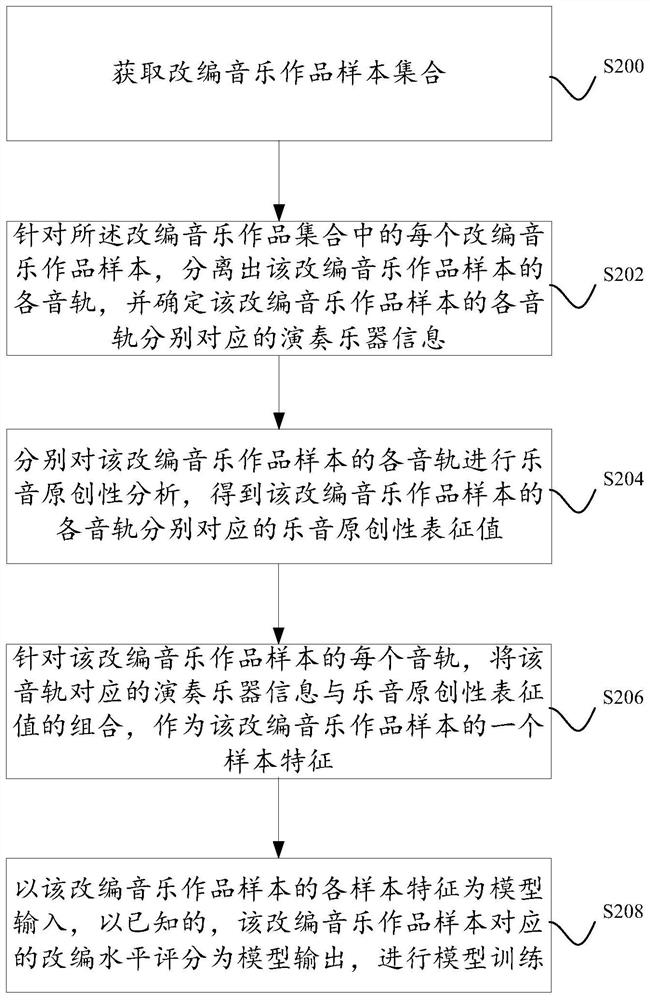
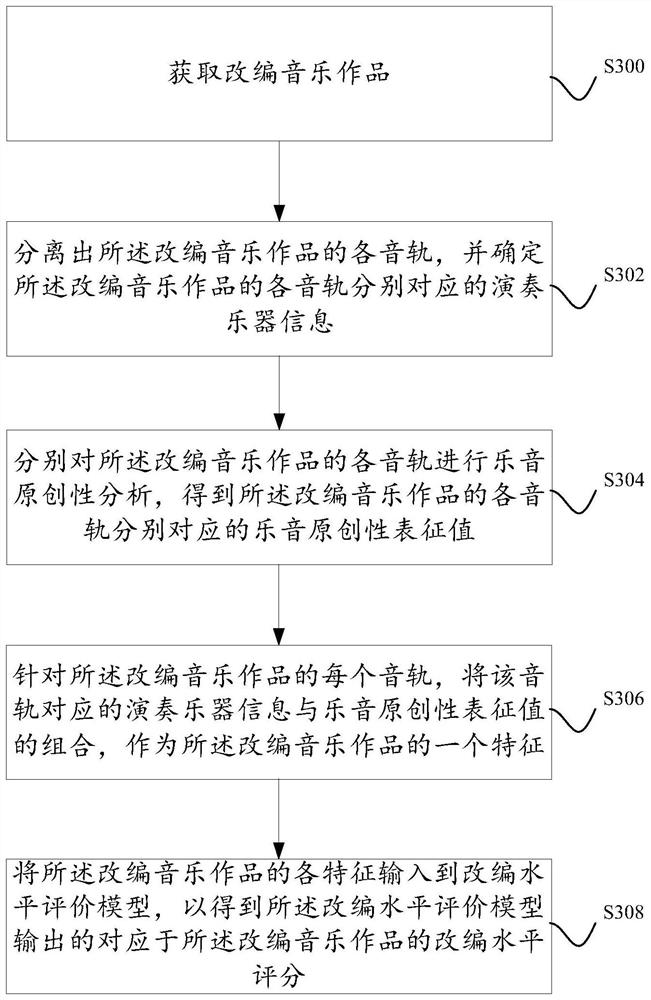
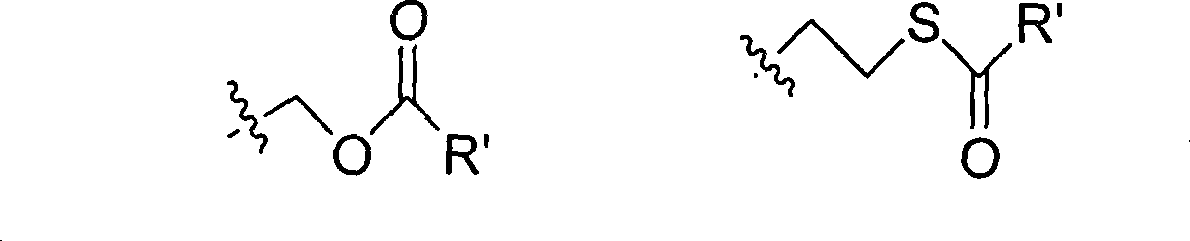Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32 results about "Derivative work" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
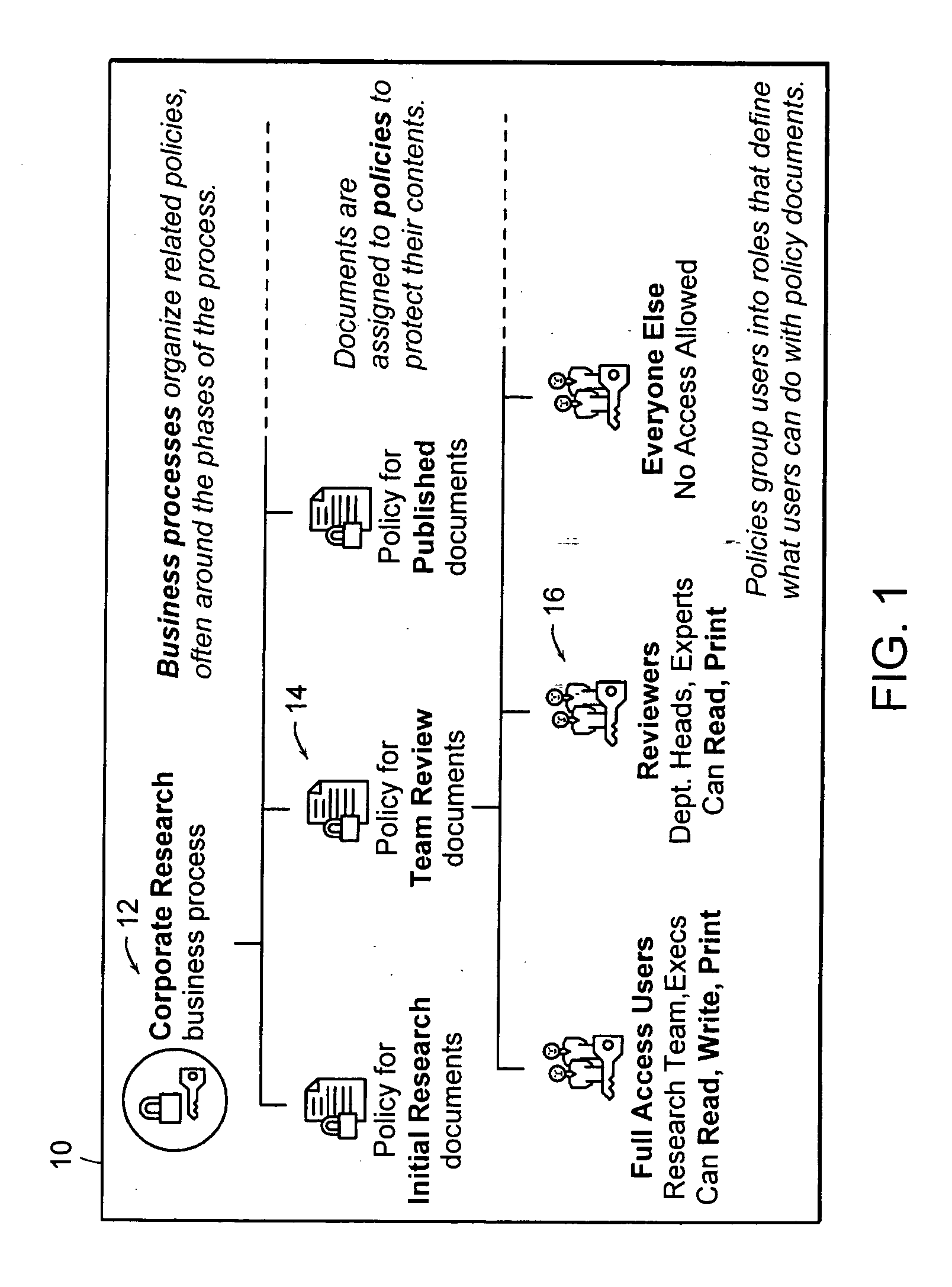
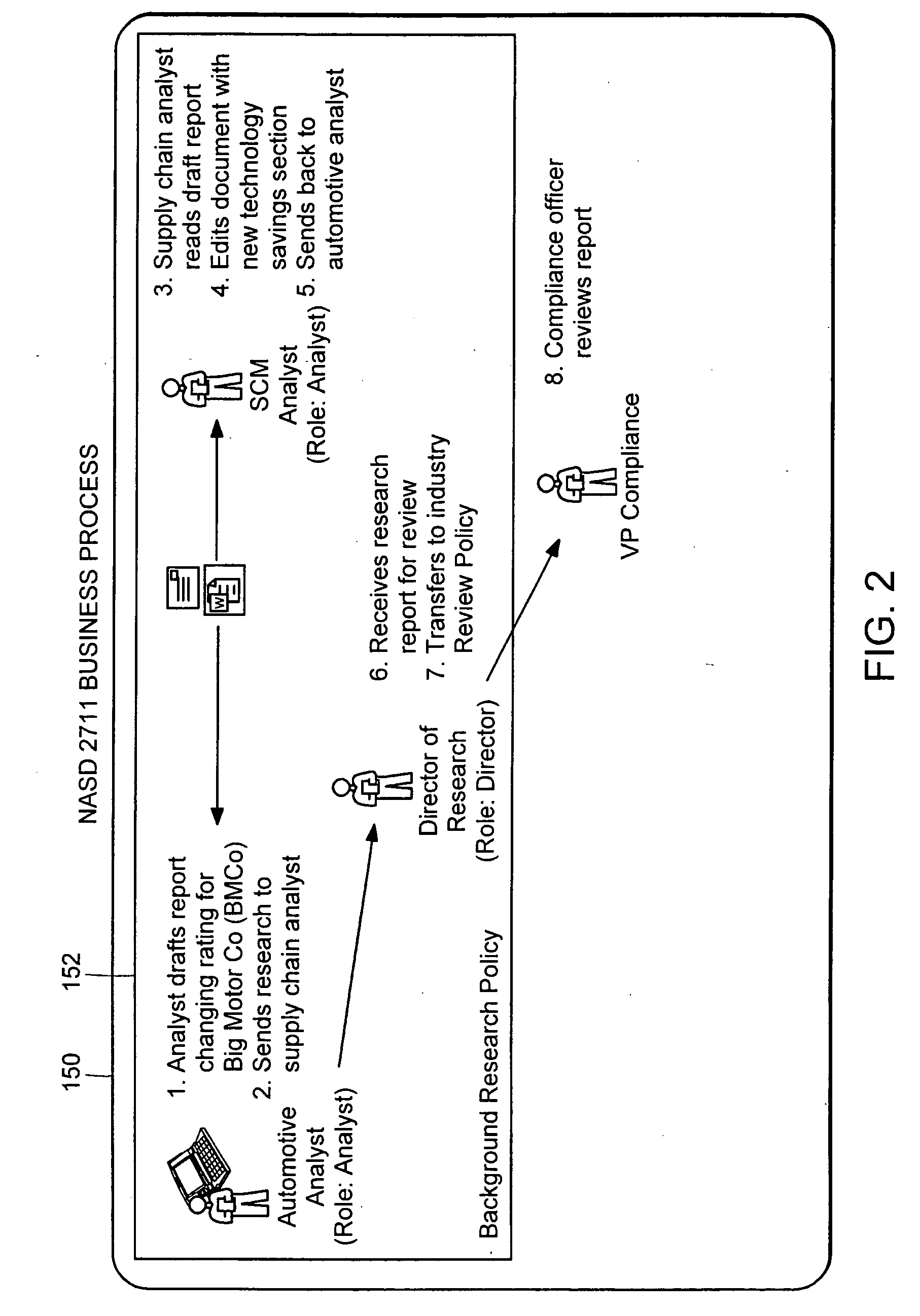
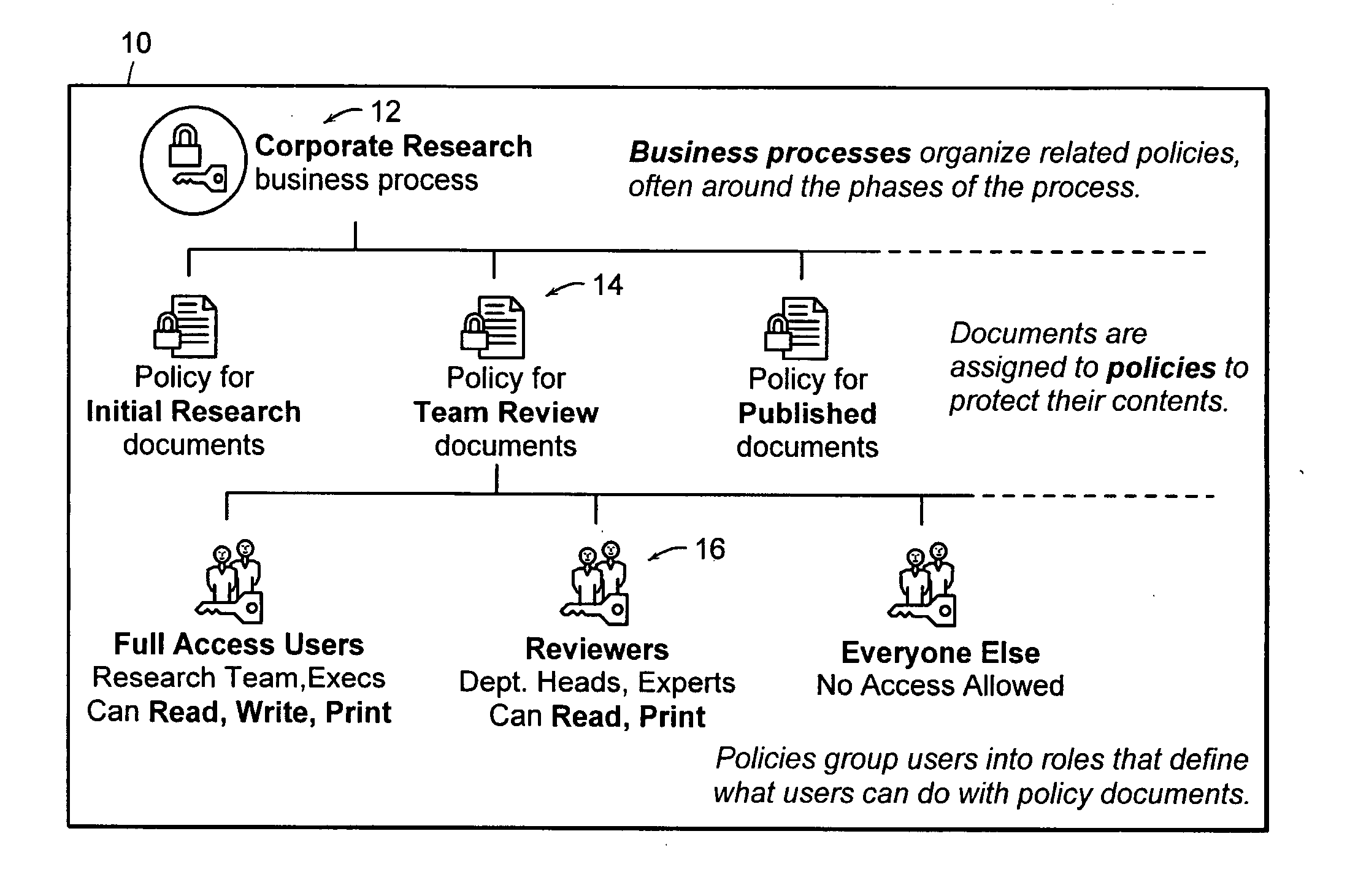
In copyright law, a derivative work is an expressive creation that includes major copyrightable elements of an original, previously created first work (the underlying work). The derivative work becomes a second, separate work independent in form from the first. The transformation, modification or adaptation of the work must be substantial and bear its author's personality sufficiently to be original and thus protected by copyright. Translations, cinematic adaptations and musical arrangements are common types of derivative works.
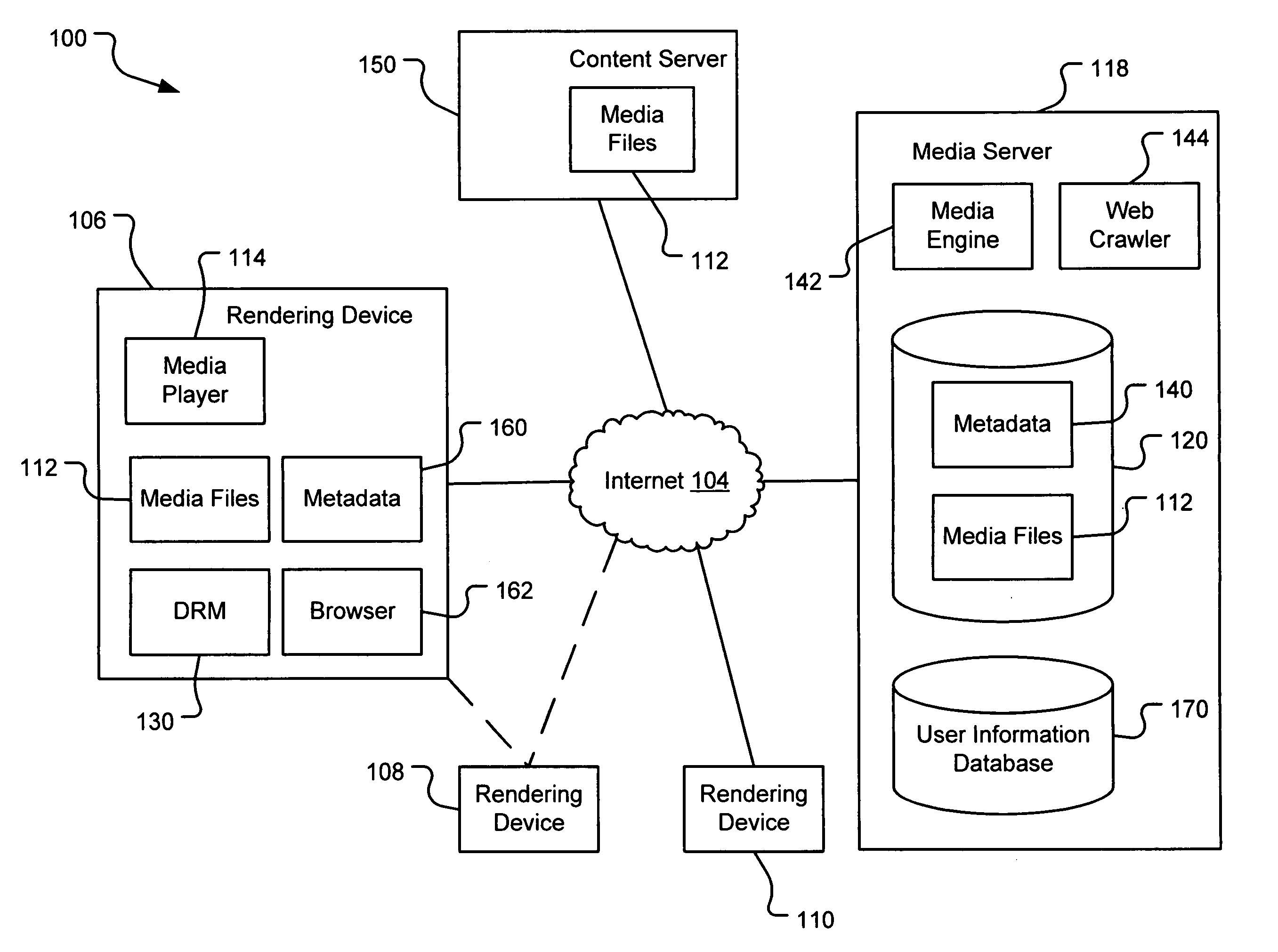
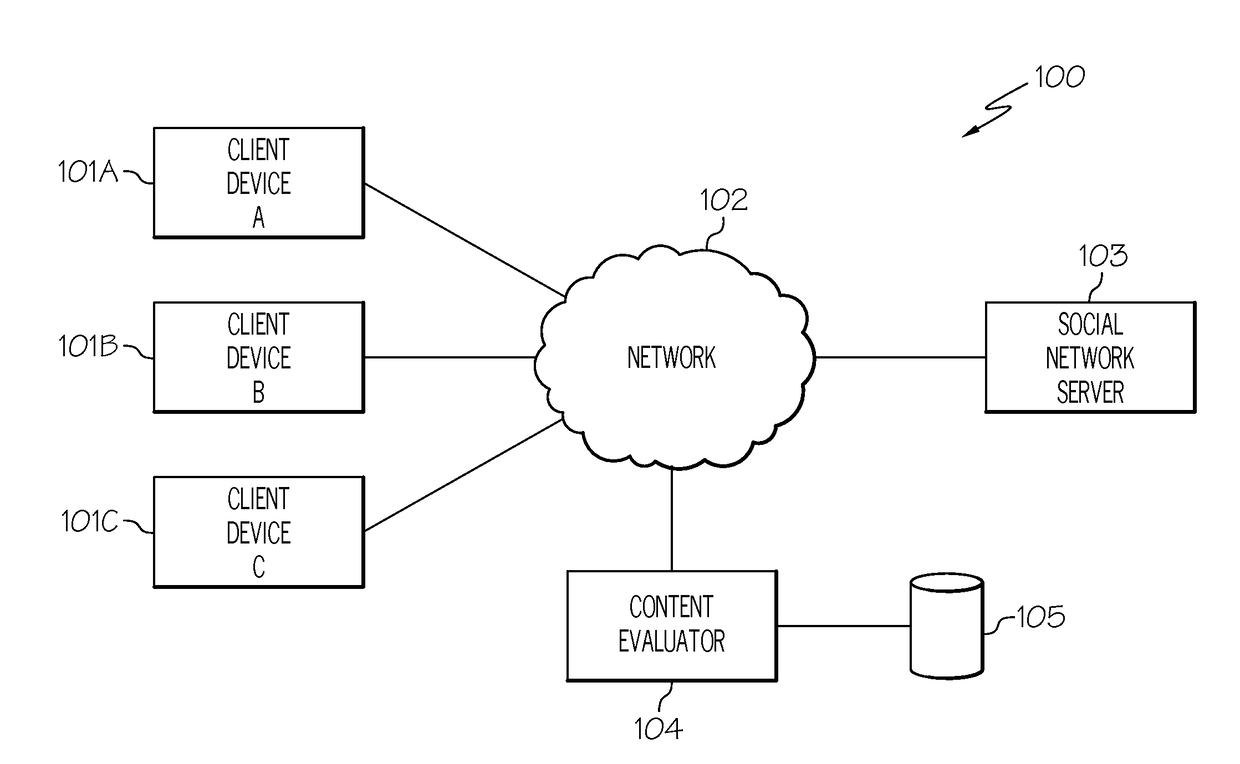
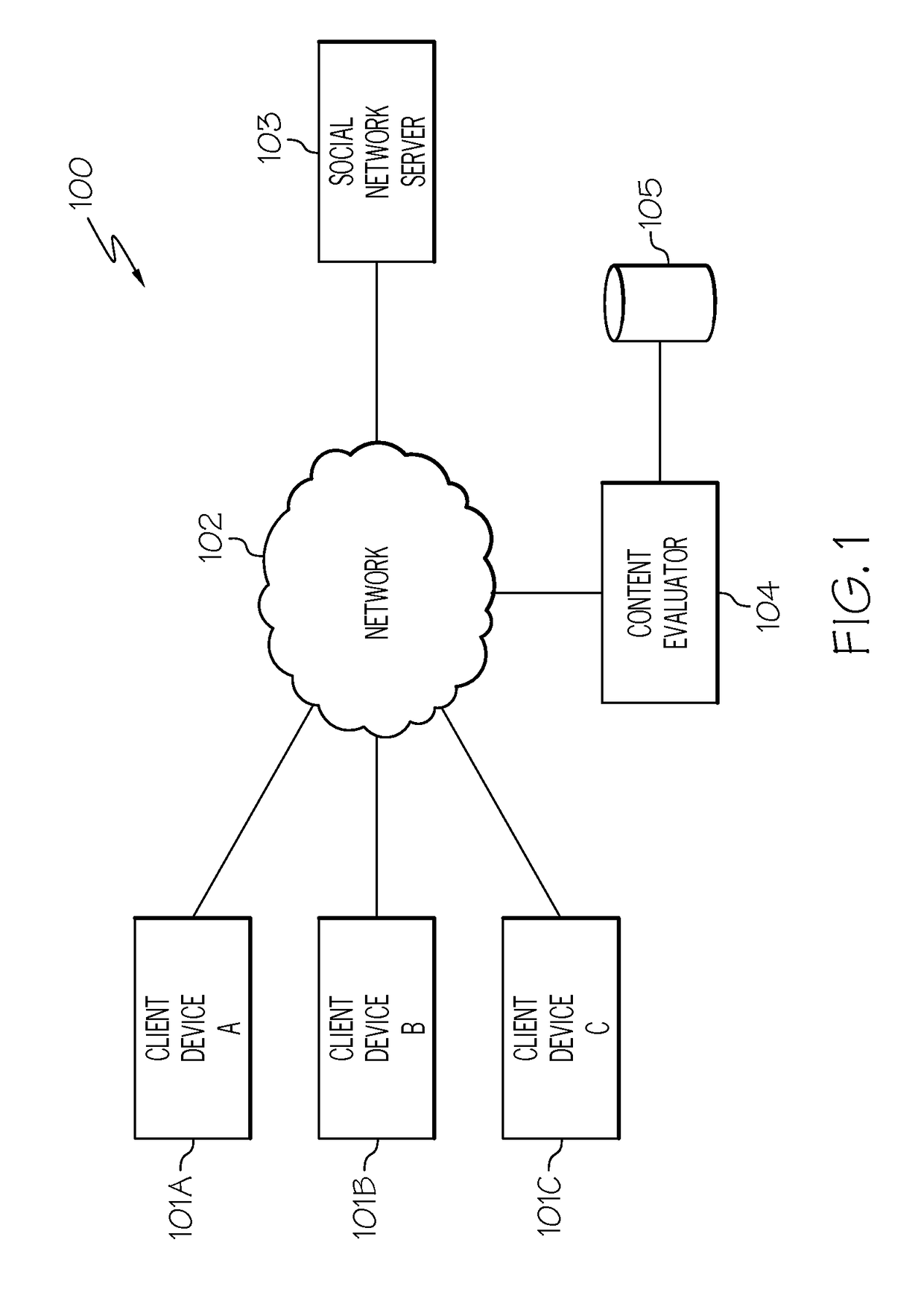
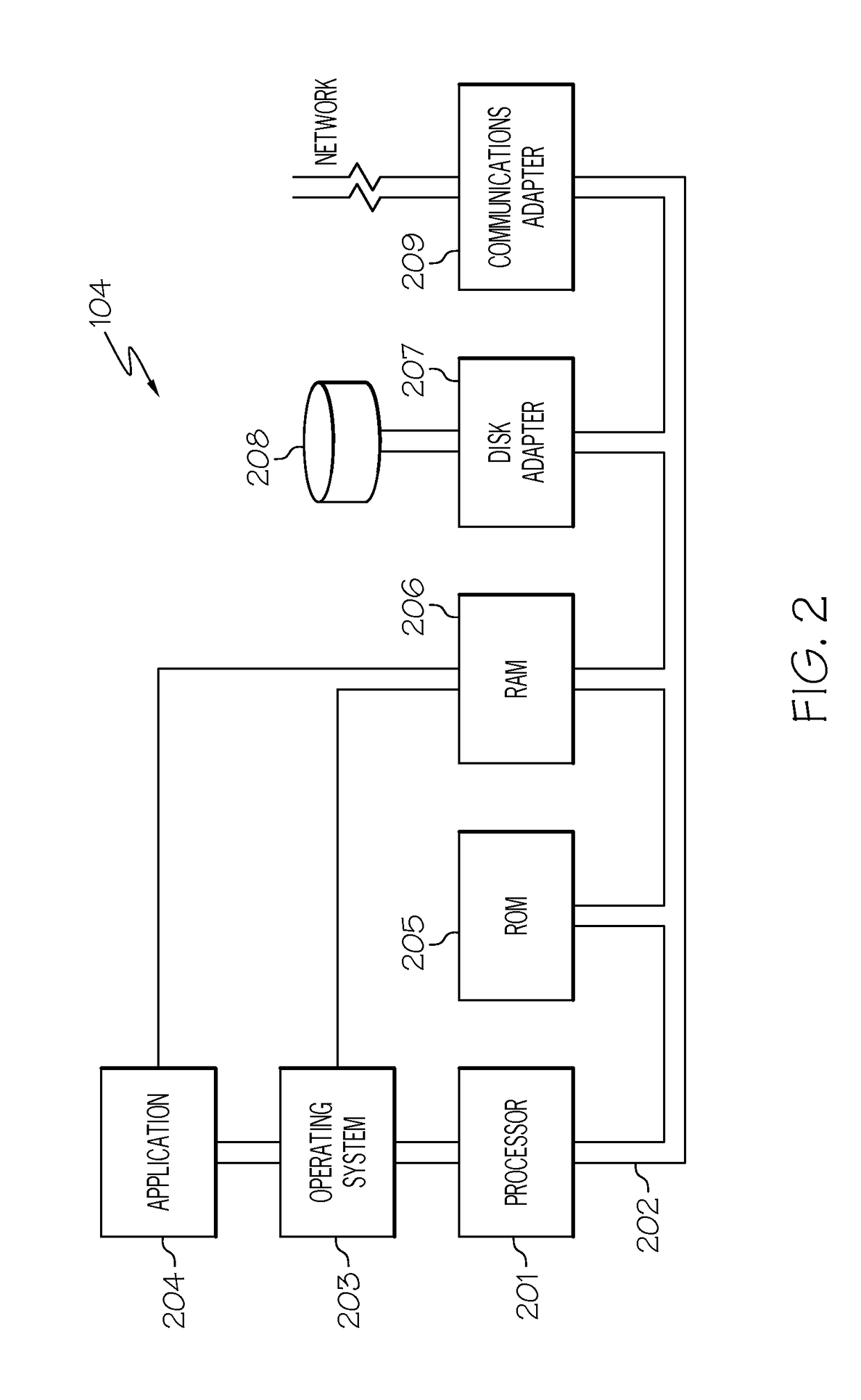
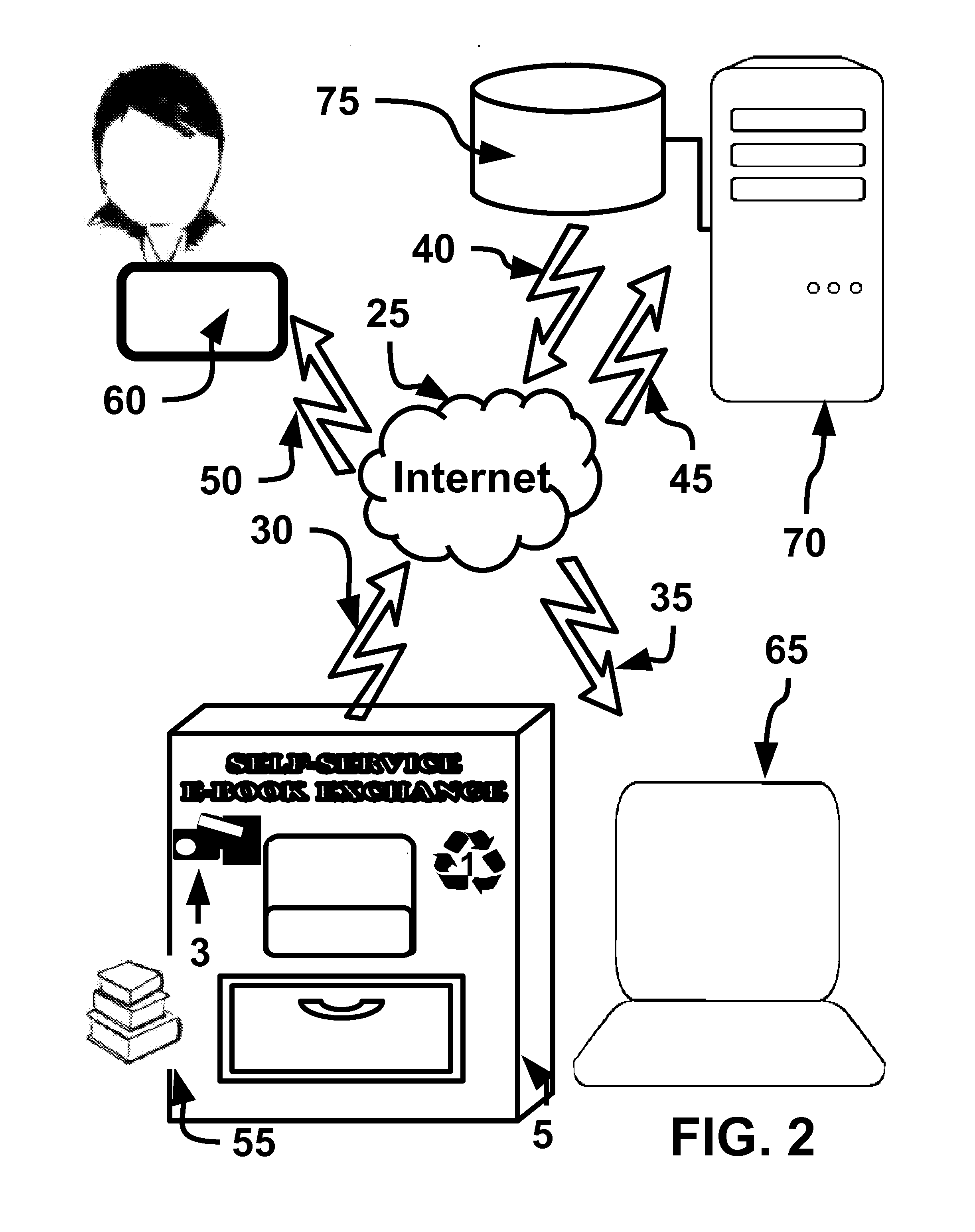
Computer method and apparatus for managing data objects in a distributed context
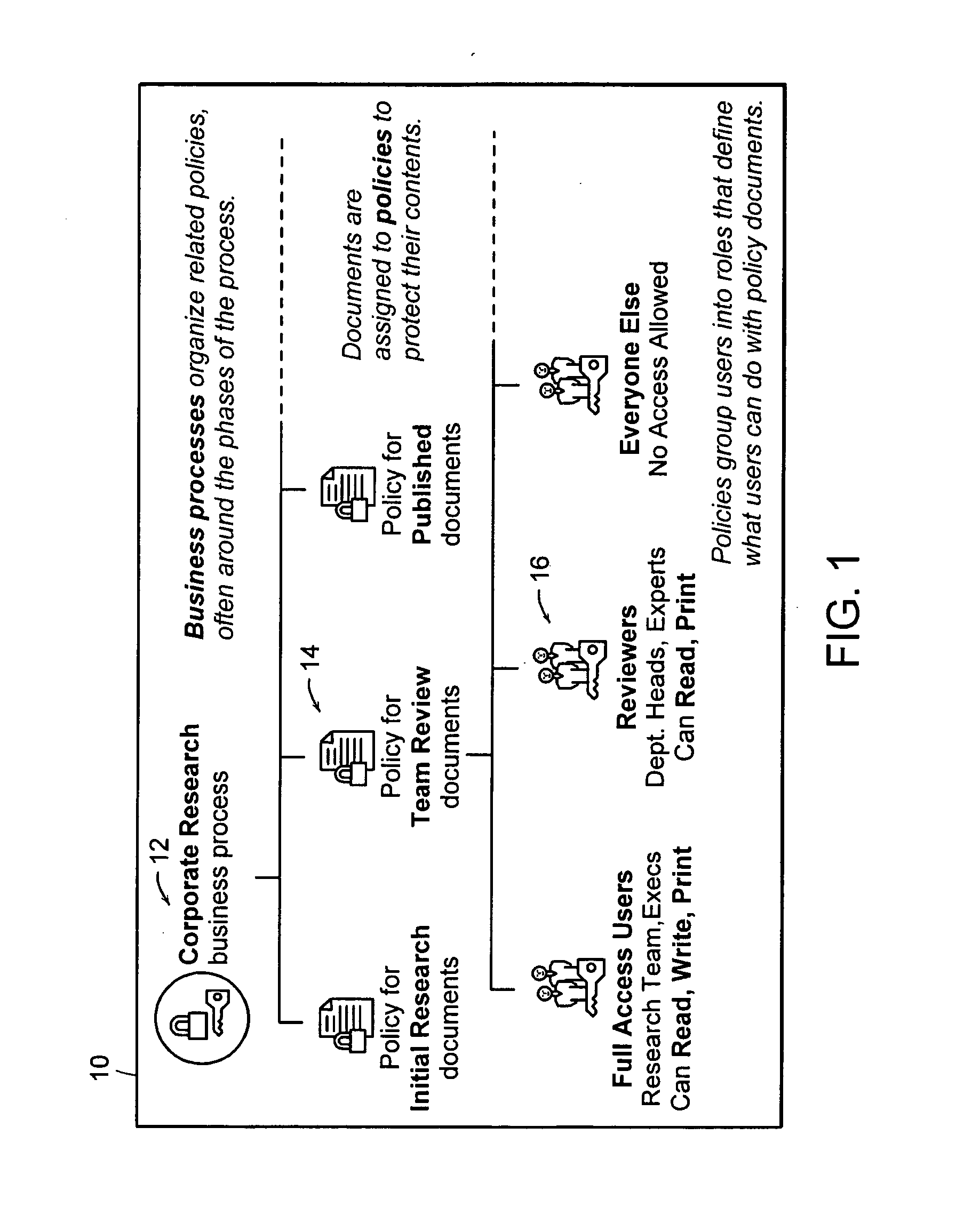
ActiveUS20050028006A1Obtaining visibility into a business processLimited historyKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsDerivative workComputer methods
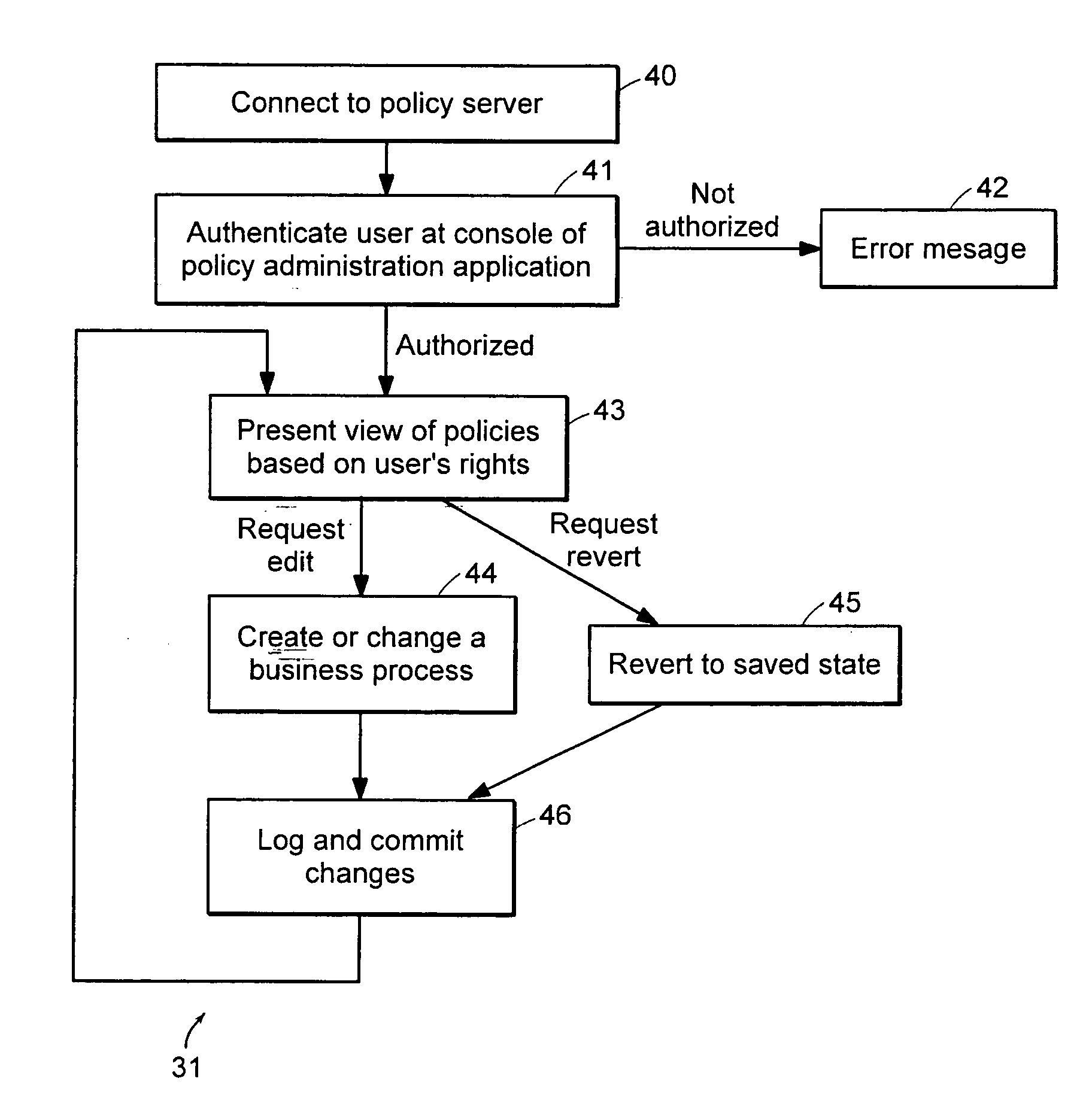
In a network of intermittently-connected computers, a method and apparatus for maintaining and managing control over data objects authored, accessed, and altered by users in dynamic, distributed, and collaborative contexts. The invention method and apparatus attach to each data object an identification of a respective control policy. Each control policy comprises at least an indication of a subset of the users who may access the data object, an indication of the privileges granted to each subset of users able to access the data object, and an indication of a subset