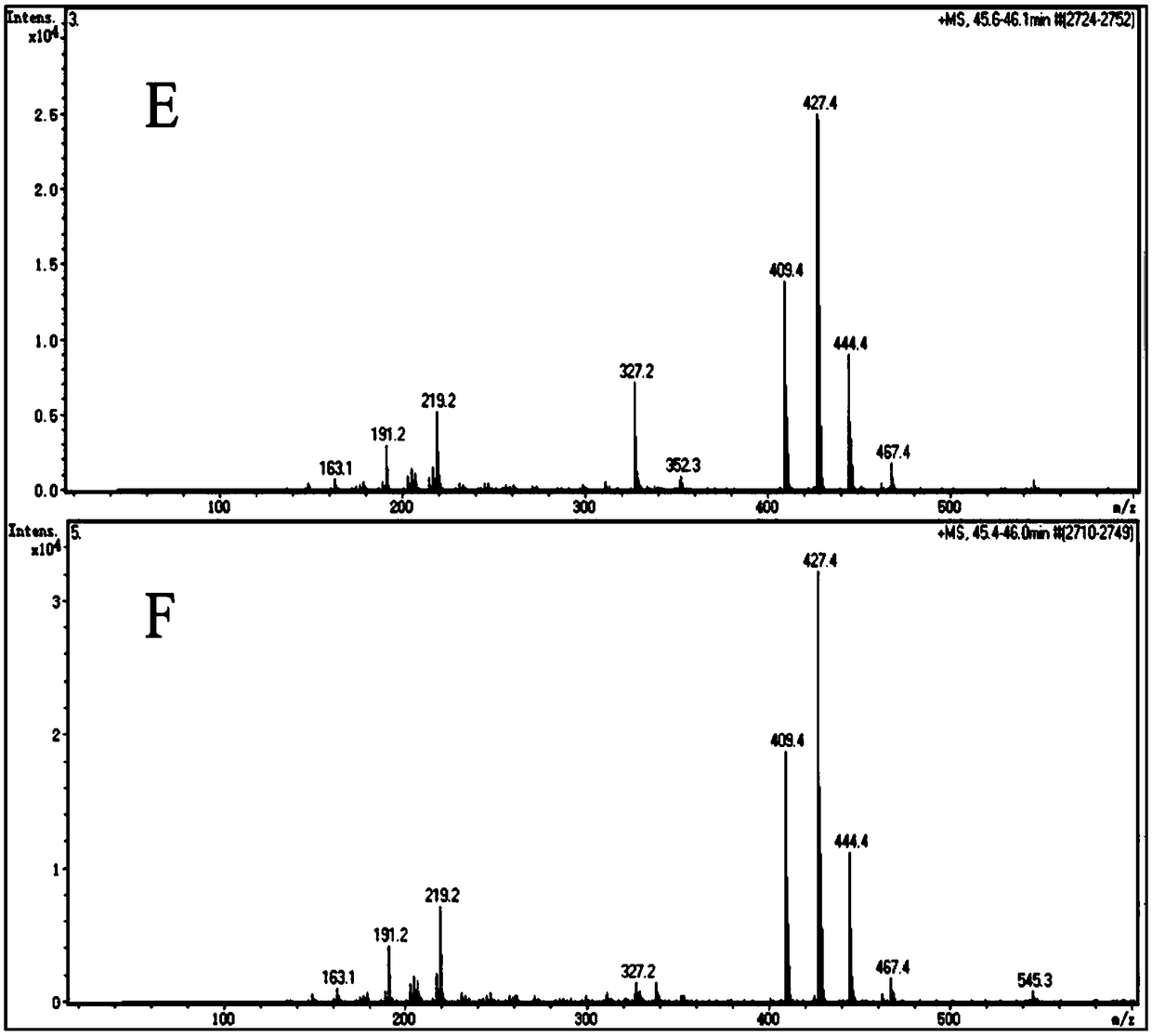
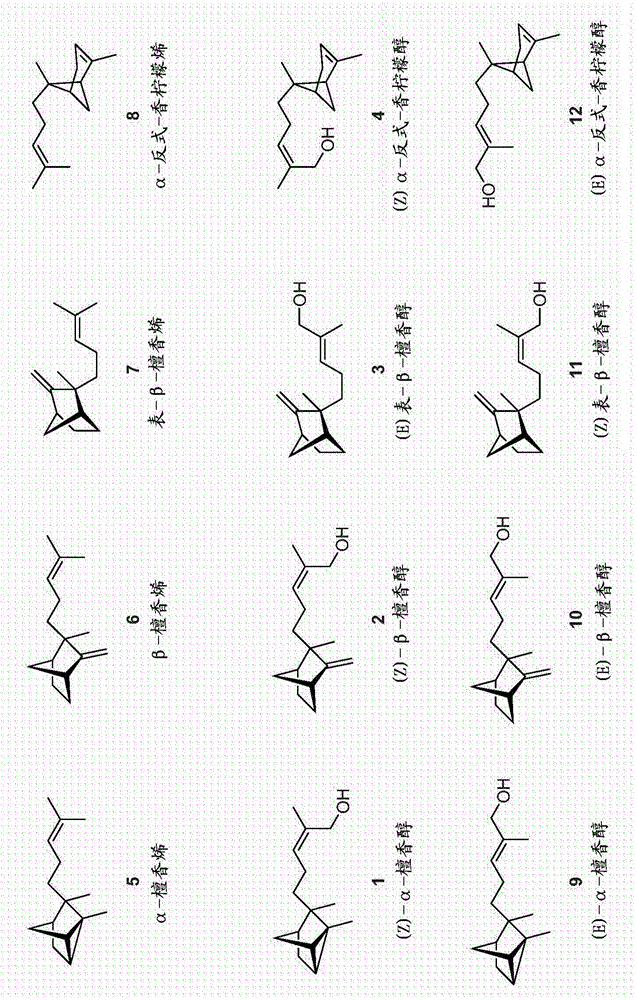
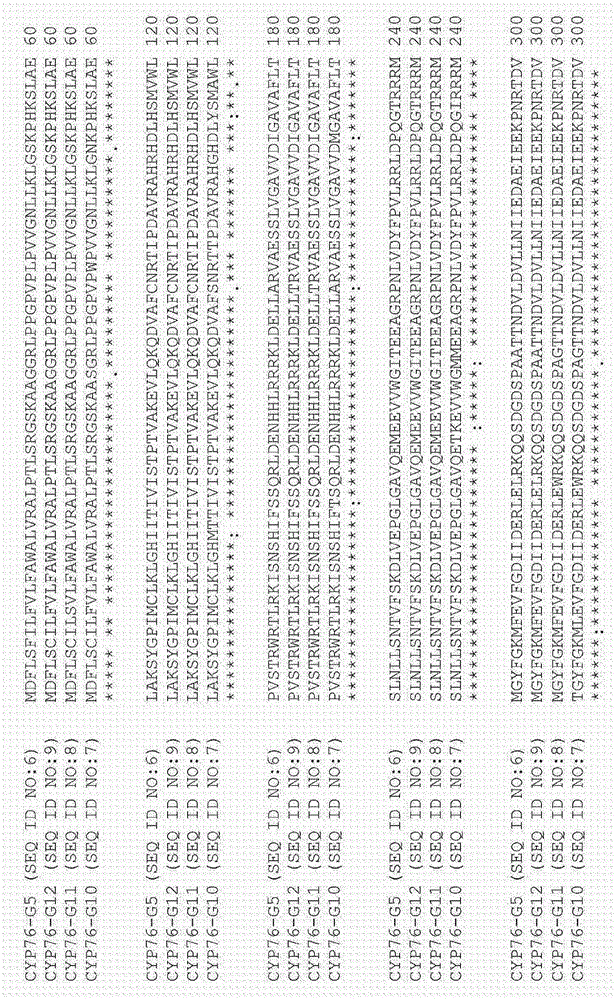
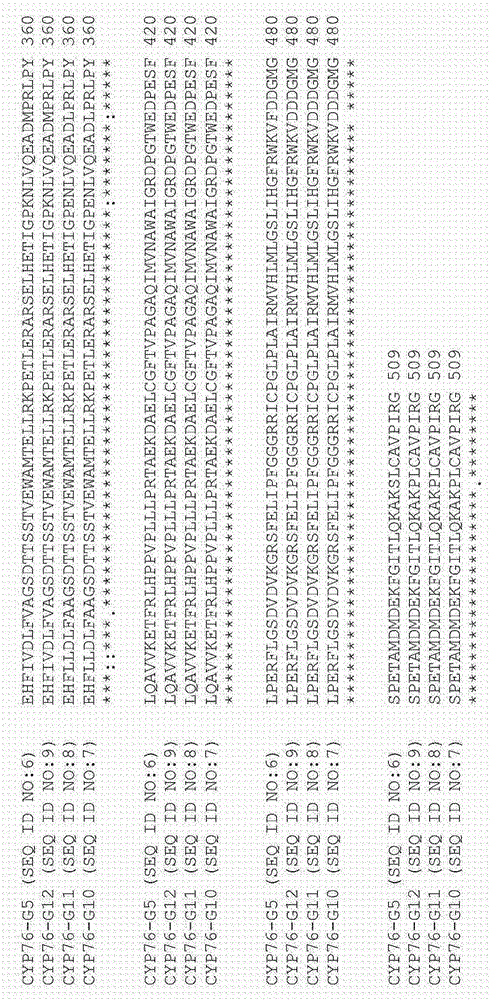
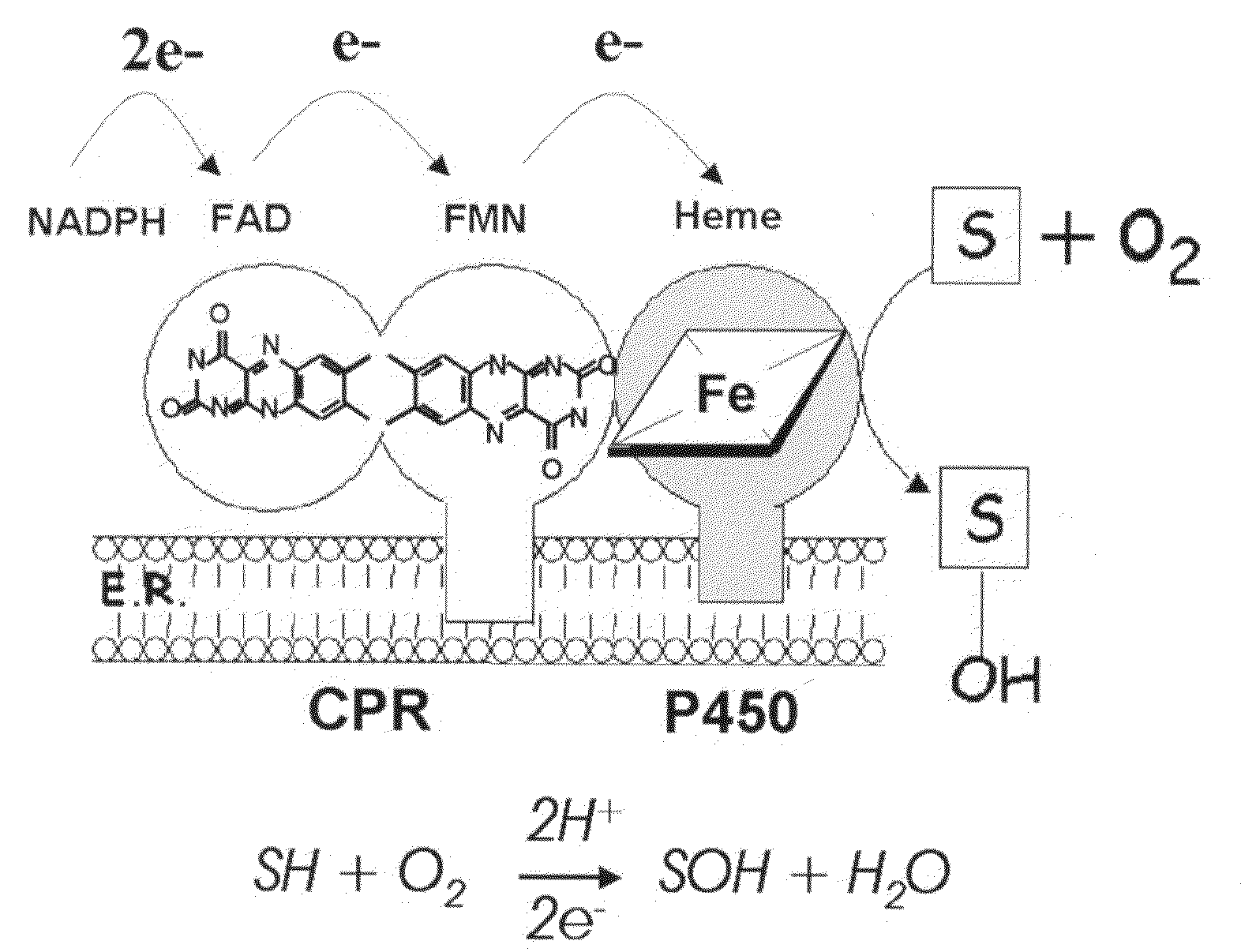
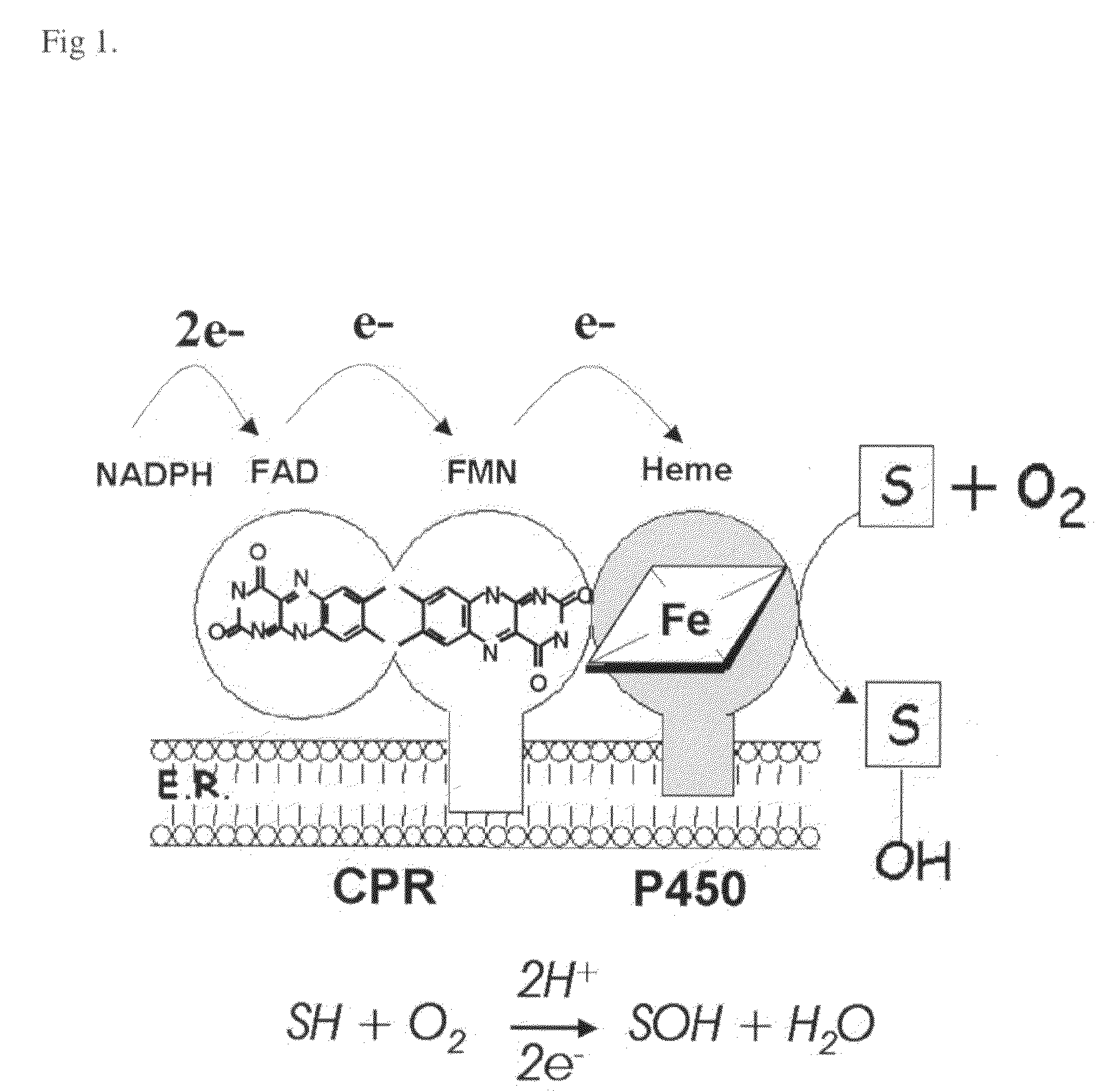
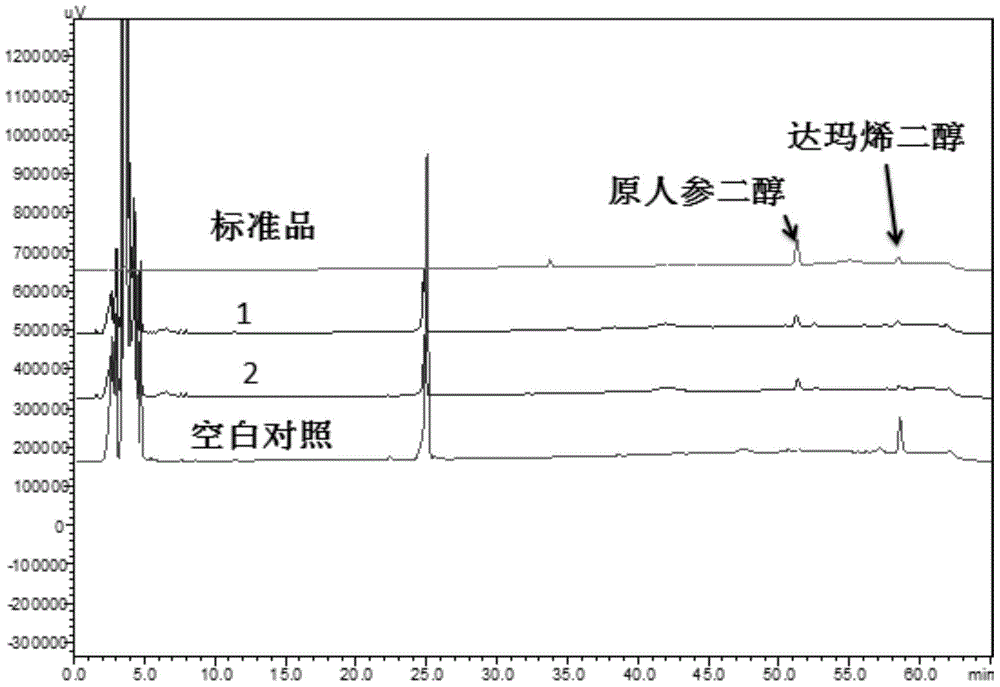
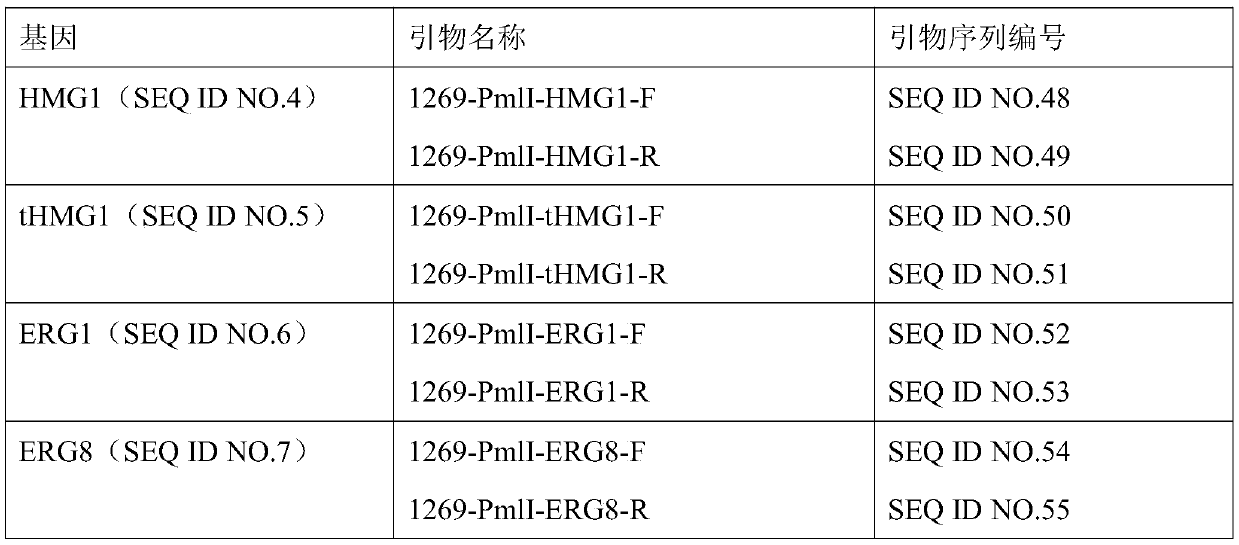
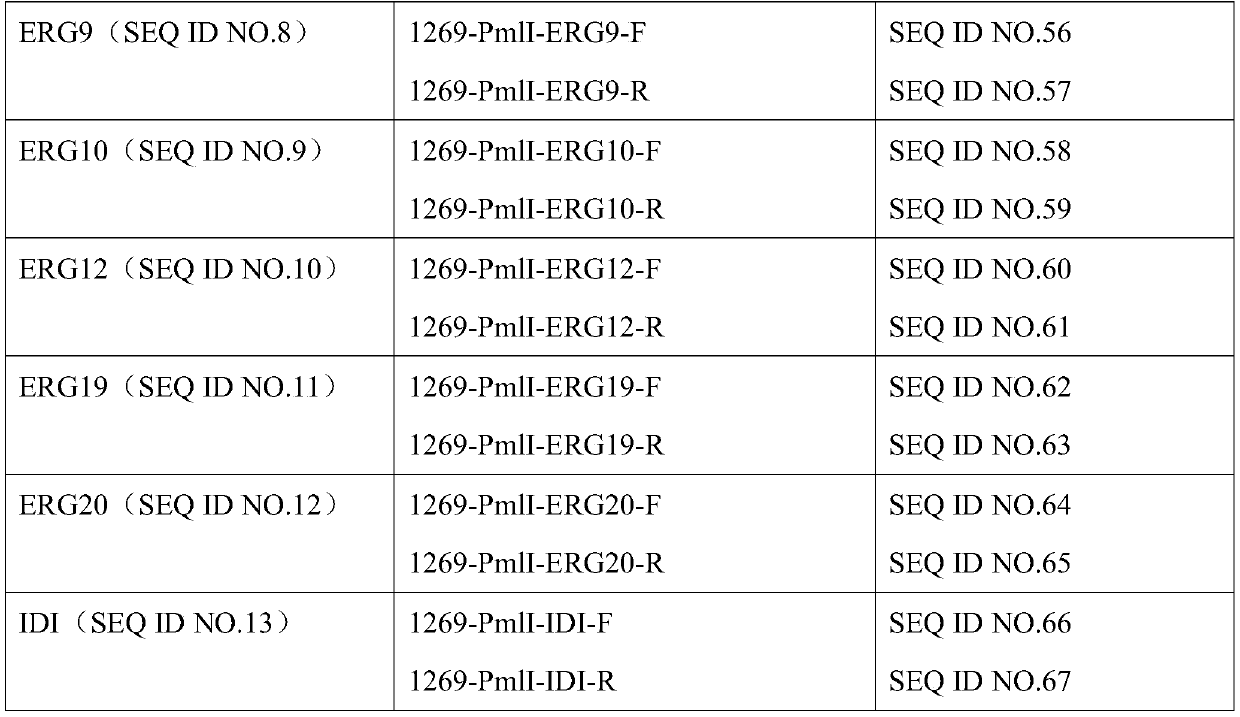
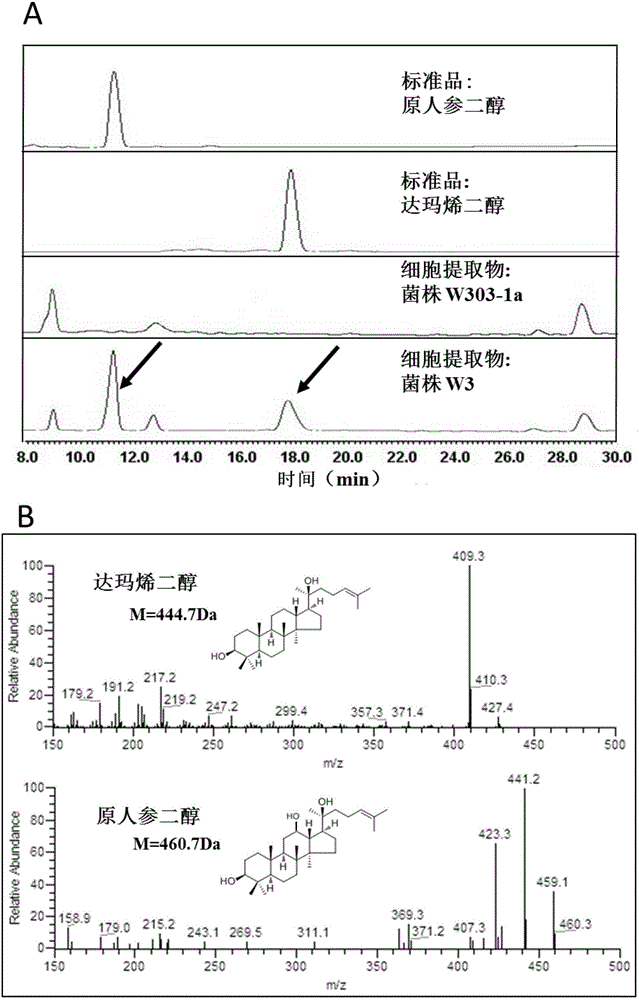
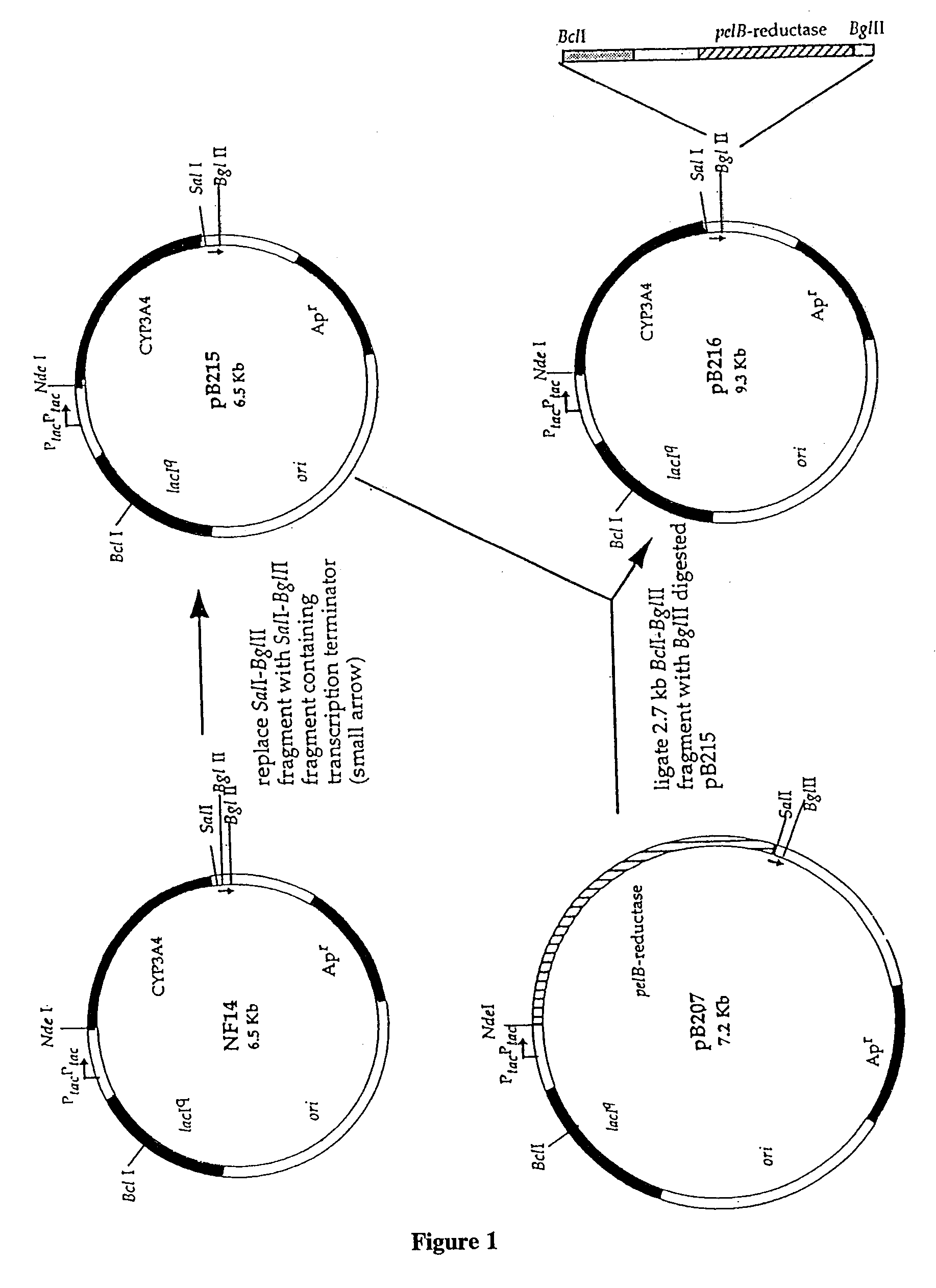
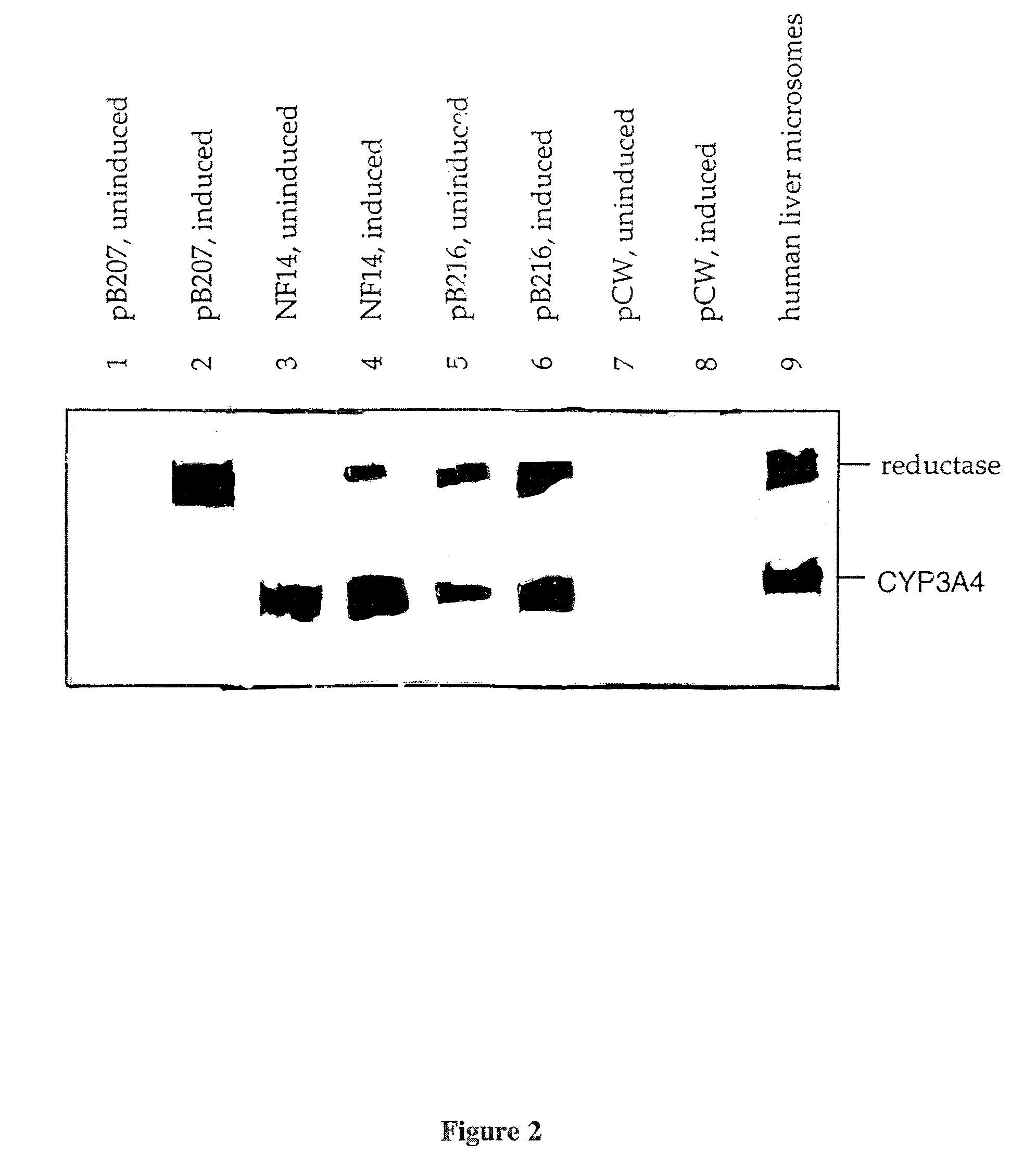
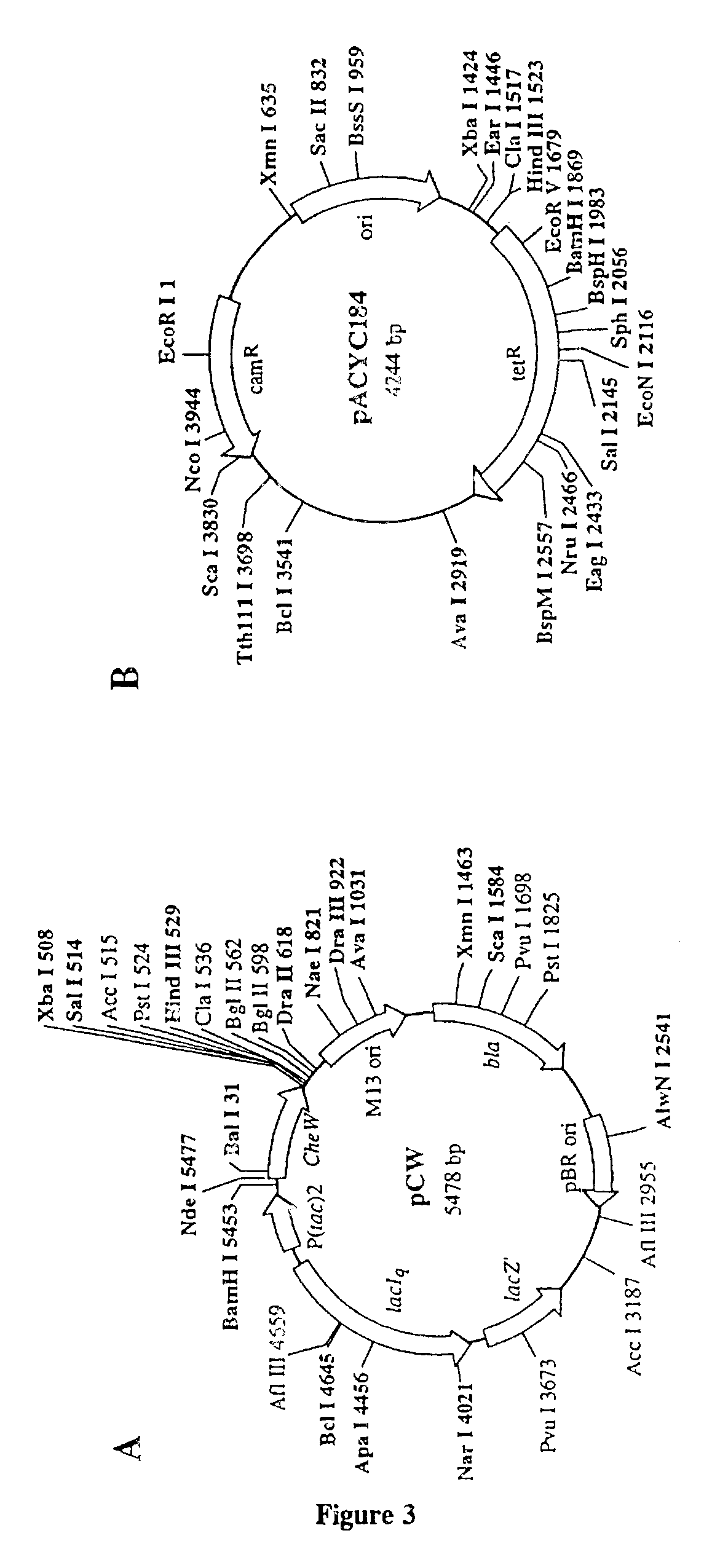
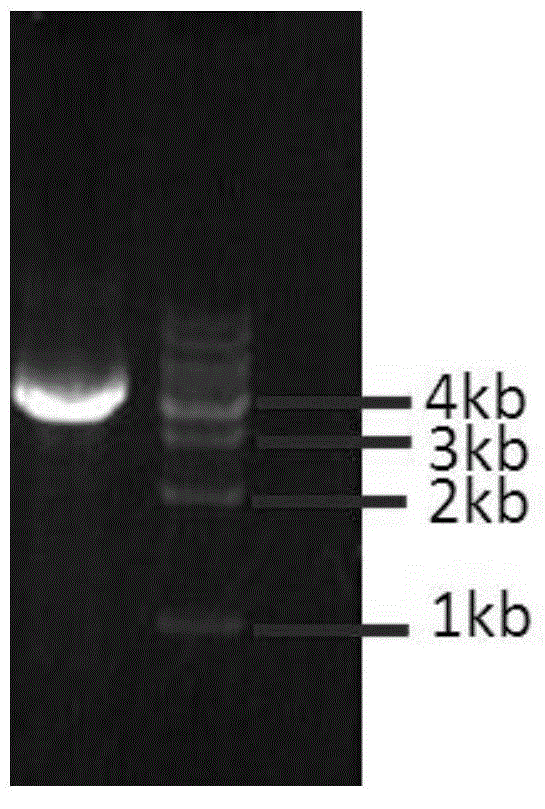
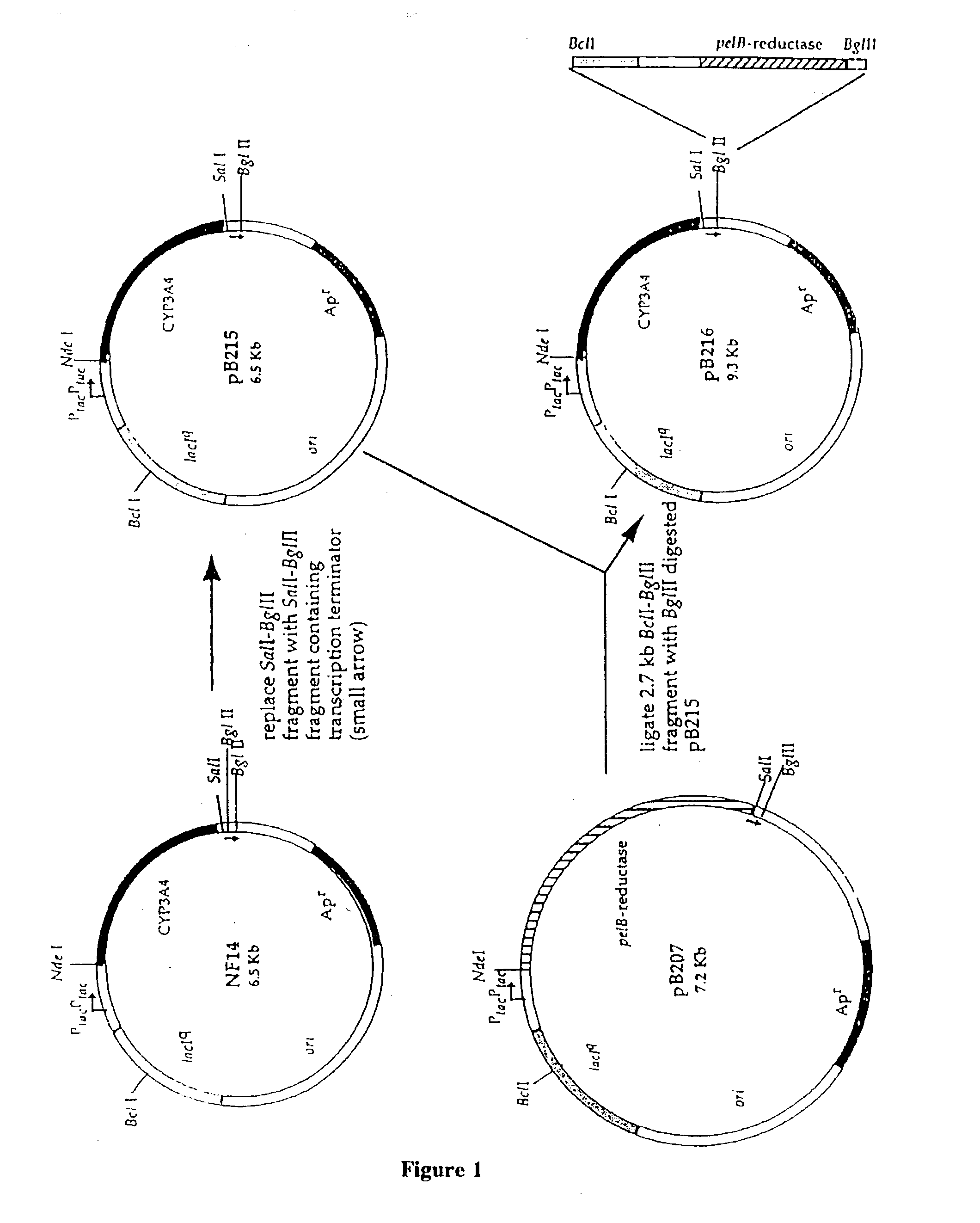
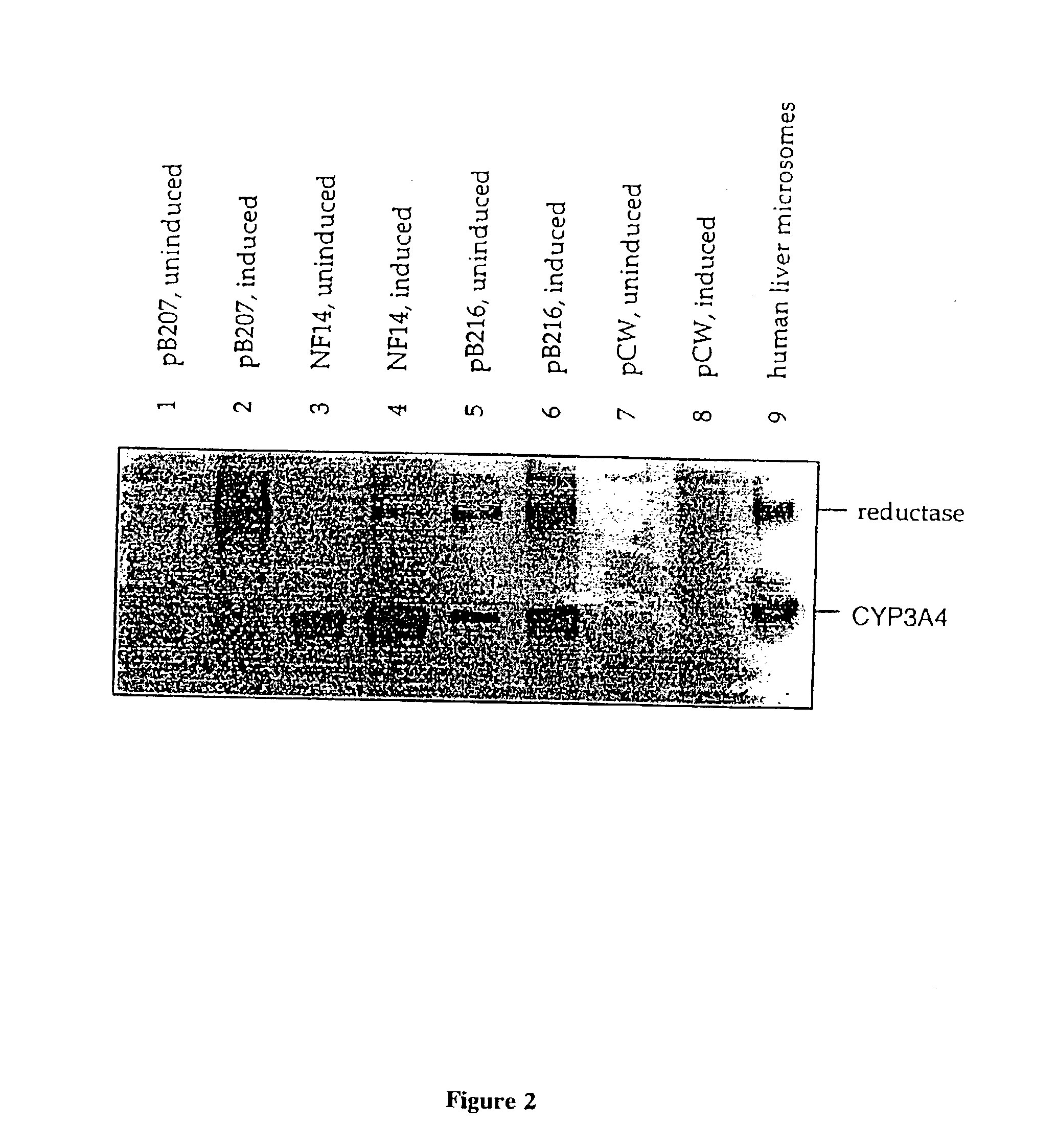
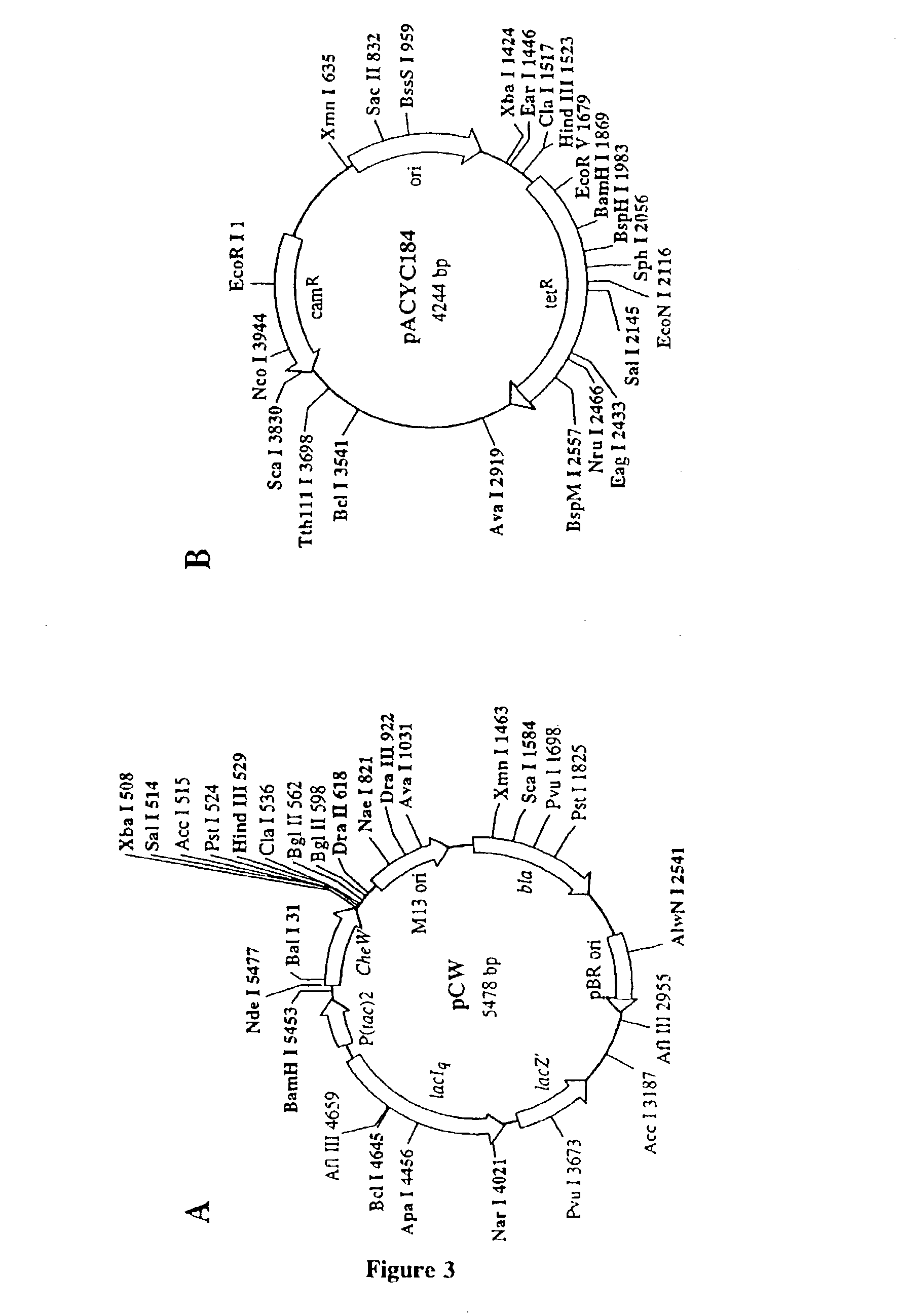
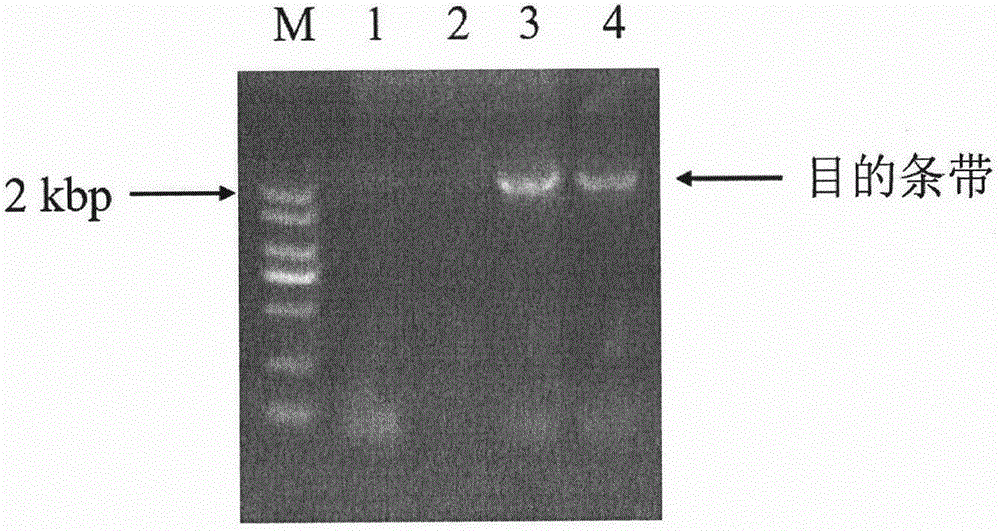
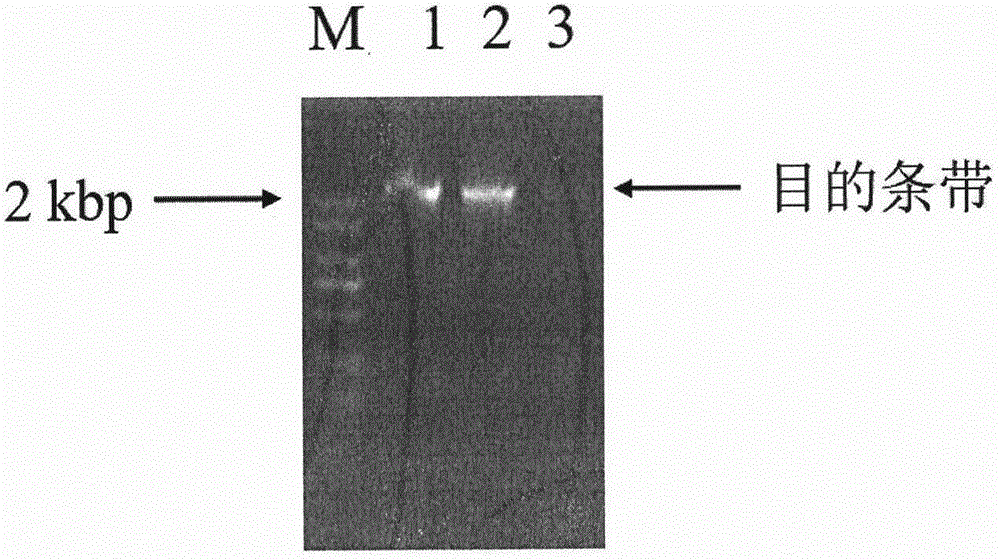
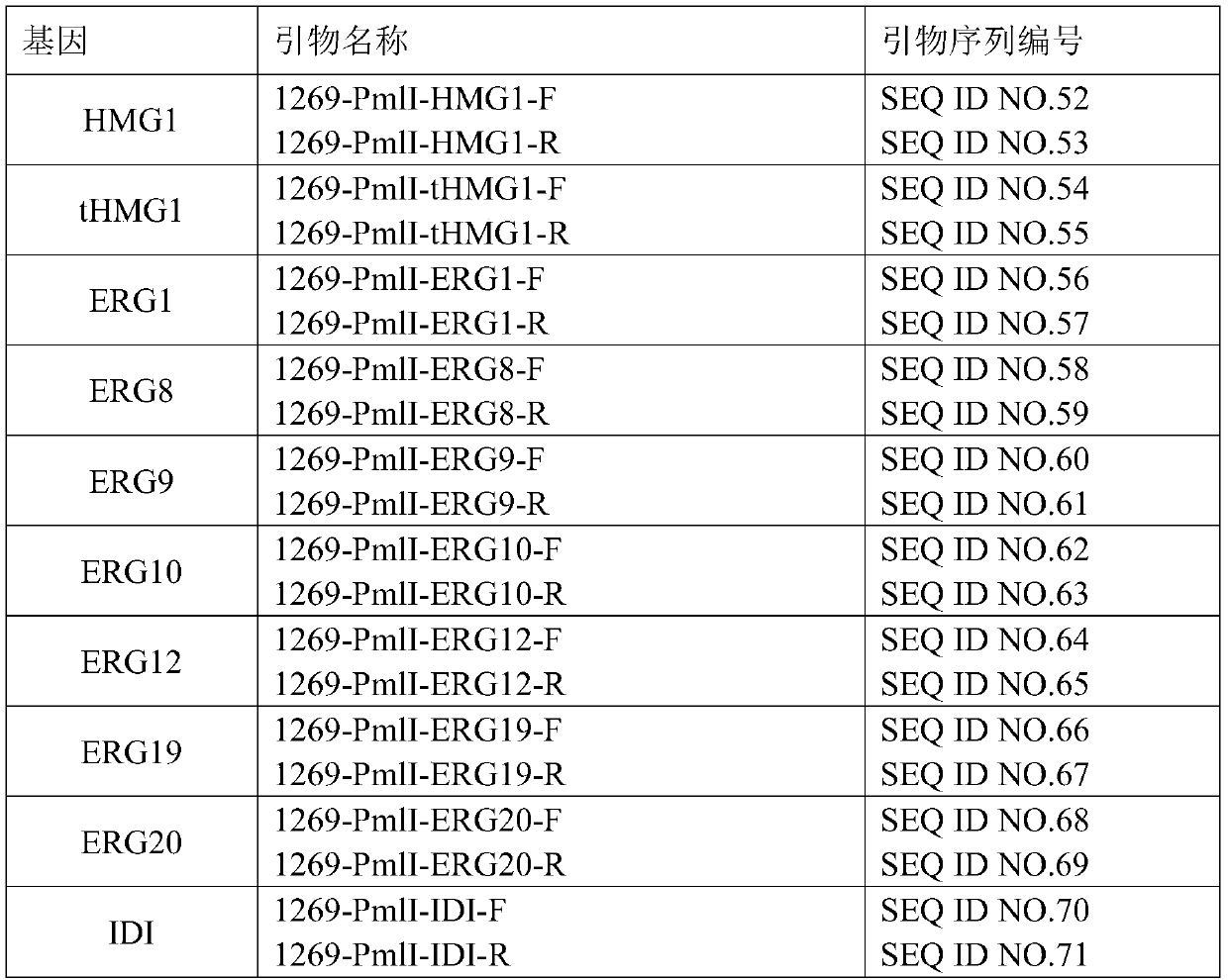
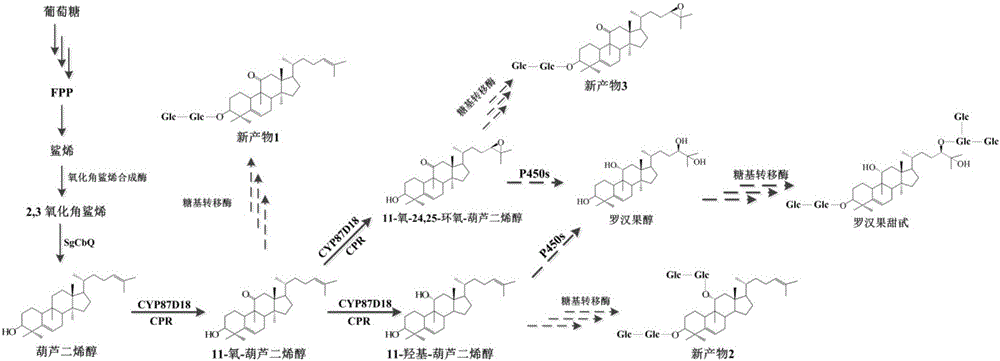
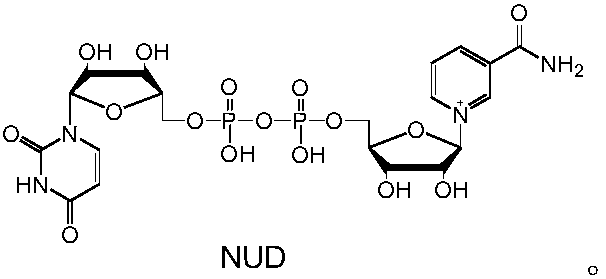
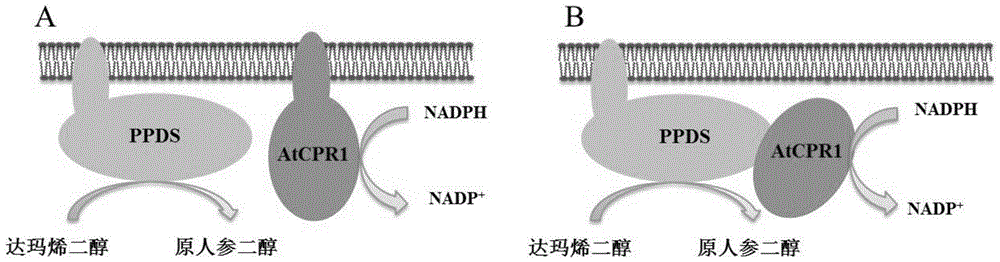
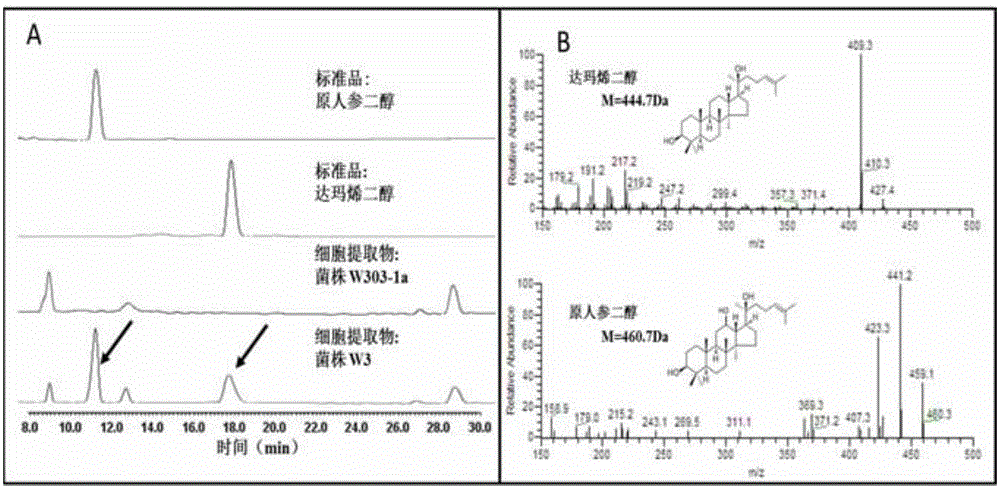
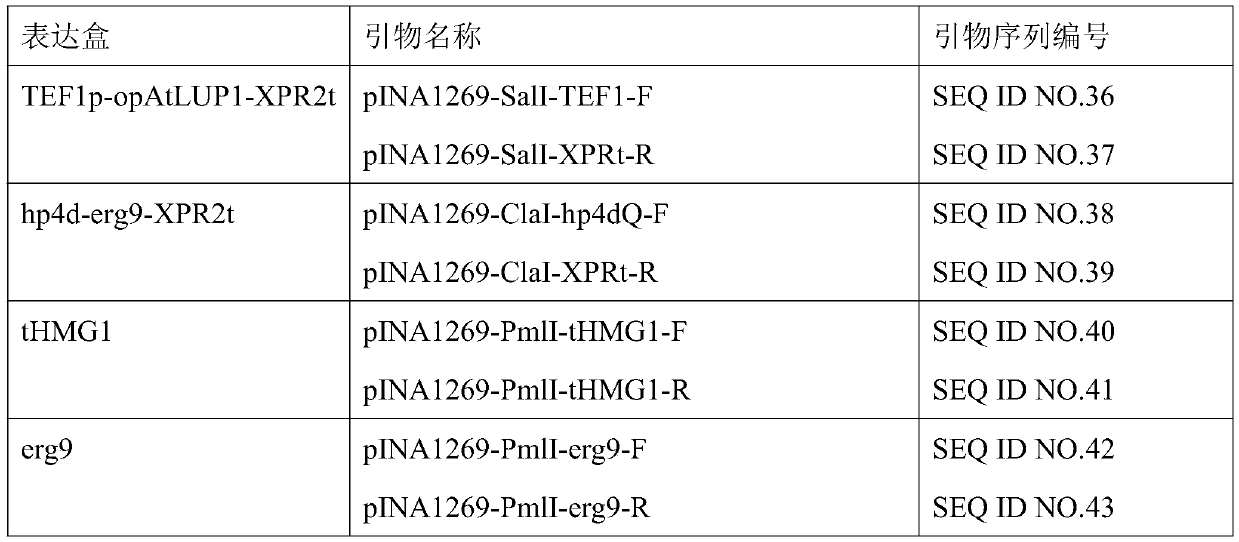
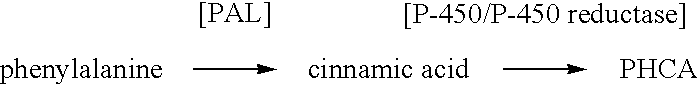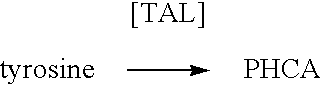Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
49 results about "Cytochrome Reductases" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
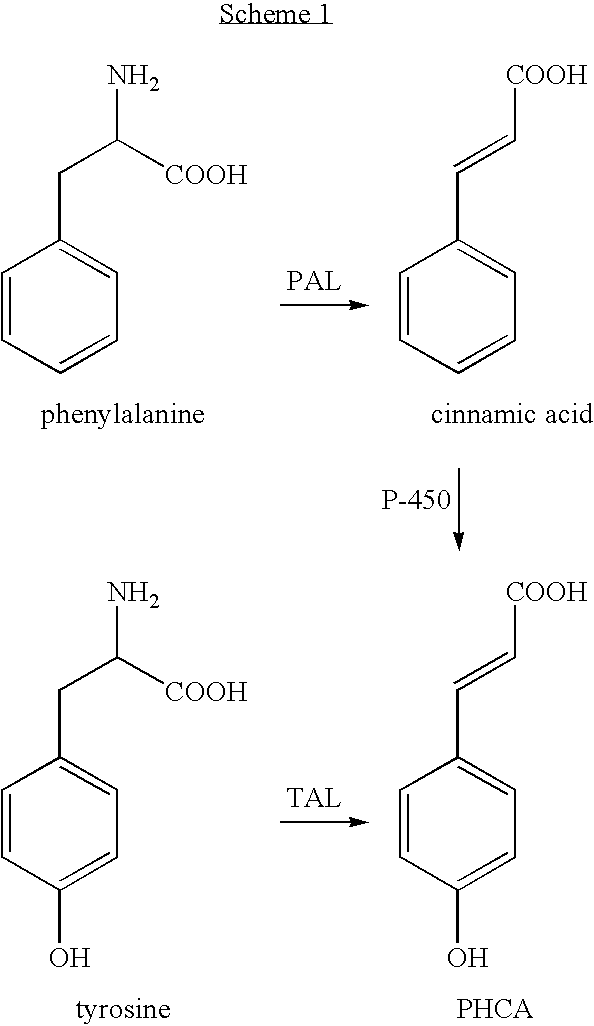
Bioproduction of para-hydroxycinnamic acid
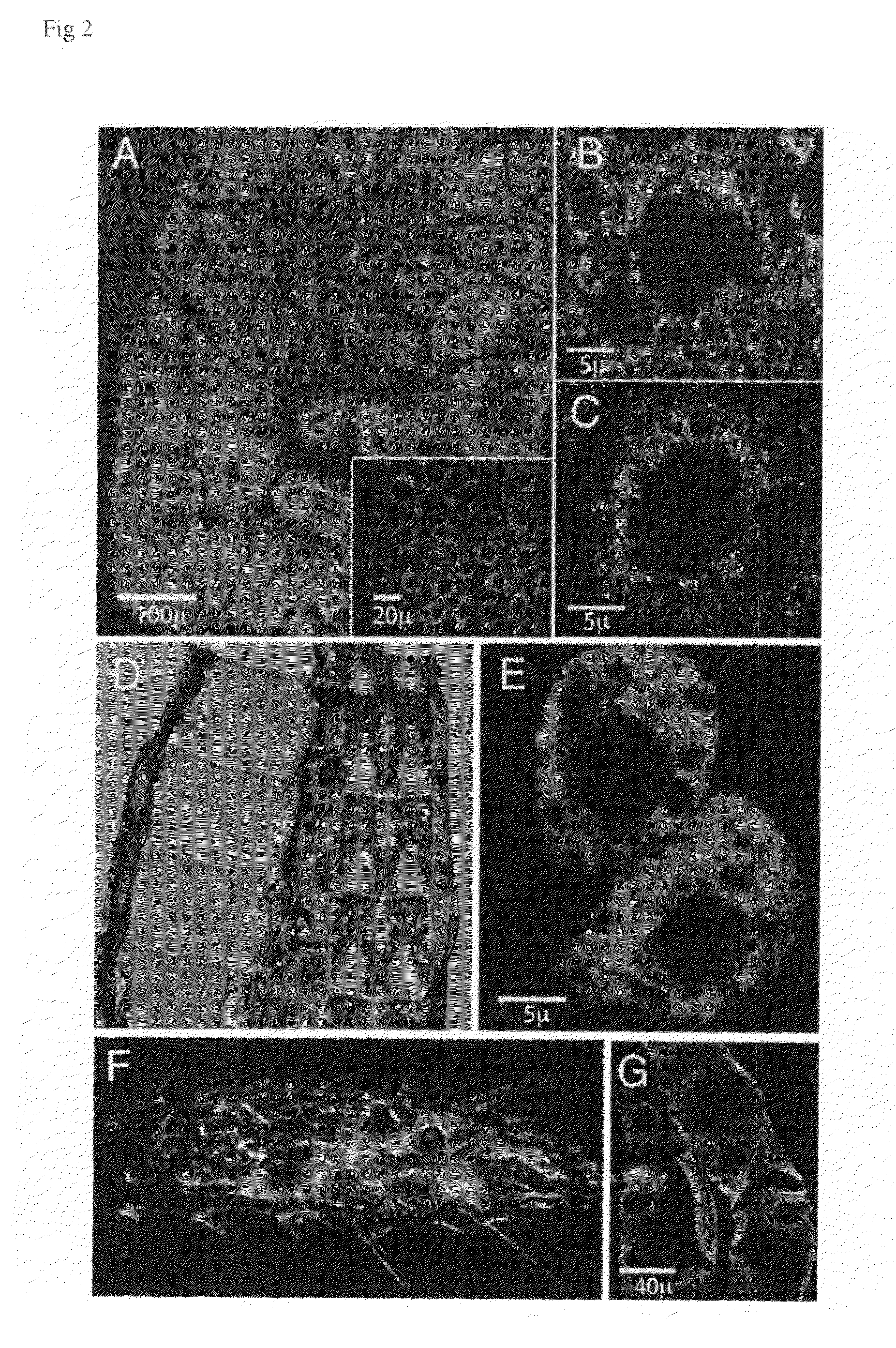
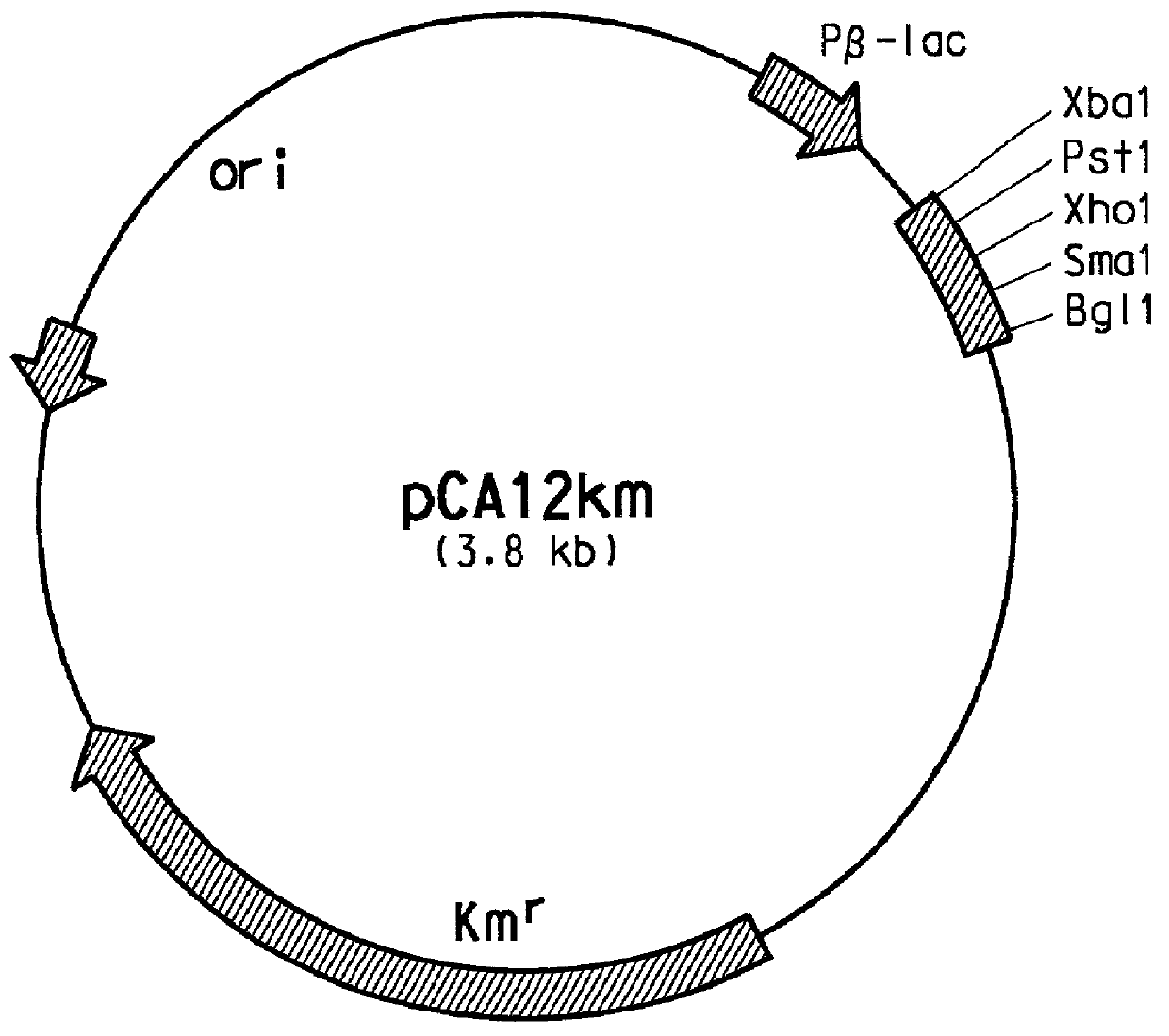
