Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
275 results about "Emerin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
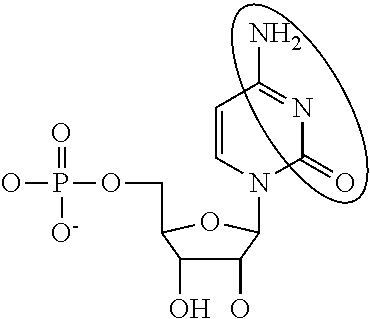
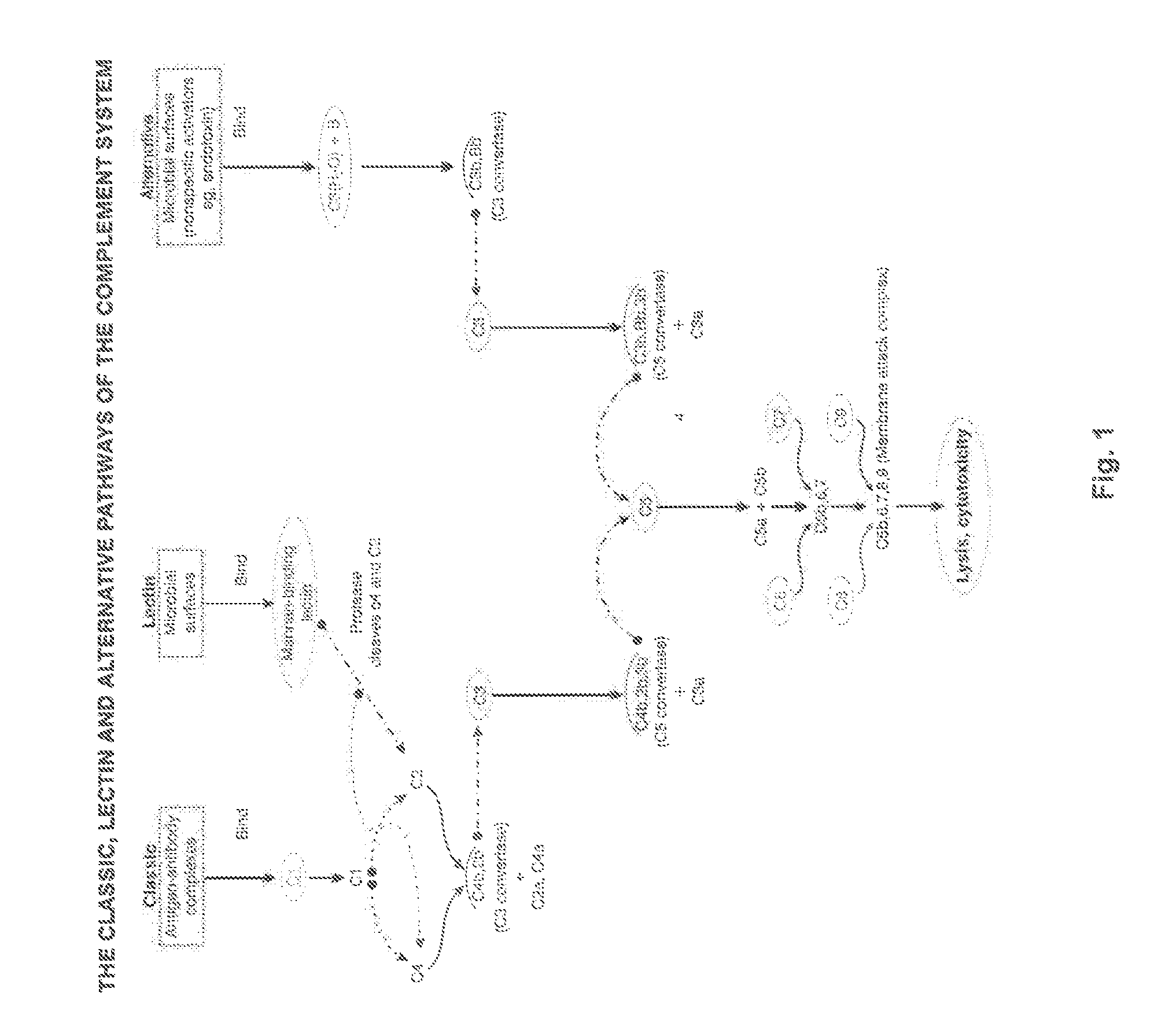
Emerin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EMD gene, also known as the STA gene. Emerin, together with LEMD3, is a LEM domain-containing integral protein of the inner nuclear membrane in vertebrates. Emerin is highly expressed in cardiac and skeletal muscle. In cardiac muscle, emerin localizes to adherens junctions within intercalated discs where it appears to function in mechanotransduction of cellular strain and in beta-catenin signaling. Mutations in emerin cause X-linked recessive Emery–Dreifuss muscular dystrophy, cardiac conduction abnormalities and dilated cardiomyopathy.
Crispr/cas systems for genomic modification and gene modulation
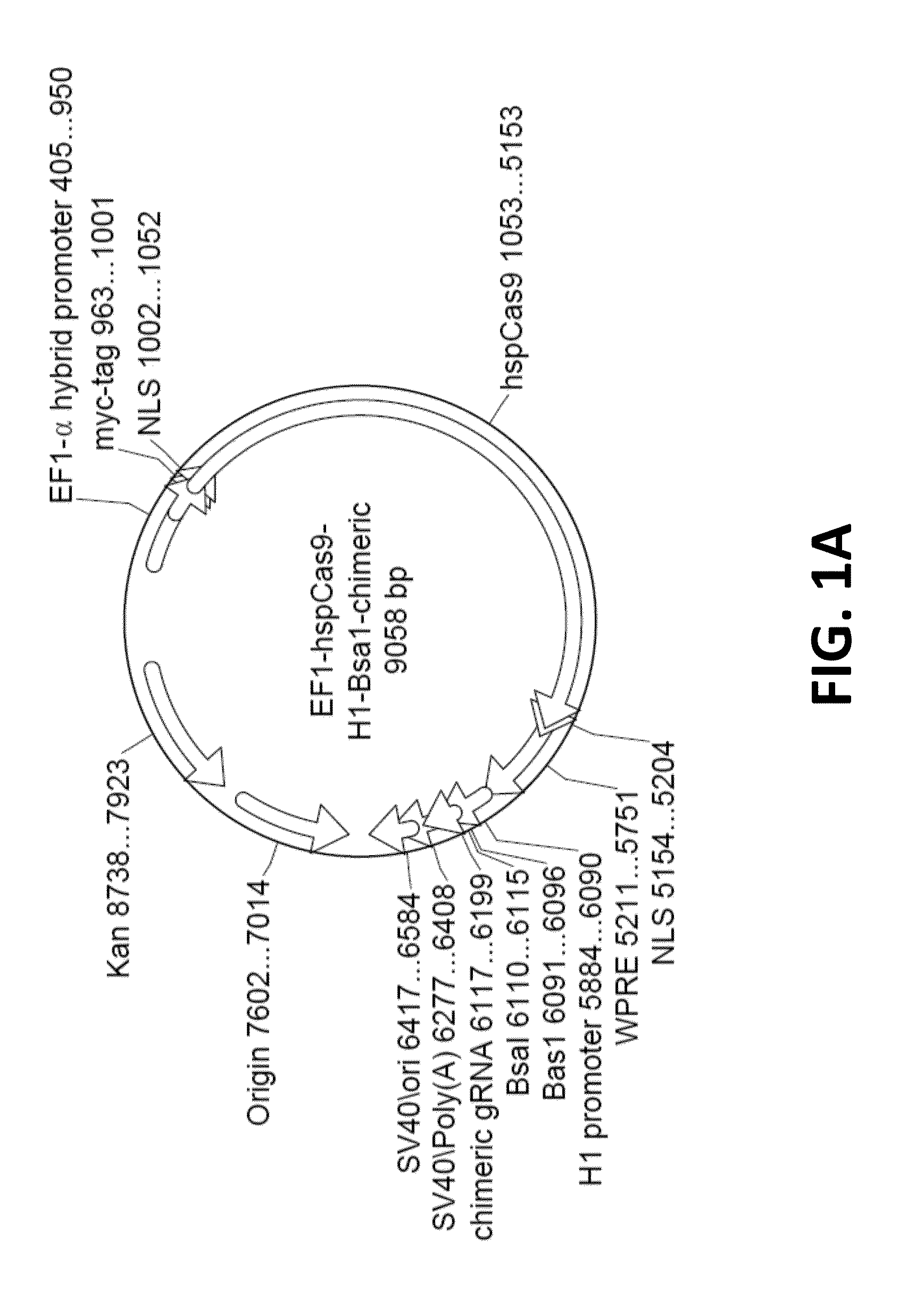
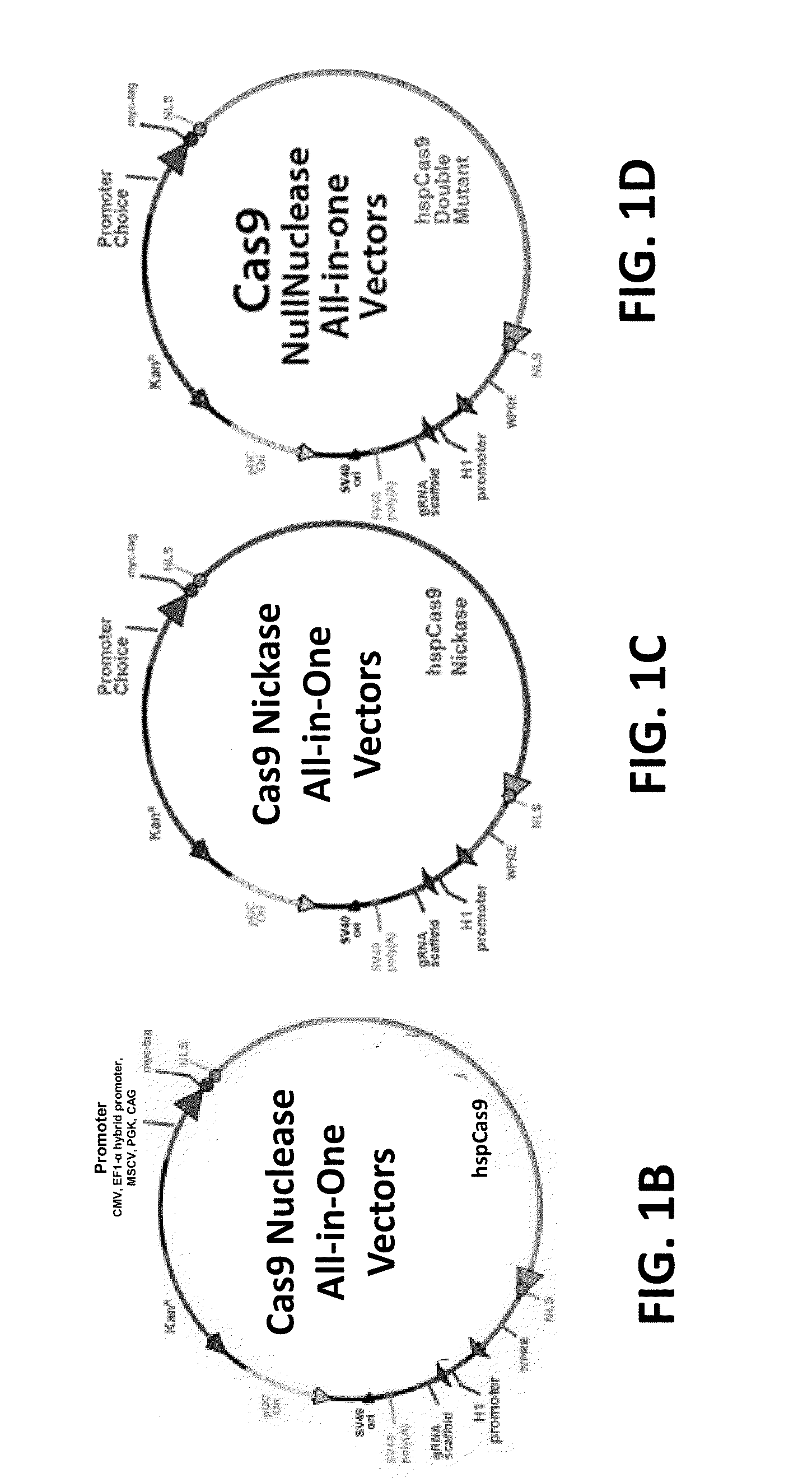
The invention relates to engineered CRISPR / Cas9 systems for genomic modification and regulation of gene expression in mammalian cells. The specification describes the design and validation of polynucleotides encoding the Streptococcus pyogenes (S. pyogenes) Cas9 gene and protein and variants of that protein, where the nucleotide sequence has been optimized for expression in mammalian cells, and also modified by fused sequences that enhance various aspects of the CRISPR / Cas system. The specification also describes systems for RNA-guided genome engineering and gene regulation in mammalian cells, including human cells.