of users who may define or edit the control policy. The invention method and apparatus separate the management of the control policies of data objects from the creation and use of the data objects. The invention method and apparatus automate common policy changes, distribution of policy changes to the enforcement agents, and propagation of control policies to derivative works.
Owner:LIQUID MACHINES
Computer method and apparatus for securely managing data objects in a distributed context
InactiveUS20050008163A1Obtaining visibility into a business processLimited historyKey distribution for secure communicationUnauthorized memory use protectionDerivative workComputer methods
In a network of intermittently-connected computers, a method and apparatus for maintaining and managing control over data objects authored, accessed, and altered by users in dynamic, distributed, and collaborative contexts. The invention method and apparatus attach to each data object an identification of a respective control policy. Each control policy comprises at least an indication of a subset of the users who may access the data object, an indication of the privileges granted to each subset of users able to access the data object, and an indication of a subset of users who may define or edit the control policy. The invention method and apparatus separate the management of the control policies of data objects from the creation and use of the data objects. The invention method and apparatus automate common policy changes, distribution of policy changes to the enforcement agents, and propagation of control policies to derivative works.
Owner:LIQUID MACHINES
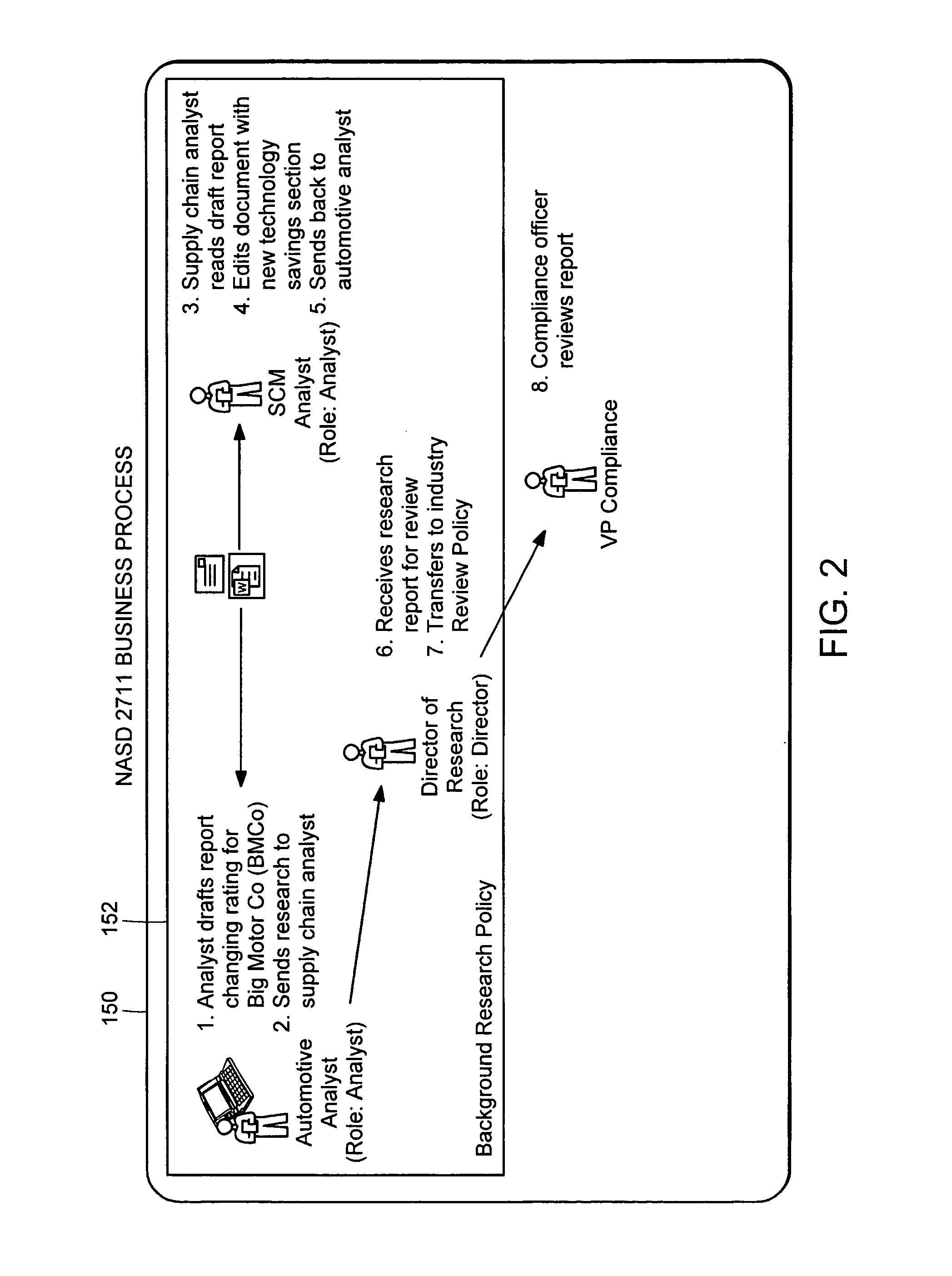
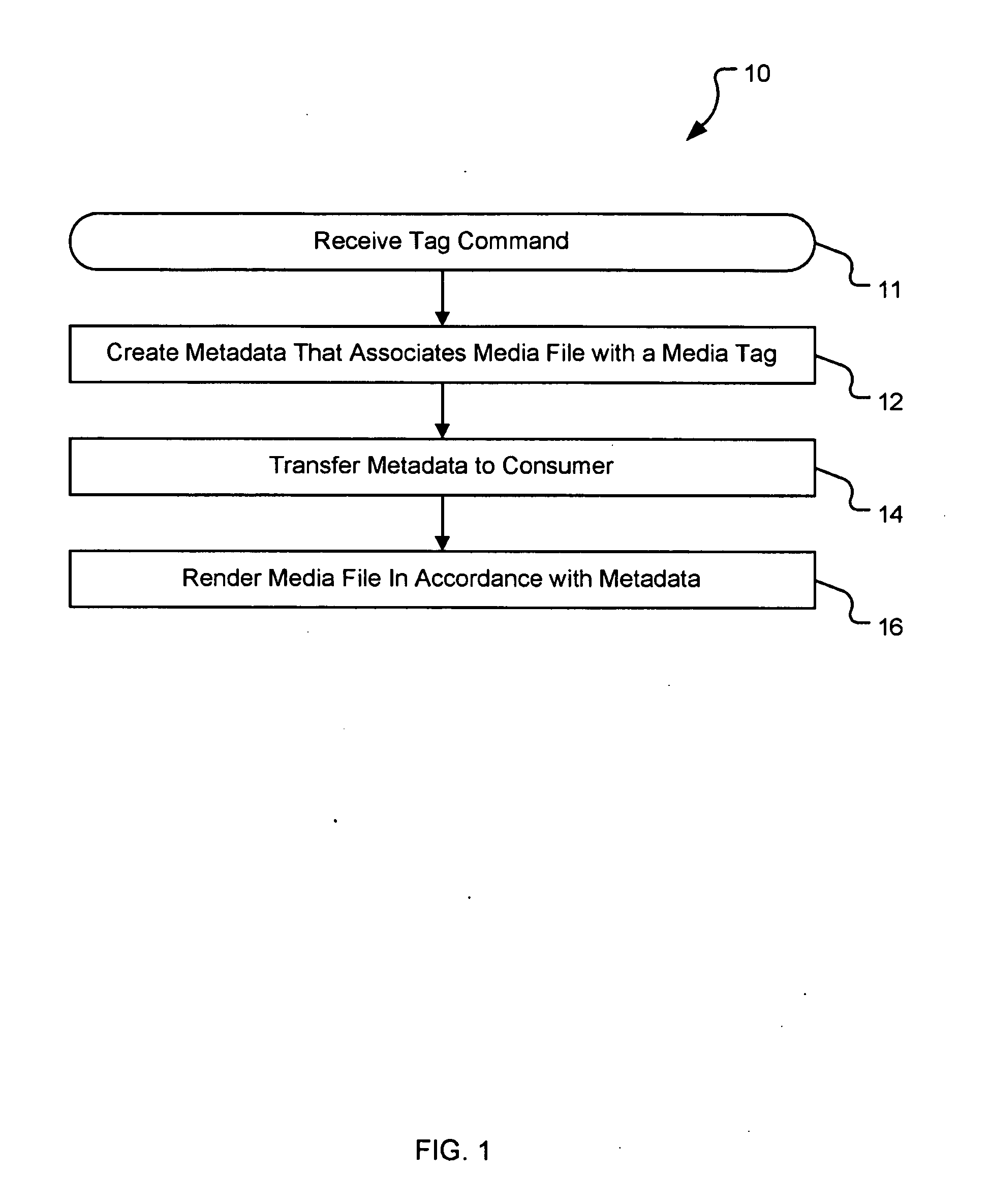
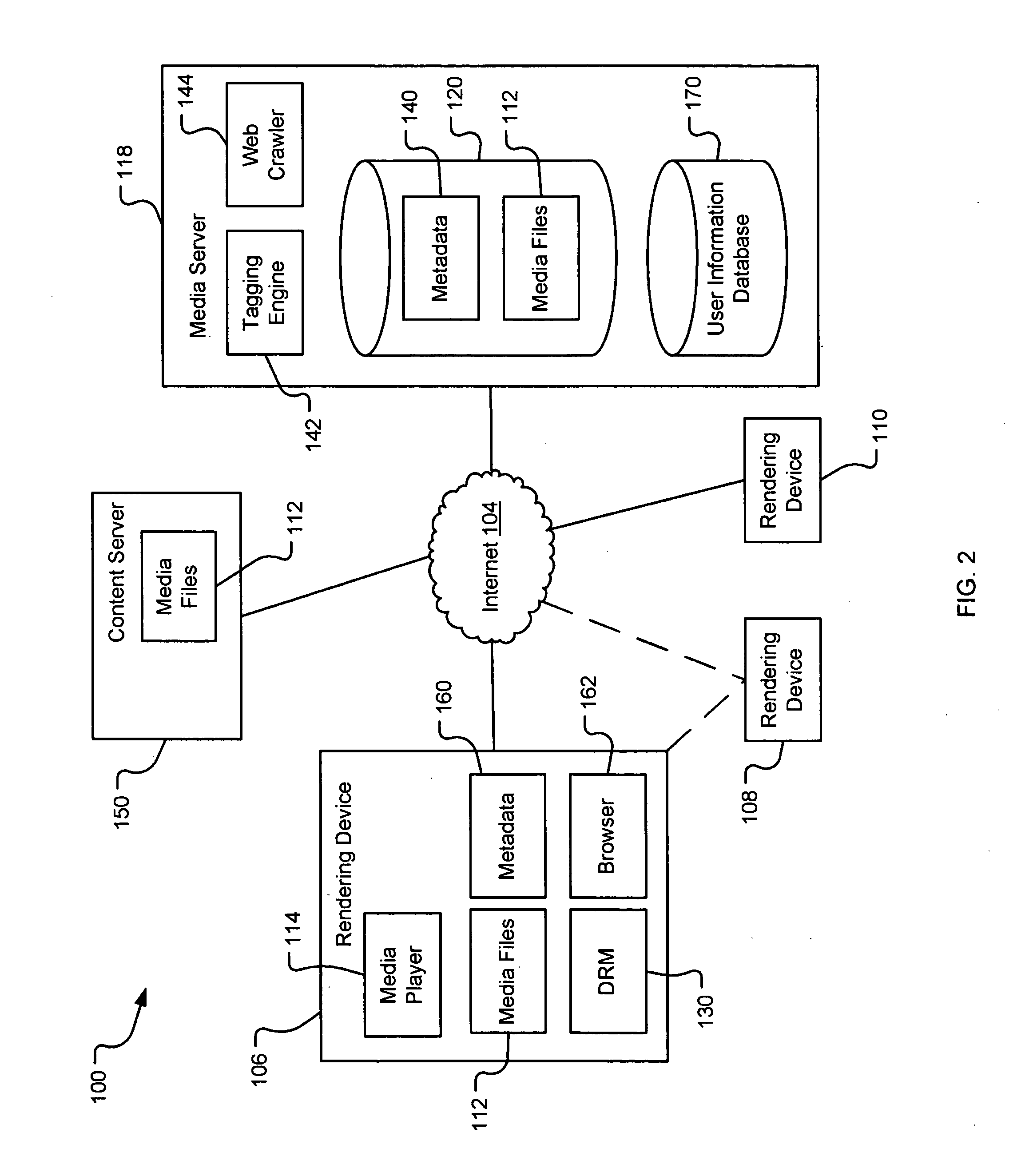
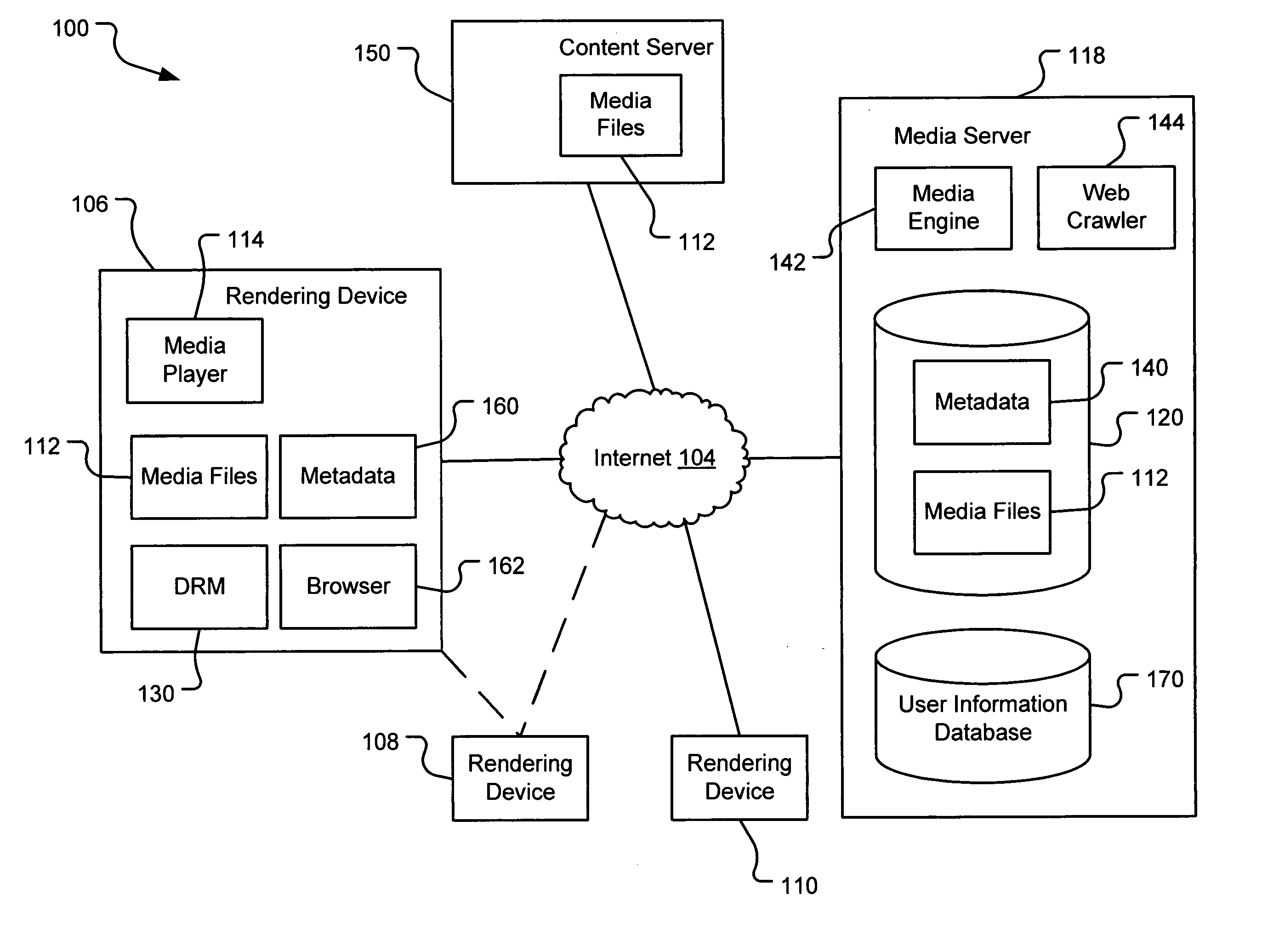
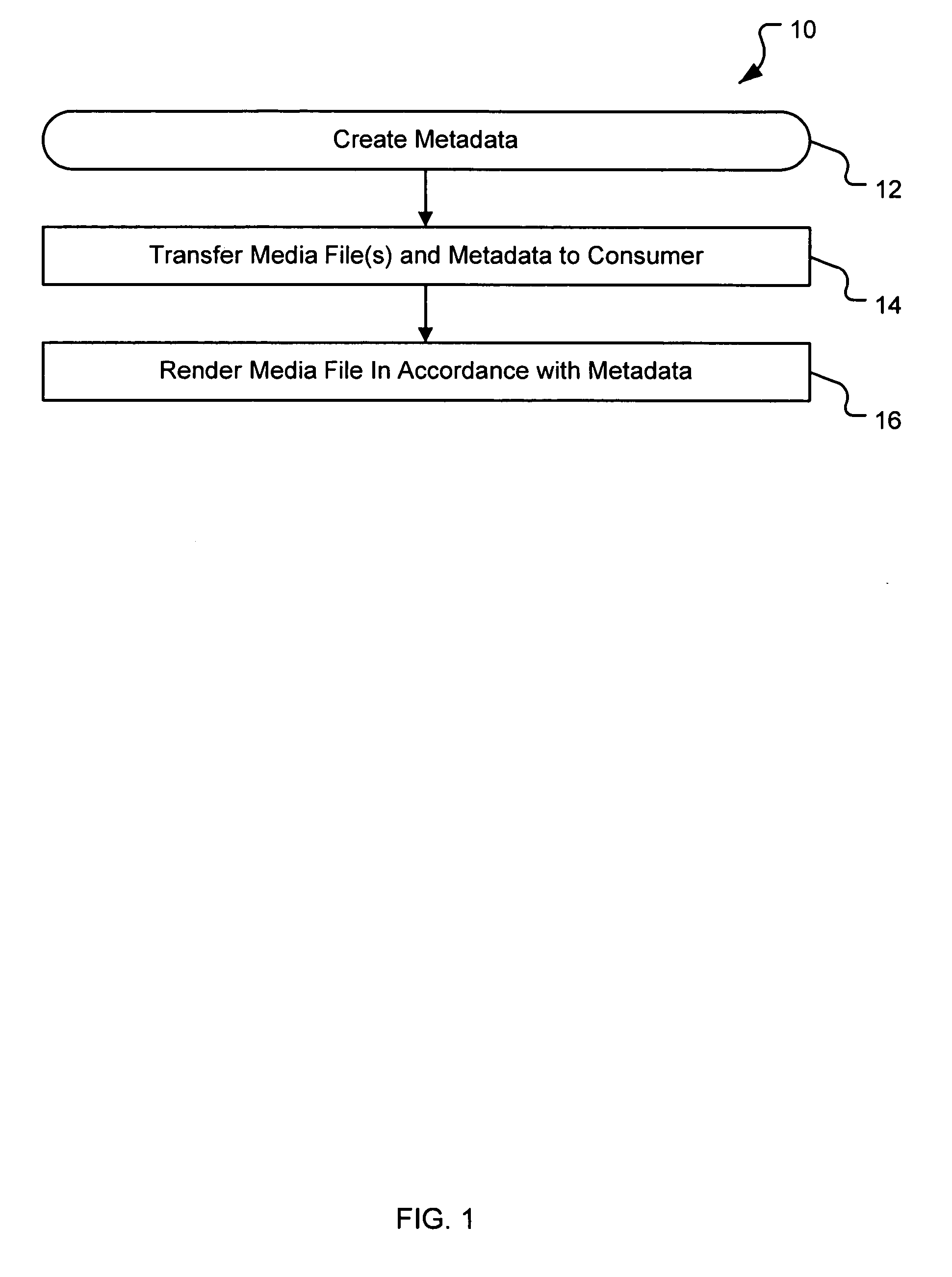
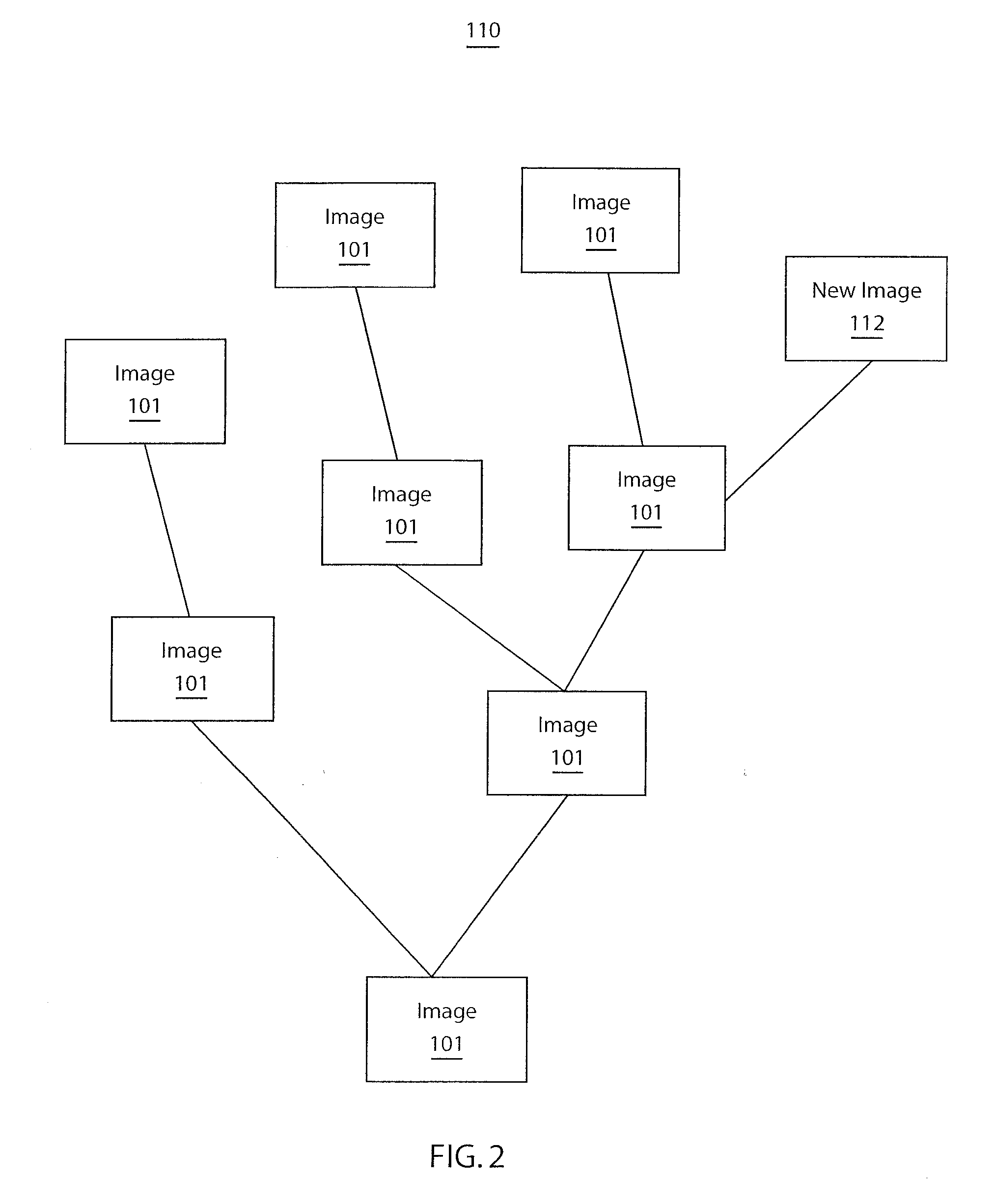
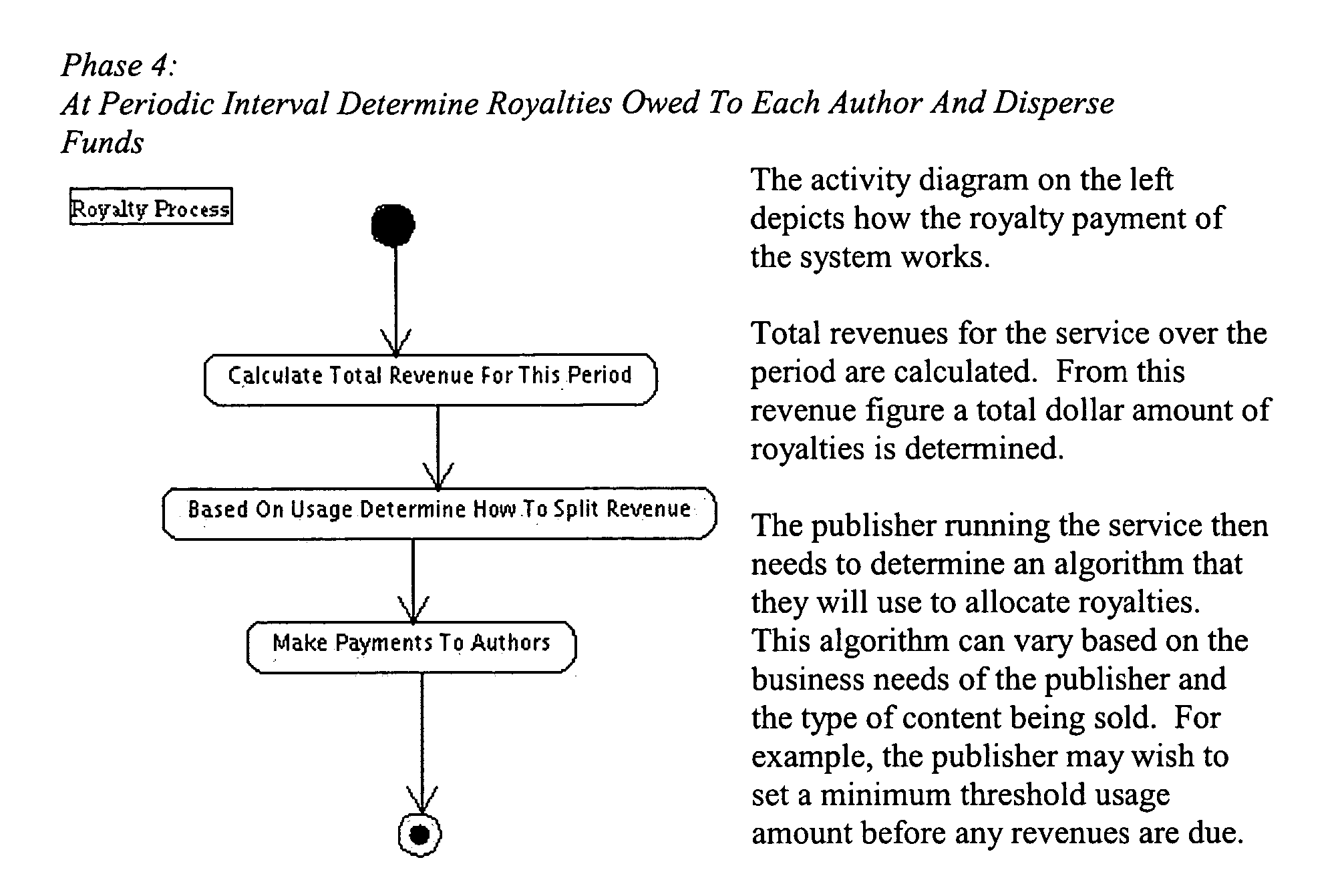
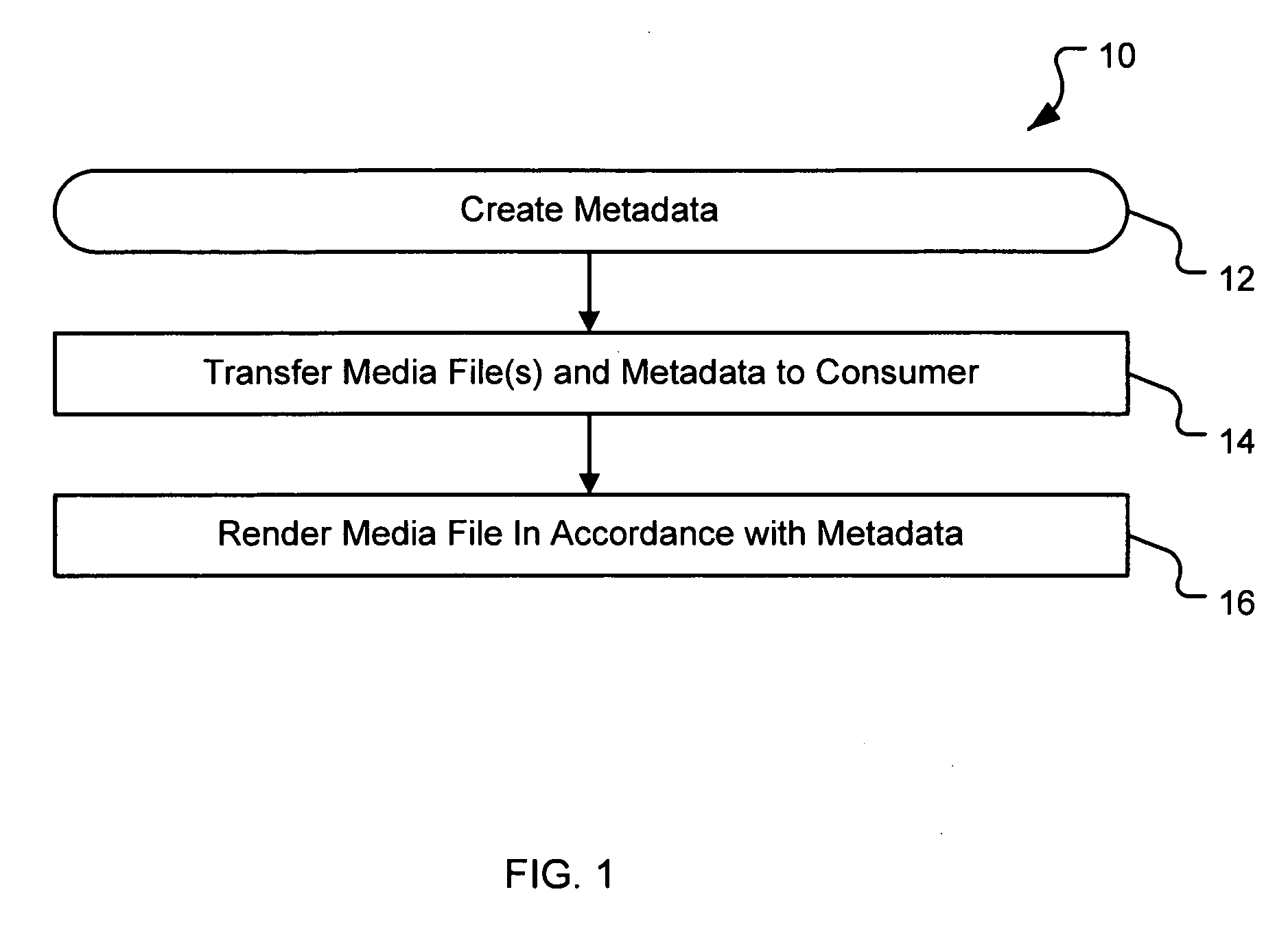
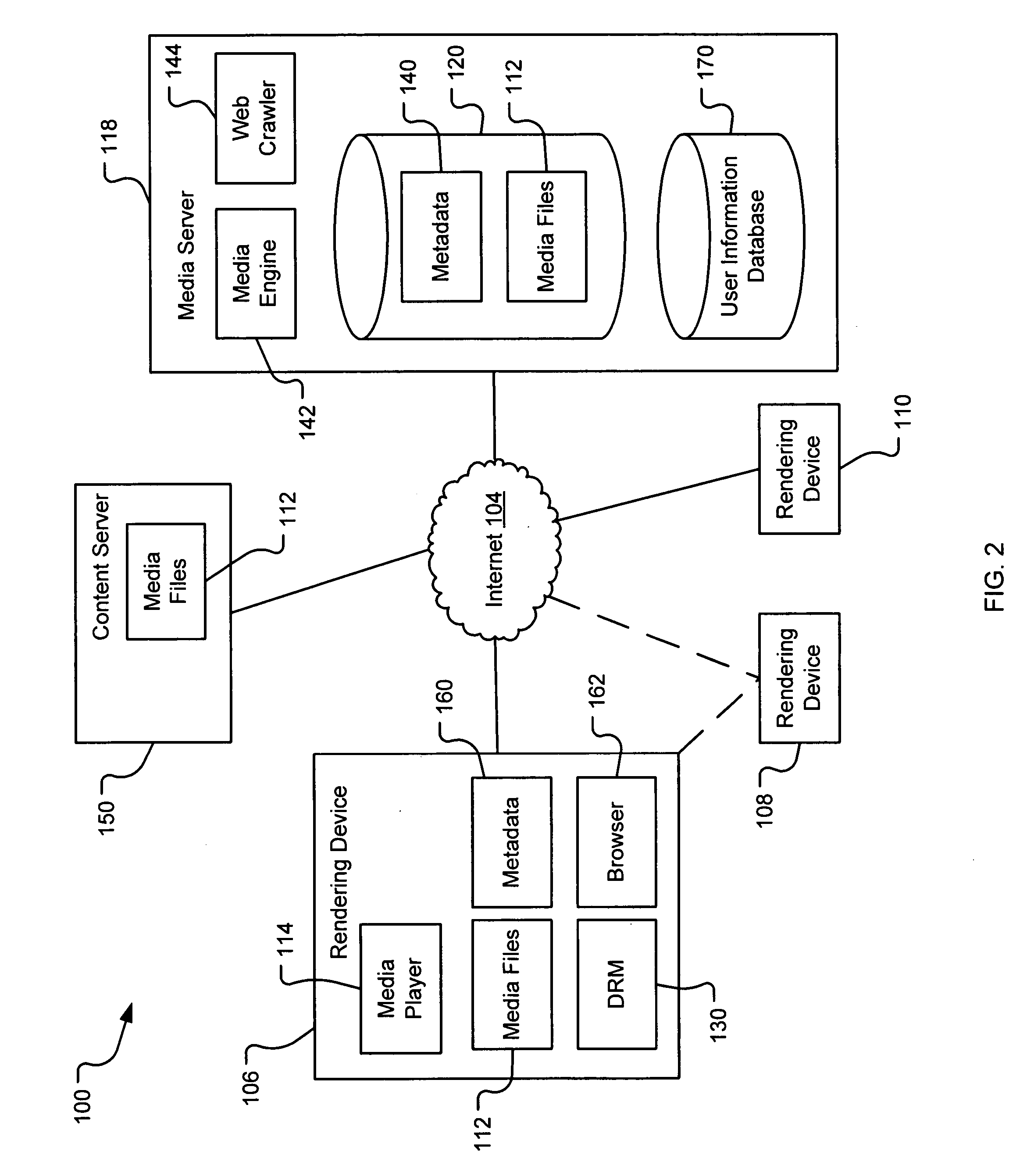
