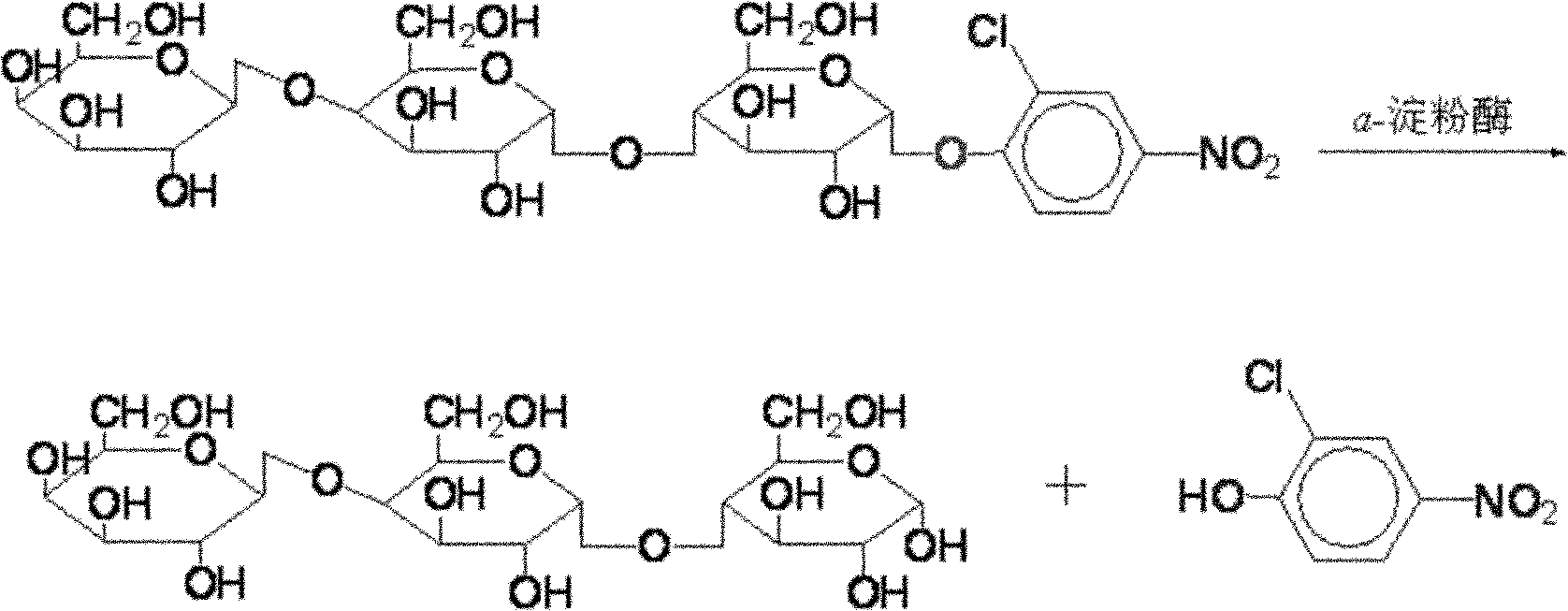
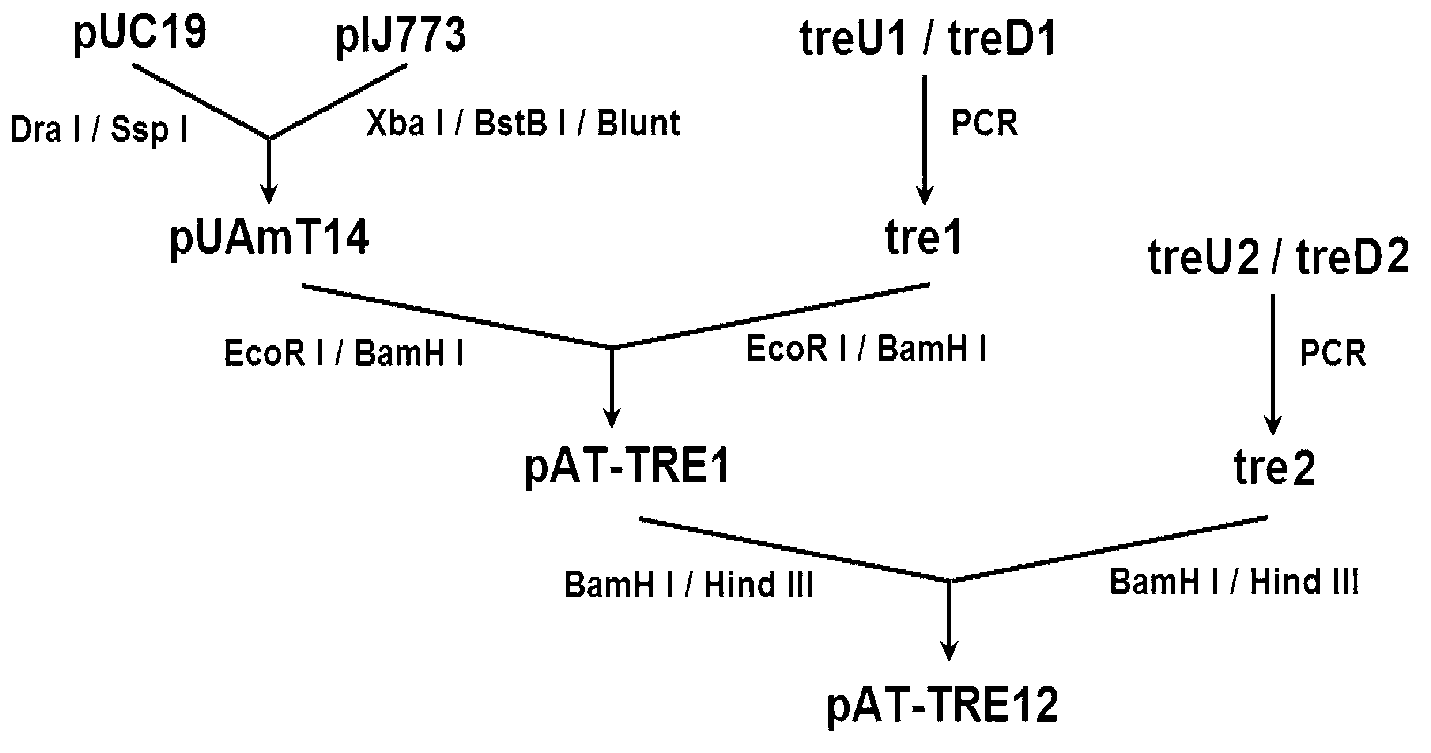
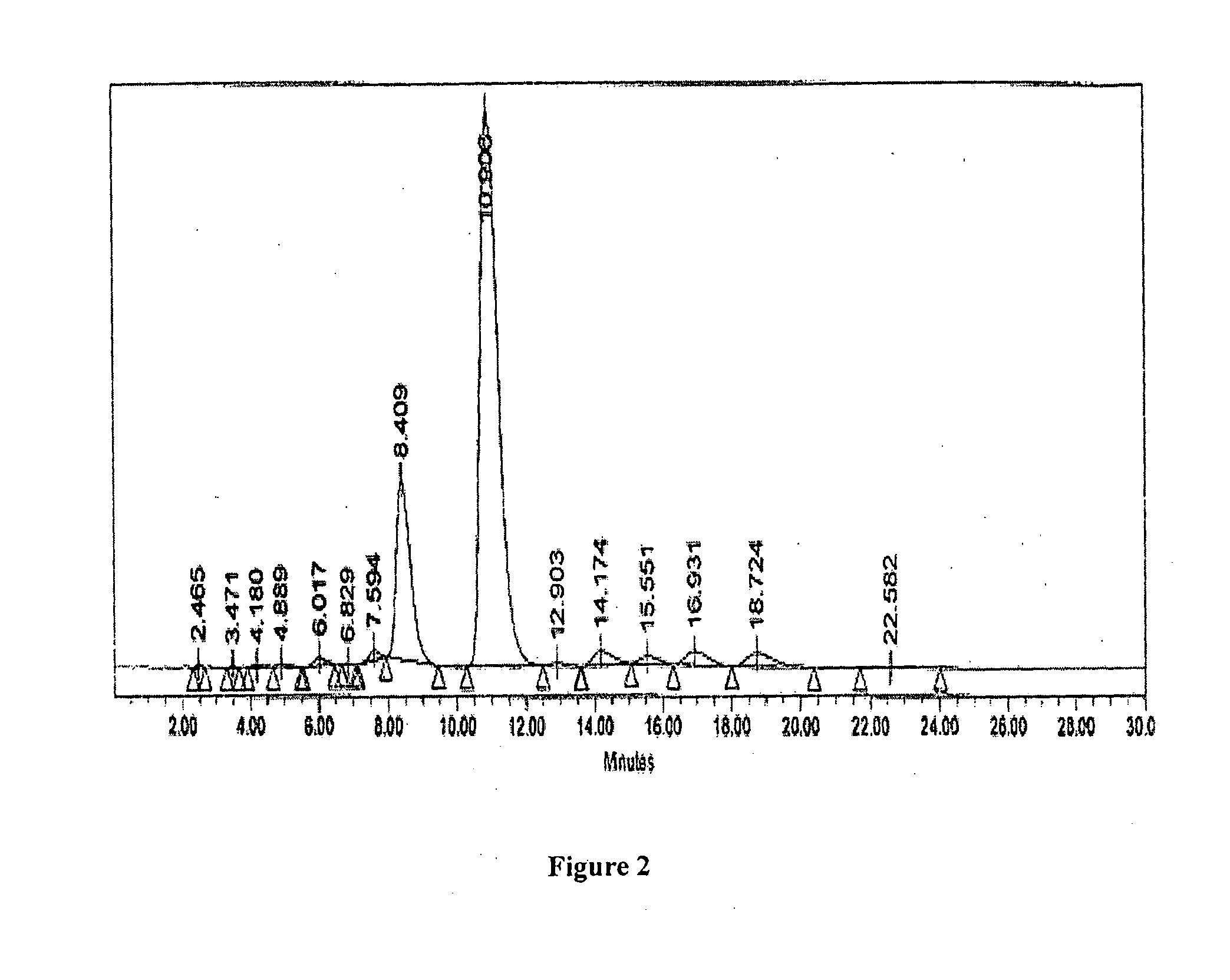
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32 results about "Actinoplanes sp." patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Macrocyclic lactone compounds and their production process
InactiveUS6187568B1Antibacterial agentsMicroorganism based processesMacrocyclic lactoneActinoplanes sp.
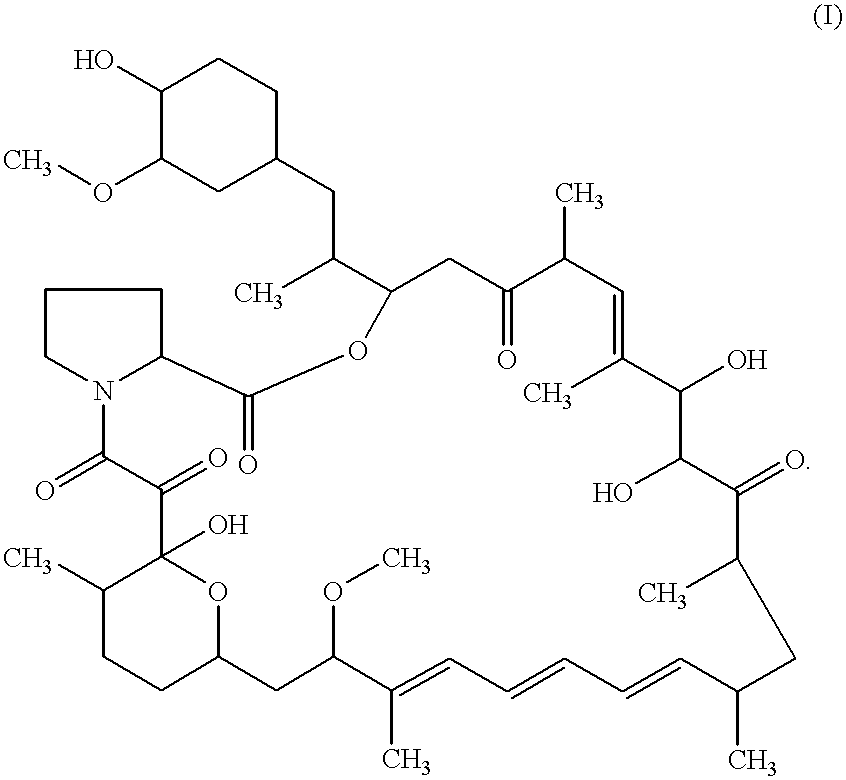
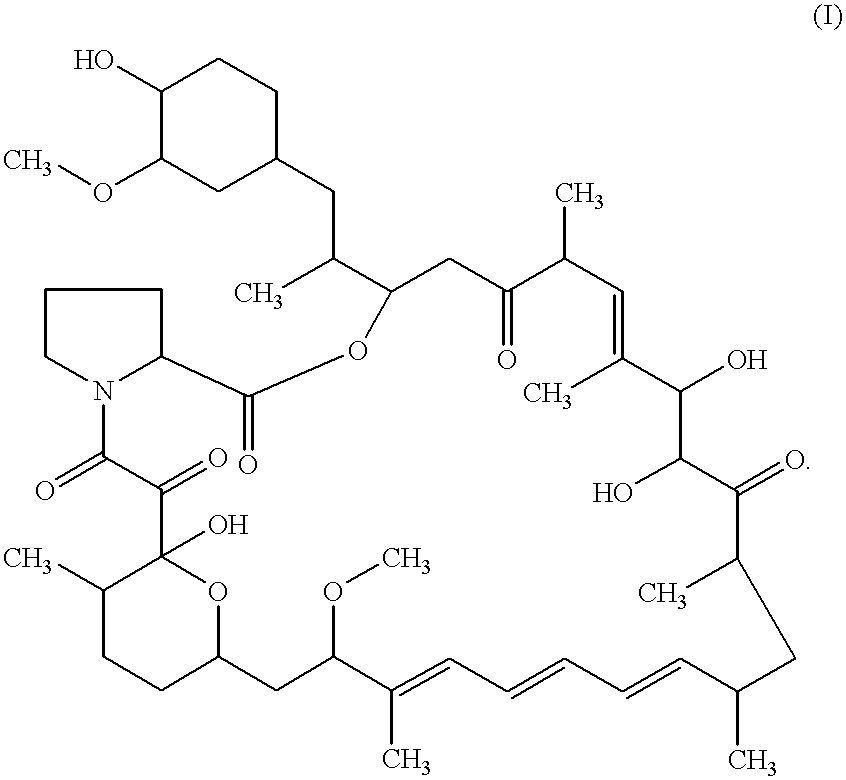
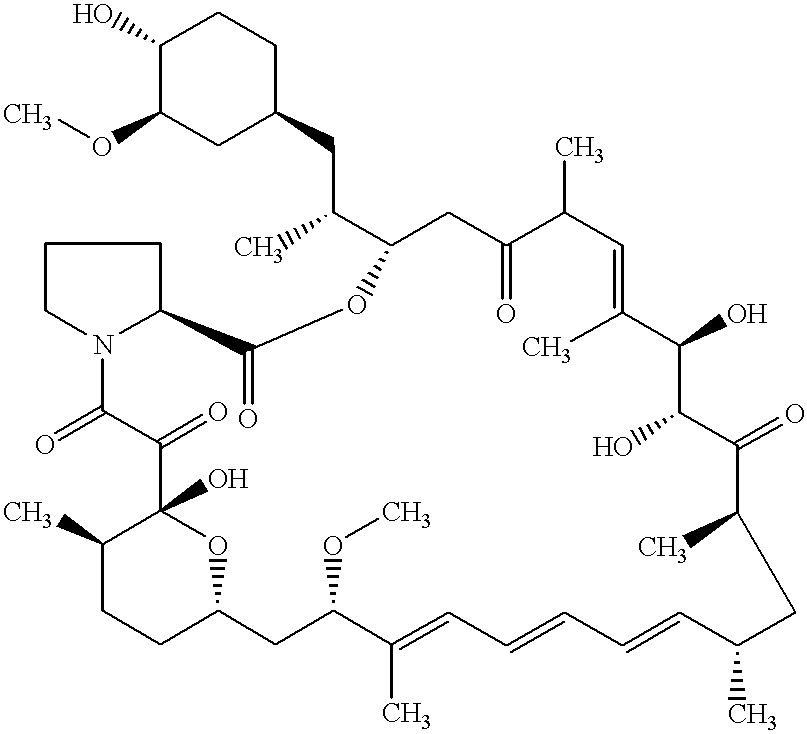
This invention provides a process for producing a macrocyclic lactone compound, which comprises cultivating Actinoplanes sp. FERM BP-3832, in the presence of L-proline, L-hydroxyproline or L-nipecotic acid, and then isolating a macrocylic lactone compound from the fermentation broth. The compounds produced by this process include a compound of the following formula:The present invention also relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same, which is useful as immunosuppressive, antimycotic, antitumor agent or the like.
