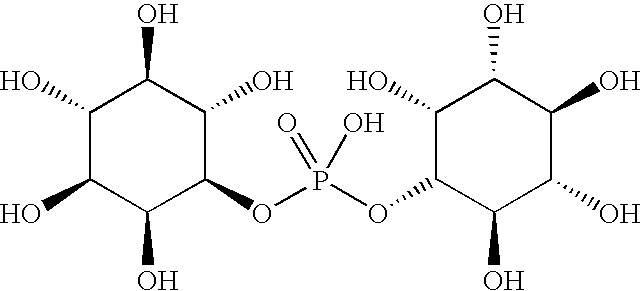
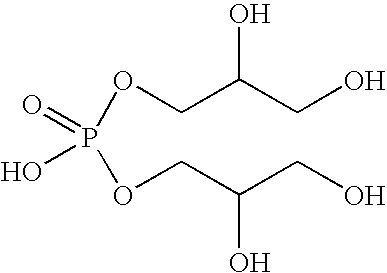
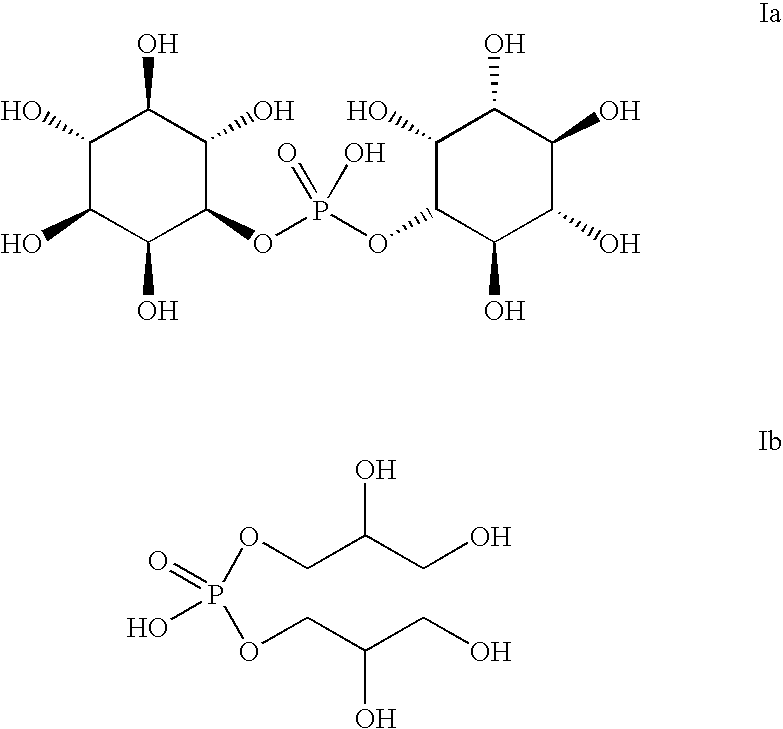
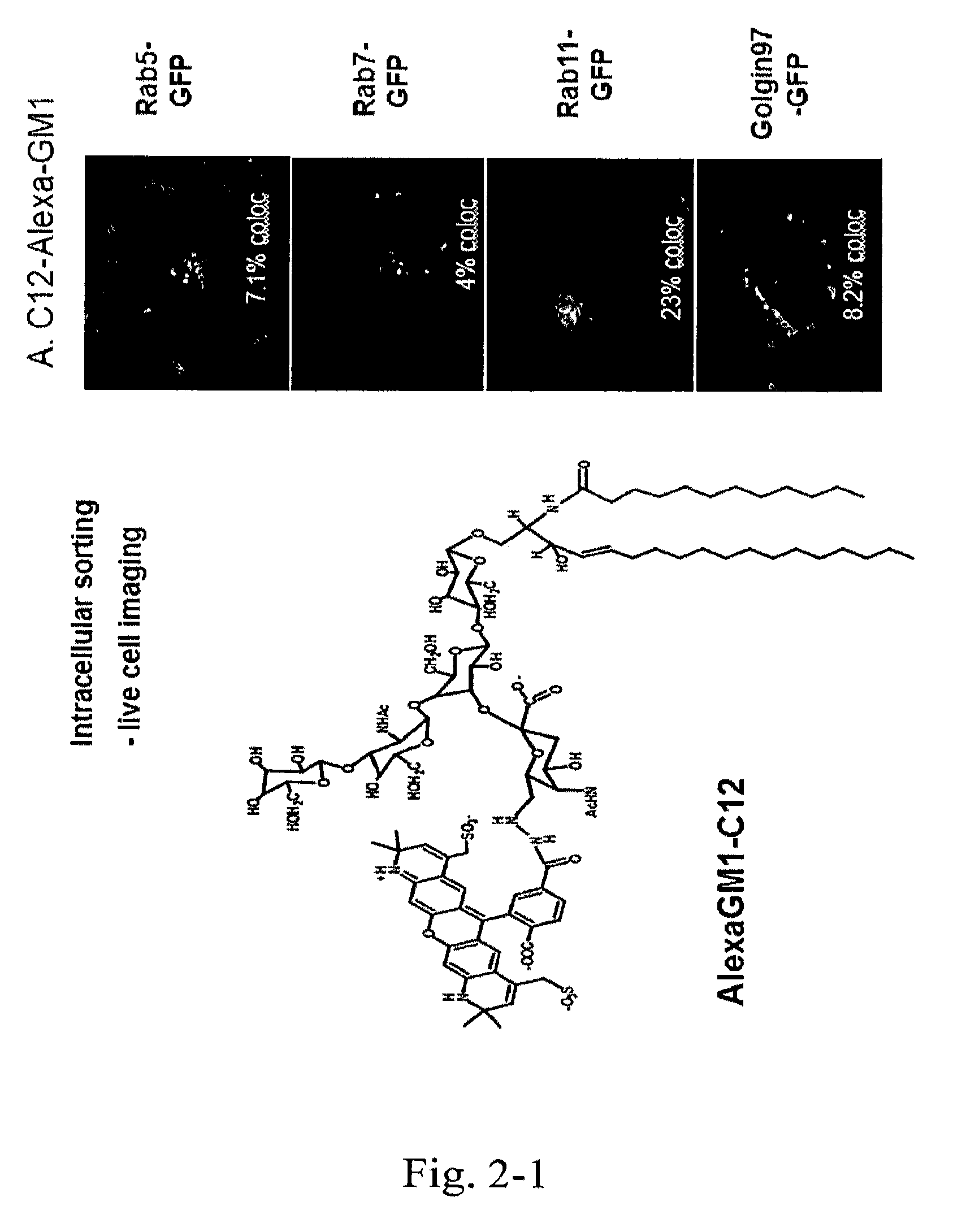
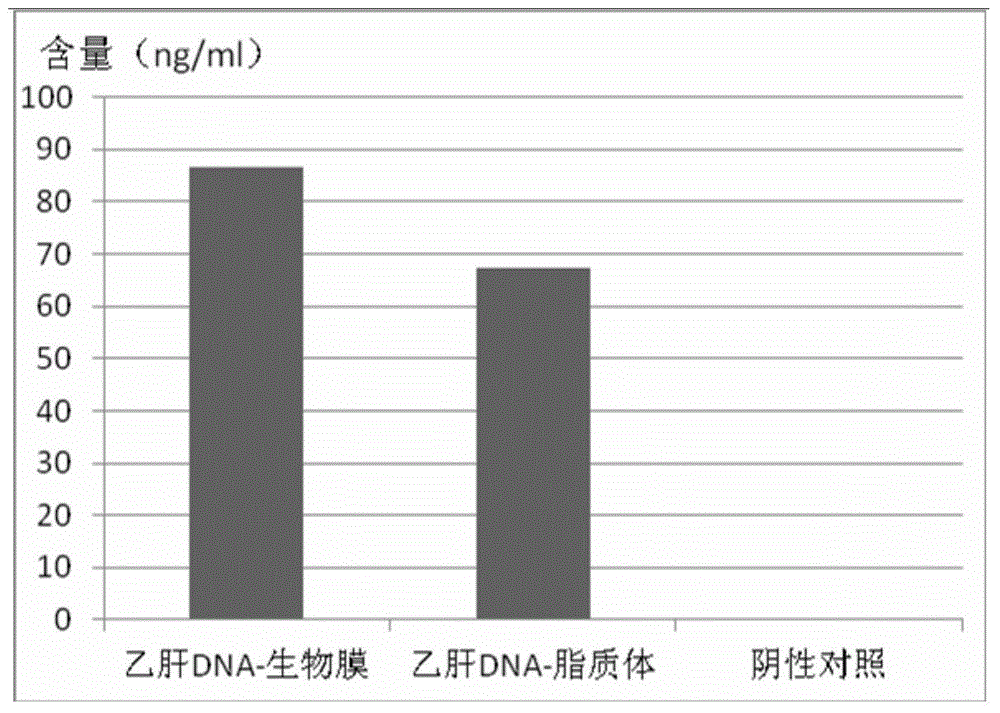
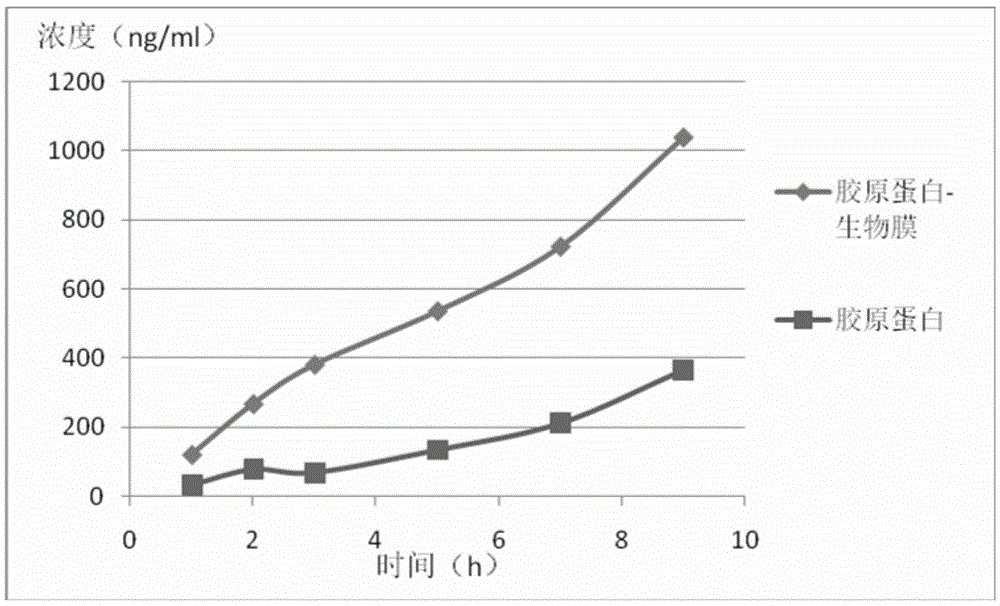
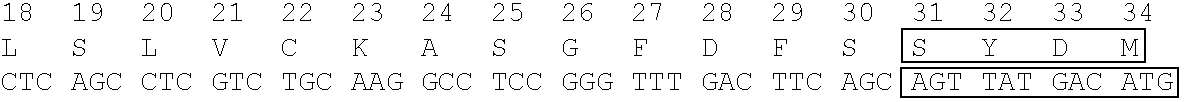Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
73 results about "Cellular compartment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
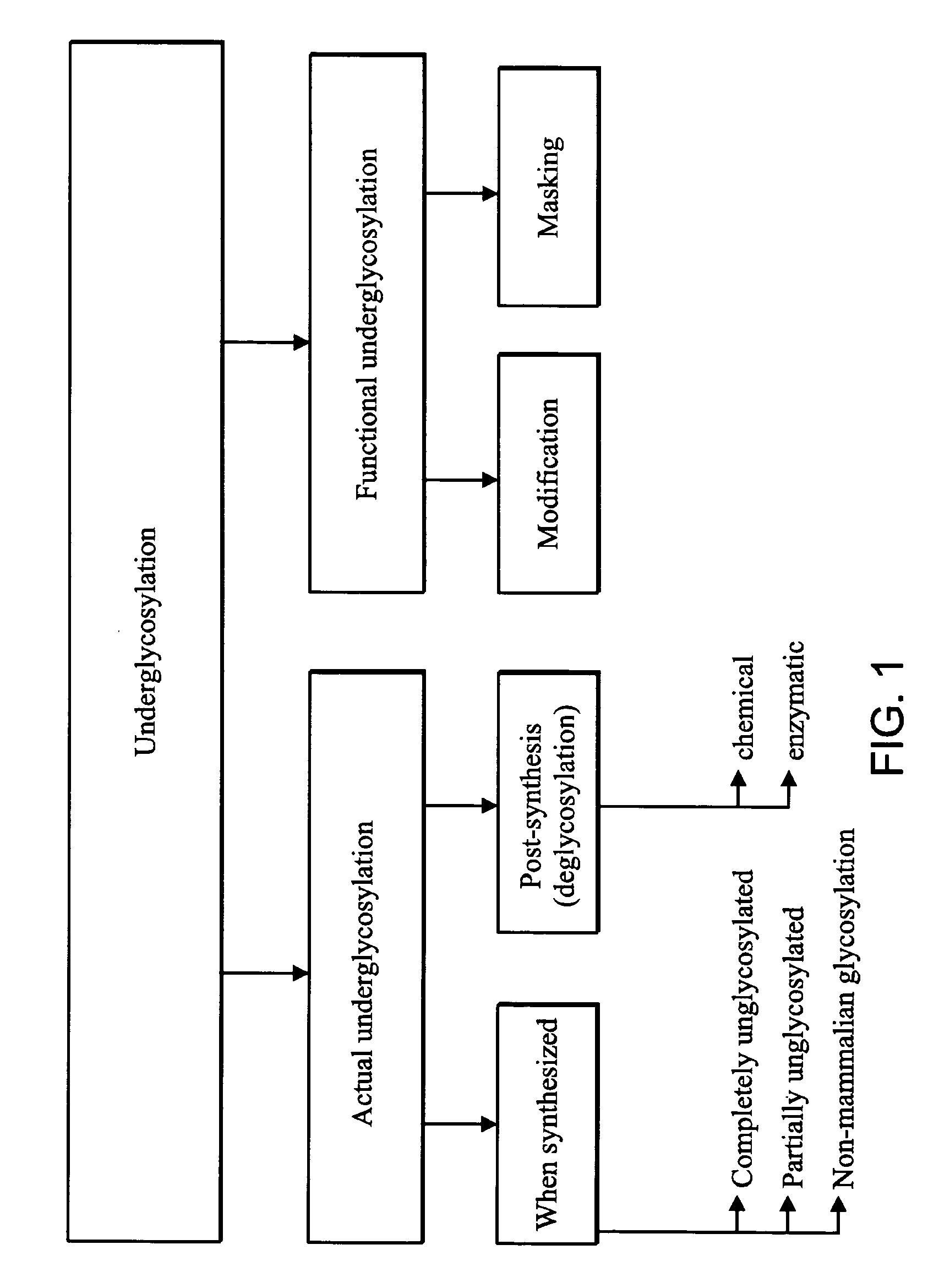
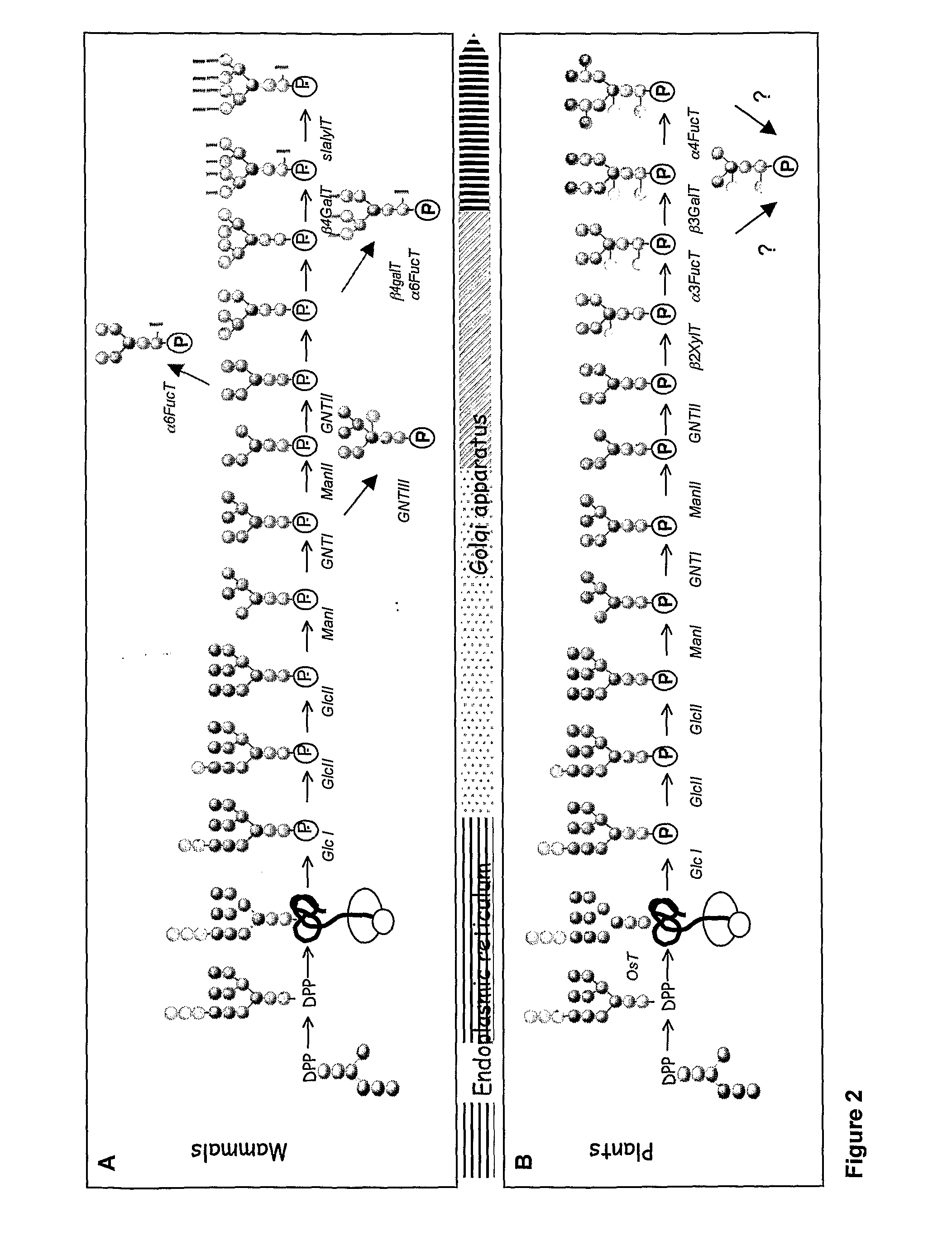
Cellular compartments in cell biology comprise all of the closed parts within the cytosol of a eukaryotic cell, usually surrounded by a single or double lipid layer membrane. These compartments are often, but not always, defined as membrane enclosed regions. The formation of cellular compartments is called compartmentalization.
Targeted therapeutic proteins
InactiveUS7560424B2Convenient treatmentSimple preparation processPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesLysosomeTherapeutic protein
Targeted therapeutics that localize to a specific subcellular compartment such as the lysosome are provided. The targeted therapeutics include a therapeutic agent and a targeting moiety that binds a receptor on an exterior surface of the cell, permitting proper subcellular localization of the targeted therapeutic upon internalization of the receptor. Nucleic acids, cells, and methods relating to the practice of the invention are also provided.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
System and method for automatic color segmentation and minimum significant response for measurement of fractional localized intensity of cellular compartments
ActiveUS20070016373A1Improve throughputInteraction is complexBioreactor/fermenter combinationsImage enhancementSystems approachesComputer science
A system, a method, and a programmed device for measurement of translocational activity among cellular compartments process magnified images of cellular material exposed to an agent by segmenting and compartmentalizing the images and then measuring fractional localized intensity of two or more components in the segmented, compartmentalized image. The measured fractional localized intensities are compared to determine translocation of cellular material among the measured components caused by the agent.
Owner:VALA SCI
Systems, methods and kits for characterizing phosphoproteomes
InactiveUS20050164324A1Quick filterImprove developmentMicrobiological testing/measurementIsotope separationPhosphorylationSystems approaches
The invention provides systems, software, methods and kits for detecting and / or quantifying phosphorylatable polypeptides and / or acetylated polypeptides in complex mixtures, such as a lysate of a cell or cellular compartment (e.g., such as an organelle). The methods can be used in high throughput assays to profile phosphoproteomes and to correlate sites and amounts of phosphorylation with particular cell states.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Formulations for targeted release of agents to low ph tissue environments or cellular compartments and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20150073041A1Easy to optimizeEfficient deliveryOrganic active ingredientsOther foreign material introduction processesCell specificActive agent
