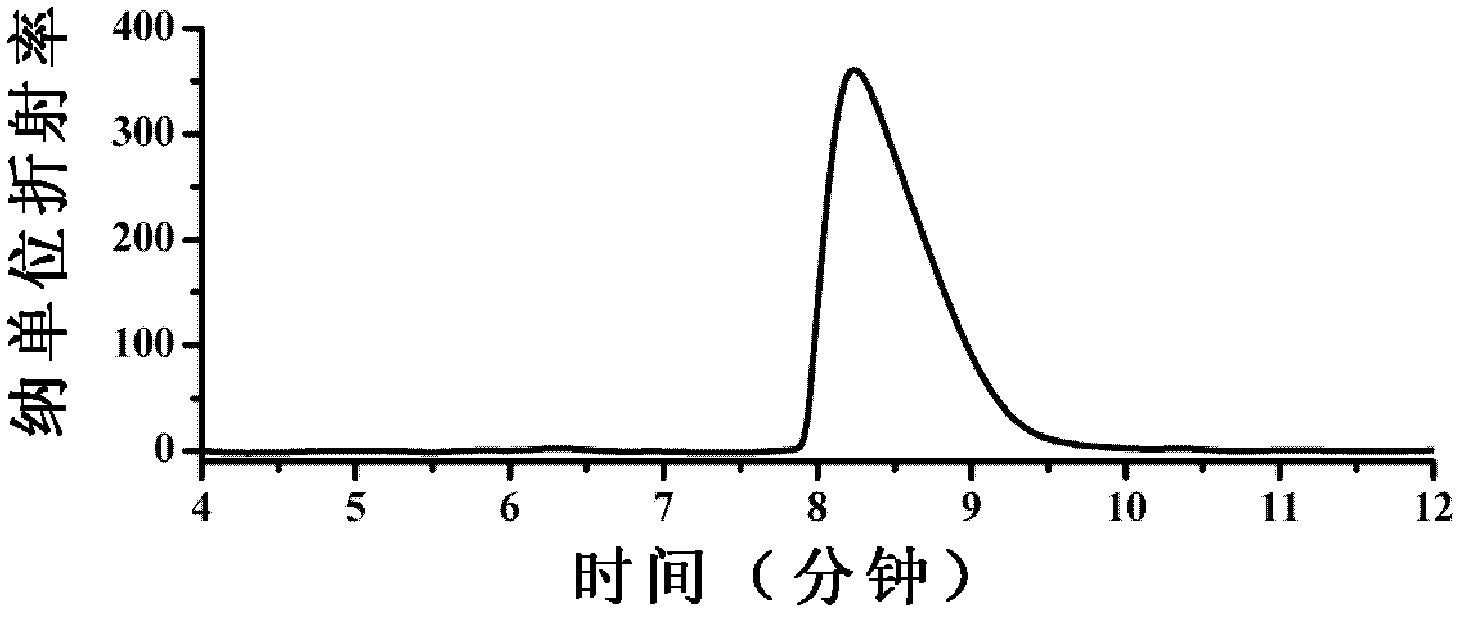
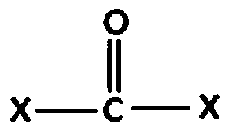Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
44 results about "1,2-Butanediol" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
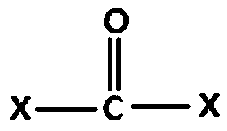
1,2-Butanediol is the organic compound with the formula HOCH₂(HO)CHCH₂CH₃. It is classified as a vic-diol (glycol. It is chiral, although typically it is encountered as the racemic mixture. It is a colorless liquid.
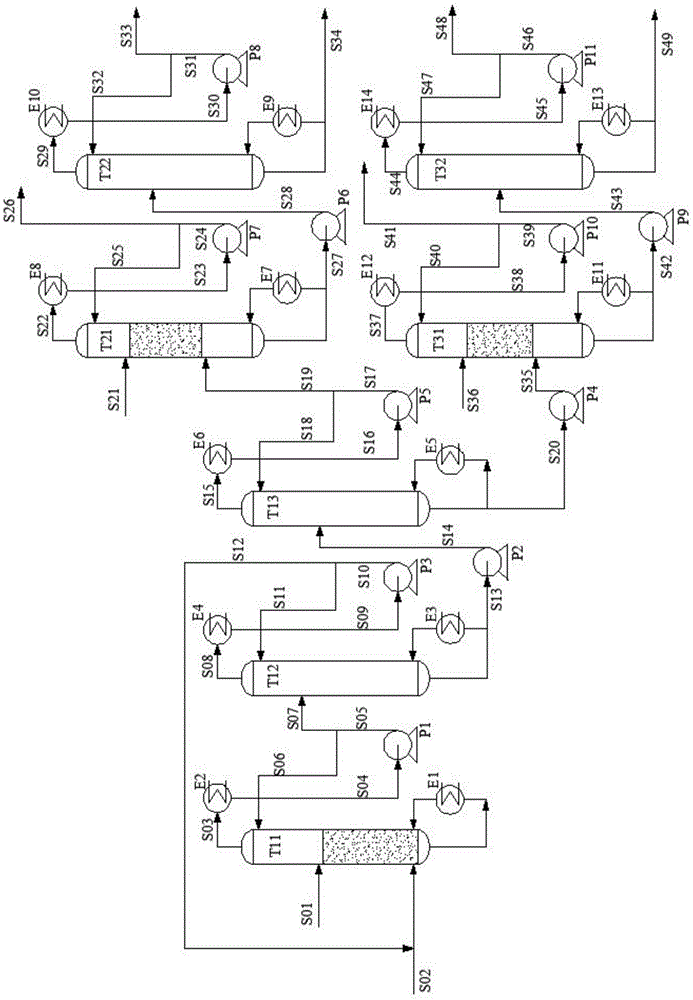
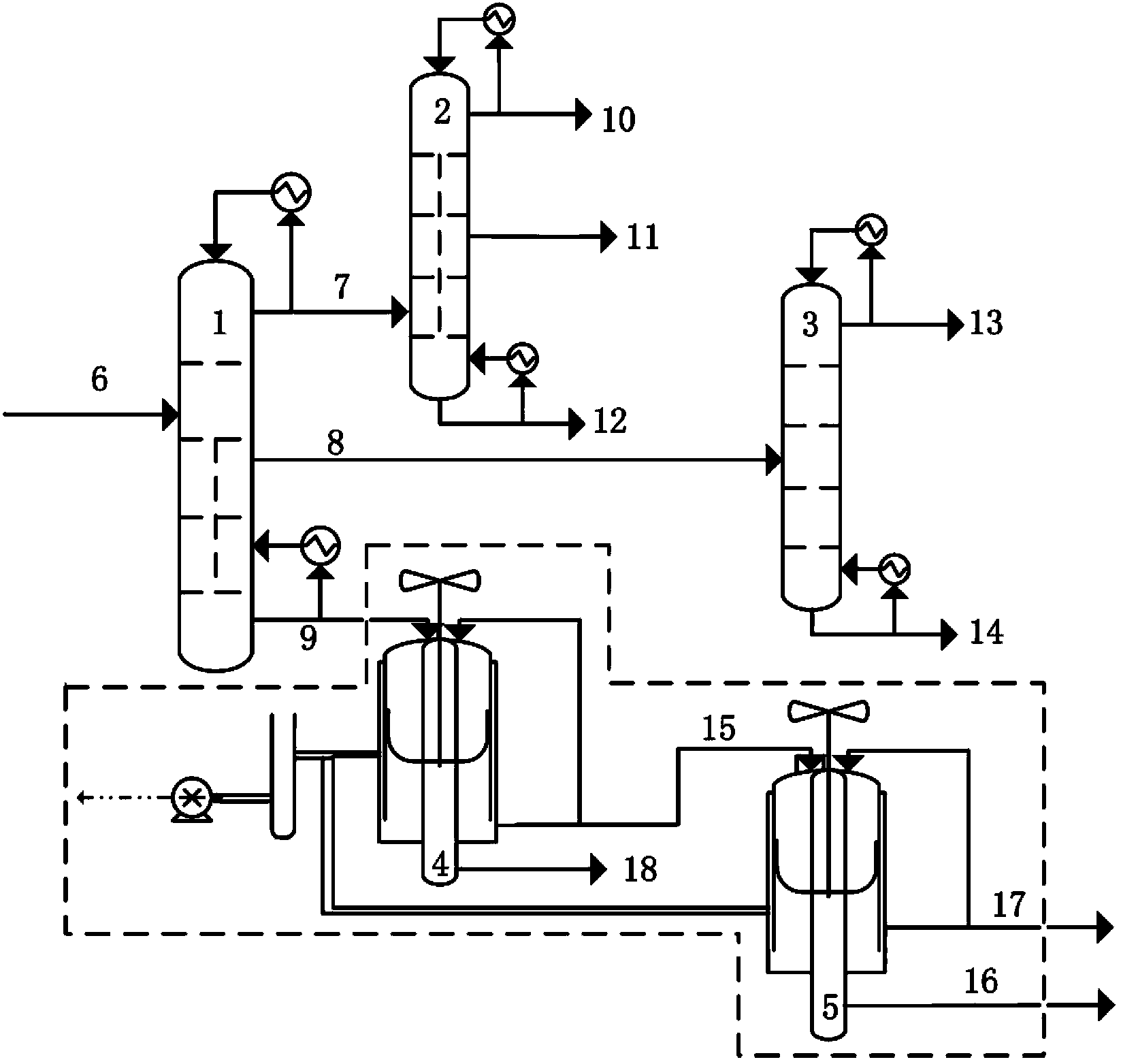
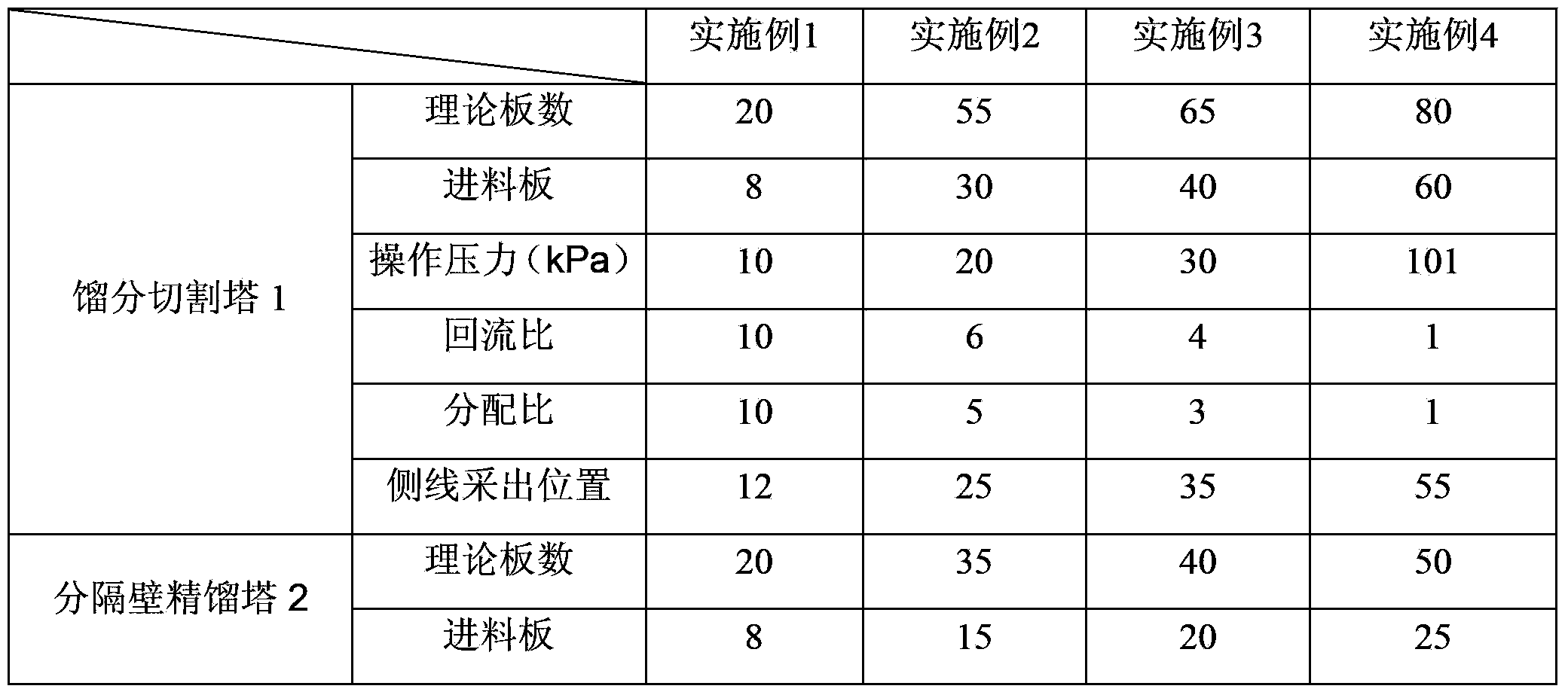
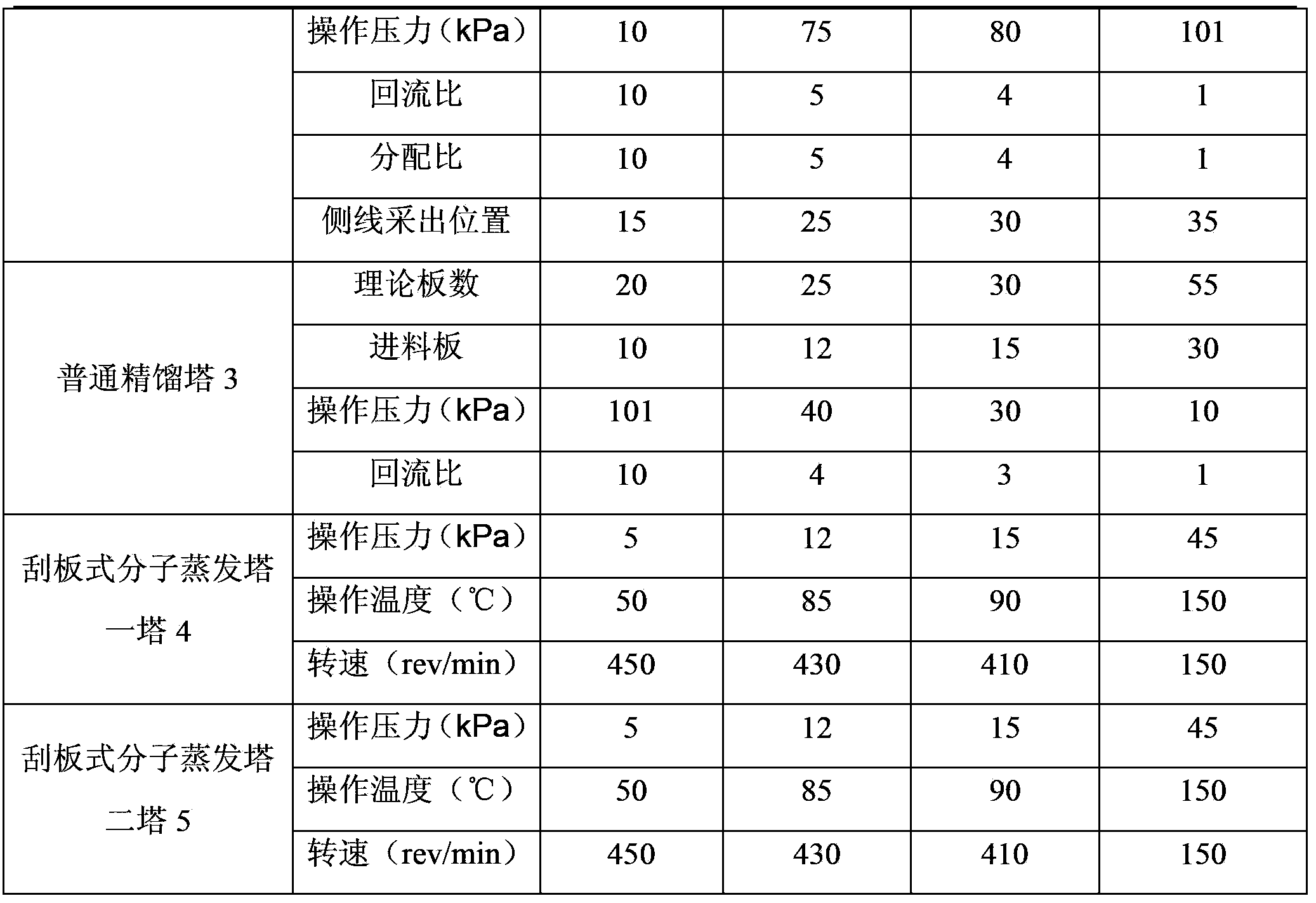
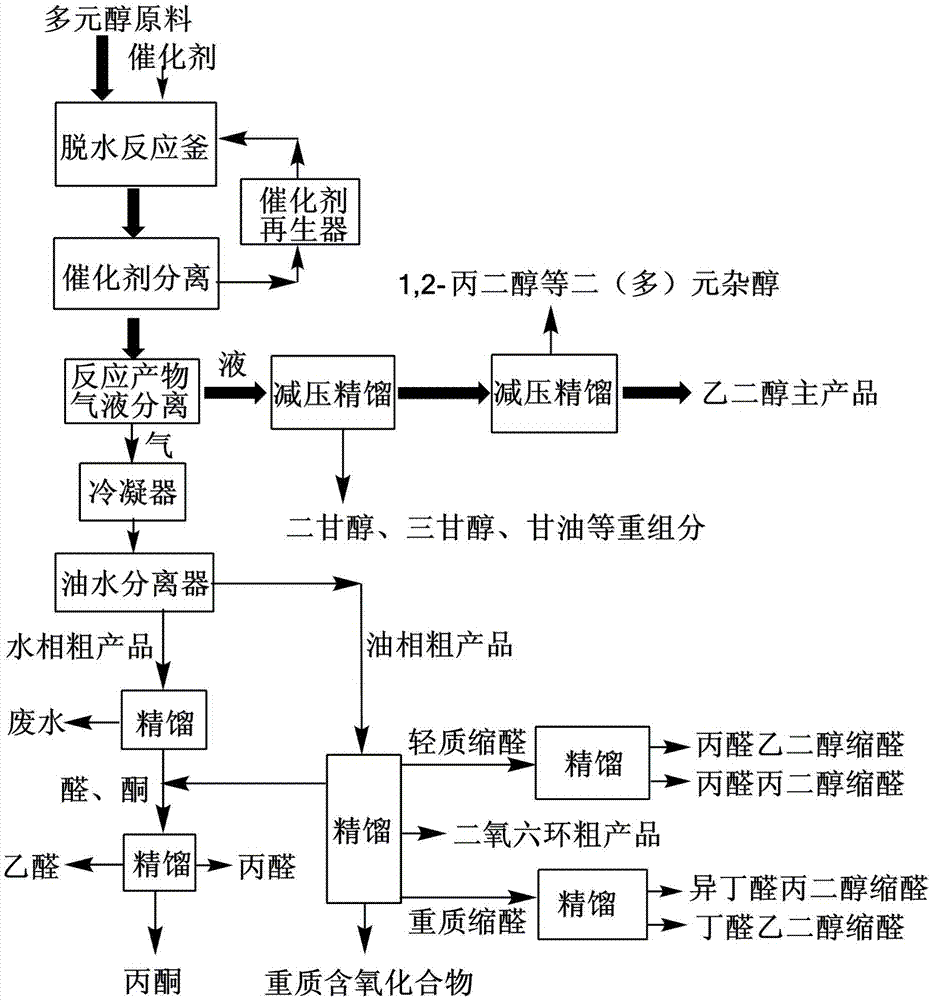
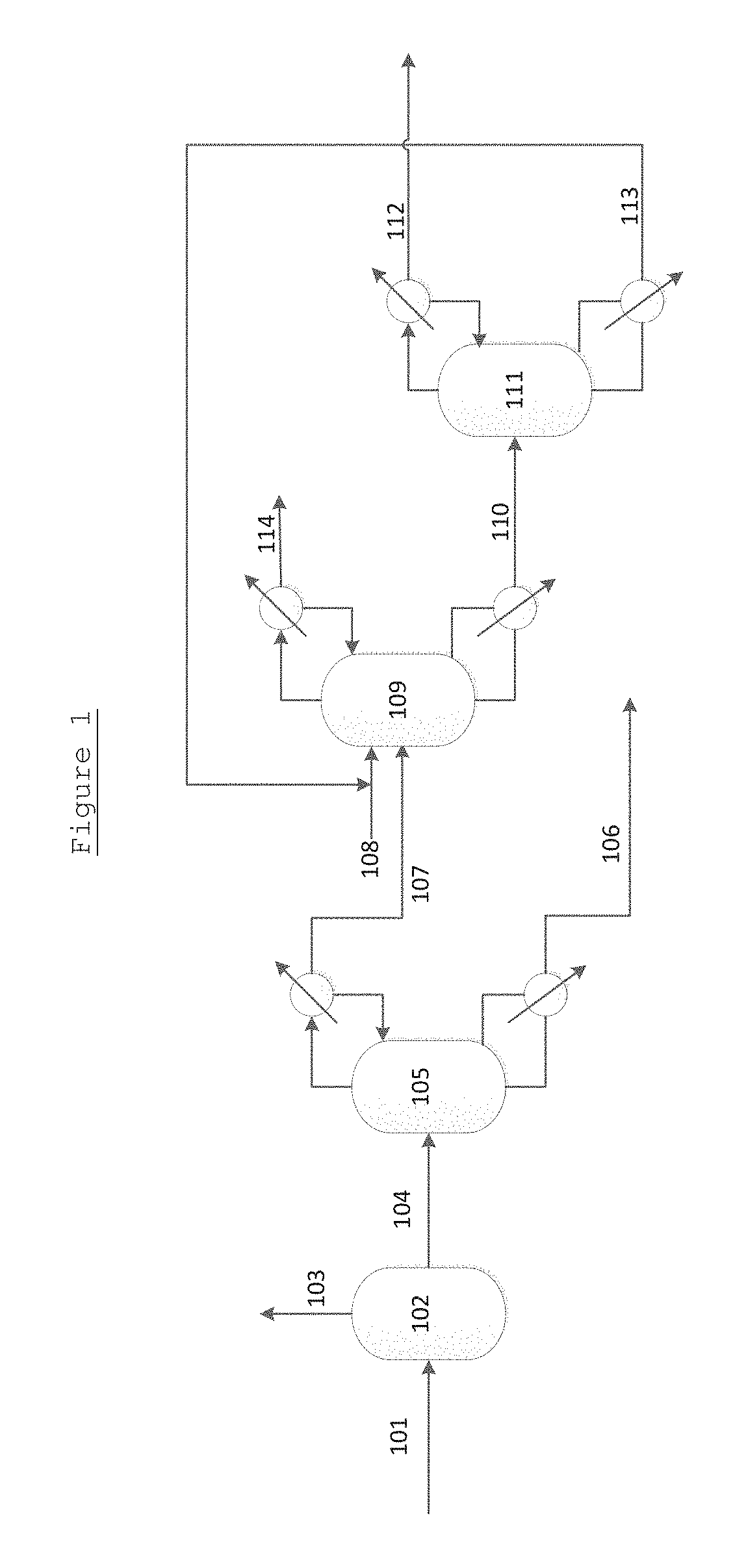
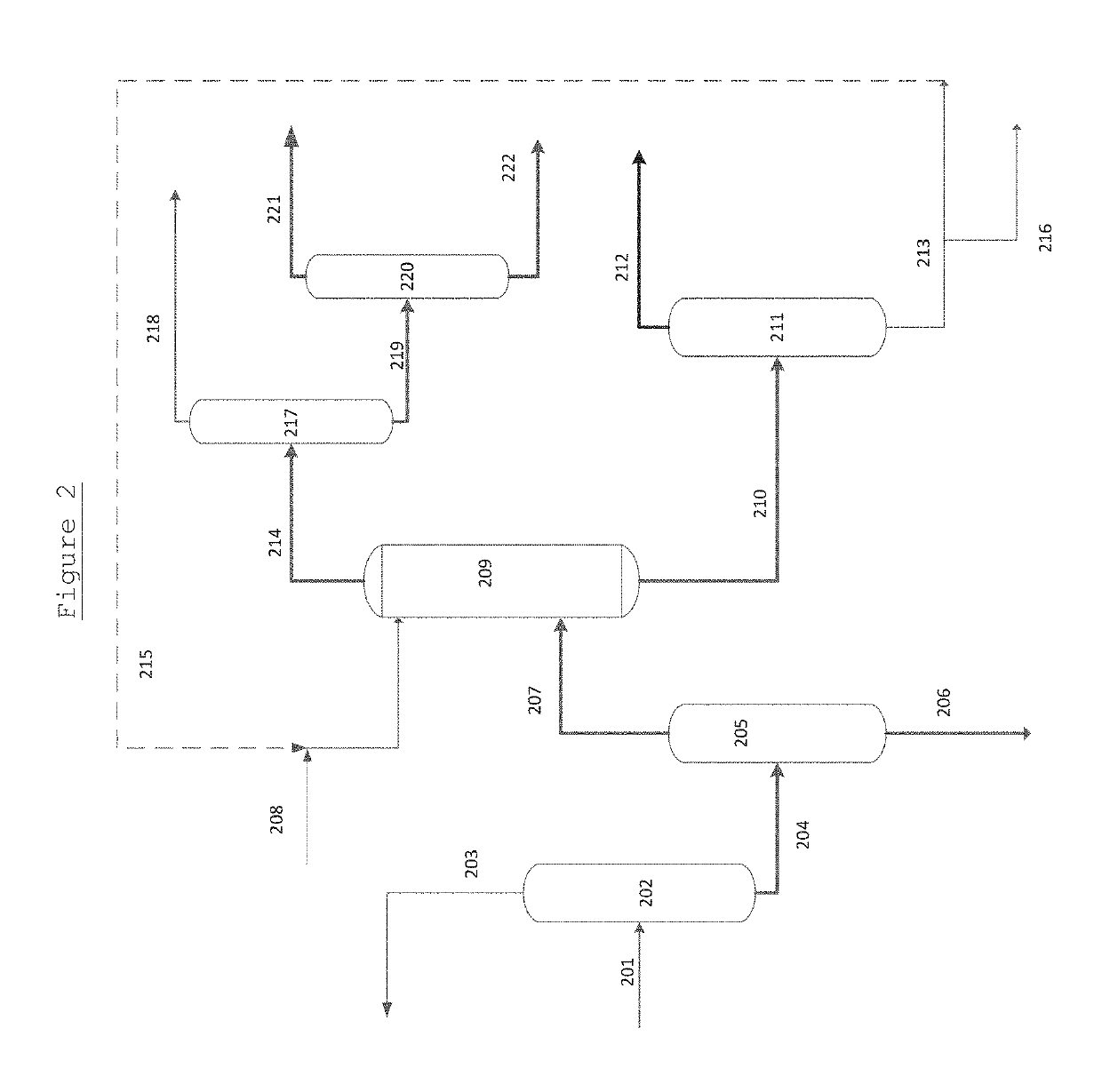
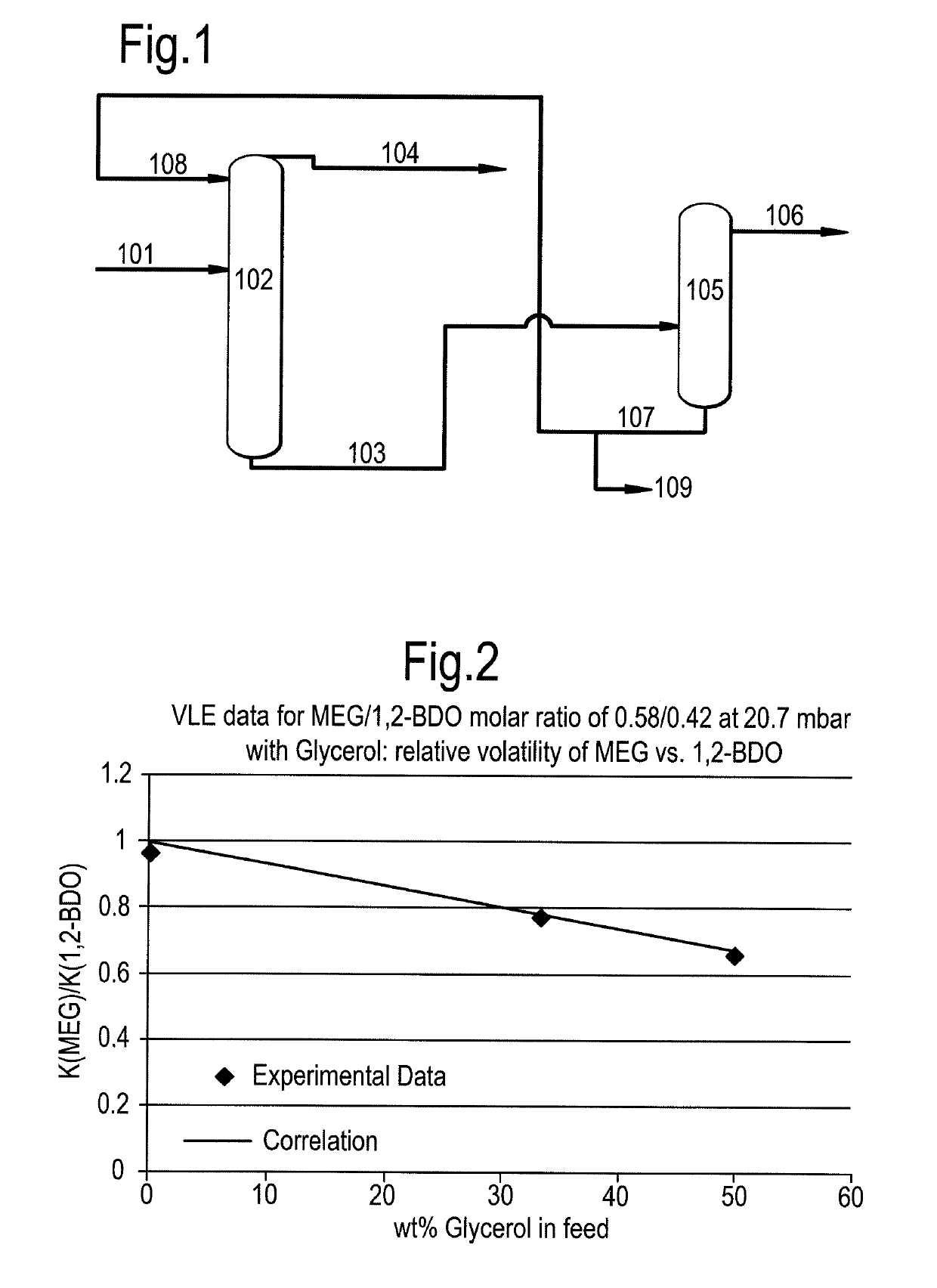
Process for separating ethylene glycol and 1, 2-butanediol
ActiveUS20130284584A1High purityBig investmentOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationButanediolGlycol synthesis
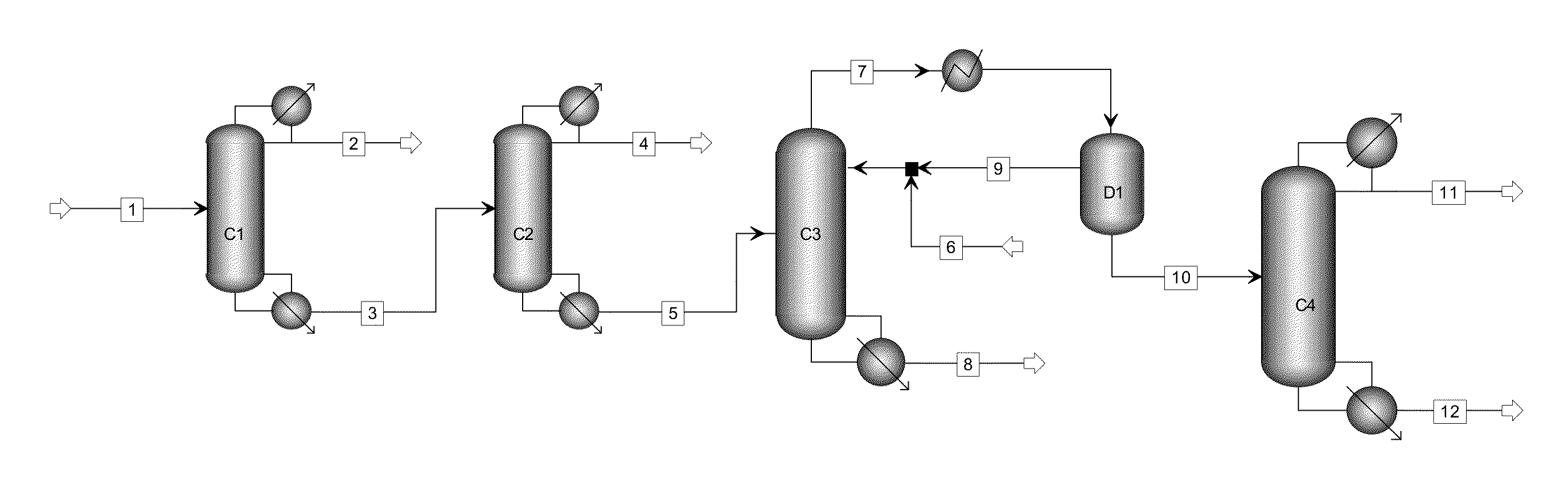
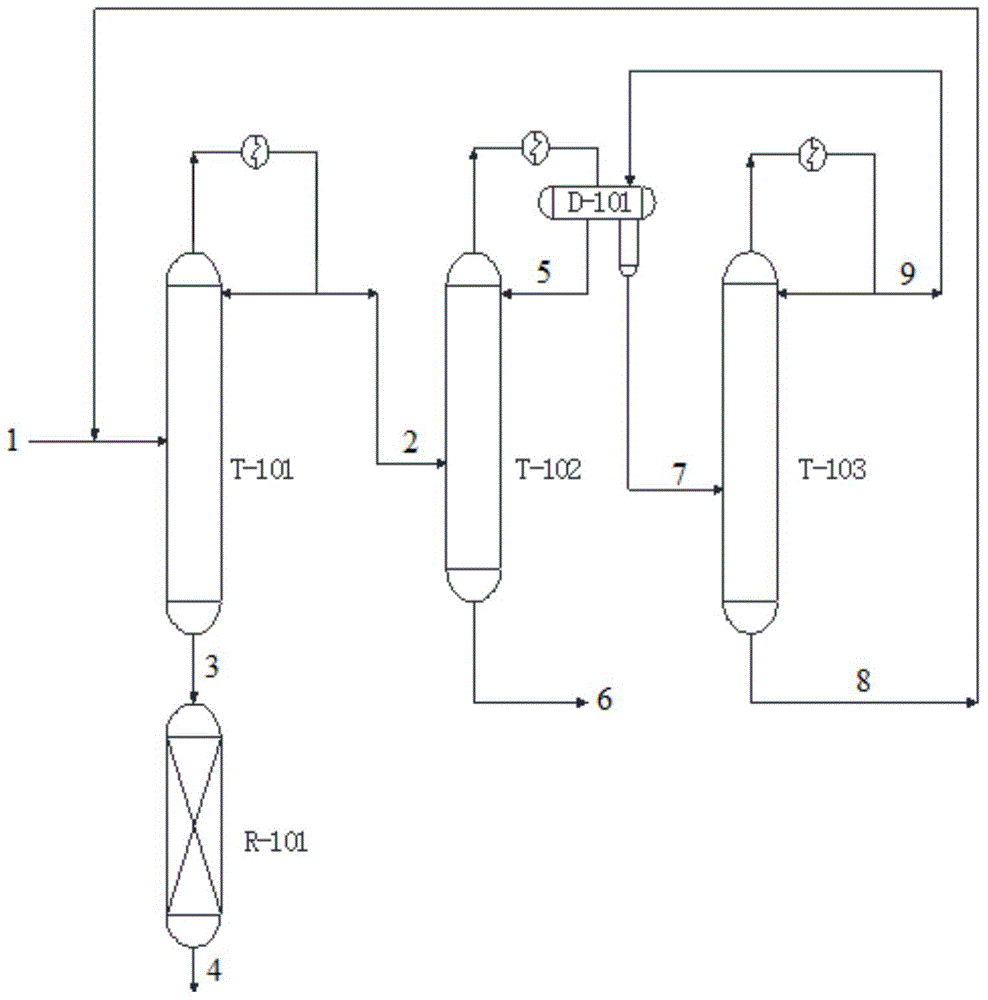
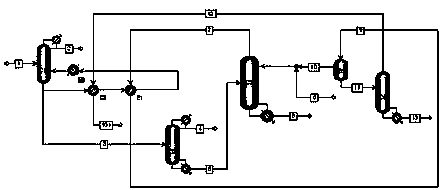
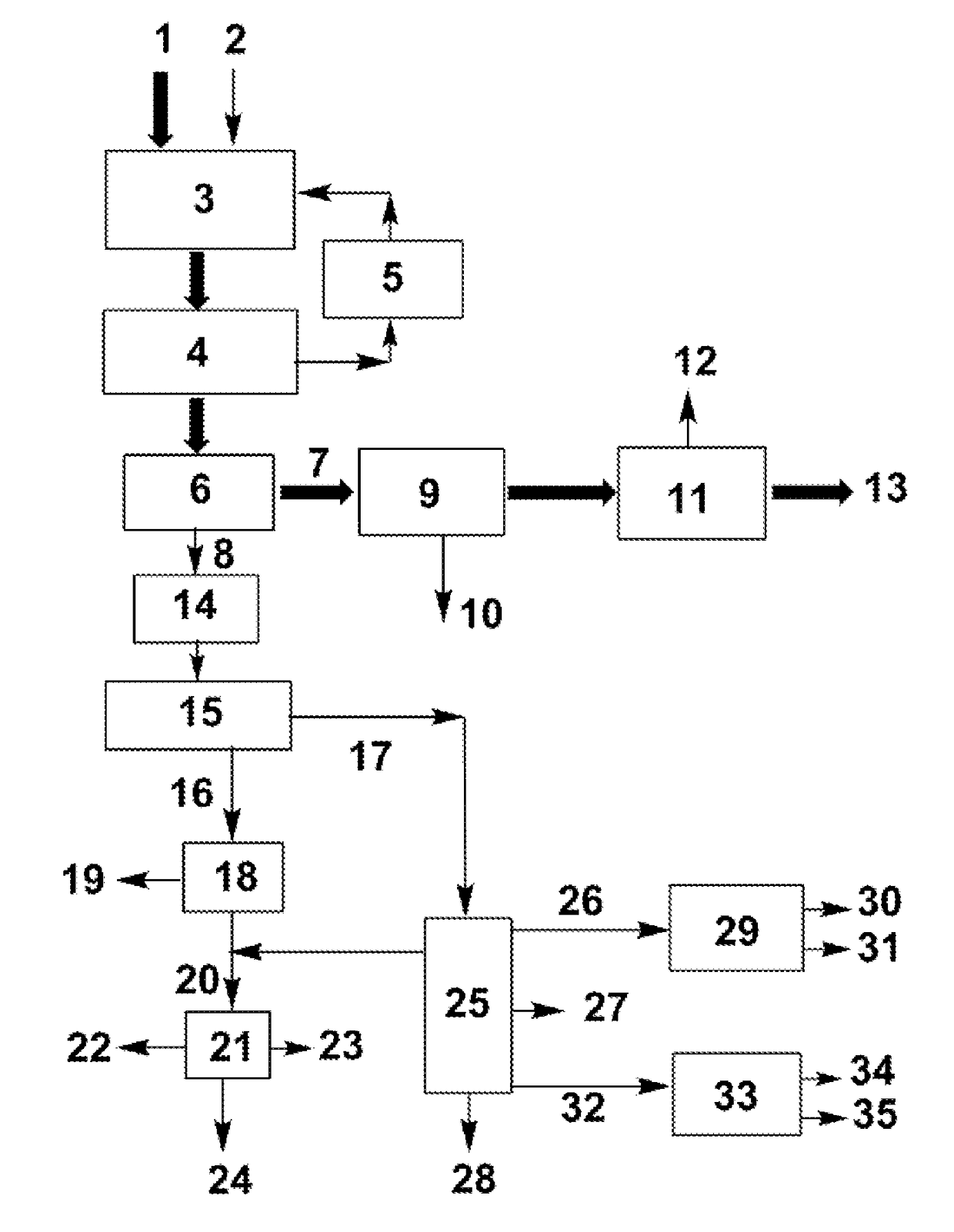
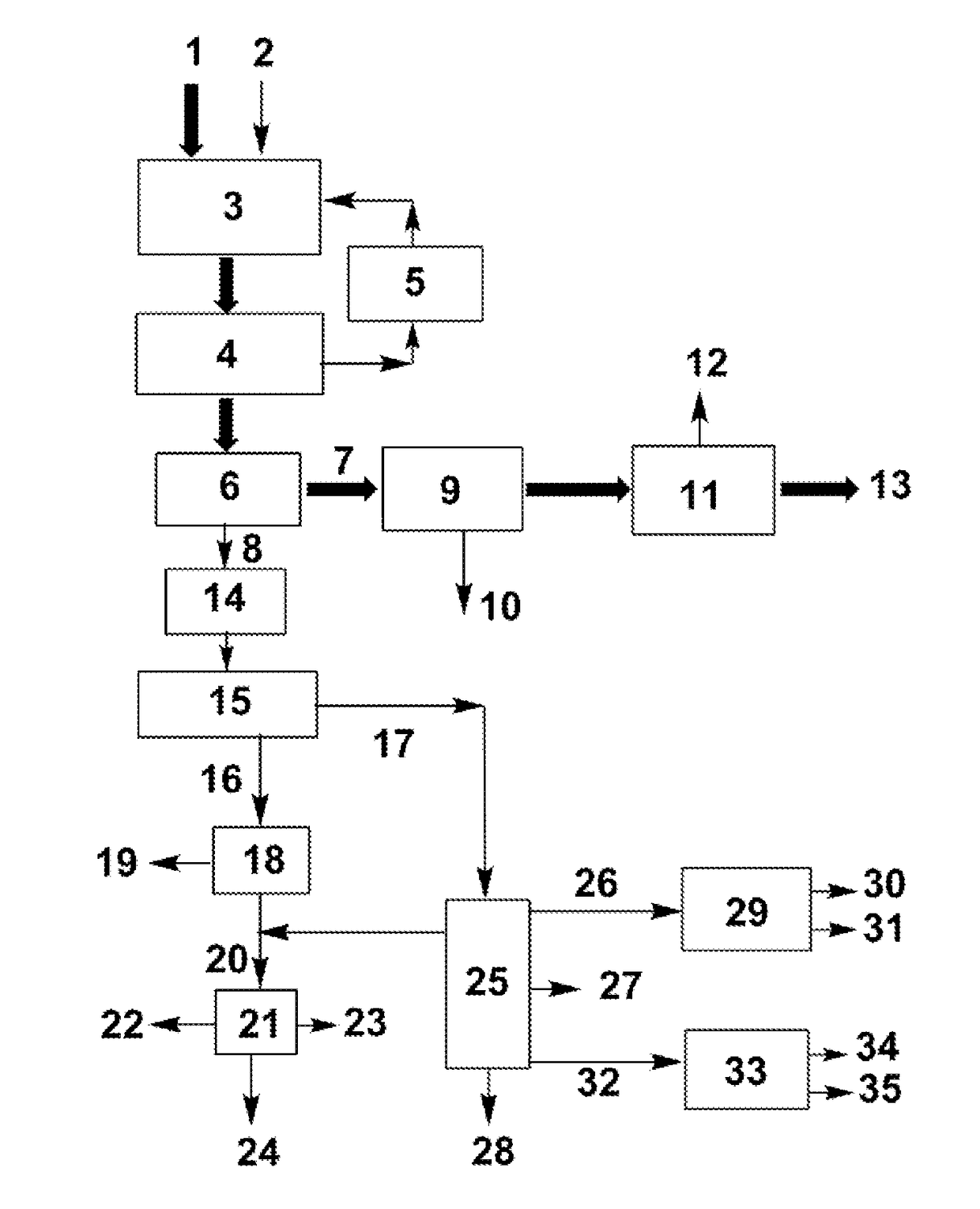
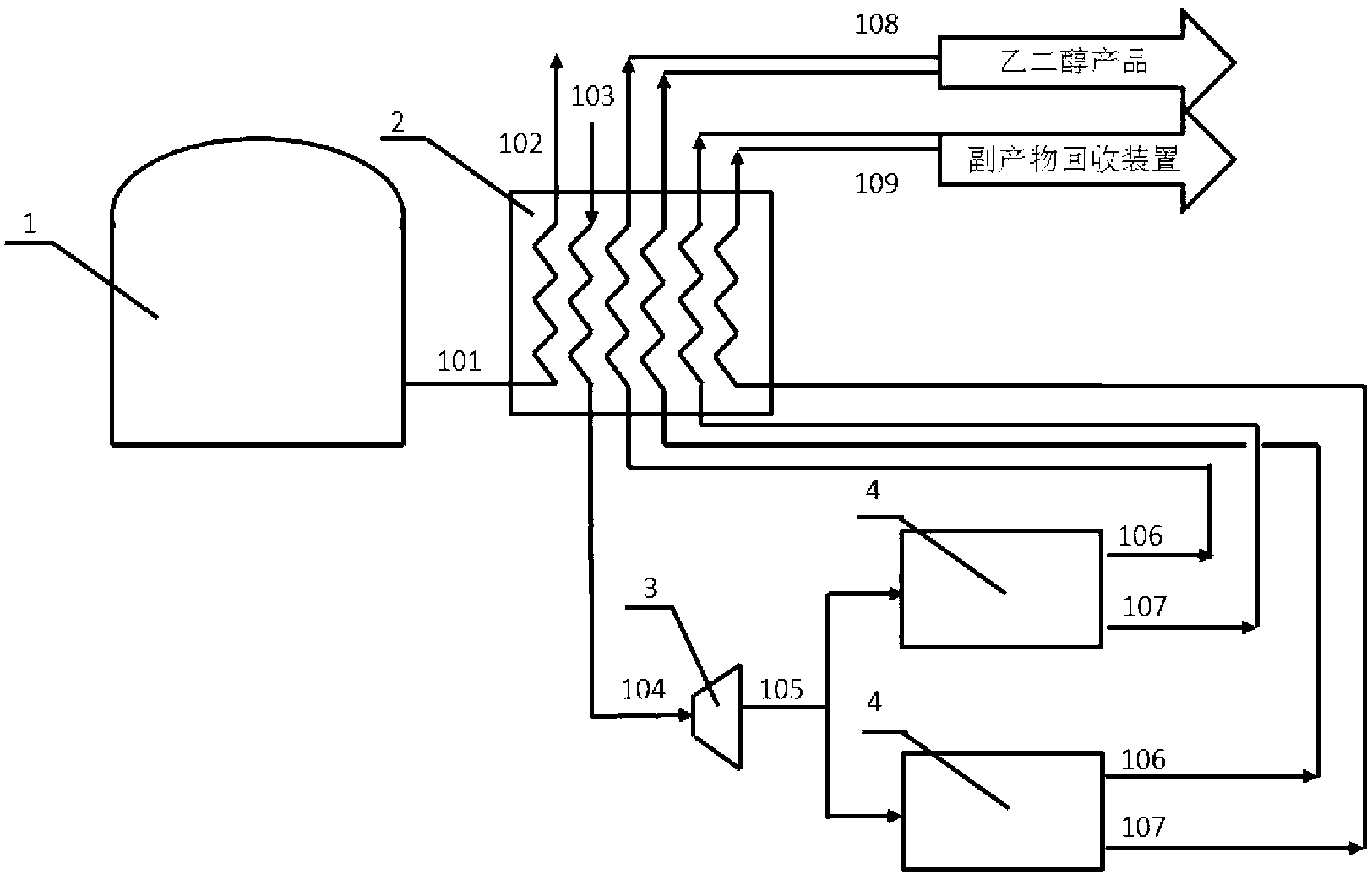
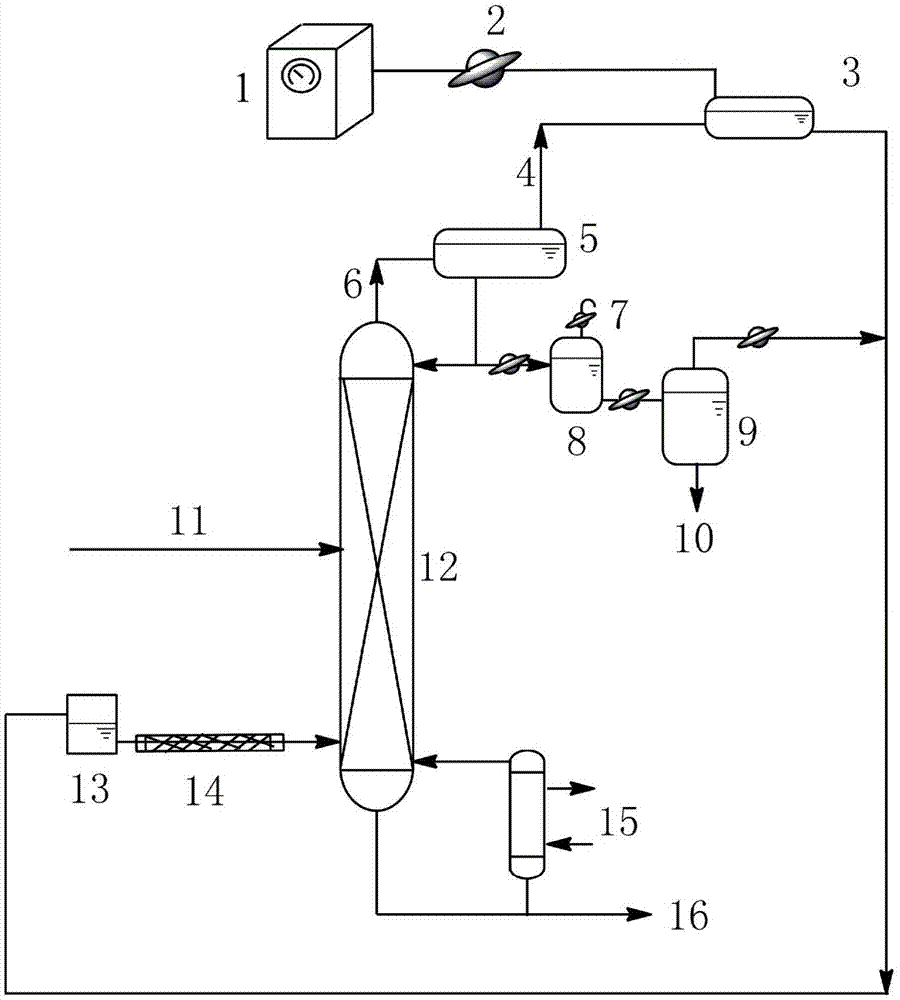
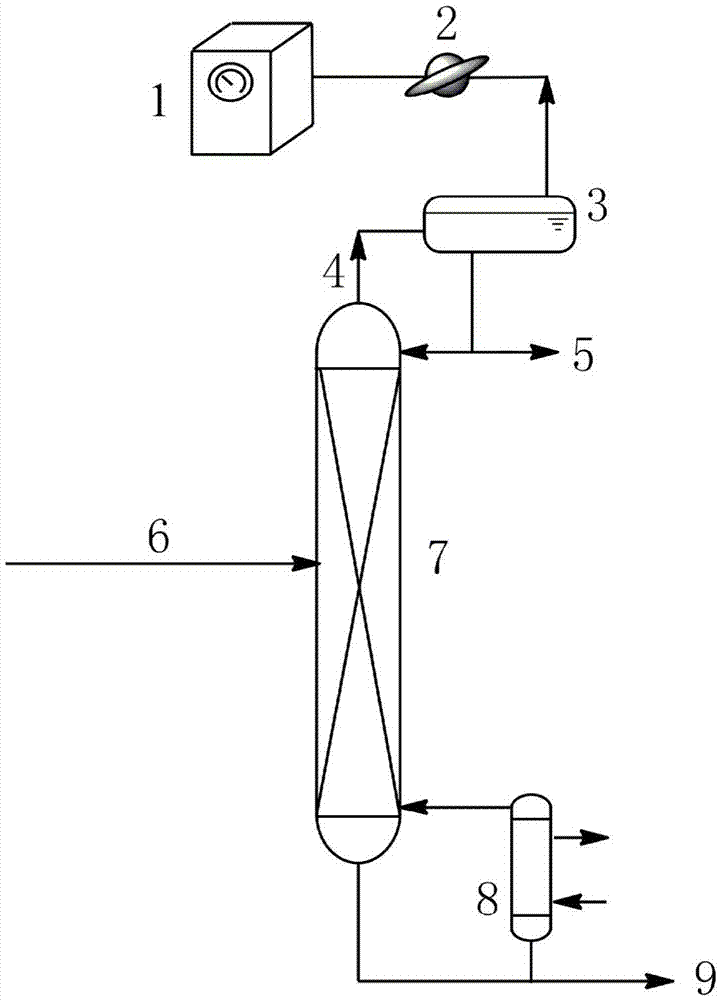
The present invention relates to a process for separating ethylene glycol and 1,2-butanediol. A material flow containing ethylene glycol and 1,2-butanediol gets into the lower-middle part of the azeotropic rectification column C3 after the light components are removed by the separating columns C1 and C2, wherein the ethylene glycol and the azeotropic agent added from the top of the column form azeotrope which is distilled out from the top of the column and gets into the phase separator D1 after being condensed, the upper phase enriched with azeotropic agent after the phase was separated returns to the top of the column to continue to participate in azeotropy, and the lower phase enriched with ethylene glycol gets into the fourth separating column C4 to be refined to obtain the ethylene glycol product.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
Method for separating glycol and 1,2-butanediol
InactiveCN103772146AReduce solubilityImprove solubilityOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationTheoretical plateReflux
