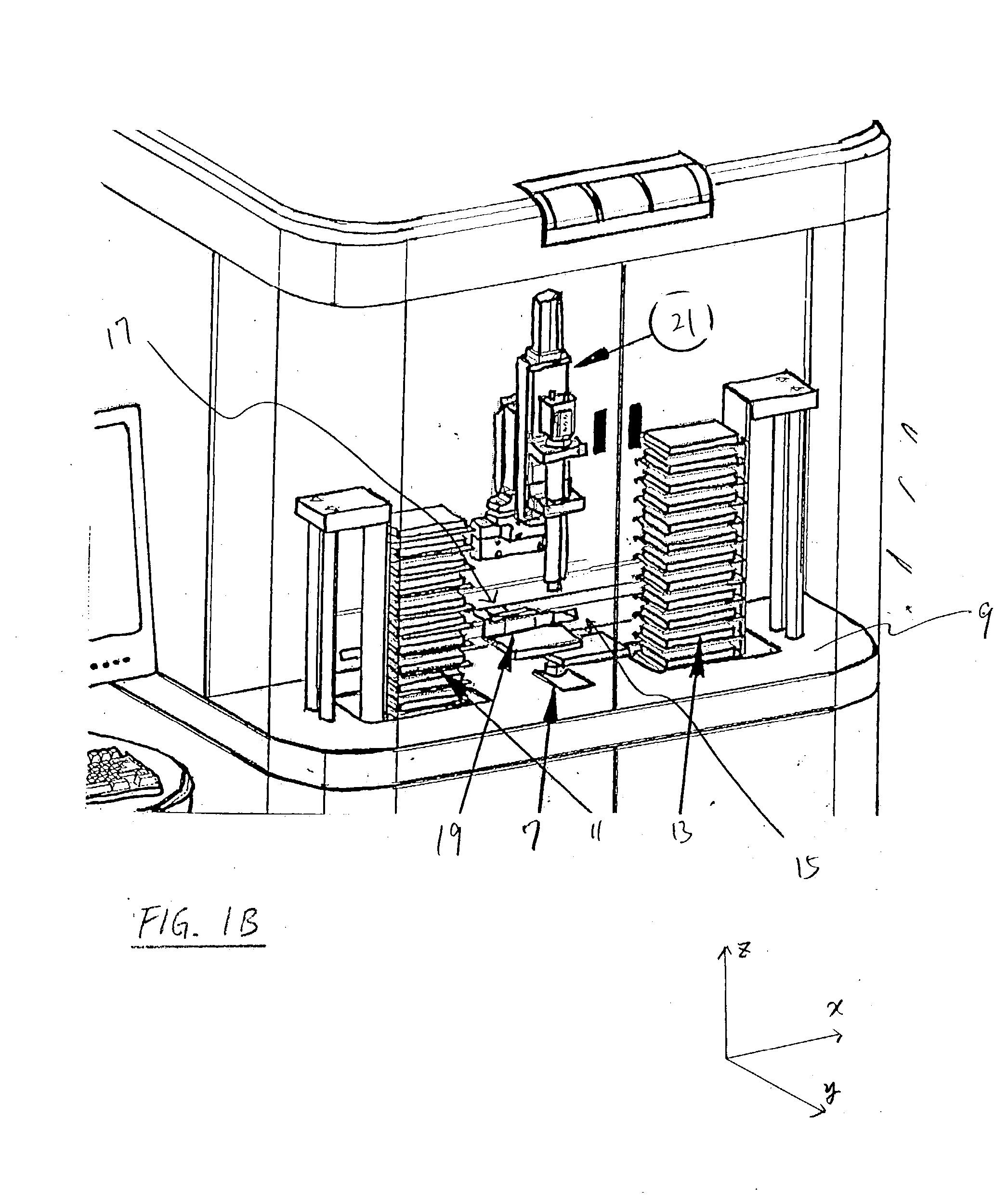
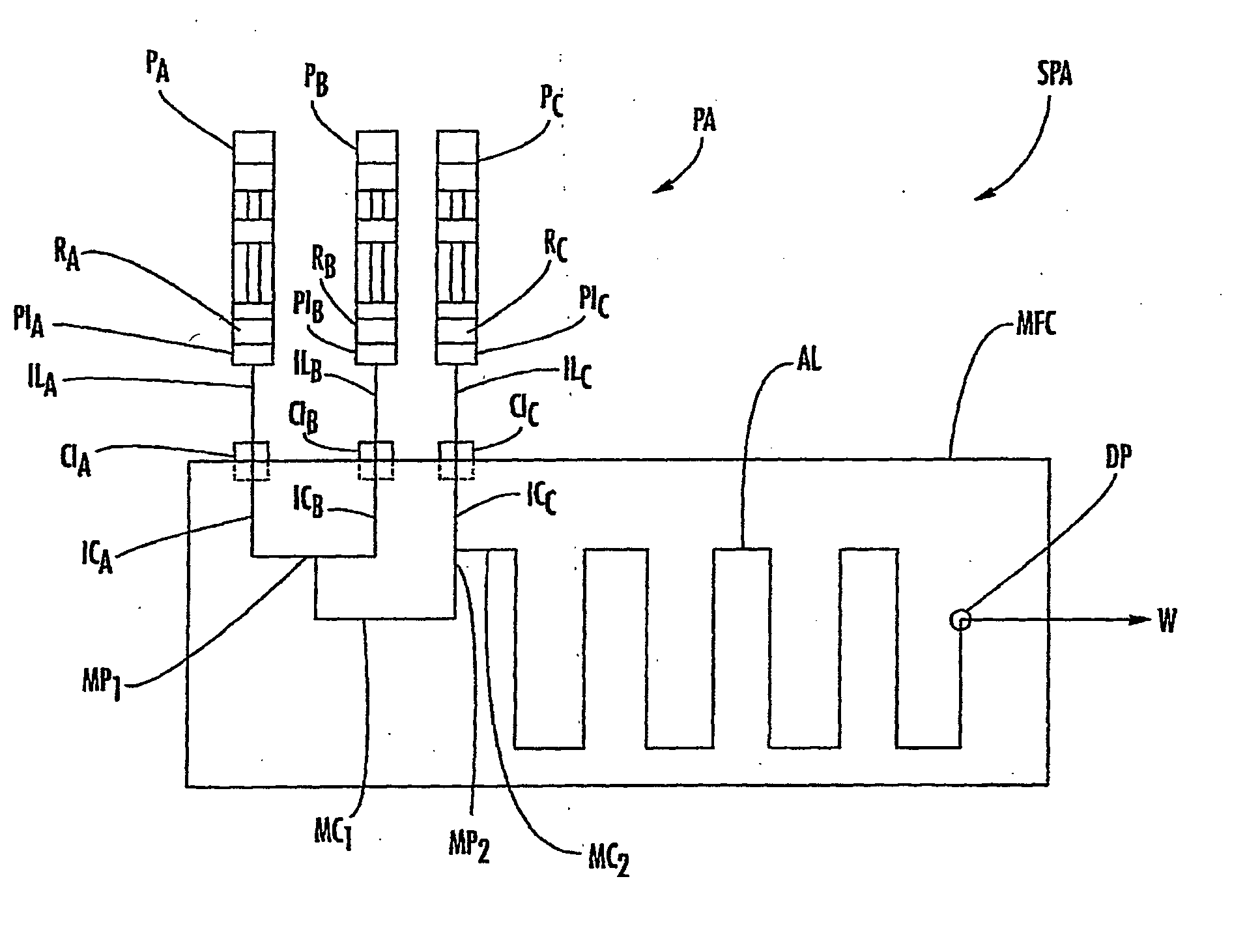
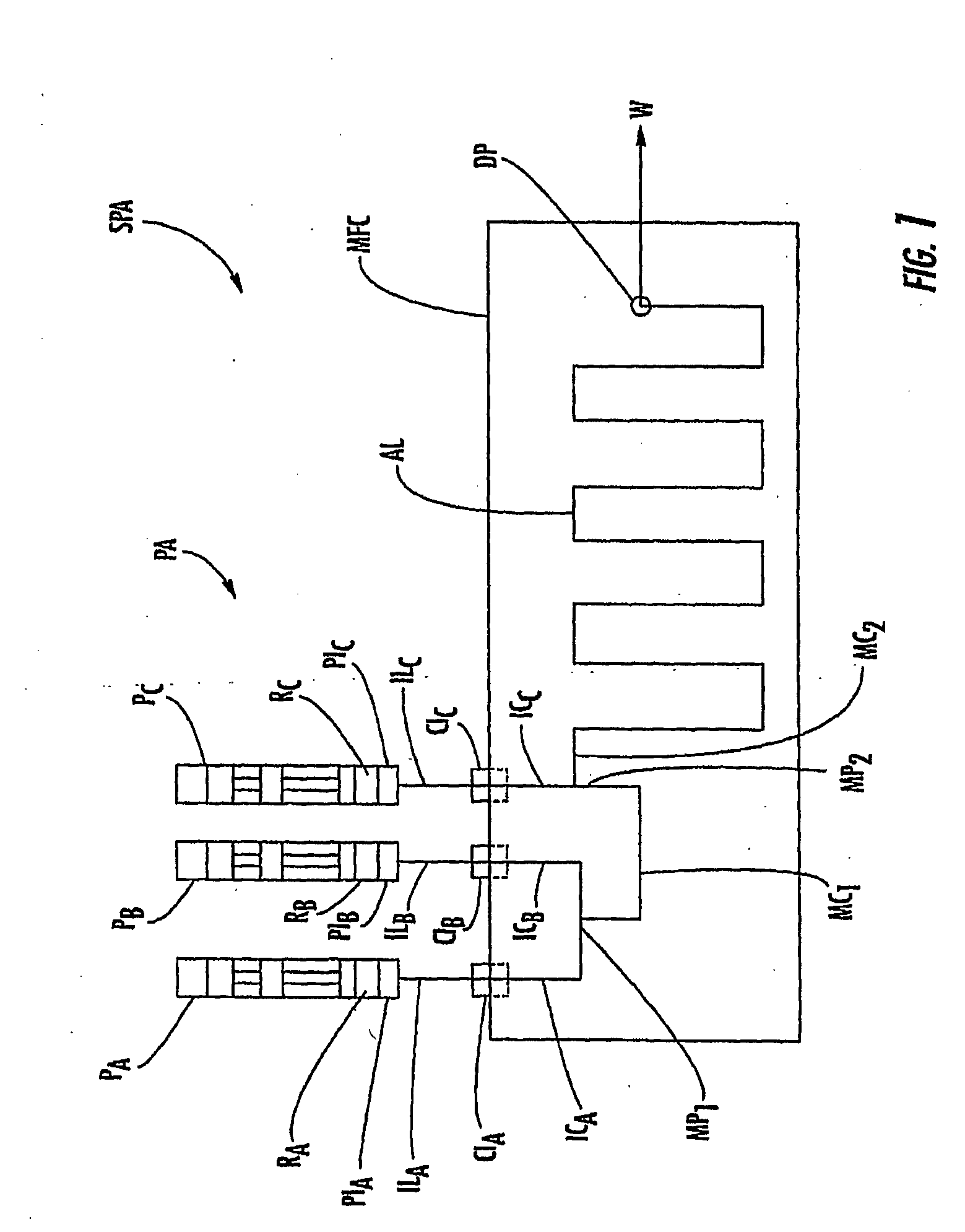
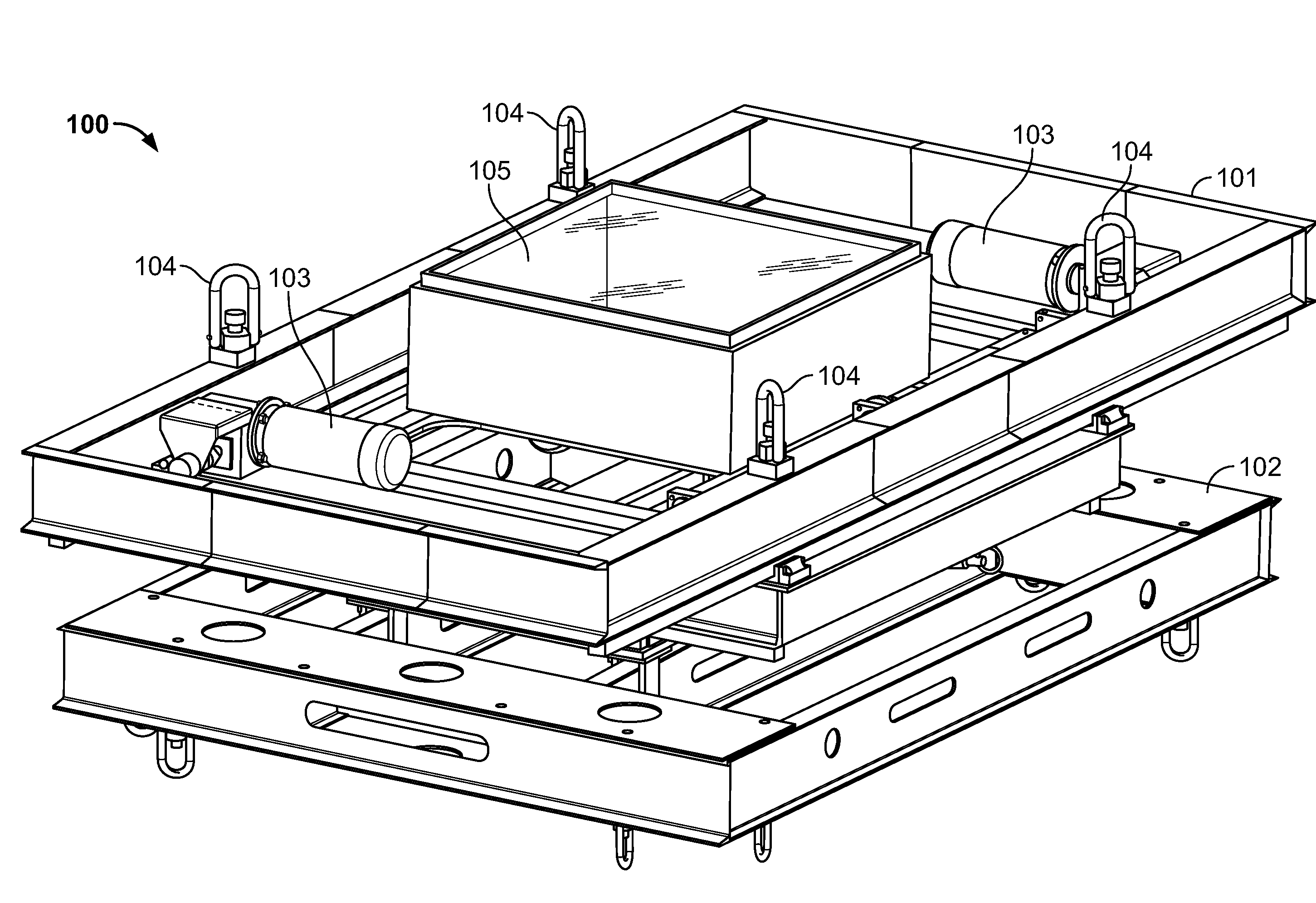
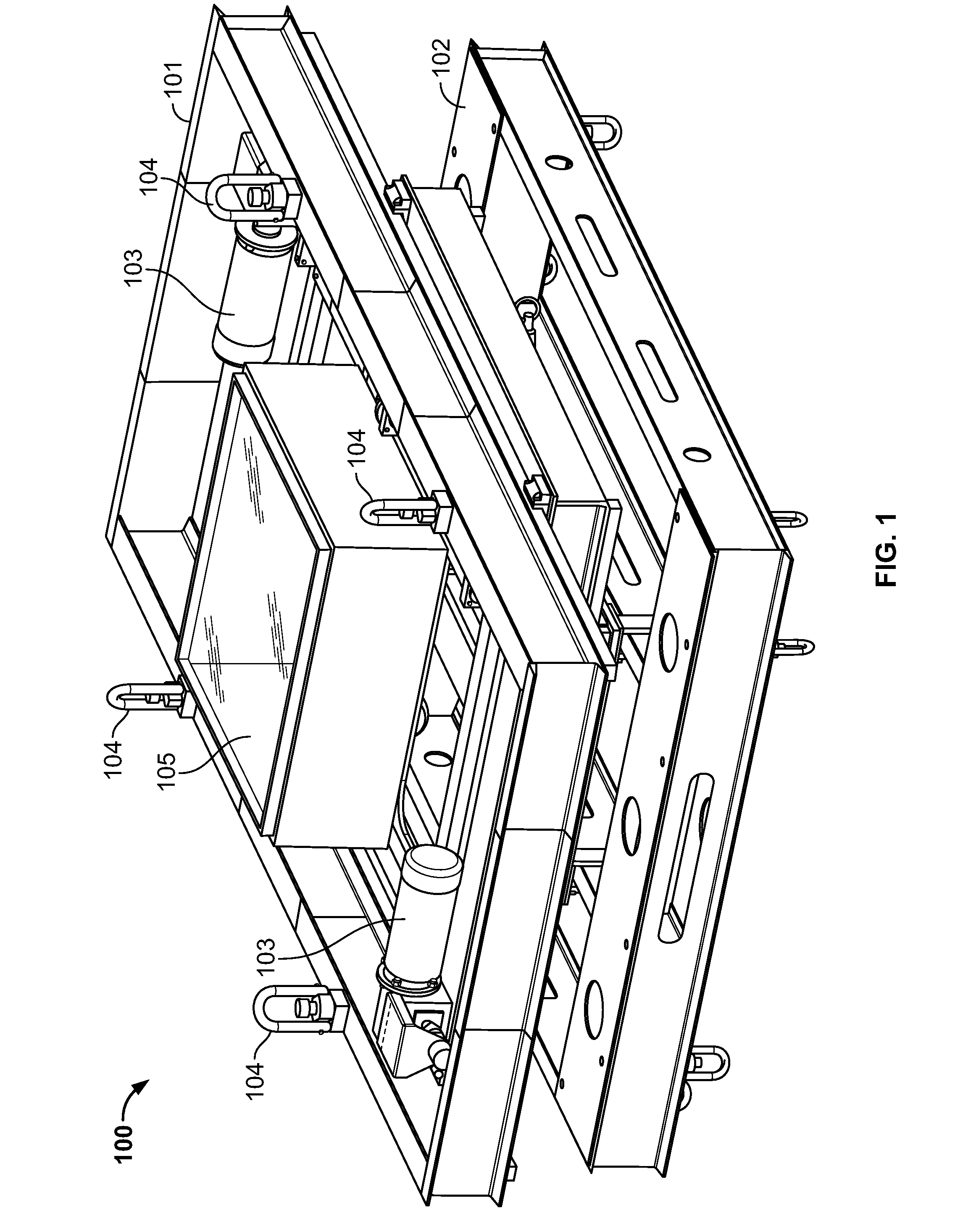
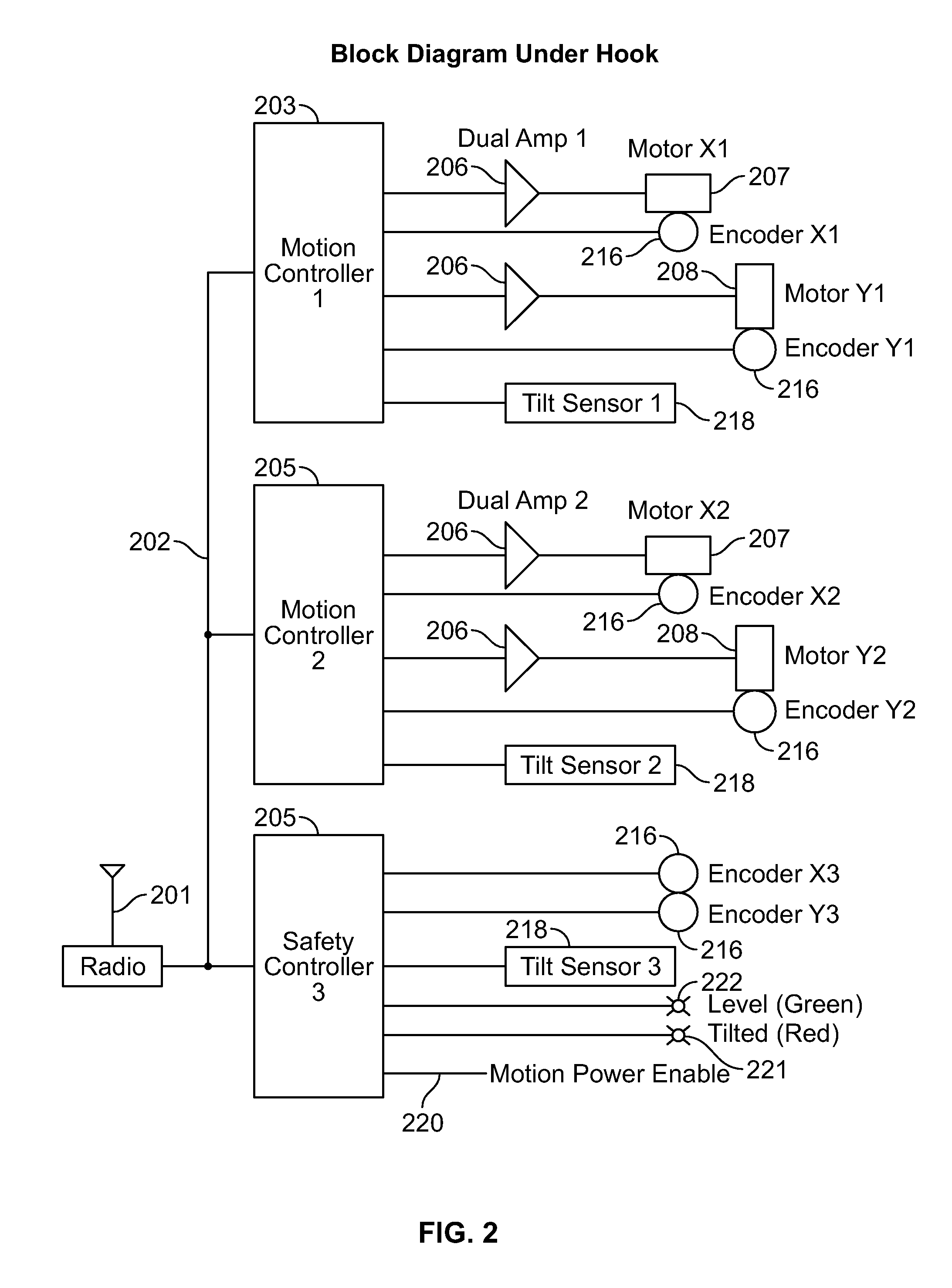
Apparatus for high-throughput non-contact liquid transfer and uses thereof
Disclosed is an apparatus for high-throughput non-contact liquid transfer. The high-throughput non-contact liquid transfer apparatus may be implemented for high-throughput biological, chemical and biochemical, synthesis and / or screening. In one variation, the apparatus comprise of an acoustic emitter, one or more X / Y linear stage with associated handling device, one or more storage queue, and an image detection system. The apparatus may be controlled by a centralized system controller with associated electronic and / or software. The apparatus may further be integrated within a frame with environment and safety enclosure. The system controller may control positioning of source vessel and target device relative to an acoustic emitter device. The system controller may also track the location of all the source well plates and target well plates, thus providing for user-defined association of any well on any source well plate with any well on any target well plate for liquid transfer.