Polyamine-co-ester-co-ortho ester) polymers, methods of forming active agent-load nanoparticles therefrom, and methods of using the nanoparticles for drug delivery are disclosed. The nanoparticles can be coated with an agent that reduces surface charge, an agent that increases cell-specific targeting, or a combination thereof. Typically, the loaded nanoparticles are less toxic, more efficient at drug delivery, or a combination thereof compared to a control or other transfection reagents.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Manipulation of the phenolic acid content and digestibility of plant cell walls by targeted expression of genes encoding cell wall degrading enzymes
InactiveUS20060005270A1Improve usabilityOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationPlant cellFerulic acid esterase
Described herein are methods to enhance the production of more highly fermentable carbohydrates in plants, especially forage grasses. The invention provides for transgenic plants transformed with expression vectors containing a DNA sequence encoding ferulic acid esterase I from Aspergillus, preferably A. niger. The expression vectors may optionally comprise a DNA sequence encoding xylanase from Trichoderma, preferably T. reesei. Expression of the enzyme(s) is targeted to specific cellular compartments, in specific tissues and under specific environmental conditions. Uses of this invention include, but are not limited to, forage with improved digestibility for livestock, and enhanced biomass conversion.
Owner:GENENCOR INT INC
Method and composition for a protein transduction technology and its applications
ActiveUS20090298111A1Efficient deliveryBest protein transduction efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsMicroencapsulation basedSpectroscopyFluorophore
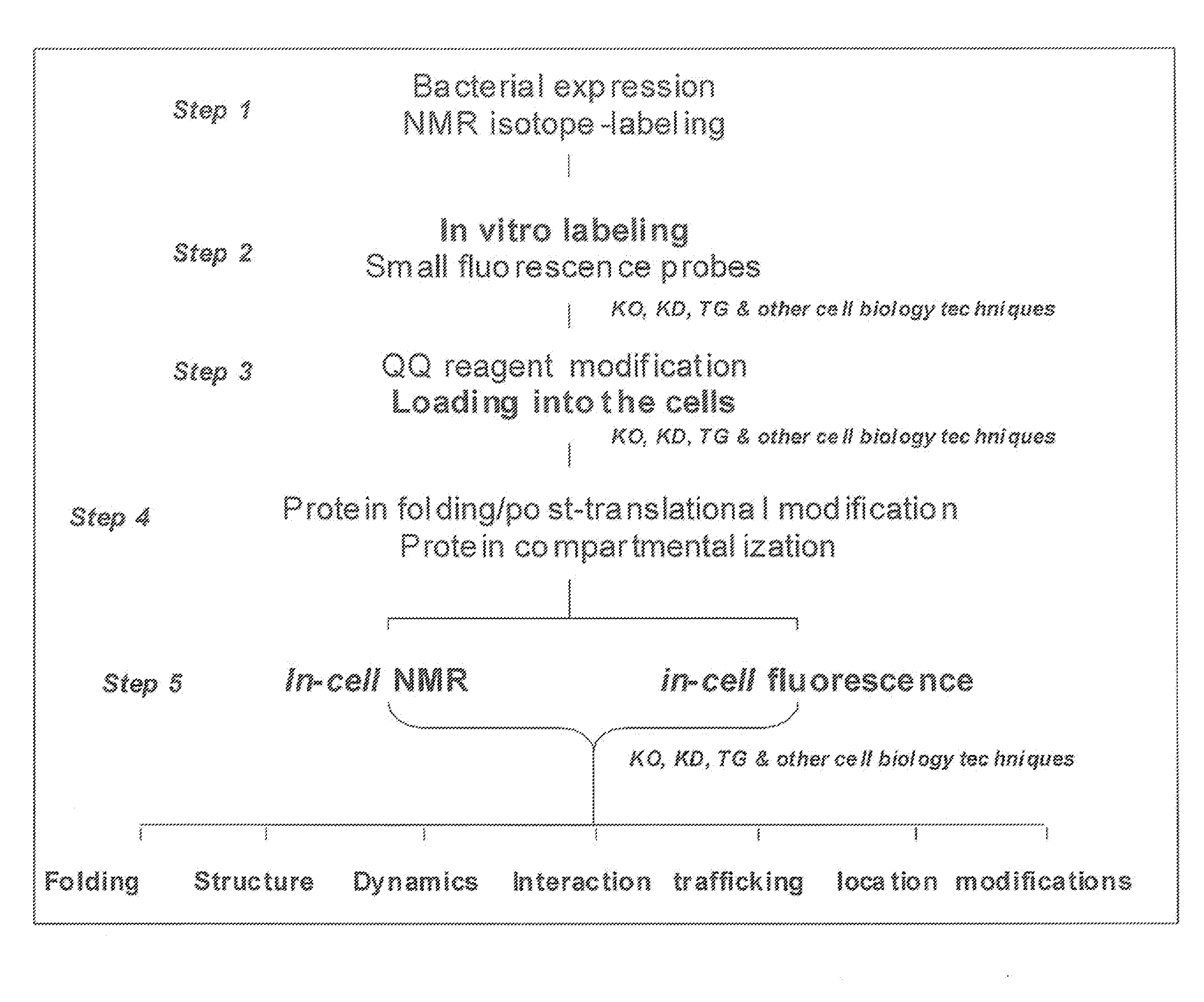
A protein transduction method for efficiently delivery of exogenous proteins into mammalian cells is invented, which has the capability of targeting different cellular compartments and protection from degradation of the delivered proteins from cellular proteases. A composition for treat proteins has cation reagents, lipids and enhancers in a carrier. The method can be used in a number of ways including: production of large quantities of properly folded, post-translationally modified proteins using mammalian cell machinery, a in-cell fluorescence spectroscopy and imaging using small molecule fluorophores and a in-cell NMR spectroscopy using living mammalian cells. The method permits cell biology at atomic resolution that is physiologically and pathological relevant and permits protein therapy to treat human diseases. The method can also be used to deliver exogenous protein inside mammalian cells, wherein the exogenous proteins follow a similar secretion pathway as that of the endogenous protein.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
Protein subcellular localization assays using split fluorescent proteins
ActiveUS20060257942A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceDirect observation
The invention provides protein subcellular localization assays using split fluorescent protein systems. The assays are conducted in living cells, do not require fixation and washing steps inherent in existing immunostaining and related techniques, and permit rapid, non-invasive, direct visualization of protein localization in living cells. The split fluorescent protein systems used in the practice of the invention generally comprise two or more self-complementing fragments of a fluorescent protein, such as GFP, wherein one or more of the fragments correspond to one or more beta-strand microdomains and are used to “tag” proteins of interest, and a complementary “assay” fragment of the fluorescent protein. Either or both of the fragments may be functionalized with a subcellular targeting sequence enabling it to be expressed in or directed to a particular subcellular compartment (i.e., the nucleus).
