Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2018 results about "Home use" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
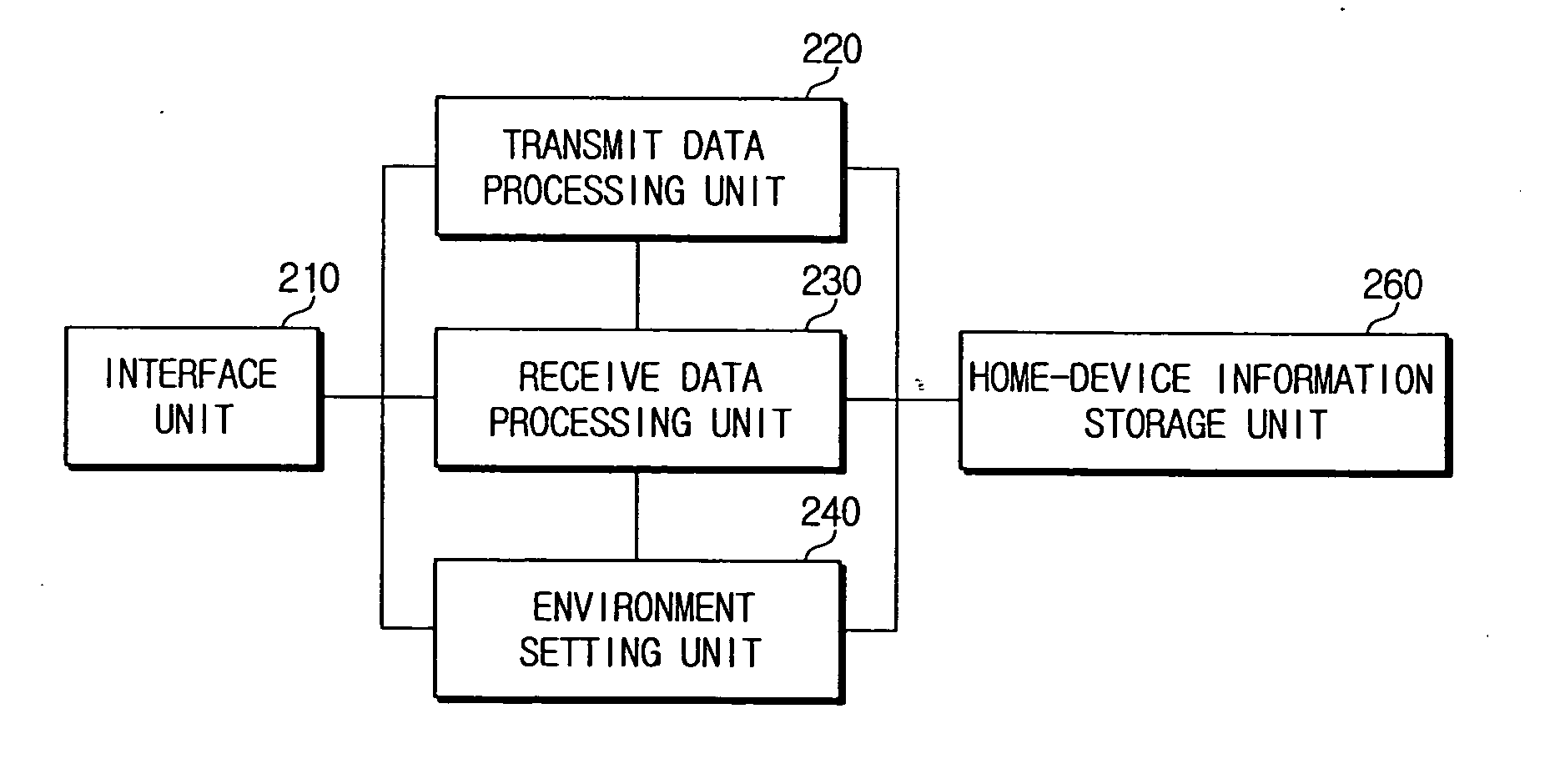
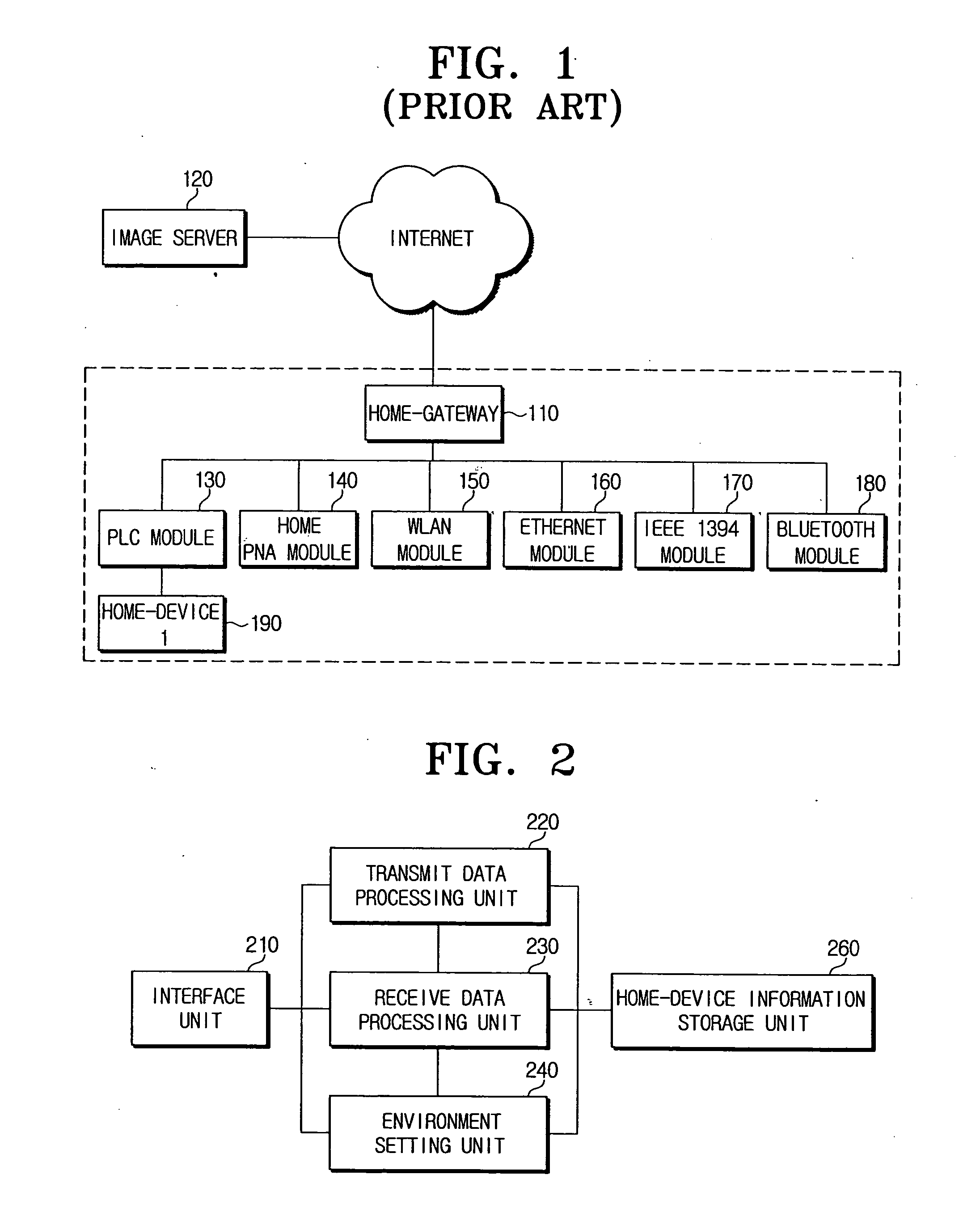
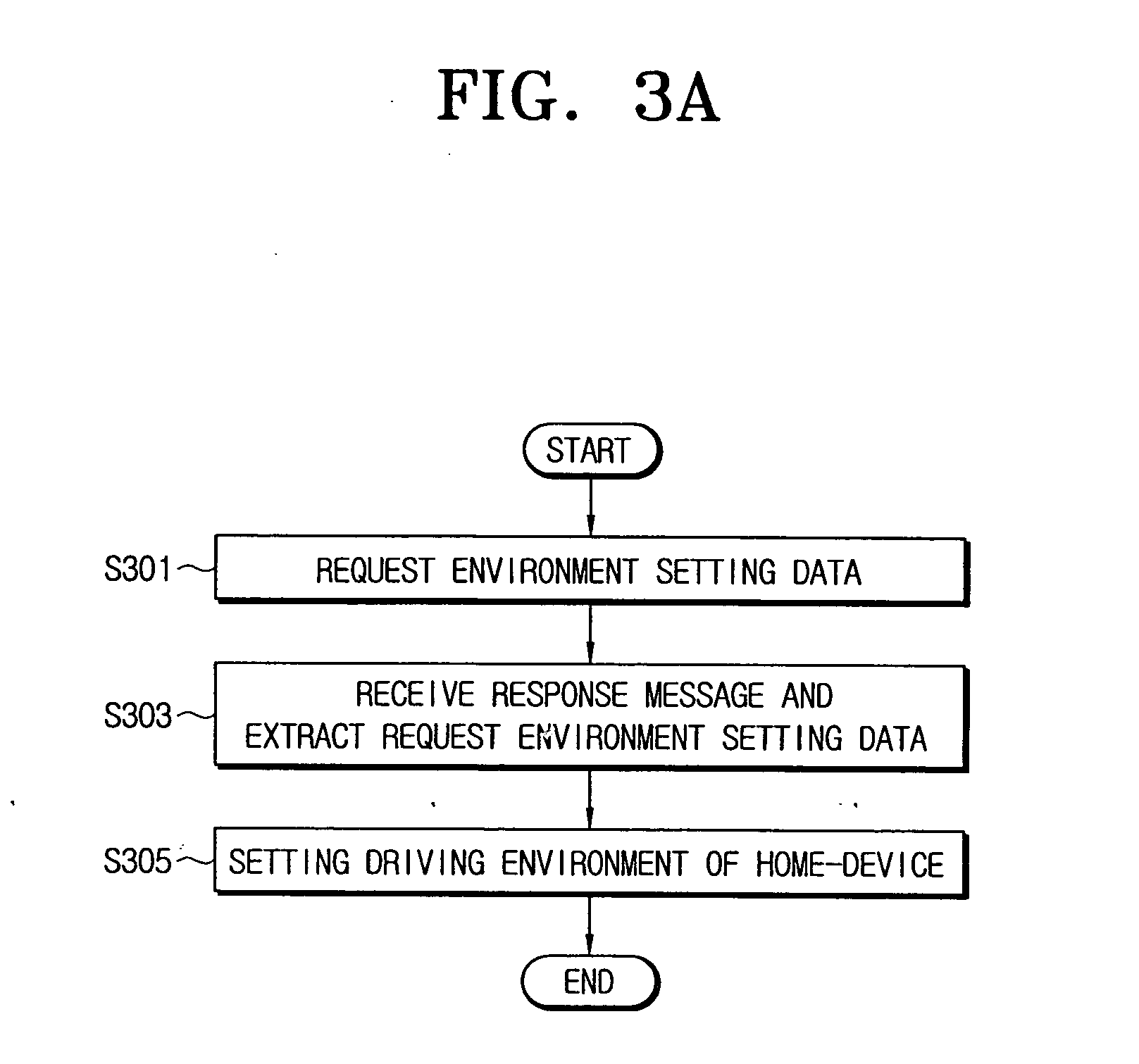
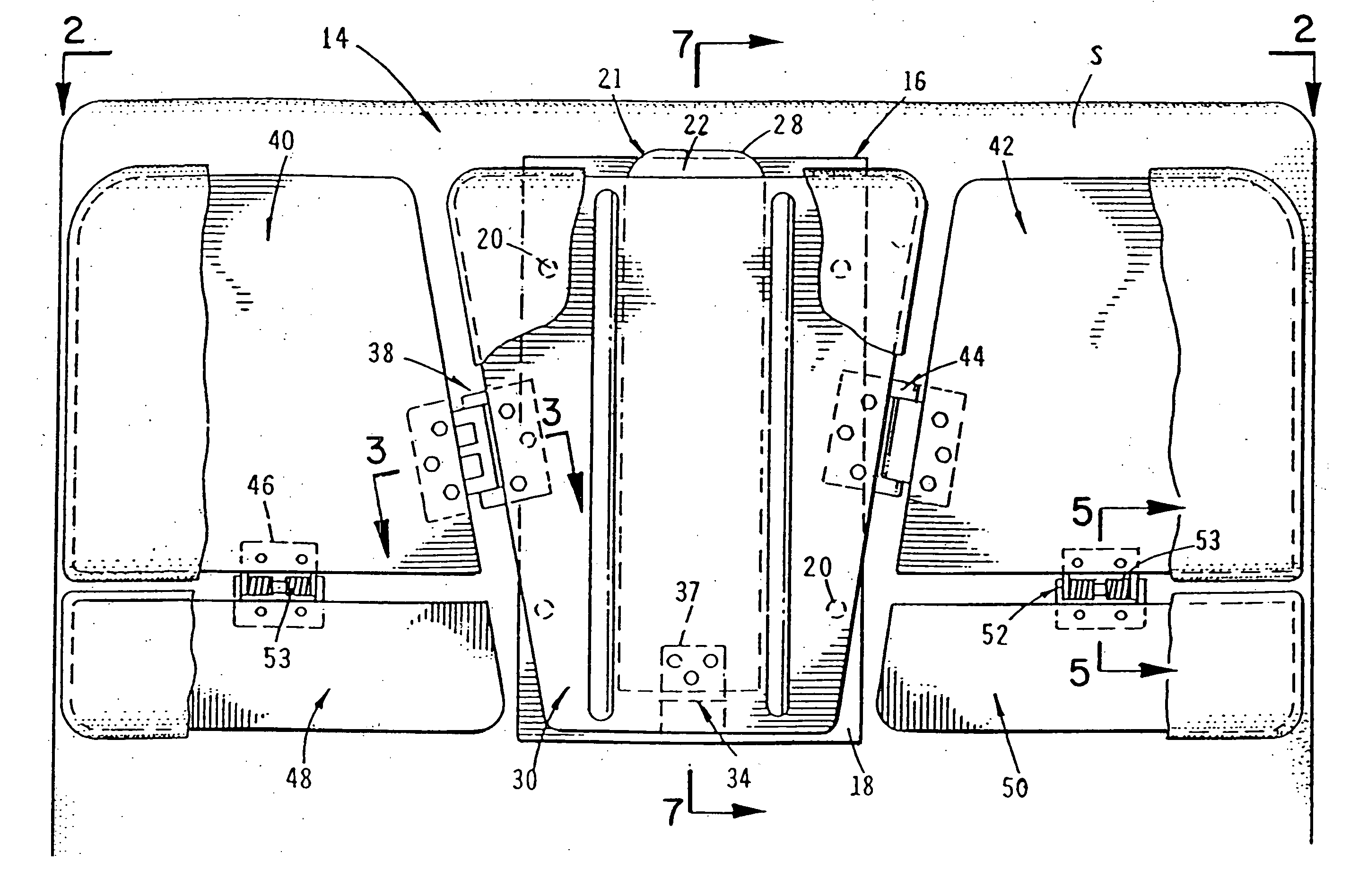
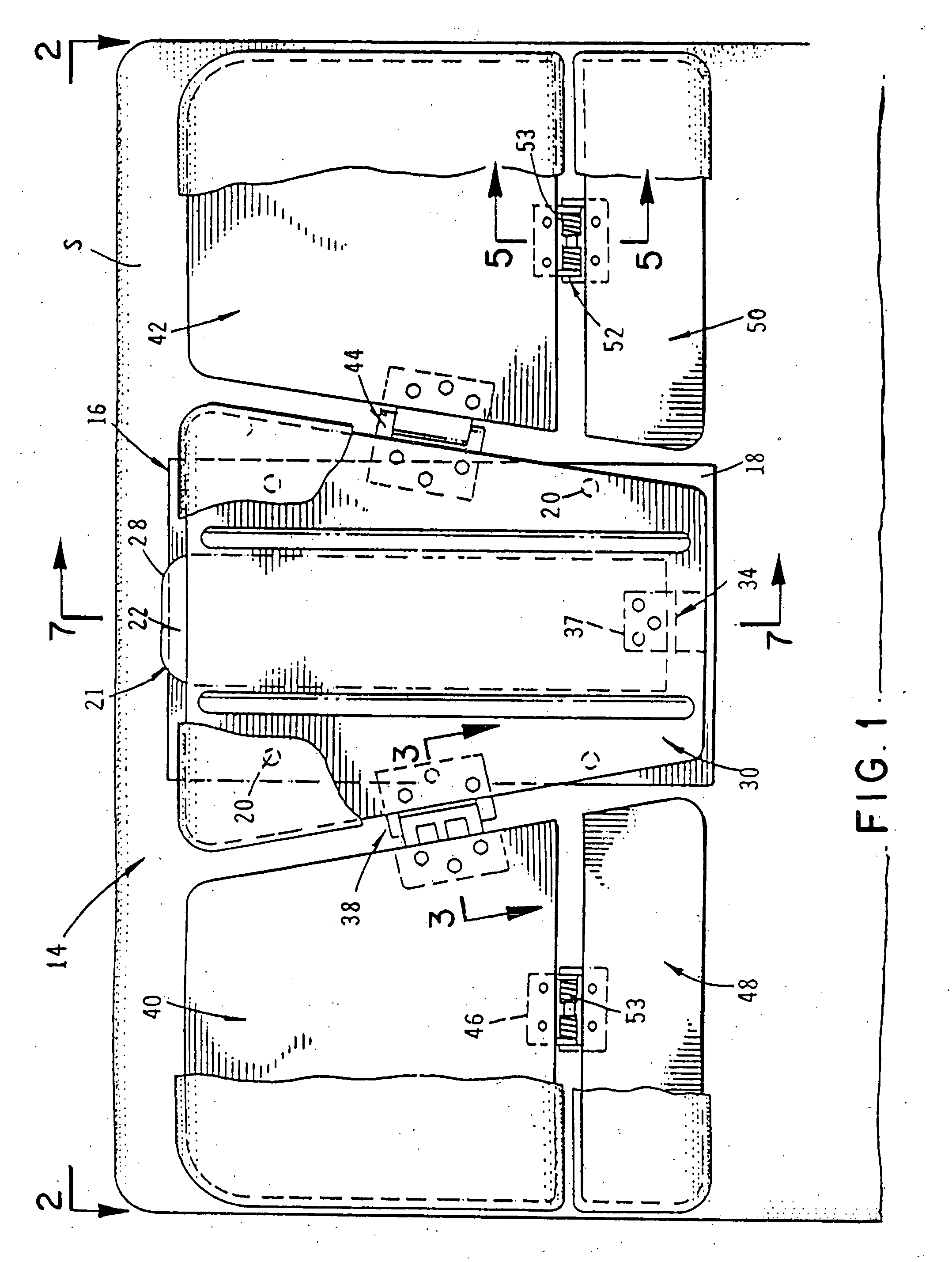
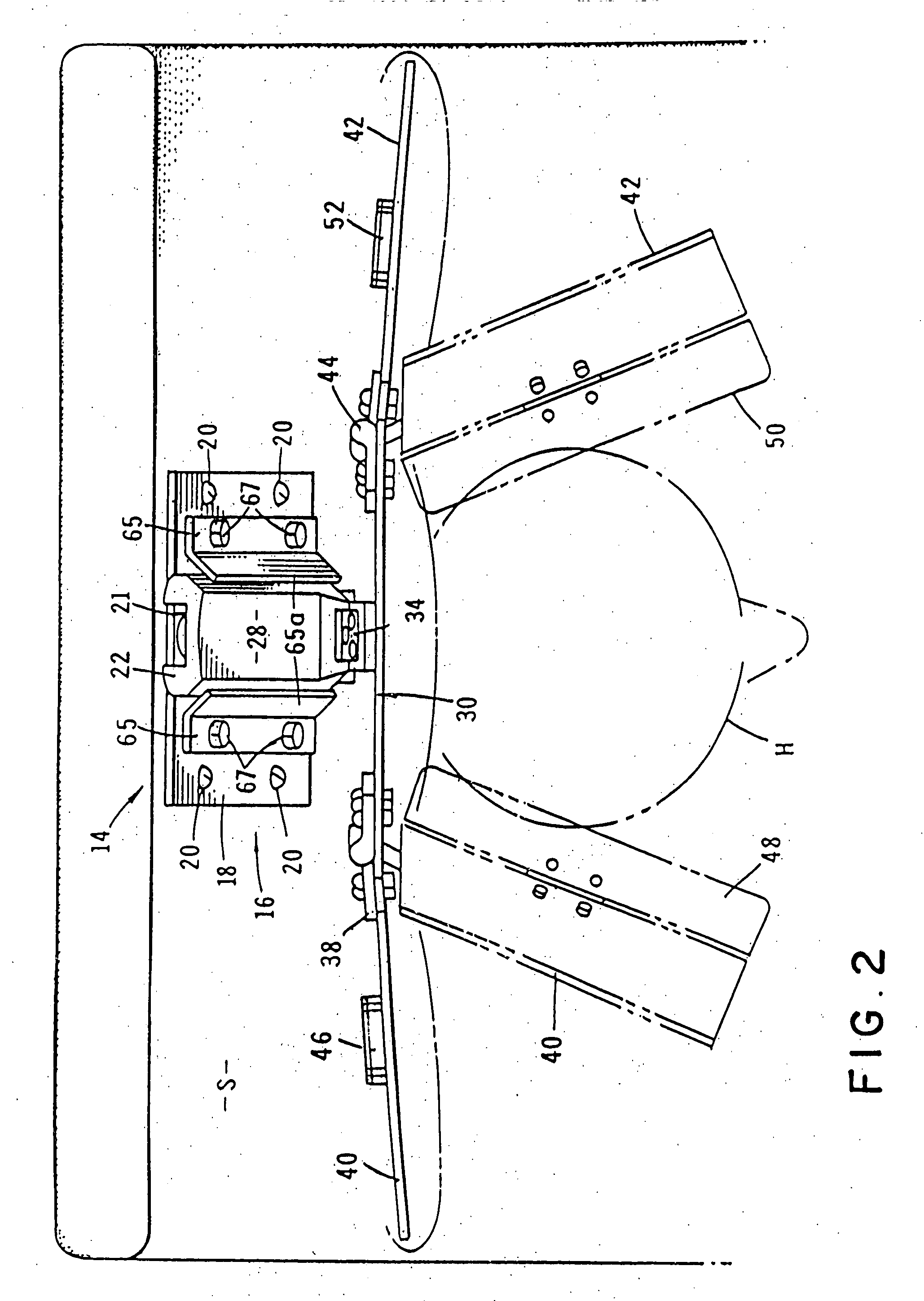
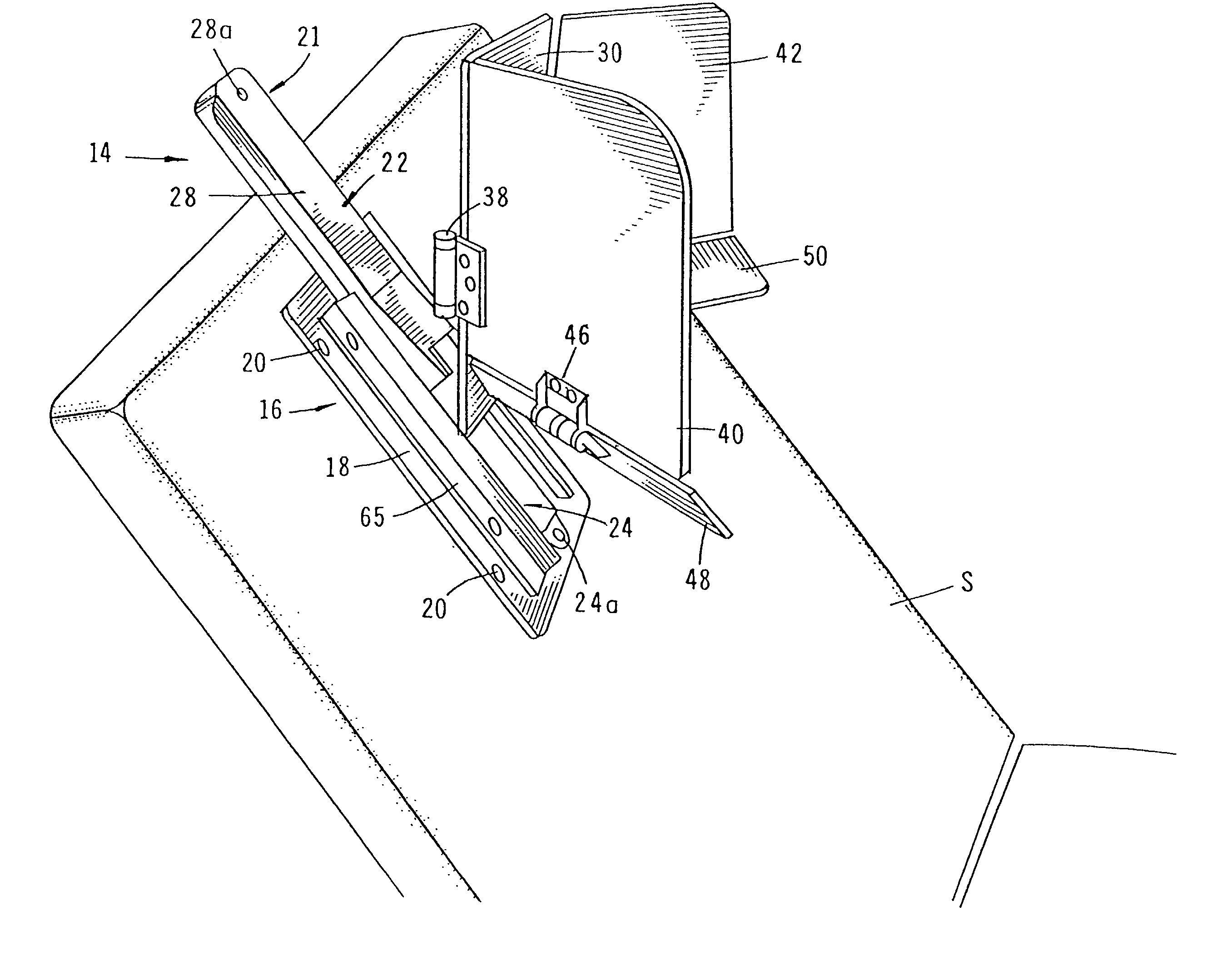
Apparatus for managing home-devices remotely in home-network and method thereof
An apparatus for providing an interface between a home-network and a external network and remotely managing the home-device connected to the home-network. The apparatus includes a transmit data processing unit for transmitting information on the home-device to a provider server connected to the external network, and requesting environment setting data for setting a driving environment of the home-device; a receive data processing unit for receiving a response message based on the request, from the provider server, and extracting the environment setting data included in the response message; and an environment setting unit for setting the driving environment for the operation of the home-device, based on the environment setting data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
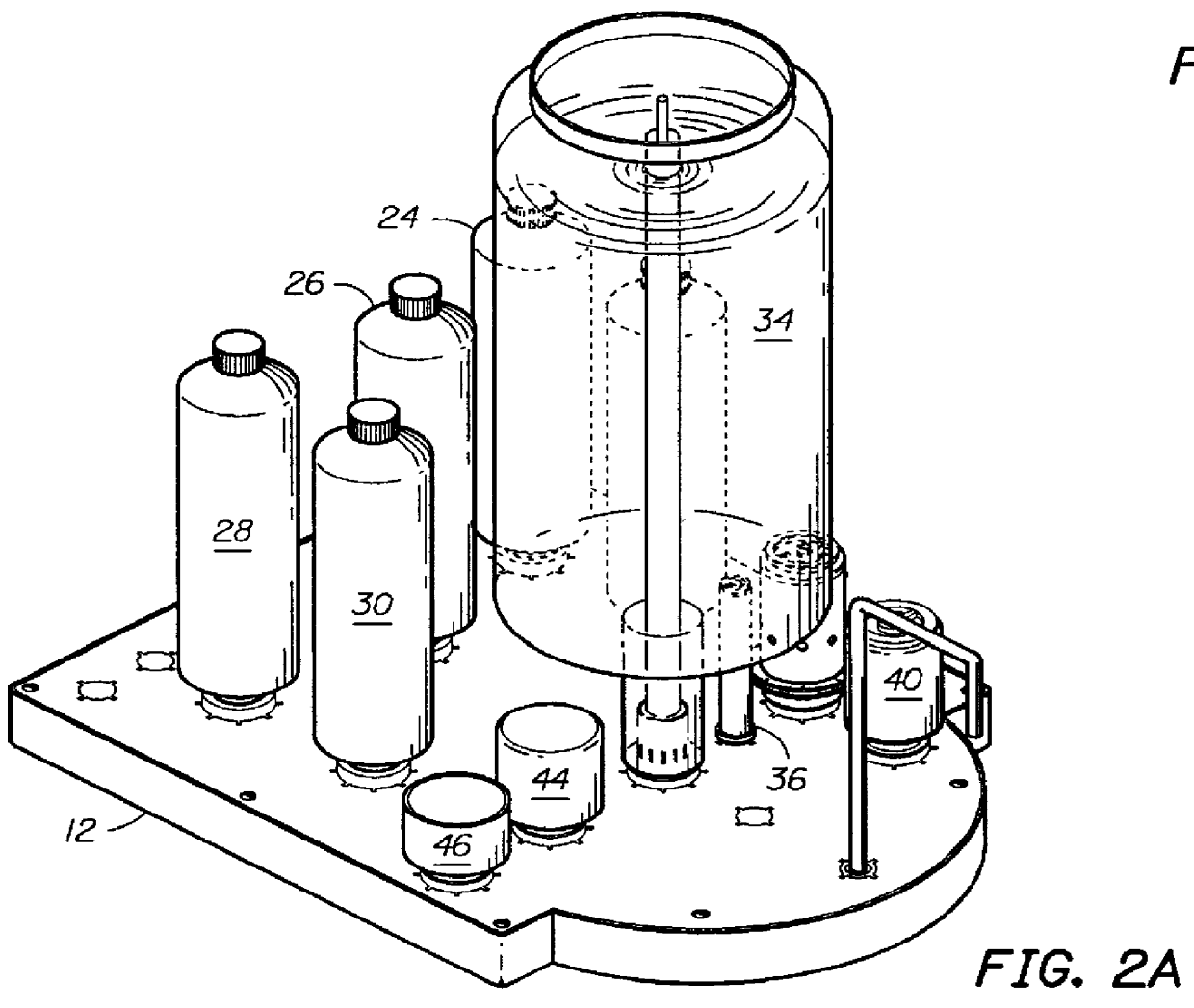
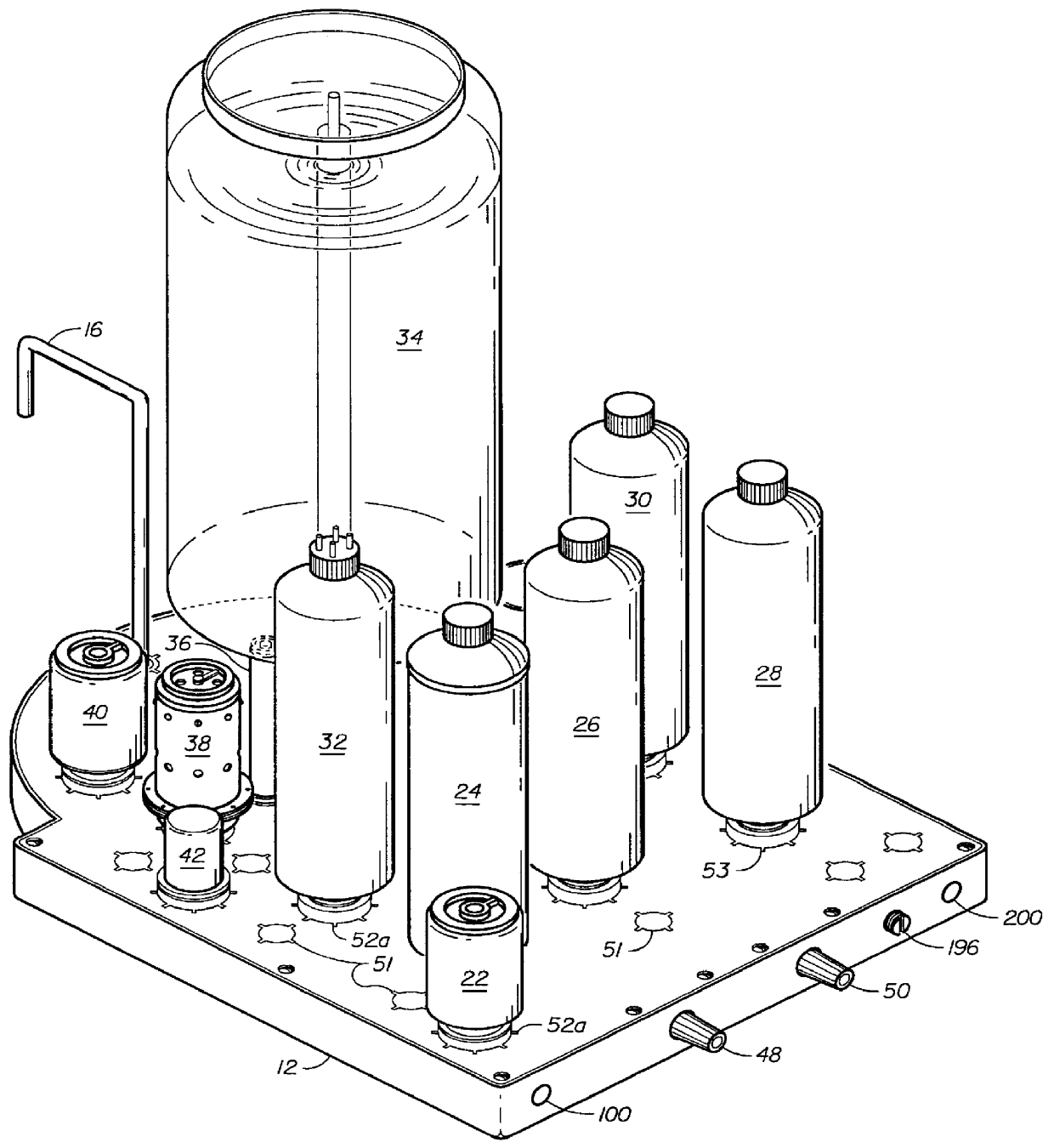
Counter top reverse osmosis water purification system
InactiveUS6099735AEasy to operate and maintainSafely maintainSolid sorbent liquid separationReverse osmosisIon exchangeCarbon adsorption
A counter top reverse osmosis water purification system, suitable for home use, is connected to a water supply and contains a closed fluid treatment circuit extending to a water outlet. The closed fluid circuit flows through a plurality of replaceable water treatment modules mounted on a flowboard and each having a specific water treatment function, such as the removal of a particular material from the water by the use of reverse osmosis, filtration, carbon adsorption, ion exchange or the addition of a chemical to balance the desired water conditions. Preferably the circuit also includes traversing a radiation device, for example an ultraviolet light, for the purpose of sanitizing the water.
