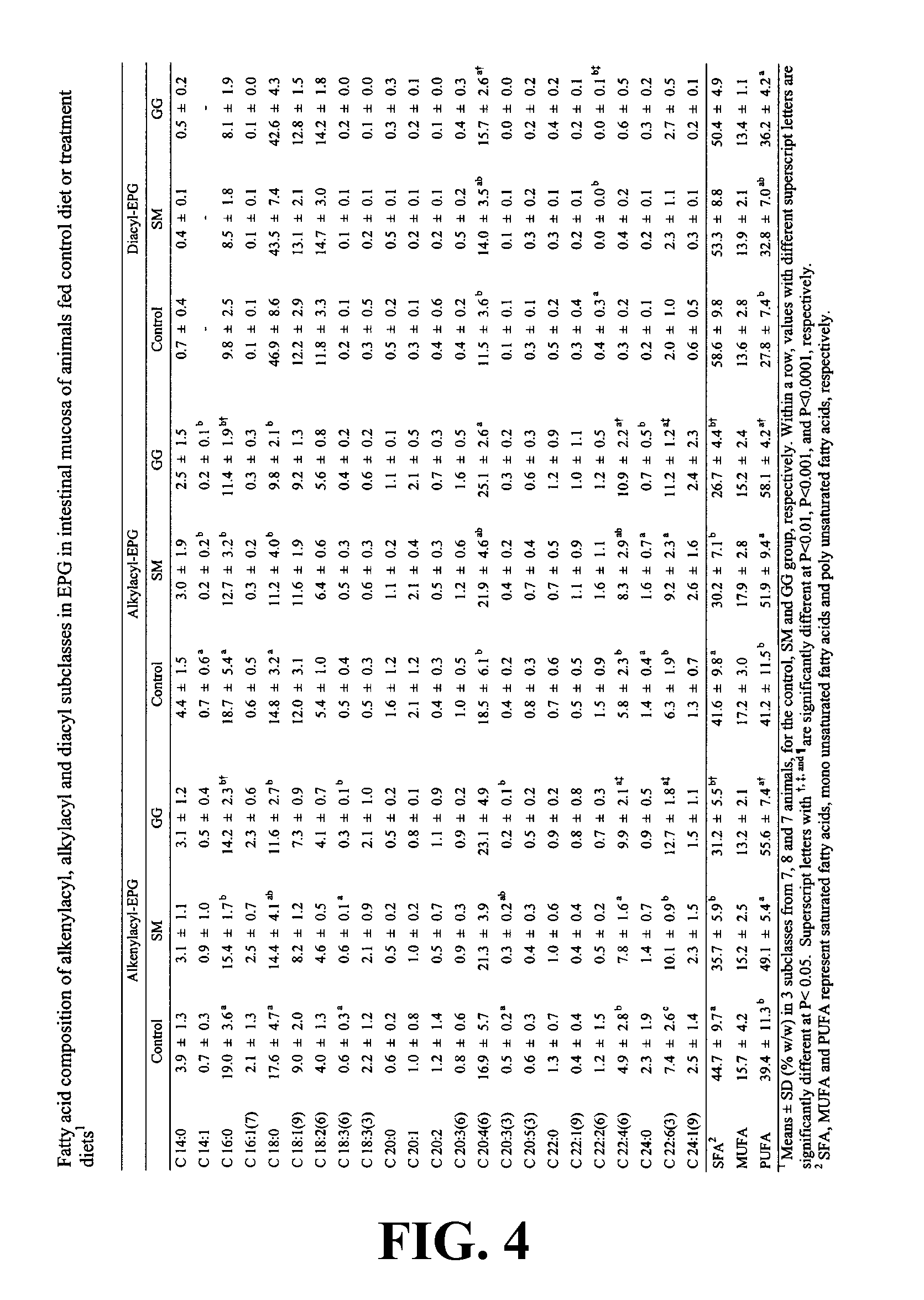
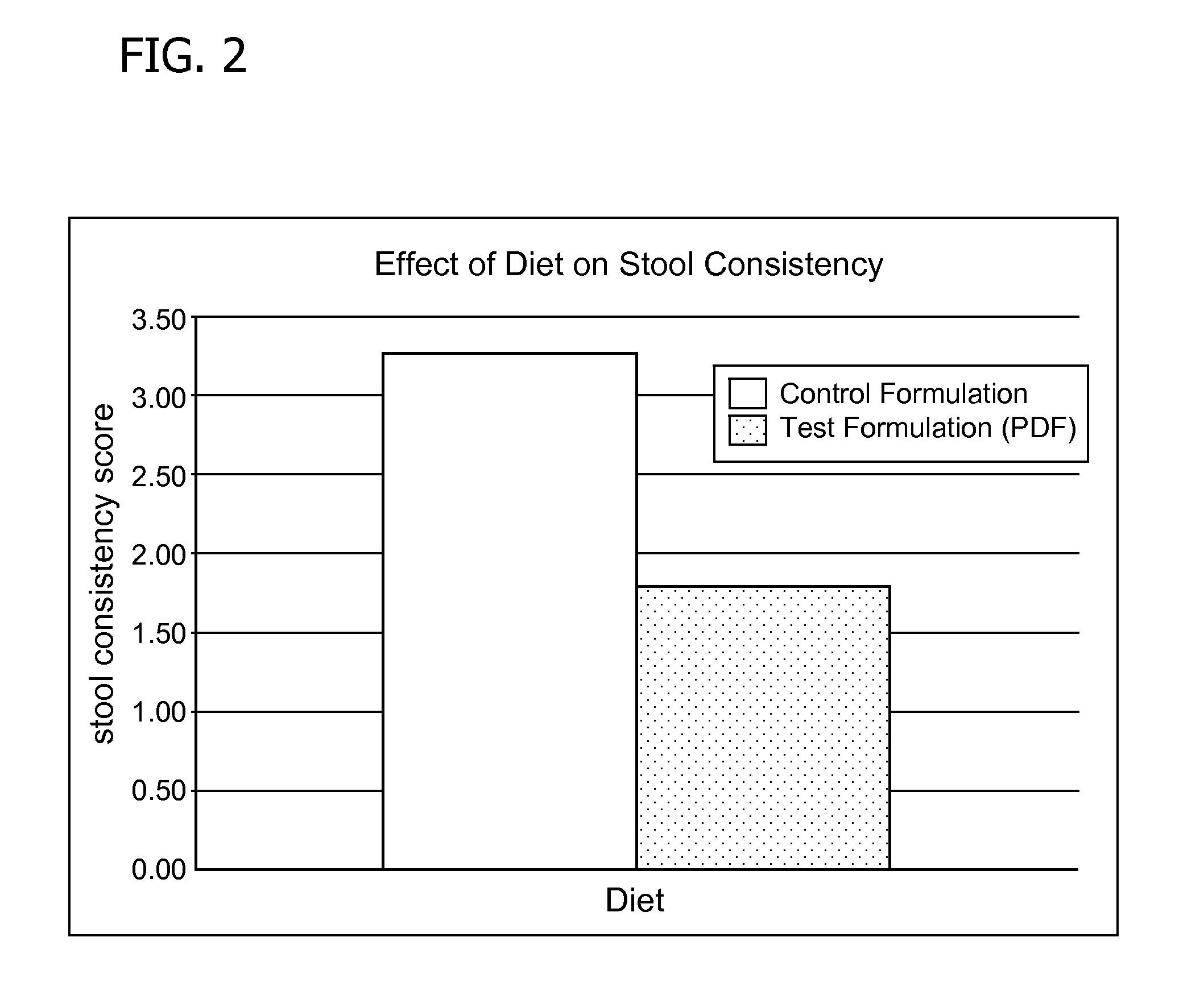
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
89 results about "Necrotizing enterocolitis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a medical condition where a portion of the bowel dies. It typically occurs in newborns that are either premature or otherwise unwell. Symptoms may include poor feeding, bloating, decreased activity, blood in the stool, or vomiting of bile.
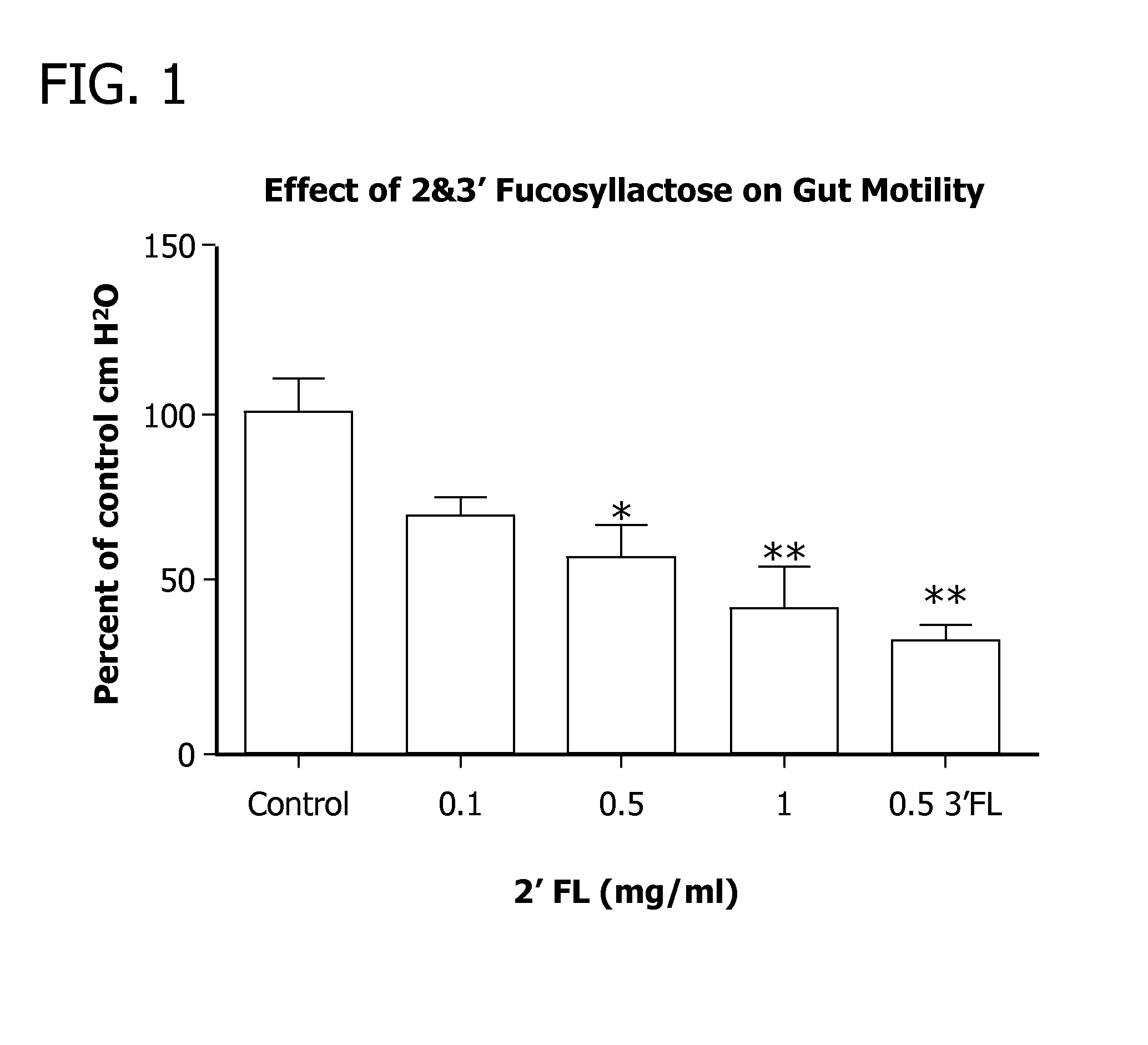
Methods for decreasing the incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis in infants, toddlers, or children using human milk oligosaccharides
ActiveUS20120172319A1Improve immune system systemImprove system enteric nervous systemOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseMorbidity aspects
Disclosed are methods of reducing the incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis in an infant, toddler, or child using nutritional compositions including human milk oligosaccharides. The nutritional compositions including the human milk oligosaccharides are effective in reducing inflammation and the incidence of inflammatory diseases.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
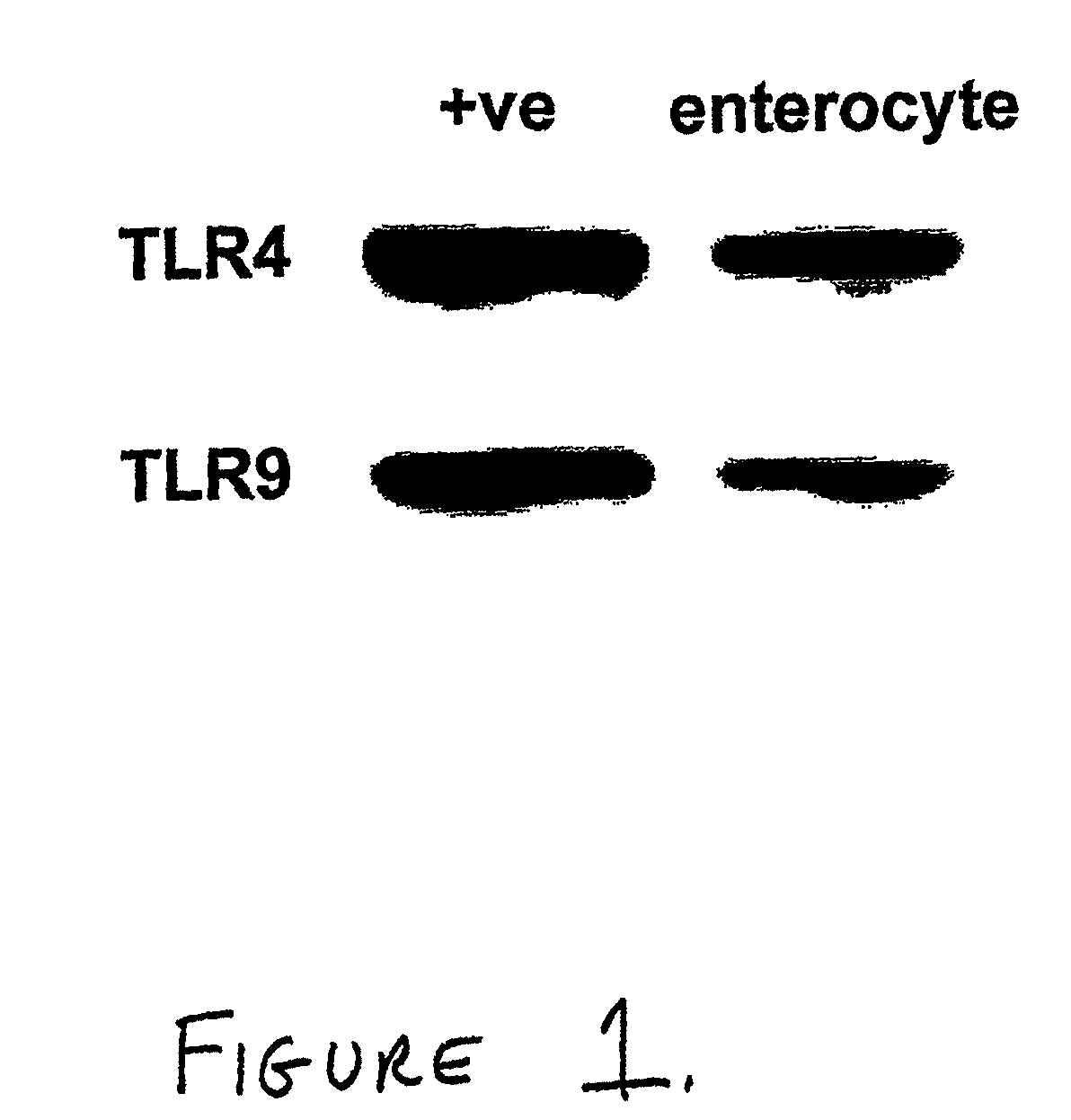
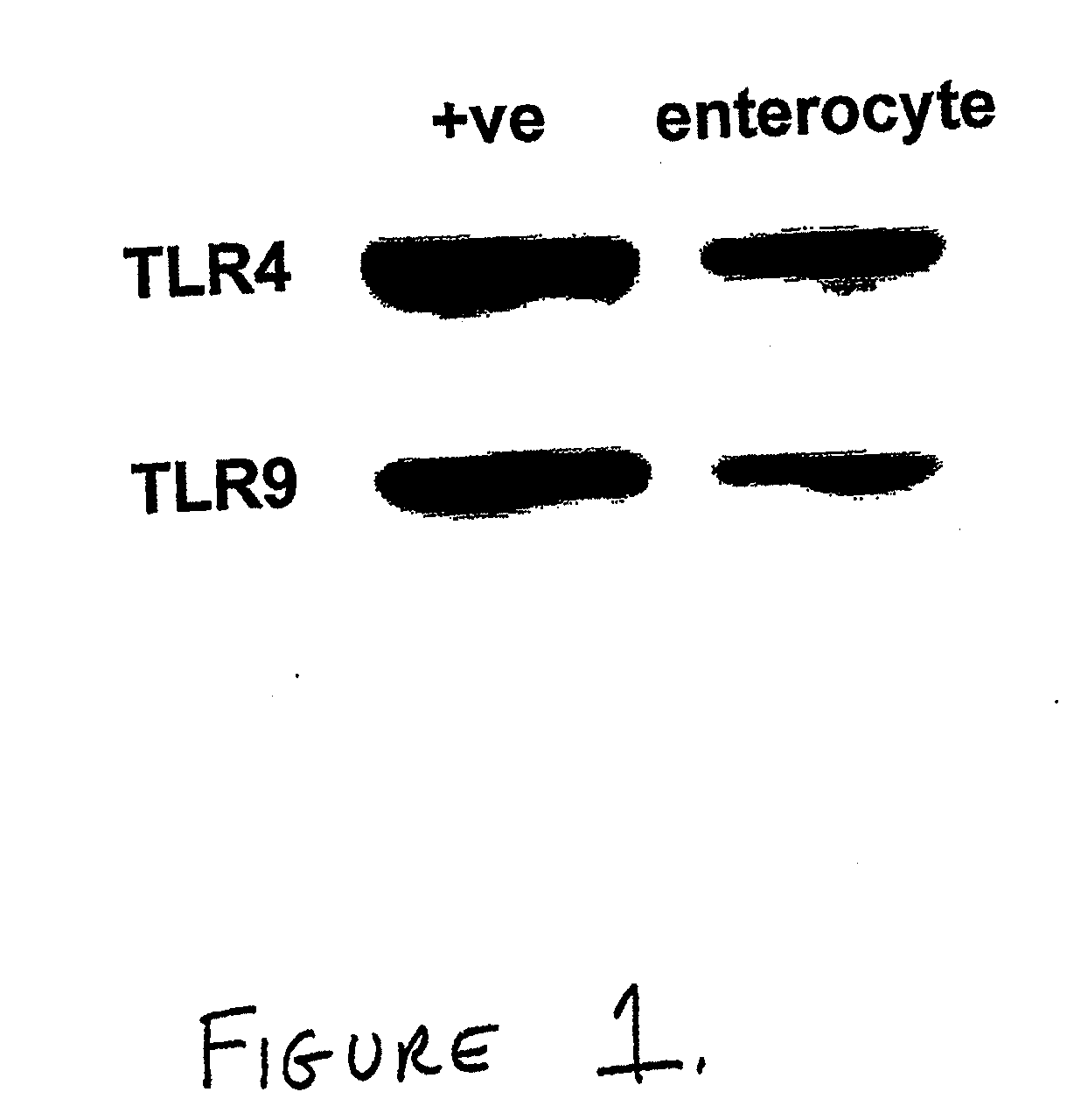
Use of toll-like receptor-9 agonists, toll-like receptor-4 antagonists, and/or nuclear oligomerization domain-2 agonists for the treatment or prevention of toll-like receptor-4-associated disorders
ActiveUS8188058B2Reduce marksReduce signalingAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiseaseNK1 receptor antagonist
The present invention relates to the use of a TLR9 agonist and / or a TLR4 antagonist and / or a NOD2 agonist for treatment or prevention of disorders involving TLR4 activation, such as systemic sepsis and necrotizing enterocolitis.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
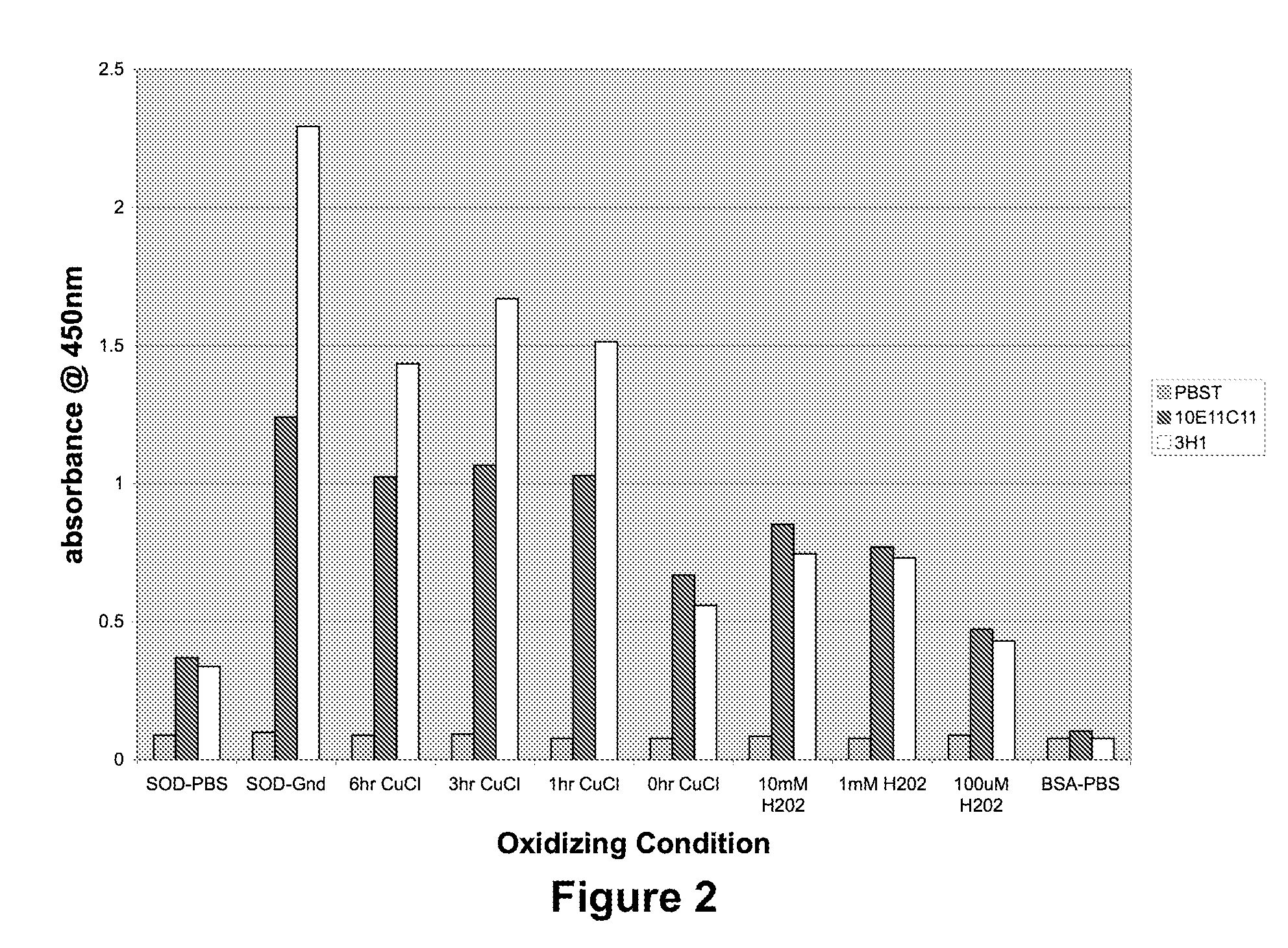
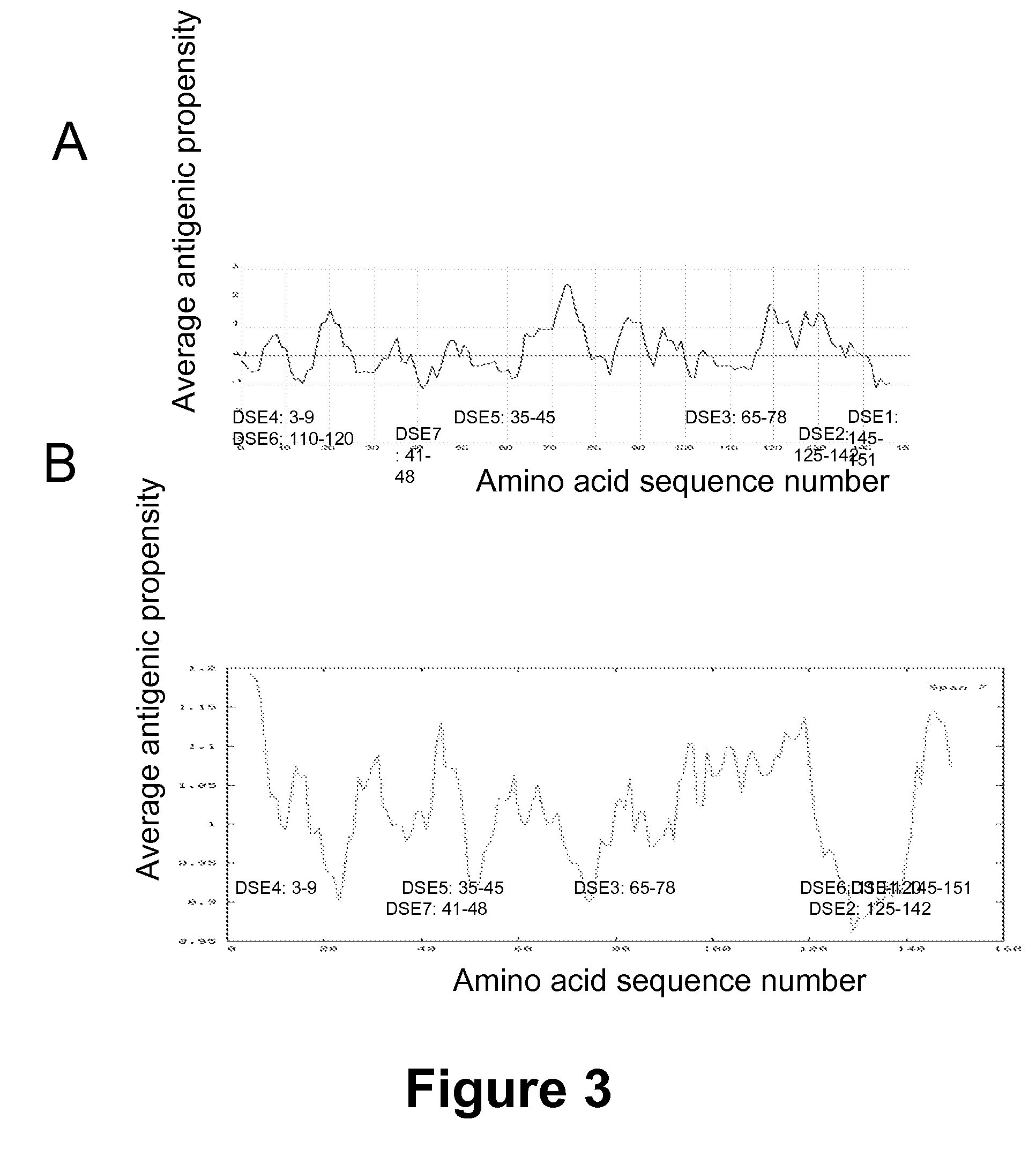
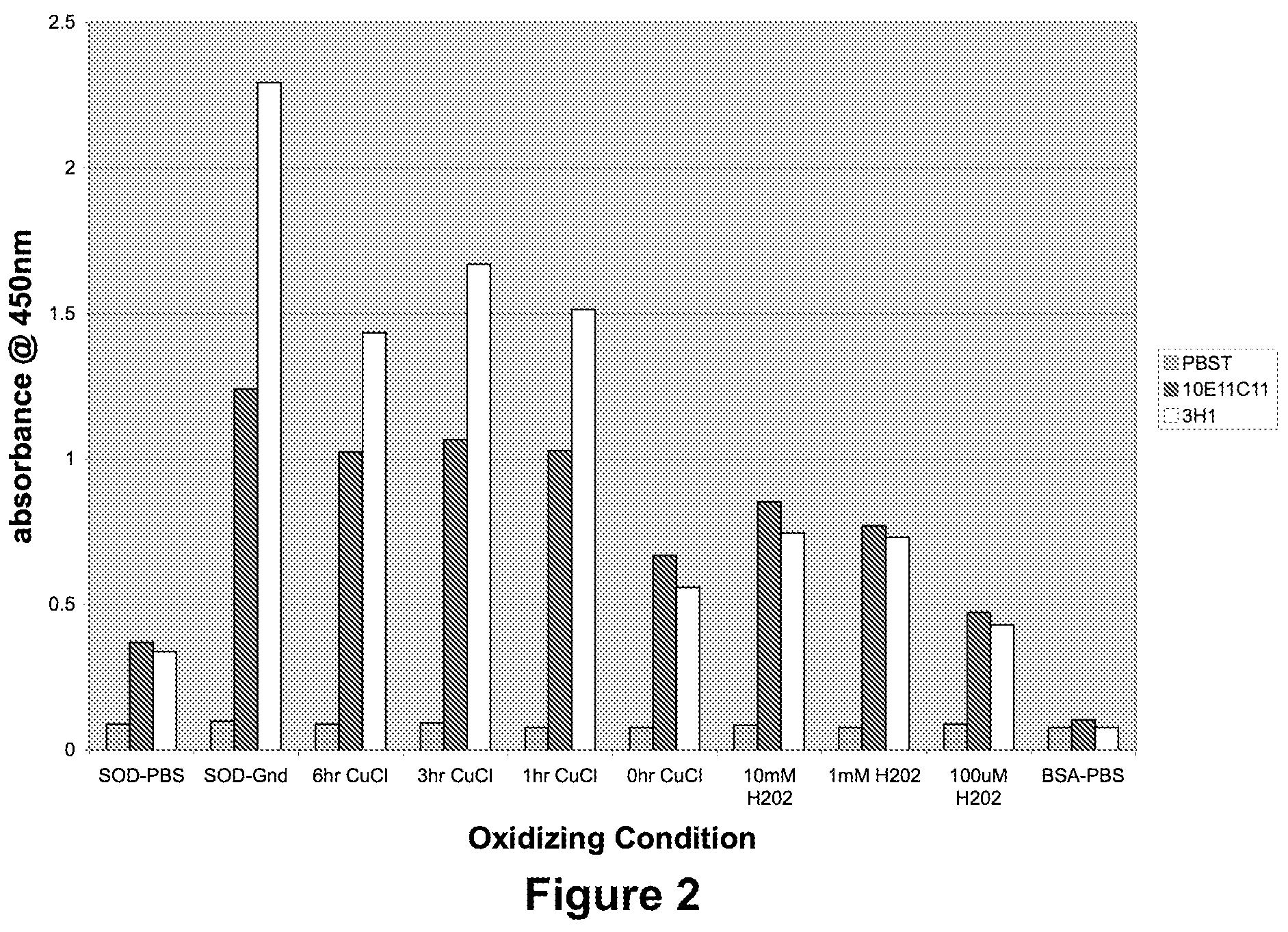
Methods and Compositions to Treat and Detect Misfolded-SOD1 Mediated Diseases
ActiveUS20080206251A1Reduce and inhibit participationInhibit and neutralize toxic effectOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderInflammatory Bowel DiseasesCerebral infarction