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
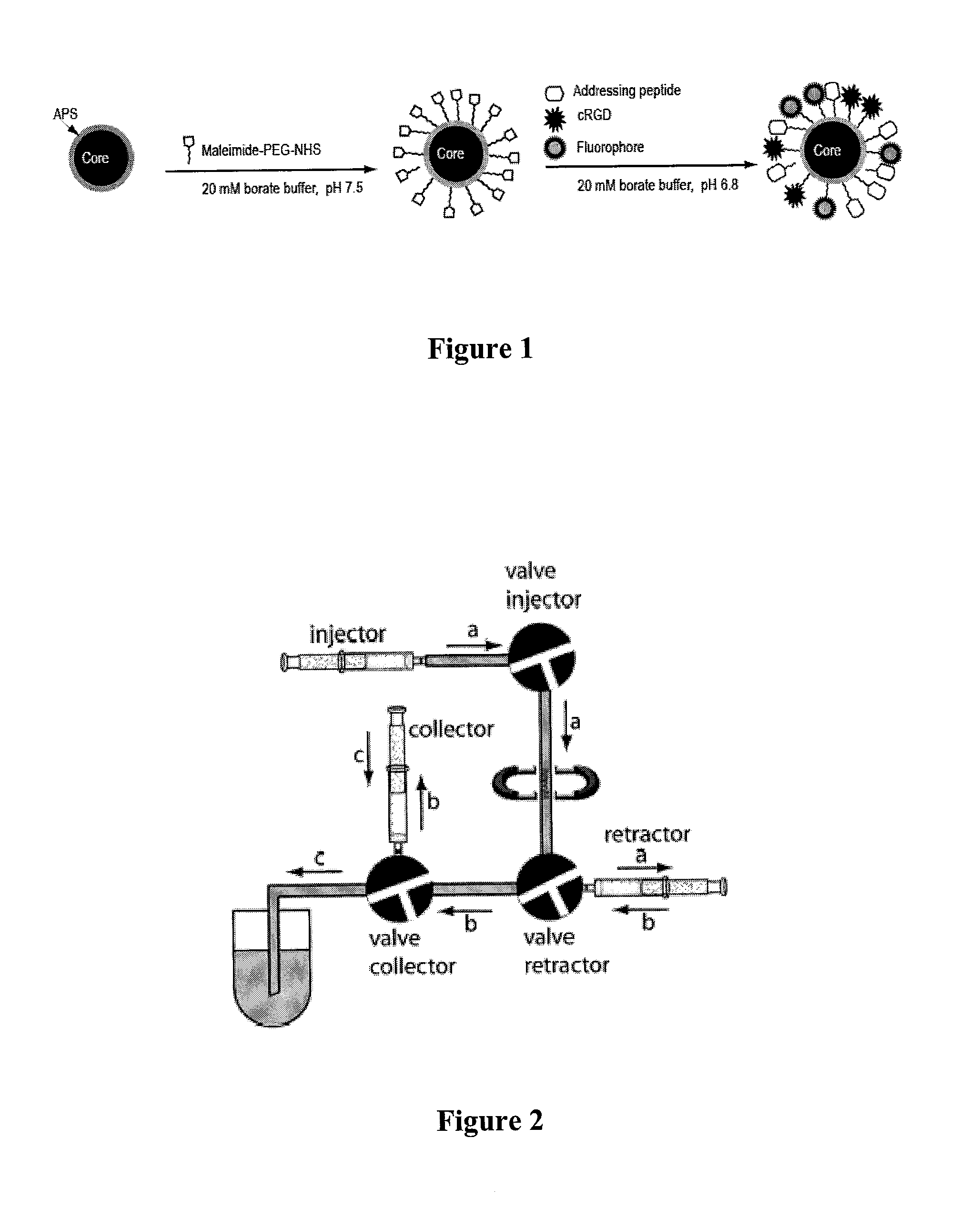
Magnetic, paramagnetic and/or superparamagnetic nanoparticles
The present invention relates to nanoparticles having a mean diameter of <500 nm and comprising, at their surface, a selected material. The nanoparticles are taken up by cells under physiological conditions and can be used to isolate interaction partners of the selected material within the cells. The present invention provides important advantages in that it opens up new ways of identifying cellular components and of delivering a substance of interest specifically to a selected cell compartment. The nanoparticles are also useful as a tool of diagnosis and for the constitution of chemical libraries.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
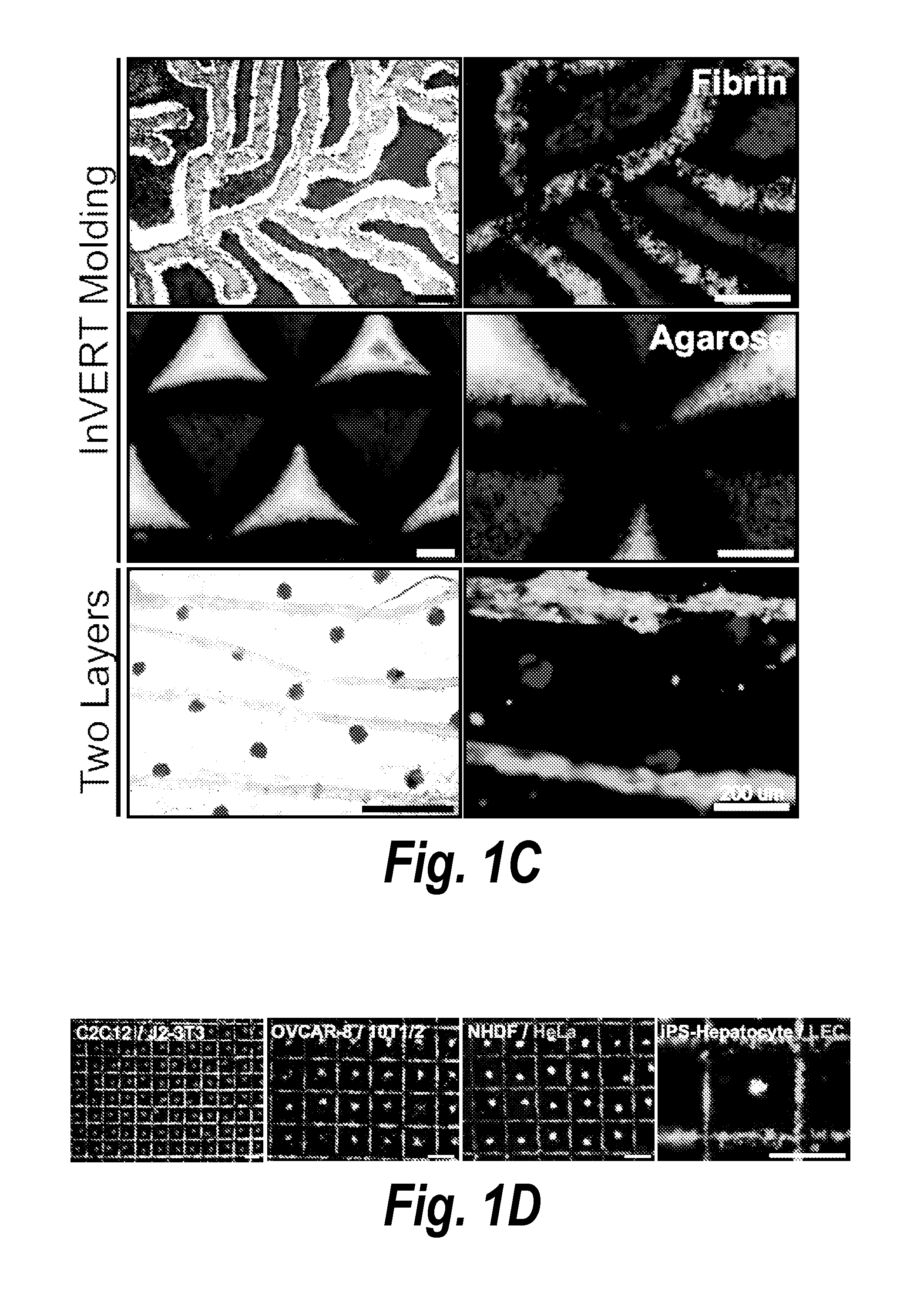
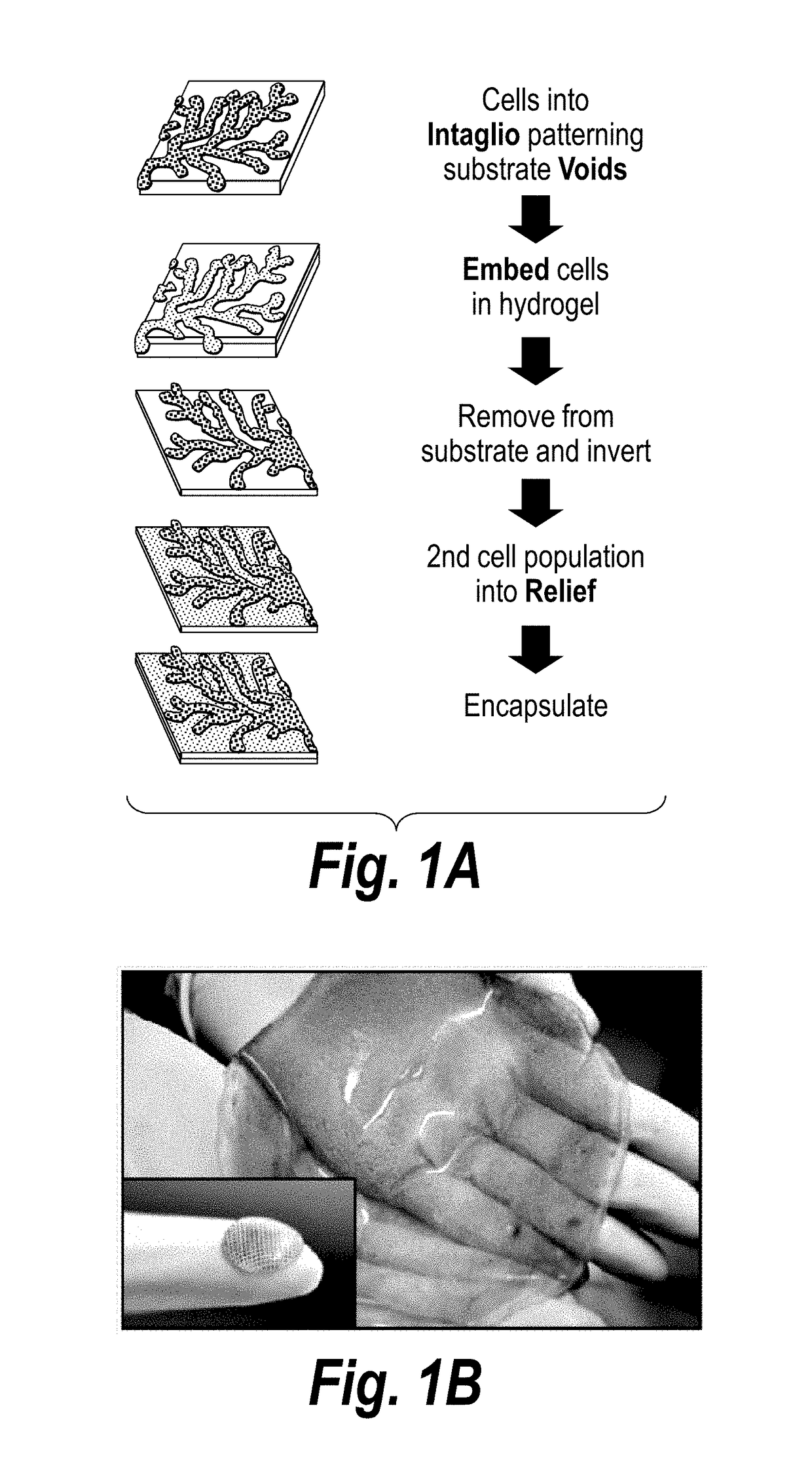
Inverse patterning process for three-dimensional multi-compartmental micro-organization of multiple cell types
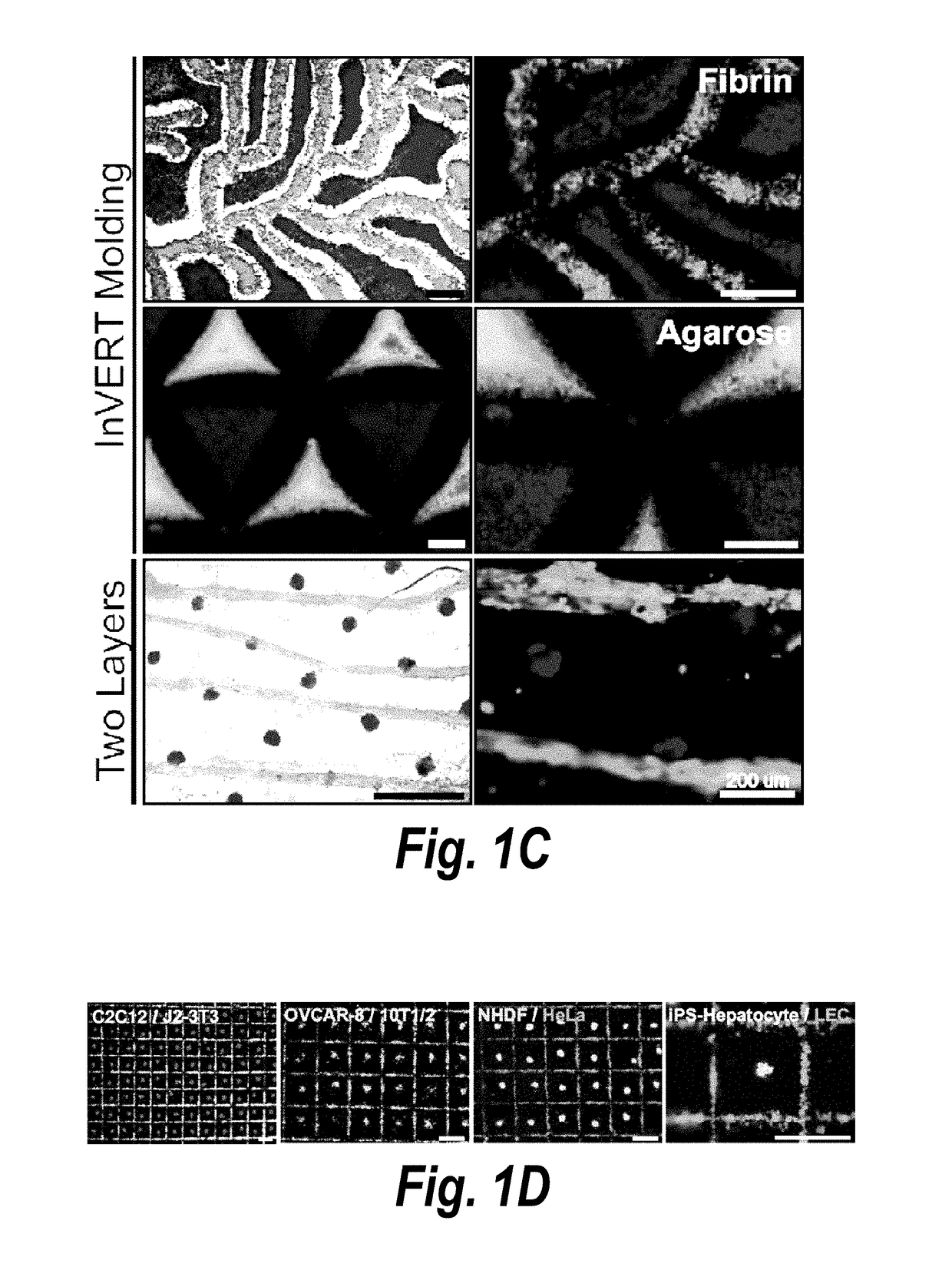
The invention features an “inverse patterning” or “Intaglio-Void / Embed-Relief Topographic (In VERT) molding” manufacturing process for generating high-resolution three-dimensional (3D) multi-cellular microstructures in distinct cellular compartments of a single hydrogel. The platform has general utility in the development of engineered tissues for human therapies, drug testing, and disease models. Additionally, the platform can serve as a model system for studying 3D cell-cell interactions in fields as diverse as stem cell biology to the development of cancer therapeutics.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
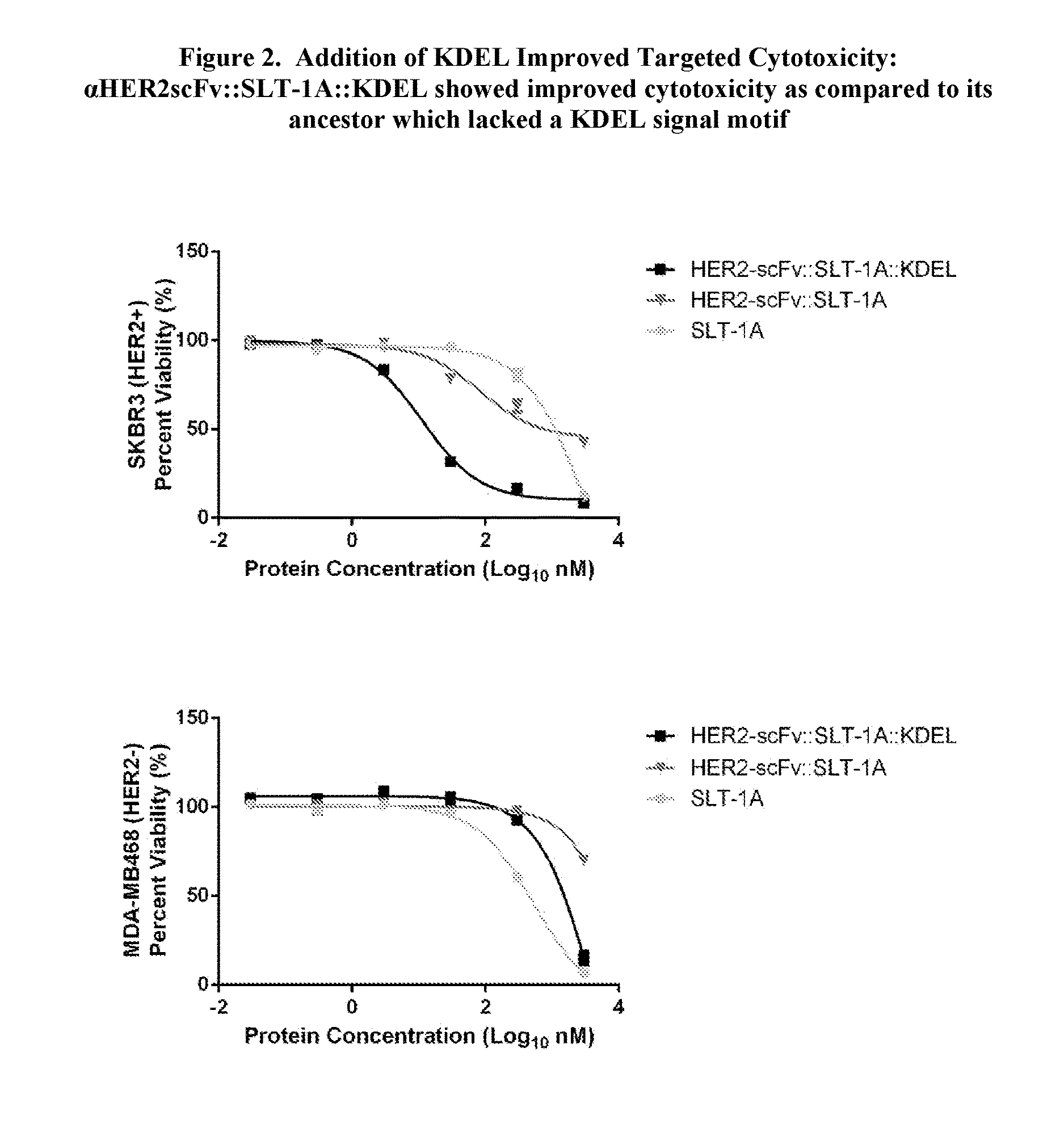
Proteins comprising binding regions, shiga toxin a subunit effector regions, and carboxy-terminal, endoplasmic reticulum localization signal motifs
The present invention provides proteins comprising binding regions for cell-type specific targeting, Shiga toxin effector regions derived from A Subunits of members of the Shiga toxin family for providing Shiga toxin effector functions (e.g. cellular internalization and cytotoxicity), and carboxy-terminal endoplasmic reticulum localization signal motifs. The presently disclosed proteins can comprise additional exogenous materials, such as, e.g., antigens, cytotoxic agents, and detection-promoting agents, and are capable of targeted delivery of these additional exogenous materials into the interiors of target cells. The proteins of the present invention have uses in methods such as, e.g., methods involving targeted killing of target cells, delivering exogenous materials into target cells, labeling subcellular compartments of target cells, and diagnosing and / or treating a variety of conditions including cancers, tumors, other growth abnormalities, immune disorders, and microbial infections.
Owner:MOLECULAR TEMPLATES
Multiple-compartment eukaryotic expression systems
InactiveUS20060183231A1Efficient expressionEfficient workVectorsArtificial cell constructsHeterologousIn vivo
Method and constructs for expressing heterologous sequences of interest in eukaryotic cells using multiple-compartment expression systems. These systems, which may be comprised of a single construct or multiple constructs, utilize at least two different promoters which are each active within a different subcellular compartment of the same eukaryotic cell. The system and constructs of the invention are particularly useful for achieving enhanced in vivo expression of RNA molecules capable of modulating the expression of target genes.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARM INC
Cosmetic formulations