Owner:KELADA MAHER I
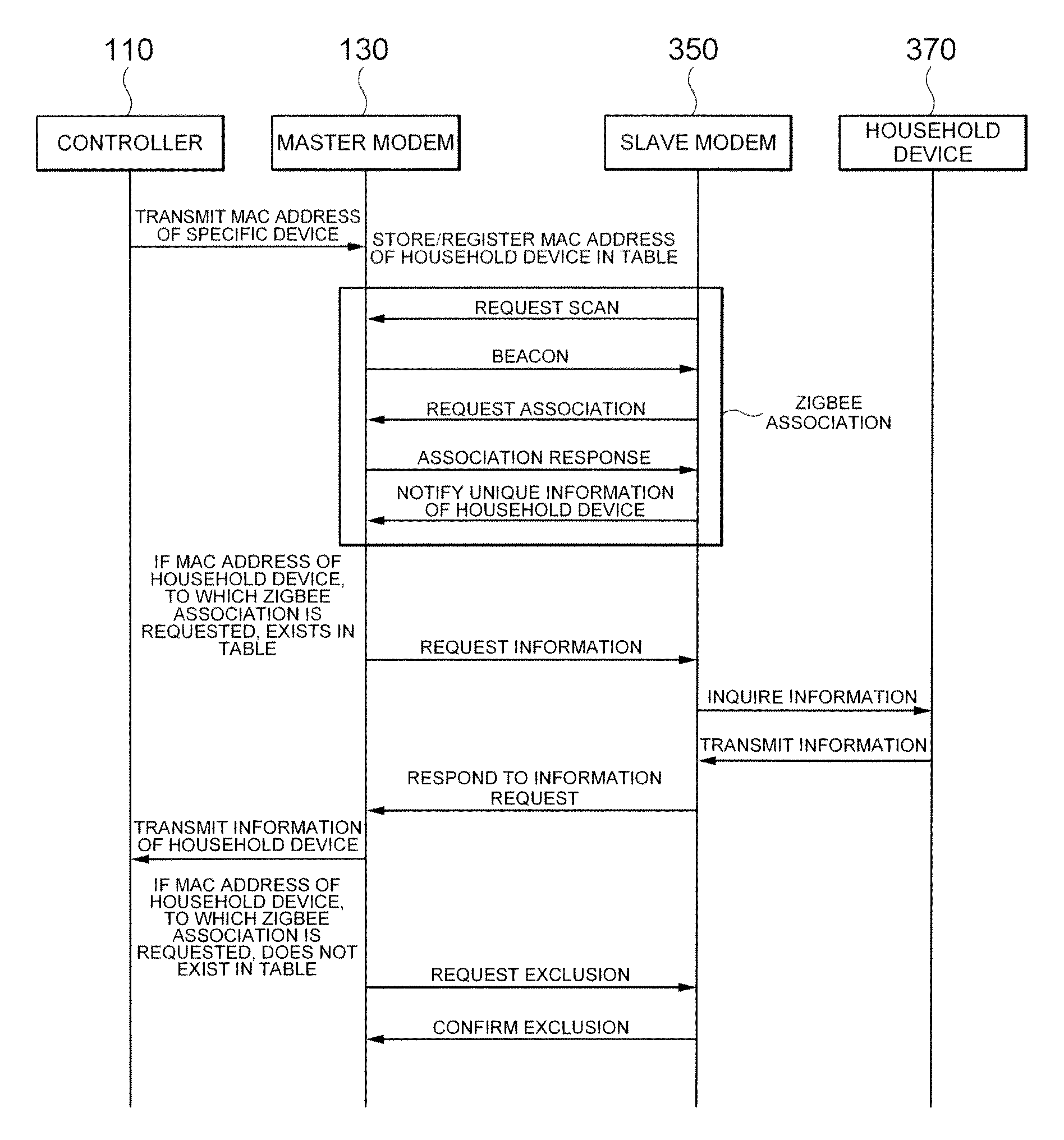
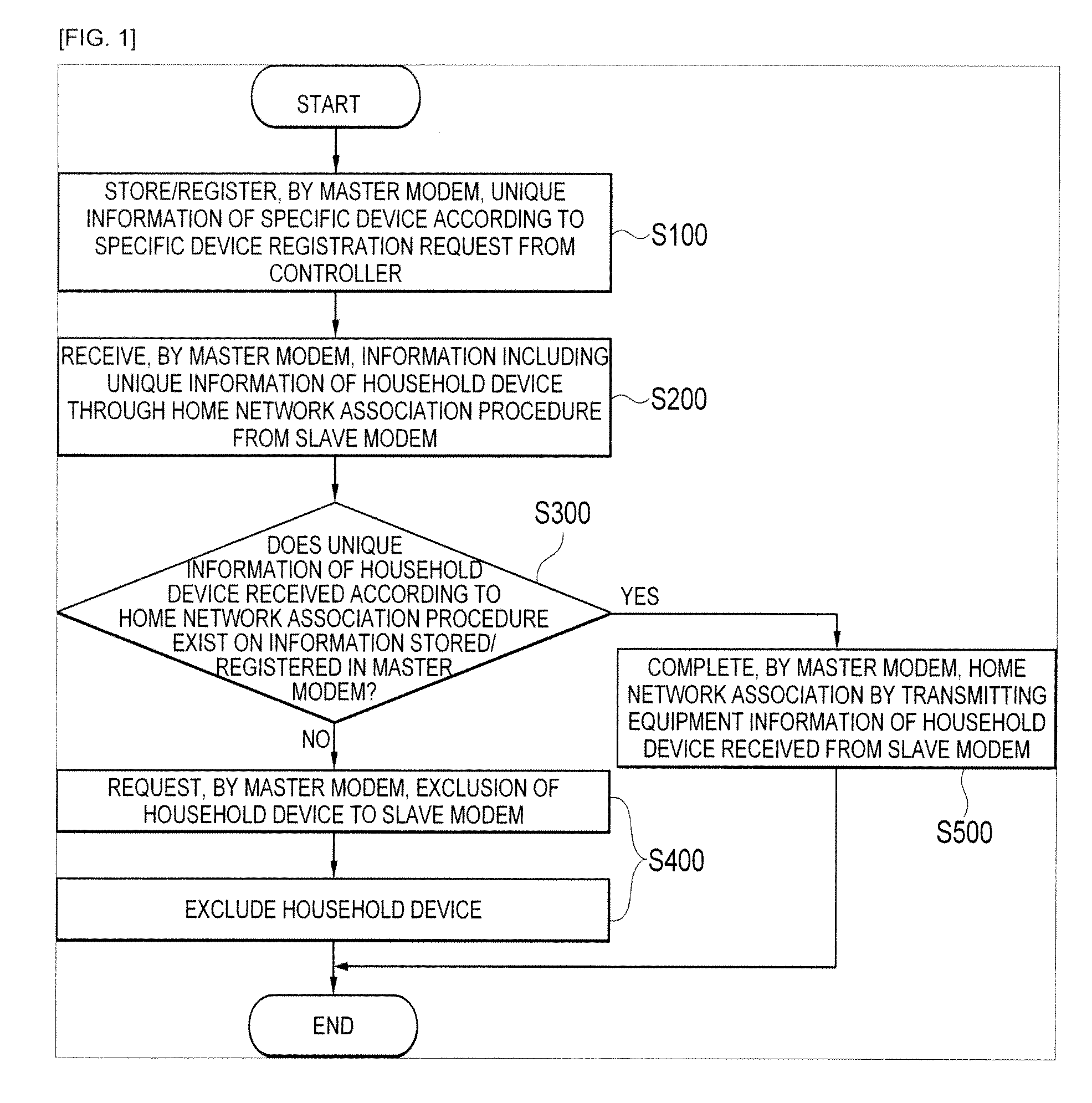
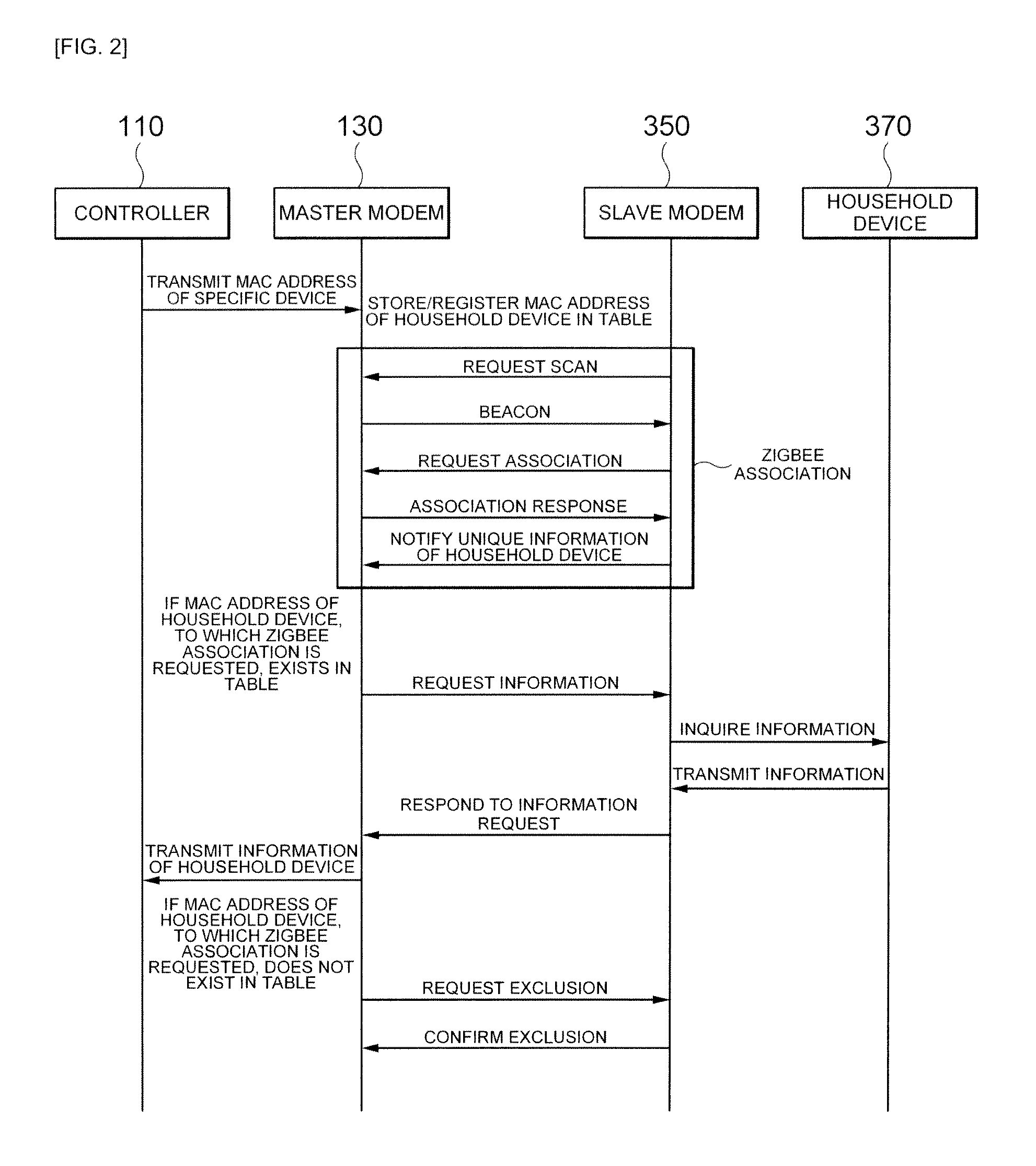
Method and system for association between controller and device in home network
InactiveUS20130077664A1ErrorHome automation networksDuplex signal operationModem deviceHome area network
A system and method for associating a controller and a device in a home network. The method includes using a master modem for: (a) registering unique information of a specific device when a controller requests a registration of the specific device; (b) receiving information including unique information of a household device from a slave modem using the home network; (c) determining whether the unique information of the household device exists on the registered information; (d) if it is determined that the unique information of the household device does not exist, requesting an exclusion of the household device requesting the association and excluding the household device from the home network association; and (e) if it is determined that the unique information of the household device exists, performing the home network association by transmitting the unique information of the household device, which is received from the slave modem, to the controller.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
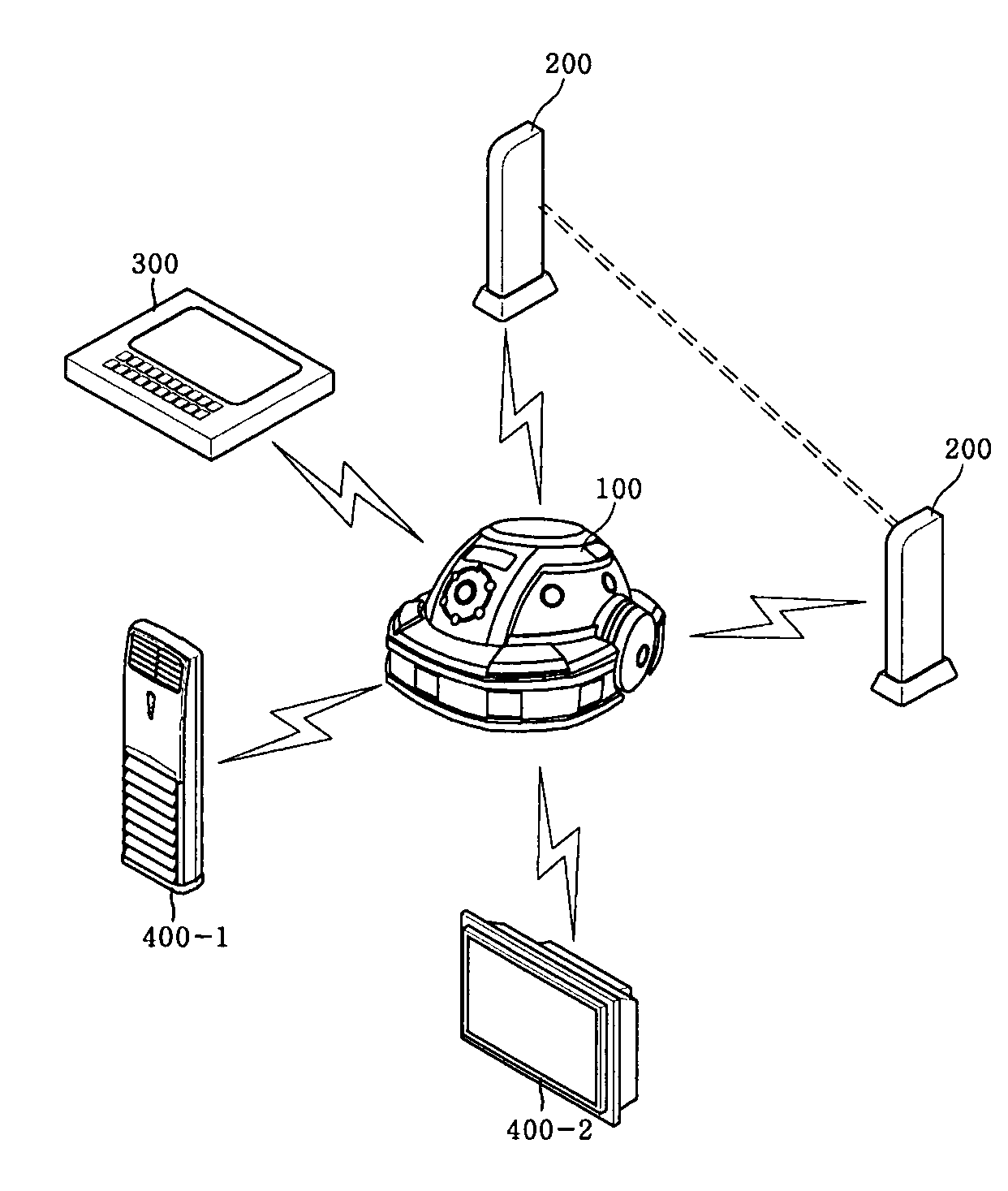
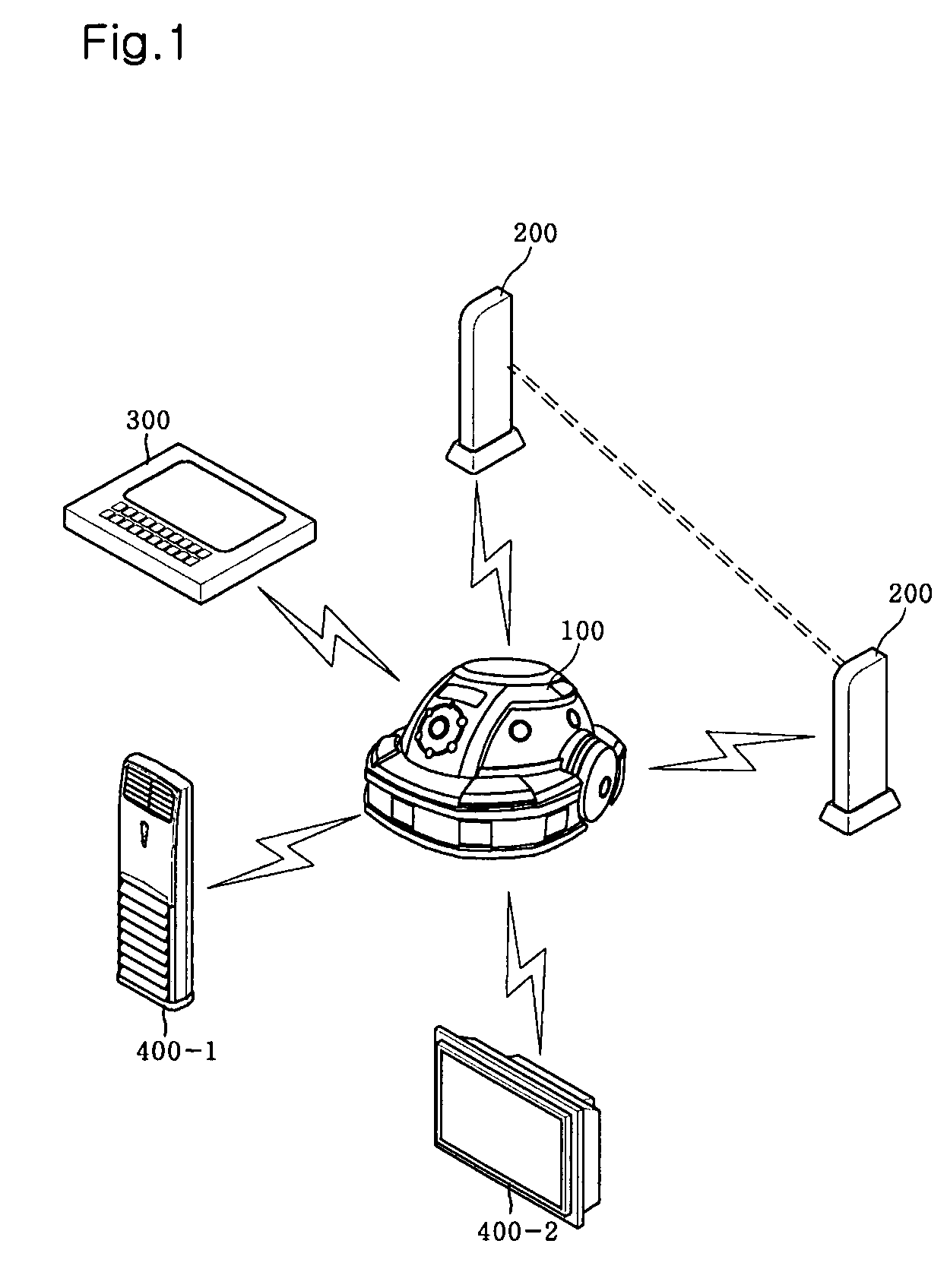
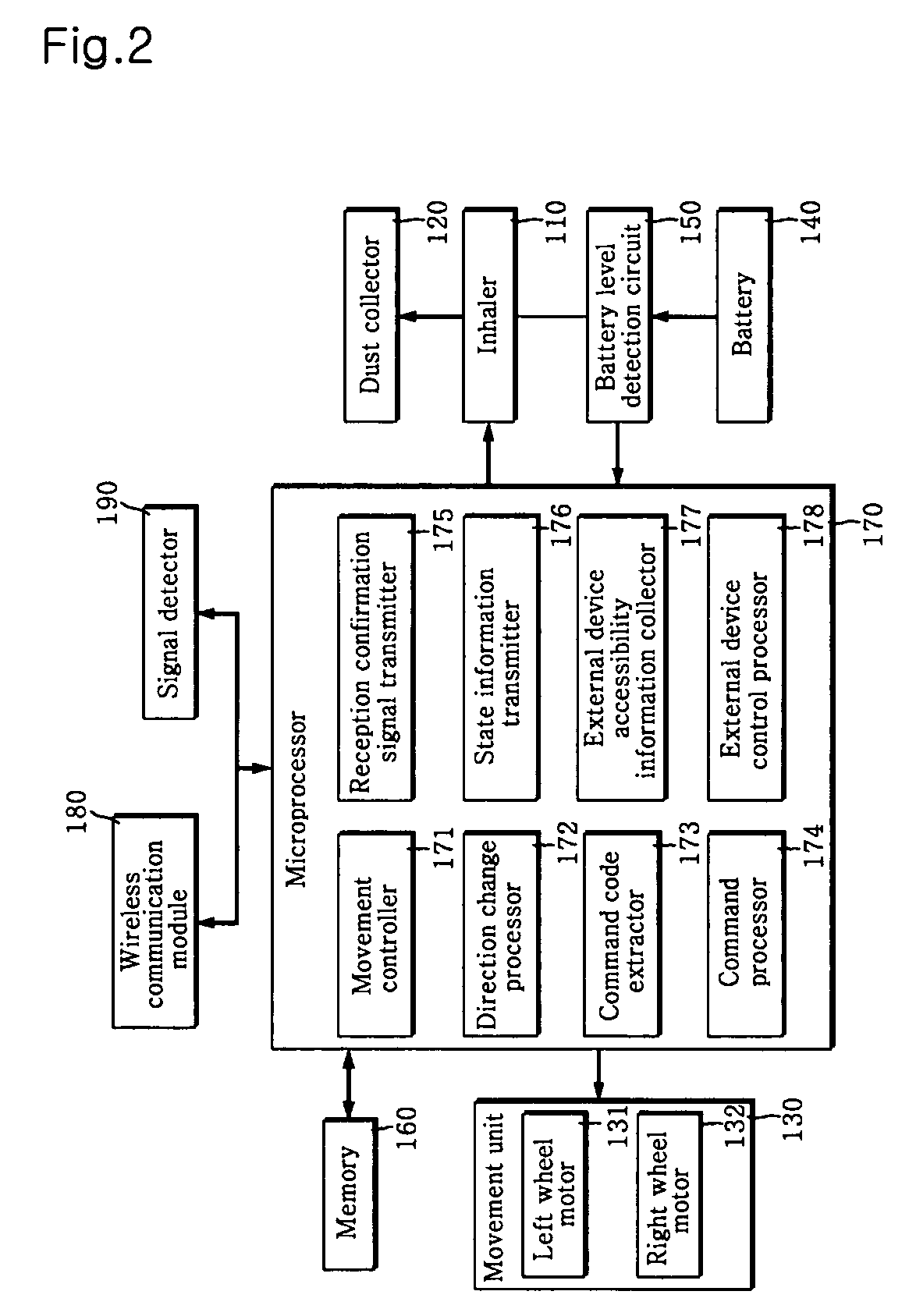
Home networking system using self-moving robot
InactiveUS20070021867A1Special service provision for substationSubstation remote connection/disconnectionWireless controlControl signal
A home networking system using a self-moving robot is provided. The self-moving robot and household devices connected via a network can be wirelessly controlled indoors or outdoors. The self-moving robot receives an operating command transmitted from a wireless operating unit, transmits information, indicating whether or not the command has been received, to the operating unit, executes a task corresponding to the command, and outputs a control signal to an accessible household device. Each signal transmission device is driven according to a drive signal transmitted within a specific range from the robot, transmits its state information including identification information to the robot when driven, and transmits a direction change signal for the robot in a specific direction. The operating unit displays the command reception information and / or state information of the signal transmission device transmitted from the self-moving robot and outputs a control signal to an accessible household device through the robot.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
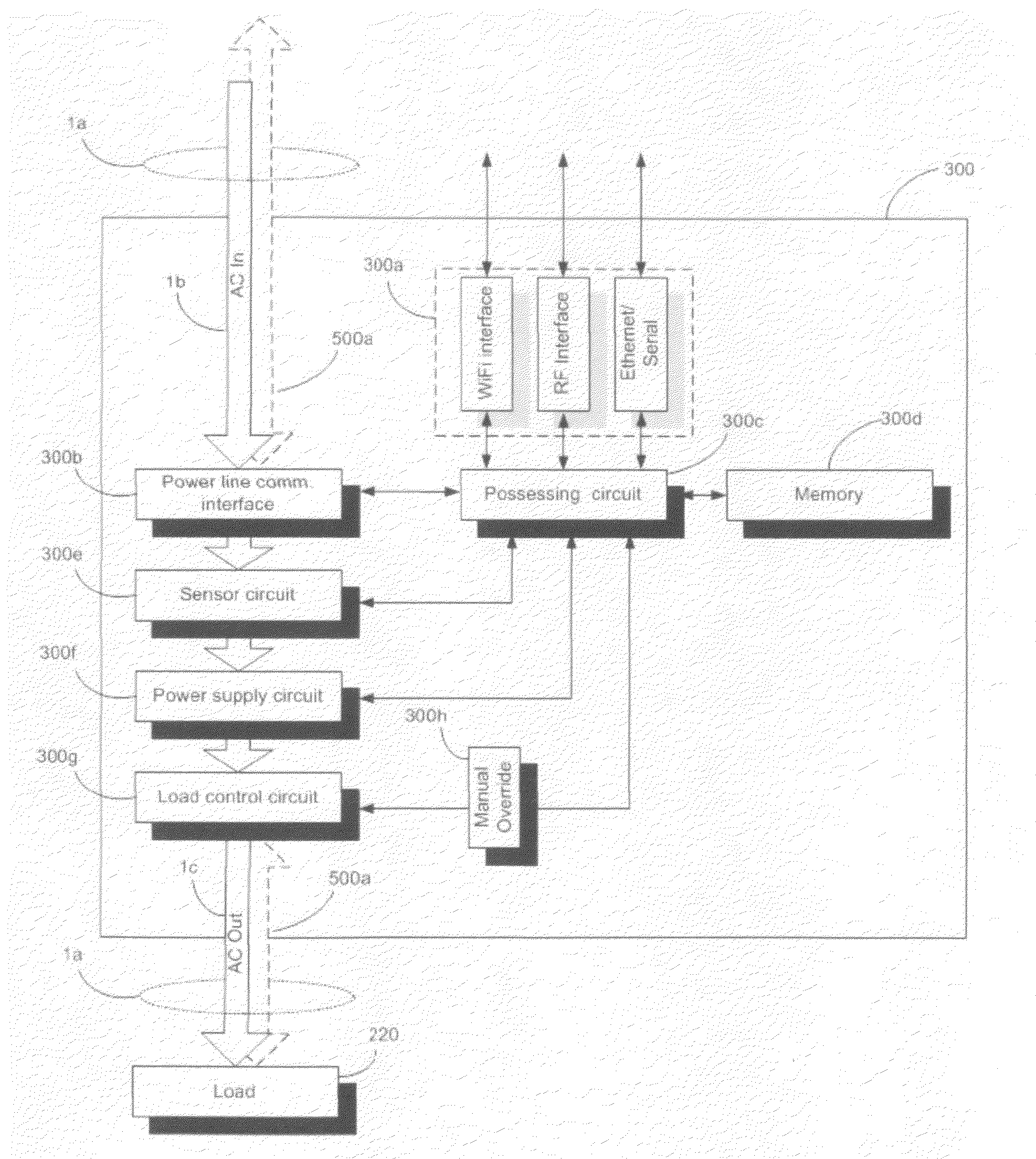
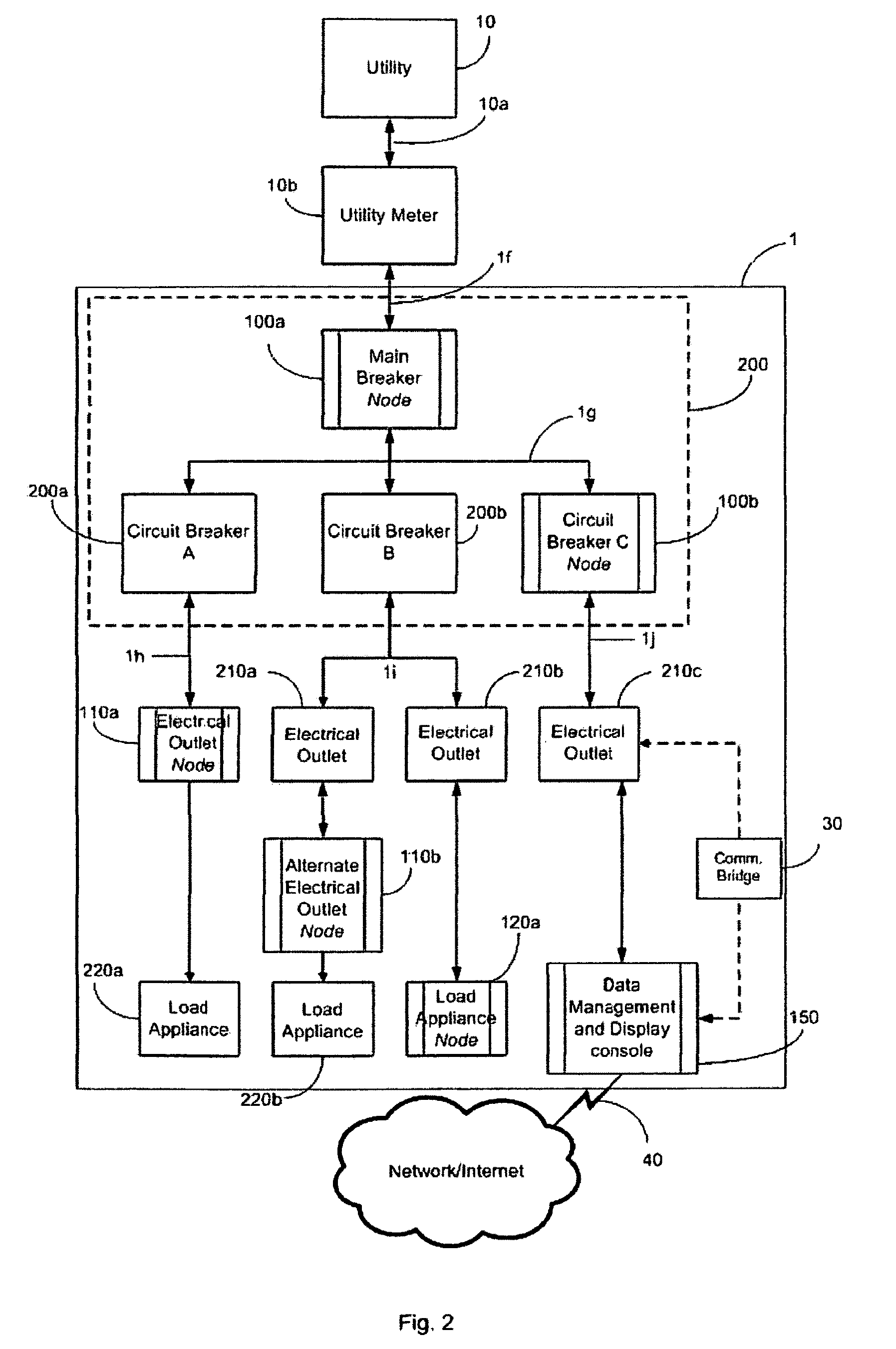
Electrical Energy Usage Monitoring System
ActiveUS20100094475A1Limited stateEasy to demonstrateInput/output for user-computer interactionLevel controlEmbedded systemCircuit breaker
A system and method consisting of networked modular sensors and a data processing / display system to detect, process, manage and present both real-time and historic electrical energy usage data (metrics, statistics, etc), additionally allowing the intelligent management of energy usage through consumer education as well as both manual and automated usage controls.Wherein sensors are integrated into the standardized form-factor components typical of household and commercial electrical interfaces, such as circuit breakers, wall outlets, light switches, plug ends, power strips, etc, additionally allowing integration with appliances or other load devices and being capable of processing data;Wherein sensors and the associated processing, display and management systems are capable of communicating with each other.
