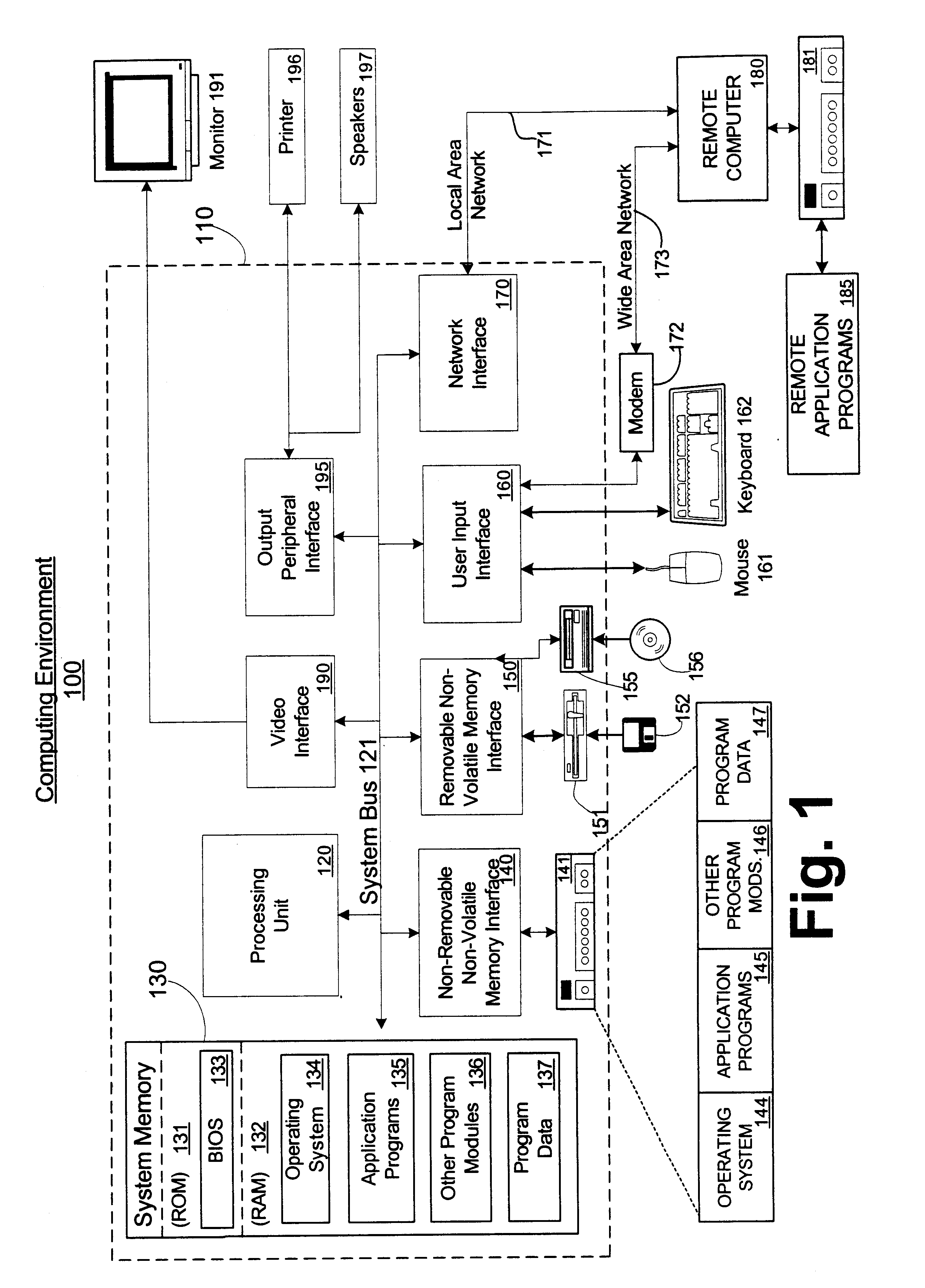
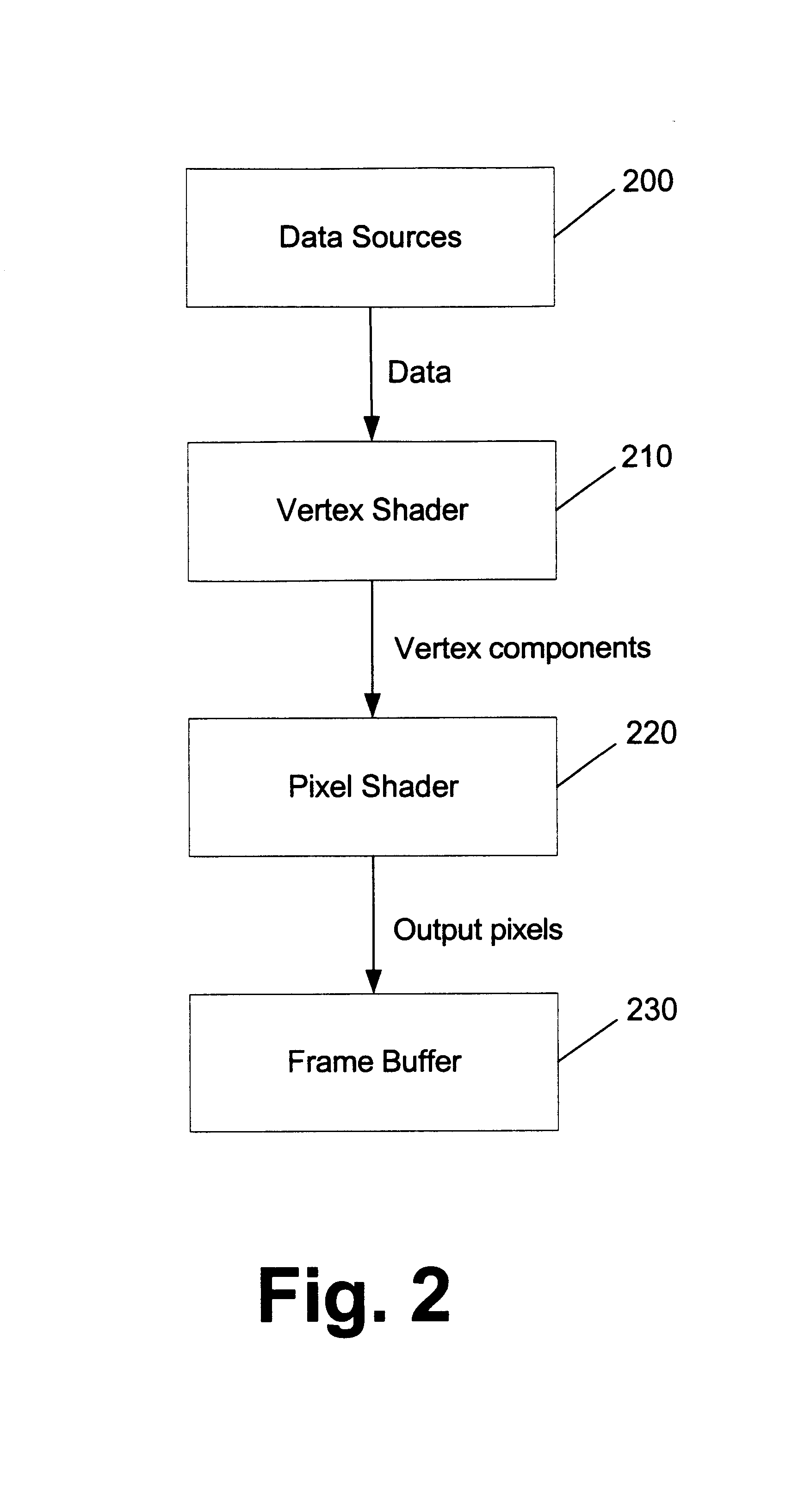
Patents
Literature
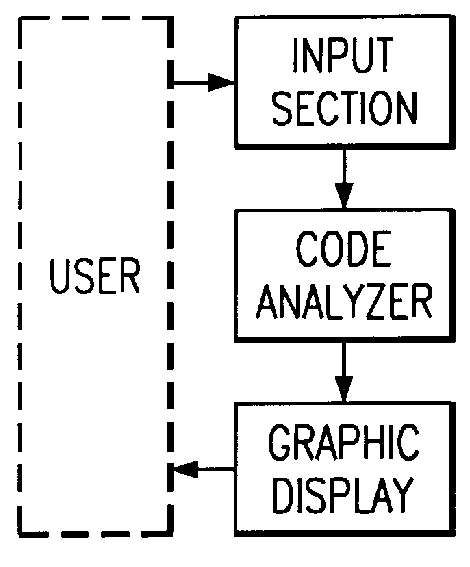
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
180 results about "Assembly language" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
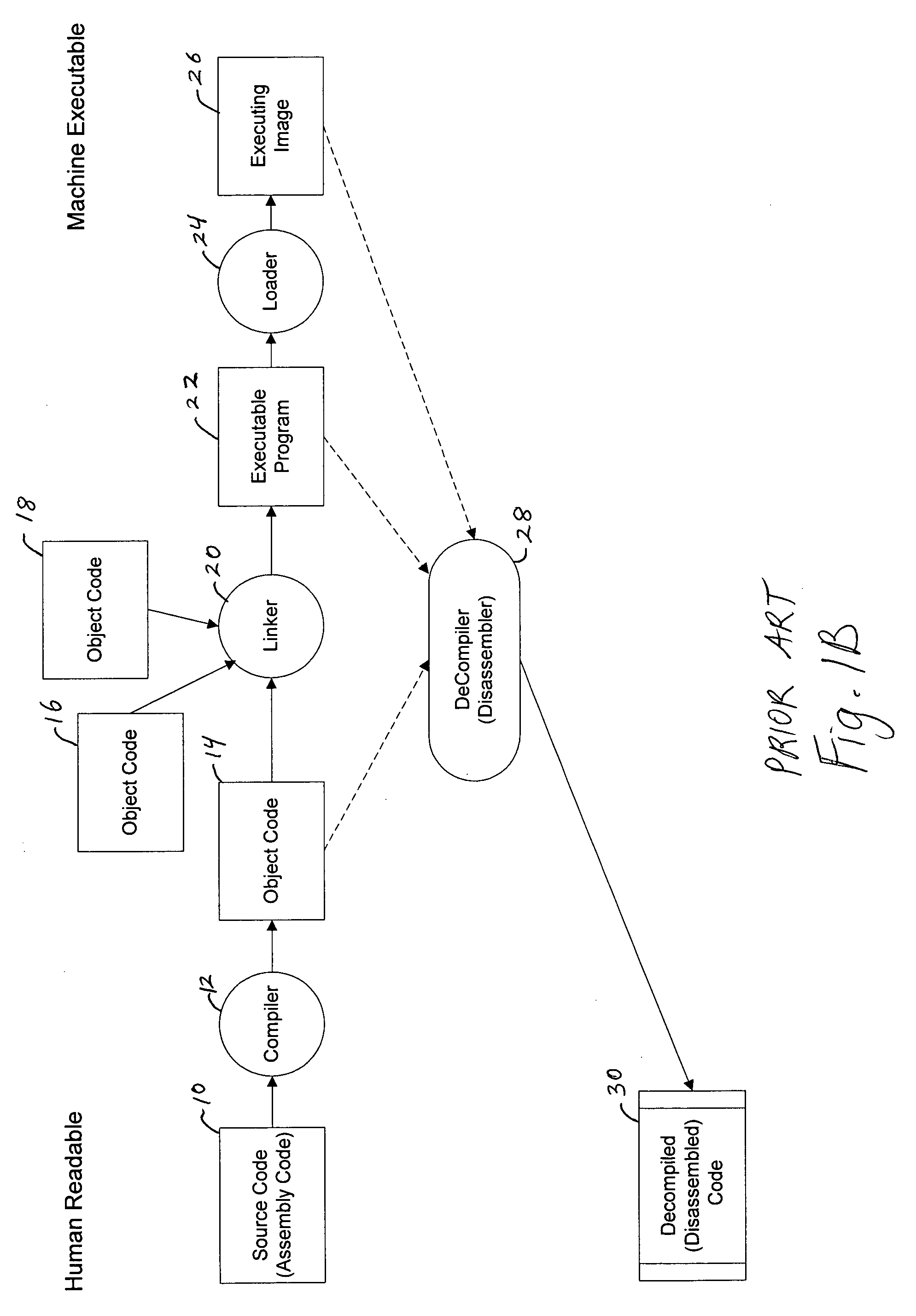
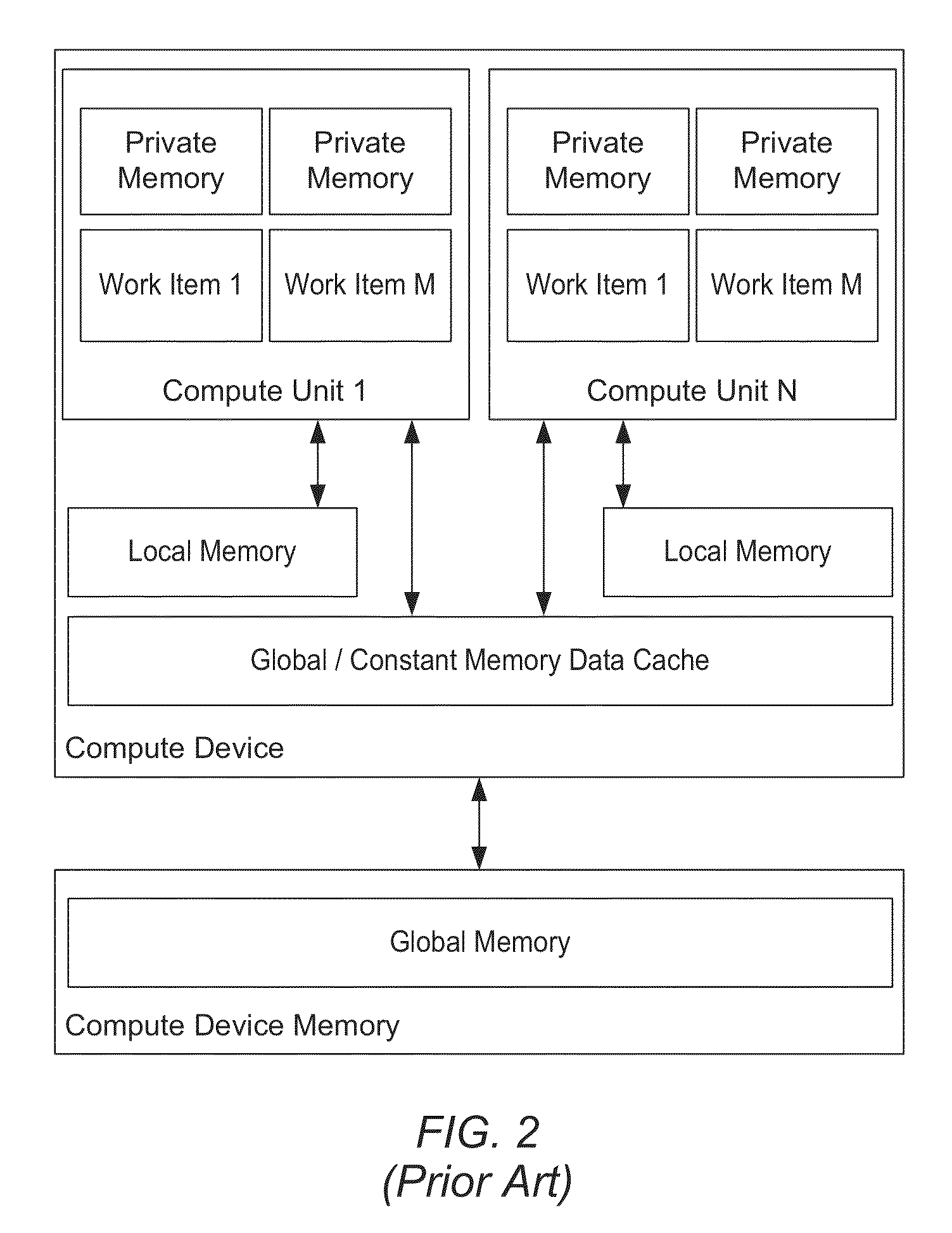
In computer programming, assembly language (or assembler language), often abbreviated asm, is any low-level programming language in which there is a very strong correspondence between the instructions in the language and the architecture's machine code instructions. Assembly language may also be called symbolic machine code.
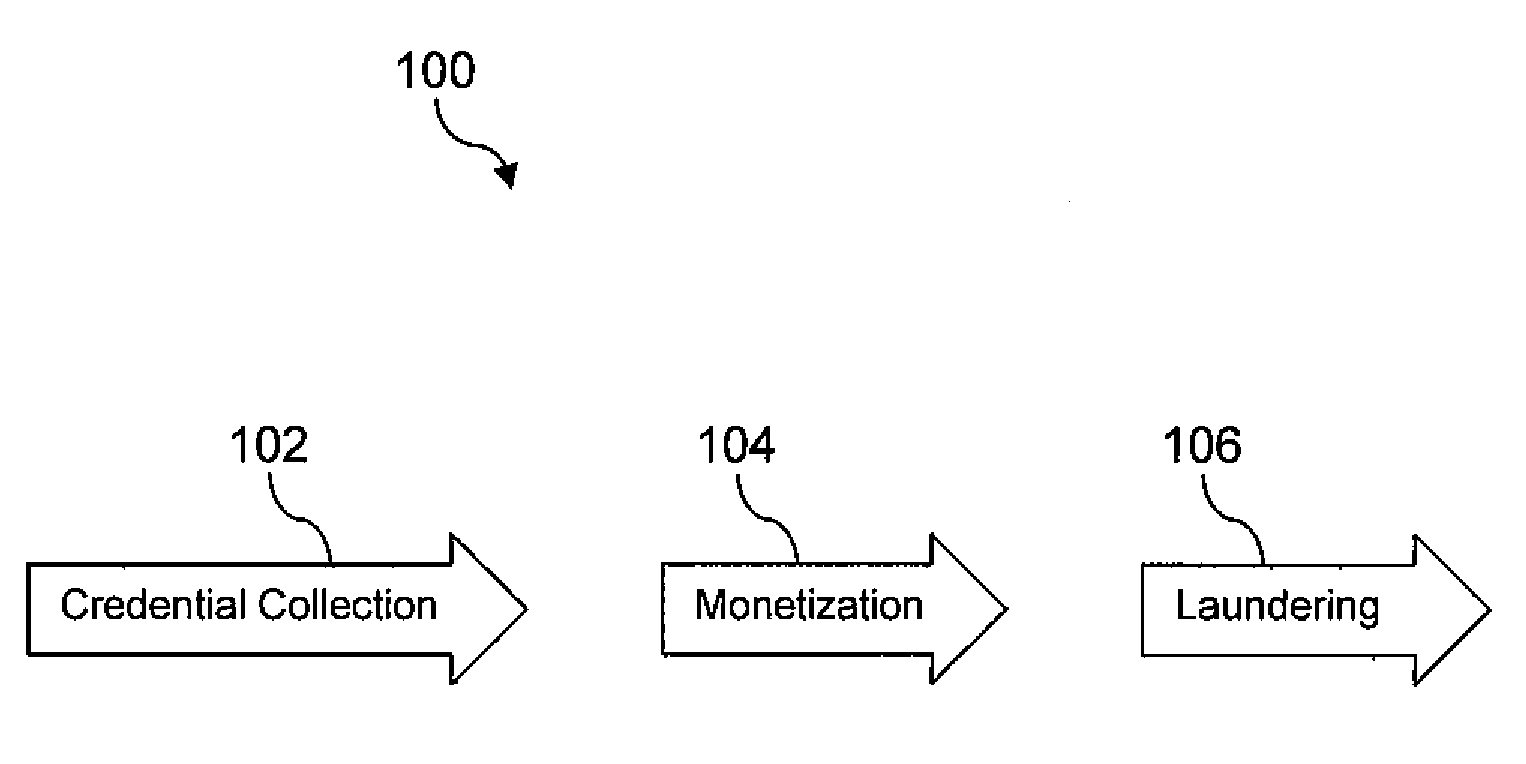
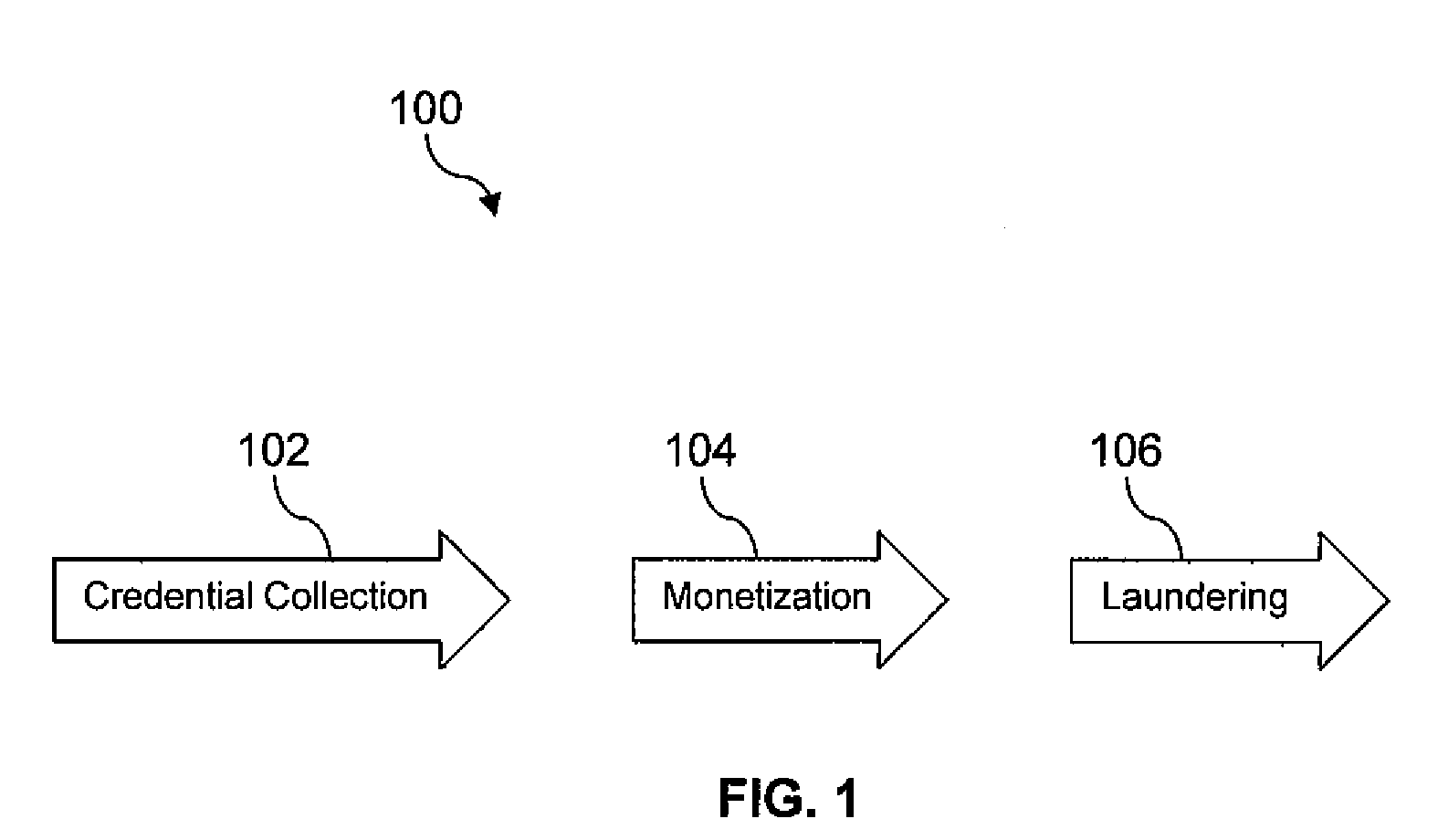
Electronic Crime Detection and Tracking
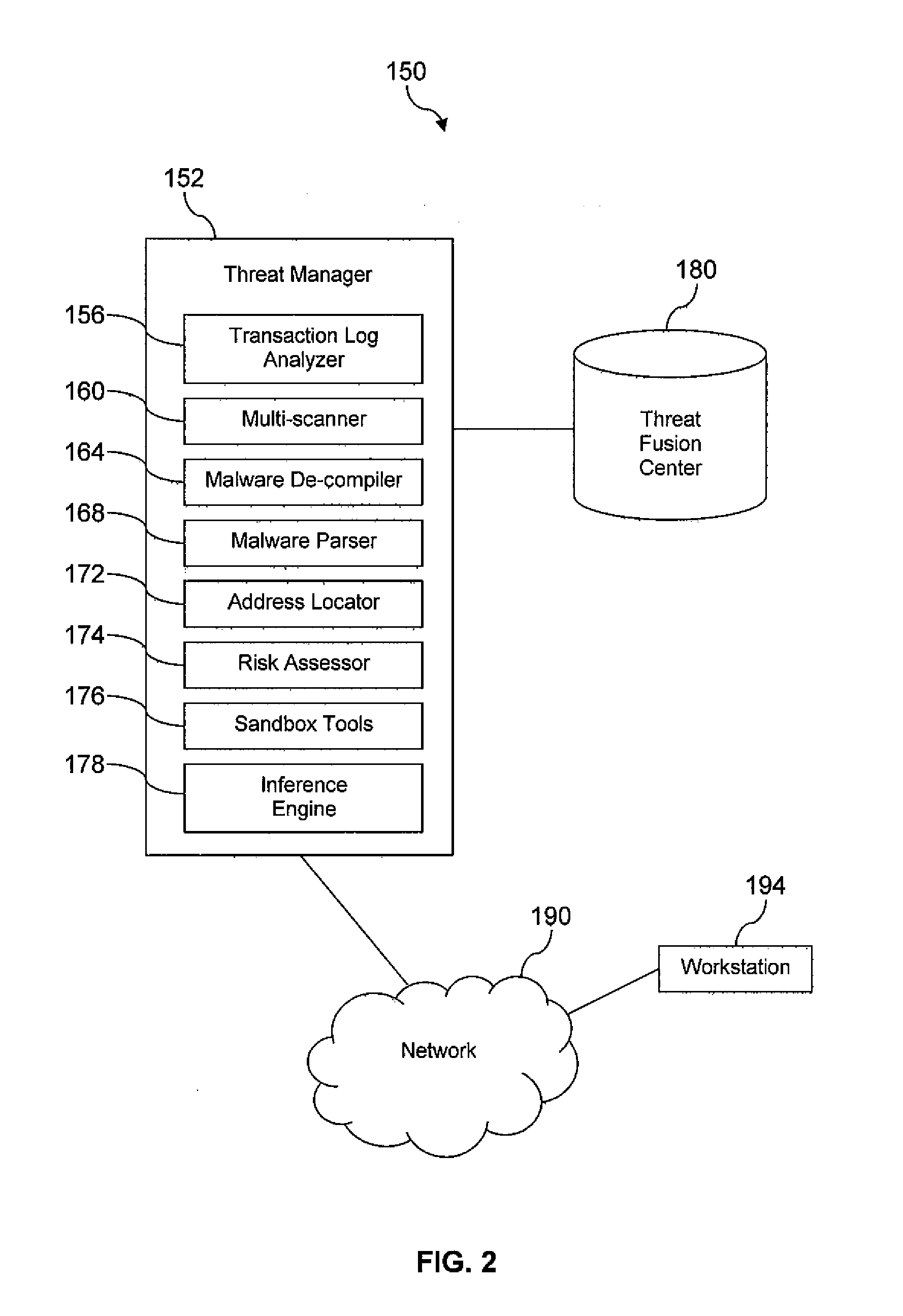
A system for electronic crime reduction is provided, comprising a computer system, a database, a malware de-compiler, a malware parser, and an inference engine. The database contains information that associates electronic crime attack signature data with at least one of an individual, a group, and a location. The malware de-compiler, when executed on the computer system, translates a first malware executable to an assembly language version. The first malware is associated with an electronic crime that has been committed. The malware parser, when executed on the computer system, analyzes the assembly language version to identify distinctive coding preferences used to develop the first malware. The inference engine, when executed on the computer system, analyzes the distinctive coding preferences identified by the malware parser application in combination with searching the database to identify one of an individual, a group, and a location associated with the electronic crime.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Usage semantics
InactiveUS6839062B2Improve the level ofFlexible workflowData processing applicationsImage data processing detailsData streamData set
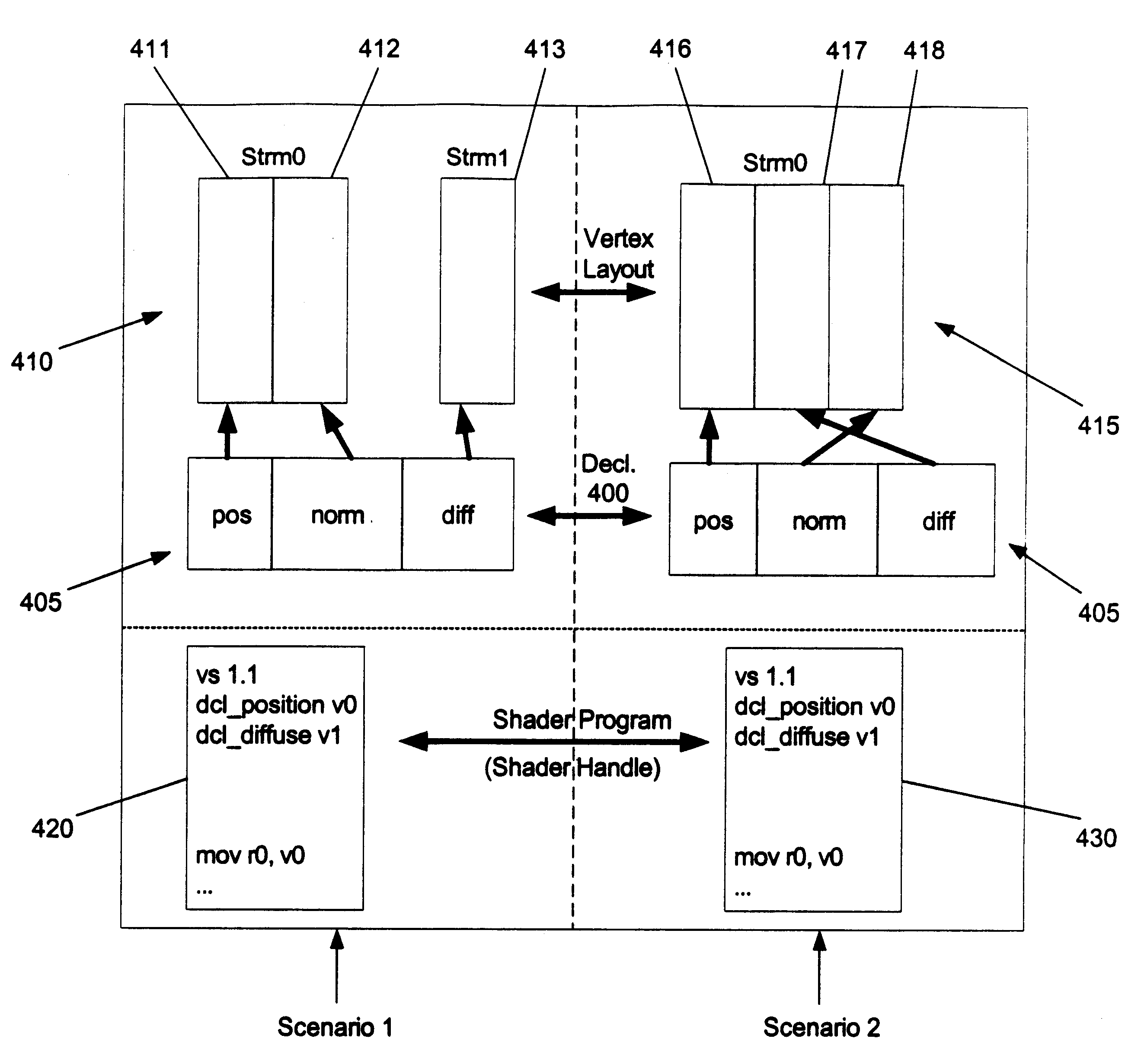
Usage semantics allow for shaders to be authored independently of the actual vertex data and accordingly enables their reuse. Usage semantics define a feature that binds data between distinct components to allow them to work together. In various embodiments, the components include high level language variables that are bound by an application or by vertex data streams, high level language fragments to enable several fragments to be developed separately and compiled at a later time together to form a single shader, assembly language variables that get bound to vertex data streams, and parameters between vertex and pixel shaders. This allows developers to be able to program the shaders in the assembly and high level language with variables that refer to names rather than registers. By allowing this decoupling of registers from the language, developers can work on the language separately from the vertex data and modify and enhance high level language shaders without having to manually manipulate the registers. This also allows the same shaders to work on different sets of mesh data, allowing the shaders to be reused. Generally, semantics can be used as a data binding protocol between distinct areas of the programmable pipeline to allow for a more flexible workflow.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System for obfuscating computer code upon disassembly
InactiveUS7065652B1Avoid disassemblyDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationObfuscationDerivative work
Owner:SAFENET DATA SECURITY ISRAEL
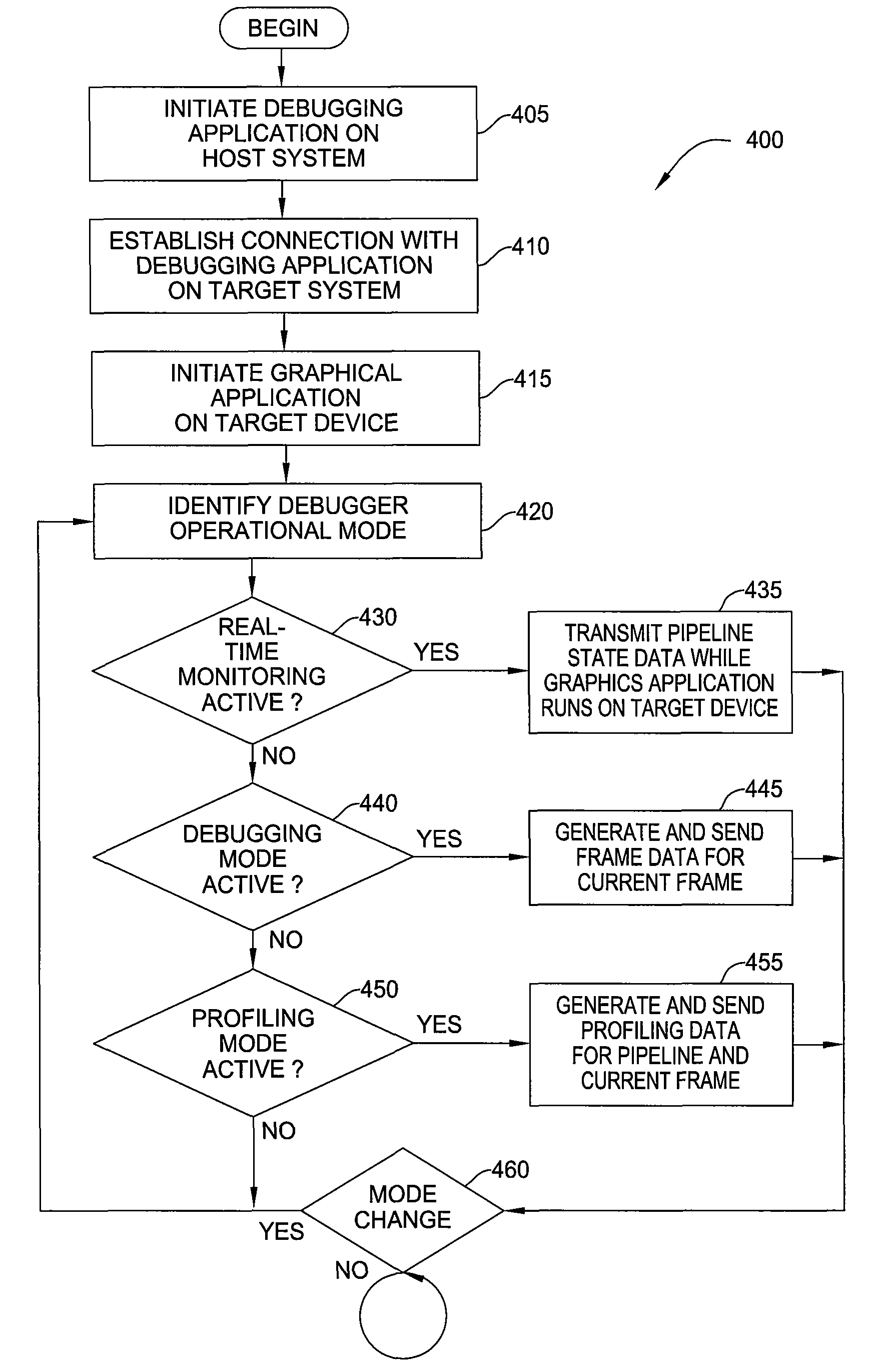
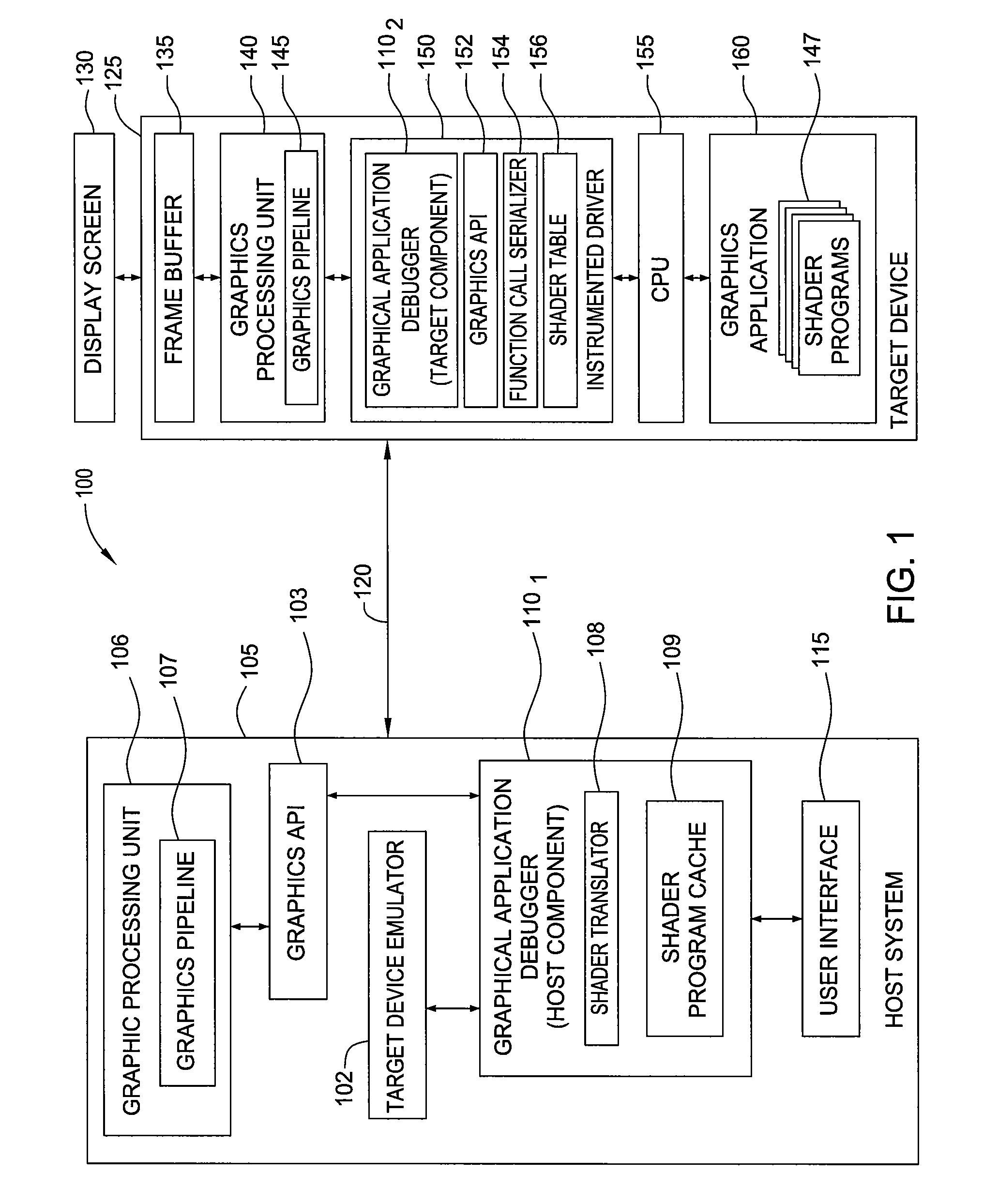
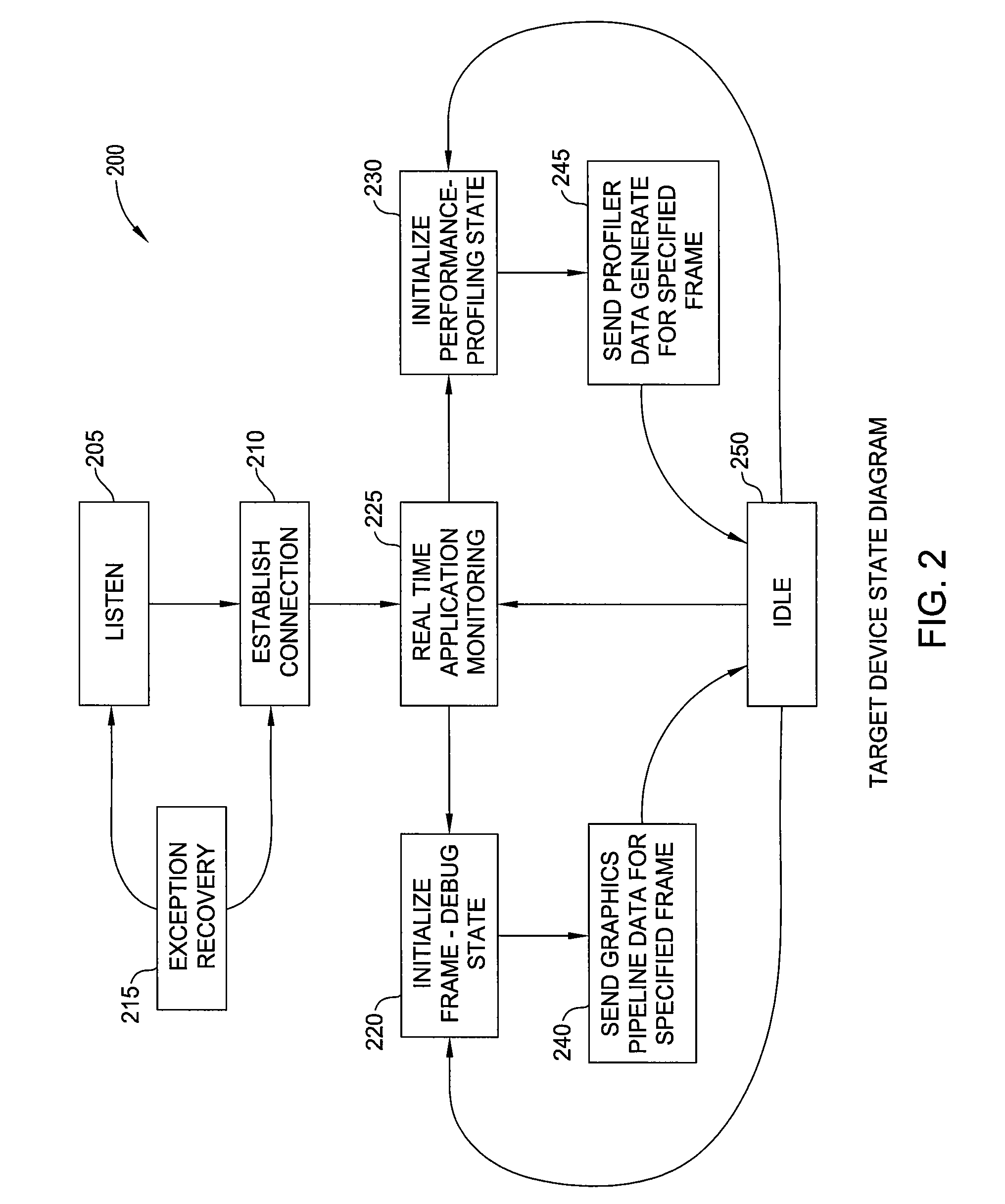
Translation of a shader assembly language binary for debugging a graphics application running on a remote device
ActiveUS8001531B1Error detection/correctionMultiple digital computer combinationsCommunication linkSerialization