Generating a stream of media data containing portions of media files using location tags
InactiveUS20070078876A1Recording carrier detailsDistributed storage methodsData streamDerivative work
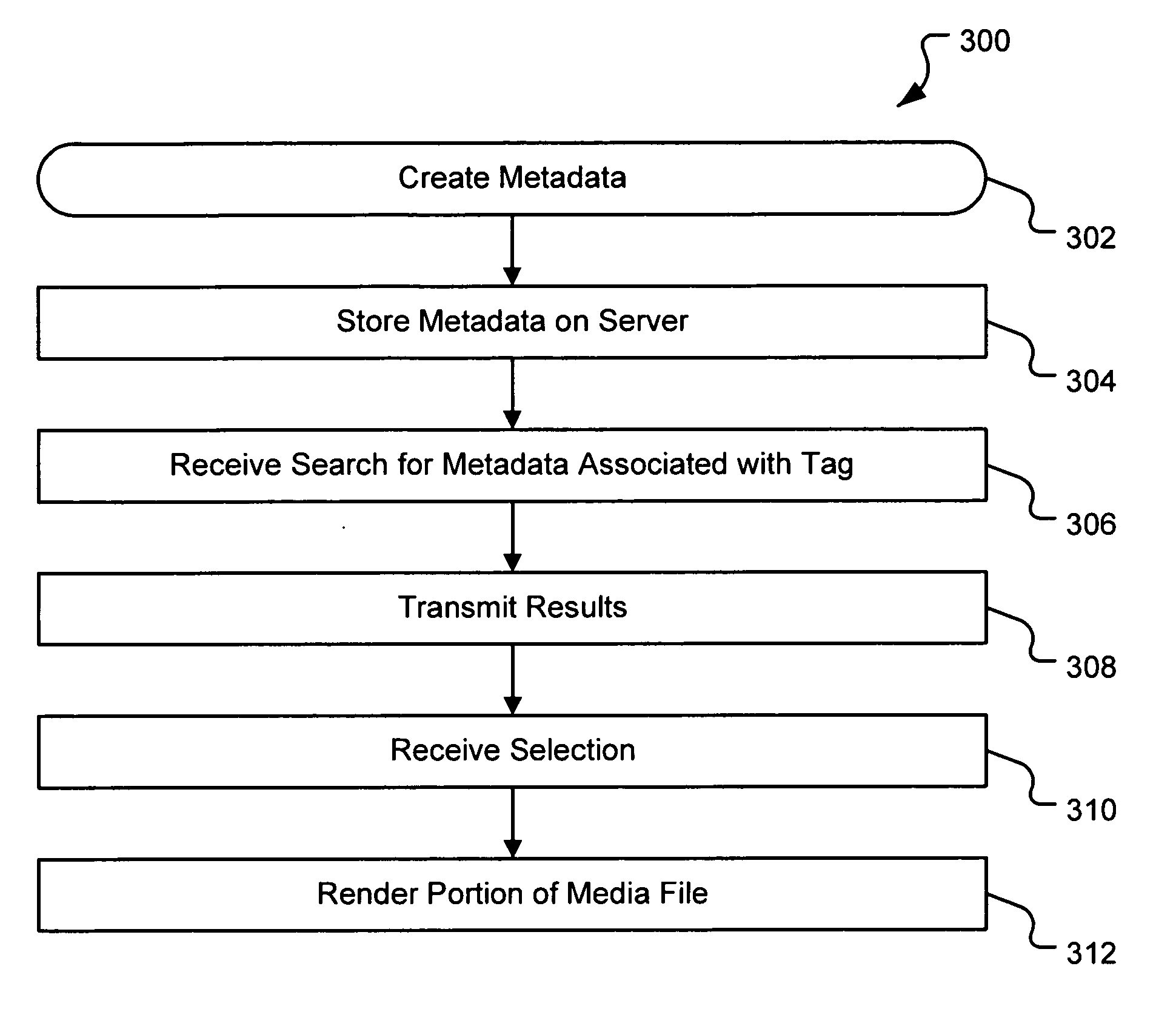
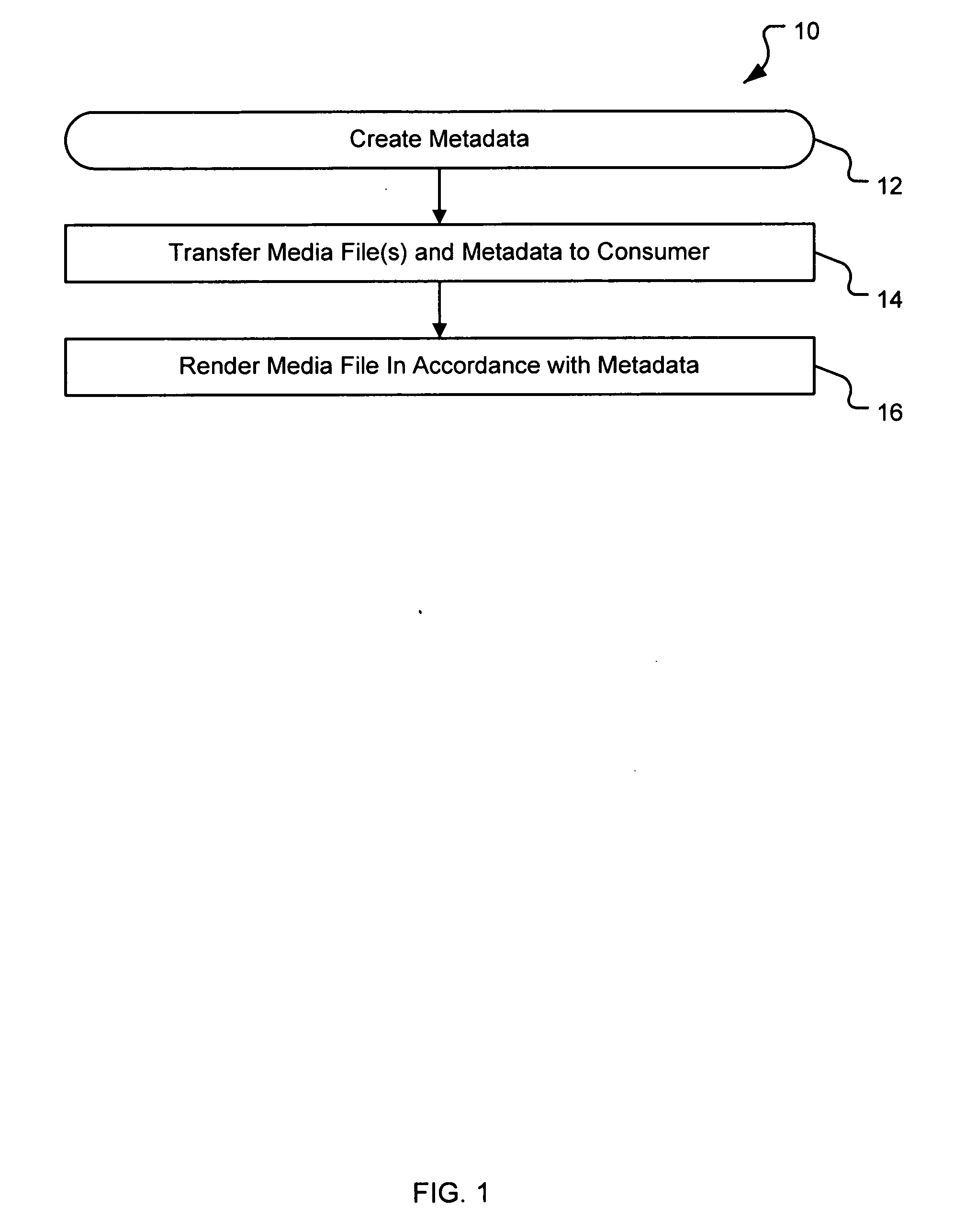
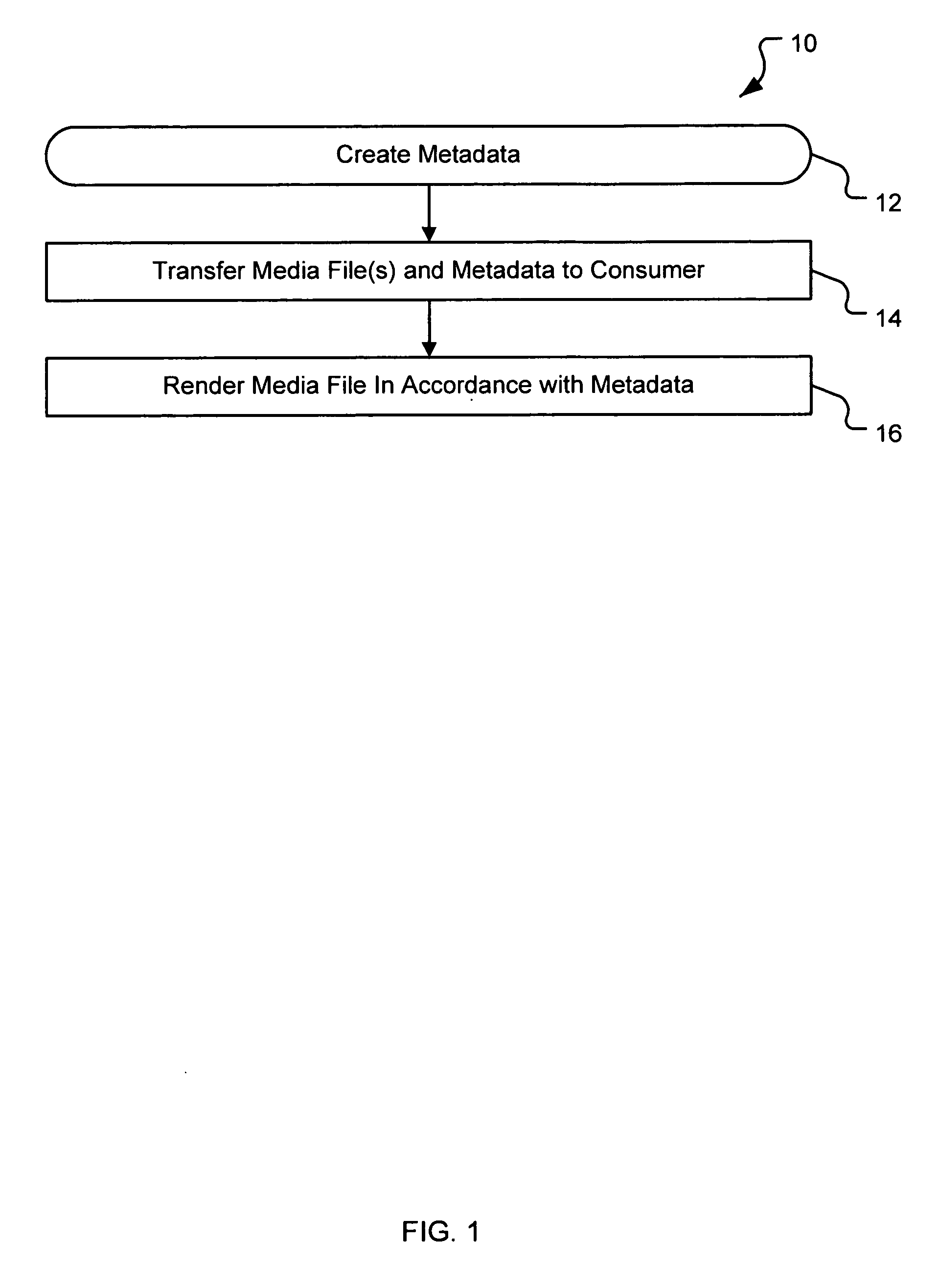
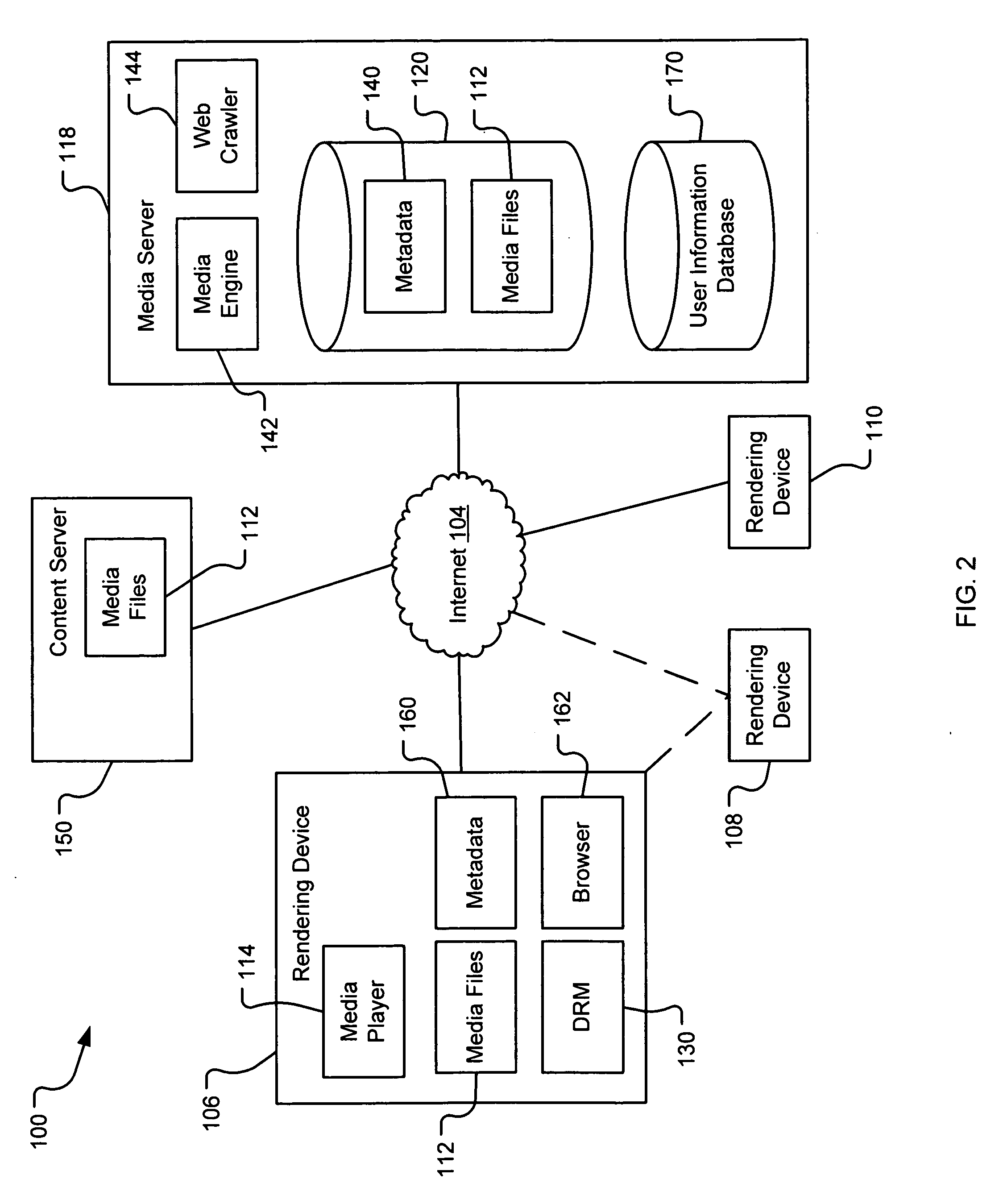
A system and method are provided for identifying discrete locations and / or sections within a pre-existing media file without modifying the media file. The discrete locations and / or sections can be associated with one or more user-selected descriptors. The system and method allows for the identifying information to be communicated to consumers of the media file and the media file to be selectively rendered by the consumer using the identifying information, thus allowing a consumer to render only the portion of the media file identified or render from a given discrete location in the media file. In an embodiment, the system and method can be performed without modifying the media file itself and thus no derivative work is created.
Owner:OATH INC
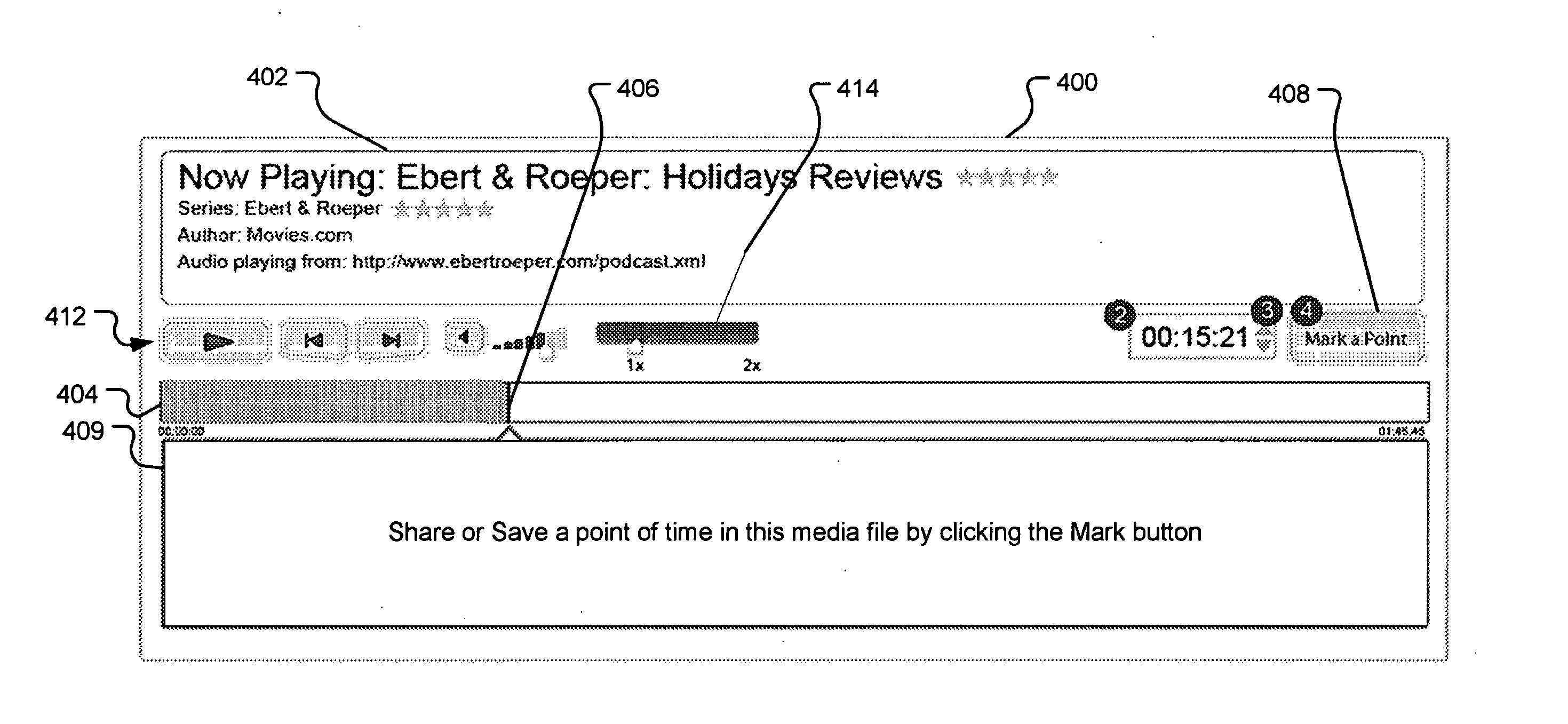
Picture tagging
InactiveUS20070079321A1Specific information broadcast systemsDigital computer detailsComputer graphics (images)Derivative work
A system and method for tagging discrete locations and / or sections within a pre-existing media file with images without modifying the media file are disclosed. The system includes a rendering device that receives user tag selections and creates information that can be used when rendering the media file in the future. When a tagged media file is rendered by a device capable of interpreting the information, the images are concurrently displayed on the interface of the rendering device. The discrete locations and / or sections can be associated with one or more user-selected image files. In an embodiment, the system and method can be performed without modifying the media file itself and thus no derivative work is created.
