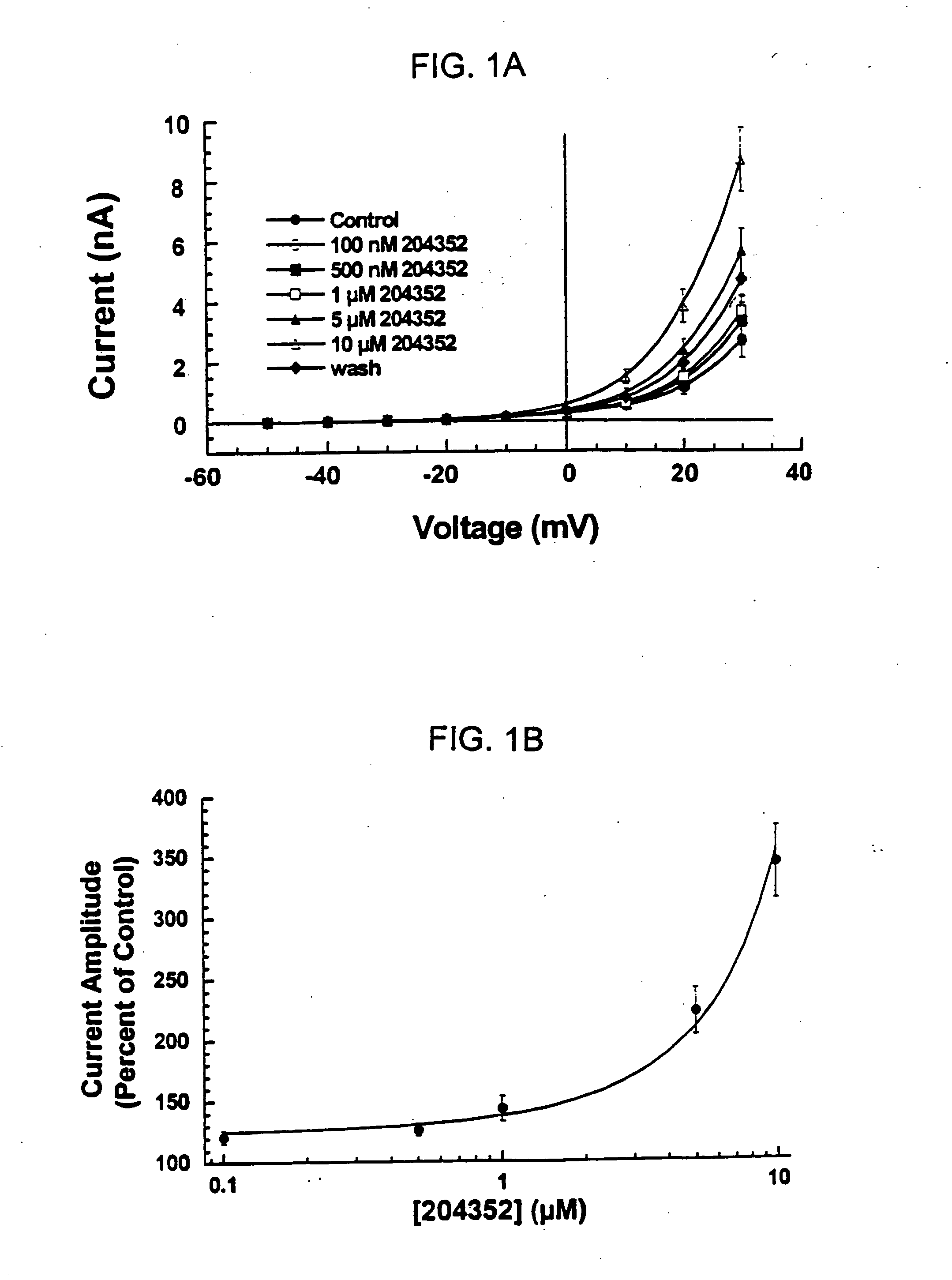
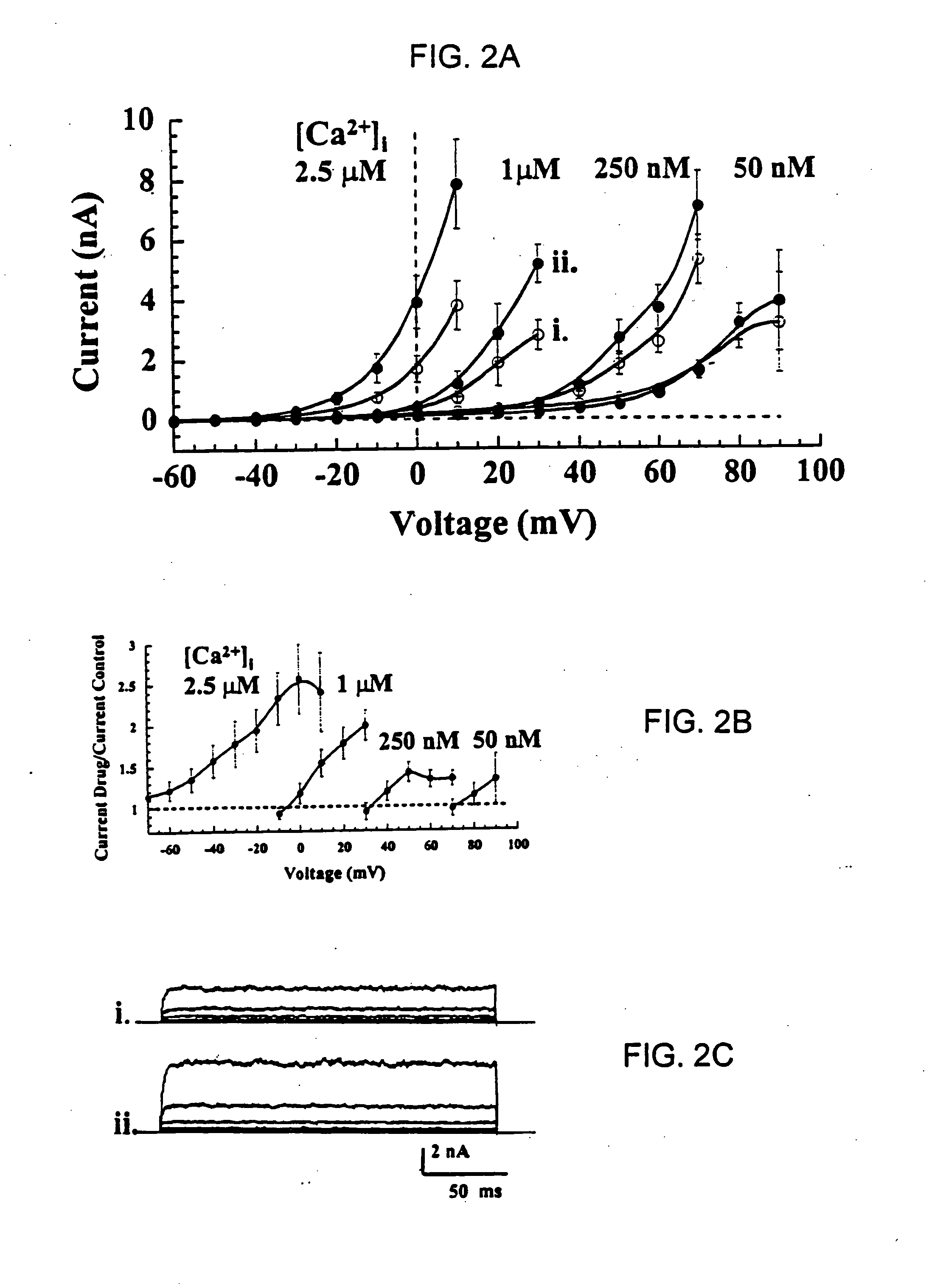
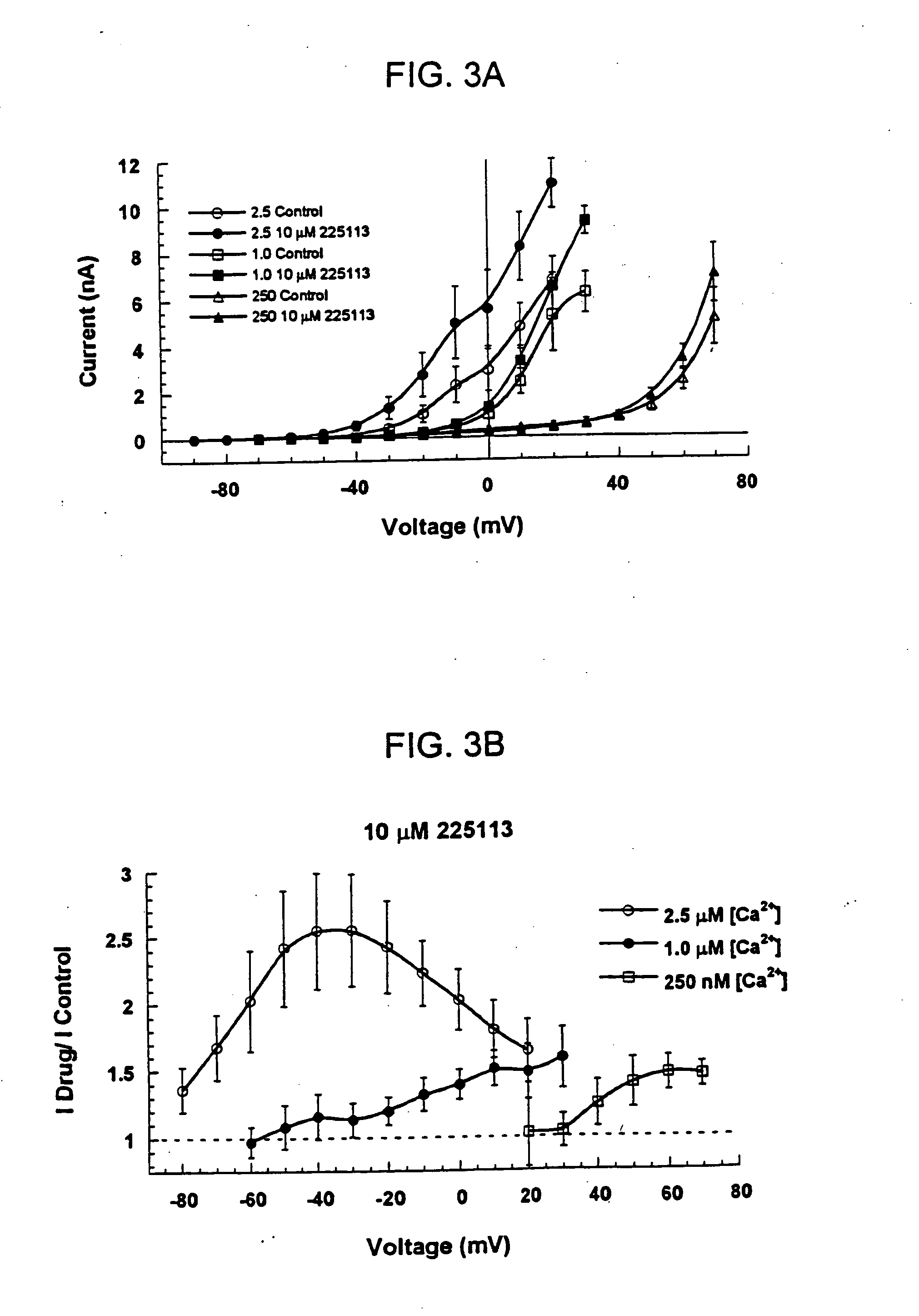
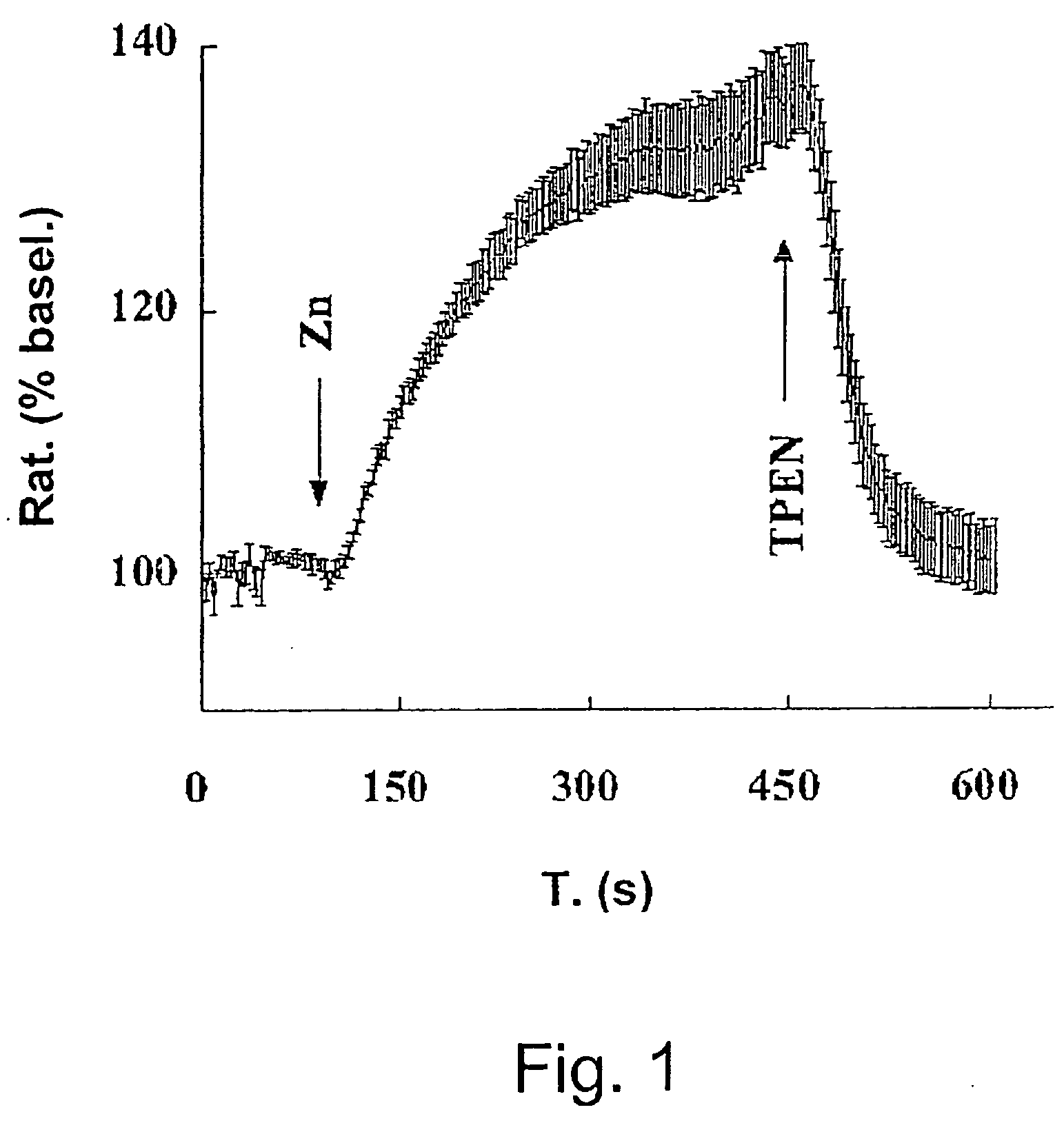
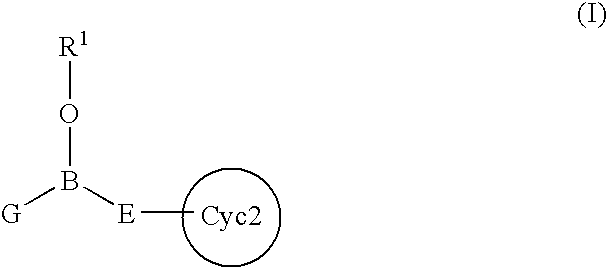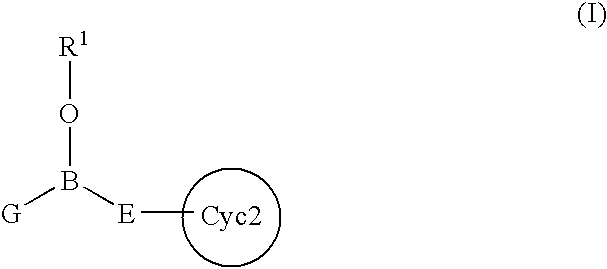Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
43 results about "Intracellular ca" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Intracellular calcium concentration increase inhibitors
InactiveUS7217701B2Effective controlImprove effective controlBiocideSenses disorderBronchial epitheliumBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
An intracellular calcium concentration increase inhibitor containing as the active ingredient (1) a boron compound represented by the formula (I).The compound represented by the formula (I) inhibits the increase of the intracellular calcium concentration, and therefore it is deemed to be useful as an agent for the prophylaxis and / or treatment of platelet aggregation, ischemic diseases in hearts and brains, immune deficiency diseases, allorgosis, bronchial asthma, hypertension, cerebrovascular spasm, various renal diseases, pancreatitis, Alzheimer's disease, etc.
Owner:MIKOSHIBA KATSUHIKO
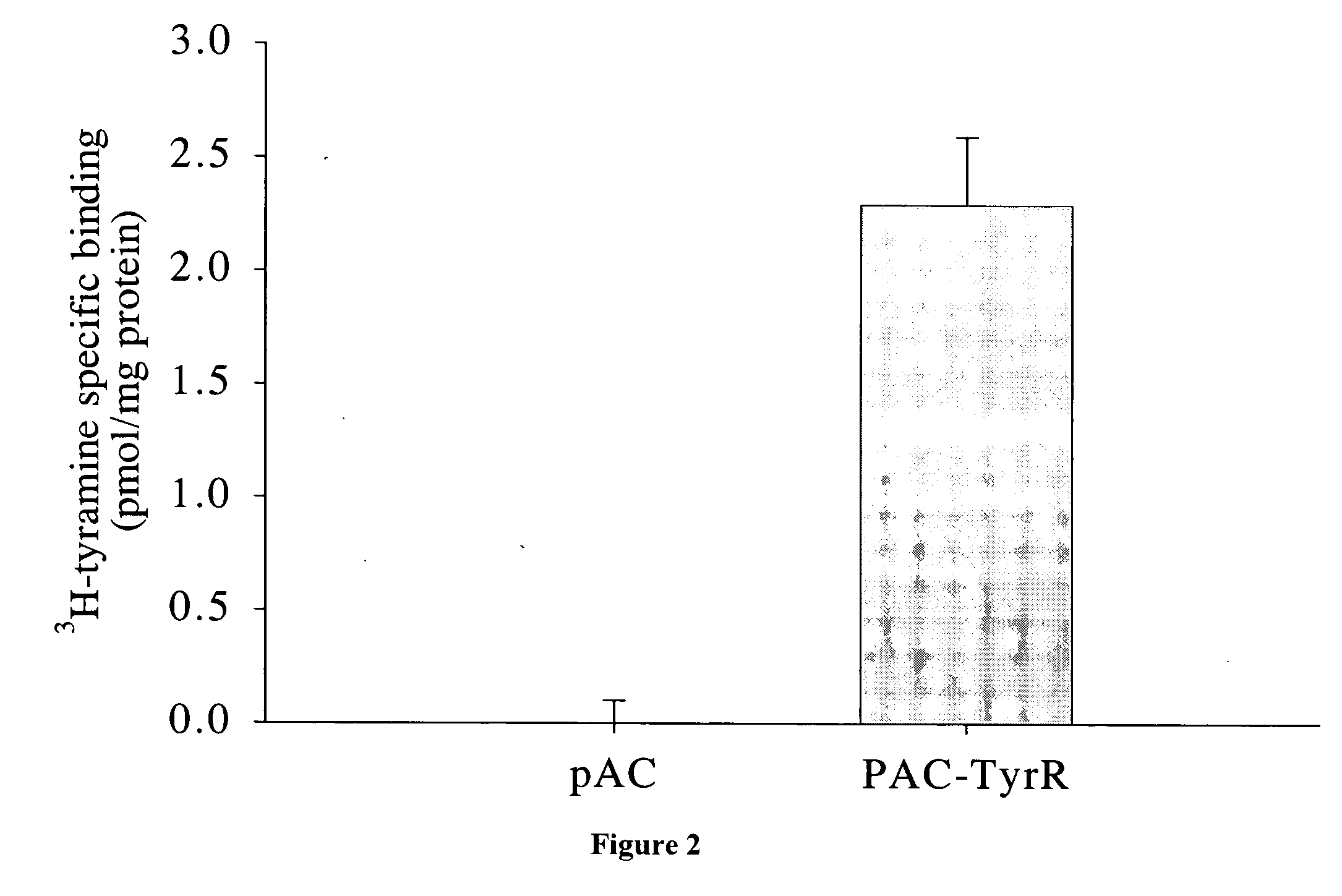
Compositions and methods for controlling insects involving the tyramine receptor
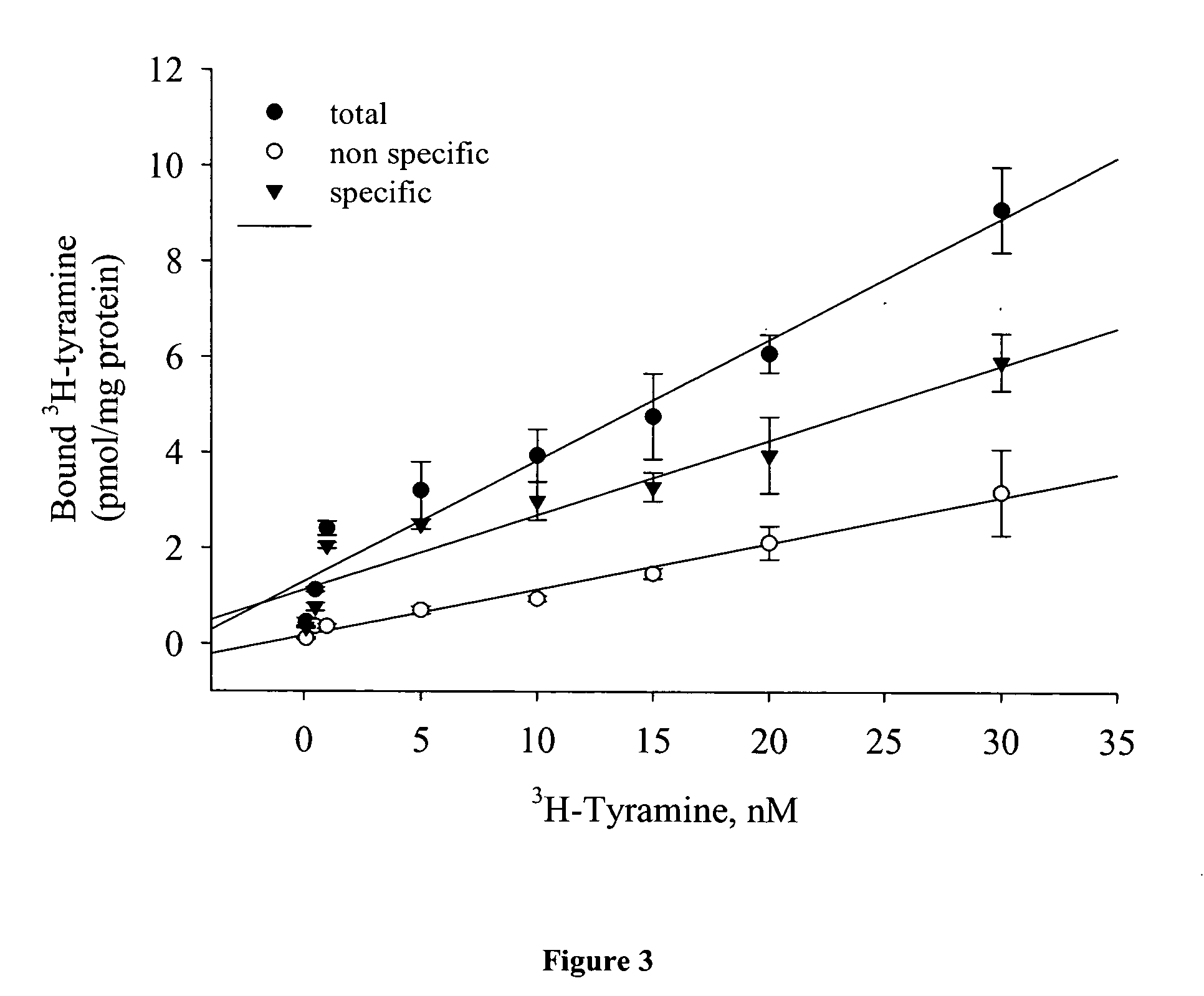
InactiveUS20060263403A1Improve the level ofHigh affinityBiocideCompound screeningCompound (substance)Tyramine receptors
An exemplary method of screening compositions for insect control activity includes, providing an insect cell expressing a receptor of the insect olfactory cascade or fragment thereof, contacting a test composition to the insect cell, measuring at least one parameter selected from olfactory cascade receptor binding affinity, intracellular cAMP levels, and intracellular Ca2+ levels, and selecting a compound capable of altering at least one of parameter selected from increased olfactory cascade receptor binding affinity, altered intracellular cAMP levels, and altered intracellular Ca2+ levels. An exemplary isolated eukaryotic cell is transformed with a nucleic acid encoding an insect olfactory cascade receptor protein or fragment thereof. An exemplary method for controlling an insect includes, contacting a composition including a compound having a binding affinity for an olfactory cascade receptor of an insect.
