Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30results about How to "Lot of radiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
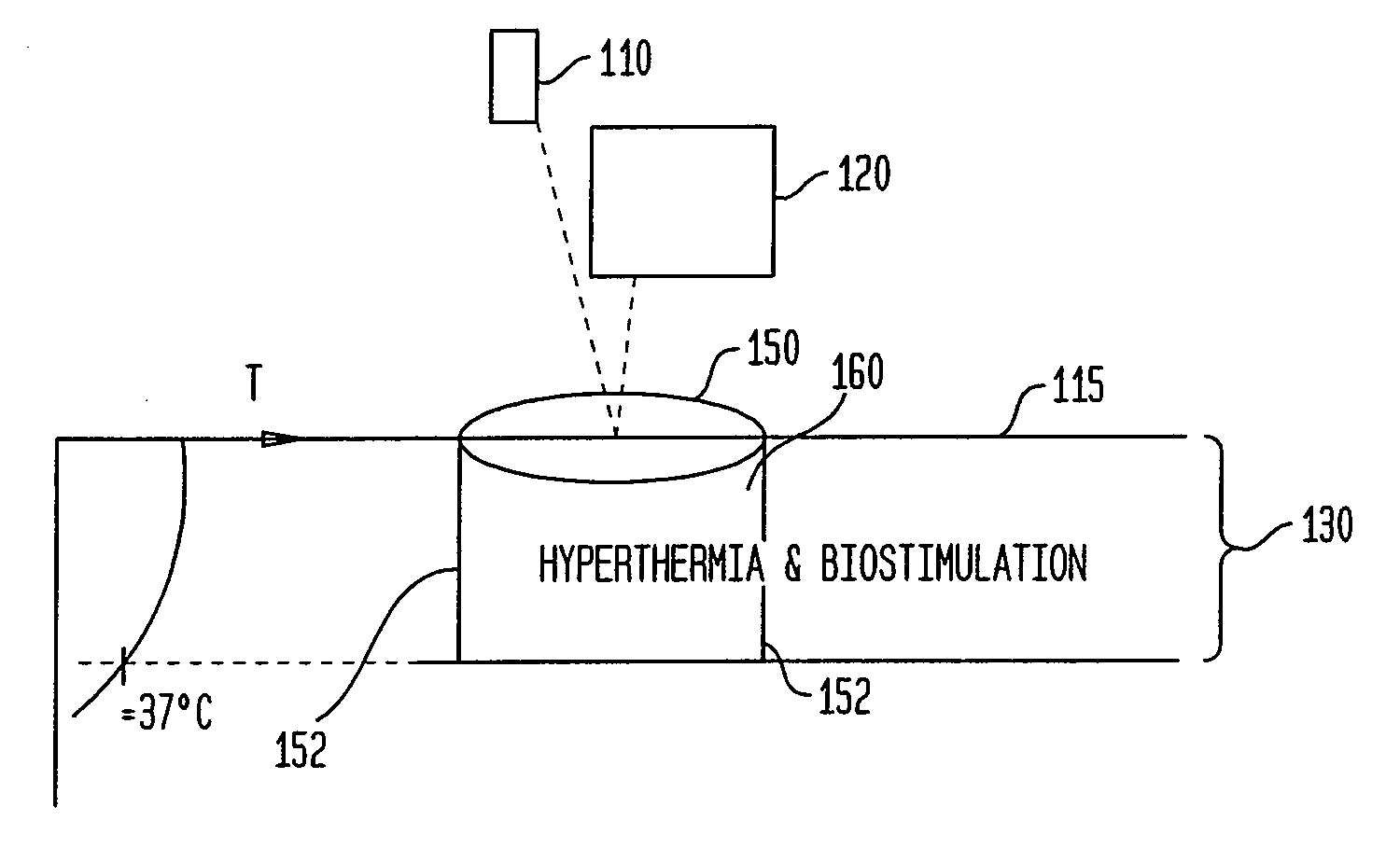
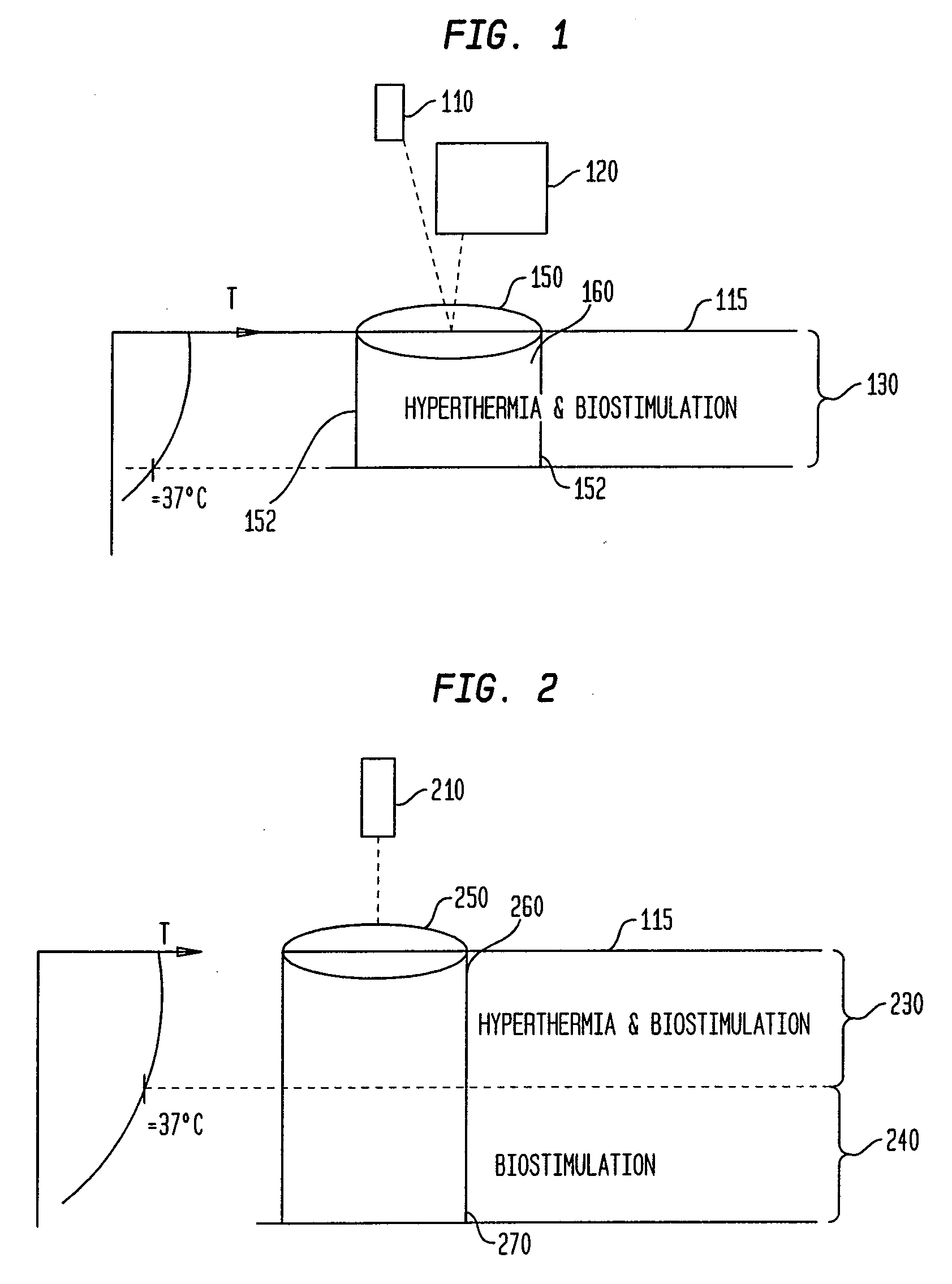
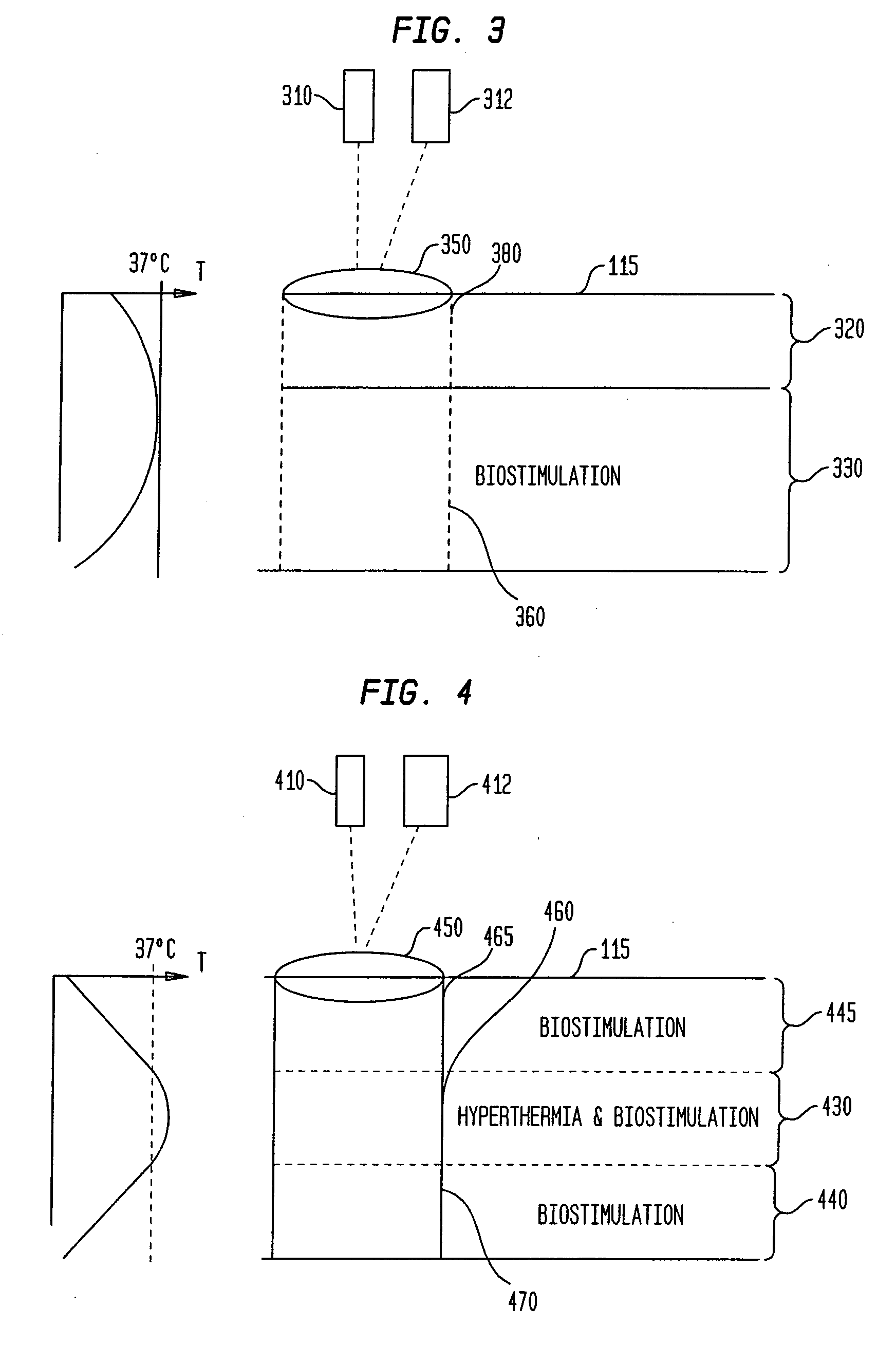
Methods and apparatus for performing photobiostimulation
InactiveUS20080033516A1Modulate efficacyLot of radiationSurgical instrument detailsLight therapyDiseaseMedicine
The present invention provides methods and devices for modulating the efficacy and / or increasing the efficiency of treatment of disease and / or cosmetic conditions through photobiostimulation combined with heating and / or cooling of the treatment region. In one aspect, methods and devices of the present invention are directed to modulating the efficacy of photobiostimulation in a target region by controlling the temperature in the region and / or its surrounding volume. According to some aspects of the present invention, tissue is heated such that biostimulation is applied to tissue that is hyperthermic. Alternatively, portions of the target region can be cooled to selectively target biostimulation to a specific region at a desired depth below the skin surface. A feedback mechanism is also provided so that the temperature of the target region can be selectively and accurately controlled.
Owner:PALOMAR MEDICAL TECH
CT detector-module having radiation shielding for the processing circuitry
InactiveUS6982423B2Lot of radiationHigh X-ray absorption coefficientMaterial analysis by optical meansComputerised tomographsX-rayComputer module
A CT detector-module-for detecting X-rays comprising: a matrix of photosensors, each of which generates signals responsive to photons incident thereon; a scintillator mounted over the matrix that converts X-rays incident on the scintillator to photons to which the photosensors are sensitive; an anti-scatter collimator mounted over the scintillator; and electronic circuitry located in close proximity to the photosensors to which each of the photosensors is connected for processing the signals generated by the photosensors; wherein parts of the module are formed from an absorbing material having a high X-ray absorption coefficient and shield the circuitry from radiation.
Owner:PHILIPS MEDICAL SYST TECH
Corrections for pulse reverberations and phasefront aberrations in ultrasound imaging
InactiveUS6905465B2Good estimateReduce impactUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound imagingSonification
A method of correcting for pulse reverberations in ultrasound imaging using two-dimensional transducer arrays, and uses such reduction in element signals and beam signal before estimation of corrections for phase front aberrations of the ultrasound wave. The pulse reverberation is estimated by two transmit events, where the second event is determined by measurement and processing on measurement on echoes of the first event. In a second embodiment of the invention, the reverberation is estimated by a single transmit event, using two receive beams and processing on these. In a third embodiment of the invention the reverberation from very strong scatterers is reduced by adjustment of the active transmit aperture.
Owner:ANGELSEN BJ O SLASHED RN A J +1
Display device
InactiveUS20090231297A1Long-life and highly brightLot of radiationOptical light guidesIlluminated signsLight sourceSurface plate
The display device has an LCD panel, a light source, and a digitizer disposed on the back surface of the LCD panel. The display device further contains a U-shaped first heat-dissipation plate made of a non-magnetic material. The first heat-dissipation plate is disposed on at least one end of the periphery of the LCD panel in a way that the opening of the U-shape faces toward the LCD panel. The light source is mounted on the first heat-dissipation plate, and an end section of the digitizer is covered with the opening of the plate.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
Gas burner
InactiveUS20010036610A1Simple and inexpensive in constructionPrevents any burn backBurner material specificationsGaseous fuel burnerEngineeringPerforated metal
A radiative heat gas burner is described of the type which may be used to fire a domestic grill. The burner head has an inlet port and comprises a pressing which together with a perforated metal sheet defines a chamber in which a combustion gas flows prior to flowing through the perforations in the sheet and combusting thereon. The sheet of metal sealingly connected to the pressing forms a combustion surface on which the combustion of gas flowing through the perforations occurs, but the invention lies in the discovery that it is not necessary to provide large apertures in the sheet which reveal portions of gauze sheets disposed parallely behind the combustion surface and which glow and thus radiate heat during operation of the burner. It is merely necessary to provide a pattern of small perforations over the entire surface of the combustion sheet, the number of said perforations being sufficient to allow for sufficient gas flow therethrough to support stable combustion, and their pattern being ideally in rows which intersect with other rows in a substantially perpendicular manner.