Owner:DALCHEMY INC
Polymeric ballistic material and method of making
PendingUS20060013977A1Dissipating projectile energySlow its forward motionLayered productsArmour platesBallistic impactPolymer
This invention relates to a polymeric ballistic material comprising a high molecular weight, high density polyethylene (HMW-HDPE) and / or composite, and to articles made from this ballistic material suitable for stopping projectiles. The articles may include backstops for firing ranges and home use, armor for vehicles, personnel, and aircraft, training targets, protection for temporary or mobile military and / or police installations, buildings, bunkers, pipelines or any “critical” need equipment that might require protection from ballistic impact, and the like.
Owner:BALLISTICS RES +1
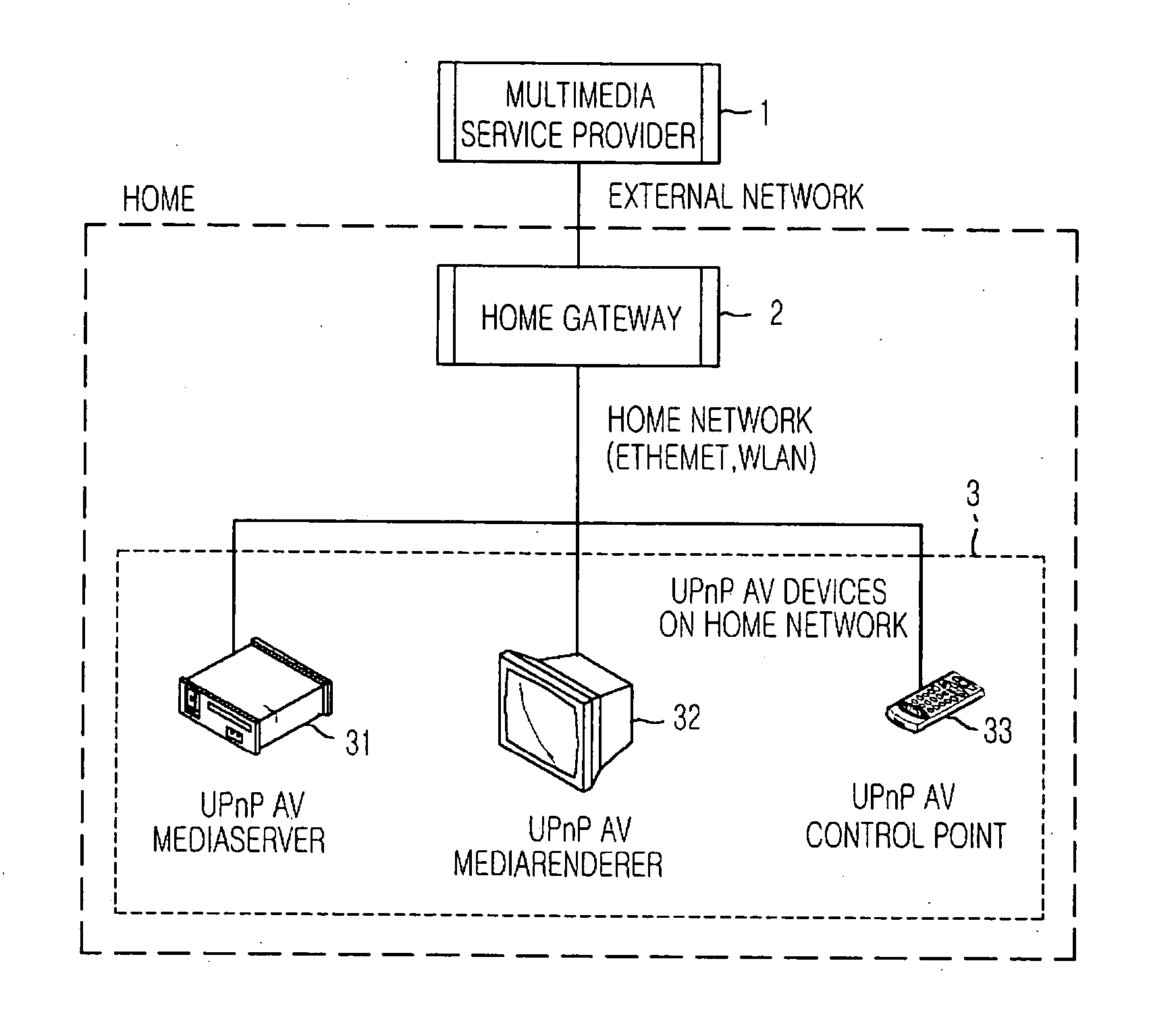
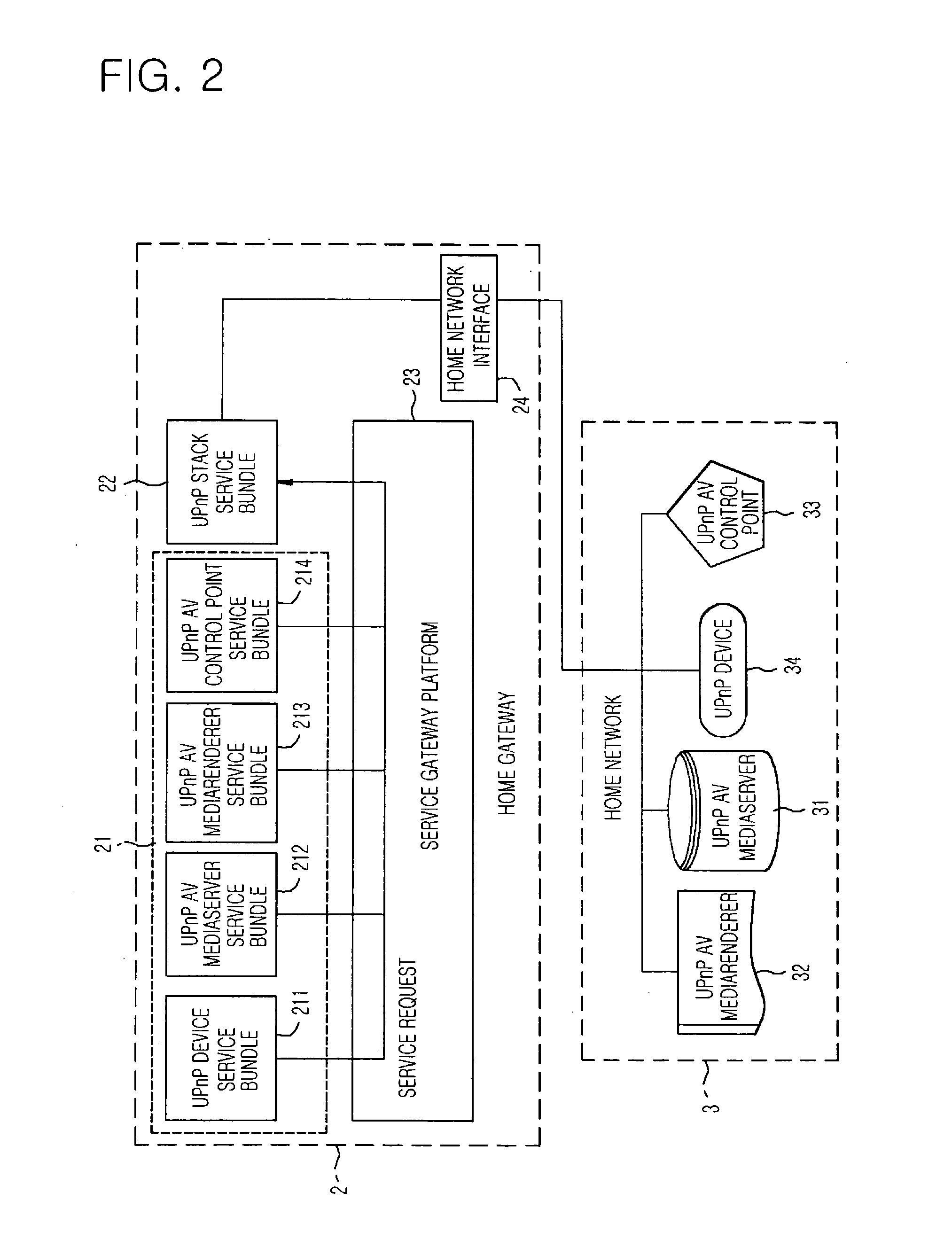
Multimedia service apparatus and method for multimedia service providers outside home to UPnP devices inside home using home gateway and service gateway platform
InactiveUS20060133391A1Good choiceMultiple digital computer combinationsTwo-way working systemsHome useService gateway
A multimedia service apparatus and method for multimedia service providers outside home to UPnP devices inside home using a home gateway and a service gateway platform is provided. In the multimedia service apparatus and method, the home gateway and the service gateway platform such as an open service gateway initiative (OSGi) service platform are used inside a home so that the multimedia service providers outside home can provide a multimedia content on a home network to a universal plug and play (UPnP) audio / video (AV) MediaRenderer following a UPnP AV structure based on UPnP, to reproduce or store the multimedia content in a UPnP AV MediaServer. The multimedia service apparatus includes: a UPnP AV (audio / video) device connected to a home network by the multimedia service provider of an external network; and a gateway device providing a multimedia service to the UPnP AV device using the service gateway platform.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
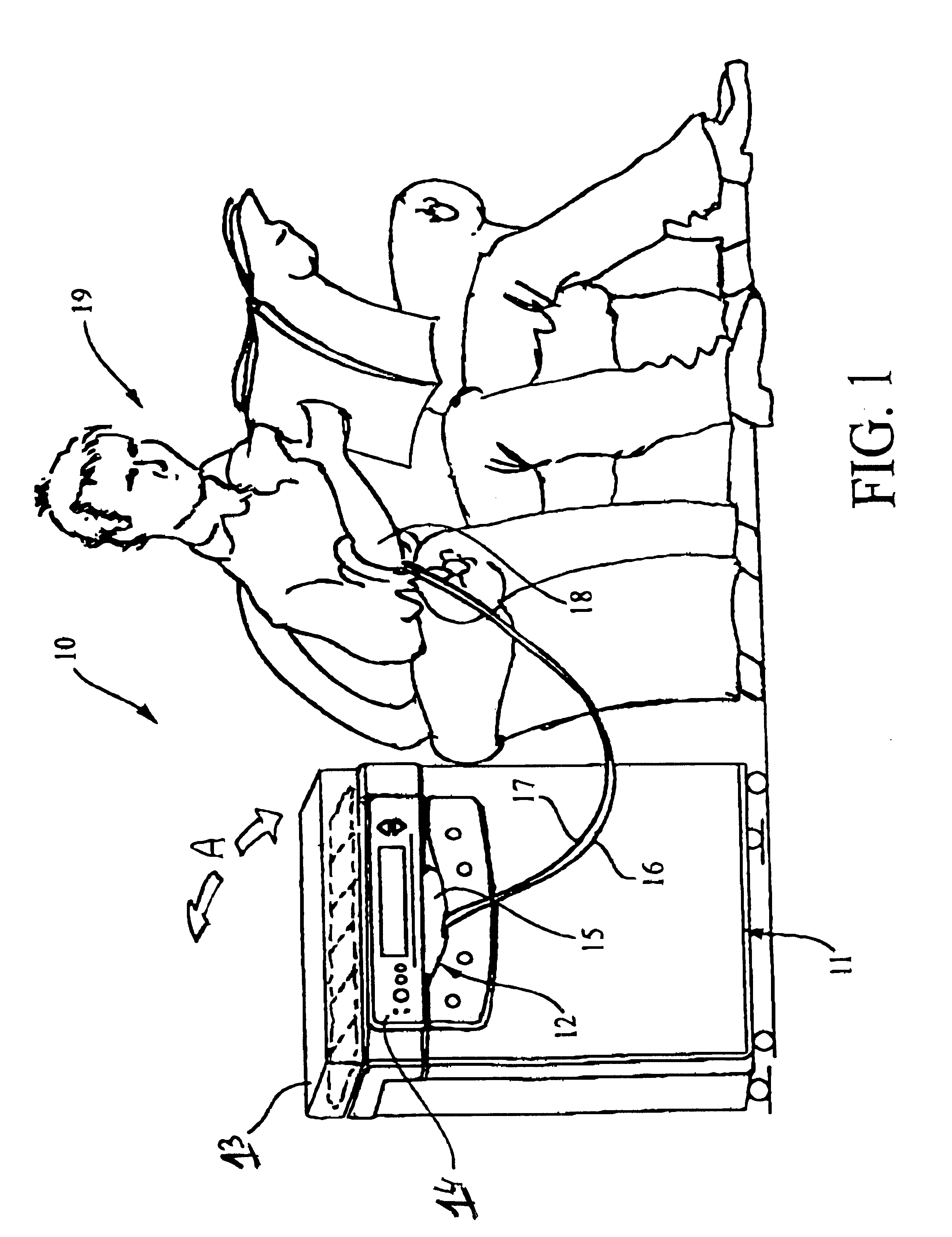
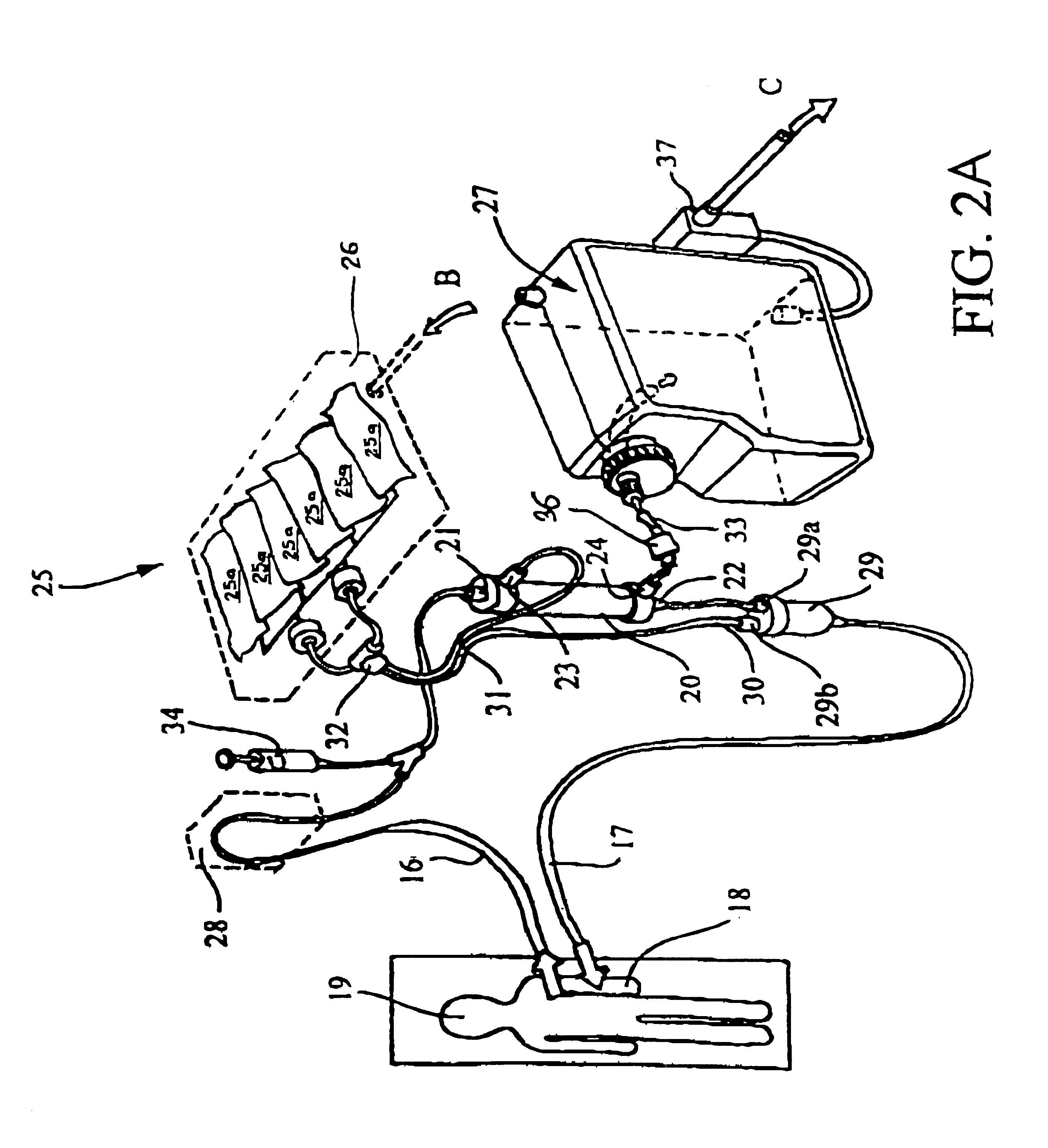
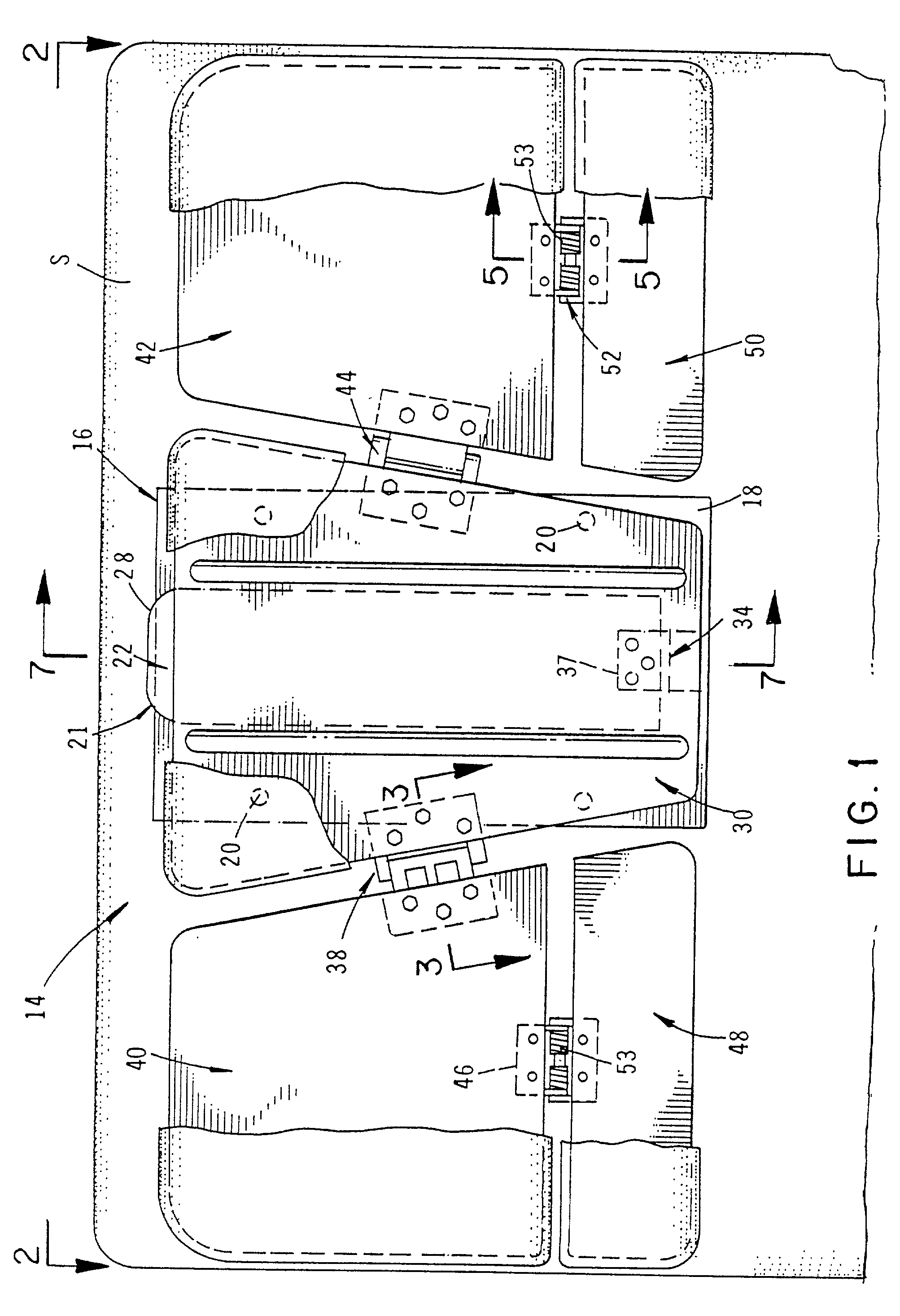
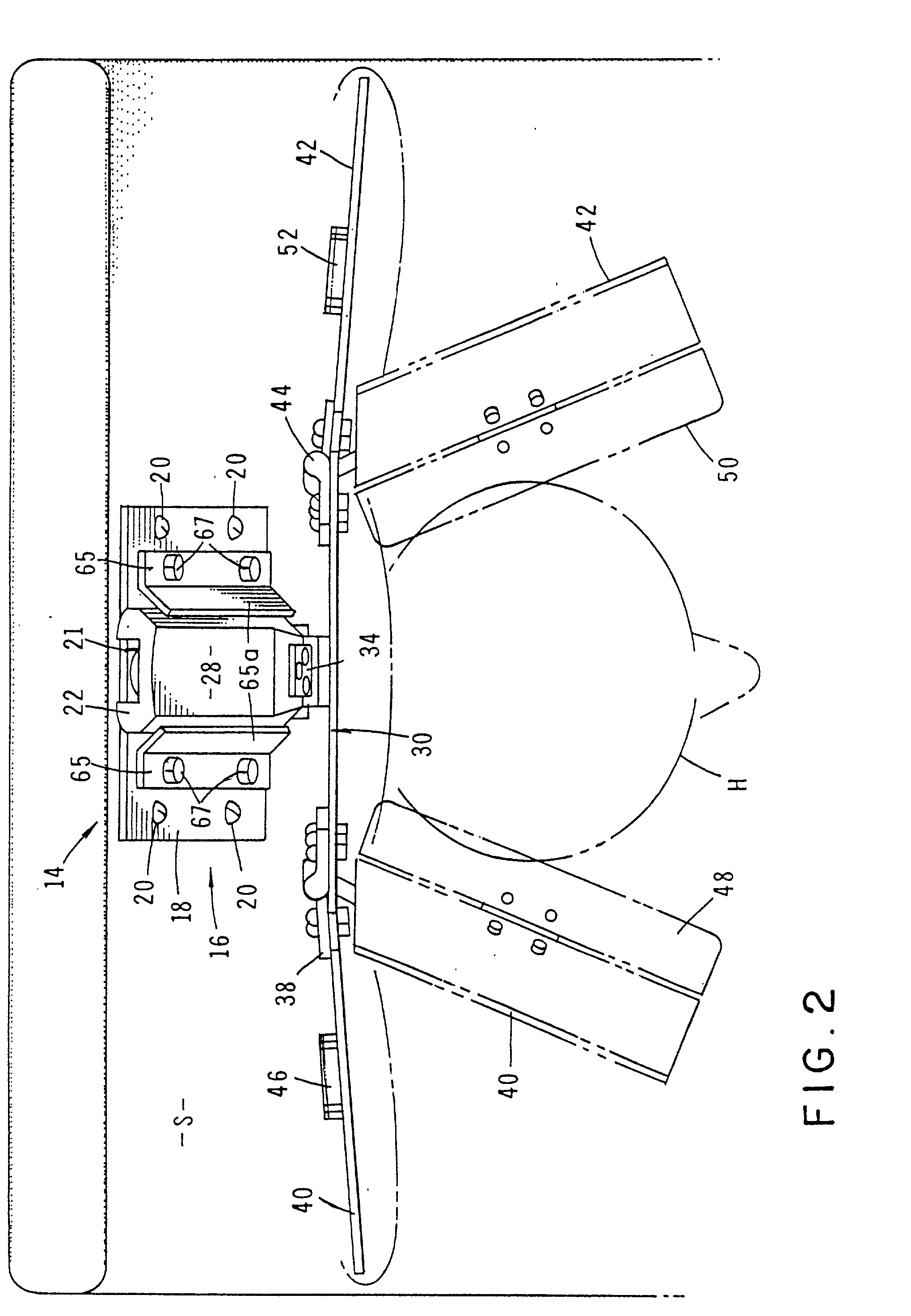
Dialysis machine, in particular for home use
The invention concerns a dialysis machine (10) comprising a dialyzer (20) having a first inlet (21) and a first outlet (22) for the bloodstream, dialysate supply mechanism (25), an arterial line (16) connected between the patent's arteriovenous fistula and the dialyzer, a venous line (17) connected between the arteriovenous fistula and the dialyzer, a pump (28) coupled with the arterial line, a dialysate supply line (31), connected between the dialysate supply mechanism and the dialyzer, a dialysate evacuation line (33) connected between a dialysate recuperating container (27) and the dialyzer. The sterile dialysate bags are arranged in a chamber (26) under a gas pressure.
