Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
80 results about "GgNMOS" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
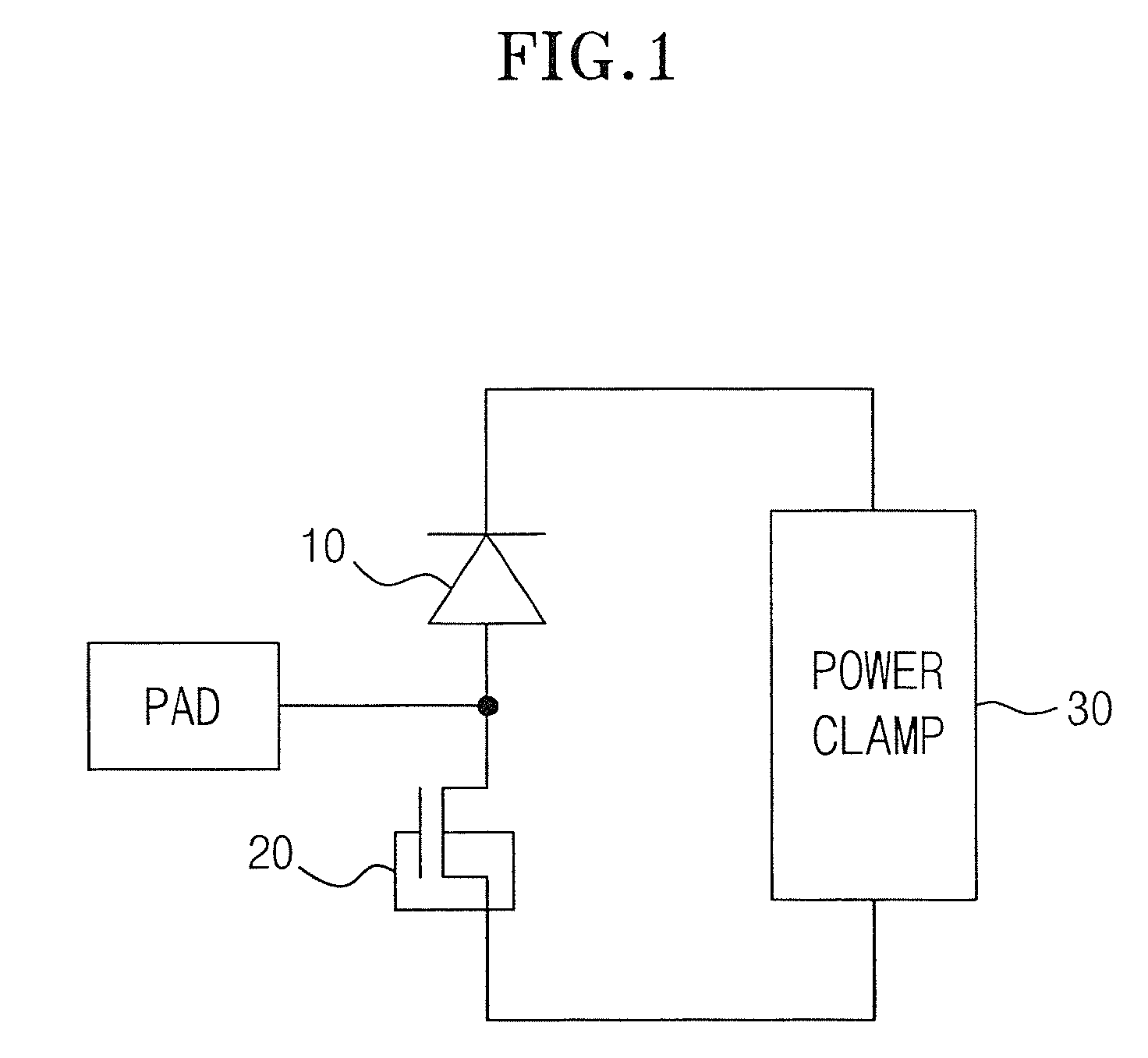
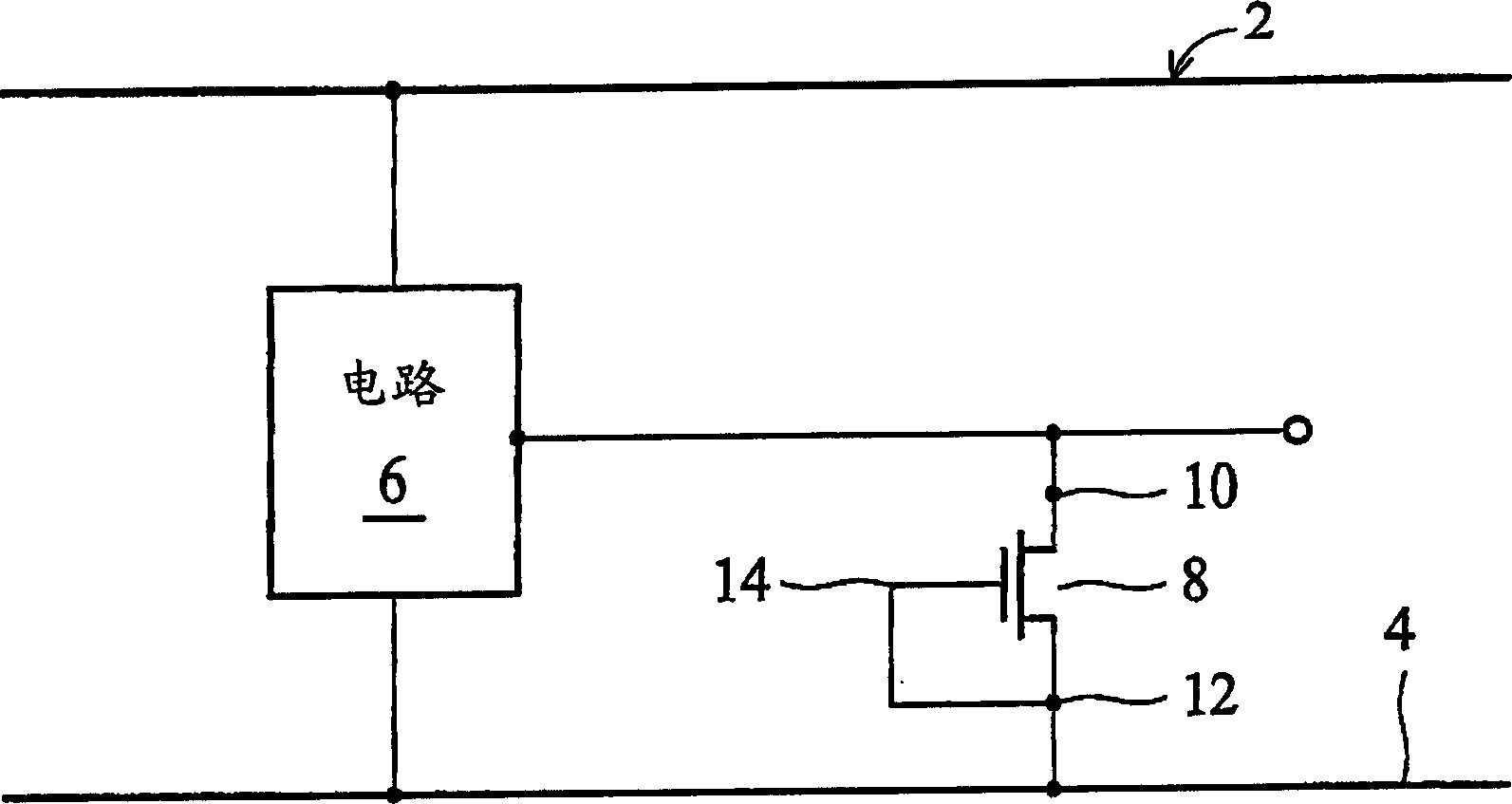
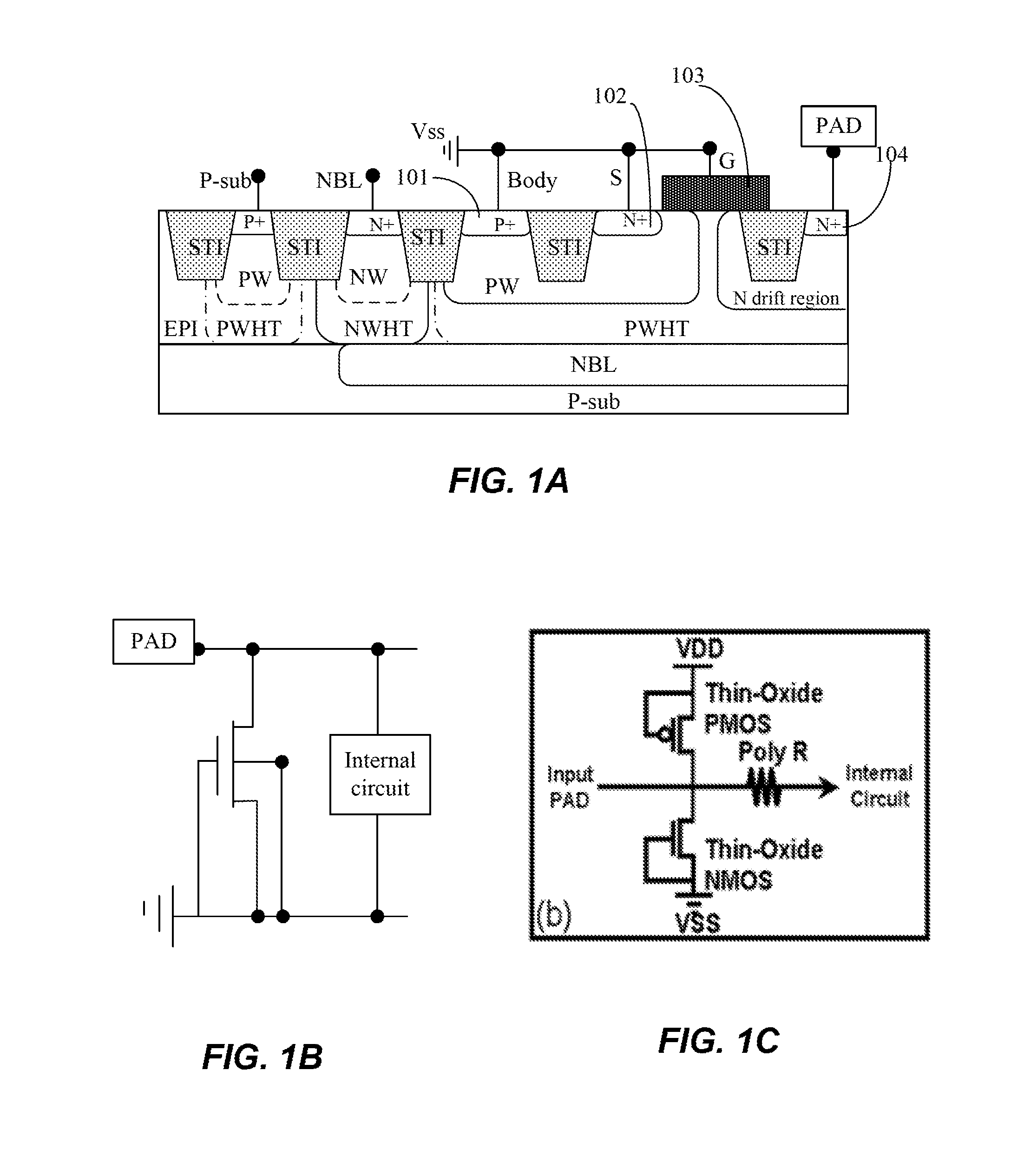
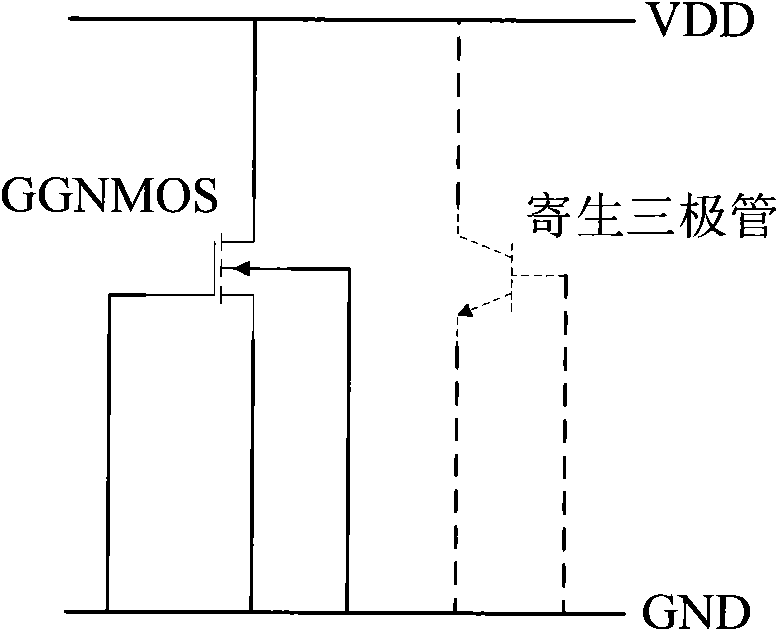
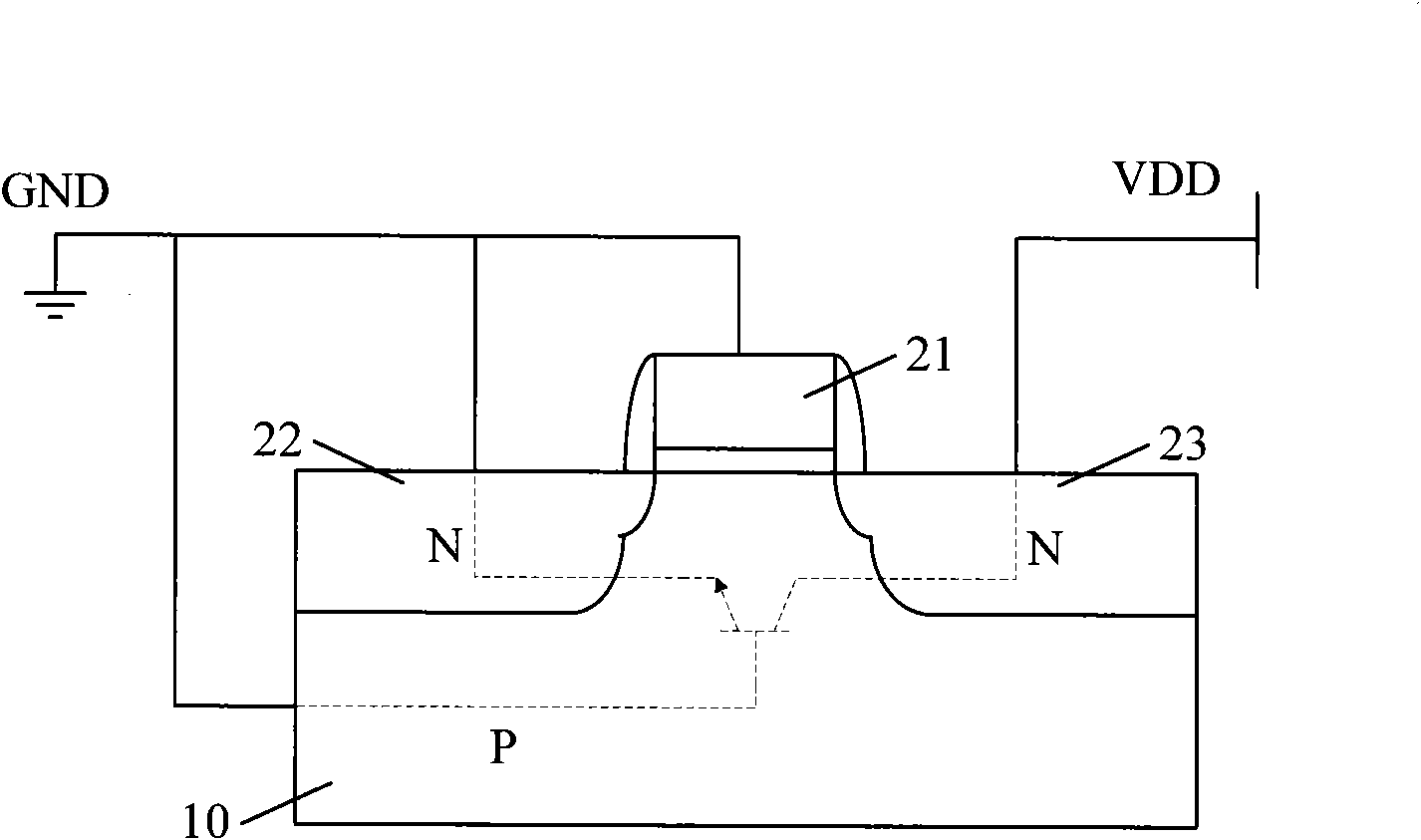
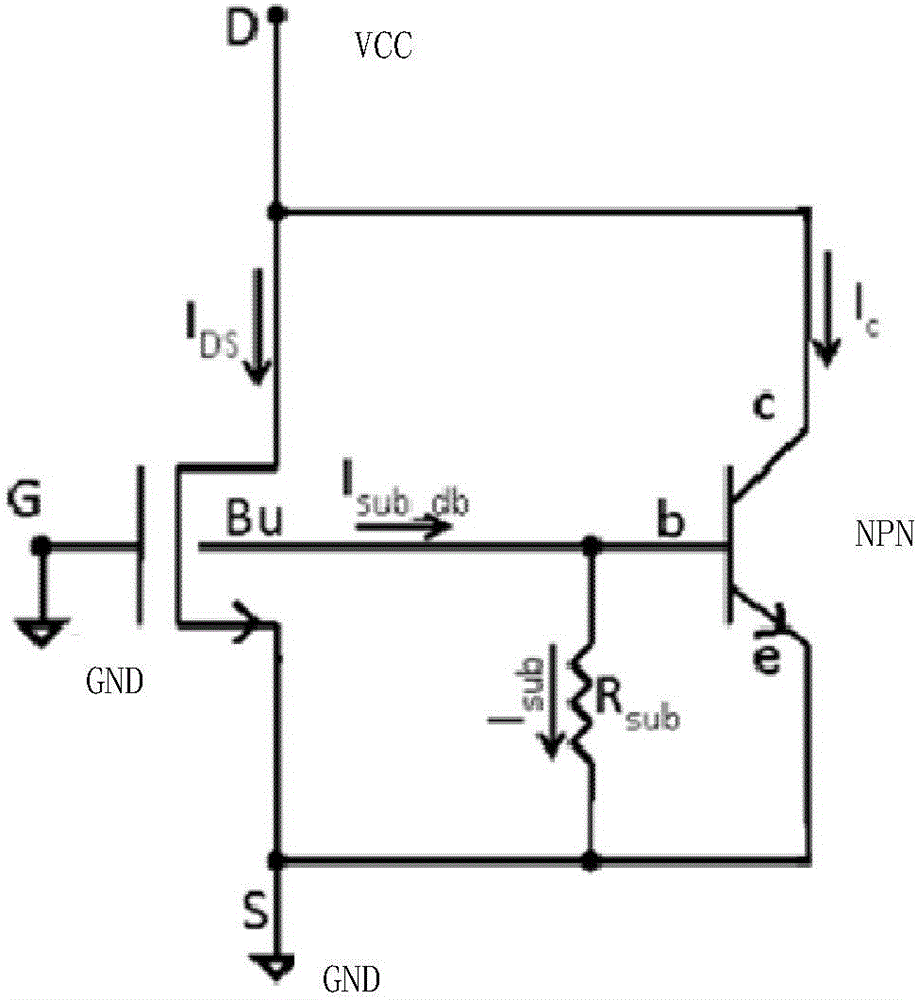
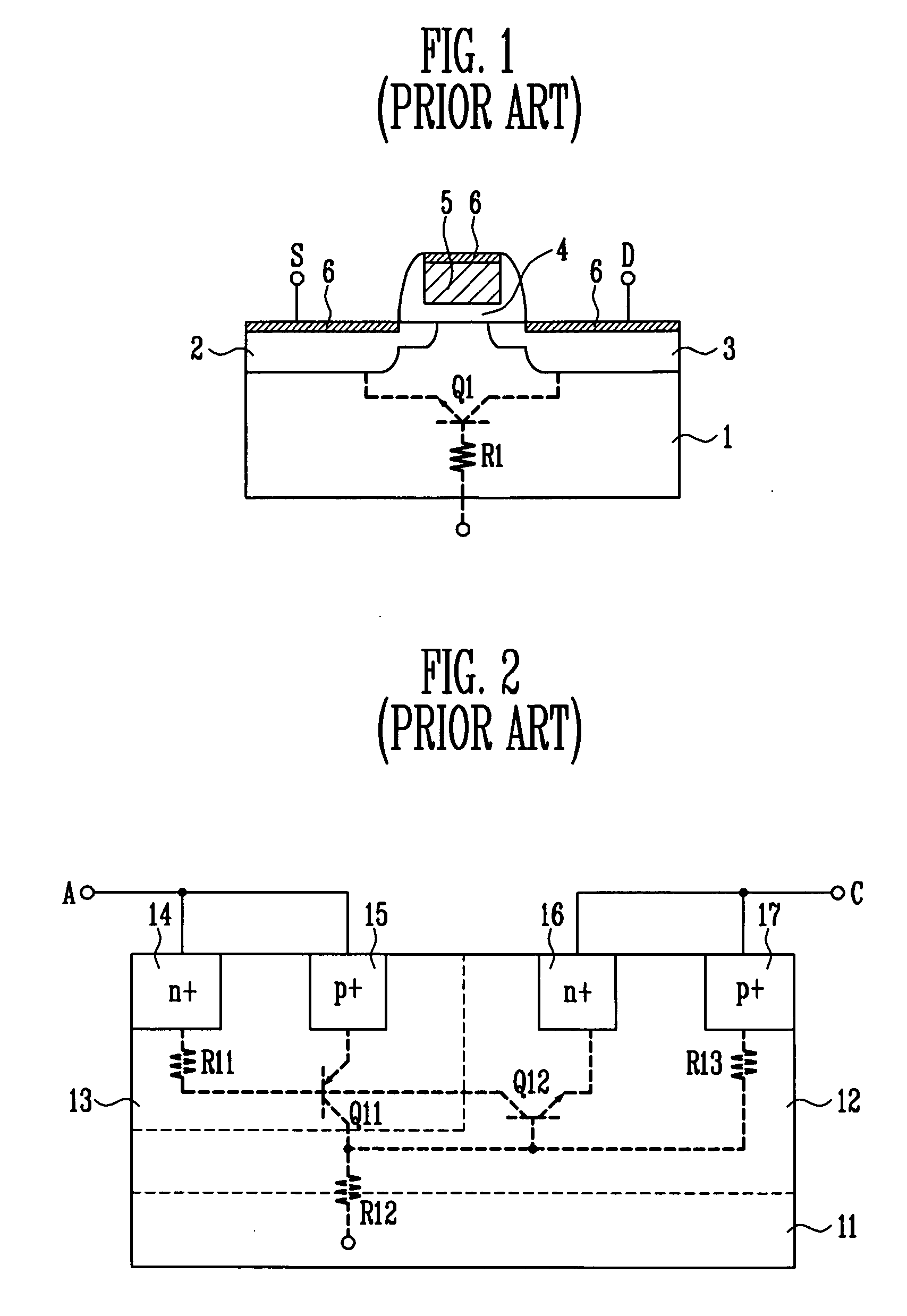
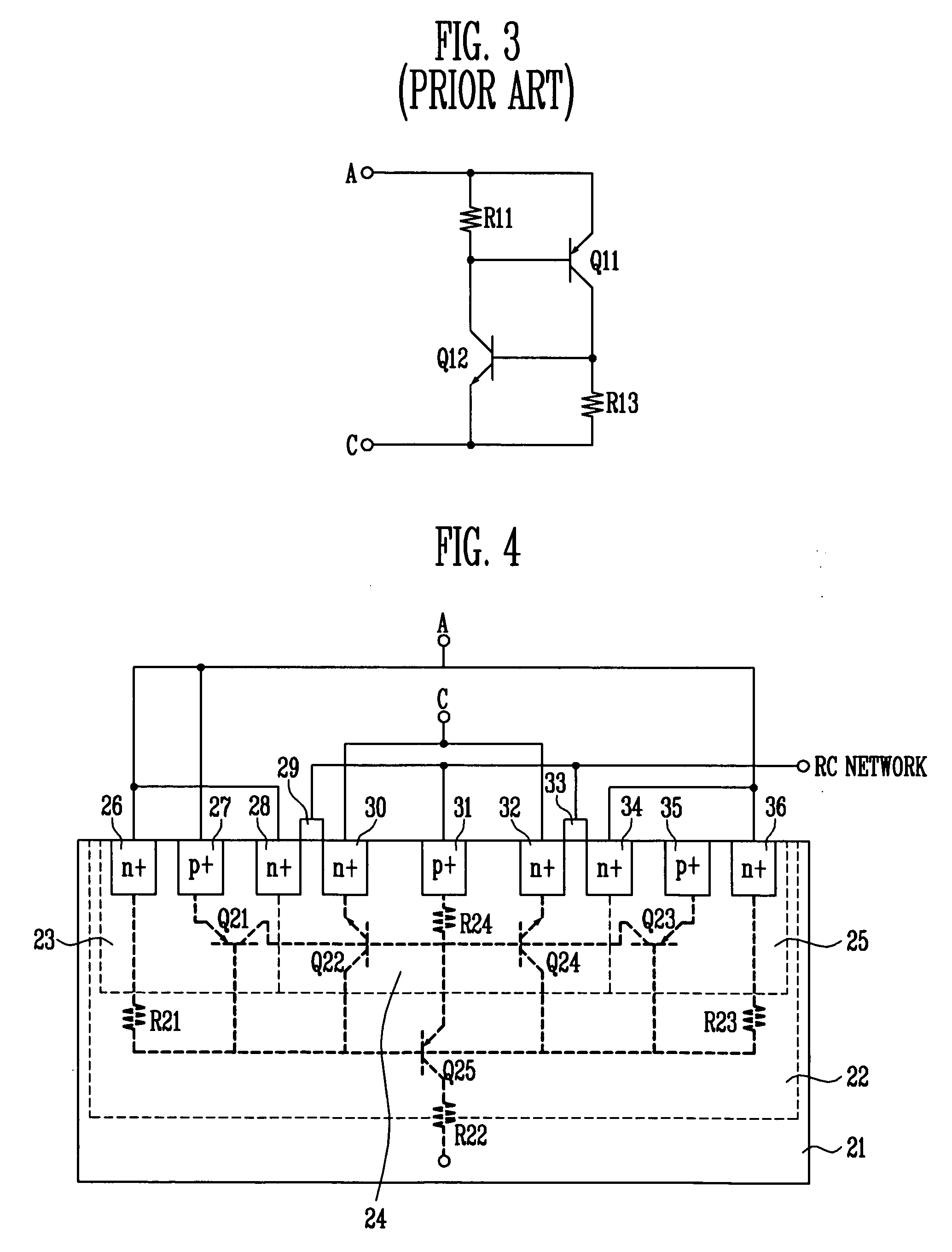
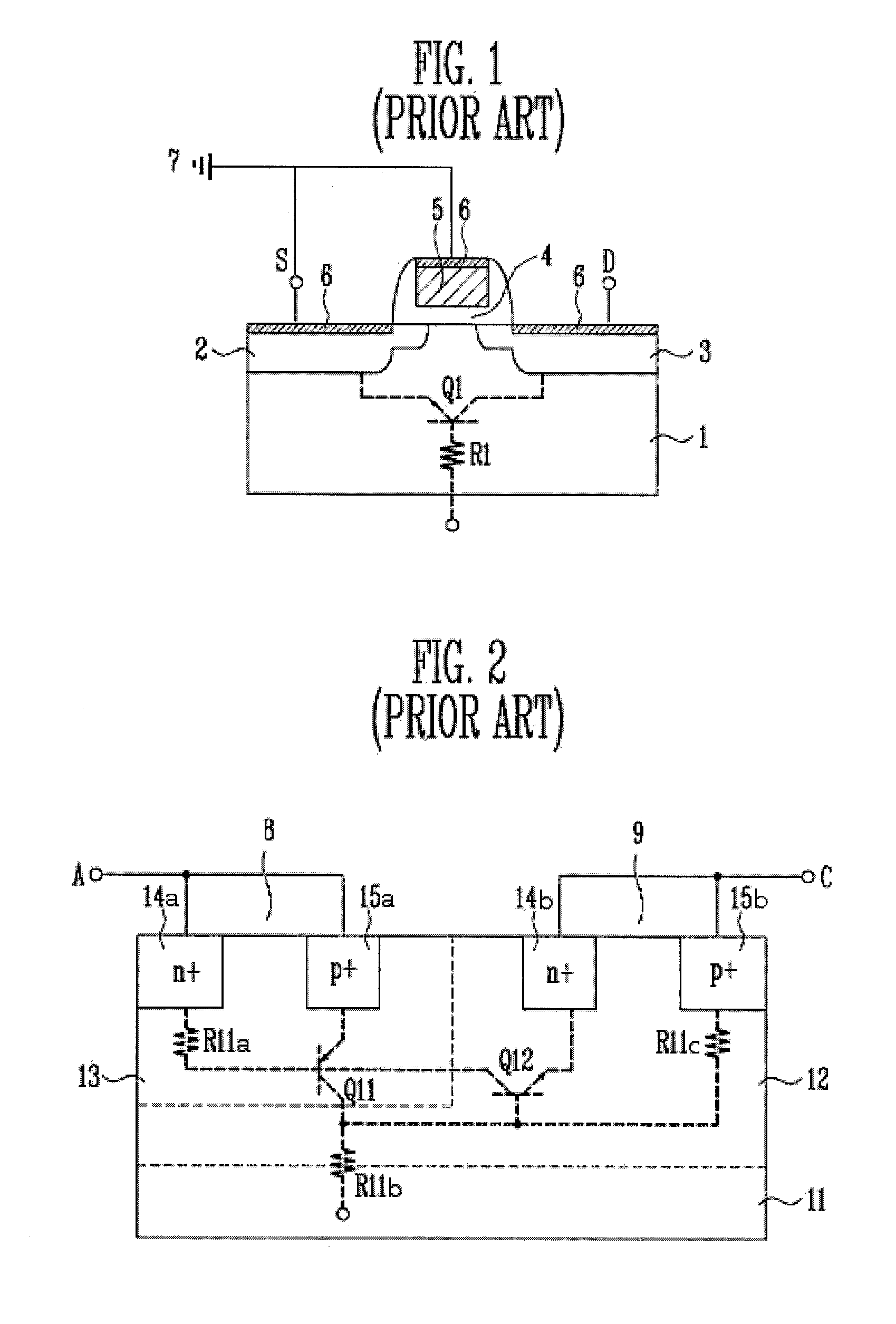
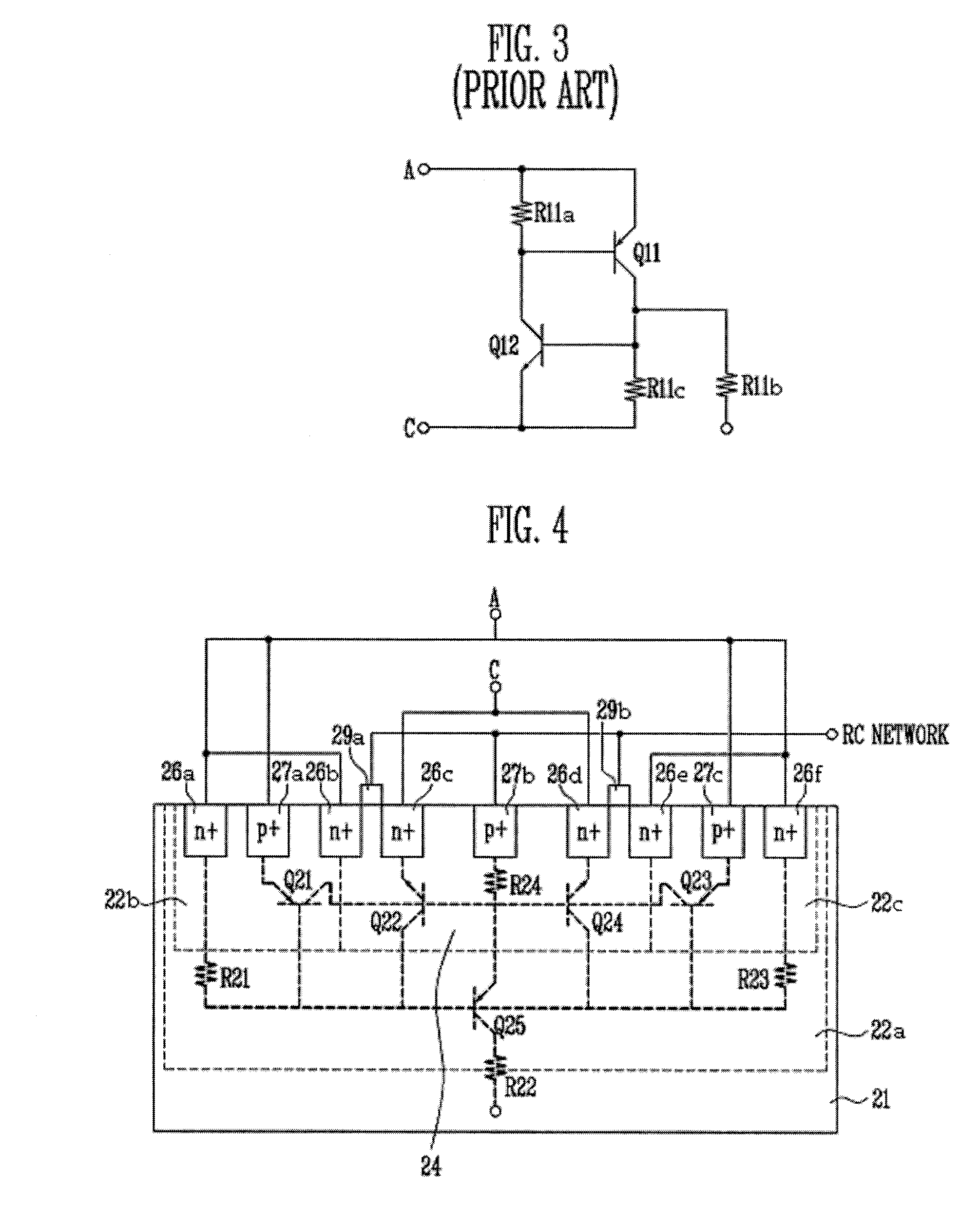
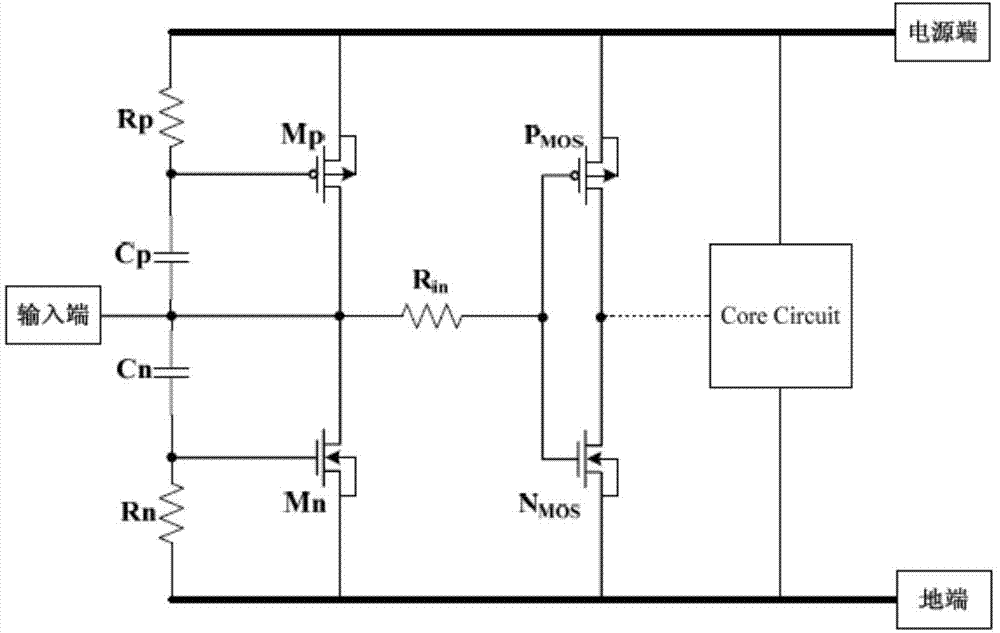
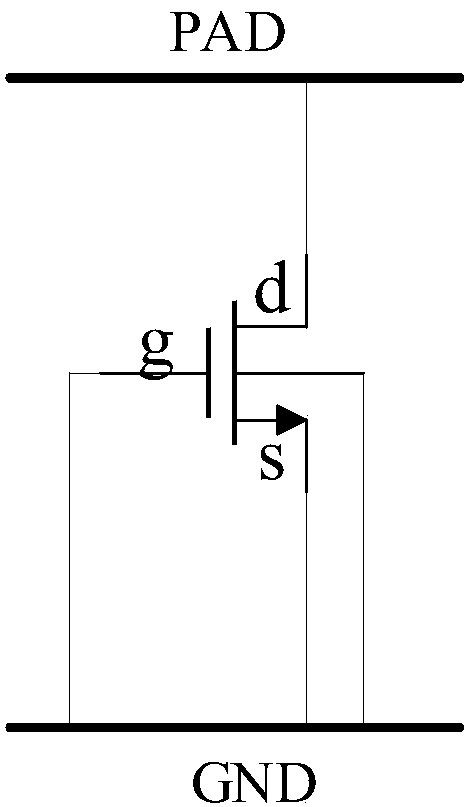
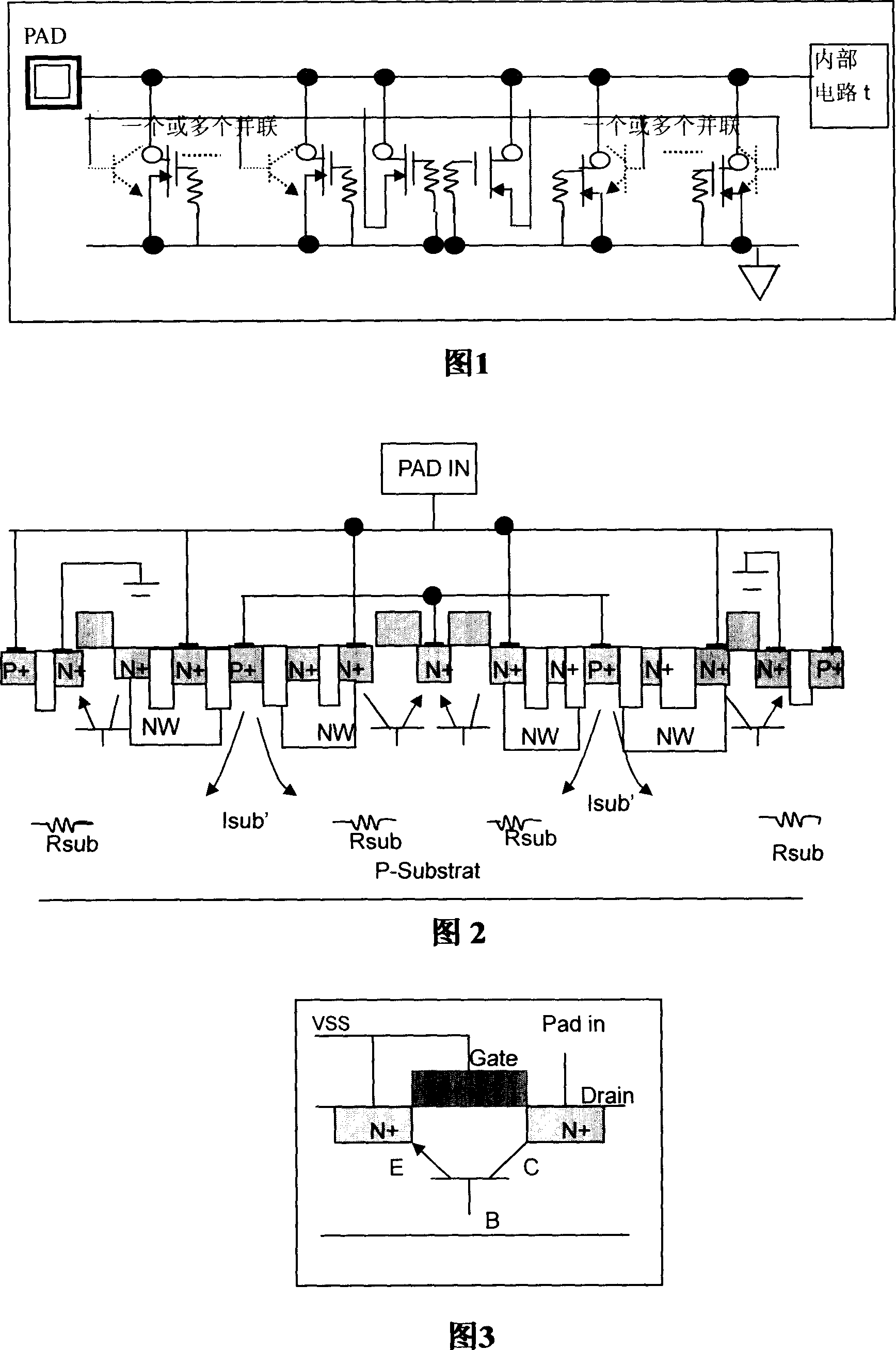
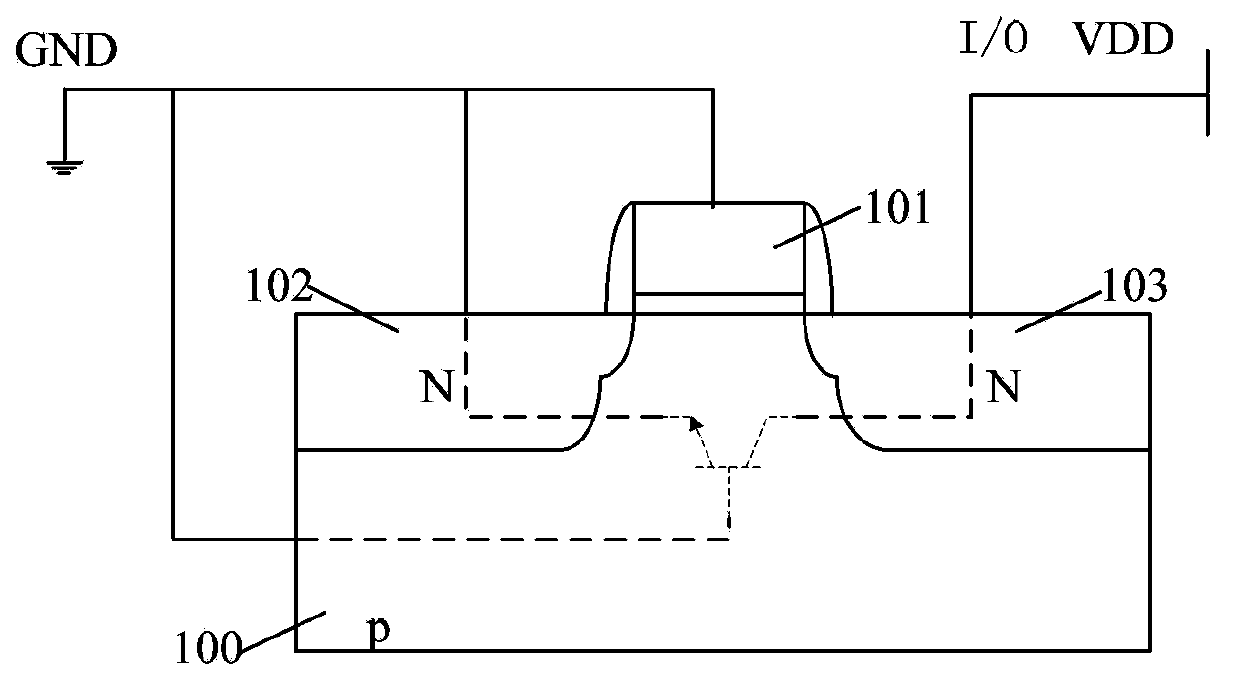
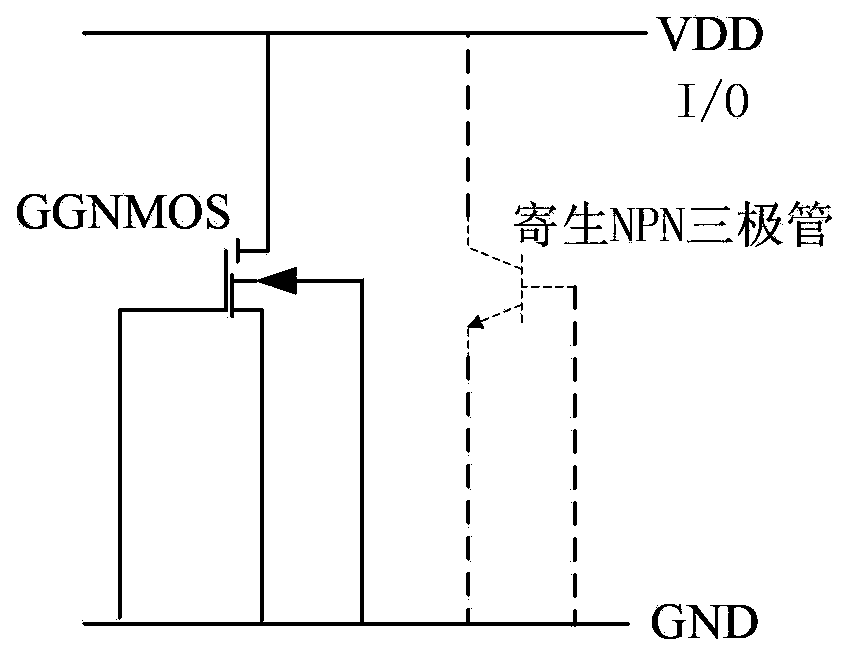
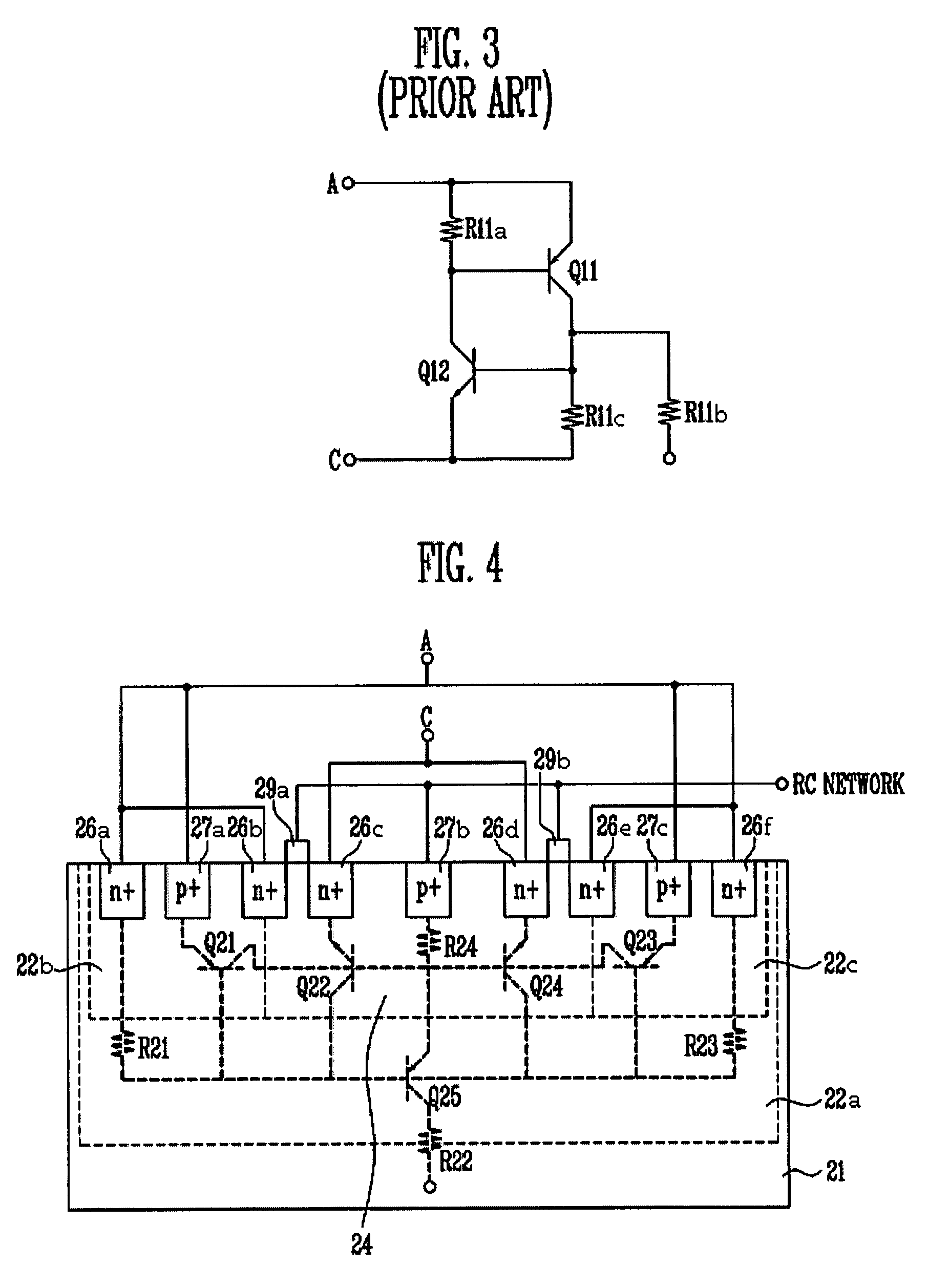
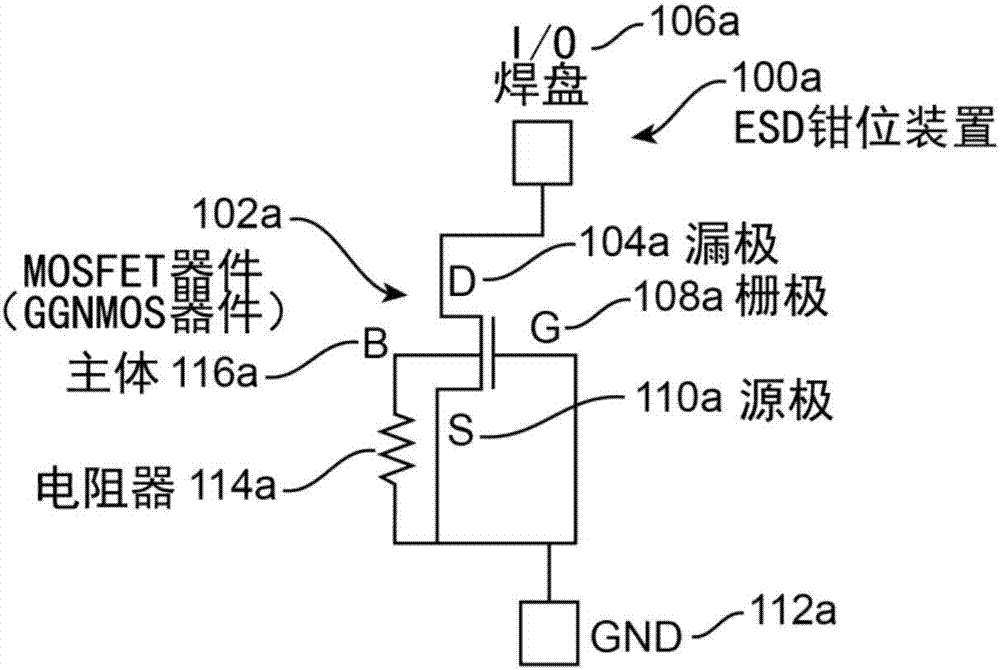
