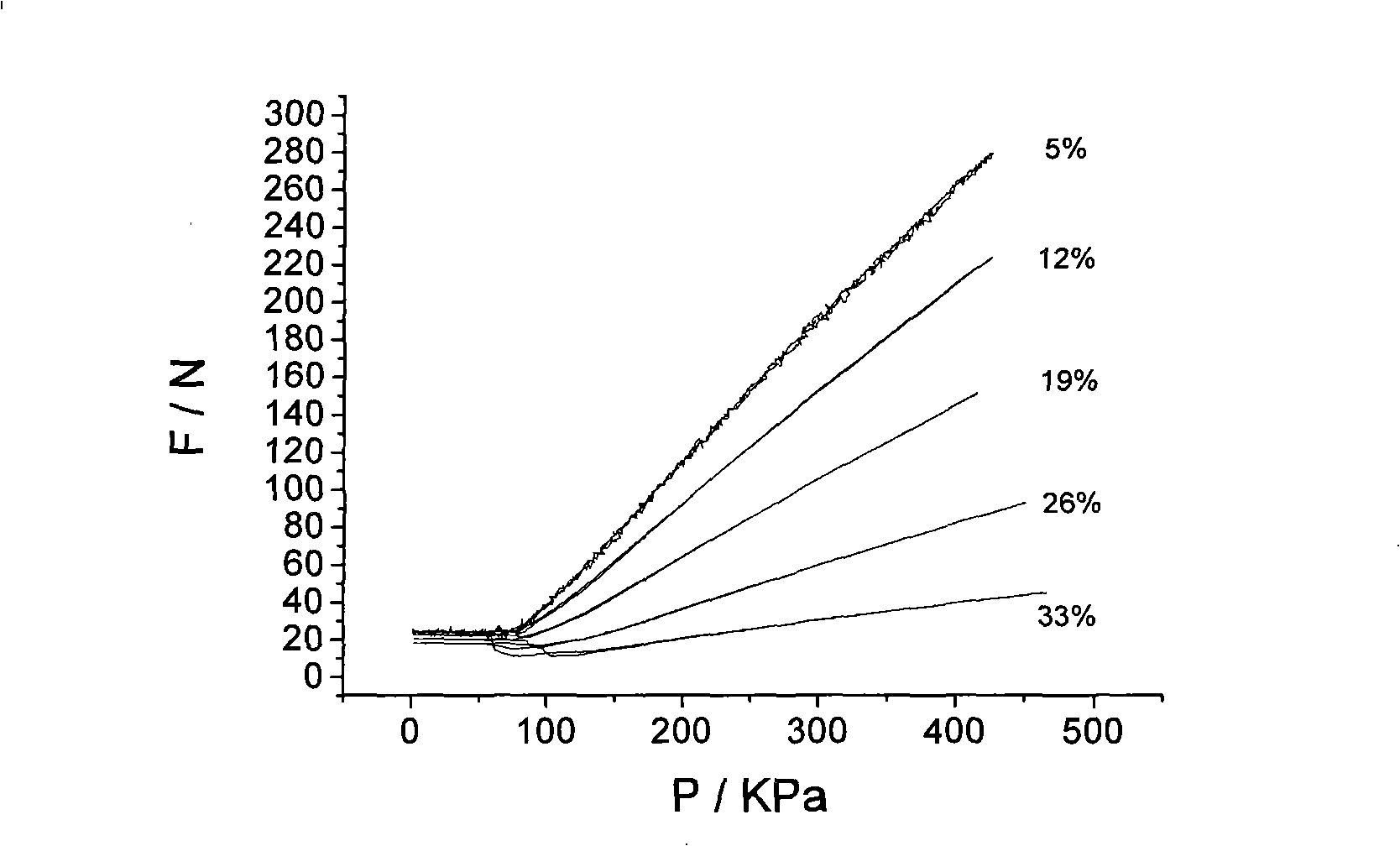
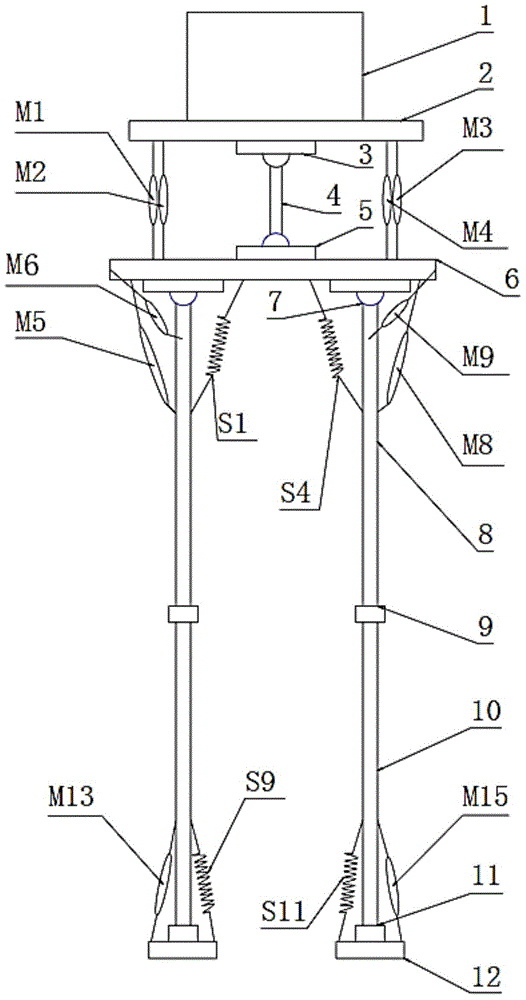
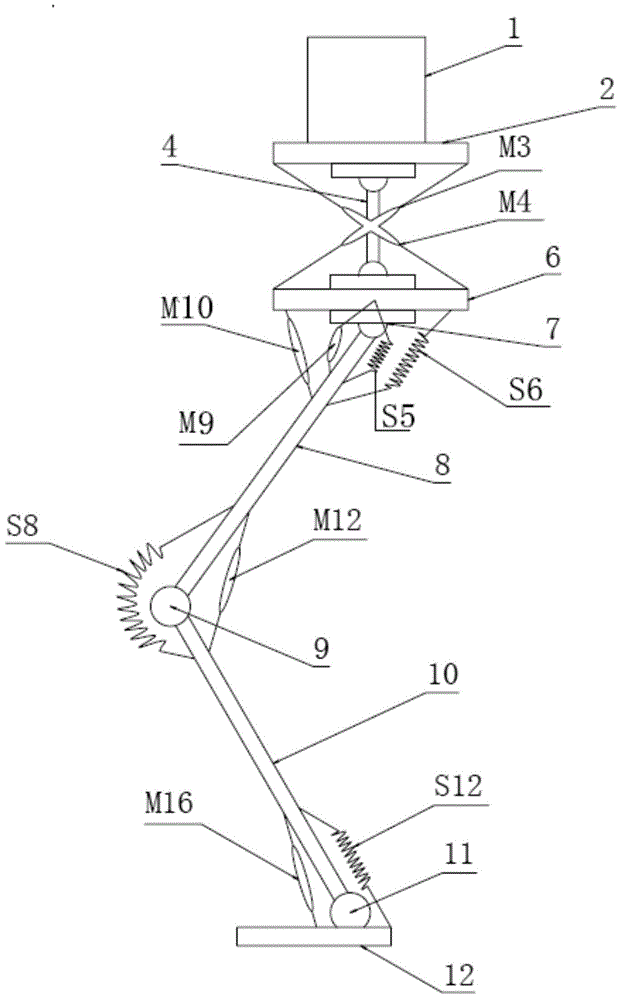
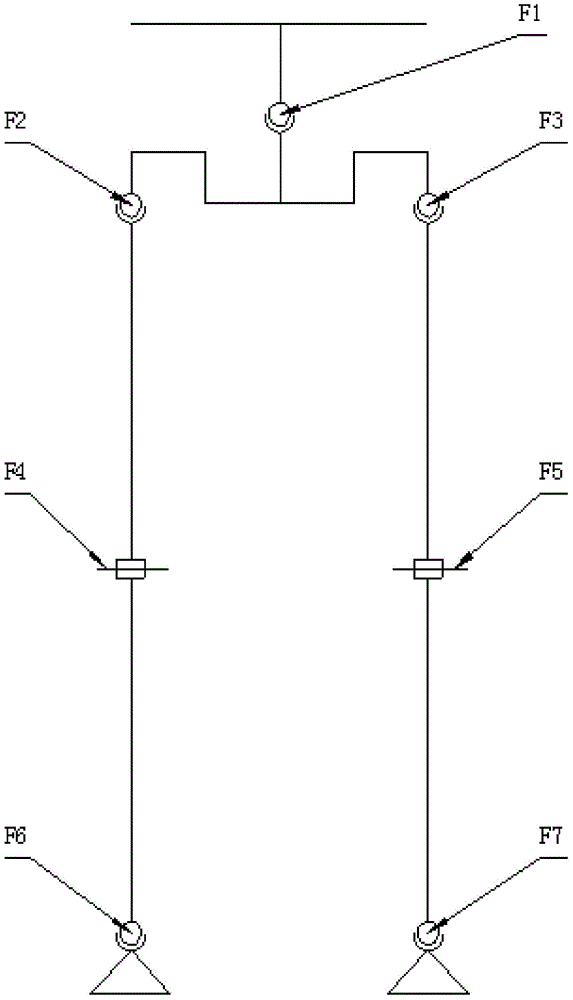
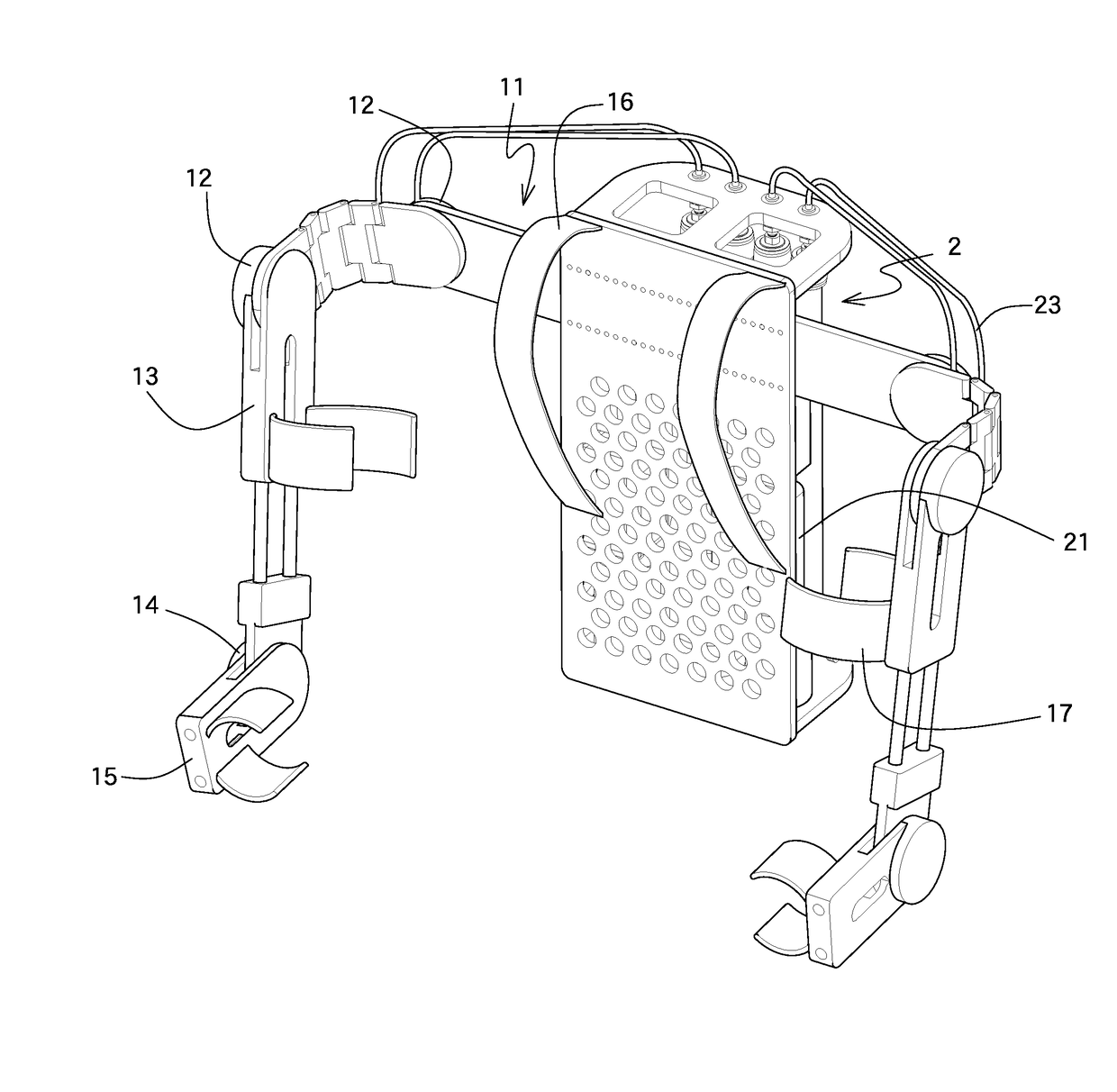
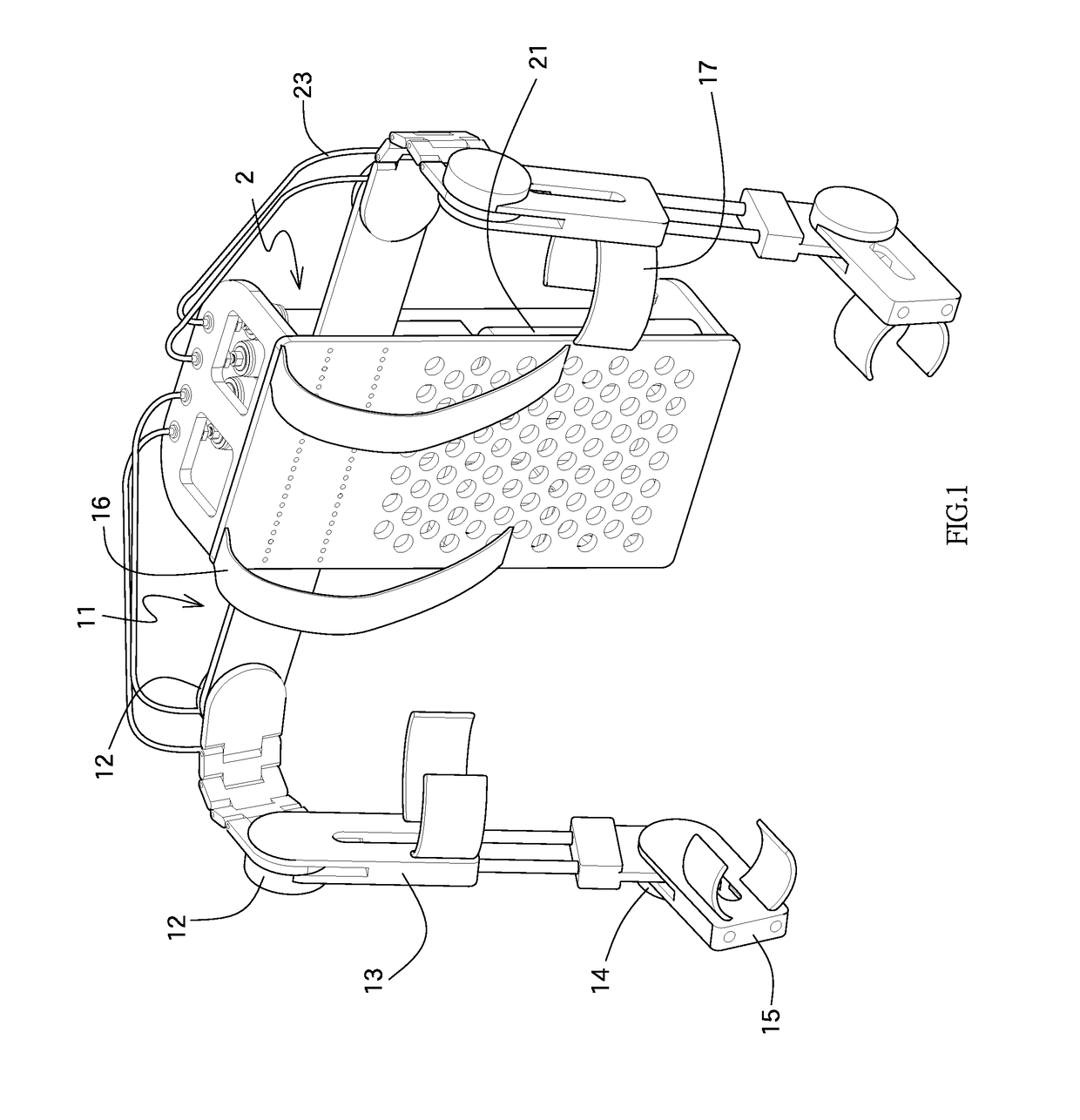
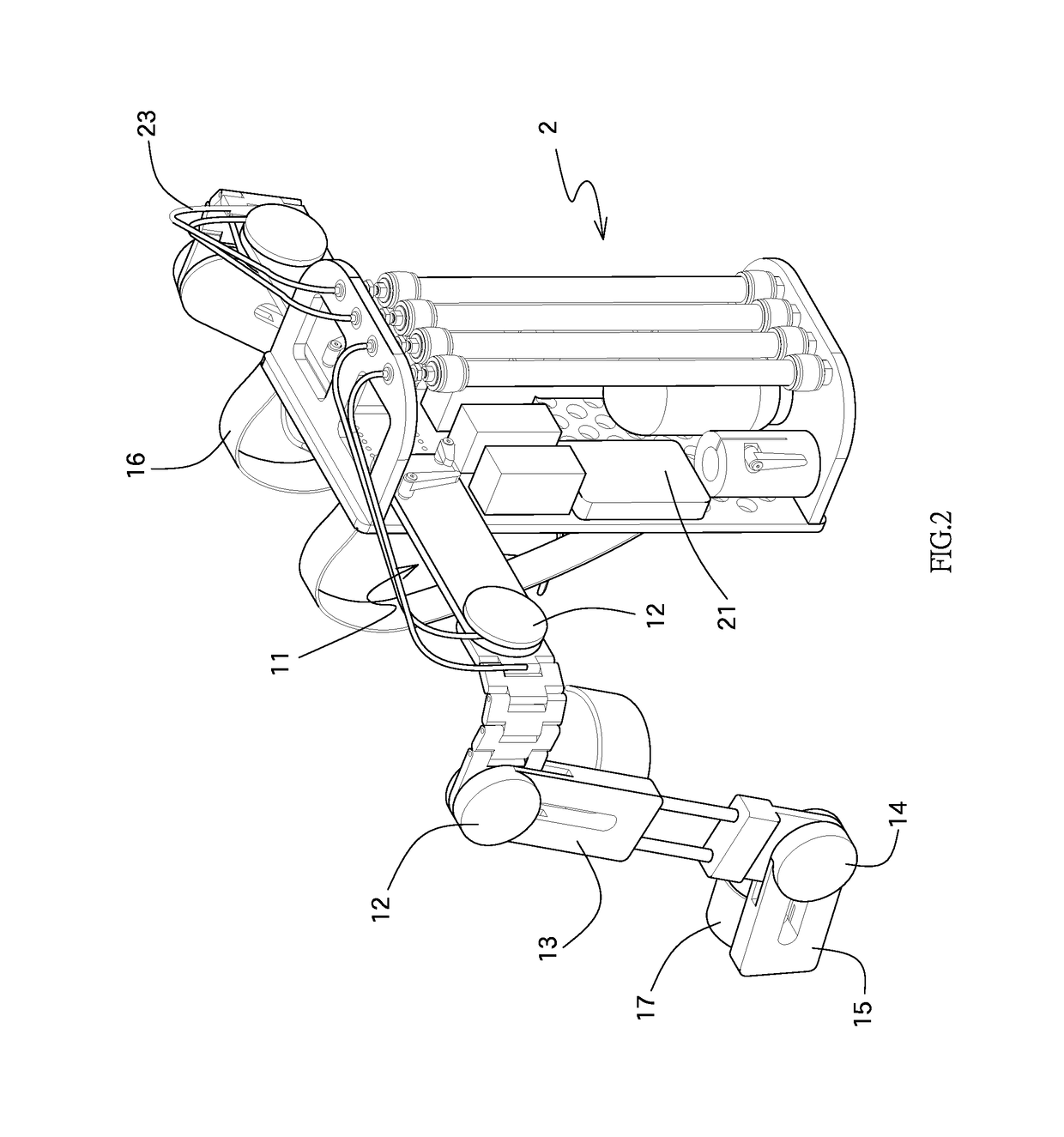
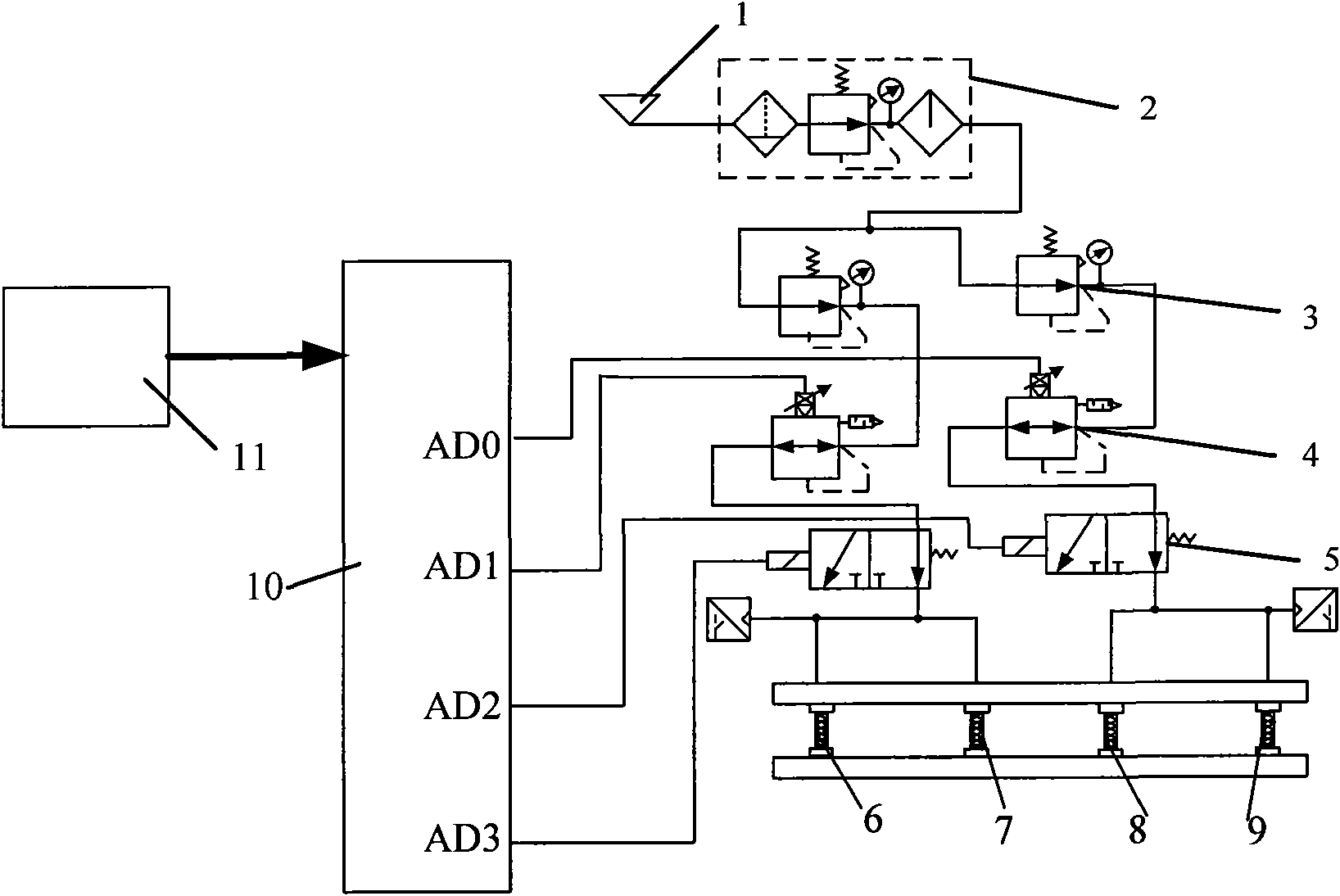
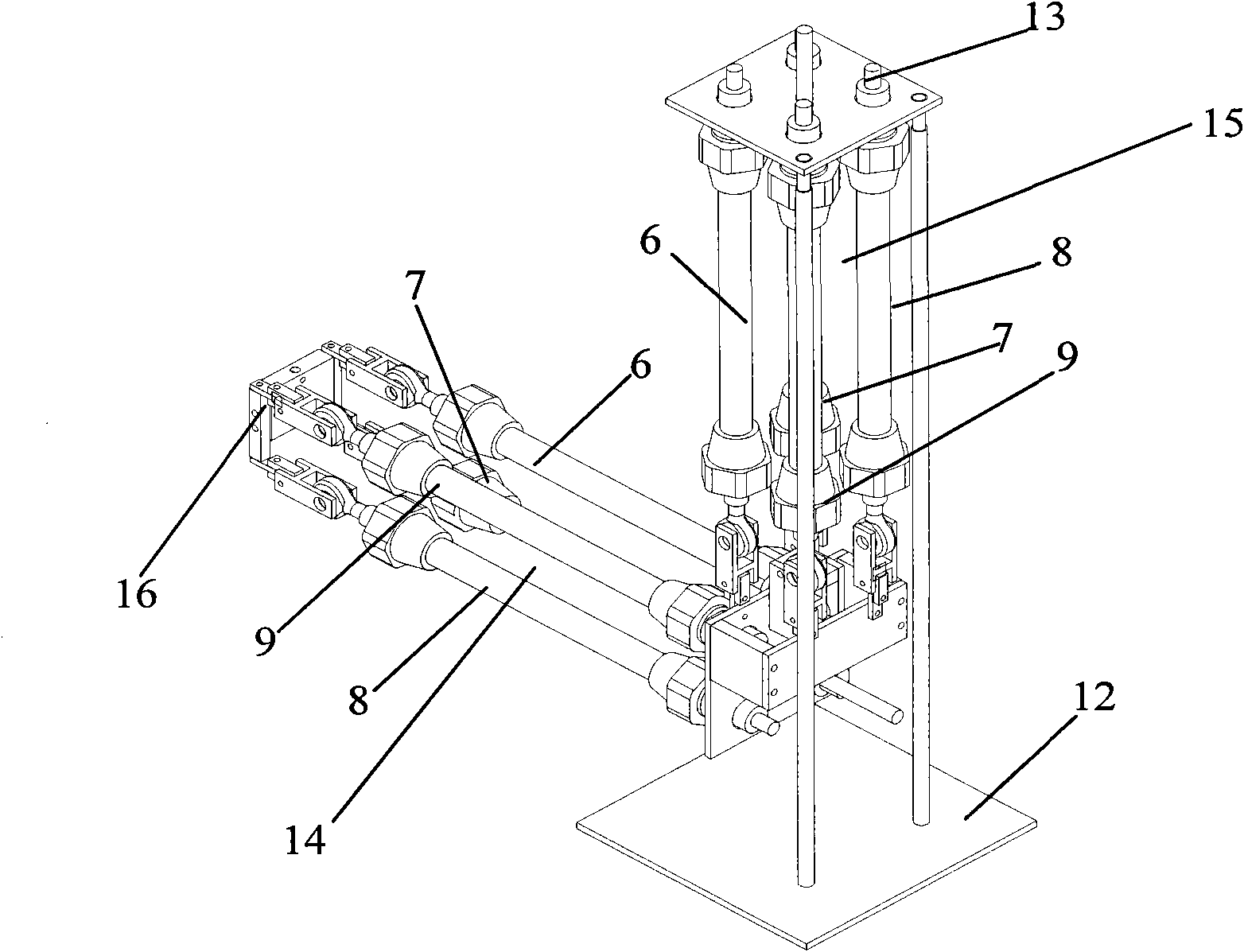
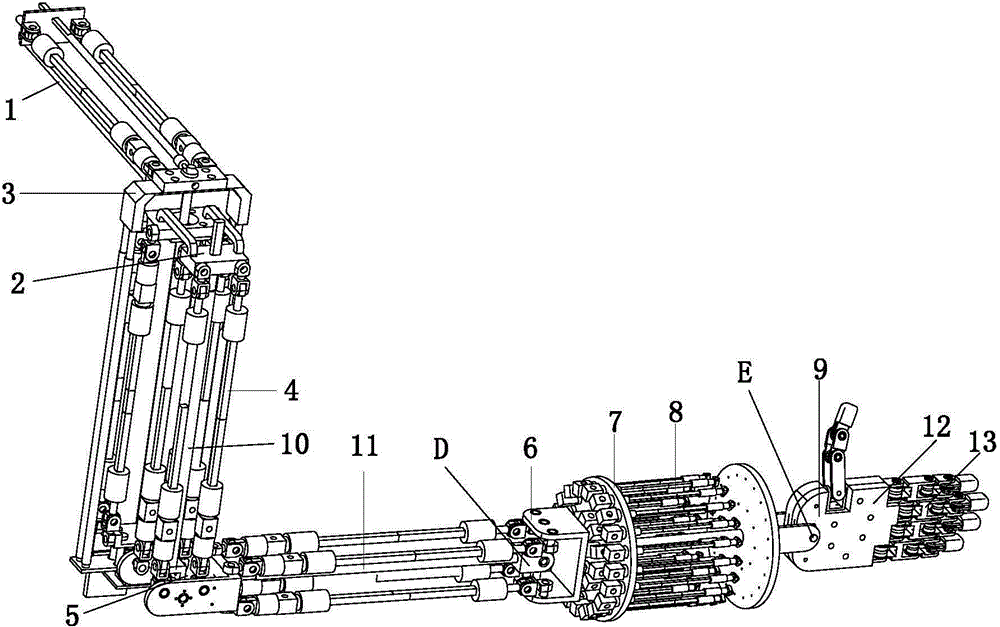
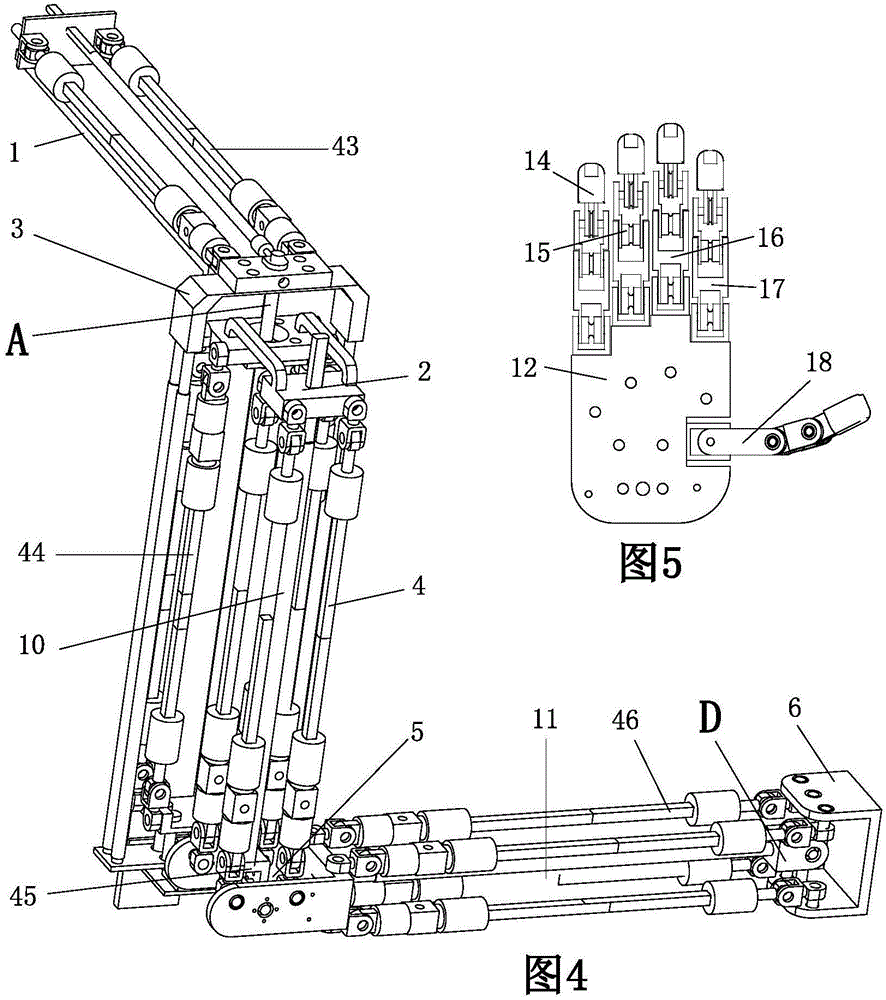
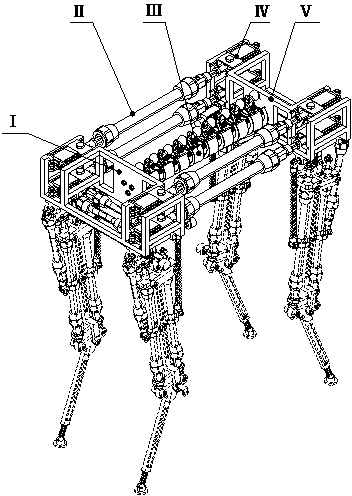
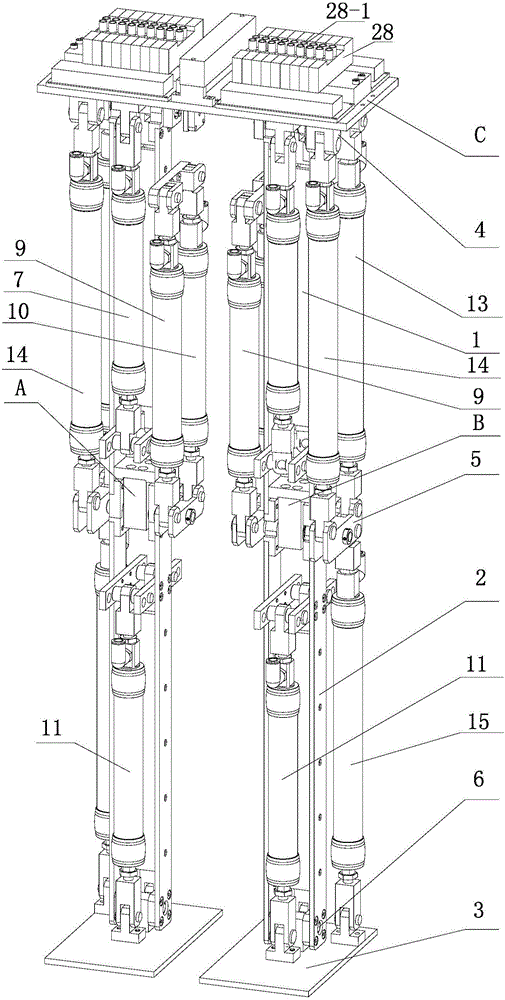
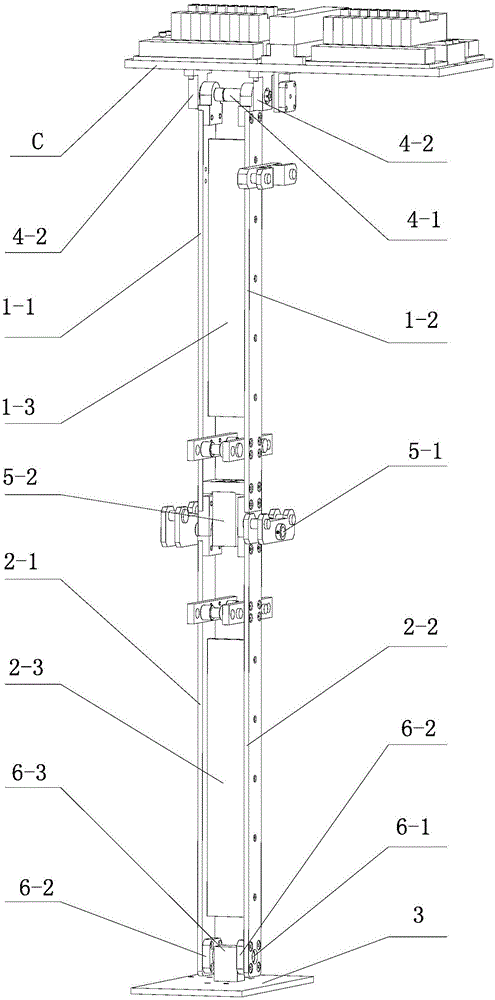
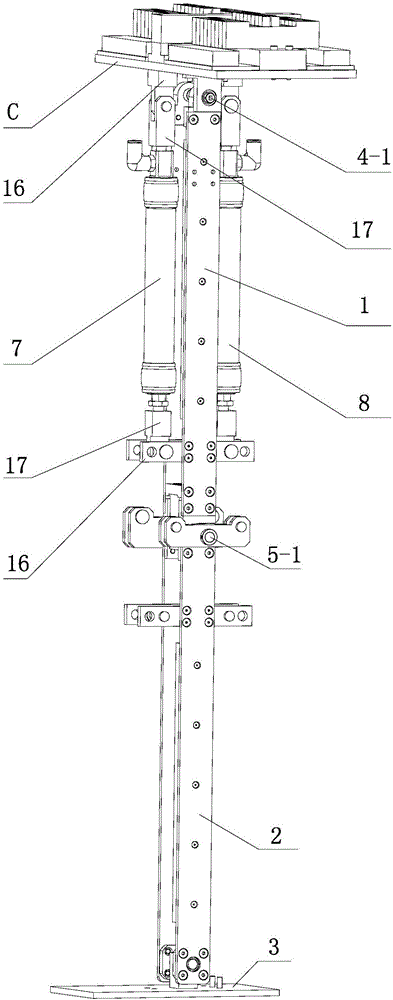
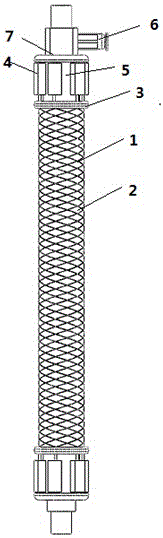
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
183 results about "Pneumatic artificial muscles" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Pneumatic artificial muscles (PAMs) are contractile or extensional devices operated by pressurized air filling a pneumatic bladder. In an approximation of human muscles, PAMs are usually grouped in pairs: one agonist and one antagonist.
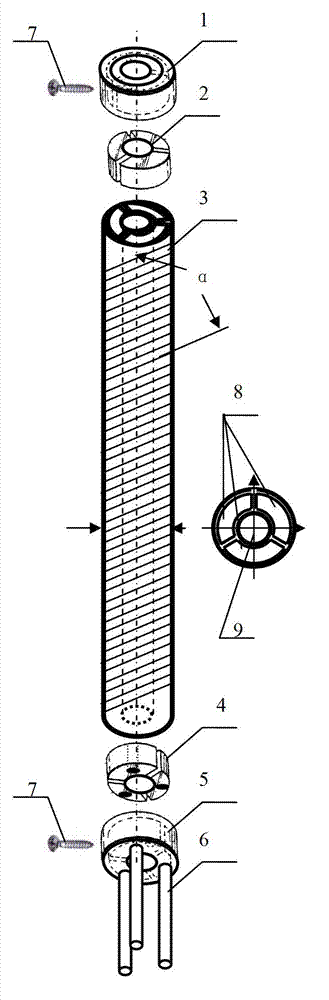
Pneumatic artificial muscles
InactiveCN101306535ASelf-bufferingSelf-dampingProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsEngineeringPneumatic artificial muscles
The invention belongs to the pneumatic technology field, and relates to pneumatic artificial muscle. The artificial muscle consists of an outer mesh grid, an inner expansion tube, a sealing component and a sealing component with air vents. The outer mesh grid is aligned with the inner expansion tube at two ends and sleeved on the inner expansion tube, with the original length thereof a little longer than that of the inner expansion tube; and one end of the outer mesh grid is inserted into the sealing component, and the other