Owner:TYRATECH
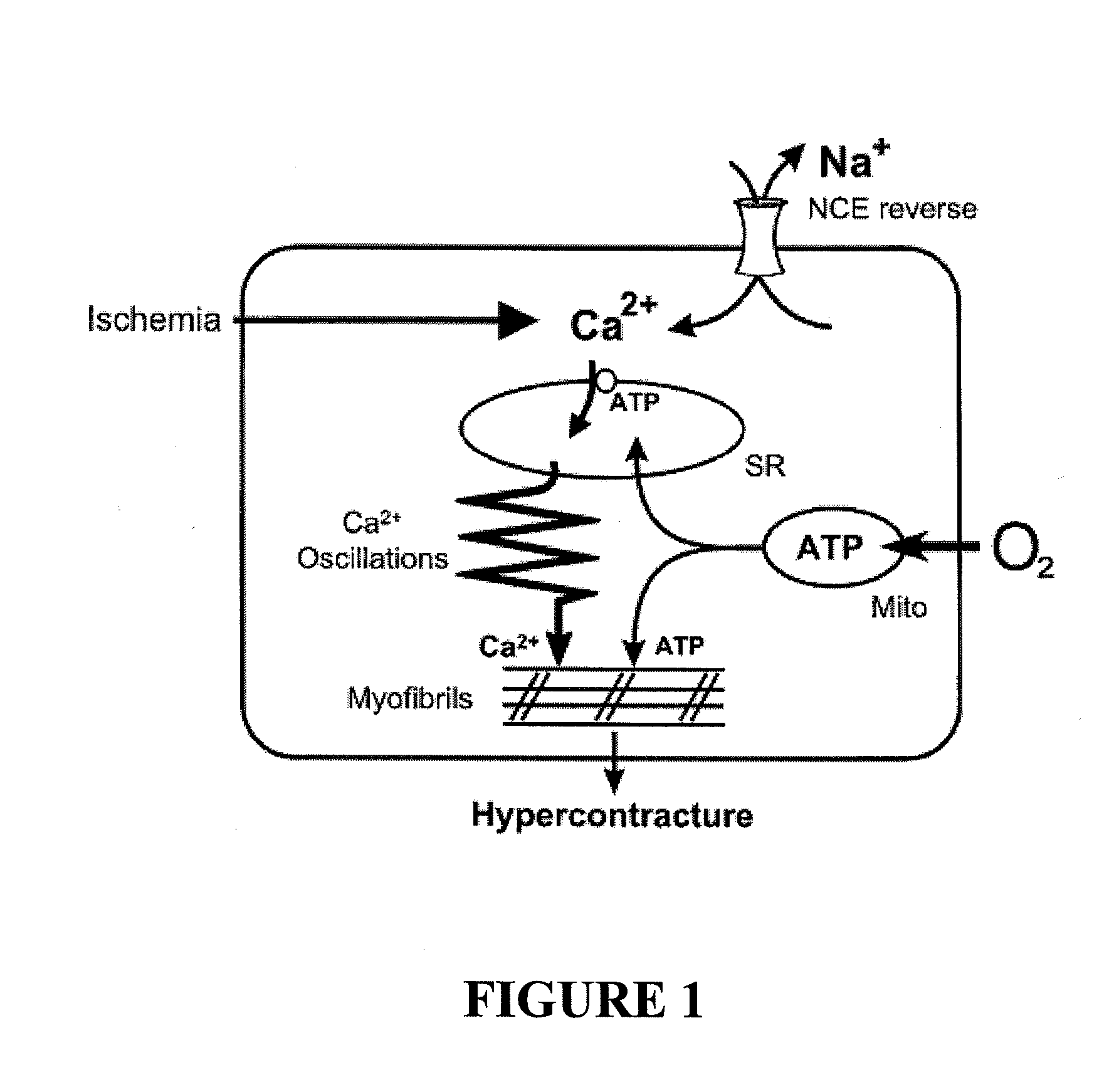
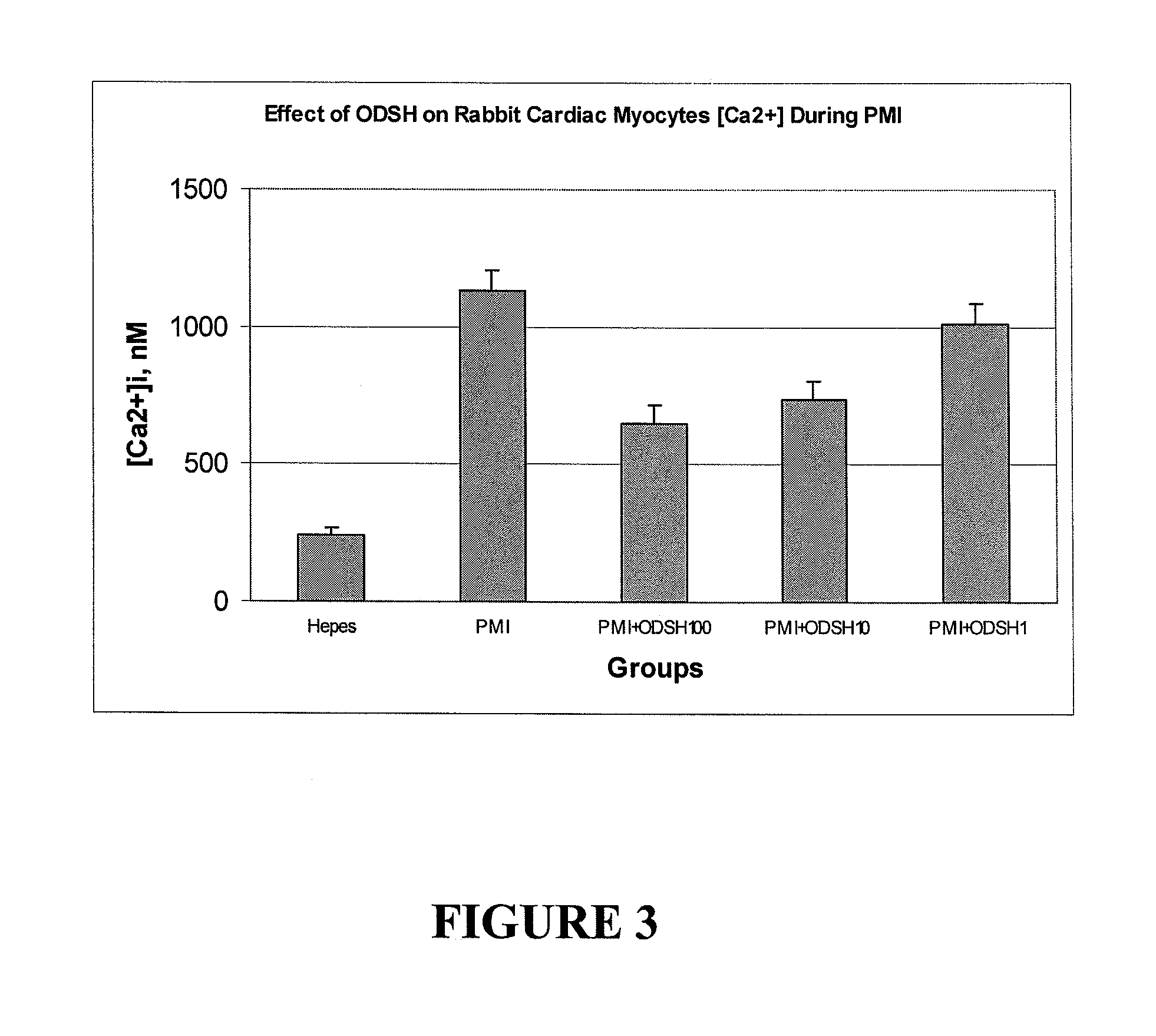
Methods for controlling intracellular calcium levels associated with an ischemic event
InactiveUS20090238852A1Loss of function of bodyOrganic active ingredientsTubular organ implantsO-desulfated HeparinEndocrinology
Described herein are methods for controlling the intracellular calcium concentration in a subject prior to experiencing an ischemic event, while experiencing an ischemic event, or while suffering from ischemia. The methods comprise administering an effective amount of O-desulfated heparin to the subject. The methods described herein are also useful in treating the symptoms associated with ischemic events or ischemia.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
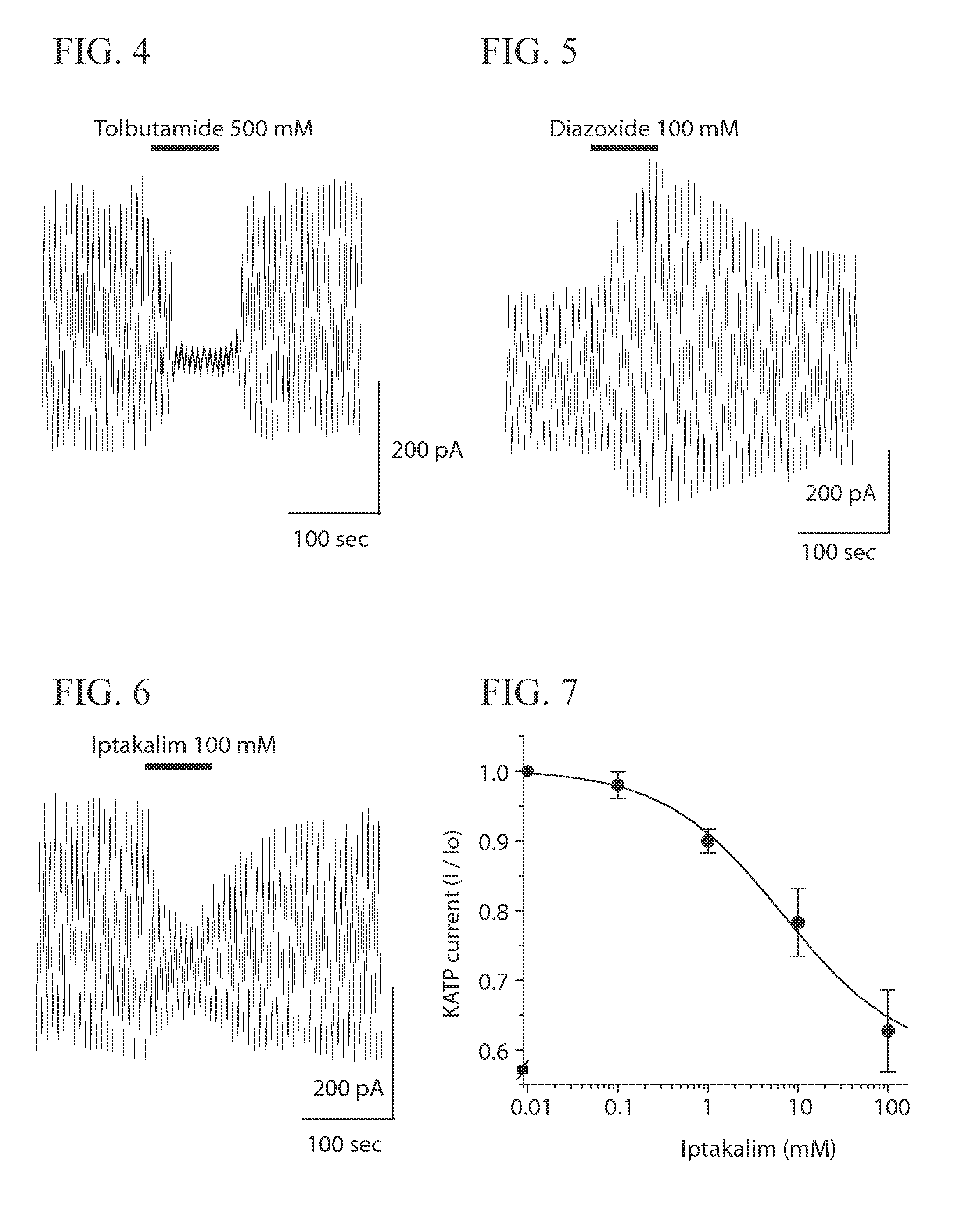
Method for Decreasing Blood Glucose Levels
InactiveUS20070231273A1Lower blood sugar levelsFacilitated releaseBiocidePill deliveryGlucose polymersD-Glucose
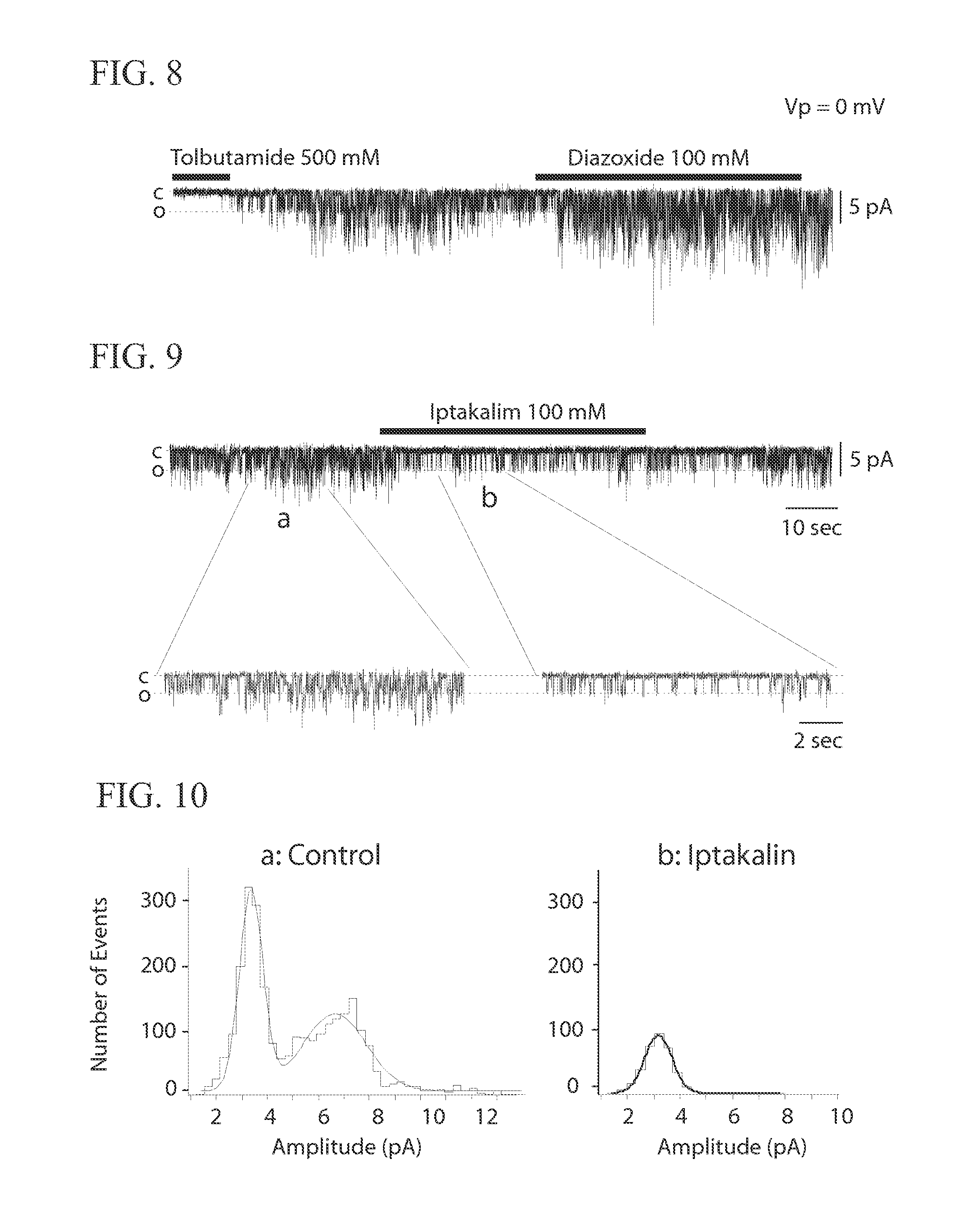
A method for decreasing blood glucose levels is disclosed. Iptakalim hydrochloride (a SUR1 subunit-dependent KATP channel blocker and a SUR2 subunit-selective KATP channel opener) is used to block pancreatic β-cell KATP channels, which depolarizes β-cells, elevates intracellular Ca2+ concentrations, and in turn increases insulin release. Therefore, in some implementations, iptakalim hydrochloride is an optimal treatment for type-2 diabetic patients with cardiovascular disorders.
Owner:WU JIE
Airway-specific trypsin-like enzymes and method of using the same
The subjects of the present invention are to provide a method of screening a compound or a polypeptide which inhibits the activity of AST, or inhibits PAR activation, mucus production promotion, cell proliferation, intracellular calcium influx or EGFR pathway activation due to AST, and further to provide a method of assaying AST in vivo and in biological cells or samples. The present invention further includes the following inventions. ASTs whose each is protein comprising the whole amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1 or 2 or a part thereof or a mammalian AST protein having a 66% or more homology with the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1 and in whose each a propeptide moiety is bound to a trypsin-like protein moiety via a disulfide bond. Nucleic acids encoding the same. Antibodies binding to the same. A method for assaying AST by using these antibodies. Further a method of assaying the inhibitory activity of a compound or a polypeptide to be assayed against AST or PAR activation, mucus production promotion, cell proliferation, intracellular calcium influx or EGFR pathway activation due to the AST.
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
Therapeutics
The present invention relates to the use of a compound of formula (1): wherein: R1 comprises a carbonyl group and R2 is a hydrocarbyl group; optionally wherein said ring is further substituted; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof; in the manufacture of a medicament for use in one or more of: modulating the release of intracellular calcium from a store controlled by nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate; modulating calcium spikes in mammalian cells; treating diseases in one or more of brain, heart, pancreatic cells (e.g. pancreatic acinar and pancreatic beta cells), immune cells, T-cells, haemopoietic cells including phagocytes; treating diseases in one or more of brain, heart, pancreatic cells (e.g. pancreatic acinar and pancreatic beta cells), immune cells, T-cells, haemopoietic cells including phagocytes by modulating the release of intracellular calcium from a store controlled by nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate; treating diseases in one or more of brain, heart, and T-cells by modulating calcium spikes in mammalian cells.