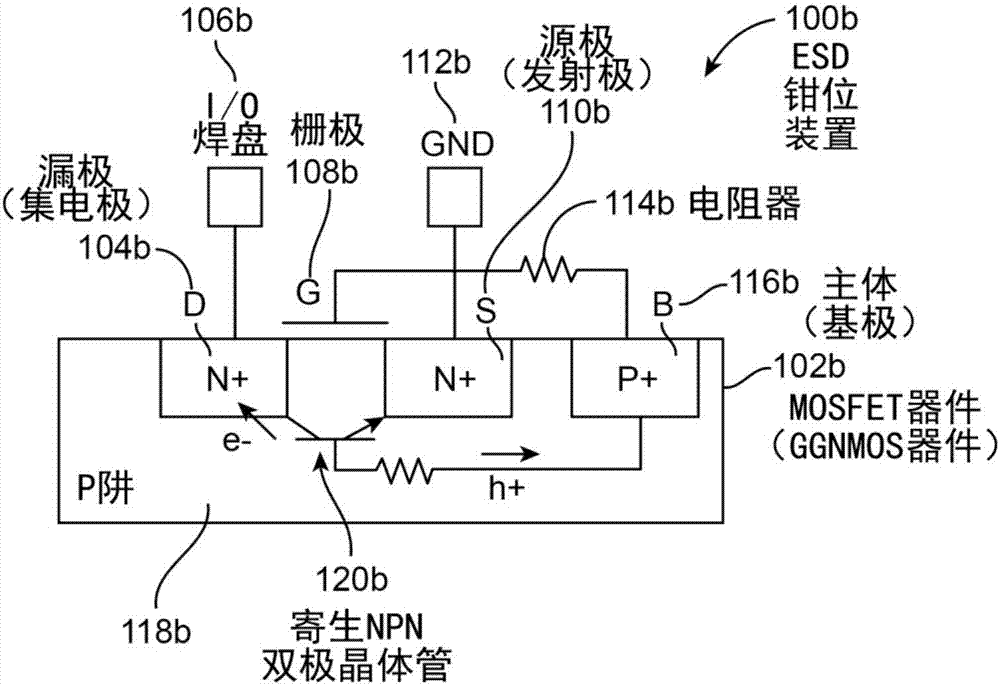
Grounded-gate NMOS, commonly known as ggNMOS, is an electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection device used within CMOS integrated circuits (ICs). Such devices are used to protect the inputs and outputs of an IC, which can be accessed off-chip (wire-bonded to the pins of a package or directly to a printed circuit board) and are therefore subject to ESD when touched. An ESD event can deliver a large amount of energy to the chip, potentially destroying input/output circuitry; a ggNMOS device or other ESD protective devices provide a safe path for current to flow, instead of through more sensitive circuitry. ESD protection by means of such devices or other techniques is important to product reliability: 35% of all IC failures in the field are associated with ESD damage.