Owner:PFIZER INC
Protein-deamidating enzyme, gene encoding the same, production process therefor, and use thereof
InactiveUS7279298B2Increase in functionality of proteinFunction increaseSugar derivativesBacteriaAmidogenActinoplanes sp.
A novel enzyme which has an activity to release side chain carboxyl groups and ammonia from a protein by acting upon side chain amido groups in the protein. This invention relates to a method for the production of an enzyme, which comprises culturing in a medium a strain that belongs to a bacterium classified into Cytophagales or Actinomycetes and has the ability to produce an enzyme having a property to deamidate amido groups in protein, thereby effecting production of said enzyme, and subsequently collecting said enzyme from the culture mixture. It also relates to a method for the modification of protein making use of a novel enzyme which directly acts upon amido groups in protein as well as to an enzyme which has a property to deamidate amido groups in protein and a gene which encodes said enzyme.
Owner:AMANO ENZYME INC
Actinoplanes utahensis and application thereof in preparing acarbose
ActiveCN105838645AImprove qualityEasy accessBacteriaMicroorganism based processesActinoplanes utahensisFermentation
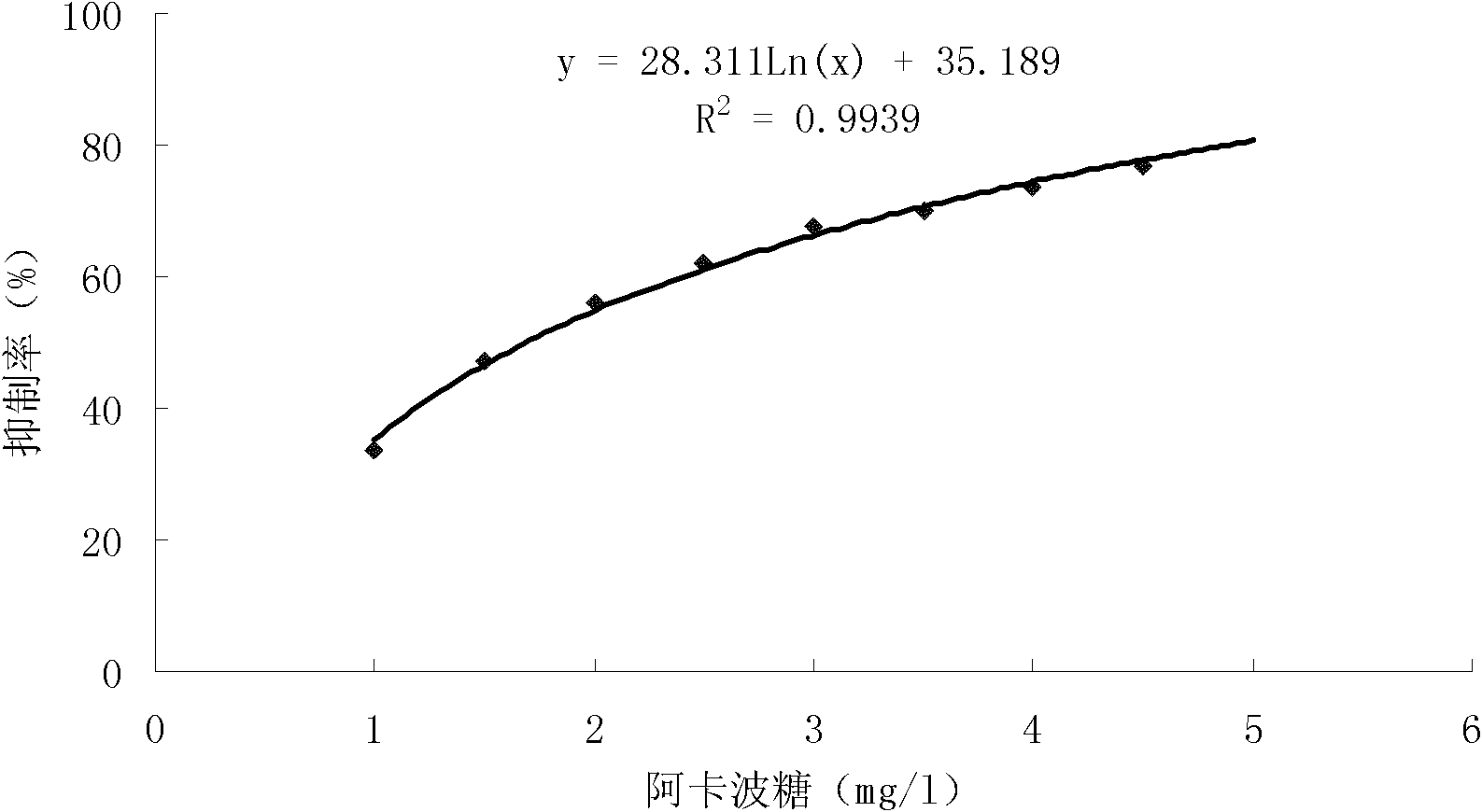
The invention discloses Actinoplanes utahensis MYIH97 and application thereof, the strain is preserved by China Center for Type Culture Collection, the preservation number is CCTCC NO:M 2016237, and the preservation date is May 3<rd>, 2016 .The invention further discloses a method for preparing acarbose through fermentation of the strain .For the fermentation process, it is proved through mass production practice that the fermentation unit is high, the impurities are less, the post-extraction difficulty is greatly reduced, the fermentation process is suitable for industrial mass production, and the quality of the obtained acarbose products is high.
Owner:HANGZHOU HUADONG MEDICINE GRP PHARMA RES INST +2
Alpha-amylase inhibitor producing strain and screening method thereof
ActiveCN102127508AShort analysis timeEasy to operateMicroorganismsMicroorganism based processesAmylase inhibitorsScreening method
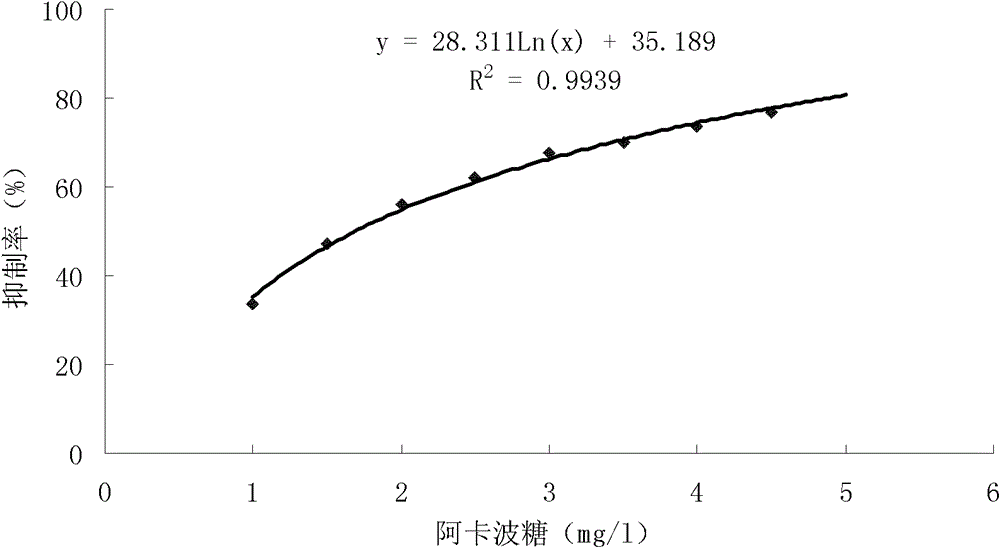
The invention discloses an alpha-amylase inhibitor producing strain, i.e. Actinoplanes sp.ZJB-08196 preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection located in Wuhan university, Wuhan Province, China on Feb. 16th, 2009 with the preservation number of CCTCC No. M209022. The alpha-amylase inhibitor is acarbose. The invention also discloses a screening method of the alpha-amylase inhibitor producing strain. The screening method provided by the invention is simple and effective, can screen a great amount of samples in a short time, has high sensitivity, reduces the long processes for processing and analyzing samples through HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography), and the like and improves detection efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +2
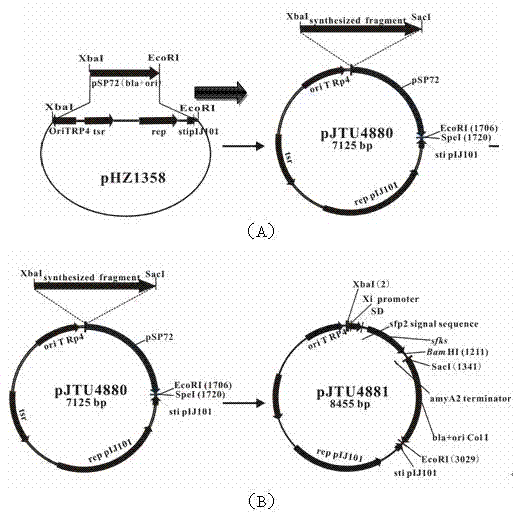
Construction method for streptomycete expression plasmids and production method for keratinase
InactiveCN102533833AIncrease productionHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionAmylaseSrc family kinase
The invention relates to a construction method for streptomycete expression plasmids and a production method for keratinase. The construction method for streptomycete expression plasmids includes the following steps: a promoter Xi of actinoplanes missouriensis xylose isomerase and a terminator of streptomycete avermitilis amylase are sleeved, and the promoter-shine-dalgarno (SD) sequence comes from 90 to 269bp of an actinoplanes missouriensis xylose isomerase gene; a cloned src family kinases (sfks) gene is inserted in a construction expression frame structure of a synthetic Xi promoter-SD-amyA2 terminator fragment, and then a conventional method is used for constructing the streptomycete expression plasmids. The production method for keratinase includes: leading the streptomycete expression plasmids into an expression host of streptomycete lividans TK24 through conjugal transfer, performing recombinant expression and generating the keratinase. Specific activity of a crude enzyme solution is 1700 U / mg after expression of the expression plasmids in the streptomycete lividans TK24 and is improved by 50 times compared with specific activity of starting strain streptomycete fradiae varieties S-221, and yield of the keratinase is much higher than starting strains after the expression.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Acarbose engineering bacterium as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103305544AC component impurity content is reducedReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesImpurityActinoplanes
The invention relates to an acarbose engineering bacterium, a method for preparing the engineering bacterium and an application of the engineering bacterium. The acarbose engineering bacterium provided by the invention is prepared by inactivating treY gene of actinoplanes by introducing homologous recombination fragments by using a conjugational transfer method. The content of the generated acarbose C-component impurity of the acarbose engineering bacterium after the acarbose engineering bacterium is fermented is greatly reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HISUN PHARMA CO LTD
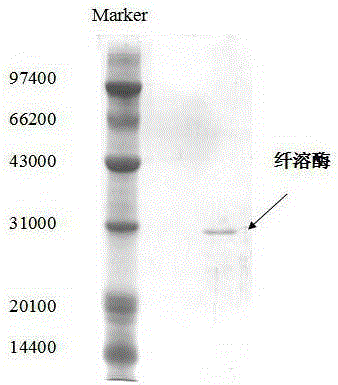
Preparation method of actinomycetes fibrinolytic enzyme
InactiveCN105219754AHigh recovery rateReduced purification processMicroorganism based processesPeptidasesFreeze-dryingSepharose
The invention relates to a preparation method of an actinomycetes fibrinolytic enzyme. Specifically, the method comprises the following steps: (1) adding ammonium sulfate powder to a fermentation supernatant containing actinomycetes fibrinolytic enzyme until a saturation degree is 25-35%W / V, standing by for a whole night at 4 DEG C and centrifuging so as to obtain a supernatant, adding ammonium sulfate powder to the supernatant once again until a saturation degree is 55-65%W / V, standing by for a whole night at 4 DEG C, centrifuging so as to obtain a precipitate, and dissolving the precipitate by virtue of a PB buffer solution so as to obtain crude enzyme liquid; and (2) centrifuging the crude enzyme liquid obtained from the step (1) at low temperature so as to remove impurities; purifying an obtained supernatant subsequently through Octyl-Sepharose FF hydrophobic interaction chromatography and Phenyl-Sepharose HP hydrophobic interaction chromatography so as to obtain a chromatographically pure enzyme; dialyzing and desalting the enzyme, and freeze-drying the enzyme so as to obtain fibrinolytic enzyme freeze-dried powder which can be preserved for a long time at minus 20 DEG C. The separation and purification method of the actinomycetes fibrinolytic enzyme disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple operation steps and high recovery rate.
