Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
58results about How to "Light transmittance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
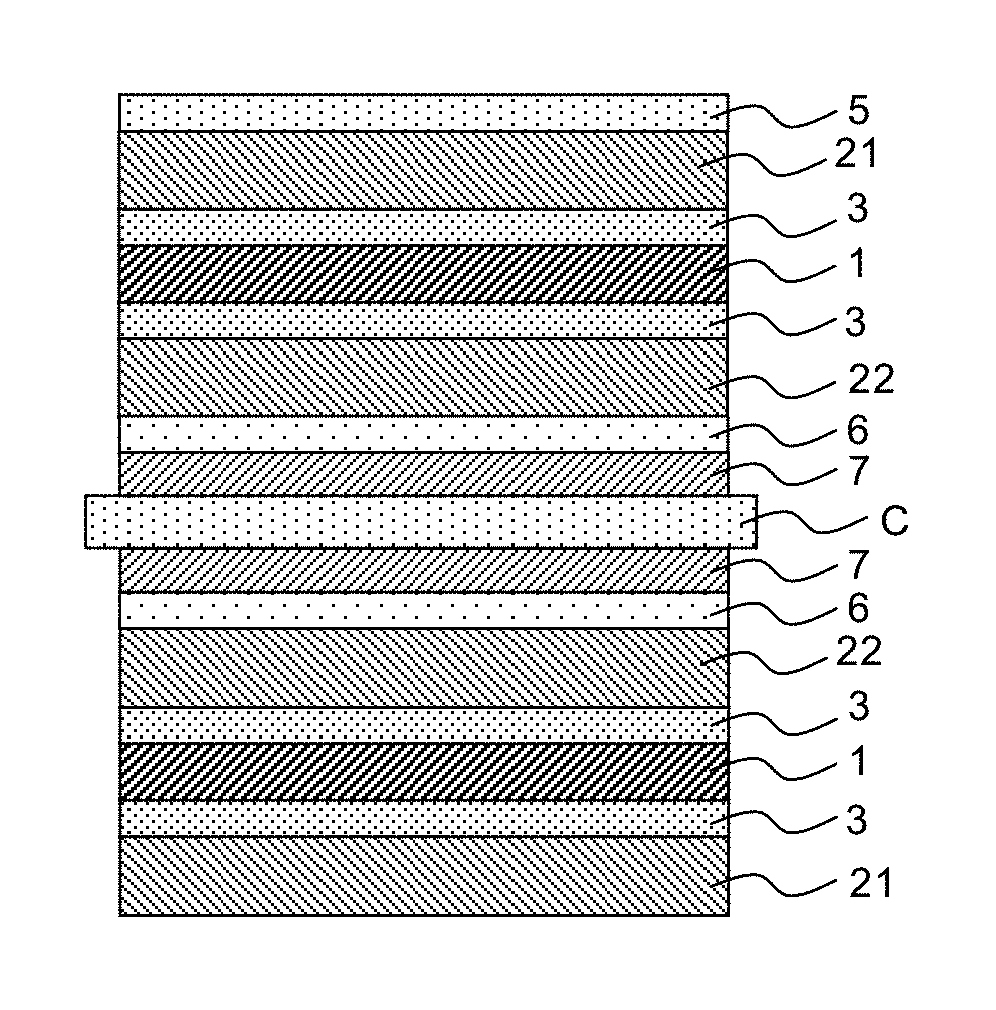
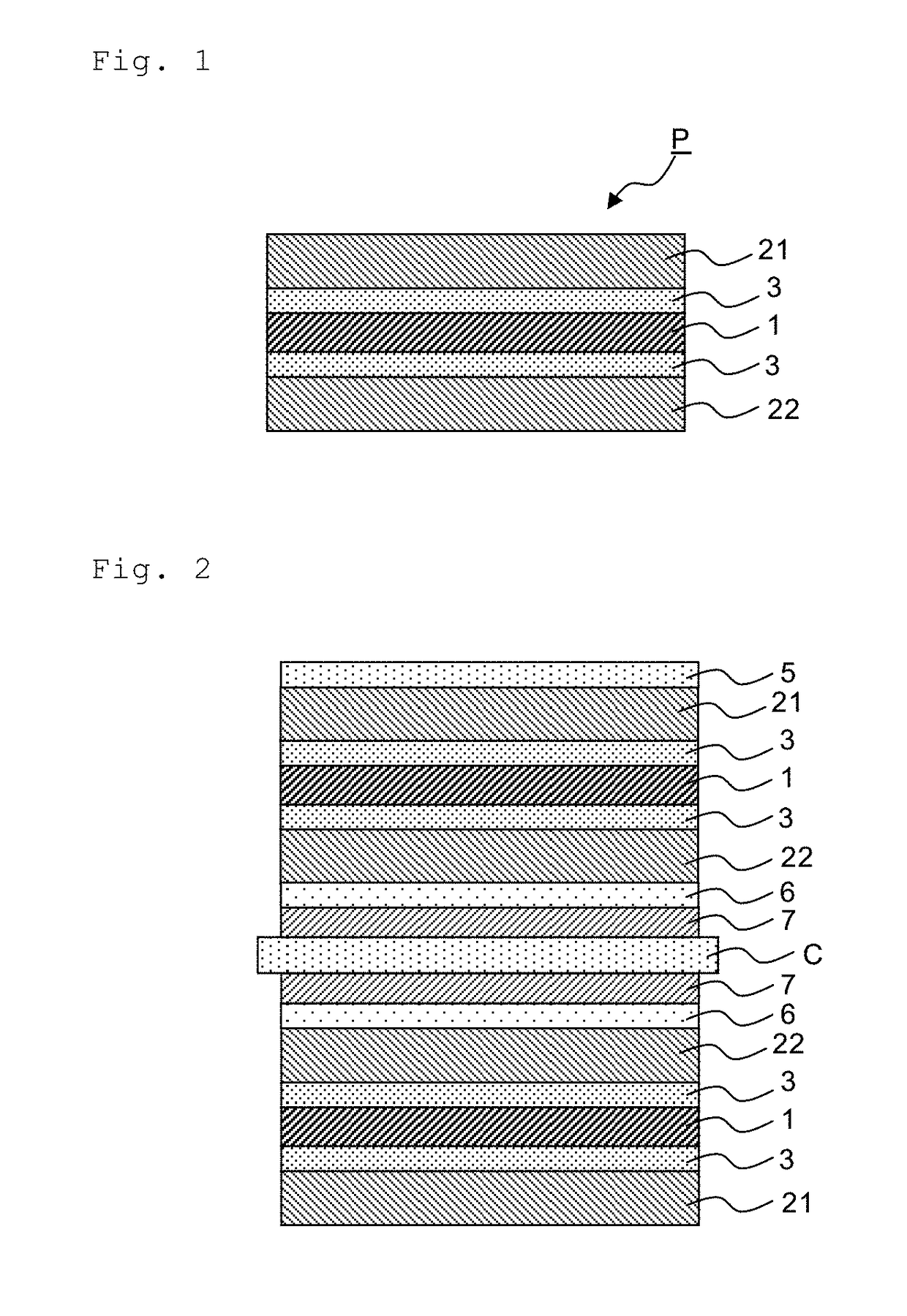
Optical glass, shaped glass material for press-molding, optical element and process for producing optical element
Disclosed is an optical glass having high-refractivity and high-dispersion properties and having little coloring, said glass containing P2O5, Nb2O5 and TiO2 as glass components, containing Sb2O3 in an amount of over 0% by weight but not more than 1% by weight based on the total content of the glass components excluding Sb2O3, having a refractive index (nd) of 1.91 or more and an Abbe's number (νd) of 21 or less and having a light transmittance that comes to be 70% at a wavelength of 500 nm or less.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Thermoplastic Resin Composition And Formed Article Using The Same
InactiveUS20080014376A1Good shading effectLight transmittanceLiquid crystal compositionsOrganic active ingredientsMass ratioBlock effect
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Optical glass, shaped glass material for press-molding, optical element and process for producing optical element
Owner:HOYA CORP
Absorbent Product for Protection from Ultraviolet Ray
InactiveUS20090084698A1Light transmittanceLess ultraviolet transmittanceContainers for flexible articlesDiagnosticsUv blockingTransmittance
An absorbent product comprises (i) a package and (ii) at least one disposable absorbent article contained in the package. The package comprises a window area and an ultraviolet barrier area. The window area allows more light transmittance than the ultraviolet barrier area. The ultraviolet barrier area allows less ultraviolet transmittance than the window area. The absorbent article comprises a liquid permeable topsheet, a liquid impermeable backsheet, an absorbent core disposed between the topsheet and the backsheet, and a reinforcement adhesive having a basis weight of not less than about 10 g / m2. The absorbent article comprises a graphic which is at least partially visible through the window area. The reinforcement adhesive is covered by the ultraviolet barrier area.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBNE CO
Dental Restorative Material
InactiveUS20150272833A1High loading of inorganic fillerExcellently reducesImpression capsPhotomechanical apparatusPolymer scienceRestorative material
A dental restorative material including a photocurable composition that contains a polymerizable monomer component (A), an inorganic filler component (B) having an average particle size of not smaller than 0.07 μm, and a photo polymerization initiator (C),the inorganic filler component (B) being contained in an amount of 100 to 1500 parts by mass per 100 parts by mass of the polymerizable monomer component (A), andthe polymerizable monomer component (A) and the inorganic filler component (B) being so selected as to satisfy a condition (X1) represented by the following formulas (1a) and (1b):nF−0.005<nM<nF+0.005 (1a)nF+0.020<nP<nF+0.040 (1b)wherein,nM is a refractive index of the polymerizable monomer component (A) at 25° C.,nP is a refractive index at 25° C. of a polymer obtained by polymerizing the polymerizable monomer component (A), andnF is a refractive index of the inorganic filler component (B) at 25° C.