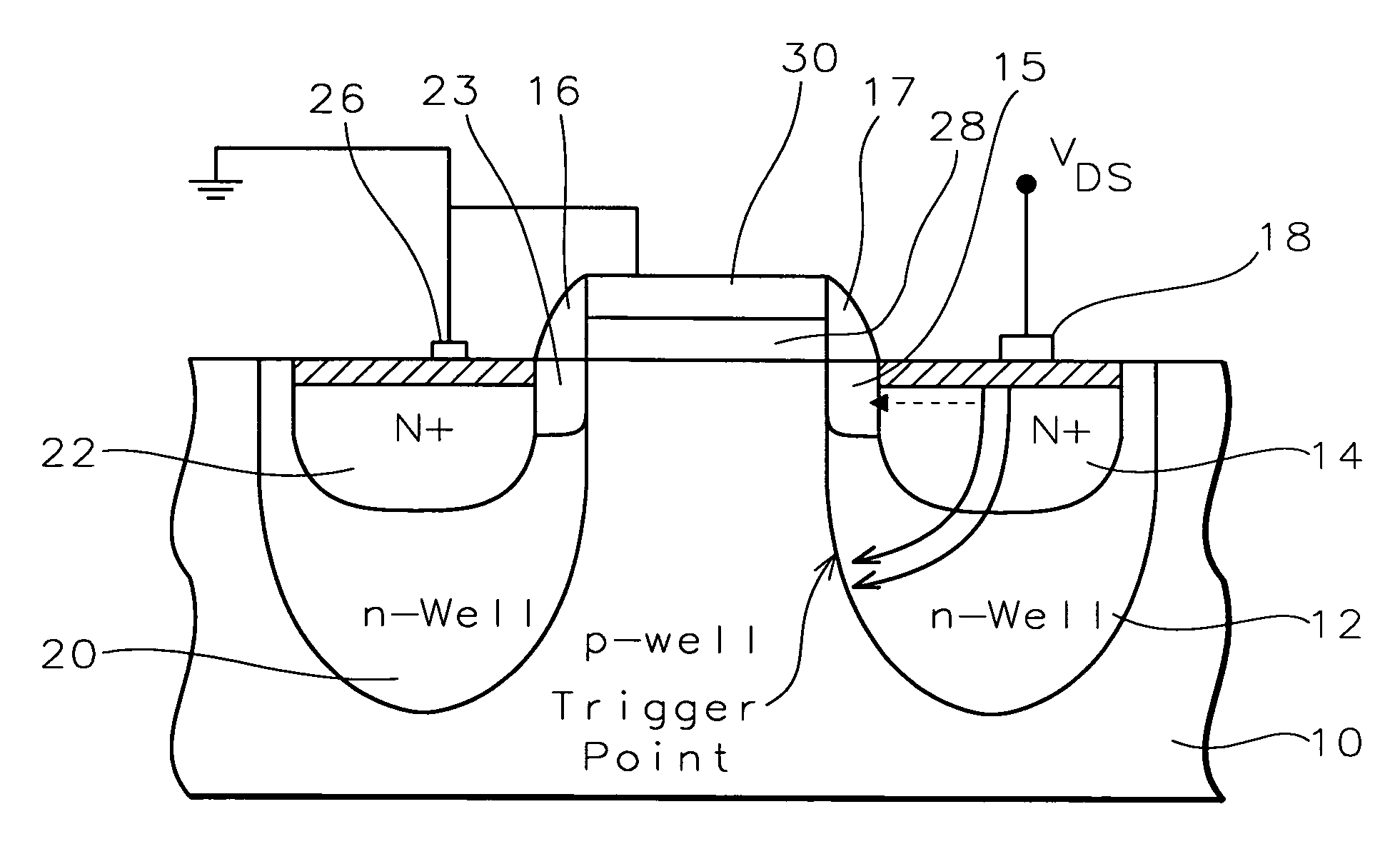
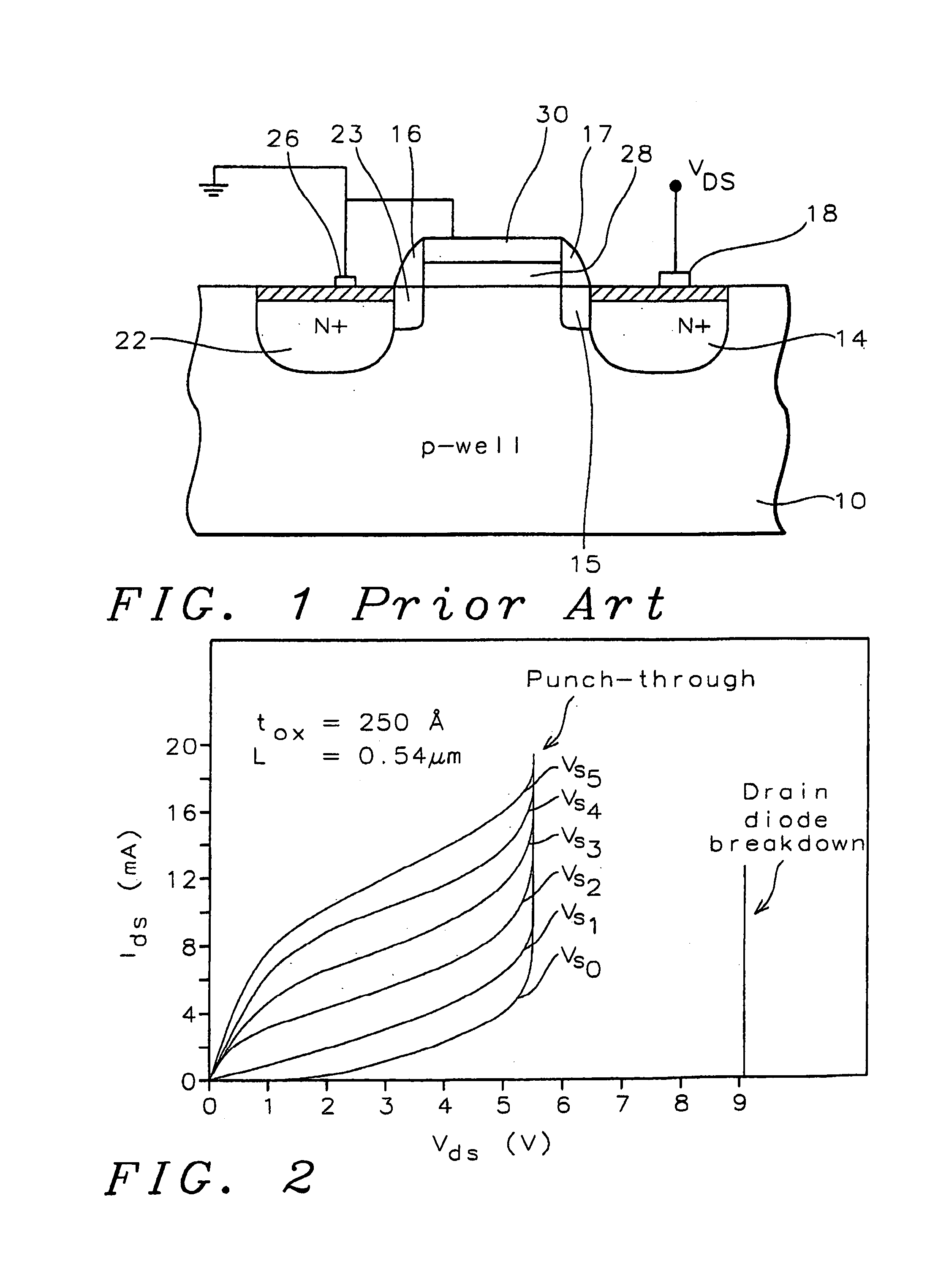
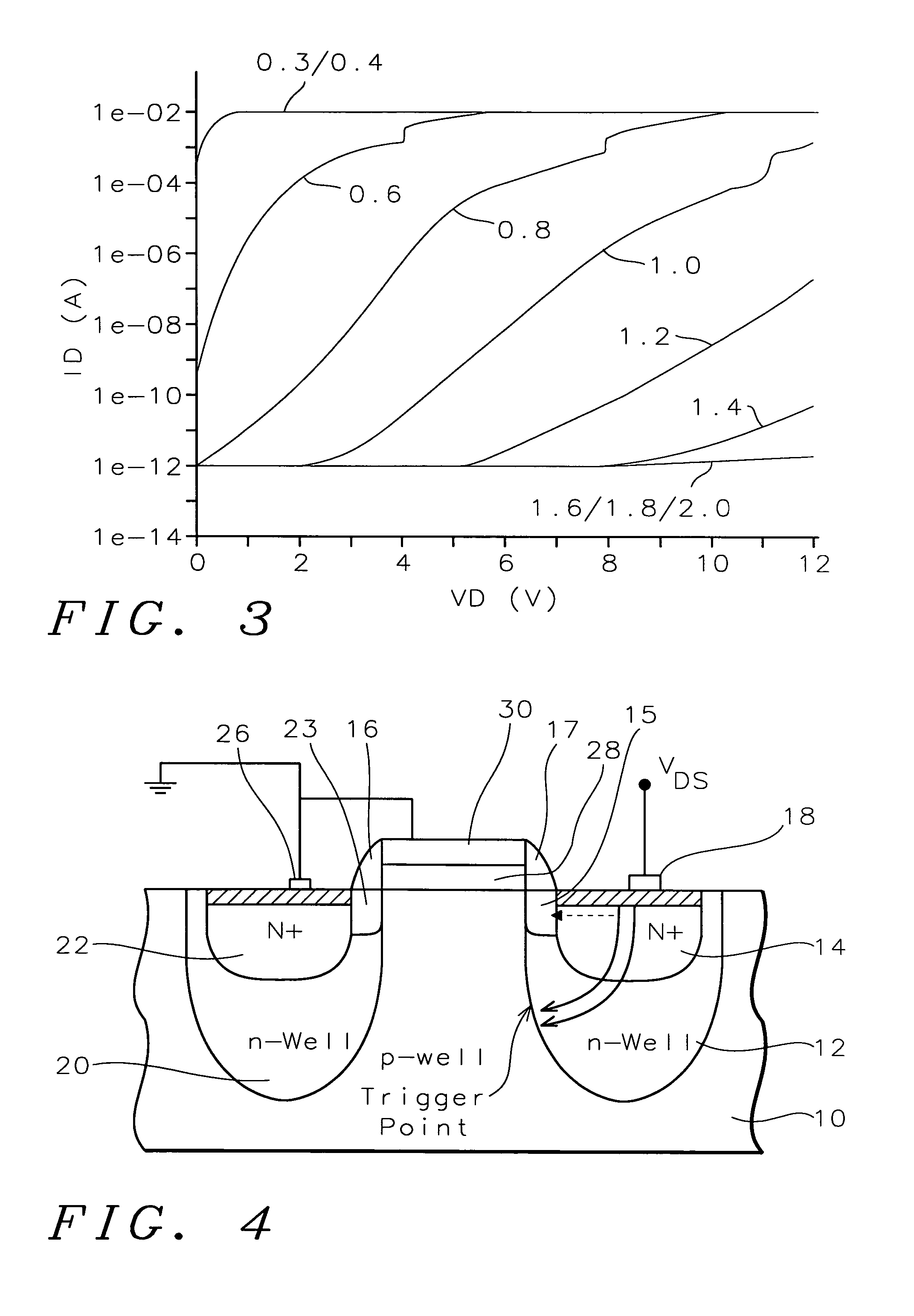
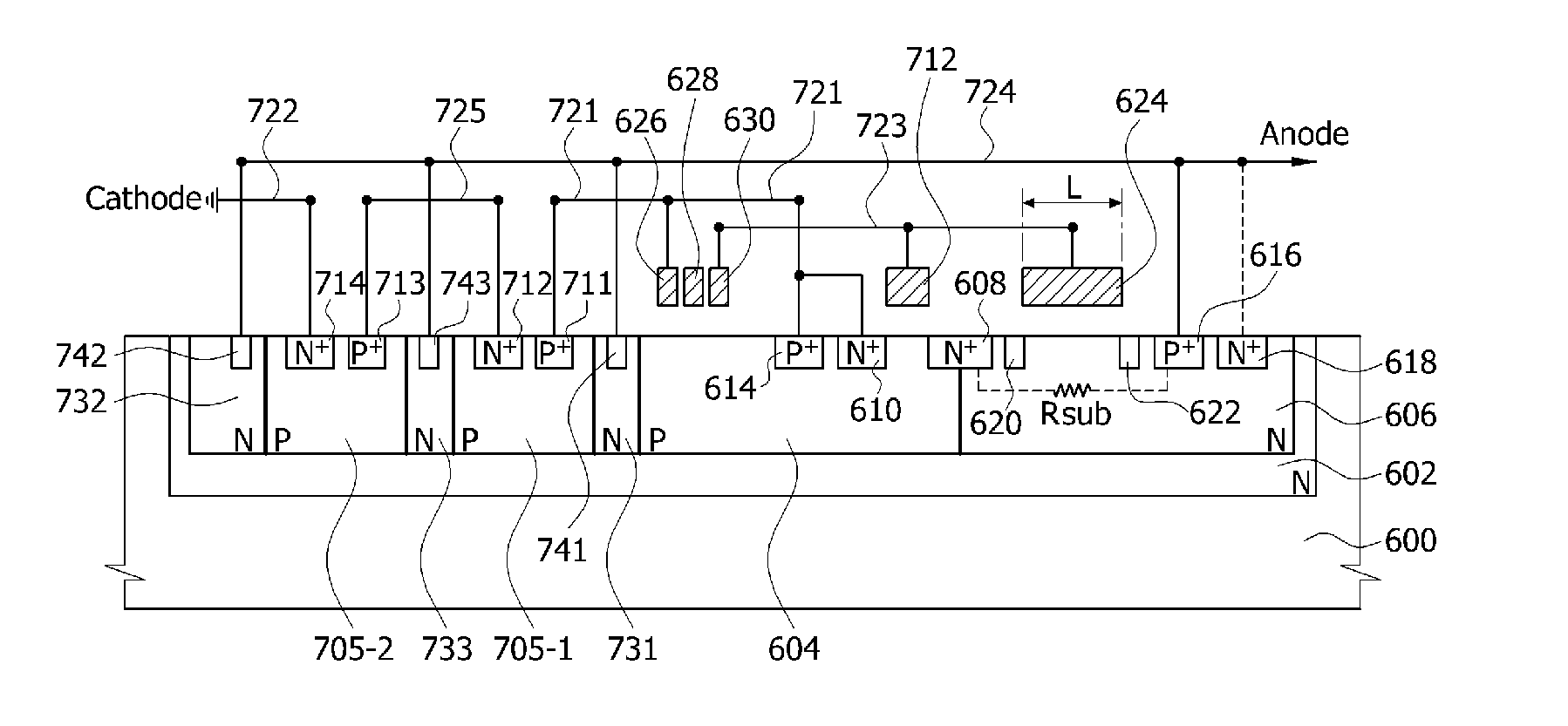
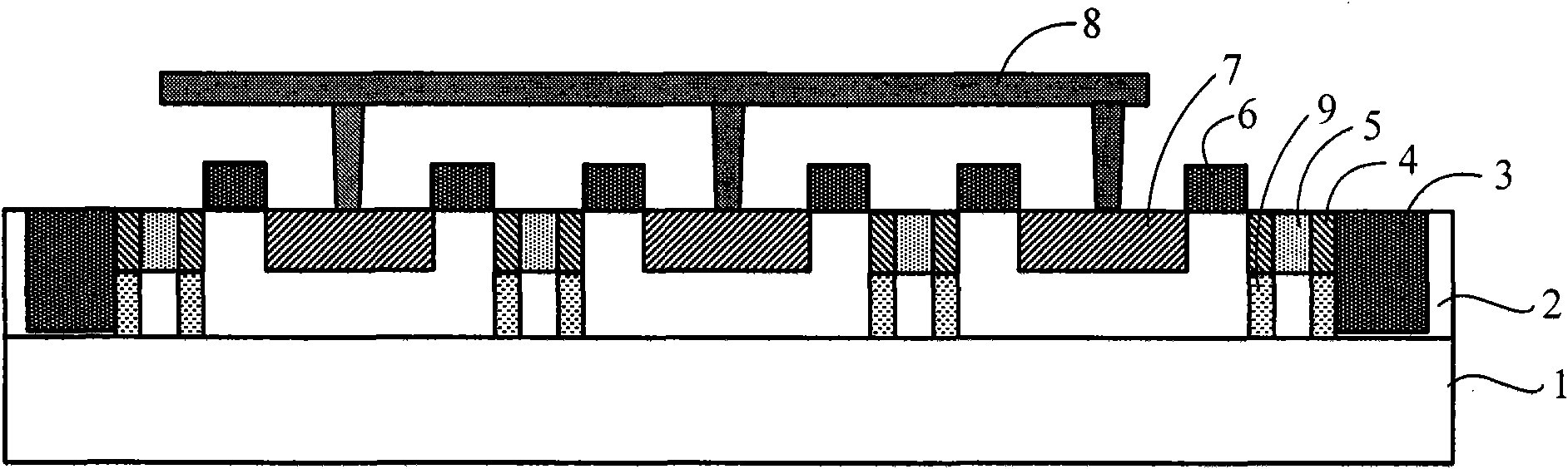
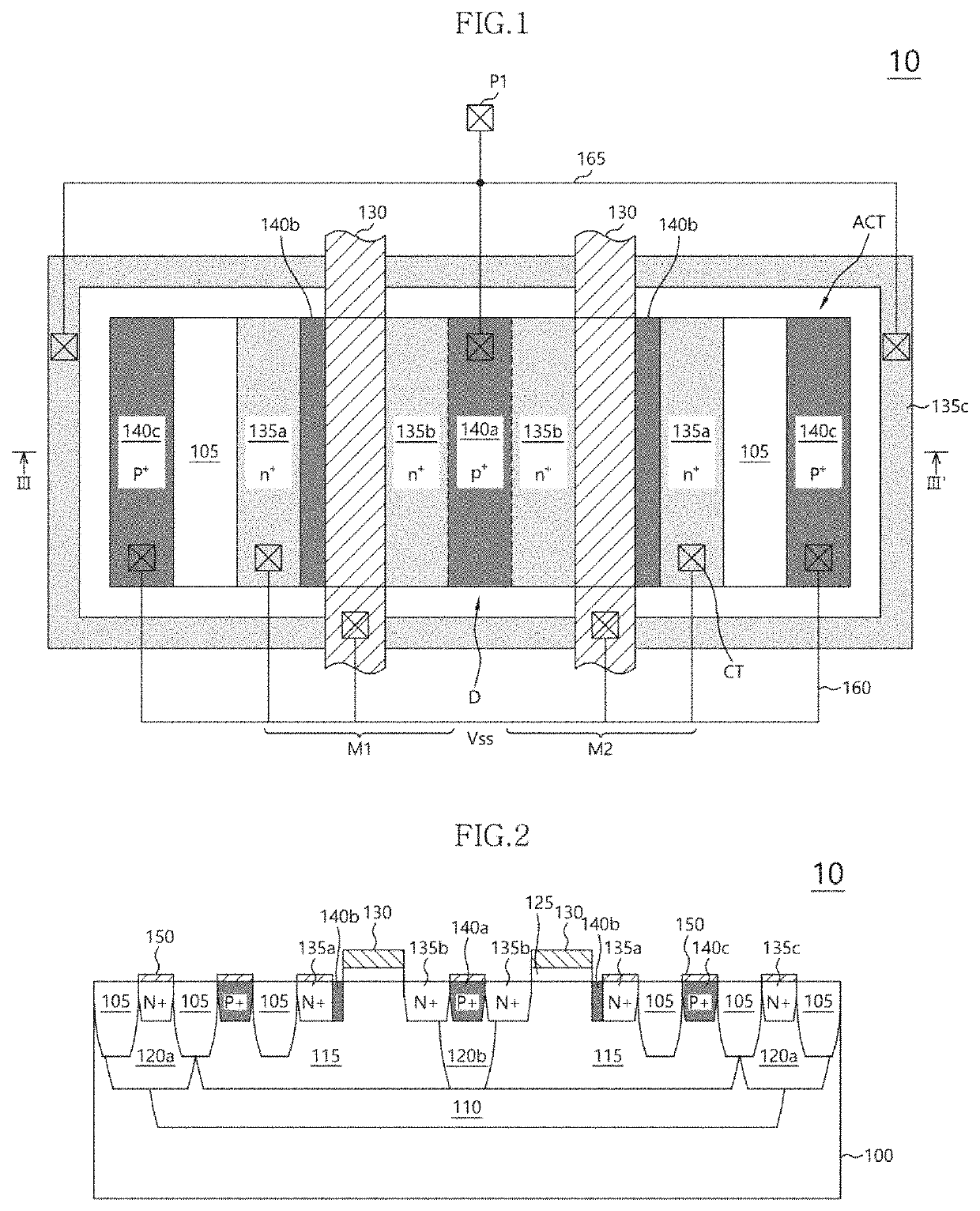
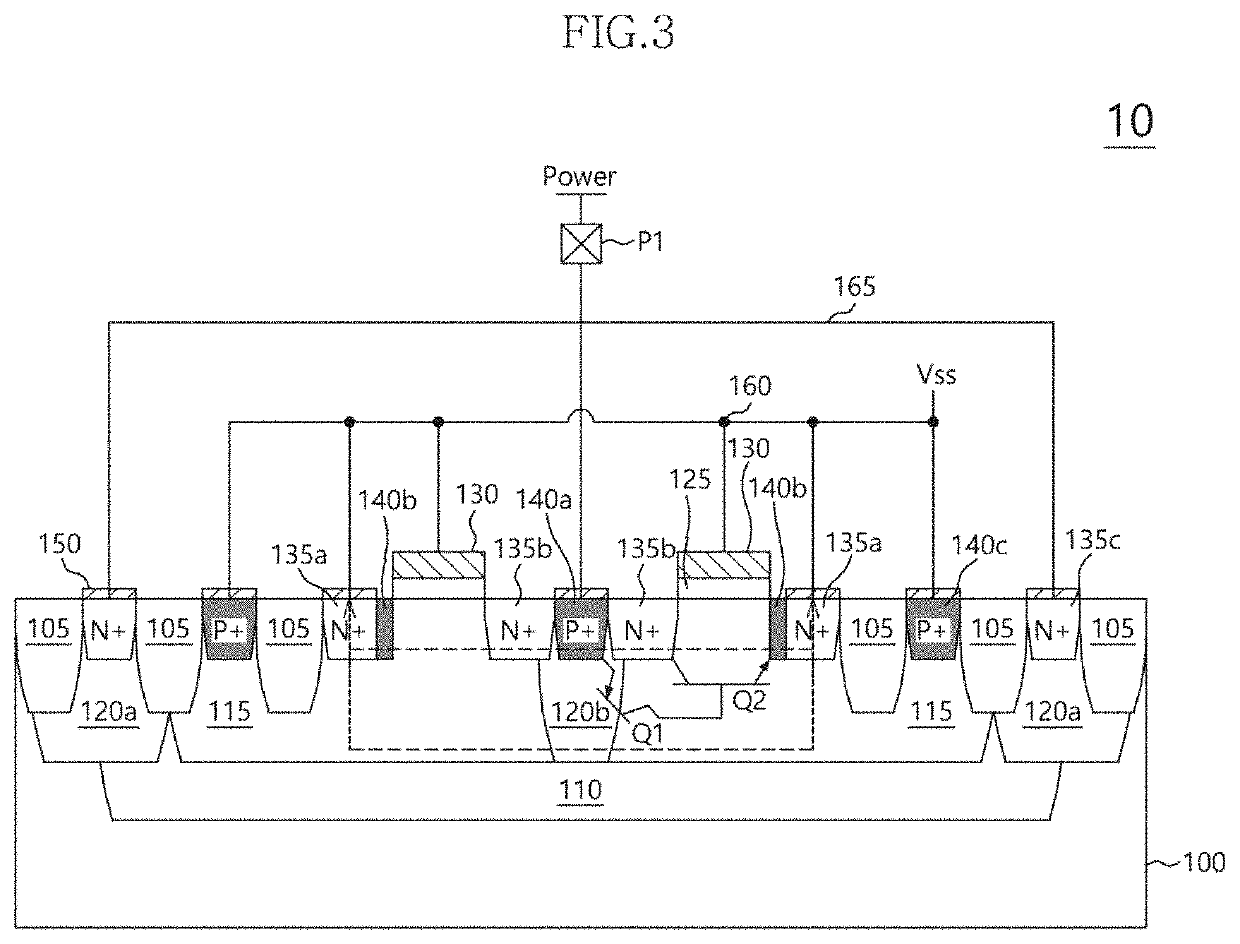
Fully silicided NMOS device for electrostatic discharge protection
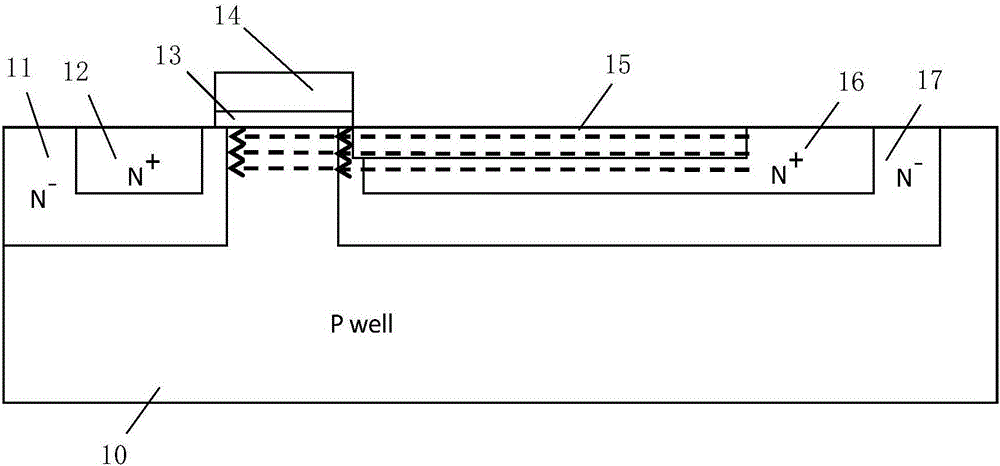
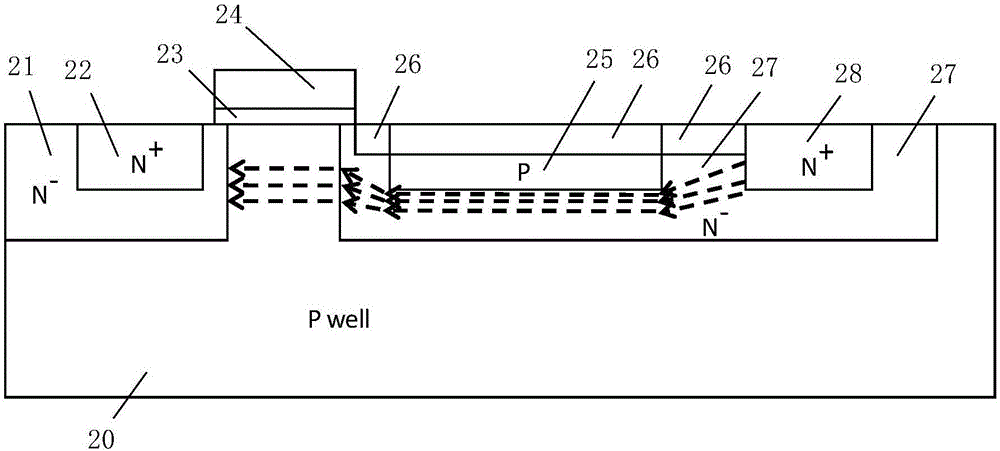
A device and method are described for forming a grounded gate NMOS (GGNMOS) device used to provide protection against electrostatic discharge (ESD) in an integrated circuit (IC). The device is achieved by adding n-wells below the source and drain regions. By tailoring the dopant concentration profiles of the p-well and n-wells provided in the fabrication process, peak dopant concentrations are moved below the silicon surface. This moves ESD conduction deeper into the IC where thermal conductivity is improved, thereby avoiding thermal damage occurring with surface conduction. The device does not require a salicidation block or additional implantation and uses standard NMOS fabrication processing steps, making it advantageous over prior art solutions.