Owner:SYST BIOSCI
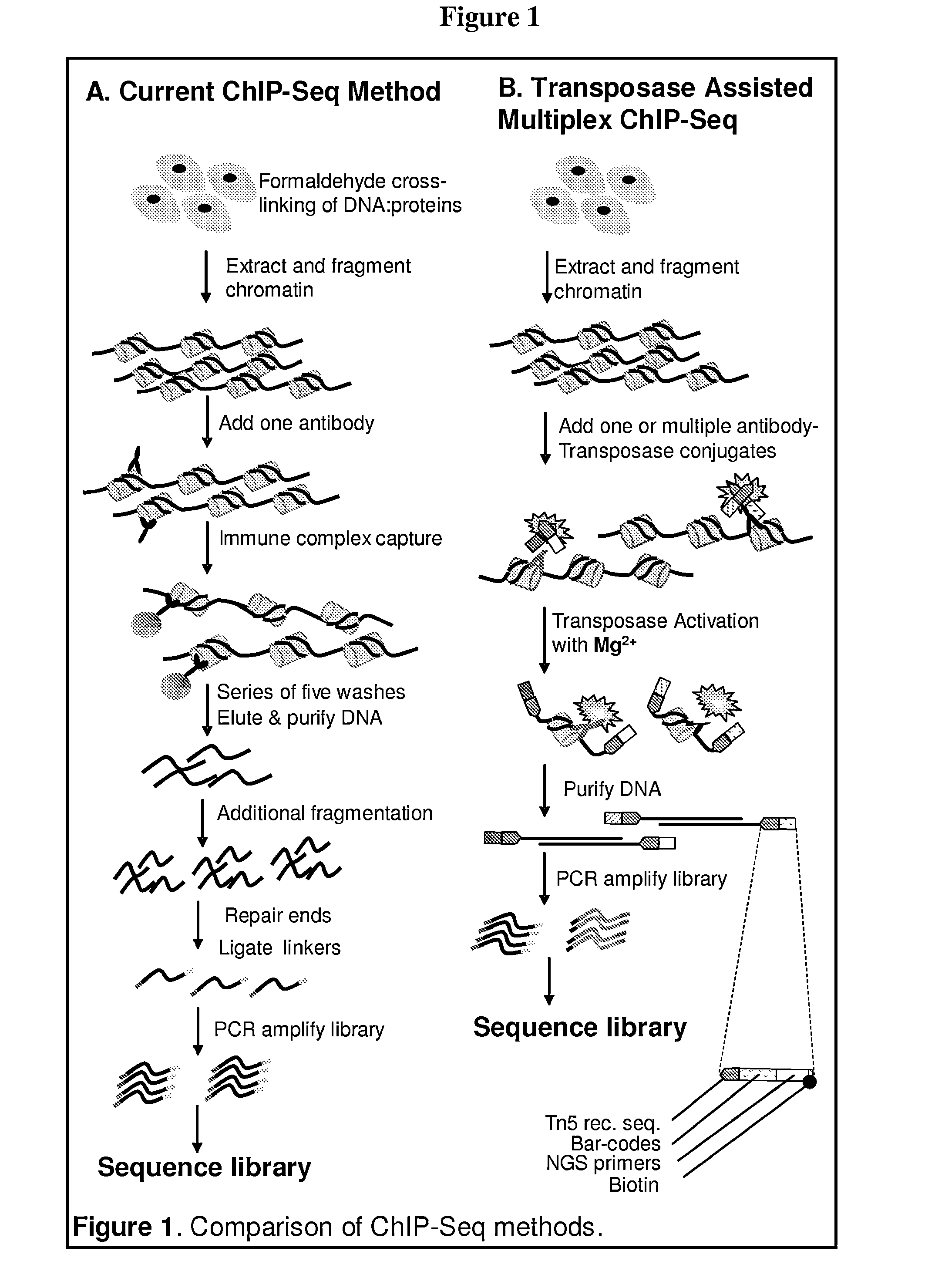
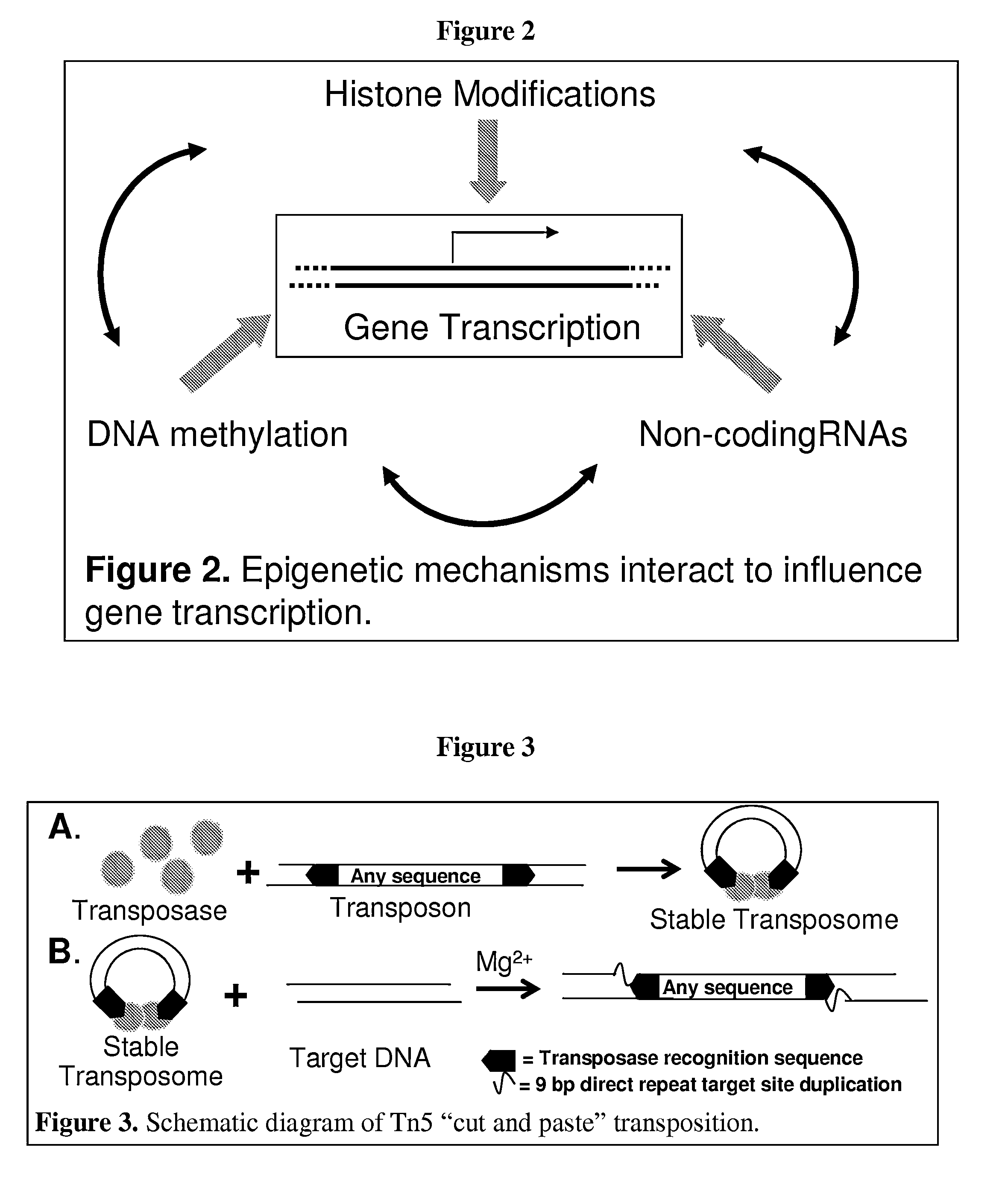
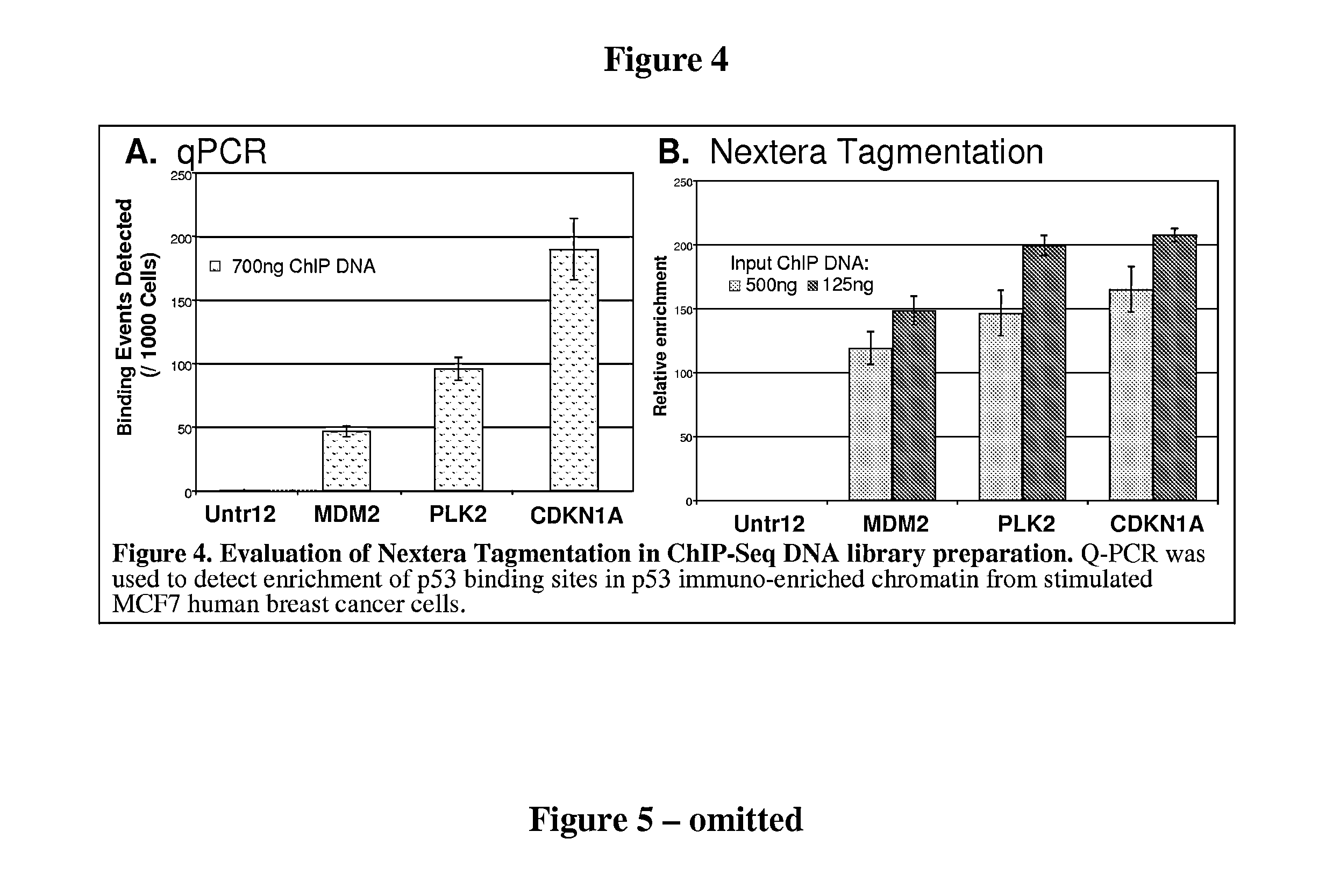
Multiplex isolation of protein-associated nucleic acids
ActiveUS20150111788A1Microbiological testing/measurementEnzyme stabilisationGenomeChromatin immunoprecipitation
The invention provides novel methods and materials for genetic and genomic analysis using single or multiplex isolation of protein-associated nucleic acids, including transposase-assisted chromatin immunoprecipitation (TAM-ChIP) and antibody-oligonucleotide proximity ligation. These methods comprise tagging and isolating chromatin or other protein-associated nucleic acids and using antibody-oligonucleotide complexes that recognize the proteins associated with such nucleic acids.
Owner:ACTIVE MOTIF INC
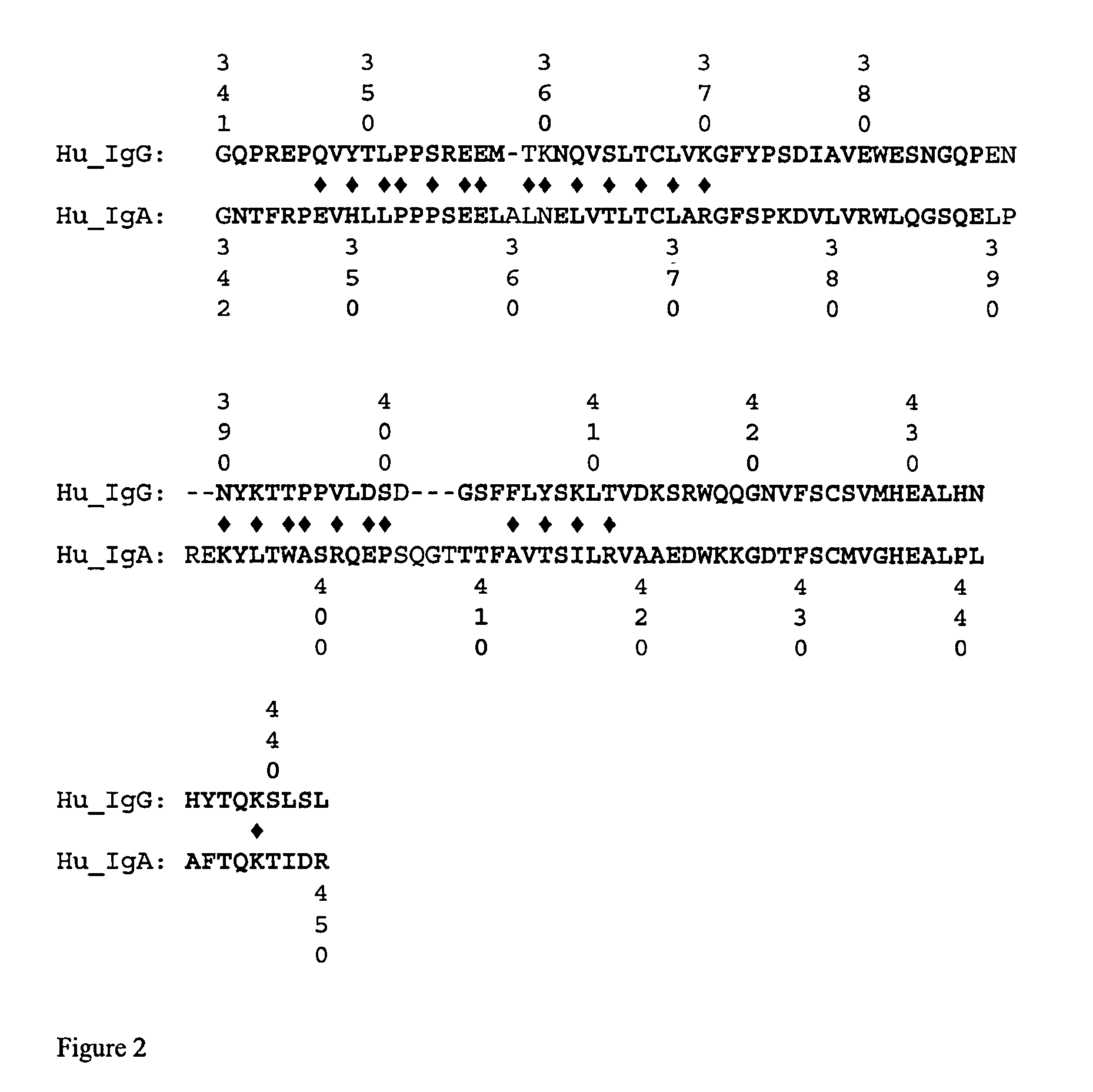
Engineered heterodimeric protein domains
ActiveUS8871912B2Strong specificityEasy to assembleHybrid immunoglobulinsSugar derivativesBiotechnologyAmino acid
The present invention provides an engineered multidomain protein including at least two nonidentical engineered domains, each of which contains a protein-protein interaction interface containing amino acid sequence segments derived from two or more existing homologous parent domains, thereby conferring on the engineered domains assembly specificities distinct from assembly specificities of the parent domains. In particular, the engineered domains form heterodimers with one another preferentially over forming homodimers. Methods of designing and using the engineered proteins are also included.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Method for predicting sensitivity to EGFR inhibitor
InactiveUS20160002741A1Accurate SensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisKRASWild type
A method for predicting sensitivity to an EGFR inhibitor includes: (a) determining whether there is a KRAS gene-derived nucleic acid or a protein thereof in a blood sample which has been collected from a subject, and whether the KRAS gene-derived nucleic acid or the protein thereof in the blood sample is wild type or mutant; and (b) determining that there is a high possibility that a tumor of the subject is sensitive to an EGFR inhibitor when a wild type KRAS gene-derived nucleic acid or a protein thereof is detected and no mutant KRAS gene-derived nucleic acid or a protein thereof is detected in the blood sample in the process (a).
Owner:TOPPAN PRINTING CO LTD
Modified mrnas encoding cell-penetrating polypeptides
InactiveUS20140371302A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesCell biologyNucleic acid
This invention relates to modified nucleic acid compositions encoding cell-penetrating polypeptides to provoke an innate immune response in a cell and methods of delivering protein-binding partners to target cells.