The invention provides a method for treating a medical condition, disease, or disorder mediated by a misfolded form of superoxide dismutase (SOD) in a subject in need of treatment. The method optionally comprises administering to the subject a composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable vehicle and an agent selected from (1) an exogenous antibody or fragment thereof that binds selectively to the misfolded form of SOD, and / or (2) an immunogen that elicits production of an endogenous antibody that binds selectively to the misfolded form of SOD, and / or (3) a nucleic acid sequence encoding (1) or (2). In certain embodiments, the invention provides methods of treating diseases such as Alzheimer's Disease, Parkinson's Disease or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and macular degeneration, glaucoma, ischemia, cerebral infarction, myocardial infarction, atherosclerosis, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel disease, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease or necrotizing enterocolitis using disease-specific epitopes, and compositions including these epitopes. The invention also provides antibodies that bind to monomeric or misfolded SOD1, and not on the molecular surface of native homodimeric SOD1. In addition, the invention includes methods of diagnosing Alzheimer's Disease, Parkinson's Disease or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in a subject. Also, the invention provides methods of identifying substances for the treatment or prevention of Alzheimer's Disease, Parkinson's Disease or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and kits using the binding proteins of the invention.
Owner:PROMIS NEUROSCI
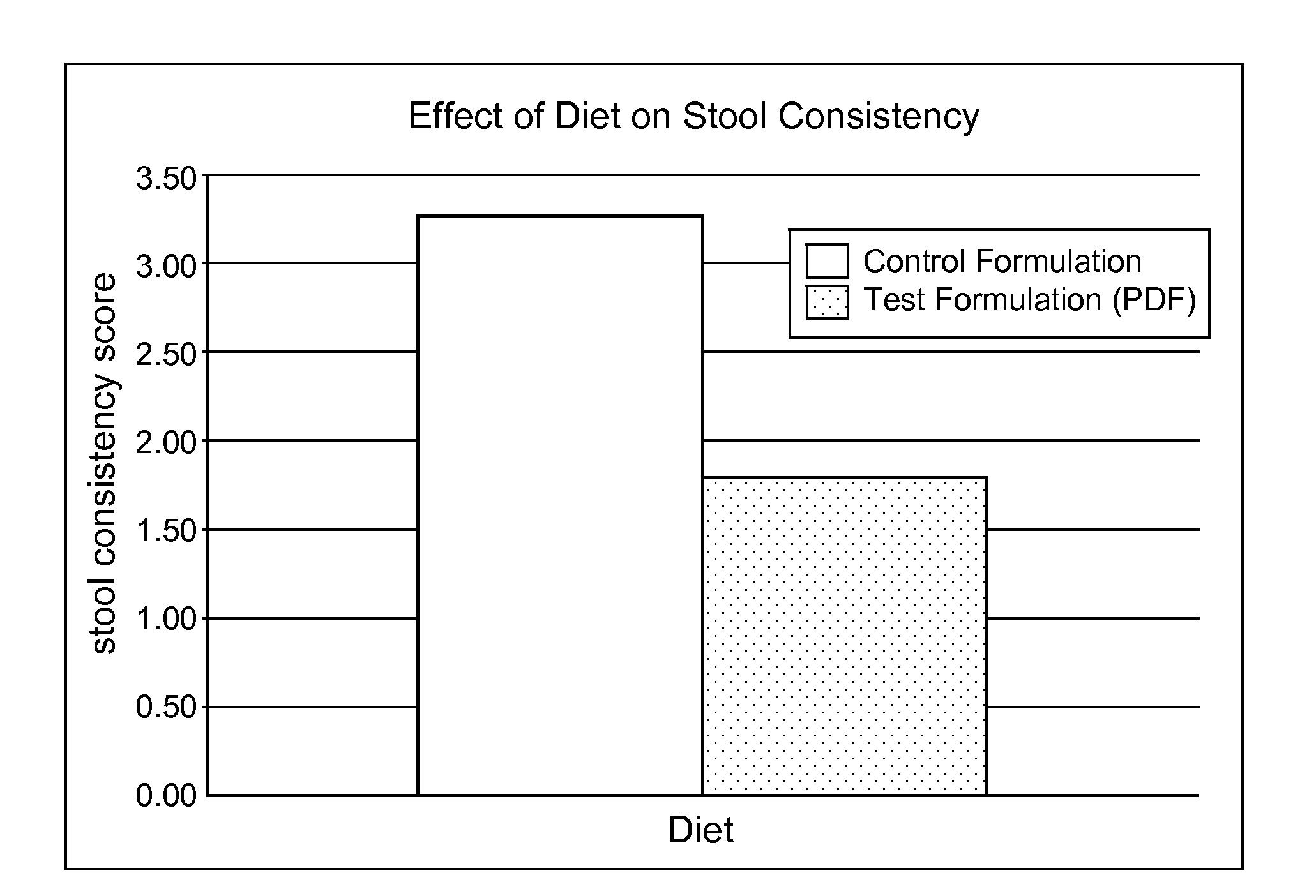
Formulations for mediating inflammatory bowel disorders
InactiveUS20070173480A1Reduce cholesterol absorptionReduce absorptionBiocideSugar derivativesInflammatory Bowel DiseasesLower blood cholesterol
The invention provides formulations and methods for mediating inflammation, in particular an inflammatory bowel disorder such as necrotizing enterocolitis, and for. Further, the formulations are effective in lowering blood cholesterol and decreasing blood cholesterol absorption. The formulations comprise at least one ganglioside, which may be selected from the group consisting of: GD3, GM1, GM2, GM3, and GD1b. The invention provides a method of treating or preventing inflammatory diseases, such as necrotizing enterocolitis by delivery of at least one ganglioside to a subject in need thereof. Supplementation of foods or liquids with gangliosides, fore example infant formula or infant foods, can be employed according to the invention.