Owner:QIQIHAR UNIVERSITY
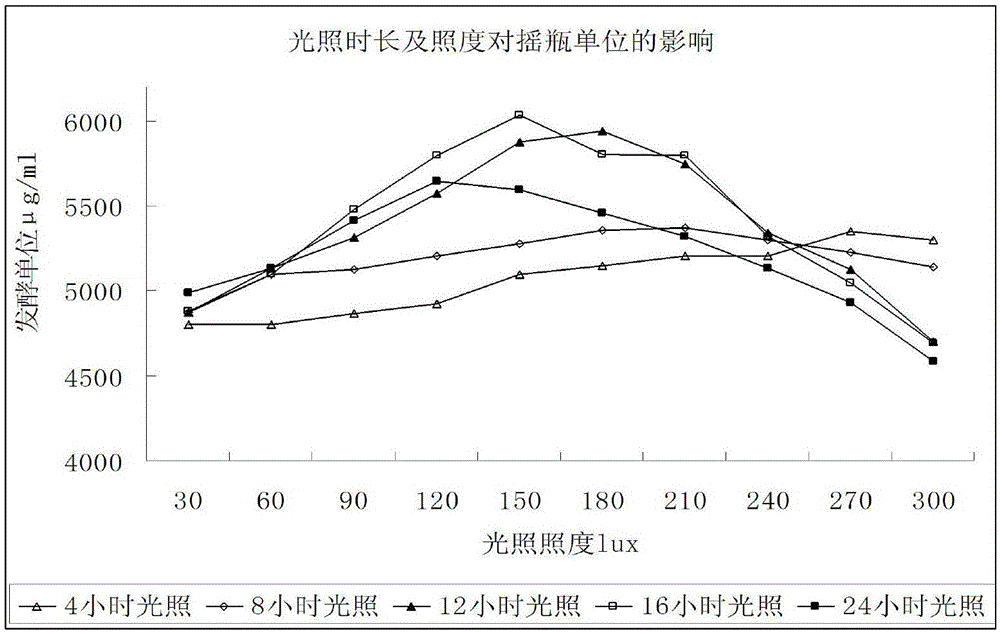
Method for increasing fermentation unit of acarbose
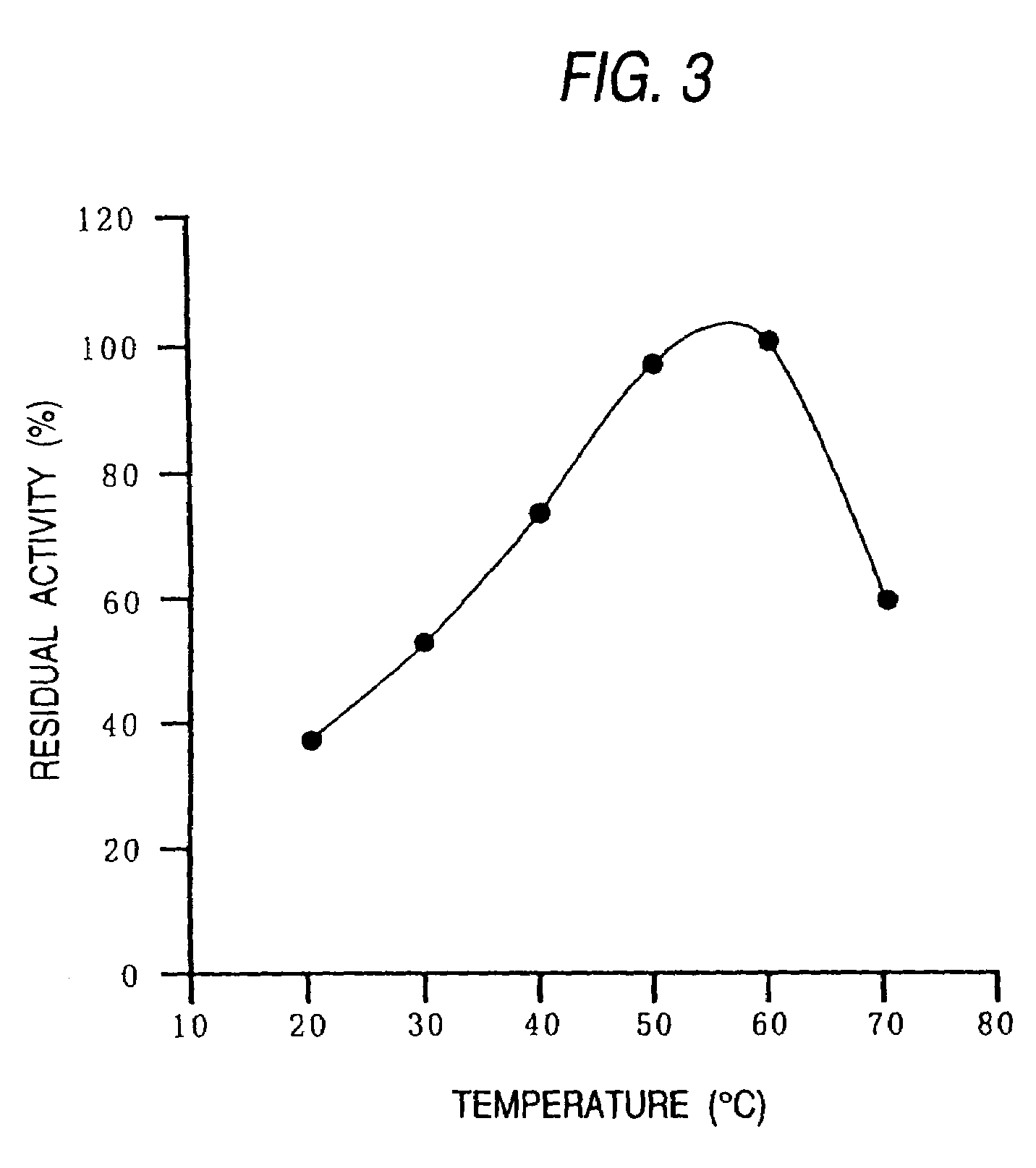
The invention relates to a method for increasing the fermentation unit of acarbose. The fermentation unit is increased through control of slant strain cultivation conditions of Actinoplanes sp.. Experimental results show that incandescent lamps serve as light sources during slant cultivation of the Actinoplanes sp.; when illumination time is controlled within 12-20h / day and illuminance is controlled within 120-180lux, the fermentation unit can be increased; particularly, when the illumination time is controlled within 12-16h / day and the illuminance is controlled within 150-180lux, the fermentation unit is increased remarkably.
Owner:CSPC SHENGXUE GLUCOSE CO LTD
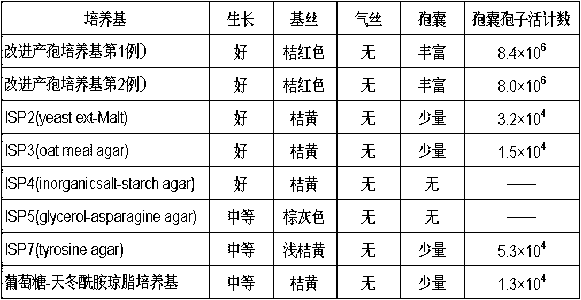
Preservation method of actinoplanes teichomyceticus
The invention provides a culture method for promoting an actinoplanes teichomyceticus industrial production strain to generate rich zoosporangiophore, in the formula of a strain culture medium, wheatgerm powder is selected as a main carbon and nitrogen source for spore germination, asparagine and ammonium sulfate are used as supplementary nitrogen sources, and trace elements supplement iron, manganese, cobalt and zinc ions. The culture temperature is controlled by stages. Glycerol and scleroglucan are used as composite cryoprotectants for -80 DEG C or ultralow-temperature liquid nitrogen preservation to prepare a strain library, so that the preservation stability of the strain library is greatly improved.
Owner:NCPC NEW DRUG RES & DEV
Preparation method of high purity ramoplanin single components
ActiveCN102838662AEfficient removalHigh yieldPeptide preparation methodsChromatographic separationMicrosphere
The invention discloses a method of utilizing an Actinoplanes sp. fermentation culture material to prepare three ramoplanin single components. The method includes: conducting decoloration on a ramoplanin fermentation solution through macroporous decolorization resin, then carrying out macroporous resin adsorption, desorption as well as concentration so as to obtain a ramoplanin crude extract containing the three single components: A1, A2, and A3; and dissolving the crude extract with a solvent, then performing chromatographic separation by means of a polymer microsphere, thus obtaining the products of three high purity ramoplanin single components A1, A2 and A3. The invention has the advantage that when using the polymer microsphere to perform chromatographic separation on the product, the sample treatment amount is large, and the obtained single components have high purity. As the price of a polymer microsphere medium is 30% of that of the reverse phase silica gel C18, and the separation effect is equivalent, the preparation cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:NCPC NEW DRUG RES & DEV
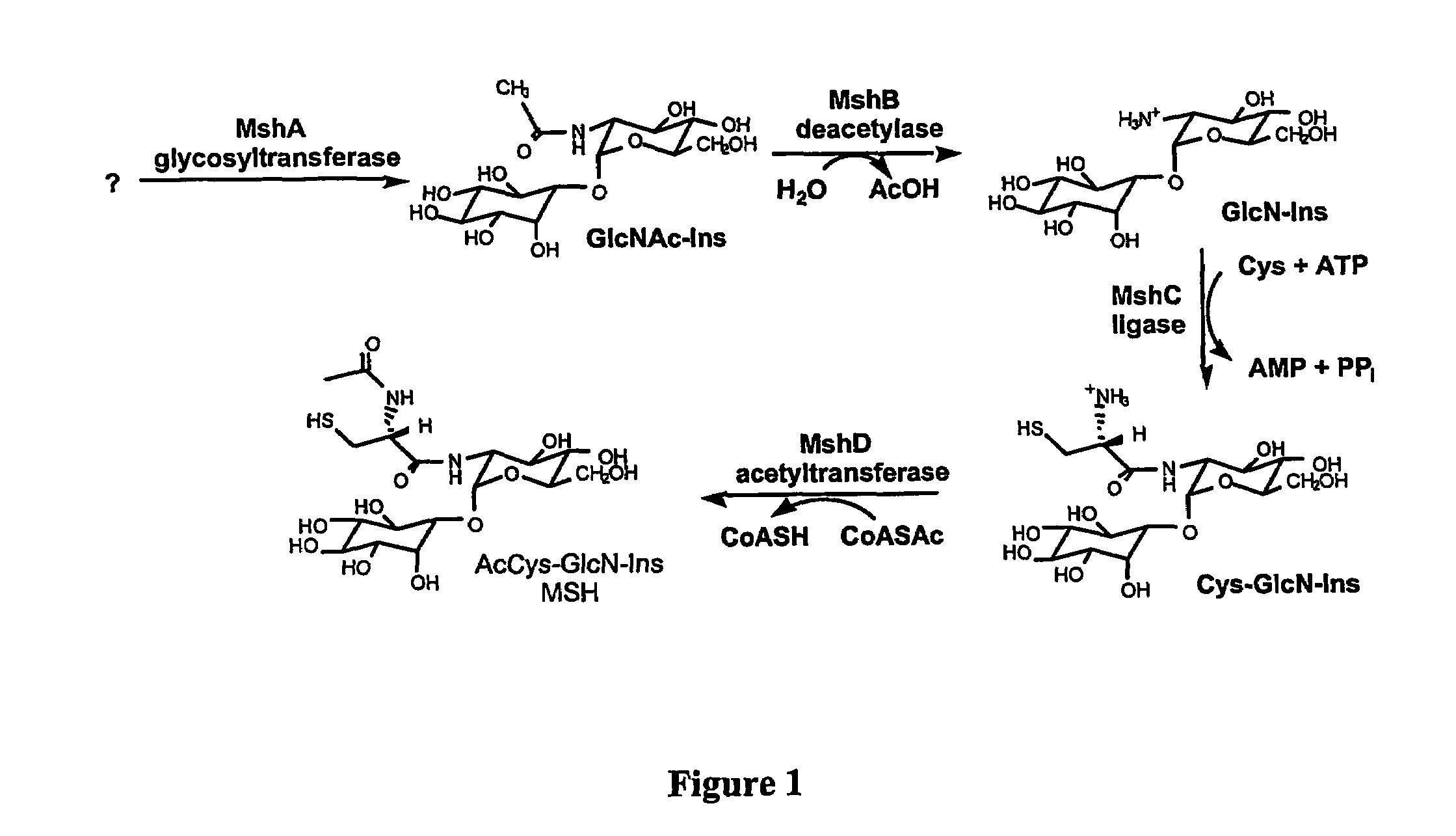
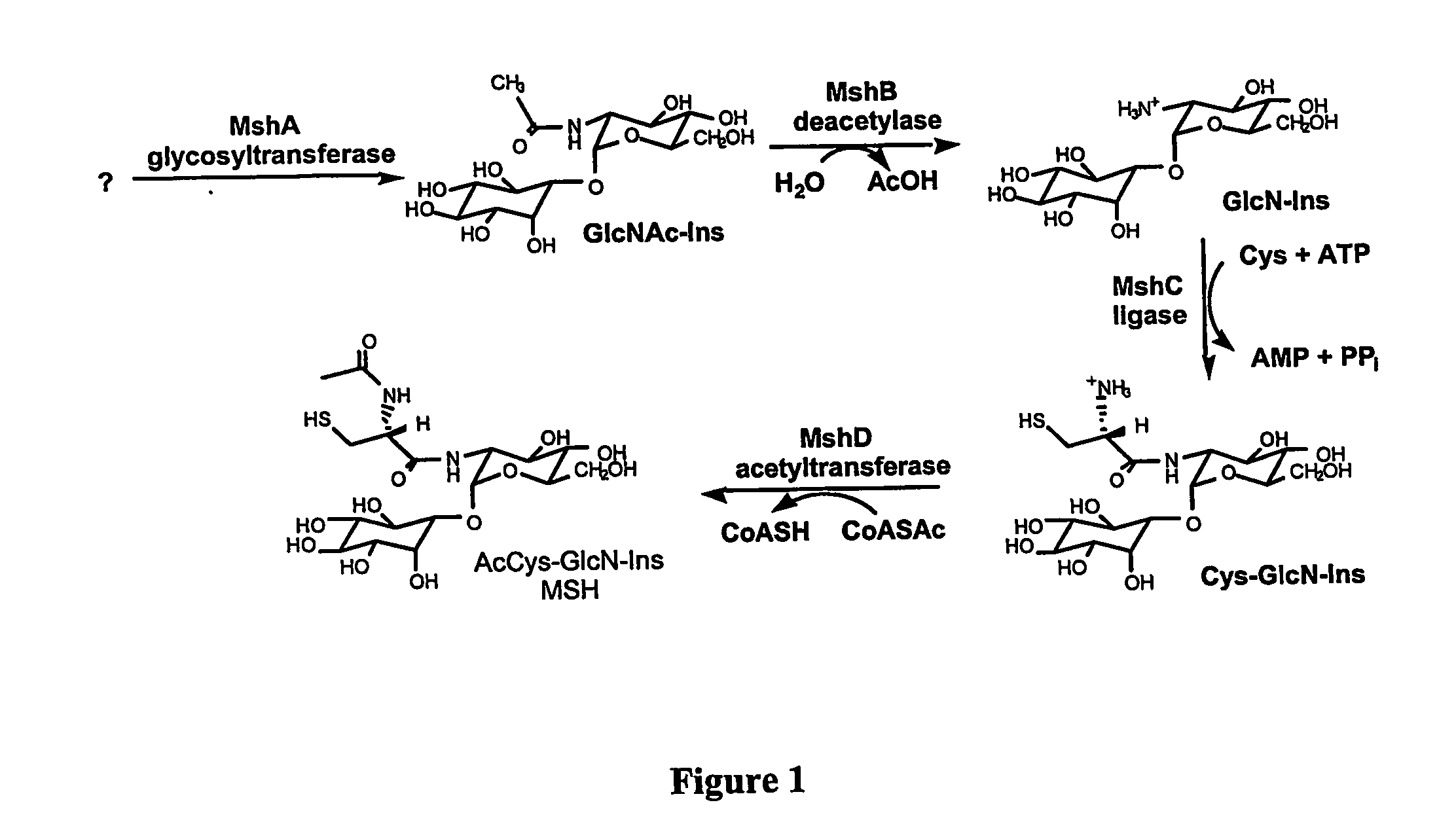
Acetyl glucosaminyl inositol deacetylase, a mycothiol biosynthetic enzyme, and methods of use
InactiveUS20050124021A1Growth inhibitionReduced activityBiocideBacteriaVirulent characteristicsMammal