Owner:TOKUYAMA DENTAL CORP
Optical multilayer disk, multiwavelength light source, and optical system using them
InactiveUS20060193231A1Improve light absorptionLight transmittanceIntegrated optical head arrangementsOptical beam sourcesRecording layerWaveguide
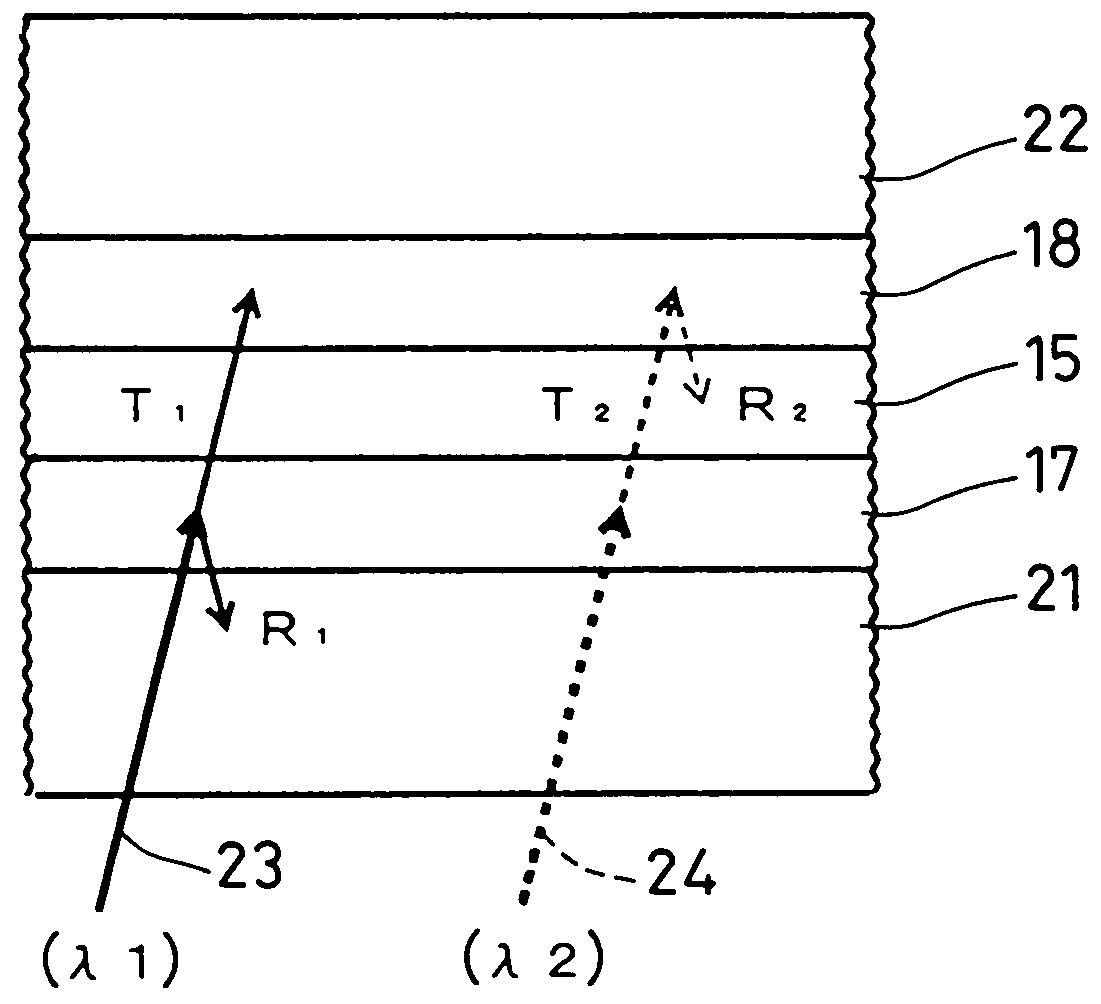
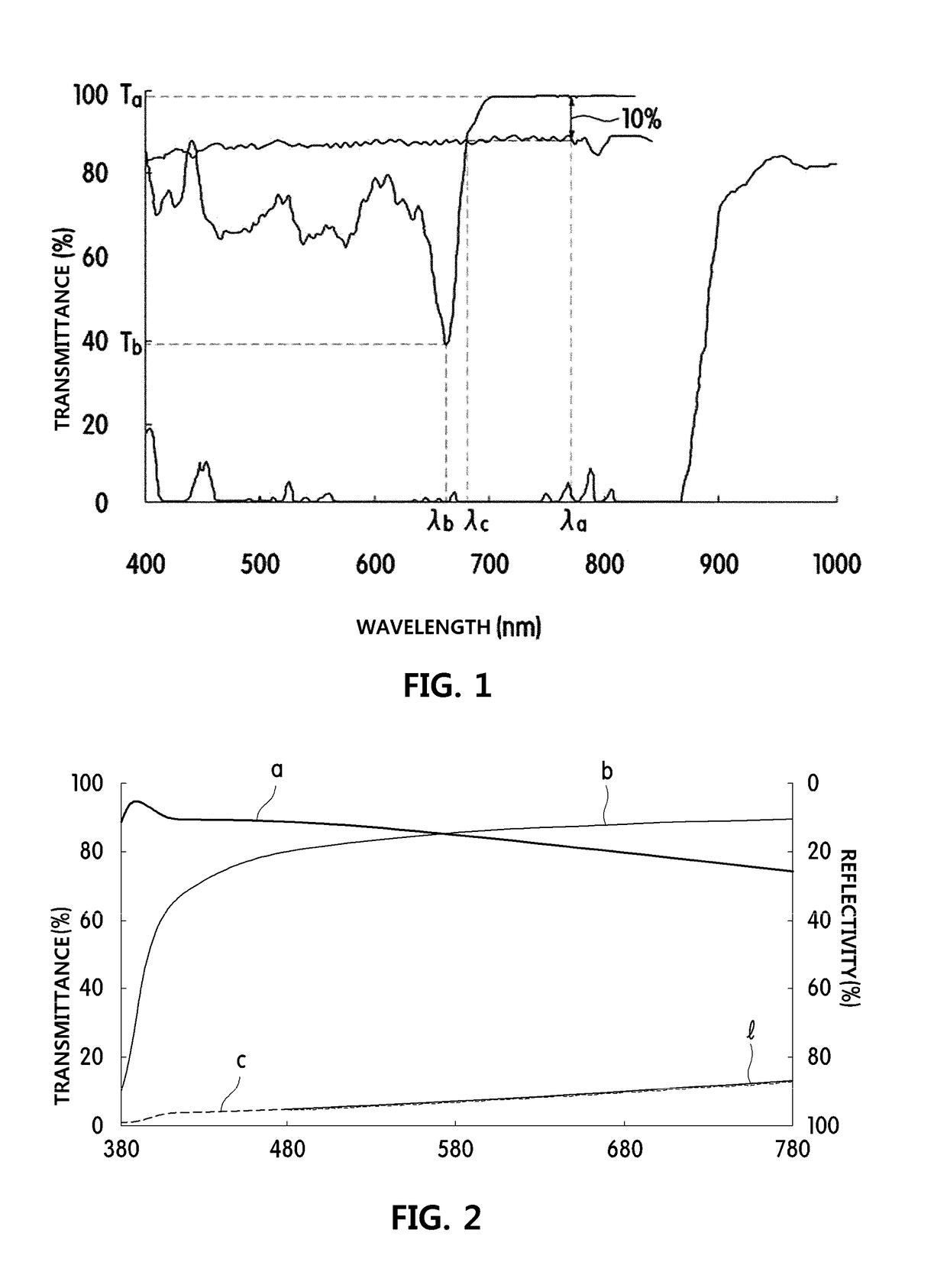
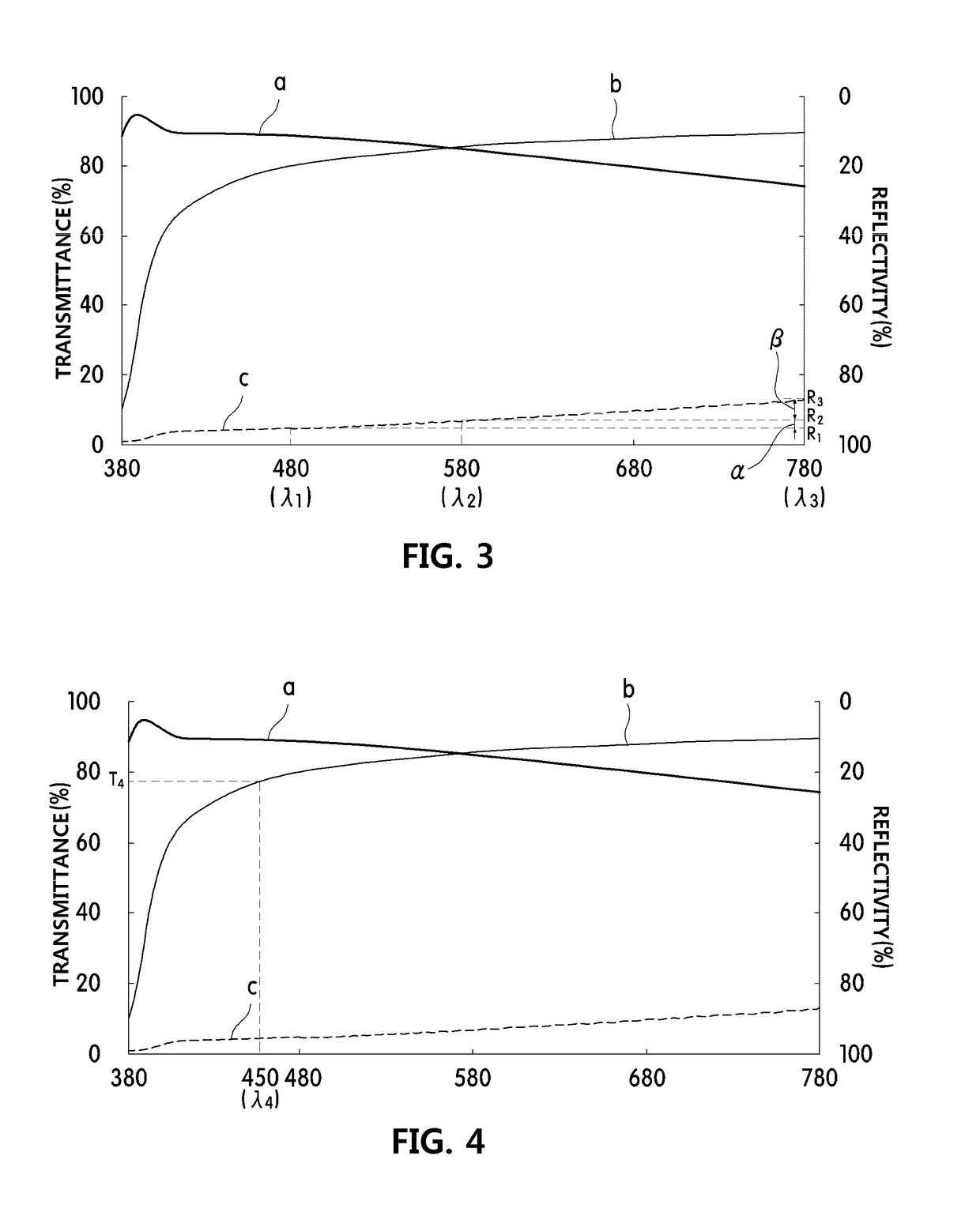
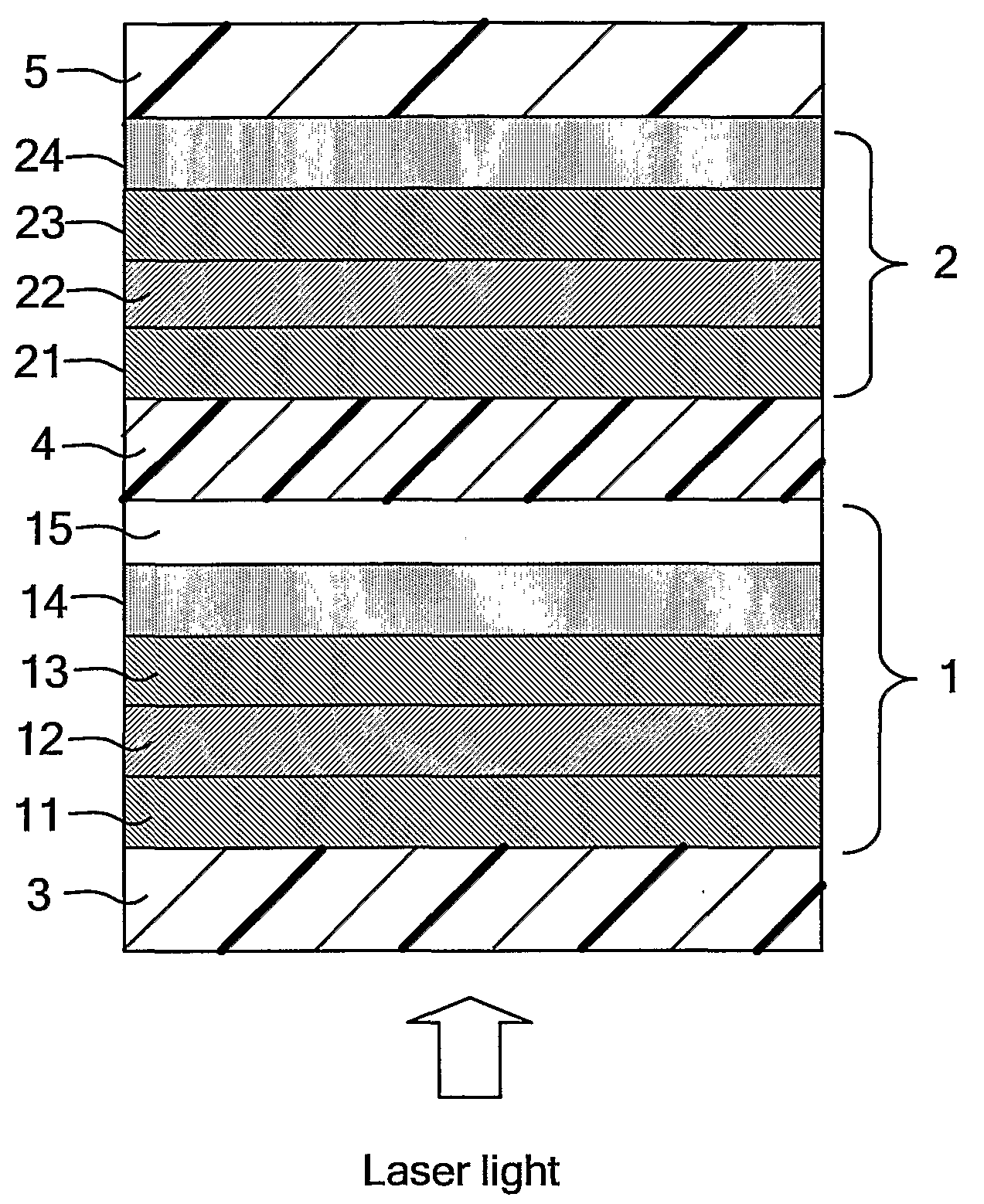
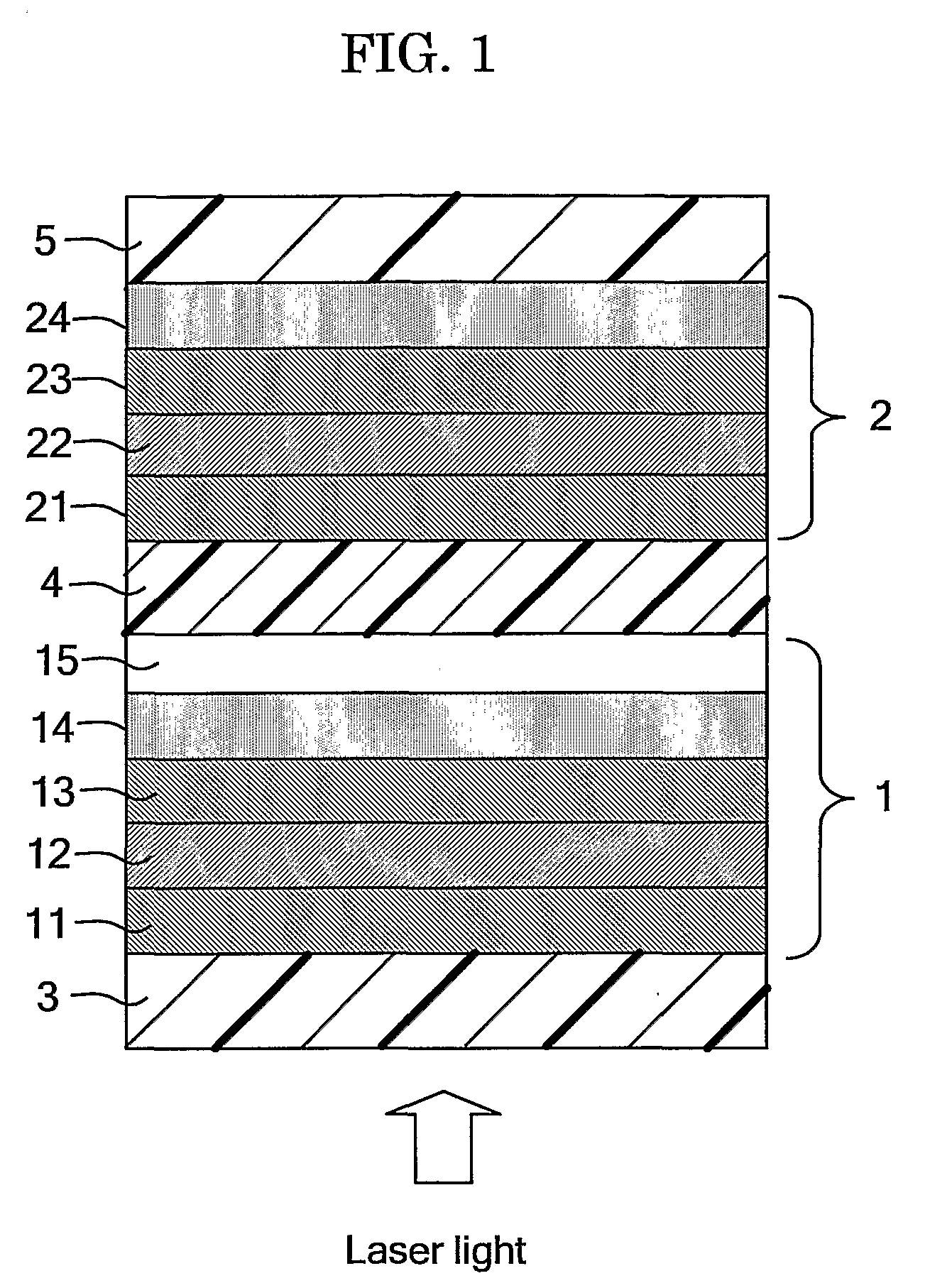
When a wavelength of a first laser beam with which a first recording medium including a first recording layer is recorded and reproduced is indicated as λ1 (nm), a wavelength of a second laser beam with which a second recording medium including a second recording layer is recorded and reproduced as λ2 (nm), the relationship between the wavelength λ1 and the wavelength λ2 is set to be expressed by 10≦|λ1−λ2|≦120. The first recording layer has a light absorptance ratio of at least 1.0 with respect to the wavelength λ1. The light transmittance of the first recording medium with respect to the wavelength λ2 is set to be at least 30 in both the cases where the recording layer is in a crystal state and in an amorphous state. In order to record and reproduce the optical multilayer disk with the above-mentioned characteristics, a multiwavelength light source with the following configuration is used. Wavelengths of fundamental waves with different wavelengths from injection parts formed at one end of a plurality of optical waveguides, which satisfy phase matching conditions different from one another and are formed in the vicinity of the surface of a substrate, are converted simultaneously, and the first and second laser beams are emitted from emission parts formed at substantially the same position at the other end of the optical waveguides. This enables an optimum optical system for high density recording and reproduction to be obtained.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Optical multilayer disk, multiwavelength light source, and optical system using them
InactiveUS7065035B1Improve recording densityEasy to controlIntegrated optical head arrangementsOptical beam sourcesHigh densityOptical transmittance
When a wavelength of a first laser beam with which a first recording medium including a first recording layer is recorded and reproduced is indicated as λ1 (nm), a wavelength of a second laser beam with which a second recording medium including a second recording layer is recorded and reproduced as λ2 (nm), the relationship between the wavelength λ1 and the wavelength λ2 is set to be expressed by 10≦|λ1−λ2|≦120. The first recording layer has a light absorptance ratio of at least 1.0 with respect to the wavelength λ1. The light transmittance of the first recording medium with respect to the wavelength λ2 is set