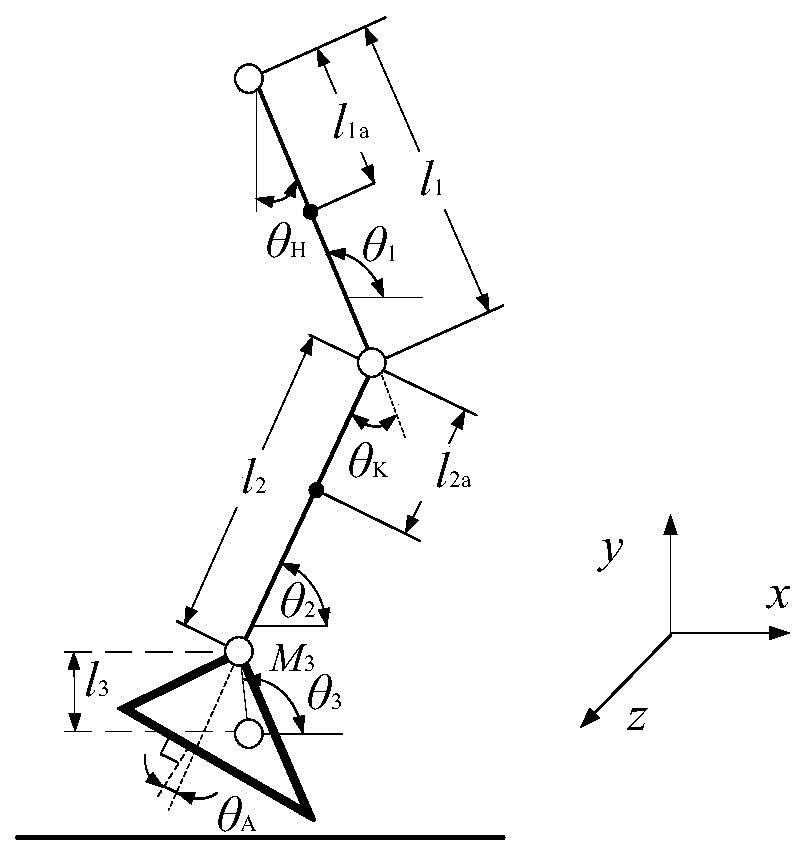
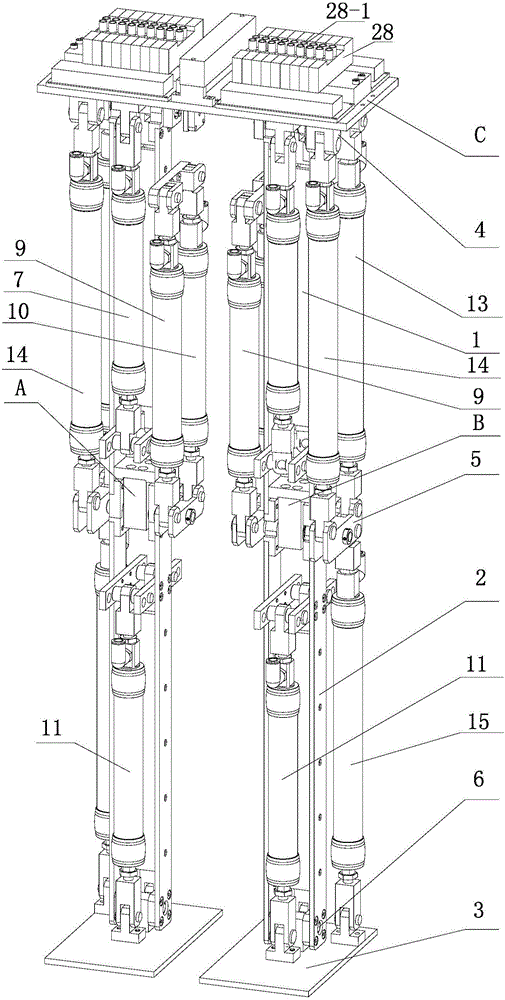
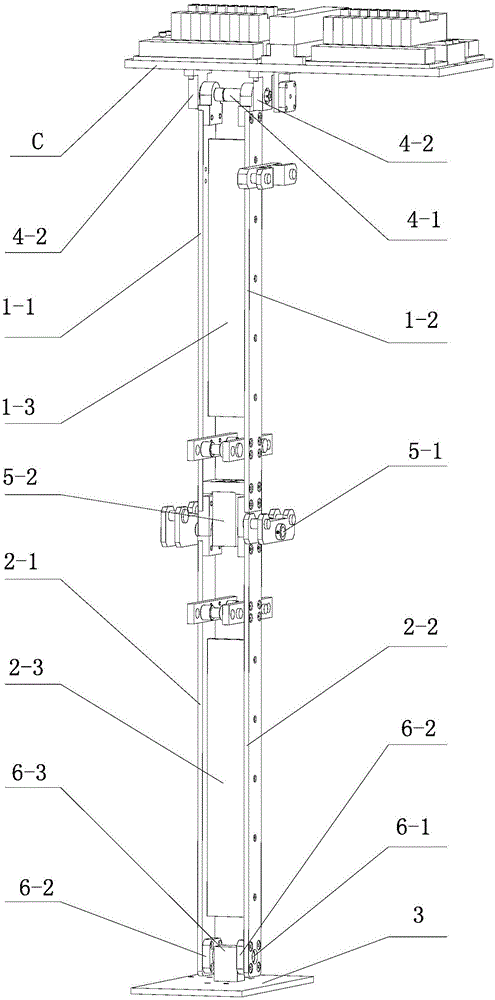
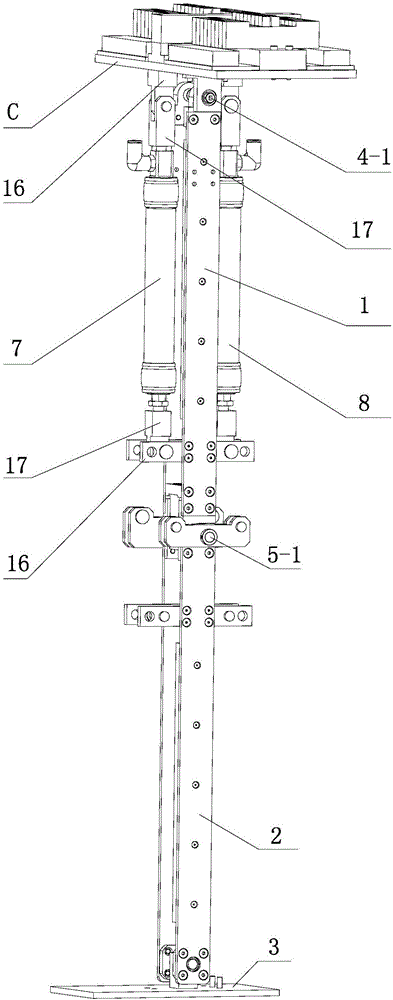
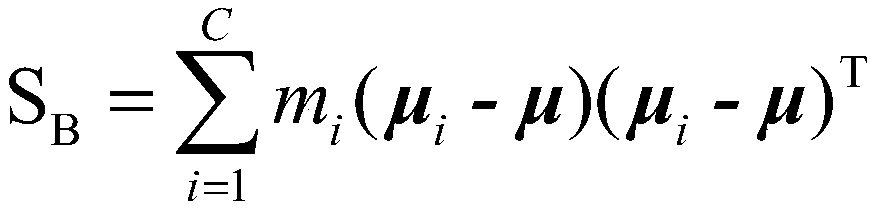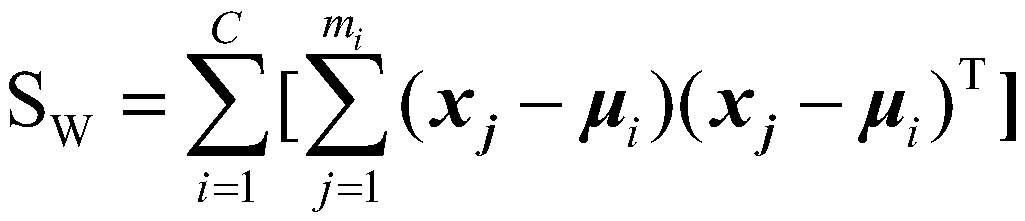Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
56 results about "Gastrocnemius muscle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
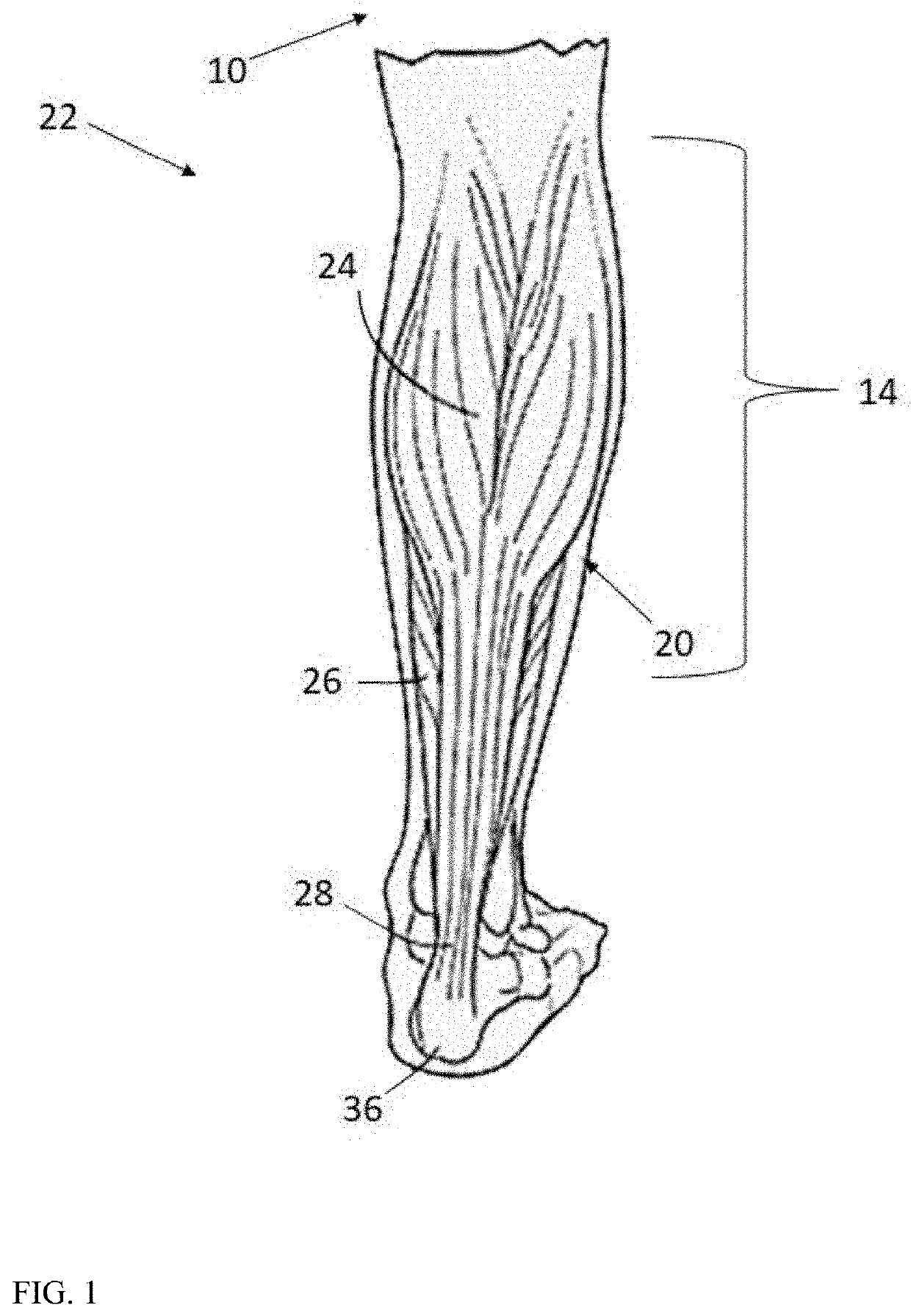
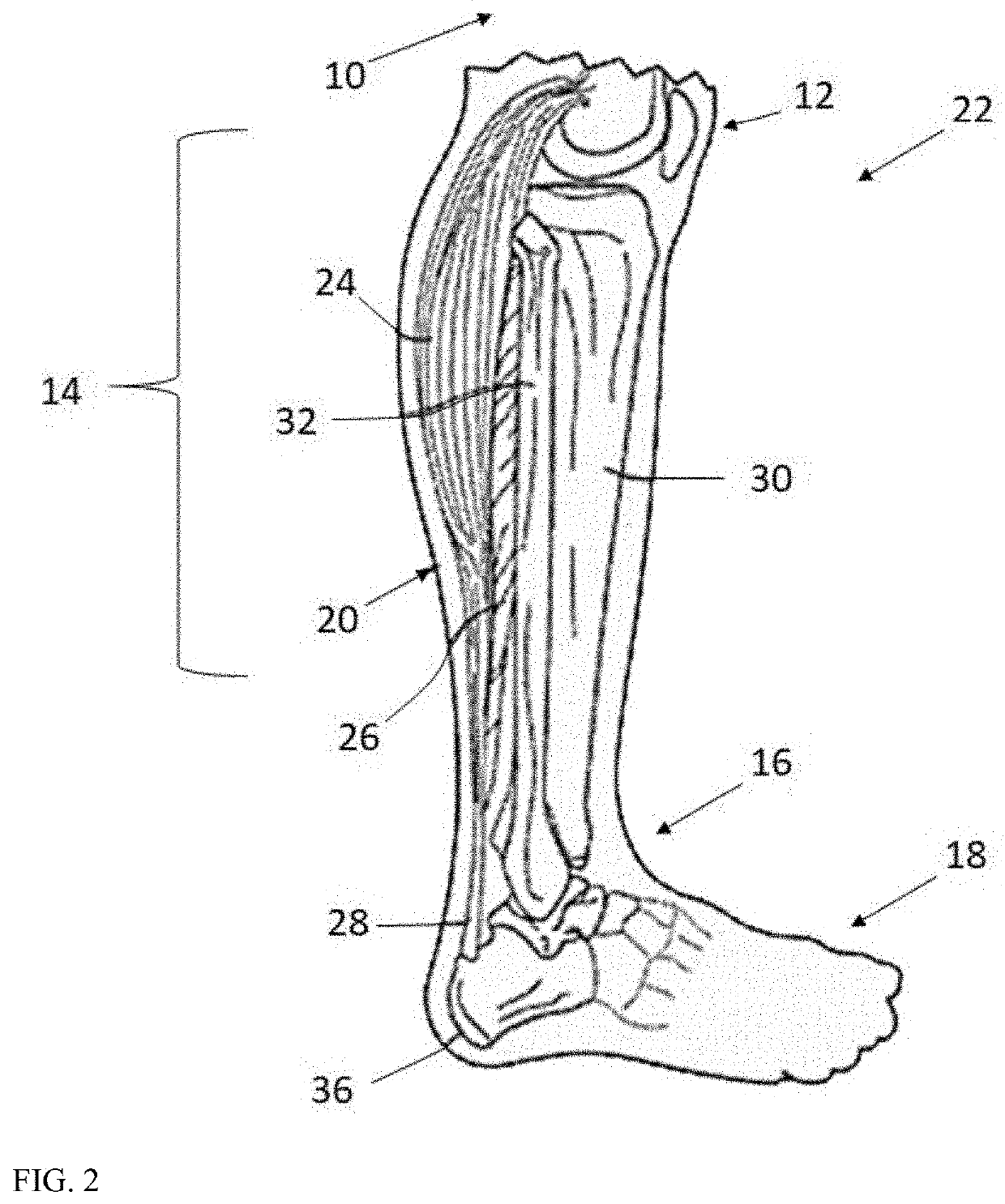
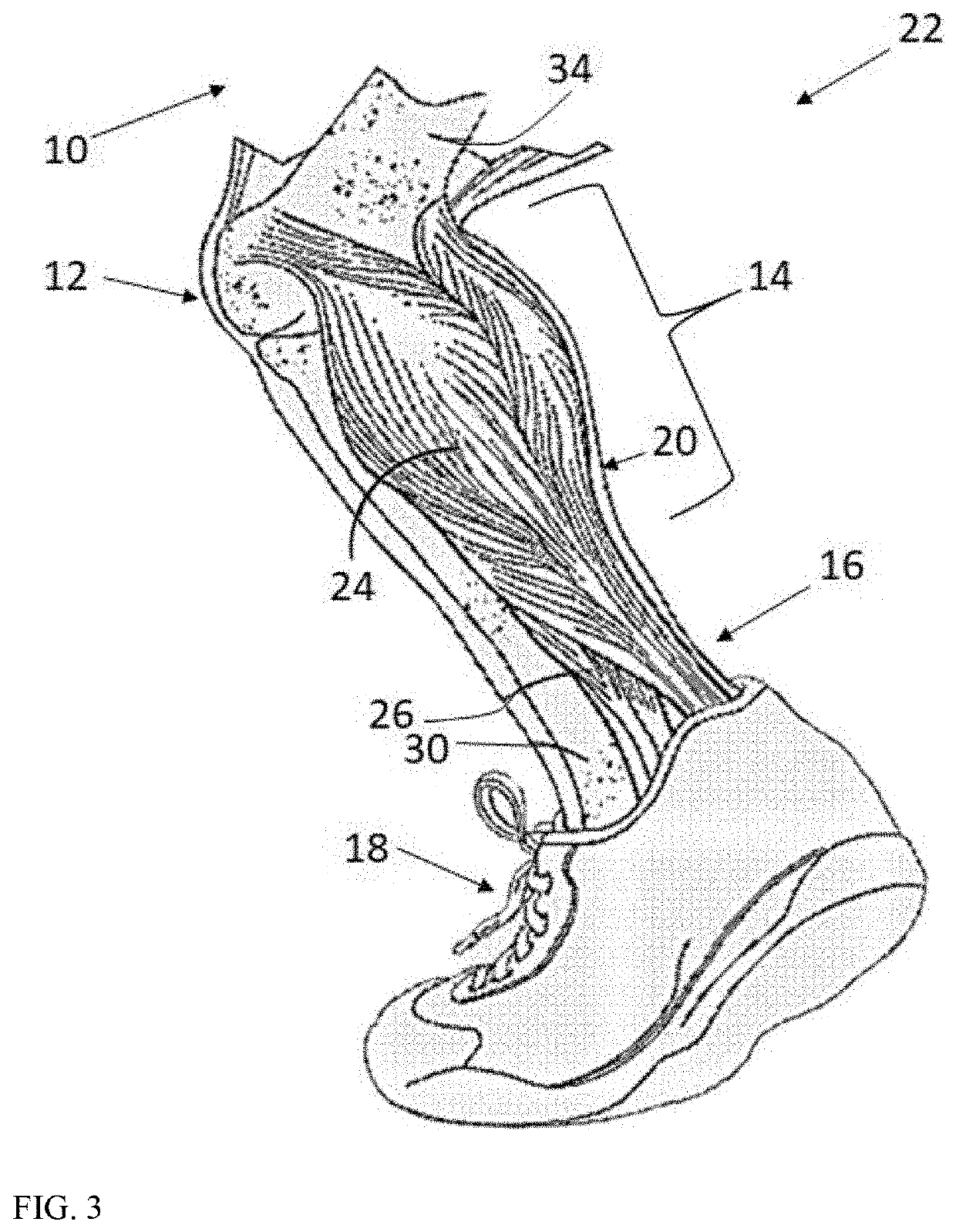
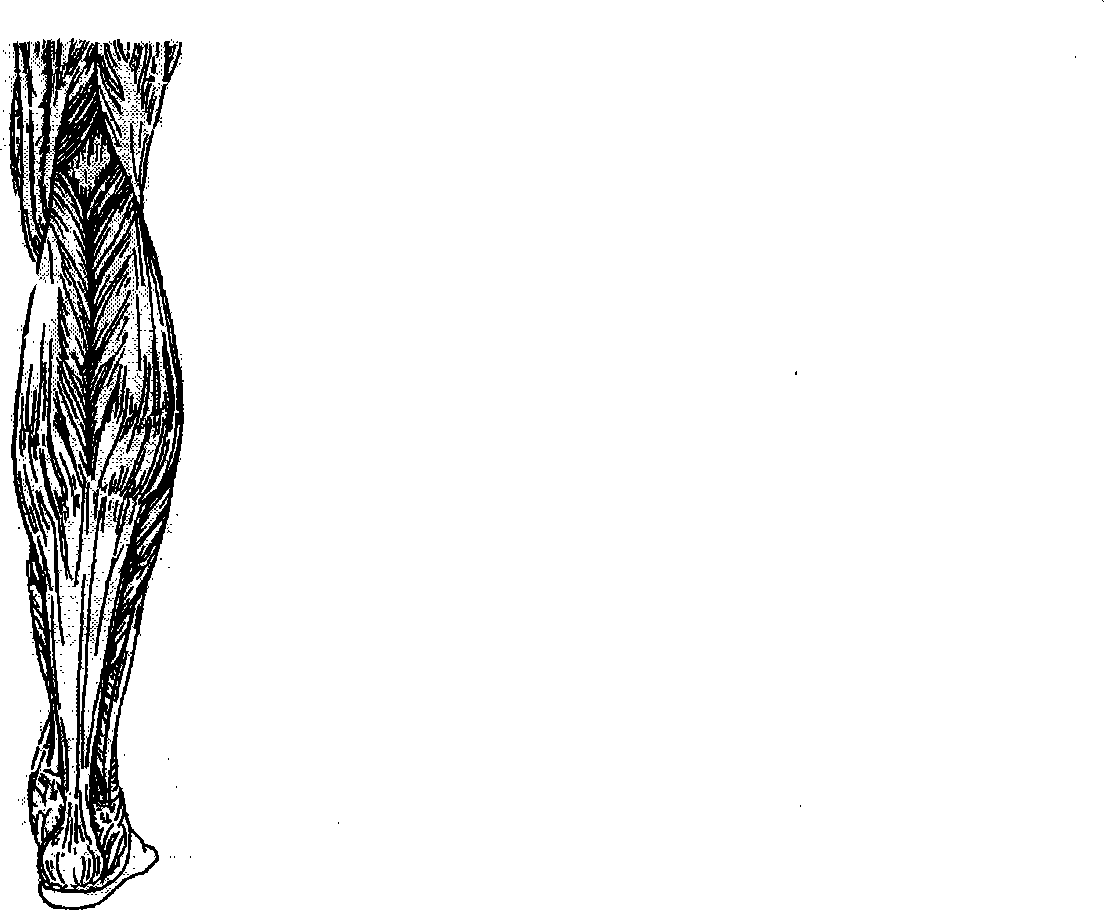
The gastrocnemius muscle (plural gastrocnemii) is a superficial two-headed muscle that is in the back part of the lower leg of humans. It runs from its two heads just above the knee to the heel, a three joint muscle (knee, ankle and subtalar joints). The muscle is named via Latin, from Greek γαστήρ (gaster) "belly or stomach" and κνήμη (knḗmē) "leg"; meaning "stomach of leg" (referring to the bulging shape of the calf).
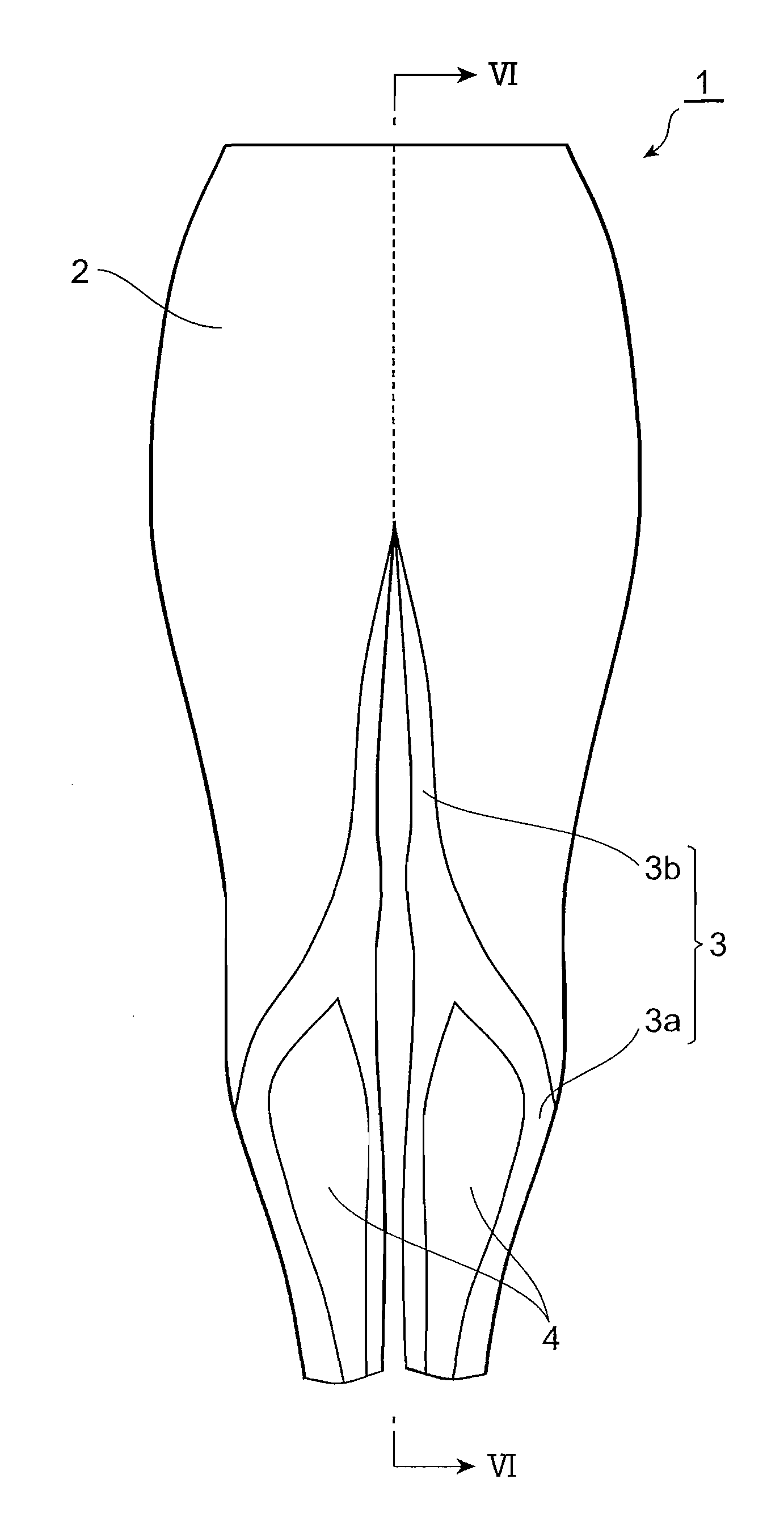
Garment with crotch part
InactiveUS20090007311A1Heat dissipationImprove breathabilityGarment special featuresTrousersThighEngineering
A conditioning bottom has a main body and a strong tightening portion which is in the form of a belt and has a tightening force stronger than a tightening force of the main body. This strong tightening portion has first strong tightening portions and a second strong tightening portion. When the conditioning bottom is worn, the first strong tightening portions extend so as to surround gastrocnemius muscles of a wearer along outer edges of the gastrocnemius muscles, and the second strong tightening portion is coupled to the first strong tightening portions and extends through the inside of the wearer's lower leg and thigh to a position of the wearer's crotch. Also, a first mesh portion having a tightening force weaker than the tightening force of the strong tightening portion is formed in a section surrounded by the first strong tightening portions.