The present invention provides several methods for biological production of para-hydroxycinnamic acid (PHCA). The invention is also directed to the discovery of new fungi and bacteria that possess the ability to convert cinnamate to PHCA. The invention relates to developing of a new biocatalyst for conversion of glucose to PHCA by incorporation of the wild type PAL from the yeast Rhodotorula glutinis into E. coli underlining the ability of the wildtype PAL to convert tyrosine to PHCA. The invention is also directed to developing a new biocatalyst for conversion of glucose to PHCA by incorporation of the wildtype PAL from the yeast Rhodotorula glutinis plus the plant cytochrome P-450 and the cytochrome P-450 reductase into E. coli. In yet another embodiment, the present invention provides for the developing of a new biocatalyst through mutagenesis of the wild type yeast PAL which possesses enhanced tyrosine ammonia-lyase (TAL) activity.
Owner:GATENBY ANTHONY A +4
Bioproduction of para-hydroxycinnamic acid
InactiveUS20010053847A1Increased substrate specificityEnhanced TAL activitySugar derivativesBacteriaTyrosine ammonia-lyase activityTyrosine
The present invention provides several methods for biological production of para-hydroxycinnamic acid (PHCA). The invention is also directed to the discovery of new fungi and bacteria that possess the ability to convert cinnamate to PHCA. The invention relates to developing of a new biocatalyst for conversion of glucose to PHCA by incorporation of the wild type PAL from the yeast Rhodotorula glutinis into E. coli underlining the ability of the wildtype PAL to convert tyrosine to PHCA. The invention is also directed to developing a new biocatalyst for conversion of glucose to PHCA by