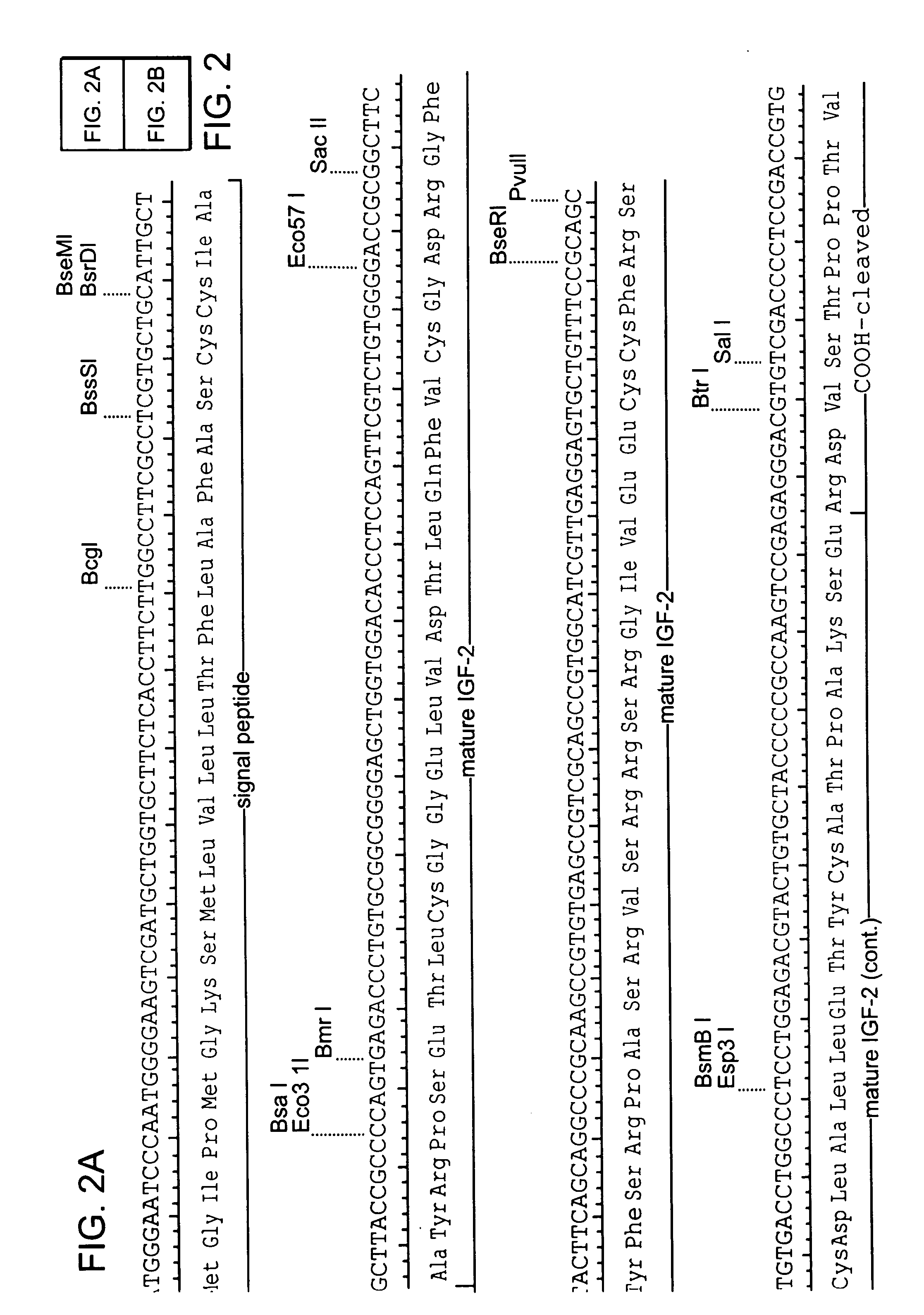
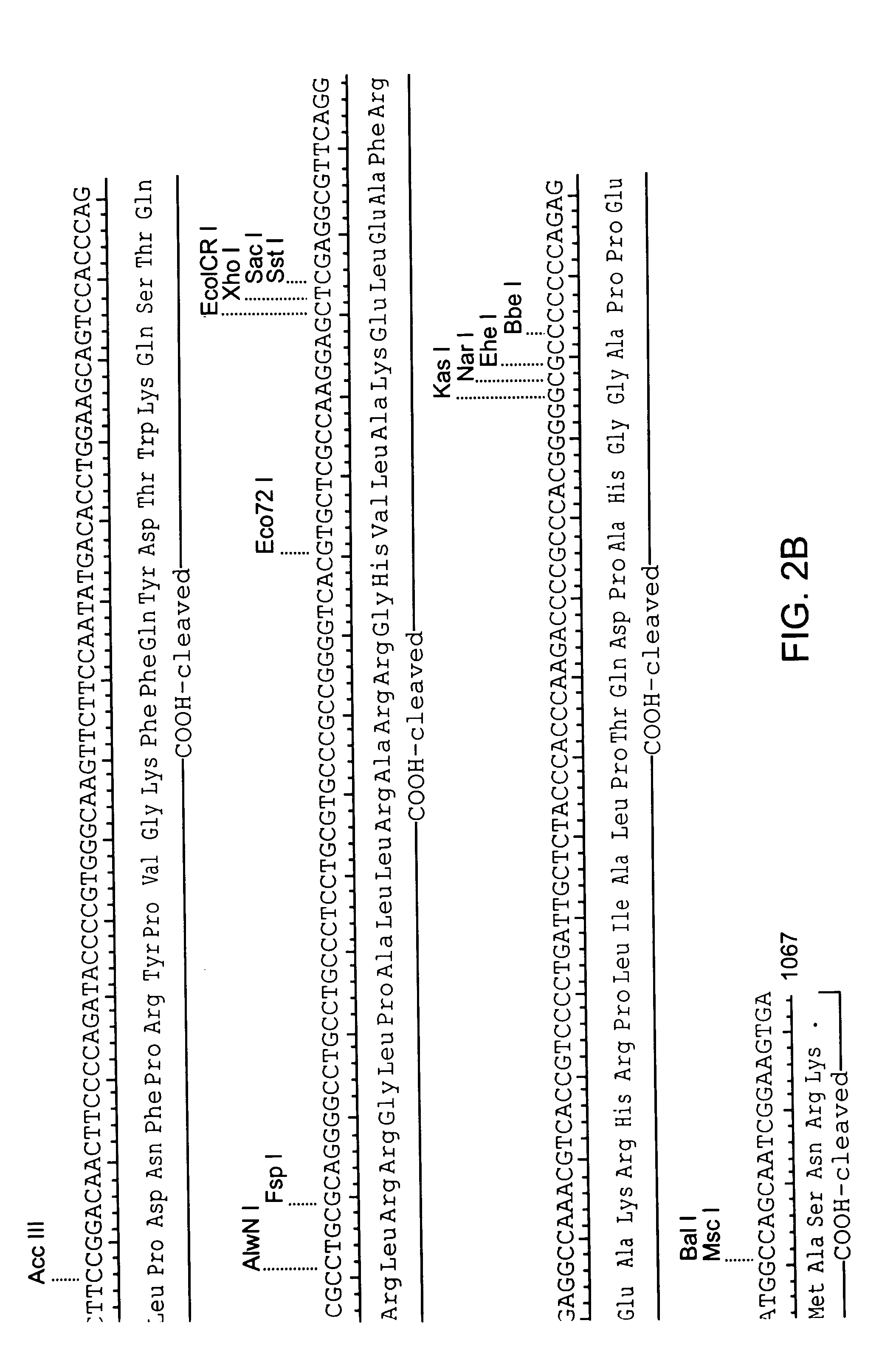
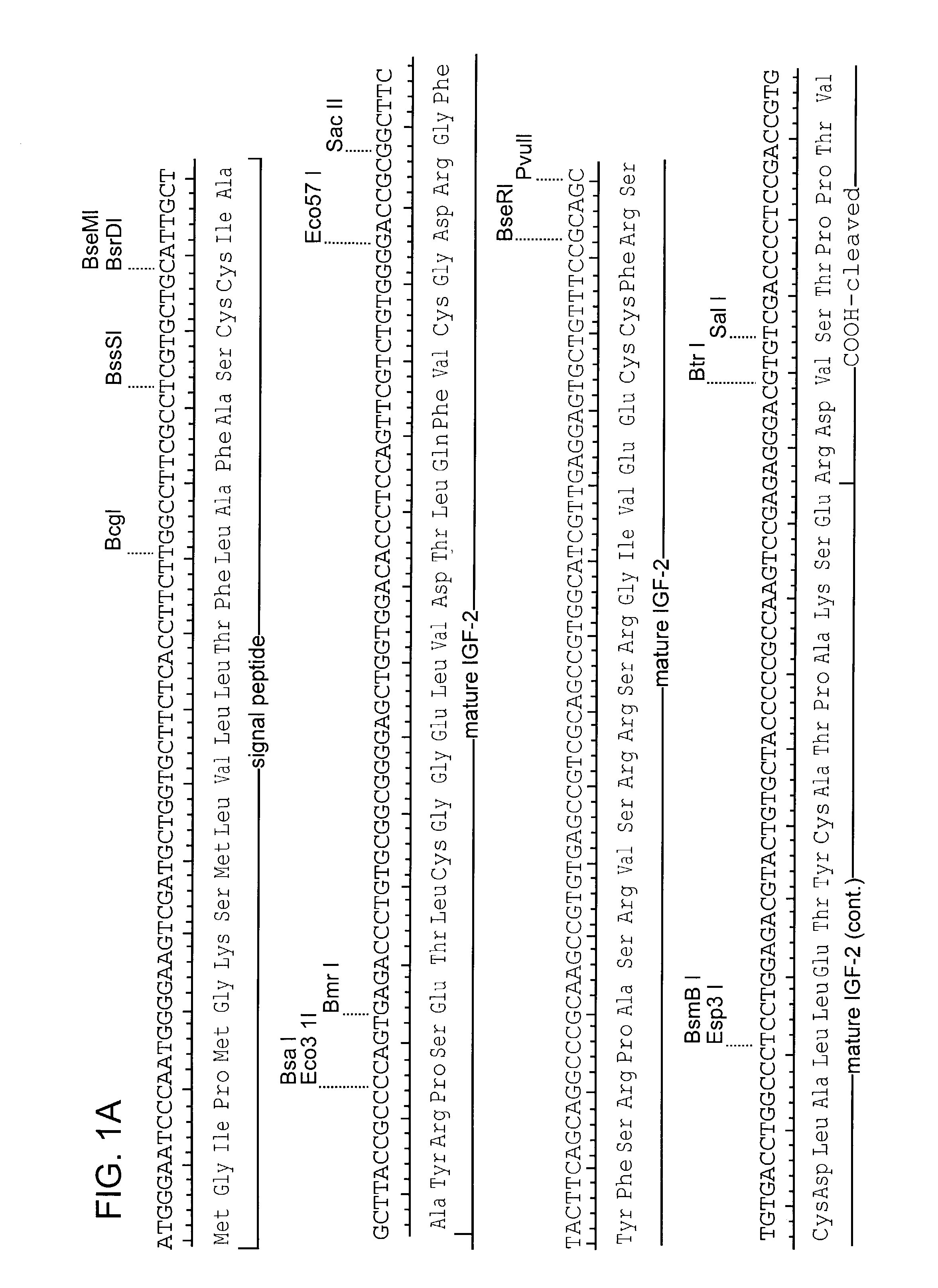
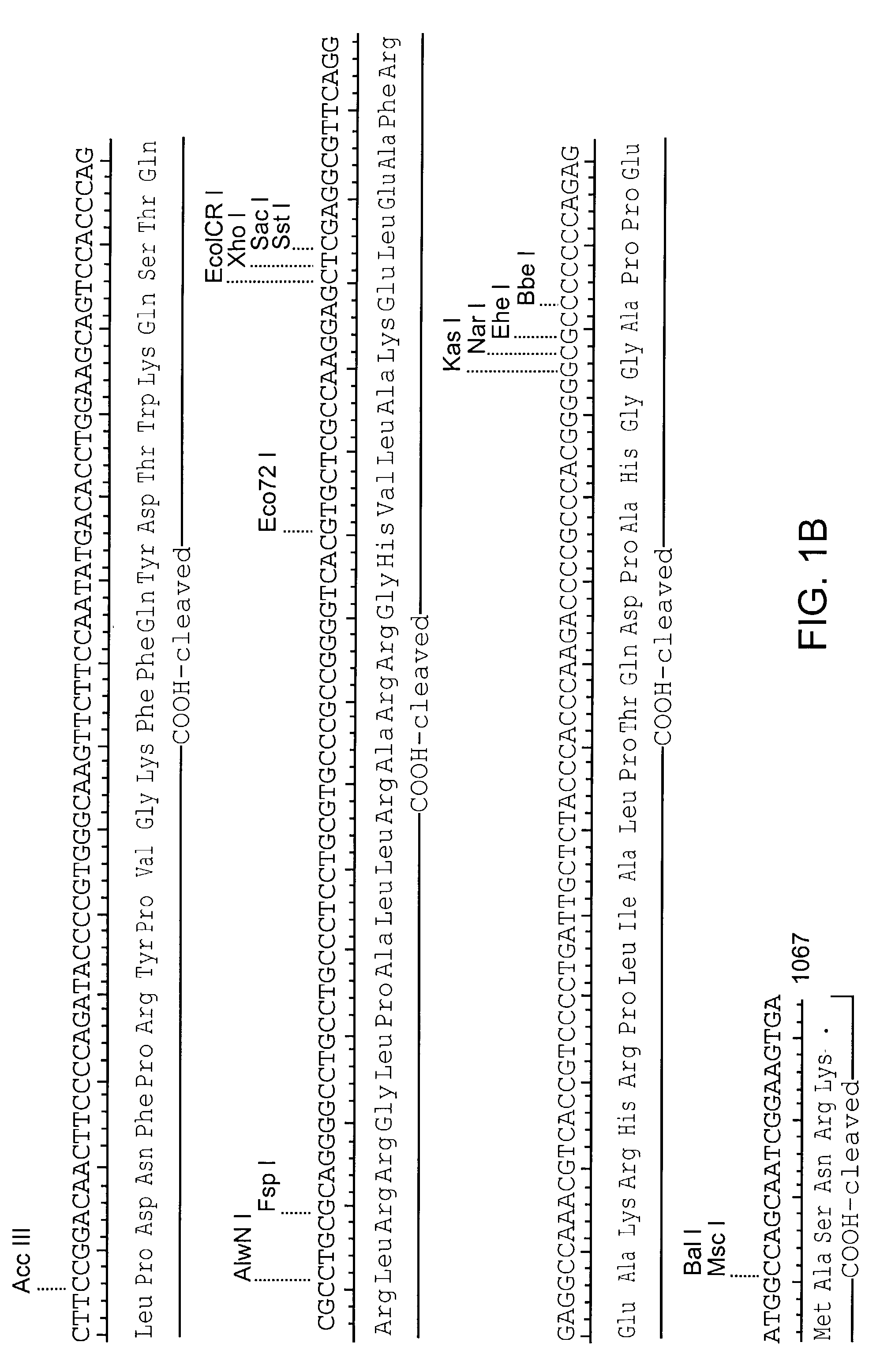
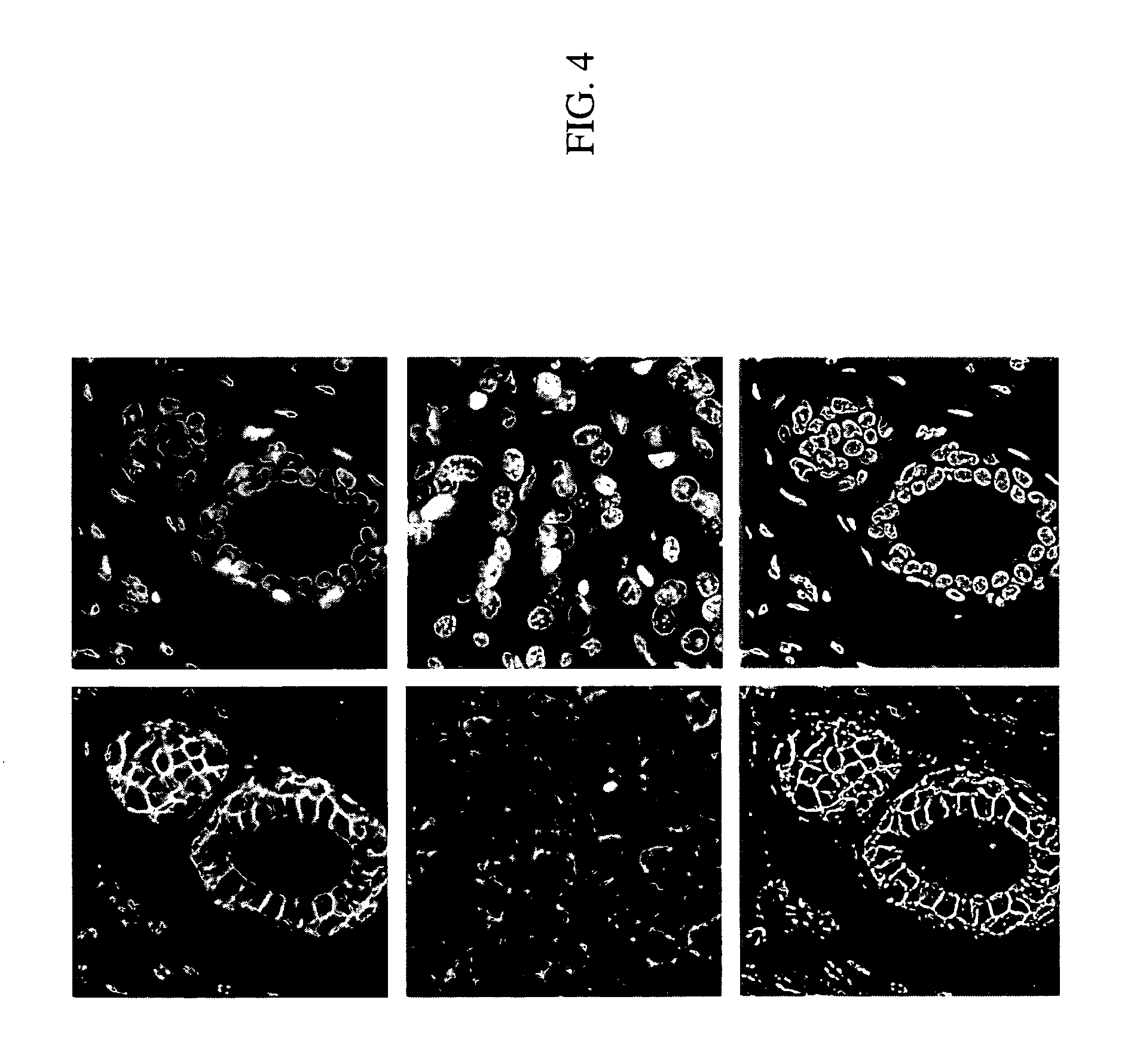
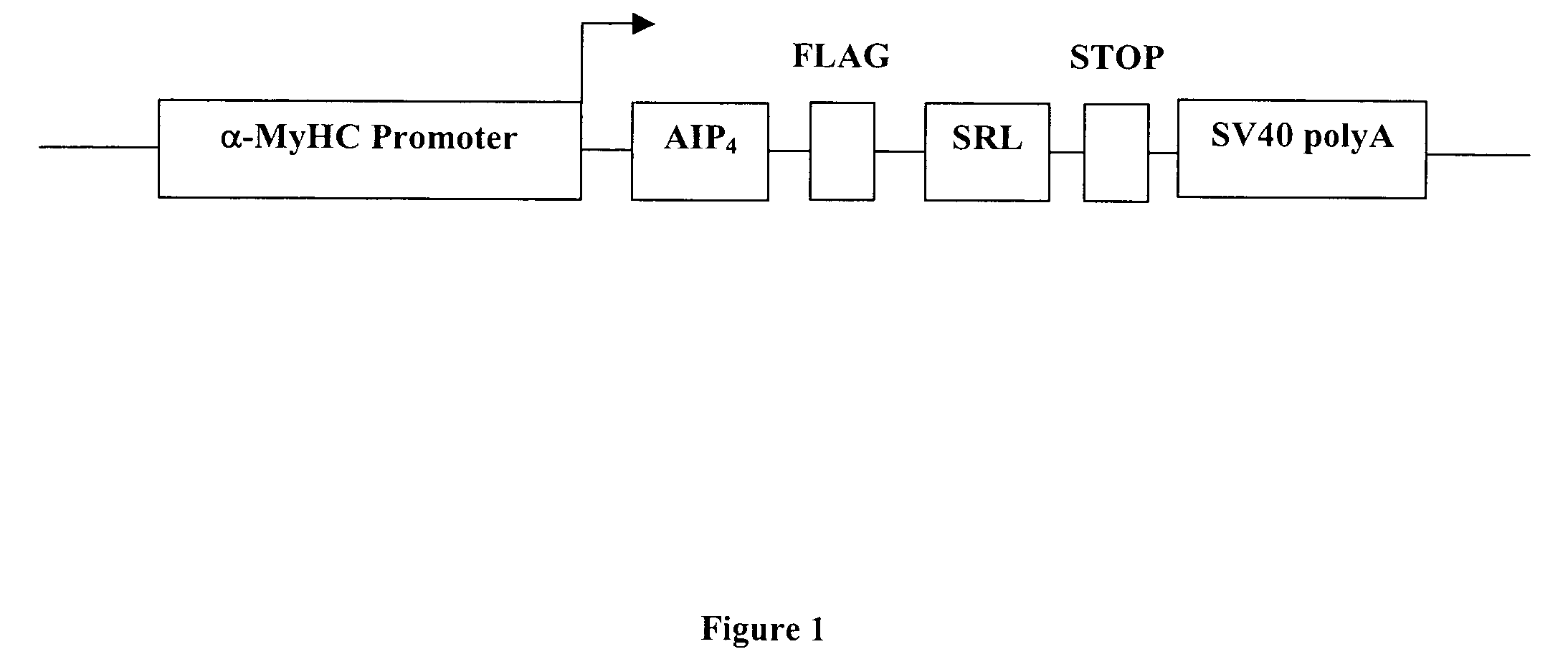
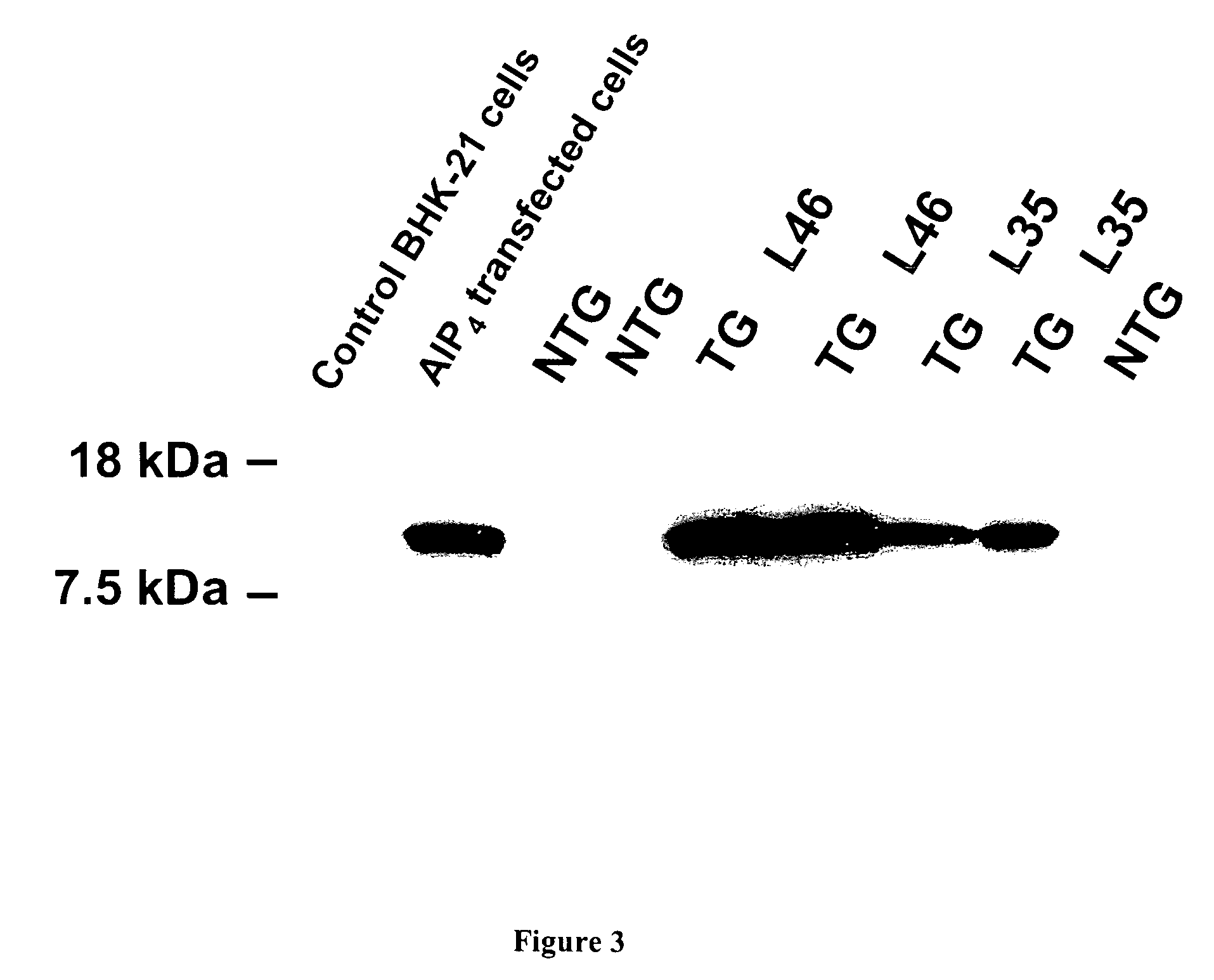
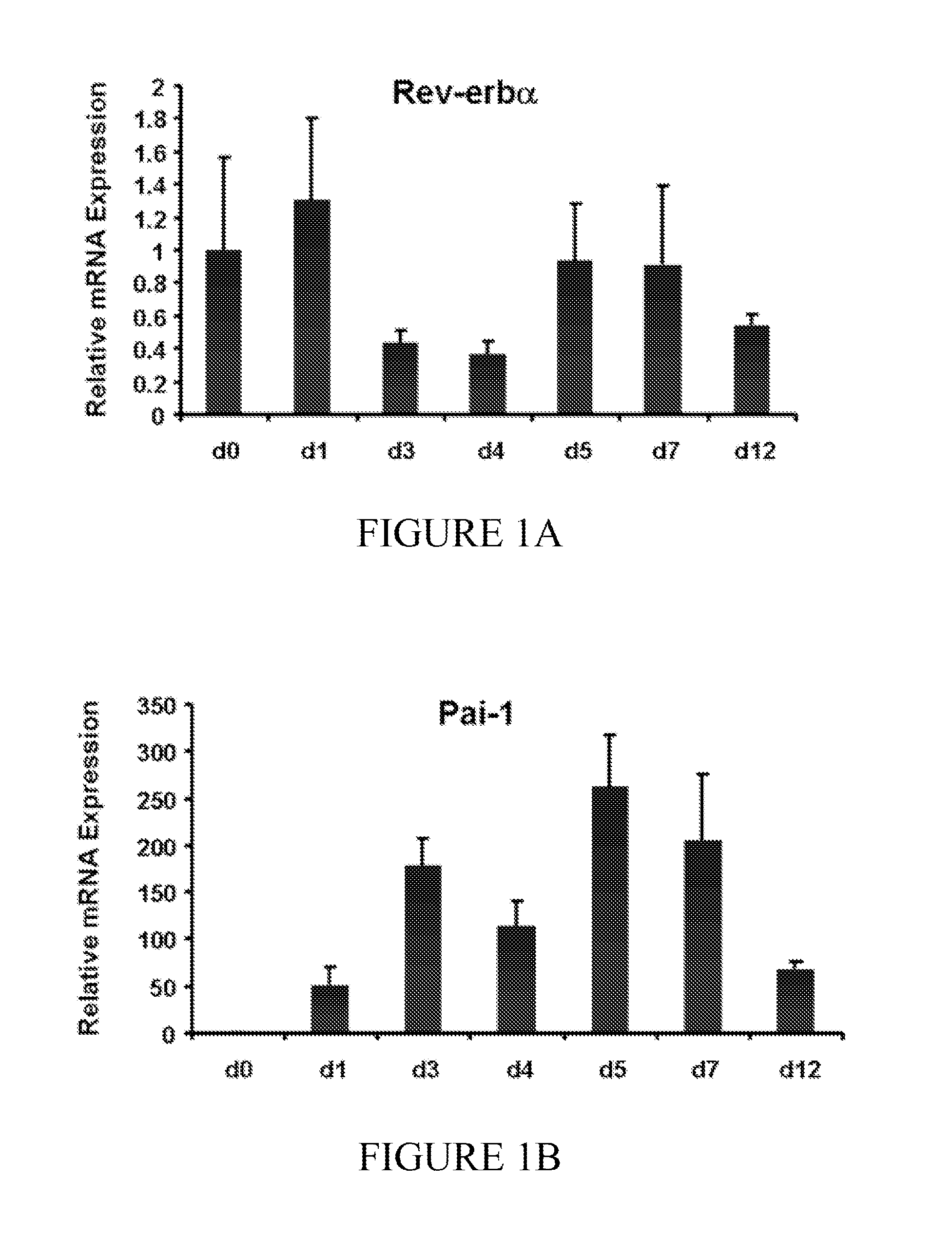
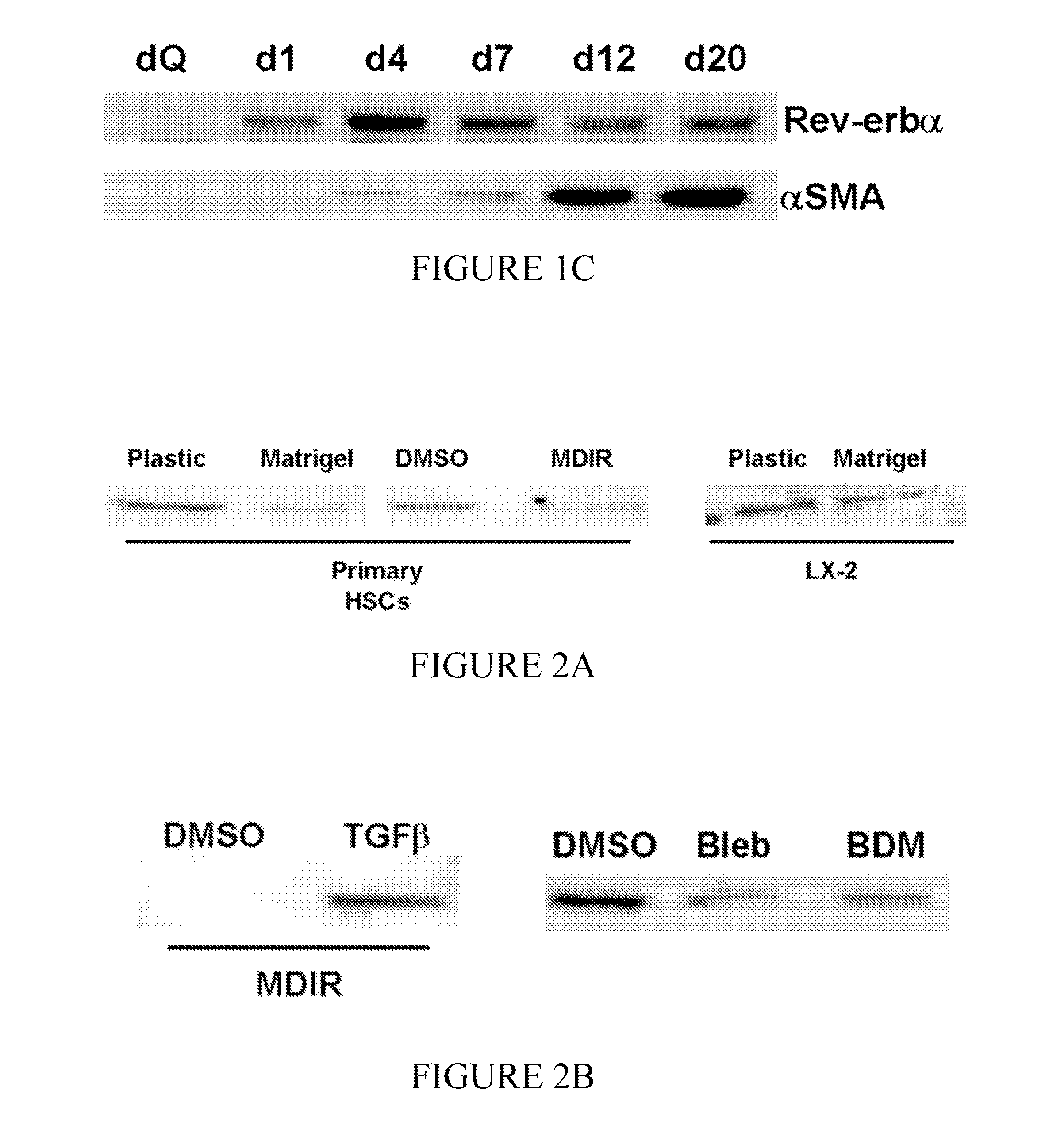
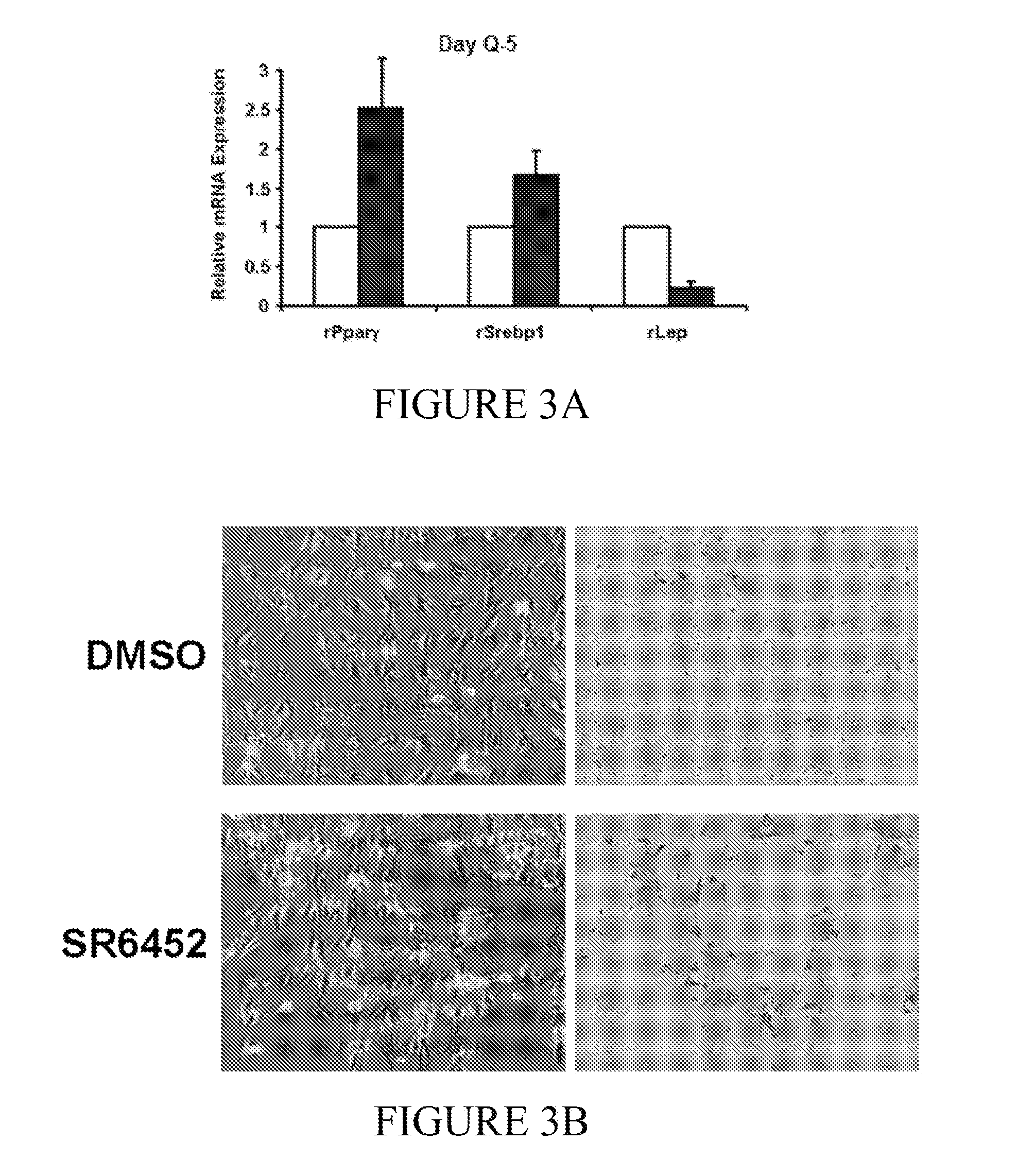
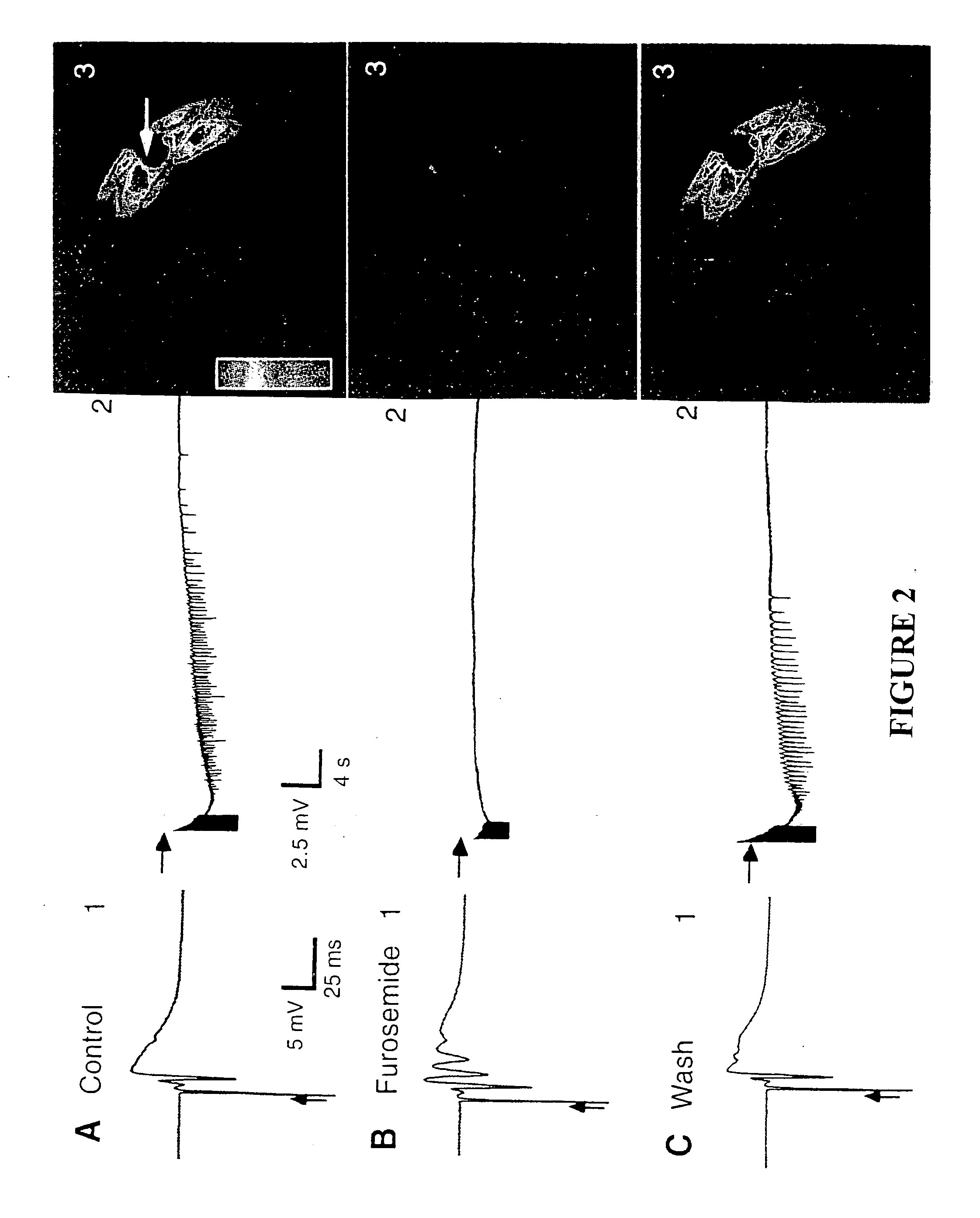
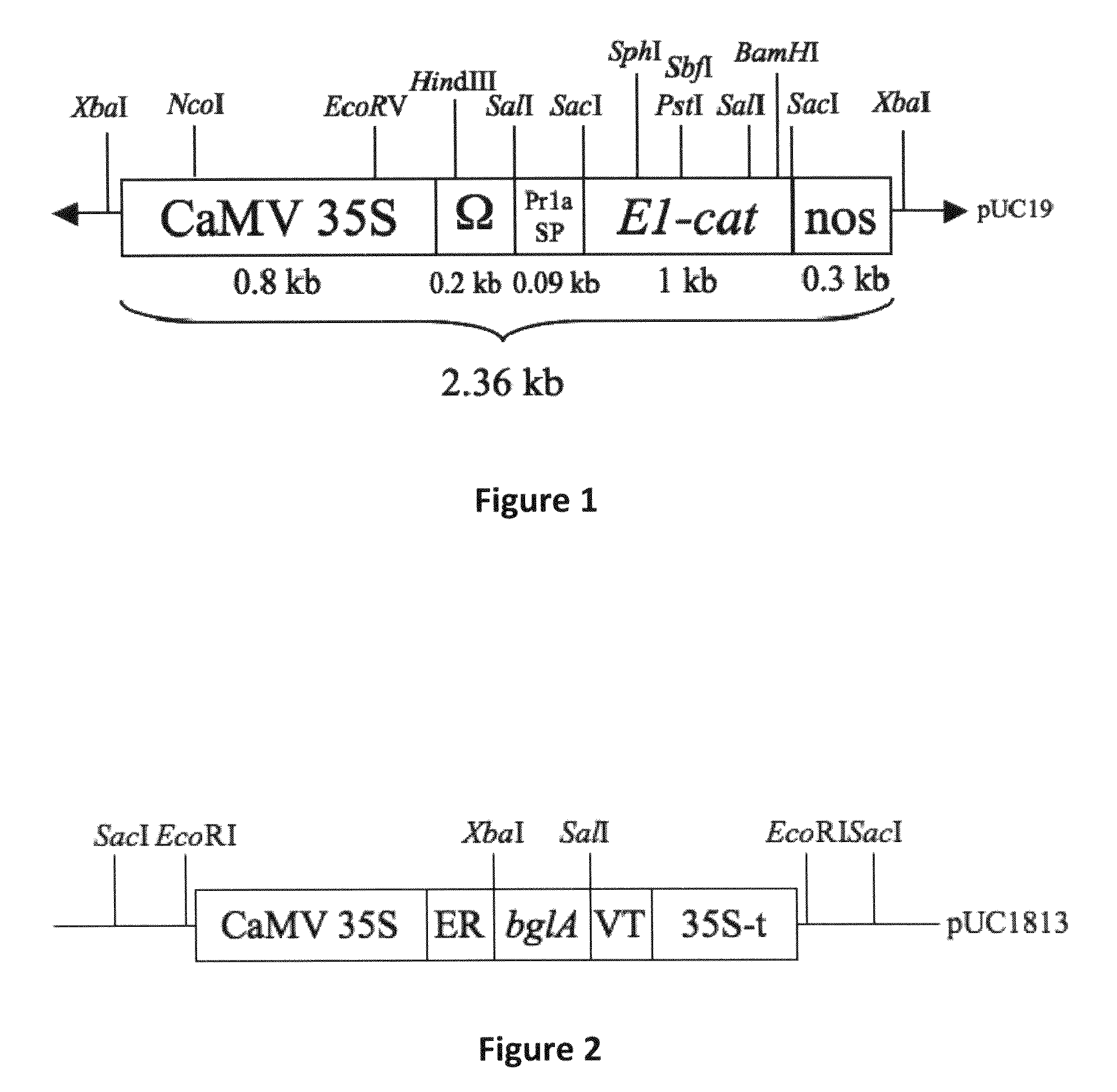