Owner:EDC BIOSYST
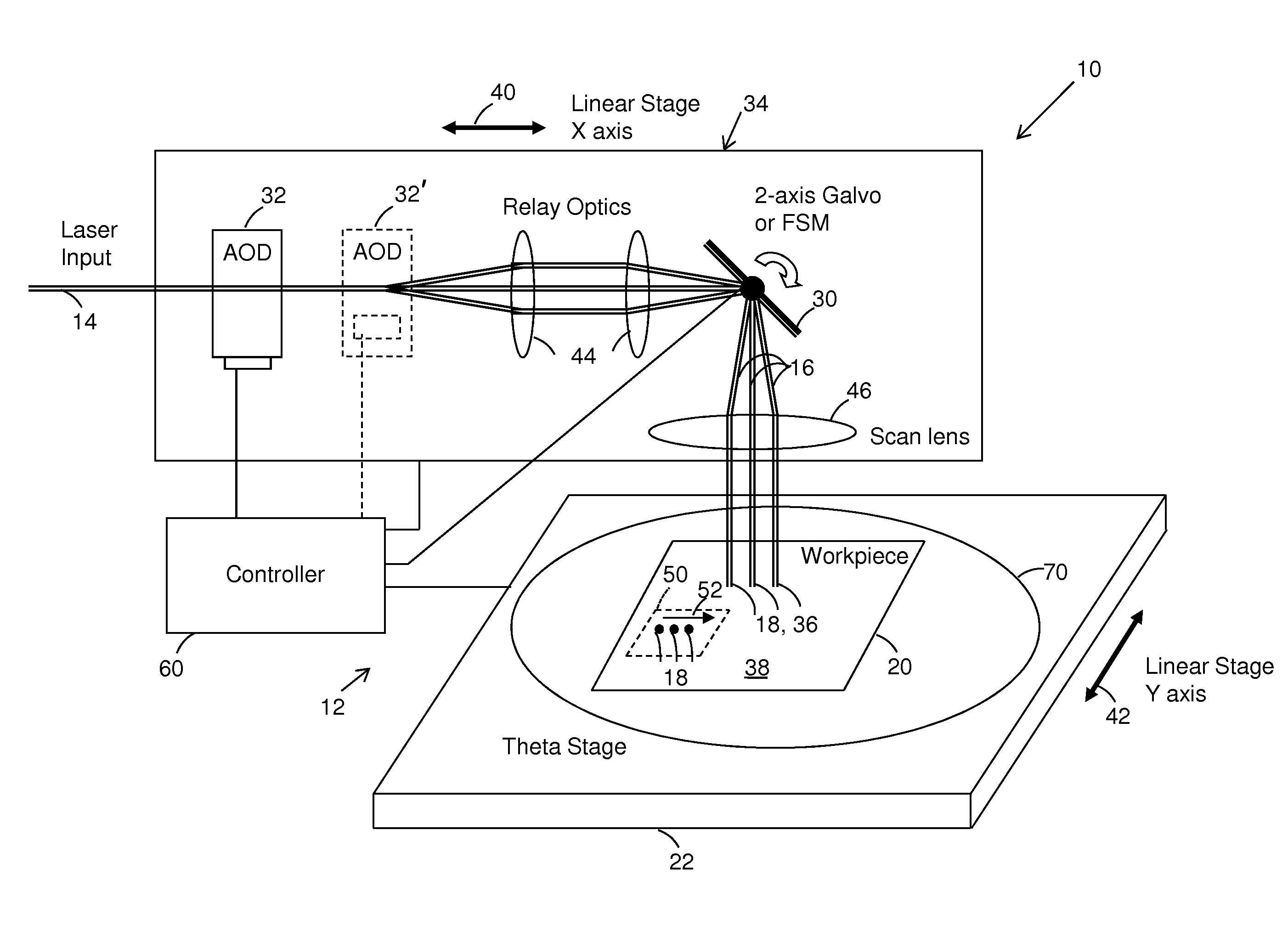
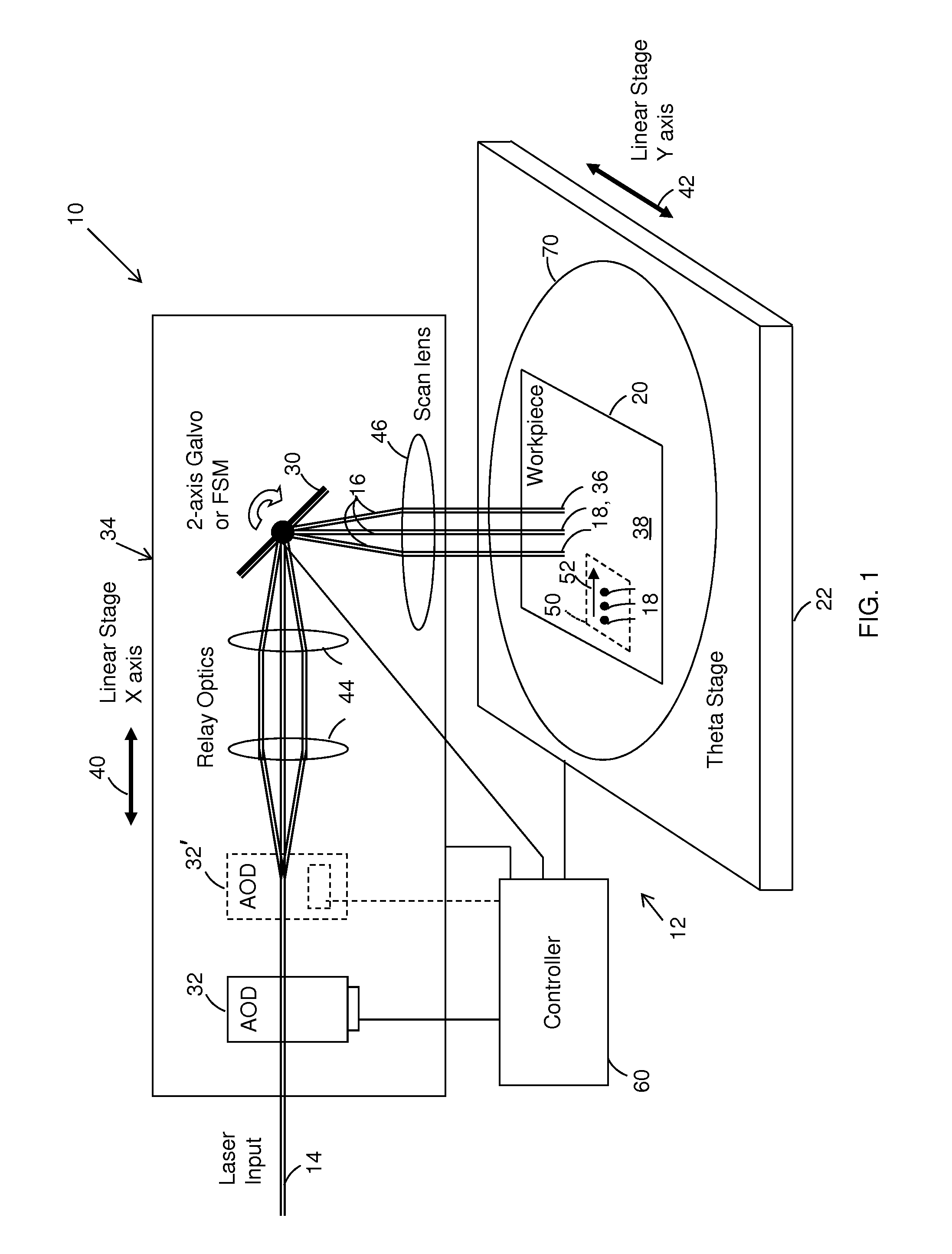
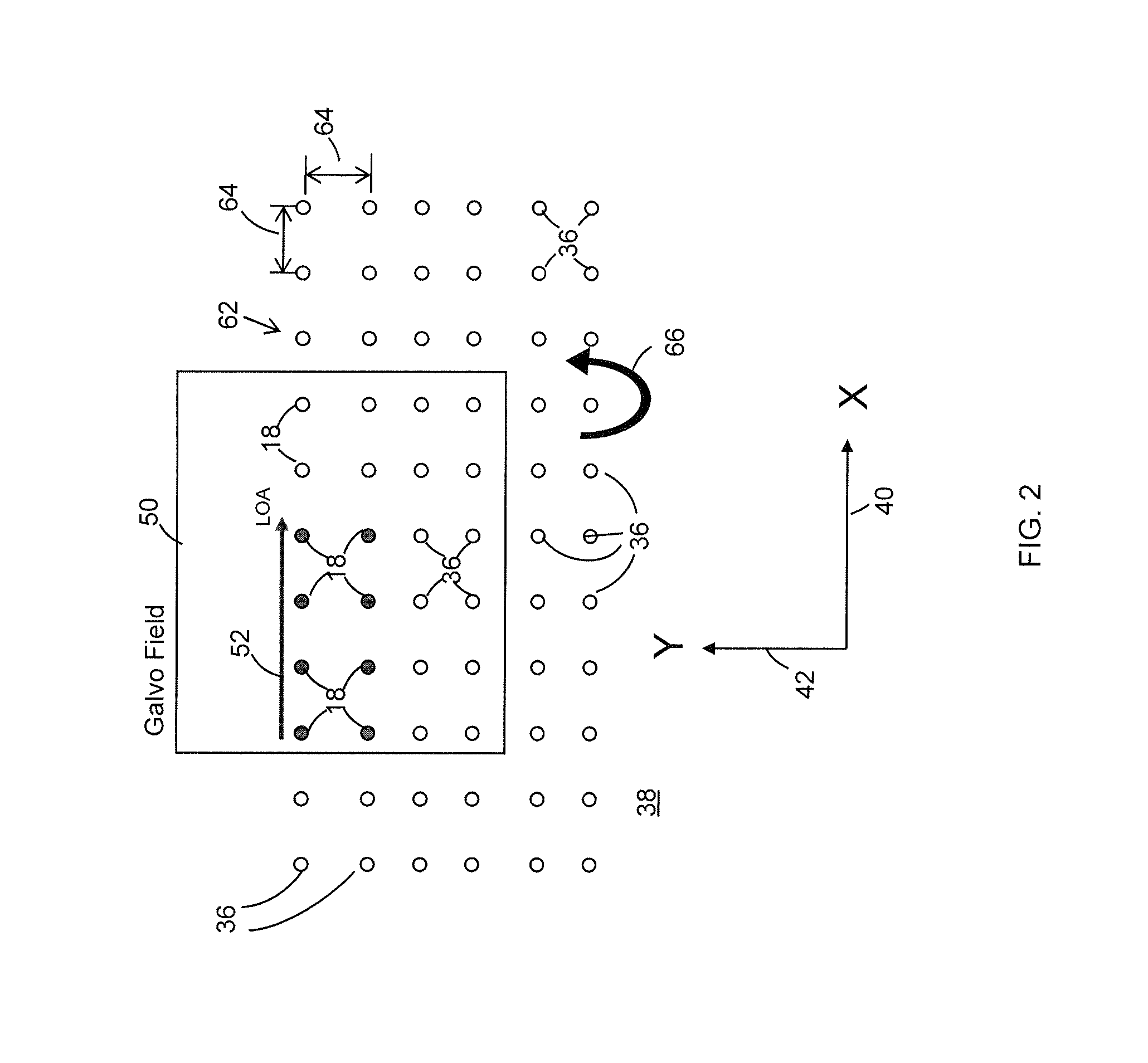
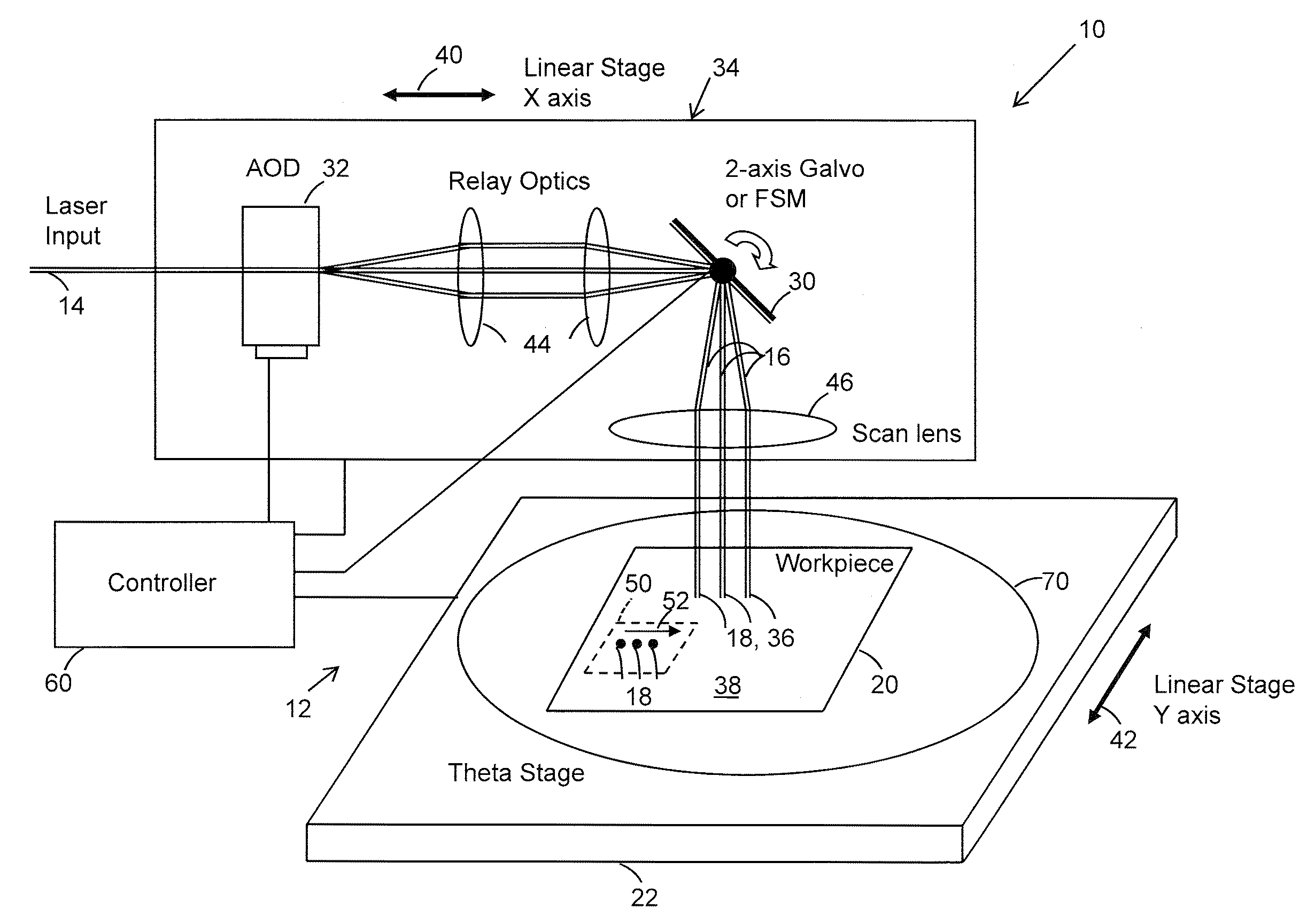
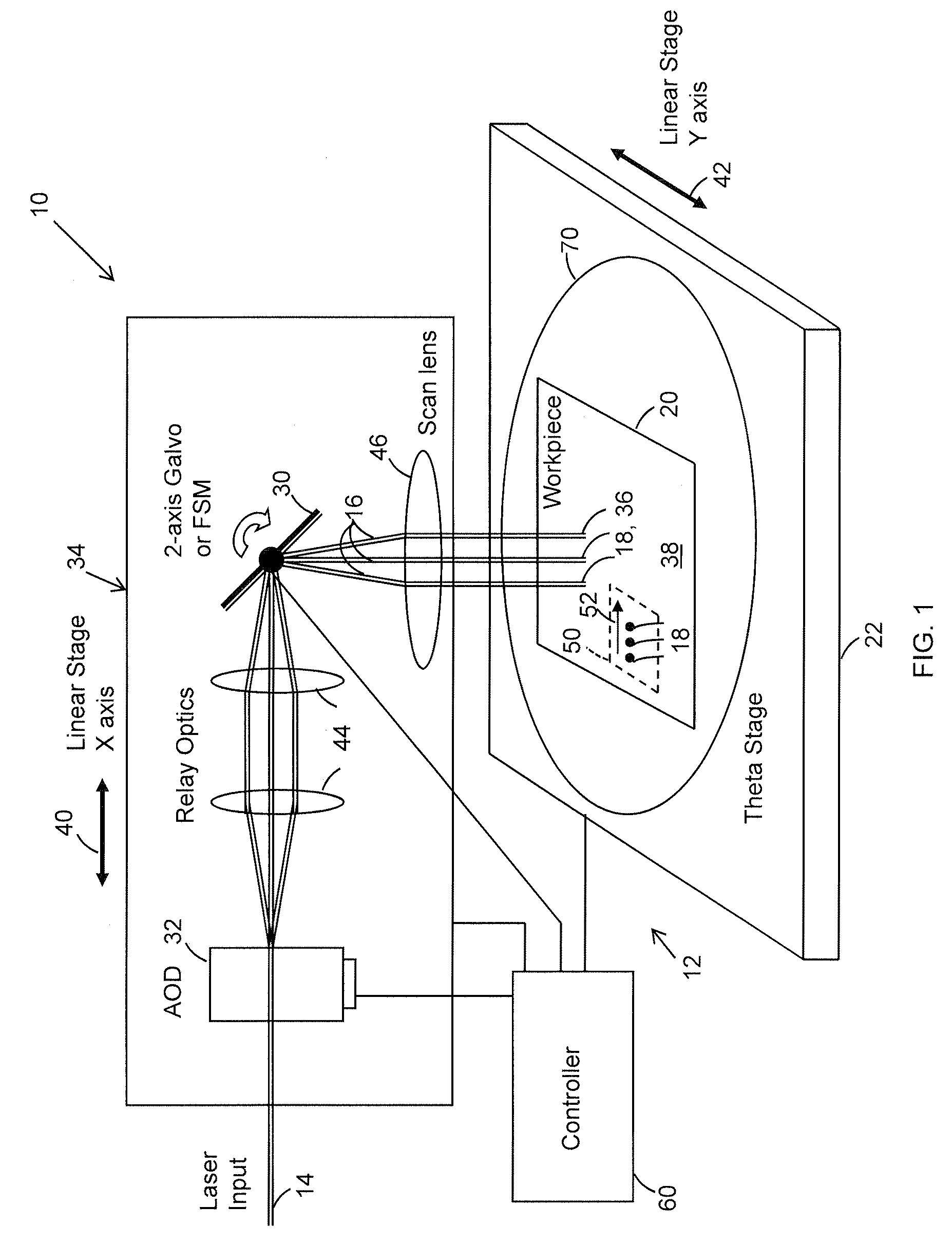
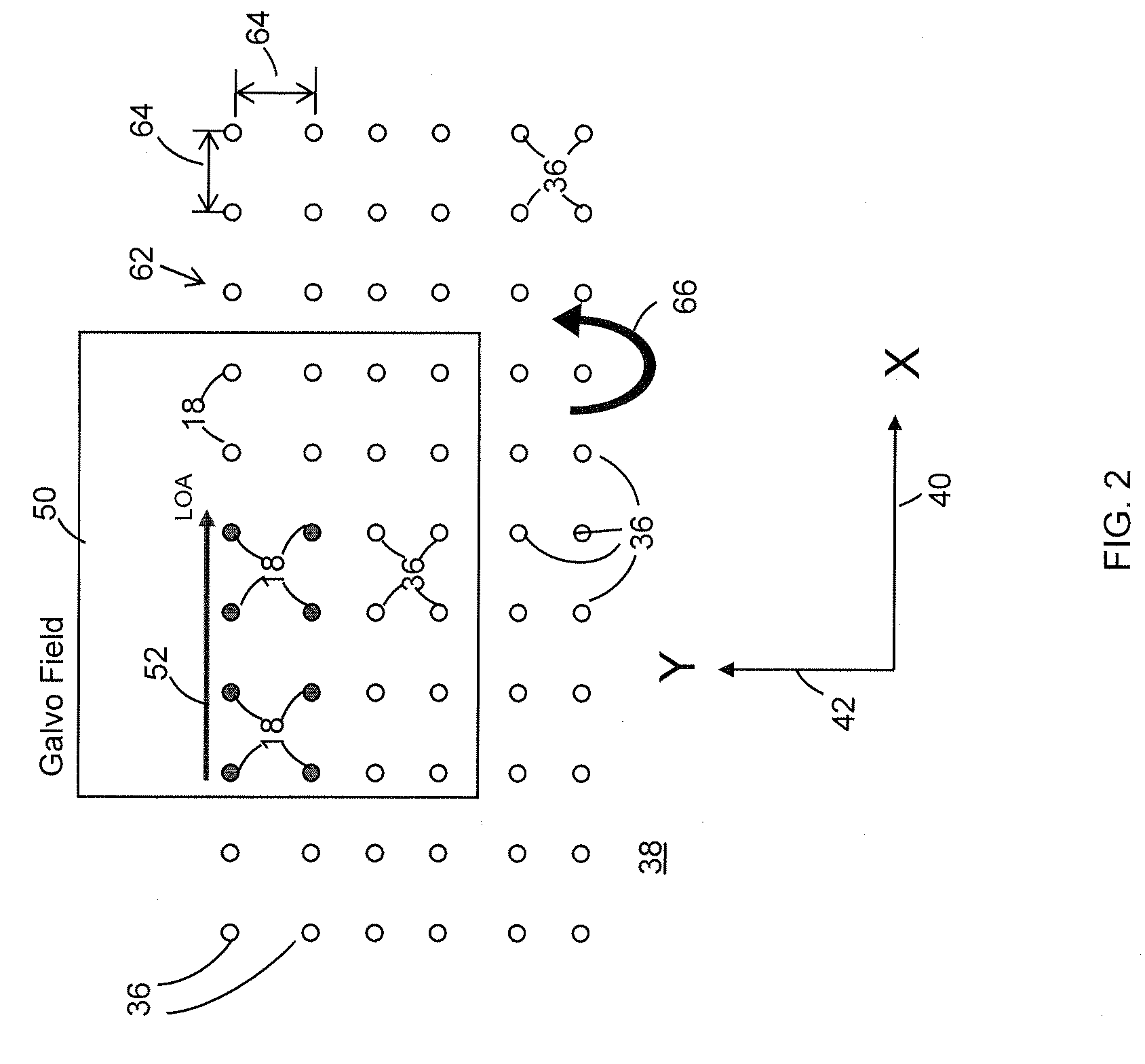
Controlling dynamic and thermal loads on laser beam positioning system to achieve high-throughput laser processing of workpiece features
ActiveUS8680430B2Minimizes inaccuracyMinimizes qualityWelding/soldering/cutting articlesPhotovoltaic energy generationLaser processingLight beam
A method of accomplishing high-throughput laser processing of workpiece features arranged in a densely spaced pattern minimizes workpiece feature processing inaccuracy and quality degradation that result from dynamic and thermal loads on laser beam positioning and optical components directing the laser beam during workpiece feature processing. A preferred embodiment is implemented with a laser beam positioning system composed of a zero-inertia optical deflector of an acousto-optic beam deflector (AOD) or an electro-optical deflector (EOD) type, a galvanometer head, and a linear stage cooperating to position the laser beam among the workpiece features.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Controlling dynamic and thermal loads on laser beam positioning system to achieve high-throughput laser processing of workpiece features
ActiveUS20100140237A1Minimizes workpiece feature processing inaccuracyMinimizes quality degradationWelding/soldering/cutting articlesPhotovoltaic energy generationLaser processingLight beam
A method of accomplishing high-throughput laser processing of workpiece features arranged in a densely spaced pattern minimizes workpiece feature processing inaccuracy and quality degradation that result from dynamic and thermal loads on laser beam positioning and optical components directing the laser beam during workpiece feature processing. A preferred embodiment is implemented with a laser beam positioning system composed of a zero-inertia optical deflector of an acousto-optic beam deflector (AOD) or an electro-optical deflector (EOD) type, a galvanometer head, and a linear stage cooperating to position the laser beam among the workpiece features.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
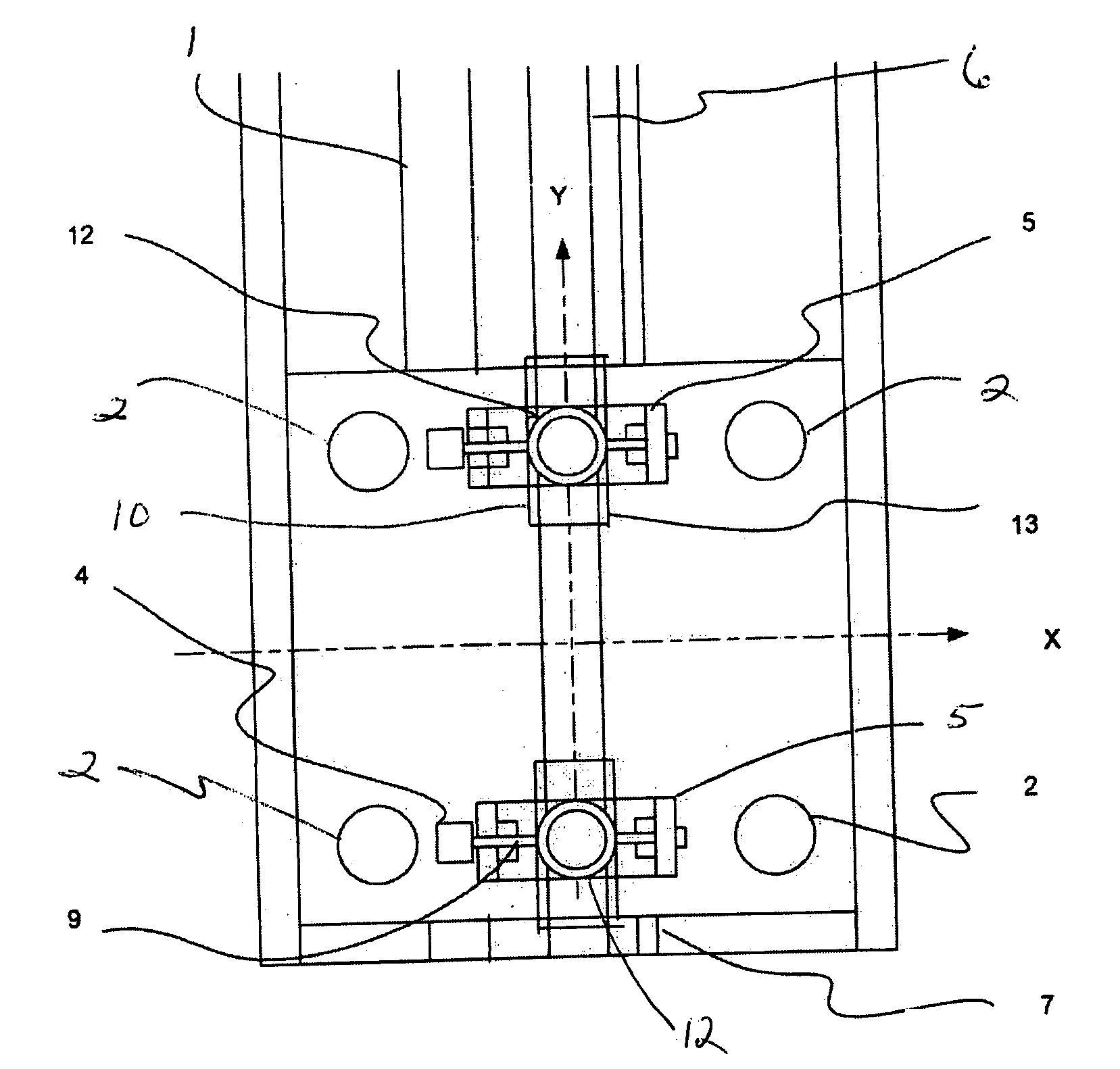
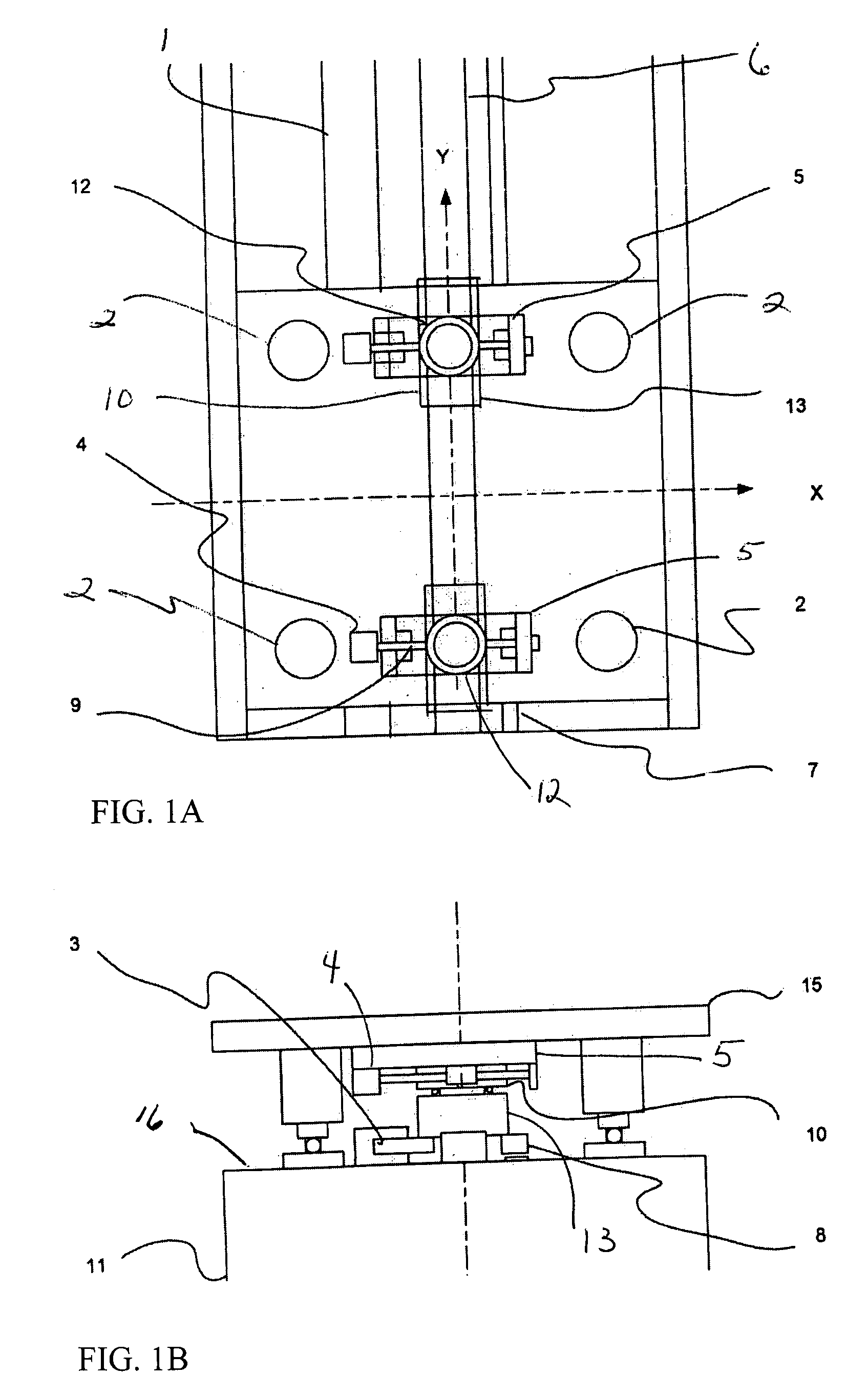
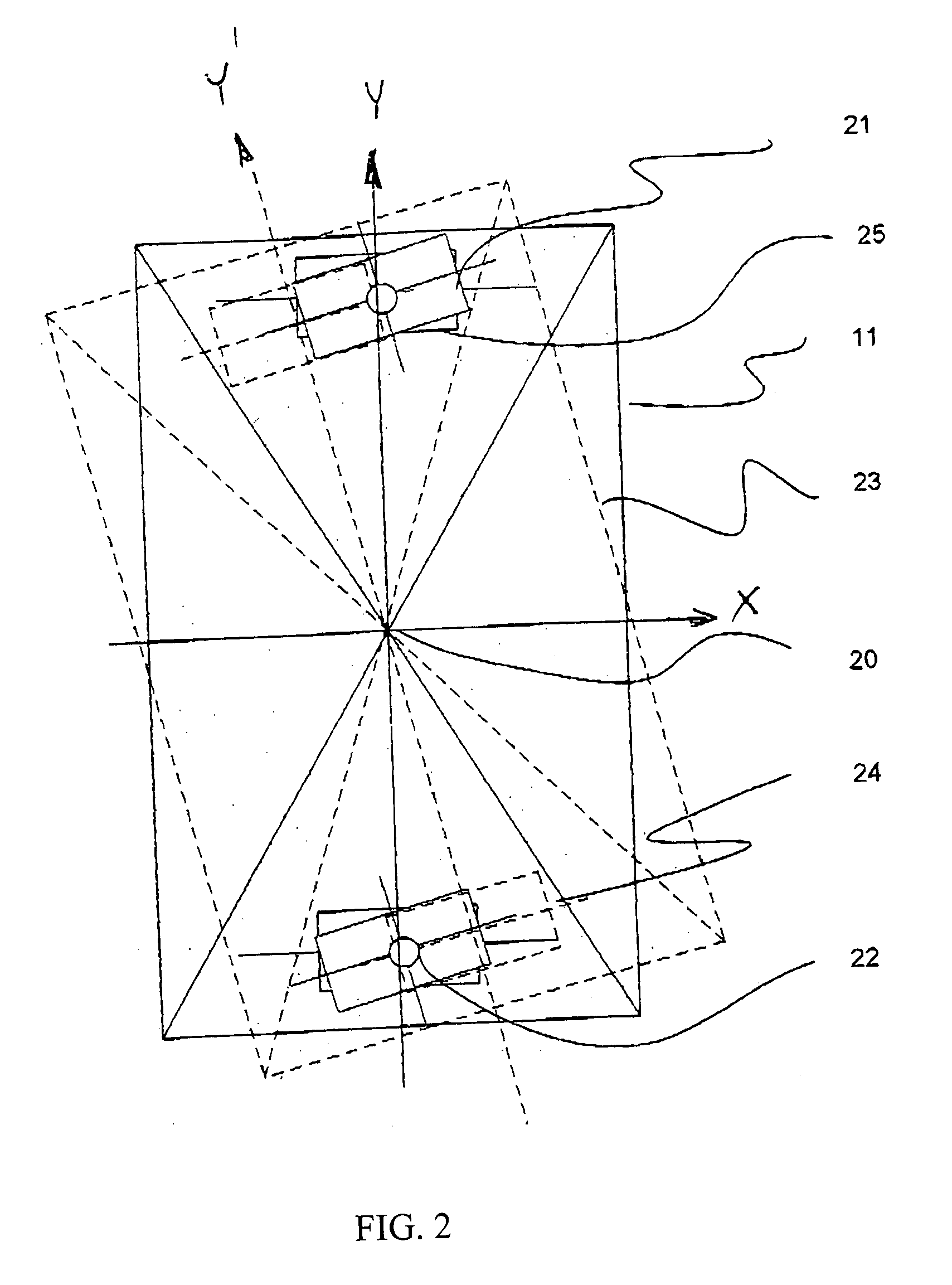
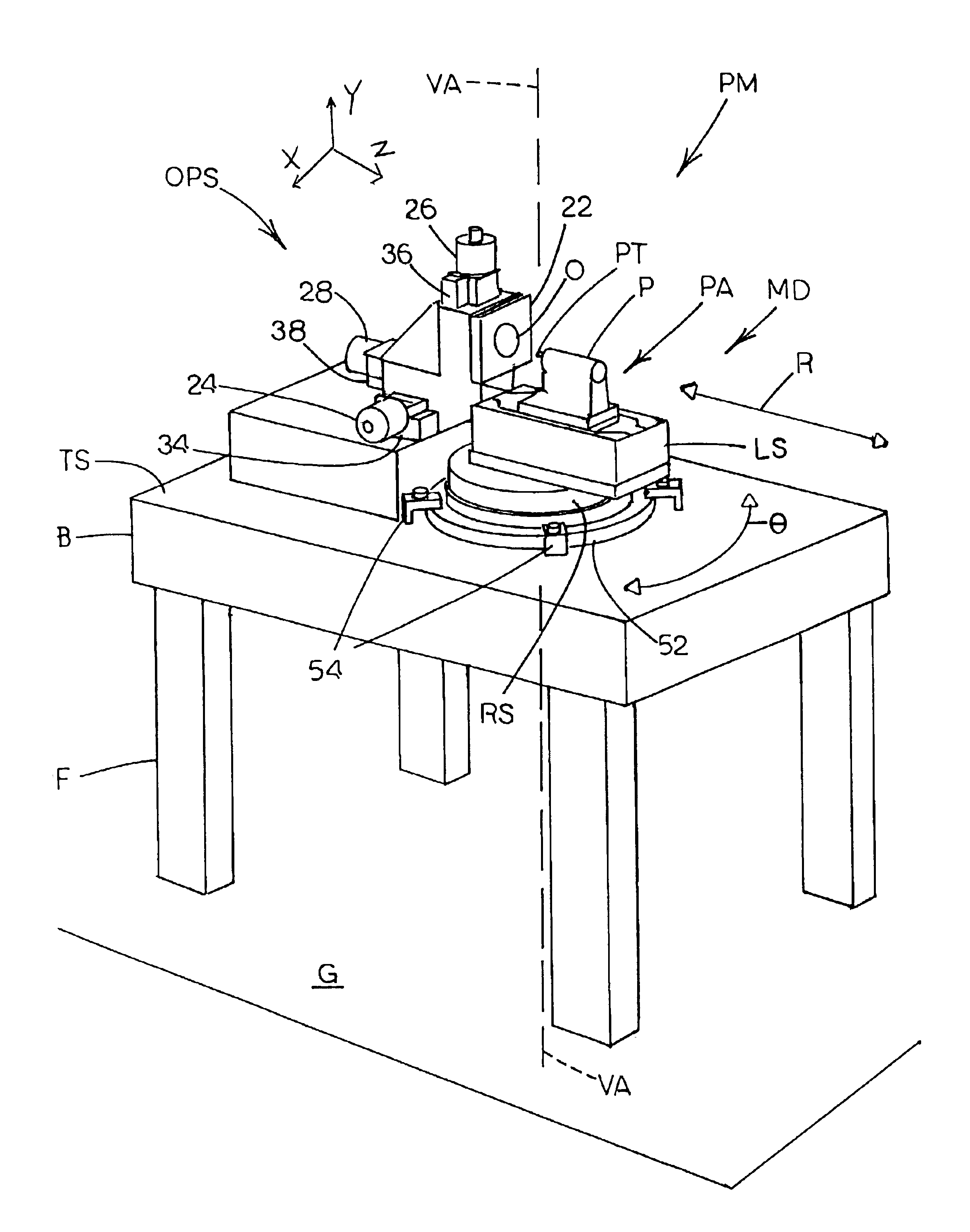
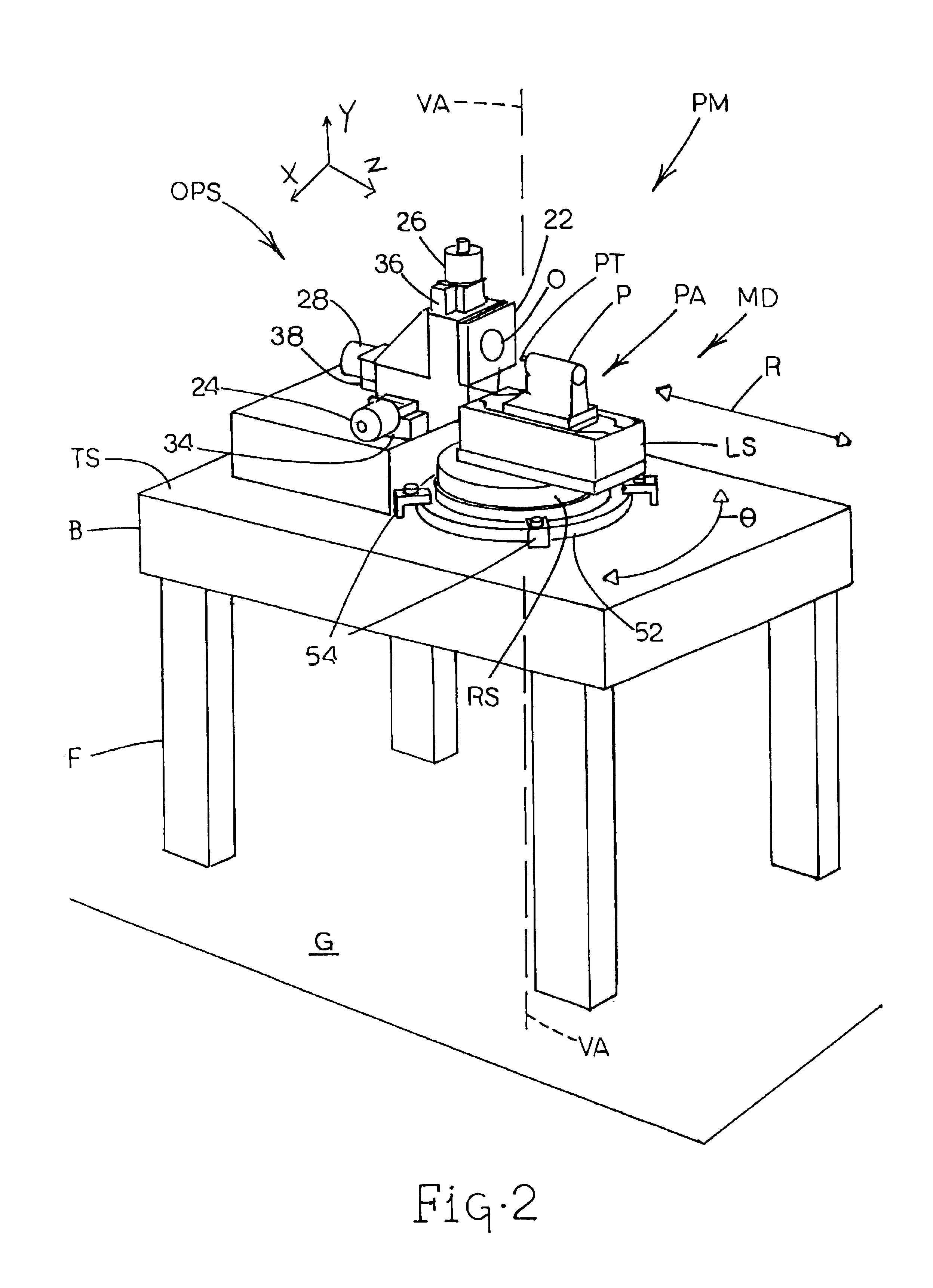
Integrated large XY rotary positioning table with virtual center of rotation
InactiveUS20070216892A1Precise positioningHigh precision feedbackPhotographic printingPositioning apparatusLinear stageCentre of rotation
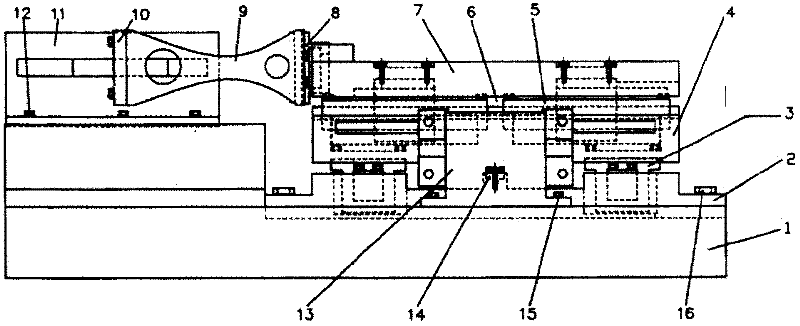
The present invention allows for a large format substrate plate to move precisely in X, Y and ⊖ Rotary directions with an integrated linear XY mechanism. The mechanism includes X1, X2 stages which are mounted to the moving substrate plate and Y1 and Y2 stages which are mounted to the machine base. The slides of the X and Y stages are connected to each other through a revolute joint. The resulting integrated X,Y mechanism can move the substrate plate in X,Y and Rotary ⊖ directions preferably by motorizing at least three of the four linear stages with feedback encoders and by using computer controller to command the three motorized stages to move to their desired positions. The relationship between the desired position of the substrate in a global XY coordinate system and the motion of each motorized stage is provided through trigonometric transformations which are integral part of this invention. This configuration can also be used to correct translation and rotational positioning errors of the substrate plate using straightness