end thereof is inserted into the sealing component with air vents. The inner expansion tube of the pneumatic artificial muscle is inflated with air with a certain pressure, so that the inner expansion deforms to cause the outer mesh grid to expand in the radial direction, so as to enable the pneumatic artificial muscle to expand in the radial direction, contract in the axial direction and output certain tensile force. The pneumatic artificial muscle has the characteristics of compact structure, simple manufacture, low price, high flexibility, high ratio of output force to dead weight, effective energy conservation, automatic buffer, pollution resistance, etc., and can be widely applied to the fields of robots, auxiliary medical apparatus and instruments, aviation, defense industry, etc.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
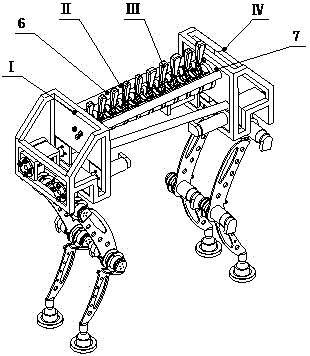
Novel biped humanoid robot system based on pneumatic artificial muscles
ActiveCN104401419AMeet the needs of multidisciplinary scientific research teachingUnique shapeVehiclesSystems designKnee Joint
The invention provides a novel biped humanoid robot system based on pneumatic artificial muscles, belongs to the technical field of robots, and in particular relates to a biped robot having powerful athletic ability and flexible humanoid characteristics. The biped humanoid robot system comprises a mechanical body and an electrical control system; the biped humanoid robot system is characterized in that the mechanical body is mainly composed of seven parts, namely a waist, a hip joint, thighs, knee joints, shanks, feet and the like, and has 13 degrees of freedom in total; in the 13 degrees of freedom, 3 degrees of freedom of the waist are realized by virtue of the cooperation of four pneumatic