Owner:WACOAL
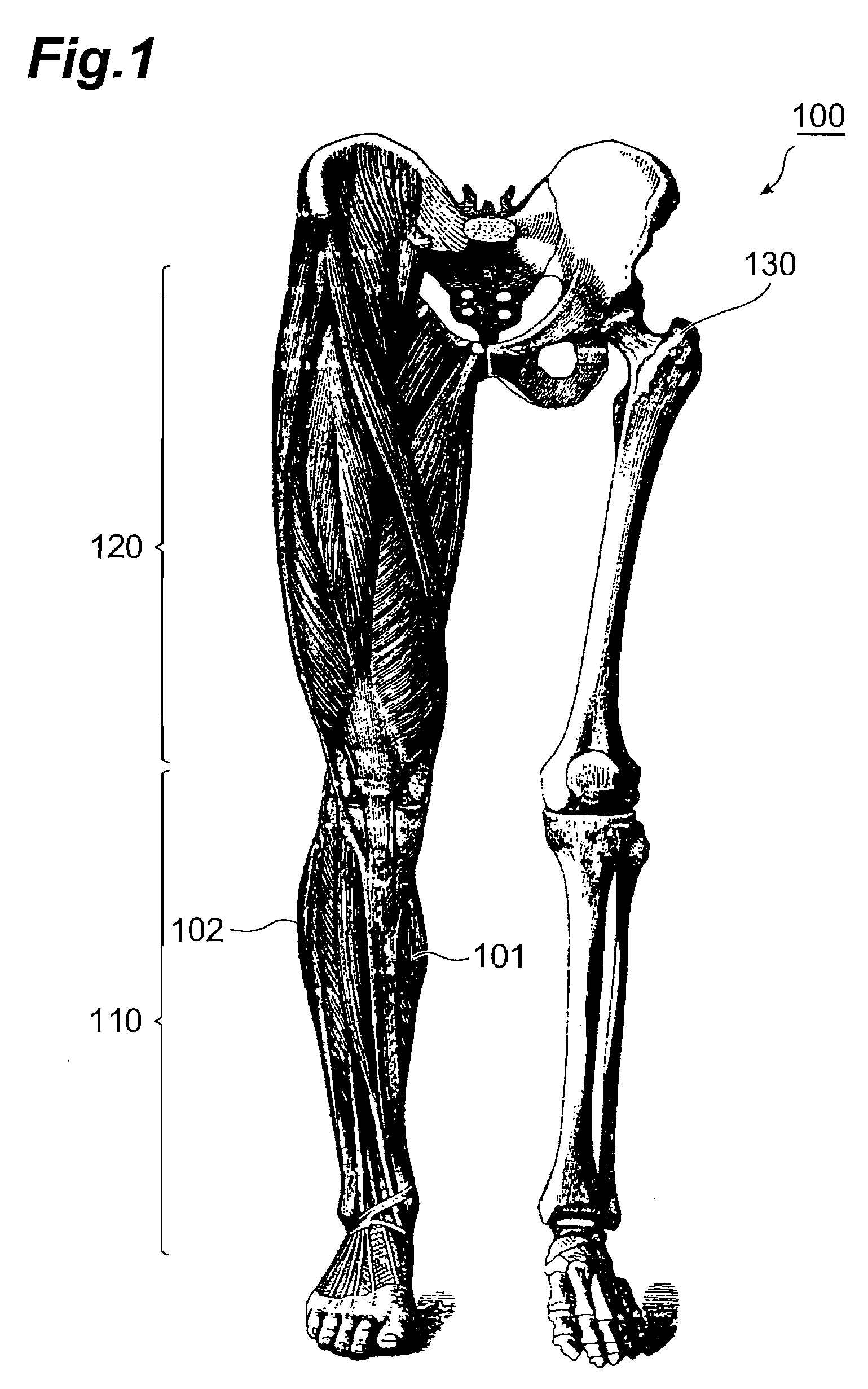
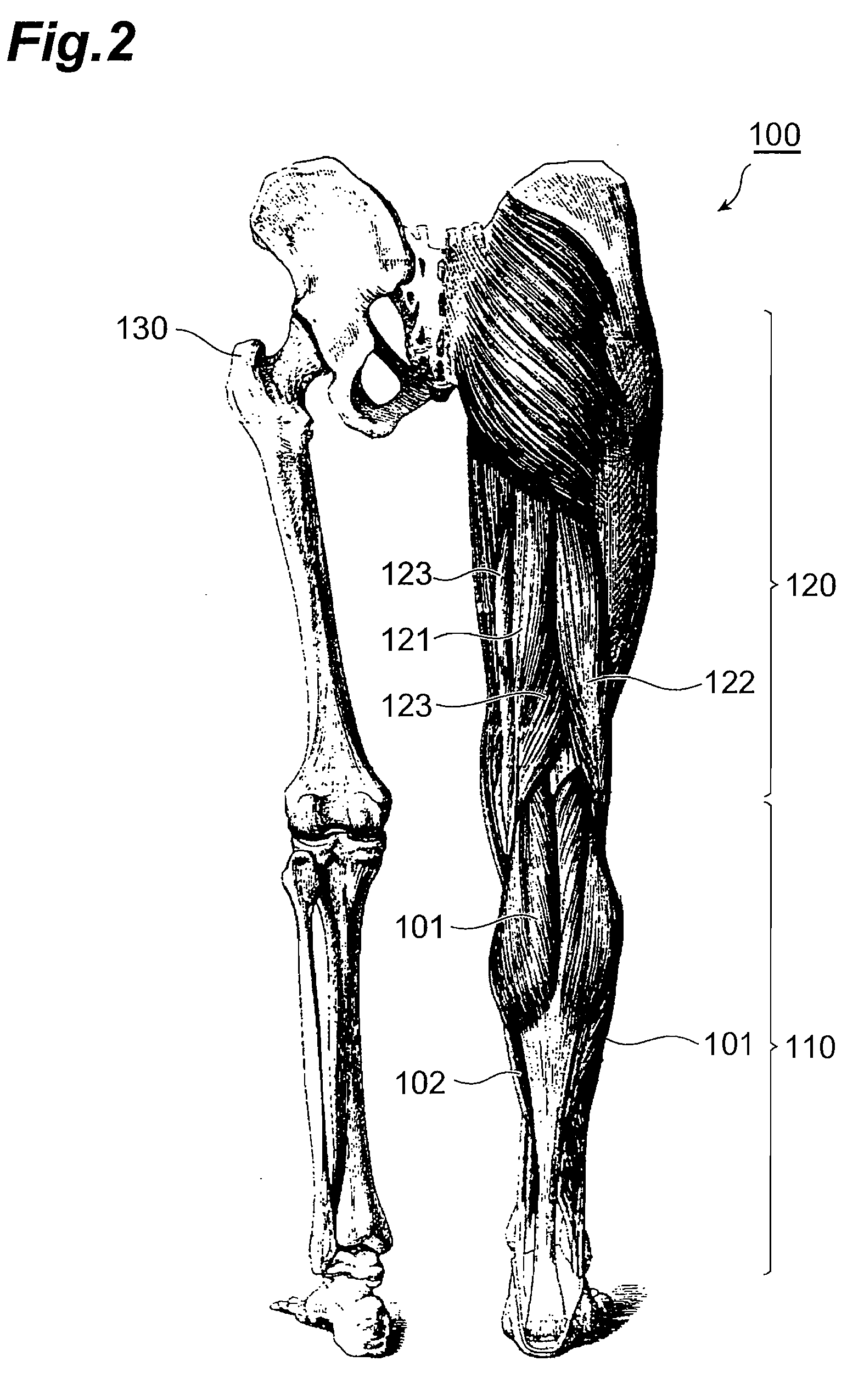
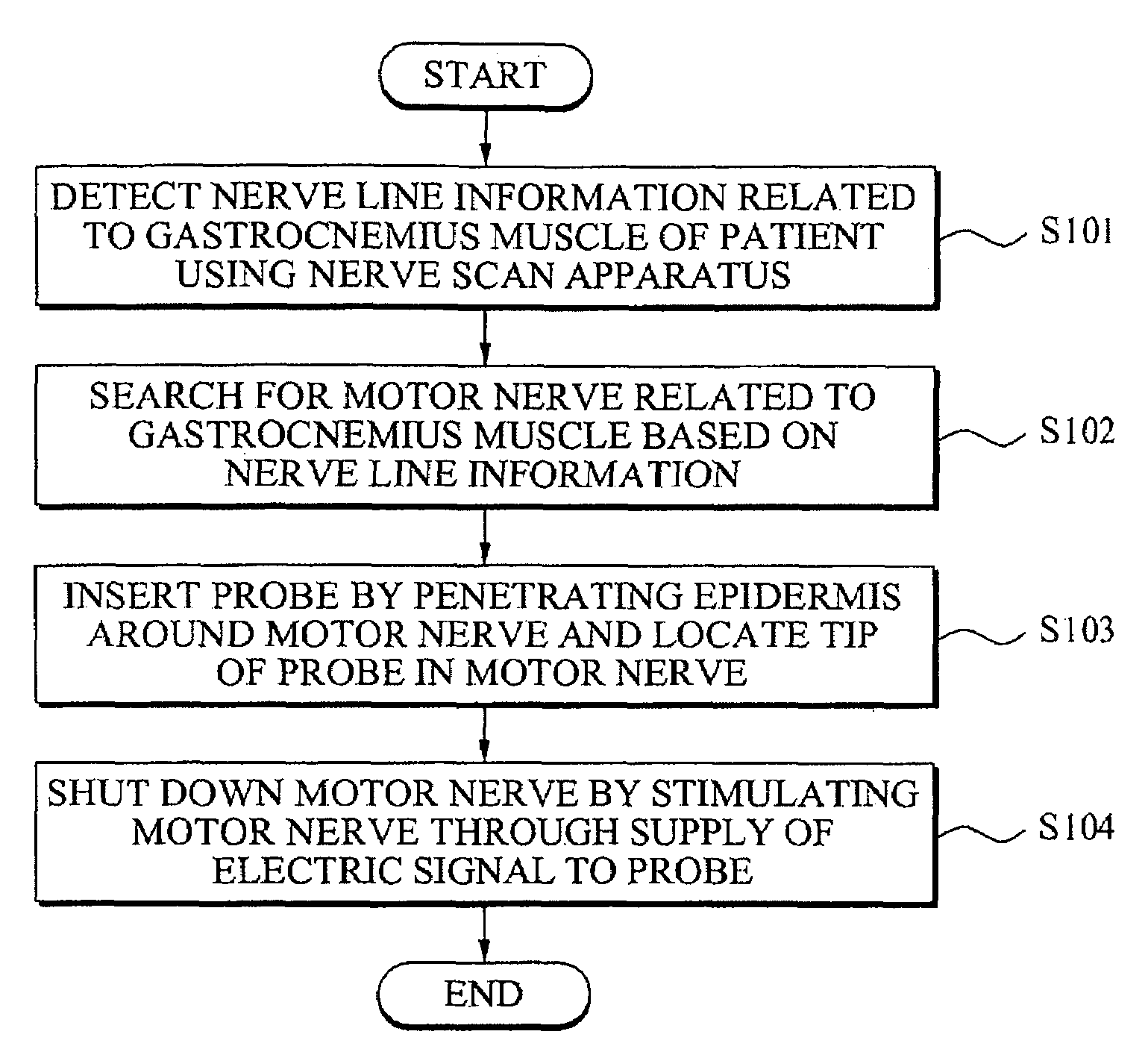
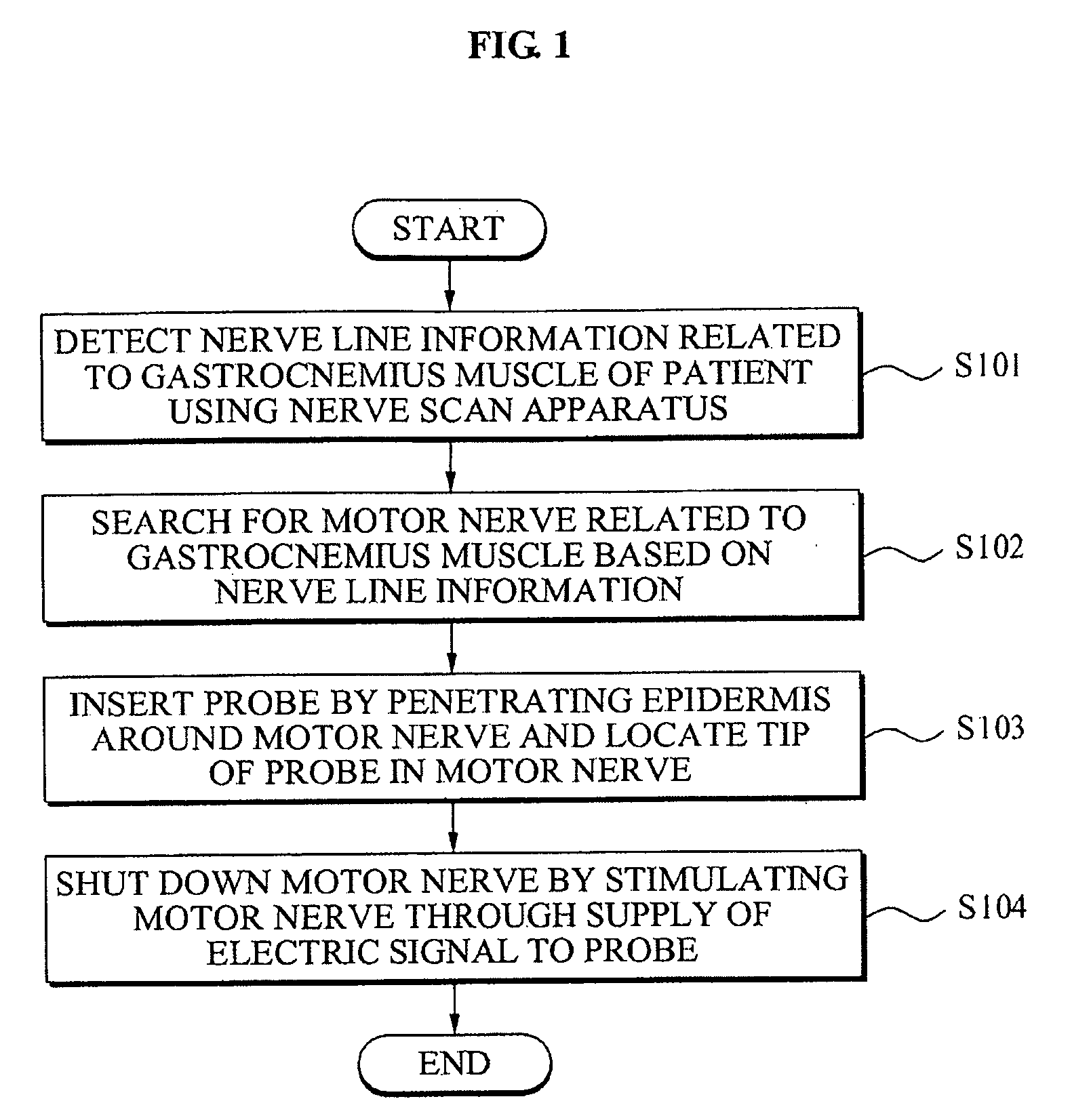
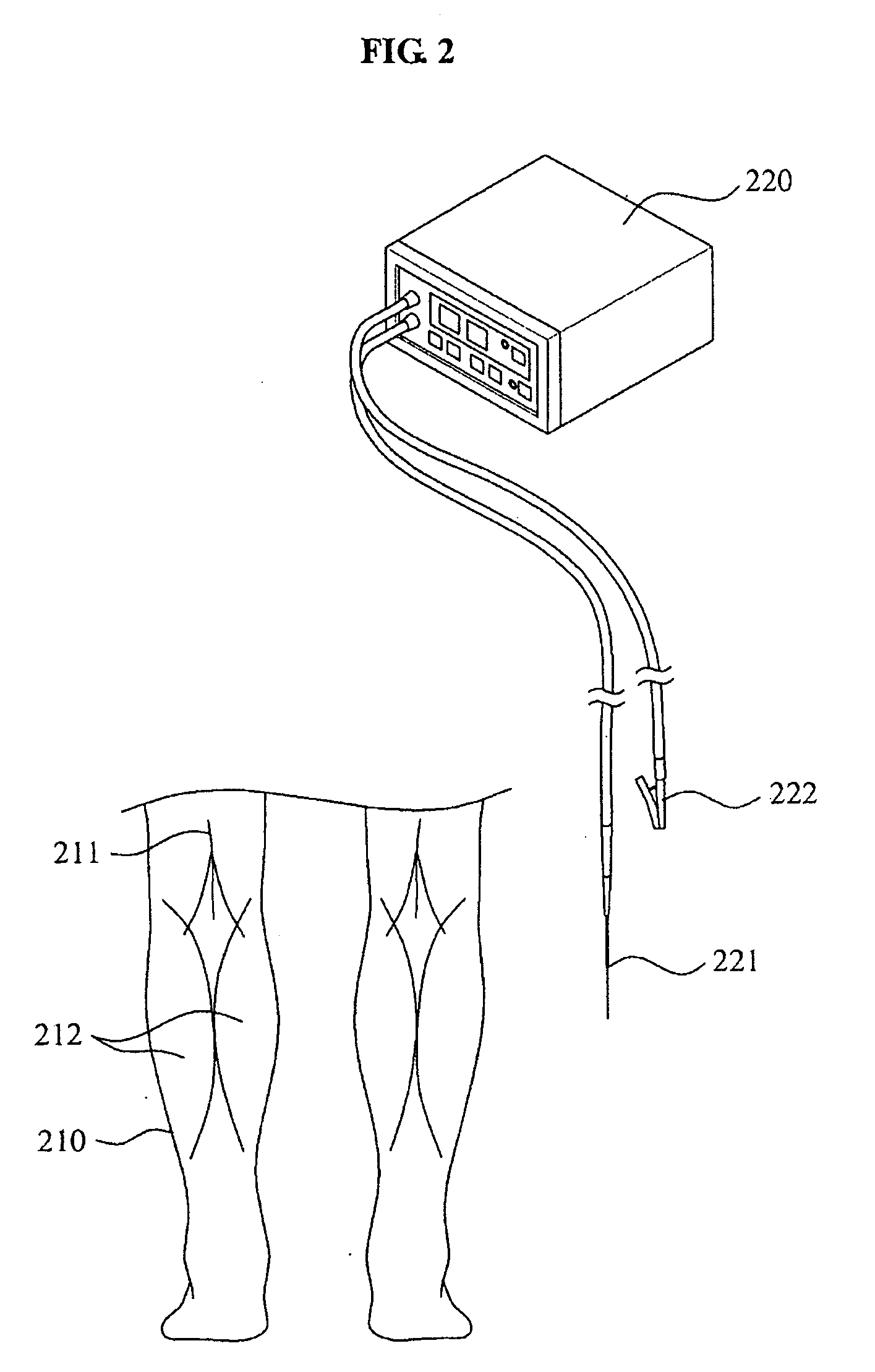
Surgical method for gastrocnemius muscle reduction
InactiveUS20100125220A1Easy and secure useMinimizeSpinal electrodesElectromyographyPhysical medicine and rehabilitationElectric signal
A surgical method for gastrocnemius muscle reduction is provided. The method may search for a motor nerve associated with a gastrocnemius muscle of a patient, inserts a probe by penetrating an epidermis around the motor nerve and locates a tip of the probe in the motor nerve, stimulates the motor nerve through supply of an electric signal to the probe, thereby shutting down the motor nerve.
