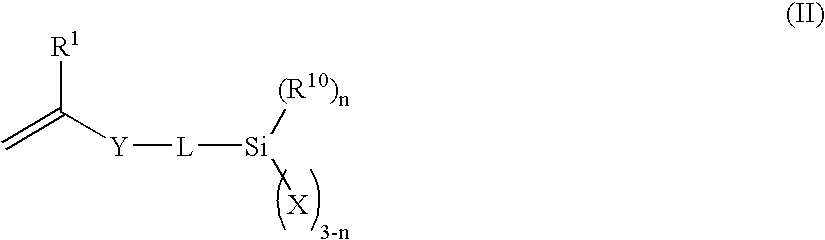Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
575results about How to "Sufficient performance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
System and method for frequency management in a communications positioning device
InactiveUS6867734B2High positioning accuracySufficient GPS performanceSynchronisation arrangementPulse automatic controlTime to first fixTransceiver
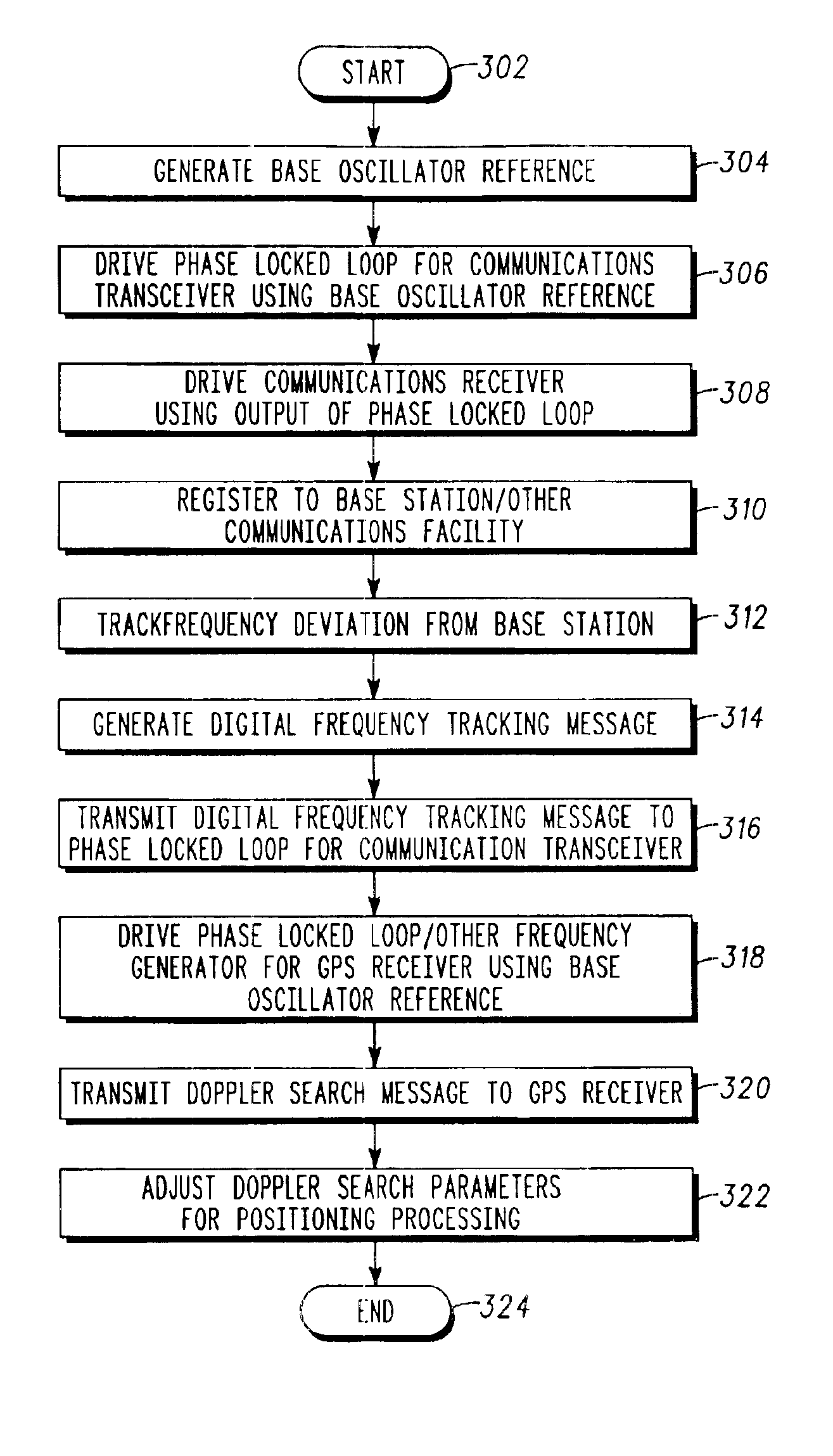
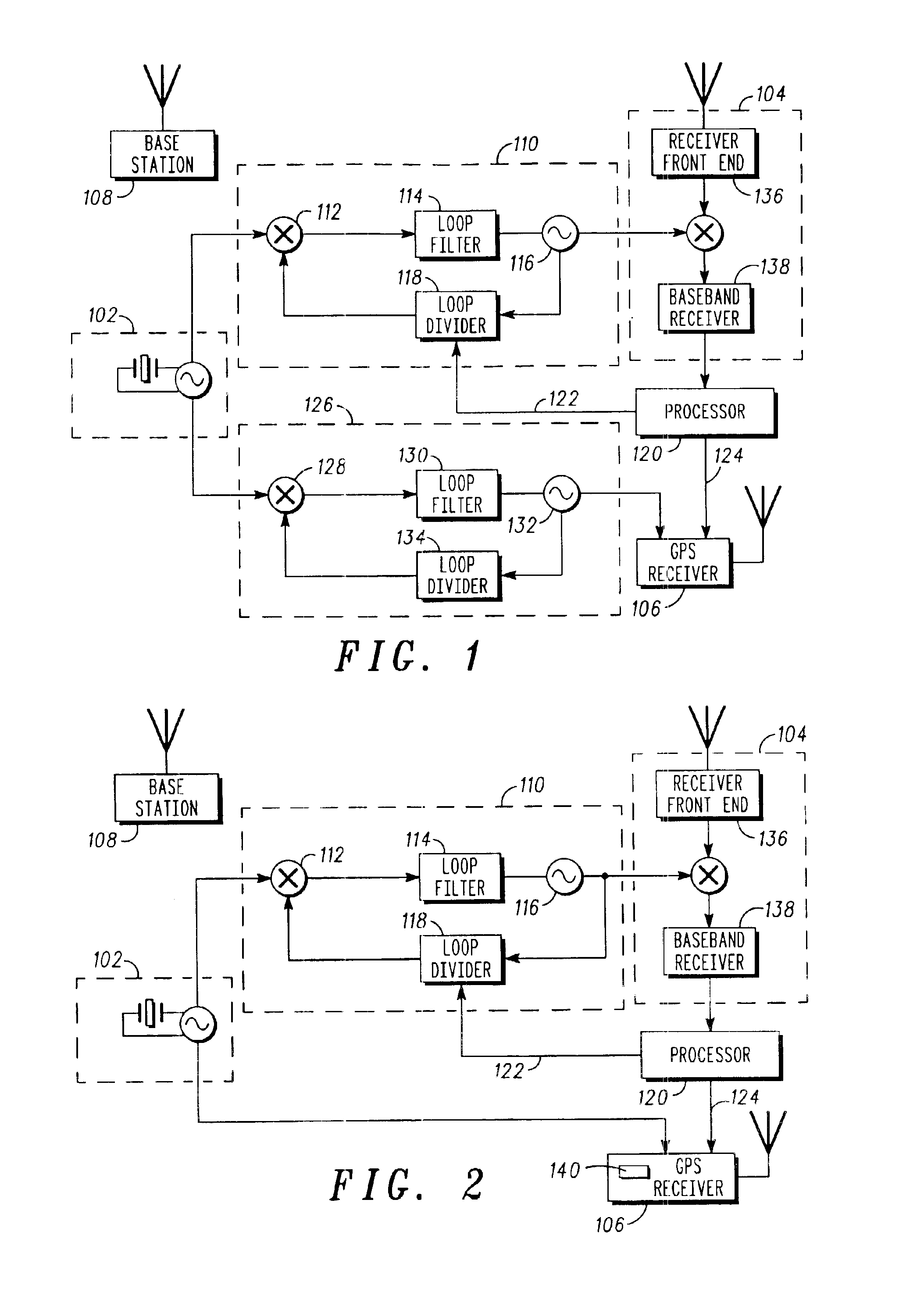
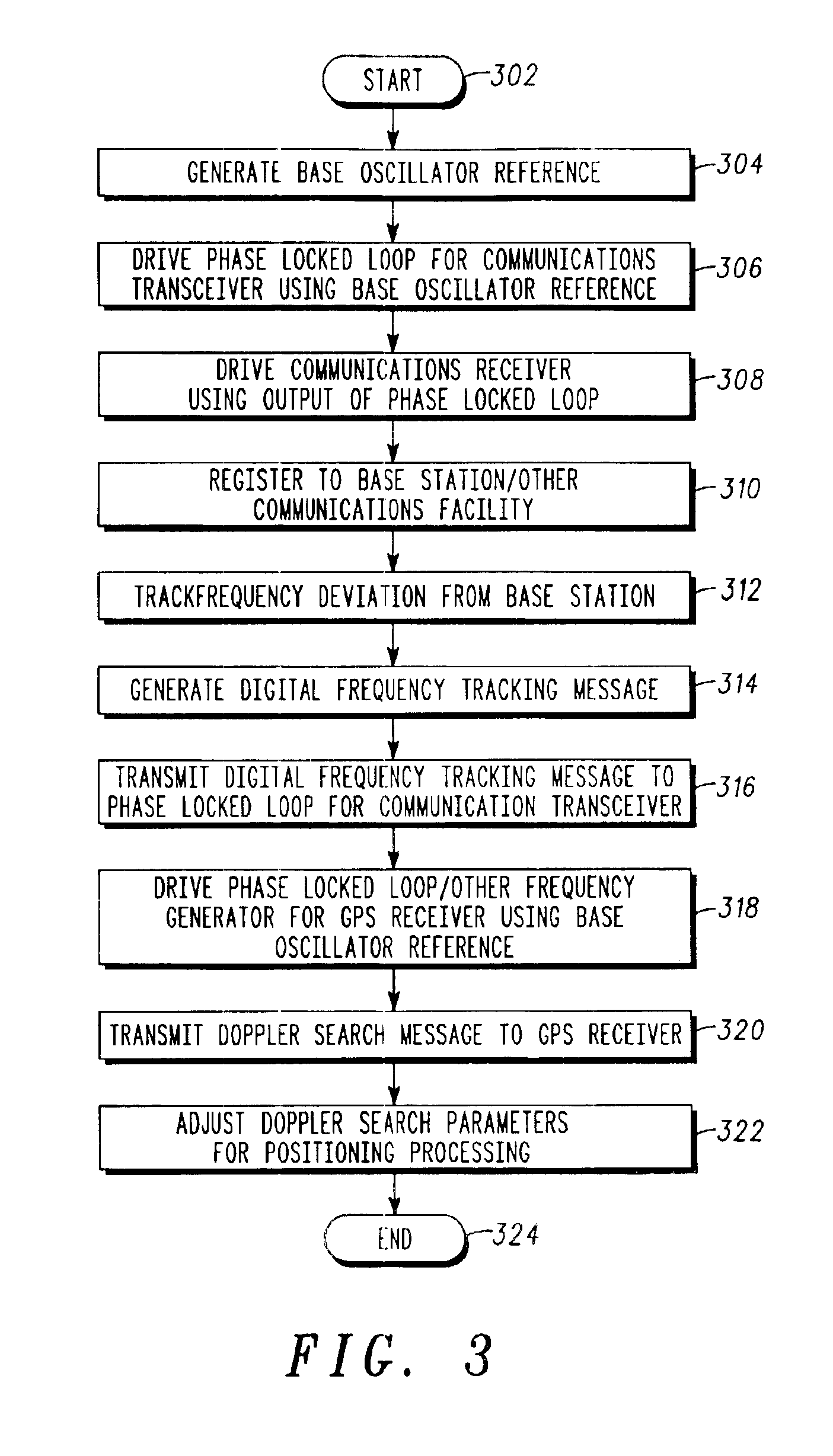
A frequency management scheme for a hybrid communications / positioning device, such as a cellular / GPS or other combined device, generates a local clock signal for the communications portion of the device, using a crystal oscillator or other part. The oscillator output may be delivered to a phase locked loop to drive a high-frequency clock for the cellular or other communications portion of the hybrid device. A processor may determine frequency error between the phase locked loop and base station or other reference, to derive a digital frequency tracking message. A Doppler search or other logical control message may likewise be communicated from the processor to a GPS or other positioning receiver. The GPS receiver circuitry may consequently adjust Doppler center, window width or other parameters to enhance time to first fix or other performance. The architecture eliminates the need for a second crystal or other direct oscillator in the GPS receiver portion of the hybrid device, while still maintaining GPS performance. The architecture of the design also eliminates the need for frequency correcting elements in the crystal oscillator or other base reference oscillator or clock. The invention can furthermore be used in any system, radio, modem, transceiver, or receiver that has two or more receivers that share one reference or base oscillator or clock.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
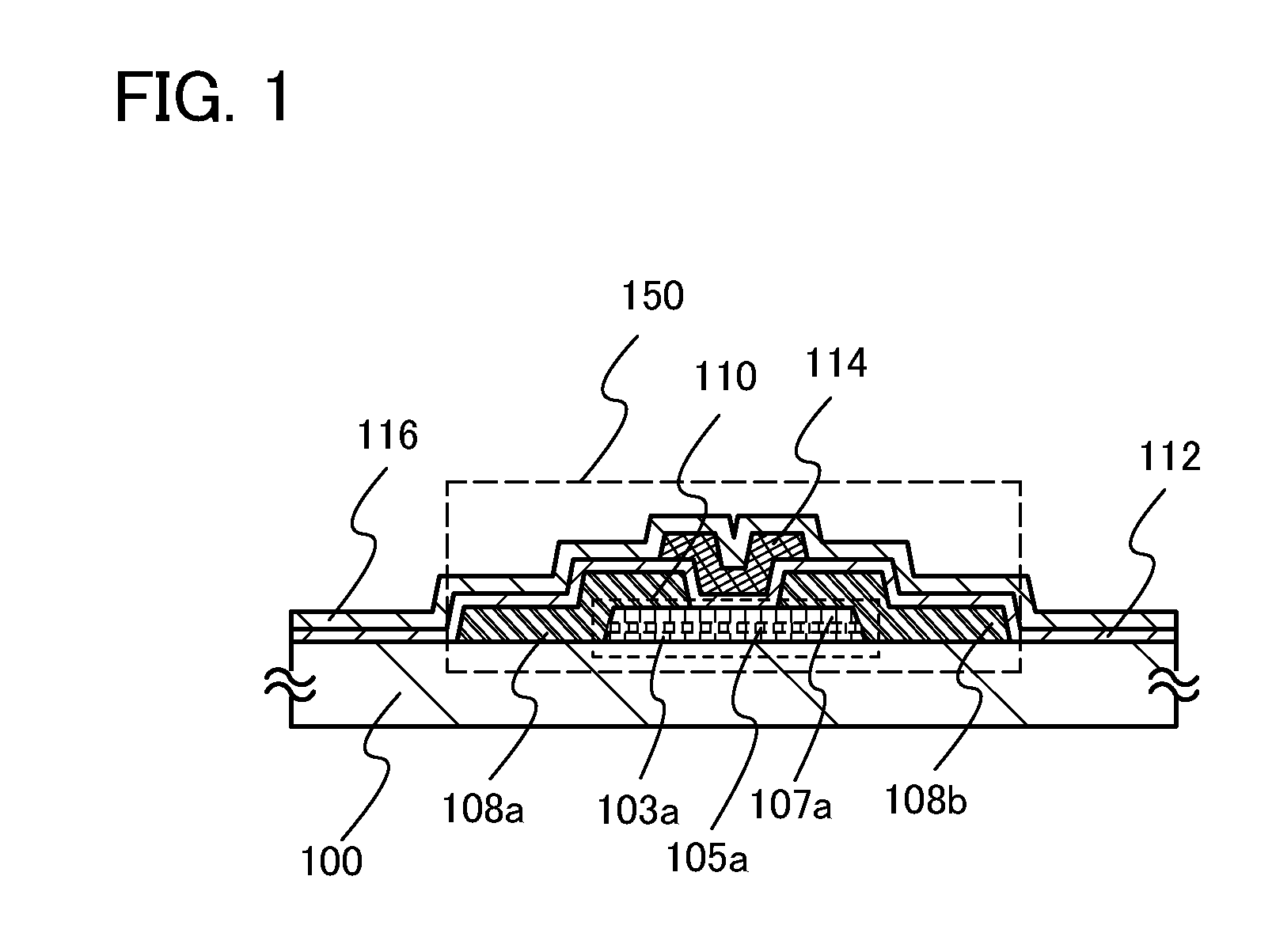
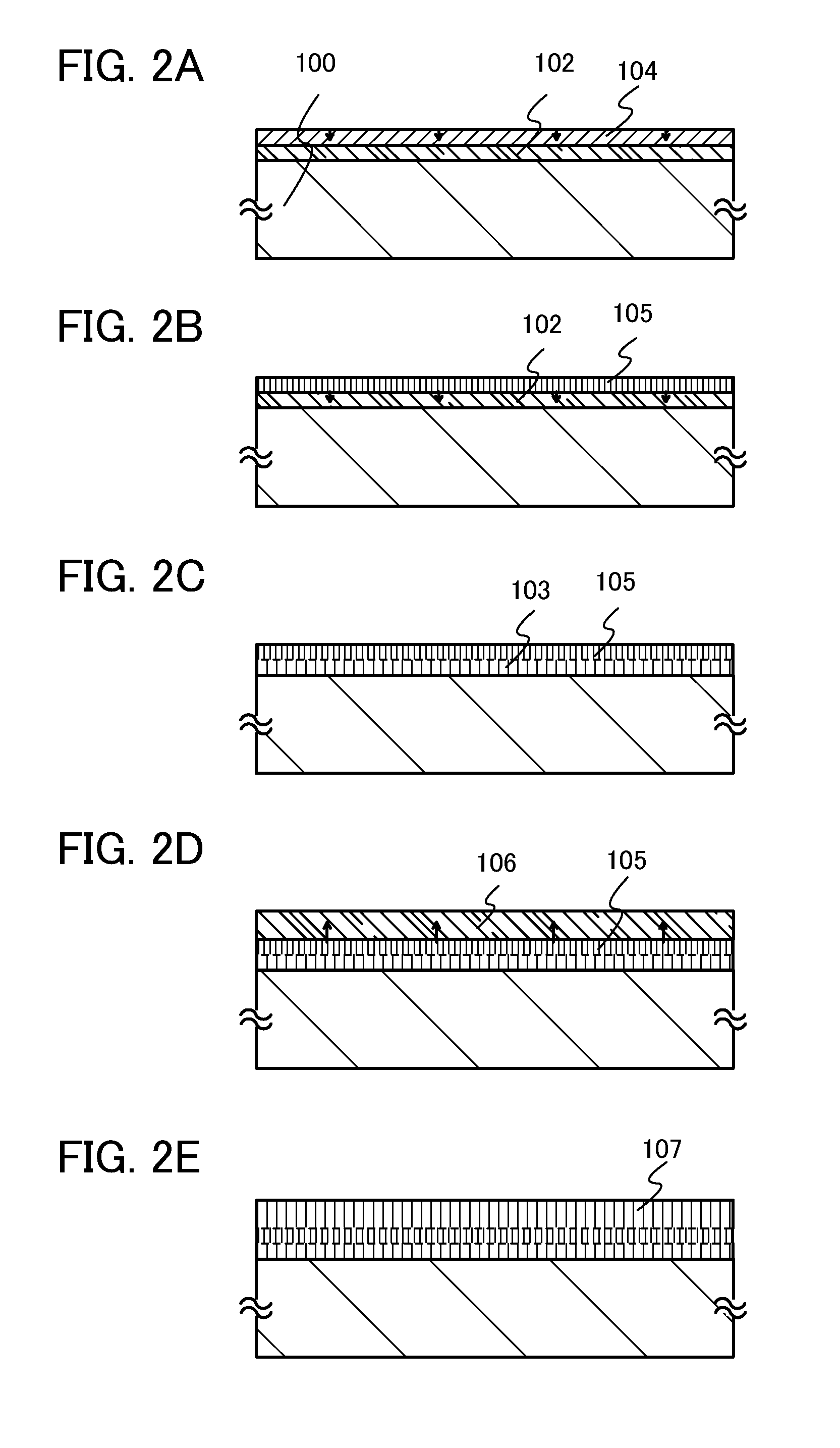
Method for manufacturing semiconductor device
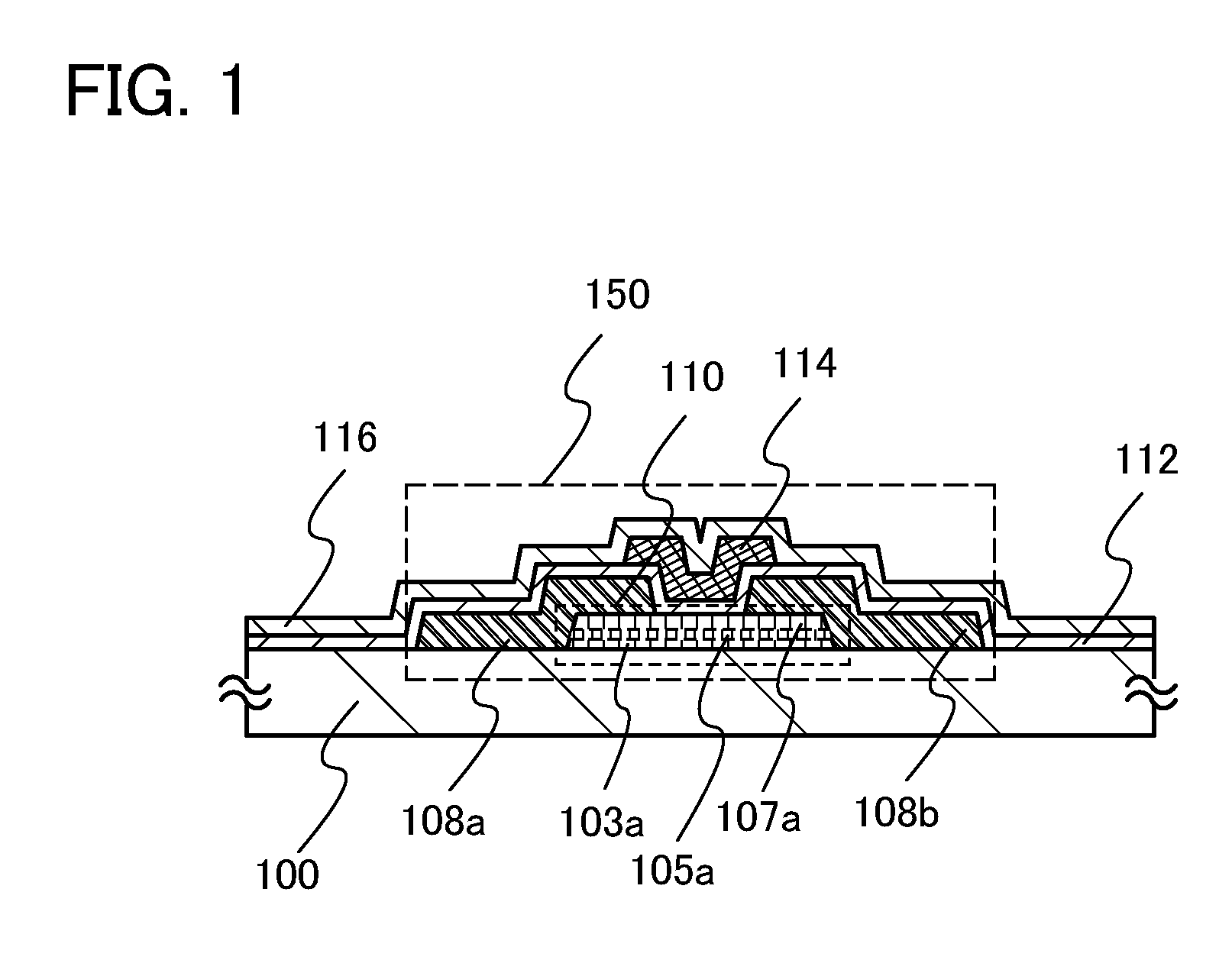
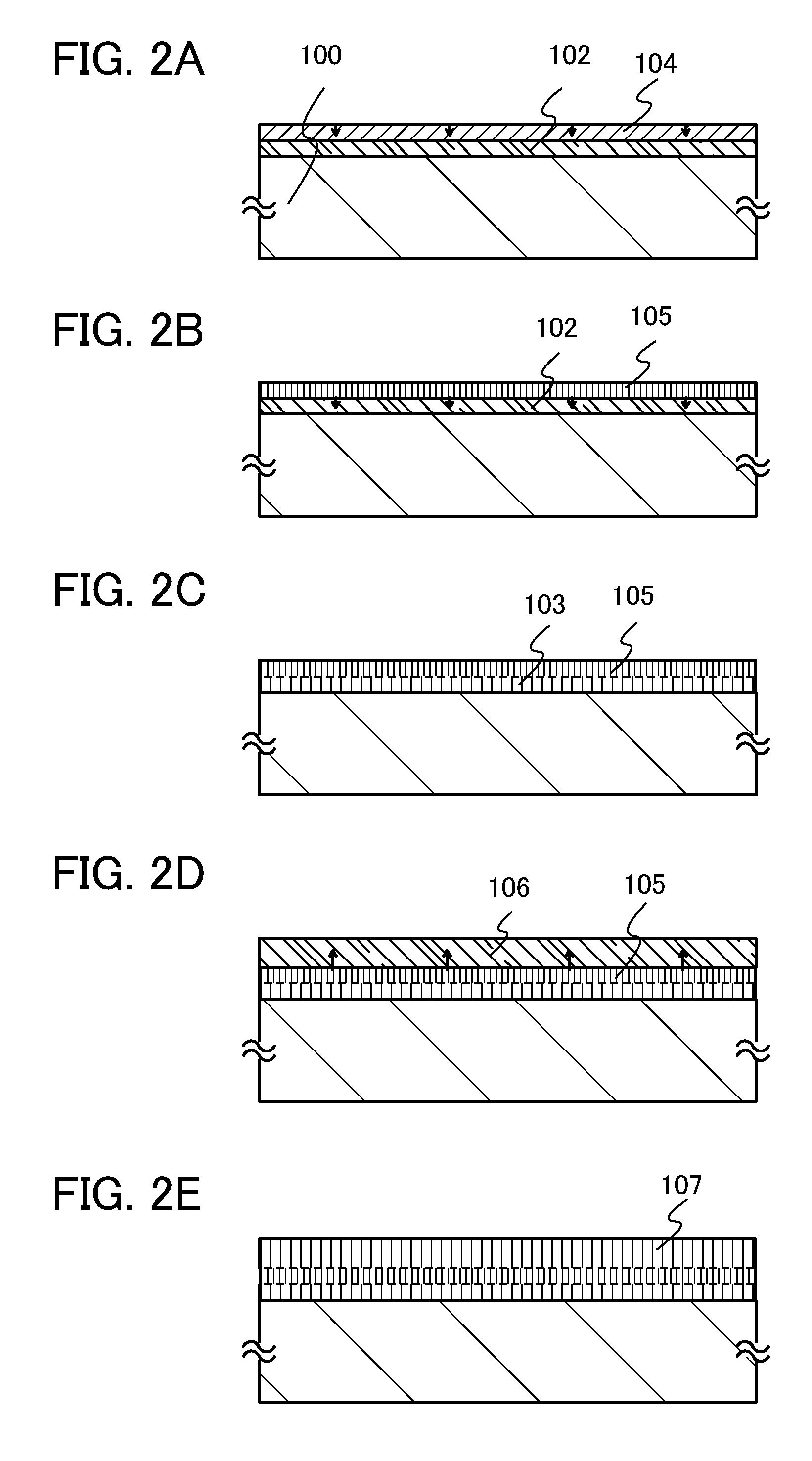
ActiveUS20110156026A1High field-effect mobilitySufficient performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay deviceSingle crystal
A larger substrate can be used, and a transistor having a desirably high field-effect mobility can be manufactured through formation of an oxide semiconductor layer having a high degree of crystallinity, whereby a large-sized display device, a high-performance semiconductor device, or the like can be put into practical use. A first multi-component oxide semiconductor layer is formed over a substrate and a single-component oxide semiconductor layer is formed thereover; then, crystal growth is carried out from a surface to an inside by performing heat treatment at 500° C. to 1000° C. inclusive, preferably 550° C. to 750° C. inclusive so that a first multi-component oxide semiconductor layer including single crystal regions and a single-component oxide semiconductor layer including single crystal regions are formed; and a second multi-component oxide semiconductor layer including single crystal regions is stacked over the single-component oxide semiconductor layer including single crystal regions.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Fiber containing filter media
InactiveUS20040038014A1Efficient removalLow efficiencySynthetic resin layered productsUltrafiltrationPolymer scienceFilter media
Improved filtration media or filter bodies can be made from fine fiber and can be formed into a filtration structure having no internal defects. The filter media or filter body comprises a collection of spot in fiber with defined fiber diameter, layer thickness and media solidity. The fine fiber is formed into a media body and obtains substantial flux and filtration efficiency. The filtration media or body can comprise single or multiple layers of fine fiber combined into the improved filter body.