and yaw maps. The mechanism of the present invention may be used to precisely position large format glass substrates in position systems for large substrate process tools. The positioning system includes a base assembly, on which the integrated XY mechanism is mounted. The moving substrate slide may be supported on the base assembly by air bearing pucks or by recirculating rail pucks. Motion in the Y direction may be provided by linear motor coil mounted to at least one of the Y pucks with a magnet mounted to the base surface in Y direction. Motion in the X direction is achieved by one or two X slides mounted to the moving plate which support the substrate in a configuration which includes, two motorized cross stages slides X1 and X2 with encoders which are connected to the Y1 Y2 slides respectively by a unique revolute joint Motion in the ⊖ direction can be achieved by opposite motion of either X1 and X2 stages or Y1 and Y2 stages or in a special double gantry configuration by all four stages where only three axes are independent.The present invention allows multiple mounting configurations of the X, Y stages which allows the user to control very large format substrates in an economic way using standard X,Y stages and low cost structural and sensing components. In addition the present invention allows the user to achieve extreme precision positioning as may be needed for process machines such as printing, laser scribing, machining, inspection and biotechnology assaying of large substrate plates by commanding the motorized stages of the mechanism to move to target position using error mapping and the kinematic formulations of this invention
Owner:EIDELBERG BOAZ
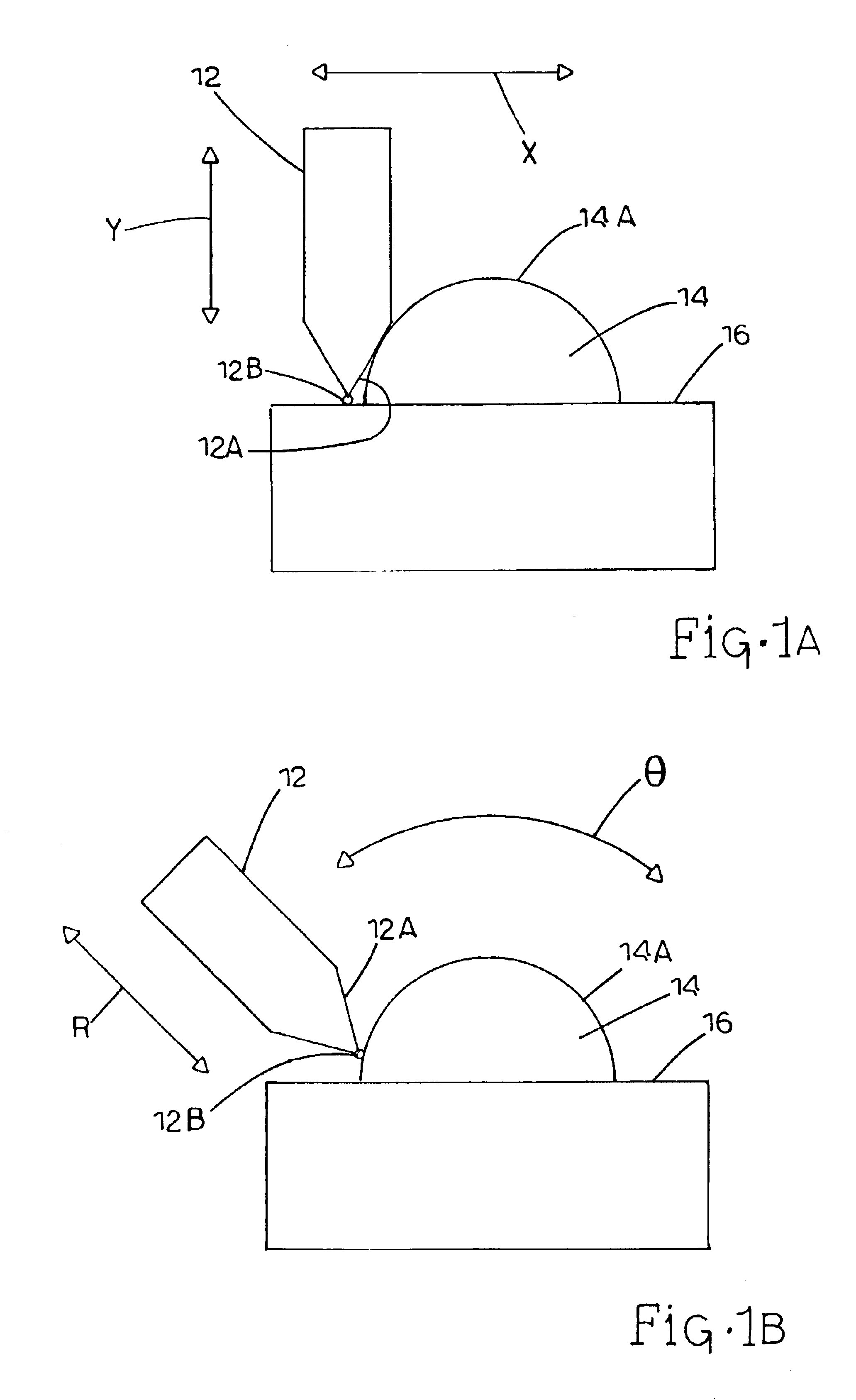
Polar coordinate-based profilometer and methods
InactiveUS6895682B2Accurate measurementAvoid interferenceMechanical counters/curvatures measurementsWind musical instrumentsRotary stageTransducer
A polar coordinate-based profilometer includes a base, a rotary stage, a linear stage, and a probe device. The rotary stage is mounted on the base and includes a rotary table rotatable about a vertical axis oriented orthogonal to the base. The linear stage is mounted on the rotary table and is rotatable therewith. The linear stage includes a linear slide member that is translatable along a radial axis orthogonal to the vertical axis. The probe device is mounted on the linear slide member and is translatable therewith. The probe device includes a probe tip that is linearly displaceable along the radial direction and communicates with a linear displacement-sensing transducer. Alternatively, the probe device scans an object without contacting the object. Methods are provided for measuring an object based on polar coordinates, and correcting for misalignment prior to measurement.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Confocal microscope with positionable imaging head
A confocal microscope for imaging tissue having an imaging head for capturing optically formed microscopic sectional images of tissue samples, a platform upon which is disposed a linear stage for moving the imaging head along a vertical dimension, and a rotary stage to rotate the linear stage and imaging head about the vertical dimension. A mounting arm couples the imaging head to the linear stage to adjust tilt of the imaging head and to rotate the imaging head about a normal axis perpendicular to an optical axis of an objective lens of the imaging head. In a first mode of operation, the imaging head is positioned to image an ex-vivo or in-vivo tissue sample upon the platform, such as ex-vivo tissue sample mounted upon a movable specimen stage, and in a second mode of operation the imaging head is positioned to image an in-vivo tissue sample beside the platform.
