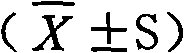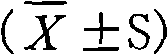Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
76 results about "Erythrocyte sedimentation rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
<ul><li>Abnormal results may include both high and low values:</li></ul><p>High values suggest infections, cancer, autoimmune diseases, Thyroid or kidney disorders, anemia or even pregnancy.</p><p>Low values infer to Leukocytosis, Congestive heart failure, lack of fibrinogen or low protein in blood, etc.</p><ul><li>Normal values are:</li></ul><p>Children - < 10 millimetres per hour</p><p>Adult female - < 20 millimetres per hour</p><p>Adult men - < 15 millimetres per hour</p><p>Elderly women - < 30 millimetres per hour</p><p>Elderly men - < 20 millimetres per hour</p>
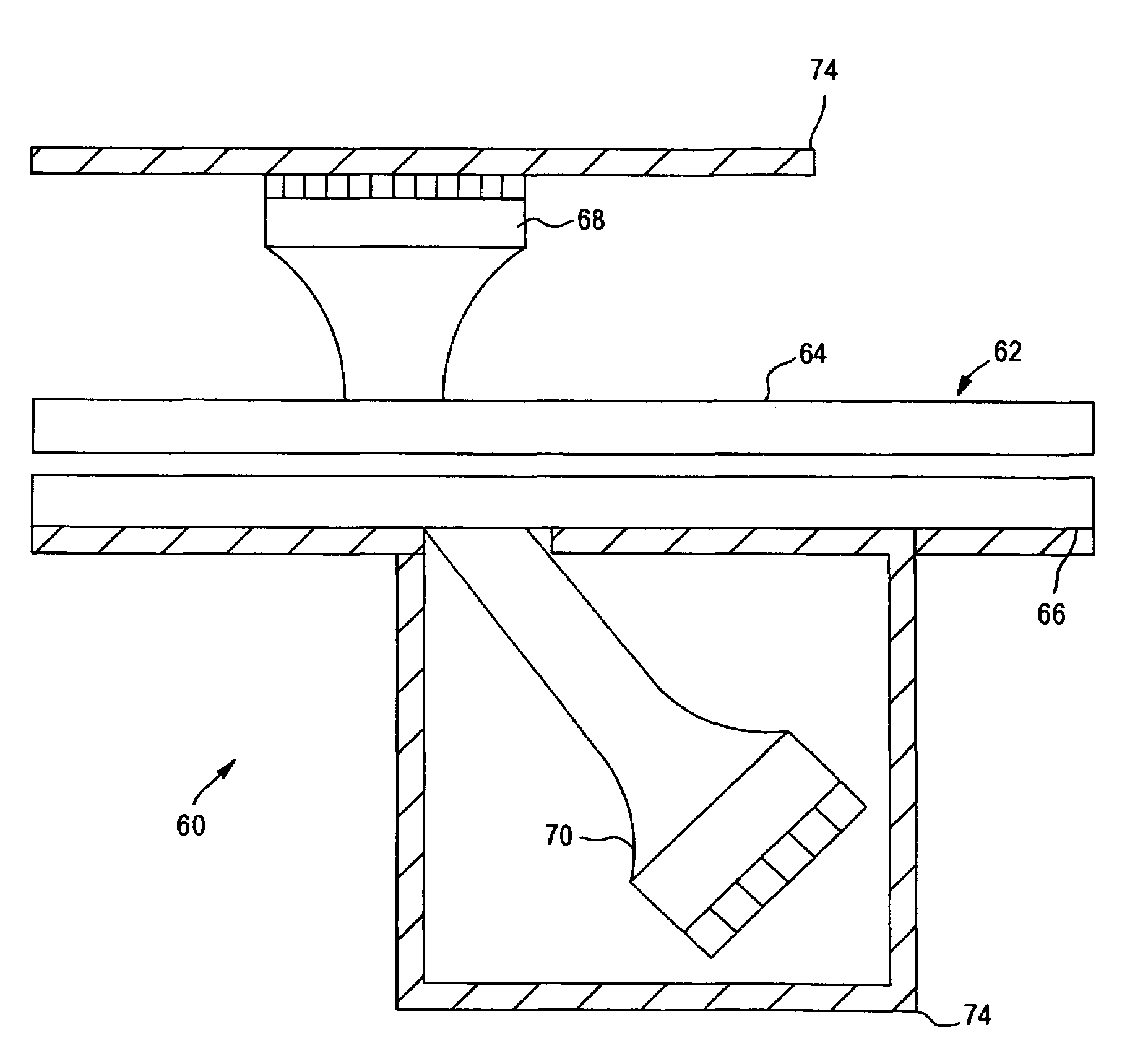
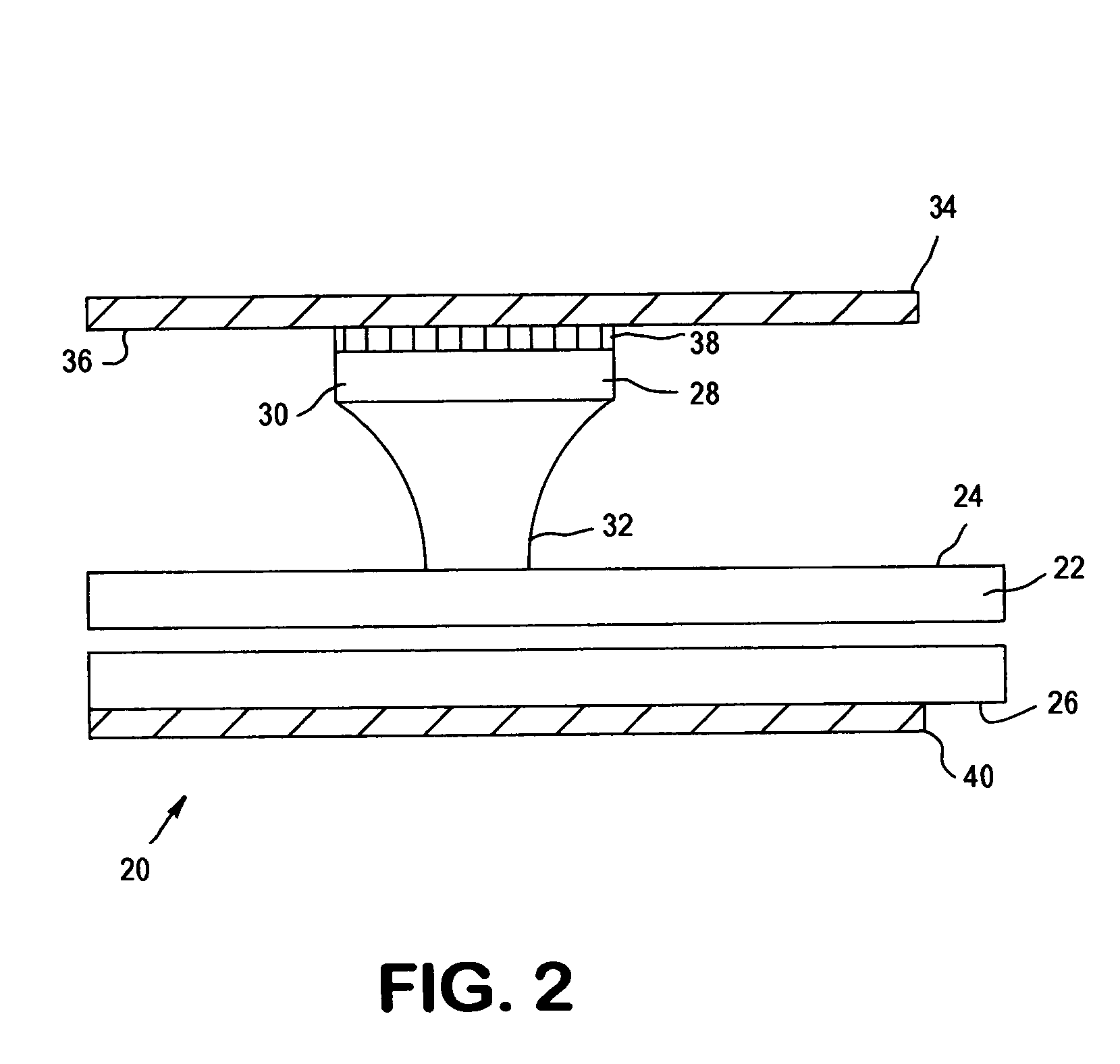
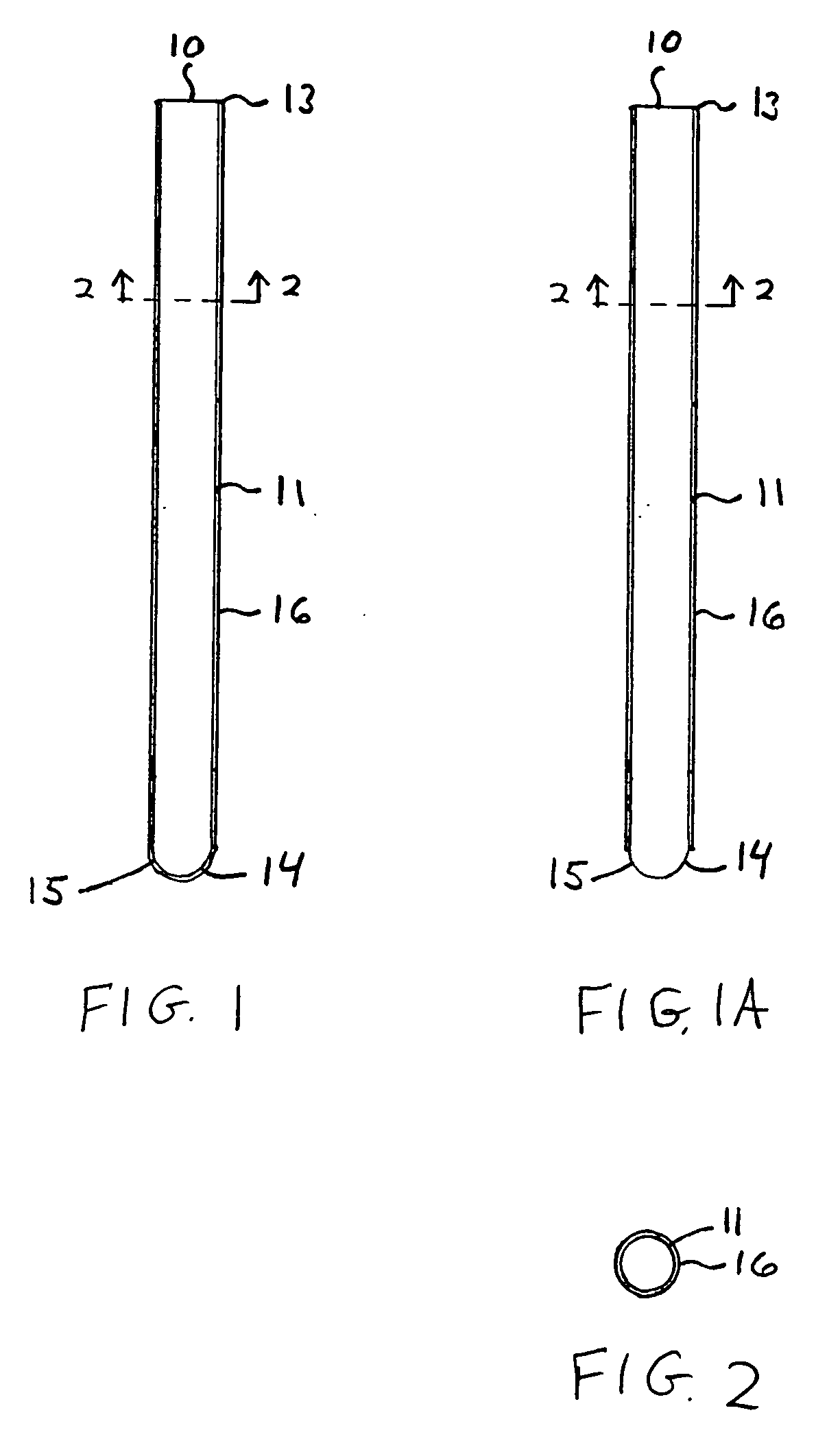
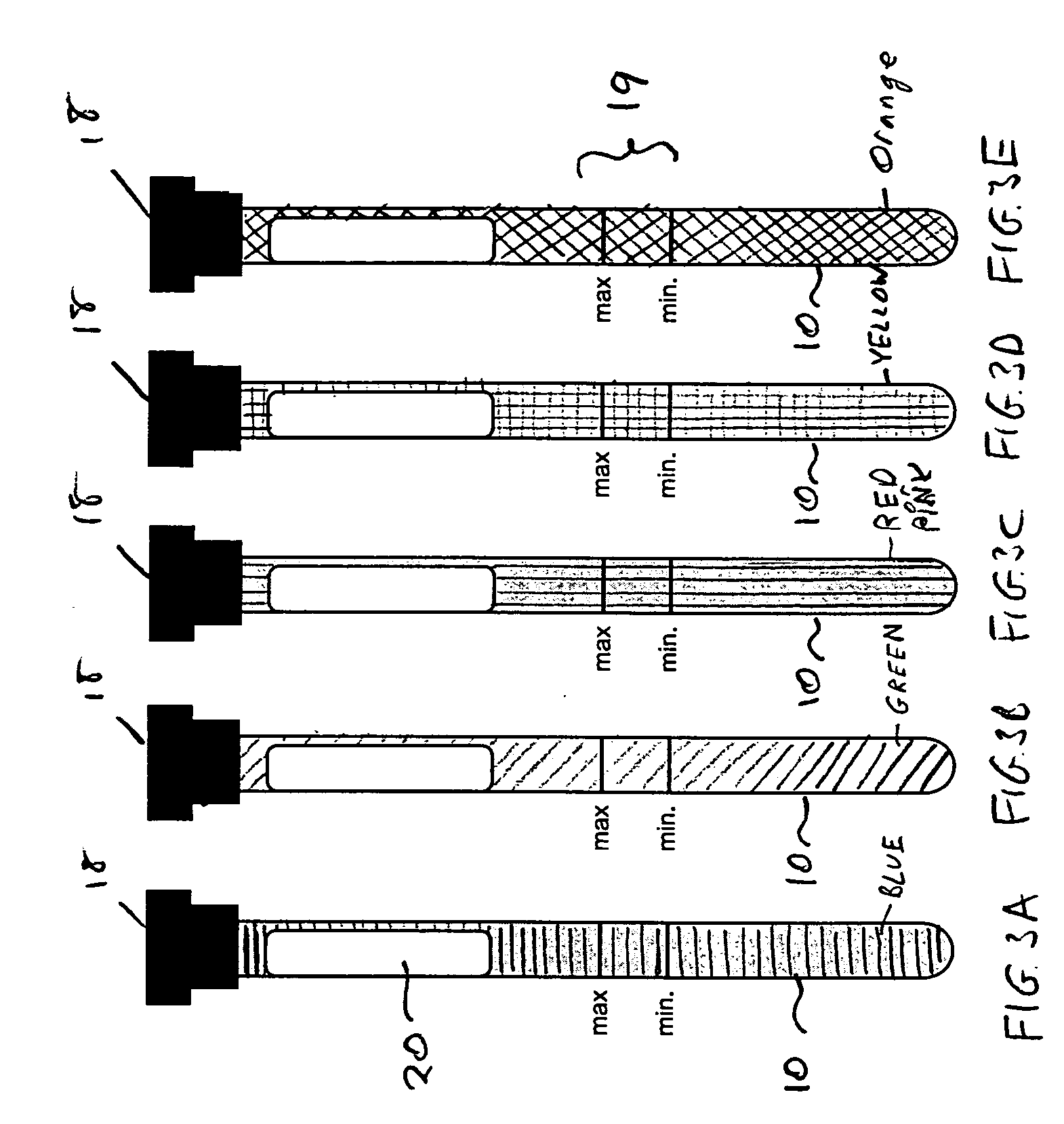
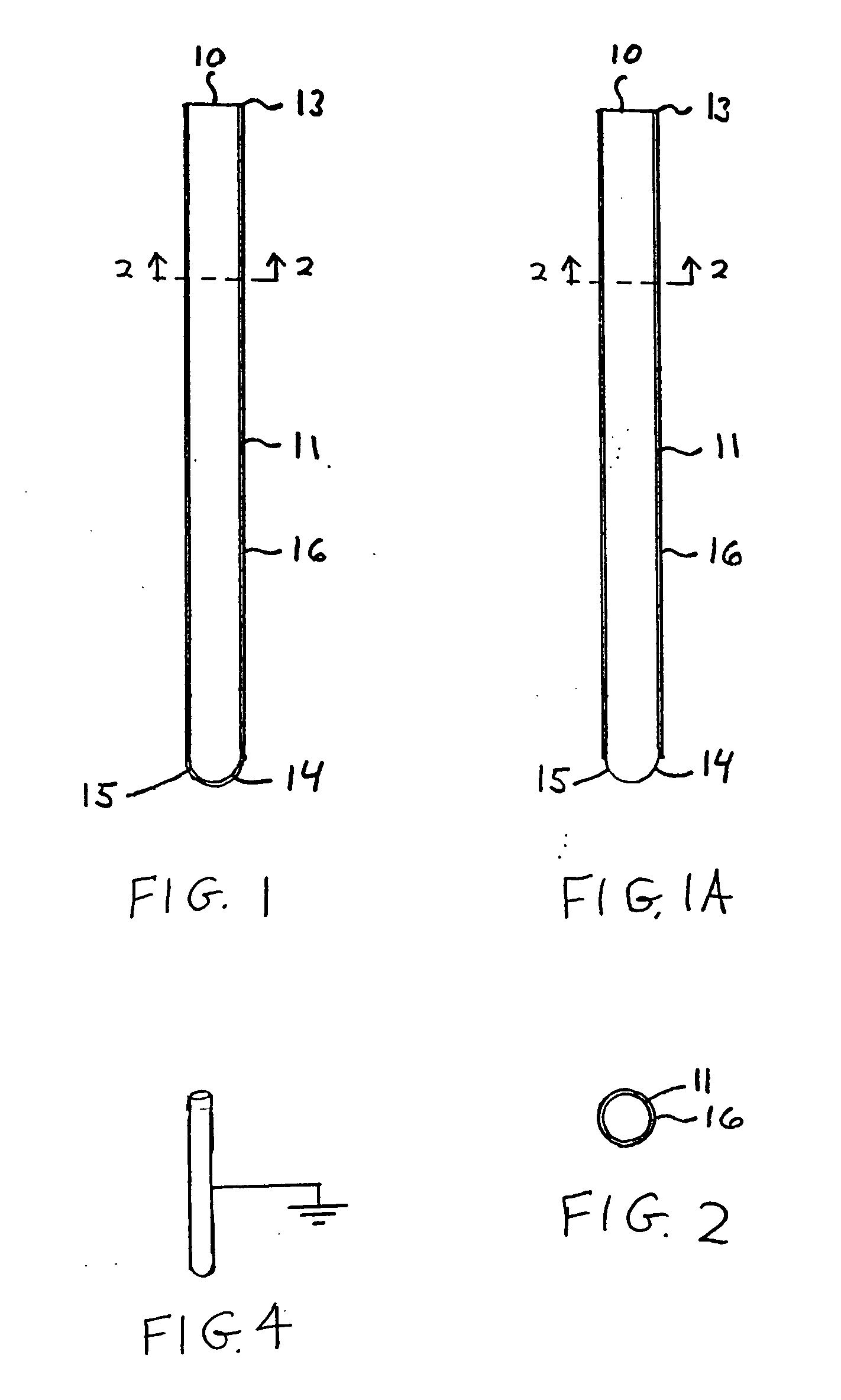
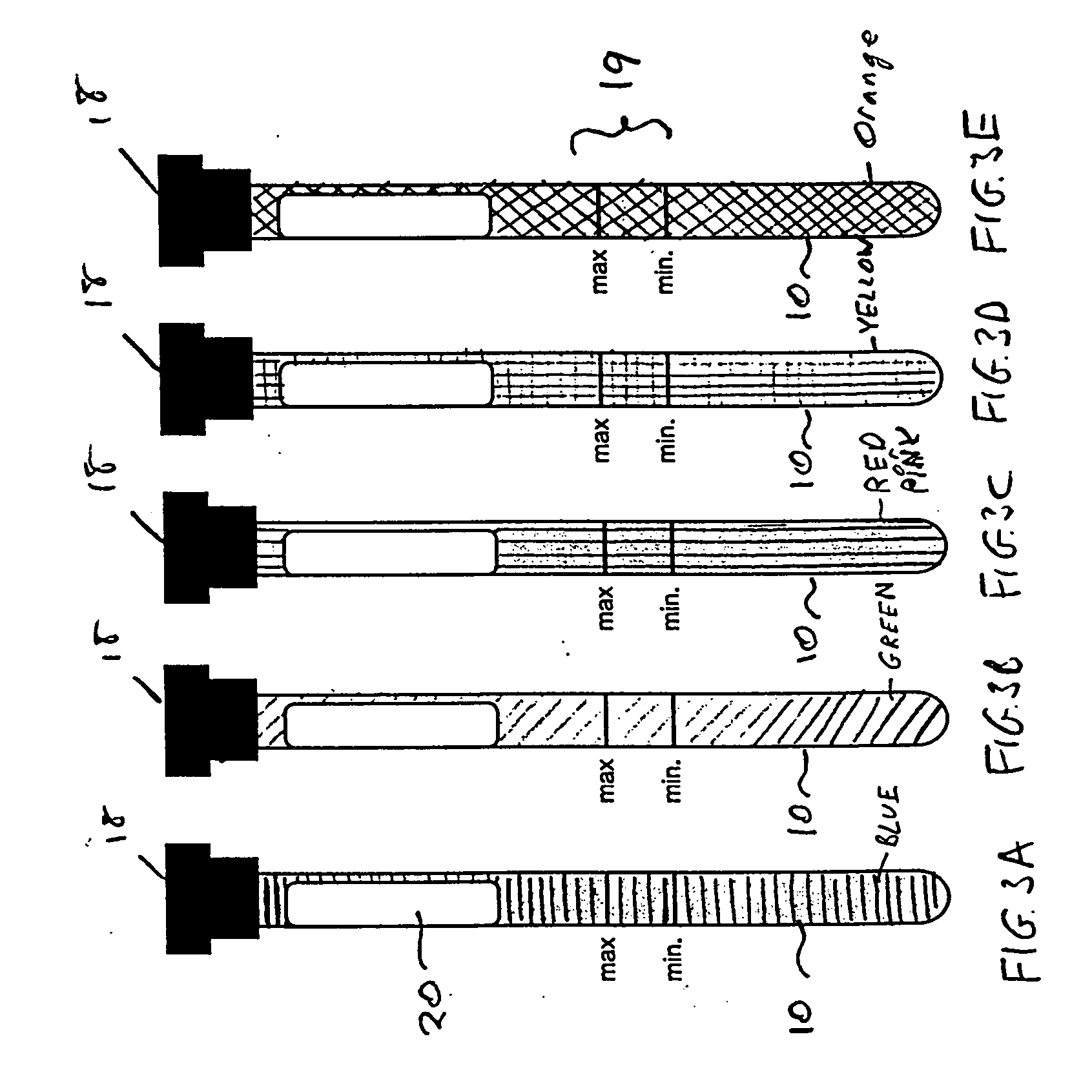
Apparatus and method for analyzing a liquid in a capillary tube of a hematology instrument
InactiveUS7207939B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesBlood capillaryHematology
An apparatus and method for determining the density and fluid-type of a fluid flowing in a capillary tube, the velocity and viscosity of a blood sample flowing in a capillary tube, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) of a blood sample after flow has been brought to an abrupt stop in a capillary tube, and / or the zeta sedimentation rate (ZSR) of a blood sample after flow has been brought to an abrupt stop in a capillary tube. These measurements are accomplished by directing a waveform pulse, such as an ultrasound pulse, at a pre-determined frequency transversely across the capillary tube and sample fluid, and by determining the flight of time of the pulse through the capillary tube and sample fluid and / or the Doppler shift of the echo signals reflecting off cells moving forwardly or transversely within a flowing, or stationary, blood sample.
Owner:COULTER INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
Glass test tube having protective outer shield
InactiveUS20060233675A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsLaboratory glasswaresPolyesterPlastic materials
An improved glass test tube is provided with a protective shield on the test tube's outer surface which protects the test tube from accidental breakage. The protective shield may be of a color which indicates that it has breakage protection. In one embodiment, the protective shield is provided by plastic material which is coated or sprayed on the outer surface of the glass test tube. In another embodiment, the protective shield is provided by one or more layers of wrapped sheet material, such as polyester film. The improved glass test tube is particularly useful in automatic analyzers that measure erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
Owner:CLINICAL DATA
Method and apparatus for measuring sedimentation rate of sediments in liquid sample
InactiveUS6336358B1Short timeAccurate measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansSedimentation analysisLine sensorBlood sampling
A measuring technology of sedimentation rate of sediments in a liquid sample capable of measuring, for example, the sedimentation rate of erythrocytes in a patient requiring an urgent medical treatment in about ¼ of the time needed in the conventional measuring method, and also capable of measuring the sedimentation rate of erythrocytes in an infant limited in the blood sampling volume. A test container filled with a liquid sample is inclined and held at a specific inclination angle, light is projected to this test container, the light passing through the test container is electrically detected by a line sensor or the like, the liquid level of the supernatant in the liquid sample and the position of the boundary of the supernatant and sediments are calculated to obtained the depth of the sediments, and the sedimentation rate of the sediments is calculated from the depth of the sediments and the measuring time.