Owner:SEONG YEON JAE
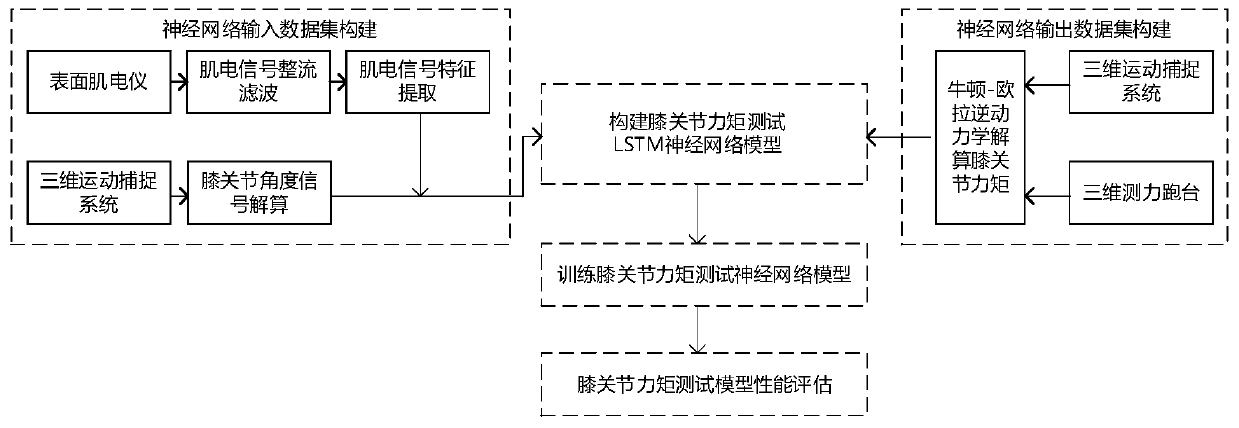
Human body knee joint force moment testing system and method based on surface electromyogram signals, and application
PendingCN110801226AIncrease sampling rateAccurate collectionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsHuman bodySimulation
The invention relates to a human body knee joint force moment testing system and method based on surface electromyogram signals, and an application. The method comprises the following steps of step 1,collecting electromyogram signals of four muscles of vastus lateralis, semitendinosus, biceps femoris long head and gastrocnemius muscle of lower limbs of a user, and performing feature extraction; step 2, synchronously collecting leg kinematics data of the user in the walking process through a three-dimensional movement acquiring system, computing knee joint angles of the user, besides, synchronously collecting the insole pressure of feet of the user in the walking process through a force measuring treadmill, constructing a simplified dynamics model of legs of the user, and performing inverse dynamics solving to obtain the calculated force moment of knee joints of the user; and step 3, constructing a training dataset and a test dataset of a knee joint force moment testing long-term and short-term memory (LSTM) neural network, and completing the training of the knee joint force moment test neural network model through data obtained in the step 1 and the data obtained in the step 2. The method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of being wide in application range and high in test precision.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
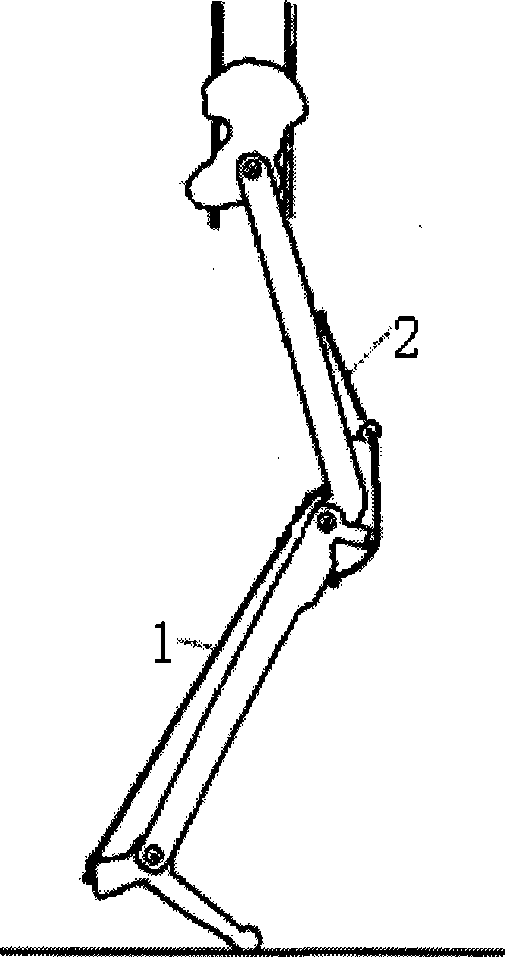
Biped robot based on pneumatic artificial muscles
The invention discloses a biped robot based on pneumatic artificial muscles and relates to biped robots. The biped robot based on the pneumatic artificial muscles aims to solve the problems that an existing active robot is driven through a rigid structure, the system structure is complicated, the flexibility is poor, and the energy efficiency of the existing active robot is low. The biped robot based on the pneumatic artificial muscles comprises a left leg, a right leg and a pelvis. The left leg and the right leg each comprise a thigh, a shank, a foot, a hip joint, a knee joint and an ankle joint. The left leg and the right leg are connected through the pelvis. The pelvis is connected with the thighs in a rotary mode through the hip joints. The thighs are connected with the shanks in a rotary mode through the knee joints. The shanks are connected with the feet in a rotary mode through the ankle joints. The iliac muscles, the gluteus maximus, the vastus lateralis muscles, the biceps femoris muscles, the semitendinous muscles and the rectus femoris muscles are arranged on the thighs. The tibialis anterior muscles, the soleus muscles and the gastrocnemius muscles are arranged on the shanks. The upper ends of the iliac muscles and the upper ends of the gluteus maximus are hinged to the pelvis respectivley. The lower ends of the iliac muscles and the lower ends of the gluteus maximus are hinged to the thighs respectively. The upper ends of the vastus lateralis muscles and the upper ends of the biceps femoris muscles are hinged to the thighs respectively. The biped robot based on the pneumatic artificial muscles belongs to the field of humanoid robots.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Differential expression of nucleic acid molecules
InactiveUS20060228775A1Treatment effectPeptide/protein ingredientsTissue cultureMyopathyMesenteric adipose tissue
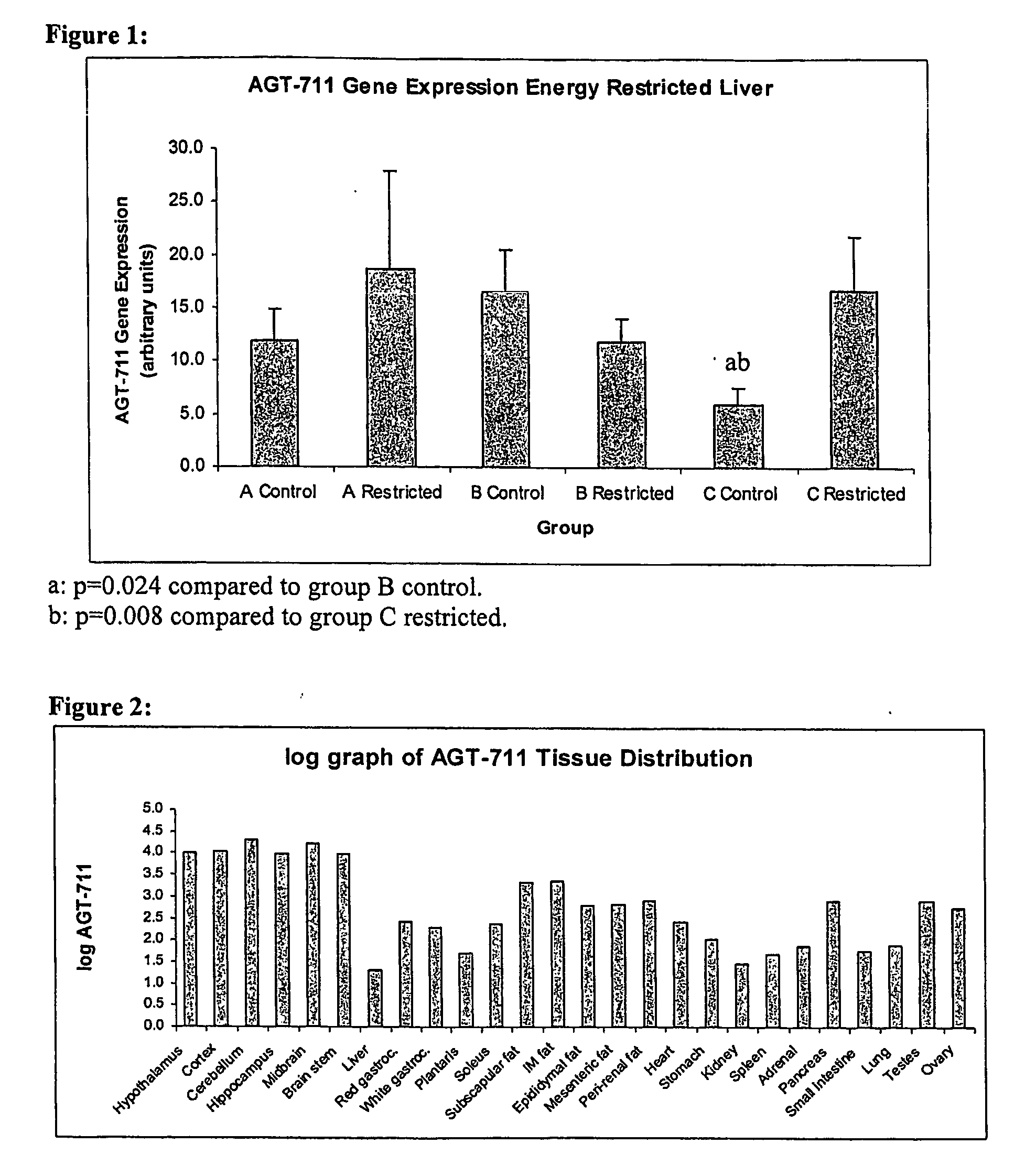
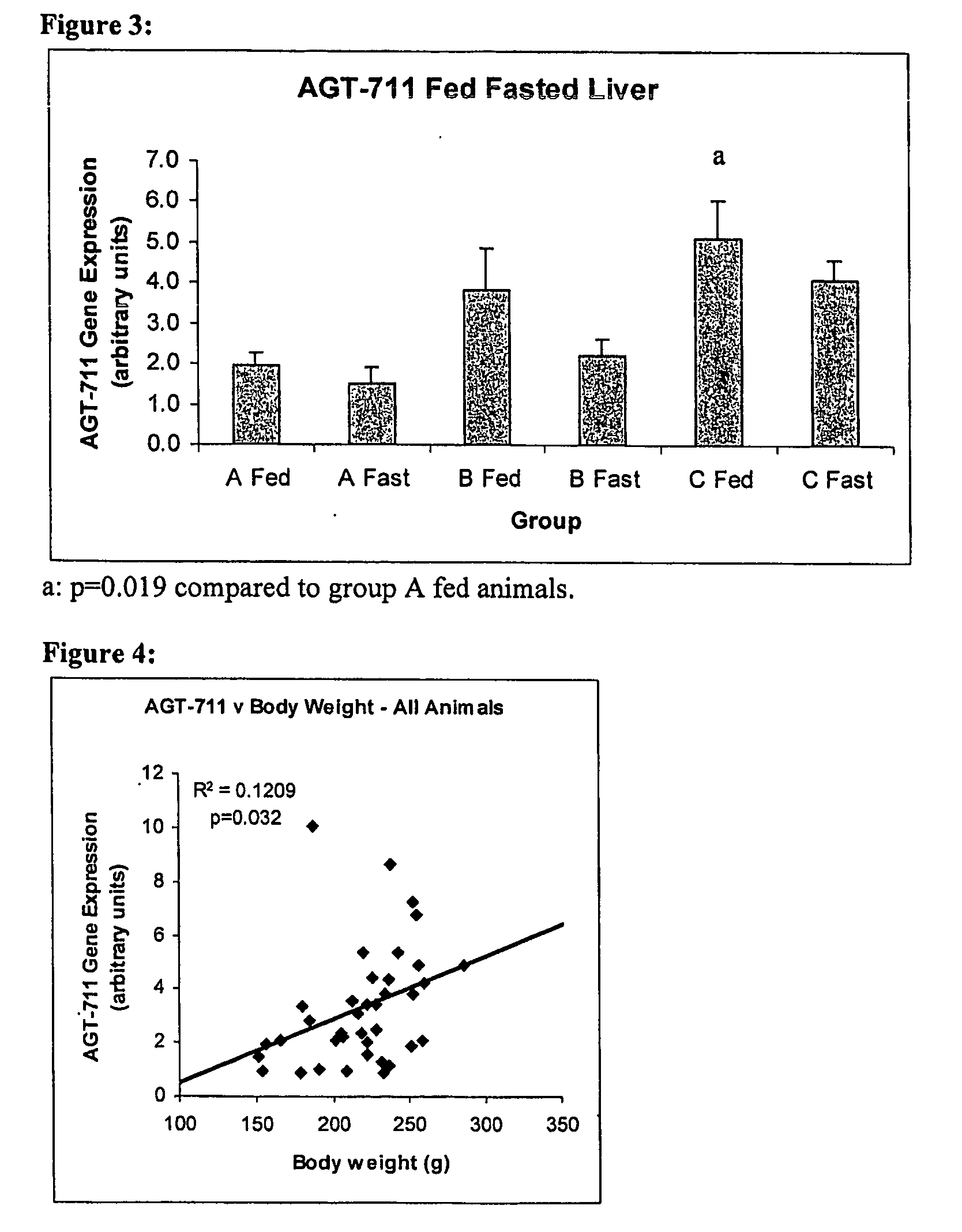
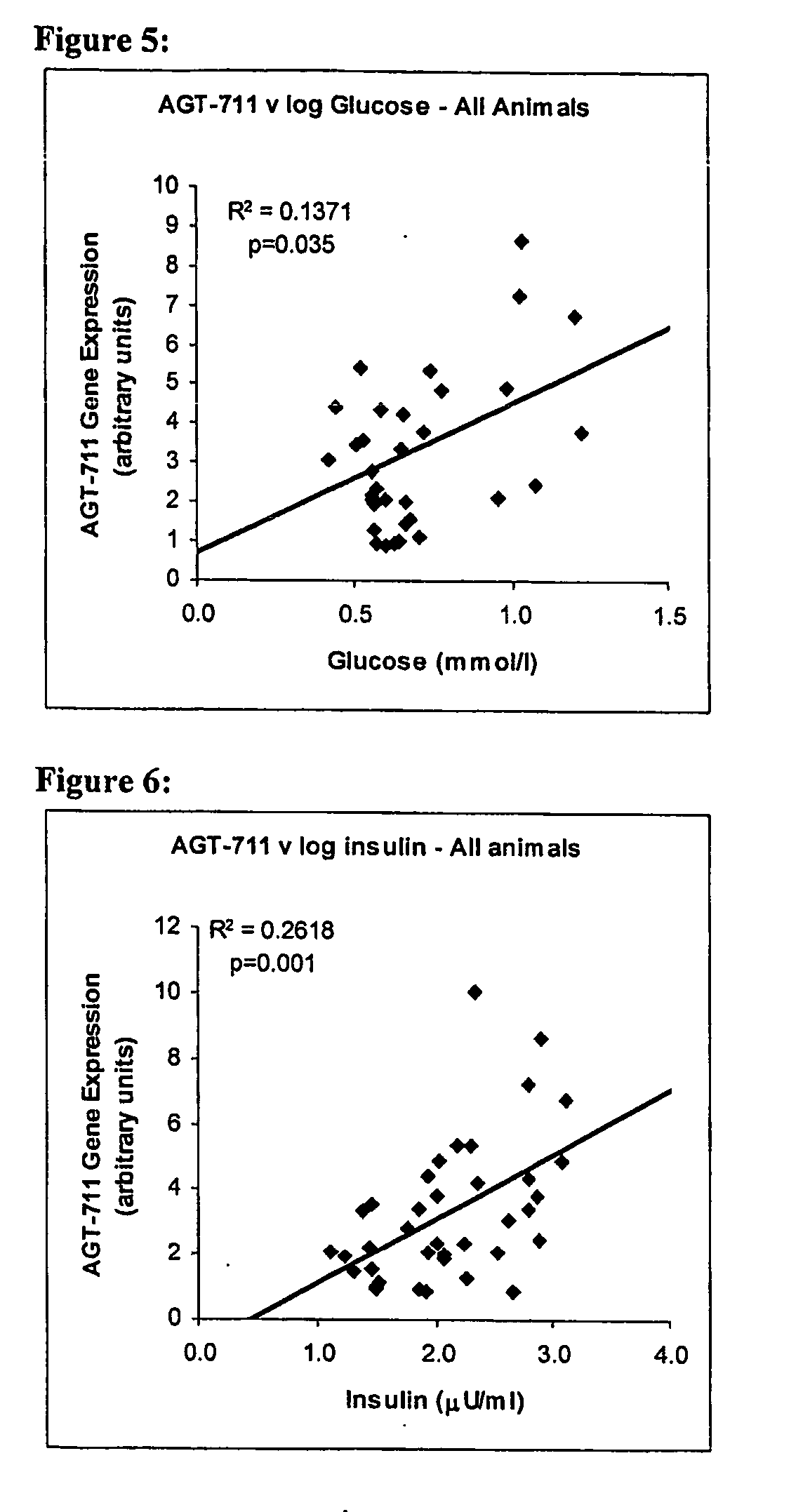
The present invention relates generally to nucleic acid molecules expressed at least in the hypothalamus, liver, mesenteric adipose tissue, or red gastrocnemius muscle conveniently identified using differential display techniques under differing physiological conditions. The nucleic acid molecules are associated with or act as markers for conditions of inter alia a healthy state, myopathy, obesity, anorexia, weight maintenance, diabetes, disorders associated with mitochondrial dysfunction, genetic disorders and / or metabolic energy levels. More particularly, the present invention is directed to a nucleic acid molecule and / or its expression product for use in therapeutic and diagnostic protocols for conditions such as inter alia a myopathy, obesity, anorexia, weight maintenance, diabetes, disorders associated with mitochondrial dysfunction, genetic disorders and / or metabolic energy levels. The subject nucleic acid molecule and expression product and their derivatives, homologs, analogs and mimetics are proposed to be useful, therefore, as therapeutic and diagnostic agents for inter alia a myopathy, obesity, anorexia, weight maintenance, diabetes, disorders associated with mitochondrial dysfunction, genetic disorders and / or metabolic energy levels or as targets for the design and / or identification of modulators of their activity and / or function.
Owner:CHEMGENEX PHARMA
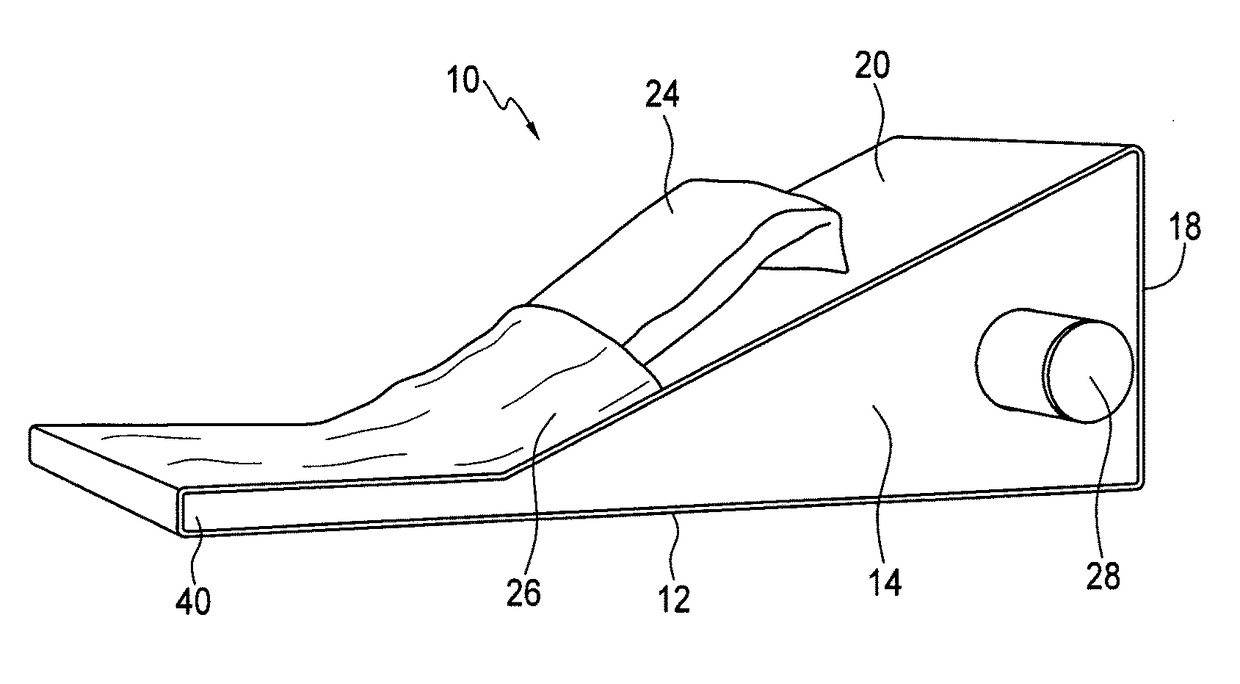
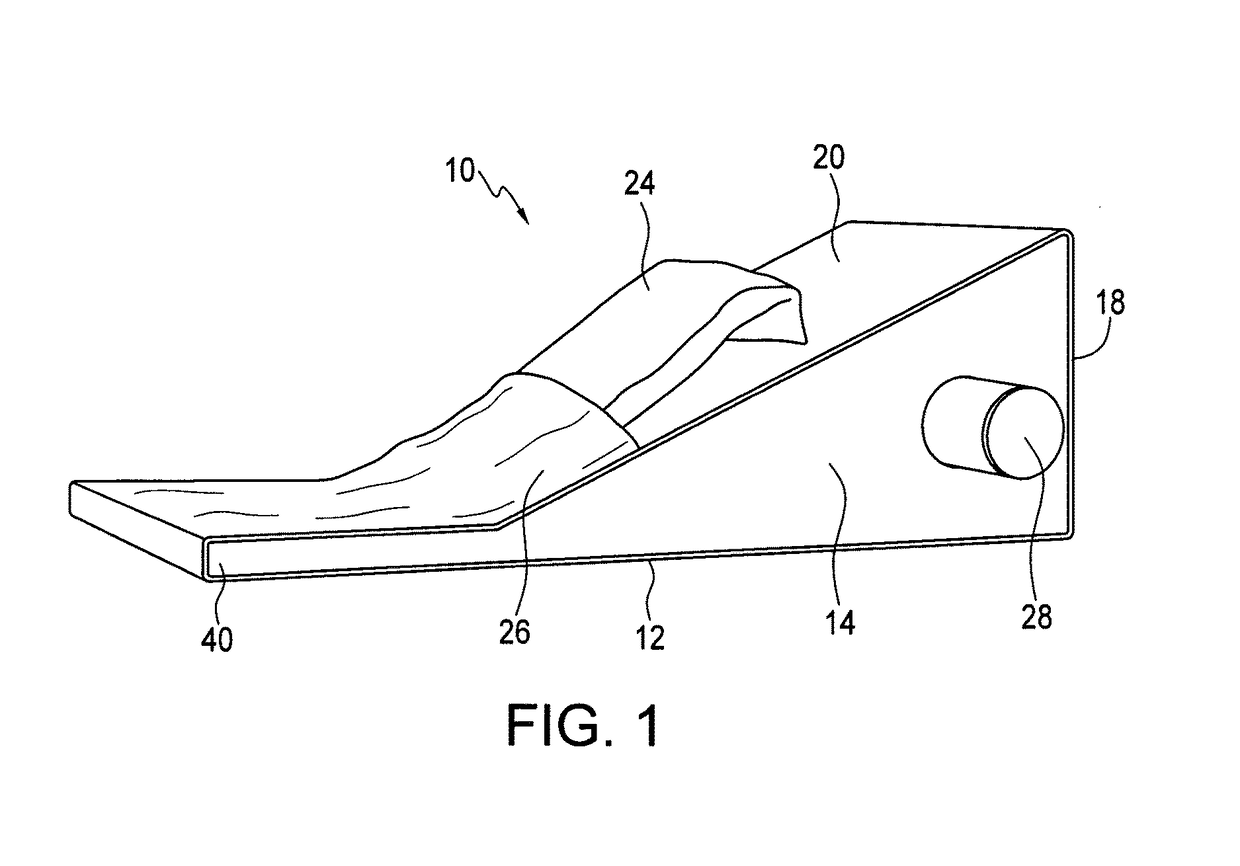
Methods for treating inflammatory symptoms associated with plantar fasciitis
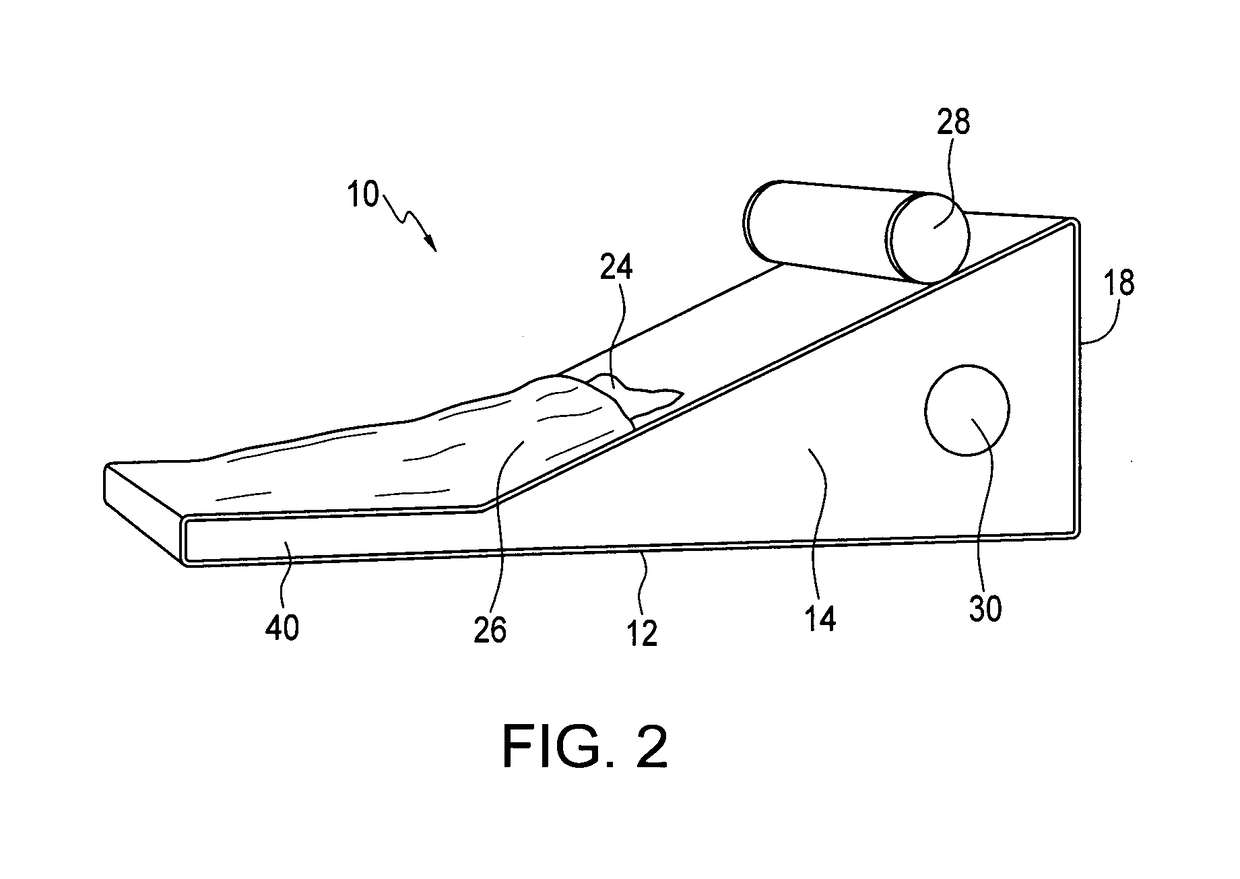
ActiveUS20160270998A1Gymnastic exercisingChiropractic devicesGastrocnemius aponeurosisPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
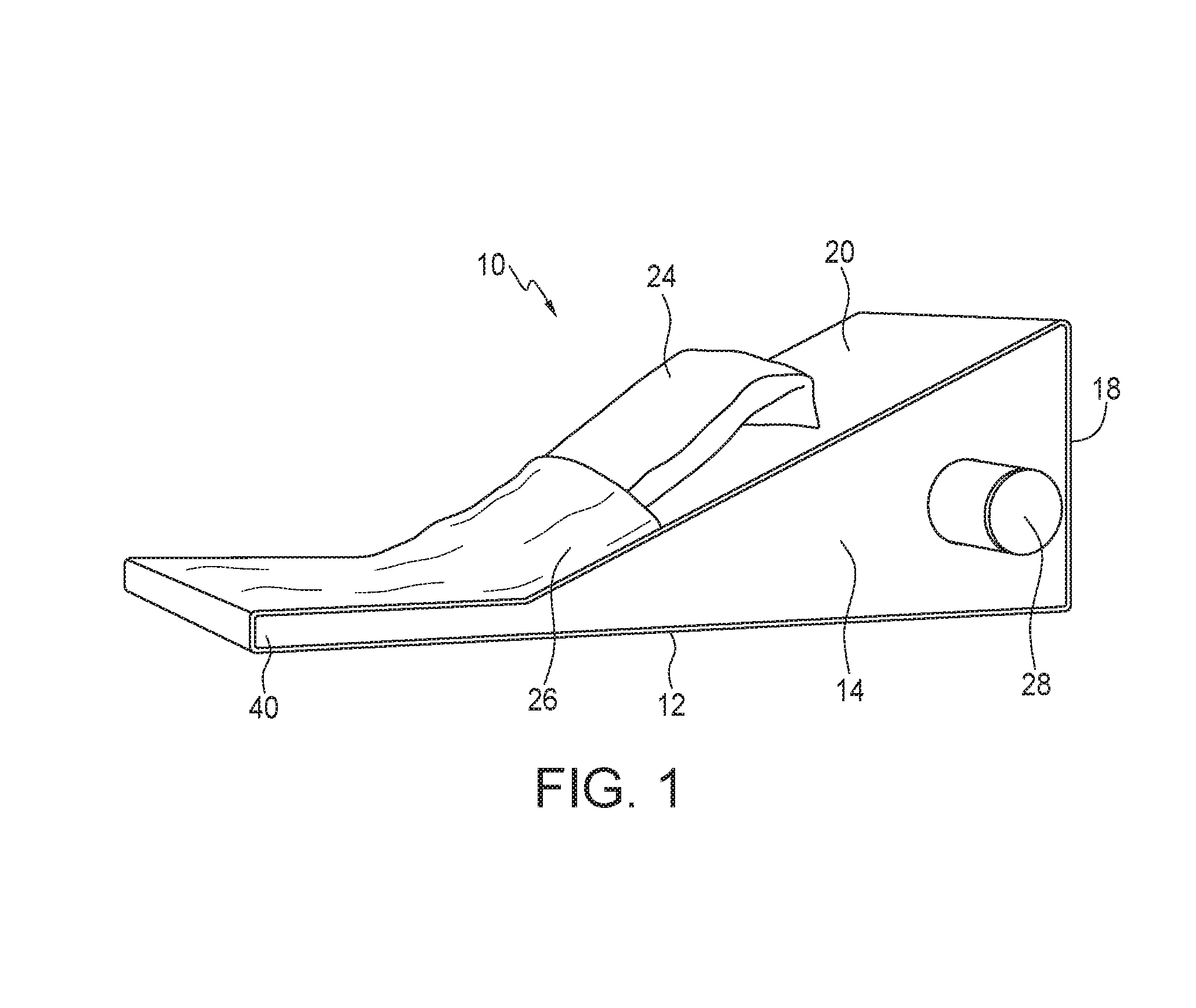
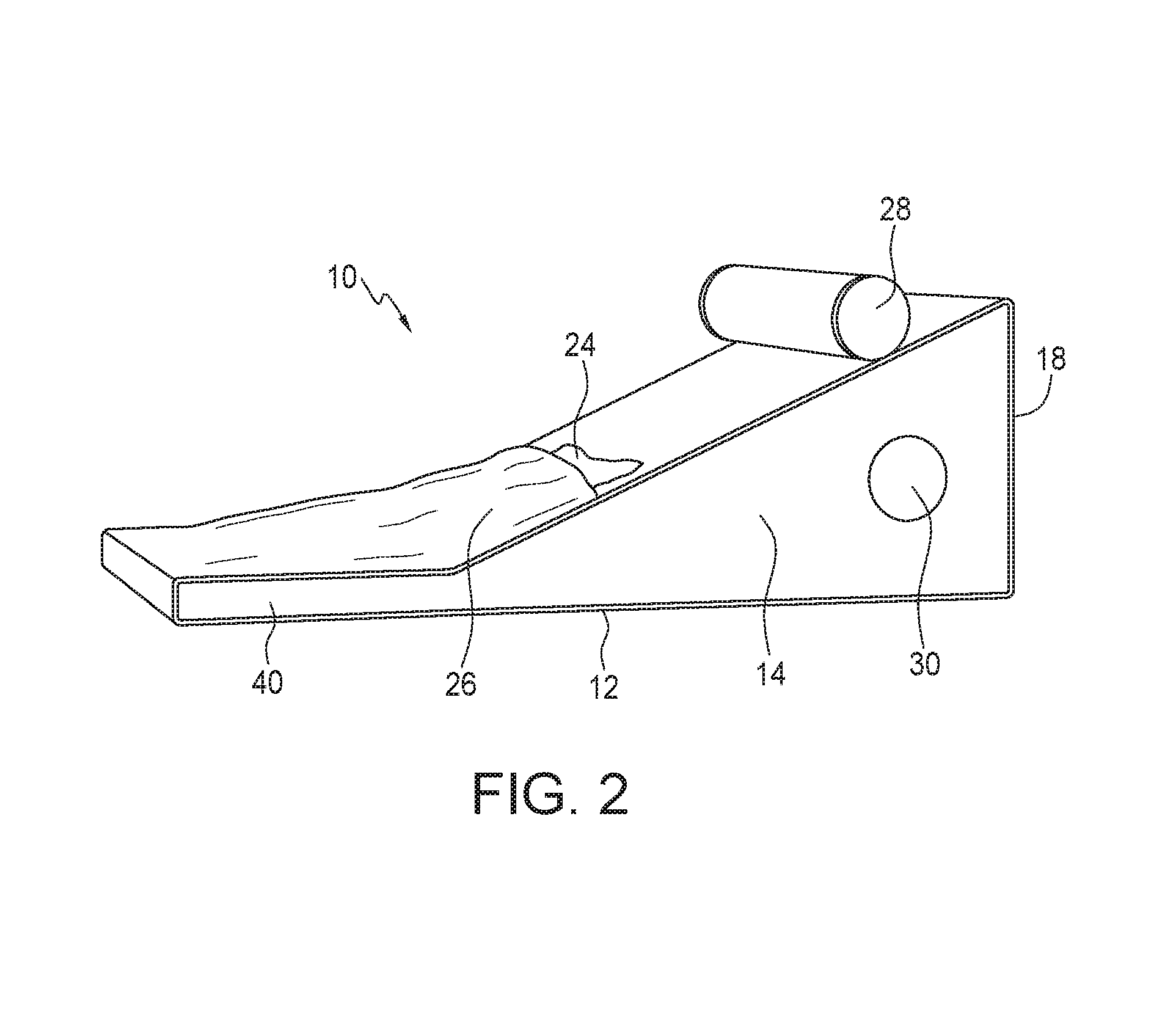
The present invention relates to a method for treating inflammatory symptoms associated with plantar fasciitis in a foot. The method involves stretching gastrocnemius and soleus muscles associated with the foot by placing the sole of the foot on an inclined ramp surface and cooling at least one portion of the sole of the foot. The method may further involve providing localized pressure to at least one portion of the plantar fascia, and to a portion of the foot below the toes, to cause dorsiflexion thereof.