The invention relates to a method for separating glycol and 1,2-butanediol, which mainly solves the problems of high investment and energy consumption due to the fact that a very high reflux ratio and very high number of theoretical plates are required when a common rectification method is employed to separate and purify a material flow containing glycol and 1,2-butanediol, and severe separation conditions or a non-ideal separation effect when a common azeotropic rectification method is employed. The method better solves the problem by employing the technical scheme that the material flow containing glycol and 1,2-butanediol and a reactor enters from the upper part and the lower part of a reaction-azeotrope rectification tower respectively, a generated reaction product forms an azeotrope with glycol at the same time, a tower kettle obtains a material flow containing 1,2-butanediol, and after the azeotrope distilled from the tower top is subjected to condensation phase splitting, a glycol-rich phase at the lower layer is further refined to form a glycol product. The method can be used for industrial production of separating the material flow containing glycol and 1,2-butanediol.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Synthetic method of polyethylene glycol terephthalate from biomass glycol
The invention discloses a synthetic method of polyethylene glycol terephthalate from biomass glycol. The glycol is prepared in to biomass through a chemical conversion method, and subjected to synthesis polyester reaction with terephthalic acid, wherein a catalyst is a composite catalyst. The biomass glycol and terephthalic acid in the molar ratio of 1.2:1-1.5:1 are added into a reaction kettle for esterification, wherein a stabilizer is triphenyl phosphate; and finally obtained by a condensation polymerization is carried out to obtain the polyester. glycol accounts for 95%-99.9% in the biomass glycol, and the trace alcohols are ethanol, 1, 2-propylene glycol, 1,2-butanediol, 1,2-pentadiol and 1,2-hexanediol. The technology of the invention is mainly to solve the influence of fusel on PET synthesis, and can synthesize PET polyester with quality standards satisfied from fusel-containing glycol.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Separating method for ethylene-glycol and 1,2-butanediol
ActiveCN103772147AReduce solubilityReduce lossesOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationTheoretical platePhase splitting
The invention relates to a separating method for ethylene-glycol and 1,2-butanediol and mainly solves the problems that when the ethylene-glycol and the 1,2-butanediol are separated and purified in the prior art, a common precise distillation method requires very high reflux ratio and theoretical plate number, resulting in large investment and high energy consumption; an azeotropic distillation method is