Owner:SEFA TECH
Coarse food mixing bean flour
InactiveCN101390585AMeet special requirementsDough treatmentFood preparationBiotechnologyESR - Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
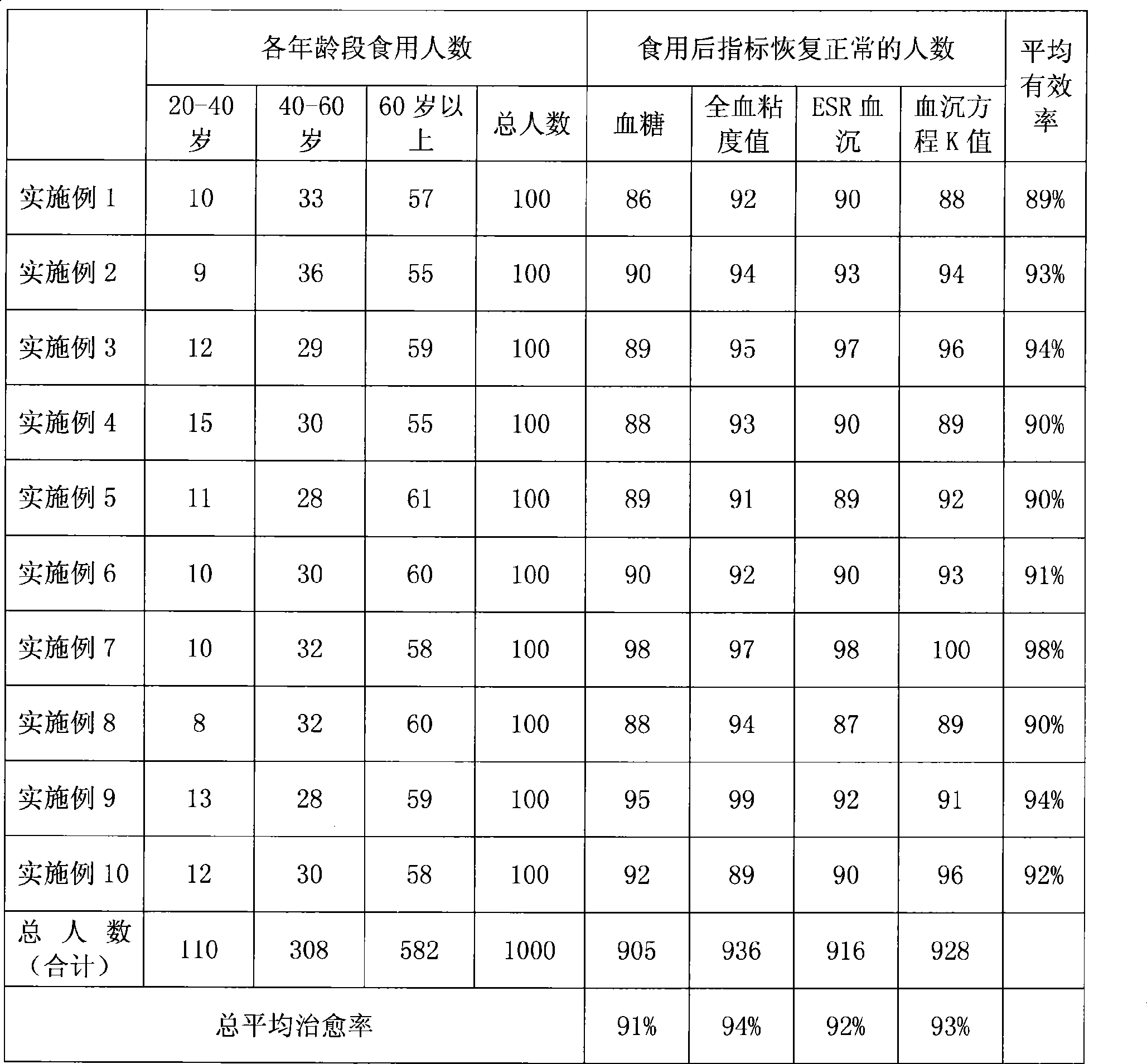
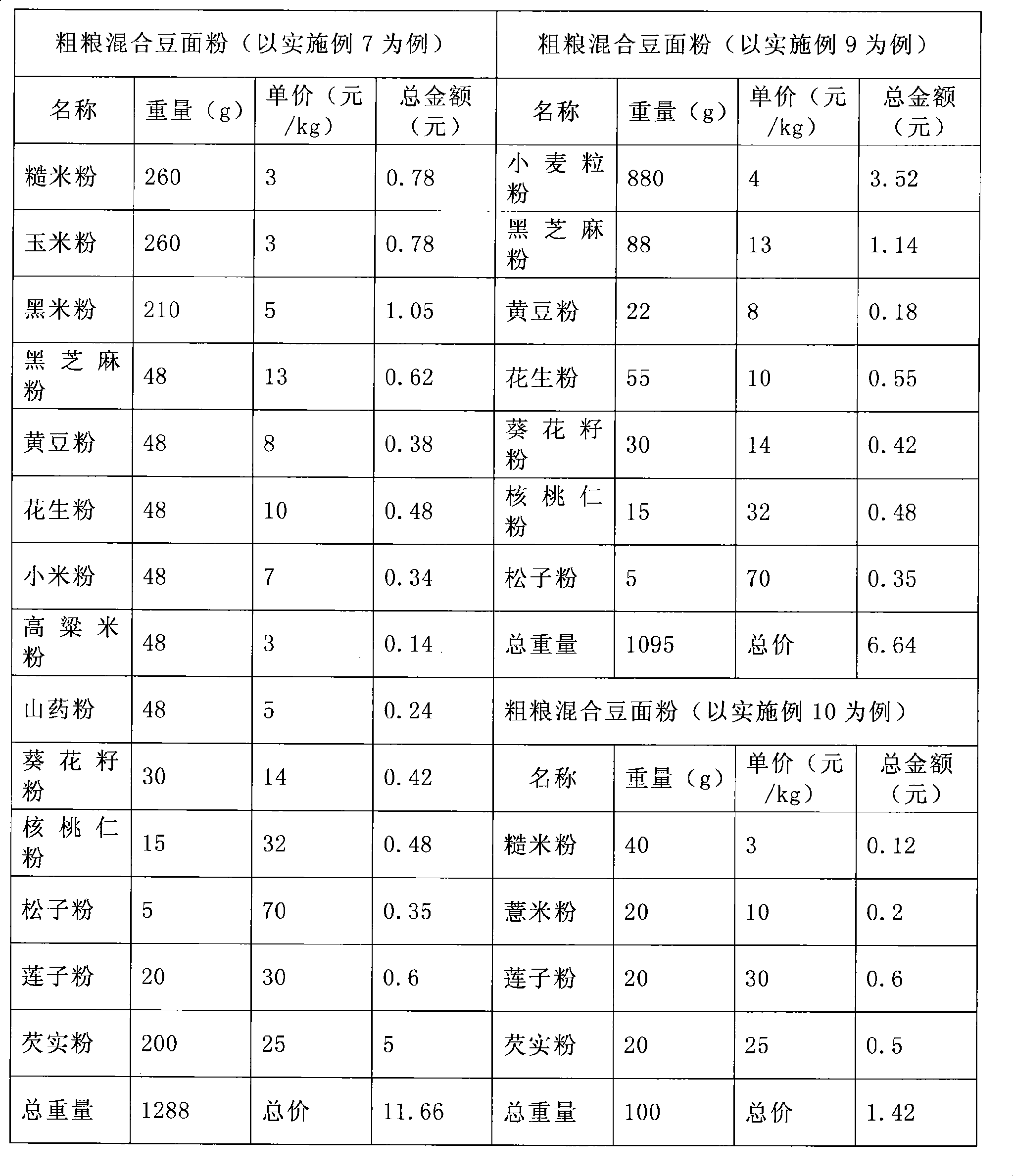
The invention relates to a kind of flour, in particular to a coarse grain mixed bean flour, wherein, the mixed bean flour comprises brown rice flour, corn flour, black rice flour, black sesame powder, soybean powder, peanut powder, millet flour, sorghum flour, potato powder, sunflower seed powder, walnut powder, pine nut powder, lotus seed powder, and Gordon euryale seed powder; or the mixed bean flour comprises wheat kernel powder, black sesame powder, soybean flour, peanut flour, sunflower seed powder, walnut powder and pine nut powder; or the mixed bean flour comprises brown rice flour, pearl barley powder, lotus seed powder and Gordon euryale seed powder. The preparation method of the coarse grain mixed bean flour adds three processing procedures on the processing method of ordinary flour production, namely, stir-frying, weighing and mixing. The coarse grain mixed bean flour has good therapeutic effects on abnormal blood glucose, whole-blood viscosity, ESR erythrocyte sedimentation rate, erythrocyte sedimentation rate equation K and other indexes; besides, the raw materials of the mixed bean flour are reasonably matched and low in price as well as rich in taste; the coarse grain mixed bean flour can be consumed by people of various ages and is an ideal product to replace the existing flour made of single material.
Owner:王斌
Glass test tube having protective outer shield
InactiveUS20060233676A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsLaboratory glasswaresPolyesterPlastic materials
An improved test tube with a glass inner surface, layer, or lining, and a protective outer shield (or layer) of a material that protects the test tube from accidental breakage. The protective shield may be of a color which indicates that it has breakage protection. In one embodiment, the protective shield is provided by plastic material which is coated or sprayed on the outer surface of the glass test tube. In another embodiment, the protective shield is provided by one or more layers of wrapped sheet material, such as polyester film. In a further embodiment, a glass tube is inserted into a plastic tube to provide such glass tube with breakage protection. The improved test tube is particularly useful in automatic analyzers that measure erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
Owner:CLINICAL DATA
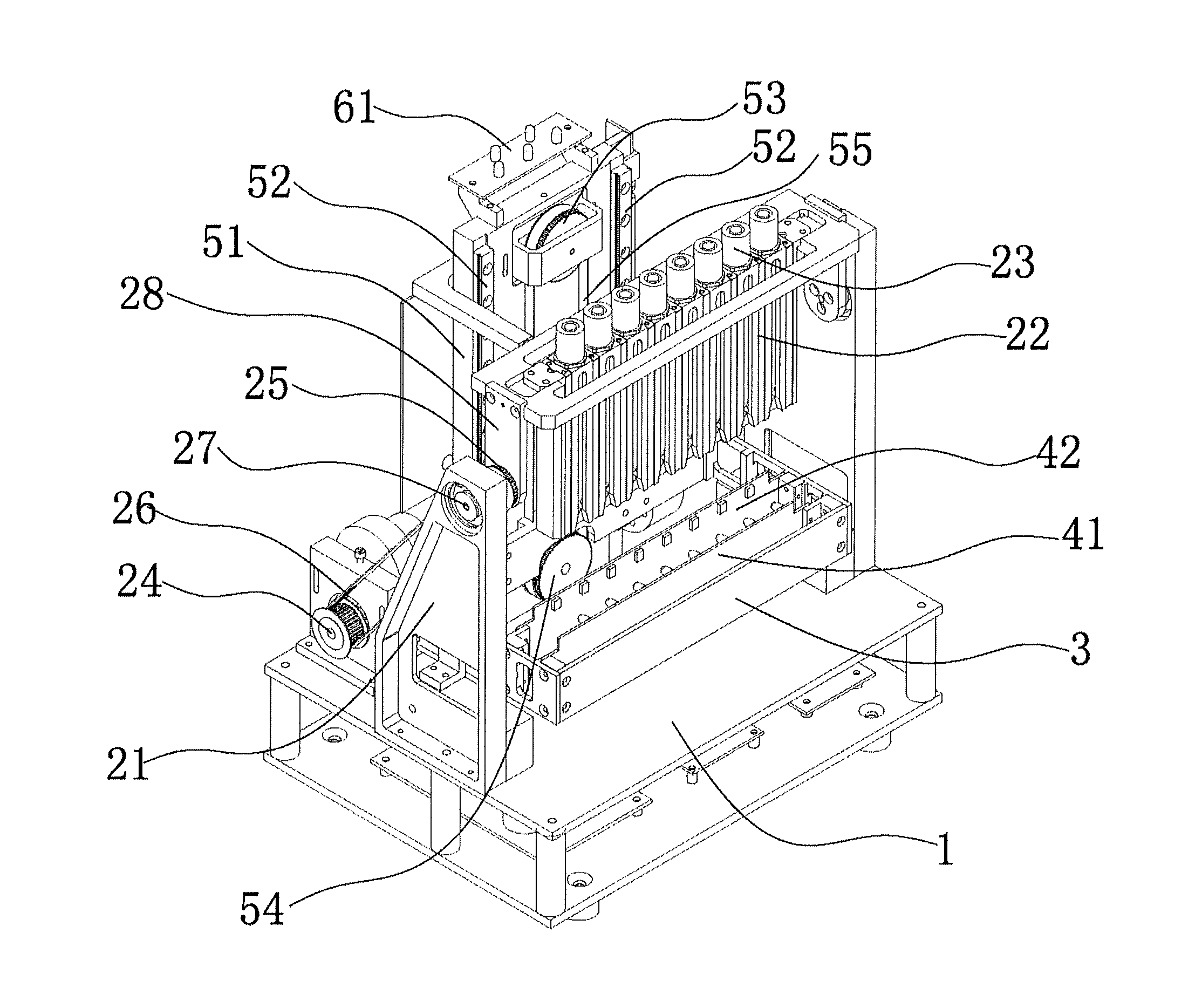
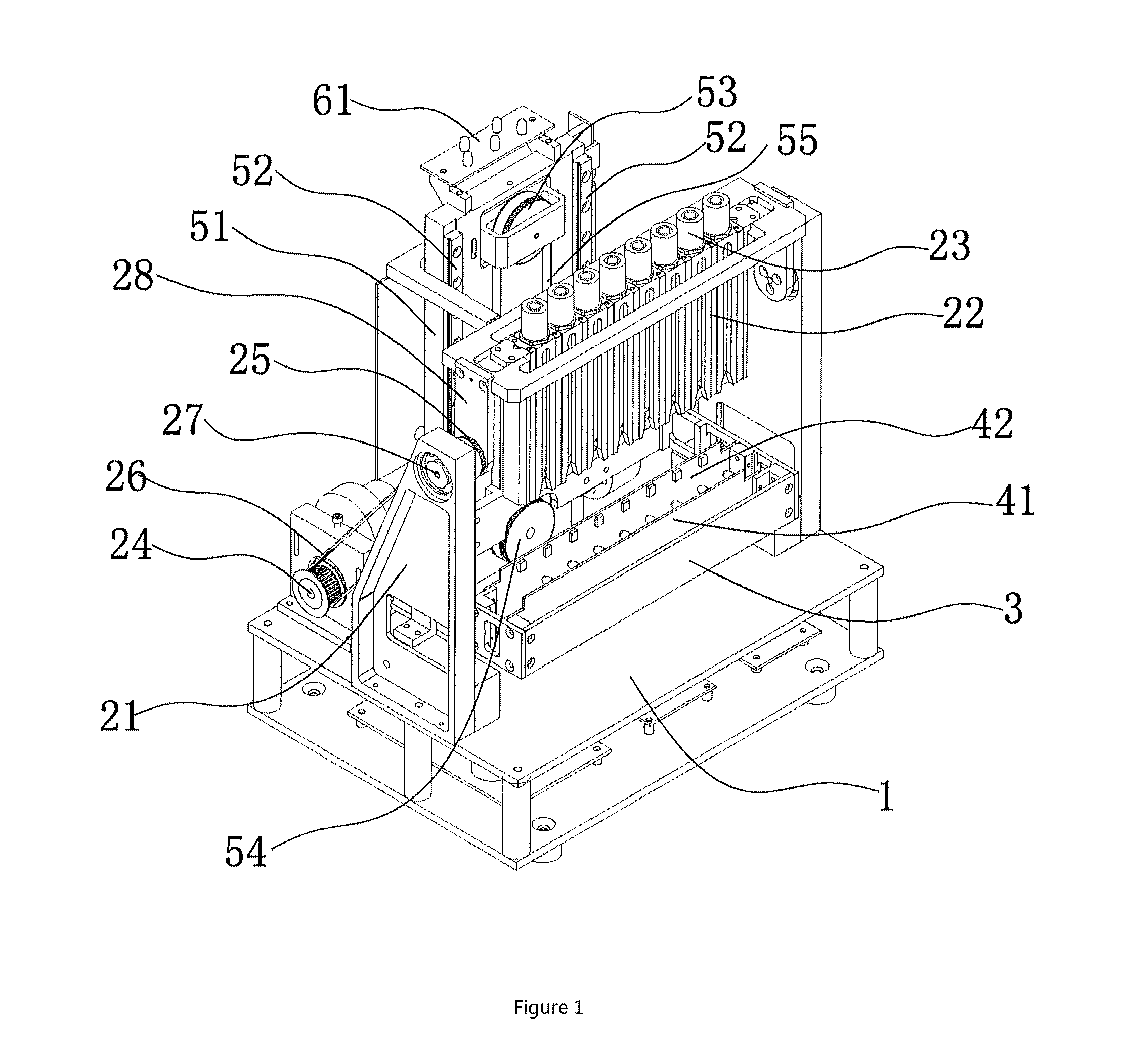
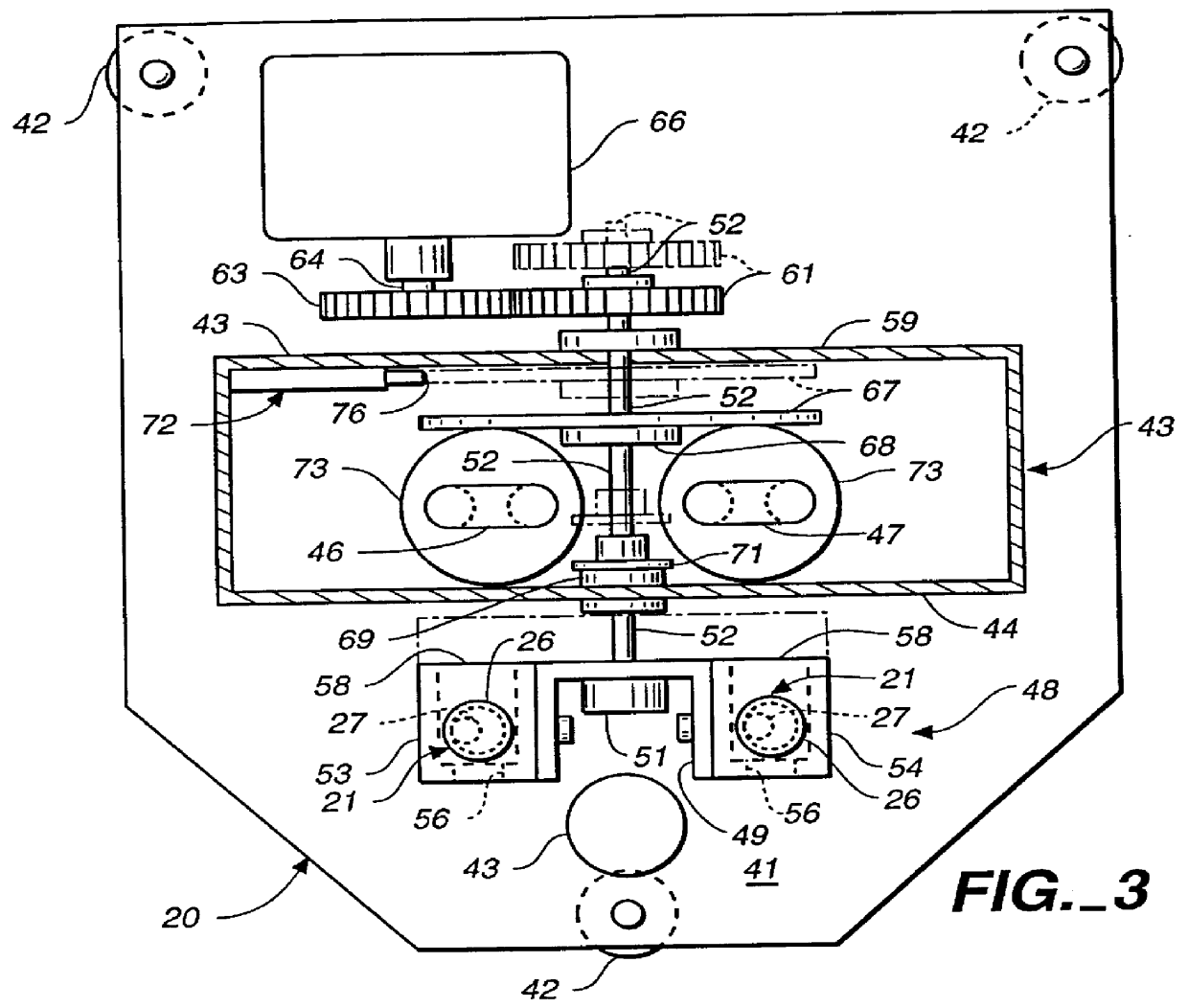
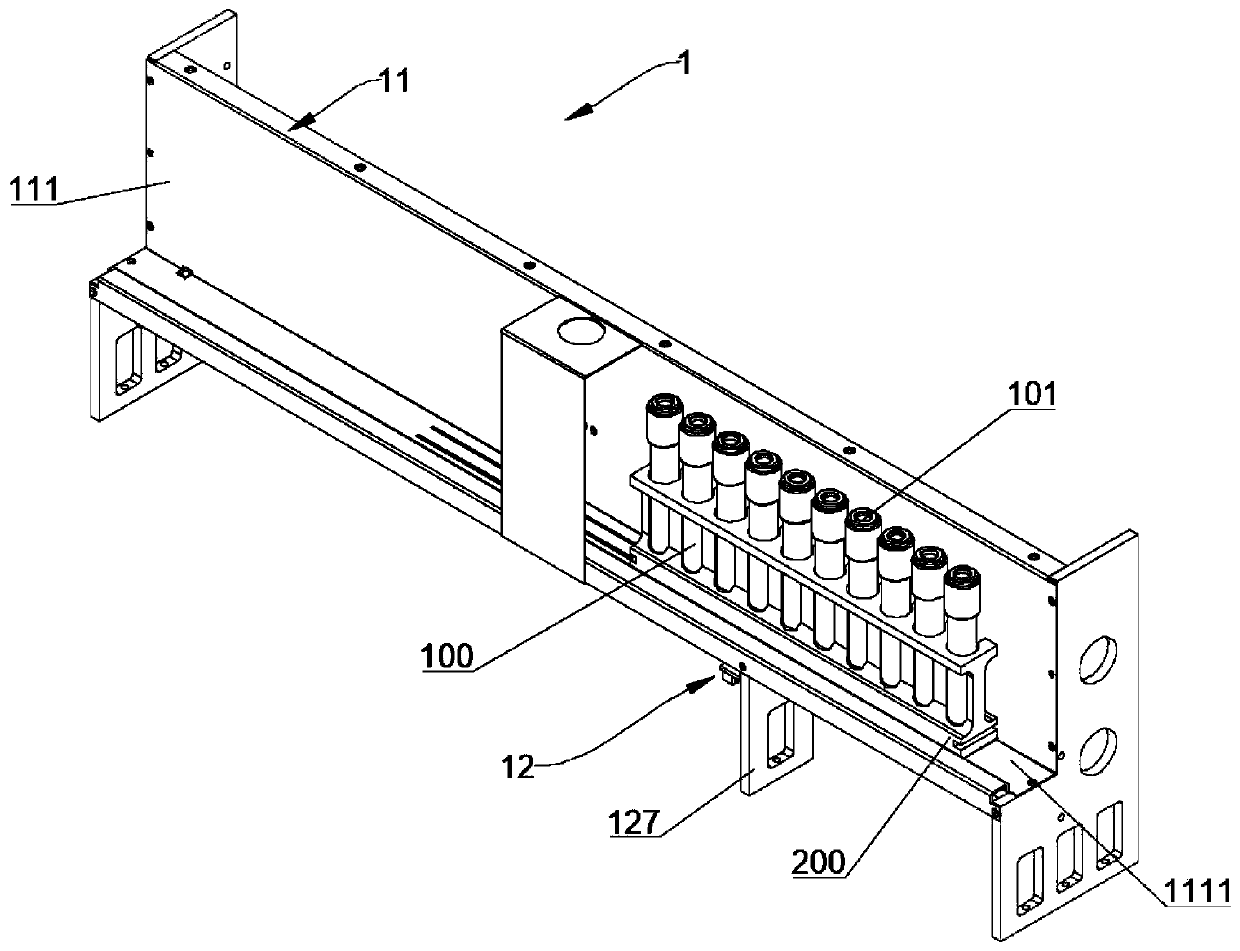
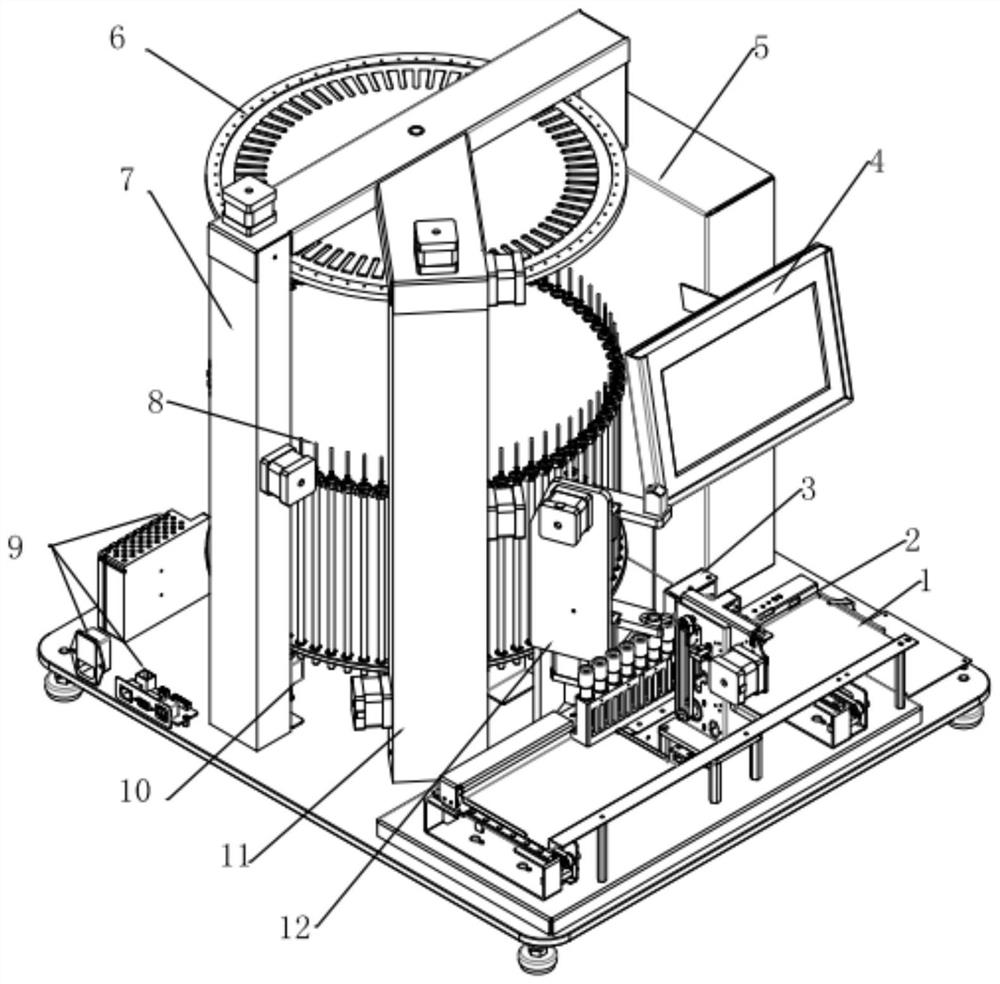
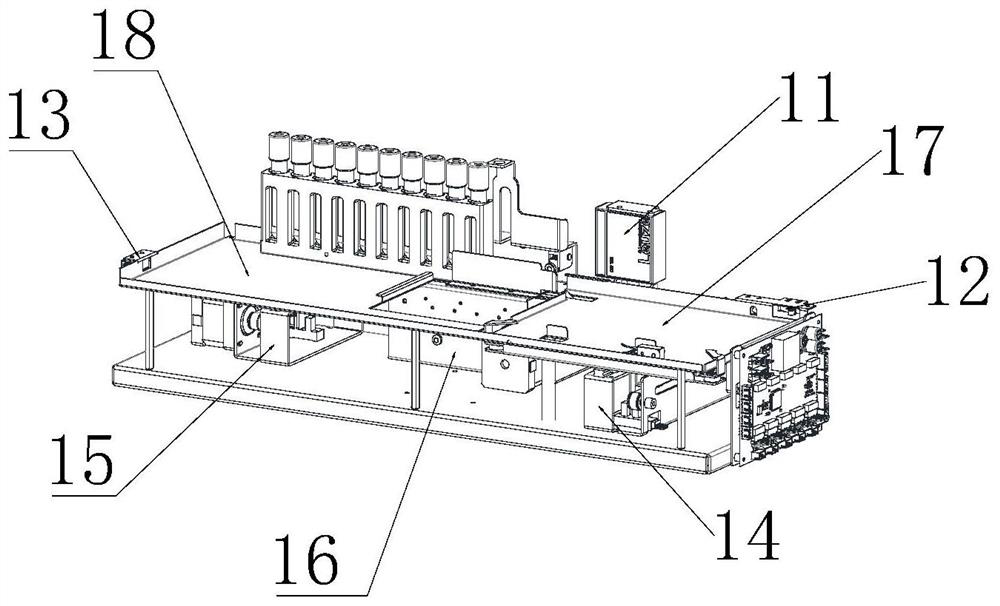
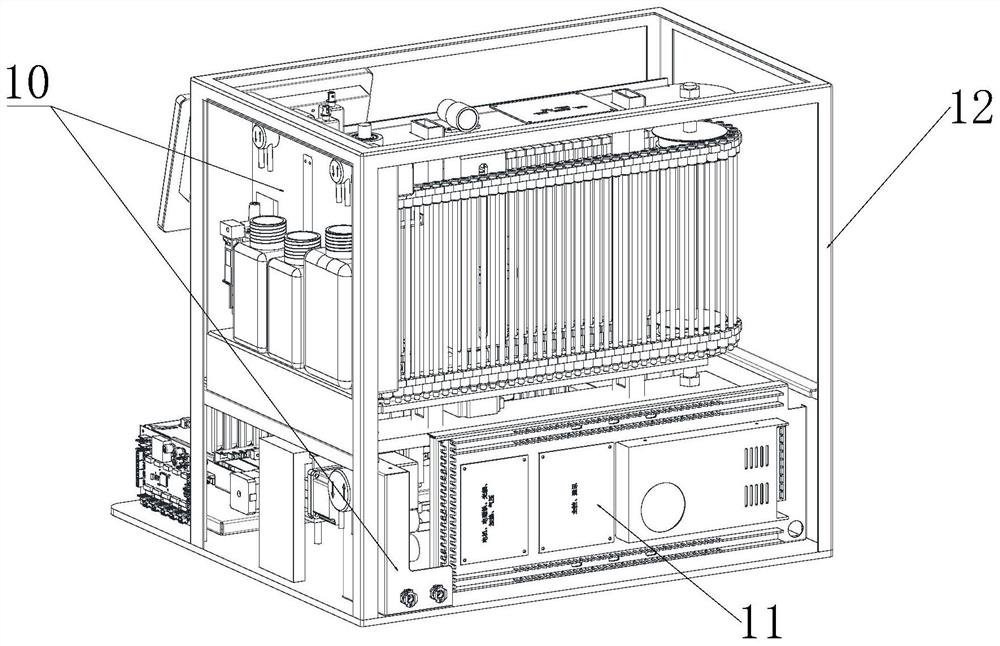
Full-automatic erythrocyte sedimentation rate analysis meter and detecting method thereof
ActiveUS20150268148A1Quickly and accurately read the sedimentation informationReduce laborRotating receptacle mixersRadiation pyrometryEngineeringTest tube
The invention provides a full-automatic erythrocyte sedimentation rate analyzer, which comprises a base as well as a blending device and a detecting device mounted on the base, wherein the blending device comprises a sample rack, a sample rack bracket and a rotating device; the sample rack bracket is arranged on the base, and is connected to the sample rack through a rotating shaft; more than one test tube rack is arranged on the sample rack; the rotating device is connected to the rotating shaft, and drives the rotating shaft to rotationally drive the sample rack to turn over up and down; a plurality of holes are arranged in each test tube rack; a fixing device is arranged in the hole, and used for placing and fixing a closed container containing samples; the detecting device comprises a guide device, a driving device, infrared transmitting and receiving devices having the same quantity as that of the test tube racks, and a mounting rack; the driving device drives the mounting rack to move up and down along the guide device; the mounting rack drives the infrared transmitting and receiving devices to move; the closed containers containing the samples are located on moving paths of the infrared transmitting and receiving devices; and infrared rays penetrate through the closed containers to realize detecting.