The invention relates to the incorporation of di-sugar alcohol phosphates of C3 to C6 sugar alcohols and / or derivatives of said compounds, e.g. acids, salts, or esters, into cosmetic or dermatological formulations for protecting the skin against environmental influences. The inventive low-molecular compounds of this type take part in the active cell protection of the cell's own free-radical scavengers, antioxidants, DNA, cell membranes and other cell compartments, protecting them against harmful environmental influences, e.g. UV radiation, IR radiation and environmental stress (thermal, chemical and physical). The compatible solution can act as a co-solvent and intensify the penetration of other active ingredients added to the cosmetic formulation, not only to stabilize said ingredients in the formulation, but also to actively transport them into deeper dermal layers.
Owner:BITOP FUR BIOTECHN OPTIMIERUNG
Manipulation of the phenolic acid content and digestibility of plant cell walls by targeted expression of genes encoding cell wall degrading enzymes
InactiveUS7453023B2Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationAnimal ForagingPlant cell
Described herein are methods to enhance the production of more highly fermentable carbohydrates in plants, especially forage grasses. The invention provides for transgenic plants transformed with expression vectors containing a DNA sequence encoding ferulic acid esterase I from Aspergillus, preferably A. niger. The expression vectors may optionally comprise a DNA sequence encoding xylanase from Trichoderma, preferably T. reesei. Expression of the enzyme(s) is targeted to specific cellular compartments, in specific tissues and under specific environmental conditions. Uses of this invention include, but are not limited to, forage with improved digestibility for livestock, and enhanced biomass conversion.
Owner:GENENCOR INT INC
Manipulation of the phenolic acid content and digestibility of plant cell walls by targeted expression of genes encoding cell wall degrading enzymes
InactiveUS7132589B2Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationAnimal ForagingPlant cell
Described herein are methods to enhance the production of more highly fermentable carbohydrates in plants, especially forage grasses. The invention provides for transgenic plants transformed with expression vectors containing a DNA sequence encoding ferulic acid esterase I from Aspergillus, preferably A. niger. The expression vectors may optionally comprise a DNA sequence encoding xylanase from Trichoderma, preferably T. reesei. Expression of the enzyme(s) is targeted to specific cellular compartments, in specific tissues and under specific environmental conditions. Uses of this invention include, but are not limited to, forage with improved digestibility for livestock, and enhanced biomass conversion.
Owner:GENENCOR INT INC
Immunoglobulin having particular framework scaffold and methods of making and using
InactiveUS20050037420A1Immunoglobulins against virusesBiological testingHigh level expressionScFv Antibodies
This invention relates to immunoglobulin molecules comprising light chain (VL) chimeric variable domains, heavy chain (VH) chimeric variable domains, e.g., scFv antibodies that are expressed at high levels within a host cell, preferably within particular cellular compartments such as, e.g., cytosol or apoplast. The VL, VH and scFv antibody molecules comprise framework scaffolds of particularly preferred framework regions. This invention also relates to nucleic acid molecules encoding the immunoglobulin molecules of this invention, vectors expressing the immunoglobulin molecules, hosts transformed with the nucleic acid molecules and vectors, and methods of using the immunoglobulin molecules. Also described are immunoglobulin libraries as well as host cells, including transgenic plants, expressing the VL, VH or scFv antibody molecules of this invention.