muscles and the waist spine, and the single degree of freedom of each of the hip joint, the knee joints and the ankle joints is realized by use of one pneumatic muscle and one spring which are pulled to each other to produce opposed rotating force. According to the design of the novel biped humanoid robot system, a control platform is provided; the system relates to the fields of control science and intelligent control in addition to robotics, and is capable of meeting the requirements of scientific research and teaching of a plurality of disciplines.
Owner:廊坊市奥联科技有限公司
Joint driving device of robot
InactiveCN101870111ASmooth motionQuick responseProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsHuman bodyMotor drive
Owner:青岛恩威机器人科技有限公司
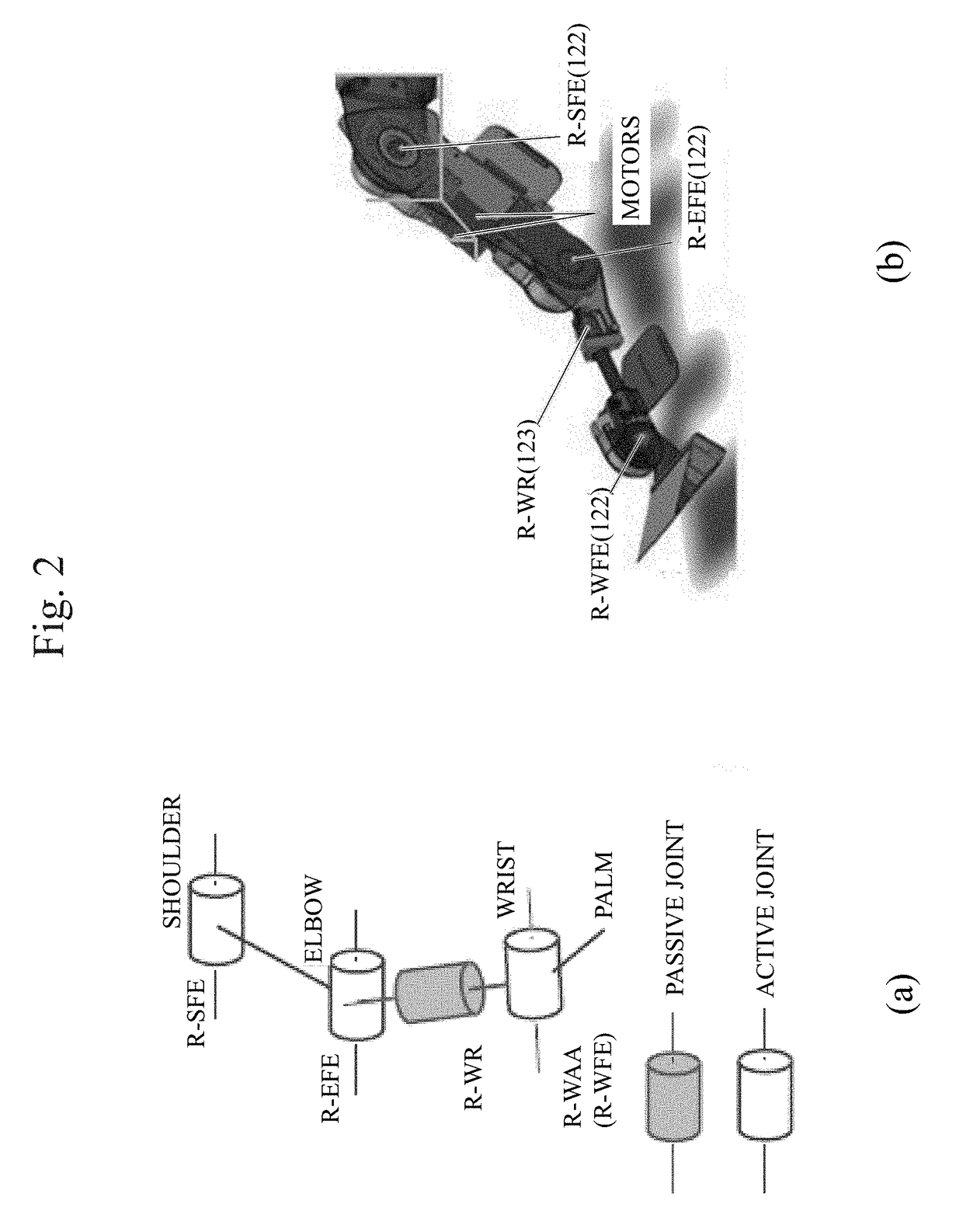
Seven degrees of freedom copy man arm of air-powered artificial muscle drive
InactiveCN101204815AAchieve flexion and extensionRealize the rotation actionArmsEngineeringDegrees of freedom
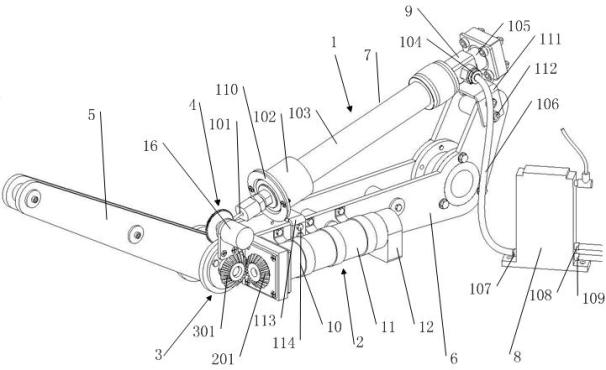
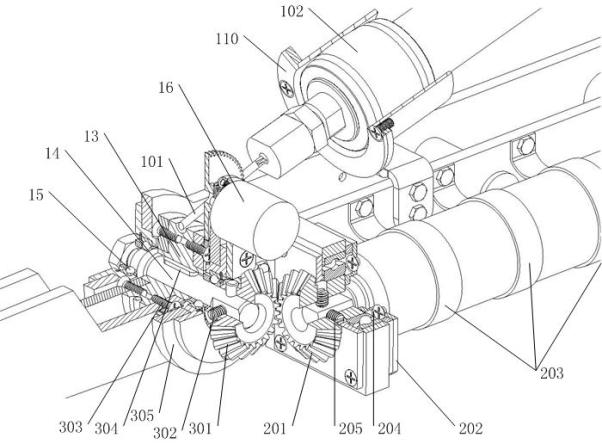
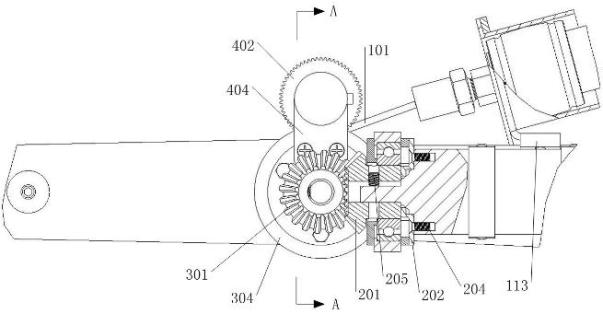
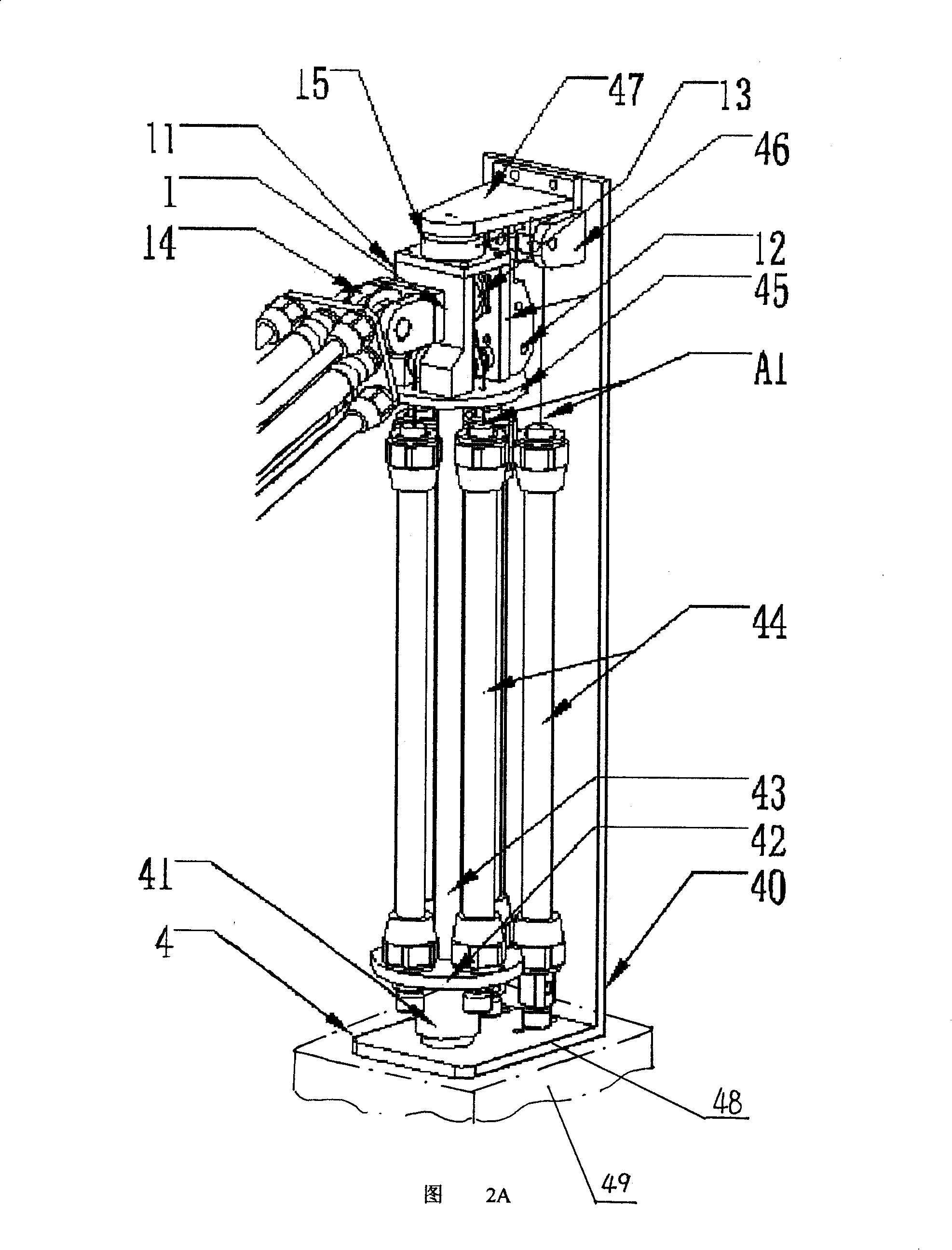
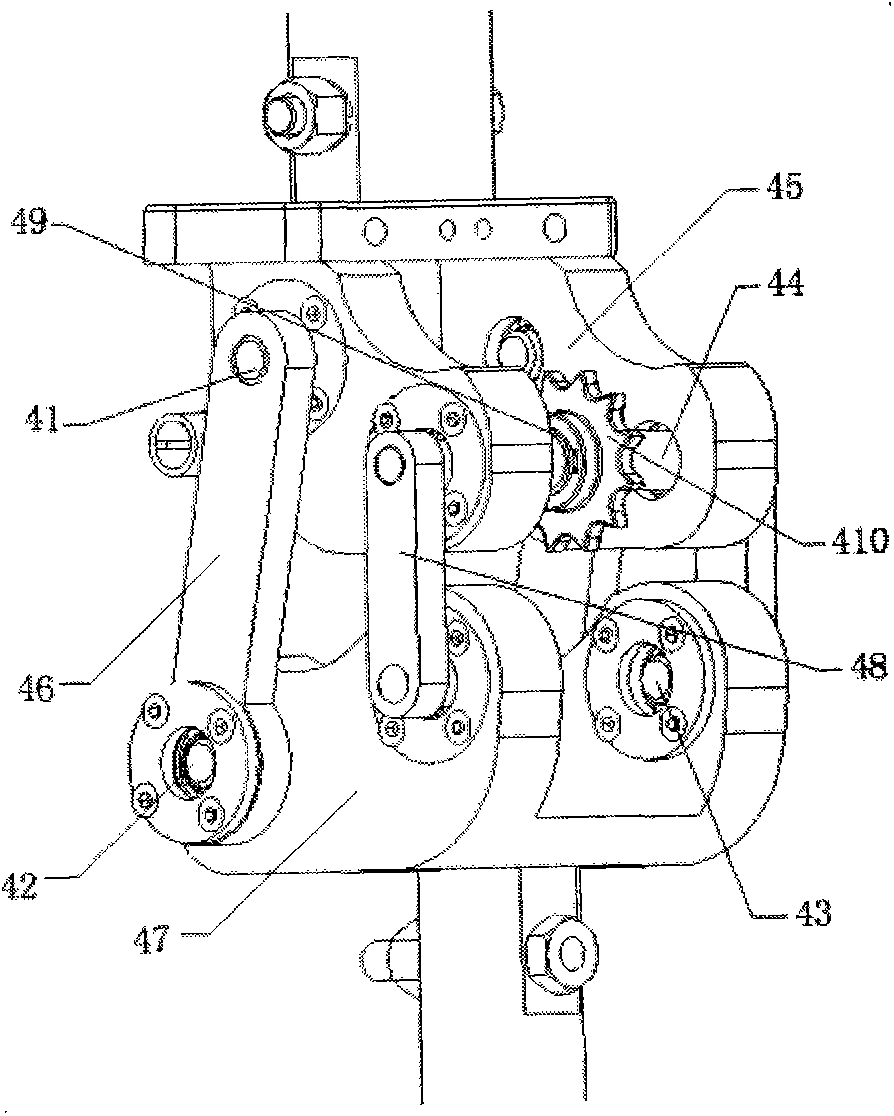
A 7-dof anthropomorphic arm driven by the pneumatic artificial muscles mainly comprises a shoulder joint (1), an elbow joint (2), a wrist joint (3), an arm support frame (4), an upper arm (5), a front arm (6) and a flexible cable (7). The arm support frame (4) is fixed with a base (49) and the pneumatic artificial muscles (44) are arranged in the arm support frame; a steel wire (A1) connected with the pneumatic artificial muscles (44) realizes the rotation of the X, Y, Z shafts through the pulley blocks (B0), (B1), (B2), (B3), (B4) and (B5); the pneumatic artificial muscles (52) driving the elbow