Owner:SHENZHEN YHLO BIOTECH
Traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating subacute thyroiditis and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103099902AImprove clinical symptoms and signsLow recurrence rateAntiviralsUnknown materialsDrug withdrawalClinical study
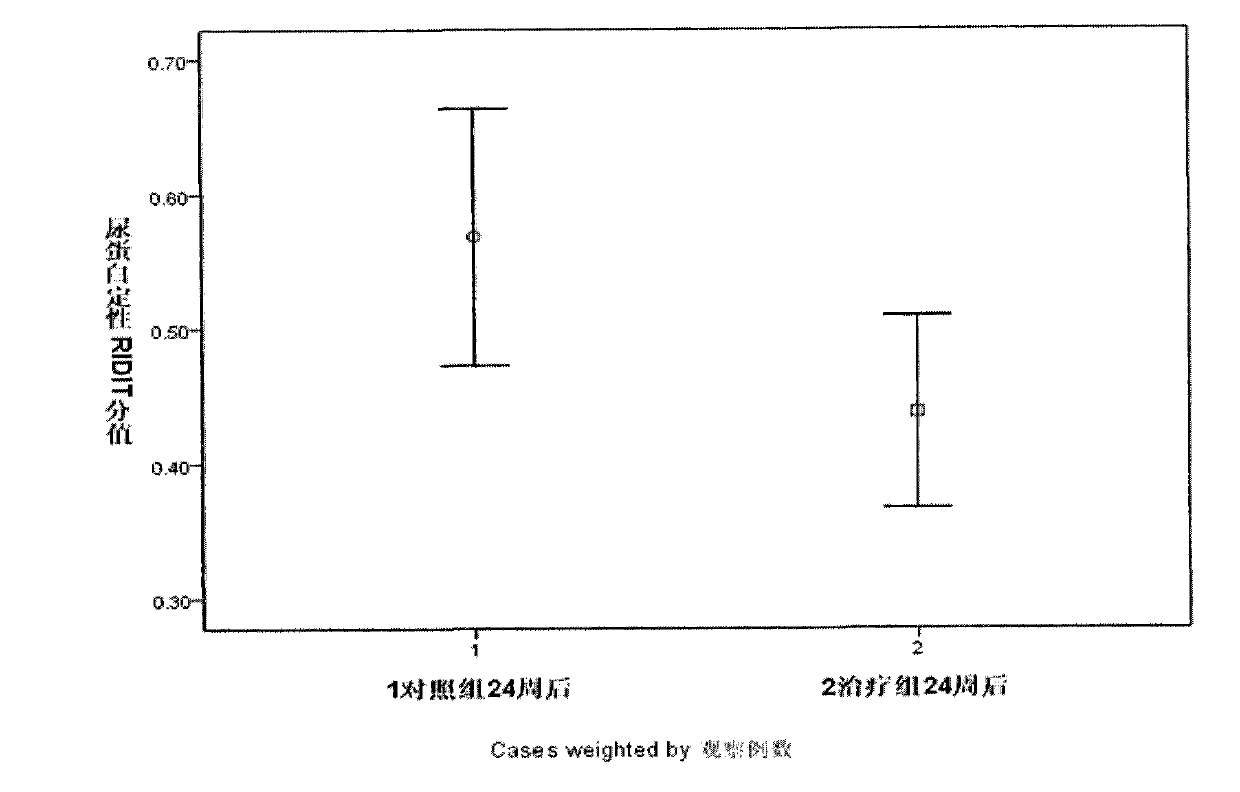
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating subacute thyroiditis. The composition is a preparation prepared from the following raw materials by weight: 15-30 parts of hedyotis diffusa, 9-15 parts of honeysuckle, 15-30 parts of dandelion, 15-30 parts of Chinese violet, 9-15 parts of root of common peony, 9-15 parts of radix scrophulariae, 9-15 parts of peach kernel, 9-15 parts of baked turtle shell and 15-30 parts of sweet wormwood. According to clinical study on the treatment of subacute thyroiditis, the traditional Chinese medicine composition provided by the invention has total effective rate of 93.34%, which is significantly better than 73.33% of a prednisone group, and can effectively reduce erythrocyte sedimentation rate and CRP of subacute thyroiditis patients, and effectively improve clinical symptoms of the patients; although the cooling time, improvement time of neck pain and regression time of neck tenderness are longer than those of the prednisone group, the goiter or nodule disappearance time shows no obvious difference from those of the prednisone group; relapse rate after drug withdrawal is 3.33%, which is significantly lower than 20% of the prednisone group; and the composition has little adverse reaction, which is significantly lower than that of the prednisone group. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the traditional Chinese medicine composition granules.
Owner:LONGHUA HOSPITAL SHANGHAI UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
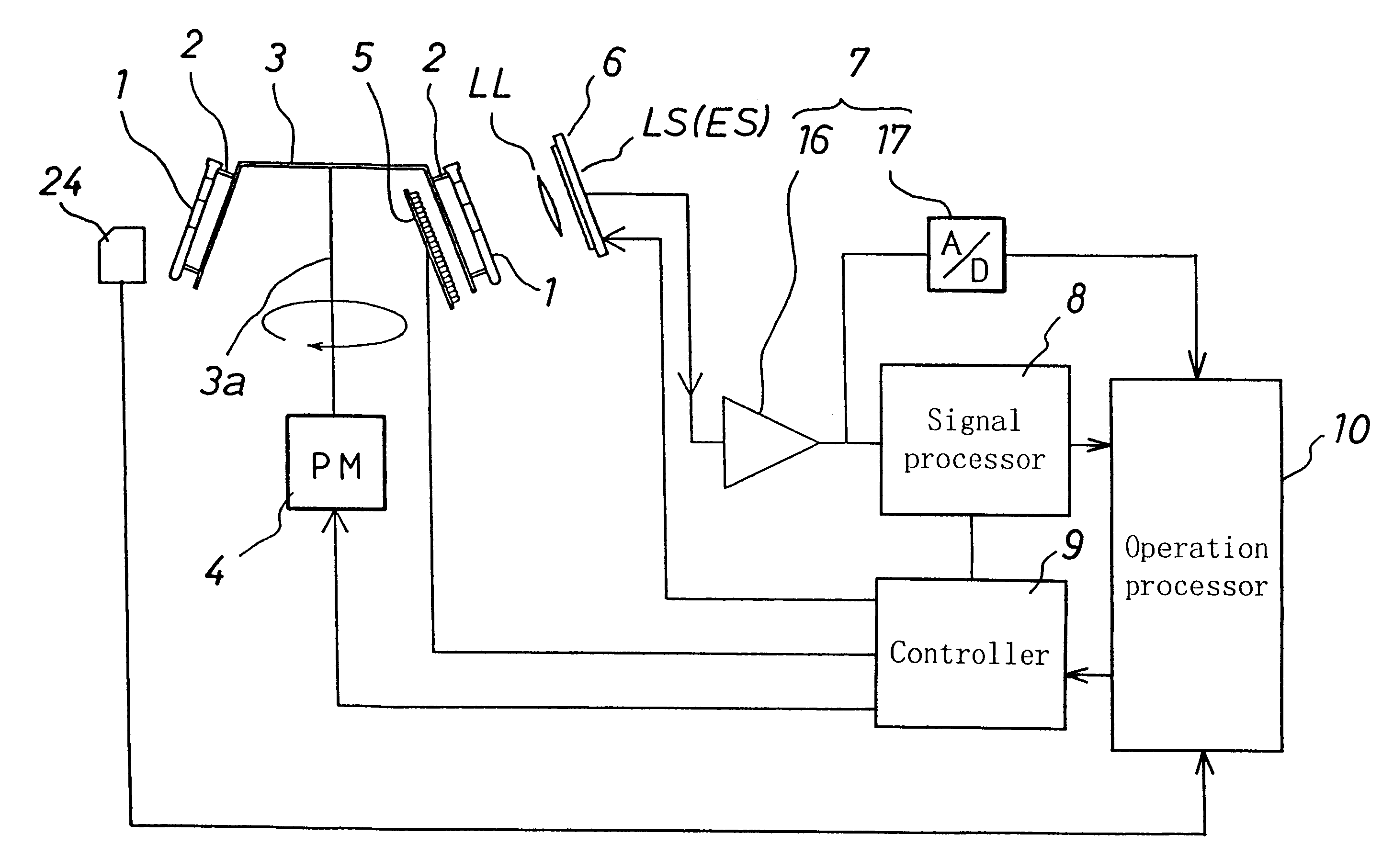
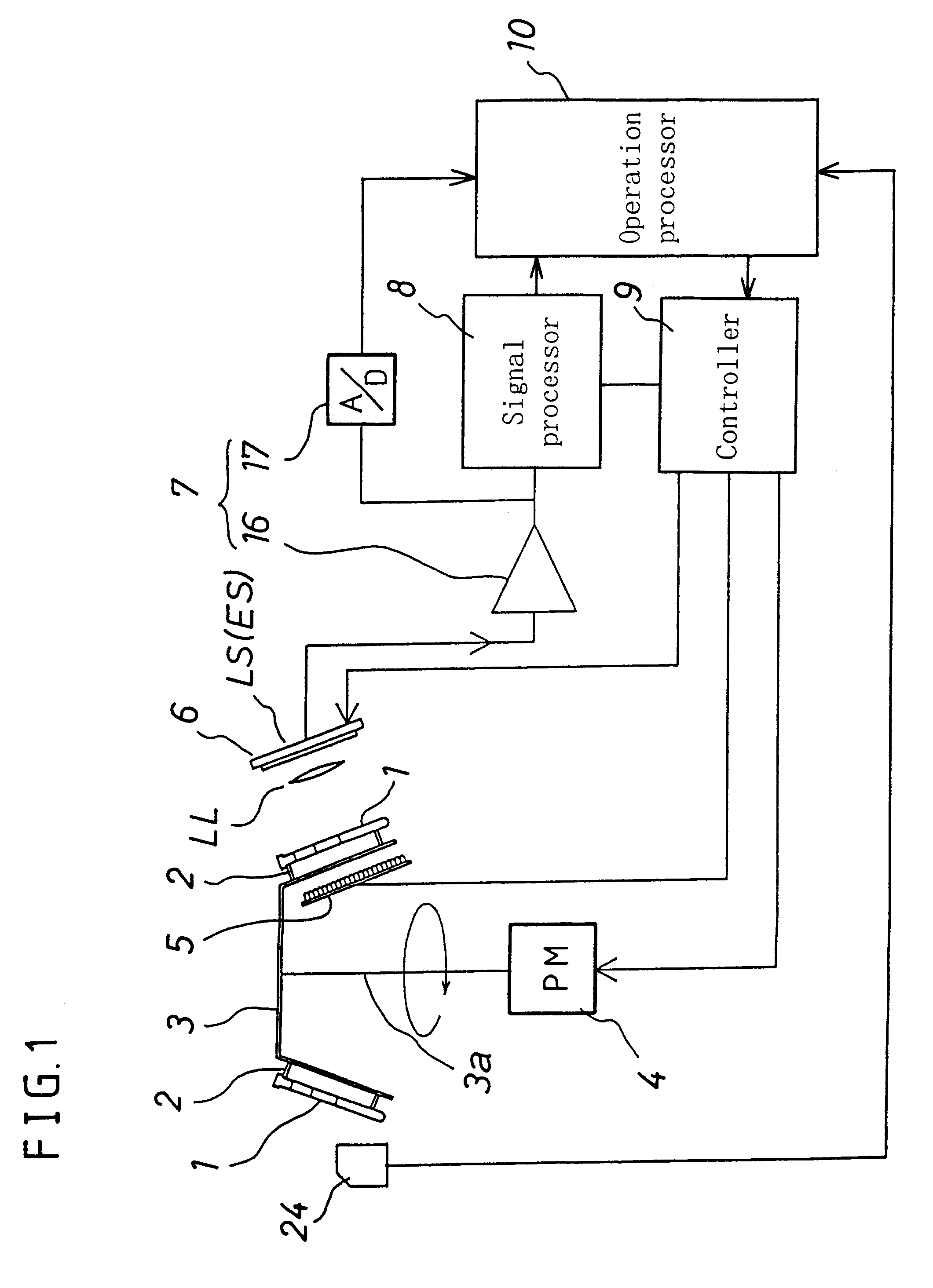
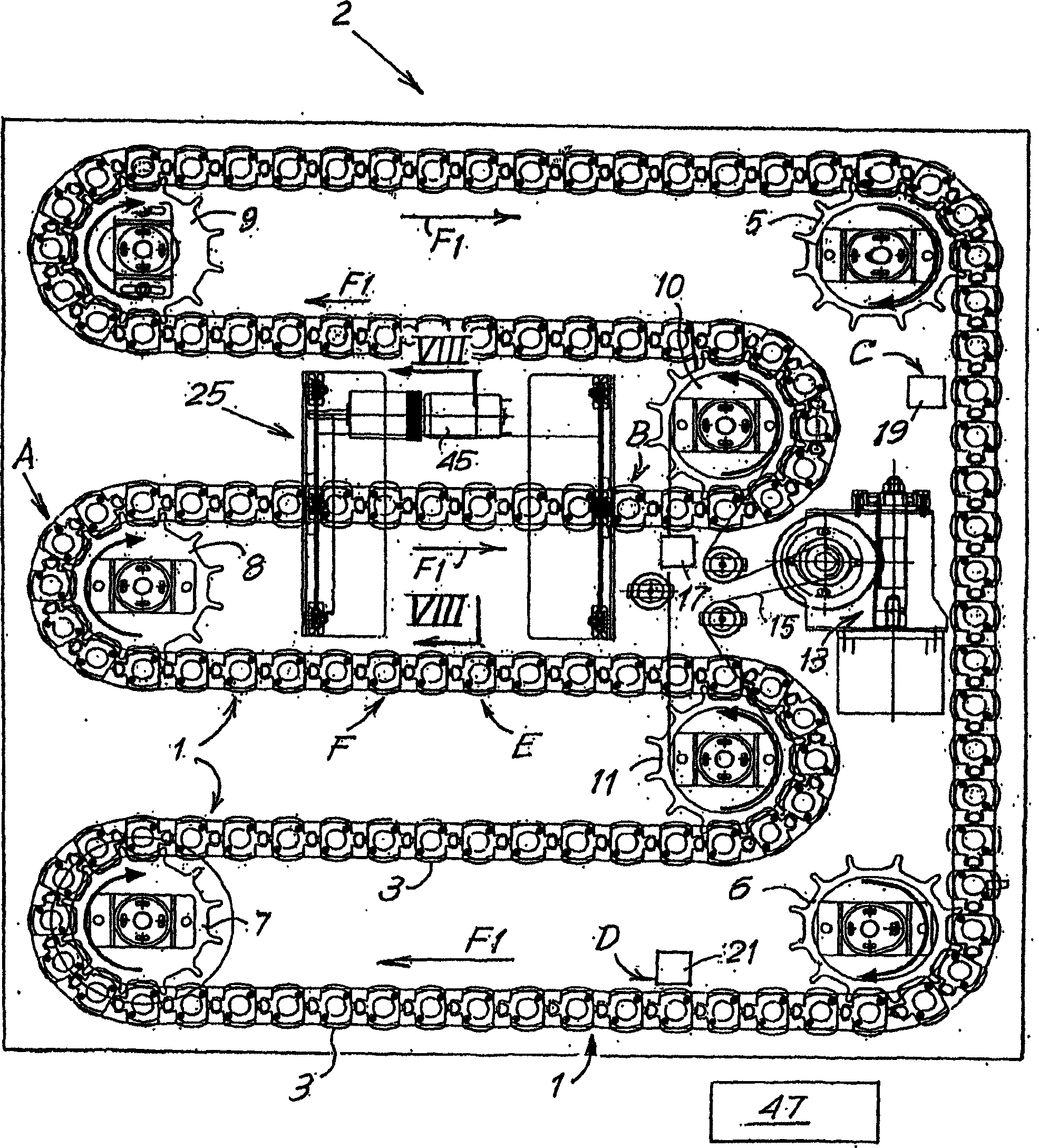
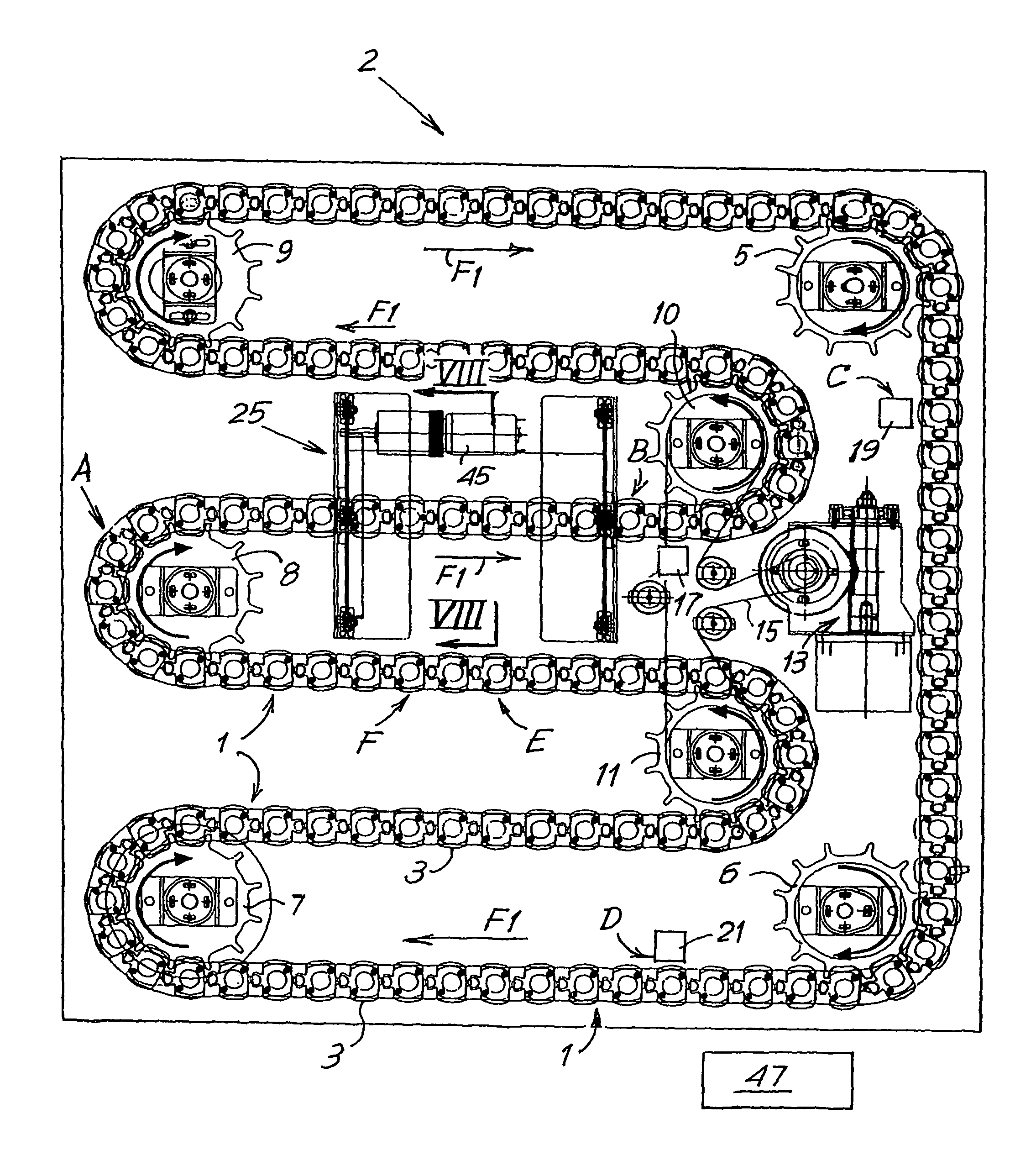
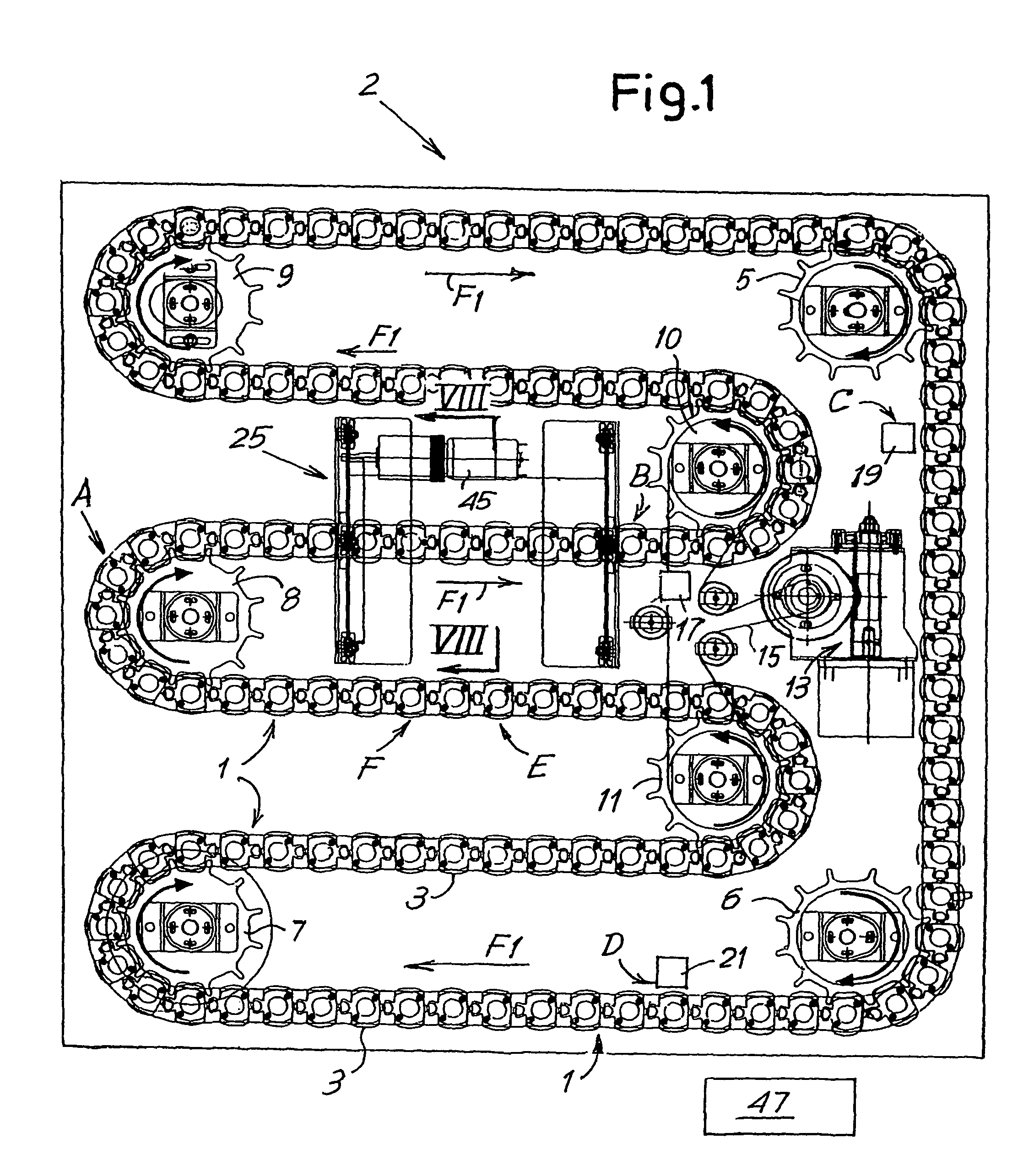
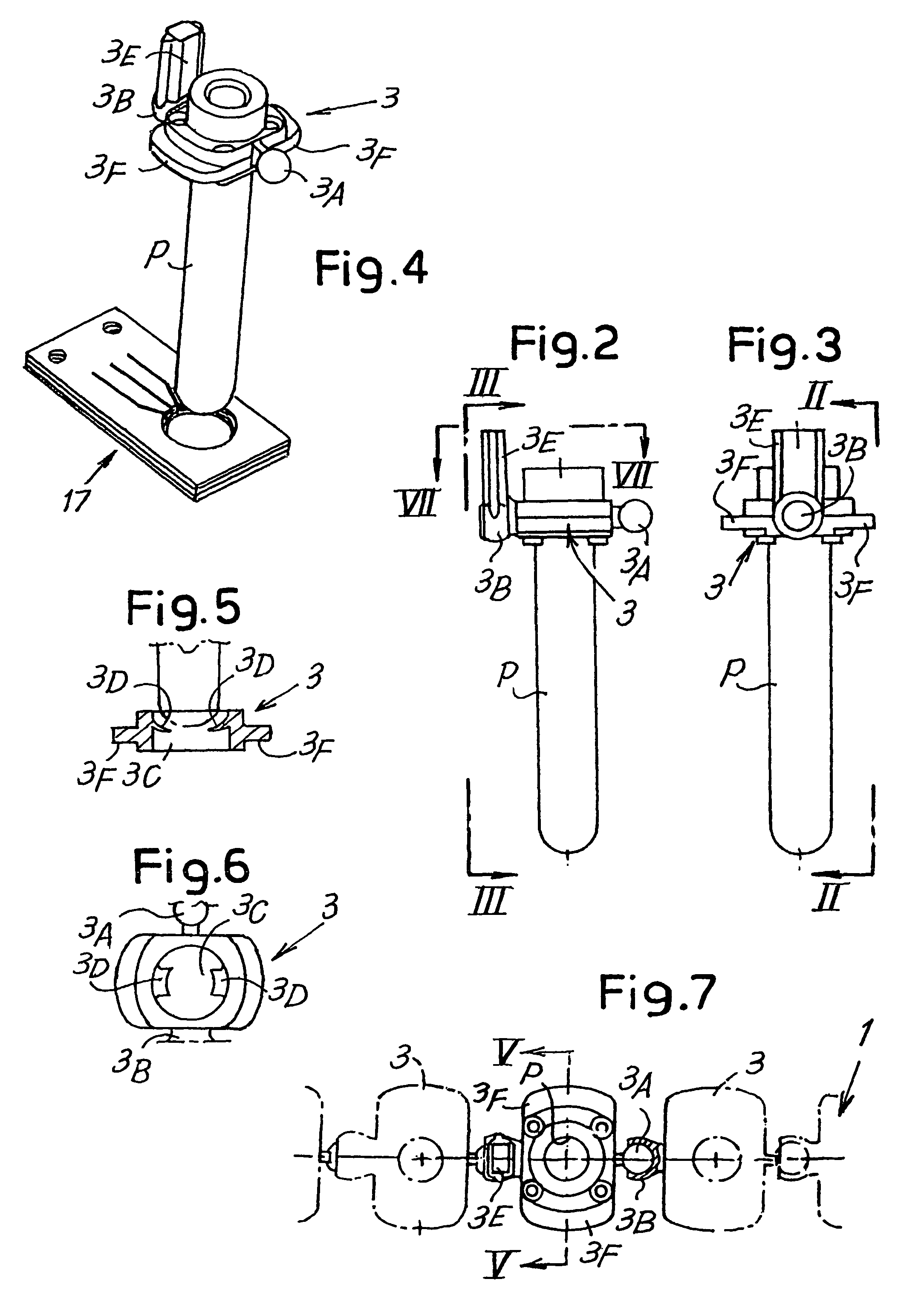
Device for performing analyses on biological fluids and related method
ActiveCN1875280AAutomatic realization of measurement resultsSimple structureSedimentation analysisBiomedical engineeringBiological fluids
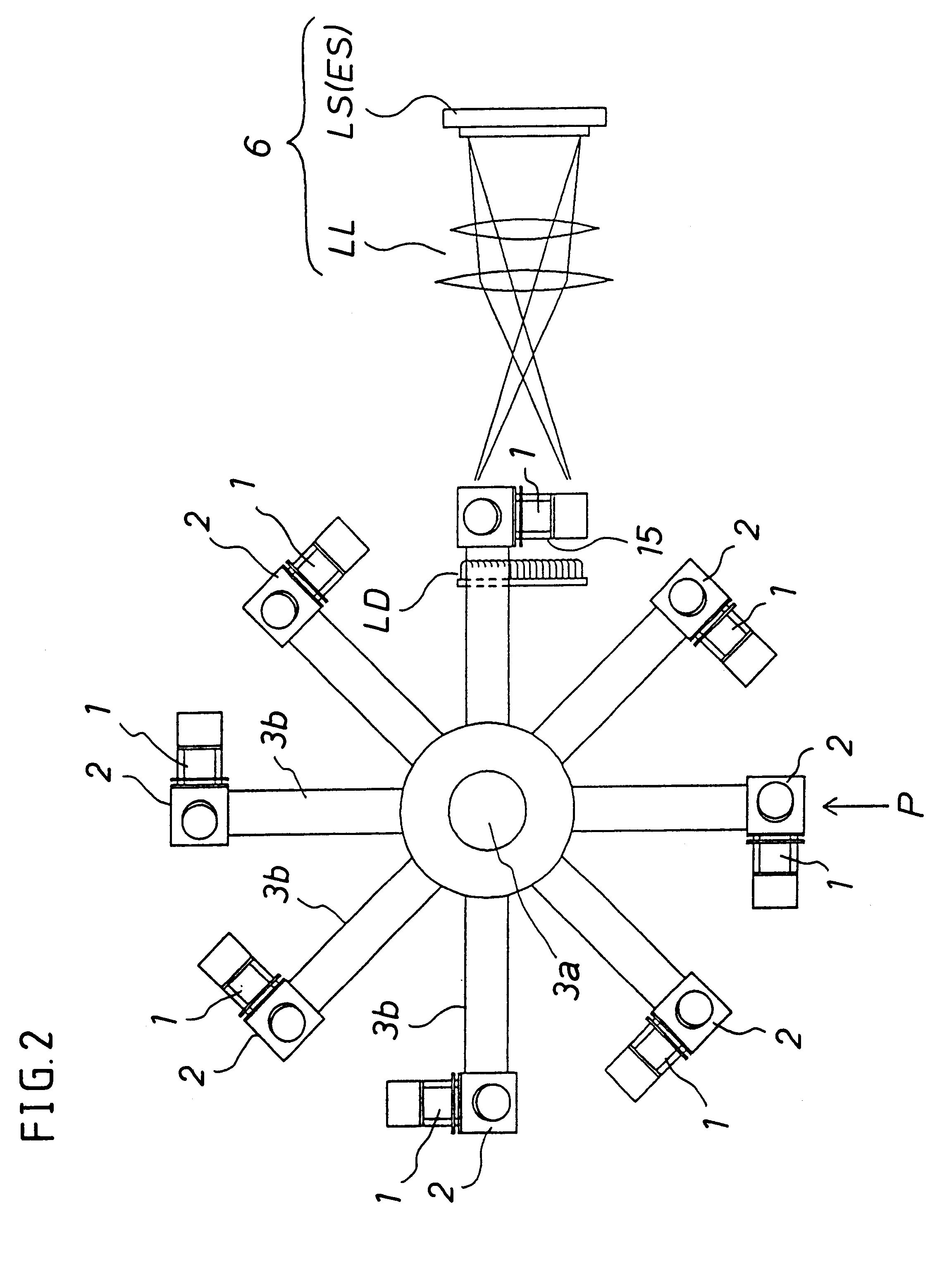
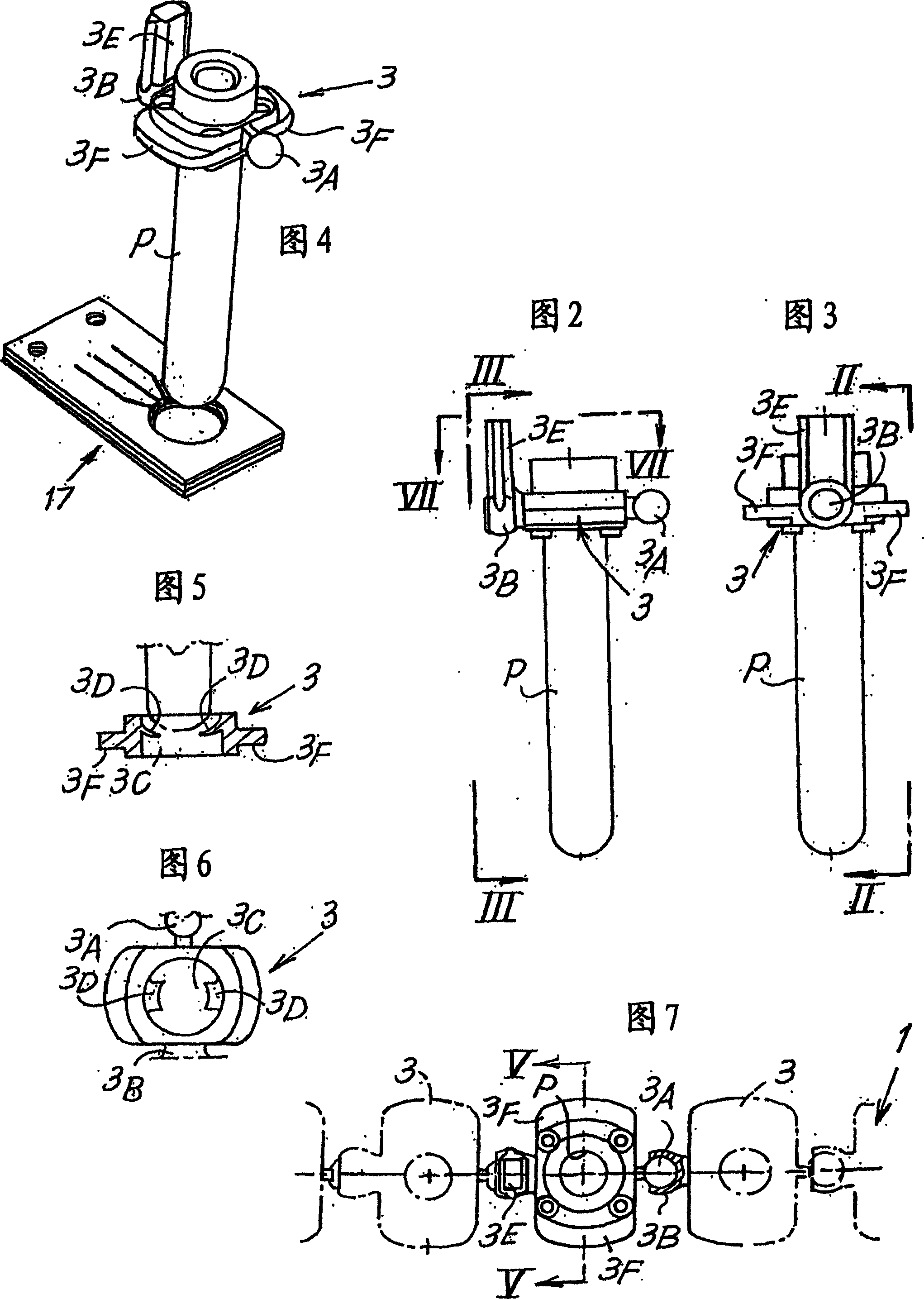
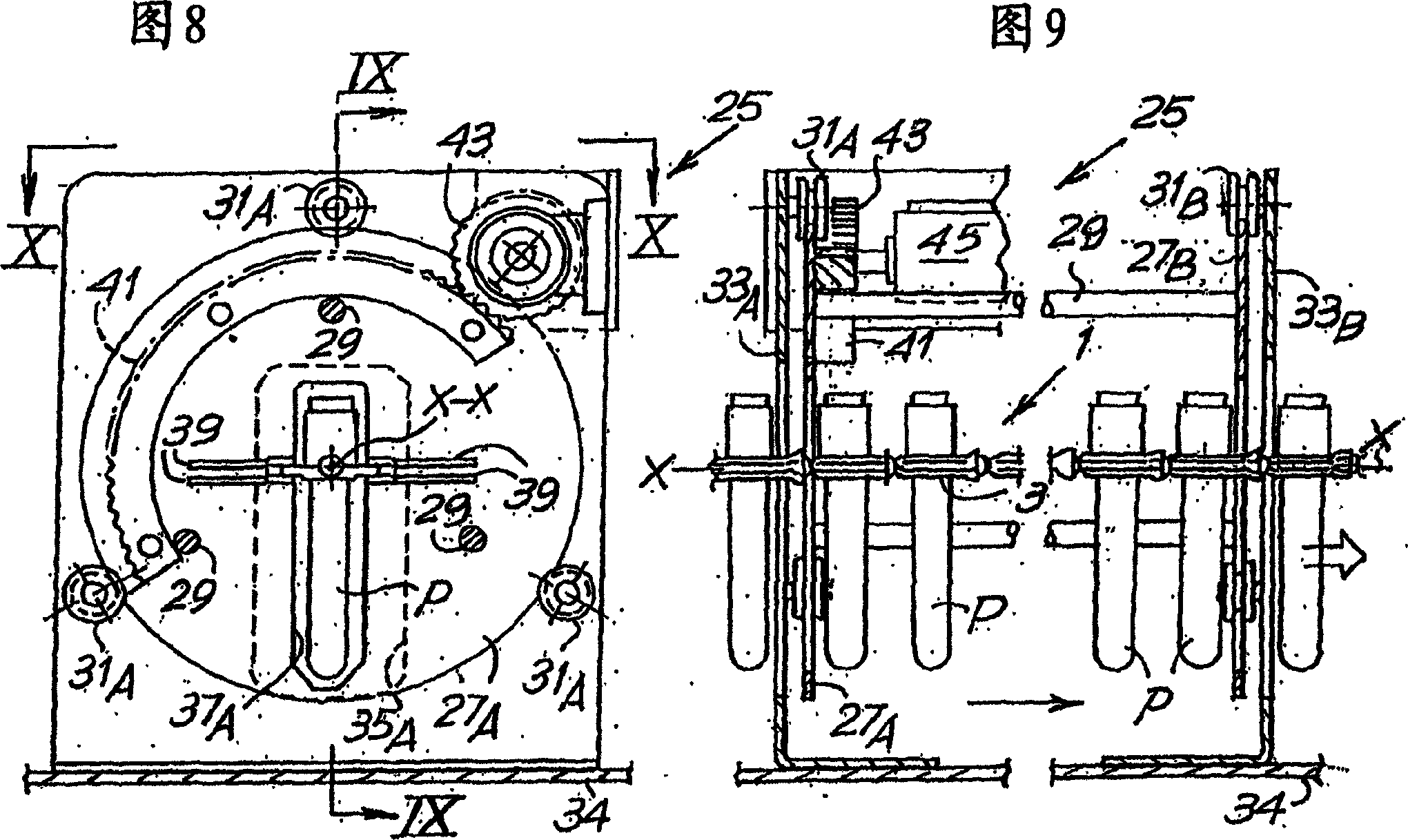
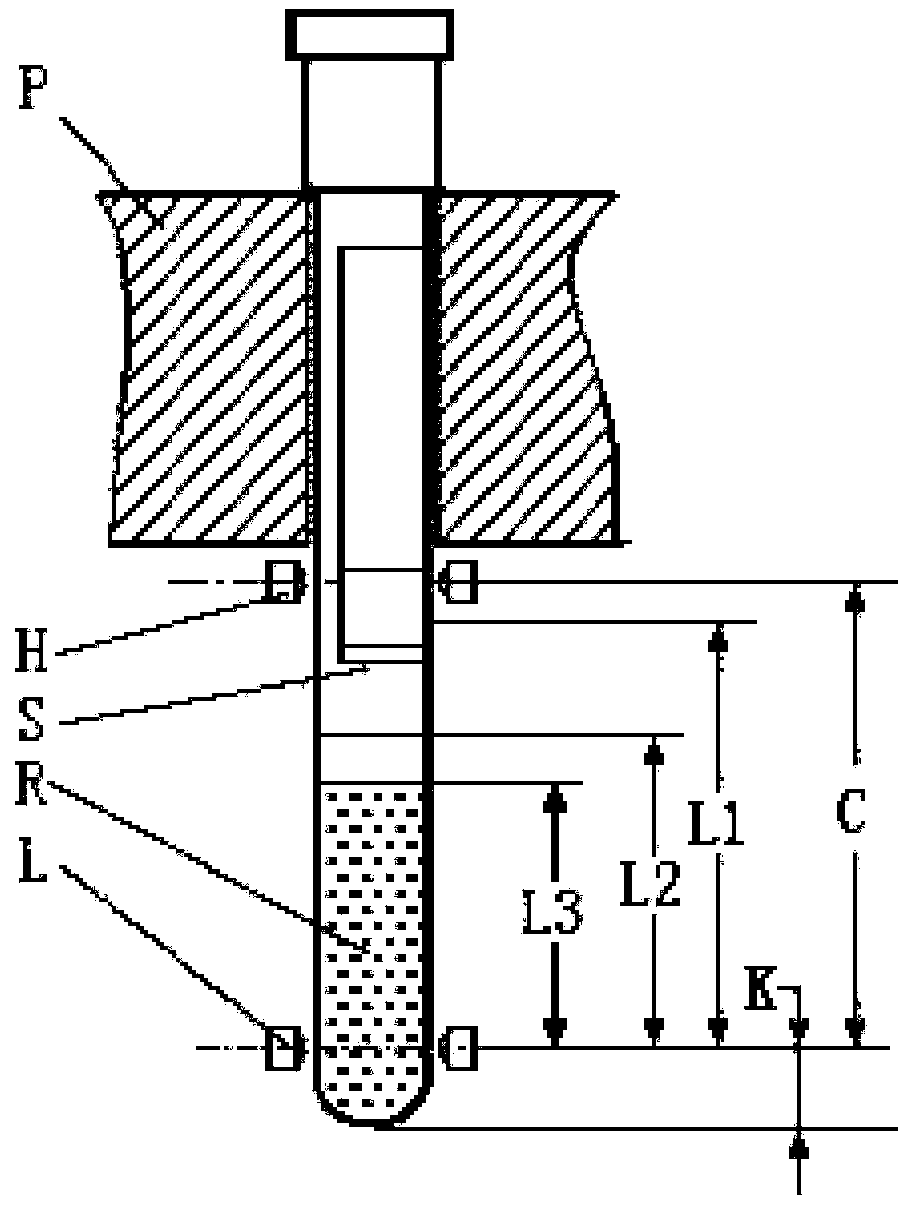
An appliance or device is described for measuring the sedimentation rate in biological fluids, and particularly the erythrocyte sedimentation rate in blood samples. The device comprises: holders (3) for test tubes (P) containing samples of biological fluid; agitator devices (25) for agitating the test tubes; at least one detector (17, 19) for reading the levels inside the test tubes. The holders together form a continuous flexible member (1) defining a closed path along which the agitator devices and the detector are arranged.