Owner:MODERNATX INC
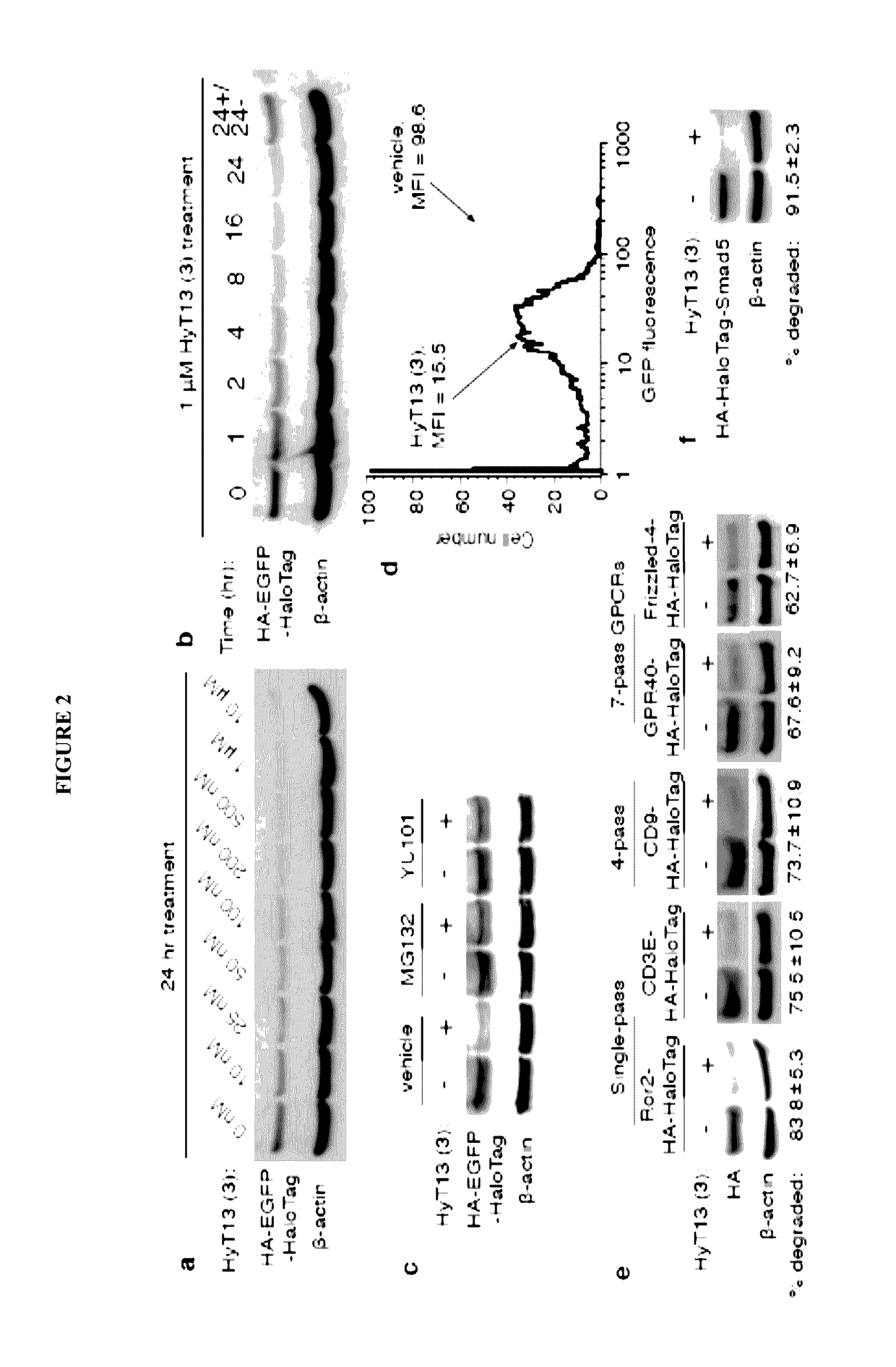
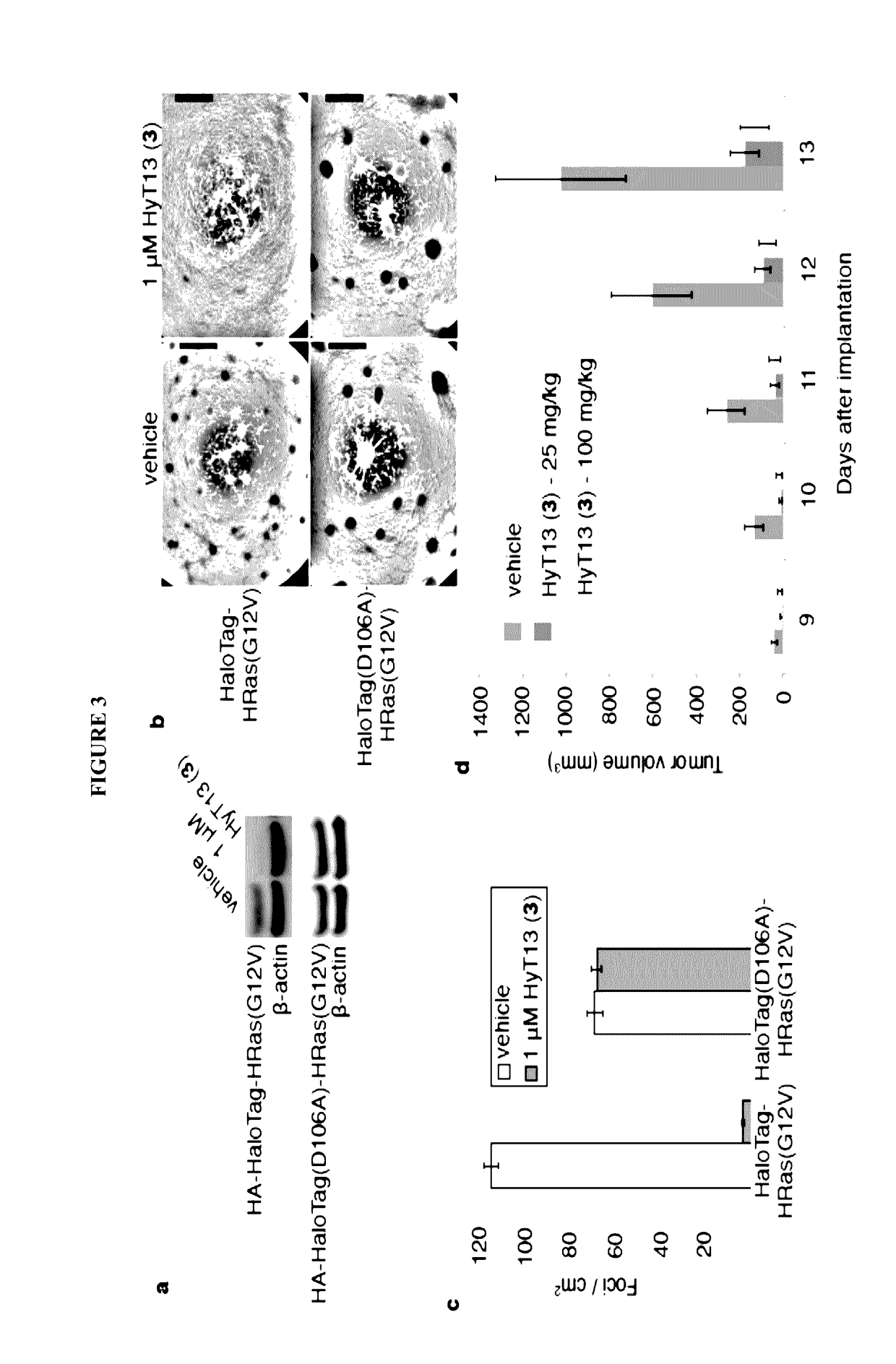
Small-molecule hydrophobic tagging of fusion proteins and induced degradation of same
The present invention includes compounds that are useful in perturbing or disrupting the function of a transmembrane or intracellular protein, whereby binding of the compounds to the transmembrane or intracellular protein induces proteasomal degradation of the transmembrane or intracellular protein. The present invention further includes a method of inducing proteasomal degradation of a transmembrane or intracellular protein. The present invention further includes a method of identifying or validating a protein of interest as a therapeutic target for treatment of a disease state or condition.
Owner:YALE UNIV
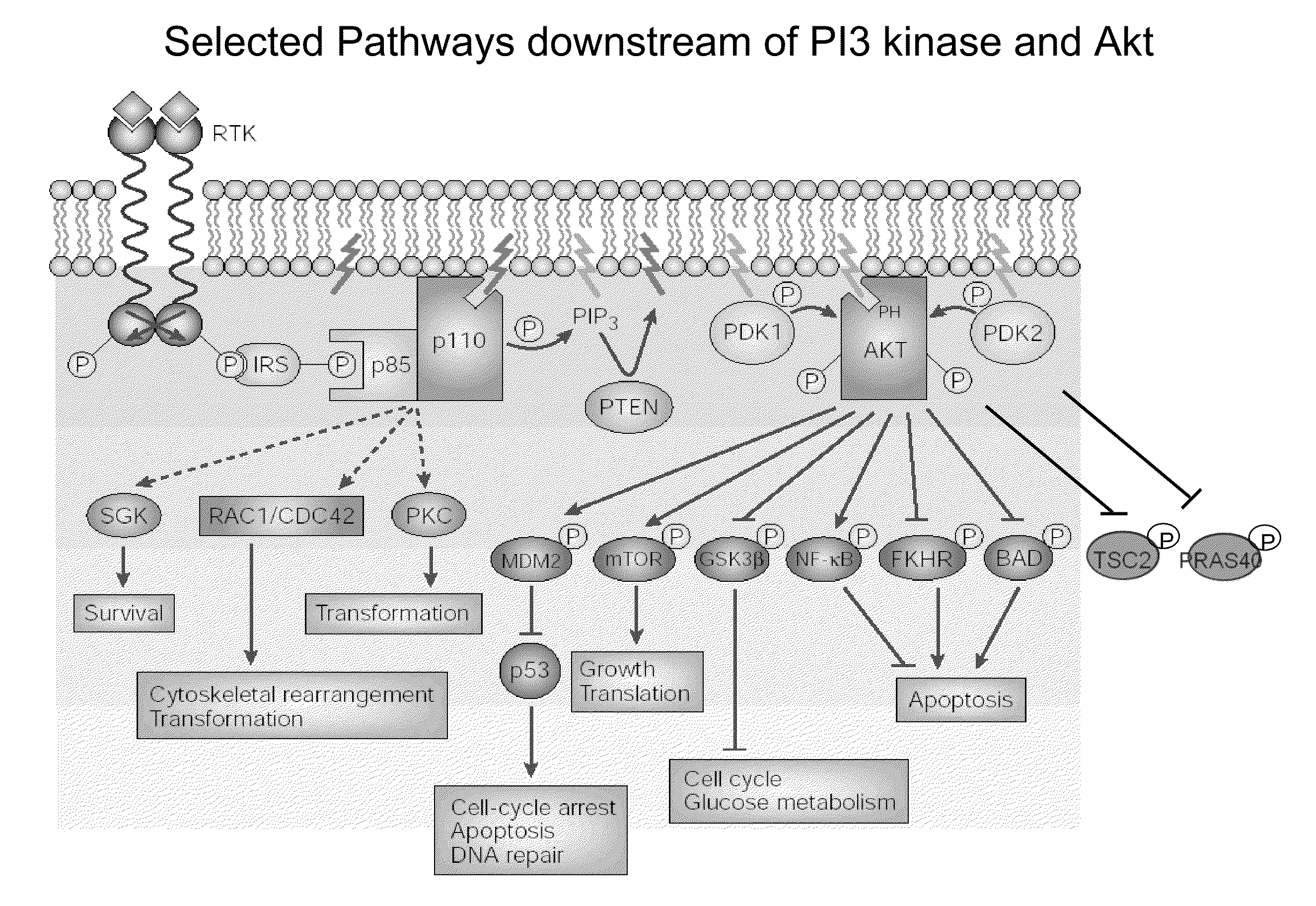
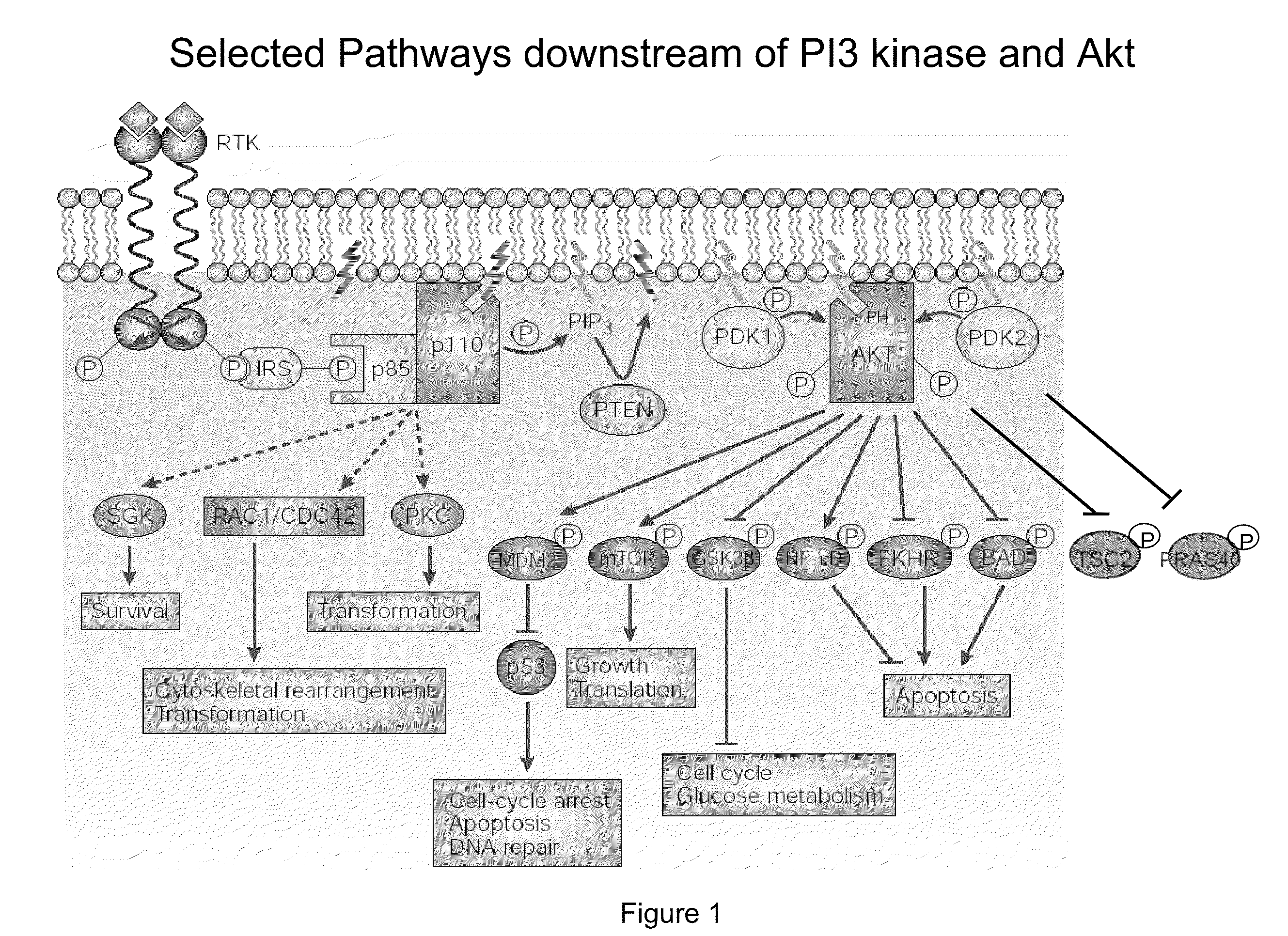
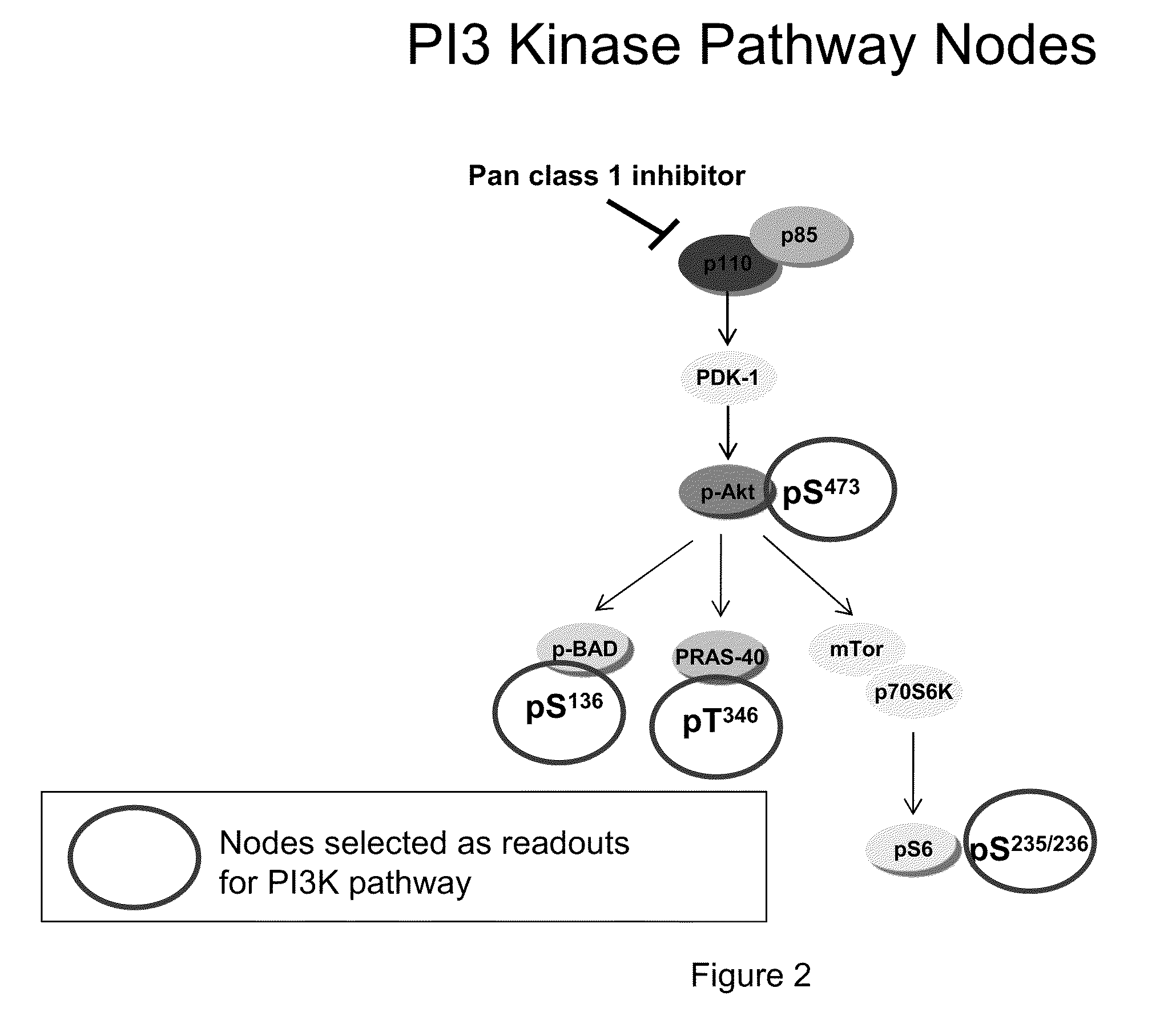
Multiple mechanisms for modulation of the pi3 kinase pathway
InactiveUS20100233733A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisPost translationalPI3 Kinases
An embodiment of the present invention is a method for measuring the post translational states and expression levels of proteins in the PI3K and / or mTor for use in diagnosis, prognosis and drug screening applications.
