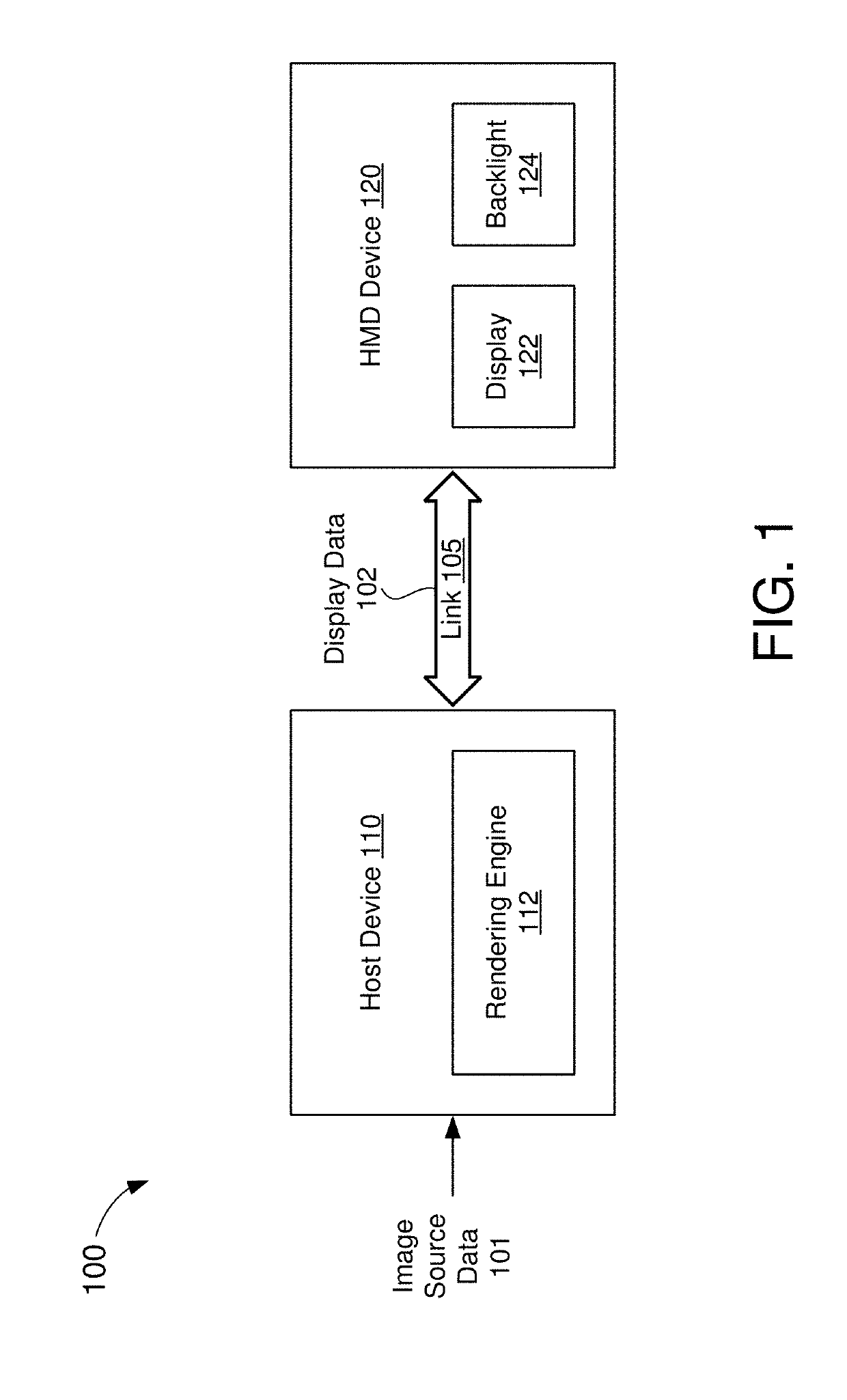
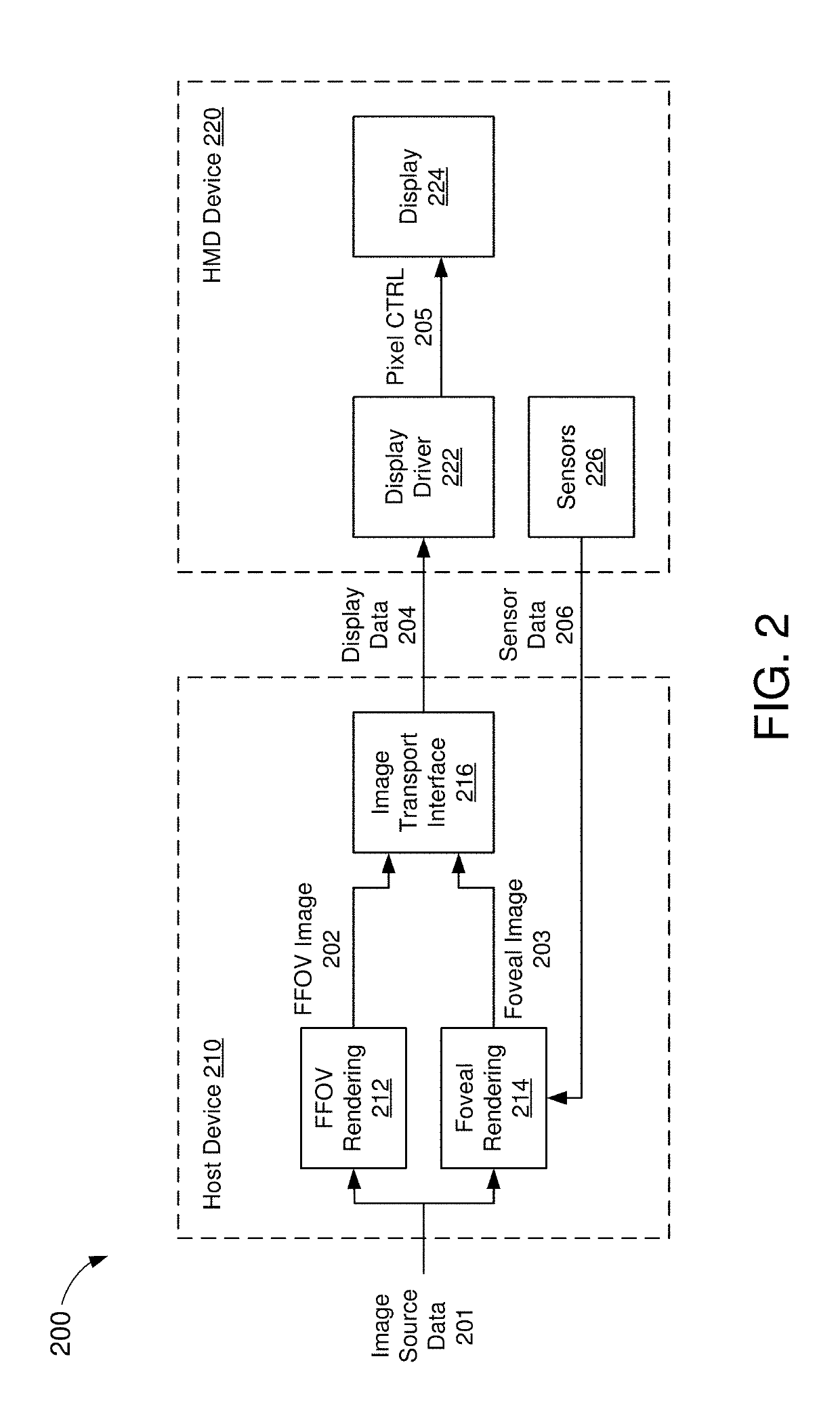
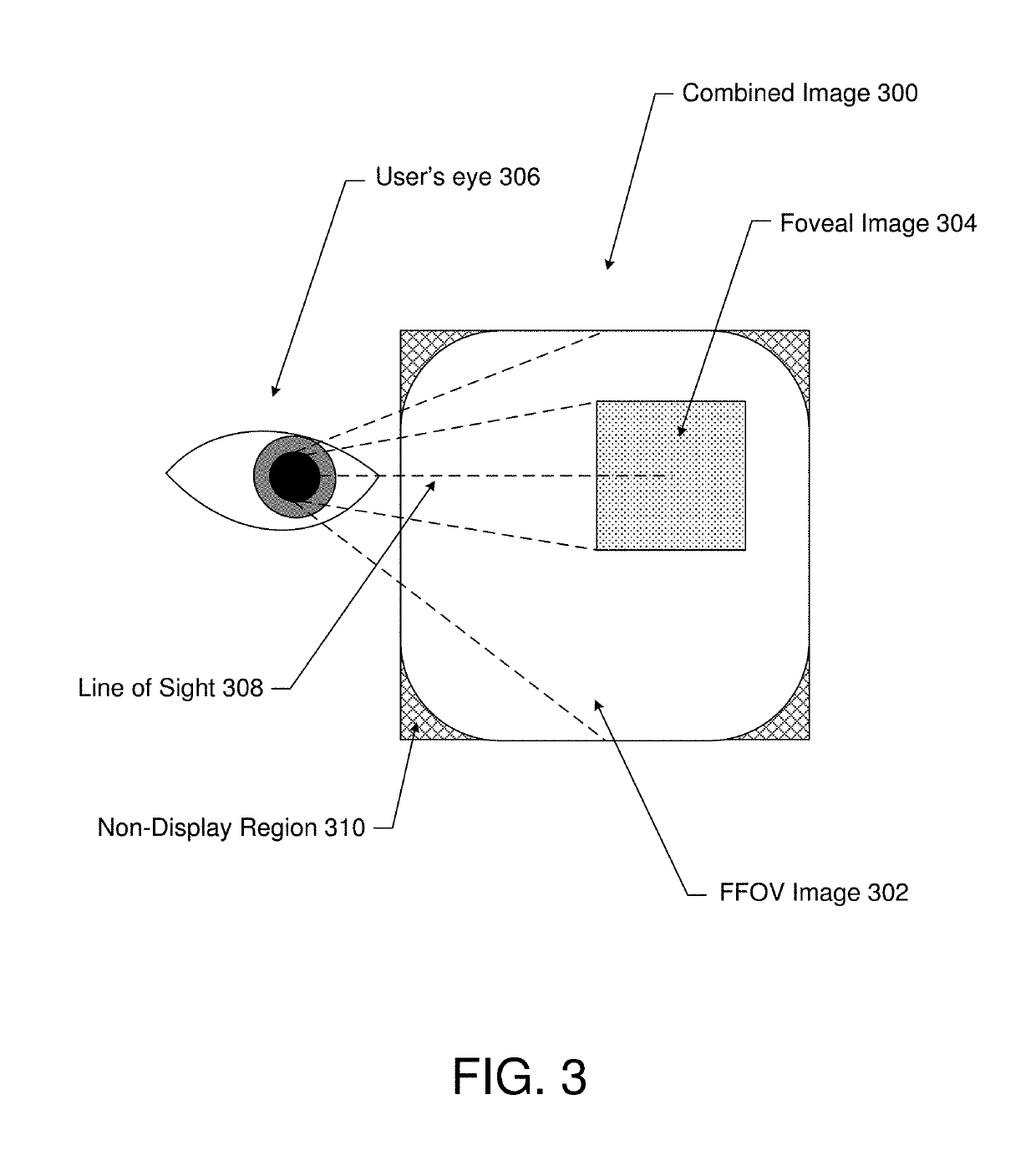
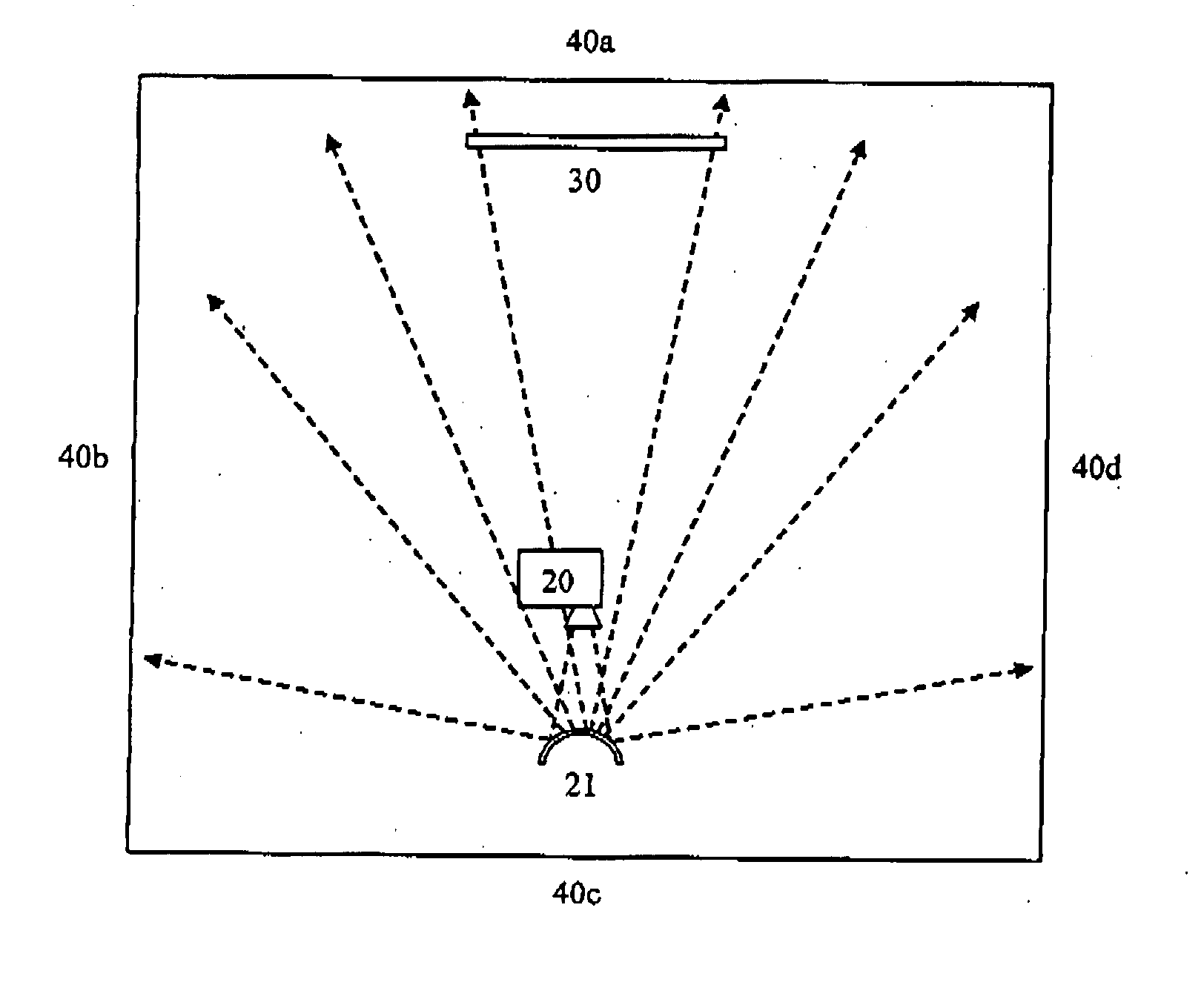
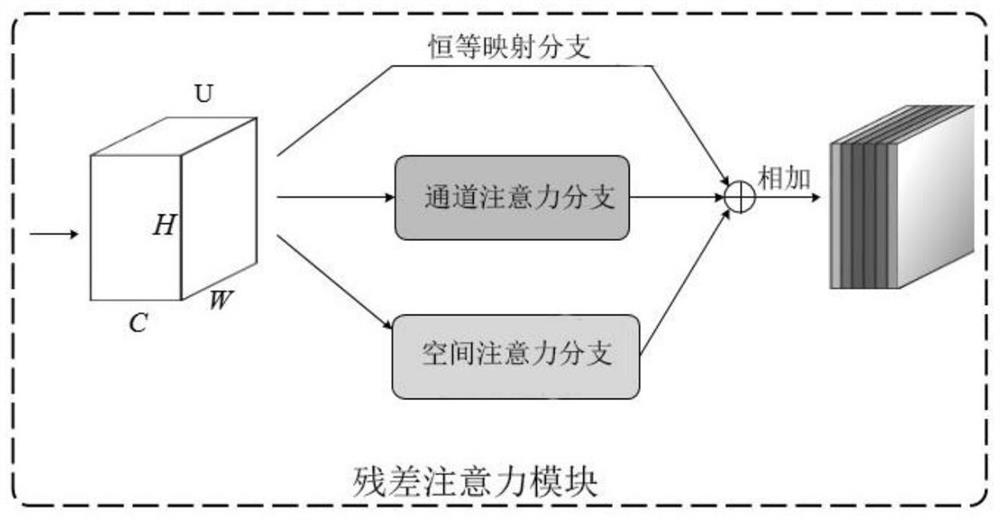
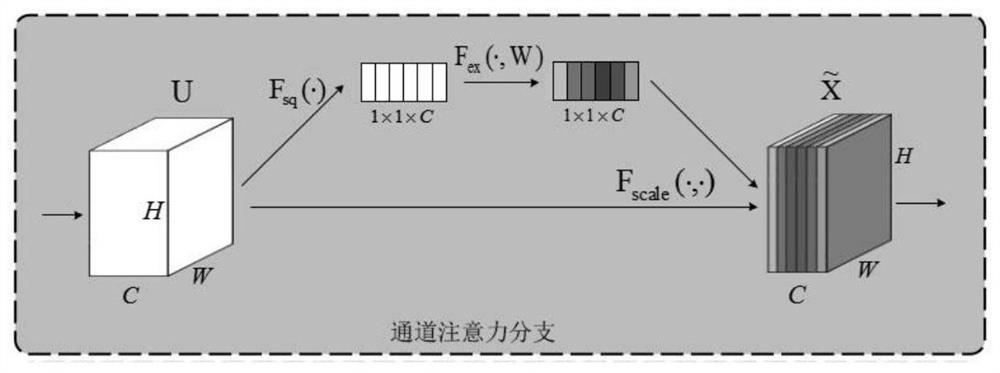
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
216 results about "Full field of view" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
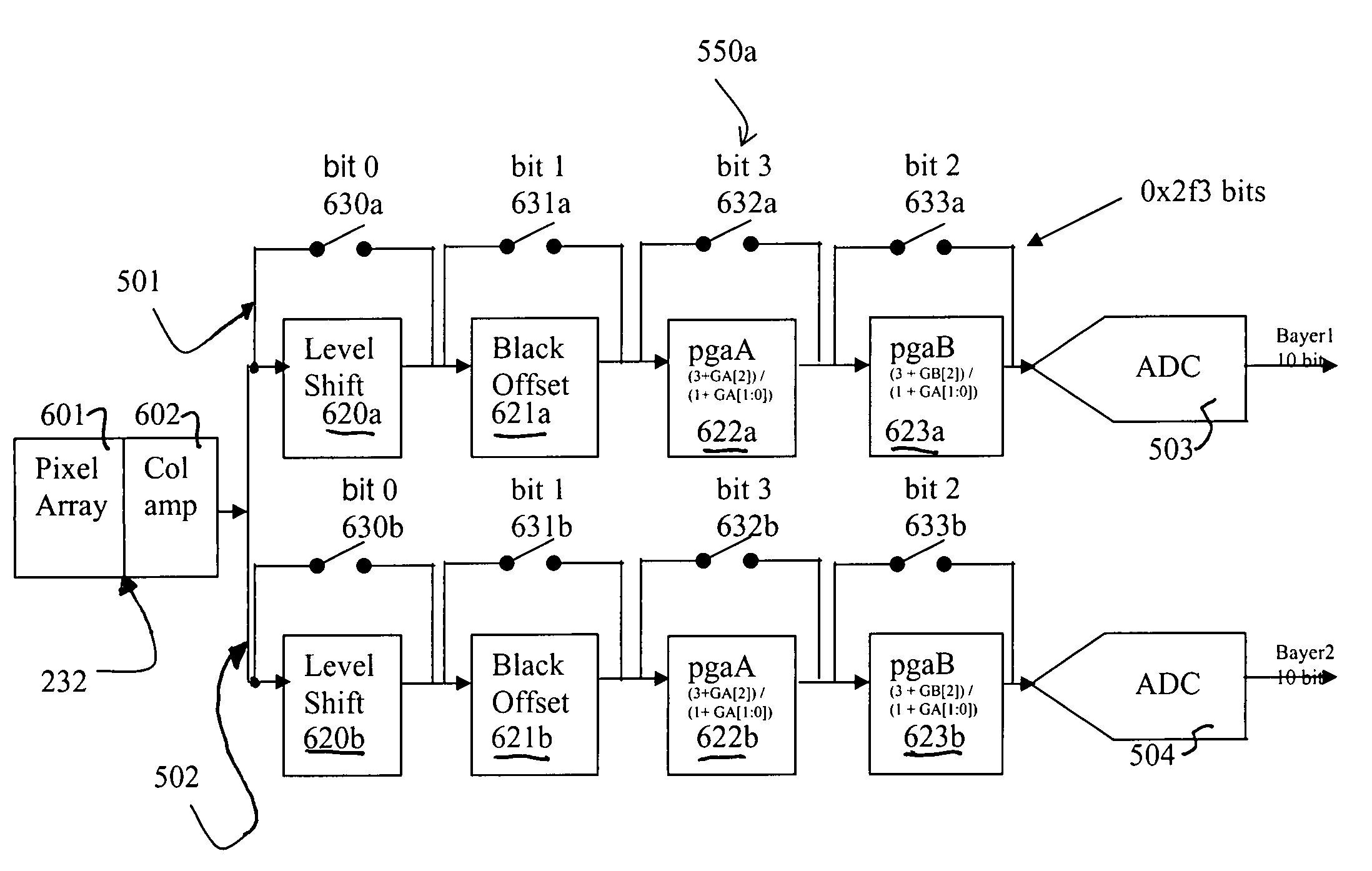
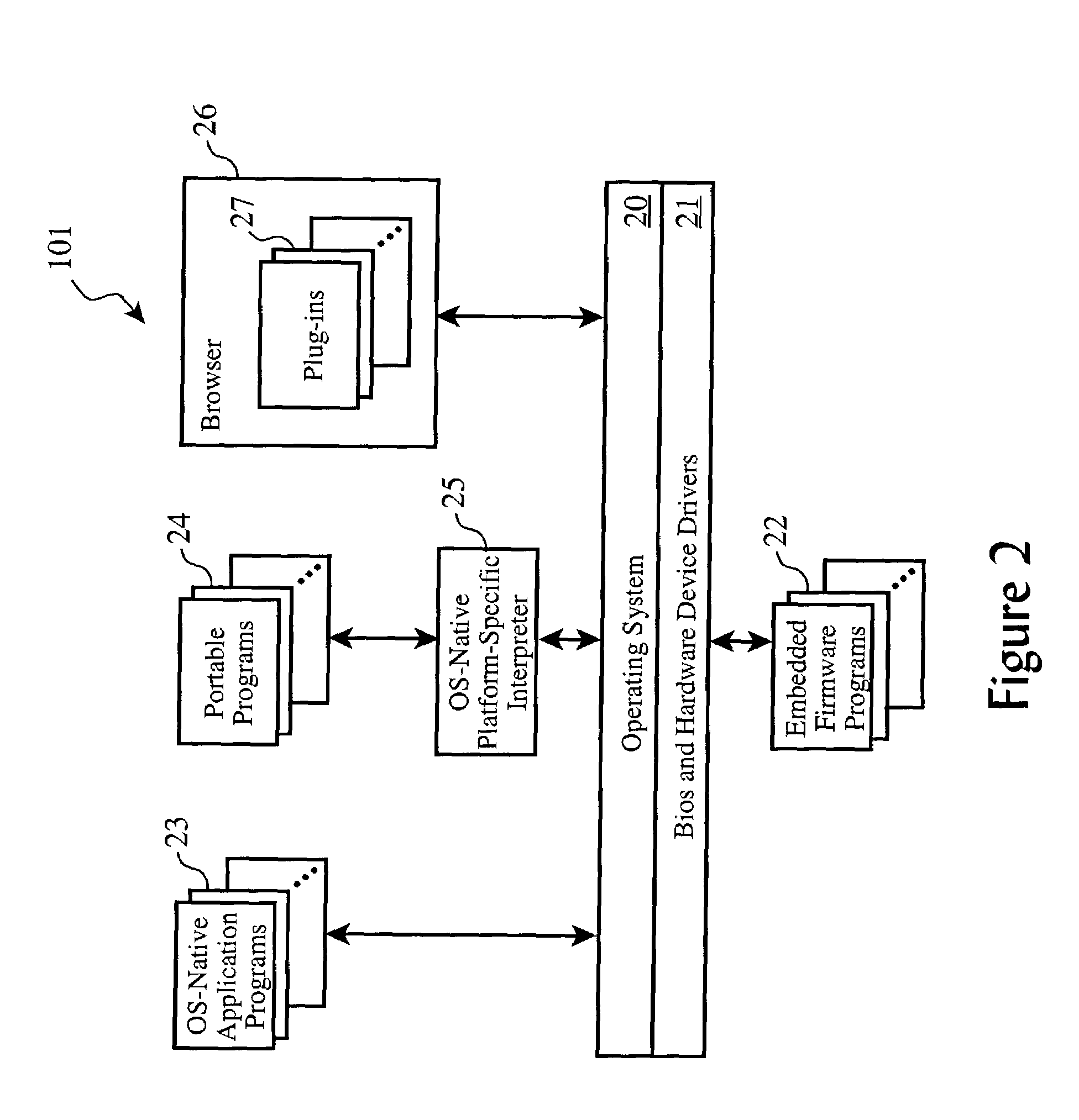
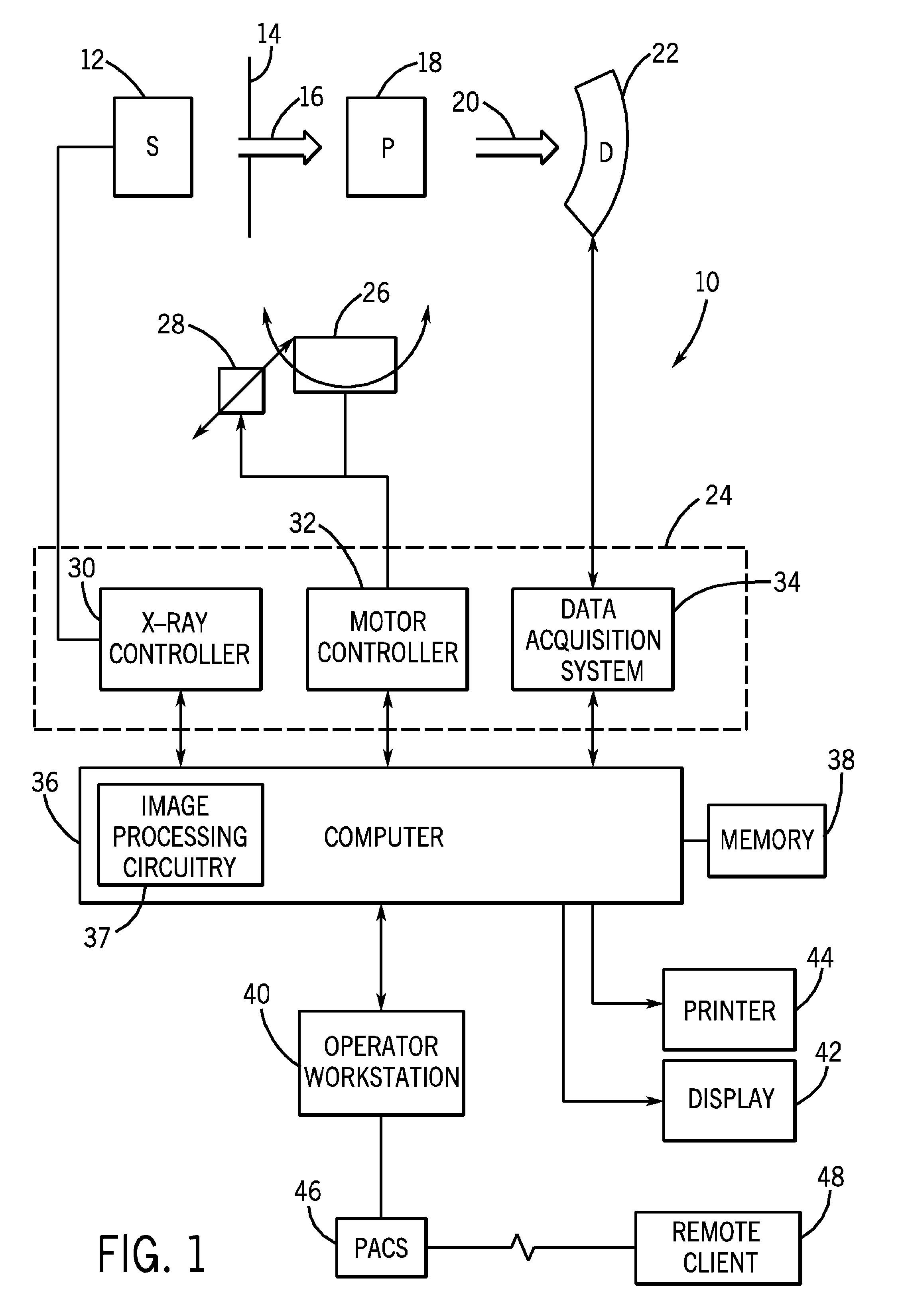
Systems and methods for power conservation in a CMOS imager
The present invention provides systems and methods capable of reducing power consumption in an imaging device. One imaging device includes two analog to digital converters that are separately programmable and can be in different power modes. Each analog to digital converter is capable of creating an image derived from a pixel array that has a full field of view, but lower resolution.
