Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
215results about How to "Reduce discharge voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
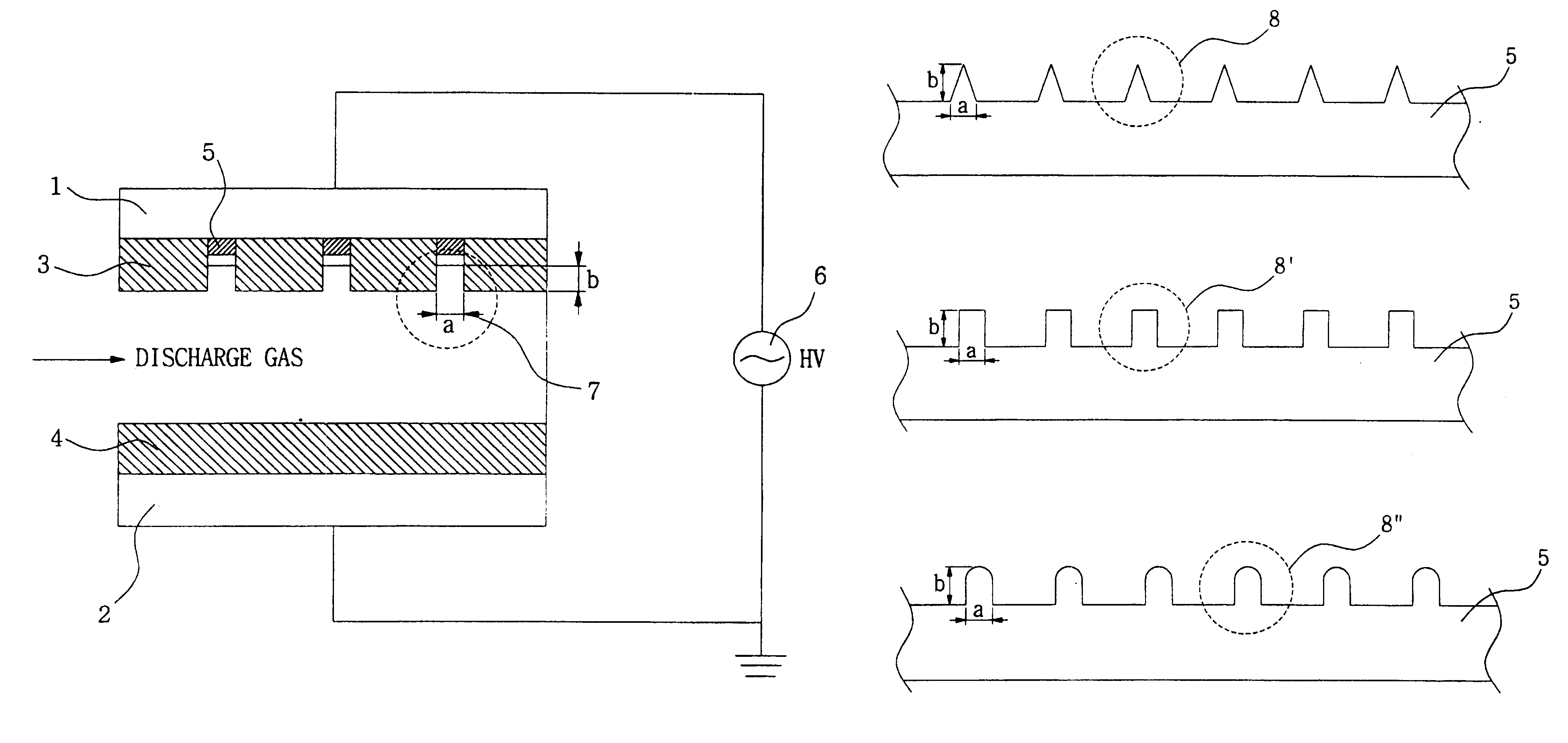
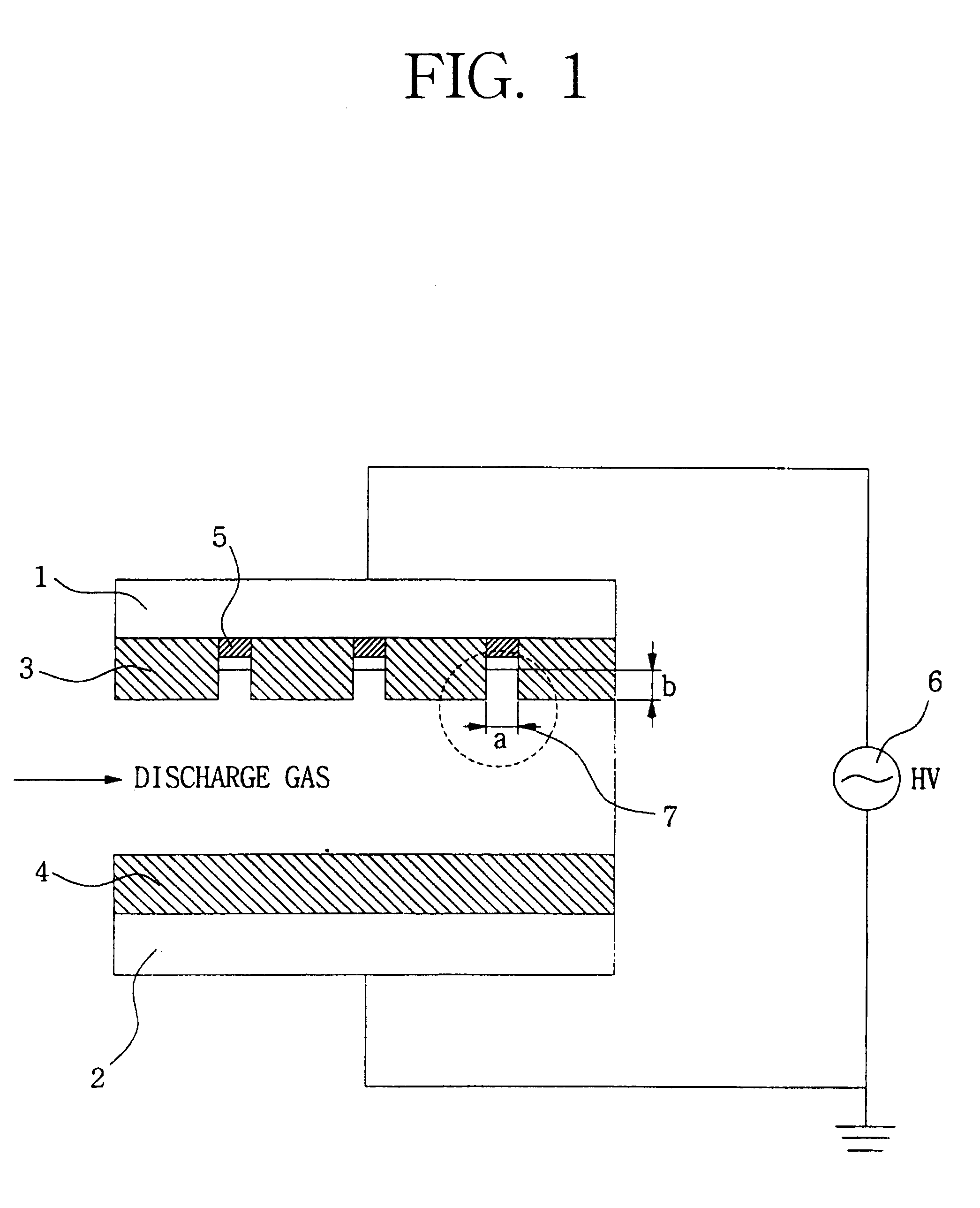
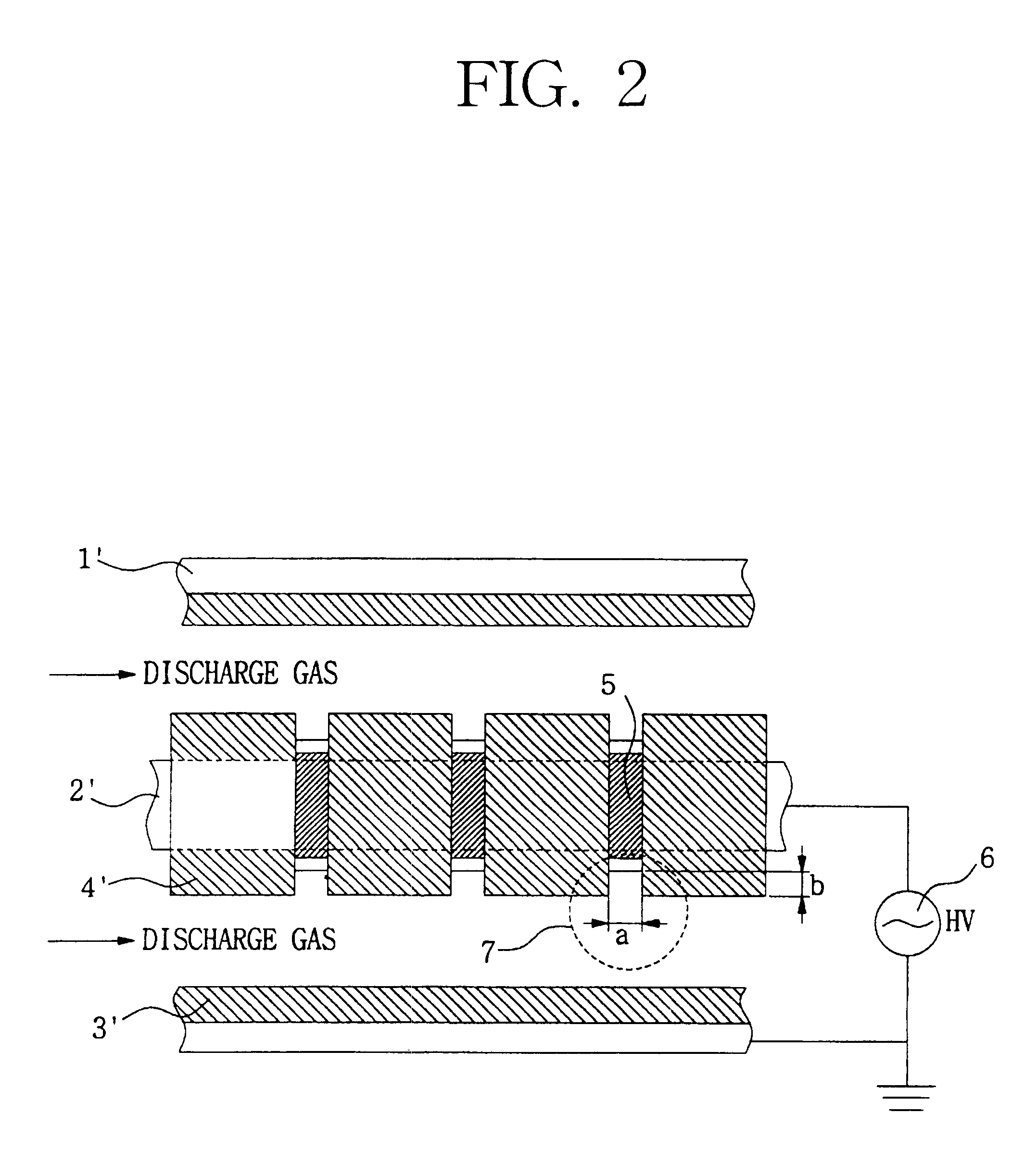
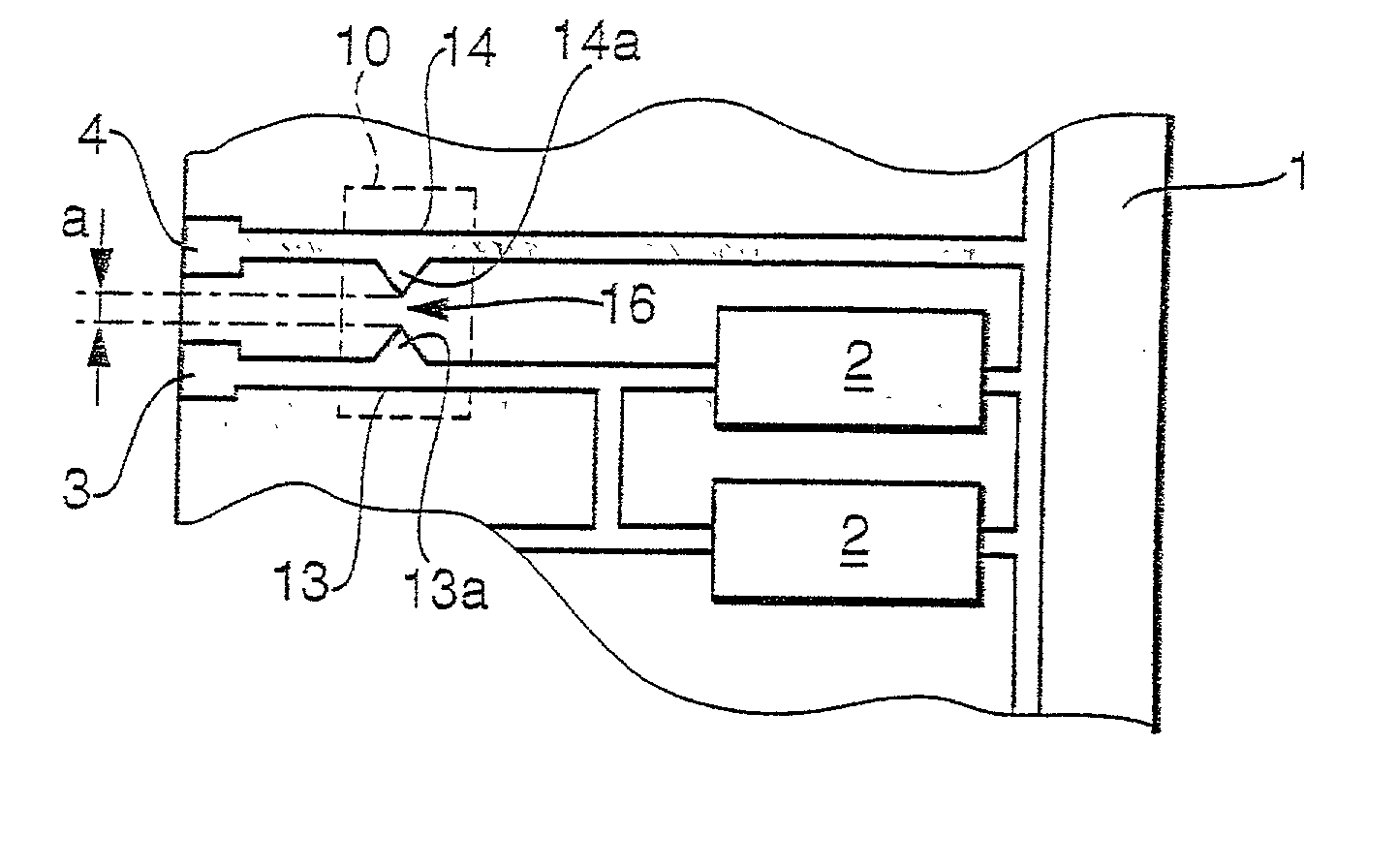
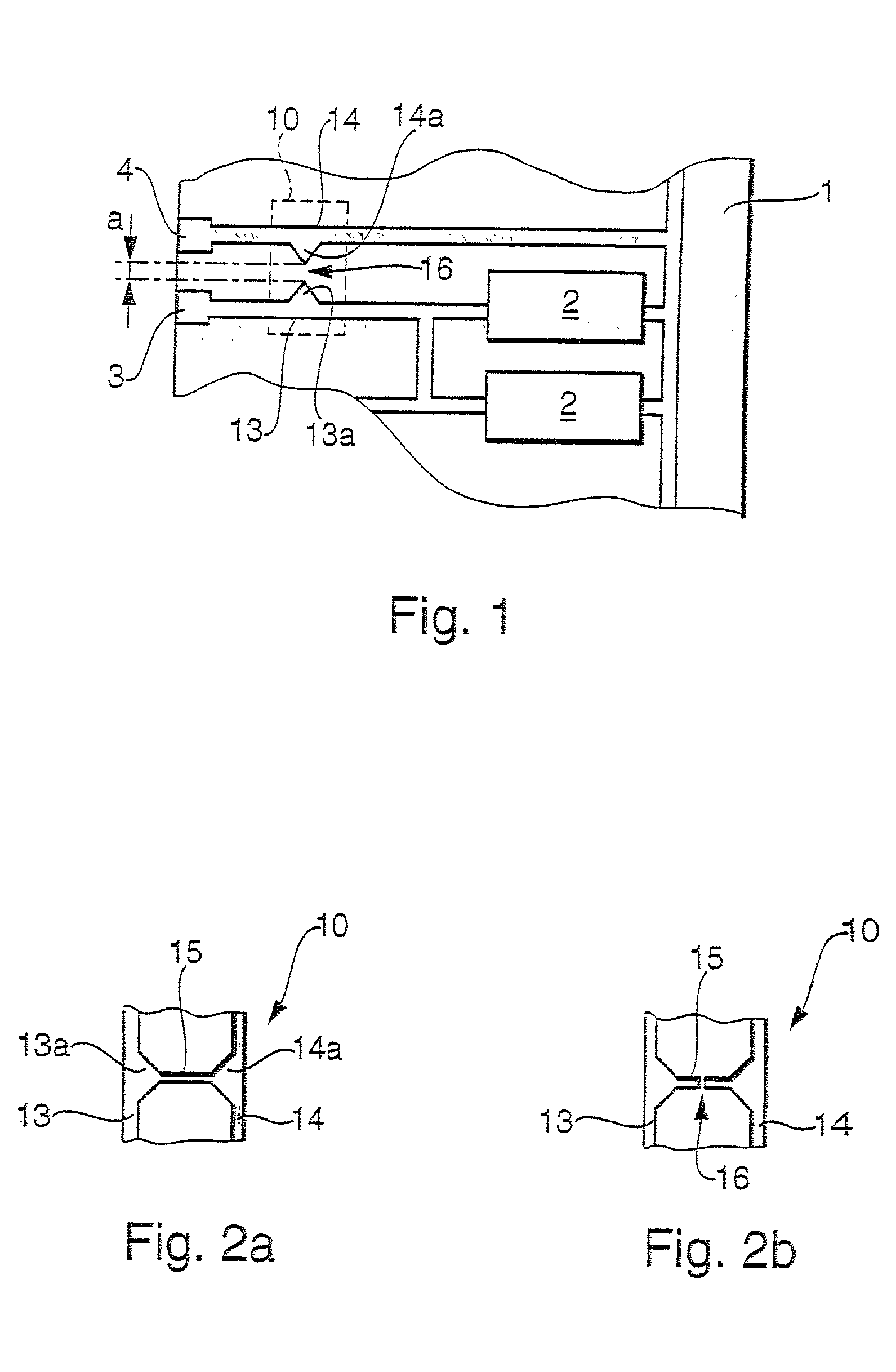
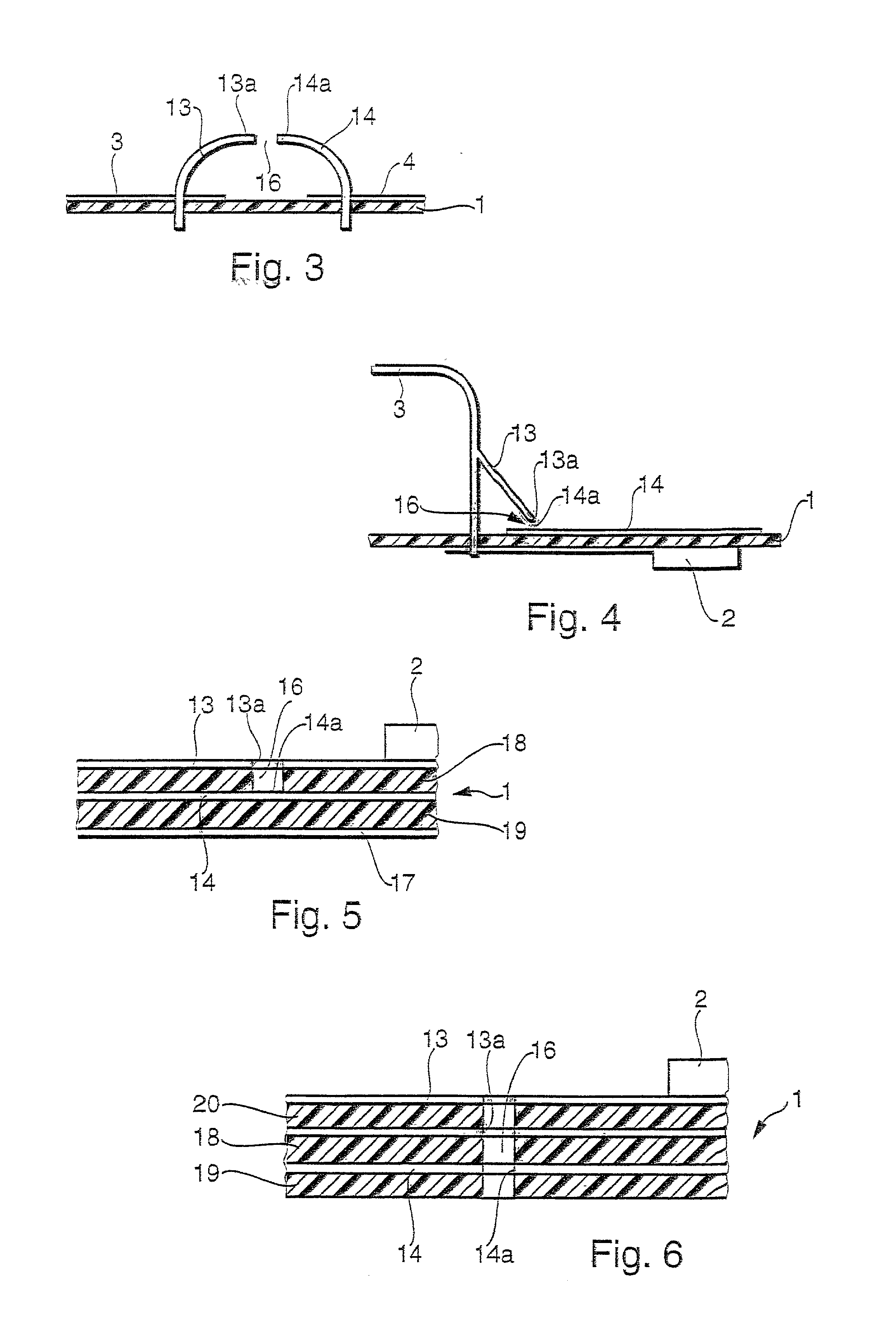
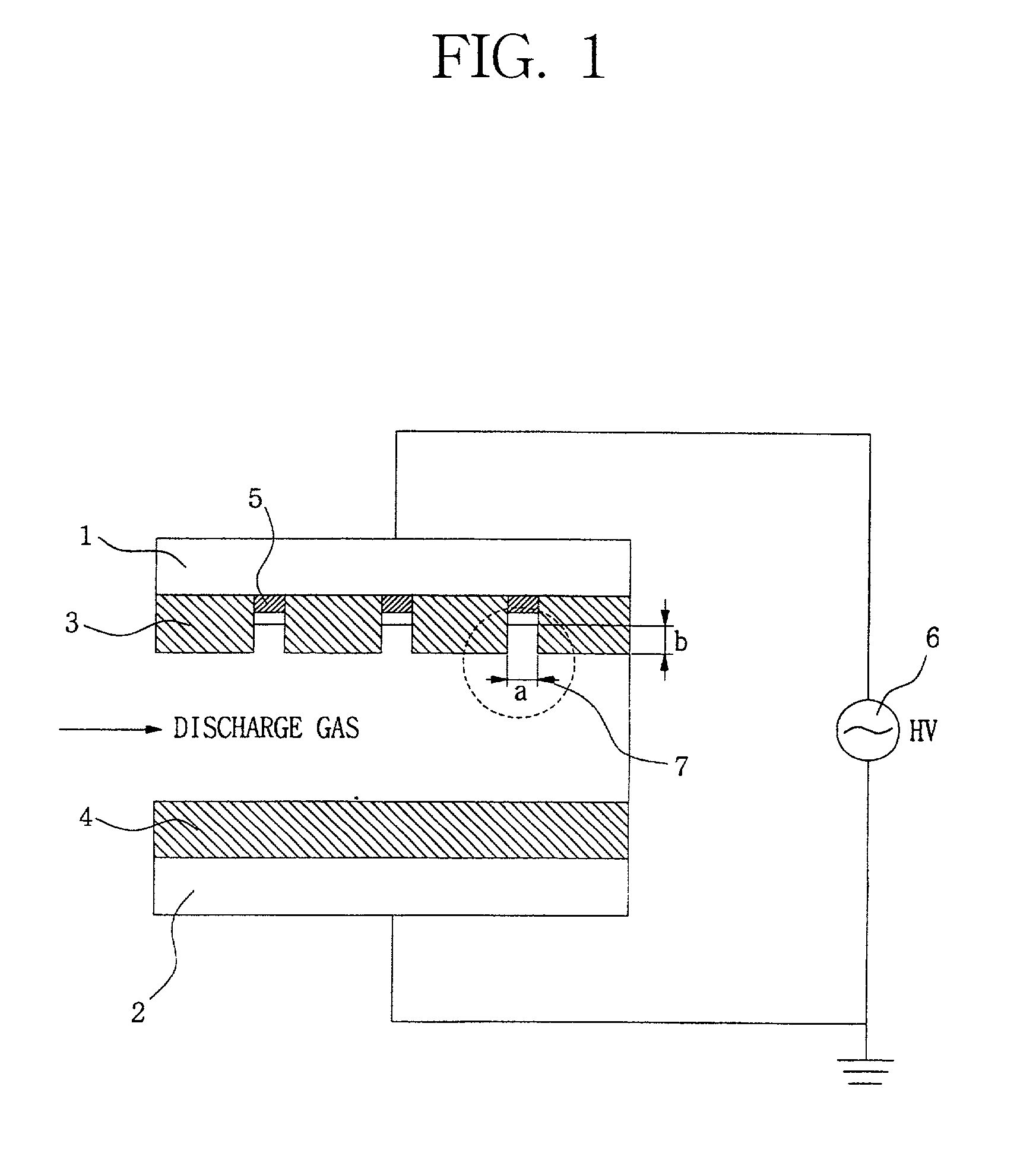
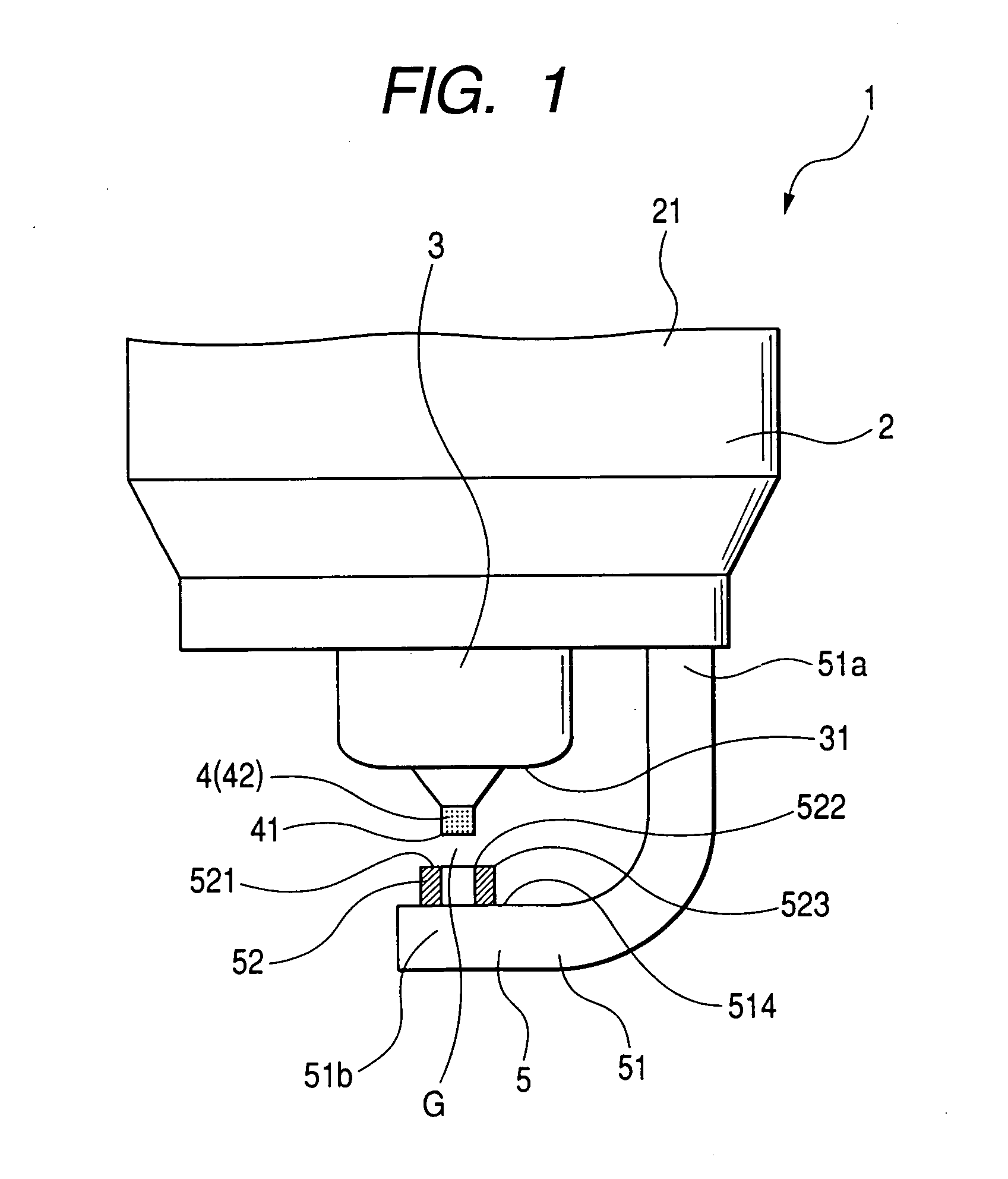
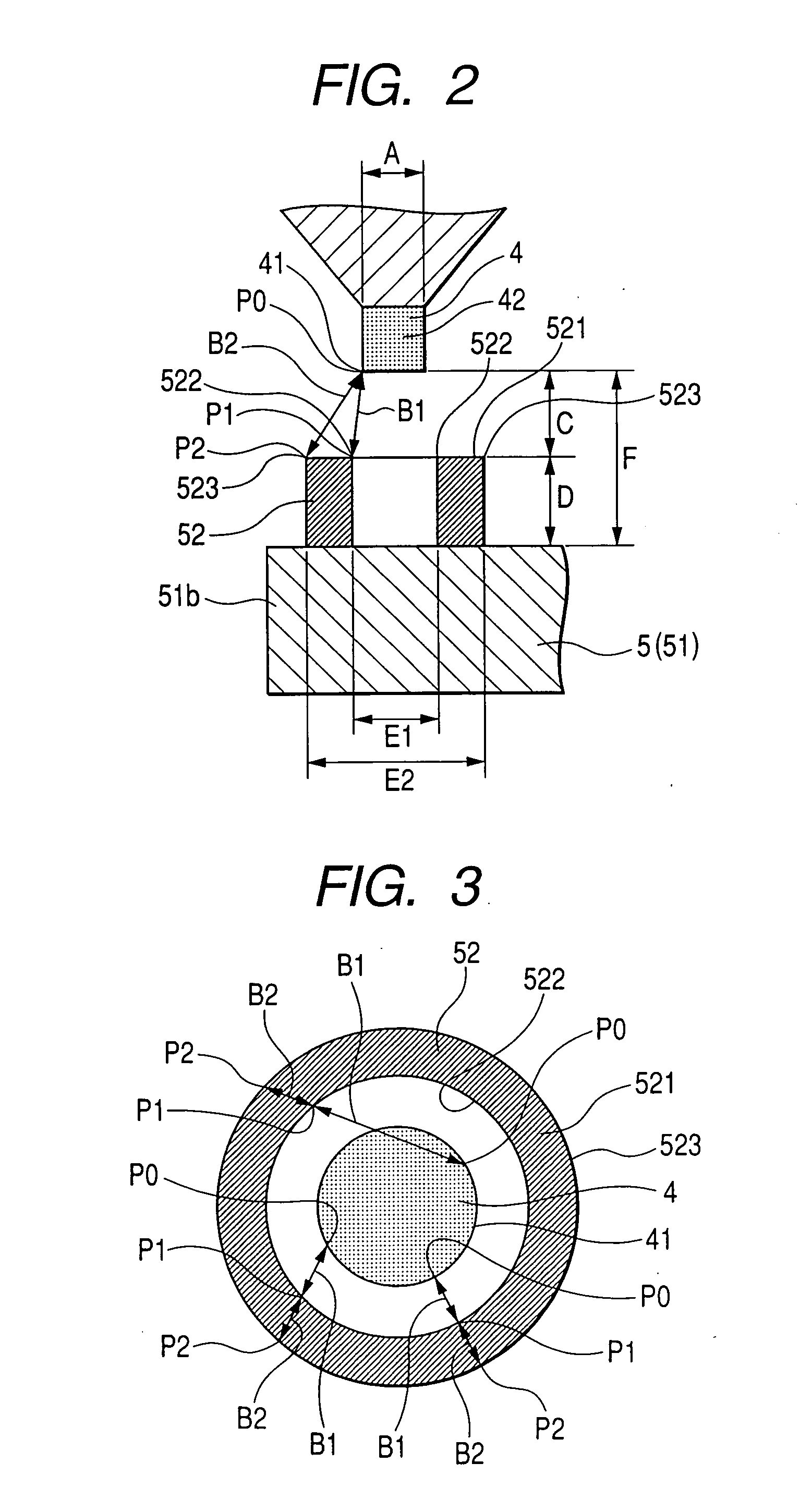
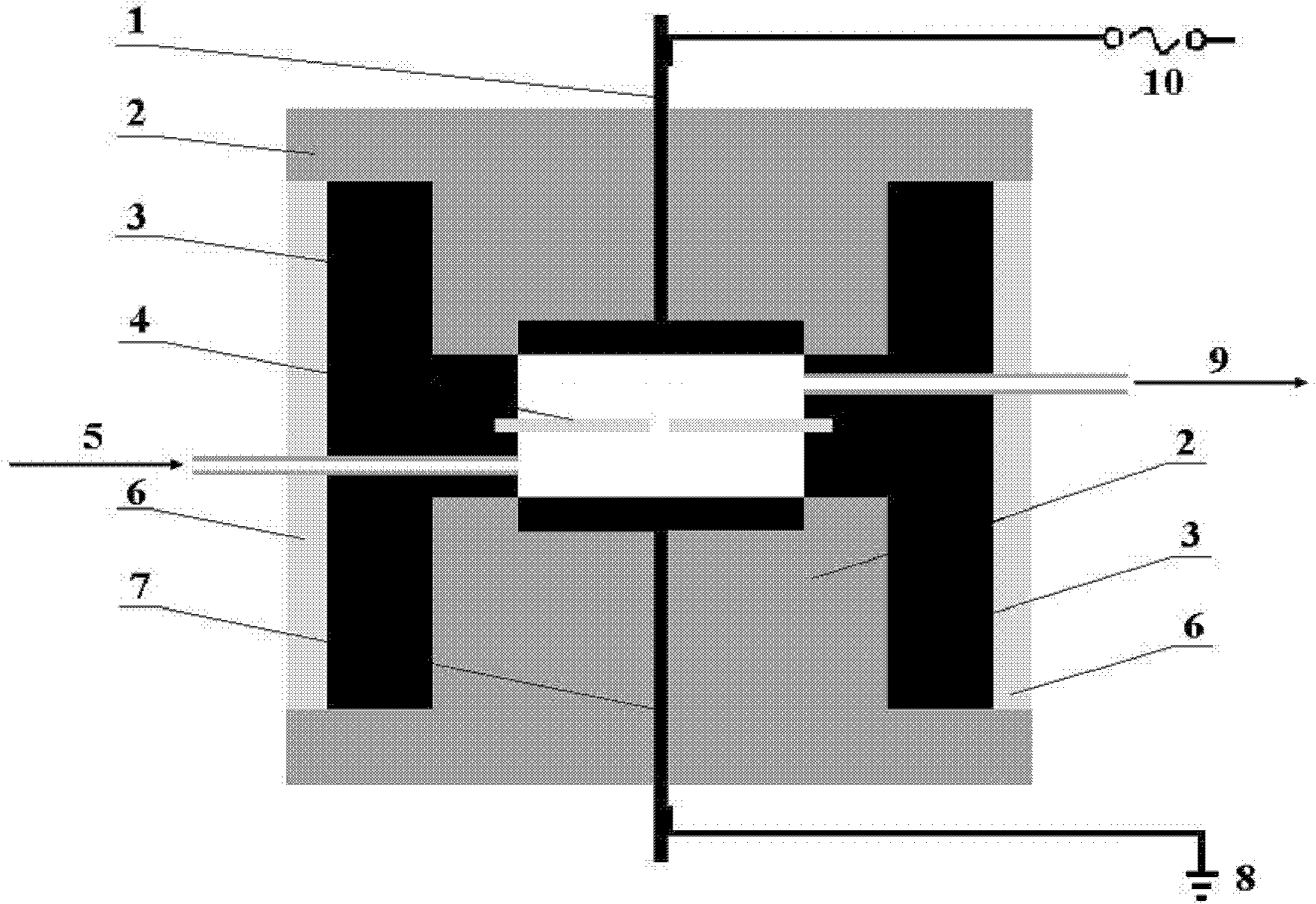
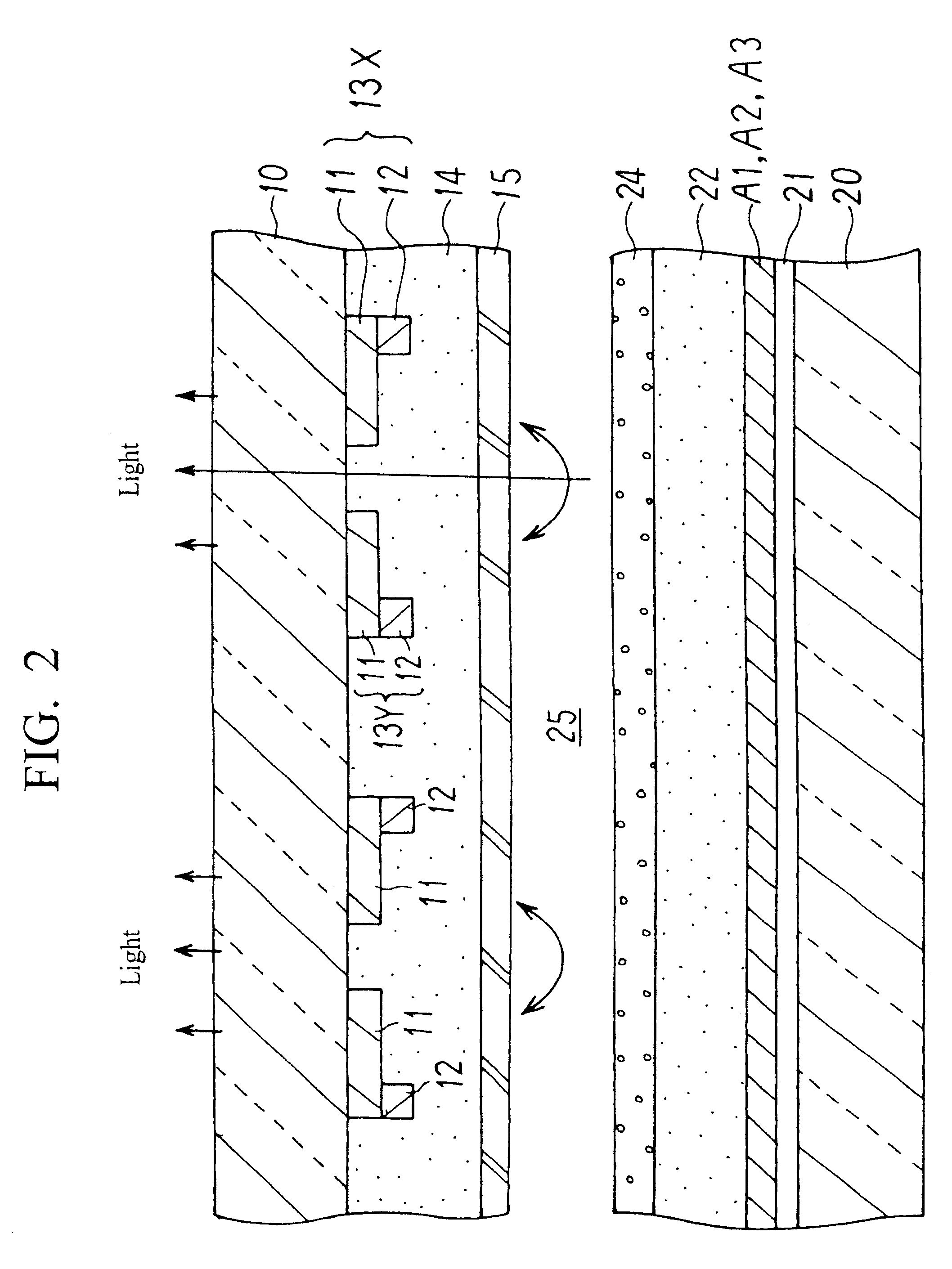
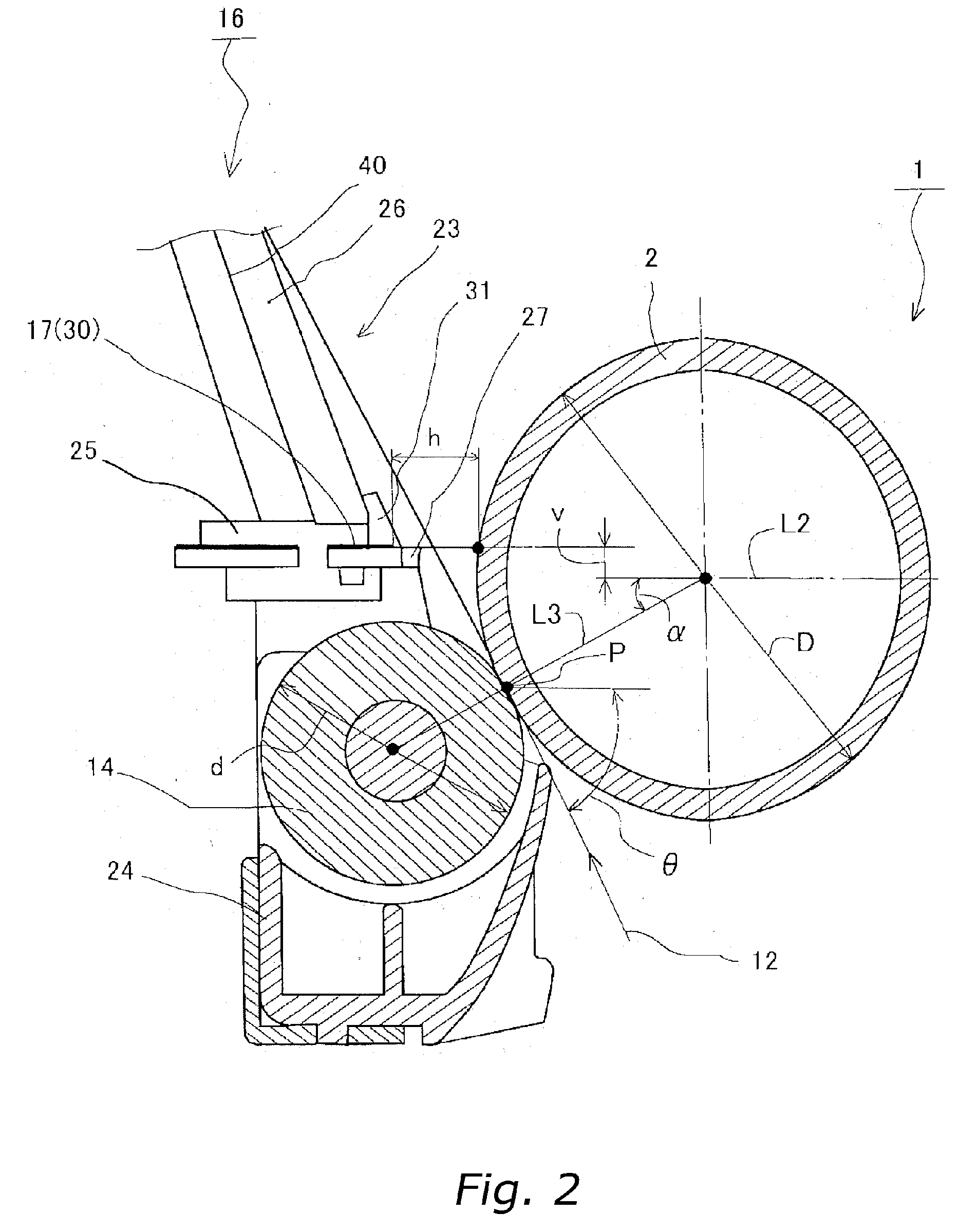
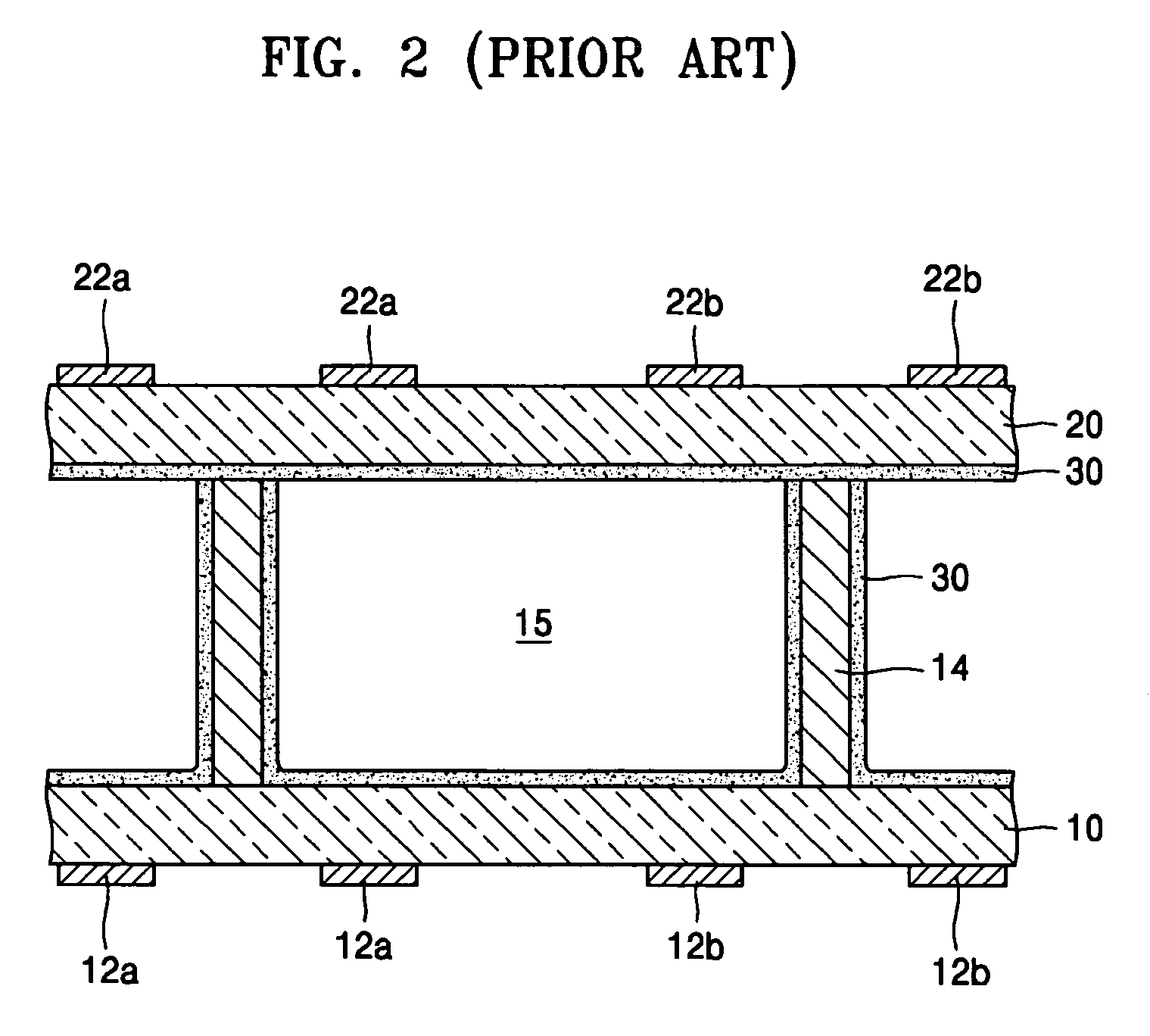
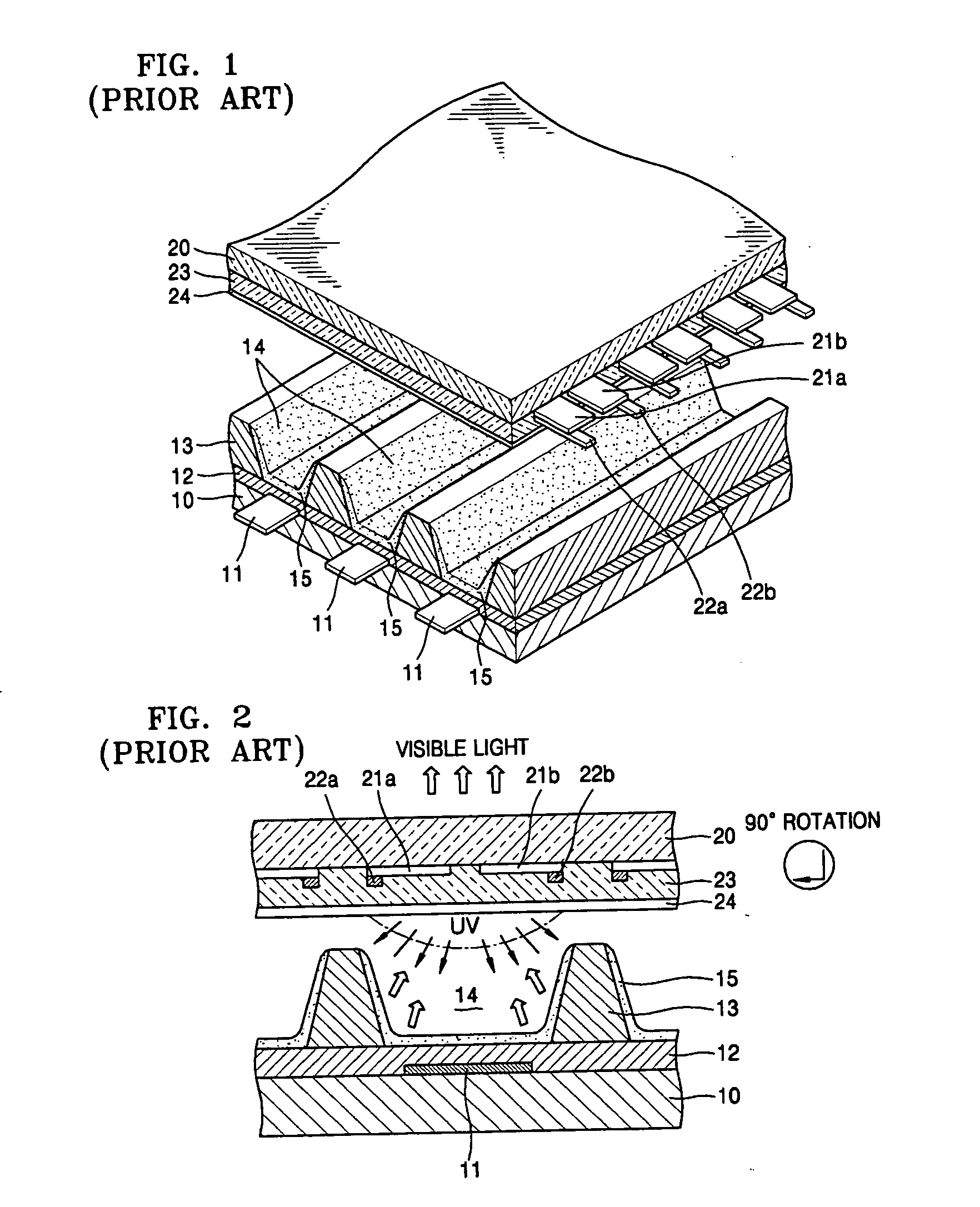
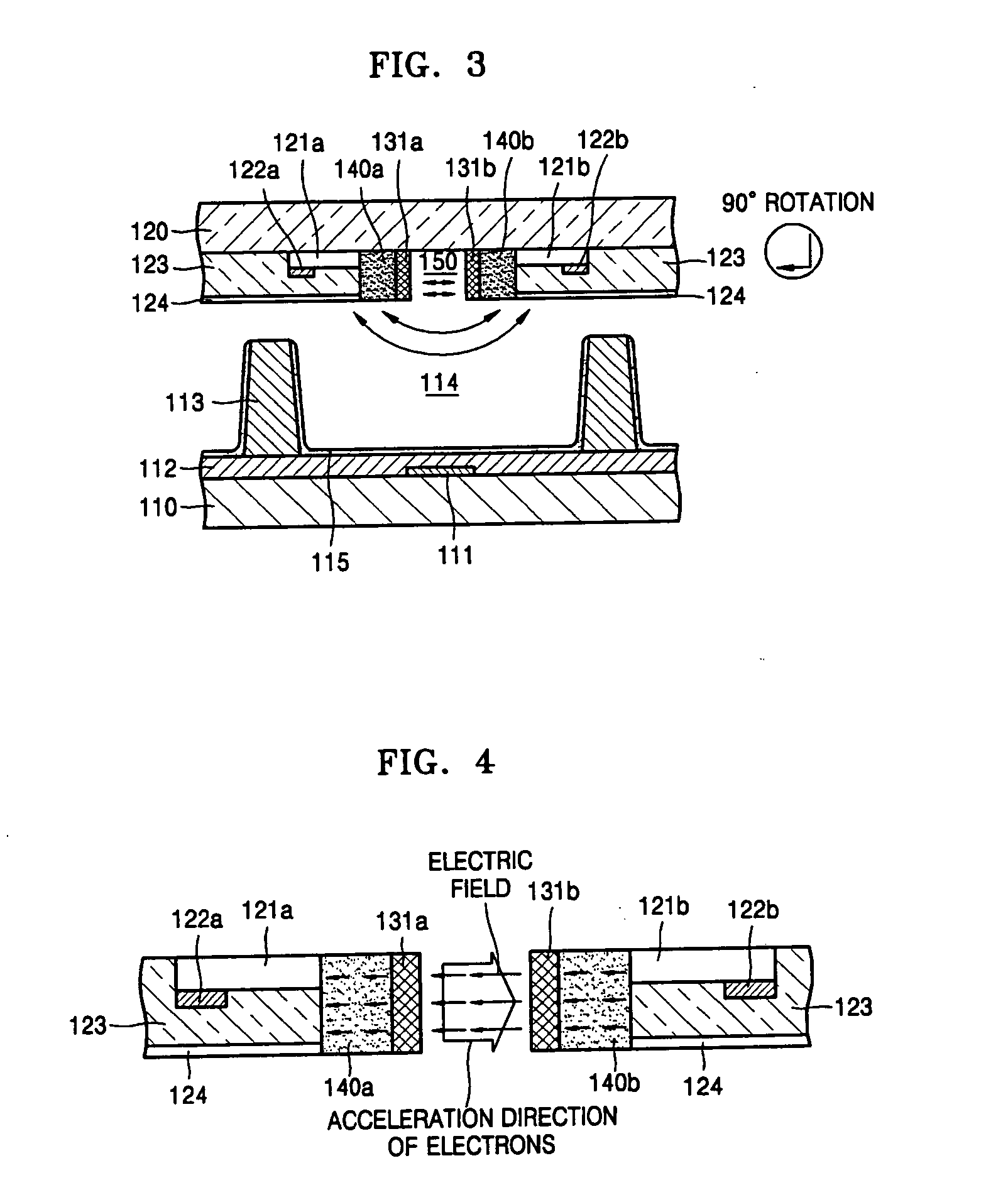
Apparatus for generating low temperature plasma at atmospheric pressure
InactiveUS6441554B1Reduce discharge voltageReduce operating and installment cost and electricity consumptionElectric discharge tubesWater treatment compoundsDielectricElectrical conductor
Owner:SE PLASMA
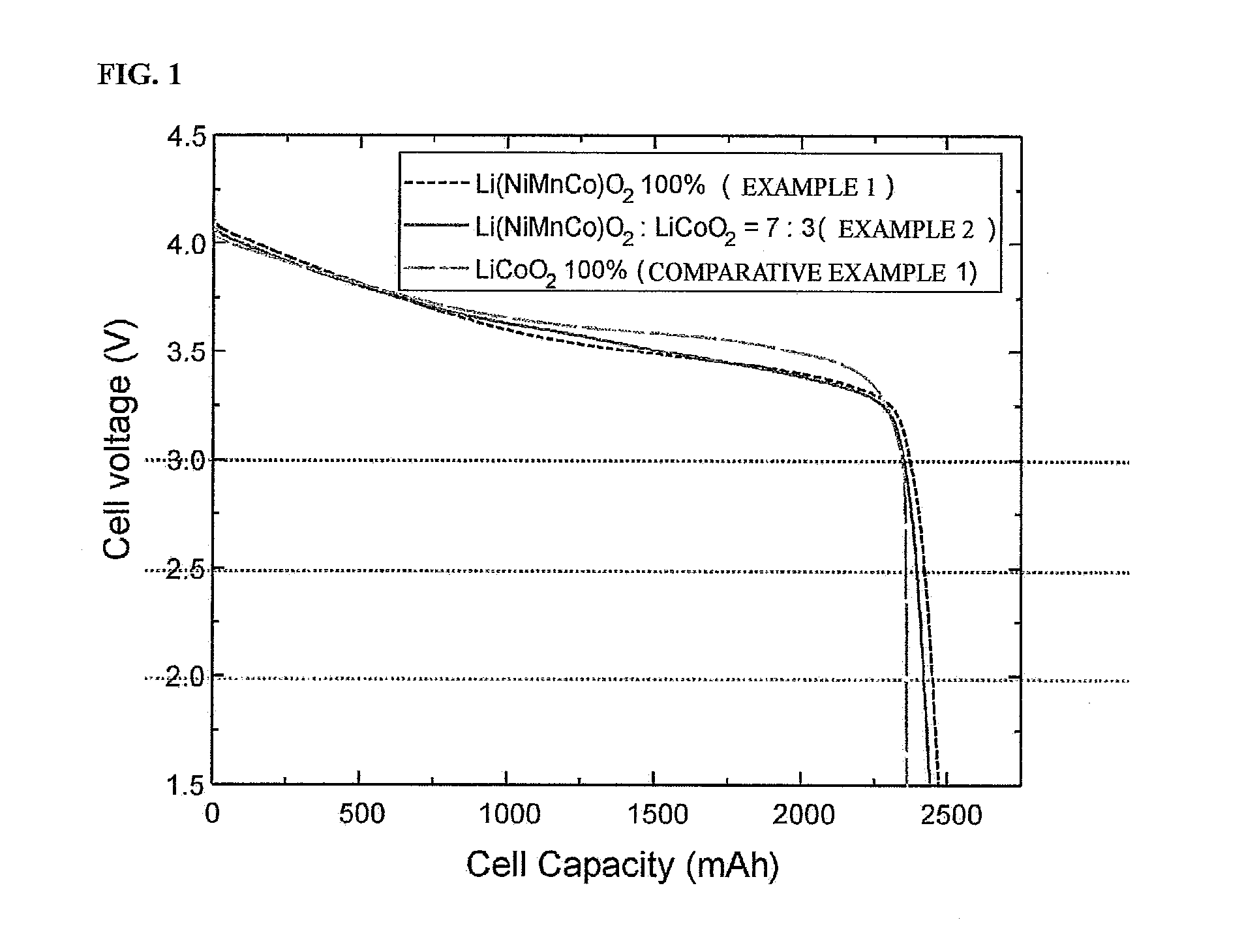
Lithium secondary battery with improved energy density
ActiveUS20120028134A1Increase battery capacityHigh capacity densityOrganic electrolyte cellsNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesMetalVoltage
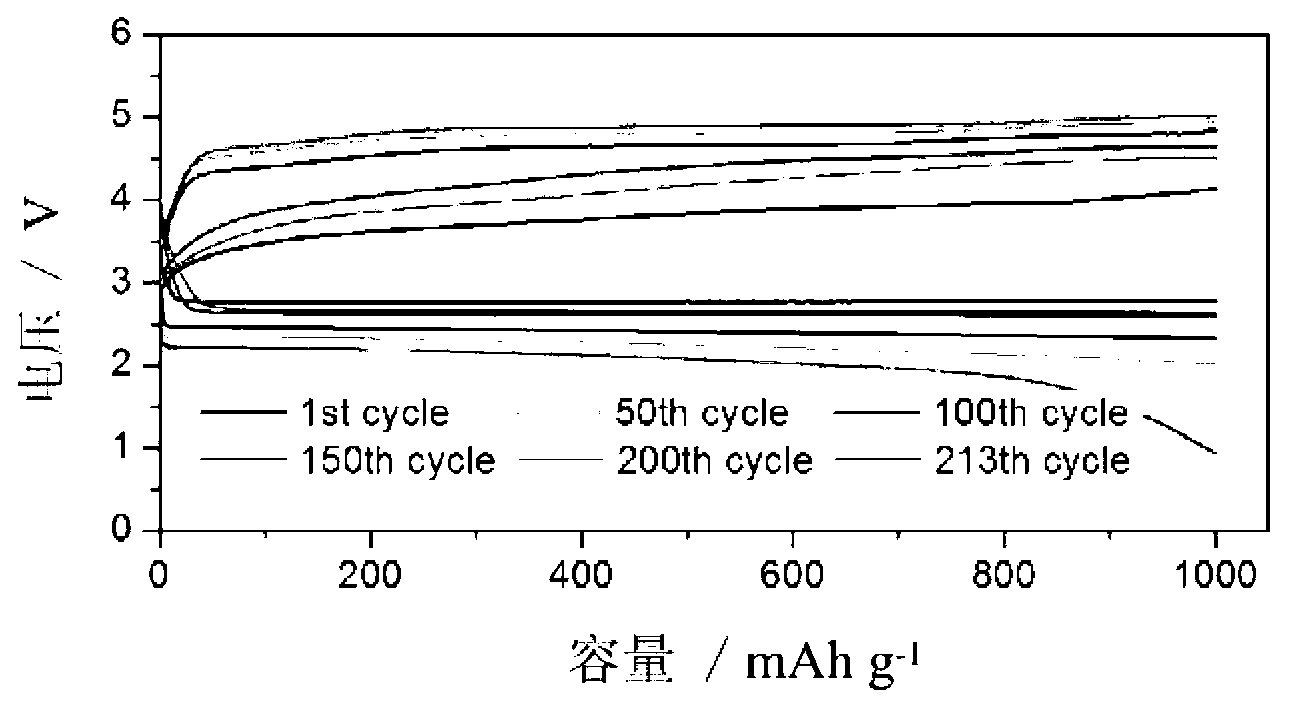