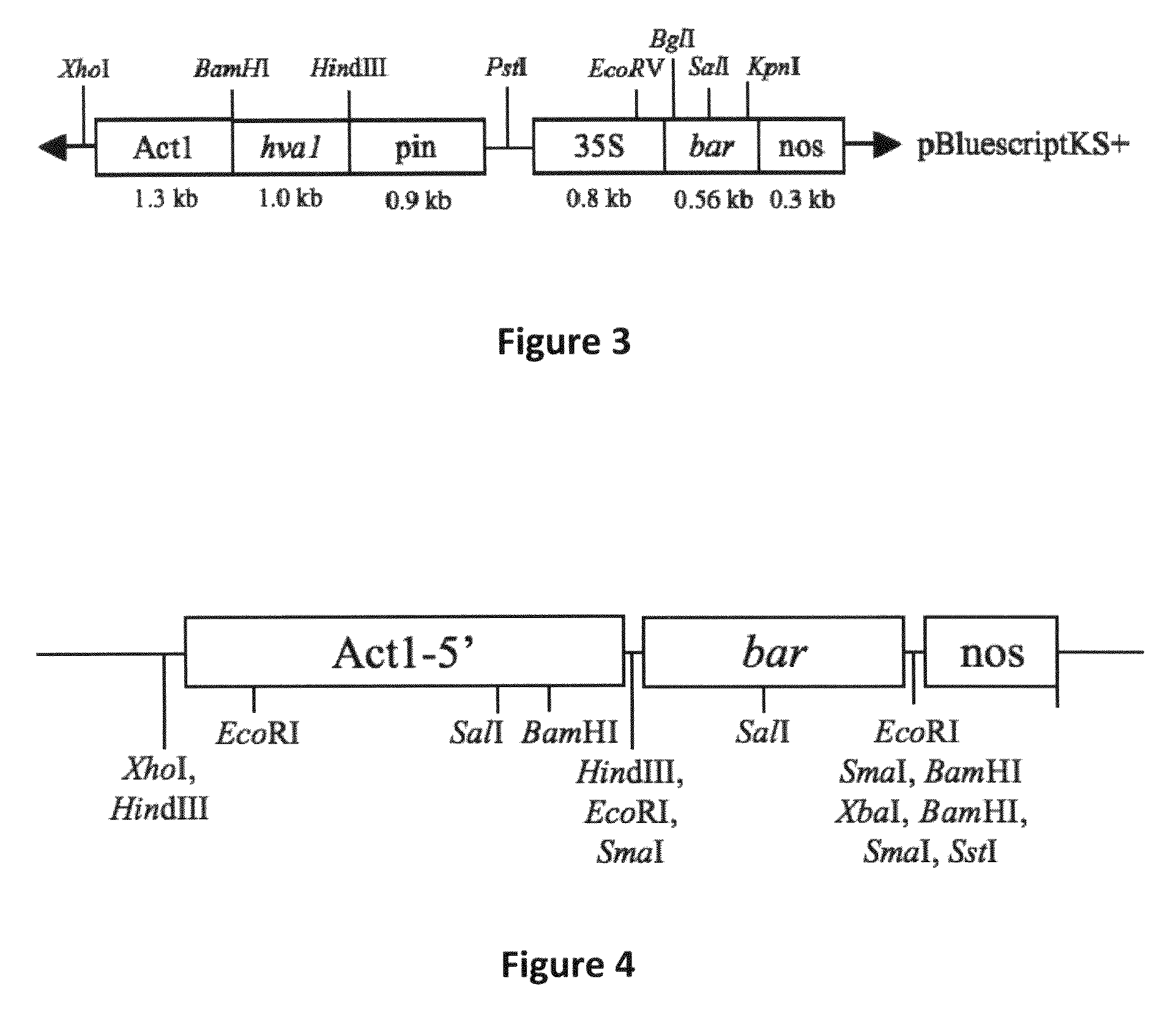
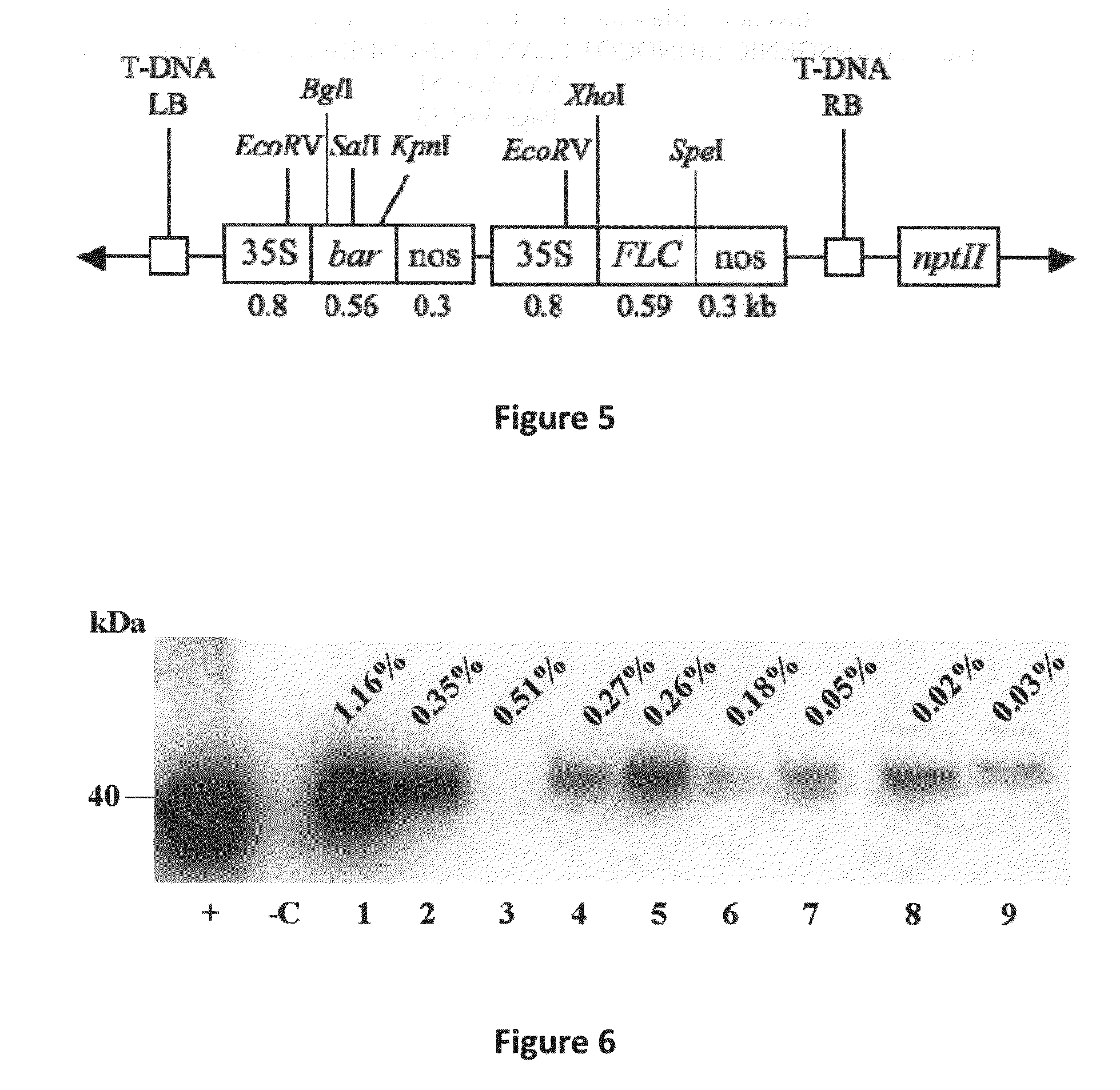
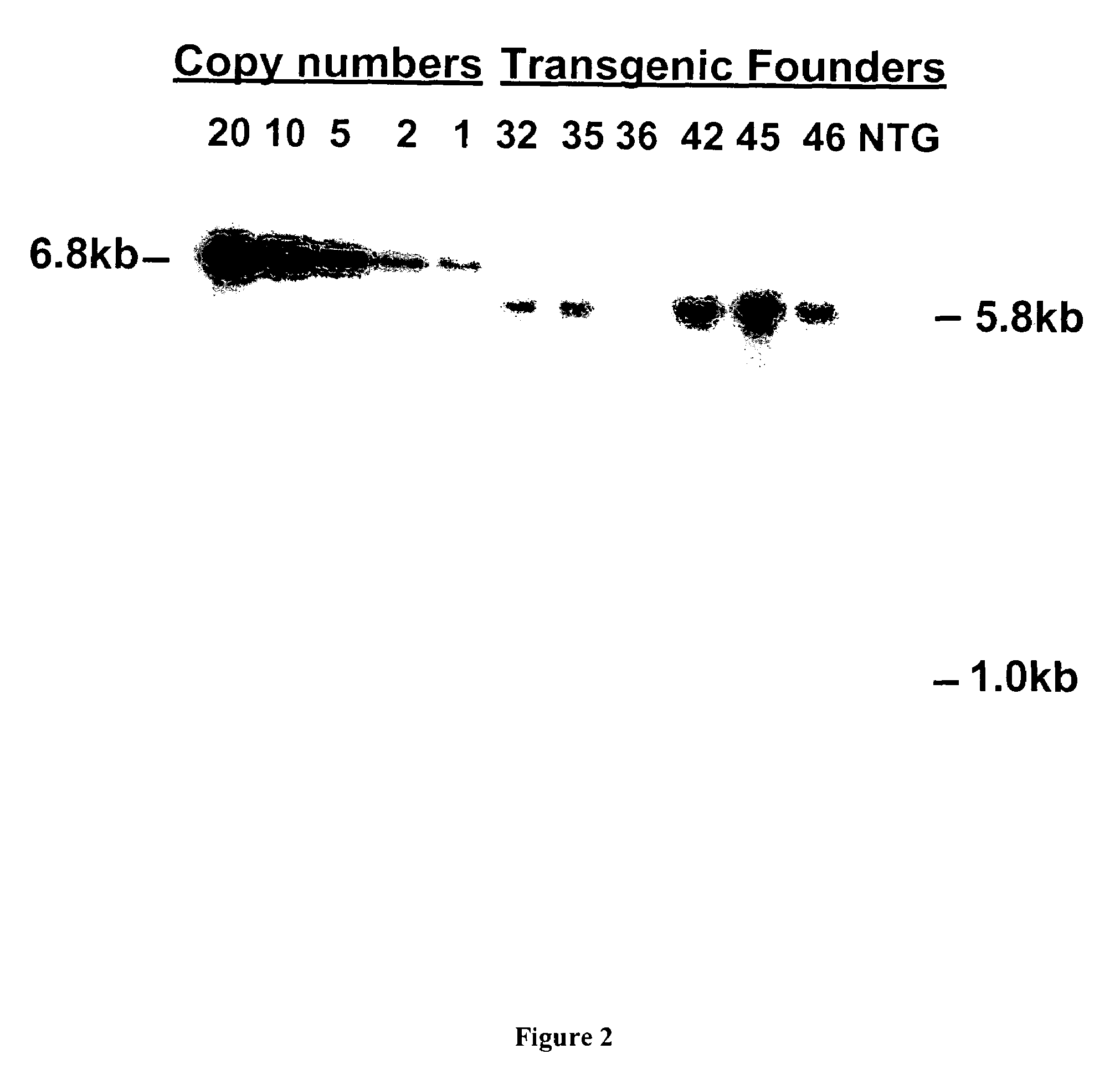Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
134 results about "Subcellular membrane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The cell membrane, or plasma membrane, is a biological membrane that surrounds the cytoplasm of a cell. In animals, the plasma membrane is the outer boundary of the cell, while in plants and prokaryotes it is usually covered by a cell wall.