Owner:CHARTERED SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING
Electrostatic discharge protection device
InactiveUS20120098046A1Increased avalanche breakdown voltageUnified operationTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsGgNMOSEngineering
An ESD protection device is provided. The ESD protection device includes a first group of electrostatic discharge protection devices connected to a first terminal and including at least one of an LORGGR and an HORGGR, and a second group of electrostatic discharge protection devices connected in series to the first group of electrostatic discharge protection devices and a second terminal and including at least one of a GGNMOS, a GGPMOS and a diode.
Owner:BAUABTECH
High holding voltage ESD protection structure and method
The holding voltage (the minimum voltage required for operation) of a LVTSCR-like device is increased to a value that is greater than a dc bias on a to-be-protected node. The holding voltage is increased by reducing the size of the p+ emitter defined by the LVTSCR-like device. As a result, the LVTSCR can be utilized to provide ESD protection to power supply pins, having better current capabilities than a GGNMOS and better holding voltage characteristics than a LVTSCR.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
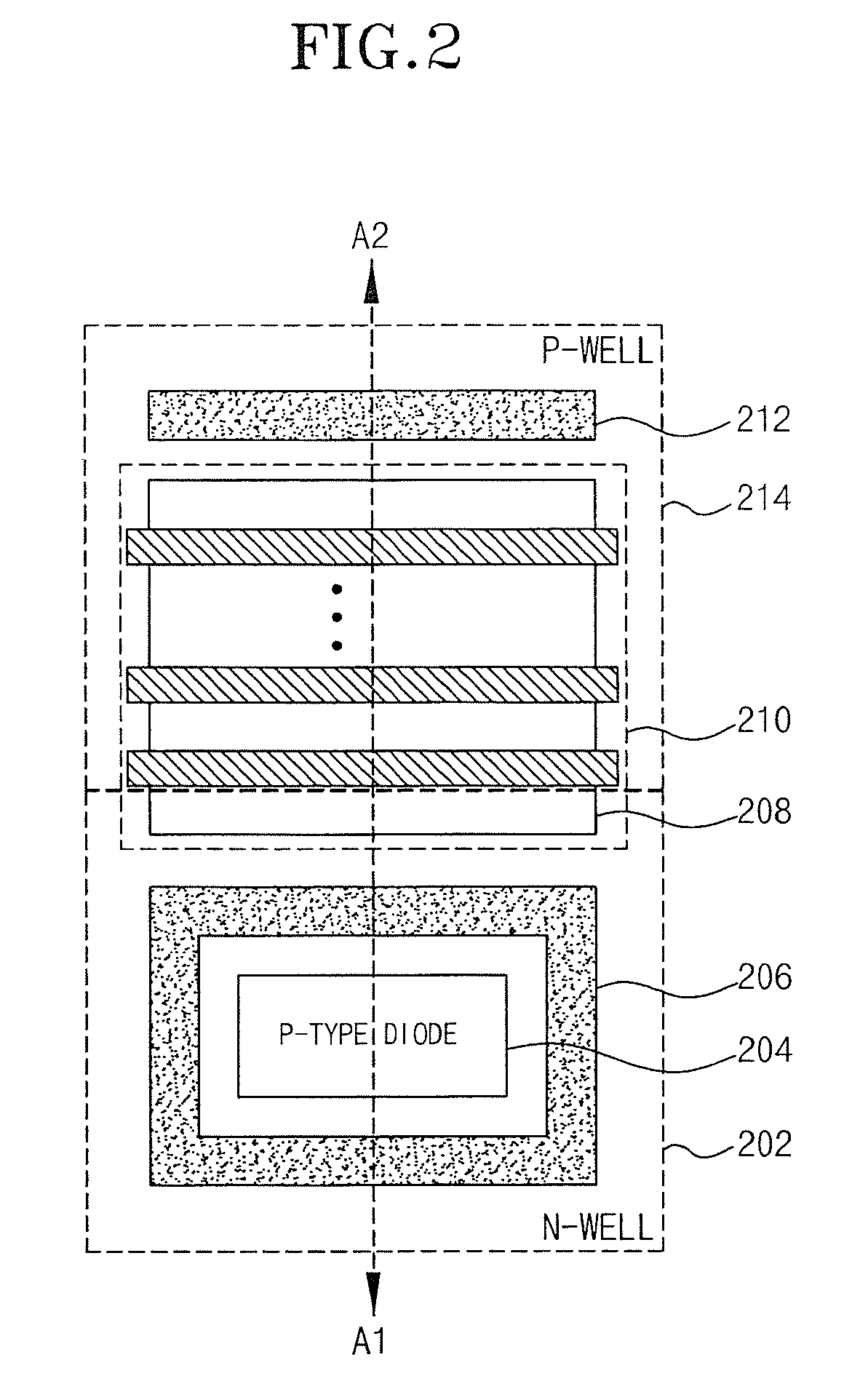
Electrostatic discharge protection element having an improved area efficiency
InactiveUS20080198519A1Improve area efficiencyReduce voltageTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsGgNMOSImpurity
An electrostatic discharge protection element is disclosed for protecting an internal circuit from electrostatic current. The electrostatic discharge protection element forms an embedded LVTSCR by adding a prescribed impurity region within an N-well region having a P-type diode formed therein. A P-well region having a GGNMOS transistor is also formed in the electrostatic discharge protection element. The embedded LVTSCR improves area efficiency, reduces a resistance, and lowers an operational voltage by reducing the distance between the P-type diode and the LVTSCR to allow high-speed operatation.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
GGNMOS device used in ESD protective circuit
ActiveCN101866922ASolve the problem of inconsistent triggeringTransistorElectrical resistance and conductanceGgNMOS
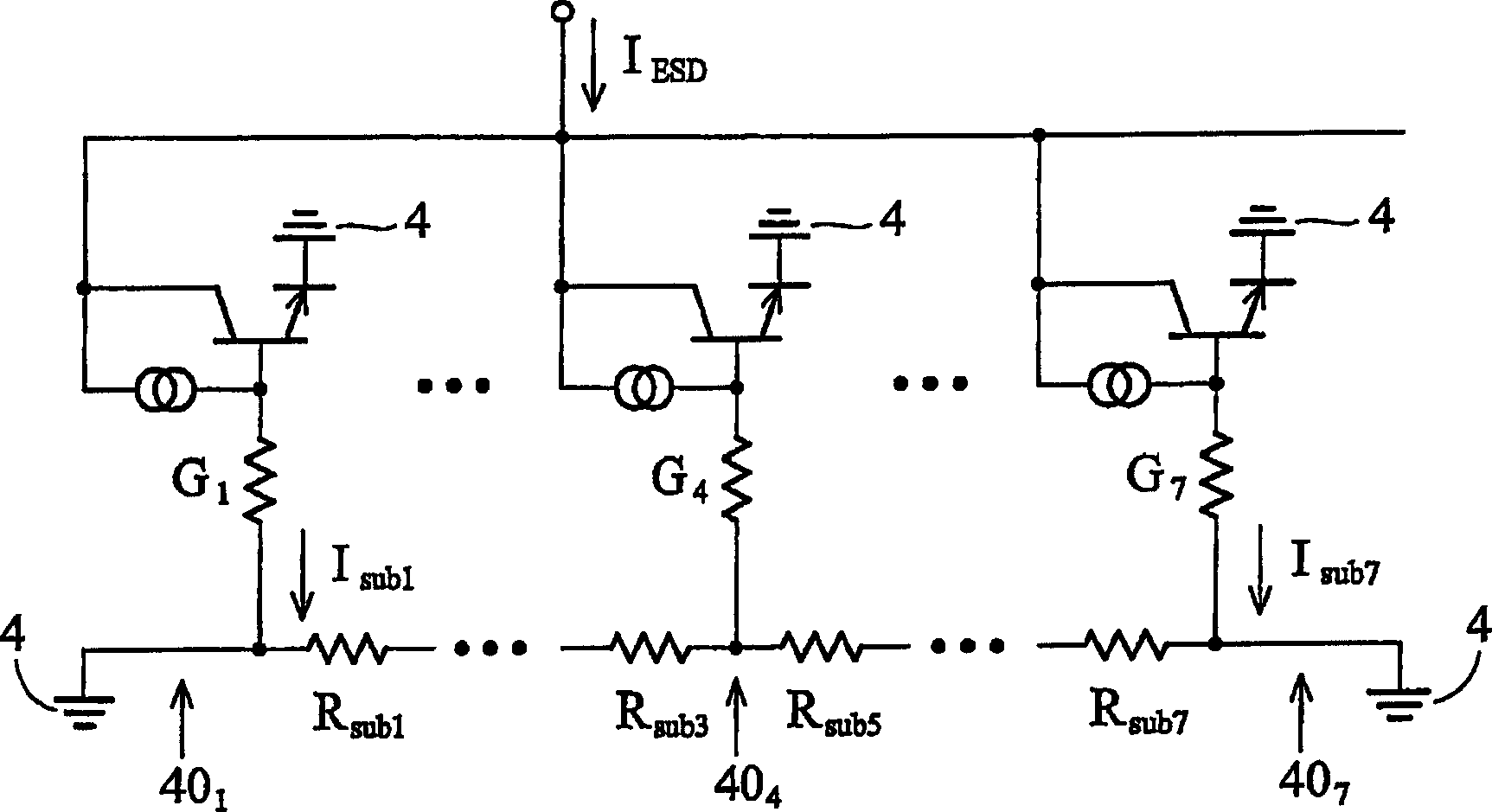
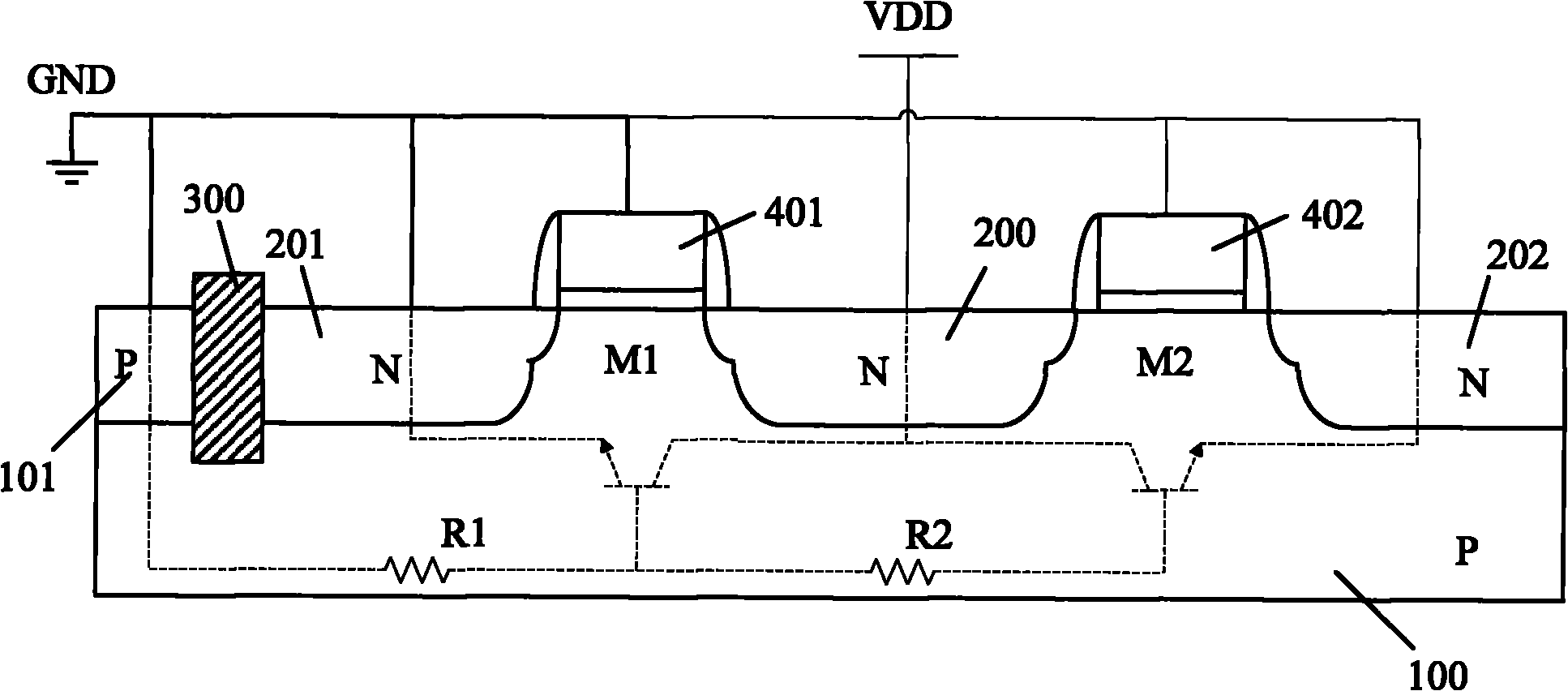
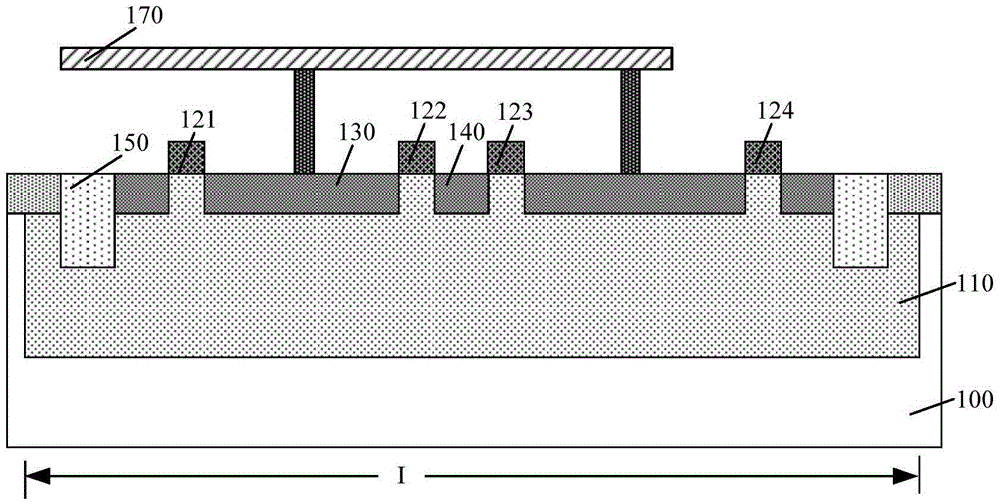
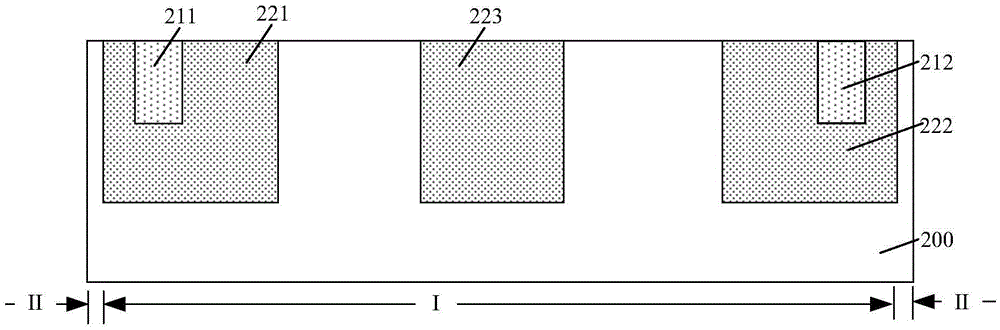
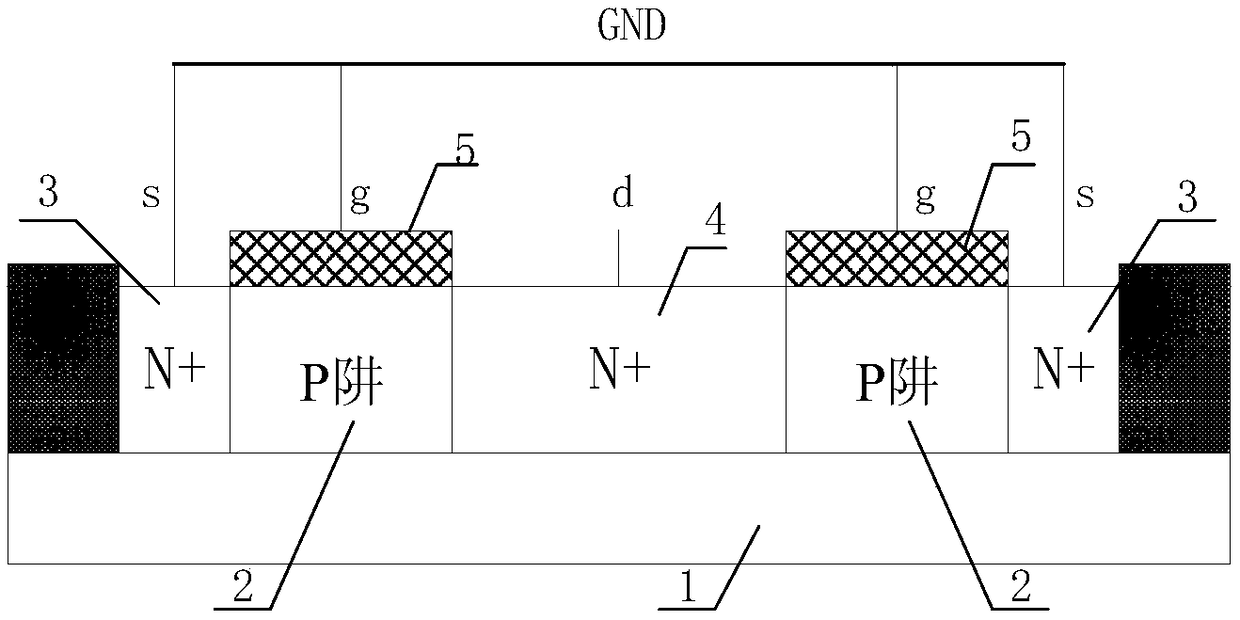
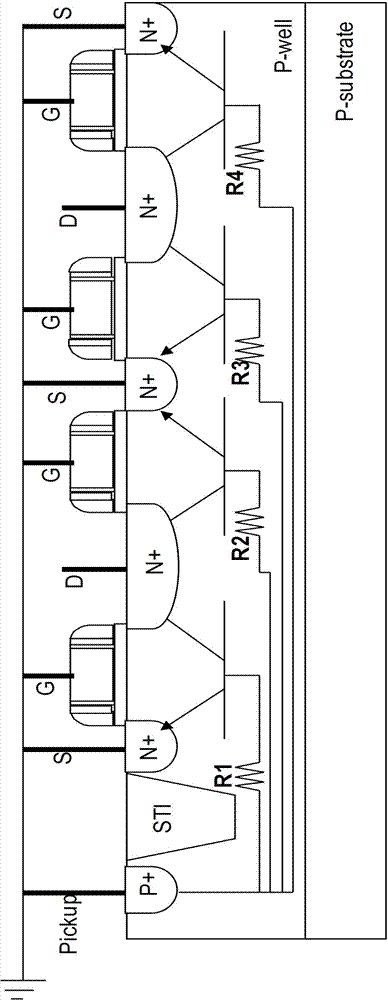
The invention provides a GGNMOS device used in an ESD protective circuit. The device comprises a substrate and a P trap region positioned on the substrate, wherein a plurality of drain electrode regions are arranged in the P trap region; the surface of the P trap region and two sides of the drain electrode regions are provided with grid electrode regions; the P trap region and the other sides of the grid electrode regions are provided with source electrode regions; P type doped regions are arranged among the source electrode regions; and a position below the source electrode regions and close to the source electrode regions is provided with an N trap region. The GGNMOS device used in the ESD protective circuit not only can solve non-uniform triggering problems, but also can solve the problems of resistance reduction, trigger voltage raising and difficult leakage of electrostatic current in a leakage path.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Grounded-grid NMOS (N-channel metal oxide semiconductor) unit for antistatic protection and antistatic protection structure thereof
InactiveCN102201446AOpen smoothlyImprove ESD Protection CapabilitiesTransistorSolid-state devicesGrounding gridElectrical resistance and conductance
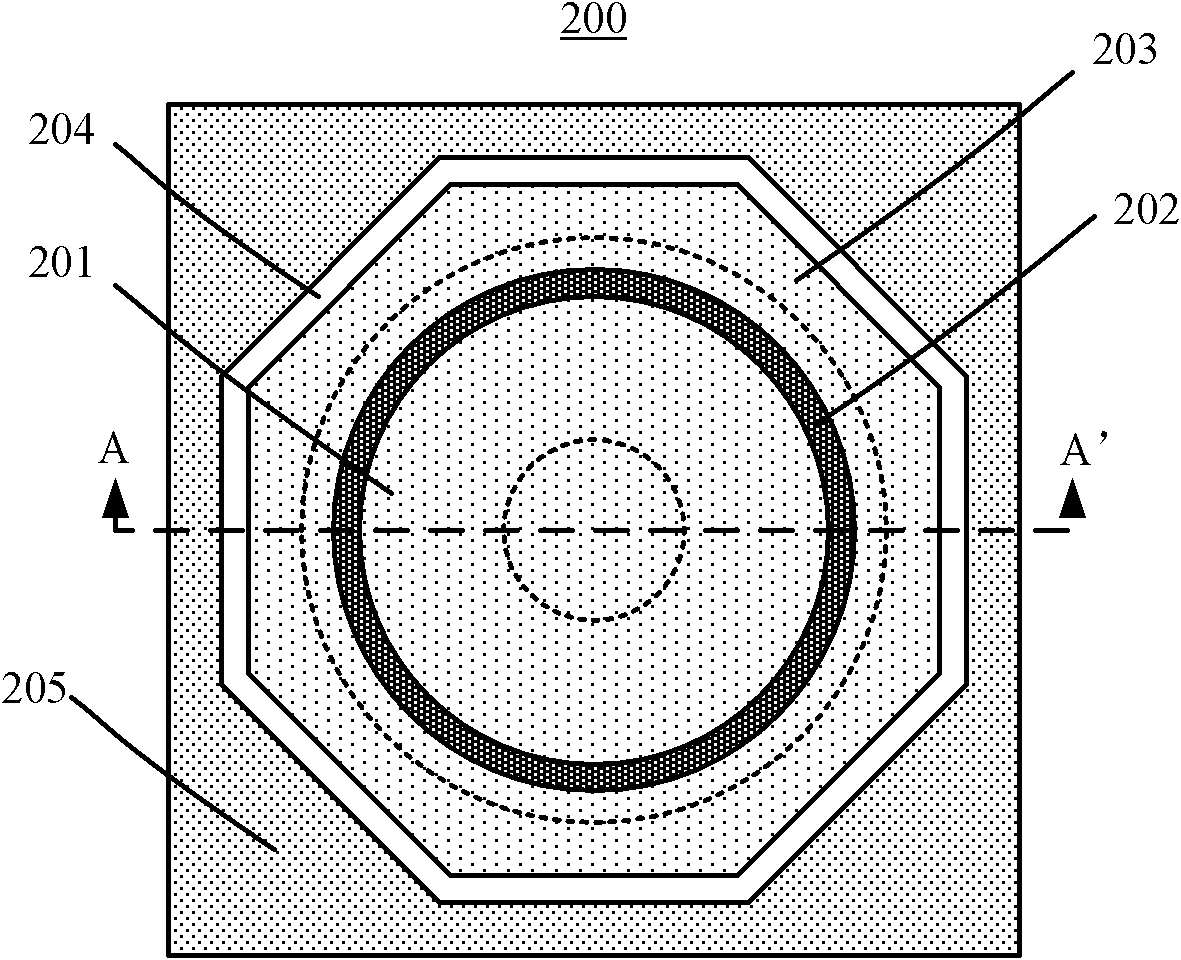
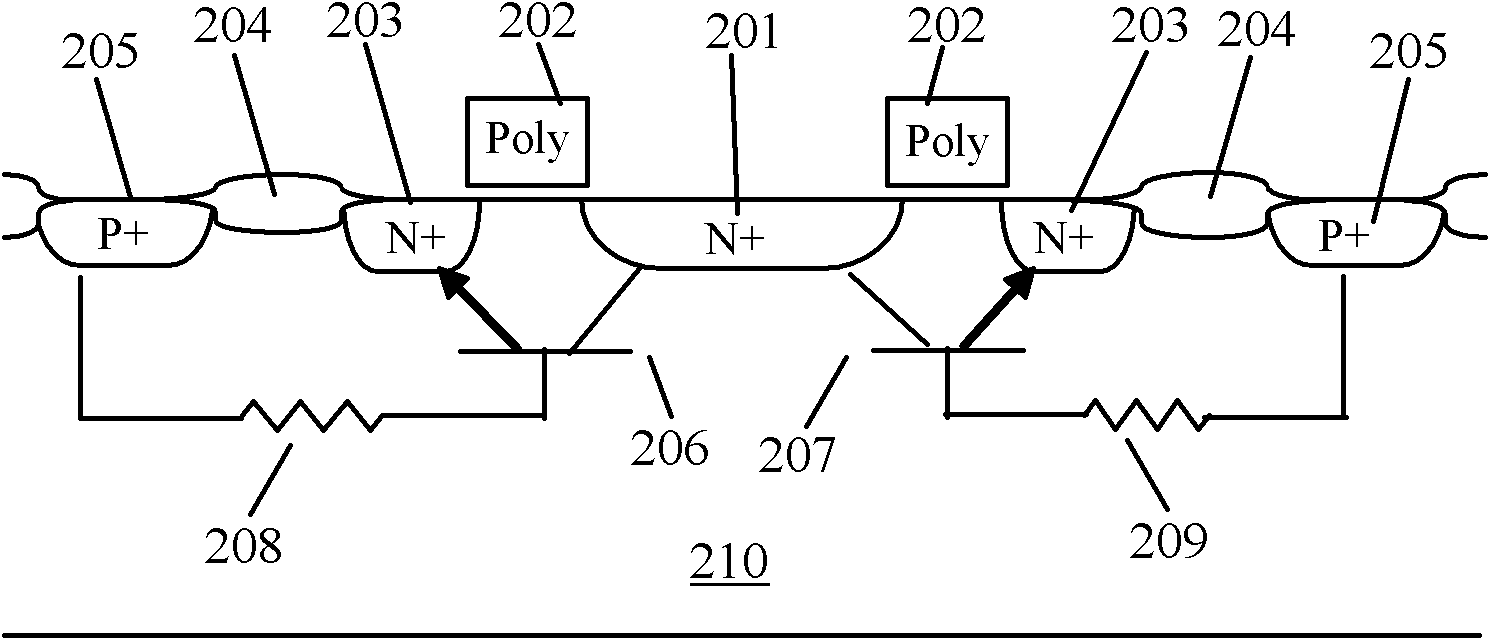
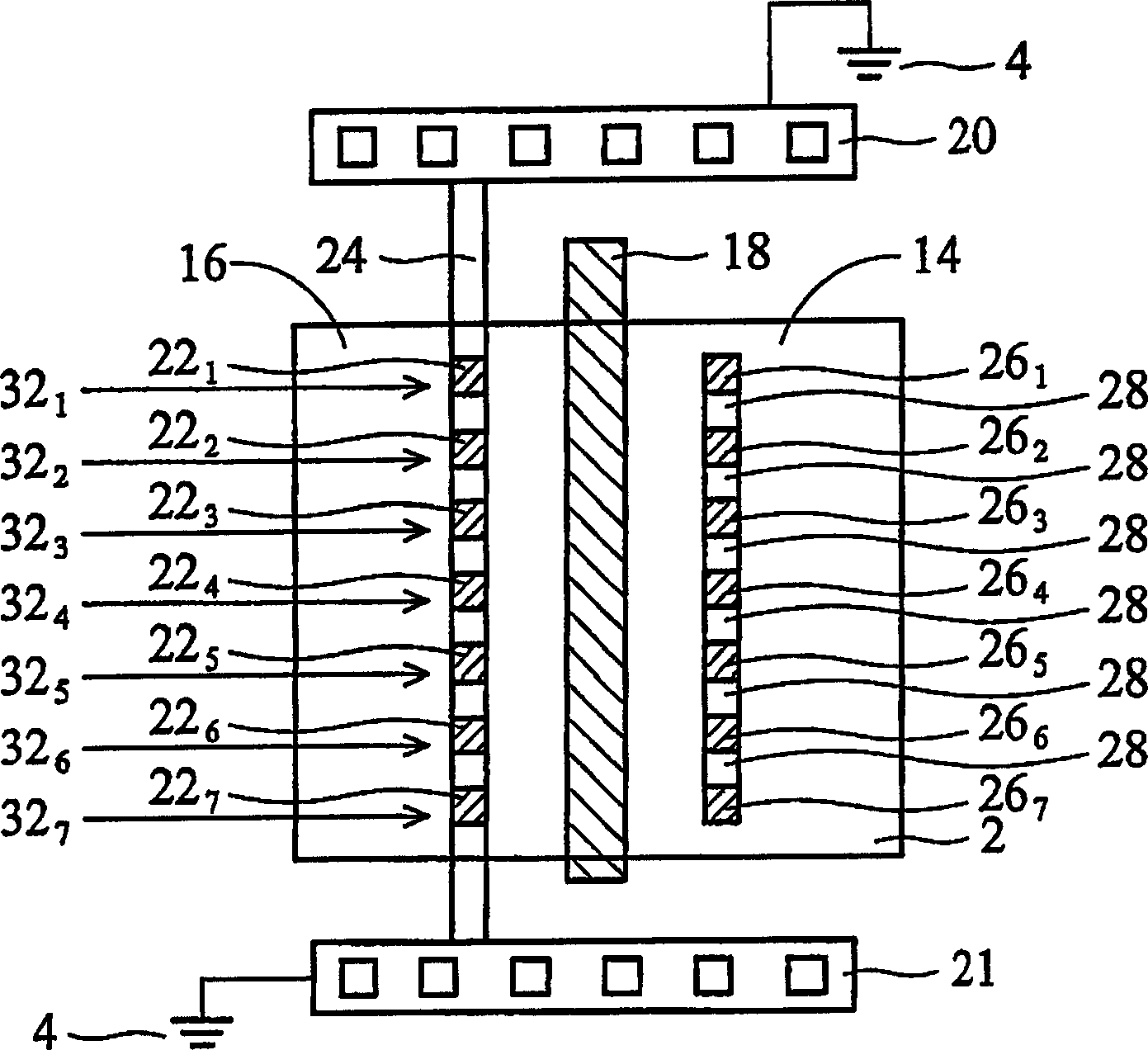
The invention provides a GGNMOS (Grounded-Grid N-channel metal oxide semiconductor) unit for antistatic protection, which is of a regular polygon shape, wherein a drain of the GGNMOS unit is closed by a circular grid; the circular grid is surrounded by a source of a regular polygon concentric with the regular polygon; the outer side of the source is provided with a regular polygonal circular substrate grounding area being concentric with the source and having the same distance with any place of the source; and the source and the regular polygonal circular substrate grounding area are evenly spaced by a field oxygen area. And correspondingly, the invention also provides an antistatic protection structure based on the GGNMOS unit. The circular grid is used for closing the drain by changing the plane layout structure of the GGNMOS unit; and resistance values of serially-connected resistors of the base of a parasitic triode are equal by adopting the method of surrounding the source through the concentric substrate grounding area. All ESD (Electronic Static Discharge) protection device units can be uniformly switched on in the antistatic protection structure provided the invention when the static is generated, thus high ESD protection capacity of above HBM 8 kV can be achieved.