Provided is a lithium secondary battery with enhanced energy density including a cathode using a cathode active material containing lithium mixed transition metal oxide absorbing and discharging lithium ions, wherein a final discharge voltage is in the range of about 1.5 V to about 2.75 V. A final discharge voltage can be reduced to 1.5 V to 2.75 V from 3.0 V by using various lithium mixed transition metal oxides as a cathode active material, or by using the various lithium mixed transition metal oxides with the LCO-based cathode material mixed. Compared to typical LCO-based cathode materials of which capacity and energy density do not change even if a final discharge voltage is decreased, a cathode material of the present invention results in further improving capacity by 10-20% as the final discharge voltage is decreased.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
Device for protecting an electric and/or electronic component arranged on a carrier substrate against electrostatic discharges
InactiveUS20020151200A1Low production costReduce discharge voltagePrinted circuit assemblingFinal product manufactureOvervoltageContact element
The proposal relates to a device for protecting an electrical and / or electronic component, arranged on a carrier substrate, from electrostatic discharges, an overvoltage occurring in the case of discharge at a carrier-substrate contact element connected to the component being diverted to a ground connection, bypassing the component. It is proposed that the protective device include a first electroconductive structure conductively connected to the jeopardized contact element, and a second electroconductive structure arranged adjacent to the first structure on the carrier substrate