joint (2) and the wrist joint (3) to act are arranged in the upper arm (5) and directly operate and control an elbow shaft (21) through a rope (A2) connected with the pneumatic artificial muscles or are respectively attached on a wrist (32) and a palm (34) through a casing tube steel wire (A2) and a casing tube steel wire (A3) so as to realize the rotation round the front arm (6) and the lateral movement. The invention has the advantages of large output force, compliant operation and control, simple structure and small weight simple and easy use, maintenance and repair.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
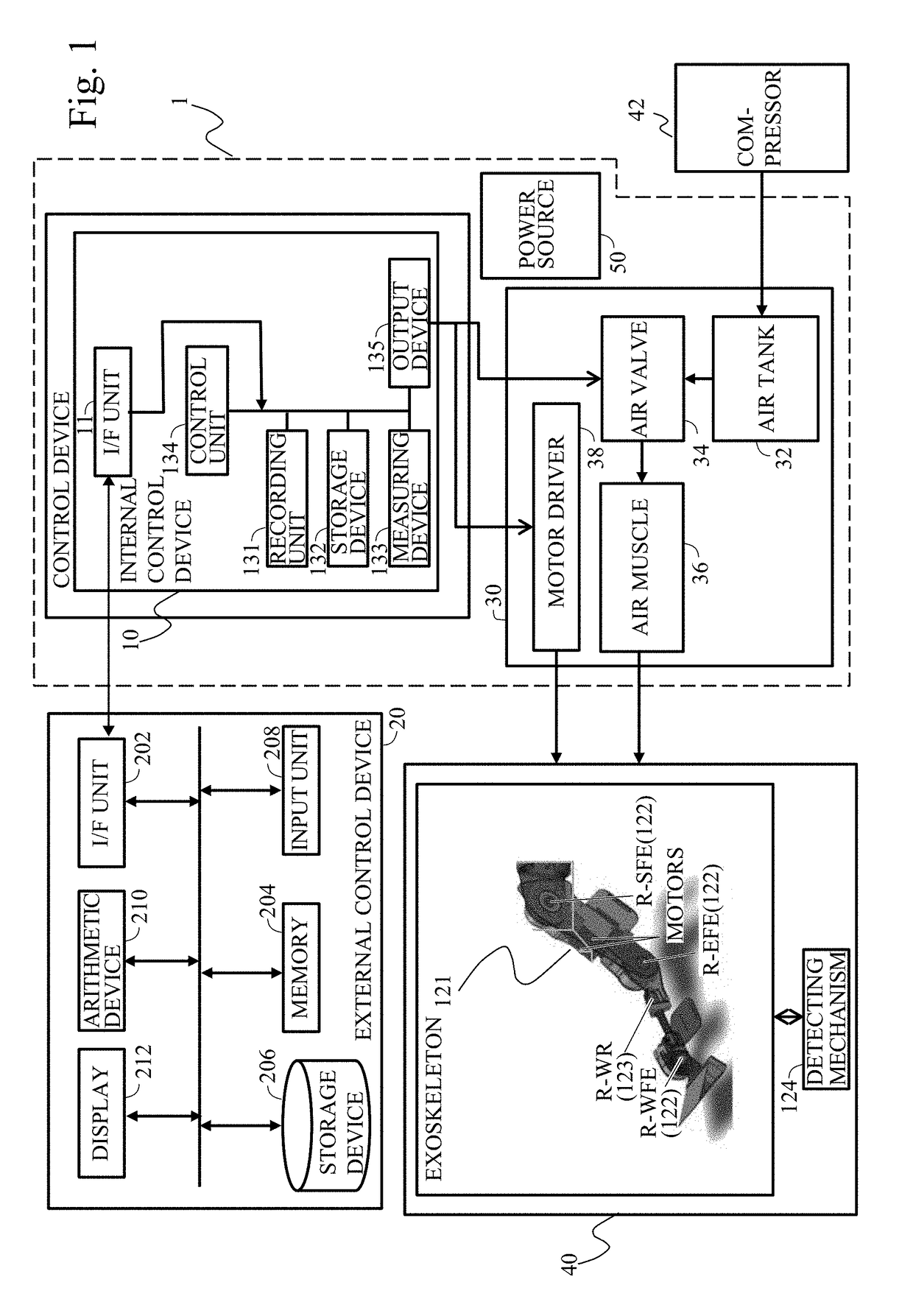
Exoskeleton apparatus driven by pneumatic artificial muscle with functions of upper limb assist and rehabilitation training
ActiveUS20170296418A1Action providedSolve the lack of flexibilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorChiropractic devicesPressure senseEngineering
An exoskeleton apparatus driven by a pneumatic artificial muscle with functions of upper limb assist and rehabilitation training includes an upper limb frame, a shoulder joint mechanism, and an elbow joint mechanism which are driven by utilizing a processing unit, a first angle sensing unit, a second angle sensing unit, a first proportional pressure valve, a pressure sensing unit and a pneumatic muscle device. The exoskeleton apparatus can be independently used as an upper limb exoskeleton assistive device or can be combined to form an upper limb exoskeleton rehabilitation training system to simulate the upper limb movements in daily life through the upper limb frame to assist with the movements of the wearer's upper limbs, accomplishing the rehabilitation training of each upper and lower arm joint and neurological function.