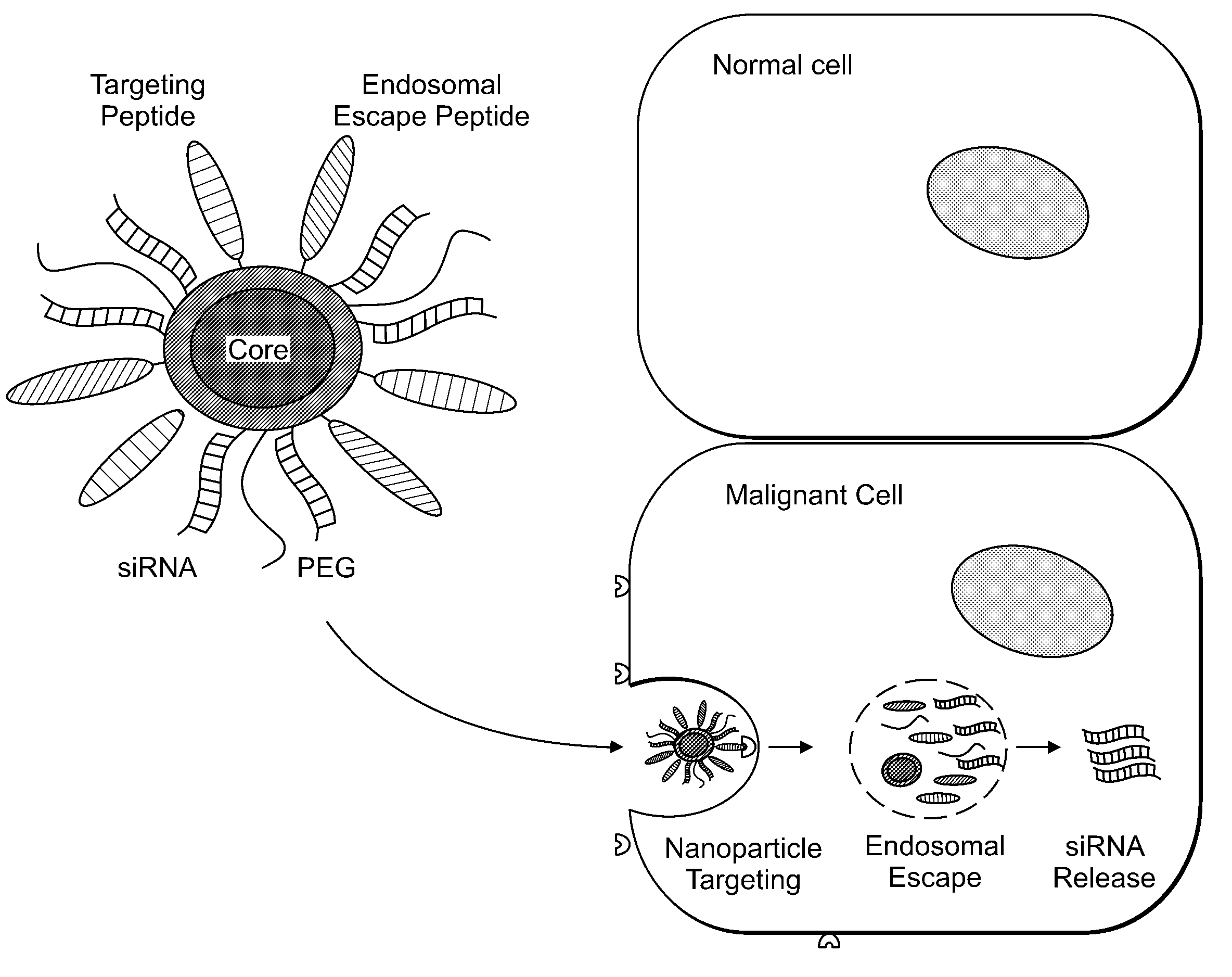
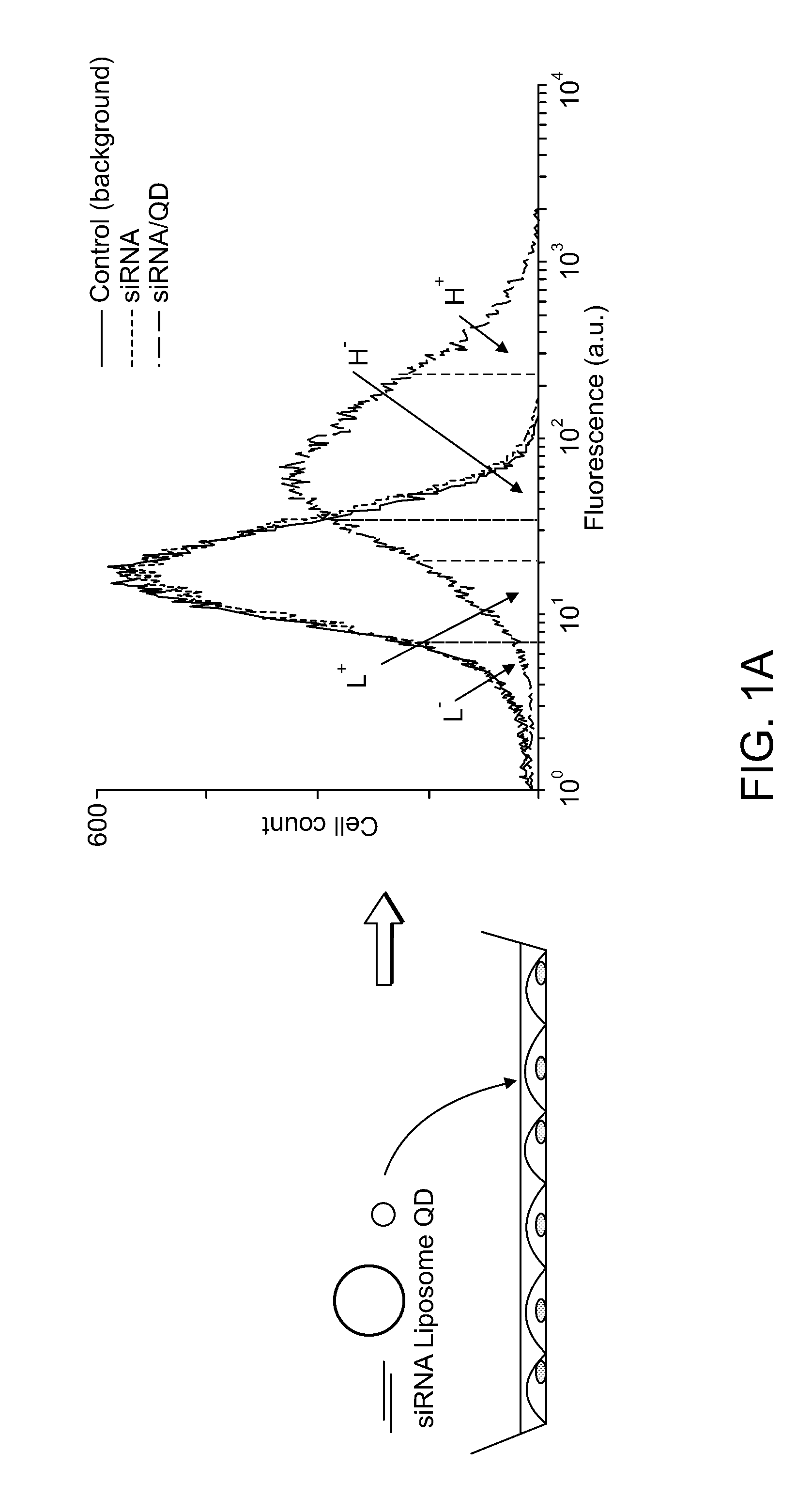
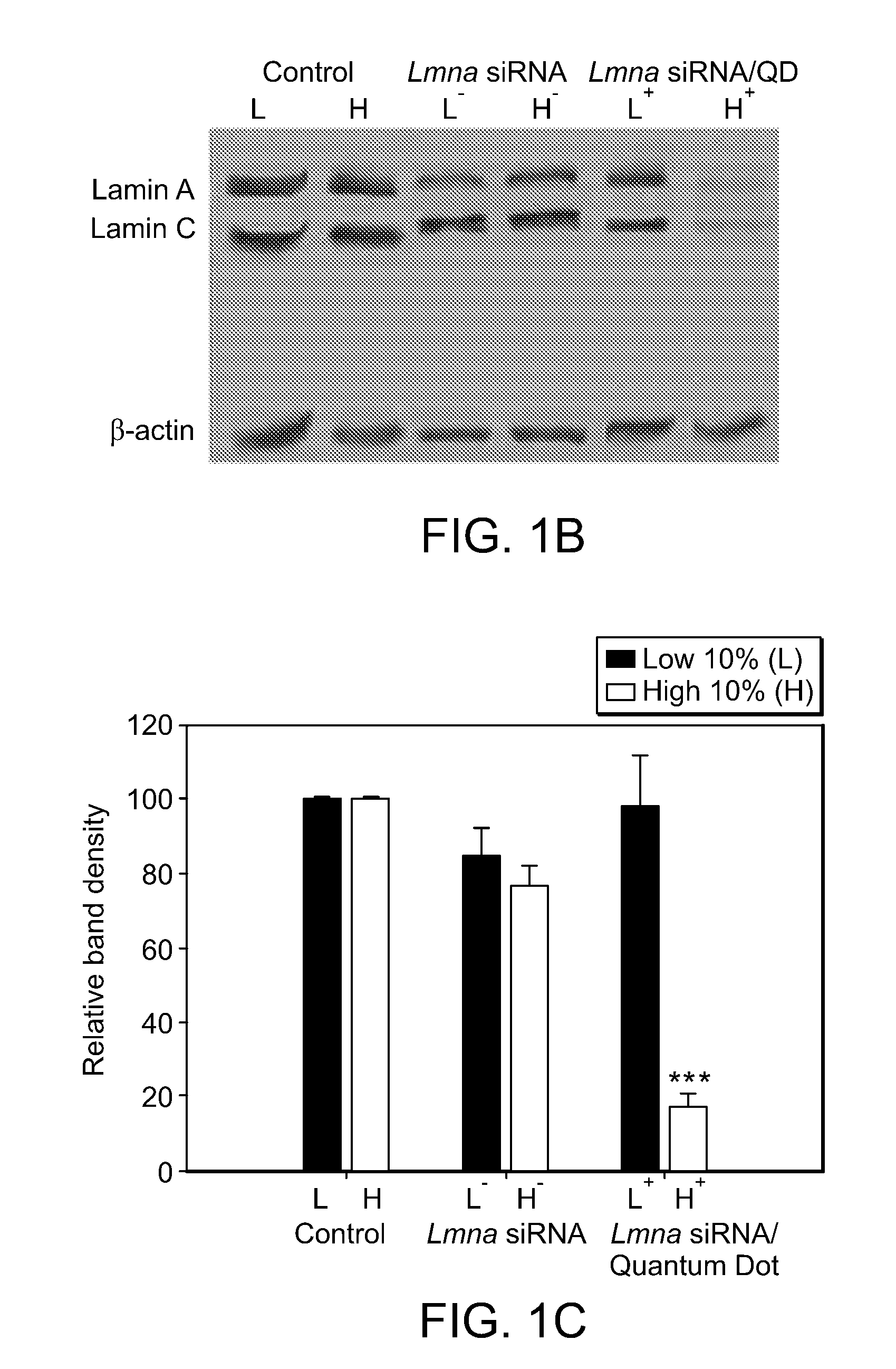
Delivery of Nanoparticles and/or Agents to Cells
InactiveUS20080213377A1Extended circulation timeReduce degradationPowder deliverySugar derivativesDiagnostic agentNanoparticle
The present invention provides systems, methods, and compositions for targeted delivery of nanoparticles and / or agents to tissues, cells, and / or subcellular locales. In general, compositions comprise a nanoparticle (e.g. quantum dot, polymeric particle, etc.), at least one modulating entity (such as a targeting moiety, transfection reagent, protective entity, etc.), and at least one agent to be delivered (e.g. therapeutic, prophylactic, and / or diagnostic agent). The present invention provides methods of making and using nanoparticle entities in accordance with the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Targeted therapeutic proteins
InactiveUS20050281805A1Extended half-lifeReduce the binding forcePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTherapeutic proteinLysosome
Targeted therapeutics that localize to a specific subcellular compartment such as the lysosome are provided. The targeted therapeutics include a therapeutic agent and a targeting moiety that binds a receptor on an exterior surface of the cell, permitting proper subcellular localization of the targeted therapeutic upon internalization of the receptor. Nucleic acids, cells, and methods relating to the practice of the invention are also provided.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
Subcellular targeting of therapeutic proteins
InactiveUS7396811B2Convenient treatmentSimple preparation processNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsLysosomeTherapeutic protein
Targeted therapeutics that localize to a specific subcellular compartment such as the lysosome are provided. The targeted therapeutics include a therapeutic agent and a targeting moiety that binds a receptor on an exterior surface of the cell, permitting proper subcellular localization of the targeted therapeutic upon internalization of the receptor. Nucleic acids, cells, and methods relating to the practice of the invention are also provided.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
Targeted therapeutic proteins
InactiveUS7560424B2Convenient treatmentSimple preparation processPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesLysosomeTherapeutic protein
Targeted therapeutics that localize to a specific subcellular compartment such as the lysosome are provided. The targeted therapeutics include a therapeutic agent and a targeting moiety that binds a receptor on an exterior surface of the cell, permitting proper subcellular localization of the targeted therapeutic upon internalization of the receptor. Nucleic acids, cells, and methods relating to the practice of the invention are also provided.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
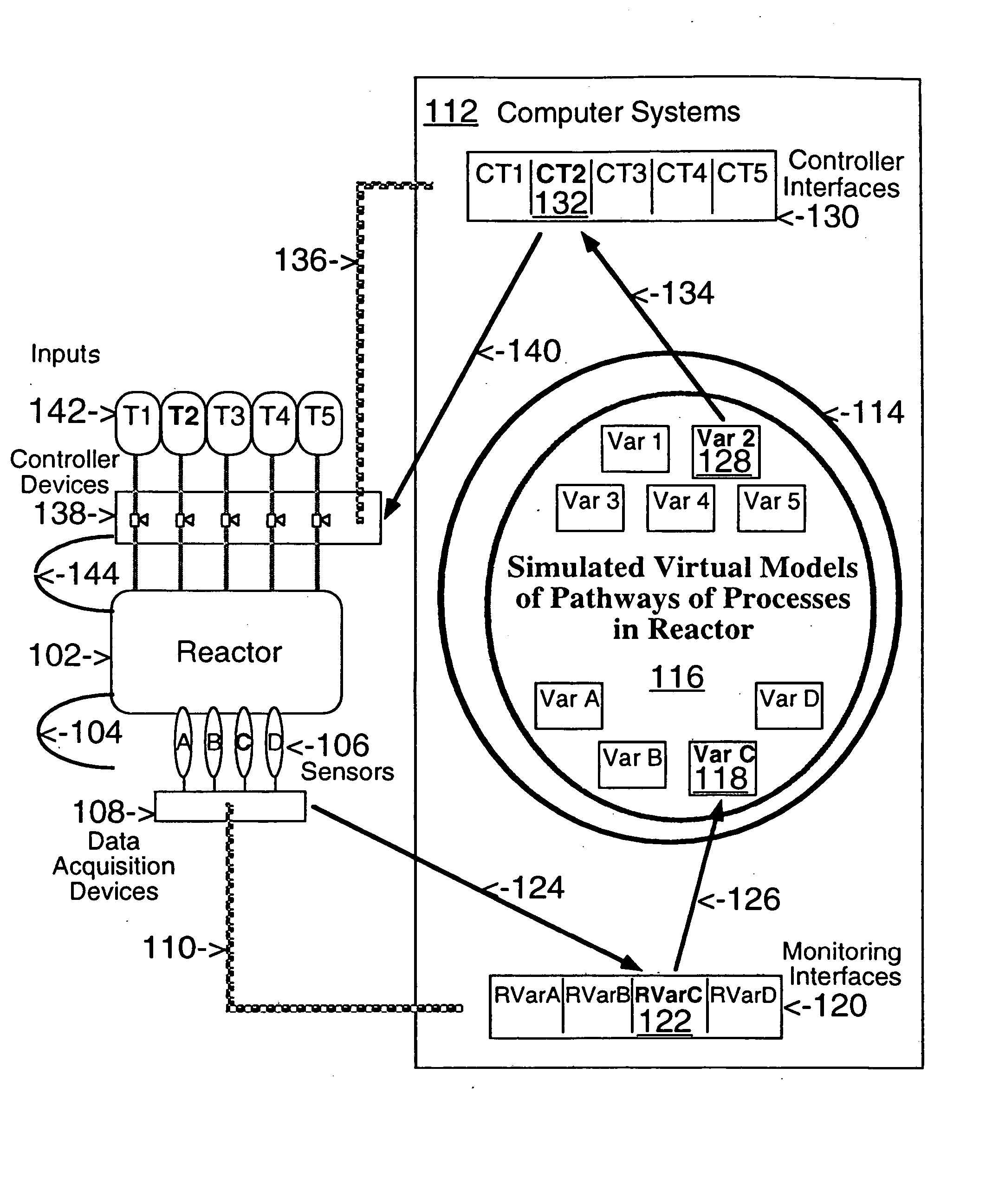
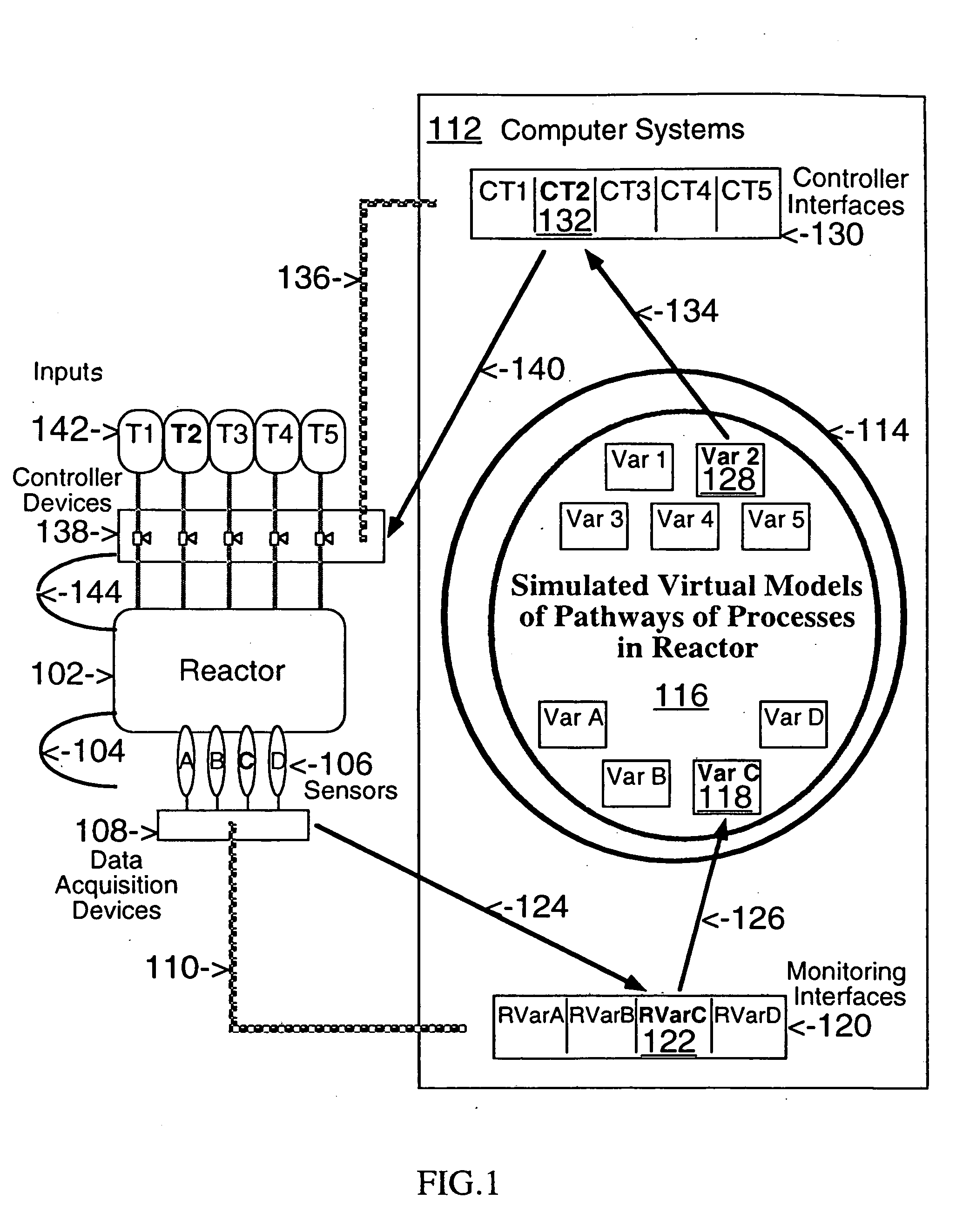
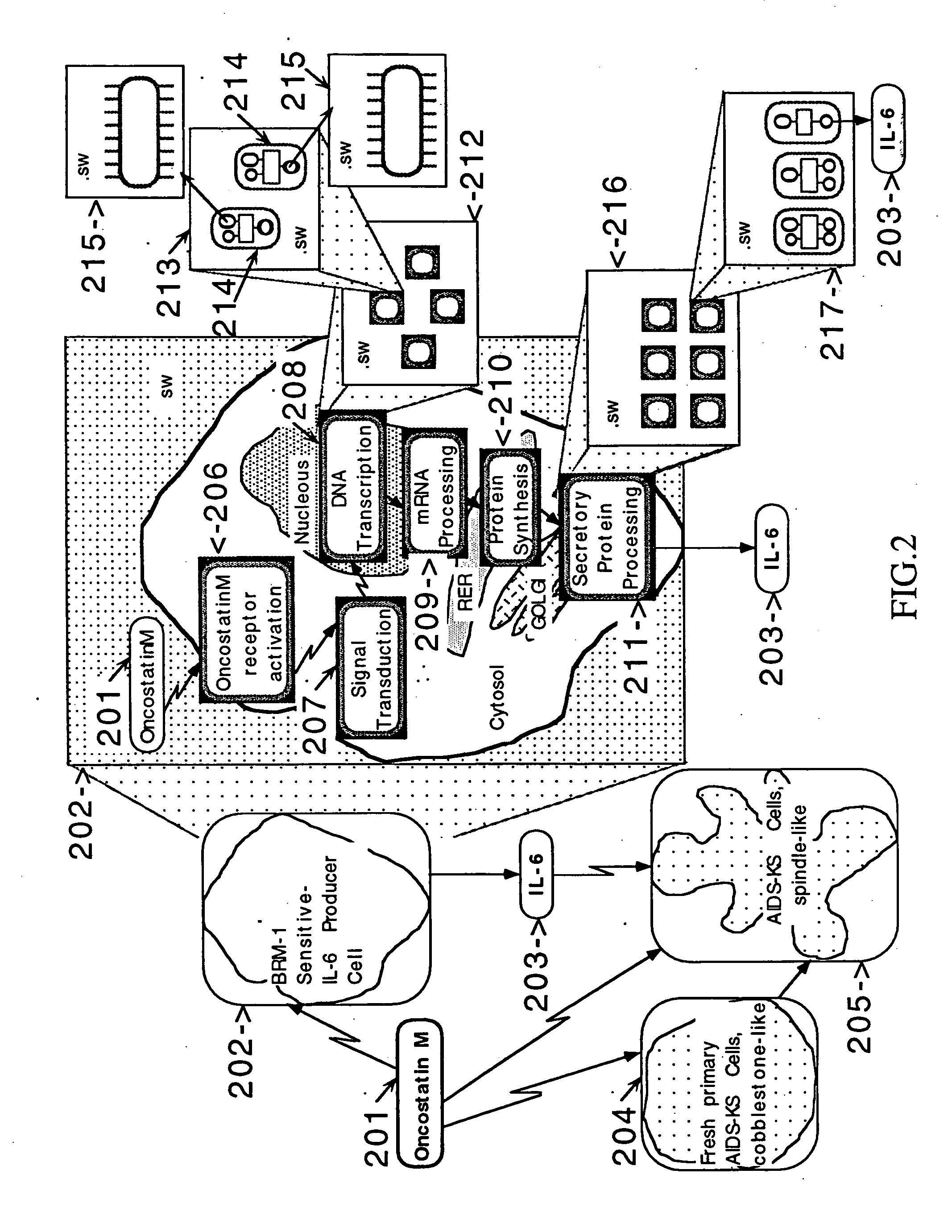
Network models of biological complex systems
This invention describes computer based systems and methods for modeling and simulation of complex biological systems from the cellular, or subcellular, to the organism and population level, for using said models to predict functions of components of the biological systems and to simulate physiological and pathological states at the various levels, and for using said models in drug development for testing in a computer system substances for possible use as therapeutics by simulating their effects on the physiological and pathological states.