Owner:ZHANG MEI YUN +5
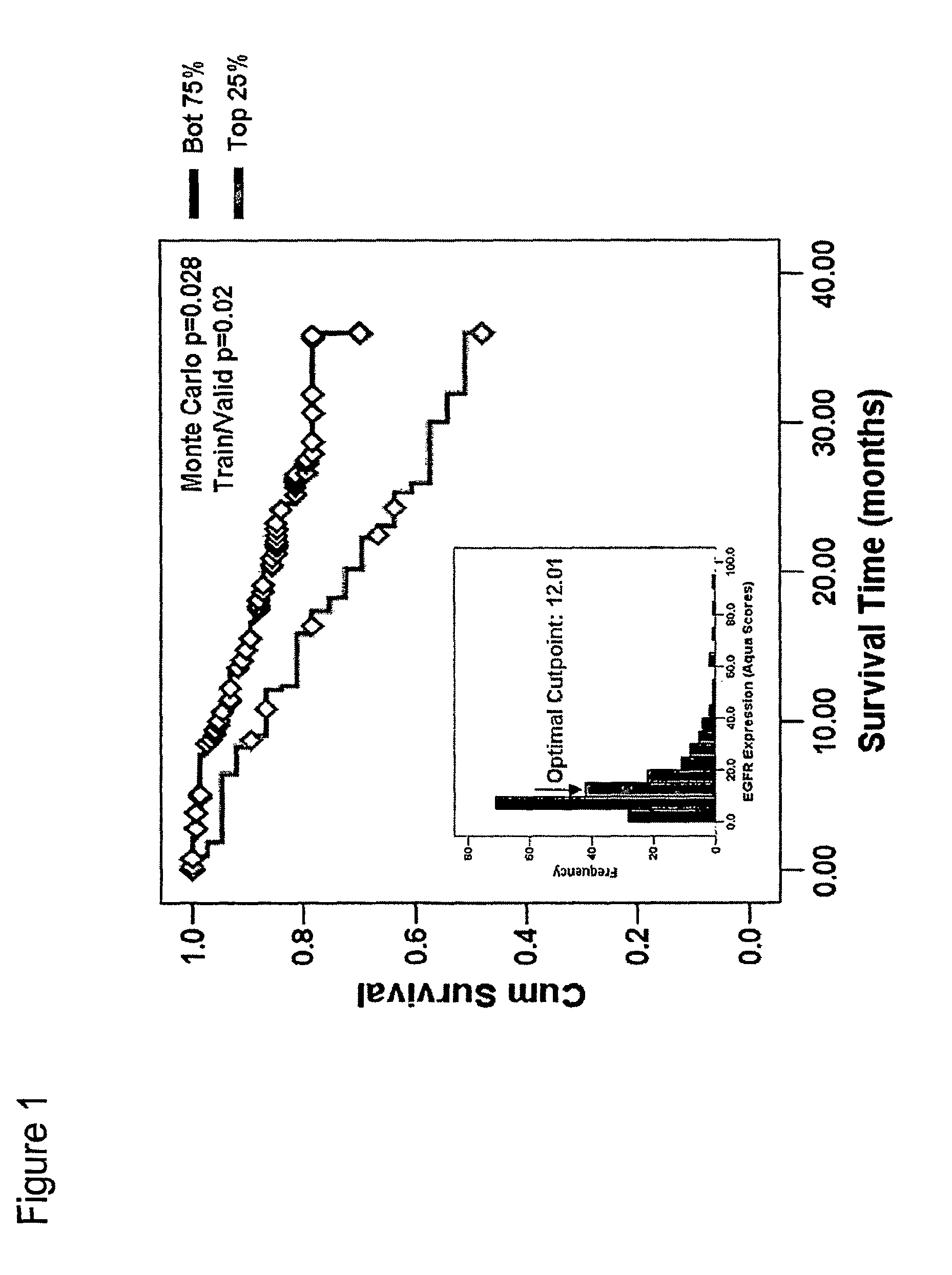
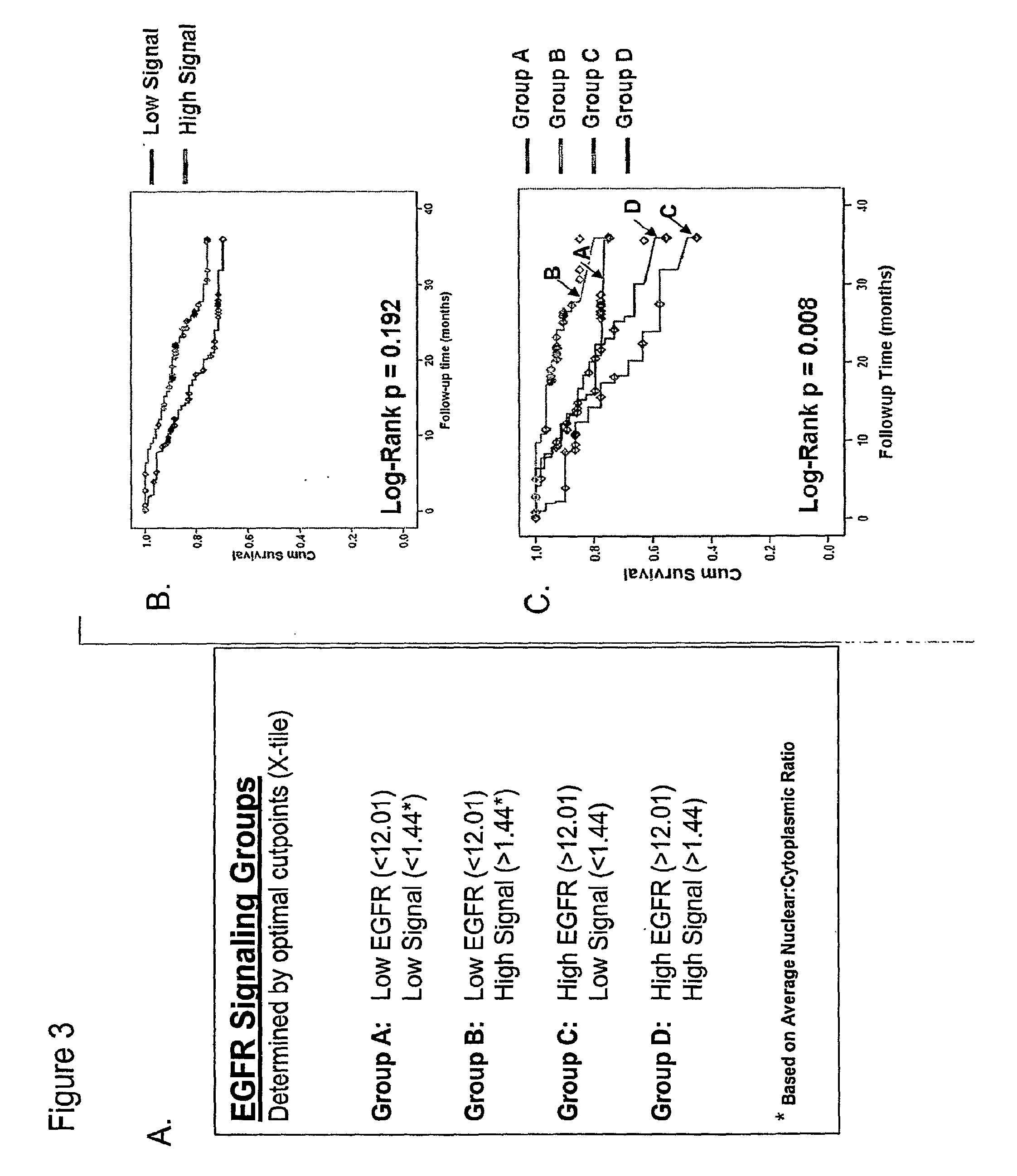
Methods for determining signal transduction activity in tumors
ActiveUS20100062452A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunohistochemistry techniqueBiology
The method of the invention pertains to determining the signal transduction activity in a tissue section by immunohistochemistry techniques. The expression level of the receptor of interest is determined as well as the expression levels of one or more effector molecules of the receptor signal transduction pathway. Furthermore a combined ratio of expression levels of effector molecules in subcellular compartments with the receptor expression was found to have prognostic significance.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG +1
Electronic device
InactiveUS20140118928A1Suitable for slim electronic deviceUniform forceDigital data processing detailsCooling/ventilation/heating modificationsThermal radiationCellular compartment
An electronic device comprises a case, a heat source and a radiator. The heat source is disposed inside the case. The radiator is disposed on the case and the radiator is kept away from the heat source at a distance. The radiator comprises a case body. A plurality of cellular compartments formed by a plurality of partition plates is disposed inside the case body. The cellular compartments are filled with a heat dissipation material. The radiator absorbs the heat of the heat source through thermal radiation.
Owner:INVENTEC PUDONG TECH CORPOARTION +1
Method and composition for a protein transduction technology and its applications
ActiveUS8722348B2Efficient deliveryImprove efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsMicroencapsulation basedSpectroscopyFluorophore
A protein transduction method for efficiently delivery of exogenous proteins into mammalian cells is invented, which has the capability of targeting different cellular compartments and protection from degradation of the delivered proteins from cellular proteases. A composition for treat proteins has cation reagents, lipids and enhancers in a carrier. The method can be used in a number of ways including: production of large quantities of properly folded, post-translationally modified proteins