Owner:ADVANCED SEMICON MFG CO LTD
A semiconductor structure for electrostatic discharge protection
ActiveCN1773704AImprove equalityUniform conductionTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsGgNMOSSemiconductor structure
The invention relates to a semiconductor structure for electrostatic discharge protection, which includes a ground gate NMOS, and the ground gate NMOS has a substrate, a gate, a source and a drain. A plurality of contact plugs are formed on the source and drain sides. A plurality of first-level vias are electrically coupled to the GGNMOS and have a substantially asymmetrical layout in the source and drain regions. One or a group of second-level vias directs the ESD current to the desired first-level vias. The uniformity of current flow in the GGNMOS is thus improved.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
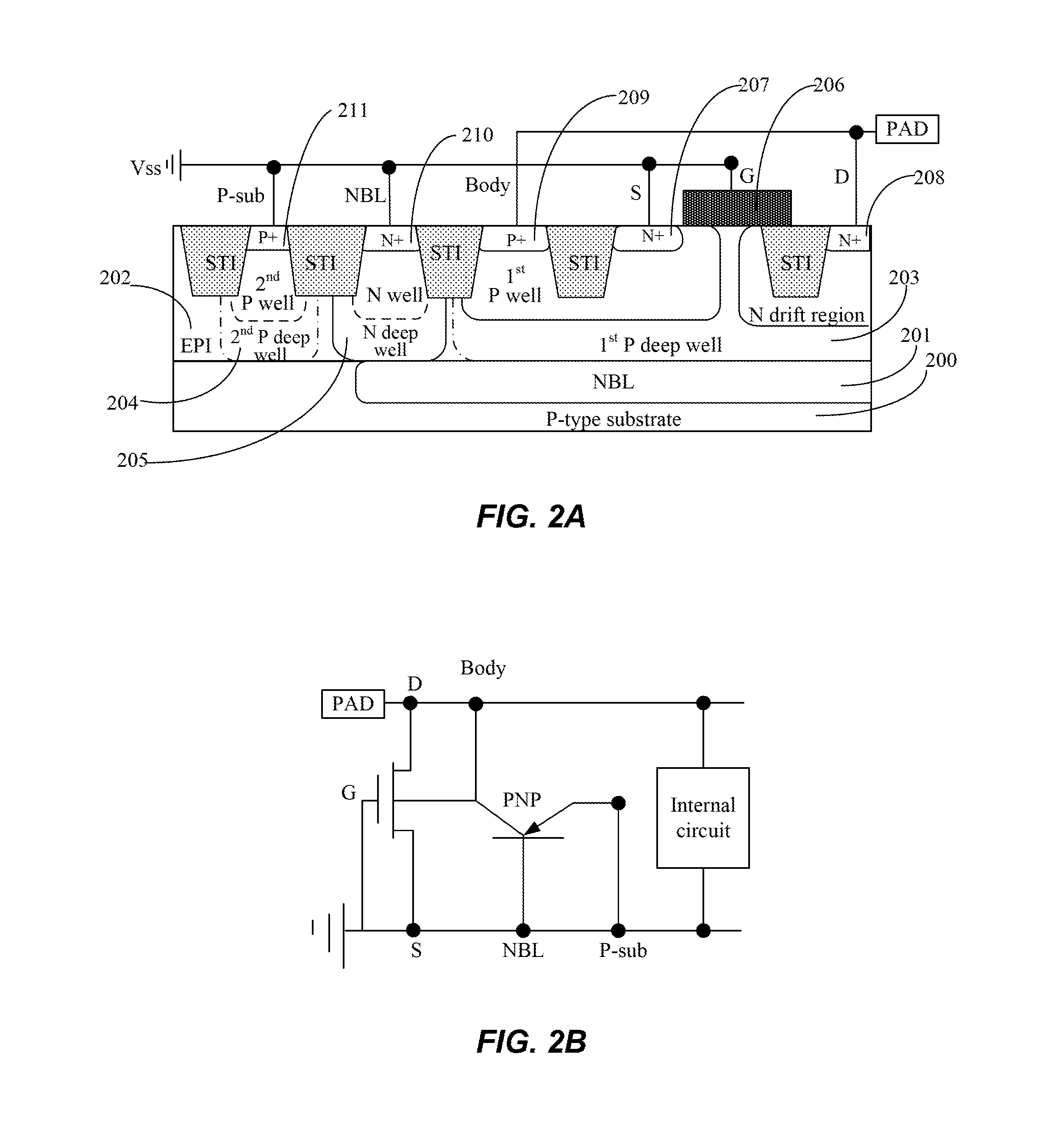
Electrostatic discharge protection structure in a semiconductor device
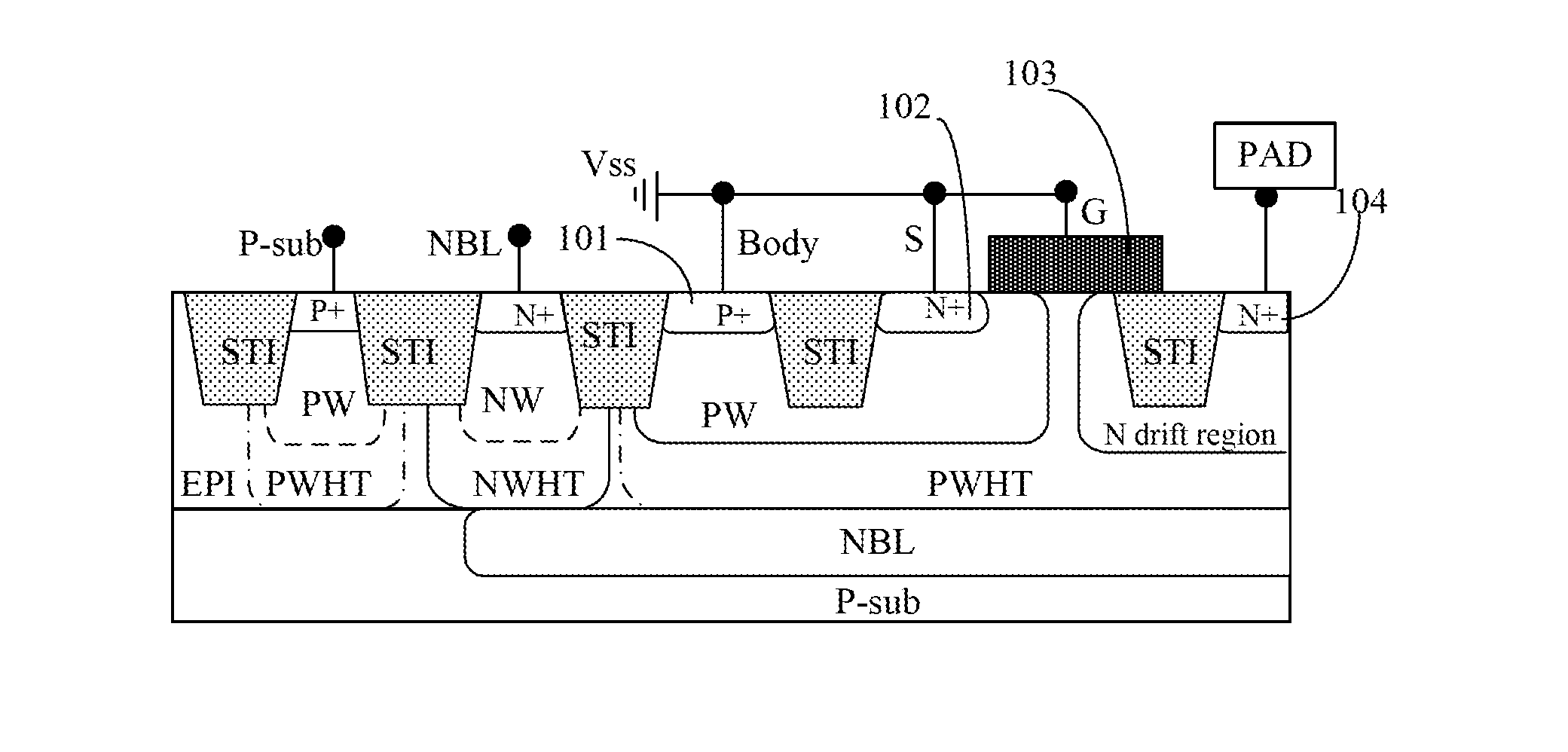
An electrostatic discharge protection structure includes a laterally diffused metal oxide semiconductor (LDMOS) device. The LDMOS device includes an embedded bipolar junction transistor. A gate, a source, a buried layer lead-out area, and a substrate lead-out area of the LDMOS device are grounded. A drain and a body region lead-out area of the LDMOS device are electrically connected to a pad input / output terminal. In an embodiment, the embedded bipolar junction transistor includes a PNP transistor operative to transmit a reverse electrostatic discharge current. An N+ drain, a gate, an N+ source, and a P+ substrate lead-out area form a grounded-gate NMOS (GGNMOS) operative to transmit a forward electrostatic discharge current.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
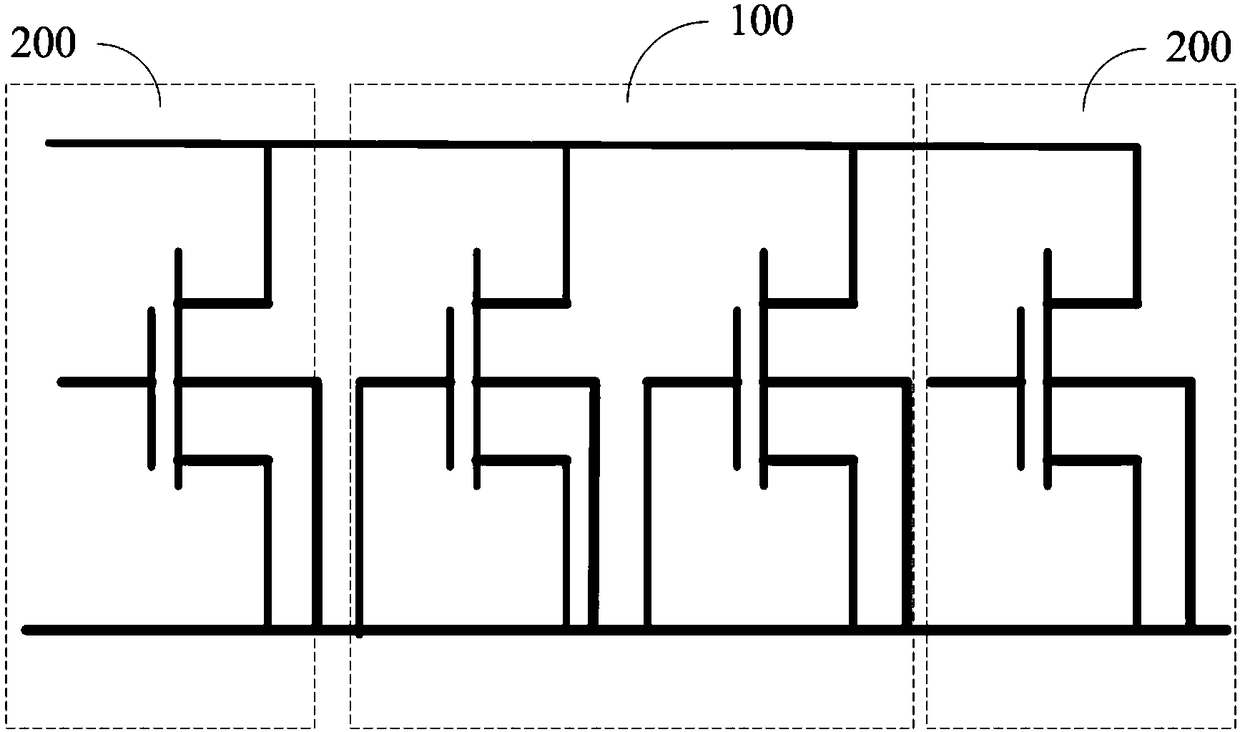
Multi-finger strip-type gate-ground N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (GGNMOS) and electrostatic protection circuit
ActiveCN102315217AChange the parasitic internal resistanceImprove conduction uniformityTransistorSolid-state devicesGgNMOSEngineering
The invention provides a multi-finger strip-type gate-ground N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (GGNMOS) and an electrostatic protection circuit. The multi-finger strip-type GGNMOS comprises a P-type semiconductor substrate, at least two N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) transistors formed in a device region, and an N-type connecting pit positioned in a semiconductor substrate arranged between drains of adjacent NMOS transistors; the P-type semiconductor substrate comprises the device region; the N-type connecting pit is connected with the drains on the two sides of the N-type connecting pit; and an N-type connecting region is formed in a surface region of the N-type connecting pit. The multi-finger strip-type GGNMOS provided by the invention has high conduction uniformity.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
High-voltage ESD protective circuit
ActiveCN106033756ACause malfunctionIncrease the trigger voltageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesGgNMOSHigh pressure
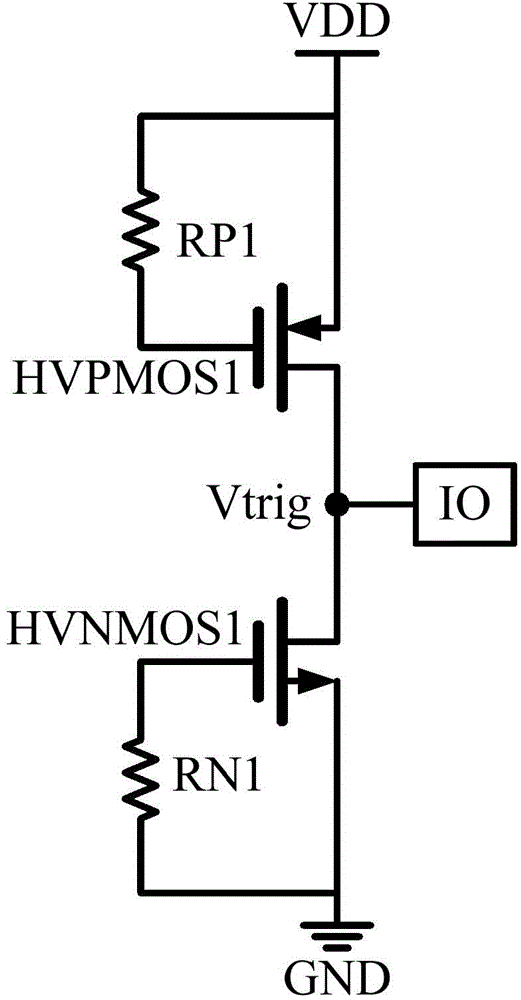
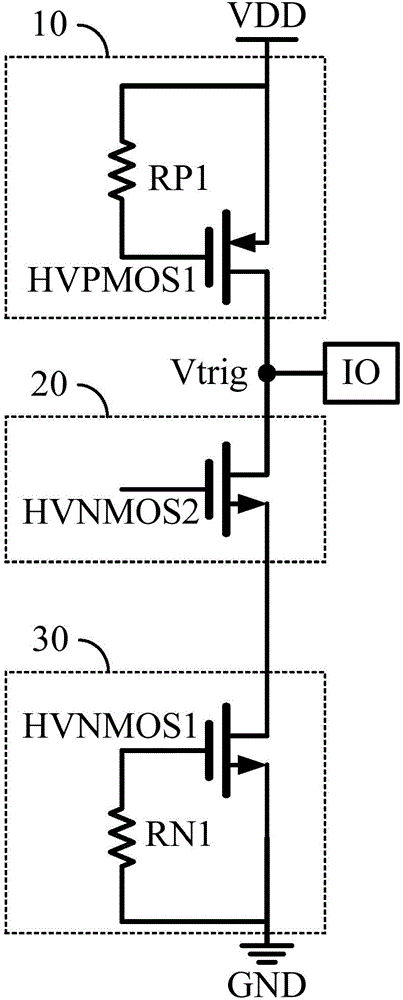
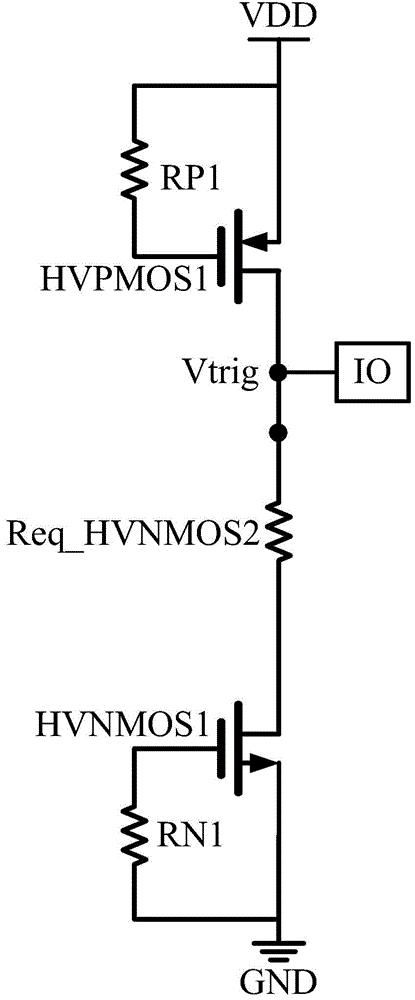
The invention provides a high-voltage ESD protective circuit which is used for discharging ESD current that flows from an IO PAD. The high-voltage ESD protective circuit at least comprises the components of a GDPMOS discharging unit which is arranged between a power supply and the IO PAD; an auxiliary discharging unit which is arranged between the IO PAD and ground and is connected with the GDPMOS discharging unit; and a GGNMOS discharging unit which is connected with the auxiliary discharging unit, wherein the auxiliary discharging unit is used for supplying an auxiliary discharging path of the GGNMOS discharging unit. The auxiliary discharging unit of the invention can supply the auxiliary discharging path of the GGNMOS discharging unit and improves ESD capability. By means of the stacked structure for aiming at high-voltage process, ESD capability of the circuit can be improved, and furthermore triggering voltage and noise resistance of the whole high-voltage ESD protective circuit can be improved, thereby preventing misoperation of the whole high-voltage ESD protective circuit caused by noise.