Owner:INTERTECH VENTURES
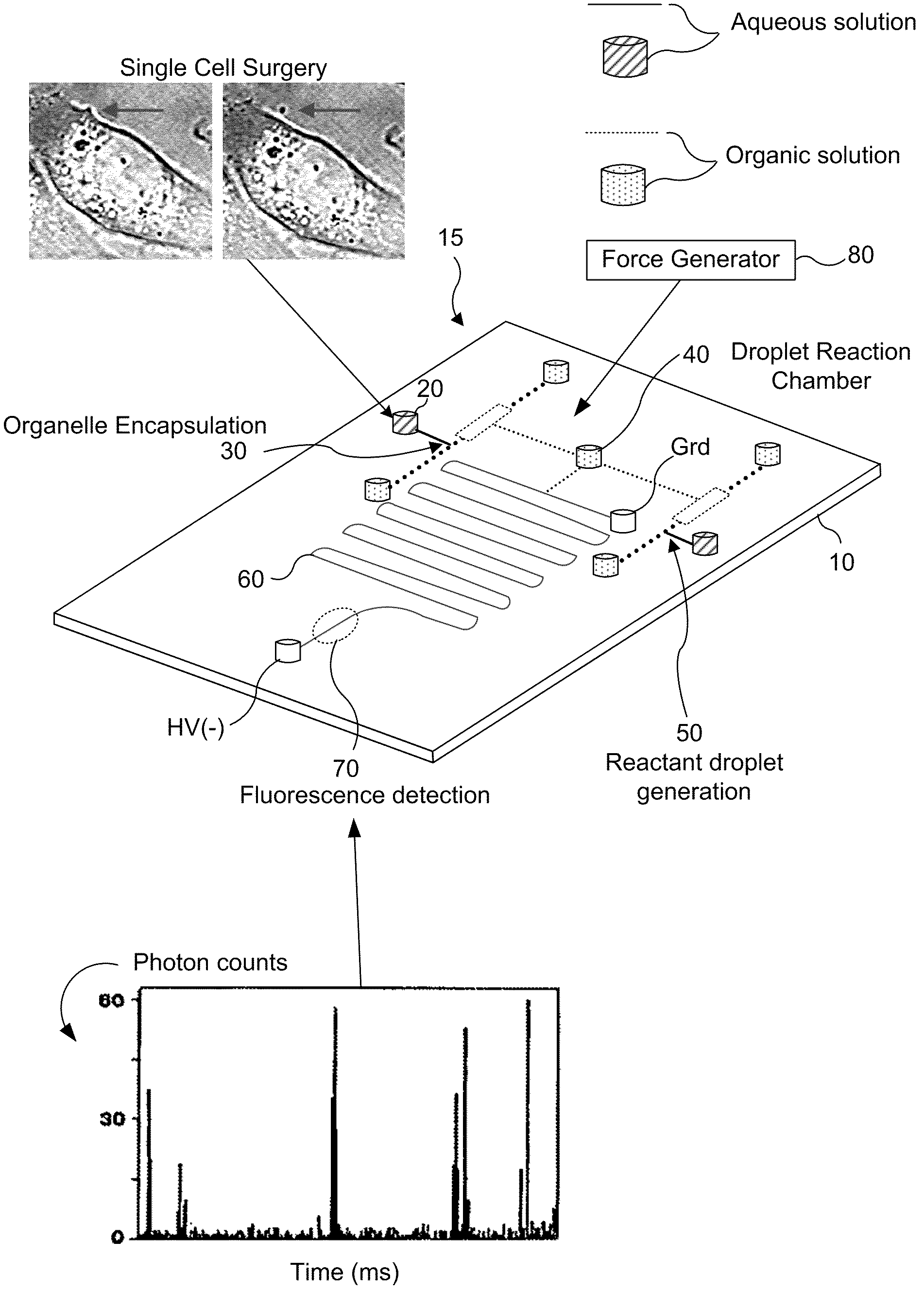
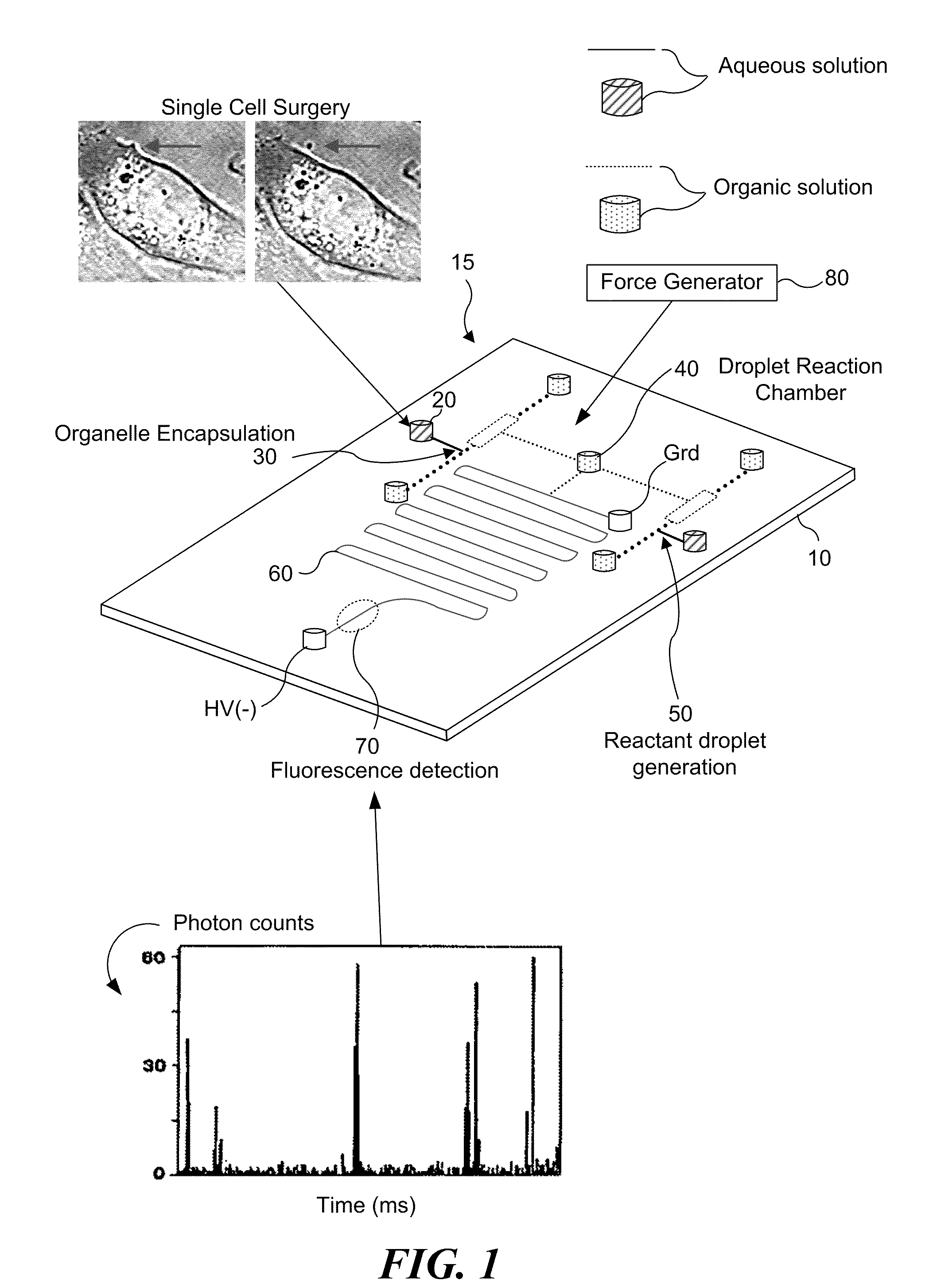
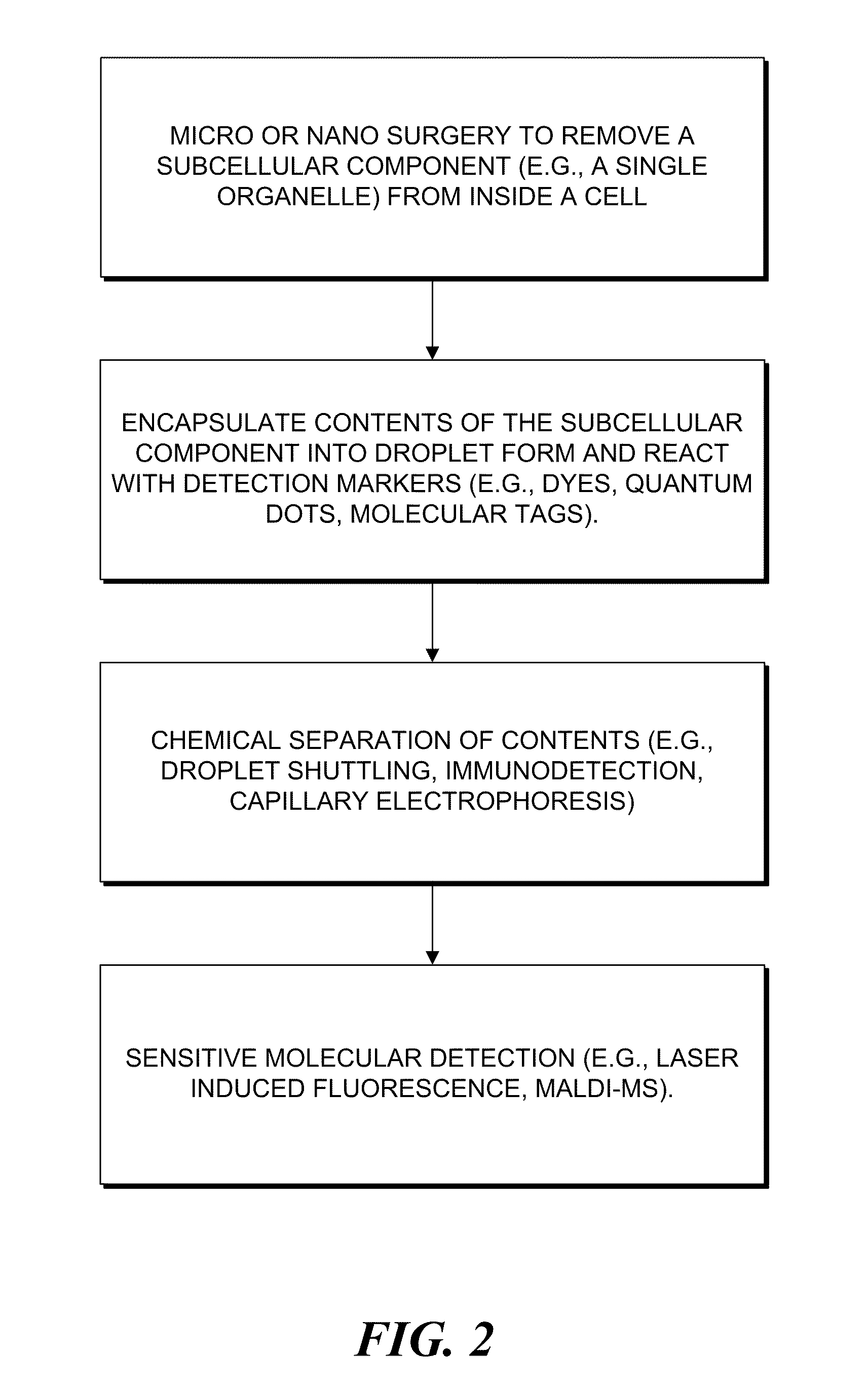
Method and device for biochemical detection and analysis of subcellular compartments from a single cell
InactiveUS7767435B2Improve spatial resolutionMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological cellIntegration platform
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
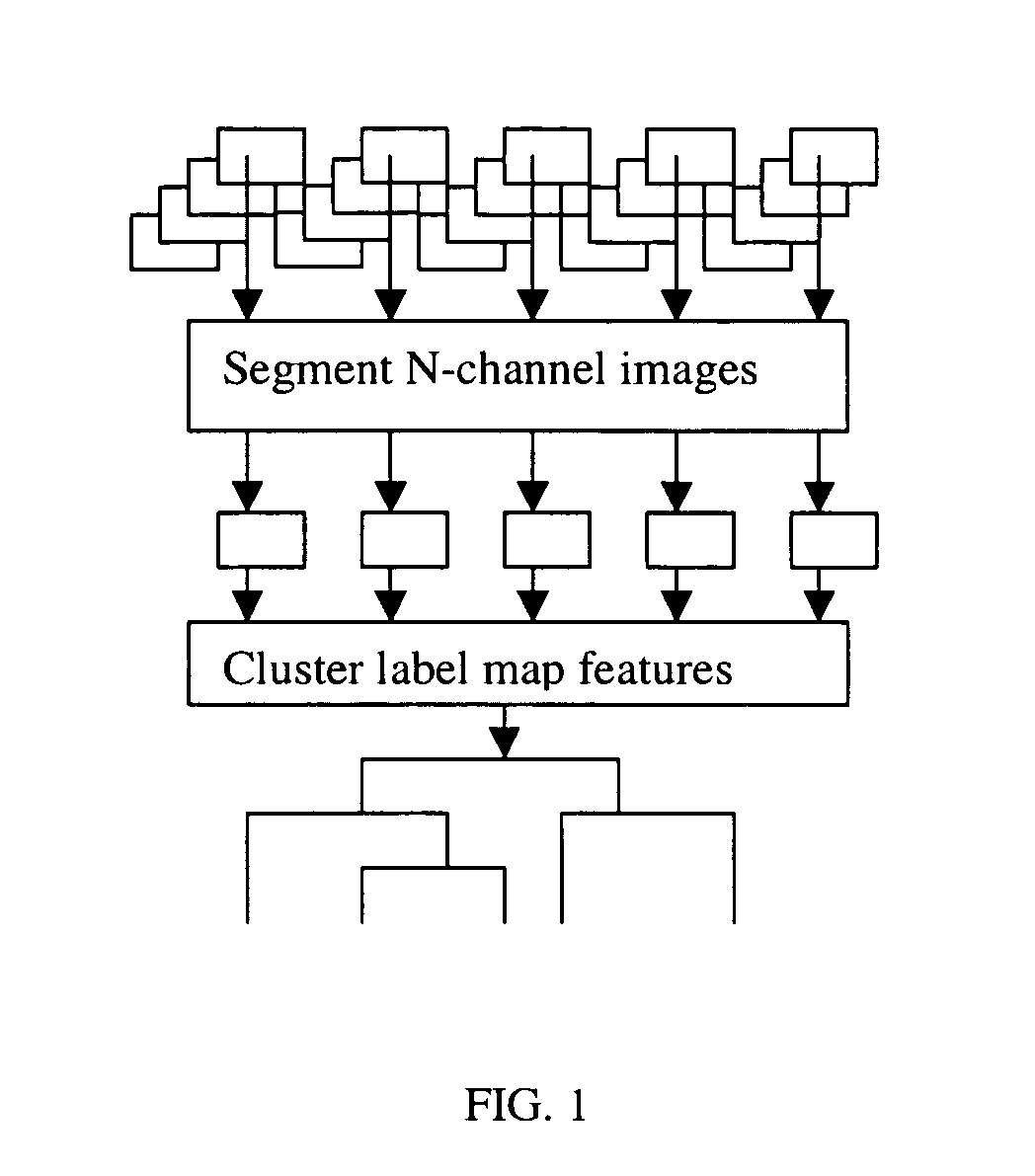
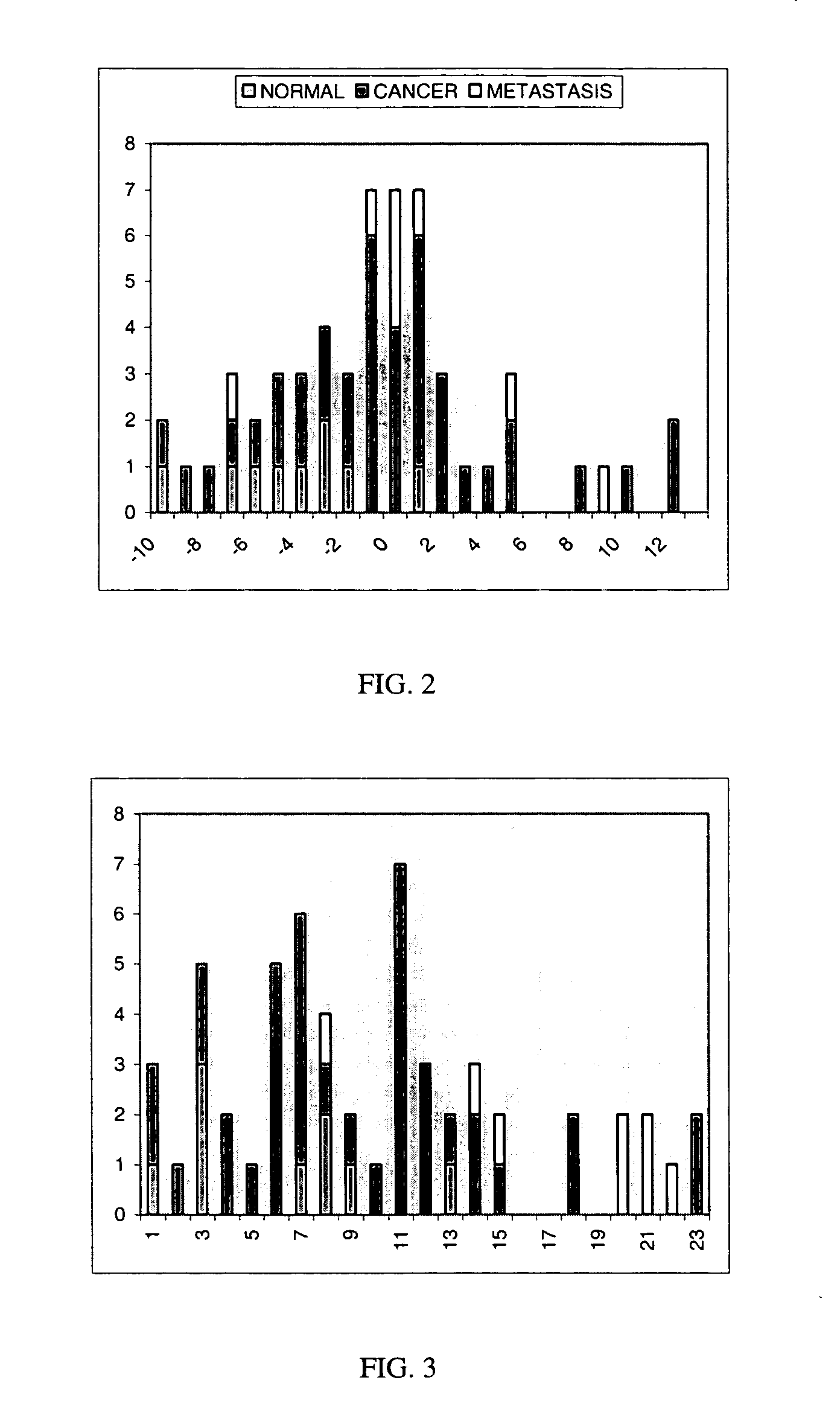
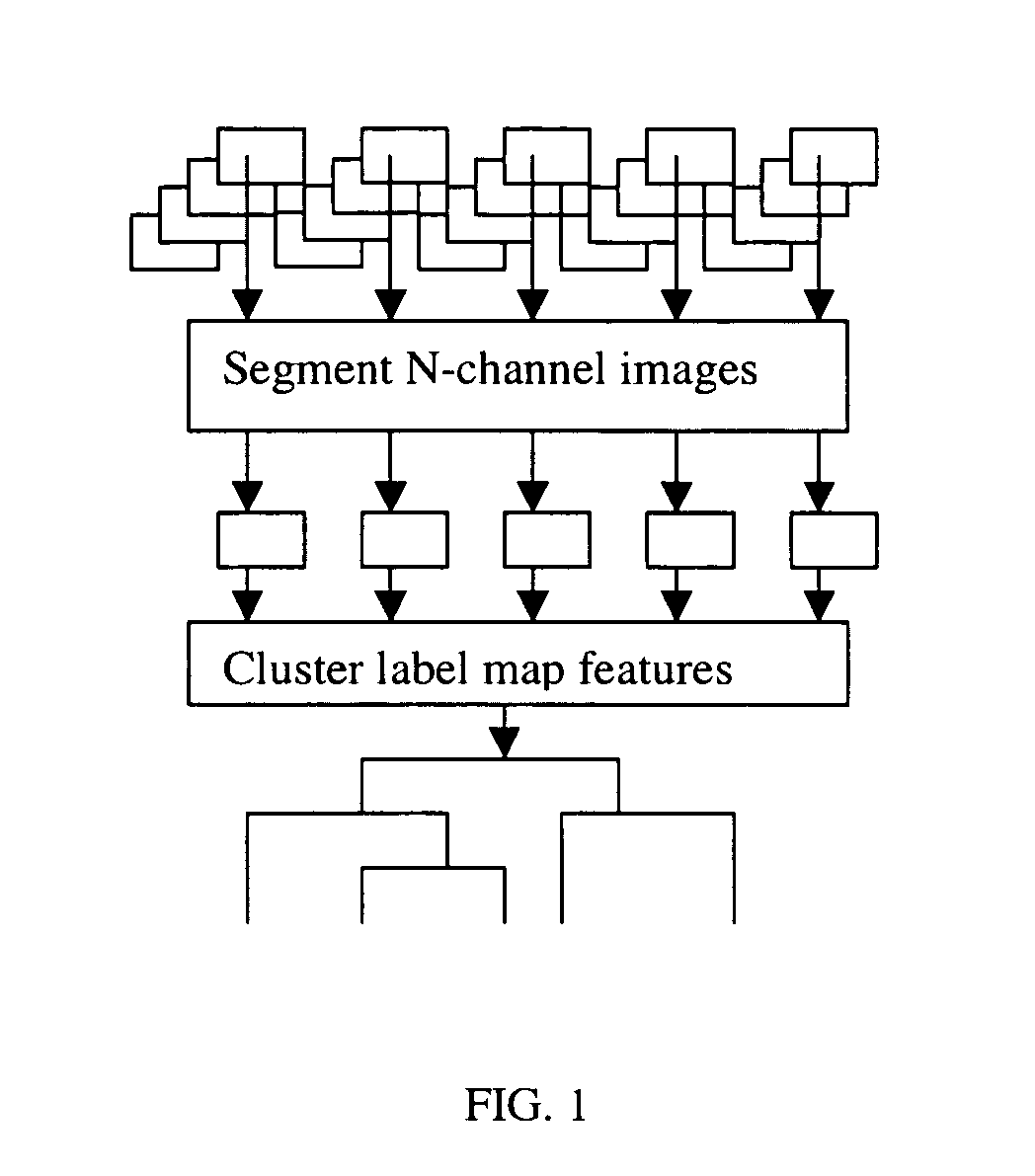
System and methods for scoring images of a tissue micro array
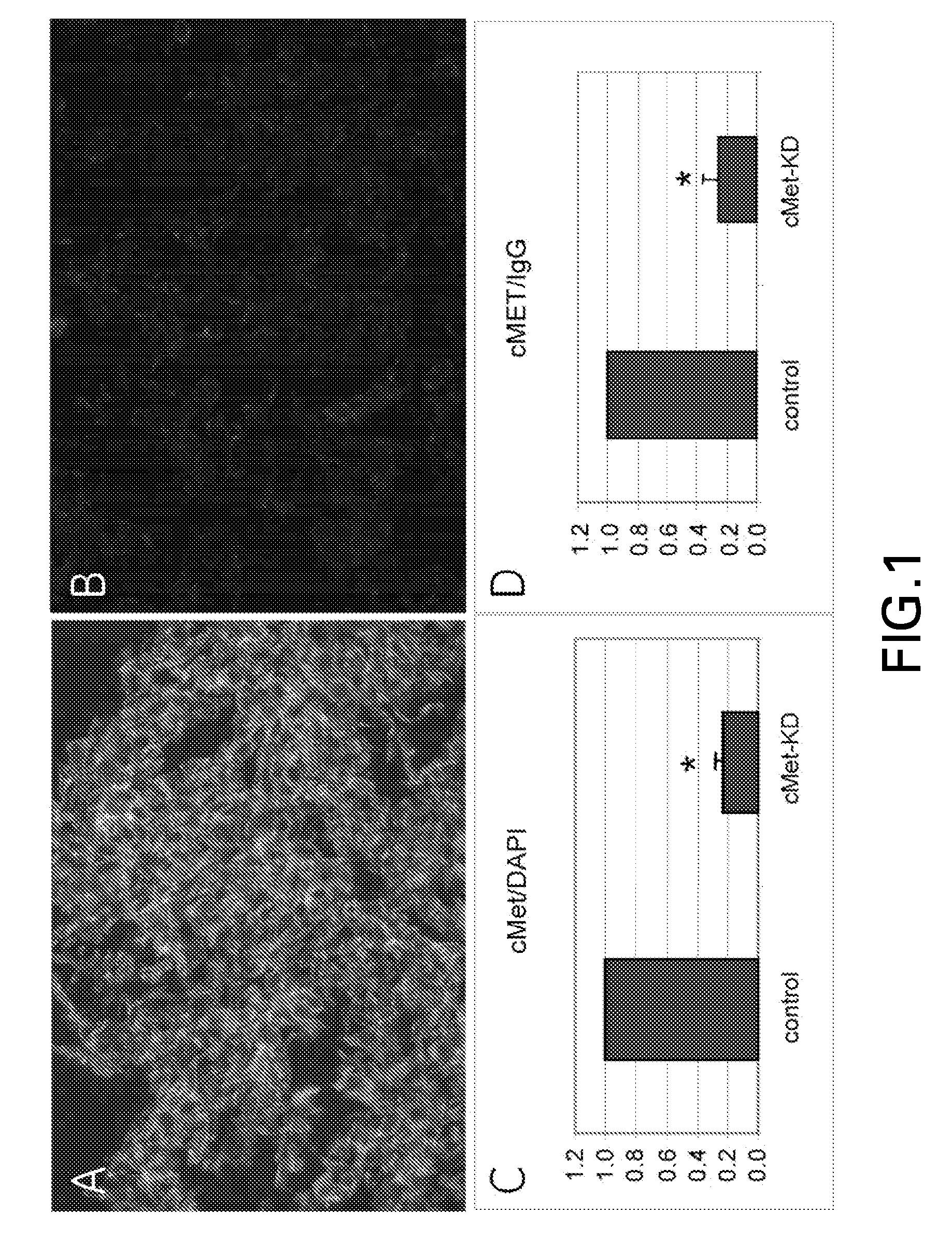
A system for analyzing tissue samples, that generally comprises, a storage device for at least temporarily storing one or more images of one or more cells, wherein the images comprise a plurality of channels; and a processor that is adapted to determine the extent to which a biomarker may have translocated from at least one subcellular region to another subcellular region; and then to generate a score corresponding to the extent of translocation.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Signal for targeting molecules to the sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum
Owner:NEWVA CAPITAL PARTNERS LP
Chemical address tags
The present invention provides methods and compositions related to the fields of chemoinformatics, chemogenomics, drug discovery and development, and drug targeting. In particular, the present invention provides subcellular localization signals (e.g., chemical address tags) that influence (e.g., direct) subcellular and organelle level localization of associated compounds (e.g., drugs and small molecule therapeutics, radioactive species, dyes and imagining agents, proapoptotic agents, antibiotics, etc) in target cells and tissues. The compositions of the present invention modulate the pharmacological profiles of associated compounds by influencing the compound's accumulation, or exclusion, from subcellular loci such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, cytoplasm, vesicles, granules, nuclei and nucleoli and other subcellular organelles and compartments. The present invention also provides methods for identifying chemical address tags, predicting their targeting characteristics, and for rational designing chemical libraries comprising chemical address tags.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Circulating flow device for assays of cell cultures, cellular components and cell products
InactiveUS20050266393A1Fast resultsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCellular componentCell substance
In vitro culture devices and methods are described. The subject methods and devices provide a means whereby cells and / or subcellular material are grown or held in a culture device that maintains the cells and / or subcellular material in a physiologically representative environment, thereby improving the predictive value of toxicity and metabolism assays, and the relevance of experimental results derived from such assays to actual in vivo conditions, processes and outcomes. The culture devices of the invention comprise a fluidic channel connected to or otherwise integrated with at least one chamber, preferably integrated in a chip format. The specific chamber geometry is designed to provide cellular interactions, liquid flow, and liquid residence and other parameter values that correlate with those found in or produced by the corresponding cell, organs or tissues, or components or products thereof, in vivo. Each device comprises at least one chamber and at least one inlet and one outlet port that allow for recirculation of the culture medium. The device will usually include a mechanism for obtaining signals from the cells and culture medium.