Owner:TRANSCHIP ISRAEL
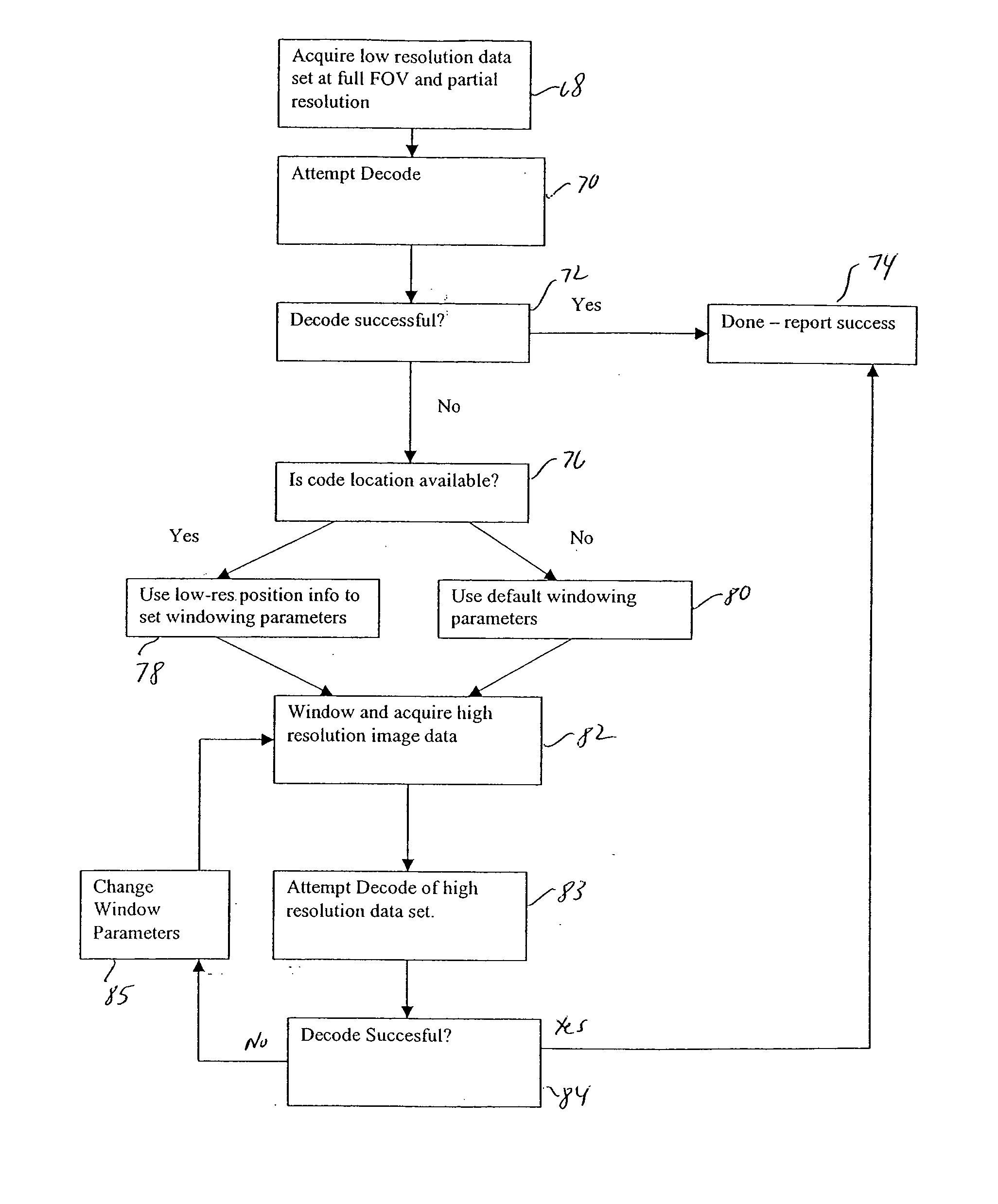
Method and apparatus for high resolution decoding of encoded symbols
InactiveUS20060027657A1Visual representatino by photographic printingSensing by electromagnetic radiationImage resolutionHigh resolution image
A method for scanning and decoding encoded symbols comprises processing low resolution image data from a full field of view and / or high resolution image data from one or more windowed segments of the field of view to provide imaging that is easily adaptable to different types of symbols and varying environmental conditions. The scanning method can be switched between the low resolution mode and the high resolution mode automatically based on whether the low resolution data is sufficiently accurate to decode the symbol.
Owner:COGNEX TECH & INVESTMENT
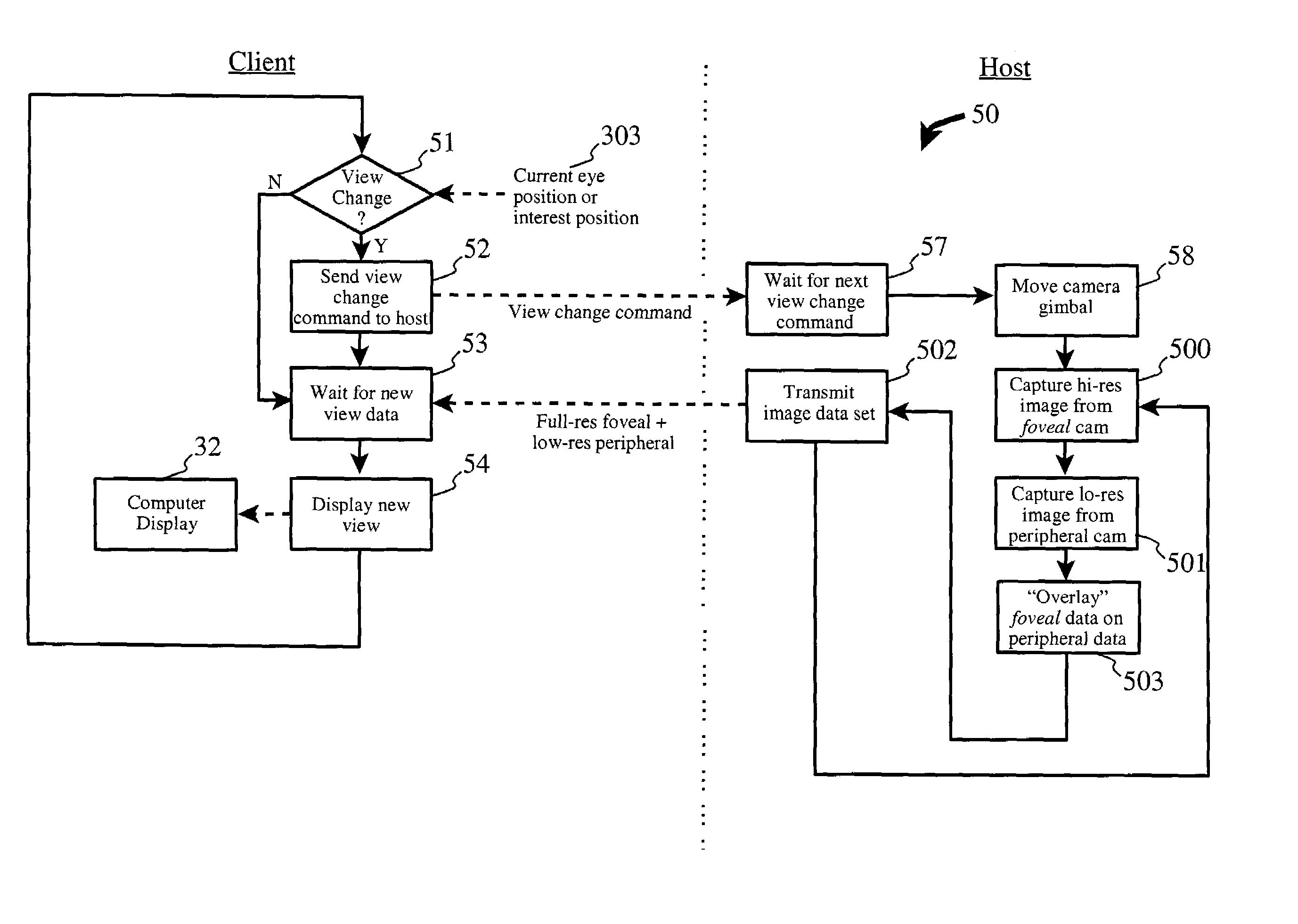
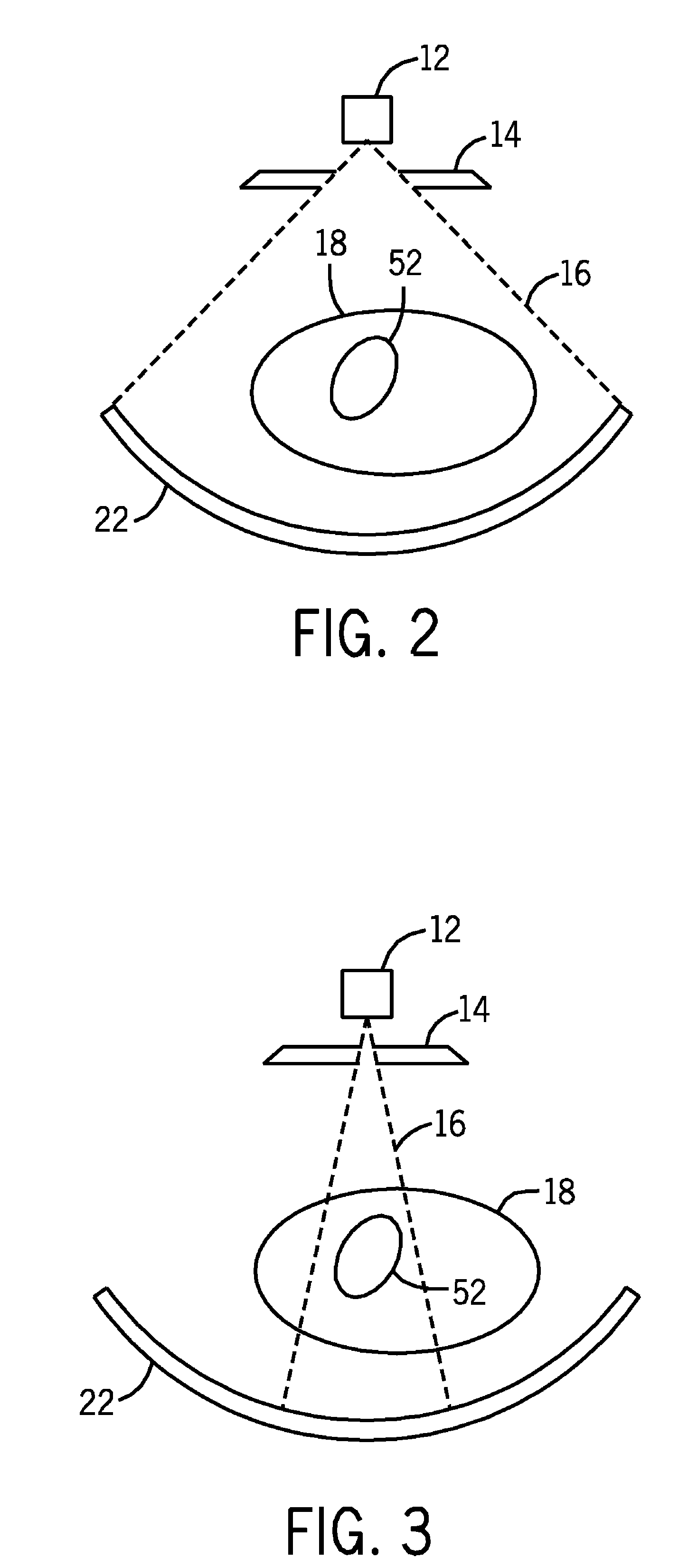
Rendering system and method for images having differing foveal area and peripheral view area resolutions
ActiveUS7129981B2Reduce image transmission bandwidthReduced time requirementsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsFovealClient machine
A client-server arrangement for camera viewing using digital cameras across a computer network. A camera server controls a motorized gimbal which determines the viewing angles of a set of cameras according to signals from a client computer which is equipped with an eye movement tracking system. Movements of the viewer's eyes result in changes in viewing angle of the remote cameras. A high resolution foveal field of view image centered on the user's point of interest is captured and overlaid on a lower resolution full filed of view image, rendering a combined image having a low resolution peripheral area and a high resolution foveal area, and being significantly reduced in size compared to a full resolution, full field of view image. This combined image is transmitted to the client for display to the user.
Owner:TOBII TECH AB
Flying craft camera and sensor mechanized lift platform
Disclosed herein is a mechanized lift platform for extending a camera and sensor, individually or collectively, out of a flying craft and retracting the camera and sensor back into the flying craft upon completion of use. The camera and sensor in the fully extended position provides a full field of view. The camera and sensor is extended and retracted through concealment doors. The concealment doors are closed when the camera and sensor are in the fully retracted position such that the lift platform and camera and sensor are not subject to any outside environment and the flying craft is able to retain its original flying characteristics. The camera and sensor mechanized lift platform has particular application for aerial photography, video, sound collection and multimedia. A method of capturing images, sounds and data comprising the steps of: Providing a device for extending a camera and sensor outside a flying craft whereby the camera and sensor can be completely retracted into the aircraft, having a platform structure to mount a camera and sensor, a power source, mechanized liner motion structure installed in flying craft to stabilize and guide the camera and sensor mounting platform during extension and retraction, concealment doors to open and close, relay switches to the flying craft cockpit and / or cabin to operate the lift platform and concealment doors, viewing and recording equipment connected to camera and sensor; and opening the concealment doors and extending the camera and sensor during flight to collect images, sounds and data or any combination thereof and display said collected images in a live graphical display in aircraft or to a remote site and upon completion of camera and sensor activities, retracting the lift platform inside the aircraft and closing the concealment doors. In a preferred embodiment of the invention the camera and sensor mechanized lift platform is extended through opened concealment doors during flight to collect images, sounds and data or any combination thereof and upon completion of camera and sensor activities, the lift platform is retracted inside the aircraft and the concealment doors are closed such that the original flying craft speed, maneuverability and aerodynamic characteristics are not altered.