using mammalian cell machinery, a in-cell fluorescence spectroscopy and imaging using small molecule fluorophores and a in-cell NMR spectroscopy using living mammalian cells. The method permits cell biology at atomic resolution that is physiologically and pathological relevant and permits protein therapy to treat human diseases. The method can also be used to deliver exogenous protein inside mammalian cells, wherein the exogenous proteins follow a similar secretion pathway as that of the endogenous protein.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
Ph-sensitive dendritic polymeric micelles
InactiveUS20120003322A1Facilitates overall micelle preparation processEasy to synthesizePowder deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsIonic strengthElectrostatic interaction
The present invention relates to a pH-sensitive PIC (polyion complex) type polymeric micelle formed by electrostatic interaction between a dendritic block copolymer and another polymer of opposite charge. The presence of a dendritic block copolymer confers high stability to the micelles in physiological conditions, while in the acid medium of tumor tissues (pH 6.5) or cell compartments, such as the endosome / lysosome (pH 5.0-5.5), the micelles tend to become destabilized, being able to selectively release drugs or macromolecules encapsulated therein. The micelles are characterized by high stability against ionic strength, dilution and temperature. They can further be lyophilized and conserved in solid state.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SANTIAGO DE COMPOSTELA
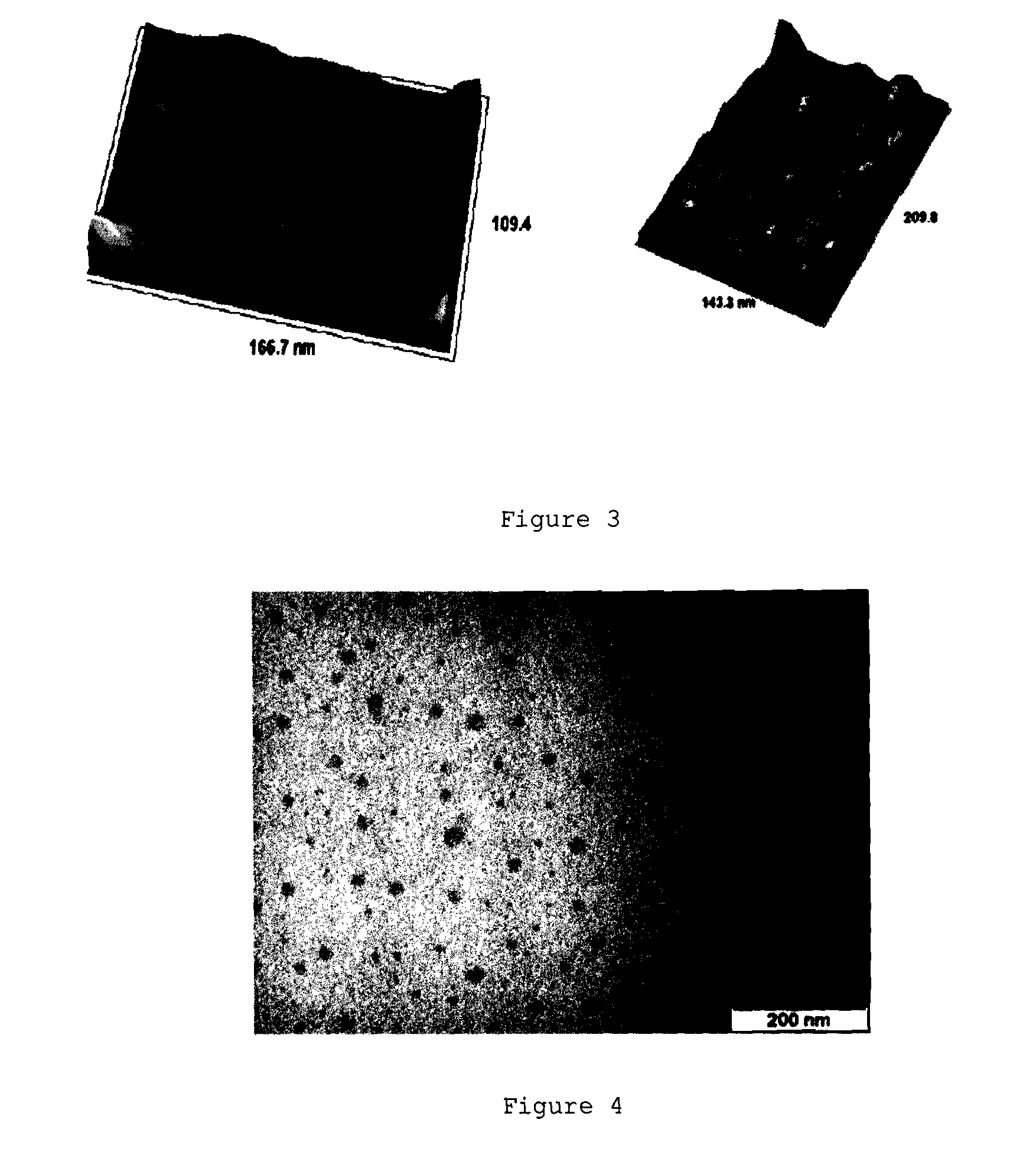
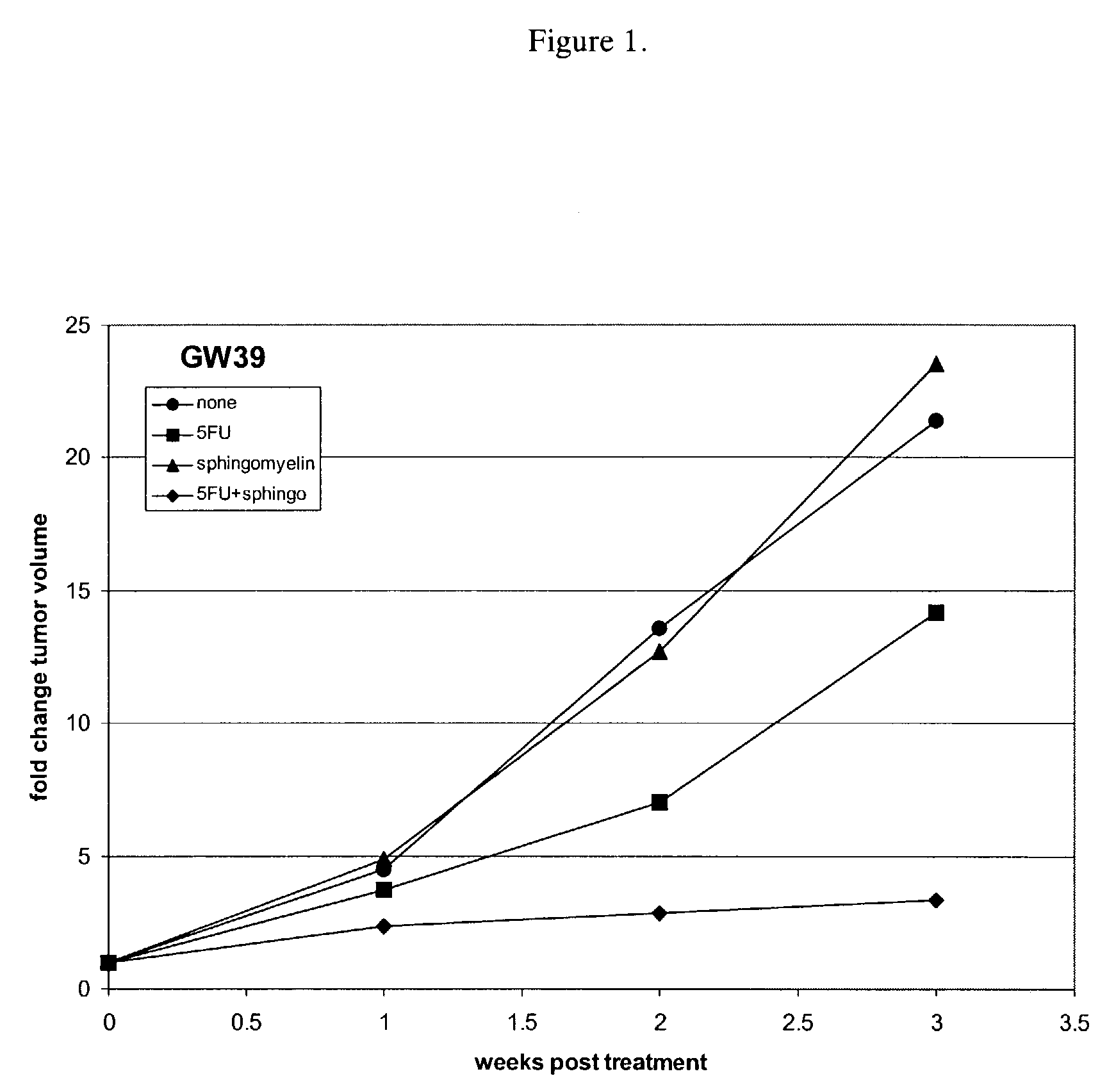
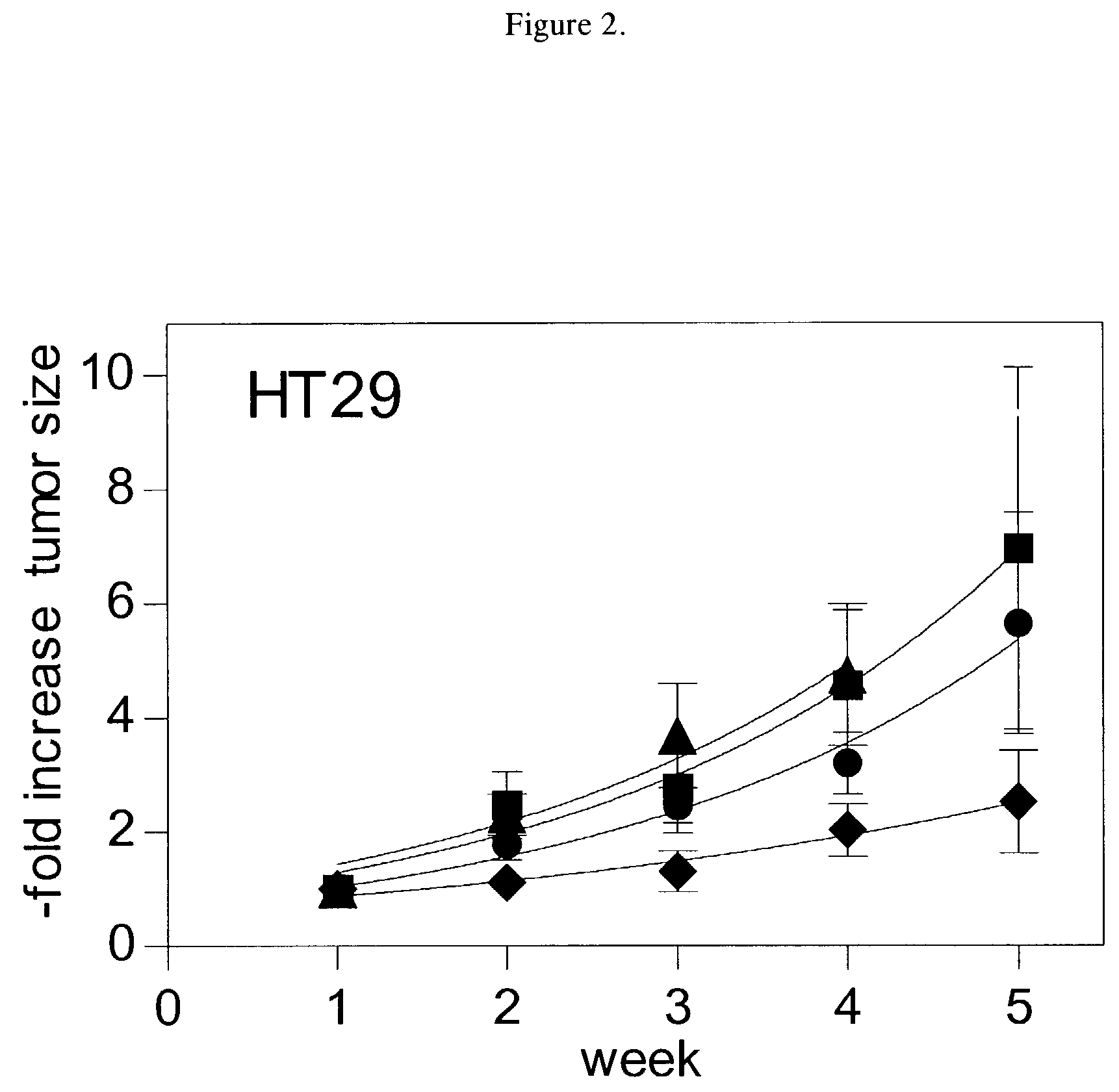
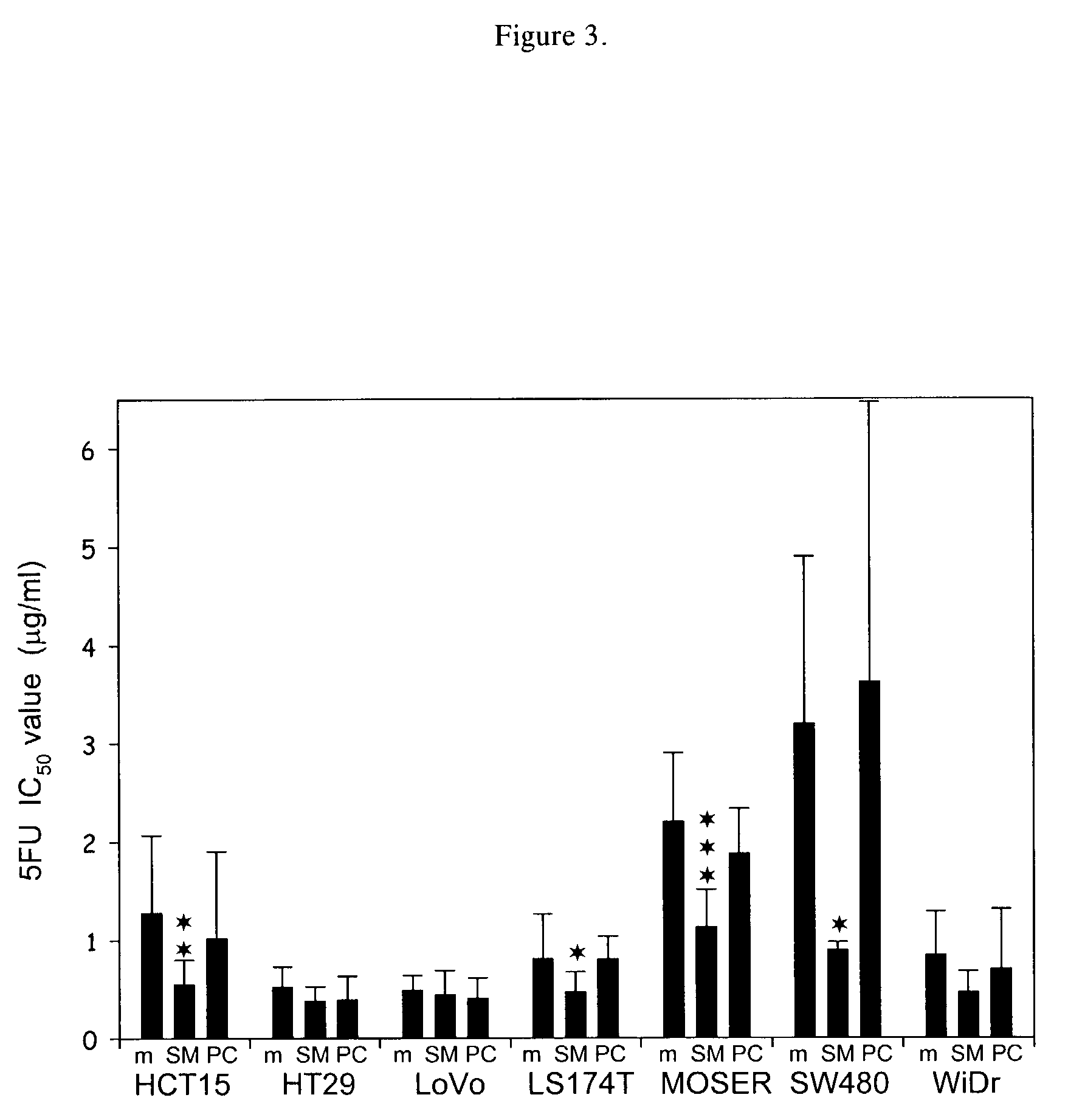
Sphingomyelin enhancement of tumor therapy
InactiveUS7288534B2Enhancing tumor therapyIncrease productionBiocideAntipyreticCo administrationCytotoxicity
Cytotoxic tumor therapy in a patient is enhanced by co-administration of sphingomyelin. The invention most likely enhances a tumor cell's ability to undergo ceramide-induced apoptosis by increasing the levels of sphingomyelin in all cellular compartments, thereby providing sufficient substrate for activated sphingomyelinase. A method of treating rheumatoid arthritis also is provided.