Owner:ATHENA CAPITAL PARTNERS
Targeted therapeutic proteins
InactiveUS7629309B2Convenient treatmentSimple preparation processPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTherapeutic proteinLysosome
Targeted therapeutics that localize to a specific subcellular compartment such as the lysosome are provided. The targeted therapeutics include a therapeutic agent and a targeting moiety that binds a receptor on an exterior surface of the cell, permitting proper subcellular localization of the targeted therapeutic upon internalization of the receptor. Nucleic acids, cells, and methods relating to the practice of the invention are also provided.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
Apparatus and method for cell migration assays
InactiveUS20080032324A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFiberCell Migration Assay
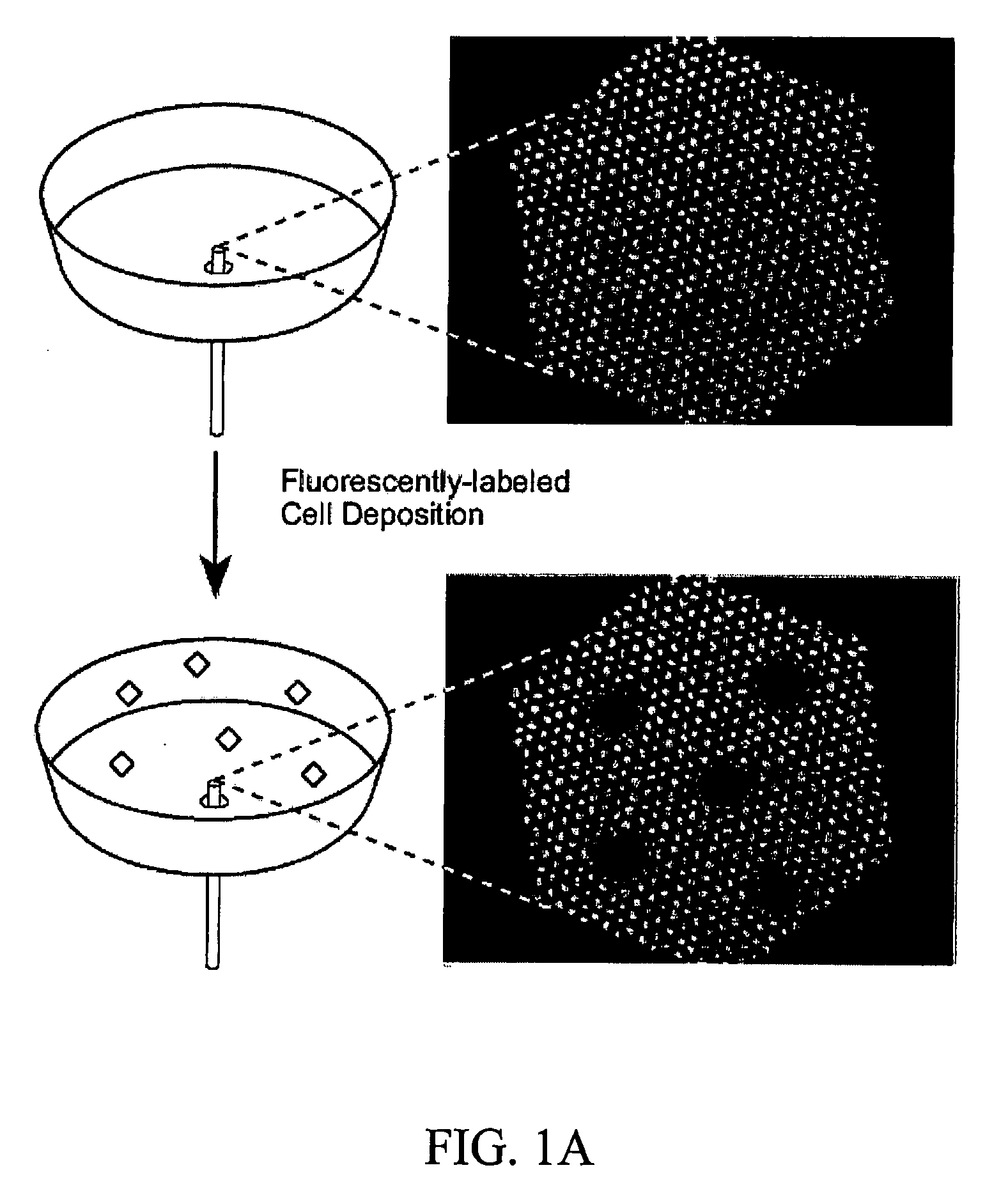
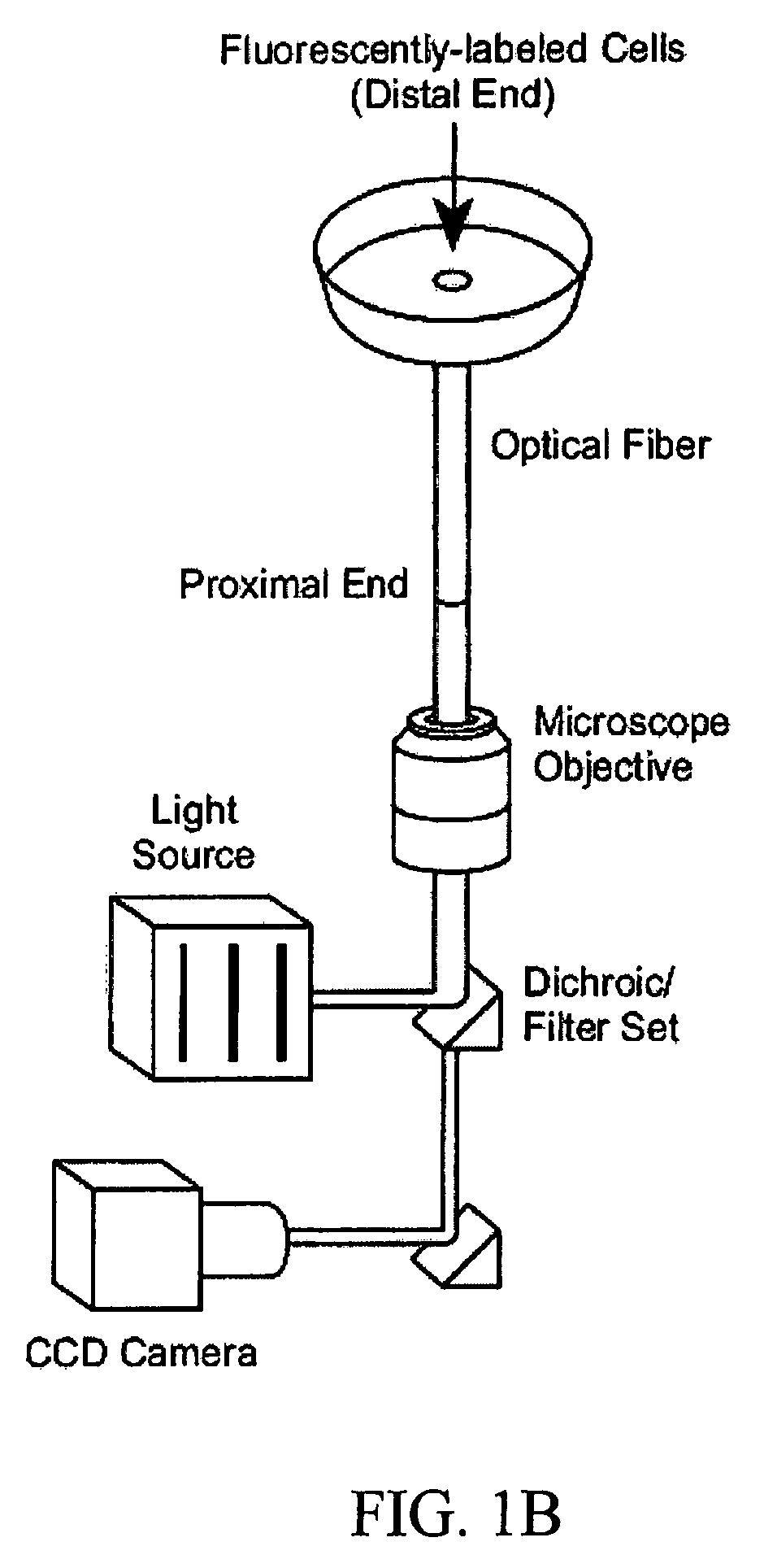
The present invention is directed to a method and apparatus for detecting and analyzing cell migration. More specifically, the present invention is directed to novel technology for analyzing cellular movement, including whole cell migration and subcellular component movement. Cells are distributed onto a substrate and monitored for migration or movement. According to one embodiment, when a labelled cell or portion of a cell passes over one of the delineations between detection units, such as individual fibers in a fiber optic bundle, the label causes a large intensity increase, which stays for a given “residence time” until the cell departs from the detection unit.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGETHE
Targeted therapeutic proteins
InactiveUS20090203575A1Convenient treatmentSimple preparation processPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsLysosomeTherapeutic protein
Targeted therapeutics that localize to a specific subcellular compartment such as the lysosome are provided. The targeted therapeutics include a therapeutic agent and a targeting moiety that binds a receptor on an exterior surface of the cell, permitting proper subcellular localization of the targeted therapeutic upon internalization of the receptor. Nucleic acids, cells, and methods relating to the practice of the invention are also provided.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
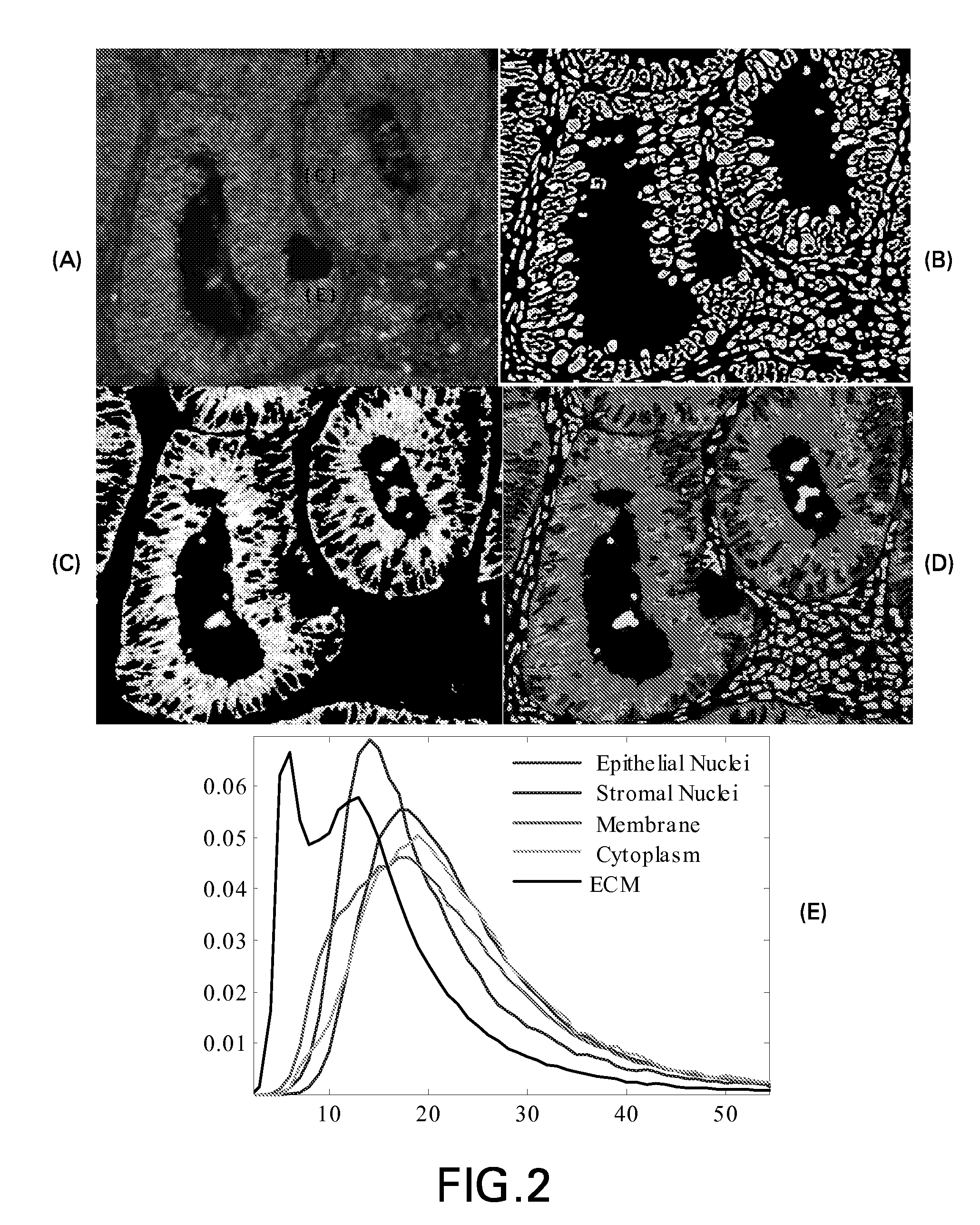
System and methods for analyzing images of tissue samples
A system for analyzing tissue samples, comprising: a storage device for at least temporarily storing one or more images of one or more cells, wherein at least one of the images is indicative of one or more channels comprising a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK); and a processing device that determines an extent to which one or more of the RTKs may have translocated from at least one subcellular region to another subcellular region of one or more of the cells; and generates a score based at least in part on the RTK translocation.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Transmission electron microscope processing method for insect antenna samples