Owner:LOWE JERRY D +1
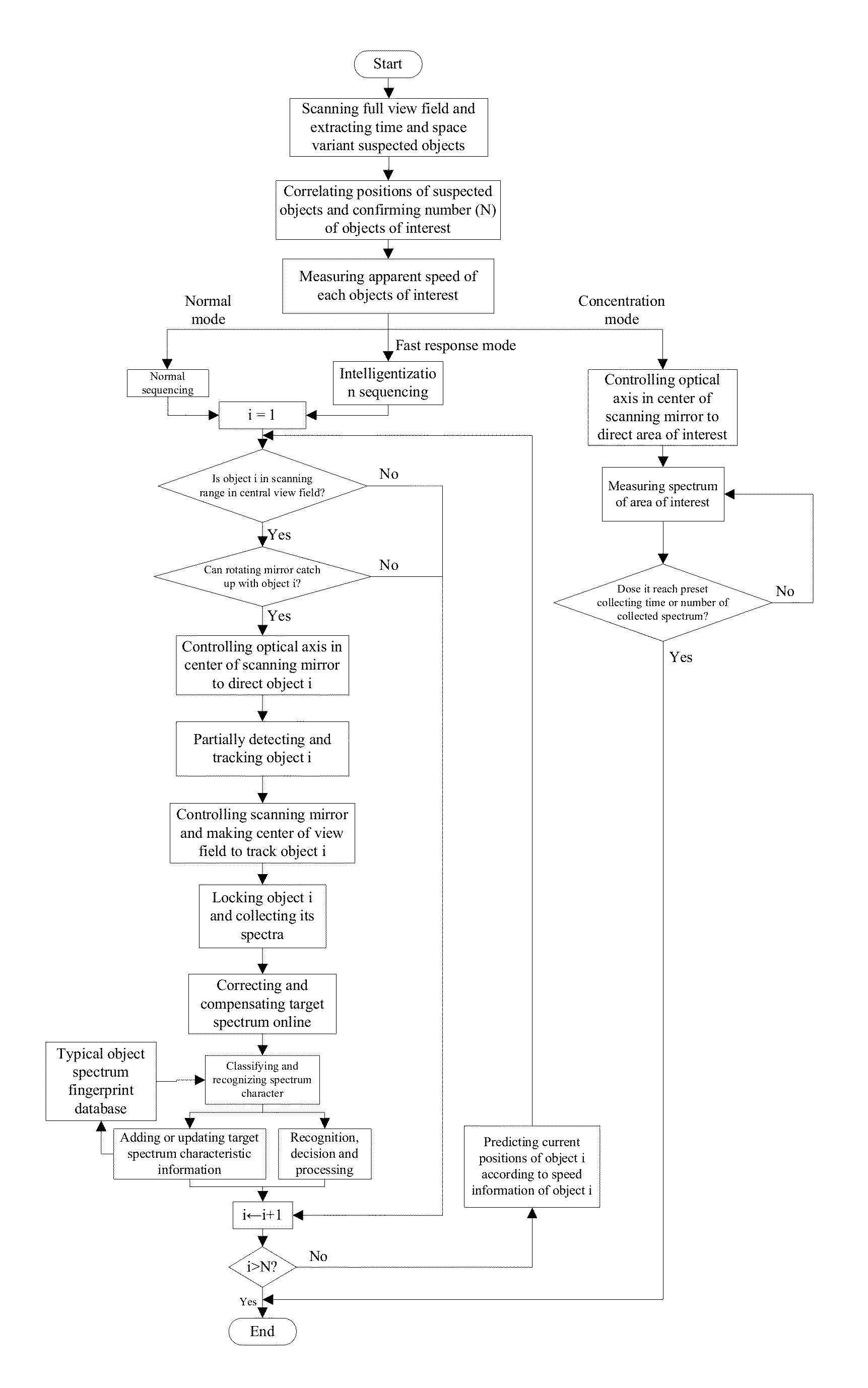
Method and apparatus for detecting spectral characteristics of multi-band moving objects
ActiveUS20130214164A1Quick checkQuick identificationSpectrum investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
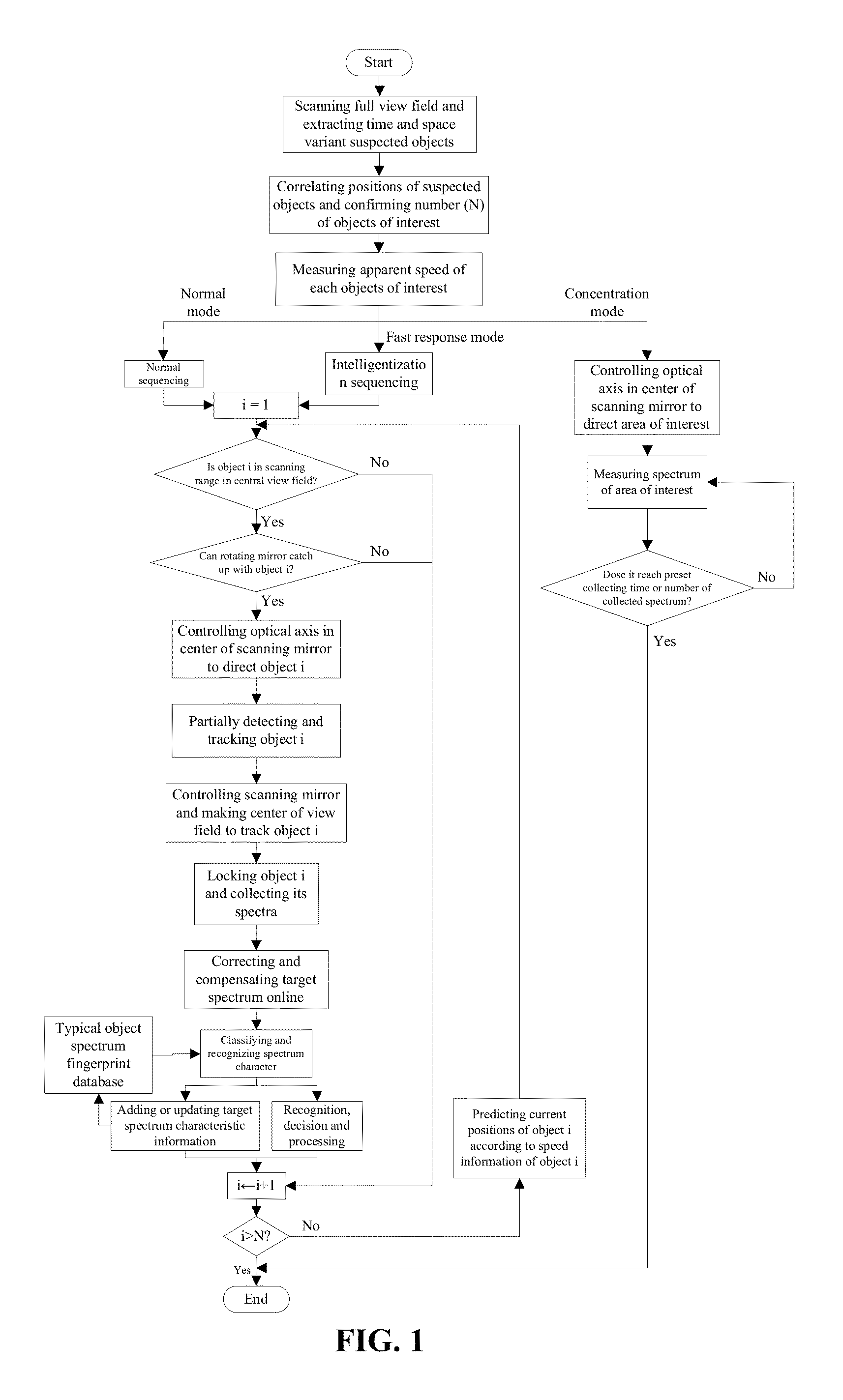
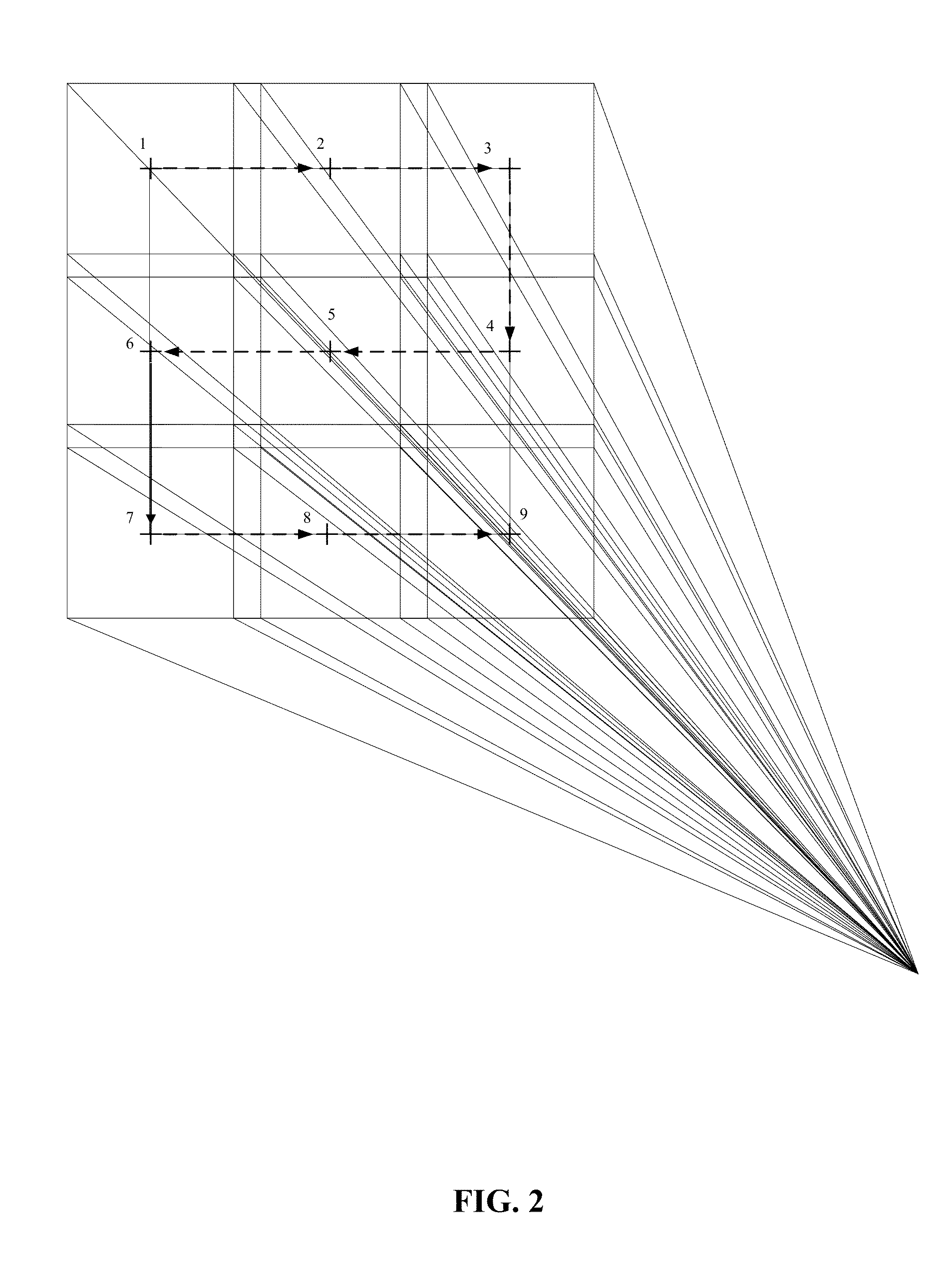
A method for detecting spectral characteristics of multi-band moving objects. The method includes: 1) dividing a full field of view into several subfields of view, and scanning and extracting suspected objects in each subfield one by one; 2) correlating interrelated suspected objects in adjacent subfields via coordinates to determine objects of interest that exist in the full field of view; 3) calculating the speeds of the objects of interest; 4) calculating average speed of all of the objects of interest and classifying the objects of interest according to their average speed; 5) compensating and rectifying the objective spectrum obtained from calculation; and 6) matching the compensated and rectified objective spectrum with a spectrum fingerprint database whereby realizing recognition of the multi-band moving objects.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Laser radar two-step calibration method based on calibration field
ActiveCN107167790ABreaking high flatness requirementsBreak flatness requirementsWave based measurement systemsDistance correctionTheodolite
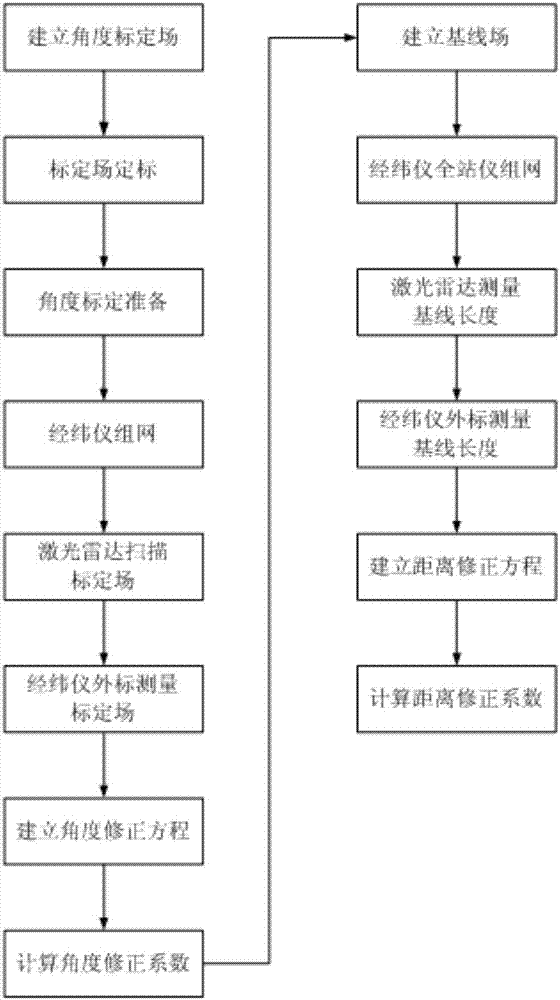
The invention discloses a laser radar two-step calibration method based on a calibration field. The method comprises steps of establishing a calibration field; carrying out calibration; preparing angle calibration; networking a theodolite; scanning a laser radar; measuring the theodolite; establishing an angle correction equation; calculating an angle correction coefficient; establishing a base line field; measuring the laser radar; measuring the theodolite; establishing a distance correction equation; and calculating a distance correction coefficient. According to the invention, rapid calibration of the laser radar is achieved without taking a precisely designed and processed calibration device as a calibration standard; a problem of too high requirements on a test place, the calibration field and the calibration device in the normal method is solved; through cooperation of a rotation bench, the whole test process is achieved, the test difficulty level is reduced and a difficulty in ensuring precision of full field-of-view angle correction in the normal method is solved; and through the test of the calibration field and the base line field step by step, effects of correcting separation distances in a calibration model are achieved and disadvantages in mutual coupling of distance parameters and angle parameters in the normal method are overcome.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
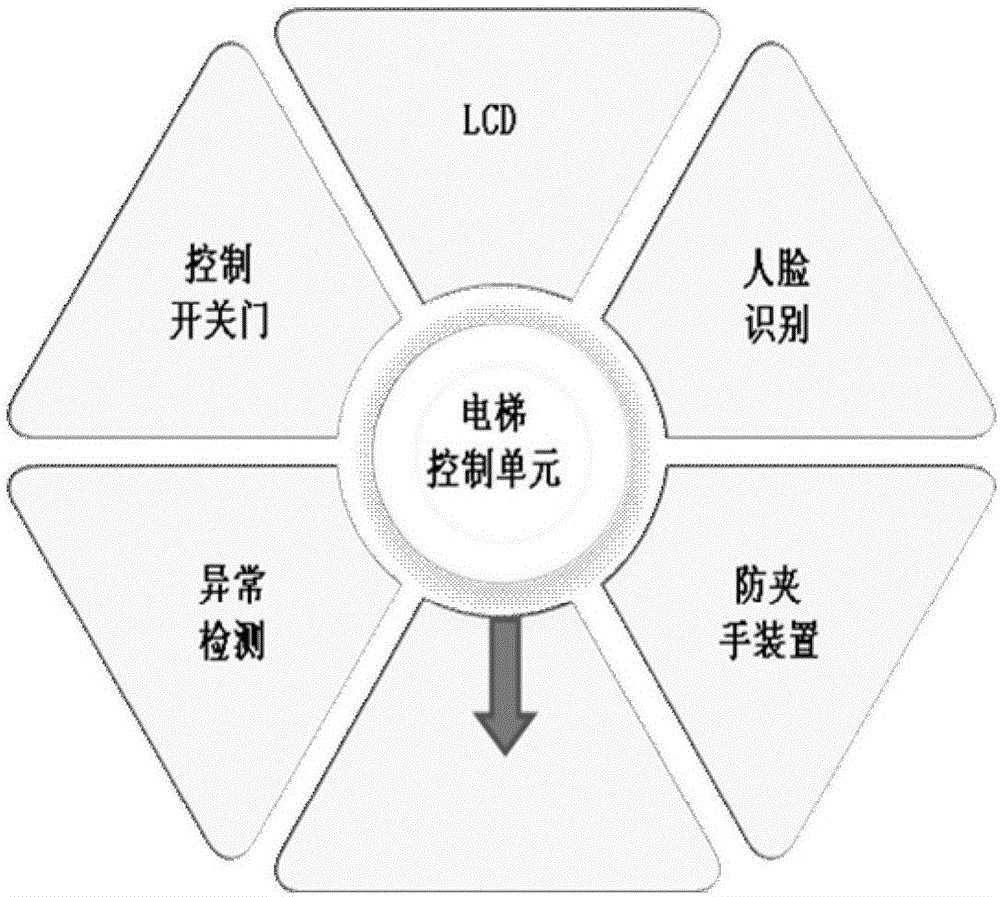
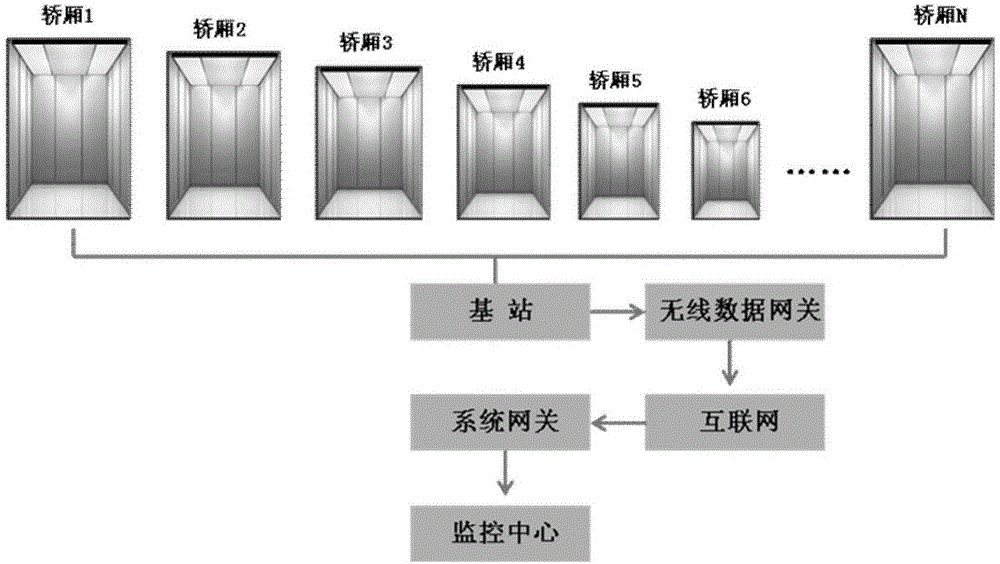
Elevator operation and maintenance monitoring method based on intelligent visual light curtain
ActiveCN106219367AExpand the scope of monitoringControl switchElevatorsBuilding liftsTreatment resultsSimulation
The invention relates to an elevator operation and maintenance monitoring method based on an intelligent visual light curtain. The method comprises the following steps that a camera and a processor are mounted in each elevator lift car, wherein the camera and the processor conduct communication transmission through a data line, and the camera is mounted in the middle above a door frame of an elevator door; each camera acquires video images in real time and transmits the images to the corresponding processor; each processor achieves full field-of-view automatic visual analysis for the area space of the corresponding elevator lift car door through an intelligent visual algorithm, and elevator faults are discovered and treated in time; and analysis and treatment results are gathered to obtain elevator operation and maintenance data which are transmitted to an elevator operation and maintenance monitoring center. Omnibearing monitoring is achieved by adoption of the elevator intelligent visual light curtain, dead zones do not exist, and the shortcomings that an infrared light curtain cannot discover small objects or is insensitive in distinguishing of the small objects are fundamentally overcome; and the monitoring range is expanded, opening and closing of the elevator door are better controlled, namely the delay door closing function is achieved, and equipment does not move along with opening and closing of the elevator door and is not prone to being intervened by external force.