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
Semiconductor apparatus, method of manufacturing semiconductor apparatus, method of designing semiconductor apparatus, and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20110233702A1Improve performanceSufficiently exhibiting performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
A semiconductor device including a first material layer adjacent to a second material layer, a first via passing through the first material layer and extending into the second material layer, and a second via extending into the first material layer, where along a common cross section parallel to an interface between the two material layers, the first via has a cross section larger than that of the second via.
Owner:SONY CORP
Solar Cell And Manufacturing Method Therefor
InactiveUS20070209697A1Sufficient performanceFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationSolar cellSubstrate surface
When forming an electrode by printing several times, the cross section area of the electrode is increased and the resistance is reduced while more electrode material is required, which leads to a cost up and waste of resources. There is provided a solar cell manufacturing method for forming an electrode of a predetermined pattern by repeating printing on a substrate surface by a predetermined number of times. A mask pattern for printing the entire predetermined pattern is used at least once among the predetermined number of printings while mask patterns, each for printing a part of the predetermined pattern, are used in the other printings, thereby forming the electrode of the predetermined pattern.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
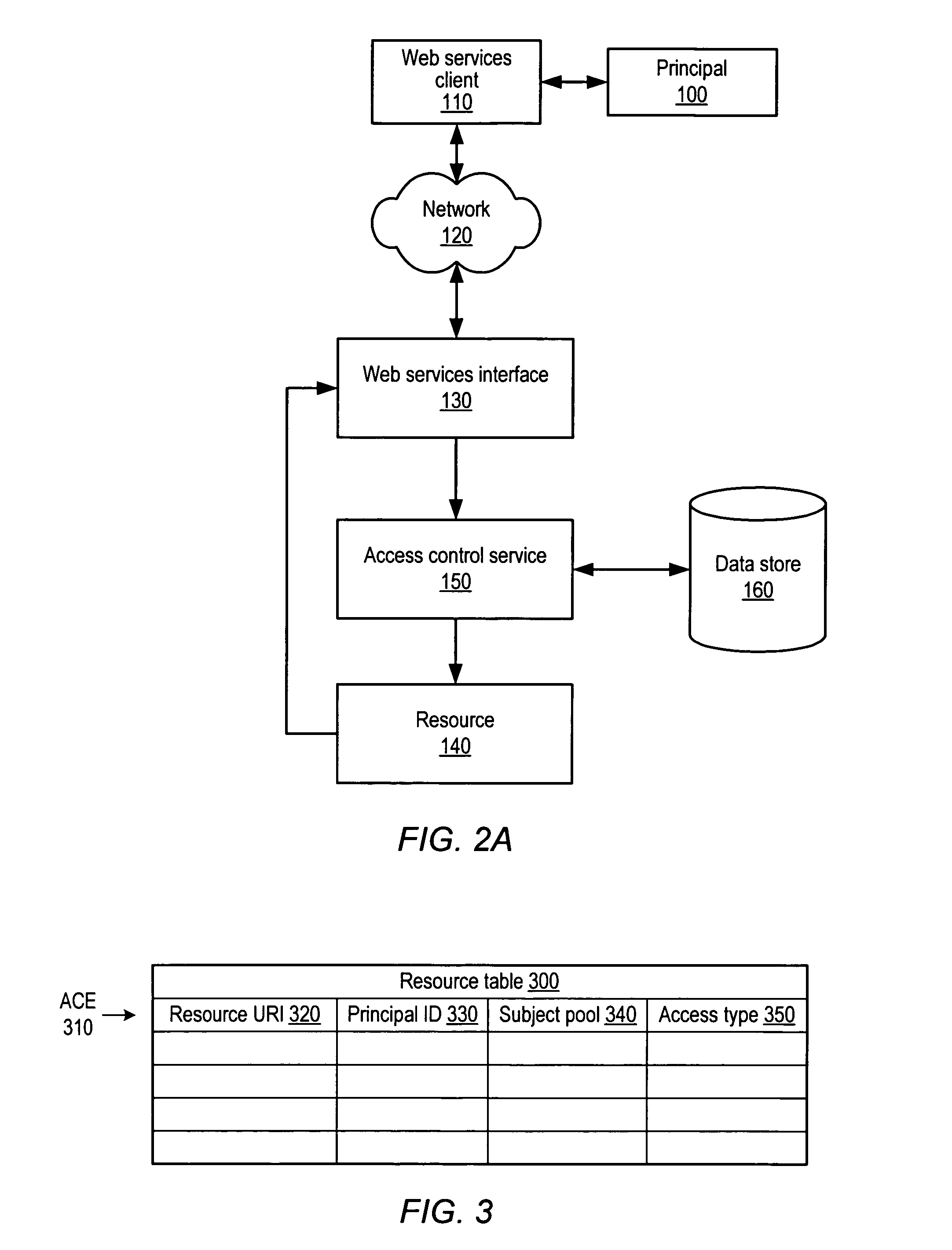
System and method for controlling access to web services resources
ActiveUS8447829B1Sufficient performanceSpecific access rightsComputer security arrangementsStore instructionNetsniff-ng
A system and method for controlling access to web services resources. A system may include a storage medium configured to store instructions and one or more processors configured to access the storage medium. The instructions may be executable by at least one of the processors to implement a web services access control system (ACS) configured to receive requests. Each request specifies an access operation to be performed with respect to a corresponding resource. Each of the requests is associated with a corresponding principal. For each received request, the ACS may be further configured to determine whether an access control entry exists that is associated with both the resource and principal associated with the request and that specifies an access type sufficient to perform the access operation. If no such entry exists, the ACS may deny the request.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
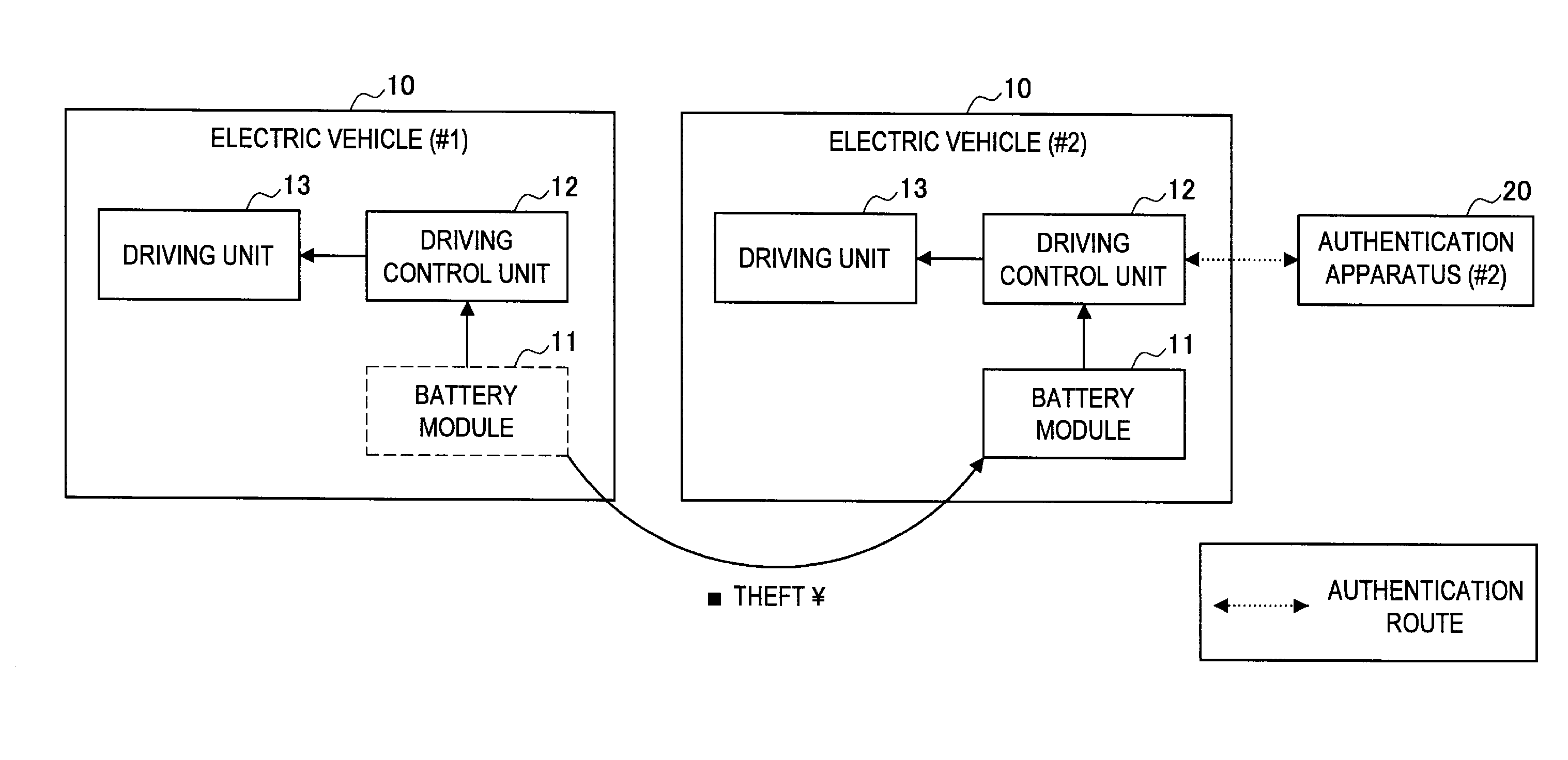
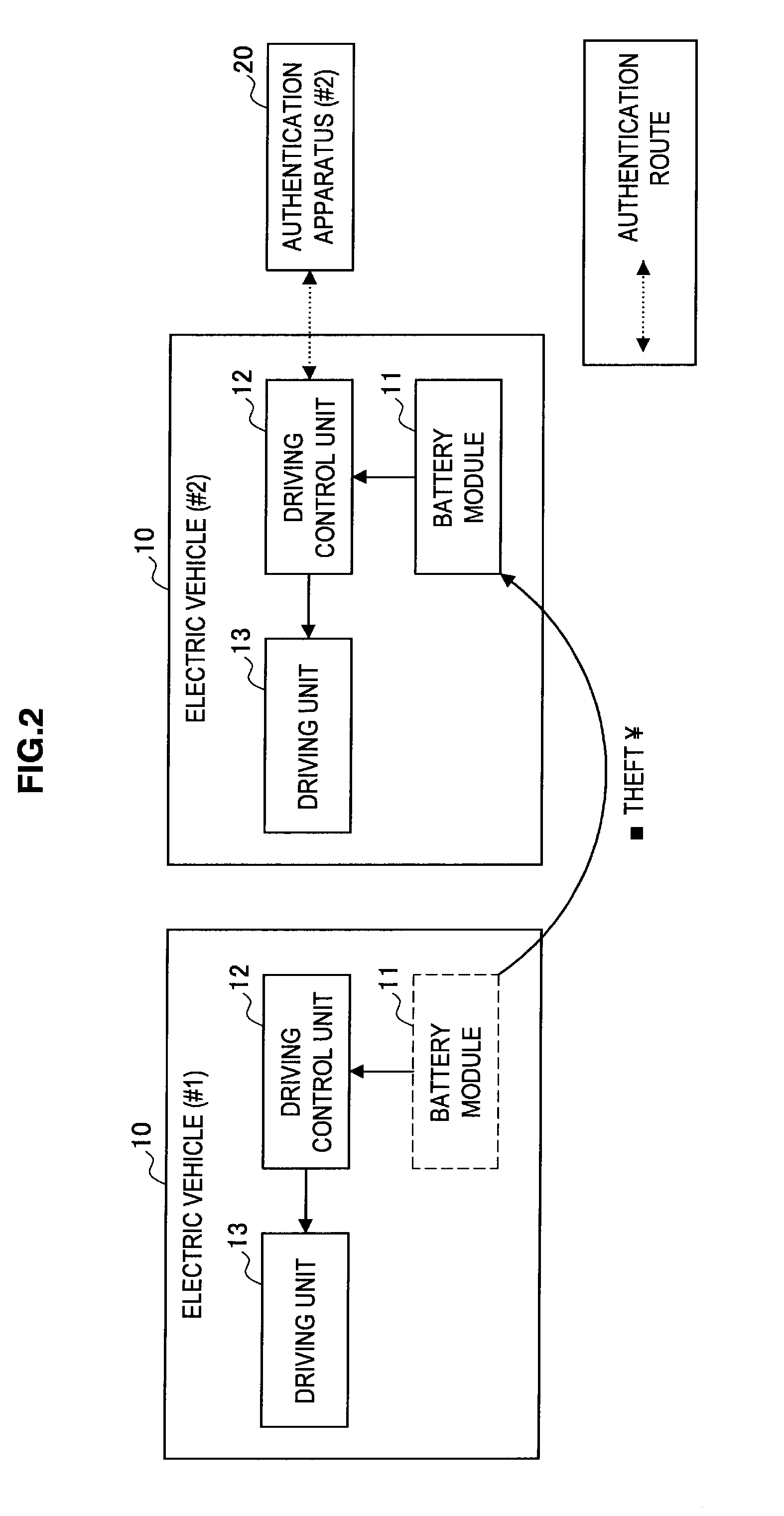
Battery module, electric vehicle, authentication apparatus, and discharging control method for battery module
InactiveUS20110270480A1Sufficient performanceMaintaining security against theftDigital data processing detailsVehicular energy storageElectrical batteryComputer module
There is provided a battery module including: a power storage unit storing power; a first authentication unit carrying out first authentication via a first authentication route; a second authentication unit carrying out second authentication via a second authentication route; and a discharging control unit controlling discharging from the power storage unit to an external appliance, wherein the first authentication unit is operable, when the first authentication has succeeded, to share key information to be used in the second authentication with an authentication party for the second authentication, the second authentication unit carries out the second authentication using the key information shared with the authentication party, and the discharging control unit is operable, when the second authentication has succeeded, to permit discharging from the power storage unit.