Owner:DIESSE DIAGNOSTICA SENESE
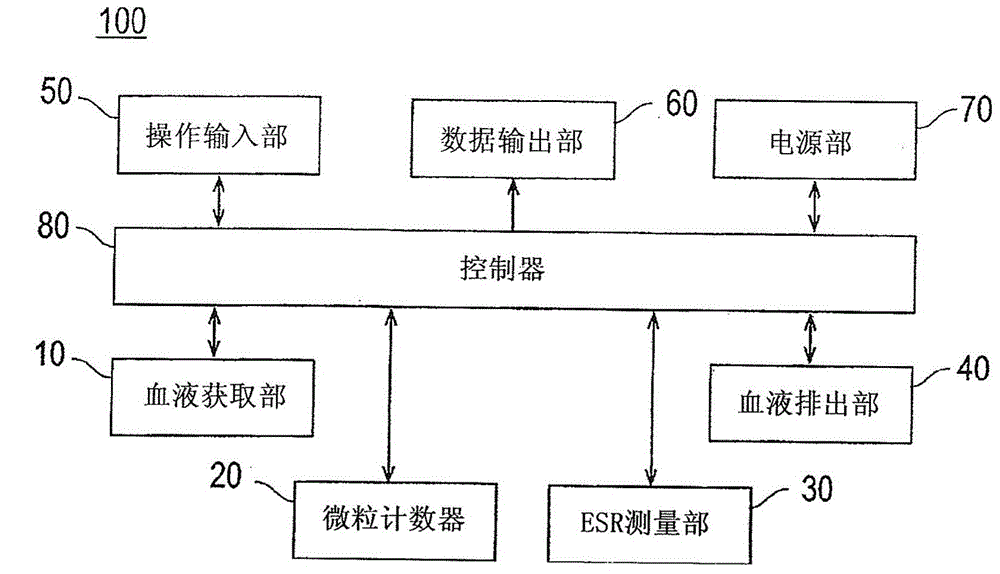
Blood Testing Apparatus And Blood Testing Method
InactiveCN104931398AShorten the timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMedicineBlood test device
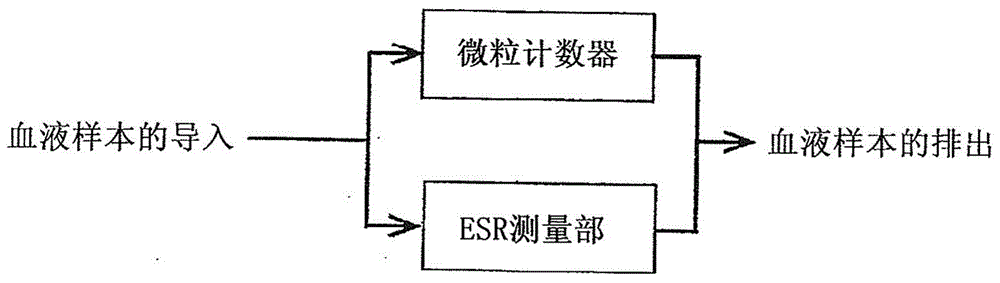
A blood testing apparatus (100) includes a blood acquiring section (10) that acquires a blood sample, a particle counter (20) that measures a particle count in the blood sample, and an erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) measuring section (30) that measures a erythrocyte sedimentation rate in the blood sample. The particle counter (20) and the ESR measuring section (30) being arranged in parallel.
Owner:NIHON KOHDEN CORP
Device for performing analyses on biological fluids and related method
ActiveUS8211381B2Automatic detectionReliable controlAnalysis using chemical indicatorsSamplingBiological fluidsBiomedical engineering
A device for measuring the sedimentation rate in biological fluids, and particularly the erythrocyte sedimentation rate in blood samples. The device comprises: holders (3) for test tubes (P) containing samples of biological fluid; agitator devices (25) for agitating the test tubes; at least one detector (17, 19) for reading the levels inside the test tubes. The holders together form a continuous flexible member (1) defining a closed path along which the agitator devices and the detector are arranged.
Owner:DIESSE DIAGNOSTICA SENESE
Blood analysis
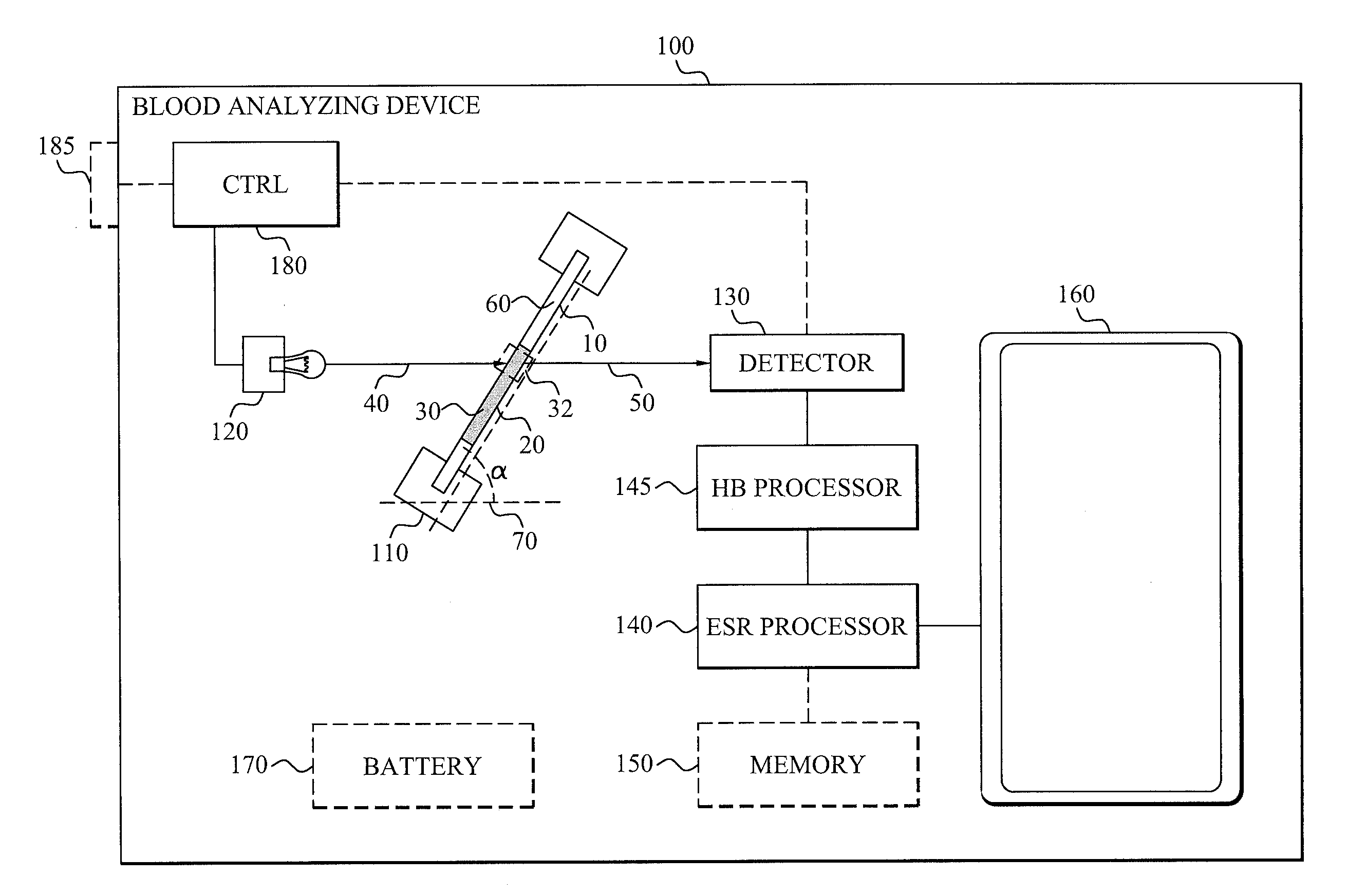
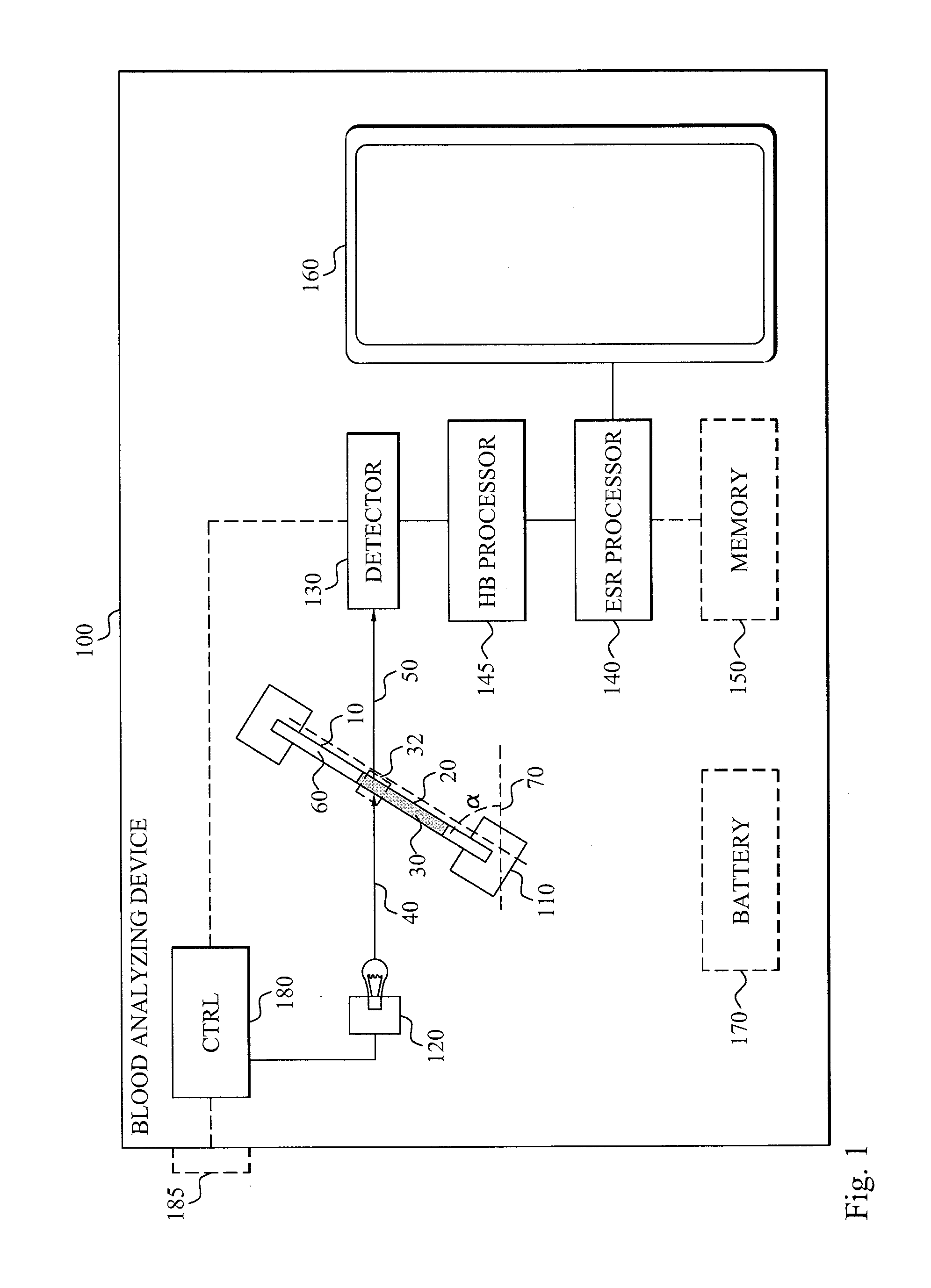
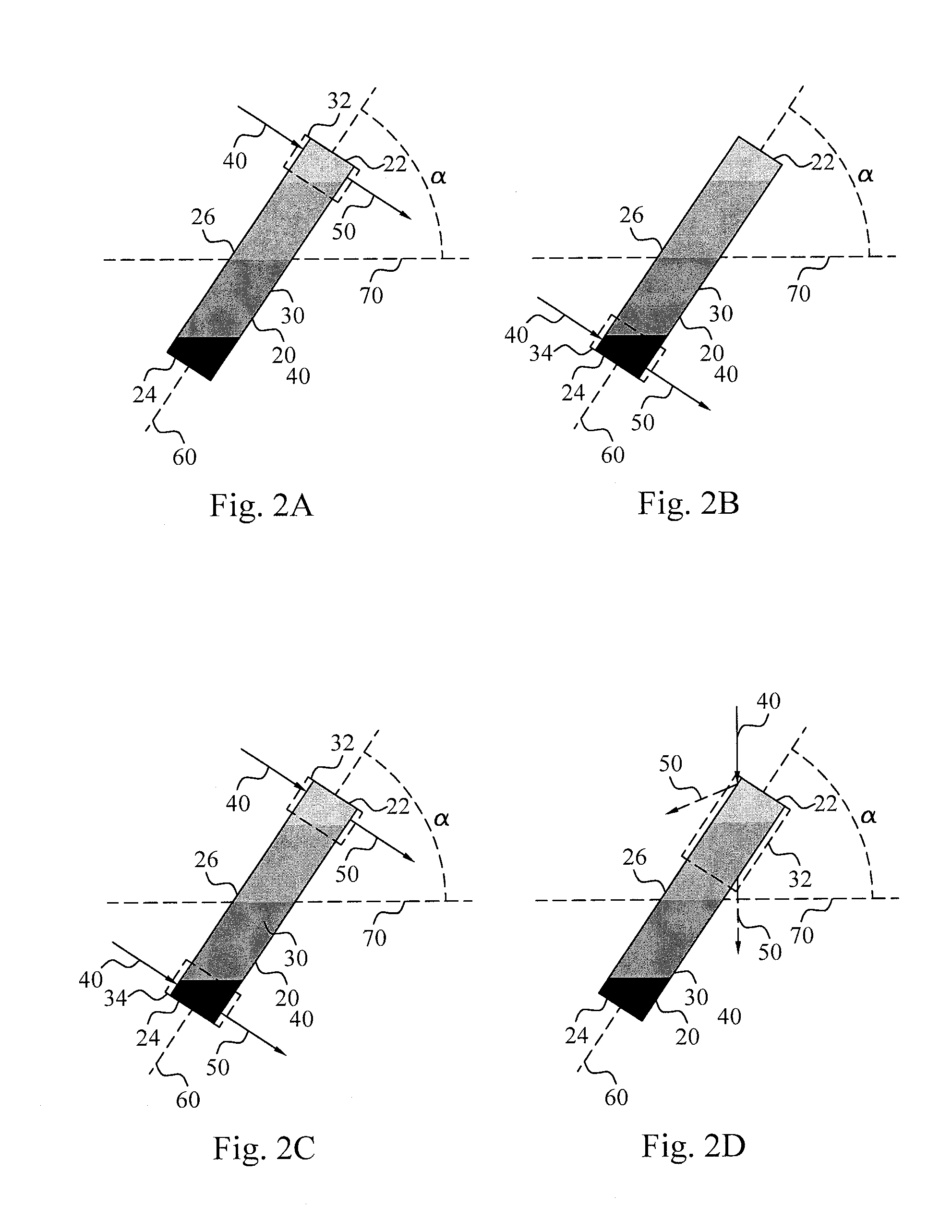
InactiveUS20150055121A1Shorten the timeShorten test timeTransmissivity measurementsSedimentation analysisKinetic informationCuvette
The invention discloses a blood analyzing device (100) comprising a holder (110) arranged for carrying a container (10) having a cuvette (20) containing a blood sample (30). The container (10) is positioned in the holder (110) so that a longitudinal axis (60) of the cuvette (20) is angled relative a horizontal axis (70). A light source (120) provides light (40) into the sample (30) and a detector (130) detects the output light (50) from a sub-portion of the blood sample (30). Kinetic information indicative of the change in hemoglobin concentration in a measuring volume (32, 34) is determined by a Hb processor (145) from the detected output light (50). An ESR processor (140) determines the erythrocyte sedimentation rate of the sample (30) based on the kinetic information.