Owner:MTI META TECH
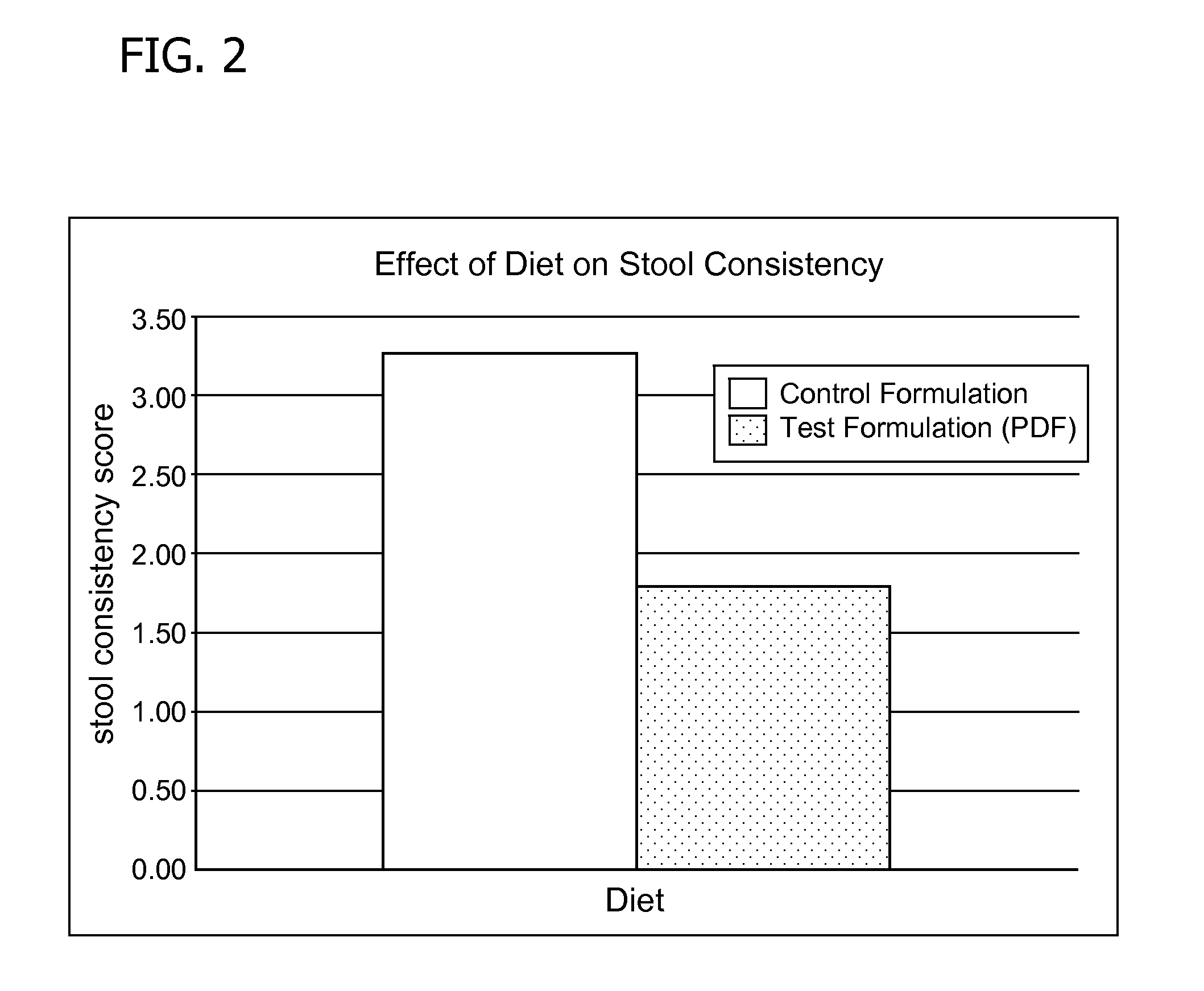
Methods for improving tolerance, digestion, and lipid soluble nutrient absorption in an infant, toddler, or child
ActiveUS20120172434A1Reduce the burden onImprove infant fat digestionBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsPremature thelarcheMonoglyceride
Disclosed are nutritional formulations including predigested fats that can be administered to preterm infants, infants, toddlers, and children for improving tolerance, digestion, and absorption of nutrients and for reducing the incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis, colic, and short bowel syndrome. The predigested fats include fatty acid-containing monoglycerides and / or a fatty acid component.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
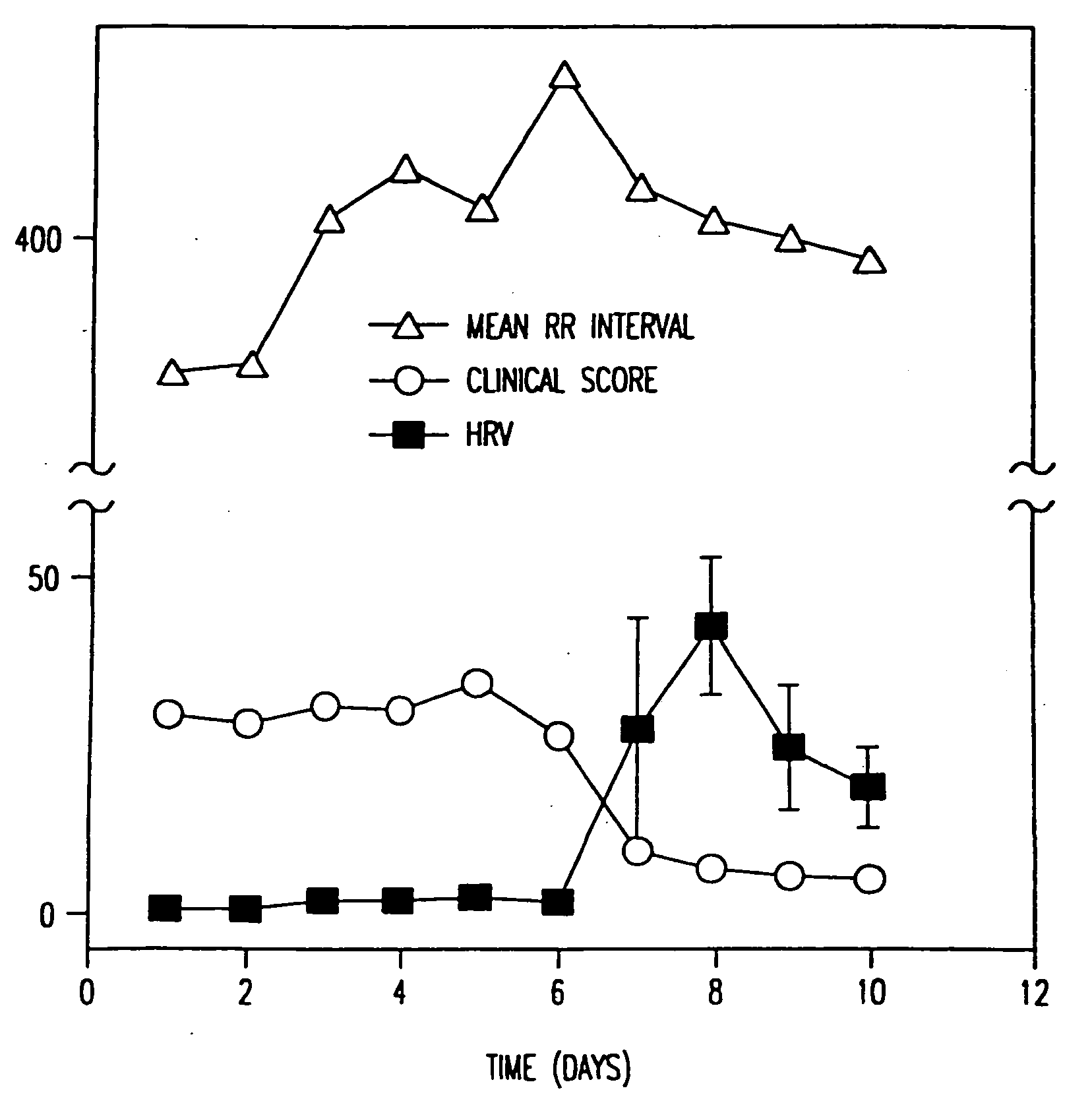
Method for the early diagnosis of subacute, potentially catastrophic illness
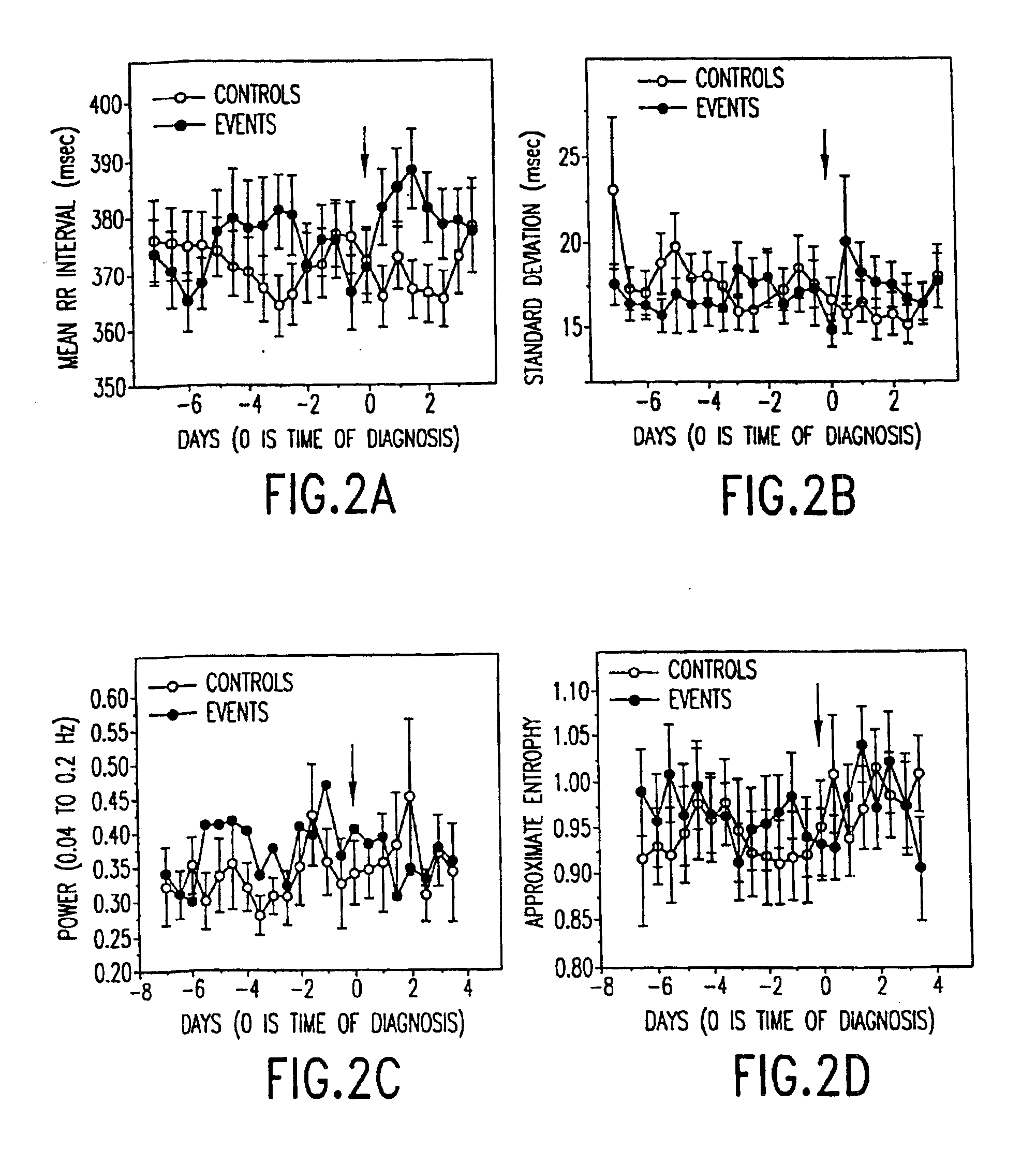
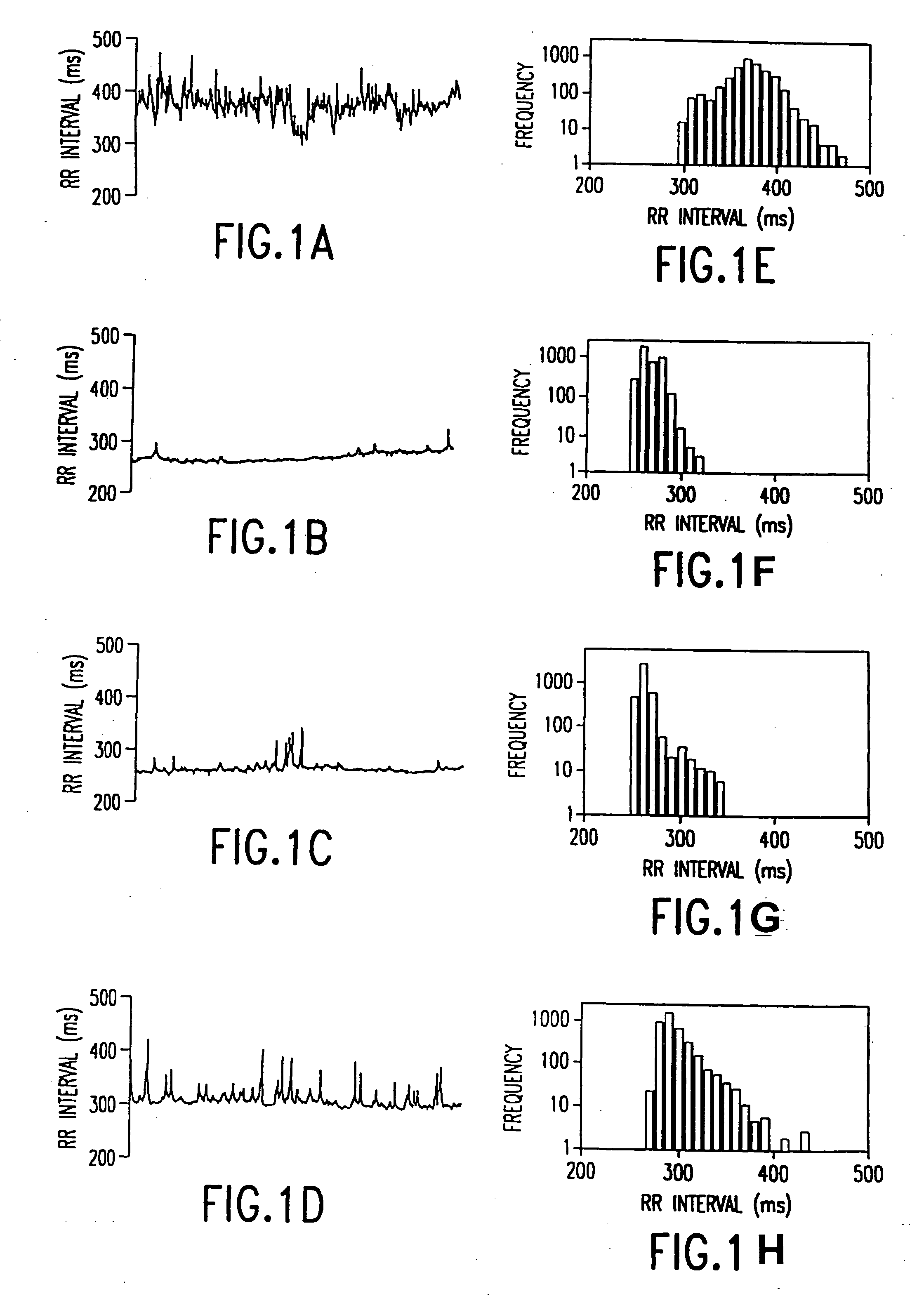
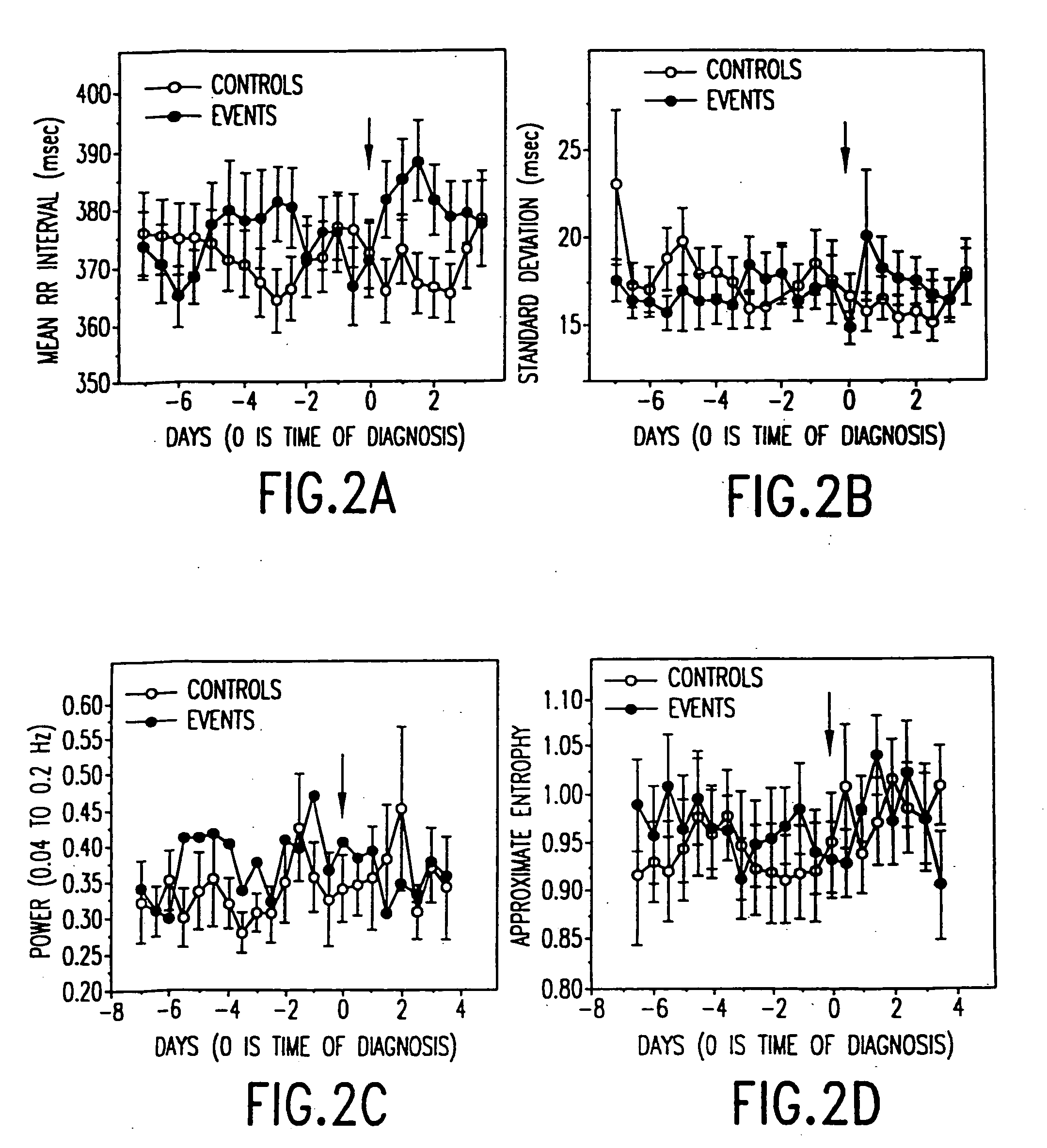
In one aspect of the invention, there is provided a method for early detection of subacute, potentially catastrophic illness in an infant. The method comprises: (a) monitoring heart rate variability in the infant; and (b) identifying at least one characteristic abnormality in the heart rate variability that is associated with the illness. This method can be used to diagnose illnesses such as, but not limited to, sepsis, necrotizing enterocolitis, pneumonia and meningitis. In another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a method for early detection of subacute, potentially catastrophic illness in an infant, which comprises: (a) monitoring the patient's RR intervals; (b) generating a normalized data set of the RR intervals; (c) calculating one or more of (i) moments of the data set selected from the third and higher moments and (ii) percentile values of the data set; and (d) identifying an abnormal heart rate variability associated with the illness based on one or more of the moments and the percentile values.