and conductively connected to the ground connection. Mutually facing sections of the electroconductive structures are set apart spatially from one another by a defined gap in such a way that an overvoltage transmitted to the contact element is transferred by a spark discharge in the gap from the section of the first electroconductive structure to the section of the second electroconductive structure, and is diverted to the ground connection.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
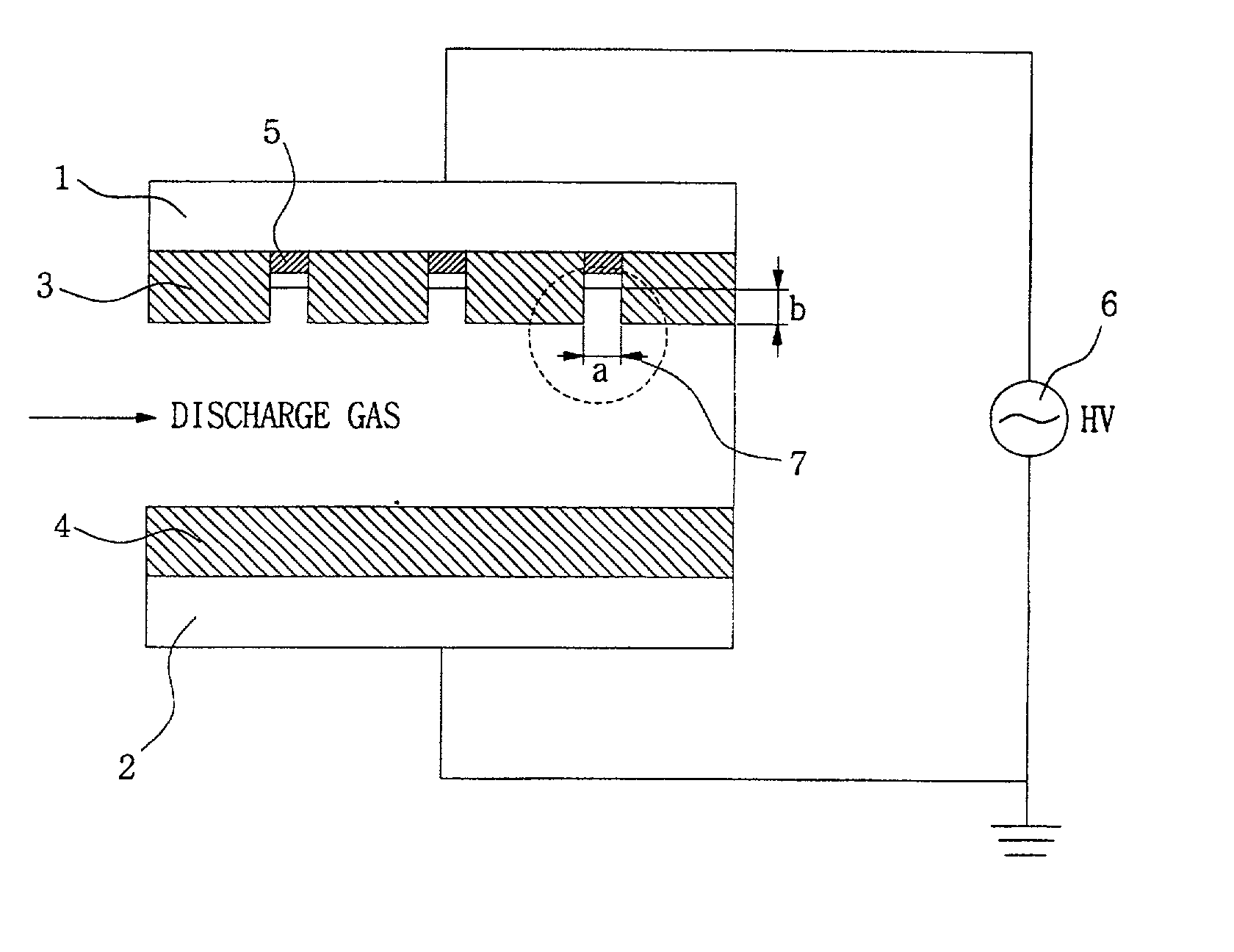
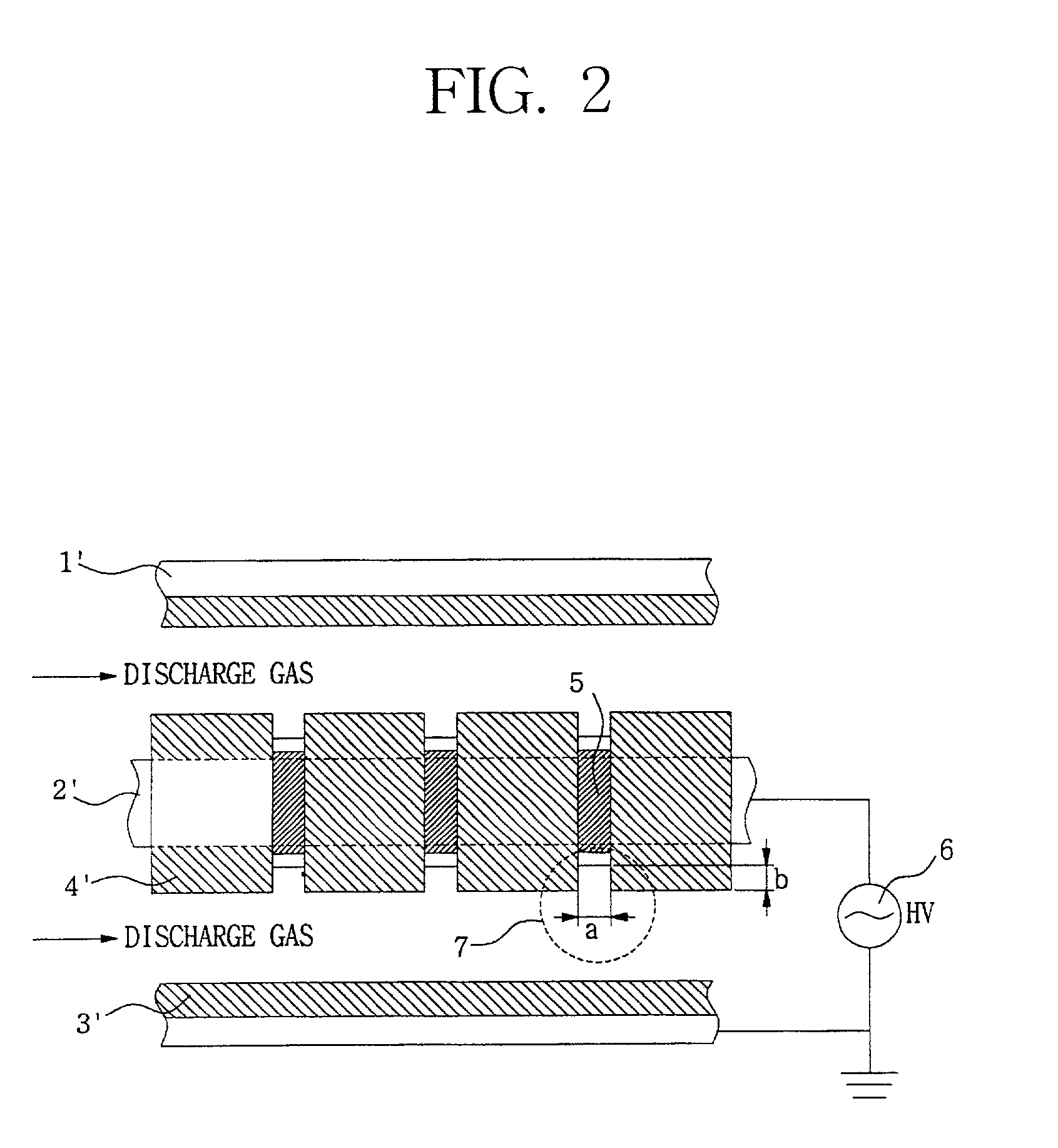
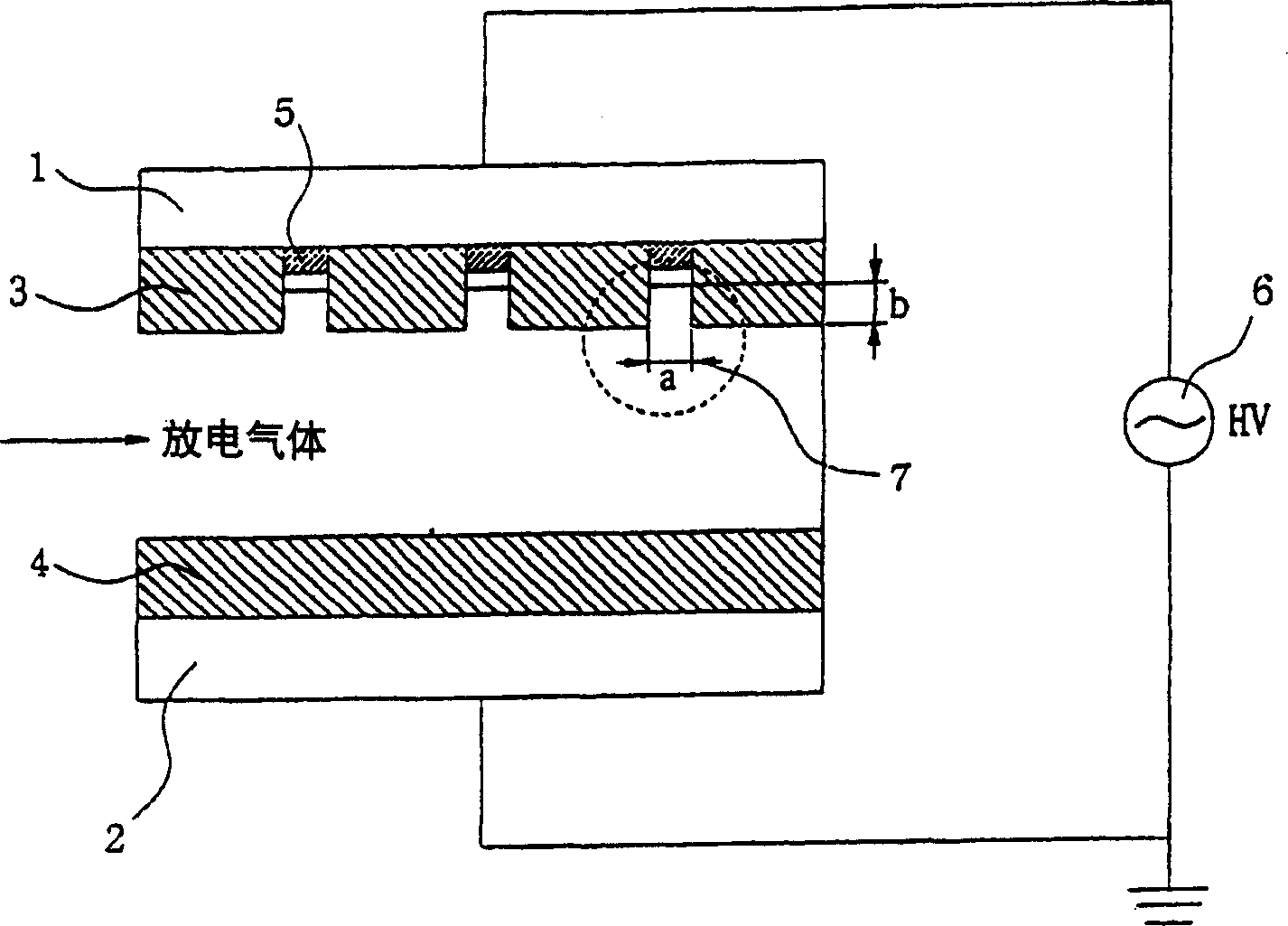
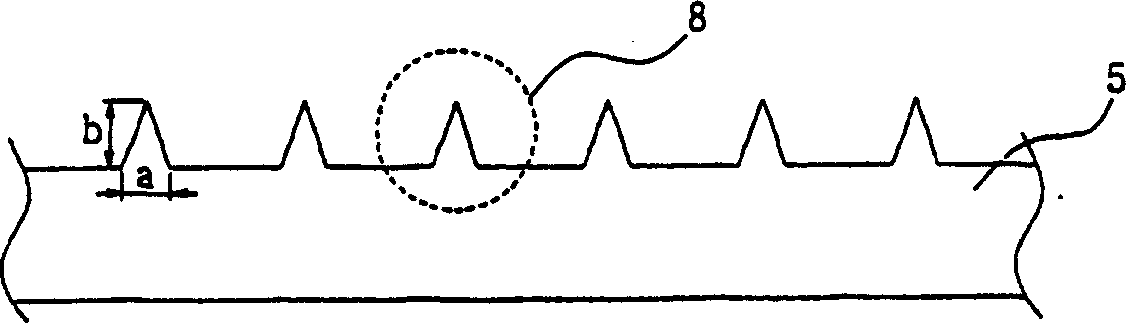
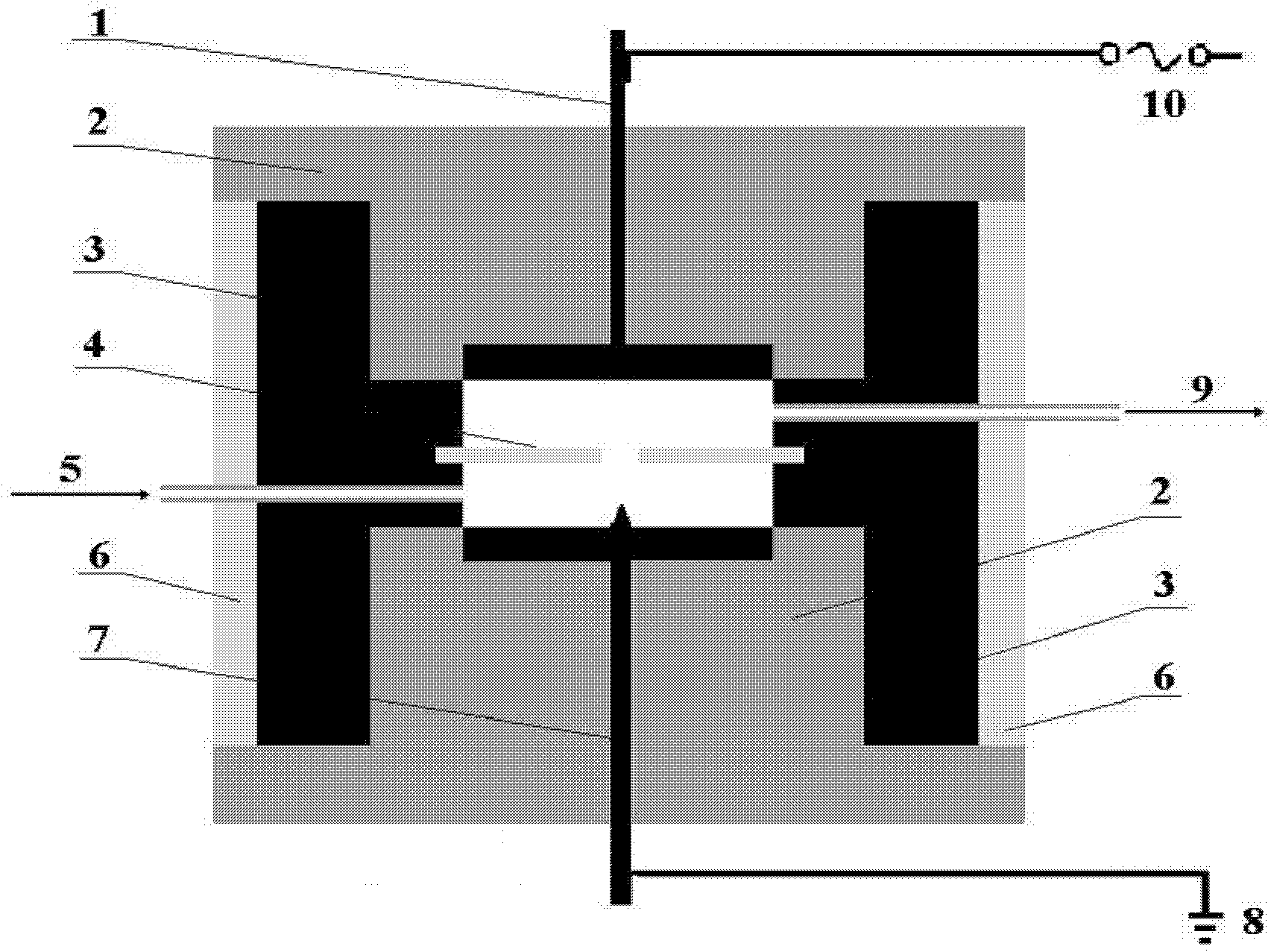
Appaaratus for generating low temperature plasma at atmospheric pressure
InactiveUS20020063537A1Reduce discharge voltageReduce operating and installment cost and electricity consumptionWater treatment compoundsElectric discharge tubesDielectricElectrical conductor
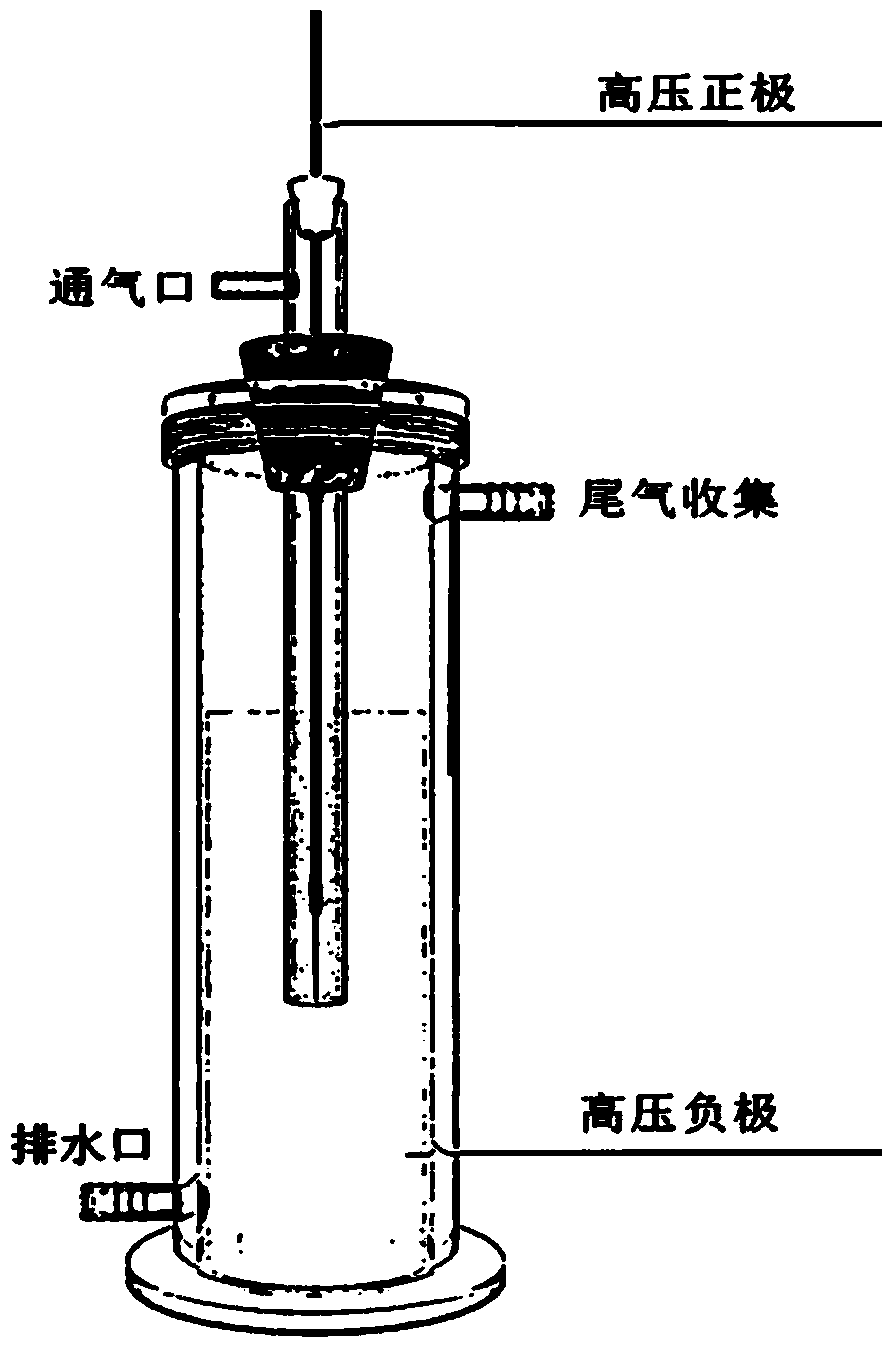
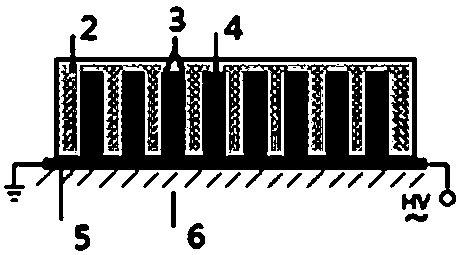
Disclosed is an apparatus for generating low-temp plasma at atmospheric pressure, comprising: a couple of electrodes facing each other at a distance, one of them being connected to a power supply, the other being grounded; a couple of dielectrics with a thickness of 25 mum-10 mm, positioned on the facing surfaces of the electrodes in such a way as to face each other, one of them having at least one discharge gap therein; and a conductor electrode having at least one tip positioned within the