to be at least 30 in both the cases where the recording layer is in a crystal state and in an amorphous state. In order to record and reproduce the optical multilayer disk with the above-mentioned characteristics, a multiwavelength light source with the following configuration is used. Wavelengths of fundamental waves with different wavelengths from injection parts formed at one end of a plurality of optical waveguides, which satisfy phase matching conditions different from one another and are formed in the vicinity of the surface of a substrate, are converted simultaneously, and the first and second laser beams are emitted from emission parts formed at substantially the same position at the other end of the optical waveguides. This enables an optimum optical system for high density recording and reproduction to be obtained.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method of utilizing dual-layer photoresist to form black matrixes and spacers on a control circuit substrate
InactiveUS6958792B2Improve throughputIncrease process marginNon-linear opticsOptoelectronicsOptical density
Owner:HANNSTAR DISPLAY CORPORATION
Apparatus and method for measuring transmittance
InactiveUS20120162651A1Light transmittanceInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsTransmissivity measurementsTransmittanceRelative motion
A device to measure the amount of light able to transmit through a liquid. The device uses a light detector and light source mounted to a support mechanism such that the detector and light source define a path of light emitted by the light source and detected by the detector. The device uses a structure designed to surround a liquid to be tested such that the structure allows light to transmit through the structure and the liquid. An actuator engenders relative motion between the support mechanism and the structure such that at certain times the light propagating between the light source and the detector passes substantially through the structure and the liquid to be tested such that the amount of light able to transmit through the liquid is detected by the detector, and at other times the light propagates directly from the light source to the detector without passing through the structure or the liquid such that the amount of light emitted from the light source is directly detected by the detector. A microprocessor then uses the two sets of detector readings to allow the transmittance measurement of the liquid to be compensated for errors introduced by drift and fluctuations in the amount of light emitted by the light source and also by drift in the light detector and electronics. Such fluctuation and drift is very common in light sources and is due primarily to changes in temperature and imperfections in the light source itself and the power supply.