Owner:POTTER BARRY VICTOR LLOYD +4
Methods and compositions for modulating C5-a-mediated inflammatory responses
InactiveUS7763708B2Impair C5a anaphylatoxin bindingHigh activityPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsEnprofyllineIn vivo
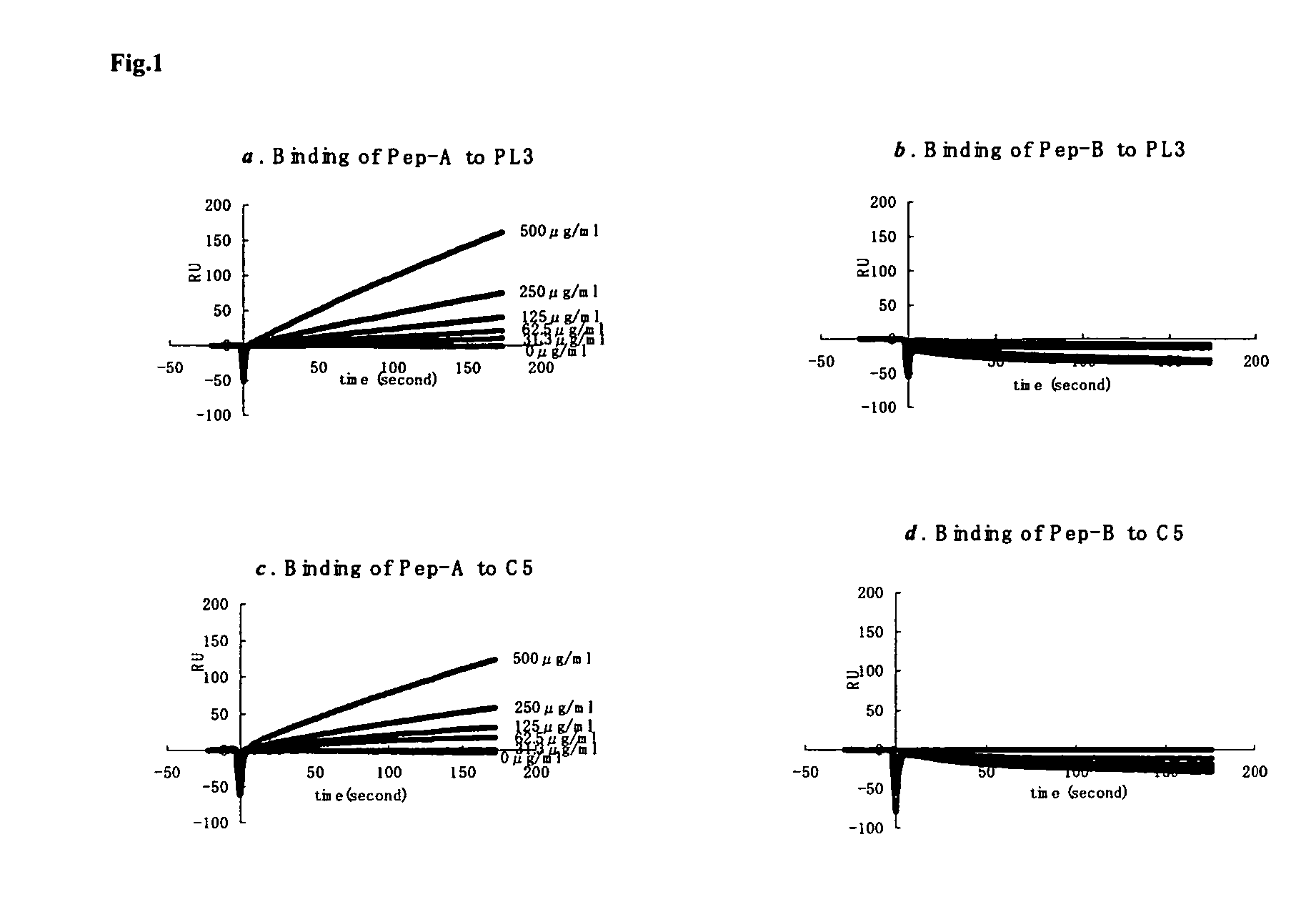
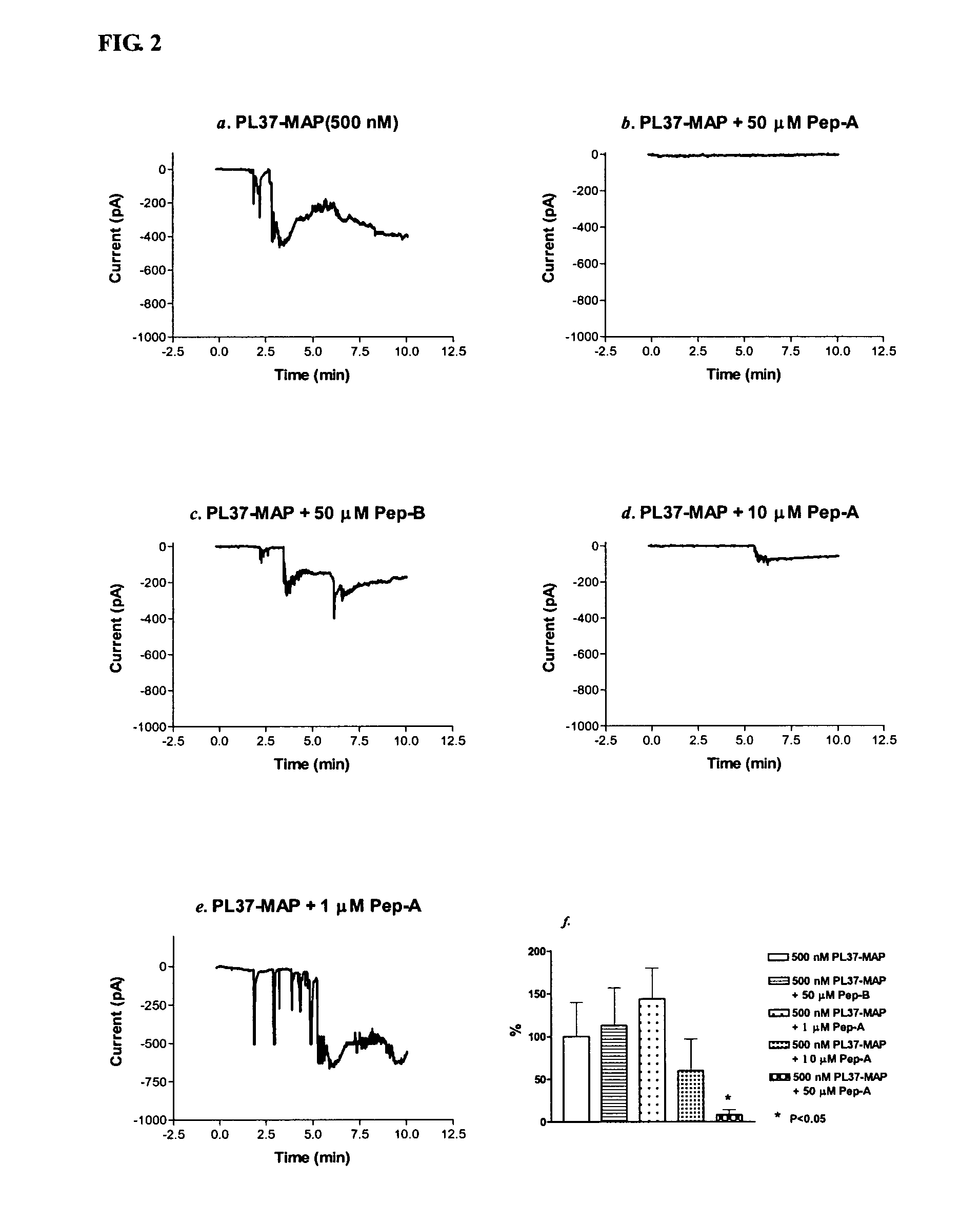
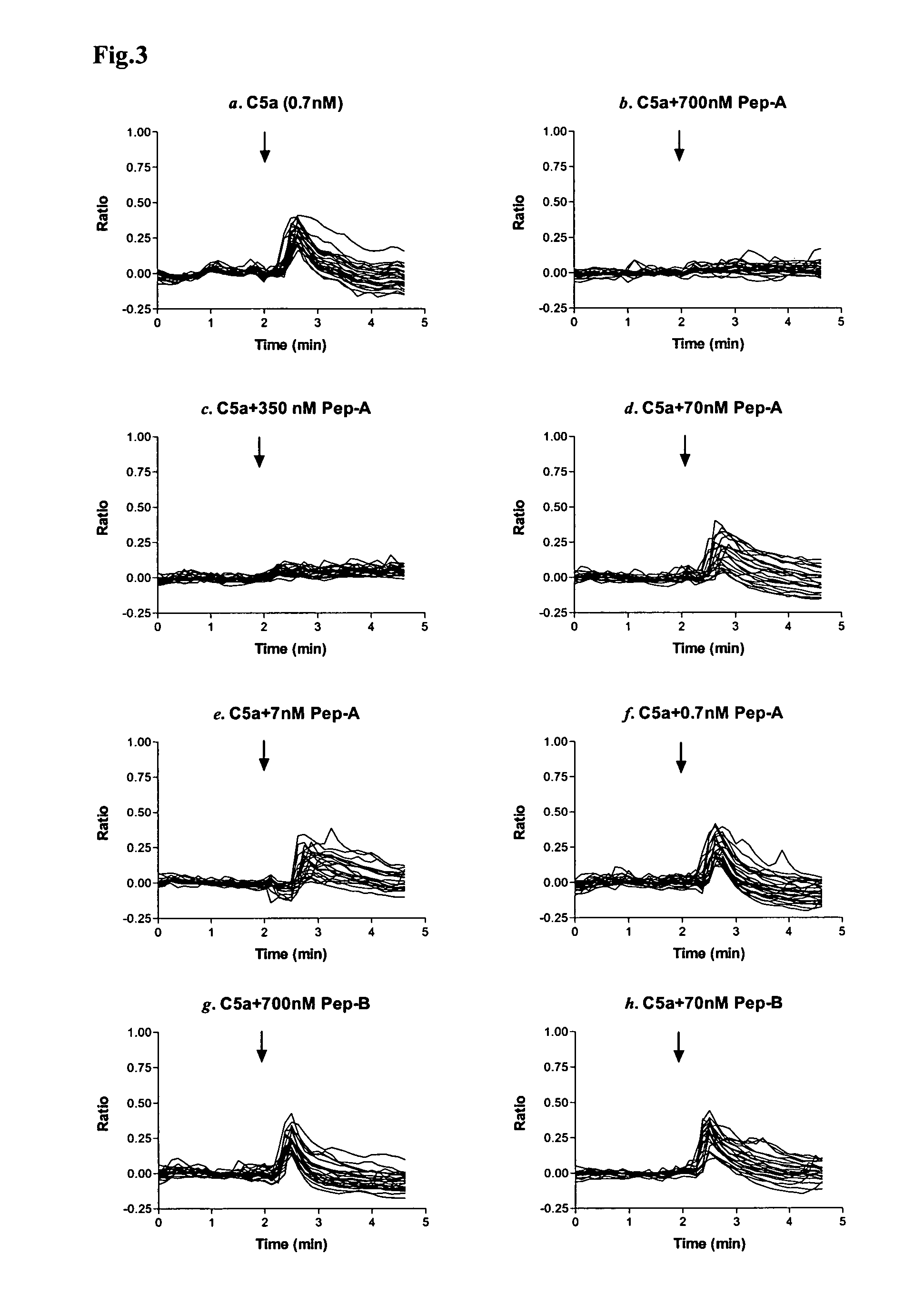
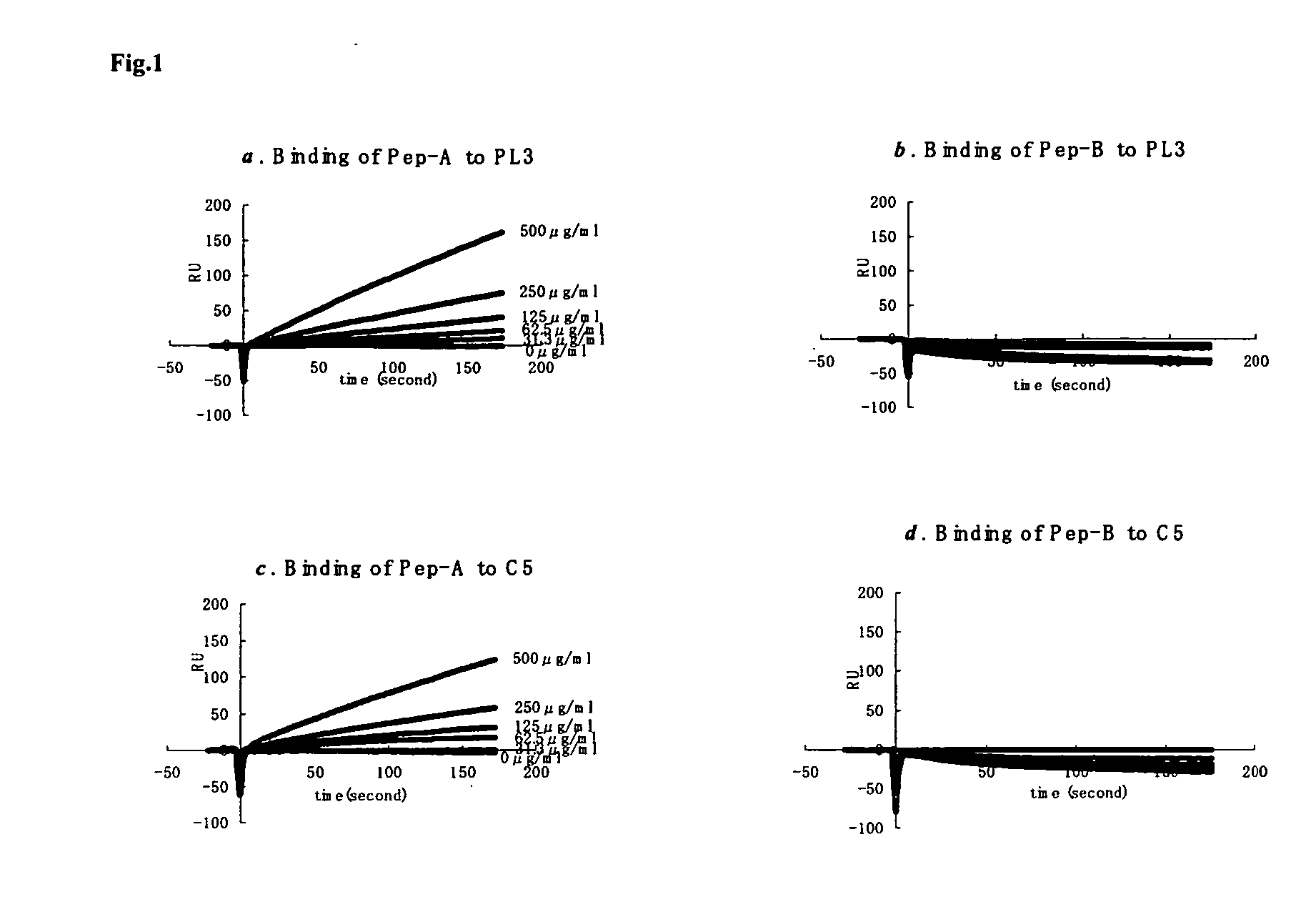
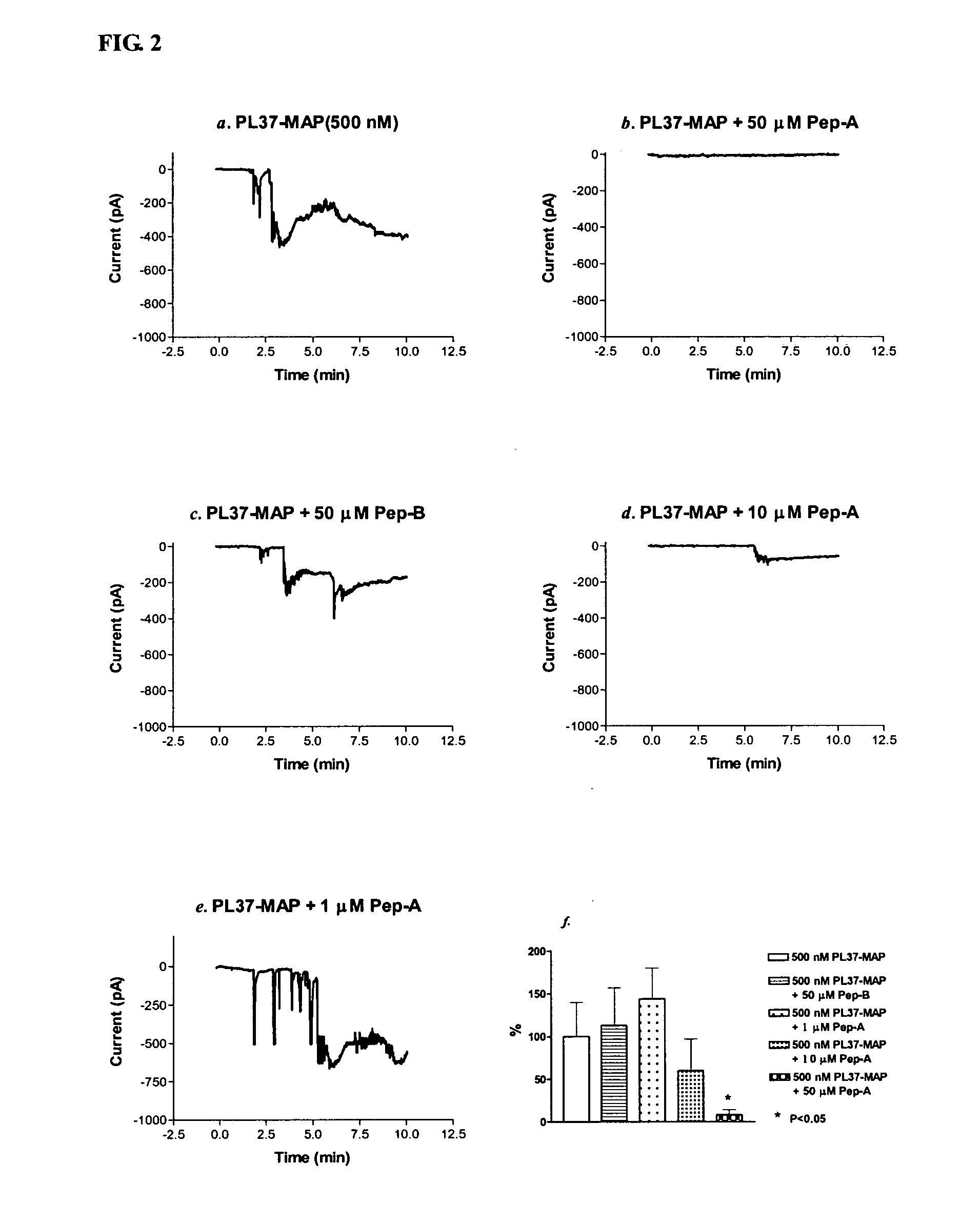
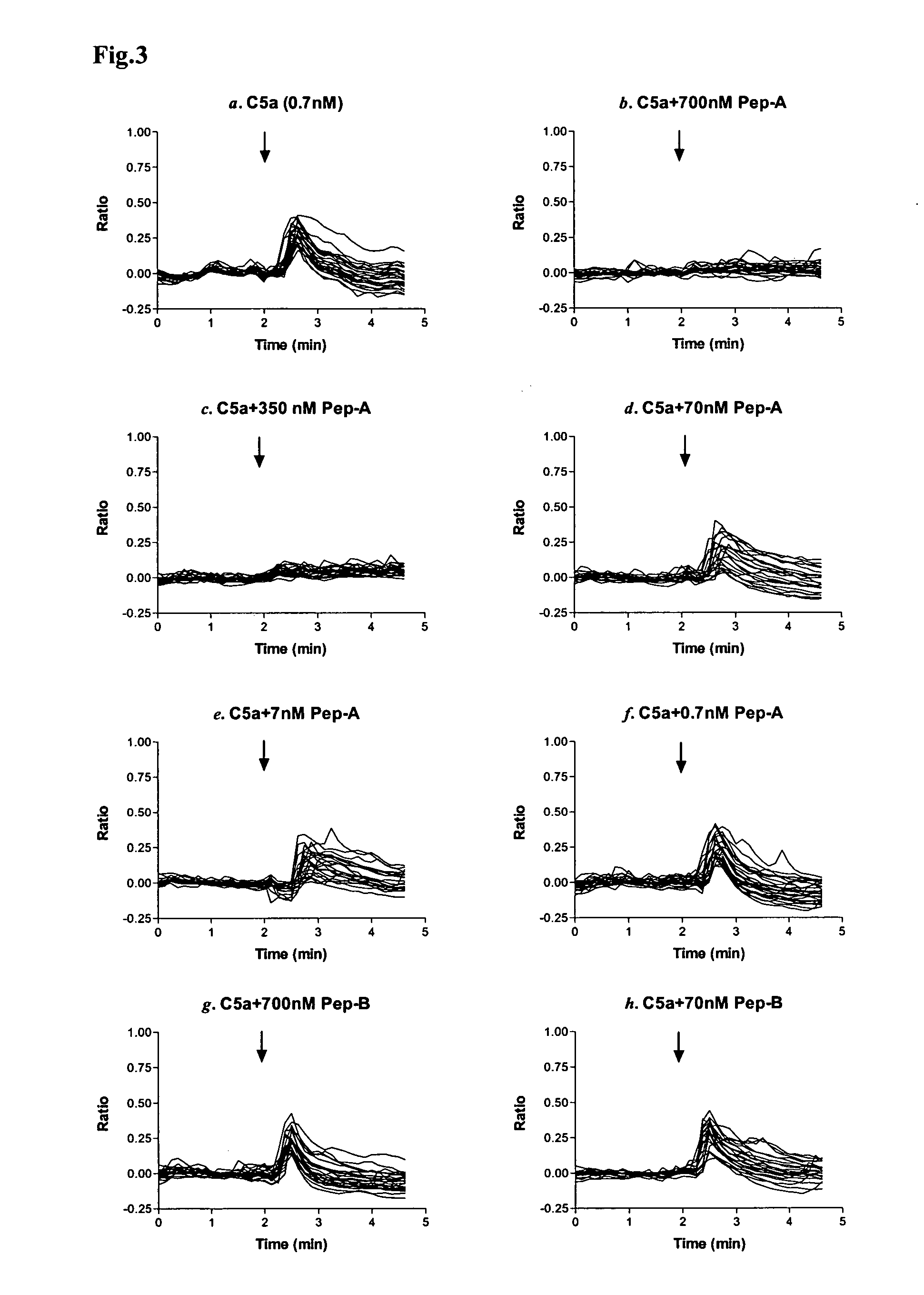
PL37 (RAARISLGPRCIKAFTE [SEQ ID NO: 2]) is an Antisense Homology Box peptide composed of amino acids 37 to 53 of C5a-anaphylatoxin. Complementary peptides, ASGAPAPGPAGPLRPMF (Pep-A [SEQ ID NO: 1]) and ASTAPARAGLPRLPKFF (Pep-B [SEQ ID NO: 3]) were designed and characterized. Pep-A bound to PL37 and to C5a with very slow dissociation, whereas Pep-B failed to bind at all. C5a was inactivated by 7 nM or more of Pep-A and this concentration of Pep-A inhibited induction of intracellular Ca++ influx in neutrophils. Patch clamp studies also showed the effectiveness of Pep-A in C5a-receptor-expressing neuroblastoma cells. Pep-A administration prevented rats from C5a-mediated rapid lethal shock. A-Pep-A (Pep-A acetylated with alanine at the amino-terminus) was more stable in vivo and showed stronger inhibition of inflammatory reactions in mice and rats. Chemical modification of Pep-A (e.g., acetylation, or single or multiple amino acid replacement, insertion, or deletion within the native Pep-A sequence) will yield effective inhibitors, and will often improve inhibitory function on C5a anaphylatoxin. In such modified constructs it will often be desired to conserve some or all 5 prolines found in Pep-A to preserve inhibitory function on C5a.
Owner:RES INST FOR PROTEIN SCI
1,3,4-oxadiazole derivative and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102827098AThe measurement result is accurateAvoid damageOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementWittig reactionSynthesis methods
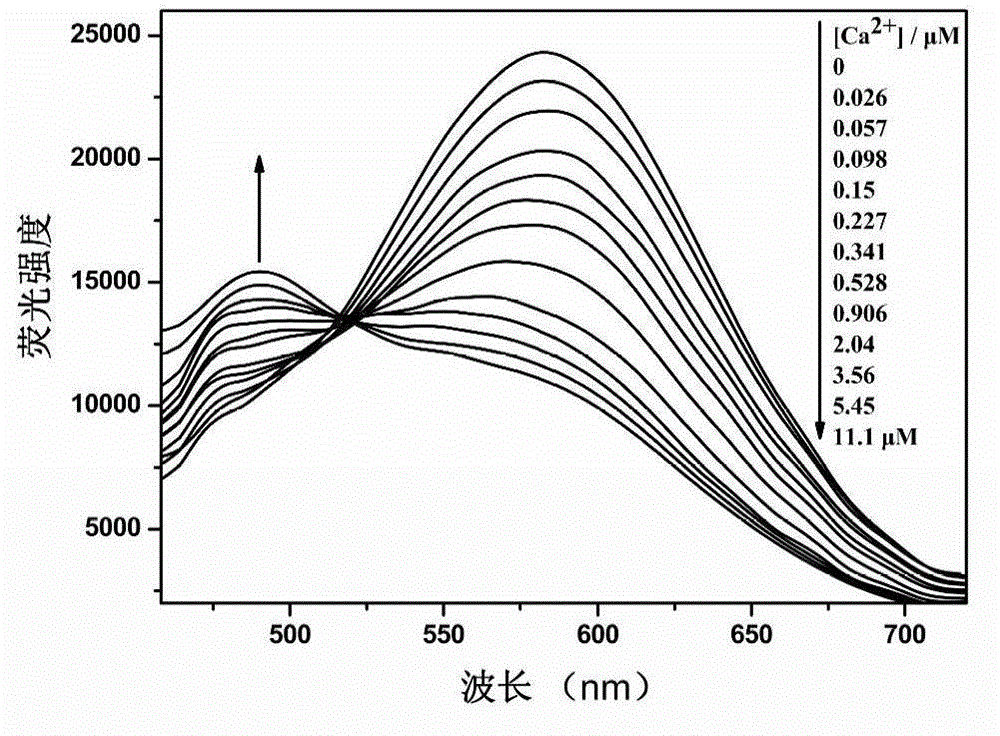
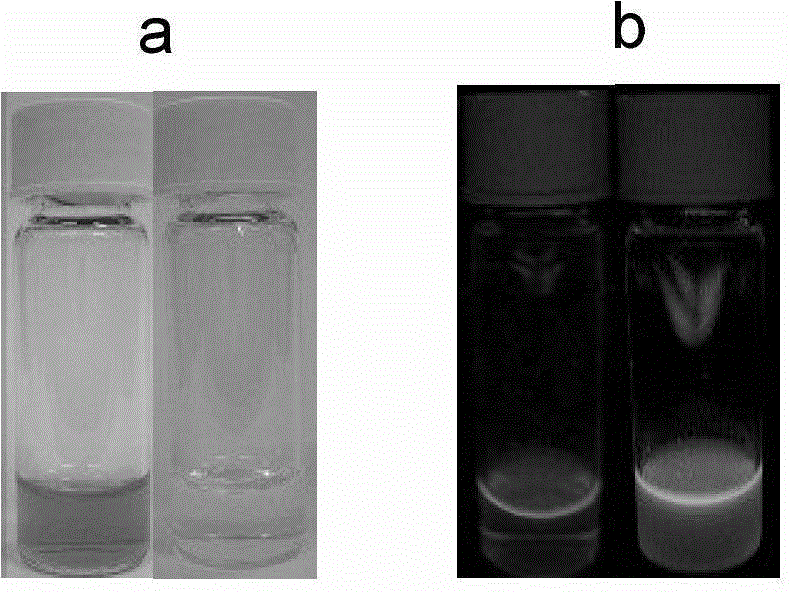
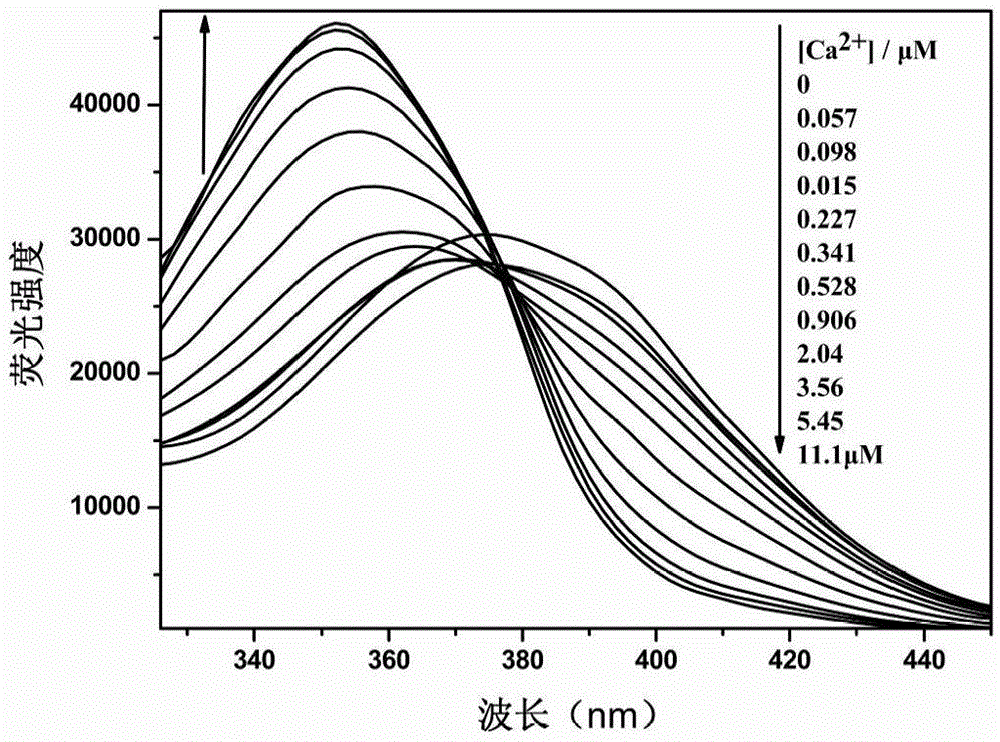
The invention discloses a 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivative and a synthetic method thereof, and an application of the derivative serving as a fluorescent indicator to detection of intracellular calcium ions (Ca<2+>). The method comprises the following steps of: under the protection of inert gas, performing a wittig reaction on the 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivative and a calcium ion response group to obtain a crude product; and concentrating the crude product, and separating through a silica gel column to obtain a pure product. The 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivative has the advantages of high sensitivity and high selectivity on Ca<2+>, large Stocks displacement, proportional measurement and the like; the color of the indicator changes greatly before and after bonding with Ca<2+>, so that identification and judgment can be performed conveniently through naked eyes; and moreover, the indicator can be loaded into cells, so that an intracellular Ca<2+> signal and the concentration thereof can be detected conveniently under a laser confocal microscope.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