Owner:OATH INC
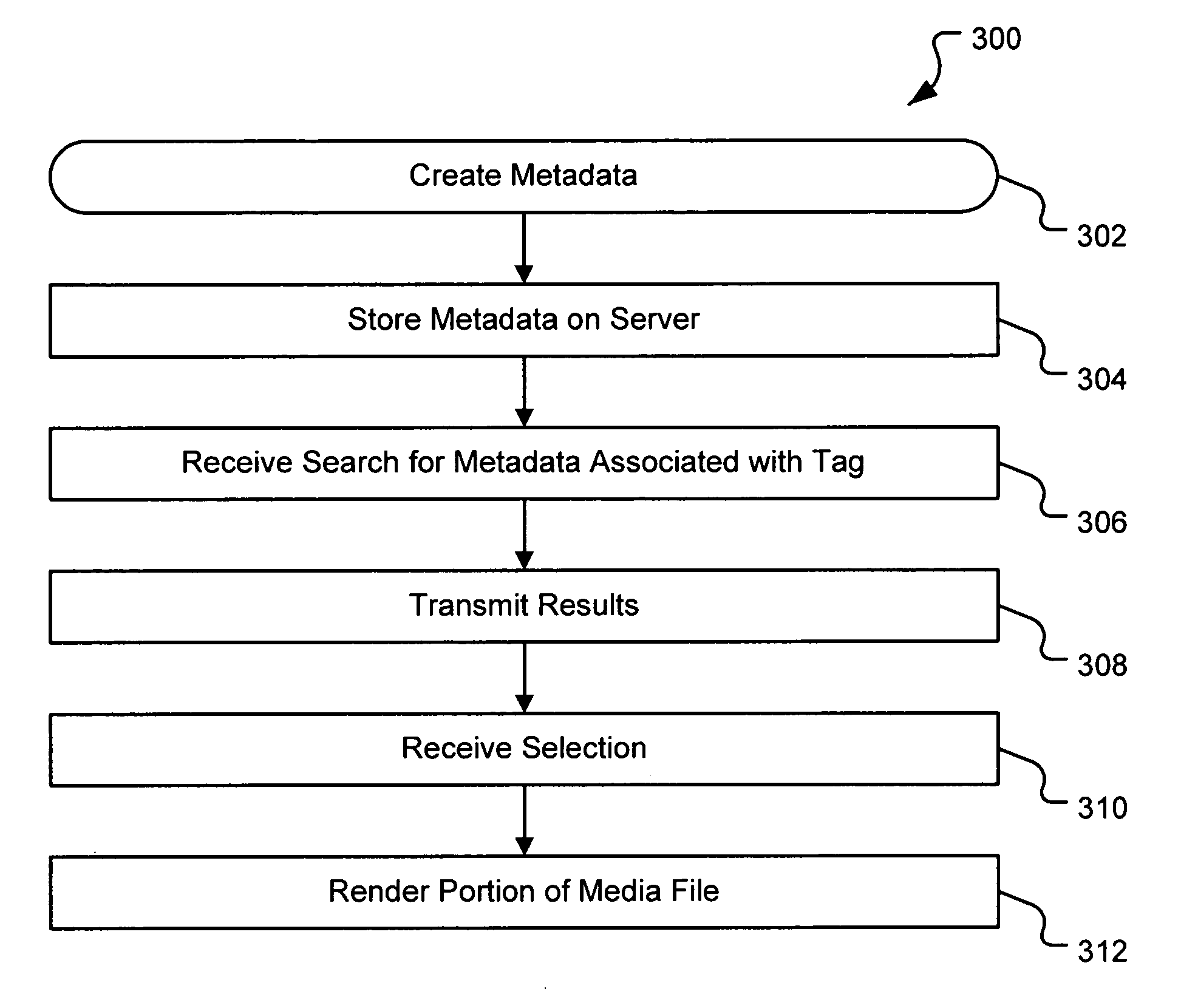
Server-based system and method for retrieving tagged portions of media files
InactiveUS20070078898A1Digital data processing detailsMetadata multimedia retrievalDerivative workWorld Wide Web
A system and method are provided for identifying discrete locations and / or sections within a pre-existing media file without modifying the media file. The discrete locations and / or sections can be associated with one or more user-selected descriptors. The system and method allows for the identifying information to be communicated to consumers of the media file and the media file to be selectively rendered by the consumer using the identifying information, thus allowing a consumer to render only the portion of the media file identified or render from a given discrete location in the media file. In an embodiment, the system and method can be performed without modifying the media file itself and thus no derivative work is created.
Owner:OATH INC
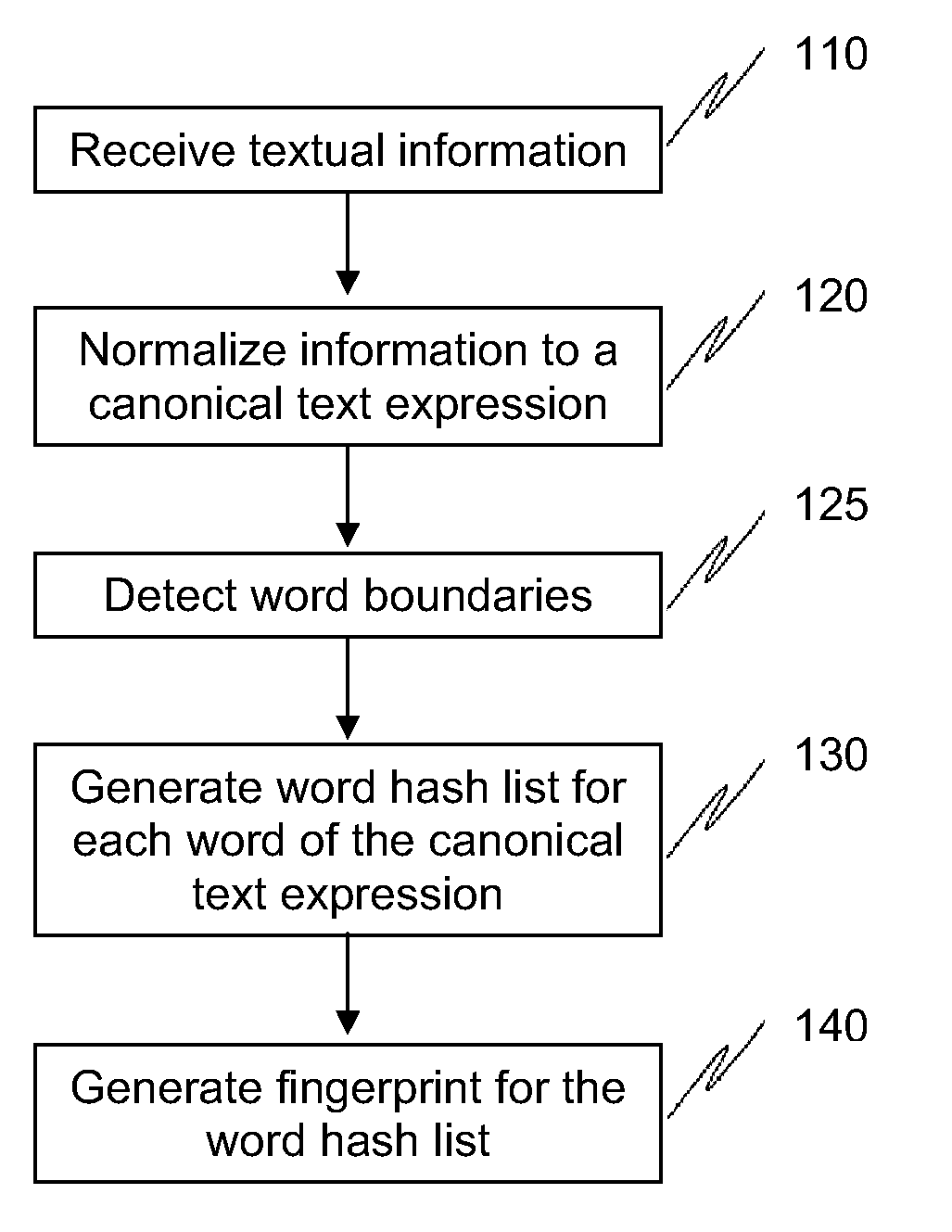
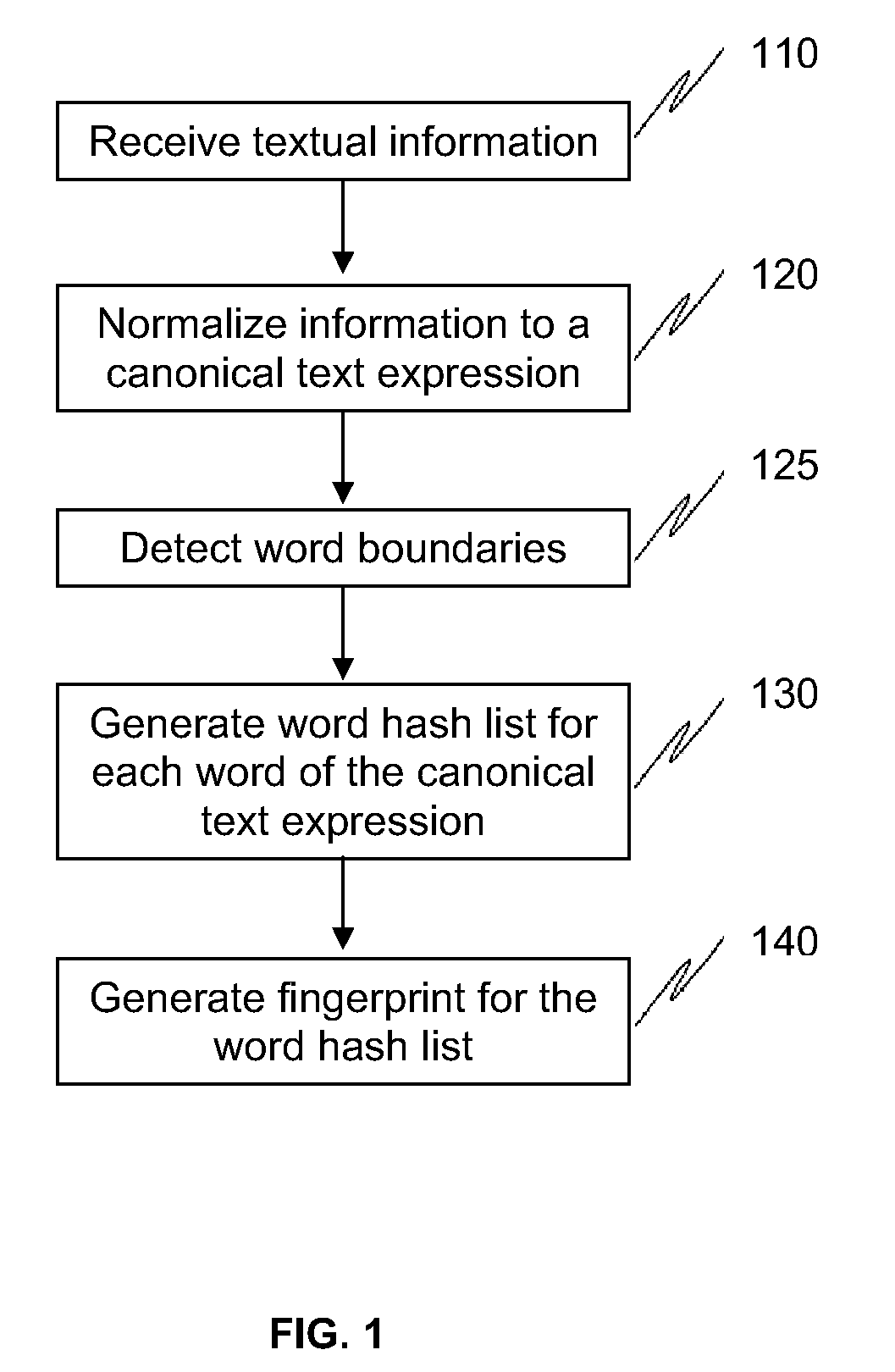
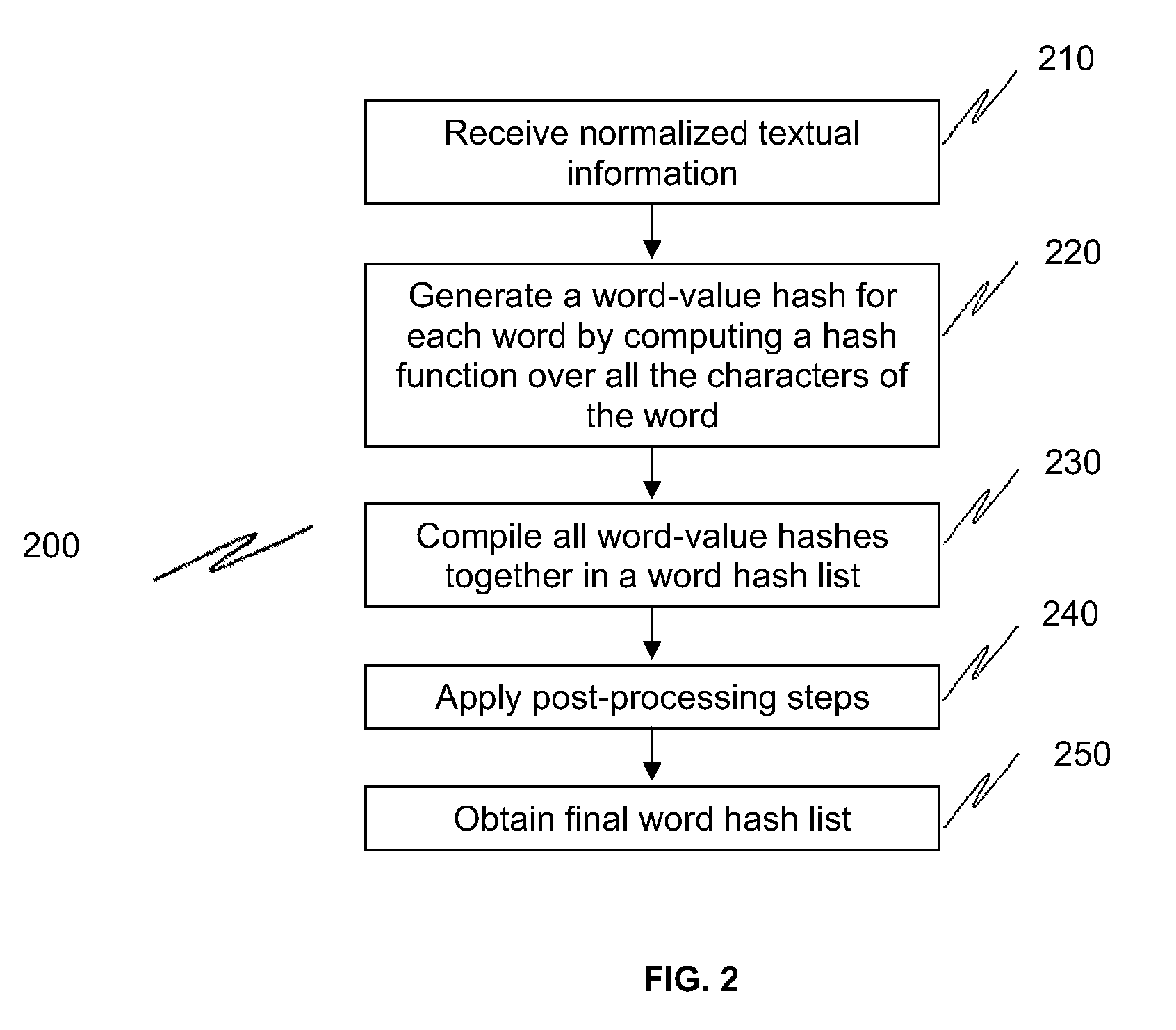
Methods and systems to fingerprint textual information using word runs
ActiveUS20100017850A1Fast and efficient and scalable meanEfficiently fingerprintDigital data processing detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsDerivative workResource efficiency
The present invention provides methods and systems to enable fast, efficient, and scalable means for fingerprinting textual information using word runs. The present system receives textual information and provides algorithms to convert the information into representative fingerprints. In one embodiment, the fingerprints are recorded in a repository to maintain a database of an organization's secure data. In another embodiment, textual information entered by a user is verified against the repository of fingerprints to prevent unauthorized disclosure of secure data. This invention provides approaches to allow derivative works (e.g., different ordering of words, substitution of words with synonyms, etc.) of the original information to be detected at the sentence level or even at the paragraph level. This invention also provides means for enhancing storage and resource efficiencies by providing approaches to optimize the number of fingerprints generated for the textual information.
Owner:FREEDOM SOLUTIONS GROUP
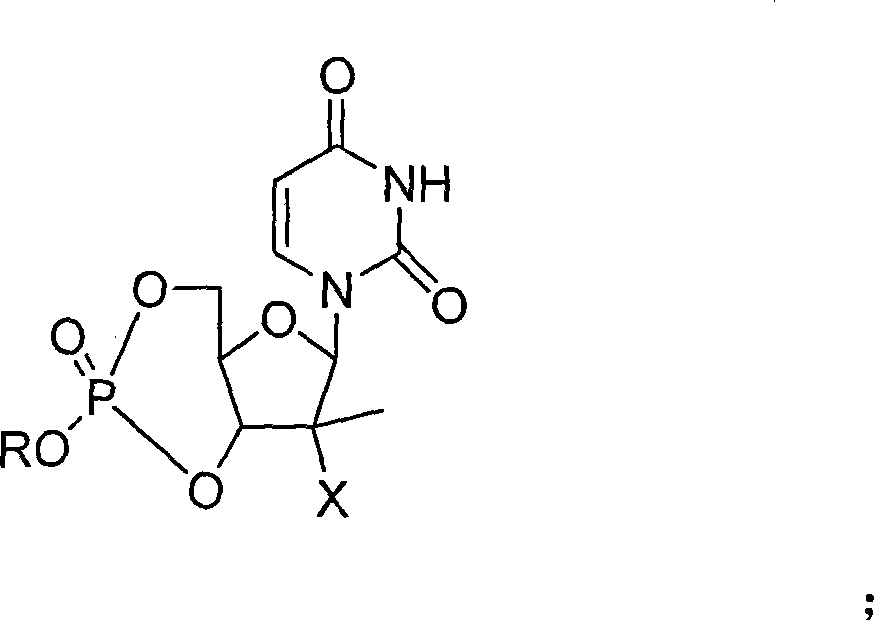
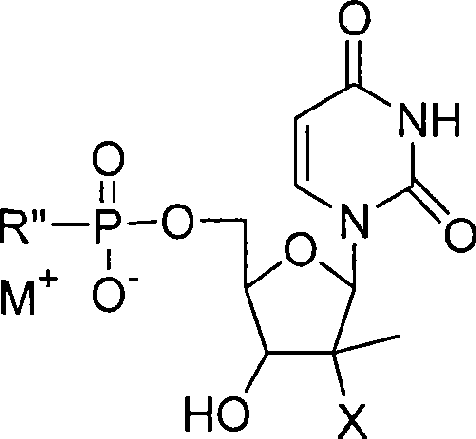
Process for preparation of nucleoside phosphoric acid ester compound and application thereof
The invention provides the nucleoside phosphate compound and the preparation and application, which comprises the nucleoside 3', 5'-cyclic phosphate and the 5'-phosphodiester compound. Wherein, the 3', 5'-cyclic phosphate and the derivatives work as the novel HCV inhibitor and the structural formula is shown in the drawing (I), wherein, X equals to OH and F; R equals to H, NH4, R' 4N, R' 3NH and metals such as Na, K, Ca and Li or the structural formula in the drawing (II), R' equals to linear chain or substituted alkane or cyclane, aromatic hydrocarbon, or substituted aromatic hydrocarbon or heterocyclic aromatic hydrocarbon; the four R' and three R' in the amine are the same or different. The invention has the advantages that the nucleoside phosphate compound is used for treating the HCV or is combined with the Alpha-interferon, ribavirin or other anti-HCV drugs to treat the infection of the hepatic c virus or HCV.
Owner:冷一欣
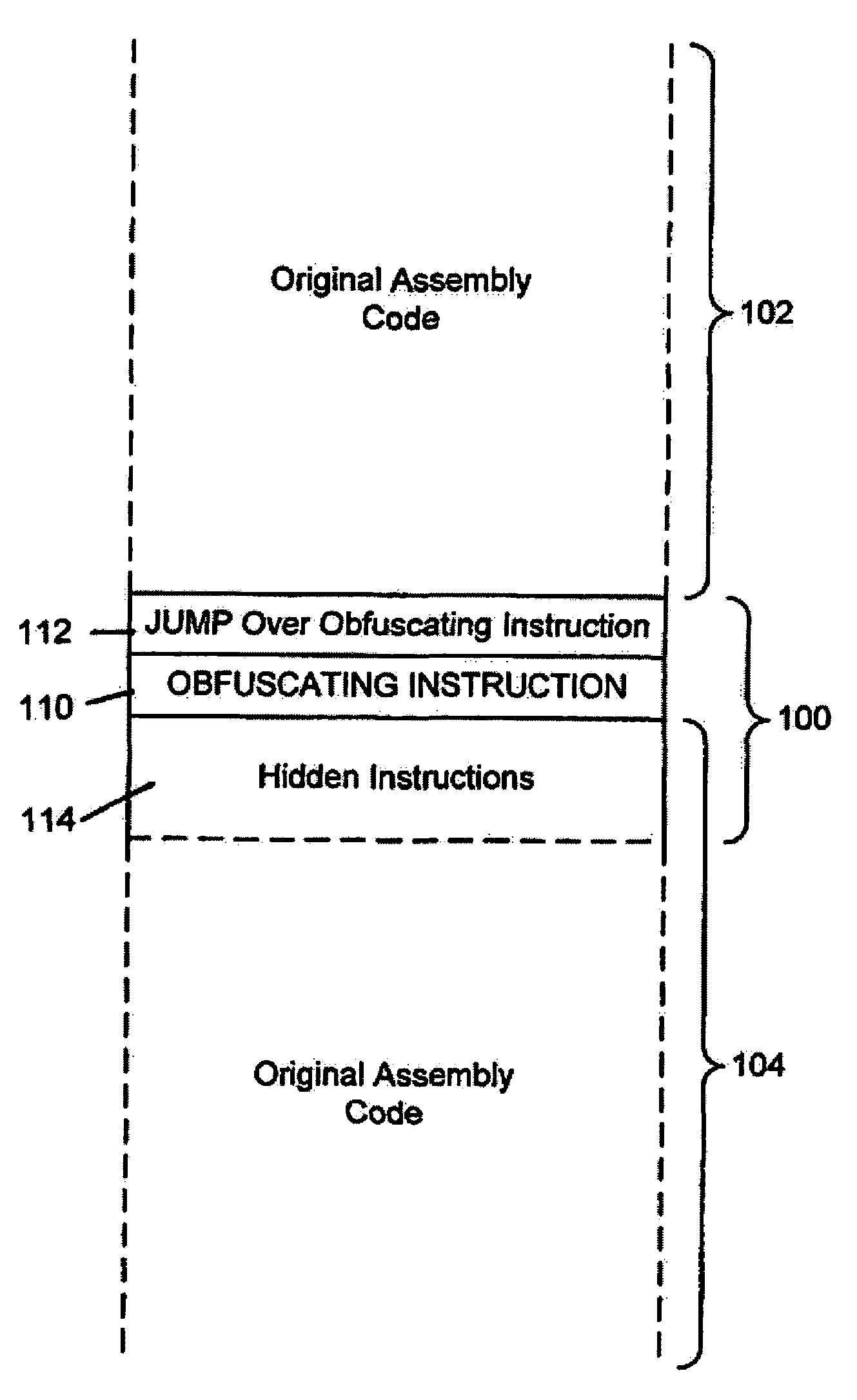
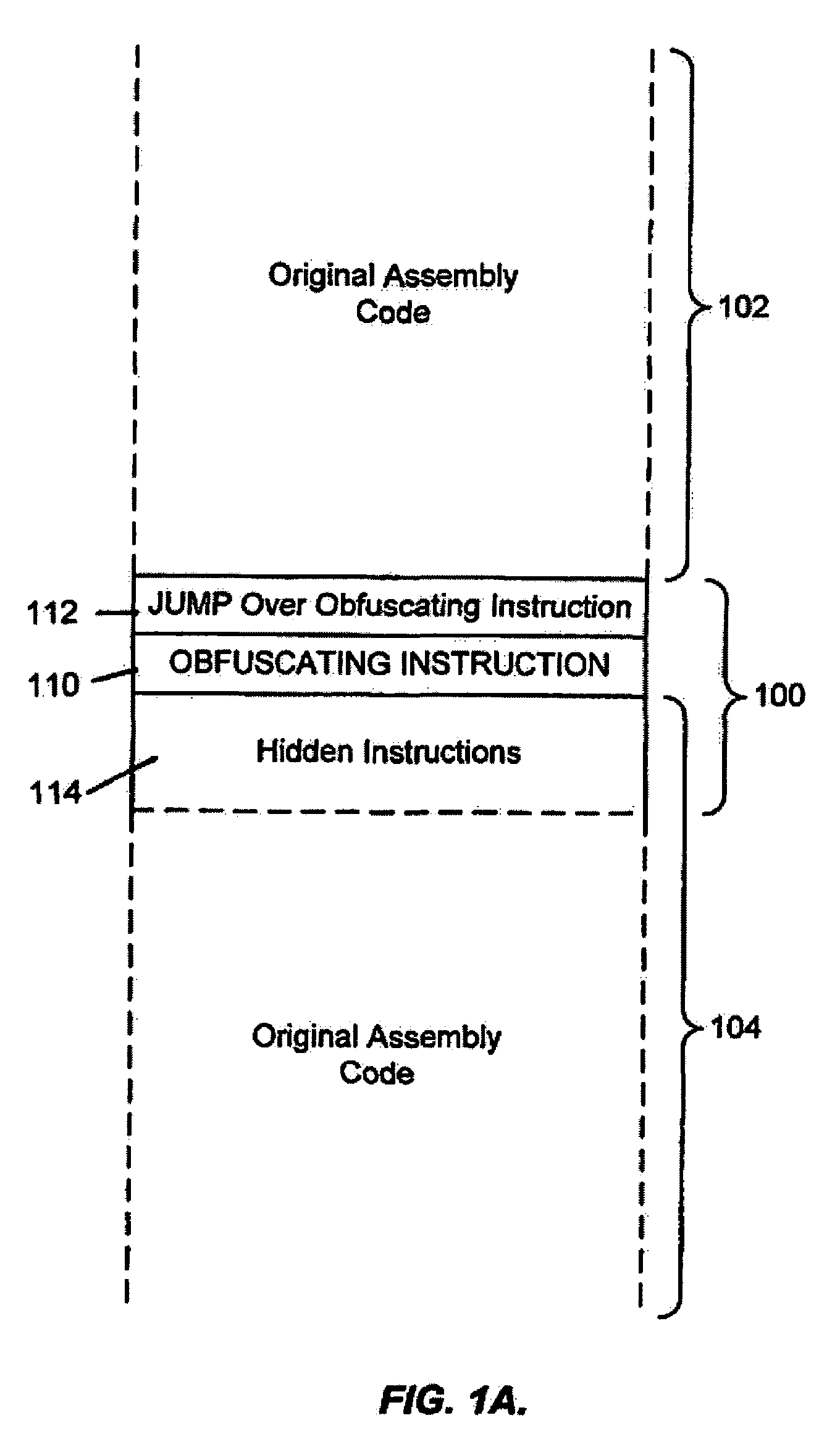
