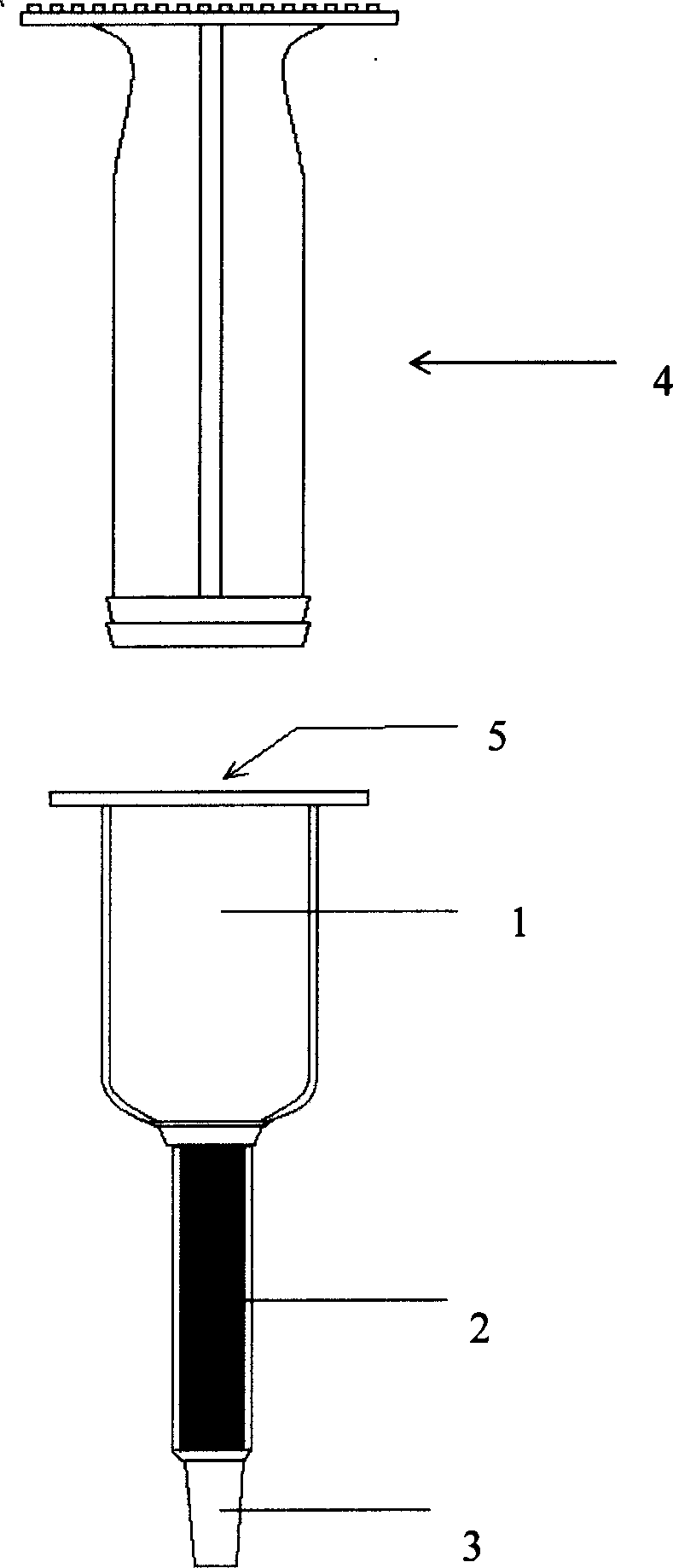
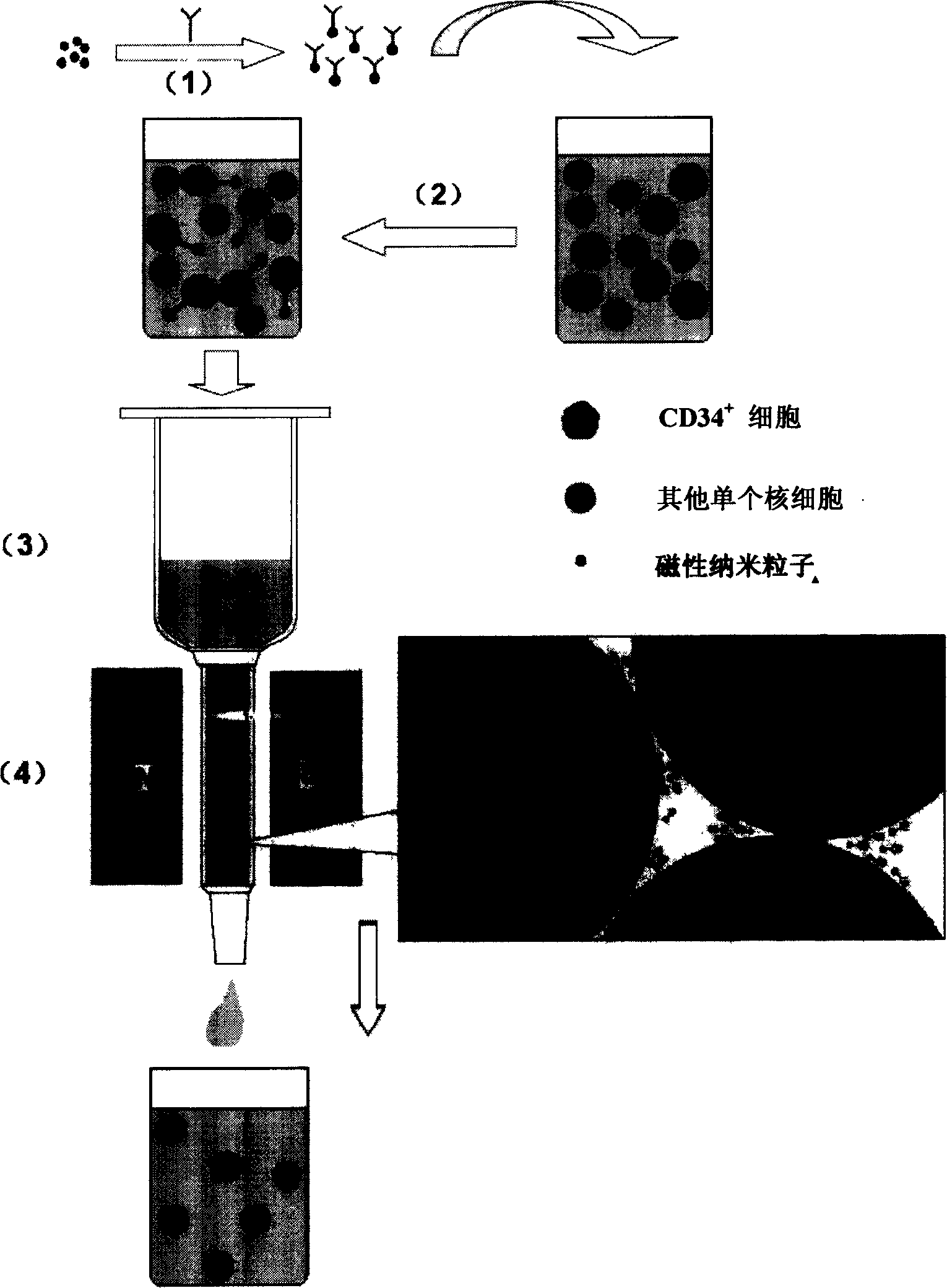
Magnetic separating colume and its use in spearating biological samples
A technology for magnetic separation and biological samples, applied in the fields of magnetic separation, solid separation, inorganic material magnetism, etc. It can solve the problems of improving separation efficiency and low magnetic induction intensity, and achieve easy mass production, uniform size, and simple and fast operation. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Preparation of filler pellets: prepared by splash quenching method.
[0042] Take three parts of soft iron material, its composition and weight percentage are respectively: iron 99.0% + carbon 0.04%, iron 99.5% + carbon 0.001%, and iron 99.8% + carbon 0.01%, and the balance contains a very small amount of aluminum, Sodium, zinc, chromium, nickel, copper, manganese and other elements. The three materials are melted at a high temperature of 1500°C-1800°C, and the molten soft iron is sprayed at a speed of 3-50 m / s, dropped from a high altitude or centrifugally thrown out, and the surface tension of the liquid phase is used to automatically shrink into a ball. Falling into the water, it suddenly condenses into a small iron ball.
Embodiment 2
[0044] Particle size screening: Most of the particle sizes of the three kinds of material pellets prepared in Example 1 are 0.2-1mm, and the magnetic properties of the iron balls are different with different particle sizes. The present invention adopts a sampling sieve to carry out particle size screening: a sampling sieve with a suitable mesh number is selected to screen pellets with target particle sizes of 0.01-0.1mm, 0.1-0.2mm