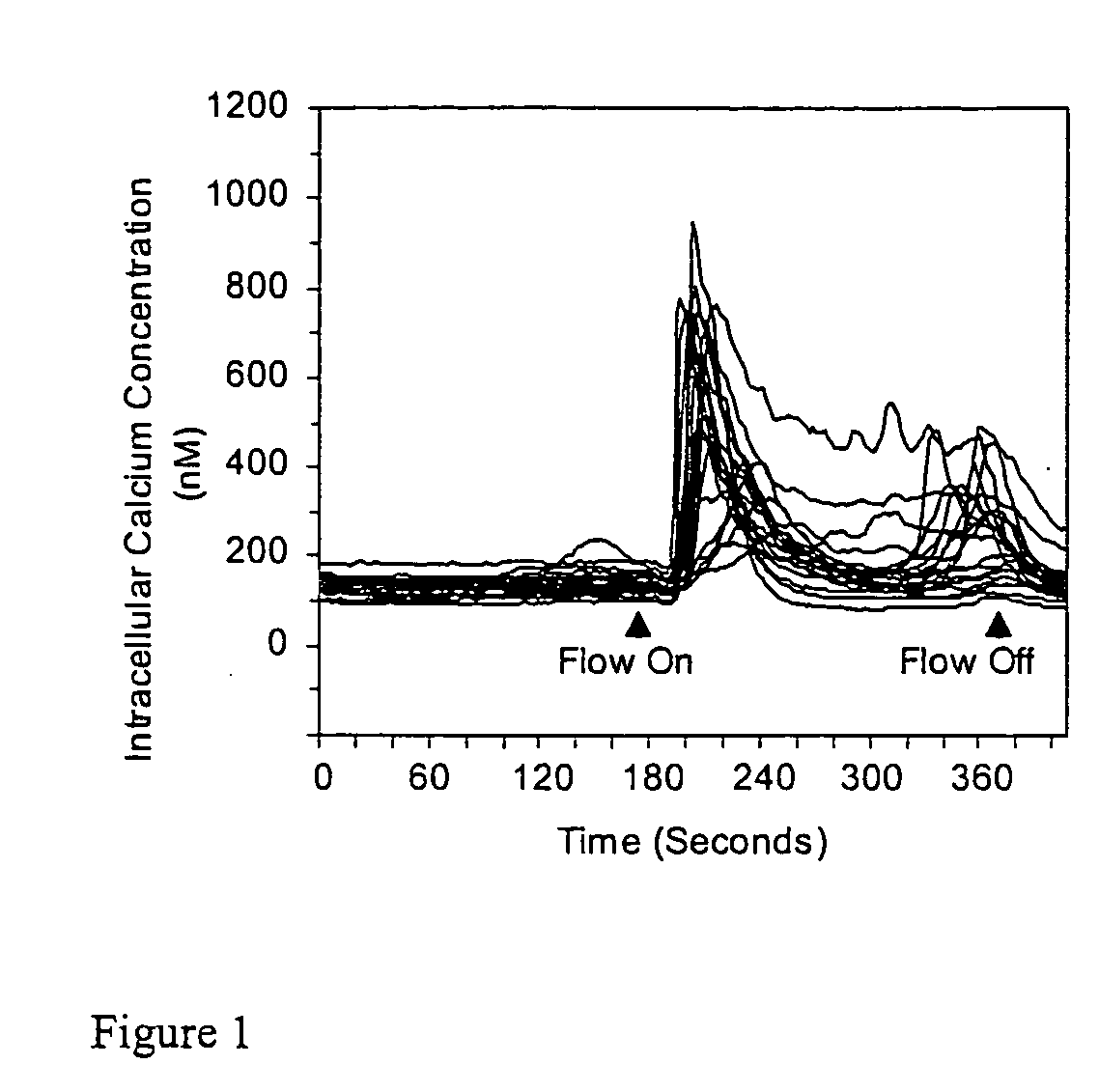
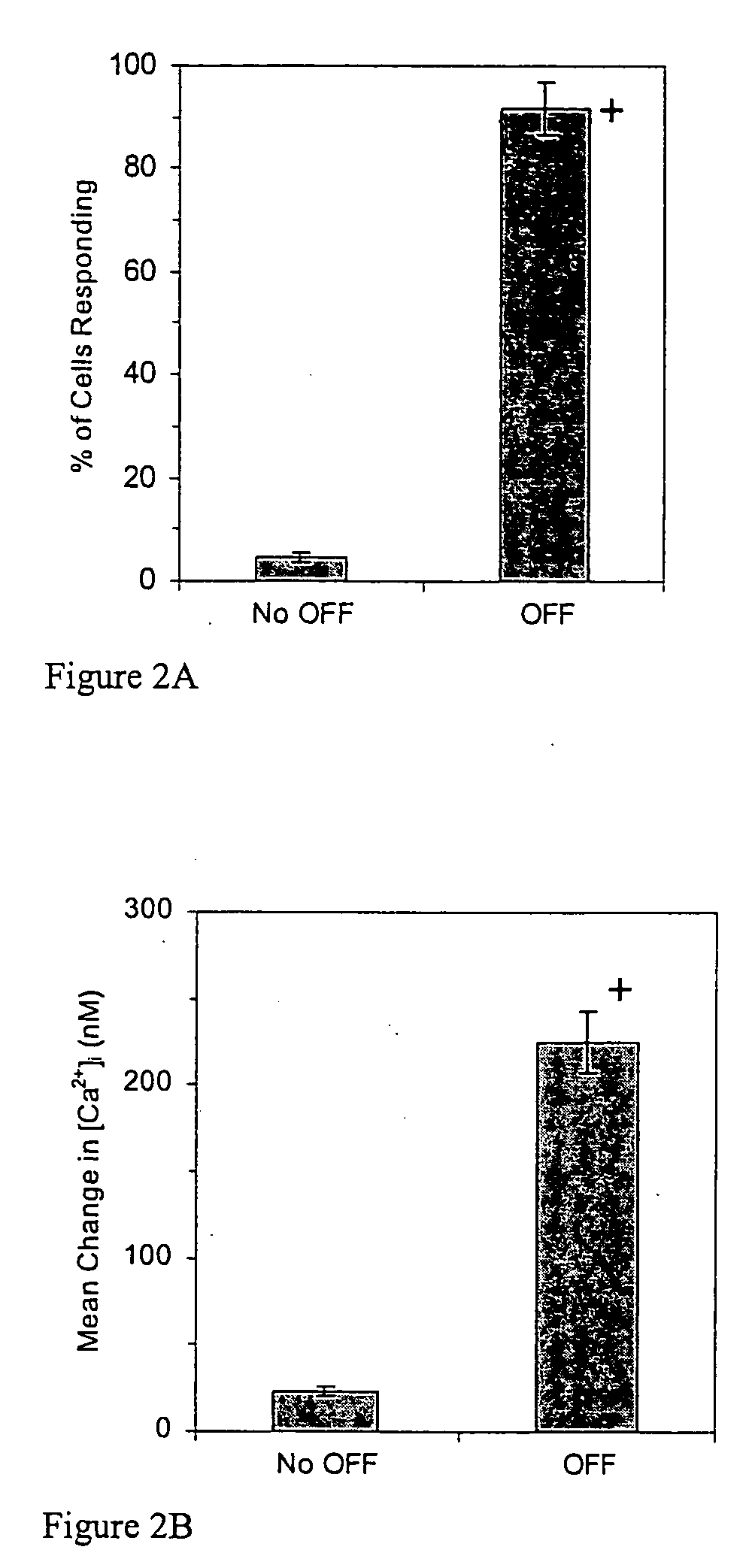
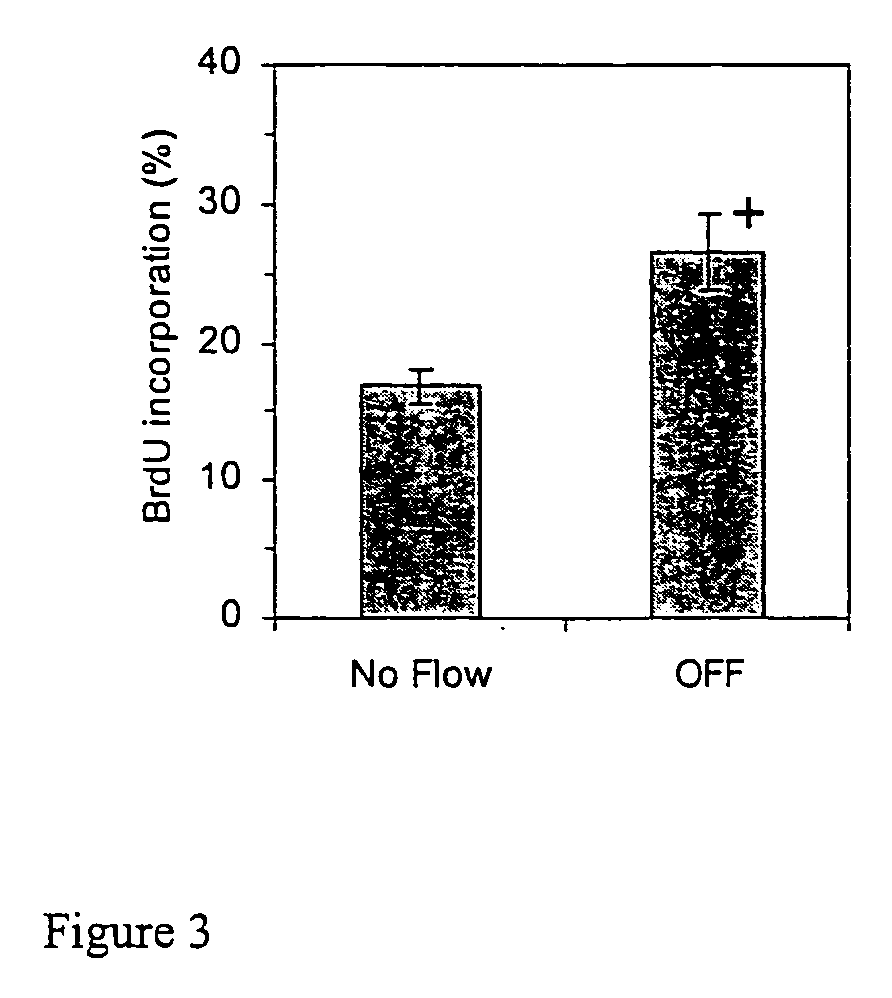
Modulation of stem and progenitor cell growth by oscillatory fluid flow
InactiveUS20070117203A1Use of materialCulture processArtificial cell constructsProgenitorGene expression
Stem or progenitor cells, including cells derived from bone marrow, exhibit increased intracellular Ca2+ mobilization and alterations in gene expression and proliferation when subjected to an oscillatory fluid flow.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
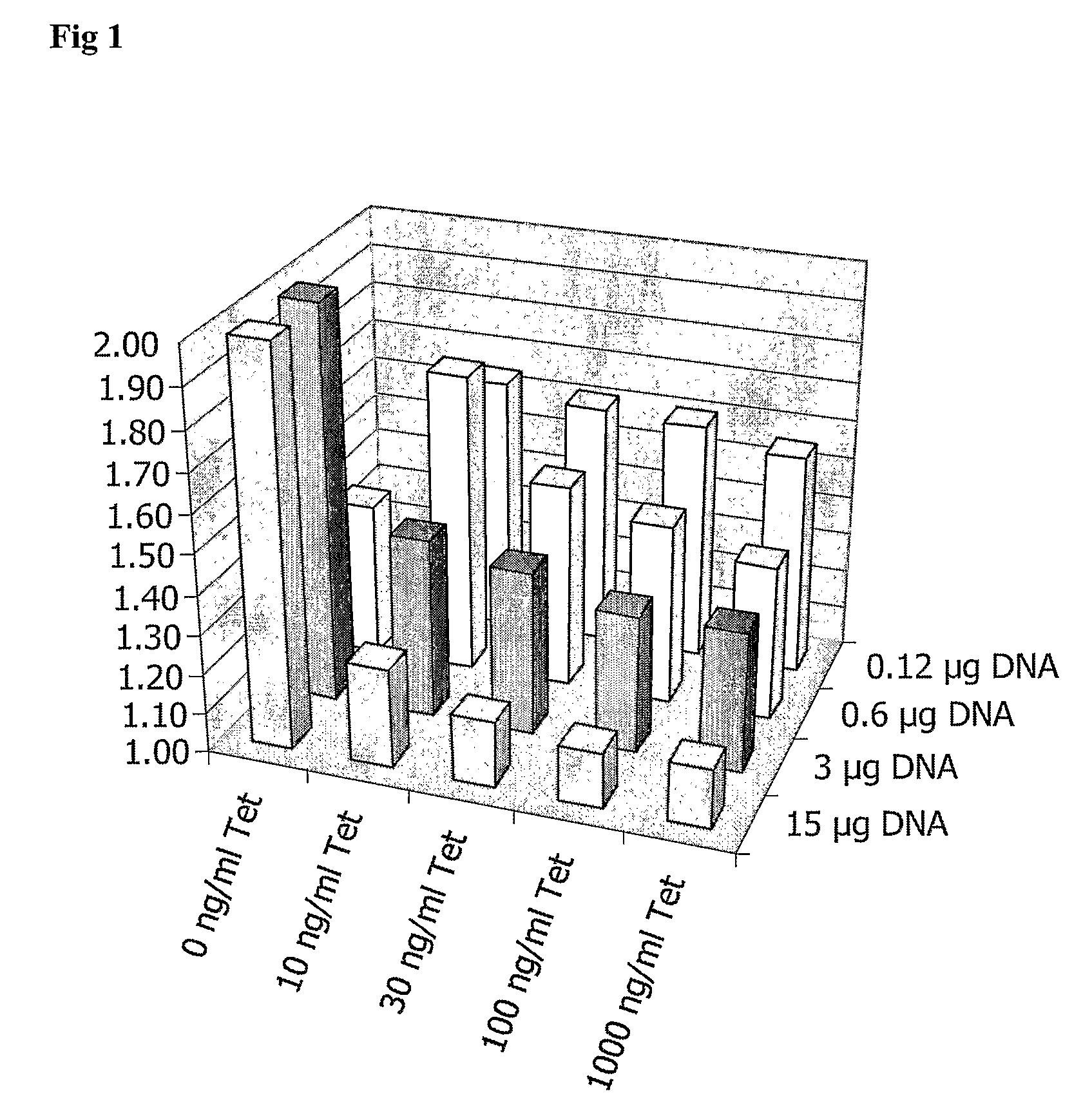
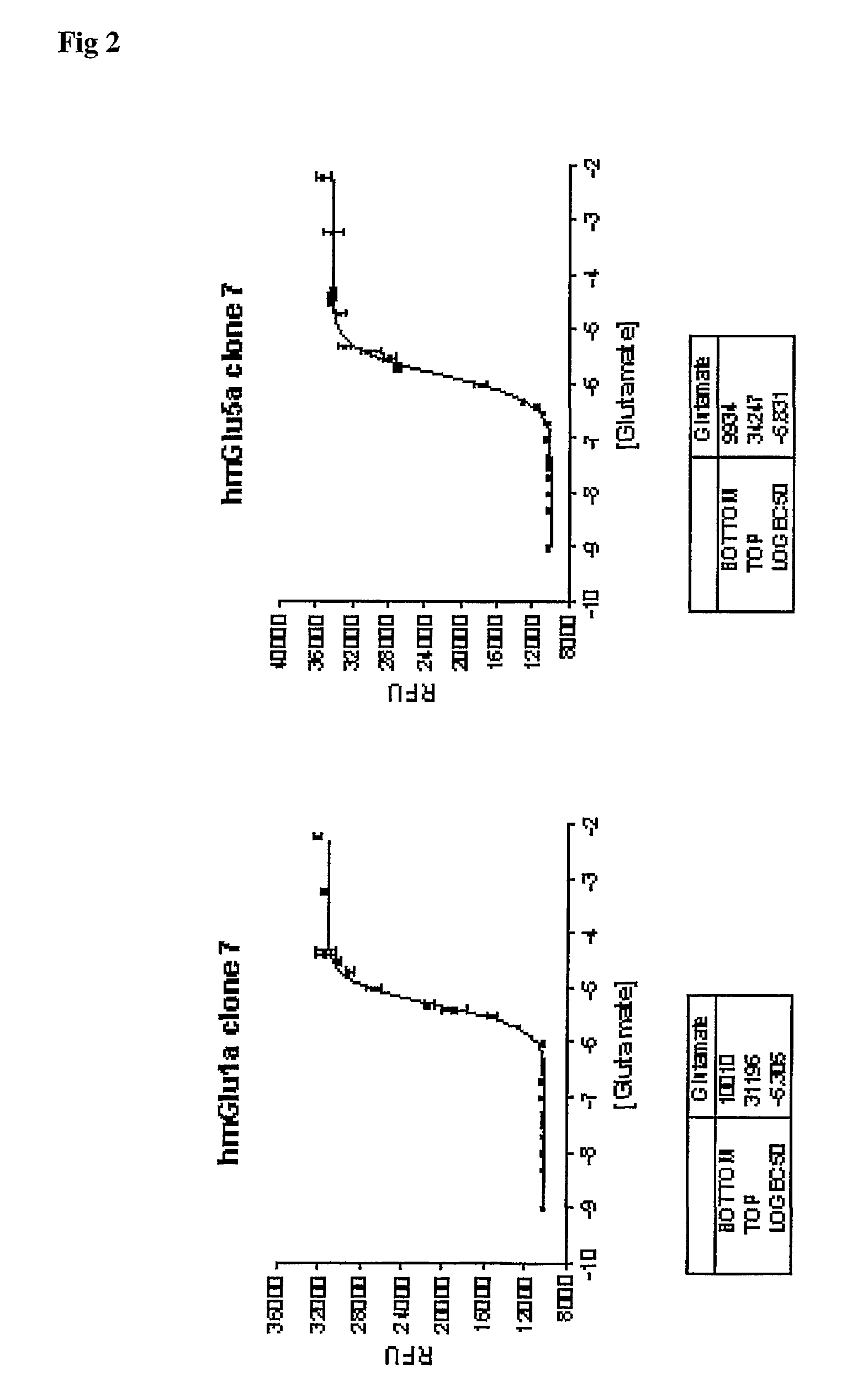
Functional Screening Assay
InactiveUS20070292898A1Determine effectMicroorganism preservationBiological testingFluorescenceNucleotide
In a first aspect the present invention provides an inducible expression vector encoding a metabotropic glutamate receptor. In particular a tetracycline inducible expression vector such as for example the commercially available pcDNA4 / TO mammalian expression vector (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, Calif. USA) comprising the nucleotide sequence encoding for a member of the Group I mGluRs, in particular for the human mGluR1a (SEQ ID No1) or mGluR5 receptor (SEQ ID No.3). In a more preferred embodiment the inducible expression vector is selected from the tetracycline inducible expression plasmids hmGlu1a-pcDNA4 / TO (FIG. 4) and hmGlu5a-pcDNA4 / TO (FIG. 5). In a second aspect, the present invention provides a cell line comprising any of the aforementioned inducible expression vectors. In particular the T-Rex-293 cells stably transfected with the tetracycline inducible expression plasmids hmGlu1a-pcDNA4 / TO (FIG. 4) and hmGlu5a-pcDNA4 / TO (FIG. 5) which where deposited at the Belgian Coordinated Collections of Microorganisms (BCCM) as T-Rex-293-hmGlu1a-pcDNA4 / TO clone on Jun. 24, 2004. In a third aspect the present invention provides a method to identify compounds capability to modulate the activity of a metabotropic glutamate receptor said method comprising the steps of; contacting the aforementioned cell line with the compound to be tested, and determining the effect of said test compound on the metabotropic glutamate receptor activity. The effect on the metabotropic glutamate receptor activity is typically determined by assessing the change in intracellular calcium, in particular using a fluorescent dye such as for example fluo-3-AM. It is also an object of the present invention to provide a method to identify a compound capable to interact with a metabotrobic glutamate receptor, in particular with a Group I mGluR receptor, said method comprising the steps of contacting the cells according to the invention with the compounds to be tested under appropriate conditions and determining the binding of said test compounds to the cells.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
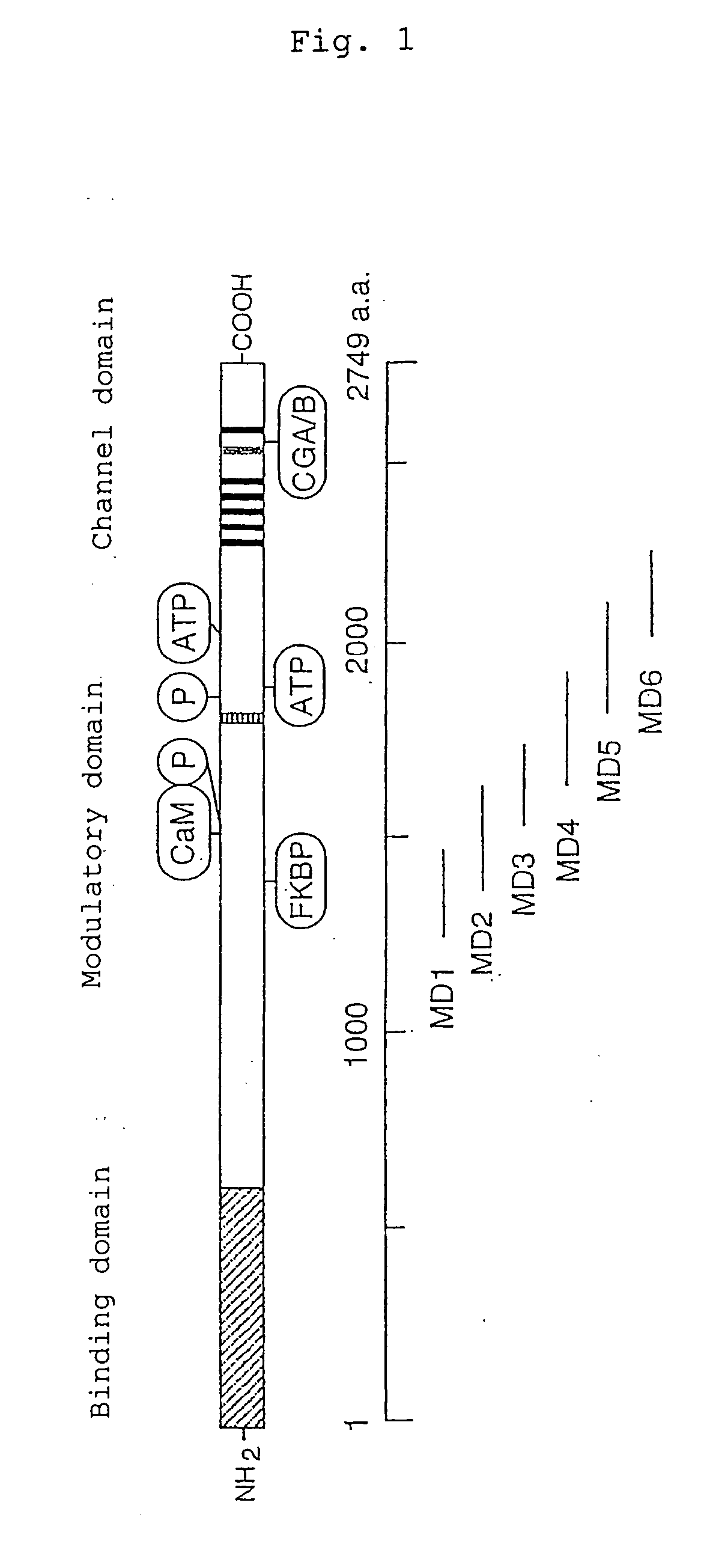
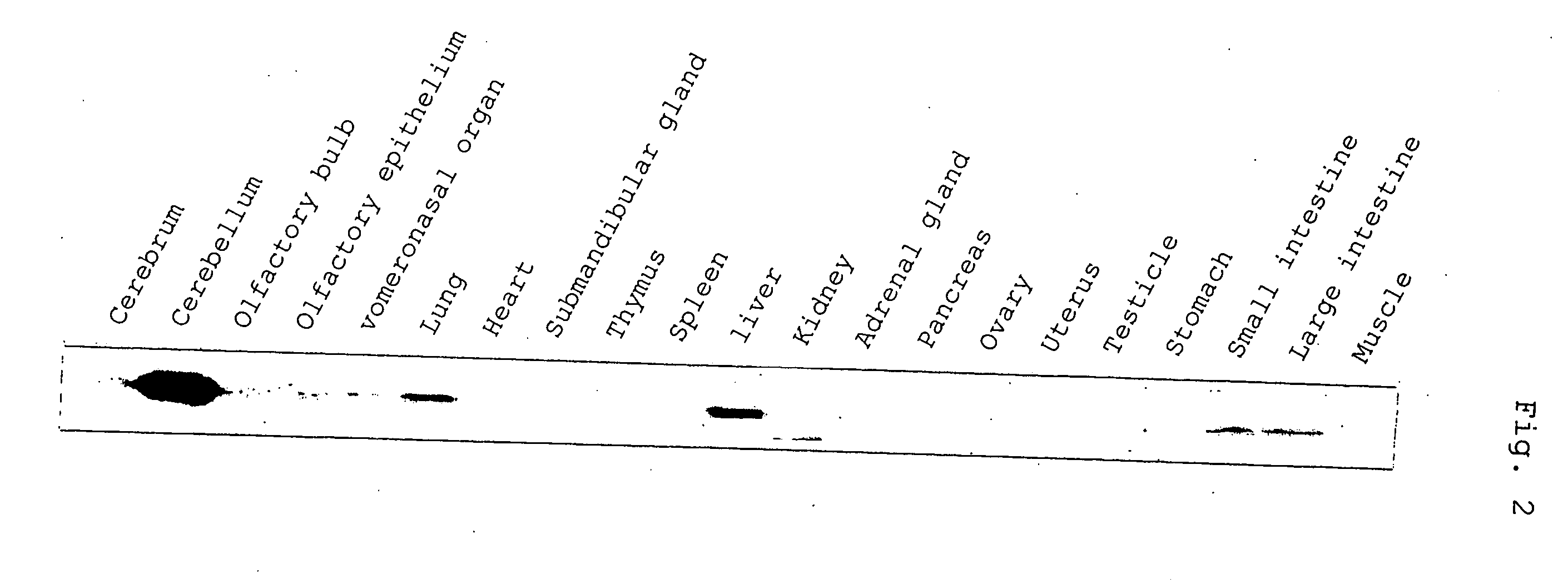
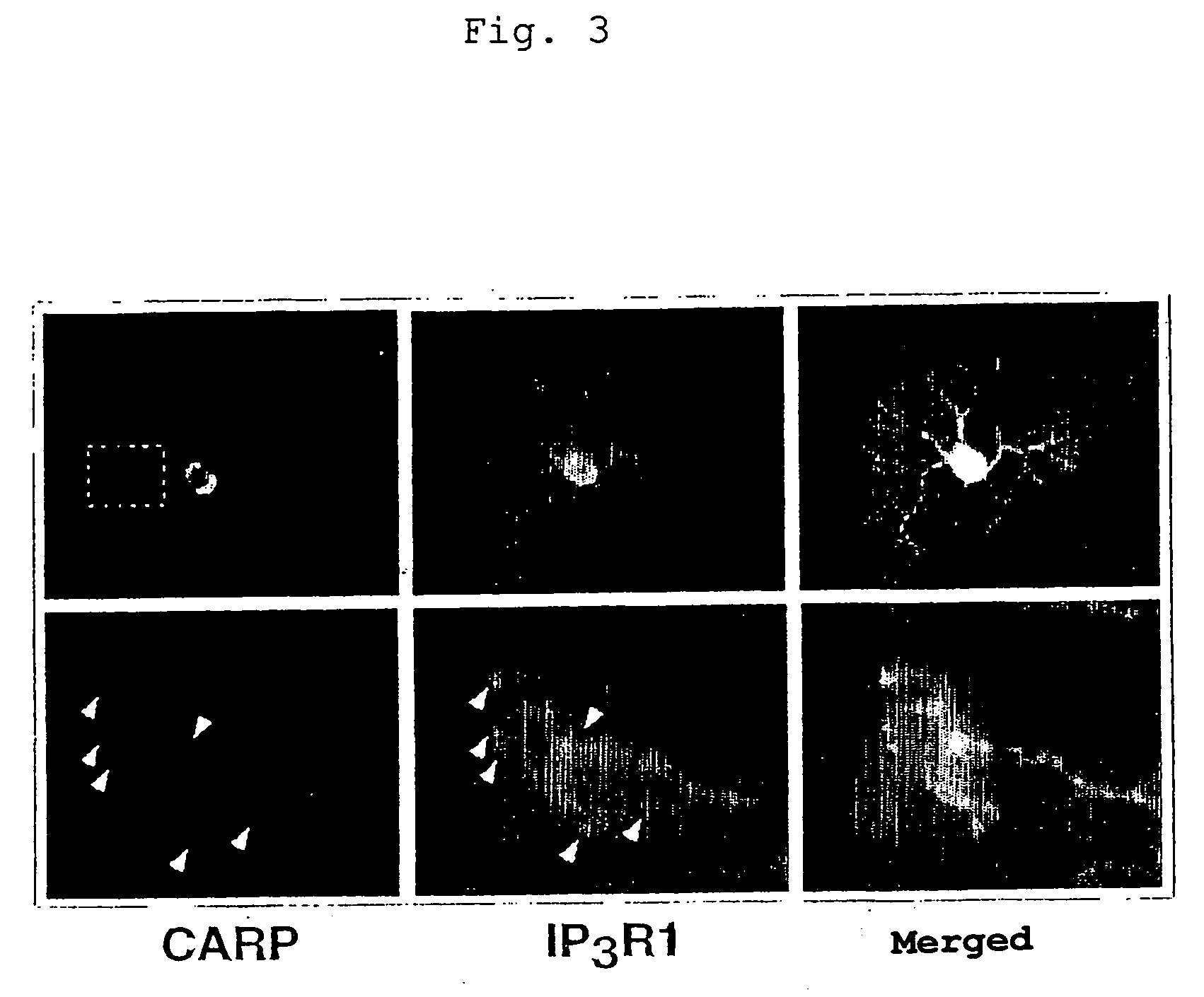
Control of function of intracellular Ca ion
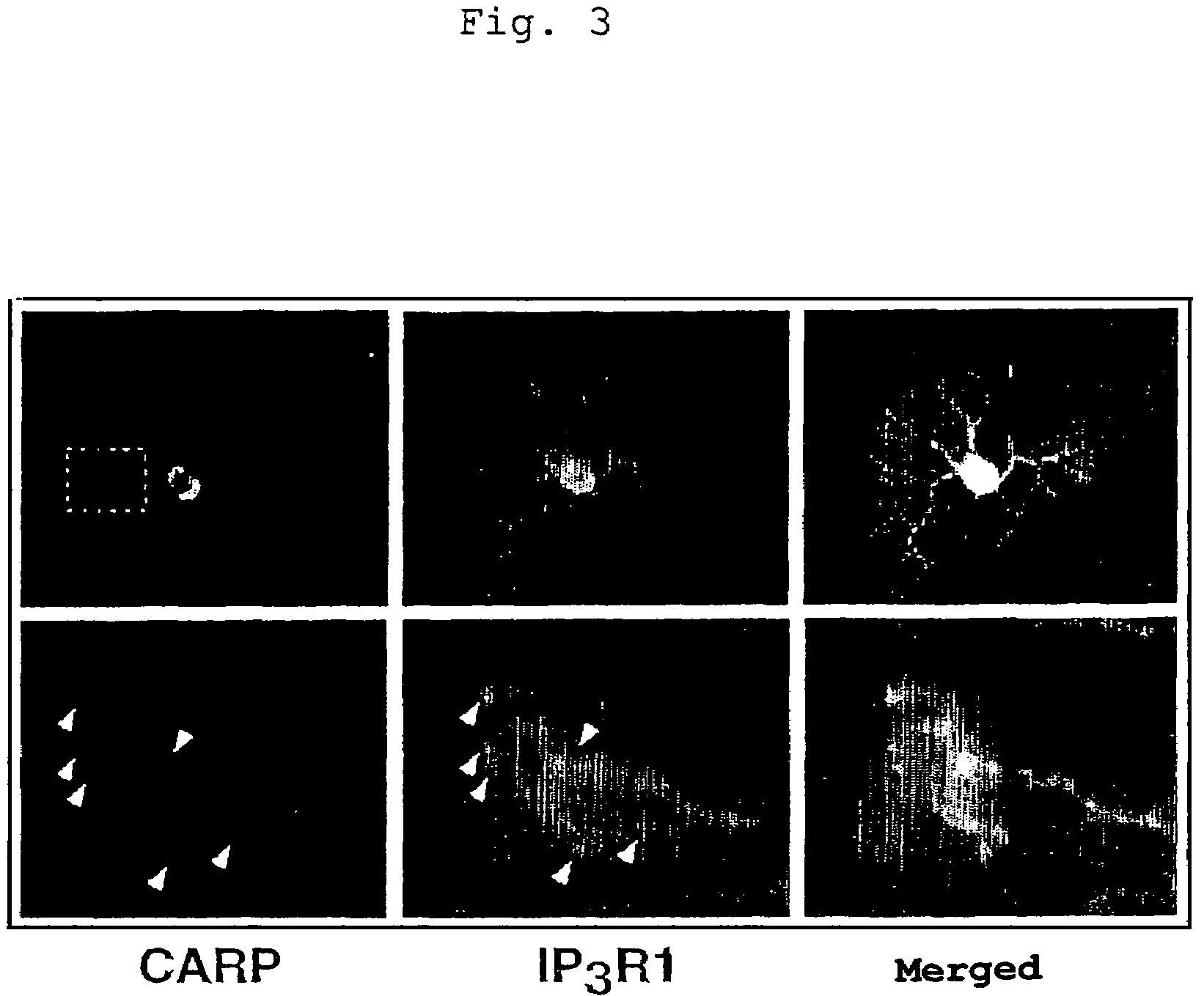