Owner:002134761 ONTARIO
Carpet unit comprising optical sensor
InactiveUS20110285296A1Good light distributionReduce light absorptionVehicle arrangementsElectric circuit arrangementsOptical transducersMechanical engineering
The invention provides a carpet unit comprising a laminate of a tufted primary backing layer providing a carpet unit top face, an intermediate adhesive layer, and a backing layer providing a carpet unit back face, wherein the carpet unit is selected from the group consisting a carpet and a carpet tile, wherein the carpet unit further comprises an optical sensor, arranged to generate a sensor signal, wherein, seen from carpet unit top face, the optical sensor is arranged behind the primary backing layer, and wherein the carpet unit is arranged to transmit light from the carpet unit top face to the optical sensor.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV +1
Indium oxide based material and method for preparing the same
ActiveUS20070170400A1Improve conductivityConvenient lightingConductive materialOxide conductorsTransmittanceWavelength range
An indium oxide based material containing carbon, and a method for preparing the same are provided. In such a method, the carbon is added to the indium oxide based material film so that the electrical resistivity of the indium oxide based material film is decreased, and the light transmittance of the indium oxide based material in the shorter wavelength range is increased, and also the light can transmit through such a material over a broader short wavelength range. The indium oxide based material prepared by the method of the present invention has higher electrical conductivity and higher light transmittance in comparison with the conventional one without adding carbon.