Embodiments of the invention provide a debugging tool configured to translate a pre-compiled binary shader as part of debugging a graphics application running on a remote device. An instrumented driver may capture and serialize each graphics API call invoked by a graphics application running on the remote device along with any pre-compiled binary shader programs supplied by the graphics application. The graphical application debugger may translate the shader program into a form appropriate for graphics hardware present on the host system. By replaying the same sequence of API calls invoked on the target device using the same shader programs, the graphical application debugger may generate and display the same image displayed on the target device without the latency of waiting for a full set of framebuffer data to be transmitted over the communication link for each frame rendered on the target device.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Firmware ROM Patch Method
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
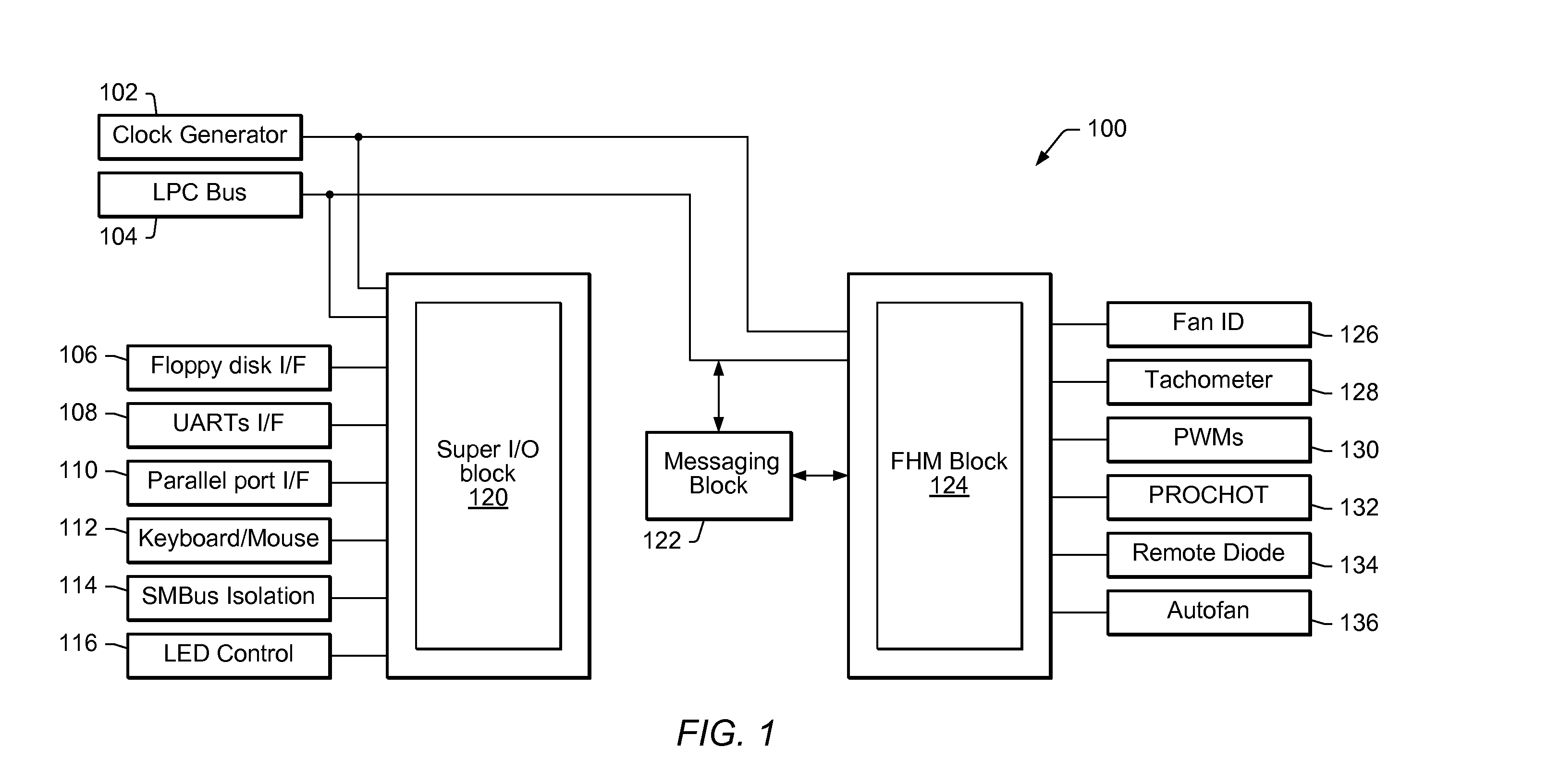
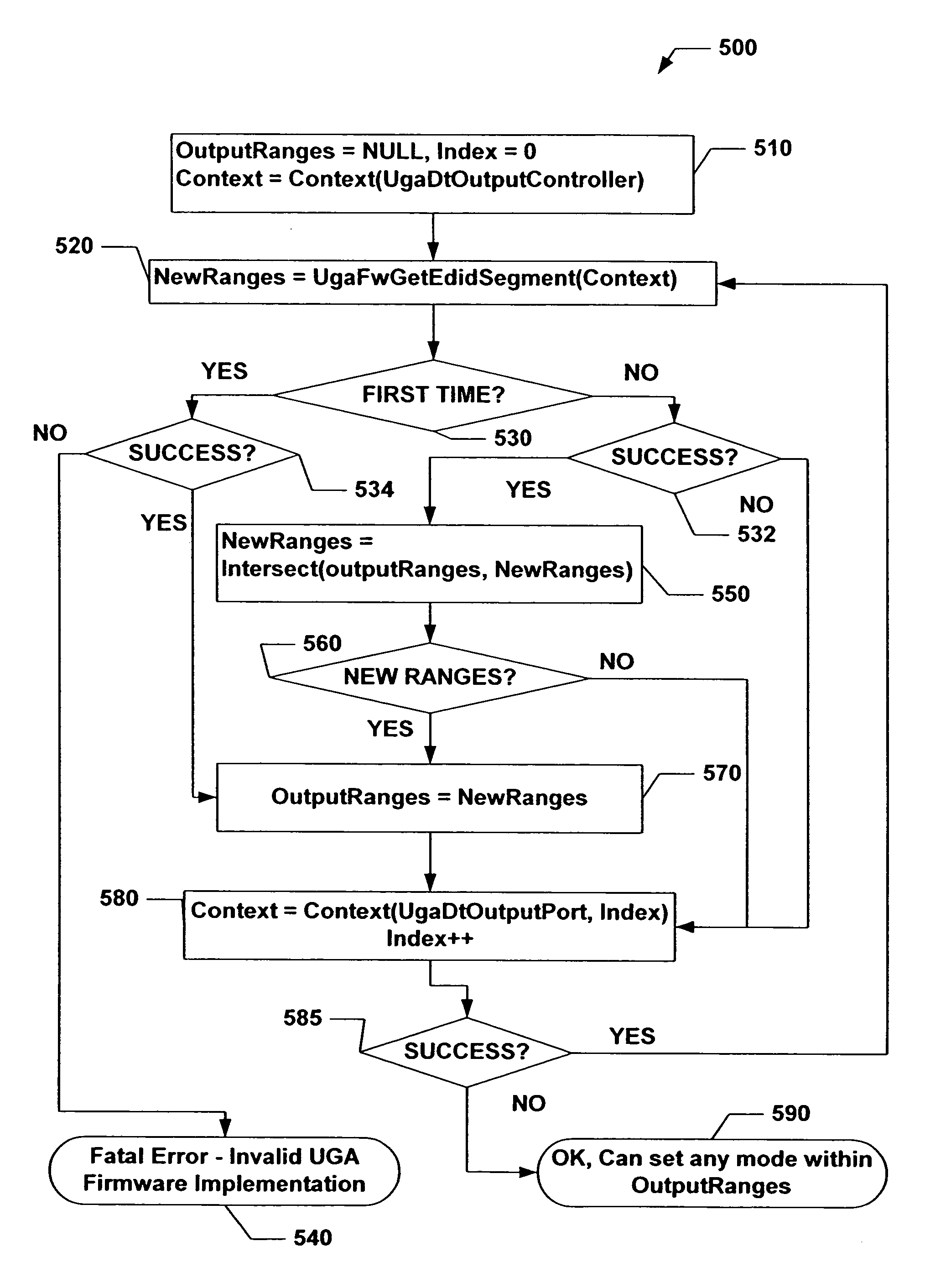
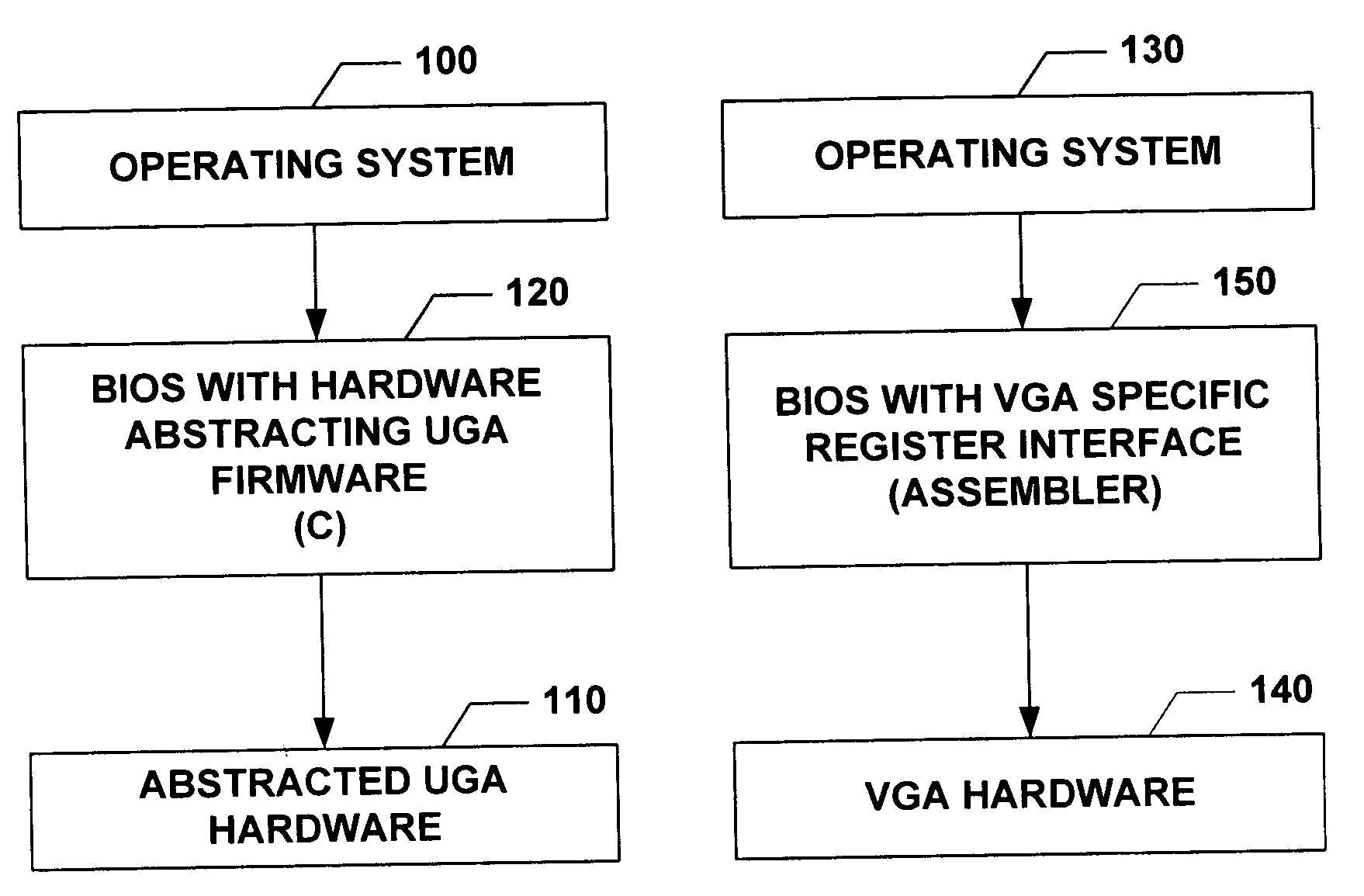
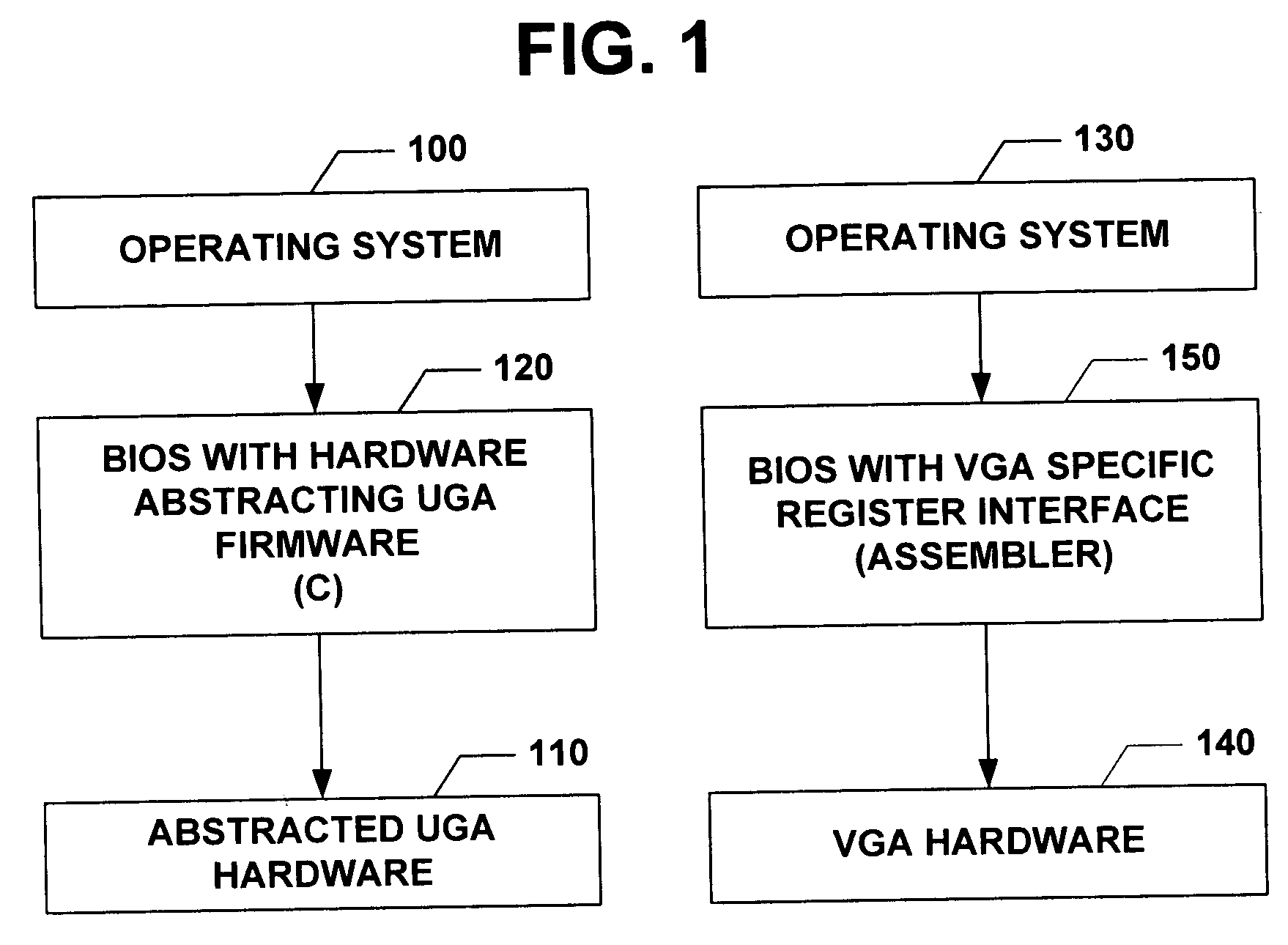
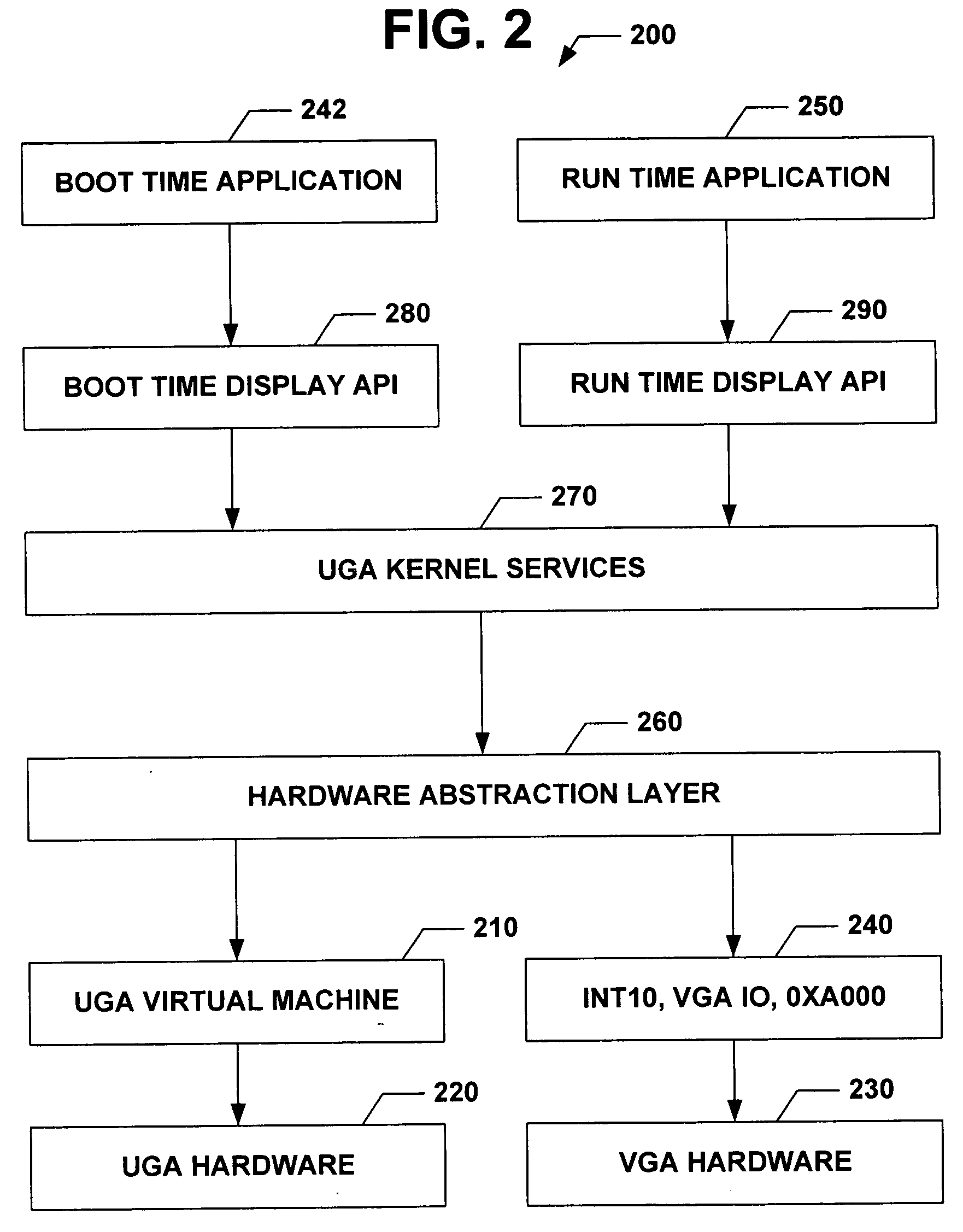
Universal graphic adapter for interfacing with hardware and means for determining previous output ranges of other devices and current device intial ranges
InactiveUS7257650B2Easy to updateQuality improvementDigital computer detailsData resettingProcessor registerAssembly language
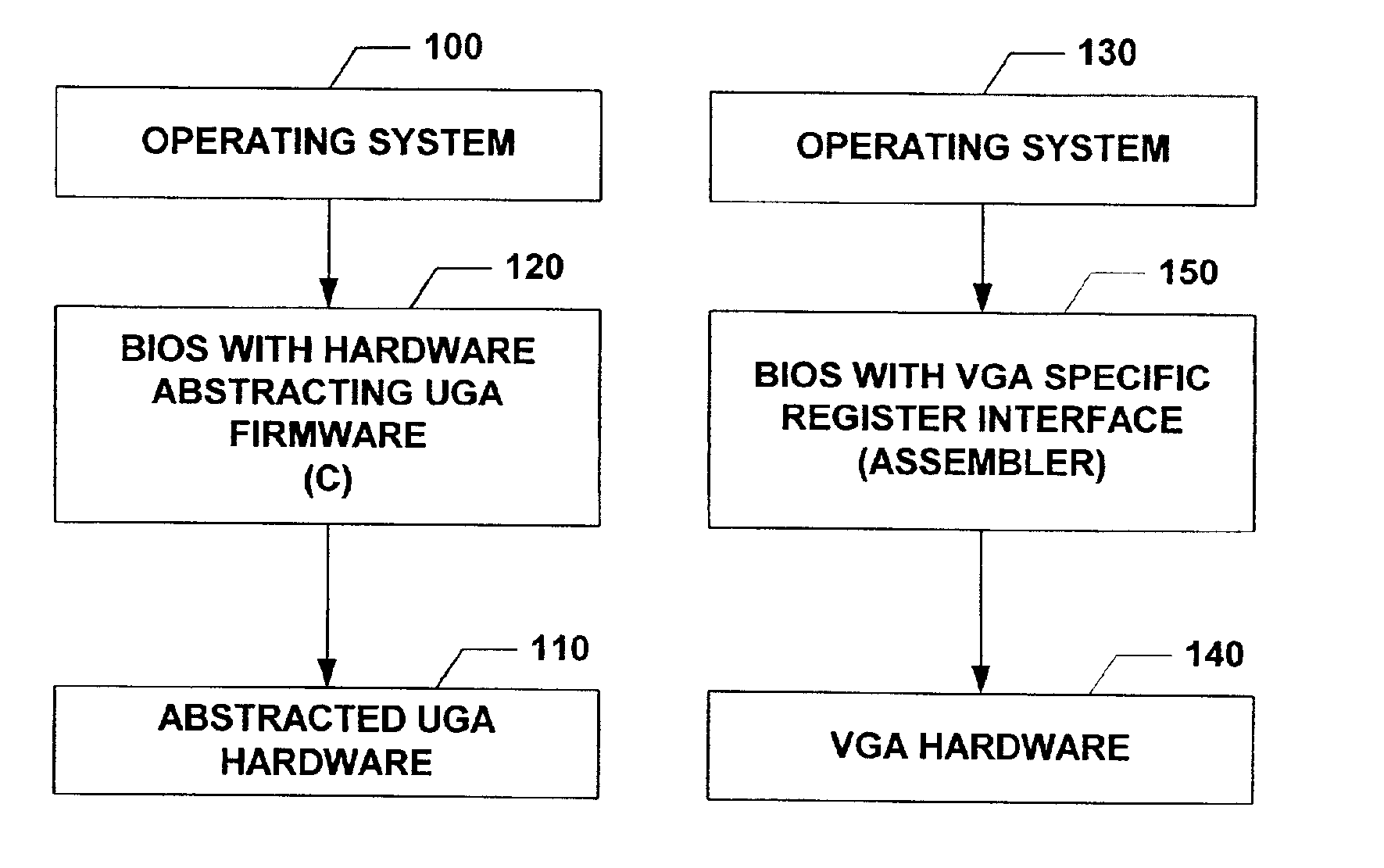
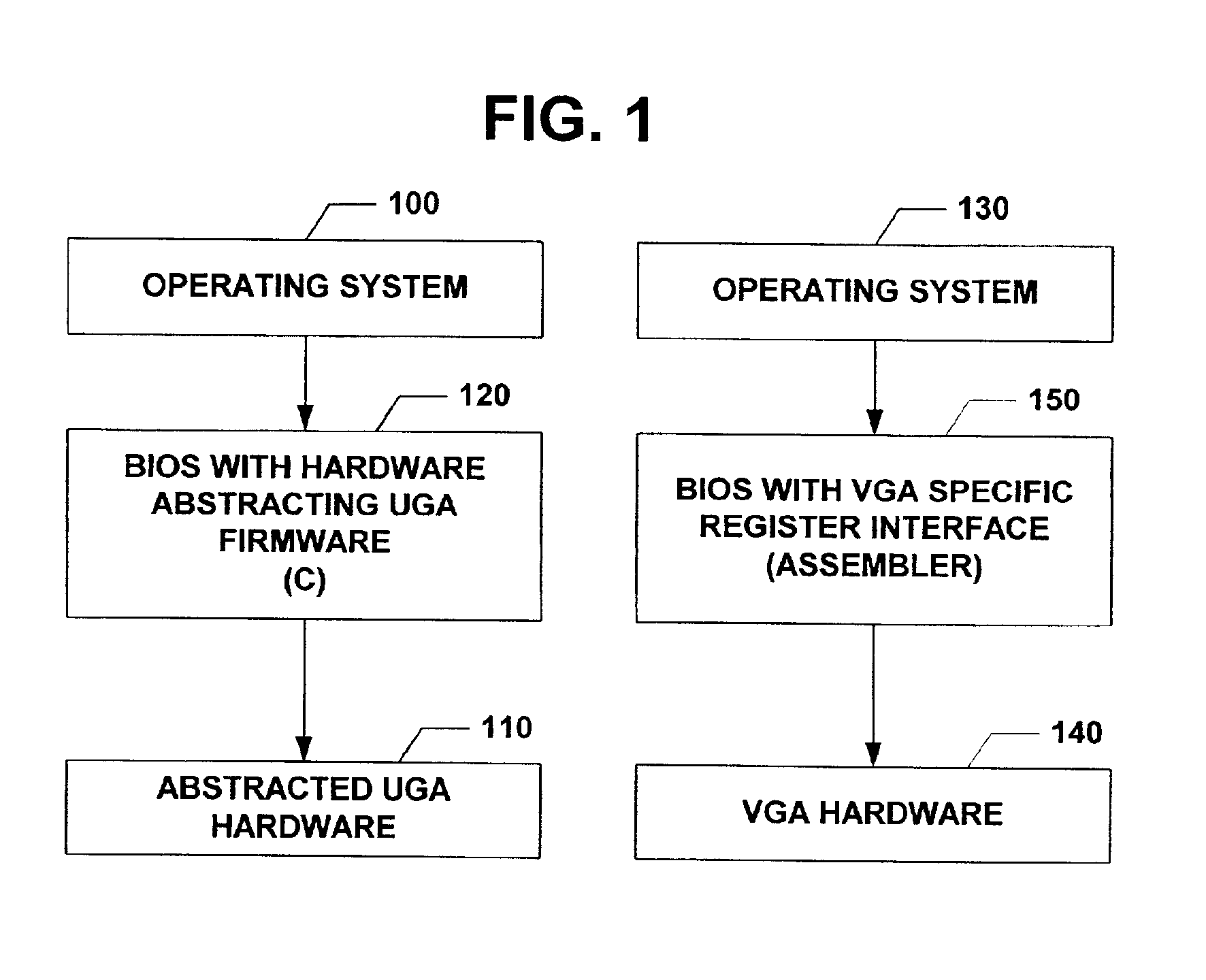
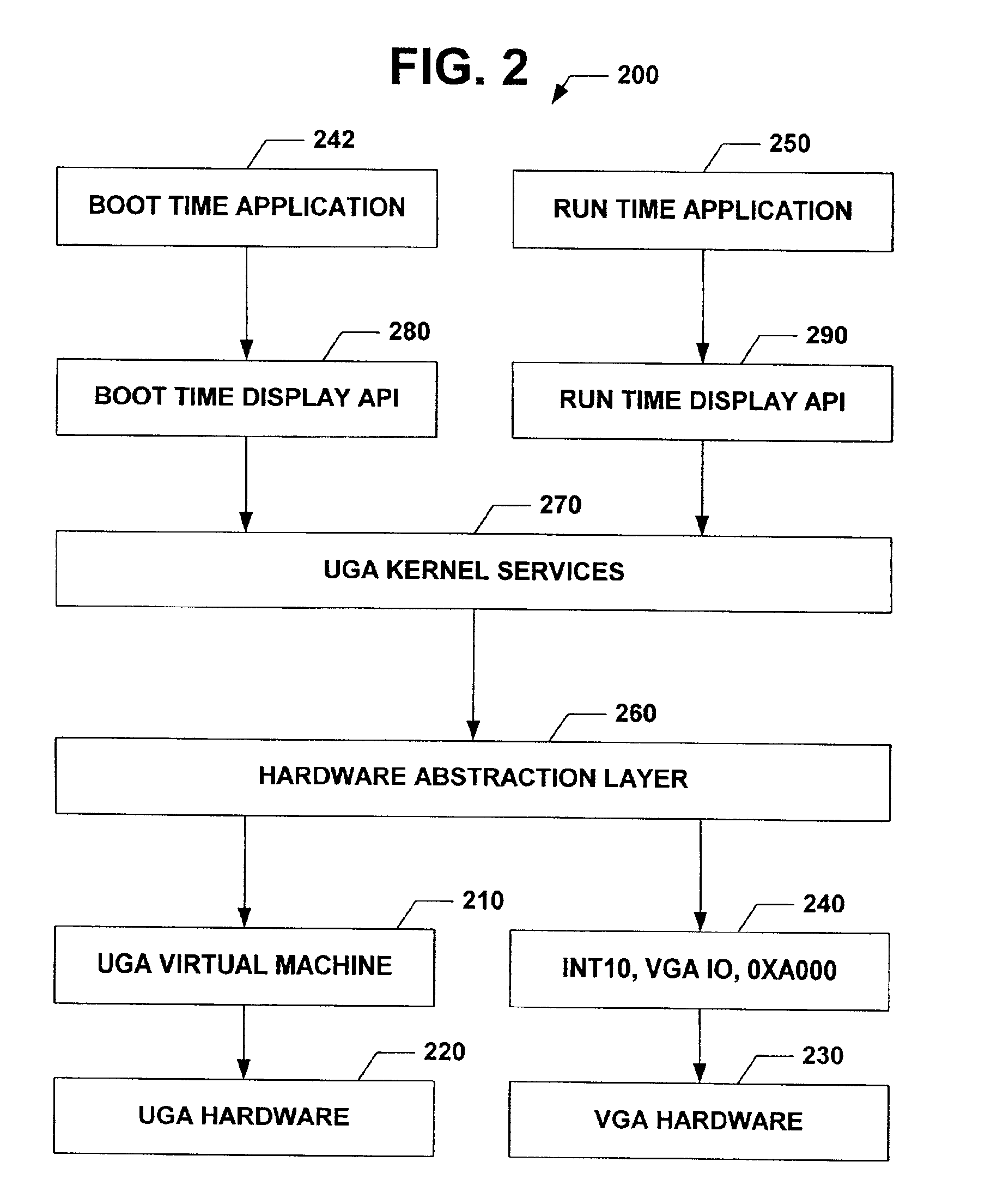
The subject invention relates to a Universal Graphics Adapter (UGA) that is a hardware-independent design that encapsulates and abstracts low-level graphics hardware in a standard manner through firmware. UGA is a firmware standard, intended to wrap existing or planned hardware, including VGA. UGA does not require the use of real-mode assembly language, direct hardware register, or frame buffer access to program, thus providing advantages over conventional systems. UGA supports basic drawing operations, continuous display modes, and power management. As a firmware-based standard, UGA facilitates updating a system to support both evolving and new hardware features.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Memory-network processor with programmable optimizations
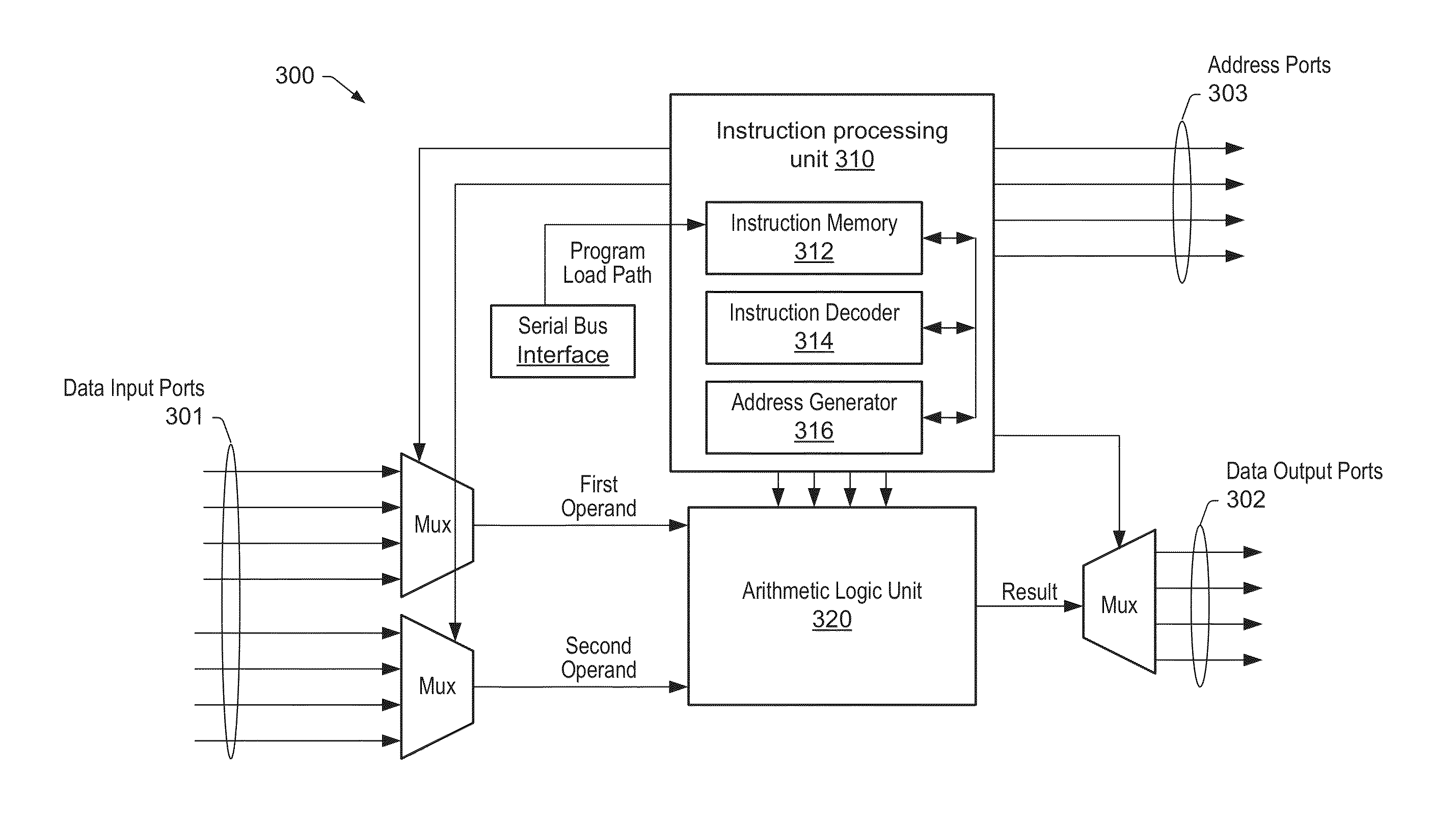
ActiveUS20140351551A1Efficient executionInstruction analysisMemory adressing/allocation/relocationAddress generation unitMulti processor
Various embodiments are disclosed of a multiprocessor system with processing elements optimized for high performance and low power dissipation and an associated method of programming the processing elements. Each processing element may comprise a fetch unit and a plurality of address generator units and a plurality of pipelined datapaths. The fetch unit may be configured to receive a multi-part instruction, wherein the multi-part instruction includes a plurality of fields. A first address generator unit may be configured to perform an arithmetic operation dependent upon a first field of the plurality of fields. A second address generator unit may be configured to generate at least one address of a plurality of addresses, wherein each address is dependent upon a respective field of the plurality of fields. A parallel assembly language may be used to control the plurality of address generator units and the plurality of pipelined datapaths.
Owner:COHERENT LOGIX
System and method to display raster images with negligible delay time and reduced memory requirements