Owner:THERMAWEDGE ENTERPRISES
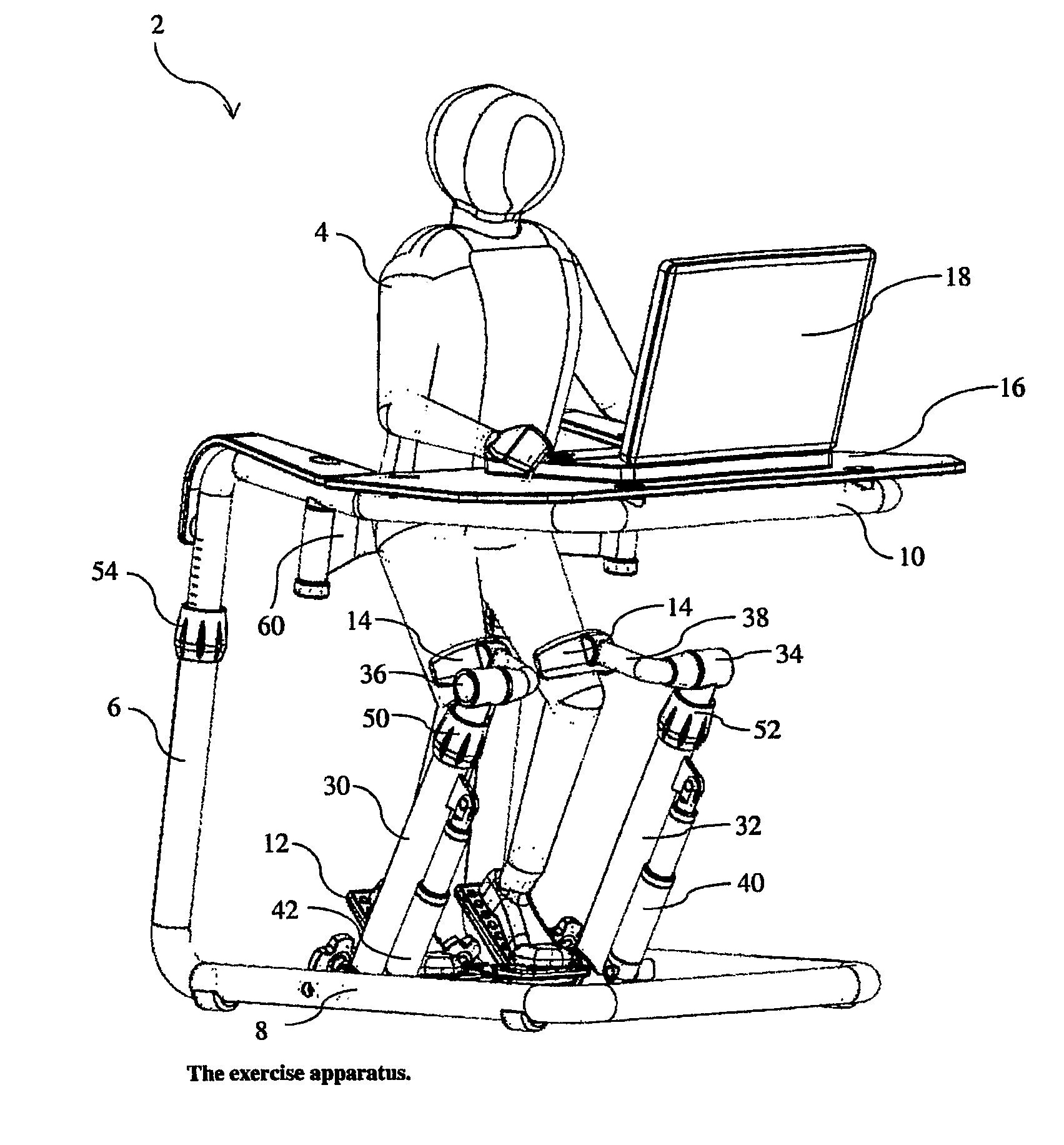
Ankle joint exercising device and control method thereof
The invention relates to an ankle joint exercising device used for solving technical problems of cerebrovascular sequelae in the neurology department, foot drops, muscle atrophy and venous thrombosis by driving ankle joints to move. The ankle joint exercising device comprises a fixing support, a pedal and a driving device, wherein the fixing support comprises a bottom support and a calf fixing support; the pedal is rotationally connected with the fixing support; the driving device can drive the pedal to rotate relative to the bottom support. Limbs are fixed on the calf fixing support and the pedal, the driving device drives the pedal to rotate so as to drive the ankle joints to move, calf gastrocnemius muscle and Achilles tendons can be effectively exercised, and Achilles tendon contracture and calf muscle disuse atrophy conditions are reduced. The invention further relates to a control method of the ankle joint exercising device.
Owner:徐增良
Method and device for activating lipid and blood glucose reduction through gastrocnemius passive movement
The invention discloses a method and device for activating lipid and blood glucose reduction through gastrocnemius passive movement. The device is provided with a bottom plate, a leg fixing frame is fixed to the rear end of the bottom plate, leg fixing bands and an ankle joint fixing band are arranged on the leg fixing frame, pedals are hinged to connecting positions of the bottom plate and legs, one or more pedals are arranged, and a driving device for driving the pedals to ascend or descend is arranged between each pedal and the bottom plate and comprises an air bag located between each pedal and the bottom plate, the upper and lower surfaces of the air bags are connected with the pedals and the bottom plate respectively, the air bags are connected with gas pipes, and the gas pipes are connected with a pressure-adjustment automatic charging and discharging gas pump. Compared with the prior art, the device is simple in structure and convenient to use, contracting and loosening of the gastrocnemius can be achieved, the effect of the gastrocnemius pump can be achieved, backflow of lower limb blood can be promoted, deep venous thrombosis can be effectively prevented, and circulation of lower limb blood can be improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN CHANGER MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
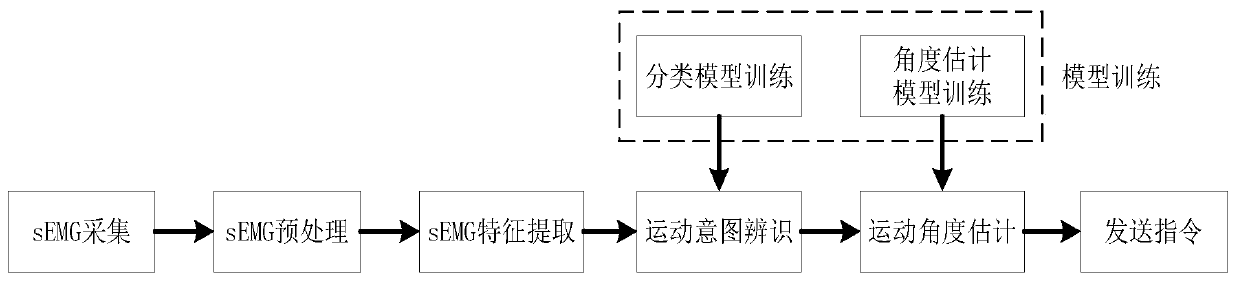
Control method for active rehabilitation treatment by using sEMG on affected side of patient
InactiveCN109758336AEasy to adaptEasy to operateChiropractic devicesControllers with particular characteristicsAnkle rehabilitationTarget–action
The invention relates to a control method for active rehabilitation treatment by using sEMG on an affected side of a patient. The control method comprises a model training stage and an online active rehabilitation treatment stage. The method utilizes the antagonistic relationship between the tibialis anterior muscle and the gastrocnemius muscle during ankle joint movement, enables the action typeof the ankle joint correlated with the contraction of a single muscle group, and achieves the movement intention identification; continuous estimation of a motion angle is completed and a continuous smooth joint motion angle estimation curve is obtained by utilizing a normalized characteristic value; then, the identified motion intention and the estimated joint motion angle serve as inputs to be sent to an ankle joint rehabilitation robot, the robot assists the patient to achieve a target action, and corresponding active rehabilitation treatment is completed. The method can meet the requirements of patients for simple control, safety and reliability of the exoskeleton type ankle rehabilitation device. For patients in different rehabilitation stages, only a small amount of parameters need to be modified, an off-line model can be well adapted, and the off-line model is more convenient, fast and easy to operate.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Leg supporter
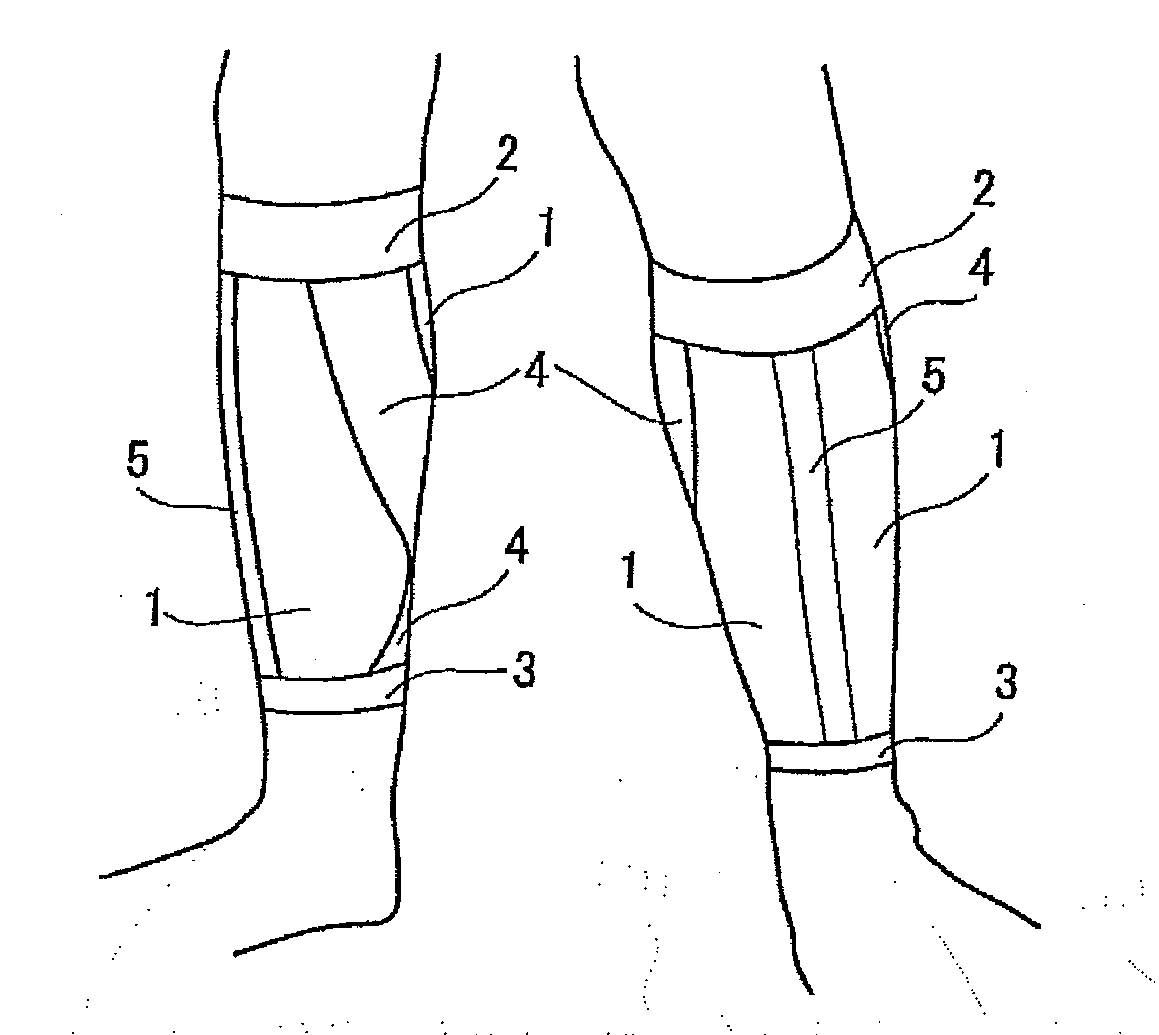
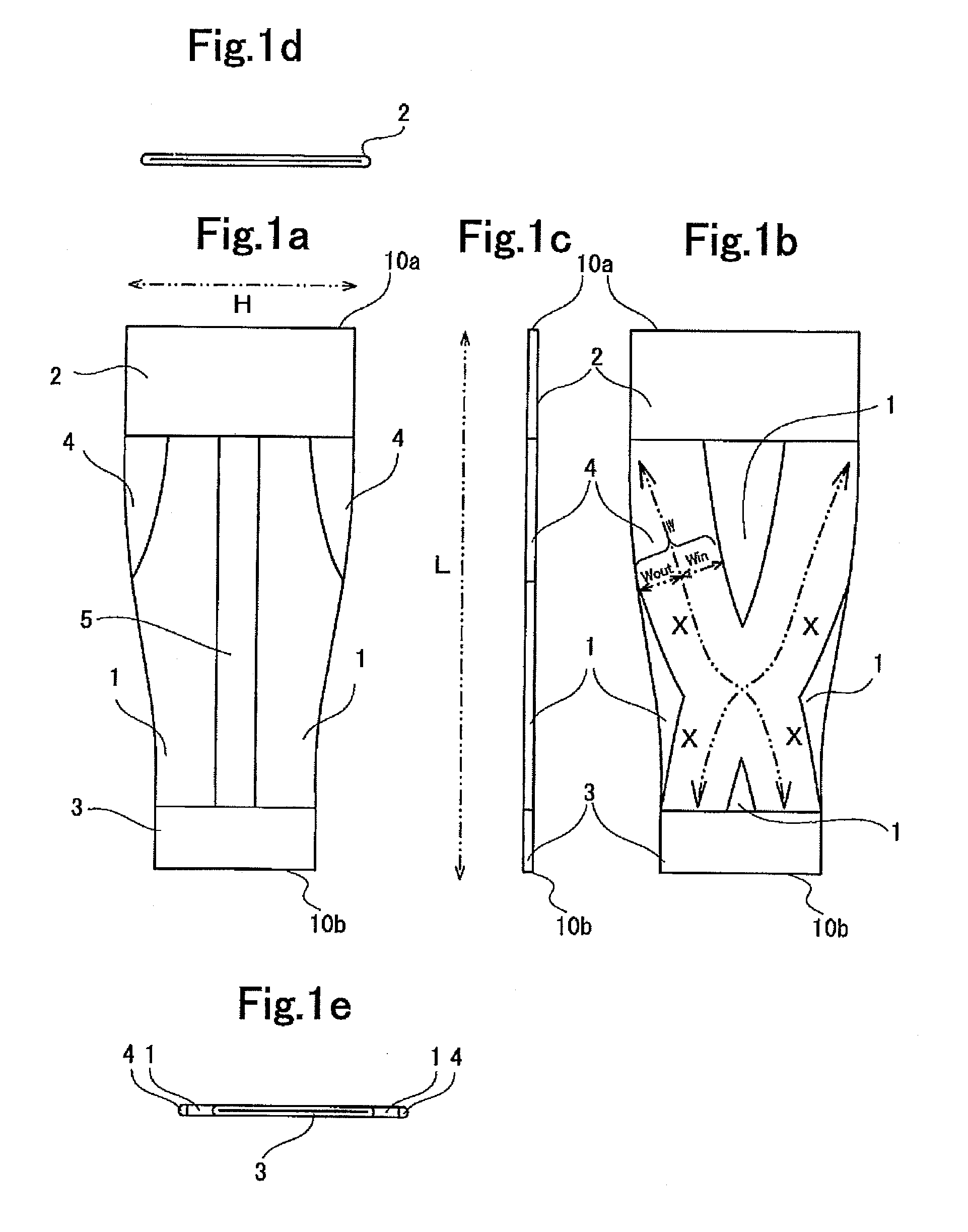
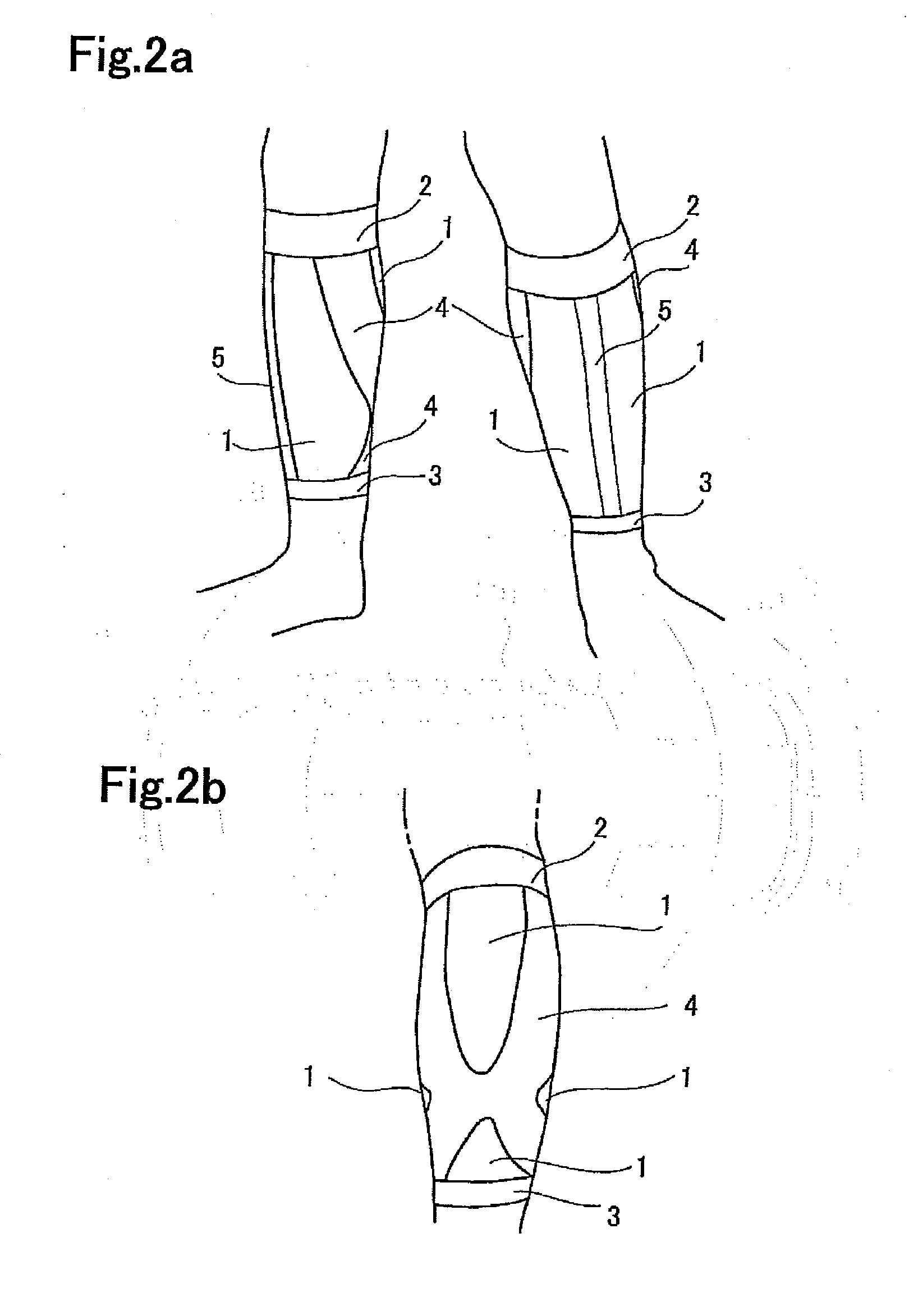
ActiveUS20130281903A1Ensure safetyReduce wearer 's fatigueWeft knittingFeet bandagesPhysical therapyAnkle
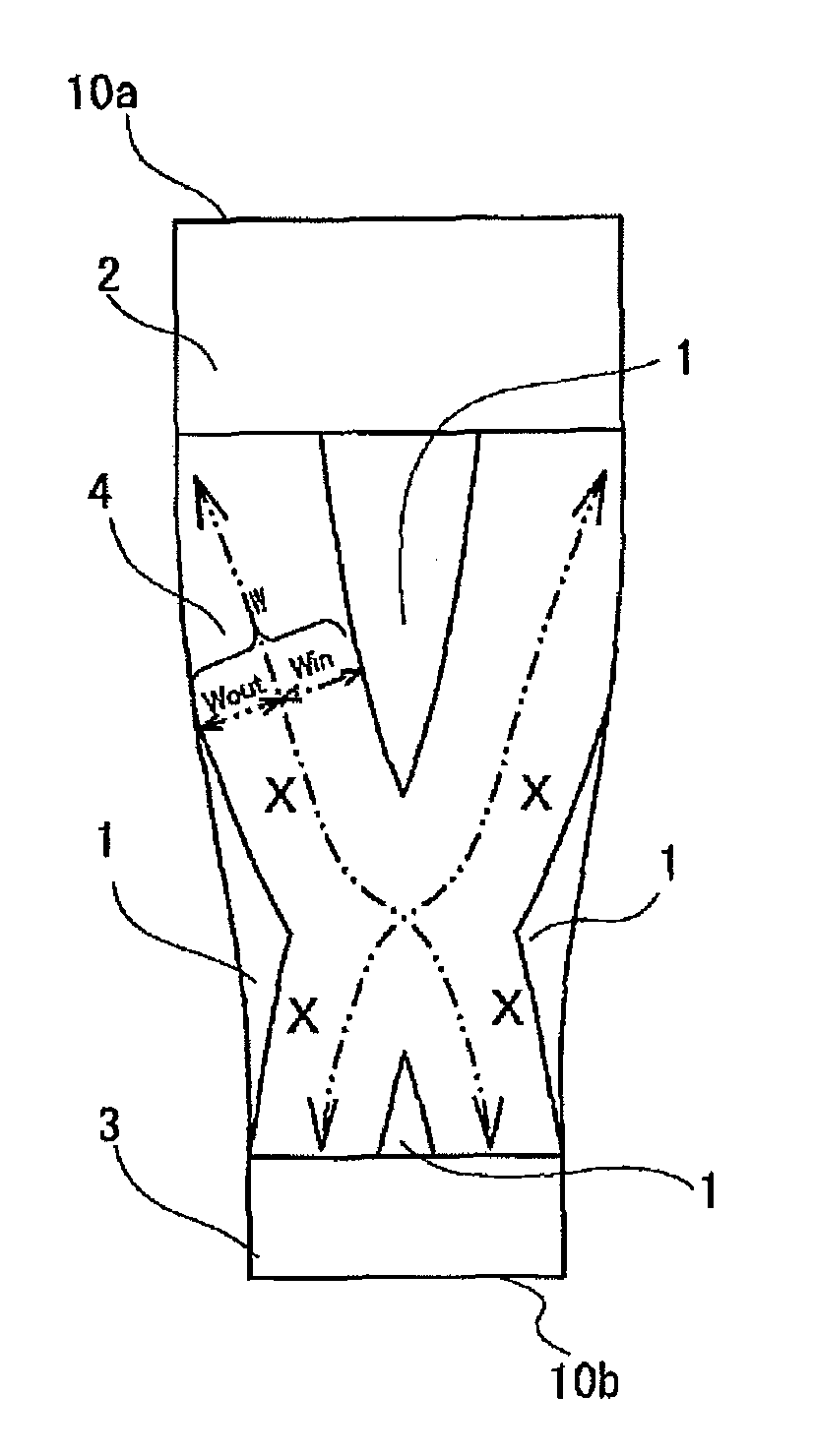
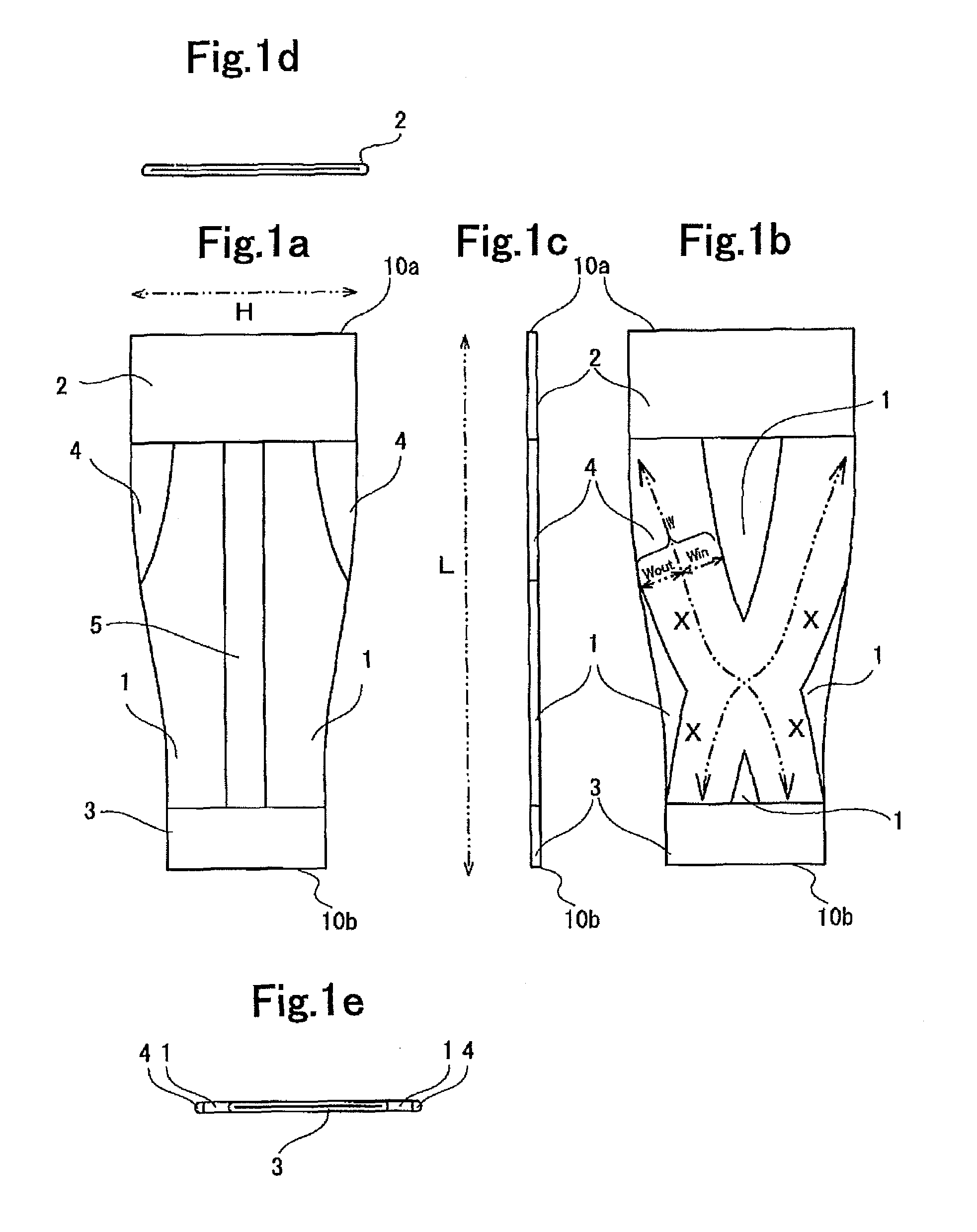
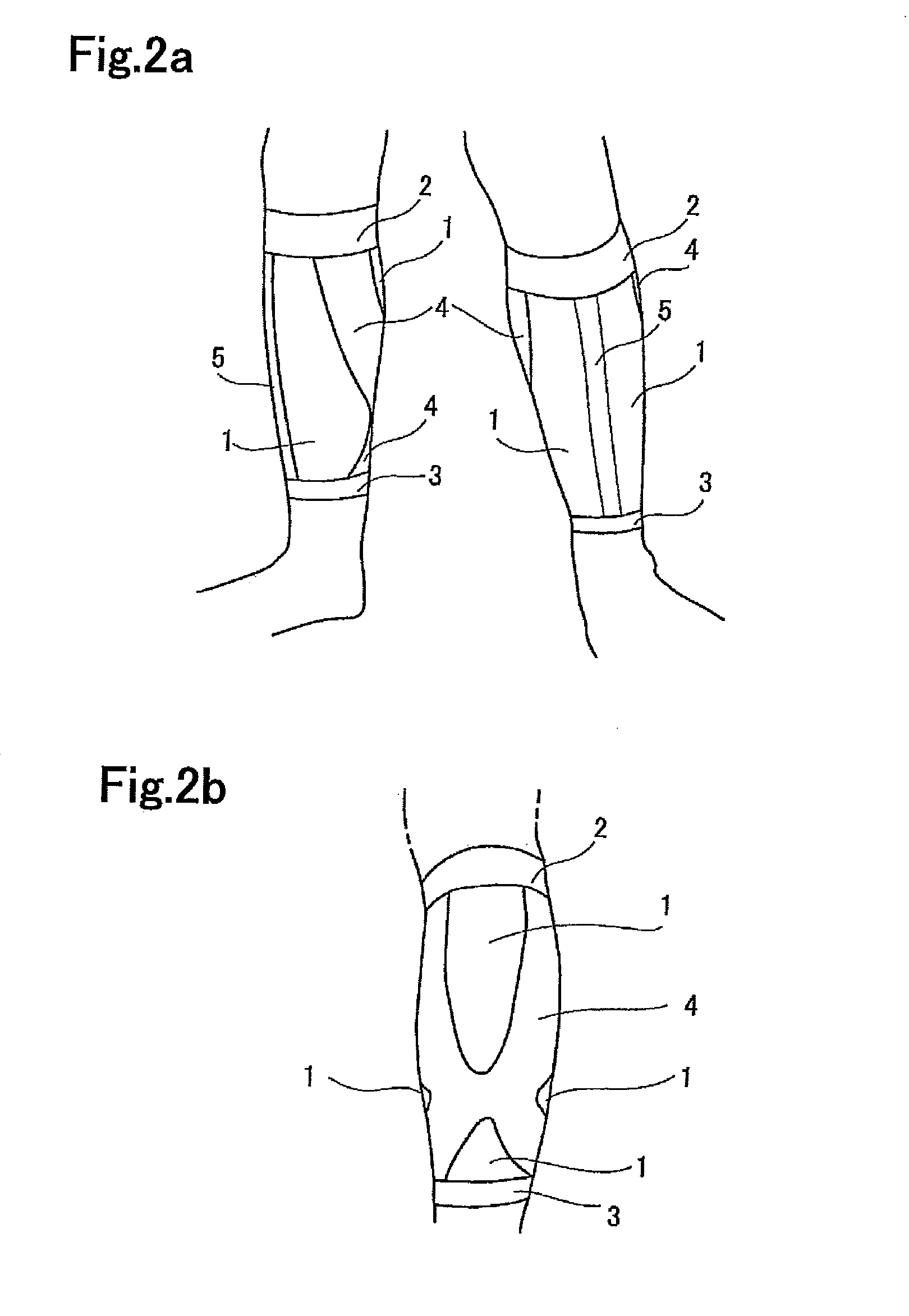