Owner:CENT FOR MOLECULAR BIOLOGY & MEDICINE
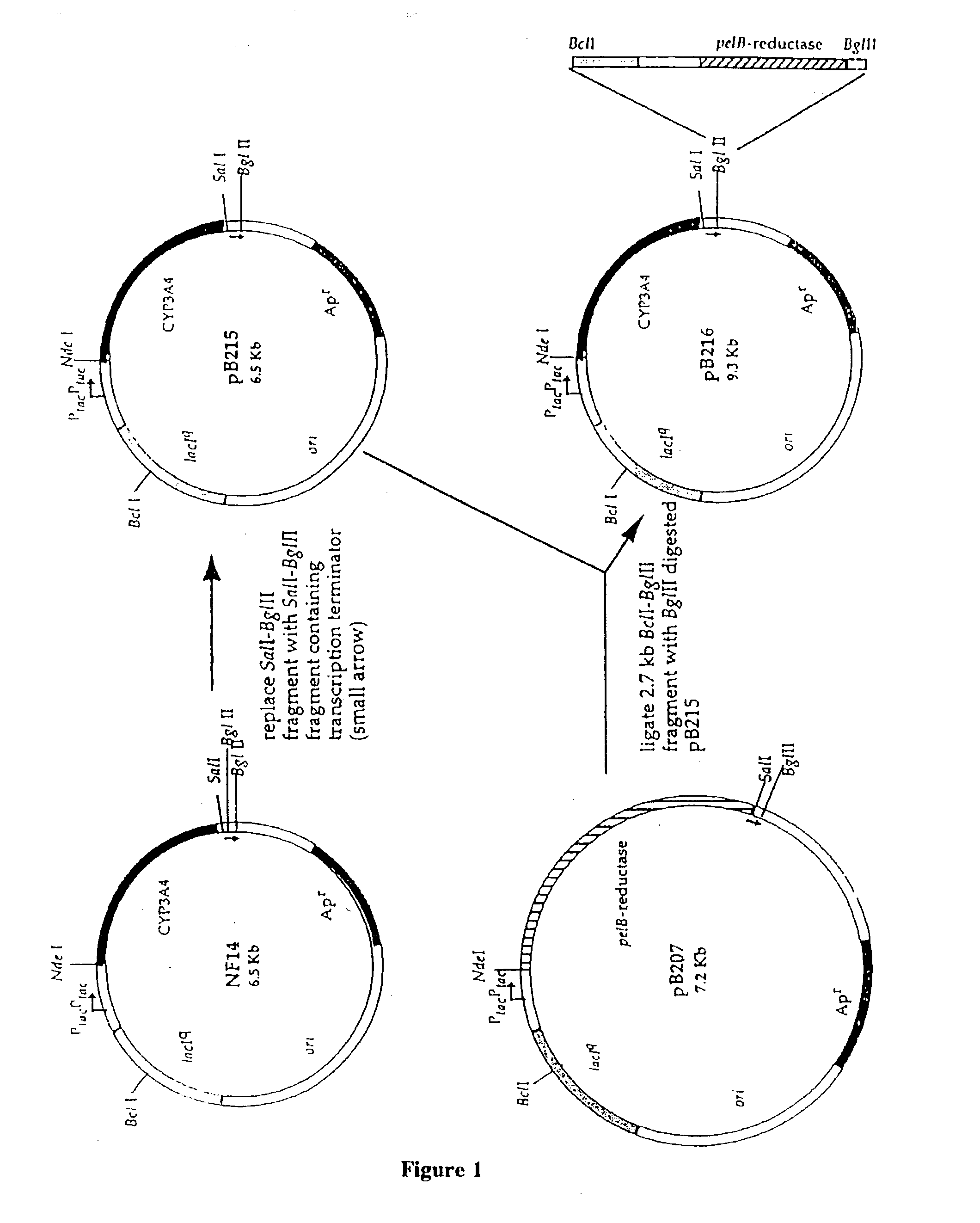
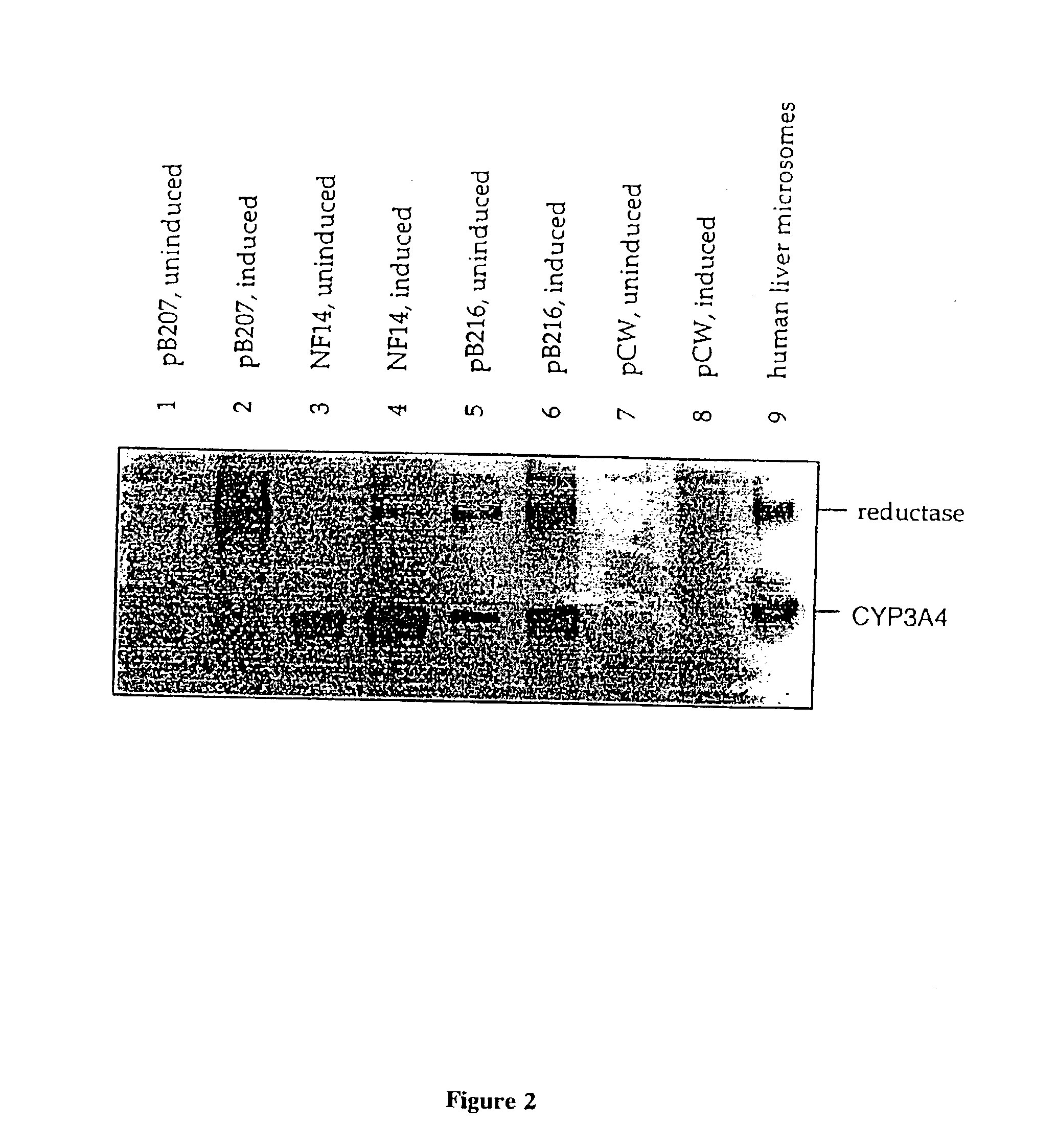
Cytochrome P450 expression in enterobacteria
InactiveUS20030215915A1Reduce degradationHigh expressionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBacteriaCytochrome P450 reductaseCell membrane
A bacterial cell containing a functional cytochrome P450 monooxygenase system, said cell comprising a genetic construct capable of expressing a cytochrome P450 and a genetic construct capable of expressing, separately from said cytochrome P450, a cytochrome P450 reductase wherein the N-terminus of the cytochrome P450 and the N-terminus of the cytochrome P450 reductase are each adapted to allow functional coupling of said cytochrome P450 and said cytochrome P450 reductase within said cell. A bacterial cell containing a cytochrome P450 comprising a genetic construct encoding, and capable of expressing, said cytochrome P450 wherein the cytochrome P450 comprises an N-terminal portion which directs the cytochrome P450 to a cellular compartment of membrane of the bacterial cell. The bacterial cells are useful as, for example, bioreactors, in drug testing and mutagenicity testing and as a source of cytochrome P450.
Owner:BTG INT LTD
Inverse patterning process for three-dimensional multi-compartmental micro-organization of multiple cell types
ActiveUS10072257B2Rapid cell patternsMinimal damageHepatocytesMammal material medical ingredientsDiseaseCell–cell interaction
The invention features an “inverse patterning” or “Intaglio-Void / Embed-Relief Topographic (In VERT) molding” manufacturing process for generating high-resolution three-dimensional (3D) multi-cellular microstructures in distinct cellular compartments of a single hydrogel. The platform has general utility in the development of engineered tissues for human therapies, drug testing, and disease models. Additionally, the platform can serve as a model system for studying 3D cell-cell interactions in fields as diverse as stem cell biology to the development of cancer therapeutics.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
System and method for automatic color segmentation and minimum significant response for measurement of fractional localized intensity of cellular compartments
ActiveUS8116982B2Large responseImage enhancementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsUltimate tensile strengthCellular material
Owner:VALA SCI
Application of biomembrane or closed structure or cellular compartment with biomembrane properties as cosmetic or cosmetic carrier
InactiveCN104997718AImprove stabilityImprove solubilityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsNatural sourceBiomedicine
Owner:HANGZHOU UMOTOR BIOTECH CO LTD
System and method for automatic color segmentation and minimum significant response for measurement of fractional localized intensity of cellular compartments
InactiveUS20130004053A1Large responseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsImage enhancementCellular materialComputer science
A system, a method, and a programmed device for measurement of translocational activity among cellular compartments process magnified images of cellular material exposed to an agent by segmenting and compartmentalizing the images and then measuring fractional localized intensity of two or more compartments in the segmented, compartmentalized image. The measured fractional localized intensities are compared to determine translocation of cellular material among the measured components caused by the agent.
Owner:VALA SCI
Mucosal delivery of therapeutic molecules, proteins, or particles coupled to ceramide lipids
Described herein are compositions and methods useful for allowing for the absorption (passage) of agents of interest, such as therapeutic agents, across epithelial and mucosal barriers and / or into certain subcellular compartments of the cell, such as the recycling endosome (RE), Golgi, and the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Application of biological membrane obtained by natural source and/or self-assembly technology, and closed structure or cellular compartment with biological membrane property as medicine carriers
InactiveCN104888230AFull penetrationGood curative effectOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsNatural sourceProtein
The invention relates to application of a biological membrane obtained by a natural source and / or a self-assembly technology, and a closed structure or a cellular compartment with biological membrane property as medicine carriers. The biological sources of the biological membrane and the closed structure or the cellular compartment with the biological membrane property are animals, plants or microorganisms; the obtained biological membrane is intact or segmented, and is of a lipid bilayer structure in form; the constituents mainly are lipid and protein; and in addition, a small amount of saccharides are combined with the lipid or protein through covalent bonds. According to the biological membrane and the closed structure or the cellular compartment (hereinafter referred to as biological membrane) with the biological membrane property disclosed by the invention as the medicine carriers, the targets of improving the stability, the solubility and the curative effects of medicines can be reached; the toxicity or irritation is reduced; and the long-term effect and the targeting property are slowly released.
Owner:HANGZHOU UMOTOR BIOTECH CO LTD
Systems and methods for multiplexed biomarker quantitation using single cell segmentation on sequentially stained tissue
Improved systems and methods for the analysis of digital images are provided. More particularly, the present disclosure provides for improved systems and methods for the analysis of digital images of biological tissue samples. Exemplary embodiments provide for: i) segmenting, ii) grouping, and iii) quantifying molecular protein profiles of individual cells in terms of sub cellular compartments (nuclei, membrane, and cytoplasm). The systems and methods of the present disclosure advantageously perform tissue segmentation at the sub-cellular level to facilitate analyzing, grouping and quantifying protein expression profiles of tissue in tissue sections globally and / or locally. Performing local-global tissue analysis and protein quantification advantageously enables correlation of spatial and molecular configuration of cells with molecular information of different types of cancer.