harsh in separation condition and undesirable in separating effect. According to the method adopting the technical scheme that material flow containing the ethylene-glycol and the 1,2-butanediol enters into an azeotropic rectification column from the lower part and an azeotropic agent enters the azeotropic rectification column from the top to obtain an azeotrope of the ethylene-glycol and the azeotropic agent at the top, the material flow containing the 1,2-butanediol is obtained in a tower kettle; after the azeotrope is subjected to condensation and phase-splitting, the azeotropic agent-rich phase at the upper layer returns to the azeotropic rectification column and continues performing azeotropic reaction while an ethylene-glycol-rich phase at the lower layer is subjected to refining to obtain the ethylene-glycol product, and the problems are well solved. Therefore, the method can be used for industrial production for separating the ethylene-glycol and the 1,2-butanediol.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for separating ethylene glycol and 1,2-butanediol
ActiveCN104926608AReduce heatReduce energy consumptionOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationPhase splitterButanediol
The invention relates to a method for separating ethylene glycol and 1,2-butanediol, and is used for mainly solving the problem of high separation energy consumption in the prior art. The problem is better solved by adopting the technical scheme that the method includes the following steps: a) coarse ethylene glycol enters a product tower, an azeotrope of 1,2-butanediol and ethylene glycol is obtained at the tower top, and ethylene glycol is obtained at a tower kettle; b) the azeotrope of 1,2-butanediol and ethylene glycol enters an azeotropic rectification tower, an azeotropic agent is added from the tower top of the azeotropic rectification tower, an azeotrope of ethylene glycol and the azeotropic agent is obtained at the tower top, and the 1,2-butanediol product is obtained in the tower kettle; c) the azeotrope of ethylene glycol and the azeotropic agent is condensed, then enters a phase splitter, and is divided into an upper-layer material flow rich in the azeotropic agent and a lower-layer material flow rich in ethylene glycol; the upper-layer material flow returns to the tower top of the azeotropic rectification tower; and d) the lower-layer material flow enters an azeotropic agent recovery tower, a tower top material flow is circulated to the azeotropic rectification tower, and a tower kettle material flow is circulated to a product tower. The method can be used in industrial production of separation of ethylene glycol and 1,2-butanediol.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method, process and apparatus for separation of ethylene glycol and 1,2-butanediol