Owner:FORSELL TOMMY
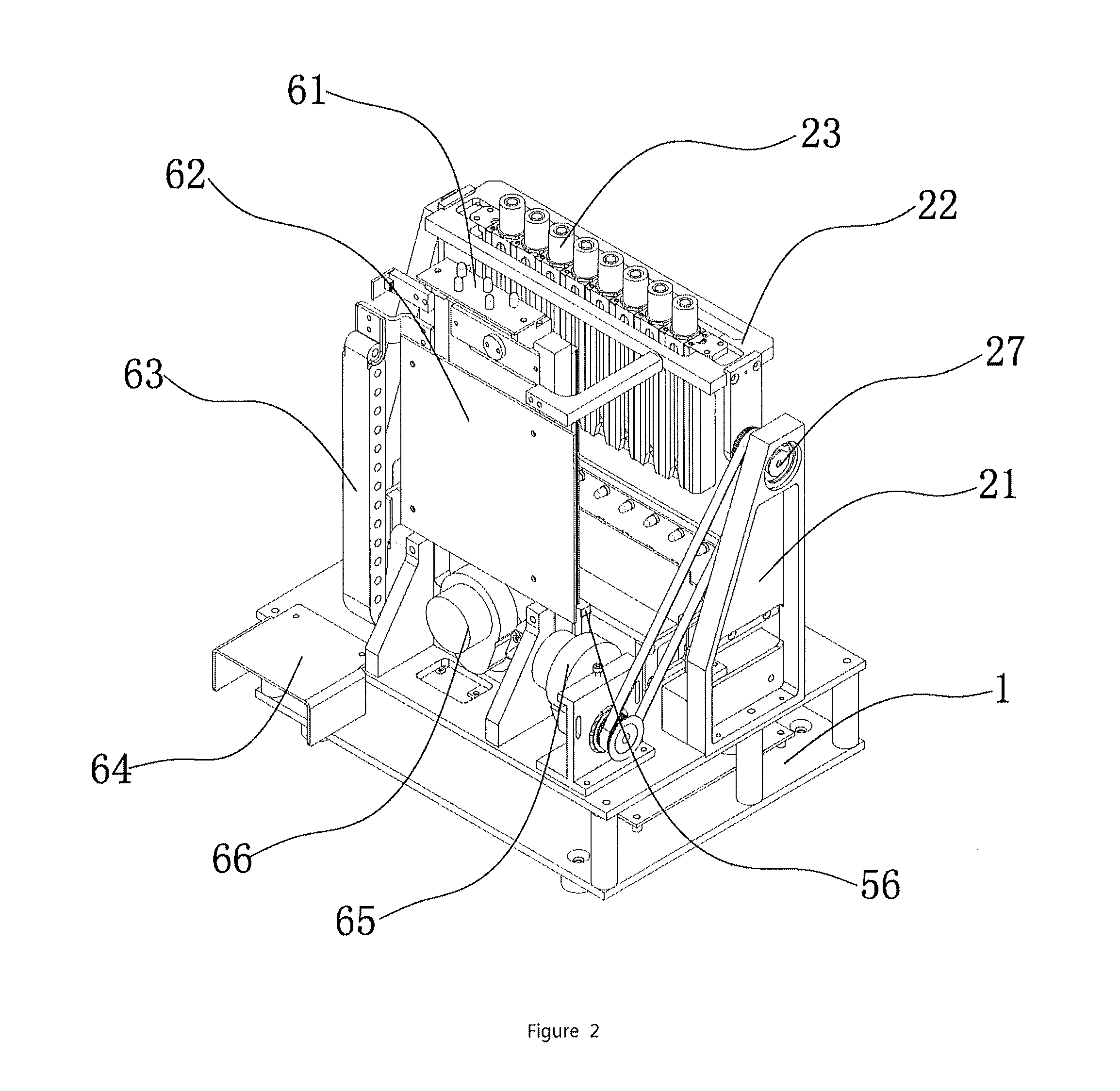
Method and apparatus for rapid determination of blood sedimentation rate
InactiveUS6098451AImprove trustAccelerates the lag phaseRead-only memoriesSedimentation analysisGravitational sedimentationBiology
An apparatus and method for rapid determination of erythrocyte sedimentation rates for a blood specimen (29) which can be linearly transposed to Westergren sedimentation rates. The method includes the steps of inducing accelerated rouleaux formation in the specimen (29) in an amount sufficient to begin settling at substantially the decantation rate for the specimen. In one embodiment a structure (27) which produces a very thin cross-sectional region (37) of the specimen (29) inside the lumen (23) of a specimen container (21) is provided to accelerate rouleaux formation. In an alternative embodiment (120), accelerated rouleaux formation is accomplished using a centrifuge (122). A third embodiment employs a movable rod (223) mounted inside the specimen tube (221) to induce accelerated rouleaux formation. All embodiments of the process next employ gravity settling the specimen in a near horizontal oriented container (21, 121, 221). Thereafter, the amount of settling occurring is determined. A sealed specimen container (21, 121, 221) which permits thorough mixing of blood in a very small diameter container for use in performing the method also is provided.
Owner:BULL BRIAN S
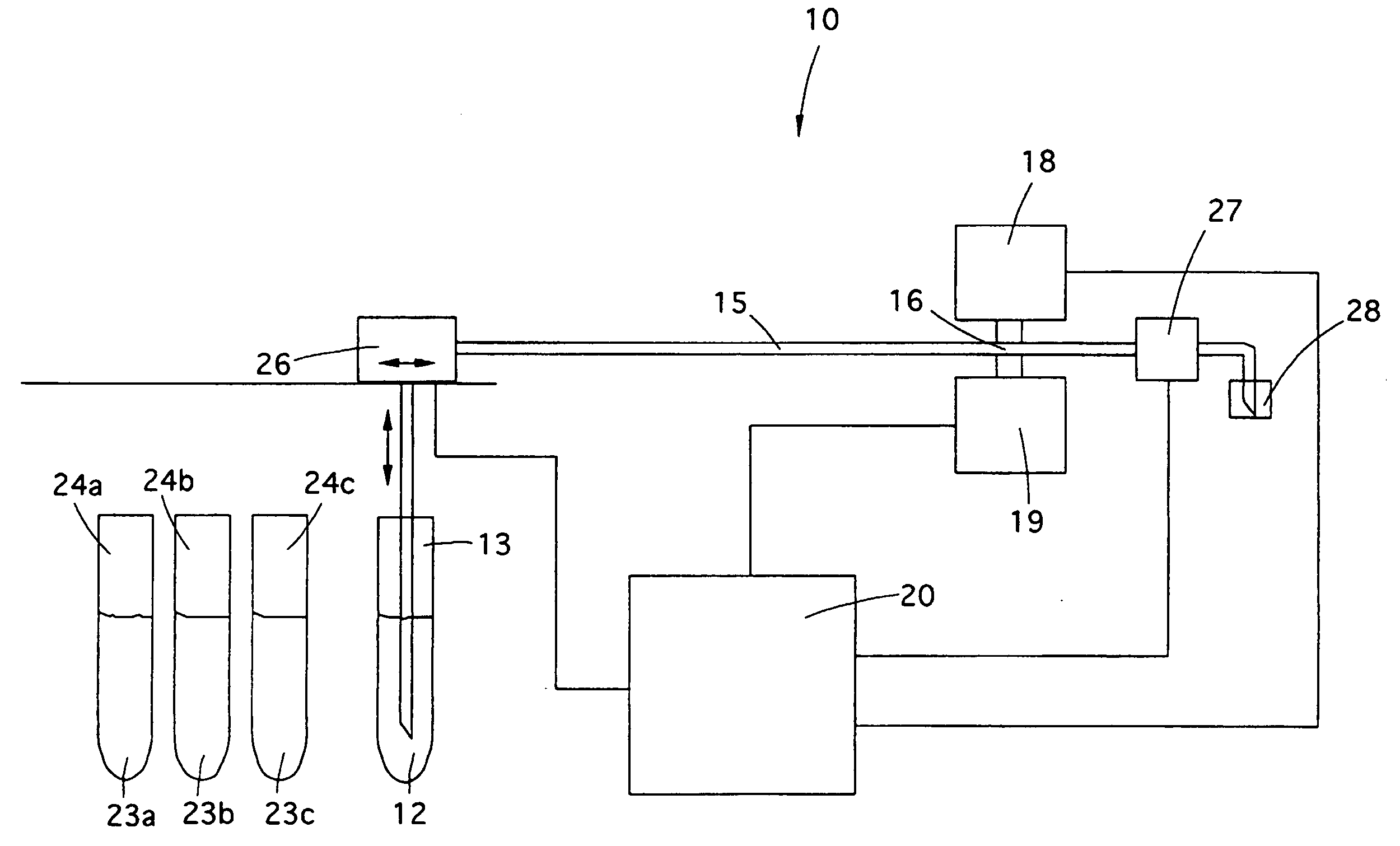
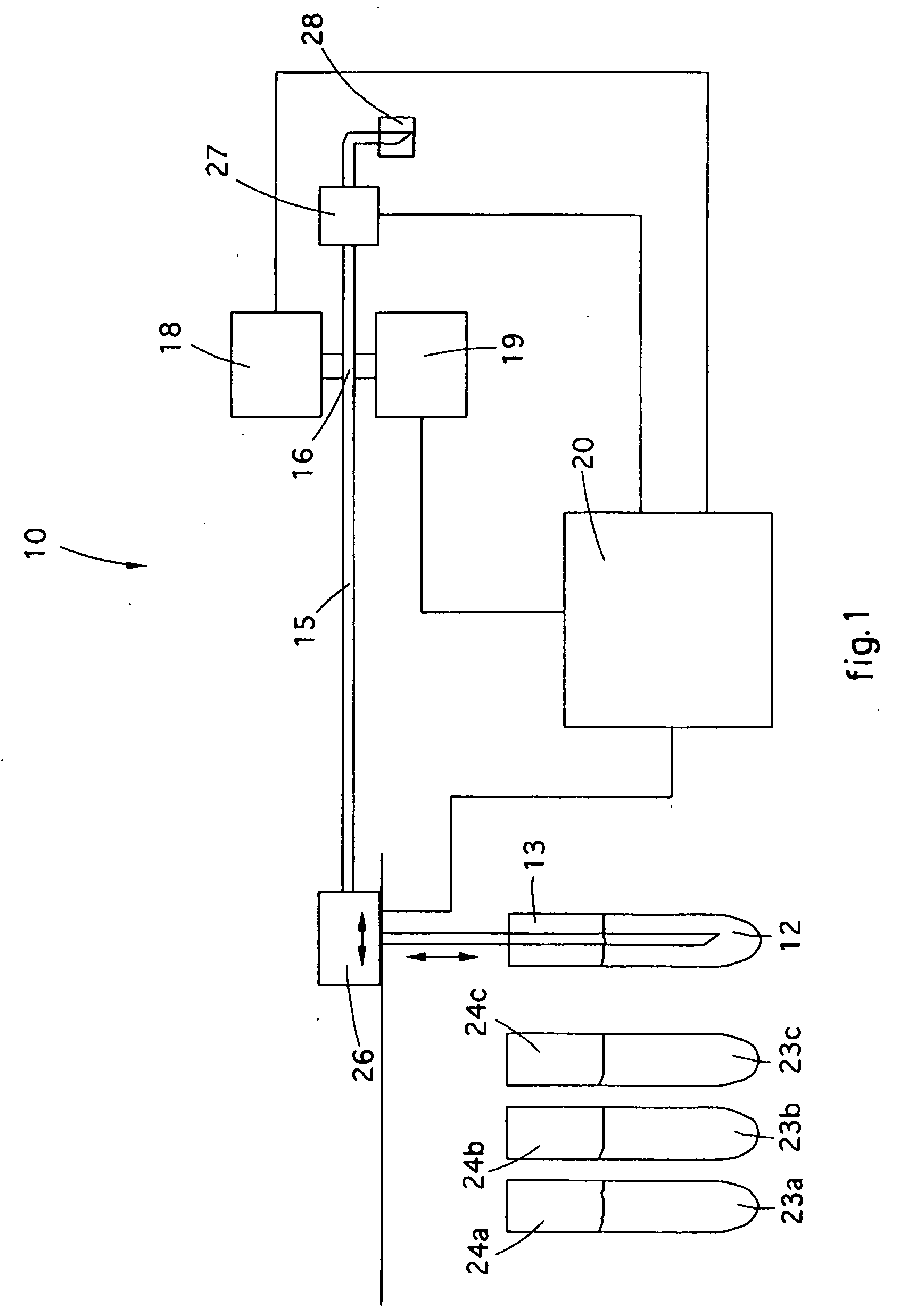
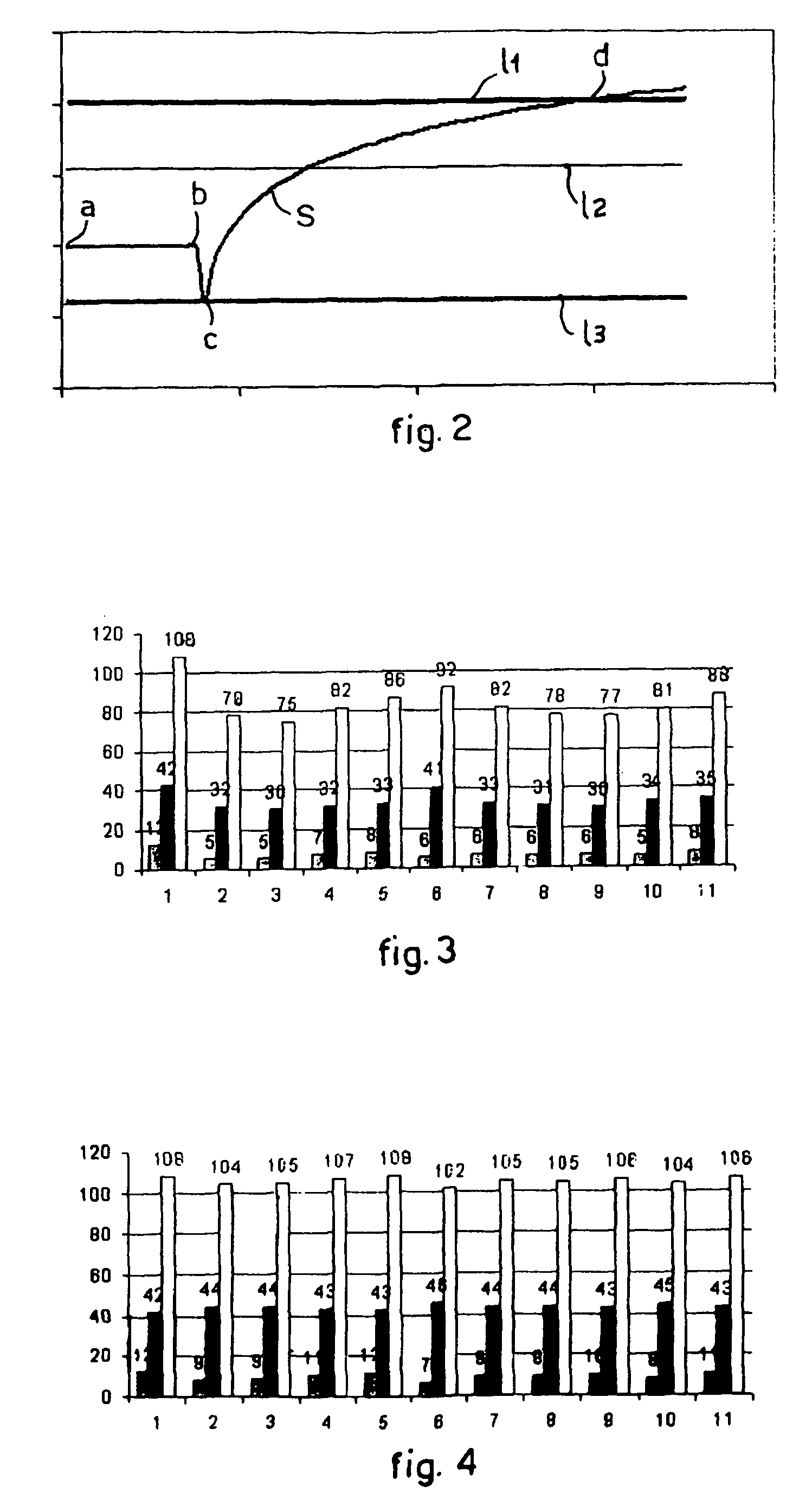
Method for Calibrating Machines for the Analysis of Characteristic Parameters of the Blood Connected To Its Density, Such as Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate and/or Red Corpuscles Aggregation Rate
ActiveUS20090120157A1Improve accuracyLimited rangeMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMaterial analysis by optical meansRed blood cellAggregation rate
A method for calibrating machines suitable to effect an analysis of a blood sample by means of measuring the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and / or aggregation of the red corpuscles, wherein said measurement is effected by exploiting the optical density kinetics obtained from the measurement of the variation in the optical density of the blood sample in an interval of time, comprises a measuring step in which, by means of the same machine with which the measurement of the optical density is effected on said blood sample, a measurement is effected of the optical density of two latexes, or turbidimetric samples. Each of the two latexes has a known optical density, reproducible, measurable and different from each other. The method also comprises a comparison step, in which the difference is calculated between the values of optical density of the latexes as obtained from the measurement performed by the machine and the known values of optical density, to allow to determine at least one correction factor usable to calibrate said machine.
Owner:ALIFAX
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) test measurement instrument of unitary design and method of using the same
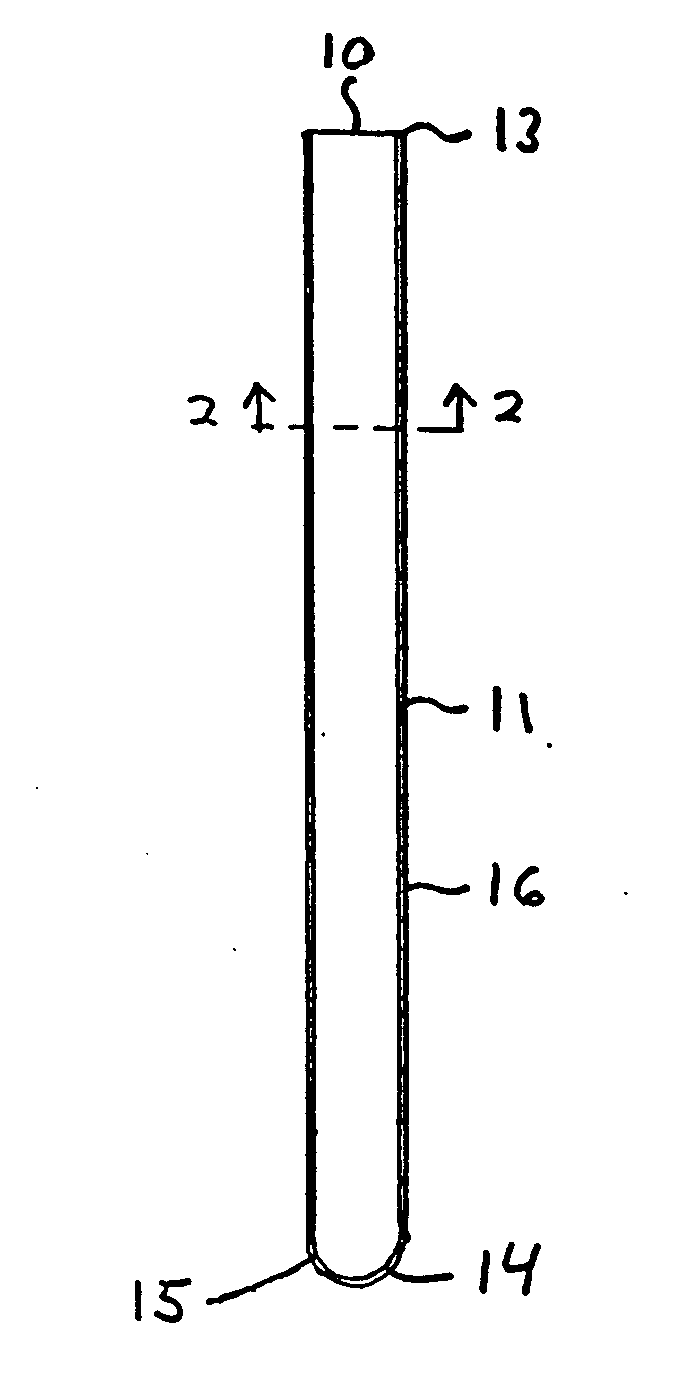
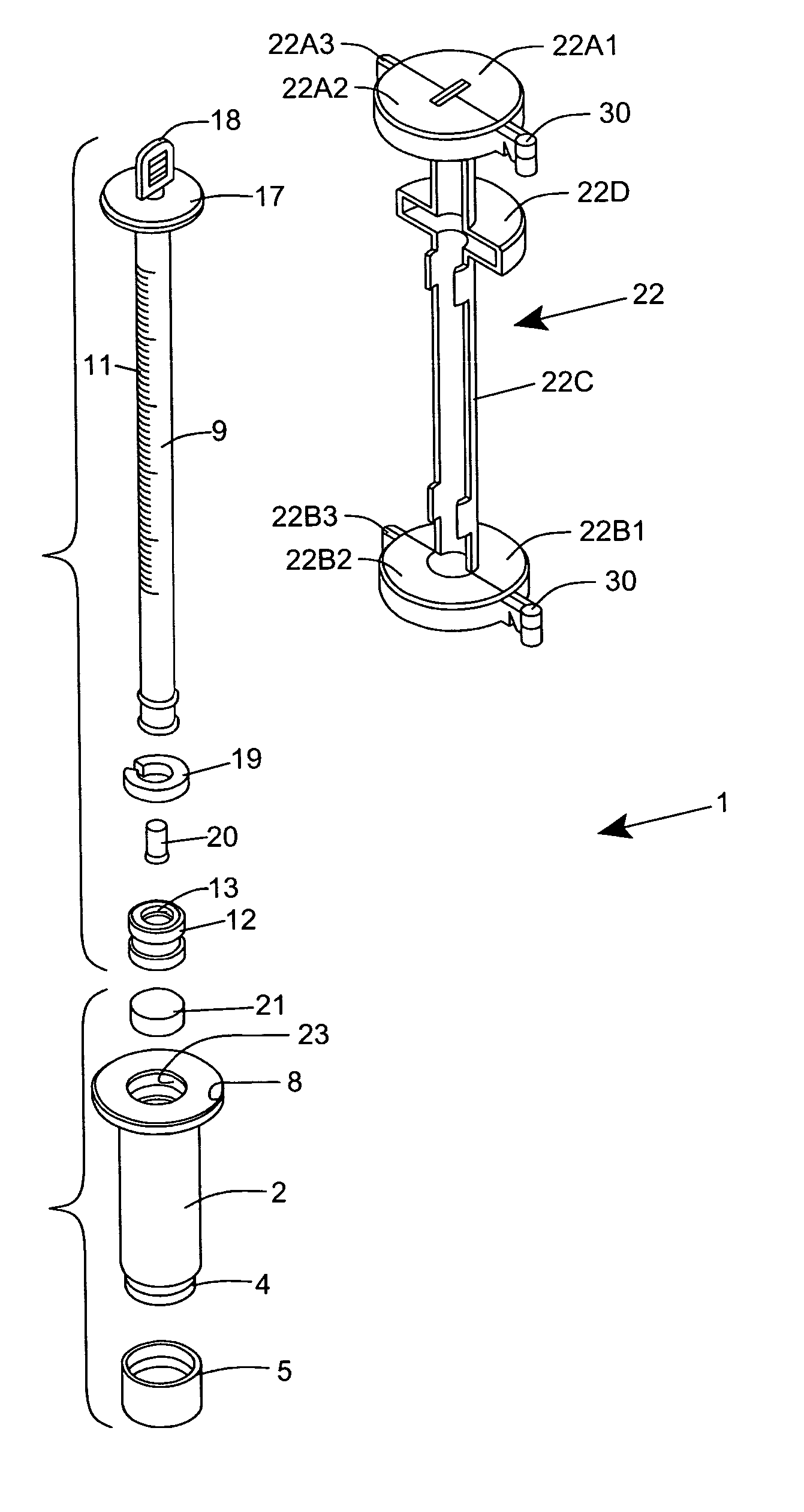
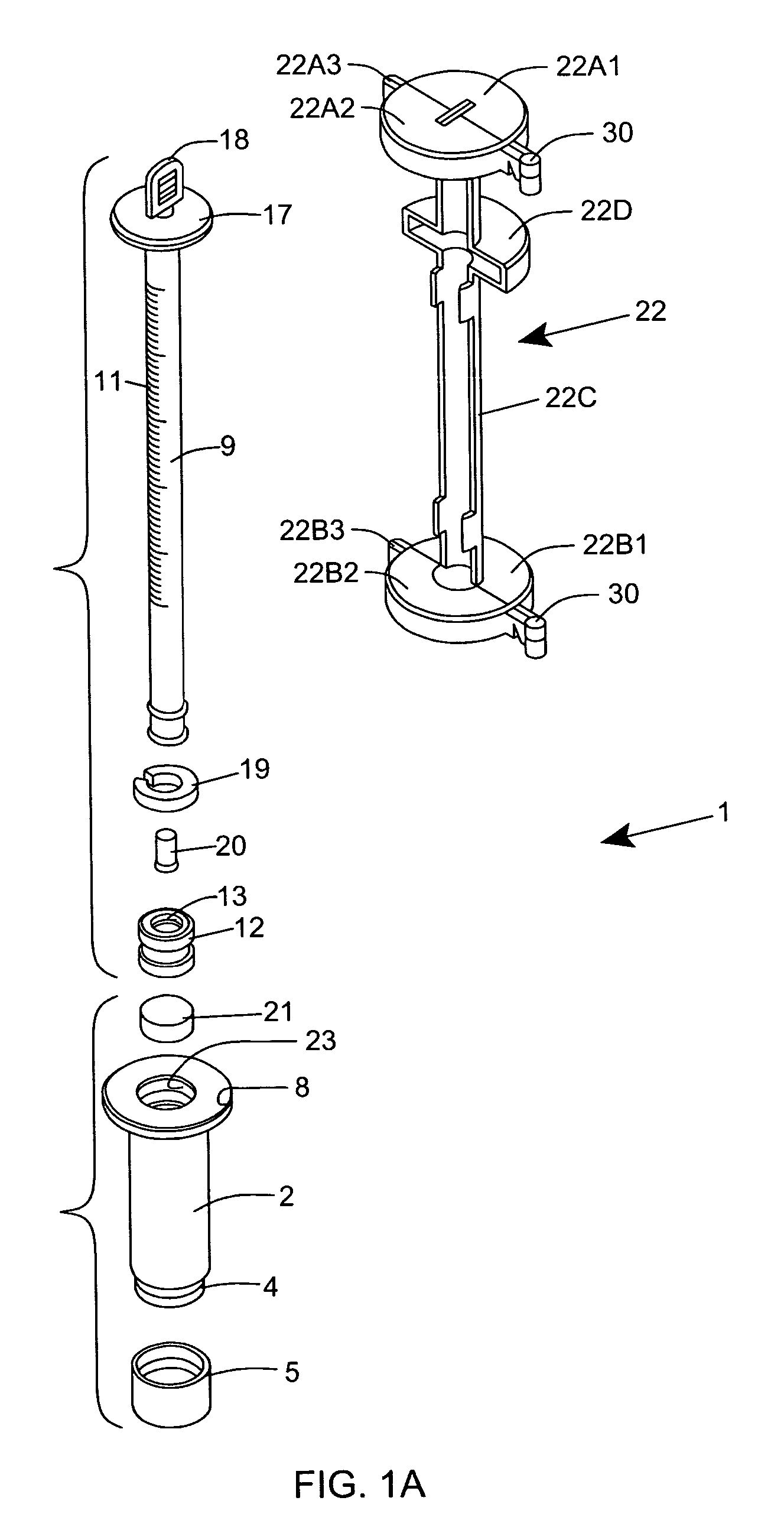
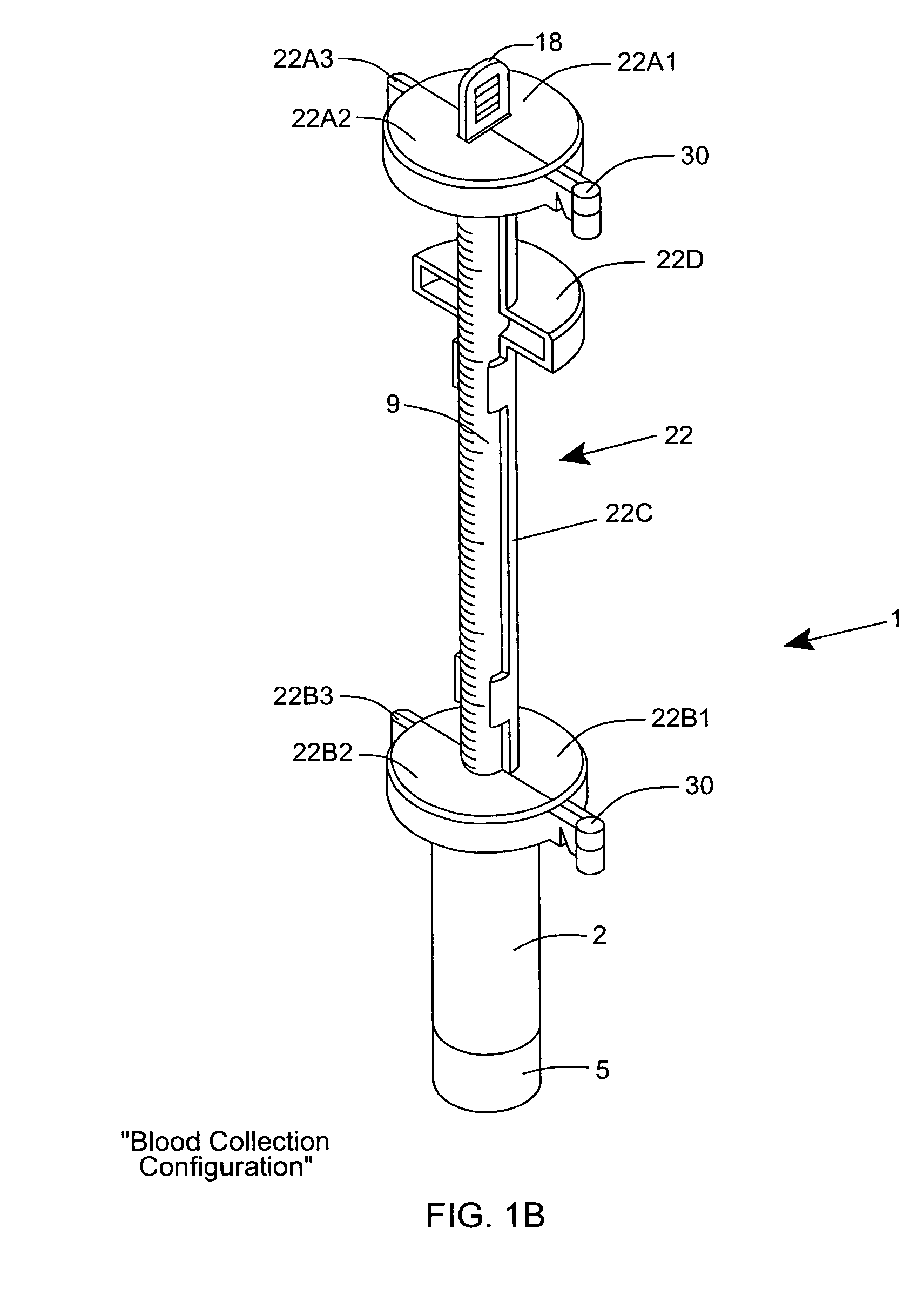
InactiveUS20060216829A1Avoid collectingSedimentation analysisBiological testingBlood Collection TubeBLOOD FILLED
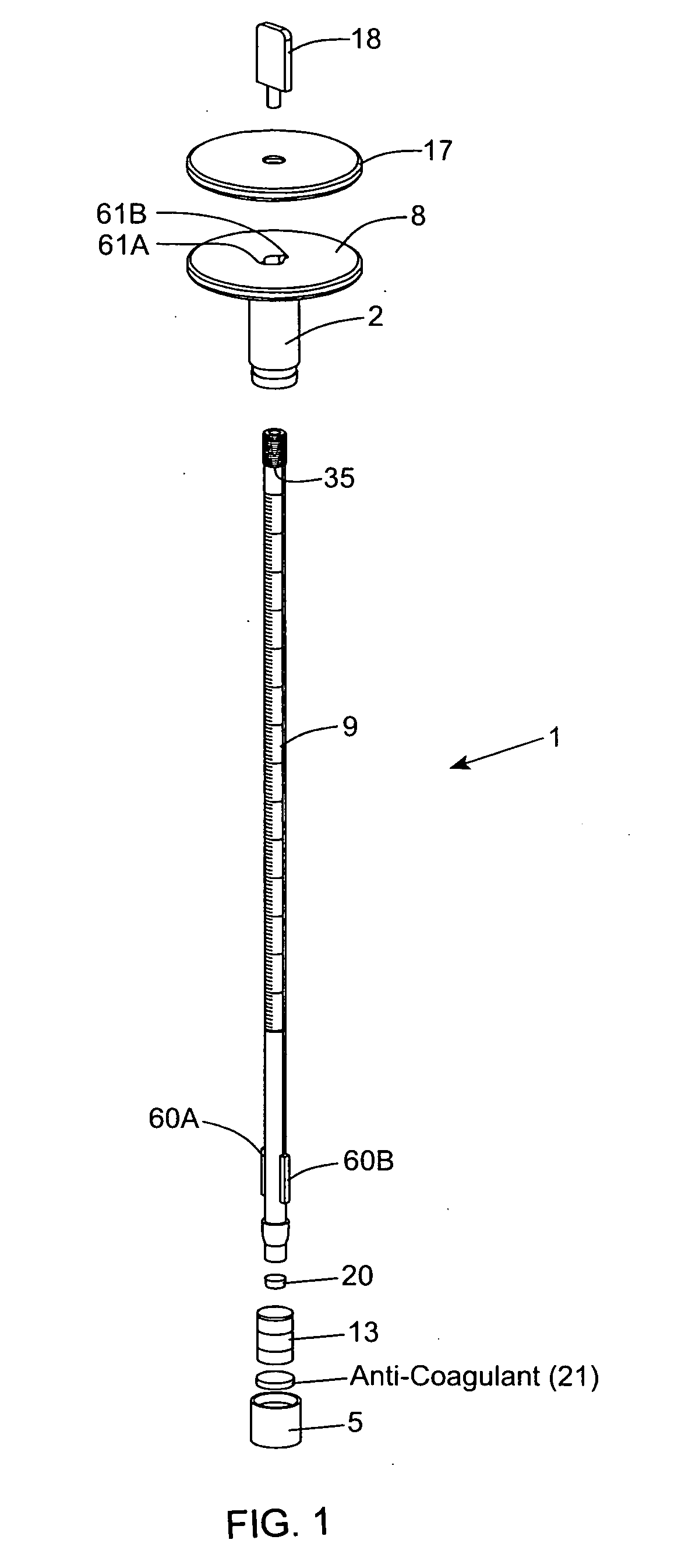
An erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) measurement instrument having a Blood Collection Configuration and an ESR Measurement Configuration. The ESR measurement instrument comprises a sedimentation measurement tube having an hollow interior volume containing a predetermined quantity of blood sample diluting agent therewithin and being air / fluid sealed with respect to the ambient environment; and a blood collection tube having a hollow interior volume containing a predetermined quantity of anti-coagulant and being vacuum-sealed with respect to the ambient environment, and physically coupled to the air-sealed sedimentation measurement tube, by at least a portion of the sedimentation measurement tube being inserted within a portion of the hollow interior volume of the blood collection tube. The sedimentation measurement tube and the blood collection tube are maintained stationarily fixed relative to each other as a unitary assembly having a syringe-like form factor when the ESR measurement instrument is arranged in the Blood Collection Configuration. During this configuration, a needle-supporting connector can be connected to the blood collection tube and a sample of whole blood from a patient vacuum-drawn and injected into the blood collection tube. After the sample of anti-coagulated blood has been collected in the blood collection tube and the needle-supporting connector is disconnected therefrom, the air / fluid seal of the sedimentation measurement tube can be broken and then the sedimentation measurement tube can be manually plunged into and to the bottom of the hollow interior volume of said blood collection tube, using a single-handed operation to rearrange the ESR measurement instrument into the ESR Measurement Configuration. The anti-coagulated sample of blood fills up a substantially portion of the sedimentation measurement tube and mixes with the blood sample diluting agent to enable the blood plasma / erythrocyte cell (P / E) interface level within the sedimentation measurement tube to settle downwards toward the blood collection tube during a predetermined time period when said ESR measurement instrument is oriented in a gravity vertical position. By virtue of the present invention, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) of the collected blood sample can be measured by determining how far the P / E interface level has moved against graduation markings formed along the length of the sedimentation measurement tube during the predetermined time period.