Owner:PHYSIDIA
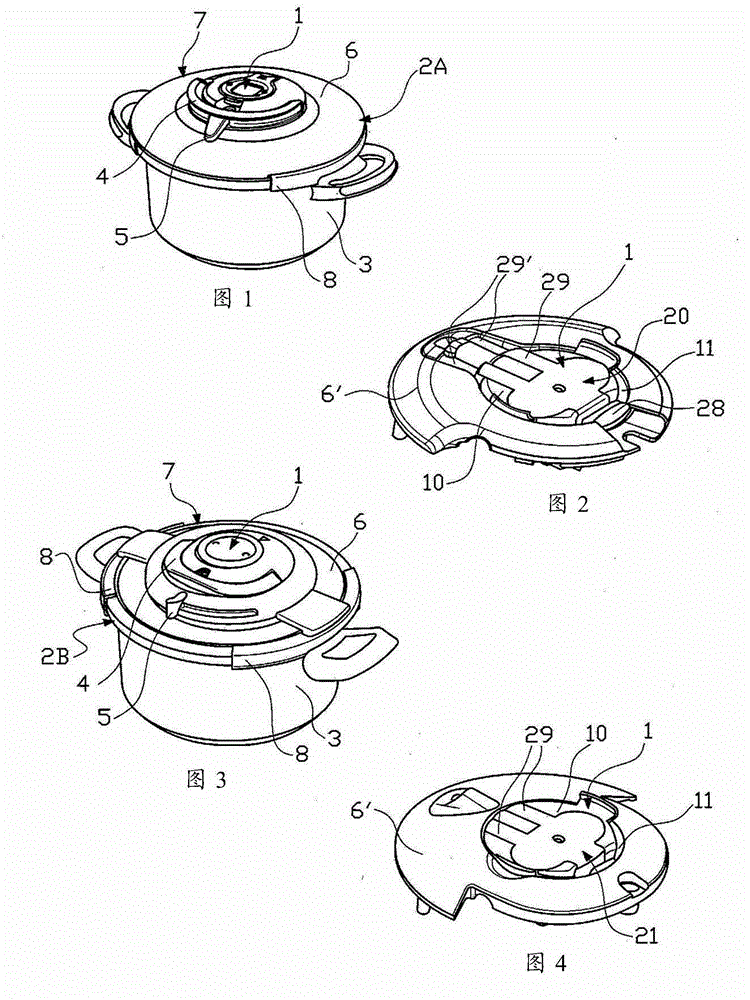
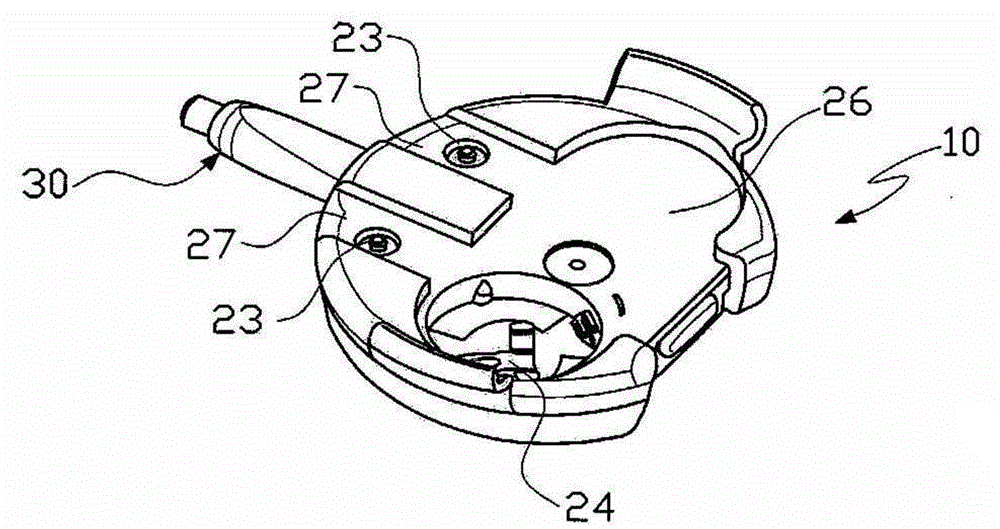
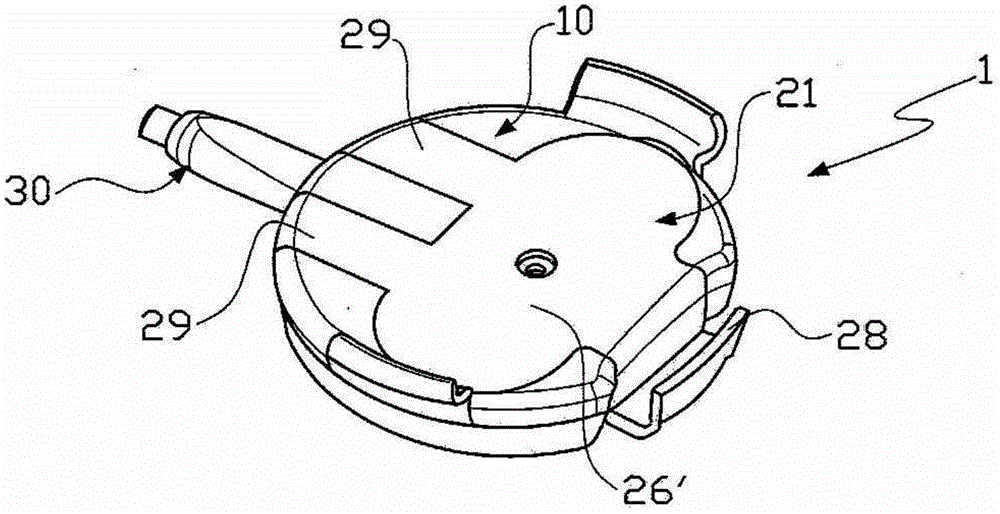
Electronic assembly with information on the operation of household appliances
The invention relates to an electronic assembly (1) with information on the operation of household appliances, for providing the user with information on the operation of at least two different models of household appliances and thereby forming at least one first pattern (2A) and at least a second pattern (2B), said assembly comprising: - a universal connection base(10) to be mounted either on said at least one first pattern (2A) or said at least one second model (2B), said base comprising: at least a first sensor for giving information of operation of said first model (2A) and at least a second sensor for giving operation information of said second model (2B), an electronic assembly for processing signals which may come from the first sensor and the second sensor, - at least two adapter modules. - Household Appliances.
Owner:SEB SA
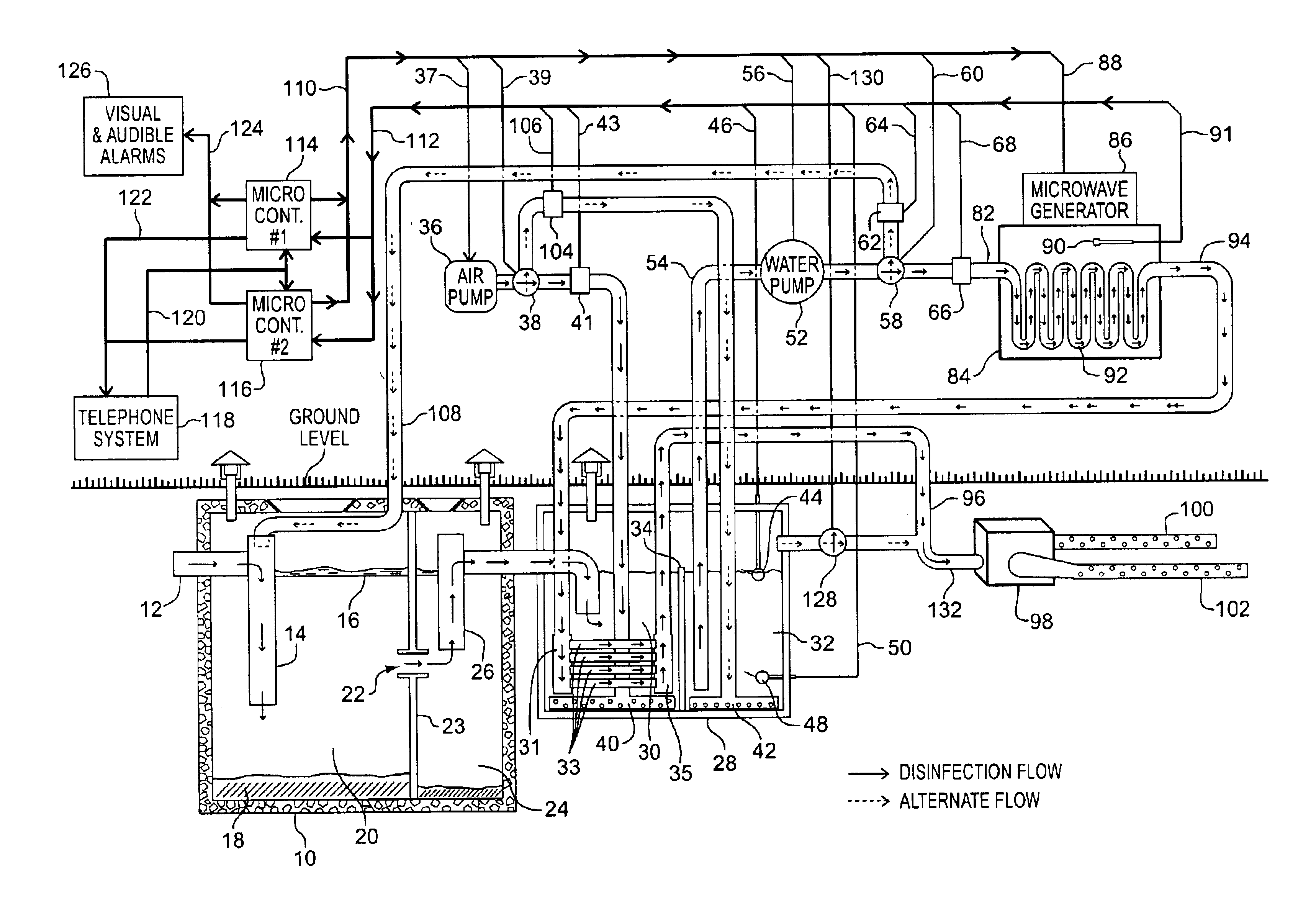
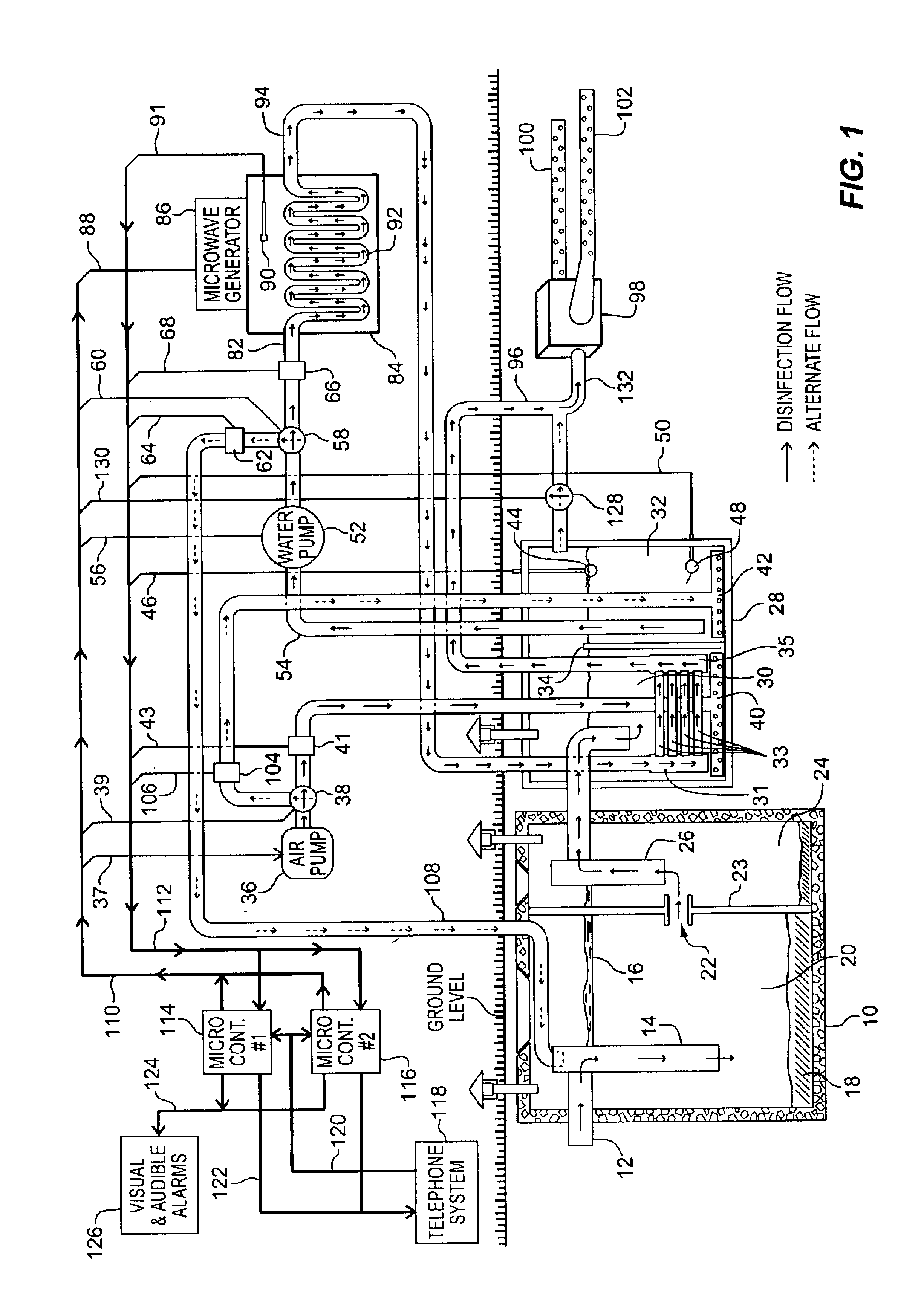
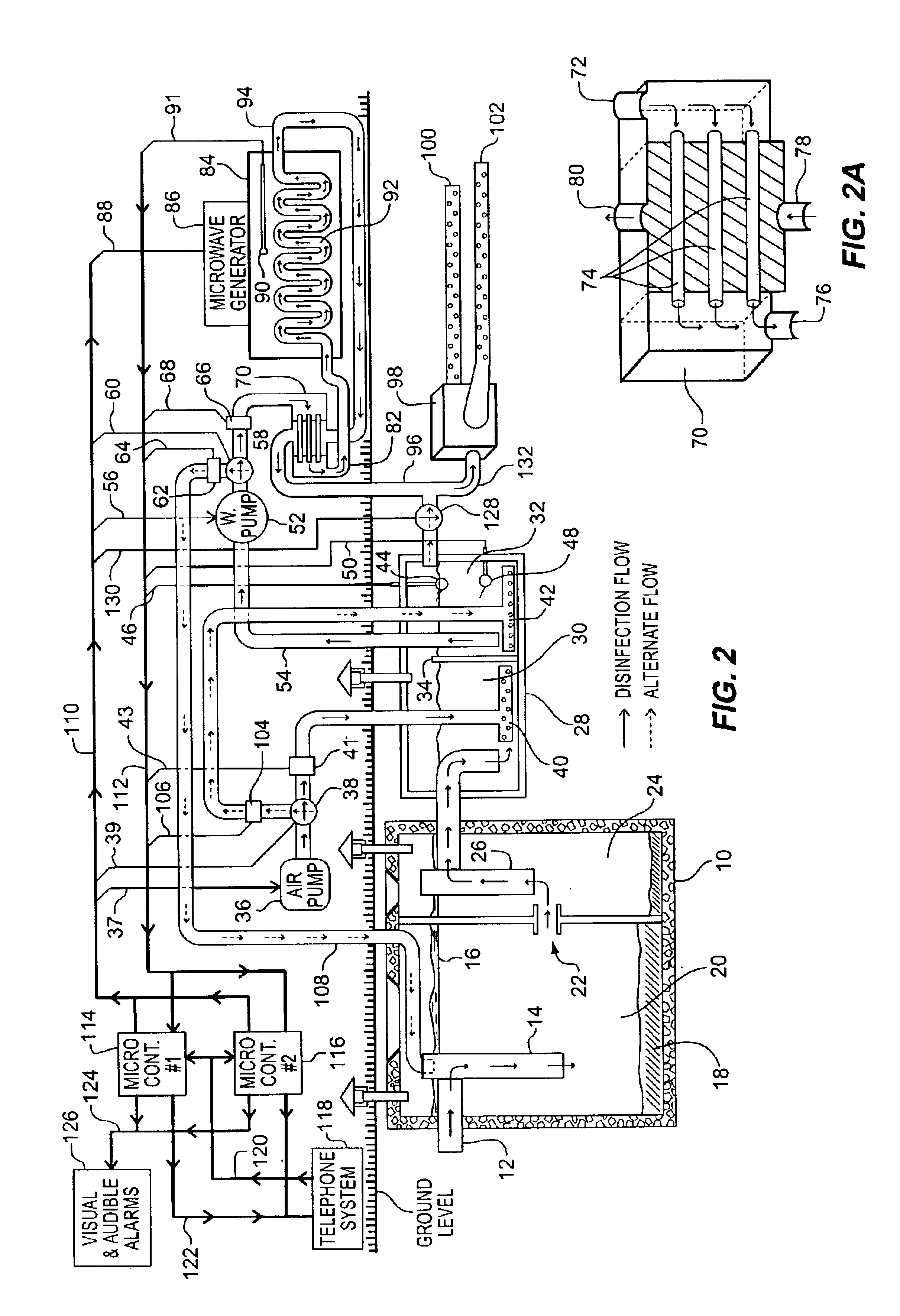
Automated, self-contained, home sewage treatment system
InactiveUS6863805B1Avoiding overflow conditionRaise the water levelGeneral water supply conservationLiquid displacementElectrical batterySolar cell
A small and cost effective sewage treatment system intended for unattended use in individual homes, small industries or businesses in locations where a central sewage treatment plant is not available. The sewage treatment system comprises a conventional septic tank which drains into a smaller aerated holding tank, a pump to transfer effluent from the holding tank into a disinfecting chamber, a regenerative heat exchanger used to raise the temperature of the effluent while being aerated in the holding tank, means for pumping the effluent at a controlled rate through a microwave field, and a conventional drain field used to release the disinfected water into the surrounding soil. Operation of this system is fully regulated by a micro-controller, thereby eliminating the need for human intervention during normal use. This invention also incorporates electronic means for detecting various fault conditions which may impede effective disinfection, means for diagnosing what part of the system is at fault, means for reporting the fault and diagnose to a central municipal location via a telephone or transponder system, an emergency battery backup system, and means for reverting system operation to that of a conventional septic tank and drain field system is case of a total power failure (both A / C and DIC) or water pump failure. Conventional household alternating current or a battery recharged via a wind generator or solar cells may power the sewage treatment system.
Owner:BARRERAS SR FRANCISCO J +1
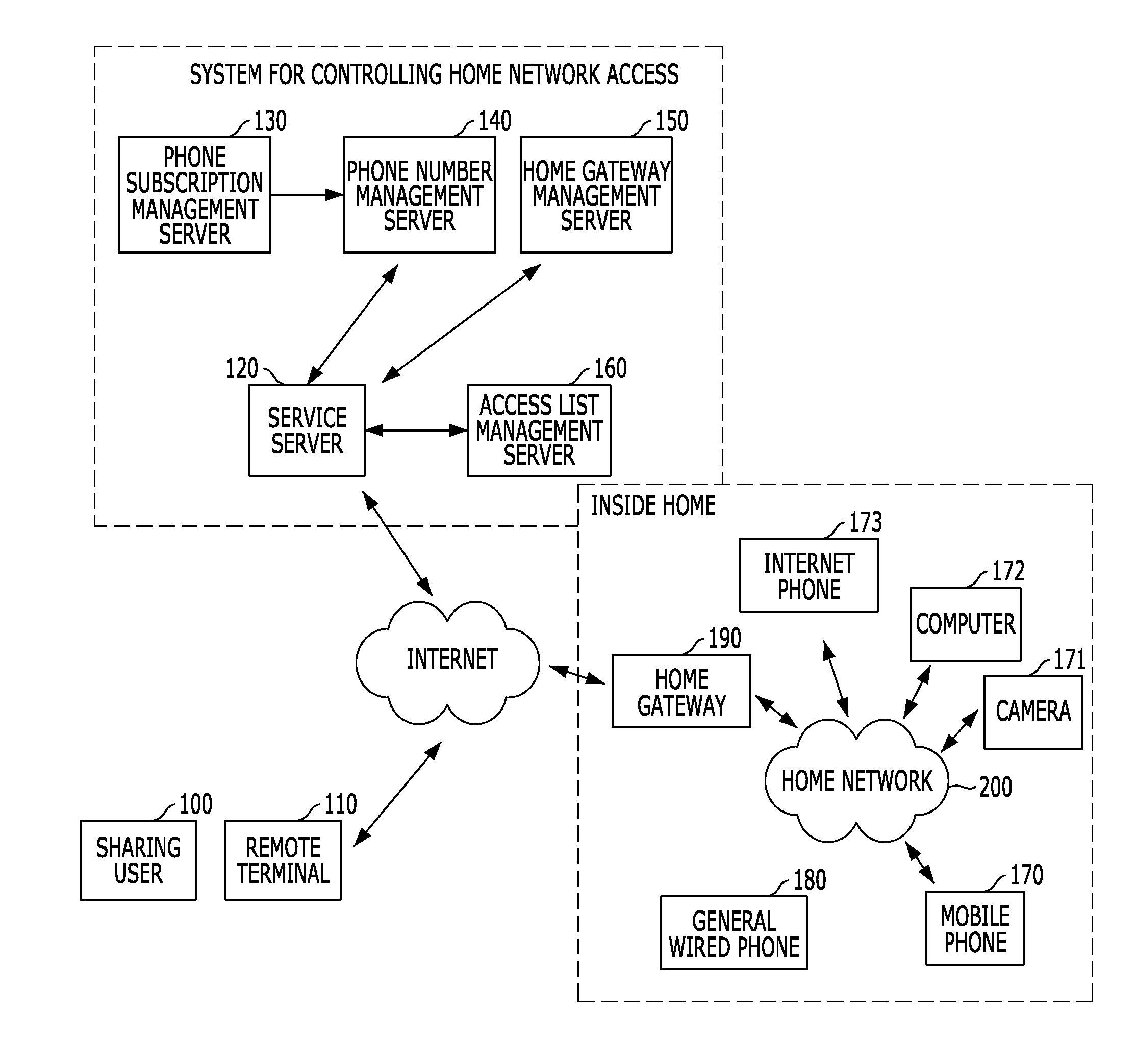
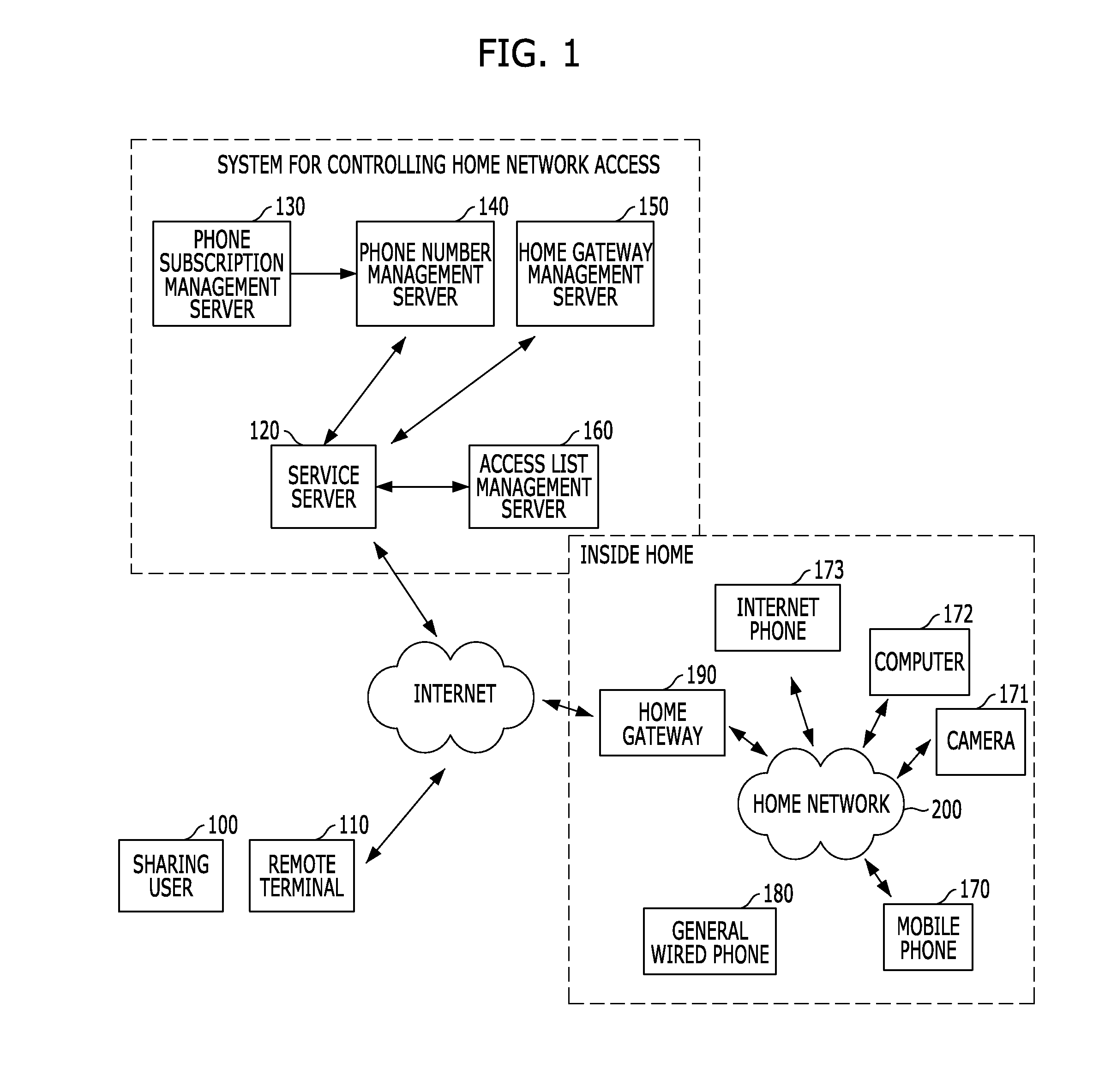
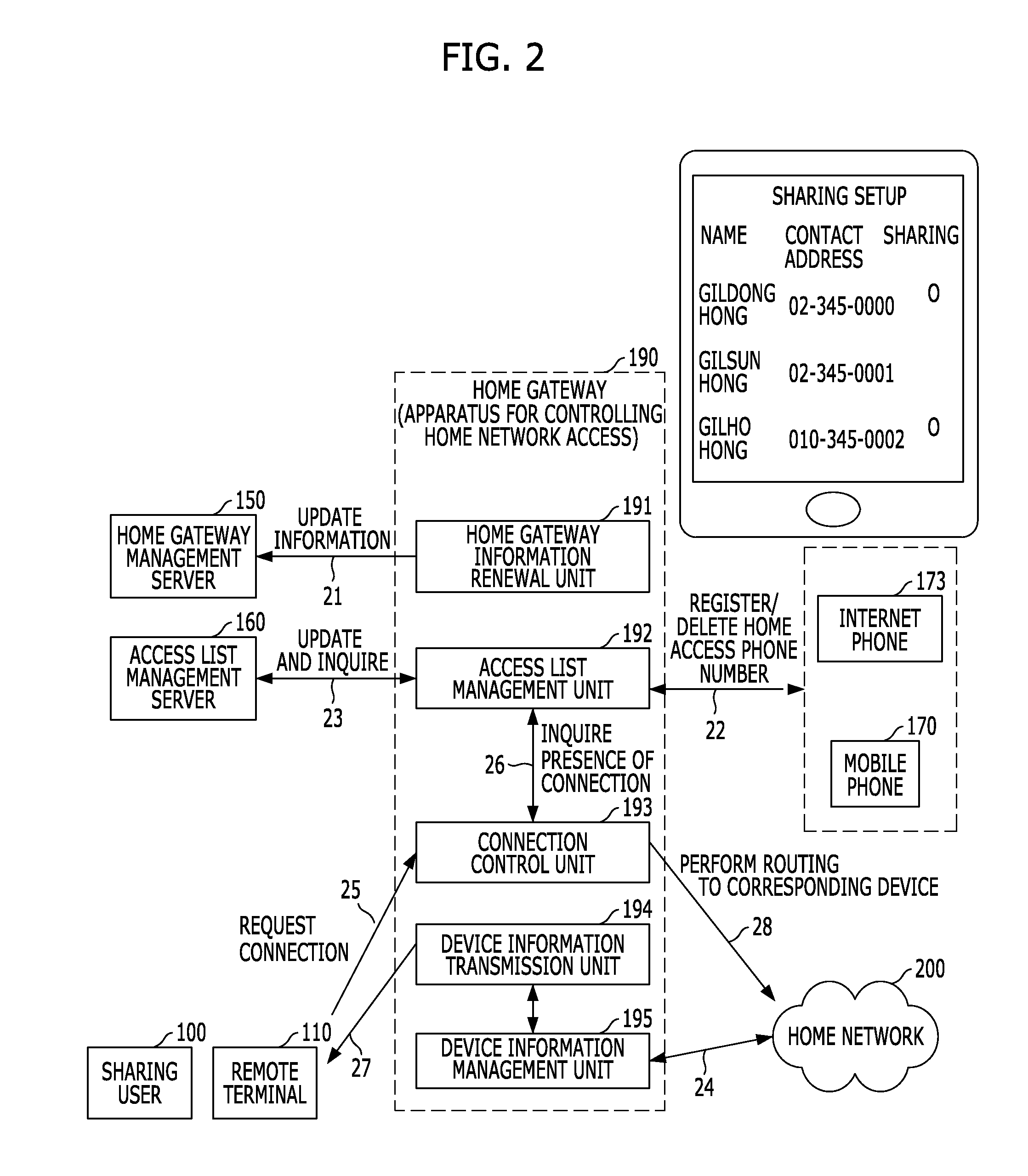
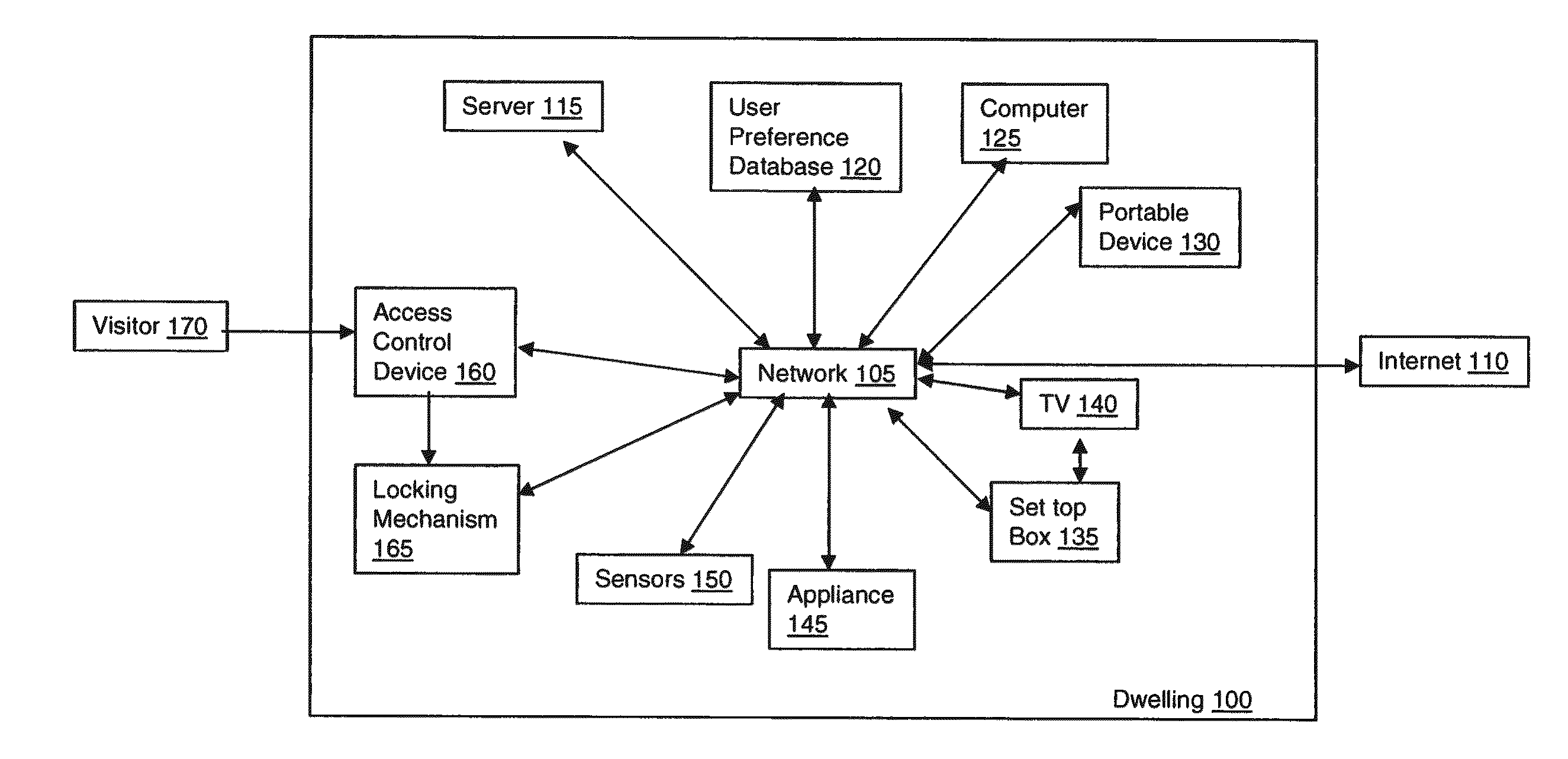
Method and apparatus for controlling home network access using phone numbers, and system thereof
ActiveUS20120151058A1Special service provision for substationData taking preventionHome useComputer terminal
A method and apparatus for controlling a home network access using phone numbers, and a system thereof, which enables a sharing user to simply set and manage sharing environment based on a telephone number capable of being easily recognized by the sharing user, and enables sharing users to simply access a sharing device inside a home using telephone numbers previously recognized by the sharing users when sharing contents of a UPnP device connected to a home network with the sharing users outside the home. The system includes a phone number management server for managing phone number information and a linked home gateway identifier, an access list management server for managing an access list, a home gateway management server for managing state information and access information of a home gateway, and a service server for receiving a service request from a remoter terminal and processing the received service request.