Owner:CHANG CHUNG CHENG
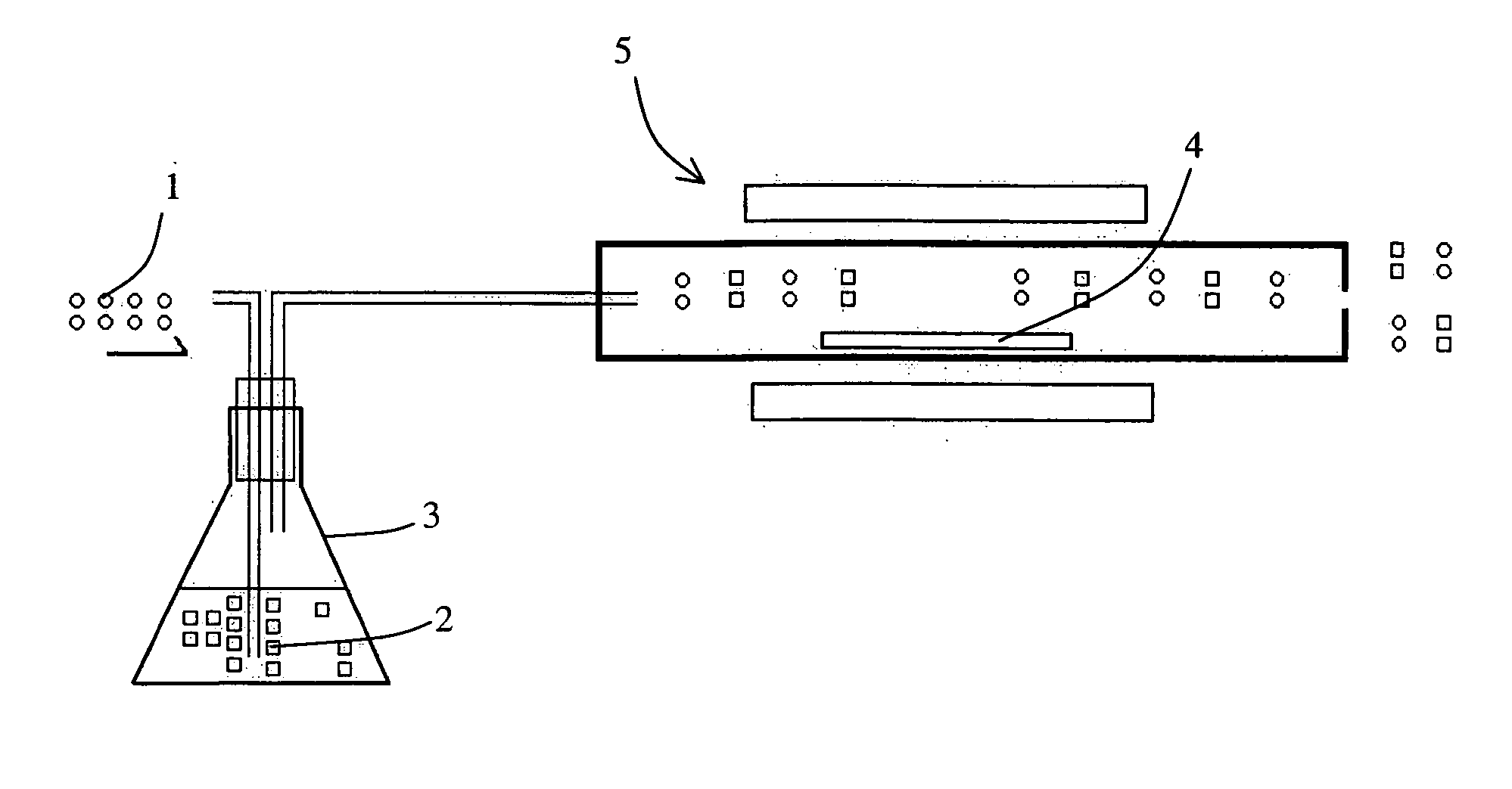
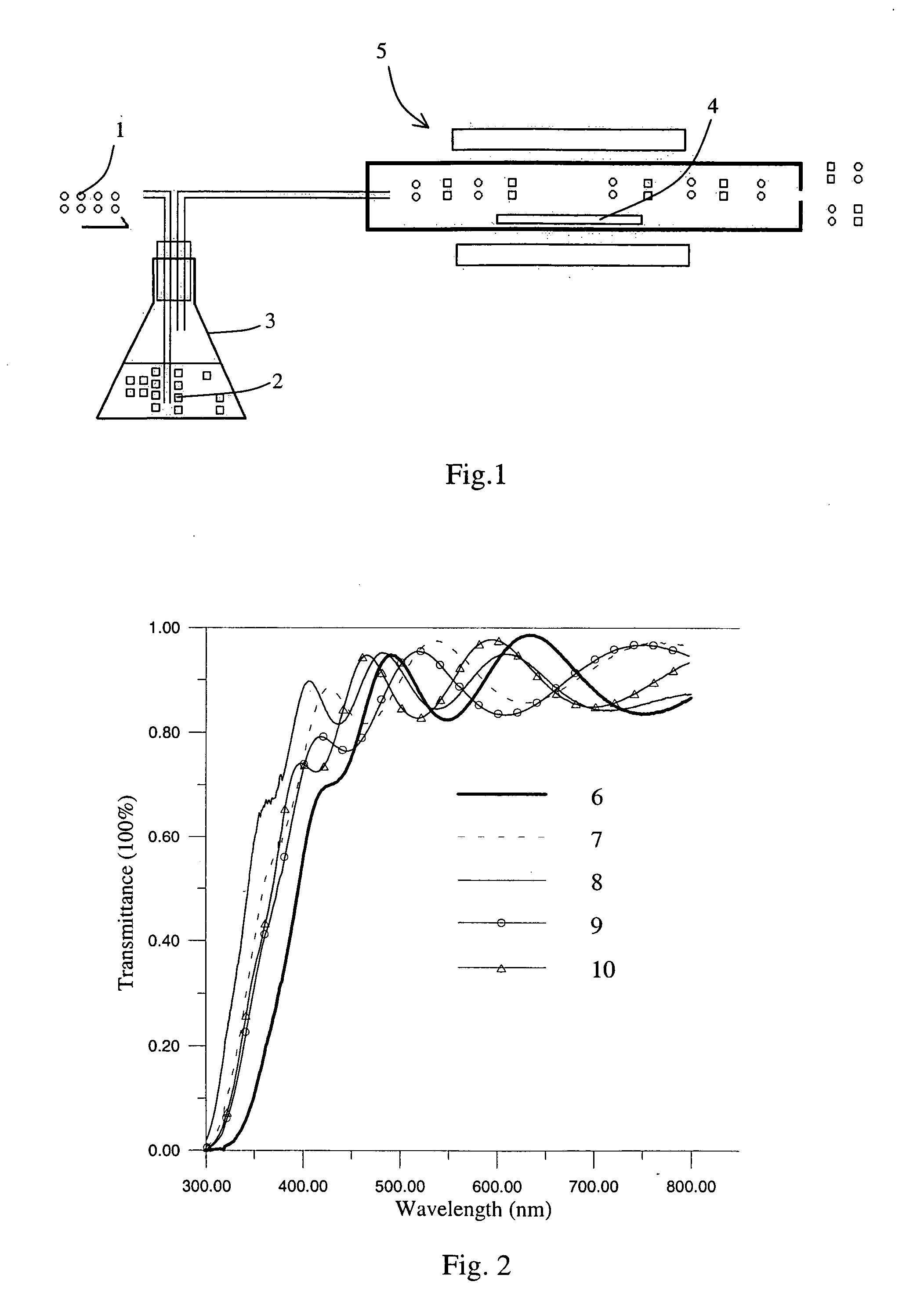
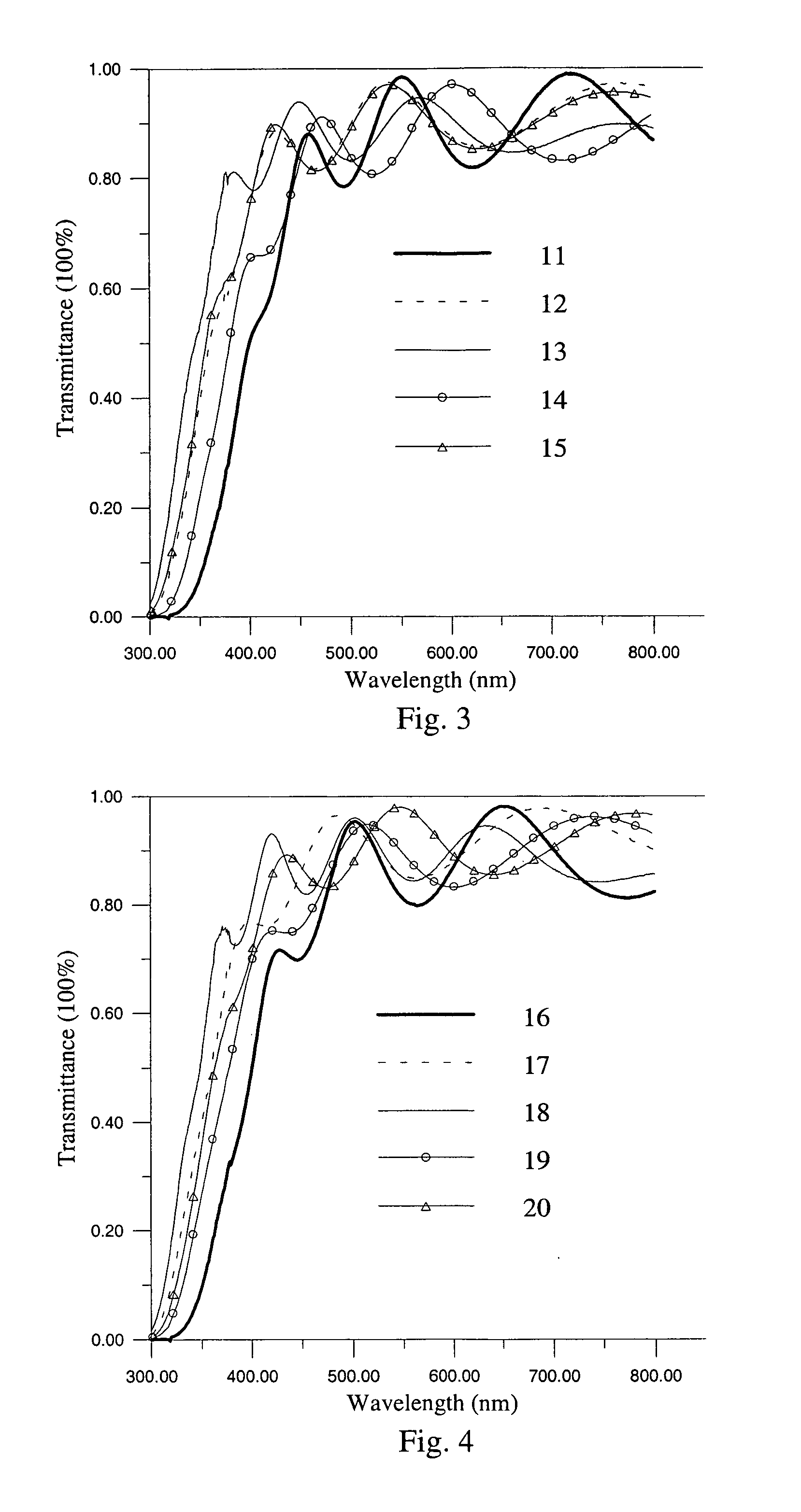
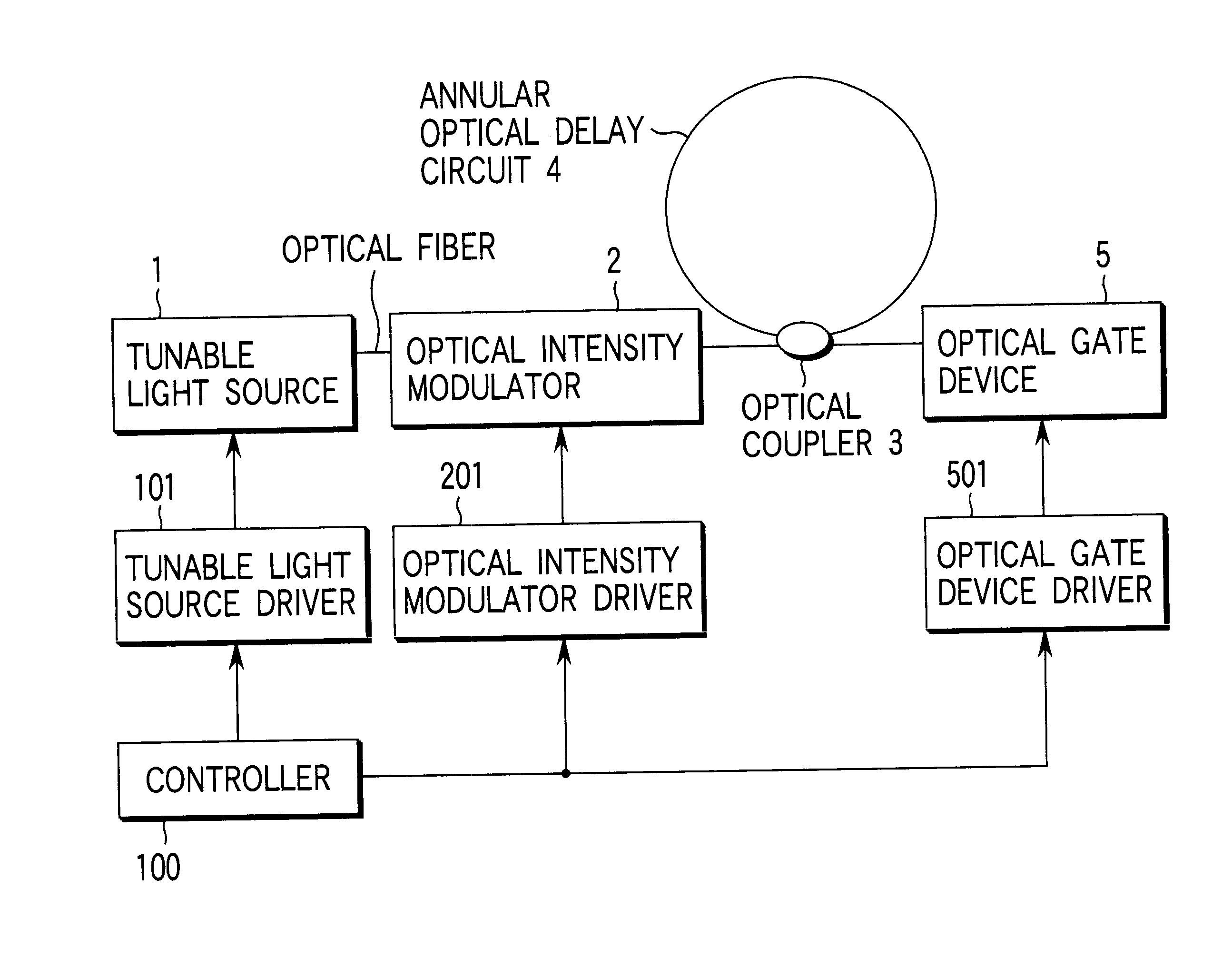
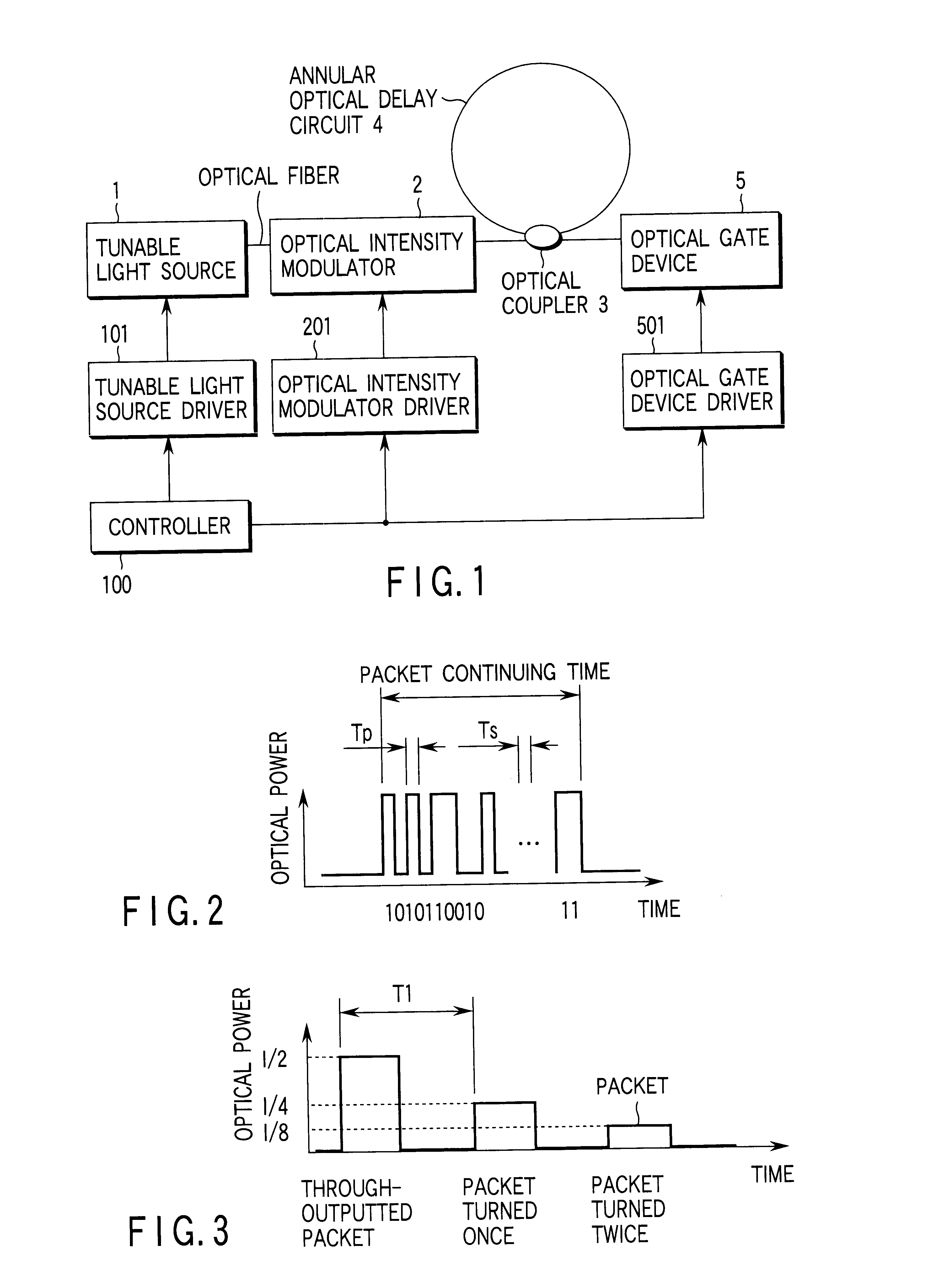
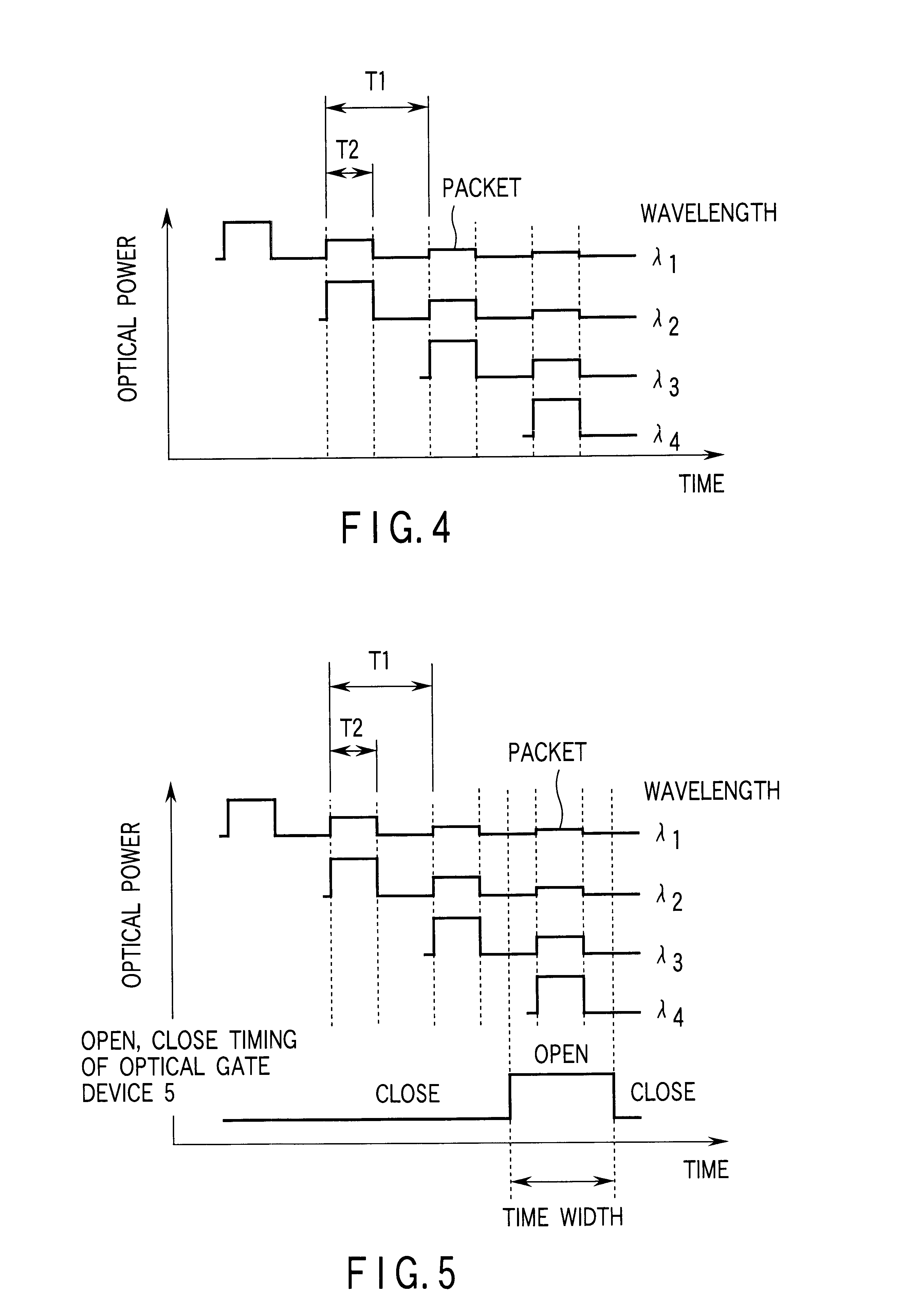
Multiwavelength light source device employing annular optical delay circuit
InactiveUS6792215B1Easy to storeHigh light transmittanceTime-division optical multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsSignal lightLength wave
A multi-wavelength light source apparatus includes a tunable light source, optical intensity modulator, optical coupler, annular optical delay circuit, and optical gate device. The tunable light source successively changes and outputs a plurality of output lights different in wavelength from one another. The optical intensity modulator outputs a modulated signal light obtained by modulating an amplitude of the output light outputted from the tunable light source over a predetermined time. The optical coupler is optically connected to the optical intensity modulator, and receives the light outputted from the optical intensity modulator. The annular optical delay circuit is optically connected to the optical coupler, and delays a part of the output light outputted from the optical intensity modulator over a time longer than the predetermined time. The optical gate device is optically connected to the optical