Owner:BRAY BURNERS
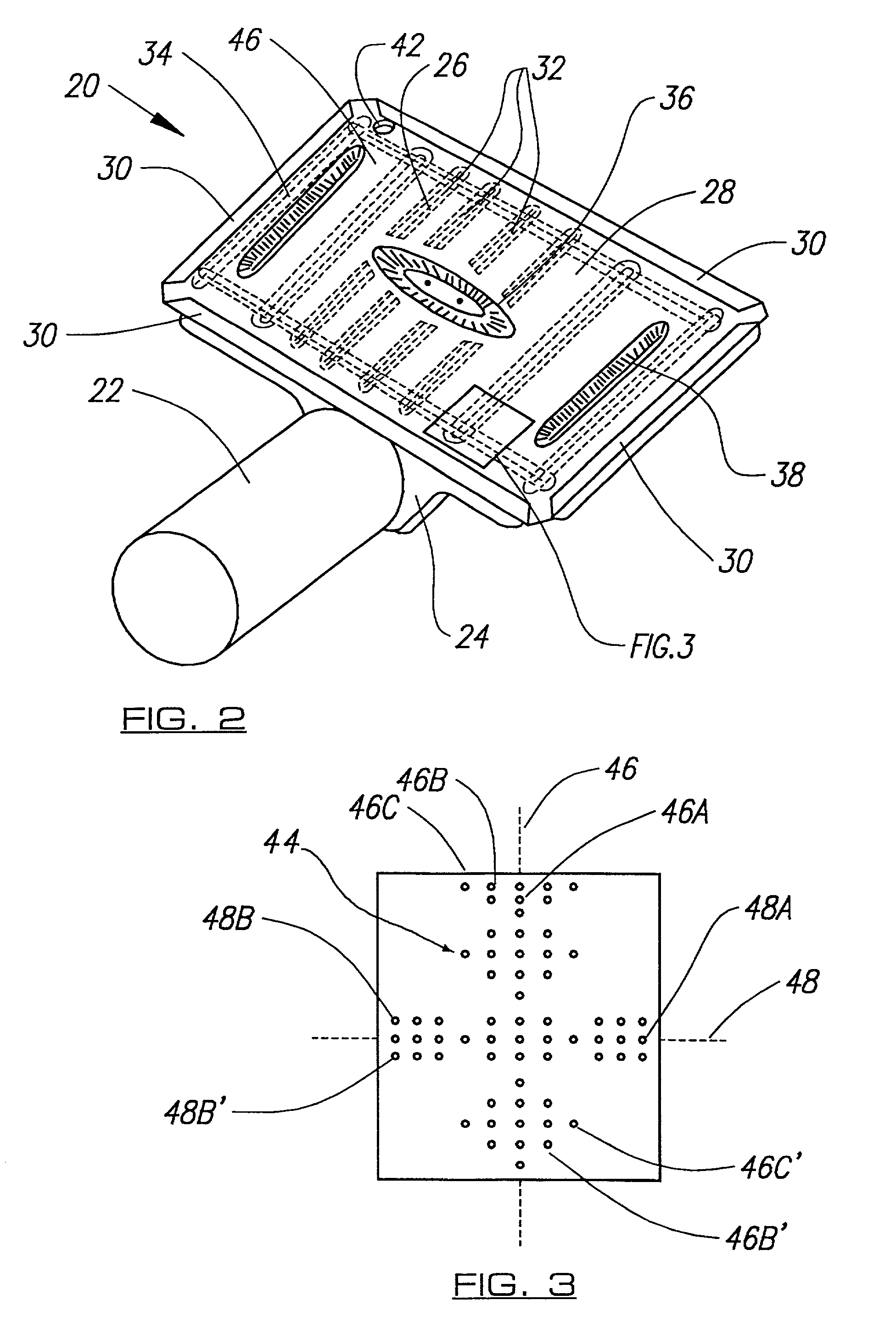
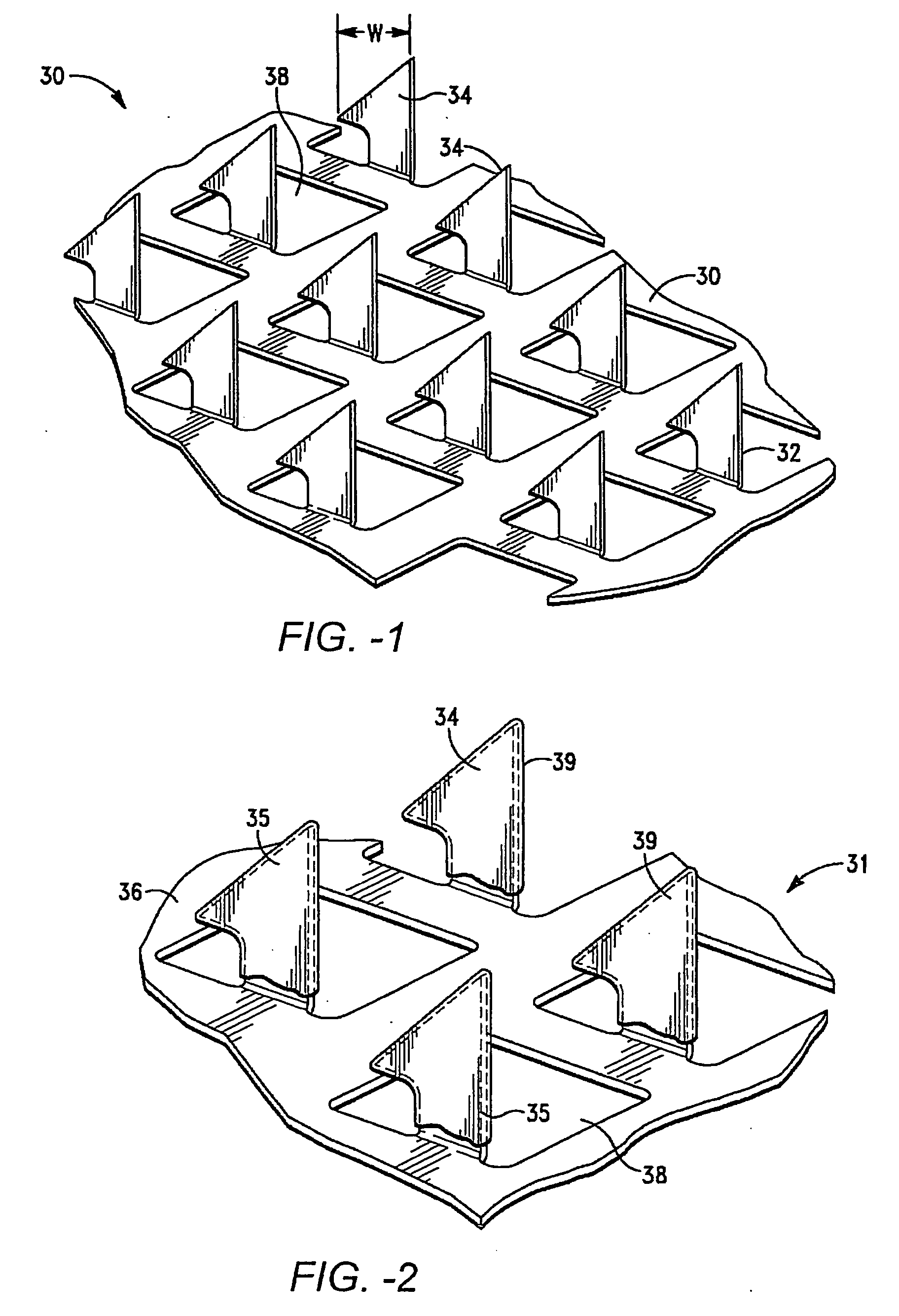
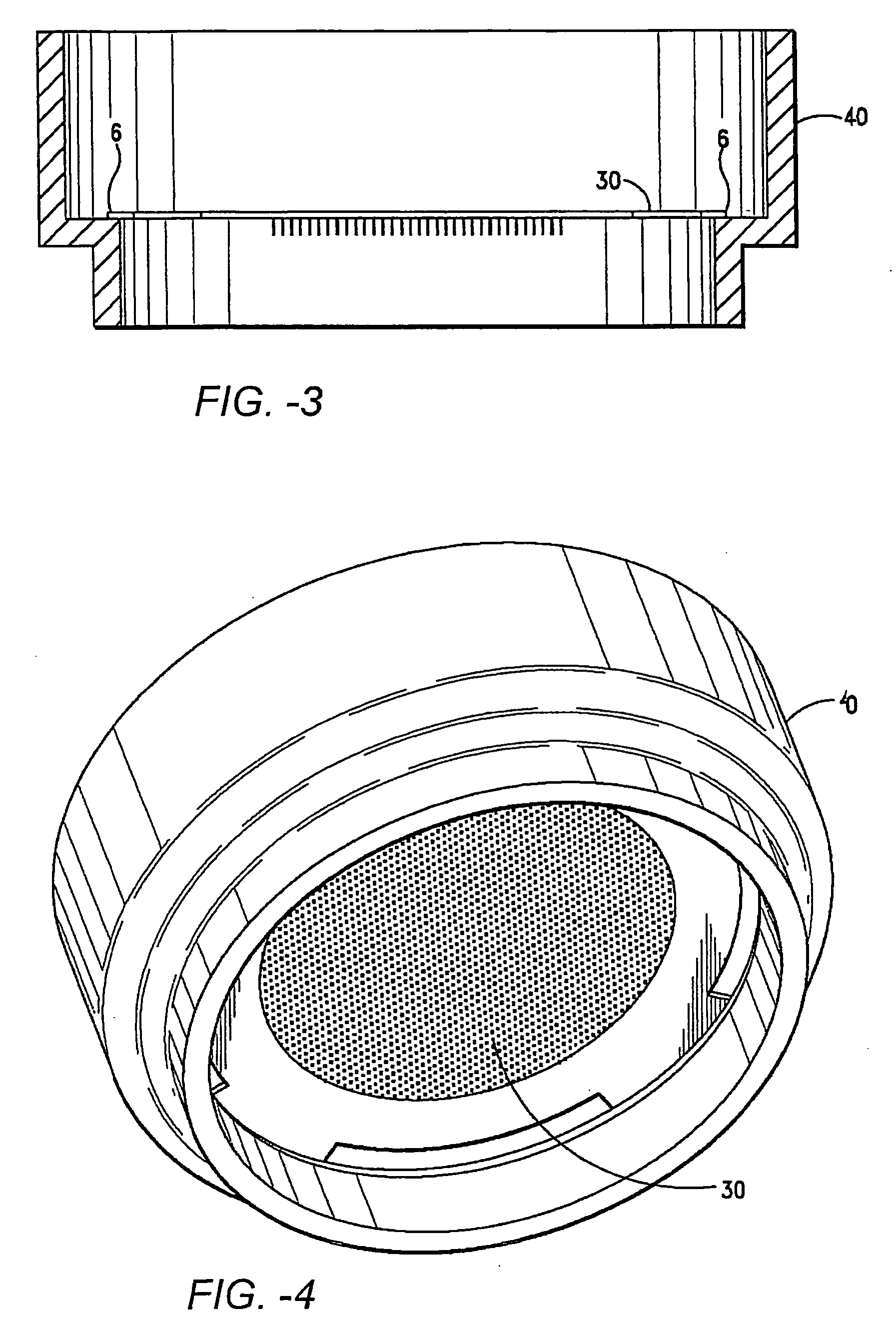
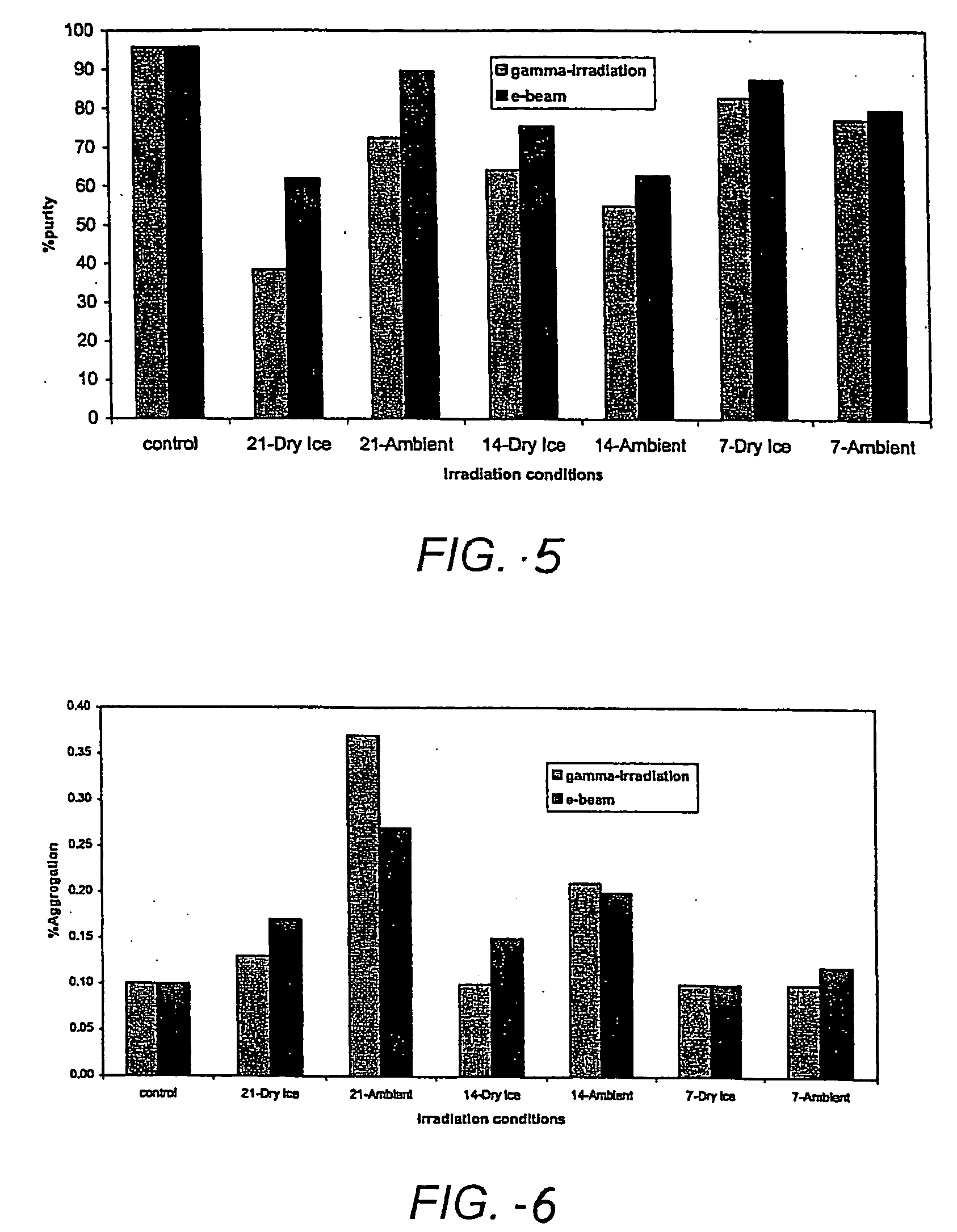
Method for terminal sterilization of transdermal delivery devices
InactiveUS20060275170A1Reduce moisture contentLot of radiationEnergy modified materialsMicroneedlesMedicineStratum corneum
An method and system for providing a terminally sterilized transdermal device adapted to delivery a PTH-based agent. A microprojection member that includes a plurality of stratum comeum-piercing microprojections is coated with PTH-based agent formulation an exposed to sufficient radiation to sterilize the microprojection member while retaining sufficient activity of the PTH-based agent. Preferably, the microprojection member is sealed in packing with an inert atmosphere and reduced moisture. The sterilizing radiation can be gamma radiation or e-beam, preferably delivered in a dose in the range of approximately 5-50 kGy. Also preferably, the irradiation is performed at −78.5-25° C. In preferred embodiments, the radiation is delivered at a rate greater than 3.0 kGy / hr.
Owner:ALZA CORP
Method and apparatus for manufacturing resin stamper, imprint method, magnetic recording medium, and magnetic recording/reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS20100239889A1Low costEasy to replaceRecord carriersConfectioneryCompression moldingResin composite
The present invention provides a technique capable of manufacturing a resin stamper at a low cost. A method of manufacturing a plate-shaped resin stamper includes: pressing a resin composite base material against a mother stamper having a pattern formed on the surface thereof by compression molding to transfer the pattern of the mother stamper to the composite base material; and punching the composite base material. In the manufacturing method, the resin composite base material includes at least one curing resin. In addition, during the compression molding, a portion of the composite base material is cured by active energy beams or heat, the pattern is transferred to the composite base material, and the composite base material is punched, thereby manufacturing the resin stamper.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Organic light emitting display
ActiveUS20070045616A1Heat conduction distanceImprove radiation efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight emissionRadiation
An organic light emitting display provided according to the invention maintains light emission efficiency and elongates its lifetime by radiating heat generated from organic light emitting elements to the outside of an encapsulated area. In the organic light emitting display, a part of a cathode is extended to the outside of the encapsulated area of a main substrate to form a radiation section integrally with the cathode. Heat generated from organic light emitting elements is diffused and radiated from the radiation section so that the heat can be discharged therefrom.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Printed circuit (PC) board module with improved heat radiation efficiency
InactiveUS20080218979A1Lot of radiationMagnetic/electric field screeningPrinted circuit aspectsIntegrated circuitRadiation