Analysis of substance capable of binding with inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate (IP3) receptor (IP3R), preferably with a regulation domain of IP3R; analysis of the function of IP3R; and establishing of a method of treatment or diagnosis for various malfunctions and diseases associated with IP3R. In particular, control of the activity of intracellular Ca2+ release. More specifically, a regulator for the activity of inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate (IP3) receptor (IP3R), comprised of carbonic anhydrase related protein (CARP); a control agent for intracellular calsium release, comprised of carbonic anhydrase related protein (CARP); and a method of control therewith.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
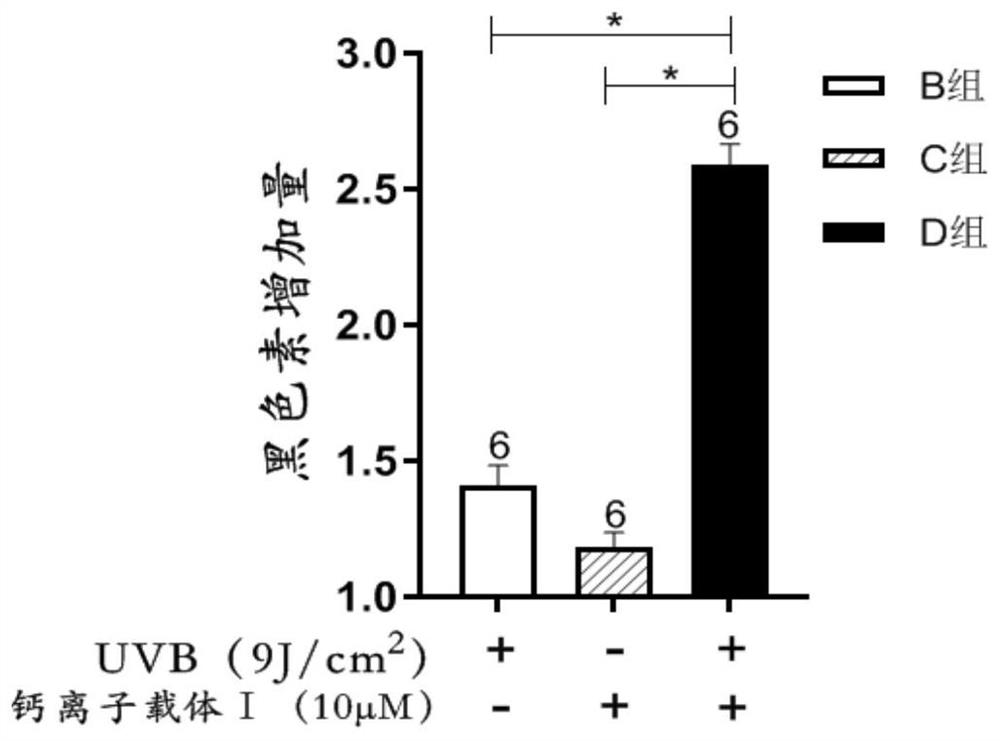
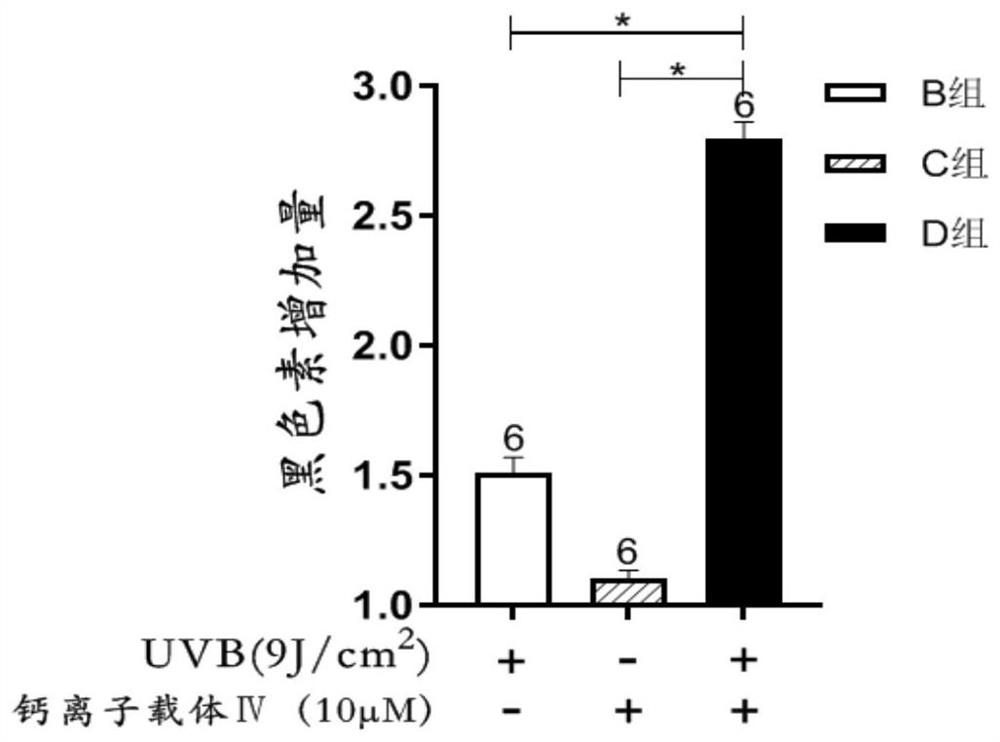
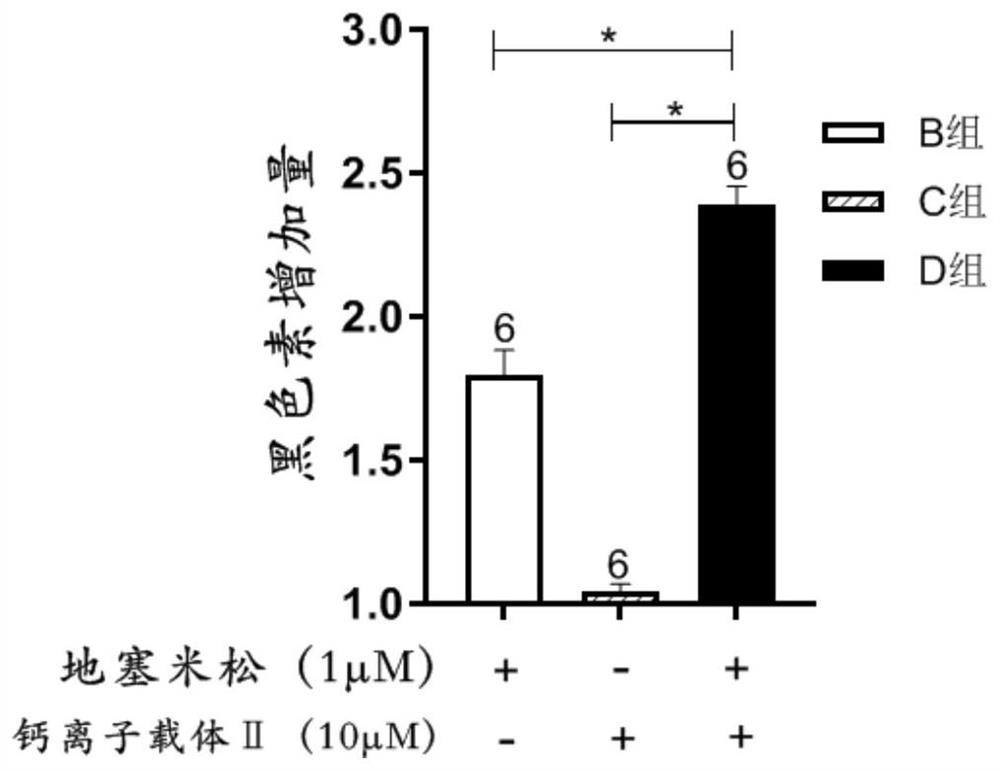
Application of calcium ion carrier in leucoderma treatment
ActiveCN111840560AIncrease intakeImprove satisfactionTetracycline active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDiseaseMelanocyte
The invention provides an application of a calcium ion carrier and derivatives thereof in preparation of a medicine for treating leucoderma, and aims to solve the problem that melanocytes at an affected part of leucoderma have obstacles in uptake and transport of calcium ions. The calcium ion carrier is smeared on the affected part to increase the intake of calcium ions by melanocytes at the affected part so that the calcium steady state of the melanocytes is improved and recovered, a better intracellular calcium environment is provided for leucoderma treatment, the synthesis and transportation of melanin are promoted, and the defense of the melanocytes to free radicals and oxidative stress is enhanced. The application aims to serve as an adjuvant drug of the existing leucoderma treatmentdrug and method, and the existing treatment drug and method are assisted by improving the calcium environment in melanocytes of the affected part of leucoderma so that the treatment effect of the existing drug and method is improved, the treatment result is consolidated, and the disease recurrence rate is reduced.
Owner:GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
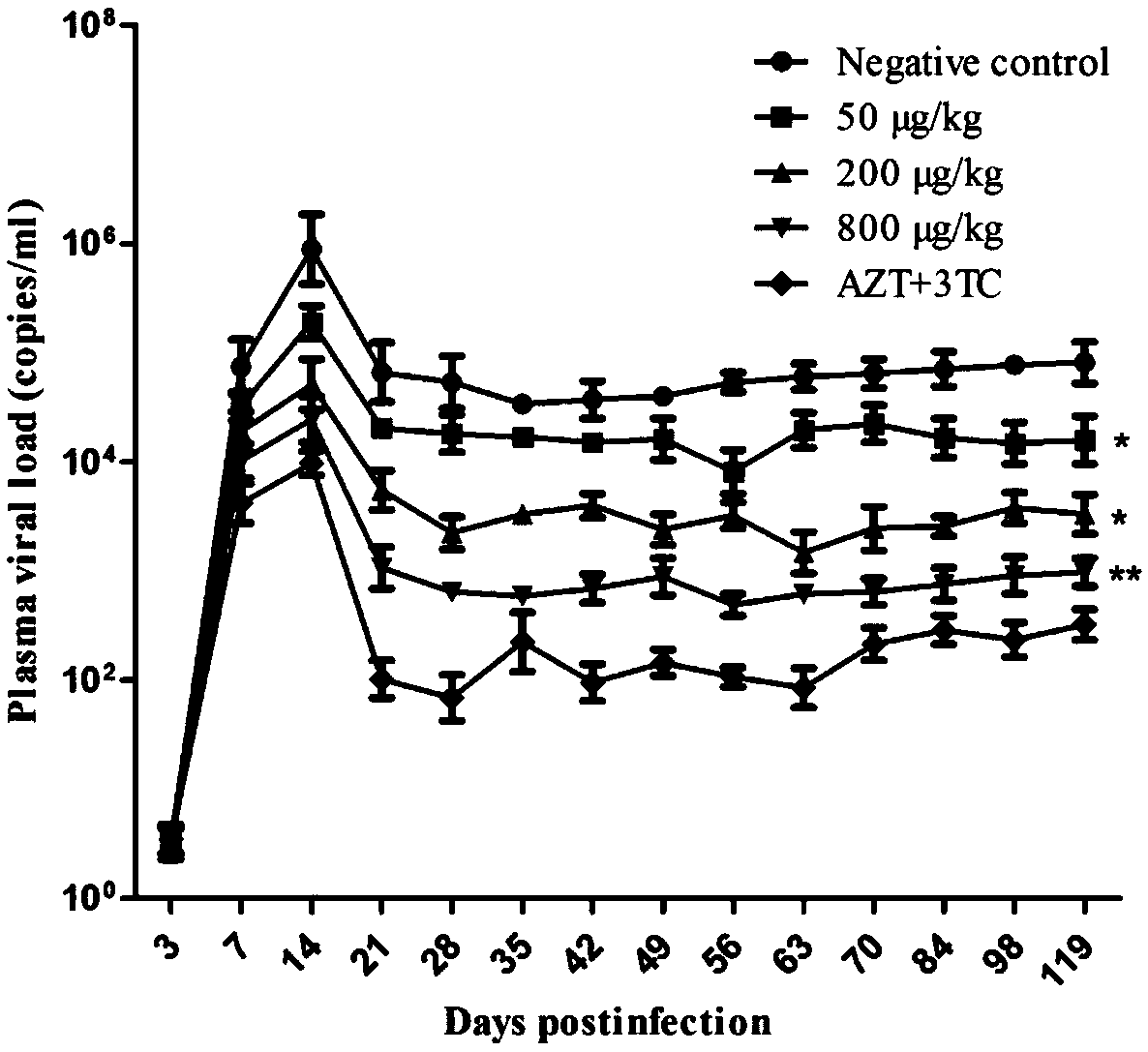
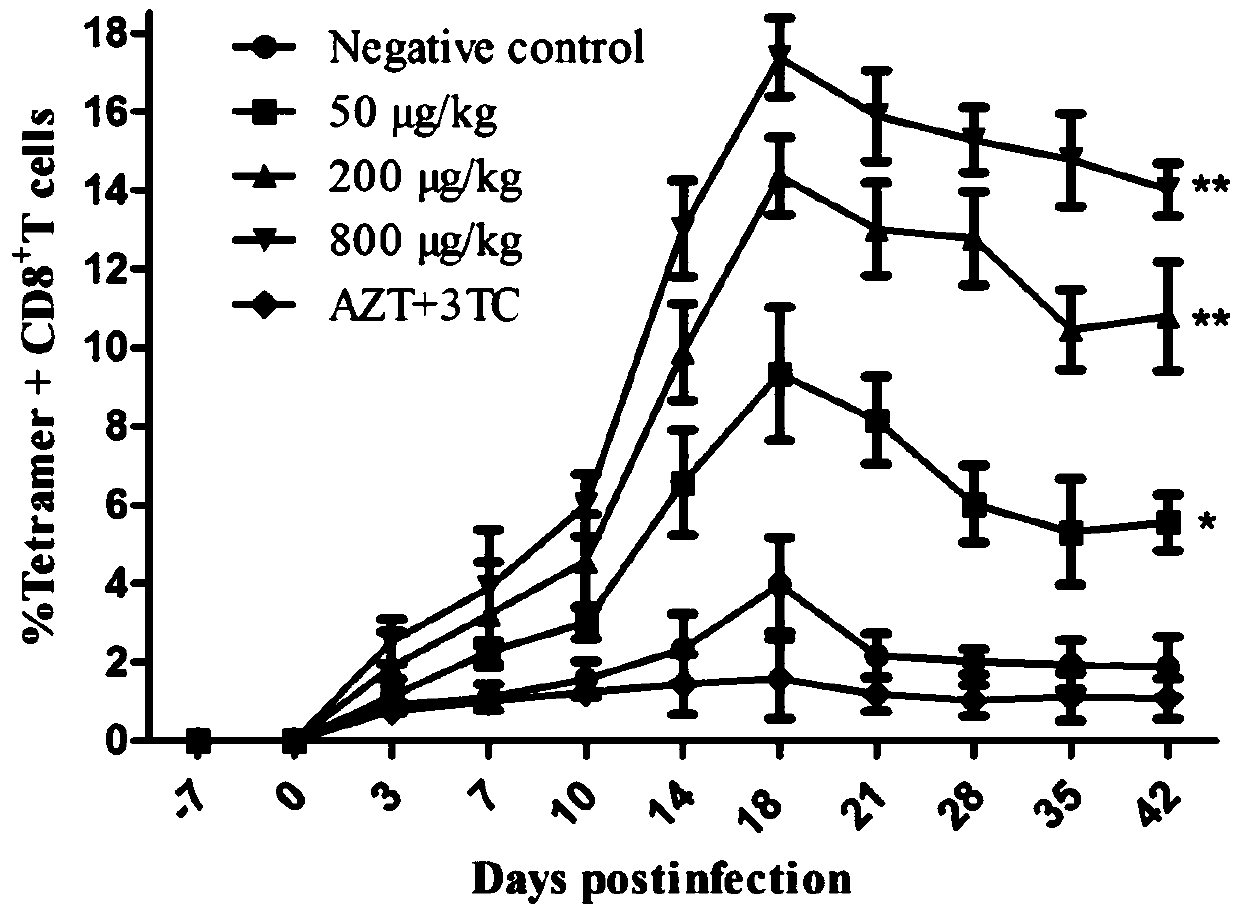
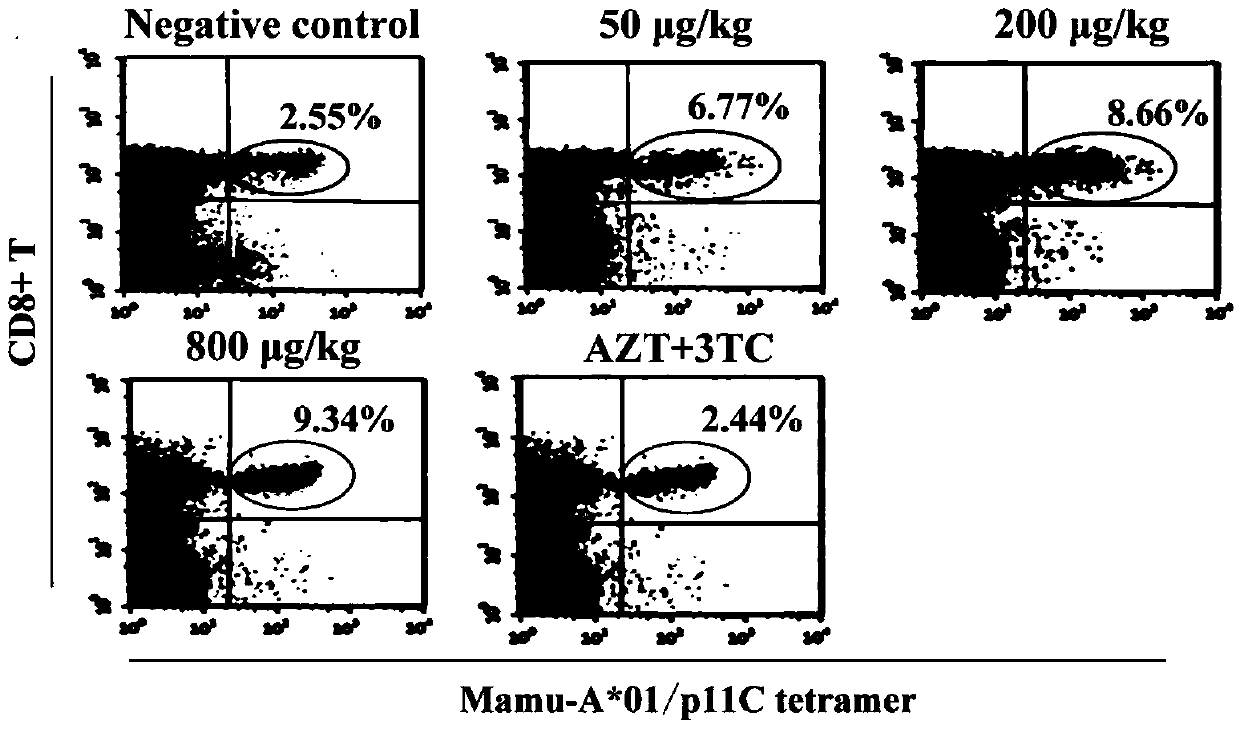
VMIP-II for inducing dephosphorylation of CD8<+> T cells to form Tcm and application of vMIP-II in medicines
The invention discloses application of virus macrophage inflammatory protein vMIP-II for inducing dephosphorylation of CD8<+> T cells to form Tcm. The vMIP-II for inducing dephosphorylation of the CD8<+> T cells to form the Tcm is developed in a laboratory and is verified by the National Institute for Control of Pharmaceutical and Biological Products. According to the invention, the CD8<+> T cellsare researched through a rhesus SIV infection model. The research finds that: the vMIP-II can enable Tcm to be proliferated depending on the dosage of the vMIP-II, and the differential gene of the proliferative cell is mainly enriched in a chemokine receptor and a phosphorylation pathway. The research further finds that: the proliferation is as follows: the vMIP-II closes a CD8<+> T chemokine receptor, promotes low expression of G protein, reduces the concentration of intracellular Ca<2+> and mitochondrial membrane potential, inhibits phosphorylation related genes, and promotes low expressionof phosphorylated proteins ERK1 / 2 and Akt, so that a CD8<+> T phosphorylation signal is weakened, metabolic reprogramming is carried out, and the CD8<+> T is converted into the Tcm. Therefore, the discovery of the vMIP-II action mechanism provides a brand-new strategy for drug research and development of HIV / SIV infected AIDS, provides a new means for adoptive immunotherapy of virus resistance and tumor resistance, and has important clinical application value.