ActiveCN105622338AHigh purityEfficient separationOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound separation/purificationLiquid productBoiling point
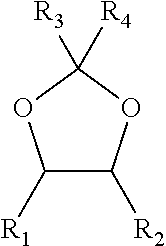
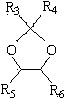
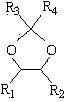
The invention relates to a method, a process and an apparatus for separation of ethylene glycol and 1,2-butanediol. The method includes, (1) subjecting ethylene glycol and 1,2-butanediol to reaction through acetal / ketal to produce acetal / ketal liquid product mixture correspondingly, (2) separating the acetal / ketal liquid product mixture containing ethylene glycol and 1,2-butanediol by a series of rectifying columns, (3) separating different acetal / ketal products by rectifying according to difference of boiling points of acetal or ketal, (4) respectively hydrolyzing the acetal / ketal products to obtain an ethylene glycol primary product and a 1,2-butanediol primary product, and (5) purifying the ethylene glycol primary product and the 1,2-butanediol primary product respectively by rectifying to obtain an ethylene glycol product and a 1,2-butanediol product. The purity of the ethylene glycol product can be up to 99.9% and the recovery thereof can be up to 99.5%; the purity of the 1,2-butanediol product can be up to 98.5%. By a reversible-reaction conversion method, the difficulty in separating ethylene glycol and 1,2-butanediol which are of similar boiling points and low relative volatility and are azeotropic is changed into the problem about separation of acetal / ketal products which are easy to separate relatively.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
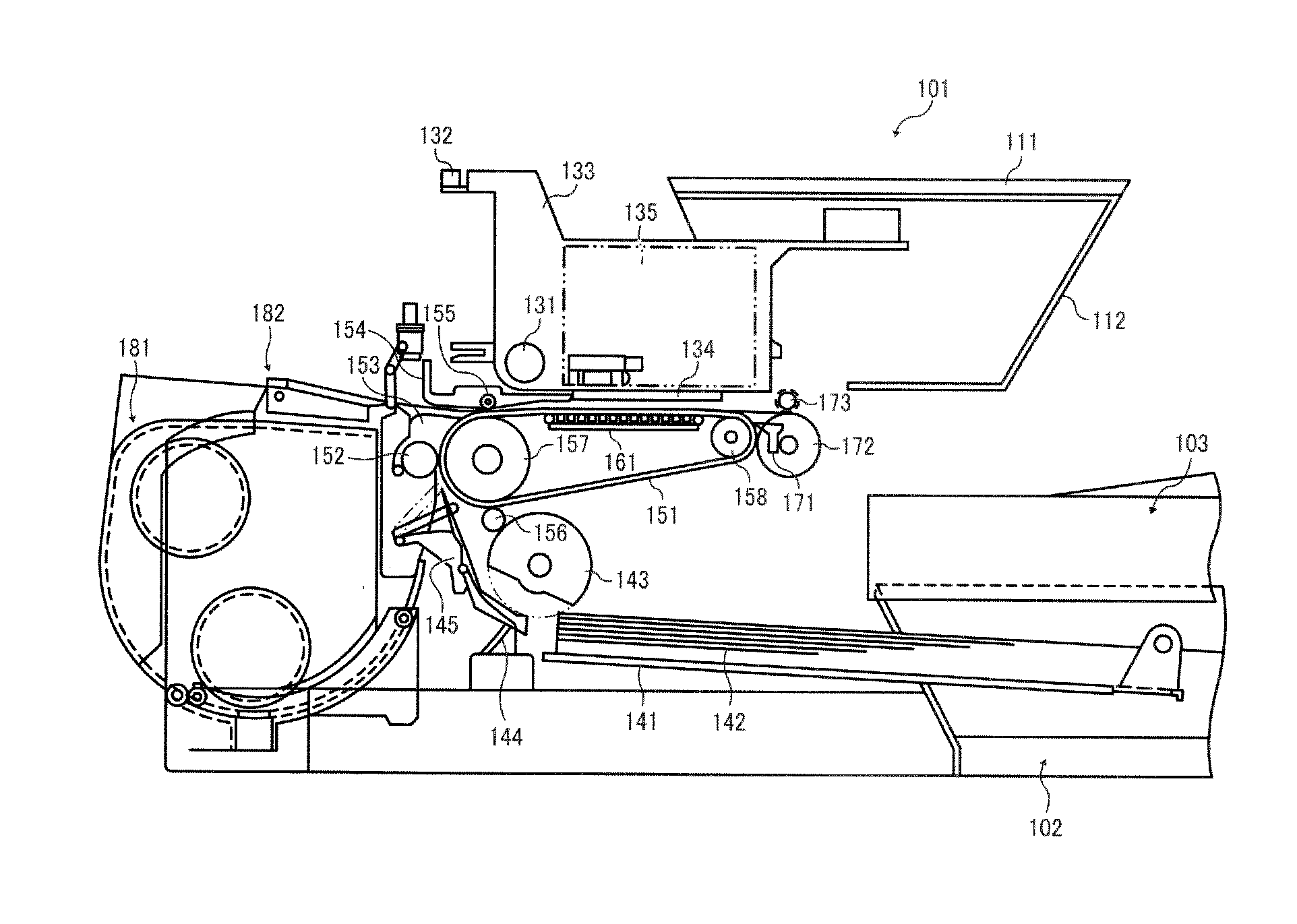
Cleaning liquid for inkjet recording apparatus, method for cleaning inkjet recording apparatus, recording method, and cleaning and filling liquid
ActiveUS20170015102A1Organic detergent compounding agentsNon-surface-active detergent compositionsOrganic solventBoiling point
A cleaning liquid for an inkjet recording apparatus is provided. The cleaning liquid includes an organic solvent having a boiling point of less than 250° C. and no organic solvent having a boiling point of 250° C. or more. The organic solvent having a boiling point of less than 250° C. includes two or more methoxy-group-containing organic solvents and at least one of 1,2-propanediol, 1,3-propanediol, 1,2-butanediol, and 2,3-butanediol.