The present invention is directed to a general purpose raster image system. The present invention performs transformations on an original raster image, and optimizes the raster image decoding and display techniques, to dramatically increase the display performance capabilities by a factor of up to fifteen times the performance provided by previous raster devices. The present invention employs two primary enhanced display features to produce fast raster image decode and display results: (1) data reduction and transformations and (2) optimized algorithmic implementations. Data reduction and transformations operate as follows: a raster image is divided into strips, which are processed individually. A feature of the optimized algorithmic implementation is to increase processing thruput of the display process by optimizing the use of available resources required to decode and display the raster images. In one embodiment, scaling operations are converted from calculation based algorithms, to data lookup tables indexed by the position of the raster image data in the original scan line. Raster image decoding algorithms are changed from iterative conditional loops to redundant code segments individually tailored for specific occurrences of raster image data. Additionally implementation of assembly language in time critical sections of display procedures allocates CPU register resources more efficiently and significantly increases performance.
Owner:UNISYS CORP
Memory-network processor with programmable optimizations
ActiveUS9430369B2Efficient executionInstruction analysisMemory adressing/allocation/relocationAddress generation unitMulti processor
Various embodiments are disclosed of a multiprocessor system with processing elements optimized for high performance and low power dissipation and an associated method of programming the processing elements. Each processing element may comprise a fetch unit and a plurality of address generator units and a plurality of pipelined datapaths. The fetch unit may be configured to receive a multi-part instruction, wherein the multi-part instruction includes a plurality of fields. A first address generator unit may be configured to perform an arithmetic operation dependent upon a first field of the plurality of fields. A second address generator unit may be configured to generate at least one address of a plurality of addresses, wherein each address is dependent upon a respective field of the plurality of fields. A parallel assembly language may be used to control the plurality of address generator units and the plurality of pipelined datapaths.
Owner:COHERENT LOGIX
Binary program vulnerability discovery method and system
ActiveCN105678169AExcavate accuratelyAccurate locationPlatform integrity maintainanceCode conversionAssembly language
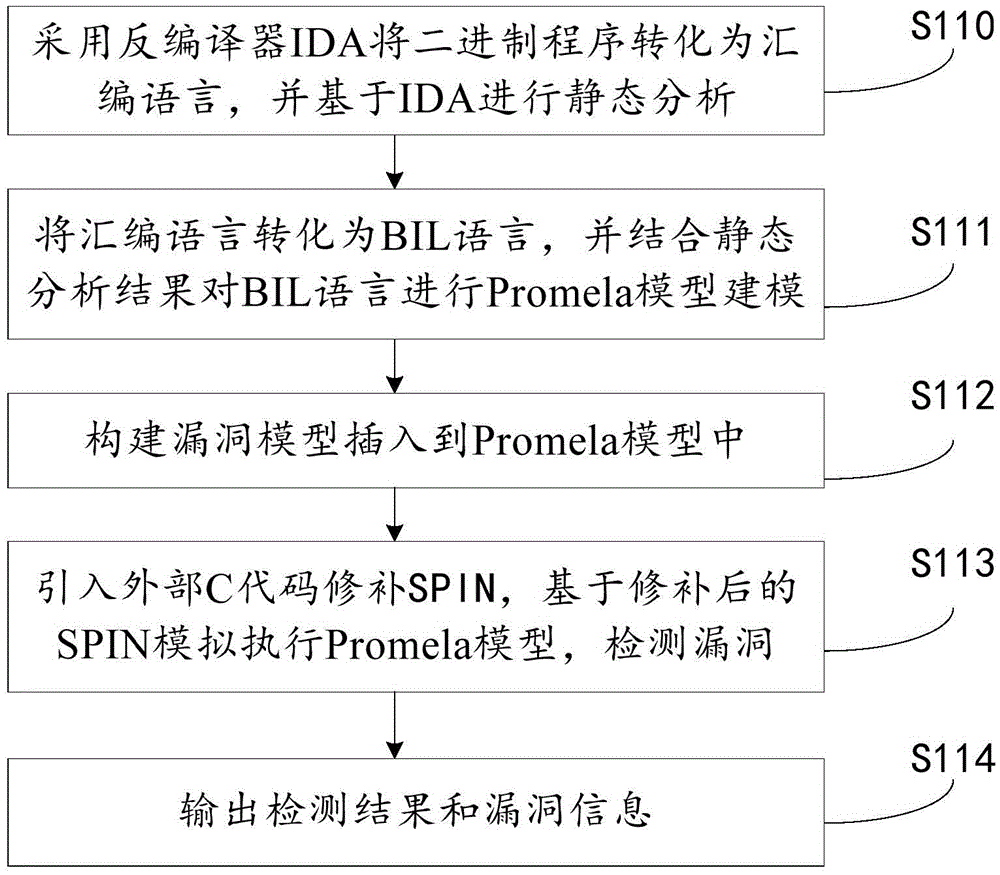
The invention provides a binary program vulnerability discovery method. The binary program vulnerability discovery method comprises steps of converting a target binary program into an assembly language, and carrying out static analysis to the assembly language; carrying out Promela model modeling to an intermediate language by combining the analysis result of the static analysis; establishing a vulnerability model and inserting the vulnerability model into the Promela model; introducing an external C code, simulating and executing the Promela model based on an SPIN, and detecting the vulnerability. The invention also provides a binary program vulnerability discovery system comprising a preprocessor module, a code conversion module and a model detection module. With respect to the binary program vulnerability discovery method and system, the intermediate language BIL is introduced to serve as a conversion bridge through which the binary program is converted into the Promela model, automatic modeling of the binary program is achieved, the embedded C function of the SPIN is employed to achieve simulation and execution, and the external C code is introduced to correct the defect of model detection. Experimental results show that the binary program vulnerability discovery method can effectively detect memory destructive vulnerabilities of binary programs.