Owner:沈阳聚德视频技术有限公司
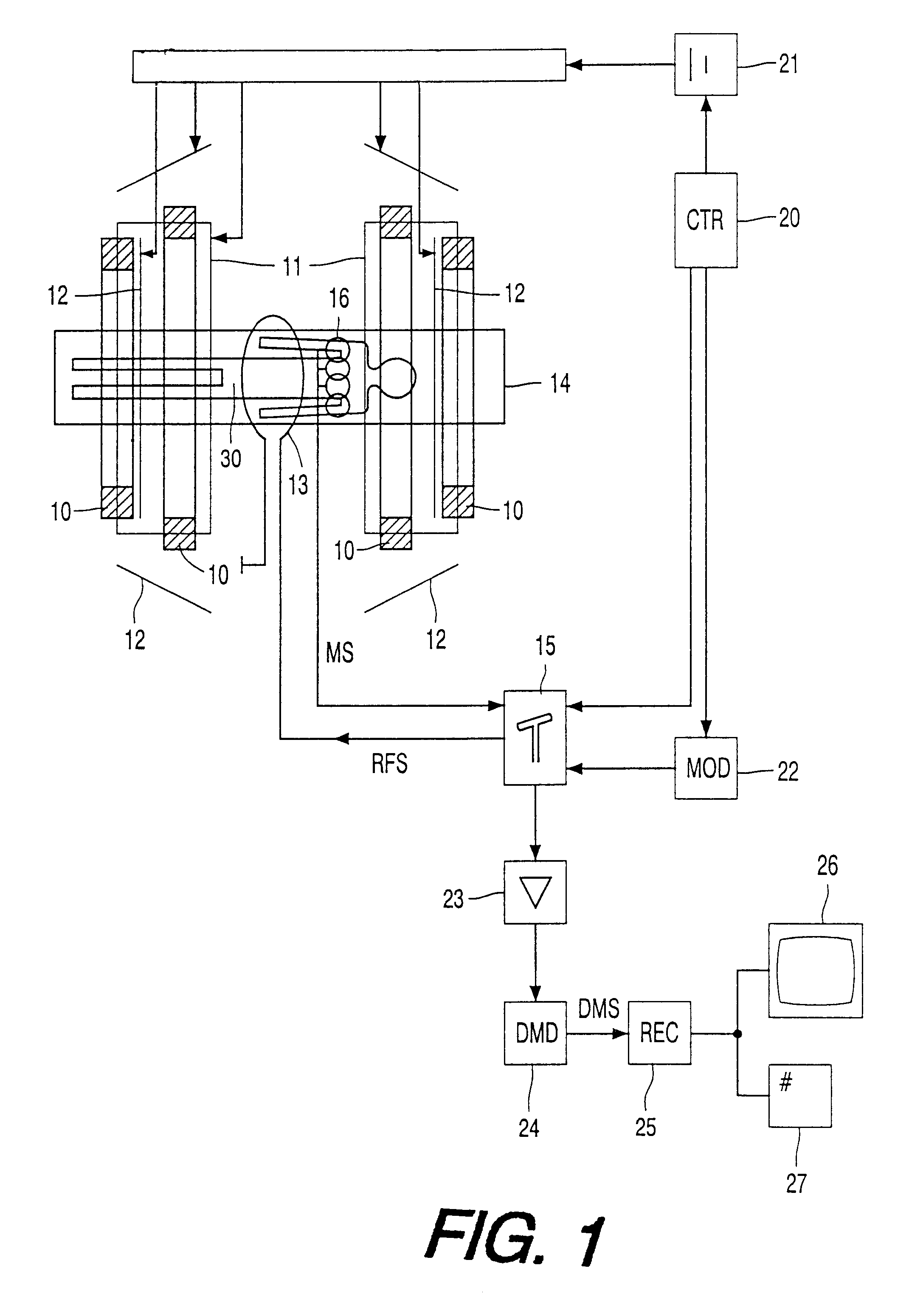
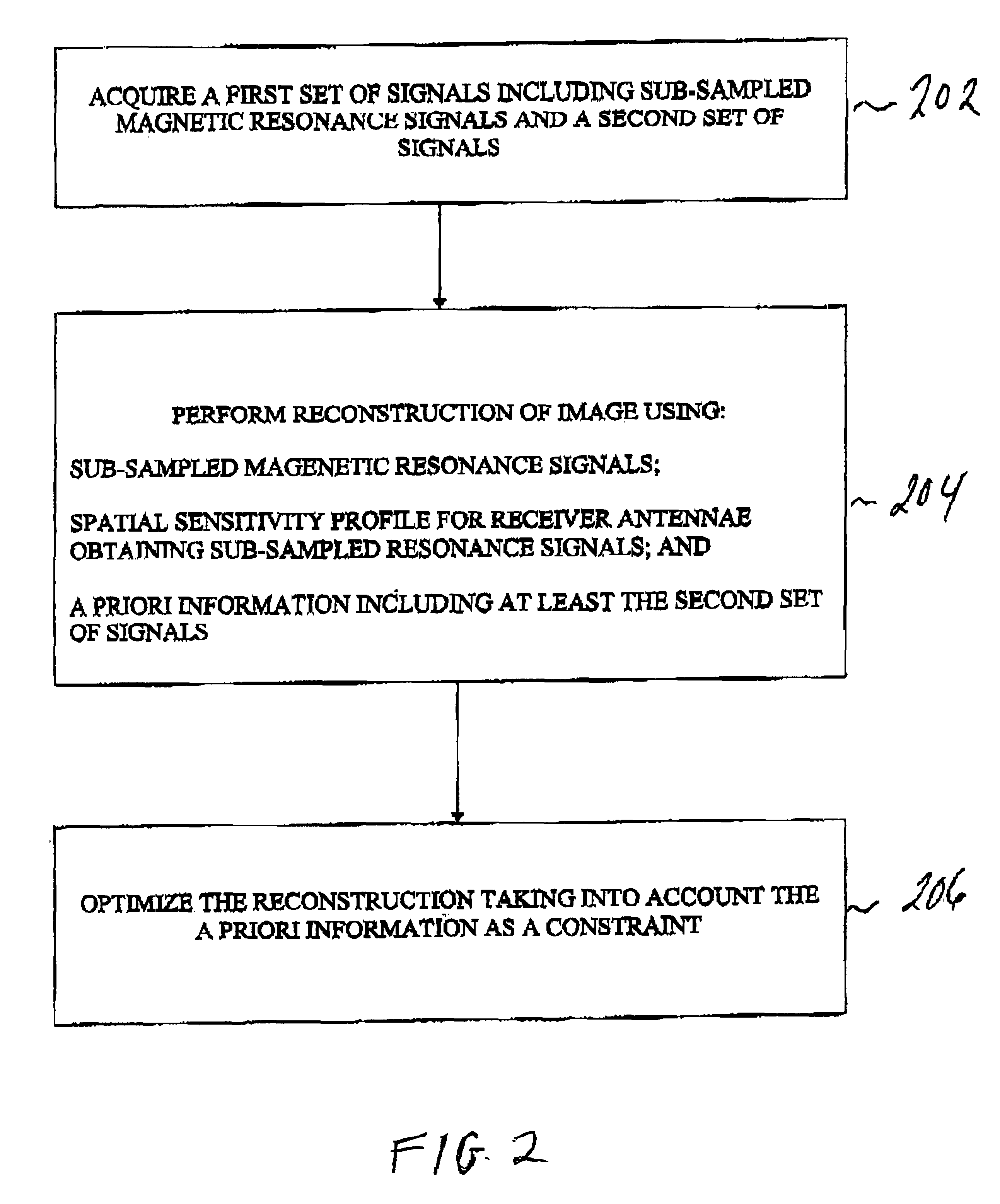
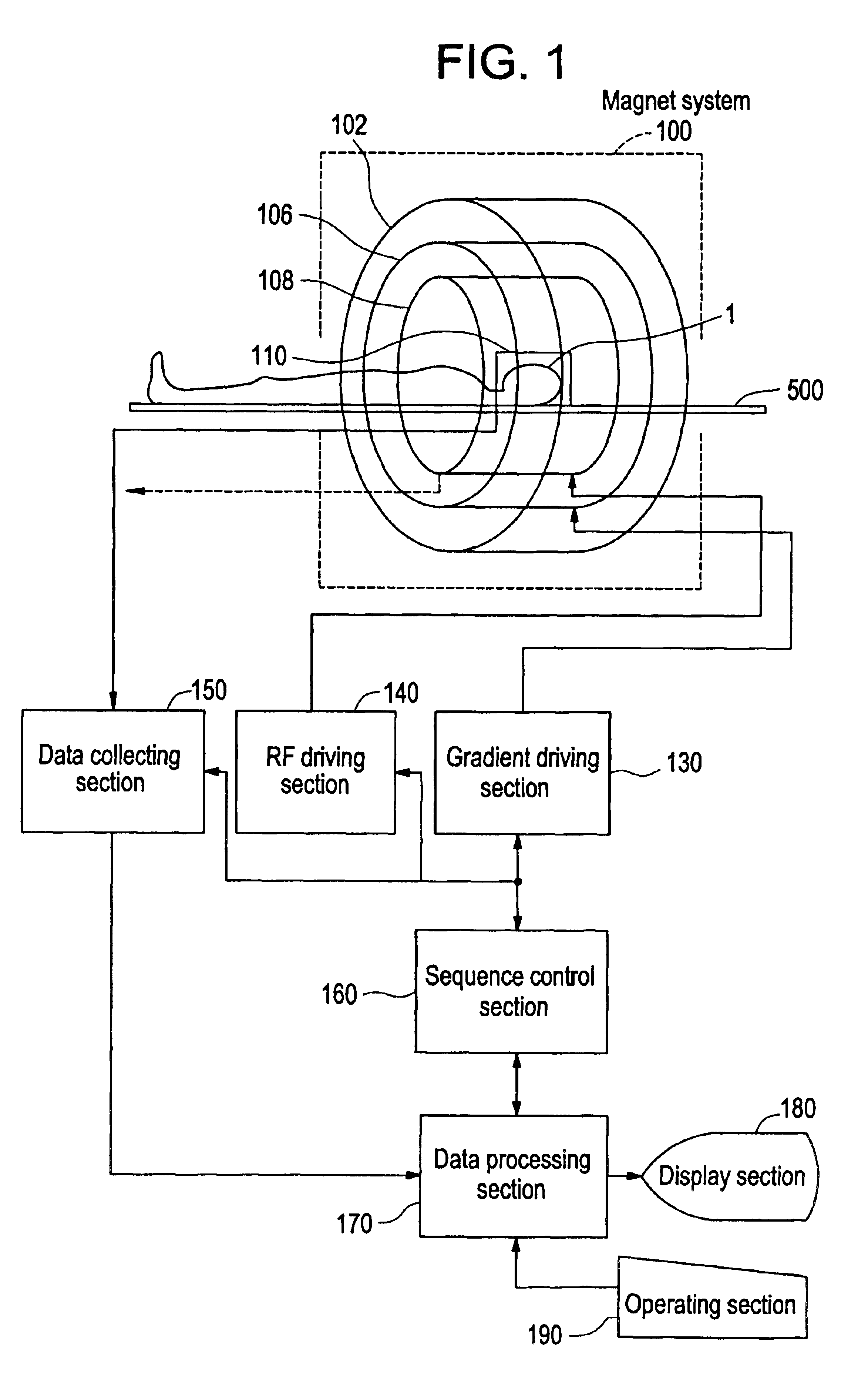
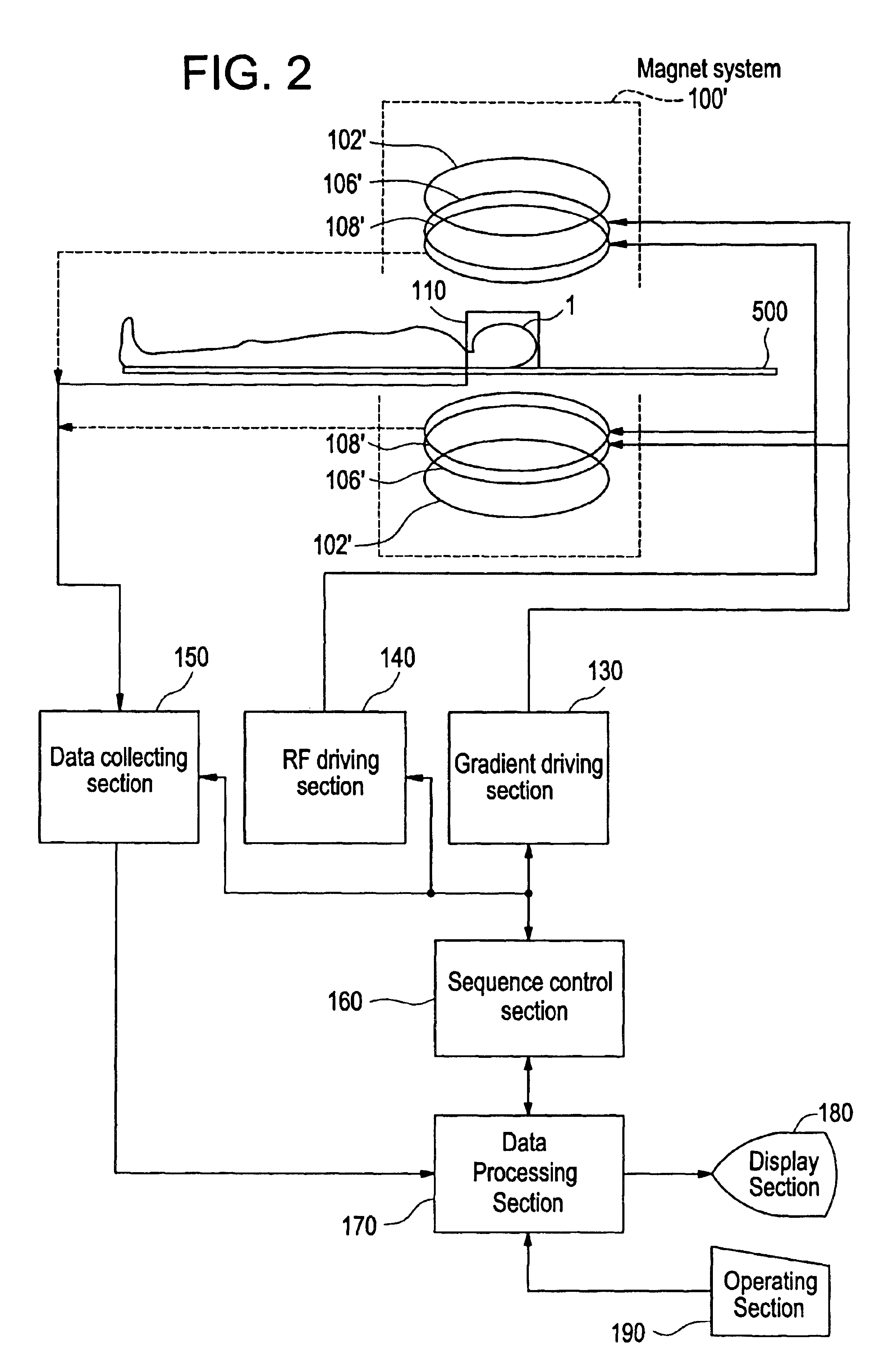
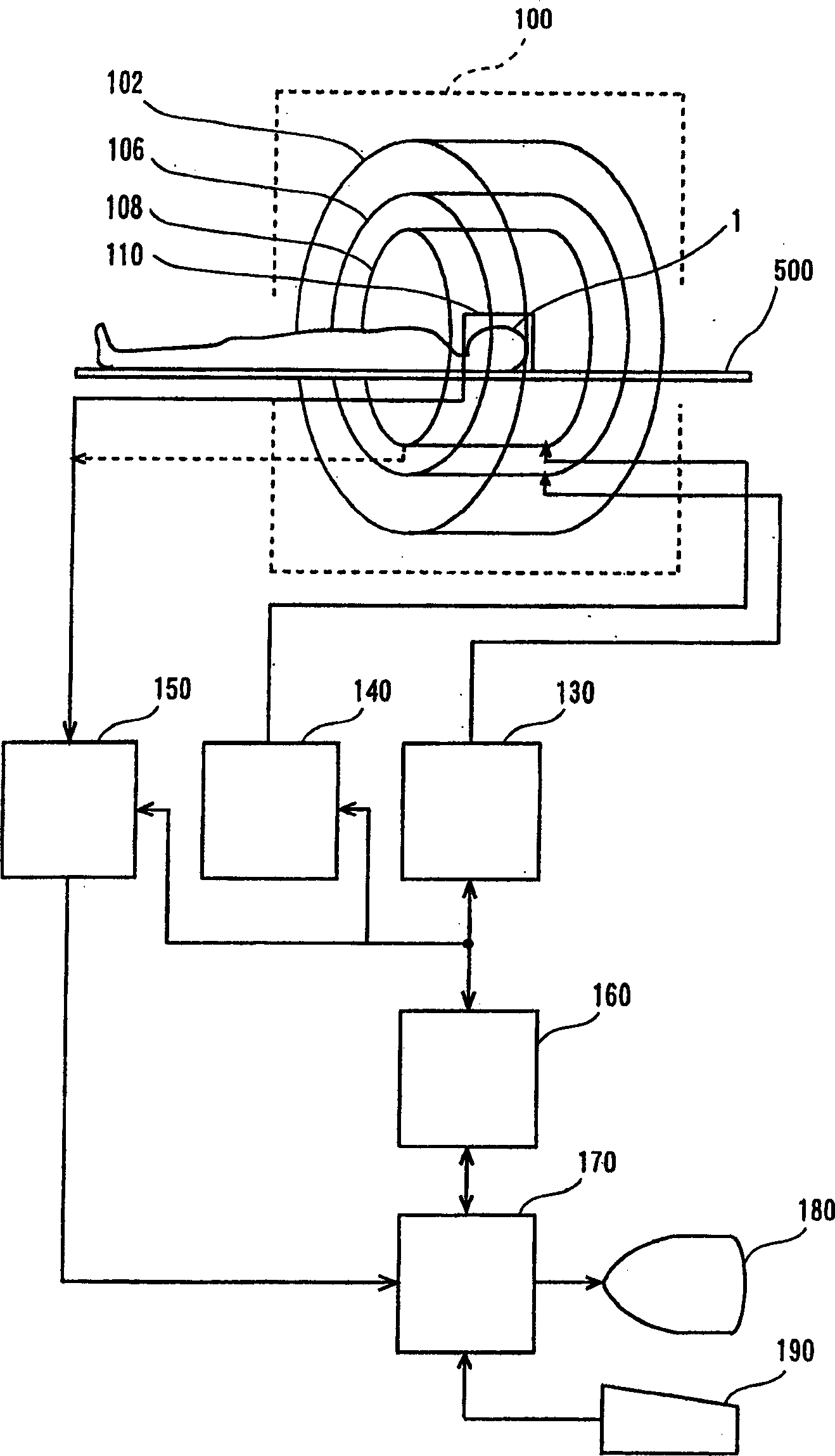
Magnetic resonance imaging method with sub-sampled acquisition
A magnetic resonance imaging method employs sub-sampled signal acquisition from a number of receiver coils such as surface coils. A full field-of-view magnetic resonance image is reconstructed on the basis of the sensitivity profiles of the receiver coils, for example on the basis of the SENSE technique. The reconstruction is carried out mathematically as an optimization, for example, requiring a minimum noise level in the magnetic resonance image. According to the invention, a priori information is also involved in the reconstruction and the a priori information is taken into account especially as a constraint in optimization.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
360-degree full field-of-view angle diffractive optical element and method for designing same
The invention relates to a 360-degree full field-of-view angle diffractive optical element and a method for designing the same. The diffractive optical element comprises a substrate layer and a plurality of nanometer bricks etched and arranged periodically on the working surface of the substrate layer. The substrate layer can be divided into a plurality of unit structures corresponding to the nanometer bricks. The unit structures have the same length, width, and height. Each individual unit structure has a square working surface with a side length of 400nm. All the nanometer bricks have the same size. The length, the width, and the height of each nanometer brick are 200nm, 120nm, and 310nm respectively and are all sub-wavelength scales. The nanometer bricks are arranged on the corresponding unit structures with different orientation angles, wherein each different orientation angle is half of the phase of the corresponding nanometer brick. The diffractive optical element ingeniously utilizes the geometrical phase and the electromagnetic resonance effect of a nanometer brick array material, realizes a simultaneous front and back transmission function which cannot be realized by a traditional diffractive optical element, expands the reachable range of diffracted light, and realizes half transmission energy and half reflection energy in a specific wavelength and precise and continuous phase control.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
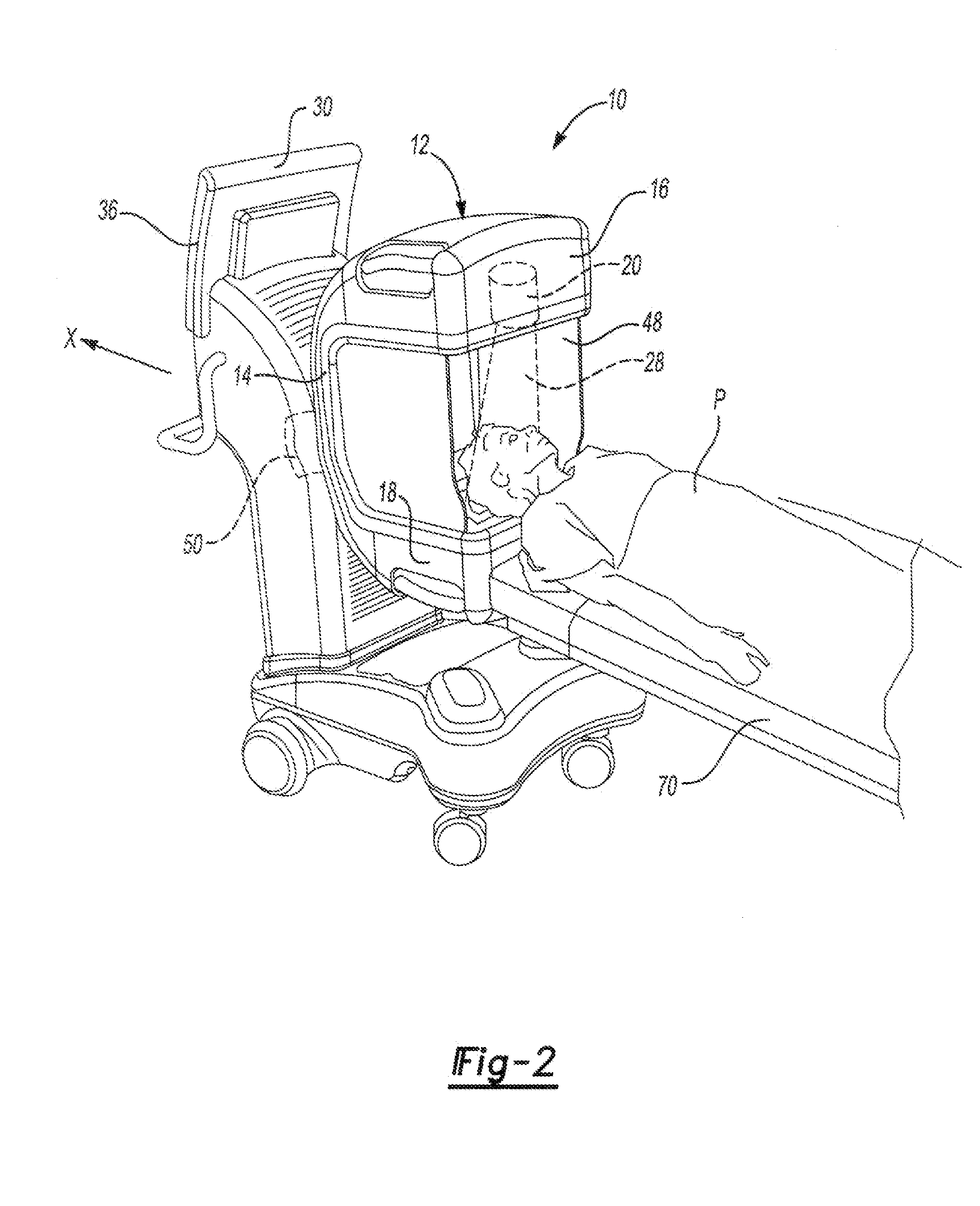
Ct scanner with automatic determination of volume of interest
InactiveUS20070237287A1Reduce X-ray exposureMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingThree dimensional ctCt scanners
A CT scanner automatically determines a volume of change based upon anatomical changes in a patient. During surgery, the CT scanner takes a sufficient number of two-dimensional initial images using a full field of view. The CT scanner compares the initial images to pre-operative data. Based upon the comparison, the CT scanner automatically determines the volume of change plus some margin to define a volume of interest. The CT scanner then collimates an x-ray source to perform an intra-operative updated CT scan of the volume of interest. The CT scanner updates the pre-operative data with the data from the intra-operative updated CT scan of the volume of interest to form a fully updated three-dimensional CT image. The initial images and the pre-operative data can be taken at a lower resolution than the intra-operative updated CT scan of the volume of interest to reduce the x-ray exposure of the patient.