incorporation of the wildtype PAL from the yeast Rhodotorula glutinis plus the plant cytochrome P-450 and the cytochrome P-450 reductase into E. coli. In yet another embodiment, the present invention provides for the developing of a new biocatalyst through mutagenesis of the wild type yeast PAL which possesses enhanced tyrosine ammonia-lyase (TAL) activity.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
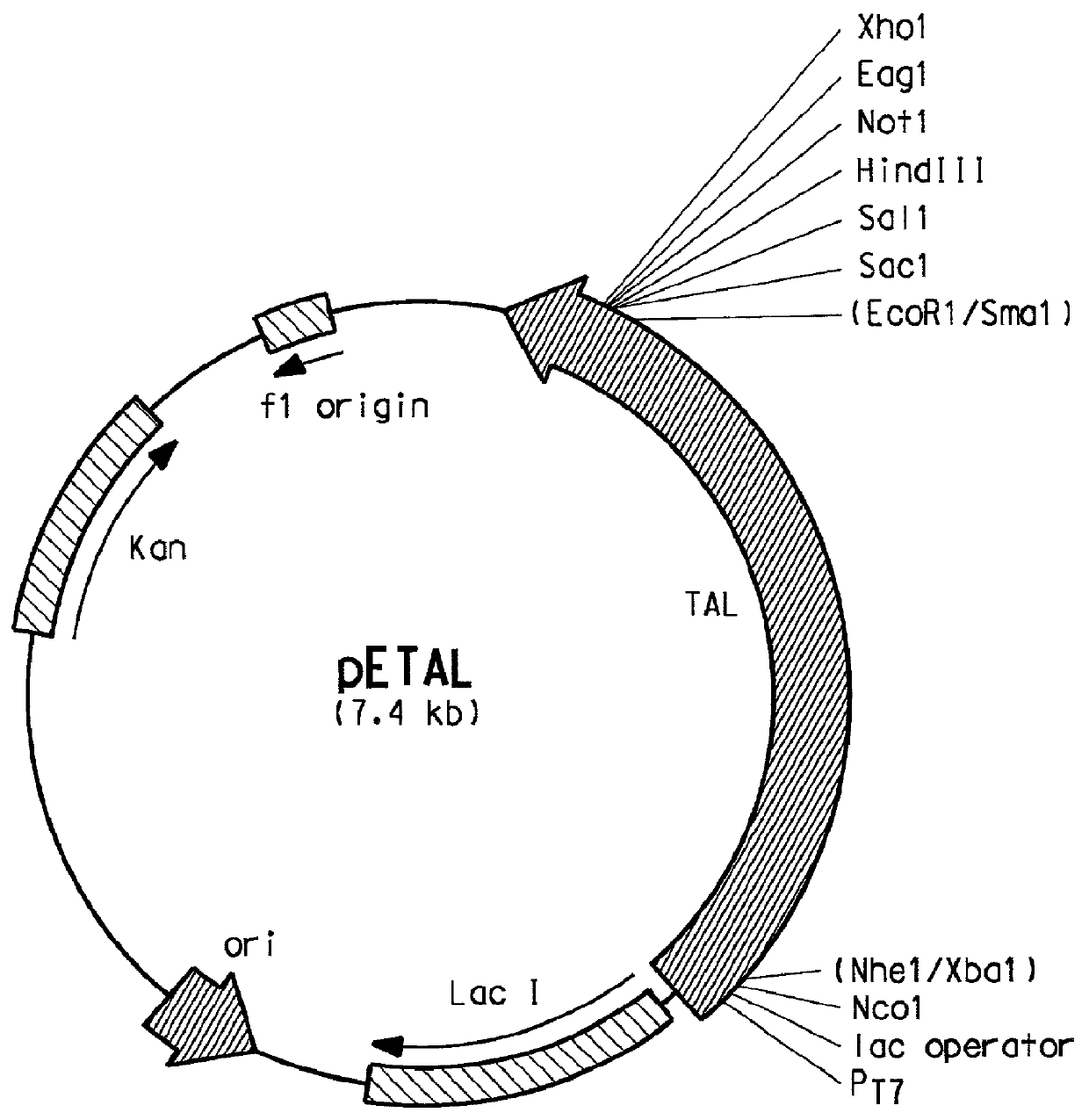
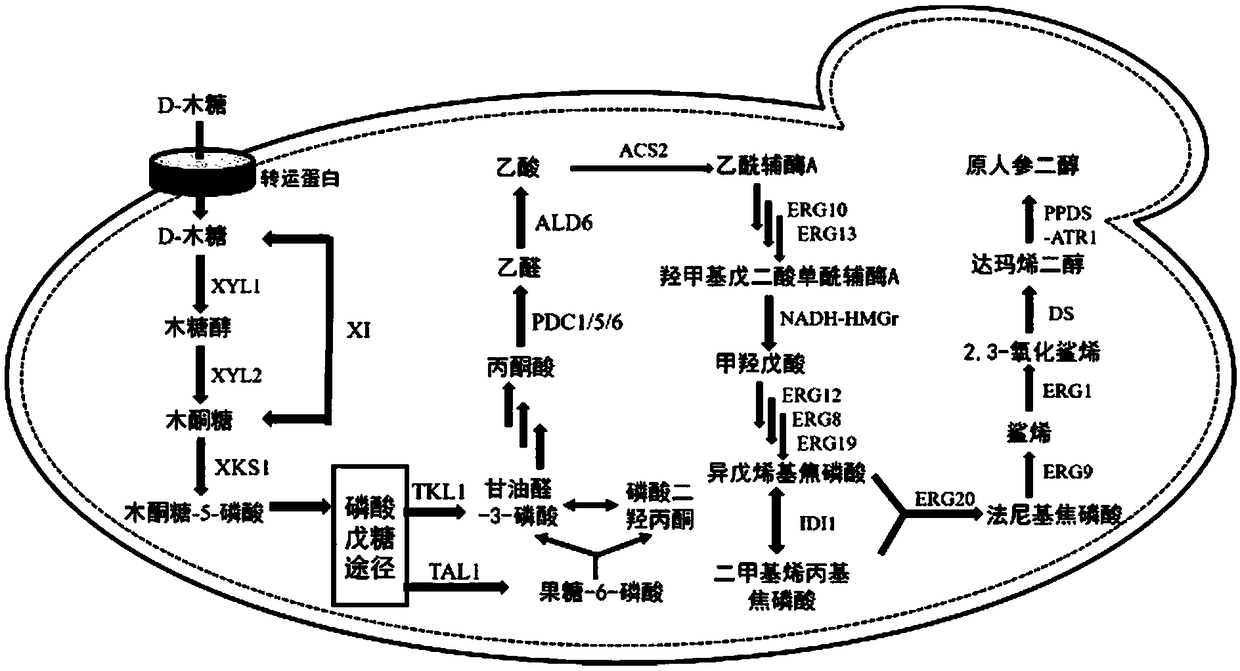
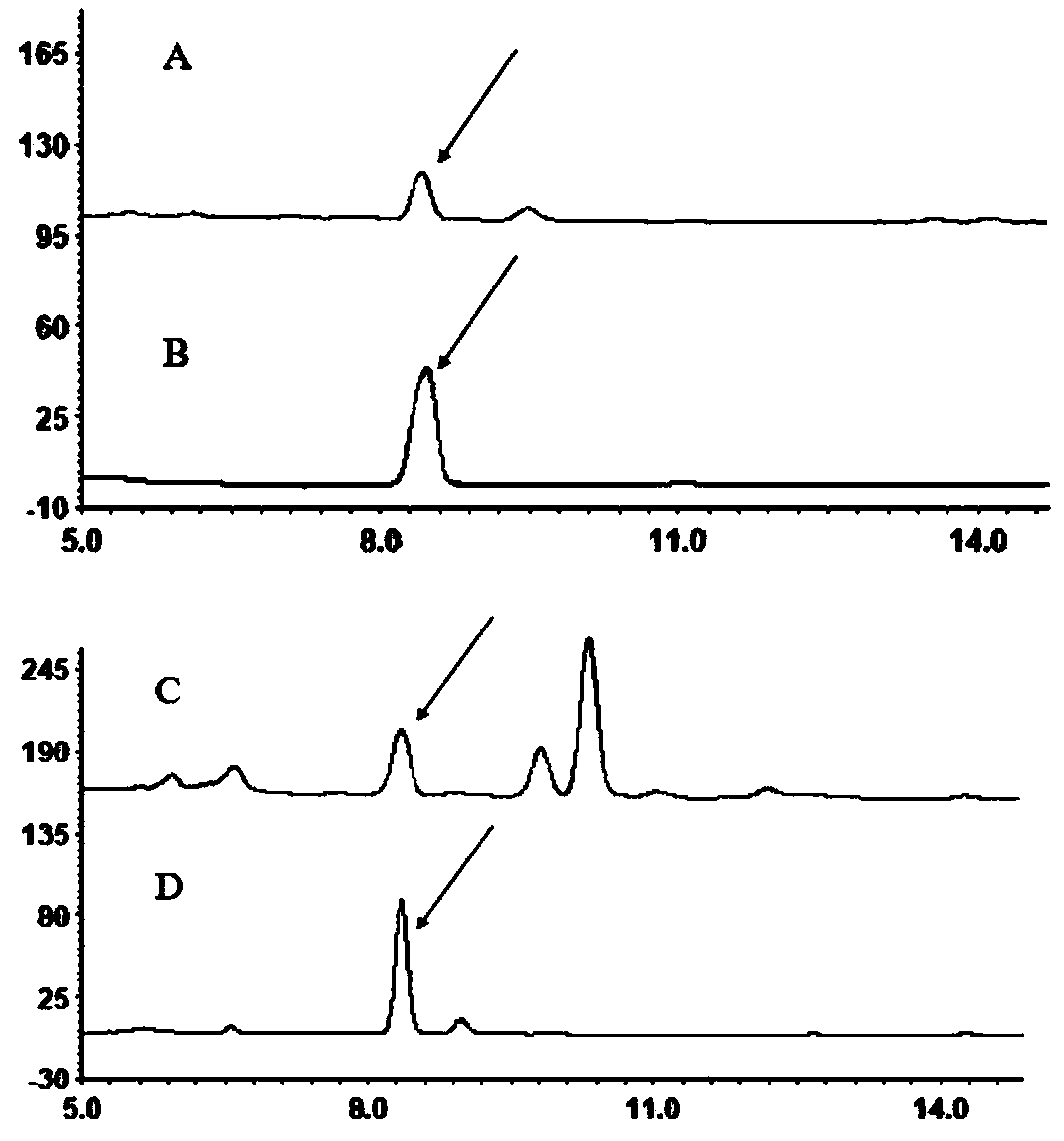
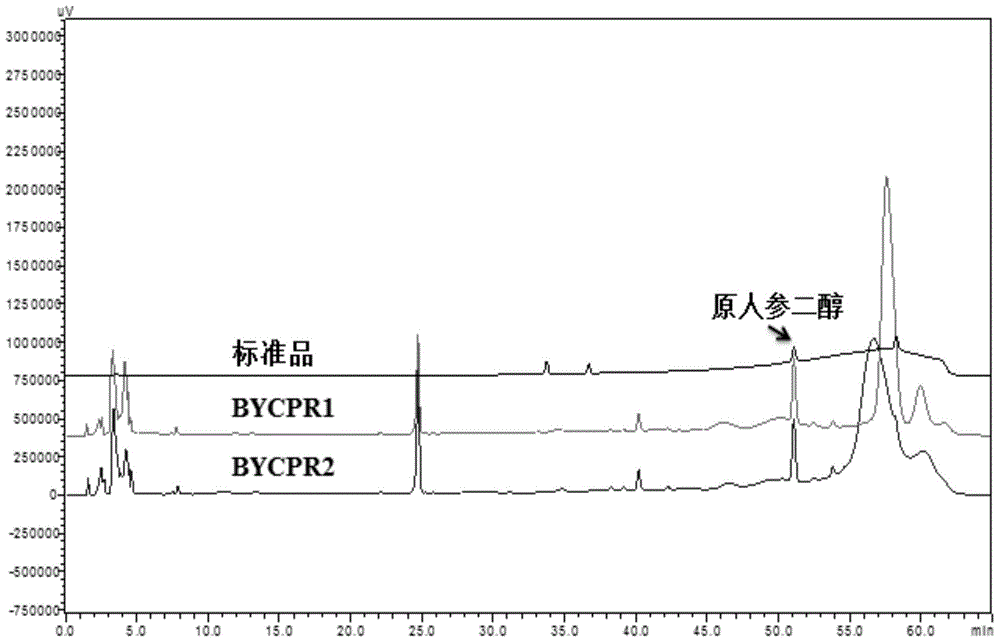
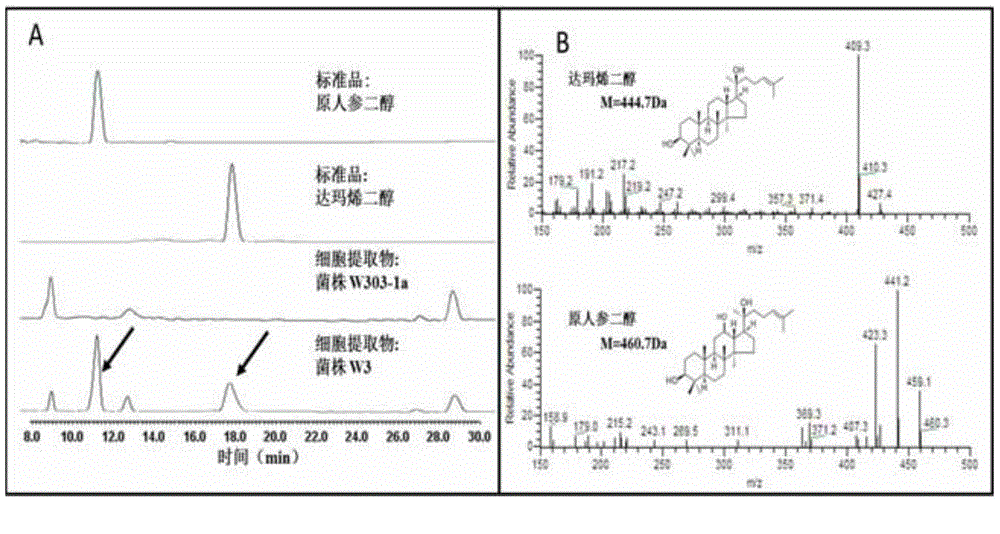
Recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing dammarenediol and protopanoxadiol using xylose and construction method
The invention discloses recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing dammarenediol and protopanoxadiol using xylose and a construction method. The construction method comprises the steps of replacing a promoter of a saccharomyces cerevisiae xylulokinase gene XKS1 with a promoter PFBA1 by virtue of a homologous recombination method, introducing xylose reductase XYL1 and a xylitol dehydrogenase XYL2 expression cassette, increasing the activities of transketolase TKL1 and transaldolase TAL1 so as to obtain recombinant bacteria 1, introducing a farnesyl-diphosphate farnesyltransferase gene ERG9, a squalene monooxygenase gene ERG1 and a dammarenediol synthase gene DS into the recombinant bacteria 1 so as to obtain recombinant bacteria 2, and introducing a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene NADH-HMGr, farnesyl diphosphatesynthase ERG20 and a protopanoxadiol synthase-cytochrome P450 reductase fusion protein gene PPDS-ATR1 into the recombinant bacteria 2, so as to obtain recombinant bacteria 3. According to the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae, dammarenediol and protopanoxadiol can be artificially synthesized by virtue of xylose.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Cytochrome p450 and cytochrome p450 reductase polypeptides, encoding nucleic acid molecules and uses thereof
The invention provides cytochrome P450 polypeptides, including cytochrome P450 santalene oxidase polypeptides, cytochrome P450 bergamotene oxidase polypeptides and cytochrome P450 reductase polypeptides. Also provided are nucleic acid molecules encoding the cytochrome P450 polypeptides. Cells containing the nucleic acids and / or the polypeptides are provided as are methods for producing terpenes, such as santalols and bergamotols, by culturing the cells.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA +1
Use of cytochrome P450 reductase as insecticidal target
InactiveUS20090010888A1Reduced activityReduce expressionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsCytochrome P450 reductaseOrganic chemistry
The invention provides a method of enhancing the effectiveness of pesticides, as well as pesticidal formulations. Furthermore, it also provides the means for the de novo rational design of pesticides. The present invention also relates to a method of screening agents for potential use in insecticides, particularly against mosquitoes.