Owner:CALIBER IMAGING & DIAGNOSTICS
CSI-based indoor positioning method
InactiveCN109151731AHigh precisionImprove efficiencySpatial transmit diversityParticular environment based servicesMultipath interferenceLinear stage
The invention provides a CSI-based indoor positioning method. The method comprises: carrying out filtering and linear transformation processing on CSI amplitude and phase data to obtain stable and robust data features; carrying out fusion of the processed amplitude and phase information to perform indoor positioning; applying naive Bayes classification to training and testing of a positioning mode, collecting a signal feature of an unknown position in real time at a linear stage, carrying out data processing to obtain amplitude phase information of the point, carrying out online matching witha fingerprint database based on a naive Bayesian classification algorithm, outputting an optimal result, and completing position estimation of a test point. According to the positioning method, defects of low accuracy and stability of the traditional indoor positioning method are overcome; the multipath interference in an indoor environment is reduced by processing and utilizing the data feature of the CSI effectively; and indoor high-precision passive positioning is realized without the need for the user to carry other devices.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
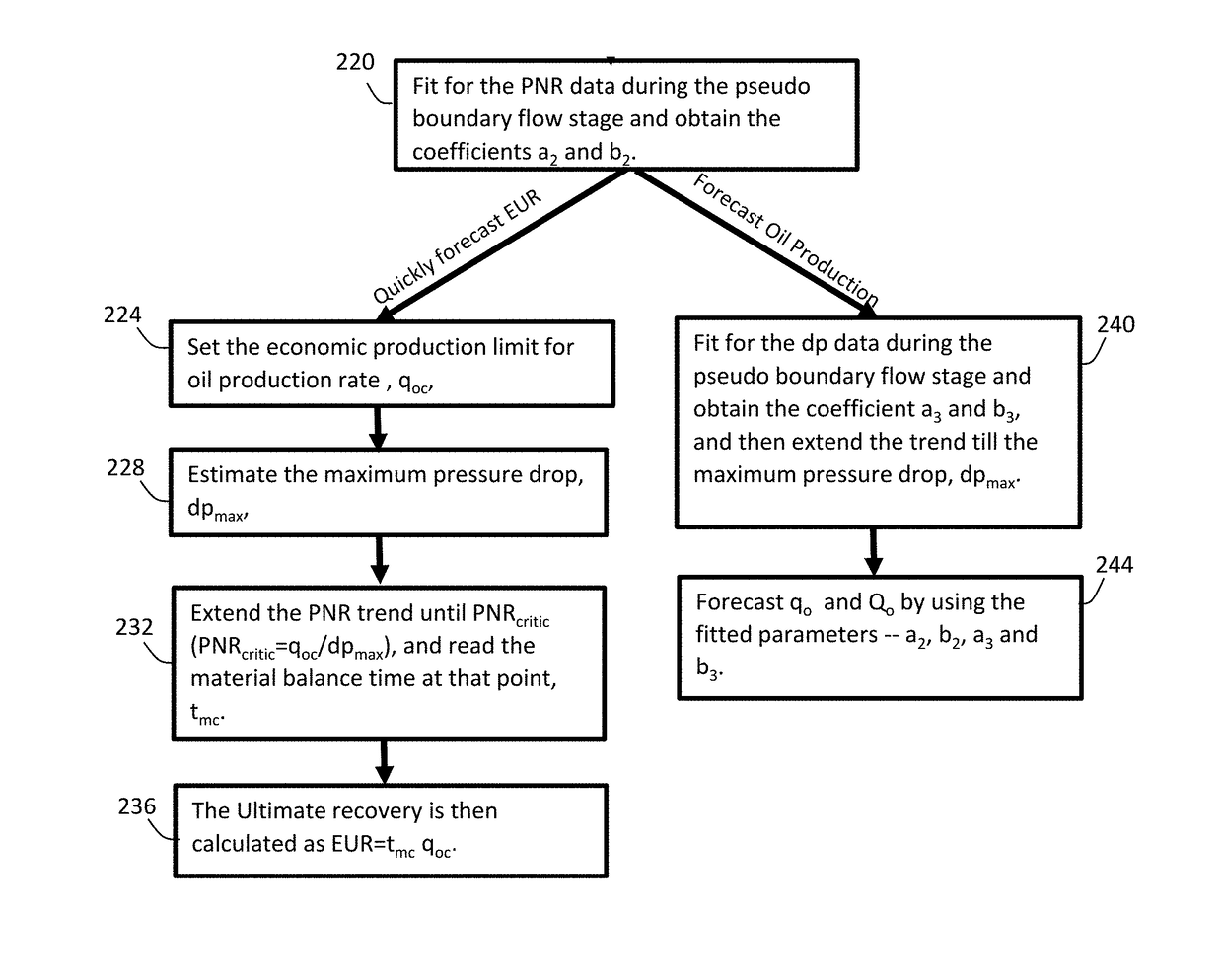
Forecasting ultimate recovery of oil and oil production for a multiply-fractured horizontal well
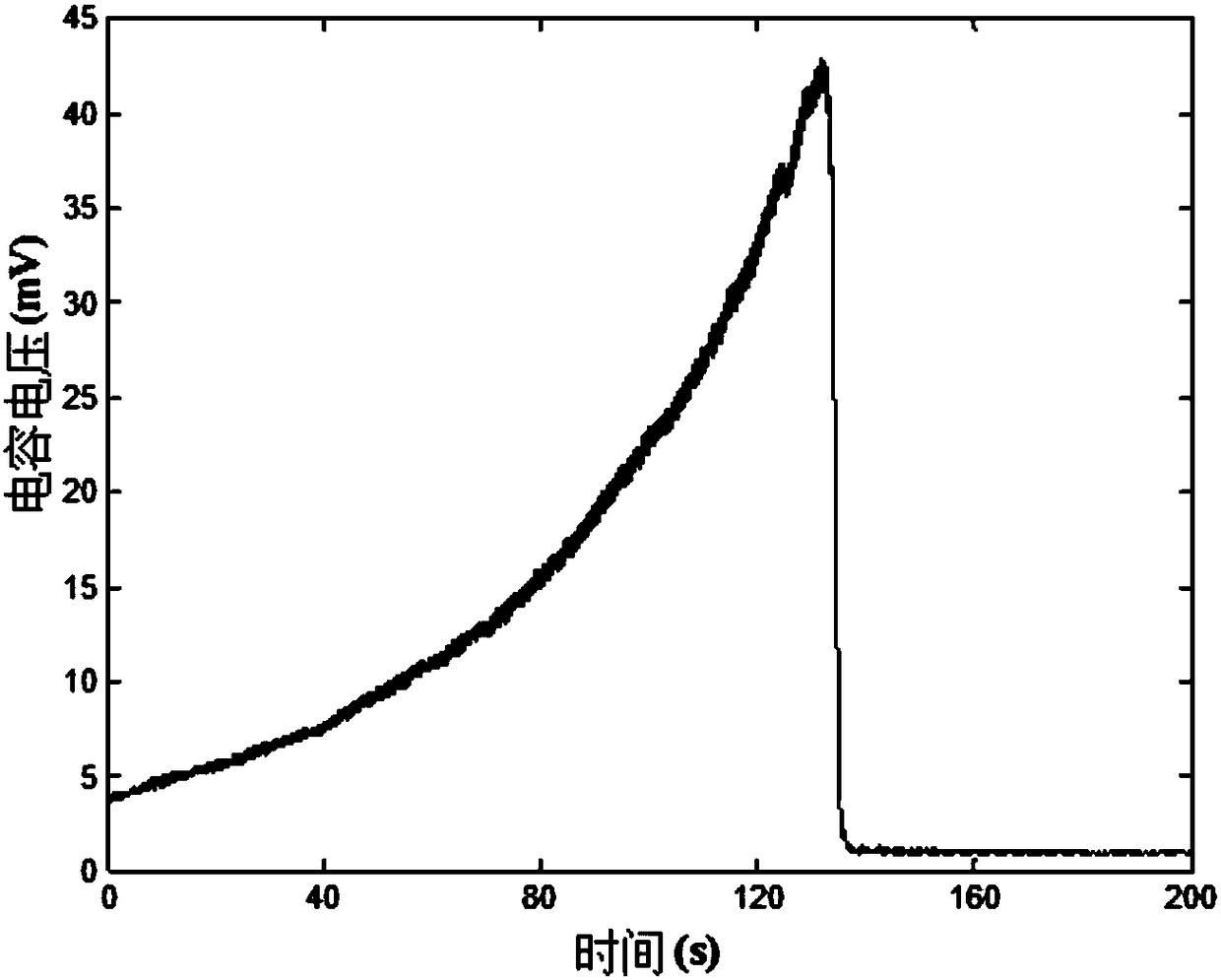
A system and method to forecast oil production and estimated ultimate recovery of oil from a multiply-fractured horizontal shale oil well. The method includes determining oil flow behavior of the oil well during linear stage flow and pseudo boundary stage flow of a well. Oil production forecasts and estimated ultimate recovery are determined based on the flow behaviors of the well and historical oil production rate data obtained from sensors disposed in or around the well. The system includes said sensor for measuring properties of the well and, optionally, a computer processor for executing the method.
Owner:TAO QINGFENG
Double-switch power supply modulator for envelope tracking system
InactiveCN104883139AImprove efficiencyIngenious structural designAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierSystem requirements
The invention discloses a double-switch power supply modulator for an envelope tracking system and belongs to the field of integrated circuits. The double-switch power supply modulator for the envelope tracking system mainly solves the problem that a power supply modulator of an envelope tracking amplifier in the prior art is low in efficiency and cannot well meet system requirements. The power supply modulator is of a double-switch converter structure and comprises a linear amplifier stage, a main switch converter stage and a compensation switch stage, output current is combined into an output signal of the whole power supply modulator, and power is supplied to a radio frequency power amplifier. Due to the fact that current output from a linear stage is compensated for by adding the compensation switch stage, the output current of a low-efficiency linear amplifier is reduced, and the overall efficiency of the system is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
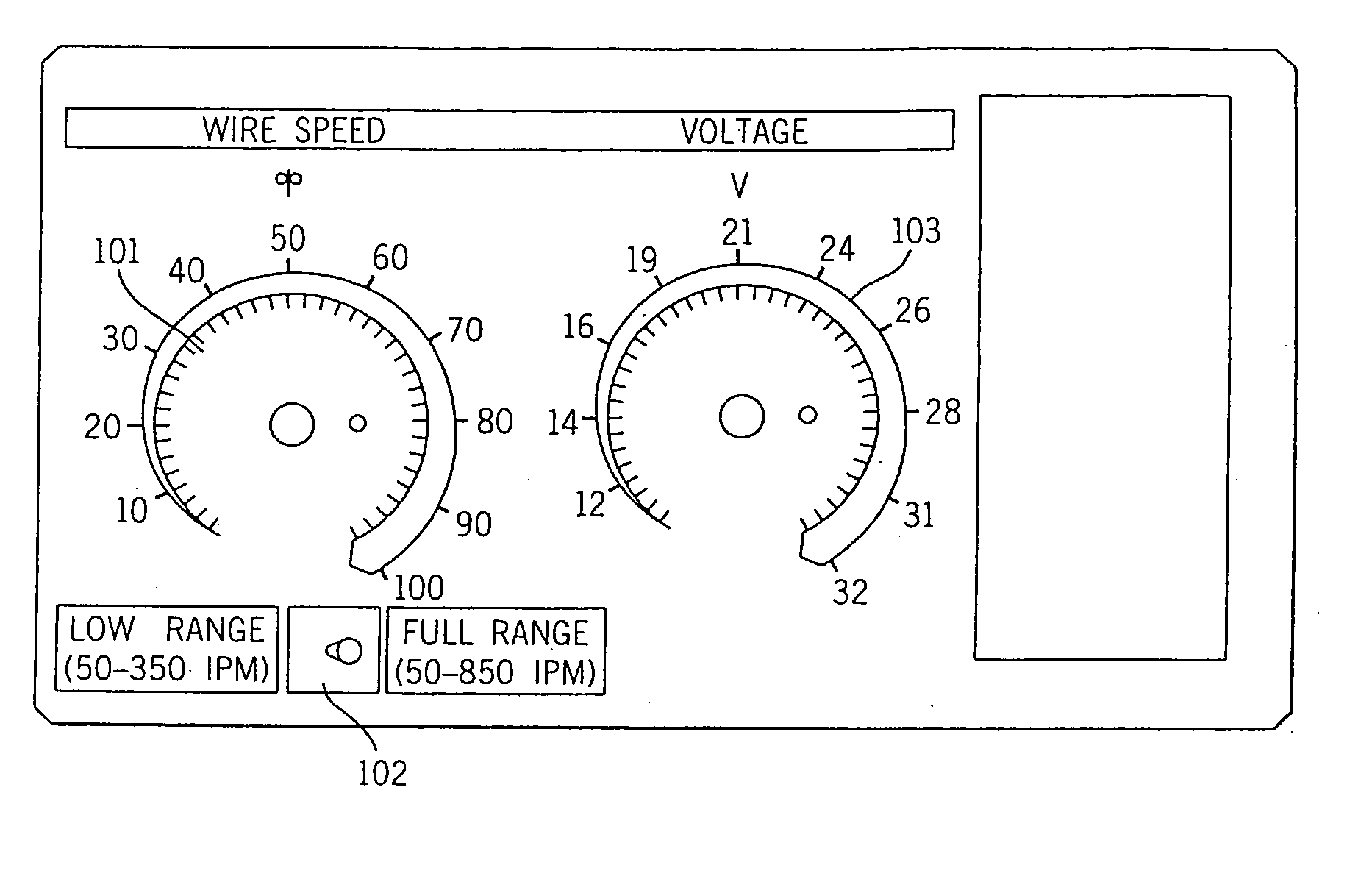
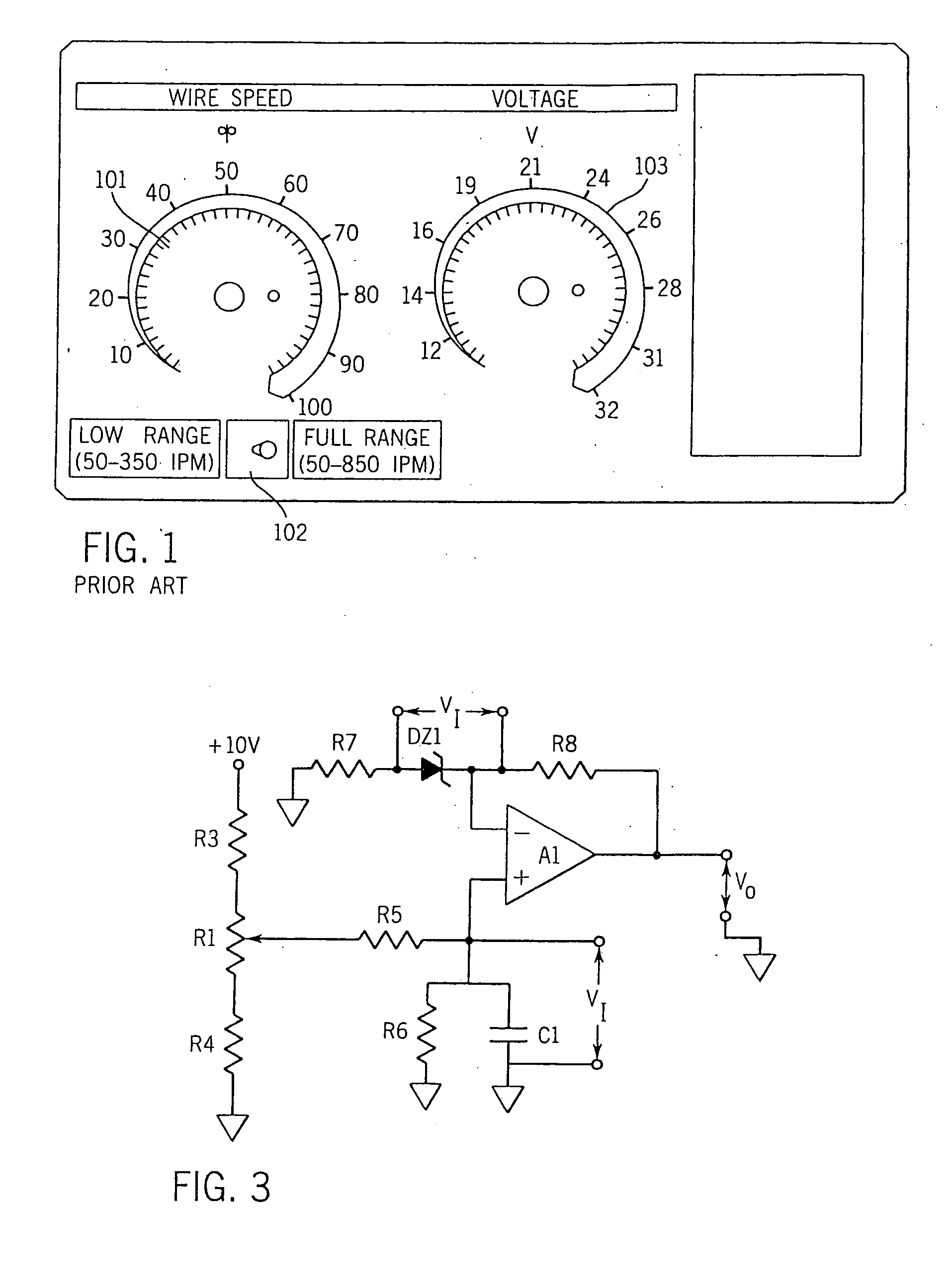
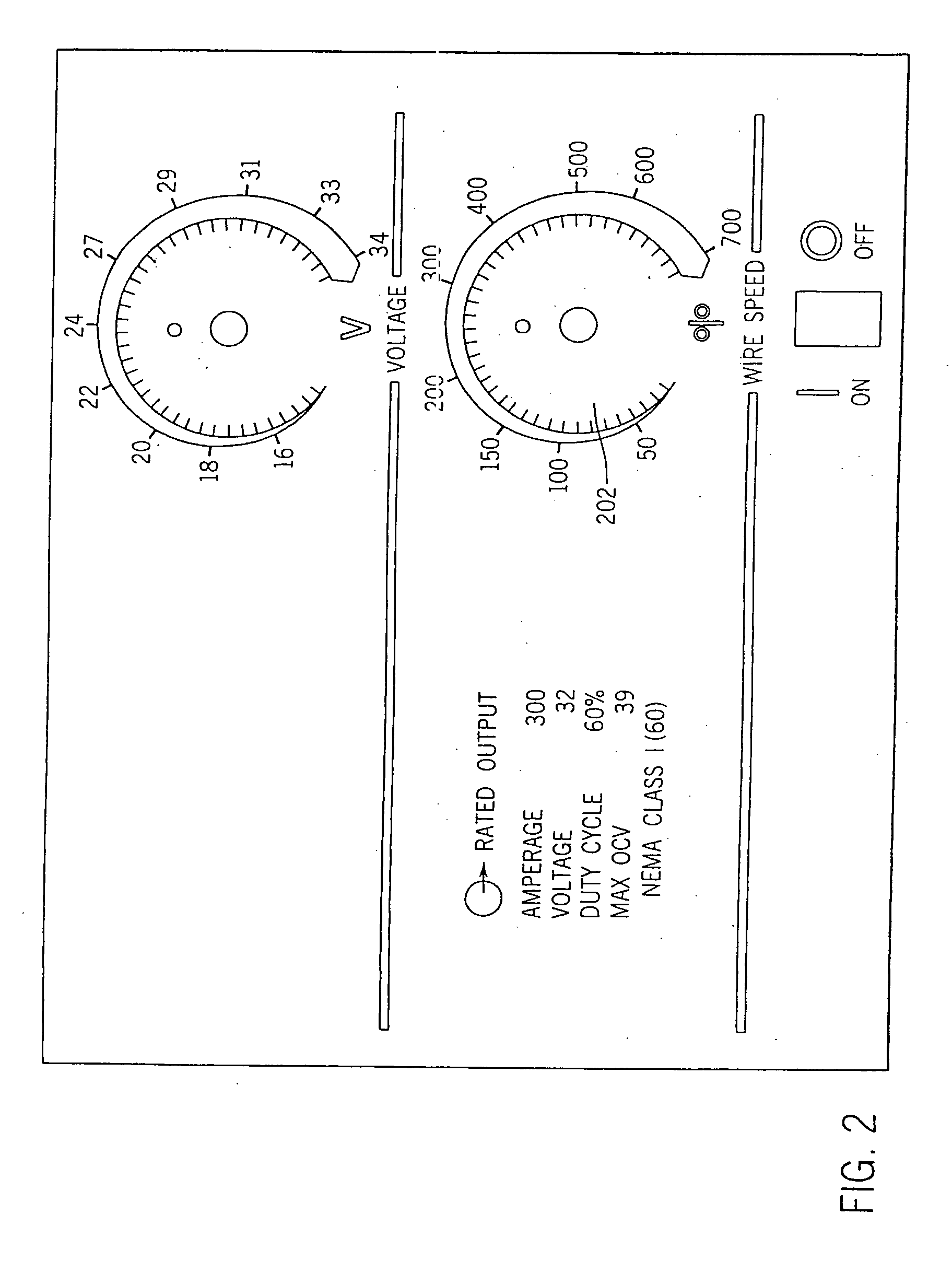
Wire feeder with non-linear speed control
A welding machine with a wire feeder and a controller is disclosed. The wire feeder includes a wire feed motor with a motor speed input. The controller is coupled to the motor speed control input. A user selectable wire feed speed input is also connected to the controller. The controller has an input circuit coupled with a non-linear stage such that the relationship between the user selectable wire feed speed input and the actual wire feed speed is not linear. The selectable input may be a potentiometer mounted on a front panel as the user selectable wire feed speed input. The non-linearity may be continuous or two discrete gains.
Owner:NOWAK ALBERT M +2
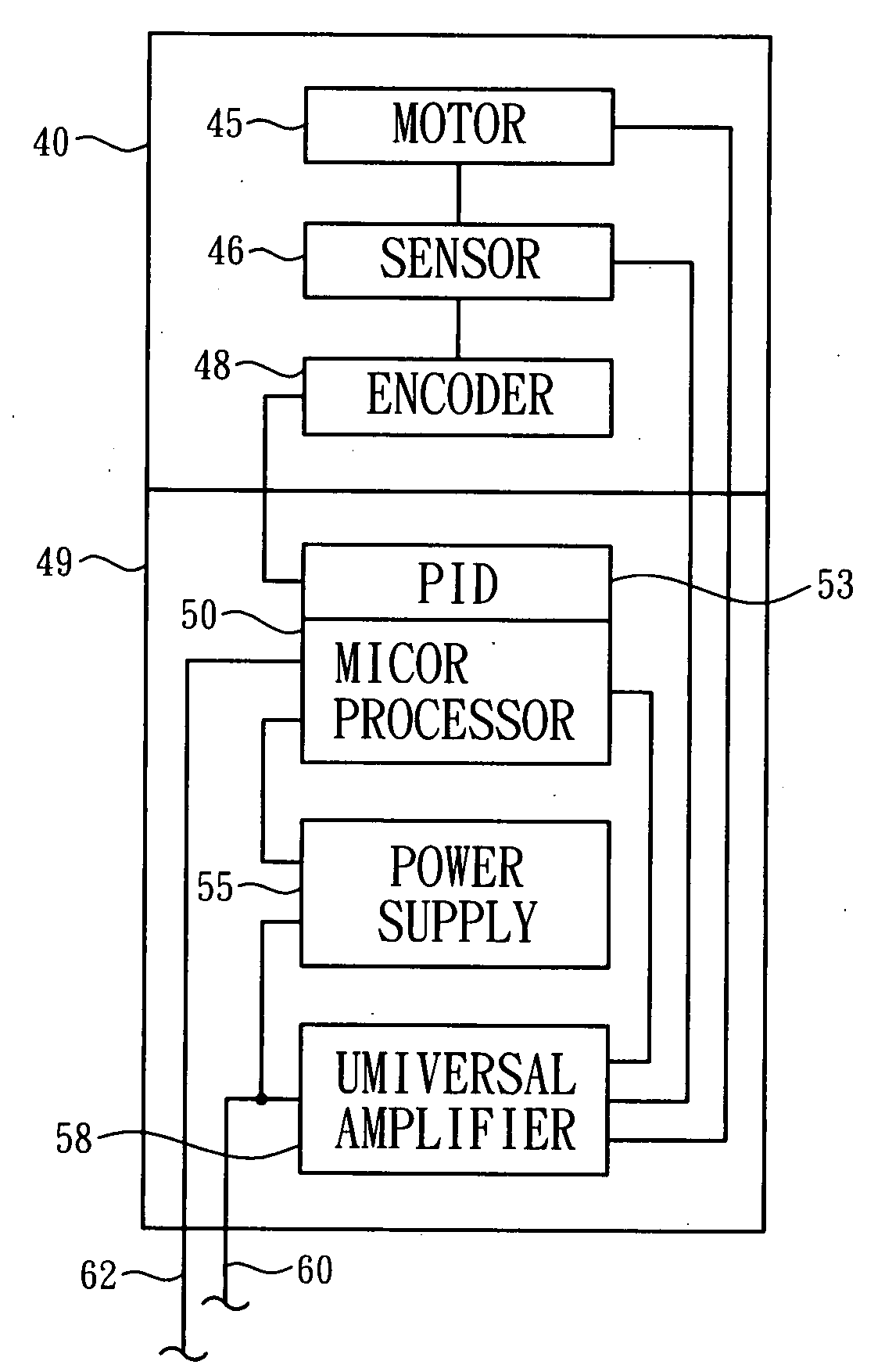
Integrated linear motor
InactiveUS20080169774A1Low costMitigated risk of mal operationProgramme controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersLinear motorAmplifier
The present invention provides an integrated linear motor, which comprises a linear stage and a controller coupled to the linear stage, wherein the linear stage comprises a Hall sensor, an encoder, and a linear motor integrated thereon and the controller comprises a microprocessor, an amplifier, and a power supply integrated therein.