Owner:LUNGHWA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Soft manipulator based on pneumatic artificial muscles
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Self-adaption MDOF (Multi-Degree Of Freedom) humanoid manipulator based on pneumatic artificial muscle
InactiveCN104589310AReduce volumeMeet performance needsProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsControl systemMulti degree of freedom
The invention relates to a self-adaption MDOF (Multi-Degree Of Freedom) humanoid manipulator based on pneumatic artificial muscle and aims at providing a manipulator which has certain functions of human hands and also has the characteristics of practicability, smoothness, safety, small size, lightness, easiness in control and simple mechanism. According to the technical scheme, the self-adaption MDOF humanoid manipulator based on the pneumatic artificial muscle comprises an air course control system, a manipulator mechanism and an artificial muscle system, wherein the manipulator mechanism comprises a mechanical big arm, a mechanical forearm, a hand and five fingers; the artificial muscle system comprises a plurality of third pneumatic artificial muscles, a plurality of fourth pneumatic artificial muscles, a plurality of first pneumatic artificial muscles, a plurality of fifth pneumatic artificial muscles and a plurality of second pneumatic artificial muscles; the mechanism big arm is driven by the third pneumatic artificial muscles and the fourth pneumatic artificial muscles; the mechanism forearm is driven by the first pneumatic artificial muscles; a wrist joint is driven by the fifth pneumatic artificial muscles; the five fingers are driven by the second pneumatic artificial muscles.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Bionic flexible machine body capable of lateral bending and up-down bending
The invention relates to a bionic flexible machine body capable of lateral bending and up-down bending and belongs to the technical field of bionic robots. The bionic flexible machine body comprises a front machine body, a back machine body, a pneumatic artificial muscle component, a bionic spine and a sliding block moving mechanism. The pneumatic artificial muscle component is connected with the front machine and the back machine body through the sliding block moving mechanism respectively. The front end and the back end of the bionic spine are connected with the front machine body and the back machine body through screws respectively. The bionic flexible machine body can achieve lateral bending and up-down tilting bending moving and has the advantages of being good in pliability, flexibility, bionic effect and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Flexible body of bionic robot
InactiveCN103144101AFlexibleBionicProgramme-controlled manipulatorSpinal columnPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The invention relates to a flexible body of a bionic robot, and belongs to the technical field of bionic robots. The flexible body comprises a front body, a back body, an artificial spine, and pneumatic artificial muscles, wherein the artificial spine is formed by sequentially arranging a plurality of bionic spine units from small to large, the bionic spine units are completely same in structure and are different in size, and each bionic spine unit consists of a bionic spine, a bionic intervertebral disc soft cushion and a spring. The flexible body has the advantages that a leg mechanism is assisted to realize the flexible and in-place steering function of the bionic robot, the mobility of the robot adapting to the complicated environment is improved, the flexibility is high, the bionic effect is good, and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Flexible snakelike arm with variable rigidity
ActiveCN109877819AStiffness variable and controllableHigh movement precisionProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringPneumatic artificial muscles
The invention discloses a flexible snakelike arm with variable rigidity. The flexible snakelike arm with the variable rigidity comprises a plurality of rigid-flexible units which are detachably connected into a whole; the rigid flexible units comprise rigid end plates, soft pneumatic artificial muscle groups, ultra-elastic multi-rod mechanisms and limiting partition plates; each ultra-elastic multi-rod mechanism comprises a plurality of ultra-elastic rods, one end of each ultra-elastic rod is assembled on one end plate, and the other end penetrates through the other end plate and then extend into the ultra-elastic rod of the adjacent rigid-flexible unit; the soft pneumatic artificial muscle groups comprise a plurality of pneumatic artificial muscles which are arranged between every two endplates and outside the ultra-elastic multi-rod mechanisms; the limiting partition plates are arranged outside the ultra-elastic multi-rod mechanisms in a sleeving mode; and the two adjacent rigid-flexible units are detachably connected through the end plates. The soft pneumatic artificial muscle groups are utilized to provide flexible bending motion capability, the plurality of ultra-elastic rodsplay a motion guiding role, and through the interaction force formed by the pneumatic artificial muscles and the super-elastic rods, the rigidity of the snake-shaped arm is variable and controllableso that the snakelike arm can reach different positions, and the motion precision of the operation end of the snakelike arm is thus improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Lower jaw masticatory robot based on pneumatic artificial muscle
InactiveCN106239480AImprove biomimicryFlexibleProgramme-controlled manipulatorM. masseterPneumatic circuit
The invention relates to the field of biomimetic robots, in particular to a lower jaw masticatory robot based on pneumatic artificial muscle. The lower jaw masticatory robot is good in softness and compact in structure. According to the technical scheme, the lower jaw masticatory robot based on the pneumatic artificial muscle comprises a support, a vertical plate of the support is fixedly provided with an upper jaw fixed platform, and a lower jaw movable platform is arranged between the upper jaw fixed platform and a base plate of the support; a temporalis mechanism and a wing muscle mechanism are connected between the support and the lower jaw movable platform; a masseter mechanism is arranged between the upper jaw fixed platform and the lower jaw movable platform; and the temporalis mechanism, the masseter mechanism and the wing muscle mechanism each comprise the pneumatic muscle, the pneumatic muscle is connected with pneumatic circuits through gas circuits, and the pneumatic circuits are electrically connected with a control system. The lower jaw masticatory robot based on the pneumatic artificial muscle is provided.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Actuator device, power assist robot and humanoid robot
ActiveUS20170231787A1Reduce inertiaProgramme-controlled manipulatorChiropractic devicesBowden cableHumanoid robot nao
[Object] To provide a hybrid actuator attaining both driving force and responsiveness, capable of reducing inertia of a movable portion.[Solution] A pneumatic air muscle has a cylinder (112) provided in a flexible member (100) forming a pneumatic artificial muscle. At the center of an upper lid element (109) of the cylinder, a through hole is opened, and an inner wire (103) of a Bowden cable passes through this through hole and is coupled by means of a spring (106) to a bottom portion of the cylinder. When the pneumatic artificial muscle contracts, the inner wire (103) and the pneumatic air muscle move together because of the stopper (105), and the contraction force is transmitted. In contrast, when the pneumatic air muscle extends, the stopper (105) is disengaged, while the tension of inner wire (103) is kept by the spring (106) to prevent slacking.
Owner:ATR ADVANCED TELECOMM RES INST INT
Pneumatic space bending flexible joint
InactiveCN103786165AJoints are compactFlexibility and flexibilityJointsThree degrees of freedomEngineering
The invention discloses a pneumatic space bending flexible joint which comprises constraint elements, a joint framework, air bags, an upper end cover, a lower end cover, upper sealing heads, lower sealing heads and fluid inlets. The constraint elements are arranged between the upper end cover and the lower end cover and are coaxially connected in series and densely arranged to form a columnar structure, four tubular cavities with parallel axes are formed in the columnar structure, the axis of one of the tubular cavities overlaps with the axis of the columnar structure to form a first tubular cavity, the other three tubular cavities expect the first tubular cavity are called as second tubular cavities, the air bags are arranged in the second tubular cavities, the two ends of the air bags are connected with the upper sealing heads and the lower sealing heads respectively and the lower sealing heads are provided with the fluid inlets. A driving device of the joint is combined with the joint to form an integral structure which is equivalent to three pneumatic artificial muscles in parallel connection and has three degrees of freedom, and composite actions such as bending and extension of a bionic joint in random directions of space can be achieved.