A Printed Circuit (PC) board module is structured such that heat generated by an Integrated Circuit (IC) device can be sufficiently radiated to the outside. The PC board module includes: a first PC board having a first conductive ground pad arranged therein; a plurality of via holes contained within the first PC board and positioned below the first ground pad; a plurality of conductive via lines contained within the plurality of via holes; a second PC board arranged below the first PC board; and a second conductive ground pad arranged on the second PC board and contacting the plurality of via lines.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Weather-resistant article, weather-resistant film and optical member
InactiveUS20110165394A1Sufficient weather resistanceLot of radiationLayered productsChemical vapor deposition coatingWeather resistanceUltraviolet
Provided is a support exhibiting excellent weather resistance, which is usable in an outdoor location for a long duration and is a support capable of sufficiently shielding UV radiation; and further provided are a weather-resistant article, a weather-resistant film, and an optical member which exhibit sufficient weather resistance even though receiving influences by heat, light or moisture. Disclosed is a weather-resistant article of the present invention possessing a support and provided thereon, a polymer layer containing a light stabilizer and a UV radiation reflective layer containing plural materials each having a different refractive index, the UV radiation reflective layer provided on the polymer layer.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
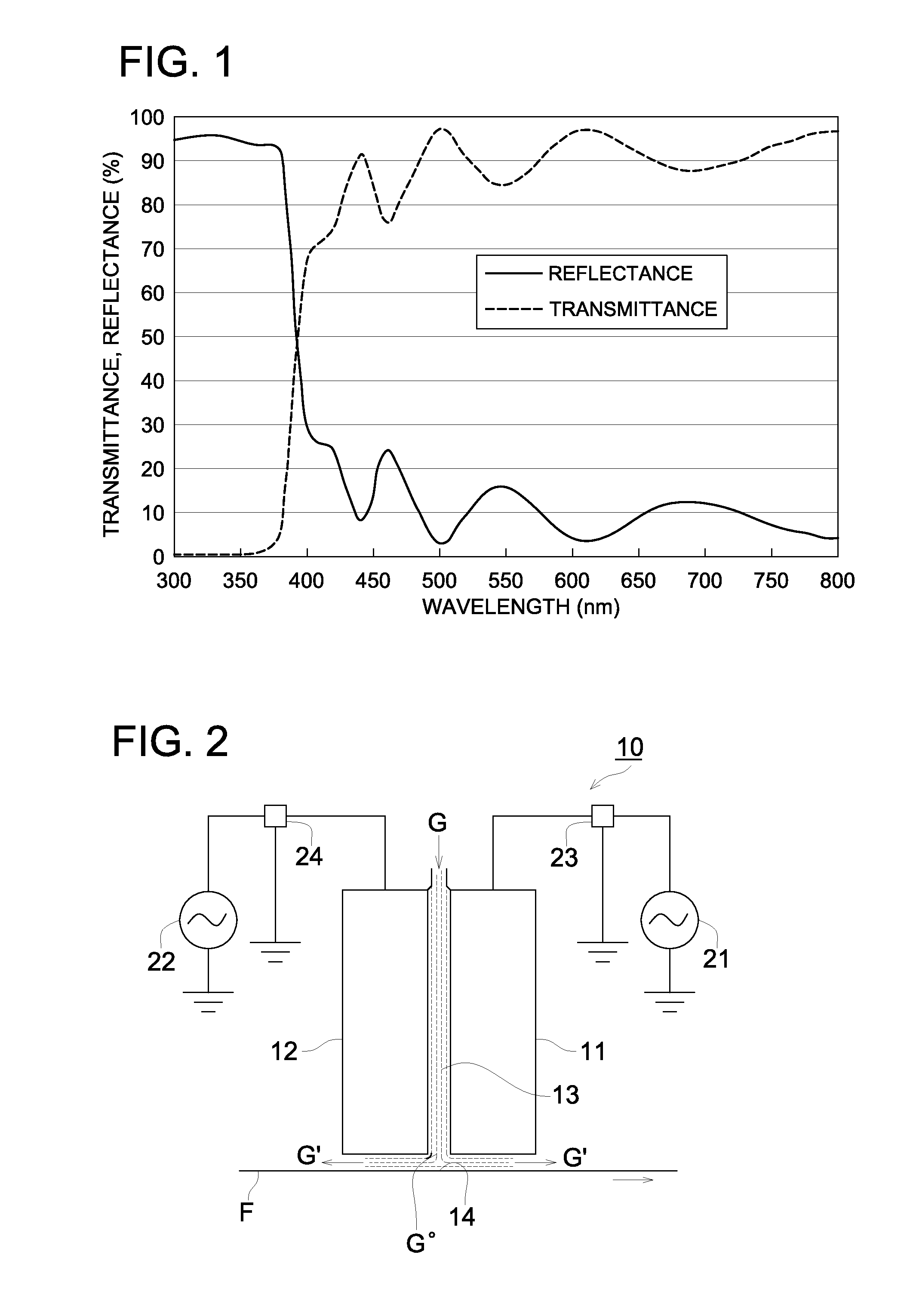
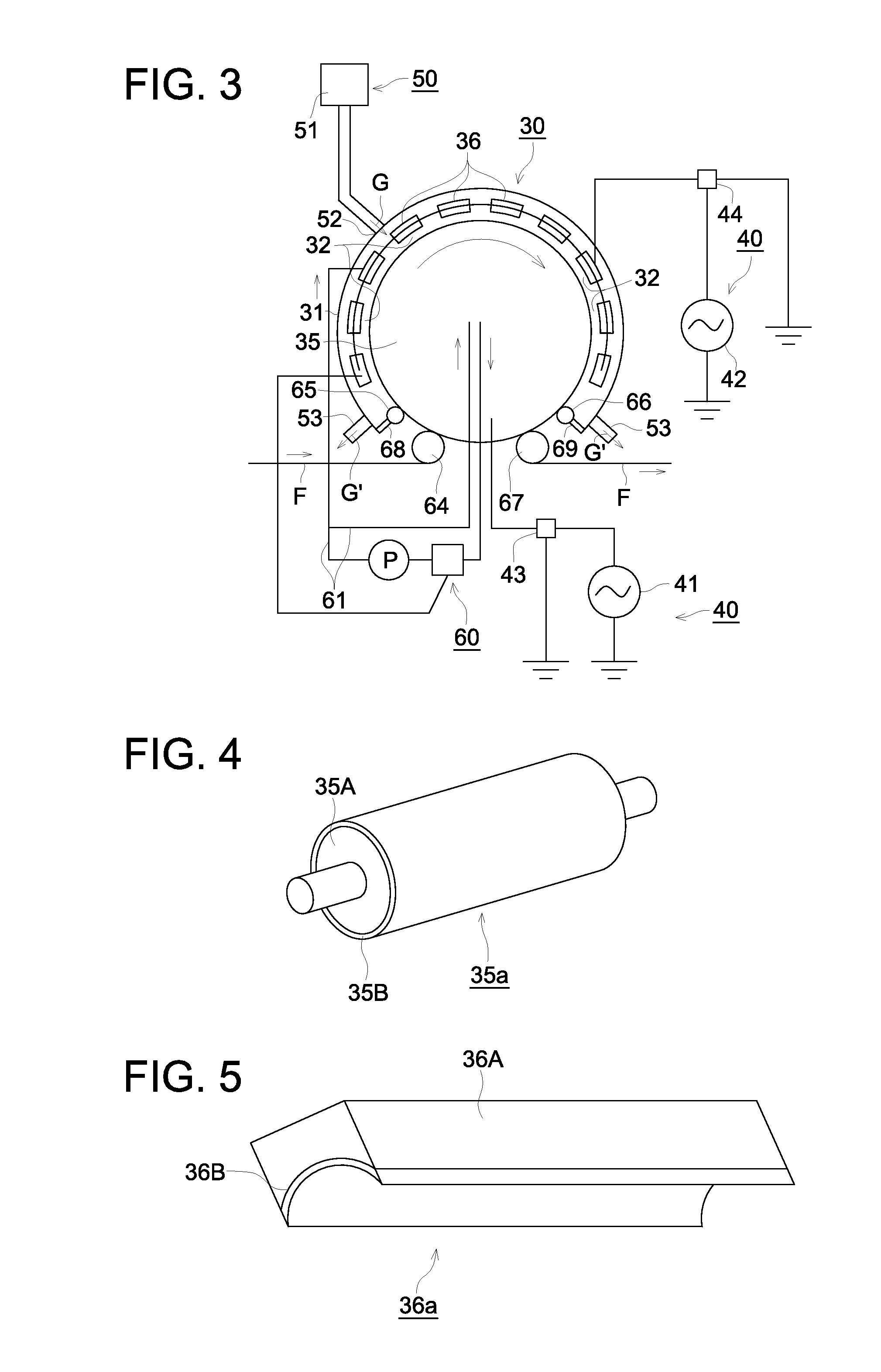
Reactor and method of producing the reactor
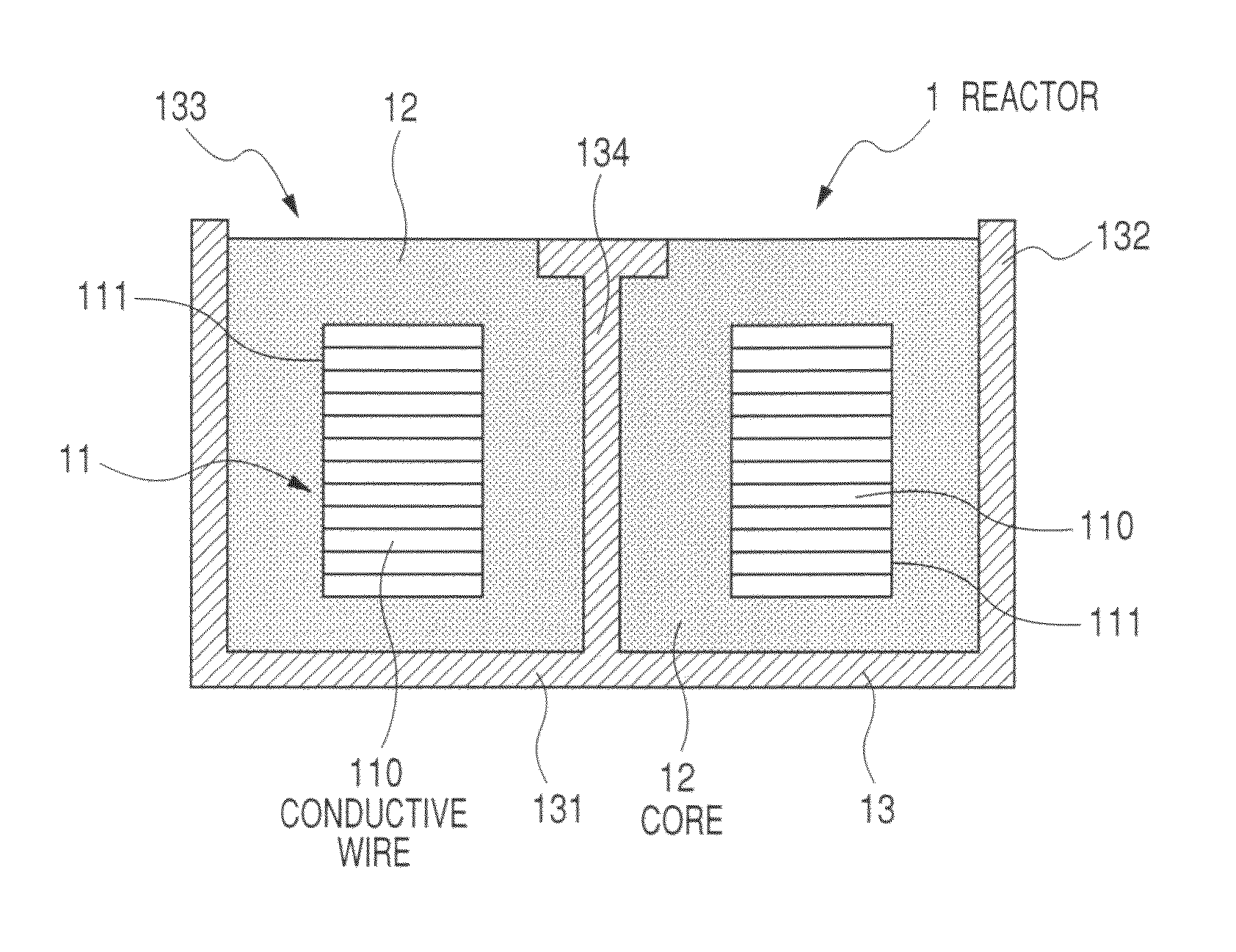
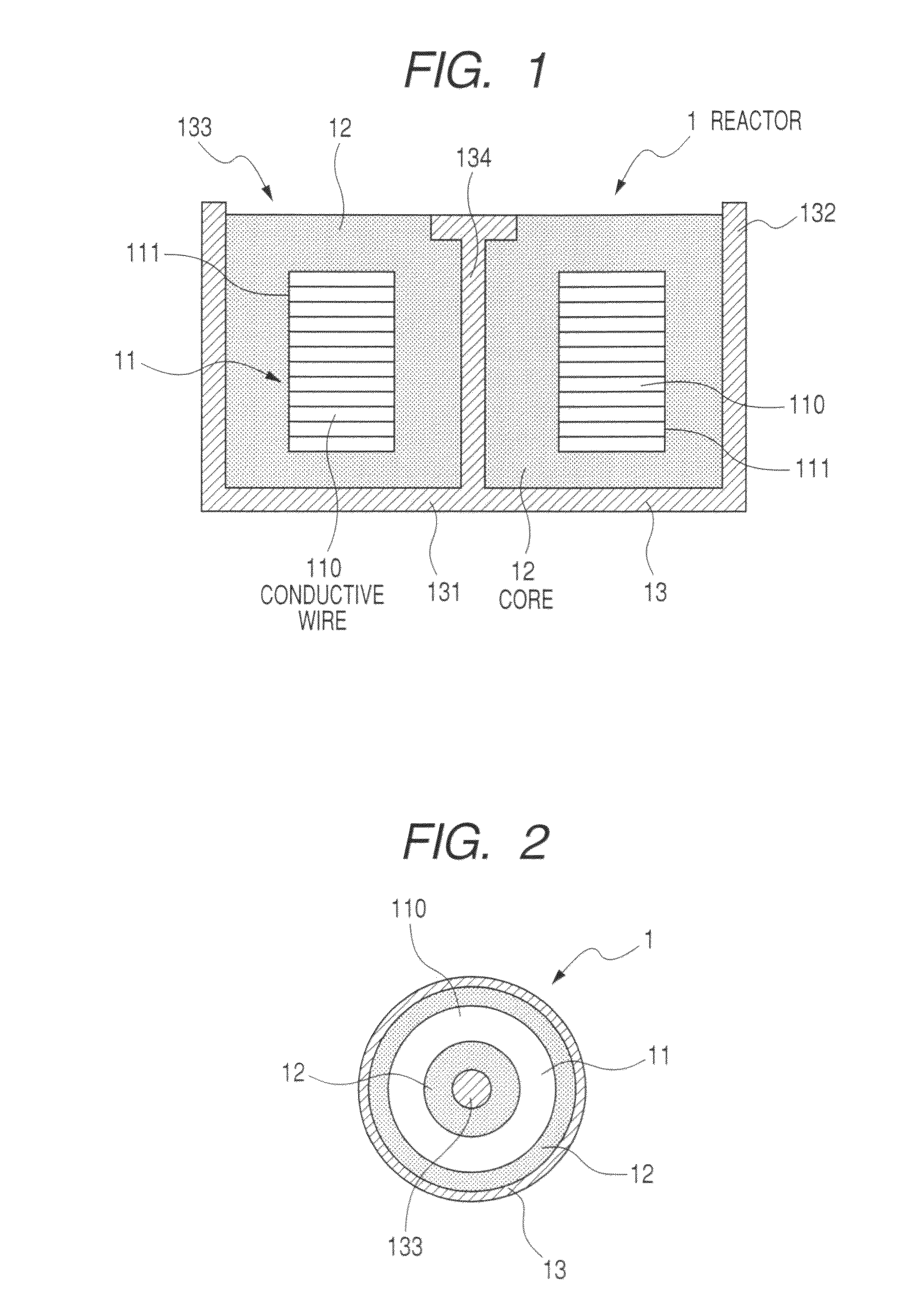
ActiveUS20100123541A1Lower elastic modulusAvoid damageTransformers/inductances coolingTransformers/inductances casingsMetallurgyNon magnetic
A reactor is composed of a coil and a core placed in the inside area and outer peripheral area of the coil in a container. The core is composed of magnetic powder, non-magnetic powder, and resin. The nom-magnetic powder is composed of main component powder and low elastic modulus powder. The main component powder as a main component of the non-magnetic powder is made of one or more kinds of powder of a heat conductivity which is larger than that of the resin. The low elastic modulus powder is made of one or more kinds of powder of an elastic modulus which is smaller than that of the powder forming the main component powder.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
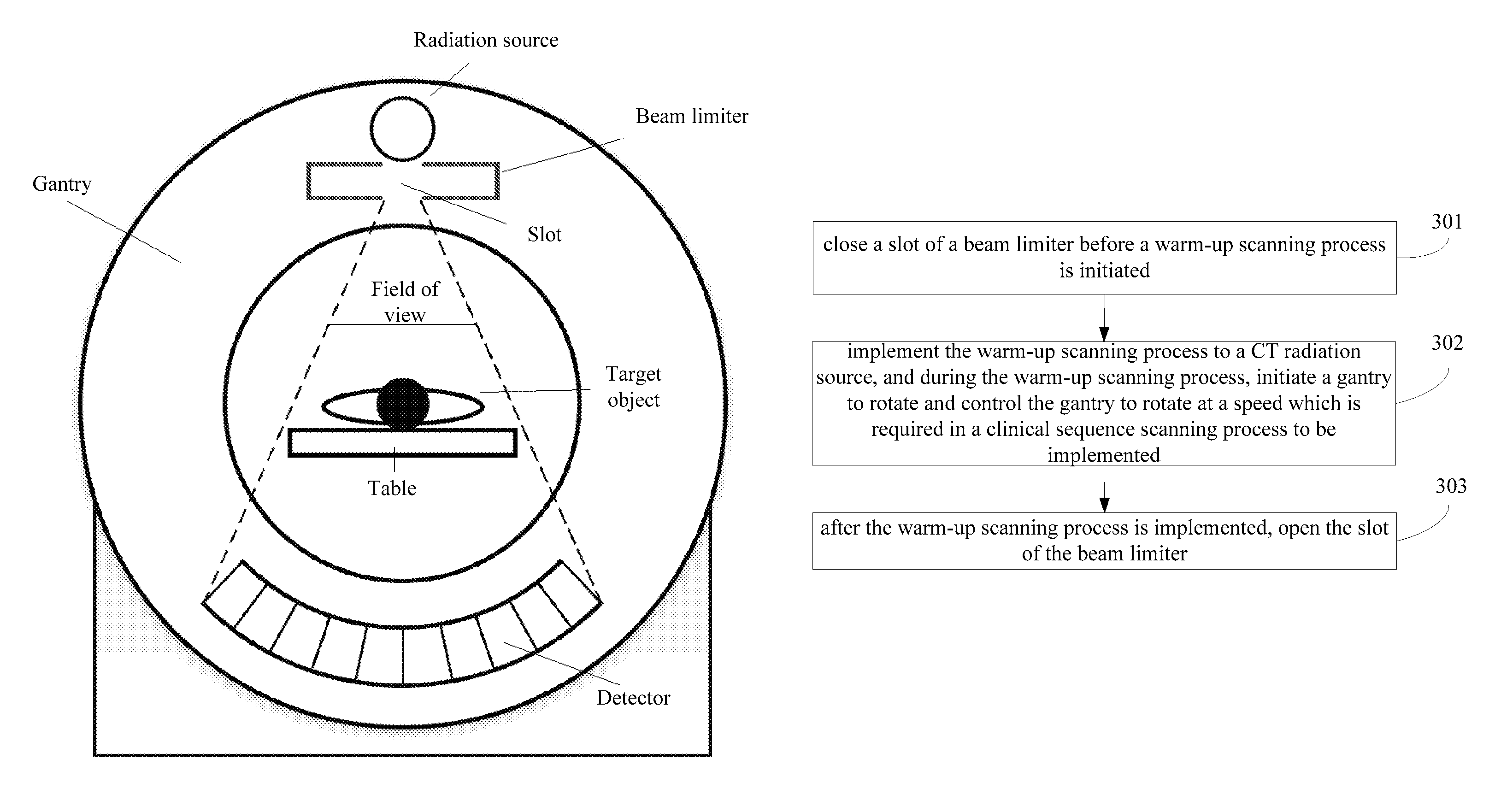
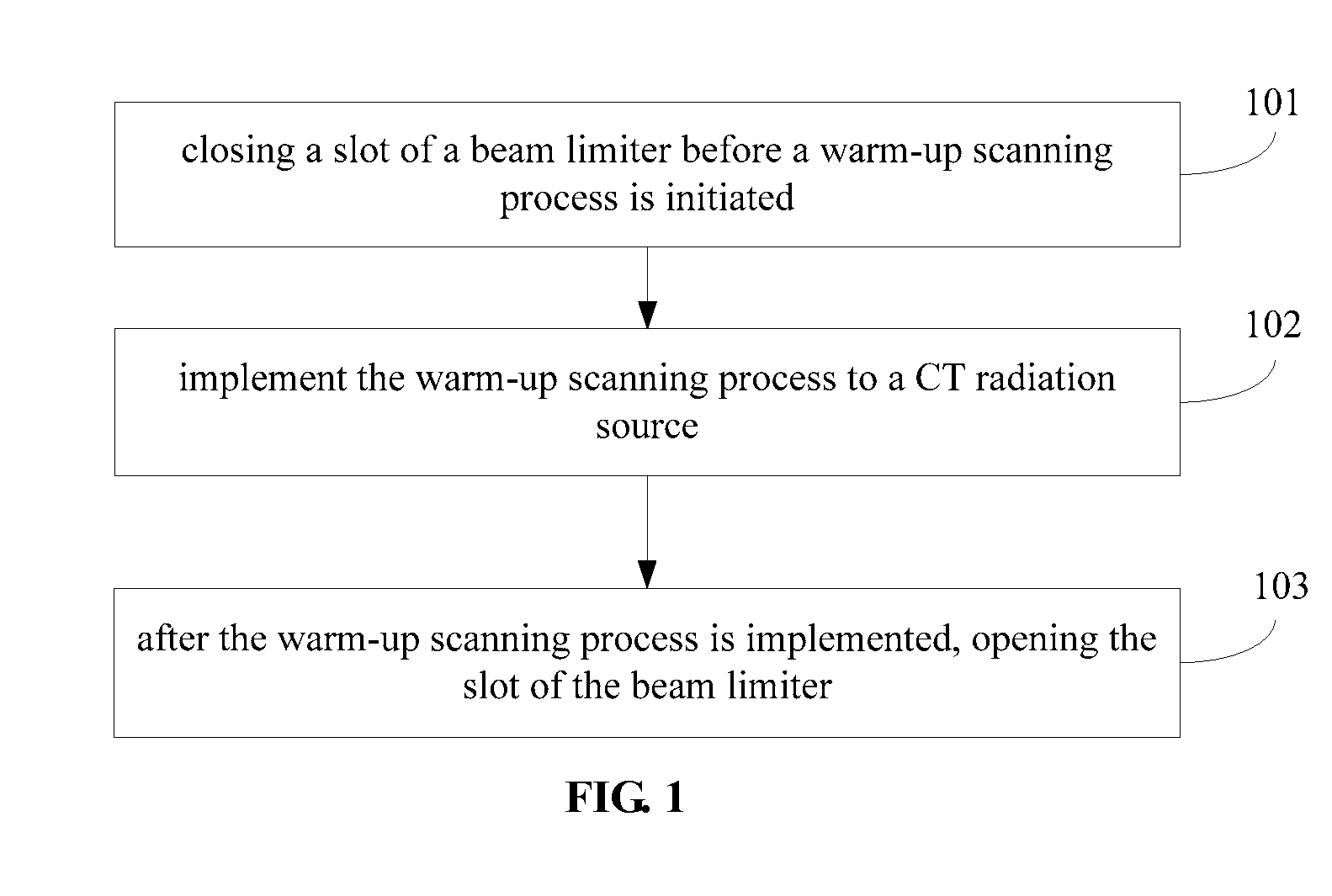
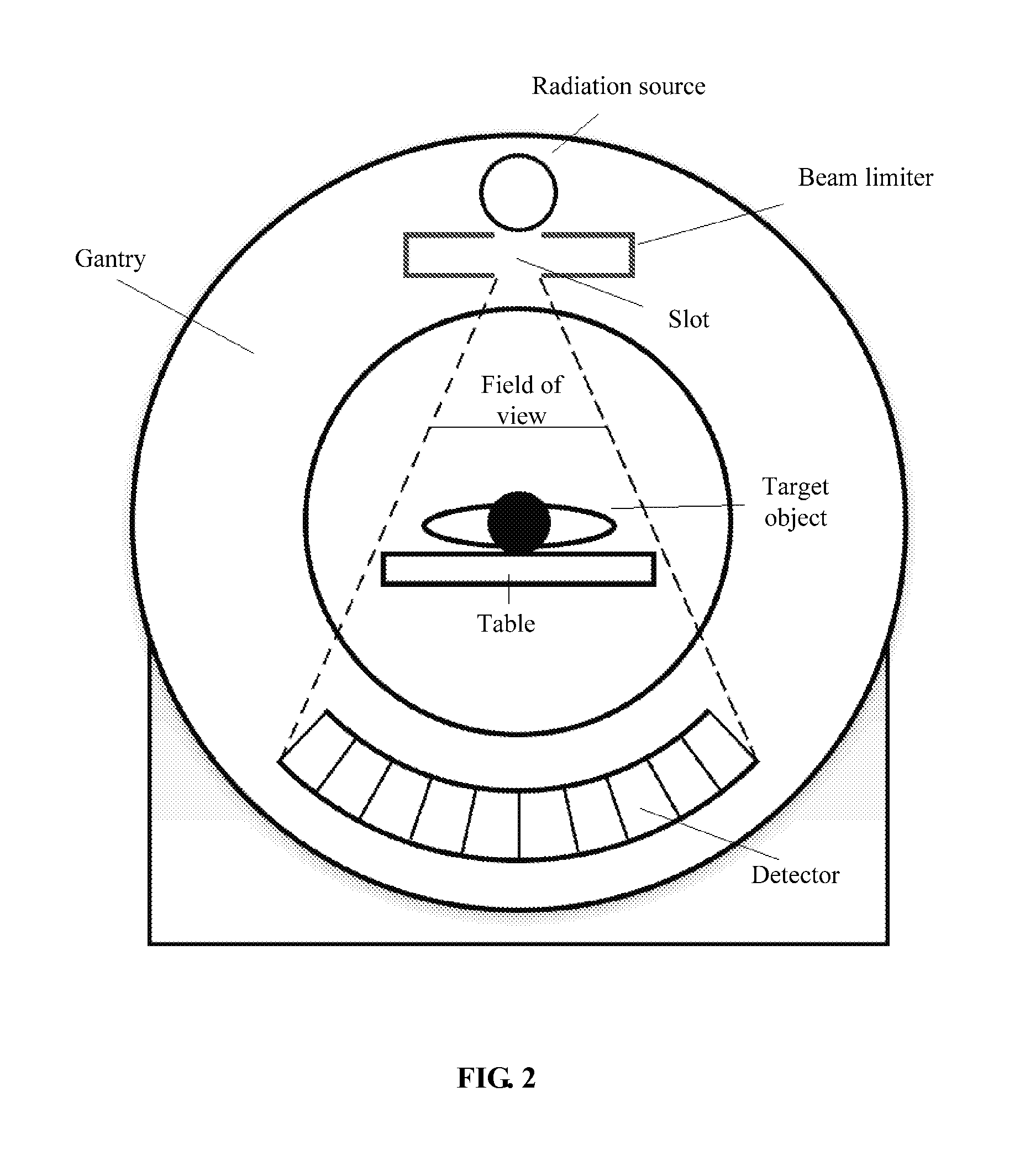
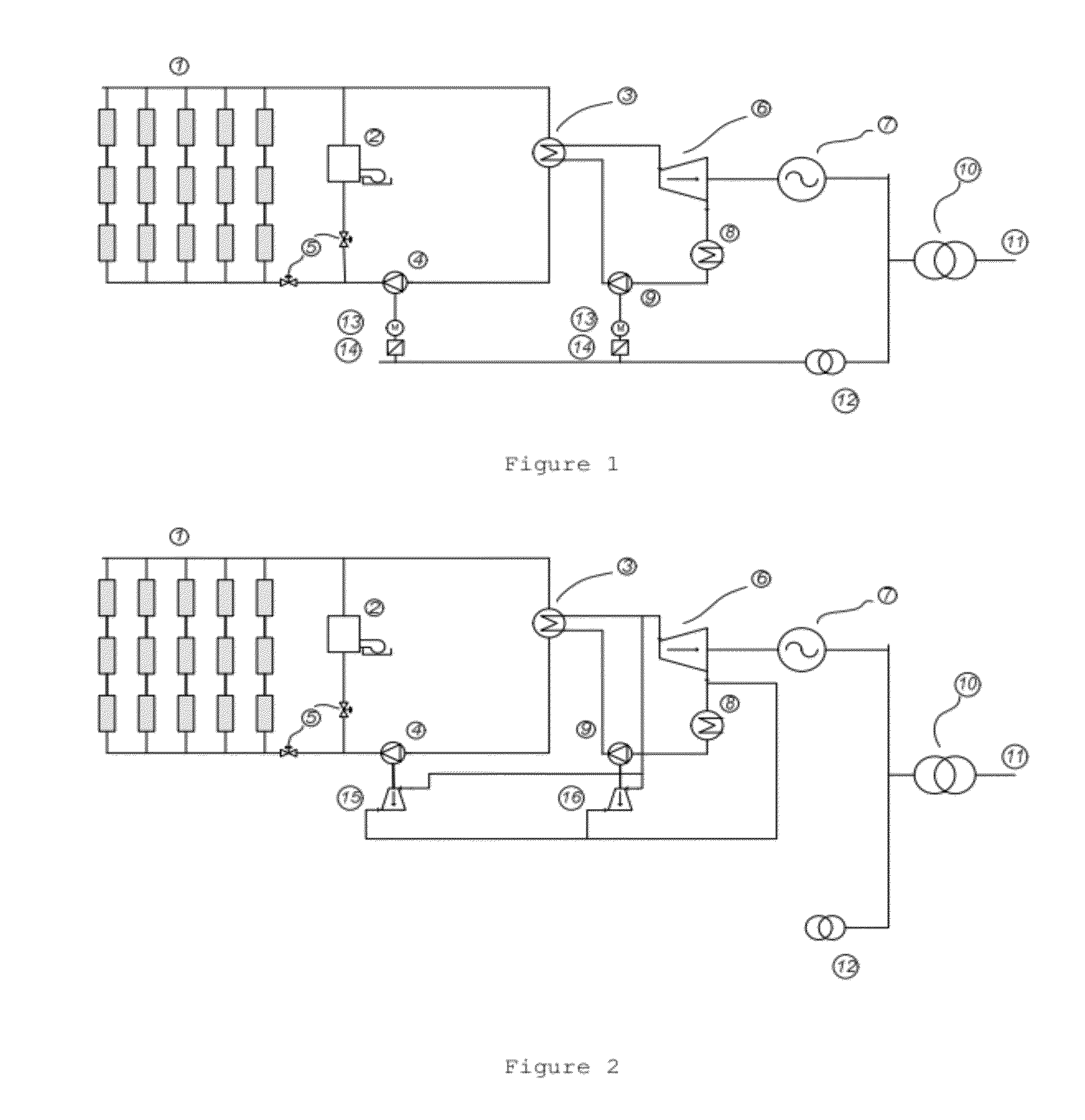
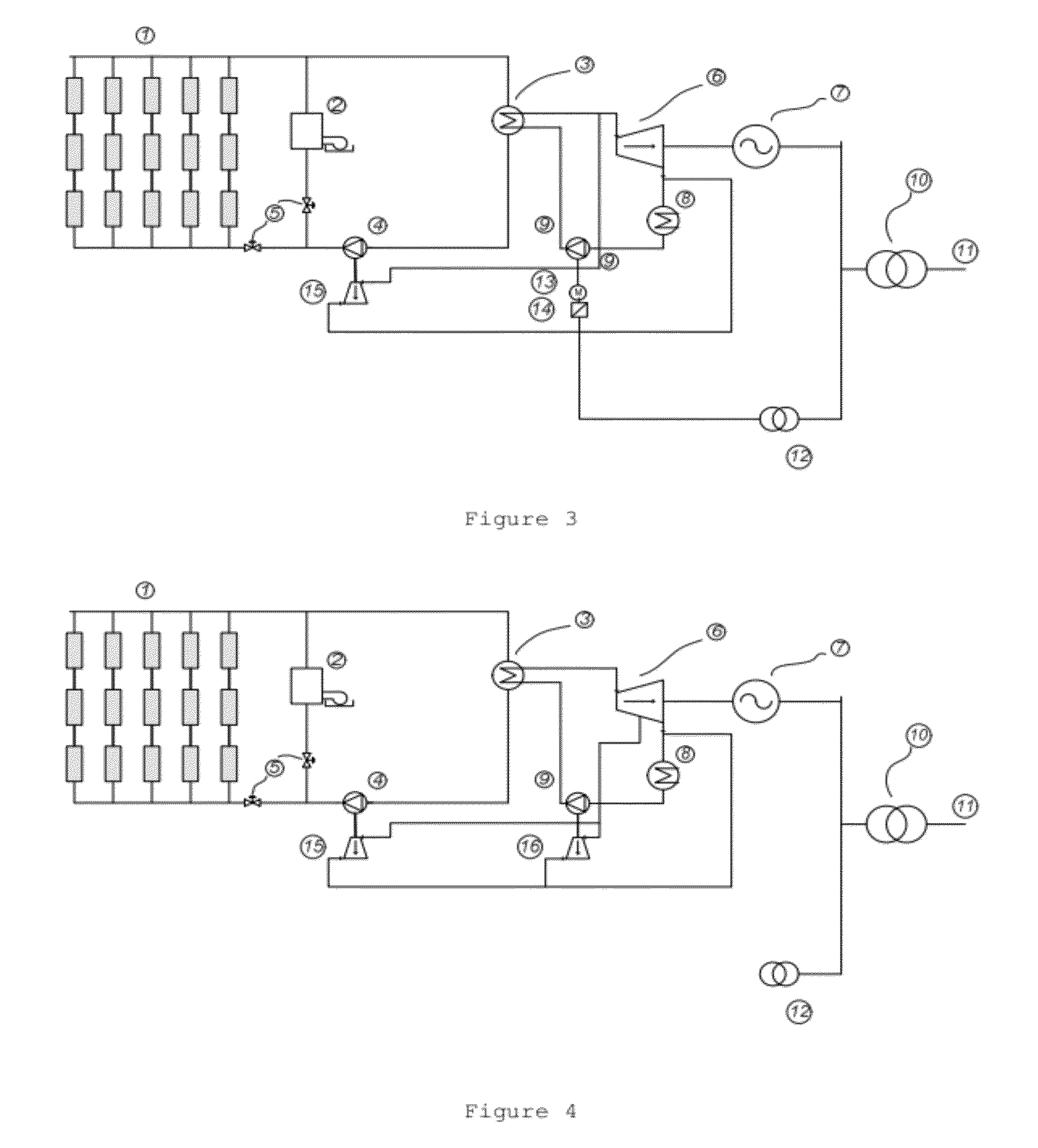
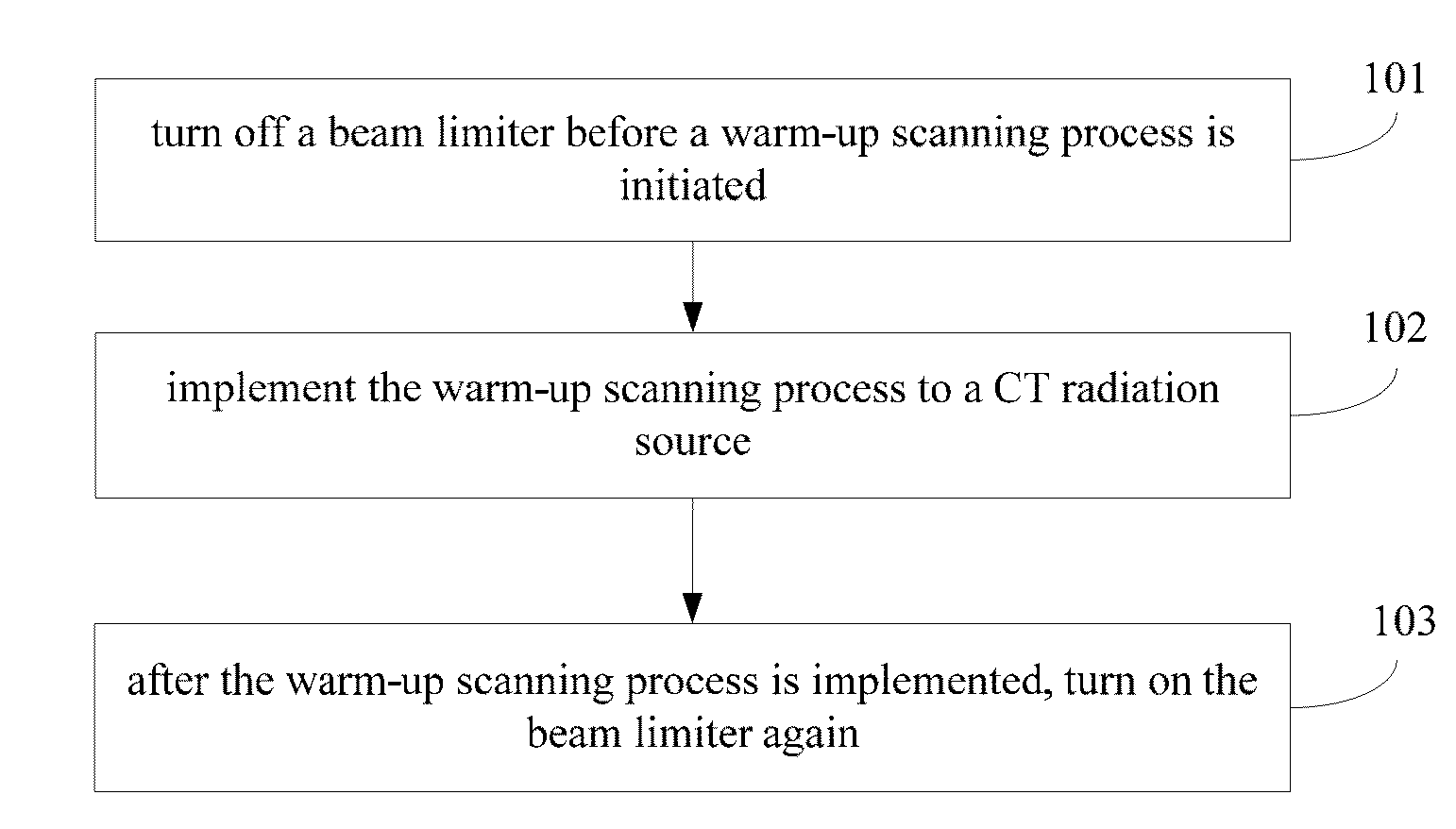
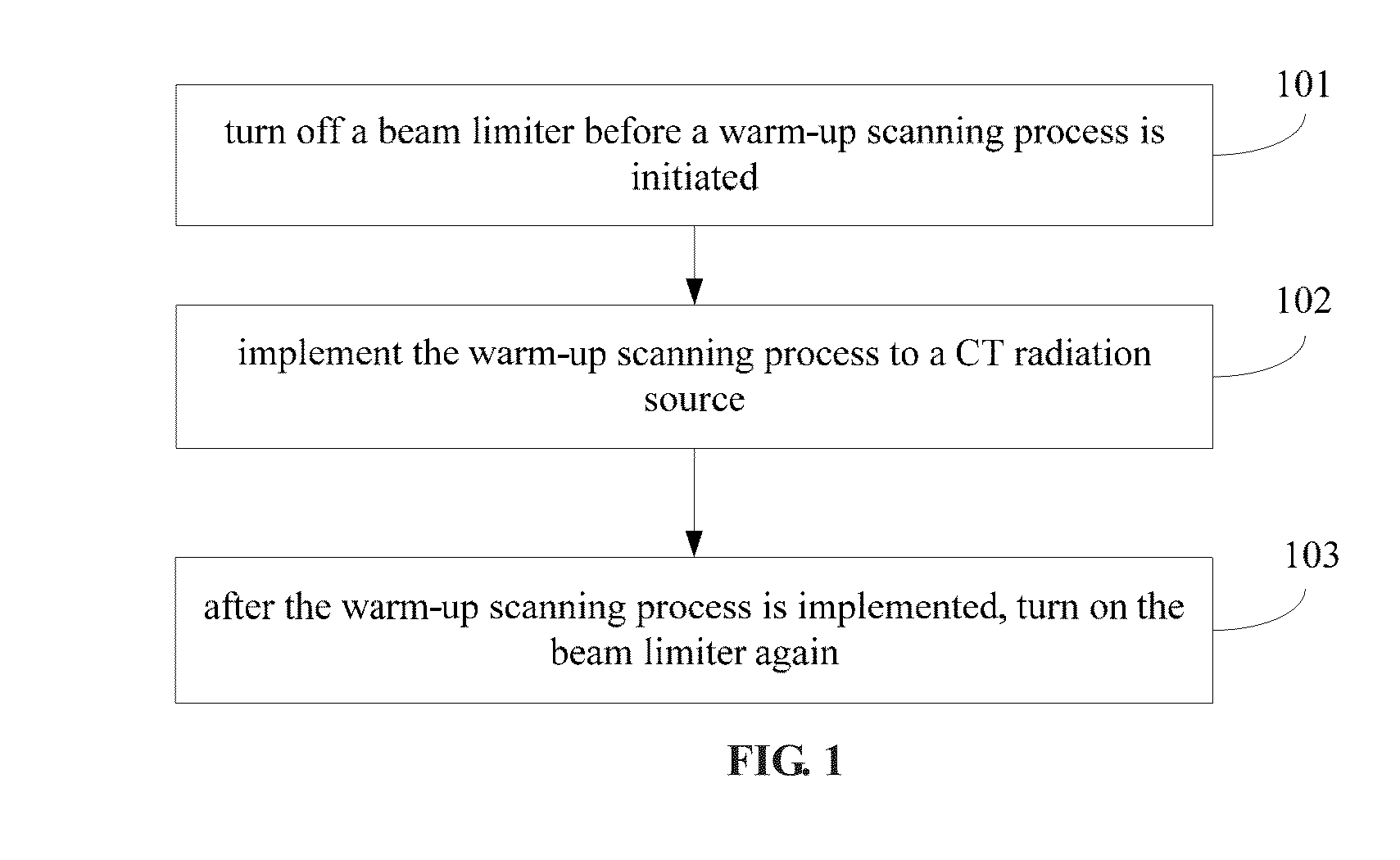
System and method for implementing warm-up scanning in CT device
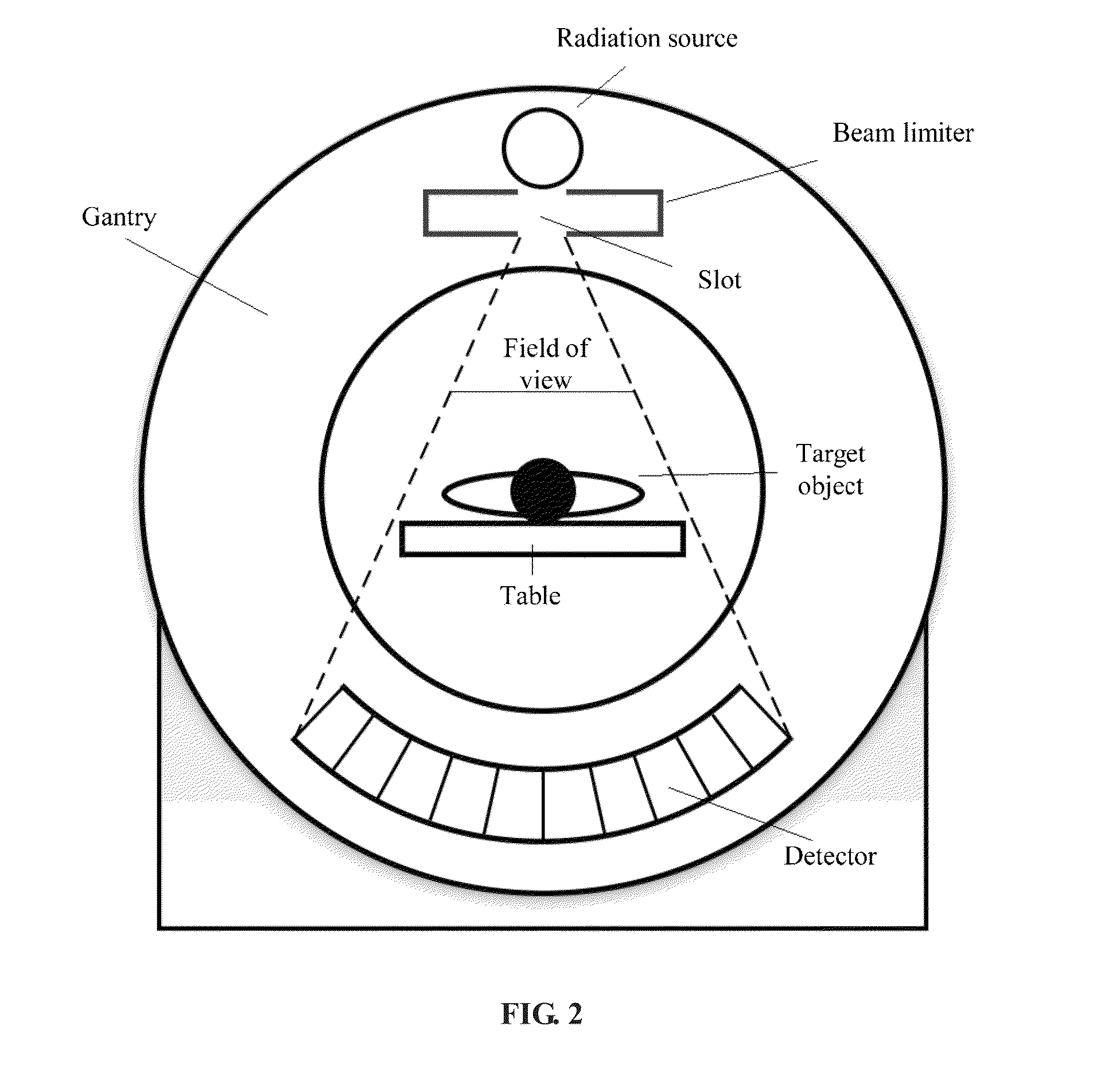
ActiveUS9220466B2Lot of radiationQuality improvementRadiation diagnostic device controlHandling using diaphragms/collimetersLight beamIonization
A system and a method for implementing warm-up scanning in a CT device are provided. The method includes: closing a slot of a beam limiter before a warm-up scanning process is initiated; implementing the warm-up scanning process to a CT radiation source; and opening the slot of the beam limiter after the warm-up scanning process is finished. The target object may not need to move during the warm-up scanning process. Therefore, a second time scout image scanning is no longer necessary and extra ionization radiation may be avoided.
Owner:NEUSOFT MEDICAL SYST CO LTD
Method for increasing the net electric power of solar thermal power stations