Owner:SONY CORP
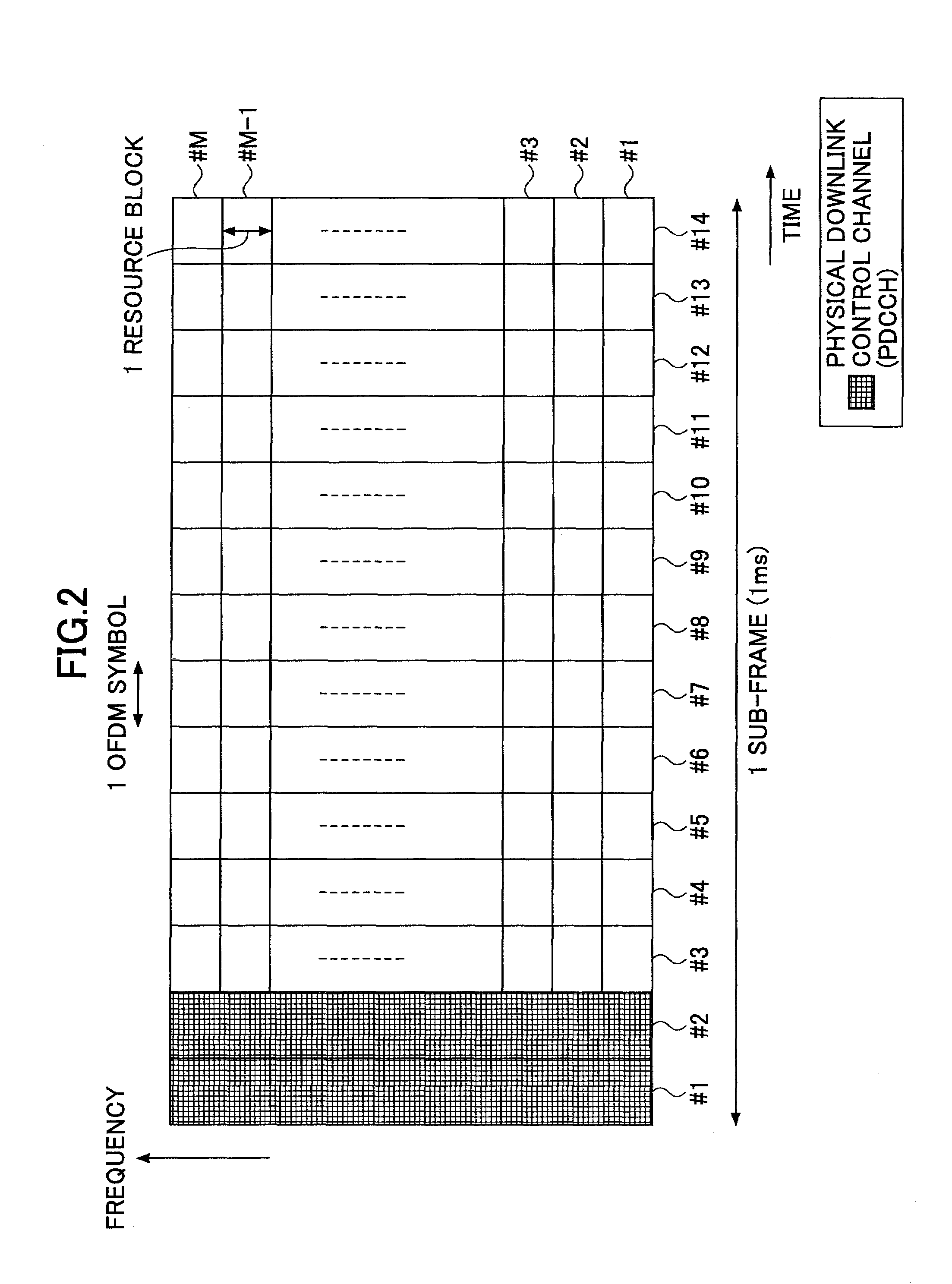
Base station apparatus and communication control method
InactiveUS20100091724A1Sufficient performancePower managementTransmission systemsControl channelCommunication control
A base station apparatus is disclosed that includes a selection unit selecting user equipment terminals to which radio resources are allocated based on priority levels indicating a priority order of allocating the radio resources for a shared channel and a resource determination unit determining a transmission power level of a control channel and resources for the control channel, the control channel indicating communications of the shared channel to the selected user equipment terminals. In the base station apparatus, when the sum of the transmission power of the control channel related to the selected user equipment terminals exceeds a predetermined first threshold value or when a sum of control resources for the control channel related to the selected user equipment terminals exceeds a predetermined second threshold value, the resource determination unit transmits the control channel to some user equipment terminals among the selected user equipment terminals.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
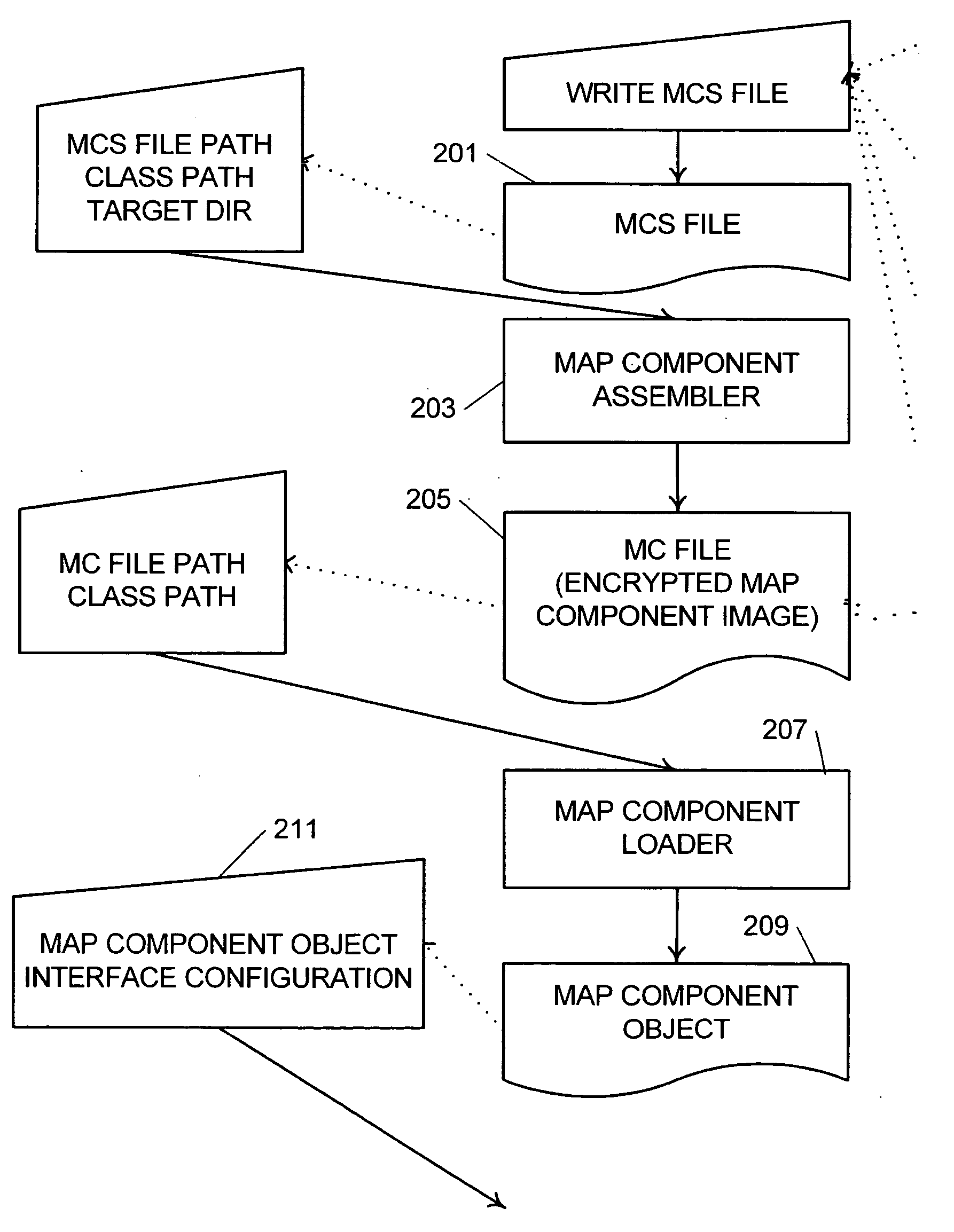
System and method for data transformation using dataflow graphs
ActiveUS20050097561A1Sufficient performanceDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsData warehouseData stream
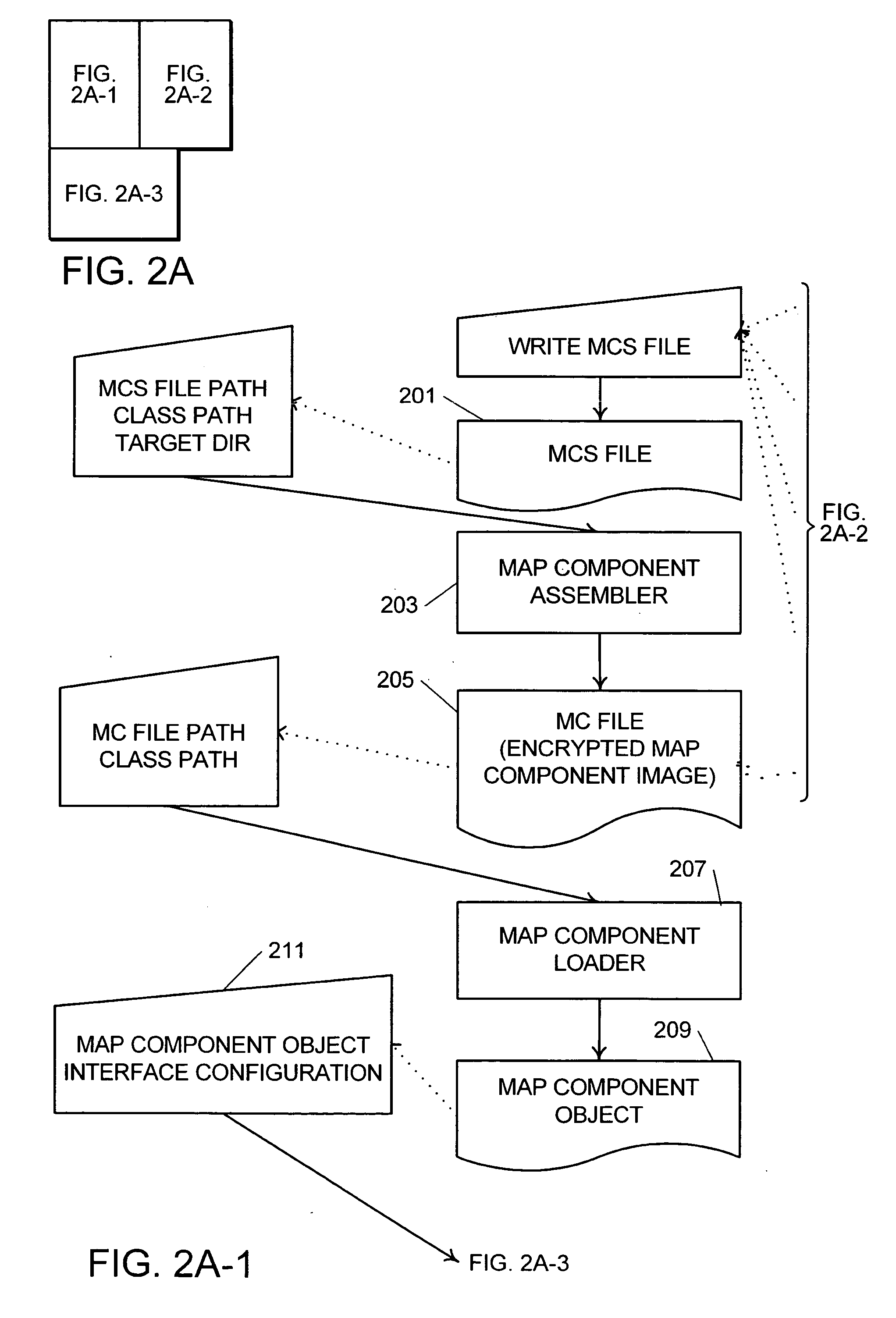
A system and method for managing data, such as in a data warehousing, analysis, or similar applications, where dataflow graphs are expressed as reusable map components, at least some of which are selected from a library of components, and map components are assembled to create an integrated dataflow application. Composite map components encapsulate a dataflow pattern using other maps as subcomponents. Ports are used as link points to assemble map components and are hierarchical and composite allowing ports to contain other ports. The dataflow application may be executed in a parallel processing environment by recognizing the linked data processes within the map components and assigning threads to the linked data processes.
Owner:ACTIAN CORP
Method and Apparatus for Automated Monitoring and Tracking of the Trajectory of Patients' Center of Gravity Movements
InactiveUS20060293613A1Sufficient performanceLessen the burden on the bodyPerson identificationSensorsCushionOccupational therapy
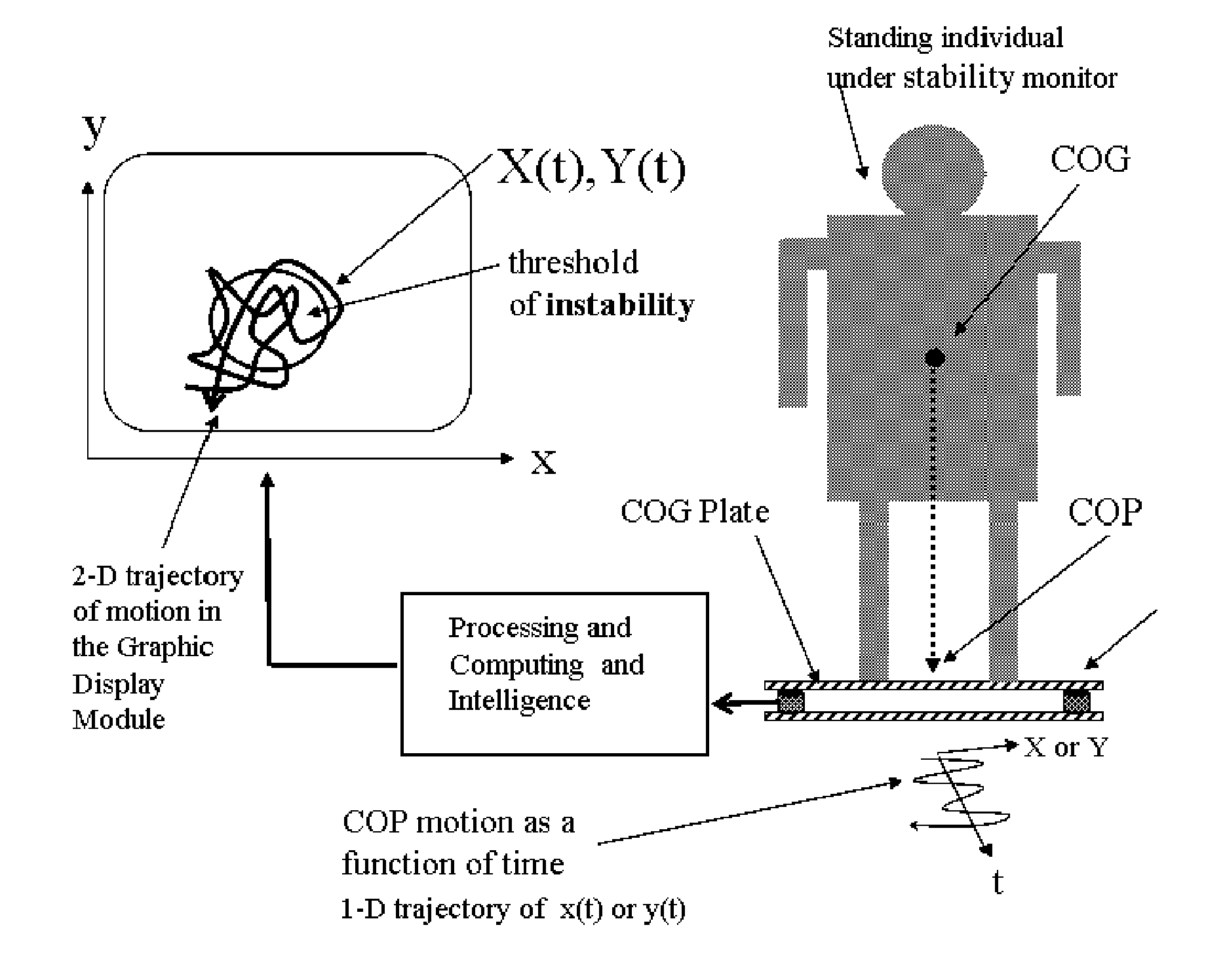
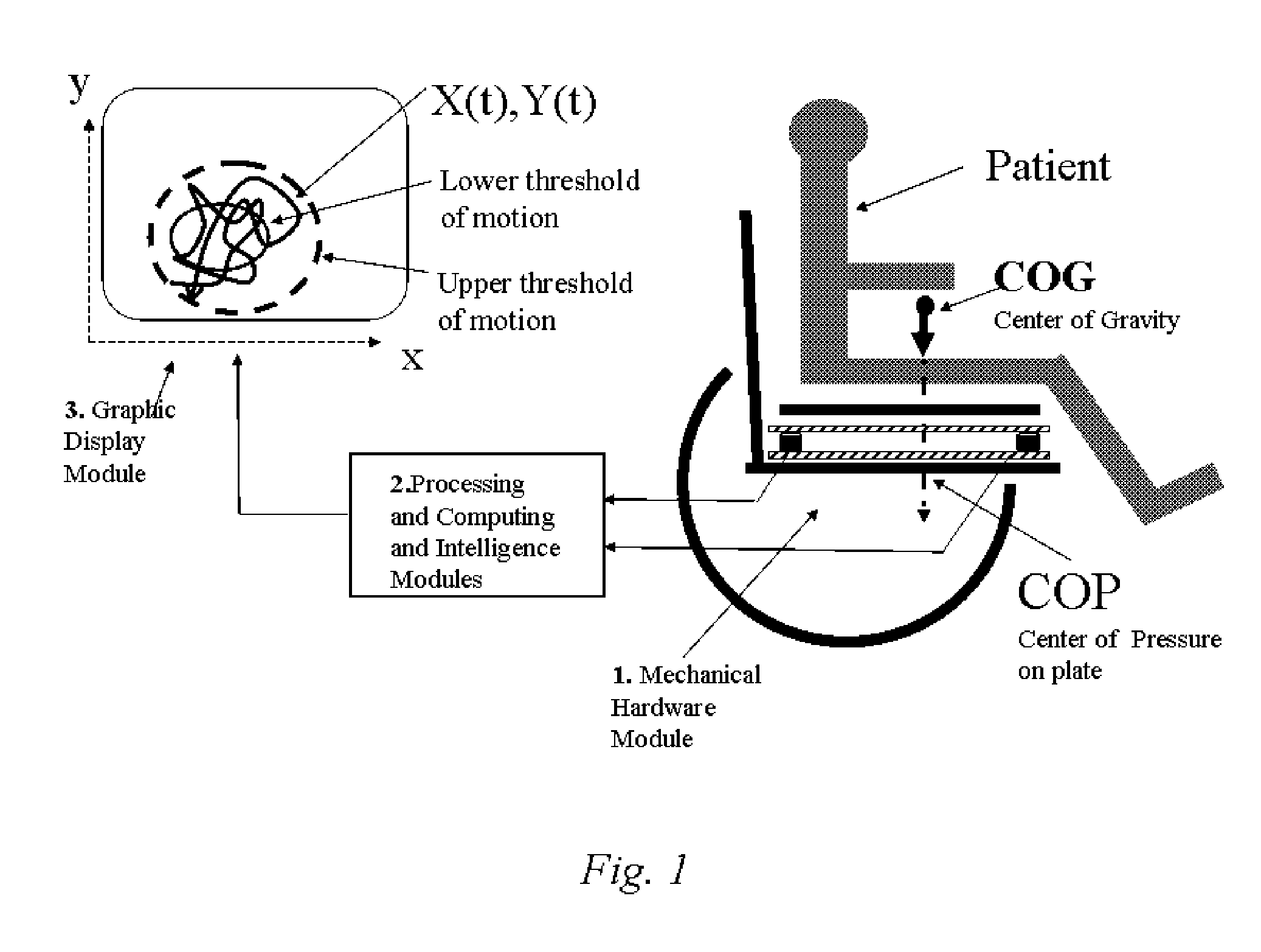
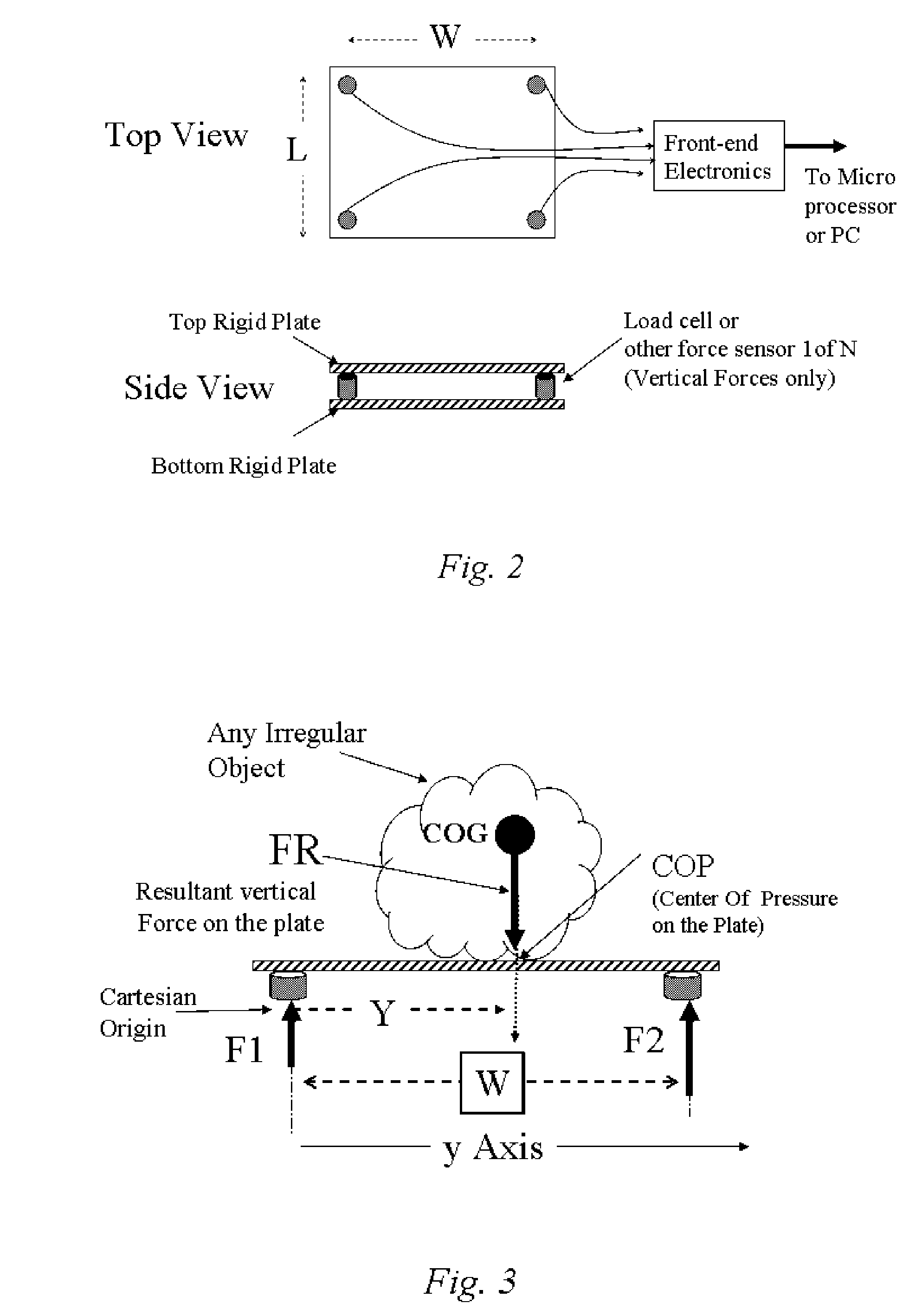
This application describes a revolutionary device to help prevent the development of pressure ulcers. The device works by using a small number of sensors in the wheelchair or bed to determine and track the projection of the patient's center of gravity (COP) onto the plane of the chair or bed. The sensor data are processed by various algorithms which determine when the danger of pressure ulcer development arises and alerts an attendant to reposition the patient. The repositioning is likewise monitored, and if it is inadequate, a higher-level alarm is issued. This device also maintains a history of patient position and movement, which is potentially useful for diagnostic purposes, such as tracking the degree of improvement resulting from a course of treatment or therapy. The archival record can also provide verification of proper care in the event of lawsuits or insurance claims. Operation of the device is non-intrusive and does not disturb either the patient or the caregiver unless repositioning of the patient is needed. The invention is based on simple, fundamental principles of physics and engineering. It is implemented with a few force sensors, microprocessors, and wireless networking technology—all of which are readily available. The unique attributes of this apparatus are: Real time performance coupled with maintenance of an archival history. Inexpensive hardware platform. Fully self-contained apparatus. Flexible algorithms for processing the sensor data and tracking motion trajectories in a quantitative manner. The hardware portion of the apparatus may adapted to be placed in the wheelchair or bed under the normal cushions, for mobility-impair patients, or it may be used as a force platform, much like a bathroom scale, for standing stability monitoring or gait training. It transmits the instantaneous COP position information over a wired or wireless network to a processing and monitoring station. It does not employ any external components such as video cameras, local GPS transmitters, etc. Aside from a tool for prevention of pressure in mobility-impaired patients, various embodiments of this system has applications in physical and occupational therapy, gait training, mental training (biofeedback), sports and athletic training, (e.g., golf swing training, baseball batting practice), gymnastics, yoga, dance / ballet, sports paraphernalia design, and a host of other areas, etc.