The present invention provides a family of bacterial acetyl glucosaminyl inositol deacetylases (MshB) with deacetylase activity against acyl glucosaminyl inositol and which play a key role in mycothiol biosynthesis. The invention deacetylases are characterized by a conserved 100 amino acid N-terminal region and three highly conserved histidine-containing regions and by having deacetylase activity as well as amide hydrolase activity. The invention further provides methods for using the invention deacetylases in drug screening assays to determine compounds that inhibit activity. The invention provides for treatment of actino-mycete infections in mammals using antibiotics that inhibit production or activity of MshB and thereby reduce the production of mycothiol and the virulence of the infecting bacteria.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA +1
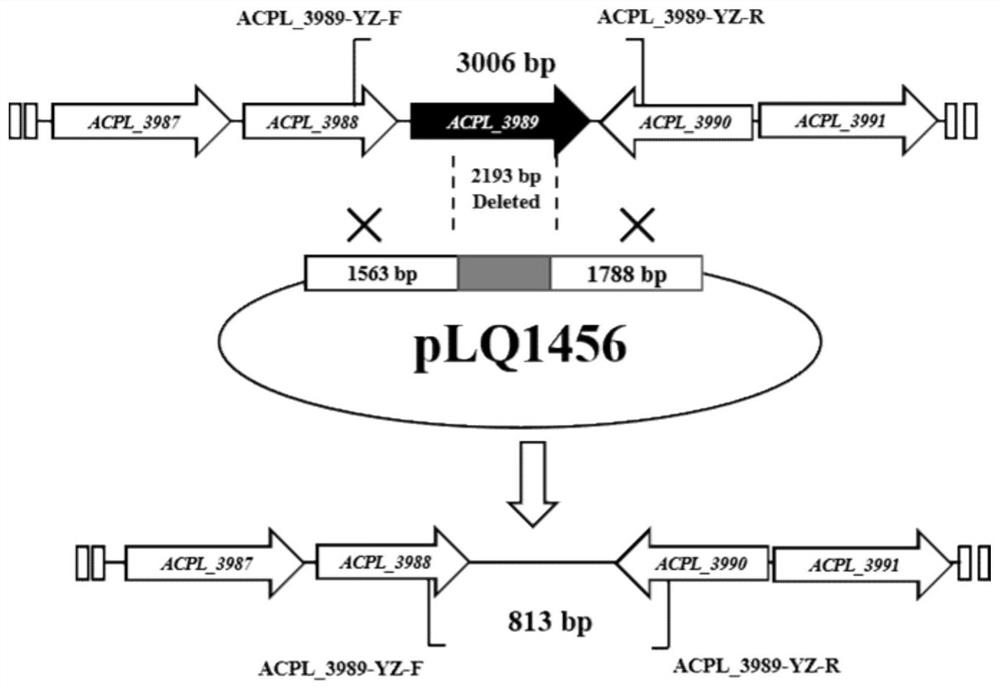
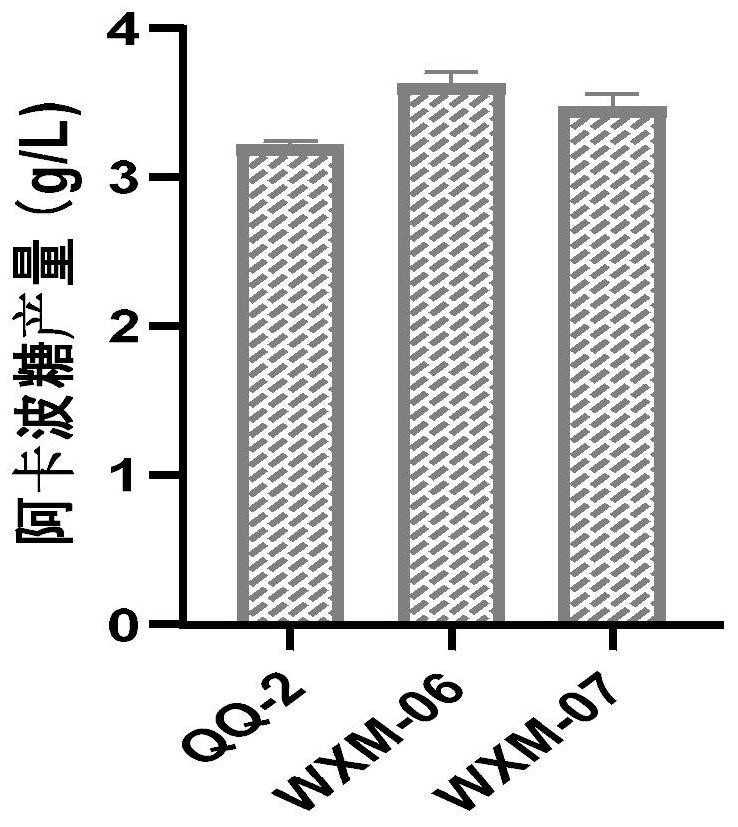
Method for knocking out negative regulatory protein genes to improve fermentation level of acarbose
ActiveCN112522174AIncreased transcription levels of biosynthetic genesImprove fermentation yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiosynthetic genesMicrobiology
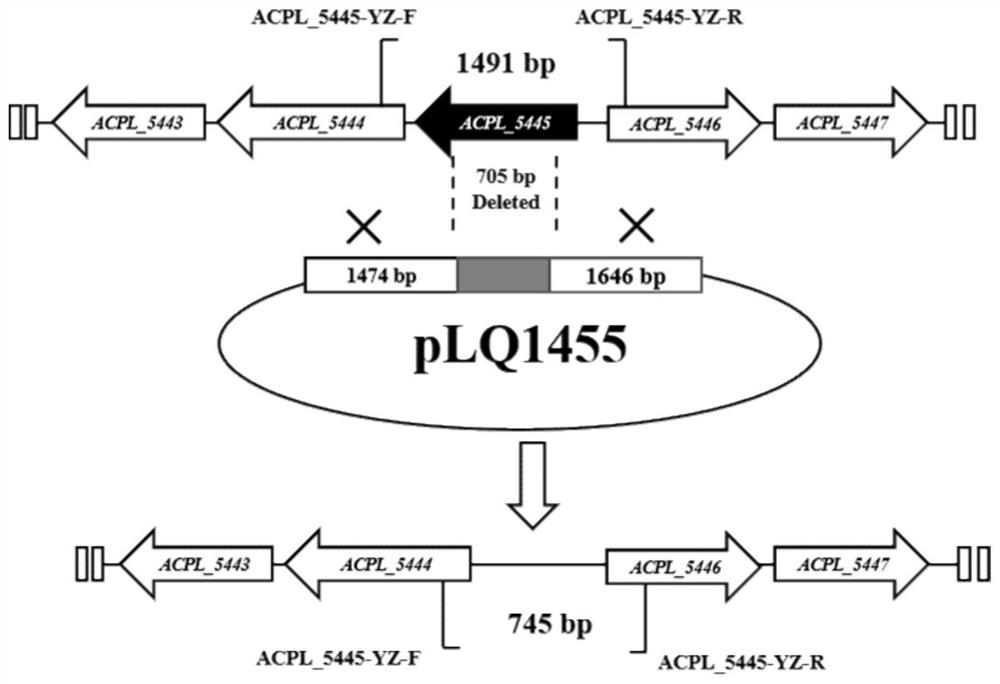
The invention discloses a method for knocking out negative regulatory genes to improve the fermentation level of acarbose. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, the negative regulatory protein genes ACPL_5445 and ACPL_3989 are knocked out from actinoplanes to obtain acarbose high-yield mutant strains. By knocking out the negative regulatory protein genes, the expression of acarbose biosynthetic genes can be promoted, and finally the acarbose yield is obviously increased. Compared with an original strain, the high-yield strains obtained by the invention have the advantages that thefermentation yields are improved by 13% and 8%, and the laboratory shake flask fermentation levels reach 3.62 g / L and 3.47 g / L.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
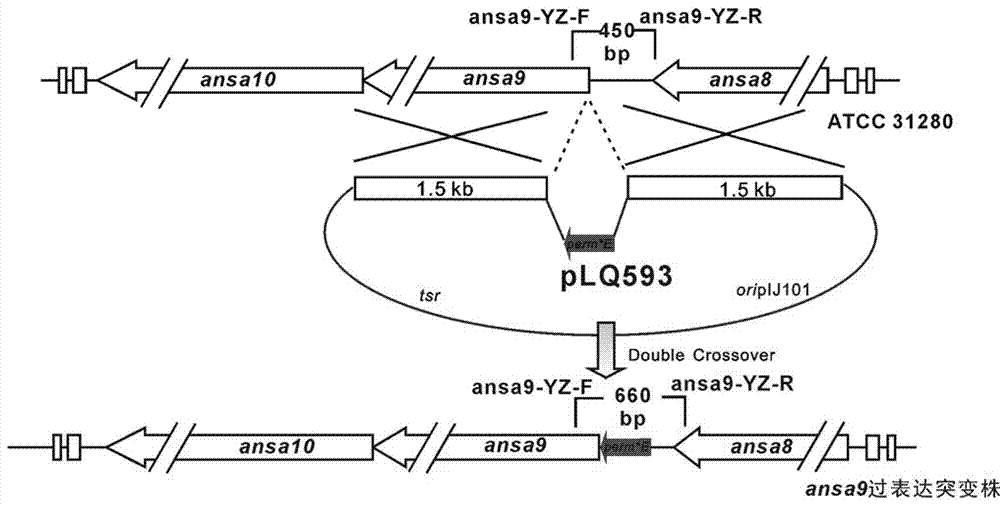
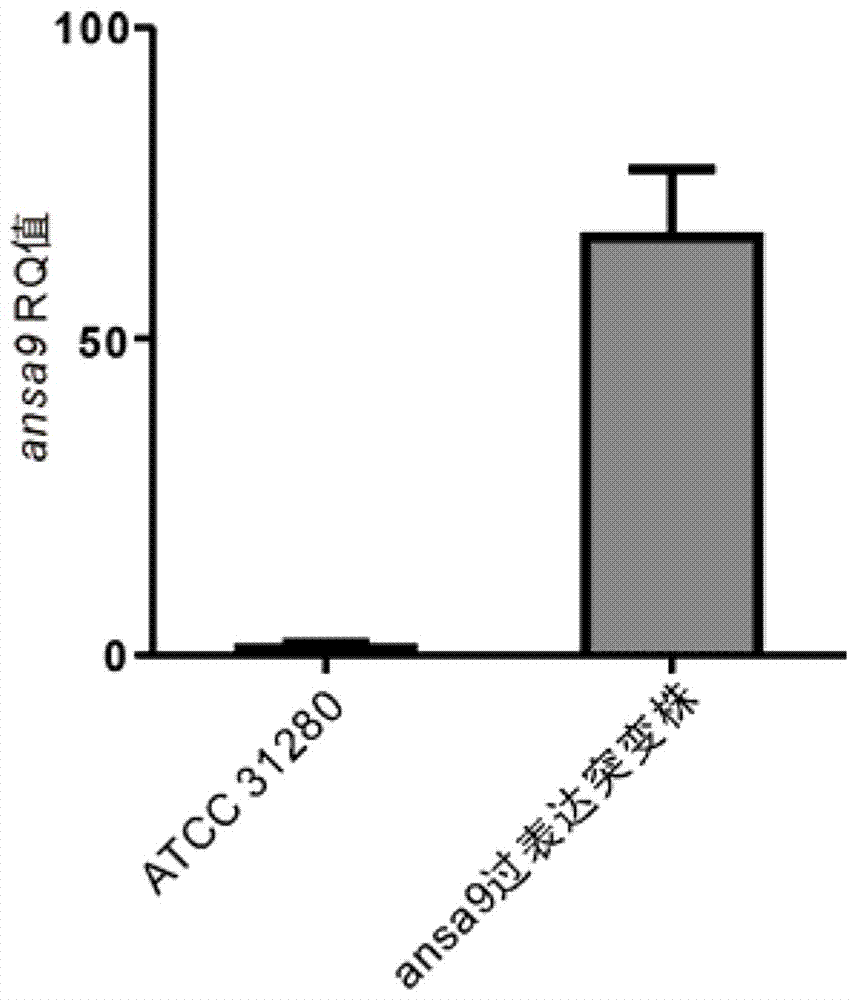
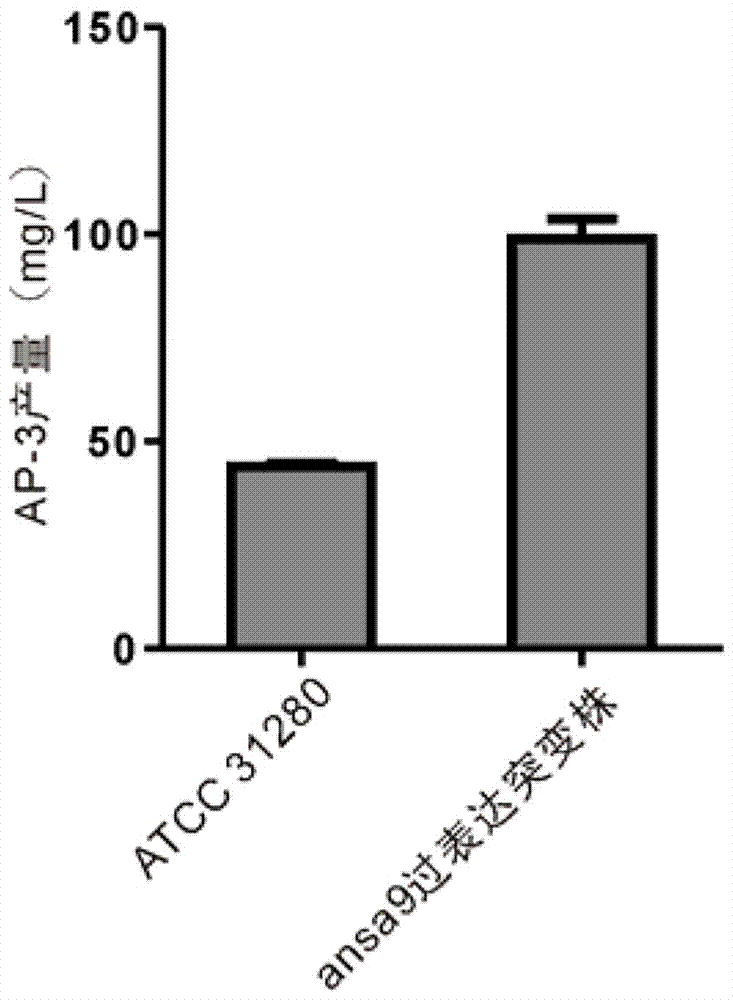
High-yield ansamitocin strain for reinforcing polyketide synthase gene transcriptional level and preparation method thereof
PendingCN107881139AIncrease productionImprove the effect of increasing productionBacteriaStable introduction of DNAEnzyme GeneResistant genes
The invention provides a high-yield ansamitocin strain for reinforcing the polyketide synthase gene transcriptional level and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of biological medicine. The yield of ansamitocin can be increased by improving the rate-limiting enzyme gene expression level in biosynthetic pathway. In the rare actinosynnema pretiosum ATCC31280, the expression level of PKS gene ansa9 is reinforced by utilizing erythrocin resistance gene promoter, the biological synthesizing capacity of actinosynnema pretiosum can be reinforced, and the yield of actinosynnema pretiosum can be increased. The ansamitocin fermenting final yield of engineering strains is increased by about 125 percent in comparison with that of the original strain, and the lab shaking flask level reaches 99mg / L.