Owner:CHINA RESOURCES MICROELECTRONICS (CHONGQING) CO LTD
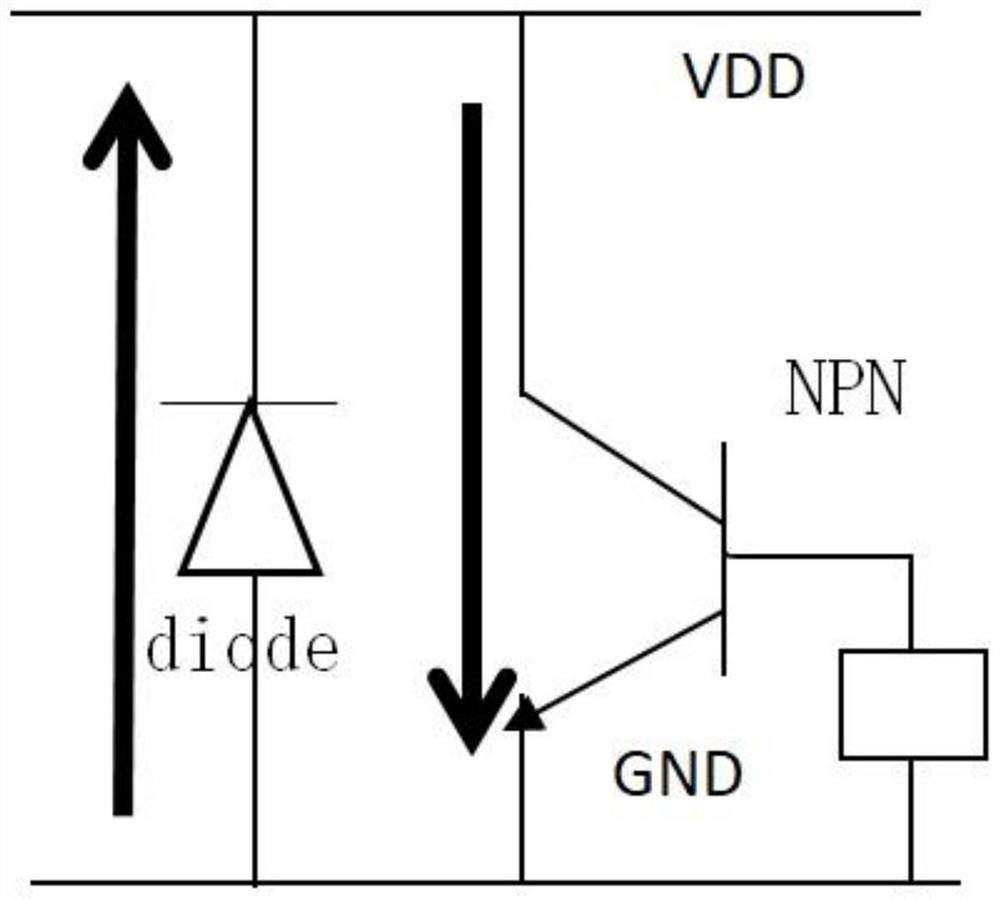
Circuit-level modeling method and model circuit which are used for GGNMOS
ActiveCN106709201ASimple structureEasy to implementCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsElectrical resistance and conductanceGgNMOS
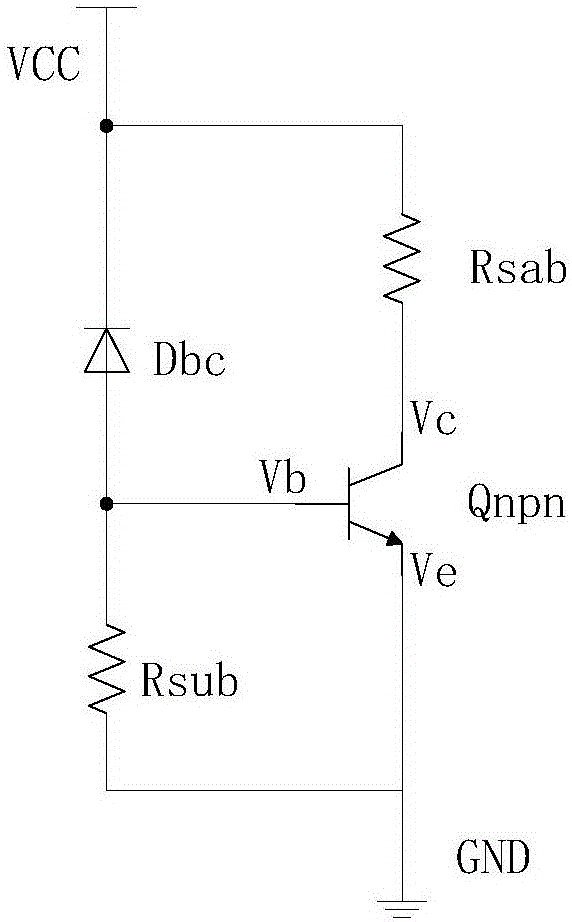
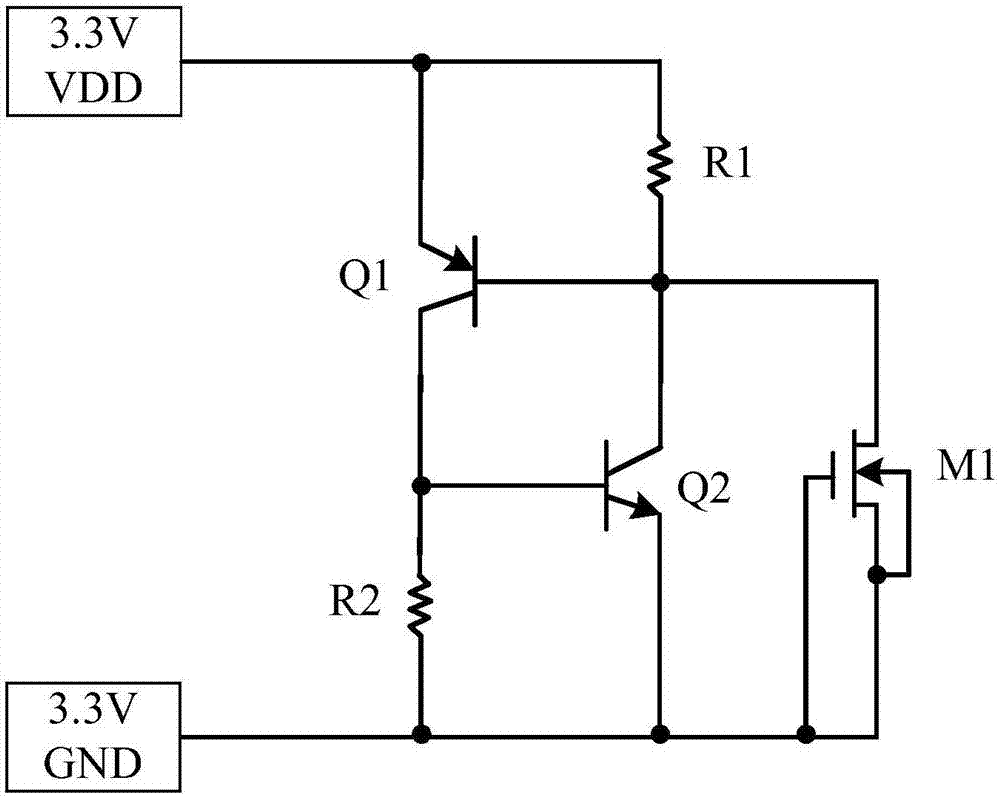
The invention discloses a circuit-level modeling method and a model circuit which are used for a GGNMOS. The model circuit comprises a triode, a first resistor, a second resistor and a diode. One end of the first resistor is in connection with a power ground, the other end of the first resistor is connected with the positive pole of the diode, the negative pole of the diode is connected with a power supply, the base of the triode is connected with a connection node between the diode and the first resistor, the emitter of the triode is connected with the power ground, and the collector of the triode is connected with the power supply through the second resistor. According to the circuit-level modeling method used for the GGNMOS, modeling is conducted on the GGNMOS, the clamping ability that the GGNMOS impacts on an ESD can be obtained by simulation within a short time by means of the model circuit, the structure is simple, the method is simple to implement, compared with an existing method that physical modeling is conducted by adopting a parameter extraction mode, the efficiency is higher, and the design cost is low.
Owner:SHENZHEN STATE MICROELECTRONICS CO LTD
Electrostatic discharge protection circuit using triple welled silicon controlled rectifier
InactiveUS20060125016A1Improve discharge performanceLower the trigger voltageThyristorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSilicon-controlled rectifierGgNMOS
Provided is an electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection circuit using a silicon controlled rectifier (SCR), which is applied to a semiconductor integrated circuit (IC). A semiconductor substrate has a triple well structure such that a bias is applied to a p-well corresponding to a substrate of a ggNMOS device. Thus, a trigger voltage of the SCR is reduced. In addition, two discharge paths are formed using two SCRs comprised of PNP and NPN bipolar transistors, with the result that the ESD protection circuit can have great discharge capacity.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Electrostatic discharge protection circuit using triple welled silicon controlled rectifier
ActiveUS20080128817A1Lower the trigger voltageImprove discharge performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSilicon-controlled rectifierGgNMOS
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
MSMV (Multi-supply Multi-voltage) integrated circuit ESD protection network under epitaxial technology
InactiveCN107482004AAvoid risk of failureEfficient designSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesGgNMOSIntegrated circuit
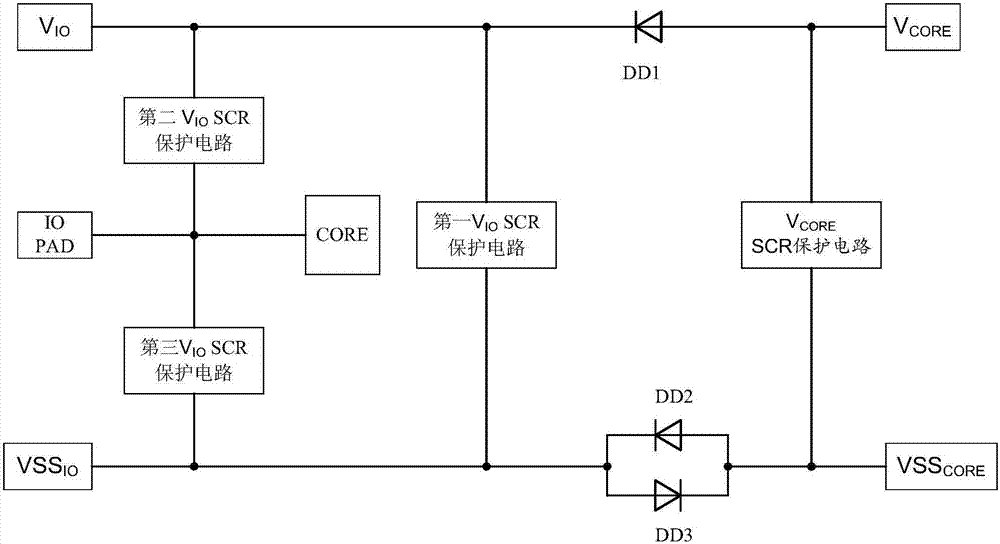
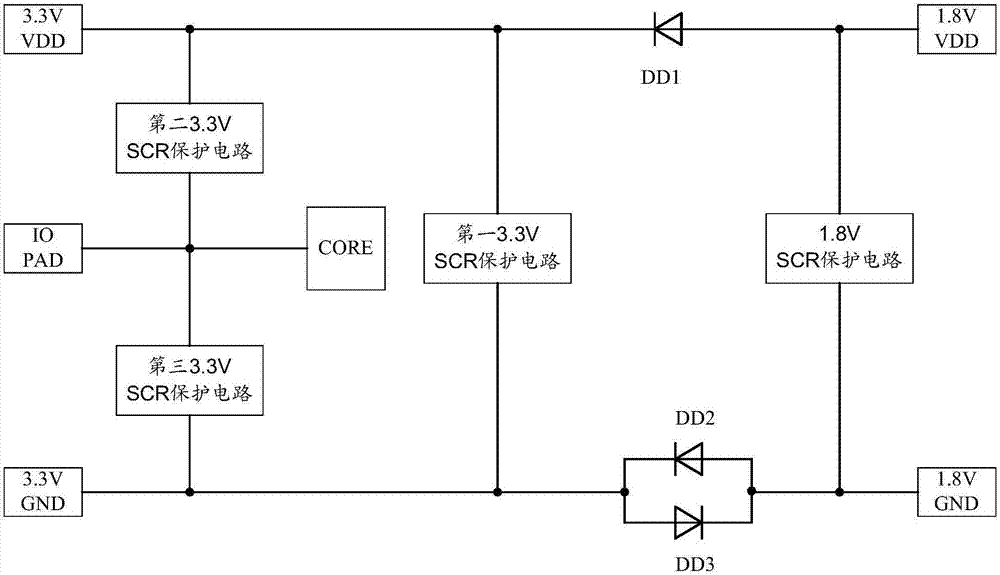
A MSMV (Multi-supply Multi-voltage) integrated circuit ESD protection network under an epitaxial technology comprises a power supply VIO, an earth VSSIO, a power supply VCORE, an earth VSSCORE, a diode DD1, a diode DD2, a diode DD3, a first VIOSCR protection circuit, a second VIOSCR protection circuit, a third VIOSCR protection circuit, a VCORESCR protection circuit and an IO PAD; the first VIOSCR protection circuit is arranged between the power supply VIO and the earth VSSIO; the VCORESCR protection circuit is arranged between the power supply VCORE and the earth VSSCORE; the second VIOSCR protection circuit and the third VIOSCR protection circuit are respectively arranged between the IO PAD and the power supply VIO and between the IO PAD and the earth VSSIO for protections. The normal ESD design (GGNMOS) under the epitaxial technology has a protection failure problem, and a MSMV (Multi-supply Multi-voltage) integrated circuit ESD is hard and complex to design; the MSMV (Multi-supply Multi-voltage) integrated circuit ESD protection network under the epitaxial technology can solve said problems, thus effectively realizing MSMV (Multi-supply Multi-voltage) integrated circuit ESD protections; the protection network uses a limited layout area, provides a strong ESD robustness, and can improve the ESD protection efficiency.