Owner:XIAN HUMEN NETWORK TECH CO LTD
Using an embedded processor to implement a finite state machine
ActiveUS7131077B1CAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationVirtual finite-state machineAssembly language
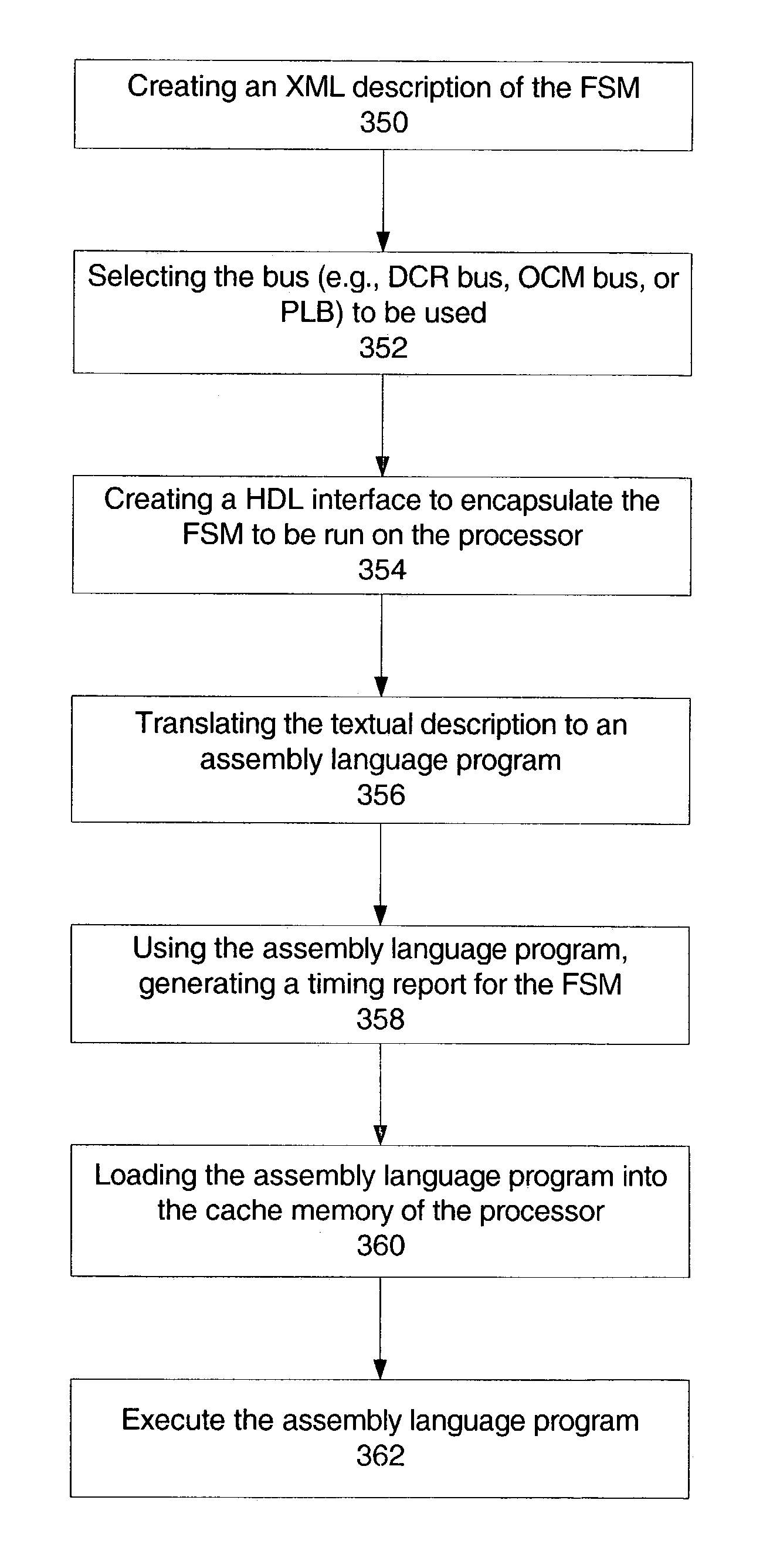
Method and System for implementing a Finite State Machine (FSM) using software executed on a processor and having accurate timing information is described, where the accurate timing information is determined without the need to execute the software. An exemplary embodiment includes an IC having an embedded processor and a programmable logic fabric, where part or all of an FSM is implemented using assembly language code stored in a memory, for example, a cache memory, of the embedded processor.
Owner:XILINX INC
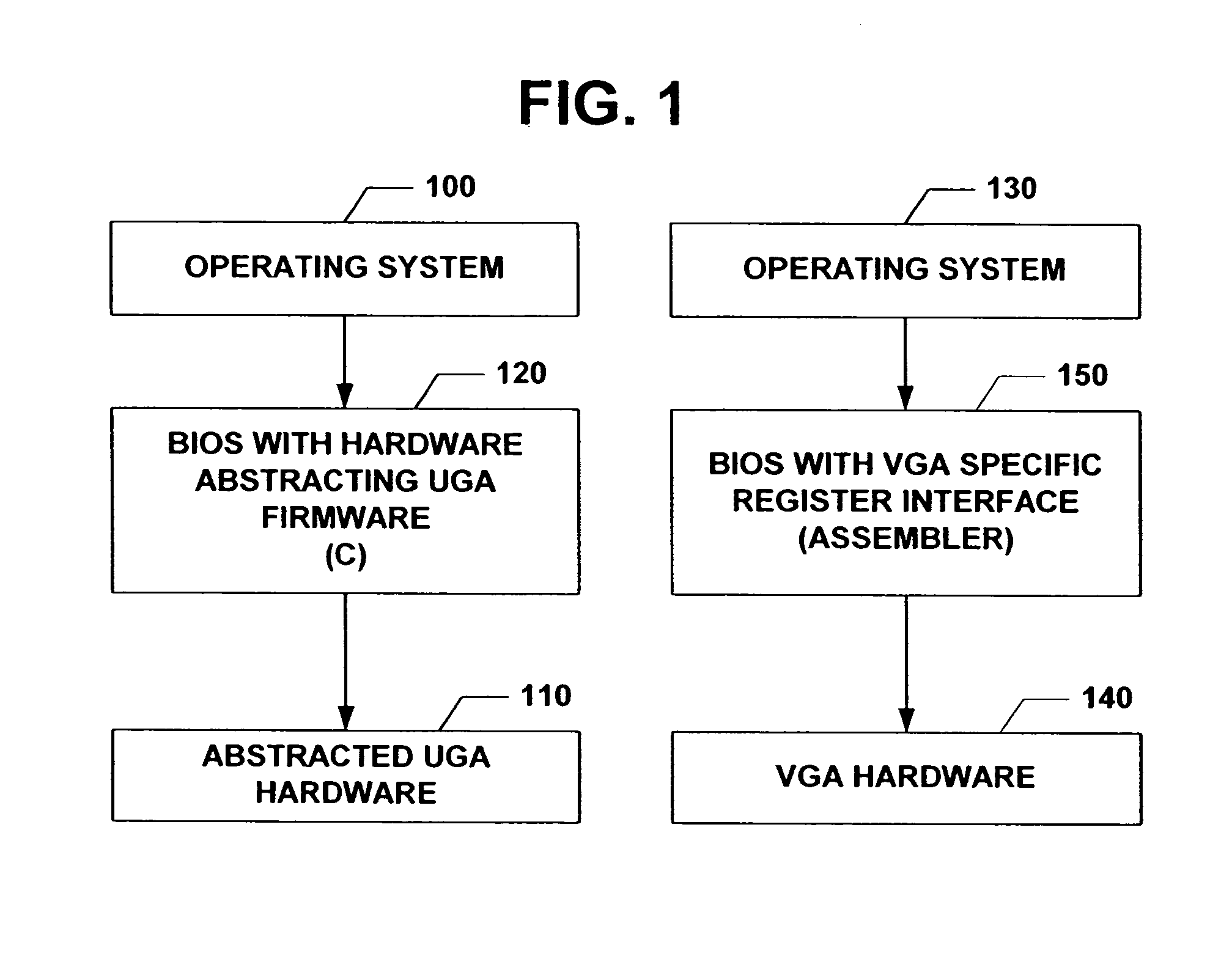
Universal graphic adapter for interfacing with hardware and means for encapsulating and abstracting details of the hardware
InactiveUS6907482B2Easy to updateQuality improvementDigital computer detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsProcessor registerAssembly language
The subject invention relates to a Universal Graphics Adapter (UGA) that is a hardware-independent design that encapsulates and abstracts low-level graphics hardware in a standard manner through firmware. UGA is a firmware standard, intended to wrap existing or planned hardware, including VGA. UGA does not require the use of real-mode assembly language, direct hardware register, or frame buffer access to program, thus providing advantages over conventional systems. UGA supports basic drawing operations, continuous display modes, and power management. As a firmware-based standard, UGA facilitates updating a system to support both evolving and new hardware features.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
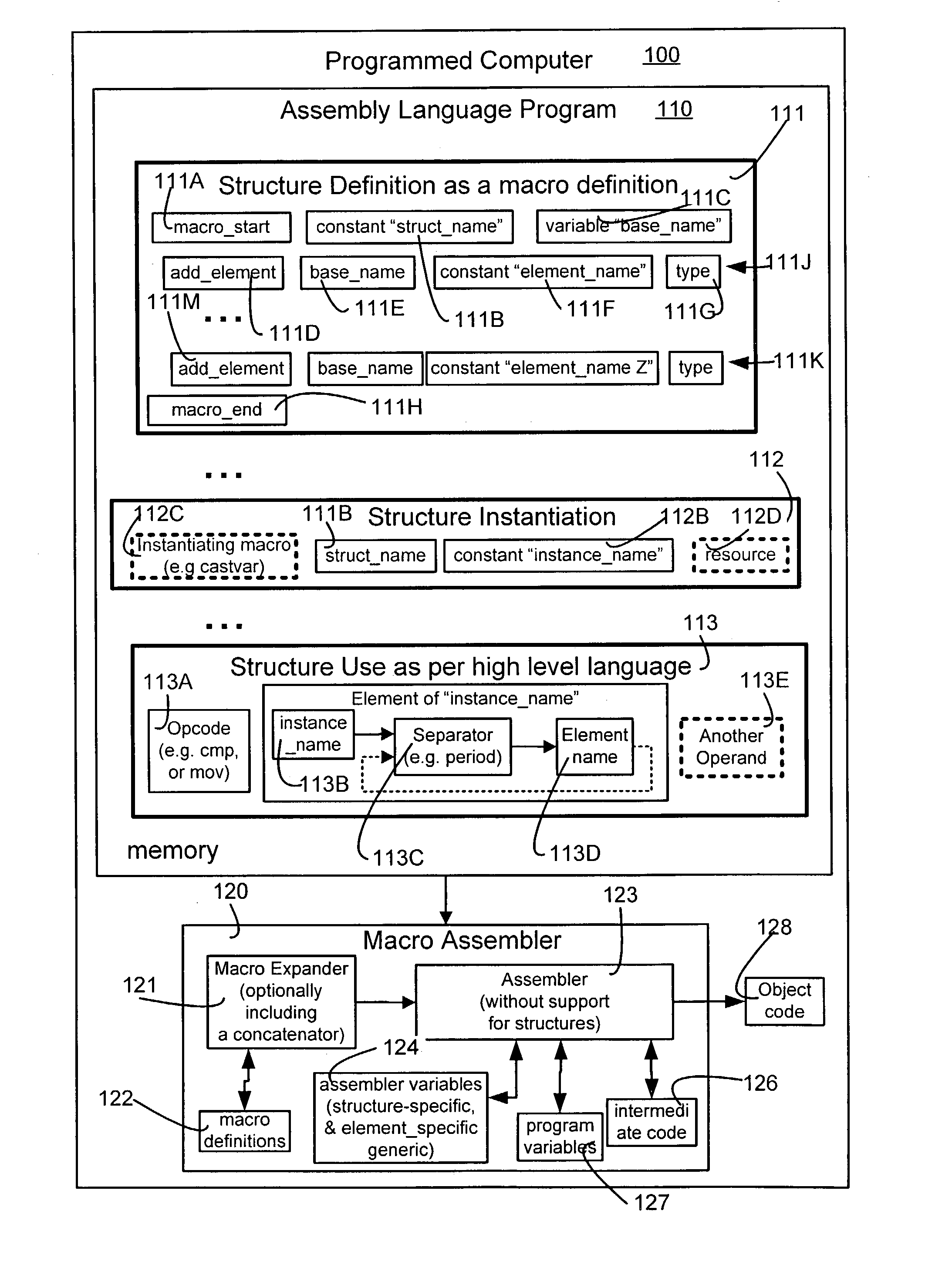
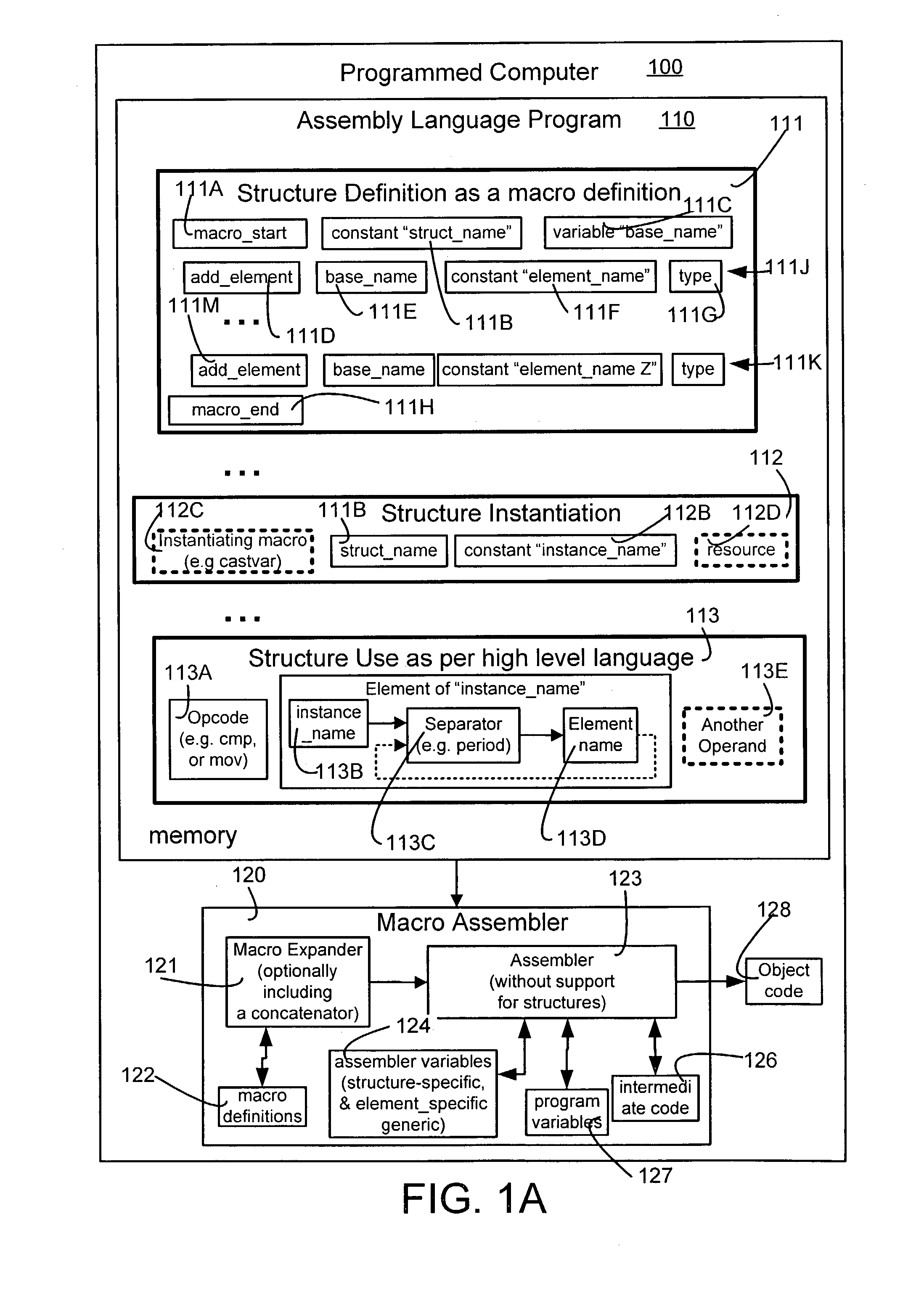
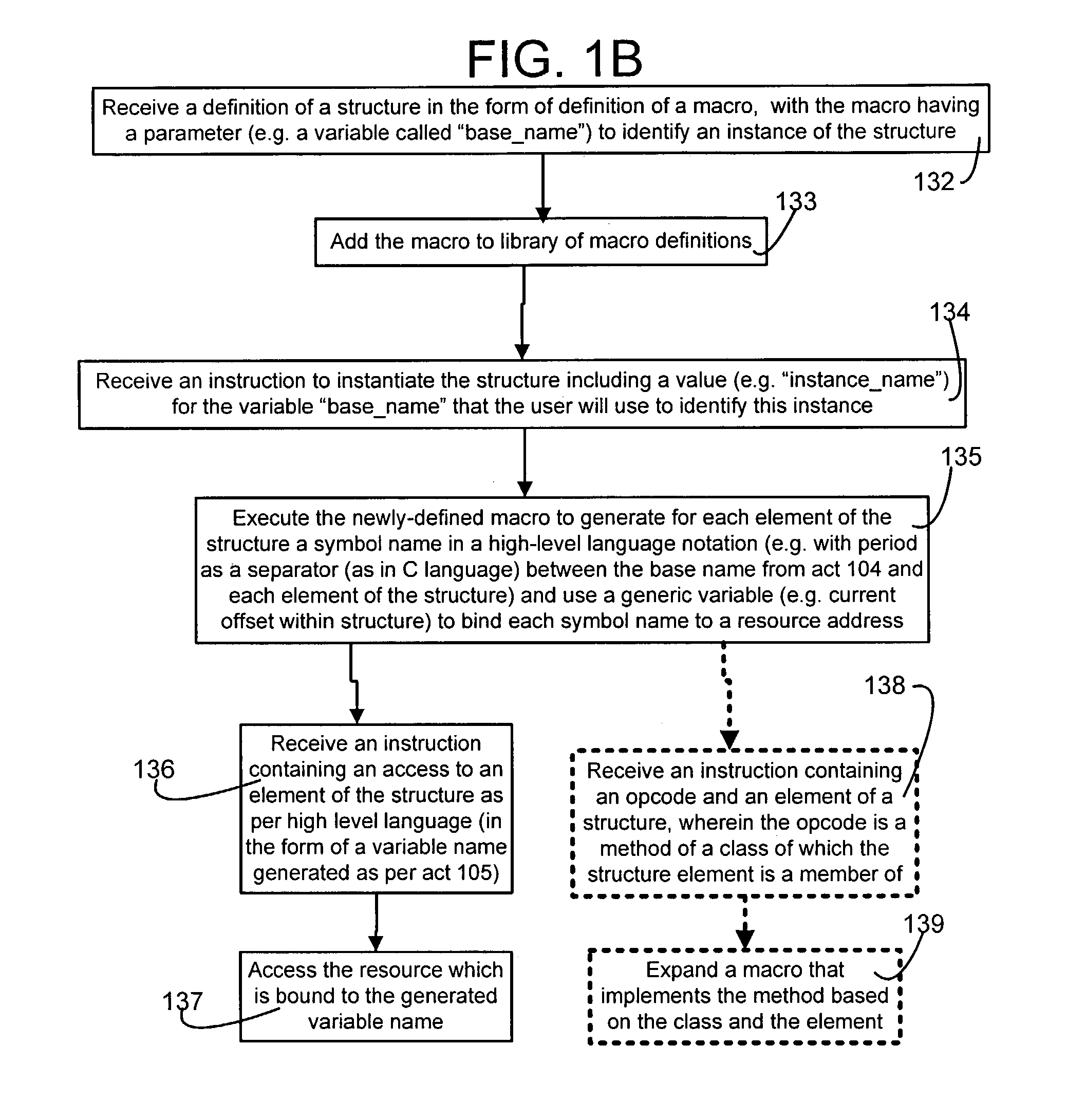
Macros to support structures for an assembler that does not support structures
An assembler incapable of supporting structures of the type supported in the “C” language receives and processes an assembly language program that contains one or more definitions of structures, structure instantiations and structure uses. Specifically, structure definitions are presented in the form of macro definitions. Moreover, a name to be used to identify the structure is passed as a parameter to the macro being defined (also called “structure-definition macro”). Furthermore, one or more members of a structure are presented in the form of arguments to a respective number of one or more macros that are invoked between the beginning and end of the structure-definition macro. During instantiation, variable names are created for each member of the structure, and these names are bound to appropriate addresses of resources. Thereafter, these variable names are used in the assembly language program to access data mapped to the member name.
Owner:OL SECURITY LIABILITY CO
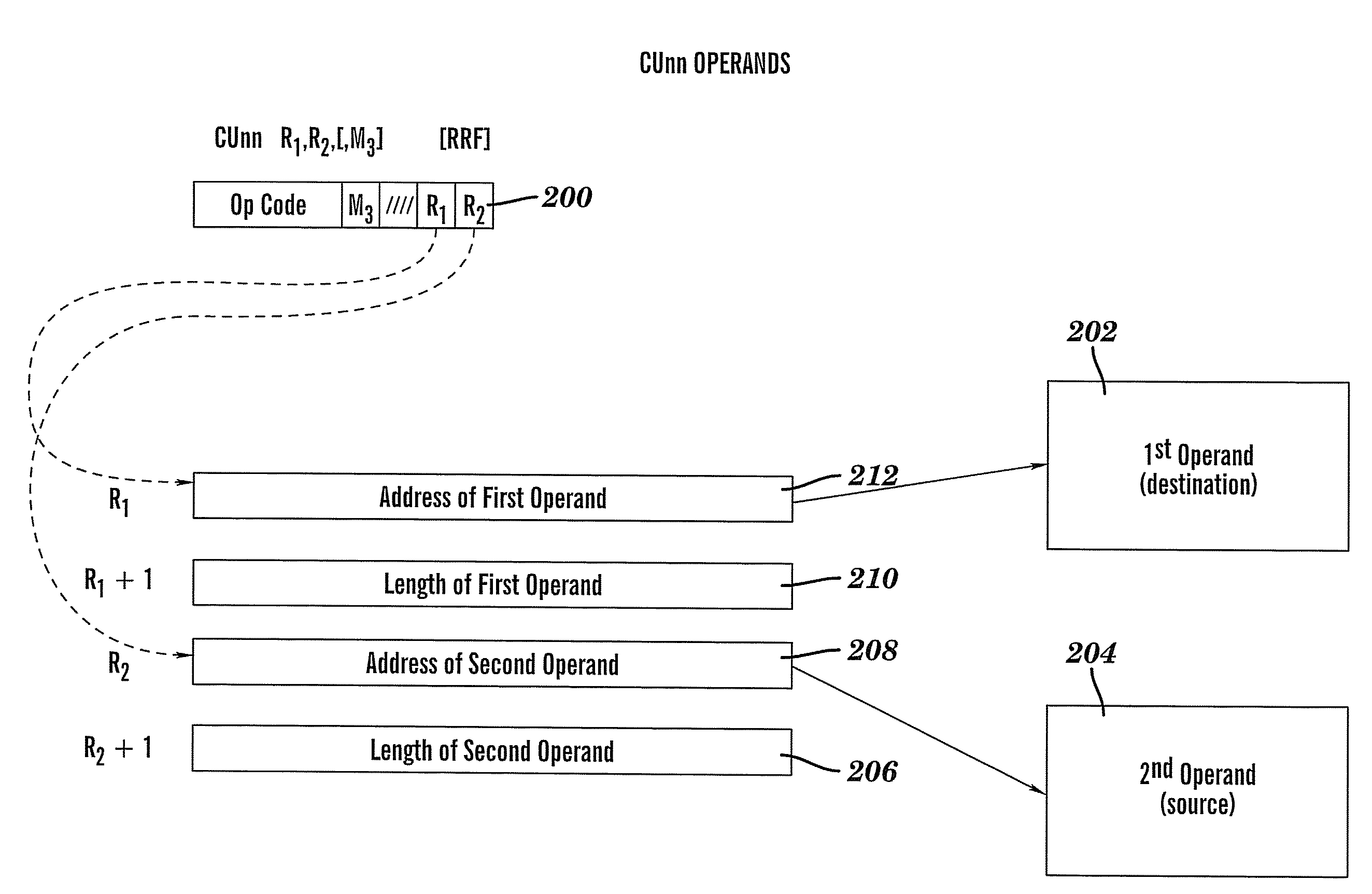
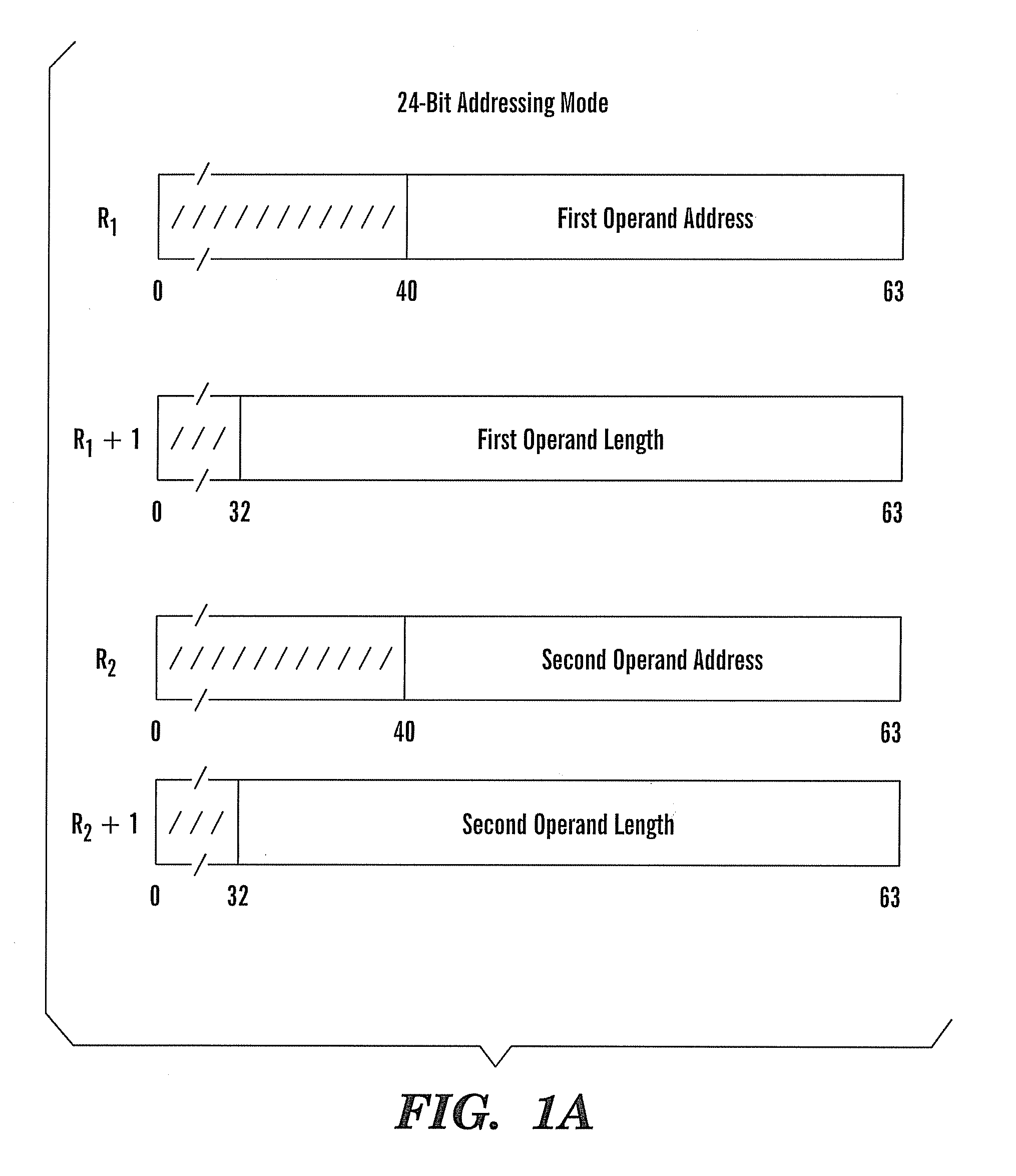
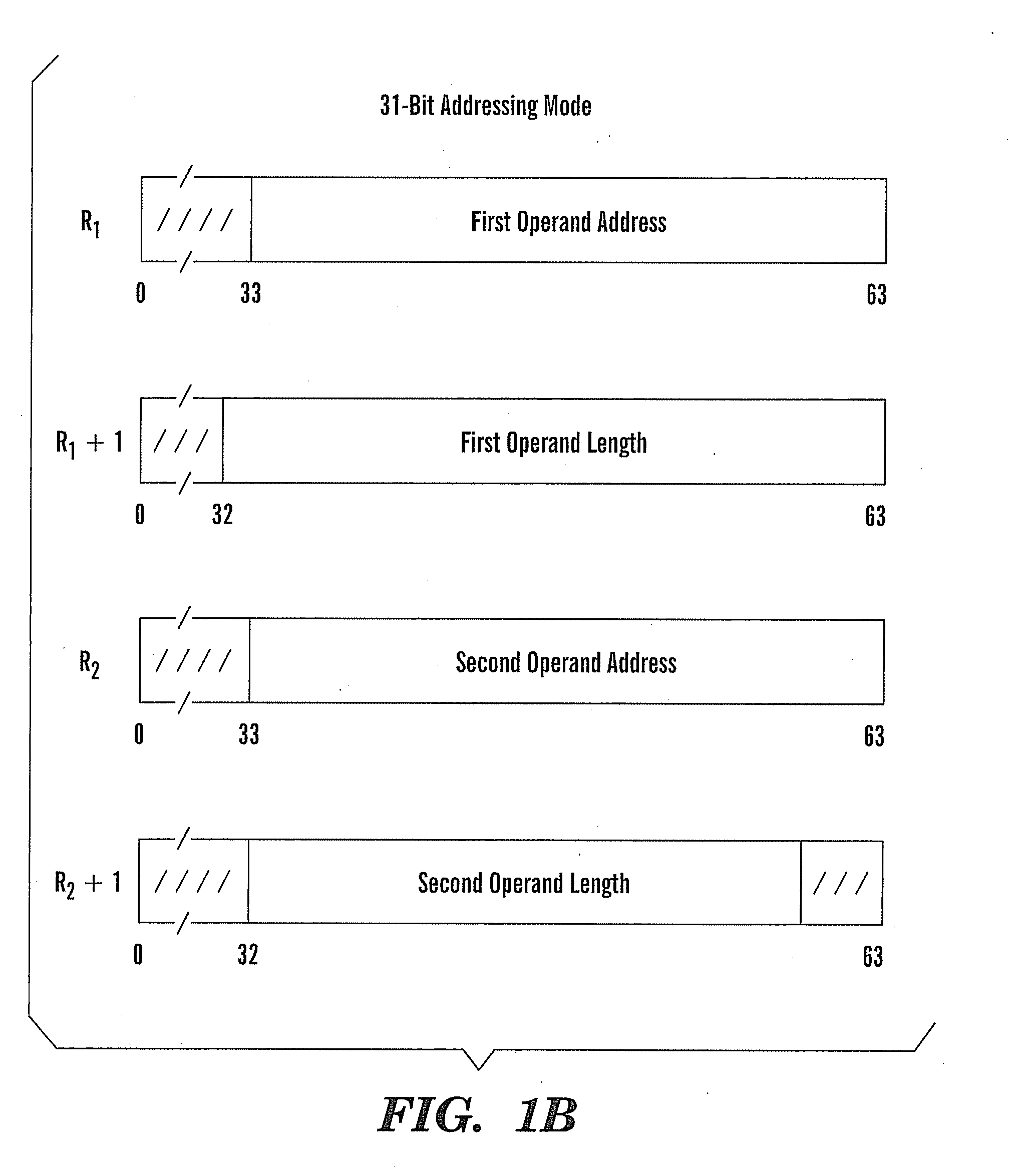
Method of employing instructions to convert utf characters with an enhanced extended translation facility
ActiveUS20080127122A1Natural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsOperandAssembly language
A method, article, and system for providing an effective implementation of assembler language instructions to convert Unicode and Unicode-tranformation-format (UTF) characters implemented on 21, 31, and 64-bit architectures, while maintaining backward compatibility with existing systems. The enhanced Extended-Translation Facility 3 (ETF3) instruction set introduces a new operand in an unused field (M3) that facilitates a change in the original instruction format and its intended function. With the ETF3-Enhancement Facility installed, a value of zeros in the M3 field indicates that instruction operation is to continue as originally defined. When a nonzero value is coded in the M3 field a new function is carried out. The assembler accommodates the changes by making the new M3 field optional when coding the instructions. If the M3 field is not coded, the assembler defaults to providing zeros in the M3 field (as found in the original instruction format), and backward compatible operation is provided.