Owner:UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF DUNDEE +1
NADPH-cytochrome P450 reducing ferment and application thereof
Provided is a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADPH)-cytochrome P450 reductase and a use thereof. Also provided is a polynucleotide encoding the NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase, an expression vector and a host cell which express the NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase, and a method for producing the protopanoxadiol.
Owner:SYNBIOTECH (SUZHOU) CO LTD
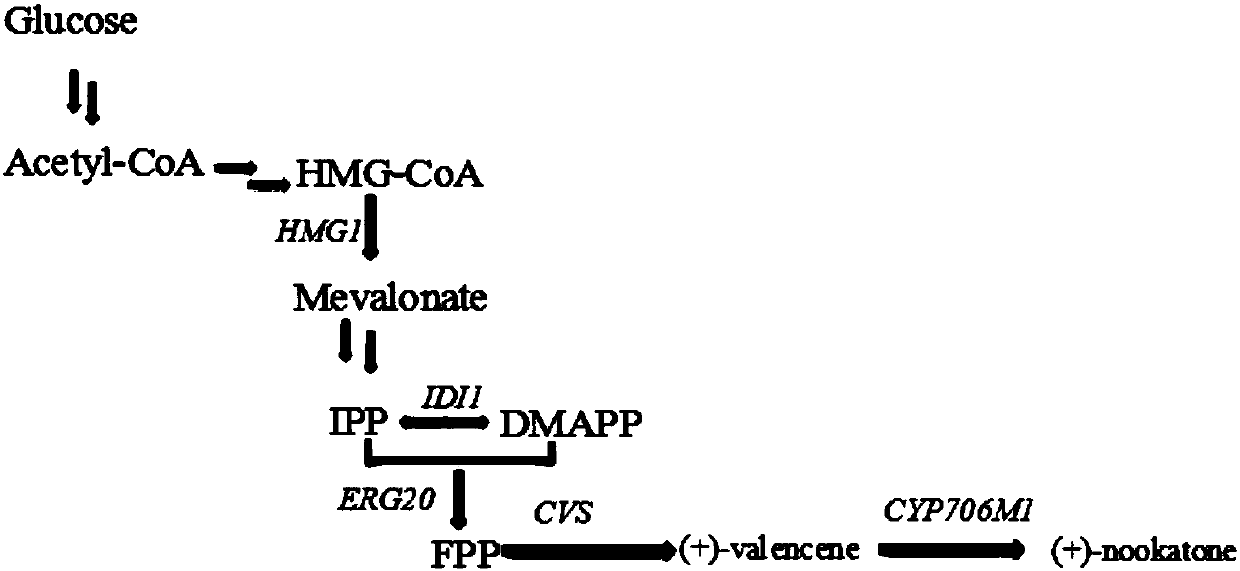
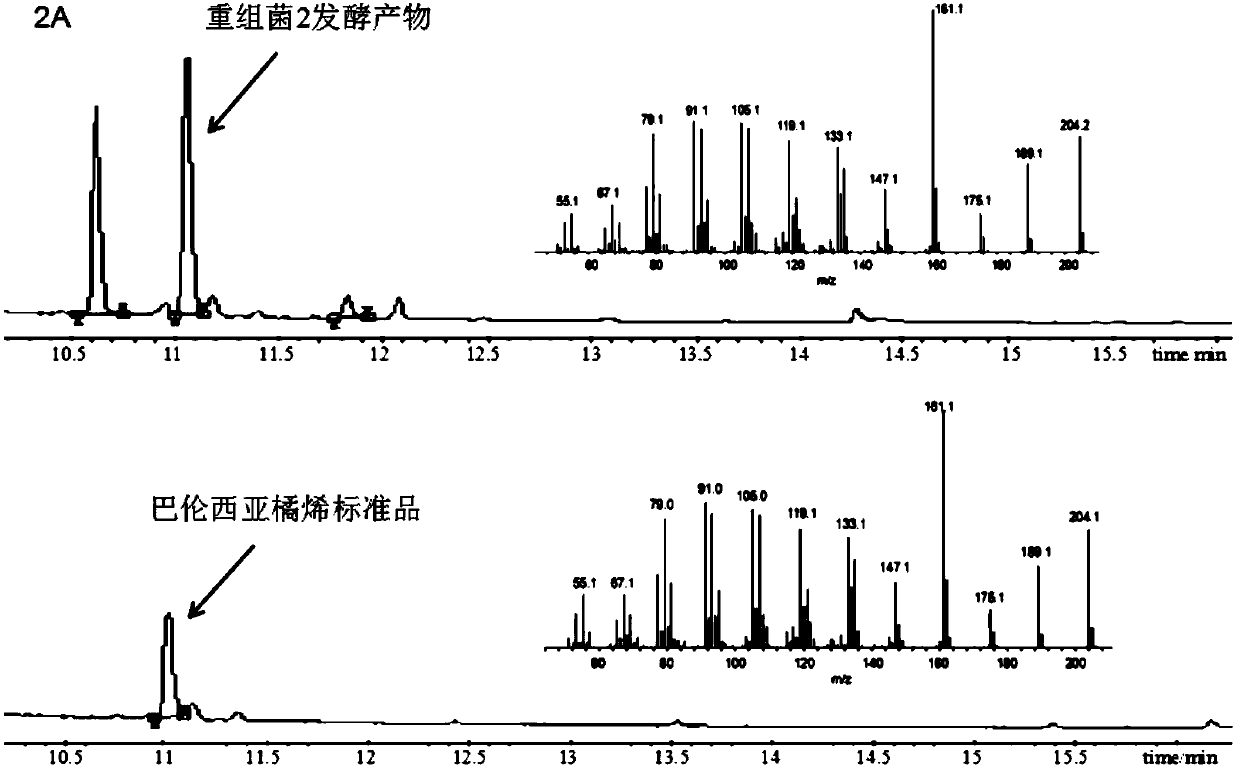
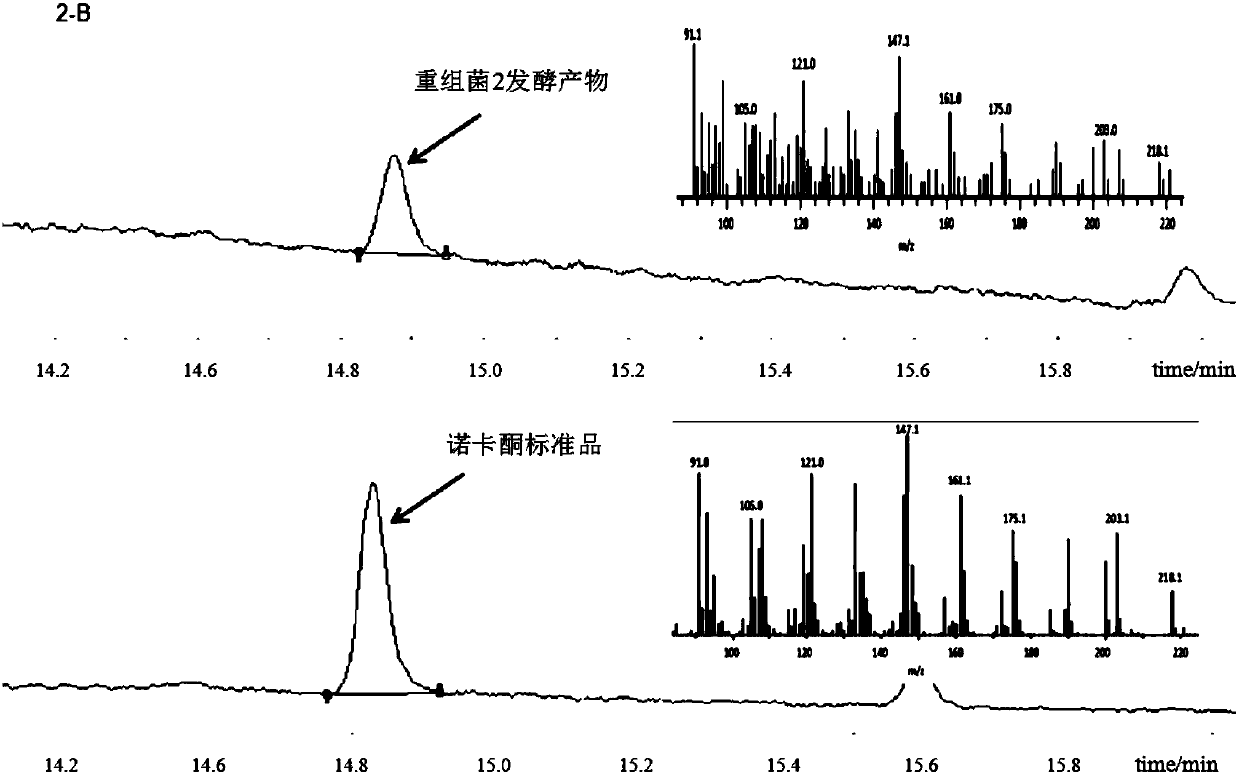
Recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica for producing Valencene and (+)-Nootkatone, and construction method thereof
The invention discloses a construction method of a recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica for producing Valencene and (+)-Nootkatone. The method is characterized in that a Valencene synthase coding gene CVSexpression cassette, a (+)-Nootkatone synthase coding gene CYP706M1 expression cassette and a cytochrome P450 reductase coding gene AtCPR expression cassette are introduced into the rDNA site of Yarrowia lipolytica through a homologous recombination technology to obtain the recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica 1 for producing Valencene and (+)-Nootkatone. Experiments prove that the recombinant Yarrowialipolytica for producing Valencene and (+)-Nootkatone, obtained by the homologous recombination technology, can increase the yield of the Valencene and the (+)-Nootkatone, and allows the yield of theValencene to be 6.5 to 18 mg / L and the yield of the (+)-Nootkatone to be 30 [mu]g / L to 0.5 mg / L. The method provides a basis for the artificial synthesis of the Valencene and (+)-Nootkatone.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
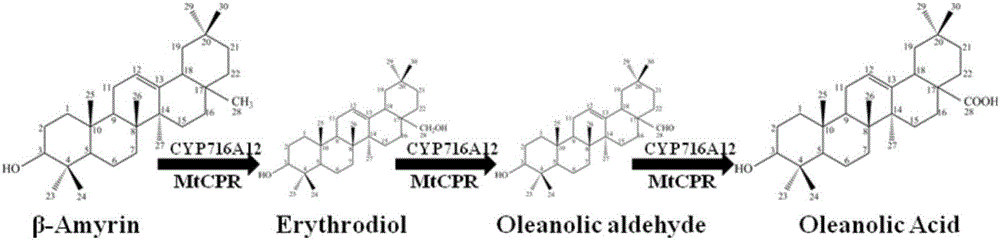
Recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica for heterogeneous synthesis of beta-amyrin and oleanolic acid and construction method
The invention discloses recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica for heterogeneous synthesis of beta-amyrin and oleanolic acid and a construction method. The construction method comprises the step of introducing an optimized beta-amyrin synthase coding gene, an optimized oleanolic acid synthase coding gene and an optimized cytochrome-NADPH-reductase 1 coding gene into Yarrowia lipolytica, thereby obtaininga recombinant strain 2. Proven by experiments, the recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica capable of yielding the beta-amyrin and the oleanolic acid is obtained through a homologous recombination method, and thus, the yield of the beta-amyrin and the oleanolic acid is increased; and the method disclosed by the invention provides a foundation for artificial synthesis of the beta-amyrin and the oleanolicacid.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
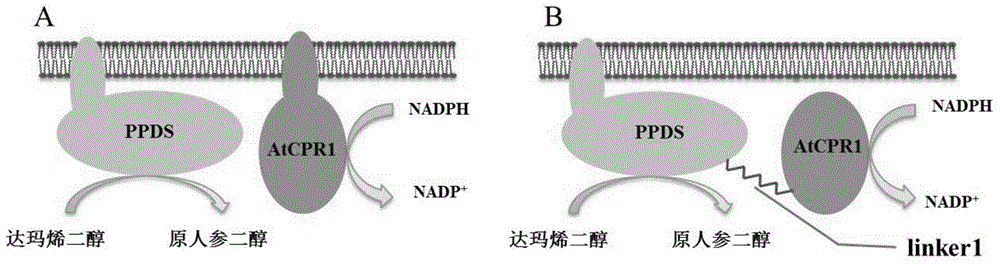
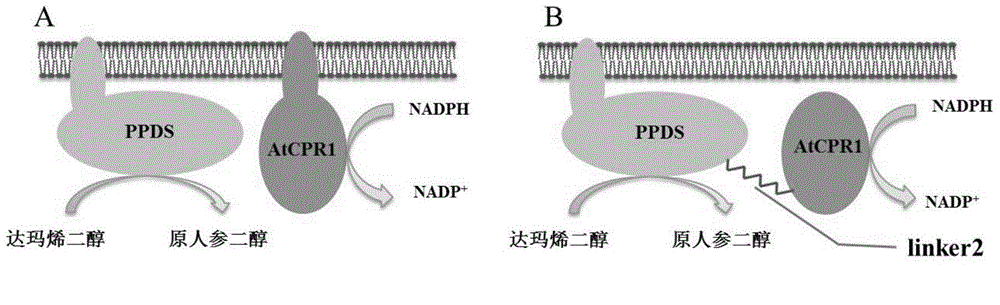
Fusion protein capable of improving dammarenediol conversion efficiency, construction method and application
ActiveCN104611303AImprove conversion efficiencyEfficient synthesisMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesProtopanaxadiolTransformation efficiency
The invention discloses fusion protein capable of improving dammarenediol conversion efficiency, a construction method and application. The construction steps comprise: excising first 138 bases at 5' end of arabidopsis thaliana cytochrome-NADPH-reductase 1 gene AtCPR1, so as to obtain a sequence shown as SEQ ID NO. 2; (2) removing a termination codon TAA at 3' end of ginseng protopanaxadiol synthase gene PPDS with a sequence shown as SEQ ID NO. 3, and connecting with the base sequence which at 5' end of the sequence shown as SEQ ID NO. 2 and used for coding polypeptide GSTSSGSG, so as to construct a gene member of fusion protein; and (3) connecting the gene member of the fusion protein with saccharomyces cerevisiae cell endogenous promoter and terminator, so as to construct a fusion protein gene expression cassette, and transforming into saccharomyces cerevisiae cell for expression. The fusion protein constructed by the method is capable of improving the conversion rate of dammarenediol to protopanaxadiol.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Amaryllidaceae plant lycoris aurea cytochrome P450 reductase 2 and coding gene and application thereof
The invention relates to a cytochrome P450 reductase and a coding gene and application thereof. The invention discloses a cytochrome P450 reductase 2 of an amaryllidaceae plant lycoris aurea for the first time, and the cytochrome P450 reductase 2 has good coenzyme specificity and can assist a cytochrome P450 enzyme to develop the catalytic activity to oxidatively modify a substrate synthetic product thereof. The invention further discloses a polynucleotide for coding the cytochrome P450 reductase, a carrier for expressing the cytochrome P450 reductase and a method for producing a caffeic acid.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Expression of functional cytochrome P450 monooxygenase system in enterobacteria
InactiveUS6566108B1Fast testImprove catalytic performancePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBacteriaBacteroidesCytochrome P450 reductase
A bacterial cell containing a functional cytochrome P450 monooxygenase system, said cell comprising a genetic construct capable of expressing a cytochrome P450 and genetic construct capable of expressing, separately from said cytochrome P450, a cytochrome P450 reductase, wherein each of the cytochrome P450 and the cytochrome P450 reductase have at their N-terminus a bacterial signal peptide. The cytochrome P450 and the cytochrome P450 reductase may be encoded by different constructs or the same construct. A bacterial cell containing a cytochrome P450 comprising a genetic construct encoding, and capable of expressing, said cytochrome P450 wherein the cytochrome P450 has, at is N-terminal, a bacterial signal peptide. The bacterial cells are useful as, for example, bioreactors, in drug testing and mutagenicity testing and as a source of cytochrome P450.