InactiveUS20120023942A1Increase powerImprove powerAuxillary drivesFrom solar energyEngineeringElectric consumption
The present invention allows increasing the net electric power supplied to the network by the solar thermal power plants of the cylindrical parabolic collector type by using the solar field in a more efficient manner, generating steam to drive the main ancillaries by means of steam turbines (turbo pumps), reducing electric consumption of the ancillary services and therefore increasing the net electric power of the plant.On days when the solar radiation is greater than the designed radiation, part of the solar field must stop being used since the generator and the turbine would exceed its designated power. The present system proposes harnessing the unused portion of the solar field for generating steam to drive the main ancillaries of the plant, energy which would otherwise not be harnessed.In addition, the overall operating performance of the ancillary service pumps is better when using steam to drive the pumps through a steam turbine (turbo pumps) instead of driving them with electric motors (motor pumps).
Owner:UNIV MADRID POLITECNICA
System and method for implementing warm-up scanning in ct device
ActiveUS20150063530A1Lot of radiationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation diagnostic device controlLight beamIonization
A system and a method for implementing warm-up scanning in a CT device are provided. The method includes: turning off a beam limiter before a warm-up scanning process is initiated; implementing the warm-up scanning process to a CT radiation source; and turning on the beam limiter after the warm-up scanning process is finished. The target object may not need to move during the warm-up scanning process. Therefore, a second time scout image scanning is no longer necessary and extra ionization radiation may be avoided.
Owner:NEUSOFT MEDICAL SYST CO LTD
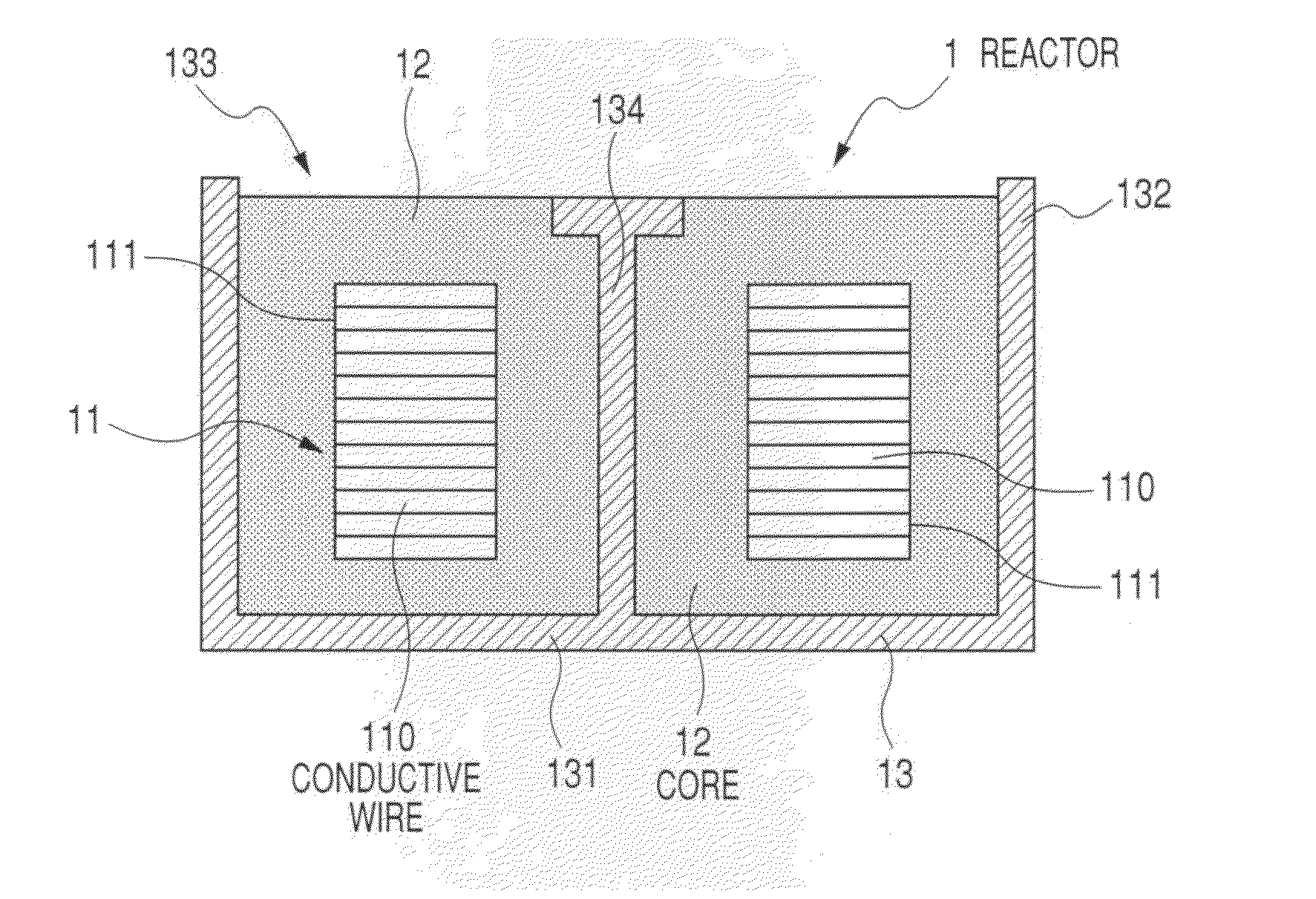
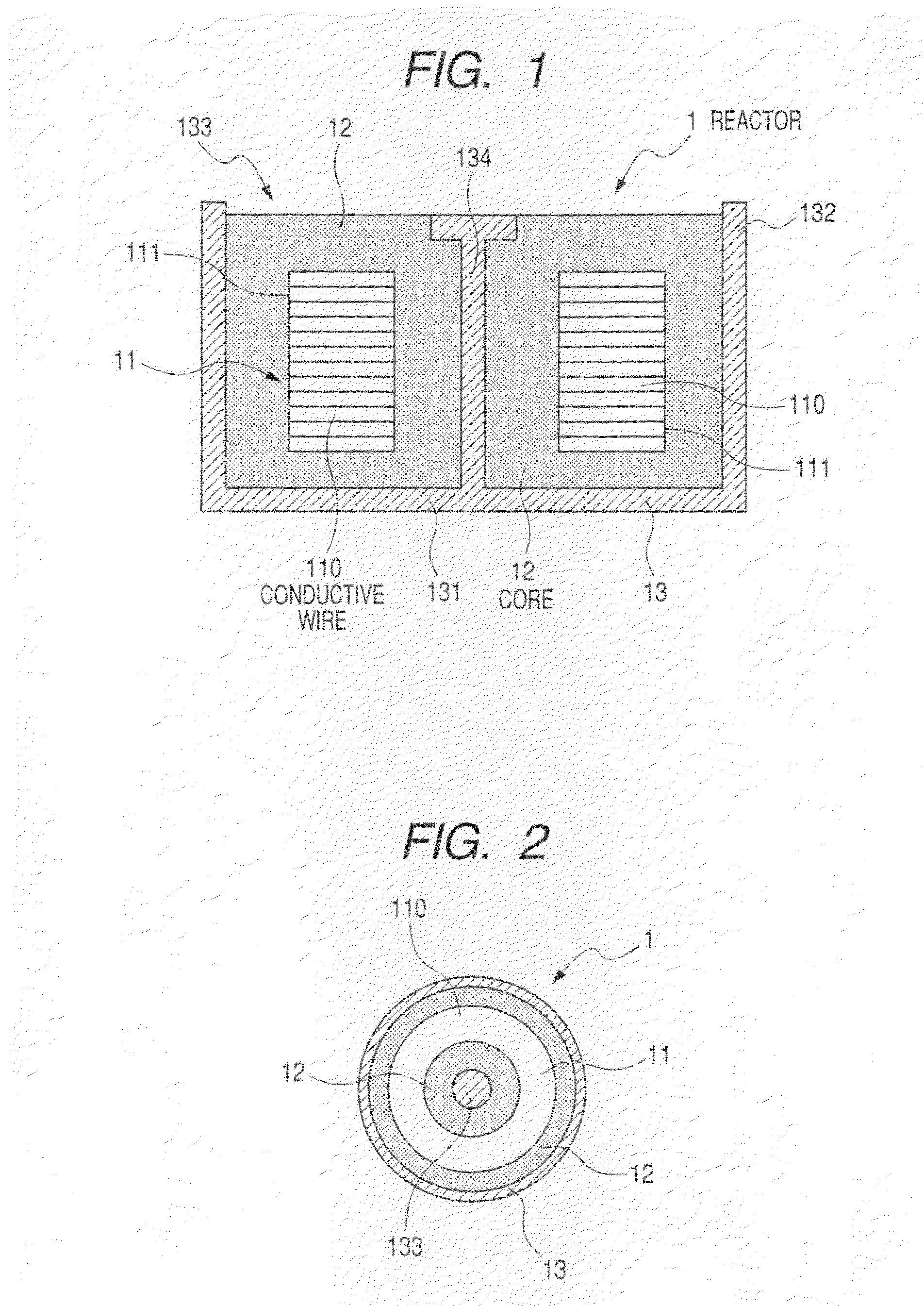
Reactor and method of producing the reactor
ActiveUS8416044B2Lower elastic modulusAvoid damageTransformers/inductances coolingTransformers/inductances casingsMetallurgyNon magnetic
A reactor is composed of a coil and a core placed in the inside area and outer peripheral area of the coil in a container. The core is composed of magnetic powder, non-magnetic powder, and resin. The non-magnetic powder is composed of main component powder and low elastic modulus powder. The main component powder as a main component of the non-magnetic powder is made of one or more kinds of powder of a heat conductivity which is larger than that of the resin. The low elastic modulus powder is made of one or more kinds of powder of an elastic modulus which is smaller than that of the powder forming the main component powder.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
Ostomy mounting wafer and a method of preparing it
InactiveUS7935095B2Lot of radiationNot to damageNon-surgical orthopedic devicesColostomyHigh absorptionLaser light
An ostomy body side mounting wafer and a method of preparing the ostomy body side mounting wafer, where the wafer is assembled from two parts using laser welding. The laser light is provided through one of the parts having a low or lower absorption of the laser light. The other part has a higher absorption of the laser light, whereby the interface between the two parts is heated at the welding zone(s) of the laser light. In this manner, an assembly is obtained independently of the thicknesses of the materials and even close to openings or other edges.