Owner:RICOH KK
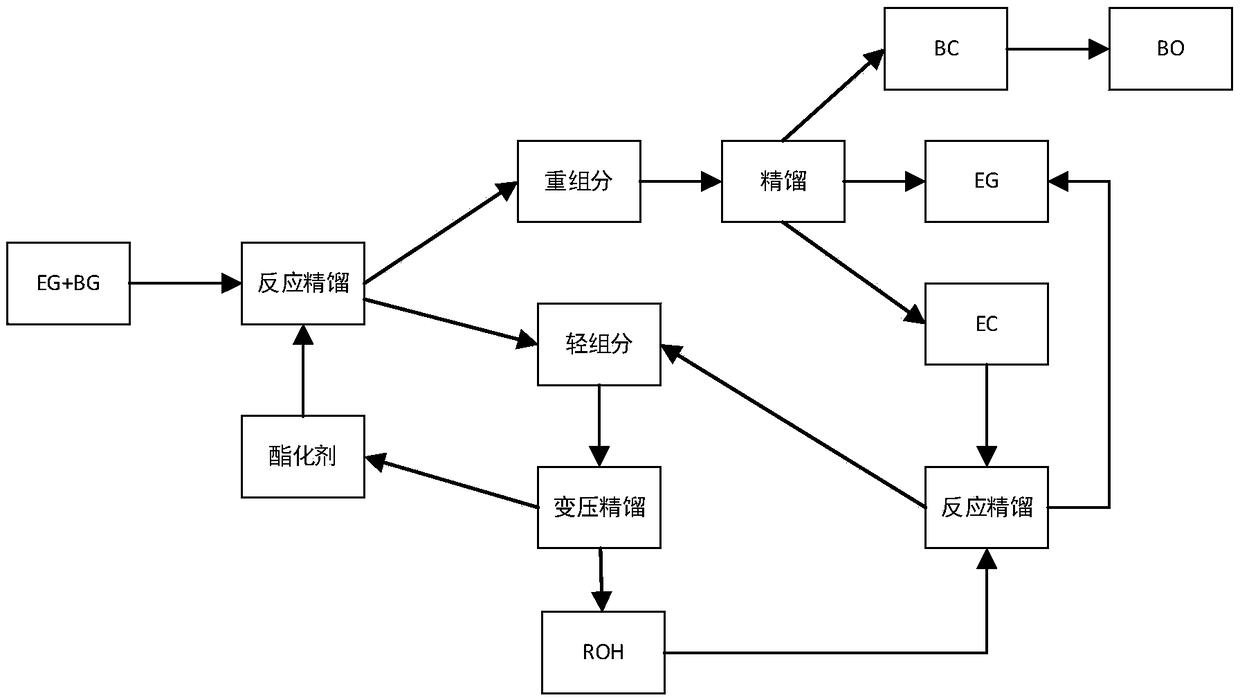
Reaction-rectification-separation-refinement novel method, technique and device of ethylene glycol and 1,2-butanediol
ActiveCN105541551AHigh purityEfficient separationOrganic compound preparationChemical industryKetoneReversible reaction
The invention relates to a separation method, technique and device of ethylene glycol and 1,2-butanediol. The method comprises the following steps: reacting a diol mixture and aldehyde or ketone in a reaction rectification tower by acetal or ketal reversible reaction to generate an acetal / ketone mixture, rectifying to separate the acetal / ketone mixture, and carrying out reaction, rectification and hydrolysis to obtain the high-purity ethylene glycol and 1,2-butanediol products. By using the technique for separation and purification, the purity of the main product ethylene glycol can reach 99.9% or above, the recovery rate can reach 99.5% or above, and the purity of the 1,2-butanediol product can reach 98.5% or above. By using the reaction rectification method, the difficulty in separating azeotropic ethylene glycol and 1,2-butanediol with approximate variable boiling point and low relative volatility becomes the problem of separation of the separable acetal / ketone product, thereby effectively implementing the high-efficiency separation on the ethylene glycol and 1,2-butanediol.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
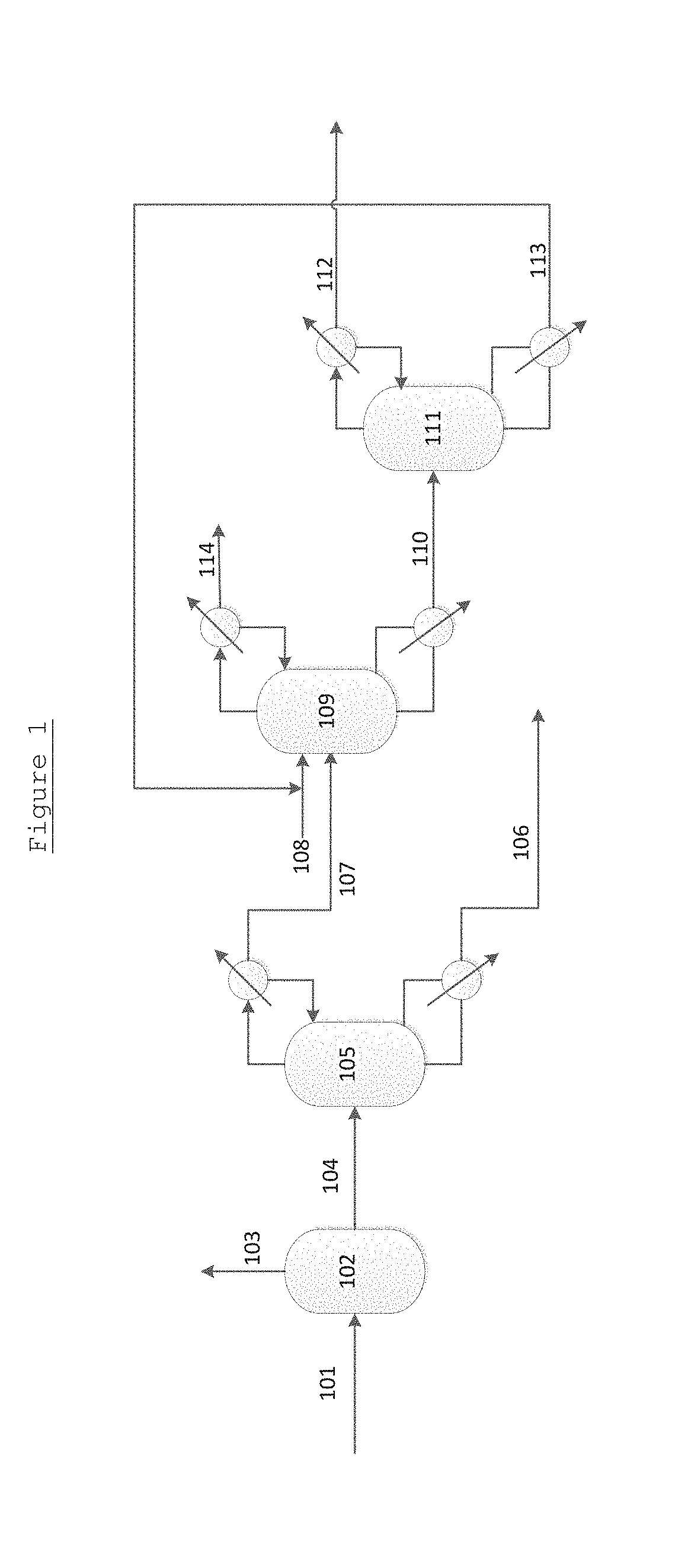
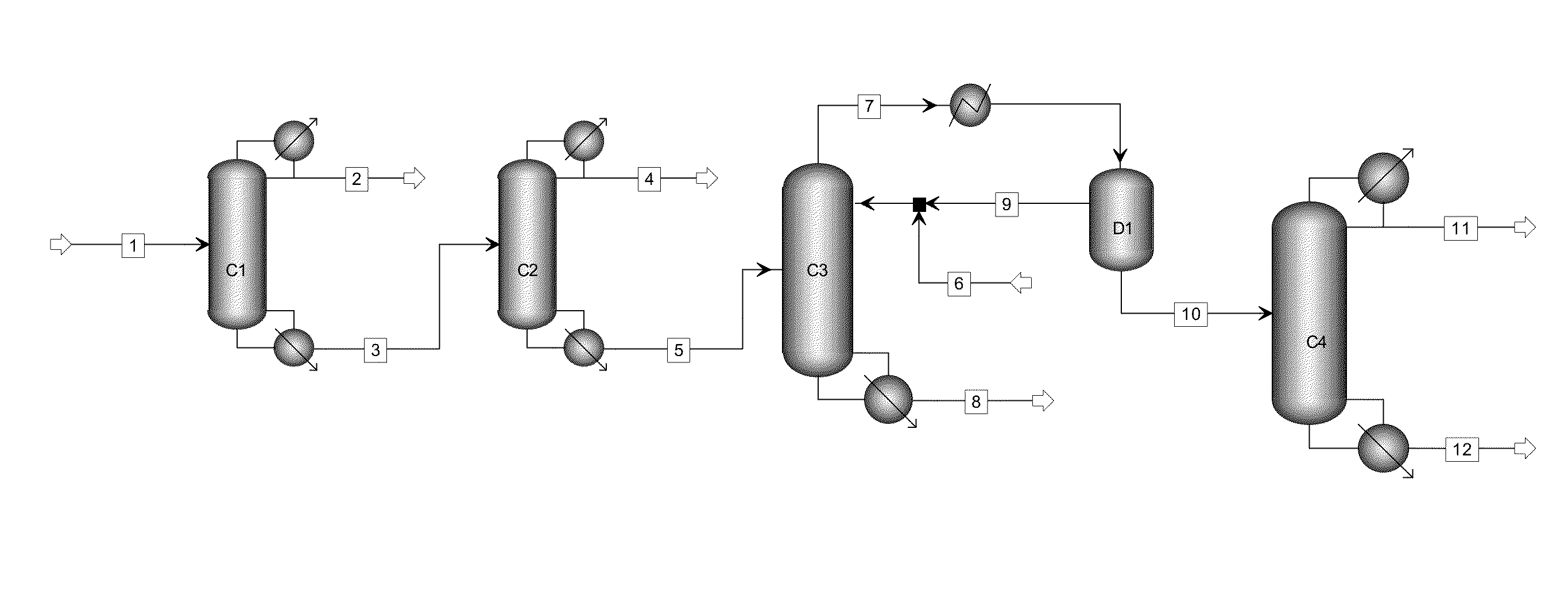
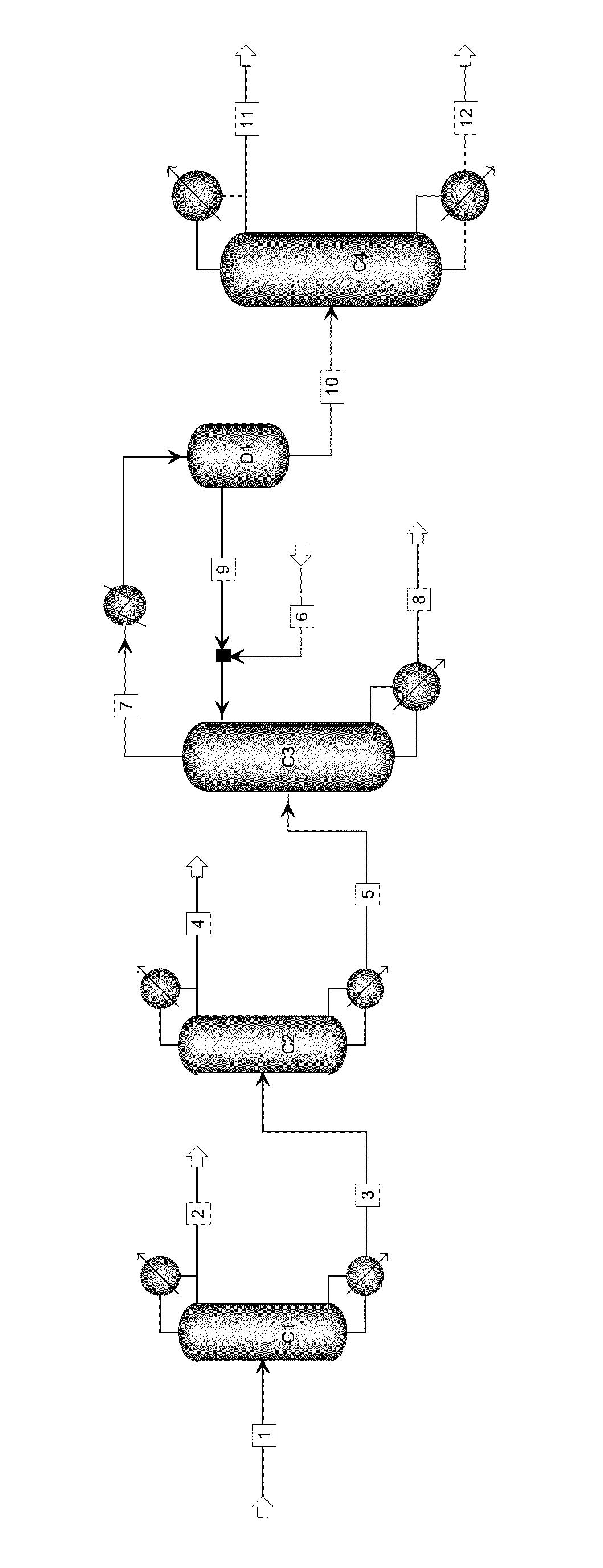
Method with heat integration function for separating ethylene glycol from 1,2-butylene glycol
ActiveCN103664522AReduce solubilityReduce lossesOrganic compound preparationChemical industryReboilerHigh energy
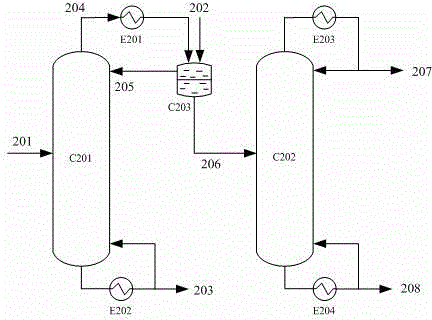
The invention relates to a method with a heat integration function for separating ethylene glycol from 1,2-butylene glycol, which is mainly used for solving the problem of high energy consumption existing in the prior art. According to the method disclosed by the invention, a technical scheme adopting a process flow including a first separating tower C1, a second separating tower C2, a third separating tower C3 and a fourth separating tower C4 is used, wherein a part of heat needed by the first separating tower C1 comes from a material flow 7 of the third separating tower 3 and the other part of heat needed by the first separating tower C1 comes from a tower kettle reboiler E0 of the first separating tower C1, and thus the problem is well solved. The method can be applied to industrial production for separating the material flow containing ethylene glycol and 1,2-butylene glycol.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Rectification method for separating ethylene glycol and 1,2-butanediol
ActiveCN104447200AReduce investmentReduce energy consumptionOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationPhase splittingHigh energy
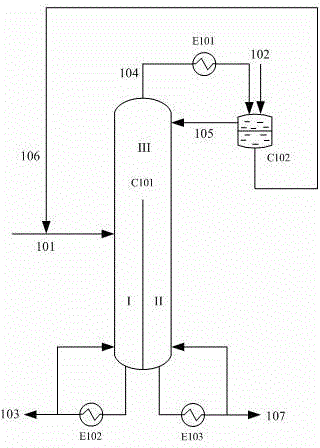
The invention relates to a rectification method for separating ethylene glycol and 1,2-butanediol, which mainly solves the technical problems of long rectification separation process, high investment and high energy consumption in the ethylene glycol and 1,2-butanediol separation process in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps: a raw material containing ethylene glycol and 1,2-butanediol enters a divisional rectification tower divisional section feed side (I), the ethylene glycol and a fresh azeotrope former added from a phase splitter form an azeotrope which is distilled off from the tower top, the supernatant azeotrope-former-rich phase subjected to condensation phase splitting returns to a divisional rectification tower common rectifying section (III) to continue participating in azeotropy, the understratum ethylene-glycol-rich phase is mixed with the raw material and returns to the divisional section feed side (I) to continue refinement, and separation is performed to obtain the ethylene glycol at the bottom of the divisional section feed side and obtain the 1,2-butanediol from the bottom of the other side (II) of the divisional section. The technical scheme well solves the technical problems, and can be used for industrial production for separating ethylene glycol and 1,2-butanediol.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
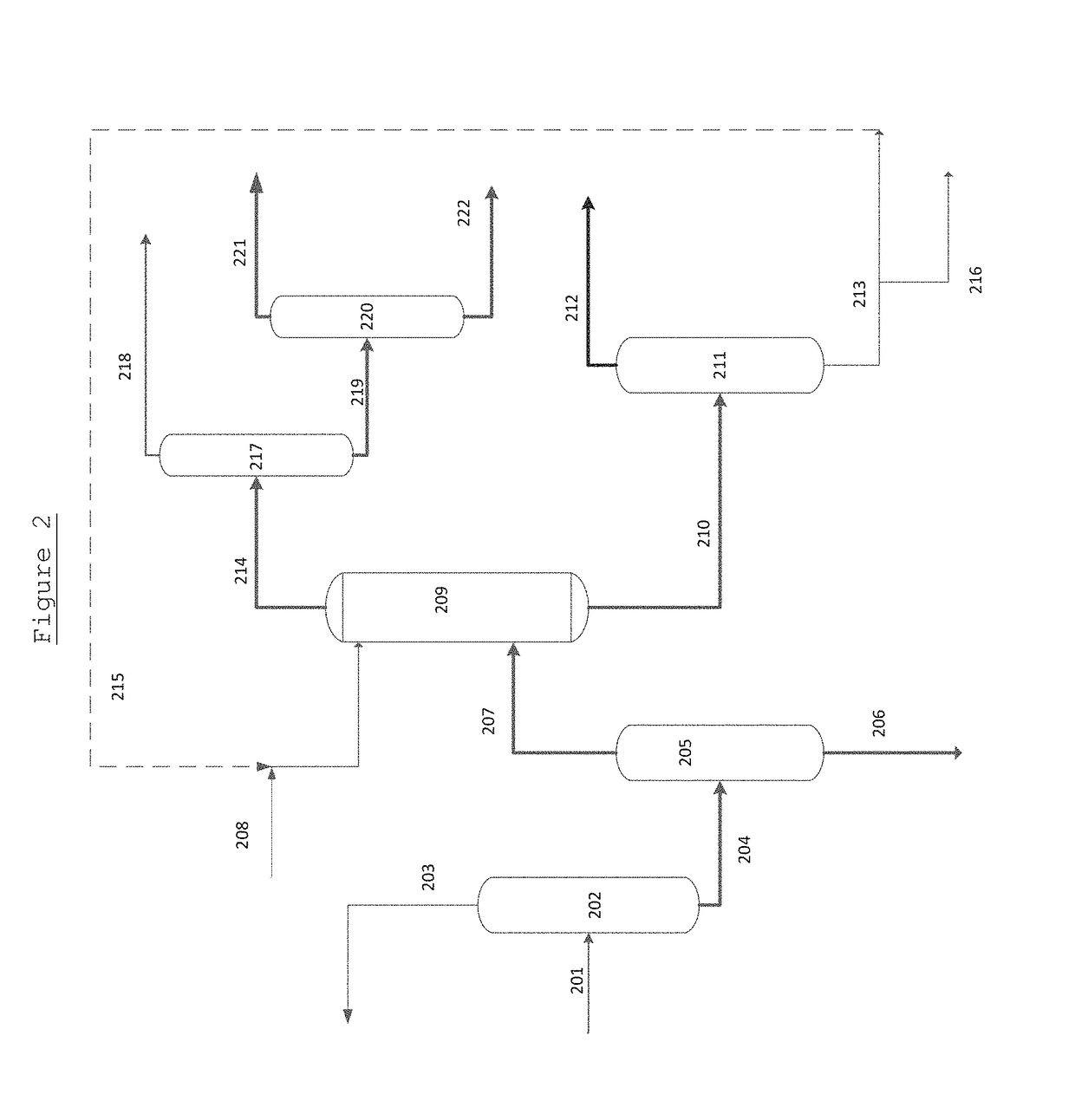
Separation method and separation device of synthesis gas ethylene glycol product
ActiveCN103435482ALess investmentReduce energy consumptionCarboxylic acid esters separation/purificationHydroxy compound separation/purificationEvaporationButanediol