Owner:莱卡微系统 CMS +1
Set of sequences for targeting expression and control of the post-translational modification of a recombinant polypeptide
InactiveUS20110195452A1Improve stabilityImprove production yieldPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsSequence signalPost translational
The present invention provides new tools useful for controlling the post-translational modifications of recombinant polypeptides. These tools are particular signal peptides allowing the targeting of recombinant polypeptides during their synthesis in a host cell to specific sub-cellular compartments and a specific designing of said recombinant polypeptides within said sub-cellular compartments. These signal peptides are SEQ ID no 1 to SEQ ID no 31 disclosed herein. The present invention relates therefore also to a process for producing a recombinant polypeptide, in particular to a post-translationally modified polypeptide comprising the steps of transfecting or transforming a cell with at least one numleic acid vector encoding a recombinant protein which is the polypeptide before being post-translationally modified or a recombinant protein different to said polypeptide, said recombinant protein comprising a peptide signal according to the present invention; growing the transfected cell; and harvesting the post-translationally modified polypeptide; wherein, when said recombinant protein is different to said polypeptide, the method also comprises a step of transfecting said cell with at least one vector encoding said polypeptide. The present invention allows advantageously, for example, to increase the yield of production of recombinant polypeptides, to prevent immunogenicity if recombinant polypeptides and to obtain therapeutically active recombinant polypeptides that are the exact copy of their natural counterpart. This invention relates particularly to the field of reorientation of plants made pharmaceuticals (PMP).
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
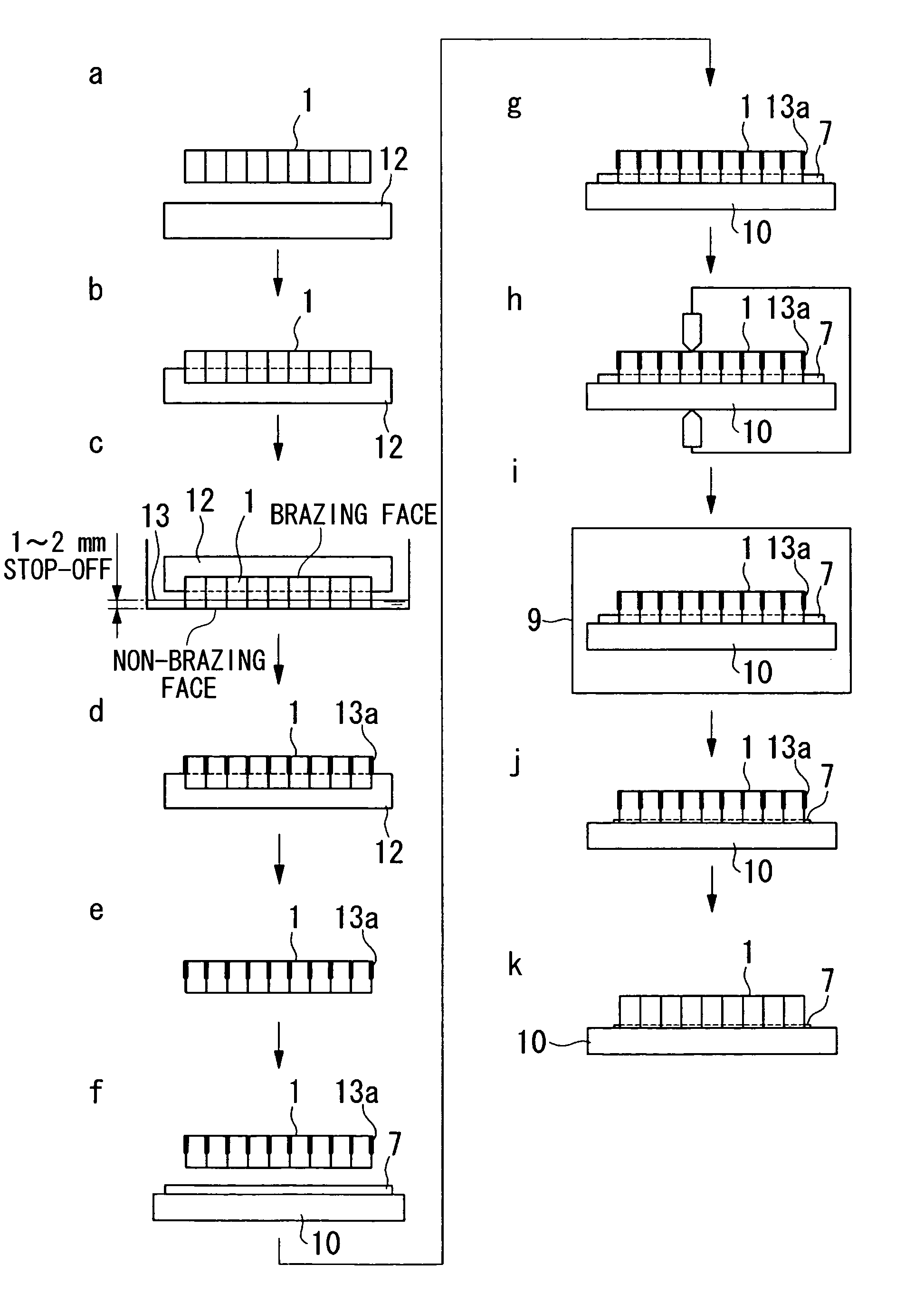
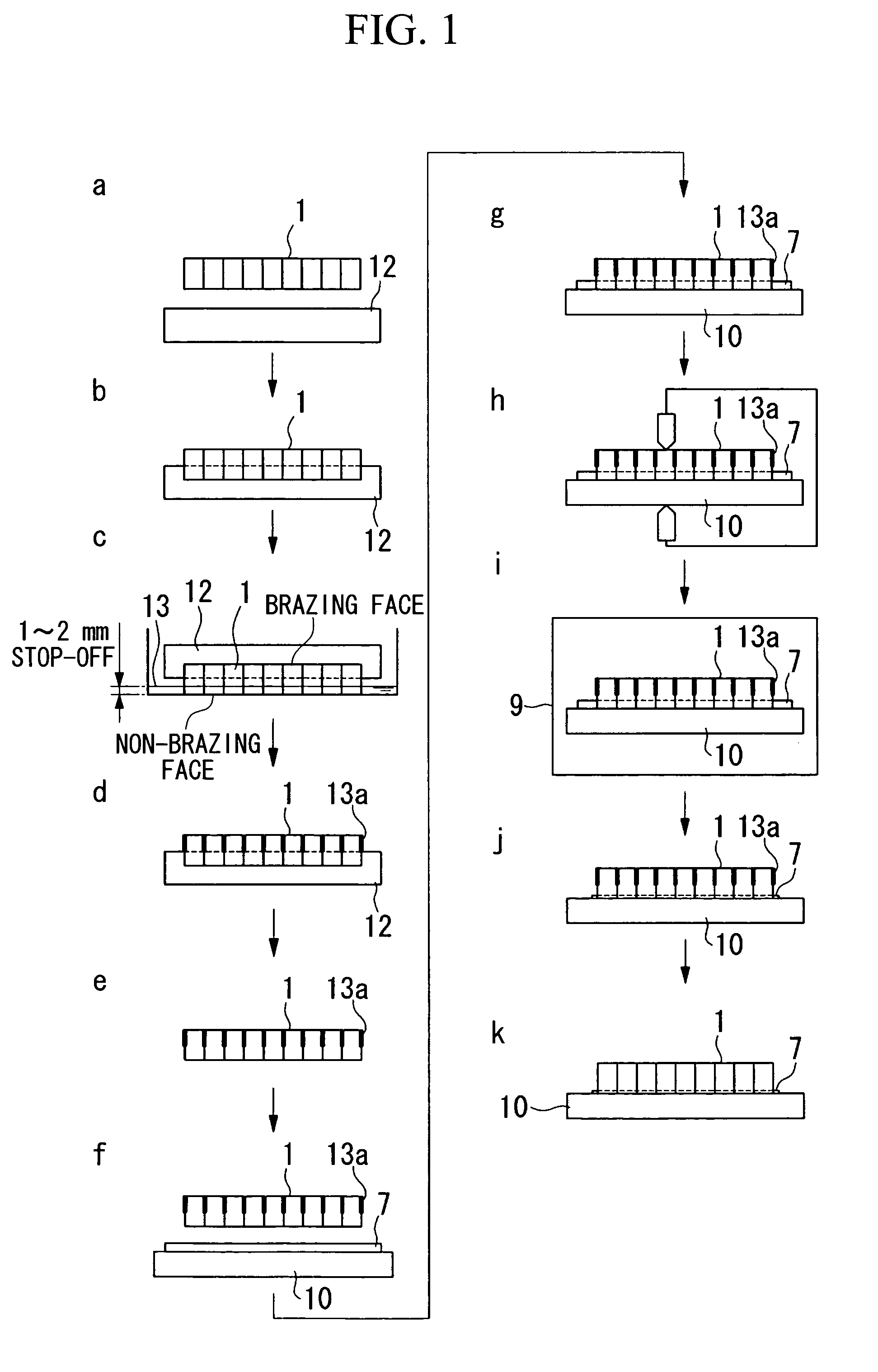
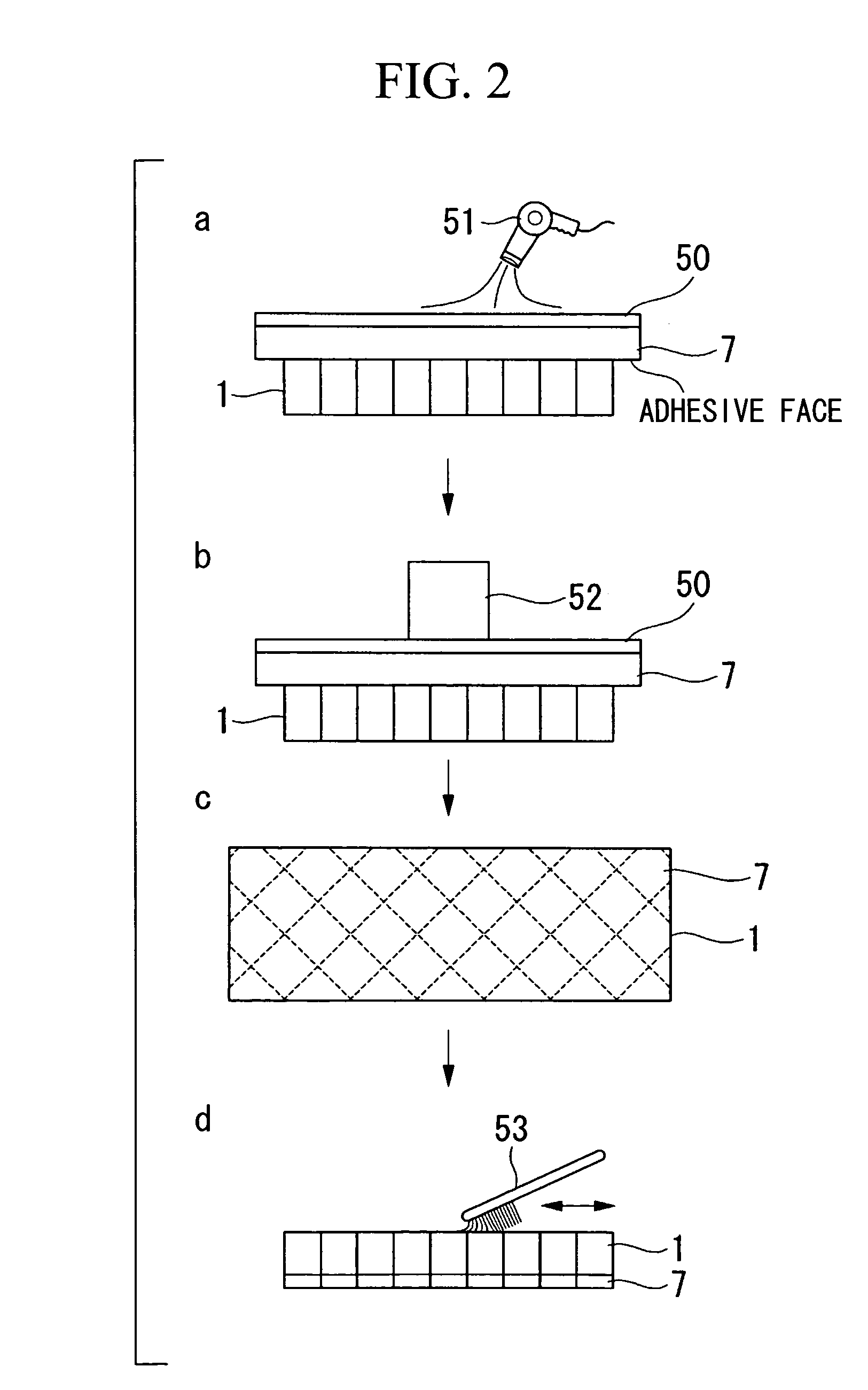
Brazing construction and method of brazing an abradable sealing material
ActiveUS7105219B2Prevent penetrationEqually distributedLayered productsSoldering apparatusHoneycombHoneycomb like
A brazing construction and method of brazing an abradable sealing material onto a base material is provided. The abradable sealing material is a tabular member having a cellular compartment construction in honeycomb form having empty compartments and partitions formed by overlapping a plurality of thin corrugated sheets. The abradable sealing material is brazed on the main material by, applying a stop-off agent on a side surface of the abradable sealing material except on a portion of the side surface close to a brazing face to form a stop-off area that prevents infiltration of a brazing filler metal in an overlapping part; superposing the brazing face of the abradable sealing material on the base material, such that the brazing filler metal is provided between the abradable sealing material and the base metal; and brazing the abradable sealing material to said base material.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com