A lower leg supporter supports a gastrocnemius muscle from upper, lower, left, and right sides without interfering with movement of an Achilles tendon and which can suppress excessive vibration or deformation of such muscle to reduce a wearer's fatigue. The lower leg supporter includes a first anchor section that secures a tubular knitted fabric to a below-knee part, a second anchor section that secures the tubular knitted fabric to an above-ankle part, and an X-shaped gastrocnemius muscle support section located at a joining part of such muscle and an Achilles tendon on the back surface side of the tubular knitted fabric. Two ends of the X-shaped knitted fabric are joined to the first anchor section to support the gastrocnemius muscle. The other two ends of the X-shaped knitted fabric are joined to the second anchor section, and extend to both edges of the Achilles tendon.
Owner:KOWA CO LTD
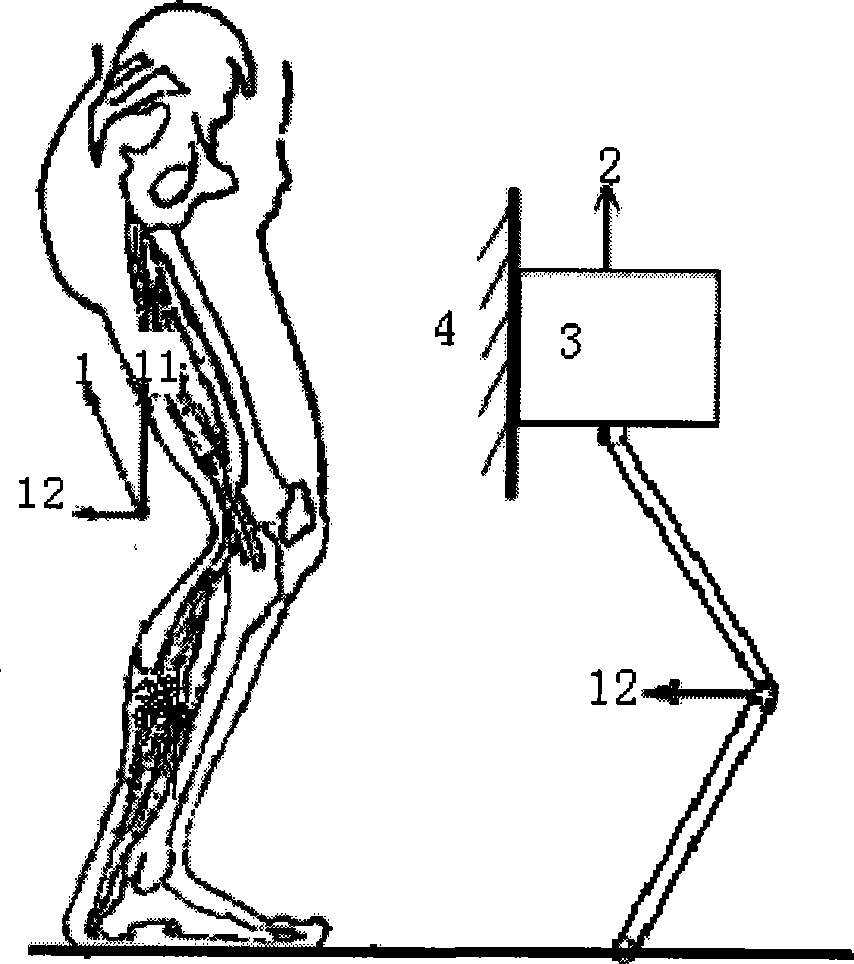
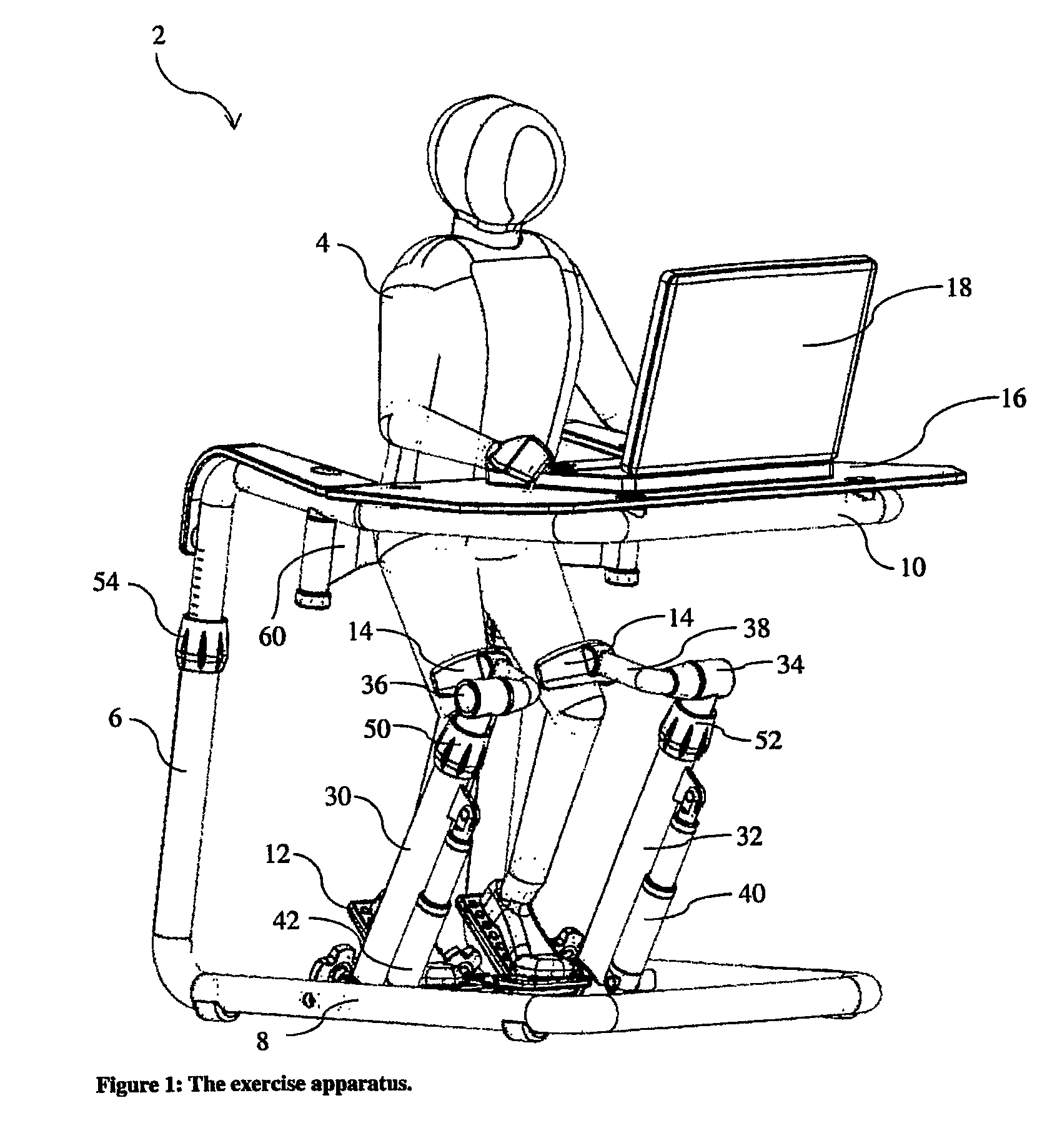
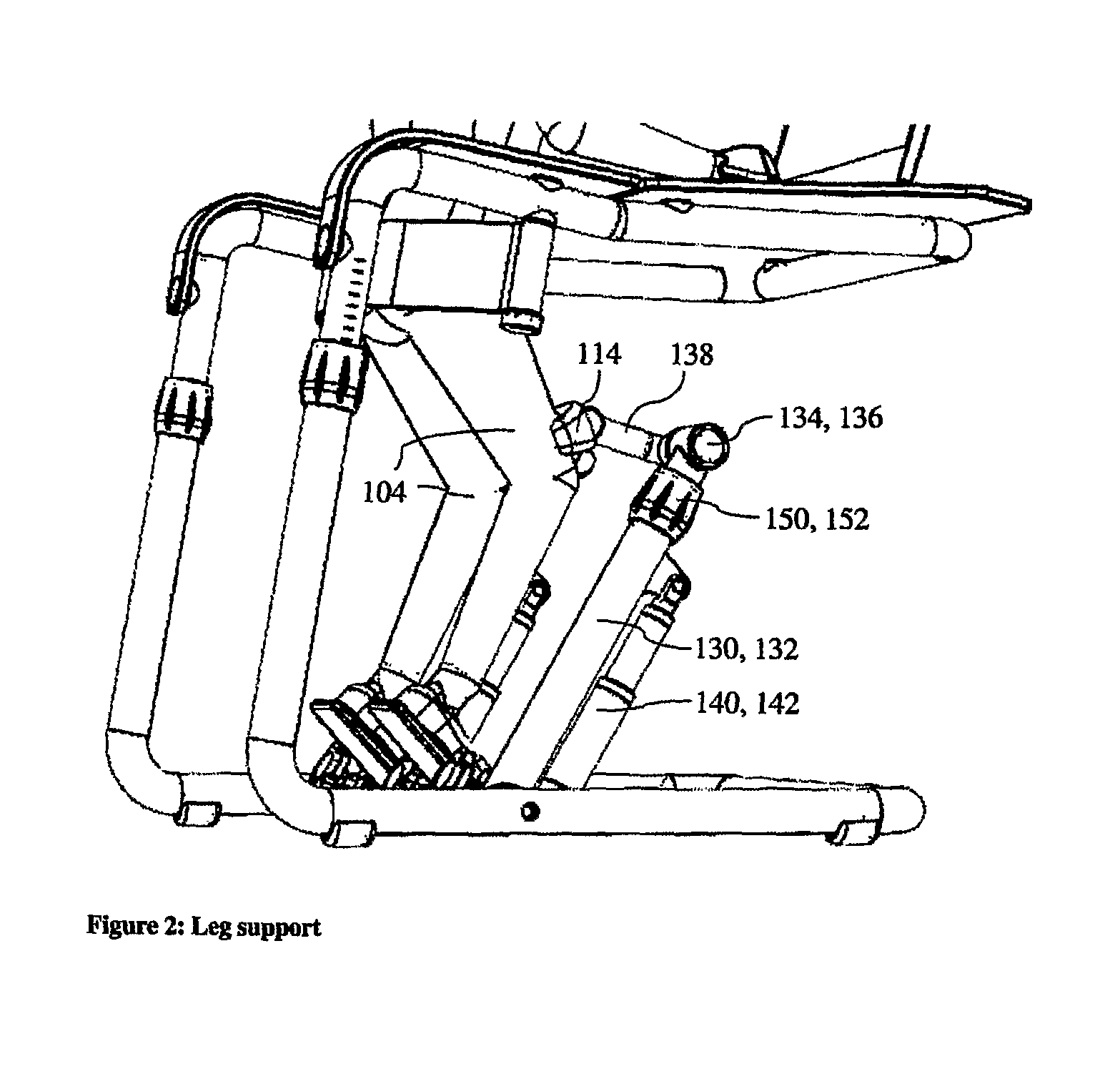
Exercise equipment intended for exercising legs of a person
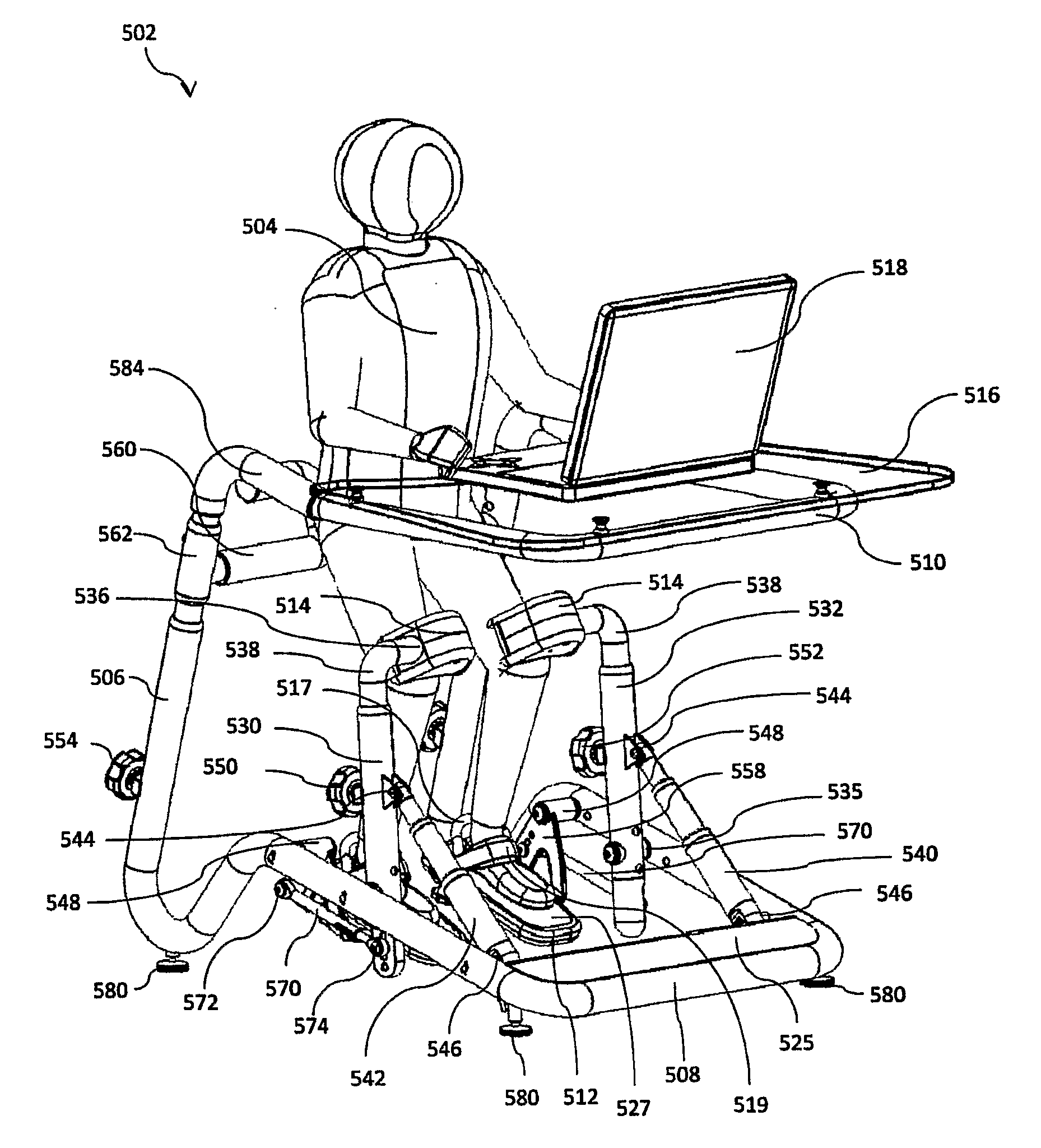
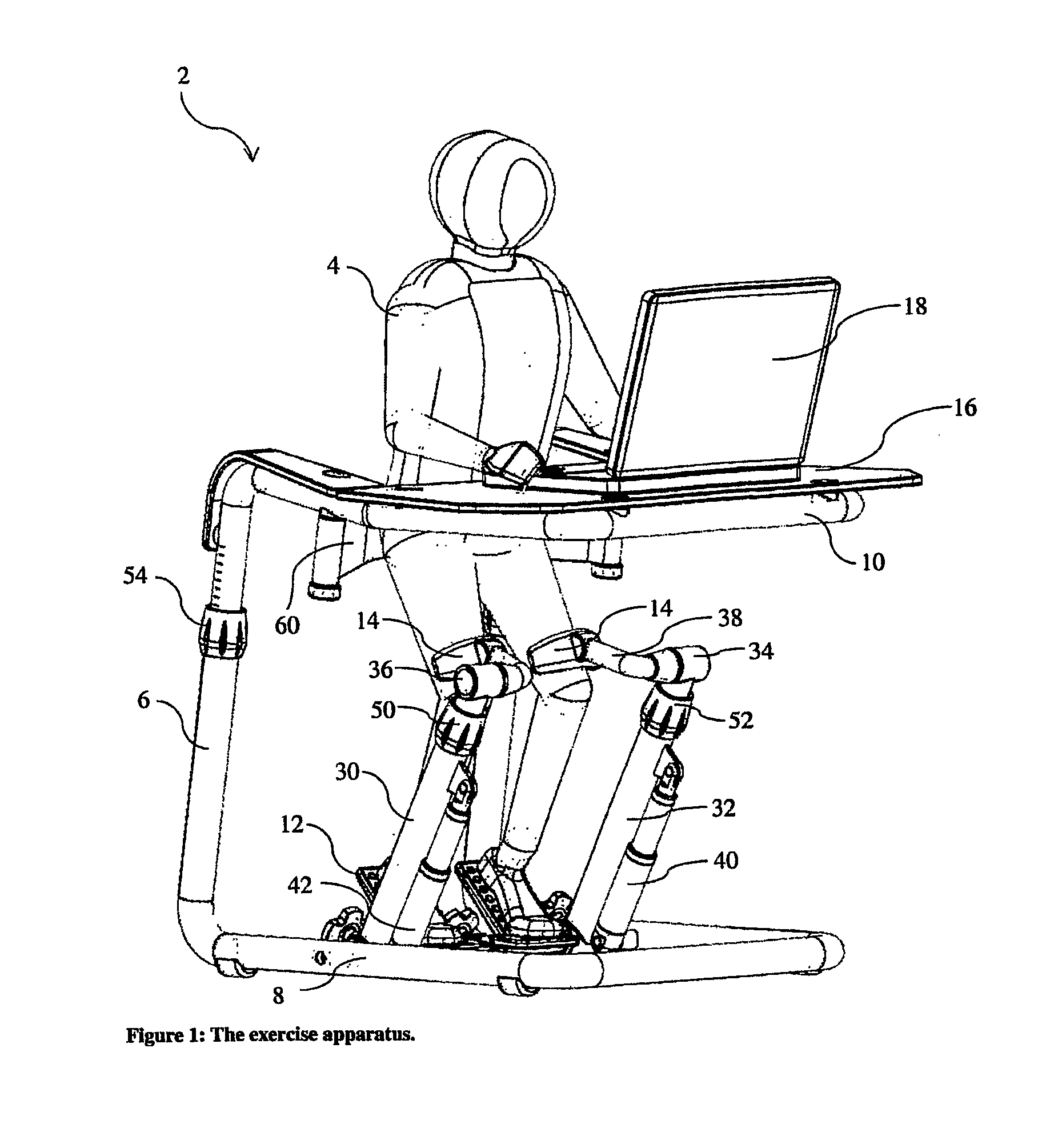
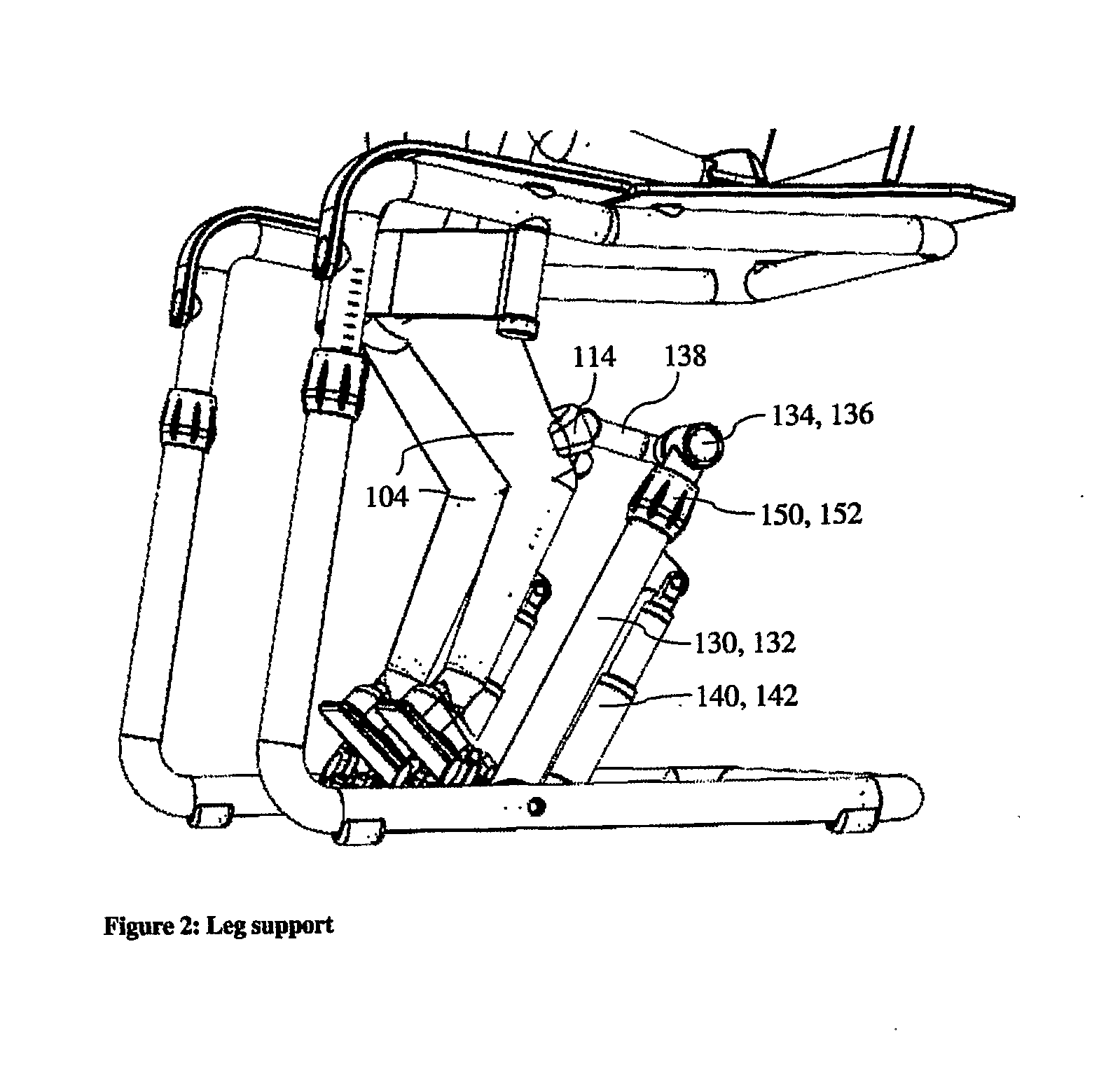
The present invention relates to an exercise apparatus for exercising muscle groups in a person's legs by stretching and / or retraction, which exercise apparatus comprises at least a first frame and at least a first foot platform which foot platform is rotatable fastened to a hearing, which hearing is placed in relation to the person's foot for exercise at least plantar flexion and / or dorsal flexion, which exercise apparatus further includes a leg support. Hereby can be achieved exercising of the muscle groups by stretching and / or retraction (quadriceps lemons, biceps femoris, semitendinosus, semimembranosus, gastrocnememius, tibialis posterior, tibialis anterior, peroneus longus, peroneus brevis and soleus) in the legs of a person, and the muscles (soleus, gastrocnemius, tibialis posterior, peroneus brevis, peroneus longus, biceps femoris, semitendinosus, semimembranosus) at the back side of the legs.
Owner:INNOVAID
Obesity-related genes
The present invention relates generally to a nucleic acid molecule which is expressed in at least red gastrocnemius muscle or its equivalent under particular physiological conditions. It is proposed that the nucleic acid molecule is differentially expressed under differing conditions of healthy state, myopathy, obesity, anorexia, weight maintenance, diabetes, disorders associated with mitochondrial dysfunction, genetic disorders, cancer, heart disease, inflammation, disorders associated with the immune system, infertility, disease associated with the brain and / or metabolic energy levels. The subject nucleic acid molecule and / or its expression product is proposed to be used in therapeutic and diagnostic protocols for conditions such as healthy state, myopathy, obesity, anorexia, weight maintenance, diabetes, disorders associated with mitochondrial dysfunction, genetic disorders, cancer, heart disease, inflammation, disorders associated with the immune system, infertility, disease associated with the brain and / or metabolic energy levels or as targets for the design and / or identification of modulators of their activity and / or function.
Owner:AUTOGEN RES +1
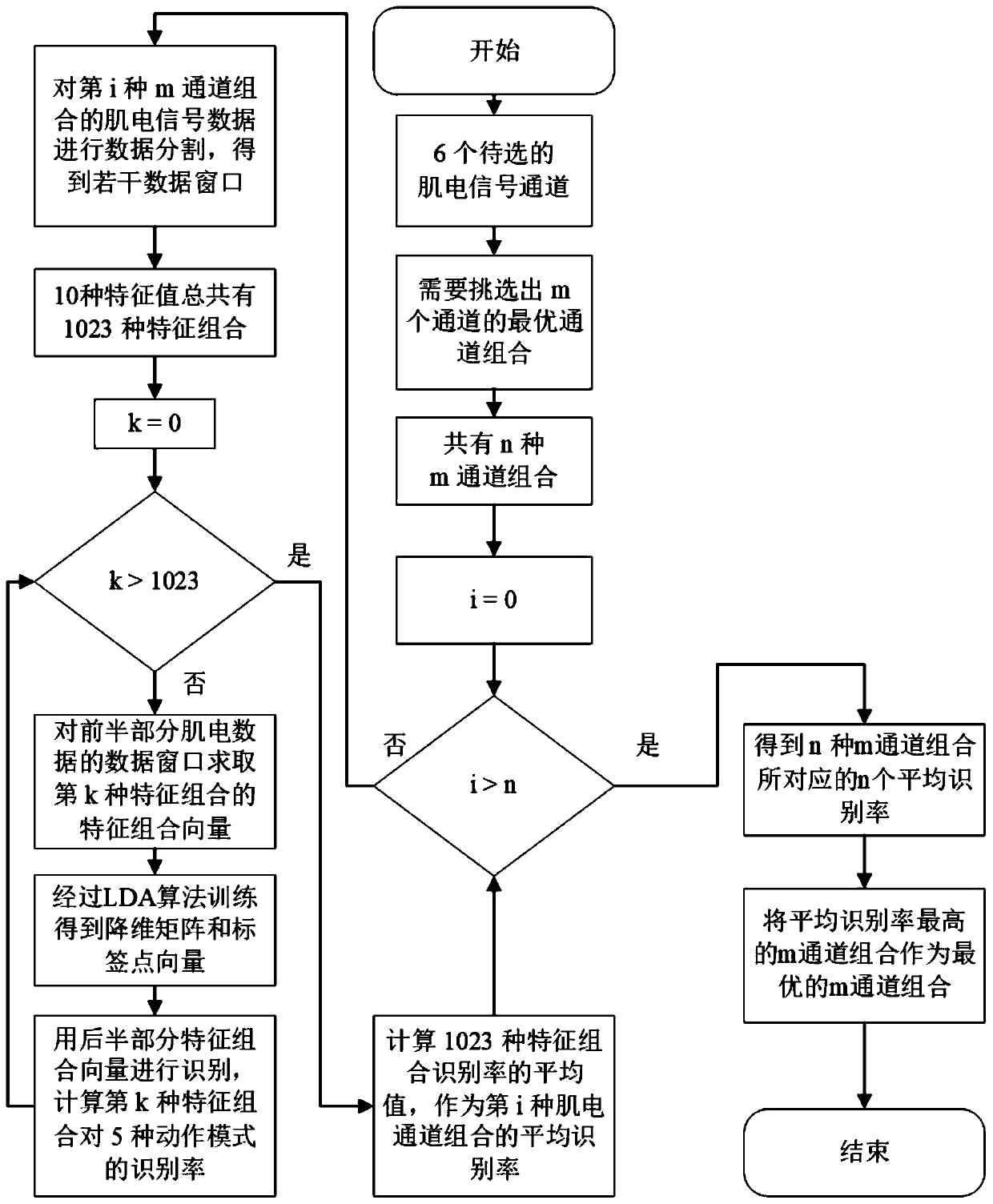
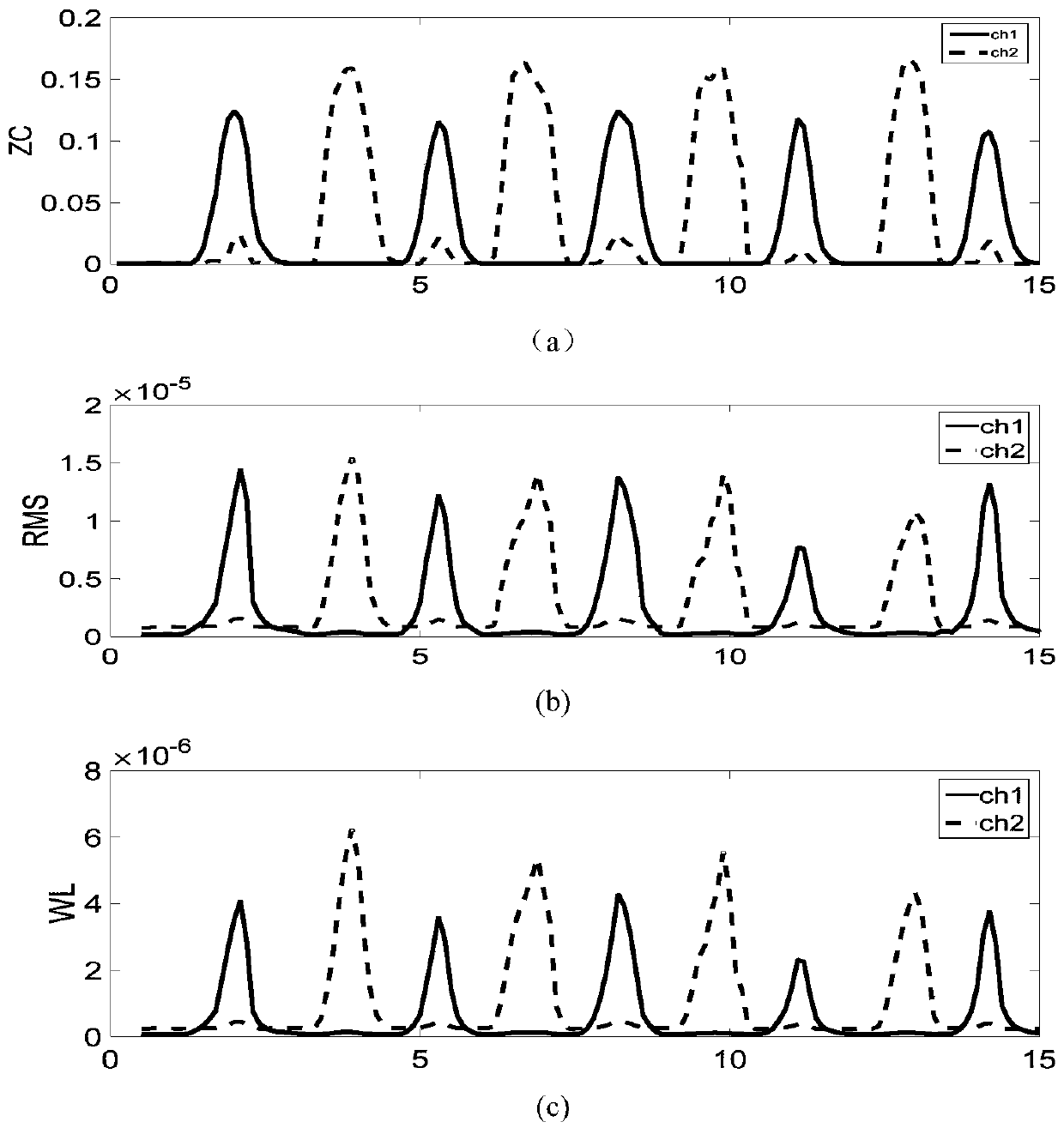
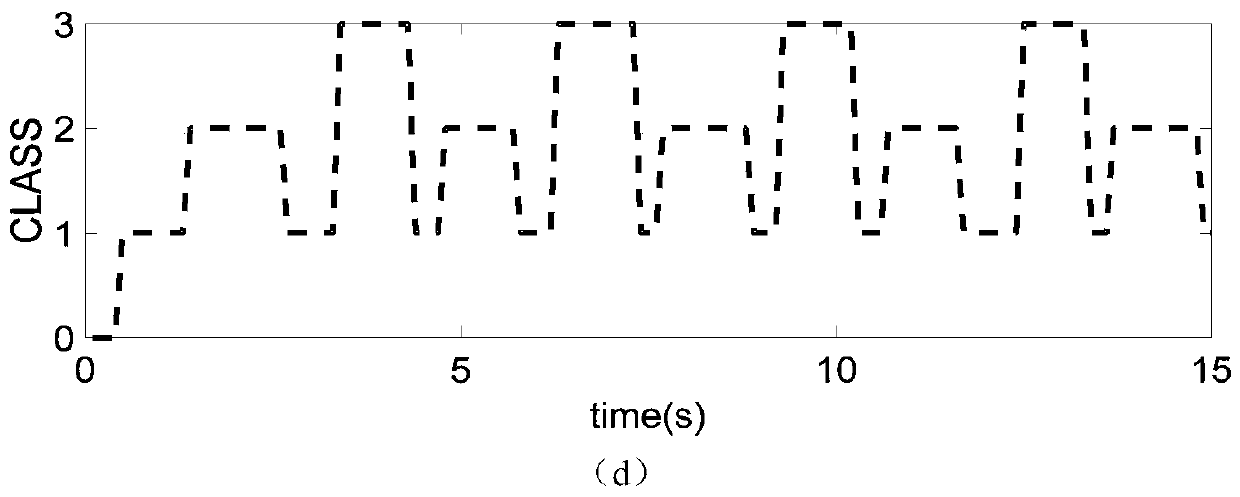
Channel selection method for surface electromyography signal based on LDA algorithm
InactiveCN110537913AImprove recognition rateDiagnostic signal processingCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionDorsal flexion
The invention discloses a channel selection method for surface electromyography signal based on an LDA algorithm. The method comprises the steps of selecting different combinations from six alternative electromyographic signal channels including tibialis anterior muscle, peroneus longus and soleus, outer gastrocnemius muscle, inner gastrocnemius muscle of medial leg and inner gastrocnemius muscleof posterior leg, for quantitative electromyographic signal channel combinations; calculating the average recognition rate of five action patterns of ankle including relaxation, dorsal flexion, plantar flexion, eversion and enstrophe, for each channel combination by using an accuracy calculation algorithm based on the LDA algorithm; and obtaining an optimal channel combination through comparing the average recognition rates of all the channel combination. The optimal electromyographic signal channel combination is determined through recognition rate calculation based on the LDA algorithm. Compared to a method of determining a channel combination by experience, the channel selection method disclosed by the invention is more scientific and accurate, and can recognize the five action patternsof ankle with a high recognition rate by using less electromyographic signal channels.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Novel lithotomy position surgery leg bracket