Owner:HEMOVATIONS
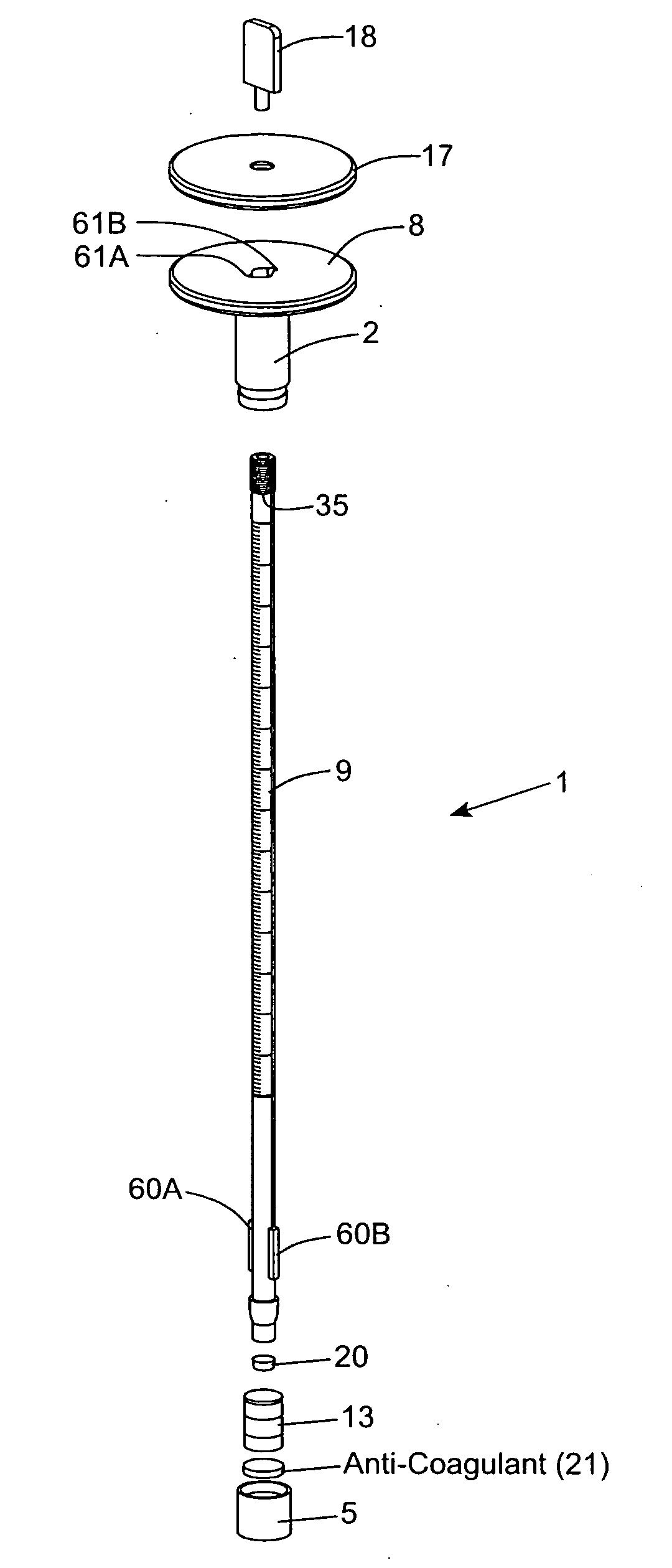
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) test measurement instrument of unitary design and method of using the same
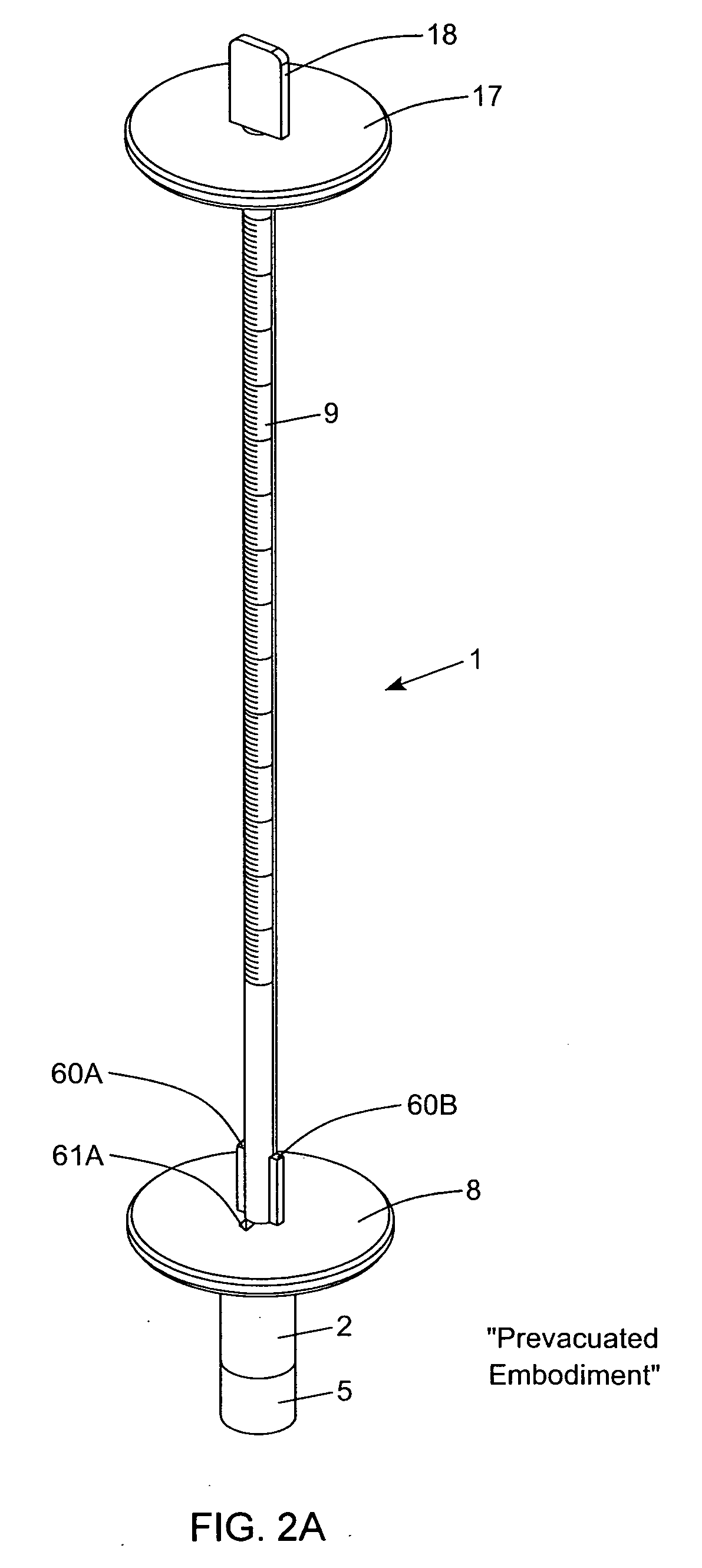
InactiveUS20070274865A1Avoid collectingEasy to manufactureSedimentation analysisBlood Collection TubeMeasuring instrument
A disposable erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) measurement instrument comprising a sedimentation measurement tube having a plunger portion, a blood collection tube having an upper portion, and an integrated locking mechanism provided between the blood collection tube and the sedimentation measurement tube. The locking mechanism permits the blood collection tube to be plunged into the blood collection tube upon rotating the sedimentation tube and the blood collection tube relative to each other, and thereafter pushing the sedimentation measurement tube into the blood collection tube. In a pre-evacuated embodiment of the present invention, the blood collection is pre-evacuated to withdraw a predetermined amount of blood during blood collection operations. In non-evacuated embodiment of the present invention, the plunger portion of the sedimentation measurement tube is inserted within the upper portion of the blood collection tube, at the time of assembly and manufacture, and is ready to be withdrawn by a predetermined about in order to manually evacuate the blood collection tube prior to use so that the blood collection tube is vacuum-pressurized to automatically draw a predetermined quantity of blood from a patient during blood collection operations.
Owner:BOUBOULIS DENIS A
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate tester and erythrocyte sedimentation rate testing method
PendingCN109991433AReduce labor intensityReduce errors in manual readingsBiological particle analysisMaterial analysisTester deviceDisplay device
The invention discloses an erythrocyte sedimentation rate tester and an erythrocyte sedimentation rate testing method, and belongs to the technical field of medicine detection. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate tester comprises a sample introduction device, a code scanning device, a blending and cap pulling device, a sample adding device, a testing device and a display device, wherein the sampleintroduction device is configured to drive a first test tube to move along a sample introduction direction; the code scanning device is configured to scan the identification code of the first test tube; the blending and cap pulling device is configured to blend liquid in the first test tube and pull the test tube cap of the first test tube; the sample adding device is configured to convey liquid in the first test tube to a second test tube; the testing device is configured to carry out liquid level monitoring on liquid in the second test tube; and the display device is configured to output a testing result. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate testing method adopts the above erythrocyte sedimentation rate tester to finish erythrocyte sedimentation rate testing. The erythrocyte sedimentationrate tester provided by the invention can replace a manual operation, automatically monitors the liquid level of a blood sample in a standard erythrocyte sedimentation rate glass tube, and improves detection efficiency and accuracy while labor intensity is lowered.
Owner:北京众驰伟业科技发展有限公司
Chinese medicinal composition for relieving hormone side effect
ActiveCN101850080AImprove clinical symptomsElevated red blood cell countAntinoxious agentsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismSide effectAsiatic pennywort
The invention relates to a Chinese medicinal composition for relieving the hormone side effect of a western medicament when systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is treated. In the medicament, drying rehmannia root, mix-fried turtle shell, largetrifoliolious bugbane rhizome, spreading hedyotis herb, sweet wormwood herb, asiatic pennywort herb, red paeony root, fried coix seed, fingercitronsliced and raw liquoric root are combined, so that the Chinese medicinal composition can improve clinical symptoms of an SLE patient, contributes to raising the red blood cell count of the patient, lowers levels of triglyceride, cholesterol, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, urine protein and hematuresis of the SLE patient, reduces the using amount of the hormone, reduces the relapse rate, improves the overall curative effect, and can be combined with the western medicament to treat the systemic lupus erythematosus.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CHINESE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
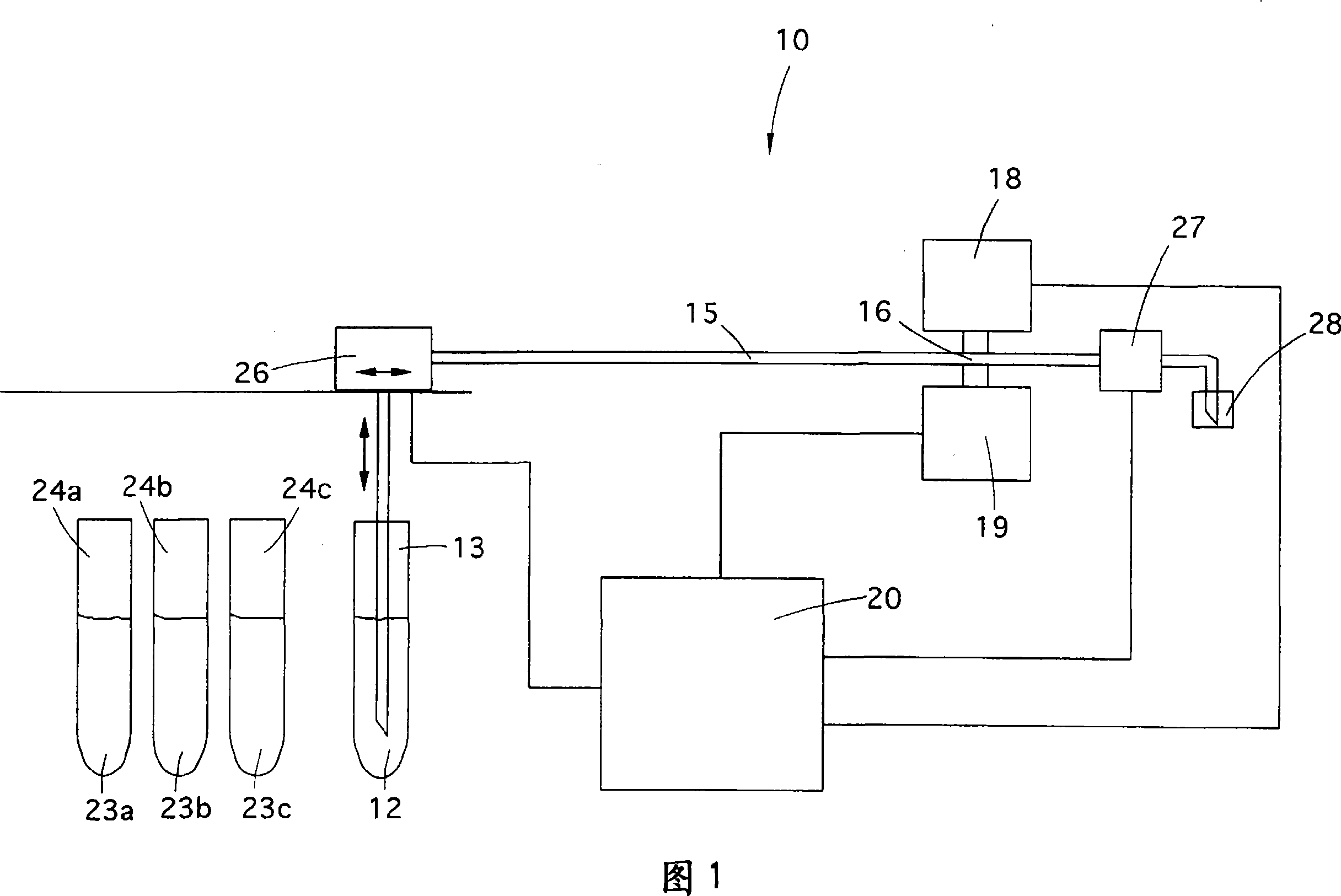
Method for calibrating machines for the analysis of characteristic parameters of the blood connected to its density, such as erythrocytesedimentation rate and/or red corpuscles aggregation rate
ActiveCN101228426AImprove accuracyLimited margin of errorMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSedimentation analysisOptical density measurementRed blood cell
A method for calibrating an instrument (10) adapted to perform the analysis of a blood sample (12) by measuring erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and / or erythrocyte aggregation, wherein said measurement is performed by using a Realized by the optical density kinetics obtained by measuring the optical density change of a blood sample (12) over a certain time interval, the method comprises the step of measuring, wherein by the same instrument (10) that performs the optical density measurement on said blood sample (12) The optical density of at least two latexes (23a, 23b, 23c) or turbidimetric samples is measured. Each of said at least two latexes (23a, 23b, 23c) has a known optical density that is reproducible, measurable and mutually distinct. The method also includes a comparison step in which the difference between the optical density values of said latex (23a, 23b, 23c) obtained from measurements made by the instrument (10) and known optical density values is calculated to allow determination of At least one correction factor may be used to calibrate said instrument (10).
Owner:ALIFAX
Levonorgestrel tablet and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN103877058AQuality improvementRapid dissolutionOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMagnesium stearateChemistry
The invention discloses a levonorgestrel tablet and a preparation process thereof. The tablet is prepared from levonorgestrel, lactose, pregelatinized starch, hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose, carboxymethyl starch sodium, polysorbate-80, 12% pregelatinized starch for slushing, aerosil, magnesium stearate and gastric-soluble film coating premixed agent. The preparation process comprises the following steps: preparing a tablet core, coating and the like. Application on 30 females indicates that the levonorgestrel tablet has a good contraception effect, hardly influences erythrocyte sedimentation rate, has the total effective rate of 95 percent, and has the characteristics of few administration times, smooth plasma concentration, long duration and the like.
Owner:邵娜
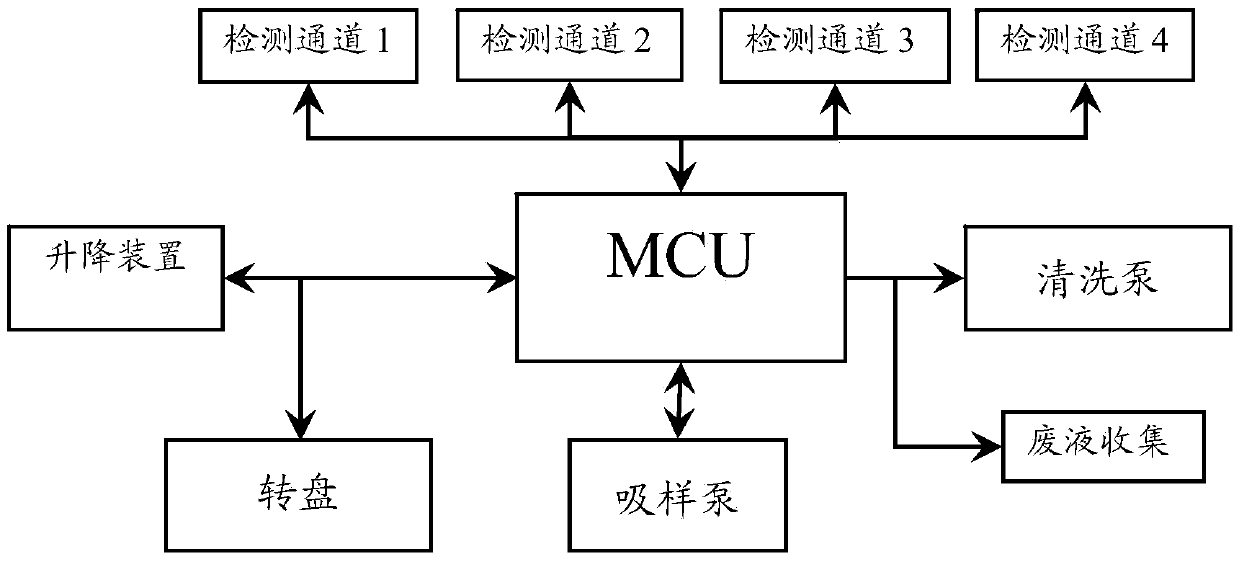
Automatic control device for detecting erythrocyte sedimentation rate data
InactiveCN105547937ASatisfy precise testing requirementsESR results are accurateSedimentation analysisAutomatic controlEngineering
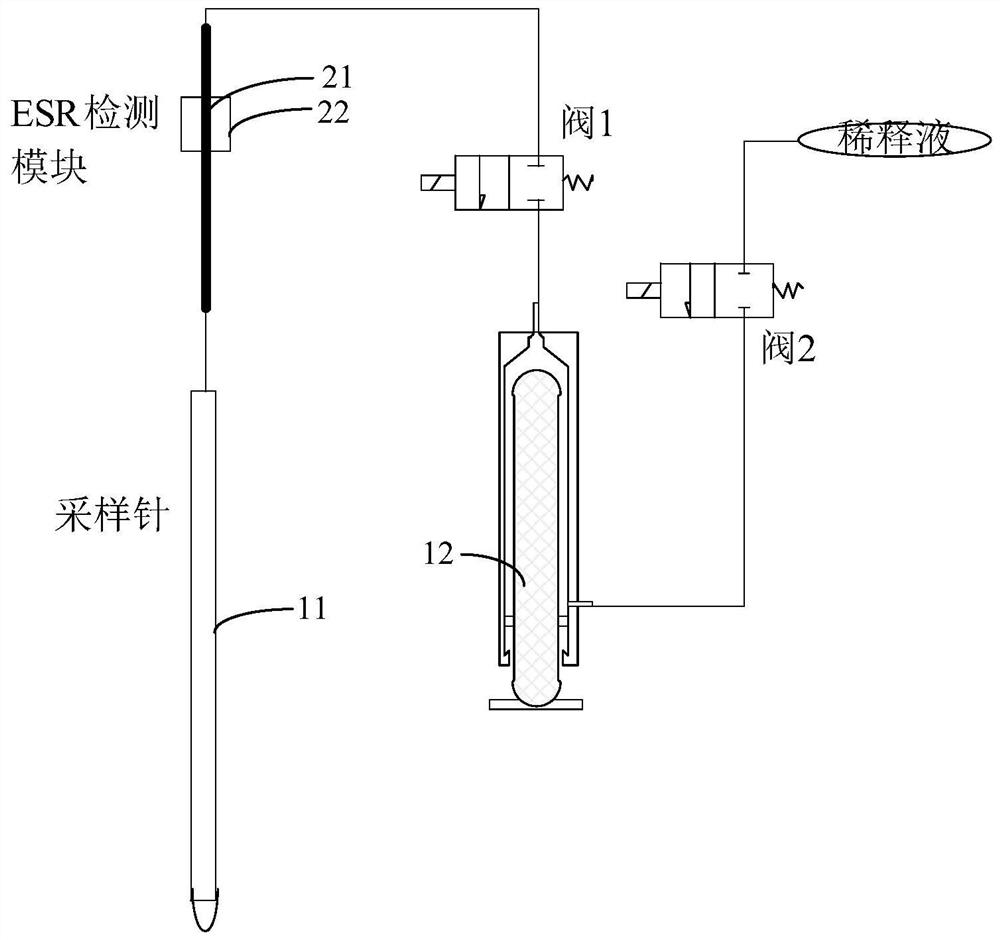
The invention provides an automatic control device for detecting erythrocyte sedimentation rate data. The automatic control device comprises a sample introduction syringe, a first control valve, an erythrocyte sedimentation rate detecting tube, a sample suction pump, a cleaning pump and an erythrocyte sedimentation rate detection platform, wherein one end of the sample introduction syringe is inserted into a blood sample while the other end of the sample introduction syringe is connected with one end of the first control valve, the other end of the first control valve is connected with one end of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate detecting tube, the other end of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate detecting tube is connected with one end of the sample suction pump, the other end of the sample suction pump is communicated with atmosphere, the other end of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate detecting tube is further connected with one end of the cleaning pump, the other end of the cleaning pump is connected with a cleaning solution, and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate detecting tube is placed on the erythrocyte sedimentation rate detection platform. Through automatic sample injection and automatic reading, erythrocyte sedimentation rate detection results, i.e., Westergren-process erythrocyte sedimentation rate results, are more accurate and reliable; so requirements for clinical accurate detection are met and accurate clinical diagnosis service is provided.
Owner:重庆异符科学仪器有限责任公司
Sample density separation liquid and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106047795ASpeed up the sinkingImprove permeabilityEpidermal cells/skin cellsCulture processExfoliative cytologySemi automatic
The invention discloses sample density separation liquid which comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 5-10% of glycerin, 3-5% of ethanol, 3-5% of sodium chloride, 79.8-88.9% of double distilled water and 0.1-0.2% of tea saponin. By adopting the sample density separation liquid, the cells of diagnostic value can naturally sedimentated more quickly while the erythrocyte sedimentation interference is reduced, thus a microscopic examination slice has clearer microscopic examination view and good cell dyeing contrast, and the sample density separation liquid can be widely applied to the exfoliative cytology specimens of gynecology, non-gynecology and the like and to a manual, semi-automatic or full-automatic liquid-based cell slide preparation process.