Owner:HIWIN MIKROSYST
Upper extremity rehabilitation device
ActiveUS9375598B1Reduce manufacturing costImprove competitivenessClubsChiropractic devicesUpper limbMotor Drive Unit
An upper extremity rehabilitation device includes: a base, a rotary shaft unit, a rotation drive unit, a brake unit, a linear move unit, a hand gripping assembly, a first and a second connecting rods. The rotary shaft unit is pivoted to the base. The rotation drive unit is disposed on the base and includes a drive portion connected to the first shaft portion. The brake unit includes an outer pipe disposed on the rotary shaft, and an inner pipe movably disposed in the outer pipe. The linear move unit includes a linear seat pivoted to the second shaft portion, and a linear platform movably disposed on the linear seat. The hand gripping assembly is disposed on the linear platform. The first connecting rod is pivoted to the brake unit. The second connecting rod is pivoted to the first connecting rod and the linear seat.
Owner:HIWIN TECH
Apparatus and method for handling fluids at nano-scale rates
ActiveUS20090142198A1Minimizing out-of-phase thermal pumpingMinimize temperature differenceMaterial nanotechnologyHeating or cooling apparatusEngineeringThermal contact
Owner:SCIEX
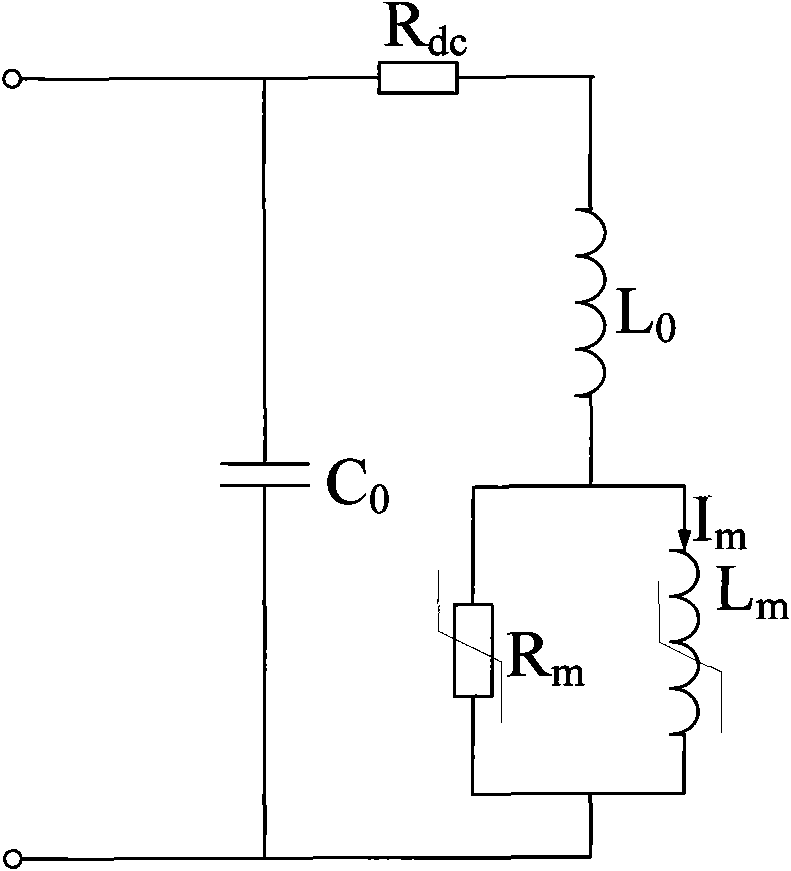
Analytical model for saturable reactor for converter valve
ActiveCN101930492APhysical concepts are clearClear expressionSpecial data processing applicationsElectrical resistance and conductanceCapacitance
The invention provides an analytical model for a saturable reactor for a converter valve. The saturable reactor for the converter valve consists of a coil and an iron core; and the working state of the iron core has a linear stage and a nonlinear stage under rated operation. In order to better perform electrical design and electrical analysis on the saturable reactor, the invention provides an analytical model for the saturable reactor for the converter valve. The analytical model comprises a coil resistance, a coil inductance, a core inductance, a core resistance, a terminal capacitance and other parameters. Corresponding electrical parameters of saturable reactors with different shapes and dimensions can be calculated. The analytical model has the advantages of clear physical conception, and capacities of easily acquiring each parameter needed in the model through a real object and providing a foundation for deep analysis of the saturable reactor.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Systems for producing precision magnetic coil windings
A system for producing precision magnetic coil windings is provided. The system includes a wire disposing assembly having a support, an axial traverser sub-assembly, and a support arm. The support is configured to receive a plurality of turns of a wire. The axial traverser sub-assembly is operatively coupled to the support. The support arm includes a wire disposing device. The system further includes a linear stage, a monitoring unit, a feedback unit, and a controller unit. The linear stage is operatively coupled to the support arm. Moreover, the controller unit is configured to axially position an incoming portion of the wire and provide reference trajectories for tracking.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
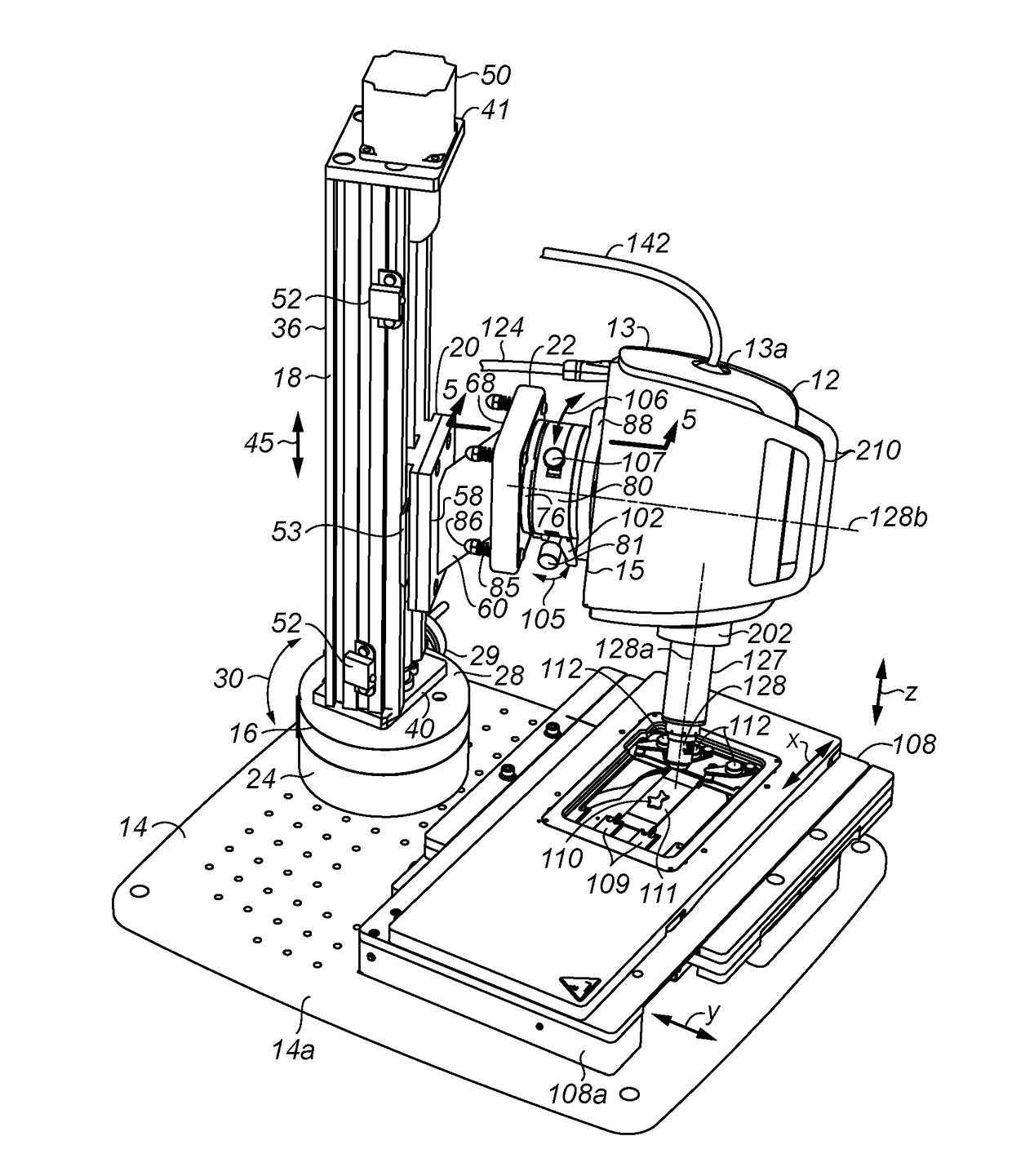
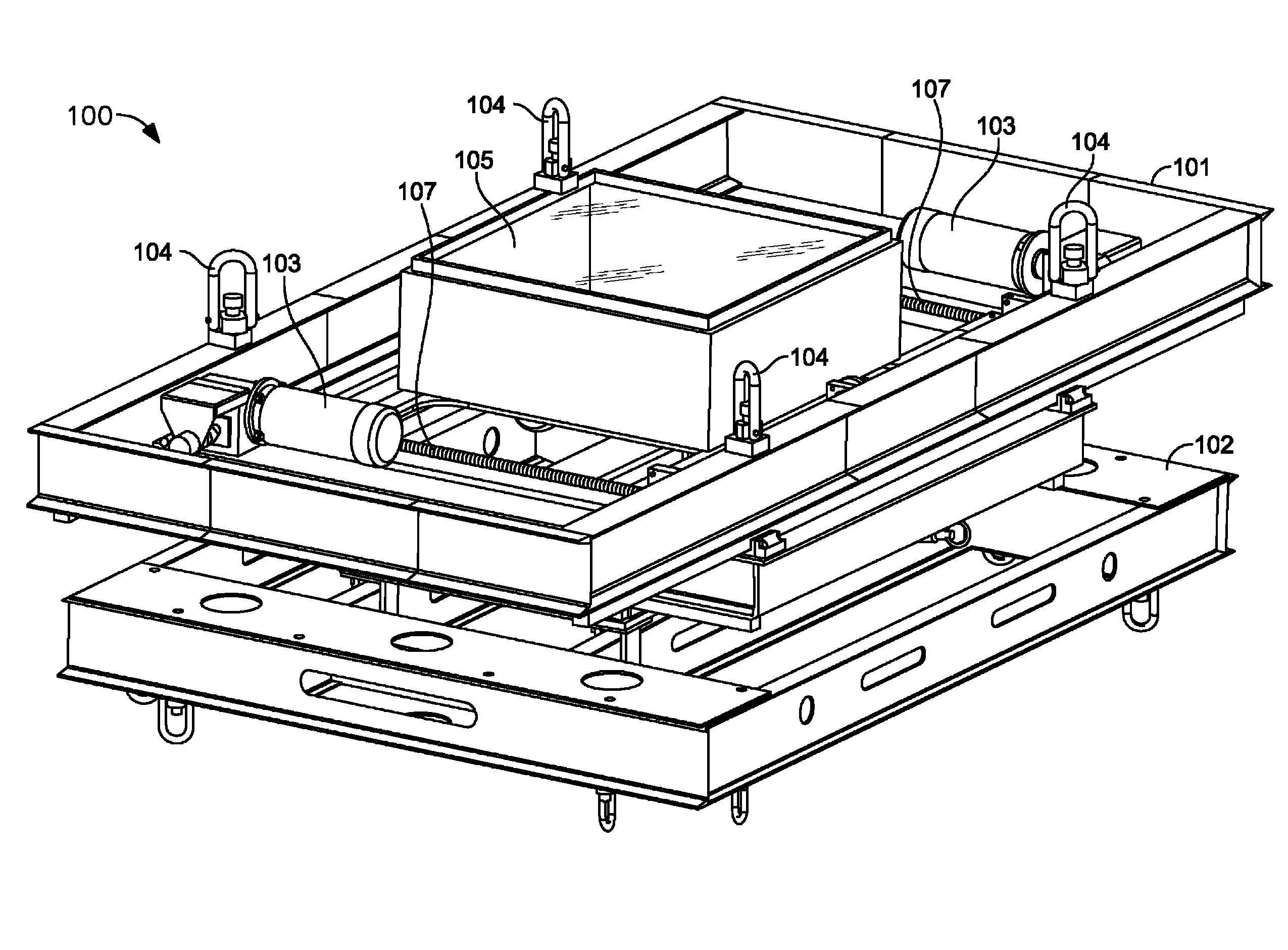
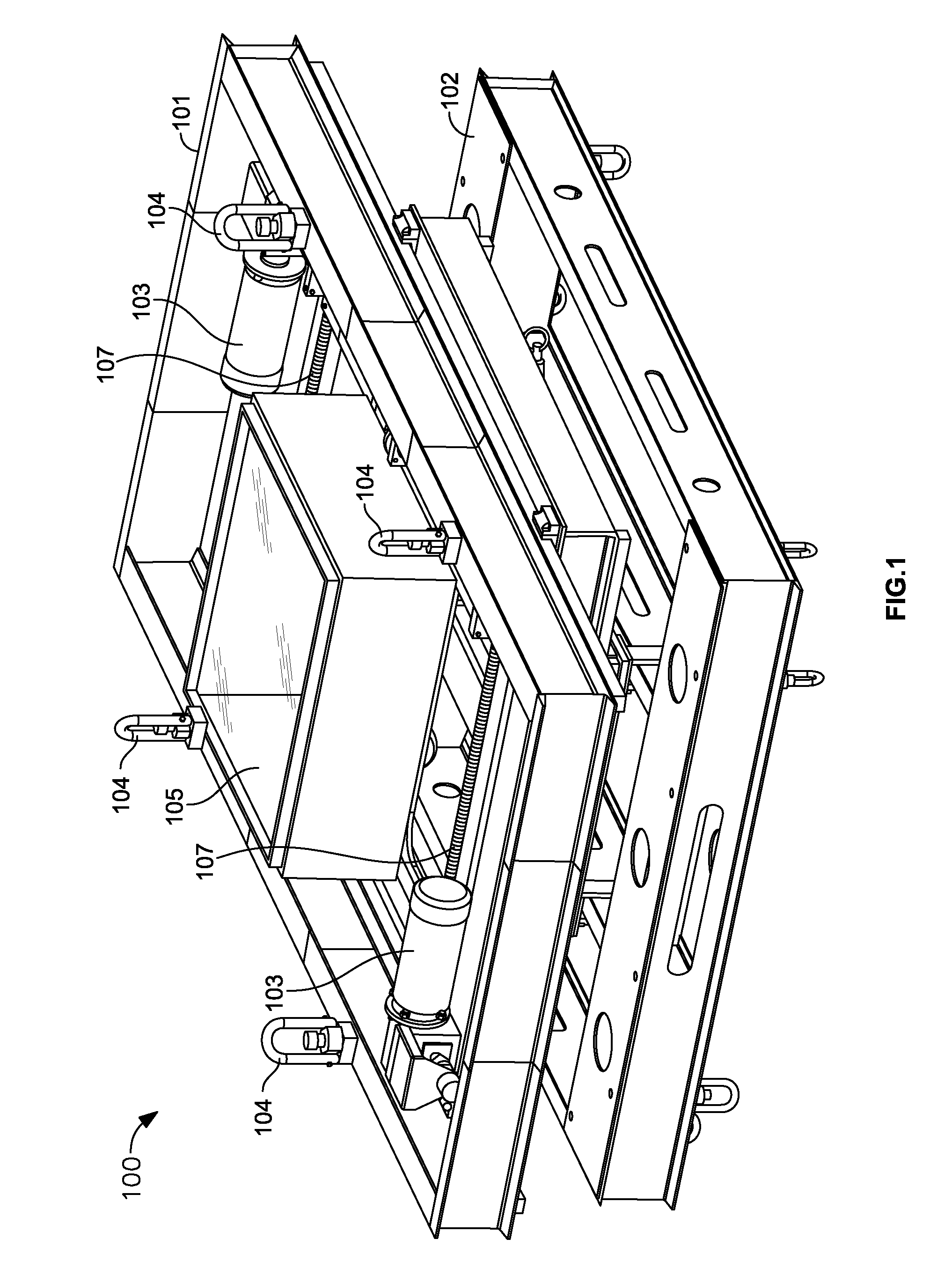
Air bushing linear stage system
A linear stage system is provided. The linear stage system includes a base, a carriage plate, a first shaft, a first air bushing coupled to the base, a first motor coupled to the base and the carriage plate, and a first position encoder. The first air bushing is configured to support the carriage plate via the first shaft, wherein the first air bushing utilizes the first shaft as a guide surface and is configured to support positioning of the carriage plate along an axis. The first motor is configured to create a linear motion parallel to the axis in a first motor element coupled to the carriage plate to position the carriage plate along the axis in response to a first control signal. The first position encoder is configured to determine a position of the carriage plate relative to the base.
Owner:ALIO INDS
Self-adjusting load bar
A method is provided for assembling a load bar assembly. The method includes providing a first linear stage having a first alignment mechanism that is configured to move the load bar assembly in a first direction. A second linear stage is provided that includes a second alignment mechanism that is configured to move the load bar in a second direction that is different from the first direction. The first alignment mechanism is positioned with respect to the second alignment mechanism such that the first alignment mechanism and the second alignment mechanism are prevented from being back-driven. The first alignment mechanism and the second alignment mechanism are configured to lock if one of the first alignment mechanism and the second alignment mechanism fails.