ActiveCN103115809AEffective immobilizationEffective preservationPreparing sample for investigationElectron microscopeBiology
The invention belongs to the field of experimental sample processing technologies, relates to insect antenna sample processing methods and particularly relates to a transmission electron microscope processing method for insect antenna samples. The method sequentially comprises the following steps of: (A) preparing fixing liquid; (B) preparing various embedding agents; (C) dissecting, fixing and rinsing; (D) dewatering and soaking; and (E) gathering, so as to obtain the samples. The method has the advantages that the problems of difficulty in fixing liquid soaking and insufficiency in embedding agent soaking during the process of insect antenna transmission processing are solved, finally-obtained sample slices can be relatively flat, the phenomena of sample wrinkling, damaging and losing are greatly reduced, internal structures of the sample slices are all effectively fixed, and subcellular structures are clearly visible.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Systems for analyzing tissue samples
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
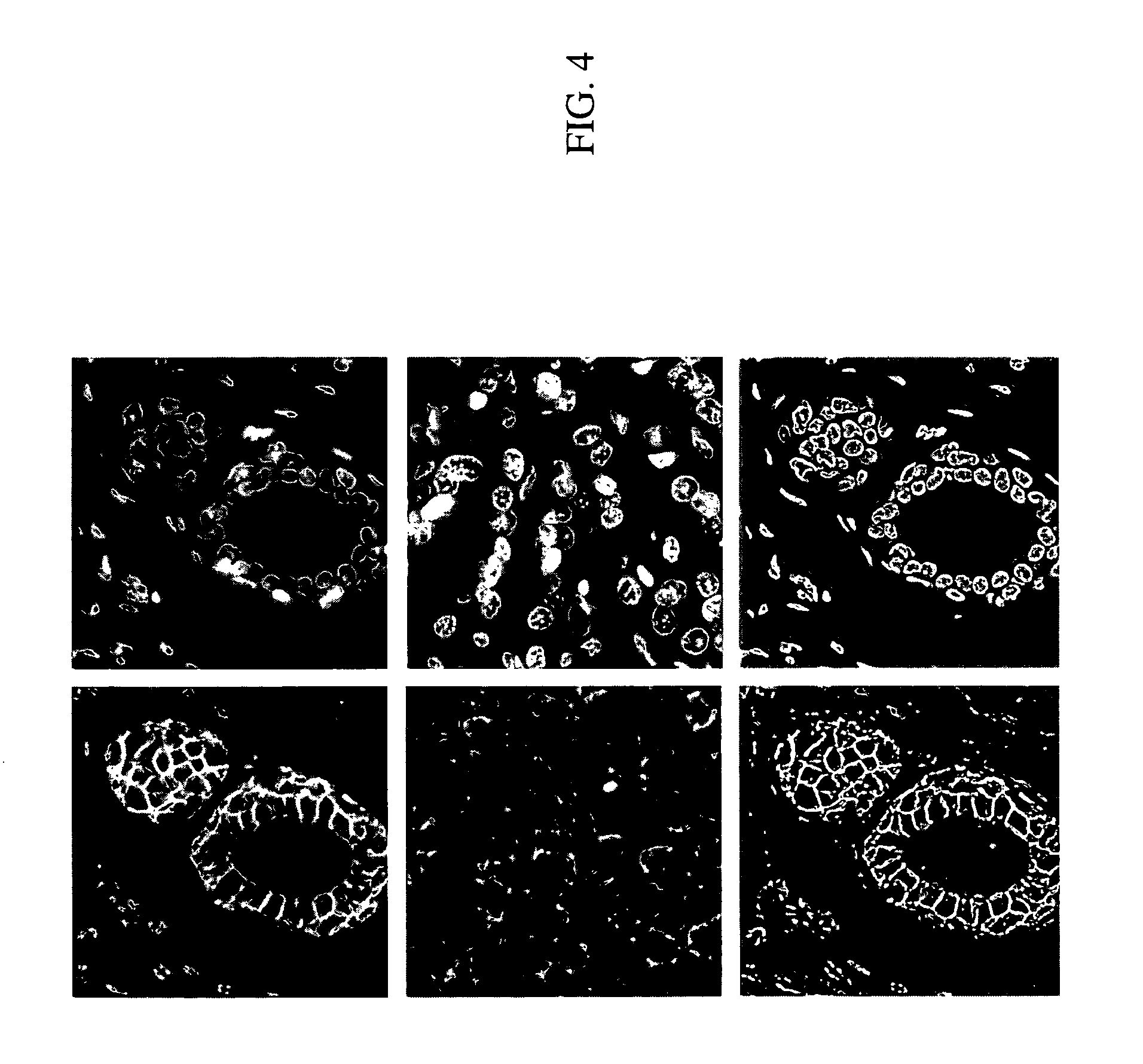
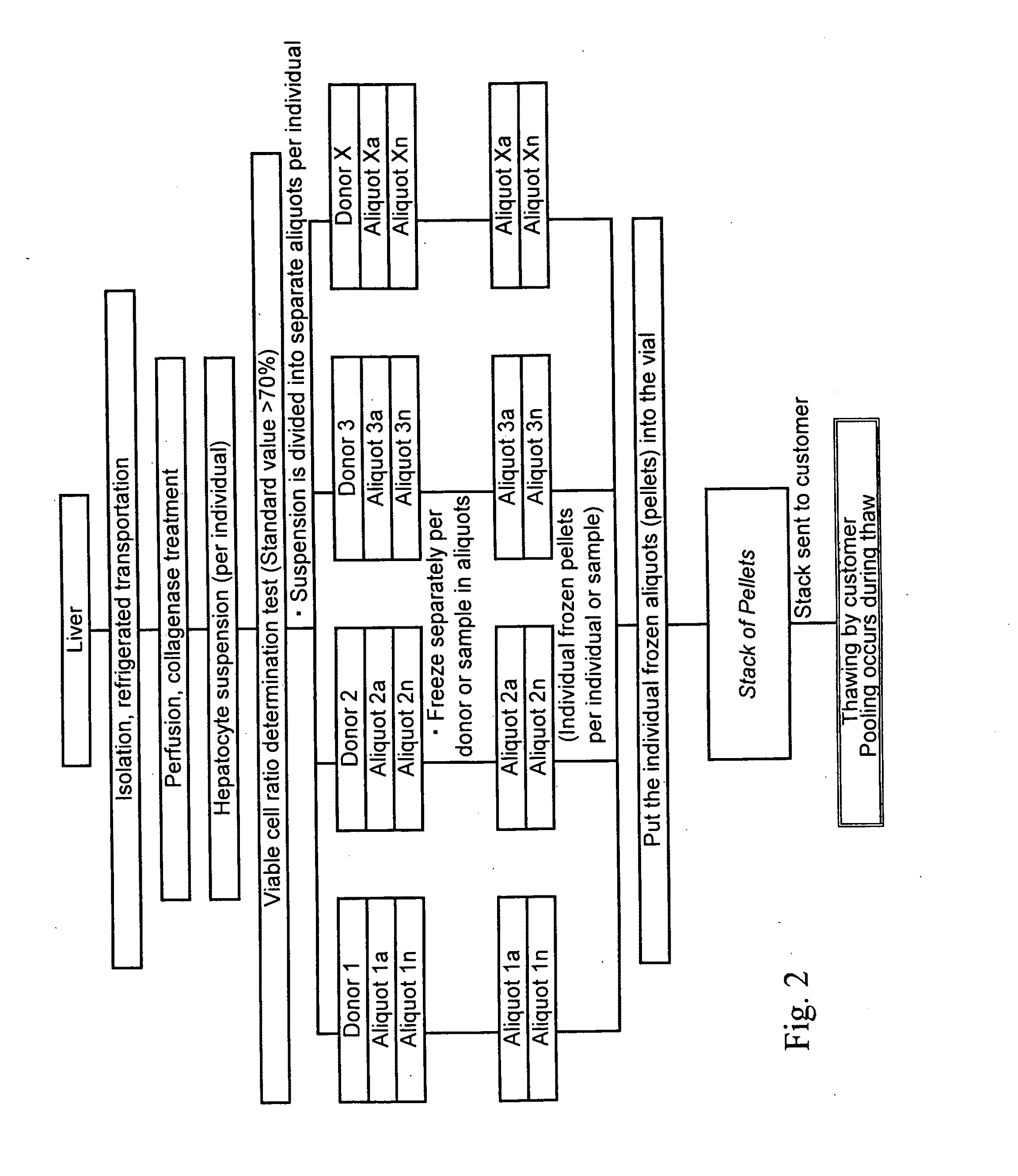
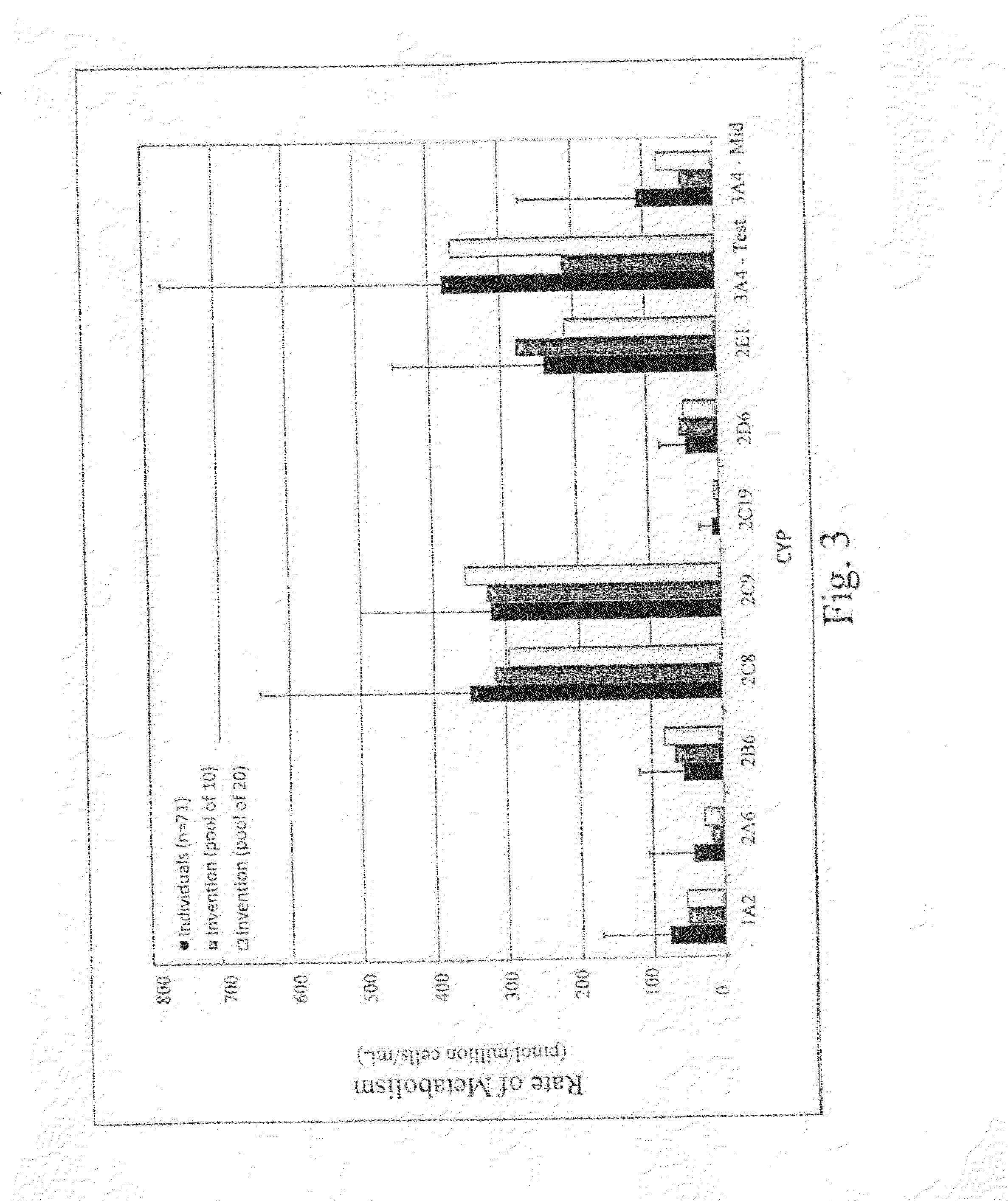
Cryopreservation of cells and subcellular fractions
InactiveUS20110105359A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCryopreservationBiology
Owner:XENOTECH CALIFORNIA
Methods of Treating Portal Hypertension
ActiveUS20150313871A1BiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBiological activationSubcellular localization
Owner:CHARLOTTE MECKLENBURG HOSPITAL AUTHORITY
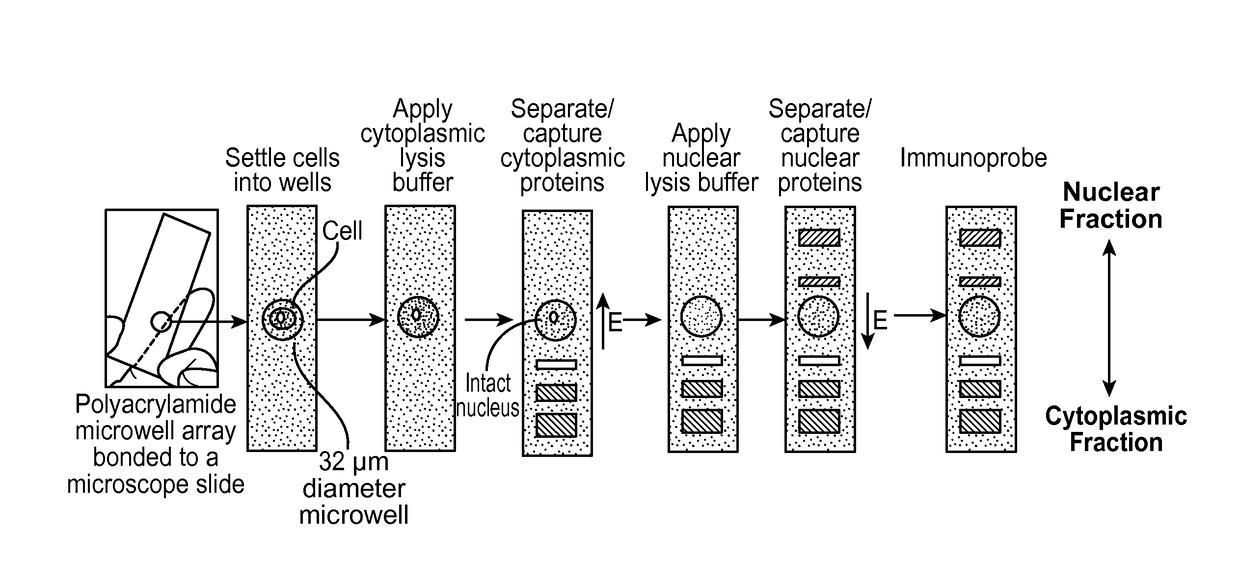
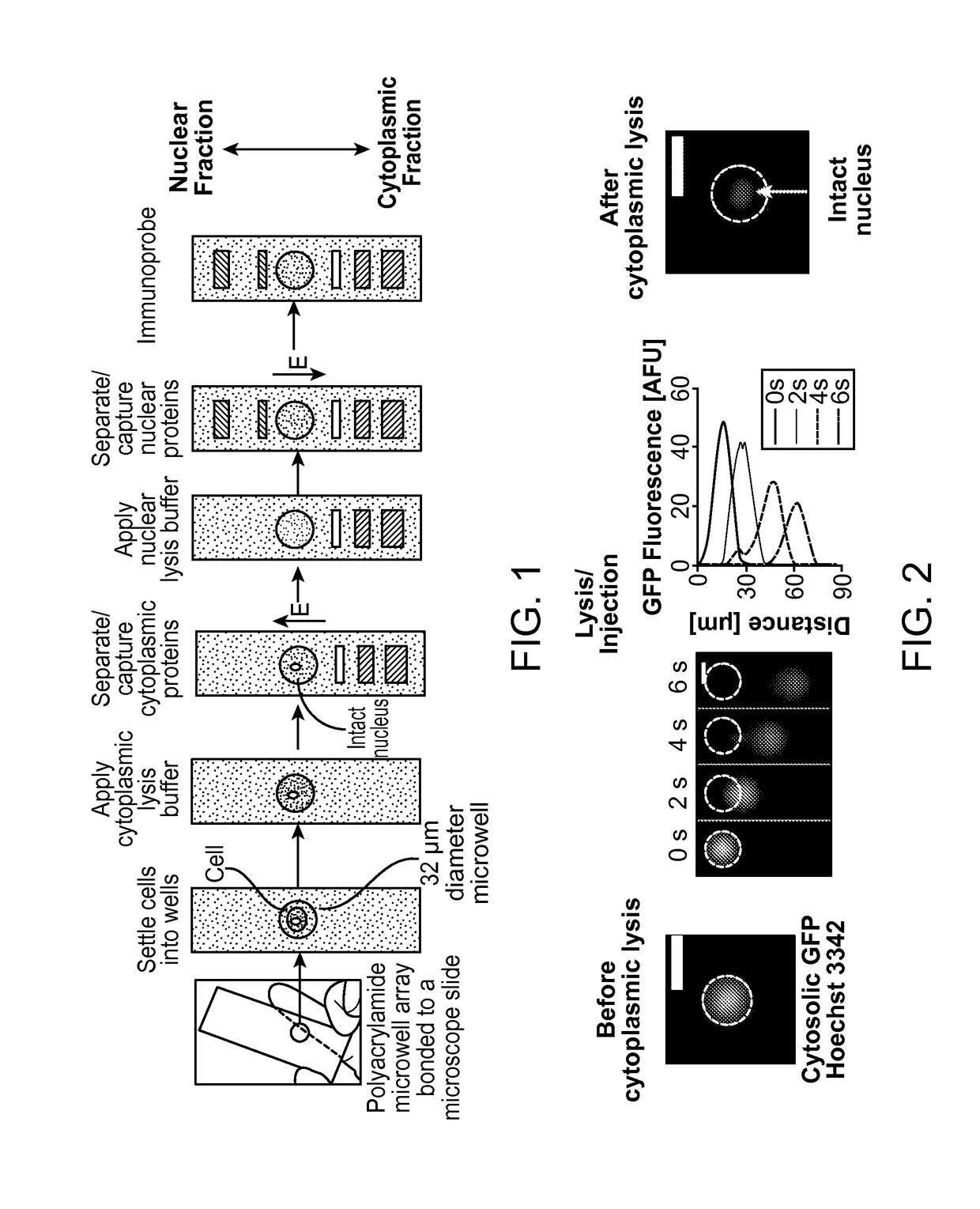
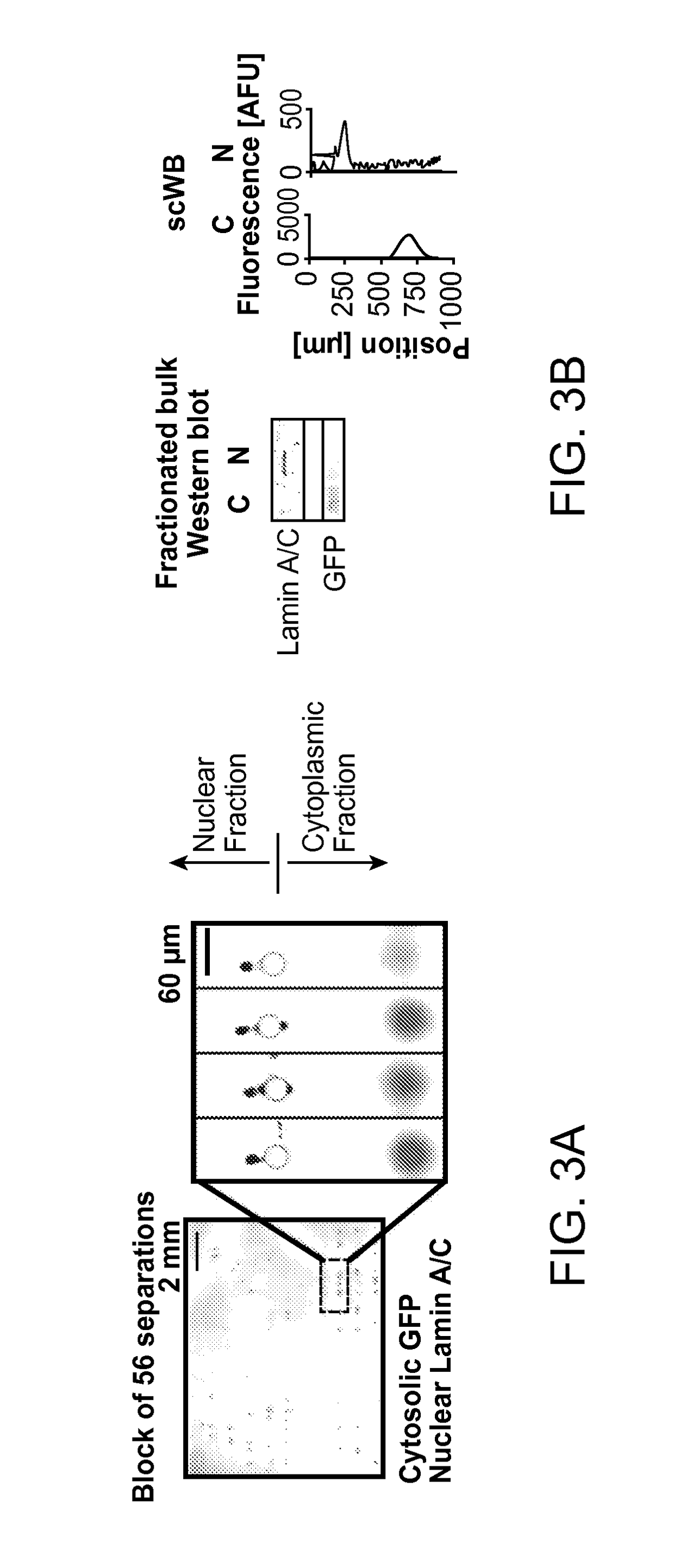
Subcellular Western Blotting of Single Cells
ActiveUS20170242020A1Electrophoretic profilingMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrophoresisAnalytical chemistry
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Multi-level specific targeting of cancer cells with IL-13
A compound comprising, in combination: a cell surface binding ligand or internalizing factor, such as an IL-13Rα2 binding ligand; at least one effector molecule (e.g., one, two, three or more effector molecules); optionally but preferably, a cytosol localization element covalently coupled between said binding ligand and said at least one effector molecule; and a subcellular compartment localization signal element covalently coupled between said binding ligand and said at least one effector molecule (and preferably with said cytosol localization element between said binding ligand and said subcellular compartment localization signal element). Methods of using such compounds and formulations containing the same are also described.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
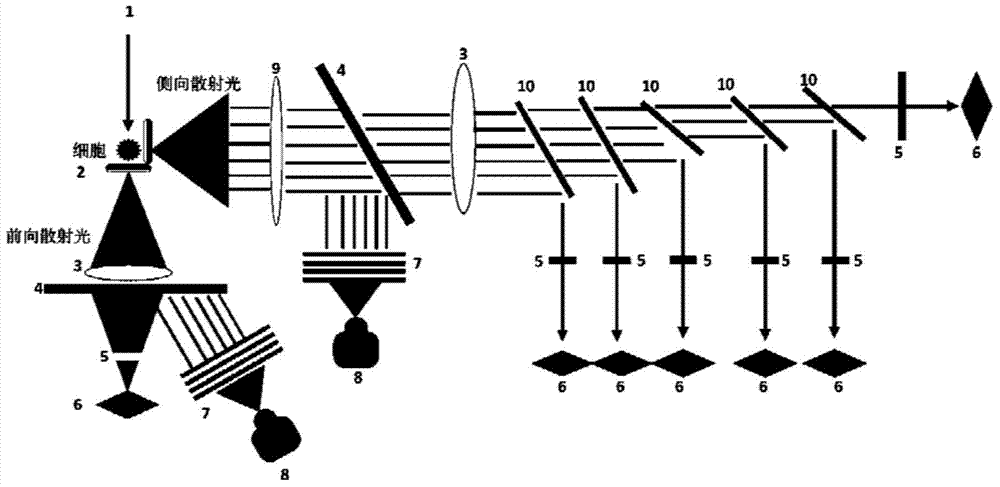
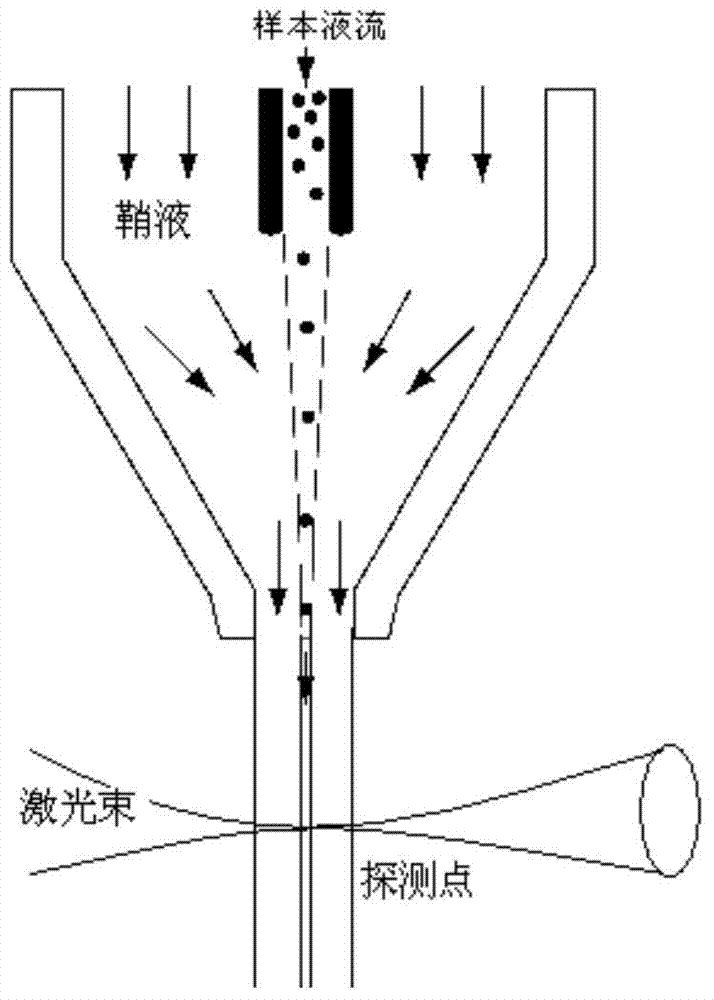
High content image flow biological microscopic analysis system