Owner:IBM CORP
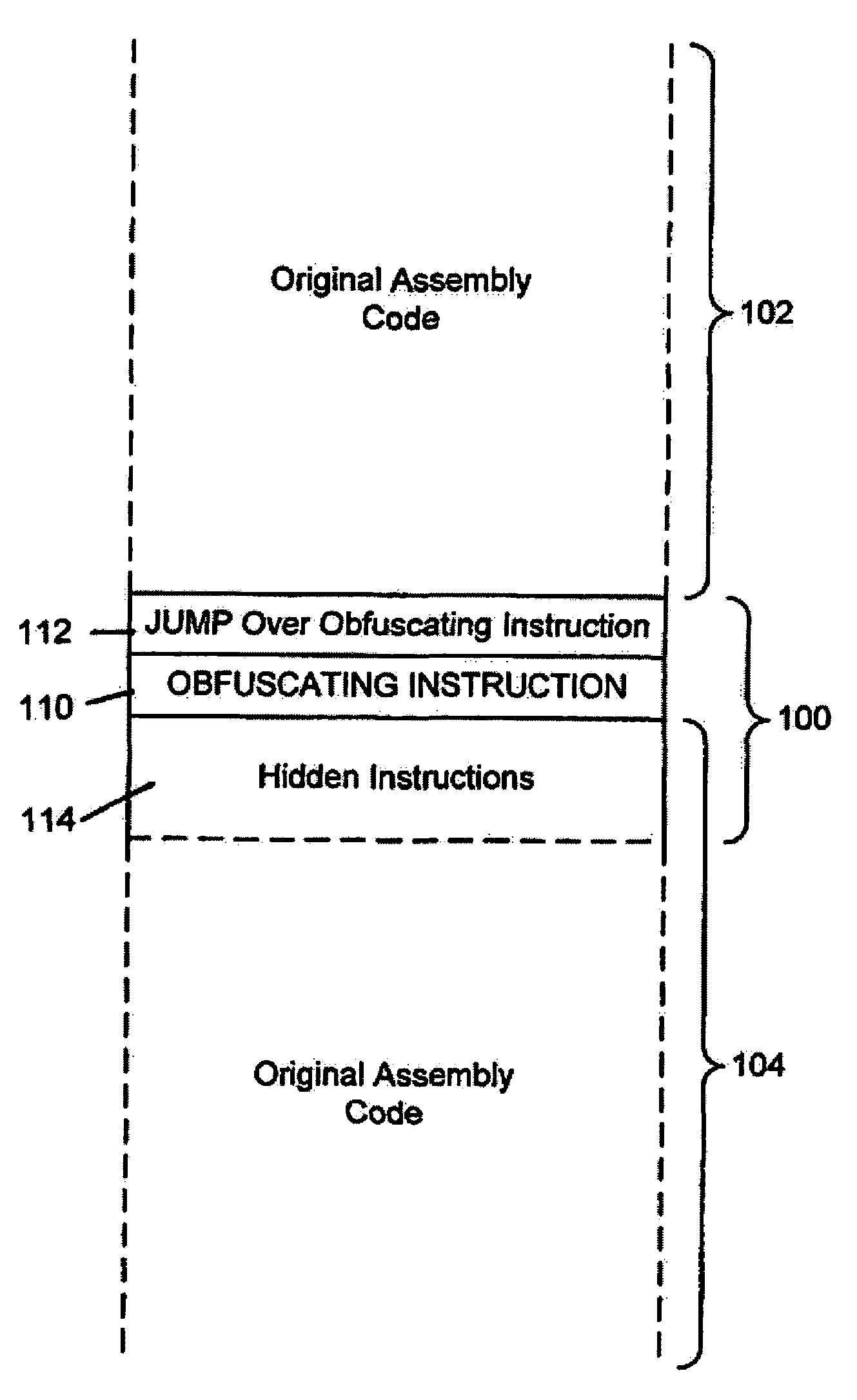
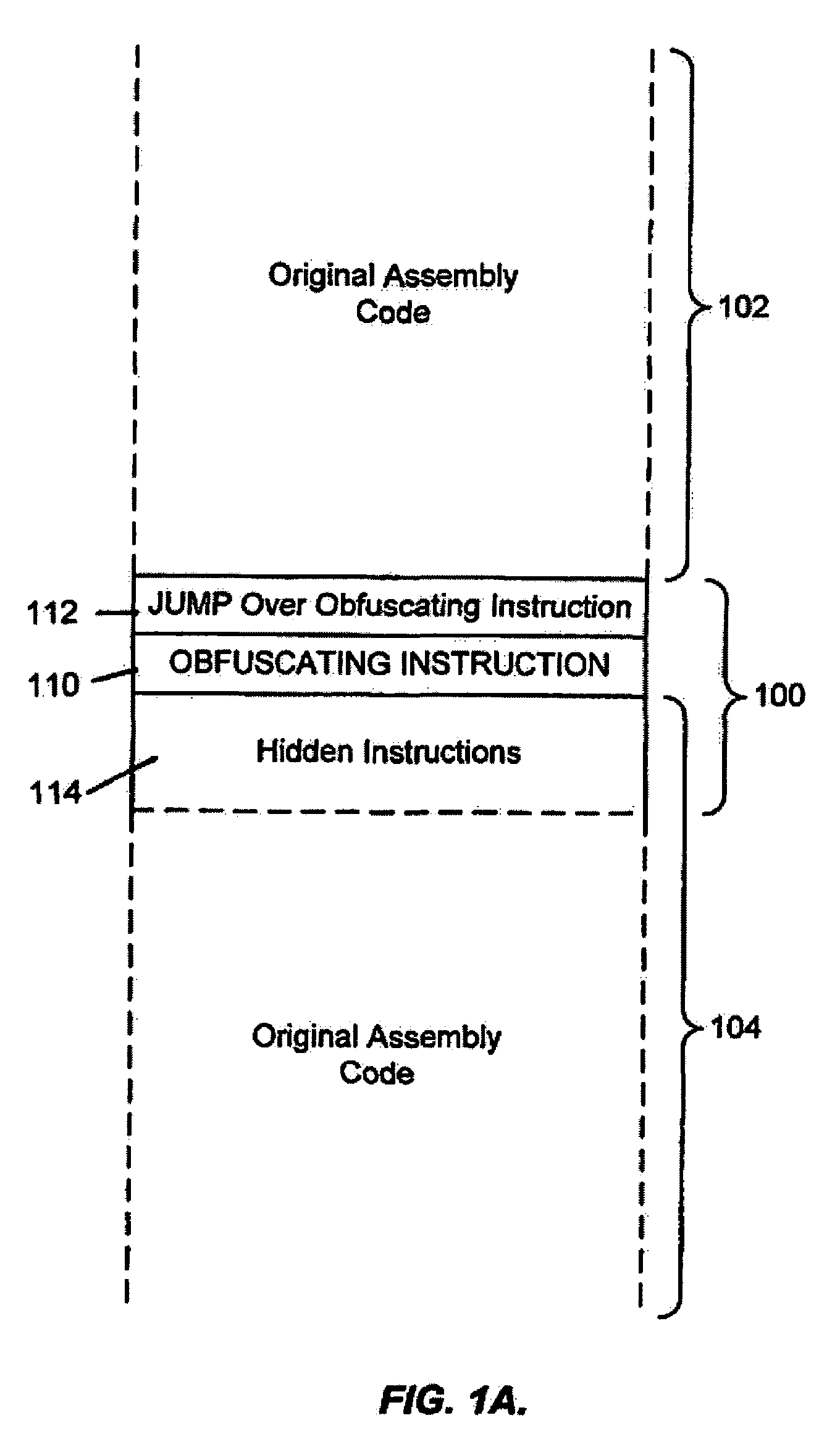
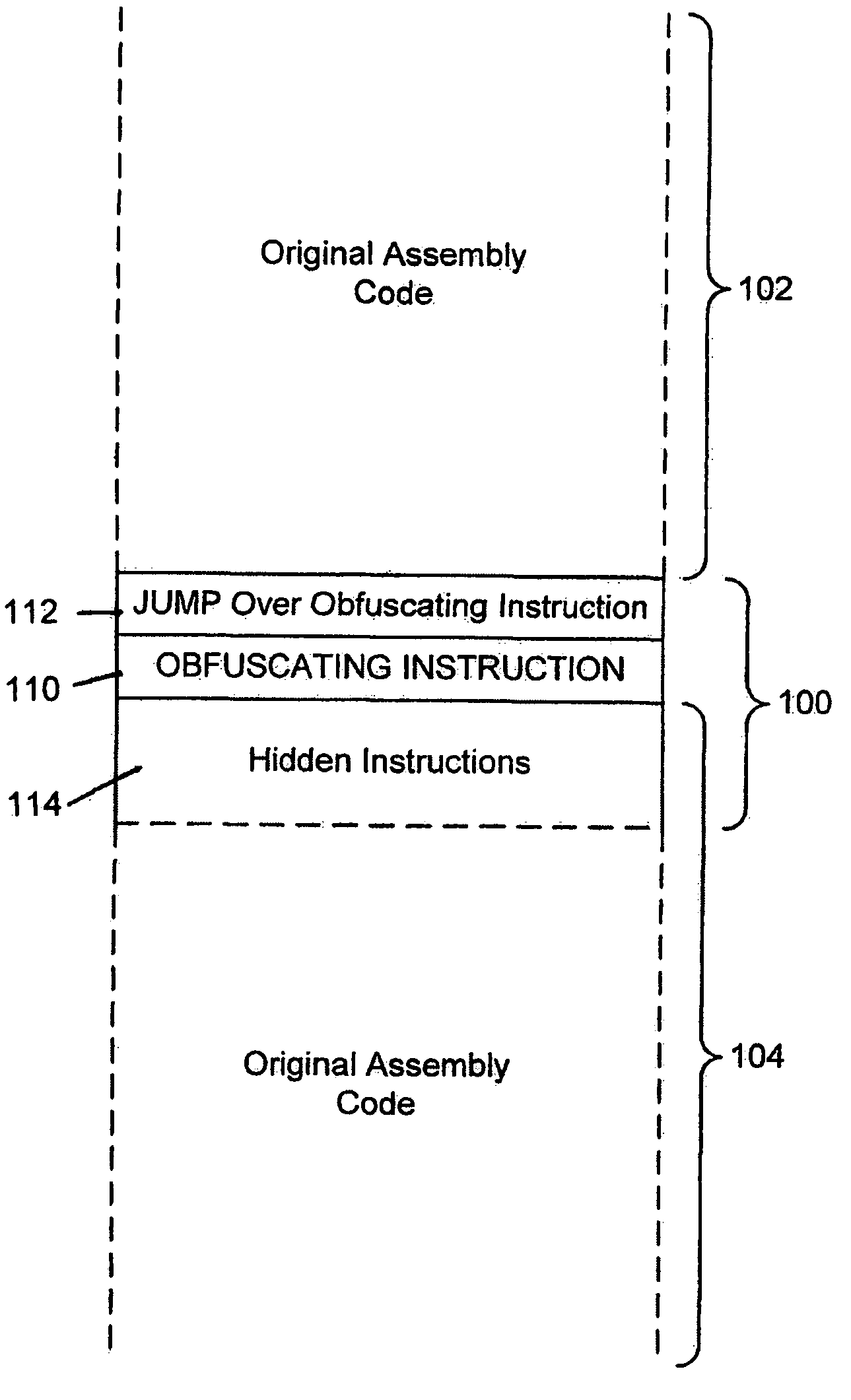
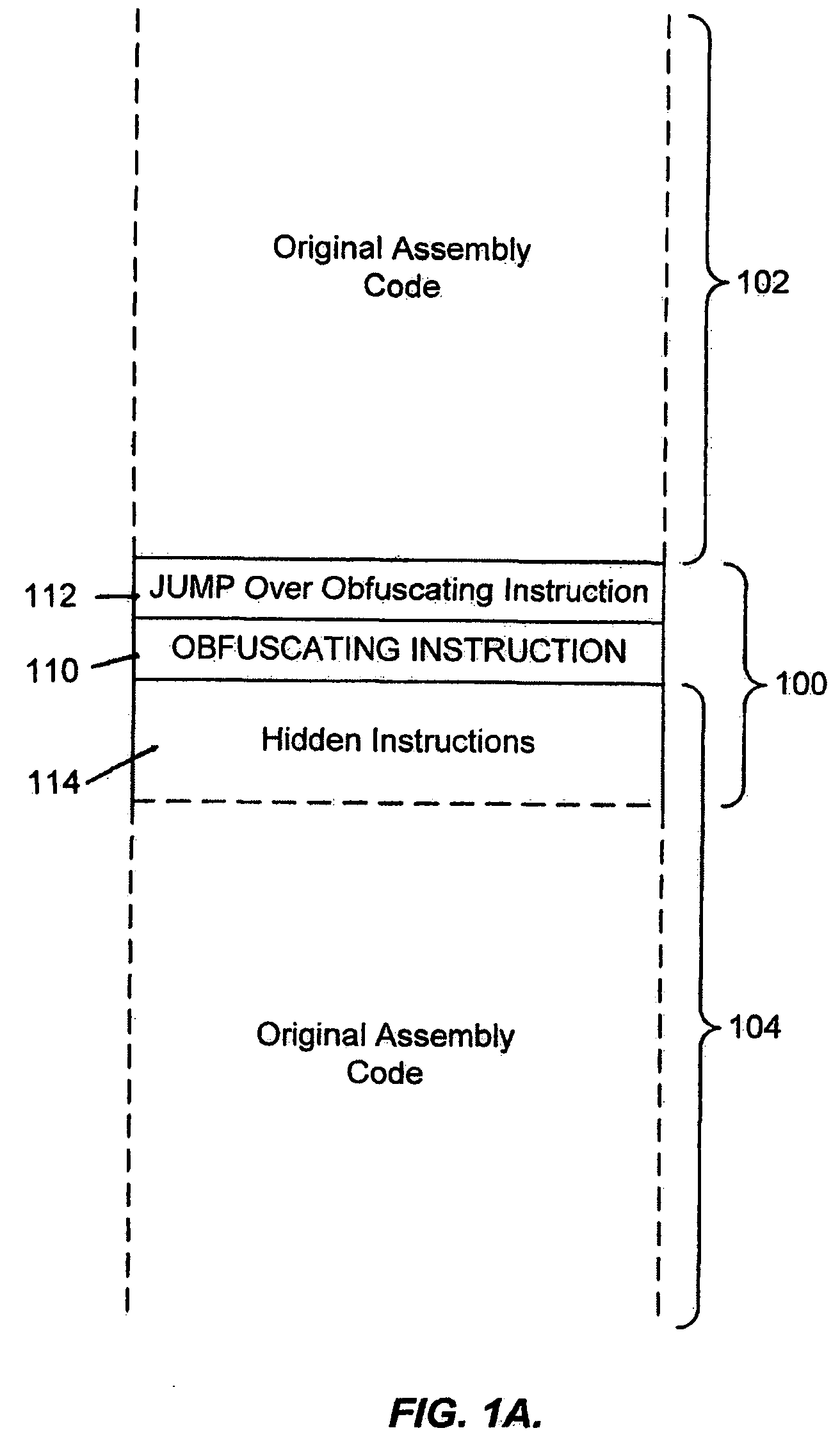
System for obfuscating computer code upon disassembly
InactiveUS20060053307A1Avoid disassemblyUnauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringObfuscationDerivative work
A system for preventing accurate disassembly of computer code. Such code masking, referred to as “obfuscation,” is useful to prevent unwanted parties from making copies of an original author's software, obtaining valuable information from the software for purposes of breaking into a program, stealing secrets, making derivative works, etc. The present invention uses assembly-language instructions so as to confuse the disassembler to produce results that are not an accurate representation of the original assembly code. In one embodiment, a method is provided where an interrupt, or software exception instruction, is used to mask several subsequent instructions. The instruction used can be any instruction that causes the disassembler to assume that one or more subsequent words, or bytes, are associated with the instruction. The method, instead, jumps directly to the bytes assumed associated with the instruction and executes those bytes for a different purpose. A preferred embodiment works with a popular Microsoft “ASM” assembler language and “DASM” disassembler. The instructions used to achieve the obfuscation include “INT” instructions. Using this approach up to 17 bytes of obfuscation can be achieved with five instructions. Each instruction remains obfuscated until executed and returns to an obfuscated state afterwards.
Owner:ALADDIN KNOWLEDGE SYSTEMS
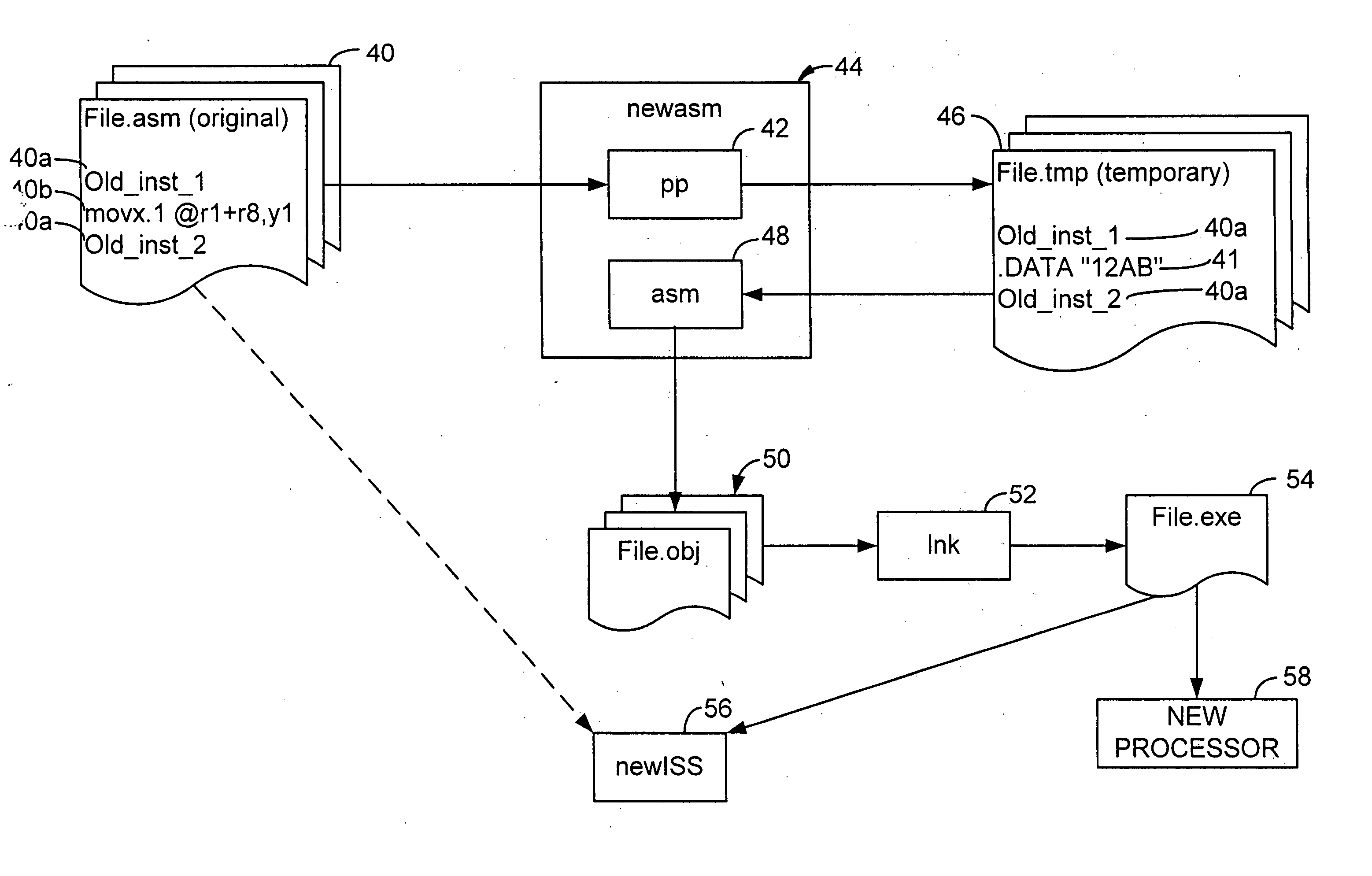
Assembly language code compilation for an instruction-set architecture containing new instructions using the prior assembler
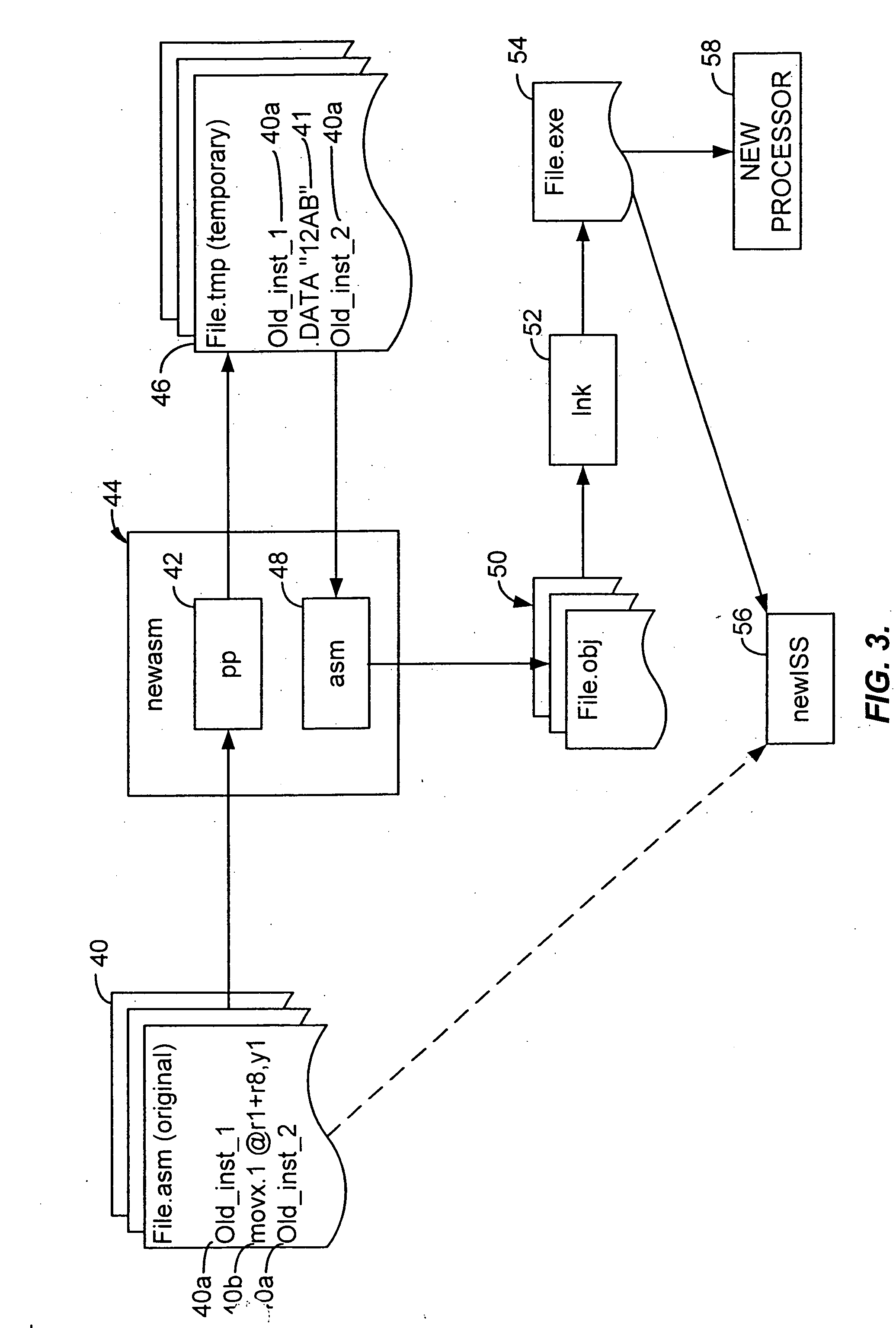
InactiveUS20060101432A1The process is simple and effectiveSoftware engineeringProgram controlObject codeAssembly language
A assembler extended instruction set architecture ISA is formed from a current ISA to which is added new instructions. Assembly of source code listing of a mixture of current and new assembly language instructions is accomplished by preprocessing the source code to create a temporary file that contains the old instructions and data directives for each of the new assembly instructions that have, as the data arguments, the object code equivalent of such new instruction. The temporary file is then applied to the old assembler to produce, for each of the old assembly language instructions, the corresponding object code. The result, after linking, is an executable, machine language program for the new ISA.