Owner:辽宁斯韦尔生物科技有限公司 +1
Methods of use of the enzymes of mycothiol synthesis
InactiveUS7560229B2Low toxicityReduced activityCompound screeningBiocideBacteroidesVirulent characteristics
The present invention utilizes three families of bacterial enzymes, which play a key role in mycothiol biosynthesis. The three families are bacterial cysteine:glucosaminyl inositol ligases (MshC) with catalytic ligase activity for ligation of glucosaminyl inositol and cysteine, bacterial acetyl-CoA:Cys-GlcN-Ins acetyltransferases (MshD) with catalytic activity for addition of an acetyl group to Cys-GlcN-Ins and bacterial MshA glycosyltransferase with catalytic activity for production of GlcNAc-Ins. The invention provides methods for using the mycothiol biosynthesis ligases, acetyltransferases or glycosyltransferases in drug screening assays to determine compounds that inhibit activity. The invention provides for treatment of actinomycete infections in mammals using antibiotics that inhibit production or activity of the enzymes of mycothiol biosynthesis, in particular MshC, MshD or MshA, and thereby reduce the production of mycothiol and the virulence of the infecting bacteria. Additionally, the invention provides a live mutant with a genome containing a modification in an endogenous enzyme of mycothiol biosynthesis gene. The invention also provides an expression vector comprising polynucleotides of mshA, mshB, mshC and mshD.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
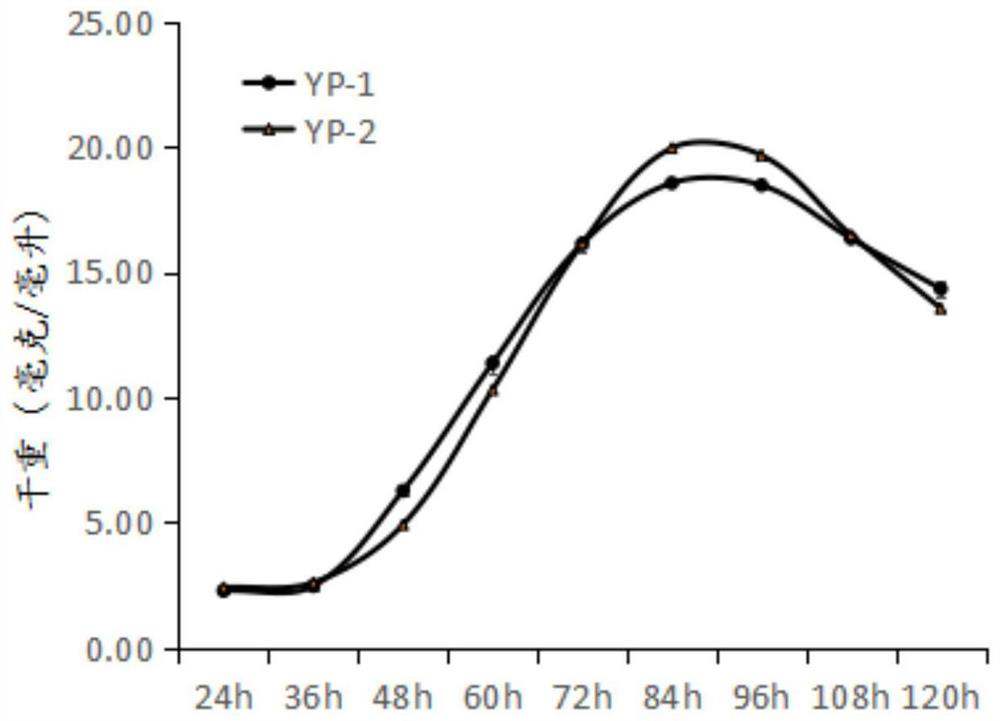
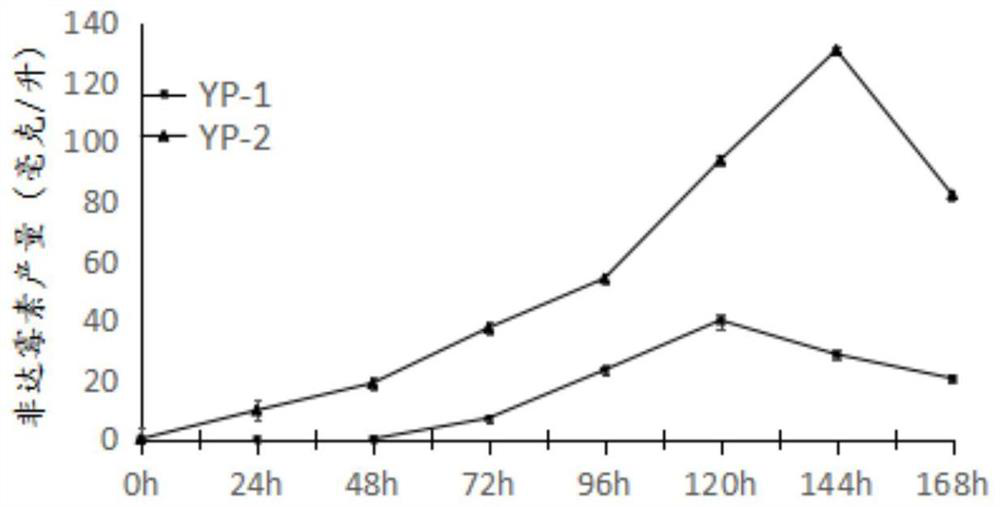
A kind of fidaxomicin genetically engineered bacteria and its construction method and application
ActiveCN108841769BAvoid buyingEasy to operateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesClostridium difficile infectionsActinoplanes deccanensis
The invention discloses a high-yield fidaxomicin genetically engineered bacterium Actinomycetes deccanensis YP‑2 (Actinoplanes deccanensis YP‑2) and a construction method. Among the Actinomycetes Deccanum YP‑1, the genetically engineered Actinomycetes YP‑2 with a high yield of fidaxomicin was screened out, and the yield was 400% to 500% higher than that of the original strain, up to 130mg / L, has a good application prospect. The method of the invention is efficient, accurate and easy to operate, and provides a new research method for the construction of the efficient biosynthesis pathway of the actinomycete drug. The fidaxomicin genetically engineered bacterium Actinomyces deccanum YP‑2 can be used in the preparation of medicines for treating diarrhea caused by Clostridium difficile infection.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Deleted high-yield ansamitocin strain and preparation method thereof
PendingCN107881138AEliminate competitionIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAnsamitocinsWild type strain
The invention provides a deleted high-yield ansamitocin strain and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of biological medicine. The ansamitocin fermenting level is improved based on the N-glycosyltransferase expression gene of inactivated ansamitocin, and the N-glycosyltransferase expression gene ansa30 inactivated in rare actinosynnema pretiosum ATCC31280, which has 97%homology with the asm25 gene in the rare actinosynnema pretiosum ATCC31565, so that the distribution of ansamitocin bio-synthesis by the method can be reduced, and the ansamitocin yield can be increased. The fermentation final yield of the mutant strain NXJ-22 ansamitocin is increased by 68 percent in comparison with that of a wild strain, and the lab shake flask level reaches 74mg / L.
Owner:辽宁斯韦尔生物科技有限公司 +1
An improved process for the preparation of fidaxomicin
The present invention provides an improved process for the preparation of fidaxomicin by culturing Actinoplanes deccanensis in the culture medium of the invention wherein the fidaxomicin is produced in a yield of greater than 500 mg / L broth. The present invention also provides a whole broth extraction process for the isolation of fidaxomicin from the fermentation broth. The present invention also provides fidaxomicin having purity of greater than 97% area by HPLC.