Owner:BEIJING MXTRONICS CORP +1
ESD (Electro-Static Discharge) protective circuit suitable for RFID (Radio Frequency Identification Devices) and RFID chip
InactiveCN104505816AImprove protectionDelayed startEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentElectrical resistance and conductanceGgNMOS
The invention discloses an ESD (Electro-Static Discharge) protective circuit suitable for RFID (Radio Frequency Identification Devices). The ESD protective circuit comprises a GC-GGNMOS (Gate Coupled Gate Grounded N-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor), wherein the GC-GGNMOS takes a stray capacitor in an inherent grid and drain overlapped region as a coupling capacitor, and the RC parameters of the GC-GGNMOS are regulated by changing the resistance value of a polycrystalline silicon resistor which connects the grid to the ground. The invention also discloses an RFID chip, and the RFID chip comprises packaged pins, an RFID chip internal circuit and the ESD protective circuit which is positioned between the packaged pins and the RFID chip and has a protective effect, wherein the ESD protective circuit comprises the GC-GGNMOS, the GC-GGNMOS takes the stray capacitor in the inherent grid and drain overlapped region as the coupling capacitor, and the RC parameters of the GC-GGNMOS are regulated by changing the resistance value of the polycrystalline silicon resistor which connects the grid to the ground. The embodiment of the invention reduces the robustness index of the protective circuit and reduces the robustness of the protective circuit.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV +1
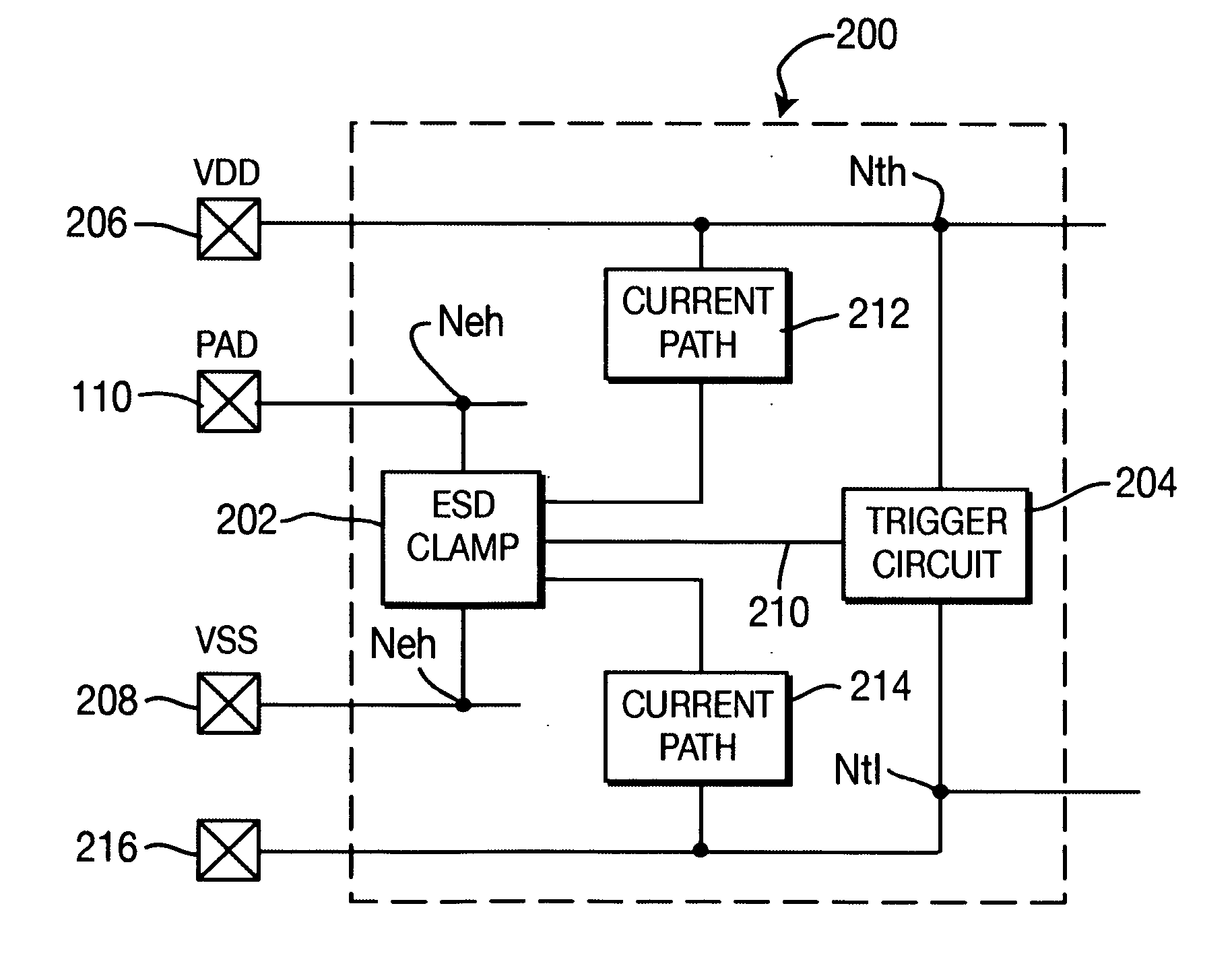
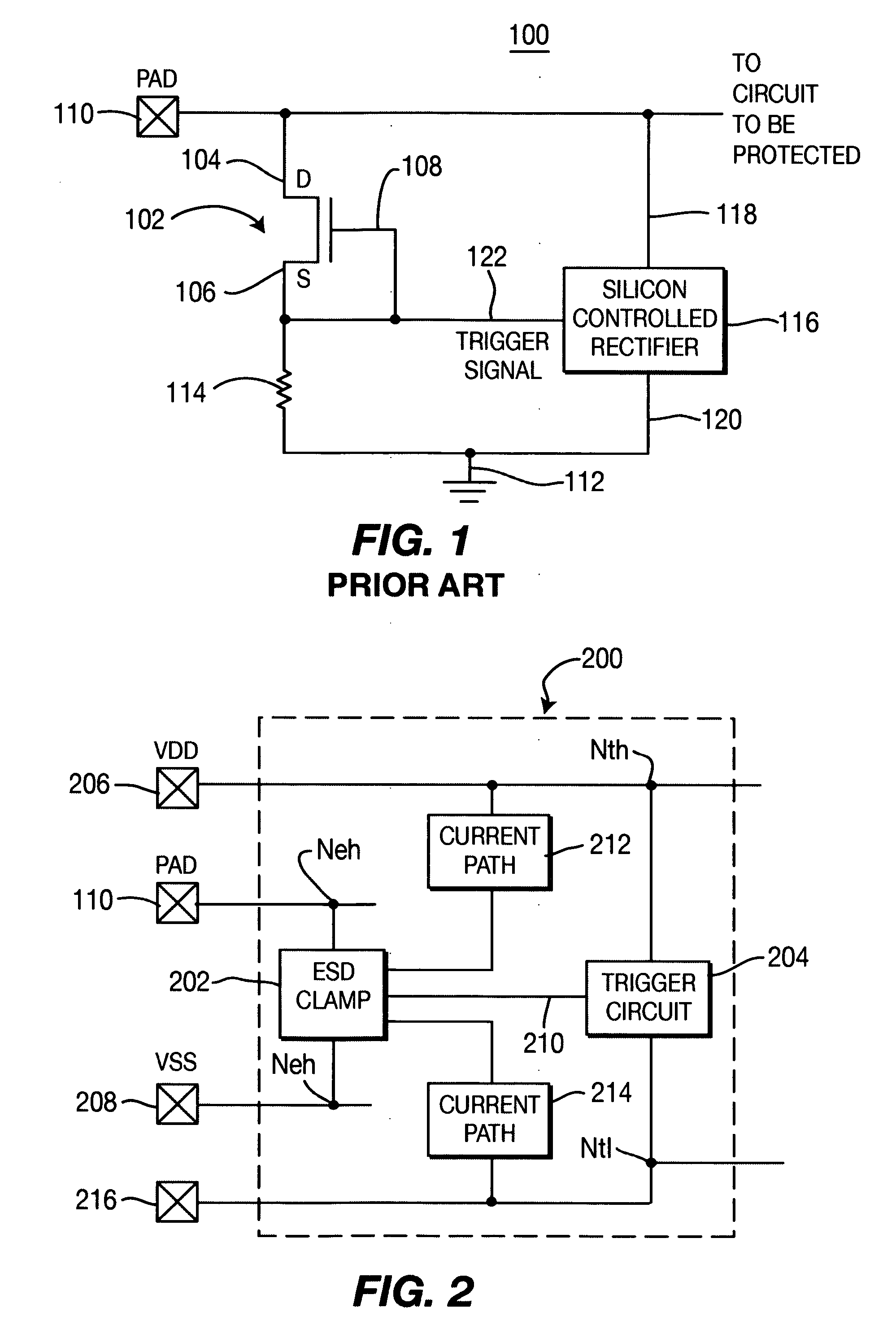
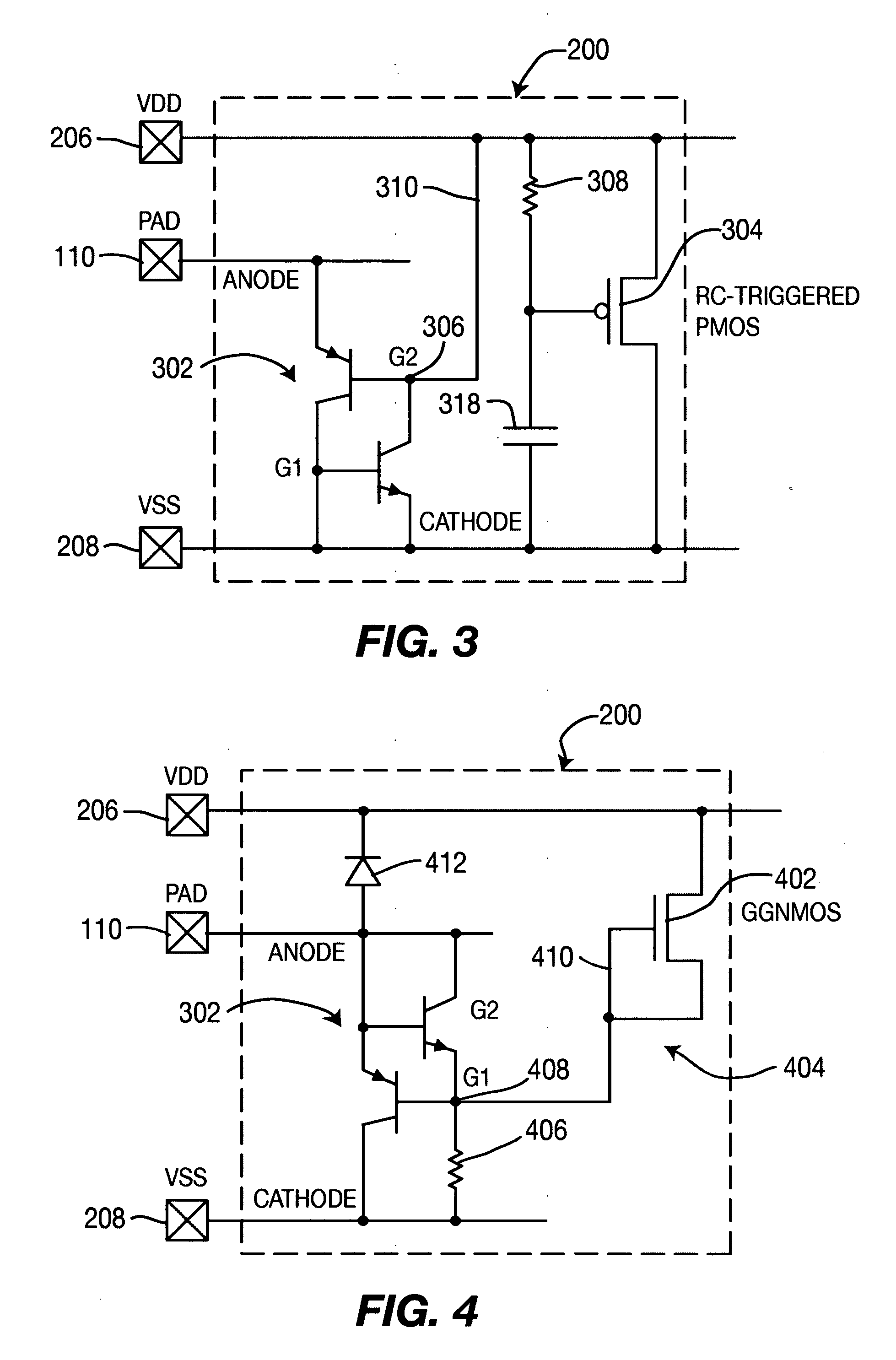
Apparatus for ESD protection
InactiveUS20060268477A1TransistorEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentSilicon-controlled rectifierGgNMOS
Apparatus for ESD circuit protection including a trigger subcircuit coupled between a first voltage reference potential and second voltage reference potential and an ESD shunt subcircuit coupled to the trigger subcircuit between a circuit device to be ESD-protected and the second voltage reference potential. The ESD shunt subcircuit is adapted for connection by a pad of an integrated circuit (IC) connection. The ESD shunt subcircuit is a silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR) that has an anode connected to the circuit device to be ESD-protected and a cathode connected to the second voltage reference potential. The trigger subcircuit is either an RC-triggered PMOS or a GGNMOS and series connected resistor.
Owner:SARNOFF CORP +1
Semiconductor structure, forming method thereof, and electrostatic protection circuit
ActiveCN105489503AReduce parasitic capacitanceWork fasterTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductor structureTime delays
The invention provides a semiconductor structure, a forming method thereof, and an electrostatic protection circuit. The forming method includes the following steps: providing a substrate including a device zone; forming a plurality of well regions, in the substrate of the device zone, that are isolated through the substrate; forming grid structures on the surfaces of the well regions; and forming a source region at one side of each grid structure in the corresponding well region, and forming a drain region at the other side of each grid structure in the substrate, wherein the drain regions cross the adjacent well regions, and the adjacent grid structures share the source regions and the drain regions. A plurality of well regions are formed in the substrate of the device zone and are isolated by means of the substrate, so part of the drain regions are positioned in the well regions and part of the drain regions are positioned in the substrate. The stray capacitance of a GGNMOS (Gated Grounded NMOS) is influenced by the concentration of doped ions, and the lower the concentration of the doped ions is, the lower the stray capacitance is, while the concentration of doped ions of the substrate is smaller than the concentration of doped ions of the well regions. Therefore, the stray capacitance of the GGNMOS can be made to be reduced, the input / output time delay can be reduced, and the working speed of a chip can be increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Electrostatic protection device based on SOI (Silicon-On-Insulator) technology and formed electrostatic protection circuit
InactiveCN108063133AEnhanced reverse ESD protectionQuick responseTransistorSolid-state devicesGgNMOSEngineering
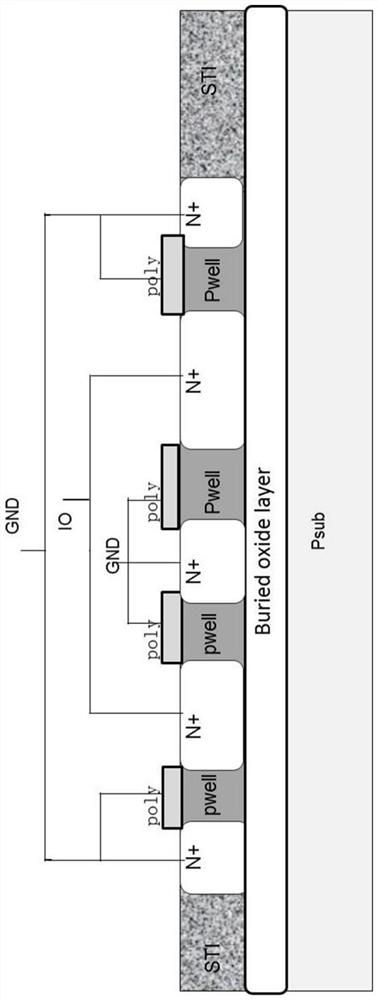
The invention provides an electrostatic protection device based on a SOI (Silicon-On-Insulator) technology and a formed electrostatic protection circuit. The device is a GGNMOS with a multiple parallel structure, and comprises a buried oxide layer, a P well area, a source, a drain, a gate, a P+ contact area and a pseudo gate, wherein the P+ contact area is arranged at one side, far away from the drain, of the source; the P+ contact area is separated from the source through the P well area; and the pseudo gate covers the P well area between the P+ contact area and the source. Thus, the reverseESD protection capability can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Anti-electrostatic protecting structure by NMOS
InactiveCN1983588ASolve the problem that the protection ability cannot be fully exertedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesGgNMOSEngineering
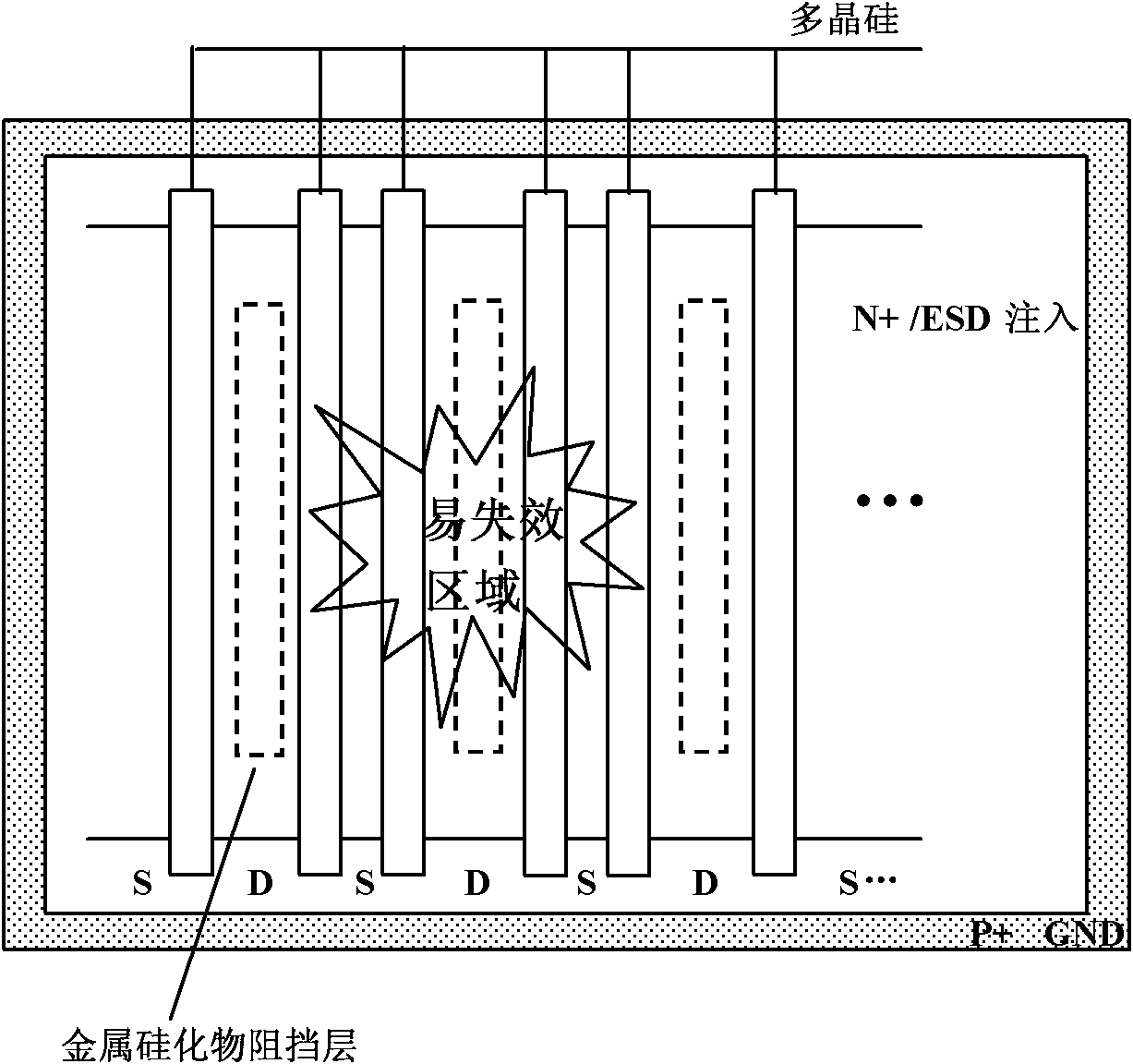
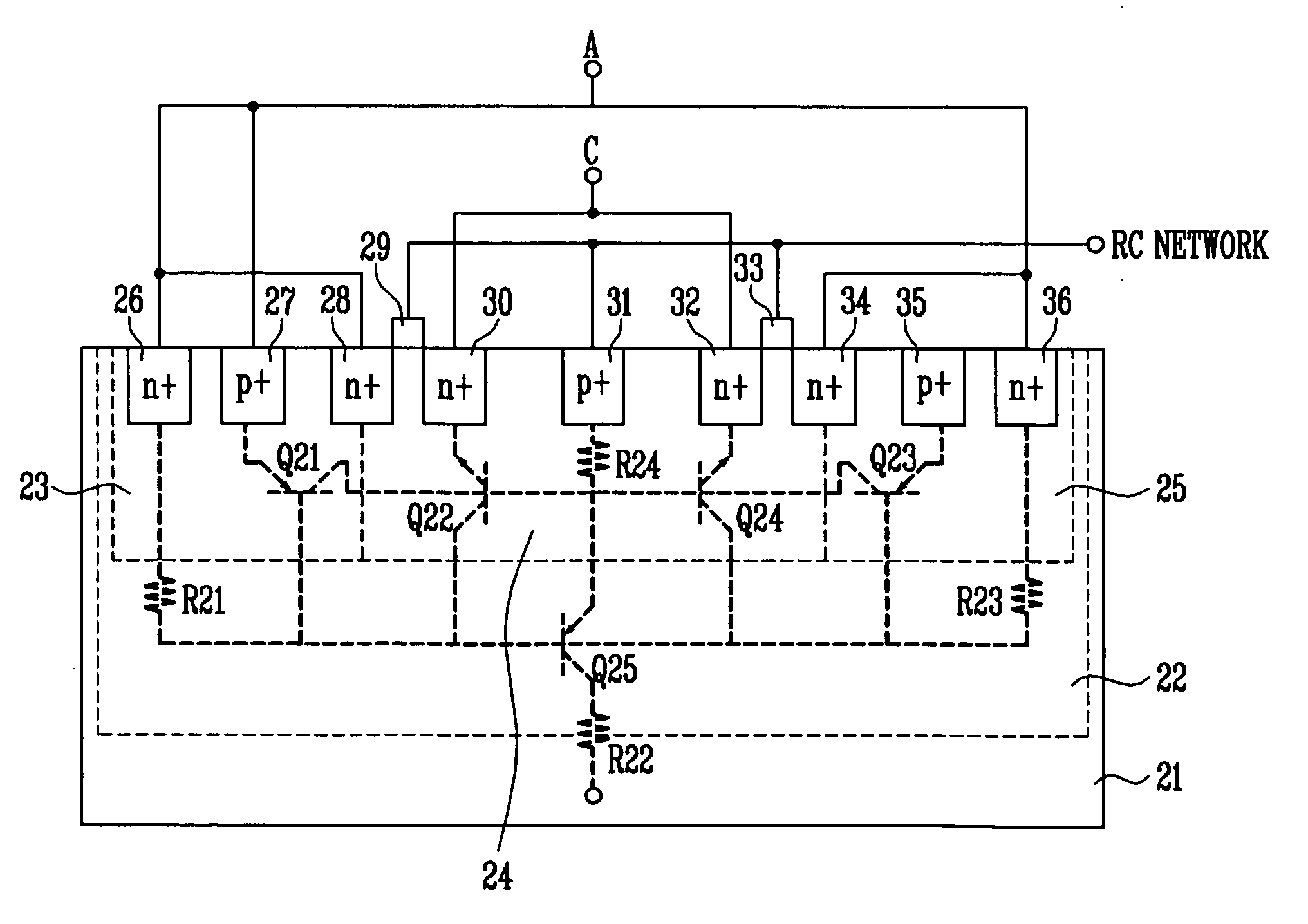
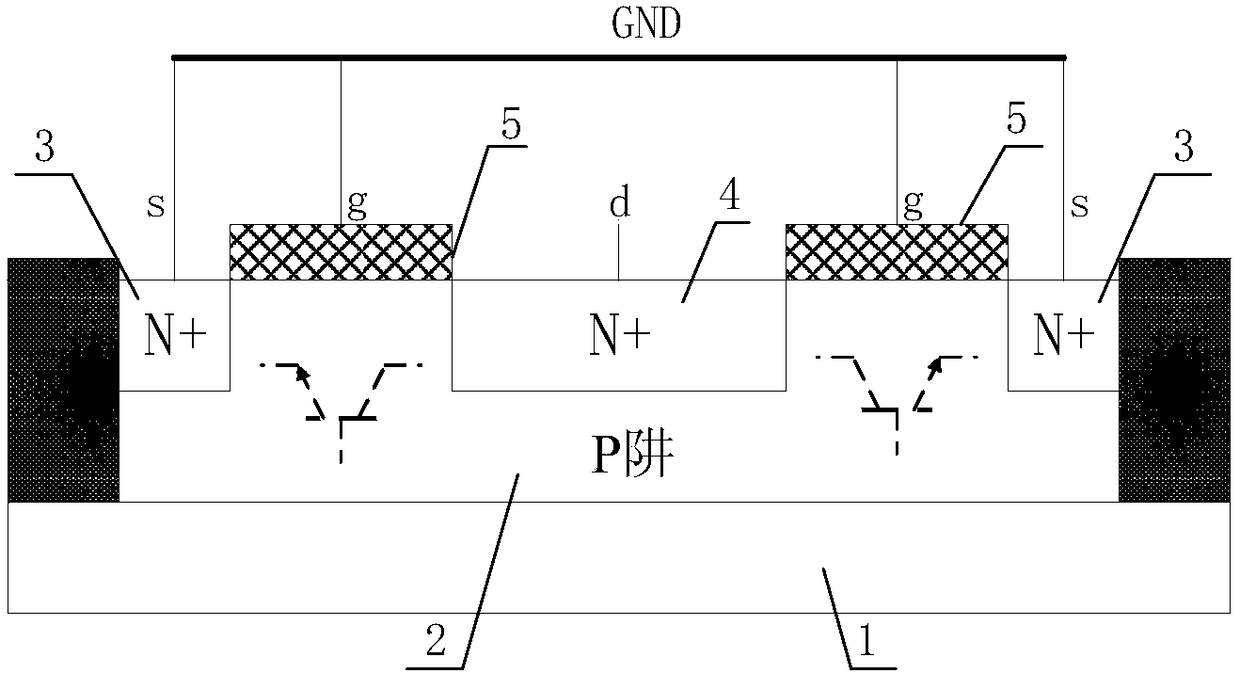
The invention is concerned with electrostatic-proof protecting structure using NMOS as the basic device of static protecting structure. The number of NMOS is even and is not less than four and adding N well resistance in confined field at the drain area. Set two NMOS at the center of static protecting structure and those grids connect in parallel connection, while the drain pole is in parallel connection. Except the central NMOS, the NMOS drain pole on the both sides is in parallel connection with the central NMOS, and source pole and grid connect with central NMOS in parallel connection and the earth. The source pole of central NMOS connects with the underlay of the parallel NMOS on both sides, i.e. the group pole of parasitical NPN. When the parasitical NPN of central NMOS is expedite, the current distributes to the group poles of parasitical NPN to parallel NMOS on both sides and the group poles are positive expedite with sending pole. This invention solves the problem that protective tube cannot expedite flow equably and the protection ability of ESD is low, when the GGNMOS structure is as the protection of ESD.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUA HONG NEC ELECTRONICS
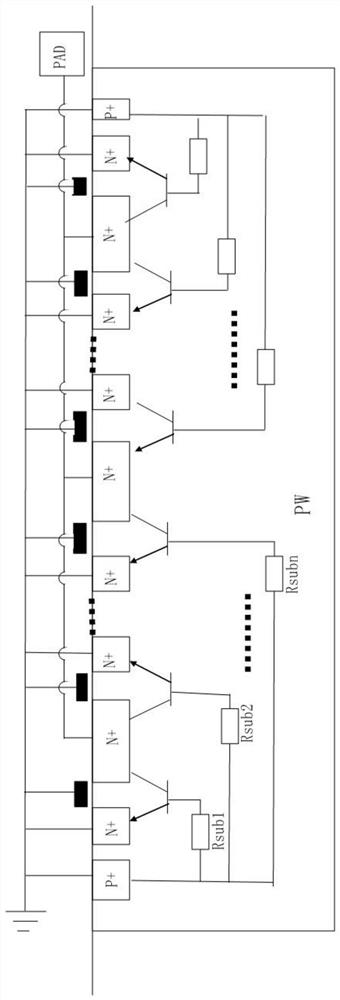
Static discharge protection circuit
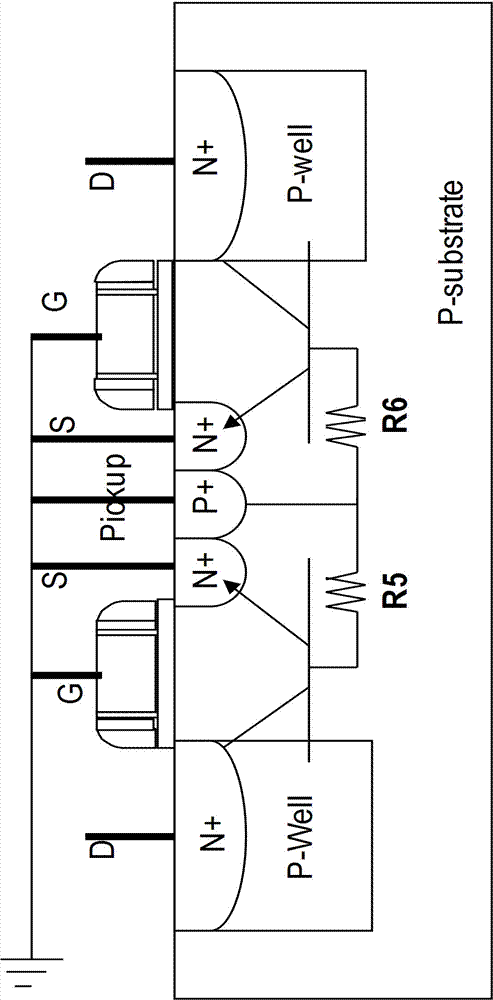
ActiveCN103094271AIncreased ESD Protection LevelsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGgNMOSMetal
The invention provides a static discharge protection circuit which is characterized by comprising a plurality of N-metal-oxide-semiconductor (NMOS) transistors. The adjacent NMOS transistors share source diffusion zones or drain diffusion zones. P traps are formed below the drain diffusion zones. A picking area is formed in the central area of the shared source diffusion zones. Grids and sources of the NMOS transistors are grounded. The picking area is also grounded. According to the static discharge protection circuit, when static discharge occurs, each finger in a grounded-gate N-metal-oxide-semiconductor (GGNMOS) simultaneously starts static discharge protection, and improves static discharge protection level measured by human body model (HBM).
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
A semiconductor device having an electrostatic discharge protection structure and a layout structure thereof
InactiveCN109216343AIncrease flexibilityFlexible modificationTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETGgNMOS
The invention relates to a semiconductor device with an electrostatic discharge protection structure and a layout structure thereof, the device includes an internal circuit and a GGNMOS, the internalcircuit includes a MOSFET, the semiconductor device further includes an active region, A MOSFET is arrange in that active region, characterized by, GGNMOS is also arrange in that active region, and the MOSFET is arranged on both lateral sides of the GGNMOS in the same active region, The active region comprises a P well, an N-type doped region of the GGNMOS and an N-type doped region of the MOSFETare arranged in the P well, the semiconductor device further comprises a P-type doped region as a substrate, and the P-type doped region is arranged on the outer sides of the MOSFET on both sides. When the electrostatic discharge occurs, if the MOSFET of the internal circuit is turned on, the substrate current is formed, thereby increasing the gate voltage of the intermediate GGNMOS, enabling theGGNMOS to be turned on more easily and improving the ESD capability.