Owner:HITACHI AMERICA
Malware identification using multiple artificial neural networks
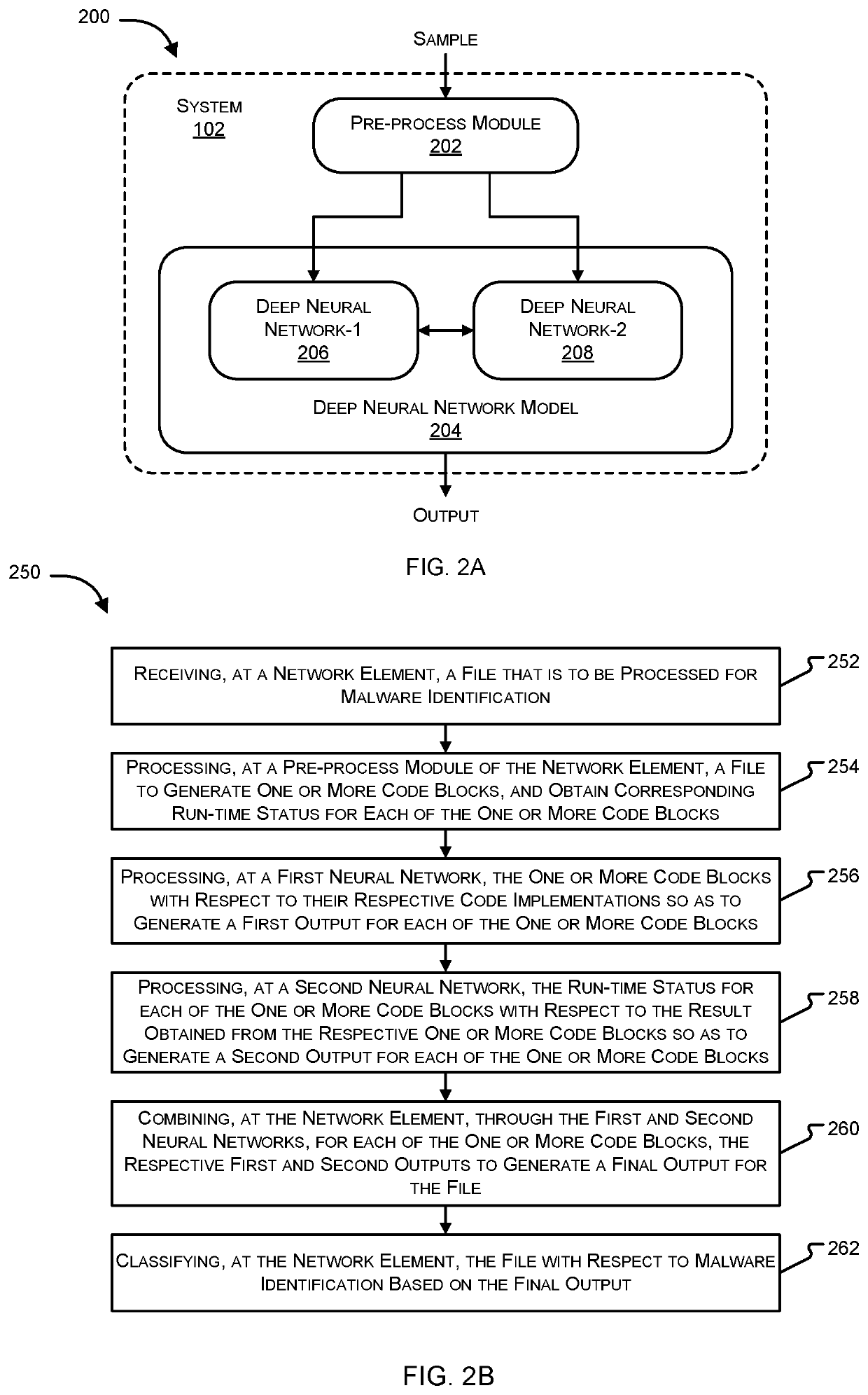
ActiveUS20200042701A1Character and pattern recognitionPlatform integrity maintainanceCoding blockEngineering
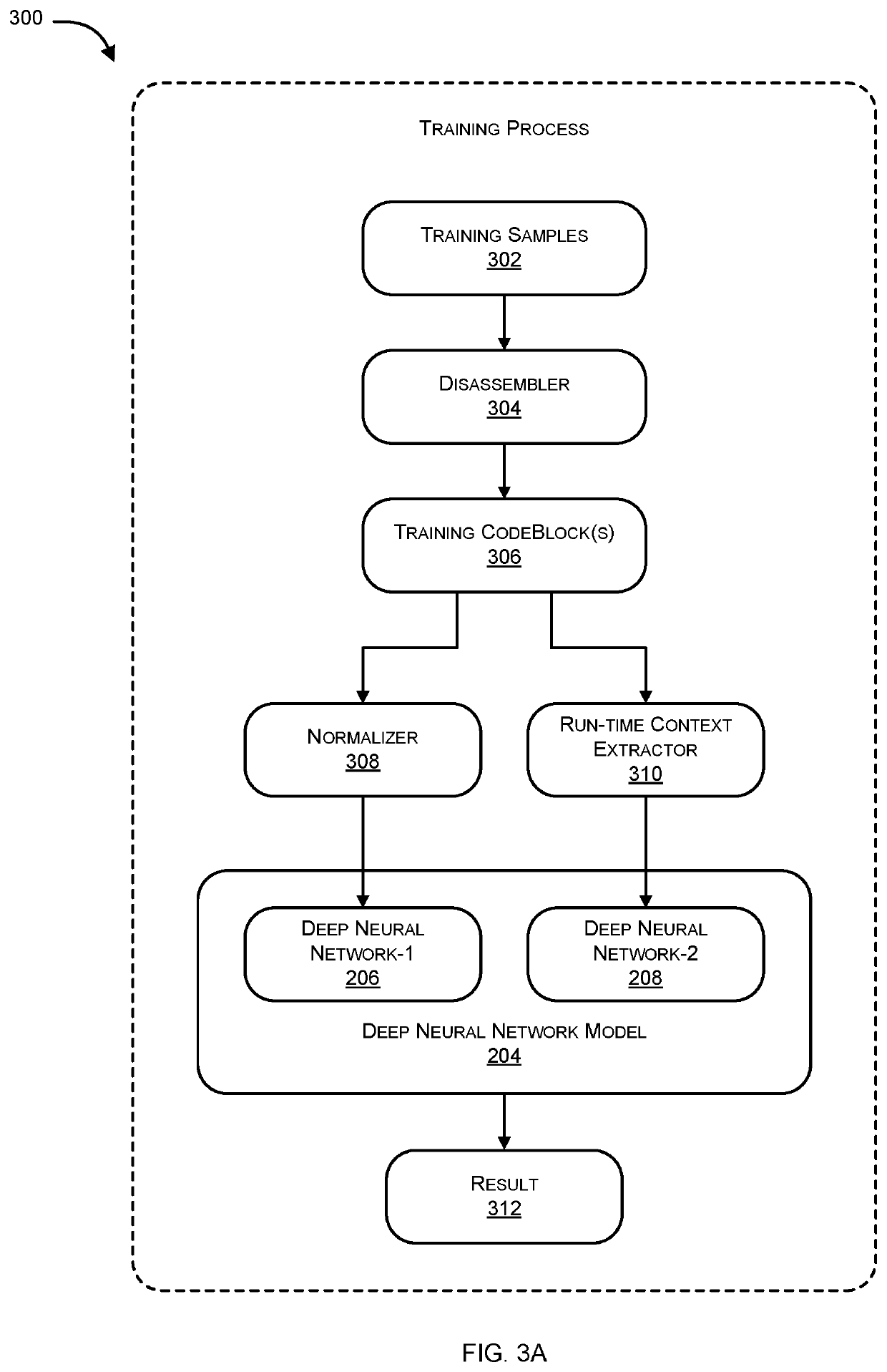
Systems and methods for malware detection using multiple neural networks are provided. According to one embodiment, for each training sample, a supervised learning process is performed, including: (i) generating multiple code blocks of assembly language instructions by disassembling machine language instructions contained within the training sample; (ii) extracting dynamic features corresponding to each of the code blocks by executing each of the code blocks within a virtual environment; (iii) feeding each code block into a first neural network and the corresponding dynamic features into a second neural network; (iv) updating weights and biases of the neural networks based on whether the training sample was malware or benign; and (v) after processing a predetermined or configurable number of the training samples, the neural networks criticize each other and unify their respective weights and biases by exchanging their respective weights and biases and adjusting their respective weights and biases accordingly.
Owner:FORTINET
Locality-sensitive hash-based detection of malicious codes
ActiveUS9361458B1Platform integrity maintainanceSpecial data processing applicationsAssembly languageLocality-sensitive hashing
Malicious code is detected in binary data by disassembling machine language instructions of the binary data into assembly language instructions. Opcodes of the assembly language instructions are normalized and formed into groups, with each group being a subsequence of a sequence of machine language instructions of the binary data. The subsequence is delimited by a predetermined machine language instruction. Locality-sensitive hashes are calculated for each group and compared to locality-sensitive hashes of known malicious machine language instructions to detect malicious code in the binary data.
Owner:TREND MICRO INC
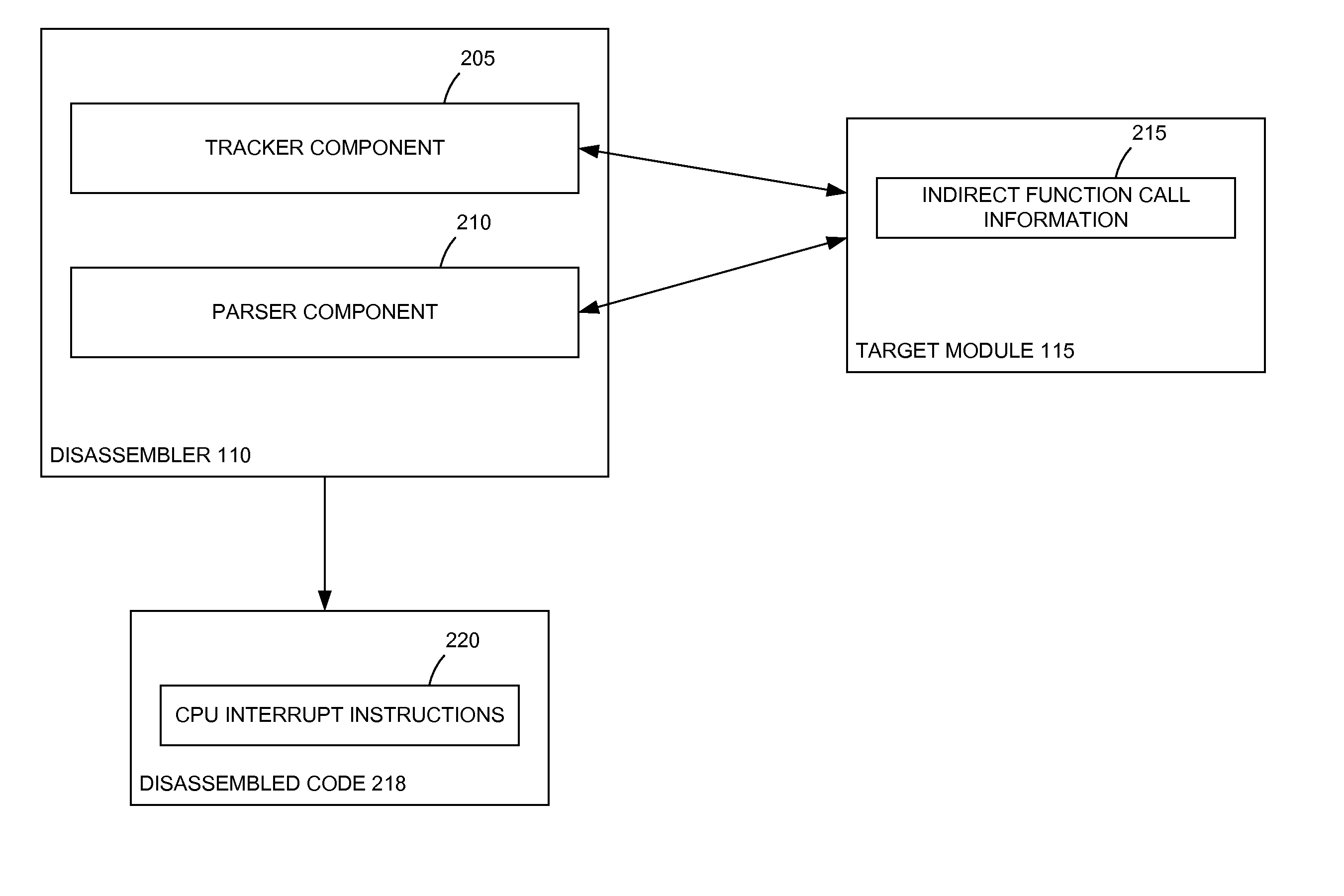
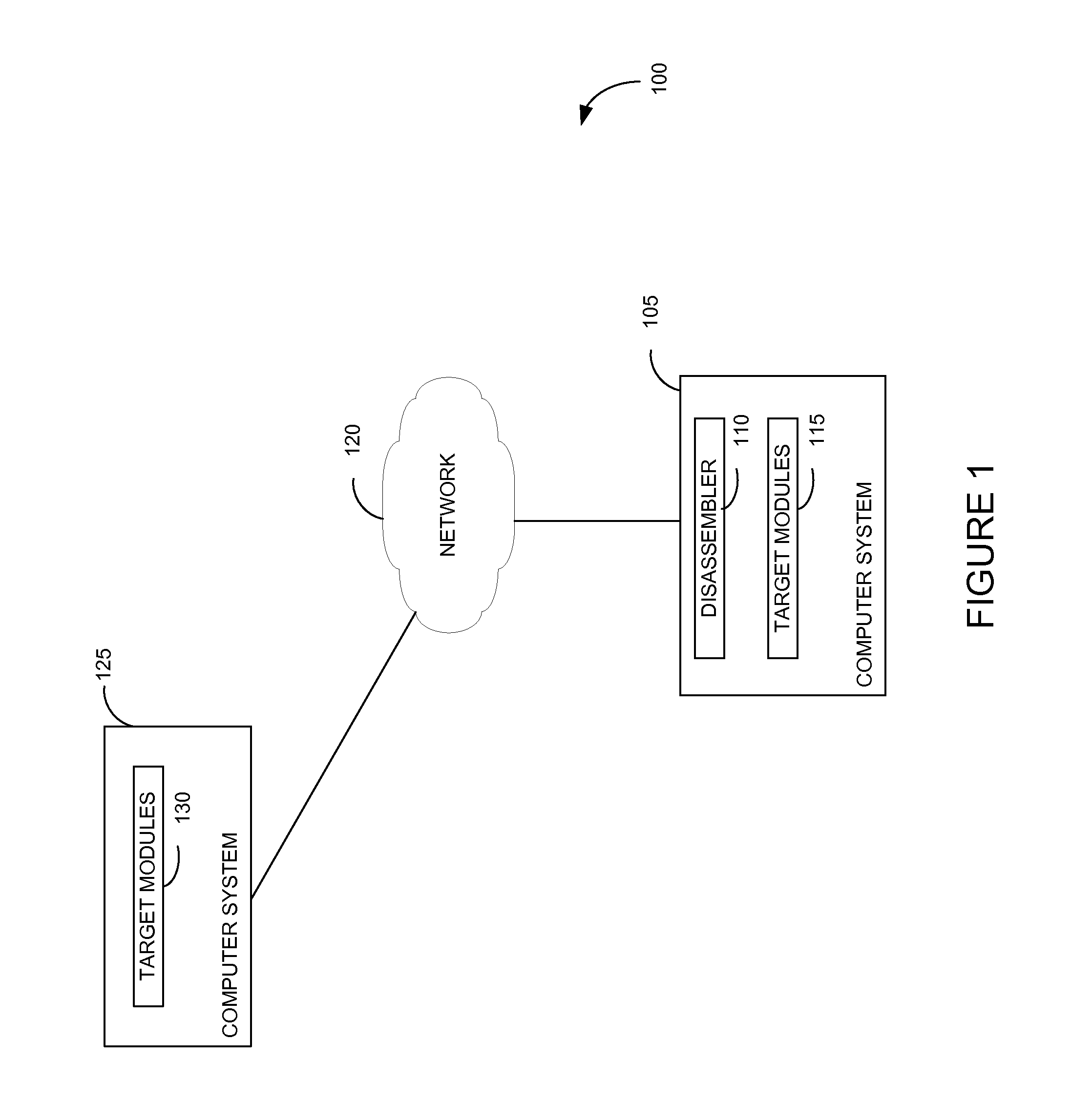
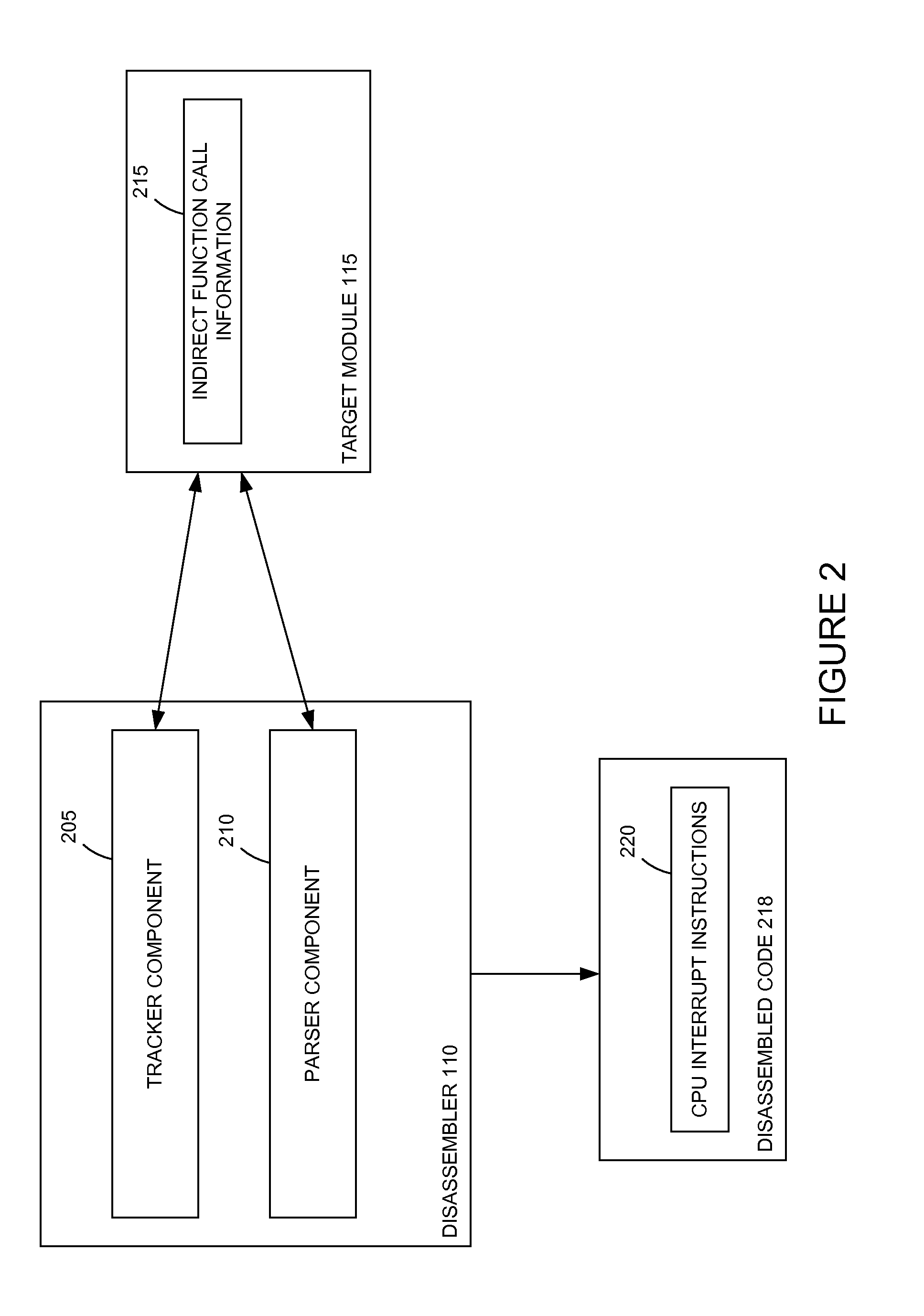
Dynamic call tracking method based on CPU interrupt instructions to improve disassembly quality of indirect calls
Embodiments presented herein describe techniques to track and correct indirect function calls in disassembled object code. Assembly language source code is generated from a binary executable object. The assembly language source code may include indirect function calls. Memory addresses associated with the function calls are identified. A central processing unit (CPU) interrupt instruction is inserted in the disassembled source code at each indirect function call. The disassembled source code is executed. When the interrupt at each indirect function call is triggered, the function name of a function referenced by a register may be determined.
Owner:CA TECH INC
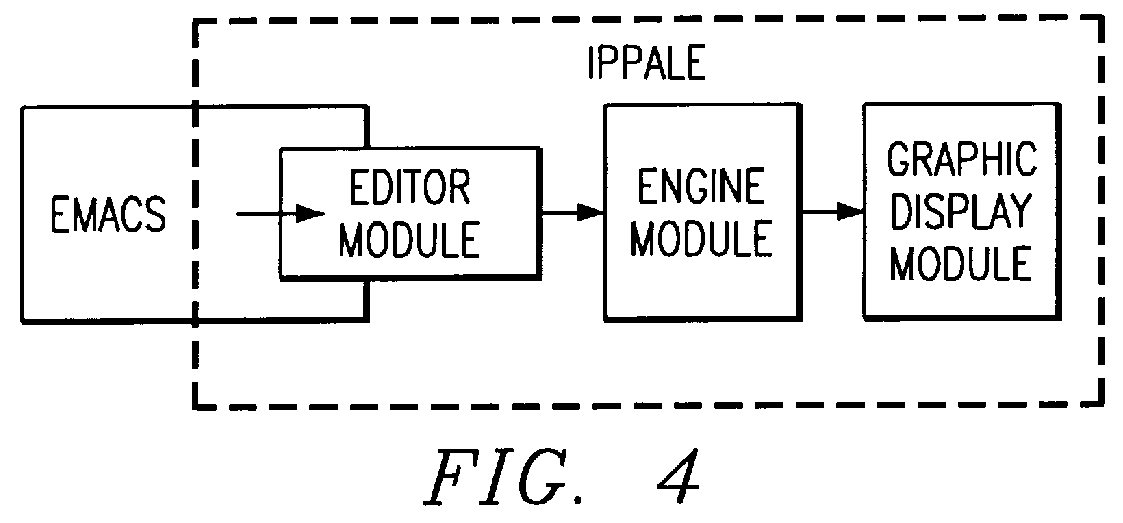
System and method for displaying and editing assembly language source codes
This application describes the Interactive PP Assembly Language Editor (IPPALE), a software tool intended to help programmers write parallel PP instructions quickly and effectively. IPPALE consists of an editor that (on command from the user) extracts the current assembly language instruction, assembles it, and displays a graphical representation of how the instruction uses the resources of the processor. This allows the programmer to see immediately whether the instruction is legal, and also whether there are idle resources that could potentially still be used. The result is that programmers can experiment with a whole set of parallel instructions without ever invoking the PP assembler. We expect this to lead to faster learning, reduced programmer frustration, and improved overall productivity.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Software long-distance loading and solidifying method based on TI DSP
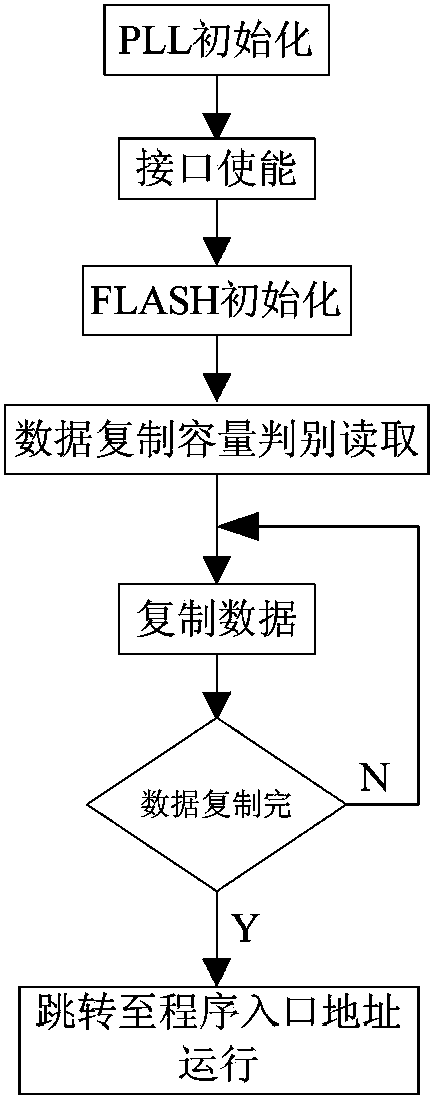
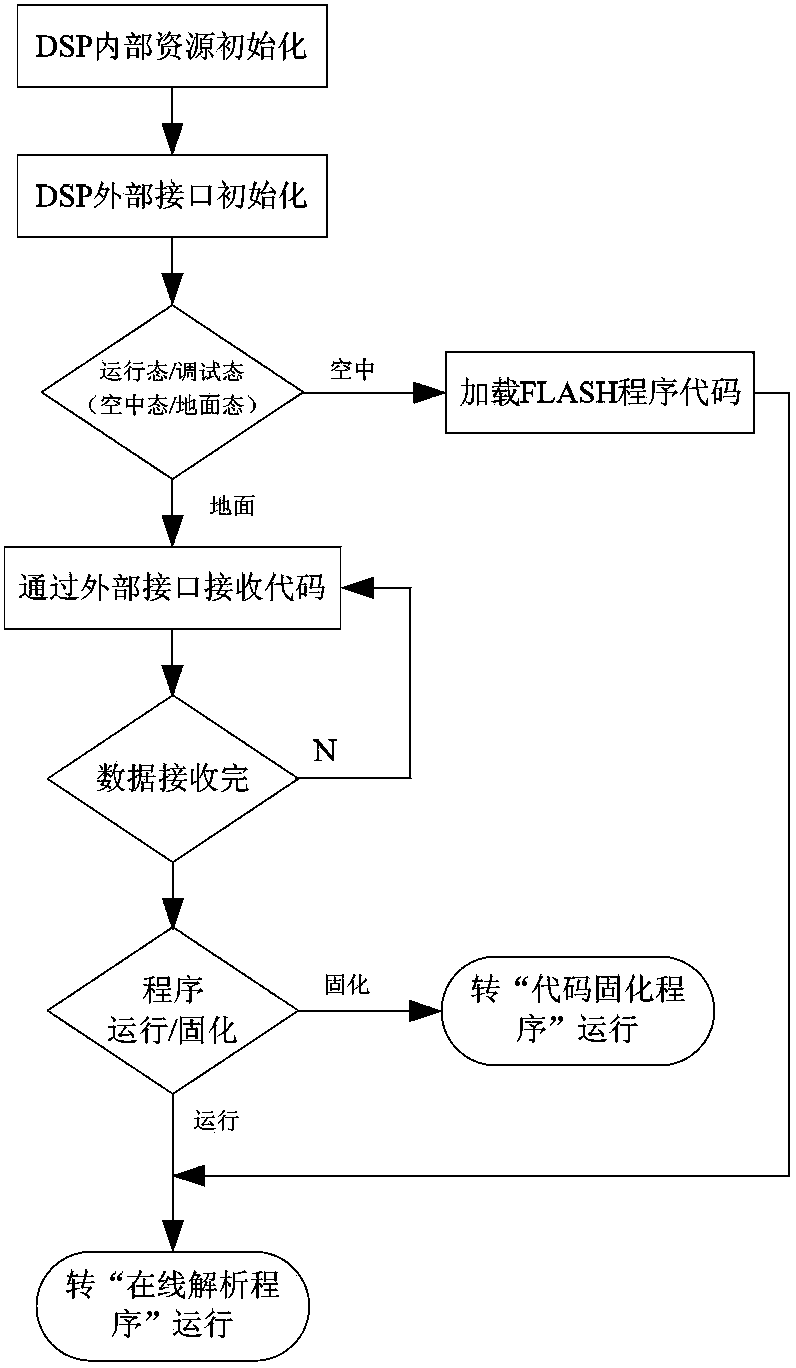
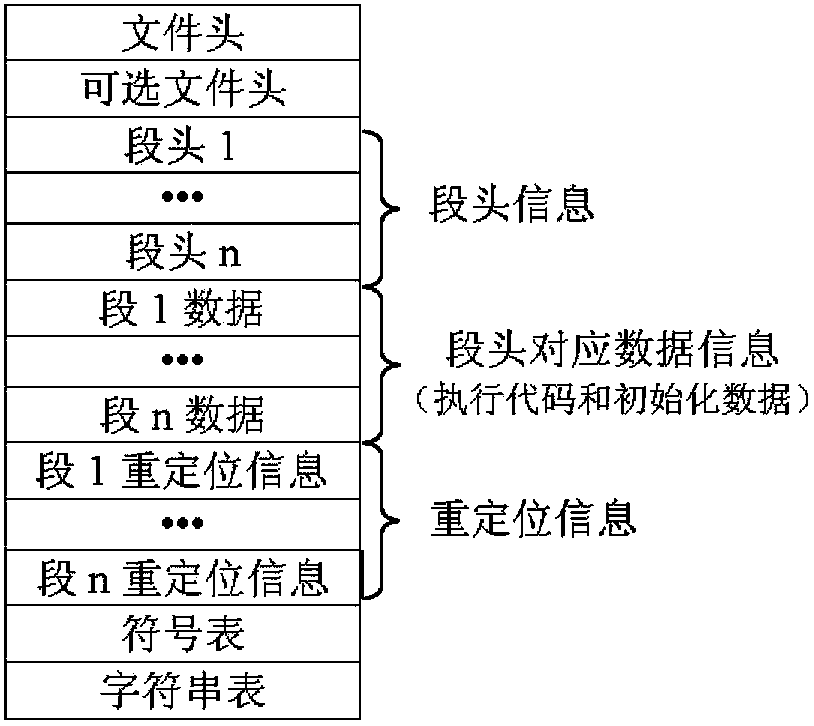
InactiveCN103902305AImplement remote code transferRealize functionProgram loading/initiatingMaintainabilityAssembly language
The invention relates to a software long-distance loading and solidifying method based on TI DSP. The method comprises the steps of assembling a one-level code guide program assembled through languages, initializing DSP, transmitting and receiving code in long distance, analyzing codes on line, and solidifying the codes. The invention provides the method capable of simplifying application debugging and maintenance upgrading of the TI DSP. The method can realize software long-distance loading, debugging and solidifying on the basis of the TI DSP so as to effectively improve the flexibility, the reliability and the maintainability of the application of a TI DSP system.