Owner:CONCEPT DEV GROUP
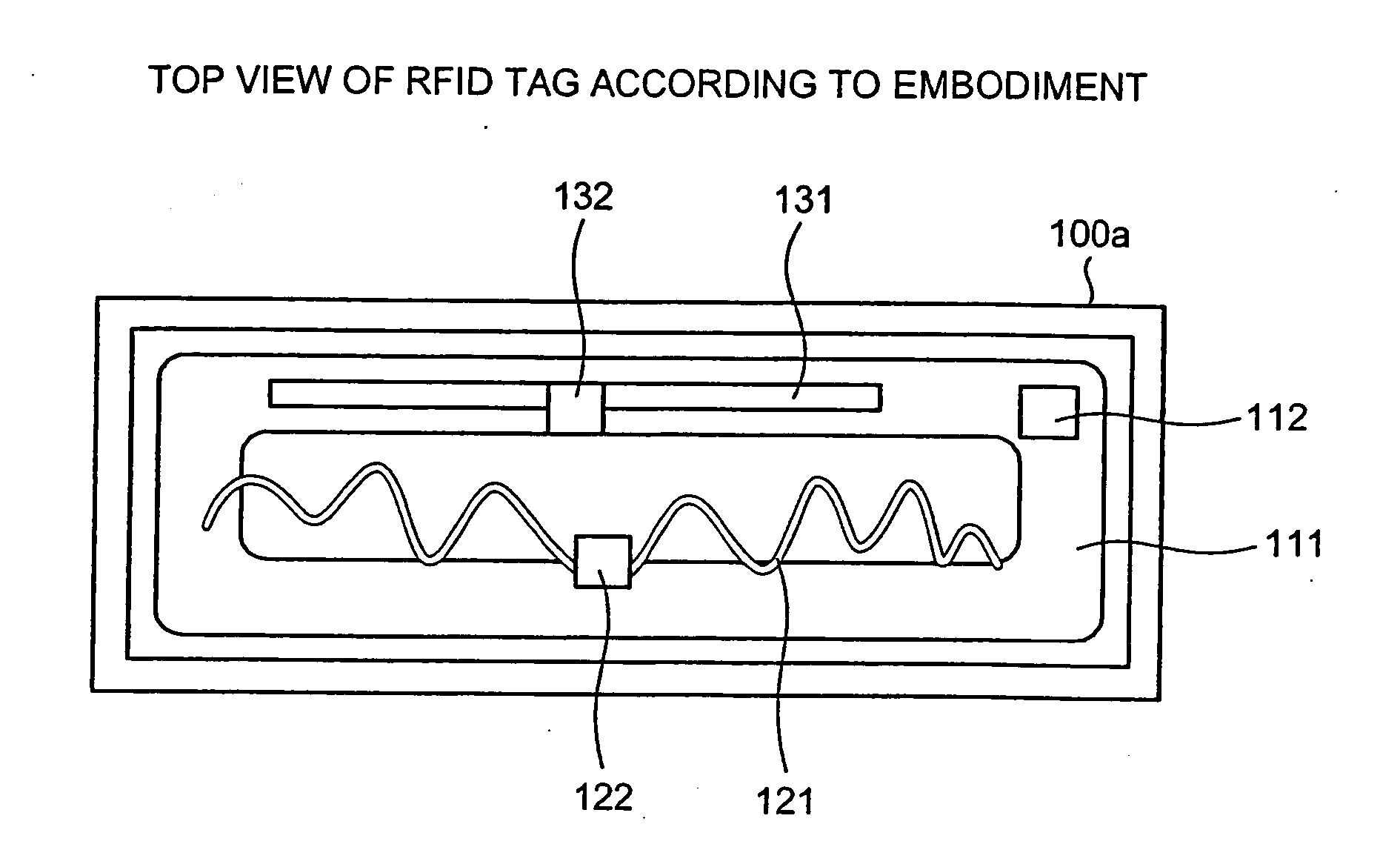
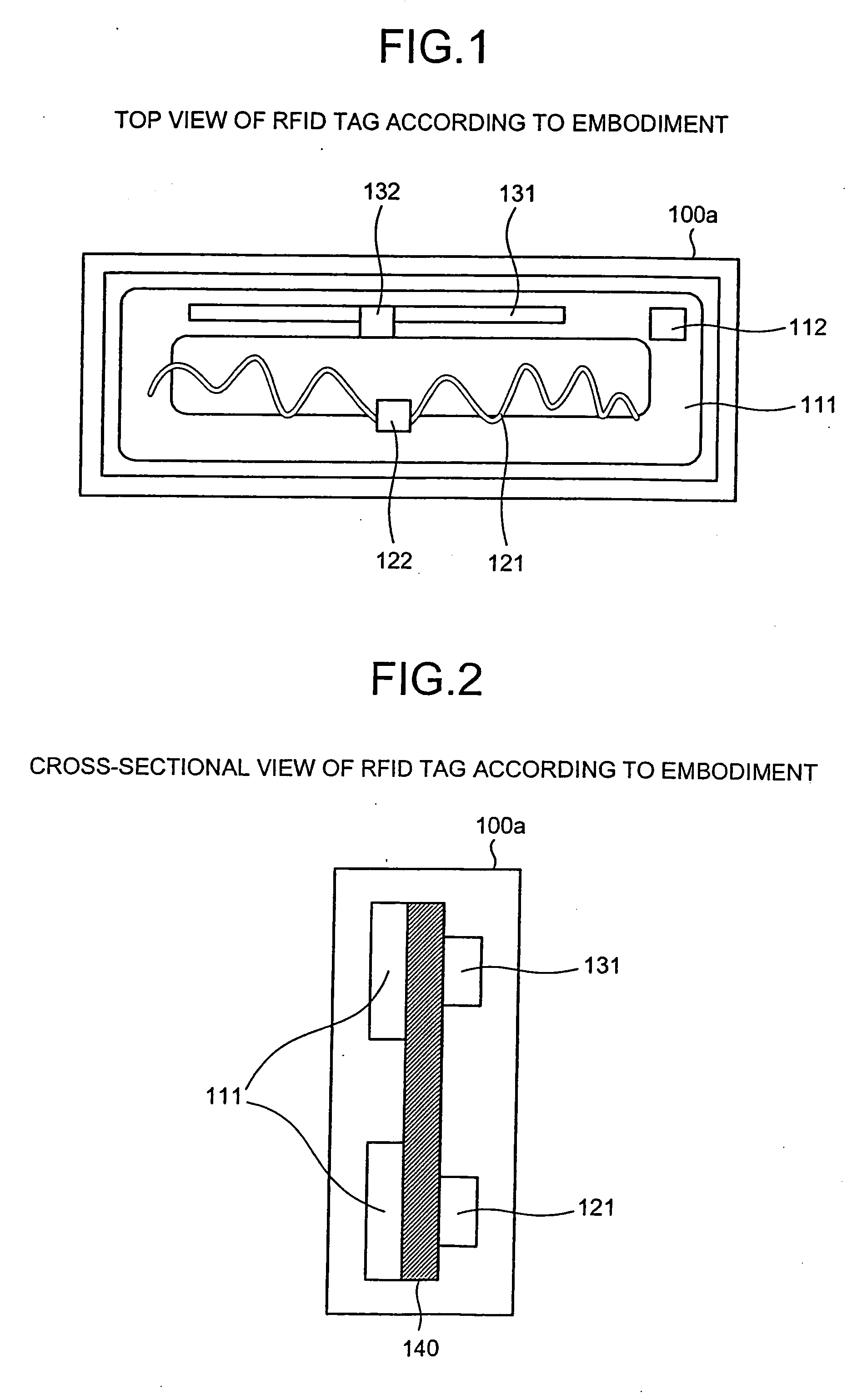
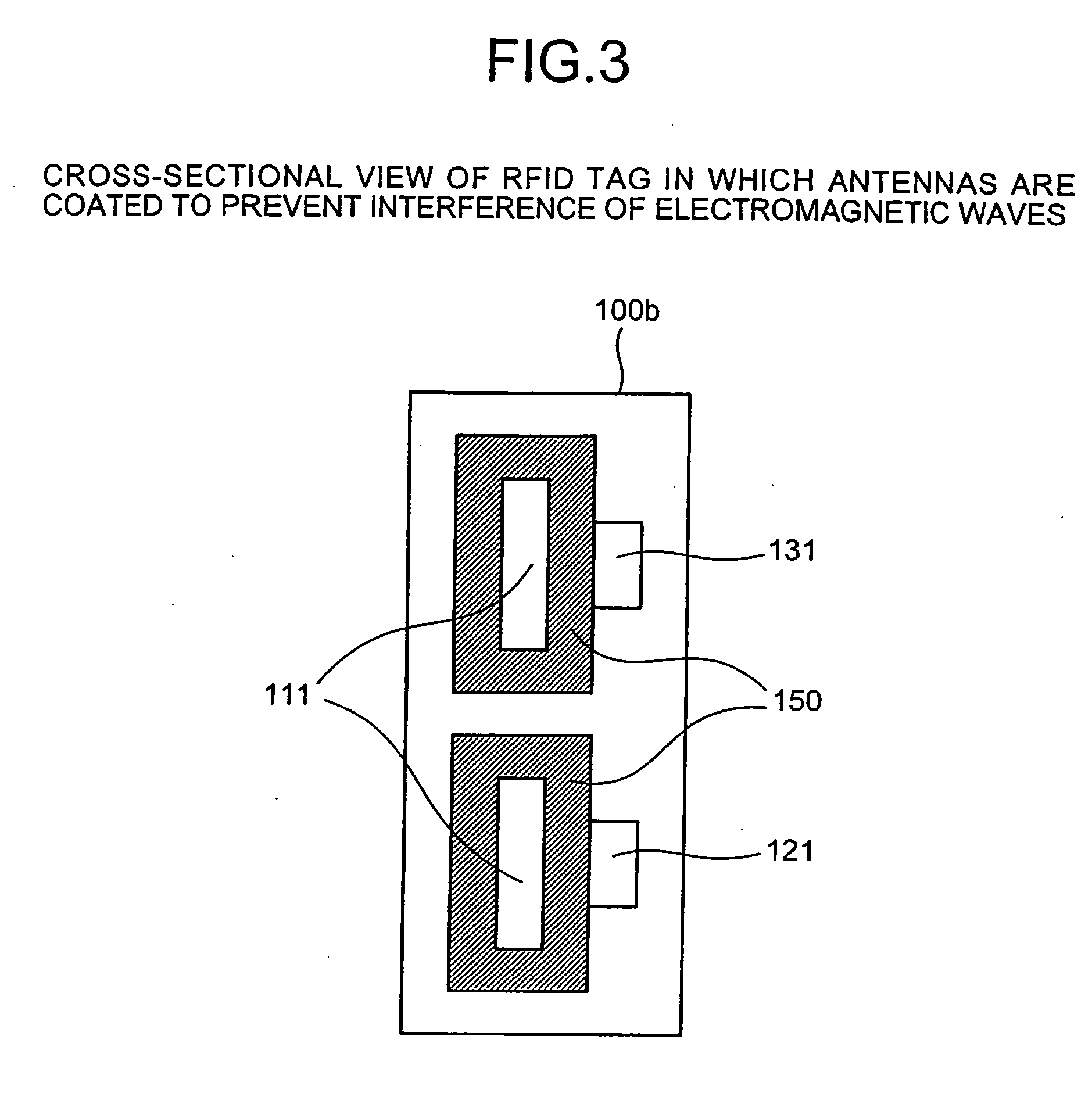
RFID tag and antenna arranging method
InactiveUS20060232419A1Avoid interferenceSufficient performanceSimultaneous aerial operationsRecord carriers used with machinesEngineeringIntegrated circuit
A non-contact integrated circuit (IC) tag accepts a plurality of frequency bands and provides sufficient performance in a compact size by freely arranging a plurality of antennas therein such that the antennas occupy a minimum area and by preventing interference between the antennas with an insulator.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
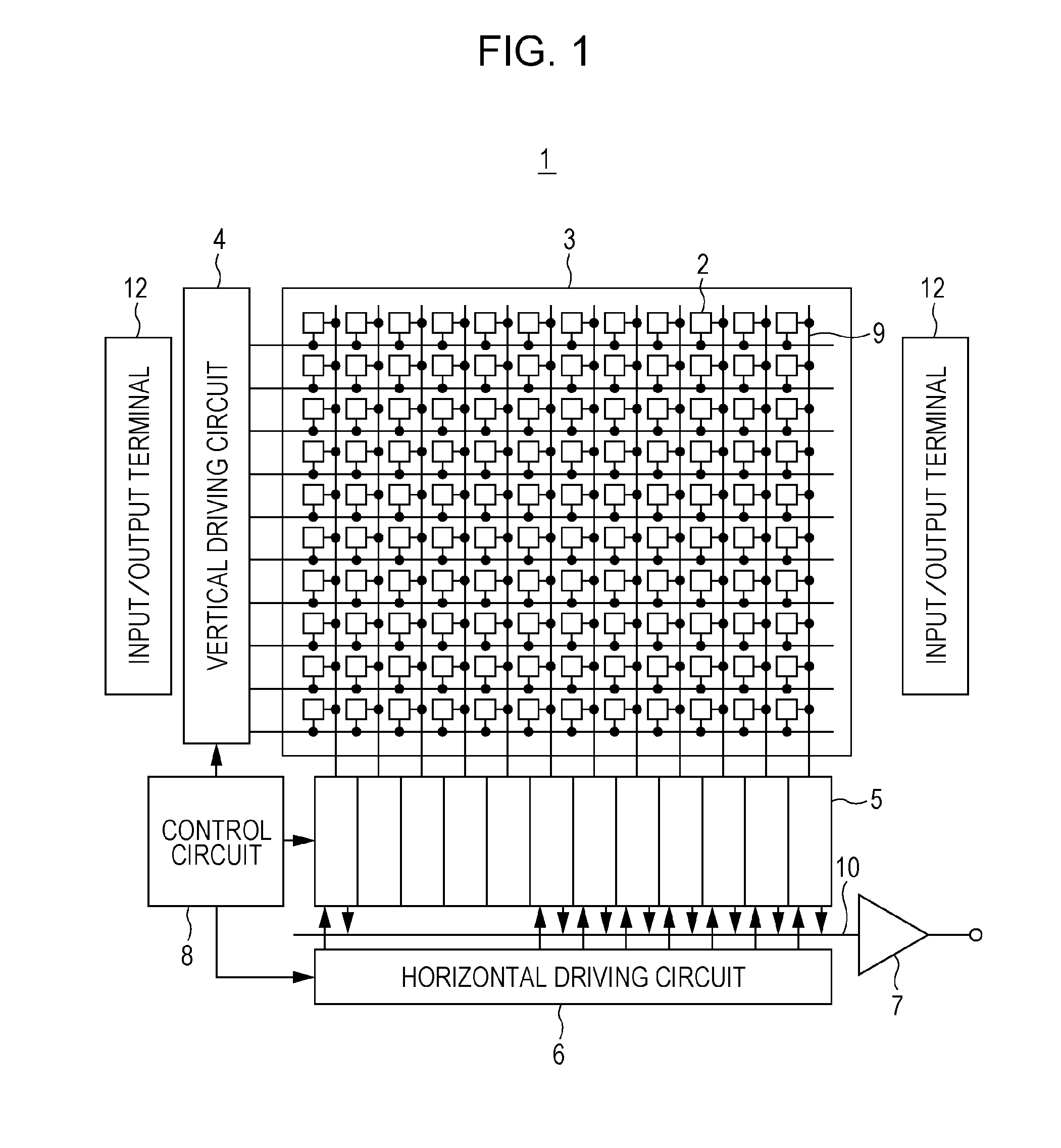
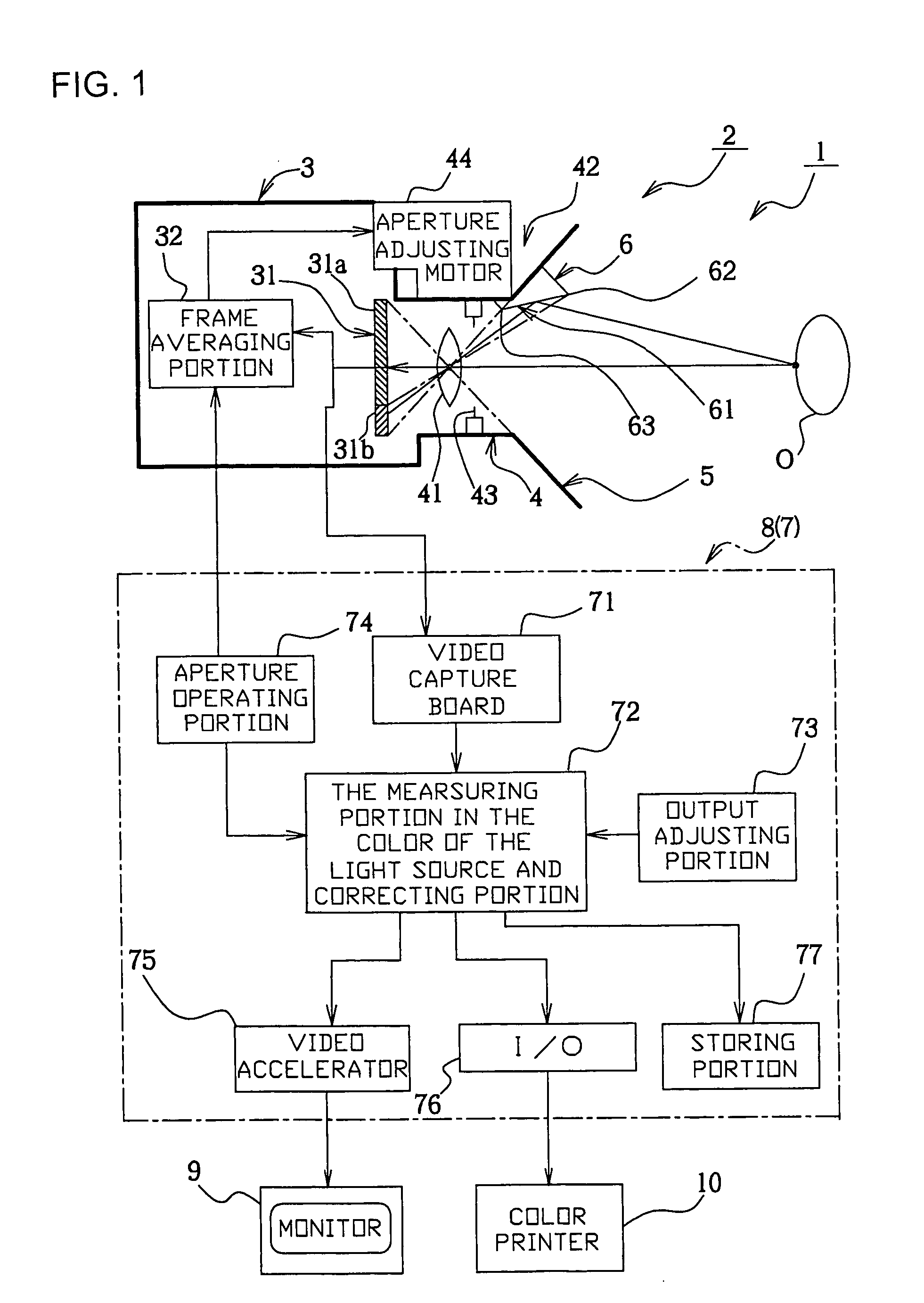
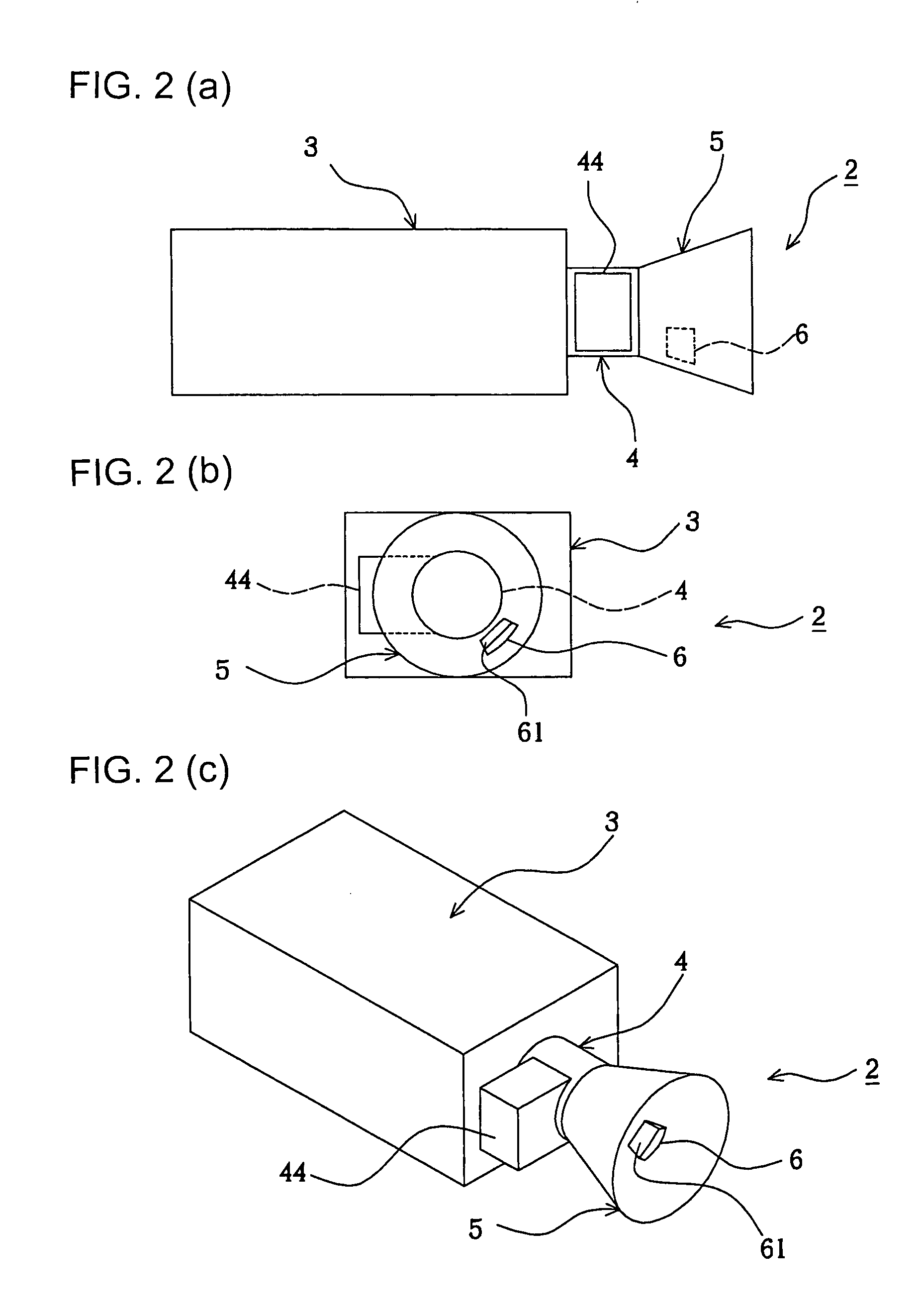
Image pickup system, image processor, and camera
InactiveUS20050117045A1Easy CalibrationColor stableTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsImaging processingReference image
An image capturing system, image processing system, and camera in which color can be precisely corrected to realize invariability of color through simple calibration while decreasing the area of a reference image part. The system comprises a camera having a lens, an image capturing system device, and a reflecting surface. Reference signal values (rn, gn, bn) are determined by averaging the intensities of the reflected lights of a reference scene received by the image capturing system device from the respective color channels of a plurality of pixel parts. The reference signal values represent the light source color, and a main image is corrected using the reference signal values.