Owner:COLOPLAST AS
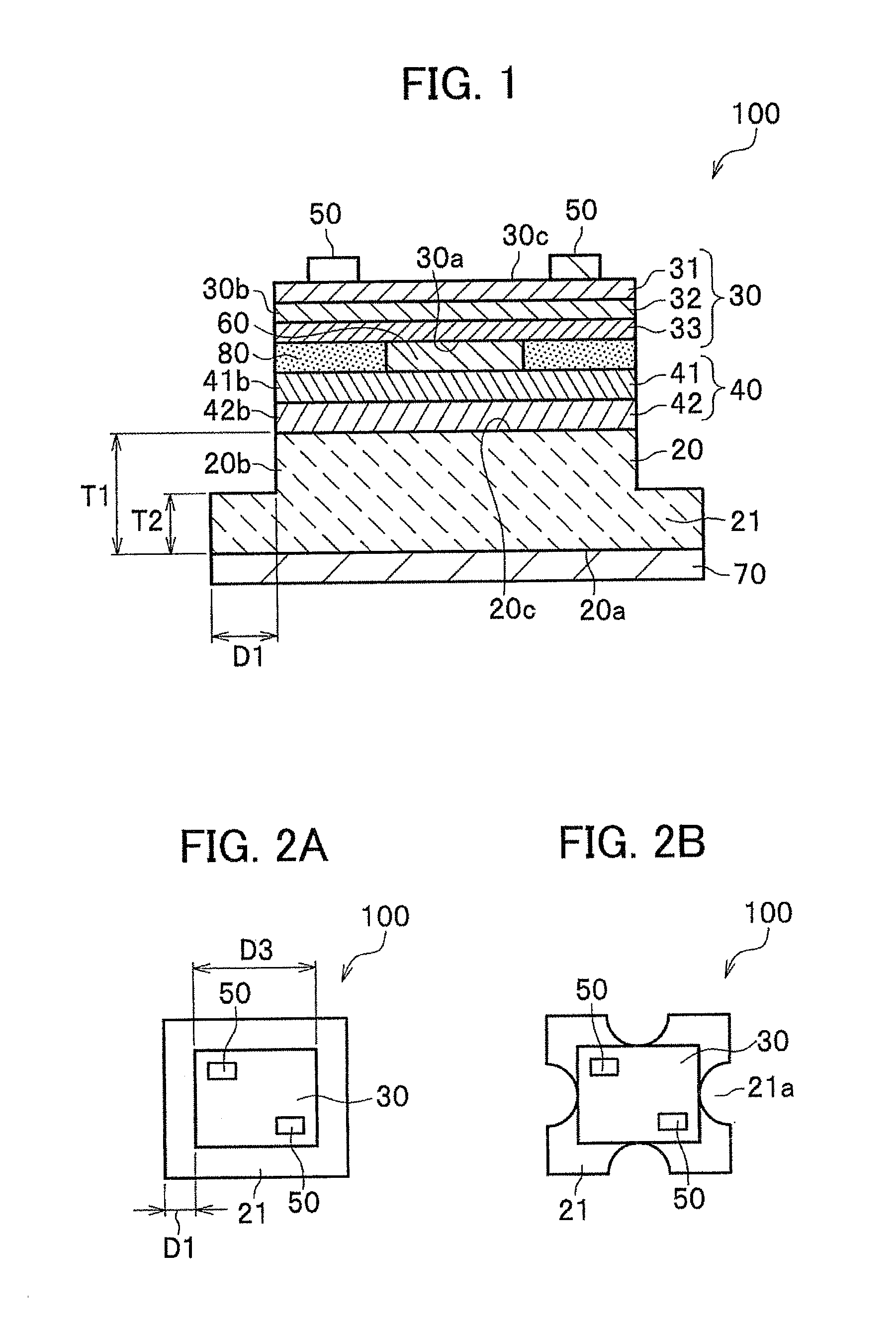
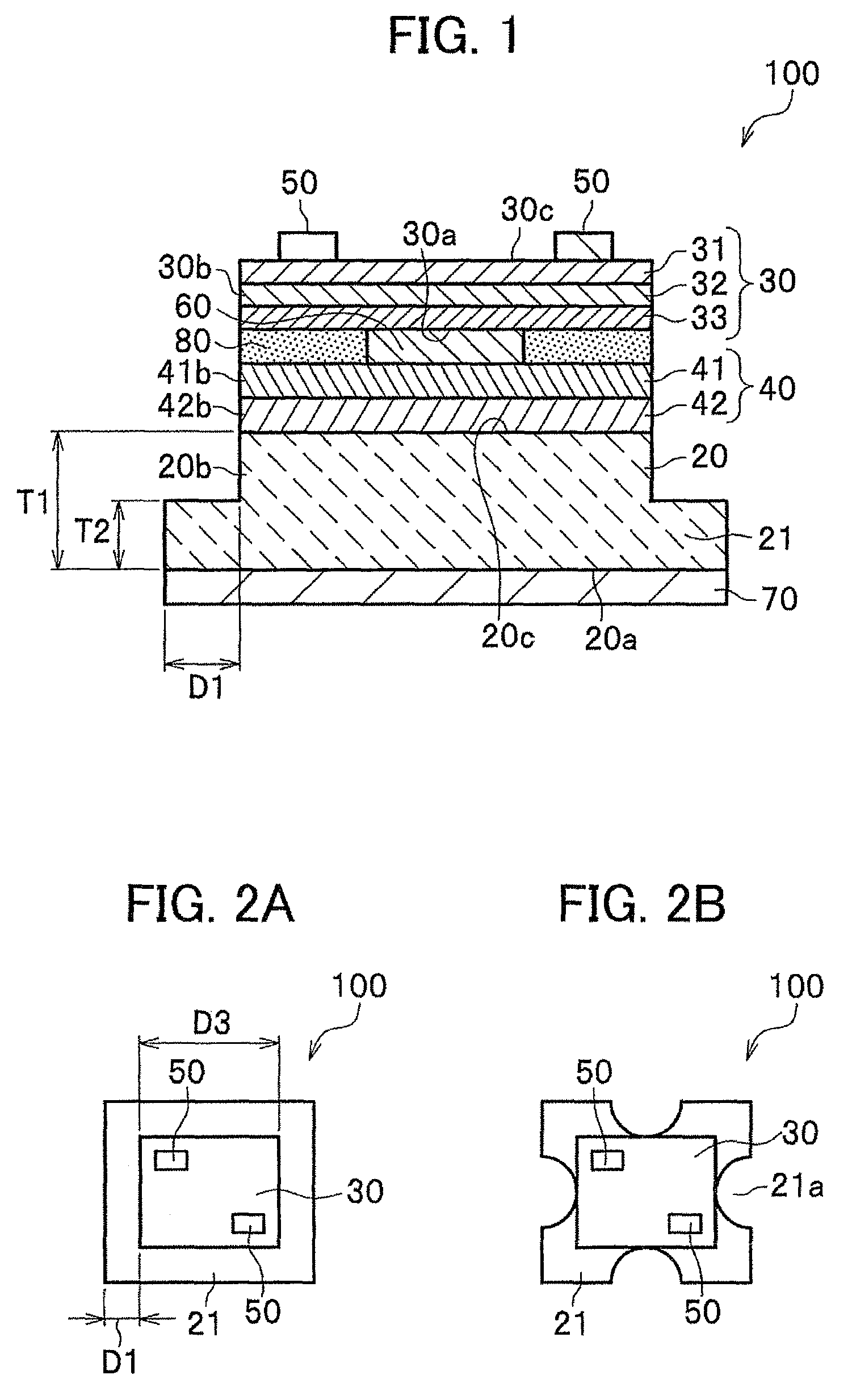
Vertical nitride semiconductor device and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20130256739A1Improve adhesionIncrease in temperatureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesOptoelectronicsFlange
Disclosed is a vertical nitride semiconductor device including a conductive substrate; a semiconductor layer bonded to the conductive substrate via a second electrode; a metal layer formed on the conductive substrate; a first electrode formed on the semiconductor layer; and a bonding layer formed between the conductive substrate and the second electrode. The conductive substrate has a flange part, which extends from a side surface of the conductive substrate, on a side of the other front surface thereof. The flange part is formed in a manner in which the conductive substrate and the semiconductor layer are bonded together and then a remaining part of the conductive substrate is divided, the remaining part being formed by cutting off the semiconductor layer and part of the conductive substrate in a thickness direction so as to expose a side surface of the semiconductor layer and the side surface of the conductive substrate.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Display device
InactiveUS8164583B2Long-life and highly brightLot of radiationTransmission systemsGraph readingDisplay deviceNon magnetic
The display device has an LCD panel, a light source, and a digitizer disposed on the back surface of the LCD panel. The display device further contains a U-shaped first heat-dissipation plate made of a non-magnetic material. The first heat-dissipation plate is disposed on at least one end of the periphery of the LCD panel in a way that the opening of the U-shape faces toward the LCD panel. The light source is mounted on the first heat-dissipation plate, and an end section of the digitizer is covered with the opening of the plate.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
Weather-resistant article, weather-resistant film and optical member
InactiveUS9279982B2Lot of radiationSolve the lack of resistanceLayered productsChemical vapor deposition coatingWeather resistanceRefractive index
Provided is a support exhibiting excellent weather resistance, which is usable in an outdoor location for a long duration and is a support capable of sufficiently shielding UV radiation; and further provided are a weather-resistant article, a weather-resistant film, and an optical member which exhibit sufficient weather resistance even though receiving influences by heat, light or moisture. Disclosed is a weather-resistant article of the present invention possessing a support and provided thereon, a polymer layer containing a light stabilizer and a UV radiation reflective layer containing plural materials each having a different refractive index, the UV radiation reflective layer provided on the polymer layer.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Automatic original document transport device and image forming device equipped with the same
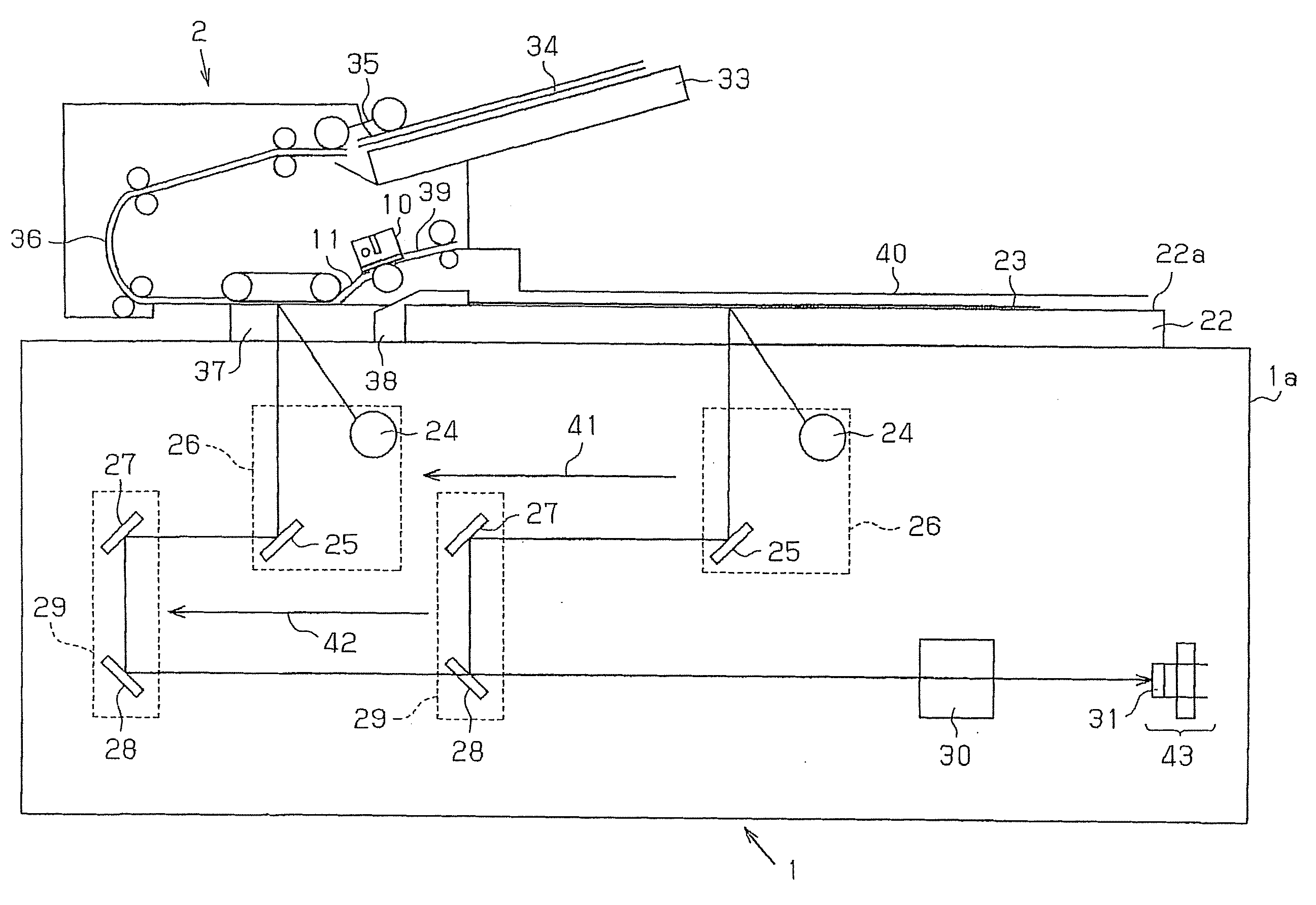
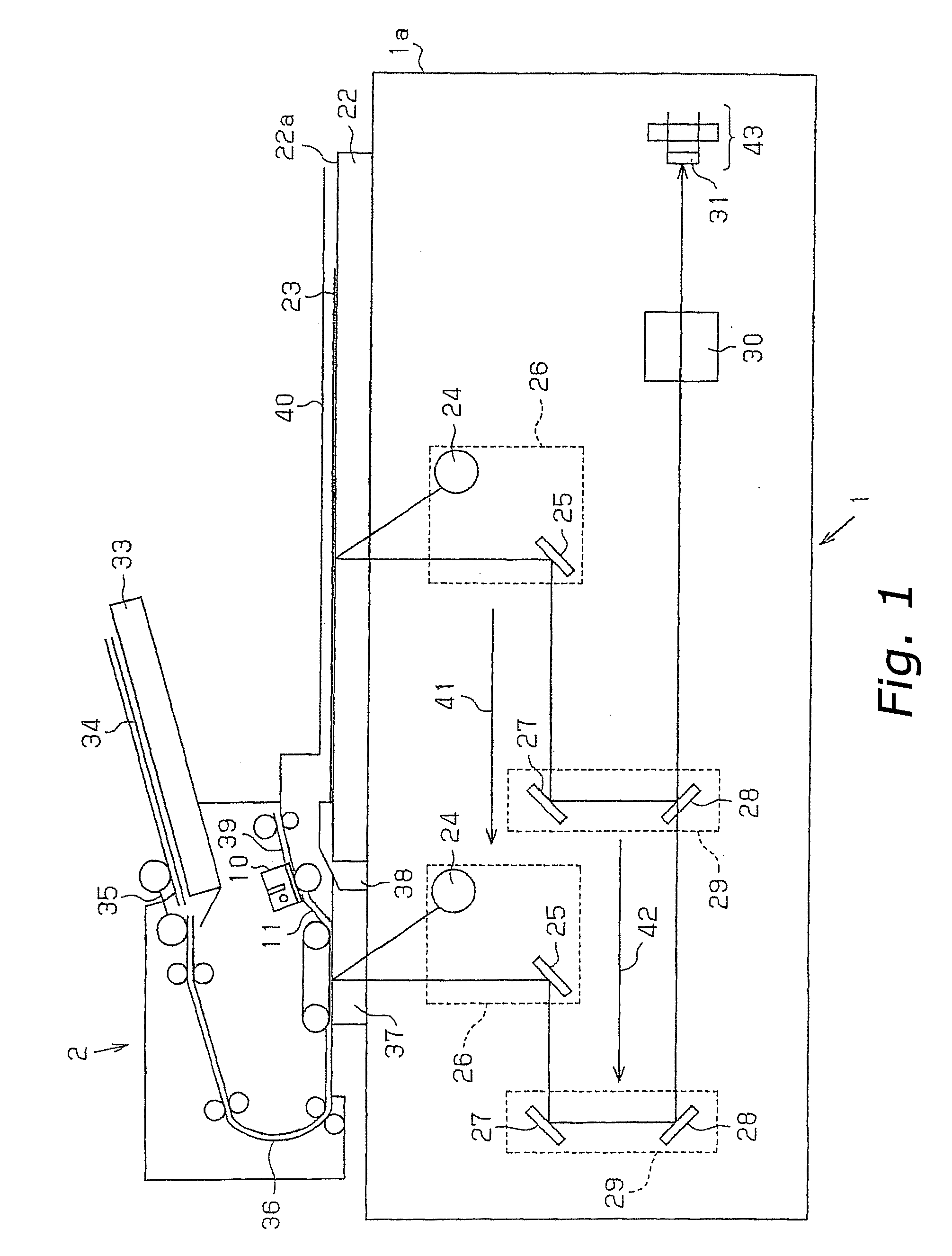
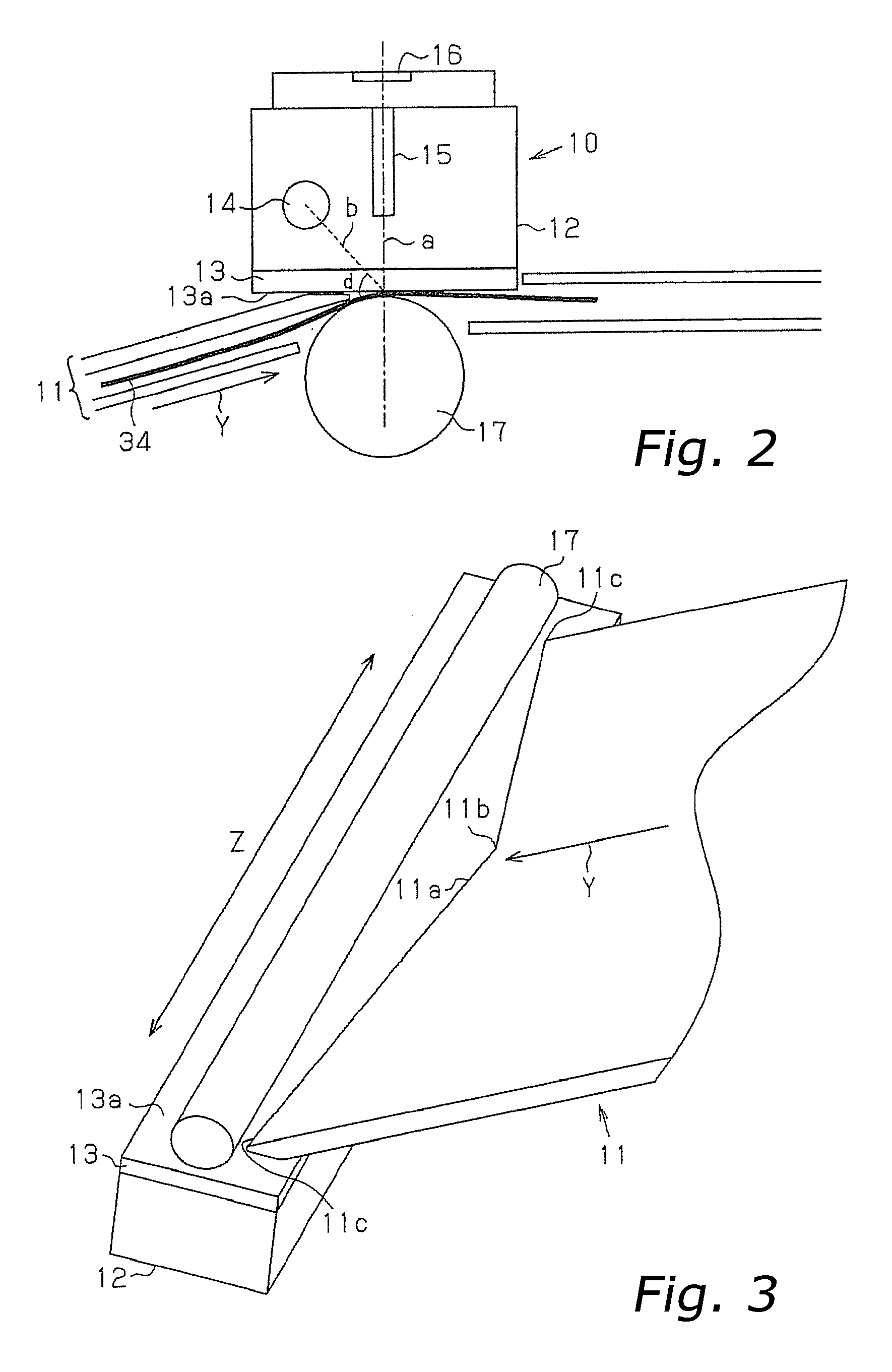
InactiveUS20070091389A1Increase in sizeExcellent imagePictoral communicationPaper documentDocument preparation
In an automatic original document transport device, there are provided a contact image sensor 10 for scanning an image of an original document 34, and an original document guide member 11 for guiding the original document 34 to the original document scanning surface 13a so as to incline with respect to the original document scanning surface 13a. Therefore, an angle d formed by the optical axis b of the light source 14 and transported original document 34 becomes large, resulting in sufficient radiation of light from the light source 14 to the light source 14. Therefore, when the original document 34 is scanned, an excellent image is obtained, and particularly when a pasted original document is scanned, the problem of a pasted end appearing on the image as a line can be effectively avoided.