The invention provides a high content image flow biological microscopic analysis system. The system comprises a liquid flow system and an optical system, wherein the liquid flow system enables cells in sample cell suspension to be focused in the center of a liquid flow under the constraint of the system sheath liquid flow and to flow through a detection window of a flow chamber one by one; the optical system comprises optical sources, an optical path system and an optical filter stack; the optical sources include a halogen lamp and a laser; through the optical path system and the optical filter stack formed by a plurality of dichroscopes, the optical system generates a bright field cell image, a six-channel fluorescent cell image and six PMT (photomultiplier tube) optical intensity signals with different wave bands. The high content image flow biological microscopic analysis system integrates flow cytometry and fluorescence microscopic imaging, has a plurality of detection channels, can collect the cell images of the cells passing through the flow chamber one by one and can carry out quantitative analysis on each cell image by utilizing analysis software, thus providing the statistical data of a cell group and the information of the cell morphology, cell structures and subcellular signal distribution.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
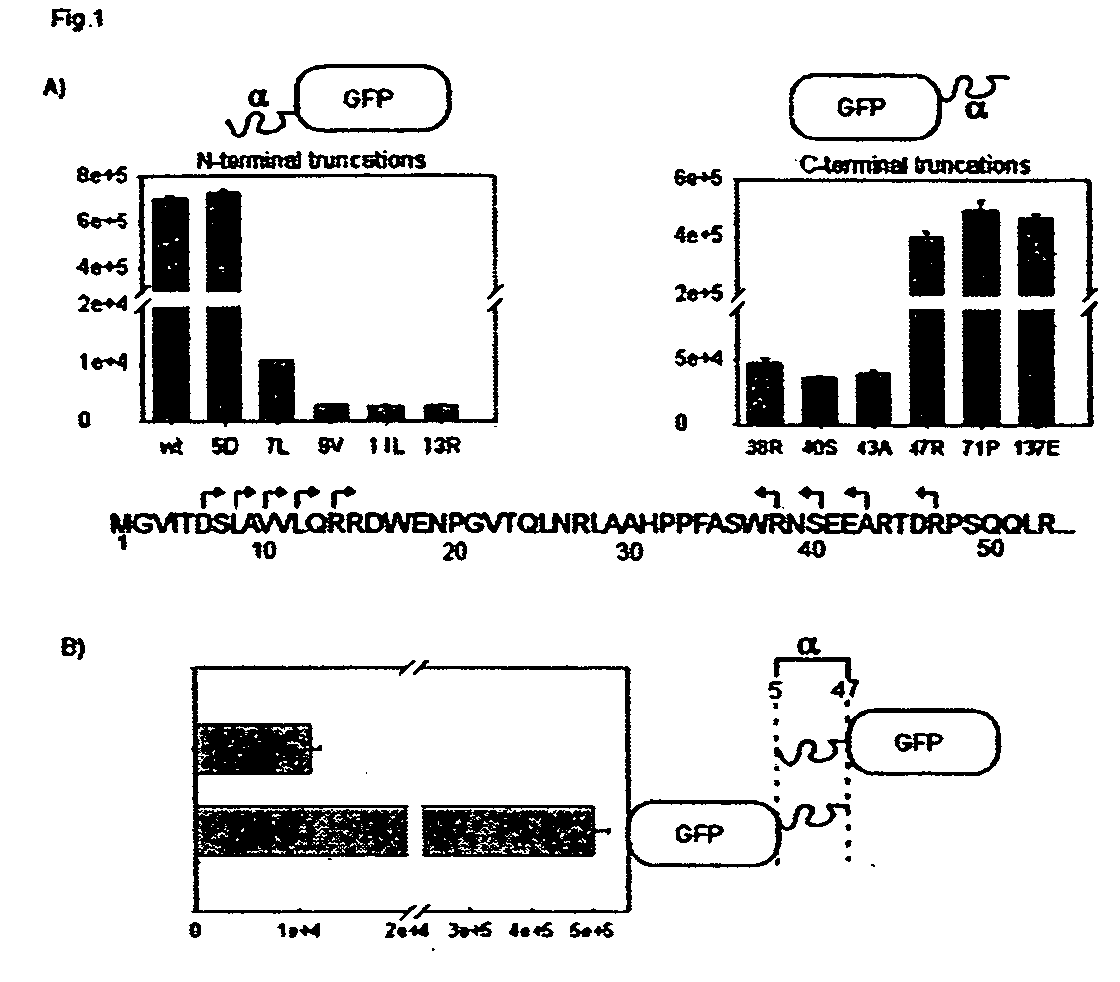
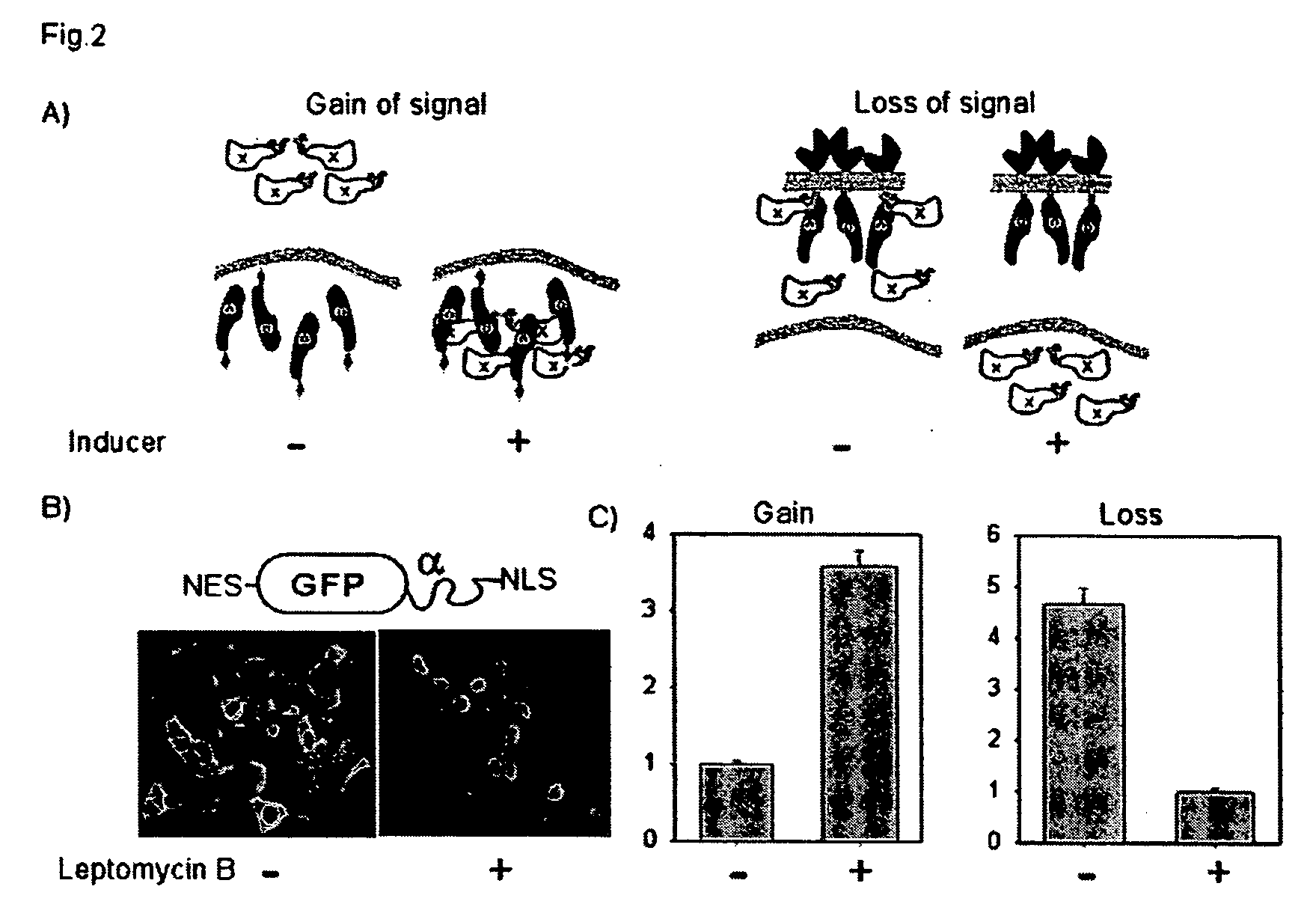
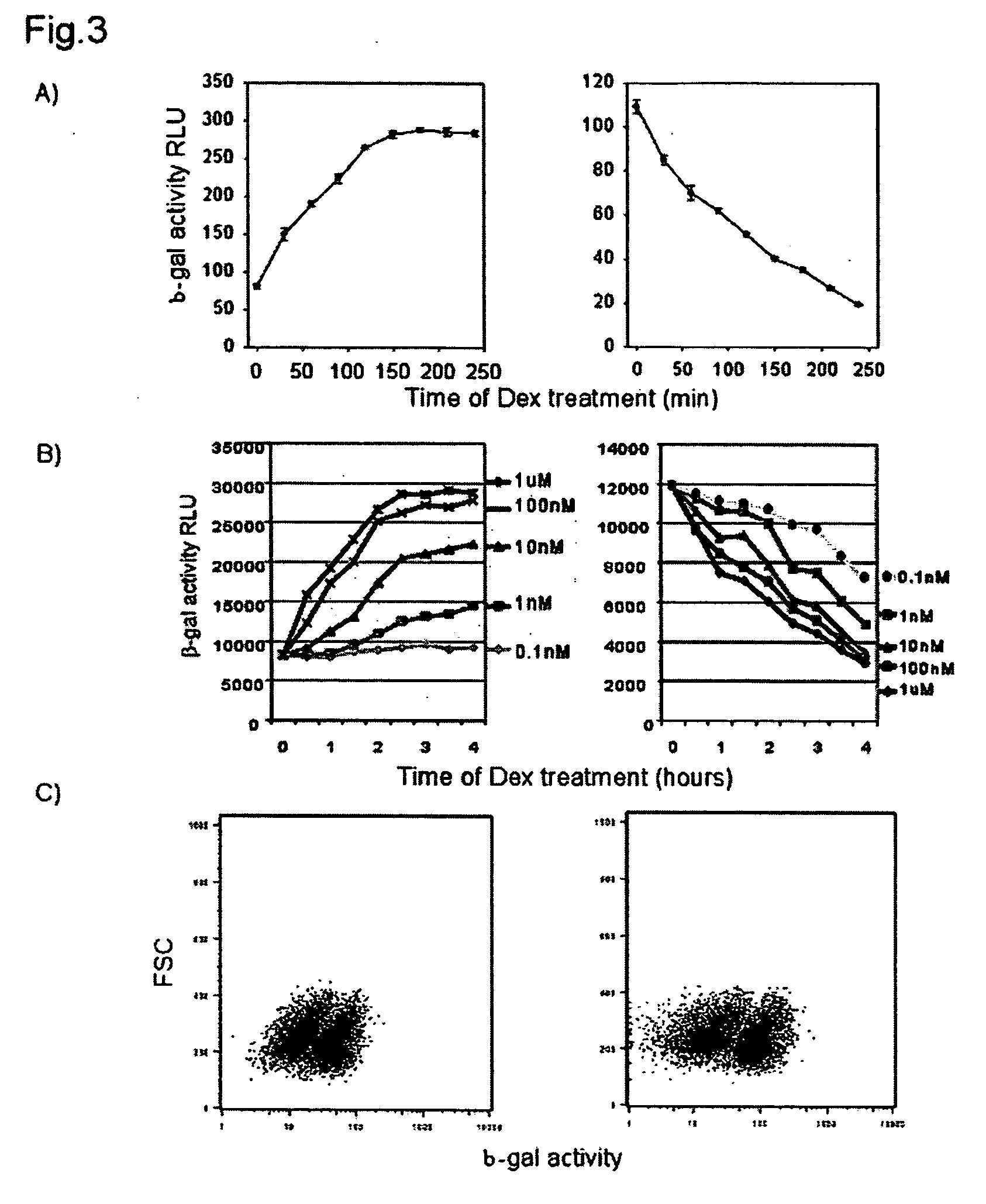
Detection of protein translocation by beta-galactosidase reporter fragment complementation
ActiveUS20050287522A1Precise and accurate monitoringMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisBeta-GalactosidasesElisa assay
Methods and compositions are provided for detecting molecular translocations, particularly protein translocations within and between subcellular copartments, using at least two components that exhibit a localization-dependent difference in complementation activity. In particular, alpha-complementing β-galactosidase fragments are provided. These β-galactosidase reporter fragments display significantly enhanced enzymatic activity when one fragment is localized in a membrane. Methods for carrying out no-wash ELISA assays based on the reporter component system are also provided.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
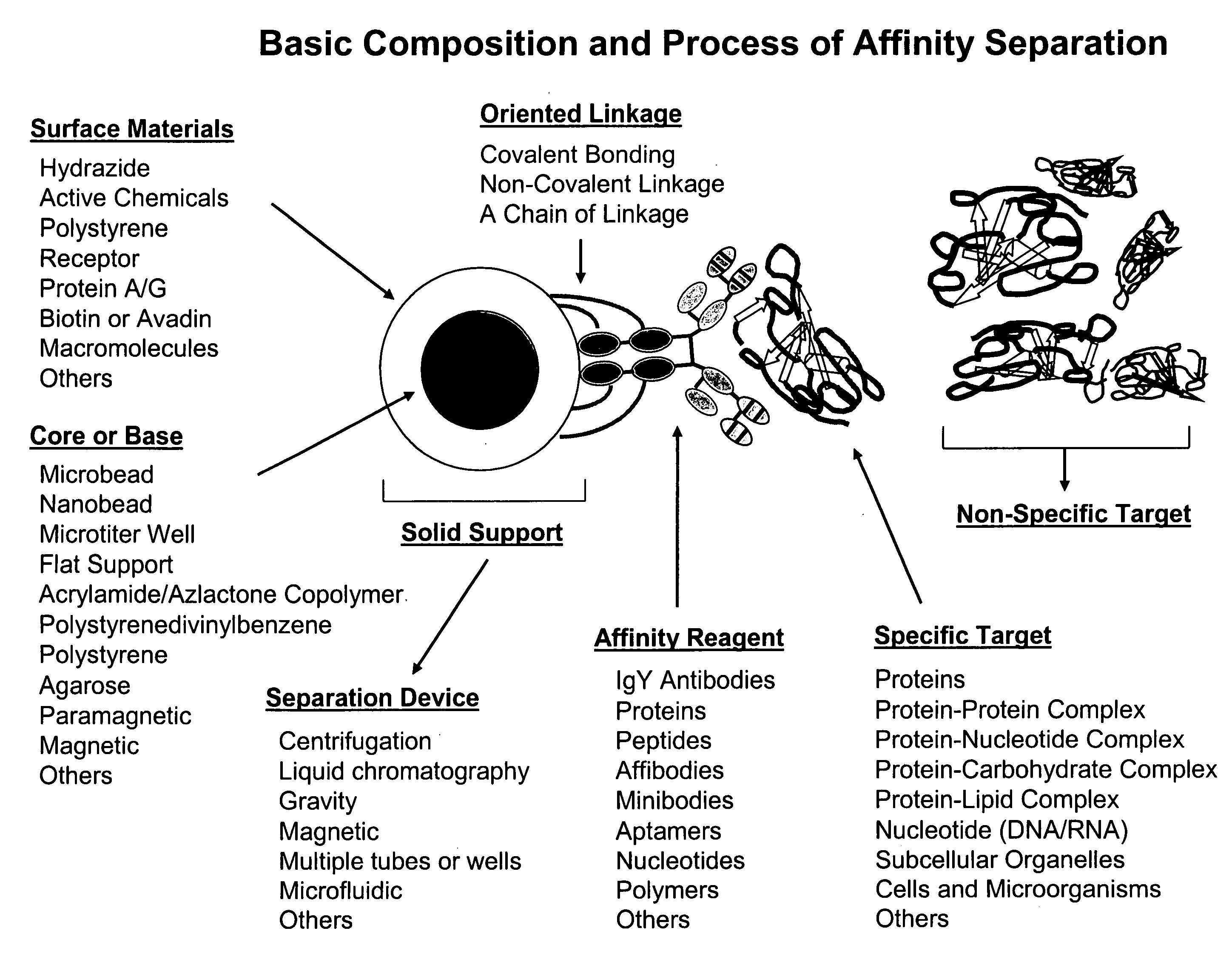
Novel high protein tortillas
InactiveUS20050095726A1Easy to adaptBetter meetingEgg immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansProtein-protein complexSubcellular organelle
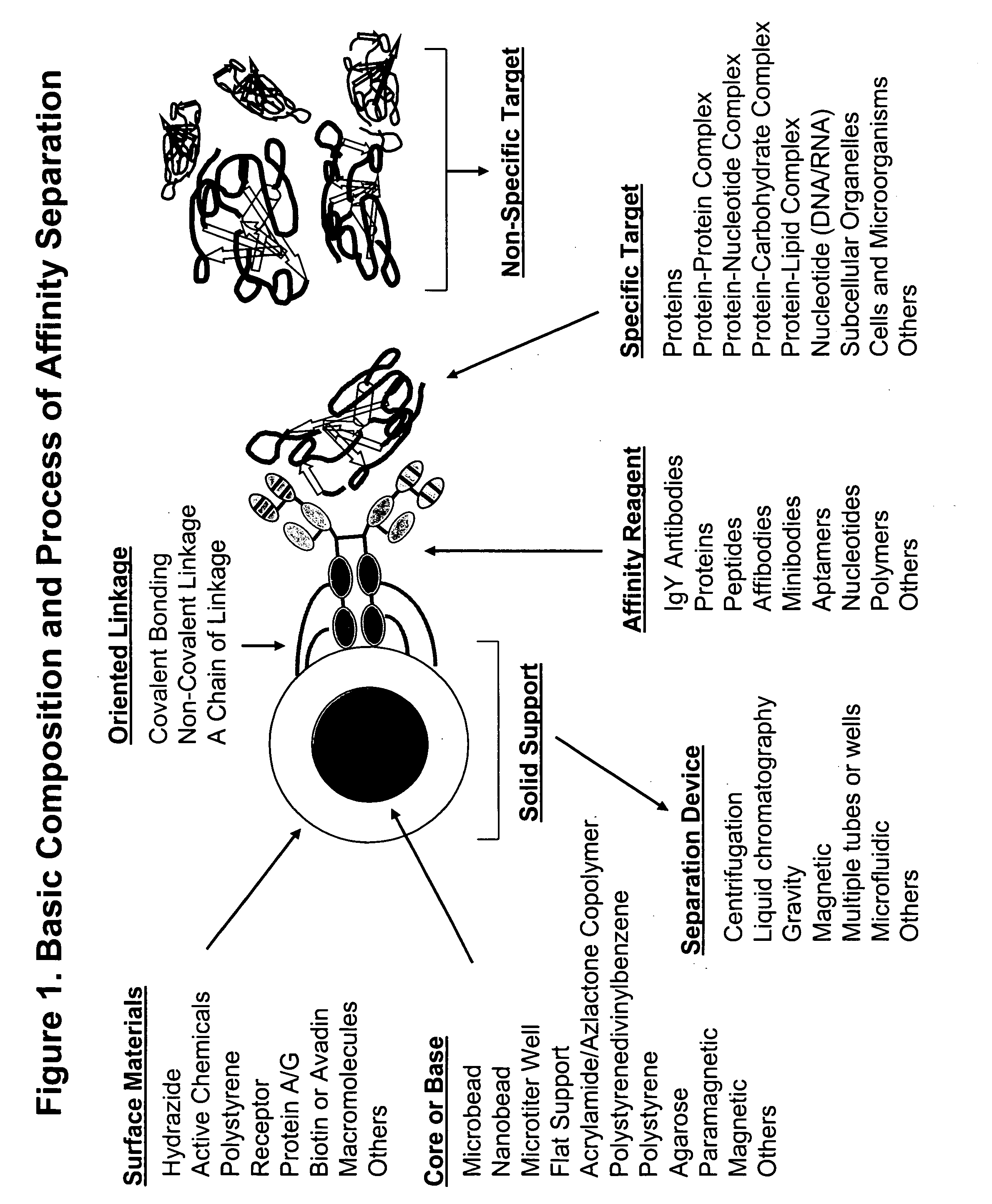
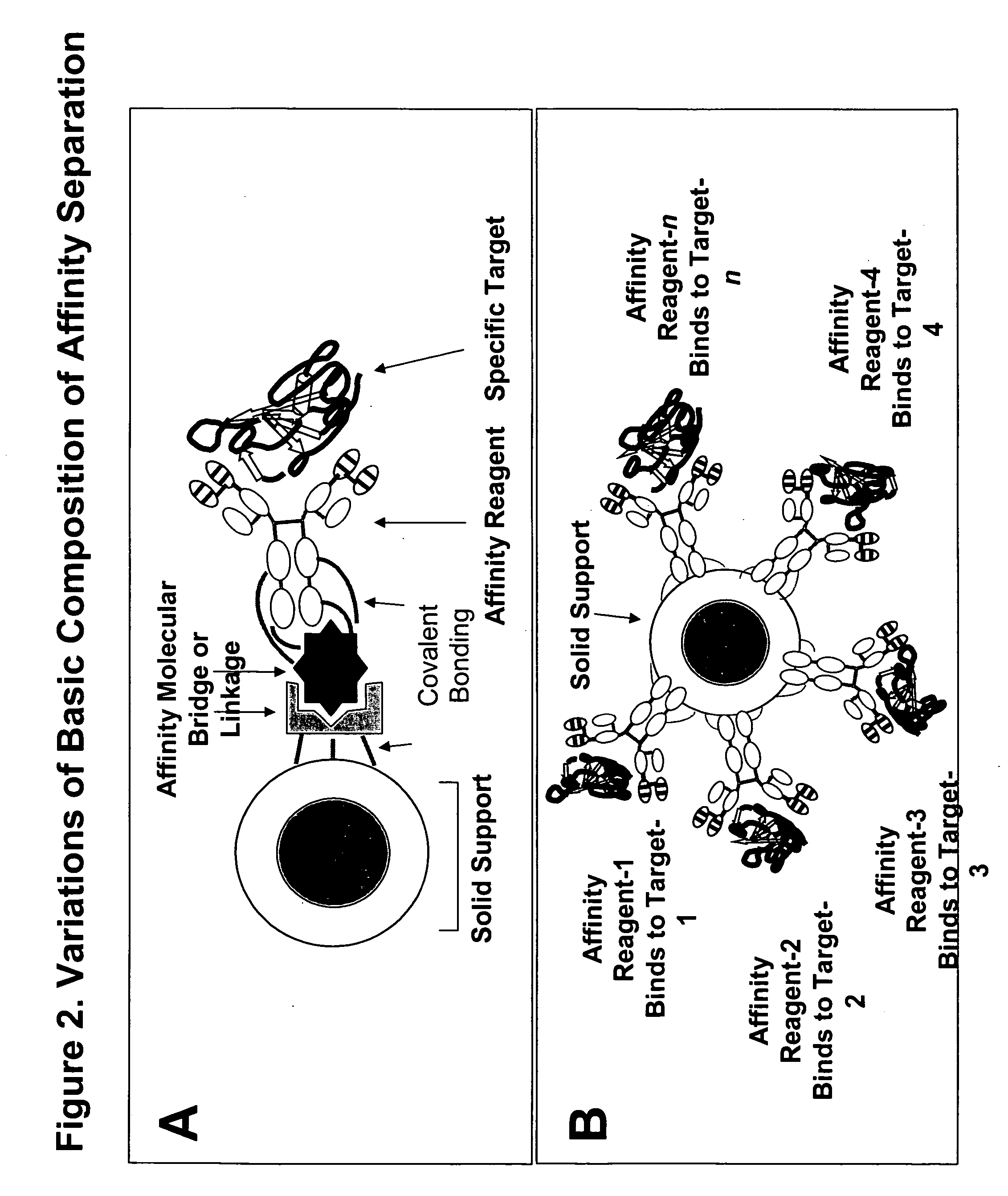
Affinity separation compositions and methods are disclosed for separating targets from complex mixtures. Affinity reagents are bound to a solid support oriented in a manner to facilitate the activity of the affinity reagents which are capable of binding specific targets by affinity recognition. Affinity reagents include IgY antibodies, proteins, peptides, nucleotides and polymers. Targets include proteins, protein-protein complexes, protein-nucleotide complexes, nucleotides, cells and subcellular organelles.
Owner:GENWAY BIOTECH
Methods and systems for assessing biological material using optical detection techniques
InactiveUS20050119552A1Improve throughputHigh sensitivityOrganic active ingredientsDiagnostic recording/measuringHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsSurvivability
Optical detection techniques for the assessment of the physiological state, health and / or viability of biological materials are provided. Biological materials which may be examined using such techniques include cells, tissues, organs and subcellular components. The inventive techniques may be employed in high throughput screening of potential diagnostic and / or therapeutic agents.