Owner:VIRGINIA UNIV OF THE +1
Methods for improving tolerance, digestion, and lipid soluble nutrient absorption in an infant, toddler, or child
ActiveUS8754126B2Improved tolerance and digestion and absorptionReduce morbidityBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsPremature thelarcheMonoglyceride
Disclosed are nutritional formulations including predigested fats that can be administered to preterm infants, infants, toddlers, and children for improving tolerance, digestion, and absorption of nutrients and for reducing the incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis, colic, and short bowel syndrome. The predigested fats include fatty acid-containing monoglycerides and / or a fatty acid component.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
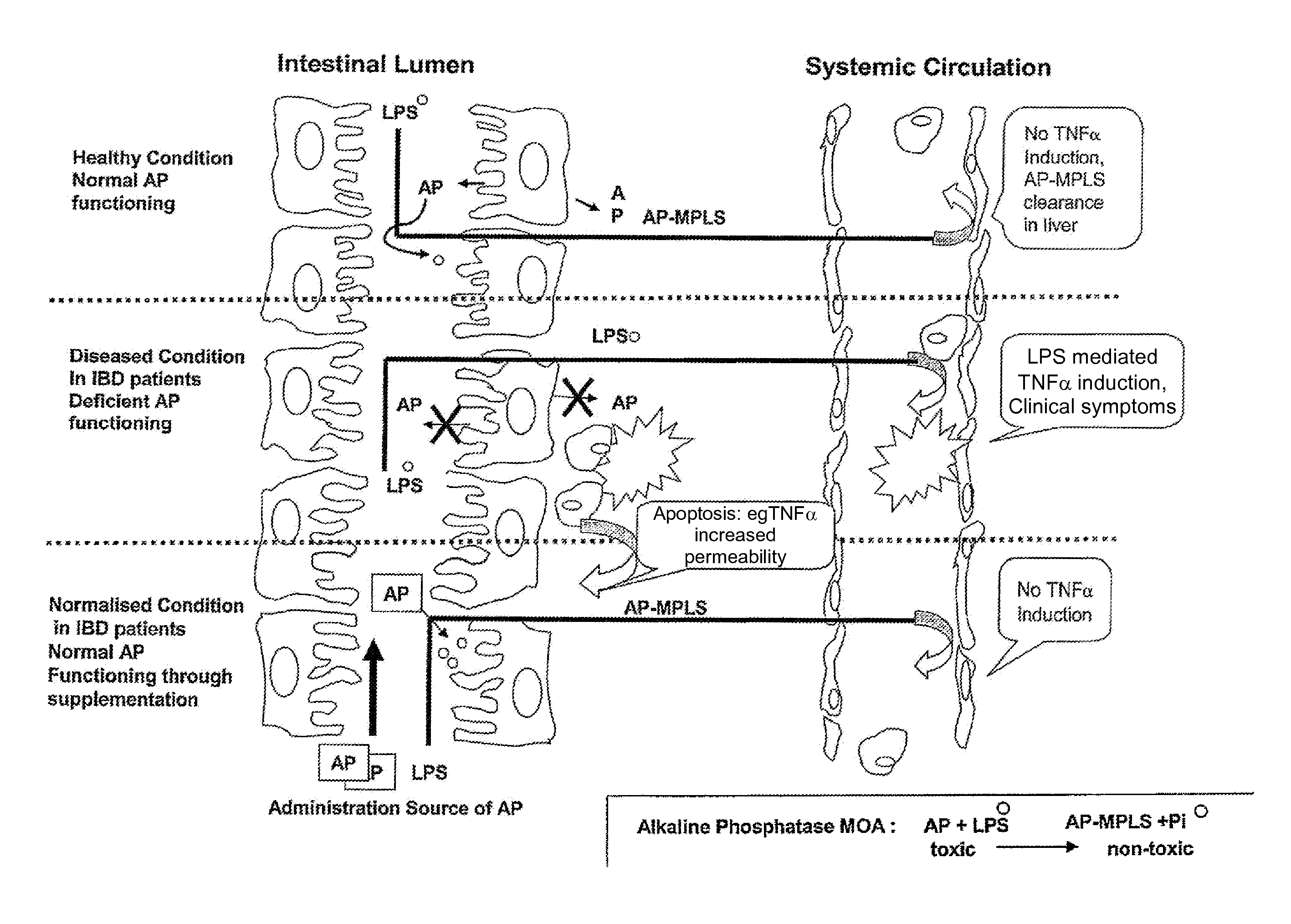
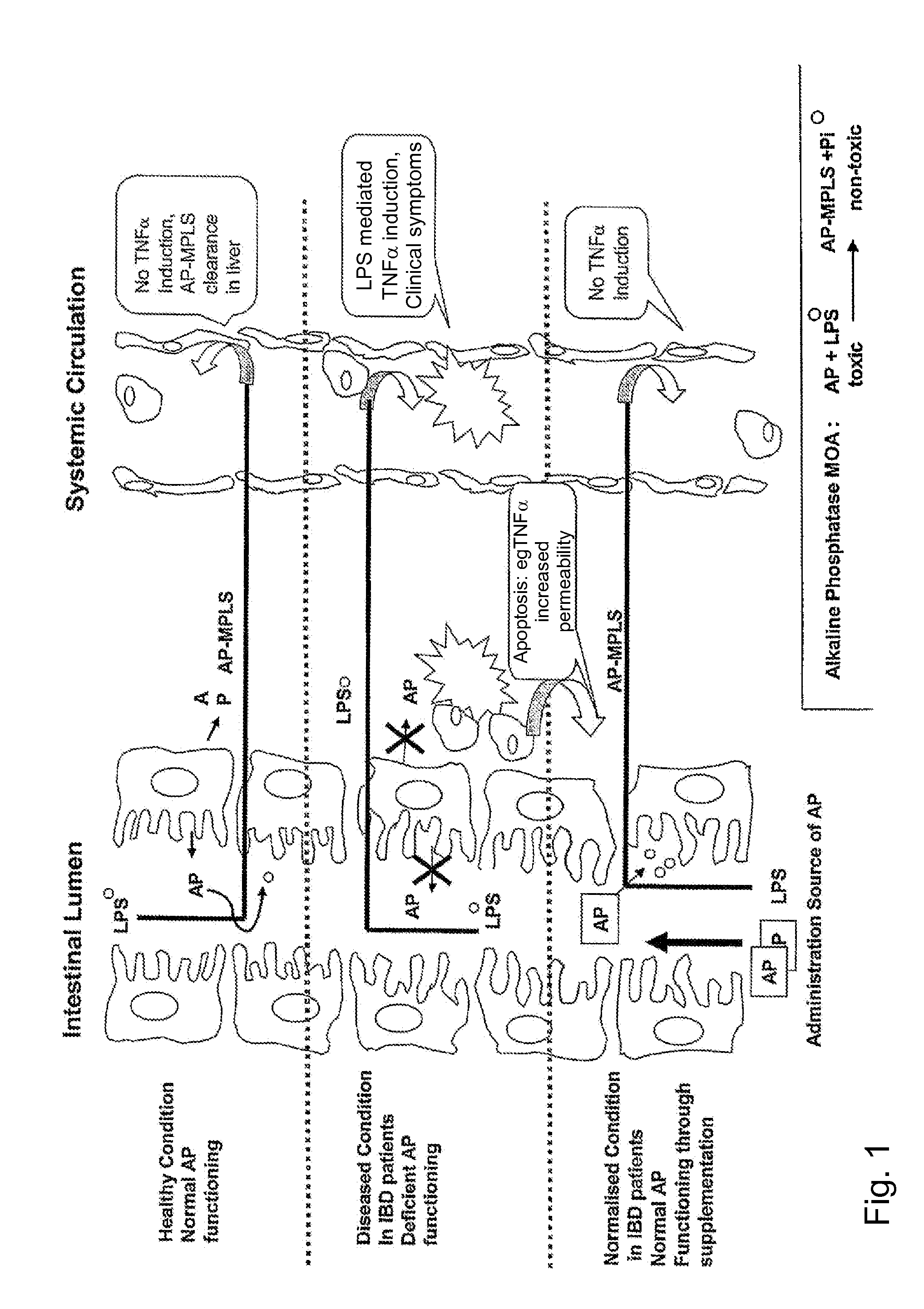
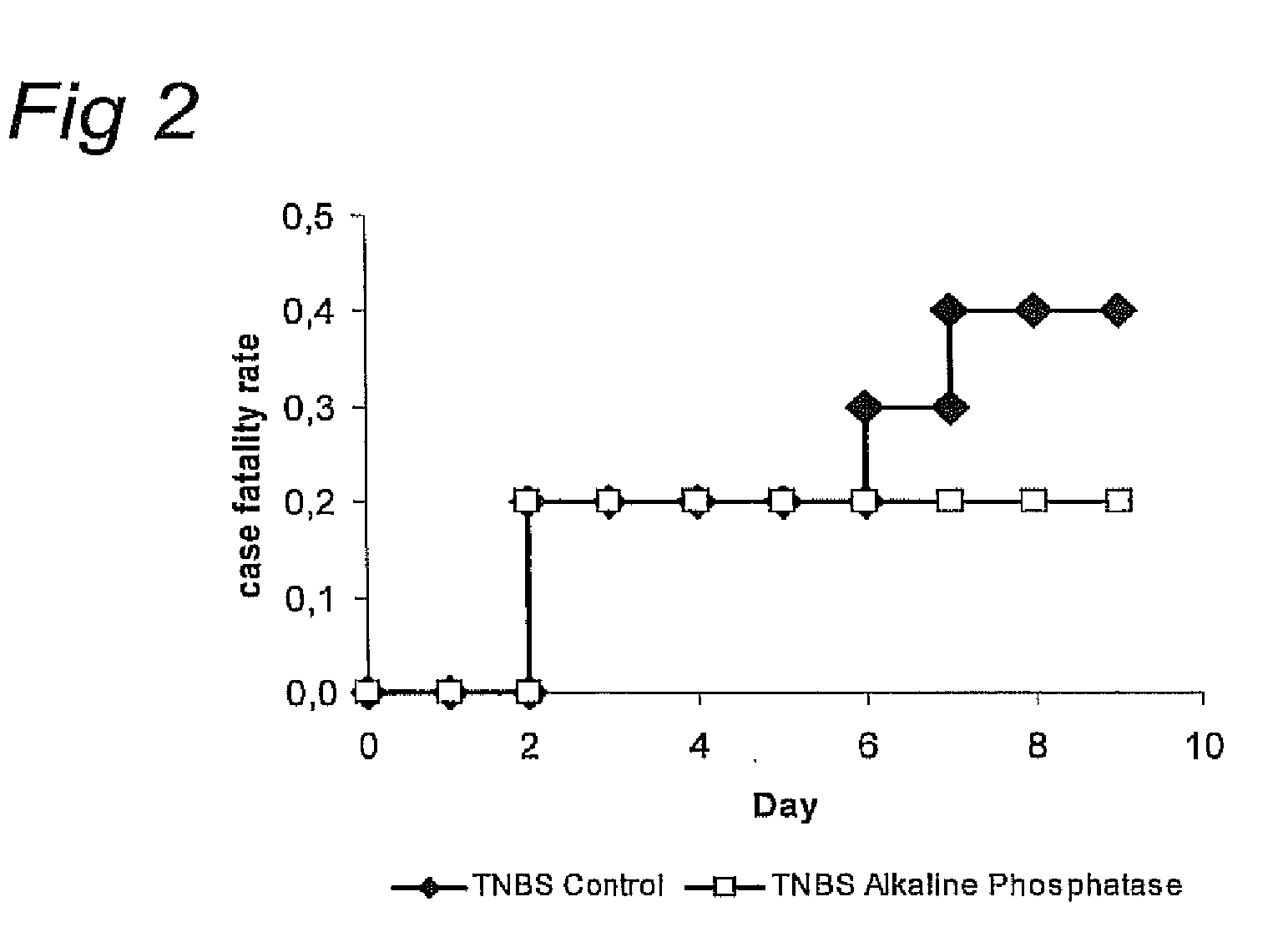
Means and method for treating and/or preventing necrotizing enterocolitis
InactiveUS20110142817A1Reduce outputPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesDiseaseNecrotizing enterocolitis
Compositions comprising a source of alkaline phosphatase that prevent or reduce toxic influx of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) through mucosal layers of a mamalian body cavity and methods of using these compositions for those purposes are disclosed. Such a source of alkaline phosphatase, preferably in a medical food such as infant milk formula, is eaten, drunk or otherwise administered for prophylaxis or treatment of LPS-mediated or LPS-exacerbated disease.
Owner:PHARMAAWARE SEPSIS
Use of toll-like receptor-9 agonists, toll-like receptor-4 antagonists, and/or nuclear oligomerization domain-2 agonists for the treatment or prevention of toll-like receptor-4-associated disorders
ActiveUS20080311112A1Reduce marksReduce signalingAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiseaseNK1 receptor antagonist
The present invention relates to the use of a TLR9 agonist and / or a TLR4 antagonist and / or a NOD2 agonist for treatment or prevention of disorders involving TLR4 activation, such as systemic sepsis and necrotizing enterocolitis.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Method and apparatus for the early diagnosis of subacute, potentially catastrophic illness
In one aspect of the invention, there is provided a method and apparatus for early detection of subacute, potentially catastrophic infectious illness in a premature newborn infant. The method comprises: (a) continuously monitoring heart rate variability in the premature newborn infant; and (b) identifying at least one characteristic abnormality in the heart rate variability that is associated with the illness. This method can be use to diagnose illnesses such as, but not limited to, sepsis, necrotizing enterocolitis, pneumonia and meningitis. In another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a method and apparatus for early detection of subacute, potentially catastrophic infectious illness in a patient. The method comprises: (a) continuously monitoring the patient's RR intervals; (b) generating a normalized data set of the RR intervals; (c) calculating one or more of (i) moments of the data set selected from the third and higher moments and (ii) percentile values of the data set; and (d) identifying an abnormal heart rate variability associated with the illness based on one or more of the moments and the percentile values.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Nutritional products including monoglycerides and fatty acids
ActiveUS20120171350A1Reduce the burden onImprove infant fat digestionHydroxy compound active ingredientsMetabolism disorderMonoglycerideMedicine
Disclosed are nutritional formulations including predigested fats that can be administered to preterm infants, infants, toddlers, and children for improving tolerance, digestion, and absorption of nutrients and for reducing the incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis, colic, and short bowel syndrome. The predigested fats include fatty acid-containing monoglycerides and / or a fatty acid component.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Traditional Chinese medicine for treating bacterial diseases in poultry
ActiveCN102552502AGood curative effectFast playAntibacterial agentsAluminium/calcium/magnesium active ingredientsEscherichia coliEnterovirus
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine for treating bacterial diseases in poultry, which is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 10-15 parts of wild chrysanthemum flower, 5-10 parts of Chinese goldthread, 8-10 parts of Scutellaria baicalensis, 8-10 parts of golden cypress, 10-15 parts of Chinese thorowax, 10-12 parts of Cape jasmine, 20-25 parts of Fagopyrum cymosum root, 25-30 parts of common andrographis herb, 8-10 parts of burdock, 25-30 parts of Chinese pulsatilla root and 30-35 parts of folium artemisiae argyi. The traditional Chinese medicine for treating the bacterial diseases in the poultry, disclosed by the invention, has the effects of preventing and treating the bacterial diseases caused by colibacillosis, salmonellosis, necrotizing enterocolitis, enterovirus syndromes, cholera fowls and the like in the poultry.