Owner:BTG INT LTD
Fusion protein capable of increasing conversion efficiency of dammarendiol, construction method and application
ActiveCN104450633AImprove conversion efficiencyEfficient synthesisAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMicroorganism based processesAgricultural scienceProtopanaxadiol
The invention discloses a fusion protein capable of increasing the conversion efficiency of dammarendiol, a construction method and an application. The construction method comprises the following steps: (1) excising the front 138 basic groups of the end 5' of the cytochrome-NADPH-reductase 1 gene AtCPR1 in arabidopsis to obtain a sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 2; (2) removing the termination codon TAA of the end 3' of the synthase gene PPDS of protopanoxadiol in ginseng shown in SEQ ID NO. 3, and connecting with a base sequence of an encoding polypeptide GSTSSG for the end 5' of a sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 2 to construct a genetic element of the fusion protein; (3) connecting the genetic element of the fusion protein with the internal promoter and the terminator of a saccharomyces cerevisiae cell to construct a genetic expression kit of the fusion protein, and transforming to enter the saccharomyces cerevisiae cell for expression. The fusion protein constructed by the method disclosed by the invention is capable of increasing the conversion efficiency of converting from dammarendiol to protopanoxadiol.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
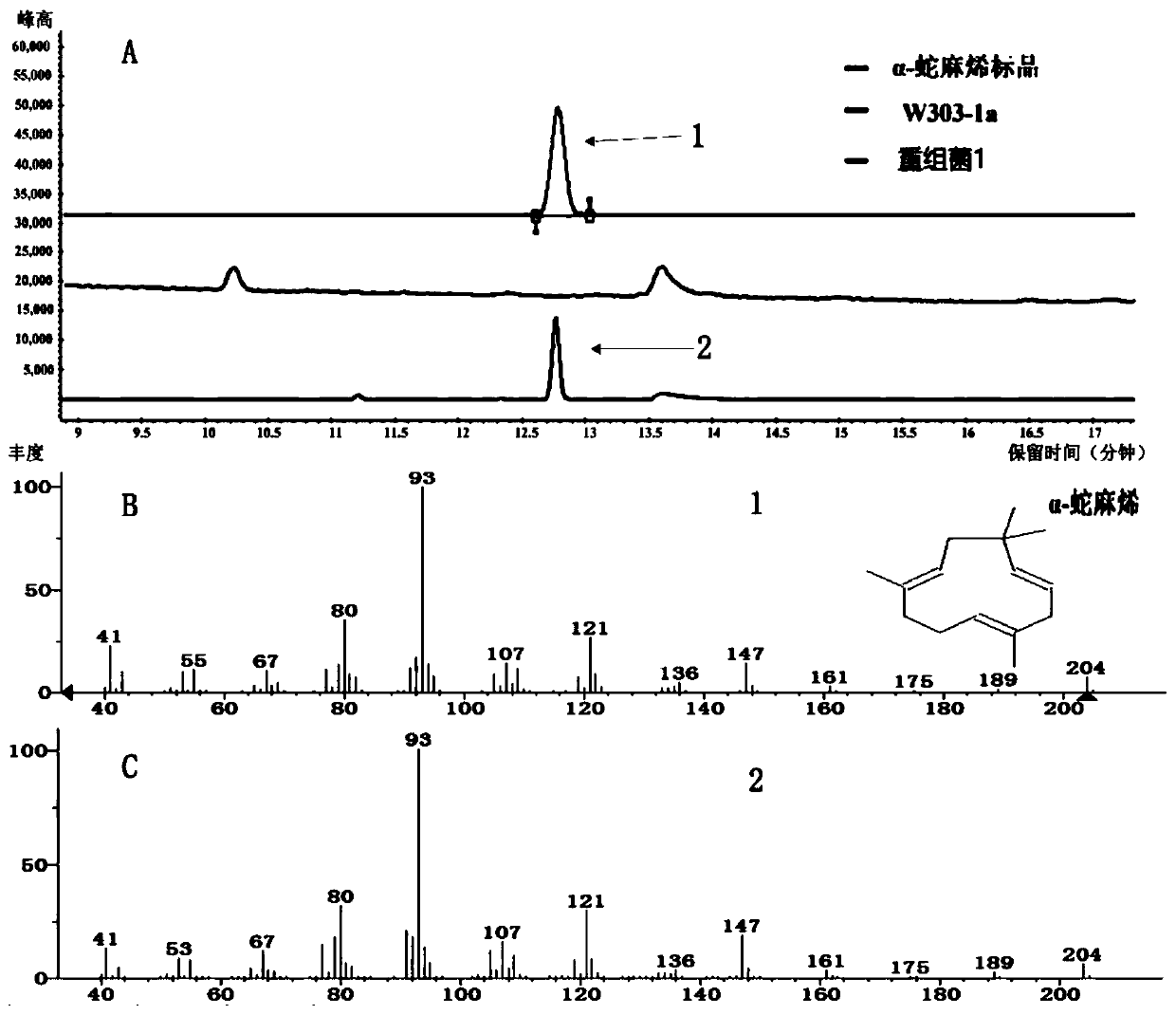
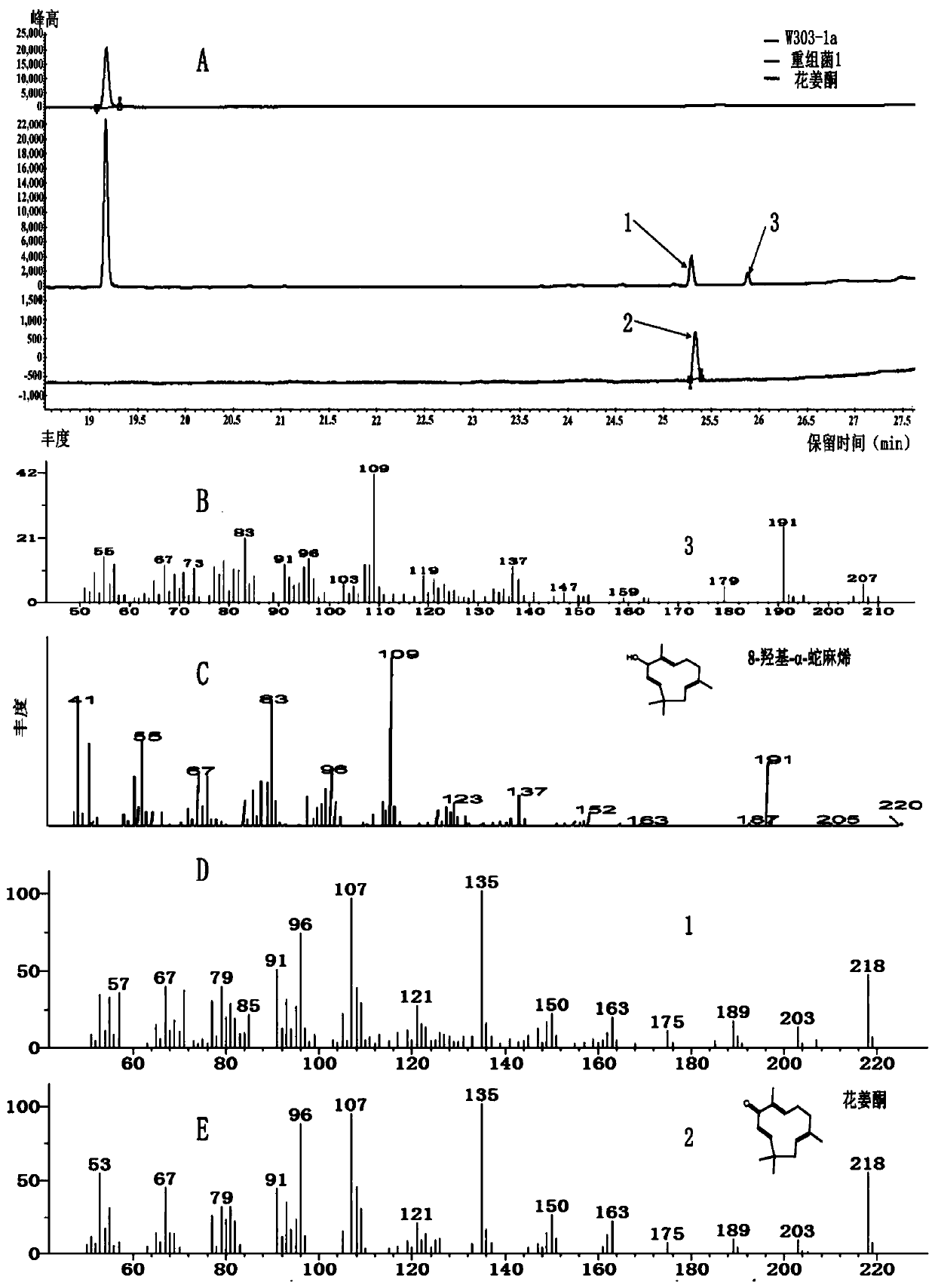
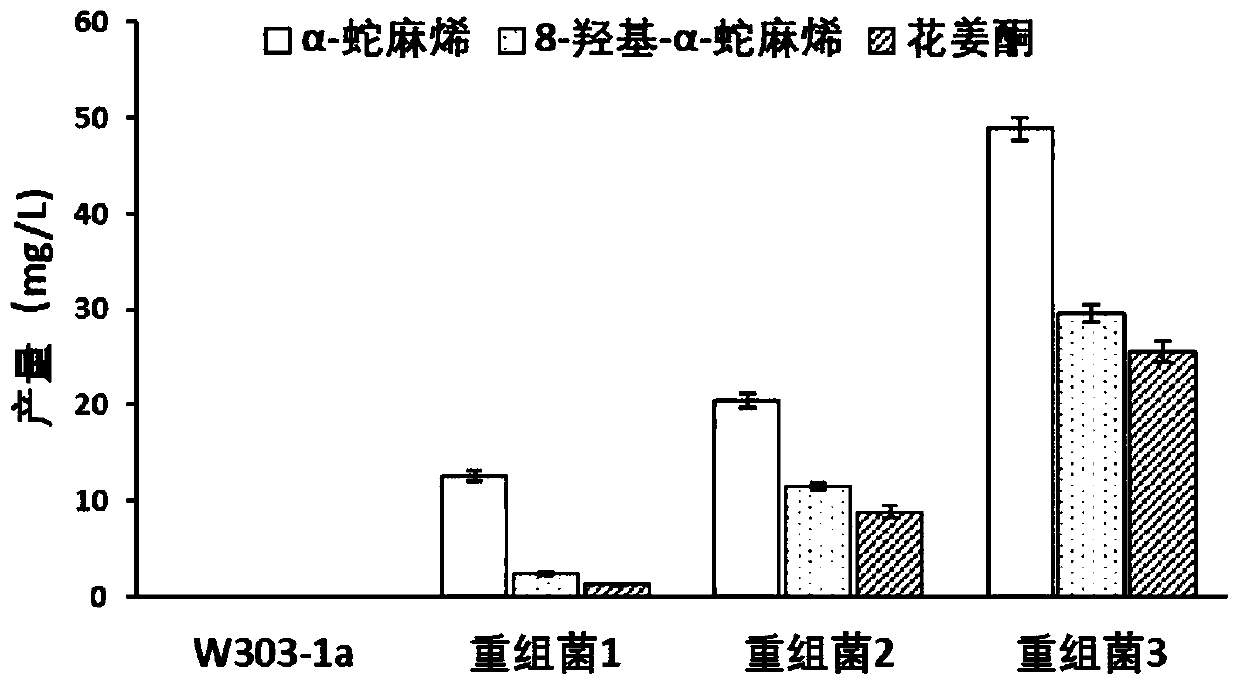
Saccharomyces cerevisiae recombinant bacterium capable of producing alpha-humulene, 8-hydroxy-alpha-humulene and zerumbone and construction method thereof
PendingCN111041041AIncrease productionHigh activityFungiMicroorganism based processesCytochrome P450 reductaseMicrobiology
The invention discloses a saccharomyces cerevisiae recombinant bacterium capable of producing alpha-humulene, 8-hydroxy-alpha-humulene and zerumbone and a construction method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: introducing an optimized alpha-humulene synthase encoding gene ZSS1, an optimized cytochrome P450 enzyme encoding gene CYP71BA1, an optimized cytochrome P450 reductase encoding gene AtCPR1 and an optimized dehydrogenase encoding gene ZSD1S114A into saccharomyces cerevisiae by utilizing homologous recombination; and obtaining a saccharomyces cerevisiae recombinant bacterium 1 capable of producing alpha-humulene, 8-hydroxy-alpha-humulene and zerumbone. Experiments prove that the saccharomyces cerevisiae recombinant bacterium capable of producing alpha-humulene, 8-hydroxy-alpha-humulene and zerumbone, constructed by the invention, can produce alpha-humulene, 8-hydroxy-alpha-humulene and zerumbone, and lays a foundation for synthesizing alpha-humulene, 8-hydroxy-alpha-humulene and zerumbone by artificial cells.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
P450 enzyme of anisodus acutangulus and application of P450 enzyme to preparation of tropinone
The present invention discloses a P450 enzyme of anisodus acutangulus. 4-(1-methyl-2-pyrrolidyl)-3-oxobutanoic acid may be converted into tropinone due to the combined catalysis of the P450 enzyme anda cytochrome P450 reductase. The method disclosed by the present invention is environment-friendly and mild in reaction condition and has an industrial development prospect.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
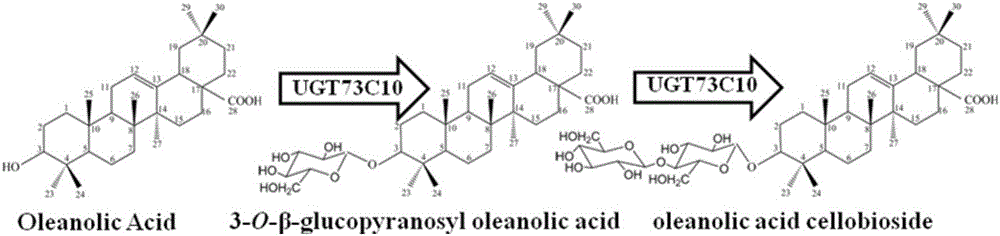
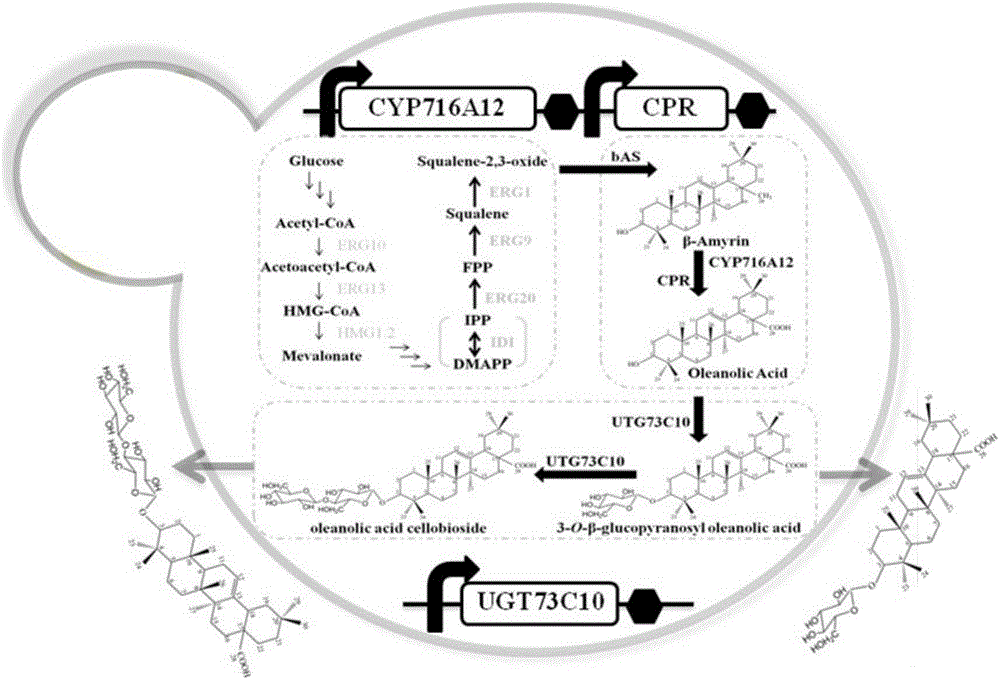
Method for synthesizing 3-O-glucose-based oleanolic acid and cellobiose oleanolic acid by using saccharomyces cerevisiae
ActiveCN106318966AIncrease productionThe fermentation process is simpleFungiMicroorganism based processesSolubilityUdp glucosyltransferase
The invention provides a method for synthesizing 3-O-glucose-based oleanolic acid and cellobiose oleanolic acid by using saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. The method comprises the following steps: synthesizing a codon optimized P450 cytochrome monooxygenase gene, a cytochrome reductase gene and a UDP-glucosyltransferase gene by a chemical method; constructing corresponding gene expression boxes by combining a saccharomyces cerevisiae promoter with a terminator; constructing gene expression vectors by a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) klenow fragment assembling method, and importing the gene expression vectors into the saccharomyces cerevisiae capable of producing beta-amyrin. Direct synthesis of the 3-O-glucose-based oleanolic acid and the cellobiose oleanolic acid serving as plant secondary metabolites in the saccharomyces cerevisiae is realized for the first time; in addition, two synthesized compounds can span cytomembrane of the saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria, and a downstream separation and extraction process is simplified, so that a new idea is provided for producing pentacyclic triterpene compounds with low water solubility and difficulty in spanning membranes by using the saccharomyces cerevisiae. The method is simple in process and can be used for producing the 3-O-glucose-based oleanolic acid and the cellobiose oleanolic acid by fermenting.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Recombinant yarrowia lipolytica for heterogeneous synthesis of alpha-amyrin and ursolic acid and construction method
The invention discloses recombinant yarrowia lipolytica for heterogeneous synthesis of alpha-amyrin and ursolic acid and a construction method. The construction method comprises steps as follows: an optimized mixed amyrin synthase encoded gene, an optimized ursolic acid synthase encoded gene and an optimized cytochrome-NADPH-reductase encoded gene are imported into yarrowia lipolytica, and recombinant bacteria 2 are obtained; and experiments prove that the recombinant yarrowia lipolytica for producing alpha-amyrin and ursolic acid is obtained with a homologous recombination method, so that theyield of alpha-amyrin and ursolic acid is improved. the method provides a basis for artificial synthesis of alpha-amyrin and ursolic acid.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Cytochrome P450 expression in enterobacteria
InactiveUS20030215915A1Reduce degradationHigh expressionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBacteriaCytochrome P450 reductaseCell membrane
A bacterial cell containing a functional cytochrome P450 monooxygenase system, said cell comprising a genetic construct capable of expressing a cytochrome P450 and a genetic construct capable of expressing, separately from said cytochrome P450, a cytochrome P450 reductase wherein the N-terminus of the cytochrome P450 and the N-terminus of the cytochrome P450 reductase are each adapted to allow functional coupling of said cytochrome P450 and said cytochrome P450 reductase within said cell. A bacterial cell containing a cytochrome P450 comprising a genetic construct encoding, and capable of expressing, said cytochrome P450 wherein the cytochrome P450 comprises an N-terminal portion which directs the cytochrome P450 to a cellular compartment of membrane of the bacterial cell. The bacterial cells are useful as, for example, bioreactors, in drug testing and mutagenicity testing and as a source of cytochrome P450.
Owner:BTG INT LTD
Cytochrome P450 reductase 1 of lycoris aurea as amaryllidaceae plant as well as coding gene and application thereof
The invention relates to cytochrome P450 reductase as well as coding gene and application thereof. The invention discloses cytochrome P450 reductase 1 of lycoris aurea as an amaryllidaceae plant for the first time; the cytochrome P450 reductase 1 has favorable coenzyme specificity and can be used for assisting a cytochrome P450 enzyme in exerting catalytic activity to modify a synthetic product of a substrate of the cytochrome P450 enzyme in an oxidative manner. The invention also discloses a polynucleotide for coding the cytochrome P450 reductase, a carrier and a host cell for expressing the cytochrome P450 reductase and a method for producing p-coumaric acid.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica for producing dammarendiol and protopanoxadiol and application
The invention discloses a recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica for producing dammarendiol and protopanoxadiol and application. The recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica is constructed by the following steps: introducing an optimized dammarendiol synthase encoding gene DS expression cassette, an optimized protopanoxadiol synthase encoding gene PPDS expression cassette and an optimized encoding gene expressioncassette of cytochrome-NADPH-reductase 1 into Yarrowia lipolytica so as to obtain a recombinant yeast 2, and cutting 1500 nucleotides from the 5'end of a gene HMG1 for encoding 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase to obtain a truncated gene tHMG1 for encoding the 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase; and introducing the truncated gene tHMG1 into recombinant yeast 2 to obtainrecombinant yeast 3. Experiments prove that the yield of dammarendiol and protopanoxadiol is increased by acquiring the recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica through a homologous recombination method. Themethod disclosed by the invention provides a basis for artificially synthesizing the dammarendiol and the protopanoxadiol.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Synthesis method of terpenoid and glycosylation products thereof in synthesis route of mogrol