The invention discloses a separation method and a separation device of a synthesis gas ethylene glycol product. The separation method comprises the steps of 1), allowing the raw synthesis gas ethylene glycol product to enter an effluent fraction tower, obtaining a light component, a mixture of methyl glycolate and dimethyl oxalate, and a heavy component respectively, 2), allowing the light component to enter a dividing wall rectifying tower, extracting methanol from the tower top, extracting an ethanol solution containing little water from a side line, 3), allowing the mixture containing methyl glycolate and dimethyl oxalate to enter a common rectifying tower, extracting methyl glycolate from the tower top, extracting dimethyl oxalate from a tower kettle, 4), allowing the heavy component to enter a scraper molecular evaporation tower I, extracting ethylene glycol from an inner wall of the tower, extracting a mixture of 1,2-propylene glycol and 1,2-butanediol from an outer wall, allowing partial mixing solution to return to the scraper molecular evaporation tower I, allowing partial mixing solution to return to a scraper molecular evaporation tower II, and 5), extracting 1,2-propylene glycol from an inner wall of the scraper molecular evaporation tower II, and extracting 1,2-butanediol from an outer wall of the scraper molecular evaporation tower II. According to the method and the device, each product is separated effectively, and the method has the characteristics of simple technology and low energy consumption.
Owner:SHAANXI COAL & CHEM TECH INST
Pre-separation method for ethanediol and 1,2-butanediol-containing raw material and preparation method of epoxybutane
ActiveCN108794300ALow investment costEasy to operateOrganic compound preparationChemical industryReactive distillationButanediol
The invention discloses a preparation method of epoxybutane. The preparation method comprises the following steps: performing reactive distillation on an ethanediol and 1,2-butanediol-containing raw material and an esterifying agent under the action of an esterifying catalyst to respectively obtain a light component containing a reaction product corresponding to the esterifying agent and a heavy component containing ethylene carbonate and butylene carbonate, rectifying the heavy component containing the ethylene carbonate and the butylene carbonate to respectively obtain the ethylene carbonateand the butylene carbonate, and decarboxylating the butylene carbonate under the action of a decarboxylating catalyst to obtain the epoxybutane. According to the preparation method of the epoxybutane, the ethanediol and 1,2-butanediol-containing raw material and the esterifying agent are subjected to ester exchange reaction, so that 1,2-butanediol is converted into the butylene carbonate which isnot azeotropic with ethanediol to purify the ethanediol, and the butylene carbonate obtained by the conversion of the 1,2-butanediol is decarboxylated to obtain the epoxybutane with a relatively highadditional value.
Owner:昌德新材科技股份有限公司
Method for Separation of Close-Boiling Mixture of Polyols
ActiveUS20170327446A1Consumption of wasteCost of wasteIon-exchanger regenerationHydroxy compound preparationDistillationPinacol rearrangement
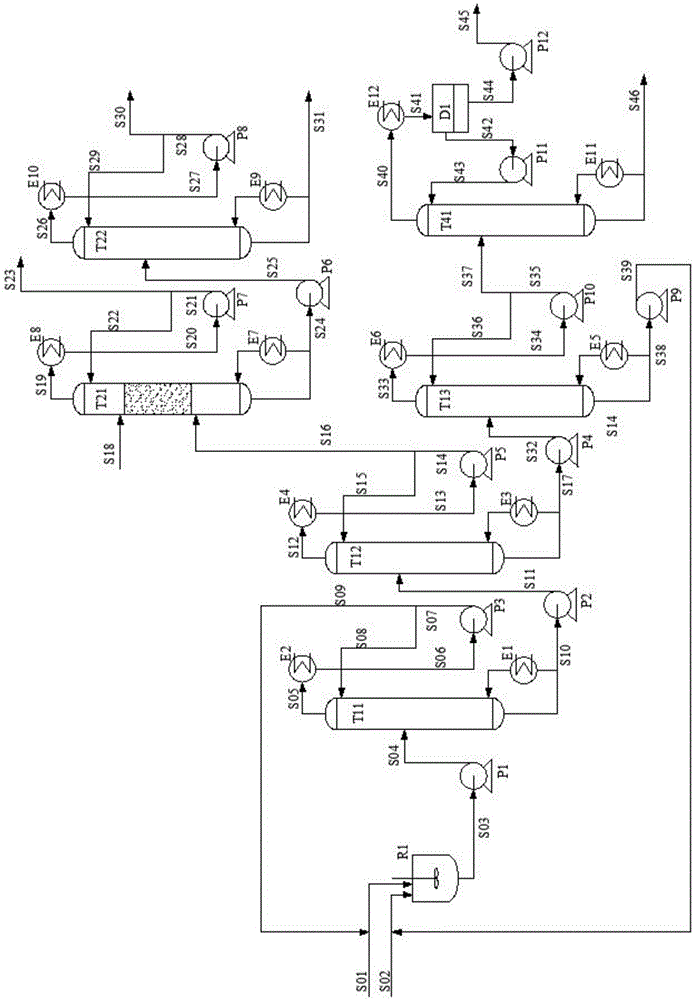
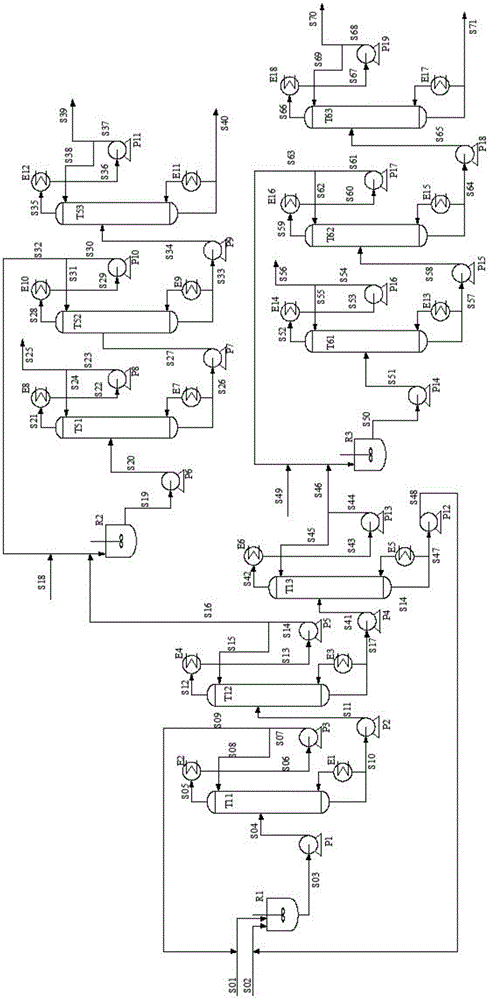
This invention discloses an approach for the separation of the close-boiling mixture of polyols. The raw material is ethylene glycol containing miscellaneous polyols (such as 1,2-propylene glycol and 1,2-butanediol). Over an acid catalyst, these miscellaneous polyols, through (1) a dehydration reaction, (2) pinacol rearrangement, and (3) acetalization or ketalization reaction, are converted into aldehydes (small amounts), acetals, and ketals (trace amount), which are simultaneously and readily separated via distillation. Meanwhile, after the reaction, the mixture is further separated to obtain an ethylene glycol product at a high purity. The invention provides a technique to remove the miscellaneous polyols from ethylene glycol via liquid-phase dehydration reactions under mild conditions, with low energy consumption. In particular, this approach is markedly effective for the removal of 1,2-butanediol that is difficult to be removed via conventional techniques. The purity of the resulting ethylene glycol product is high, and value-added acetals or ketals are co-produced.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Inkjet ink, ink cartridge, inkjet recording device, and ink printed matter
ActiveUS20150030818A1Decorative surface effectsDuplicating/marking methods2,3-Butanediol1,3-Propanediol
Inkjet ink contains water, hydrosoluble organic materials; and a colorant, wherein the hydrosoluble organic materials account for 30% by weight to 50% by weight of the inkjet ink, wherein the hydrosoluble organic materials contain 3-methoxy-1-butanol, herein the hydrosoluble organic materials contain at least one of 1,3-butane diol, 3-methyl-1,3-butane diol, 1,2-butane diol, 2,3-butane diol, 1,2-pentane diol, 3-methyl-3-hydroxymethyl oxetane, 1,2-propane diol, or 1,3-propane diol in an amount of 1% of the inkjet ink.