Owner:NODALITY
Mammallian cell culture process for protein production
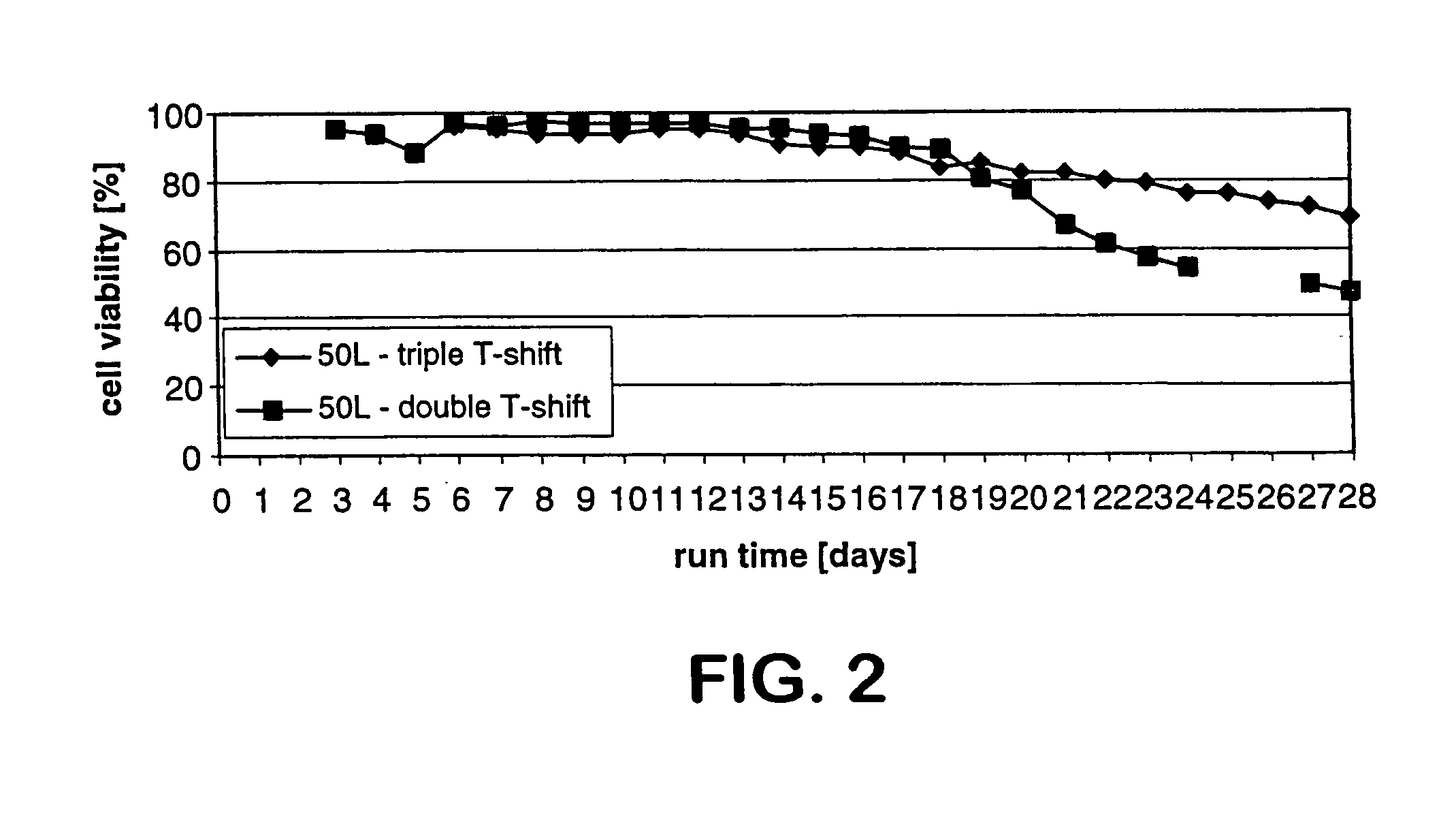
InactiveUS20120015438A1Enhance cell viabilityEnhanced final titer and concentrationAnimal cellsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsGrowth phaseSialic acid
The present invention describes methods and processes for the production of proteins, particularly glycoproteins, by animal cell or mammalian cell culture, preferably, but not limited to, fed-batch cell cultures. In one aspect, the methods comprise at least two temperature shifts performed during the culturing period, in which the temperature is lower at the end of the culturing period than at the time of initial cell culture. Throughout their duration, the culturing processes of the invention involving two or more downward shifts in temperature sustain a high viability of the cultured cells, and can yield an increased end titer of protein product, and a high quality of protein product, as determined, e.g., by sialic acid content of the produced protein. In another aspect, the methods comprise the delayed addition of polyanionic compound during the culturing period. The delayed addition of polyanionic compound sustains a high viability of the cultured cells, and can extend the growth phase, delay the onset of the death phase, and arrest the death phase.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Use of endo-lysosomal system and secreted vesicles (exosome-like) in treatments and diagnostics based on small RNA and experimental study of small RNA
InactiveUS20110177054A1Increase reduce activityGood effectOrganic active ingredientsBiocideRegulatory rnaLipid formation
The present invention relates to a method for determining the delivery rates and / or efficiency of a siRNA, miRNA or related molecule to target organs or cells, a kit and the use of proteins or lipids involved in the formation of the endolysosomal system for modulating the activity and / or the cell-to-cell transfer of RNA, small RNA, for example miRNA, siRNA and piRNA, mRNA or non-coding RNA.It finds many applications in particular in methods for identifying the target(s) of miRNA or siRNA therapeutics, in methods for determining the efficiency of a treatment with siRNA and / or miRNA therapeutics, in methods for determining the efficiency of a treatment with siRNA and / or miRNA therapeutics, and in methods for genotyping and / or characterizing the condition of a person, a tumor or a fetus.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
Fusion proteins
InactiveUS20110091437A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBinding siteCytotoxicity
A single chain, polypeptide fusion protein, comprising: a non-cytotoxic protease, or a fragment thereof, which protease or protease fragment is capable of cleaving a protein of the exocytic fusion apparatus of a nociceptive sensory afferent; a dynorphin Targeting Moiety that is capable of binding to a Binding Site on the nociceptive sensory afferent, which Binding Site is capable of undergoing endocytosis to be incorporated into an endosome within the nociceptive sensory afferent; a protease cleavage site at which site the fusion protein is cleavable by a protease, wherein the protease cleavage site is located between the non-cytotoxic protease or fragment thereof and the dynorphin Targeting Moiety; and a translocation domain that is capable of translocating the protease or protease fragment from within an endosome, across the endosomal membrane and into the cytosol of the nociceptive sensory afferent. Nucleic acid sequences encoding the polypeptide fusion proteins, methods of preparing same and uses thereof are also described.
Owner:HEALTH PROTECTION AGENCY +1
Baculoviral vectors comprising repeated coding sequences with differential codon biases
ActiveUS8697417B2Improve stabilityReduced expression levelAnimal cellsSugar derivativesViral vectorParvovirus
The present invention relates to production of proteins in insect cells whereby repeated coding sequences are used in baculoviral vectors. In particular the invention relates to the production of parvoviral vectors that may be used in gene therapy and to improvements in expression of the viral rep proteins that increase the productivity of parvoviral vectors.
Owner:UNIQURE IP BV
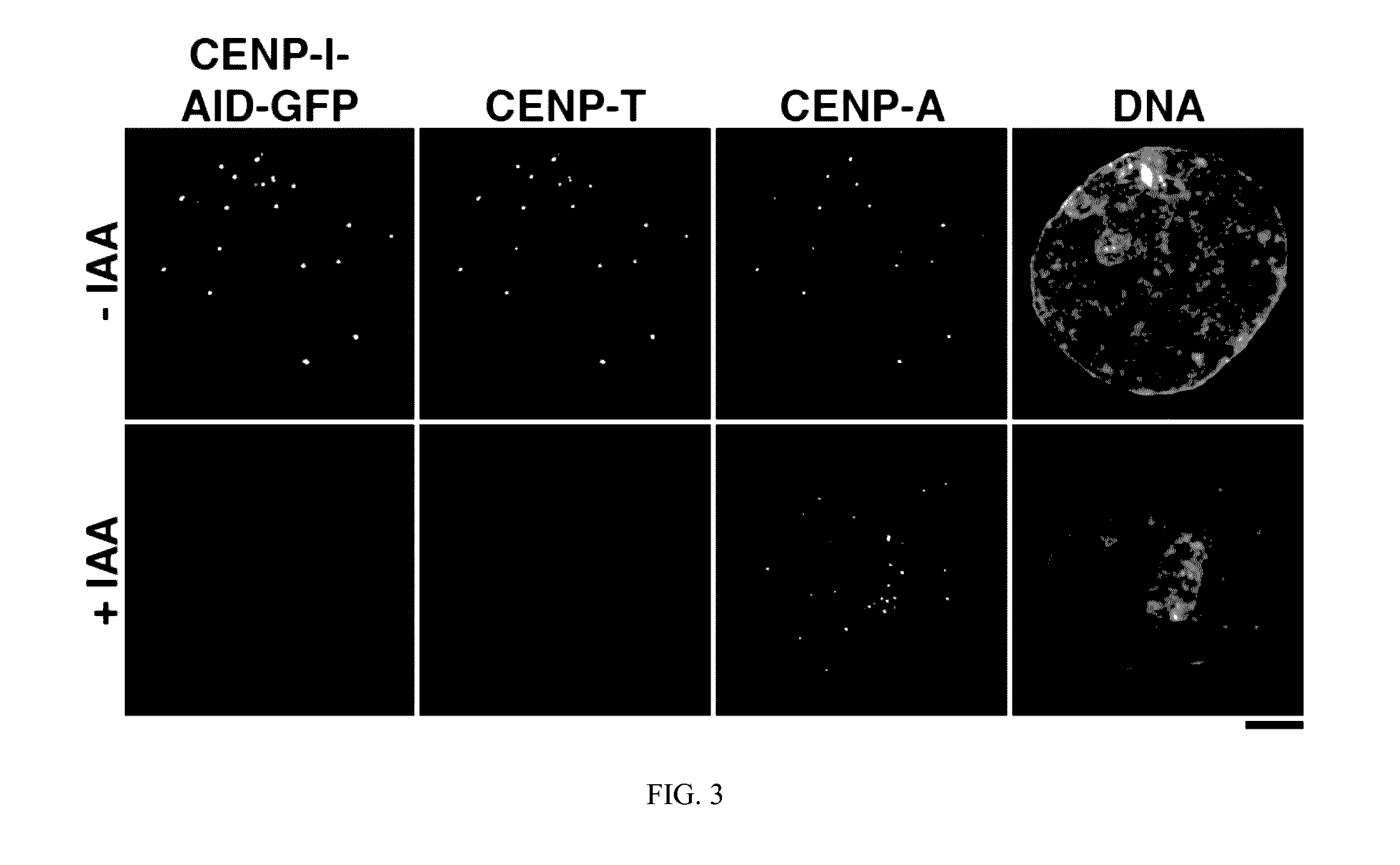
CRISPR-Mediated Genome Engineering for Protein Depletion
InactiveUS20170009242A1Efficient removalMinimal timeHydrolasesFusion with degradation motifCancer researchGenome engineering
The present invention provides compositions and methods for tagging a target gene with a degron (e.g., auxin-inducible degron) in a variety of eukaryotic cells using the CRISPR genome-editing technology. Also provided are cells that have been genetically modified using such compositions and methods.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
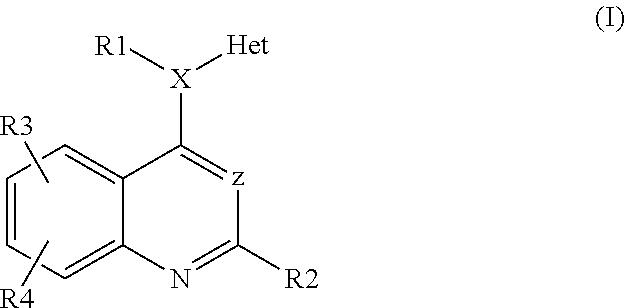
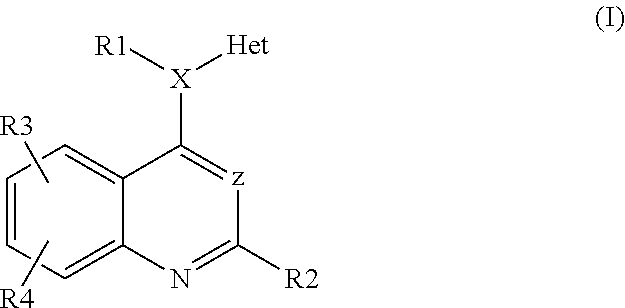
Heteroarylaminoquinolines as tgf-beta receptor kinase inhibitors
InactiveUS20120225875A1Promote accumulationInhibit swellingBiocideNervous disorderKinaseTGF beta receptors
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
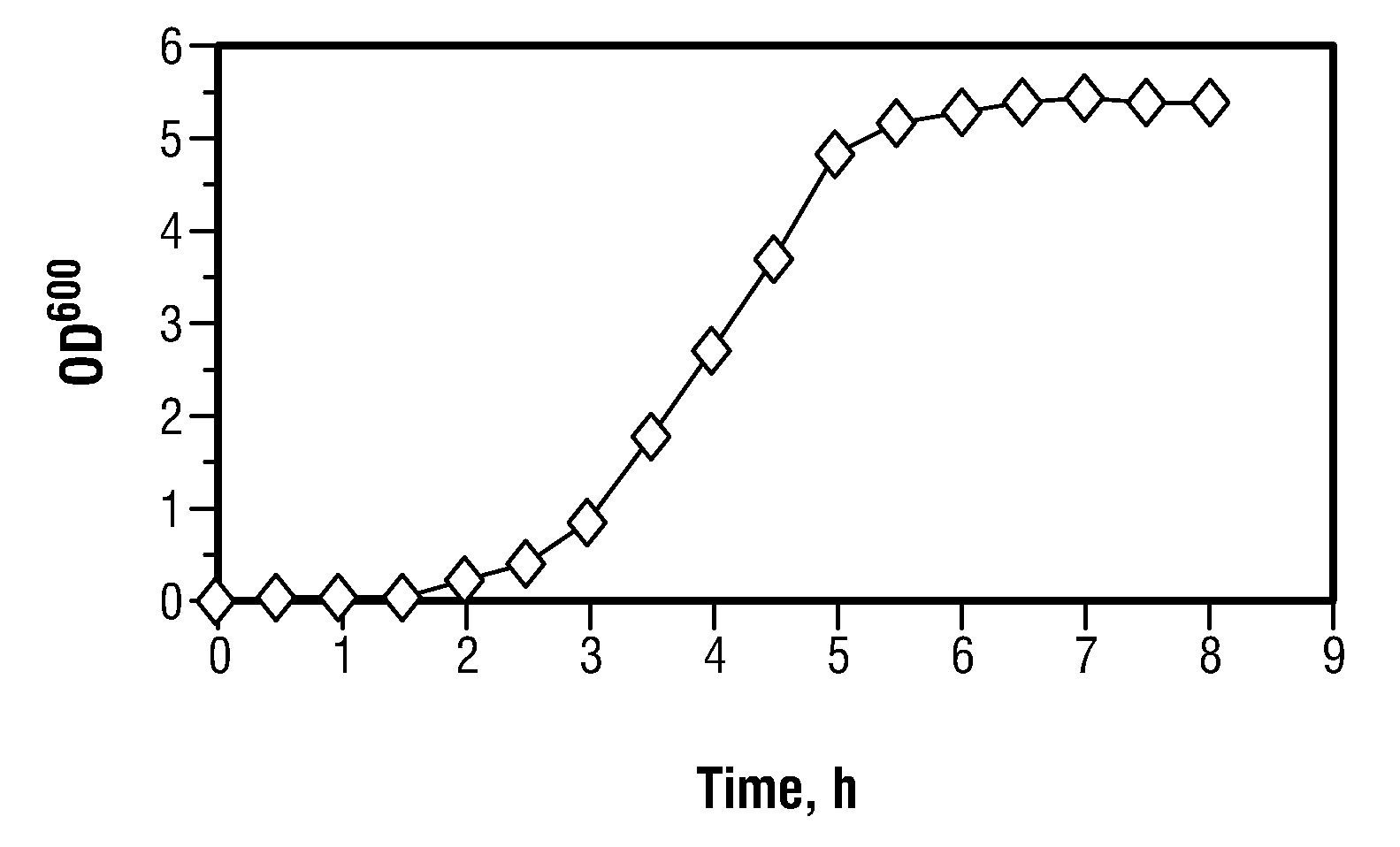
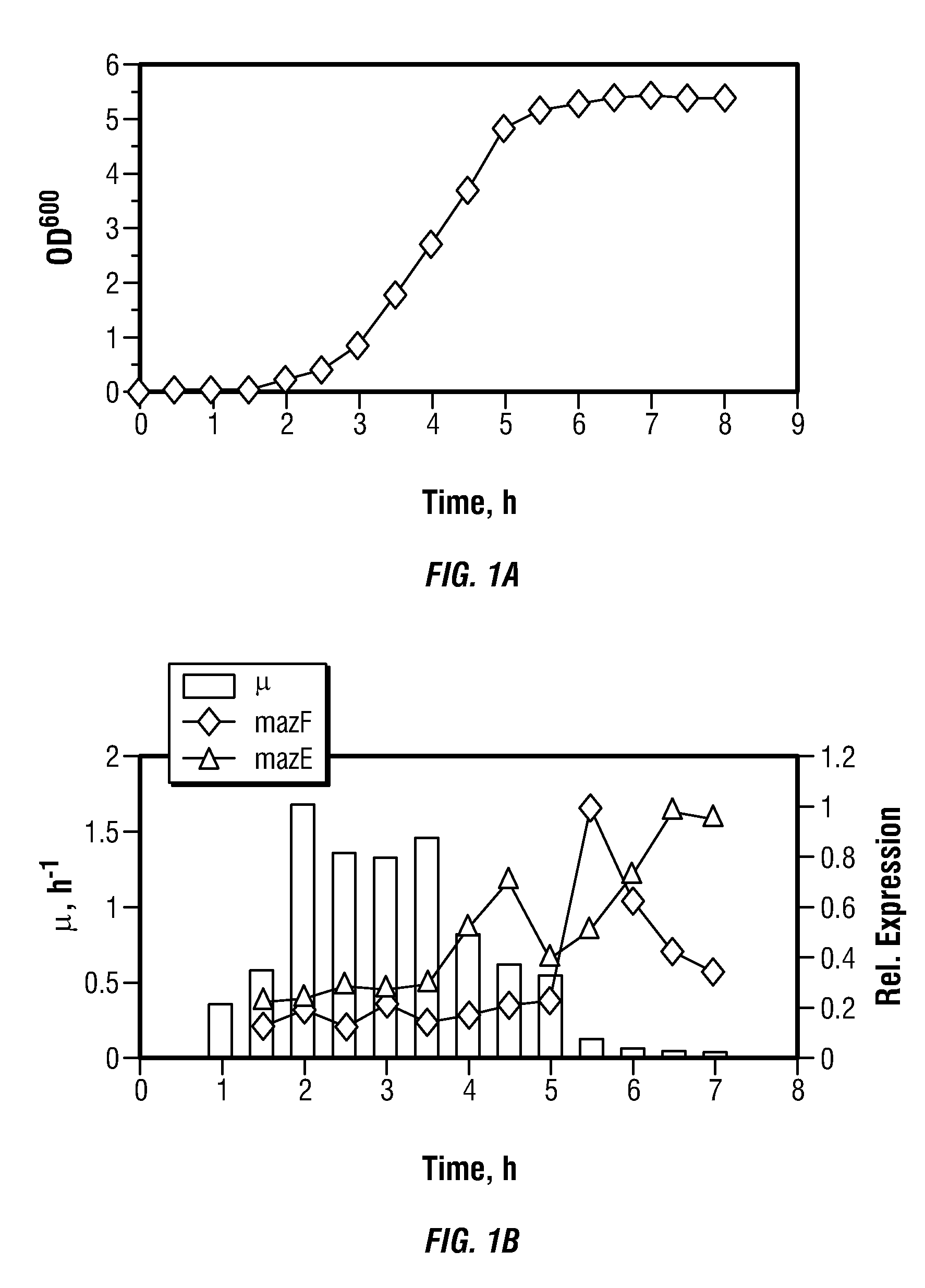