Owner:河南天纳图生物科技有限公司
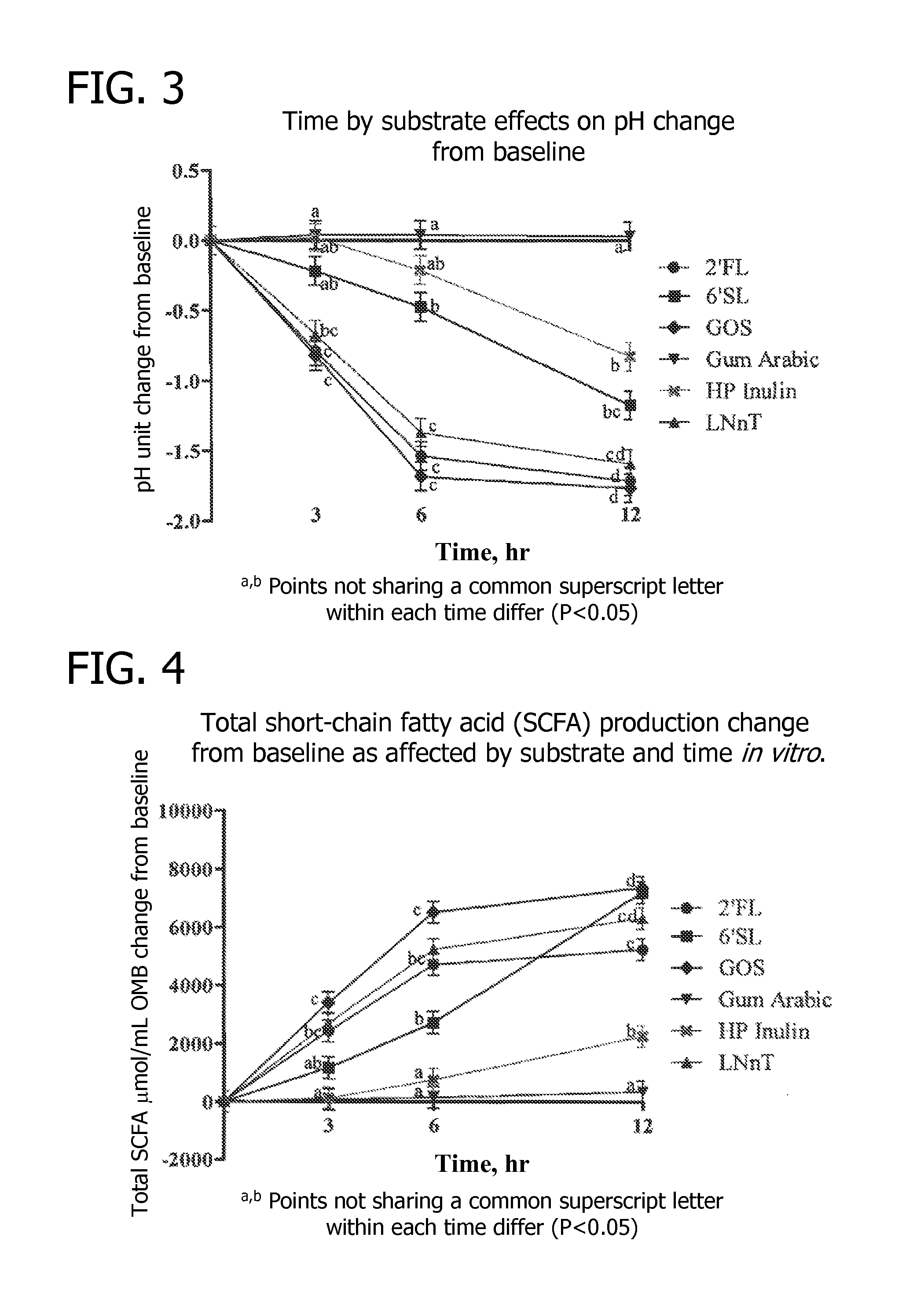
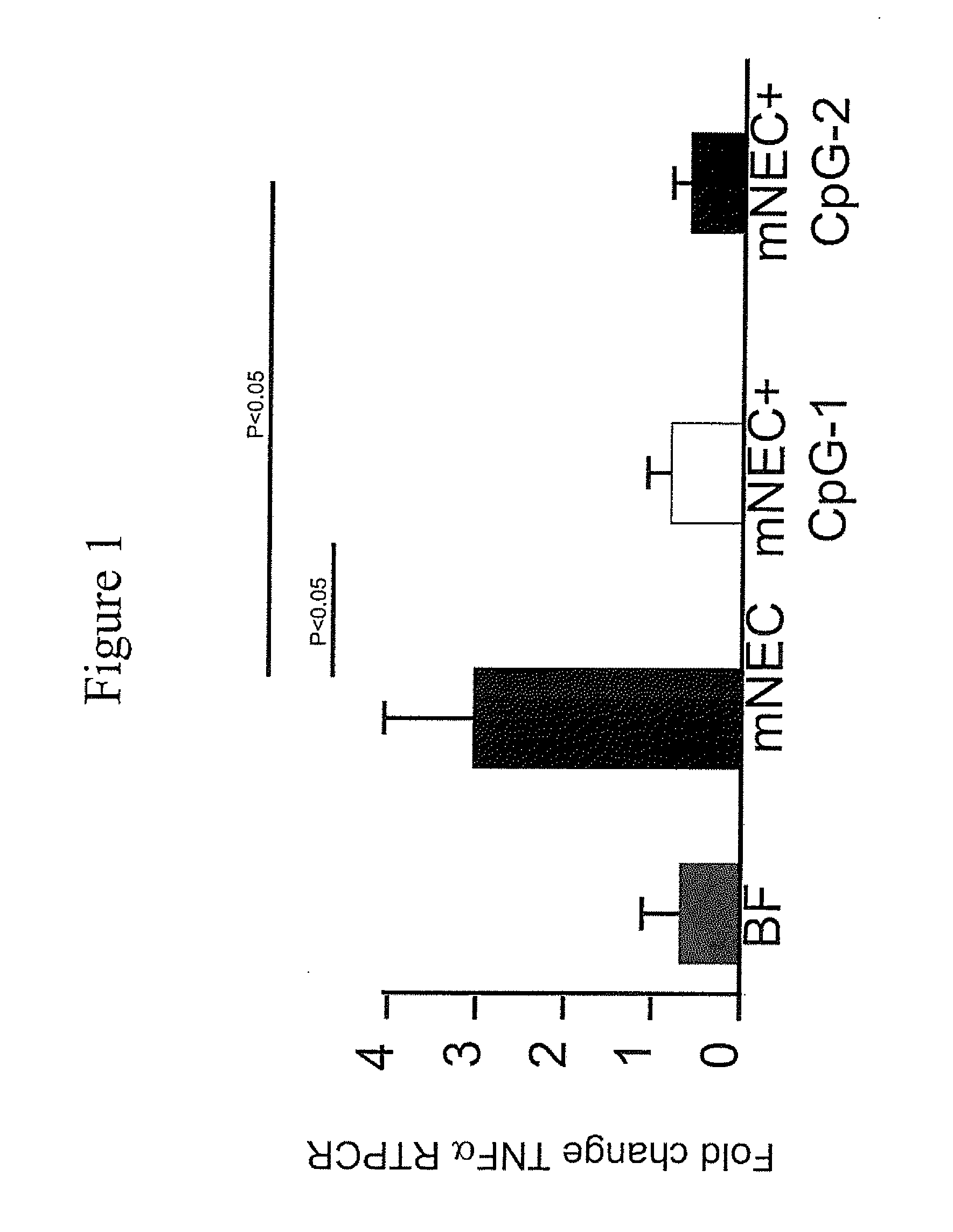
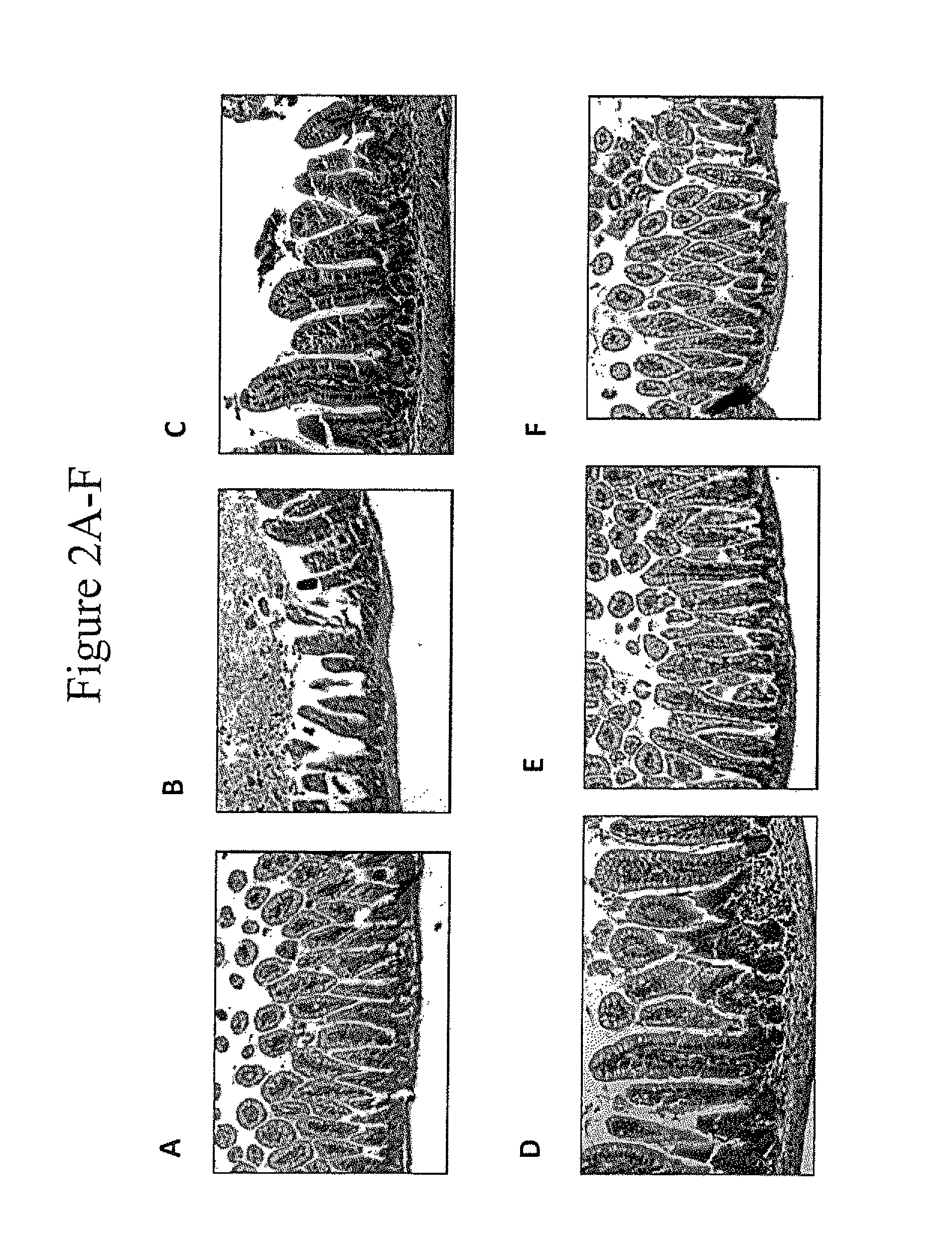
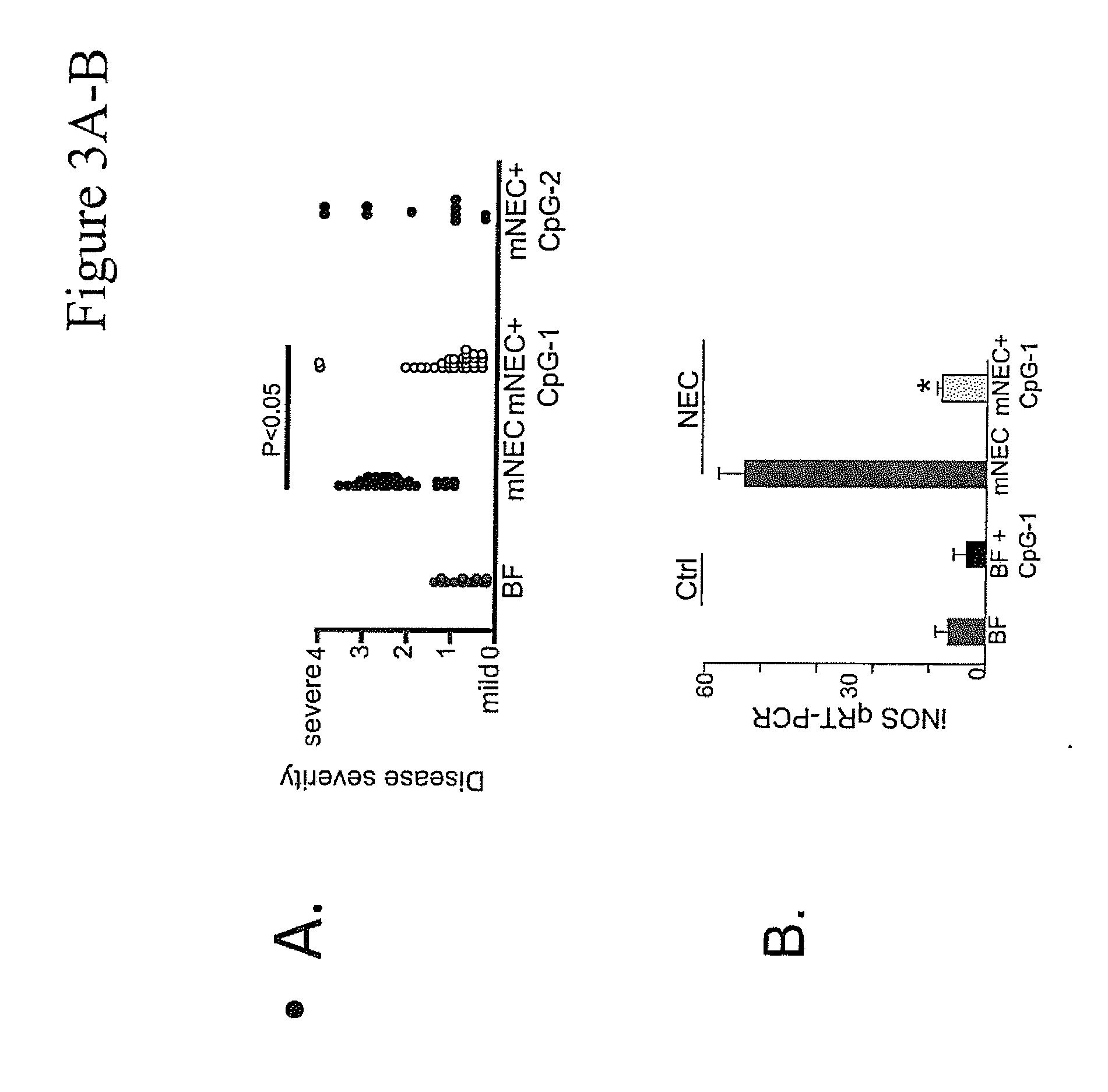
Oral therapy of necrotizing enterocolitis
The present invention relates to methods of treating or reducing the risk of necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) in an infant comprising orally administering an effective amount of a CpG-ODN. It is based, at least in part, on the results of experiments in which orally administered CpG-ODNs were observed to reduce the histopathology and markers of inflammation in a murine model for NEC. The present invention further provides for oral formulations of CpG-ODN for administration to infants.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Nutritive preparation containing butyric acid
InactiveCN107736614AAffect the tasteSolve the technical problems of prevention and controlMilk preparationFood ingredient functionsNecrotizing enterocolitisButyric acid
The invention provides a nutritive preparation containing butyric acid. The nutritive preparation comprises a nutrient composition and a butyric acid compound, wherein the concentration of the butyricacid compound in the nutritive preparation is 0.5-200mM(mmol / L); and the butyric acid compound is selected from at least one of butyric acid, butyrate and butyric acid derivatives. The butyric acid compound is added to the nutrient composition, so that necrotizing enterocolitis can be prevented and treated, and besides, the nutritive preparation has the effects of promoting growth, and promotingdevelopment of the immune system and maturation of intestinal tracts.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PEDIATRIC RES +1
Compositions for use in the prevention or treatment of necrotizing enterocolitis in infants or young children born by c-section
ActiveUS20160296542A1Gut protectionImprove developmentOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemNecrotizing enterocolitisOligosaccharide
The present invention relates to a composition comprising at least one human milk oligosaccharide and / or a precursor thereof, for use in preventing and / or treating necrotizing enterocolitis in infants or young children born by C-section.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
Methods and compositions to treat misfolded-SOD1 mediated diseases
ActiveUS7887803B2Reduce and inhibit participationInhibit and neutralize toxic effectOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderUlcerative colitisCerebral infarction
The invention provides a method for treating a medical condition, disease, or disorder mediated by a misfolded form of superoxide dismutase (SOD) in a subject in need of treatment. The method optionally comprises administering to the subject a composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable vehicle and an agent selected from (1) an exogenous antibody or fragment thereof that binds selectively to the misfolded form of SOD, and / or (2) an immunogen that elicits production of an endogenous antibody that binds selectively to the misfolded form of SOD, and / or (3) a nucleic acid sequence encoding (1) or (2). In certain embodiments, the invention provides methods of treating diseases such as Alzheimer's Disease, Parkinson's Disease or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and macular degeneration, glaucoma, ischemia, cerebral infarction, myocardial infarction, atherosclerosis, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel disease, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease or necrotizing enterocolitis using disease-specific epitopes, and compositions including these epitopes. The invention also provides antibodies that bind to monomeric or misfolded SOD1, and not on the molecular surface of native homodimeric SOD1. In addition, the invention includes methods of diagnosing Alzheimer's Disease, Parkinson's Disease or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in a subject. Also, the invention provides methods of identifying substances for the treatment or prevention of Alzheimer's Disease, Parkinson's Disease or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and kits using the binding proteins of the invention.