Owner:CYTOSCAN SCI
Transgenic monocot plants encoding beta-glucosidase and xylanase
Plant proteins isolated from monocot plants from transformation of the monocot plant with DNA at least 80% homologous to the bglA gene encoding β-glucosidase from a rumen bacterium which is Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens H17c and targeted to a subcellular compartment. The transformed plant is ground after the β-glucosidase has been accumulated, and the protein is extracted or used directly with the ground plant material to degrade cellobiose, in particular, to produce sugars used in fermentations, particularly to produce ethanol. Also, a gene at least 80% homologous to DNA XYL1 gene encoding a xylanase is also provided in a transformed plant and used to produce sugars.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
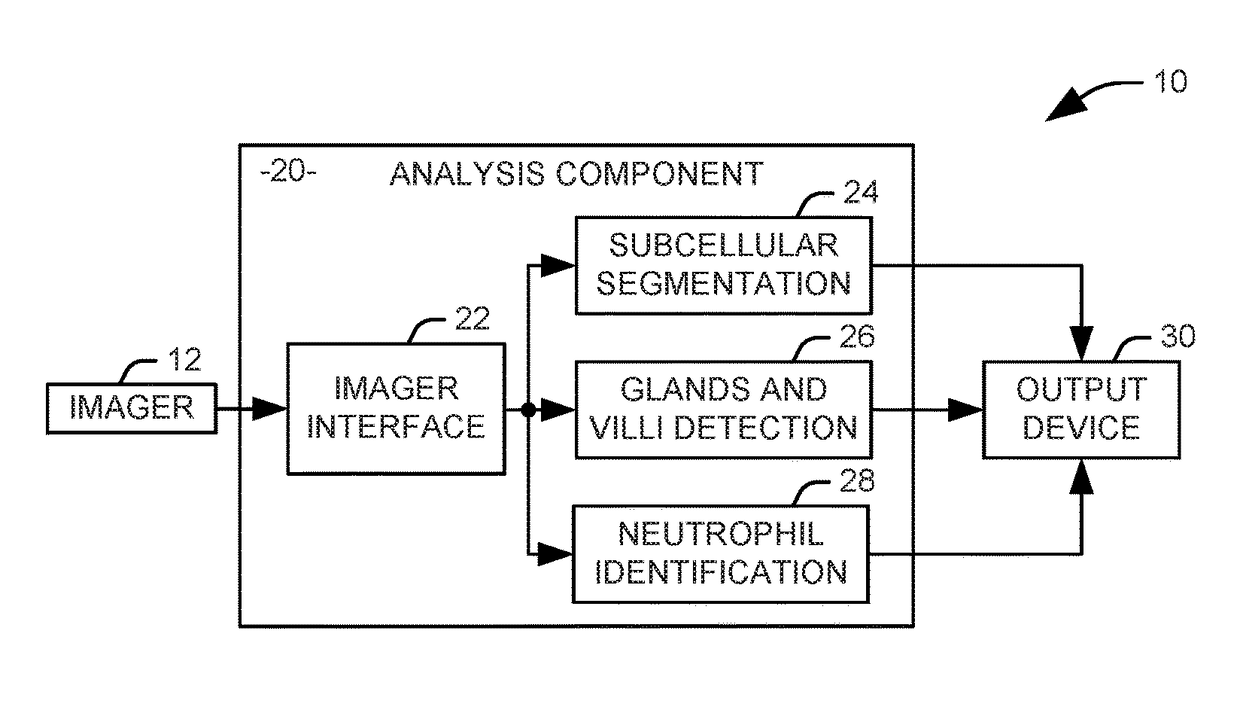
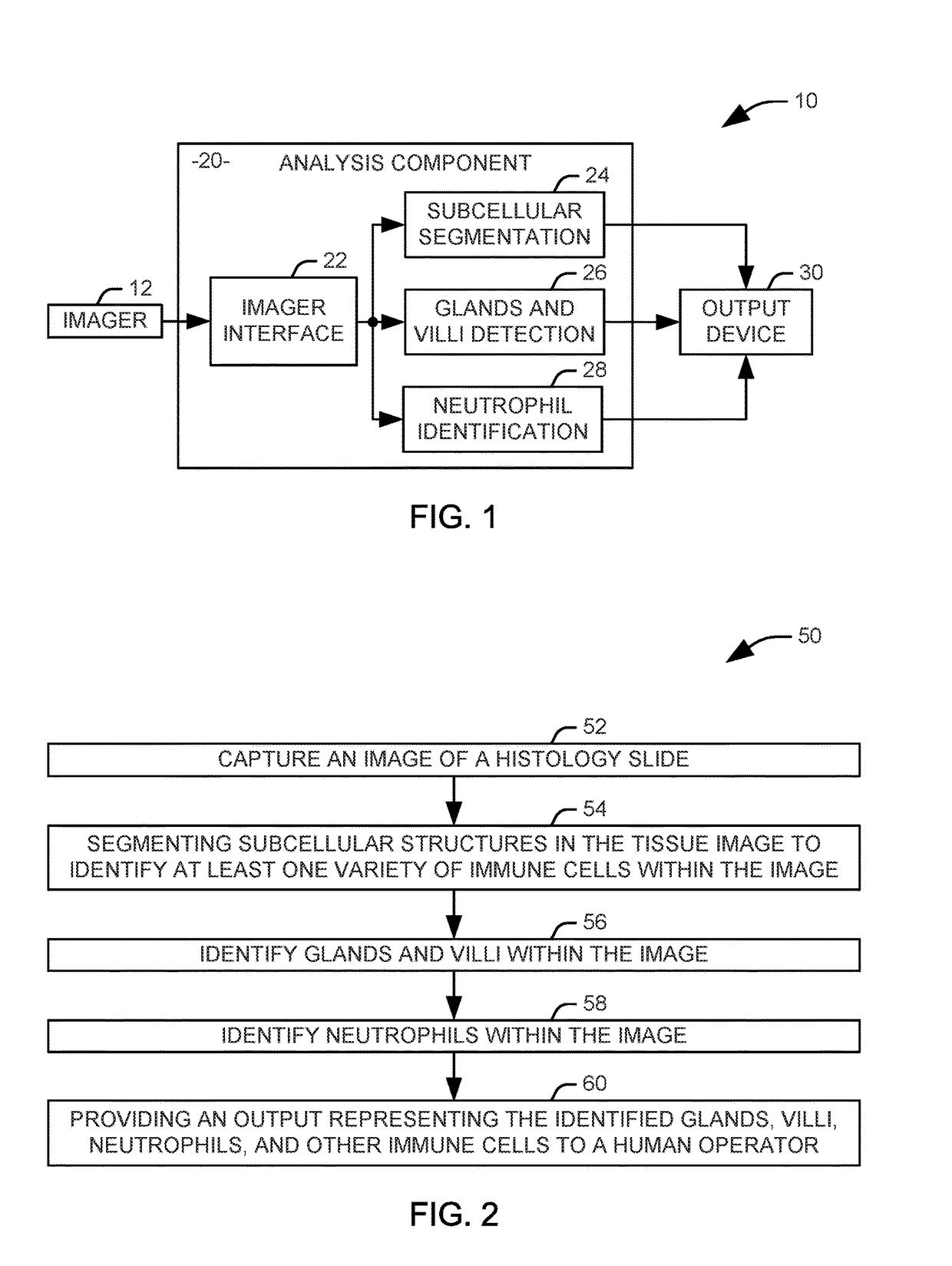
Identification of inflammation in tissue images
Systems and methods are provided for identifying markers for inflammation in a tissue image. The tissue image is captured as an image of a histology slide. Subcellular structures in the tissue image are segmented via a first automated process to identify at least one variety of immune cells within the image. Glands and vilii are identified within the tissue image via a second automated process. Neutrophils are identified within the tissue image via a third automated process. An output representing the identified glands, villi, neutrophils, and other immune cells is provided to a human operator.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
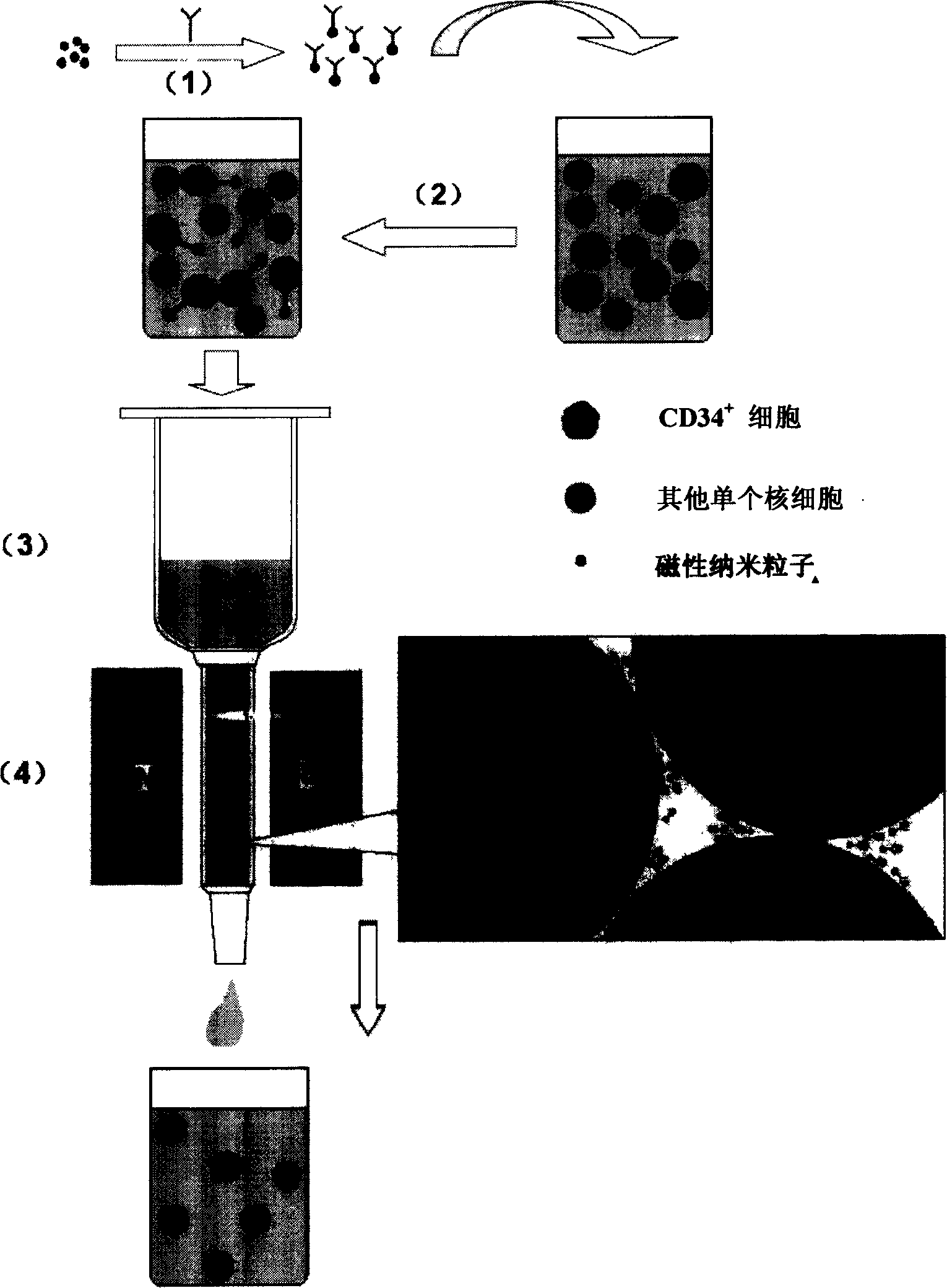
Magnetic separating colume and its use in spearating biological samples
InactiveCN1899698AEasy to makeEase of mass productionLiquid surface applicatorsInorganic material magnetismBiological pumpEngineering
The present invention relates to a kind of magnetic separating column and its application in separating biological samples. The magnetic separating column has structure comprising a material holding section, a filler column, a discharge port and a pushing plug. The filler column is filled with small magnetic soft iron balls of sizes 0.01-0.1mm, 0.1-0.2mm and 0.2-1mm separately. During separation, the sample fed through the inlet in the upper end is made to flow through the filler column and the discharge port under the gravity action, and the pushing plug applies pressure to push out the blocked sample. Under the action of outer magnetic field, the magnetic separating column can generate high gradient magnetic field for effective fast separation of various kinds of cells, subcellular matters, bacteria, viruses, nucleic acids, proteins and other biological samples.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for expressing proteins by using plant petal cell protoplast
The present invention relates to a method for expressing proteins by using plant petal cell protoplast. The method comprises: (1) adopting plant petals as a material, and carrying out enzymolysis to obtain petal cell protoplast; (2) standing the petal cell protoplast for 20-40 min at a temperature of 2-8 DEG C; and (3) transforming plasmid into the protoplast by using a PEG and Ca<2+>-mediated method, and expressing the target protein. Compared with the method in the prior art, the method of the present invention has the following beneficial effects that: the target protein can be expressed in a short time, the protoplast protein expression system can be used for research on target protein subcellular positioning and protein molecule interaction, the activity of the protoplast is normal, and the target protein expression detection results show that the method can be used for research on gene transcription level, protein expression level and substance metabolism level change in living cells and is the rapid and convenient target gene function research method.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
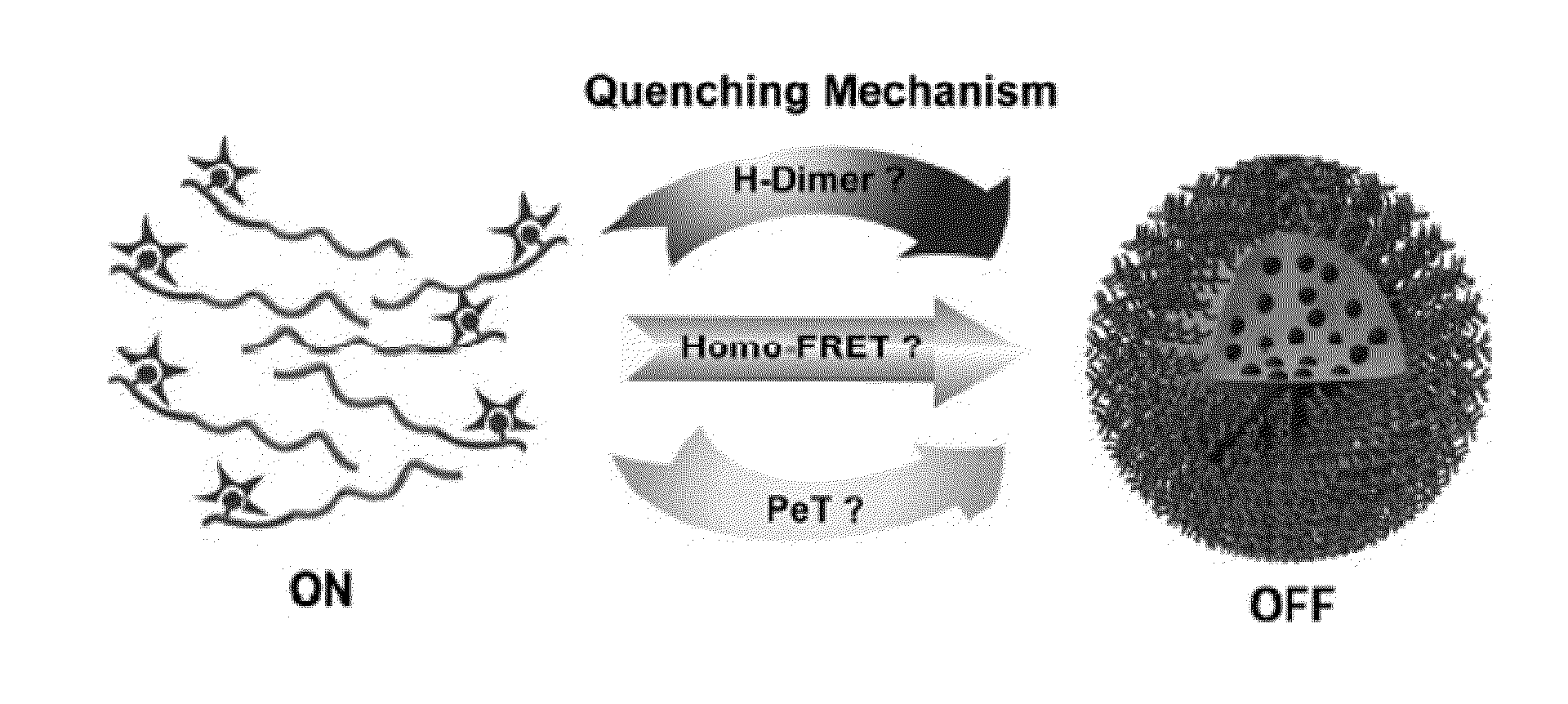
MULTICOLORED pH-ACTIVATABLE FLUORESCENCE NANOPLATFORM
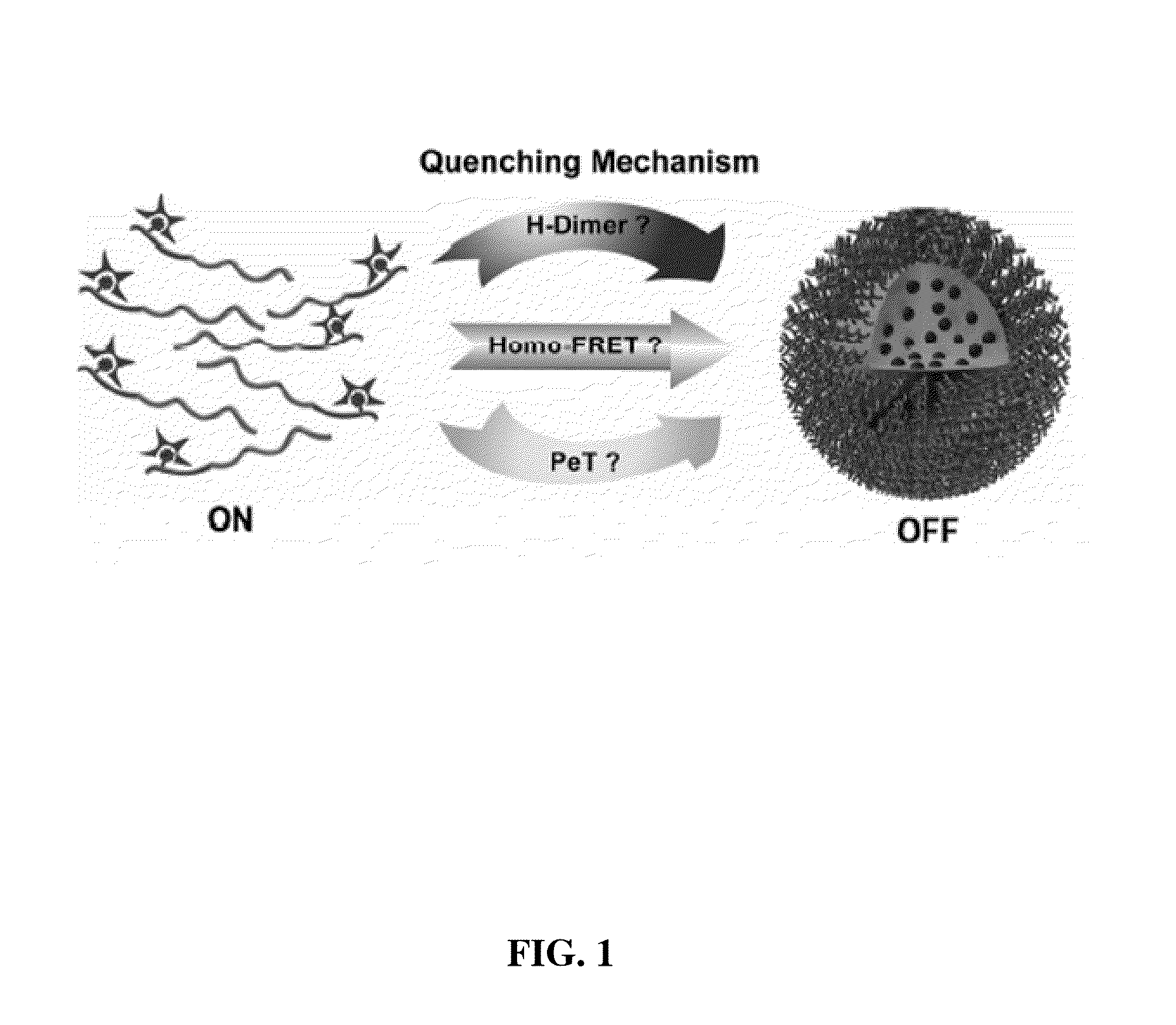
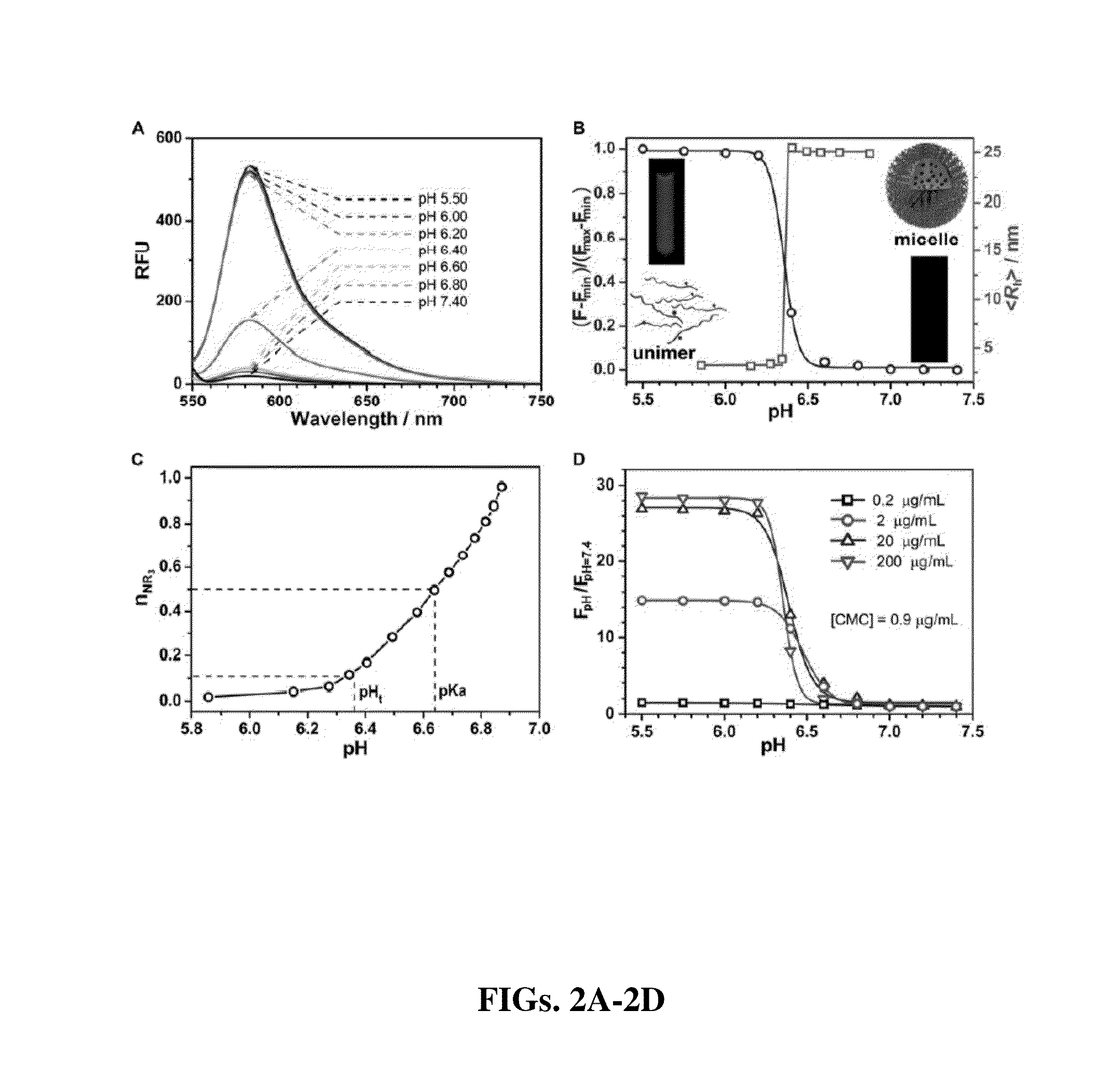
ActiveUS20130330278A1Improved labelingSharp contrastUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceLysosome
The present invention relates to pH-tunable, highly activatable multicolored fluorescent nanoplatforms and methods of using the nanoplatforms in a variety of applications including, but not limited to, investigating fundamental cell physiological processes such as pH regulation in endocytic vesicles, endosome / lysosome maturation, and effect of pH on receptor cycling and trafficking of subcellular organelles.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
System and method of label-free cytometry based on brillouin light scattering
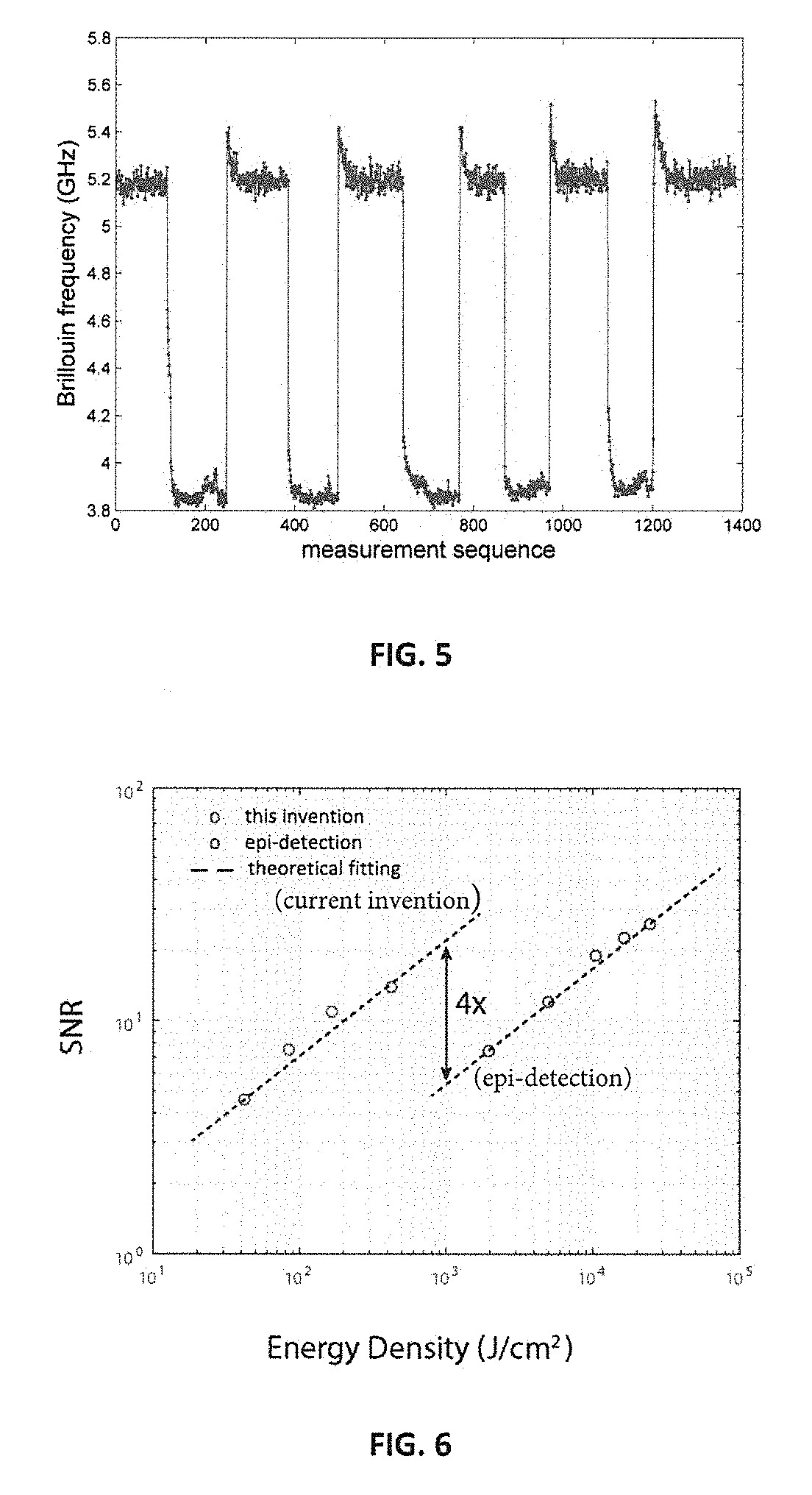
ActiveUS20170176318A1Material analysis by optical meansBiological particle analysisSpectroscopyMultiple point
The present invention relates to a method and system for a label-free cell analysis based on Brillouin light scattering techniques. Combined with microfluidic technologies according to the present invention, Brillouin spectroscopy constitutes a powerful tool to analyze physical properties of cells in a contactless non-disturbing manner. Specifically, subcellular mechanical information can be obtained by analyzing the Brillouin spectrum of a cell. Furthermore, a novel configuration of Brillouin spectroscopy is provided to enable simultaneous analysis of multiple points in a cell sample.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com