Toxin/antitoxin systems and methods for regulating cellular growth, metabolic engineering and production of recombinant proteins
The present invention provides compositions and method for regulating cellular growth and metabolism, intra- and extracellular enzymatic activities, and synthesis of endogenous and / or heterologous proteins, comprising the steps of cloning genes encoding an mRNA interferase (toxin) and its cognate antitoxin; expressing these proteins in a host cell from two separate constitutive or inducible promoters on one or more plasmid vectors or on a chromosome; and regulating the cellular growth and metabolism by controlling the ratio of toxin and antitoxin present in the host cell. Optionally, the method provides further steps of modifying an endogenous or heterologous gene of interest to substitute all mRNA recognition sequences with sequences that are not cleavable by the mRNA interferase being expressed without any change in the amino acid sequence of the protein encoded by the gene; and co-expressing the gene of interest in the same host cell.
Owner:MAZEF BIOSCI
Producing process of sterile plants, plants obtained by the process, and use of the plants
InactiveUS20110099664A1Suppress transcriptionReliable and easy to produceOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationDouble-floweredPlant cell
Transcription of a gene associated with formation of floral organs is suppressed to produce a sterile plant. A plant cell is transfected with a chimeric gene that includes (i) a coding gene of a transcription factor that promotes expression of a gene associated with formation of floral organs, and (ii) a polynucleotide that encodes a functional peptide that converts an arbitrary transcription factor into a transcription repressor, and a chimeric protein in which the transcription factor is fused with the functional peptide is expressed in the plant cell. The expression of the gene associated with formation of floral organs is dominantly suppressed by the chimeric protein, and as a result a male sterile plant is produced that cannot properly form pollen. The chimeric protein also suppresses expression of a gene associated with dehiscence of anther, and as a result a plant is produced in which dehiscence of anther is suppressed. Further, the chimeric protein suppresses expression of target genes of a transcription factor associated with formation of stamen and pistil, and as a result a double flowered plant is produced.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Peptidomimetic macrocycles
ActiveUS9505804B2Stabilize alpha-helical secondary structureImprove biological activityP53 proteinPeptide preparation methodsCross-linkDisease
Provided herein are peptidomimetic macrocycles containing amino acid sequences with at least two modified amino acids that form an intramolecular cross-link that can help to stabilize a secondary structure of the amino acid sequence. Suitable sequences for stabilization include those with homology to the p53 protein. These sequences can bind to the MDM2 and / or MDMX proteins. Also provided herein are methods of using such macrocycles for the treatment of diseases and disorders, such as cancers or other disorders characterized by a low level or low activity of a p53 protein or high level of activity of a MDM2 and / or MDMX protein.
Owner:AILERON THERAPEUTICS INC
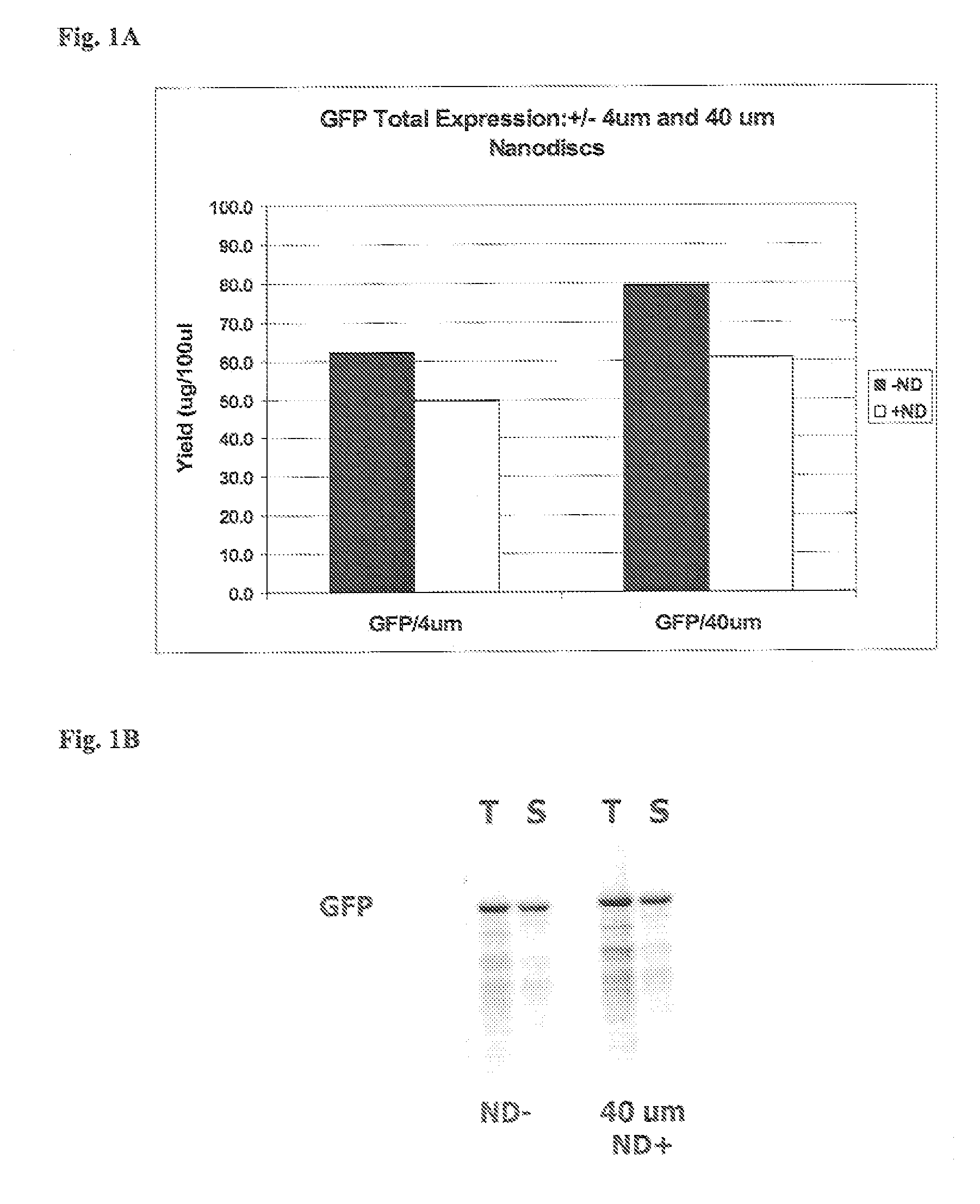
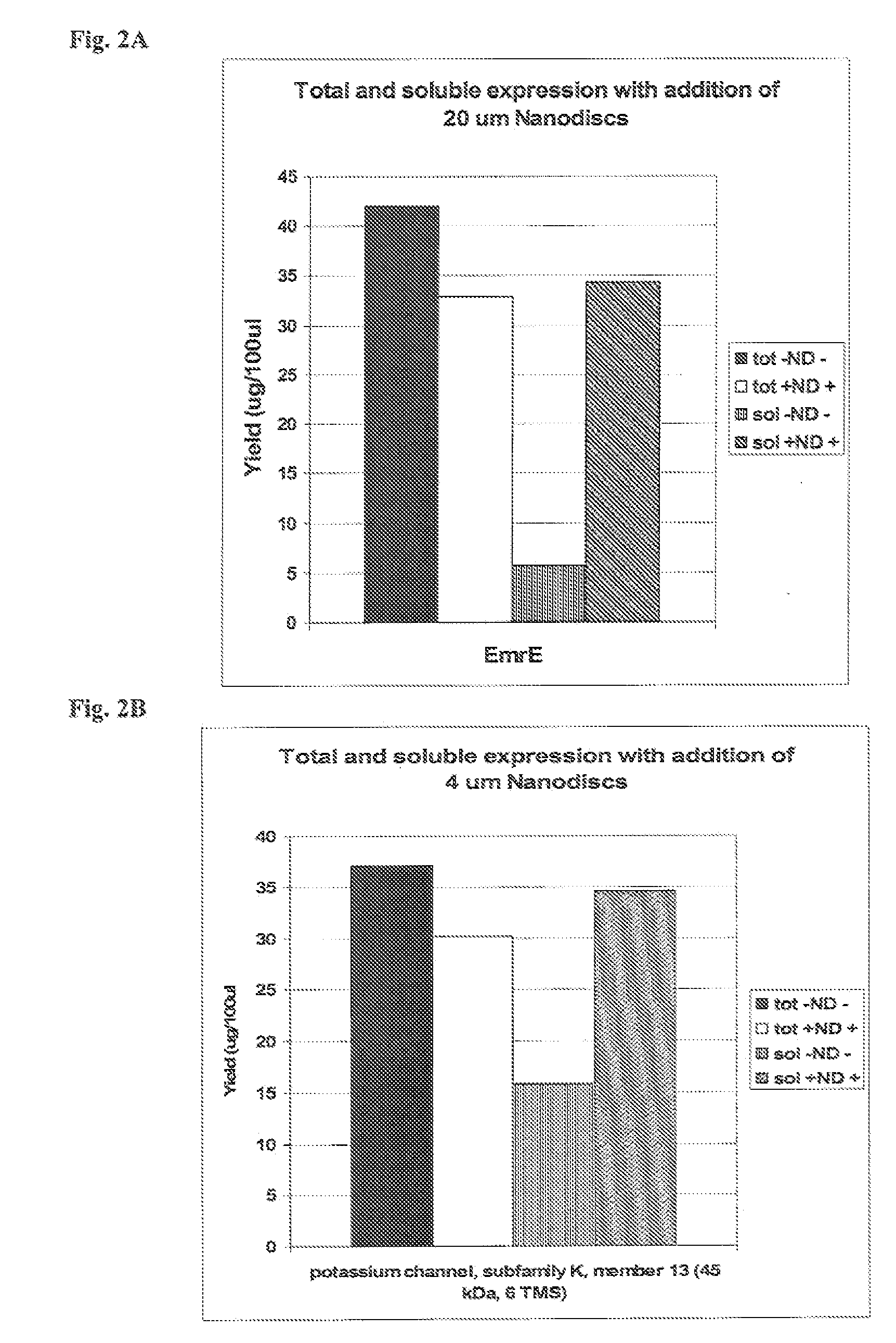
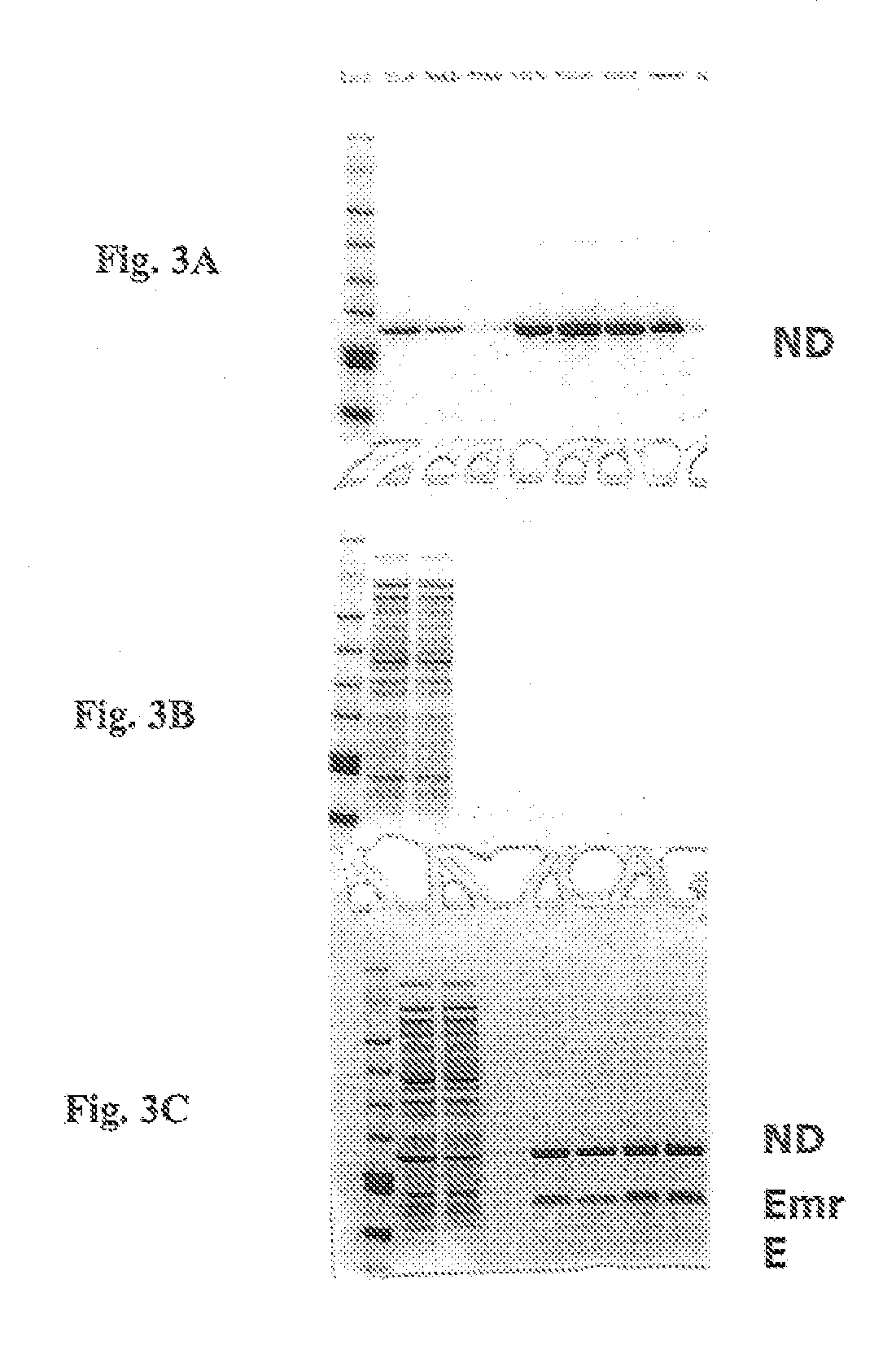
In vitro protein synthesis systems for membrane proteins that include adolipoproteins and phospholipid-adolipoprotein particles
In vitro protein synthesis systems and methods are provided that produce membrane proteins in soluble form. In some aspects, the invention provides methods of synthesizing proteins using in vitro protein synthesis systems that include an apolipoprotein, in which higher yields of soluble protein are produced than in the absence of the apolipoprotein. Apolipoproteins useful in the present invention include naturally occurring apolipoproteins, as well as sequence variants of wild-type apolipoproteins, and engineered apolipoproteins. The apolipoproteins can be provided in an in vitro protein synthesis system associated with lipid or not associated with lipid. The invention also provides compositions and kits for synthesis of proteins in soluble form, in which the compositions and kits include cell extracts for protein translation and at least one apolipoprotein biomolecule.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Method for whole surrounding surface display of target proteins using bacterial exosporium
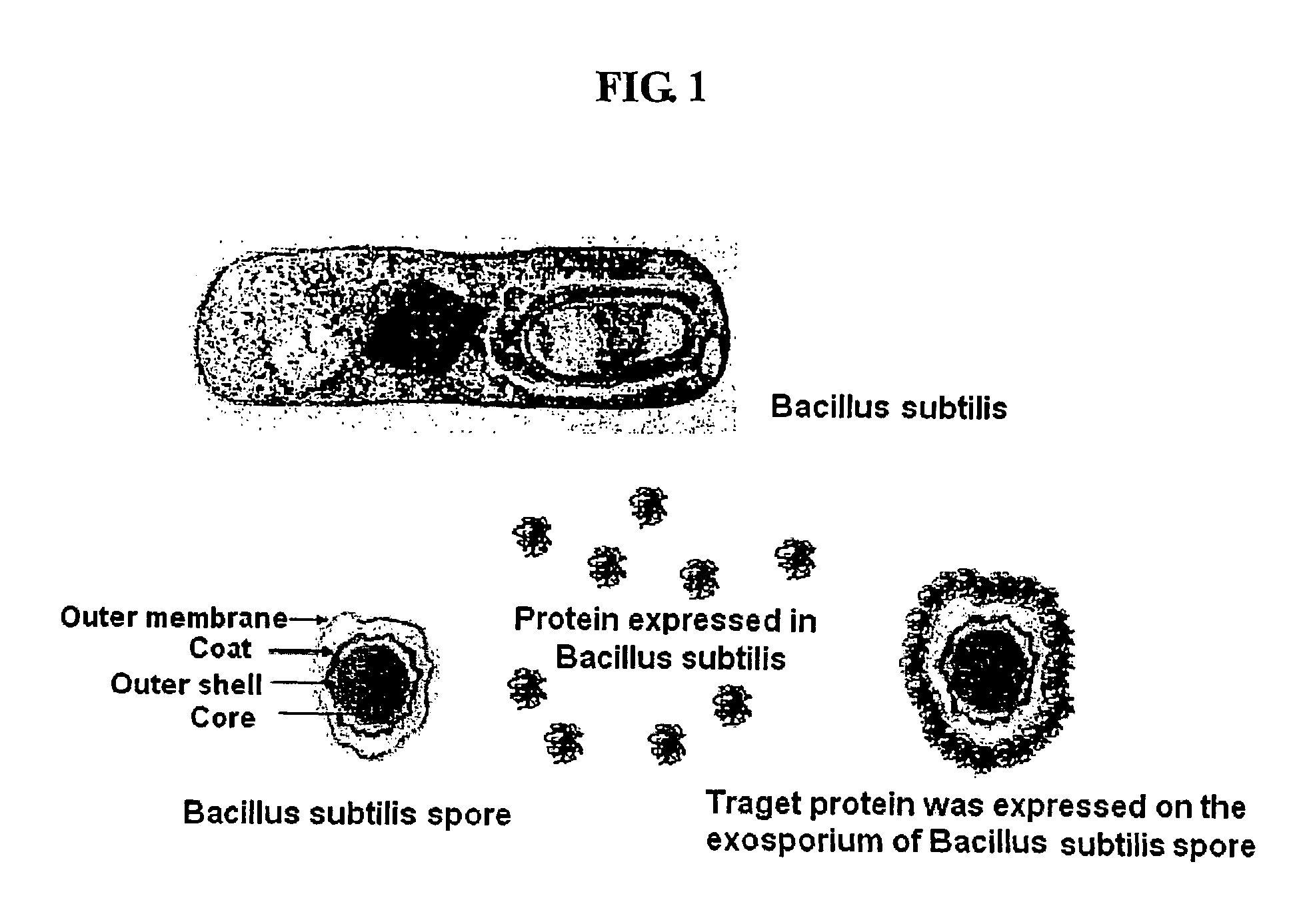
InactiveUS8030064B2Fast conductionAddressing slow performanceBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsSurface displayScreening method