Owner:KYOCERA DOCUMENT SOLUTIONS INC
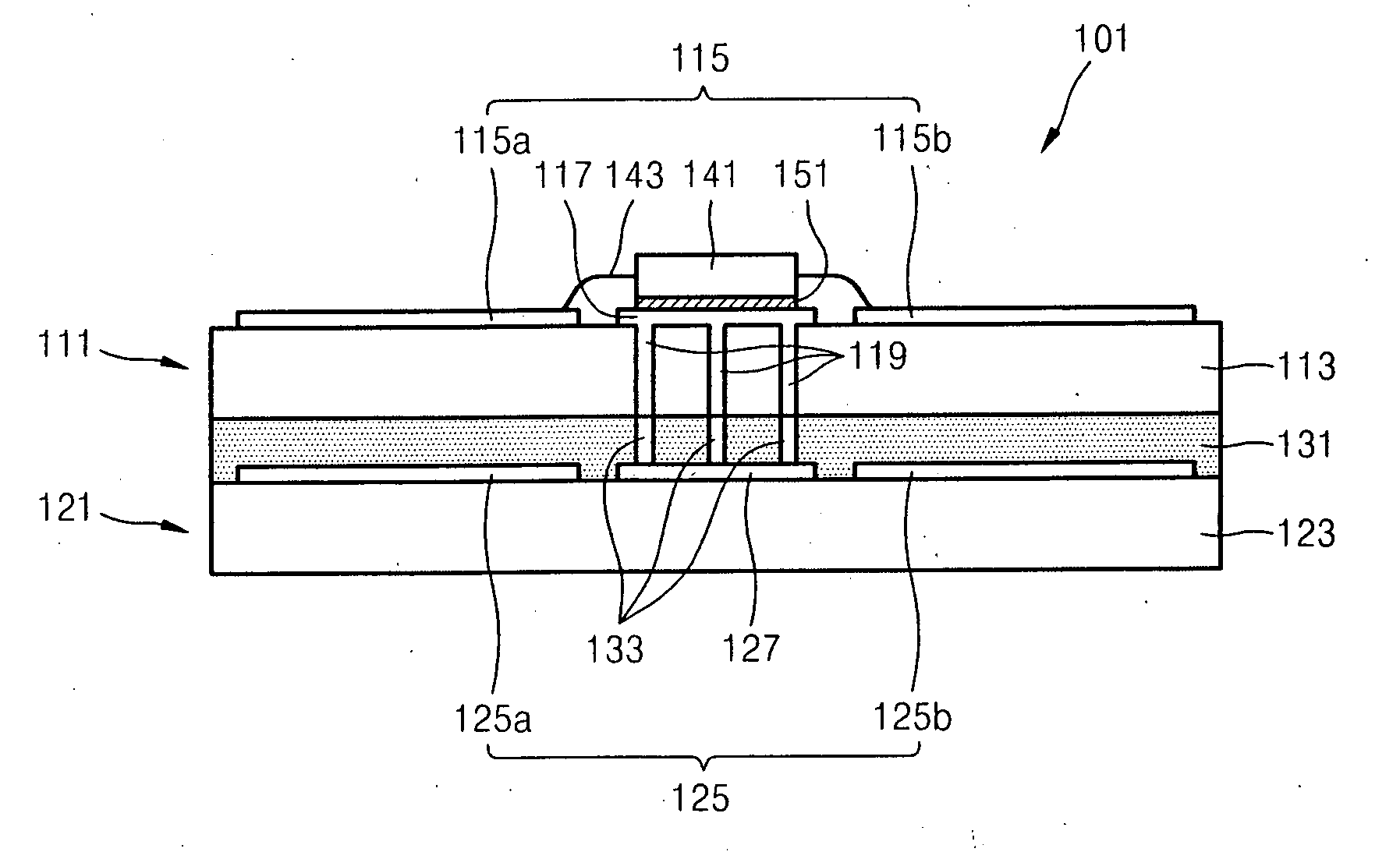
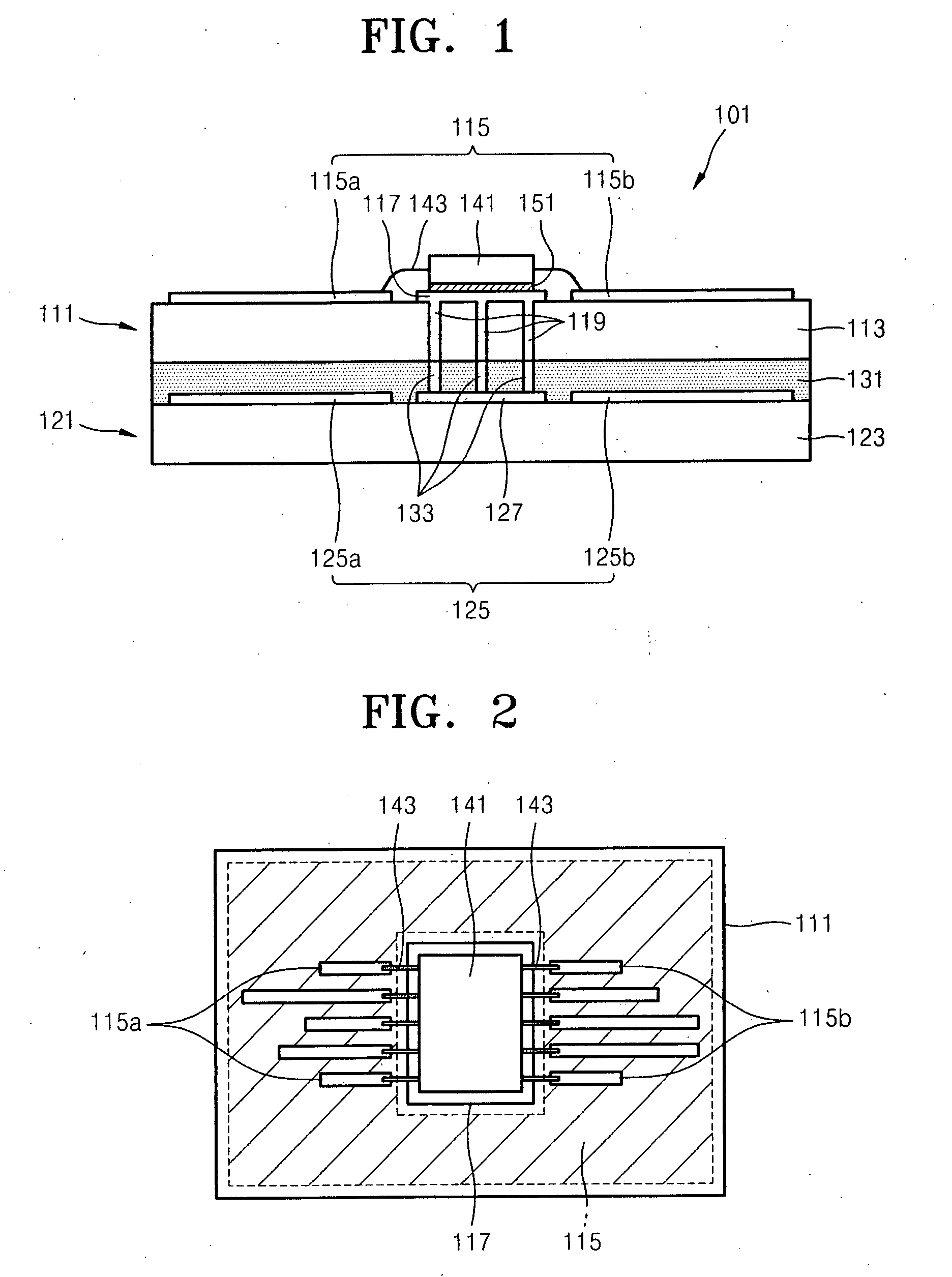
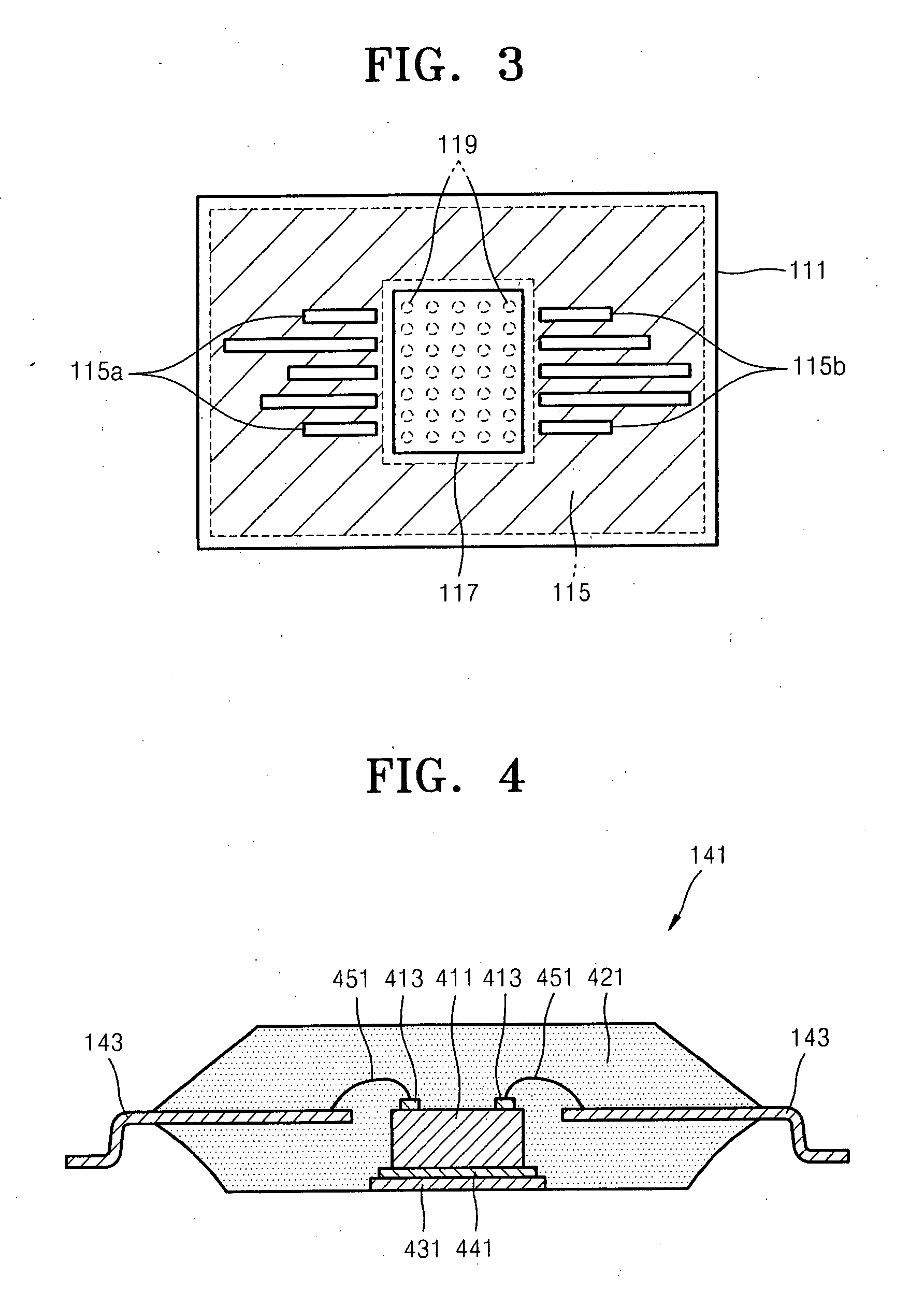
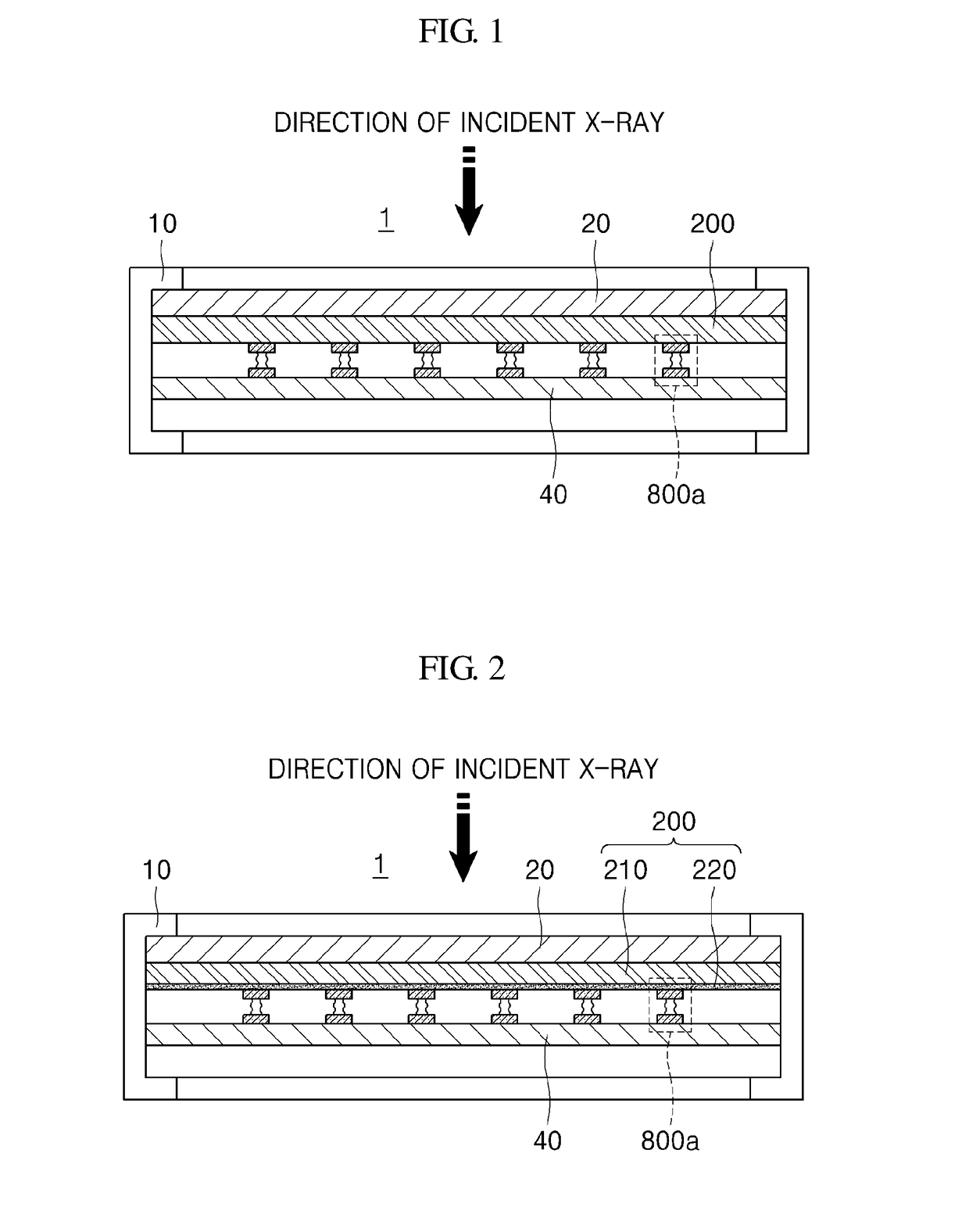
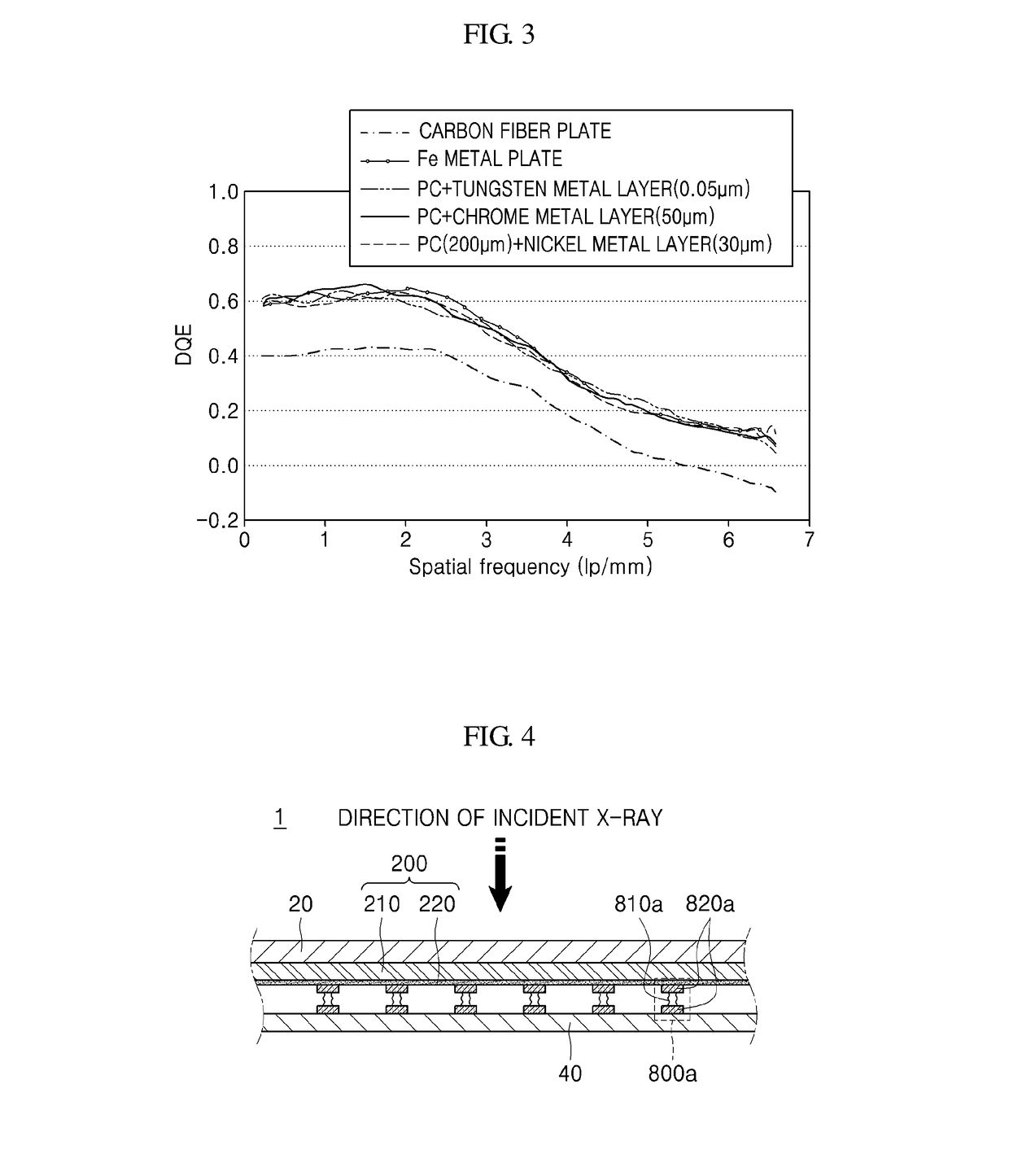
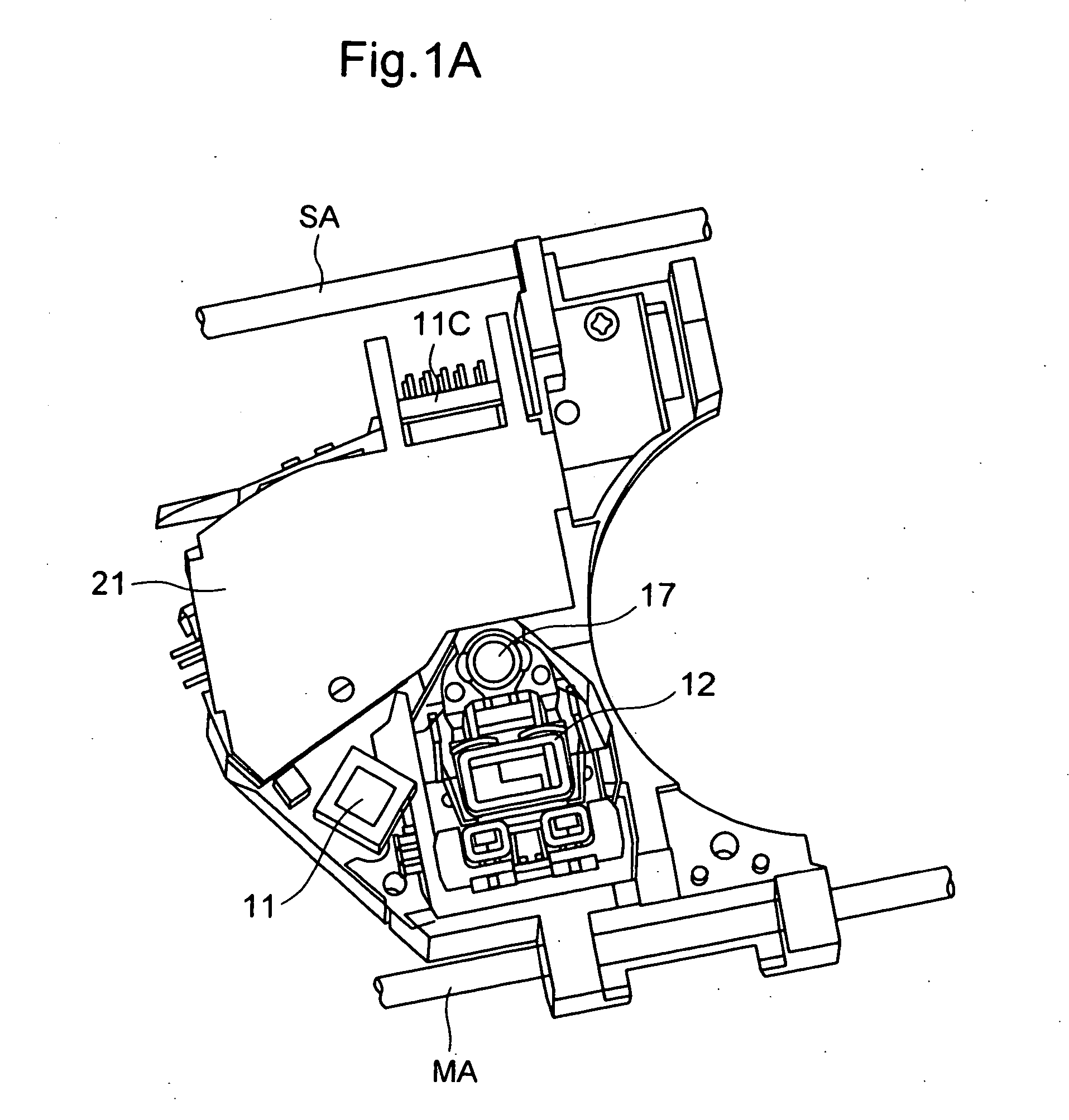
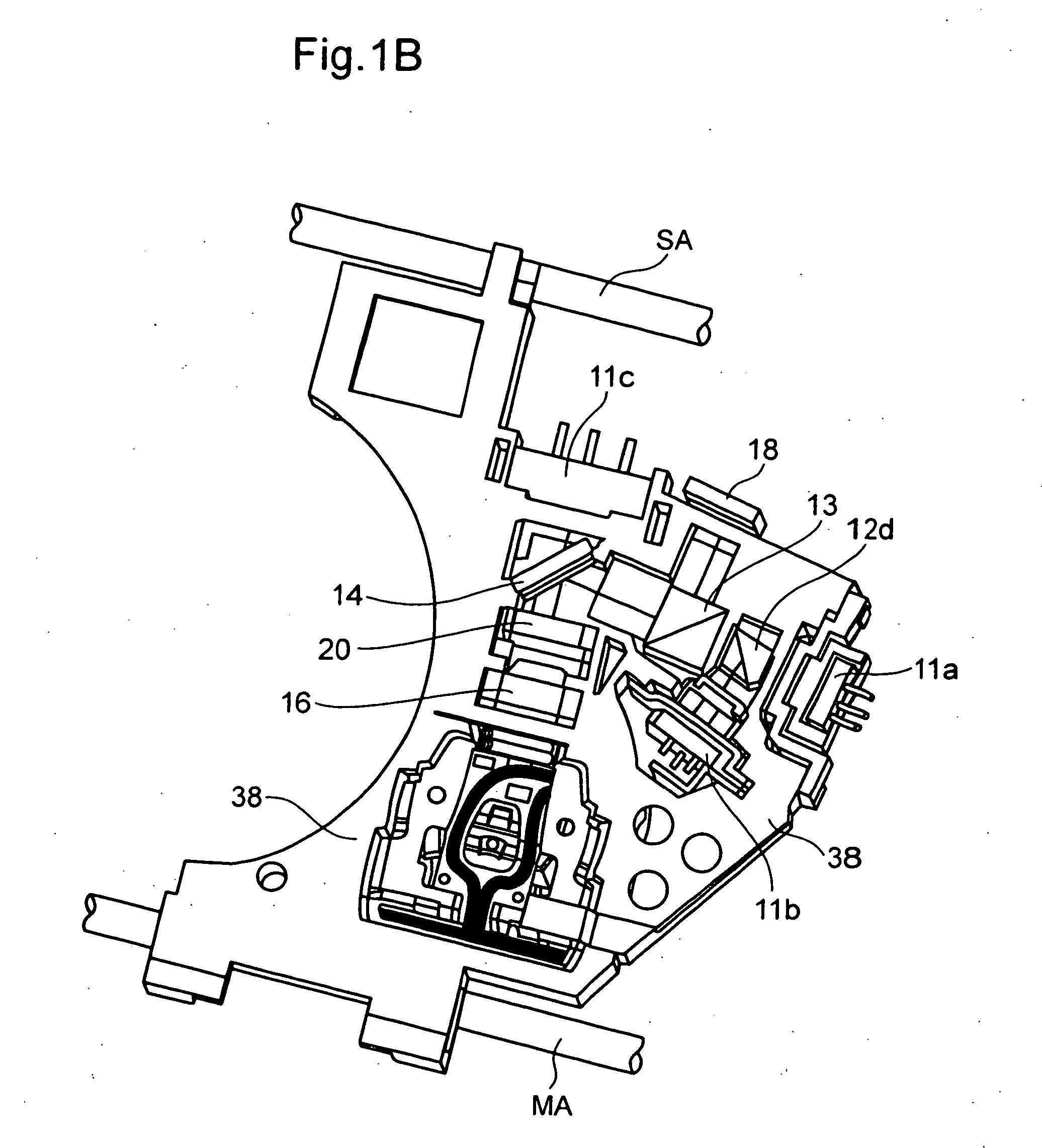
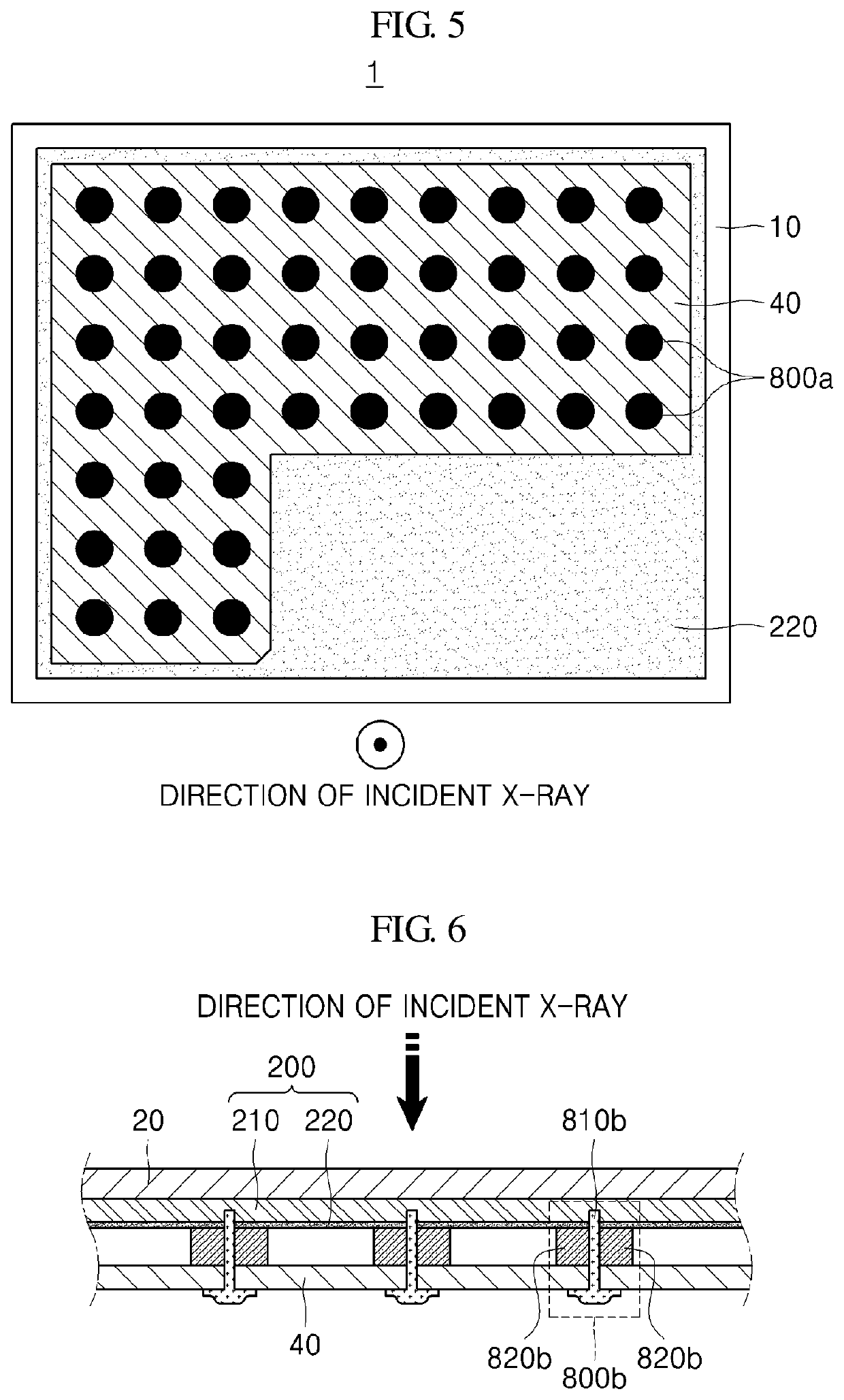
Radiation detector and radiography apparatus having the same
ActiveUS20170281103A1Noise minimizationLot of radiationPatient positioning for diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringElectricityPrinted circuit board
The present invention proposes a radiation detector including a housing, a radiation detection panel accommodated in the housing and converting radiation incident from the outside of the housing into an electric signal, a printed circuit board electrically connected to the radiation detection panel and an intermediate plate that is disposed between the radiation detection panel and the printed circuit board, supports the radiation detection panel, and is electrically connected to the ground line of the printed circuit board, wherein the intermediate plate is transmissive to the radiation.
Owner:DRTECH
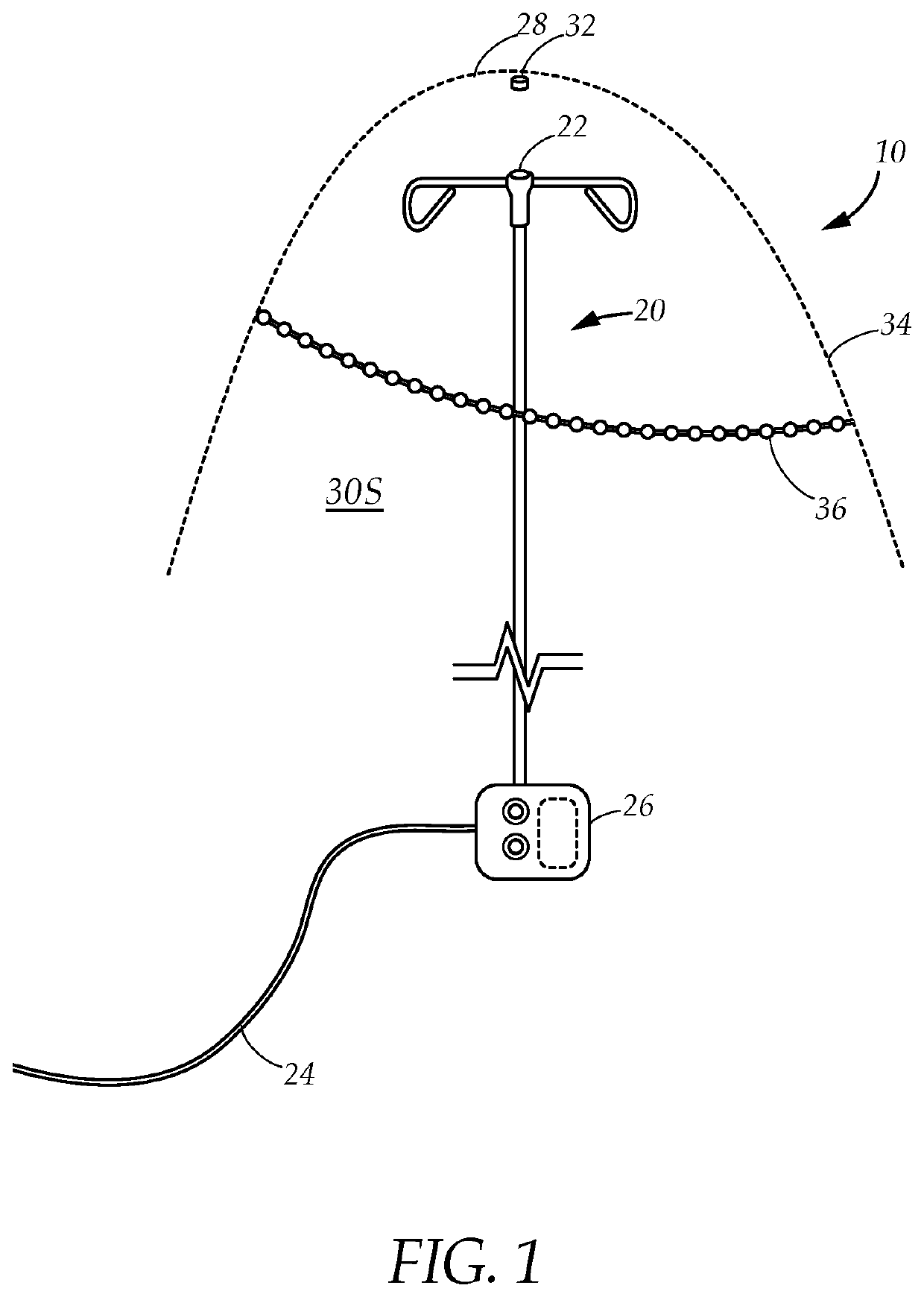
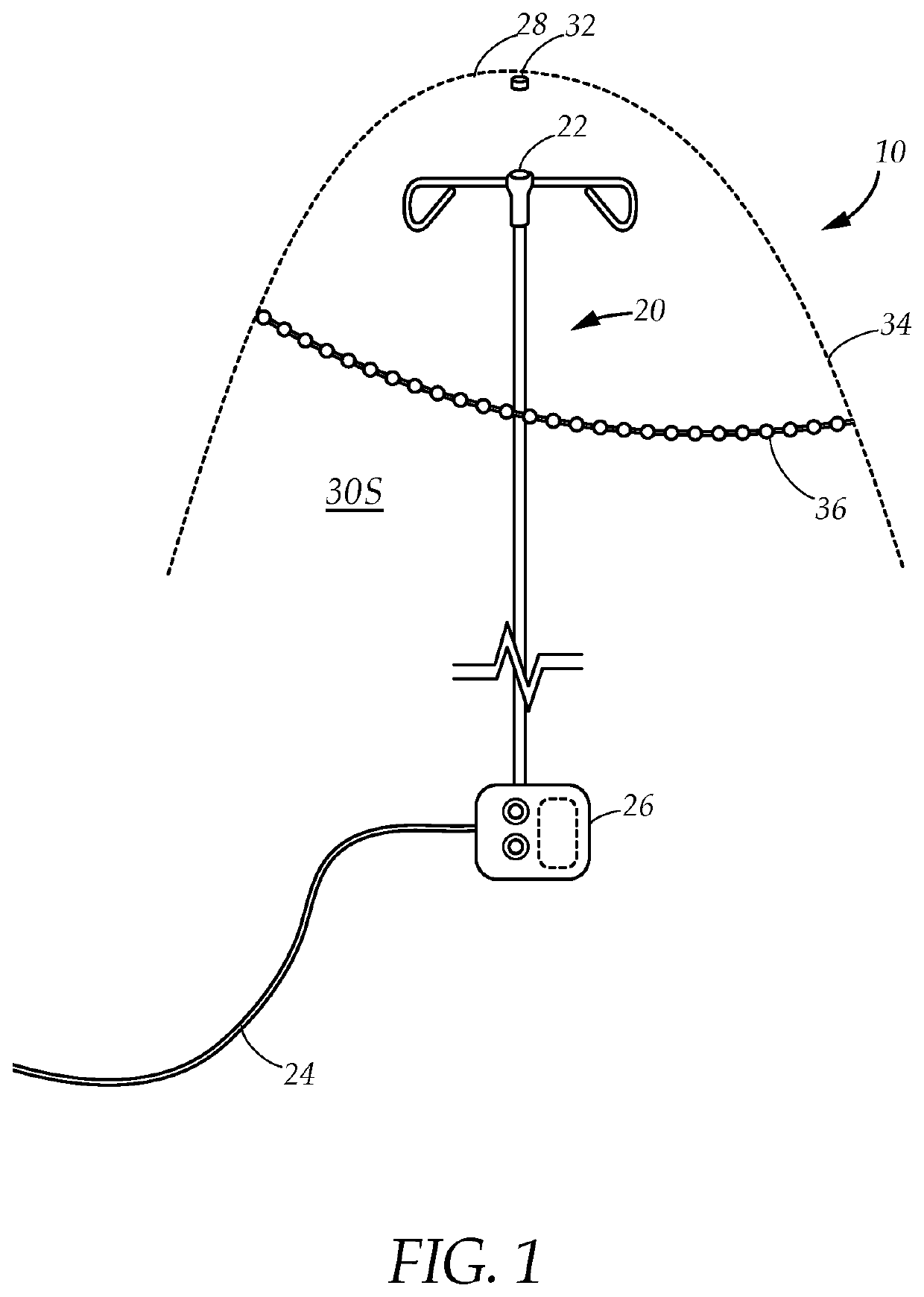
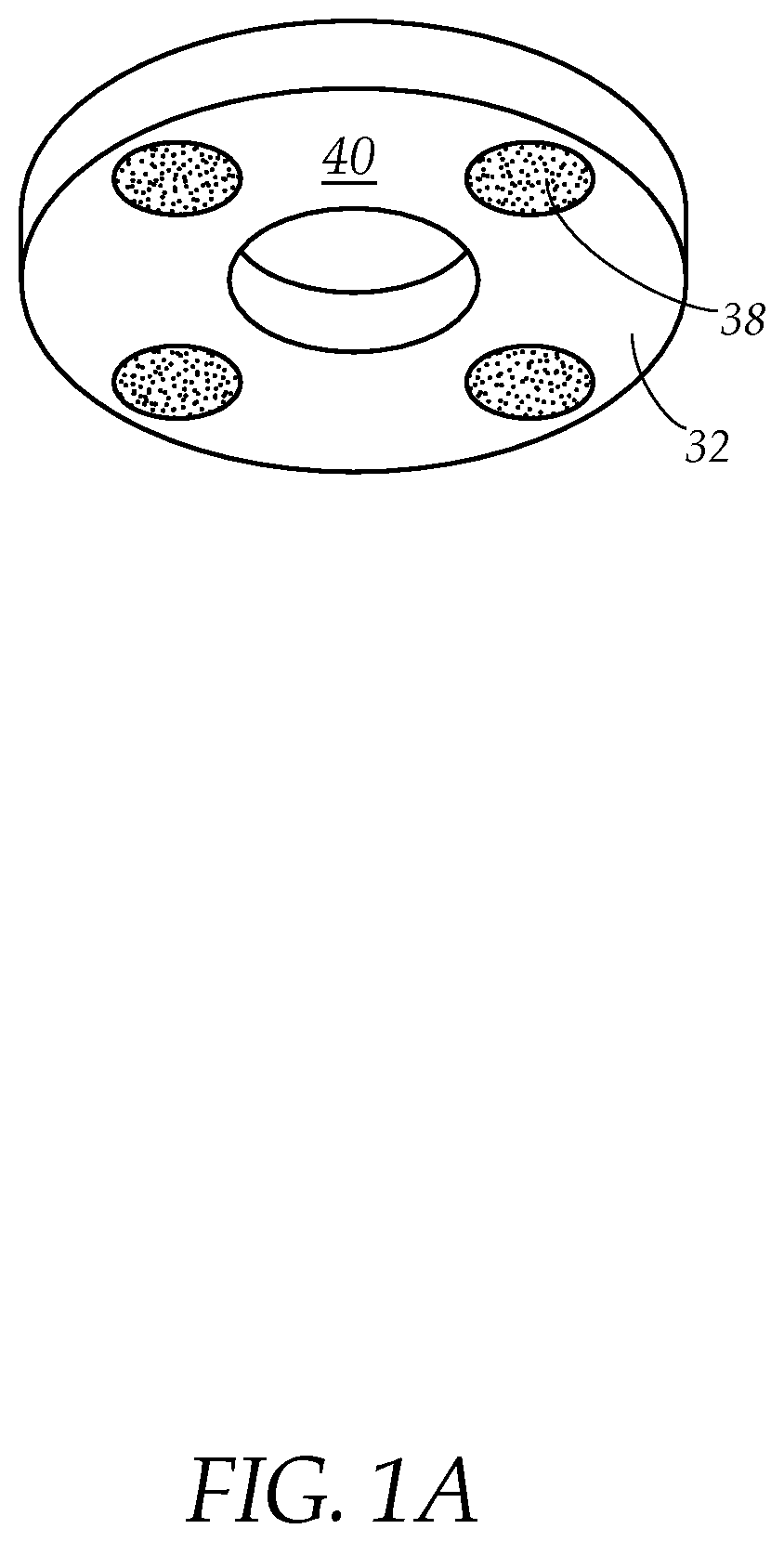
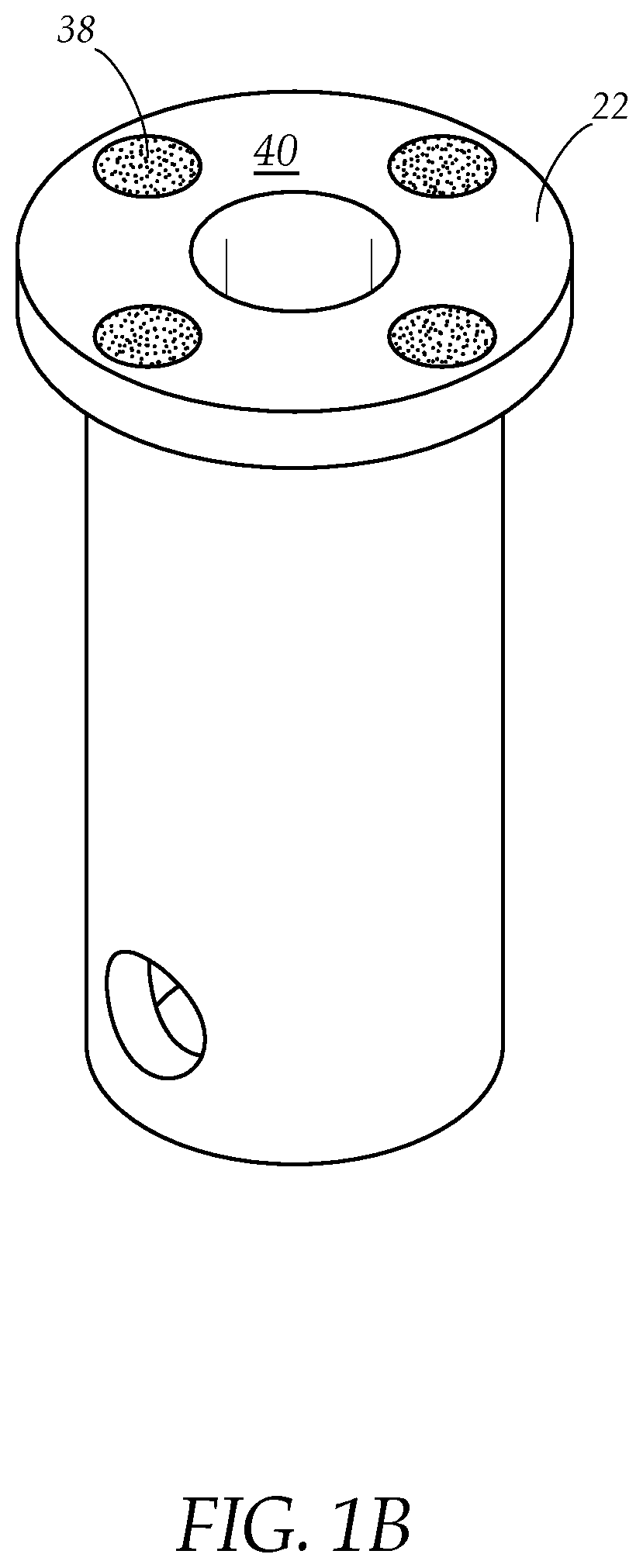
Self-sterilizing IV pole system
ActiveUS11351278B1Efficient and easy-to-useStaff time spentEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsPlanar light sourcesWheelchairUltraviolet lights
A system and method for sterilizing a wheelchair, stretcher or the like, that comprises an intravenous (IV) pole attaching to the wheelchair or stretcher having an electrical connector at the pole top, and a reflective drape having an interior lined with UV LED lights that electrically connects to the connector on top of the IV pole when draped over the wheelchair or stretcher. The UV LED lights sterilize the wheelchair or other equipment that is under the drape after a period of exposure to UV radiation without using disinfectant chemical sprays or wiping with disinfectant cloths and without staff attention.
Owner:THAKUR VISHAL
Organic light emitting display
ActiveUS7679089B2Reduced life-timeLot of radiationDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsThermal radiationLight emission
An organic light emitting display provided according to the invention maintains light emission efficiency and elongates its lifetime by radiating heat generated from organic light emitting elements to the outside of an encapsulated area. In the organic light emitting display, a part of a cathode is extended to the outside of the encapsulated area of a main substrate to form a radiation section integrally with the cathode. Heat generated from organic light emitting elements is diffused and radiated from the radiation section so that the heat can be discharged therefrom.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Optical pick-up apparatus and optical disk apparatus