Owner:RICOH KK
Method for removing dihydric alcohol or polyol impurities in glycol and increasing yield of glycol
ActiveCN106866366AHigh selectivityFulfil requirementsOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound separation/purificationDistillationButanediol
The invention discloses a method for removing dihydric alcohol or polyol impurities in glycol and increasing the yield of glycol. According to the method, glycol containing dihydric alcohols or heteropolyols (such as 1,2-butanediol) is used as a raw material; under the action of a protonic acid catalyst, dihydric alcohols or heteropolyols undergoes a dehydration reaction, a secondary in-depth dehydration reaction, an acetalation reaction; and heteroalcohols are totally converted into low-boiling-point products which are separated through distillation and condensation. Acetal in the low-boiling-point products is subjected to a hydrolysis reaction so as to produce glycol, trace heteroalcohols and aldehydes; and glycol and heteroalcohols are separated through simple distillation and returned to an in-depth dehydration reaction vessel, so the yield of glycol is increased. Meanwhile, the trace heteroalcohols are further converted in the in-depth dehydration reaction vessel; a crude glycol product having undergone two-step dehydration does not contain dihydric alcohol or polyol impurities; and since rectification for separation of the dihydric alcohol or polyol impurities with boiling points close to the boiling point of glycol is not needed, the number of rectifying towers in the whole separation flow and energy consumption are substantially reduced.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for the separation of glycols
ActiveUS20190062244A1High purityAffect volatilityOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationAlcoholBoiling point
A process for the production of high purity mono-ethylene glycol (MEG) from a product stream of a saccharide hydrogenolysis process. The process having the steps of: (i) removing solvent from the product stream to provide a solvent-lean product stream; (ii) subjecting the solvent-lean product stream to distillation to provide a bottoms stream comprising high boiling by-products and a top stream comprising a mixture comprising MEG and 1,2-butanediol (1,2-BDO); (iii) providing said mixture having MEG and 1,2-BDO as a feed to a distillation column; (iv) providing a feed comprising an extractant of C3 to C6 alcohols and mixtures thereof to the distillation column above the mixture comprising MEG and 1,2-BDO; (v) removing a stream comprising MEG and the extractant as a bottoms stream from the distillation column; and (vi) subjecting the stream comprising MEG and the extractant to distillation to provide a top stream comprising high purity MEG.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
Process for the separation of glycols
ActiveUS10308577B2High purityAffect volatilityOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationAlcoholBoiling point
A process for the production of high purity mono-ethylene glycol (MEG) from a product stream of a saccharide hydrogenolysis process. The process having the steps of: (i) removing solvent from the product stream to provide a solvent-lean product stream; (ii) subjecting the solvent-lean product stream to distillation to provide a bottoms stream comprising high boiling by-products and a top stream comprising a mixture comprising MEG and 1,2-butanediol (1,2-BDO); (iii) providing said mixture having MEG and 1,2-BDO as a feed to a distillation column; (iv) providing a feed comprising an extractant of C3 to C6 alcohols and mixtures thereof to the distillation column above the mixture comprising MEG and 1,2-BDO; (v) removing a stream comprising MEG and the extractant as a bottoms stream from the distillation column; and (vi) subjecting the stream comprising MEG and the extractant to distillation to provide a top stream comprising high purity MEG.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
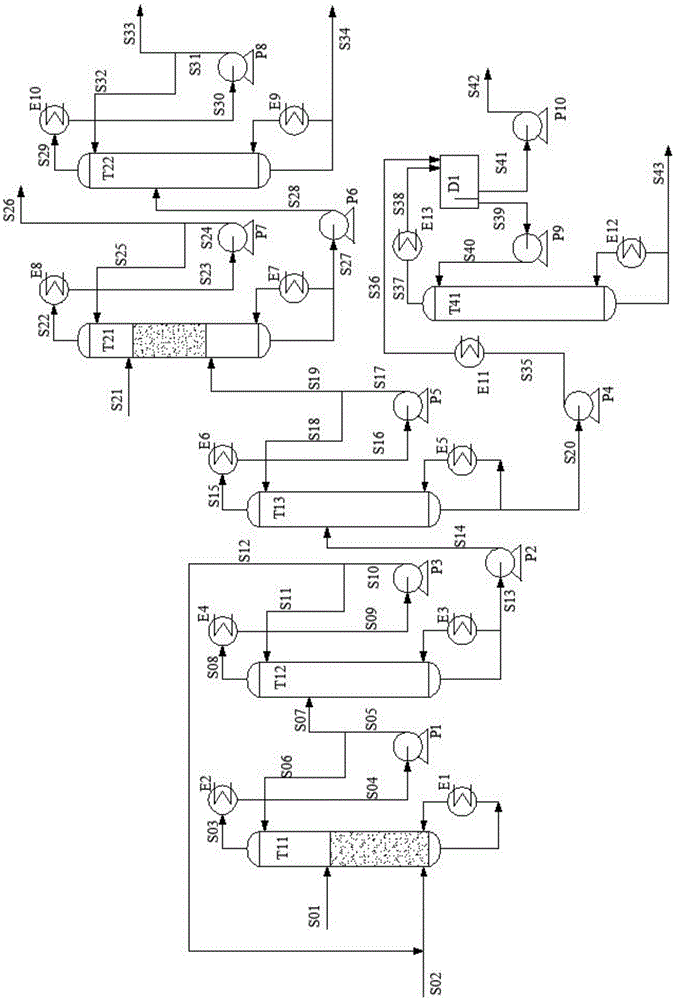
Process for separating ethylene glycol and 1,2-butanediol
ActiveUS8906205B2High purityBig investmentOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds purification/separationButanediol1,2-Butanediol
A process for separating ethylene glycol and 1,2-butanediol. A material flow containing ethylene glycol and 1,2-butanediol gets into the lower-middle part of the azeotropic rectification column C3 after the light components are removed by the separating columns C1 and C2, wherein the ethylene glycol and the azeotropic agent added from the top of the column form azeotrope which is distilled out from the top of the column and gets into the phase separator D1 after being condensed, the upper phase enriched with azeotropic agent after the phase was separated returns to the top of the column to continue to participate in azeotropy, and the lower phase enriched with ethylene glycol gets into the fourth separating column C4 to be refined to obtain the ethylene glycol product.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
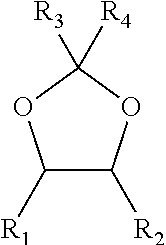
Process for the separation of glycols using glycerol
ActiveUS10246390B2Organic compound preparationDistillation regulation/controlFractionating columnGlycerol
A process for the separation of monoethylene glycol (MEG) and 1,2-butanediol (1,2-BDO) from a first mixture including MEG and 1,2-BDO, the process including providing the first mixture of MEG and 1,2-BDO as a feed to a distillation column. The process also includes providing a feed comprising glycerol to the distillation column above the first mixture. The process also includes operating the distillation column at a temperature in the range of from 50 to 250° C. and a pressure in the range of from 0.1 to 400 kPa. The process also includes removing a stream comprising MEG and glycerol as a bottoms stream from the distillation column and removing a stream comprising 1,2-BDO above the point at which the feed comprising glycerol is provided to the distillation column.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Production method of cotton-like knitted fabric
InactiveCN103668736AGood compatibilityMeet the requirements of health and environmental protectionWeft knittingWarp knittingFuranPolyester
The invention discloses a production method of cotton-like knitted fabric. The production method includes the steps of 1, making all-biomass polyester chips from, by weight, 9-8 parts of 1, 2-propanediol, 3-5 parts of 1, 2-butanediol, 4-6 parts of pentanediol, 2-4 parts of sorbitol, 3-5 parts of ethanediol, 16 parts of bio-base 1, 3-propanediol, and 1 part of bio-base 2, 5-furan diacid; 2, subjecting the all-biomass polyester chips to melt spinning at the spinning temperature of 310DE C, at the spinning speed of 1550m / min, at the drawing temperature of 90DEG C, under the pre-drawing ratio of 1.5, under the primary drawing ratio of 4-5, and under the secondary drawing ratio of 2-3, so as to obtain all-biomass polyester fiber; 3, knitting warps and wefts containing the all-biomass polyester fiber into the cotton-like knitted fabric. The knitted fabric produced by the production is more compatible with the human body and meets the requirements for health and environment protection.
Owner:CHANGSHU XINLEI KNITTING
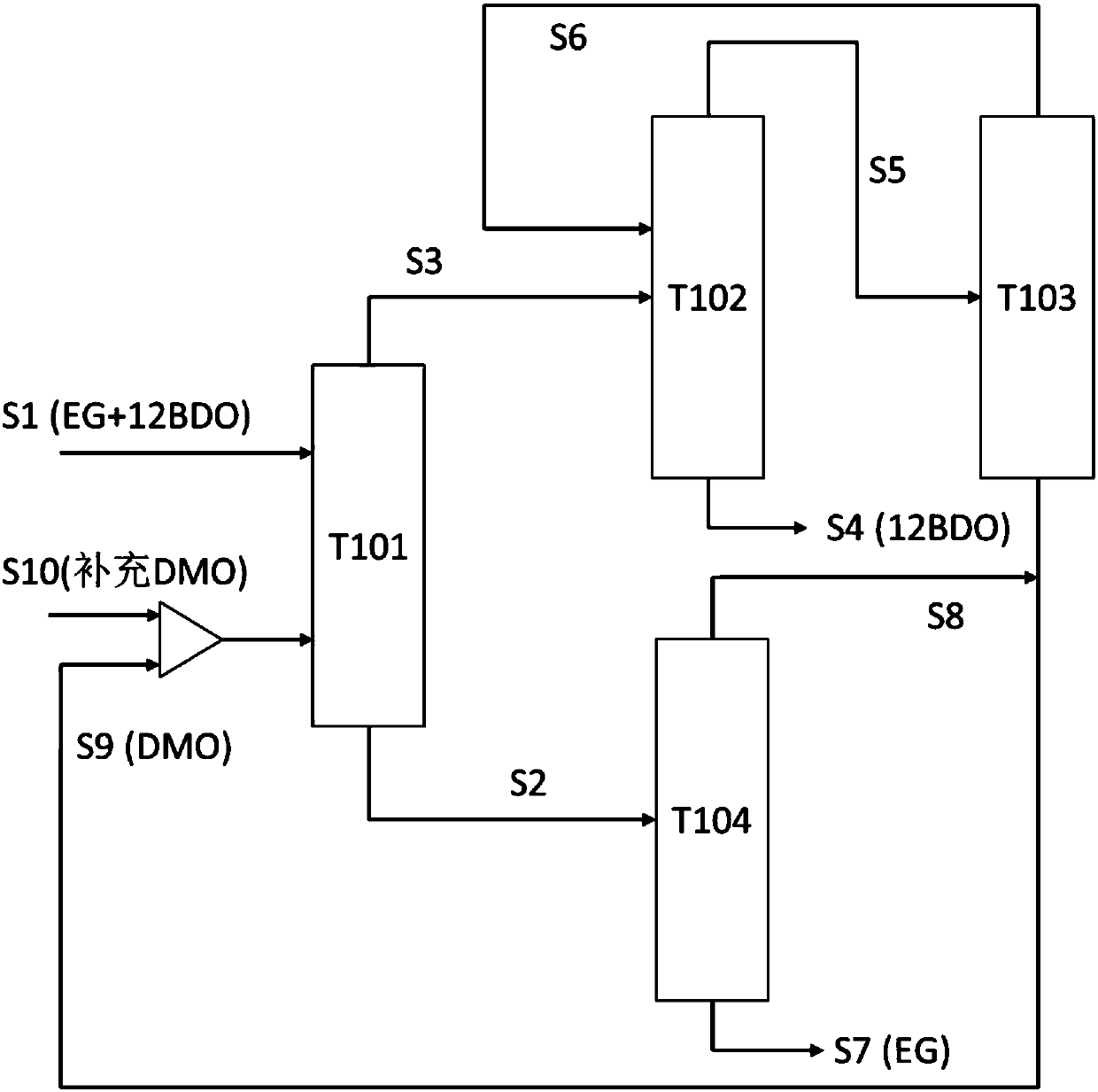
Method for separating low-concentration 1,2-butanediol from ethylene glycol by adopting azeotropic distillation
ActiveCN108017517AHigh purityHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationHigh pressureButanediol
The invention discloses a method for separating low-concentration 1,2-butanediol (12BDO) from ethylene glycol (EG) by adopting an azeotropic distillation method. The method comprises the steps of feeding EG-12BDO and an azeotrope agent DMO into an ethylene glycol separating tower, wherein a mixture of the EG and the azeotropic agent DMO is formed at a tower bottom; further refining the tower bottom mixture to obtain the EG; for an azeotrope of the 12BDO and the DMO at a tower top of the separating tower, sequentially carrying out low-pressure azeotropy and high-pressure azeotropy, and respectively separating out the 12BDO and the DMO, wherein the azeotrope agent DMO can be recycled. The method provided by the invention solves the problem that in a process for preparing the ethylene glycolthrough coal-based synthesis gas, the ethylene glycol tower top product ethylene glycol and a mixture of another byproduct dihydric alcohol are difficult to separate. According to the process providedby the invention, the main product ethylene glycol is high in purity and high in yield, and the azeotrope agent DMO can be repeatably recovered and recycled; by adopting the hydrogenation reaction raw material DMO as the azeotrope agent, the introduction of a third component is also avoided, so that a separating flow of the EG is simplified, the equipment investment and the energy consumption ofthe whole process are reduced, and the method has an important economic value.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
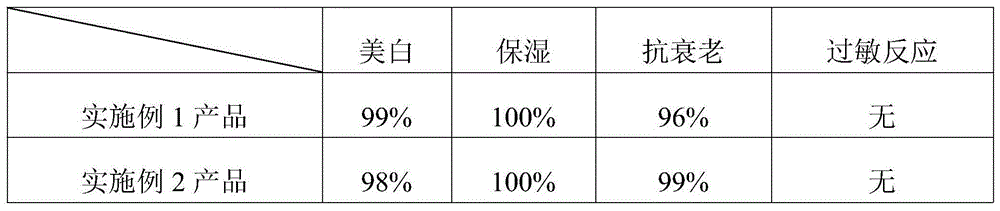
Skin-care liquid using plant to decompose melanin and preparation method thereof
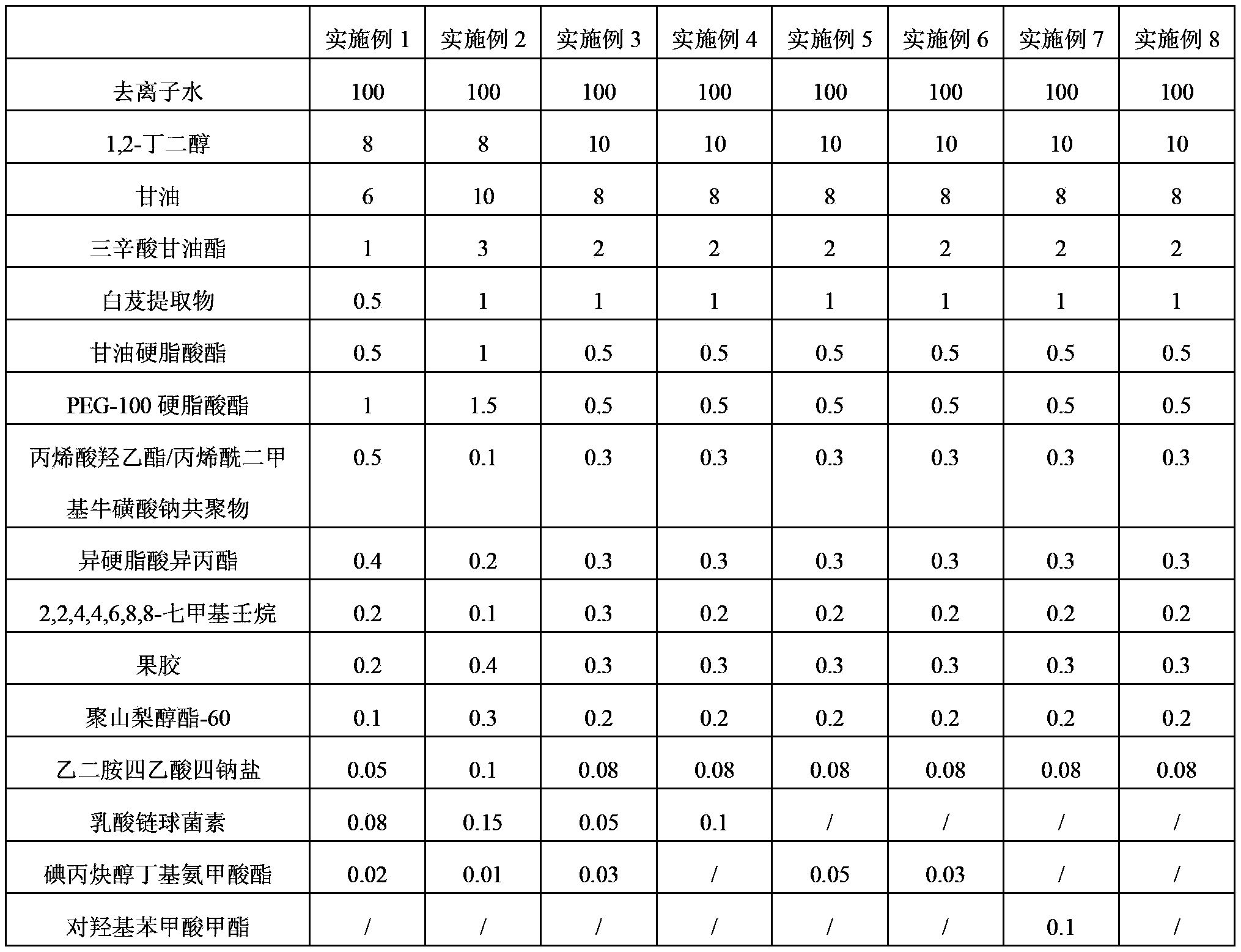
InactiveCN104367484AGood moisturizing effectImprove breathabilityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsMelaninGlucoside
The invention provides a skin-care liquid using plant to decompose melanin and a preparation method thereof. The skin-care liquid is composed of water, 1,2-butanediol, kojic acid dipalmitate, hydrogenated lecithin, resveratrol, and raspberry ketone beta-d-glucoside. The skin-care liquid is a cream, is capable of preserving moisture and whitening, is good in anti-ageing effect and good in air permeability, and can be rapidly absorbed by skin.