Owner:INNOVENTOR ENG
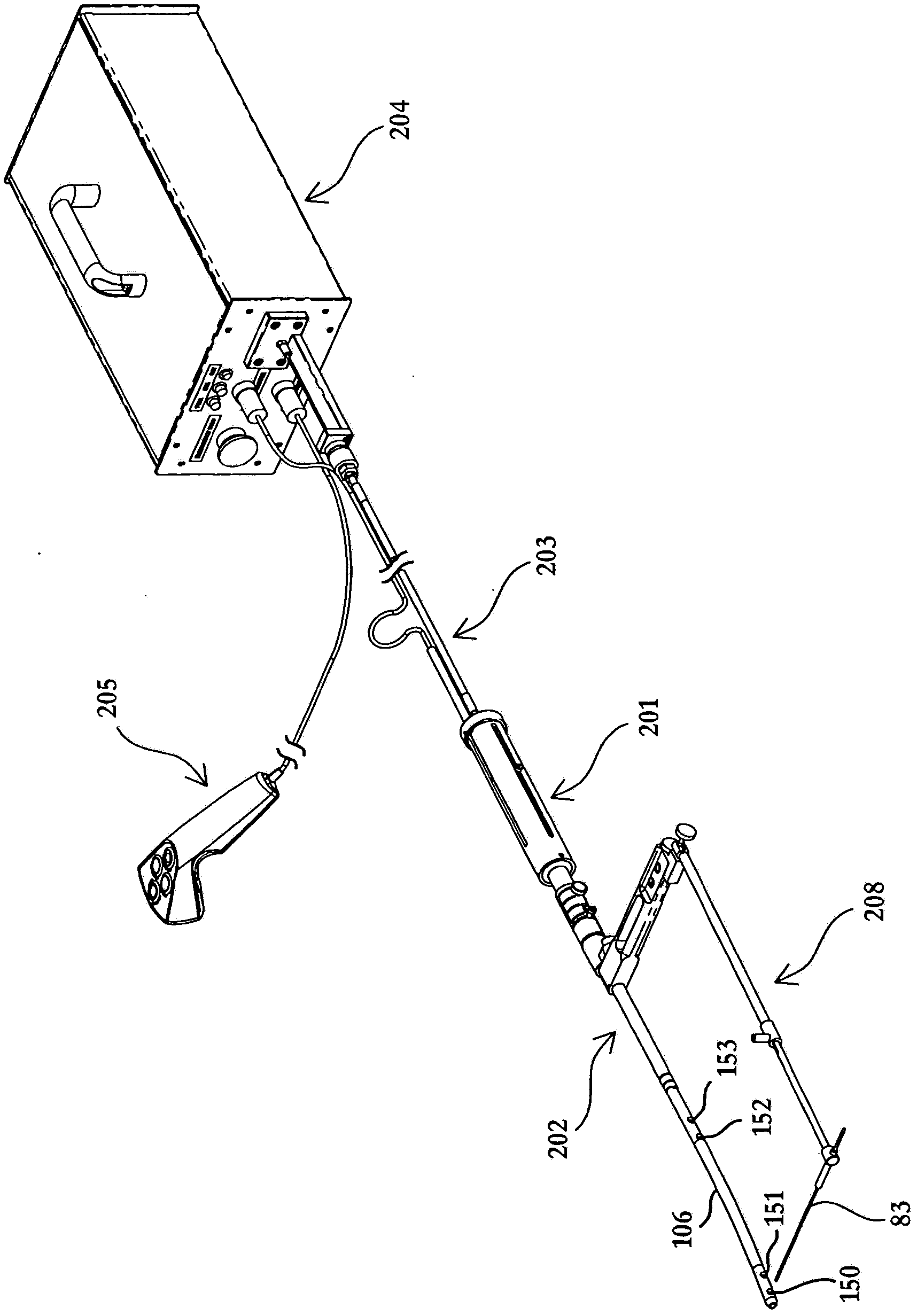
Drill assembly and system and method for forming a pilot hole
Owner:DGIMED ORTHO INC
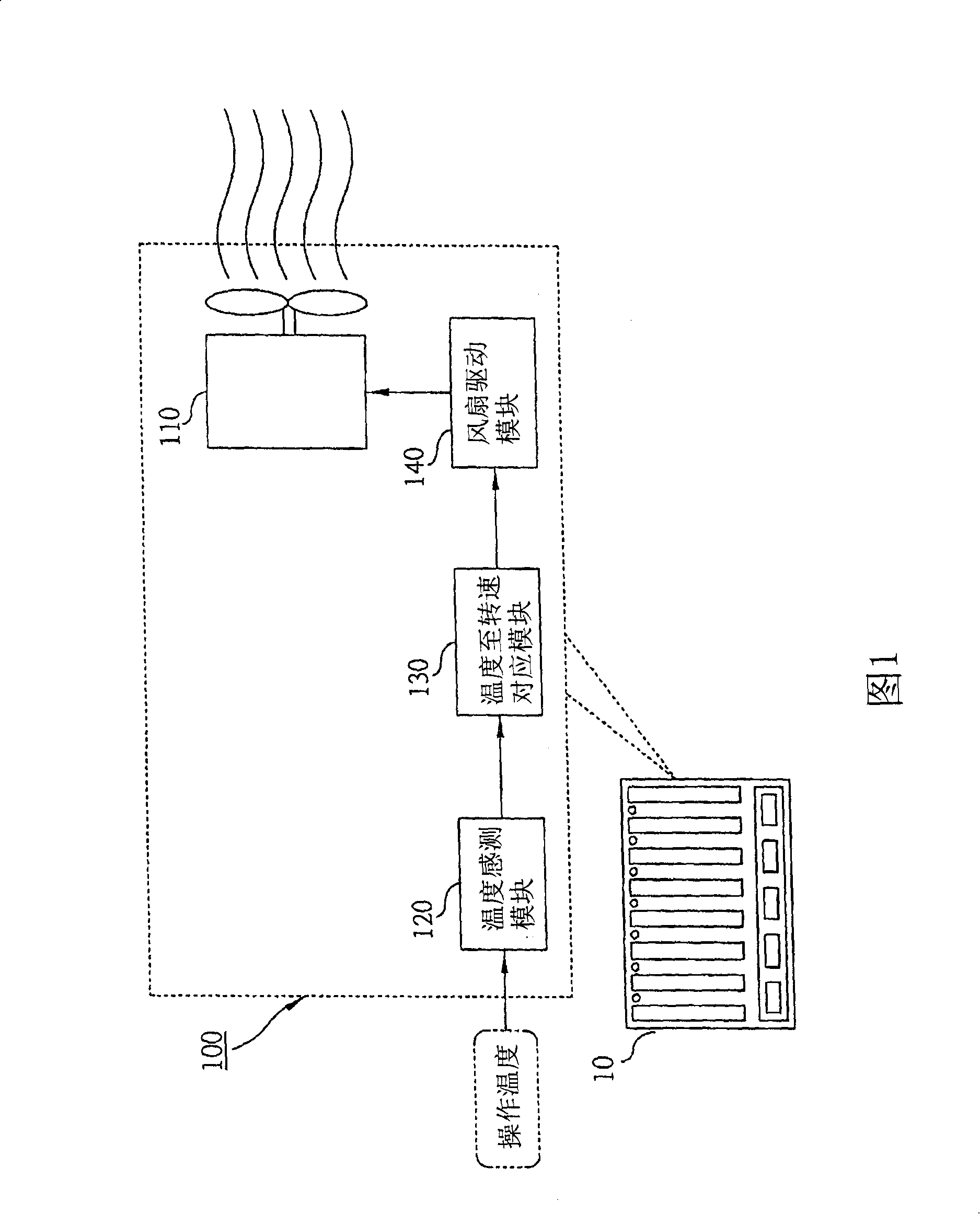
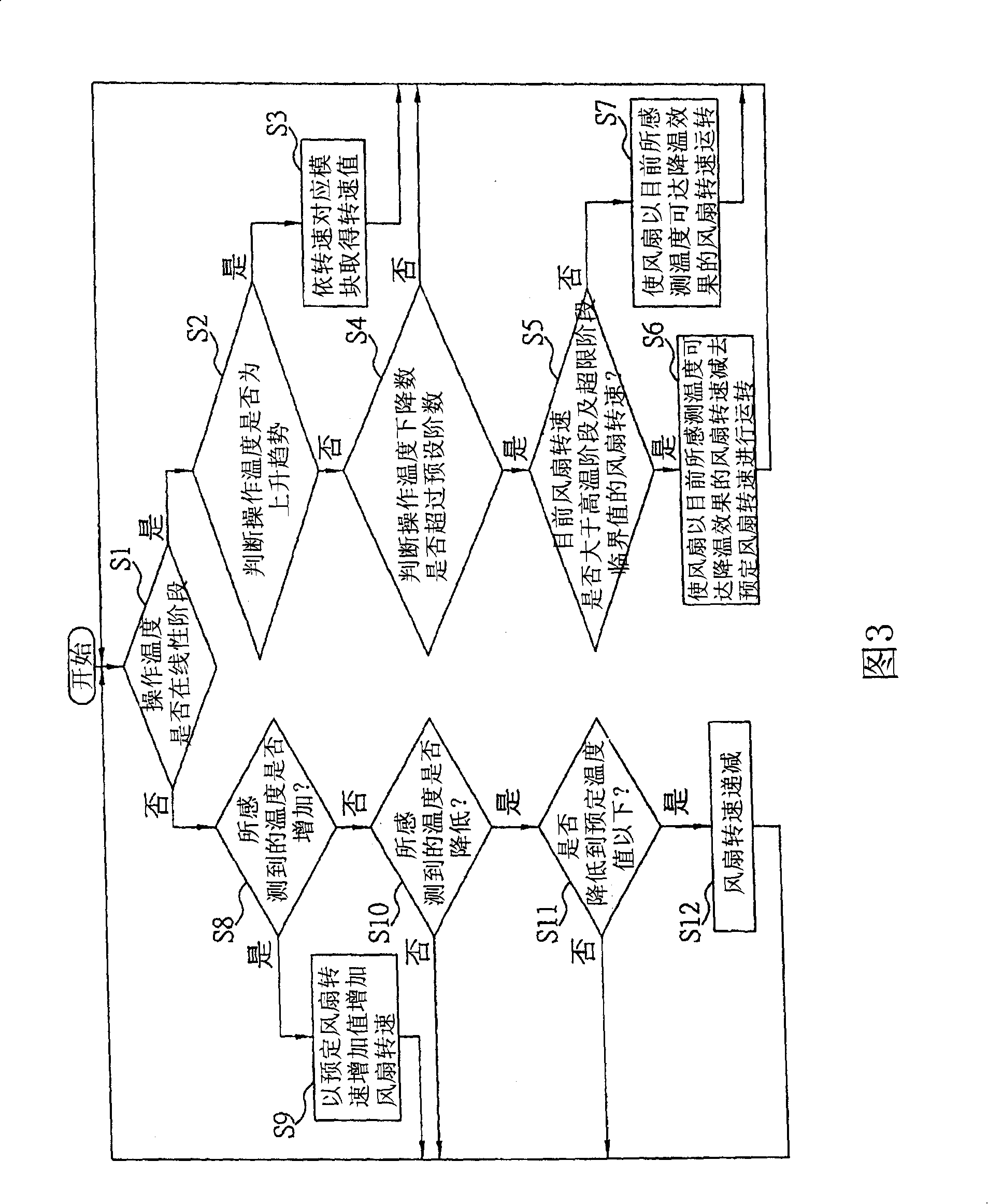
Dynamic control type electronic equipment dissipating heat method and system
InactiveCN101203126AWon't burnDigital data processing detailsTemperatue controlPersonal computerOperating temperature range
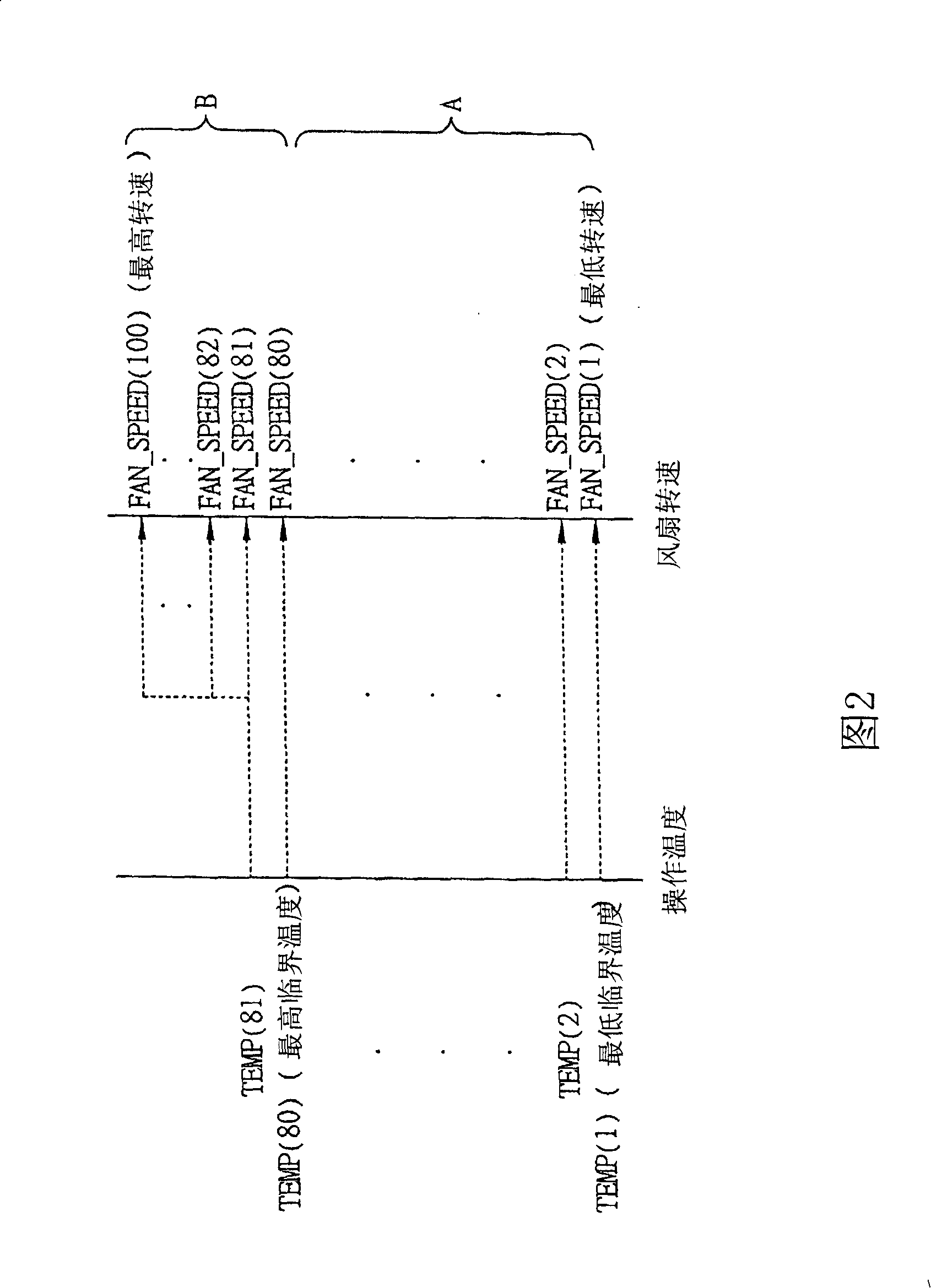
A dynamic controlling type heat dissipating method and system of electronic equipment can be used for being matched with a piece of electronic equipment such as a blade server, a desktop personal computer or a laptop to provide a dynamic controlling type heat dissipating function. The invention is characterized in that the operating temperature range of the electronic equipment is divided into two stages: a linear stage and a high temperature stage. When in the linear stage, a linear way is used for corresponding to a fan speed value; on the contrary, when in the high temperature stage, a dynamic controlling way is used for controlling the fan rotational speed to reduce the temperature to the linear stage rapidly.
Owner:INVENTEC CORP
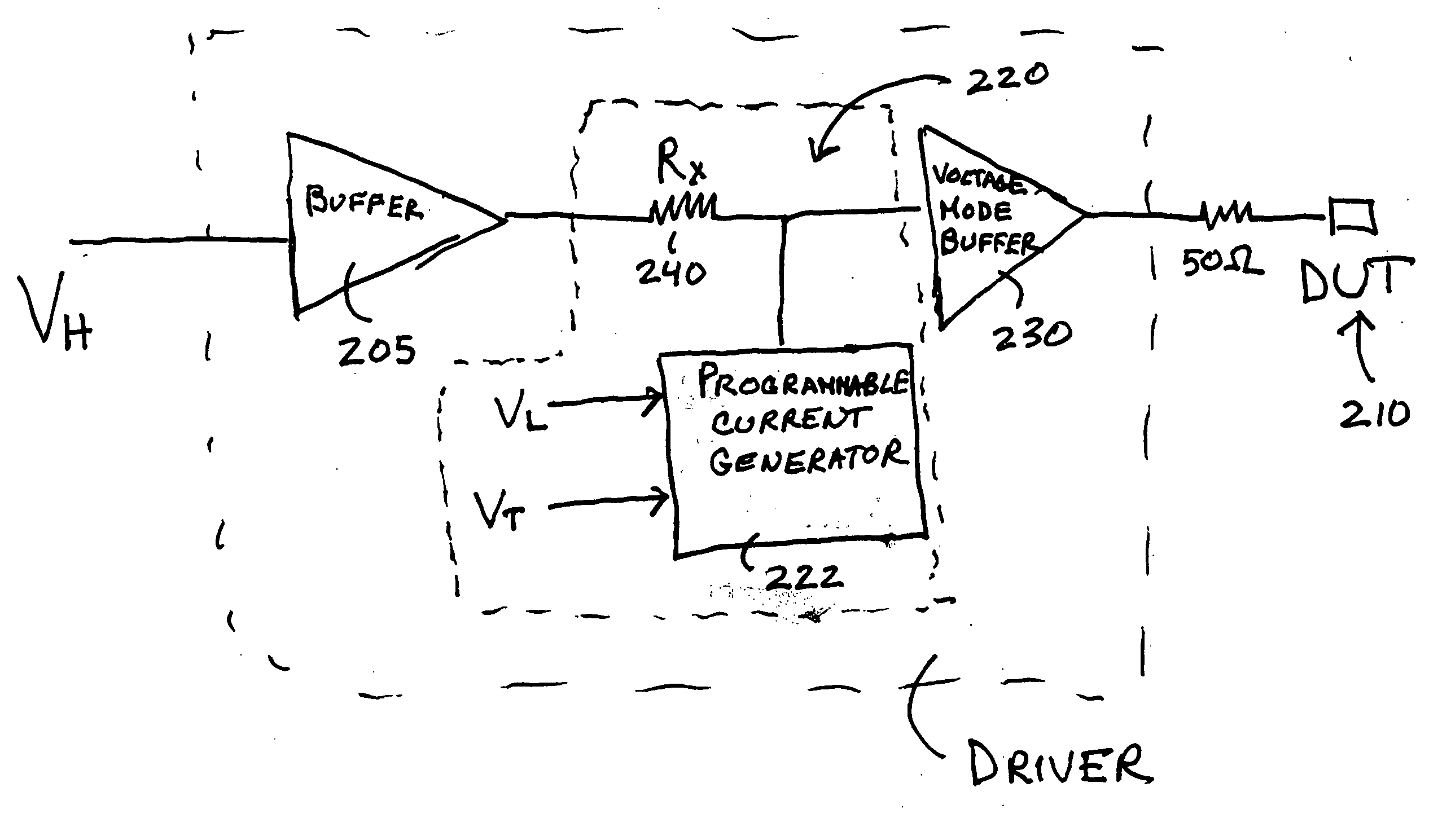
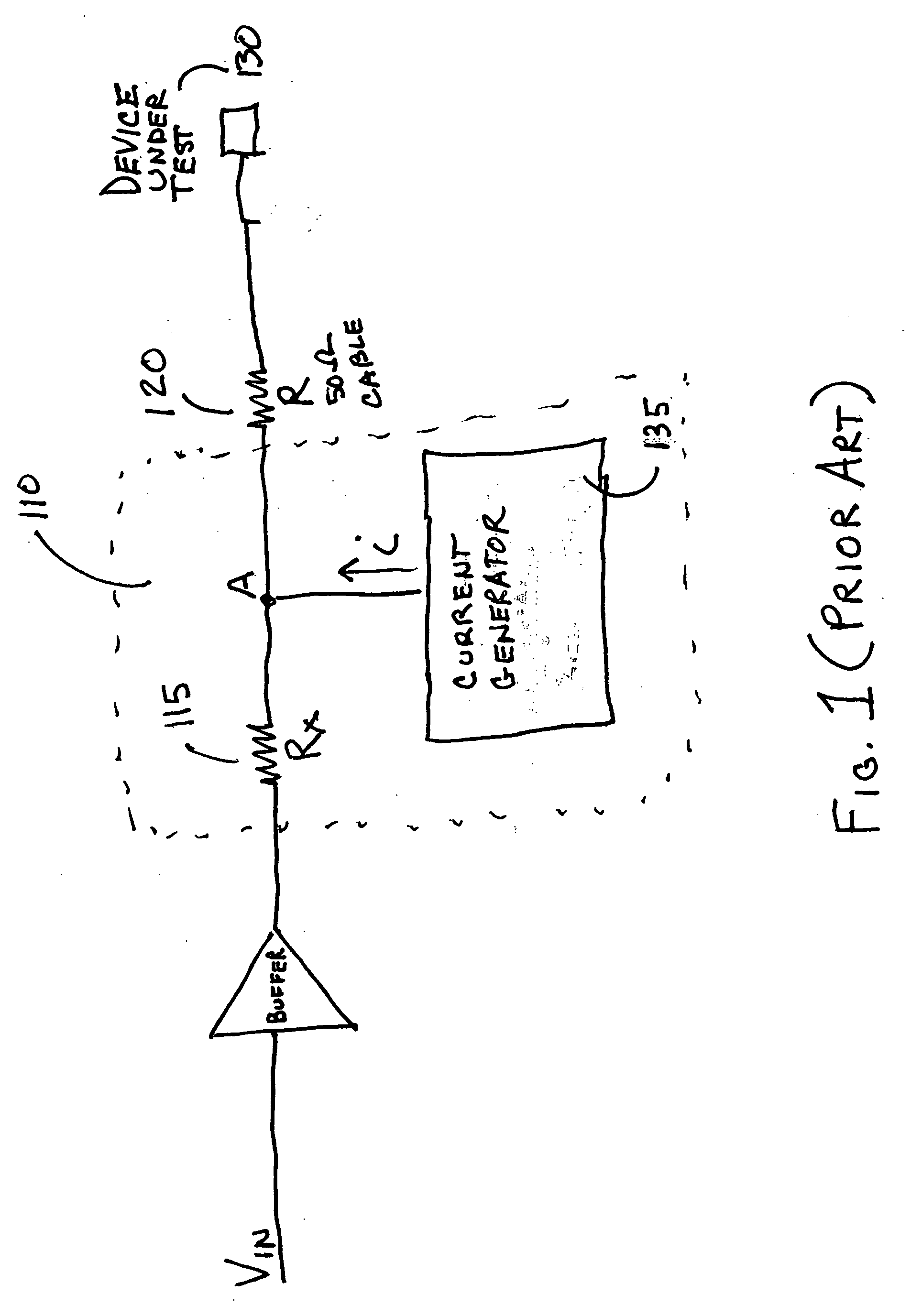
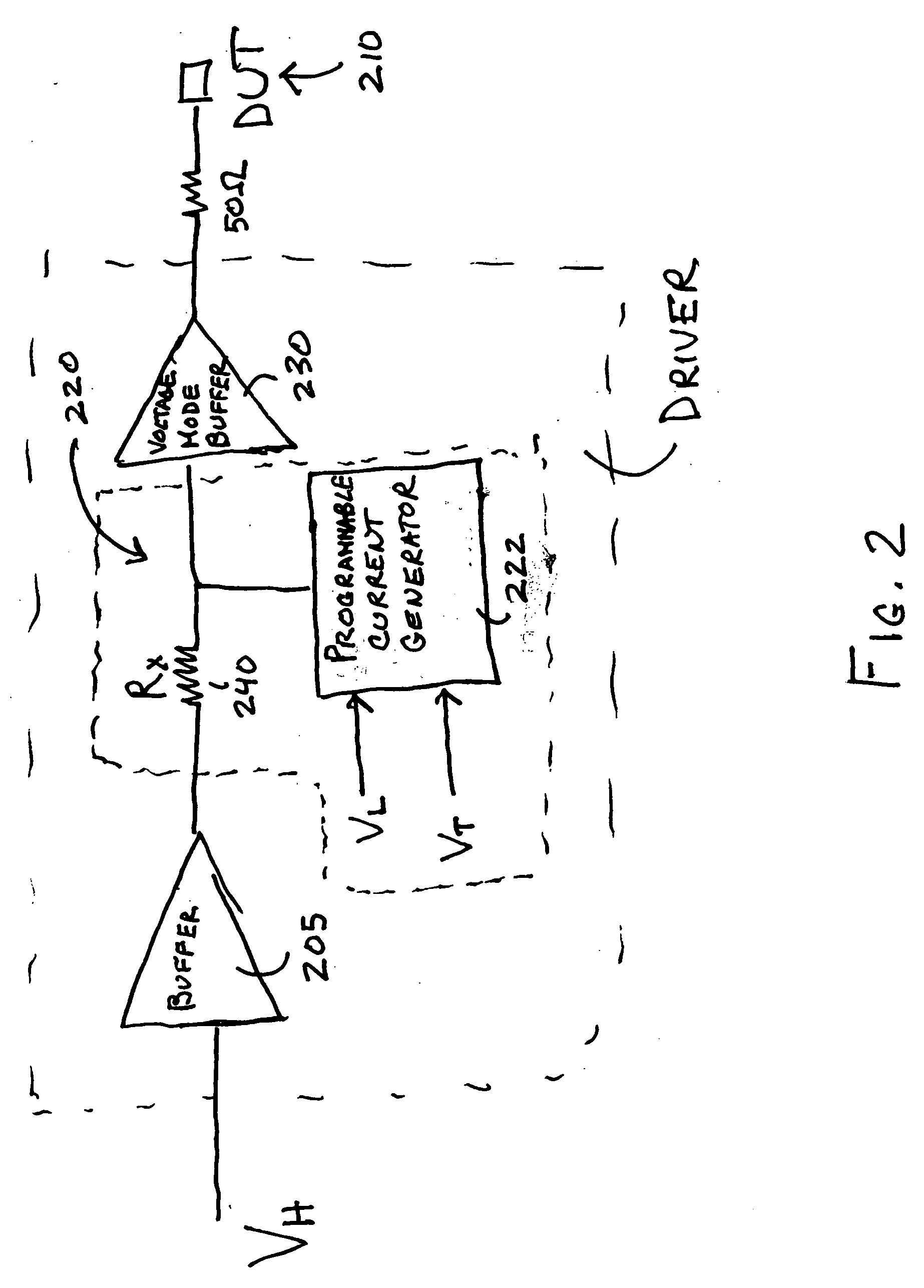
Current mode waveform generator followed by a voltage mode buffer
InactiveUS20060173641A1Quick changeRequired standing powerCurrent/voltage measurementElectrical testingPower savingLinear stage
A power saving circuit that creates a fast changing high resolution signal for testing of a pin of a device under test is disclosed. The circuit of the invention includes a current mode waveform generator followed by a voltage mode buffer. For example, the current mode waveform generator may be an A-linear or KT-linear stage. The voltage mode buffer may be a class AB output stage. By including the voltage mode buffer after the current mode waveform generator, the required standing power for the driver circuit is reduced when compared to using a current mode waveform generator alone.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Self-adjusting load bar
A method is provided for assembling a load bar assembly. The method includes providing a first linear stage having a first alignment mechanism that is configured to move the load bar assembly in a first direction. A second linear stage is provided that includes a second alignment mechanism that is configured to move the load bar in a second direction that is different from the first direction. The first alignment mechanism is positioned with respect to the second alignment mechanism such that the first alignment mechanism and the second alignment mechanism are prevented from being back-driven. The first alignment mechanism and the second alignment mechanism are configured to lock if one of the first alignment mechanism and the second alignment mechanism fails.
Owner:INNOVENTOR ENG
Linear platform of double-shaft floating stator
InactiveCN102522356AAvoid shockHigh positioning accuracySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringDrive motor
The invention provides a linear platform of a double-shaft floating stator, which comprises a base, a first direction driving device, a second direction driving device and a working platform connected with the first direction driving device and the second direction driving device are fixed on the base; when the drive motors in the first direction driving device and the second direction driving device drive the working platform to move, the stators of the drive motors move along a direction opposite to the movement direction of the working platform. According to the invention, when the rotors of the drive motors propel the working platform to move, the stators of the drive motors drive a stator to slide toward a direction opposite to the movement direction of the working platform instead of directly acting on the base of the platform under the counterforce of the stators of the drive motors so as to avoid the impact on the base and improve the locating precision and the measuring precision of the linear platform, and the linear platform can be located at a micron level of locating precision.
Owner:DG HUST MFG ENG RES INST
Apparatus and method for handling fluids at nano-scale rates
ActiveUS8021130B2Reduce the liquid flow rateIncrease the cross-sectional areaMaterial nanotechnologyHeating or cooling apparatusThermal contactLinear displacement
Apparatus and Method for Handling Fluids at Nano-Scale Rates. A linear displacement pump produces non-pulsatile liquid flow rates as low as the nl / mm range. The pump includes a servo motor, a gear reduction, a lead screw, a linear stage, a barrel, and a plunger extending into the barrel and coupled to the stage. A microfluidic interconnect device can be coupled to the barrel. One or more of these pumps can be disposed in a thermally controlled pump assembly that includes a pump housing, a thermally conductive body disposed in the housing and including first and second opposing sides, and a temperature regulating element such as a thermoelectric device disposed in thermal contact with the thermally conductive body on a side thereof opposite to the barrel or barrels of the pumps.
Owner:SCIEX
Method and apparatus for conducting real-time process control of particle and fiber generation
A linear stage moves a laser along the collection plate of an electrospinning device. The stage supports the laser that is moved through the electrospinning / electrospraying deposition field by a continuous rotation servo motor. Stage movement is controlled by a control unit. Signal voltages collected are sectioned into concentric layers so that the extinction coefficient for each layer can be calculated without including the extinction coefficient from the previous layer. The extinction coefficients were used in the Beer-Lambert law to determine the diameter of fibers being deposited on the collection plate as well as the concentration of fibers deposited indicating deposition speed.