Owner:广州溯原生物科技股份有限公司
Regulators of NFAT
Disclosed are methods of identifying an agent that modulates an NFAT regulator protein. One such method comprises contacting at least one test agent with a recombinant cell comprising at least one NFAT regulator protein or fragment or derivative thereof, assessing the effect of the test agent on an activity, interaction, expression, or binding to the NFAT regulator protein or fragment or derivative thereof, and identifying the test agent that has an effect on an activity, interaction, expression, or binding to the NFAT regulator protein or fragment or derivative thereof, whereby the identified test agent is characterized as an agent that modulates an NFAT regulator protein. Methods of identifying an agent that modulates intracellular calcium, methods to screen for an agent that modulates NFAT regulator function, methods to diagnose unexplained immunodeficiency in a subject, and methods for identifying an agent for treating or preventing a disease or disorder associated with a NFAT regulator protein or calcium signaling are also disclosed.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Mechanism of astricyte-neuron signaling
InactiveUS20080299109A1Nervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsG protein-coupled receptorNeurotransmission
The present invention relates to a novel communication mechanism between astrocytes and neurons at a synapse. More specifically, the present invention relates to a signaling mechanism between astrocytes and neurons, by activating astrocytic G-protein coupled receptors, thereby activating glutamate receptors on a membrane of neighboring postsynaptic neurons, resulting in increasing the level of intracellular Ca2+ and inducing a depolarization inward current to control neurotransmission in neurons.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
DNA encoding a prostaglandin F2alpha receptor, a host cell transformed therewith and an expression product thereof
Molecular cloning and expression of a prostaglandin F2alpha receptor which is linked to the signal transduction pathways via guanine nucleotide binding regulatory (G) proteins and measured by, for example, cAMP, IP3 or intracellular calcium. By constructing cell lines that express a prostaglandin F2alpha receptor, the affinities and efficacies of agonist and antagonist drugs with the receptor can be assessed. A recombinant DNA construct includes a vector and a DNA fragment encoding a prostaglandin F2alpha receptor. A host cell is transformed with a recombinant DNA construct, so that the DNA fragment is expressed and a prostaglandin F2alpha receptor is produced. Suitable host systems include eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells, especially mamalian cells such as rat or human. Additionally, for diagnostic purposes, antibodies to a prostaglandin F2alpha receptor can be prepared by producing all or a portion of the receptor protein and injecting these into various types of mammals. Using the resulting antibodies, expression of an F2alpha receptor cDNA, i.e. receptor protein in tissue and cells can be measured.
Owner:PHARMACIA & UPJOHN AB
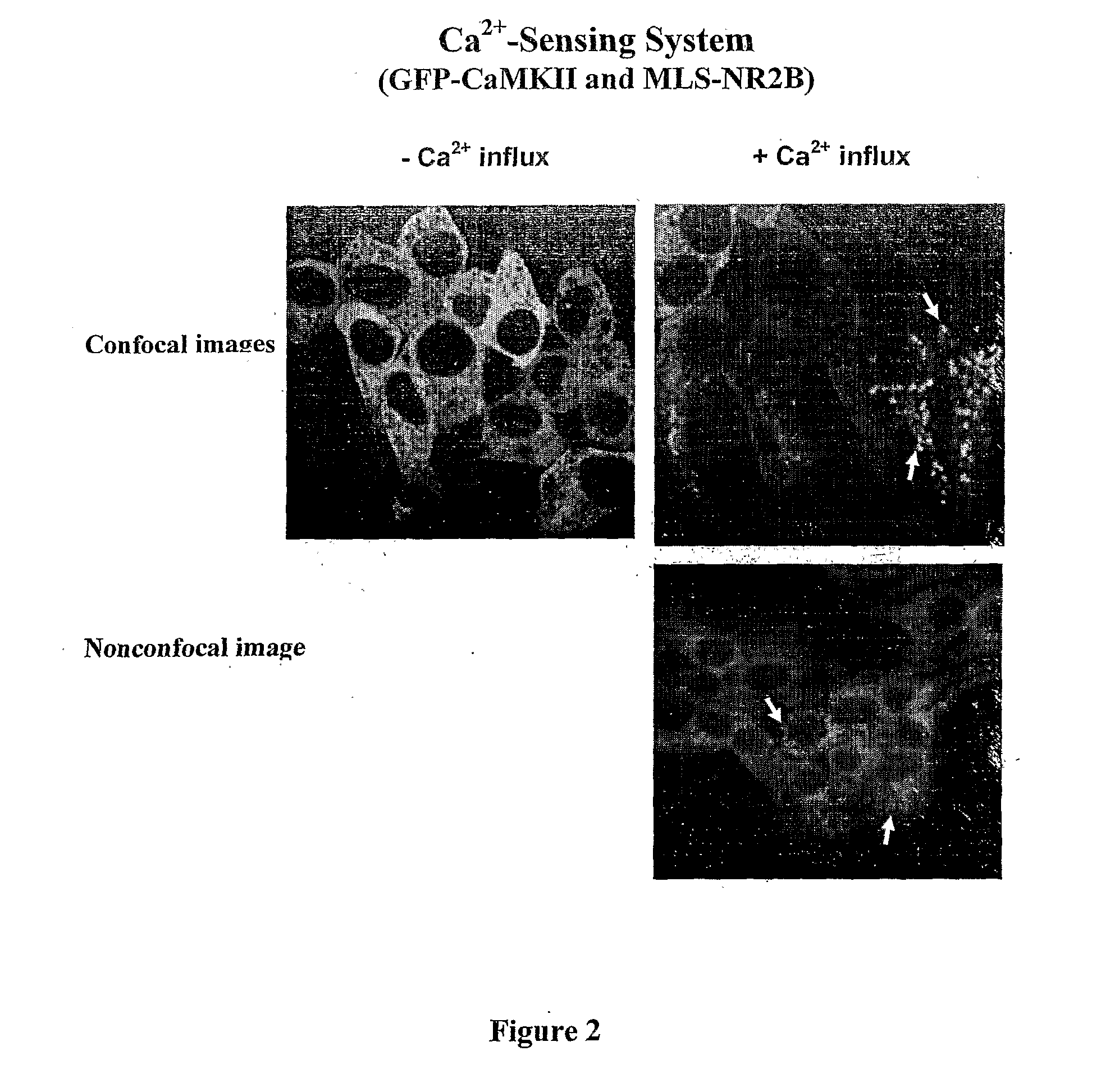
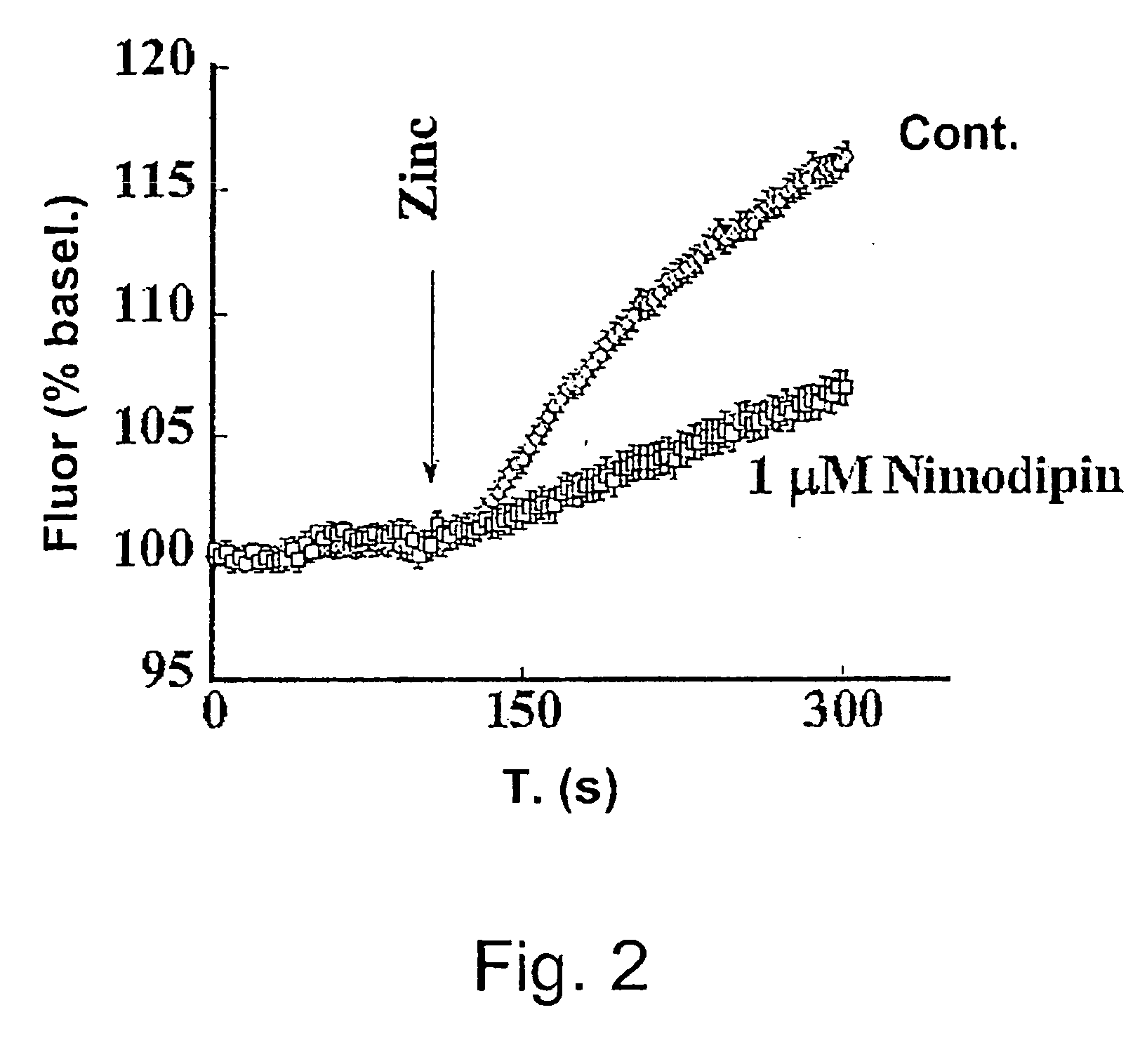
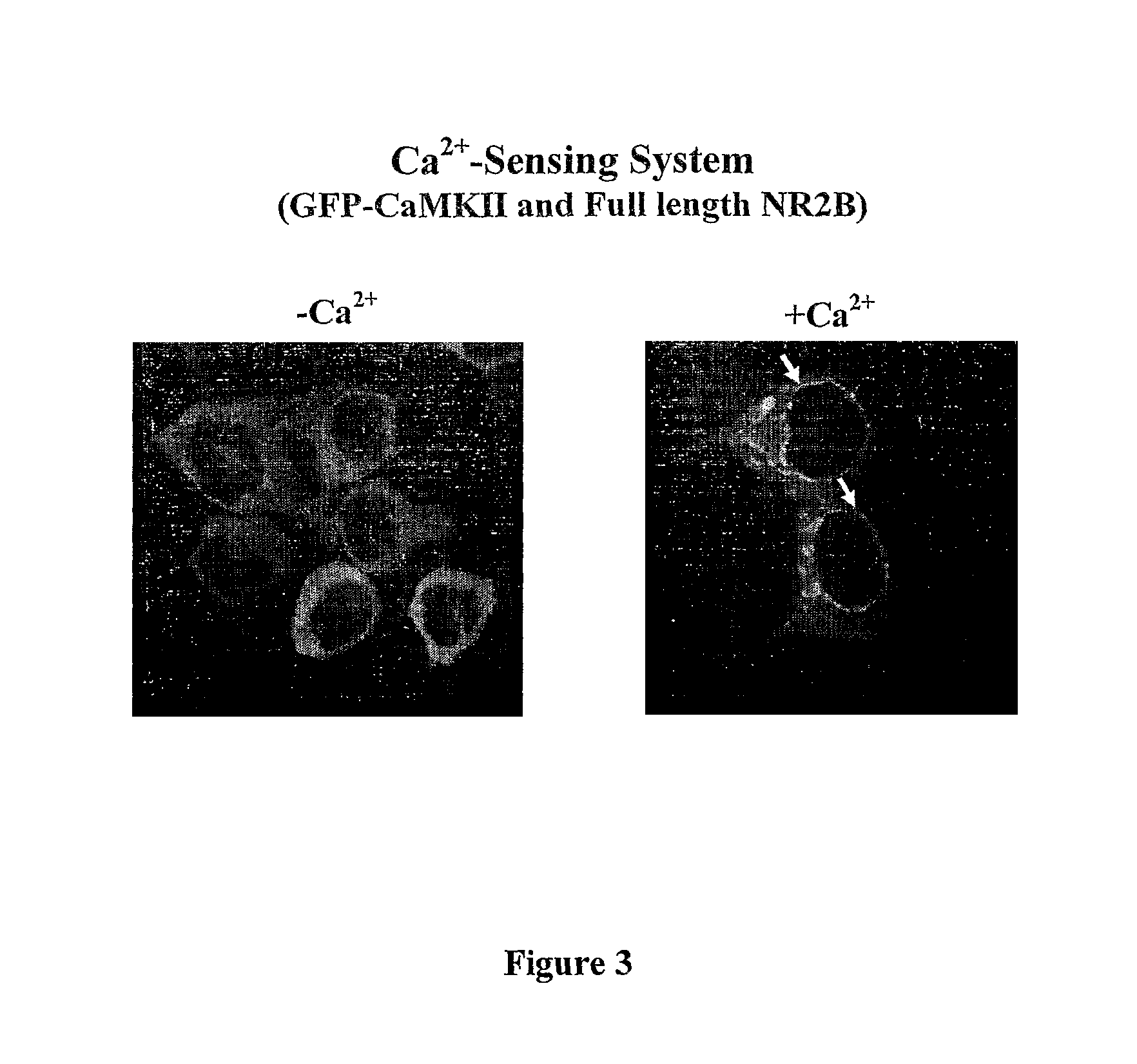
Assay for Detection of Transient Intracellular CA2+
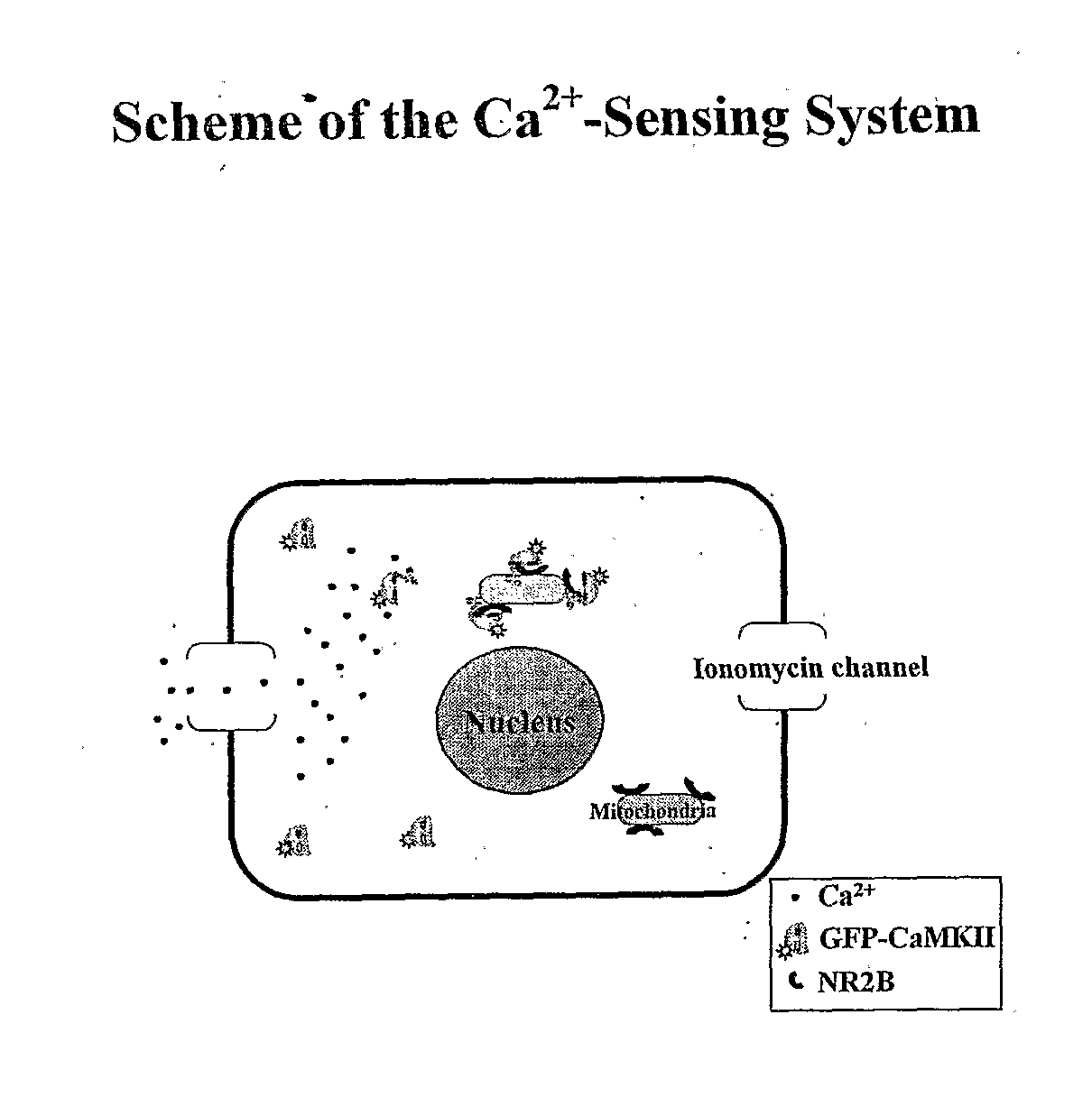
InactiveUS20100240071A1Avoid the needTransferasesBiological material analysisNR1 NMDA receptorN methyl D aspartate receptors
This invention relates to a simple end point assay for detection of transient intracellular Ca2+ with broad applicability to many Ca2+channel proteins comprising, Generation of expression constructs for the fusion proteins having the Ca2+ / calmodulin dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) phosphorylation sites of NR2A or NR2B subunits of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) or the voltage gated potassium channel of Drosophila (Eag) or any protein sequence which binds to the T-site of CaMKII similar to NR2B, conjugated to mitochondrial localizing signal sequence, or mutants of these sequences as described herein. Generation of mammalian expression constructs of α-CaMKll as a chimera with green fluorescent protein (GFP-α-CaMKII) or its mutants as described herein. Site-Directed mutagenesis, Transfection, Ca2+ stimulation, imaging and quantification of the number of cells with Ca2+-dependent signal, wherein, NMDA receptor activity assay, TRPVI receptor activity assay, GluR4 receptor activity assay are performed to detect the activity Of Ca2+ channel proteins.