Owner:XORAN TECH
Magnetic resonance imaging method with sub-sampled acquisition
A magnetic resonance imaging method employs sub-sampled signal acquisition from a number of receiver coils such as surface coils. A full field-of-view magnetic resonance image is reconstructed on the basis of the sensitivity profiles of the receiver coils, for example on the basis of the SENSE technique. The reconstruction is carried out mathematically as an optimization, for example, requiring a minimum noise level in the magnetic resonance image. According to the invention, a priori information is also involved in the reconstruction and the a priori information is taken into account especially as a constraint in said optimization.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
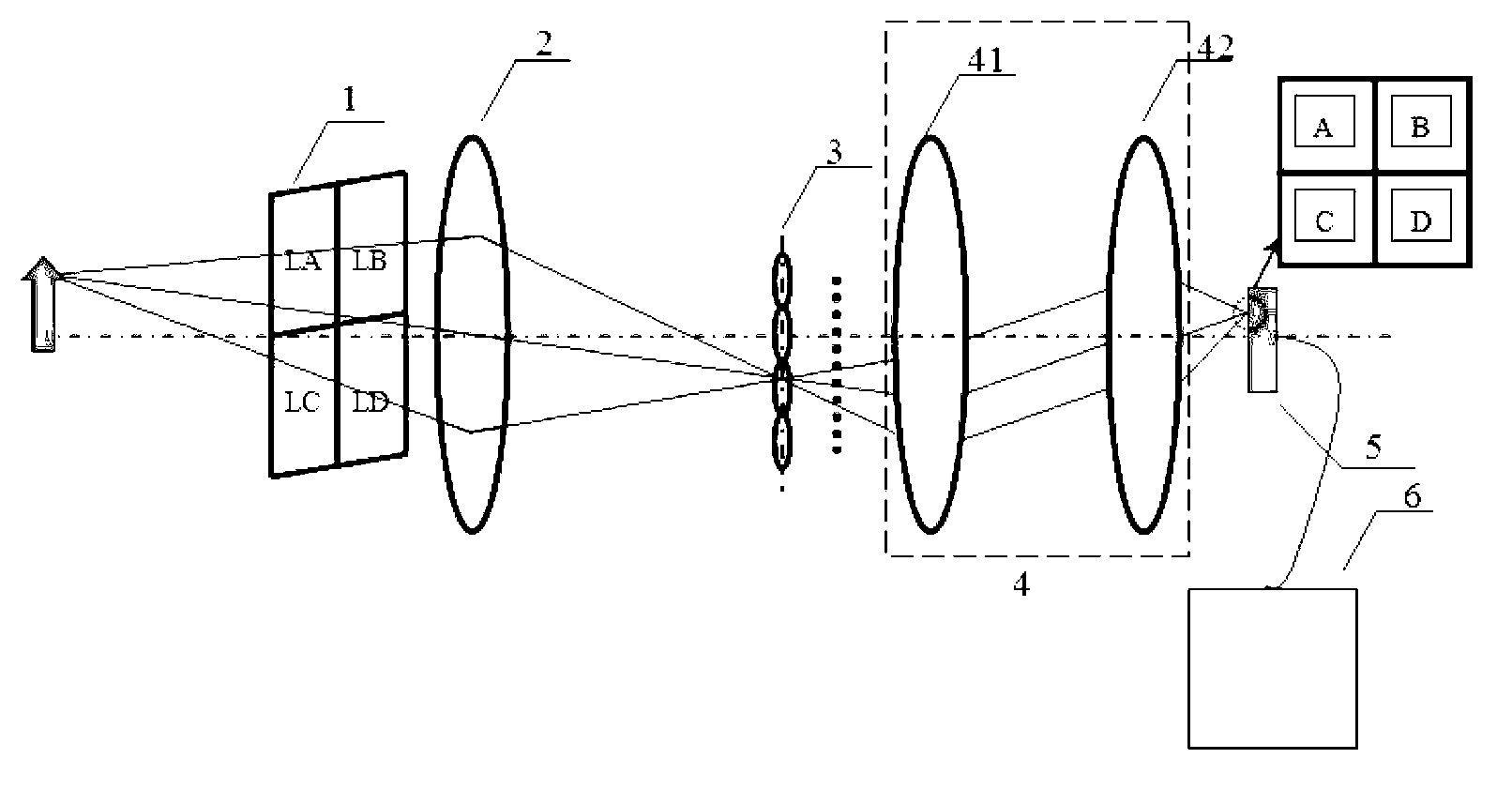
Multispectral light-field camera
InactiveCN103234527AEnabling Dynamic Multispectral ImagingStable structurePicture taking arrangementsUsing reradiationSpectral bandsLight-field camera
The invention provides a multispectral light-field camera. Along a light path direction, the camera comprises a light filter array, a main imaging lens, a micro lens array, combined sub-lenses, a detector and a signal processing system, which are sequentially arranged. An imaging method comprises the steps that: the light filter array is arranged on a pupil plane of the main imaging lens, and information of various target spectral bands is introduced with a pore size division method; with the micro lens array positioned on an image plane of the main imaging lens, the multispectral information is spatially separated; the combined sub-lenses are introduced, such that micro lens focal plane is secondarily transferred to a detector photosensitive surface; and the signal processing system calculates the data obtained by the detector, and spectral images of different wavebands are extracted and obtained. With the camera provided by the invention, multispectral information of each pixel in a full field of view can be obtained, dynamic multispectral imaging can be realized, and system structure is stable.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
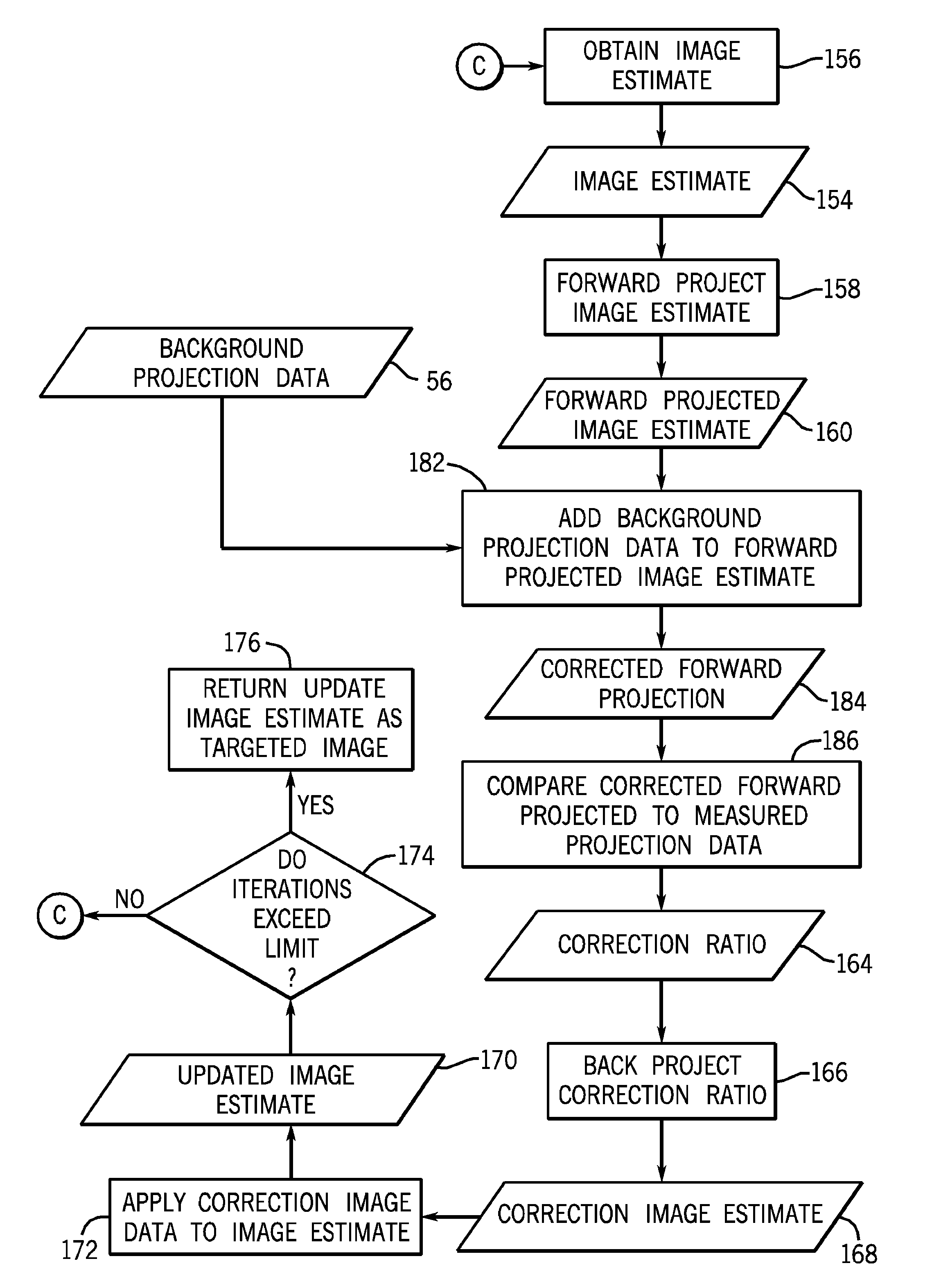
Keyhole computed tomography
ActiveUS20090225934A1Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationComputing tomographySmall target
A method of acquiring and reconstructing a computed tomography (CT) image is provided. A first scan of the full field of view (FOV) is acquired. A second scan of a smaller target FOV is then acquired by using a collimator to narrow the X-ray beam width. The CT image is iteratively reconstructed by replacing a key-hole region of the full FOV projection data with the target FOV projection data. An exemplary embodiment comprises imaging a heart (target FOV) within a torso (full FOV) over multiple heart beat cycles. A computer readable medium is further provided, including a program configured to reconstruct a CT image using the key-hole method.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
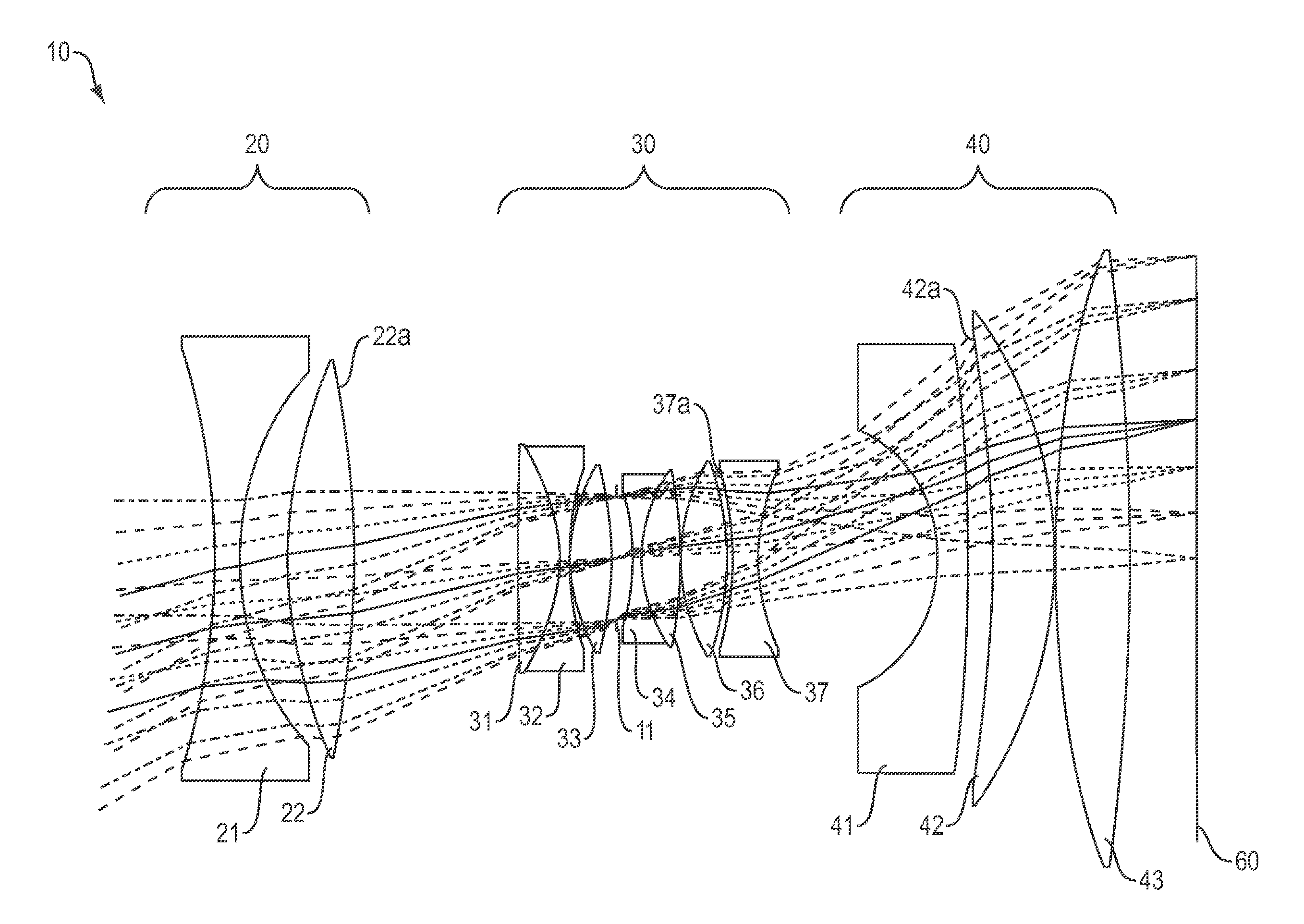
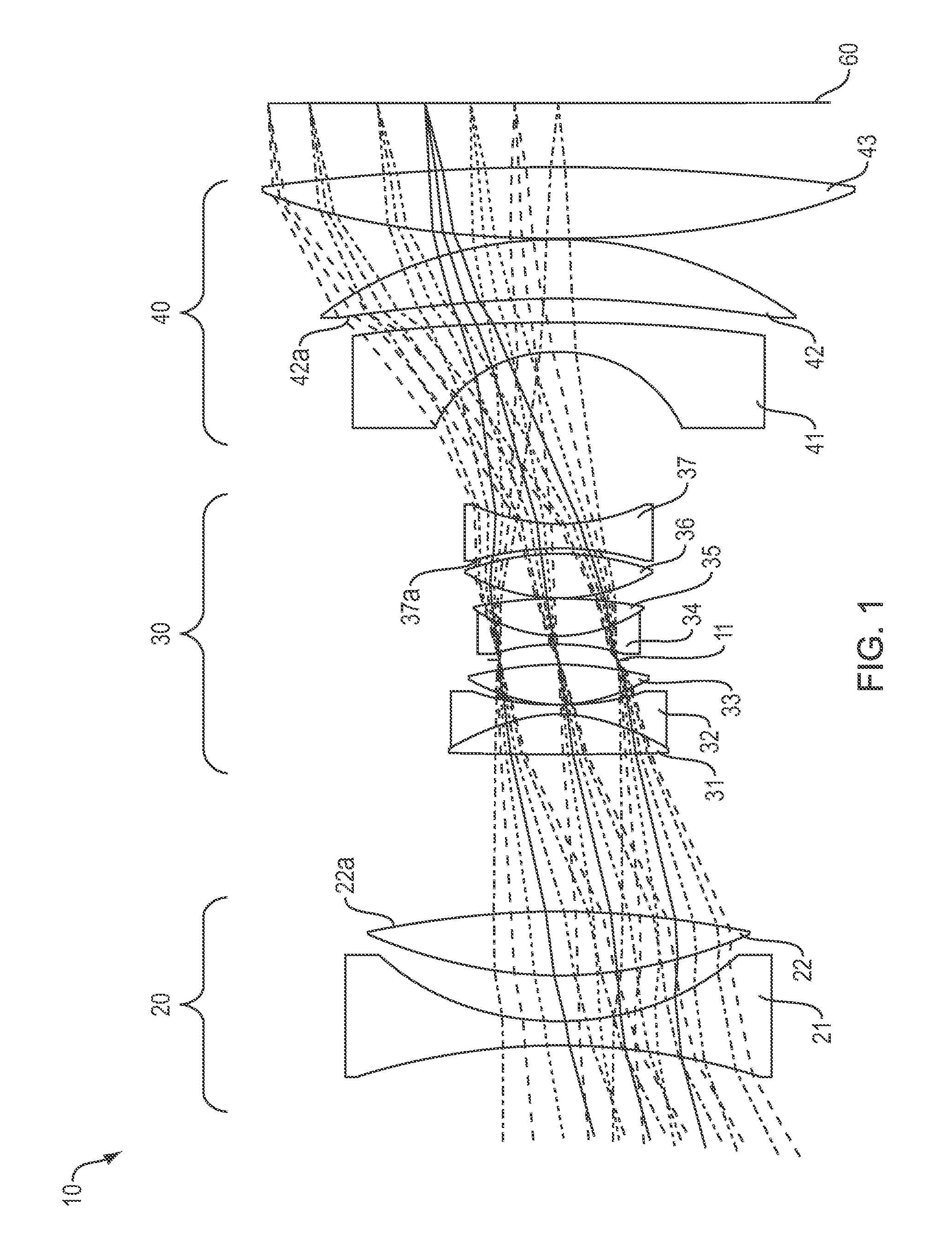
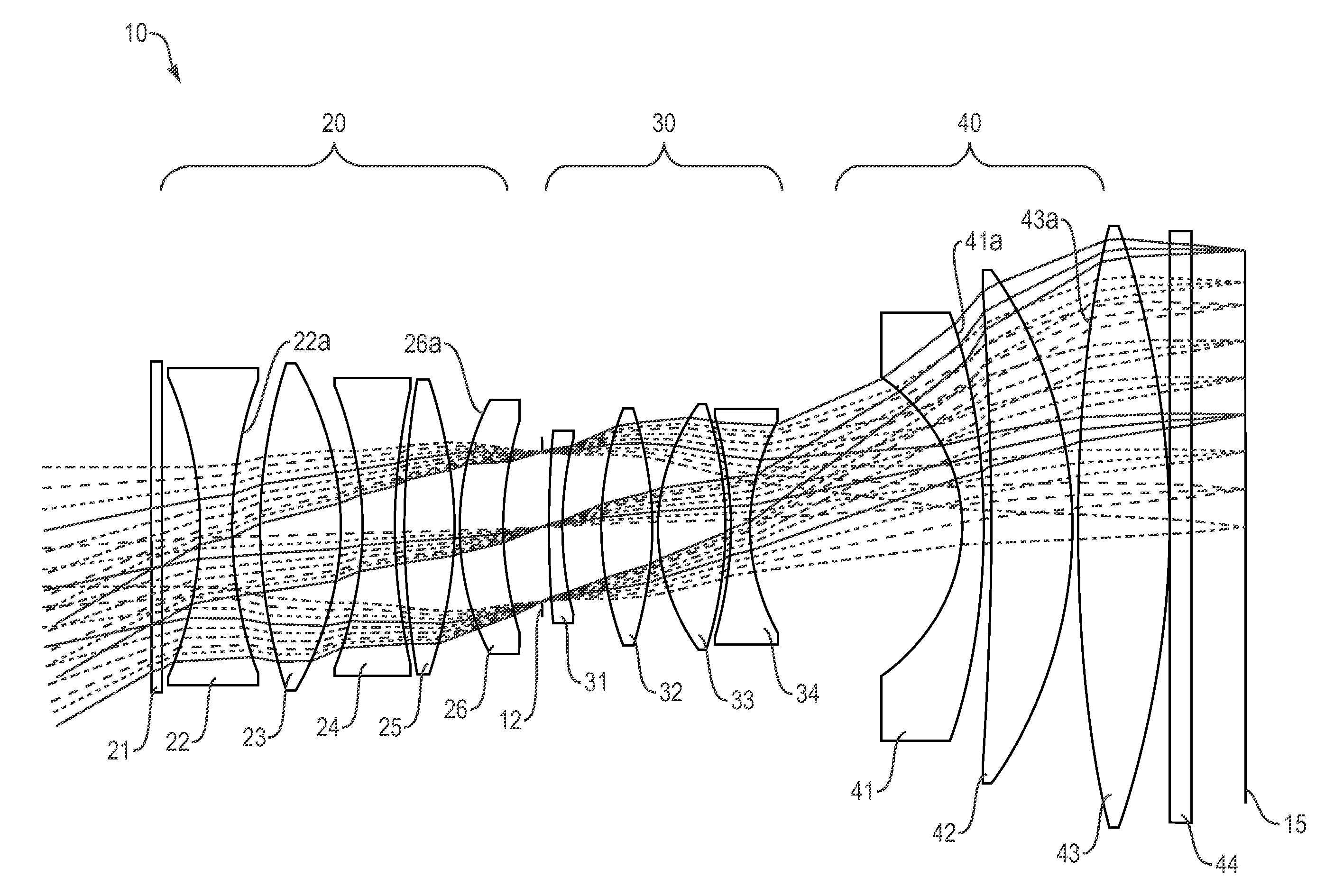
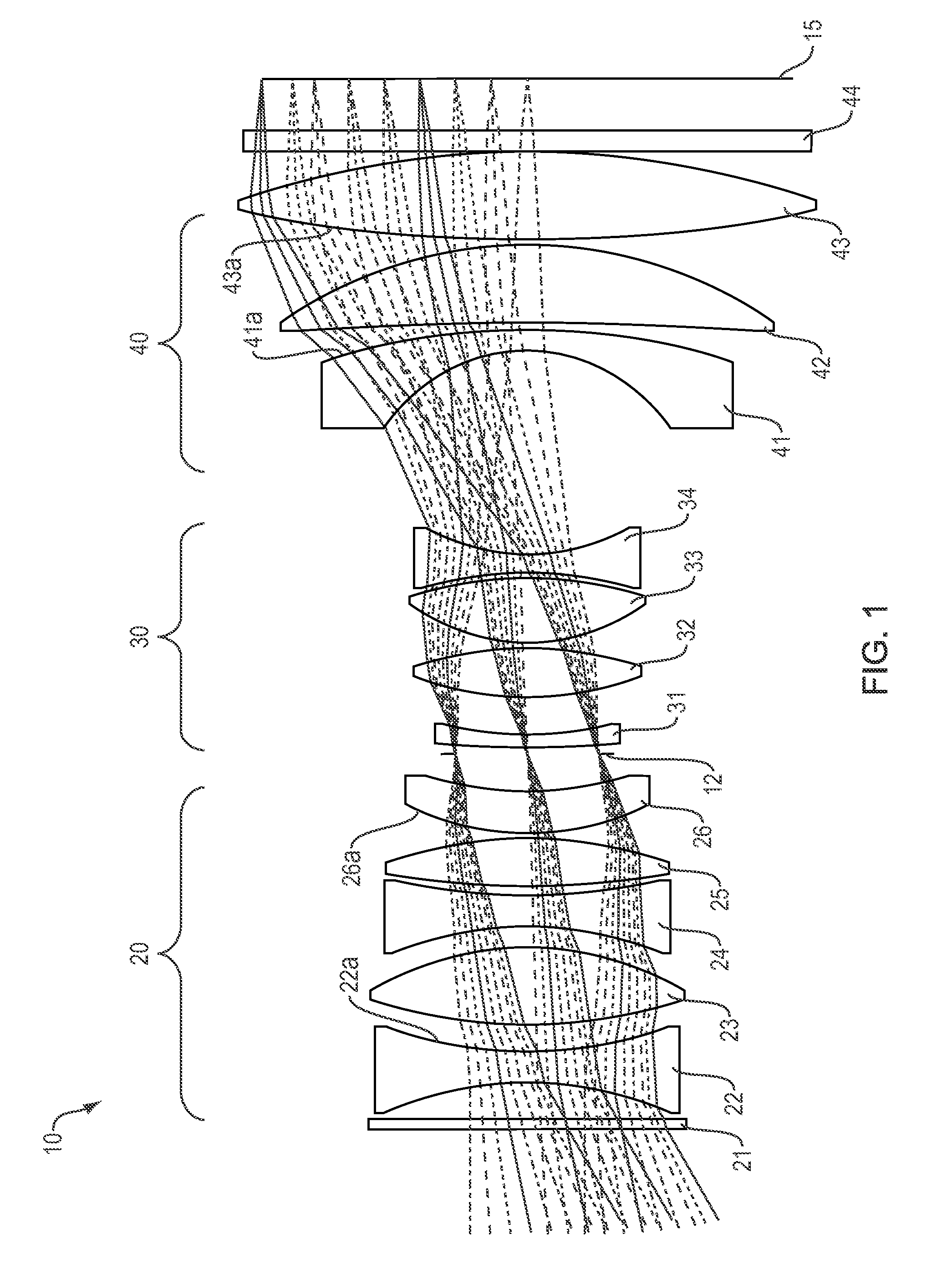
Low distortion athermalized imaging lens
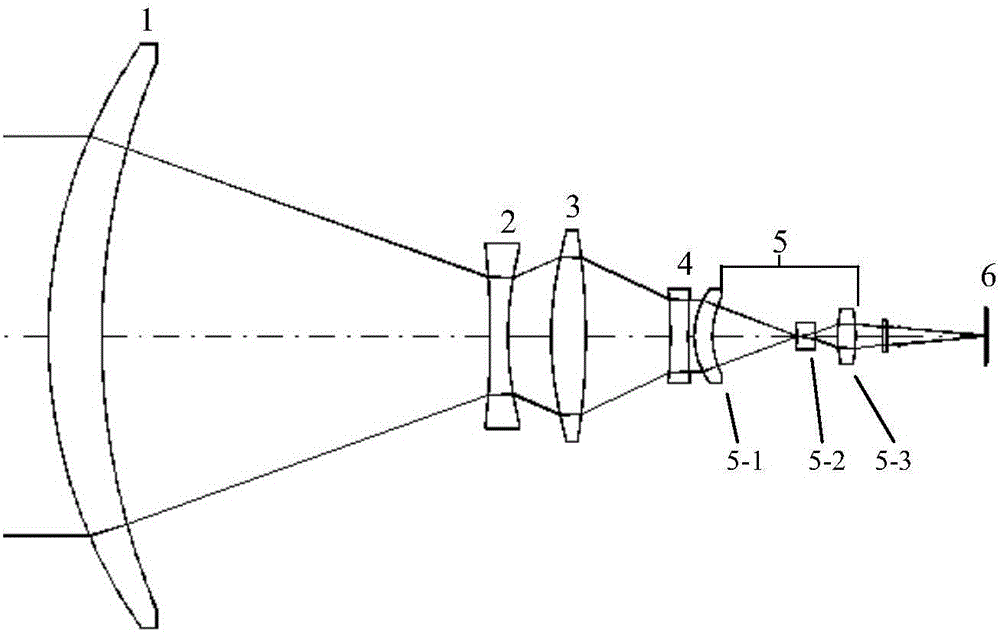
A compact, lens suitable for airborne photography and mapping has distortion less than 0.6% and is athermal from −15° C. to +40° C. The lens is near-telecentric to less than 11°, apochromatic over the wavelength range 450 nm-650 nm, and has a full field of view of 60° (high quality field over 53°). The lens can be secondary color corrected. In embodiments, the focal length is 101 mm and the back working distance is more than 10 mm. Embodiments have a focal plane diameter of 104 mm and are compatible for use with a CMOS 1.8 gigapixel multiple FPA. In embodiments, the lens comprises three groups of optical elements, with an aperture located within the second optical group. In some embodiments the first group includes two elements, the second group includes six or seven elements, and the third group include three elements. In embodiments the lens (without window) is less than 180 mm long.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
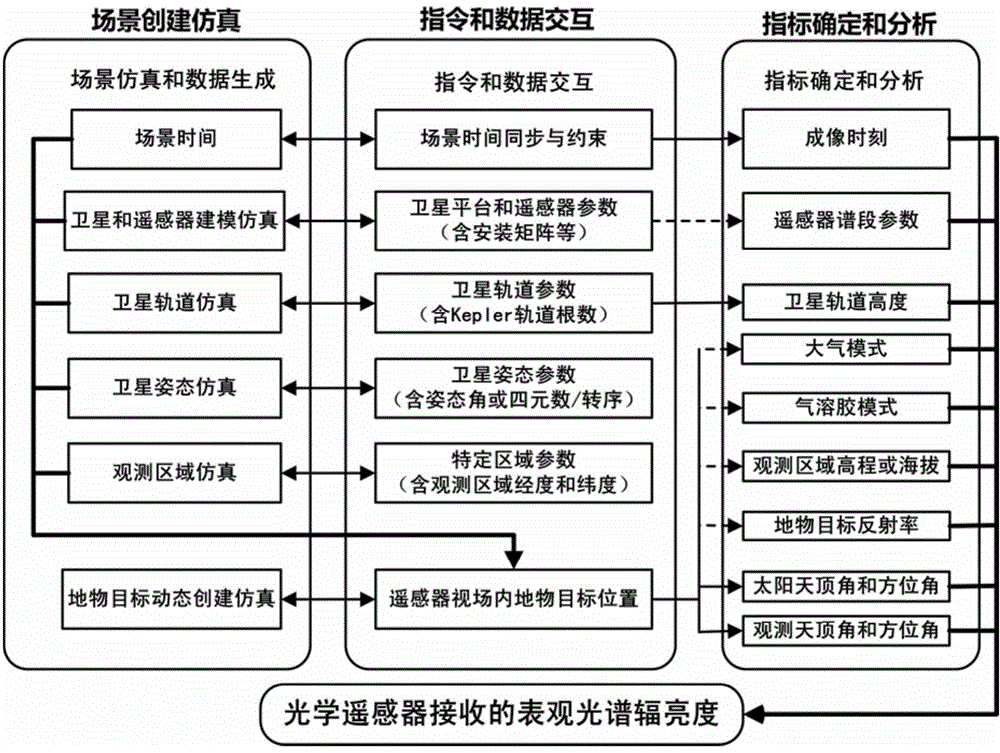
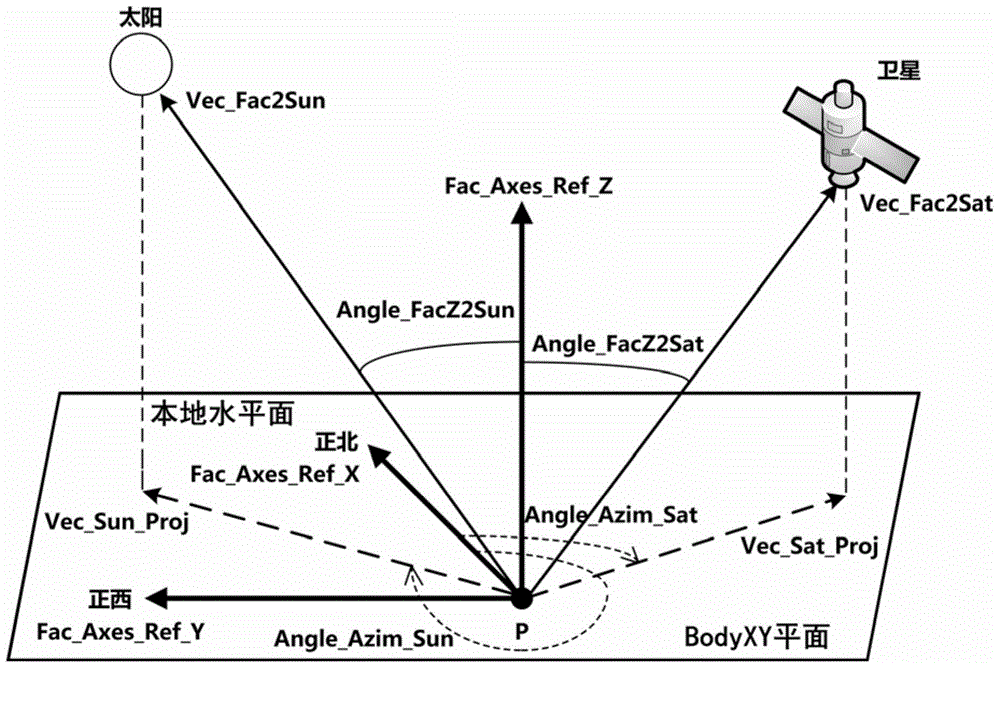
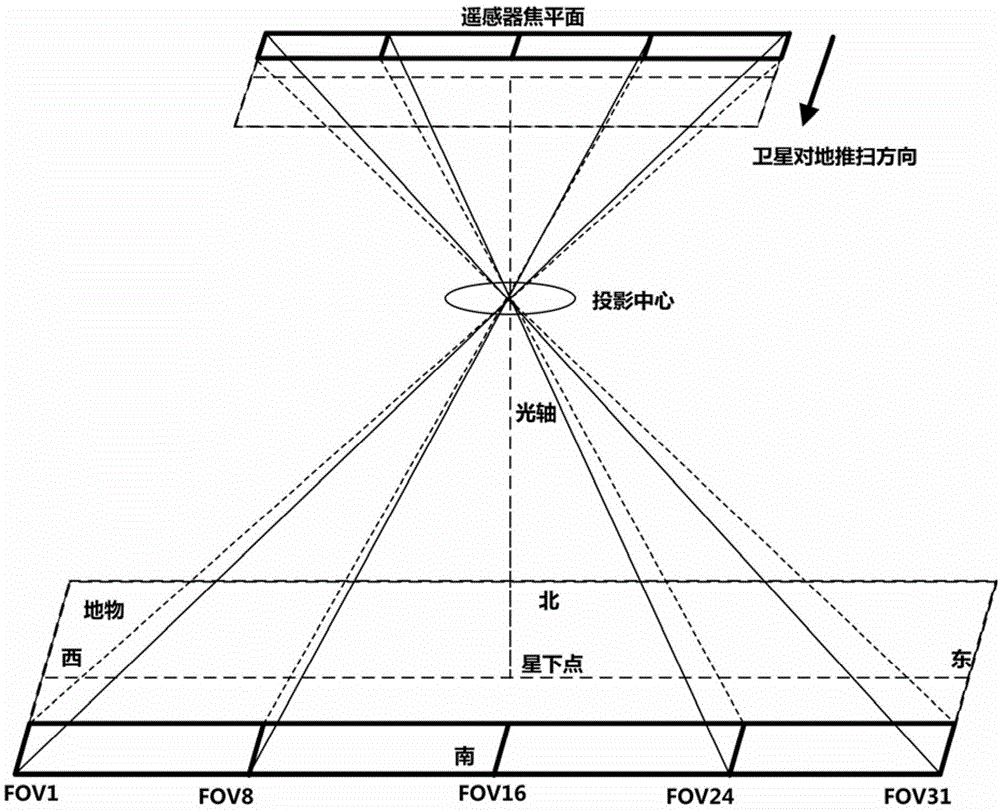
Method for determining full-field-of-view apparent spectral radiance of satellite-borne optical remote sensor
ActiveCN104573251AEliminate simplificationEliminate approximate calculationsSpecial data processing applicationsRadianceRadiative transfer theory
The invention discloses a method for determining full-field-of-view apparent spectral radiance of a satellite-borne optical remote sensor. The method comprises the steps that firstly, an optical remote sensing satellite observation model and a scene are simulated, a satellite remote sensor model, an observation object, a satellite orbit and an attitude parameter are set, and the scene is restrained; secondly, an optical remote sensing satellite full-field-of-view observation parameter is calculated; finally, the optical remote sensing satellite full-field-of-view apparent spectral radiance is determined. According to the method, determination of the apparent spectral radiance received by the remote sensor is based on a radiation transfer theory, and simulation is conducted on the whole radiation transfer link including the earth, a ground object target, the background characteristics, the atmospheric conditions and the satellite-borne optical remote sensor according to the operating characteristics of a satellite platform and the remote sensor; the apparent spectral radiance received by the view field positions corresponding to pixels at different positions of the focal plane of the remote sensor is determined according to the pixels one by one through radiation transfer model software.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
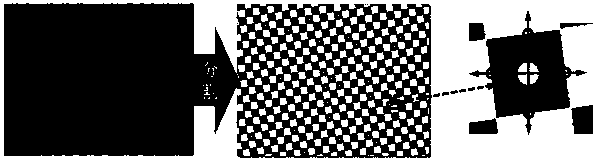
SFR test equipment and test method thereof
SFR test equipment and a test method thereof are disclosed. The equipment comprises a target plate, a light source, a base station and an image acquisition system. The target plate is a full field-of-view SFR target plate and is formed by a plurality of inclined black square blocks and a plurality of inclined white square blocks which are intersected. The light source is arranged in front of or behind the target plate. The base station supports a camera module group. The image acquisition system is connected to the camera module group so that an initial image of the target plate is transmittedto the image acquisition system. According to each knife edge inclination angle, an edge spread function (ESF) and a line spread function (LSF) are calculated. And finally, a SFR value of resolutionpower of the camera module group is determined.