Owner:NATURE TECH CO LTD
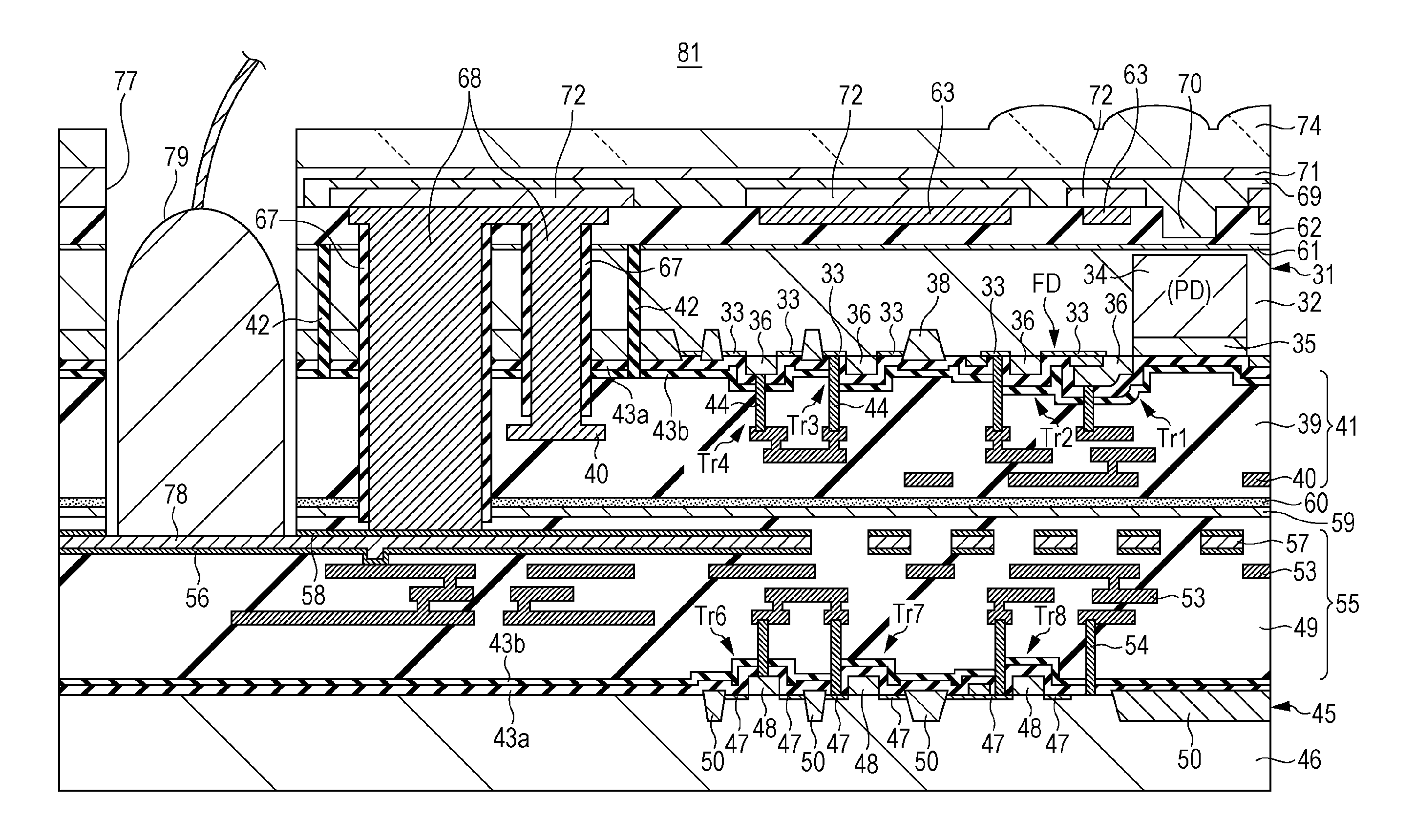
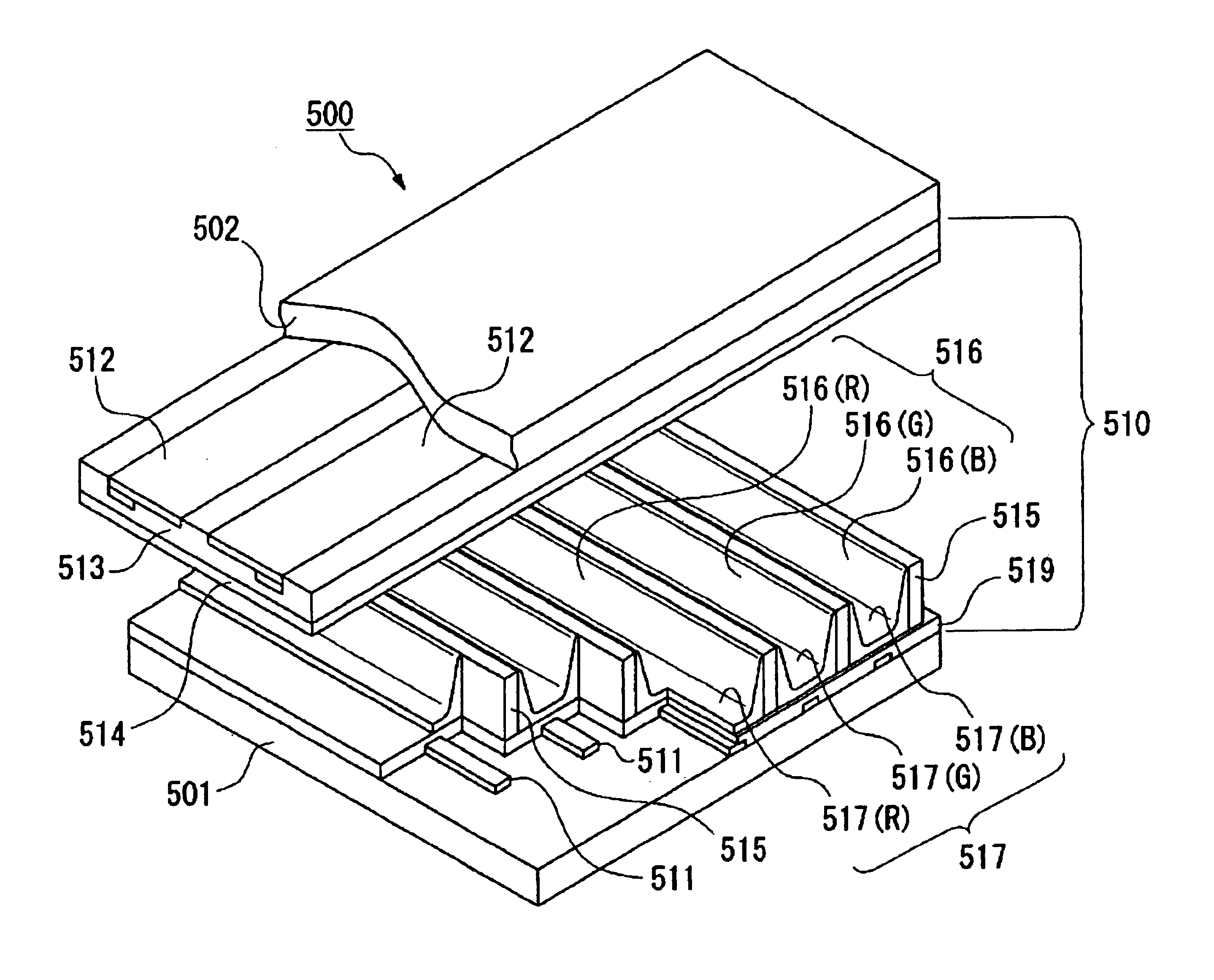
Semiconductor composite apparatus, print head, and image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20060214287A1Reduce manufacturing costSolve the lack of functionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsEngineering
A semiconductor composite apparatus, includes a first substrate, a semiconductor thin film layer, active devices, first driving circuits, and second driving circuits. The semiconductor thin film layer is formed on the first substrate and is formed of a first semiconductor material. The active devices are formed in the semiconductor thin film layer. The first driving circuits is formed of a second semiconductor material and performing a first function in which the active devices are driven. The second driving circuits are formed of a third semiconductor material and performing a second function in which the active devices are driven, the second function being different from the first function.
Owner:OKI DATA CORP
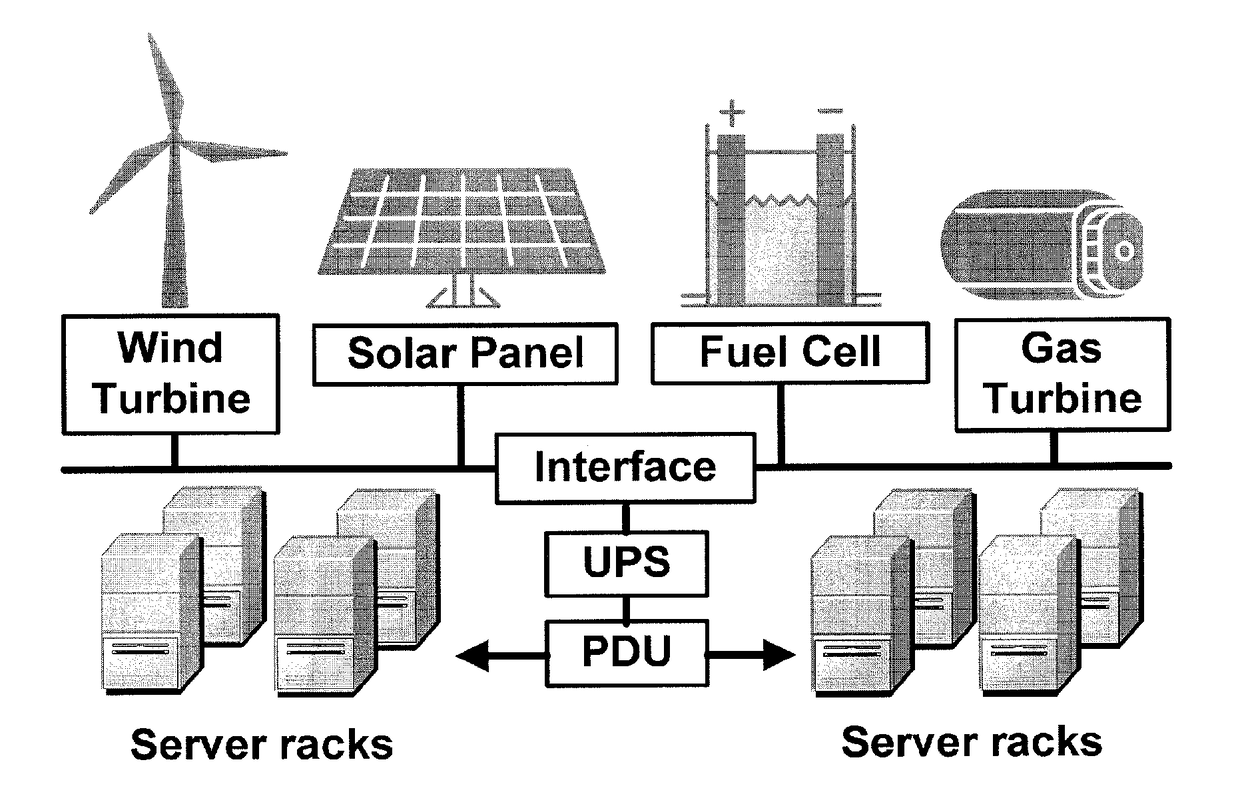
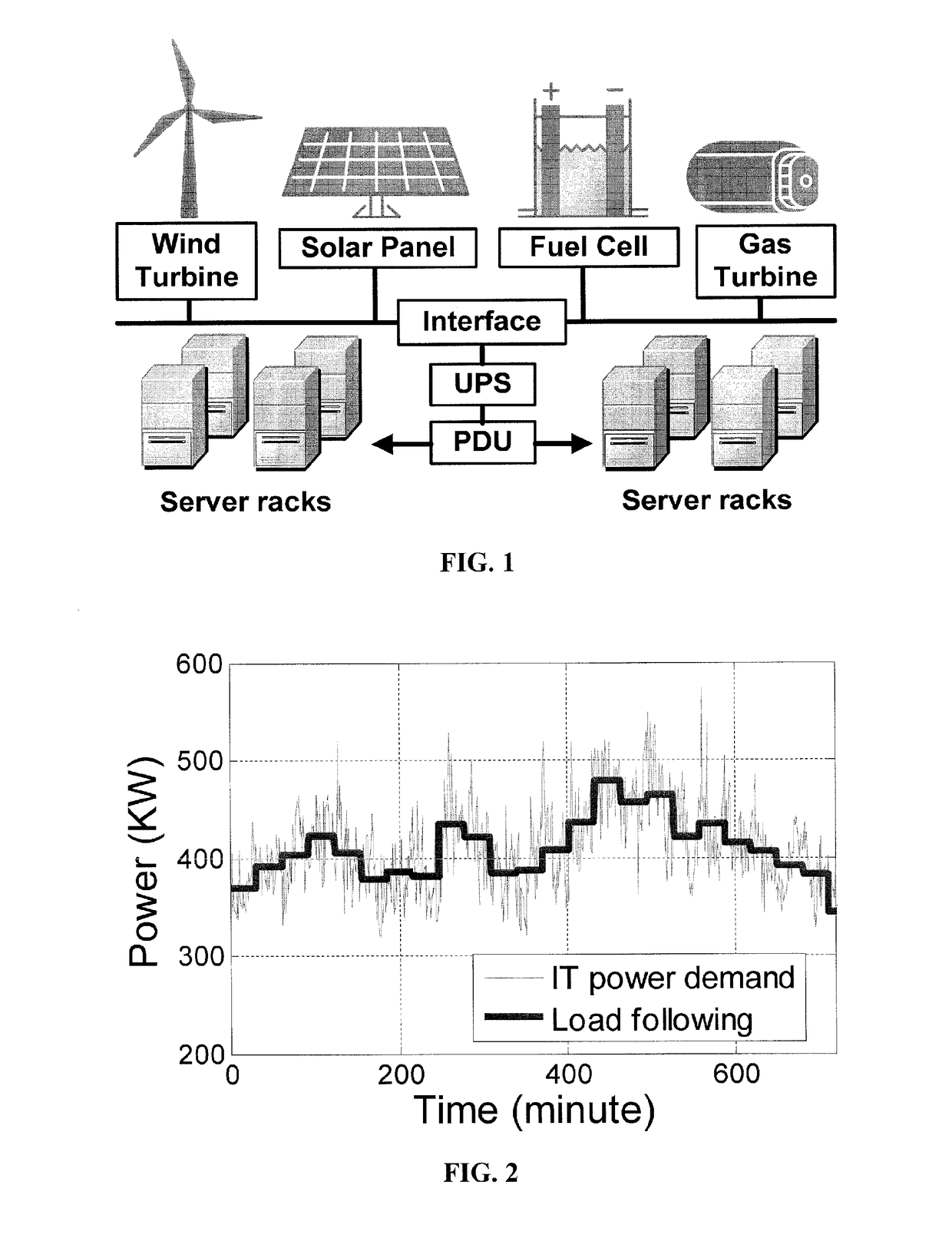
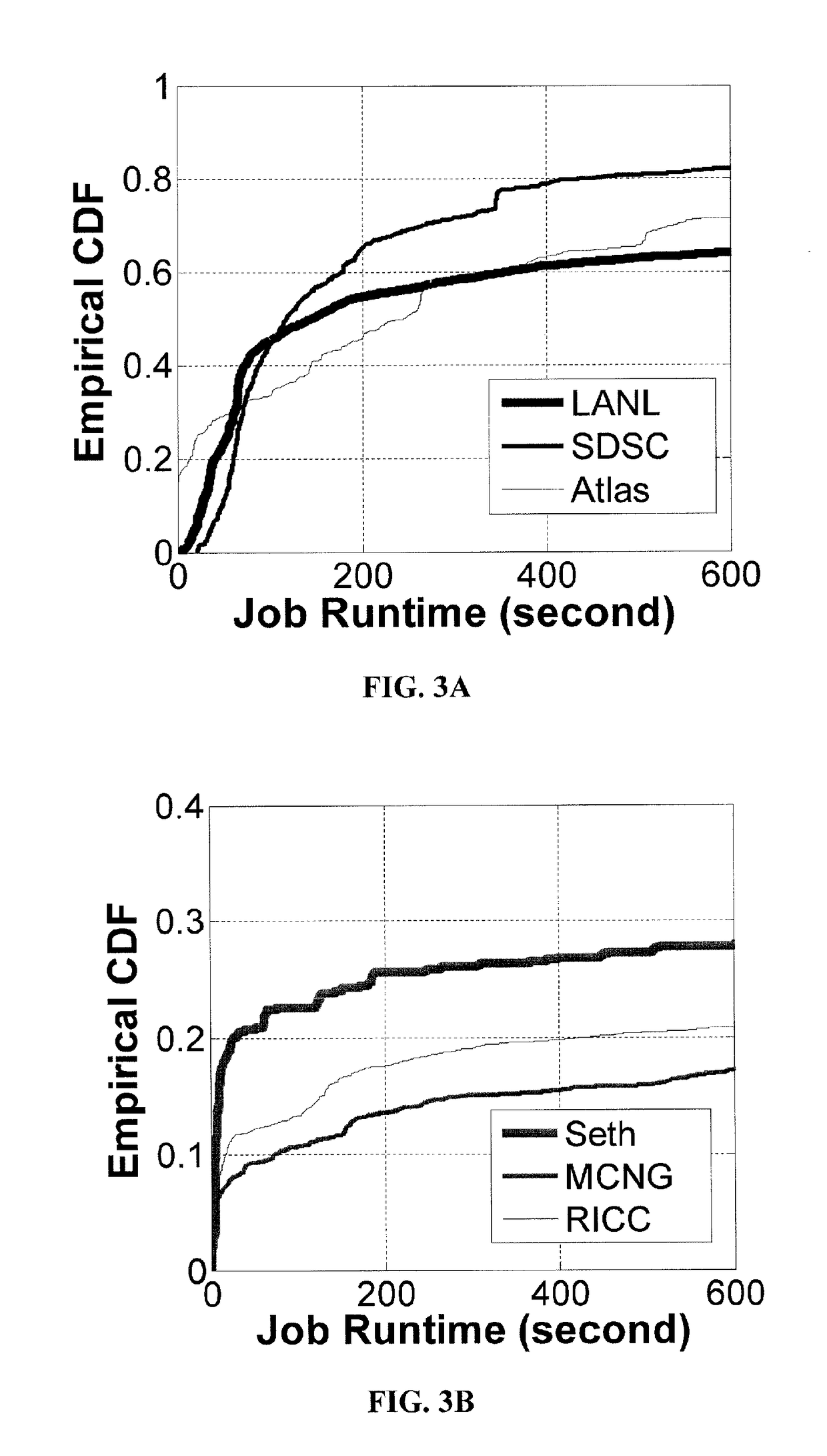
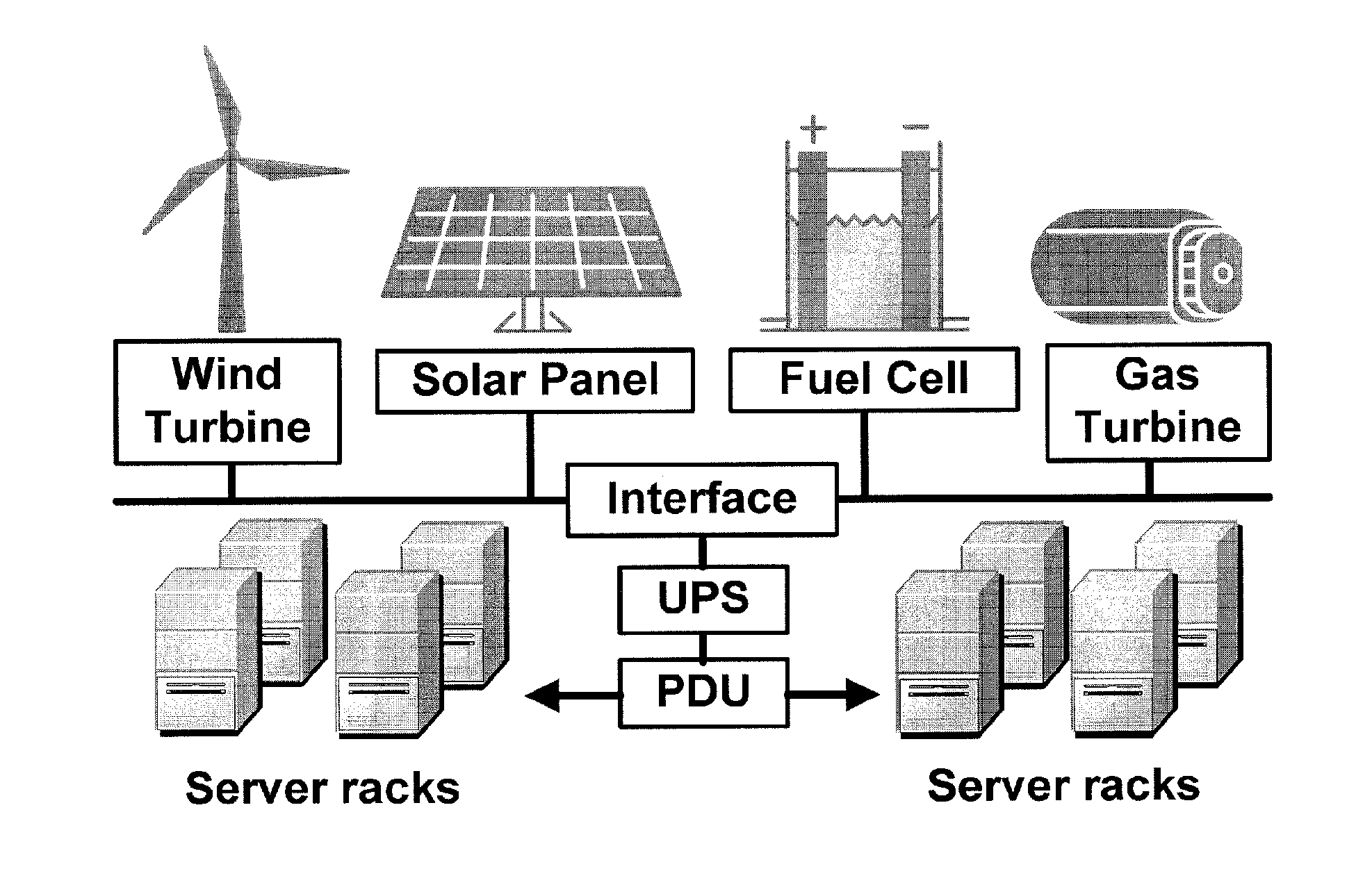
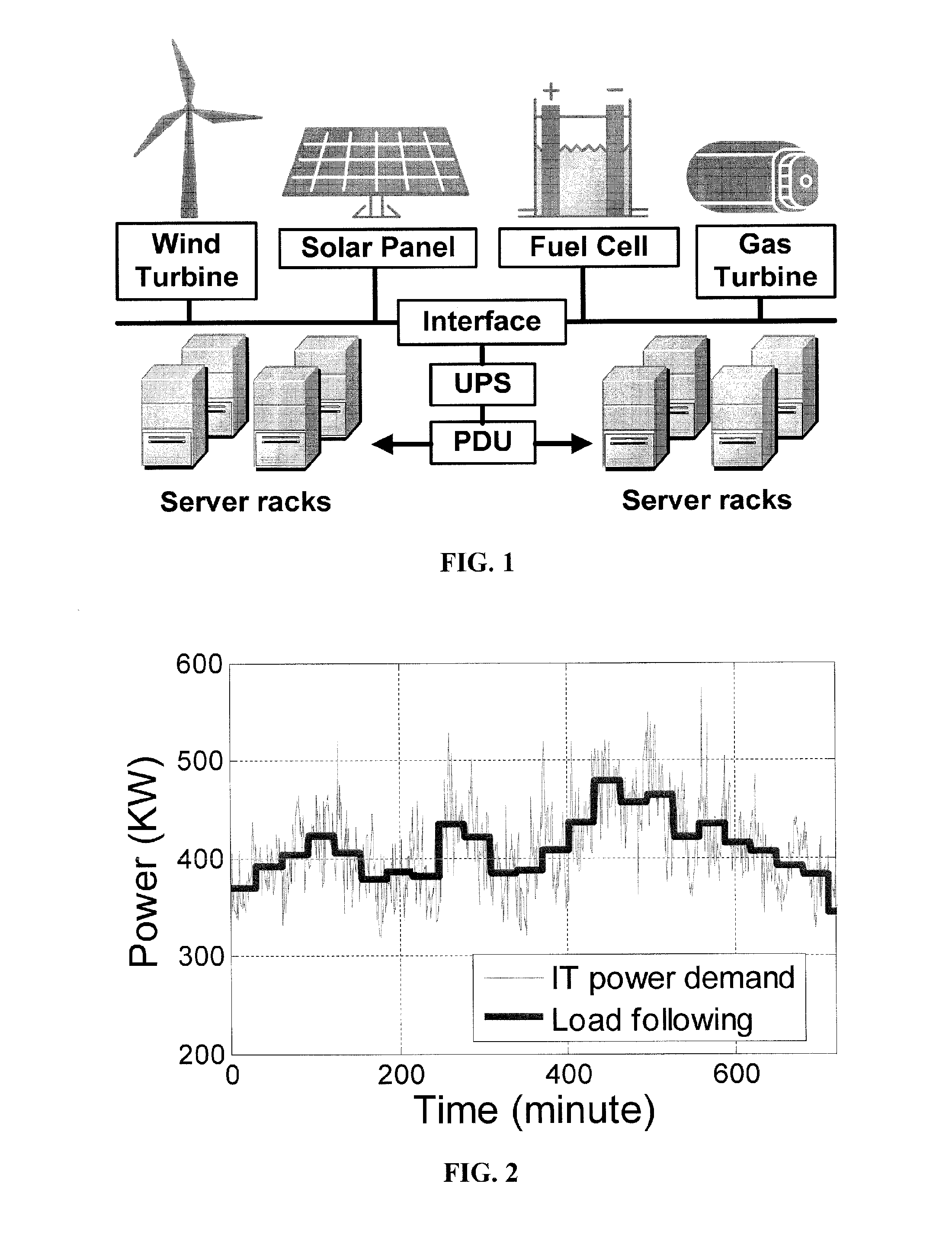
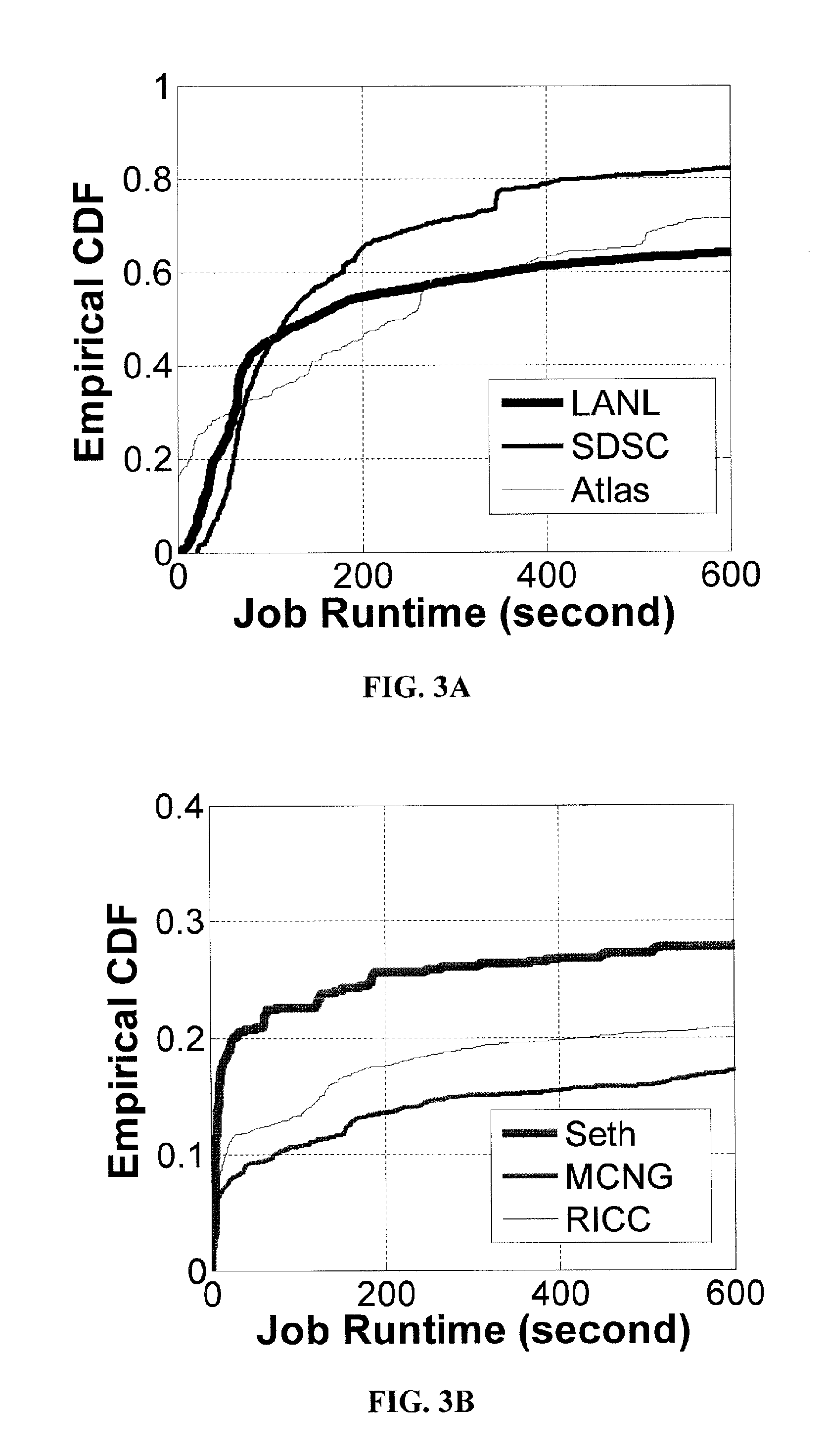
Method and apparatus for power management using distributed generation
ActiveUS9800052B2Improve performanceReduce electricity loadGeneration forecast in ac networkSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsData centerEngineering
Embodiments relate to a method and system for power demand shaping (PDS) so as to manage power generation and use. Specific embodiments relate to data center power demand shaping to achieve high-performance low-overhead data center operation. Specific embodiments can incorporate standard (utility power) energy sources, renewable energy sources, or a combination of standard (utility power) energy sources and renewable energy sources. Embodiments of the subject PDS techniques can incorporate trimming the data center load power so as to allow DG systems to follow the power demand efficiently and / or incorporate two adaptive load tuning schemes that can boost data center performance and enable near-oracle operation during power demand trimming process. To implement a cross-layer power optimization scheme, embodiments of the subject invention relate to a power management module that can reside between front-end distributed generation and back-end computing facilities to provide a coordinated tuning between the supply and load.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Method for manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveUS20120305913A1Sufficient performanceImprove conductivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay deviceSingle crystal
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
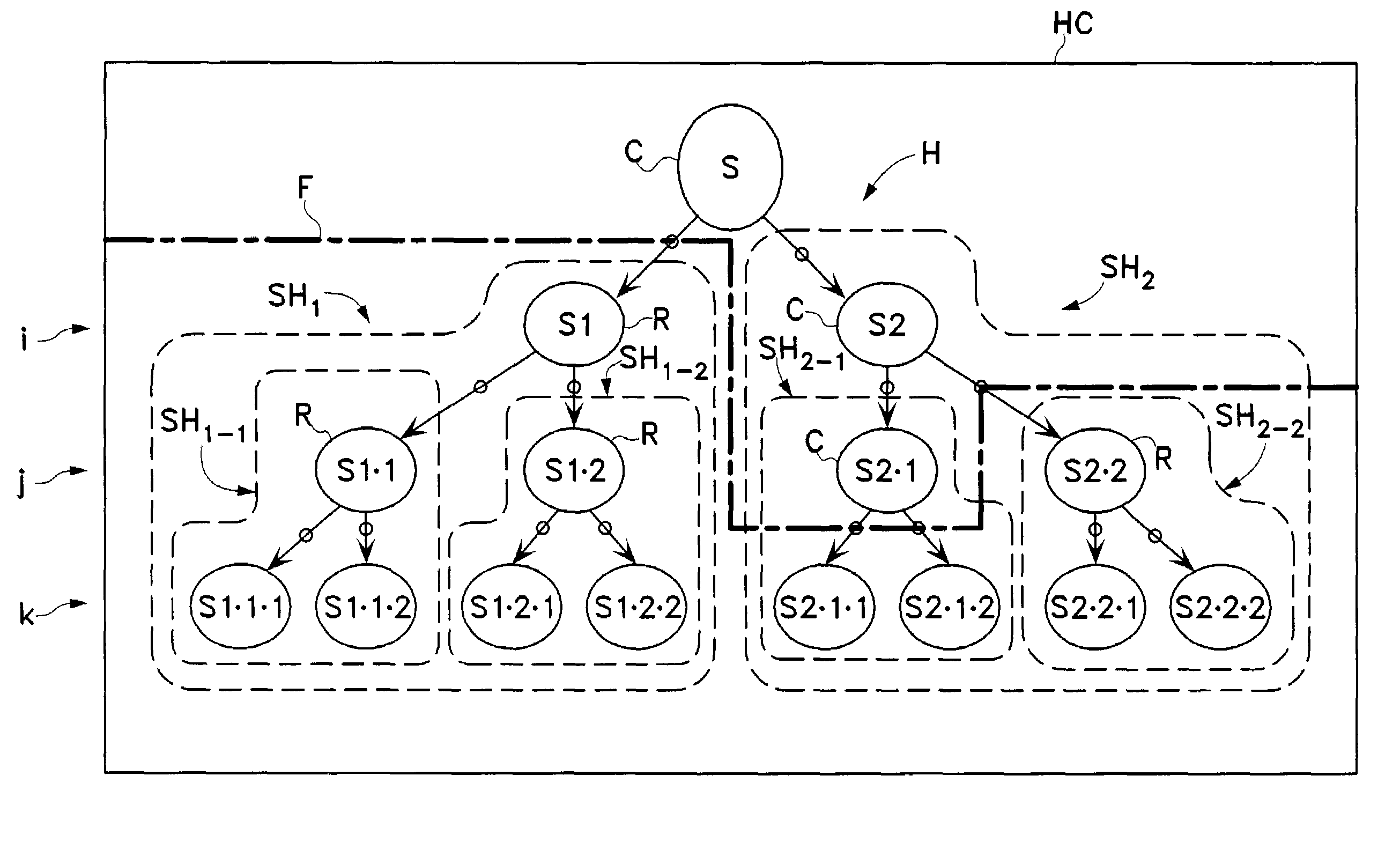
Hierarchical categorization method and system with automatic local selection of classifiers
InactiveUS7349917B2Sufficient dataSufficient performanceData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsClassification ruleLocal selection
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Adsorption desulfurization agent for desulfurizing petroleum fraction and desulfurization method using the same