Owner:HANGZHOU HEALTHSKY BIOTECH CO LTD
Leflunomide tablet and preparation technology thereof
InactiveCN103989675AQuality improvementRapid dissolutionAntipyreticAnalgesicsMagnesium stearateDissolution
The invention discloses a leflunomide tablet and a preparation technology and use thereof. The product is prepared from leflunomide, milk sugar, pregelatinized starch, hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose, carboxymethyl starch sodium, polysorbate-80, 12% slushing pregelatinized starch, magnesium stearate and a gastric soluble film coating premix. The production method comprises the steps of fabricating tablets and coatings, and the like. The leflunomide tablet disclosed by the invention is high in dissolution rate, good in stability, good in anti-inflammatory analgesic effect, and small in effect on erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and the total effective rate is 85%. The drug disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of being fewer in medication administration times, stable in plasma concentration, long in lasting time and the like.
Owner:王俊国
Full-automatic Westergren's method-based erythrocyte sedimentation rate analyzer
ActiveCN111610339AReduce manual errorsReduce reading errorsBiological testingAgainst vector-borne diseasesAssayLaboratory technicians
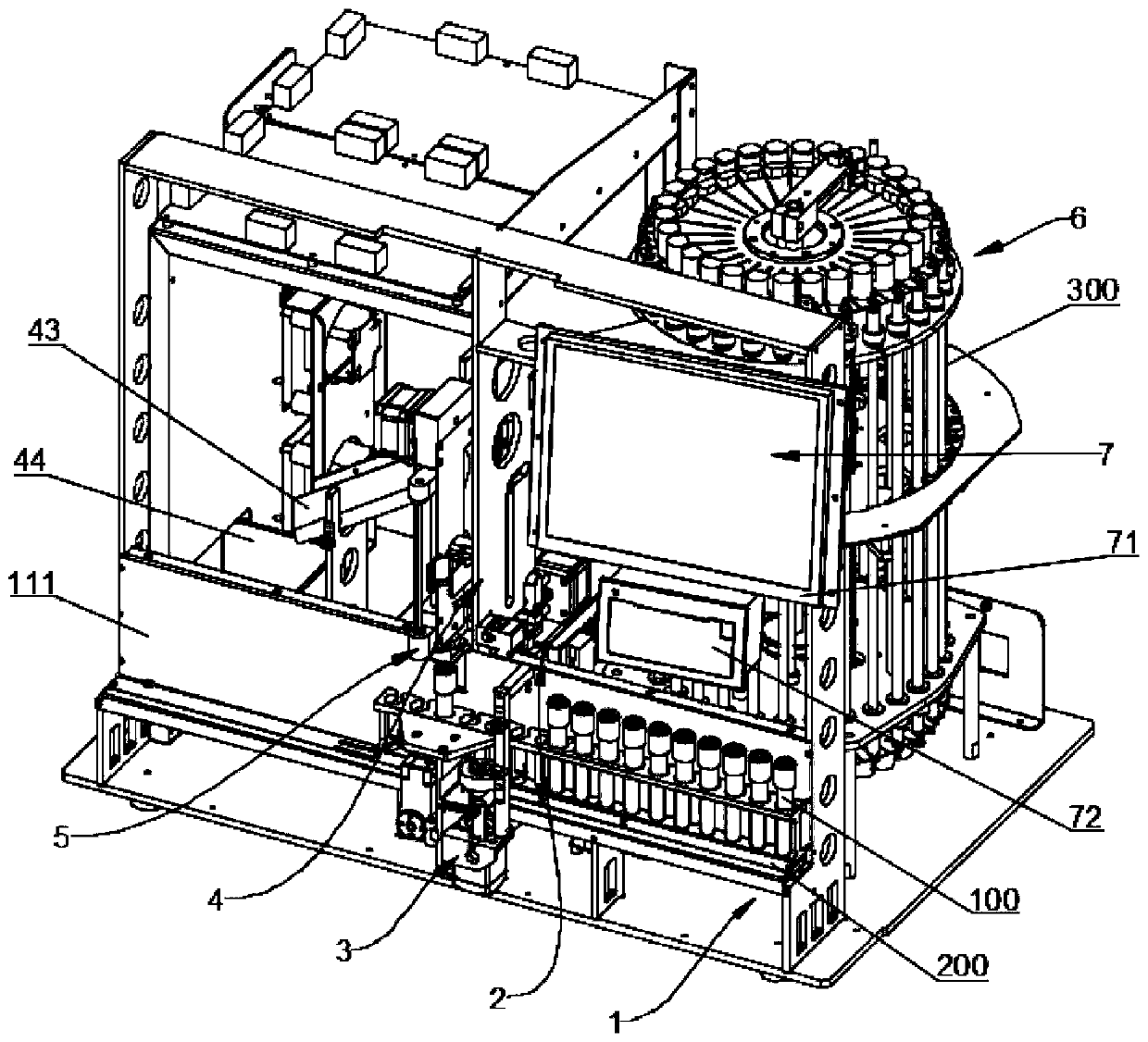
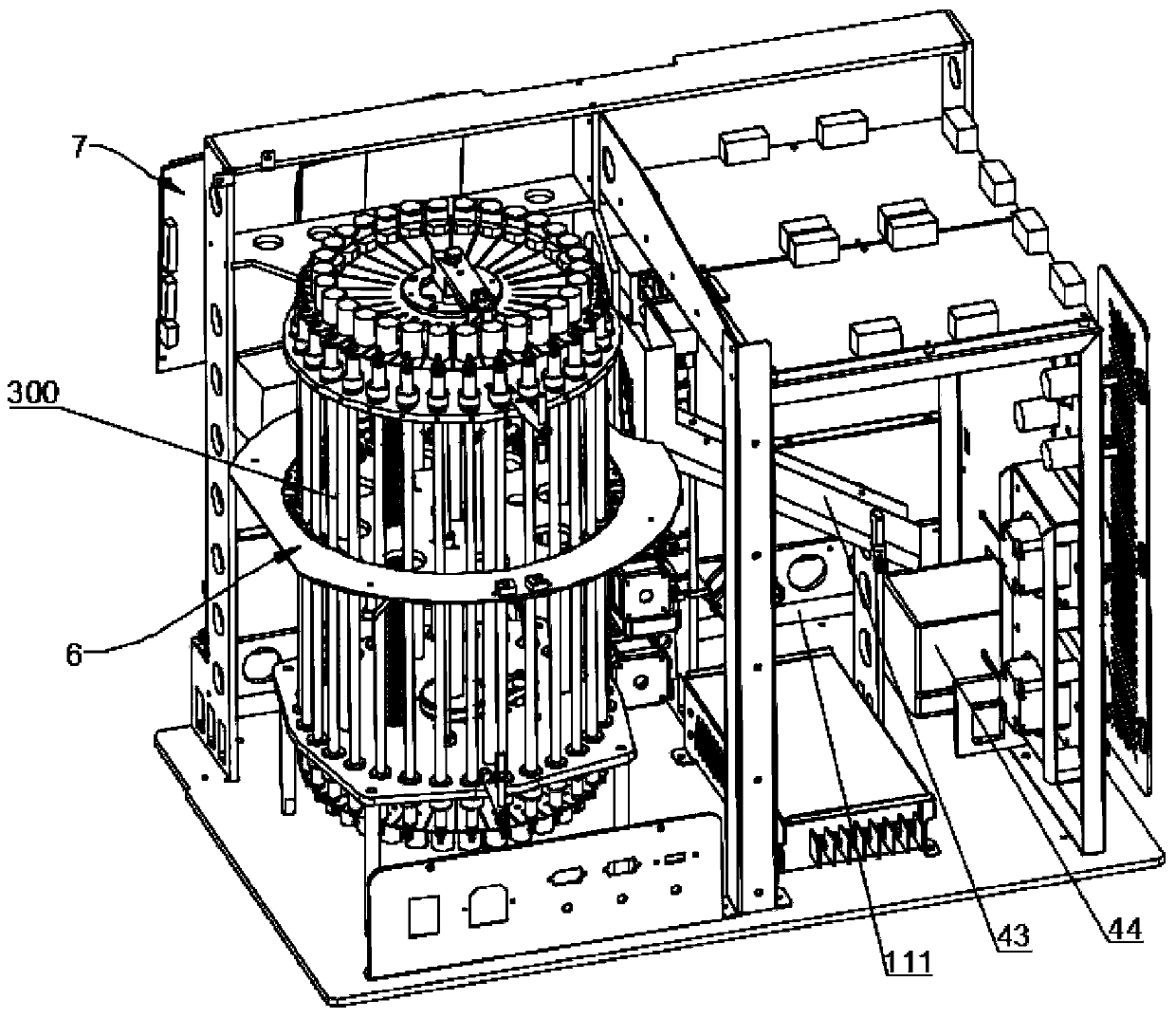
The invention relates to a full-automatic Westergren's method-based erythrocyte sedimentation rate analyzer. A sample injection frame module is arranged on the foremost side of the analyzer, a shaking-up module is arranged in the middle spare position of the sample injection frame module, a code scanning device is arranged on one side of the sample injection frame module, and a liquid path modulefor sucking samples, diluent and cleaning liquid is installed on one side of a bottom plate; a pipe placing frame module for placing a measuring pipe and driving the measuring pipe to rotate is mounted on the bottom plate; a cleaning position lifting module for pushing and pulling a piston in the measuring pipe to realize the functions of extracting cleaning liquid and releasing the liquid is mounted on one side of the pipe placing frame module; a cleaning nozzle is correspondingly arranged under the cleaning position lifting module, and a detection lifting module is arranged on one side of the pipe placing frame module; a puncture sampling module is of a double-needle structure and comprises an outer needle for puncture and an inner needle for sample suction. The erythrocyte sedimentationrate analyzer is fully automatic, thereby liberating the manpower of a laboratory technician in a laboratory, and reducing the errors of manual operation and reading; and with an advanced infrared liquid level reading technology, the measurement result is more accurate.
Owner:山东艾科达生物科技有限公司
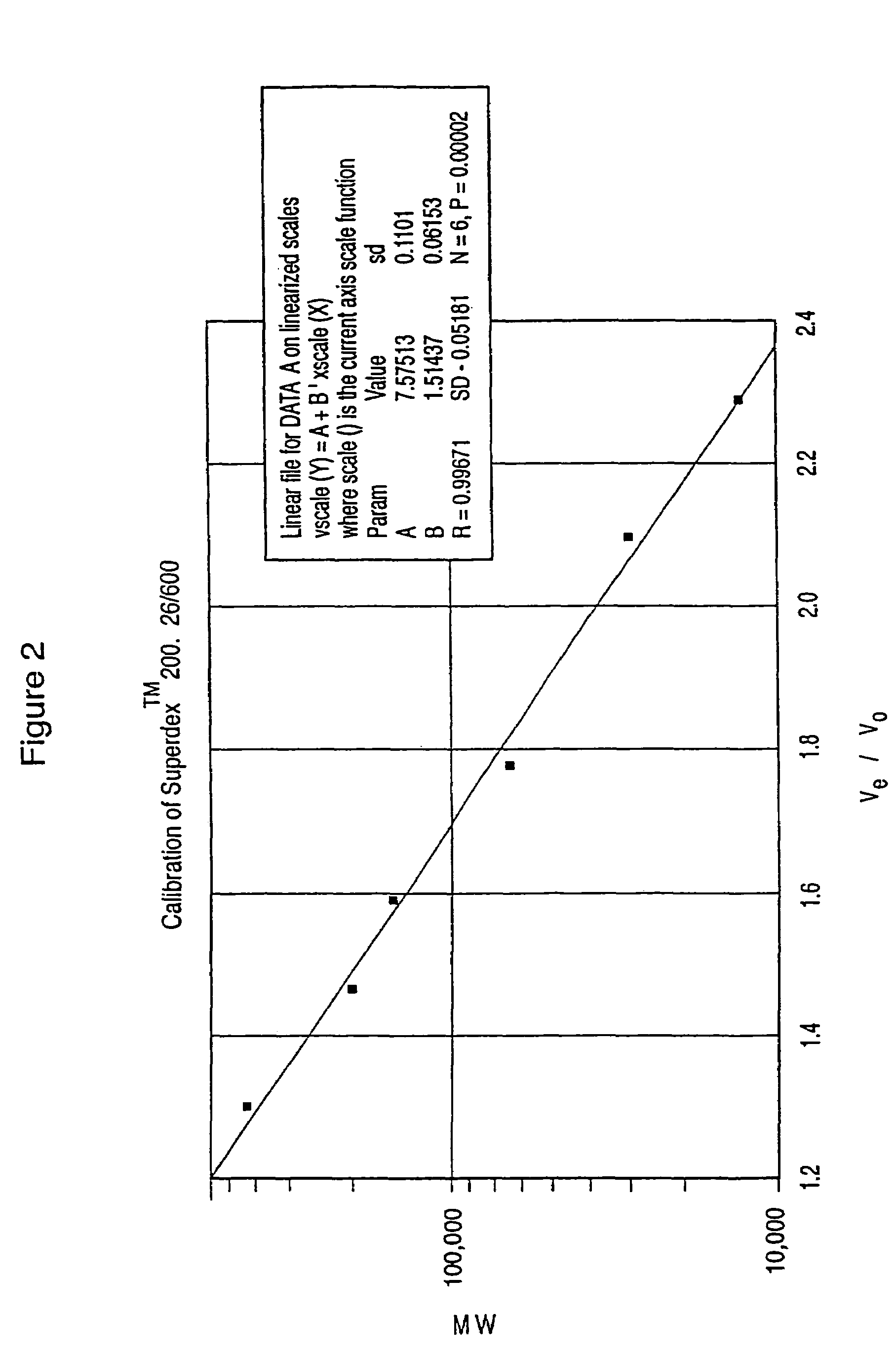
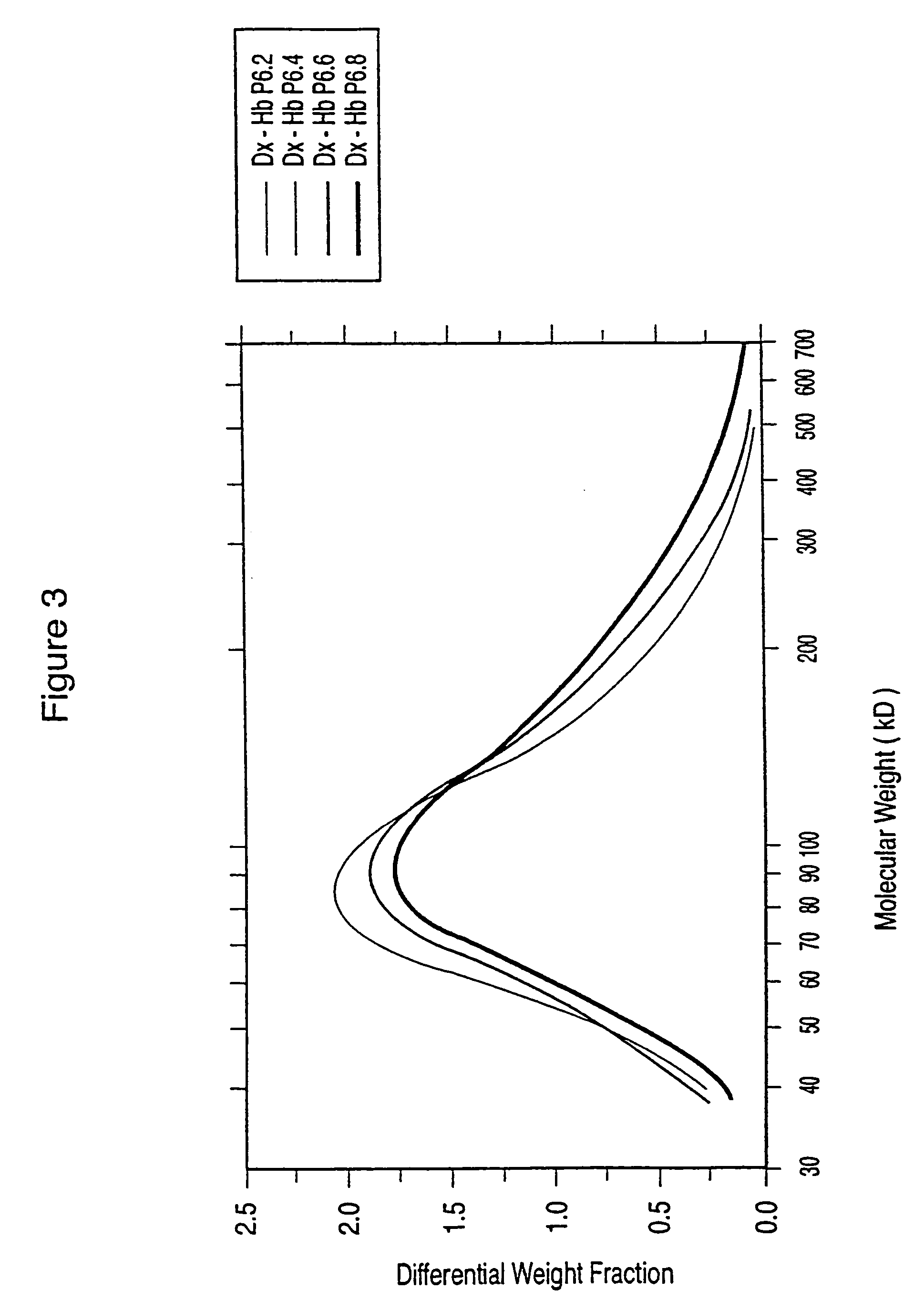
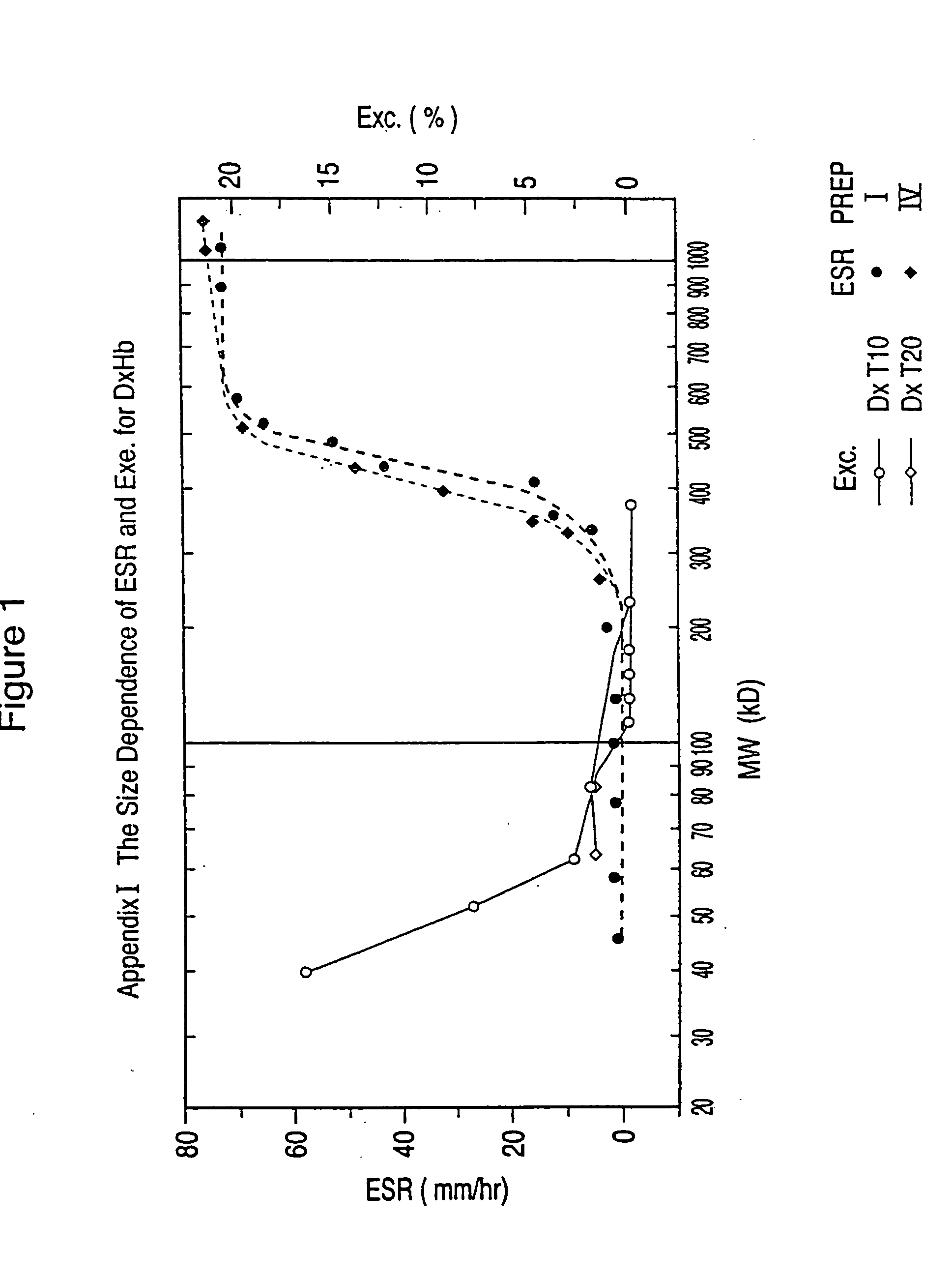
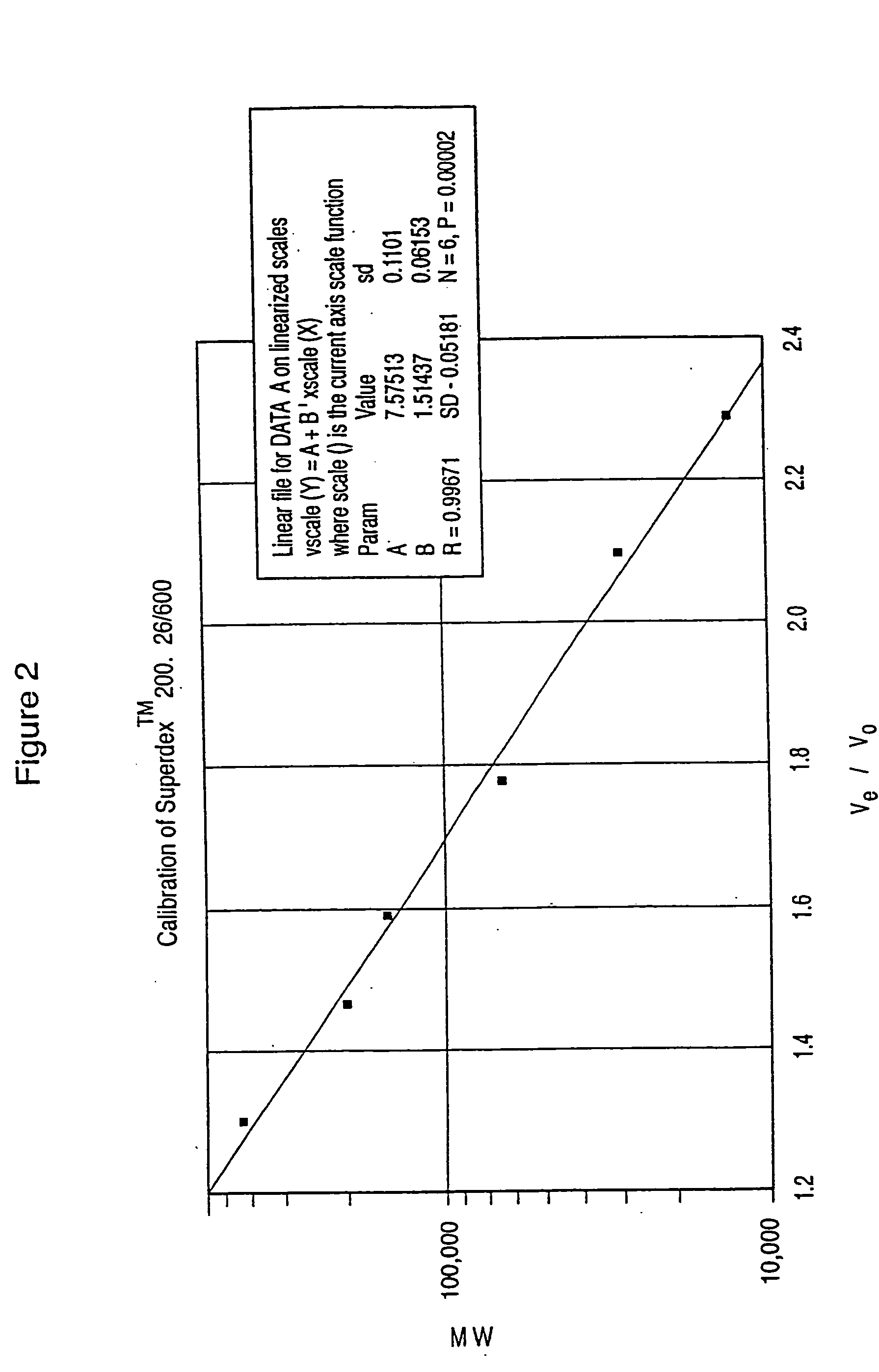
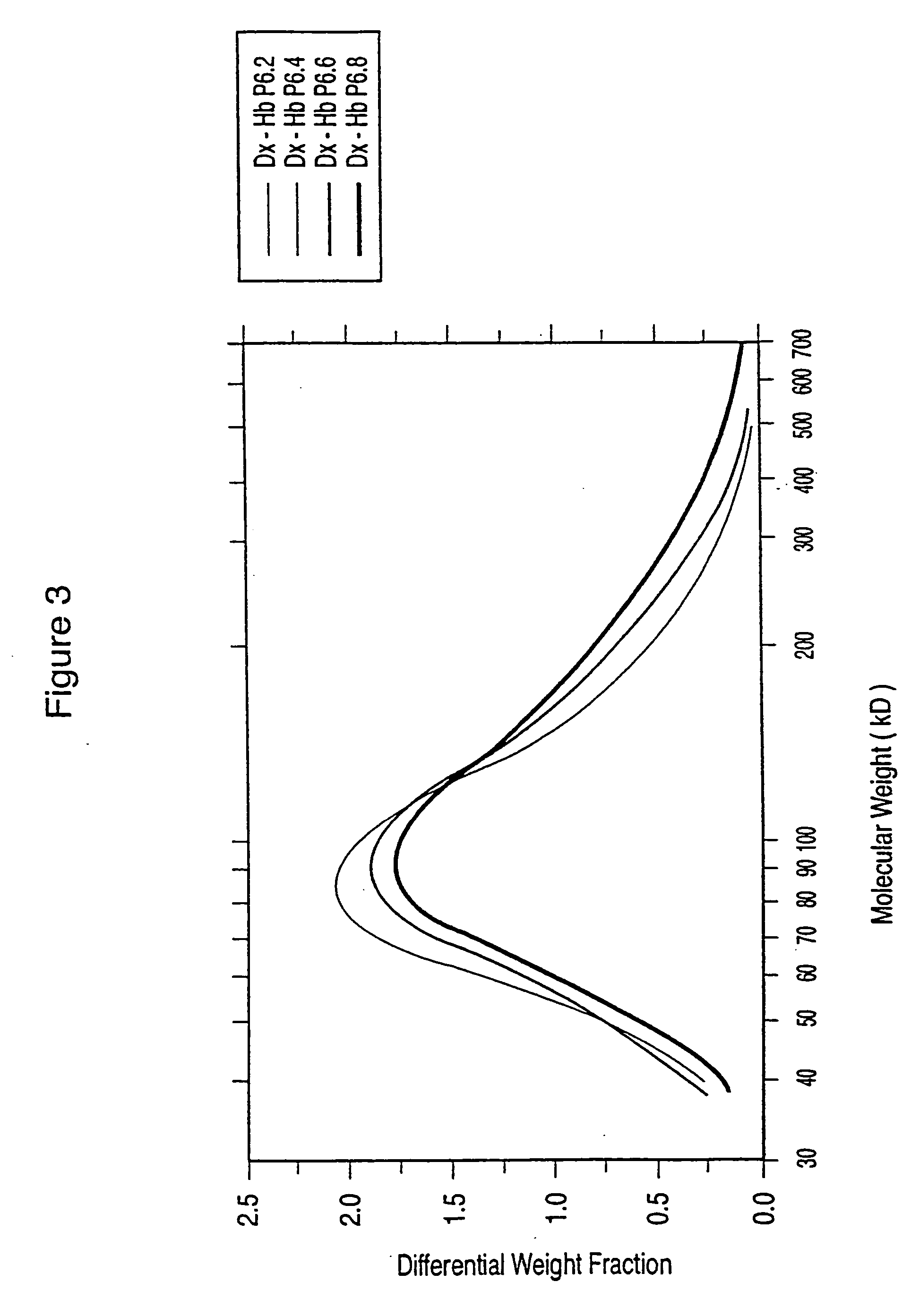
Dextran-hemoglobin conjugates as blood substitutes
An hemoglobin (Hb)-Dextran (Dx) conjugate having a molecular weight between 50 kd and 500 kD provides a blood substitute that results in acceptable erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and excretion rate (EXC) values. DxHb conjugates of the invention can be used for a variety of purposes as an alternative to blood.