Owner:KT CORP
Easy-load household automatic paper towel dispenser
There is provided a towel dispenser that includes a housing for containing toweling. The toweling includes a first towel and a second towel that are connected together and separable at a perforation formed between the first and second towel. The housing is configured to define a path P for the toweling. A motor and a perforation sensor are provided for dispensing the toweling and are electrically connected together. The perforation sensor is configured to generate a signal indicative of the presence of the perforation and the motor is configured to deactivate in response to the signal.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
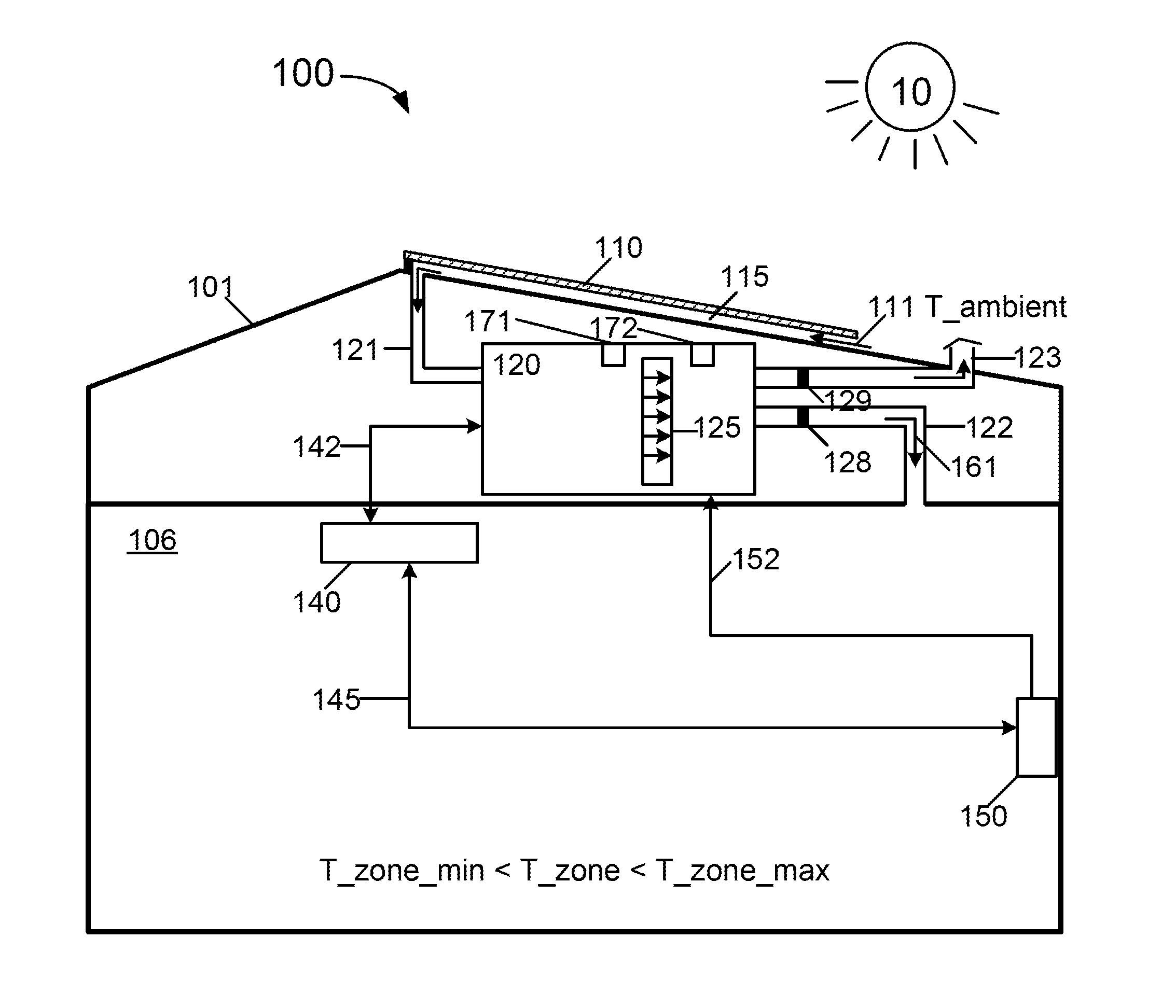
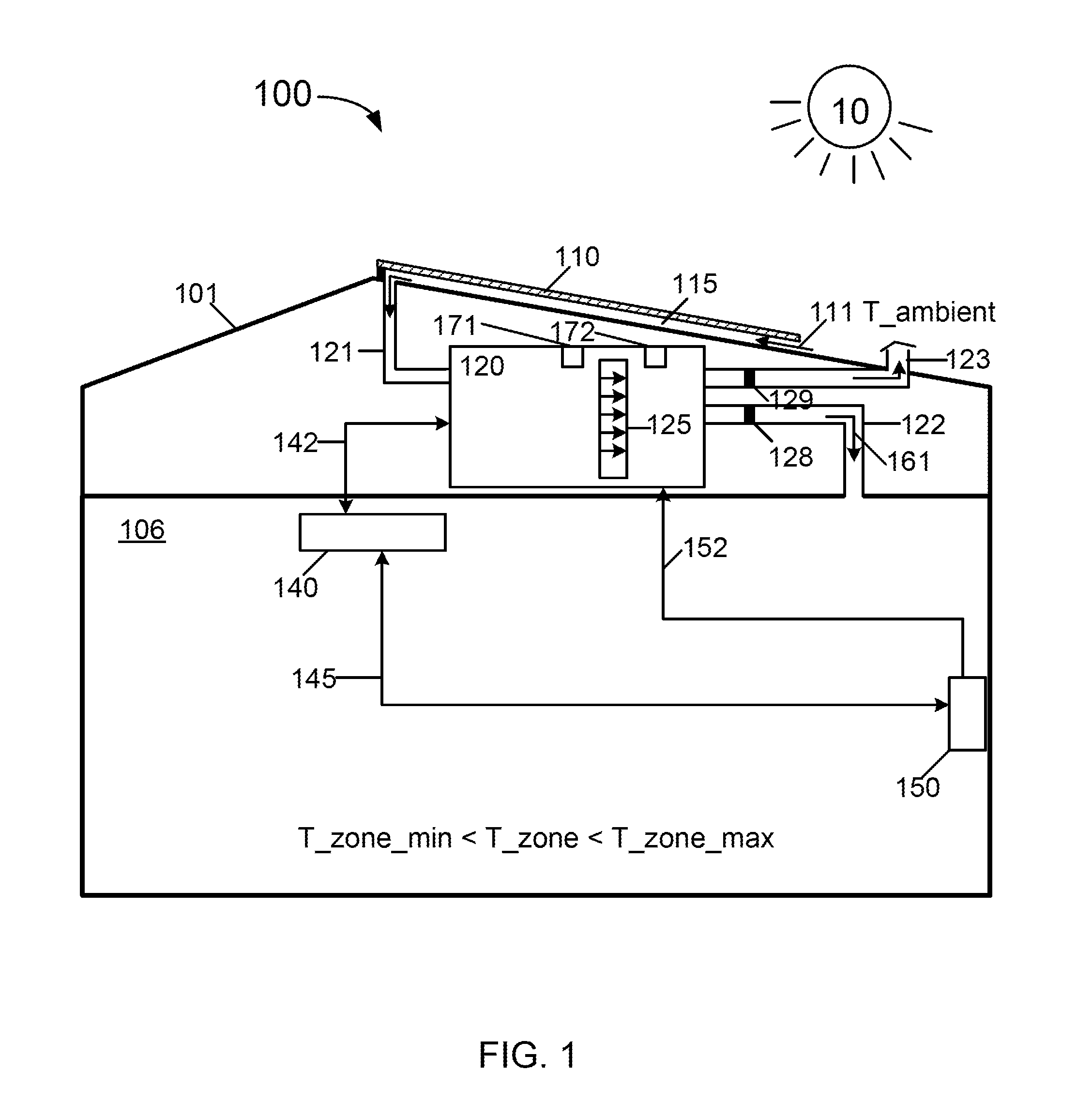
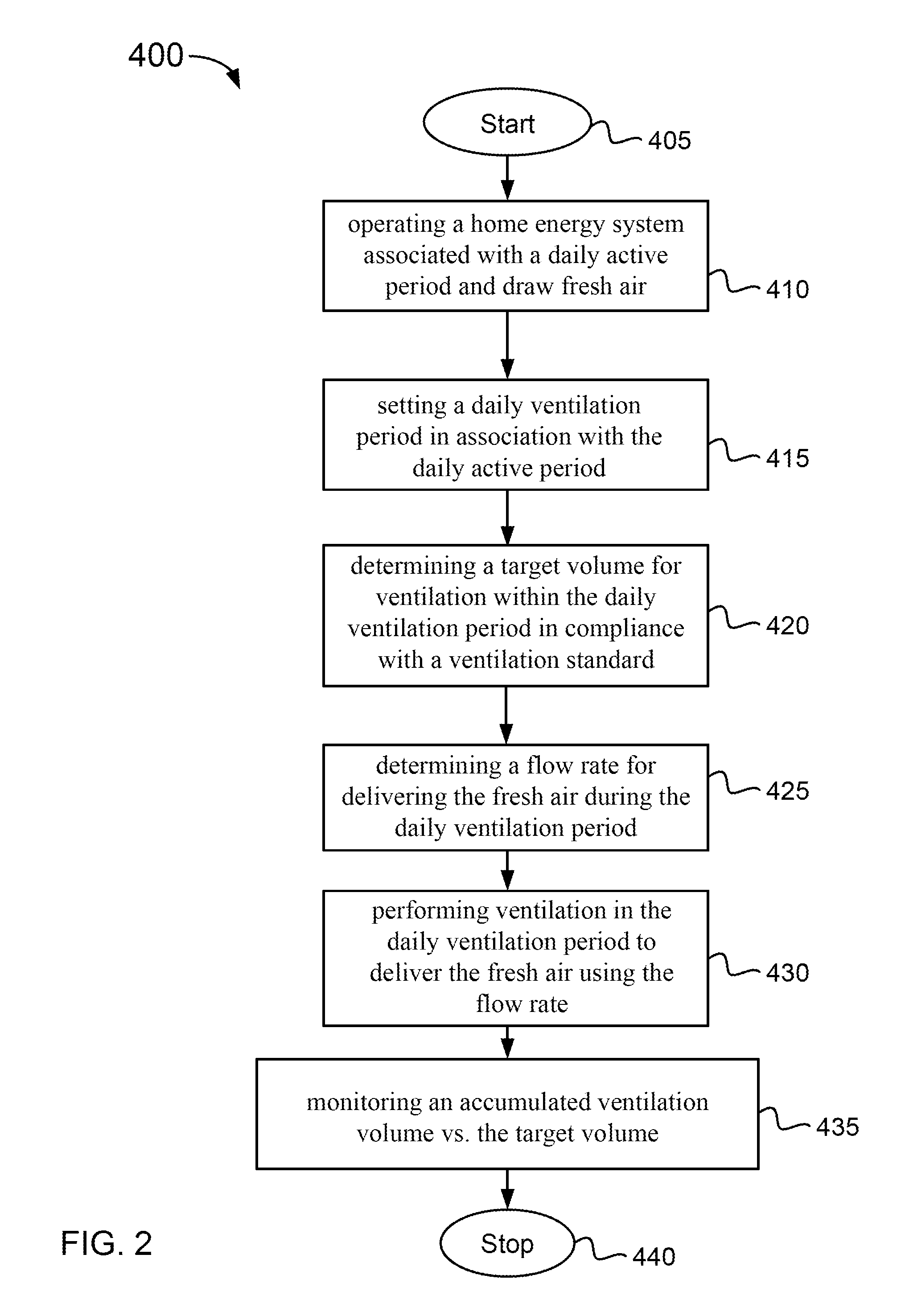
Method and system of ventilation for a healthy home configured for efficient energy usage and conservation of energy resources
InactiveUS20110223850A1Small sizeOptimize energy useMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsHome useMedicine
A method provides a ventilation control compliant with an adopted ventilation standard for efficient energy usage and conservation of energy resources. The method includes operating a home energy system to generate solar energy within a daily active period and draw fresh air from an ambient region, setting a daily ventilation period as a fractional period of a day, the ventilation period being coincident with the active period during a heating period for the home or a time period after the active period during a cooling period for the home, determining a target volume, determining a flow rate for delivering the fresh air during the ventilation period, performing ventilation in the ventilation period to deliver the fresh air into the home using the flow rate, and monitoring an accumulated total ventilation volume of the delivered fresh air until the accumulated total ventilation volume is within a vicinity of a target volume.
Owner:SUNEDISON INC
Apparatus and method for passive testing of alcohol and drug abuse
InactiveUS20100204600A1Digital data processing detailsPerson identificationCompound organicAlcohol and drug
An automated system and method for passive testing of alcohol and drug abuse. The system enters a participant or subject into the system who is to be monitored during a probationary or other program for alcohol or drug abuse offenders. The system provides a drug testing home device or a drug testing kiosk device for use by the participant. The system enrolls the biometrics information of the participant into the computer system (e.g., finger print, voice, image, volatile compound organic gas level, and pH level). When the participant is to be tested in accordance with a testing schedule, the system validates these same biometrics of the participant, conducts the test, and then analyzes the test information for determining if the participant has been using alcohol or other drugs and should be subjected to a confirming urinalysis exam.
Owner:JUSTICE EZ TRAC
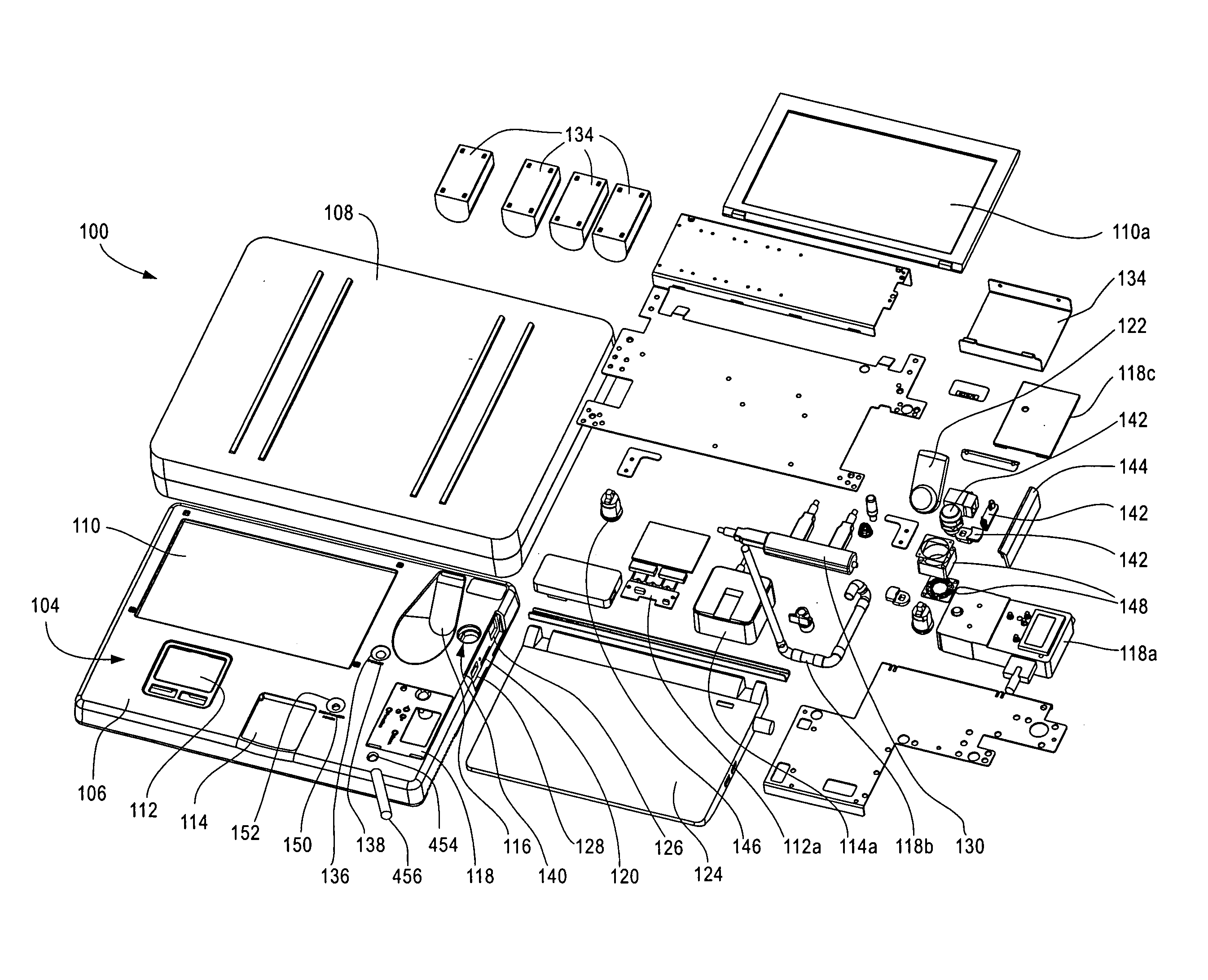
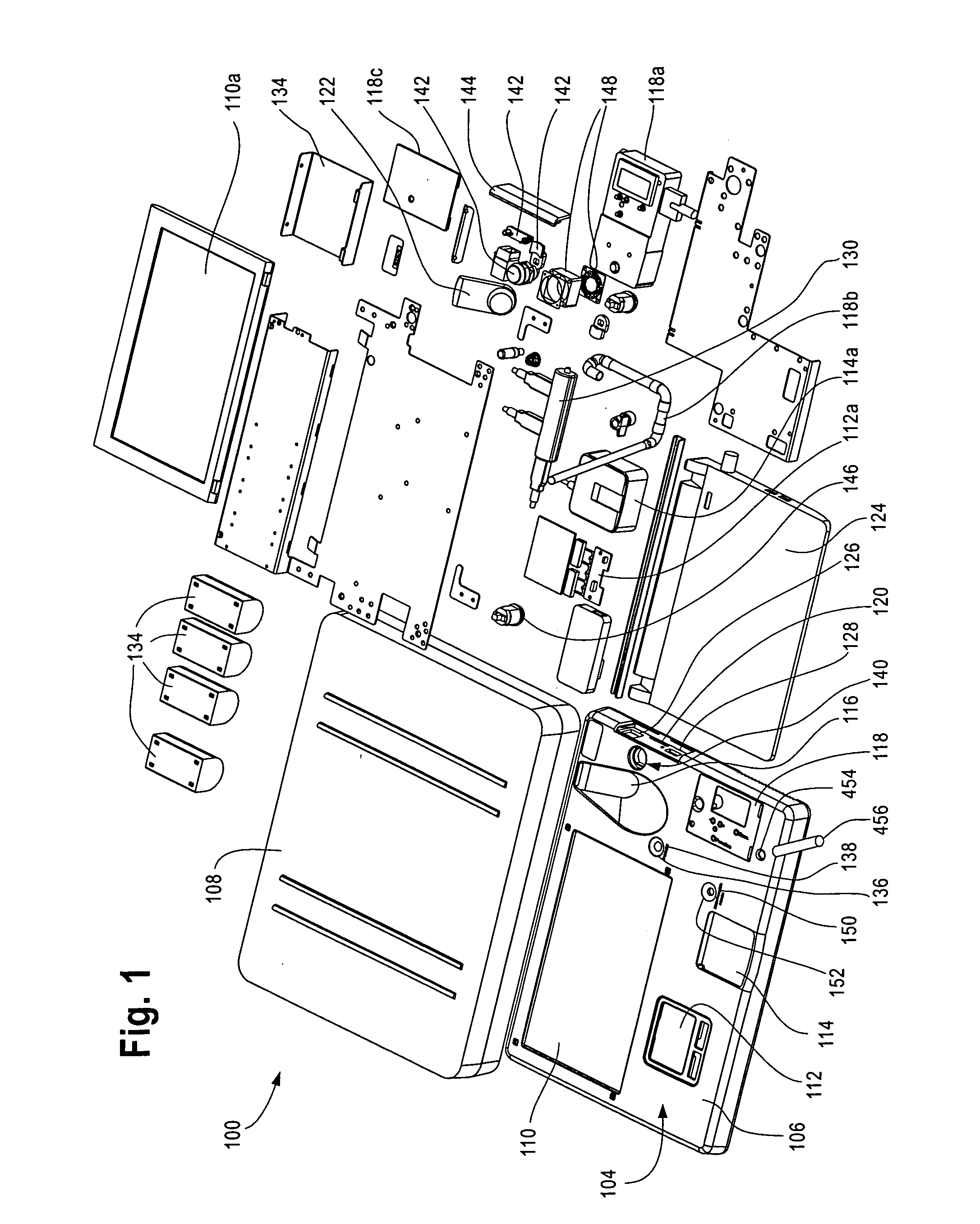
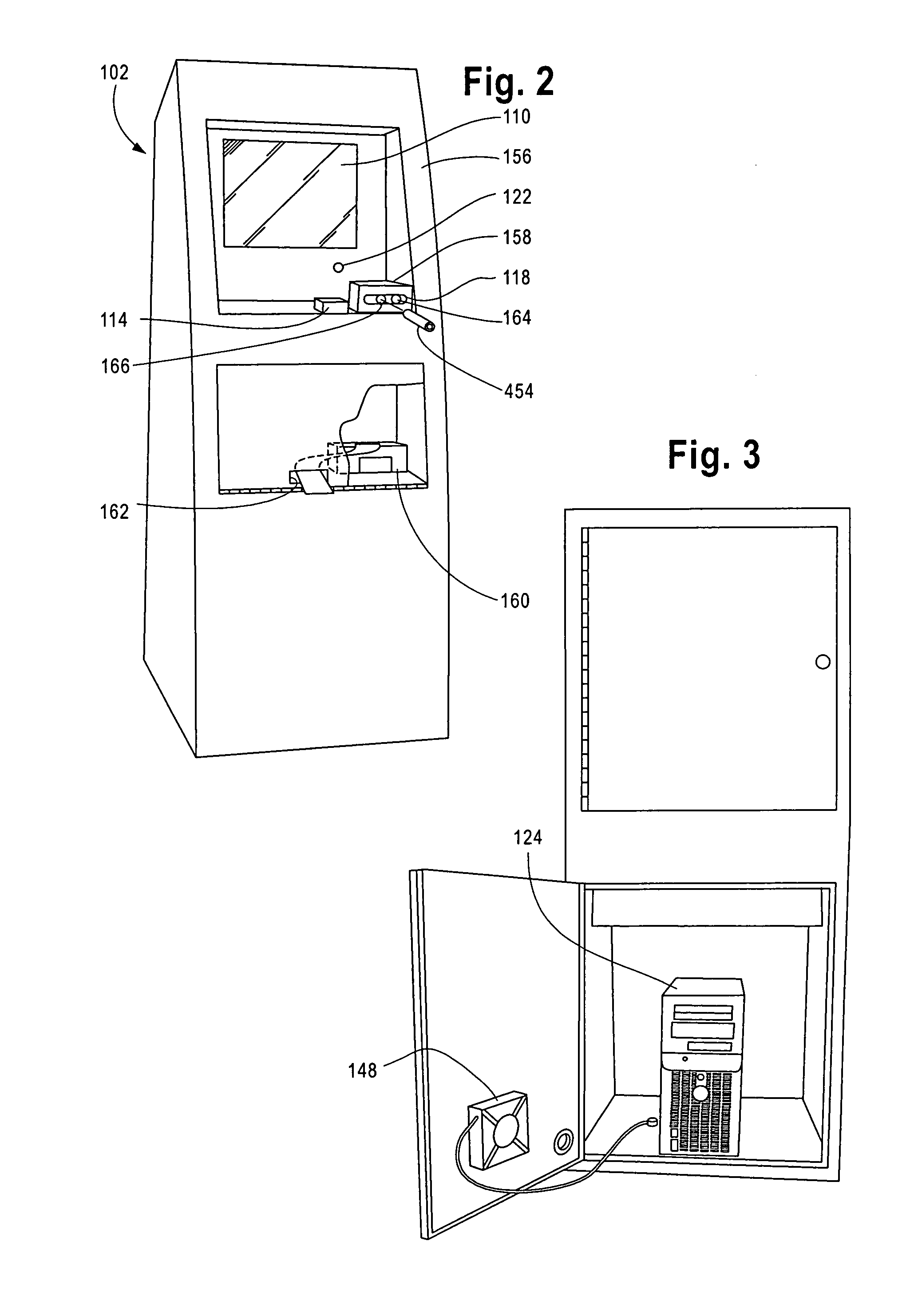
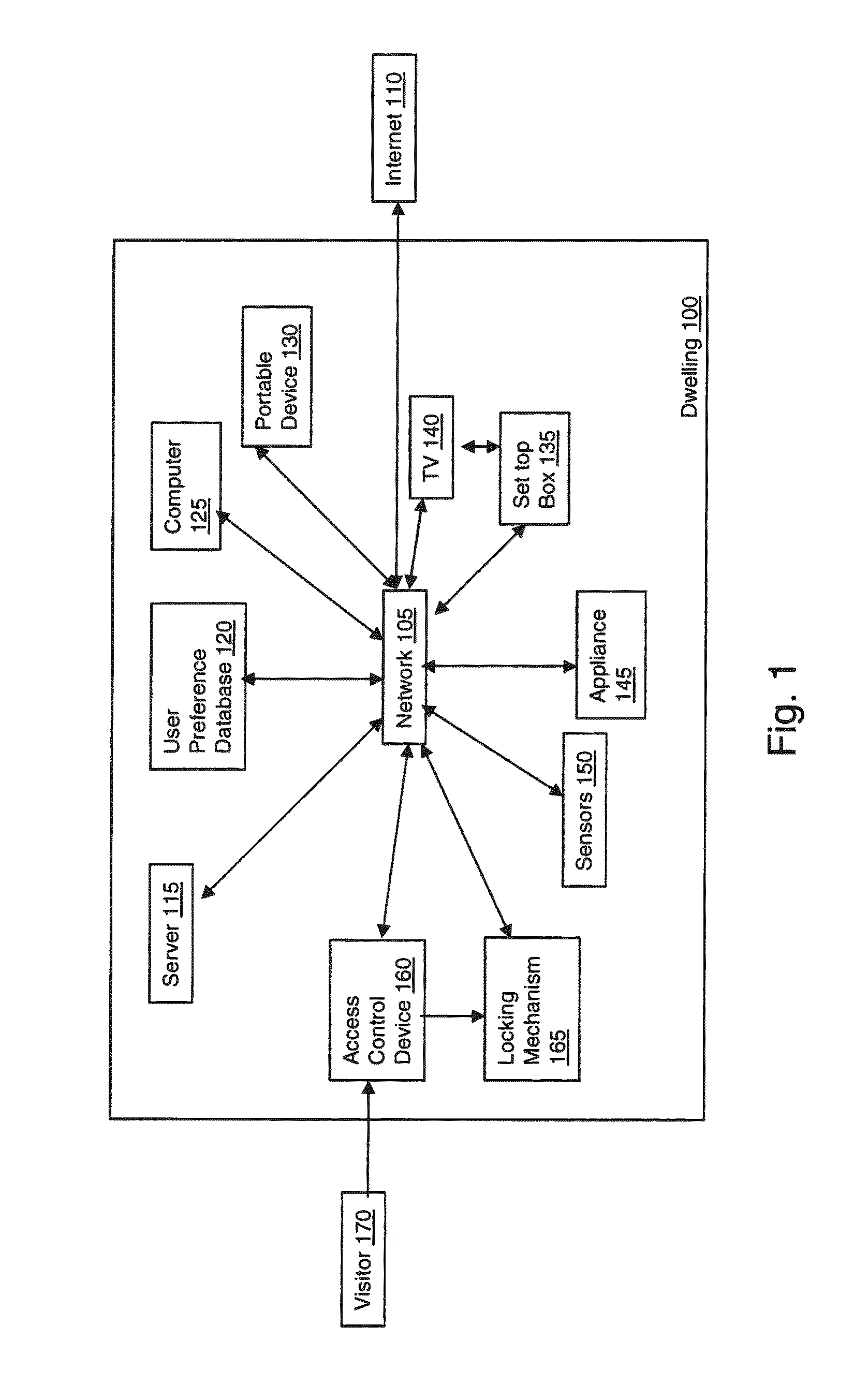
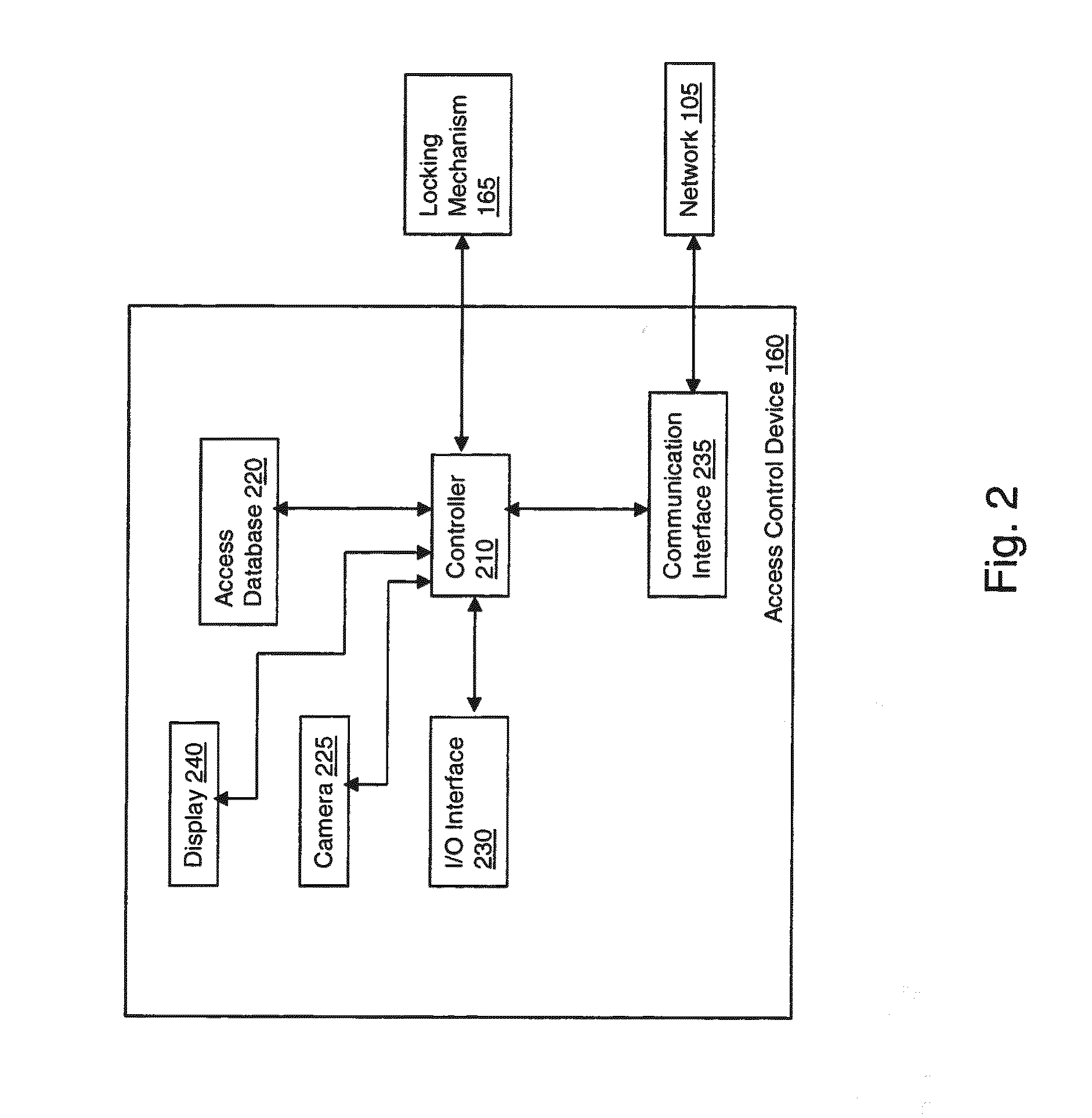
Method and apparatus for controlling access to a home using visual cues
InactiveUS20140192197A1Closed circuit television systemsIndividual entry/exit registersLocking mechanismLevel data