Owner:CSMC TECH FAB2 CO LTD
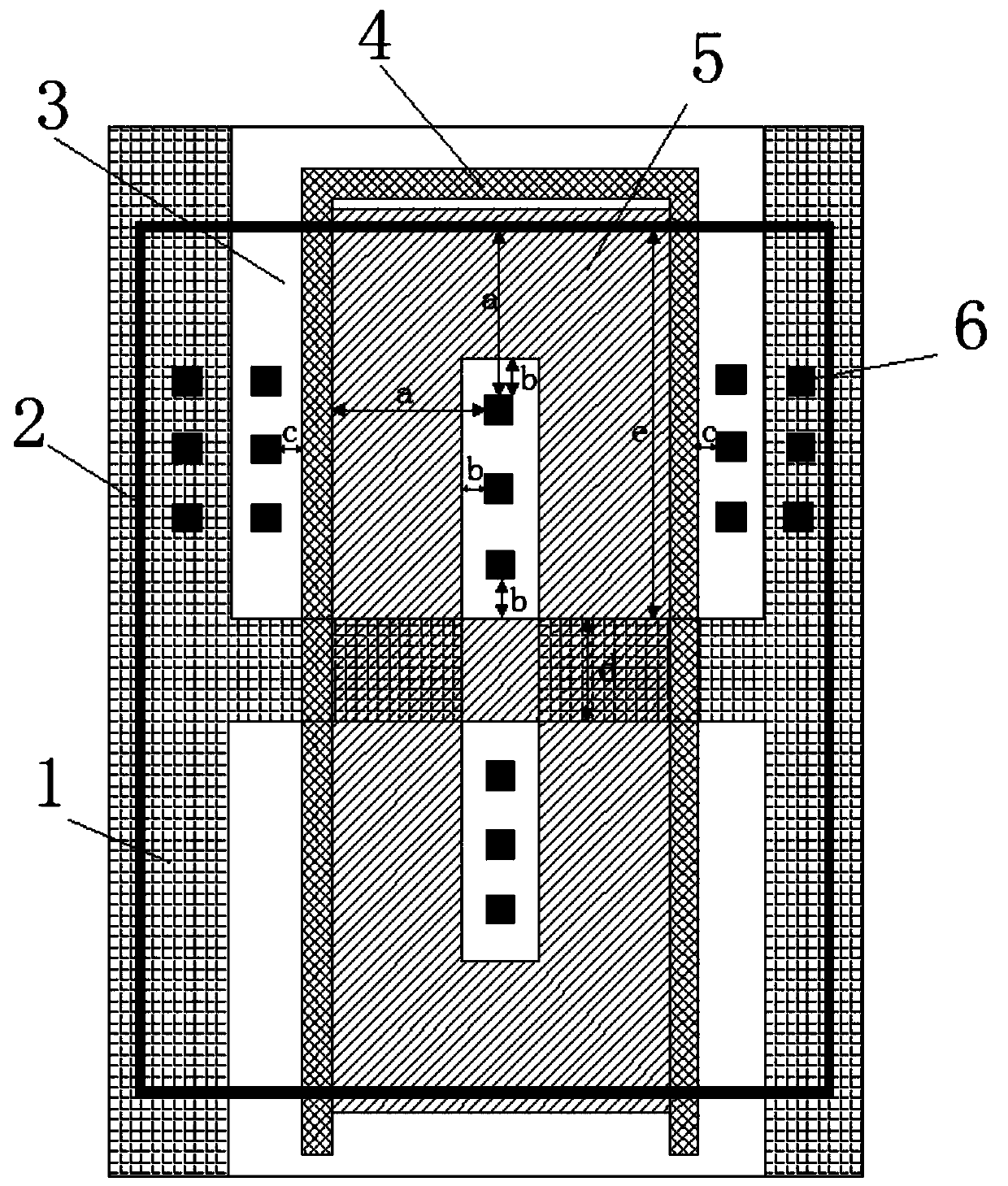
GGNMOS ESD protection device structure based on SOI process
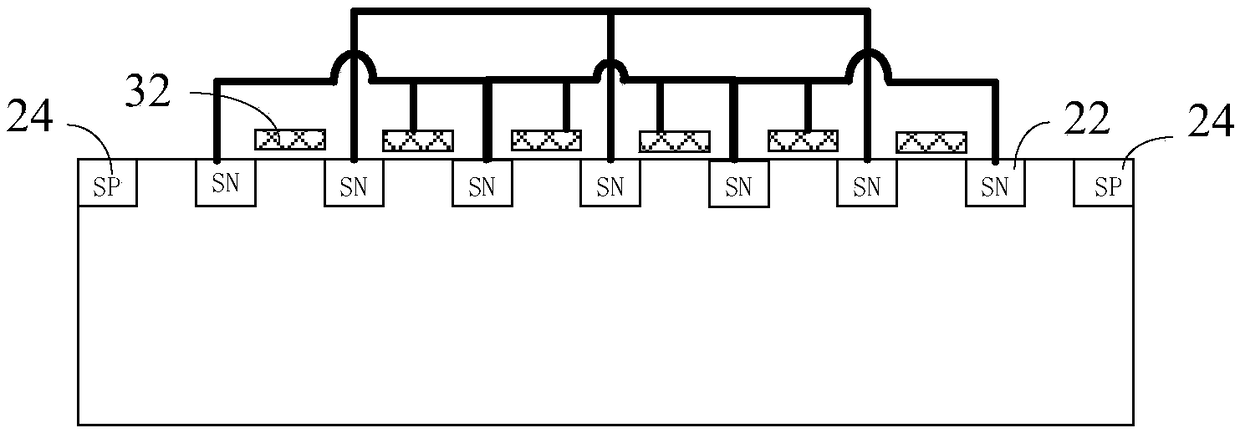
ActiveCN111508951AReduce areaFull body contactTransistorSolid-state devicesGgNMOSCondensed matter physics
The invention discloses a GGNMOS ESD protection device structure based on an SOI technology. The structure comprises an SAB layer, P-type doped source-drain units SP, N-type doped source-drain units SN, a polycrystalline gate POLY, a device active region TO and contact holes W1. P-type doped source and drain units of a strip-type NMOS tube are segmented; the body contact of the device is designedbetween every two sections of P-type doped source-drain units. A P-type doped source and a P-type doped drain of a strip-type NMOS tube are segmented; the body contact of the device is designed between every two P-type doped source drains, the N-type doped source drain units of the strip-type NMOS tube are ingeniously segmented through the structure, the range of an SN injection layer and the range of an SP injection layer are defined by the segments respectively, the process is achieved through photoetching, and by means of the design, on one hand, the area is saved, and on the other hand, the body contact is more sufficient; TLP test evaluation shows that under the same area, the ESD resistance of the SOI GGNMOS device is obviously improved by 1.2 times or above compared with that of a traditional SOI GGNMOS device.
Owner:58TH RES INST OF CETC
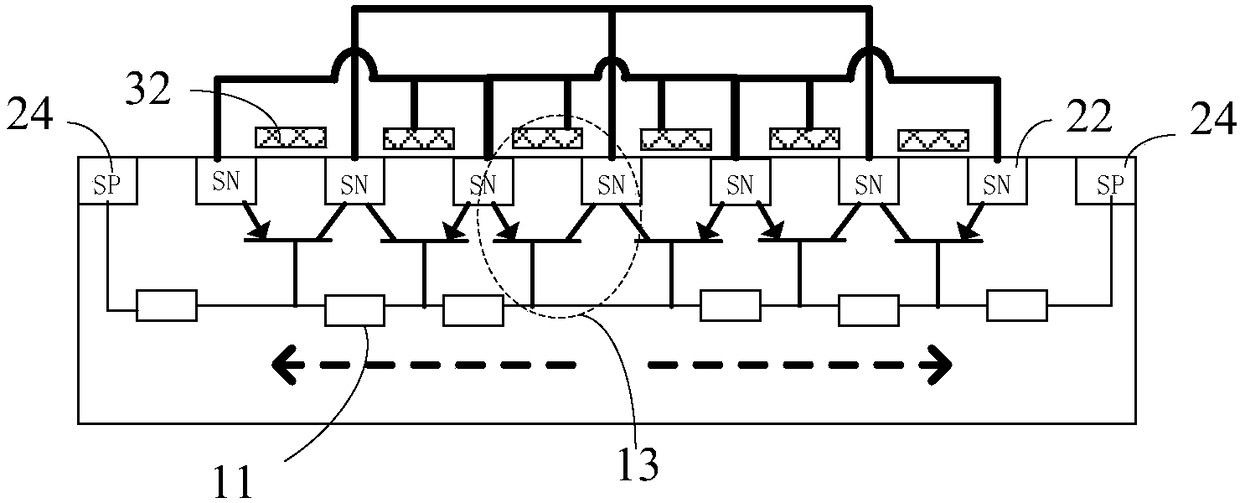
Electrostatic protection GGNMOS structure
The invention discloses an electrostatic protection GGNMOS structure, which is suitable for an interdigital GGNMOS of an SOI process. In the upper layer of the substrate, an active region is defined through an STI process, a plurality of P wells are formed in the active region, and the plurality of P wells are mutually spaced; a heavily doped N-type injection region is arranged between the P trapand the peripheral STI; heavily doped N-type injection regions are arranged between the P wells at intervals; the heavily doped N-type injection region is in transverse contact with the P trap; and aheavily doped P-type injection region is arranged between the P wells in the central region, and the heavily doped P-type injection region is in transverse contact with the P wells on the two sides ofthe heavily doped P-type injection region. According to the invention, through the P trap and the heavily doped P-type injection region in the central region, each insertion finger forms a body diodefrom S / B to the drain end, so that the ESD capability of the GGNMOS in the direction of the body diode is enhanced.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Electrostatic discharge protection device
An electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection device includes a pad, a diode, a gate ground NMOS (GGNMOS) transistor and a thyristor. The diode includes an anode connected with the pad. The GGNMOS transistor is connected between a cathode of the diode and a ground terminal. The thyristor is formed between the diode and the ground terminal when an ESD current may flow from the pad.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Electrostatic discharge protection circuit and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103872039ALead away in timeExtend working lifeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesGgNMOSWorking life
The invention discloses an electrostatic discharge protection circuit. The electrostatic discharge protection circuit comprises a gate-grounded N type metal oxide semiconductor (GGNMOS) transistor located on a semiconductor substrate, a drain electrode of the GGNMOS transistor is connected an input / output end of a chip circuit, a source electrode and a gate electrode and the semiconductor substrate are all connected to the ground; and the circuit also comprises a Peltier cooling element that is located near the GGNMOS transsitor and used for absorbing heat generated by the GGNMOS transistor. The invention also discloses a manufacturing method of the electrostatic discharge protection circuit. By adoption of the electrostatic discharge protection circuit, the working life of an ESD protection device can be prolonged.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Quick-opening uniform-conduction bidirectional electrostatic surge protection IC
PendingCN112599522AEnhanced ESD robustnessImprove robustnessTransistorSolid-state devicesGgNMOSHemt circuits
The invention discloses a quick-opening uniform-conduction bidirectional electrostatic surge protection IC, and belongs to the field of electrostatic discharge and surge protection of circuits. By introducing a reverse bias unit composed of an N type buried layer and a P well, bidirectional electrostatic surge protection is carried out on an application circuit of which the working voltage is higher than 18V; by adjusting the width of the P trap, the voltage clamping capability of the bidirectional electrostatic surge protection IC is adjusted. By introducing the on-state NMOS, the current conduction uniformity of the surface of the P trap is enhanced, and the starting speed of the bidirectional electrostatic surge protection IC is improved. By introducing a cascaded electrical structure of a GGNMOS and an on-state NMOS, the surface current discharge capability of the bidirectional electrostatic surge protection IC can be enhanced, and the ESD robustness of the bidirectional electrostatic surge protection IC can also be enhanced. On the premise that the area of the chip is not increased, the bidirectional electrostatic surge protection IC also has bidirectional ESD / TVS protection performance.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Electrostatic discharge protection circuit using triple welled silicon controlled rectifier
InactiveUS7342281B2Lower the trigger voltageImprove discharge performanceThyristorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSilicon-controlled rectifierGgNMOS
Provided is an electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection circuit using a silicon controlled rectifier (SCR), which is applied to a semiconductor integrated circuit (IC). A semiconductor substrate has a triple well structure such that a bias is applied to a p-well corresponding to a substrate of a ggNMOS device. Thus, a trigger voltage of the SCR is reduced. In addition, two discharge paths are formed using two SCRs including PNP and NPN bipolar transistors. As a result, the ESD protection circuit can have greater discharge capacity.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
GGNMOS (Gate-Grounded N-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) device applied to ESD (Electro-Static discharge) protection and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN106298777AImprove cooling effectImprove protectionTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGgNMOSEngineering
The invention discloses a GGNMOS (Gate-Grounded N-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) device applied to ESD (Electro-Static discharge) protection and a manufacturing method thereof. A P-type doping region is arranged in a drain extension region of a GGNMOS to form a floating reverse diode with a drain NLDD (N-type Lightly Doped Drain) doping region, so that distribution of drain ESD current is changed; ESD leakage current is deviated from the surface of the drain extension region and a conducting channel; the cooling capability during ESD discharge of the GGNMOS is enhanced; secondary breakdown current during snapback of the device is increased; and the ESD protection capability of the GGNMOS device is enhanced.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUALI MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Enhanced electrostatic discharge (ESD) clamp
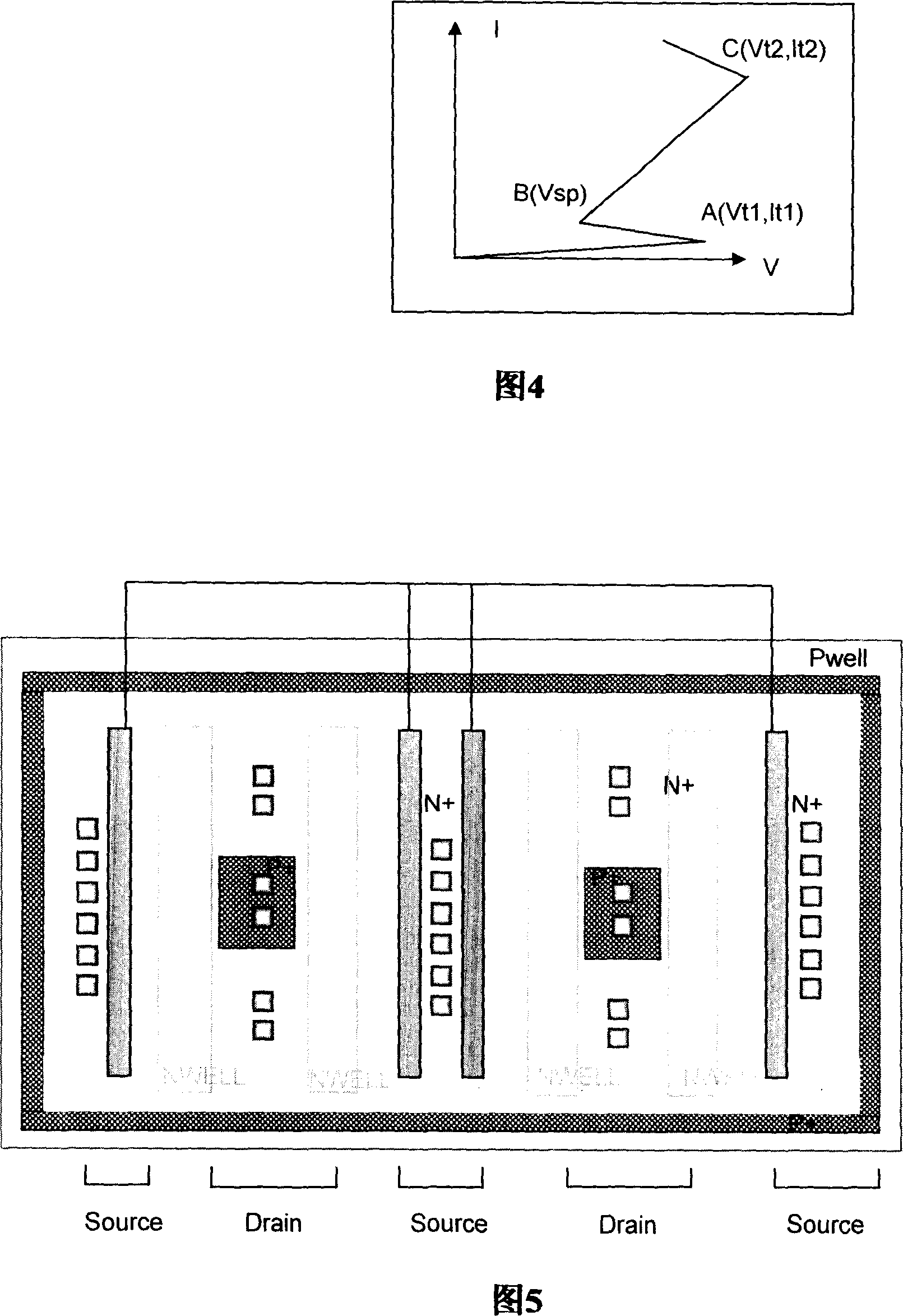
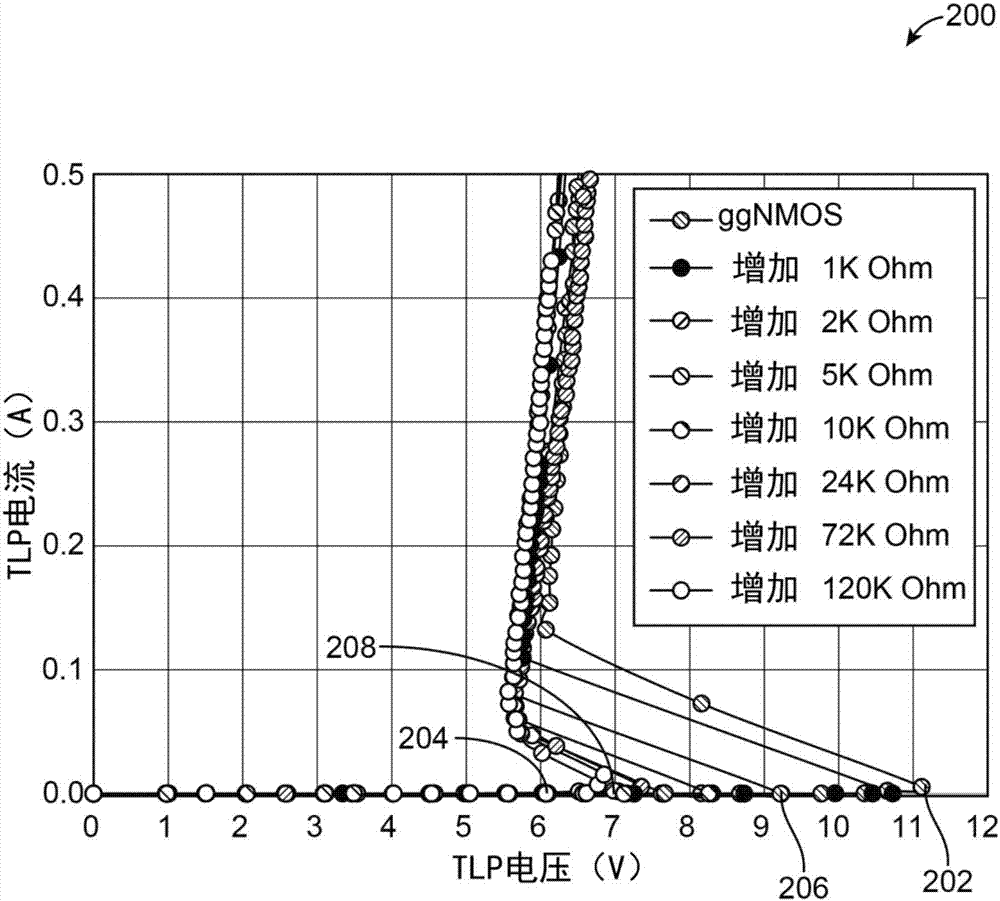
An enhanced ESD clamp is provided with a resistor connected between the body terminal and the source terminal of a MOSFET device. In one exemplary embodiment, the MOSFET device is a grounded-gate NMOS (ggNMOS) transistor device with the resistor ('body resistor') connected externally to the MOSFET device. In another embodiment, the MOSFET device is a ggPMOS transistor device. In yet another embodiment, the body resistor is disposed within and connected internally to the MOSFET device. In any event, the resistance value of the body resistor determines the level to which the trigger voltage of the ESD clamp will be reduced when an ESD event occurs.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
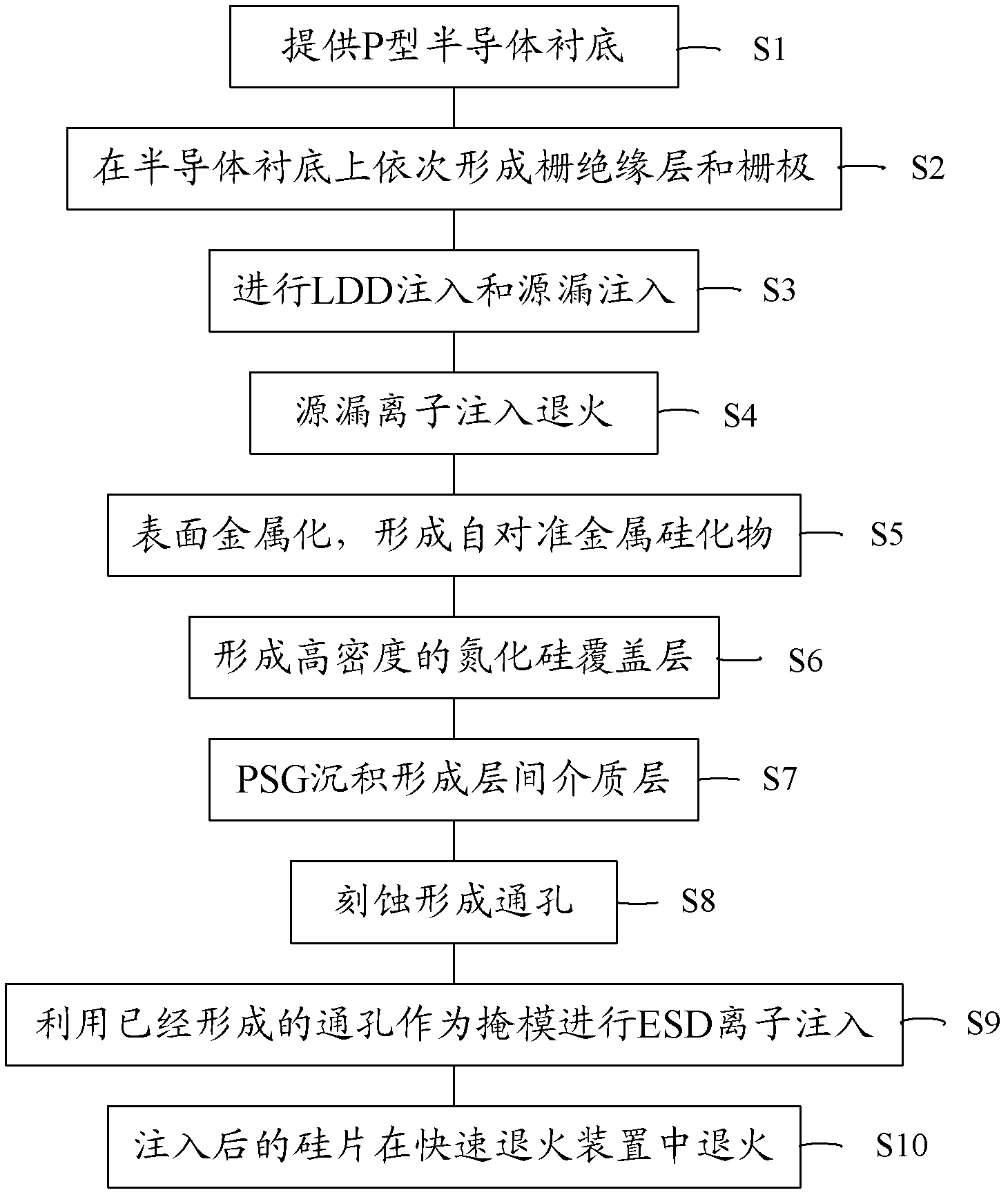
Gate-grounded NMOS manufacturing method
ActiveCN103187295AEasy to controlLower breakdown voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInsulation layerGgNMOS
The invention relates to a gate-grounded NMOS (GGNMOS) manufacturing method which includes the following steps. A P-shaped semi-conductor substrate is provided. A gate insulation layer and a grid electrode are sequentially formed on the semi-conductor substrate, source drain implantation is performed, an interlamination medium layer is formed, a through hole of a contact hole is formed in an etching mode and ESD ion filling is performed by using the formed through hole as a reticle mask. Compared with that ESD filling is performed before the contact hole is formed in manufacturing the GGNMOS, performing the ESD filling after the through hole of the contact hole is formed can not only reduce procedures of original technology, narrow down an ESD Implant zone in a drain electrode and reduce leakage, but also reduce grid leak parasitic capacitance caused by horizontal spreading and improve static protection characteristics of the GGNMOS.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com