coupler, receives the output light outputted from the optical intensity modulator and the light passed via the annular optical delay circuit to open a gate at a timing and time width such that all of the signal light modulated over the predetermined time is included one by one for each of the plurality of wavelengths.
Owner:ANRITSU CORP
Display panel
ActiveUS20100149478A1Raise the ratioImprove transmittanceLiquid crystal compositionsStatic indicating devicesLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
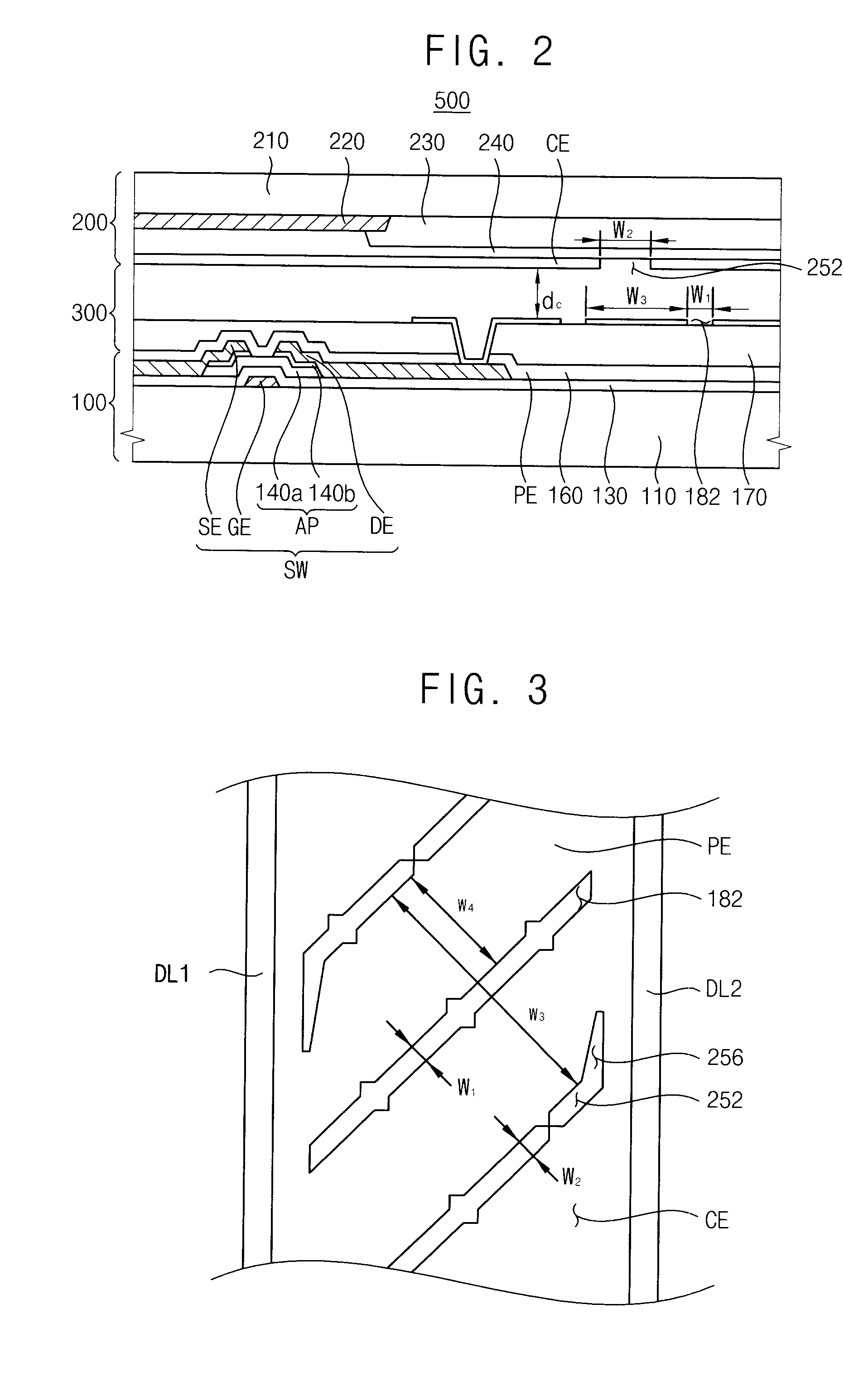
A display panel includes a first substrate, a second substrate, and a liquid crystal layer. The first substrate includes a switching element connected to a gate line and a data line crossing each other, and a pixel electrode electrically connected to the switching element. The pixel electrode includes a first domain-dividing portion extending in a direction. The second substrate is spaced apart from the first substrate to have a cell gap of about 3.1 μm to about 3.3 μm. The second substrate includes a common electrode including a second domain dividing portion formed in a region between the first domain-dividing portions adjacent to each other. The liquid crystal layer is interposed between the first and second substrates. The liquid crystal layer includes a liquid crystal composition having a refractive anisotropy (Δn) of about 0.1010 to about 0.1030.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Soundproofing structure, opening structure, cylindrical structure, window member, and partition member