Owner:SKINNER JACK L +3
Method and device for measuring motion error of linear stage
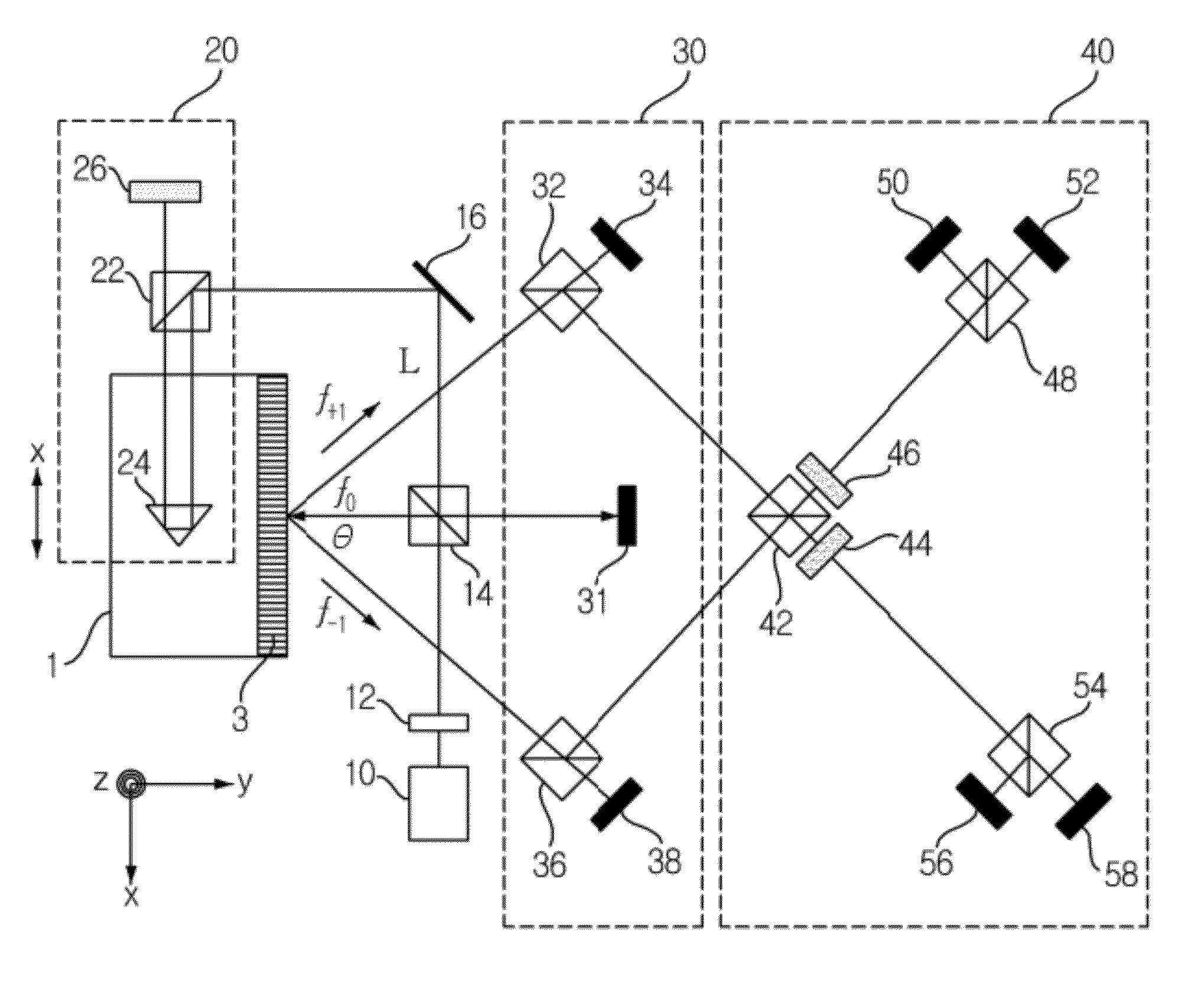
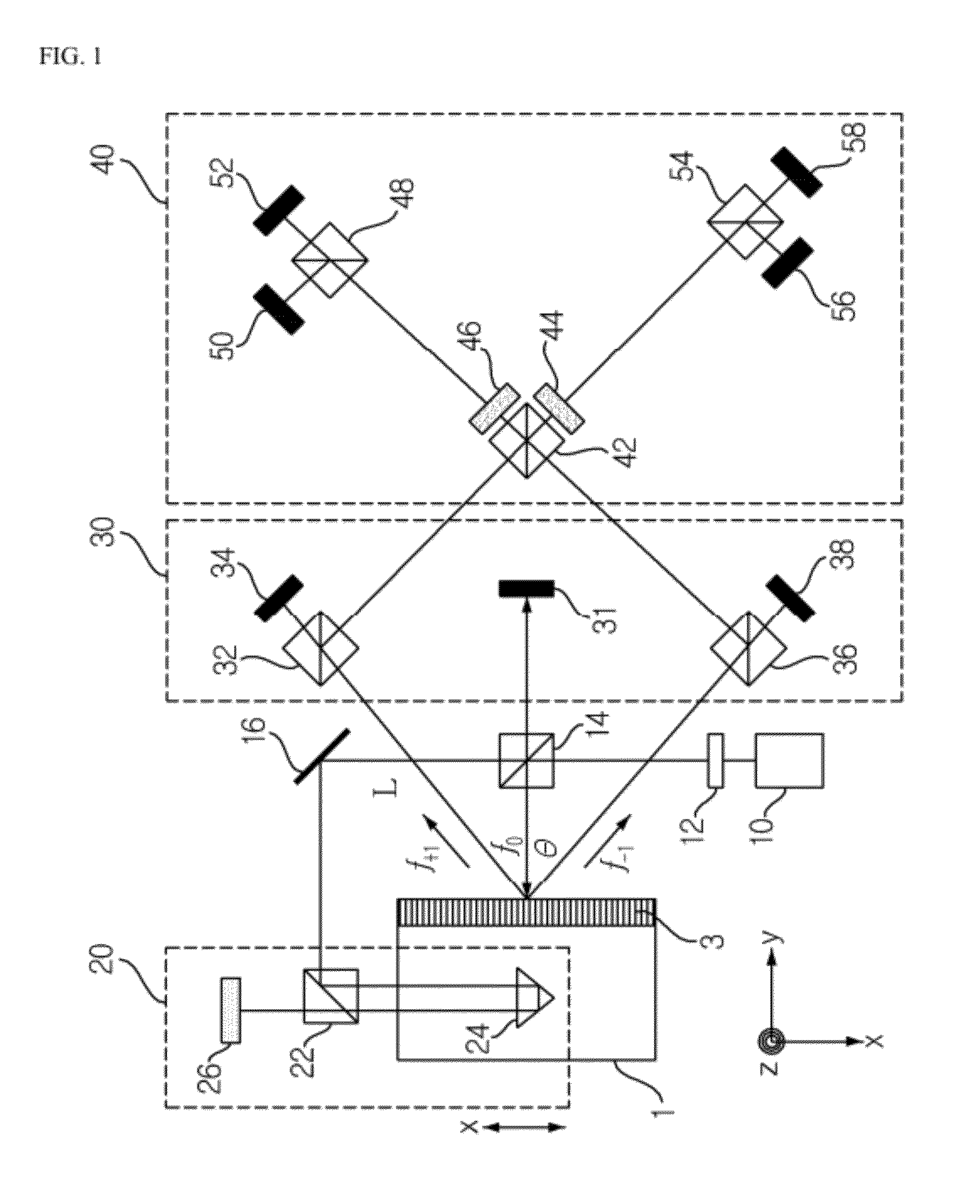
ActiveUS20120314220A1Accurate measurementInterferometersUsing optical meansLinear motionBeam splitter
Measurement of motion errors of a linear stage is performed to enable accurate measurement of motion errors in linear directions and a rotational direction in the linear stage using a diffraction grating. A first beam splitter splits a laser beam emitted from a light emitting unit. A first measurement unit measures a unidirectional linear motion error of the linear stage using one laser beam component split by the first beam splitter and a second measurement unit measures an angular motion error and another unidirectional linear motion of the linear stage error using a diffracted beam component obtained by diffracting another laser beam component split by the first beam splitter through the diffraction grating. A third measurement unit circularly polarizes the beam component diffracted through the diffraction grating to measure a third unidirectional linear motion error of the linear stage.
Owner:GWANGJU INST OF SCI & TECH
Measuring method for linear stage
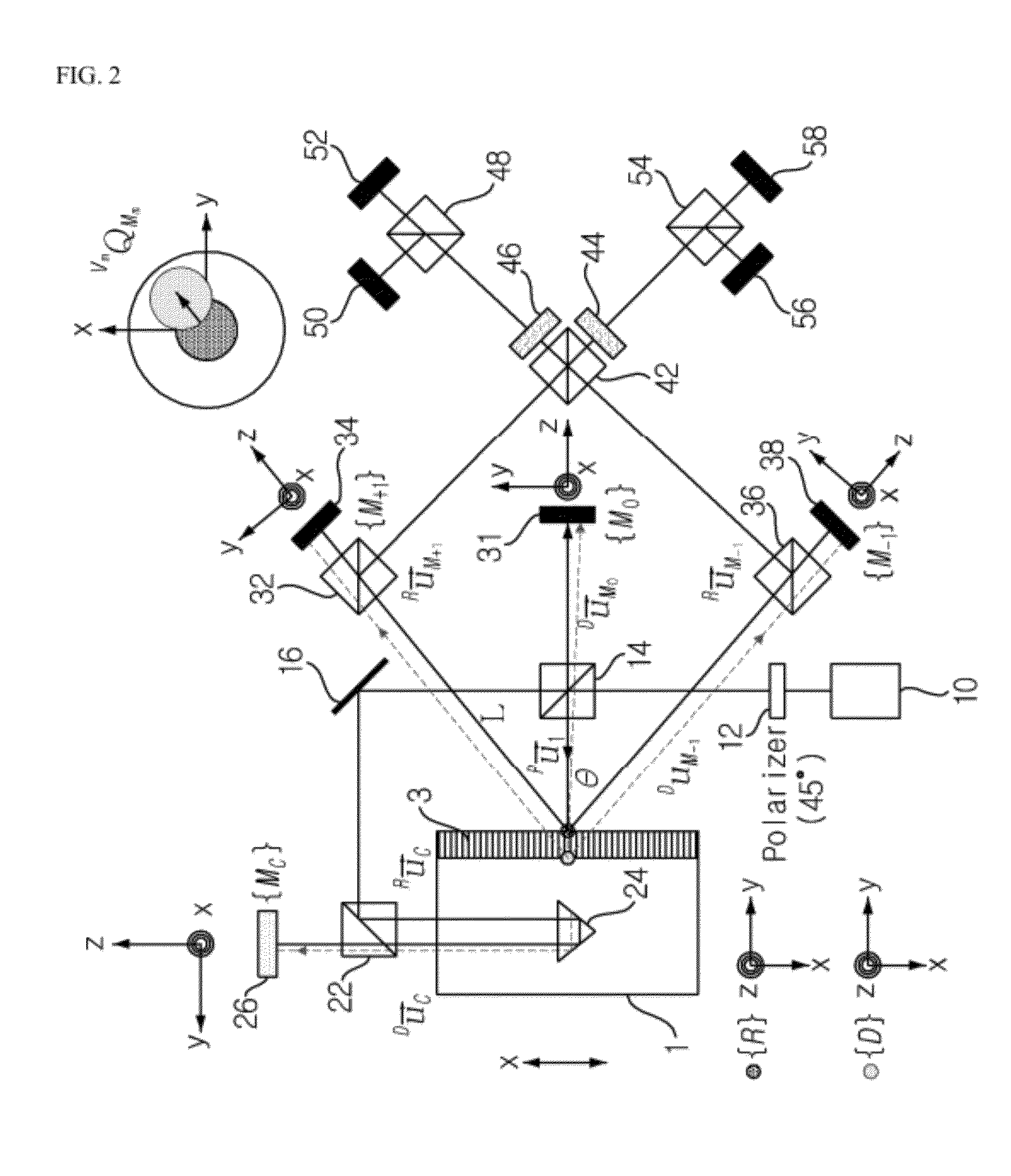
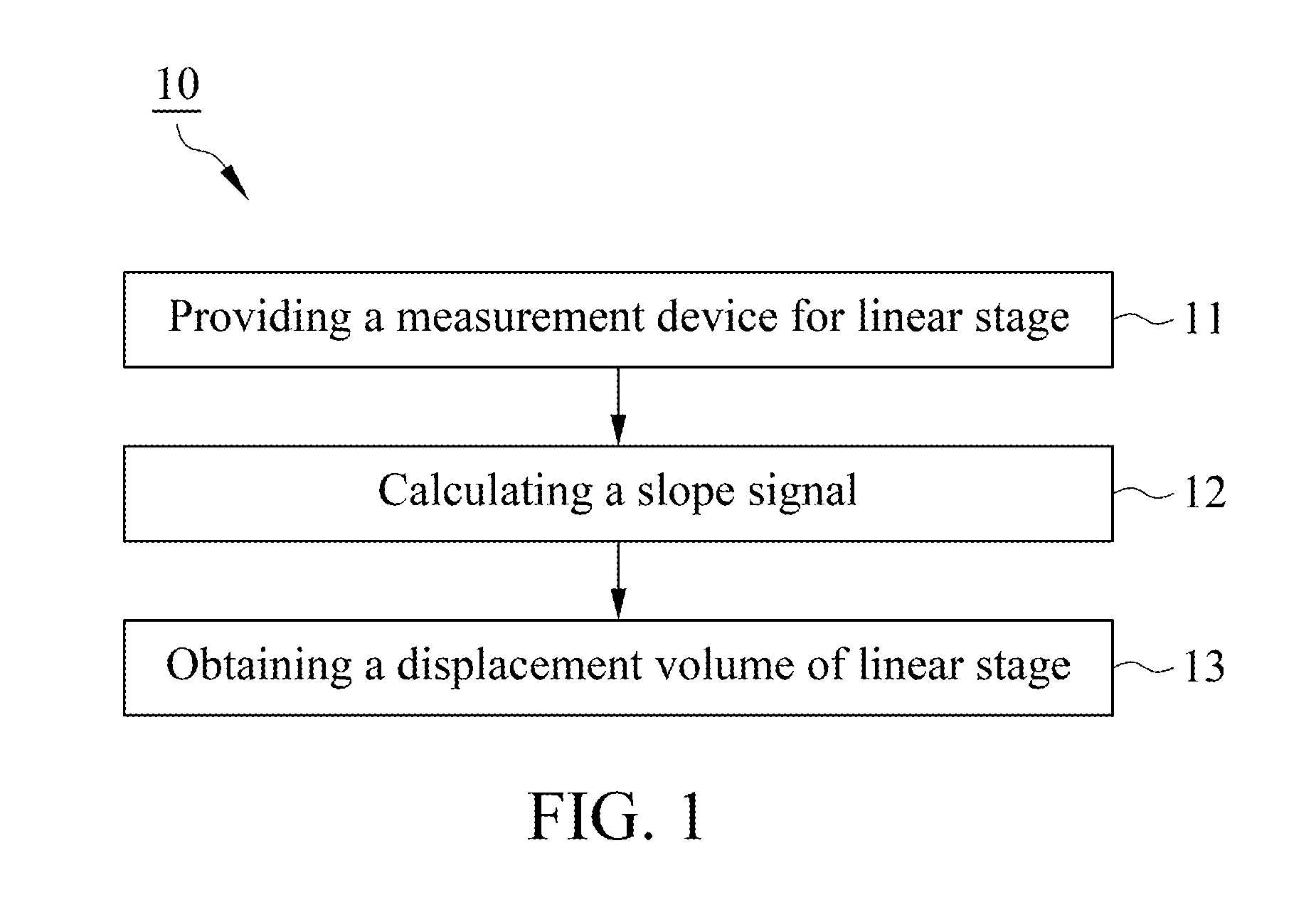
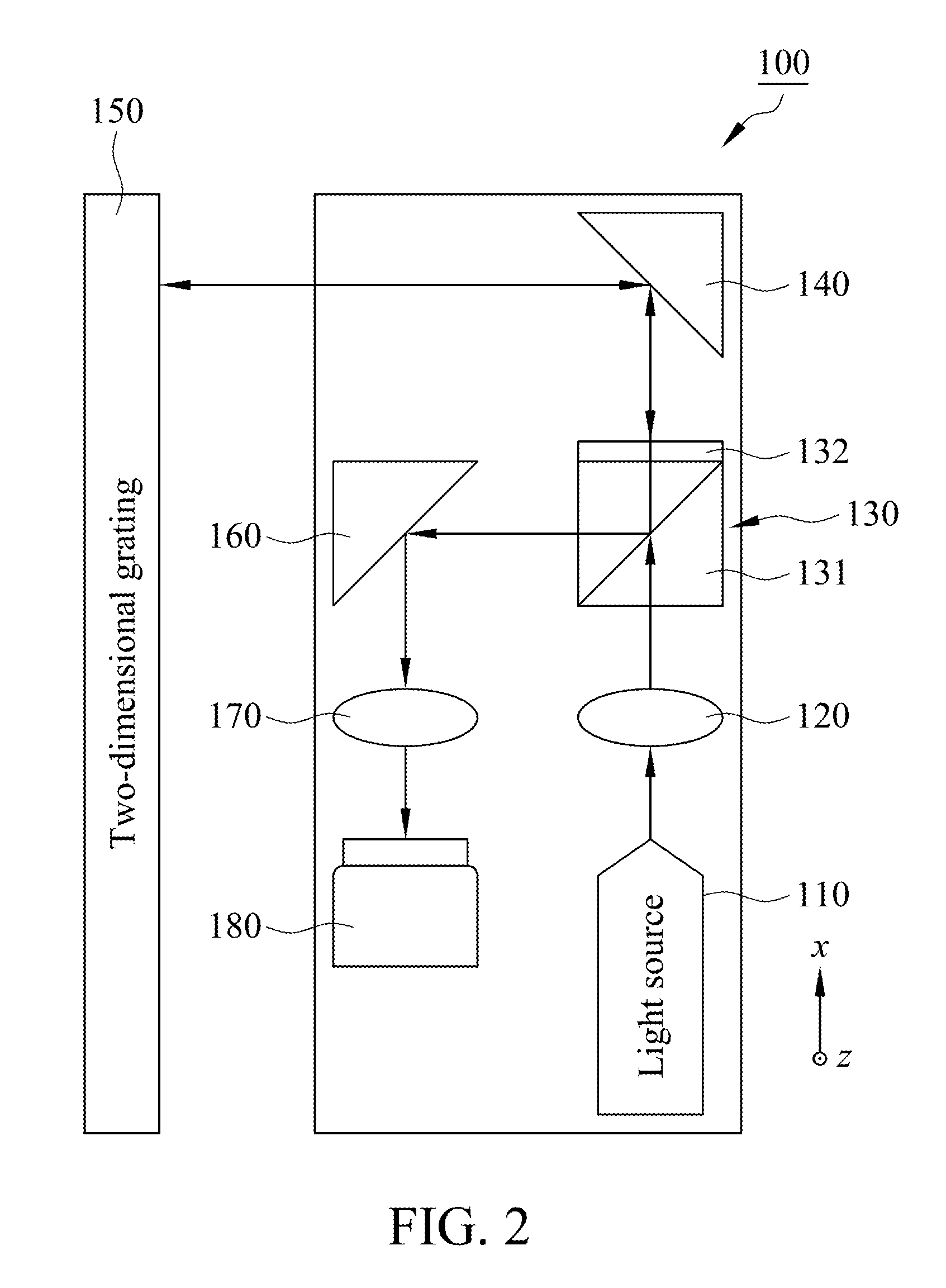
ActiveUS9255788B1Simplified and rapid calculationSuitable for measuringUsing optical meansGratingPhotodiode
A measuring method for linear stage used for measuring a displacement volume of a linear stage includes a light source, a two-dimensional grating, a quadrant photodiode and a processor. The light source provides an incident light, and the two-dimensional grating is disposed in light path of the incident light and reflects the incident to form a reflection light. The quadrant photodiode is disposed in light path of the reflection light and receives the reflection light for generating a plurality of sensing signals. The processor receives the sensing signals and utilizes the sensing signals to calculate a slope signal by a slope signal equation of the two-dimensional grating and an initial position signal and an end position signal by a position signal equation of the two-dimensional grating. The processor obtains the displacement volume of the linear stage by the slope signal, the initial position signal and the end position signal.