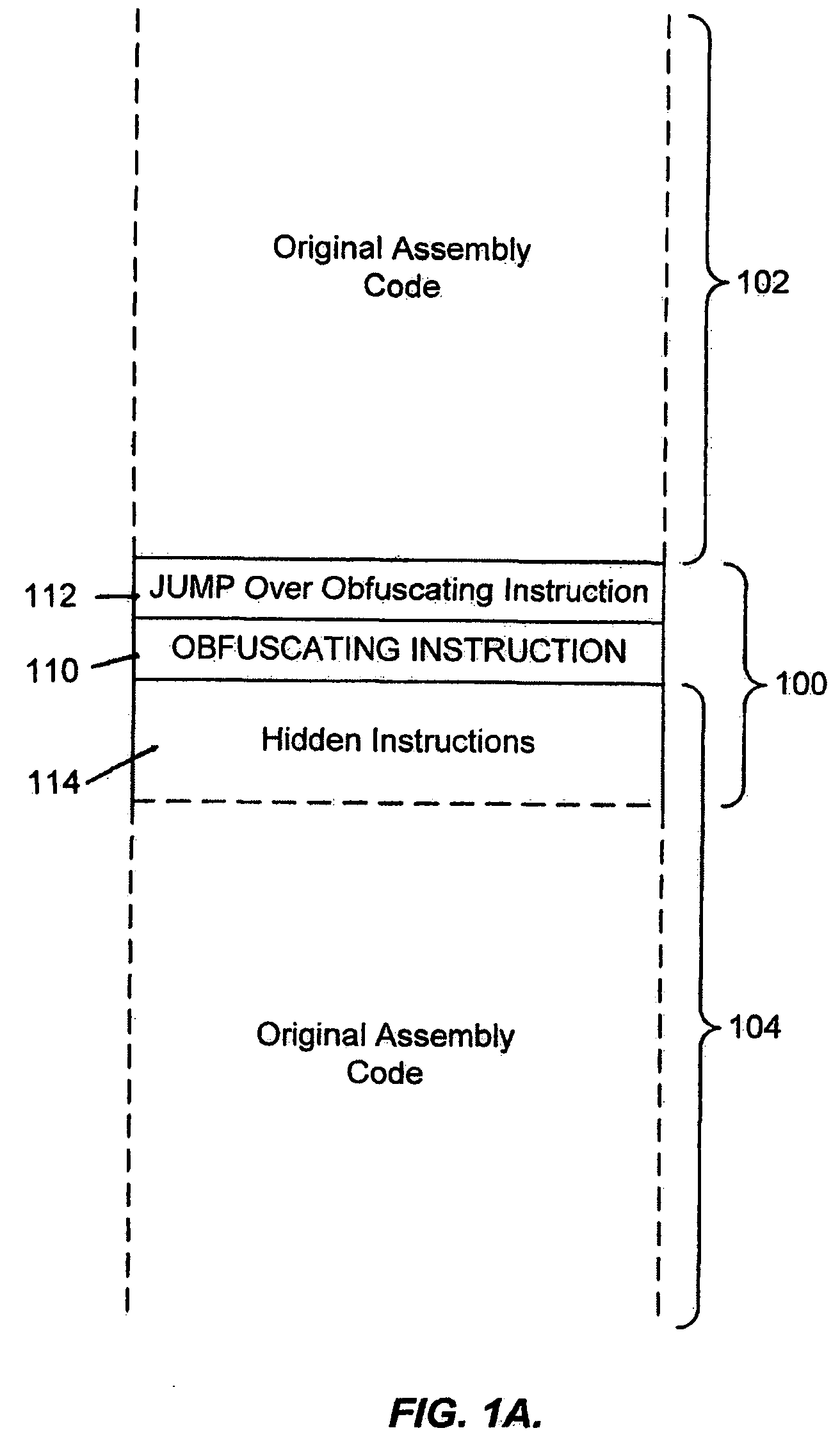
System for obfuscating computer code upon disassembly
InactiveUS7065652B1Avoid disassemblyDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationObfuscationDerivative work
Owner:SAFENET DATA SECURITY ISRAEL
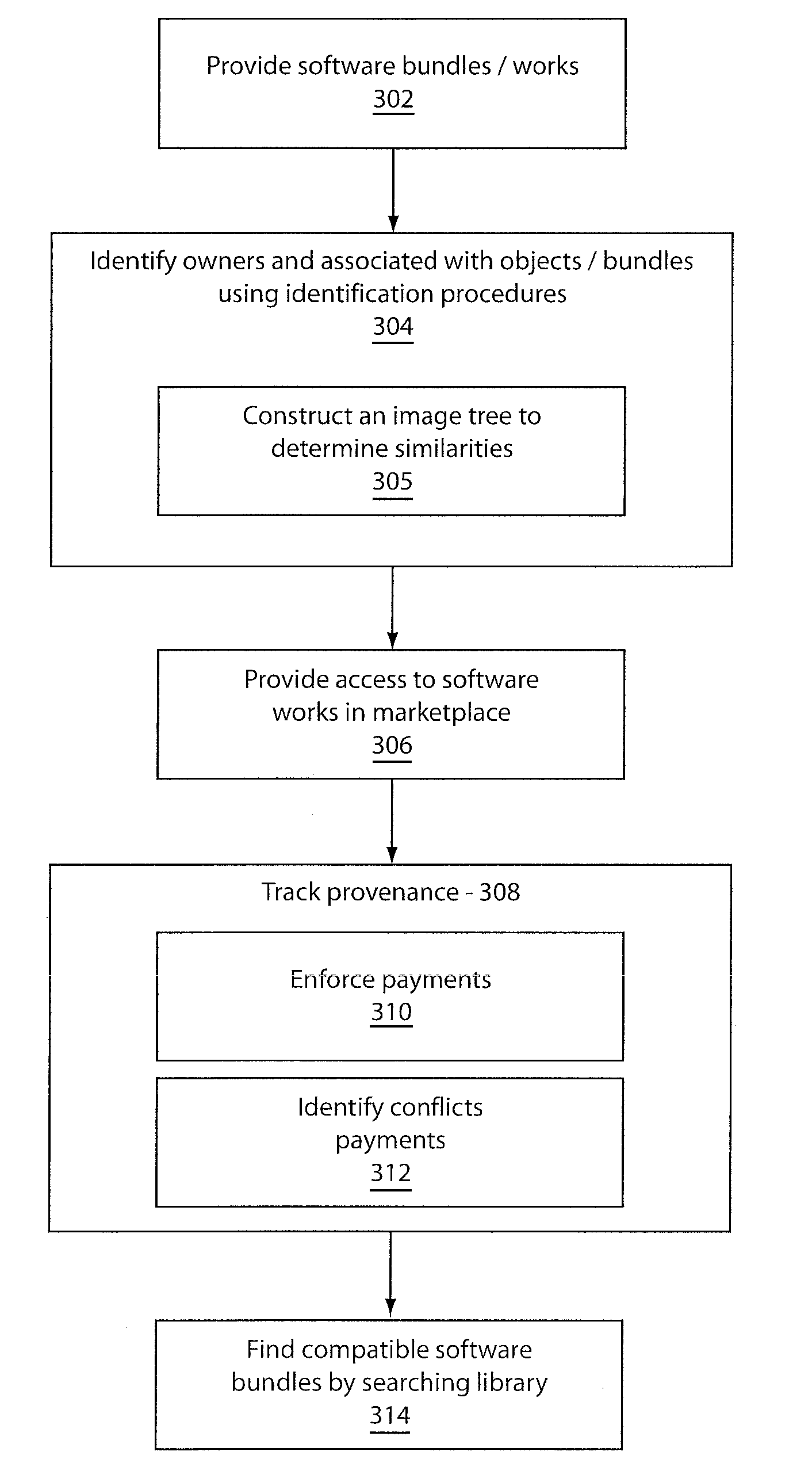
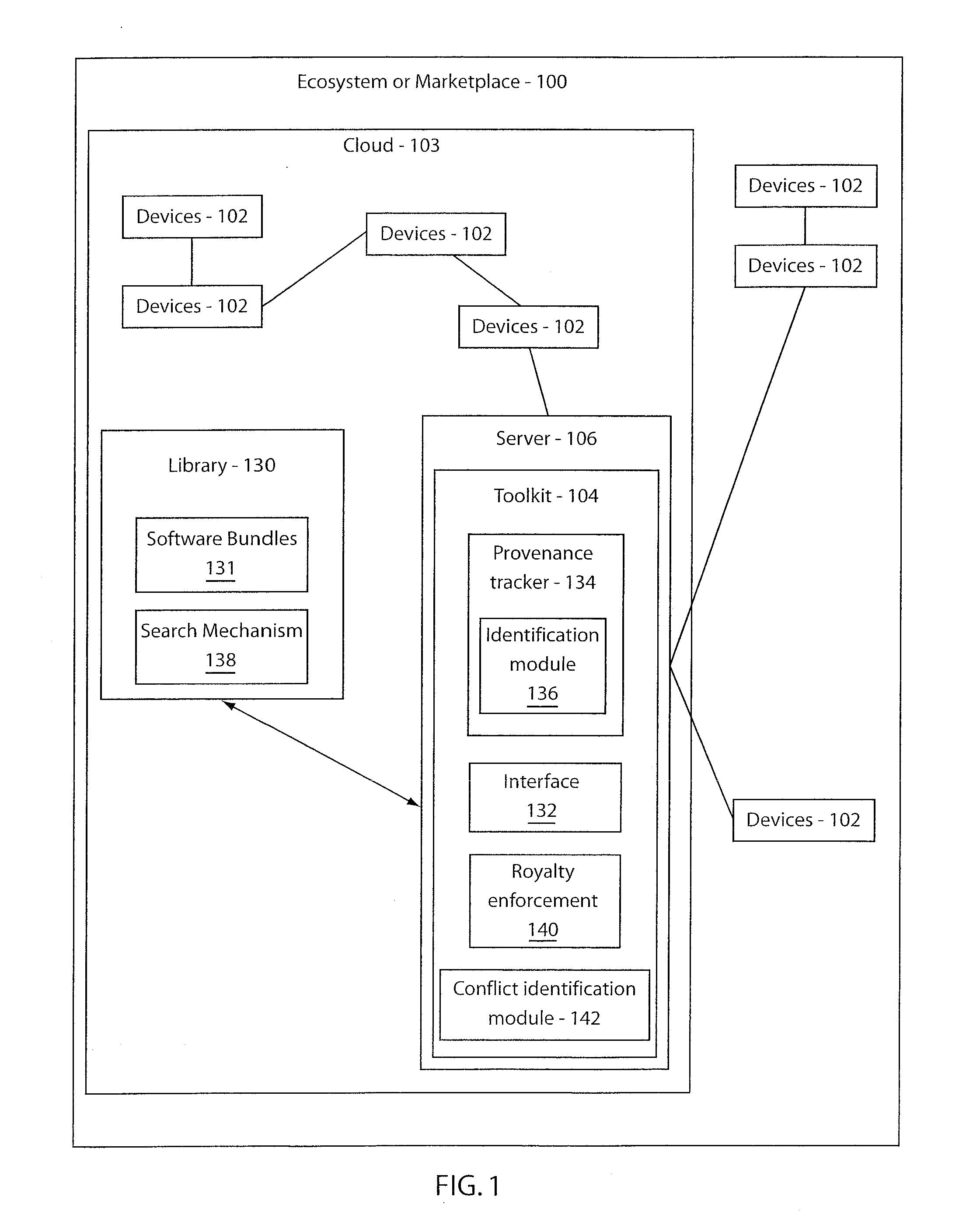
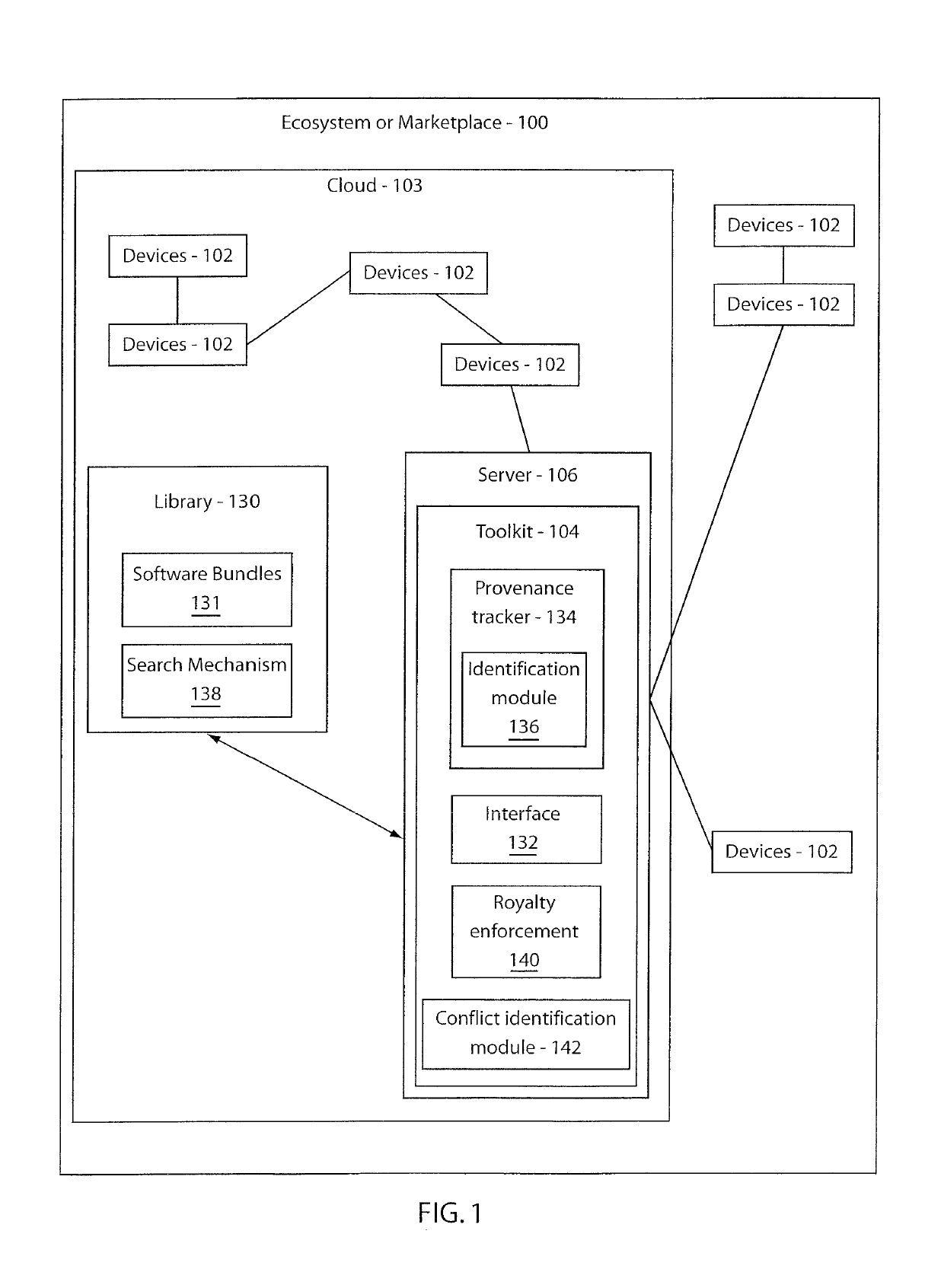
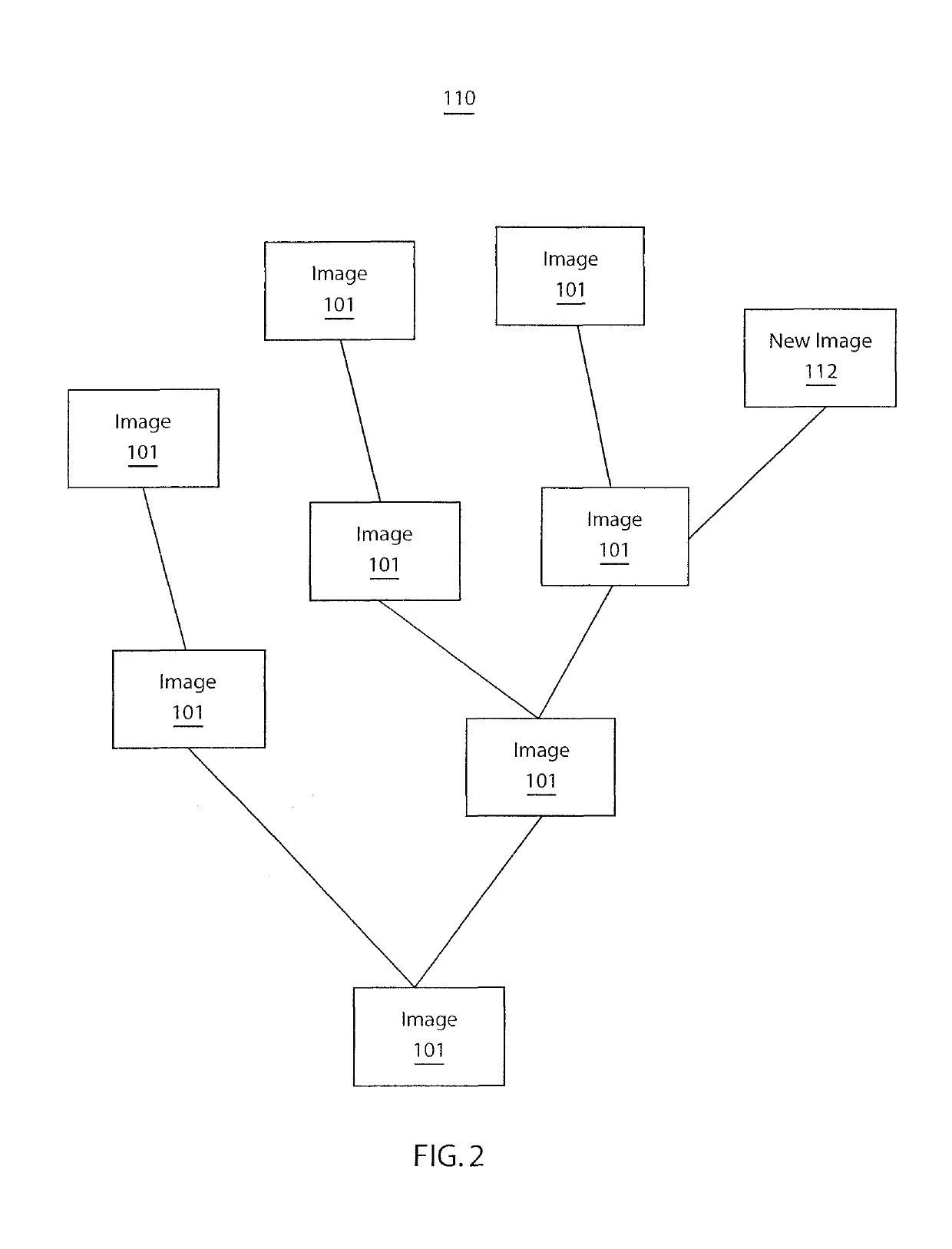
Method and system for provenance tracking in software ecosystems
InactiveUS20110218920A1User identity/authority verificationComputer security arrangementsDerivative workSoftware engineering
A system and method for tracking provenance for software use and development includes a developer toolkit program stored in memory media and accessible by a software market place wherein the software marketplace provides a library of software bundles that can be used for software development and modification of the software bundles. The developer toolkit includes a user interface configured to enable software creation of original works and derivative works. The development toolkit further includes a provenance tracker configured to track provenance of the derivative works and original works wherein the provenance tracker makes the derivative work and the provenance of the derivative work available in the software market place. The provenance tracker includes a software bundle identification module configured to identify and verify ownership of the original works and derivative works by associating an owner of the derivative works and original works with features included in portions of the derivative works and original works.
Owner:IBM CORP
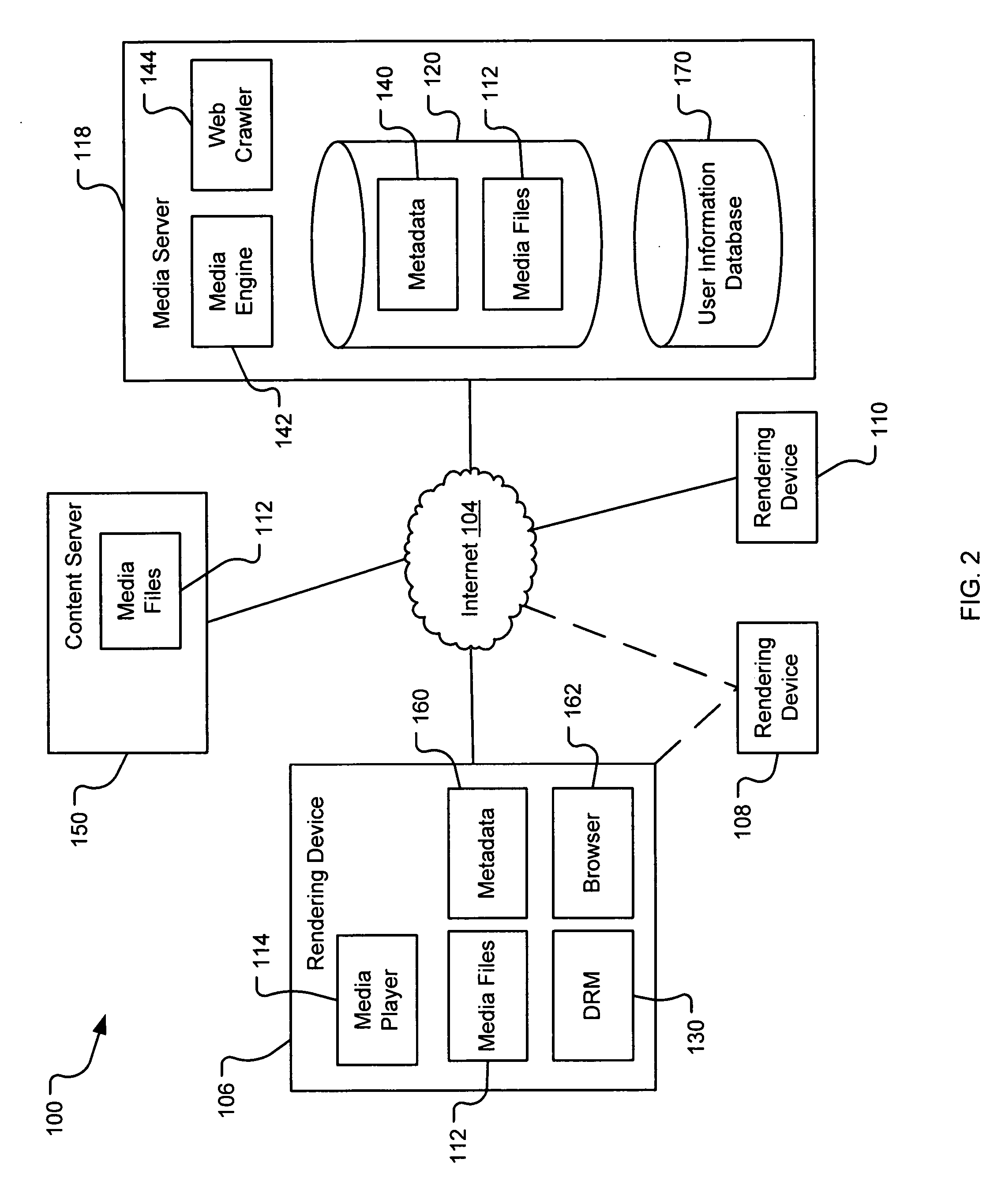
Using location tags to render tagged portions of media files
InactiveUS20070078883A1Digital data processing detailsMetadata multimedia retrievalDerivative workWorld Wide Web
A system and method are provided for identifying discrete locations and / or sections within a pre-existing media file without modifying the media file. The discrete locations and / or sections can be associated with one or more user-selected descriptors. The system and method allows for the identifying information to be communicated to consumers of the media file and the media file to be selectively rendered by the consumer using the identifying information, thus allowing a consumer to render only the portion of the media file identified or render from a given discrete location in the media file. In an embodiment, the system and method can be performed without modifying the media file itself and thus no derivative work is created.
Owner:OATH INC
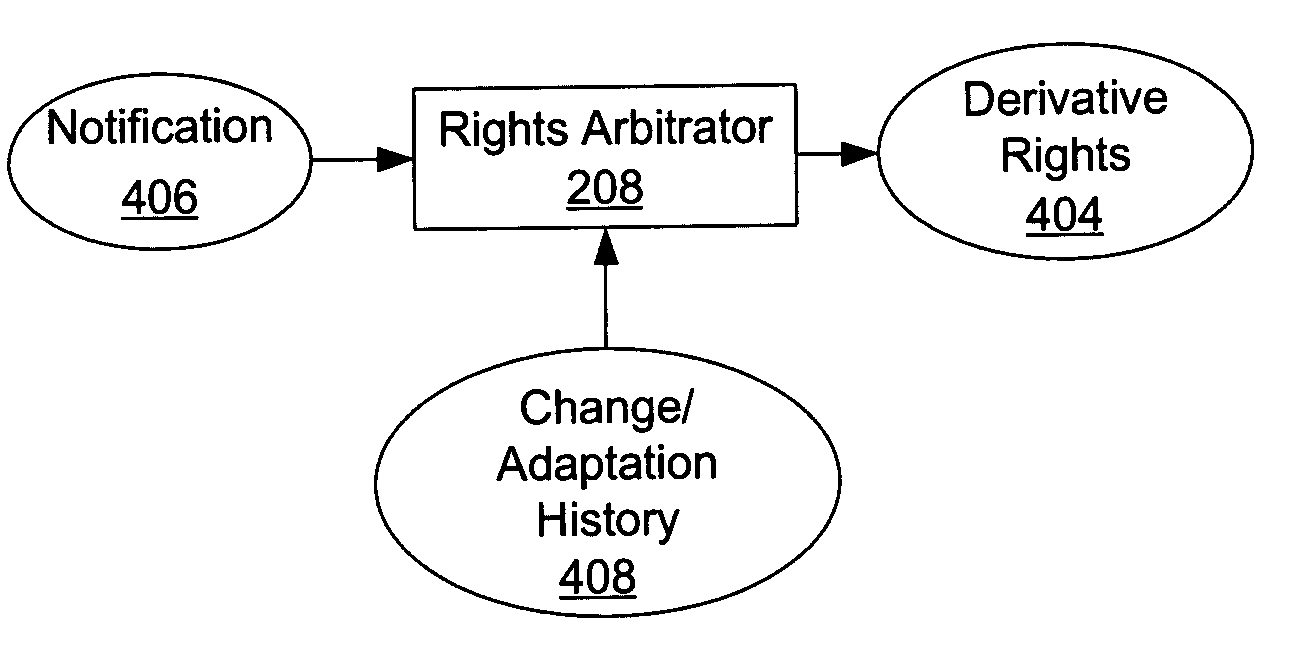
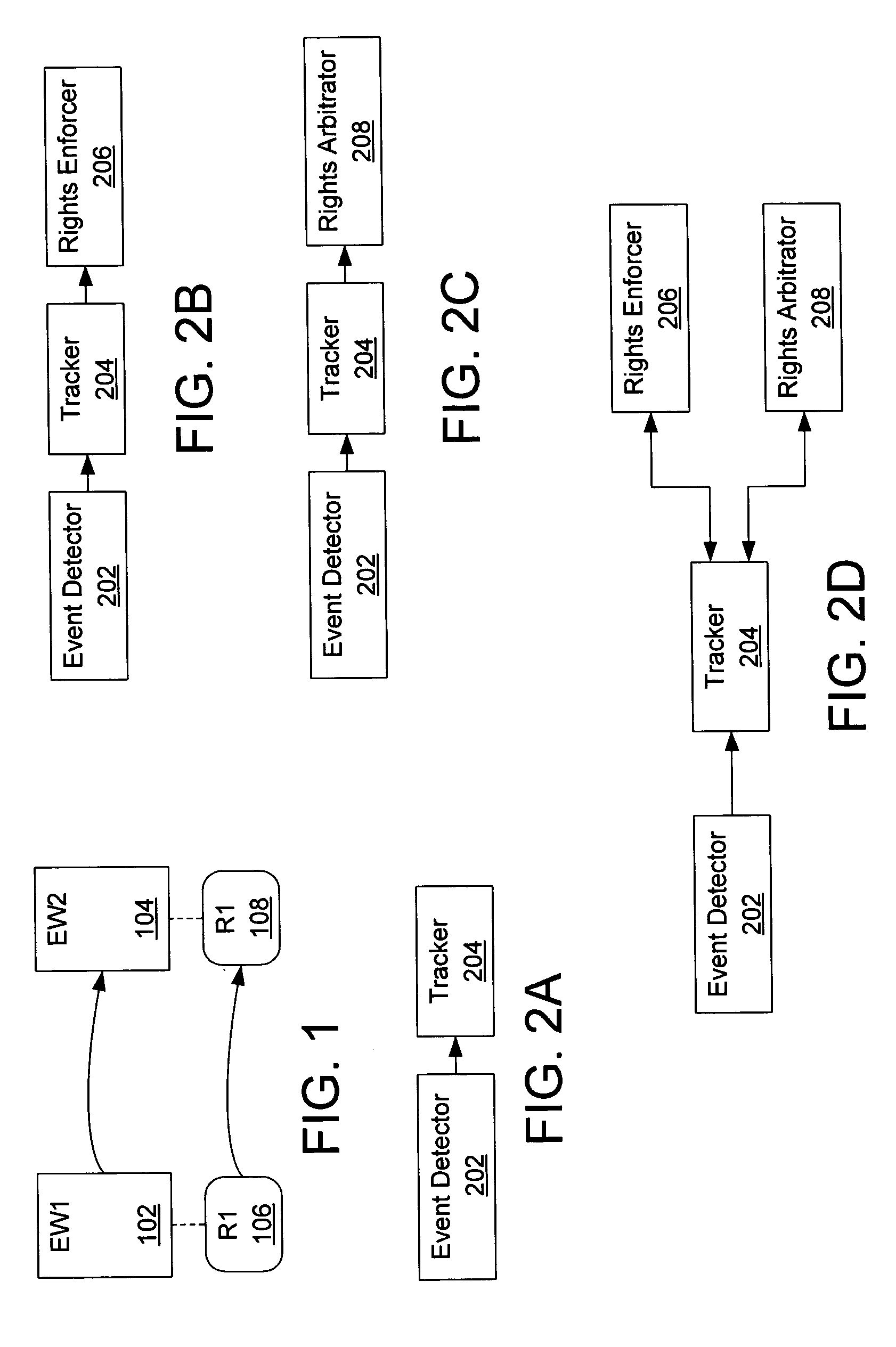
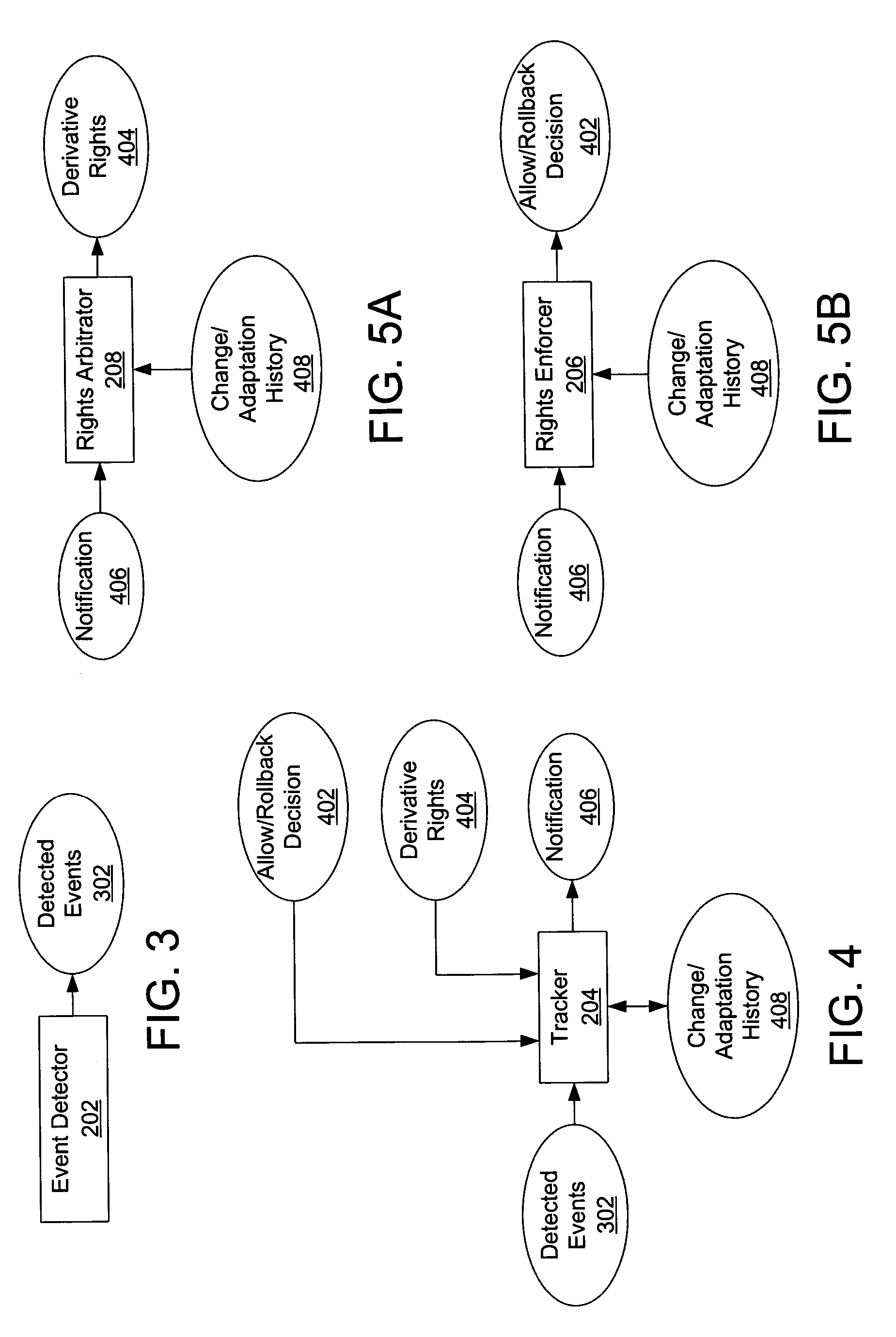
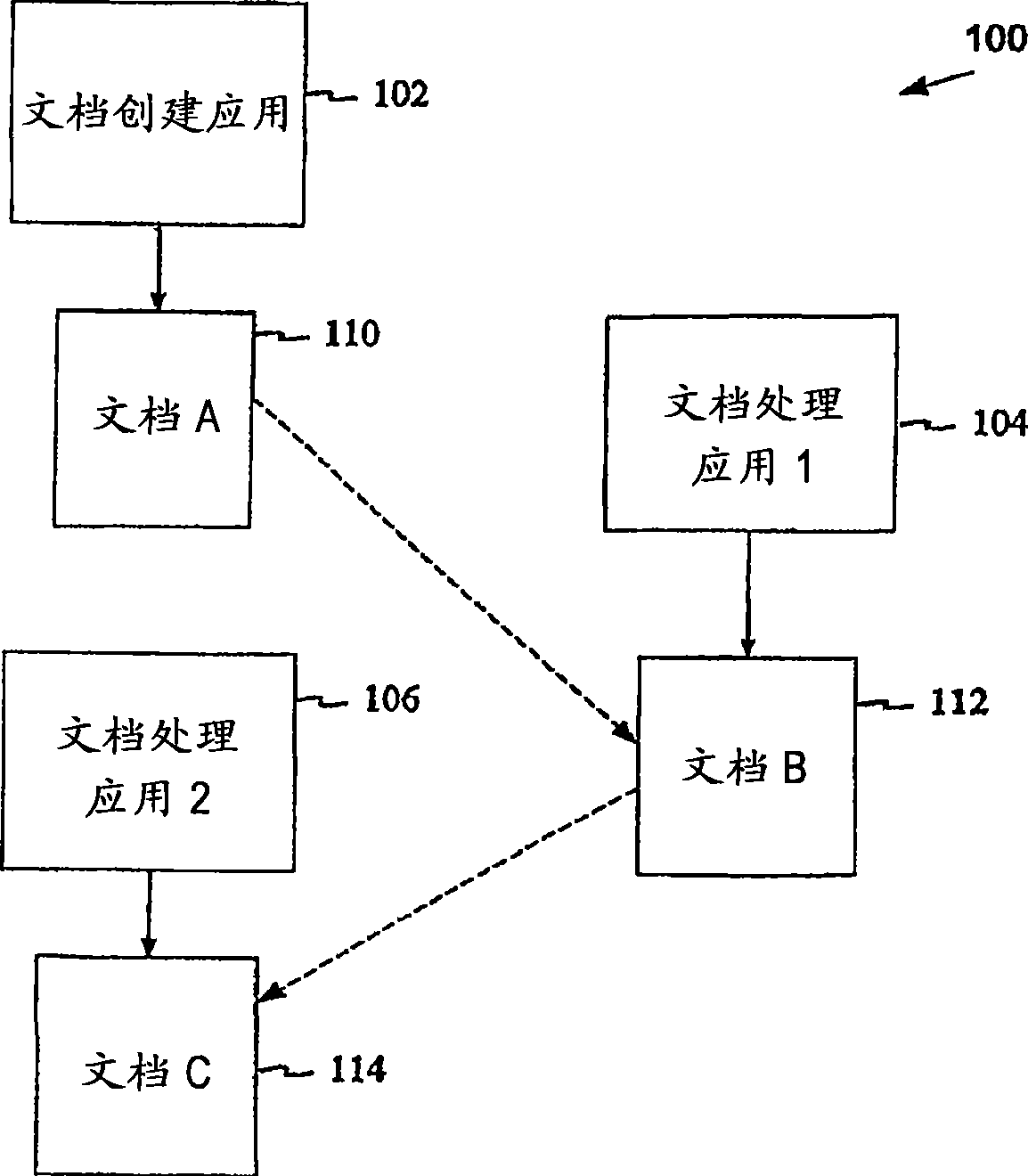
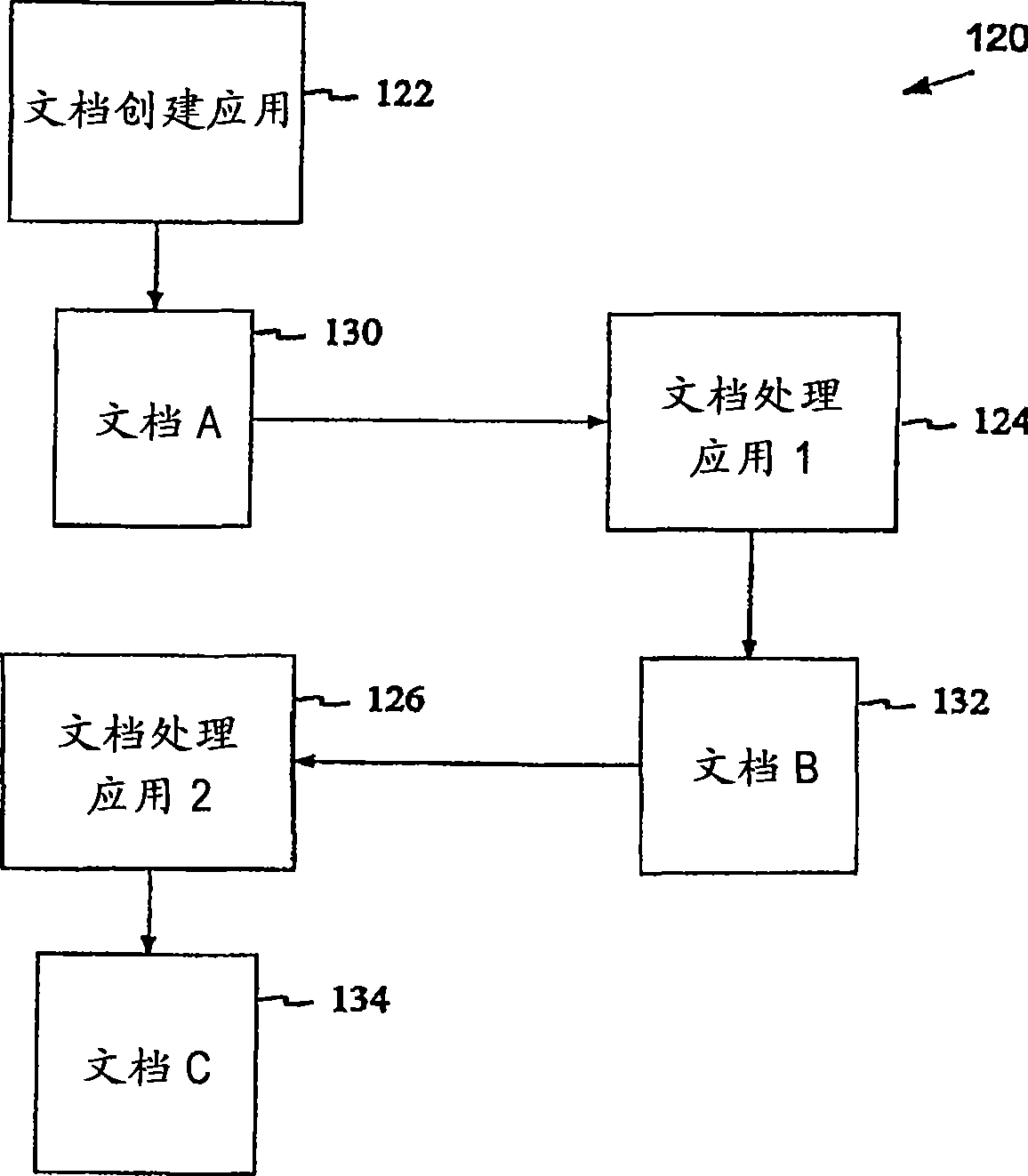
Method, system, and device for handling creation of derivative works and for adapting rights to derivative works
A method, system, and device for handling creation of derivative works and for assigning usage rights to the derivative works for enforcing usage rights associated with digital works, including detecting computer-related events that are indicative of manipulations of an original work for creating a derivative work; and maintaining a history of information, including at least one of rights associated with electronic content related to each of the events, origin of electronic content related to each of the events, and event related information that can be used to determine the origin of and rights associated with electronic content.