Owner:DEXTROSANG CORP
Dextran-hemoglobin conjugates as blood substitutes
InactiveUS20050113289A1Haemoglobins/myoglobinsMammal material medical ingredientsMedicineExcretion process
An hemoglobin (Hb)-Dextran (Dx) conjugate having a molecular weight between 50 kd) and 500 kD provides a blood substitute that results in acceptable erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and excretion rate (EXC) values. DxHb conjugates of the invention can be used for a variety of purposes as an alternative to blood.
Owner:DEXTROSANG
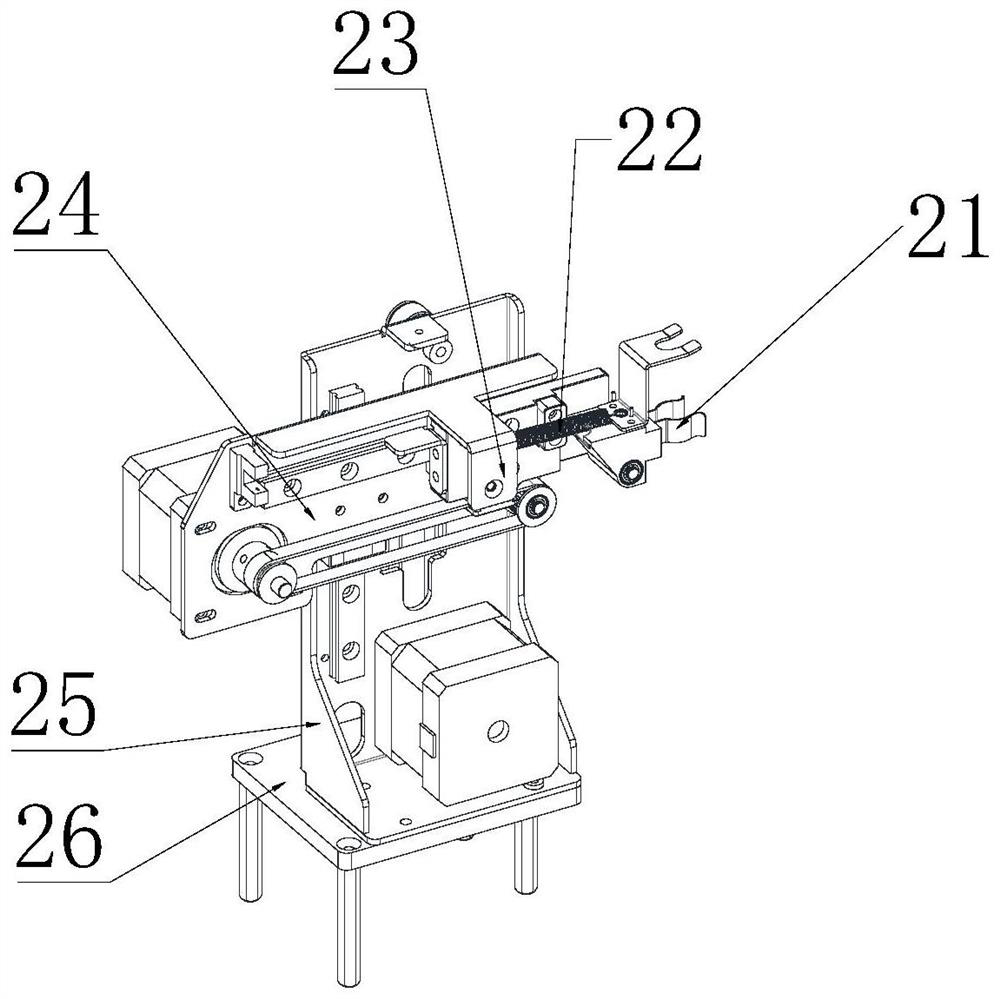
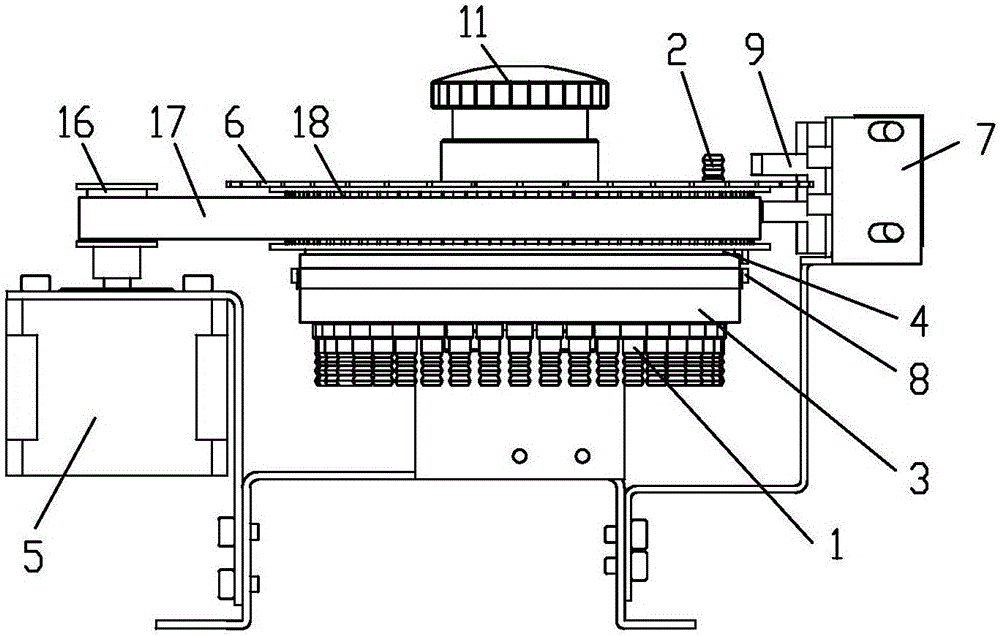
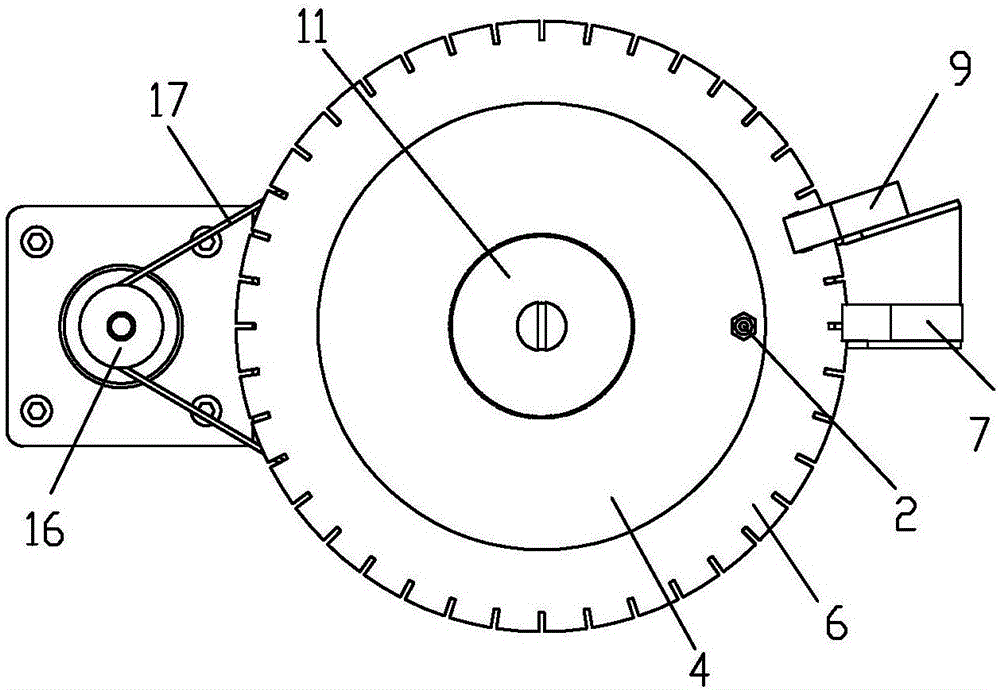
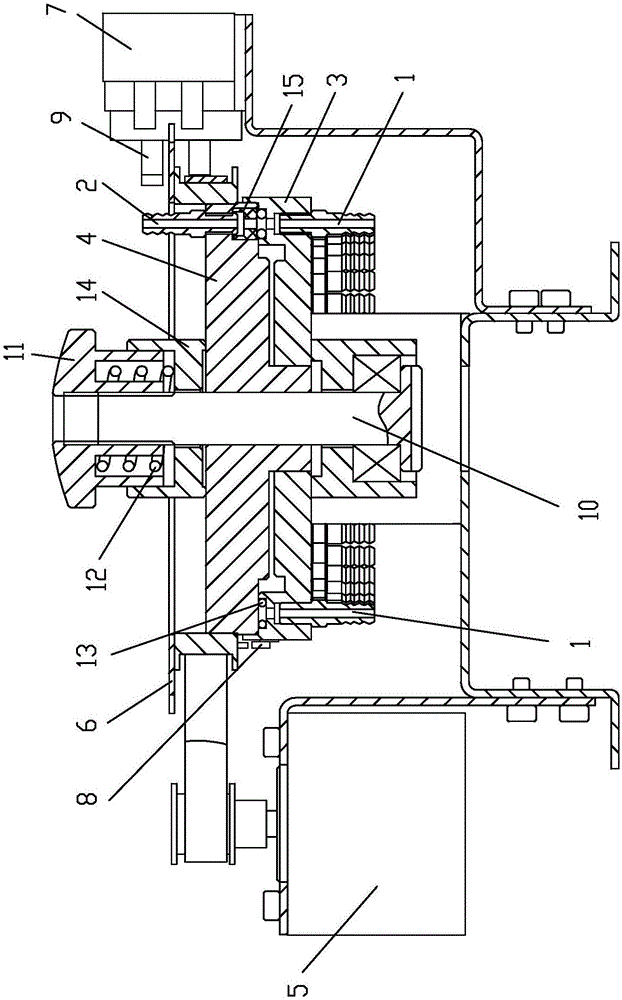
Blood sample feeding device for precise Westergren method erythrocyte sedimentation rate detector
ActiveCN106353227APrecise positioningMeet the requirements of testing instruments with high detection efficiencySedimentation analysisLocation detectionControl system
The invention disclsoes a blood sample feeding device for a precise Westergren method erythrocyte sedimentation rate detector. The blood sample feeding device comprises a control system and a sample feeding channel; the sample feeding channel is communicated through fixed connectors and a movable connector; the plurality of fixed connectors are distributed on the same circumference of a fixed disc; one movable connector is fixedly connected onto a rotary table; when the rotary table is driven by a motor through a synchronous belt transmission structure to rotate, the movable connector is communicated with the plurality of fixed connectors; an indexing plate is fixedly connected onto the rotary table; the control system is used for acquiring rotary table position information through a first position detection device and the indexing plate; the control system is further used for acquiring position information of the fixed connectors, which are communicated with the movable connector, in the plurality of fixed connectors through a second position detection device. The blood sample feeding device for the precise Westergren method erythrocyte sedimentation rate detector has the beneficial effects that the requirements on detection instruments with high detection efficiency can be effectively met; the rotary table is accurately positioned; the blood sample feeding device is simple and compact in structure, convenient to operate, low in manufacturing cost and long in service life.
Owner:CHONGQING NANFANG NUMERICAL CONTROL EQUIP
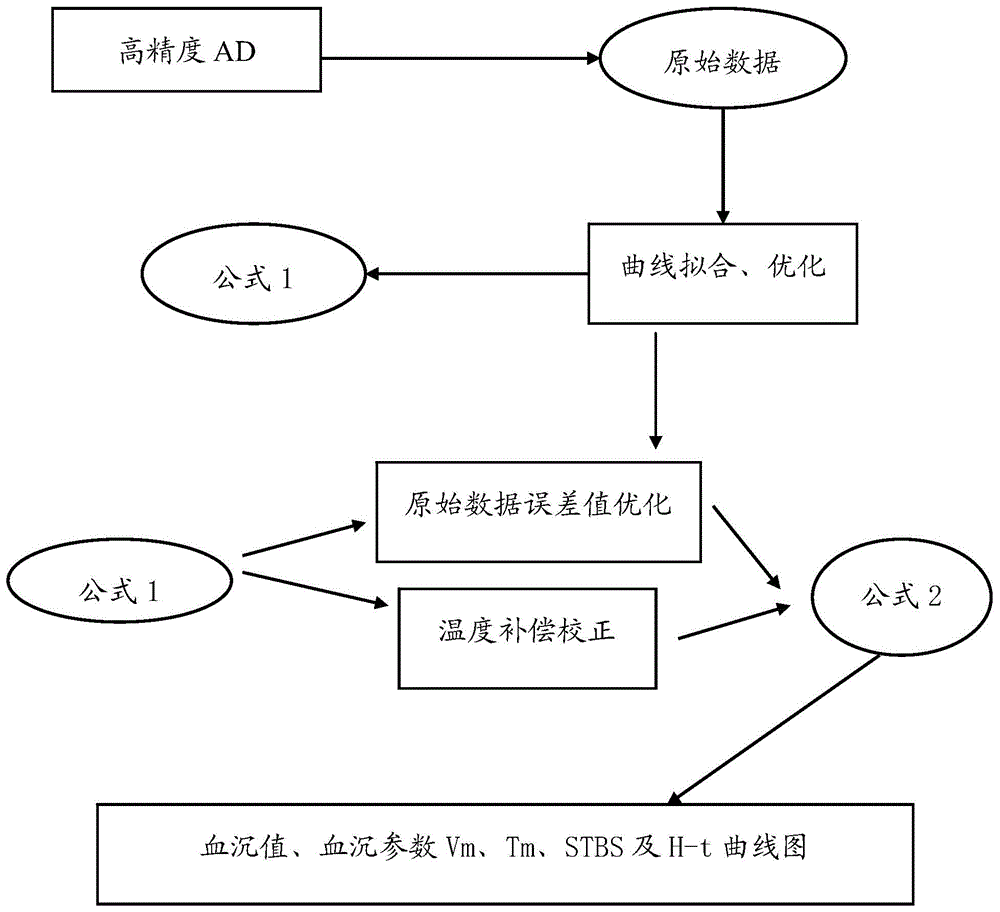
Precise detecting method for obtaining erythrocyte sedimentation data
The invention discloses a precise detecting method for obtaining erythrocyte sedimentation data. The precise detecting method comprises the following steps: step I. acquiring original erythrocyte sedimentation data by virtue of an analog-digital conversion acquiring device of an erythrocyte sedimentation deposition instrument, performing array loop traverse checking on the original erythrocyte sedimentation data, eliminating reading errors of the original erythrocyte sedimentation data, and screening the accurate original erythrocyte sedimentation data; step II, fitting the original erythrocyte sedimentation data through a least square method to generate a fitted curve to establish a mathematical model so as to obtain the initial erythrocyte sedimentation data; step III. subjecting the initial erythrocyte sedimentation data obtained in the step 2 to temperature compensation and error value elimination to obtain the final erythrocyte sedimentation data; and a step IV. feeding the calculated erythrocyte sedimentation data back to a data receiving end of the erythrocyte sedimentation deposition instrument for displaying.
Owner:重庆异符科学仪器有限责任公司
Rapid erythrocyte sedimentation rate measuring method and measuring device thereof
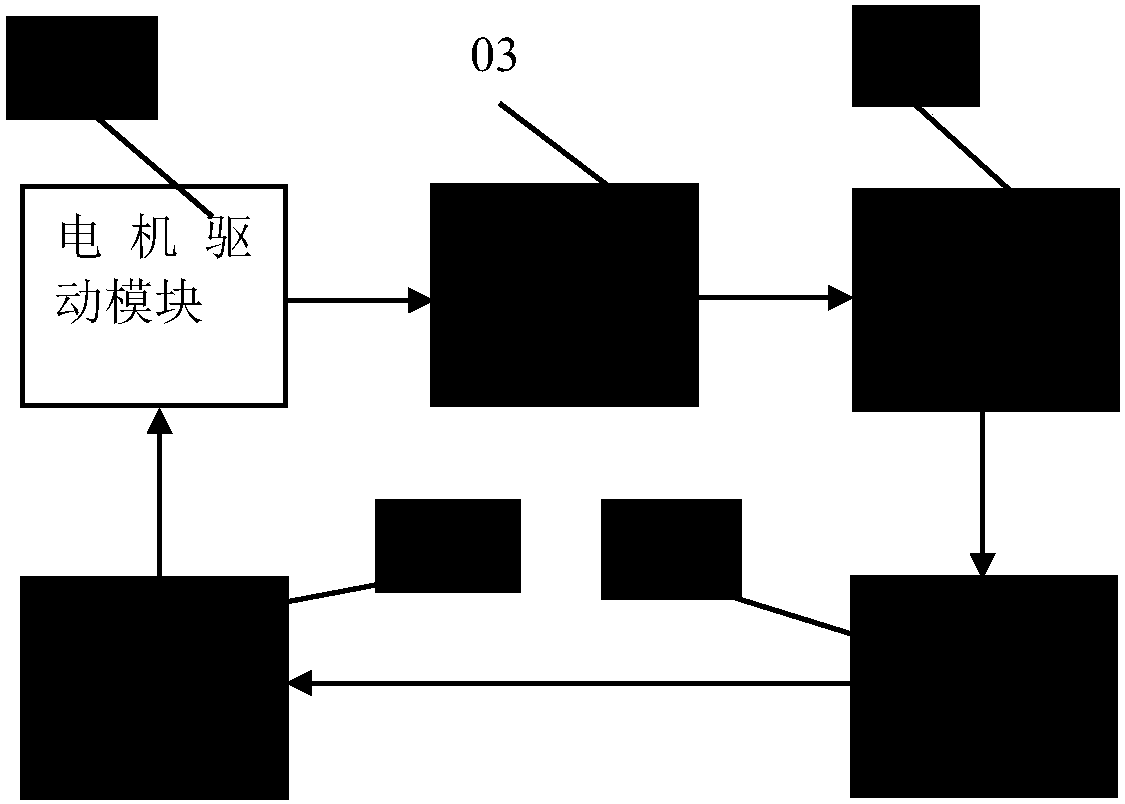
InactiveCN109752295ACalculation method is simpleReduced measurement timeSedimentation analysisMotor driveFast measurement
The invention discloses a rapid erythrocyte sedimentation rate measuring method and a measuring device thereof. The measuring method comprises the steps that the geometric size of an erythrocyte sedimentation rate tube is modified, a photovoltaic detecting sensor is used for detecting the height value change of the sedimentation surface of erythrocyte in the modified erythrocyte sedimentation ratetube in the erythrocyte sedimentation process, an erythrocyte sedimentation rate Westergren value is obtained by a modern signal processing method and a regression algorithm, the measuring time of the rapid measuring method is half the time of a traditional Westergren method, and the correlation of the rapid measuring method with the Westergren method achieves 99%. The measuring device comprisesa microprocessor 01, a motor driving module 02, a motor execution module 03, a mechanical motion module 04 and a photovoltaic module 05. A rapid erythrocyte sedimentation rate analyzing meter is established by the rapid erythrocyte sedimentation rate measuring method and the measuring device thereof, a rapid erythrocyte sedimentation, rapid painting of an erythrocyte sedimentation rate value and erythrocyte sedimentation rate process curve can be realized, erythrocyte sedimentation rate sample measuring of a large batch can be automatically carried out, and the practical value is high.
Owner:苏州泰寿健康科技有限公司
Blood cell analyzer and cleaning method thereof
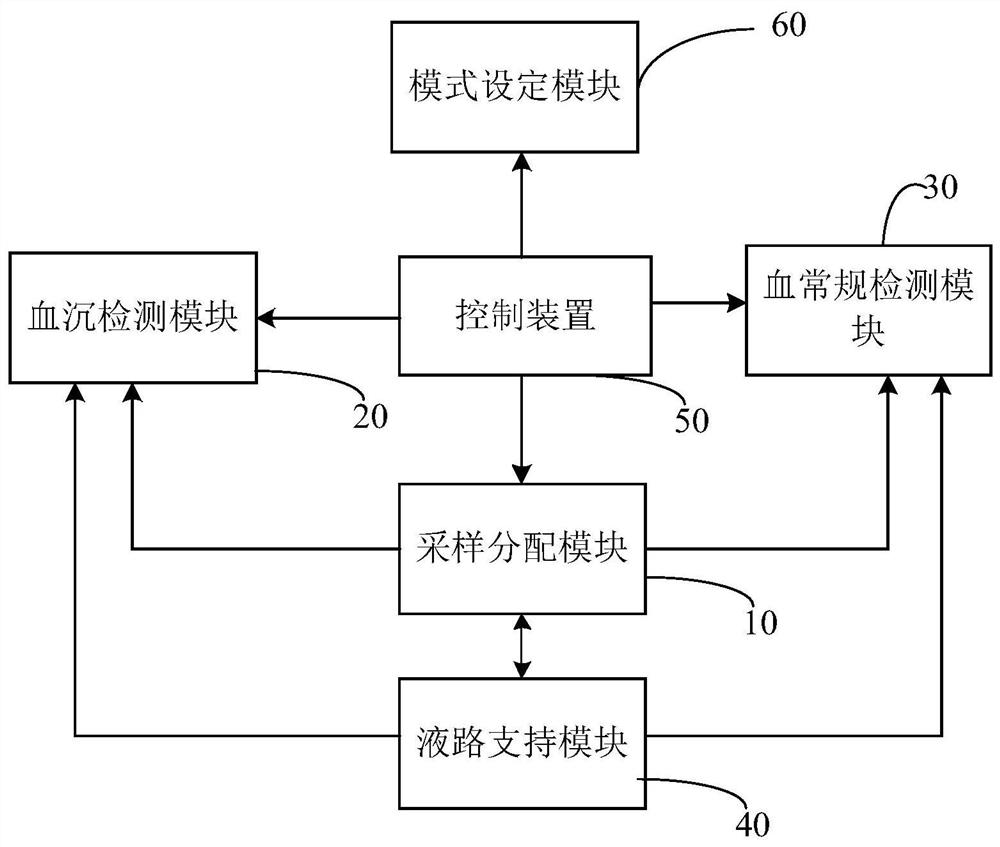
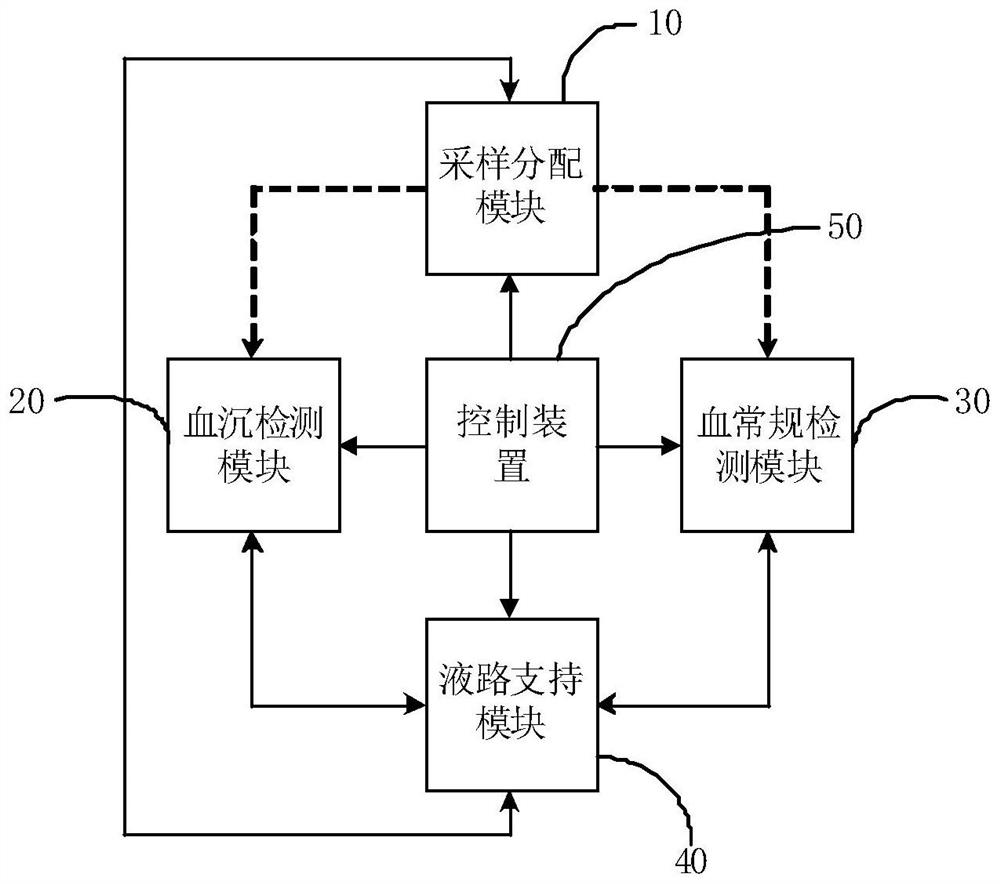
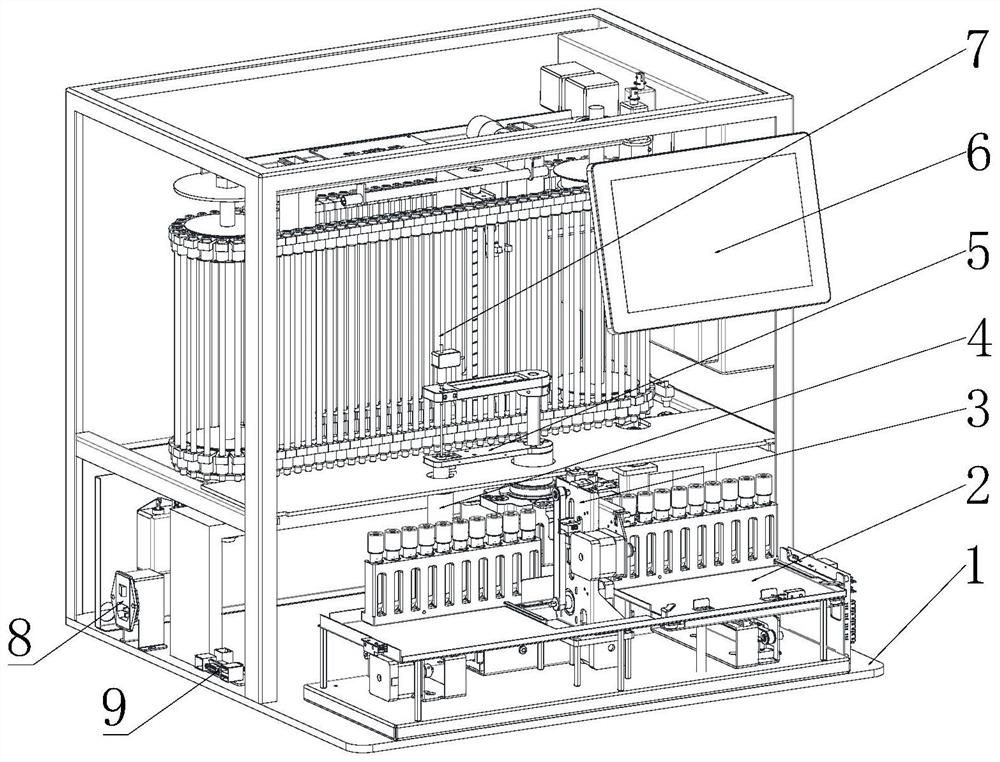
PendingCN114062205AFast measurementEasy to measureBiological particle analysisSedimentation analysisBlood specimenHematological test
The invention provides a blood cell analyzer and a cleaning method thereof. The blood cell analyzer comprises a mode setting module used for setting a working mode of the blood cell analyzer; a sampling distribution module, which is used for collecting blood samples and distributing the blood samples to the erythrocyte sedimentation rate detection module and / or the blood routine examination module; an erythrocyte sedimentation rate detection module, which is used for detecting the erythrocyte sedimentation rate of the blood sample; a blood routine detection module, which is used for performing blood routine detection on the blood sample; a liquid path supporting module, which is at least used for cleaning the sampling distribution module; a control device, which is at least used for controlling at least one of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate detection module and the blood routine detection module to operate according to a set working mode; besides, the blood cell analyzer is further provided with different cleaning modes, and the control device is further used for controlling the liquid path supporting module to execute the corresponding cleaning mode according to the set working mode so as to clean the sampling distribution module. According to the scheme, the testing speed can be increased, and the cleaning liquid consumption is reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Full-automatic dynamic erythrocyte sedimentation rate analyzer based on Westergren's method
ActiveCN111610340AWith automatic scanning functionStable structureBiological testingEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a full-automatic dynamic erythrocyte sedimentation rate analyzer based on a Westergren's method. The analyzer comprises a bottom plate; a sample injection frame module for driving a sodium citrate tube and an EDTA tube to automatically inject samples, a shaking-up module for automatically and uniformly mixing samples, a needle washing pool for washing a sampling needle, a sample adding module for adding a sample in the sample tube into a detection tube for detection, a control panel for operating an instrument and outputting a result, a turntable module, a power inputswitch, an external communication board for transmitting detection data, a filling and cleaning module for adding a sample into the detection tube, a liquid path module for cleaning, diluting and treating waste liquid, an external PCB control module, and a rack are installed on the bottom plate. The test process is processized and standardized, the test principle is the same as that of a standardWestergren's method, various interference factors of manual operation are avoided as much as possible, and the test result is objective, reliable and credible; the development of erythrocyte sedimentation rate detection in the directions of reliability, accuracy, convenience and the like is facilitated, and the test efficiency is remarkably improved.
Owner:山东艾科达生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com