Owner:PROMIS NEUROSCI
Nutritional products including a novel fat system including fatty acids
InactiveUS20120172445A1Reduce the burden onImprove infant fat digestionBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsMonoglycerideMedicine
Disclosed are nutritional formulations including predigested fats that can be administered to preterm infants, infants, toddlers, and children for improving tolerance, digestion, and absorption of nutrients and for reducing the incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis, colic, and short bowel syndrome. The predigested fats include fatty acid-containing monoglycerides and / or a fatty acid component.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Compositions for use in the prevention or treatment of necrotizing enterocolitis in infants and young children
ActiveUS20160296541A1Promoting enteral feeding tolerancePromoting gastrointestinal functional maturationOrganic active ingredientsVitamin food ingredientsEnterocolitisPhysiology
The invention discloses a composition comprising LNT and at least another human milk oligosaccharide or precursor thereof, for use in preventing and / or treating necrotizing enterocolitis in infants and young children.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
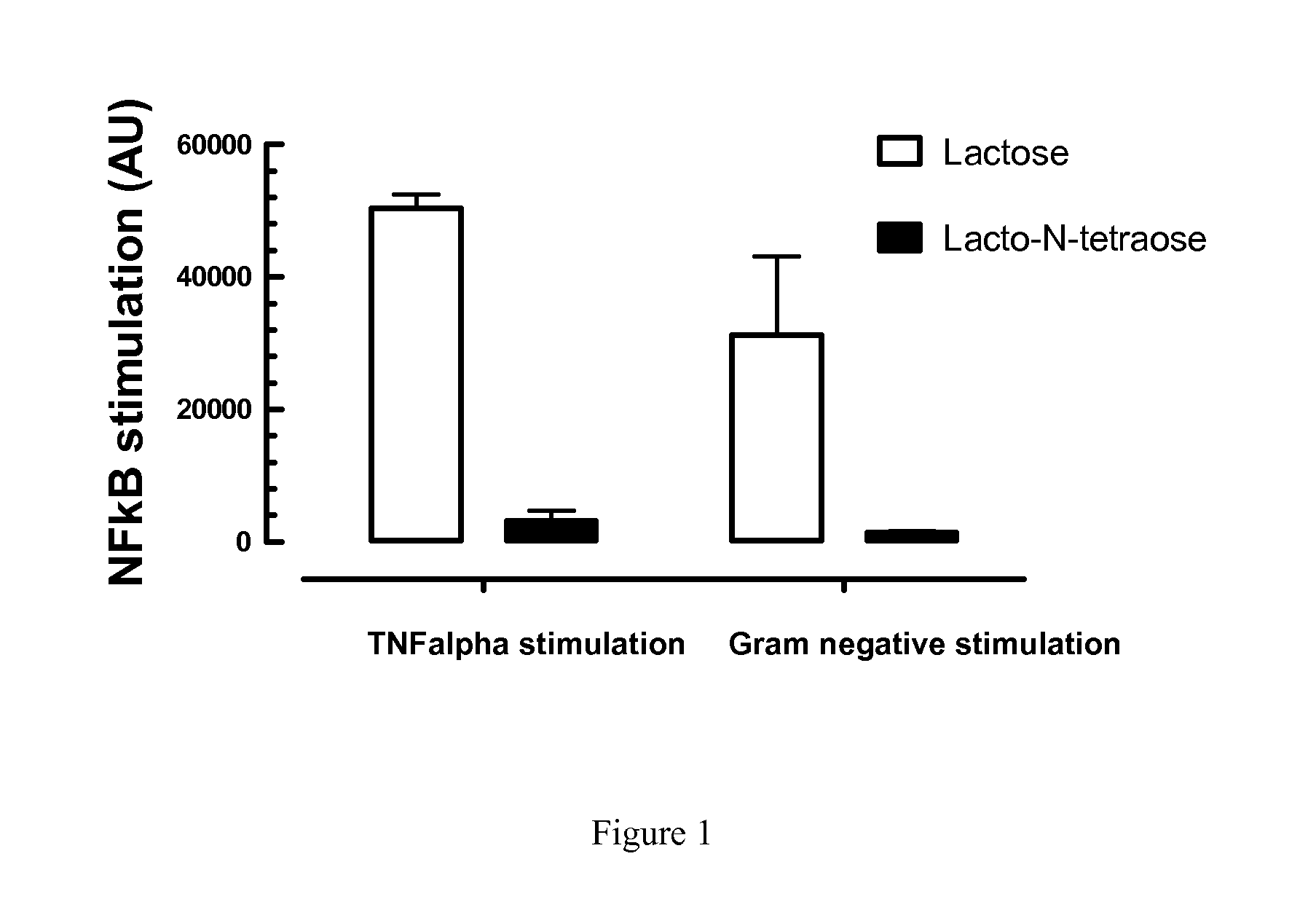
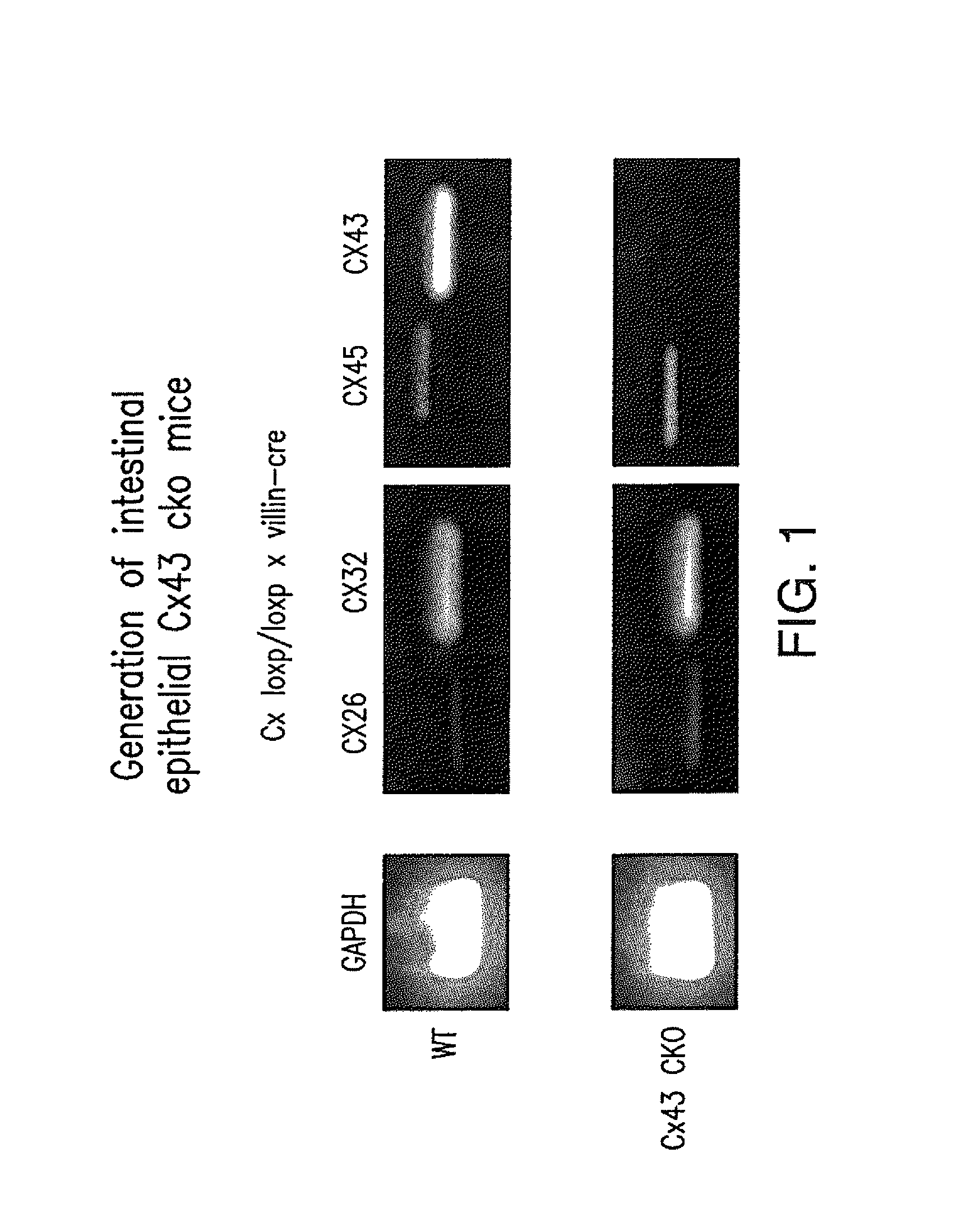
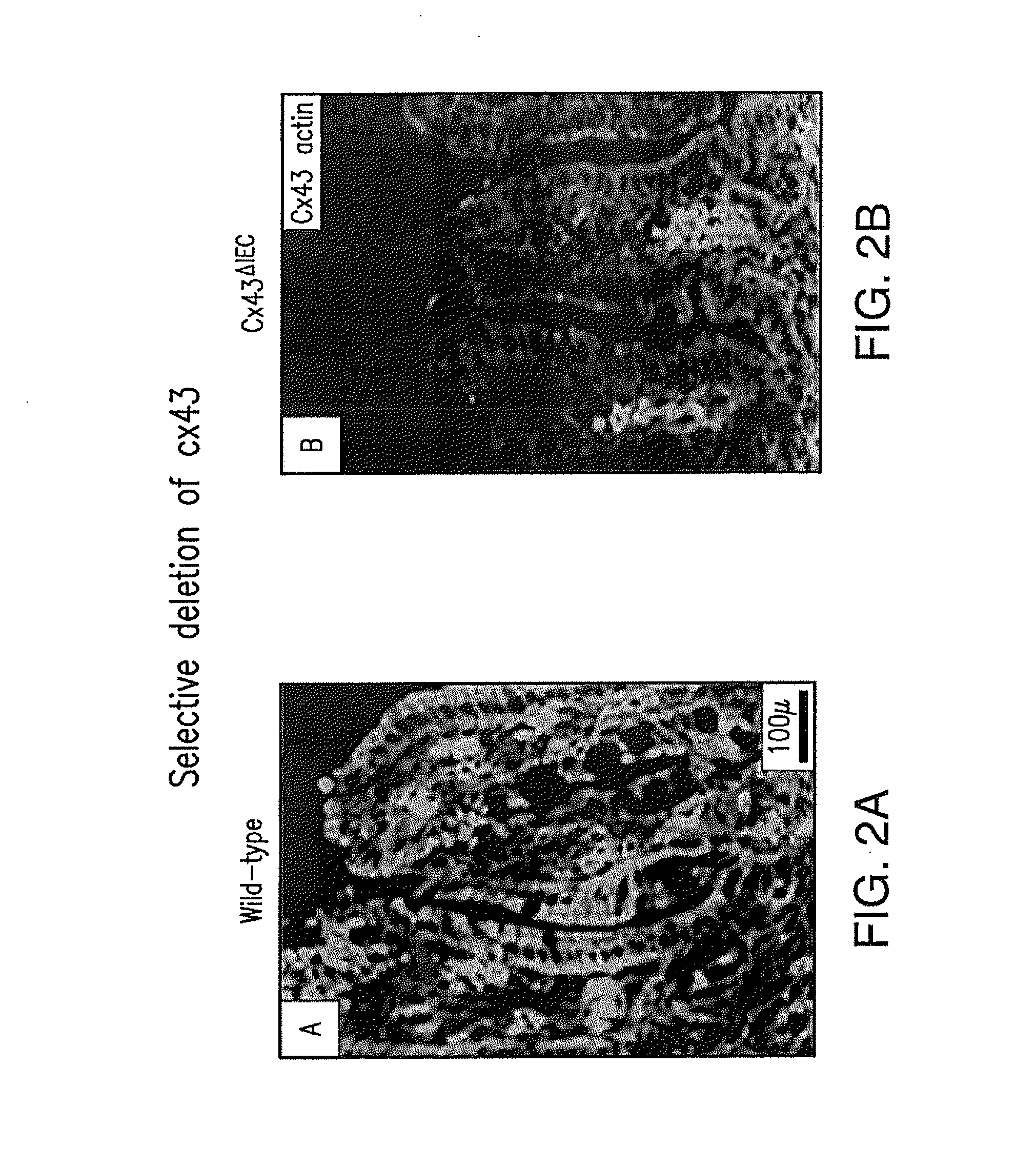
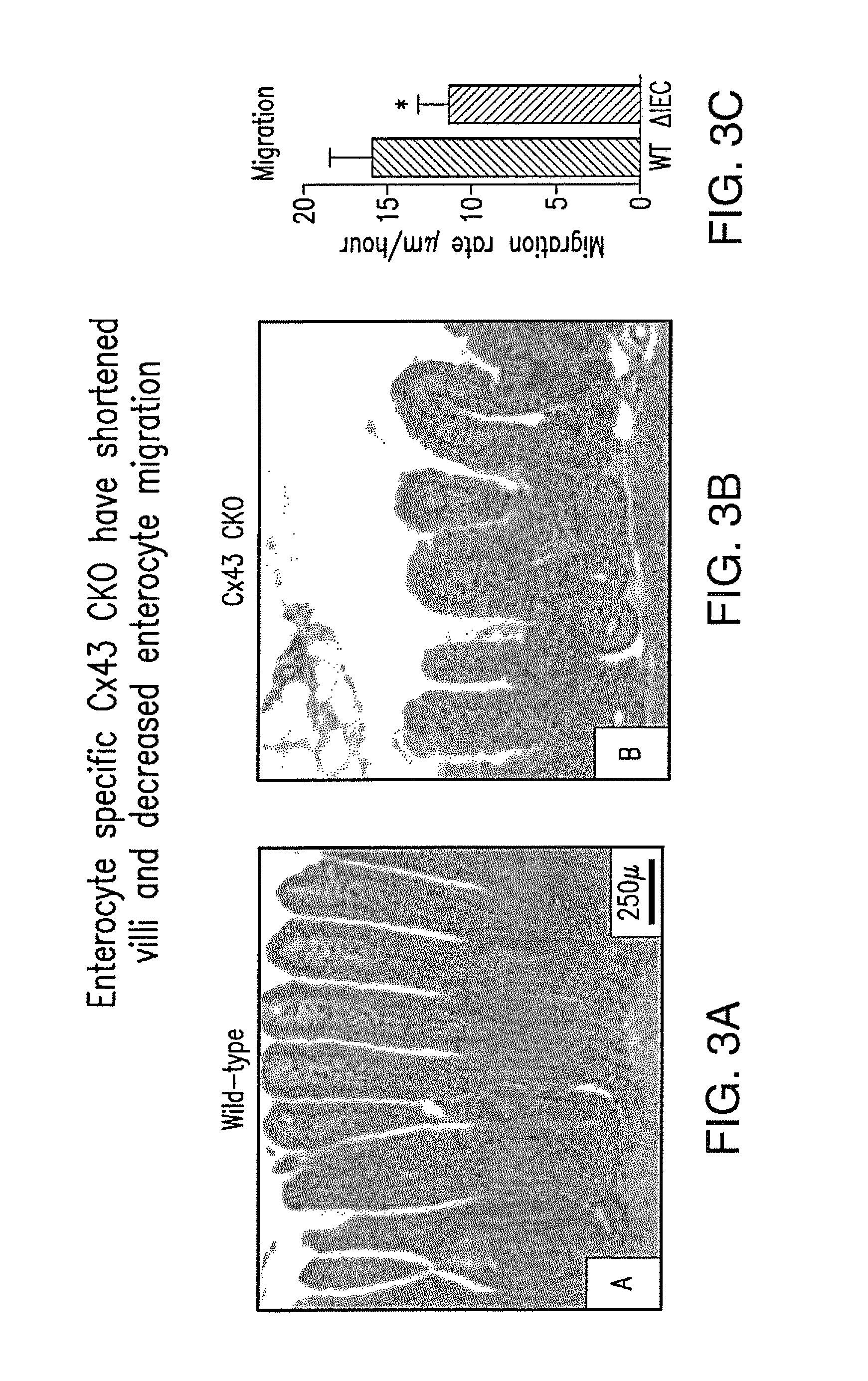
Gap Junction-Enhancing Agents for Treatment of Necrotizing Enterocolitis and Inflammatory Bowel Disease
ActiveUS20130345154A1Reduce riskImprove mobilityBiocideAntipyreticEnterocolitisIntestinal inflammation
The present invention relates to methods of reducing the risk of occurrence of, and / or treating, necrotizing enterocolitis (“NEC”) or inflammatory bowel disease (“IBD”) comprising administering, to a subject in need of such treatment, an effective amount of a gap junction enhancing agent (“GJEA”), for example a peptide (“GJP”) or peptide analog (“GJPA”). It is based, at least in part, on the discovery that greater functionality of gap junctions between enterocytes increases their rate of migration and reduces the severity of intestinal inflammation.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Use of toll-like receptor-9 agonists
The present invention relates to the use of a TLR9 agonist and / or a TLR4 antagonist and / or a NOD2 agonist for treatment or prevention of disorders involving TLR4 activation, such as systemic sepsis and necrotizing enterocolitis.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Compositions and Methods for Treating Necrotizing Enterocolitis
InactiveUS20090105188A1Prevent and slow progressionBiocideDigestive systemRecommended IntakePolymerase L
The present invention relates to a method for treating or preventing necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) in a human neonate in need thereof, comprising administering to the neonate a pharmaceutically effective amount of a composition comprising a poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase / polymerase (PARP) inhibitor. Also contemplated herein is an infant food or treatment composition comprising a PARP inhibitor in an amount that is 5 to 500 times greater than a daily recommended intake dosage for the PARP inhibitor.
Owner:NATIONWIDE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
Nutritional products including a novel fat system including monoglycerides
ActiveUS20120172443A1Reduce the burden onImprove infant fat digestionBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsMonoglycerideMedicine
Disclosed are nutritional formulations including predigested fats that can be administered to preterm infants, infants, toddlers, and children for improving tolerance, digestion, and absorption of nutrients and for reducing the incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis, colic, and short bowel syndrome. The predigested fats include fatty acid-containing monoglycerides and / or a fatty acid component.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Formulations for mediating inflammatory bowel disorders
InactiveUS7851451B2Reduce absorptionBiocideDispersion deliveryLower blood cholesterolNecrotizing enterocolitis
The invention provides formulations and methods for mediating inflammation, in particular an inflammatory bowel disorder such as necrotizing enterocolitis, and for. Further, the formulations are effective in lowering blood cholesterol and decreasing blood cholesterol absorption. The formulations comprise at least one ganglioside, which may be selected from the group consisting of: GD3, GM1, GM2, GM3, and GD1b. The invention provides a method of treating or preventing inflammatory diseases, such as necrotizing enterocolitis by delivery of at least one ganglioside to a subject in need thereof. Supplementation of foods or liquids with gangliosides, fore example infant formula or infant foods, can be employed according to the invention.
Owner:MTI META TECH
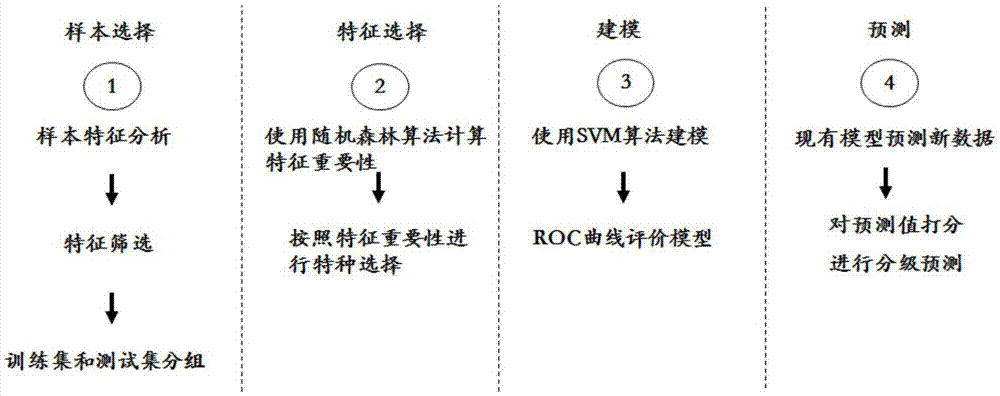
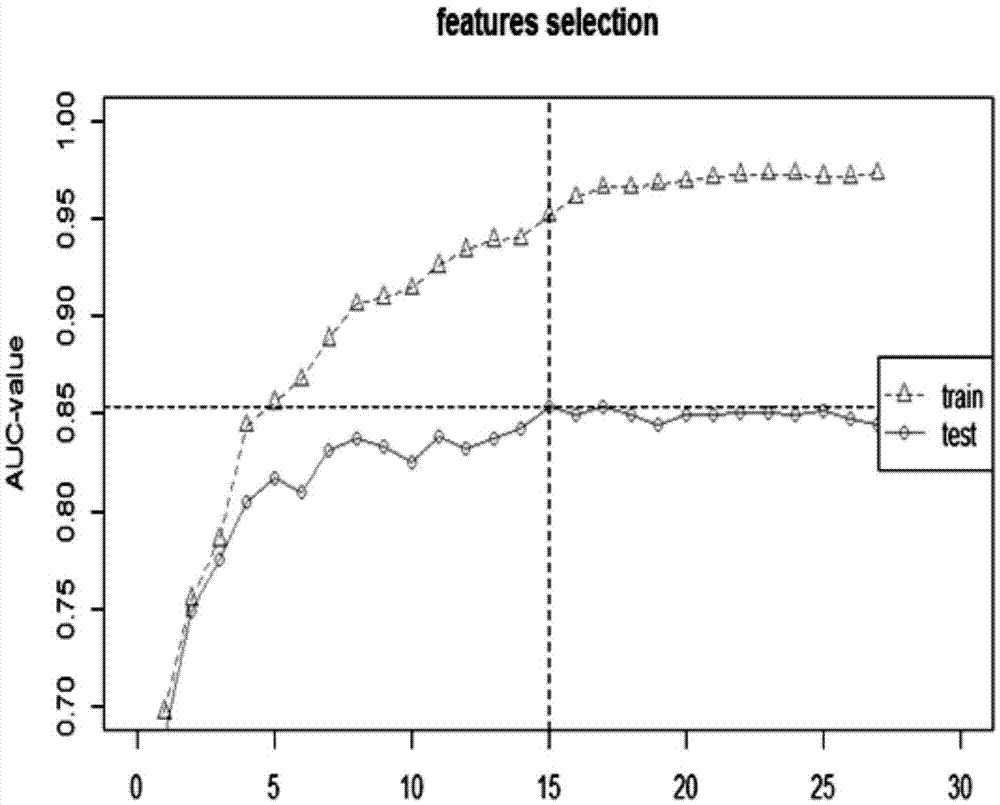
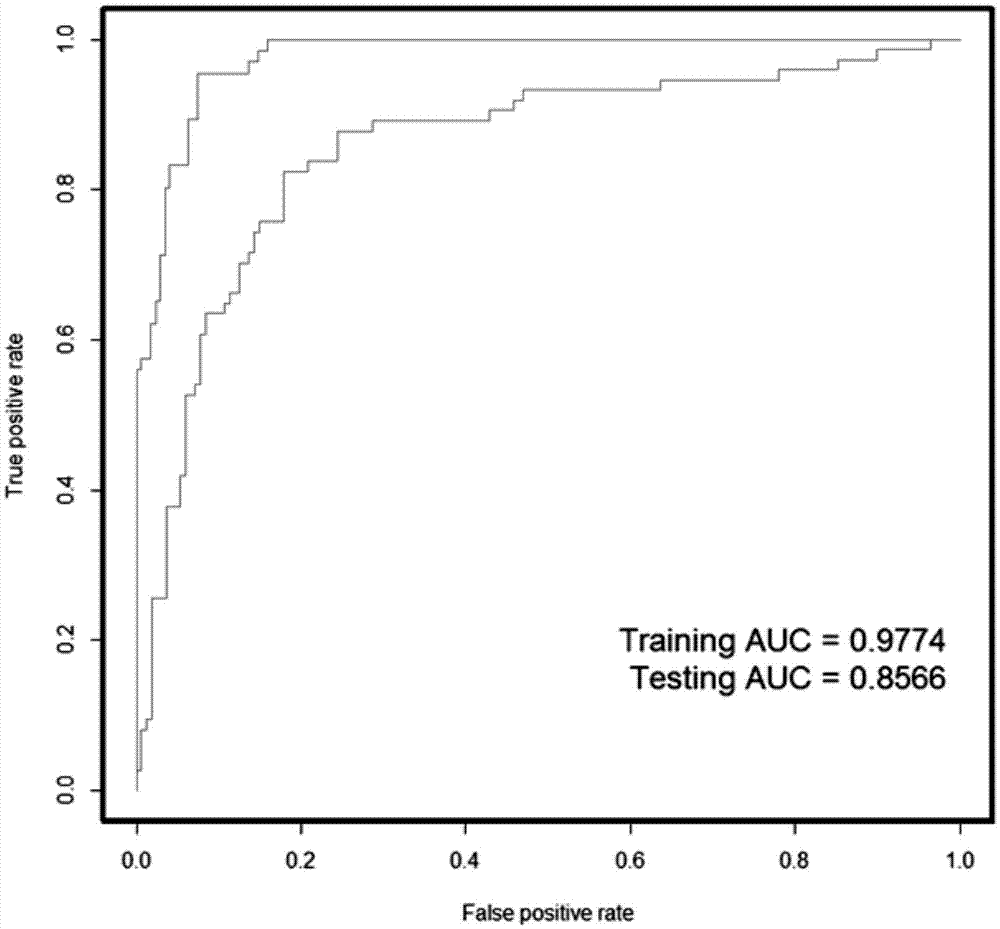
Medical data modeling-based class prediction method of necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC)
ActiveCN107194137AEffective predictionEffective judgmentSpecial data processing applicationsICT adaptationPredictive methodsData modeling
The invention provides a medical data modeling-based class prediction method of necrotizing enterocolitis(NEC). The method includes the following steps: data sample selection, feature screening, important feature selection, model establishment and prediction result scoring. According to the method, systematic analysis and modeling are carried out on relevant data of the necrotizing enterocolitis, an evaluation method of model prediction is given, through a model, effective auxiliary diagnosis can be carried out on the necrotizing enterocolitis of patients based on the data of the necrotizing enterocolitis, effective prevention, intervention and treatment are enabled to be carried out at an initial disease period, and a basis is provided for achieving the best treatment effect.