Owner:CONTENTGUARD HLDG
Filemarking pre-existing media files using location tags
InactiveUS20070078897A1Metadata multimedia retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsDerivative workWorld Wide Web
A system and method are provided for identifying discrete locations and / or sections within a pre-existing media file without modifying the media file. The discrete locations and / or sections can be associated with one or more user-selected descriptors. The system and method allows for the identifying information to be communicated to consumers of the media file and the media file to be selectively rendered by the consumer using the identifying information, thus allowing a consumer to render only the portion of the media file identified or render from a given discrete location in the media file. In an embodiment, the system and method can be performed without modifying the media file itself and thus no derivative work is created.
Owner:OATH INC
System and automate the licensing, re-use and royalties of authored content in derivative works
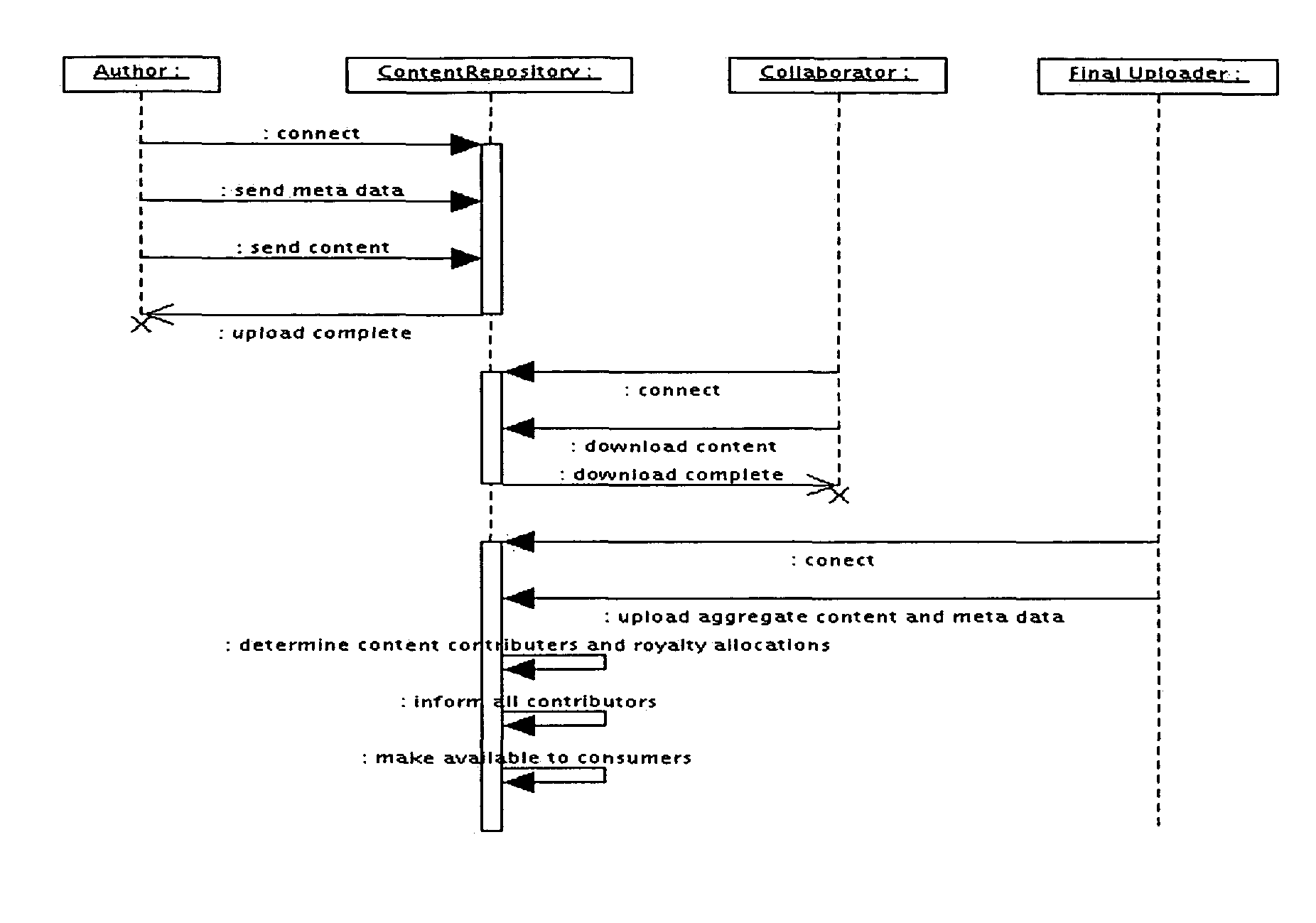
InactiveUS20050043960A1Safely included in derivativeEquitable financial participationComputer security arrangementsMarketingDerivative workComputer science
A system and method which allows authors to automate the licensing and distribution process to enable their works to be safely included in derivative works, regardless of the industry.
Owner:DISTRIBUTED ENG
Identifying portions within media files with location tags
InactiveUS20070078896A1Digital data processing detailsMetadata multimedia retrievalDerivative workWorld Wide Web
A system and method are provided for identifying discrete locations and / or sections within a pre-existing media file without modifying the media file. The discrete locations and / or sections can be associated with one or more user-selected descriptors. The system and method allows for the identifying information to be communicated to consumers of the media file and the media file to be selectively rendered by the consumer using the identifying information, thus allowing a consumer to render only the portion of the media file identified or render from a given discrete location in the media file. In an embodiment, the system and method can be performed without modifying the media file itself and thus no derivative work is created.
Owner:OATH INC
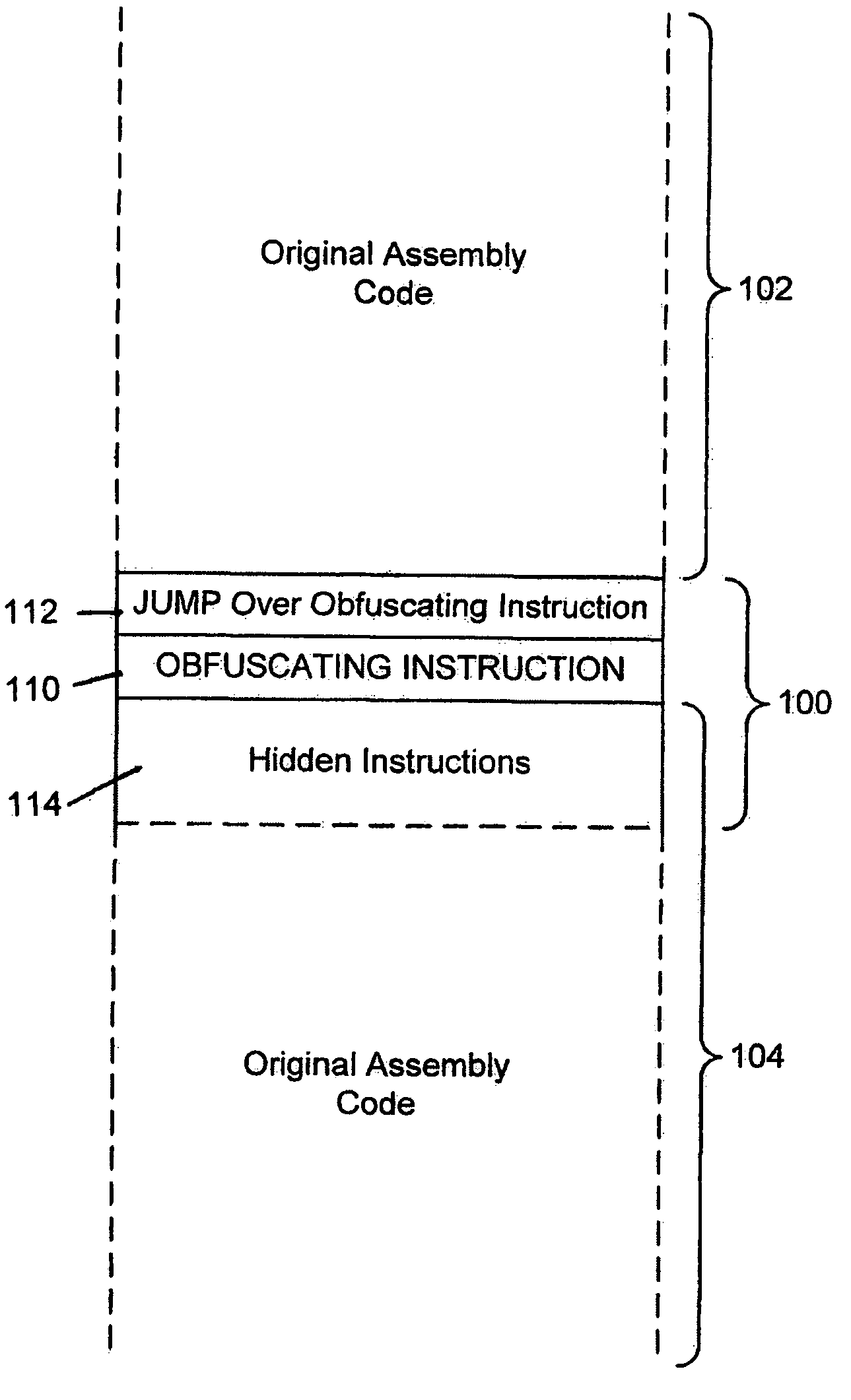
System for obfuscating computer code upon disassembly
InactiveUS20060053307A1Avoid disassemblyUnauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringObfuscationDerivative work
A system for preventing accurate disassembly of computer code. Such code masking, referred to as “obfuscation,” is useful to prevent unwanted parties from making copies of an original author's software, obtaining valuable information from the software for purposes of breaking into a program, stealing secrets, making derivative works, etc. The present invention uses assembly-language instructions so as to confuse the disassembler to produce results that are not an accurate representation of the original assembly code. In one embodiment, a method is provided where an interrupt, or software exception instruction, is used to mask several subsequent instructions. The instruction used can be any instruction that causes the disassembler to assume that one or more subsequent words, or bytes, are associated with the instruction. The method, instead, jumps directly to the bytes assumed associated with the instruction and executes those bytes for a different purpose. A preferred embodiment works with a popular Microsoft “ASM” assembler language and “DASM” disassembler. The instructions used to achieve the obfuscation include “INT” instructions. Using this approach up to 17 bytes of obfuscation can be achieved with five instructions. Each instruction remains obfuscated until executed and returns to an obfuscated state afterwards.
Owner:ALADDIN KNOWLEDGE SYSTEMS
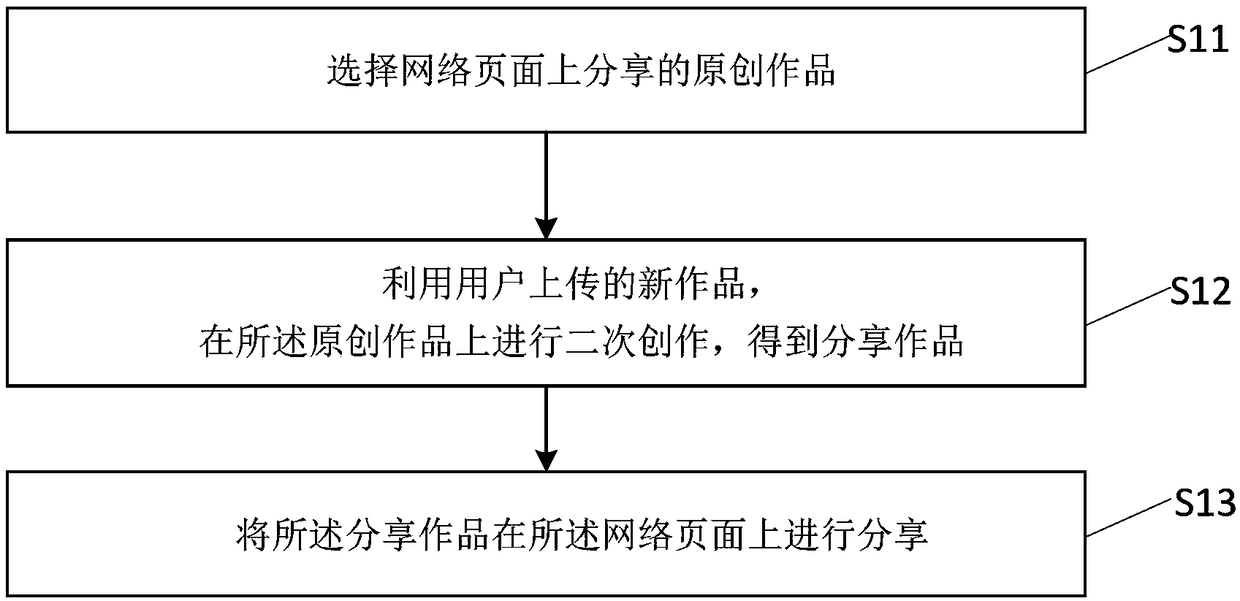
Sharing method and device of network works, server and storage medium
InactiveCN109194644AAbundant resourcesLower barriers to creationWeb data retrievalTransmissionDerivative workDistributed computing
The present invention discloses a sharing method and device of network works, a server and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting original works shared on a network page; employing new works uploaded by a user, and performing derivative work on the original works to obtain shared works; and performing sharing of the shared works on the network page. In the invention, the sharing method and device of network works, the server and the storage medium form shared works through joint derivative work of the original works and the new works to enrich the resources ofthe shared works, reduce the creation difficulty of the shared works and allow more users to take part in the creation of the shared works.
Owner:BEIJING DAJIA INTERNET INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
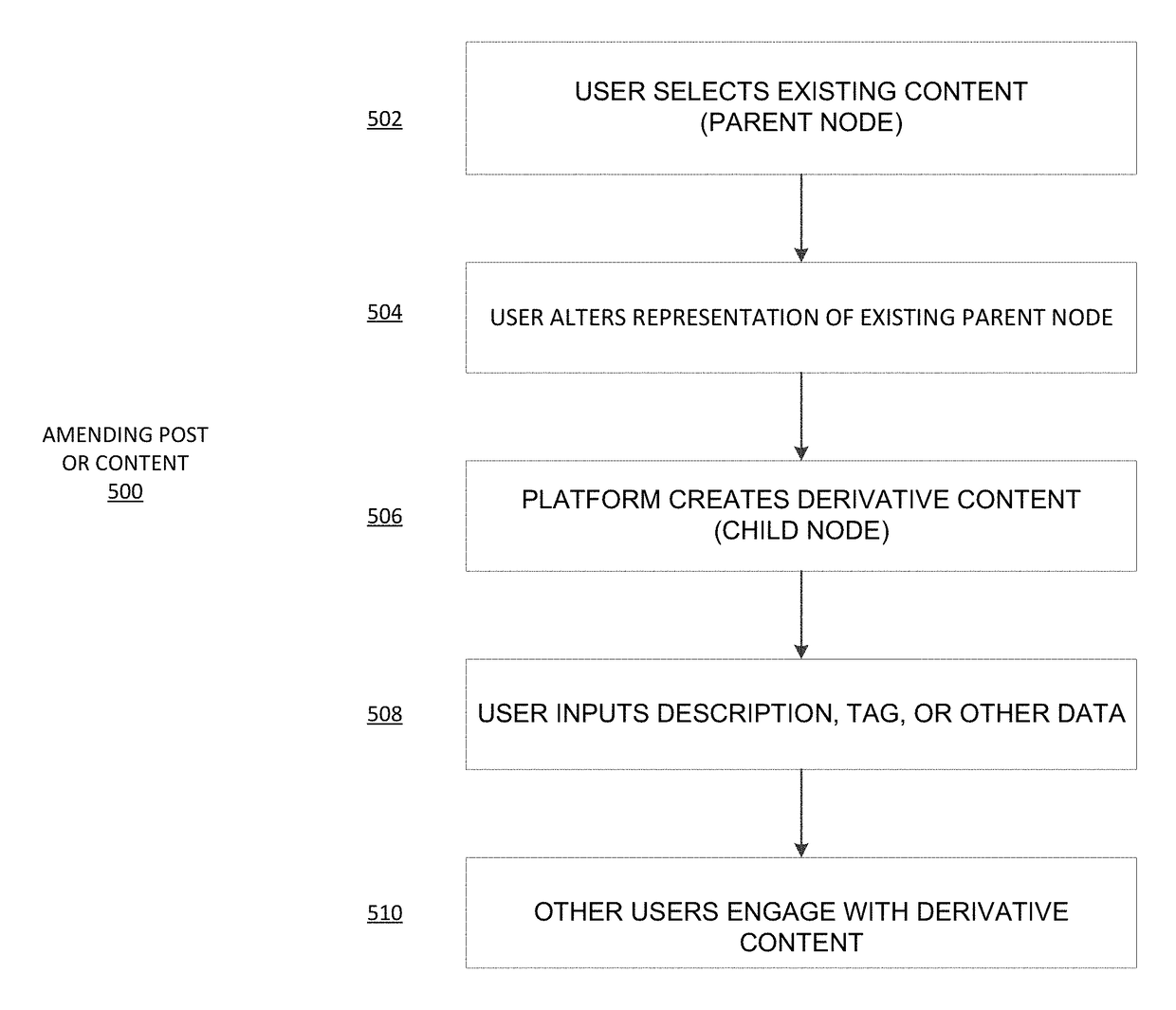
Collaboration platform
Example embodiments described herein relate to an online social content collaboration platform that allows user devices to access content and create derivative works of content. A graph structure defines content and derivative works as nodes and relationships or links between the content and derivative works as edges. The content and relationships for the content may be displayed to user device as an interface of visual elements in the form of the graph structure of nodes and edges. Example embodiments described herein relate to an online social content collaboration platform that allows user devices to access content and create derivative works of content and get rewarded. The rewards can be cryptographic tokens.
Owner:INERSI INC
System for tracking distribution for internet-distributed works of authorship
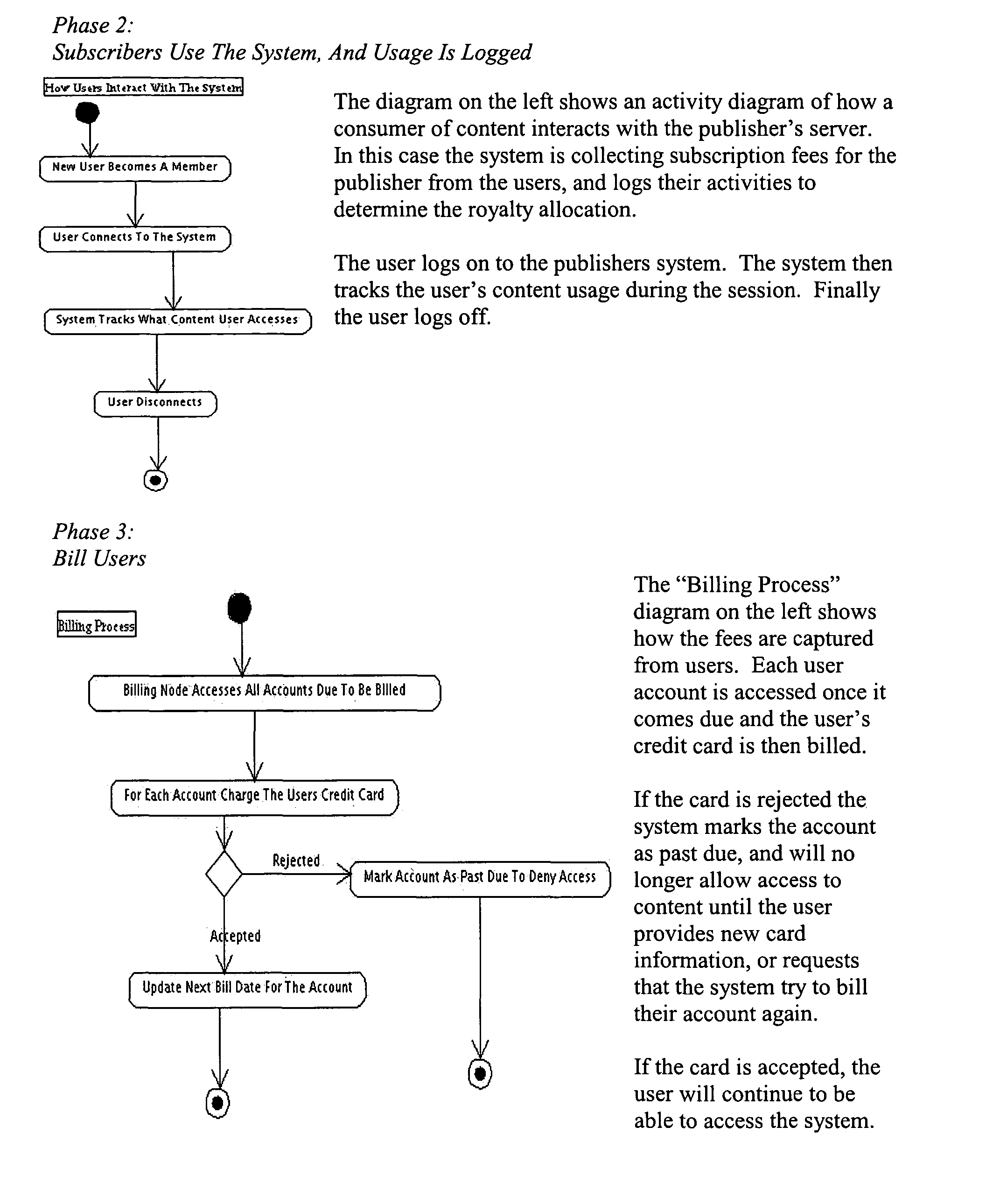
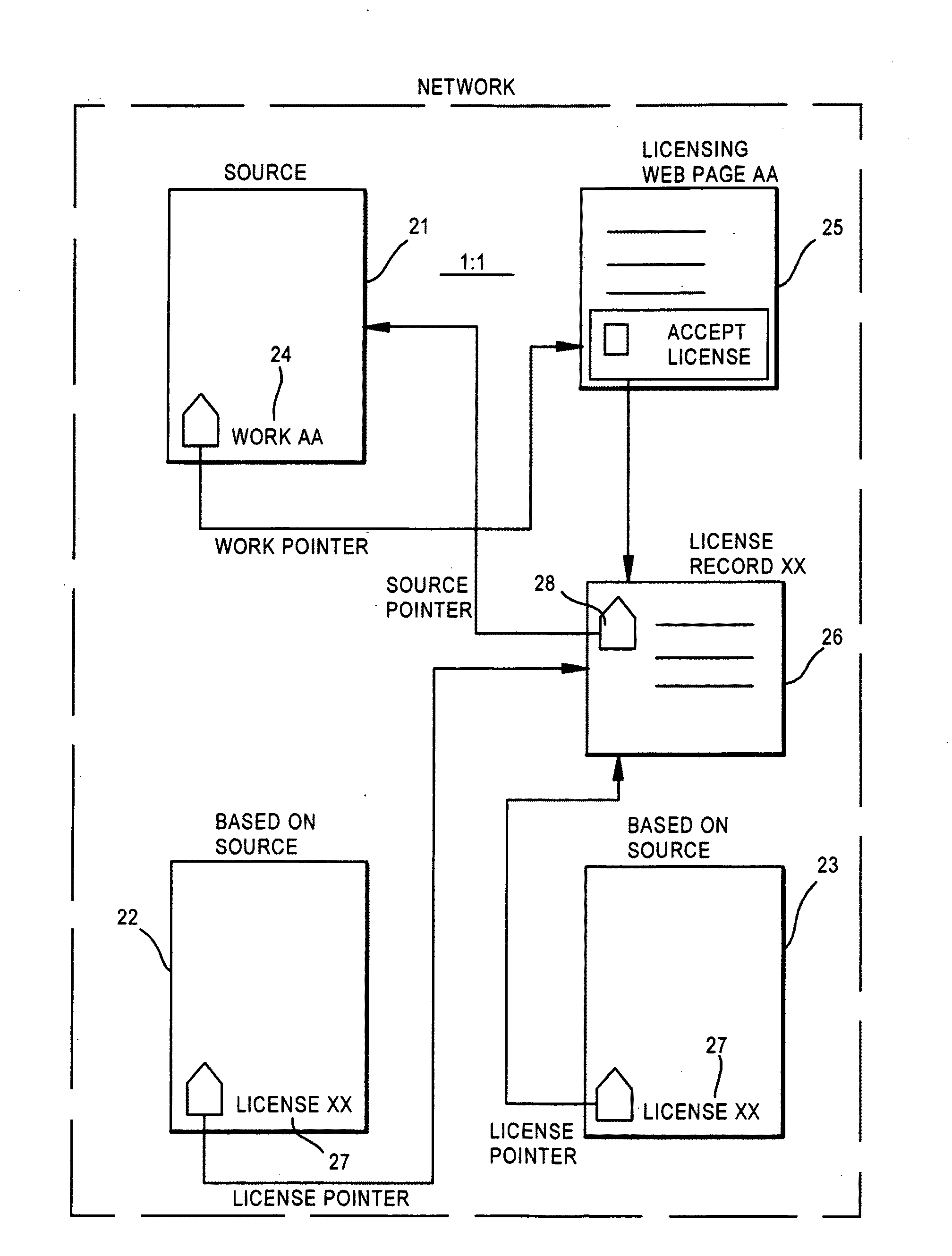
InactiveUS20100042652A1Done quickly and easilyEasy to processDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsState LicensureDerivative work
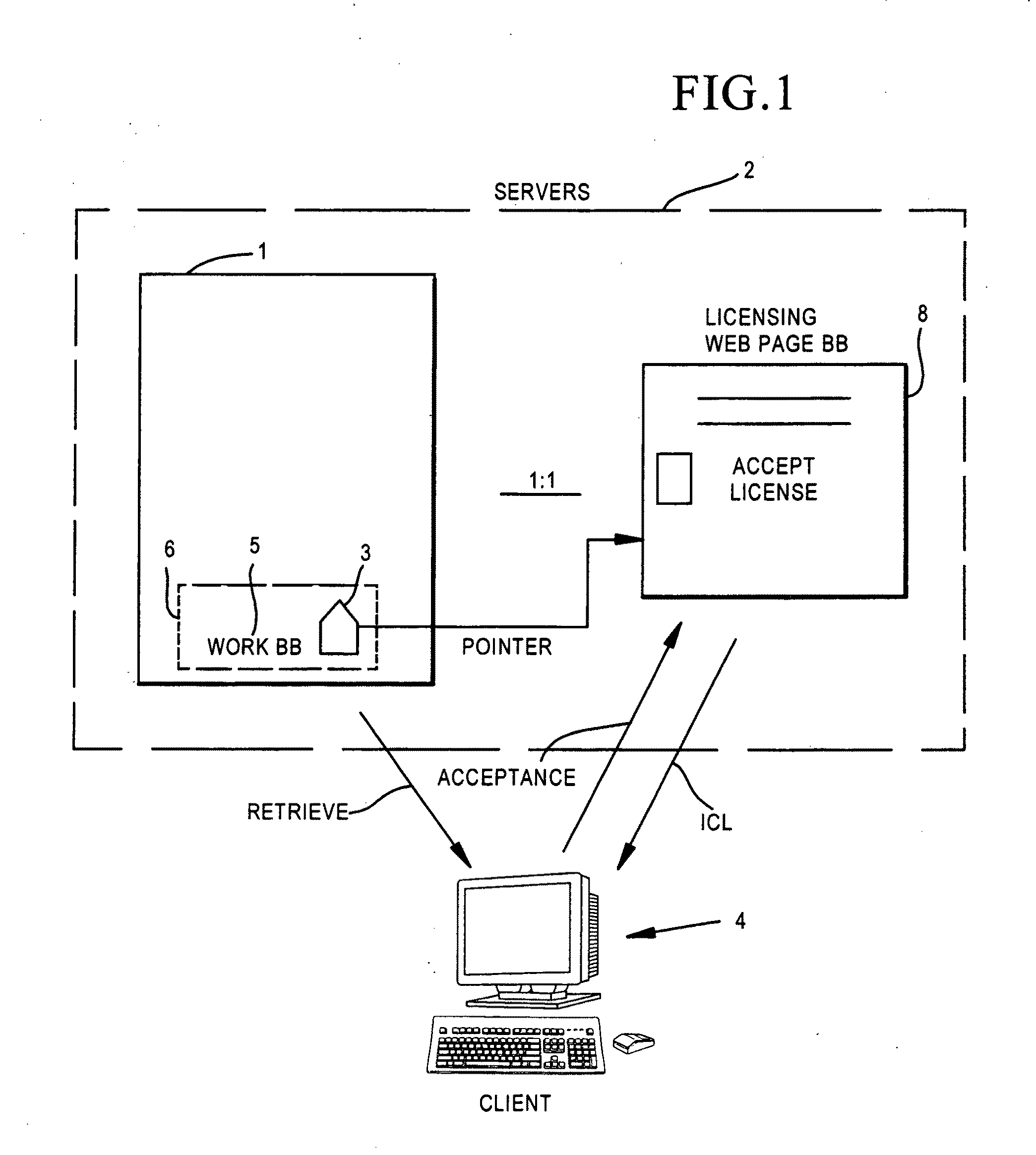
A system for use on the Internet to allow automated licensing of works of authorship and access to information about licenses which have been granted. A unique work identifier is issued to each of a large number of works of authorship, most of which are available on the Internet, but some of which are not. When the works are published, whether or not on the Internet, the unique work identifier is included. The work identifier may also identify a distributor, or chain-of-distributors, through which the work has been licensed. The unique identifier leads to a web page where a user can accept an offered license to do one or more of: reproduce, distribute, perform, display, or prepare derivative works. The system then automatically generates a unique license identifier which is placed in each copy of the work prepared by the licensee. The license identifier permits tracking of further licensing.