InactiveCN108210235AAvoid damagePrevent crushingOperating tablesAmbulance serviceFibular nervePlexus
The invention relates to a novel lithotomy position surgery leg bracket. The technical scheme of the novel lithotomy position surgery leg bracket is that, according to the position characteristic of lithotomy position surgery, a traditional scheme that popliteal space of a leg is supported is changed, popliteal space supporting is replaced by shank supporting, and all untoward effects caused by the traditional popliteal space supporting are solved. A boot-shaped design completely according with the three-dimensional physiological curve of a shank can reduce the press on the popliteal space anda gastrocnemius muscle, and avoid the damage on popliteal space plexus and fibular nerves. Cantilever type leg supporting is adopted for adjusting positions needed in surgery at will, the surgery position is controlled by an adjusting handle, and the leg bracket can stay in a desired position at will. When the position is adjusted, no medical care personnel is needed for lifting and moving the leg of a patient, and even during the surgery, the medical care personnel can still easily adjust multiple angles in a germ free condition of the leg. The work intensity of the medical care personnel isreduced, the efficiency and safety of the surgery are improved, and the surgical results are improved.
Owner:奥克兰高分子医用材料(天津)有限公司
Household simple leg massage device
ActiveCN108904247ADoes not interfere with workOut of the way of entertainmentVibration massageLeg muscleSoleus muscle
The invention relates to the technical field of leg massage, in particular to a household simple leg massage device. The device comprises a leg placing frame; a supporting block is fixedly connected to the bottom of the leg placing frame; a leg placing groove is formed in the top of the leg placing frame; a soft leather cushion is arranged in the leg placing groove; a soleus blood activating mechanism is arranged at the bottom of an inner cavity of the leg placing frame; and a gastrocnemius fatigue elimination mechanism is arranged on the soleus blood activating mechanism. The device is especially suitable for household leg muscle massage, has the advantages of good massage effect, high comfort level, low equipment cost and no obstacle to upper body actions, can effectively relieve the fatigue of the legs of a user, does not cause obstacle to office and entertainment of the user, and can beat and massage the soleus and the gastrocnemius in the two legs of the user at the same time; thestrength of beating is moderate and the comfort level is relatively high; and the efficiency and effect of leg muscle massage are improved.
Owner:温州万阳电子科技有限公司
Lower leg supporter
A lower leg supporter supports a gastrocnemius muscle from upper, lower, left, and right sides without interfering with movement of an Achilles tendon and which can suppress excessive vibration or deformation of such muscle to reduce a wearer's fatigue. The lower leg supporter includes a first anchor section that secures a tubular knitted fabric to a below-knee part, a second anchor section that secures the tubular knitted fabric to an above-ankle part, and an X-shaped gastrocnemius muscle support section located at a joining part of such muscle and an Achilles tendon on the back surface side of the tubular knitted fabric. Two ends of the X-shaped knitted fabric are joined to the first anchor section to support the gastrocnemius muscle. The other two ends of the X-shaped knitted fabric are joined to the second anchor section, and extend to both edges of the Achilles tendon.
Owner:KOWA CO LTD
Dorsiflexion/plantarflexion extension above the knee brace
ActiveUS20200206059A1Chiropractic devicesFracturePhysical medicine and rehabilitationPlantaris muscle
Devices and processes used to treat ankle conditions. More specifically, the present disclosure relates to a brace and the corresponding method of use to treat ankle conditions by stretching the Gastrocnemius muscle, soleus muscle, and plantaris muscle.