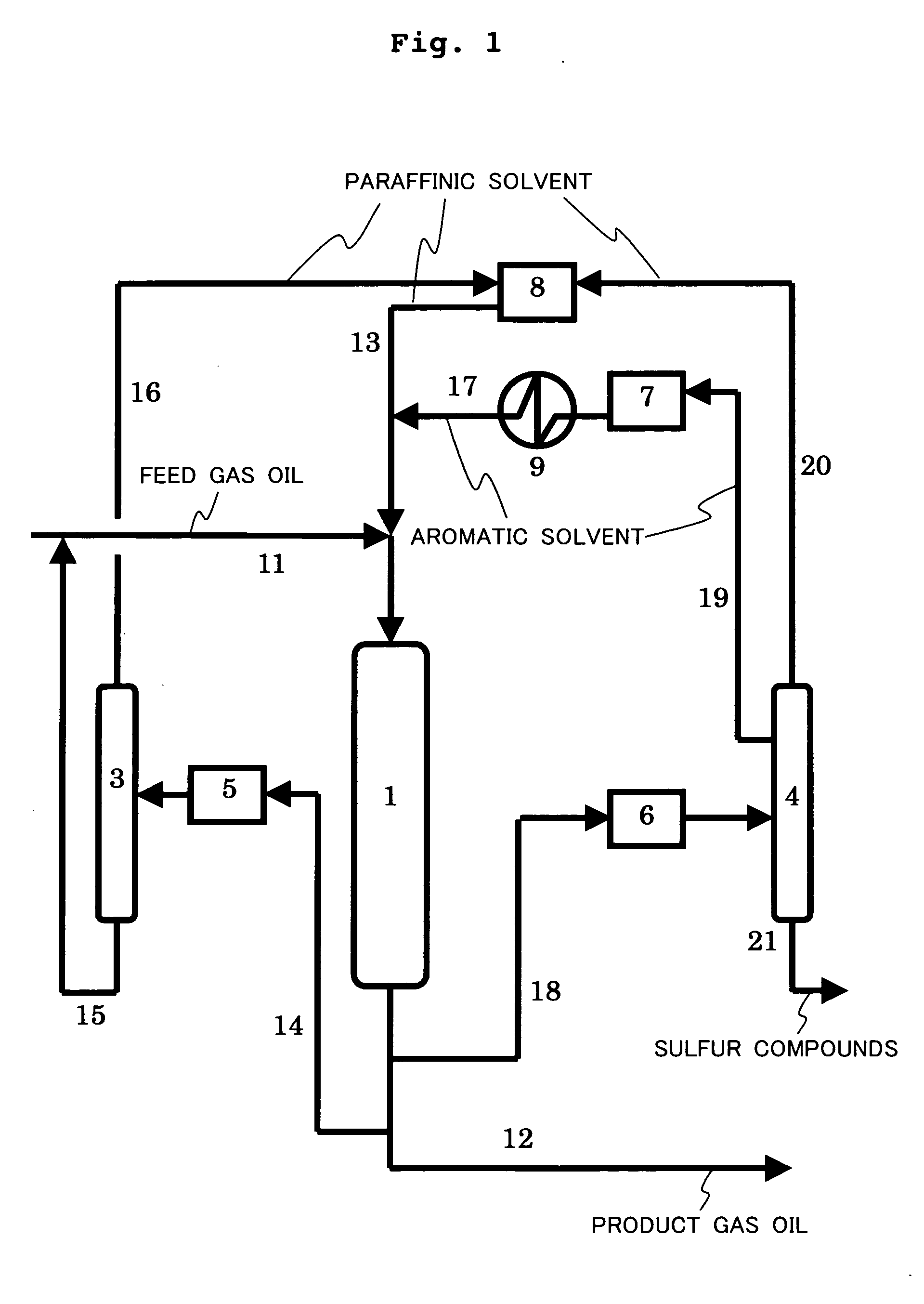
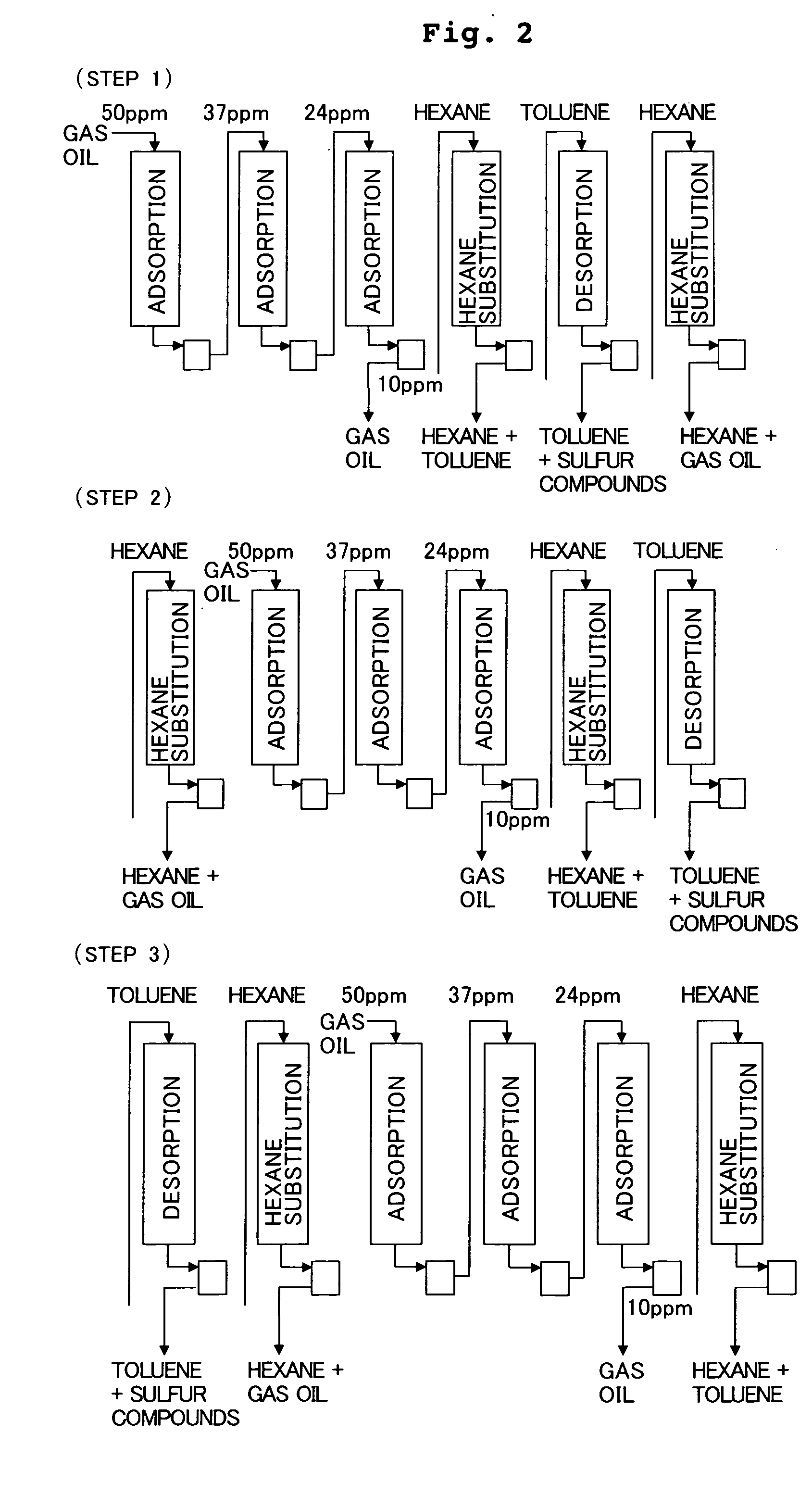
InactiveUS20050173297A1Reduce equipment costsLow running costOther chemical processesLiquid organic insulatorsDesorptionTower
A desulfurization method for a gas oil which includes a step of removing sulfur compounds contained in a gas oil distillate product by the adsorption with an adsorptive desulfurization agent formed of a fibrous active carbon and provided in an adsorption tower (1), and a desorption regeneration step of washing the used adsorptive desulfurization agent with an aromatic solvent to regenerate the desulfurization agent. The method allows the production of gas oil being satisfactorily freed of sulfur content at relatively low equipment and operation costs over a long period of time, and in the method, difficult-to-remove sulfur compounds, such as 4,6-DMDBT, and polycyclic aromatic compounds having two or more rings are selectively removed.
Owner:JAPAN ENERGY CORP
Fine inorganic oxide dispersion, coating composition, optical film, antireflection film, polarizing plate, and image display device
InactiveUS20050154086A1Improve dispersion stabilityImprove visibilityPigment treatment with organosilicon compoundsOrganic solventAlcohol
An inorganic oxide dispersion containing an organic solvent, and inorganic oxide particles surface-treated with at least one of a hydrolyzate and a partial condensate of an organosilane compound represented by formula (I), the inorganic oxide particles being dispersed in the organic solvent: (R10)m—Si(X)4−m (I) as defined herein, the surface treatment of the inorganic oxide particles being carried out in a presence of at least one of: (a) an acid catalyst; and (b) a metal chelate compound having Zr, Ti or Al as a center metal and at least one of an alcohol represented by formula: R3OH in which R3 represents an allyl group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms, and a compound represented by formula: R4COCH2COR5 as defined herein, as a ligand.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Cooling Structure For Batteries and Electrical Units
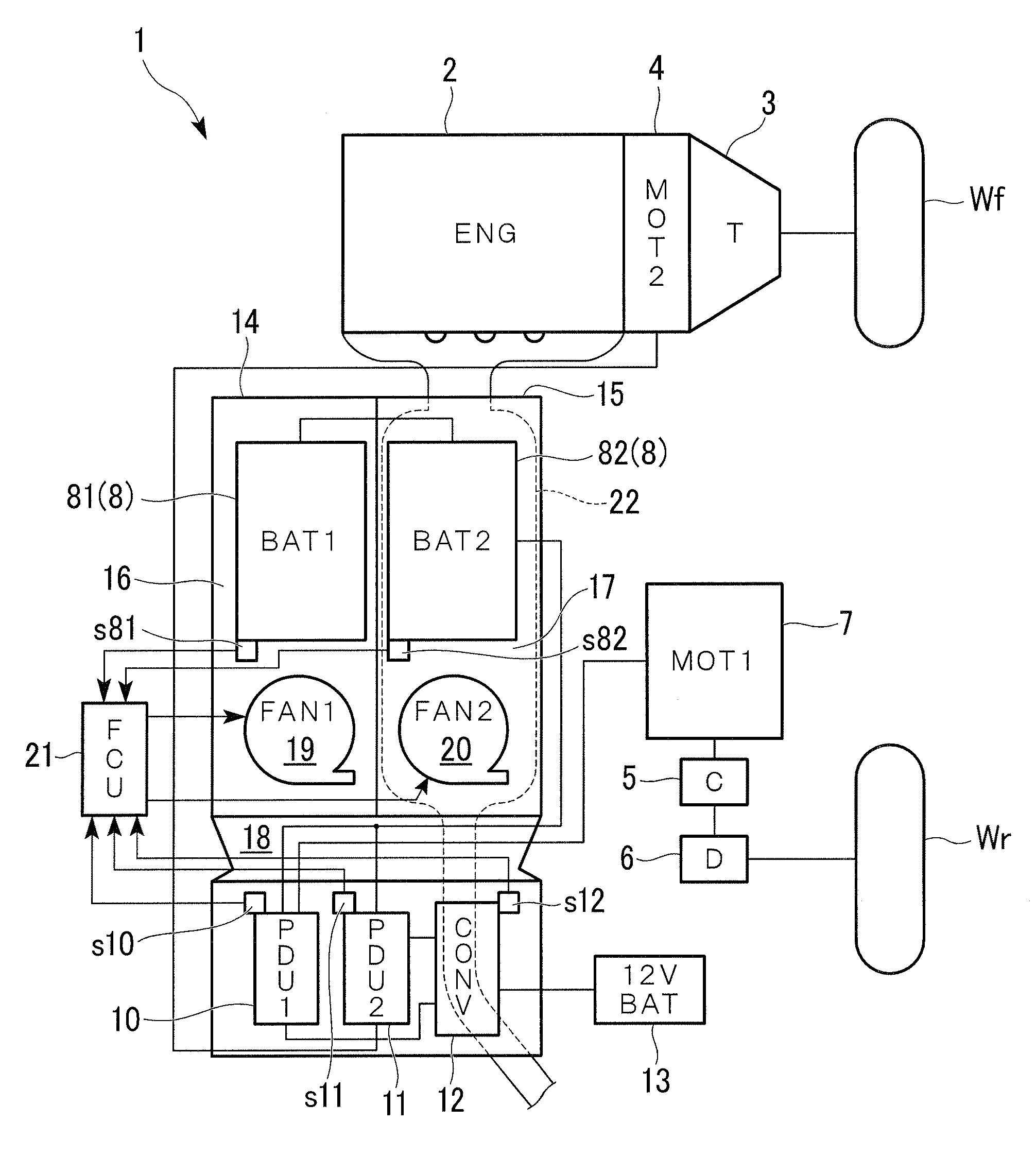
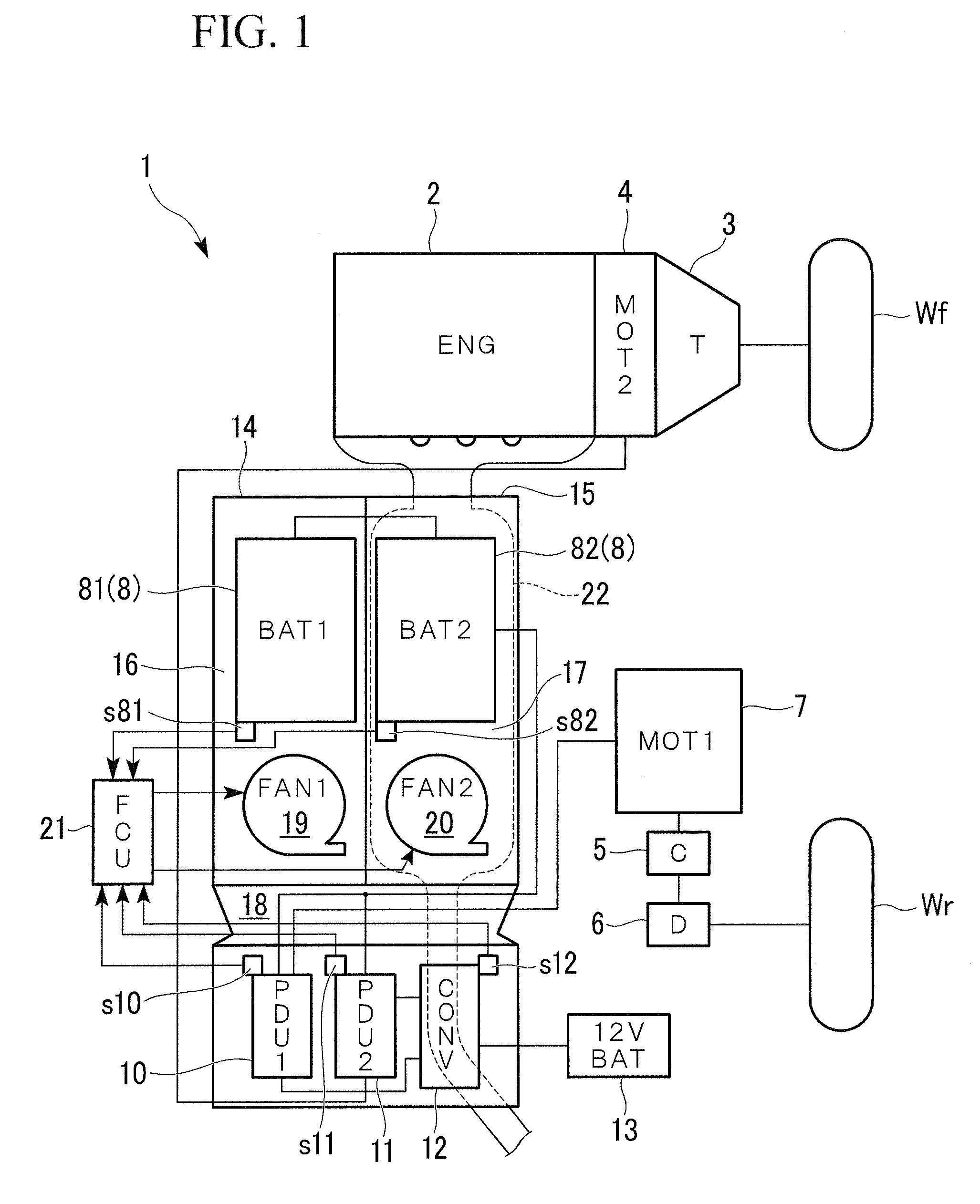
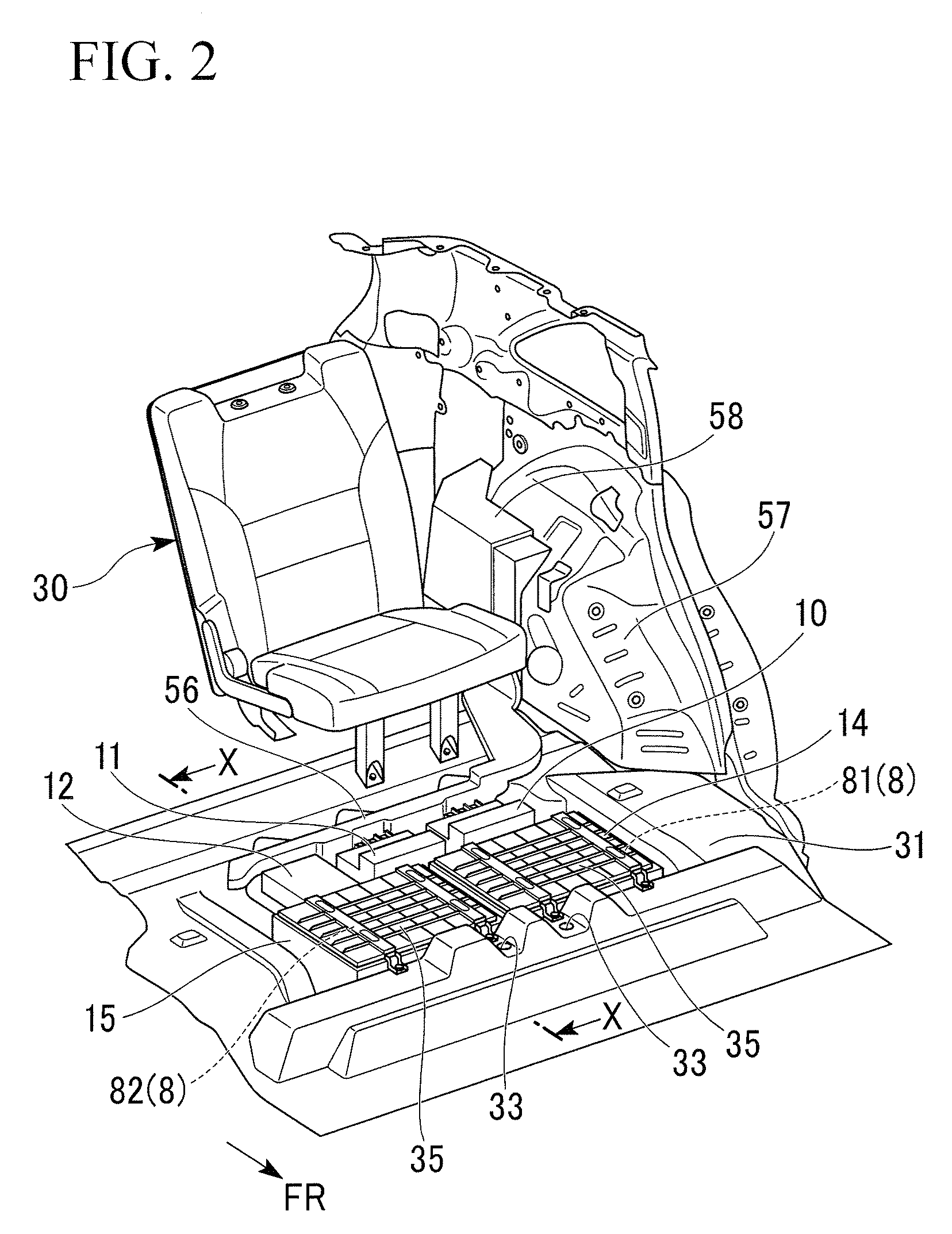
InactiveUS20080251246A1Use minimizedSuppression temperature differenceTemperatue controlSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical batteryEngineering
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
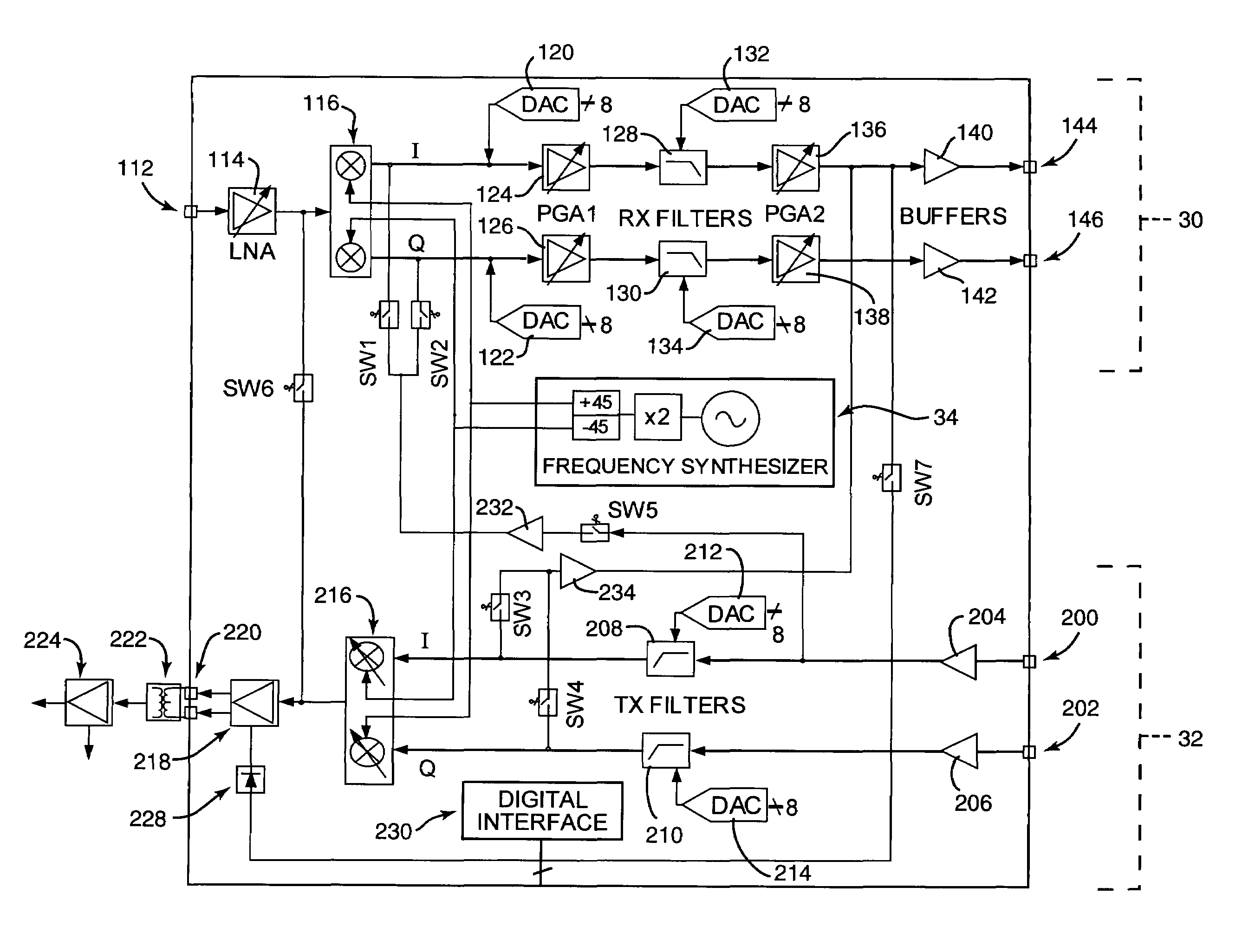
Direct-conversion transceiver enabling digital calibration
InactiveUS7715836B2Sufficient performanceTransmitters monitoringReceivers monitoringTransceiverEngineering
A transceiver for transmitting and receiving signals includes a transmitter operative to up-convert baseband signals from a baseband frequency into RF signals at a radio frequency (RF) frequency and output the RF signals, a receiver operative to receive RF signals and down-convert the RF signals into baseband signals having the baseband frequency, and a plurality of calibration paths coupling the transmitter to the receiver. Any of the calibration paths can be selected to be active when calibrating components of the transceiver. Tunable components can use calibration information to optimize transceiver performance.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Base station apparatus and communication control method