Owner:ICOPYRIGHT
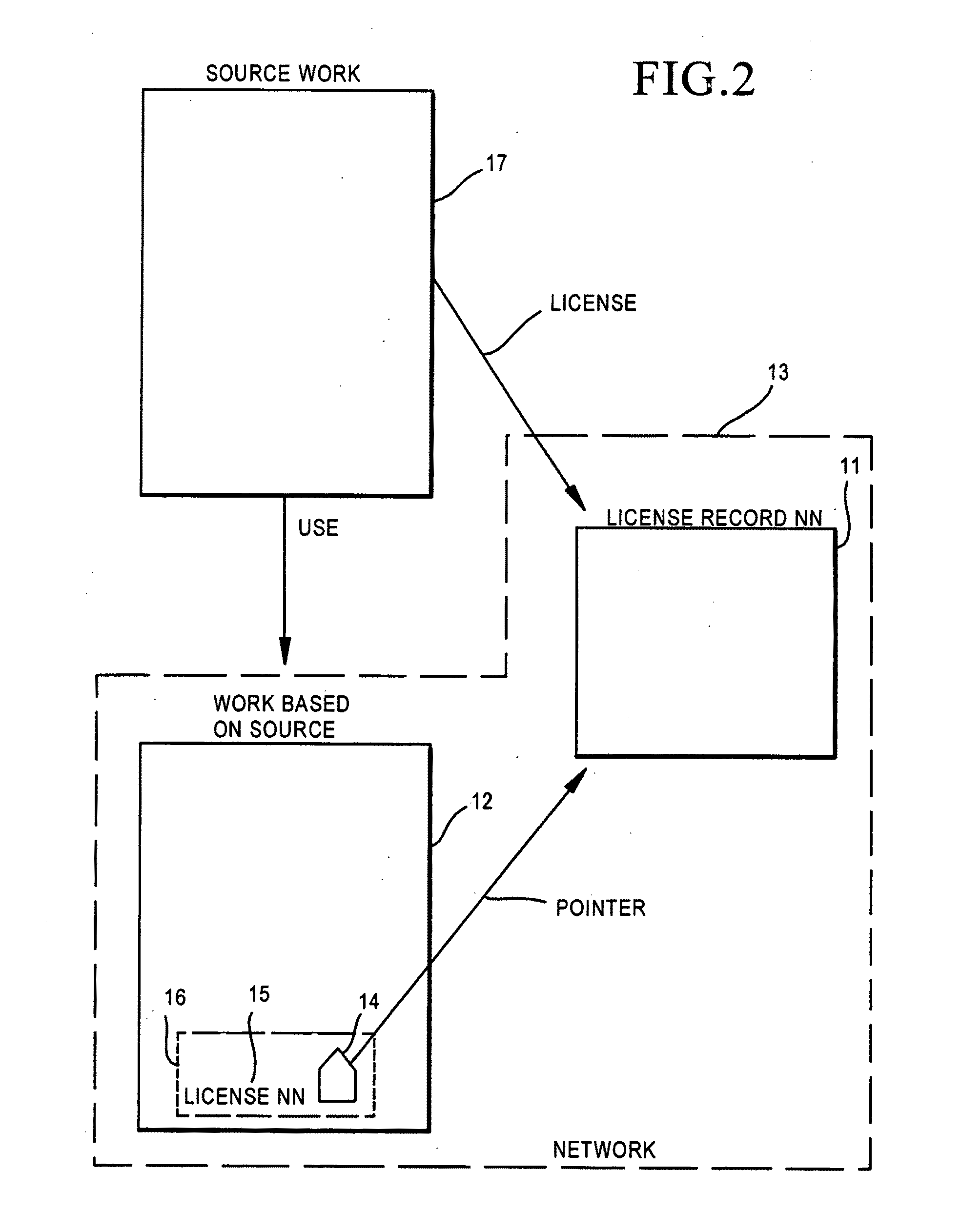
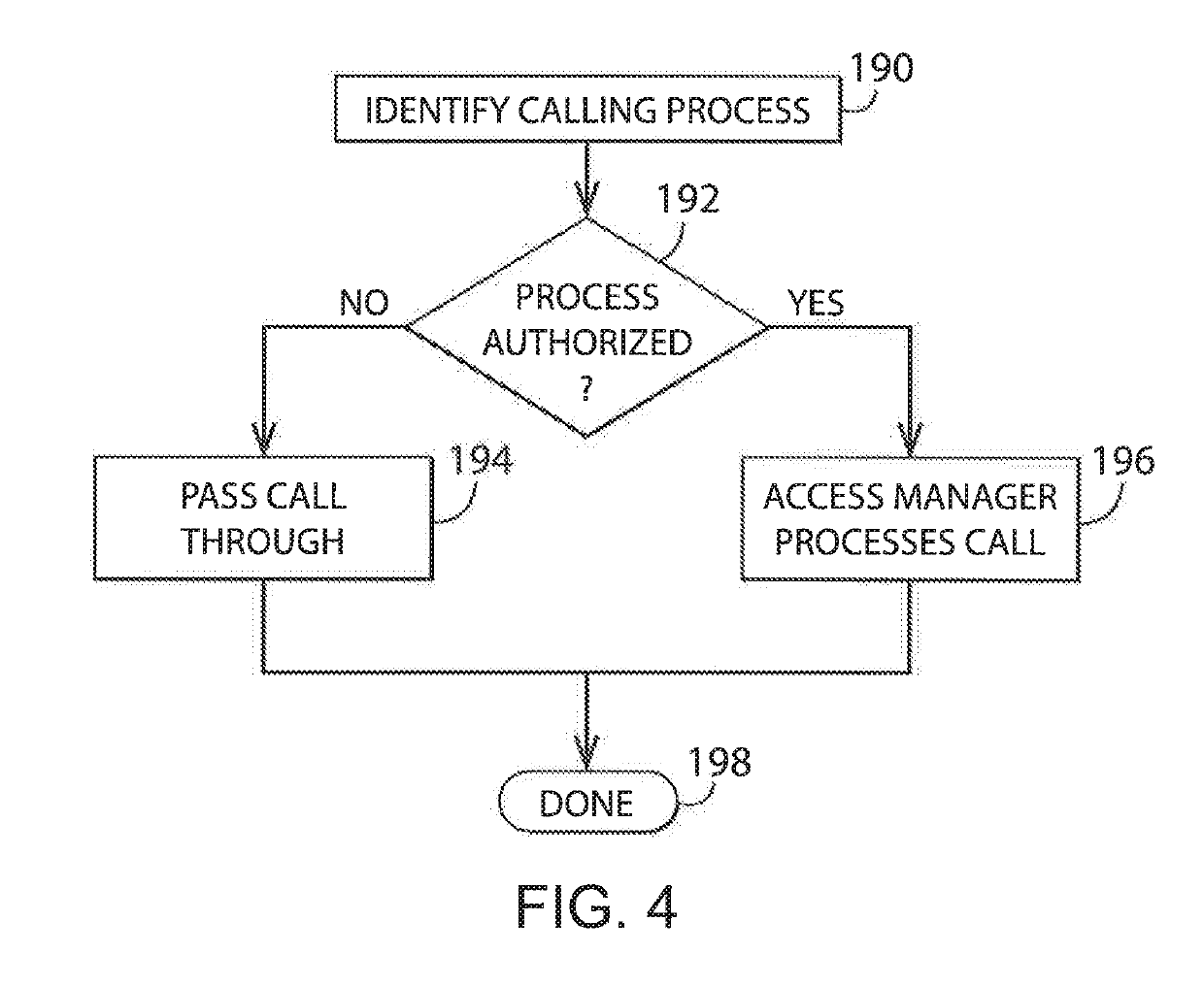
System and Method for Secure File Access of Derivative Works
An access manager that detects a derivative work and automatically transfers digital access rights associated with an original work to the derivative work executes on a computing device. The access manager detects data to be written to a storage device and generates a new file signature for the data. The access manager compares the new file signature to existing file signatures, where the file signatures include piecewise signatures. When at least one of the piecewise signatures from the new file signature matches one of the piecewise signatures in the existing file signatures, the access manager determines that the new data to be written to the storage device is a derivative work generated from the existing file. The access rights associated with the existing file signature are copied to the new file such that the file access rights associated with the original work are passed on to the derivative work.
Owner:CROWDSTRIKE
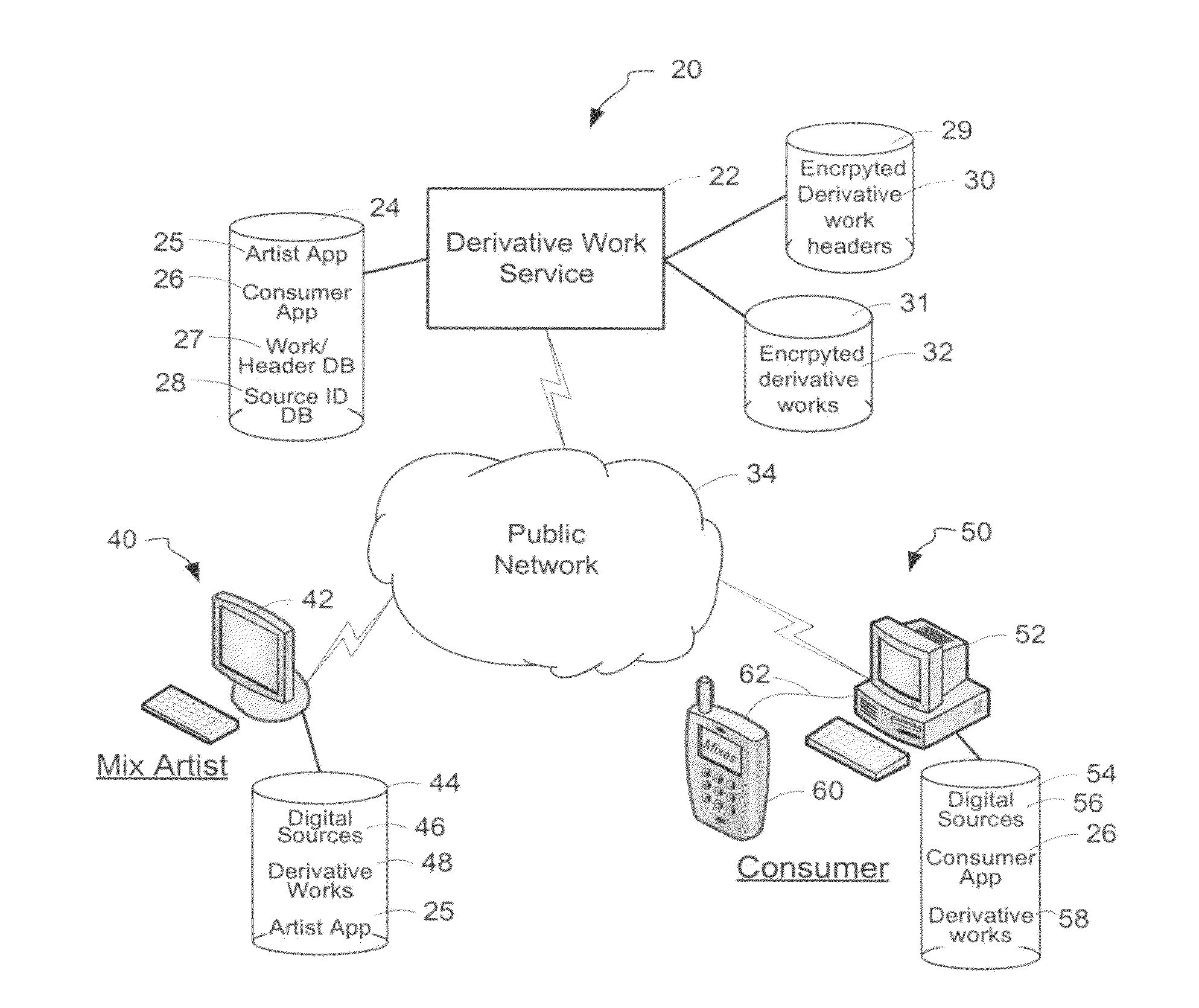
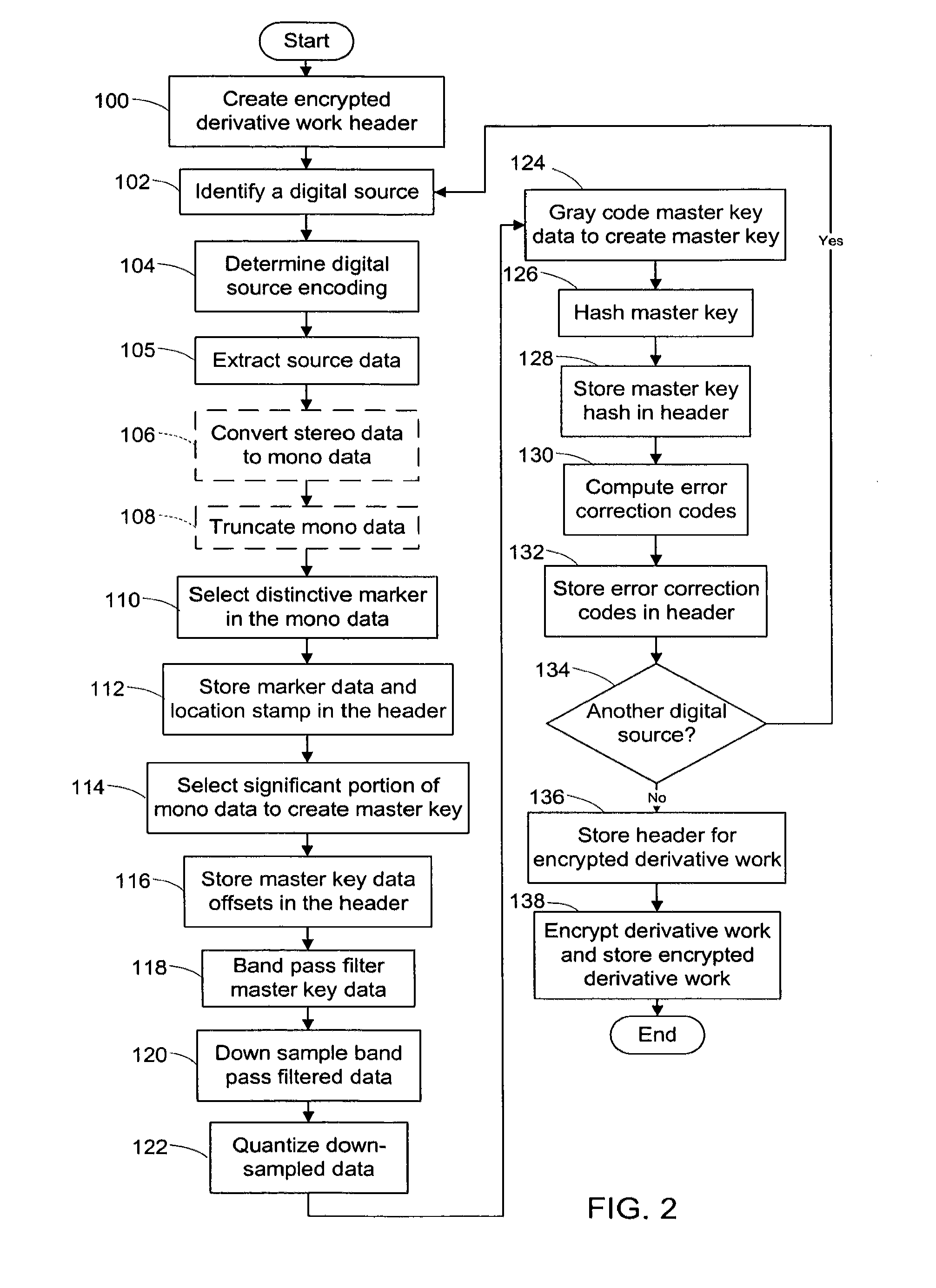
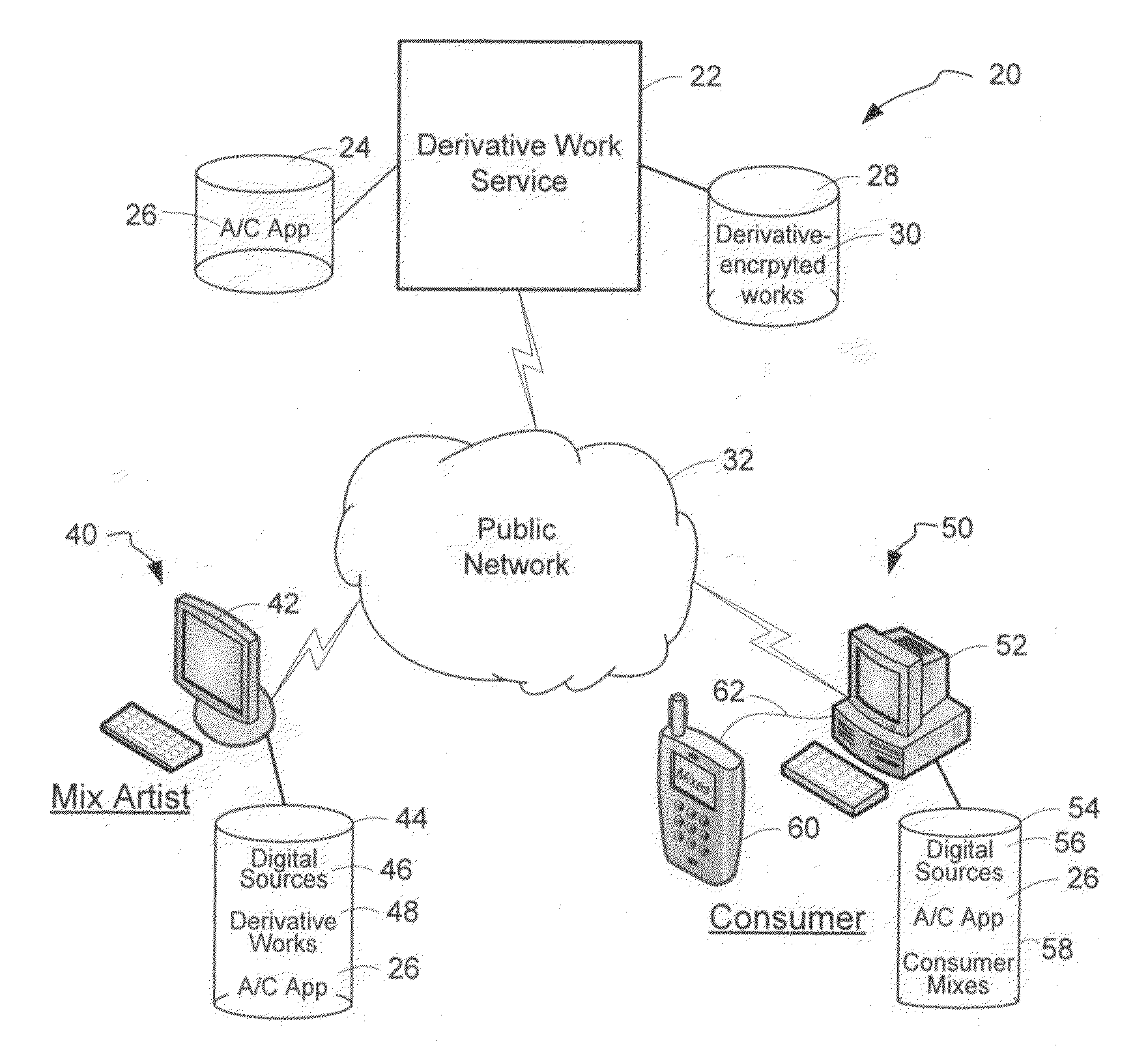
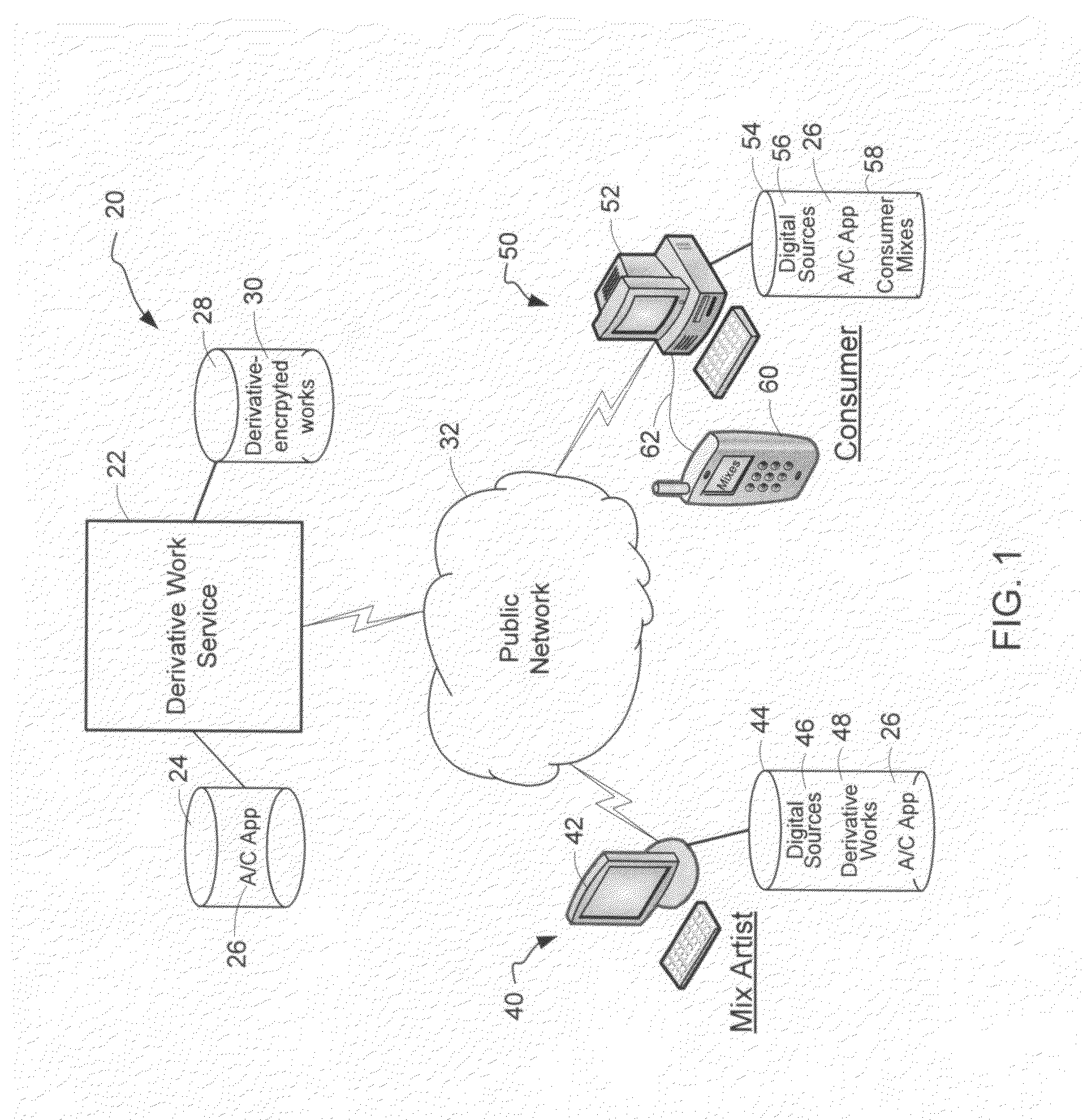
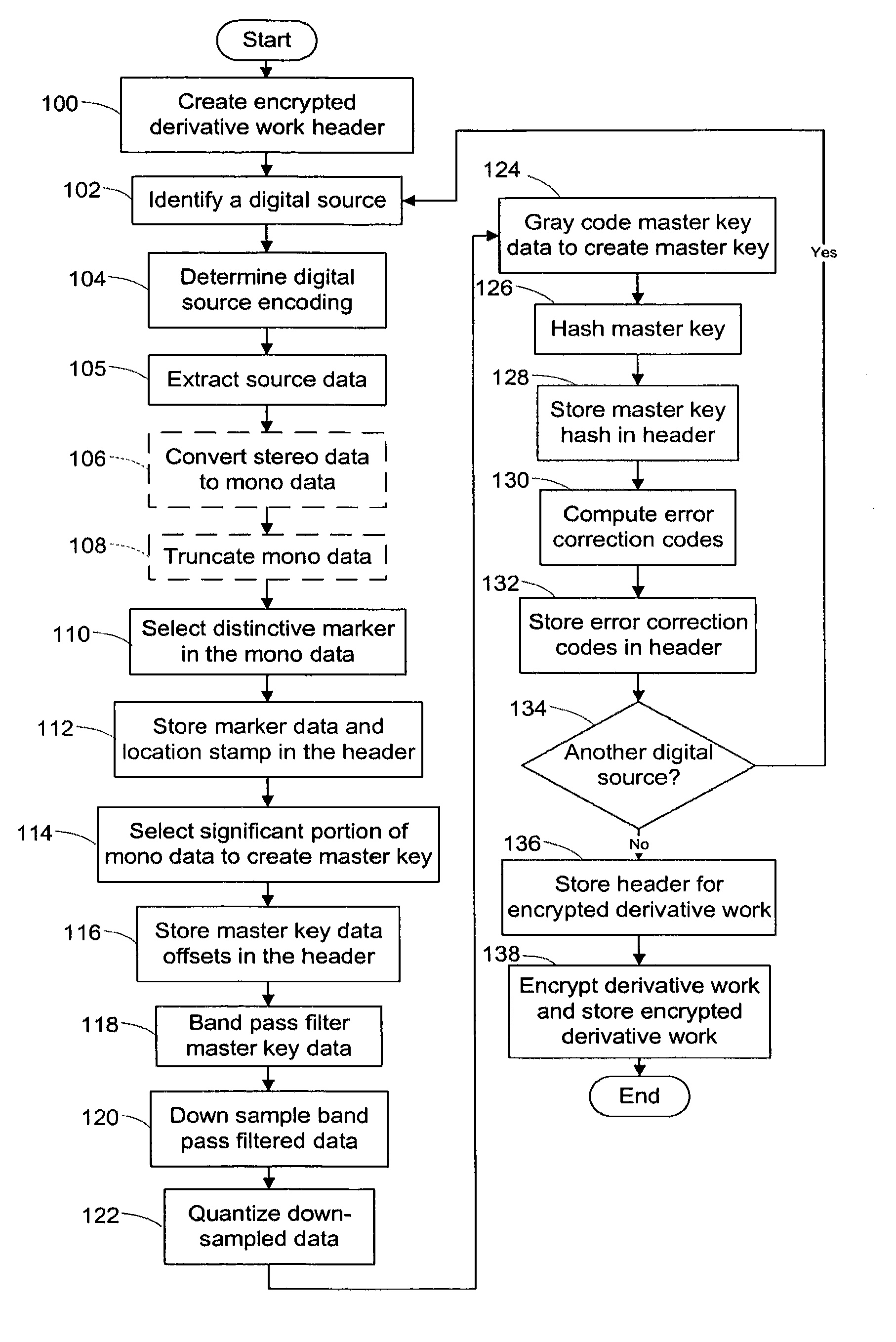
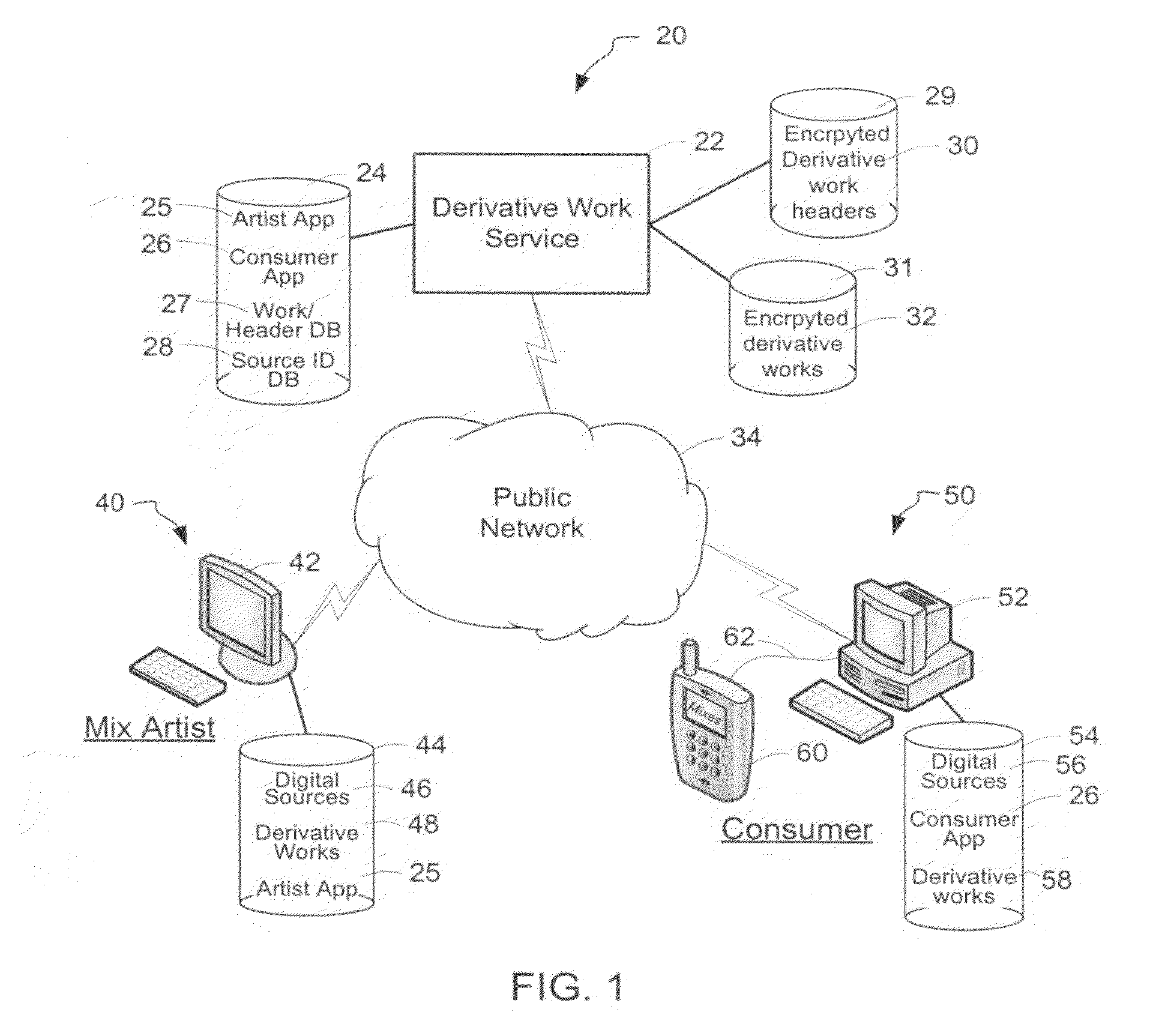
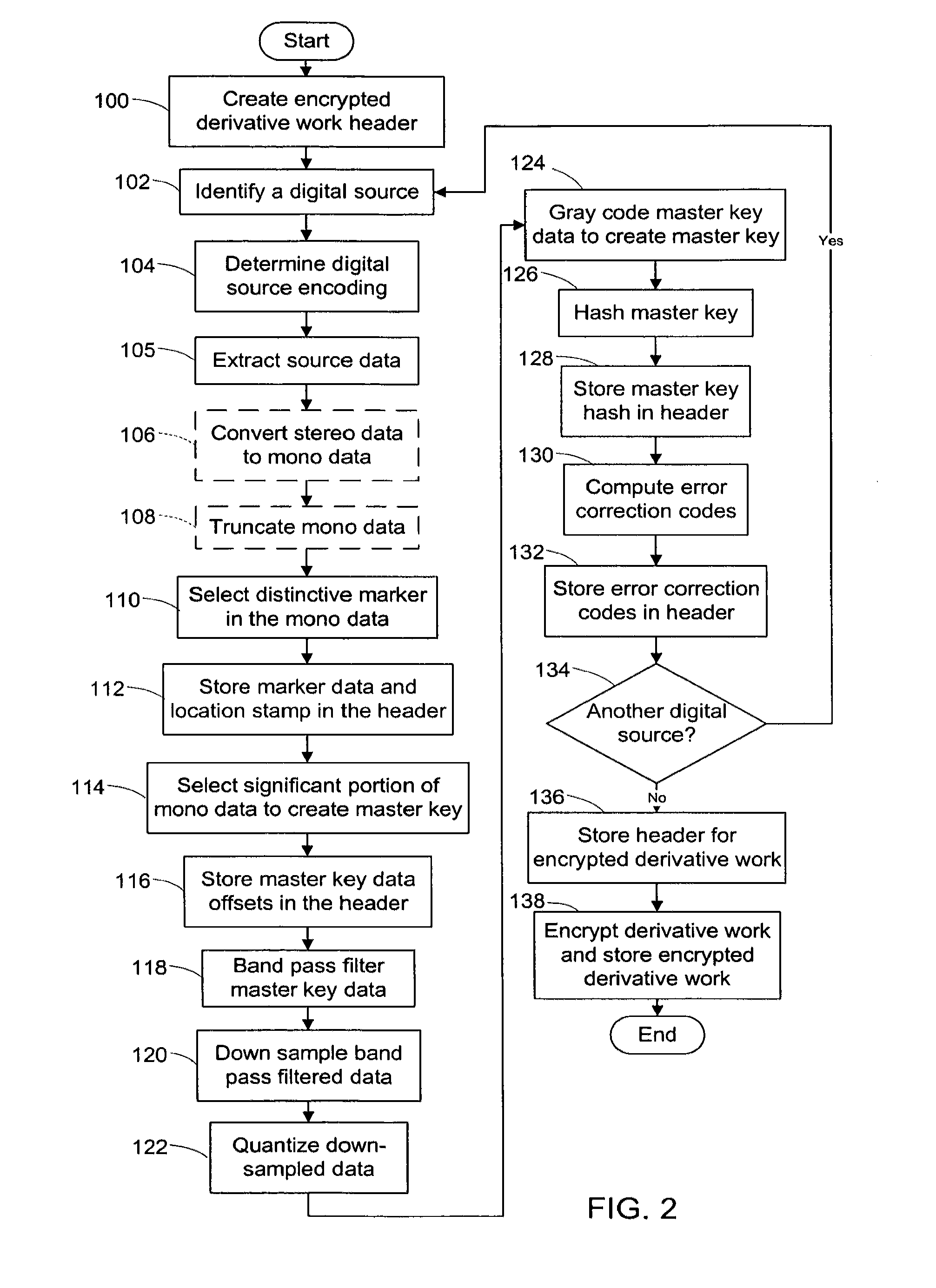
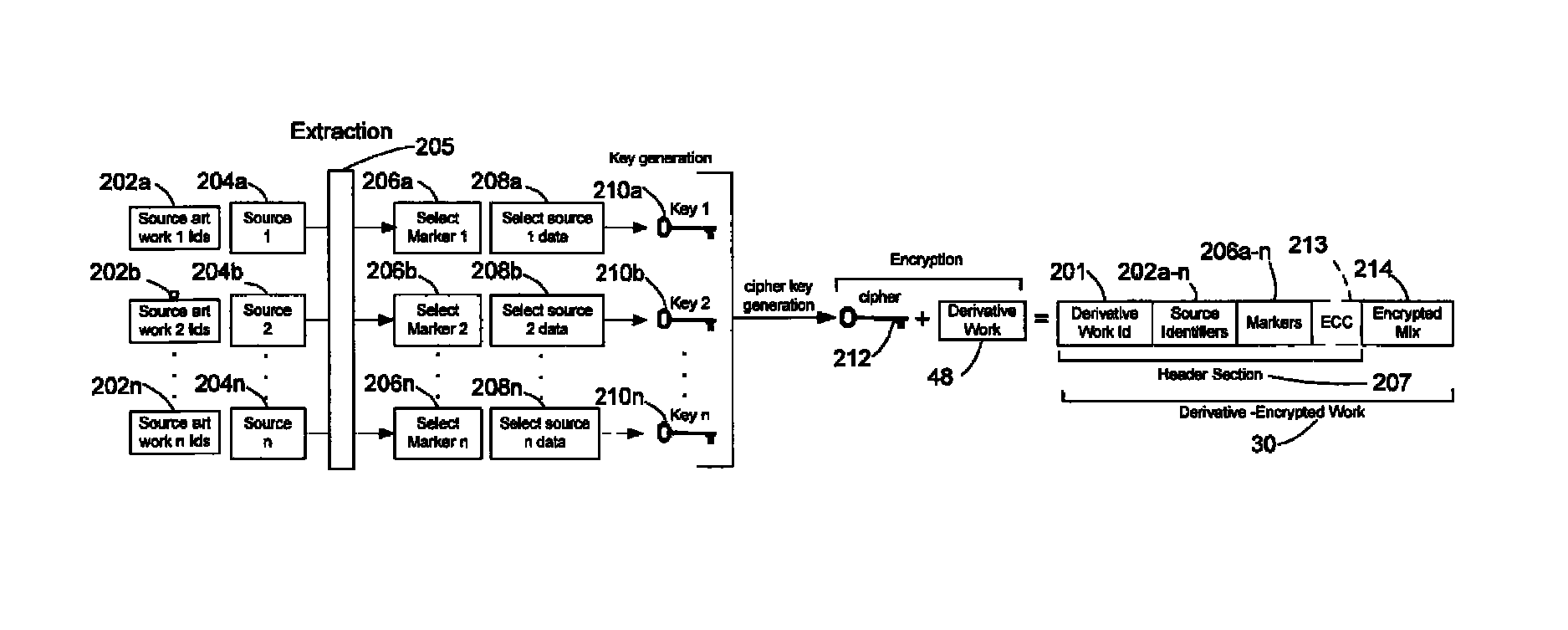
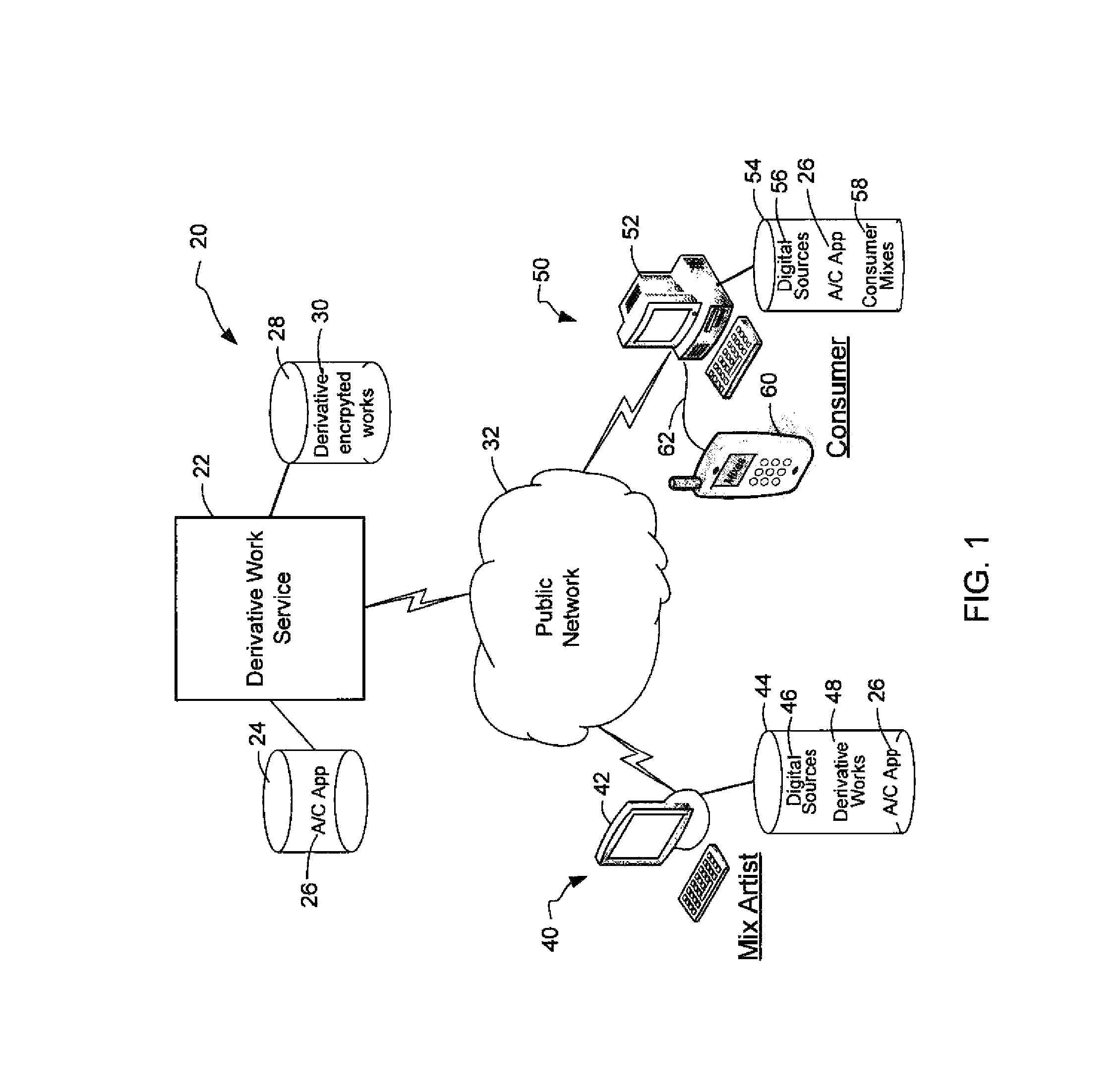
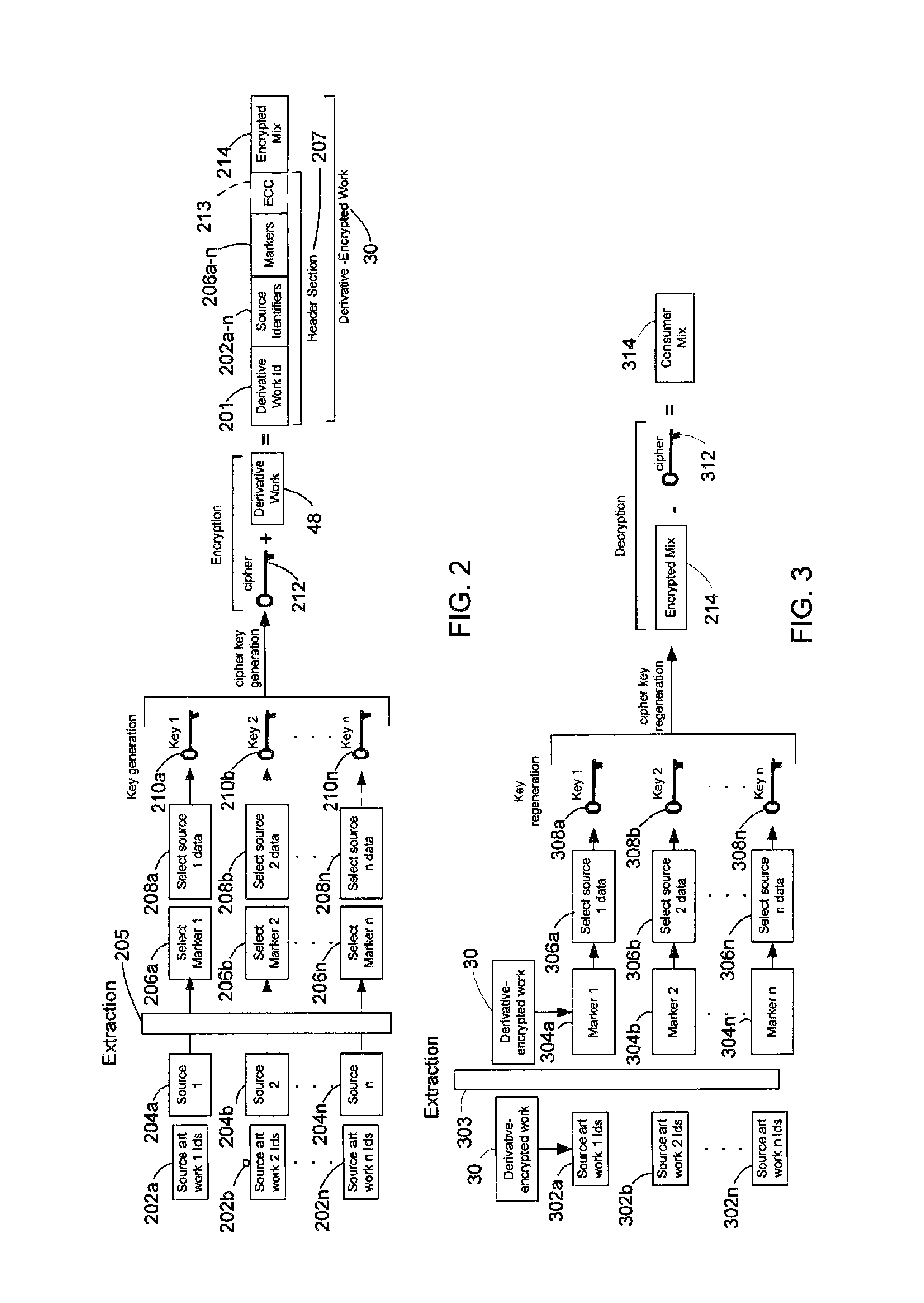
System and method of generating encryption/decryption keys and encrypting/decrypting a derivative work
InactiveUS20120096262A1Data processing applicationsUser identity/authority verificationDerivative workMaster key
A derivative work is encrypted using master keys generated from source data extracted from digital sources used to create the derivative work. A software application permits a mix artist to encrypt and stream a derivative work to a worldwide web server, where it is made available to consumers. A software application permits the consumers to acquire and decrypt an encrypted derivative work if the consumer has possession of a corresponding digital source for each of the digital sources used to encrypt the derivative work.
Owner:LEGITMIX
Evaluating an impact of a user's content utilized in a social network
ActiveUS9881345B2Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsImpact scoreDerivative work
A method, system and computer program product for evaluating an impact of a user's content utilized in a social network. Content in a document (e.g., a presentation) that has been posted on a social network environment is detected as being reused by another user in another document. The author of the reused content is then identified. A counter keeping track of the number of times this content has been adopted in derivative works is then incremented. A score (“impact score”), representing the author's ability to influence other users to adopt the author's content in other users' derivative works, is then generated based on the number of times this content has been adopted in derivative works. Social credit is then provided to the author using the impact score. In this manner, recognition is provided to the author thereby providing motivation for users to post created content in the social network.
Owner:AIRBNB
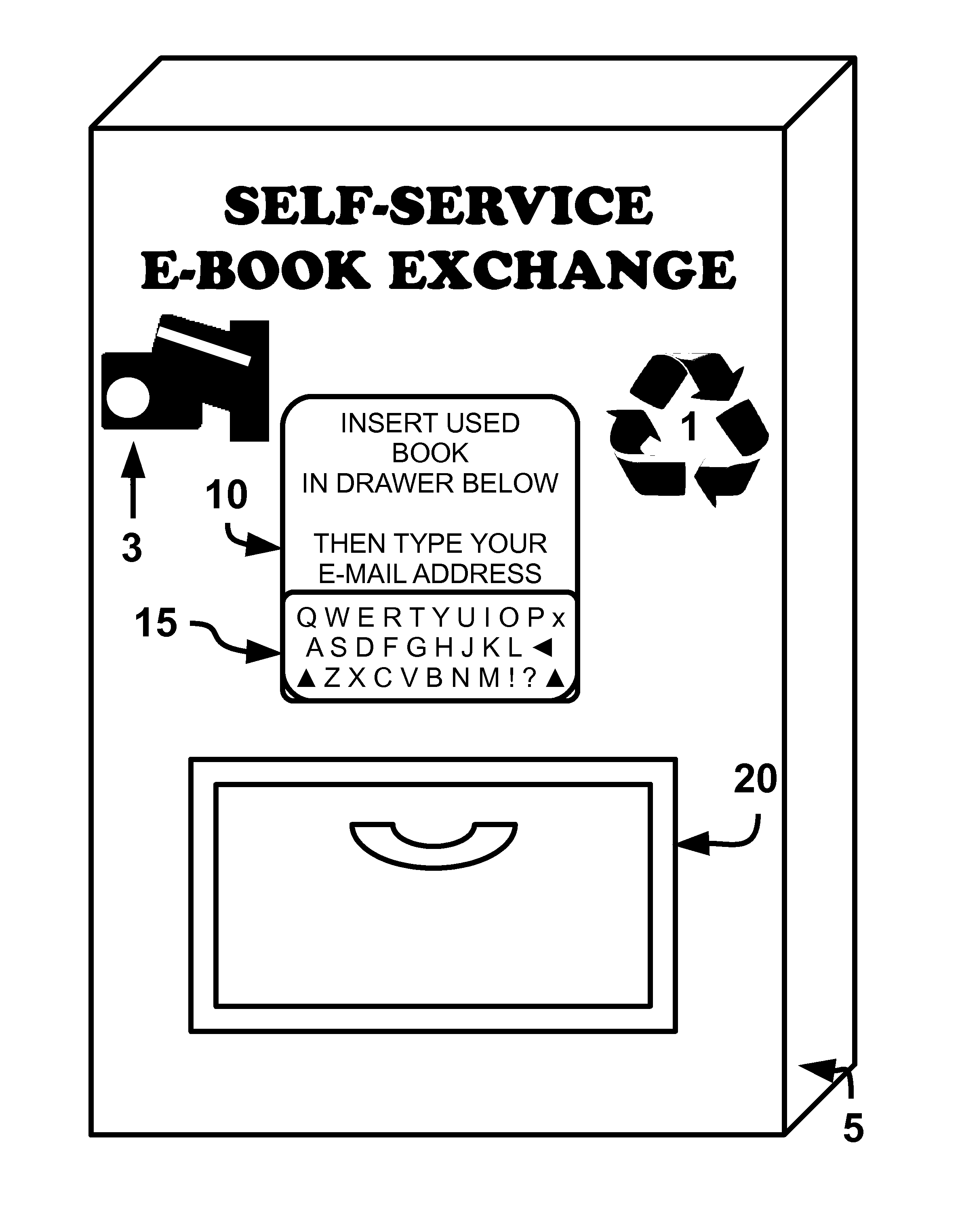
Apparatus, method and system of replacing physical versions of works with electronic versions
InactiveUS20150332233A1Function increaseAvoiding and minimizingPayment architectureBuying/selling/leasing transactionsComputer hardwareIntellectual property
Numerous methods of exchange are facilitated in which a physical copy of a previously-manufactured work embodying intellectual property in some tangible form, such as a physical book, are replaced with an electronic or digital version of similar intellectual property work, a replacement work or a derivative work. The physical item of manufacture is thereafter removed from the marketplace, or some aspect of its perceived private property value is diminished or destroyed physically or effectively so that physical items of tangible property are replaced by electronic or digital versions. To the extent first-sale doctrine under copyright law applies to physical or electronic versions of items, first-sale private property rights may be preserved for the benefit of the private property owner, even though the replacement electronic version of the work may be licensed, not sold, to the user through a disclosed mechanism of exchange.
Owner:HURNI MATTHEW WILLIAM +1
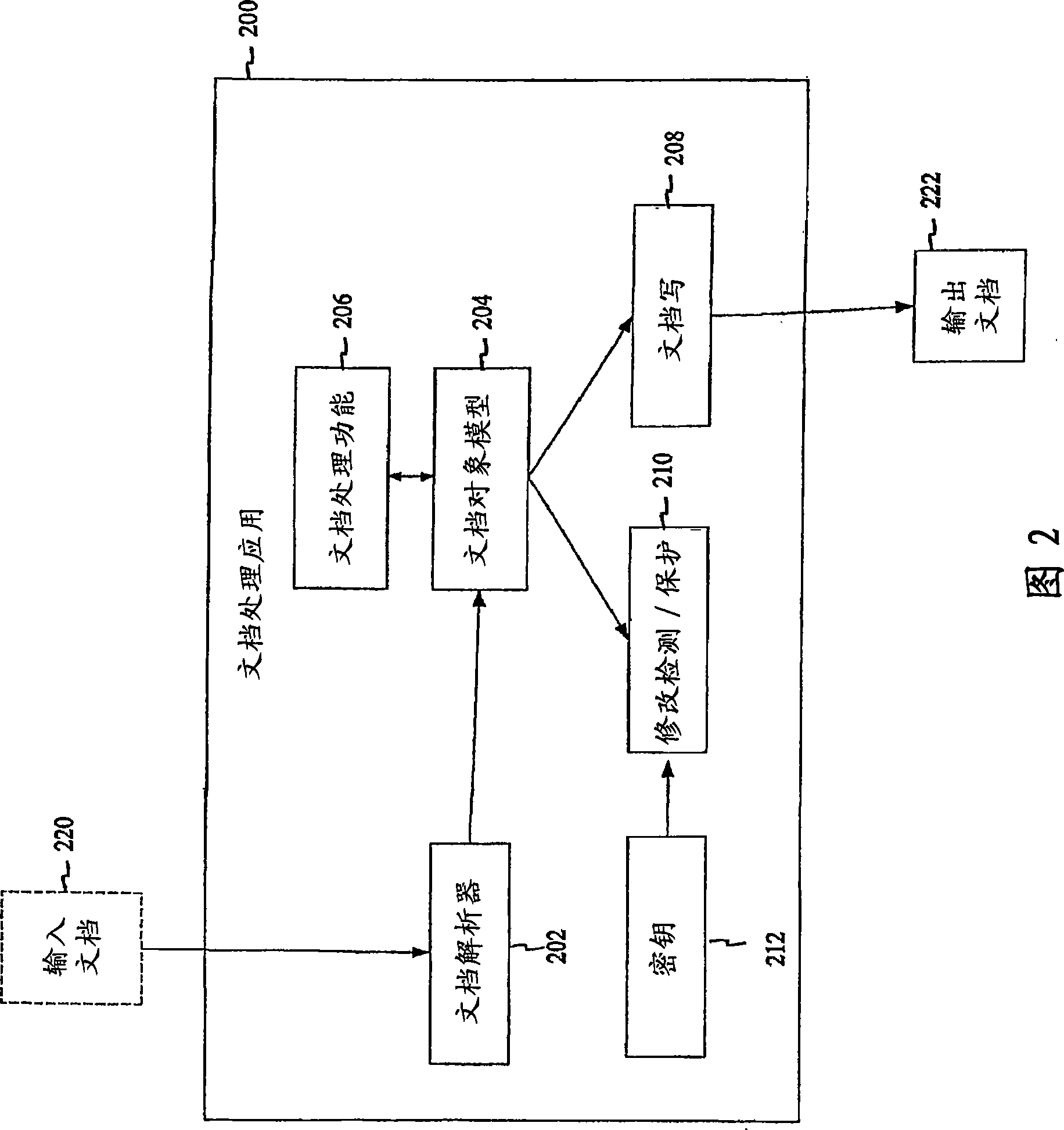
Protecting the integrity of electronically derivative works
InactiveCN101449508AVerify integrityDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationDerivative workDigital signature
Systems and methods provide a mechanism to protect the integrity of electronically derivative works. One aspect of the systems and methods includes receiving an original document including a first digital signature. After the document is derived, a second digital signature is created. The second digital signature may include the first digital signature, a message digest from the first digital signature, and a message digest for the second digital signature. A further aspect of the systems and methods include assigning a security key to a document processing application. The assigned key may be used to produce the second document signature.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
Method and system for provenance tracking in software ecosystems
InactiveUS10339575B2User identity/authority verificationComputer security arrangementsDerivative workSoftware engineering
A system and method for tracking provenance for software use and development includes a developer toolkit program stored in memory media and accessible by a software market place wherein the software marketplace provides a library of software bundles that can be used for software development and modification of the software bundles. The developer toolkit includes a user interface configured to enable software creation of original works and derivative works. The development toolkit further includes a provenance tracker configured to track provenance of the derivative works and original works wherein the provenance tracker makes the derivative work and the provenance of the derivative work available in the software market place. The provenance tracker includes a software bundle identification module configured to identify and verify ownership of the original works and derivative works by associating an owner of the derivative works and original works with features included in portions of the derivative works and original works.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