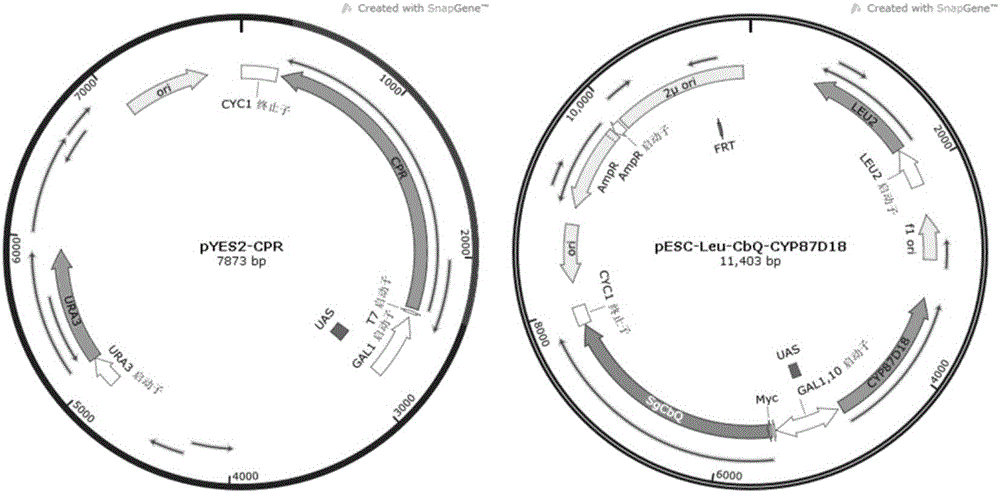
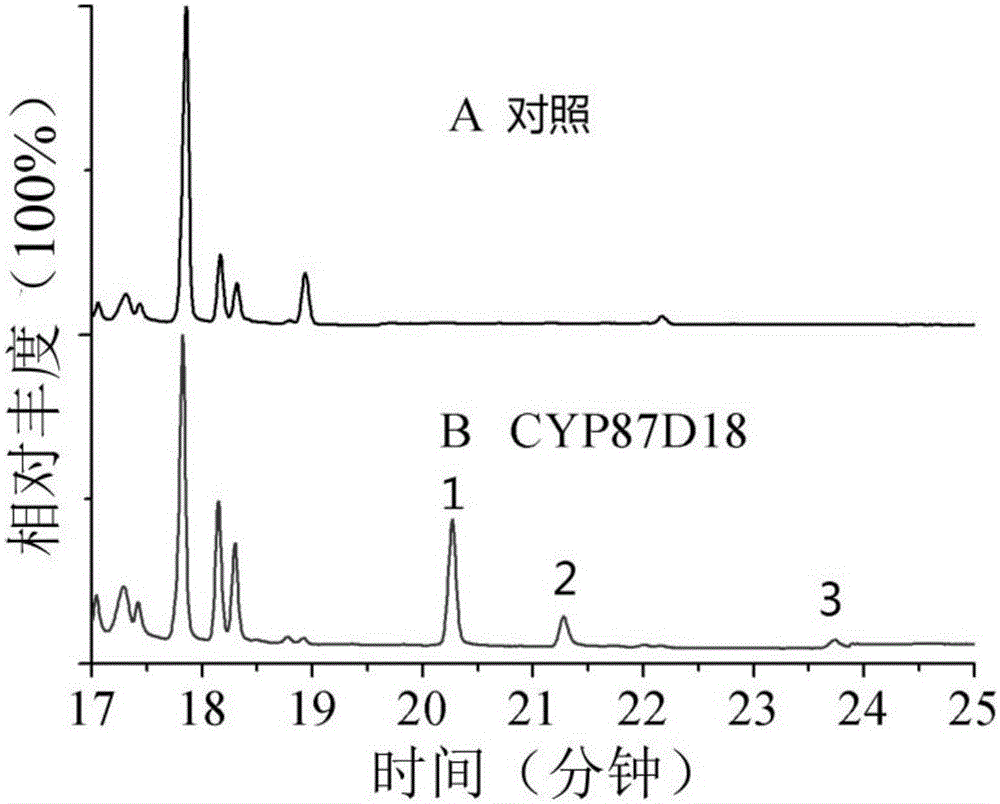
The invention discloses a microbial fermentation method for synthesizing triterpene compounds, namely a distillers yeast recombination strain SY2 containing cucurbitane dienol synthetase SgCbQ, P450 CYP87D18 and cytochrome reductase CPR, in the metabolism route of mogrol, which takes dextrose as a substrate to synthesize three new products including 11-oxygen-cucurbitane dienol, 11-hydroxy-cucurbitane dienol and 11-oxygen-24, 25-epoxy-cucurbitane dienol. The invention further discloses a metabolism route for synthesizing mogrol through cucurbitane dienol, namely the cucurbitane dienol is catalyzed through P450 CYP87D18 and synthesized into 11-oxygen-cucurbitane dienol, 11-oxygen-cucurbitane dienol is catalyzed through enzyme and synthesized into 11-hydroxy-cucurbitane dienol and 11-oxygen-24, 25-epoxy-cucurbitane dienol, and 11-hydroxy-cucurbitane dienol and 11-oxygen-24, 25-epoxy-cucurbitane dienol can be synthesized into the mogrol through other P450 or epoxide hydrolase. The invention further discloses a novel thought for obtaining more glycosylation products by catalyzing new products through glycosyl transferase. The method has significance for determining the synthesis route of mogrol and synthesizing relevant intermediate metabolites and glycosylation products through the microbial fermentation method.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
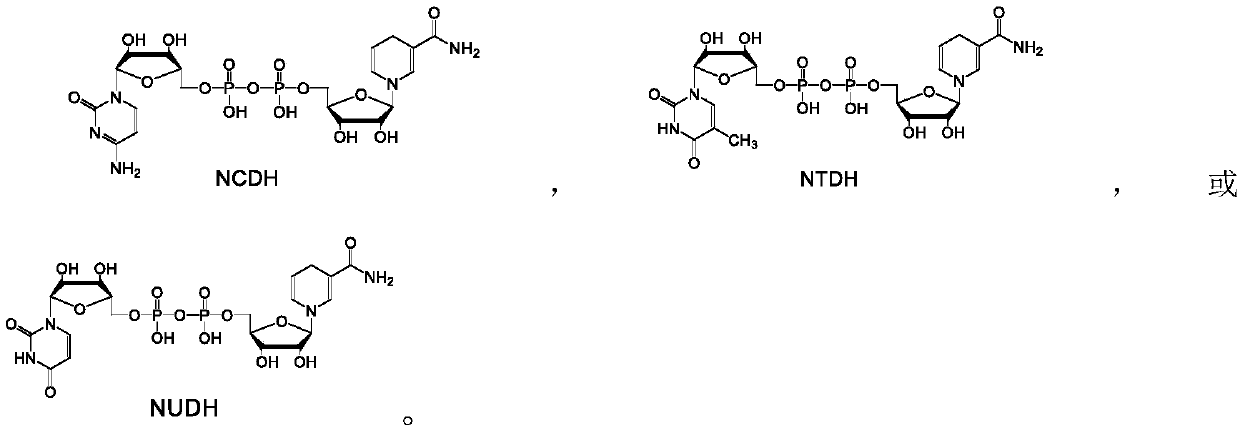
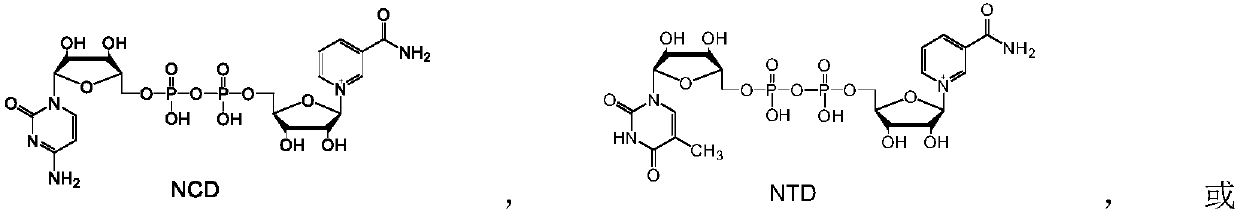
NADH analog dependent cytochrome P450 reductase and application thereof
ActiveCN111218430ACatalytic conditions are mildImprove reaction efficiencyOxidoreductasesFermentationCytochrome P450 reductaseOxidoreductase
The invention discloses an NADH analog dependent cytochrome P450 reductase and an application thereof. An NADH analogue is used as a cofactor and reducing power to catalyze electron transfer and reduce cytochrome P450 to complete catalytic circulation. The enzyme is subjected to fusion expression with different types of cytochrome P450 enzymes to construct the NADH analog-dependent, heterozygous and self-sufficient cytochrome P450 enzyme, the obtained NADH analog-dependent cytochrome P450 enzyme can be coupled with oxidoreductases of a regenerated NADH analogue, and the NADH analog is used tocatalyze corresponding substrates of different families of cytochrome P450 to be converted into products. The NADH analog-dependent cytochrome P450 reductase can be used for constructing a biologicalorthogonal metabolic pathway independent of natural cofactor NAD(P)H to realize uncoupling of P450 enzyme-catalyzed energy consumption and endogenous energy metabolism.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Fusion protein capable of increasing conversion efficiency of dammarendiol and construction method
ActiveCN104450769AImprove conversion efficiencyFacilitate efficient synthesisTransferasesOxidoreductasesGene expressionTransformation efficiency
The invention discloses a fusion protein capable of increasing the conversion efficiency of dammarendiol and a construction method. The construction method comprises the following steps: (1) excising the front 138 basic groups of the end 5' of the cytochrome-NADPH-reductase 1 gene AtCPR1 in arabidopsis to obtain a sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 2; (2) removing the termination codon TAA of the end 3' of the synthase gene PPDS of protopanoxadiol in ginseng shown in SEQ ID NO. 3, and connecting with a sequence at the end 5' of the sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 2 to construct a genetic element of the fusion protein; (3) connecting the genetic element of the fusion protein with the internal promoter and the terminator of a saccharomyces cerevisiae cell to construct a genetic expression kit of the fusion protein, and transforming to enter the saccharomyces cerevisiae cell for expression. The fusion protein constructed by the method disclosed by the invention is capable of increasing the conversion efficiency of converting from dammarendiol to protopanoxadiol.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
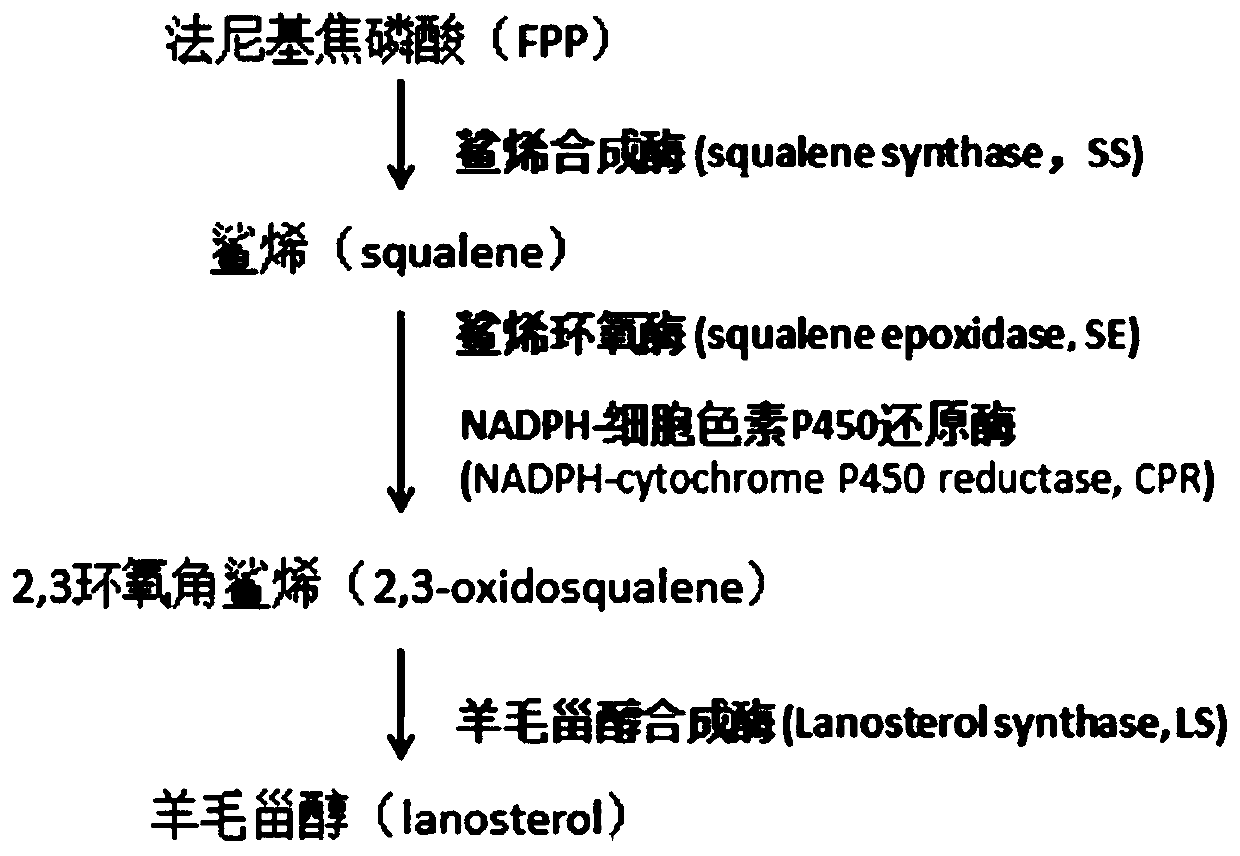
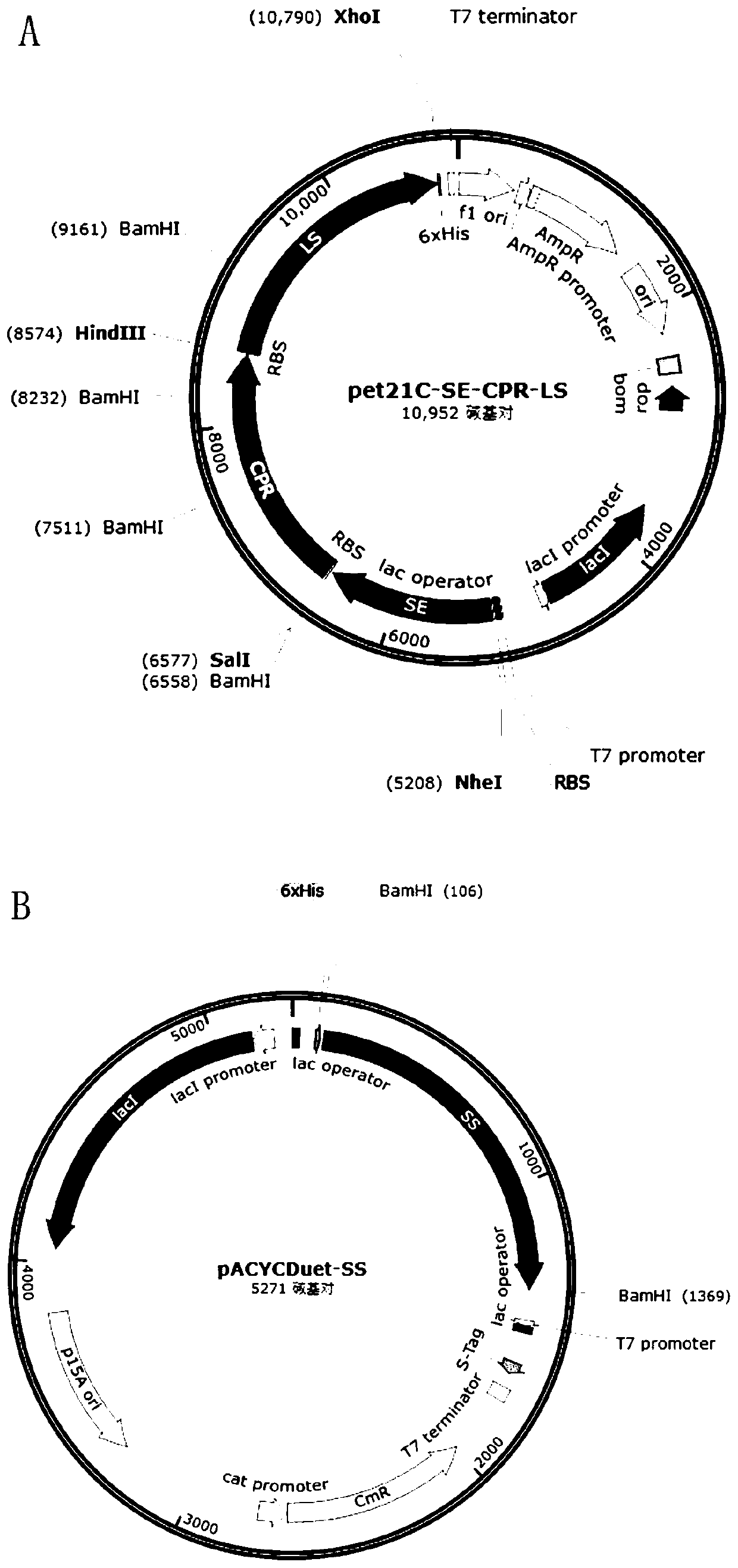
Construction method of escherichia coli bacterial strain for generating lanosterol
The invention relates to a construction method of an escherichia coli bacterial strain for generating lanosterol. The construction method comprises the steps of optimizing a codon of squalene epoxidase of methylococcus capsulatus according to an escherichia coli codon, and performing PCR amplification to obtain a squalene epoxidase genetic fragment; performing PCR amplification to obtain NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase, and lanosterol synthetase genetic fragments, performing merging to obtain a DNA fragment SE-CPR-LS, cloning the SE-CPR-LS fragment to a vector pet21c by a restriction enzyme cutting connection method, and constructing an expression vector pet21c-SE-CPR-LS; cloning the squalene synthase genetic fragment to the vector pACYCduet-1 by a homologous recombination method, and constructing an expression vector pACYCduet-SS; and transforming the vectors pet21c-SE-CPR-LS and pACYCduet-SS into escherichia coli competence cells, so as to obtain the escherichia coli bacterial strainfor generating lanosterol. Through an exogenous plasmid transforming method, an escherichia coli BL21(DE3) system is improved, so that synthesis of the lanosterol can be realized; and through a codonoptimization technique, the expression level of exogenous genes in an escherichia coli system can be increased.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
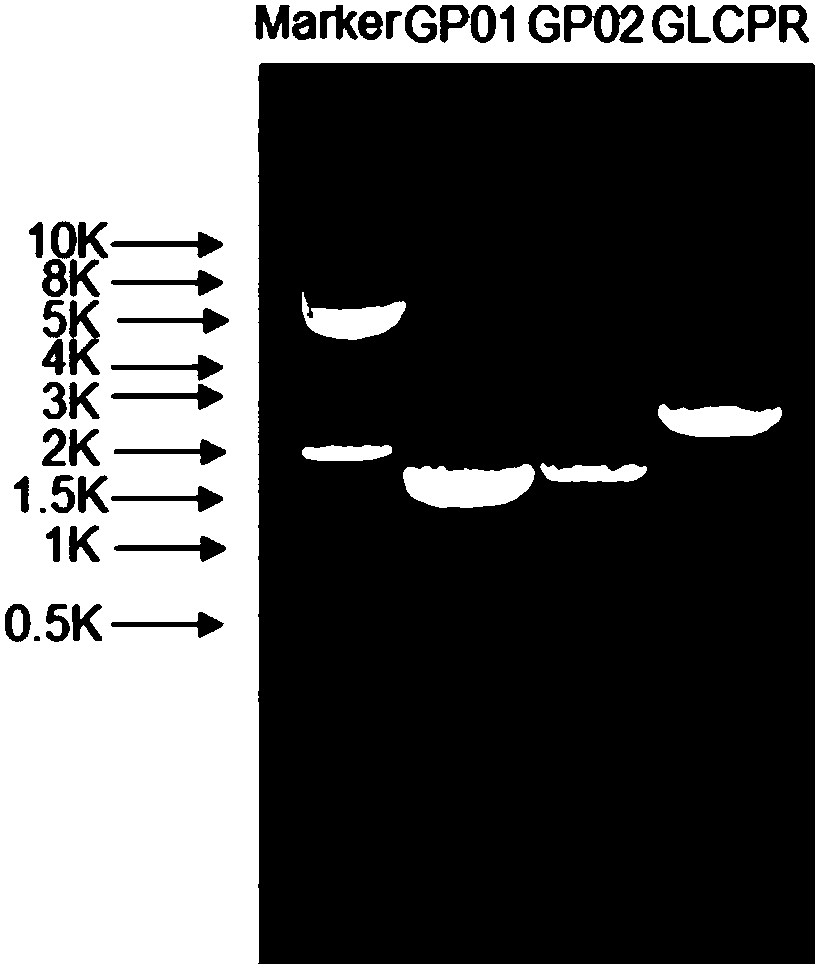
Cytochrome P450, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-cytochrome P450 reductase and application thereof
ActiveCN108866142APromote generationGood reductase propertiesOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringCytochrome P450 reductaseTriterpene
The invention relates to cytochrome P450, a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-cytochrome P450 reductase and application thereof. The invention discloses the set of new cytochrome P450 (P450 GP01 and P450 GP02) which performs the effect in the terpenoid hydroxylation catalysis and synthesis of Ganoderma triterpenes, and the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-cytochrome P450 reductase (GLCPR) which completes hydroxylation catalysis by cooperating with the cytochrome P450. In specific, the cytochrome P450 GP01 can specifically and efficiently catalyze the hydroxylation of C-23 site of a tetracyclic triterpene compound substrate. The cytochrome P450 GP02 performs hydroxylation om ganoderic acid DM and ganoderic acid TR to generate various kinds of products. The GLCPR can be paired with the cytochrome P450, and assists the cytochrome P450 to perform the hydroxylation activity.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
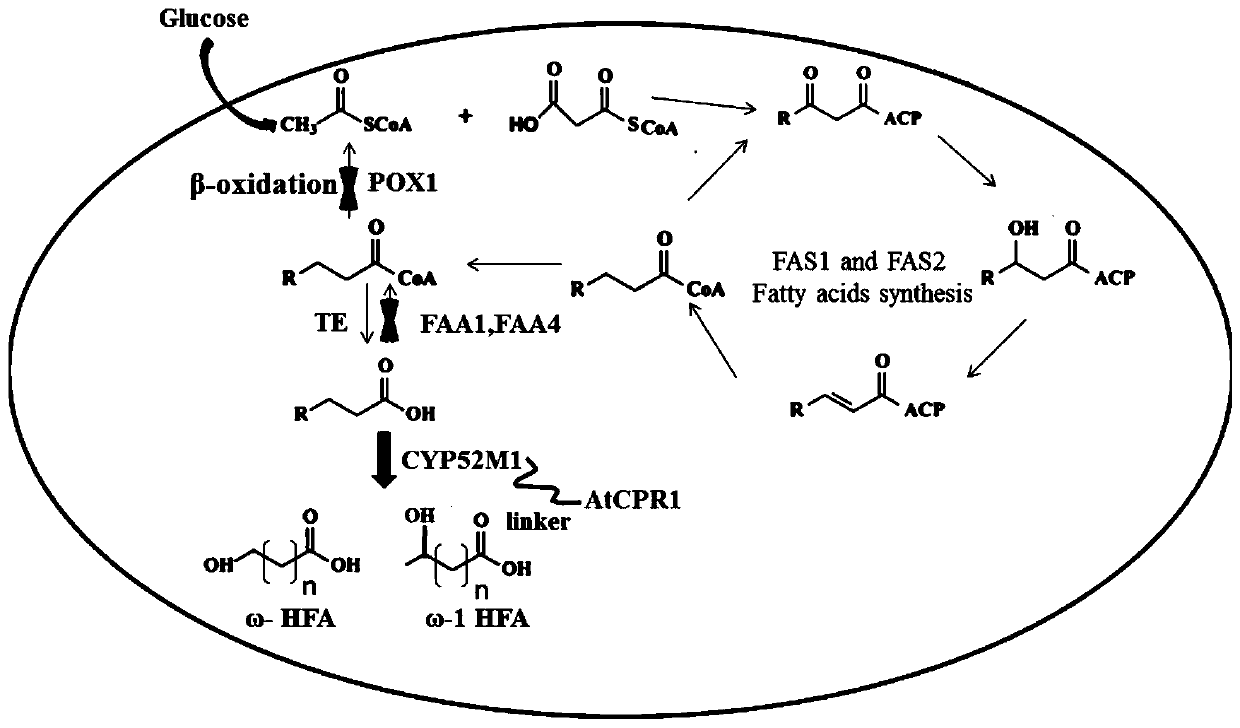
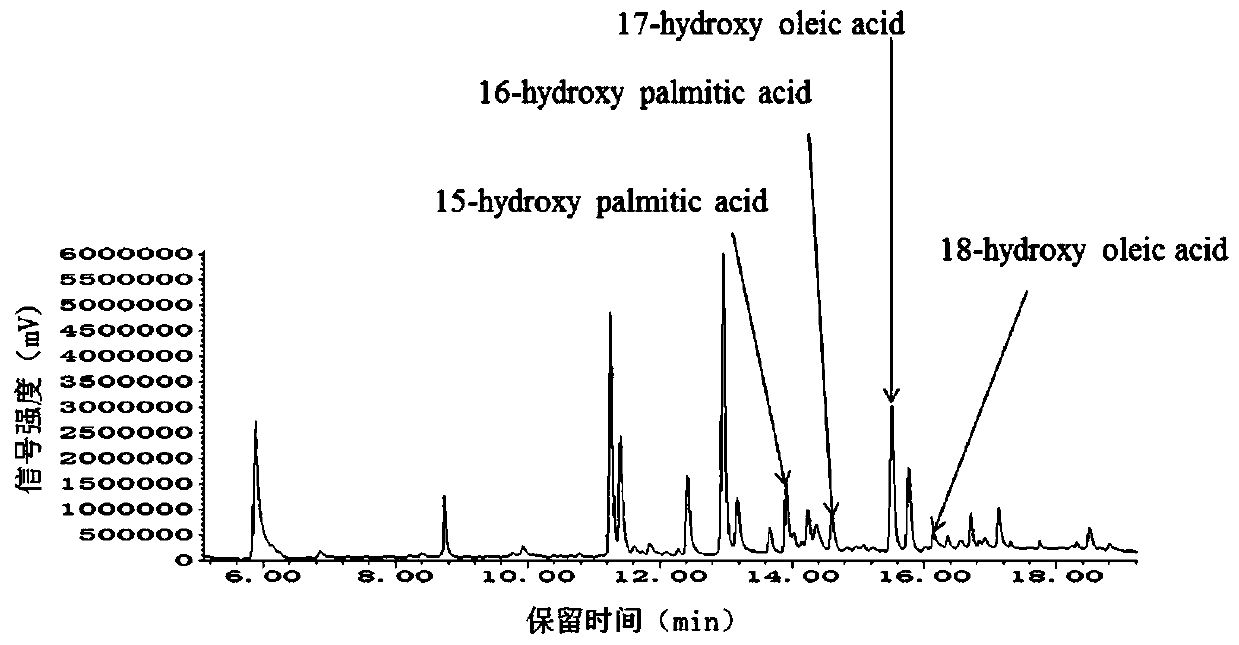
Recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiaes, construction methods of recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiaes and applications of recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiaes in production of hydroxy fatty acids
The invention discloses recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiaes, construction methods of the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiaes and applications of the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiaes in production of hydroxy fatty acids. Through a homologous recombination method, the recombinant fungi (1) are obtained by knocking out key gene acyl coenzyme A oxidase POX1 in a beta-oxidation pathway relatedto fatty acid catabolism in saccharomyces cerevisiaes and knocking out acyl coenzyme A activating enzymes FAA1 and FAA4, recombinant fungi (2) are obtained by introducing cytochrome P450 oxidase CYP52M1 and cytochrome P450 reductase SbCPR into the recombinant fungi (1), or the recombinant fungi (3) are obtained by introducing cytochrome P450 oxidase CYP52M1 and cytochrome P450 reductase AtCPR1 into the recombinant fungi (1), or the recombinant fungi (4) are obtained by introducing cytochrome P450 oxidase and cytochrome P450 reductase fusion protein gene CYP52M1-AtCPR1 into the recombinant fungi (1).