Owner:北京万灵盘古科技有限公司
Use of Toll-like receptor-9 agonists, Toll-like receptor-4 antagonists, and/or nuclear oligomerization domain-2 agonists for the treatment or prevention of Toll-like receptor-4-associated disorders
ActiveUS20120077868A1Reduce marksReduce signalingAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiseaseNK1 receptor antagonist
The present invention relates to the use of a TLR9 agonist and / or a TLR4 antagonist and / or a NOD2 agonist for treatment or prevention of disorders involving TLR4 activation, such as systemic sepsis and necrotizing enterocolitis.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
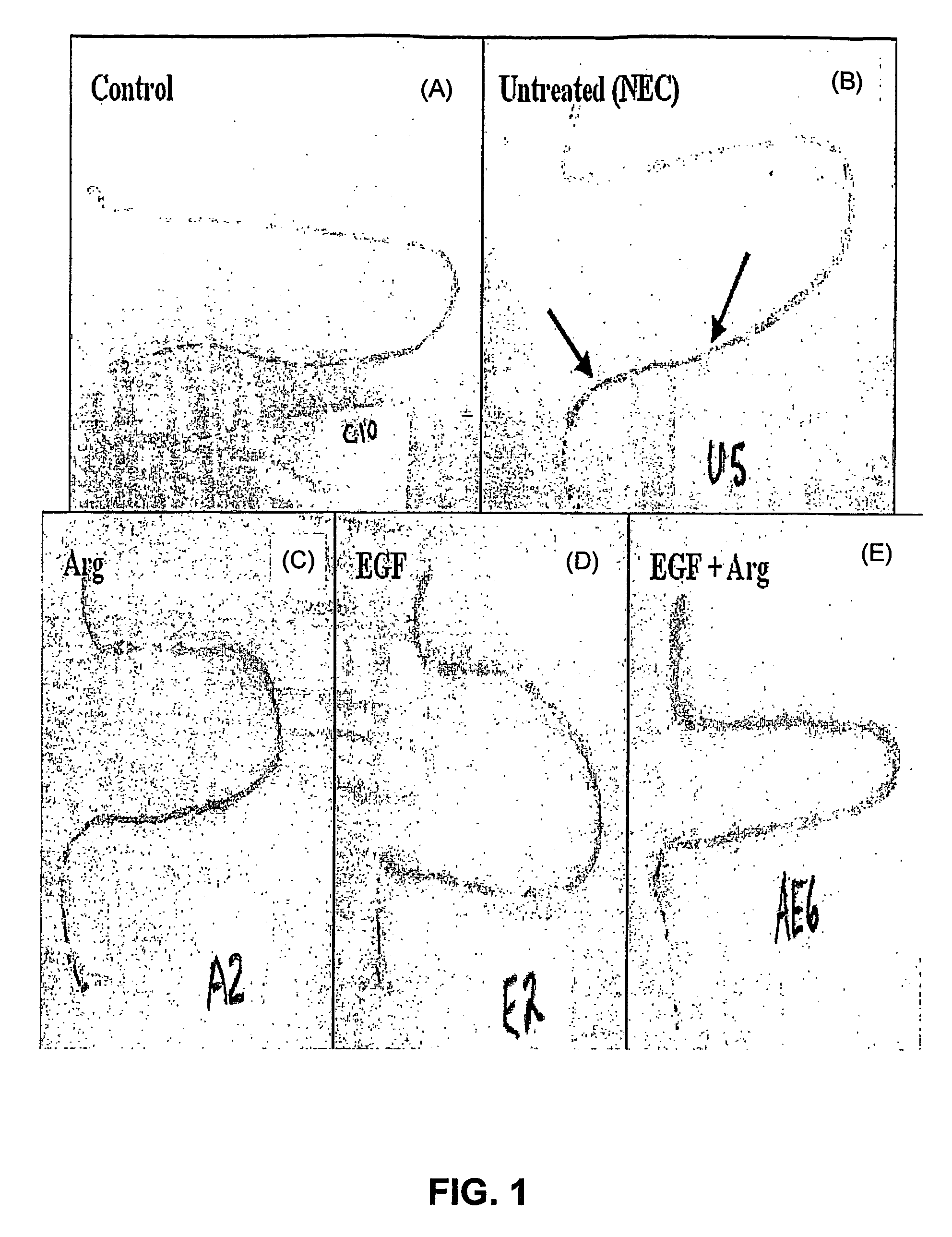
Treatment for Necrotizing Enterocolitis
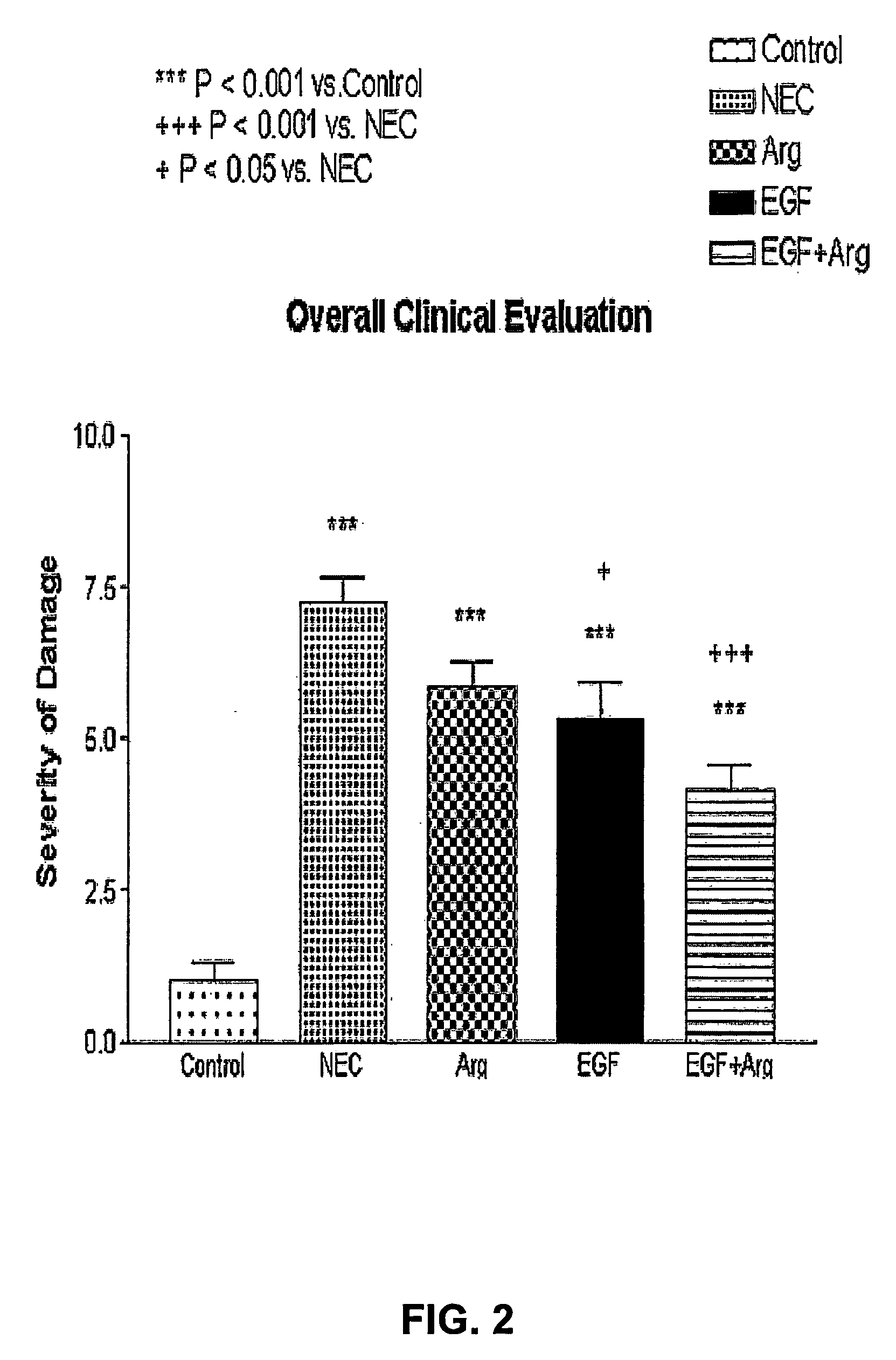
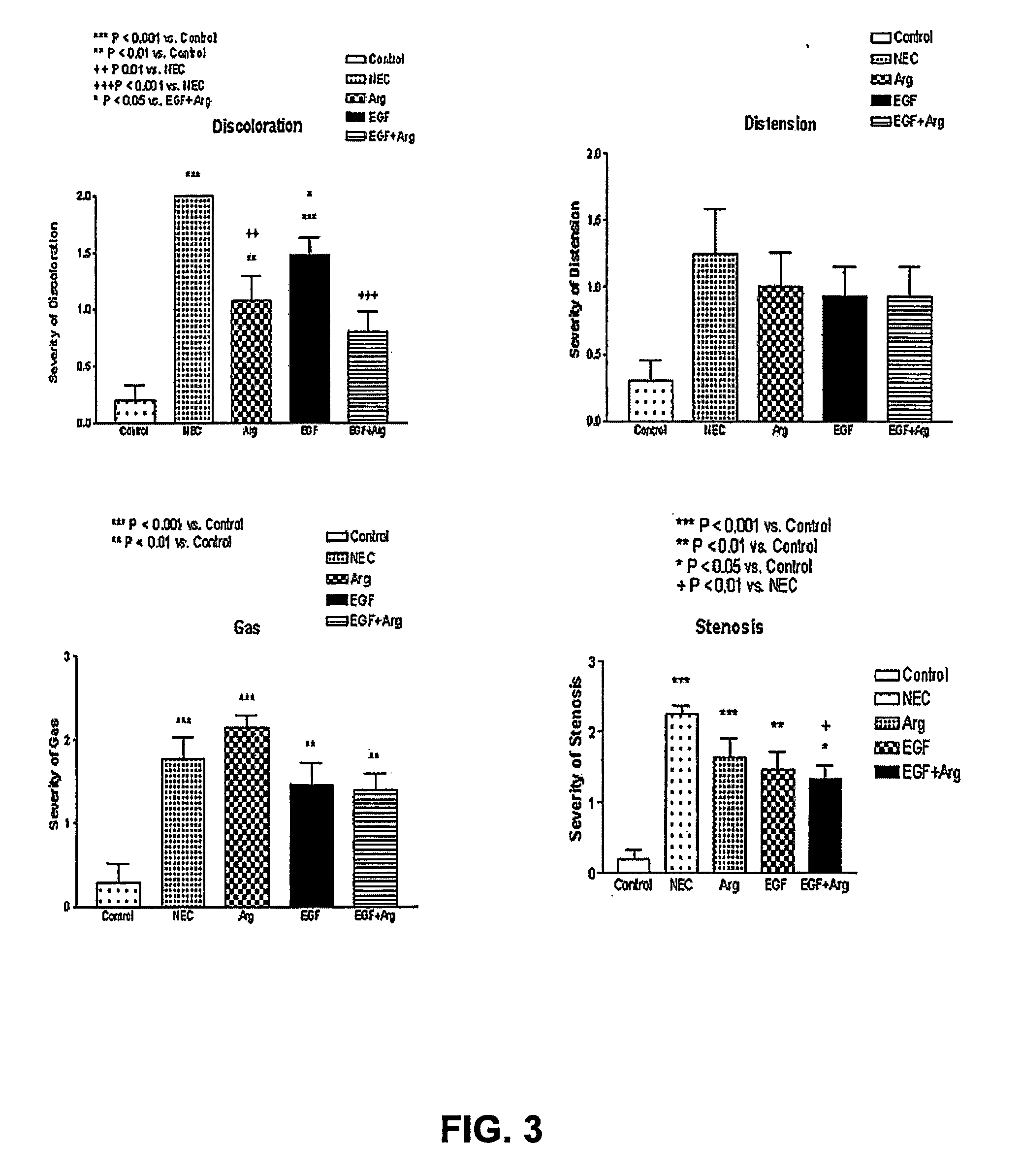
The invention provides compositions and methods for the treatment of necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC). A treatment of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor agonist and L-arginine, a bioequivalent thereof, or NO-donor showed efficacy against NEC. The invention also provides kits, unit doses and uses comprising epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor agonist and L-arginine, a bioequivalent thereof, or NO-donor for the treatment of NEC.