An apparatus and method that controls access to a dwelling is provided. An image capturing device captures an image representing an individual attempting to access the dwelling. An access database includes data identifying individuals known to a user and access level data associated with each individual known to the user, the data identifying individuals known to the user including image data representative of the individual. A controller receives the captured image data from the image capturing device and determines a level of access associated with the individual attempting access by comparing the captured image data with the image data representative of individuals stored in the access database. Upon determining that the access level indicates that access should be granted, the controller controls a locking mechanism to move from a first locked position to a second unlocked position enabling access to the dwelling.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Customized control system for electrical appliances using remote device
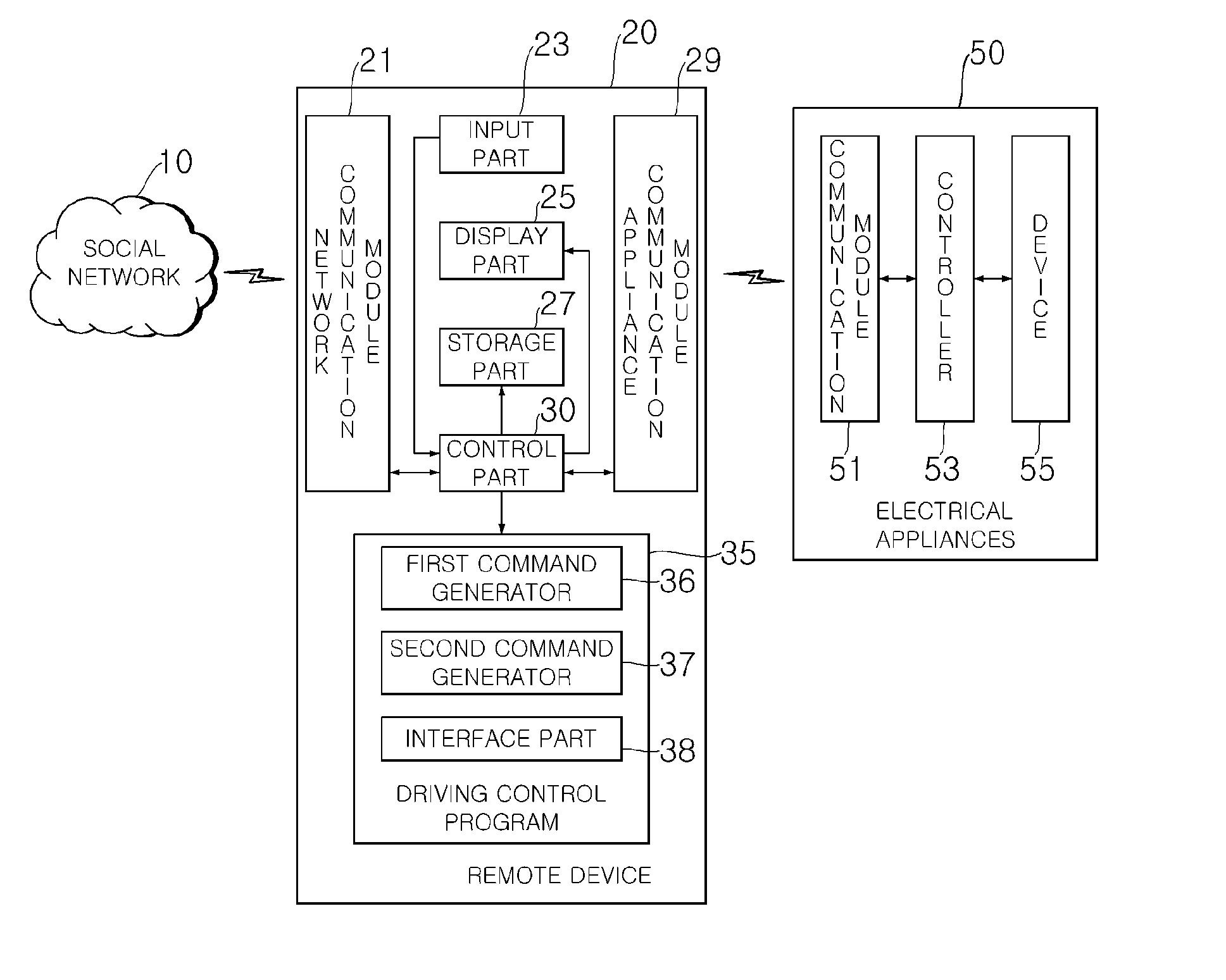
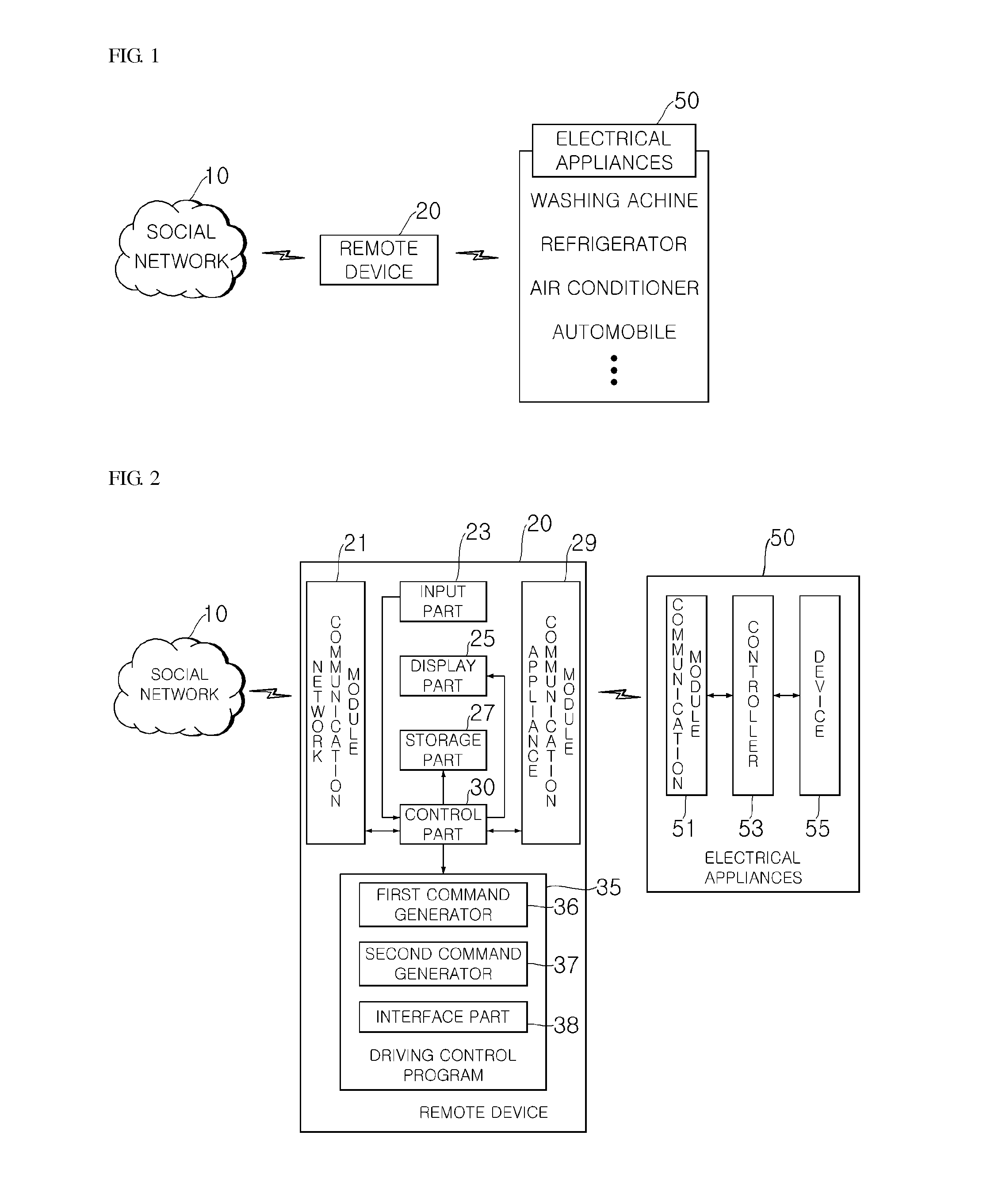
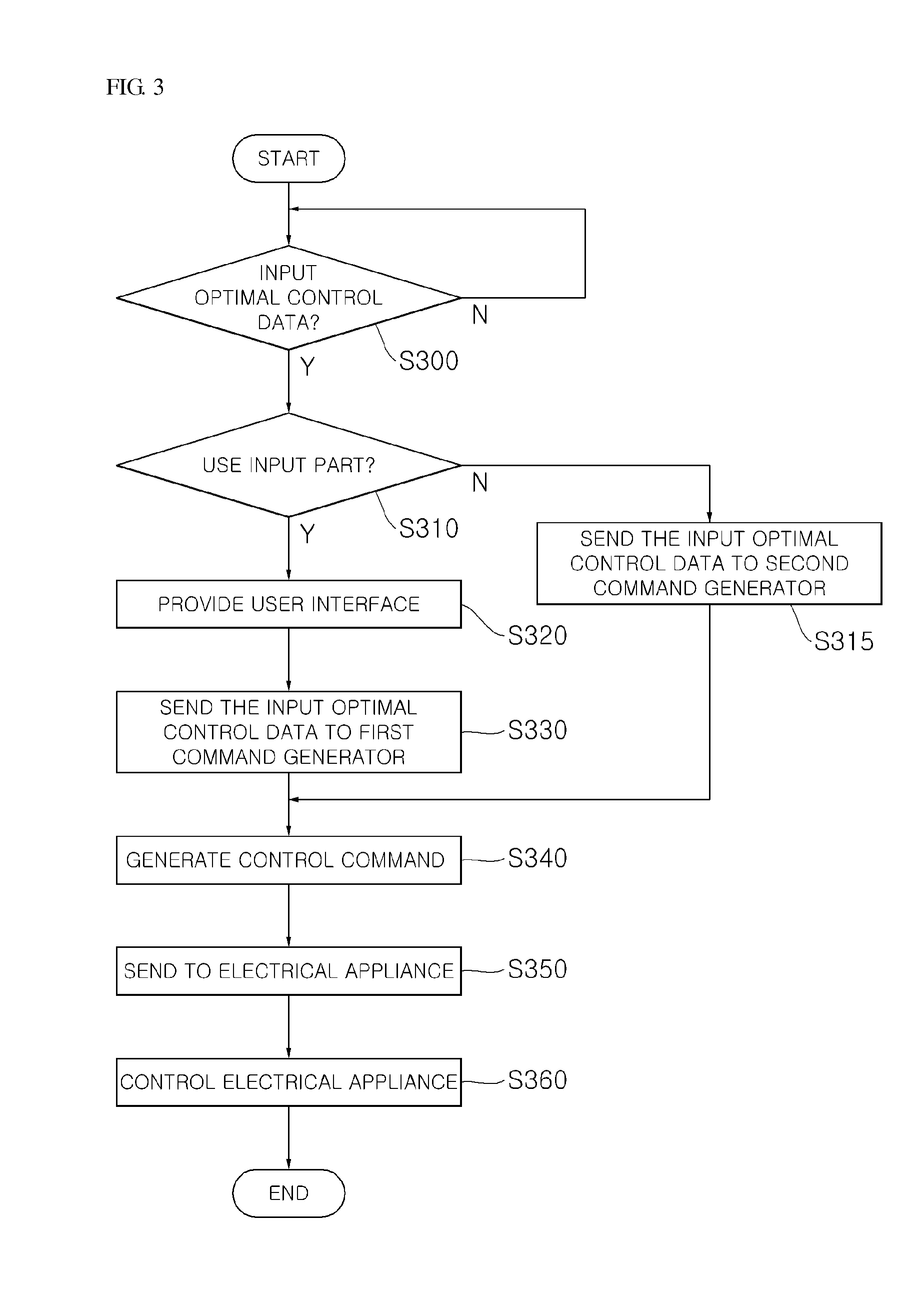
A remote device having an electrical appliance control function and an electrical appliance control system are provided. The remote device includes an appliance communication module for communicating with an electrical appliance which is used by a user inside or outside home using power; a network communication module for supporting communication with outside to obtain user set optimal control data which controls the electrical appliance to operate in some other mode than an operation mode basically provided by a manufacturer of the electrical appliance; and a control part for controlling the electrical appliance based on the user set optimal control data. Hence, user's convenience can be promoted by allowing the user to control the electrical appliance on the optimal condition.
Owner:PARK SOOHONG +1
Seat headrest
InactiveUS6666517B2Easy height adjustmentReliable lockingVehicle seatsOperating chairsChinCombined use
An adjustable headrest that provides both support and comfort to the user and one that can be used in connection with furniture including household and office furniture and also in connection with various types of passenger vehicles. The headrest includes slide means for permitting easy height adjustment of the headrest and also includes locking means for securely locking the headrest in a desired elevated position. Further, the headrest includes easily adjustable, wing-like, side-support members that are pivotally connected to a centrally located, vertically adjustable head support member by means of constant torque hinges and also includes easily adjustable chin support members that are pivotally connected to the side support members by means of constant torque hinges.
Owner:REINHOLD IND
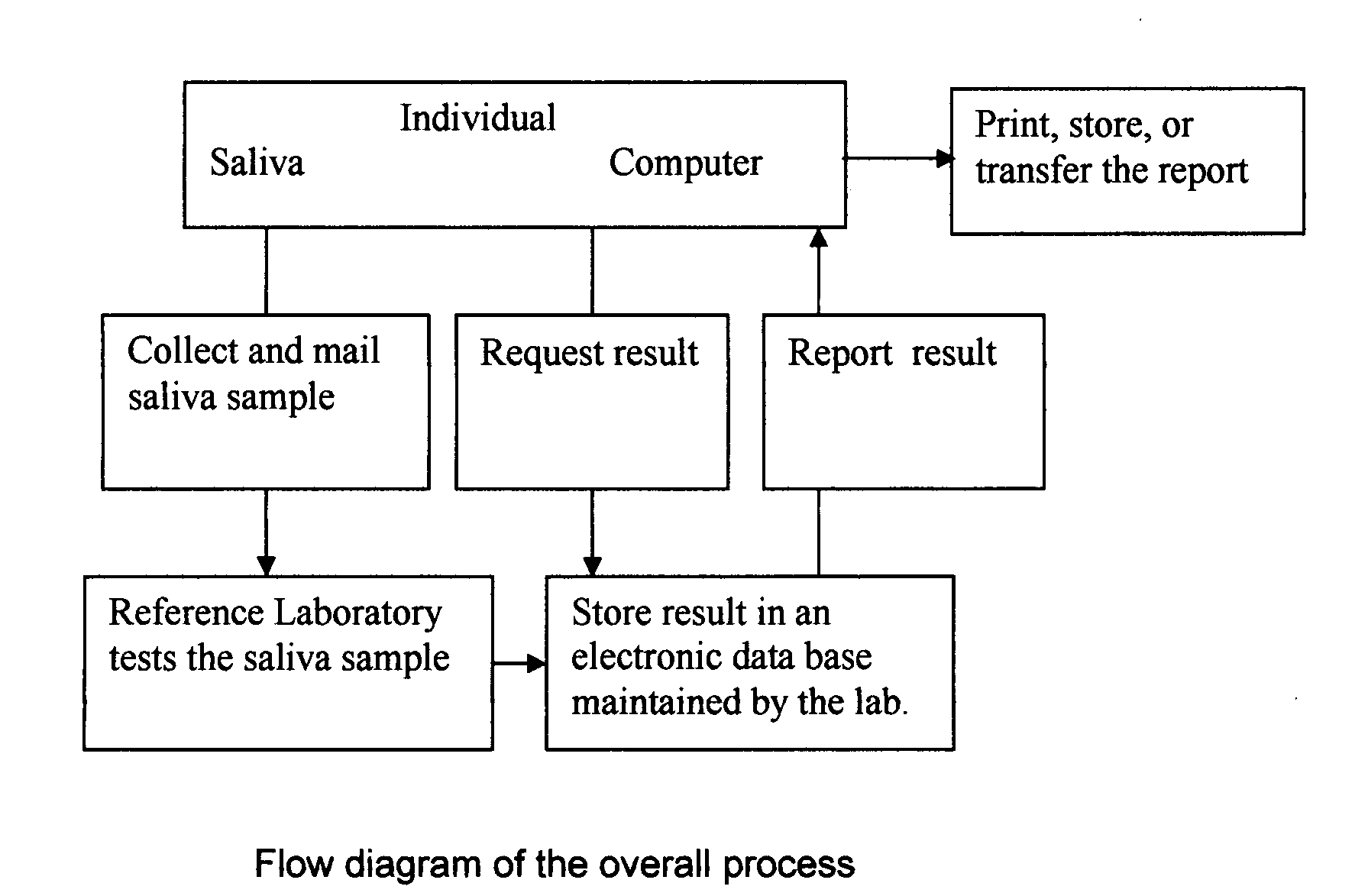
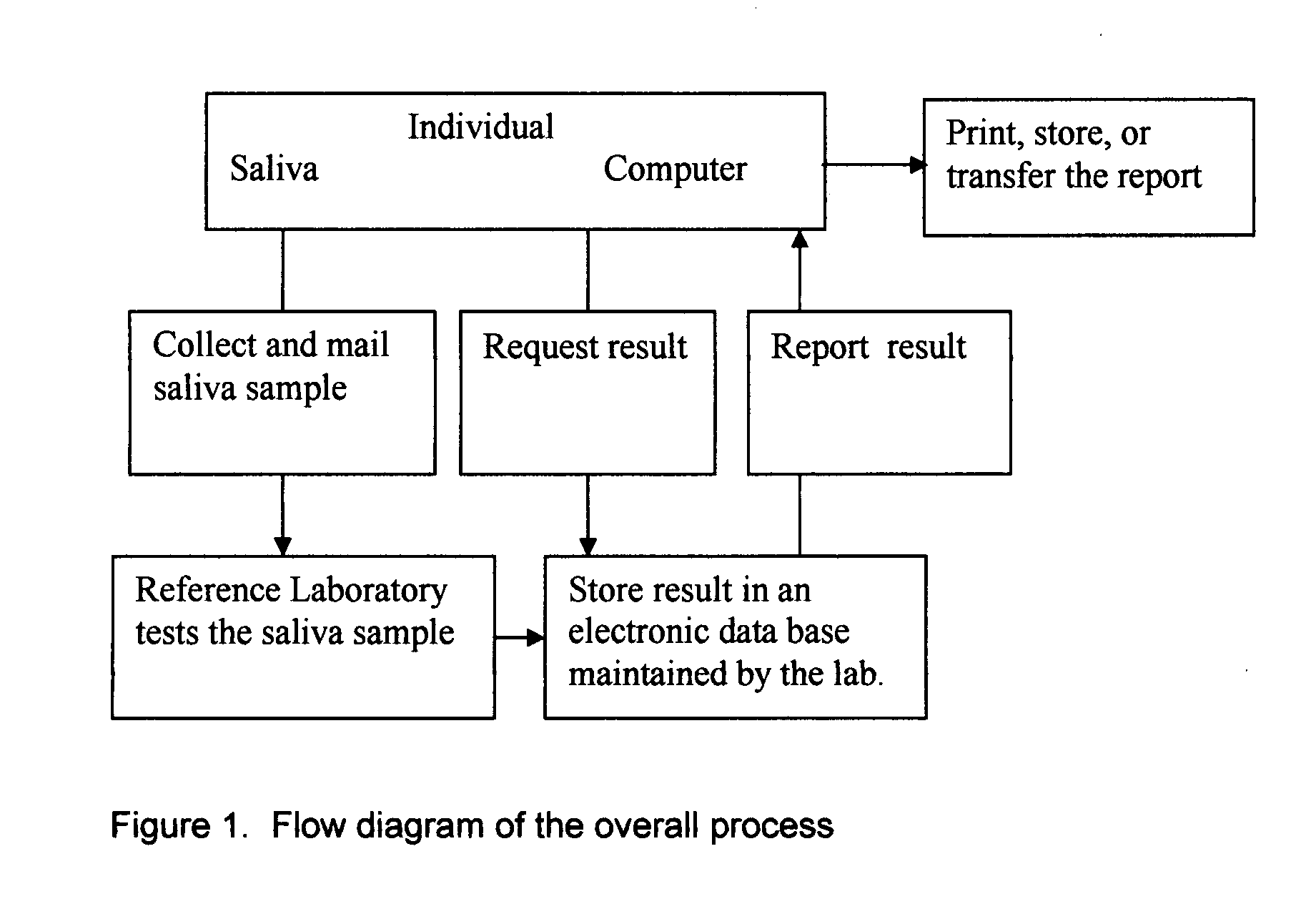
Home test for glycated albumin in saliva
InactiveUS20080227210A1Withdrawing sample devicesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsSaliva sampleSaliva collection
A home test for measuring glycated albumin levels in saliva. The saliva sample is collected at home using a standardized saliva collection kit and mailed to a testing laboratory that performs the test and reports the result directly back to the customer via the internet. The home test can be used to monitor glucose control in diabetics and in healthy individuals. It may also be used as a diagnostic aid in identifying individuals with diabetes, or who are at risk of developing diabetes.