Owner:BEIHUA UNIV
Handwork imitation dough kneading machine based on pneumatic artificial muscle
InactiveCN103168806AIncrease added valueImprove palatabilityMixing/kneading structural elementsMixing/kneading with vertically-mounted toolsGear wheelEngineering
The invention discloses a handwork imitation dough kneading machine based on pneumatic artificial muscle. The handwork imitation dough kneading machine is characterized by comprising a single-chip microcomputer controller, an artificial muscle gas distributor, a gas distribution pipe, a surface hammer ejector rod, a reset spring, a pneumatic artificial muscle surface hammer, a dough kneading motor, a small gear, a large gear, a cam, a cam shaft, a slotting cam, a slotting cam shaft, a roller ejector rod, a connecting rod, a ridge lifting shovel and a ridge lifting shovel support rod. Compared with the prior art, the handwork imitation dough kneading machine has the advantages that (1) the existing rigid kneading part is replaced by the pneumatic artificial muscle surface hammer, so that a novel and reliable dough kneading way is provided; (2) the handwork imitation dough kneading machine fully utilizes the characteristics of flexible contact, controllable extension size and the like of the pneumatic artificial muscle, thus basically realizing handwork imitation dough kneading operation; the flour products are good in palatability and high in additional value; and (3) the handwork imitation dough kneading machine solves the problem of automatic resetting of a dough after being kneaded for once, is relatively high in degree of automation, and improves the production efficiency and the safety.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Biomimetic crop picking robot
ActiveCN102873675AGuaranteed fine pickingAchieve performanceProgramme-controlled manipulatorPicking devicesProportional controlComputer module
A biominetic crop picking robot comprises picking pipes based on pneumatic artificial muscle, a generator used for feeding air pressure into inner cavities of the picking pipes, pneumatic pressure rate control valves used for controlling the air pressure fed into the inner cavity of each picking pipe, a pressure sensor used for detecting air pressure fed into the inner cavity of each picking pipe, a pneumatic pressure rate controller used for coordinating and controlling each pneumatic pressure rate control valve, a pulse type vacuum generation module used for sucking picked objects, a picking control subsystem used for controlling and performing picking action, a container used for collecting the picked objects, a microprocessor used for intelligently analyzing a video, autonomously navigating and controlling the action of the picking pipes based on the pneumatic artificial muscle and a walking part used for the work of a picking robot in a picking crop area. The biominetic crop picking robot has the advantages of excellent natural flexibility, simple mechanism, low control complexity, high picking efficiency, excellent environmental adaptability, and low manufacturing and maintenance costs.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
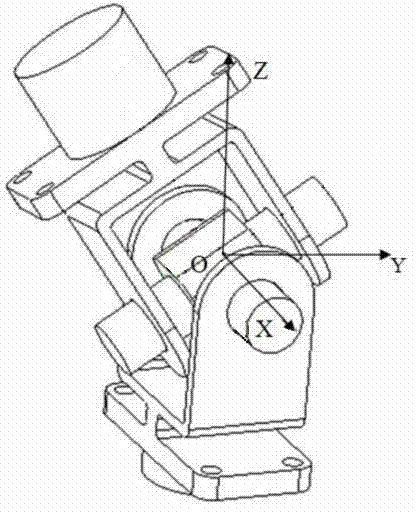
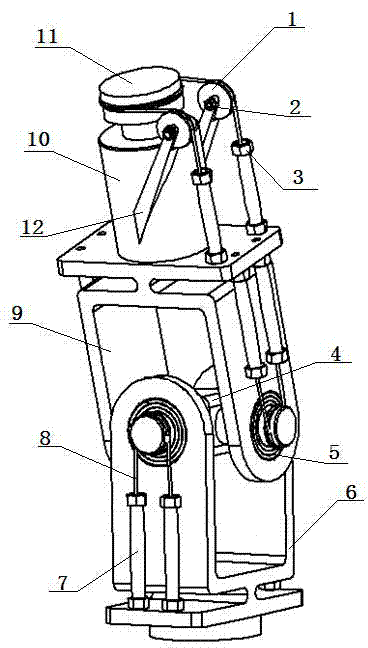
Orthorhombic three-freedom joint driven by pneumatic artificial muscles
The invention discloses an orthorhombic three-freedom joint with relatively high integration driven by pneumatic artificial muscles. The orthorhombic three-freedom joint comprises a hooke joint mechanism consisting of an X-axis bracket, a Y-axis bracket and a cross shaft, wherein an Z-axis bracket is arranged on the top of the Y-axis bracket; a steering mechanism is arranged on the Z-axis bracket; a tail end performer is arranged on the top of the Z-axis bracket; artificial muscles are arranged at one sides of the steering mechanism, the X-axis mechanism and the Y-axis mechanism; ends of the artificial muscles are connected with the bracket through a nut, and the other ends of the artificial muscles are connected with a transmission rope; the transmission rope is vertically nested on the tail end performer and the shaft shoulder of the cross shaft through the steering mechanism. The orthorhombic three-freedom joint realizes three-freedom orthogonality, simplifies motion equation, improves the control speed, strengthens the joint flexibility and expands joint working sace.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIV OF WATER RESOURCES & ELECTRIC POWER
Flexible pectoral fin swing type underwater bionic robot
InactiveCN101486377AAchieve supple movementChange the speed of movementPropulsive elements of non-rotary typeUnderwater equipmentBionicsPneumatic artificial muscles
The invention discloses a flexible pectoral fin swing type underwater bionic robot, consisting of a left swinging component, a right swinging component, a tail swinging component, a supporting component, a left flexible wing and a right flexible wing; the left flexible wing has the same structure with that of the right flexible wing, the two wings are symmetrically assembled by taking the longitudinal axis as a center to form a flexible body, the left swinging component, the right swinging component, the tail swinging component and the supporting component are arranged inside the flexible body, and an air supply is arranged outside the flexible body; the supporting component is arranged along the longitudinal axis, the left swinging component and the right swinging component are respectively arranged at the left side and the right side of the supporting component, and the tail swinging component is arranged at the rear end of the supporting component; and the left swinging component has the same structure as that of the right swinging component. The bionic robot adopts the external air supply to drive pneumatic artificial muscles, so as to realize moving forwards, turning and heave movement of the bionic robot in water.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Two-leg robot leg mechanism based on driving of artificial muscles
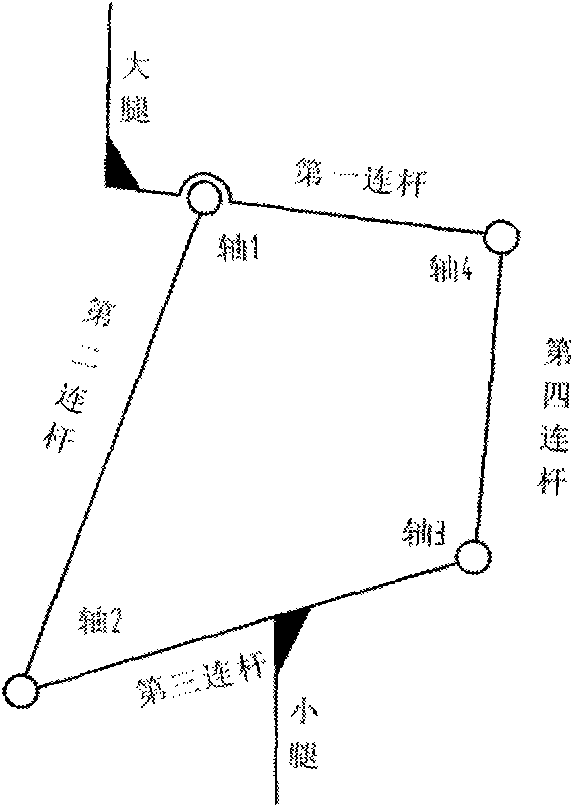
InactiveCN103707951AEffective simulationShorten the lengthVehiclesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationDrive shaft
The invention discloses a two-leg robot leg mechanism based on driving of artificial muscles. The two-leg robot leg mechanism comprises a single-shaft hip joint, thigh rods, a pneumatic artificial muscle driving mechanism, bionic knee joints, crus rods, ankle joint transmission mechanisms and artificial flexible feet, wherein the single-shaft hip joint is connected with the thigh rods, the thigh rods are connected with the bionic knee joints, the bionic knee joints, the crus rods, the ankle joint transmission mechanisms and the artificial flexible feet are sequentially connected, the pneumatic artificial muscle driving mechanism comprises a transverse rod, the transverse rod is perpendicularly fixed in the thigh rods, two pneumatic artificial muscles are arranged in parallel, one ends of the two pneumatic artificial muscles are fixedly connected with the transverse rod, the other ends of the two pneumatic artificial muscles are connected to each other through a chain, the chain is connected with a driving shaft of the bionic knee joints through a chain wheel, and driving is achieved through opposite pulling of the pair of pneumatic muscles. The two-leg robot leg mechanism has the advantages of being natural in walking gait, high in adaptability to road conditions, small in motion impact, high in walking speed, small in energy consumption, capable of achieving flexible motion of joints, simple in structure and delicate in design.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV +1
Wearable rehabilitation training device for upper limbs driven by pneumatic artificial muscles