Owner:AVIC NO 631 RES INST
Method and system for detecting stack alteration
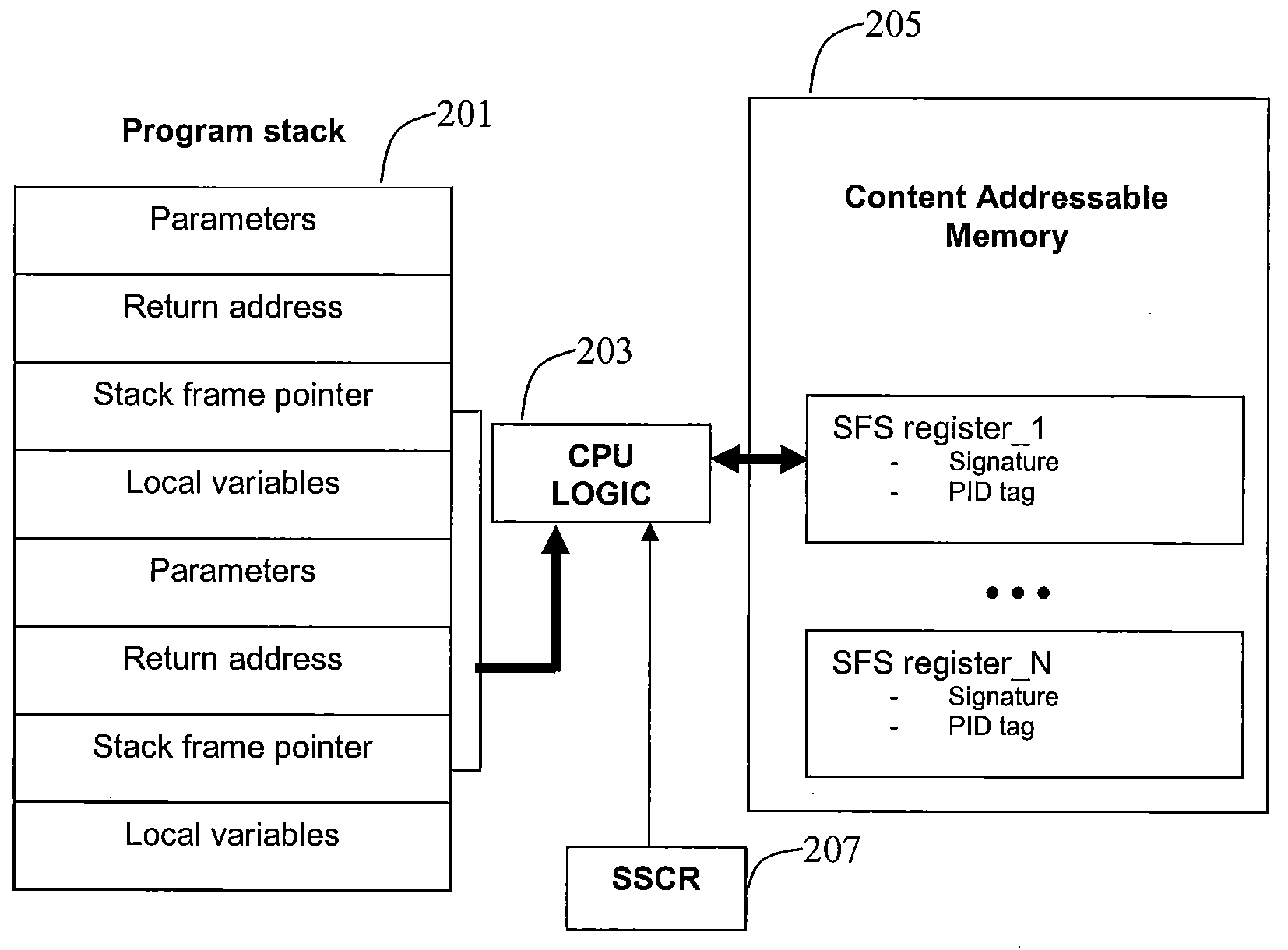
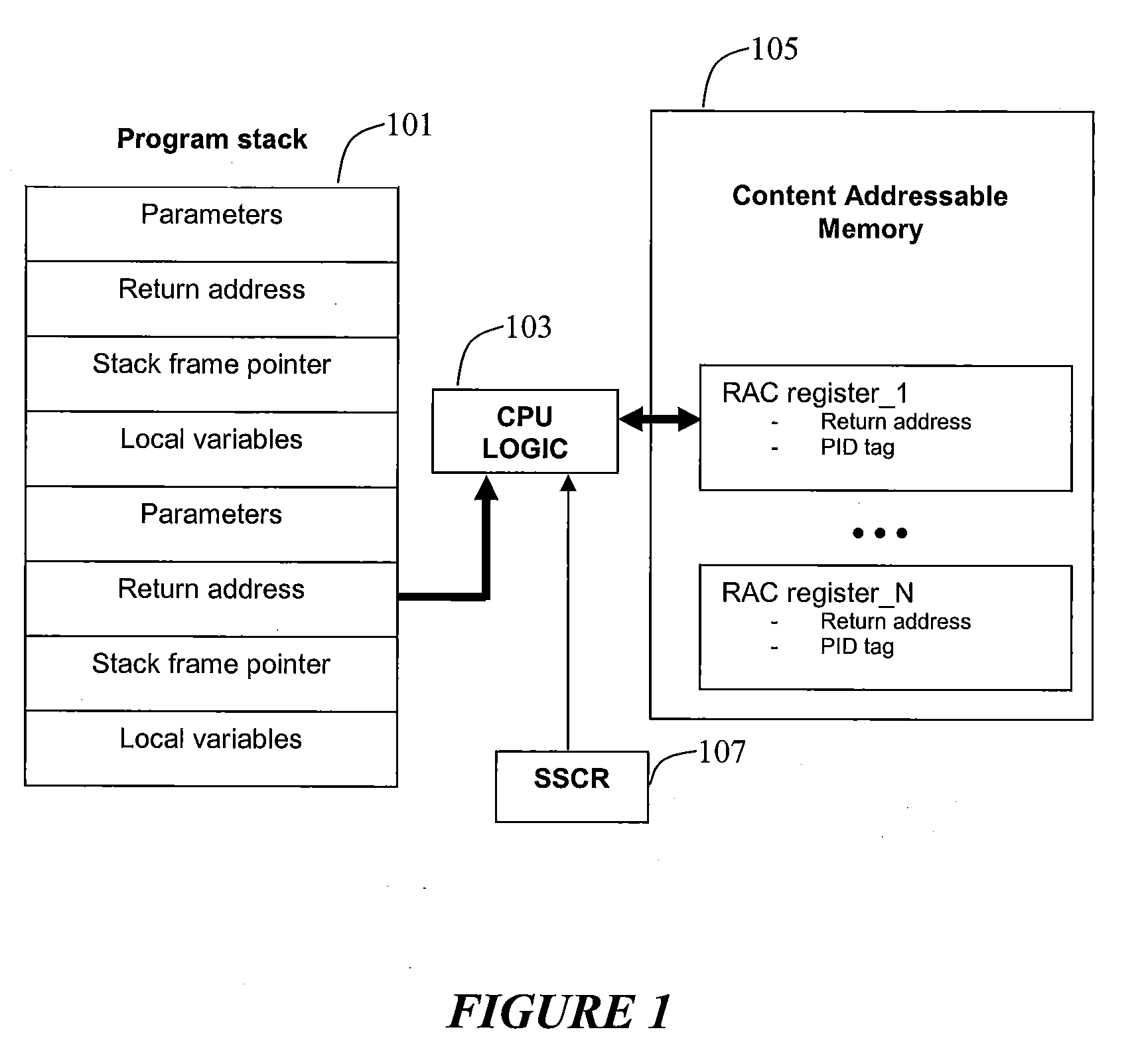
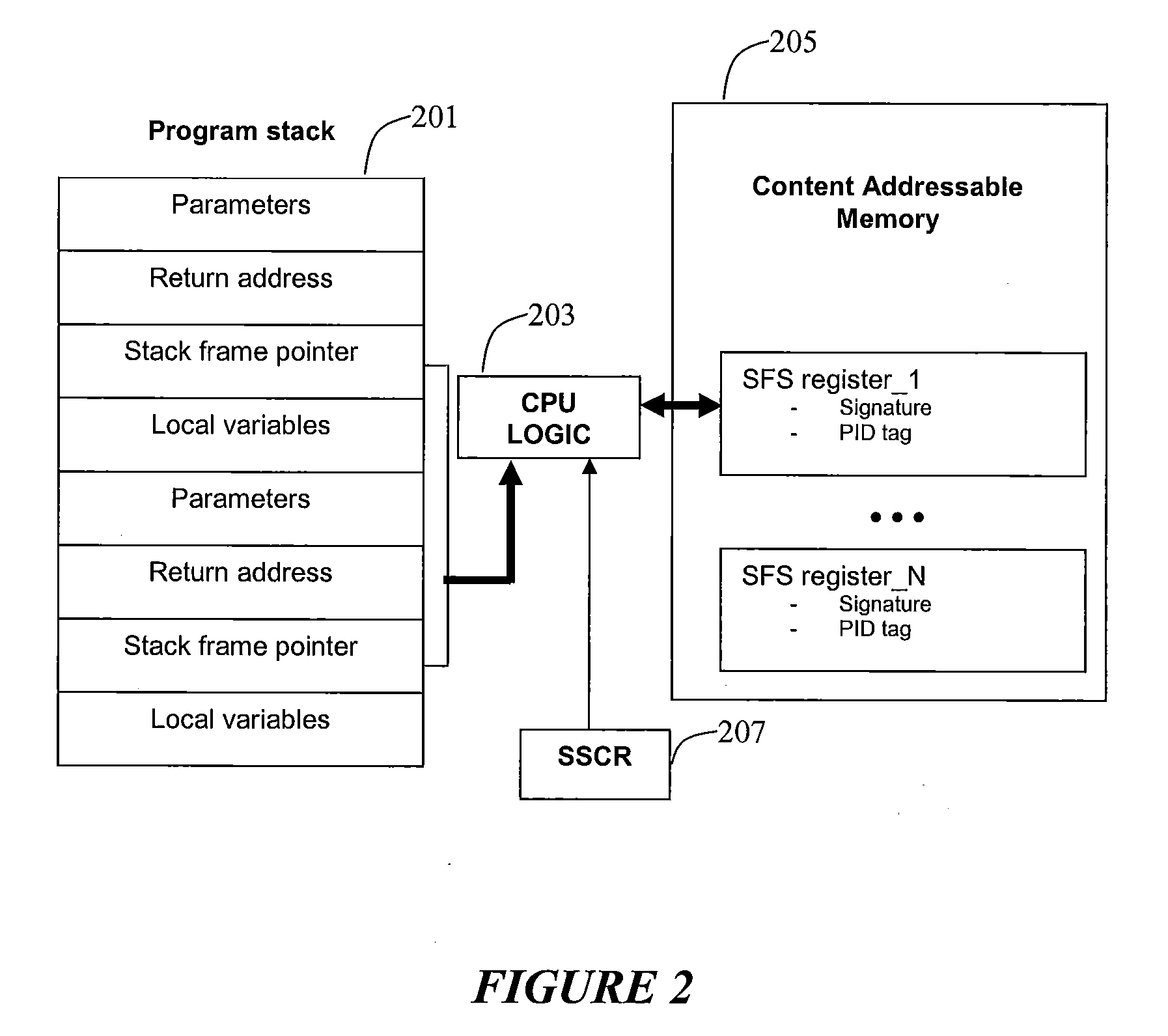
InactiveUS20090187748A1Error detection/correctionDigital computer detailsOperational systemMachine instruction
The disclosed systems and methods relate to employing one or more of machine instructions (i.e. assembler language instructions) to detect stack alterations. Aspects of the present invention also relate to employing CPU logic and one or more associated CPU registers to detect stack alterations. Aspects of the present invention may also relate to employing hidden content addressable memory (CAM) and registers that are only accessible by the CPU, and each cell in the CAM may be accessed using a PID unique to the running program, such as the process ID or thread ID assigned by the operating system scheduler.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
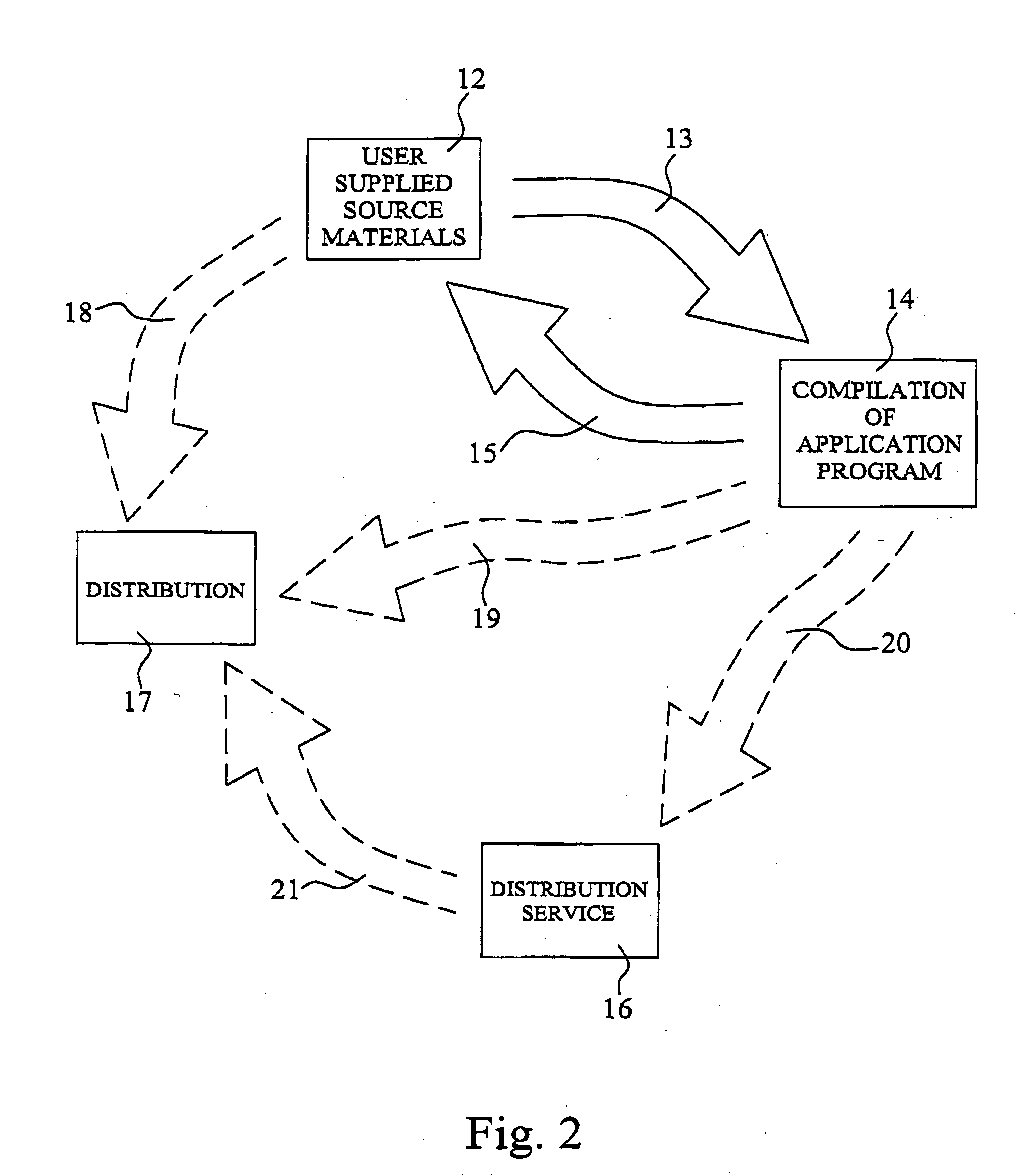
Methods and systems for producing and/or distributing electronic publications
InactiveUS20050108023A1Overcome disadvantagesMultiple digital computer combinationsOffice automationPortable document formatAssembly language
This invention relates to systems and methods for producing or providing electronic publications. A client wanting an electronic publication and obtain access to server across the Internet to request the compilation of an electronic publication. The client may provide the source files in the form of standard format files such as .PDF files and these may be used to generate an electronic publication, preferably in assembly language, incorporating additional technology such as a compiled multi-page document with a page-turn. Rather than supply software to the client for the client to produce their own publications, the client may pay as they go with a transaction taking place with each new file compiled. This also reduces the need to support distributed software and makes incrementally developing features of the software available to all clients upon introduction of the features into a group of selectable features for inclusion in the executable program forming the publication.
Owner:HEMMINGS CHRIS
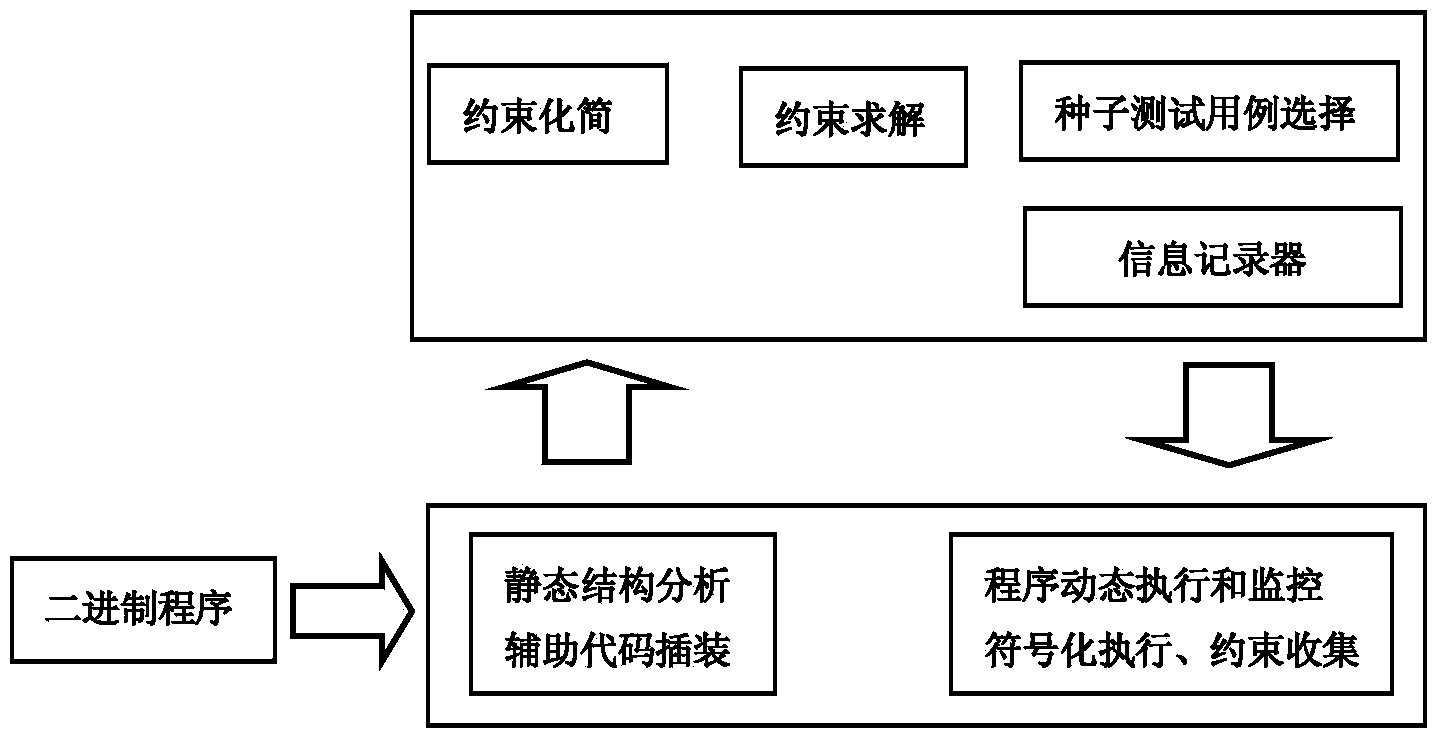
Sensitive area-oriented embedded software test case generating method
InactiveCN103714000AImprove analysis efficiencyReduce complexitySoftware testing/debuggingEmbedded softwarePath cover
The invention relates to a sensitive area-oriented embedded software test case generating method. The sensitive area-oriented embedded software test case generating method comprises the steps that firstly, binary files are analyzed, intermediary language transformation is conducted on an assembly language generated by the disassembling technology, and instrumentation is conducted on transformation results so as to obtain an instrumentation procedure; secondly, the instrumentation procedure is used for analyzing a sensitive area so as to determine taint data; thirdly, a seed test case dynamic execution procedure is used for collecting branch path constraint conditions, and when a branch jump occurs, constraint sets collected at present are reversed and output; finally, whether each constraint in the collected constraint sets comprises taints is analyzed, processing is carried out, the simplified constraint sets are sent into a constraint solver and are solved, and obtained final results are test cases which can generate input controllable branch paths covering the taint data. Compared with the single static analysis technology or the single dynamic analysis technology, the sensitive area-oriented embedded software test case generating method has higher analysis efficiency.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
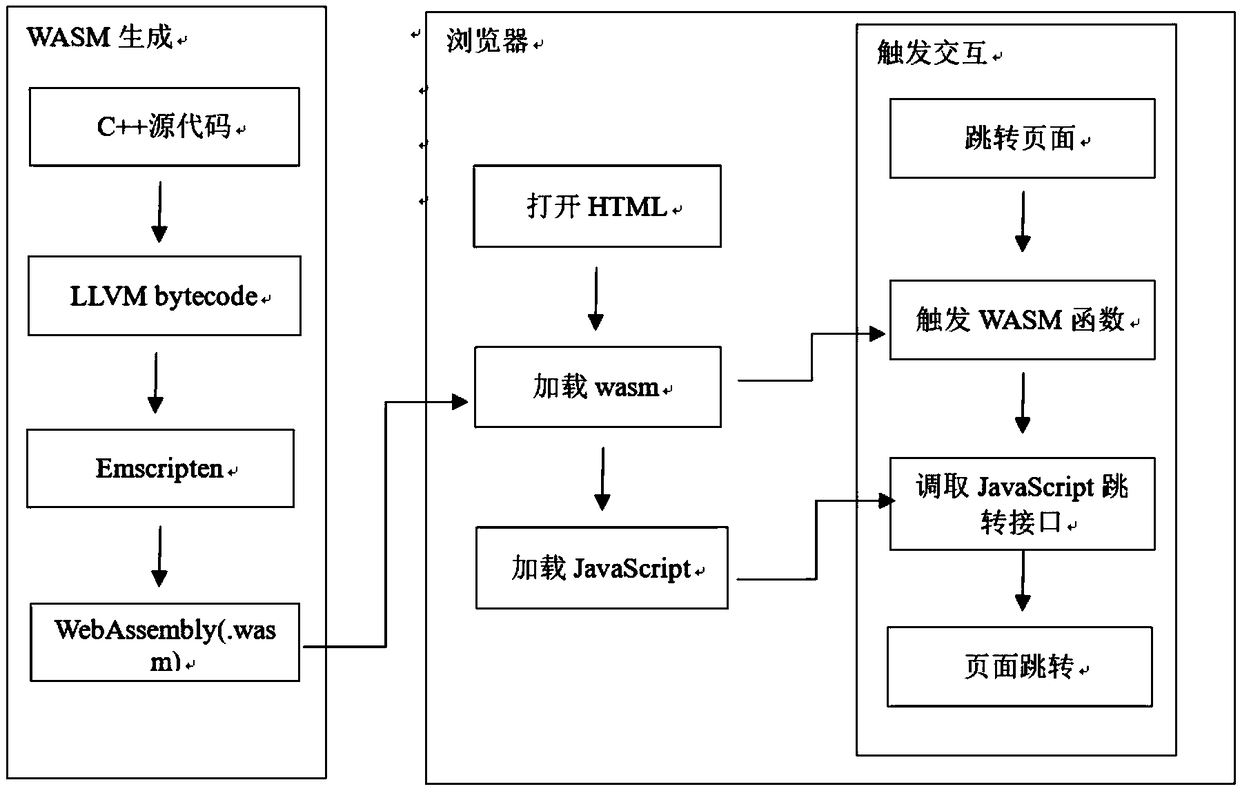
A method for controlling page jump based on web page assembly language
InactiveCN109284104AAchieve jumpEnsure safetyCreation/generation of source codeSource to sourceLanguage controlSource code
The invention relates to a method for controlling page jump based on web page assembly language, comprising the following steps: 1 compiling a function by using C + + language, obtaining a target URLaddress to be jumped in the form of a string through parameters of the function; the target JavaScript function is called and the converted character set is passed to the target JavaScript function asa parameter; 2, compiling that C + + source code into an LLVM bytecode, and converting the bytecode into WebAssembly through a compile tool; 3 rewriting a JavaScript function whose name and parameters are consistent with the called target JavaScript function in step 1; by rewriting the parameters of the JavaScript function, the target address of the web page to be jumped is obtained; 4, in the HTML page, the WebAssembly obtained in the step 2is loaded and parsed, the JavaScript function obtained in the step (3) is loaded and parsed, and the page is controlled to jump to the target address byusing the DOM standard function of the HTML.