and 0.2-1mm respectively. Iron balls with a larger particle size of 0.2-1 mm can be used to process a large number of samples, and are suitable for separating magnetically labeled biological samples with strong magnetic responses. Iron balls with a smaller particle size of 0.01-0.1 mm or 0.1-0.2 mm can generate a magnetic field with a larger gradient, which is suitable for separating magnetically labeled biological samples with weak magnetic response.
[0045] Density Screening: The main component of filler pellets is iron. During the preparation of...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Improving magnetic permeability: The stress generated by quenching makes the magnetic properties of the balls unable to meet the requirements of sorting materials. It is necessary to eliminate the stress through a suitable annealing process, so as to improve the magnetic permeability of the small iron ball and reduce its coercive force. Raise the temperature to 400-900°C with the furnace, control the temperature to 700-1000°C, keep it for 1-5 hours, and cool it down to 400-900°C at a controlled speed, preferably raise the temperature to 800°C with the furnace, control the temperature to 900°C, and keep it for 4 hours. Cool down to 500°C at controlled speed. In order to avoid the oxidation of the balls, the annealing of the balls is carried out in a vacuum furnace or a hydrogen atmosphere. The annealed pellets have fine grains, uniform structure, low hardness, low coercive force (Hc=30~150A / m) and high maximum magnetic permeability (μ max =4000~9000), which meets the b...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Maximum permeability | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com