The invention relates to a wearable rehabilitation training device for upper limbs driven by pneumatic artificial muscles. The wearable rehabilitation training device comprises a back support assembly, a shoulder joint upward-downward swing mechanism, a shoulder joint inward-outward swing mechanism, an elbow joint swing mechanism and a wrist joint swing mechanism. A left upper end of the back support assembly is rotatably connected with a first joint shaft of the shoulder joint inward-outward swing mechanism by means of plastic bearings. The left lower end of the back support assembly is rotatably connected with the lower end of a pneumatic artificial muscle assembly A by means of a bottom plate connecting part. The shoulder joint upward-downward swing mechanism is rotatably connected with a pneumatic artificial muscle assembly B, a pneumatic artificial muscle assembly C and a joint connecting part at the upper end of the elbow joint swing mechanism by means of a shoulder joint connecting part. The lower end of the shoulder joint inward-outward swing mechanism is fixedly connected with a large arm skeleton of the elbow joint swing mechanism by means of a right-angle connecting part. The lower end of the elbow joint swing mechanism is movably connected with a small arm skeleton of the wrist joint swing mechanism in an adjustable mode. The wearable rehabilitation training device for upper limbs driven by pneumatic artificial muscles is featured by being low in weight, high in bionic performance and fine in safety.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Humanoid lower limbs driven by pneumatic artificial muscles
The invention discloses humanoid lower limbs driven by pneumatic artificial muscles and relates to a robot. By the adoption of the humanoid lower limbs driven by the pneumatic artificial muscles, the problems that due to the fact that an existing active robot is driven through a rigid structure, system structure is complicated, flexibility is poor, and the energy efficiency of the robot is low are solved. The humanoid lower limbs comprise a left leg, a right leg and a pelvis, wherein the left leg and the right leg are both provided with a thigh, a shank, a foot, a hip joint, a keen joint, an upper ankle joint and a lower ankle joint, the left leg and the right leg are connected through the pelvis, and the pelvis is connected with the thighs in a rotary mode through the hip joints; each thigh is connected with the corresponding shank in a rotary mode through the corresponding knee joint, each shank is connected with an ankle joint disc in a rotary mode through the corresponding upper ankle joint, and each ankle joint disc is connected with the corresponding foot in a rotary mode through the corresponding lower ankle joint; each thigh is provided with iliacus, gluteus maximus, vastus lateralis muscles, biceps femoris muscles, semitendinosus and rectus femoris, each shank is provided with tibialis anterior muscles, musculi soleus, musculus gastrocnemius, adductor and peroneus, and the upper end of the iliacus and the upper end of the gluteus maximus are both hinged to the pelvis. The humanoid lower limbs belong to the field of humanoid robots.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
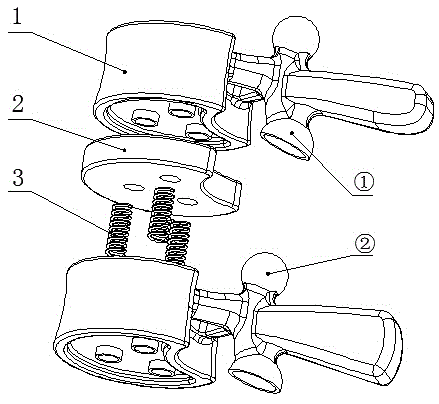
Single-degree-of-freedom joint mechanical driven by two pneumatic artificial muscle assemblies
The invention relates to a single-degree-of-freedom joint mechanical driven by two pneumatic artificial muscle assemblies, and belongs to the technical field of bio-robots. The single-degree-of-freedom joint mechanical driven by the two pneumatic artificial muscle assemblies can be used in leg joints of the four-footed bio-robots. The single-degree-of-freedom joint mechanical driven by the two pneumatic artificial muscle assemblies comprises the two pneumatic artificial muscle assemblies, two rotary parts, a thigh framework and a crus framework, wherein the two ends of the two pneumatic artificial muscle assemblies are connected with the rotary parts and pin shafts. The single-degree-of-freedom joint mechanical driven by the two pneumatic artificial muscle assemblies has the bionic advantages of being large in movement range, high in movement speed, good in flexibility and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Deformable skin structure with designable poisson ratio
The invention relates to a wing skin structure, in particular to a deformable skin structure with a designable poisson ratio, aiming at solving the problem that the existing skin structure cannot meet the requirements of lower deformation rigidity along the deformation direction and higher structural rigidity along other non-deformation directions, thus being not capable of bearing aerodynamic load and inertia load. The deformable skin structure comprises a honeycomb structure base body, a flexible elastomer and a plurality of pneumatic artificial muscles, wherein the honeycomb structure base body is a honeycomb structure body formed by arranging positive poisson ratio honeycomb unit bodies and negative poisson ratio honeycomb unit bodies in a mixed way; the flexible elastomer is poured onto the honeycomb structure base body and the plurality of pneumatic artificial muscles so as to form a flexible panel. The deformable skin structure with the designable poisson ratio is used for manufacturing aircraft wing skin.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
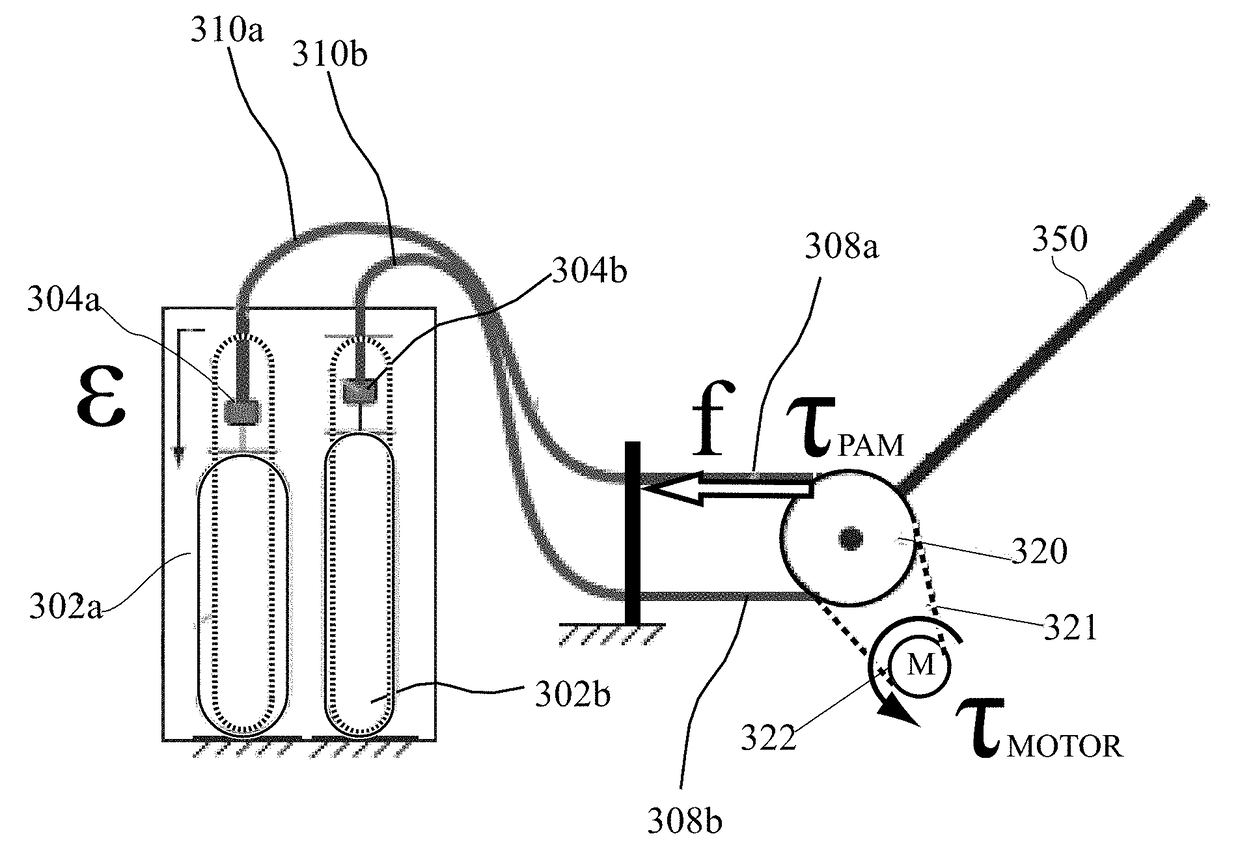
Pneumatic sensing actuator
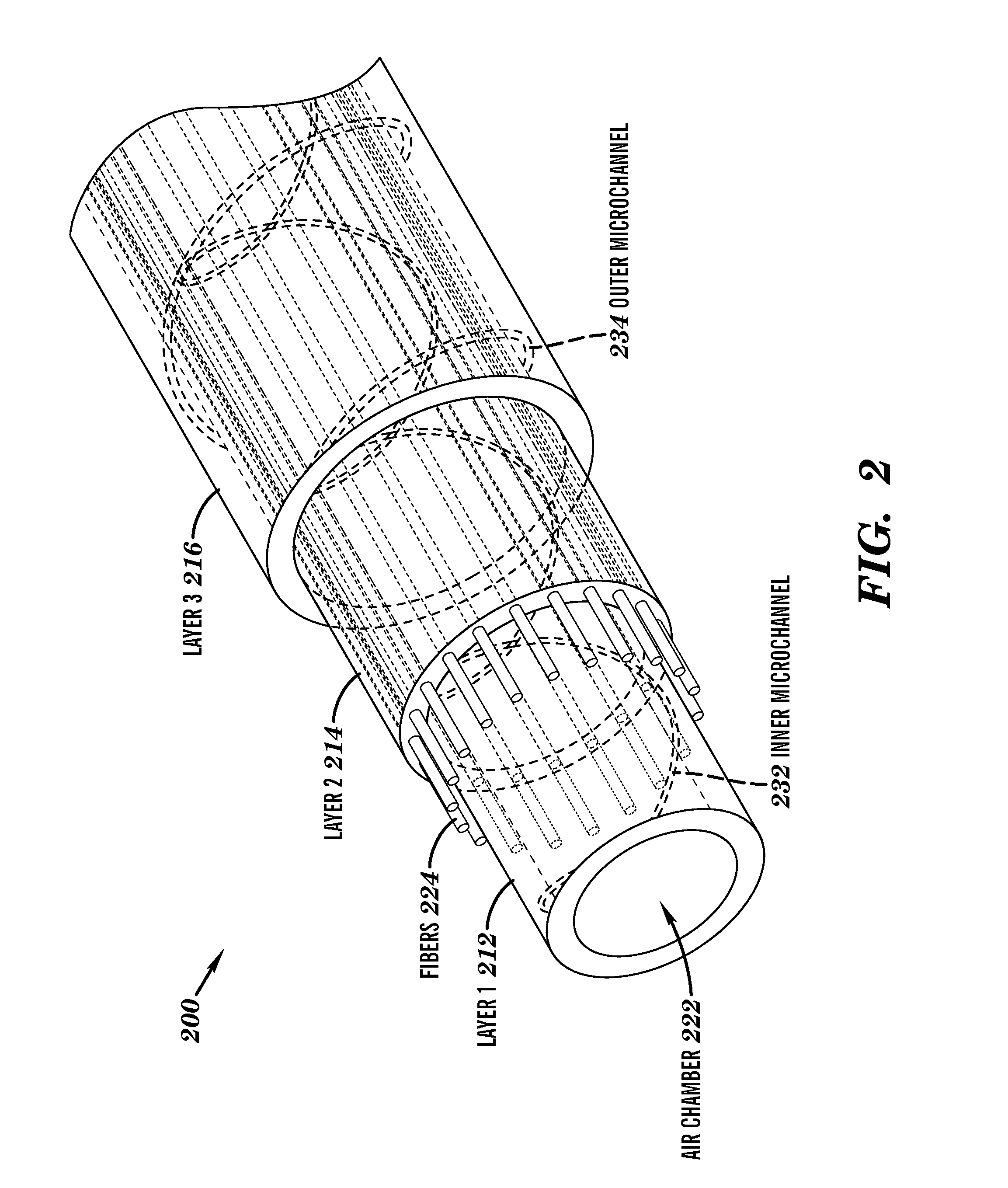
ActiveUS20150337874A1Flexible wall reciprocating enginesMouldsElectrical resistance and conductanceFiber
A pneumatic artificial muscle (PAM) actuator body can be formed from an elastic material that includes an inflatable chamber and a restraining component, such as flexible, but inextensible fibers, that causes the actuator to contract when the chamber is inflated with fluid (e.g., air or water). The actuator body can be cylindrical or flat. The actuator body can include a sensor layer formed of an elastic material including a microchannel filled with a conductive fluid to sense the expansion of the actuator body. The sensor layer can be configured to expand when the actuator body is inflated causing the electrical resistance of the conductive fluid to change. A sensor layer between the actuator body and restraining component can be used to measure changes in the contraction force of the actuator and a sensor layer outside of the restraining component can be used to measure changes in the length of the actuator.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP +1
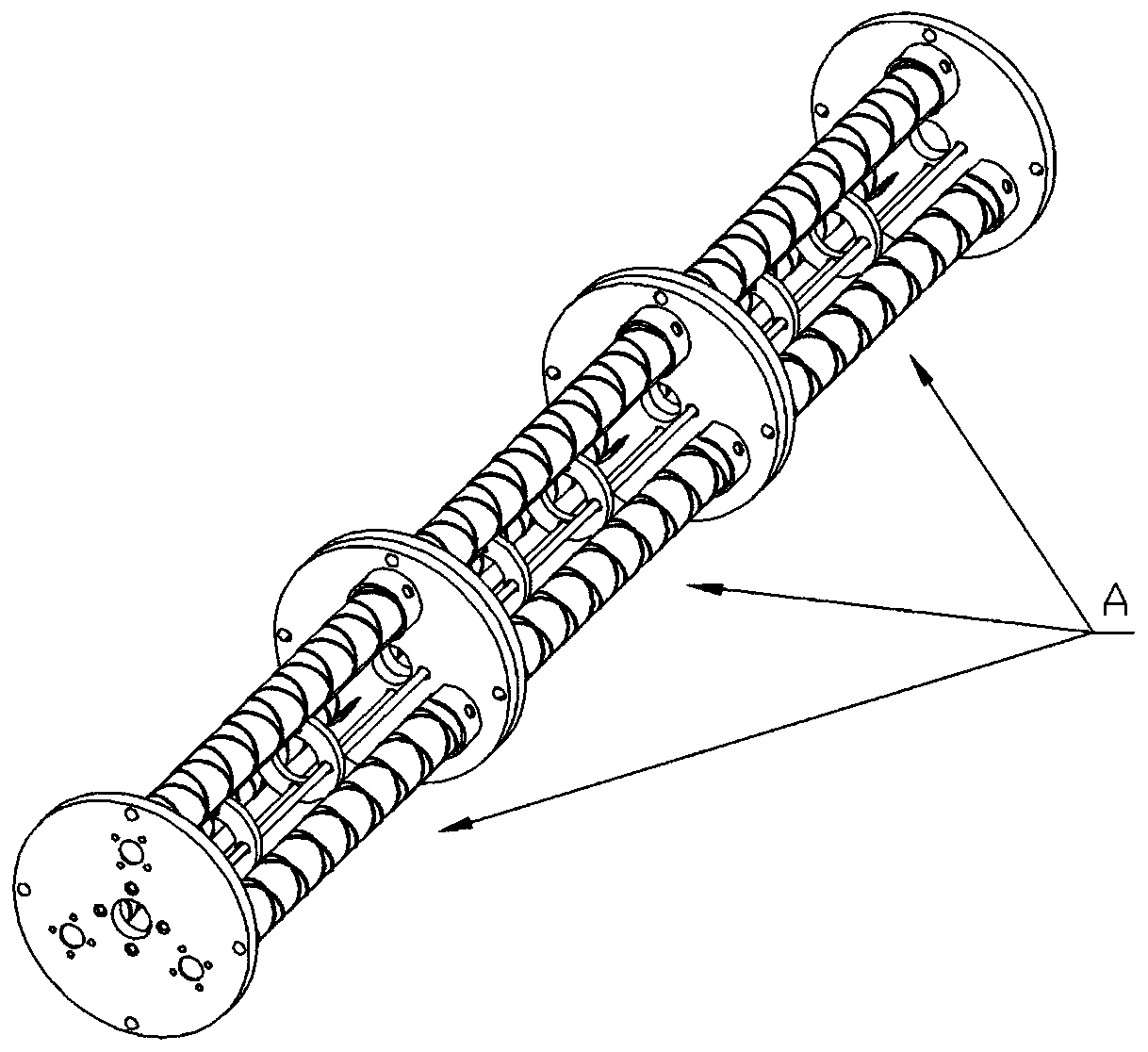
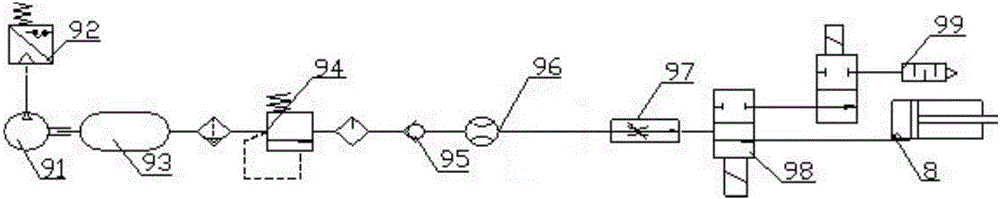
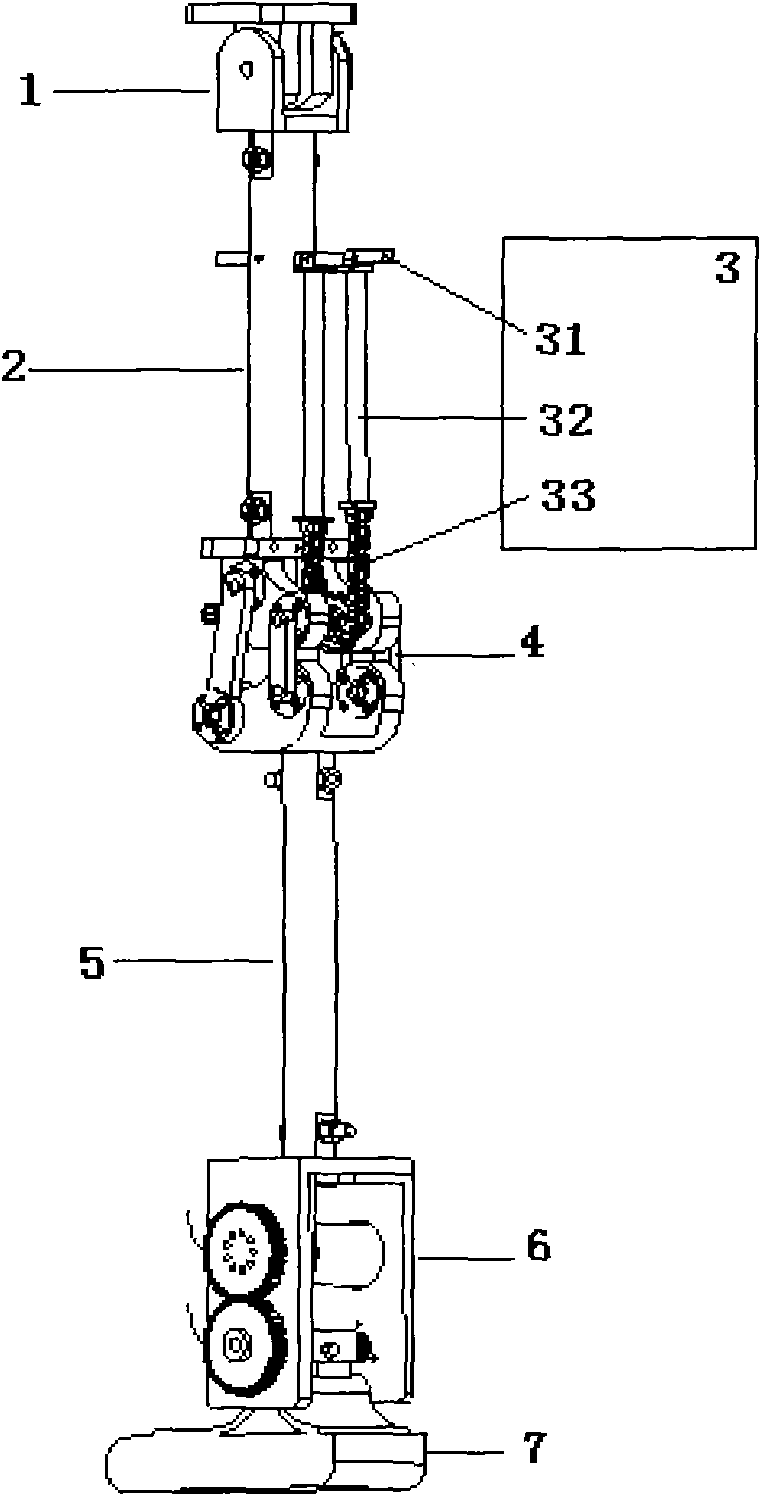
Three freedom degree motion simulator of pneumatic hybrid mechanism
InactiveCN101537621AIncrease load capacityLarge working spaceManipulatorRotational freedomThree degrees of freedom
The invention belongs to the field of pneumatic technology, relates to a gas-driven motion simulator, in particular to a three freedom degree motion simulator of a pneumatic hybrid mechanism; the invention is a novel three freedom degree motion simulator of the pneumatic hybrid mechanism, which is driven by an air cylinder and a pneumatic artificial muscle in a mixing mode to realize combination of a parallel mechanism and a serial mechanism; wherein the parallel mechanism consists of a first angle sensor, a second angle sensor, a crossing shaft, a hooker hinge, a pneumatic artificial muscle, an upper platform and a lower platform, and is used for realizing the two rotational freedom degree; the serial mechanism consists of the air cylinder, a base, a linear bearing, a guiding rail and a flange, and is used for realizing the freedom degree of up-and-down movement; the serial mechanism is connected with the lower platform of the parallel mechanism by threads; and servocontrol of the three freedom degree motion simulator is realized by a pneumatic control mechanism. The invention has the advantages of simple structure, mutual independence of three freedom degree, good controllability, fast response of pneumatic control and good softness of pneumatic artificial muscle.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
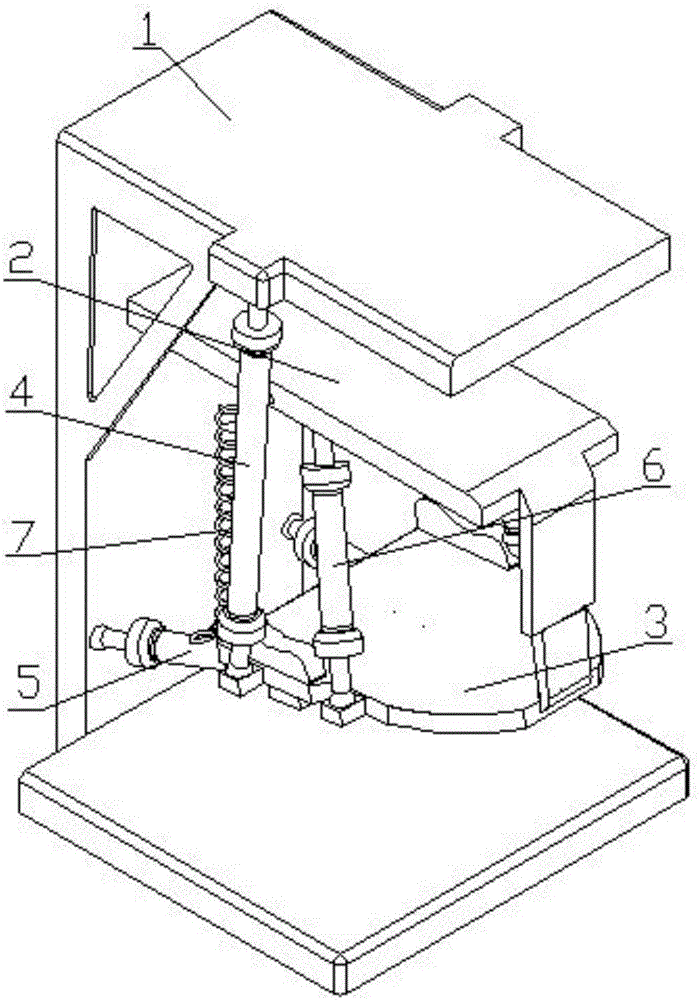
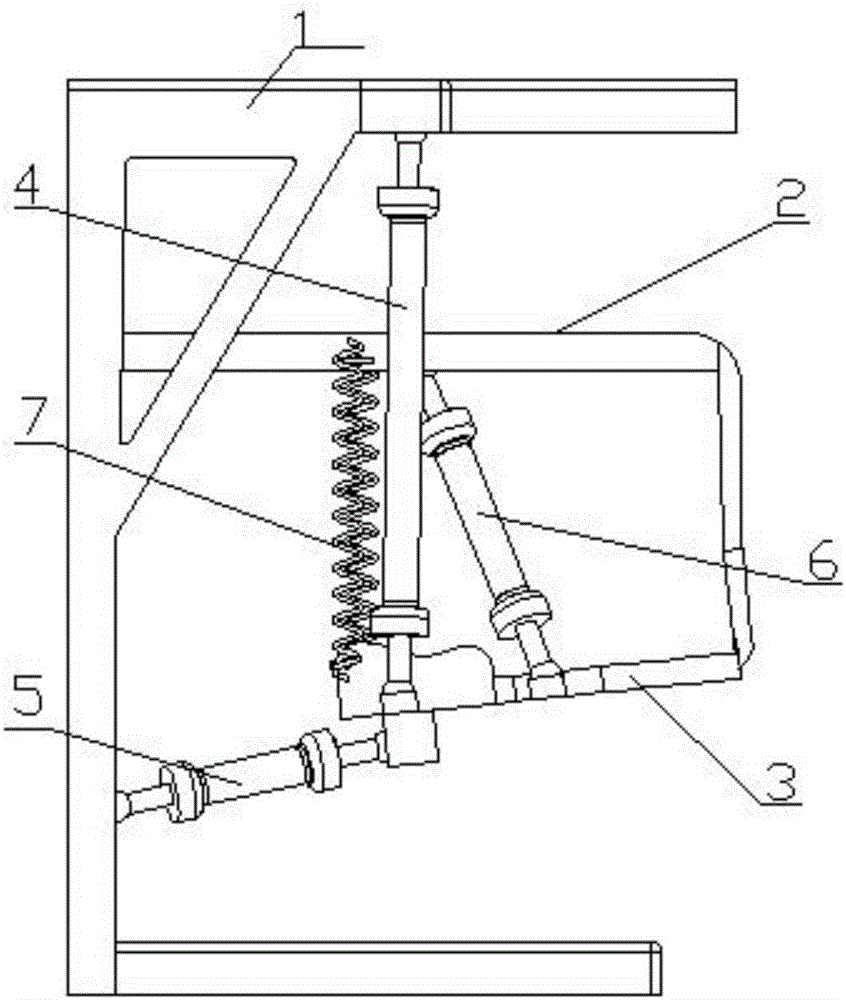
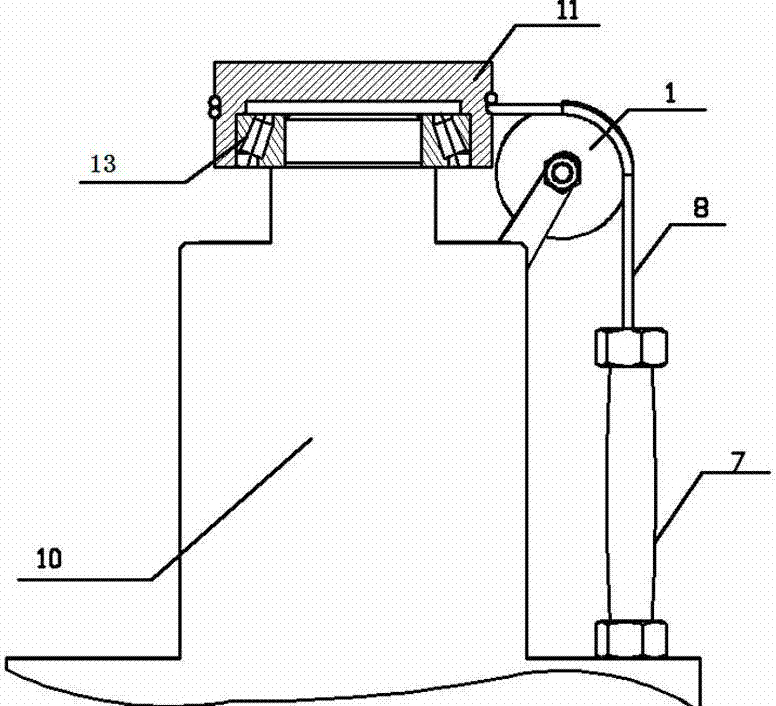
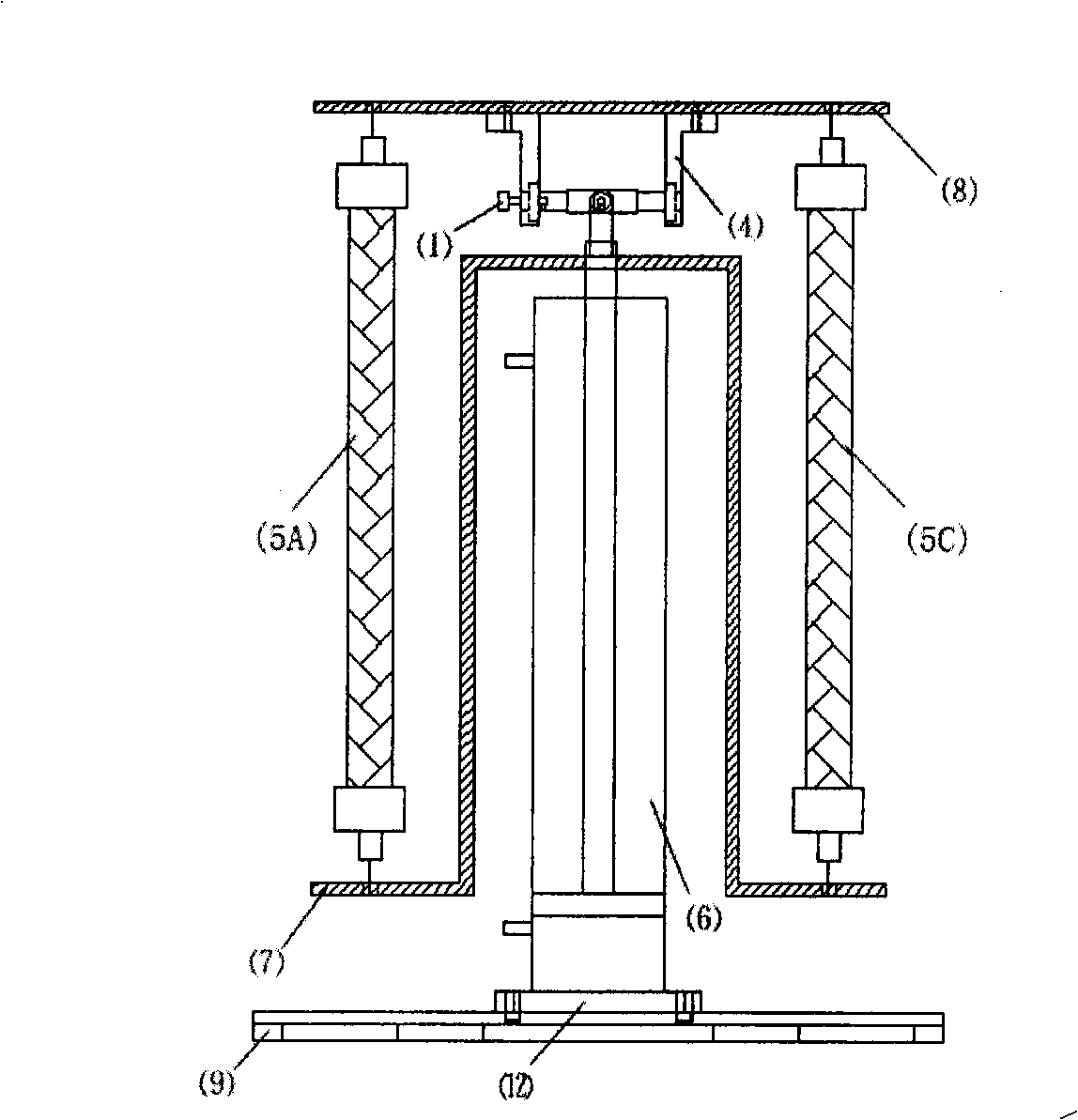
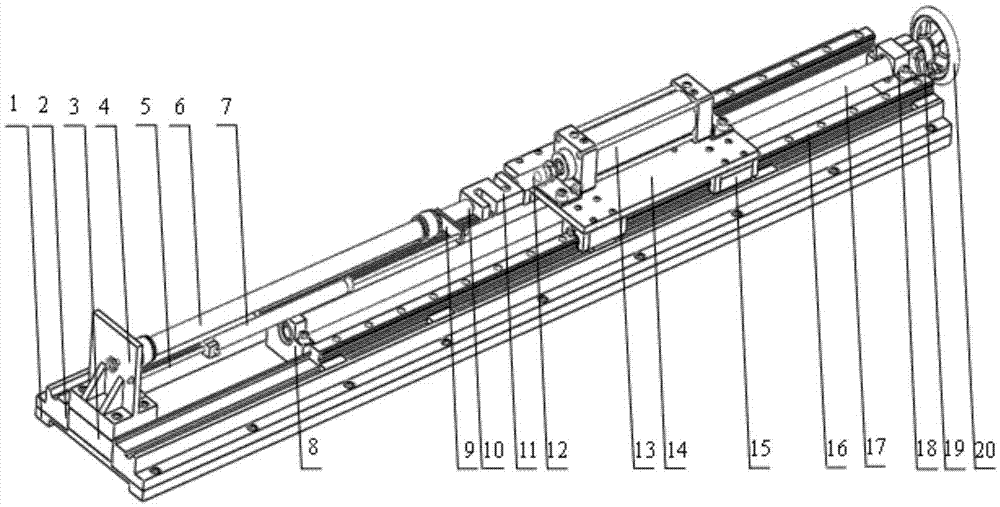
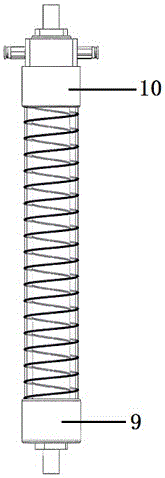
Pneumatic artificial muscle static state characteristic comprehensive testing device and driving system