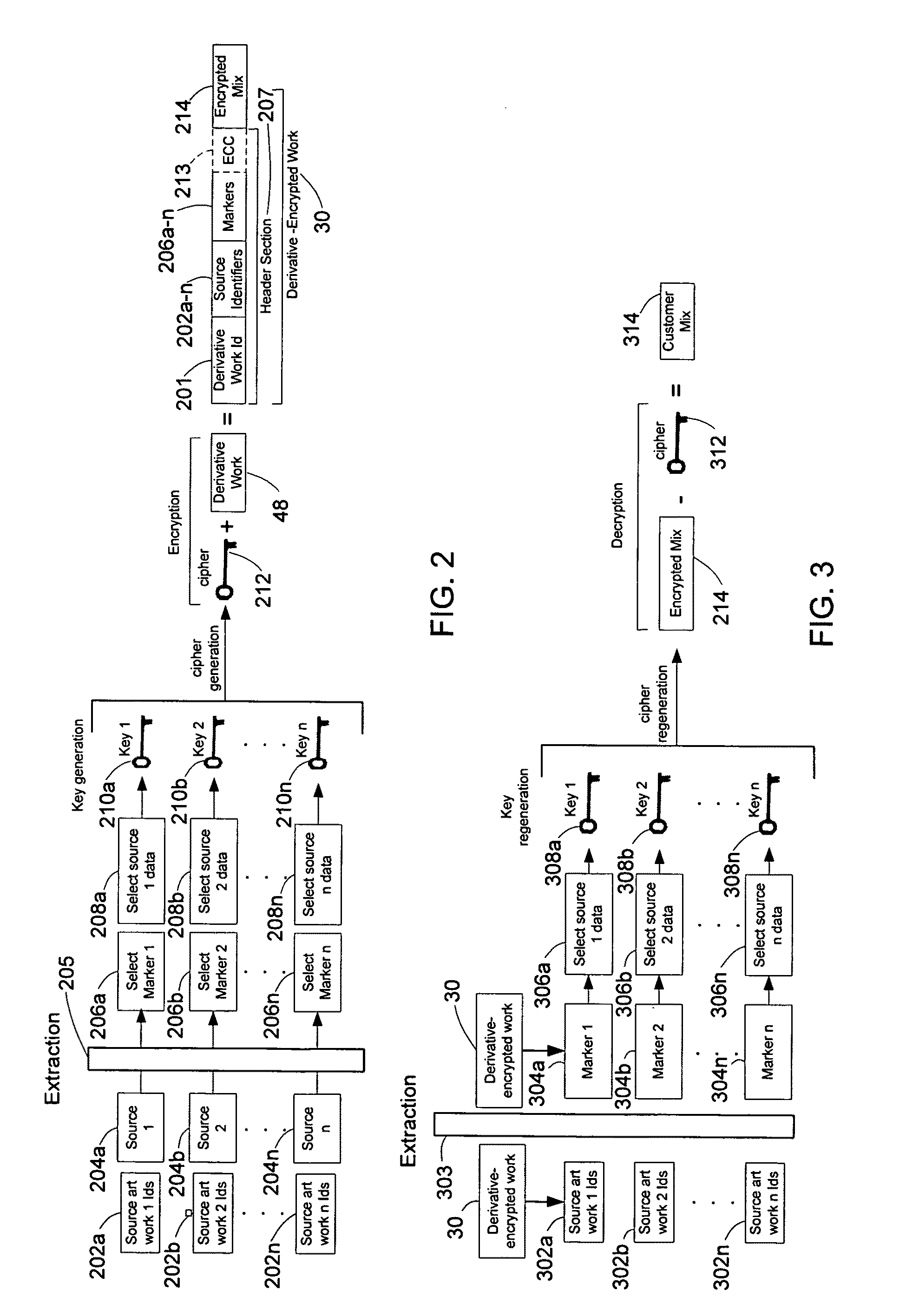
System and method of encrypting a derivative work using a cipher created from its source
InactiveUS20110258440A1Simple and reliable processUser identity/authority verificationRecord information storageDerivative workApplication software
A derivative work is encrypted using a cipher created from digital sources used to create the derivative work. A software application made available for download permits a mix artist to generate a derivative-encrypted work from a derivative work that the mix artist has created using one or more of the digital sources. The derivative-encrypted work is streamed to a worldwide web server, where it is made available for download by consumers for a fee. The software application is also available for download by the consumers and permits the consumers to purchase and download any available derivative-encrypted work. However, the derivative-encrypted works can only be decrypted if the consumer has possession of a digital source for each of the source art works associated with the digital sources used to create the derivative work.
Owner:LEGITMIX
System and method of generating encryption/decryption keys and encrypting/decrypting a derivative work
InactiveUS8925102B2Key distribution for secure communicationData processing applicationsDerivative workMaster key
A derivative work is encrypted using master keys generated from source data extracted from digital sources used to create the derivative work. A software application permits a mix artist to encrypt and stream a derivative work to a worldwide web server, where it is made available to consumers. A software application permits the consumers to acquire and decrypt an encrypted derivative work if the consumer has possession of a corresponding digital source for each of the digital sources used to encrypt the derivative work.
Owner:LEGITMIX
System and method of encrypting a derivative work using a cipher created from its source
InactiveUS8782803B2Simple and reliable processKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsDerivative workApplication software
A derivative work is encrypted using a cipher created from digital sources used to create the derivative work. A software application made available for download permits a mix artist to generate a derivative-encrypted work from a derivative work that the mix artist has created using one or more of the digital sources. The derivative-encrypted work is streamed to a worldwide web server, where it is made available for download by consumers for a fee. The software application is also available for download by the consumers and permits the consumers to purchase and download any available derivative-encrypted work. However, the derivative-encrypted works can only be decrypted if the consumer has possession of a digital source for each of the source art works associated with the digital sources used to create the derivative work.
Owner:LEGITMIX
Miniature exhaust-free hydrogen peroxide synthesizing device and method
ActiveCN108622861AReduce volumeMiniaturizationPeroxides/peroxyhydrates/peroxyacids/superoxides/ozonidesMicroreactorChemical reaction
The invention discloses a miniature exhaust-free hydrogen peroxide synthesizing device and method and belongs to the technical field of chemical reaction. The device comprises a hydrogenation microdisperser, a micro-packed bed, an oxidation microreactor, a micro-extractor and a phase separation tank connected in an order. The microreactor realizes the catalytic hydrogenation of anthraquinone-containing derivatives and oxidation of the hydrogenated anthraquinone-containing derivative work liquid. Through extraction separation, hydrogen peroxide is obtained. In synthesis, hydrogen and oxygen conversion rates are 100% so that tail gas emission is avoided. The device is free of a gas-liquid separator. The synthesis method is effectively simplified. The production economy and safety are effectively improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Application of plant dyeing yarn in infant clothes and application method
InactiveCN107156932ASolve natural dyeing and finishingSolve the antibacterialFibre treatmentHandkerchiefsYarnDerivative work
The application of plant dyed yarn in infant clothing, the infant clothing includes infant finished clothing, accessories and derivative products, it is characterized in that the infant finished clothing, accessories include male and female infants and young children's bottoming shirts, Underpants, skirts, T-shirt suspenders for outer wear, underwear, pajamas, home clothes, thermal clothing, and knitted sweaters; the derivative products include bibs, socks, hats, scarves, and gloves for boys, girls, and boys. The invention also provides an application method. The invention combines the natural fiber and plant dyeing technology and applies it to infant clothing and apparel products.
Owner:李志 +2
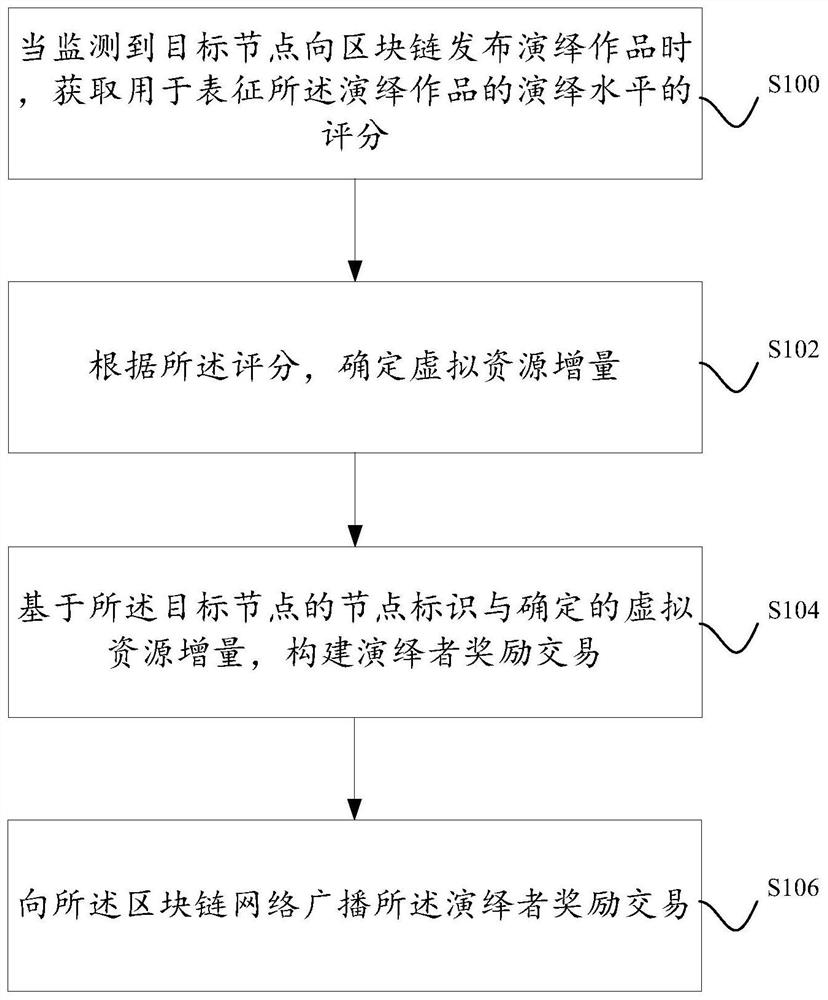
A method and device for issuing rewards to performers of works based on blockchain
ActiveCN109034891BNon-tamperableExamples cannot be limitedUser identity/authority verificationMachine learningComputer networkInternet privacy
Disclosed are a method and a device for issuing rewards to performers of works based on blockchain. The blockchain network includes a plurality of business nodes, and the business nodes have the authority to publish works to the blockchain, and the virtual resources are used as the transaction medium between the multiple business nodes to conduct copyright-related transactions. For a business node that publishes deductive works, rewards are issued to the business node through the consensus mechanism in the blockchain network, so that the virtual resources corresponding to the business node increase. In addition, the virtual resource increment corresponding to the service node is determined according to the deductive level of the deductive works released by the service node.
Owner:ADVANCED NEW TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com