InactiveUS20060143633A1Avoid swellingIncrease cooling areaRecord information storageReducing physical parameters of carriersPhotodetectorLaser light
An optical pick-up apparatus that irradiates a disk with laser light emitted from a laser light source and uses a photodetector to receive the laser light reflected by the disk to thereby perform recording / reproduction onto / from the disk, comprises: a laser diode driver that drives the laser light source; an upper cover that serves as a heat radiation means for radiating heat generated by the laser diode driver; and an optical base that serves as a heat radiation means for radiating heat generated by the laser light source and photodetector.
Owner:TOSHIBA SAMSUNG STORAGE TECHNOLOGY
Radiation detector and radiography apparatus having the same
ActiveUS11058374B2Noise minimizationLot of radiationPatient positioning for diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringMedicinePrinted circuit board
The present invention proposes a radiation detector including a housing, a radiation detection panel accommodated in the housing and converting radiation incident from the outside of the housing into an electric signal, a printed circuit board electrically connected to the radiation detection panel and an intermediate plate that is disposed between the radiation detection panel and the printed circuit board, supports the radiation detection panel, and is electrically connected to the ground line of the printed circuit board, wherein the intermediate plate is transmissive to the radiation.
Owner:DRTECH
Self-sterilizing iv pole system
PendingUS20220257816A1Efficient and easy-to-useStaff time spentEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsPlanar light sourcesWheelchairUltraviolet lights
A system and method for sterilizing a wheelchair, stretcher or the like, that comprises an intravenous (IV) pole attaching to the wheelchair or stretcher having an electrical connector at the pole top, and a reflective drape having an interior lined with UV LED lights that electrically connects to the connector on top of the IV pole when draped over the wheelchair or stretcher. The UV LED lights sterilize the wheelchair or other equipment that is under the drape after a period of exposure to UV radiation without using disinfectant chemical sprays or wiping with disinfectant cloths and without staff attention.
Owner:THAKUR VISHAL
Communication device and electronic device comprising the same