The invention discloses a pneumatic artificial muscle static state characteristic comprehensive testing device and a driving system. A support is fixed on one end of a pedestal; two guide rails are arranged on the two sides of the pedestal along the length direction through two guide rail seats which are fixedly installed; the two guide rails are connected to an air cylinder connection plate provided with an air cylinder through a sliding block; a screw rod is arranged on the support rack between the two guide rails through a screw rod support side assembly which is installed in proximity to one end of the support rack and a screw rod support seat assembly which is arranged away from one end of the support rack; one end of the screw rod is connected to a hand wheel; the driving end of the air cylinder is connected to one end of a tension sensor; the other end of the tension sensor is connected to an air non-taken terminal of a pneumatic artificial muscle to be detected through a connection plate; the air non-taken terminal of the pneumatic artificial muscle is fixed on the support rack; the support rack is connected to one end of a displacement sensor through a connection rod; and the other end of the displacement sensor is fixed on the connection plate through a bolt. The invention can realize the comprehensive test of the static state characteristic of the pneumatic artificial muscle.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
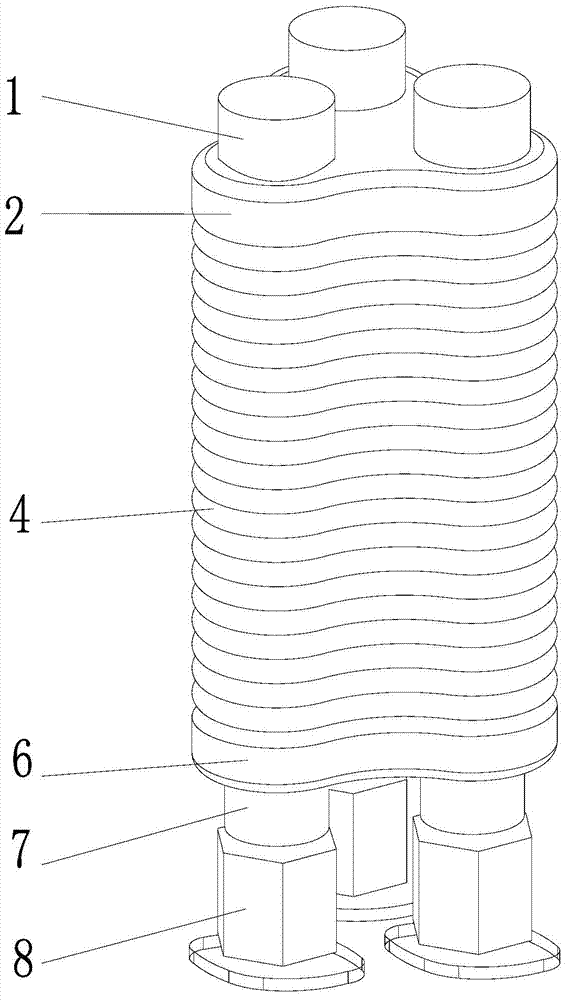
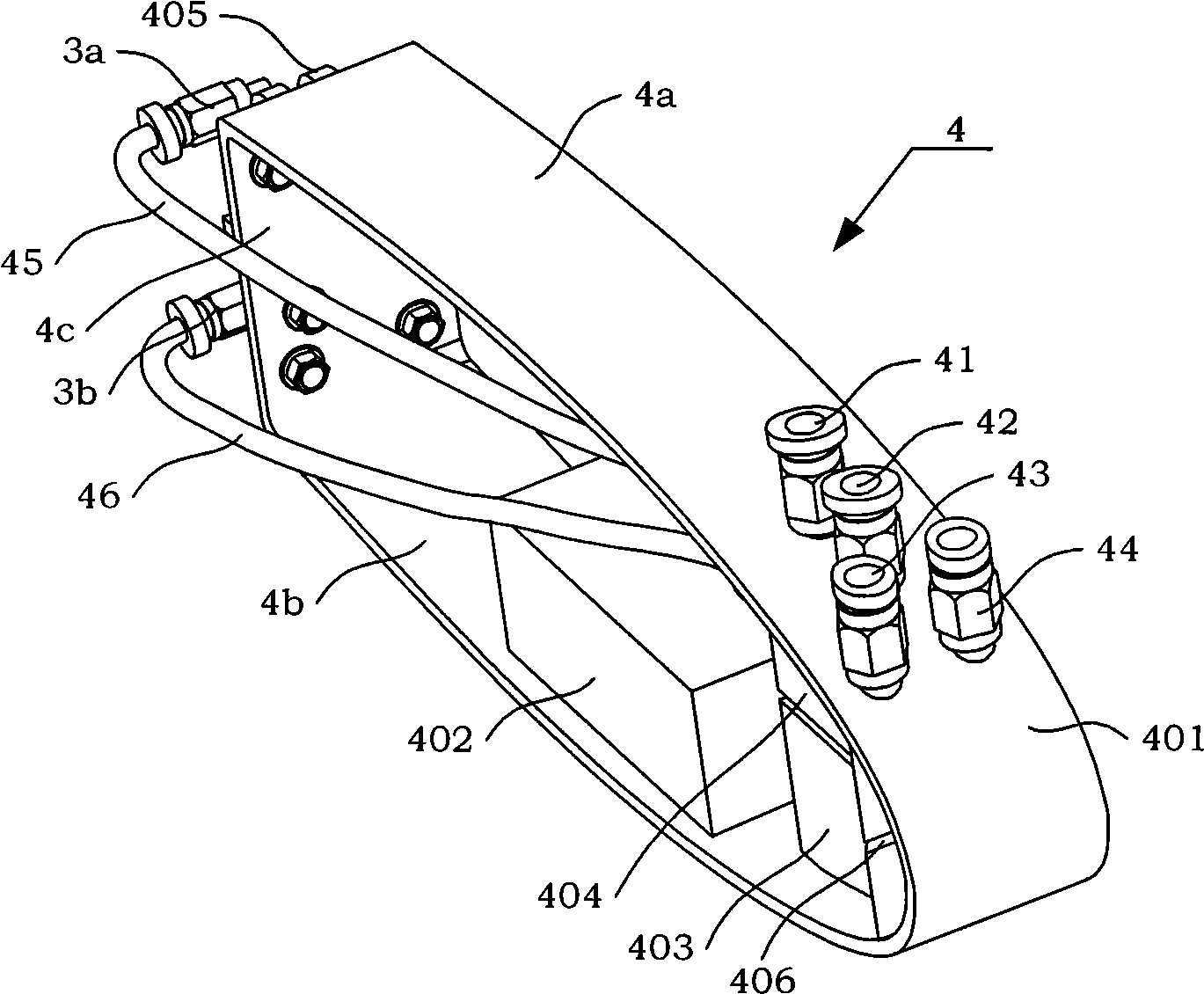
Double-tube sleeved type pneumatic artificial muscle
InactiveCN105666484AReduce frictionGuaranteed inflation and contractionProgramme-controlled manipulatorFiberDouble tube
The invention belongs to the pneumatic artificial technical field, and particularly relates to double-tube sleeved type pneumatic artificial muscle.The double-tube sleeved type pneumatic artificial muscle comprises an elastic outer tube, outer cellosilk, an elastic inner tube, inner cellosilk, a first air pipe connector, a second air pipe connector, a gap, an inner tube cavity, a first clamp, a second clamp, a gap vent and an inner tube cavity vent.By controlling the relationship of air pressure in the gap and air pressure in the inner tube cavity, active axial contraction and active axial rotation of the double-tube sleeved type pneumatic artificial muscle are achieved.Compared with pneumatic muscle of the same model in the market, the double-tube sleeved type pneumatic artificial muscle has the advantage that air consumption is lower, so that energy saving is better achieved.The performance of the pneumatic muscle is improved and enriched, functional innovation and expansion are achieved, and the double-tube sleeved type pneumatic artificial muscle is worth application.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Balance-enhanced type intelligent protective waist band with pneumatic artificial muscles
ActiveCN108041725AEasy to installEasy to replaceDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsGas cylinderProtection mechanism
The invention discloses a balance-enhanced type intelligent protective waist band with pneumatic artificial muscles. The balance-enhanced type intelligent protective waist band comprises a waist bandbody, a falling protection mechanism and a waist and back support mechanism, wherein the waist band body is longitudinally folded, and is mutually connected by first Velcro on the waist band body, andboth ends of the waist band body are mutually connected by inserting fasteners; snap fasteners, a controller, a lithium battery, a normally-closed type electromagnetic valve and a high-pressure air cylinder are arranged on the waist band body; the falling protection mechanism comprises a plurality of support layers, a longitudinal air bag and a transverse air bag, and the upper end of each support layer is connected with the waist band body through the corresponding snap fastener; the waist and back support mechanism comprises a flexible support plate, a fixing bundle band, a support rod, a support rod adjusting mechanism, and a connecting plate. The balance-enhanced type intelligent protective waist band with pneumatic artificial muscles has the advantages that the convenience in use isrealized, the weight is light, the intelligence degree is high, the safety and reliability are realized, and the like; the problems of balance enhancing and improving of safety protection of the userin the falling process are effectively solved.
Owner:合肥市明磊网络科技有限公司
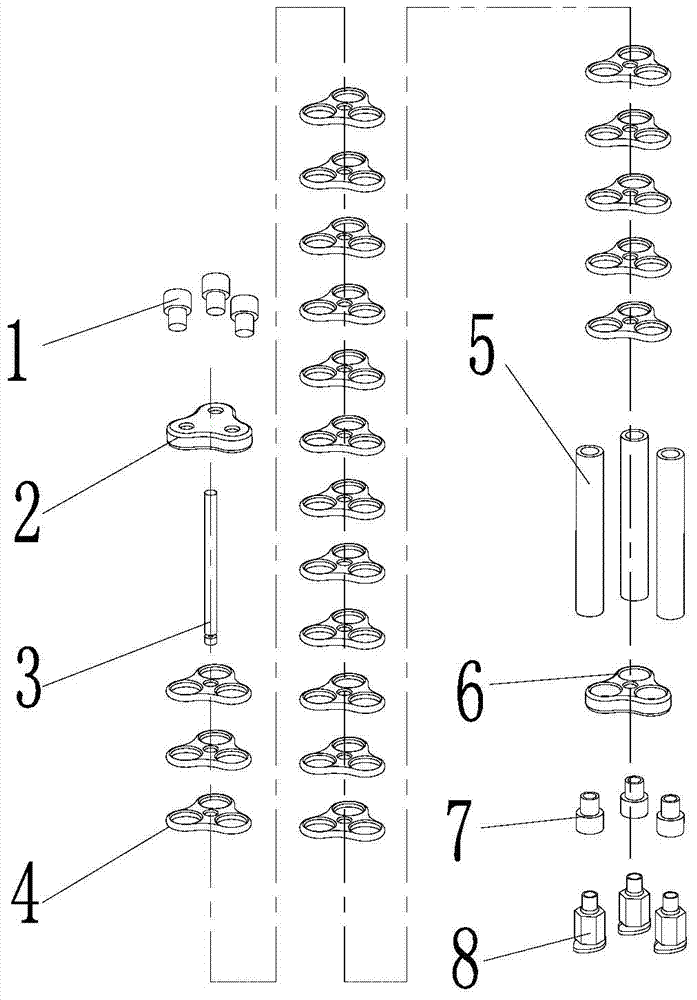
Pneumatic multidirectional bending flexible joint
The invention discloses a pneumatic multidirectional bending flexible joint which comprises constraint elements, a joint framework, air bags, an upper end cover, a lower end cover, upper sealing heads, lower sealing heads and fluid inlets. The constraint elements are arranged between the upper end cover and the lower end cover and are coaxially connected in series and densely arranged to form a columnar structure, a plurality of tubular cavities with parallel axes are formed in the columnar structure, the axis of one of the tubular cavities overlaps with the axis of the columnar structure to form a first tubular cavity, the tubular cavities expect the first tubular cavity are called as second tubular cavities, the air bags are arranged in the second tubular cavities, the two ends of the air bags are connected with the upper sealing heads and the lower sealing heads respectively and the lower sealing heads are provided with the fluid inlets. A driving device of the joint is combined with the joint to form an integral structure which is equivalent to four pneumatic artificial muscles in parallel connection and has one degree of freedom and two degrees of operation, and active bending, axial elongation and other functions of the joint in eight directions of space can be achieved.
Owner:BEIHUA UNIV
Biped robot based on pneumatic artificial muscles
The invention discloses a biped robot based on pneumatic artificial muscles and relates to biped robots. The biped robot based on the pneumatic artificial muscles aims to solve the problems that an existing active robot is driven through a rigid structure, the system structure is complicated, the flexibility is poor, and the energy efficiency of the existing active robot is low. The biped robot based on the pneumatic artificial muscles comprises a left leg, a right leg and a pelvis. The left leg and the right leg each comprise a thigh, a shank, a foot, a hip joint, a knee joint and an ankle joint. The left leg and the right leg are connected through the pelvis. The pelvis is connected with the thighs in a rotary mode through the hip joints. The thighs are connected with the shanks in a rotary mode through the knee joints. The shanks are connected with the feet in a rotary mode through the ankle joints. The iliac muscles, the gluteus maximus, the vastus lateralis muscles, the biceps femoris muscles, the semitendinous muscles and the rectus femoris muscles are arranged on the thighs. The tibialis anterior muscles, the soleus muscles and the gastrocnemius muscles are arranged on the shanks. The upper ends of the iliac muscles and the upper ends of the gluteus maximus are hinged to the pelvis respectivley. The lower ends of the iliac muscles and the lower ends of the gluteus maximus are hinged to the thighs respectively. The upper ends of the vastus lateralis muscles and the upper ends of the biceps femoris muscles are hinged to the thighs respectively. The biped robot based on the pneumatic artificial muscles belongs to the field of humanoid robots.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
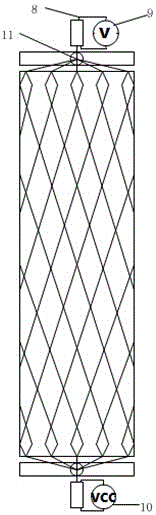
Pneumatic artificial muscle with self-sensing and driving functions
InactiveCN105856219AImprove shrinkageExpand the scope ofProgramme-controlled manipulatorFiberVoltmeter
The invention belongs to the pneumatic artificial technical field and in particular relates to a pneumatic artificial muscle with self-sensing and driving functions. The pneumatic artificial muscle comprises fibers, an elastic hose, a cylindrical sleeve pipe, a fiber collecting hoop, a fiber collecting hole, a piezoelectric body, an electrode, a sensing circuit, a drive circuit, a hoop and an air pipe joint. The pneumatic artificial muscle has the beneficial effects that via the direct piezoelectric effects of the piezoelectric body, the contractility of the fibers can be measured to obtain the external load driving force of the pneumatic muscle; meanwhile, collision of the pneumatic muscle can be self-sensed according to the real-time reading of a voltmeter; via the inverse piezoelectric effects of the piezoelectric body, the amount of contraction of the pneumatic muscle can be increased and the rigidity of the pneumatic muscle can be changed; compared with the same model of pneumatic muscle on the market, the pneumatic muscle provided by the invention can achieve the effects of detecting the external load driving force, self-sensing collision, increasing the amount of contraction of the pneumatic muscle and changing the rigidity of the pneumatic muscle; the properties of the pneumatic muscle are improved and enriched; and the pneumatic muscle has function innovation and extension and is worthy to be applied.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com