discharge gap, in which an electric field is applied at an intensity of 1-100 KV / cm through the power supply across the electrodes by use of a pulse direct current or an alternating current in a frequency bandwidth of 50 Hz-10 GHz while a reaction gas is fed between the electrodes, so as to induce a hollow cathode discharge, a capillary discharge or the high accumulation of charges from the discharge gap. With this structure, the apparatus prevents the conversion of the plasma to arcs and thus gives stable, low-temp plasma in a high density, and utilizes a broad bandwidth of frequencies in addition to being low in electricity consumption and being manufactured at a low cost. At low voltages, it can generate and maintain stable, low-temperature plasma over a large area. The plasma is suitable to form radicals of high energy and can be used for bonding, polishing, cleaning, thin films deposition, sterilization, ozone generation, printing, dyeing, etching, purification of water and air, complete combustion of fuels, manufacture of highly luminous lamps.
Owner:SE PLASMA
Separators for alkaline electrochemical cells
ActiveUS7931981B2Adequate electronic conductivity and integrityHigh voltageAlkaline accumulatorsActive material electrodesElectrical batteryElectrochemical cell
Owner:ENERGIZER BRANDS
Method of making plasma display panel with dielectric layer suppressing reduced electrode conductivity
InactiveUS6296539B1Drop in conductivitySuppresses resistance riseAddress electrodesSustain/scan electrodesIndiumIndium tin oxide