Owner:NINGBO SUNNY OPOTECH CO LTD
Method for measuring large field-of-view telescope optical system distortion and field curvature
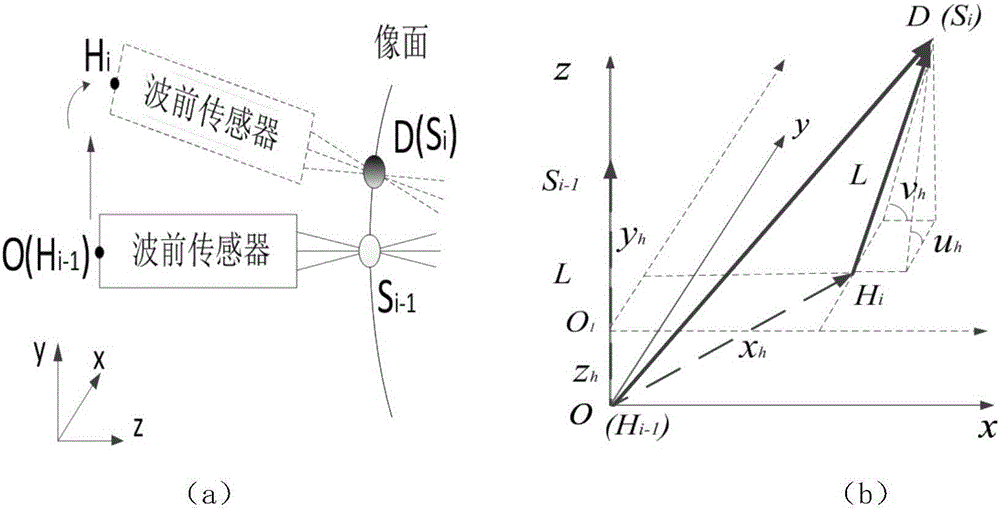
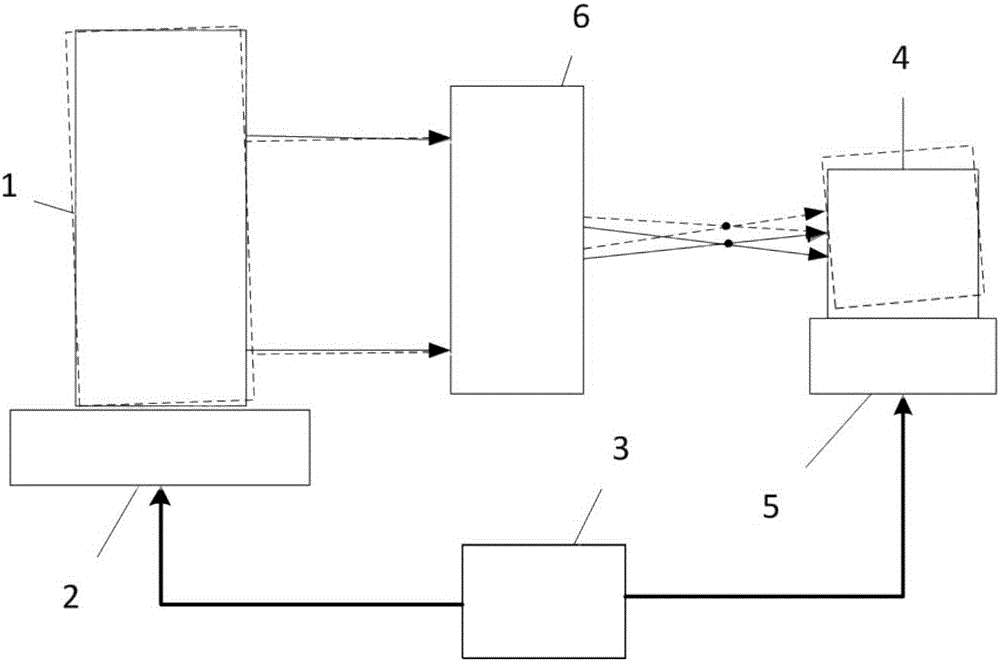
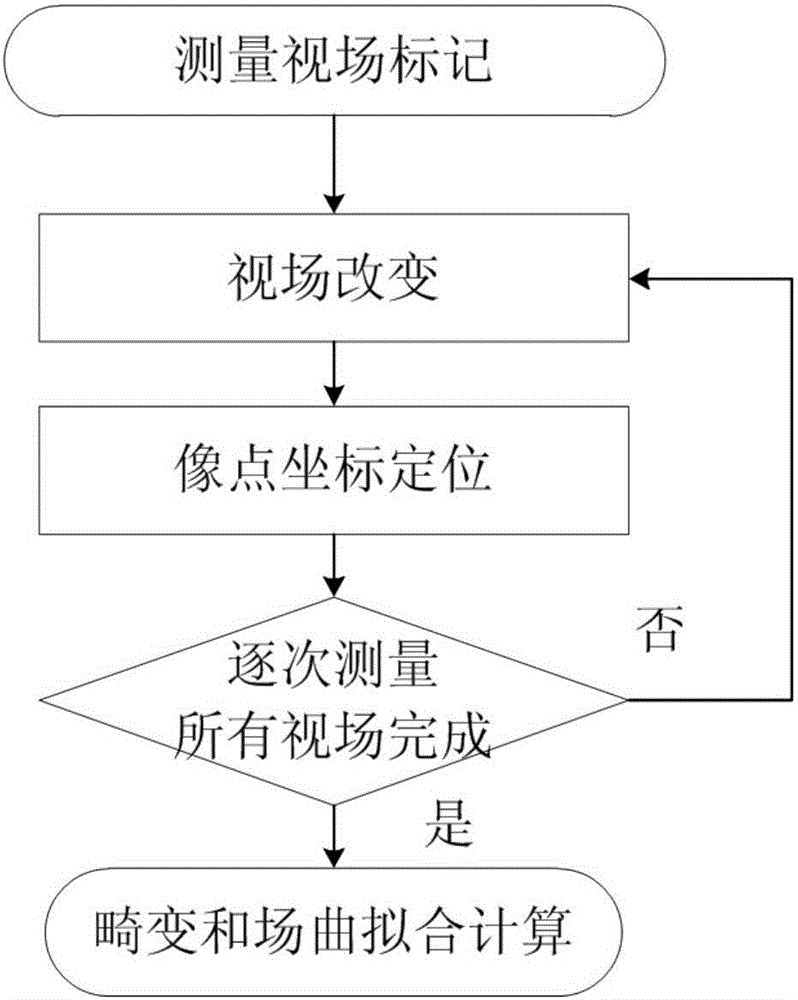
ActiveCN106404352AOvercome operabilityOvercome precisionGeometric properties/aberration measurementWavefrontClosed loop
The invention relates to a method for measuring large field-of-view telescope optical system distortion and field curvature. According to the invention, parallel light sources (1) come directly into a to-be-detected large field-of-view telescope (6). The field of view can be changed through the adjustment of the inclination and the pitching attitude of the parallel light sources (1). In the process of full field of view measurement, the to-be-detected large field-of-view telescope (6) remains to be in a fixed state. A computer (3), a wavefront detector (4) and the motion platform (5) of the wavefront detector form a closed-loop positioning structure to precisely measure and position the spatial positions of the image points of the to-be-detected large field-of-view telescope. Through the comparison of the ideal positions of the image points, the distortion and field curvature of the to-be-detected large field-of-view telescope (6) optical system can be obtained through fitting. The measuring method of the invention can be operated simply and effectively and achieves high measurement efficiency. Further, the method can perform automatic checking and can provide reliable measurement data for large field-of-view telescope optical system to correct distortion and field curvature.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
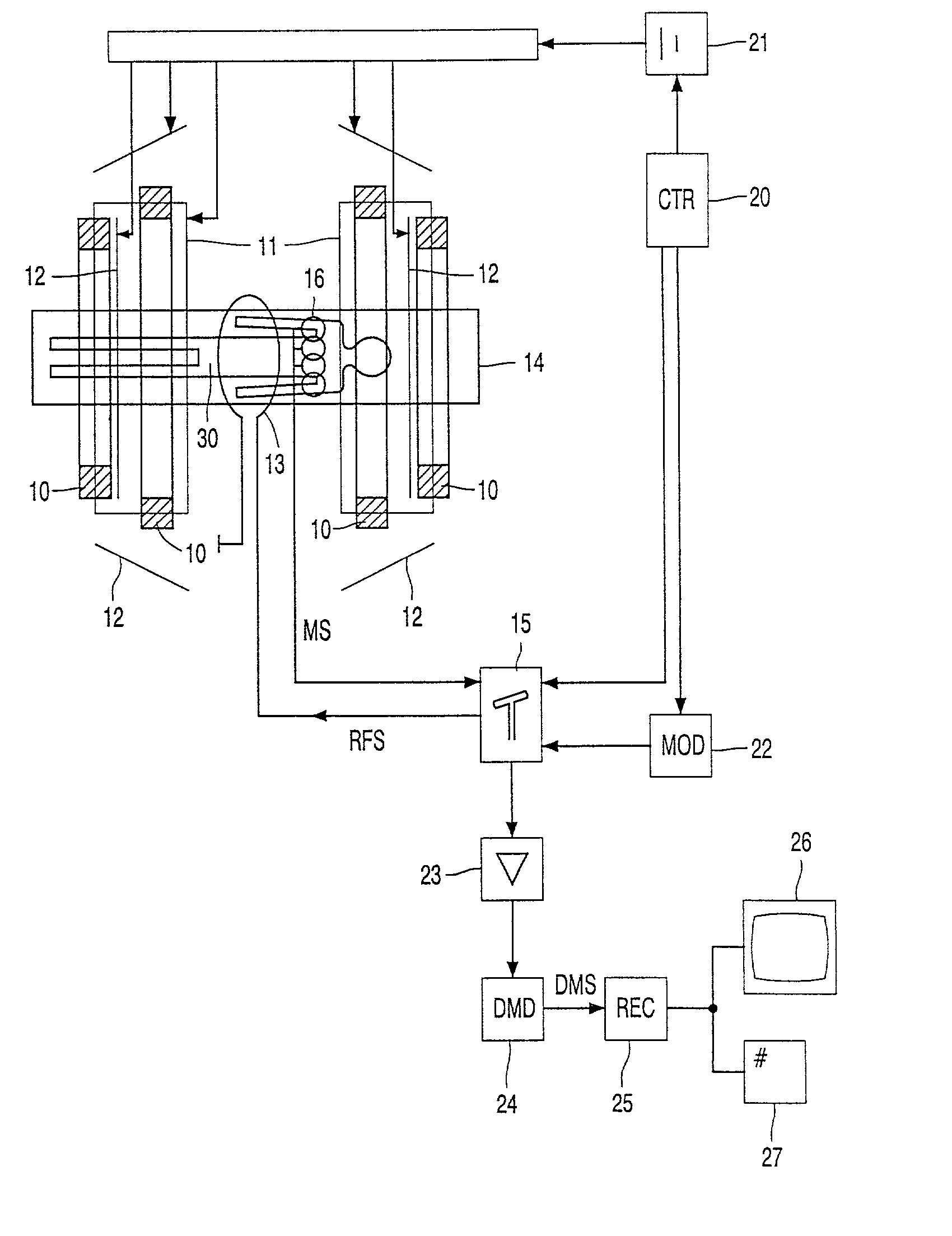
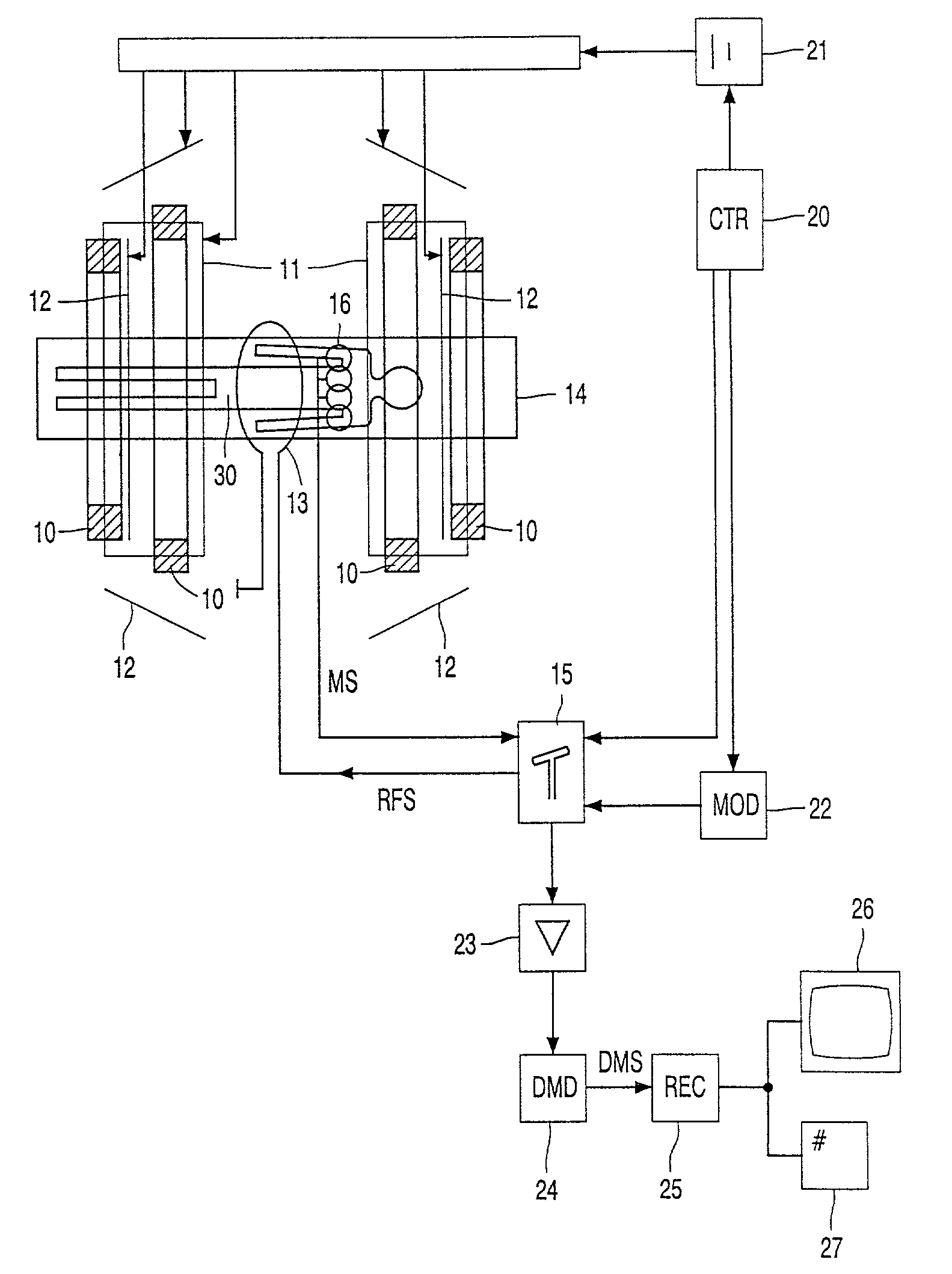
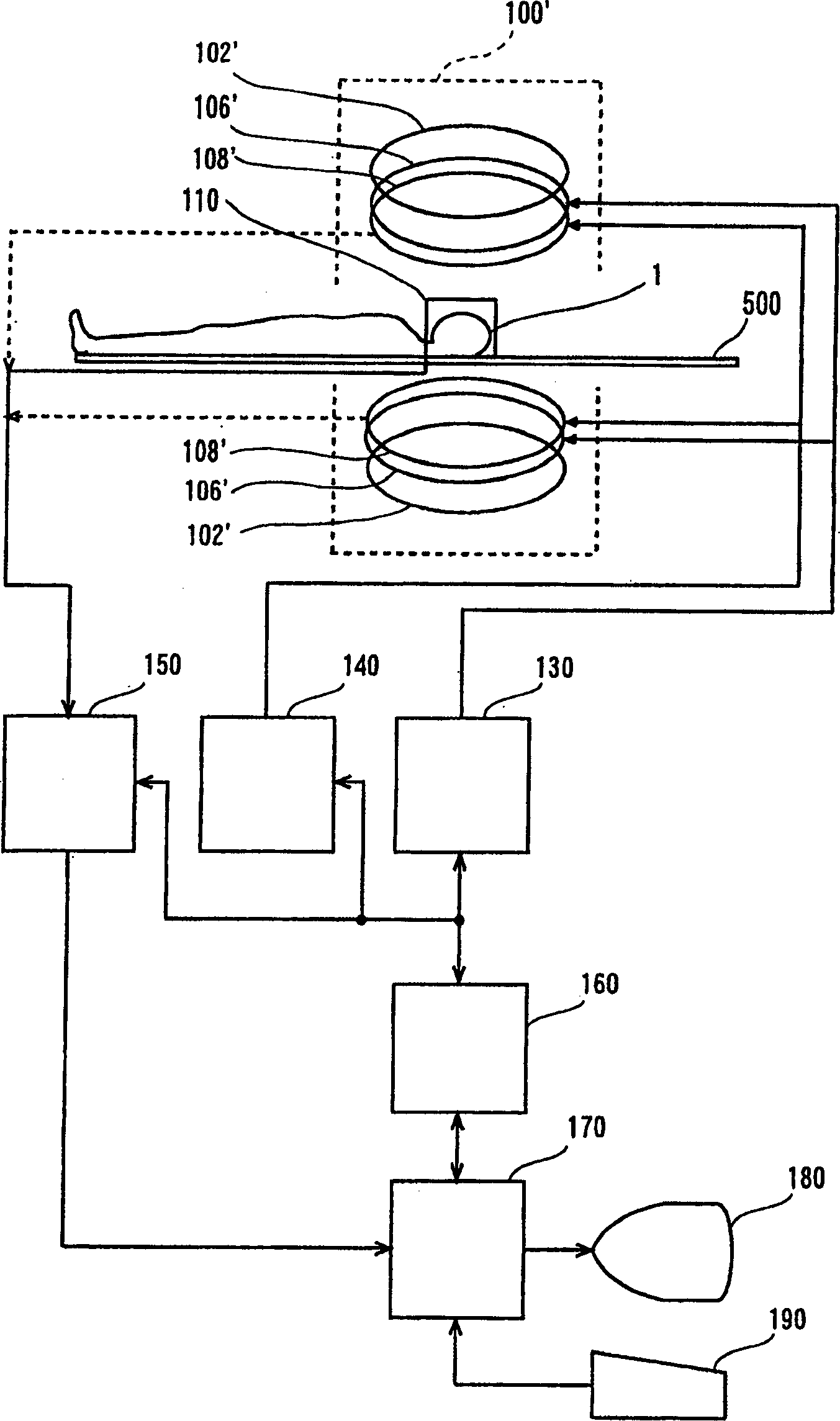
MRI systems with parallel receivers for phase correction
InactiveUS6842001B2Precision productionImprove consistencyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhase correctionIntermediate image
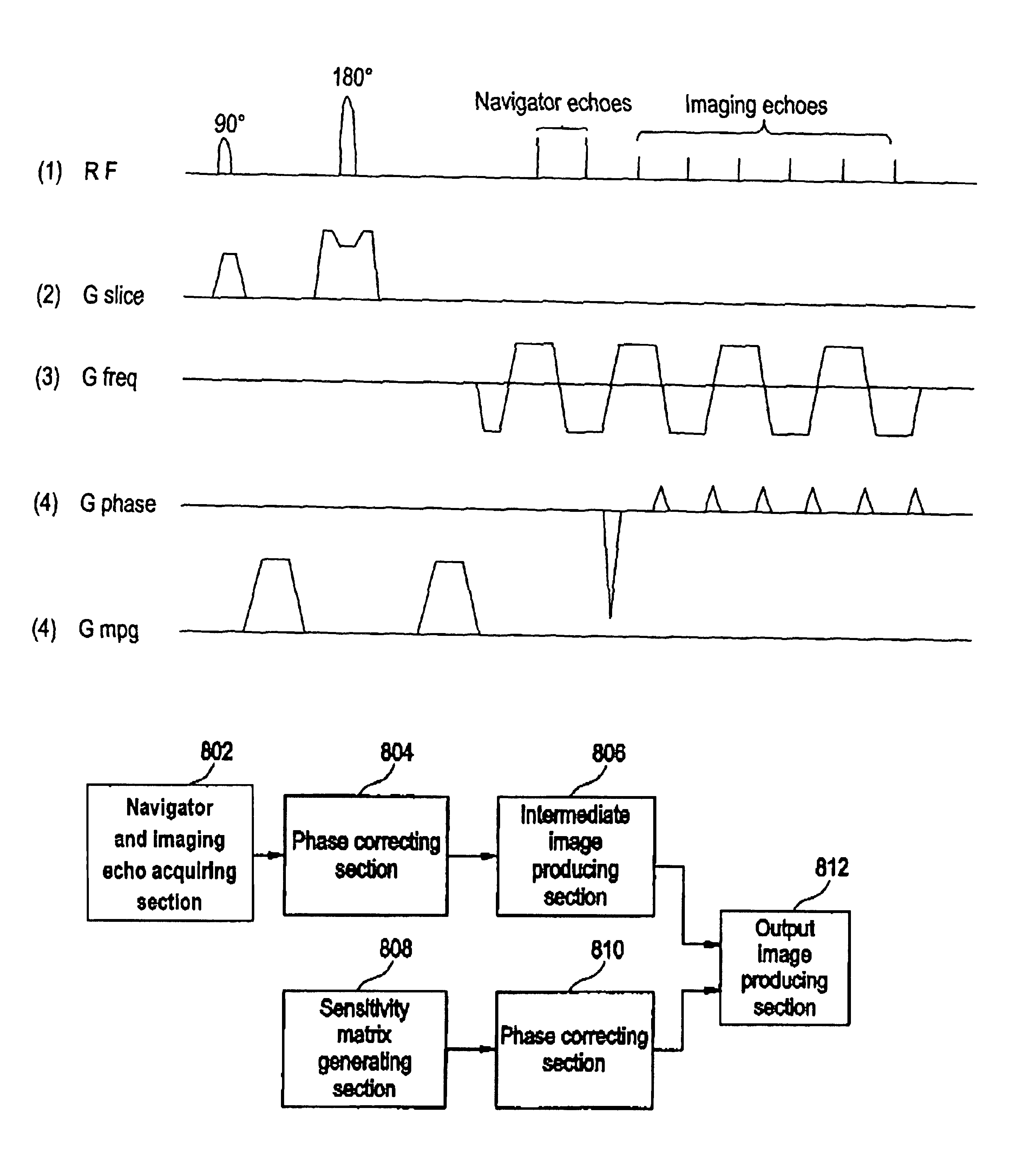
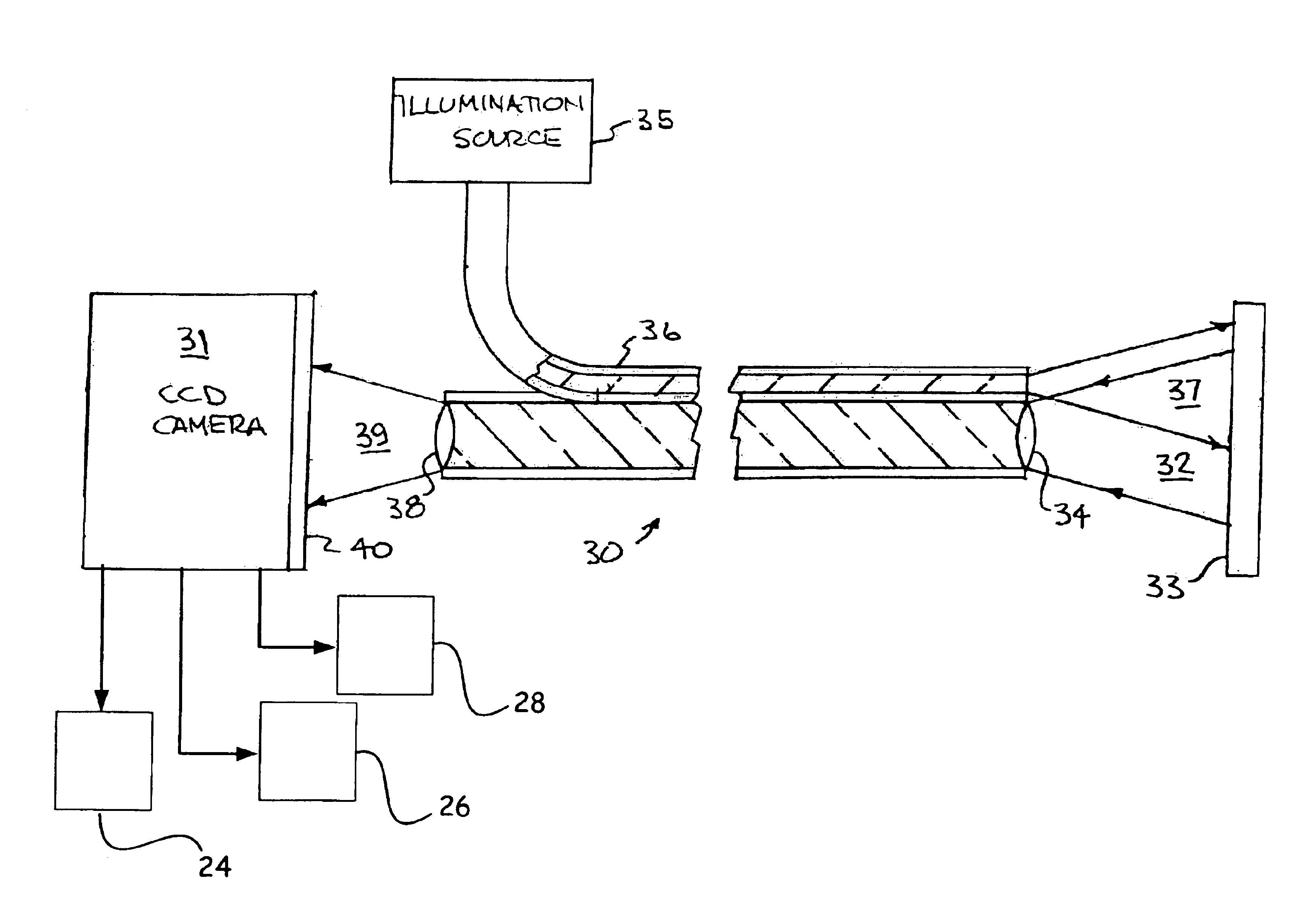
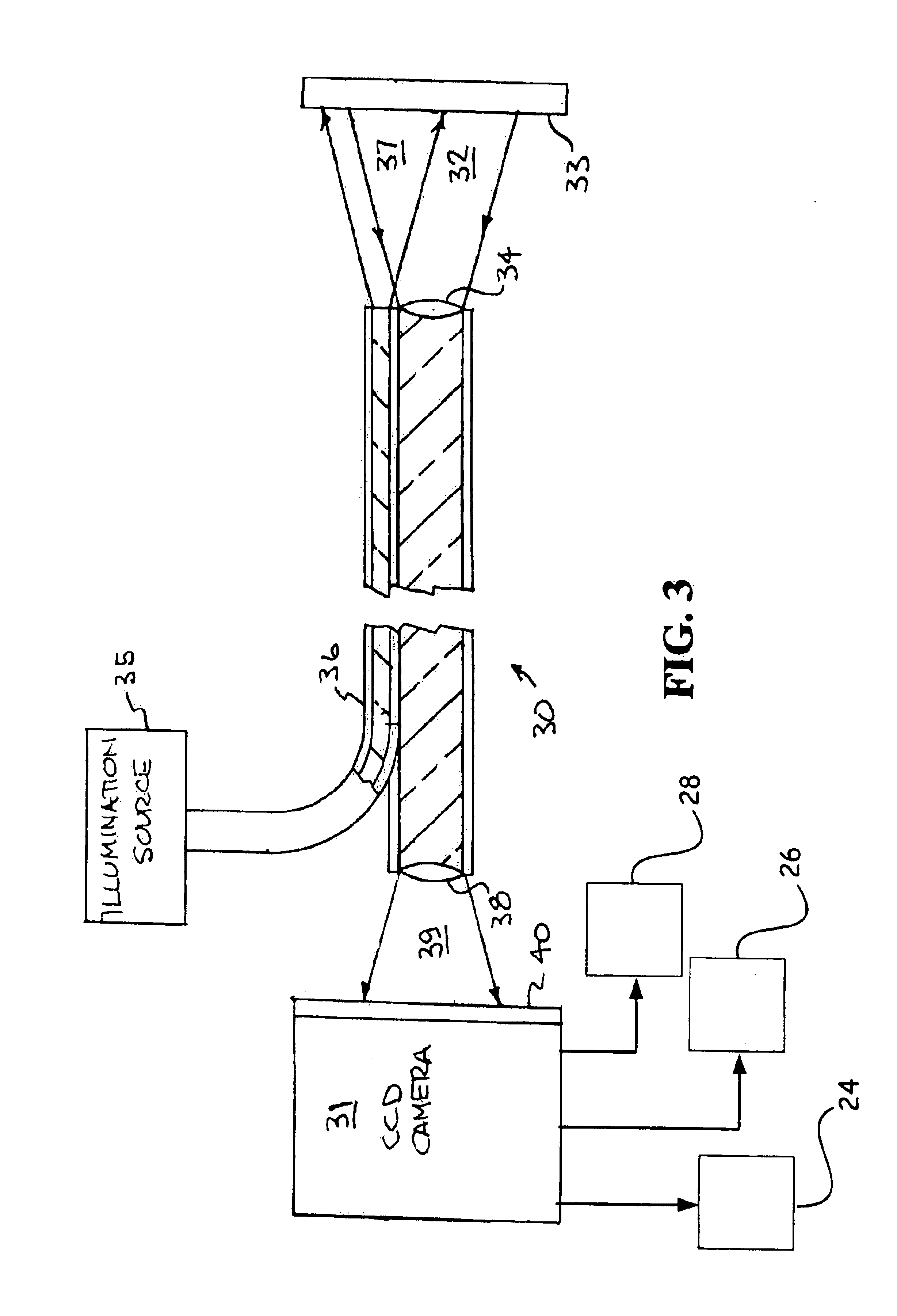
For the purpose of enabling parallel imaging even when a navigator echo is used to phase-correct an imaging echo, the present invention involves: exciting spins within a subject to acquire an imaging echo generated by the excited spins along with a navigator echo, with a reduced field-of-view via a plurality of receiver systems; conducting phase correction on the imaging echo based on the navigator echo; producing an intermediate image based on the phase-corrected imaging echo from each of the plurality of receive systems; generating a sensitivity matrix for the plurality of receiver systems; correcting the phase of matrix data in the sensitivity matrix; and producing an image with a full field-of-view based on the intermediate image and the phase-corrected sensitivity matrix.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Athermal apochromatic telecentric f-theta lens with low f-number
A compact F-theta lens suitable for precise mapping and aerial photography has an F# of not more than 4.5 and a full field of view of 60° (high quality field over) 53°. The lens is near-telecentric to less than 6°, apochromatic from 450 nm to 650 nm, and athermal from −15° C. to +40° C. Embodiments have a focal plane diameter of 104 mm and are compatible for use with a CMOS 1.8 gigapixel multiple FPA. In some embodiments the focal length is 101 mm and the back working distance is more than 10 mm. In embodiments the lens includes three groups of optical elements, with an aperture located between the first and second groups. In some of these embodiments, the first group has at least three elements, while the second and third groups have four and three elements respectively, and the diameter of the first two groups, including housing, is less than 65 mm.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Display interface with foveal compression
ActiveUS20190122642A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsSteroscopic systemsComputer graphics (images)Image resolution
A method of transporting foveal image data is disclosed. A host device receives image data from an image source and renders a full field-of-view (FFOV) image using the image data. The host device further identifies a foveal region of the FFOV image and renders a foveal image corresponding to the foveal region using the image data. More specifically, the foveal image may have a higher resolution than the foveal region of the FFOV image. The host device may then transmit each of the foveal image and the FFOV image, in its entirety, to a display device. For example, the host device may concatenate the foveal image with the FFOV image to produce a frame buffer image, and then transmit the frame buffer image to the display device.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
System and method for video processing and display
InactiveUS20070247518A1Improve immersionRemove distortionTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesComputer graphics (images)Video processing
To supplement a video display on a conventional television, a surround video stream may be projected onto wall and other surfaces adjacent the television. The surround video stream may derive from a wide angle lens camera positioned alongside the main camera. The surround video stream may be processed in a local processor to compensate for departures from planar geometry in the wall surfaces. Where no surround video stream is received, a video processor may synthesize a surround video stream from the main video signal. Moving objects represented in the main video signal may be synthesized in the surround video to provide the perception of movement across the viewer's full field of view.