Owner:SMITH HENRY
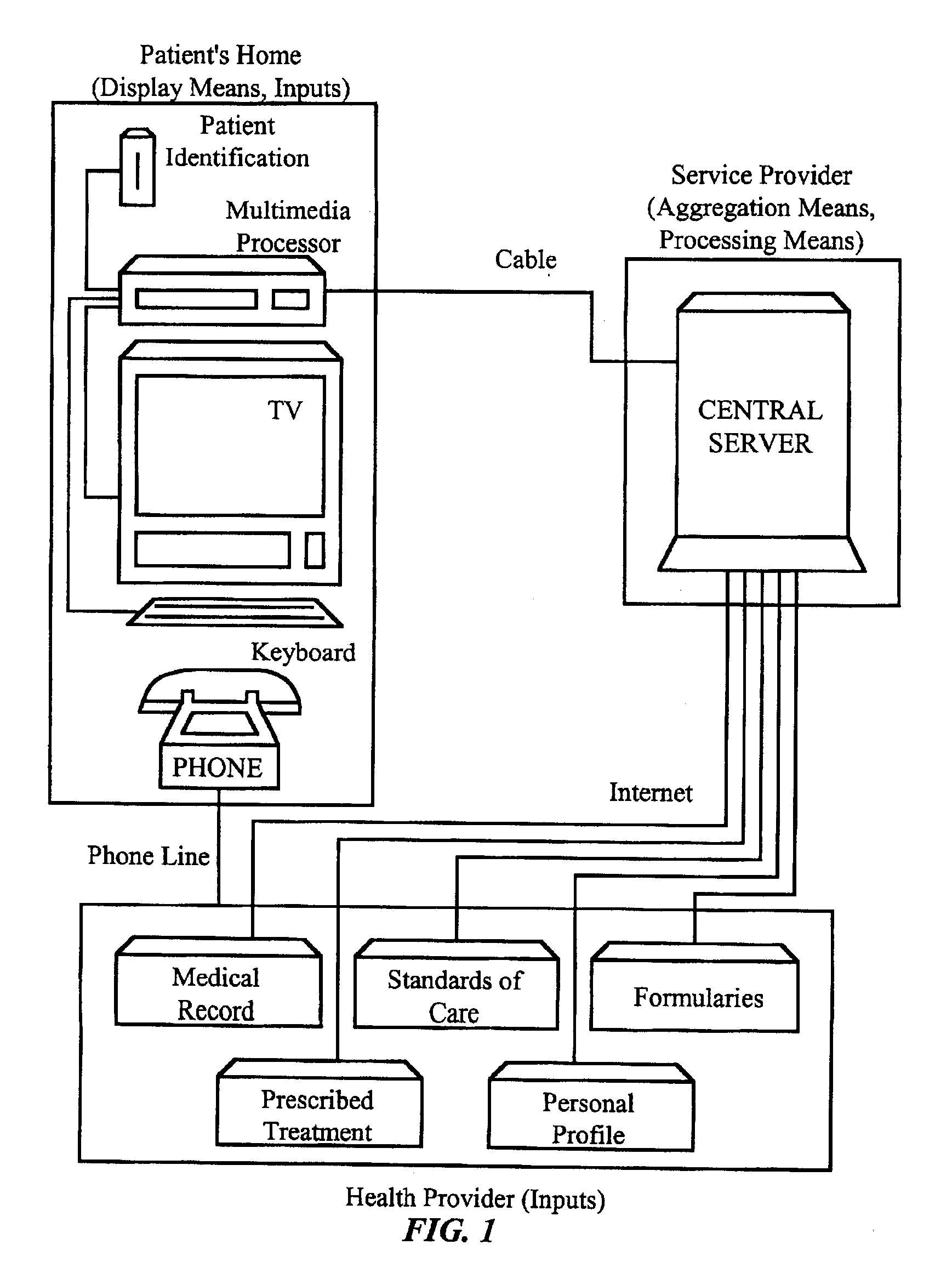
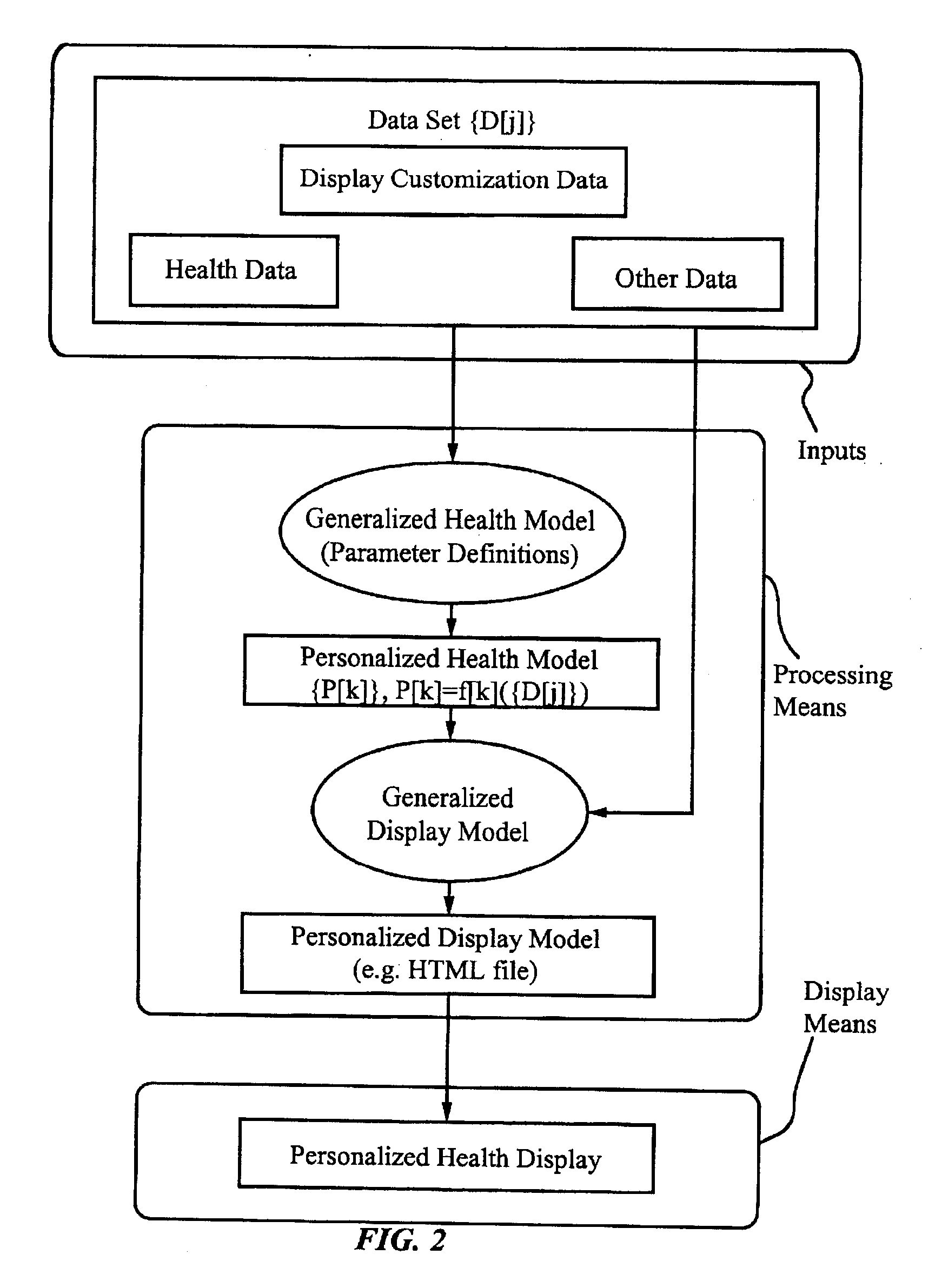
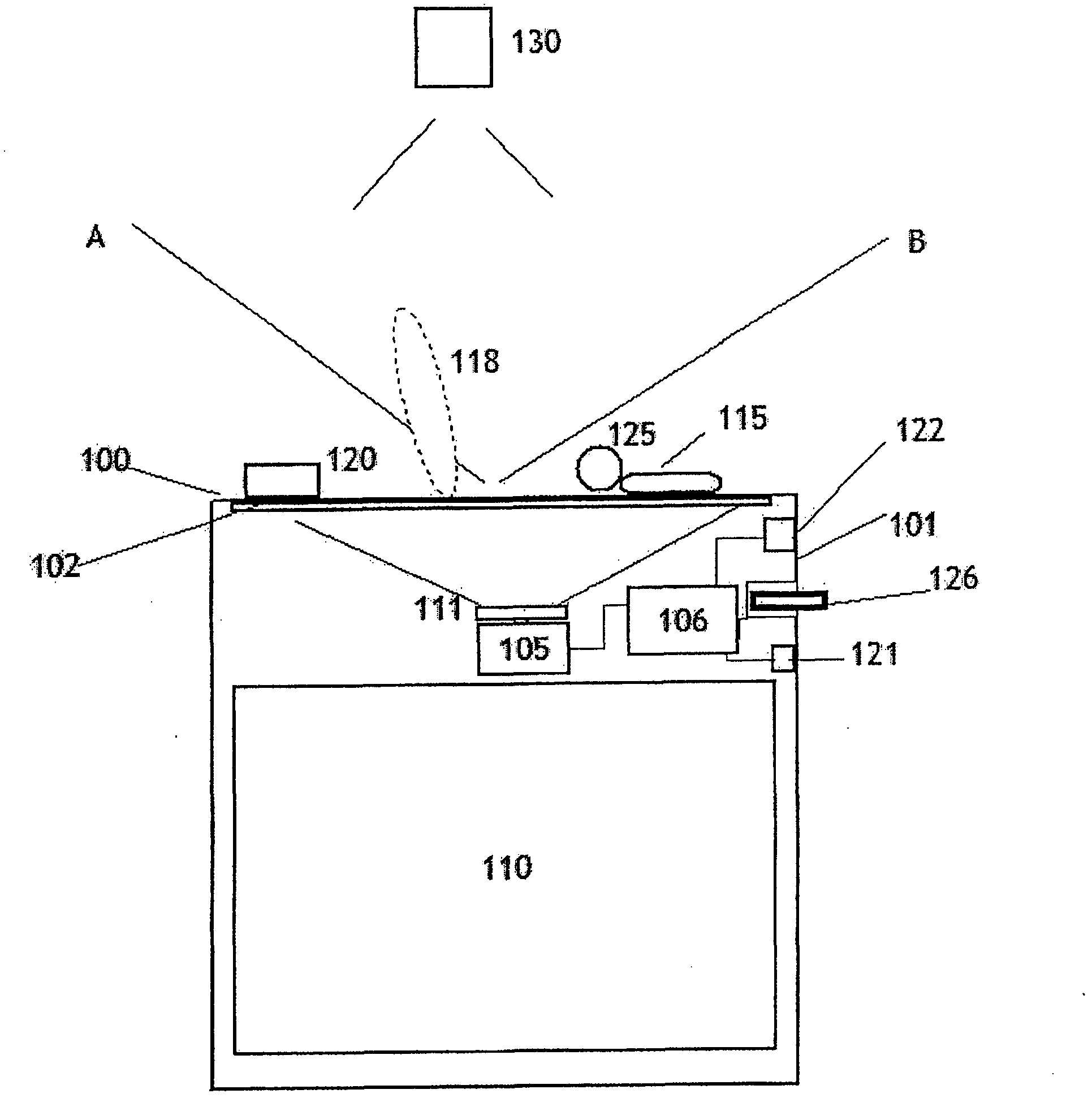
Personalized body image
Delivery of health information to a patient suffering from a chronic condition is personalized by displaying the health information directly on a customized image of a body. The patient's medical record, standards of care for the condition, prescribed treatments, and patient input are applied to a generalized health model of a disease to generate a personalized health model of the patient. The personalized health model comprises an HTML file encoding an image map of a body. The body image illustrates the health condition of the individual patient. Preferably, data is collected from health provider sources and stored in a database on a server at a service provider site. The data is processed at the server, and is displayed in the patient's home using a TV connected to a multimedia processor. The multimedia processor connects the television set to a communications network such as the Internet. Applications include preventive care of chronic diseases such as diabetes and asthma.
Owner:HEALTH HERO NETWORK
Interactive home manual with networked database
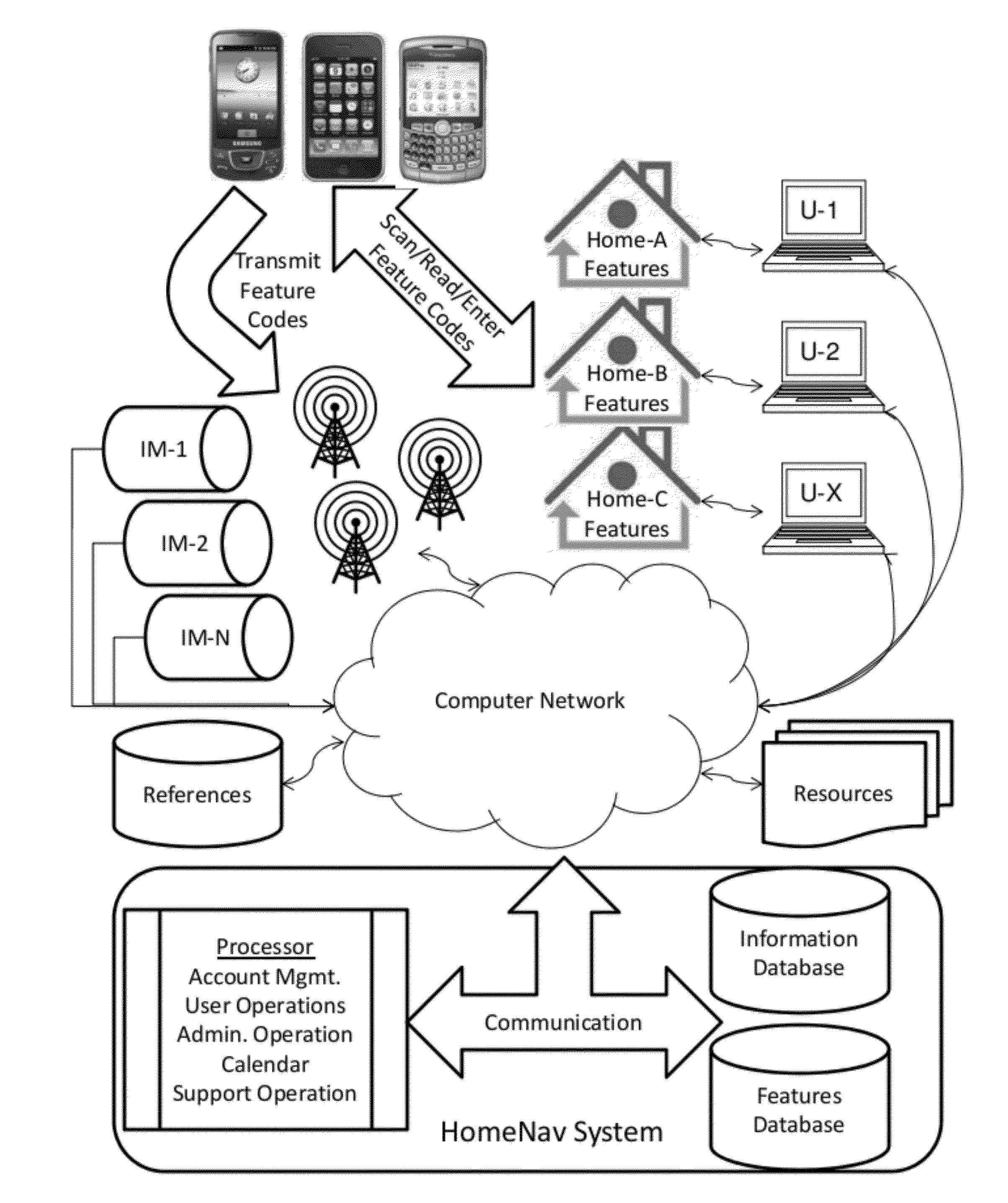
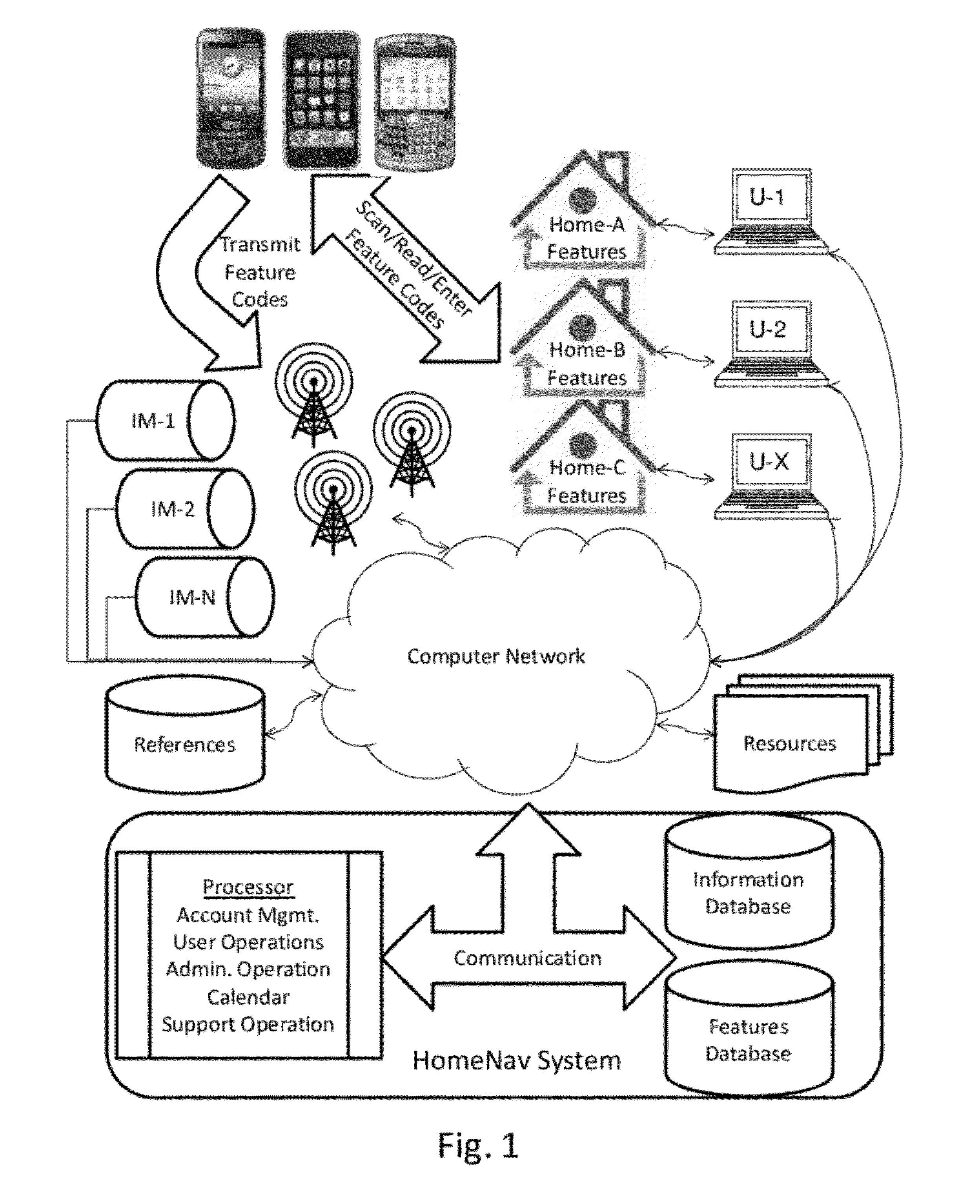
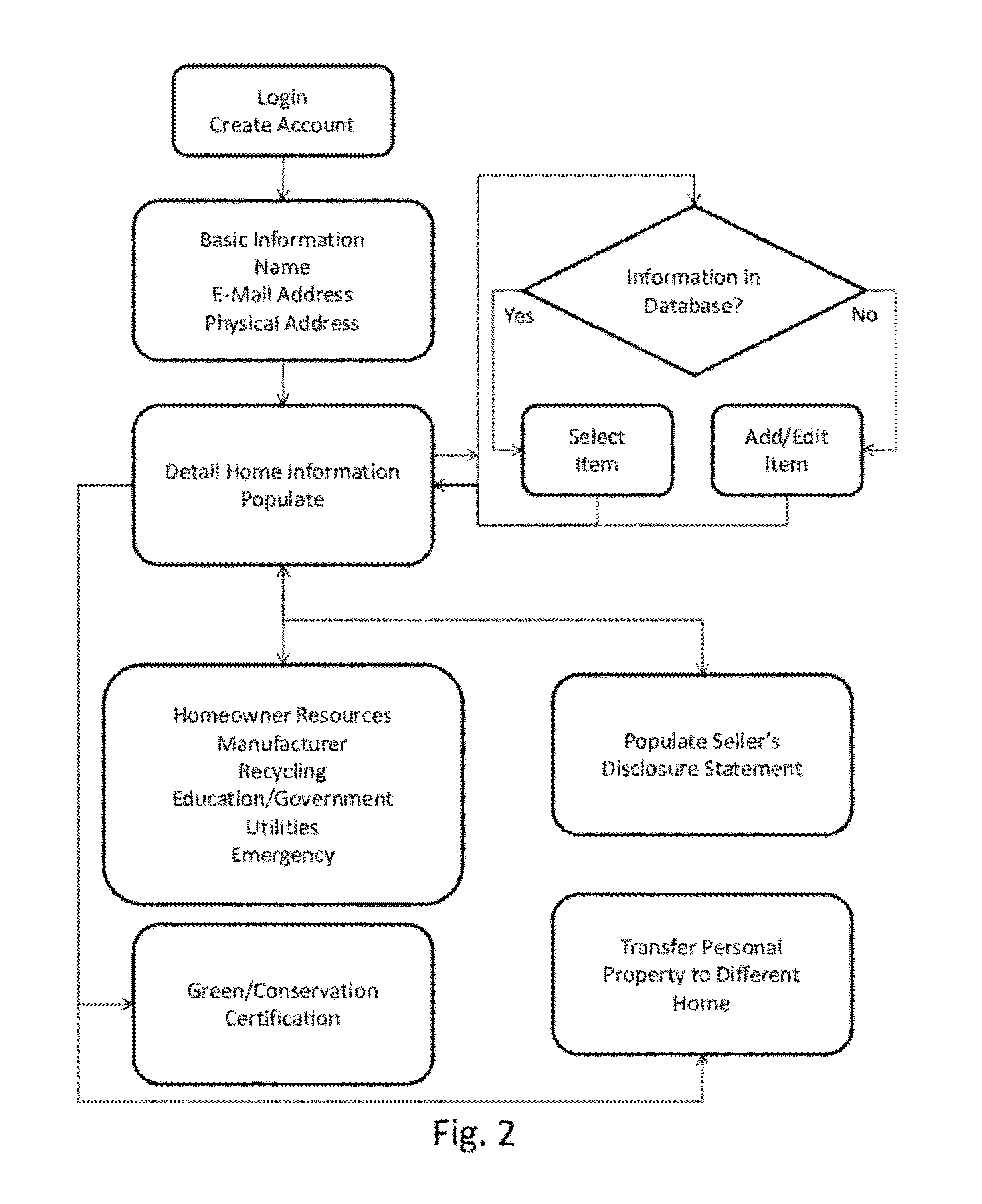
InactiveUS20120179727A1Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsHome useFeature description
A interactive home manual system has a centralized database that stores datasets with user account information, home locations, home feature descriptions, home feature information, home feature codes and a set of correlations between the stored data. A centralized computer processor has an account management module, an interactive user operations module, and an administrative operations module. The account management module correlates user accounts with the user account information in the centralized database while the operations module produces the set of correlations for the users' respective accounts and the administrative operations module manages the database. The centralized computer processor is in local communication with the centralized database and in networked communication with the users through a centralized communications module. The users preferably identify the features for their homes using feature codes that can be scanned or otherwise entered through a mobile communications device or manually.
Owner:ESSER MARLA J
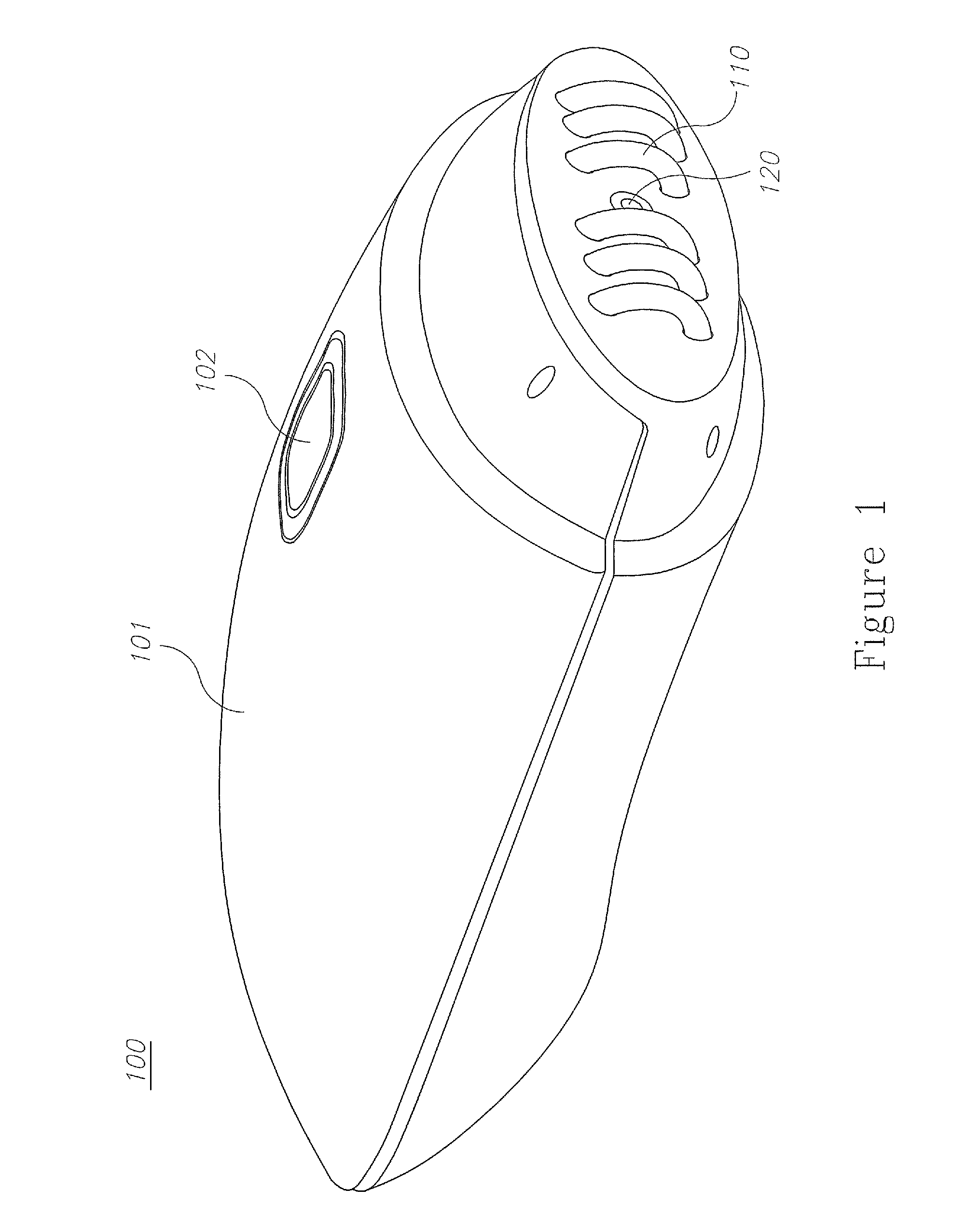
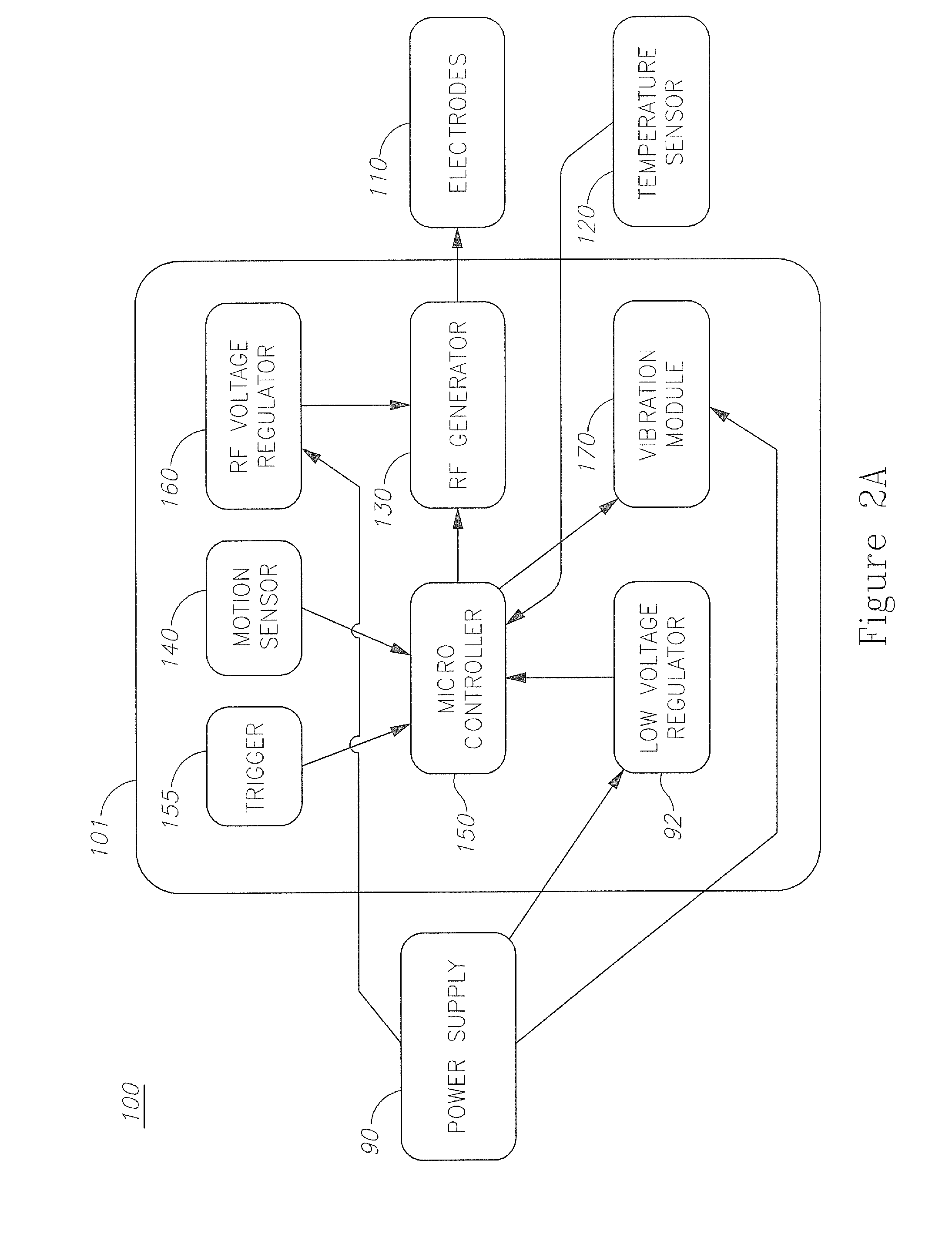
Skin treatment devices and methods
A skin treatment device for home use is provided herein. The device has enhanced safety features and improved operation efficiency. RF energy is delivered under strict control to a relatively small and well localized volume of the skin, avoiding excessive heating of the skin surface. Surface heating is monitored both by direct temperature measurement and by movement monitoring of the device to ensure proper use and prevent skin overheating and the pain associated therewith.