The present invention relates to a method for expressing a target protein on an exosporium forming the outermost surface of bacterial spores. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method for expressing a target protein on the surface of cells and spores using an exosporium as a matrix for surface expression, and methods for the production of a protein array, the production of antibodies, the separation of a certain substance from a mixture, bioconversion, and the improvement of a target protein, which are characterized by using the cells or spores having the target protein that was expressed on the surface by the above expression method. The method for expressing the target protein on the surface of the spore outer membrane of the gene carriers according to the present invention has effects in that a variety of the target proteins can be expressed and the level of surface expression of the target protein is increased compared to the existing technology, and also the structural stability of the gene carriers having the target protein expressed on their surface, the viability of the host, and the rapidity of the screening method, are greatly increased.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH +1
Filamentous fungi with inactivated protease genes for altered protein production
The invention relates to a filamentous fungal cell (e.g., Aspergillus sp.) comprising at least one inactivated protease gene chosen from apsB, a homolog of apsB, cpsA, a homolog cpsA, and combinations thereof. Nucleic acids and methods for making the inactivated mutant filamentous fungal cells are provided as well as methods for using the cells for the altered production of endogenous or heterologous proteins of interest.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
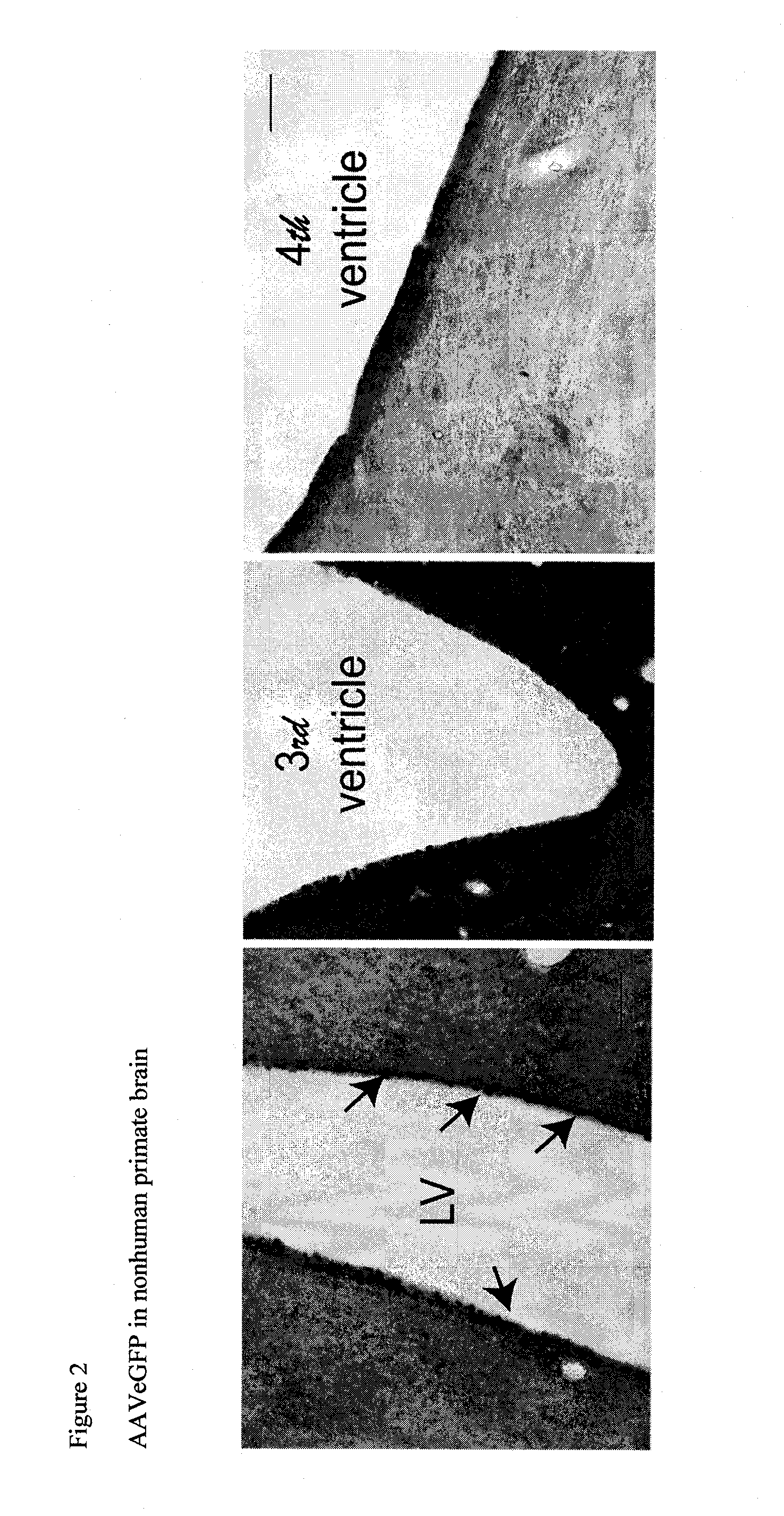
Methods and compositions for treating brain diseases
The present disclosure provides methods of treating a disease in a non-rodent mammal comprising administering to the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of the non-rodent mammal an rAAV2 particle containing a vector comprising a nucleic acid encoding a therapeutic protein inserted between a pair of AAV inverted terminal repeats in a manner effective to infect an ependymal cell in the non-rodent mammal, wherein the ependymal cell secretes the therapeutic protein so as to treat the disease.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Immunization and/or treatment of parasites and infectious agents by live bacteria
ActiveUS9486513B1Reducing or eliminating the targeted parasite, infectious diseaseSsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsHuntingtons choreaAntiparasitic
Chimeric proteins are expressed, secreted or released by a bacterium to immunize against or treat a parasite, infectious disease or malignancy. The delivery vector may also be attenuated, non-pathogenic, low pathogenic, or a probiotic bacterium. The chimeric proteins include chimeras of, e.g., phage coat and / or colicin proteins, bacterial toxins and / or enzymes, autotransporter peptides, lytic peptides, multimerization domains, and / or membrane transducing (ferry) peptides. The active portion of the immunogenic chimeric proteins can include antigens against a wide range of parasites and infectious agents, cancers, Alzheimer's and Huntington's diseases, and have enhanced activity when secreted or released by the bacteria, and / or have direct anti-parasite or infectious agent activity. The activity of the secreted proteins is further increased by co-expression of a protease inhibitor that prevents degradation of the effector peptides. Addition of an antibody binding or antibody-degrading protein further prevents the premature elimination of the vector and enhances the immune response.
Owner:BERMUDES DAVID GORDON
Proteins comprising amino-terminal proximal shiga toxin a subunit effector regions and cell-targeting immunoglobulin-type binding regions
InactiveUS20160376328A1Reduces and eliminates cytotoxicityFacilitates cellular internalizationAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsCellular pathwaysCytotoxicity
The present invention provides proteins comprising immunoglobulin-type binding regions for cell-type specific targeting and Shiga toxin A Subunit effector regions for Shiga toxin effector functions (e.g. cellular internalization, directing subcellular routing, and / or cytotoxicity), wherein the binding regions and Shiga toxin effector regions are combined such that the Shiga toxin effector regions are proximal to the amino-terminals of the proteins. The presently disclosed proteins can comprise additional exogenous materials, such as, e.g., antigens, cytotoxic agents, and detection-promoting agents, and are capable of targeted delivery of these additional exogenous materials into the interiors of target cells. The proteins of the present invention have uses in methods such as, e.g., methods involving targeted killing of target cells, delivering exogenous materials into target cells, labeling subcellular compartments of target cells, and diagnosing and / or treating a variety of conditions including cancers, tumors, other growth abnormalities, immune disorders, and microbial infections.
Owner:MOLECULAR TEMPLATES
Immunogenic composition and method of developing a vaccine based on fusion protein
The present invention relates to an immunogenic composition. More particularly, the present invention is a composition directed to eliciting an immune response to HIV fusion protein. The present invention contemplates three categories of embodiments: protein or protein fragments, messenger RNA, or DNA / RNA. DNA / RNA compositions may be either naked or recombinant. The present invention further contemplates use with a variety of immune stimulants.