The present invention relates to a plasma display panel comprising transparent electrodes and a dielectric layer covering said transparent electrodes on at least one substrate of a pair of substrates facing each other with a discharge space therebetween, the main constituent of the transparent electrodes is included in the dielectric layer. Further, the main constituent of the transparent electrode is indium oxide and indium oxide is included in the dielectric layer. By including the main constituent of the transparent electrodes in the dielectric layer, it is believed that the drop in conductivity caused by diffusion of the dielectric substance in the transparent electrodes during high-temperature processing is prevented.
Owner:HITACHT MAXELL LTD
Spark plug having ground electrode protruding member with inner and outer edges
A spark plug includes a metal shell, an insulator, a center electrode, and a ground electrode. The insulator is retained in the metal shell. The center electrode is secured in the insulator and has an end portion that protrudes from the insulator and has an end edge. The ground electrode includes a base member fixed to the metal shell and a protruding member joined to the base member. The protruding member protrudes from a surface of the base member and has a hollow end face that faces the end portion of the center electrode through a spark gap. The end face of the protruding member has an inner edge and an outer edge, both of which face the end edge of the end portion of the center electrode. With the above configuration, the spark plug can induce spark discharges with a low discharge voltage while securing the ignition capability thereof.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
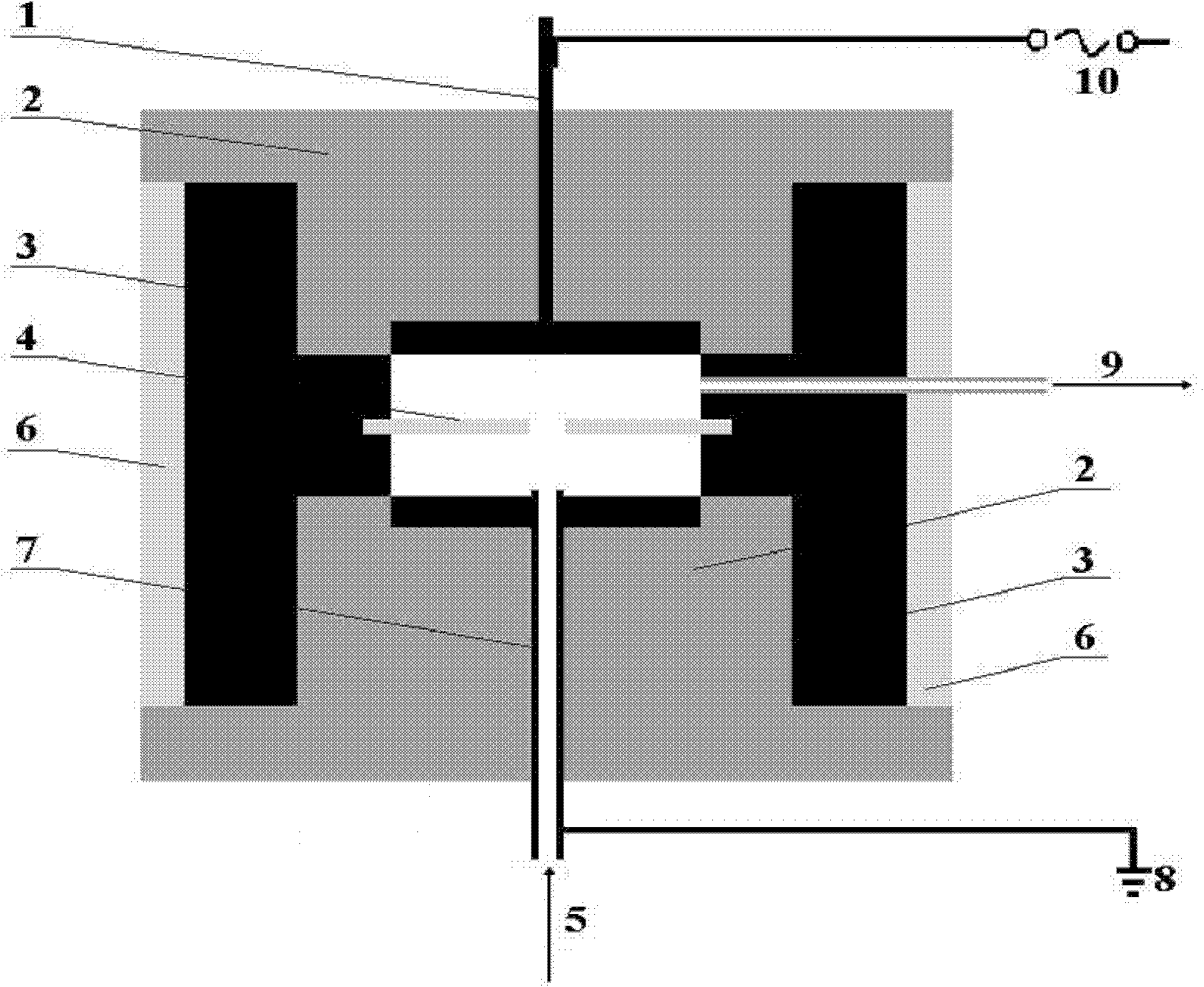
Apparatus for generating low temperature plasma at atmospheric pressure
InactiveCN1491527AReduce power consumptionReduce discharge voltageElectric discharge tubesEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesDielectricElectrical conductor
Disclosed is an apparatus for generating low-temperature plasma at atmospheric pressure, comprising: a couple of electrodes facing each other at a distance, one of them being connected to a power supply, the other being grounded; a couple of dielectrics with a thickness of 25 mum to 10 mm, positioned on the facing surfaces of the electrodes in such away as to face each other, one of them having at least one discharge gap therein; and a conductor electrode having at least one tip positioned within the discharge gap, wherein an electric field is applied at an intensity of 1-100 KV / cm through the power supply across the electrodes by use of a pulse direct current or an alternating current in a frequency bandwidth of 50 Hz to 10 GHz while a reaction gas is fed between the electrodes, so as to induce a hollow cathode discharge, a capillary discharge or the high accumulation of charges from the discharge gap. The inventive apparatus prevents the conversion of the plasma to arcs and thus gives stable, low-temperature plasma in a high density.