Owner:ENDYMED MEDICAL
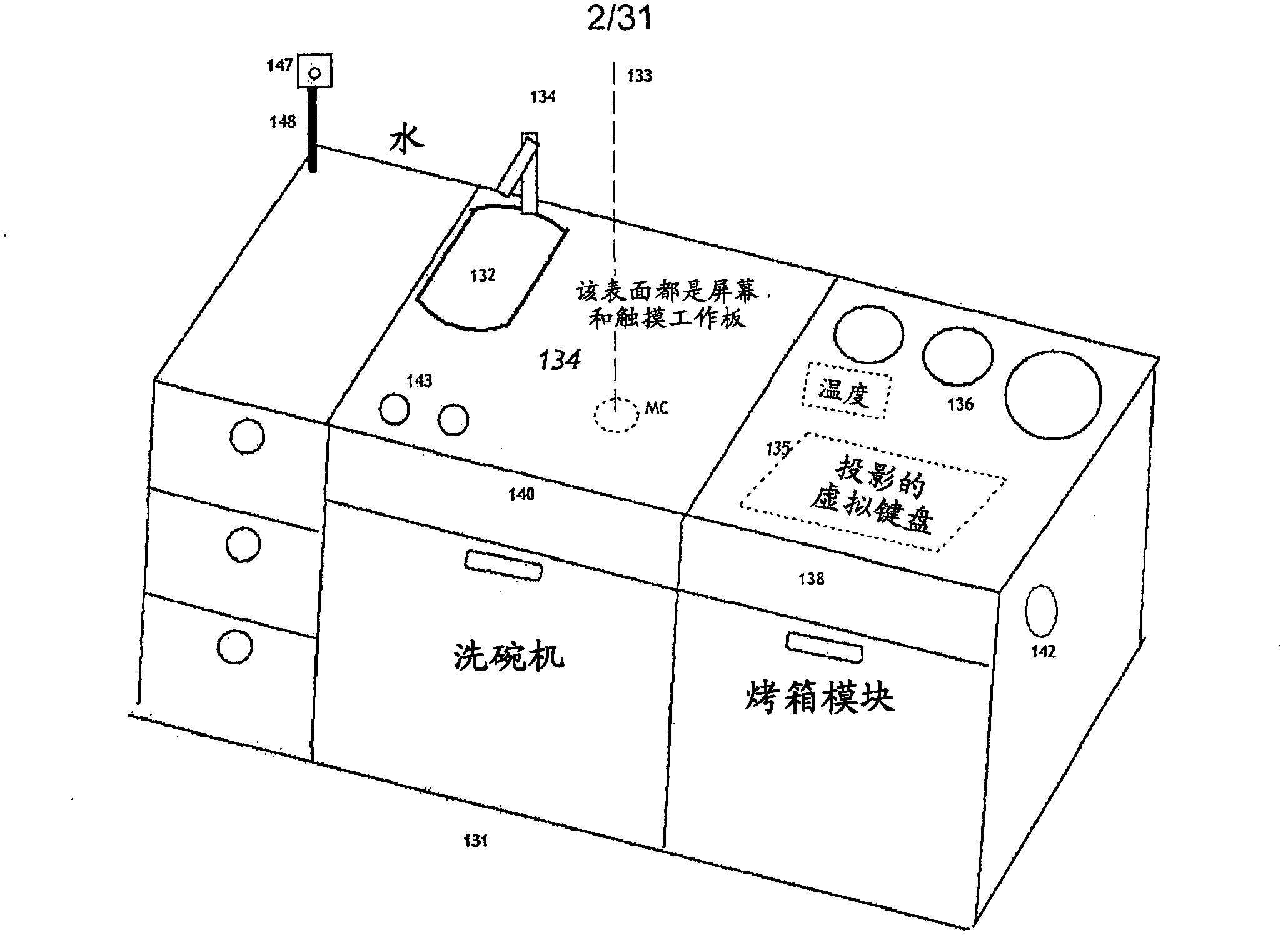
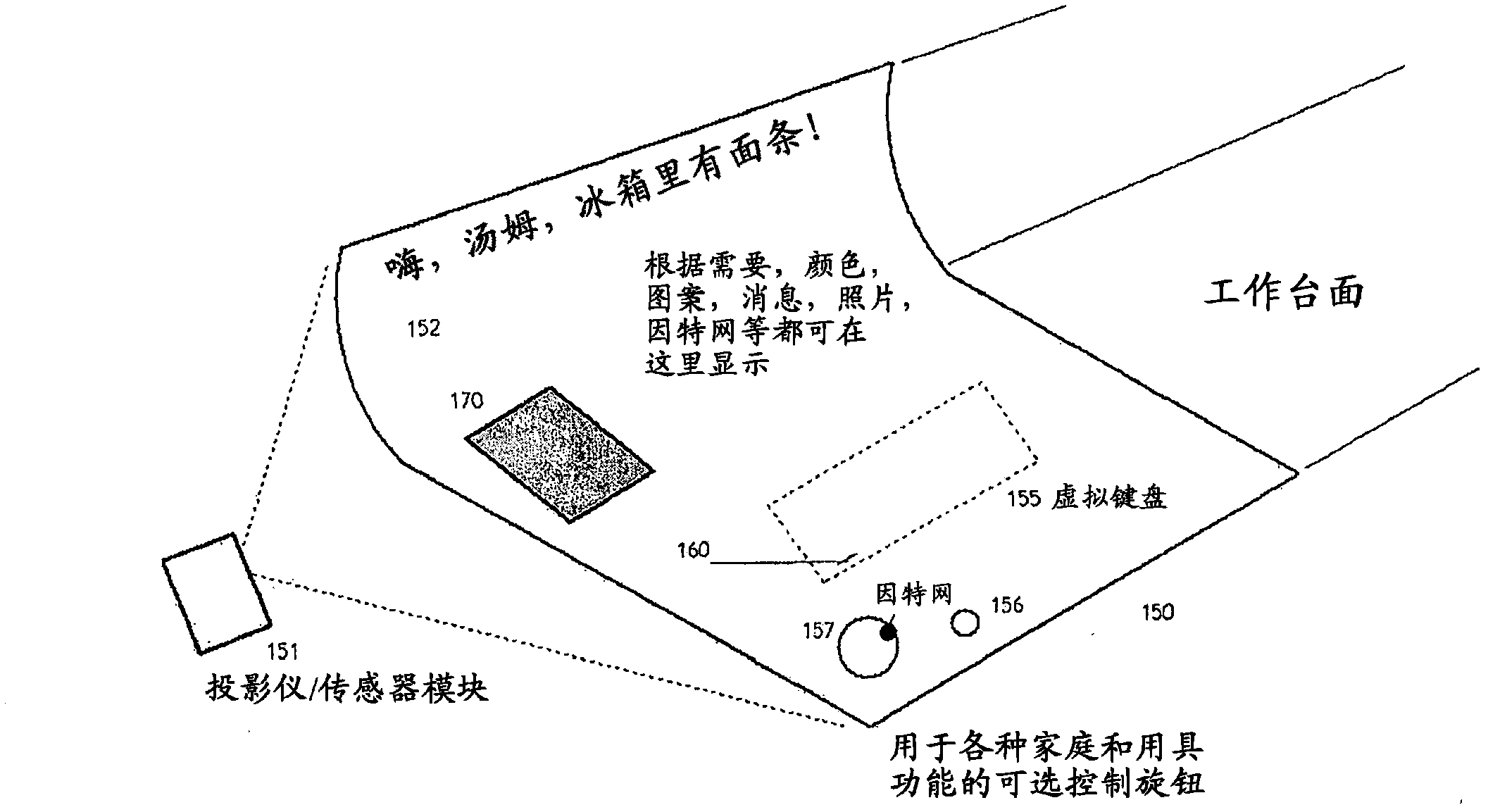
Control of appliances, kitchen and home
InactiveCN102498442AOperational securityInput/output for user-computer interactionWashing controlling processesHome useTelecommunications
The disclosed invention is generally in the field of control of appliances in the home, and in their networking and connectivity also with audio systems and internet sources and the integration of these elements in a connected manner. Preferred apparatus generally employs a video projection system and one or more TV cameras. Embodiments of the invention may be used to enhance the social interaction and enjoyment of persons in the kitchen and reduce the work of food preparation. The invention may be used in many rooms of the house, and contribute to the well being of seniors and others living therein.
Owner:APPLE INC
Outdoor home cleaning robot
InactiveUS20100106298A1Save powerShorten the timeComputer controlSimulator controlWorking environmentEngineering
A method, system and apparatus comprising an autonomous all weather outdoor cleaning robots designed to identify and clean various outdoor household objects including but not limited to personal automobiles and other vehicles and outdoor objects. The robot will autonomously navigate to a designated area and scan the vehicle or object to determine the optimum cleaning routine to render. The robot can record and learn its working environment by comparing scanned vehicles and outdoor objects with its existing database for future reference. The robot can also compare its position and store navigation data which correlates to areas previously visited and items previously cleaned so as to increase efficiency for future work by reducing travel and scanning times. The present invention is focused on autonomous outdoor cleaning robots with multiple purposive functions. Specifically, the present invention utilizes micro-processors to control cleaning, navigation and perception. More specifically, the present invention uses multi-segmented arms to perform needful chores. Even more specifically, the present invention can adapt and learn from its environment performing useful tasks.
Owner:HERNANDEZ EUSEBIO GUILLERMO +1
Outdoor home cleaning robot—system and method
ActiveUS9114440B1Save powerShorten the timeProgramme controlAutomatic obstacle detectionWorking environmentSimulation
A hardware and software method, system and apparatus comprising an autonomous all weather outdoor cleaning robot designed to identify, and clean various outdoor household objects including but not limited to personal automobiles and other vehicles. The robot autonomously navigates to a designated area and scans the vehicle or object to determine the optimum cleaning routine. The robot learns its working environment by comparing scanned vehicles and outdoor objects with its existing database for future reference. The robot also compares and stores navigation data, which correlate to areas previously visited to increase efficiency for future work by reducing travel and scanning times. The Present Invention focuses on autonomous outdoor cleaning multi-purpose robots. The robots utilize microprocessors to control cleaning, navigation and perception. More specifically, the robots use multi-segmented arms to perform needful chores. Even more specifically, a robot can adapt and learn from its environment while performing useful tasks.
Owner:COLUCCI MICHAEL A +1
Methods for laundering delicate garments in a washing machine
InactiveUS20030008799A1Improve performanceProcess can be usedInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic detergent compounding agentsEngineeringDry cleaner
A product and process for laundering delicate or dry-clean only garments in a washing machine, such as a conventional home washing machine. The process may utilize a garment container, such as a flexible wrap to protect the garments. The process also includes at least one cleaning composition specially formulated for delicate garments. The cleaning composition(s) can be in a number of suitable forms, and can be introduced into the process in a number of different manners. The products used in the process may be provided in the form of a kit. The kit may also include a pretreatment applicator.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Seat headrest
InactiveUS20040195893A1Easy height adjustmentReliable lockingVehicle seatsOperating chairsChinCombined use
An adjustable headrest that provides both support and comfort to the user and one that can be used in connection with furniture including household and office furniture and also in connection with various types of passenger vehicles. The headrest includes slide means for permitting easy height adjustment of the headrest and also includes locking means for securely locking the headrest in a desired elevated position. Further, the headrest includes easily adjustable, wing-like, side-support members that are pivotally connected to a centrally located, vertically adjustable head support member by means of constant torque hinges and also includes easily adjustable chin support members that are pivotally connected to the side support members by means of constant torque hinges.
Owner:REINHOLD IND
Seat Headrest
InactiveUS20020158499A1Readily deflatableReadily inflatableVehicle seatsOperating chairsHome usePhysical medicine and rehabilitation
An adjustable headrest that provides both support and comfort to the user and one that can be used in connection with furniture including household and office furniture and also in connection with various types of passenger vehicles. The headrest includes slide means for permitting easy height adjustment of the headrest and also includes locking means for securely locking the headrest in a desired elevated position. Further, the headrest includes easily adjustable, wing-like, side-support members that are pivotally connected to a centrally located, vertically adjustable head support member by means of constant torque hinges and also includes easily adjustable chin support members that are pivotally connected to the side support members by means of constant torque hinges.
Owner:REINHOLD IND
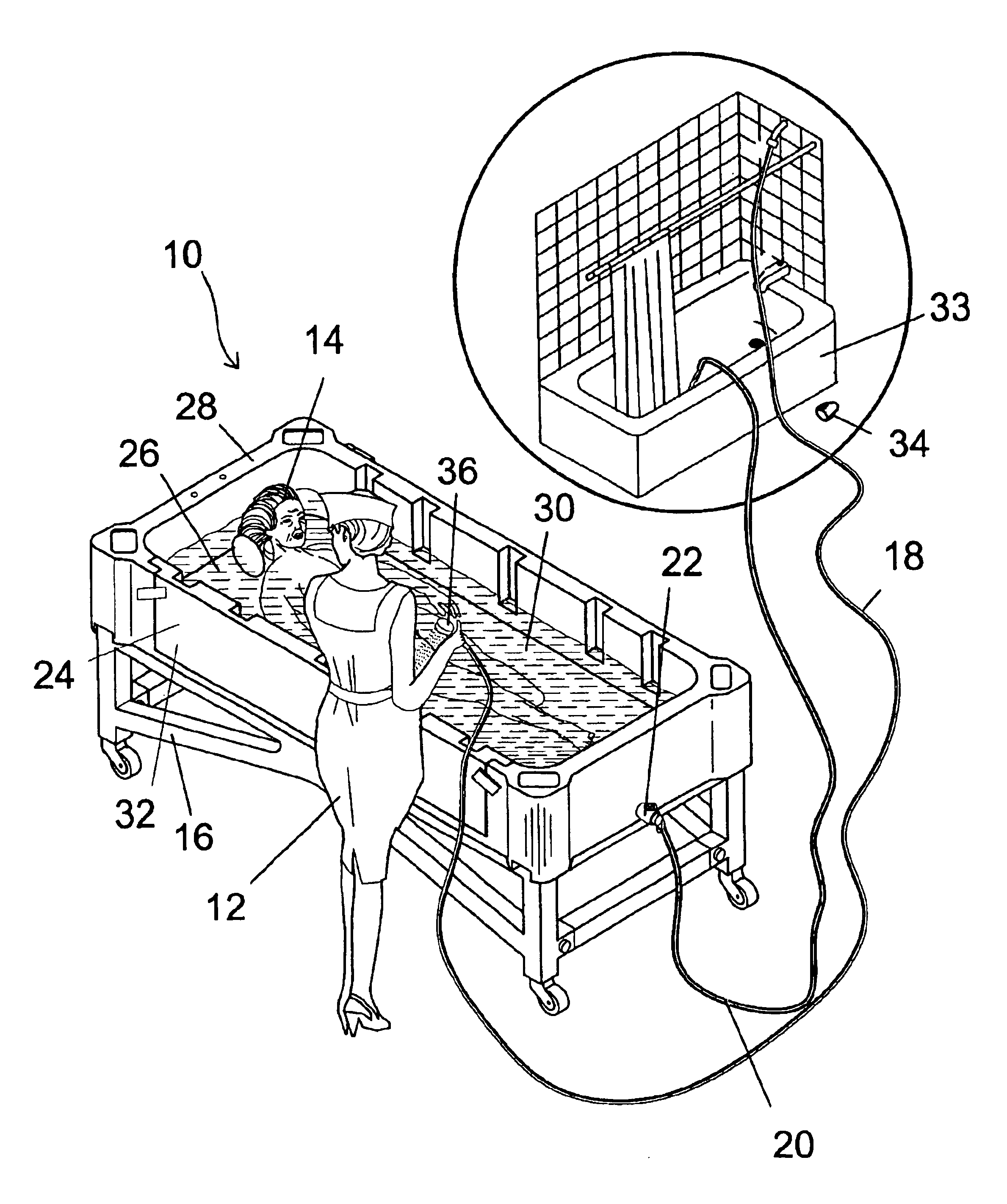
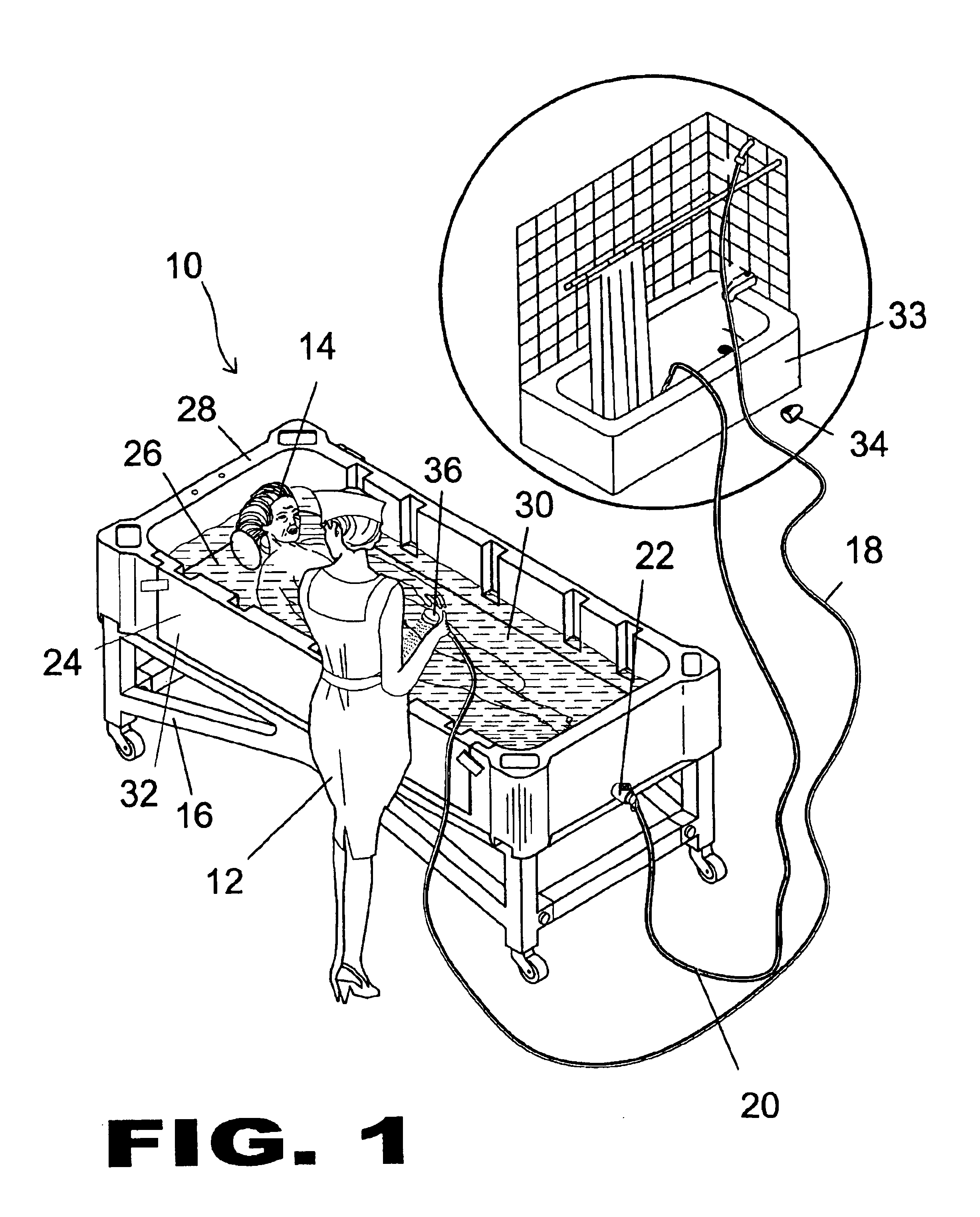
Comfort bed bath
InactiveUS6802088B1Cheap manufacturingGuaranteed economical operationBathsDouchesEngineeringGuide tube
The present invention 10 discloses a portable bed device comprising a horizontal bottom 26 surrounded by vertical walls 28 with an open top forming a tub 32 for holding water therein in order to wash a person. The tub 32 has a removable side panel 42 incorporated into at least one sidewall wherein a latching mechanism 44 is used to attach the removable side panel to the tub 32. An adjustable backrest / footrest 38 is provided in order to rest the patient's head thereon wherein the backrest / footrest element is attached by tongue 39 and groove 40 fastening means to the sidewalls of the tub 32. A headrest 48 may also be removably attached to the backrest / footrest element. A means for introducing water into the tub 32 comprises a flexible inlet conduit 18 and a flexible outlet conduit 20 wherein water may be supplied from a conventional household showerhead and diverted back for discharge into, for example, the shower or tub 33 itself The patient may be washed using the showerhead 36 attached to the end of the inlet line 18. The tub 32 may be placed onto a gurney 16 when it is not feasible to bathe the patient in the bed.
Owner:GRUNER MARK
Distributed electric power generation
InactiveUS20090115368A1Reduce lossesIdeal system efficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsSteam useHome useElectrical battery
An electric power generating system is arranged such that the system efficiency approaches 100%. In the context of this special arrangement, system efficiency is defined as the electrical energy produced divided by the amount of heat energy allocated to its production. All heat energy that is not converted to electric energy is completely used by an associated household. However, high efficiency requires that heat usage by the household is not increased as a result of this arrangement. Unlike most electric power generation, heat is not wasted, so there is no inefficiency.The motor vehicle includes an electric generator driven by a heat engine, with an optional natural gas connection to the household. The heat from the exhaust and the engine coolant is connected to household devices that make full use of that heat. As needed, operation of the heat engine is regulated such that heat discharge rate does not exceed the rate at which household devices can use that heat. Generated electricity charges vehicle batteries, with surplus going to the household and to the public utility.
Owner:BULLIS JAMES KENNETH
A home-based heliox system with carbon dioxide removal
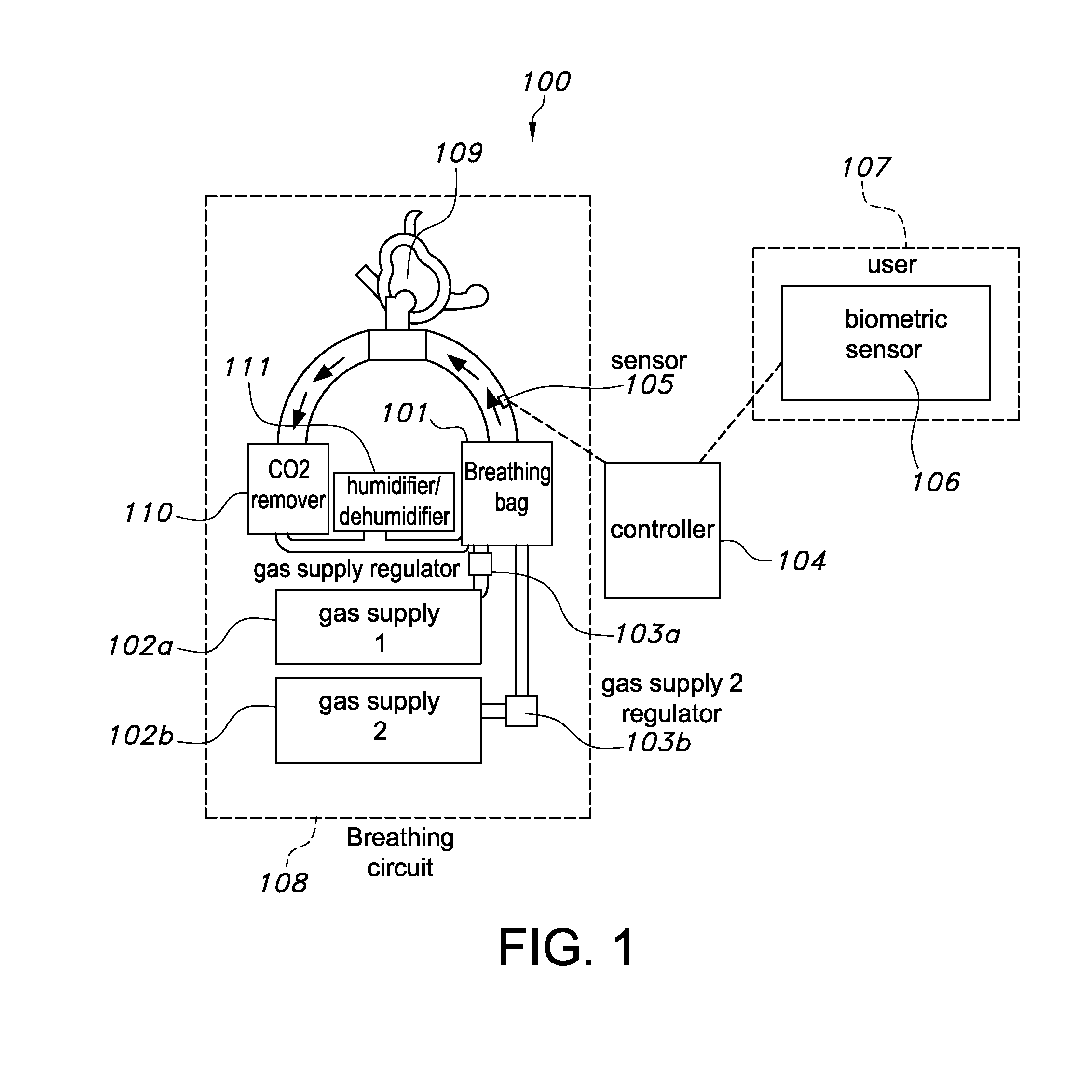
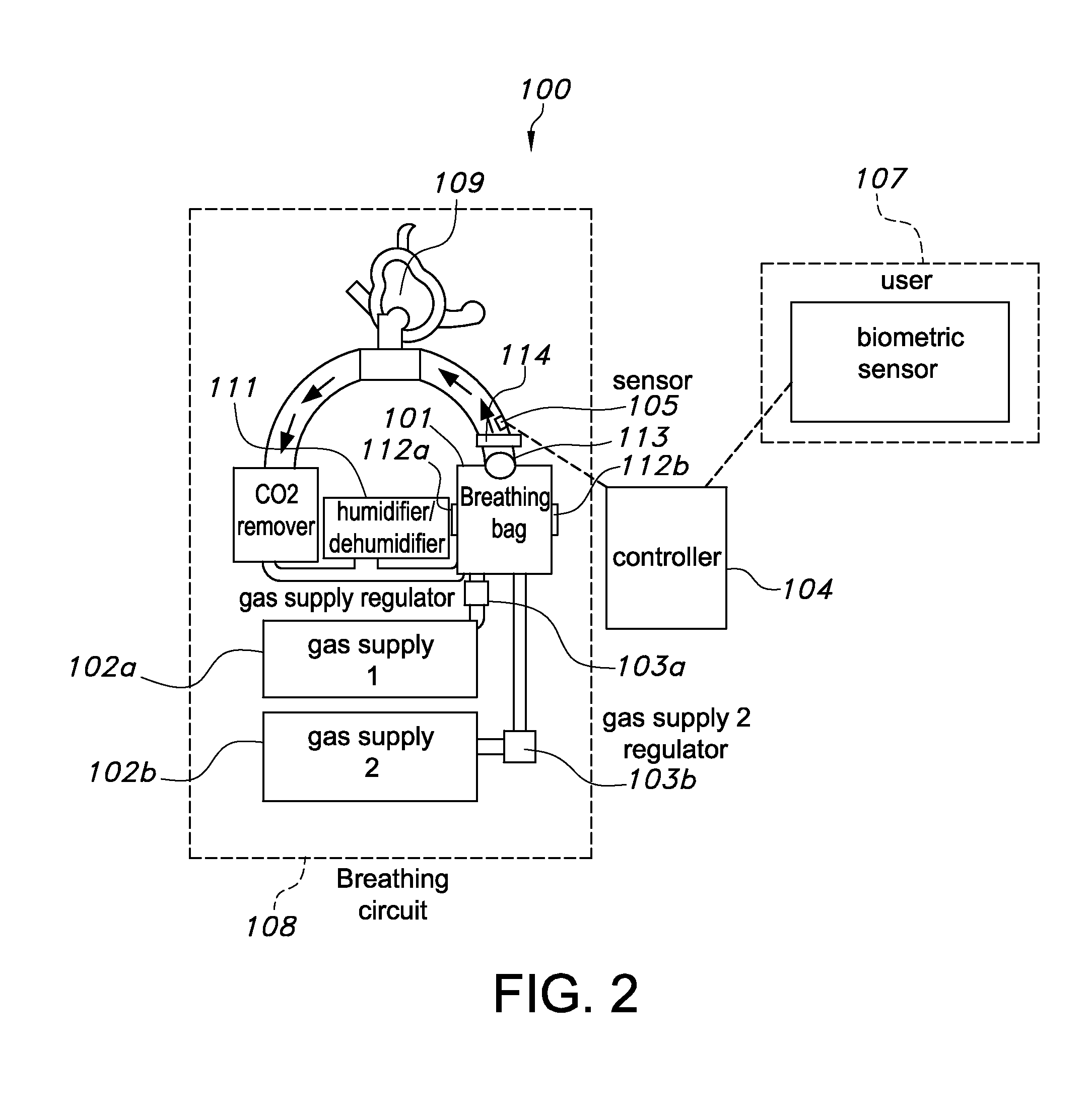
ActiveUS20160213879A1Simple for individual operationSufficiently compactRespiratorsElectrocardiographyHelioxHome based
A closed-circuit heliox delivery system and methods for alleviating symptoms of COPD and related disorders are provided. The system is self-monitoring and can be used outside of a hospital environment. The system contains a gas supply fluidly connected to a breathing circuit. The breathing circuit contains an upper airway device, such as a mask. The system contains a sensor(s) and controller. The sensors measure parameters in the system, the ambient environment, or related to the physiological state of the user. The controller can adjust the system to maintain parameters within the device, i.e. pressure, temperature, humidity, within predetermined ranges. The controller can adjust the system to maintain a target physiological state of the user, i.e. target blood oxygen levels or Work of Breathing (WOB).
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com