Owner:RAJIV GANDHI CENT FOR BIOTECH +1
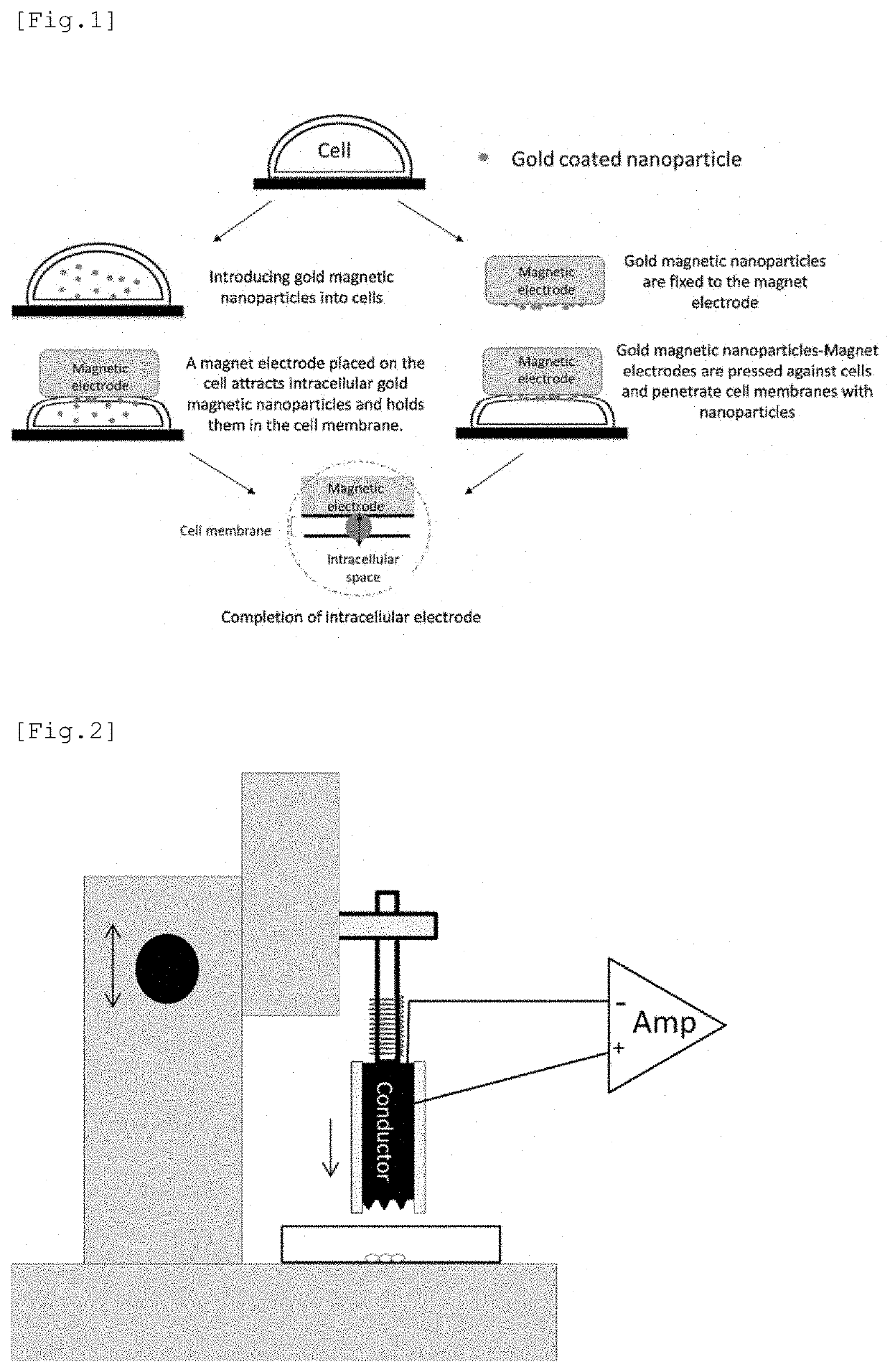
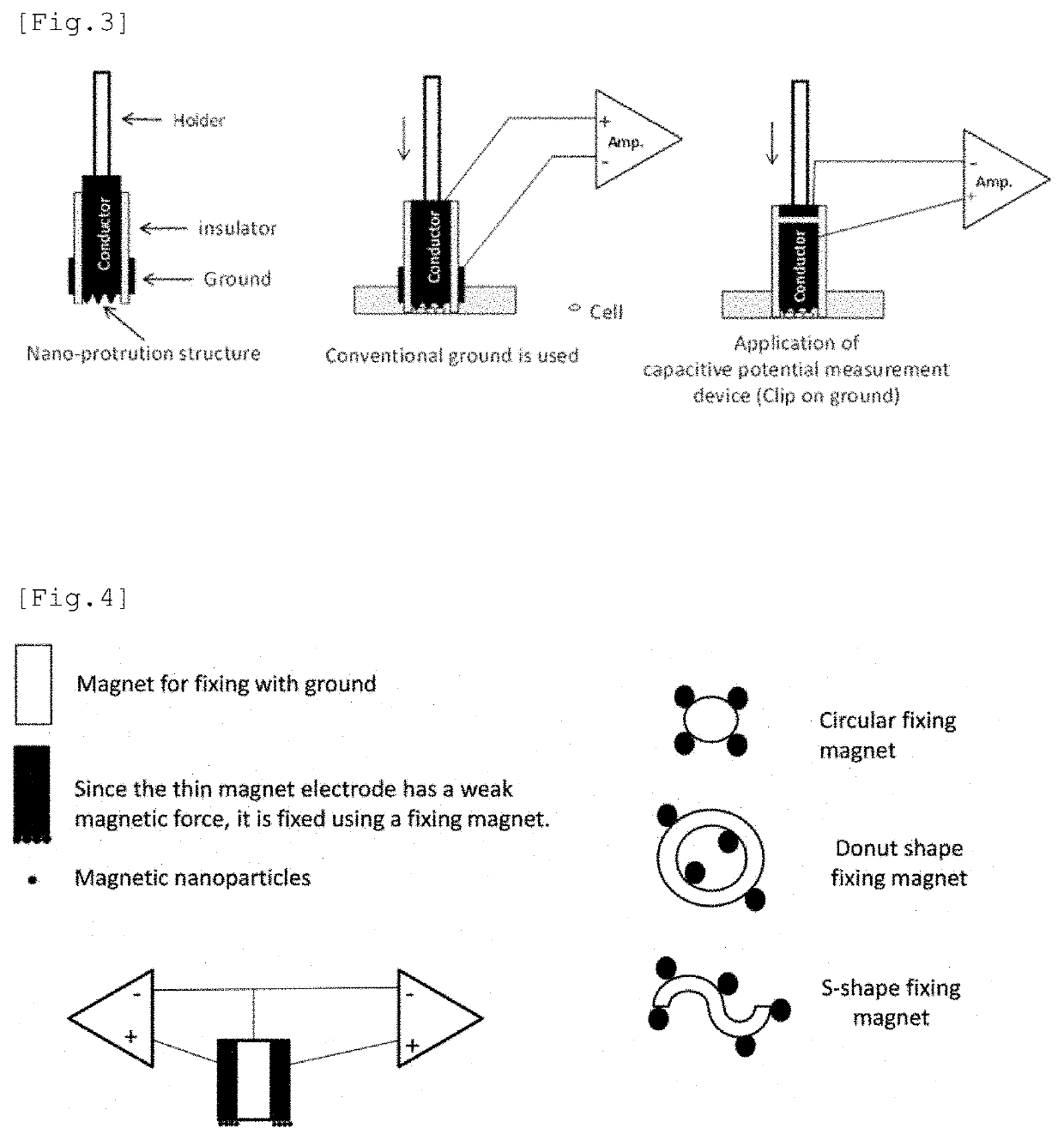
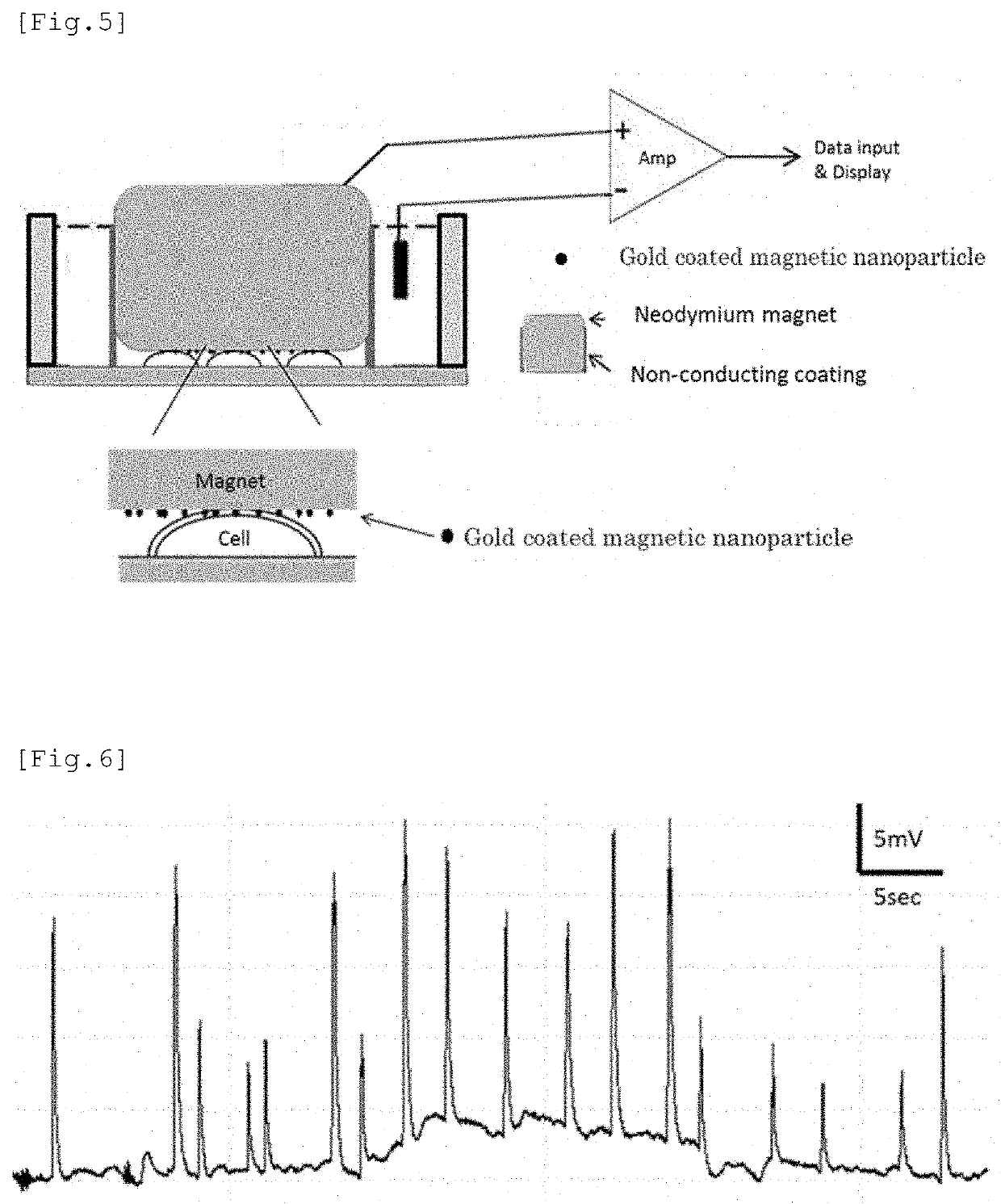
Electrode having NANO structure at tip
PendingUS20210355418A1Change in potentialEasy to measureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNano structuringRecording electrode
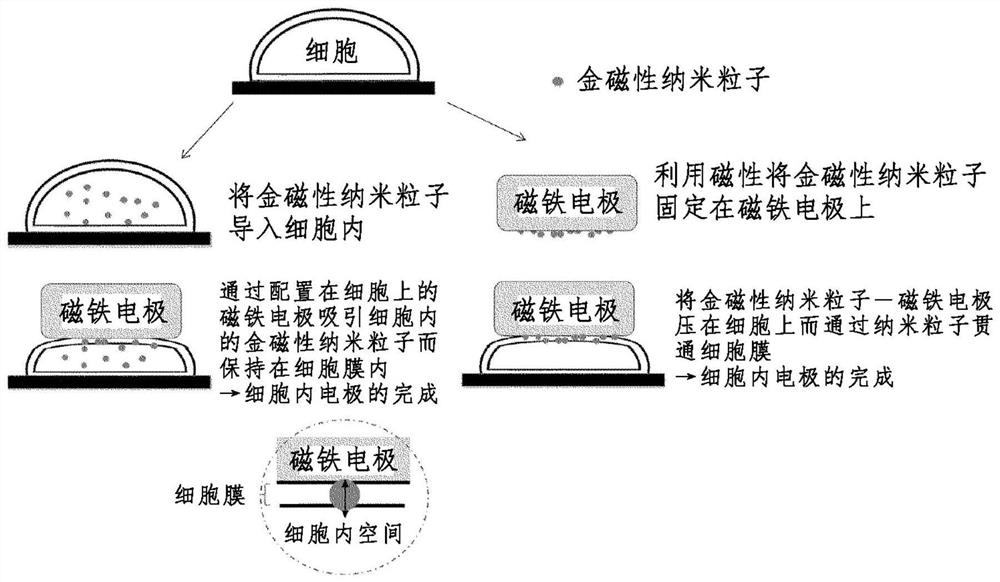
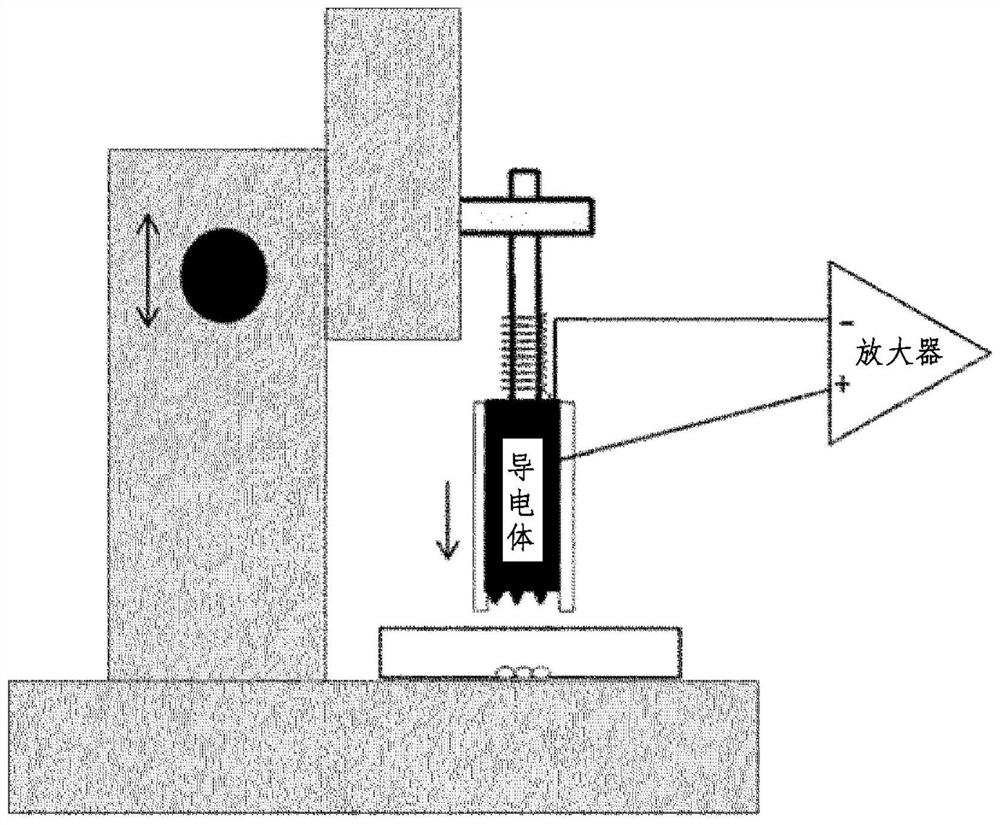
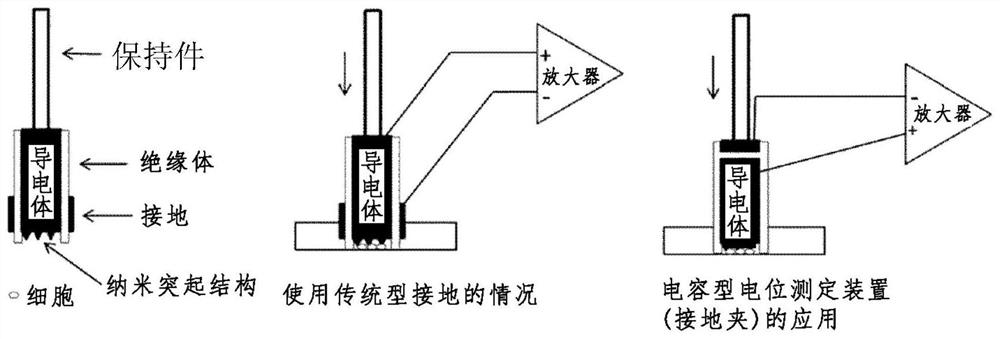
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a method which is designed to form an intracellular recording electrode for a cell by a simple operation which is less invasive to the cell and does not need a magnetic force, and with which the short-term or long-term intracellular potential can be accurately measured. More specifically, provided is a method comprising: securing, to a manipulator or the like, a holder provided on a conductor having a conductive nano structure at a tip; making the tip nano structure part penetrate a cell membrane while adjusting the amount of pressure applied to the target cell, thereby forming an intracellular recording electrode independently secured above the cell; and measuring the intracellular potential. The conductive nano structure at the tip and the conductor main body do not have to be magnetic but may be stuck together by magnetic force or may be formed as one body. When the cell membrane potential of a target cell cultured in a typical culture vessel is recorded, by forming the conductor main body of a magnetic electrode (MagEle) and independently securing same using a ring-shaped magnet that is provided on the lower surface of the culture vessel and that secures a light projection path or a light observation path through the center thereof, measurement of the intracellular potential of the target cell and fluorescent observation of changes in intracellular potential due to a light stimulus or intracellular calcium dynamics can be performed simultaneously.
Owner:ION CHAT RES CORP
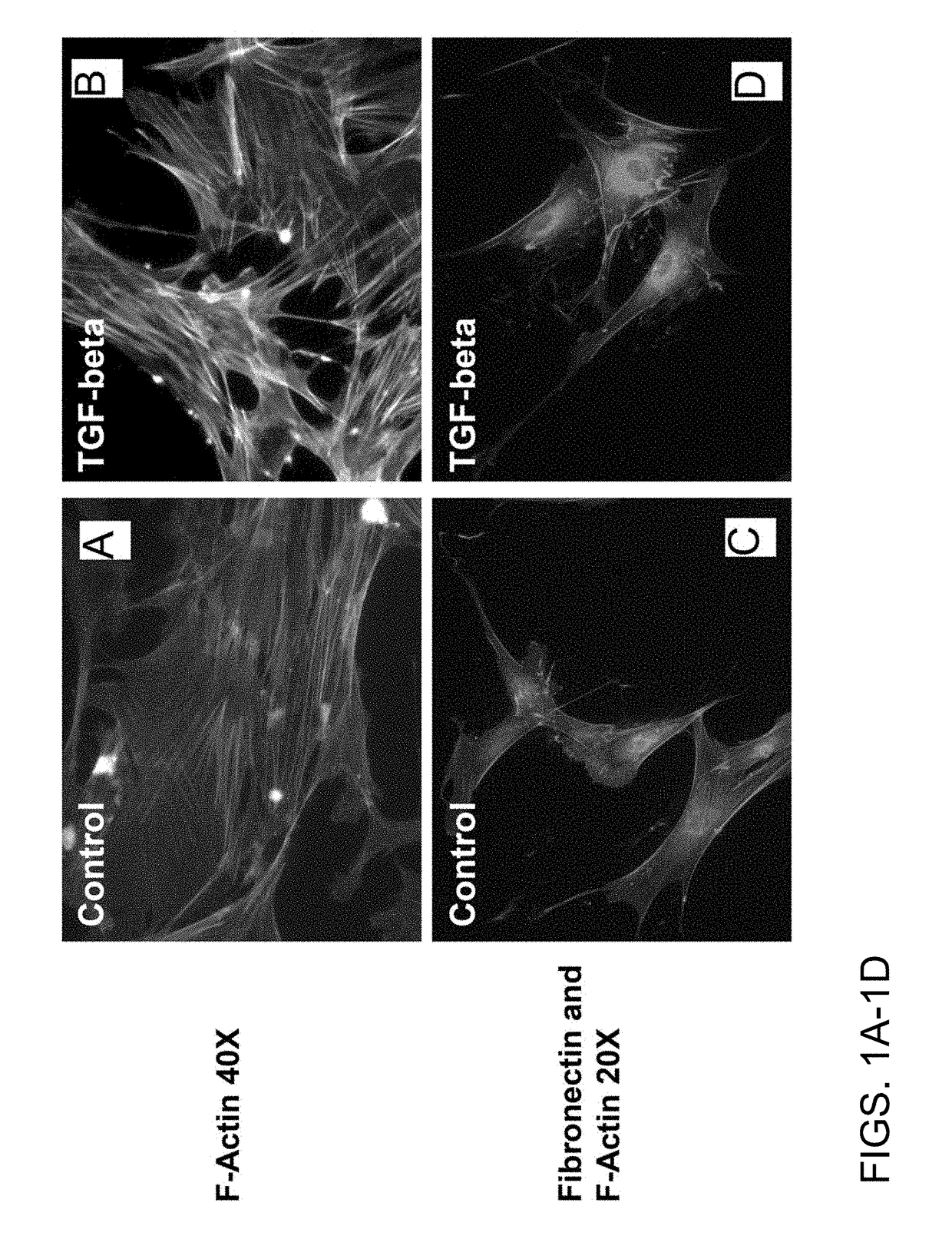
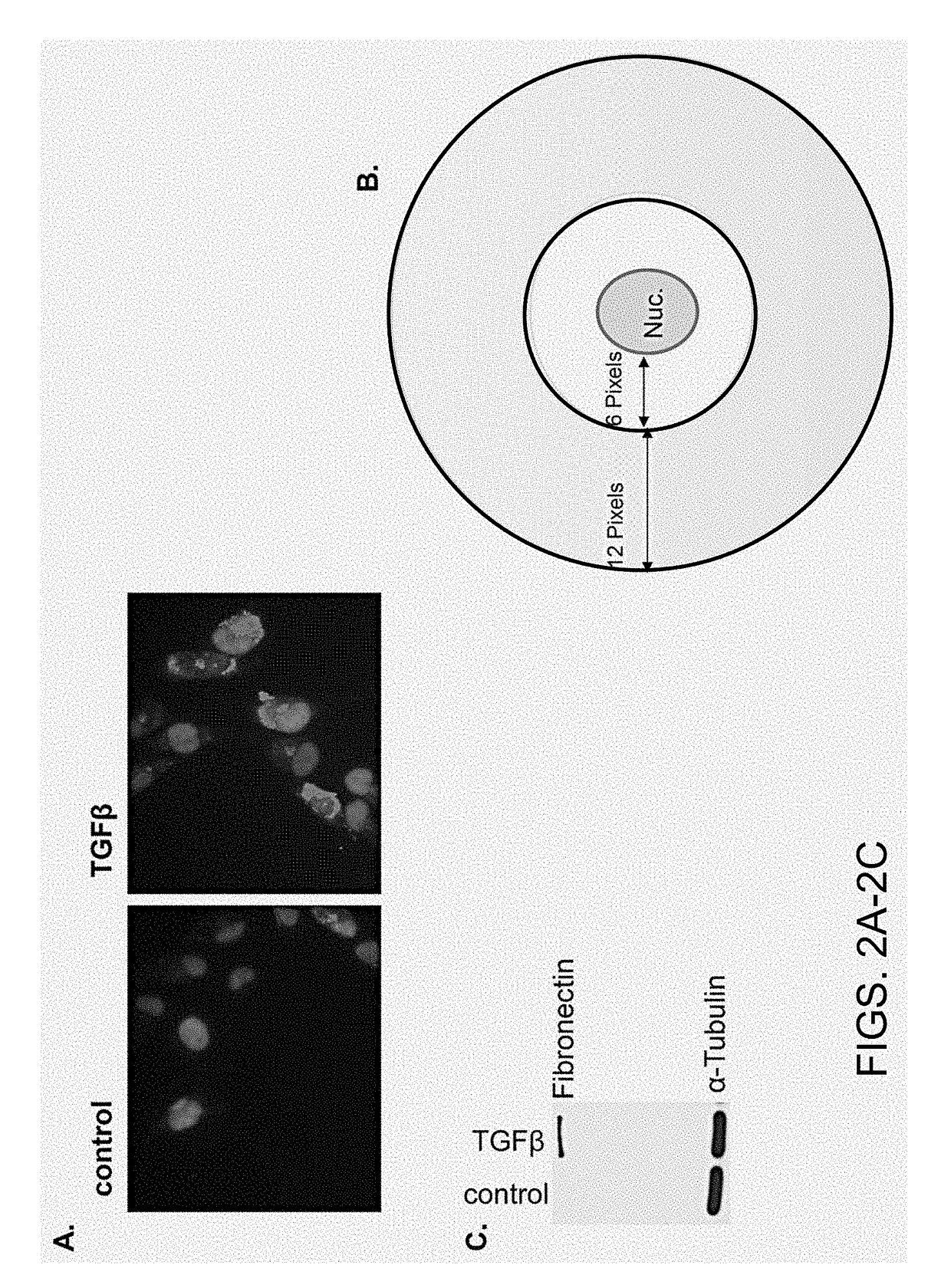
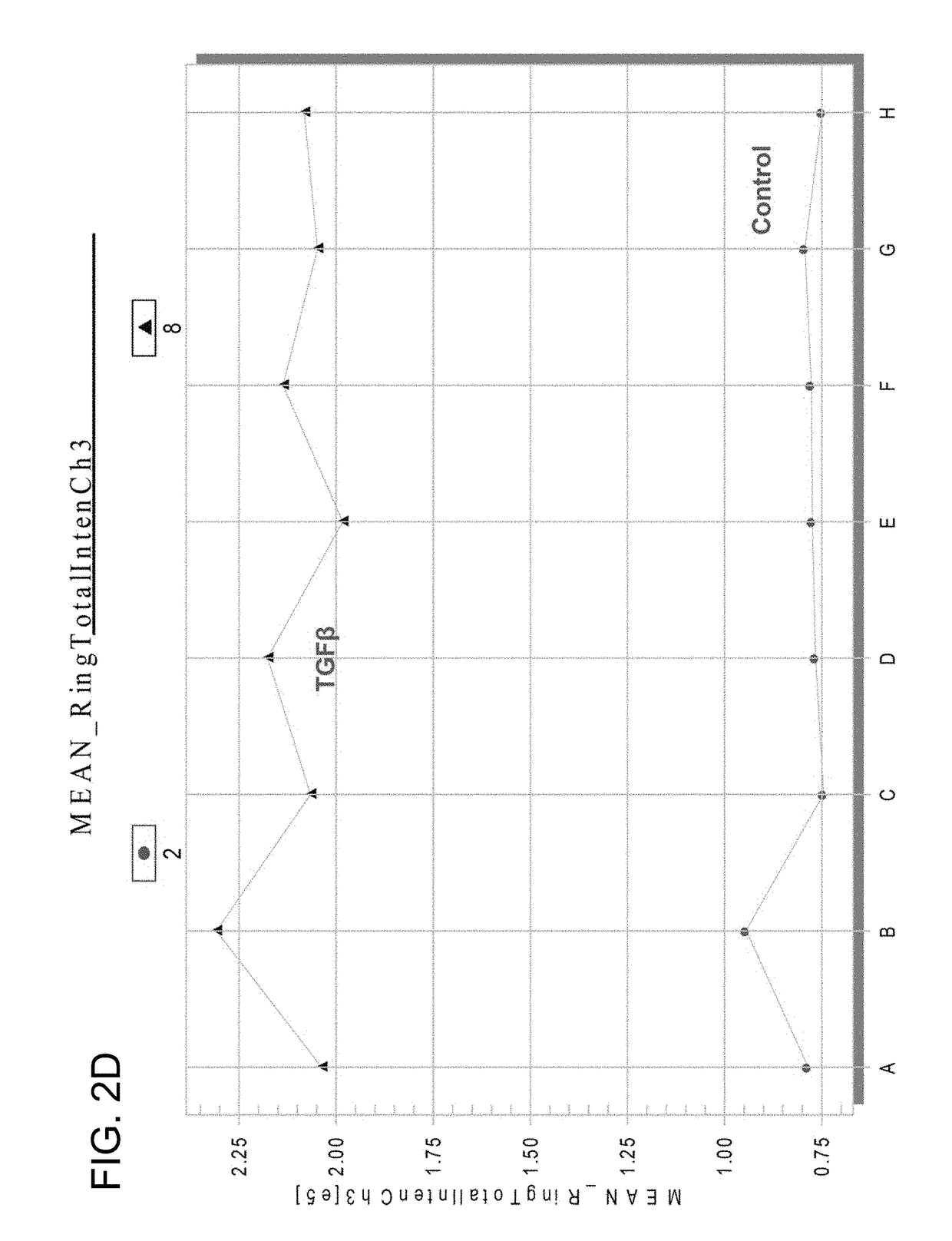
Chemicals and methods to prevent and treat tgf-beta mediated activation of fibroblasts to reduce and treat cancer and fibrosis
ActiveUS20190038655A1Increased proliferationIncreased defective apoptosisHydroxy compound active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsDiseaseEnantiomer
A method of treating an activated fibroblast associated disease or pre-disease condition in a mammal comprising, administering a pharmaceutical composition including a therapeutically effective amount of a first therapeutic, wherein the first therapeutic is one of an intracellular Ca2+ elevator, a YAP / TAZ inhibitor, both a intracellular Ca2+ elevator and a YAP / TAZ inhibitor, or pharmacologically acceptable salts, solvates, esters, amides, clathrates, stereoisomers, enantiomers, prodrugs or analogs thereof, or a combination thereof.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
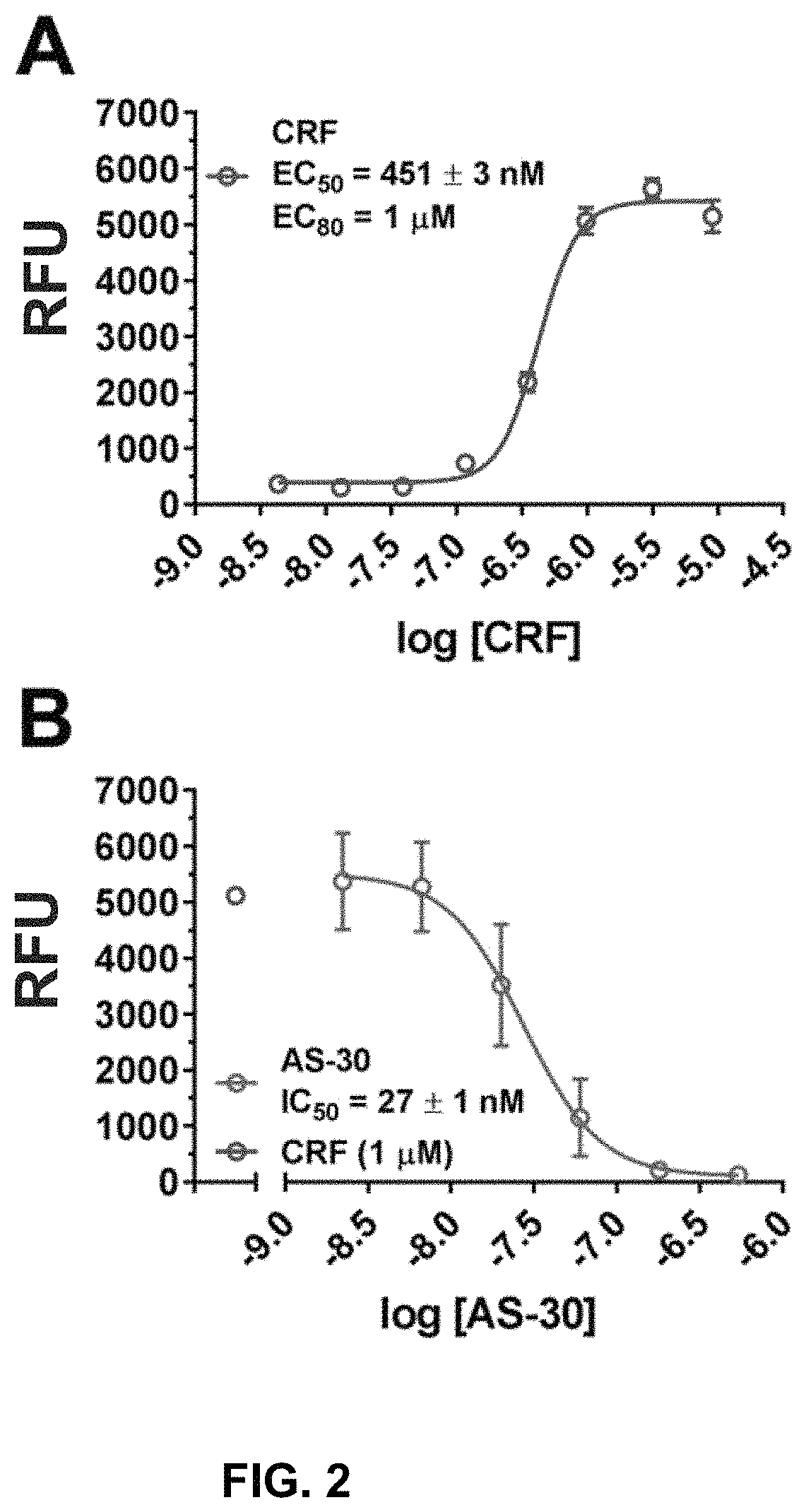
Compositions and methods for the modulation of the corticotropin releasing factor binding protein and the treatment of alcohol use disorder
ActiveUS11278527B2Organic chemistryHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsAspartic acid receptorsSubstance abuser
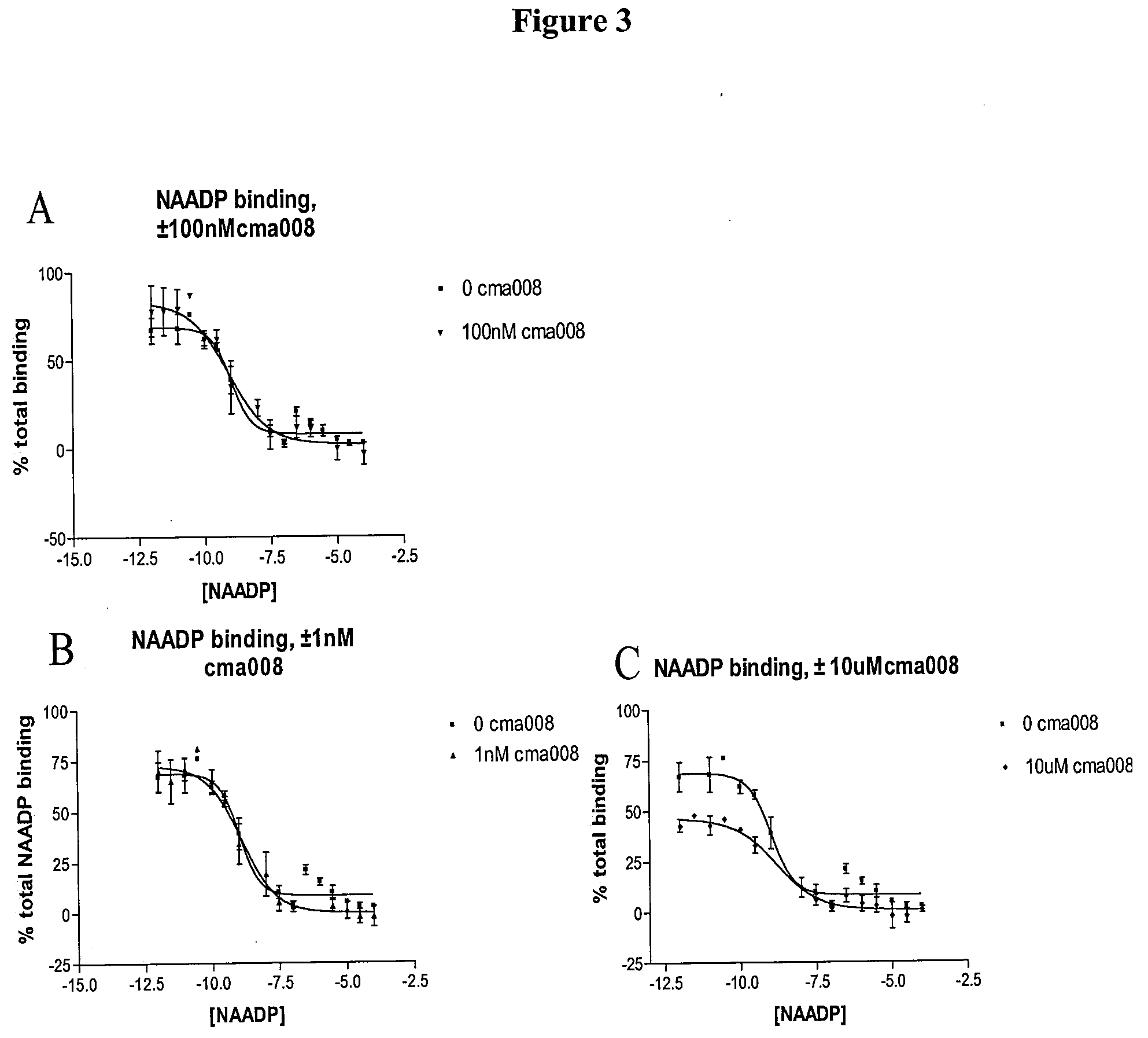
Stress responses involve corticotropin releasing factor (CRF), the two cognate receptors (CRF1 and CRF2) and the CRF-binding protein (CRFBP). Utilizing a novel cell-based assay, a C-terminal CRFBP fragment [CRFBP(10 kD)] was found to potentiates CRF-intracellular Ca2+ release, demonstrating that CRFBP possesses excitatory roles in addition to the inhibitory role established by the N-terminal fragment of CRFBP [CRFBP(27 kD)]. This interaction was CRF2-specific, as CRF1 responses were not potentiated by CRFBP(10 kD). As there were currently no small molecule ligands available that selectively interact with either CRFBP or CRF2, a cell-based assay was miniaturized, wherein CRFBP(10 kD) was fused as a chimera with CRF2α, that allowed us to a perform a high-throughput screen (HTS) of approximately 350,000 small molecules. This resulted in the identification of negative allosteric modulators (NAMs) of the CRFBP(10 kD)-CRF2 complex that blunt CRF-induced potentiation of N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor (NMDAR)-mediated synaptic transmission in dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmental area (VTA). These results provide the first evidence of specific roles for CRF2 and CRFBP in the modulation of neuronal activity and suggest that NMDARs in the VTA may be a target for the treatment of stress and substance abuse disorders such as alcohol use disorder.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
Electrode having NANO structure at tip
PendingCN112969780AEasy to measureAvoid damageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNano structuringRecording electrode
Owner:ION CHAT RES CORP +1
Photoproteins with enhanced bioluminescence and assays using the same
InactiveUS7981602B2Improved bioluminescence activityHigh affinity to calciumBacteriaTissue cultureCell based assaysPhotoprotein
The present invention relates to photoproteins with enhanced bioluminescence obtained by mutagenesis of clytin, to their use as intracellular calcium indicators and in cell-based assays.