Owner:IQ MEDICAL LLC
Ankle muscle force testing device
PendingCN107028616AInhibit transformationPortable and convenientSensorsMuscle exercising devicesMuscle forceMechanical engineering
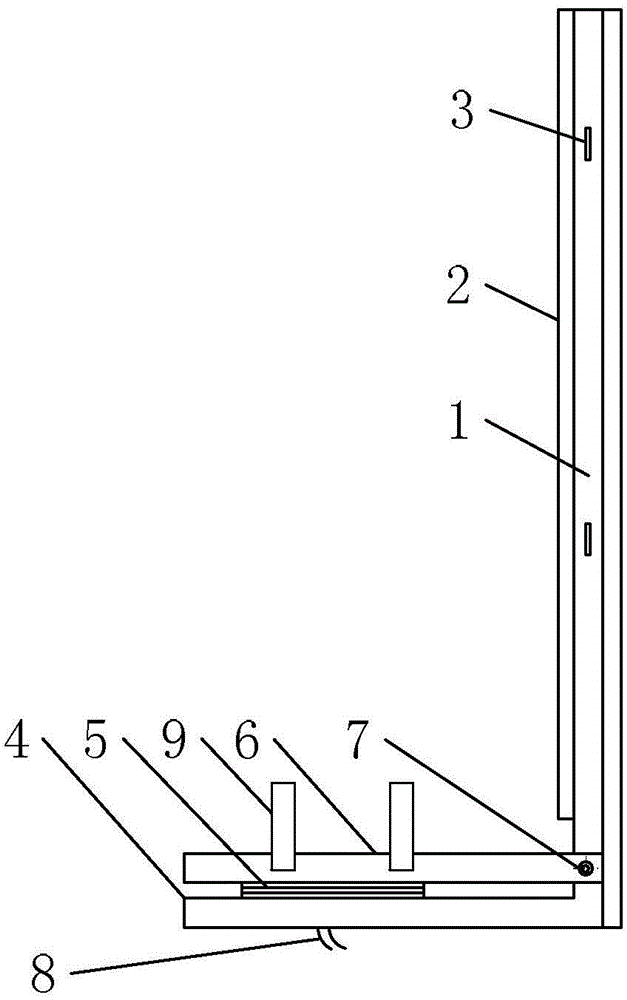
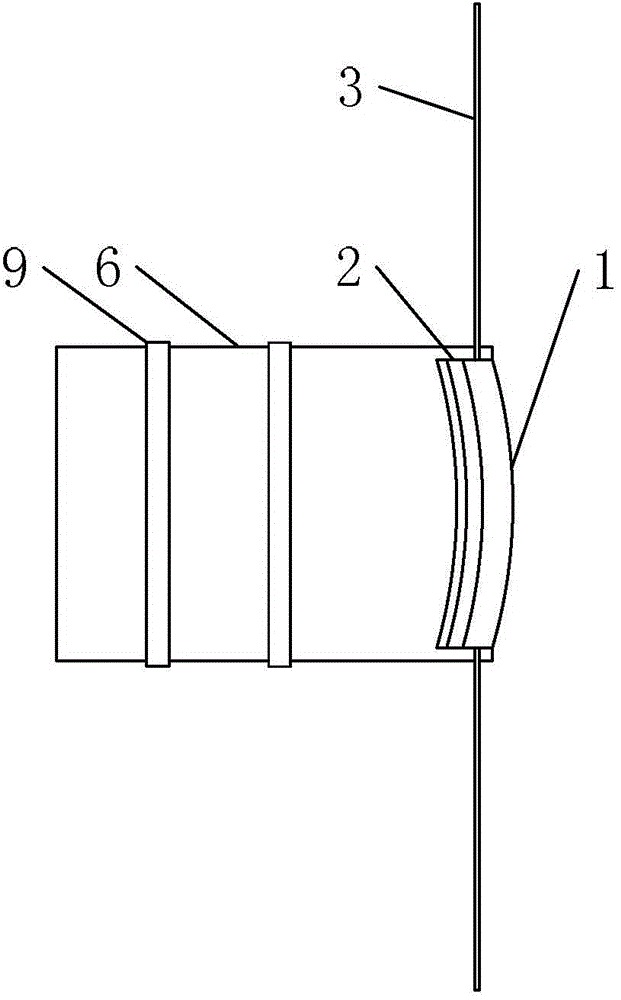
The invention discloses an ankle muscle force testing device. The ankle muscle force testing device comprises a fixed support, a pull and push dynamometer and a testing head, wherein the fixed support comprises a bottom plate, a stand column and a fixed slope, the fixed slope is fixed to the bottom plate with the stand column as support, the pull and push dynamometer is fixed to the fixed slope, the testing head is fixedly connected with a pull and push rod of the pull and push dynamometer, a window is formed in the middle and lower portion of the fixed slope, and the testing head is located in the window. The ankle muscle force testing device can be used for measuring ankle anterior tibial muscle and musculus gastrocnemius force, is convenient to carry and capable of measuring ankle dorsiflexion and plantar flexion at the same time and avoids body position changing. The ankle muscle force testing device can be used for bedside muscle force testing and used for testing ankle force of healthy people or ankle dyskinesia patients with joint injuries and cerebral apoplexy hemiplegia and facilitates rehabilitation evaluation.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZHEJIANG CHIENSE MEDICAL UNIV
CD29<+> human umbilical cord source mesenchymal stem cell and use thereof in preparation of drug for treating skeletal muscle atrophy in high-sugar and high-fat environments
ActiveCN107557332AImprove hyperlipidemiaImprove symptoms of skeletal muscle atrophyMetabolism disorderMuscular disorderAcute hyperglycaemiaAntigen
The invention discloses a CD29<+> human umbilical cord source mesenchymal stem cell and use thereof in the preparation of a drug for treating skeletal muscle atrophy in high-sugar and high-fat environments. The CD29<+> human umbilical cord source mesenchymal stem cell represents the following mesenchymal stem cell cytomembrane molecules: a human leukocyte differentiation antigen CD73, a human leukocyte differentiation antigen CD90, a human leukocyte differentiation antigen CD105 and a human leukocyte differentiation antigen CD29. According to the CD29<+> human umbilical cord source mesenchymalstem cell, the hyperlipidemia and hyperglycemia of a db<- / -> mouse can be obviously improved, muscle fiber cross sections of soleus and gastrocnemius muscle of the db<- / -> mouse can be increased, andthe contents and cell number of each myotube are increased, so that the symptoms of the skeletal muscle atrophy of the db<- / -> mouse are improved. According to the CD29<+> human umbilical cord sourcemesenchymal stem cell, the theoretical foundation and experiment basis are laid for the subsequent research and development of the drug for treating skeletal muscle atrophy in the high-sugar and high-fat environments, and the CD29<+> human umbilical cord source mesenchymal stem cell has wide application prospects.
Owner:JILIN TUO HUA BIOTECH
Apparatus for treating inflammatory symptoms associated with plantar fasciitis
ActiveUS9931264B2Gymnastic exercisingChiropractic devicesGastrocnemius aponeurosisPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The present invention relates to a method for treating inflammatory symptoms associated with plantar fasciitis in a foot. The method involves stretching gastrocnemius and soleus muscles associated with the foot by placing the sole of the foot on an inclined ramp surface and cooling at least one portion of the sole of the foot. The method may further involve providing localized pressure to at least one portion of the plantar fascia, and to a portion of the foot below the toes, to cause dorsiflexion thereof.
Owner:THERMAWEDGE ENTERPRISES
Method for promoting mammalian filial generation growth through maternal addition of phytosterol ester
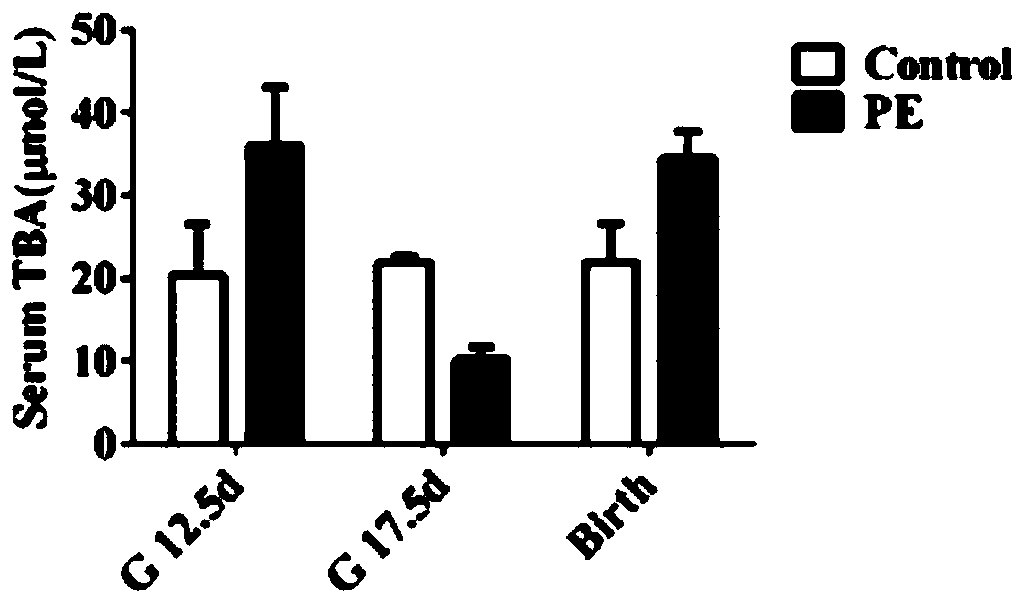
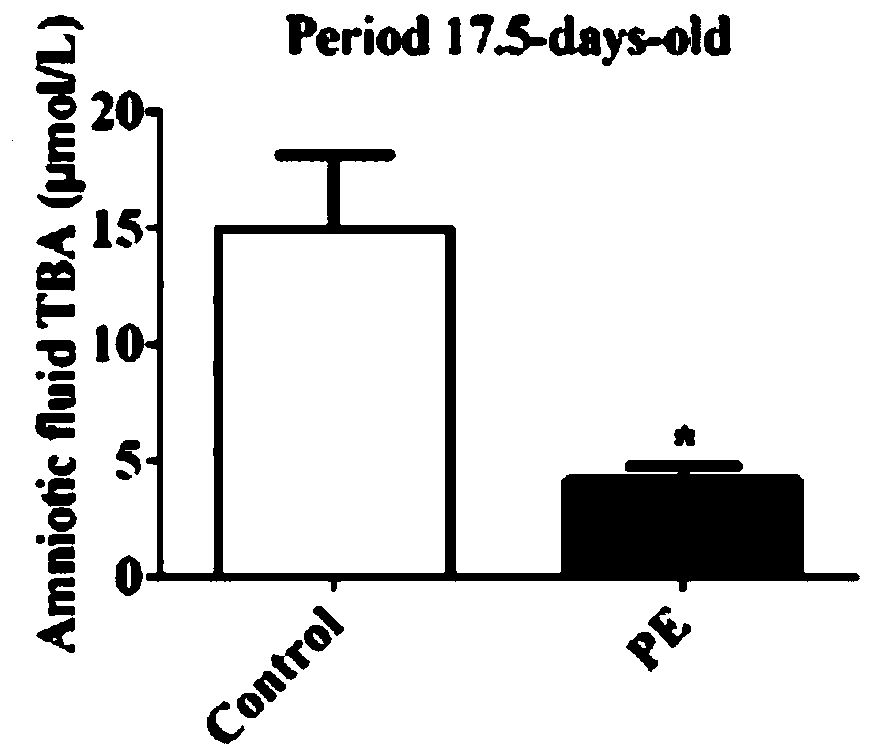
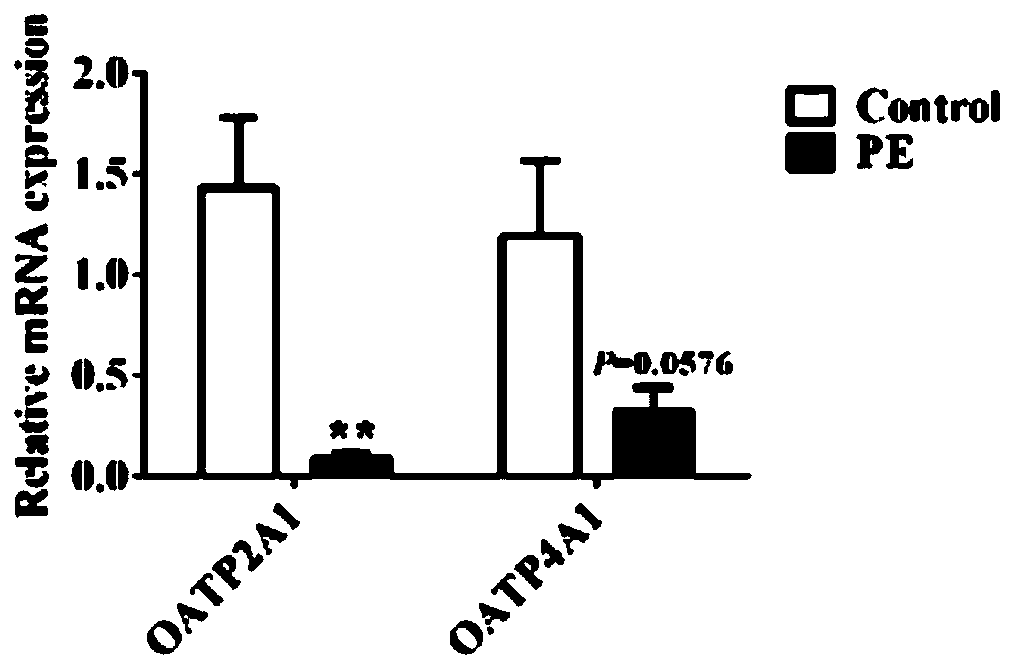
PendingCN110537631ANo metabolismRegulate metabolismOrganic active ingredientsMuscular disorderFiberSide effect
The invention discloses application of phytosterol ester in preparation of a mammal feed additive, and a method for promoting mammalian filial generation growth through maternal addition of phytosterol ester. According to the invention, the phytosterol ester replaces grease and is added into grease-free daily ration feed for mammals, so that the bile acid level in serum and amniotic fluid, the expression level of a placenta bile acid transporter and the expression level of an embryo posterior limb bud bile acid receptor can be reduced, and the weight, muscle content, gripping power, flatfish muscle fiber quantity, gastrocnemius muscle fiber cross sectional area and myosin heavy chain mRNA expression level can be improved. Besides, after entering the body of the mammal, the phytosterol ester is converted into phytosterol and fatty acid through the digestion effect of the small intestines, no toxic or side effect is generated, and therefore the phytosterol ester has wide application andpopularization value in the aspect of preparing mammal feed additives.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
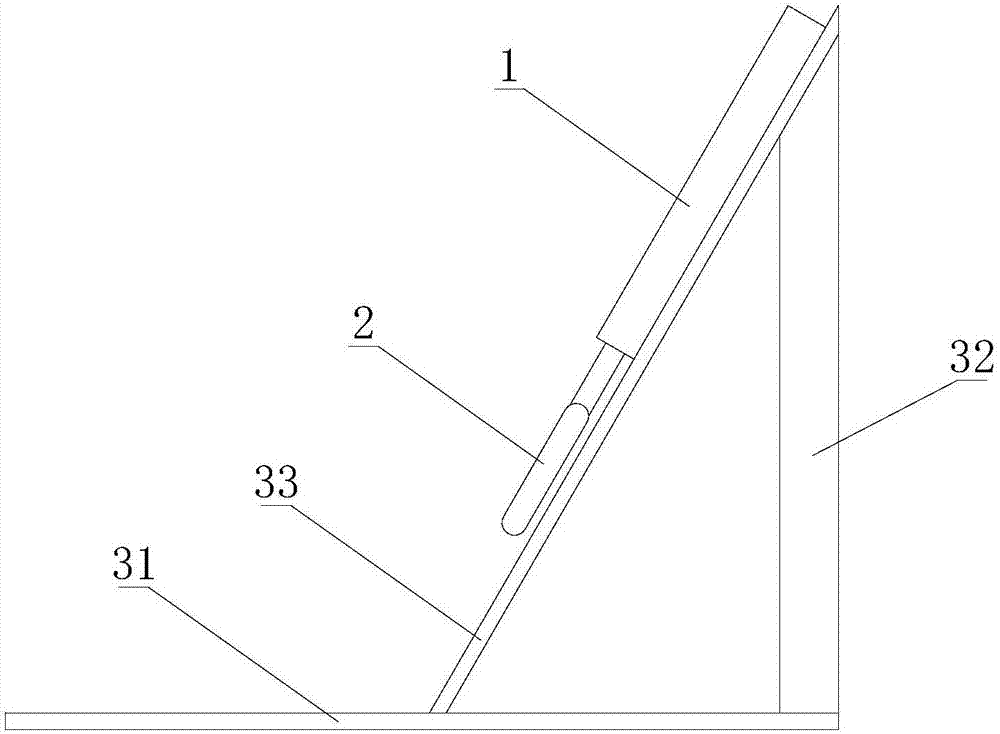
Device for isolated static stretching of the gastrocnemius (CALF) muscle
A calf-stretching device enables a user to conduct stretching exercises of the gastrocnemius muscles of the leg. The calf-stretching device includes a support base positionable on a floor surface and left and right surfaces immovably attached to the support base. Each of the left and right surfaces present a convex curved surface from a front side to a back side to receive respective feet of the user, the convex curved surface having a greater radial dimension on an inner portion than an outer portion to correspond to a foot arch of the user.
Owner:AMIS JAMES
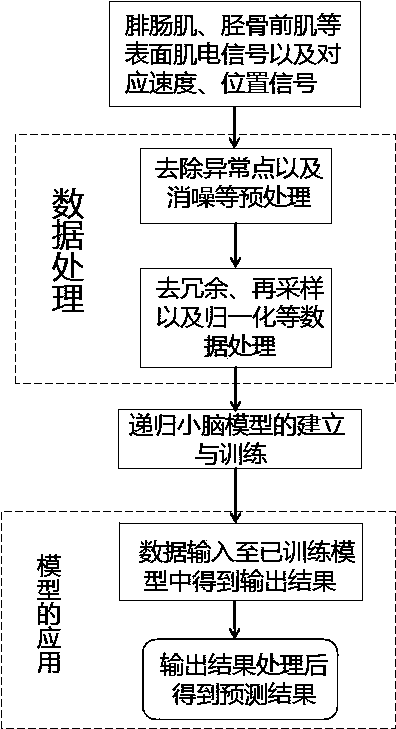
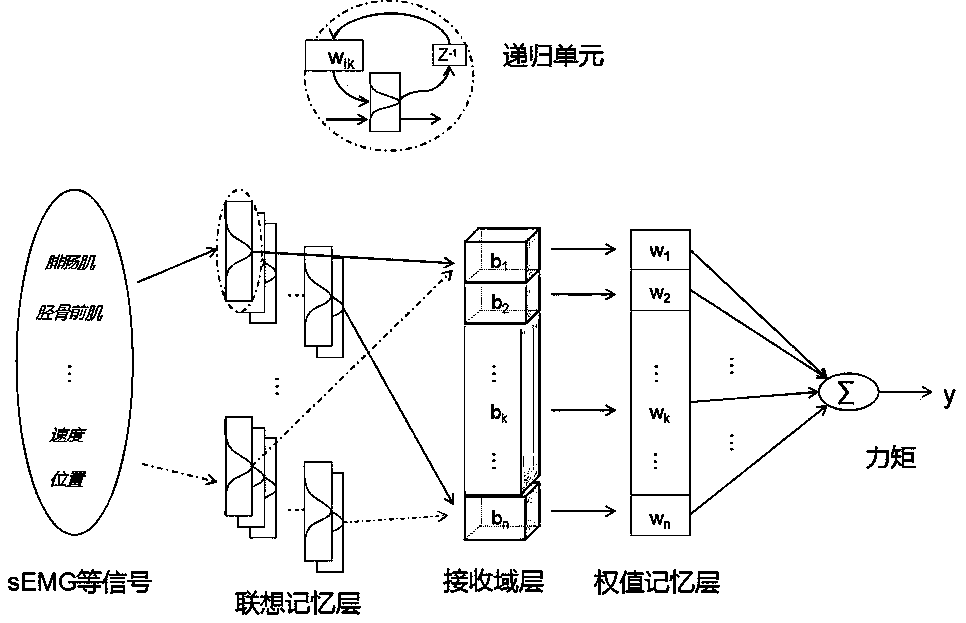
Ankle moment prediction method of recurrent cerebellar model based on surface electromyogram signal
The invention relates to an ankle moment prediction method of a recurrent cerebellar model based on a surface electromyogram signal. The method uses an sEMG (Surface Electromyogram) data of the muscle(including but not limited to the gastrocnemius muscle, the tibialis anterior, the peroneus longus and the hallucis longus) relevant to the human body ankle joint and corresponding speed and positiondata are used; and a recurrent cerebellar model neural network is used for performing moment prediction on the human body ankle joint.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Medical application of enzymatic hydrolysate of icariin and main component baohuoside I of icariin
InactiveCN112138017ALow effective dosePlay a protective effectOrganic active ingredientsMuscular disorderSkeletal muscle atrophyHydrolysate
The invention discloses a medical application of an enzymatic hydrolysate of icariin and a main component baohuoside I of the icariin, and particularly relates to an application of the enzymatic hydrolysate of icariin and the main component baohuoside I of the icariin in preparing a medicine for treating skeletal muscle atrophy. In-vitro and in-vivo experiments prove that the enzymatic hydrolysateof icariin or baohuoside I can significantly reduce the skeletal muscle atrophy degree, including increase of muscle fiber cross-sectional area, gastrocnemius muscle wet weight / body mass ratio and aerobic exercise ability, and can up-regulate skeletal muscle protein content by regulating an autophagy system, thus having great application prospects.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF T C M
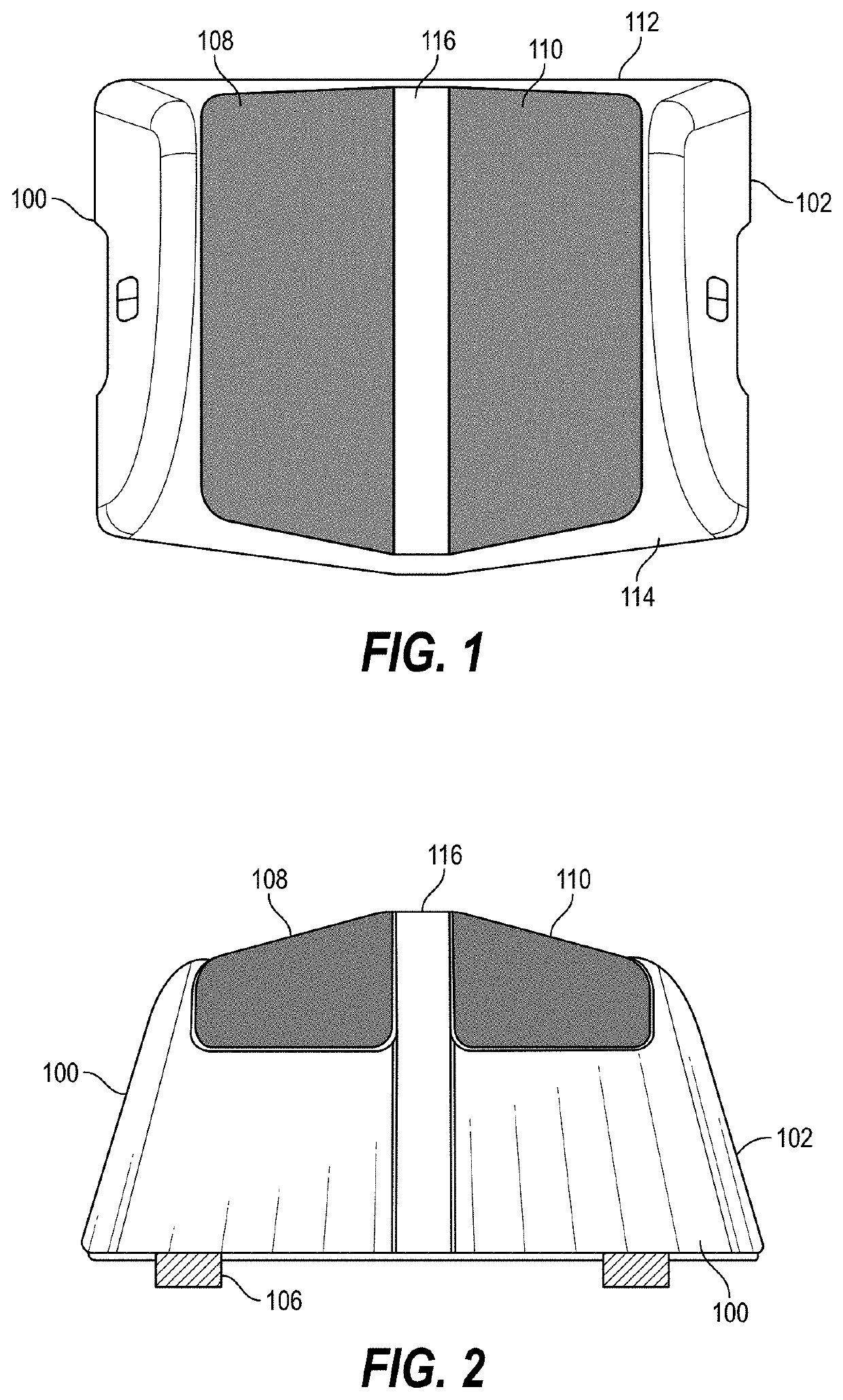
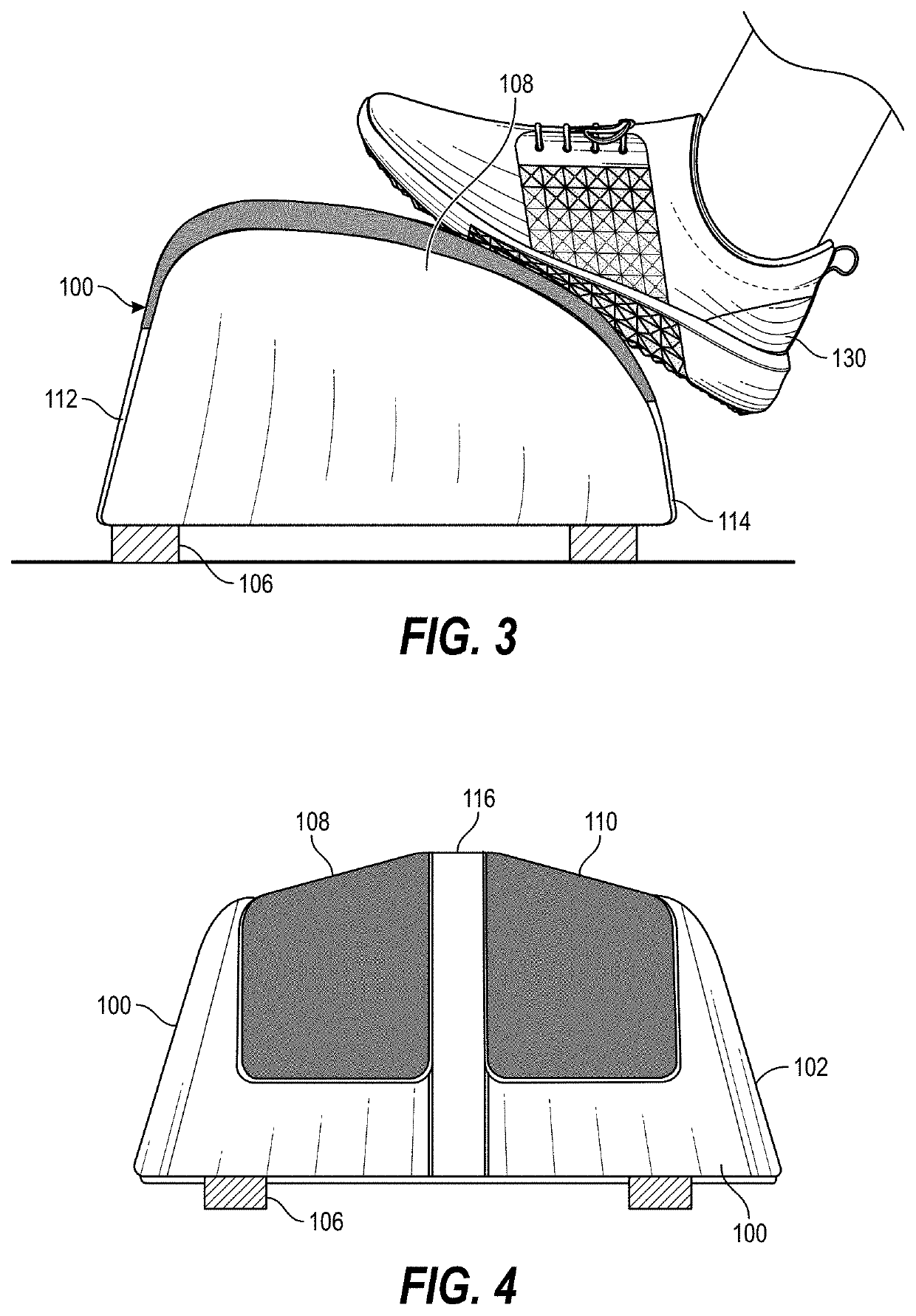
Sport shoes and trousers system simulating and reinforcing function of lower limbs gastrocnemius
The invention belongs to the field of sports instruments, and provides a sports shoe and trousers system for simulating and strengthening the functions of gastrocnemius in lower limb. The system comprises a pair of trousers and a pair of shoes, which are connected with each other, and further includes an elastic structure for simulating and strengthening gastrocnemius, which is fixedly arranged in an anatomical position corresponding to gastrocnemius of a human body through a fixing strap; a first fixing strap is arranged in the waist position of the trousers, and is arranged by being wound around waist once; a second fixing strap is arranged in the position above the knee joint of the trousers, and is arranged by being wound around legs; and the system is further equipped with a third fixing strap, with the nearest end connected with the first fixing strap and the farthest end connected with the second fixing strap. On the one hand, the invention can serve the purpose of protecting gastrocnemius from damages during intense exercises; and on the other hand, the invention can strengthen the action which is the result of gastrocnemius striding across a joint and opposite to the moment thereof in direction, thereby improving the muscular functions of gastrocnemius, and achieving the purpose of enabling athletes to perform better.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF SPORT
Exercise equipment intended for exercising legs of a person
The present invention relates to an exercise apparatus for exercising muscle groups in a person's legs by stretching and / or retraction, which exercise apparatus comprises at least a first frame and at least a first foot platform which foot platform is rotatable fastened to a hearing, which hearing is placed in relation to the person's foot for exercise at least plantar flexion and / or dorsal flexion, which exercise apparatus further includes a leg support. Hereby can be achieved exercising of the muscle groups by stretching and / or retraction (quadriceps lemons, biceps femoris, semitendinosus, semimembranosus, gastrocnememius, tibialis posterior, tibialis anterior, peroneus longus, peroneus brevis and soleus) in the legs of a person, and the muscles (soleus, gastrocnemius, tibialis posterior, peroneus brevis, peroneus longus, biceps femoris, semitendinosus, semimembranosus) at the back side of the legs.