Owner:SE PLASMA
Plate type plasma reactor for hydrogen production through ammonia decomposition
InactiveCN101863455AIncreased electron energy densityImprove energy efficiencyHydrogen productionEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesDecompositionNitrogen gas
The invention belongs to the technical field of plasma chemistry and hydrogen energy, and relates to a plate type plasma discharge reactor for hydrogen production through ammonia decomposition. The plasma reactor is characterized by being divided into a plat-plate type, a needle-plate type and a pipe-plate type according to different earth electrodes, wherein an insulating blocking medium is arranged between a high-voltage electrode and the earth electrode of the reactor, and open pores are formed on the blocking medium; the high-voltage electrode and the earth metal electrode generate plasmas to discharge through the open pores on the blocking medium to ensure that ammonia gas is decomposed into hydrogen gas and nitrogen gas in a discharge zone; and the open pores of the blocking medium not only are discharge channels, but also are inevitable channels for reactants. The plate type plasma discharge reactor with the blocking medium provided with the open pores has the advantages of reducing the discharge voltage, limiting the discharge zone, improving the energy density of the discharge zone, and further improving the efficiency of decomposing the ammonia gas directly by using non-equilibrium plasmas.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
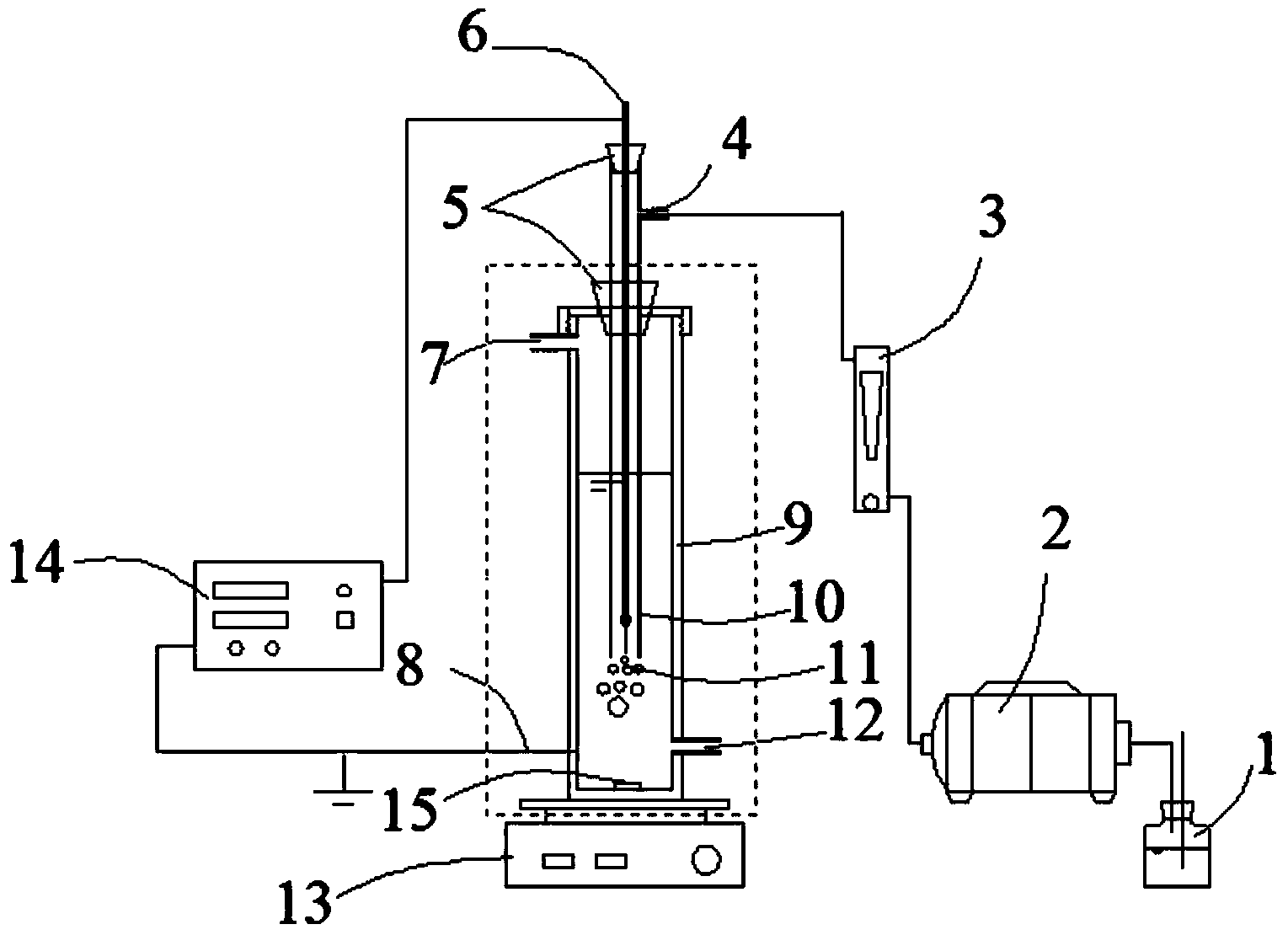
Device and method for degrading antibiotic wastewater by utilizing low temperature plasma in coordination with bismuth molybdate catalyst
InactiveCN103848484AImprove degradation rateHigh removal rateWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsCatalyst degradationBreather
The invention discloses a device and a method for treating antibiotic wastewater by utilizing low temperature plasma in coordination with a bismuth molybdate catalyst. The device for treating the antibiotic wastewater by utilizing the low temperature plasma in coordination with the bismuth molybdate catalyst comprises a barrel-shaped reactor, a breather pipe, a high voltage electrode, an alternating current high voltage power supply, an air pump and a stirrer, wherein the breather pipe is arranged inside the barrel-shaped reactor and is coaxial with the barrel-shaped reactor, the high voltage electrode is suspended inside the breather pipe, the lower port of the breather pipe is arranged at the lower bottom part inside the barrel-shaped reactor, the upper part of the breather pipe is arranged outside the barrel-shaped reactor, an air inlet is formed in the side wall of the upper part of the breather pipe, the air inlet is communicated with the outlet of the air pump by virtue of a pipeline; the alternating current high voltage power supply is respectively connected to the high voltage electrode and grounded, and the stirrer is arranged at the lower part of the barrel-shaped reactor. The device for treating the antibiotic wastewater by utilizing the low temperature plasma in coordination with the bismuth molybdate catalyst has the characteristics of simple design, low equipment investment and no secondary pollution and can be applied to the filed of treatment on antibiotic wastewater and organic wastewater difficult to be biochemically degraded, wherein a degradation reaction temperature can be increased by fully utilizing heat produced in a discharge process.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Discharge electrode structure of plasma air purification device
ActiveCN102548177ADifferent structureLimit processingDeodrantsPlasma techniqueGlow plasmaEngineering
The invention discloses a discharge electrode structure of a plasma air purification device. The electrode structure comprises a positive electrode group and a negative electrode group, wherein at least one of the positive electrode group and the negative electrode group is wrapped with insulating medium; and the two electrode groups contact directly, such that a contact point is formed. According to the invention, the discharge electrode structure is applied to the plasma air purification device, so a great amount of low temperature plasma is generated at an electrode intersection and a nearby area of the electrode intersection through the structure; the low temperature plasma has properties of glow-like plasma, wide sterilization range, high sterilization rate, short time consumption and low power consumption; in addition, the adopted net-like structure can not only ensure good air permeability but also enlarge the actual plasma function area, therefore, the sterilization rate is further improved.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
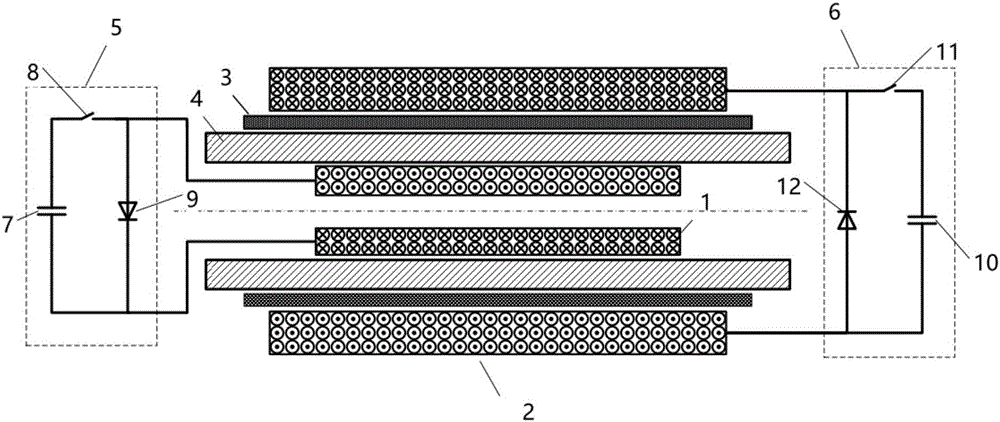
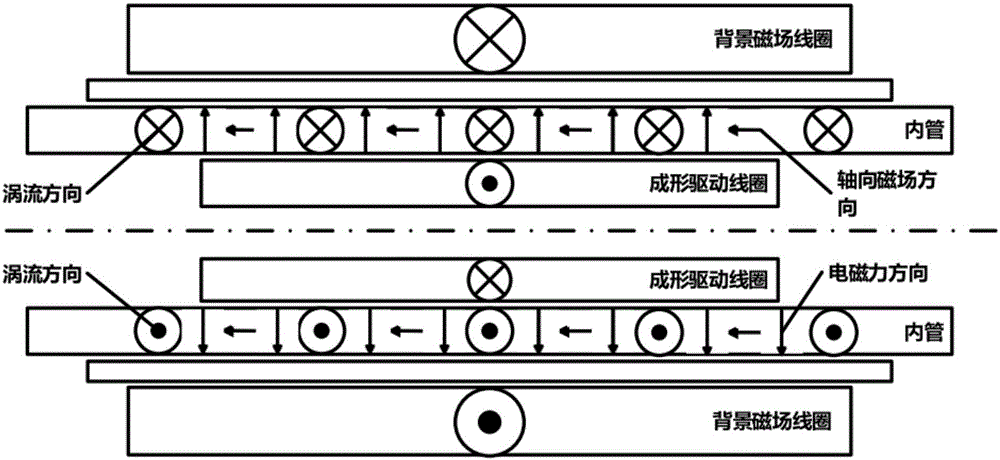
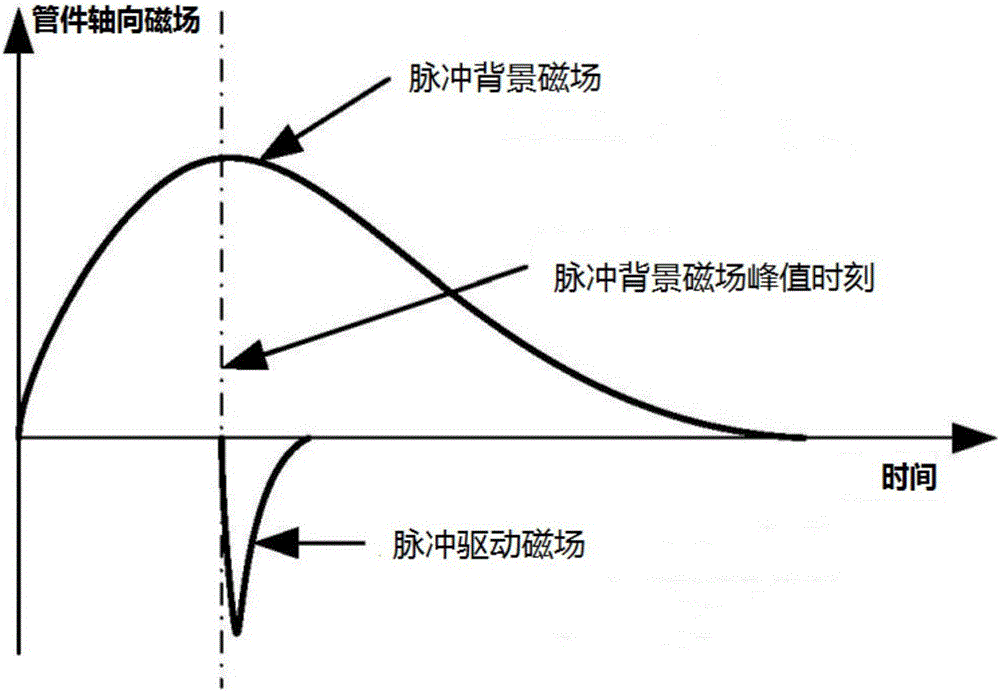
Electromagnetic forming device and method of metal pipe
ActiveCN106694681AHigh strengthSmall electromagnetic forceElectromagnetic formingUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses an electromagnetic forming device and method of a metal pipe. The device comprises a background magnetic field unit and a metal pipe forming driving coil, wherein the background magnetic field unit is used for generating a pulse background magnetic field on the metal pipe, and a pulse driving magnetic field can generate vortexes on the metal pipe; and the metal pipe forming driving coil is used for generating the pulse driving magnetic field on the metal pipe. Due to the fact that the pulse width of the pulse driving magnetic field is much smaller than that of the pulse background magnetic field, the vortexes generated by the pulse background magnetic field on the metal pipe can be ignored, meanwhile, the influences of the pulse driving magnetic field on a magnetic field on the metal pipe can be ignored, and thus, electromagnetic force is generated on the metal pipe through interaction of the pulse background magnetic field and the vortexes. By independently adjusting the pulse background magnetic field and the pulse driving magnetic field, the electromagnetic force can be improved, the metal pipe high in mechanical strength and low in conductivity can be formed, meanwhile, the design difficulty of the forming driving coil can be lowered, and the service life of the forming driving coil is prolonged.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Plasma display panel with dielectric layer suppressing reduced electrode conductivity
InactiveUS6344713B1Suppresses resistance riseReduce discharge voltageAddress electrodesSustain/scan electrodesIndiumDielectric layer
The present invention relates to a plasma display panel comprising transparent electrodes and a dielectric layer covering said transparent electrodes on at least one substrate of a pair of substrates facing each other with a discharge space therebetween, the main constituent of the transparent electrodes is included in the dielectric layer. Further, the main constituent of the transparent electrode is indium oxide and indium oxide is included in the dielectric layer. By including the main constituent of the transparent electrodes in the dielectric layer, it is believed that the drop in conductivity caused by diffusion of the dielectric substance in the transparent electrodes during high-temperature processing is prevented.
Owner:HITACHT MAXELL LTD
Alternating current driven type plasma display device
InactiveUS20010015621A1Reducing discharge initiation voltageImprove reliabilitySustain/scan electrodesDischarge tube luminescnet screensAlternating currentXenon
An alternating current driven type plasma display device characterized in that a discharge gas charged in a discharge space where discharge takes place consists of a xenon gas alone and the discharge gas has a pressure of 9.0x104 Pa or lower.
Owner:SONY CORP
Medical array type micro-plasma skin treatment device
ActiveCN105396227ASimple structureEasy to useX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapySkin treatmentsEngineering
The invention provides a medical array type micro-plasma skin treatment device comprising a shell, high voltage electrodes, a ground electrode, insulation medium tubes, an air inlet tube, a PCB, a high voltage power supply and a high voltage line. The shell is a cylindrical shell, and the internal part is provided with a separating plate of which the surface is provided with an air inlet A and a line penetrating port A. The sealing end of the shell is provided with an air inlet B and a line penetrating port B. The air inlet tube is communicated with the air inlet A through the air inlet B. The PCB, the ground electrode and a sealing cap are installed below the separating plate in turn. The sealing cap is connected with the shell in a threaded way. The ground electrode and the surface of the sealing cap are uniformly provided with through holes. The insulation medium tubes are arranged in the through holes. The high voltage electrodes are installed in the internal parts of the insulation medium tubes. The top ends of the high voltage electrodes are welded on the PCB. The surface of the PCB is uniformly provided with ventilation holes. The high voltage line is connected on the PCB. The high voltage line penetrates through the line penetrating port A and the line penetrating port B to be connected with the external high voltage power supply. The medical array type micro-plasma skin treatment device has advantages of being simple in structure, convenient to use and flexible in operation.
Owner:DALIAN NATIONALITIES UNIVERSITY
Discharge light-emitting device and method manufacture thereof
InactiveUS6744208B2Reduce voltageEasy dischargeTube/lamp vessel fillingAlternating current plasma display panelsElectric dischargeWater vapor
A discharge light-emitting device includes a gas-filled discharge spaces (30) to use electric discharge in the gas. The gas contains at least 0.01-1% water vapor by volume. The specified amount of water vapor decreases discharge voltage markedly. Water vapor is introduced between a sealing step and an evacuation step so that the gas-filled discharge spaces can finally contain a desired amount of water vapor.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Image forming device
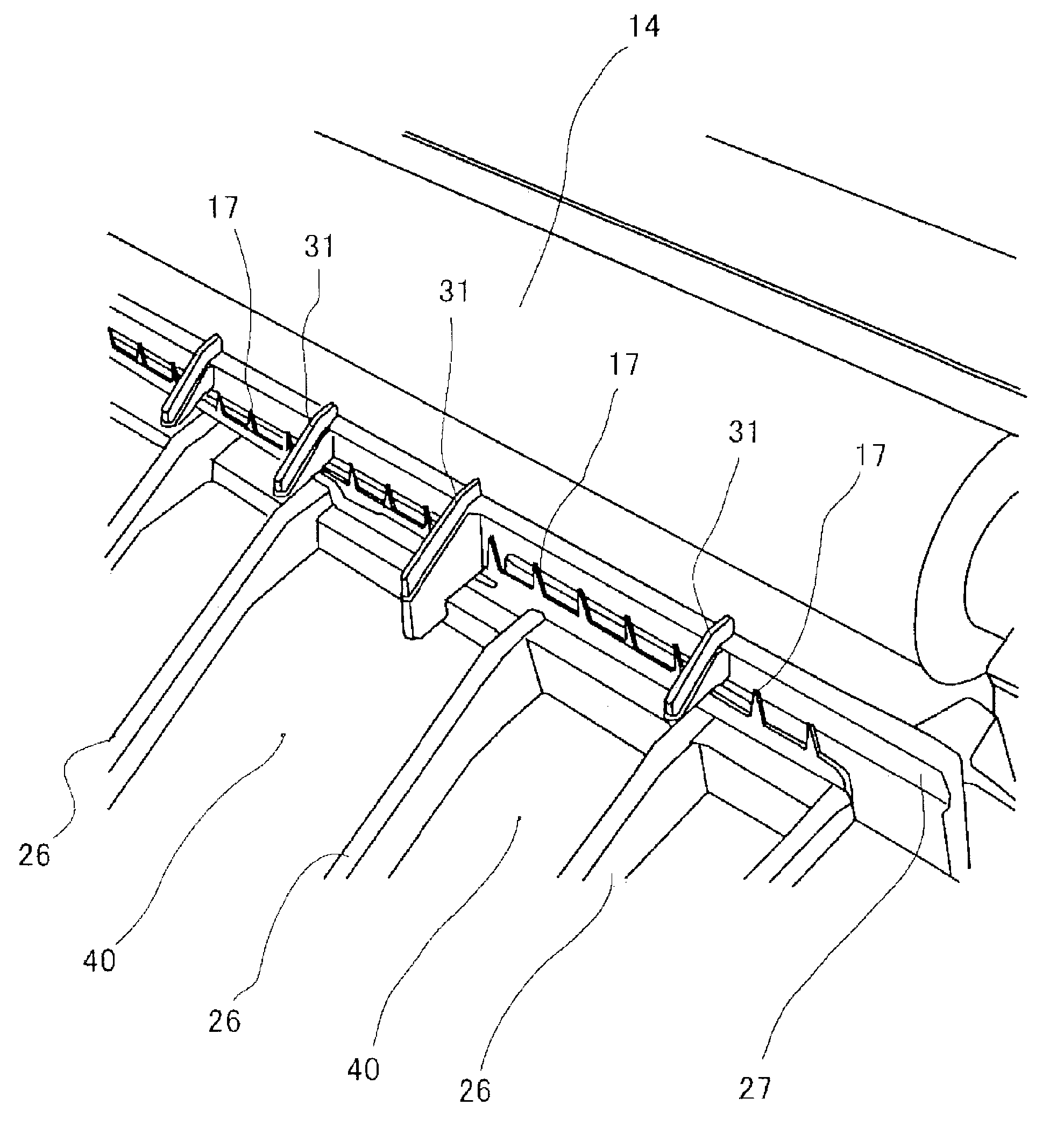
ActiveUS20060198668A1Eliminate static electricityEasy to seeElectrographic process apparatusImage formationEngineering
A plurality of separation needles are arranged downstream from a transfer roller in the sheet transport direction along a direction which is orthogonal to the sheet transport direction, and when a separation voltage is applied to the separation needles, an electrical discharge occurs between the photosensitive drum and the separation needles, and a sheet which has been charged by the transfer roller has static charge eliminated and is separated from the photosensitive drum. Furthermore, a transport unit established downstream from the separation needles in the sheet transport direction has a plurality of transport plates which guide the transport of the sheet, and a grounding plate which is located between these transport plates, and the grounding plate is connected to the grounding unit of the device body such that the grounding plate can be seen without interference from the tip end of the separation needles.