InactiveUS20100091726A1Sufficient performanceError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunication controlUser equipment
A base station apparatus capable of communicating with user equipment terminals using an uplink shared channel includes a user selection unit configured to select a user equipment terminal to which the base station apparatus allocates a radio resource based on whether the base station apparatus receives a signal for requesting allocation of the uplink shared channel from the user equipment terminal.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
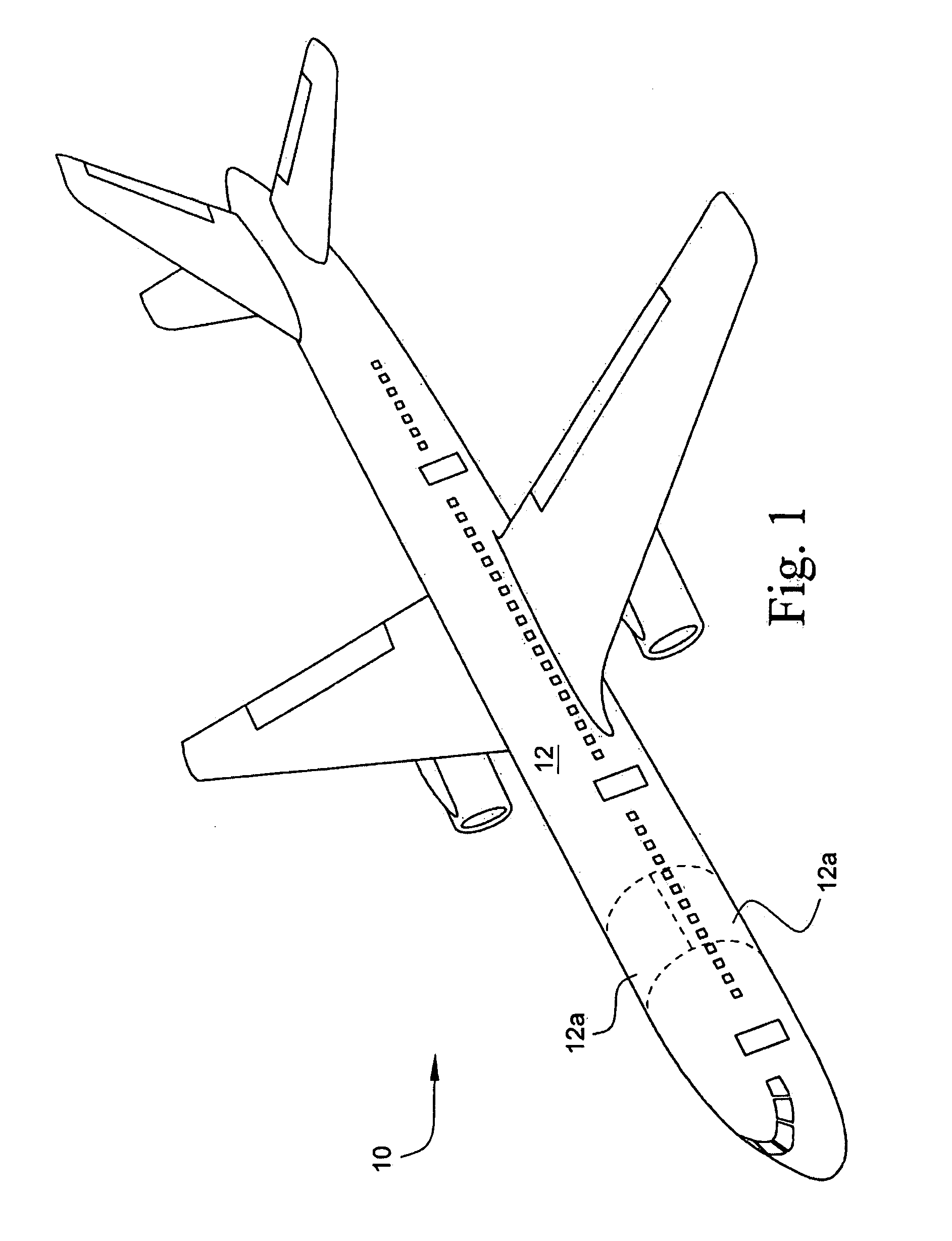
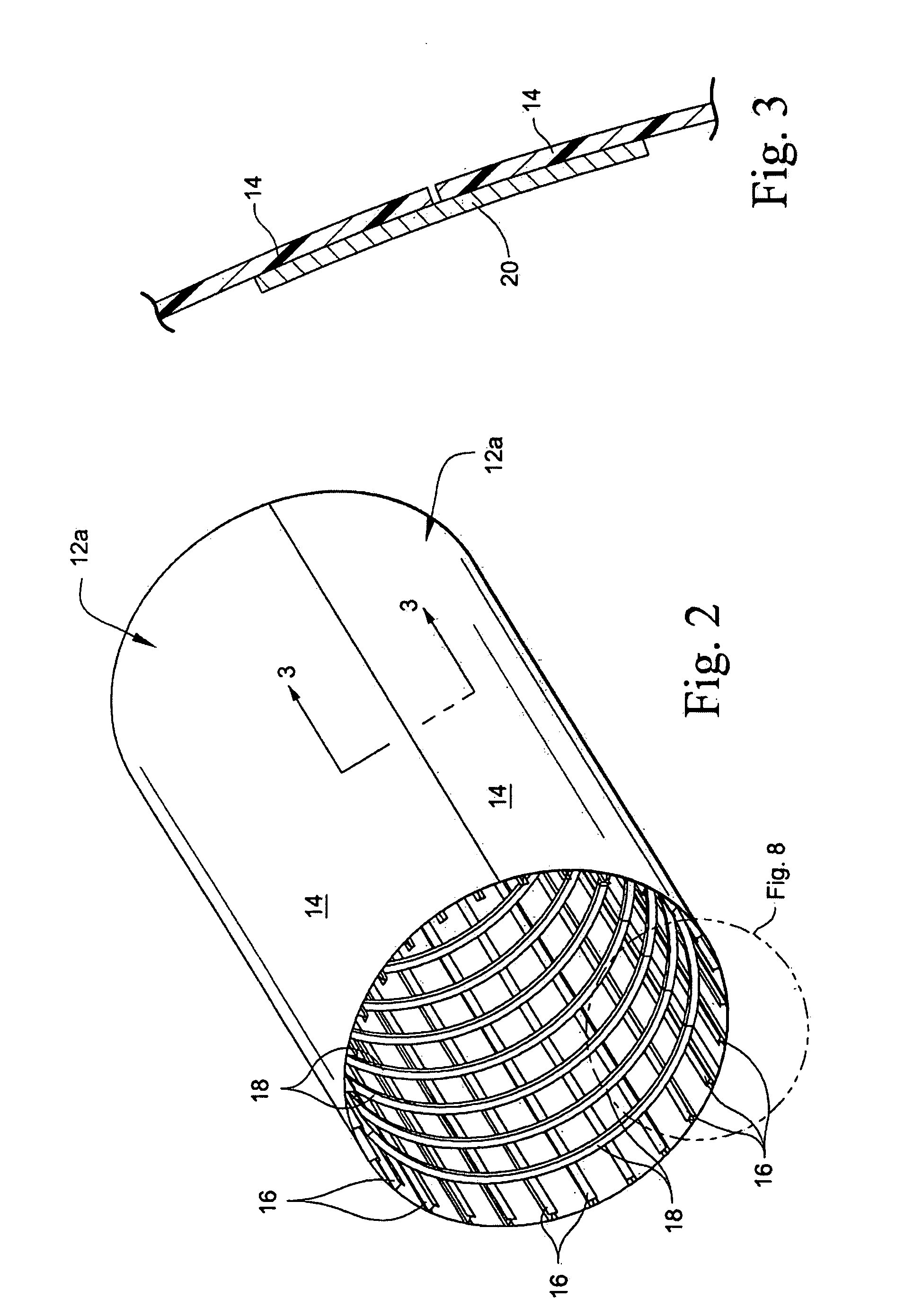
Hybrid aircraft fuselage structural components and methods of making same
InactiveUS20090277994A1Light weightEconomically manufacturedEfficient propulsion technologiesFuselage bulkheadsMetal frameworkFuselage
An aircraft fuselage assembly of basic construction in composite materials employs metallic frames with reduced quantity of metallic shear ties attached to the composite stiffened skin, formed by two or more longitudinal panels, spliced with longitudinal metallic splice members. Typically, the latitudinal metallic frame members are fastened to the inward outstanding flange portion of the composite stringers which are in turn integrated to the skin. As such, the frame members are spaced from (floating over) the fuselage skin. An electrical path may thus be established so as to protect the fuselage structure against the impact of electrical discharges commonly encountered in the atmosphere by providing metallic shear ties interconnecting the frame and splice members so as to span the space therebetween.
Owner:EMBRAER SA
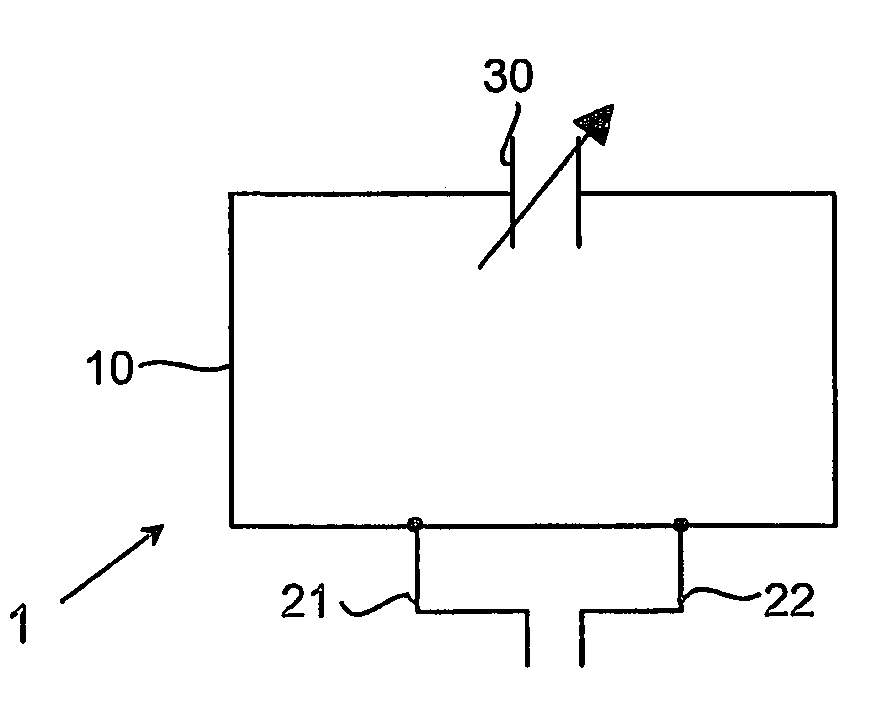
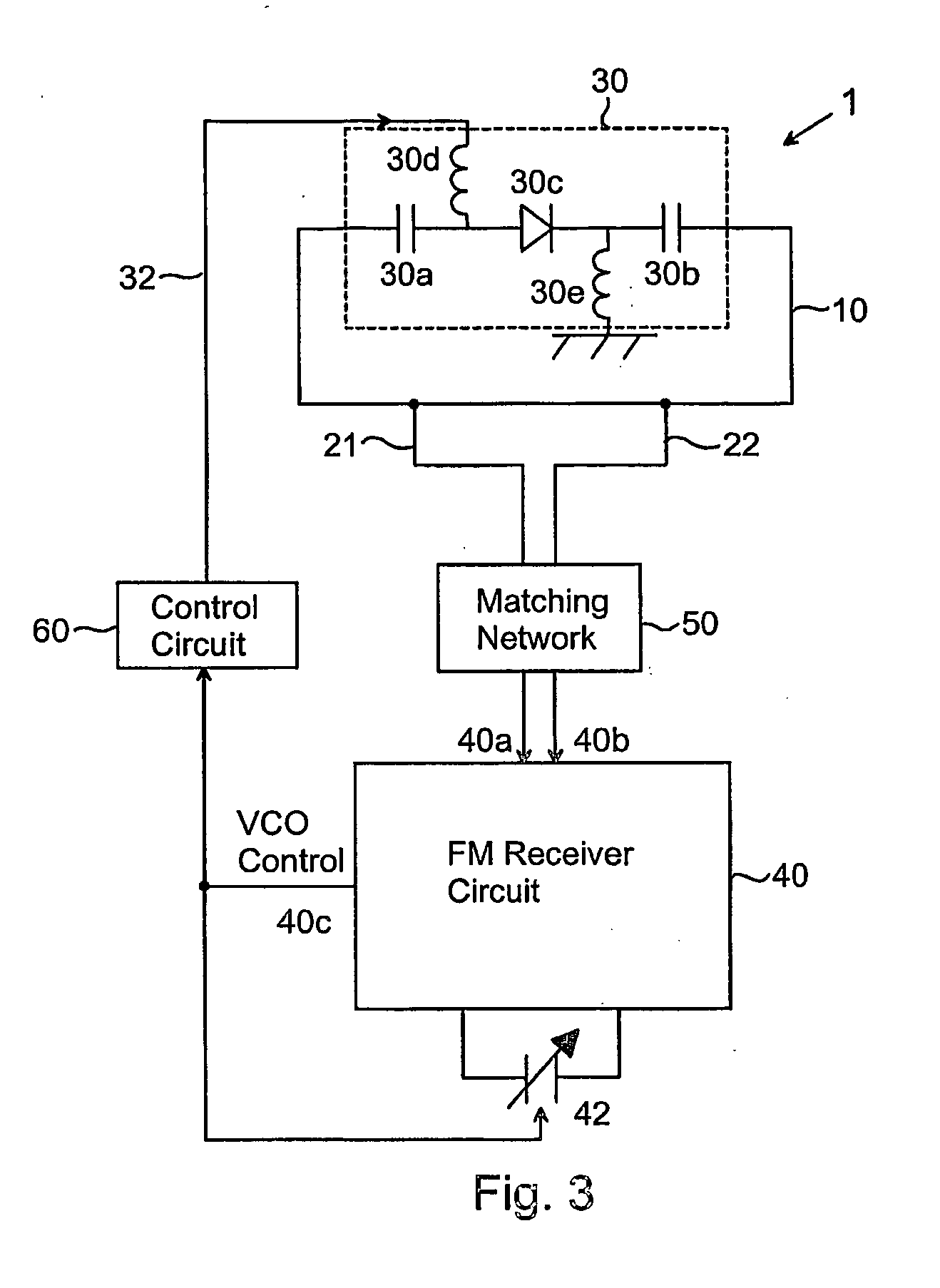
Antenna Device and Portable Radio Communication Device Comprising Such Antenna Device
InactiveUS20080287084A1Sufficient performanceImprove performanceSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsResonanceElectrical impedance
An antenna device for a portable radio communication device adapted for receiving radio signals comprises an internal radiating element (10) comprising at least one feeding portion (21, 22) connected to a receiver circuit (40). The radiating element (10) comprises an electrical impedance (30) that is controllable in dependence on the desired frequency range of the received signals, wherein the feeding portion (21, 22) is connected to a feeding input (40a, 40b) on the receiver circuit and the control input of the controllable electrical impedance (30) is connected to an output (40c) on the receiver circuit (40) intended for the control of the VCO resonance frequency of the receiver circuit. In that way an antenna device can be provided inside the casing of a small sized portable radio communication device, which has good performance throughout a narrow sub-band of a frequency band having a relatively low frequency, wherein the narrow sub-band can be adjusted in frequency so as to cover the entire frequency band, such as the FM radio band.