Owner:UNIV TECH INT
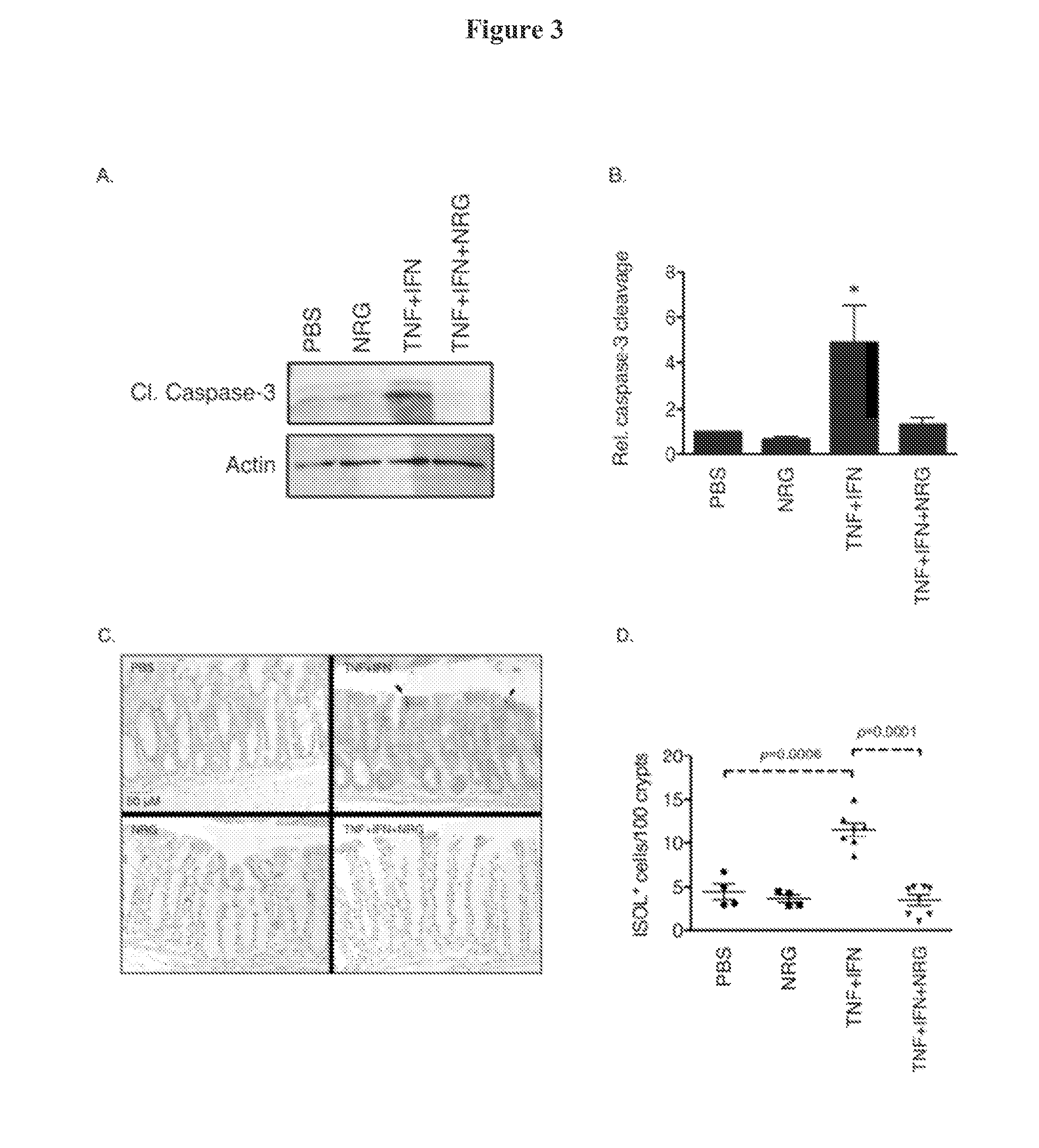
Use of neuregulin-4 for treatment of inflammatory bowel disease and necrotizing enterocolitis
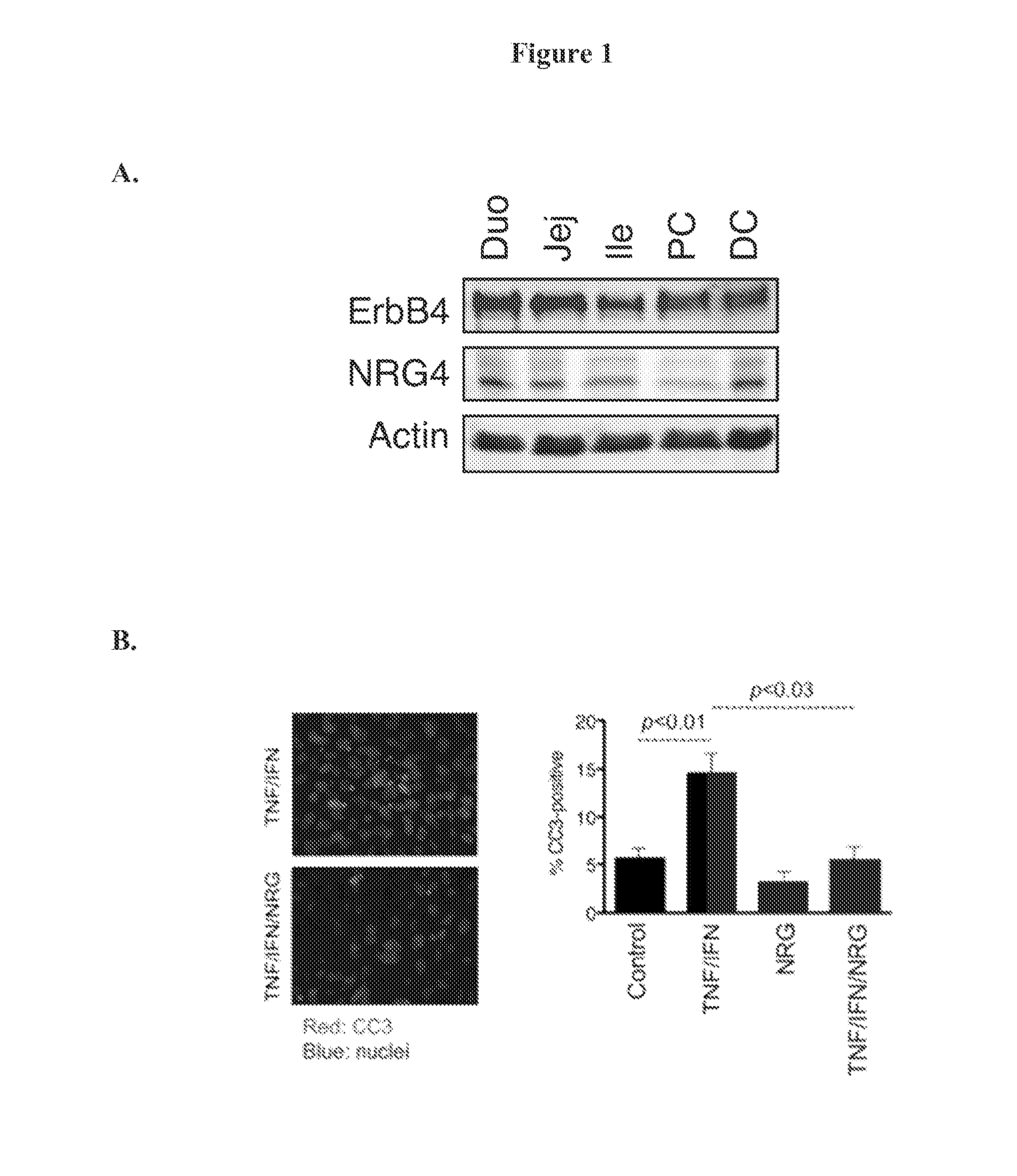
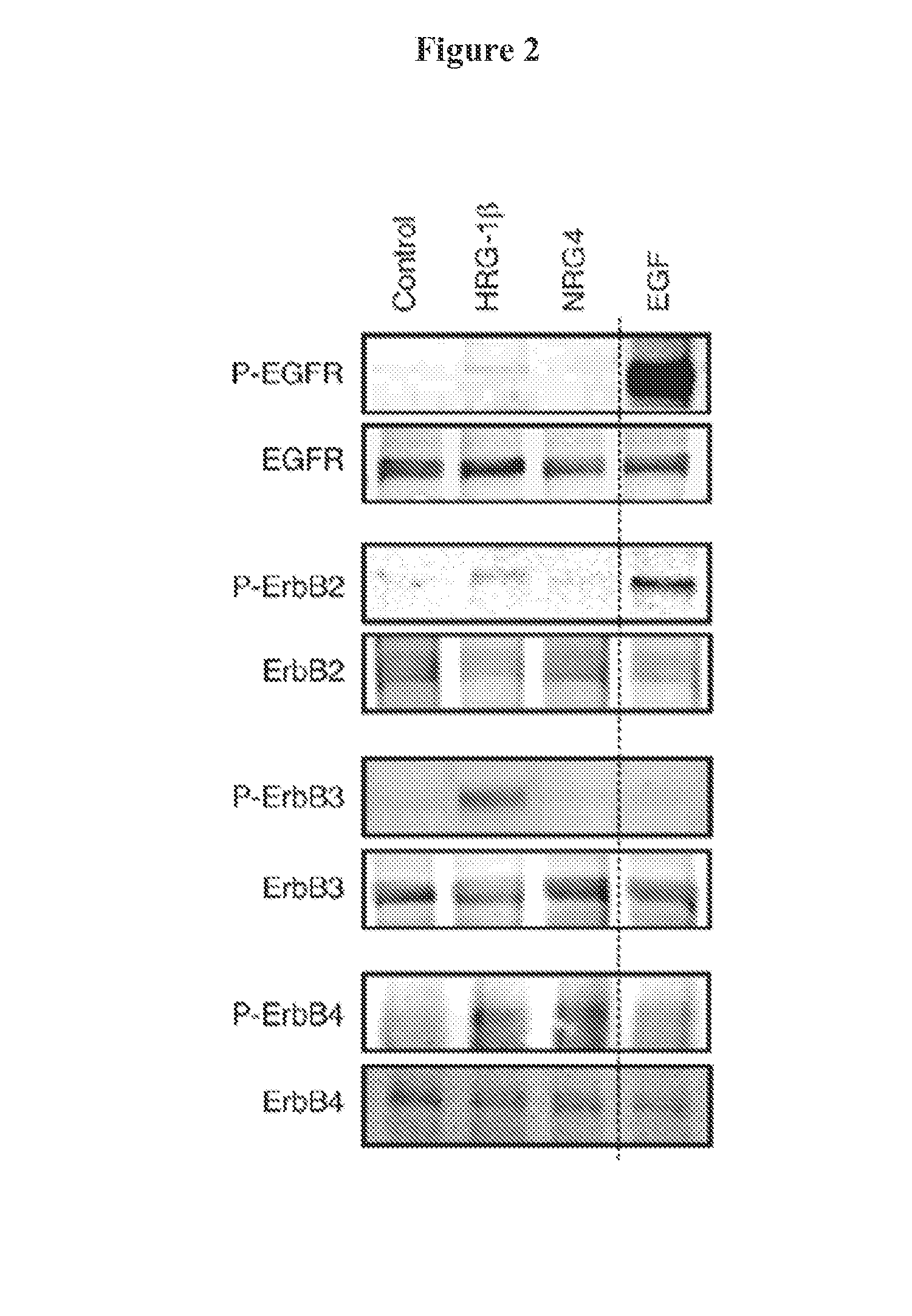
The invention provides methods, pharmaceutical compositions and kits for treating, inhibiting and / or reducing the severity of inflammatory bowel disease and necrotizing enterocolitis in a subject in need thereof by administering an effective amount of a composition comprising an activator of ErbB4.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF LOS ANGELES
Methods for decreasing the incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis in infants, toddlers, or children using human milk oligosaccharides
ActiveUS9539269B2Improving gut function and immunityAccelerated growth and maturationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsMorbidity aspectsDisease
Disclosed are methods of reducing the incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis in an infant, toddler, or child using nutritional compositions including human milk oligosaccharides. The nutritional compositions including the human milk oligosaccharides are effective in reducing inflammation and the incidence of inflammatory diseases.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Pharmaceutical combination for the treatment of tissue damage owing to an arterial irrigation defect
This invention relates to a medicine for humans, and particularly to a pharmaceutical combination comprising Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) and Growth Hormone secretagogue hexapeptide (GHRP) for use in preventing tissue damage due to blood flow suppression by enhancing tissue repair following ischemic damage. The aforementioned combination may be applied as a single pharmaceutical composition. Alternatively, an individual may also receive both EGF and GHRP in a separate manner but within a single therapeutic regime to enhance cellular survival when organs are subjected to blood flow deprivation for a critical period of time. This combination attenuates reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation and its associated cytotoxicity. It is also useful in promoting cellular survival when tissue or organs are exposed to prolonged ischemic periods. The combination is useful as a prophylactic agent in those subjects prone to multiple organ failure (MOF) such as burn victims, multiple trauma patients, hypoxic neonates, acute respiratory distress syndrome patients, and necrotizing enterocolitis patients.
Owner:CENT DE ING GENETICA & BIOTECNOLOGIA
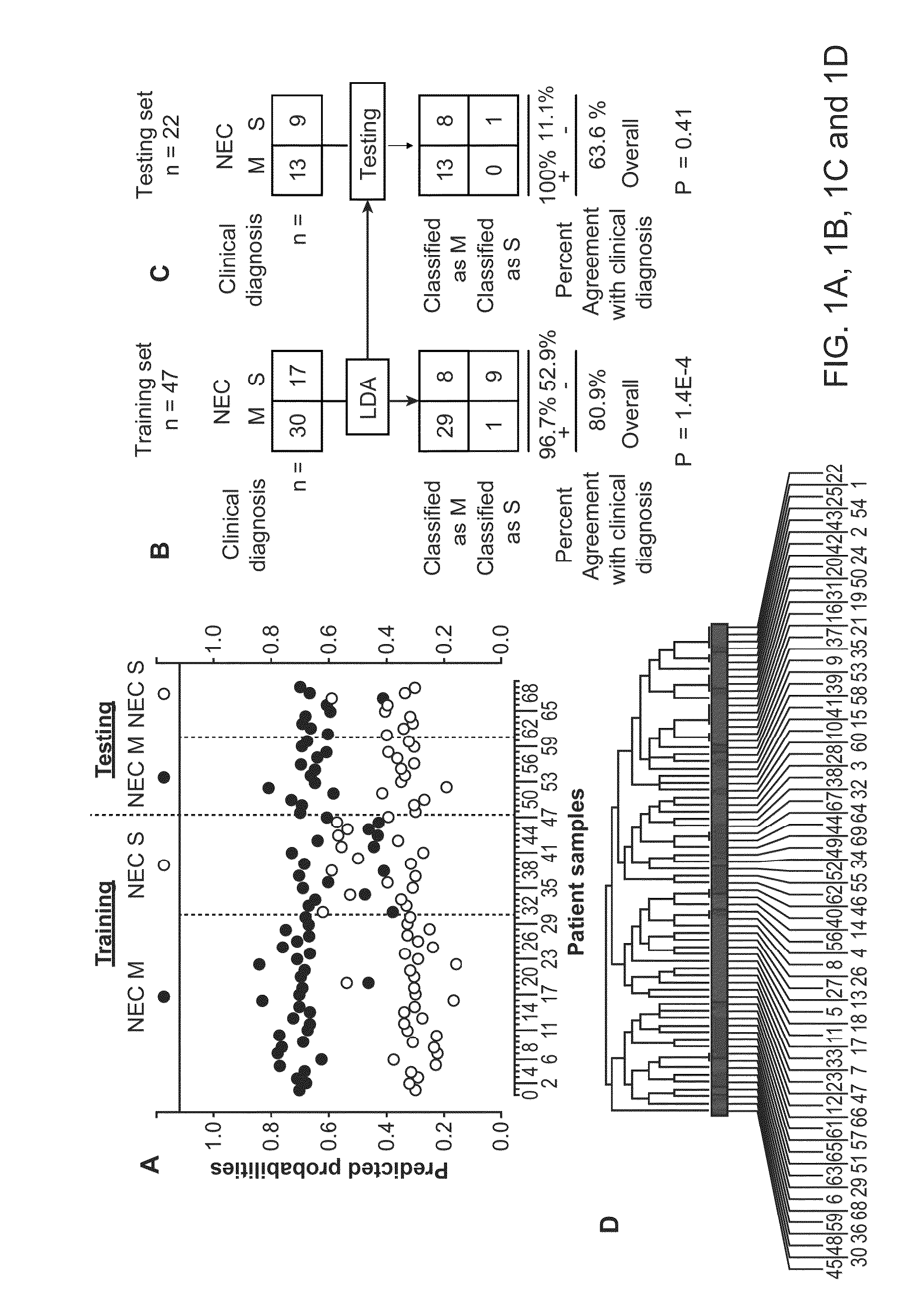
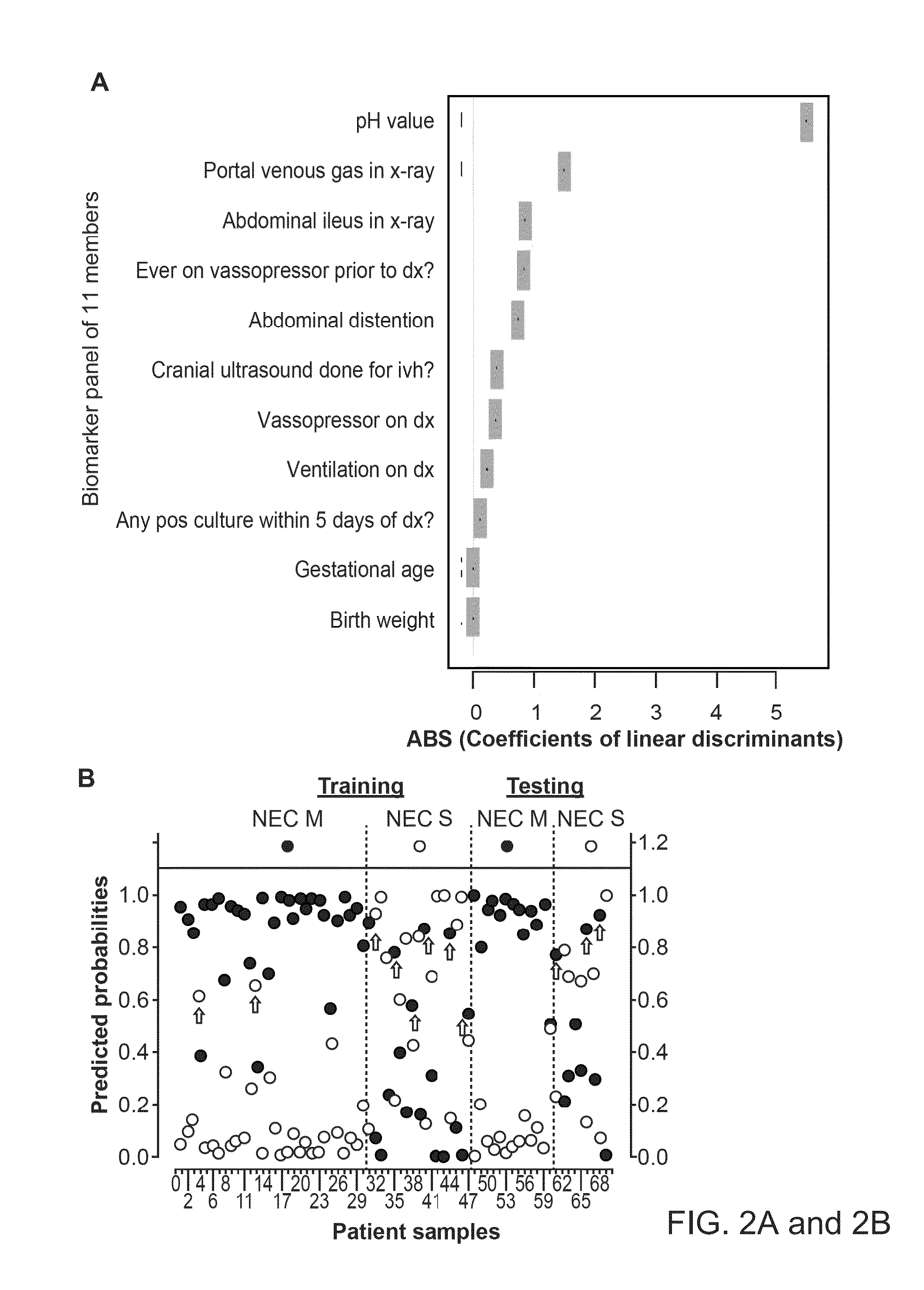
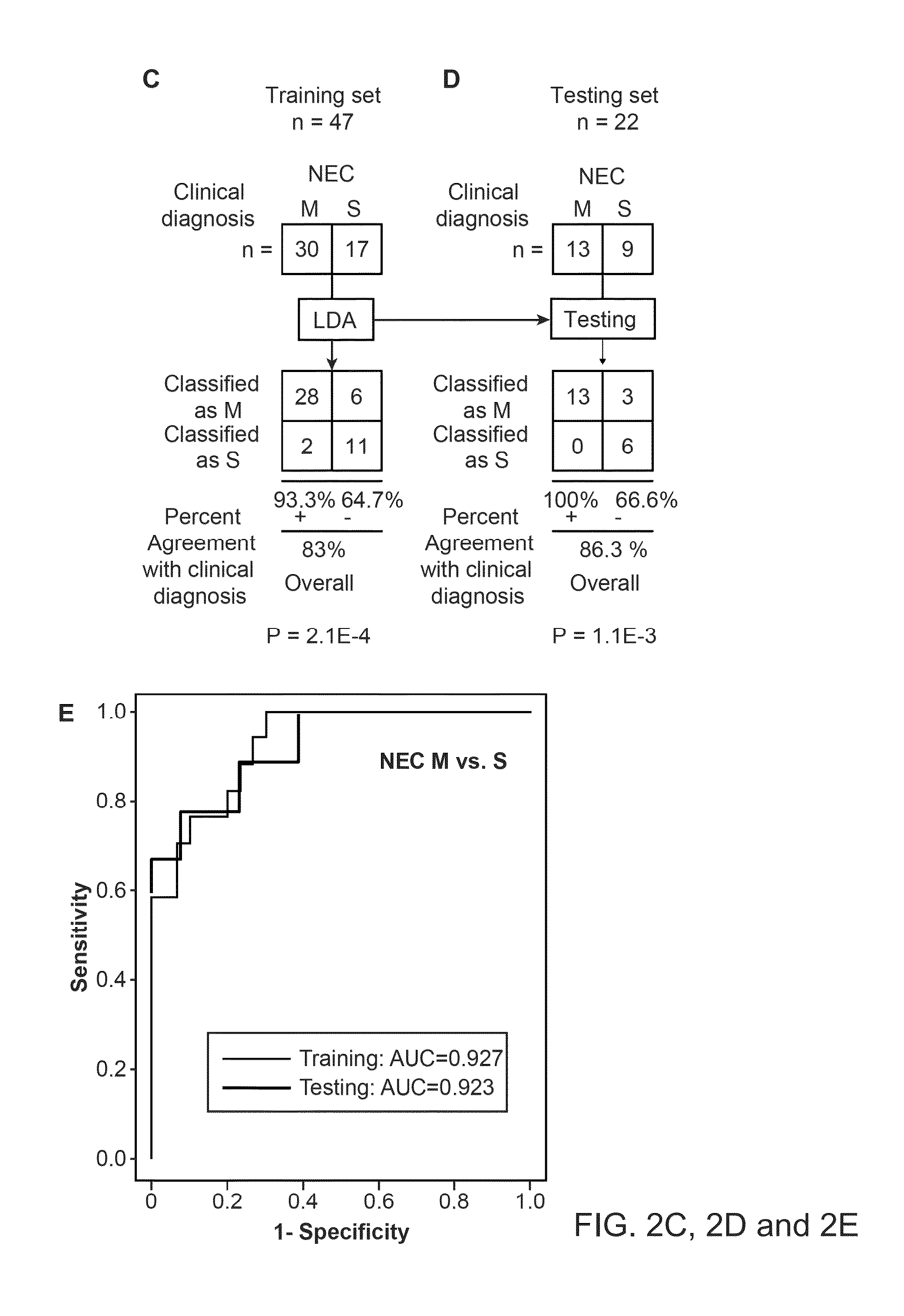
Urine biomarkers for necrotizing enterocolitis and sepsis
InactiveUS20140162370A1Prediction of responsivenessDisease diagnosisBiological testingBacteriuriaUrine biomarkers
Aspects of the invention include methods, compositions, and kits for diagnosing Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC), for diagnosing sepsis, for providing a prognosis for a patient with NEC, and for predicting responsiveness of a patient with NEC to medical intervention. These methods find use in a number of applications, such as diagnosing and treating infants who are suspected of having NEC, intestinal perforation (IP), or sepsis.
Owner:RES INST AT NATIONWIDE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com