Owner:AXXAM SRL (IT)
Selective maxi-K potassium channel openers functional under conditions of high intracellular calcium concentration, methods and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050043293A1Function increaseImprove opening rateBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseK channels
The present invention describes calcium sensitive and selective maxi-K potassium channel opener / activator compounds that function to open maxi-K channels under conditions of high intracellular calcium concentrations, and which do not significantly affect the opening of maxi-K channel proteins under conditions of low or physiologically normal intracellular calcium concentrations. Methods of assaying for and using such compounds are also provided. According to the invention, whole cell voltage patch-clamp studies newly demonstrated that the ability of opener compounds, e.g., fluoro-oxindoles and chloro-oxindoles, to open maxi-K channels was sensitive to the intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+])i, i.e., more channels opened at more negative potentials. Particular fluoro-oxindole and chloro-oxindole compounds produced significant increases in whole-cell maxi-K potassium channel-mediated outward currents only in cells having higher [Ca2+]i, compared with effects in lower [Ca2+]i. Such compounds provide Ca2+-sensitive and selective openers of maxi-K channels which show maximum effectiveness under conditions of increased [Ca2+]i and, as such, provide treatments for diseases and disorders in which cells undergo, or are subject to, traumatic stress due to high internal calcium levels, such as stroke.
Owner:GRIBKOFF VALENTIN K +5
Zinc transporter compositions for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases
InactiveUS20060166860A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicinePhysical interaction
The present invention relates to the use of ZnT-1, originally described as a zinc transporter, in the regulation of L-type calcium channels (LTCC). In this study, the inventors have unexpectedly demonstrated that ZnT-1 physically interacts with LTCC, regulating its function. Most importantly, the inventors have shown that ZnT-1 can regulate intracellular Ca2+ influx, and thus, its intracellular concentration. This is the first demonstration of a natural blocker for LTCC, and it is a promising breakthrough as a potential agent to be used in the treatment and / or prevention of cardiovascular diseases and related indications.
Owner:BEN GURION UNIVERSITY OF THE NEGEV
Assay for detection of transient intracellular CA2+
InactiveUS8304198B2Biological material analysisTransferasesNR1 NMDA receptorN methyl D aspartate receptors
This invention relates to a simple end point assay for detection of transient intracellular Ca2+ with broad applicability to many Ca2+ channel proteins comprising, Generation of expression constructs for the fusion proteins having the Ca2+ / calmodulin dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) phosphorylation sites of NR2A or NR2B subunits of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) or the voltage gated potassium channel of Drosophila (Eag) or any protein sequence which binds to the T-site of CaMKII similar to NR2B, conjugated to mitochondrial localizing signal sequence, or mutants of these sequences as described herein. Generation of mammalian expression constructs of α-CaMKll as a chimera with green fluorescent protein (GFP-α-CaMKII) or its mutants as described herein. Site-Directed mutagenesis, Transfection, Ca2+ stimulation, imaging and quantification of the number of cells with Ca2+-dependent signal, wherein, NMDA receptor activity assay, TRPVI receptor activity assay, GluR4 receptor activity assay are performed to detect the activity Of Ca2+ channel proteins.
Owner:RAJIV GANDHI CENT FOR BIOTECH +1
1,3,4-oxadiazole derivative and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102827098BHigh practical application valueThe measurement result is accurateOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceSilica gel
The invention discloses a 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivative and a synthetic method thereof, and an application of the derivative serving as a fluorescent indicator to detection of intracellular calcium ions (Ca<2+>). The method comprises the following steps of: under the protection of inert gas, performing a wittig reaction on the 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivative and a calcium ion response group to obtain a crude product; and concentrating the crude product, and separating through a silica gel column to obtain a pure product. The 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivative has the advantages of high sensitivity and high selectivity on Ca<2+>, large Stocks displacement, proportional measurement and the like; the color of the indicator changes greatly before and after bonding with Ca<2+>, so that identification and judgment can be performed conveniently through naked eyes; and moreover, the indicator can be loaded into cells, so that an intracellular Ca<2+> signal and the concentration thereof can be detected conveniently under a laser confocal microscope.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
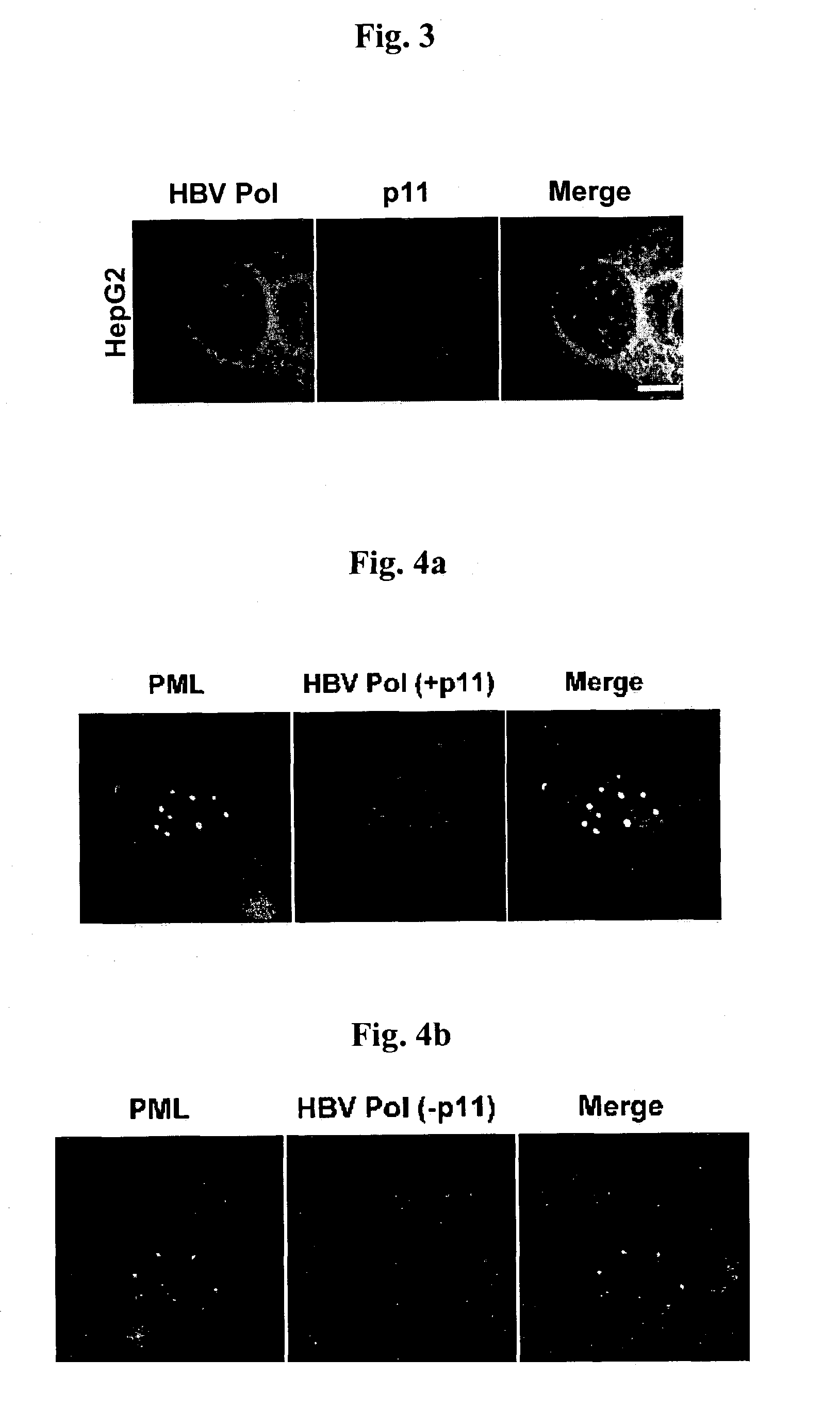
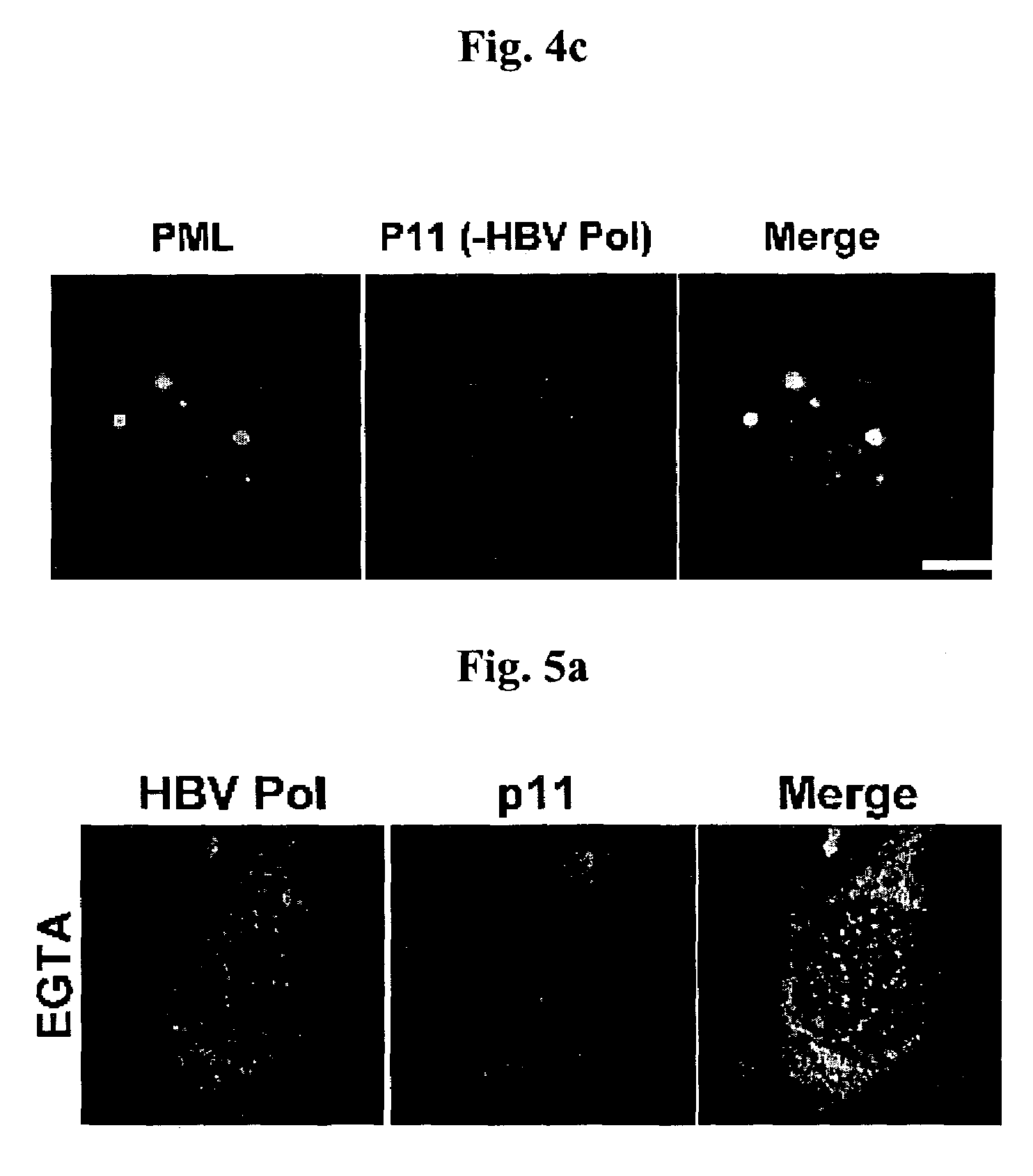
Complex of Hepatitis B virus polymerase with p11 and method for controlling movement of the complex in HepG2 cell
Disclosed is a complex of the 11 kDa Ca2+ binding protein of 11 and Hepatitis B virus polymerase (HBVPol) which moves to Promyelocytic Leukemia Nuclear Body (PMLNB). Furthermore, the present invention discloses a method for controlling movement of the HBVPol / p11 complex into the nucleus of HepG2 cell with adjusting of intracellular Ca2+ ion concentration by administrating an agent for controlling calcium ion concentration in HepG2 cells.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Methods and compositions for modulating C5-a-mediated inflammatory responses
InactiveUS20060063701A1High activityProlong half-life in vivoPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsIn vivoAmino acid change
PL37 (RAARISLGPRICKAFTE [SEQ ID NO: 2]) is an Antisense Homolgoy Box peptide composed of amino acids 37 to 53 of C5a-anaphylatoxin. Complementary peptides, ASGAPAPGPAGPLRPMF (Pep-A [SEQ ID NO: 1]) and ASTAPARAGLPRLPKFF (Pep-B [SEQ ID NO: 3]) were designed and characterized. Pep-A bound to PL37 and to C5a with very slow dissociation, whereas Pep-B failed to bind at all. C5a was inactivated by 7 nM or more of Pep-A and this concentration of Pep-A inhibited induction of intracellular Ca++ influx in neutrophils. Patch clamp studies also showed the effectiveness of Pep-A in C5a-receptor-expressing neuroblastoma cells. Pep-A administration prevented rats from C5a-mediated rapid lethal shock. A-Pep-A (Pep-A acetylated with alanine at the amino-terminus) was more stable in vivo and showed stronger inhibition of inflammatory reactions in mice and rats. Chemical modification of Pep-A (e.g., acetylation, or single or multiple amino acid replacement, insertion, or deletion within the native Pep-A sequence) will yield effective inhibitors, and will often improve inhibitory function on C5a anaphylatoxin. In such modified constructs it will often be desired to conserve some or all 5 prolines found in Pep-A to preserve inhibitory function on C5a.
Owner:RES INST FOR PROTEIN SCI
Control of function of intracellular Ca ion
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
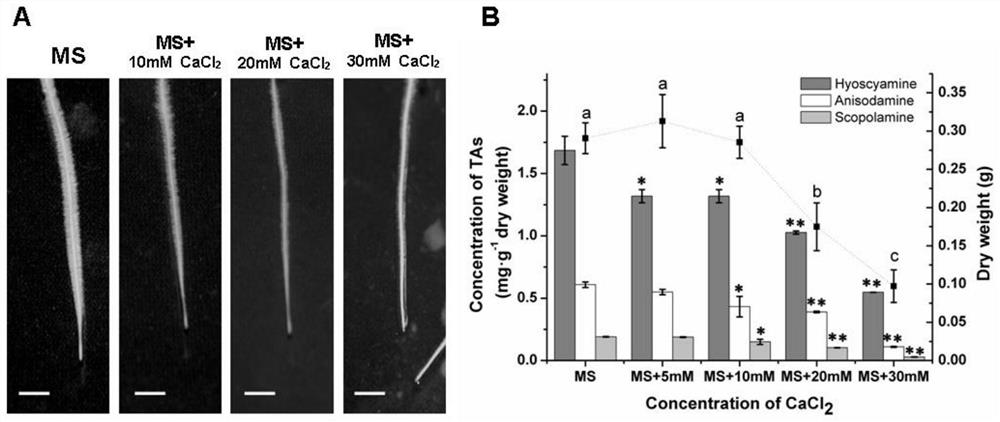
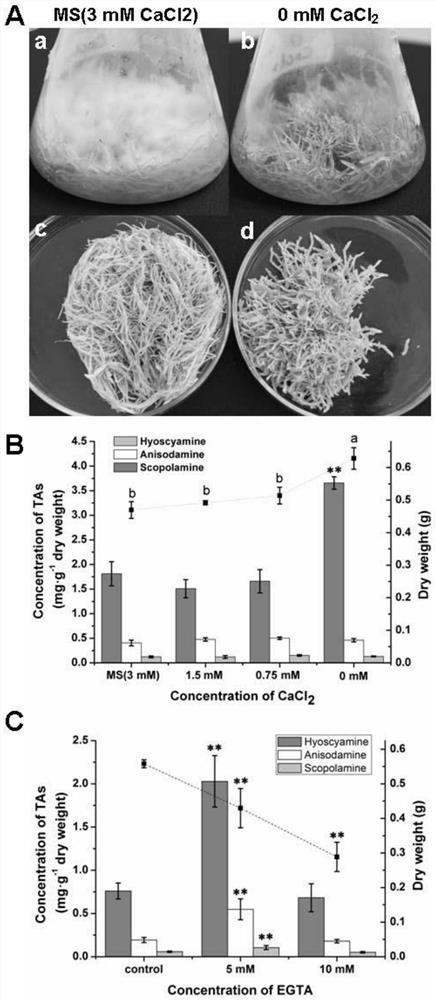
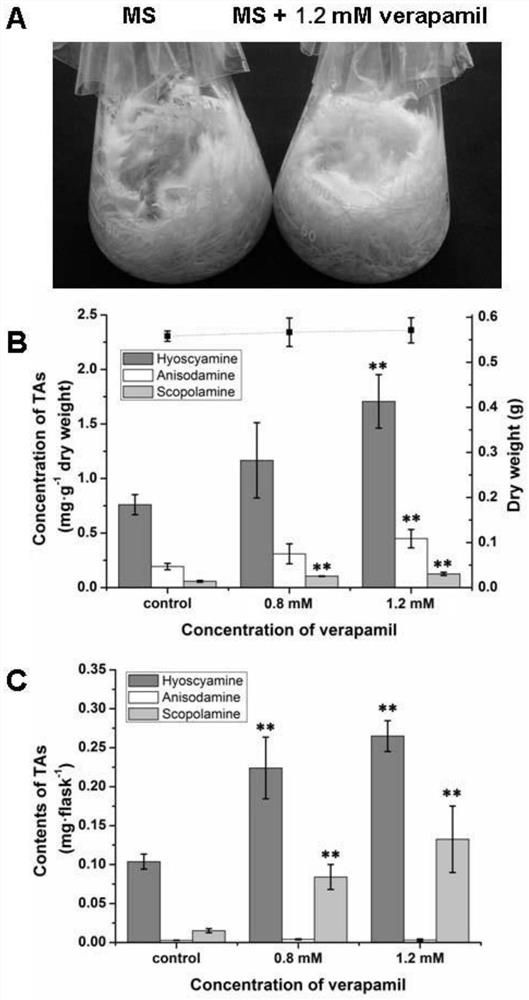
Method for increasing tropane alkaloid content in belladonna hairy roots by using calcium signal inhibitor
ActiveCN114651719ATAs content decreasedIncrease concentrationPlant genotype modificationAngiosperms/flowering plantsReceptorTropane alkaloid
The invention discloses a method for increasing tropane alkaloid content in belladonna hairy roots by using a calcium signal inhibitor, which is characterized in that extracellular Ca < 2 + > concentration is reduced by using a Ca < 2 + > specific chelating agent, or a Ca < 2 + > / CaM signal pathway in the belladonna hairy roots is inhibited by using a cell membrane Ca < 2 + > channel inhibitor or an intracellular Ca < 2 + > receptor calmodulin inhibitor, so that the content of tropane alkaloid in the belladonna hairy roots is increased. Therefore, the expression of related genes PMT, TRI, CYP80F1, H6H and ArAT4 in the synthetic route of the tropane alkaloids is induced, and the synthesis and accumulation of the tropane alkaloids hyoscyamine, anisodamine or scopolamine are promoted.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com