Owner:KYOCERA DOCUMENT SOLUTIONS INC
Alternating current driven type plasma display device
InactiveUS6713958B2Improve reliabilityIncrease contrastSustain/scan electrodesDischarge tube luminescnet screensKryptonAlternating current
An alternating current driven type plasma display device includes a plurality of sustain electrodes having a spacing less than 5x10<-5 >m and a discharge gas in a discharge space where discharge takes place. The discharge gas consists of xenon gas alone having a pressure greater than or equal to 1.0x10<4 >Pa and less than or equal to 3.0x10<4 >Pa or the discharge gas consists of krypton gas alone having a pressure less than or equal to 6.6x10<4 >Pa.
Owner:SONY CORP
Air electrode for lithium-air battery and preparation method for air electrode
ActiveCN103219527AIncrease specific energyImprove energy efficiencyCell electrodesEngineeringHierarchical porous
The invention relates to an air electrode for a lithium-air battery and a preparation method for the air electrode, which belong to the field of electrochemical energy materials, and aim to solve the technical problems of high overpotential, low charging and discharging utilization rate and few cycle times of a lithium-air battery in the prior art. The air electrode for the lithium-air battery is made of a nanocrystalline catalyst-modified hollow carbon sphere and carbon paper air electrode material with a hierarchical porous structure. When the air electrode is used for the lithium-air battery, the specific energy, energy utilization efficiency, rate capability and cycling stability of the lithium-air battery can be effectively improved, and particularly, the cycle life of the lithium-air battery is prolonged to 205 times from conventional maximum 100 times reported by documents. According to the preparation method for the air electrode, a hard template method and an electrophoretic technology are reasonably combined, a process is simple, the operation is convenient, the cost is low, an additive is avoided, a complex powder electrode preparation process is eliminated, and the stability of an air positive electrode is greatly improved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for improving activated carbon performances by self-assembling low-temperature plasma modification
InactiveCN106984269AImprove modification efficiencyShorten modification timeOther chemical processesActivated carbonSorbent
The invention discloses a method for improving activated carbon performances by self-assembling low-temperature plasma modification, and belongs to the technical field of activated carbon modification. A self-assembling low-temperature plasma modification reaction device used in the invention mainly comprises a box body, a plasma generator, a gas distribution and exhaust gas treatment system, an auxiliary facility and the like. The activated carbon modification is taken as an aim, and the activated carbon modification is realized via four processes of activated carbon screening treatment, reactor detection and setting, activated carbon modification, and exhaust gas treatment. The method for improving the activated carbon performances by the self-assembling low-temperature plasma modification can effectively reduce the loss of activated carbon, shorten the modification time and improve the modification efficiency of the activated carbon, takes air as an air source which is cheap in price and easily obtained and is simple to operate, free of ozone dissipation and waste liquid to be treated, and environmentally friendly. The method for improving the activated carbon performances by the self-assembling low-temperature plasma modification can be widely used in the activated carbon modification, and further can be popularized and applied to the modification of adsorbents of kaolin and montmorillonite.
Owner:CHONGQING TECH & BUSINESS UNIV
Discharge electrode structure of plasma air purification device
ActiveCN102548177BDifferent structureLimit processingDeodrantsPlasma techniqueEngineeringGlow plasma
The invention discloses a discharge electrode structure of a plasma air purification device. The electrode structure comprises a positive electrode group and a negative electrode group, wherein at least one of the positive electrode group and the negative electrode group is wrapped with insulating medium; and the two electrode groups contact directly, such that a contact point is formed. According to the invention, the discharge electrode structure is applied to the plasma air purification device, so a great amount of low temperature plasma is generated at an electrode intersection and a nearby area of the electrode intersection through the structure; the low temperature plasma has properties of glow-like plasma, wide sterilization range, high sterilization rate, short time consumption and low power consumption; in addition, the adopted net-like structure can not only ensure good air permeability but also enlarge the actual plasma function area, therefore, the sterilization rate is further improved.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Double-layer sleeve type corona plasma generating device
ActiveCN104128077AInto the uniformAvoid direct impactDispersed particle separationProduct gasProcess engineering
The invention relates to a double-layer sleeve type corona plasma generating device comprising a gas buffering chamber, an outer-layer processing chamber and an inner-layer processing chamber. A gas inlet is provided on the outer side of the gas buffering chamber. An insulation baffle is provided on the inner side of the buffering chamber. Airway through holes are provided on the baffle. Gas to be processed sequentially enters the outer-layer processing chamber and the inner-layer processing chamber through the airway through holes. When the gas is completely processed, the gas is discharged from a gas outlet connected to an end of the inner-layer processing chamber. According to the invention, with the buffering chamber, the gas to be processed can be uniformly and stably delivered in the processing chambers. The chambers adopt a coaxial multi-pin-plate structure, such that electric field unevenness coefficient is high, discharge voltage is low, and thus operation energy consumption is reduced. Also, voltage adjustable range is wide, and application scope is wide. With the inner-outer double layer structure, low temperature plasma dedusting and waste gas degradation are separated, such that the influence of dust in waste gas to waste gas molecule degradation is avoided, and energy utilization rate is improved. Also, reactor structure is compact. The device provided by the invention is suitable for the fields such as waste gas treatment, sterilization and disinfection, ozone synthesis, and the like.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
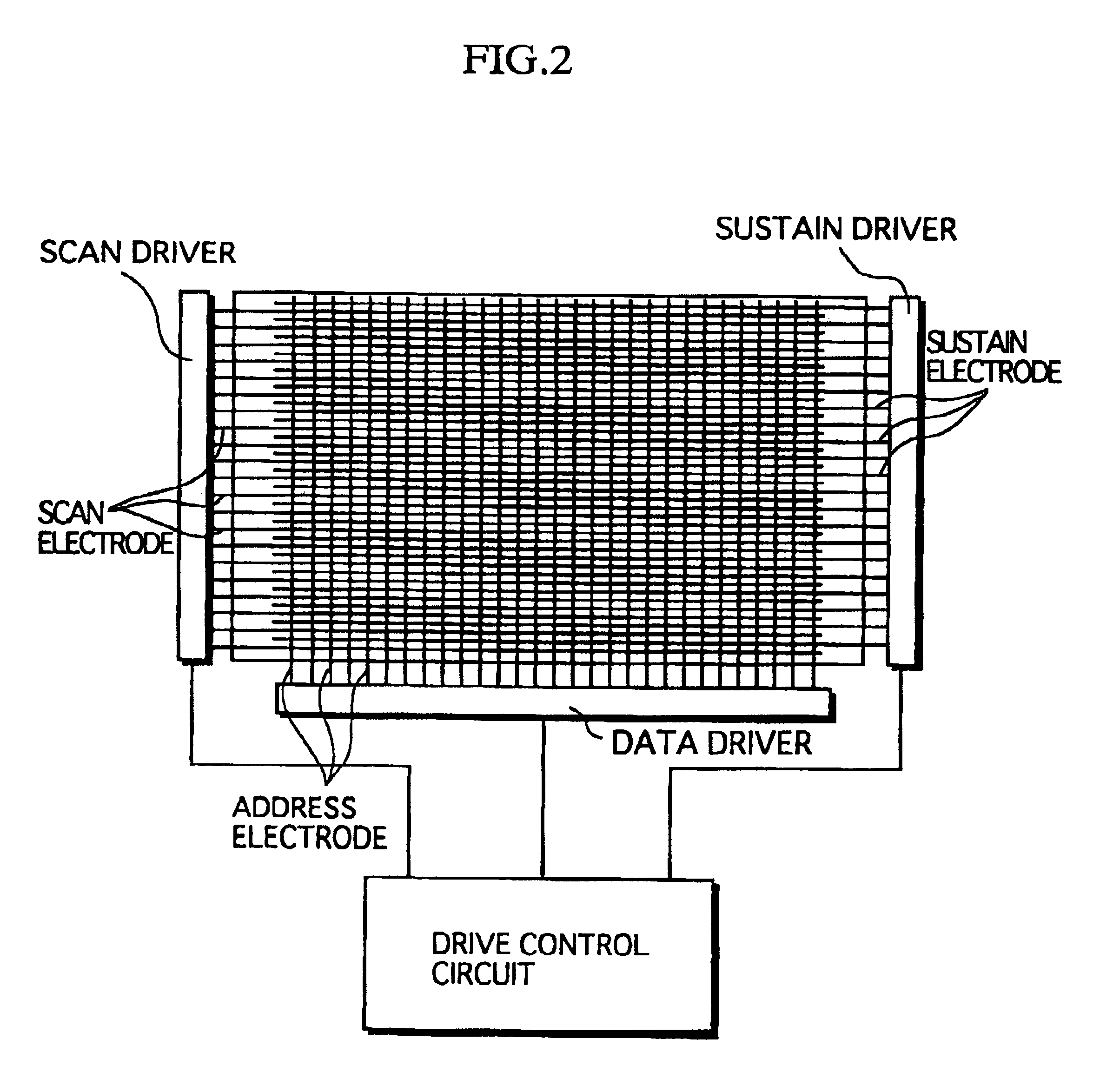
Plasma display panel having igniter electrodes
InactiveUS20050029946A1Reduce discharge voltageSmooth rideSustain/scan electrodesAuxillary electrodesEngineeringPlasma display
A plasma display panel, and particularly to a surface-discharge plasma display panel that may have an electrode structure in which a pair of discharge sustain electrodes may be arranged at respective discharge cells between two substrates to make the display discharge. The plasma display panel may include igniter electrodes formed over barrier ribs extending from discharge sustain electrodes along the barrier ribs, and protruding toward the inside of discharge cells at their ends.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Flat-type light source and liquid crystal display device having the same
InactiveUS20060043857A1Reduce discharge voltageImprove discharge efficiencyPlanar light sourcesPoint-like light sourceDischarge efficiencyLiquid-crystal display
In a flat-type light source and an LCD device incorporating the flat-type light source, the flat-type light source includes a lamp body, external electrodes and hollow electrodes. The lamp body has a plurality of discharge spaces. The external electrodes are disposed on an outer surface of the lamp body, and are partially overlapped with the discharge spaces. Each of the hollow electrodes is disposed on an inner surface of the lamp body, and is disposed in each of the discharge spaces. The hollow electrode may have a rectangular or other suitable tube shape. As a result of this construction, a discharge voltage to operate the flat-type light source may be decreased, and discharge efficiency may be increased.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Micropore-induced shock wave balloon catheter and system
ActiveCN113367767ALower the thresholdSmall discharge resistanceBalloon catheterSurgeryMedicineEngineering
The invention relates to a micropore-induced shock wave balloon catheter and system. The system is composed of electric field generating equipment and the shock wave balloon catheter; the electric field generating equipment comprises a man-machine interaction module, a control module, a power module and a high-voltage pulse output module; the electric field generating equipment is electrically connected with the shock wave balloon catheter; the shock wave balloon catheter comprises a long and thin component extending in the axial direction, a working balloon body arranged at the far end of the long and thin component, a wire and a liquid injection pipe which are arranged in a cavity of the long and thin component, an electric field generating mechanism arranged in the working balloon body, and a micropore-induced shock wave generating device wrapping the electric field generating mechanism; the electric field generating mechanism is electrically connected with the high-voltage pulse output module through a wire; a micropore mechanism penetrating through the wall of the micropore-induced shock wave generating device is arranged on the micropore-induced shock wave generating device; and the micropore mechanism can prevent liquid from entering through the surface tension of the micropore mechanism, so that the micropore-induced shock wave generating device can isolate the electric field generating mechanism from liquid flowing into the working balloon body.
Owner:南京欣科医疗器械有限公司
Flat lamp
InactiveUS20060061275A1Reduce discharge voltageImprove luminous efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsEngineeringAuxiliary electrode
Provided is a flat lamp which includes a lower substrate and an upper substrate that form discharge space therebetween disposed facing each other, a plurality of discharge electrodes formed at least on one of the lower substrate and the upper substrate, a plurality of spacers that form a plurality of discharge cells by defining the discharge space, and disposed parallel to the discharge electrodes between the lower substrate and the upper substrate, a plurality of auxiliary electrodes, to which a voltage is induced by applying a voltage to the discharge electrodes, formed on a surface of the spacers, and a fluorescent layer formed on an inner wall of the discharge cells.
Owner:SAMSUNG CORNING CO LTD
Low-temperature plasma generating device and method with stealth function
The invention discloses a low-temperature plasma generating device with a stealth function, comprising discharging patches, an electromagnetic transparent dielectric coating, a micropore, a carbon fiber discharge electrode and a metal conducting layer. A low-temperature plasma generating method with a stealth function, the discharging patches are uniformly installed on the outer surface of military equipment, and the discharging patches are connected with a high-voltage power supply; the high-voltage power supply is controlled to release pulse high voltage, the pulse voltage is connected witha carbon fiber discharge electrode, dielectric barrier discharge is carried out under the action of the electromagnetic transparent dielectric coating to release the plasma, and a plasma cloud clusteris formed. According to the device in the invention, the high-frequency high-voltage plasma generator is used for manufacturing the plasma, that is, under a high-frequency voltage condition, a dielectric barrier discharge mode is used to avalanche the air into plasma, and radar signals can be shielded.
Owner:苏州恩奇医疗器械有限公司
Composite material containing fluorine-containing titanium phosphate compound as well as preparation method and application of composite material
ActiveCN104577111AExcellent rate performanceImprove high current charge and discharge performanceNegative electrodesSecondary cellsLow voltageSodium-ion battery
The invention provides a composite material containing a fluorine-containing titanium phosphate compound as well as a preparation method for the composite material. The composite material comprises the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 60-99 percent of the fluorine-containing titanium phosphate compound and 1-40 percent of an electronic conductive material, wherein the chemical formula of the fluorine-containing titanium phosphate compound is Na3[Ti2P2O10F]. The invention further provides a lithium ion battery anode material containing the composite material, a sodium-ion battery anode material containing the composite material and corresponding batteries. Furthermore, the invention further relates to application of the composite material containing the fluorine-containing titanium phosphate compound in a lithium ion battery and a sodium-ion battery, and particularly application in a room-temperature lithium ion battery and a room-temperature sodium-ion battery. The composite material disclosed by the invention has the advantages of low cost, low voltage, high capacity, environment friendliness and the like.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Image forming device having a conductive member with separation needles
ActiveUS7457573B2Eliminate static electricityEasy to seeElectrographic process apparatusImage formationEngineering
A plurality of separation needles are arranged downstream from a transfer roller in the sheet transport direction along a direction which is orthogonal to the sheet transport direction, and when a separation voltage is applied to the separation needles, an electrical discharge occurs between the photosensitive drum and the separation needles, and a sheet which has been charged by the transfer roller has static charge eliminated and is separated from the photosensitive drum. Furthermore, a transport unit established downstream from the separation needles in the sheet transport direction has a plurality of transport plates which guide the transport of the sheet, and a grounding plate which is located between these transport plates, and the grounding plate is connected to the grounding unit of the device body such that the grounding plate can be seen without interference from the tip end of the separation needles.
Owner:KYOCERA DOCUMENT SOLUTIONS INC
Light emitting device using plasma discharge
InactiveUS20060170344A1Reduce discharge voltageImprove luminous efficiencyAuxillary electrodesAlternating current plasma display panelsLight emitting deviceElectron
A plasma-discharge light emitting device is provided. The plasma-discharge light emitting device may include: rear and front panels separated from each other in a predetermined interval, wherein at least one discharge cell may be provided between the rear and front panels, and wherein plasma discharge may be generated in the discharge cells; a pair of discharge electrodes provided on at least one of the rear and front panels for each of the discharge cells; a trench provided as a portion of each of the discharge cells between the pair of the discharge electrodes; and electron-emitting material layers provided on both sidewalls of the trench.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com