Owner:KARP NELSON M
Triple acting antimicrobials that are refractory to resistance development
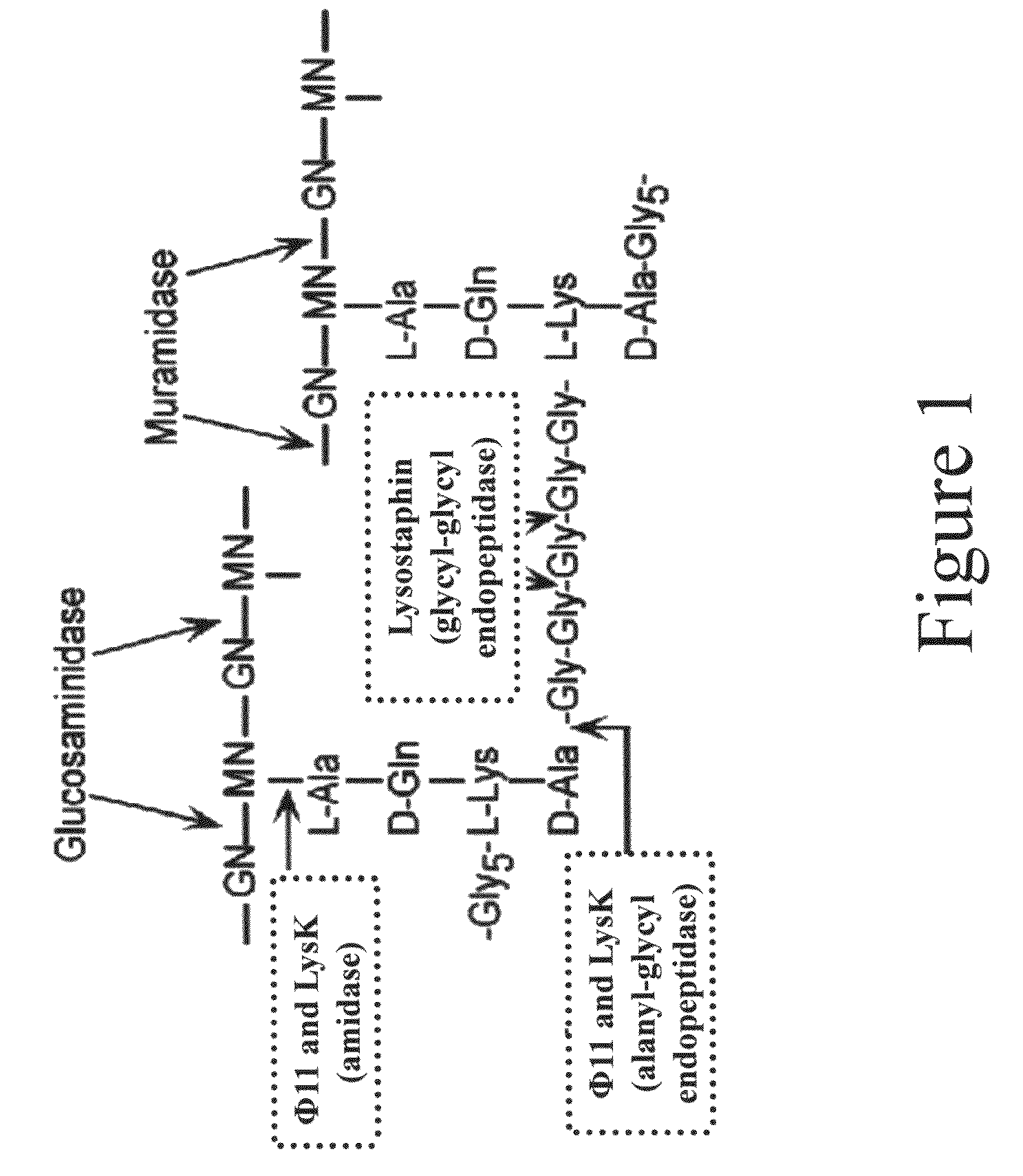
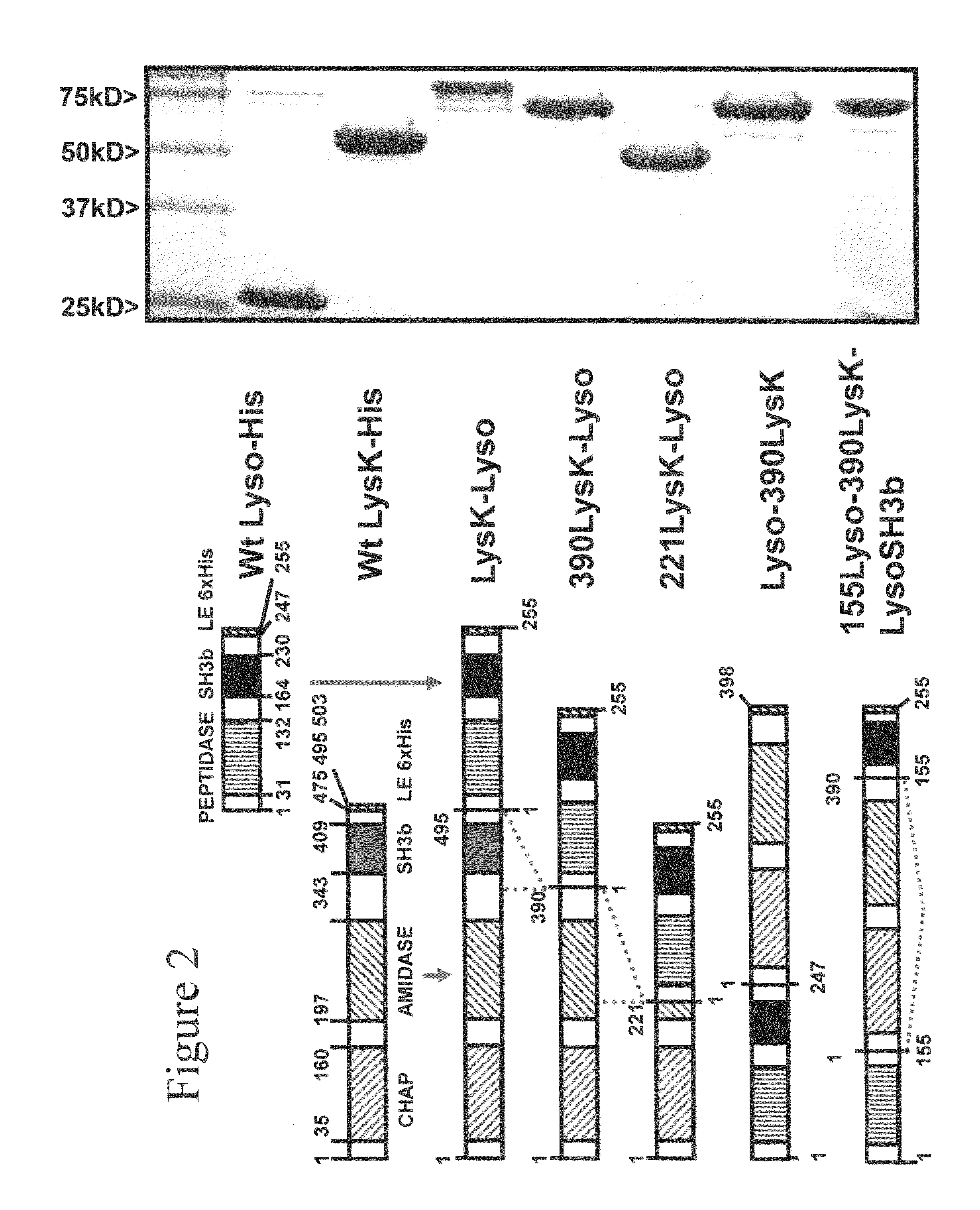
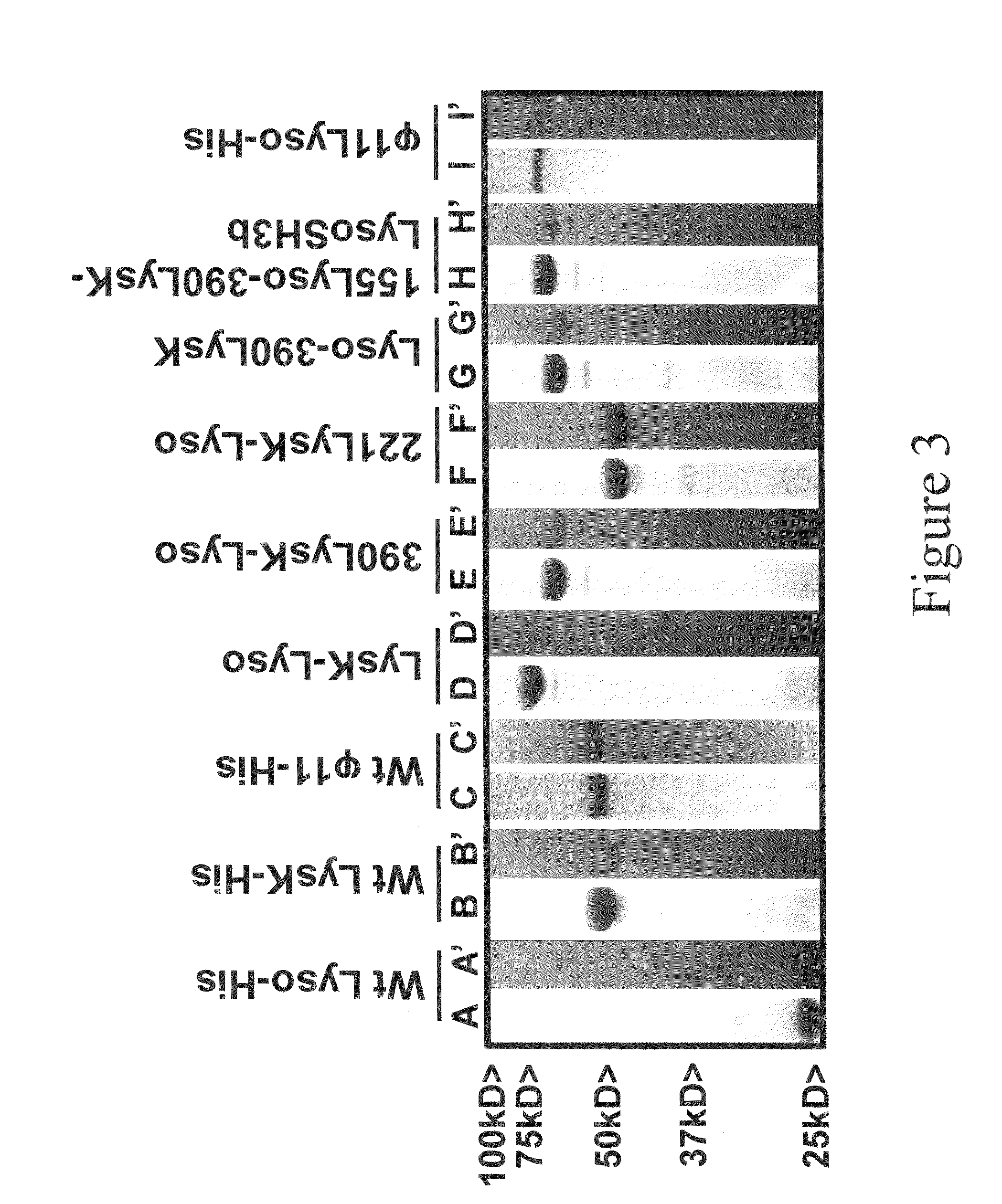
InactiveUS8481289B2Effectively lysingPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesGrowth phaseGlycyl-Glycine
Multi-drug resistant superbugs are a persistent problem in modern health care. This invention provides an antimicrobial endolysin-Lysostaphin triple fusion protein, comprising (1) an endolysin CHAP endopeptidase domain, (2) an endolysin amidase domain, and (3) a Lysostaphin glycyl-glycine endopeptidase domain. The domains are derived from two proteins that show antimicrobial synergy when used in combination. The protein has specificity and exolytic activity for the peptidoglycan cell wall of untreated, live Staphylococcus aureus from many growth phases i.e. stationary, logarithmic and biofilm growth. The recombinant triple fusion protein comprising the three functional antimicrobial domains is designed to be refractory to resistance development.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
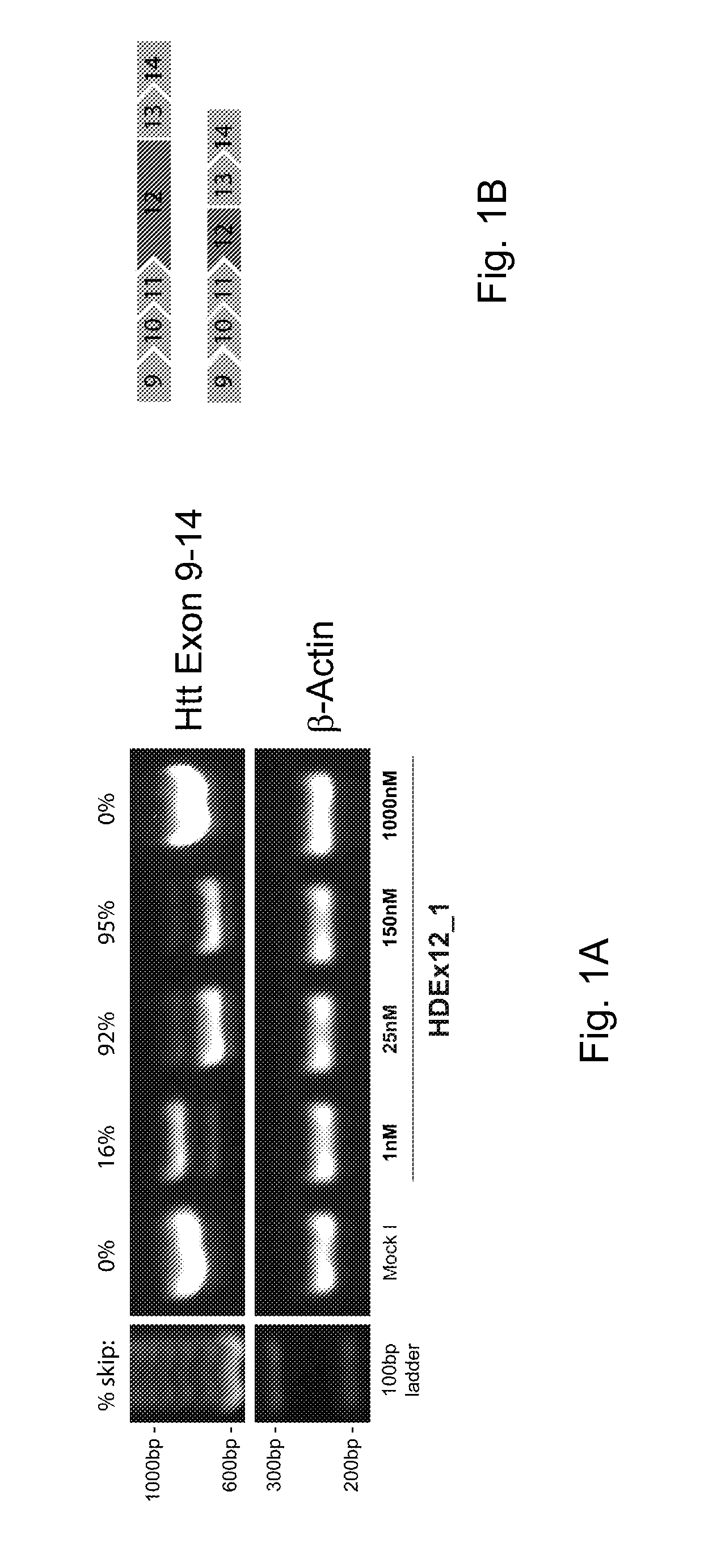
Antisense oligonucleotide directed removal of proteolytic cleavage sites from proteins
ActiveUS20130198877A1Improve the level ofLow toxicitySplicing alterationNervous disorderPrecursor mRNAProteolysis
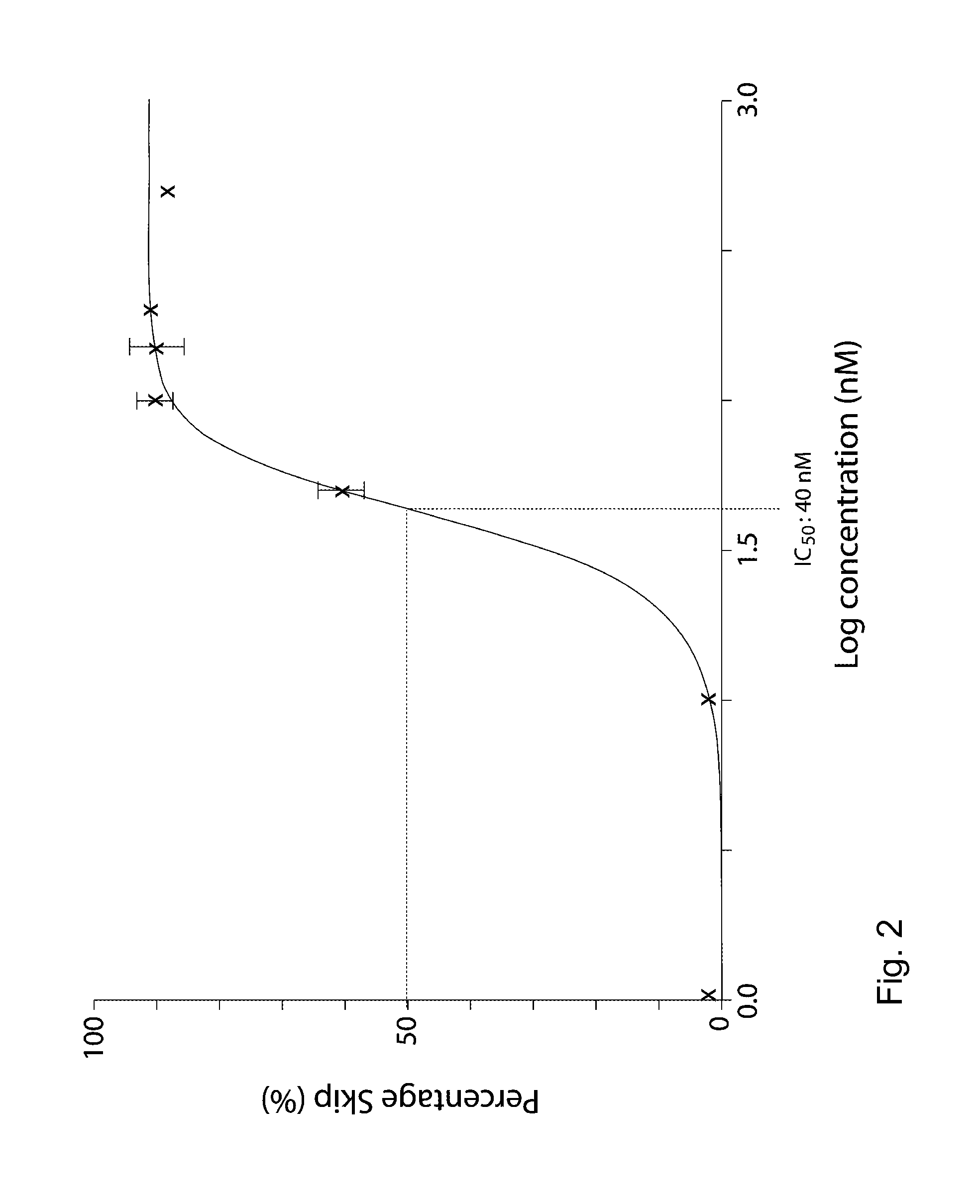
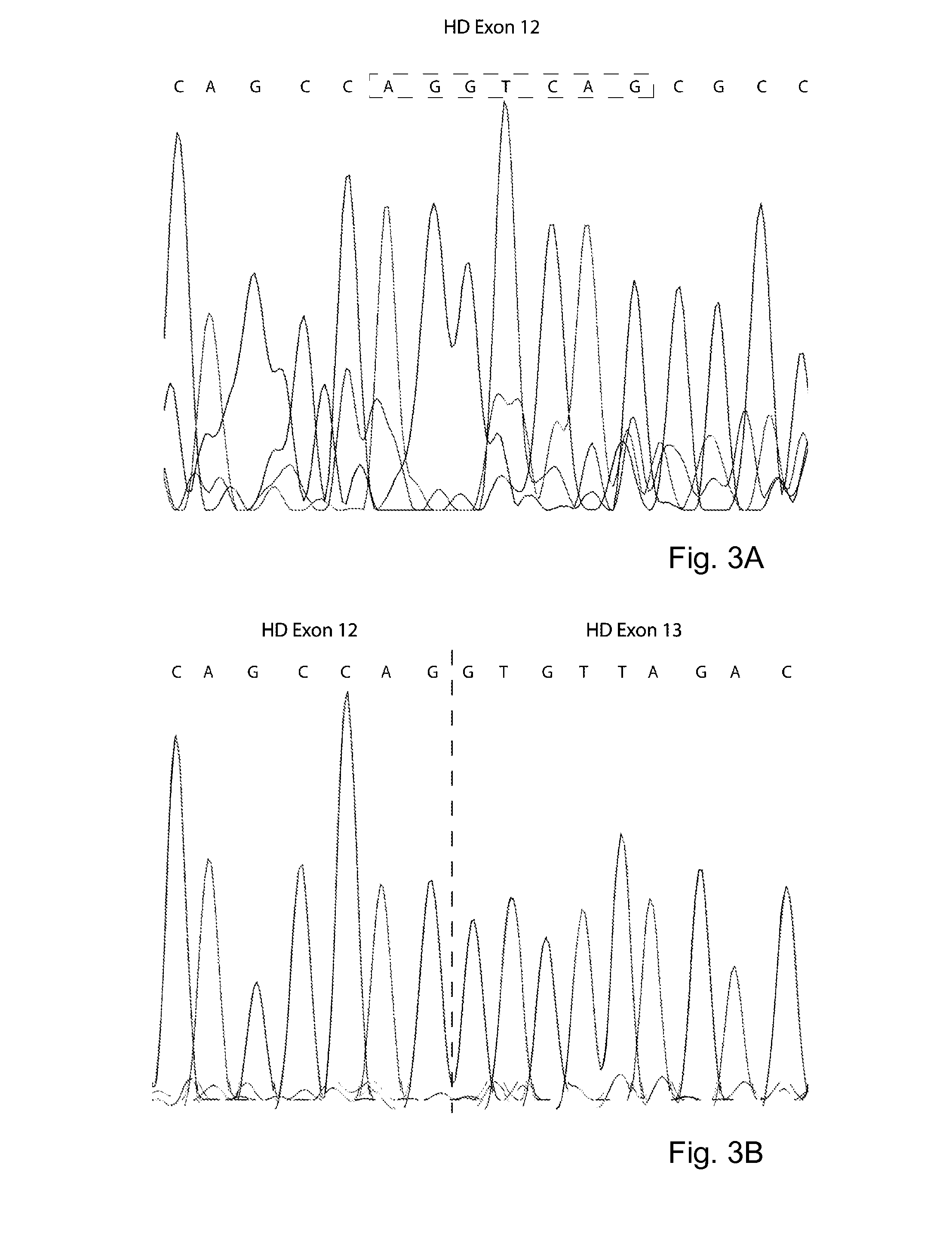
Described are means and methods for removing a proteolytic cleavage site from a protein, the method comprising providing a cell that expresses pre-mRNA encoding the protein with an anti-sense oligonucleotide that induces skipping of the exonic sequence that encodes the proteolytic cleavage site, and allowing translation of mRNA produced from the pre-mRNA.