Owner:BRITISH BROADCASTING CORP
Three-group linkage compact type high-zoom-ratio infrared continuous zooming optical system
ActiveCN106526818AReduce high-order aberrationsAchieve optical continuous zoomOptical elementsImaging qualityLight beam
The invention relates to a three-group linkage compact type high-zoom-ratio infrared continuous zooming optical system, adopts a double-compensation group design method to realize three-group linkage of a zooming group and compensation groups, realizes a large zoom ratio, and through adoption of aspheric surfaces and diffractive surfaces, high-grade aberrations, point-on-axis and off-axis point aberrations, beamlet and wide light beam aberrations and various aberration are reduced and axial space is compressed, and satisfying image quality is obtained in a full field of view and a full aperture. The advantages are that 30-time optical continuous zooming and continuously variable focal length are realized, continuously enlarged and reduced images can be obtained, and the image plane position is kept stable, and image quality is kept good in a zooming process. The axial length of the whole optical system is small, is only 180mm, and is reduced by nearly 60% than the length of an optical system of the same kind. By adoption of aspheric surface and diffractive surface design, the designed degree of freedom of the continuous zooming optical system is increased, optimization design is performed on the optical system, and optional variables are increased, so that optical system aberration design is easy to achieve an excellent result, and thus excellent image quality is obtained.
Owner:LUOYANG INST OF ELECTRO OPTICAL EQUIP OF AVIC
Optic for industrial endoscope/borescope with narrow field of view and low distortion
An optic for the imaging optics on the distal end of a flexible fiberoptic endoscope or rigid borescope inspection tool. The image coverage is over a narrow (<20 degrees) field of view with very low optical distortion (<5% pin cushion or barrel distortion), compared to the typical <20% distortion. The optic will permit non-contact surface roughness measurements using optical techniques. This optic will permit simultaneous collection of selected image plane data, which data can then be subsequently optically processed. The image analysis will yield non-contact surface topology data for inspection where access to the surface does not permit a mechanical styles profilometer verification of surface topology. The optic allows a very broad spectral band or range of optical inspection. It is capable of spectroscopic imaging and fluorescence induced imaging when a scanning illumination source is used. The total viewing angle for this optic is 10 degrees for the full field of view of 10 degrees, compared to 40-70 degrees full angle field of view of the conventional gradient index or GRIN's lens systems.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Keyhole computed tomography
ActiveUS7920670B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationComputing tomographySmall target
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
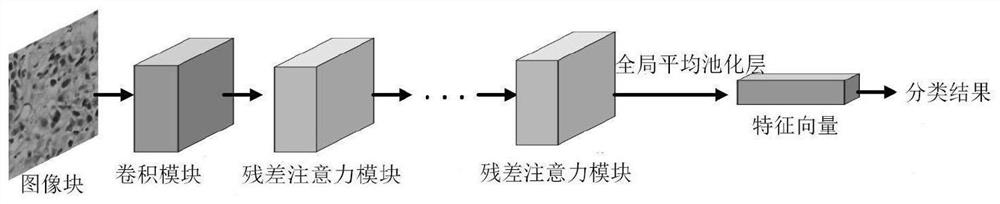
Focus area classification method and system for full-view digital pathological section
PendingCN112084930AImprove computing efficiencyImprove classification accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesAutomatic segmentationClassification methods
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
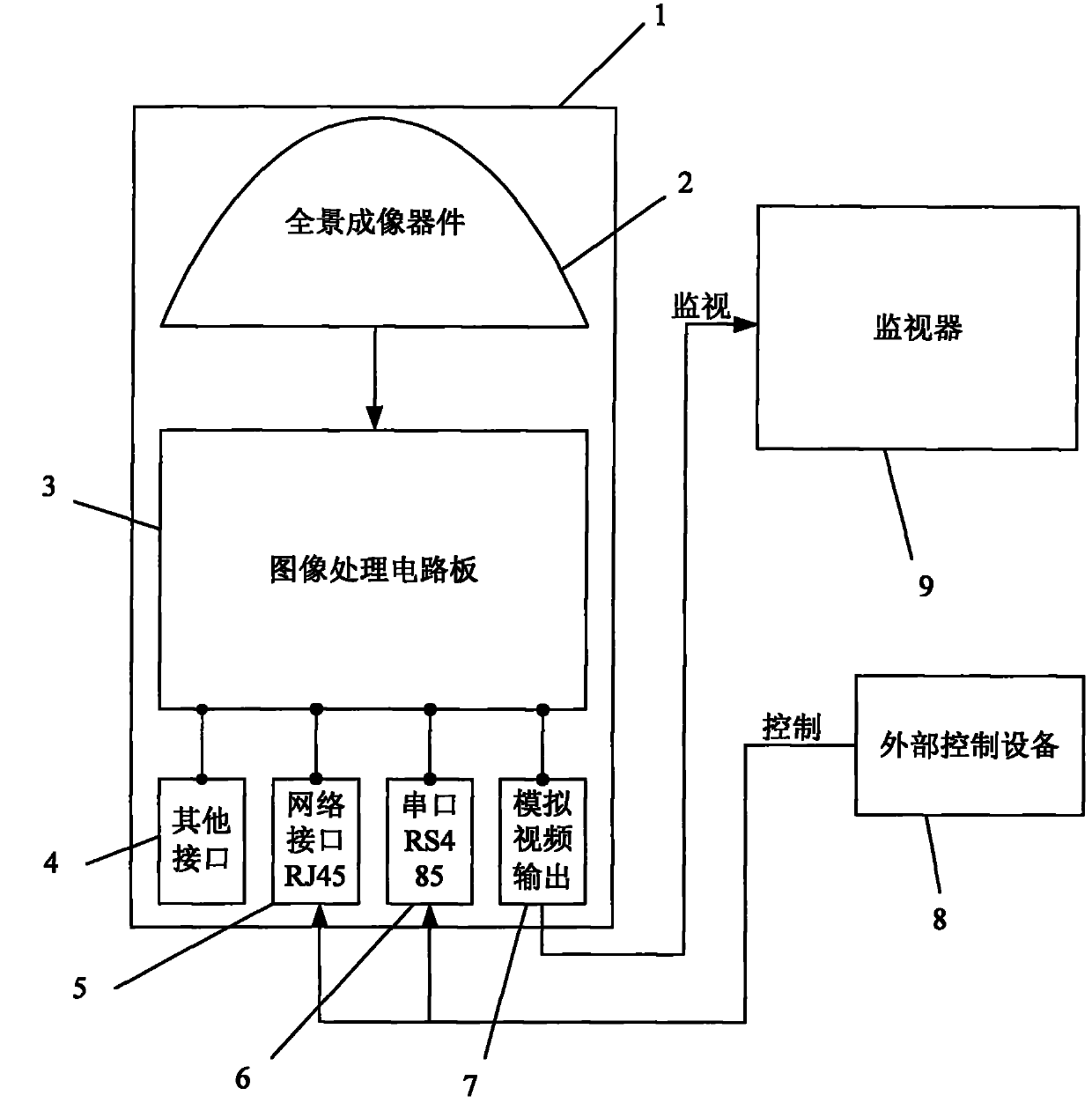
Panorama-spreading system for analog video monitor and panorama-spreading methods
InactiveCN102780871AEffective displayTelevision system detailsColor television detailsVisual field lossImaging processing
The invention discloses a panorama-spreading system for an analog video monitor. The system can directly output the analog video signals of panoramic images meeting the viewing habit of the human eyes, and can be directly connected with the monitor for monitoring. The system comprises a panoramic imaging device and an image processing circuit board, and is provided with an analog video signal interface, a network interface RJ45 and a serial port RS485, the analog video signal interface is used for outputting analog video signals, and the network interface RJ45 and the serial port RS485 are used for controlling a camera. On the basis, the invention also discloses a variety of panoramic image-spreading methods, which can spread omnidirectional images into panoramic images which are suitable for the viewing habit of the human eyes and meet analog video resolution. According to the scheme provided by the invention, the panorama-spreading system can be directly connected with the panoramic camera of the analog video monitor, thus realizing 360-degree full-visual field monitoring.
Owner:张茂军 +1
Magnetic resonance imaging equipment
InactiveCN1487305AWith full field of viewHas pixel valueMagnetic property measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringPhase correctionIntermediate image
For the purpose of enabling parallel imaging even when a navigator echo is used to phase-correct an imaging echo, the present invention involves: exciting spins within a subject to acquire an imaging echo generated by the excited spins along with a navigator echo, with a reduced field-of-view via a plurality of receiver systems (802); conducting phase correction on the imaging echo based on the navigator echo (804); producing an intermediate image based on the phase-corrected imaging echo from each of the plurality of receiver systems (806); generating a sensitivity matrix for the plurality of receiver systems (808); correcting the phase of matrix data in the sensitivity matrix (810); and producing an image with a full field-of-view based on the intermediate image and the phase-corrected sensitivity matrix (812).