Owner:雷詠麟
Method for producing R-alpha-hydroxybutyrate by using 1, 2-butanediol as substrate
ActiveCN103103222ASuccessful stereospecific synthesisAchieve stereospecific synthesisMicroorganism based processesFermentationHydroxybutyric acidHigh concentration
The invention discloses a method for producing 1,2-butanediol by using R-alpha-hydroxybutyrate as a substrate. The method comprises steps of: culturing Gluconobacter oxydans DSM 2003 by a conventional method to prepare a biological catalyst; mixing the biological catalyst with a substrate 1,2-butylene glycol aqueous solution; adding ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid and oscillating for 1-30 h under condition of 20-50 DEG C and pH of 4.0-10.0 to obtain a transformation liquid; and preparing a solution containing R-alpha-hydroxybutyrate through the transformation liquid. The method provided by the invention has the following characteristics: (1) the method employs biological catalysis, has simple reaction system, mild reaction conditions, short steps and simple operation; and the biological catalyst can be easily removed, so as to facilitate subsequent separation and purification; (2) the method has a short reaction period, and the product R-alpha-hydroxybutyrate can accumulate to a high concentration; (3) the substrate 1,2-butanediol has low price, and is easy to acquire; and (4) product enantiomer has high excessive rate reaching higher than 99%, so as to lay foundation for the efficient production of R-alpha-hydroxybutyrate.
Owner:上海肆芃科技有限公司
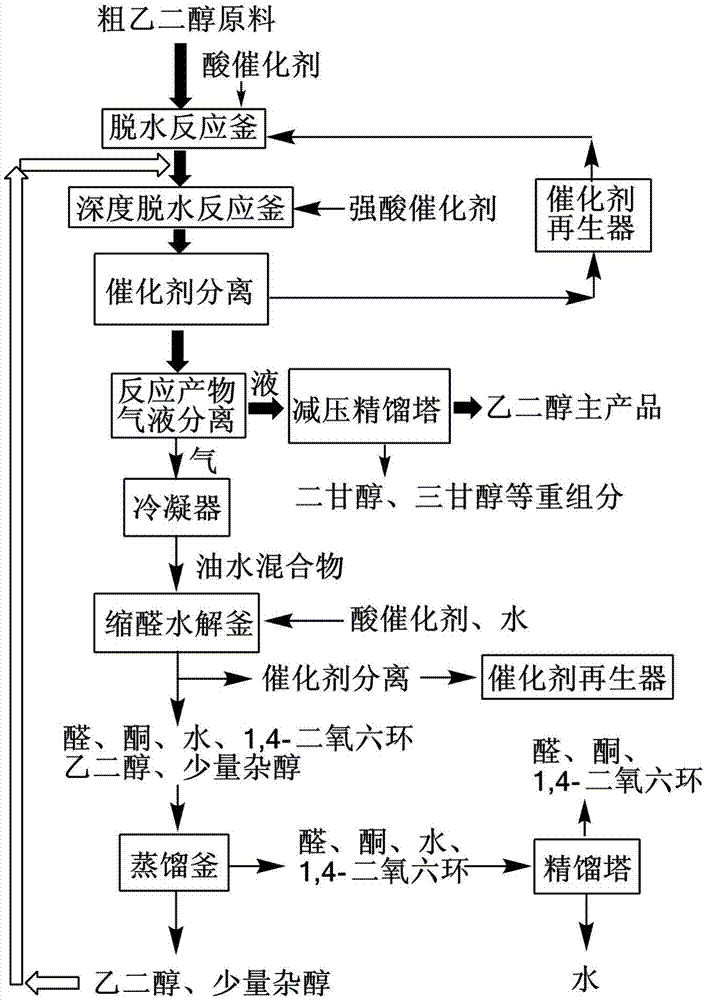
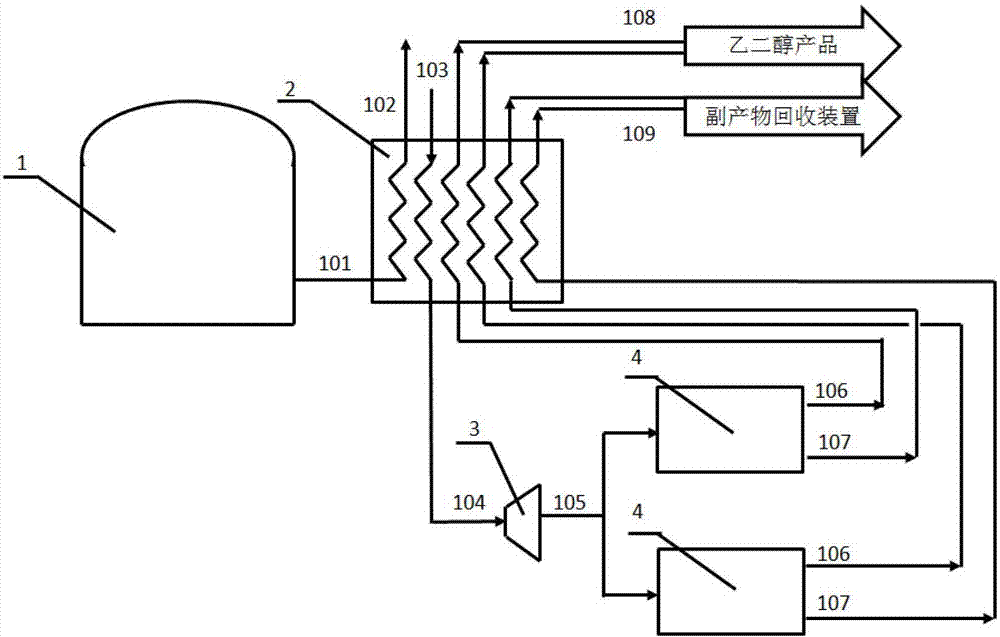
Technology for efficiently purifying glycol obtained through oxalate hydrogenation
ActiveCN103319310AImprove productivityReduce negative impactHydroxy compound separation/purificationEngineeringButanediol
The invention relates to a technology for efficiently purifying glycol obtained through oxalate hydrogenation. The technology is characterized in that LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas) low-temperature liquid is subjected to heat exchange through a heat exchange unit, after the temperature of the LNG low-temperature liquid rises to a room temperature, the LNG low-temperature liquid is liquefied, and then the liquefied LNG low-temperature liquid is conveyed to a natural gas application place outside battery limit through a natural gas conveying pipeline; a glycol crude product prepared through high-temperature high-pressure oxalate hydrogenation passes through the heat exchange unit in a direction opposite to the conveying direction of the LNG low-temperature liquid through the conveying pipeline, is precooled through the heat exchange unit and is subjected to auxiliary refrigeration through auxiliary refrigeration equipment, and after the temperature of the crude product is reduced to minus 5 DEG C to 5 DEG C, the crude product is conveyed to a separation unit through the pipeline; after the temperature of the crude product in the separation unit is reduced to minus 20 DEG C to minus 40 DEG C through freezing-separation equipment, liquefied 1, 2-propylene glycol and 1,2-butanediol serve as byproducts to be separated and recycled, and the solid glycol is directly collected, or after the glycol is heated to liquid state, the liquid glycol pure product is collected. According to the technology, the impurities, namely the 1,2-propylene glycol and the 1,2-butanediol in the glycol are separated by virtue of the characteristics of difference in solidifying points, the high-purity glycol is obtained, the productivity is high, and the cold energy of LNG is fully utilized.
Owner:JIANGSU CHINA NUCLEAR IND HUAWEI ENGDESIGN & RES
Cosmetic compositions and methods providing enhanced penetration of skin care actives
A cosmetic composition suitable for topical application is provided. In some examples, the cosmetic composition can include glycerin, hexyldecanol, a vitamin B compound, and one or more materials selected from the group consisting of 1,2-pentanediol, 1,4-pentanediol, 2,4-pentanediol, 1,5-pentanediol, 1,2-butanediol, 1,3-butanediol, 1,4-butanediol, 2,3-butanediol, 1,2-hexanediol, 1,5-hexanediol, 1,6-hexanediol, 2,5-hexanediol, hexylene glycol, and combinations thereof.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Method for separation of close-boiling mixture of polyols
ActiveUS9926251B2Consumption of wasteCost of wasteIon-exchanger regenerationHydroxy compound preparationDistillationPinacol rearrangement
This invention discloses an approach for the separation of the close-boiling mixture of polyols. The raw material is ethylene glycol containing miscellaneous polyols (such as 1,2-propylene glycol and 1,2-butanediol). Over an acid catalyst, these miscellaneous polyols, through (1) a dehydration reaction, (2) pinacol rearrangement, and (3) acetalization or ketalization reaction, are converted into aldehydes (small amounts), acetals, and ketals (trace amount), which are simultaneously and readily separated via distillation. Meanwhile, after the reaction, the mixture is further separated to obtain an ethylene glycol product at a high purity. The invention provides a technique to remove the miscellaneous polyols from ethylene glycol via liquid-phase dehydration reactions under mild conditions, with low energy consumption. In particular, this approach is markedly effective for the removal of 1,2-butanediol that is difficult to be removed via conventional techniques. The purity of the resulting ethylene glycol product is high, and value-added acetals or ketals are co-produced.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Emulsion for bletilla striata nutritive mask, bletilla striata nutritive mask and preparation method of bletilla striata nutritive mask
InactiveCN104095778AReduce dosageEasy to useCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsBletilla striataPolyethylene glycol
The invention discloses an emulsion for a bletilla striata nutritive mask, the bletilla striata nutritive mask and a preparation method of the bletilla striata nutritive mask. The emulsion for the bletilla striata nutritive mask is prepared from deionized water, 1,2-butylene glycol, glycerin, glycerin tricaprylate, bletilla striata extract, glyceryl stearate, polyethylene glycol-100 stearate, hydroxyethyl acrylate / sodium acryloyldimethyltaurate copolymer, isopropyl isostearate, 2,2,4,4,6,8,8-heptamethylnonane, pectin, polysorbate-60, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid tetrasodium salt, nisin and iodopropynyl butylcarbamate. The invention also discloses the bletilla striata nutritive mask comprising the emulsion and a fiber mask. The bletilla striata nutritive mask is suitable for all skin types, has excellent moisture retention performances, has effects of resisting aging and crease, can obviously relieve facial acne melanin and has the function of whitening.
Owner:上海珍馨化工科技有限公司
Separation method of polyol mixture
ActiveCN106866369AReduce the number of platesReduce energy consumptionOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationPolyolAlcohol
The invention discloses a separation method of a mixture of polyols with similar boiling points. Glycol containing dihydric fusels (1,2-butylene glycol and 1,2-butylene glycol) is adopted as the feedstock of a reduced pressure rectifying tower, and a weakly polar gaseous extraction agent is introduced to the bottom of the tower, so relative volatility between the 1,2-butylene glycol and 1,2-butylene glycol which have the same weak polarity and the glycol with strong polarity is improved, and the separation efficiency of rectification is improved. The invention provides a novel rectification method of the dihydric fusels from the glycol. The boiling point of the gaseous extraction agent is far lower than that of the dihydric alcohols, and the gaseous extraction agent is easy to separate and can be recycled, so the material consumption and the energy consumption in the separation process are reduced. The method allows the 1,2-butylene glycol and 1,2-butylene glycol to be separated from the glycol, and allows highly pure glycol and concentrated 1,2-butylene glycol and 1,2-butylene glycol byproducts to be obtained.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Inkjet ink, ink cartridge, inkjet recording device, and ink printed matter
Inkjet ink contains water, hydrosoluble organic materials; and a colorant, wherein the hydrosoluble organic materials account for 30% by weight to 50% by weight of the inkjet ink, wherein the hydrosoluble organic materials contain 3-methoxy-1-butanol, herein the hydrosoluble organic materials contain at least one of 1,3-butane diol, 3-methyl-1,3-butane diol, 1,2-butane diol, 2,3-butane diol, 1,2-pentane diol, 3-methyl-3-hydroxymethyl oxetane, 1,2-propane diol, or 1,3-propane diol in an amount of 1% of the inkjet ink.
Owner:RICOH KK
Technology for efficiently purifying glycol obtained through oxalate hydrogenation
ActiveCN103319310BReduce negative impactReduce energy consumptionHydroxy compound separation/purificationEngineeringHigh pressure
The invention relates to a technology for efficiently purifying glycol obtained through oxalate hydrogenation. The technology is characterized in that LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas) low-temperature liquid is subjected to heat exchange through a heat exchange unit, after the temperature of the LNG low-temperature liquid rises to a room temperature, the LNG low-temperature liquid is liquefied, and then the liquefied LNG low-temperature liquid is conveyed to a natural gas application place outside battery limit through a natural gas conveying pipeline; a glycol crude product prepared through high-temperature high-pressure oxalate hydrogenation passes through the heat exchange unit in a direction opposite to the conveying direction of the LNG low-temperature liquid through the conveying pipeline, is precooled through the heat exchange unit and is subjected to auxiliary refrigeration through auxiliary refrigeration equipment, and after the temperature of the crude product is reduced to minus 5 DEG C to 5 DEG C, the crude product is conveyed to a separation unit through the pipeline; after the temperature of the crude product in the separation unit is reduced to minus 20 DEG C to minus 40 DEG C through freezing-separation equipment, liquefied 1, 2-propylene glycol and 1,2-butanediol serve as byproducts to be separated and recycled, and the solid glycol is directly collected, or after the glycol is heated to liquid state, the liquid glycol pure product is collected. According to the technology, the impurities, namely the 1,2-propylene glycol and the 1,2-butanediol in the glycol are separated by virtue of the characteristics of difference in solidifying points, the high-purity glycol is obtained, the productivity is high, and the cold energy of LNG is fully utilized.
Owner:JIANGSU CHINA NUCLEAR IND HUAWEI ENGDESIGN & RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com