Owner:CONCORD BIOTECH
Preparation method of high purity ramoplanin single components
ActiveCN102838662BEfficient removalHigh yieldPeptide preparation methodsChromatographic separationMicrosphere
The invention discloses a method of utilizing an Actinoplanes sp. fermentation culture material to prepare three ramoplanin single components. The method includes: conducting decoloration on a ramoplanin fermentation solution through macroporous decolorization resin, then carrying out macroporous resin adsorption, desorption as well as concentration so as to obtain a ramoplanin crude extract containing the three single components: A1, A2, and A3; and dissolving the crude extract with a solvent, then performing chromatographic separation by means of a polymer microsphere, thus obtaining the products of three high purity ramoplanin single components A1, A2 and A3. The invention has the advantage that when using the polymer microsphere to perform chromatographic separation on the product, the sample treatment amount is large, and the obtained single components have high purity. As the price of a polymer microsphere medium is 30% of that of the reverse phase silica gel C18, and the separation effect is equivalent, the preparation cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:NCPC NEW DRUG RES & DEV
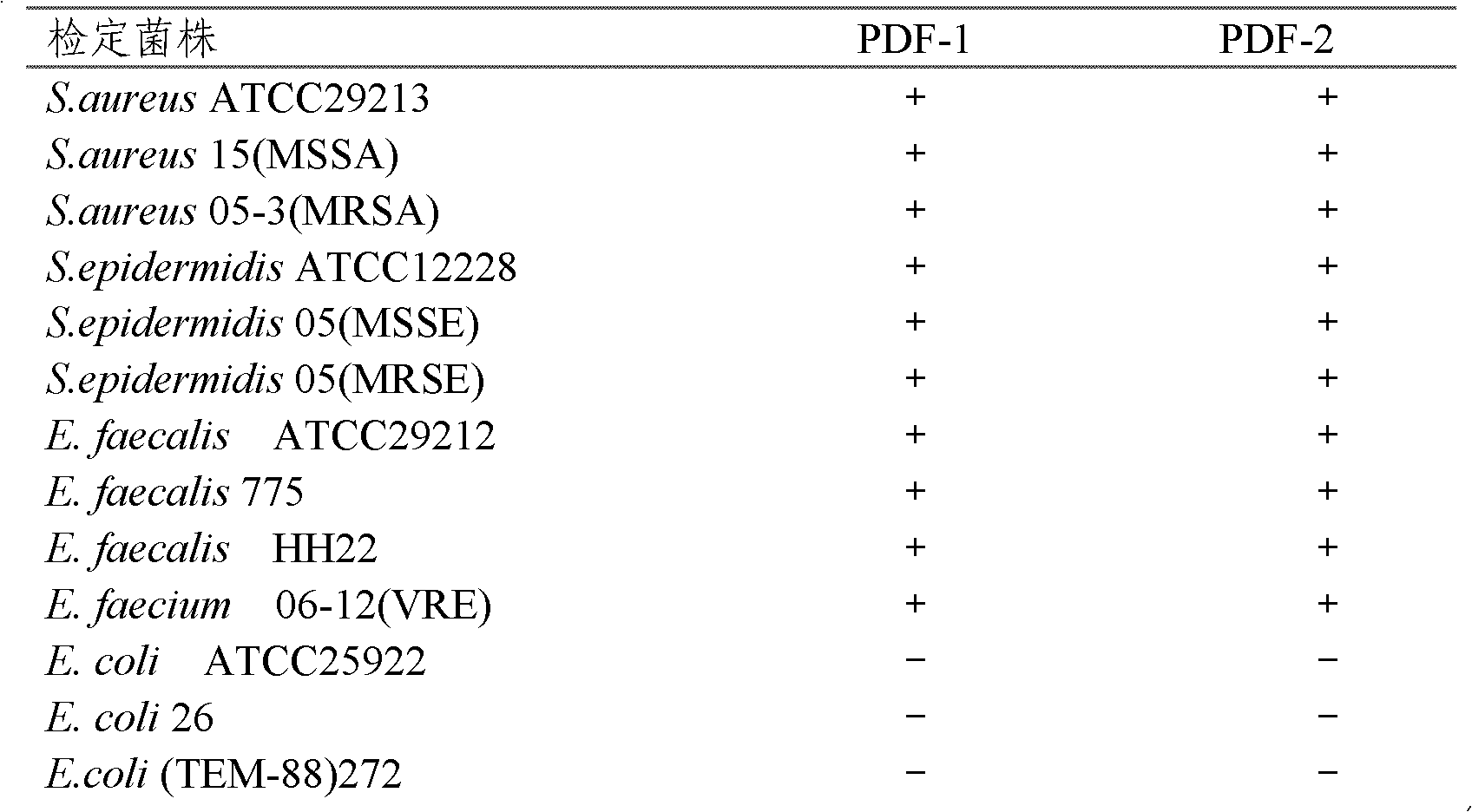
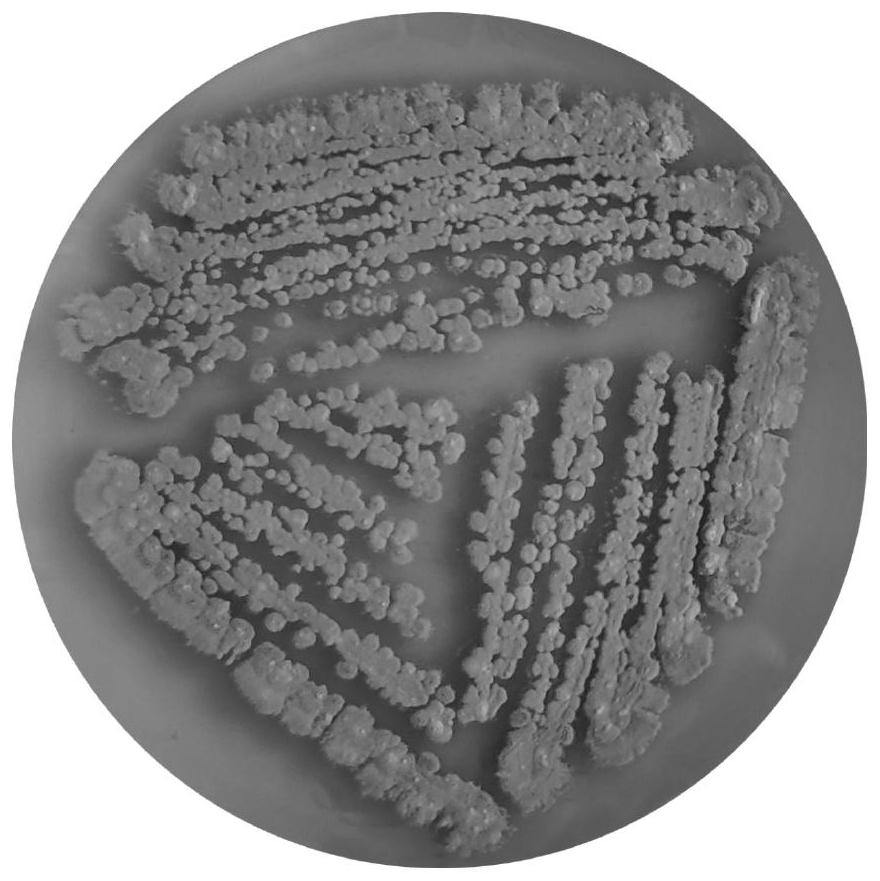
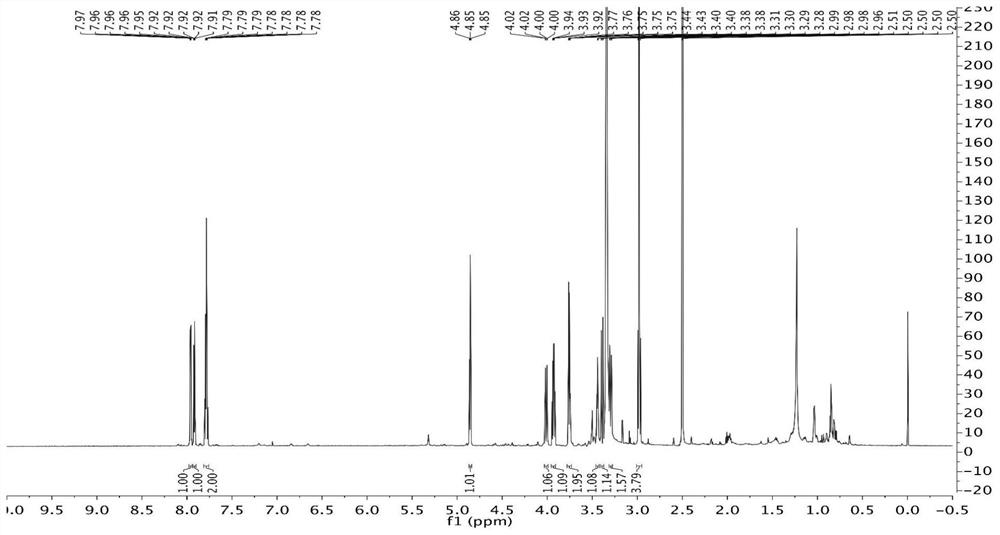
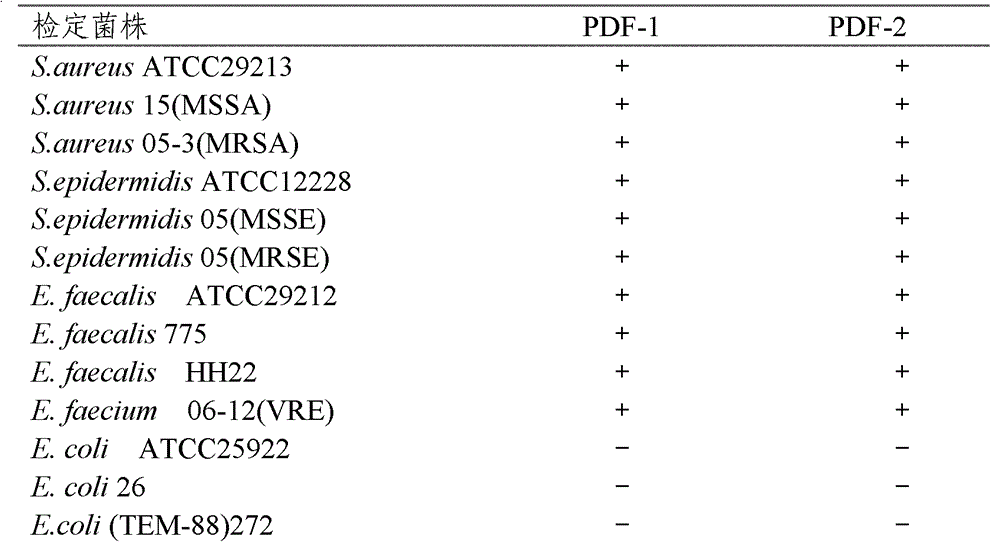
Two Actinoplanaceae strains and antibacterial application thereof
The invention provides two Actinoplanaceae strains and antibacterial application thereof. The Actinoplanaceae strains, Actinoplanes sp. PDF-1 and PDF-2, have preserving numbers of CGMCC No. 4692 and CGMCC No. 4693. The strains have effect in resisting bacteria, especially resisting drug-resistant bacteria. The strains provided by the invention are renewable microbe resources, can obtain products having activity in resisting drug-resistant bacteria, are suitable for large-scale industrial fermentation production, and have environmental pollution smaller than chemical synthesis.
Owner:MEDICINE & BIOENG INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Crystalline forms of Actinomycin D for treatment of cancer
Owner:TRANSGENEX NANOBIOTECH
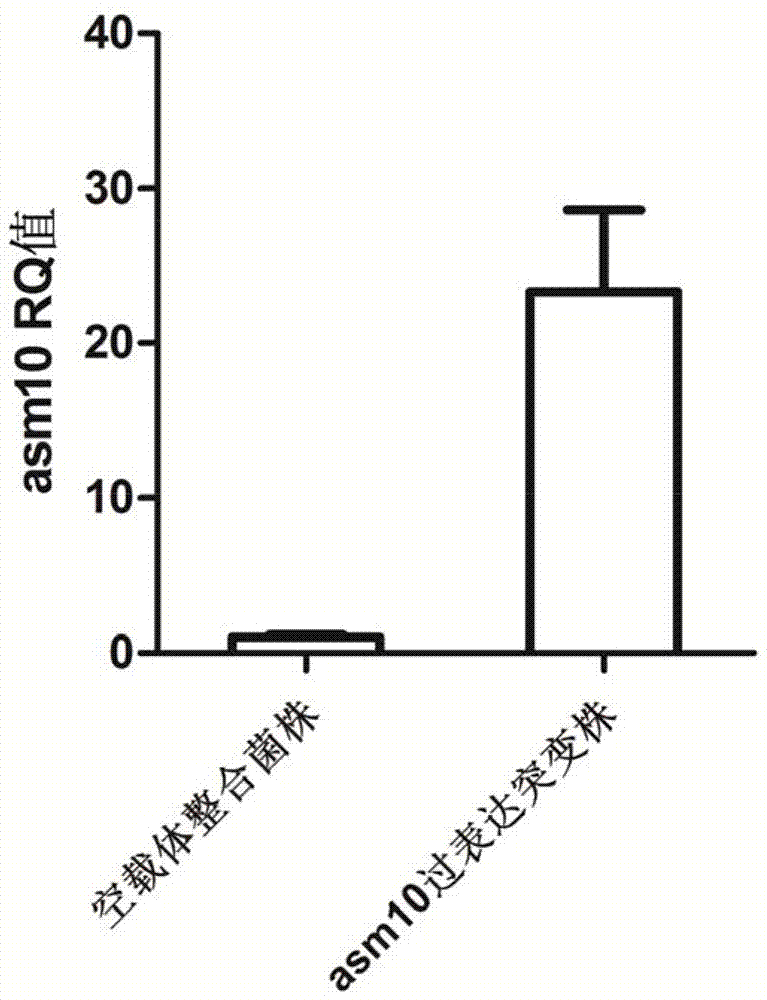
High-yield ansamitocin strain for reinforcing transcriptional level and preparation method thereof
PendingCN107881137AIncrease productionImprove fermentation yieldBacteriaTransferasesEnzyme GeneMethyltransferase
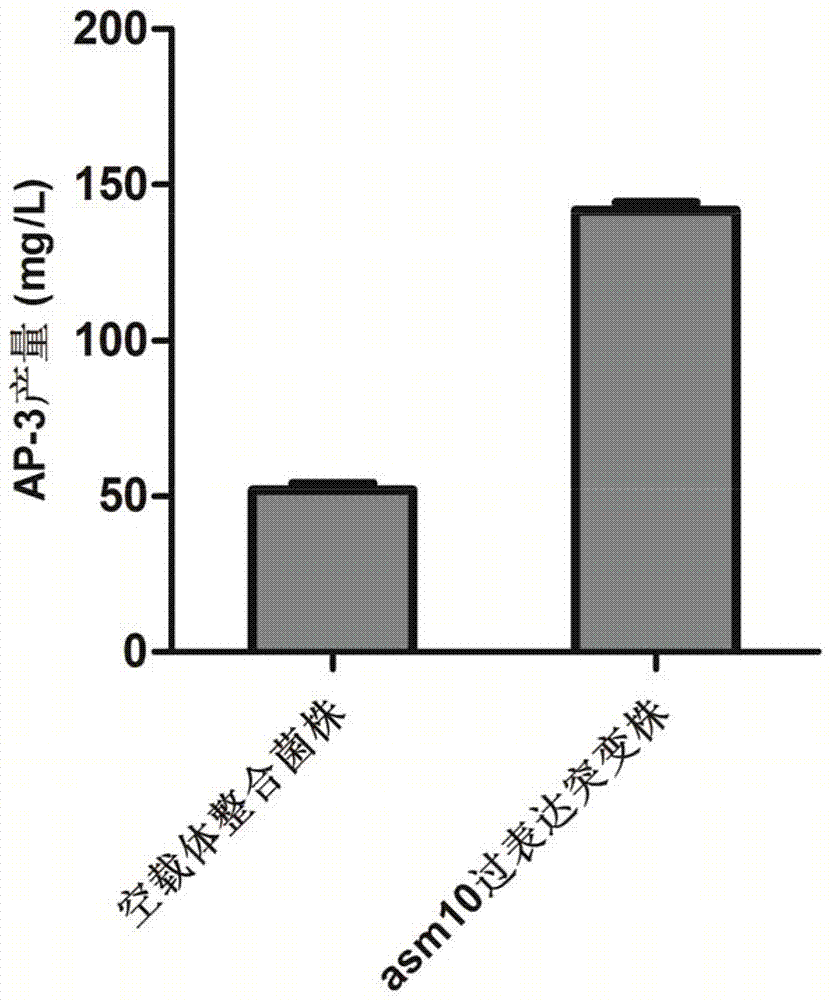
The invention provides a high-yield ansamitocin strain for reinforcing transcriptional level and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of biological medicine. The yield of ansamitocin can be increased by improving the rate-limiting enzyme gene expression level in biosynthetic pathway. The gene asm10 is modified in the deleted mutant strain NXJ-22 of the glycosyl transferase expression gene of rare actinosynnema pretiosum ATCC31280 after overexpression of strong promoter kasOp*, the methyltransferase activity can be reinforced, and the yield of ansamitocin can be improved. The ansamitocin fermenting final yield of engineering strains is increased by about 173 percent in comparison with that of a control strain, and the lab shaking flask level reaches 141.8mg / L.