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
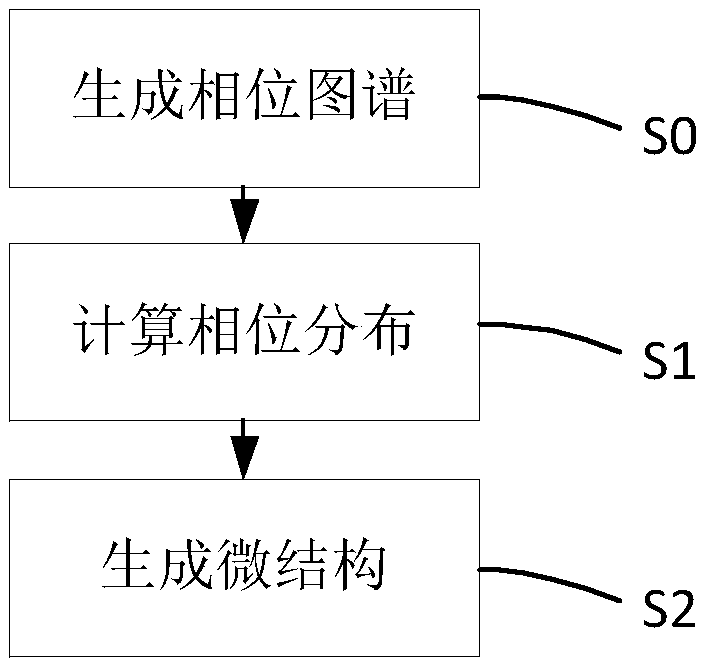
Super-lens microstructure generation method and micro two-photon microscope system based on super lens
ActiveCN109507765AReduce the impactSpeed up progressPhotomechanical apparatusMicroscopesIn vivoImaging equipment
The invention provides a super-lens microstructure generation method. The method includes the following steps of generating phase maps, calculating phase distribution and generating microstructures. The invention further relates to a micro biphoton microscopy system based on the super-lens. A super-surface lens is introduced into the field of biphoton microscopy, medium numerical aperture focusingis achieved under full field of view, the structure of a microscope is greatly simplified, the weight of the overall equipment is largely reduced, and lighter load animal experiments can be achieved.The reliability of in vivo biphoton microscopy experimental data is improved, and the method has high scientific value for micro biphoton, especially in vivo microscopic imaging; the influence of a backpack type micro microscope system on observed objects (such as mice) is further reduced. According to the system, from simulation design to processing to experiments, a super-surface lens is introduced into the biphoton microscopy imaging system, and a new generation of imaging equipment is provided for brain imaging of living animals. The progress in brain and Neuroscience research is promoted.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
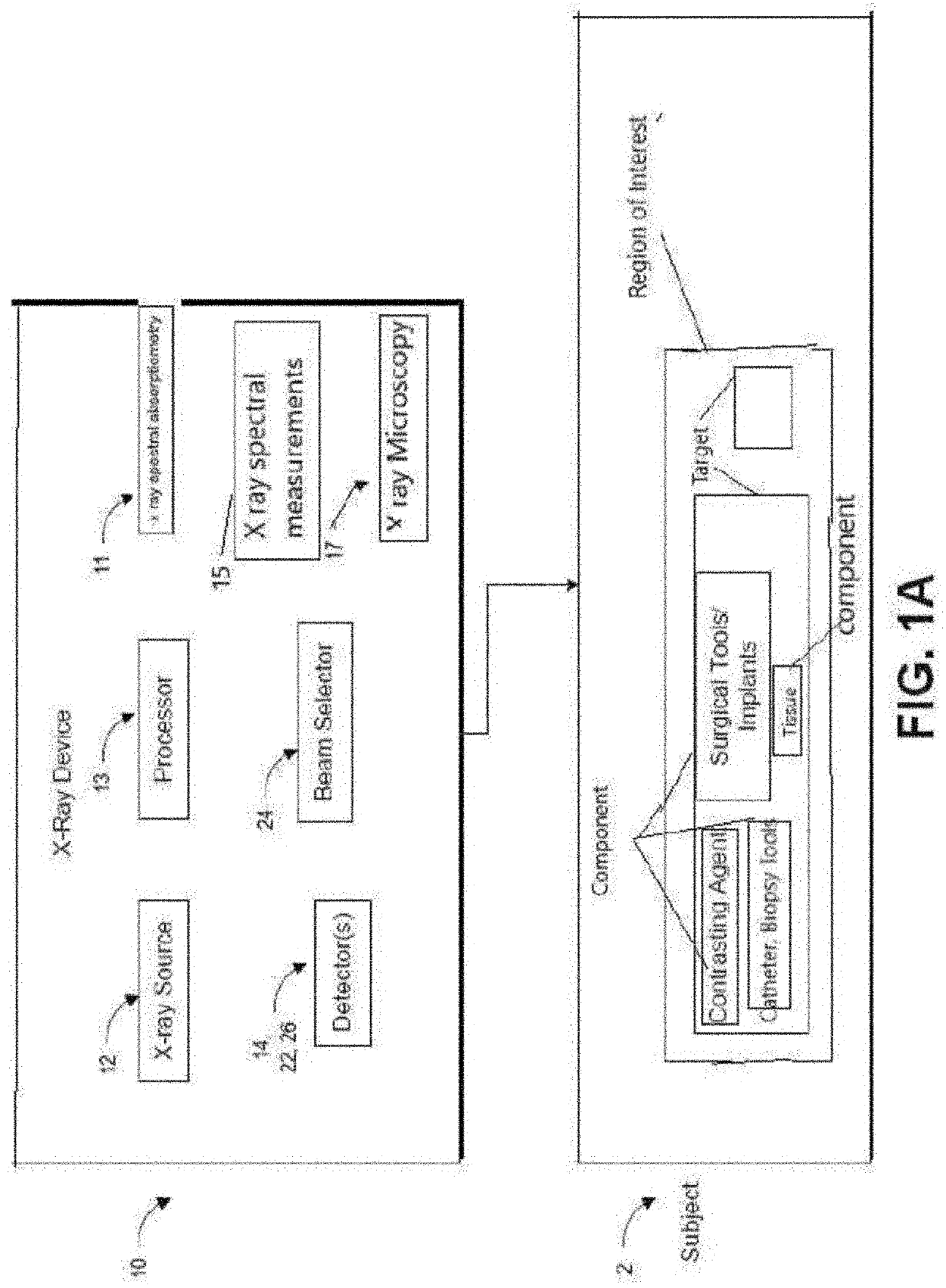
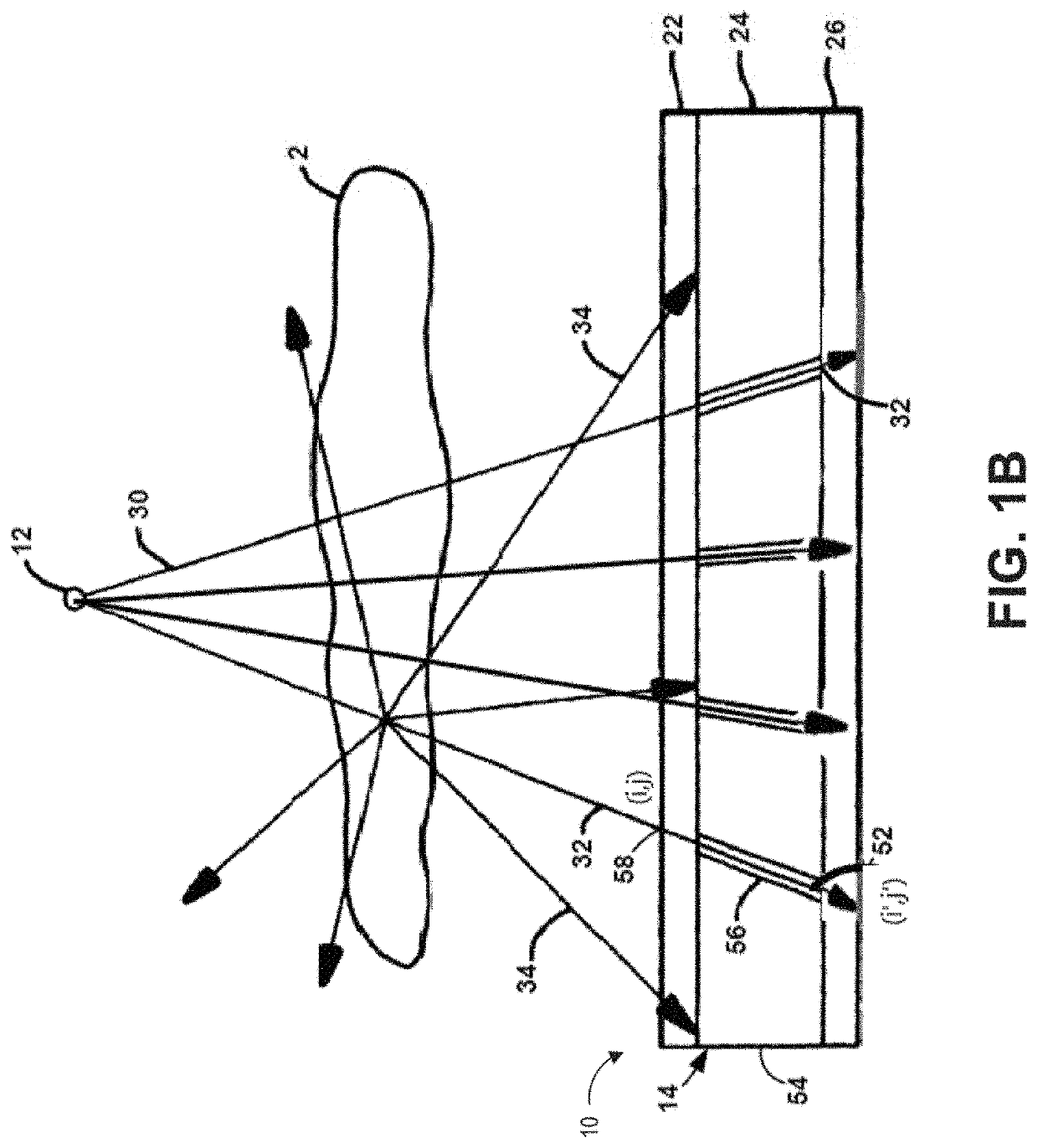
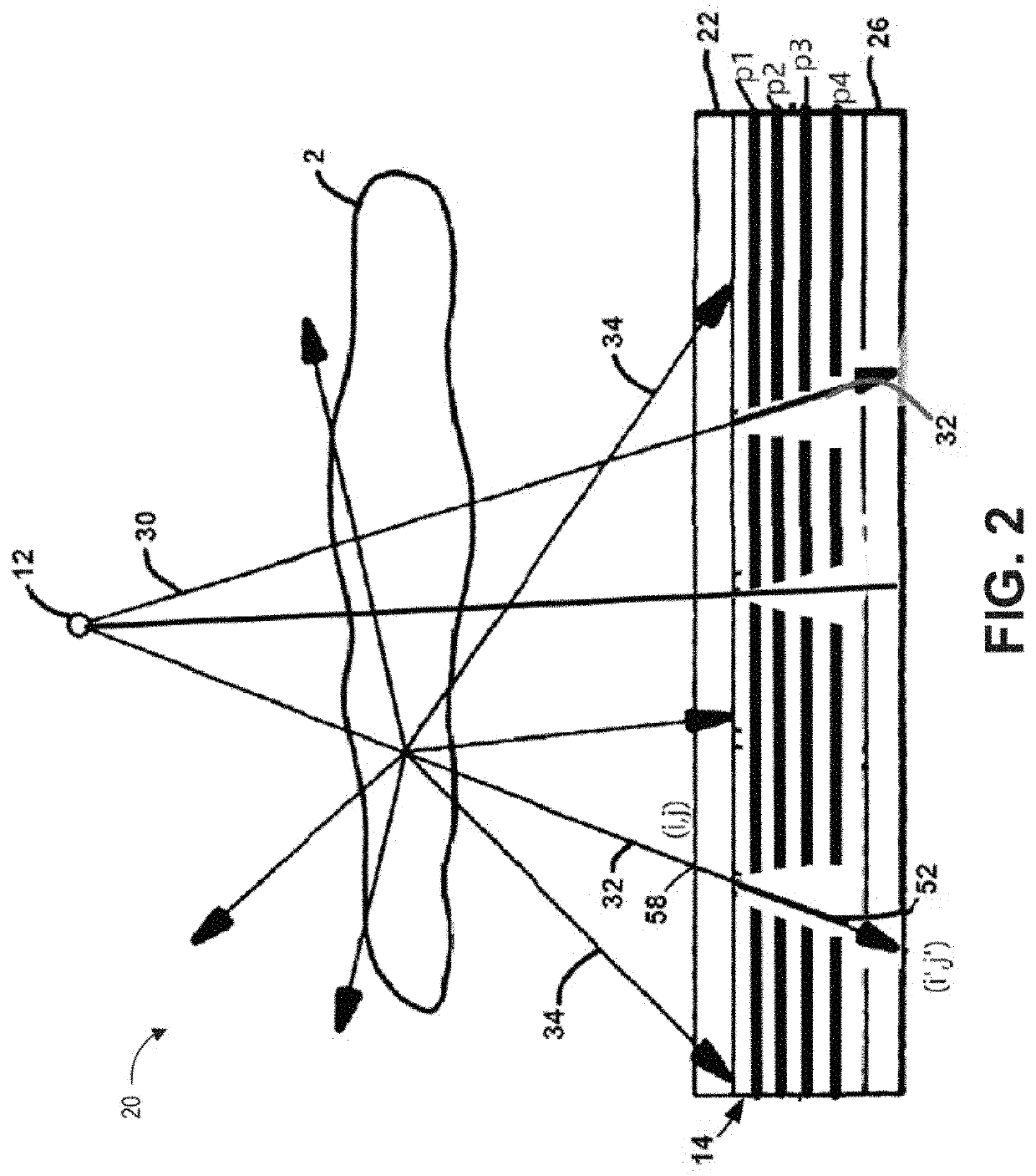
Apparatus and methods for x-ray imaging
PendingUS20210244374A1Enhance the imageIncrease speedTomosynthesisTomographyTwo dimensional detector3d image
An x-ray apparatus and method can improve x-ray imaging in a variety of ways. For example, the improve x-ray apparatus can reduce scatter from x-ray images acquired by two-dimensional detectors. An improved 2D x-ray apparatus can provide 3D imaging for medical and / or industrial applications. An improved 2D x-ray apparatus and method can produce separate material imaging, and composition analysis for characterization and correlation of image, densitometry, and composition information of individual component or individual material within a single subject. Non-rotational 3D microscopy, combining 2D or 3D full field x-ray imaging and high resolution 2D or 3D x-ray microscopy or spectral absorptiometry and spectroscopy can achieve a higher resolution and wider field of view in x-ray imaging and quantitative analysis in 3D and real time. The x-ray apparatus can improve tracking and / or surgical guidance in time and / or space.
Owner:XENSELAB LLC
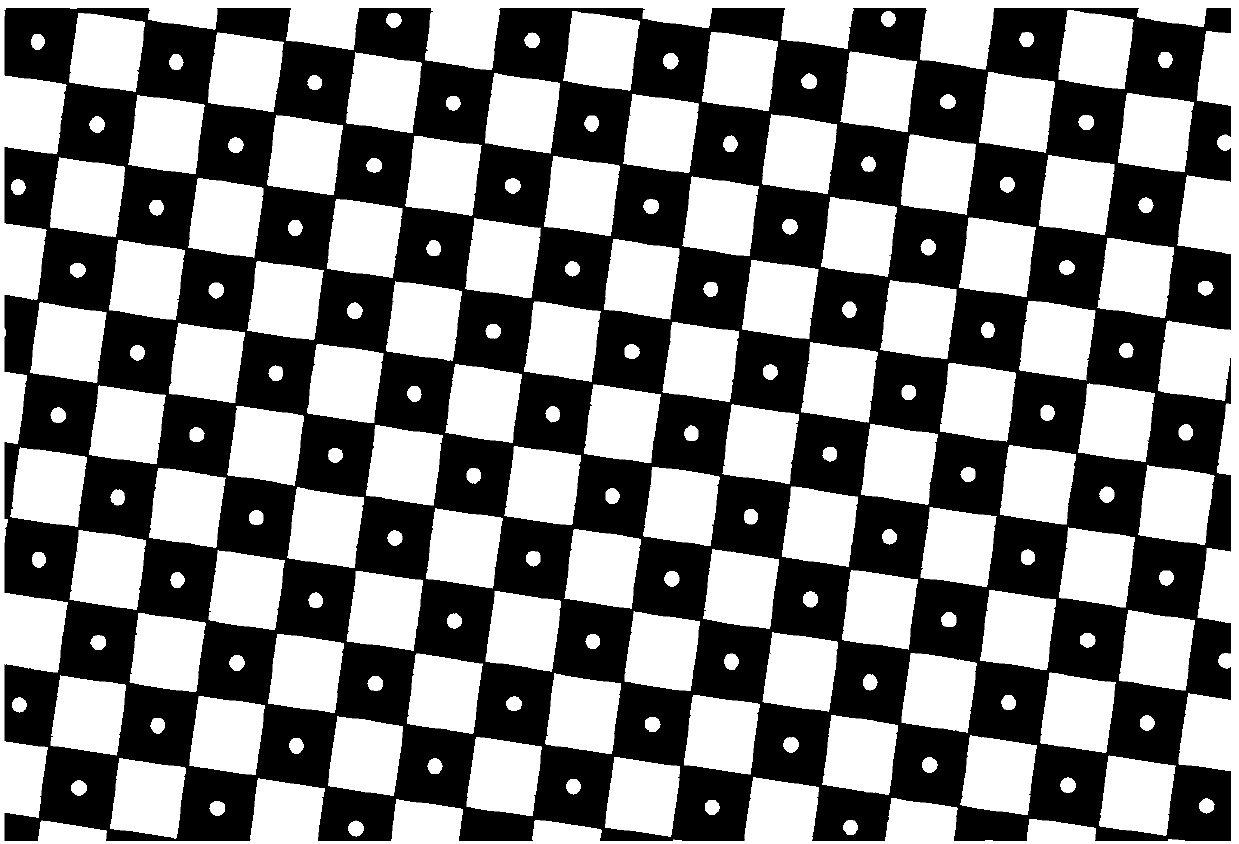
Calibration method of surface structured light three-dimensional measurement system
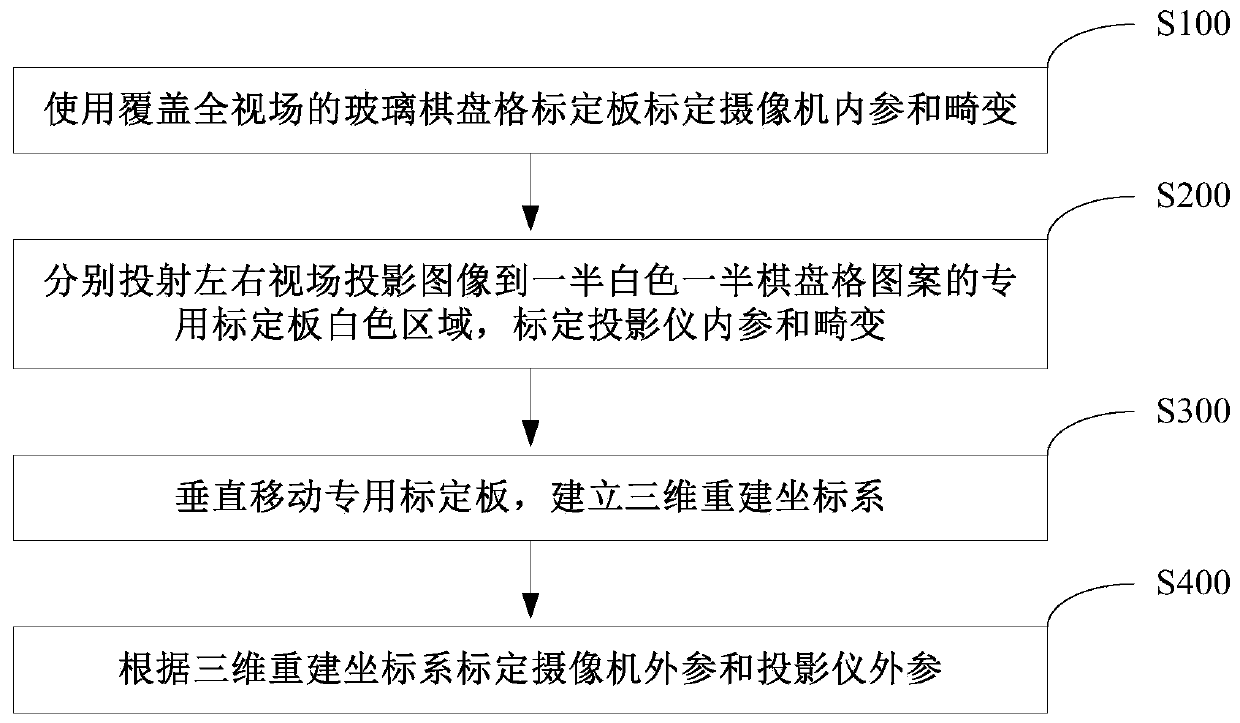
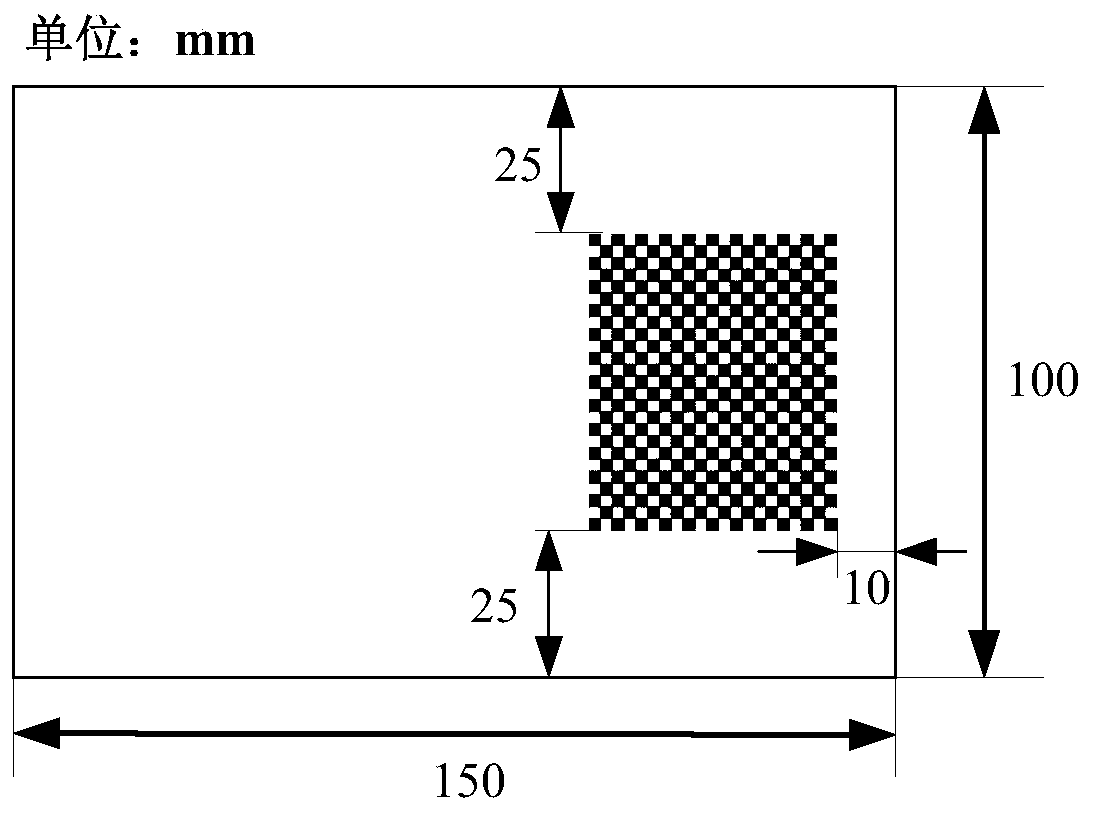
ActiveCN111028297AAvoid Error Coupling InterferenceImprove calibration accuracyImage analysisUsing optical meansComputer graphics (images)Projection image
The invention discloses a calibration method of a surface structured light three-dimensional measurement system. The method comprises the following steps: calibrating internal parameters and distortion of a camera by using a glass checkerboard calibration plate covering a full field of view; respectively projecting left and right field-of-view projection images to a special calibration board whitearea of a semi-white semi-checkerboard pattern, and calibrating the internal reference and distortion of the projector; vertically moving the special calibration plate, and establishing a three-dimensional reconstruction coordinate system; calibrating camera external parameters and projector external parameters according to the three-dimensional reconstruction coordinate system. According to thecalibration method provided by the invention, a special calibration board with half white and half checkerboard is designed; the three-dimensional reconstruction coordinate system is constructed in cooperation with the vertical lifting platform to calibrate the projector, the camera and the surface structured light system, camera calibration, projector calibration and system external parameter calibration are separated in the overall calibration scheme and do not depend on a structured light algorithm, coupling interference of various errors in the calibration process is avoided, and thereforethe calibration precision is greatly improved.
Owner:BEIJING LUSTER LIGHTTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com