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Recombinant yarrowia lipolytica strain for producing protopanoxadiol by utilizing xylose and construction method and application of recombinant yarrowia lipolytica strain
PendingCN111690549ATo achieve effective applicationBig advantageFungiTransferasesCytochrome P450 reductasePyrophosphate
The invention discloses a recombinant yarrowia lipolytica strain for producing protopanoxadiol by utilizing xylose and a construction method and application of the recombinant yarrowia lipolytica strain. Yarrowia lipolytica ATCC 201249 is used as an original strain, optimized xylose reductase XYL1, xylitol dehydrogenase XYL2 and an overexpressed endogenous xylulokinase XKS expression cassette areintroduced, and a recombinant strain 1 is obtained; a dammarendiol synthase gene DS, a protopanoxadiol synthase gene PPDS and a cytochrome P450 reductase gene ATR1 are introduced into the recombinantstrain 1 to obtain a recombinant strain 2; a gene tHMG1 for encoding nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-hydroxymethyl glutaryl coenzyme A reductase, a gene erg9 for squalene synthase and an erg20 for encoding farnesene pyrophosphate synthase in a truncated mevalonic acid pathway are introduced into the recombinant strain 2 to obtain a recombinant strain 3; and the recombinant yarrowia lipolytica isused for producing the protopanoxadiol by using the xylose, and the shake flask yield reaches 80.88 mg / L.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
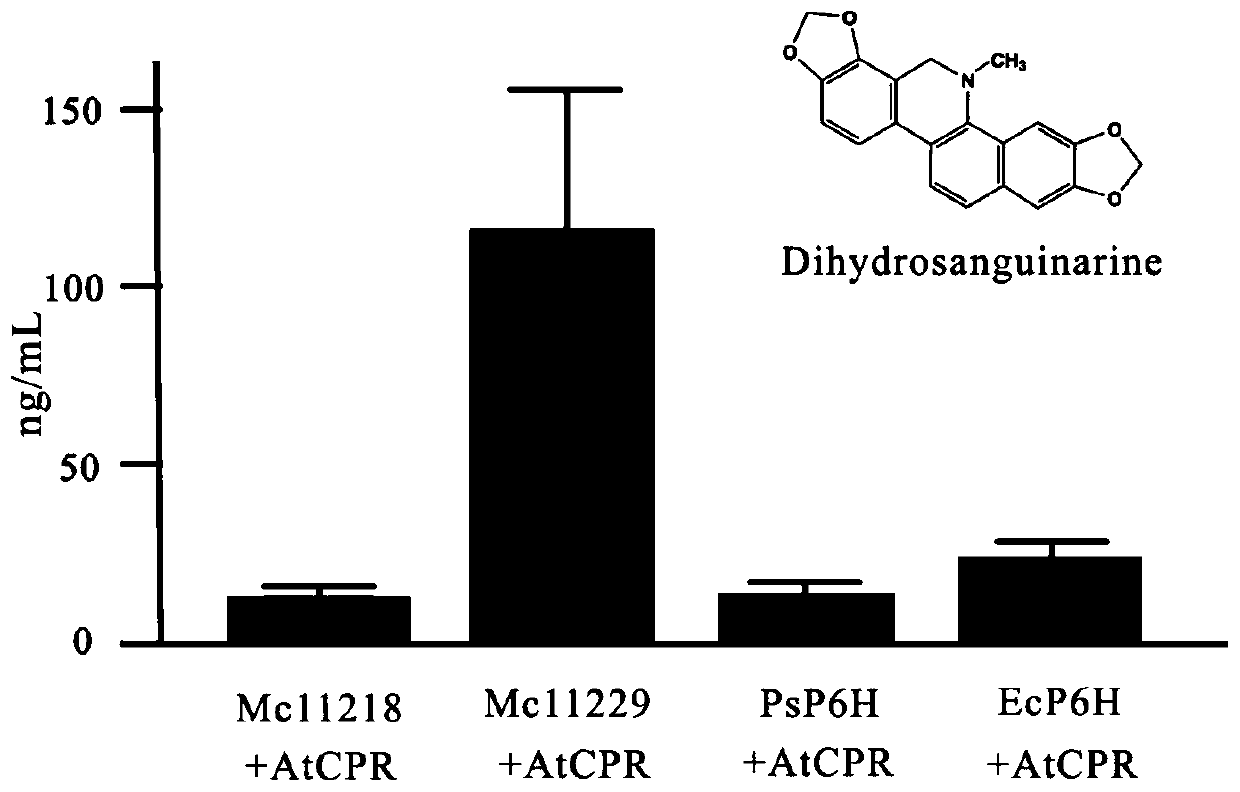
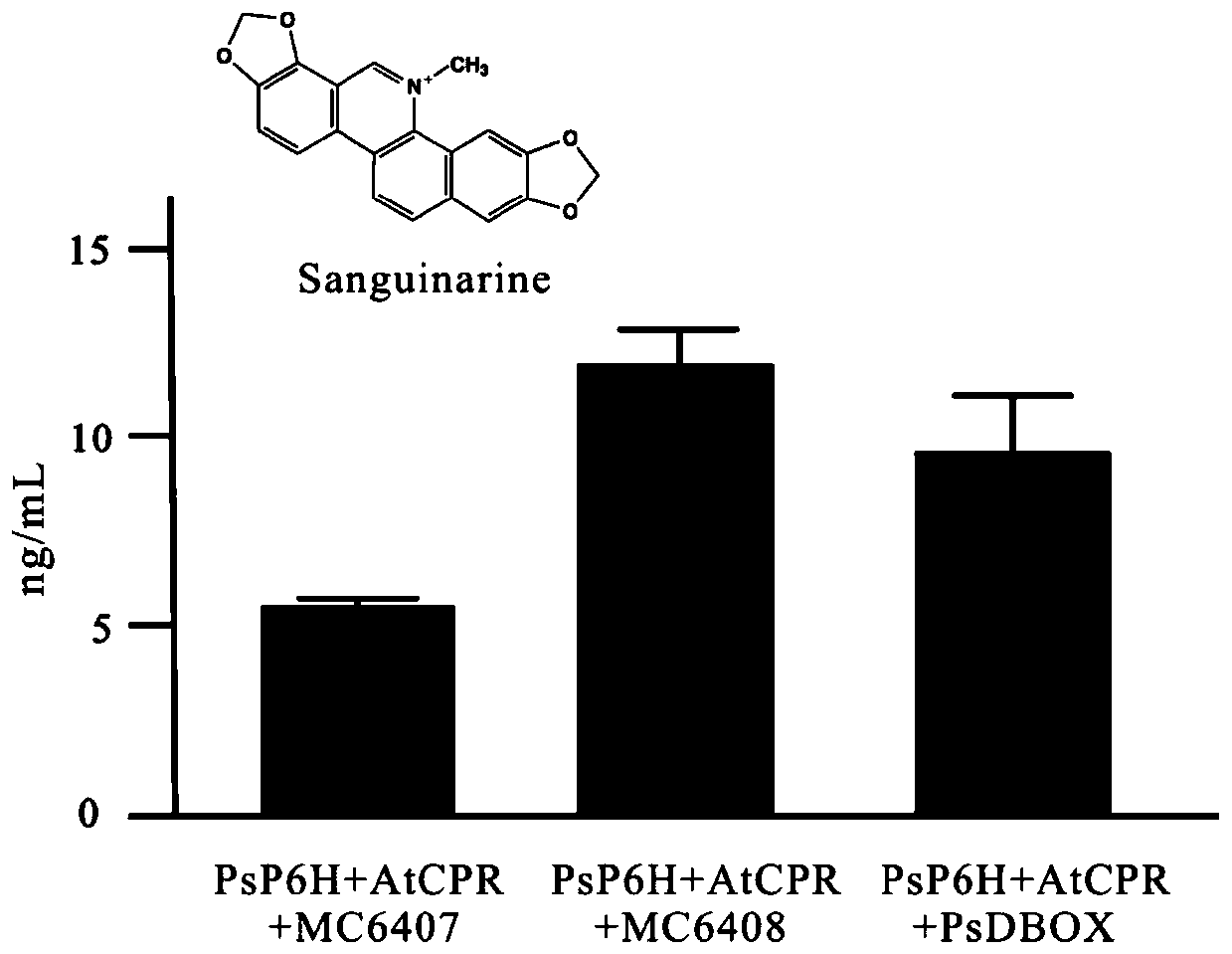
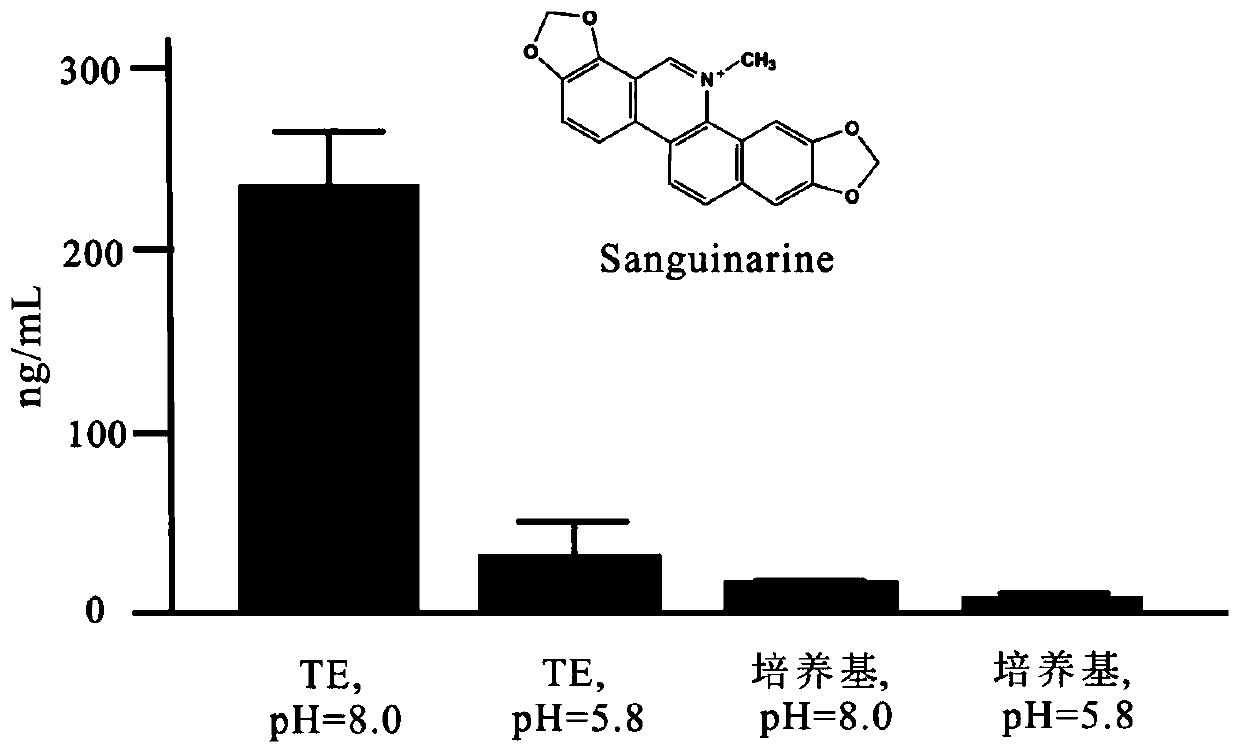
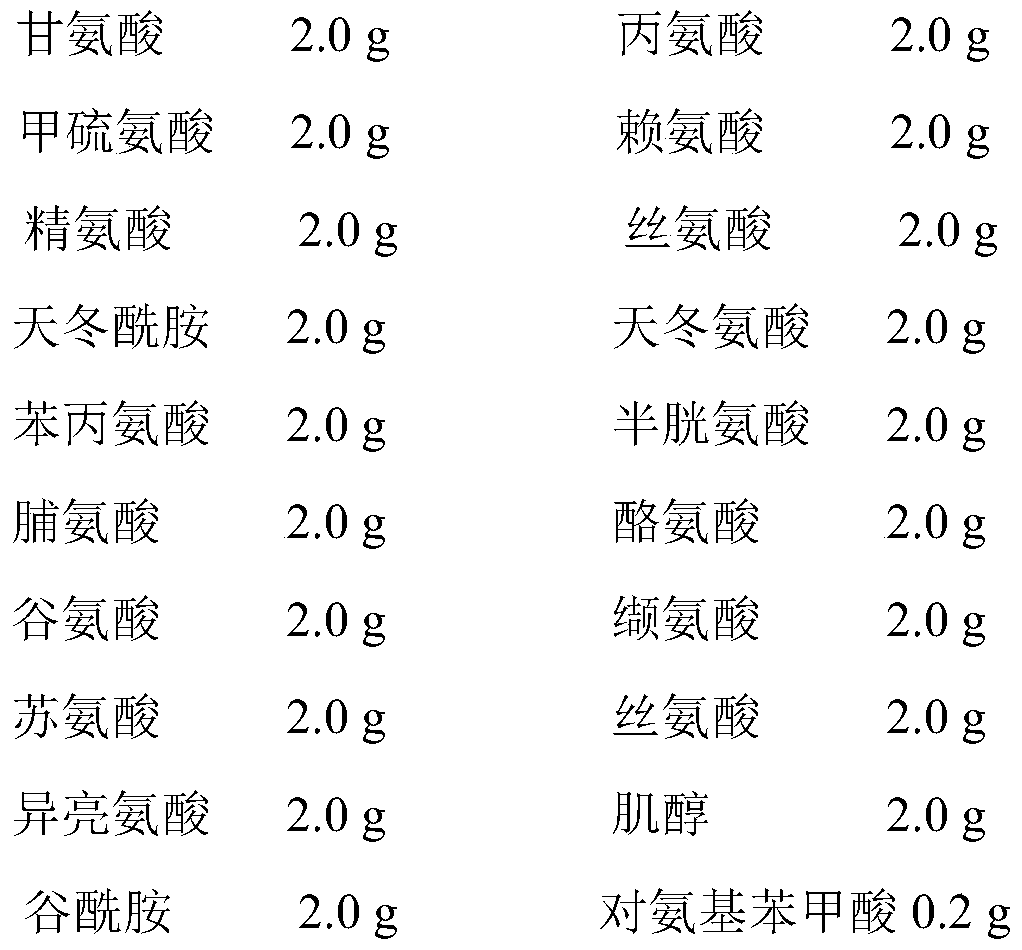
High-efficiency enzyme-catalyzed method for synthesizing sanguinarine and chelerythrine
ActiveCN109468351BIncrease contentReduce manufacturing costFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHeterologous
Owner:MICOLTA BIORESOURCE INC LTD
Recombinant yarrowia lipolytica for heterogenous synthesis of betulinic acid and construction method of recombinant yarrowia lipolytica
The invention discloses recombinant yarrowia lipolytica for heterogenous synthesis of betulinic acid and a construction method of the recombinant yarrowia lipolytica. The construction method comprisesthe following steps: by using a homologous recombination method, introducing an optimized lupeol synthase encoding gene opAtLUP1, an optimized cytochrome P450 enzyme encoding gene opCYP716A12 and anoptimized cytochrome P450 reductase 1 encoding gene opAtCPR1 into yarrowia lipolytica so as to obtain a recombinant bacterium 1; and introducing a shortcut 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase encoding gene tHMG1, a squalene synthase encoding gene Erg9 and the optimized lupeol synthase encoding gene opAtLUP1 into the recombinant bacterium 1, so as to obtain a recombinant bacterium 2. Experiments show that the recombinant yarrowia lipolytica which is constructed by using the method disclosed by the invention and applied to heterogenous synthesis of betulinic acid has a high yield ofbetulinic acid.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing levopimaric diene and levopimaric acid and construction method
PendingCN111041040AIncrease productionFungiMicroorganism based processesCytochrome P450 reductaseCytochrome p450 enzyme
The invention discloses recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing levopimaric diene and levopimaric acid and a construction method. The method comprises the following steps: introducing a modified L-pimaric diene synthase encoding gene T delta LPS, an optimized cytochrome P450 enzyme encoding gene CYP720B1 and an optimized cytochrome P450 reductase encoding gene TcCPR into saccharomyces cerevisiae to obtain a recombinant bacterium 1; introducing a 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase encoding gene tHMG1 into the recombinant bacterium 1 to obtain a recombinant bacterium 2; introducing a farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase encoding gene Erg20 into the recombinant bacterium 2 to obtain a recombinant bacterium 3; and replacing a wild squalene synthase promoter in the recombinant bacterium 3 with a Met3 promoter to obtain a recombinant bacterium 4; experiments prove that the fermentation of the recombinant bacteria disclosed by the invention can improve the yields of the levopimaric diene and the levopimaric acid; and a foundation is laid for artificial cell synthesis of the levopimaric diene and the levopimaric acid.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
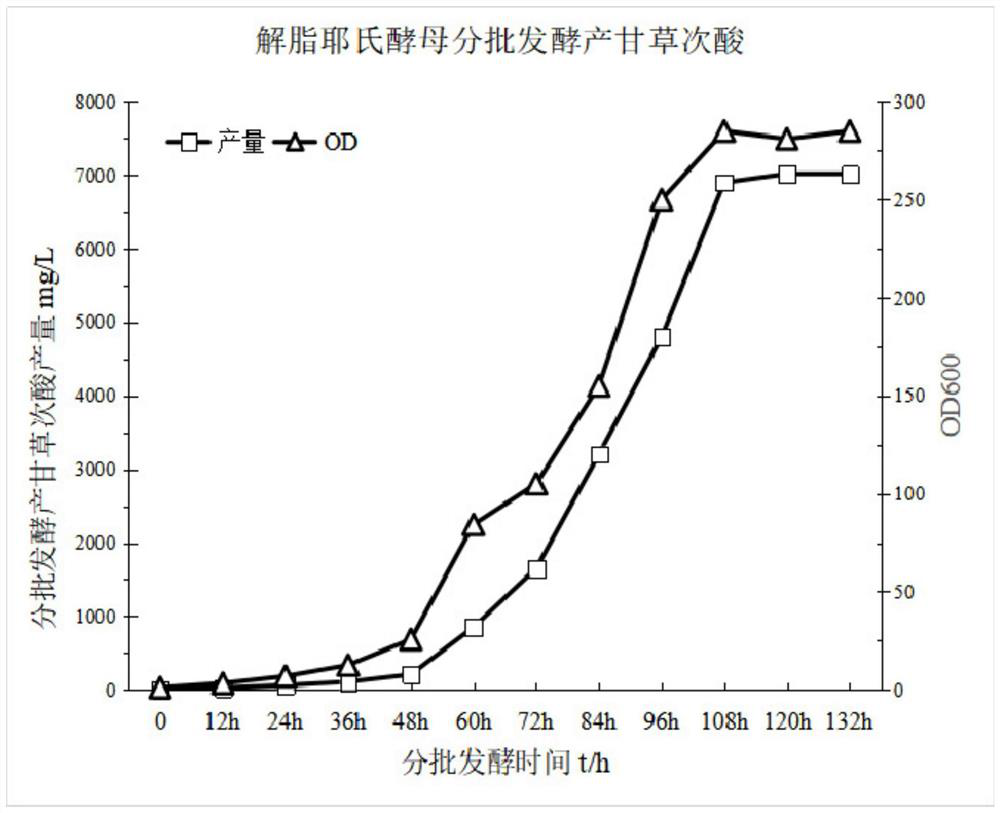
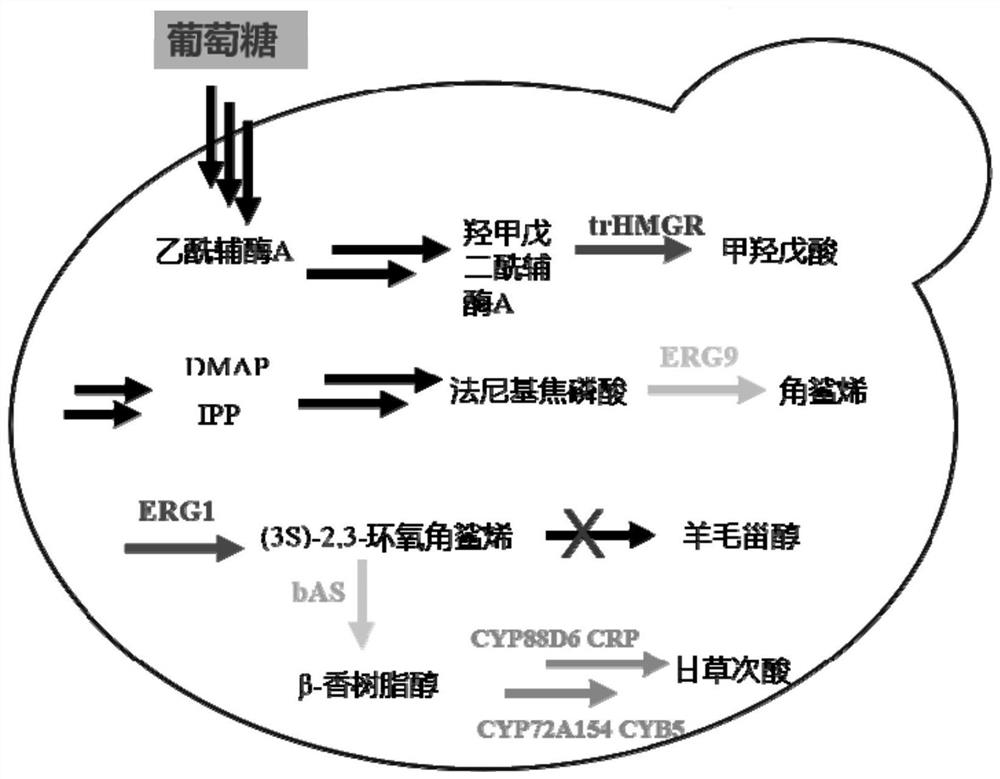
Yarrowia lipolytica engineering strain for biologically synthesizing glycyrrhetinic acid by taking glucose as substrate as well as construction and application thereof
PendingCN113930348AIncrease productionConducive to large-scale industrial productionFungiTransferasesCytochrome P450 reductaseCytochrome P450
The invention discloses a yarrowia lipolytica engineering strain for biologically synthesizing glycyrrhetinic acid by taking glucose as a substrate as well as construction and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biology. According to the engineering strain, a beta-amyrin synthase expression module, a 11 / 30 site-oxidized beta-amyrin synthase expression module, a cell P450 oxidase expression module and a cytochrome P450 reductase expression module are integrated on a genome; the construction method comprises the following steps: constructing to obtain glycyrrhetinic acid biosynthesis module plasmids: beta-amyrin synthase bAS, cytochrome P450 oxidase 88D6CYP88D6, 11 / 30-site-oxidized beta-amyrin synthase CYP725A4 and cytochrome P450 reductase CPR, integrating the glycyrrhetinic acid biosynthesis module onto a yarrowia lipolytica tool plasmid, and linearizing the plasmids integrated with the glycyrrhetinic acid biosynthesis module, and introducing the linearized plasmids into yarrowia lipolytica to obtain the yarrowia lipolytica engineering bacteria of which the genome is integrated with the glycyrrhetinic acid biosynthesis module. The yield of glycyrrhetinic acid produced by the engineering strain is remarkably improved and reaches 7g / L to the maximum.
Owner:河北维达康生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com