Owner:辽宁斯韦尔生物科技有限公司 +1
Alpha-amylase inhibitor producing strain and screening method thereof
ActiveCN102127508BEasy to operateReliable resultsMicroorganismsMicroorganism based processesAmylase inhibitorsScreening method
The invention discloses an alpha-amylase inhibitor producing strain, i.e. Actinoplanes sp.ZJB-08196 preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection located in Wuhan university, Wuhan Province, China on Feb. 16th, 2009 with the preservation number of CCTCC No. M209022. The alpha-amylase inhibitor is acarbose. The invention also discloses a screening method of the alpha-amylase inhibitor producing strain. The screening method provided by the invention is simple and effective, can screen a great amount of samples in a short time, has high sensitivity, reduces the long processes for processing and analyzing samples through HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography), and the like and improves detection efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +2
Method for enhancing positive regulatory protein gene expression to increase acarbose fermentation level
ActiveCN112592878AImprove fermentation yieldIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiosynthetic genesMicrobiology
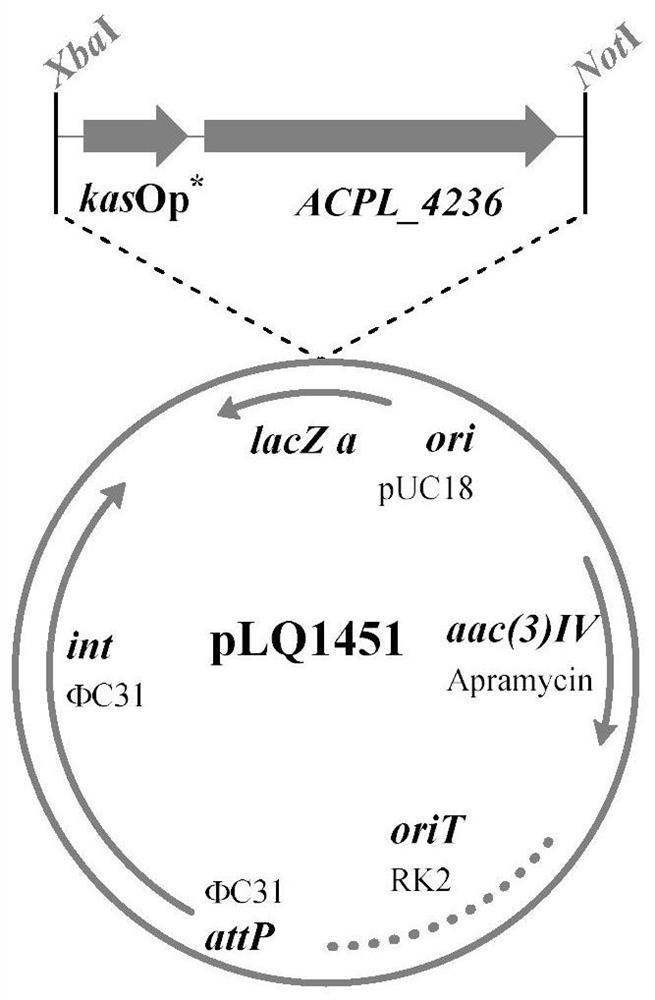
The invention discloses a method for enhancing positive regulatory protein gene expression to improve the acarbose fermentation level. In actinoplanes, positive regulatory protein genes ACPL_1889, ACPL_4236, ACPL_7303, ACPL_6479 and ACPL_8104 are respectively subjected to intensified expression by utilizing a strong promoter kasOp*, so that an acarbose high-yield mutant strain is obtained. Enhancement on the expression of the positive regulation protein genes can promote the expression of acarbose biosynthetic genes, and finally, obviously improve the acarbose yield. Compared with an originalstrain, the fermentation yields of the high-yield strains obtained by the invention are respectively improved by 25%, 18%, 26%, 22% and 15%, and the laboratory shake flask fermentation levels respectively reach 3.29g / L, 3.11g / L, 3.32g / L, 3.21g / L and 3.03g / L.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for Improving the Biosynthetic Yield of Ansamitocin p-3
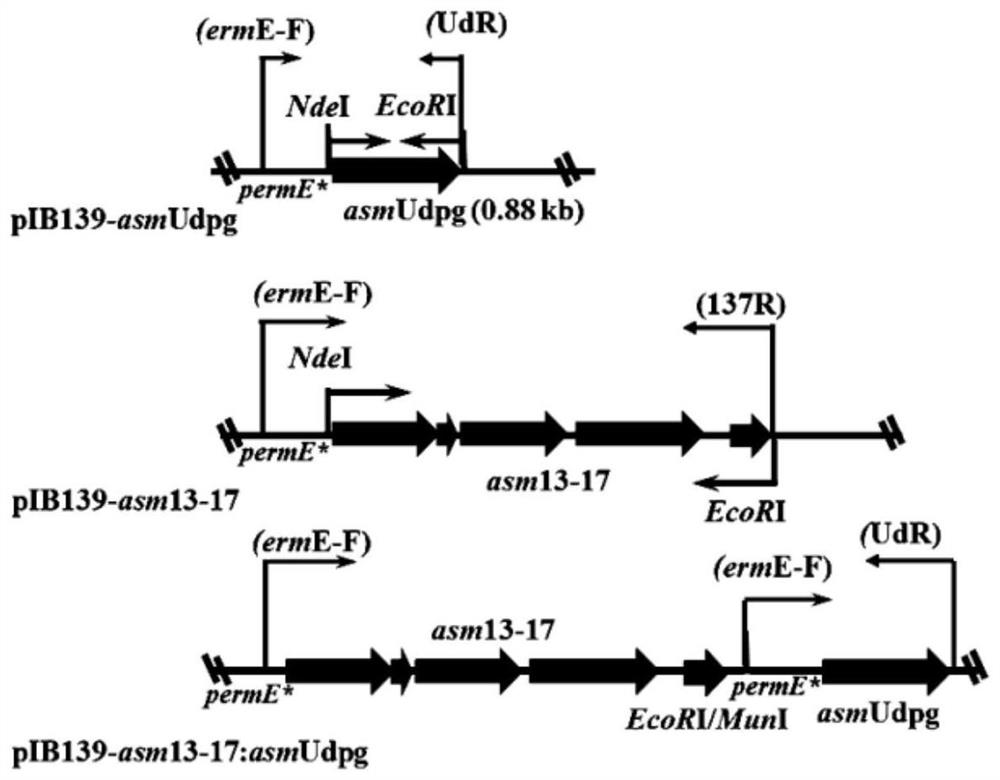
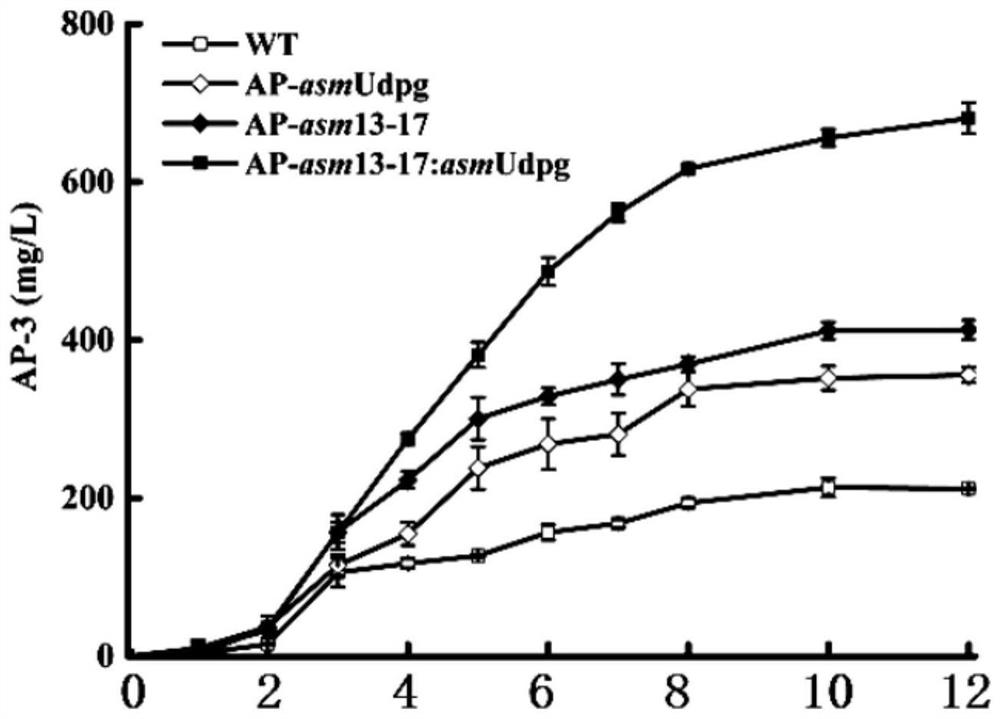
ActiveCN108456689BIncrease supplyIncrease productionFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGeneticsBiochemistry
A method for improving the biosynthetic yield of ansamitocin P-3, by constructing the expression plasmid pIB139-asm13-17 of the asm13-17 gene, constructing the expression plasmid pIB139-asmUdpg of the asmUdpg gene, and constructing the co-expression of the asm13-17 gene and asmUdpg The integrated expression plasmid pIB139‑asm13‑17:asmUdpg corresponding to the gene, and the above expression plasmids are respectively transferred into Actinosynnema pretiosum precious orange (Actinosynnema pretiosum), to achieve the improvement of biosynthetic expression, the present invention can significantly improve Fermentation levels of ansamitocin P‑3.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Novel crystalline forms of actinomycin d for treatment of cancer
ActiveUS20210053963A1Antibacterial agentsOrganic chemistry methodsPharmaceutical drugActinoplanes sp.
Owner:TRANSGENEX NANOBIOTECH
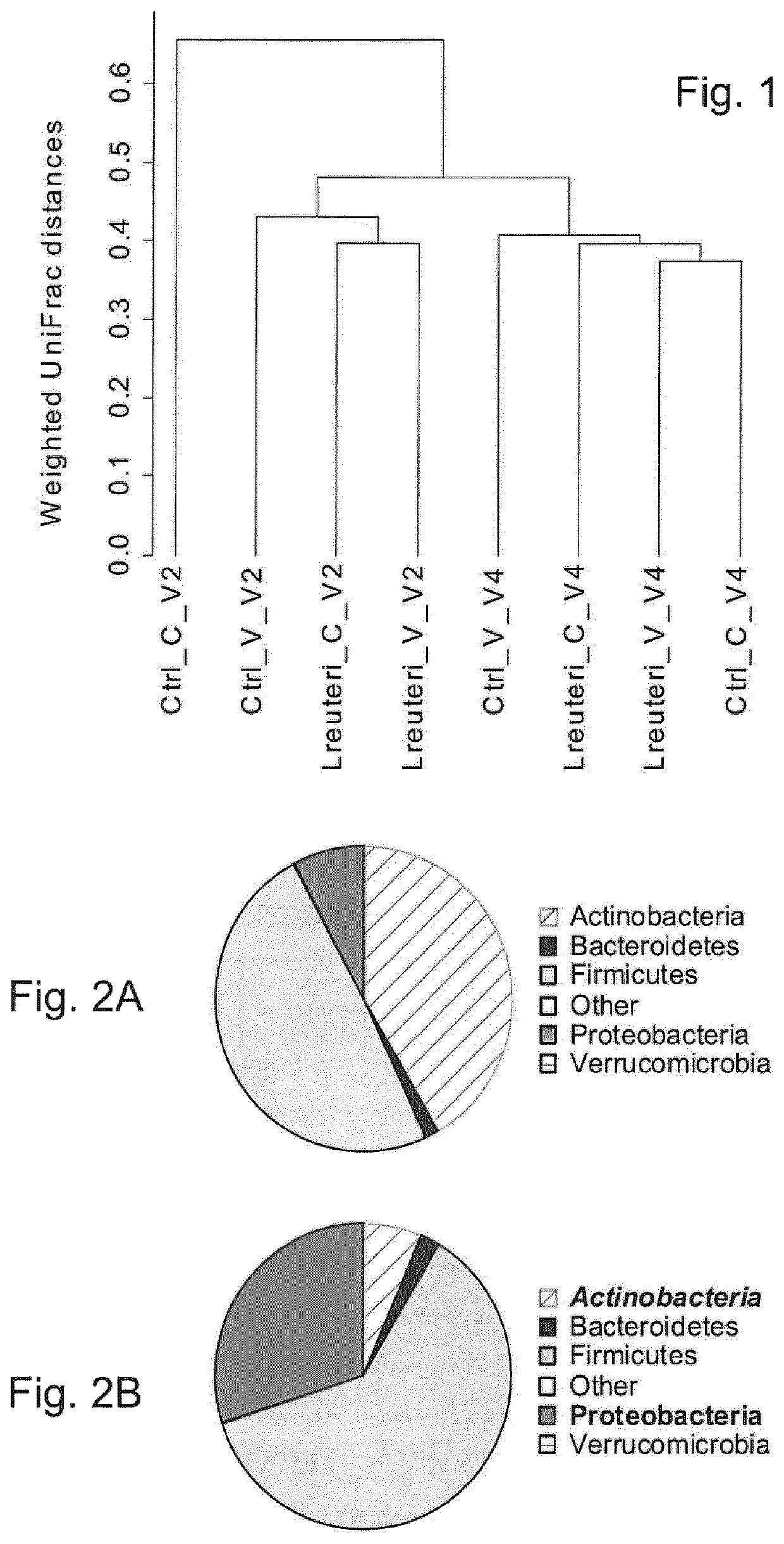
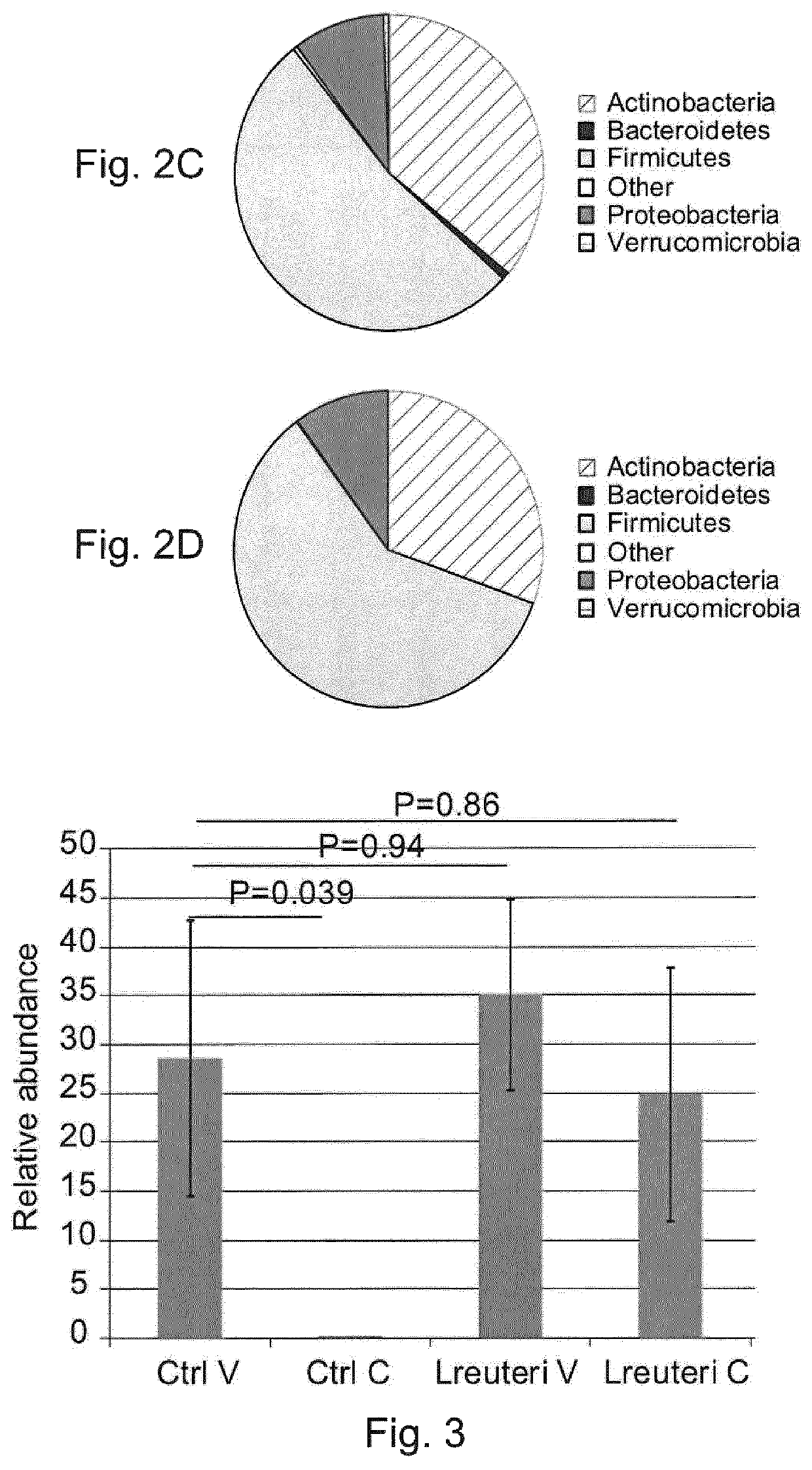
Use of L. reuteri for recovery of microbiota dysbiosis in early life
ActiveUS11369646B2Organic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderFunctional diarrheaPancreatic hormone
The invention concerns Lactobacillus reuteri for use in the prevention or treatment of microbiota dysbiosis, in particular, decreased levels of Actinobacteria and increased levels of Proteobacteria, in young mammals and in the prevention or treatment of disorders associated therewith. The microbiota dysbiosis may have been cause by numerous factors including being born by caesarean section, exposure to antibiotics in utero or after birth, or, parenteral feeding, hospitalizing, psychological stress or by gastrointestinal dysfunctions. The disorders that may be treated or prevented by preventing or treating microbiota dysbiosis include propensity to infection, allergy, type I diabetes mellitus, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, celiac disease, peripheral and central adiposity, obesity, necrotizing enterocolitis, inflammatory bowel disease, such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, and functional gastrointestinal disorders such as IBS, functional diarrhea, functional constipation, recurrent abdominal pain, and dyspepsia.