Owner:METAL INDS RES & DEV CENT
Bidirectional cantilever-type piezoelectric vibration energy collection device
InactiveCN108199618AChange the vibration amplitudePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesVertical vibrationElectricity
The invention belongs to the field of energy collection equipment, and discloses a bidirectional cantilever-type piezoelectric vibration energy collection device. The bidirectional cantilever-type piezoelectric vibration energy collection device comprises a horizontal engine base, a vertical engine base and two piezoelectric devices, wherein the vertical engine base is vertically arranged on the horizontal engine base, each piezoelectric device comprises a piezoelectric sheet clamping block, a magnet fixing block, a magnet and a piezoelectric sheet, a gap exists between the two magnets, magnetic poles at sides opposite to each other are dotted magnetic poles, so that the vibration amplitude of the piezoelectric sheet is amplified, and the collected energy is improved. By the two orthogonalpiezoelectric sheets with the magnets at tail ends and by an effect of a repulsive effect between the magnets, the deformation of the piezoelectric sheets can be caused during vertical vibration andhorizontal vibration, so that two-dimensional vibration energy can be collected, vibration enters a non-linear stage, and the collected energy is also improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
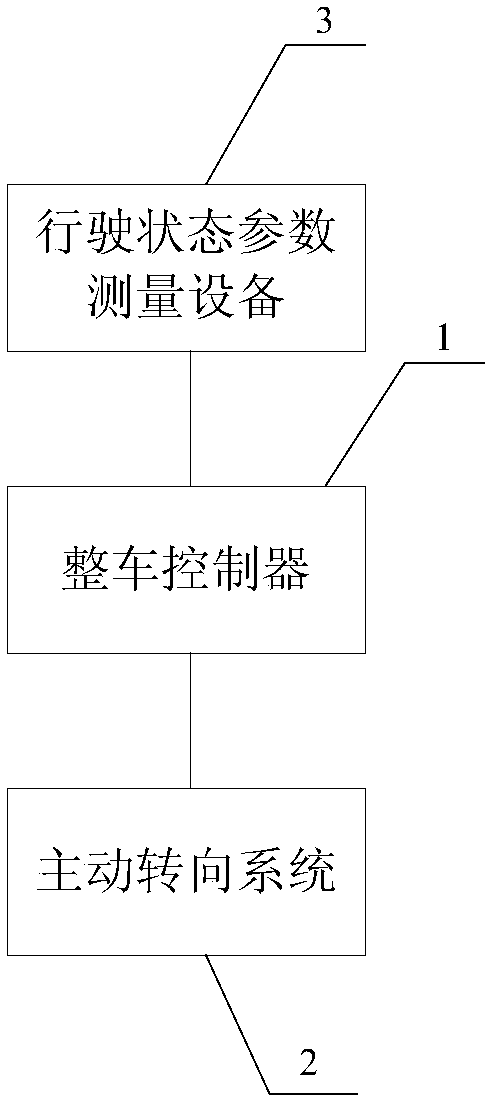
Control method and device for unstable vehicle and intelligent vehicle
The embodiment of the invention provides a control method and device for an unstable vehicle and an intelligent vehicle. The control method for the unstable vehicle comprises the steps that accordingto a speed parameter and mass center parameter of the vehicle, a first feedforward front wheel steering angle is obtained, wherein the first feedforward front wheel steering angle is a front wheel steering angle corresponding to that a front shaft lateral force of a mimical vehicle is in a linear stage of a transverse tire force model; according to the first feedforward front wheel steering angleand a tire slip angle corresponding to the front shaft lateral force of the vehicle, a second feedforward front wheel steering angle is predicted; according to the sum of the first feedforward front wheel steering angle and the second feedforward front wheel steering angle and a maximum angle of the front wheels of the vehicle allowed to be rotated, a driving front wheel steering angle is obtained, so that when the front wheel steering angle of the vehicle is controlled to be the driving front wheel steering angle, the vehicle enters a stable state from an unstable state. The control method and device for the unstable vehicle and the intelligent vehicle can make the unstable vehicle enter the stable state from the unstable state.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
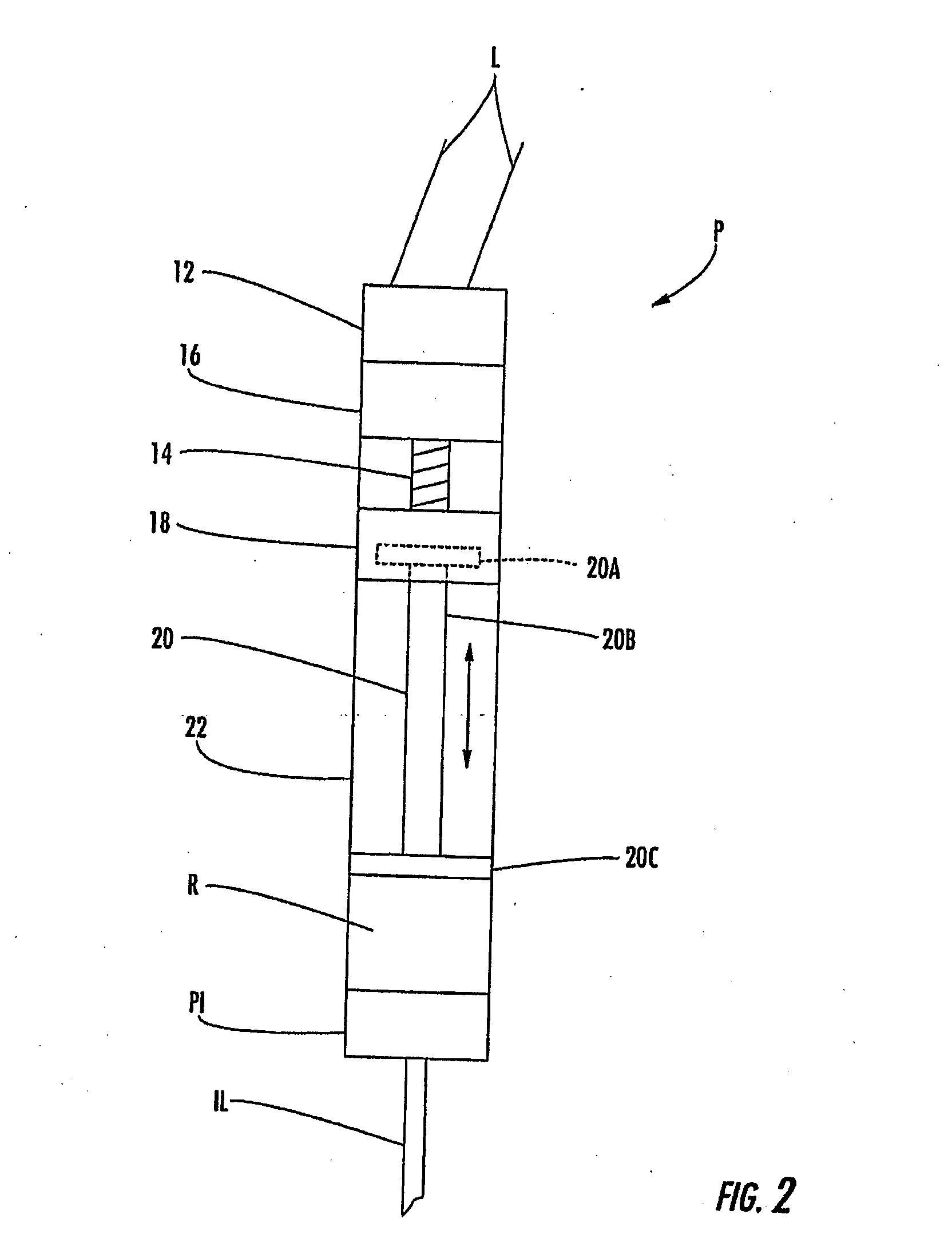
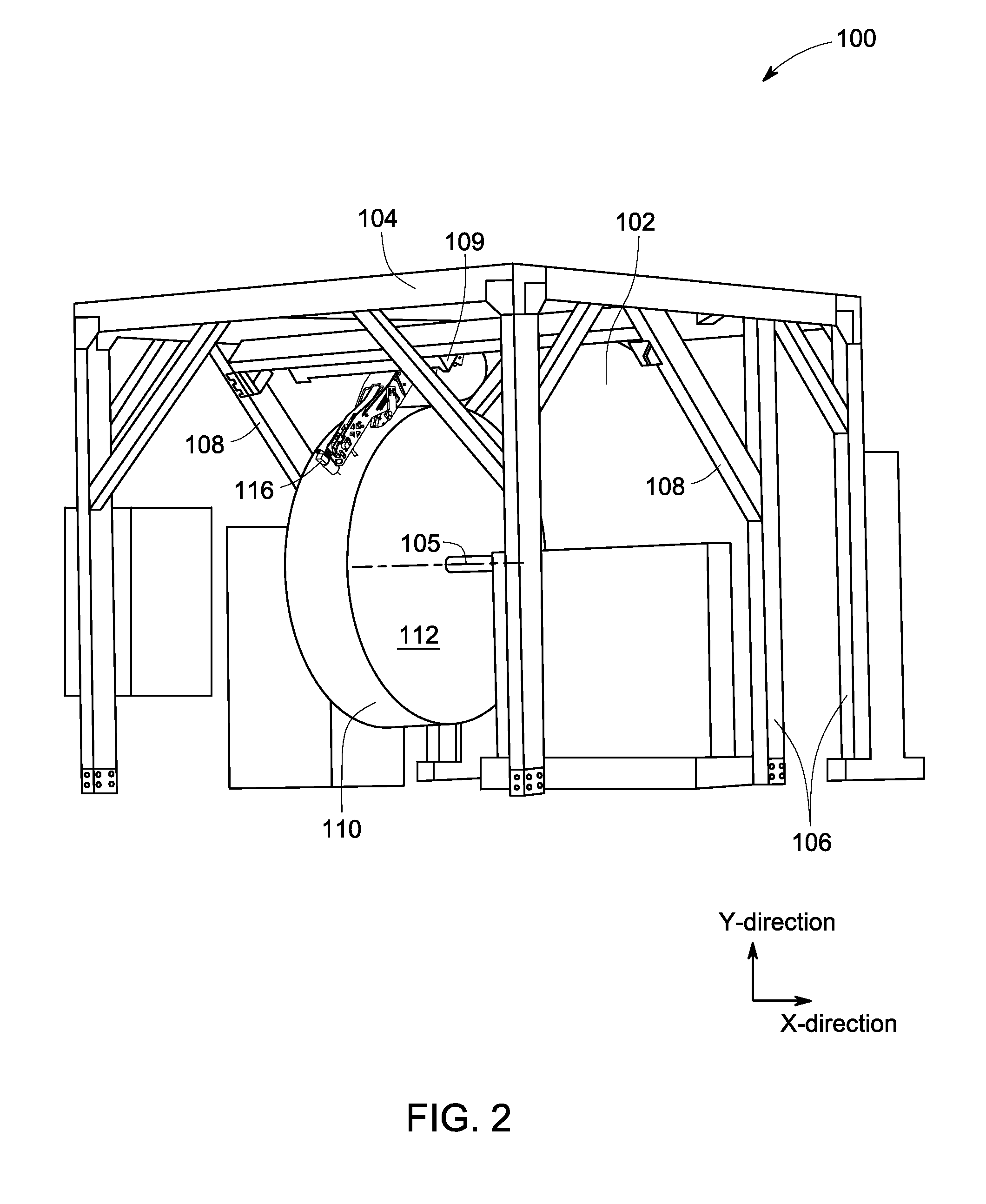
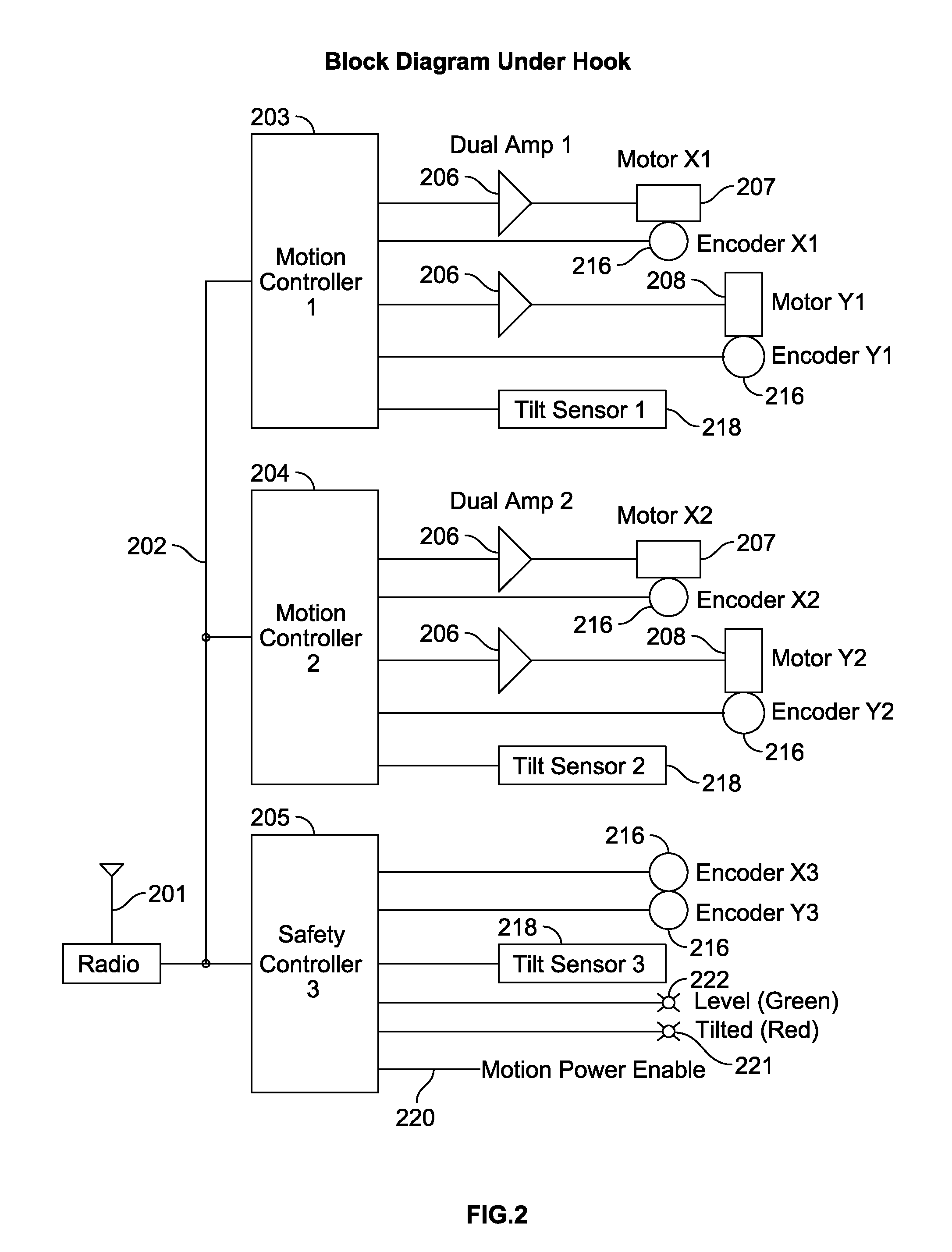
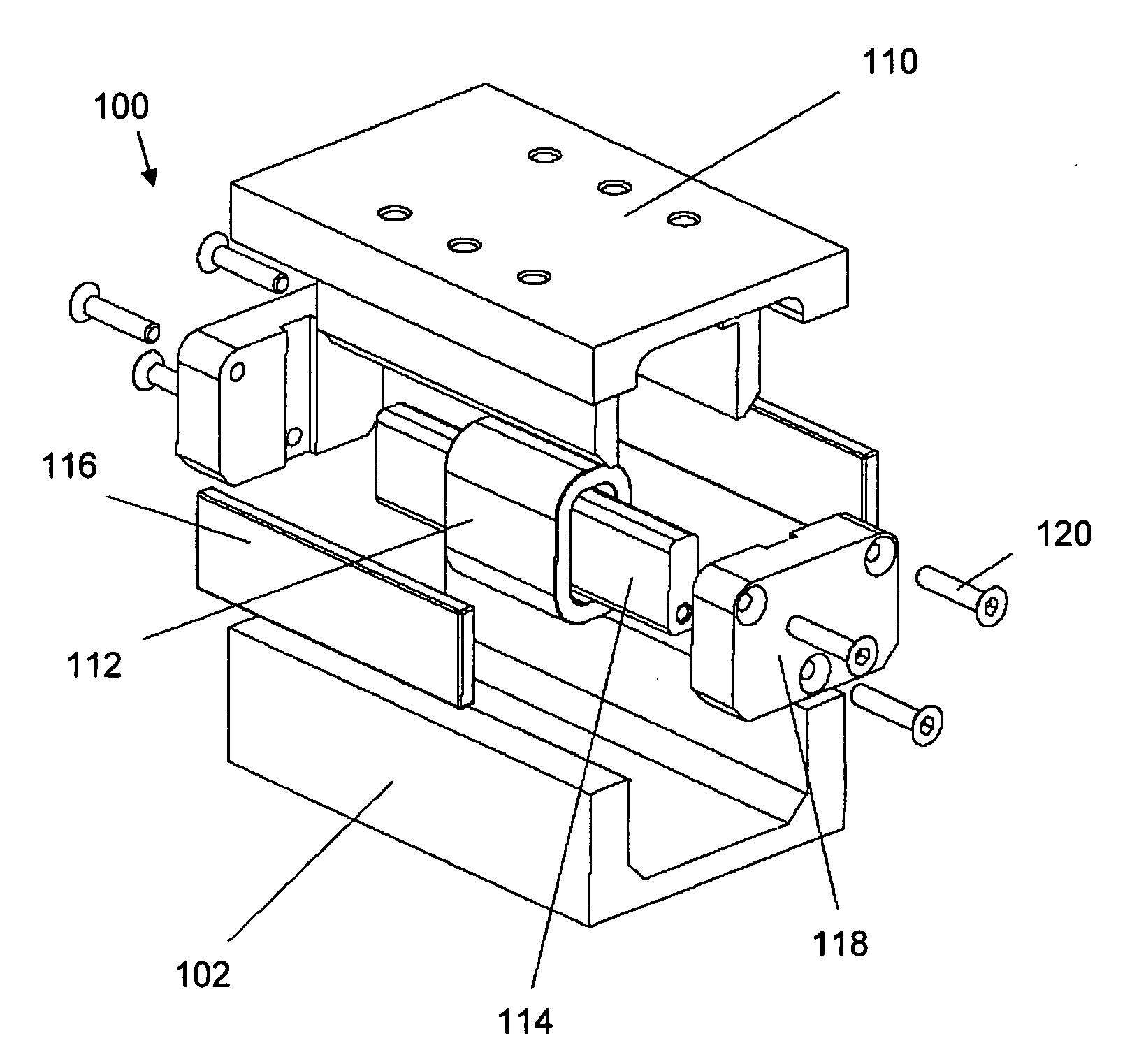
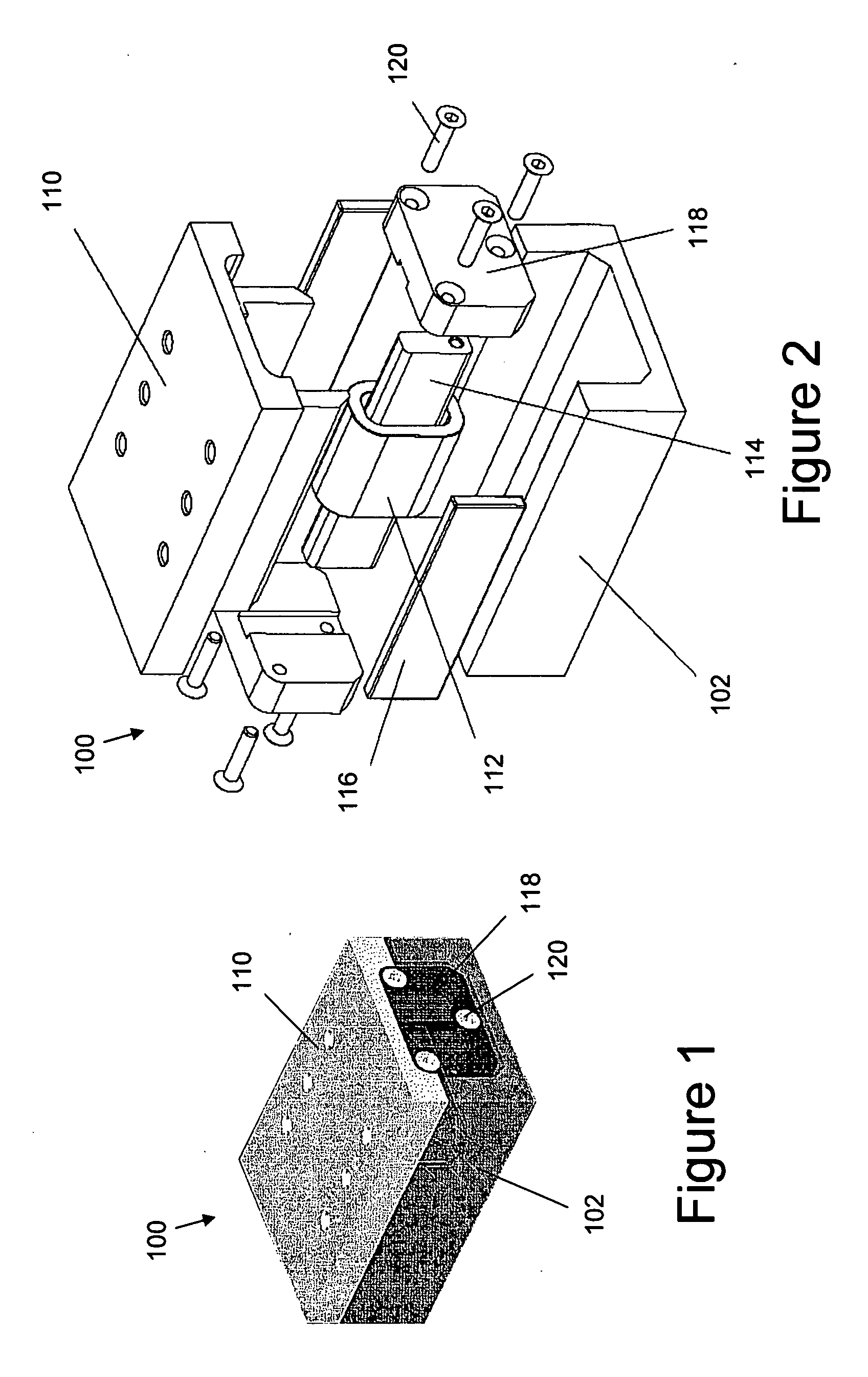
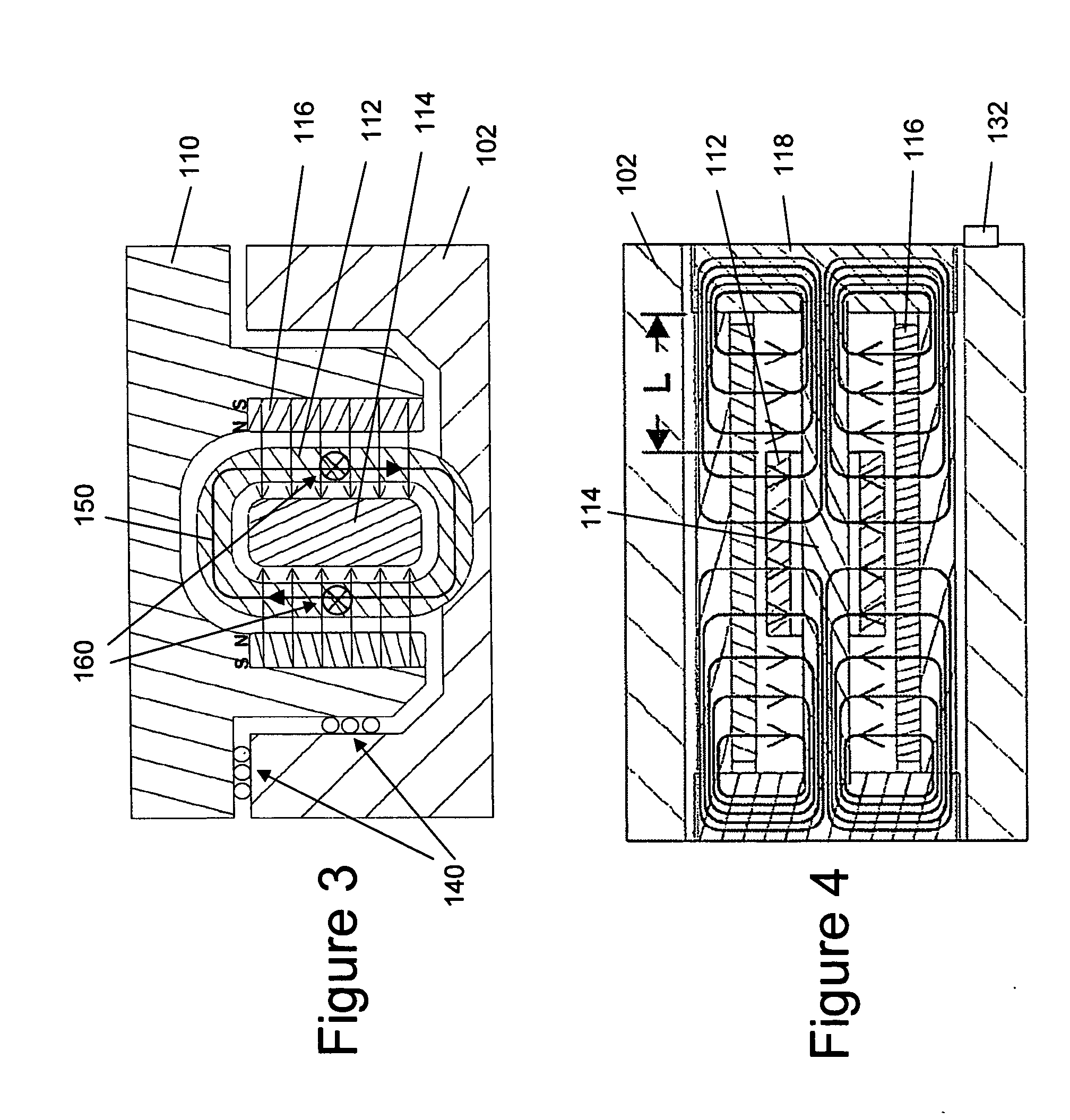
Linear stage including an integrated actuator and associated methods
InactiveUS20070133117A1Improve accuracyReduce frictionDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageMagnetic sourceEngineering
According to one example a linear translation stage is provided. The linear stage includes a first portion (e.g., a base portion) and a second portion (e.g., a stage portion) configured for relative translation with respect to each other. One of the first portion or the second portion has a coil associated therewith and the other of the first portion or the second portion has a magnetic source associated therewith. The magnetic source may include one or more magnets to produce a magnetic field that generally encompasses the coil such that current through the coil causes a force on the coil, thereby causing translation of the first portion relative to the second portion.
Owner:NEWPORT CORP
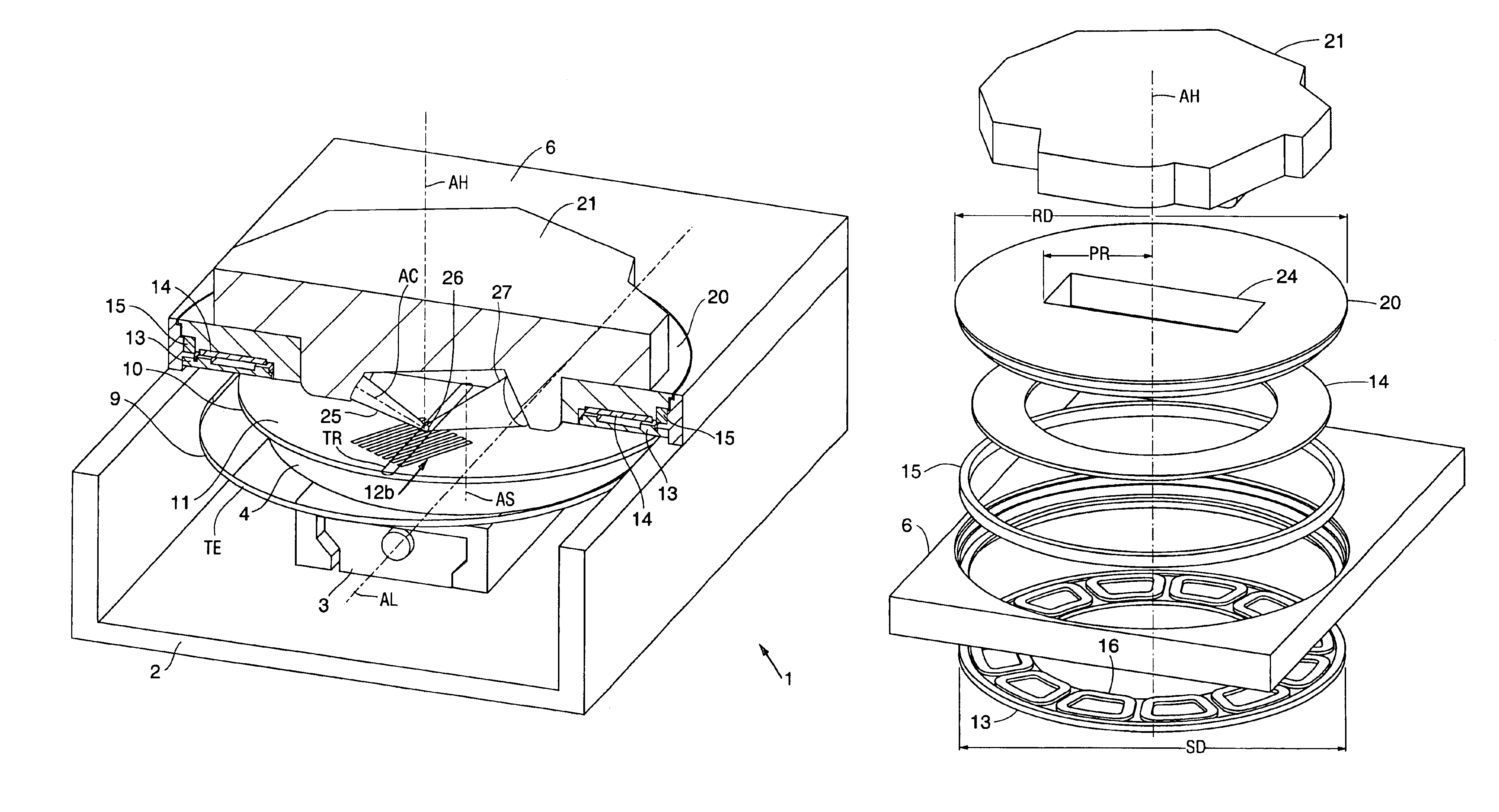
Rotating head ellipsometer
InactiveUS6882413B2Significant informationEnhanced informationPolarisation-affecting propertiesLight polarisation measurementRotary stageLight beam
An ellipsometric apparatus provides a rotating focused probe beam directed to impinge a sample in any direction. A rotating stage rotates the wafer into a linear travel range defined by a single linear axis of a single linear stage. As a result, an entire wafer is accessed for measurement with the single linear stage having a travel range of only half the wafer diameter. The reduced single linear travel results in a small travel envelope occupied by the wafer and consequently in a small footprint of the apparatus. The use of a rotating probe beam permits measurement of periodic structures along a preferred direction while permitting the use of a single reduced motion stage.
Owner:THERMA WAVE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com