Owner:ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS BIJ DE UNIV VAN AMSTERDAM ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT
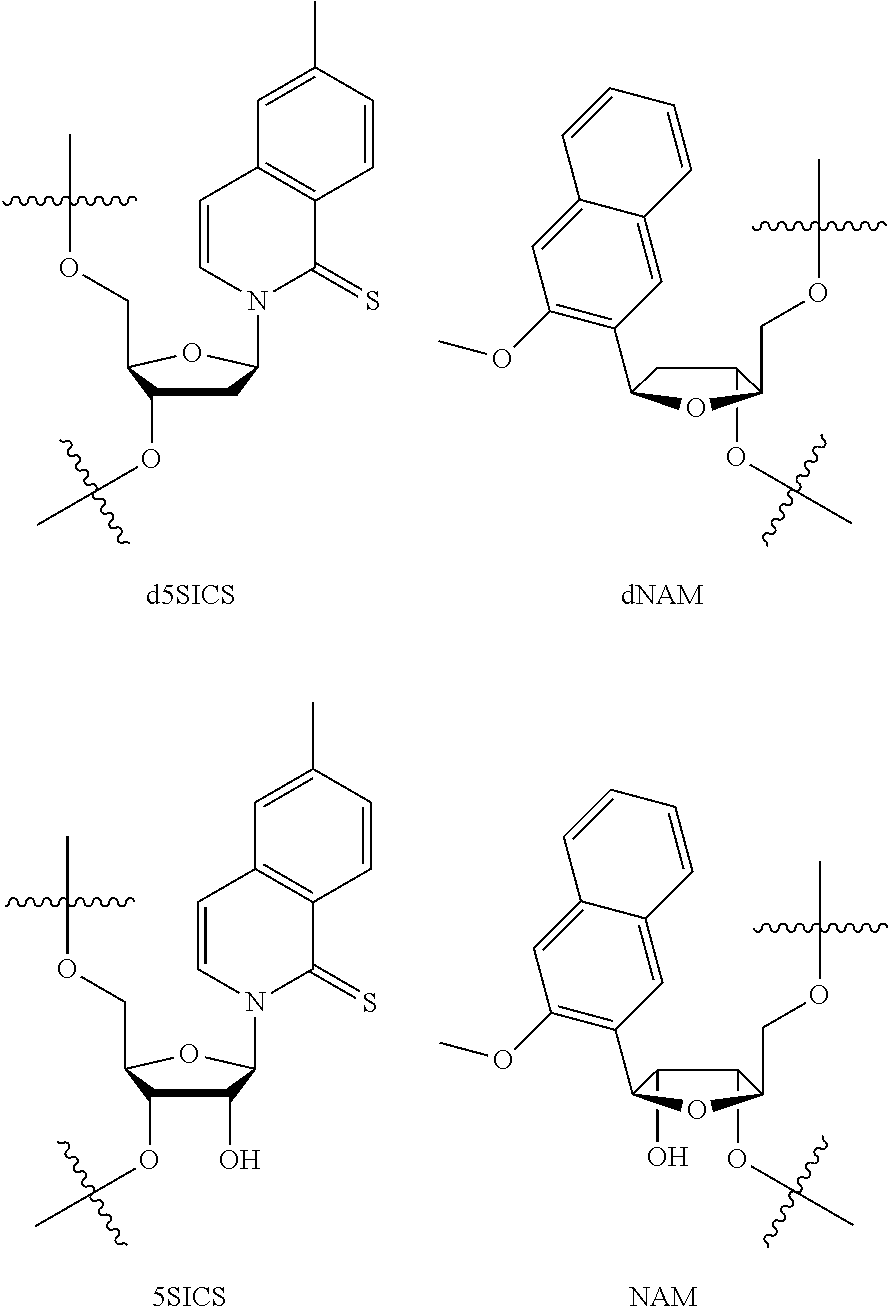
Incorporation of unnatural nucleotides and methods thereof
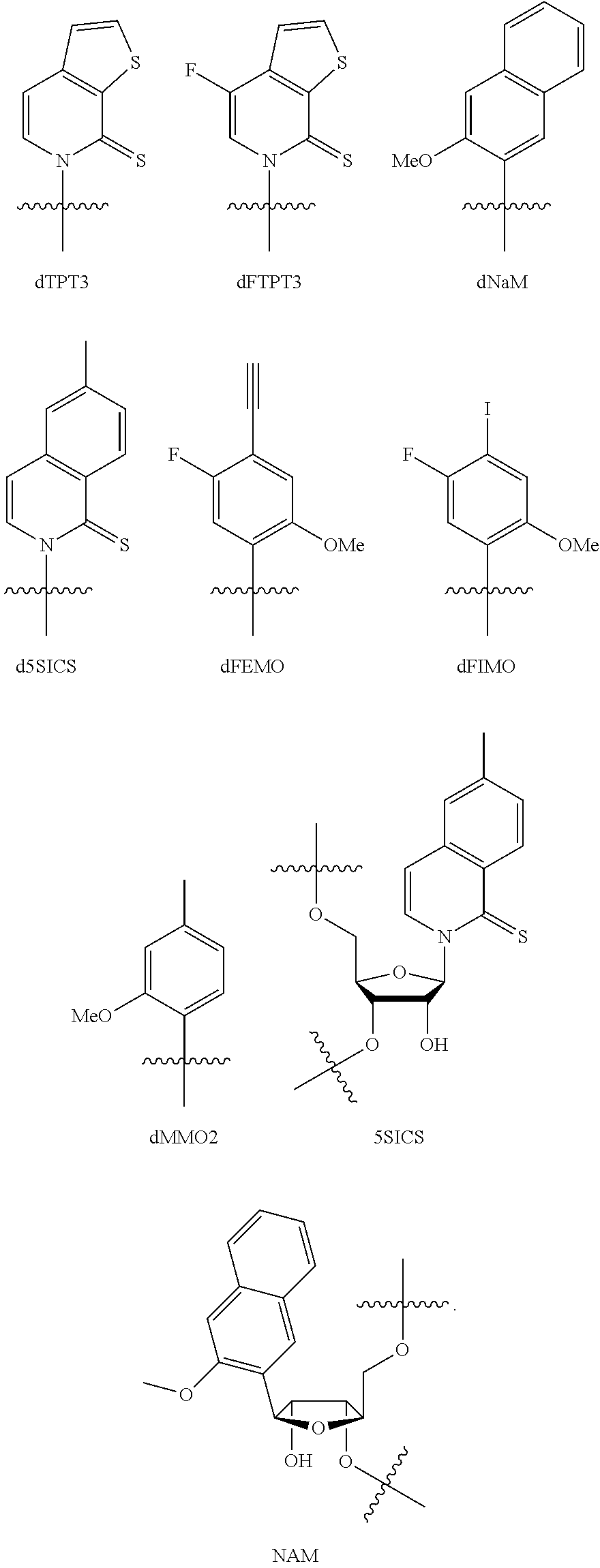
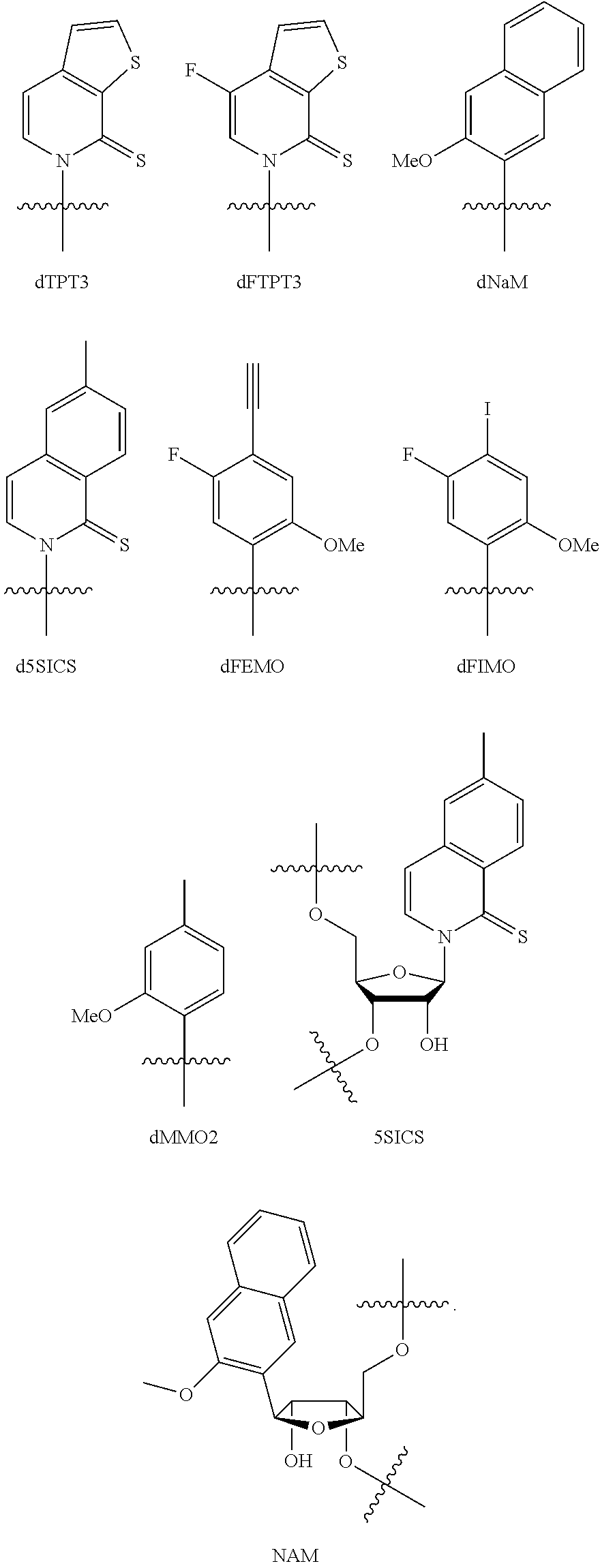
Disclosed herein are methods, composition and kits for the synthesis of proteins which comprises unnatural amino acids that utilize a mutant tRNA, wherein the mutant tRNA comprises a mutant anticodon sequence. And an additional method comprises generating nucleic acids that contain an expanded genetic alphabet.
Owner:SYNTHORX
Method for correlating gene expression profiles with protein expression profiles
InactiveUS7299134B2Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansProtein expression profileGene and protein expression
Owner:CIPHERGEN BIOSYSTEMS INC
Post labeling stabilization of radiolabeled proteins and peptides
InactiveUS6261536B1Avoid formingRadioactive preparation carriersSolution deliveryOrganic chemistryIncubation period
The subject invention relates to the use of ascorbic acid and derivatives thereof in stabilizing radiolabeled proteins and peptides against oxidation loss of radiolabel and autoradiolysis. Ascorbic acid is added after radiolabeling, including any required incubation period, but prior to patient administration.
Owner:RHOMED INCORPORATED
Translocation of non-natural chemical entities through anthrax protective antigen pore
Disclosed is a new approach for delivering compounds and drugs to the cytosol of living cells through the use of engineered protein transporters. The engineered protein transporters include a pore and a pore specific delivery protein, wherein a reagent such as a drug is attached to one or more of the engineered protein transporters.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com