Owner:BIOGAIA AB
Methods of use of the enzymes of mycothiol synthesis
InactiveUS20060183116A1Reduced virulenceReduced activityOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesChemistryAcetyltransferase
The present invention utilizes three families of bacterial enzymes, which play a key role in mycothiol biosynthesis. The three families are bacterial cysteine:glucosaminyl inositol ligases (MshC) with catalytic ligase activity for ligation of glucosaminyl inositol and cysteine, bacterial acetyl-CoA:Cys-GlcN-Ins acetyltransferases (MshD) with catalytic activity for addition of an acetyl group to Cys-GlcN-Ins and bacterial MshA glycosyltransferase with catalytic activity for production of GlcNAc-Ins. The invention provides methods for using the mycothiol biosynthesis ligases, acetyltransferases or glycosyltransferases in drug screening assays to determine compounds that inhibit activity. The invention provides for treatment of actinomycete infections in mammals using antibiotics that inhibit production or activity of the enzymes of mycothiol biosynthesis, in particular MshC, MshD or MshA, and thereby reduce the production of mycothiol and the virulence of the infecting bacteria. Additionally, the invention provides a live mutant with a genome containing a modification in an endogenous enzyme of mycothiol biosynthesis gene. The invention also provides an expression vector comprising polynucleotides of mshA, mshB, mshC and mshD.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Sponge-derived actinomycete and preparation method and application of novel sulfur-containing alkaloid produced by sponge-derived actinomycete
The invention discloses a sponge-derived actinomycete and a preparation method and application of novel sulfur-containing alkaloid produced by the sponge-derived actinomycete. According to the present invention, a biological activity test results show that a compound 1 and a compound 2, which are separated from the fermentation product of the sponge-derived actinomycete Nocardiopsis dassonvillei SCSIO 40065, have antibacterial and antitumor activity, such that the compound 1 and the compound 2 can be used for the preparation of antibacterial drugs and antitumor drugs.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Two Strains of Motile Actinomycetes and Their Application in Anti-bacteria
The invention provides two Actinoplanaceae strains and antibacterial application thereof. The Actinoplanaceae strains, Actinoplanes sp. PDF-1 and PDF-2, have preserving numbers of CGMCC No. 4692 and CGMCC No. 4693. The strains have effect in resisting bacteria, especially resisting drug-resistant bacteria. The strains provided by the invention are renewable microbe resources, can obtain products having activity in resisting drug-resistant bacteria, are suitable for large-scale industrial fermentation production, and have environmental pollution smaller than chemical synthesis.
Owner:MEDICINE & BIOENG INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
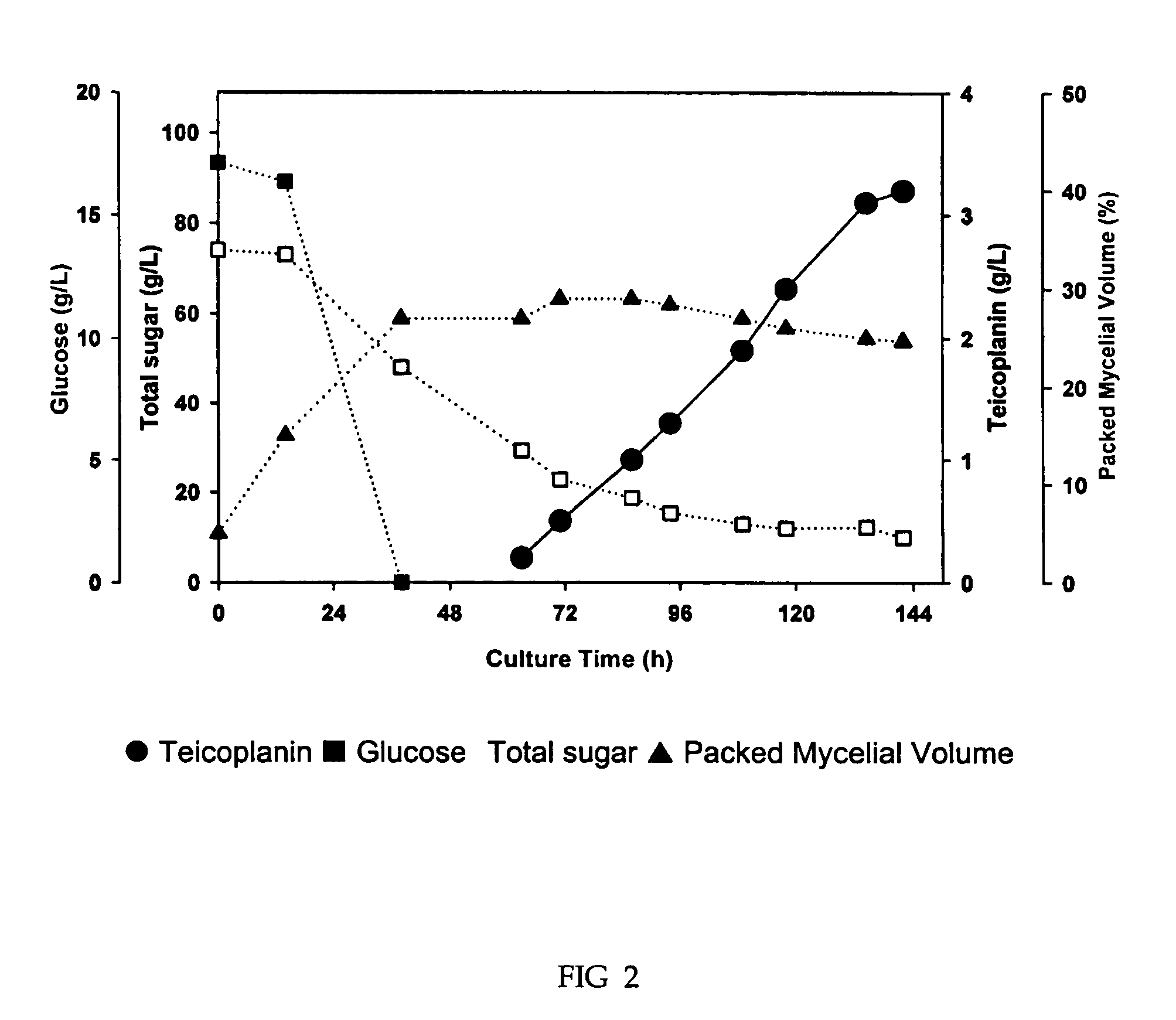
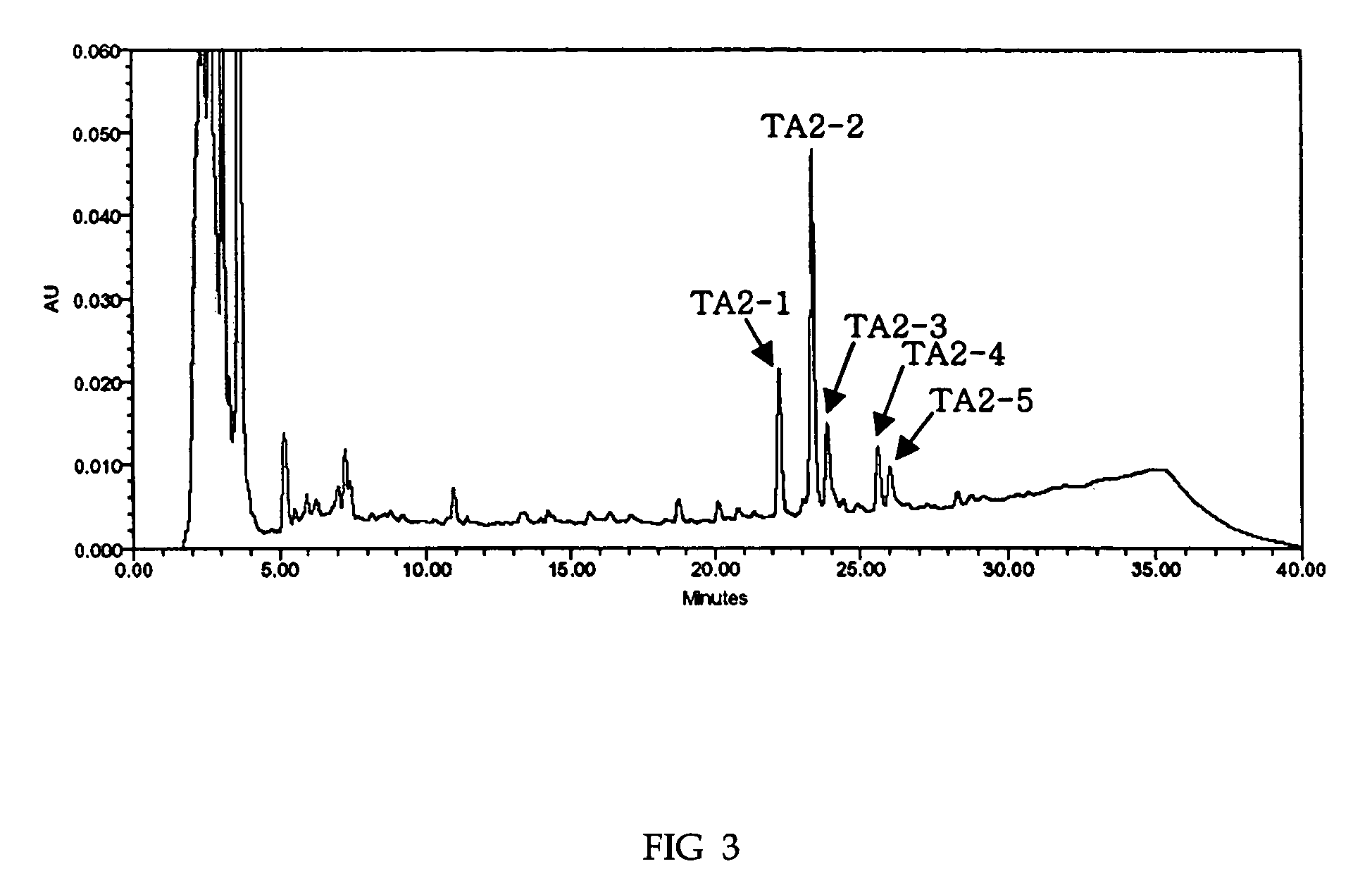
Process for the production of teicoplanin
The present invention provides a newly isolated mutant culture of Actinoplanes teichomyceticus BNG 2315. This culture is capable of producing teicoplanin more than 60 times productivity than those reported before (e.g., Actinoplanes teichomyceticus nov. sp. ATCC 31121). The present invention also provides a fermentation process for the production of teicoplanin in an aerobic condition using the mutant strain Actinoplanes teichomyceticus BNG 2315 in a culture-medium comprising carbon sources, nitrogen sources and mineral salts.
Owner:BIOGENE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com