Owner:LAIRD TECH AB (SE)
Surface treatment method, surface-treated substrate, method for forming film pattern, method for making electro-optical device, electro-optical device, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS6861377B1Thin and compactObtain uniformTransistorAntenna supports/mountingsUltravioletUltraviolet irradiation
The invention provides a surface treatment method by which a substrate with desired uniform lyophilicity is obtained in order to enhance the formation of a film pattern by an ink-jet process; a surface-treated substrate obtained by the surface treatment; and a method of forming a film pattern.A surface of a substrate is subjected to lyophobic treatment by forming a self-assembled layer composed of organic molecules. The lyophobicity is then modified by ultraviolet irradiation or the like to obtain desired lyophobicity.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
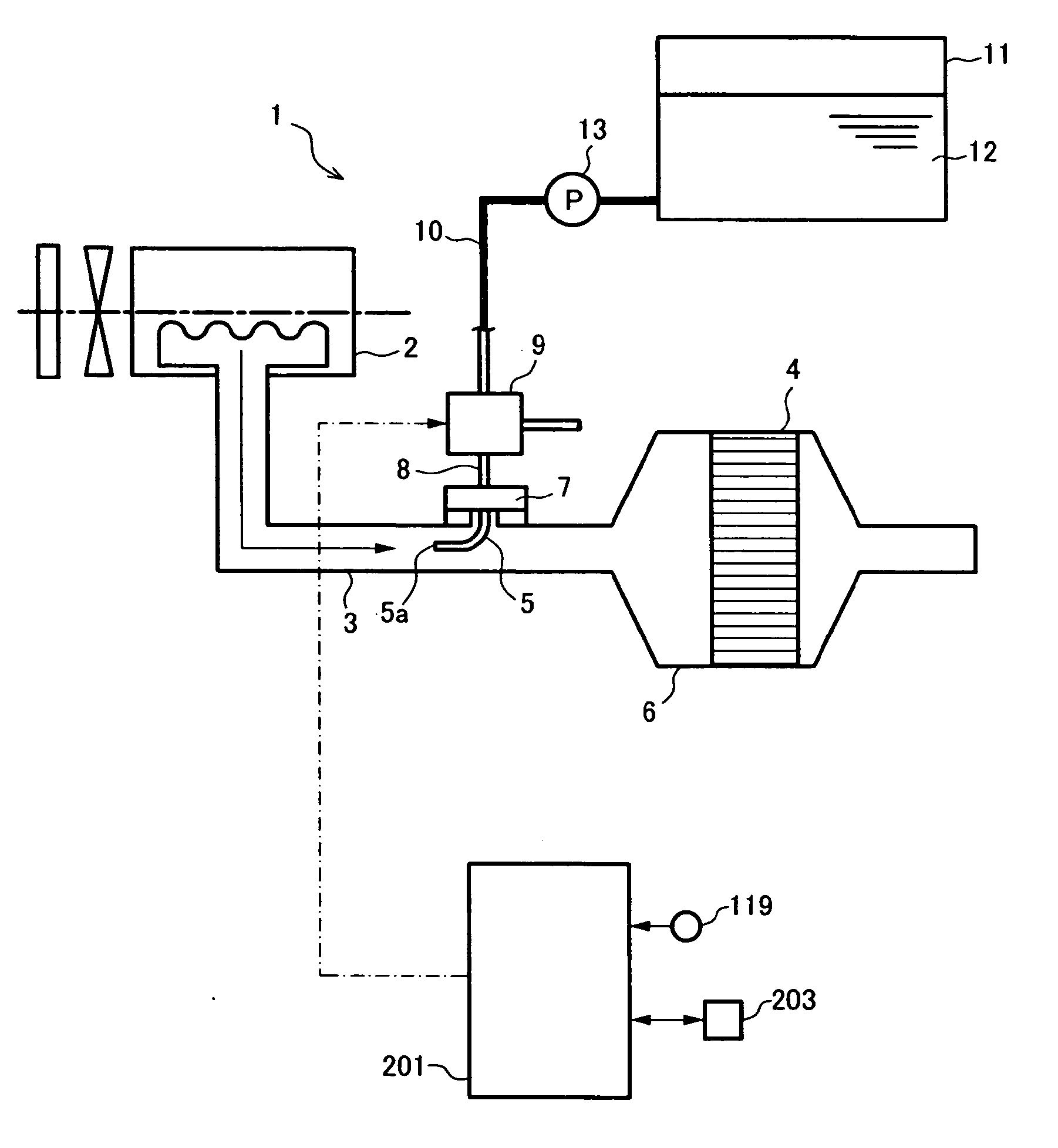
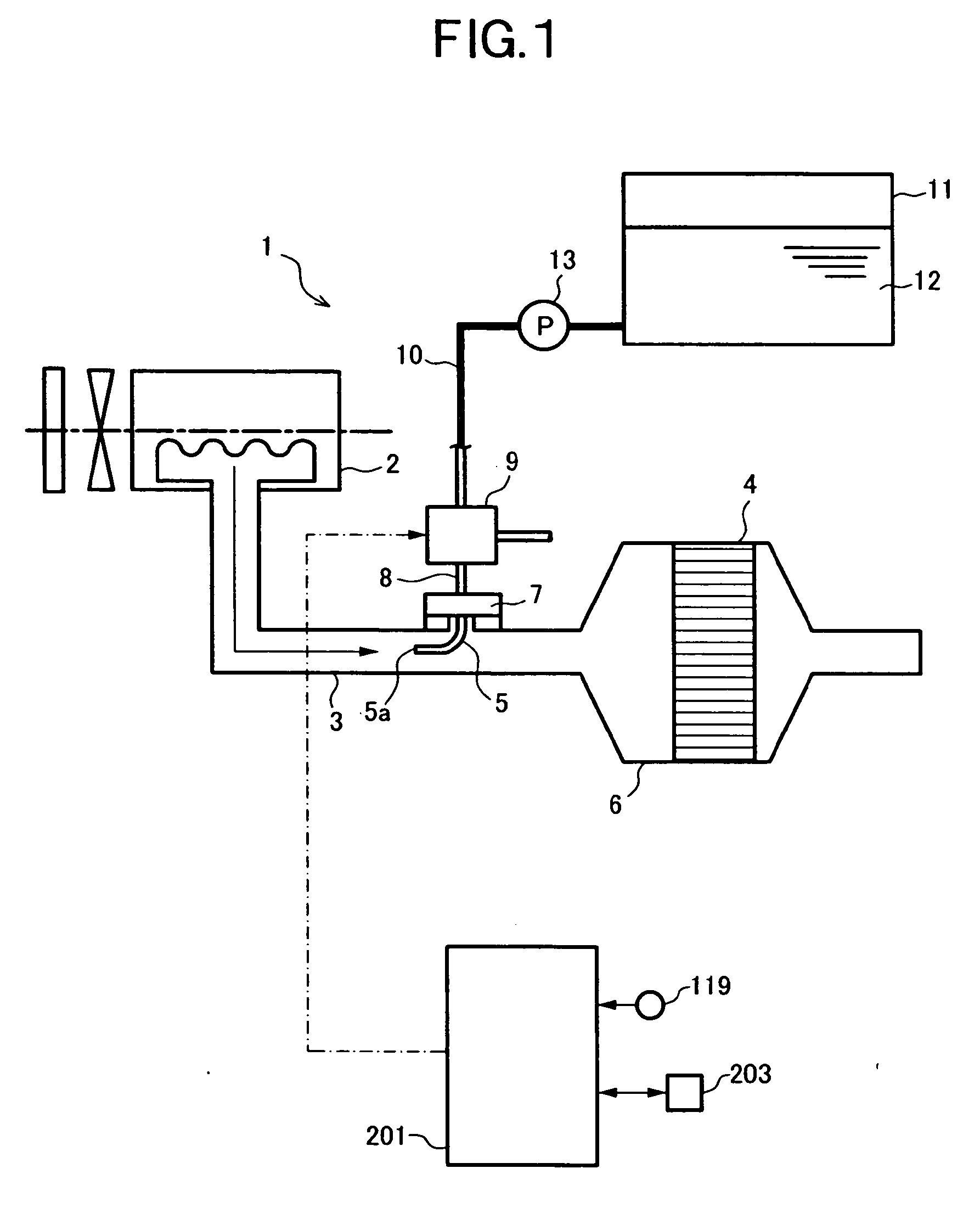
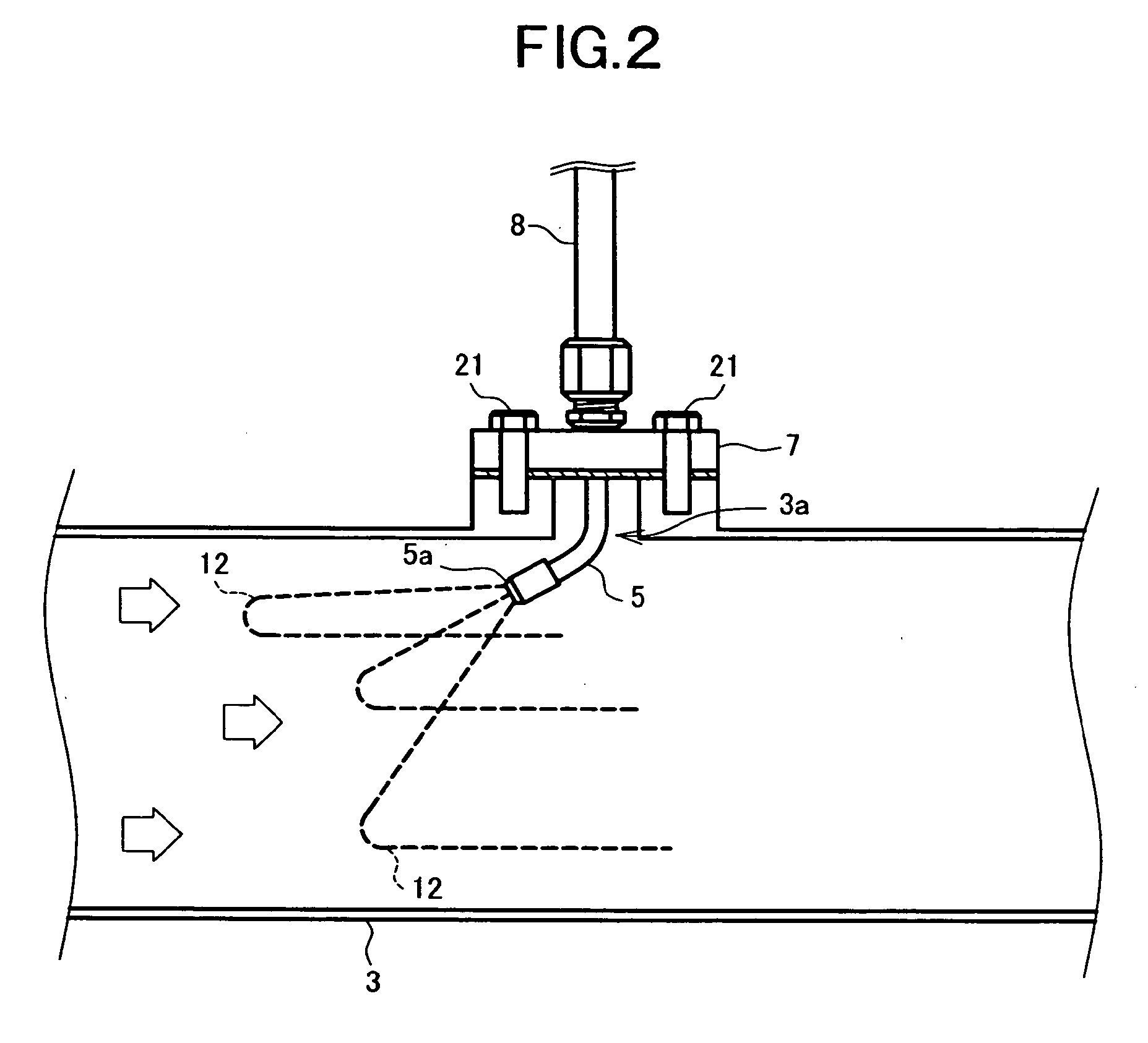
Exhaust emission purifying apparatus for internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20070035832A1Achieving Reliability RequirementsWell mixedInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusExhaust fumesEnvironmental engineering
In an exhaust emission purifying apparatus for an internal combustion engine, for adding a reducing agent for NOx to the exhaust gas to thereby purify NOx in the exhaust gas, the mixing of the reducing agent injected by an injection nozzle with the exhaust gas is accelerated. To this end, in the apparatus of the present invention, the injection nozzle for the urea water is disposed to be opposite to the flow of the exhaust gas, or to face upward in a vertical direction.
Owner:VOLVO LASTVAGNAR AB
Method and apparatus for power management using distributed generation
ActiveUS20160013652A1Sufficient performanceImprove load following efficiencyGeneration forecast in ac networkSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsData centerEngineering
Embodiments relate to a method and system for power demand shaping (PDS) so as to manage power generation and use. Specific embodiments relate to data center power demand shaping to achieve high-performance low-overhead data center operation. Specific embodiments can incorporate standard (utility power) energy sources, renewable energy sources, or a combination of standard (utility power) energy sources and renewable energy sources. Embodiments of the subject PDS techniques can incorporate trimming the data center load power so as to allow DG systems to follow the power demand efficiently and / or incorporate two adaptive load tuning schemes that can boost data center performance and enable near-oracle operation during power demand trimming process. To implement a cross-layer power optimization scheme, embodiments of the subject invention relate to a power management module that can reside between front-end distributed generation and back-end computing facilities to provide a coordinated tuning between the supply and load.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20110147739A1High field-effect mobilitySufficient performanceTransistorPolycrystalline material growthDisplay deviceSingle crystal
A larger substrate can be used, and a transistor having a desirably high field-effect mobility can be manufactured through formation of an oxide semiconductor layer having a high degree of crystallinity, whereby a large-sized display device, a high-performance semiconductor device, or the like can be put into practical use. A single-component oxide semiconductor layer is formed over a substrate; then, crystal growth is carried out from a surface to an inside by performing heat treatment at 500° C. to 1000° C. inclusive, preferably 550° C. to 750° C. inclusive so that a single-component oxide semiconductor layer including single crystal regions is formed; and a multi-component oxide semiconductor layer including single crystal regions is stacked over the single-component oxide semiconductor layer including single crystal regions.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Proton conductive composition and proton conductive membrane
InactiveUS20050130024A1Sufficient generating performanceSufficient performanceSolid electrolytesConductive materialMaterials scienceAtomic physics
The invention provides a proton conductive membrane which, even when reduced in thickness, does not allow penetration of an electrode to prevent a short circuit between electrodes and which permits sufficient generating performance. A proton conductive composition capable of forming the membrane is also provided. The proton conductive composition includes a nonconductive filler and a polyarylene having a sulfonic group. The proton conductive membrane, comprising the composition, contains the nonconductive filler in an amount of 3 to 50% by volume, and the nonconductive filler particles have diameters ranging from 3 to 90% the thickness of the membrane.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON +1
Semiconductor device having IGBT and diode
ActiveUS20070170549A1Sufficient performanceSufficient surge withstand voltageTransistorDiodeSemiconductorSemiconductor device
A semiconductor device includes: a substrate having a first side and a second side; an IGBT; and a diode. The substrate includes a first layer, a second layer on the first layer, a first side N region on the second layer, second side N and P regions on the second side of the first layer, a first electrode in a first trench for a gate electrode, a second electrode on the first side N region and in a second trench for an emitter electrode and an anode electrode, and a third electrode on the second side N and P regions for a collector electrode and a cathode. The first trench penetrates the first side N region and the second layer, and reaches the first layer. The second trench penetrates the first side N region, and reaches the second layer.
Owner:DENSO CORP
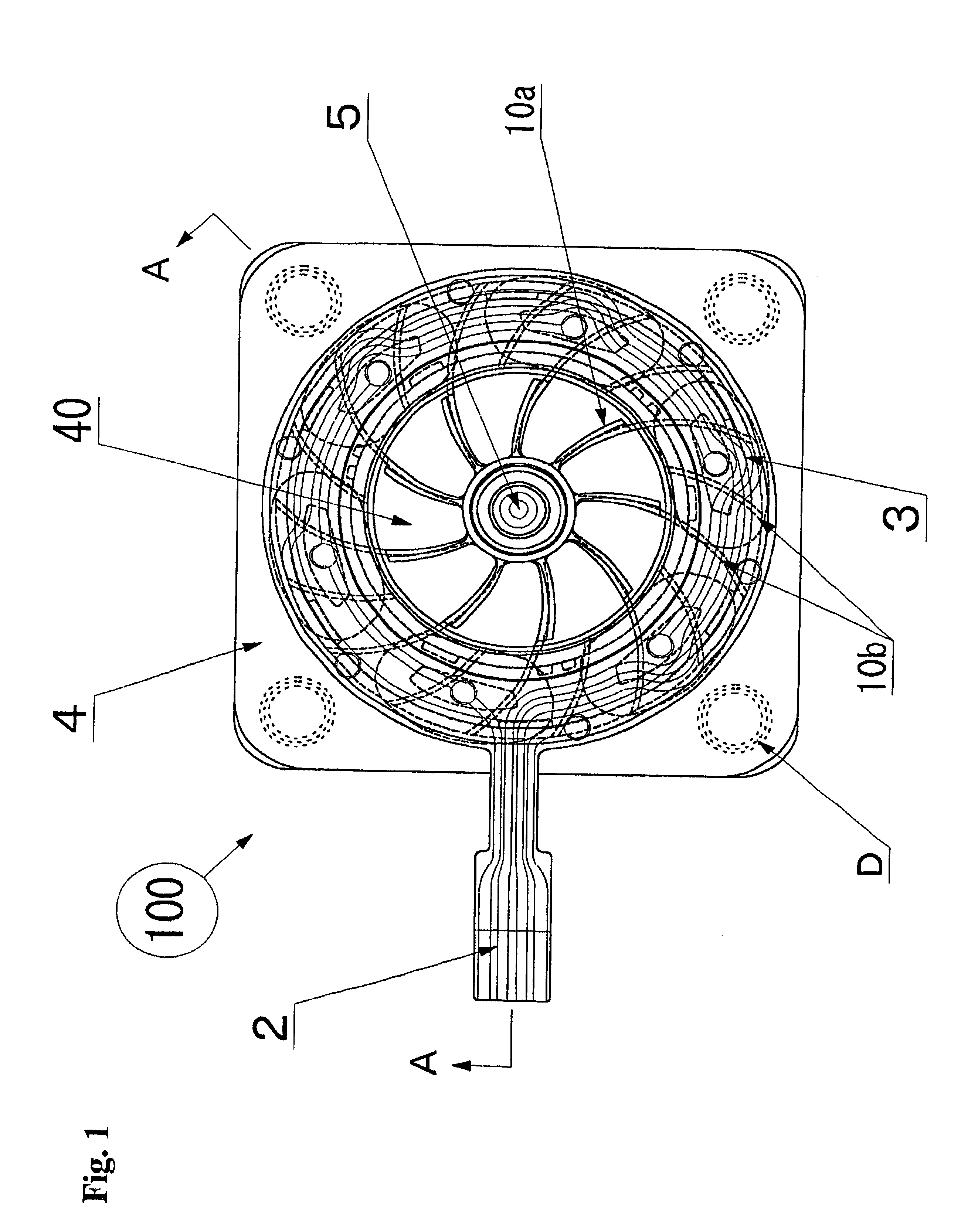
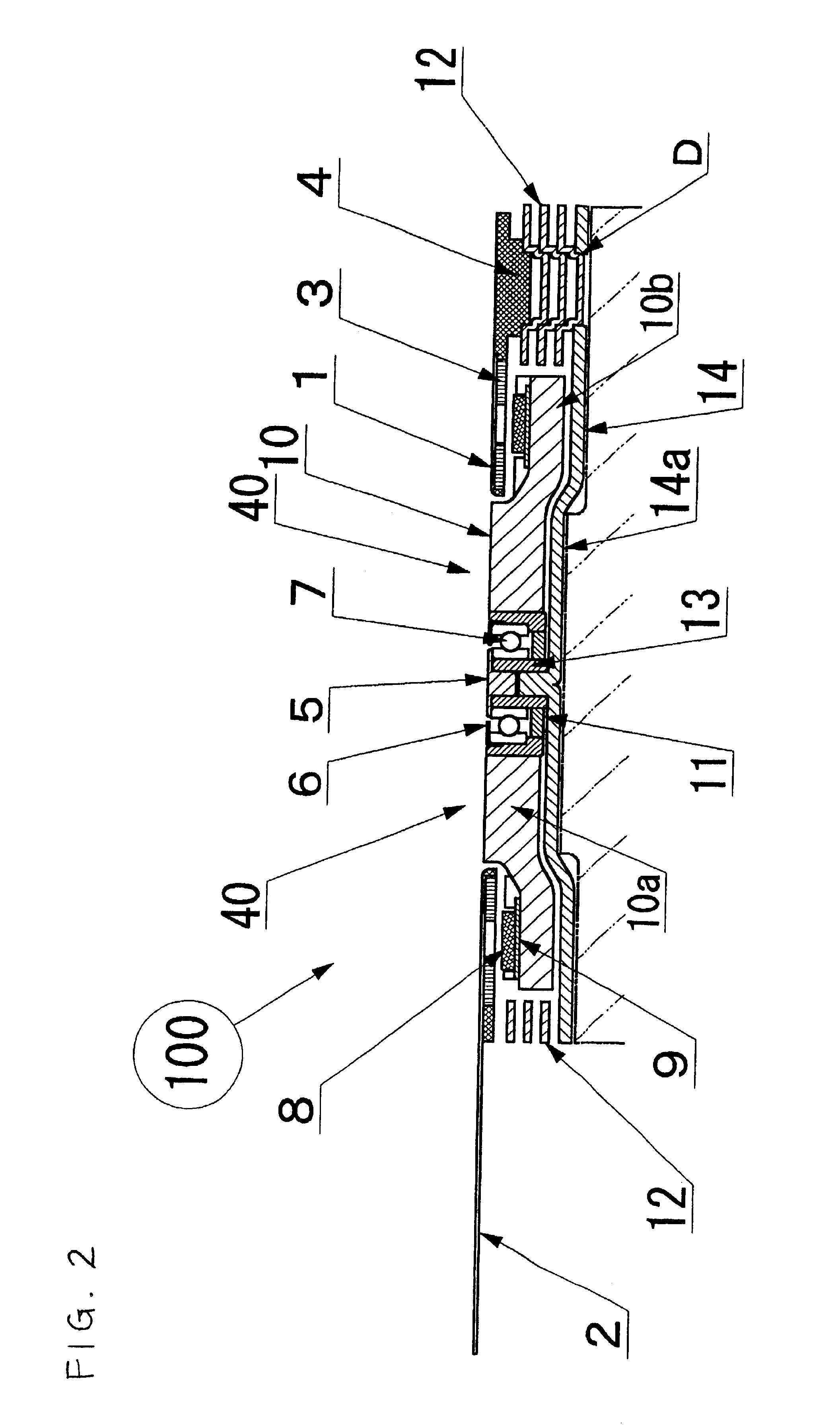
Very thin fan motor with attached heat sink
InactiveUS6873069B1Improve performanceStable speedPump componentsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsStator coilCooling effect
A very thin fan motor with an attached heat sink that has high heat radiation and air cooling effects in a small, flat, thin package, that has a simple and easily assembled overall structure as a fan motor, and that has superior cooling efficiency. A flat fan mounted in various kinds of electronic equipment that need to radiate heat, and particularly mounted directly on the CPU, characterized by having a fan motor mechanism that comprises a heat plate that supports a rotor fan that can rotate in a central position and that has a contact surface that matches the shape of the external surface of the item (such as a CPU) to be cooled, rotor magnets that are part of the rotor fan and are positioned around the periphery on the surface of the heat plate, and a stator coil substrate, by having multiple metal heat radiation fins with excellent thermal conductivity, which are thin heat-radiating fins, arranged in parallel at a fixed interval on the heat plate pointing outward from the rotor fan as cooling heat-radiation fins, and by combining the function of cooling heat sink with the heat radiation fins that conduct the heat absorbed from the heat plate and radiate it away by the action of the air moved by the rotor fan.
Owner:NAMIKI PRECISION JEWEL CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com