Owner:QINGDAO RES INST OF BEIHANG UNIV
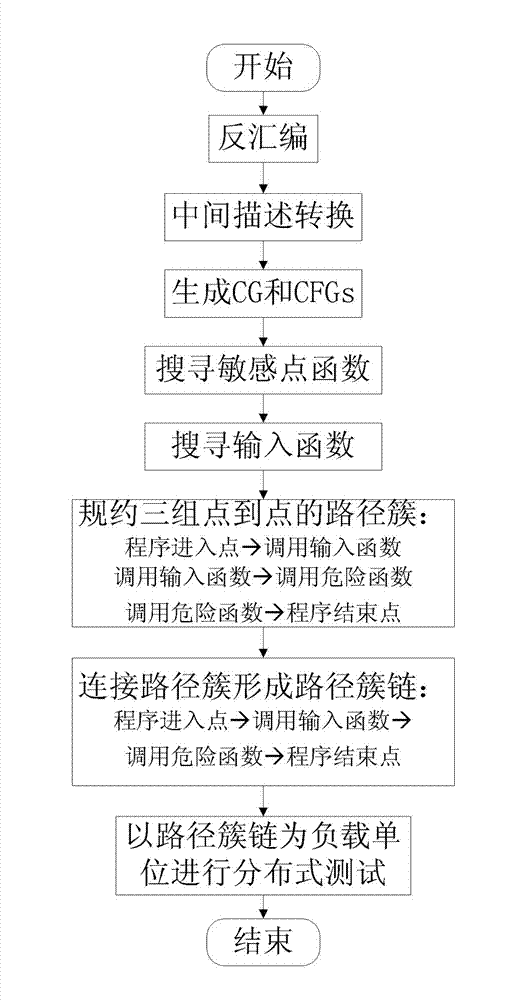
Parallel symbolic execution method based on path cluster reductions
ActiveCN103049377AReduce time overheadImprove abilitiesSoftware testing/debuggingCall graphEntry point
The invention relates to a computer software safety testing method based on program symbolic execution path cluster partitions. The parallel symbolic execution method based on path cluster reductions includes the steps of: (1) disassembling an tested executable program, (2) obtaining assembly codes of the tested executable program and transferring into uniform intermediate assembly language forms, (3) generating a function call graph and a control flow diagram of the tested executable program according to intermediate assembly language forms, (4) finding a dangerous function and an input function according to a static analysis of the function call graph; (5) respectively creating a path between a program entry point and a call input function, between the call input function and a call dangerous function, and between the call dangerous function and a program end point and reducing into path cluster, (6) subjecting the obtained paths to point-to-point connection to form an integral path cluster chain assembly from program entry point to program end point, and (7) generating corresponding test cases to perform actual program safety tests with an integral path cluster chain from program entry point to program end point formed in step (6) serving as a load unit.
Owner:CHINA INFORMATION TECH SECURITY EVALUATION CENT
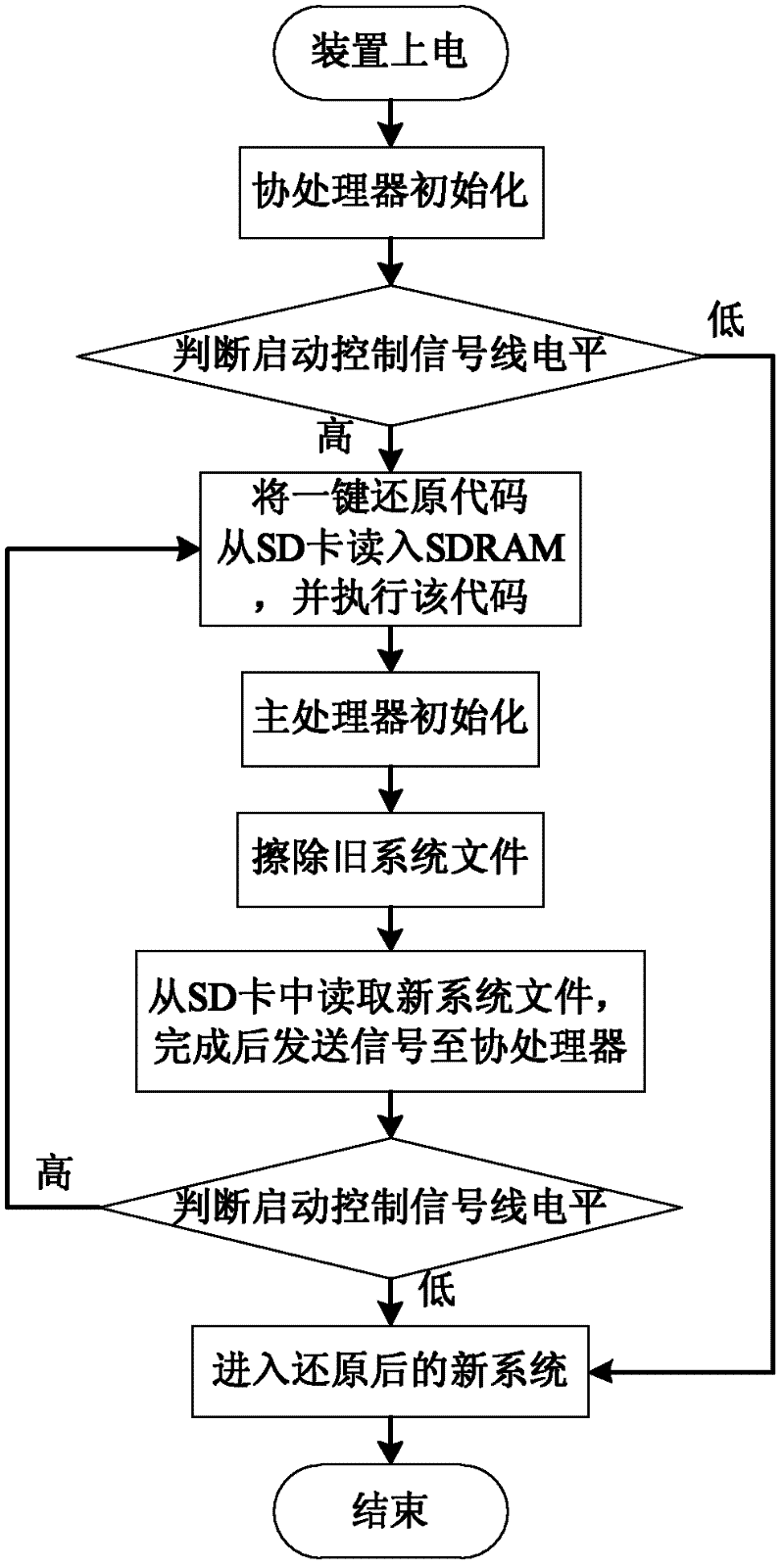
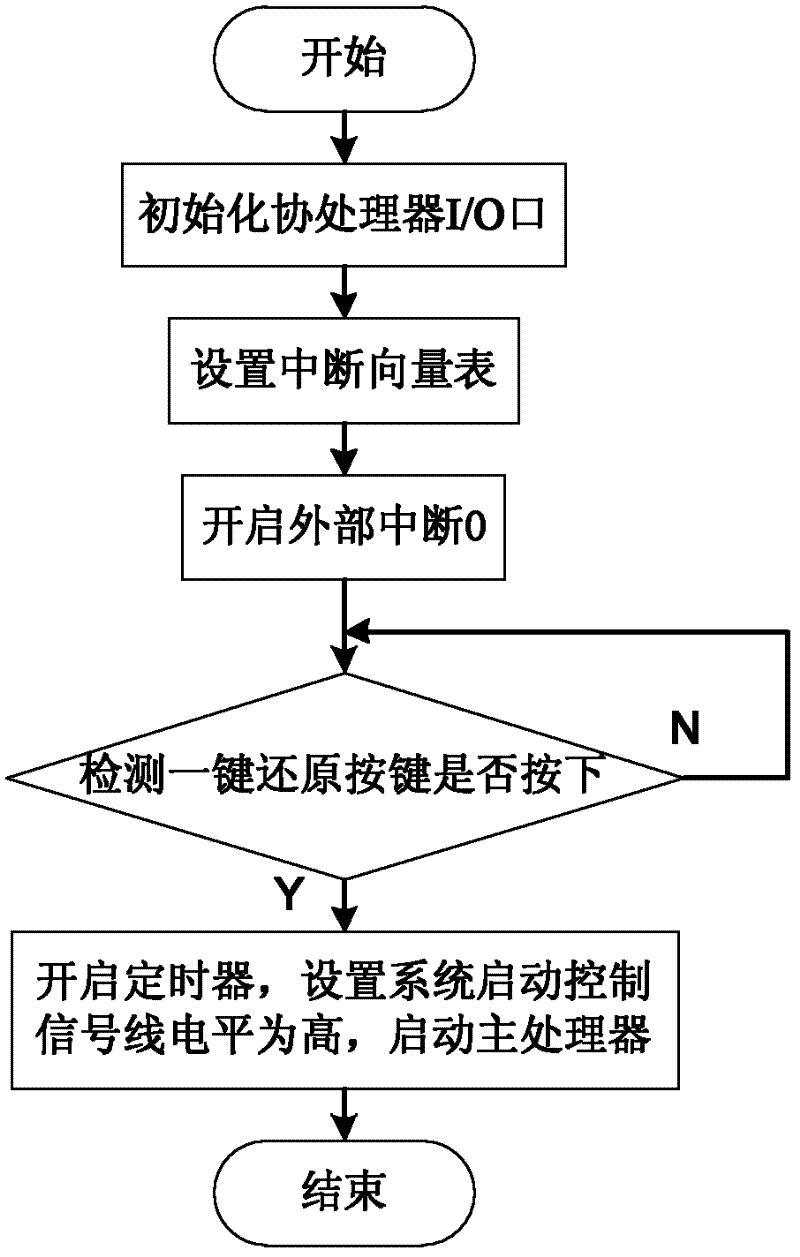
One-key reset method suitable for embedded Linux operating system
InactiveCN102520778ASolve the problem of needing to connect the upper computer to restore the systemHigh degree of intelligenceData resettingRedundant operation error correctionMicrocontrollerOperational system
A one-key reset method suitable for an embedded Linux operating system belongs to the technical field of an embedded system. The one-key reset method of the embedded operating system is constructed by C programming language and assembly language. A user starts the one-key reset of the system by a one-key reset button, and an operating system to be reset is stored in a common SD (Secure Digital) card. When the reset button is pressed, a main processor is triggered to start the level switching of a control module, and the starting mode of the main processor is changed to be in a one-key reset mode. When the reset is finished, a main processor module sends a signal to a reset module, the starting mode is changed to be a normal starting mode, the main processor module is reset, and the system is in login. The system adopts a modular design, a peripheral singlechip is additionally arranged and is taken as a coprocessor module to control the reset of the main processor and change the starting mode of the main processor. By the communication between a GPIO (General Purpose Input / Output) port and the main processor, the one-key reset method is suitable for the embedded main processors with different structures and solves the problem that a common embedded system needs to be connected with an upper computer to be reset.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
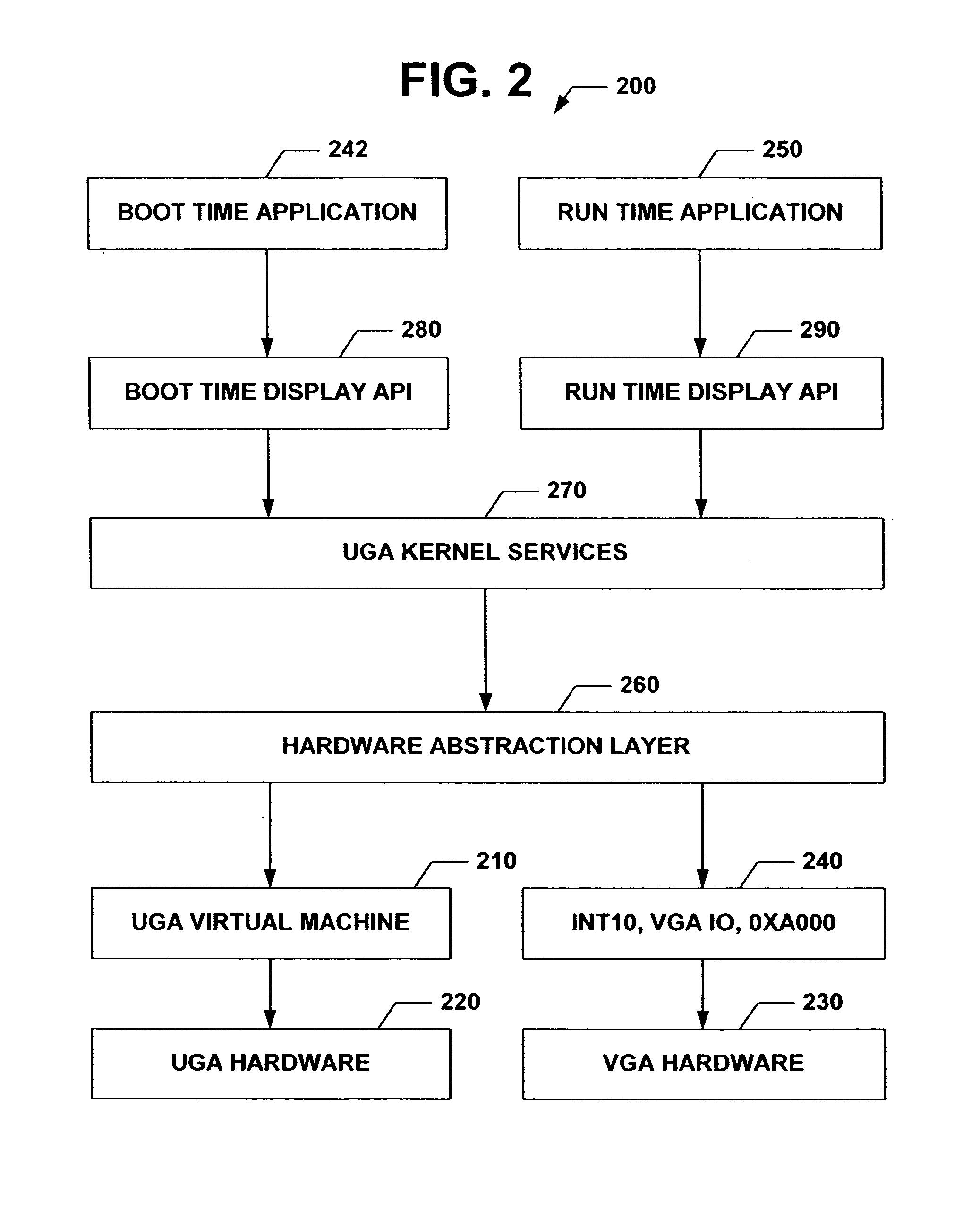
Universal graphics adapter
InactiveUS20050160191A1Easy to updateQuality improvementDigital computer detailsData resettingAssembly languageReal mode
The subject invention relates to a Universal Graphics Adapter (UGA) that is a hardware-independent design that encapsulates and abstracts low-level graphics hardware in a standard manner through firmware. UGA is a firmware standard, intended to wrap existing or planned hardware, including VGA. UGA does not require the use of real-mode assembly language, direct hardware register, or frame buffer access to program, thus providing advantages over conventional systems. UGA supports basic drawing operations, continuous display modes, and power management. As a firmware-based standard, UGA facilitates updating a system to support both evolving and new hardware features.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
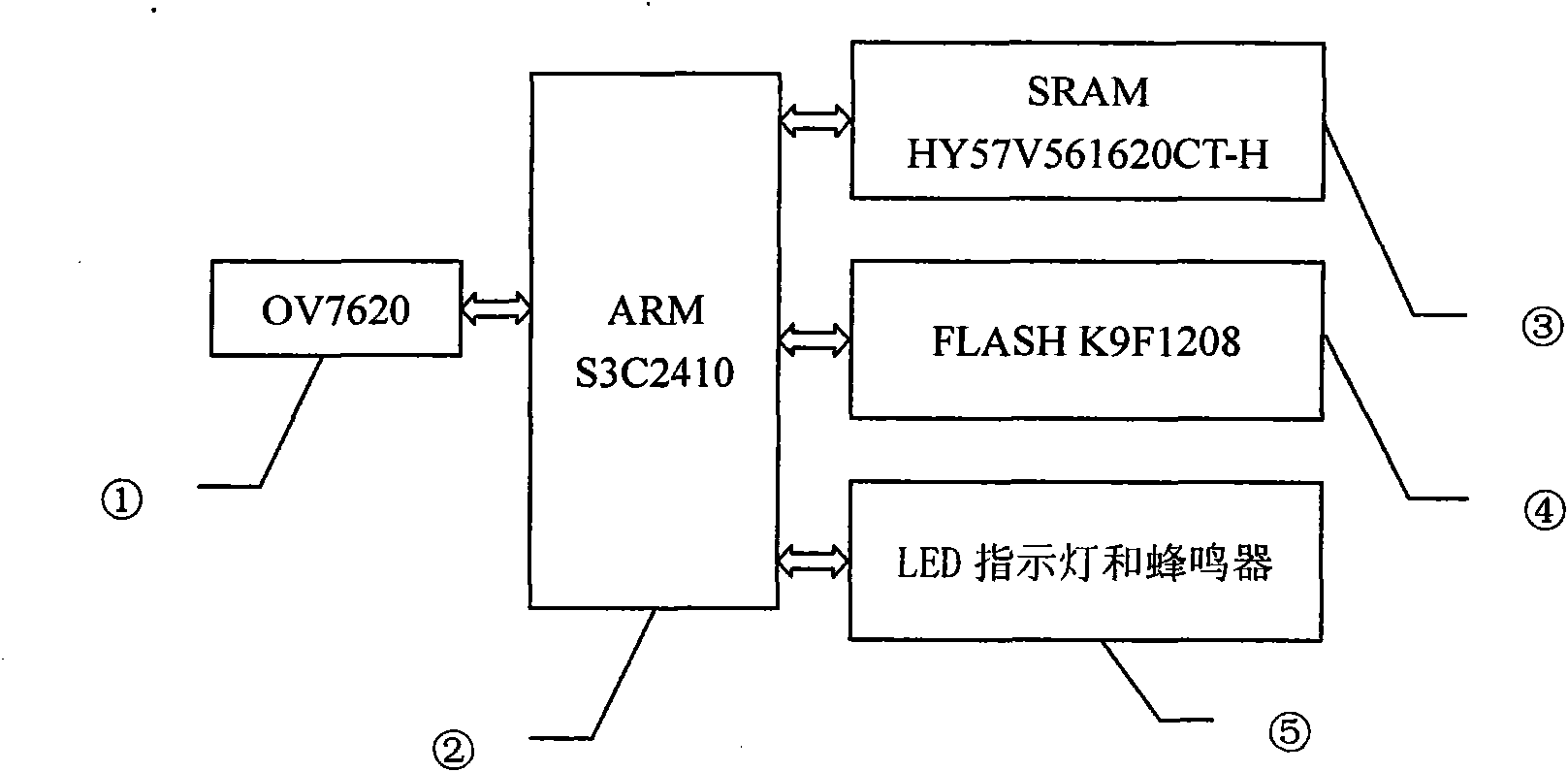
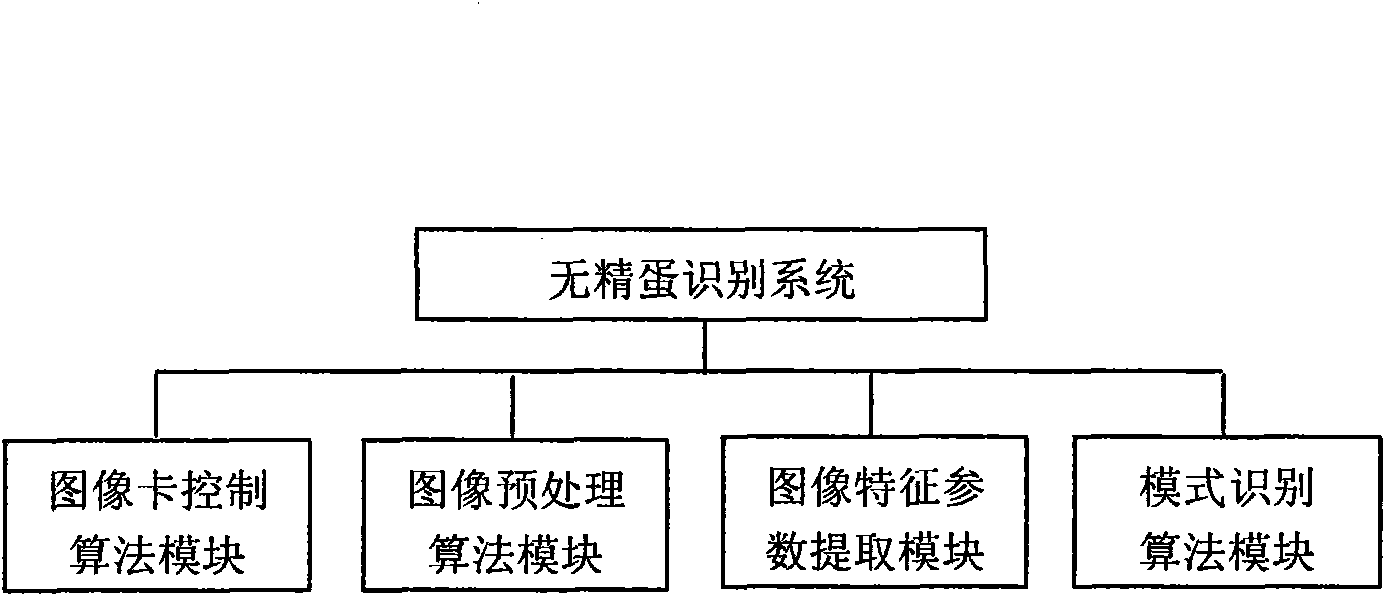
Brooding-before clear egg distinguishing method and device thereof
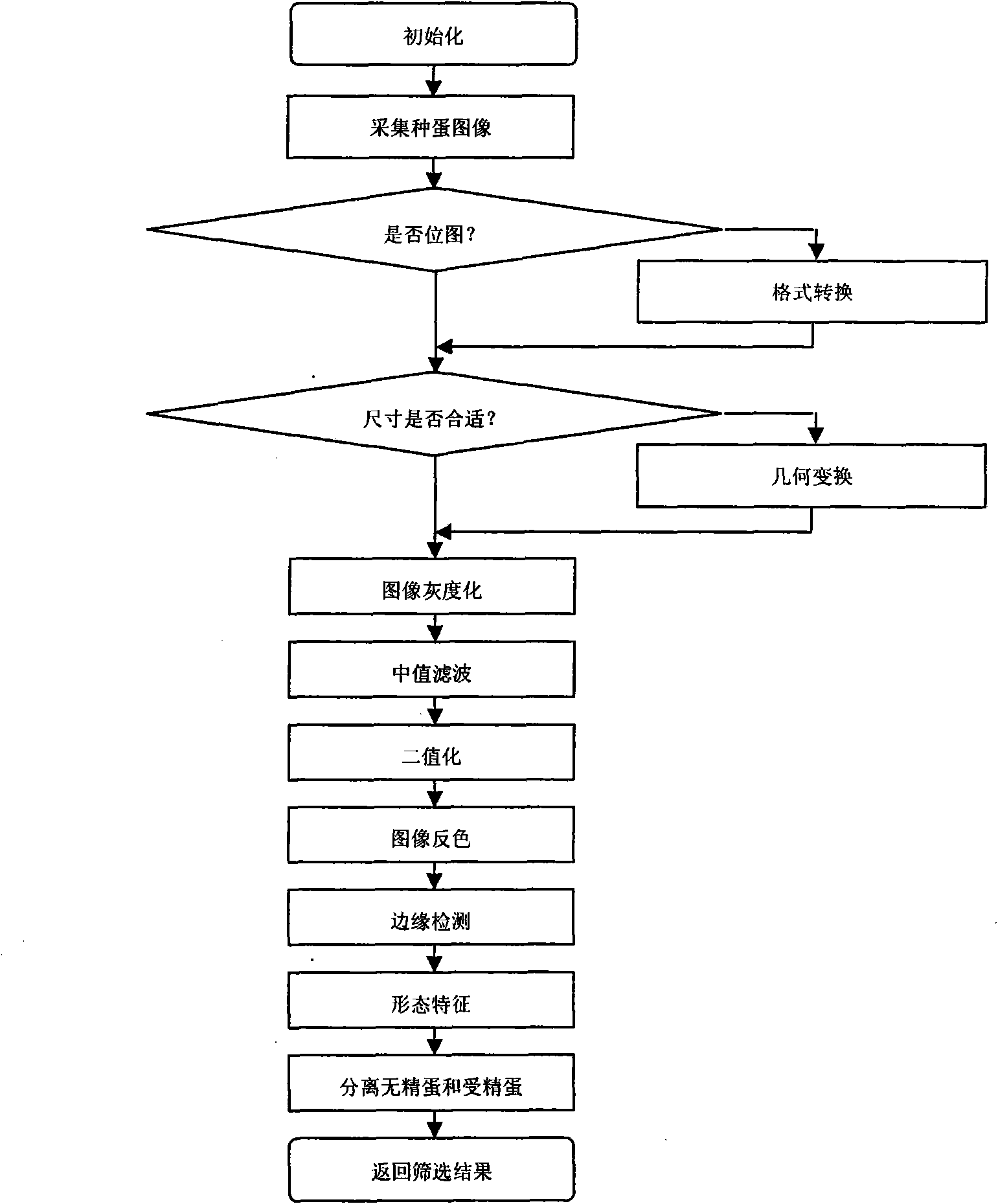
InactiveCN101916366AImprove detection accuracyThe identification method is efficient and fastBiological neural network modelsCharacter and pattern recognitionCMOSAxial ratio
The invention discloses a brooding-before clear egg detection device and a method thereof, belonging to the egg detection manufacturing technical field. The invention constructs an embedded clear egg distinguishing system, and hardware of the system are an ARM S3C2410 embedded system development board, a CMOS image sensor OV7620, an LED and a buzzer. The invention constructs clear egg distinguishing software by using C language and assembly language in the Linux environment provided by ARM S3C2410. The key components of the software include hatching egg acquisition, image border detection, characteristic parameter extraction and three-layer BP neural network; and the main function to be realized is that the neural network is utilized to distinguish clear egg and embryonated egg according to the characteristic parameters of the acquire image (including circularity, complexity, elongation, spherical property, axial ratio and coefficient of variation). The output of the neural network is 10 or 01, the output is taken as driving level and is displayed by the LED, and the buzzer makes a noise. By adopting the method and device, clear egg distinguishing is convenient and rapid, the requirement of rejecting clear egg before brooding can be completely met, thus the clear egg distinguishing system is efficient and practical.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG BAYI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Defending method based on virtual function table hijacking
InactiveCN105868641AHigh speedReduce overheadPlatform integrity maintainanceProgram slicingSemantics
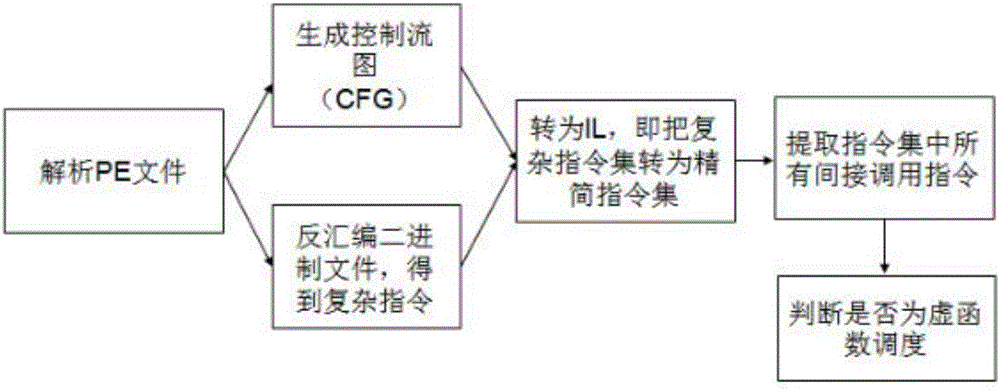
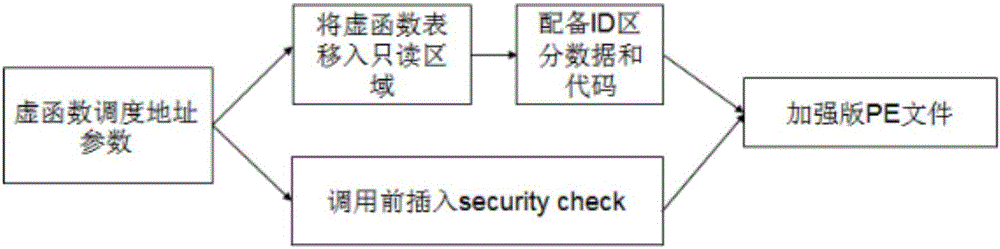
The invention provides a defense method based on virtual function table hijacking, which can determine the utilization and further attack of potential use-after-free type loopholes in binary executable files. Step 1. Use the static instruction fragmentation and extraction framework to disassemble an executable file as input and generate a control flow graph and assembly language; Step 2. Compress and simplify the assembly language obtained in Step 1; Step 3. vEXTRACTOR in Step 2 Execute backward program slicing on the obtained intermediate language; step 4, extract all low-level semantics satisfying virtual function scheduling from the first three steps, and take out the virtual function scheduling part; step 5, rewrite and configure ID; All reference parameters of the function table are changed to new addresses of vtables, and VRewriter equips each virtual function with a security check to verify the integrity of the target virtual table; step 7, put the execution code equipped with security check into a new The code segment, to ensure that most of the original code department intact.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com