Owner:INNOVAID
Method for establishing muscle tissue damage repairing animal model
InactiveCN106806025AEasy to storeMeeting the needs of damage repair researchDiagnosticsSurgeryMuscle tissueCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention belongs to the field of animal model construction, and specifically discloses a method for establishing an animal model for repairing muscle tissue damage, comprising the following steps: first anesthetizing the model animal, fixing it in a prone position, and disinfecting the hind limbs of the anesthetized experimental rat; Then, the skin and subcutaneous tissue of the sterilized hindlimb were incised sequentially through surgery to expose the gastrocnemius muscle and separate the lower part of the gastrocnemius muscle; finally, an electrode was used to clamp the gastrocnemius muscle on the exposed side, and a pulsed electric field was applied to the gastrocnemius muscle to establish an animal model of muscle tissue damage repair. . The present invention uses irreversible electroporation to establish an animal model of muscle tissue damage repair, which can provide a technical method that is simple, easy to implement, low in cost, short in modeling time, stable in model, accurate in damage, and accurate in scope and controllable, and can meet the requirements of destroying muscle cells at the same time. Requirement to preserve extracellular matrix structure.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Magnetic resonance scanning method of gastrocnemius muscles of machins
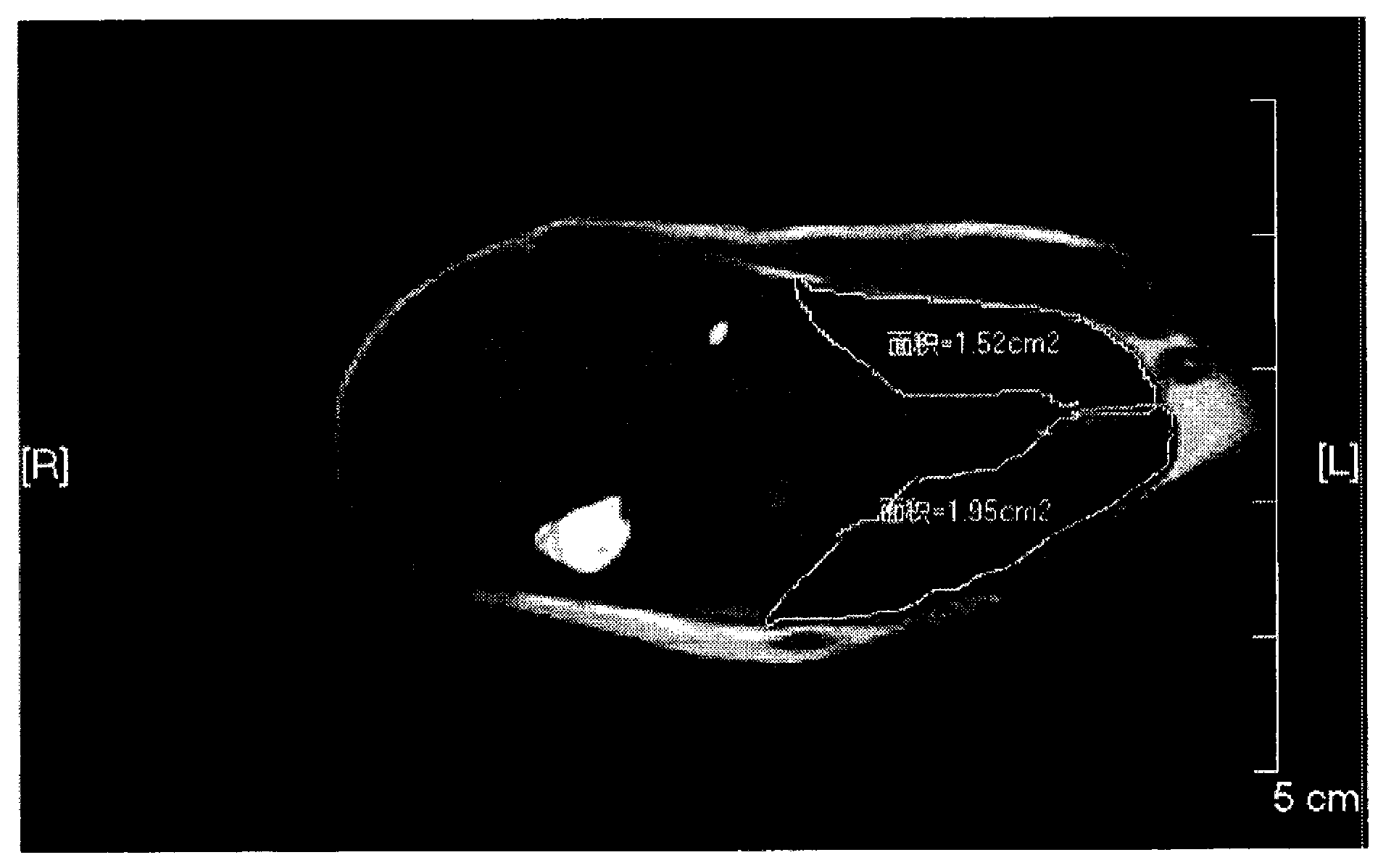
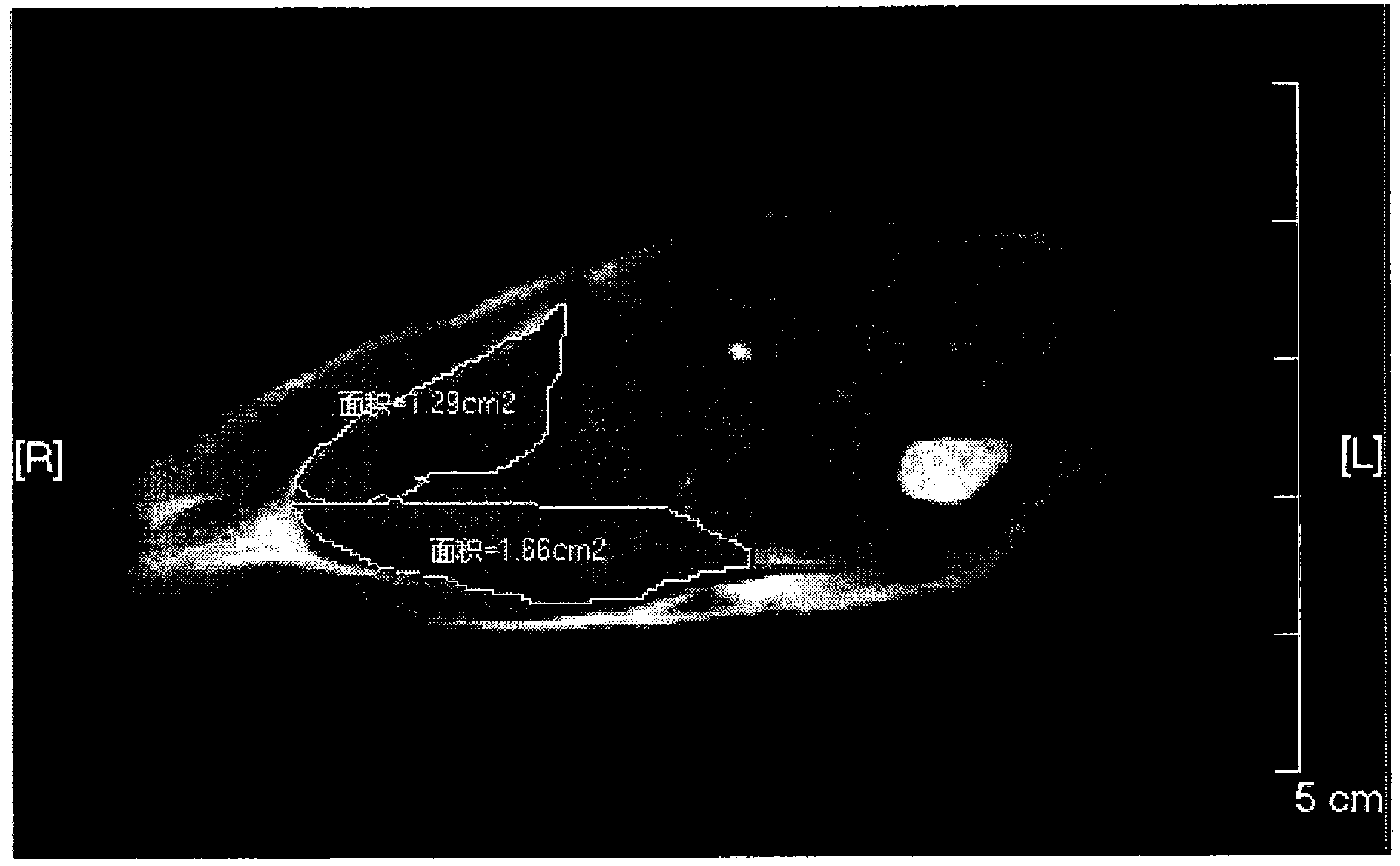
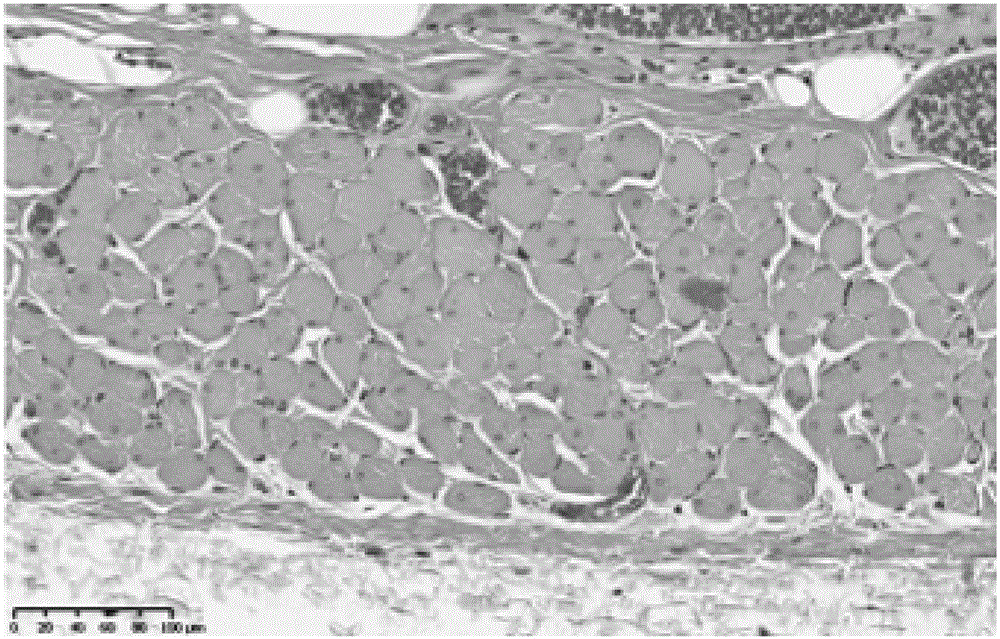
The invention provides a scanning method of the gastrocnemius muscles of machins. According to the scanning method, a PHILIPS Achieva 1.5T magnetic resonance machine is used for scanning, wherein the T1 scanning sequence is IR, the visual field is 40cm*40cm, and TR / TE is 561ms / 17ms; and a T2 weighted image scanning sequence is SE, TR / TE is 3900ms / 102ms, layer thickness / interval is 5mm / 0.5mm, and the matrix is 320*320. The magnetic resonance scanning method of the gastrocnemius muscles of the machins can provide a clear magnetic resonance image of the gastrocnemius muscles of the machins and has a larger meaning in terms of muscle volume measurement, disease research and the like.
Owner:GUANGXI WEIMEI BIOTECH
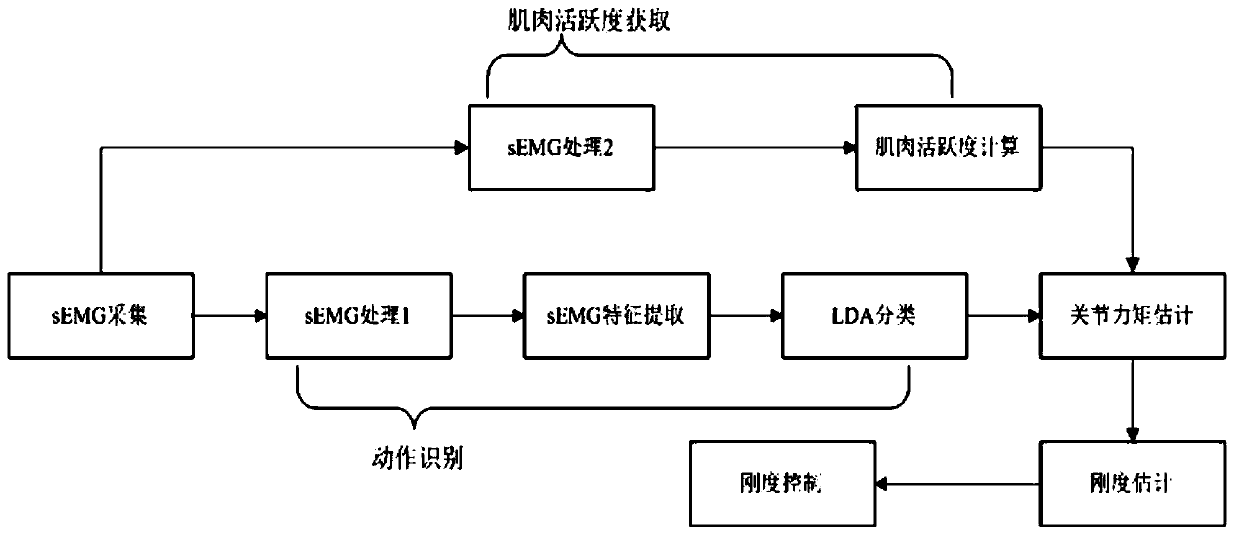
A control method using SEMG to control the stiffness of ankle joint rehabilitation equipment
ActiveCN109199783BSimple methodImprove efficiencyChiropractic devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringNerve networkPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The invention relates to a method for controlling the rigidity of ankle joint rehabilitation equipment by using sEMG, which collects sEMG signals of tibialis anterior muscle and gastrocnemius muscle.A filter is used to filter the collected sEMG signal. The eigenvalue of the filtered sEMG signal is extracted and the eigenvector is formed. Using LDA algorithm to classify the ankle movements, different ankle movements can be obtained. According to the results of classification, the corresponding neural network is selected and the corresponding muscle activity is obtained to estimate the joint torque. The model of ankle joint torque and ankle joint stiffness is established to estimate ankle joint stiffness and control ankle joint stiffness. The method can meet the requirements of safety, comfort and anti-interference of the wearable ankle joint equipment of the patient. Moreover, for patients with different rehabilitation conditions, it is not necessary to retrain the neural network model, only need to modify individual model parameters, the method is simple and efficient.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
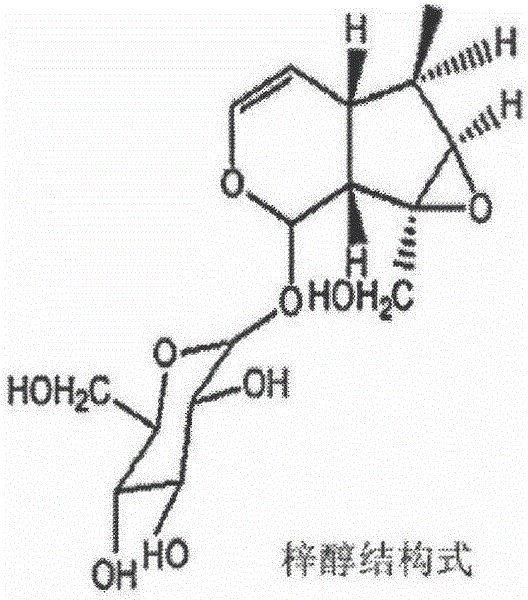
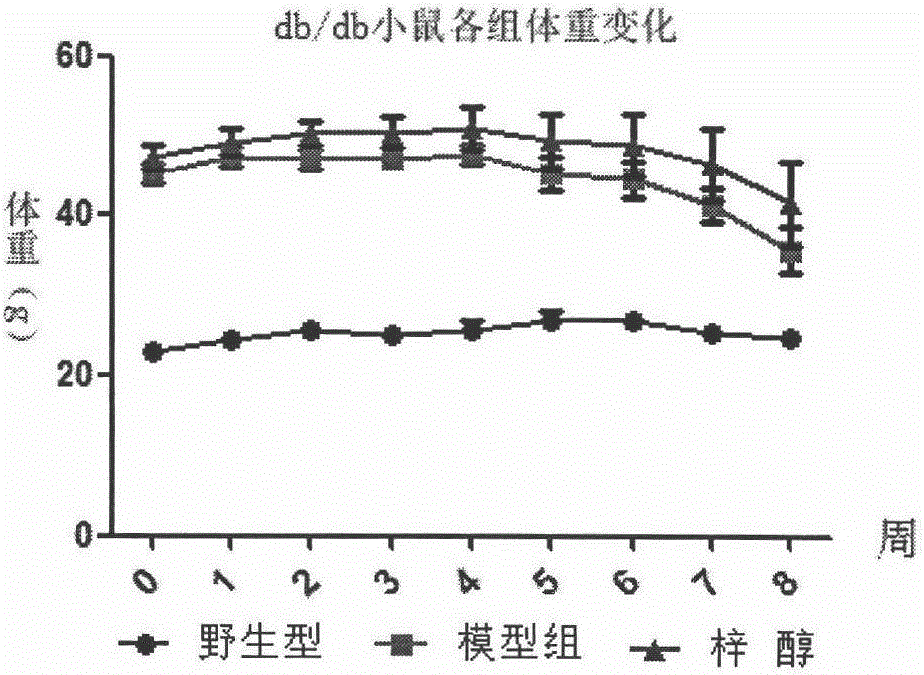
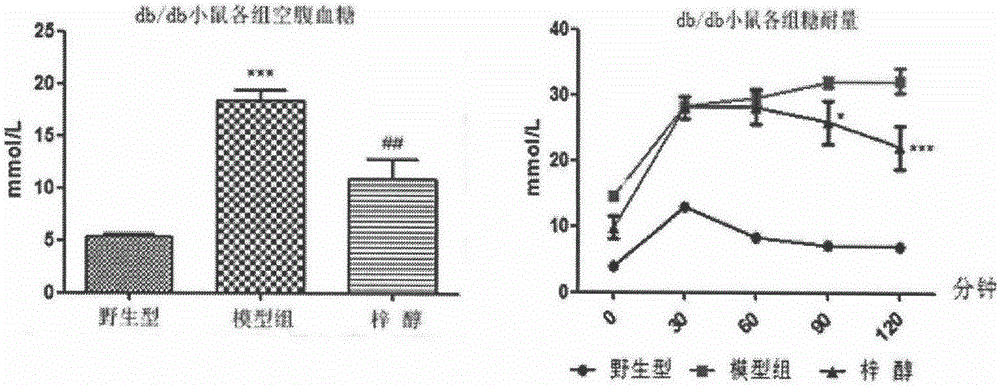
Application of catalpol in preparation of medicine for preventing and curing or delaying myasthenia and/or amyotrophia
InactiveCN106265709ALow priceEasy to getOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderType i muscle fibersAmyotrophia
The invention discloses a medicinal application of catalpol. Experiments find that catalpol can remarkably improve myasthenia and amyotrophia caused by diabetes and reverse the loss of I type muscle fibers in skeletal muscles due to diabetes. Results show that catalpol can enhance the holding power of the skeletal muscles, improve the reduced motor ability caused by diabetes, increase the total weight of the skeletal muscles as well as the weight of gastrocnemius muscles and soleus muscles, improve insulin resistance and reduce fasting blood glucose, thereby improving myasthenia and amyotrophia caused by diabetes. Accordingly, catalpol can be used for preventing and curing or delaying myasthenia and / or amyotrophia caused by diabetes. Catalpol can be extracted from traditional Chinese medicines and is cheap, safe, effective and easily available and has great market prospect accordingly.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com