ActiveUS10607512B2Improve efficiencySimple patternStampsNear-field transmissionTelecommunicationsCommunication device
Owner:ATEC IOT CO LTD
Vertical nitride semiconductor device and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS9196793B2Improve efficiencyIncrease productionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesNitride semiconductorsMetal
Disclosed is a vertical nitride semiconductor device including a conductive substrate; a semiconductor layer bonded to the conductive substrate via a second electrode; a metal layer formed on the conductive substrate; a first electrode formed on the semiconductor layer; and a bonding layer formed between the conductive substrate and the second electrode. The conductive substrate has a flange part, which extends from a side surface of the conductive substrate, on a side of the other front surface thereof. The flange part is formed in a manner in which the conductive substrate and the semiconductor layer are bonded together and then a remaining part of the conductive substrate is divided, the remaining part being formed by cutting off the semiconductor layer and part of the conductive substrate in a thickness direction so as to expose a side surface of the semiconductor layer and the side surface of the conductive substrate.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Communication device and electronic device comprising the same
ActiveUS20180366041A1Improve antenna radiation efficiencySimple patternStampsNear-field transmissionEngineeringElectric devices
A communication device according to an embodiment comprises: an antenna unit; and a grounding region for emitting a communication signal of the antenna unit, wherein the grounding region cannot overlap with another region inside the communication device, which includes a region in which the antenna unit is disposed.
Owner:ATEC IOT CO LTD
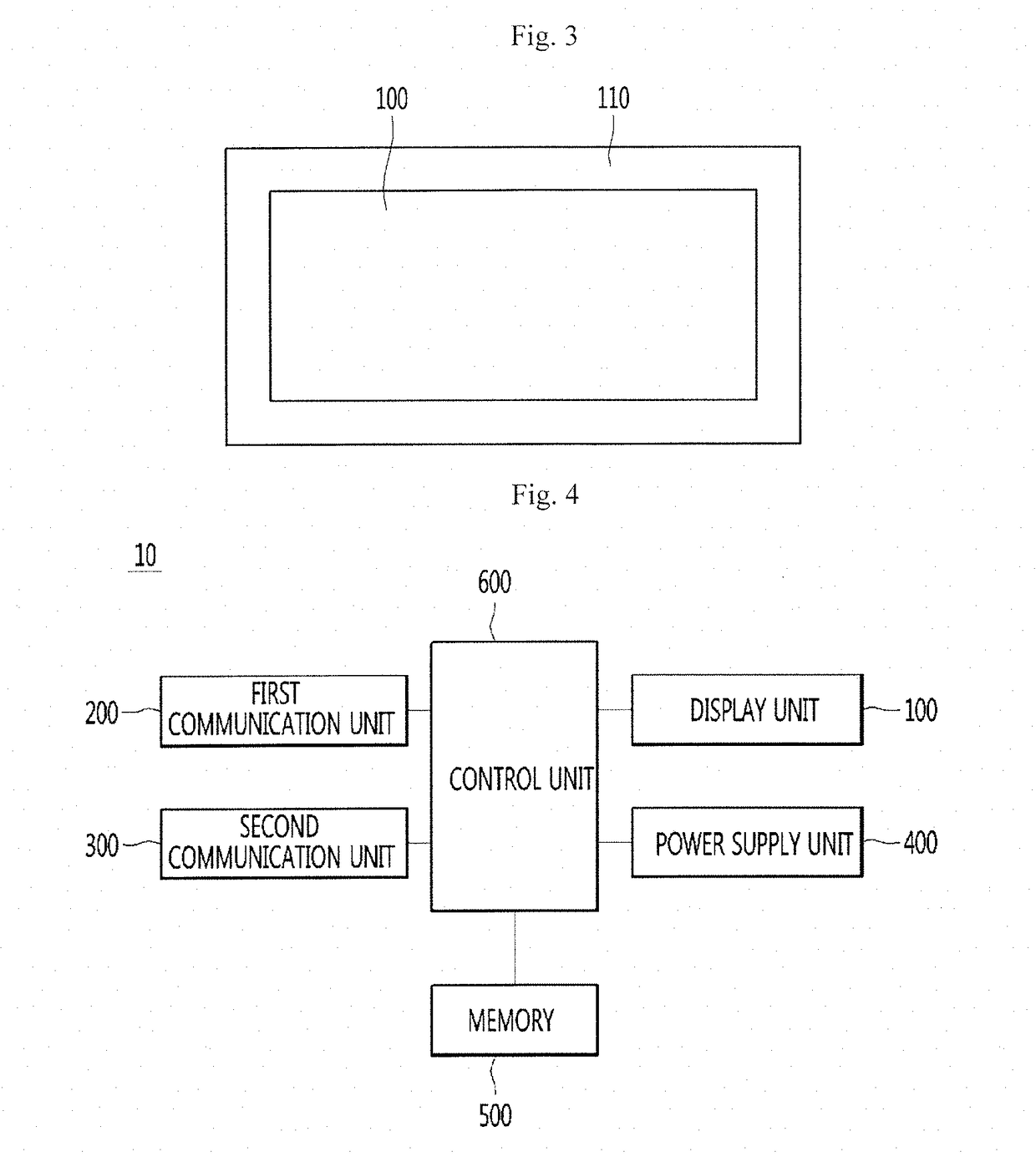
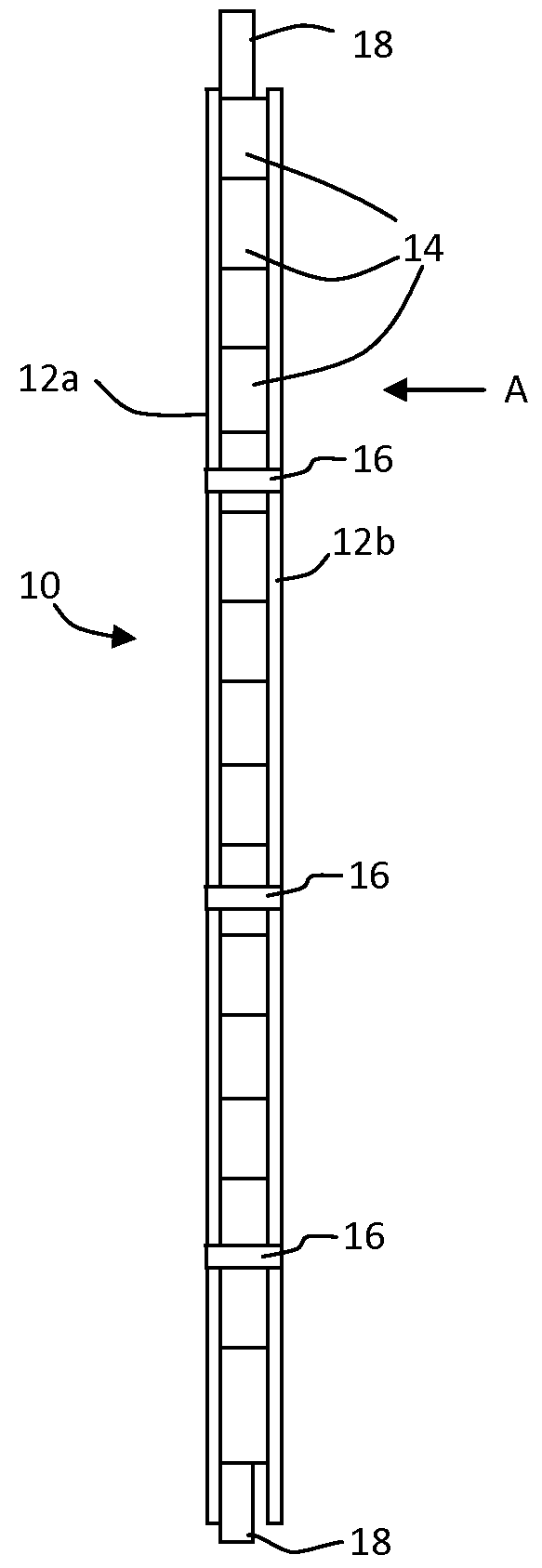
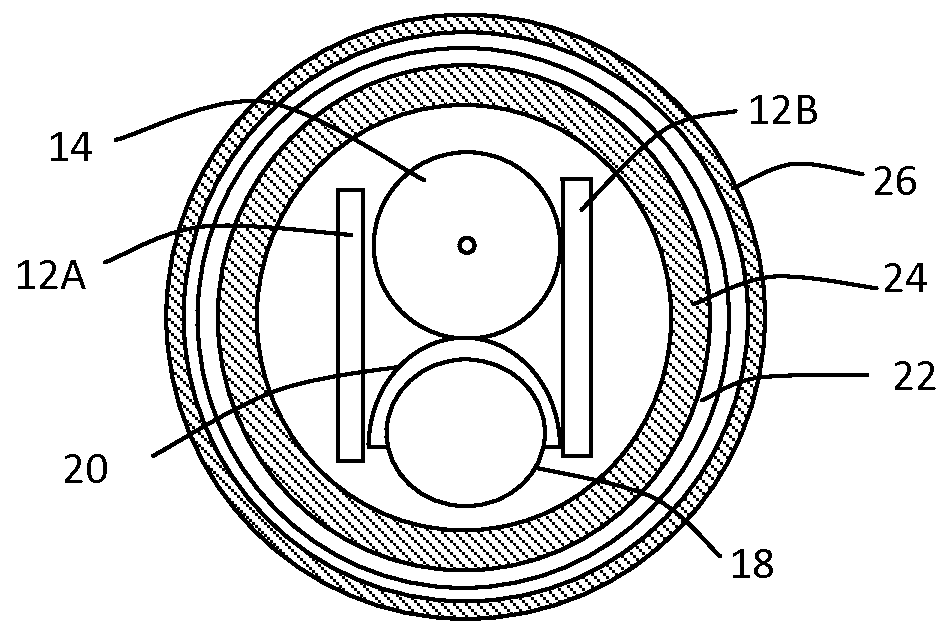
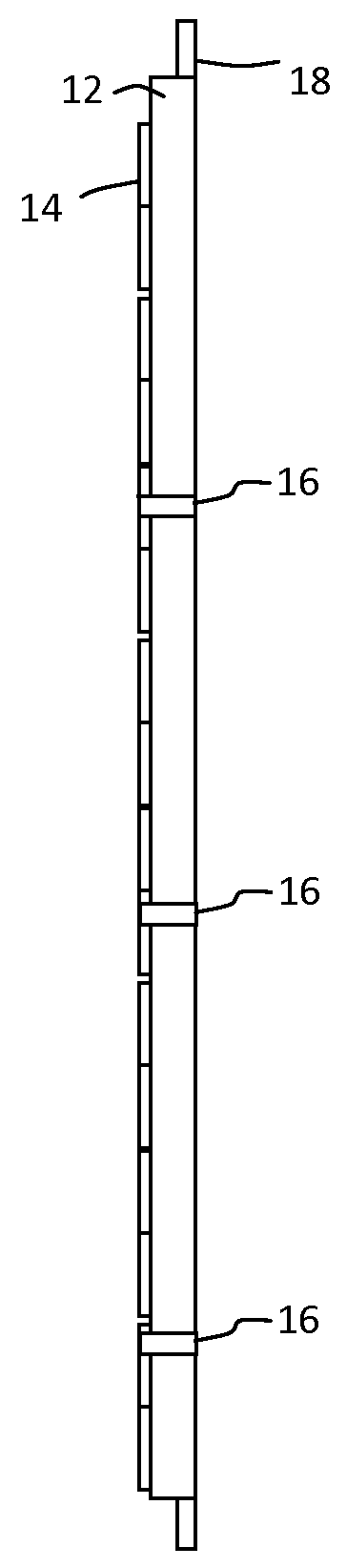
Radiation detector for density or level measurements
ActiveUS9360407B2Increase temperatureProtect environmentMachines/enginesLevel indicatorsLevel measurementData treatment
A nucleonic density profiler includes a detector probe, for detecting ionizing radiation, includes an array of sources of ionizing radiation, an array of radiation detectors and a circuit board including at least two circuit board portions. A power source and electronic apparatus includes a control unit and a signal and data processor for calculating a density profile of the material phases using signals generated by the detectors in response to radiation received from the radiation sources.
Owner:JOHNSON MATTHEY PLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com