ActiveUS10373599B2Improve performanceEnsure ventilation propertyWallsLayered productsSound sourcesTransmittance
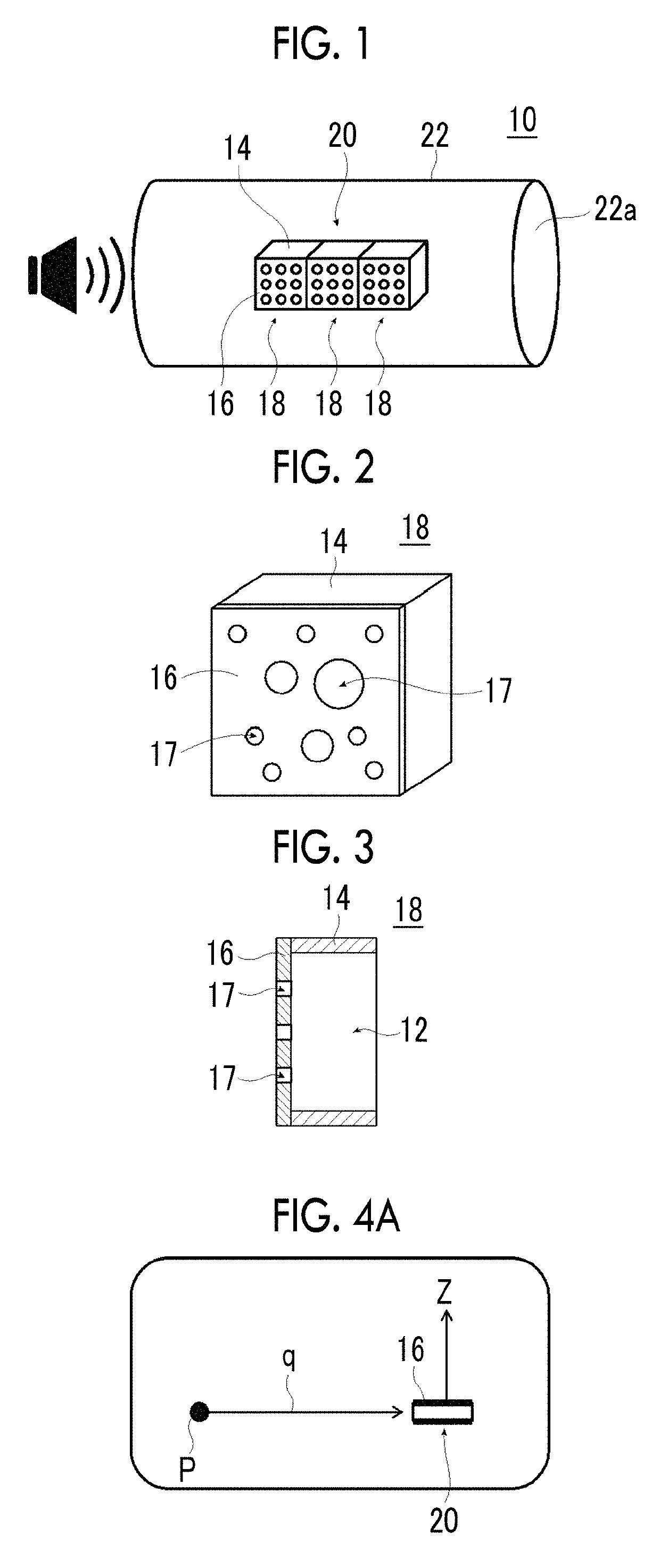
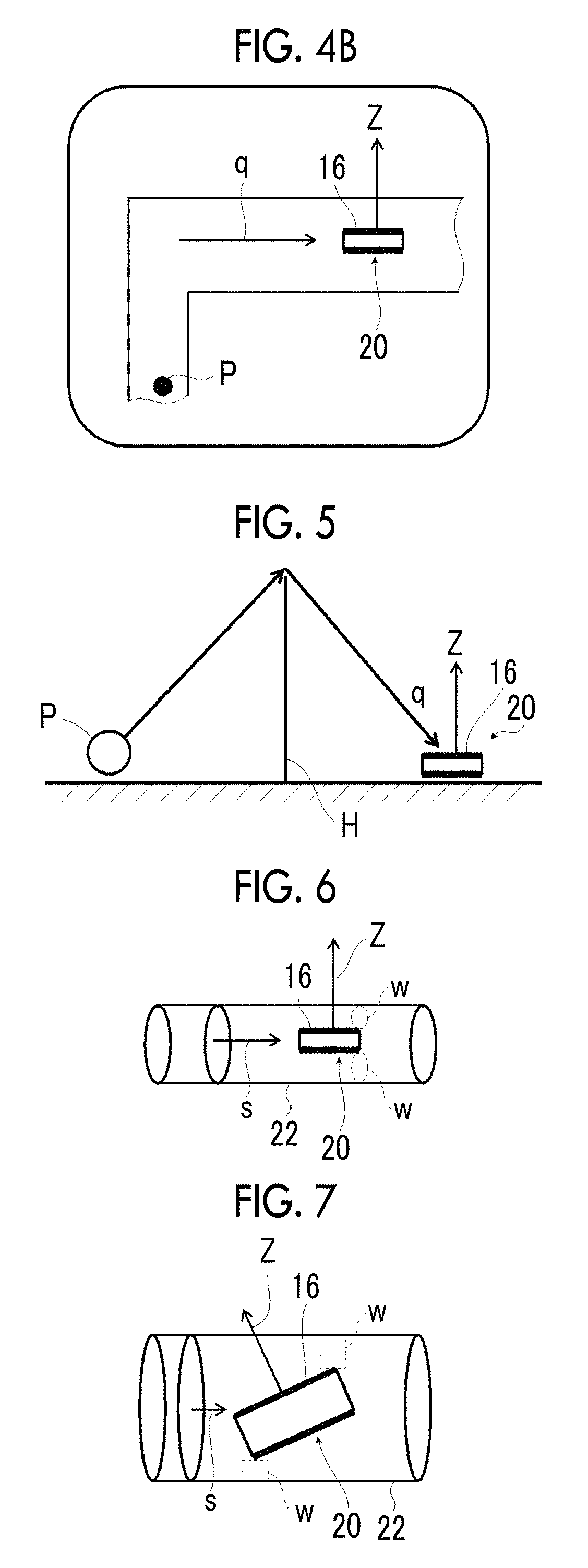
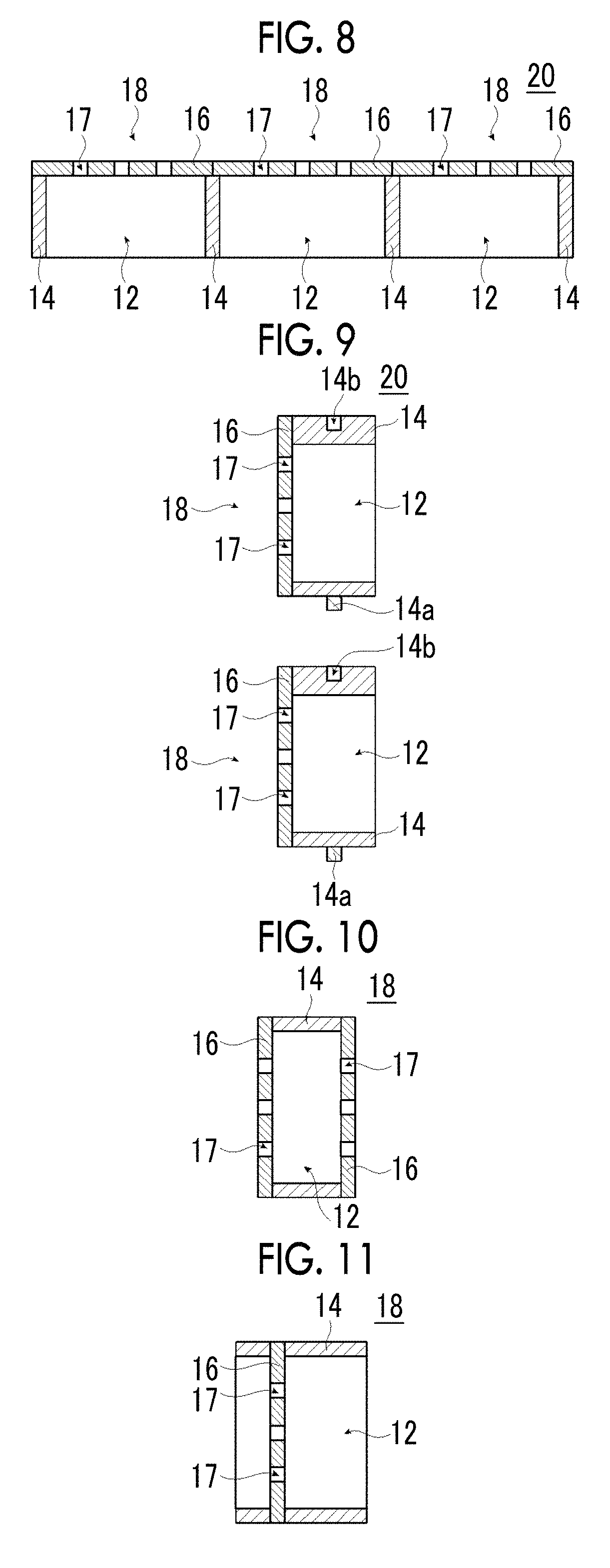
An object is to provide a soundproofing structure which exhibits high soundproofing performance in a broad frequency band, can be miniaturized, can ensure ventilation properties, and has a light transmittance, and a cylindrical structure, a window member, and a partition member including this soundproofing structure. Provided is a soundproofing structure including: a soundproofing cell which includes a frame having a frame hole portion passing therethrough and a film that covers the frame hole portion and is fixed to the frame, in which the film has a plurality of through-holes passing therethrough in a thickness direction, an average opening diameter of the through-holes is in a range of 0.1 μm to 250 μm, and a vertical direction of a film surface is disposed so as to be inclined with respect to a direction of a sound source to be soundproofed.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
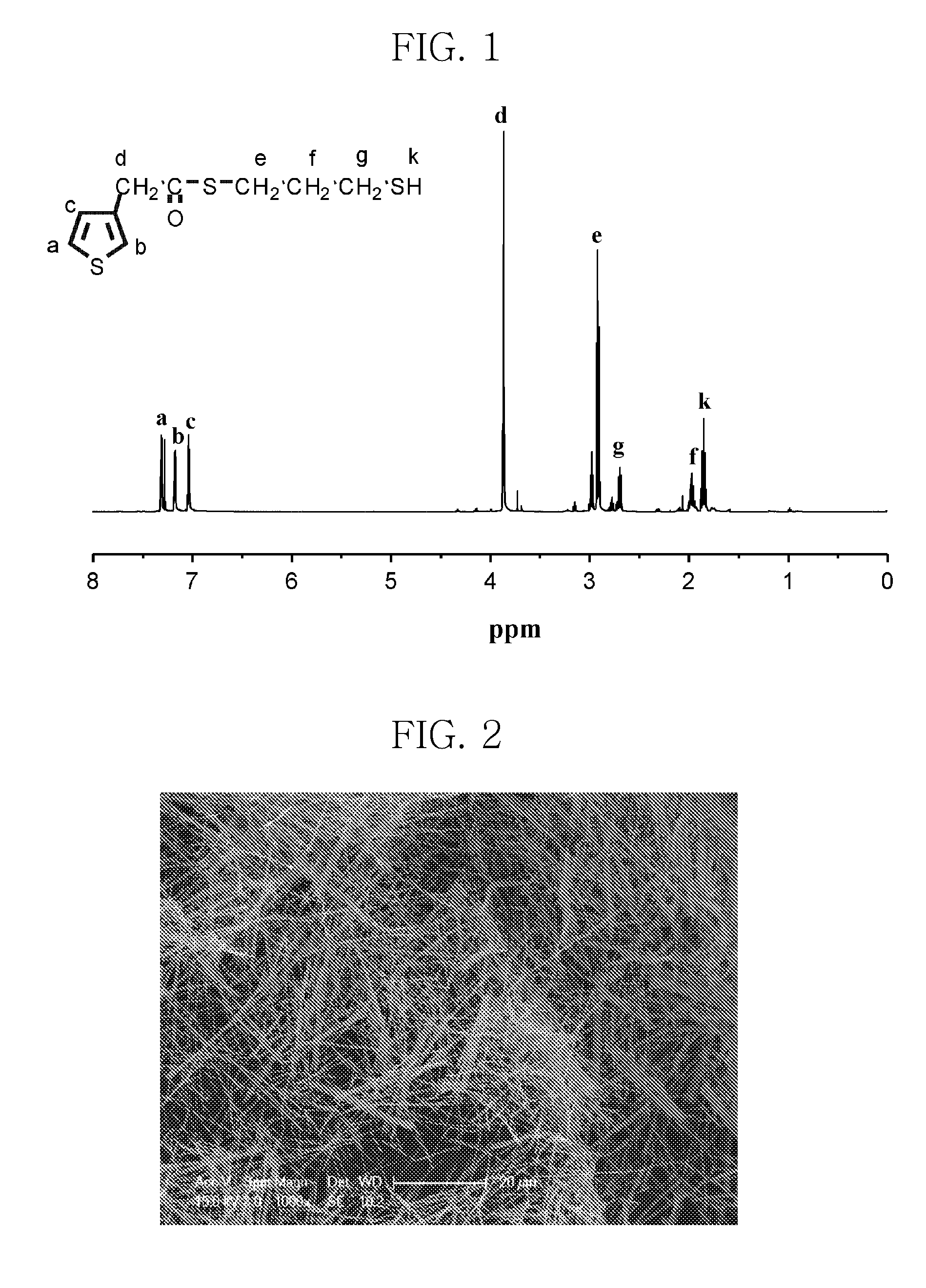
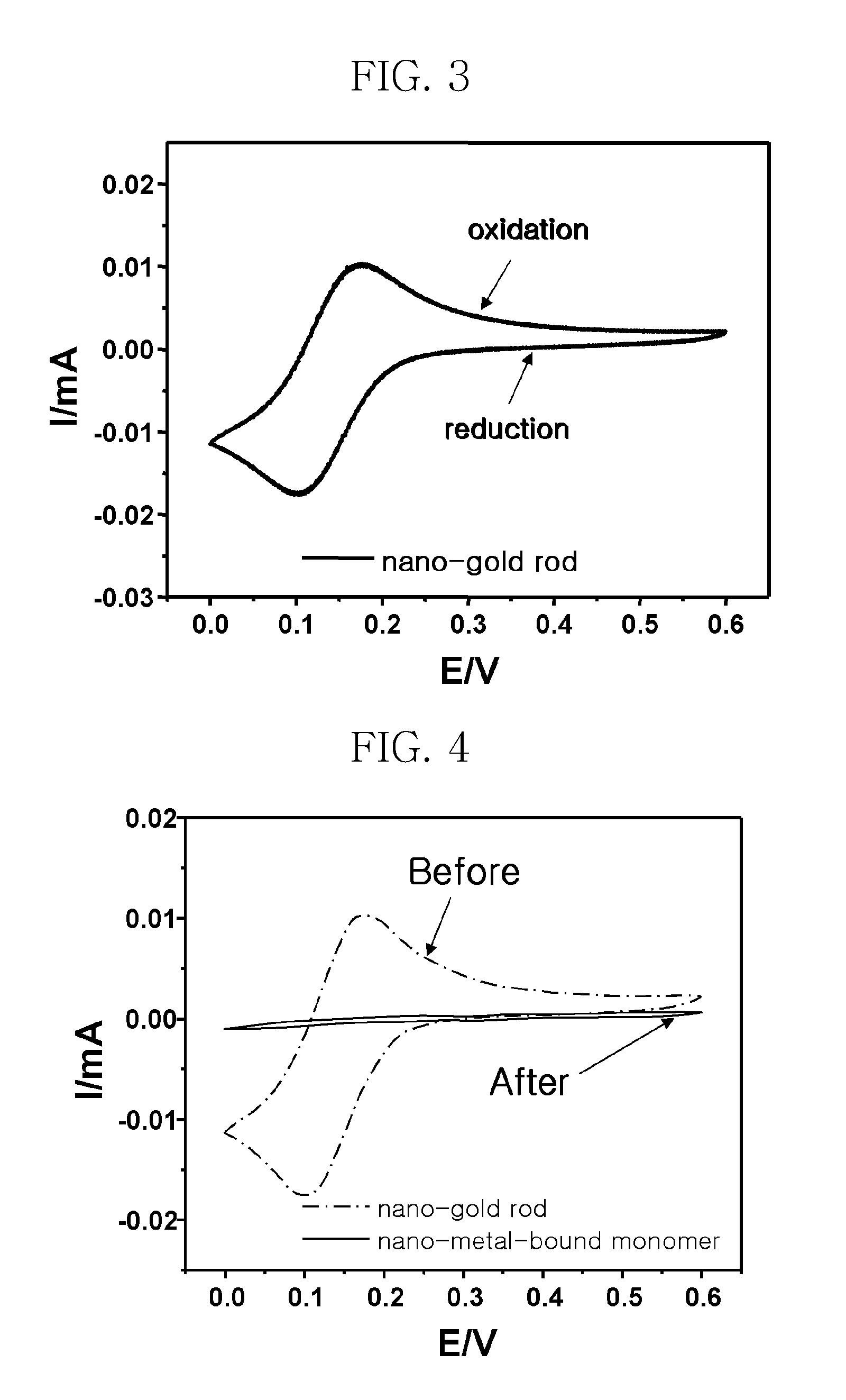
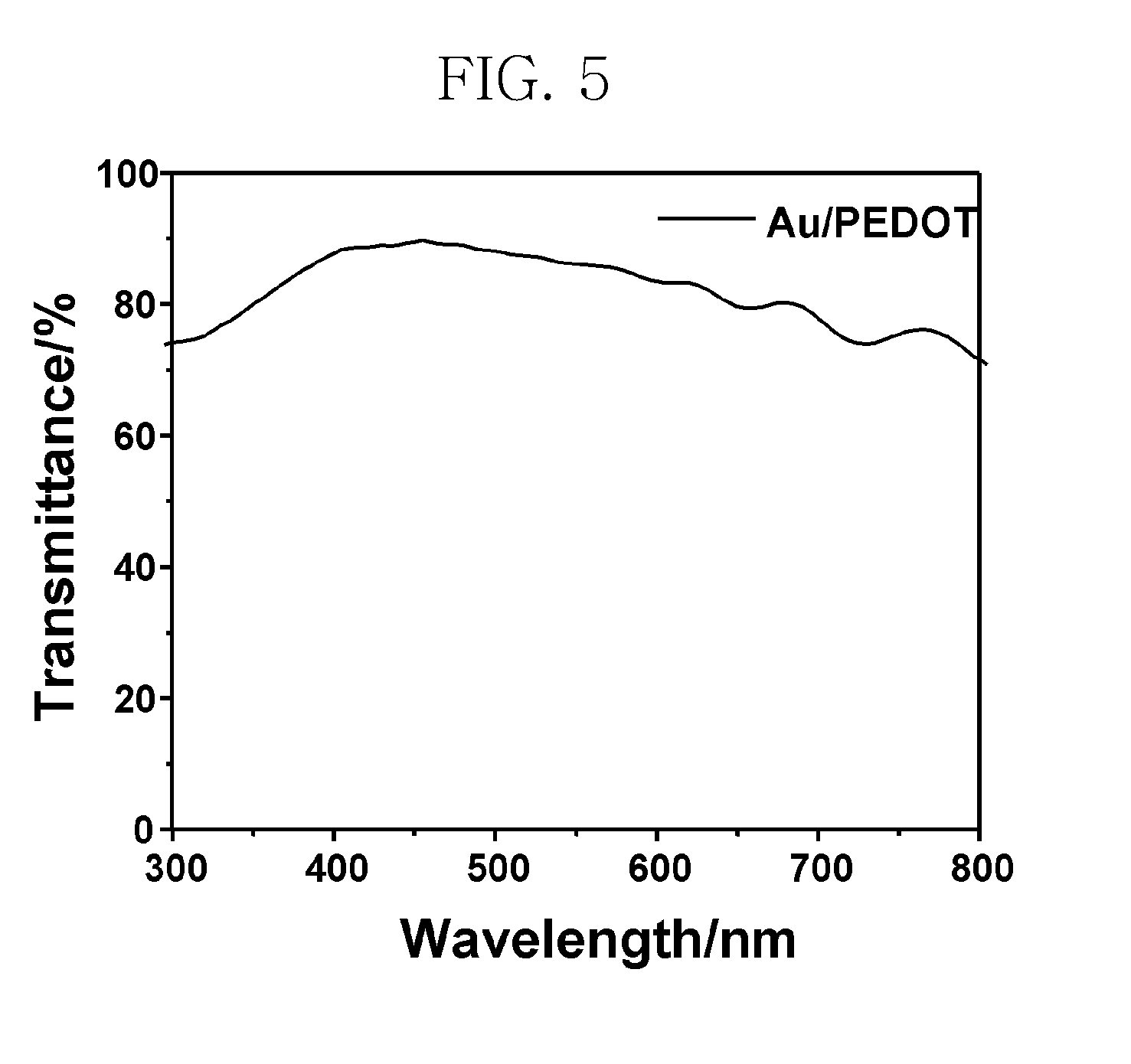
Monomer for binding nano-metal, conductive polymer composite and method of preparing the conductive polymer composite
ActiveUS20090286082A1Improve conductivityImprove solubilityMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic chemistryConductive polymer compositeElectrical conductor
Disclosed herein is a monomer for binding nano-metal, which is useful for the preparation of a conductor having increased conductivity with ensuring flexibility and transparency. Polymerization of the monomer for binding nano-metal provides a conductive polymer composite including a nano-metal rod. A method of preparing the conductive polymer composite is also provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Polishing pad
ActiveUS9126304B2High accuracy optical end-point detectionPrevent leakageAbrasion apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSlurrySemiconductor
An object of the present invention is to provide a polishing pad which enables high accuracy optical end-point detection in a state where polishing is carrying out, and which can prevent slurry leakage from a polishing layer to a cushion layer even in the case of being used for a long period. Another object is to provide a method for producing a semiconductor device using the polishing pad. The present invention relates to a polishing pad in which a polishing layer having a polishing region and a light-transmitting region, and a cushion layer having a through hole are laminated via a double-sided adhesive sheet such that the light-transmitting region and the through hole are laid one upon another, wherein a transparent member is stuck on an adhesive layer of the double-sided adhesive sheet in the through hole.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
Flexible display panel and flexible display device
ActiveUS20210081063A1Reduce the arrangement densityImprove the display effectSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal gridMetal mesh
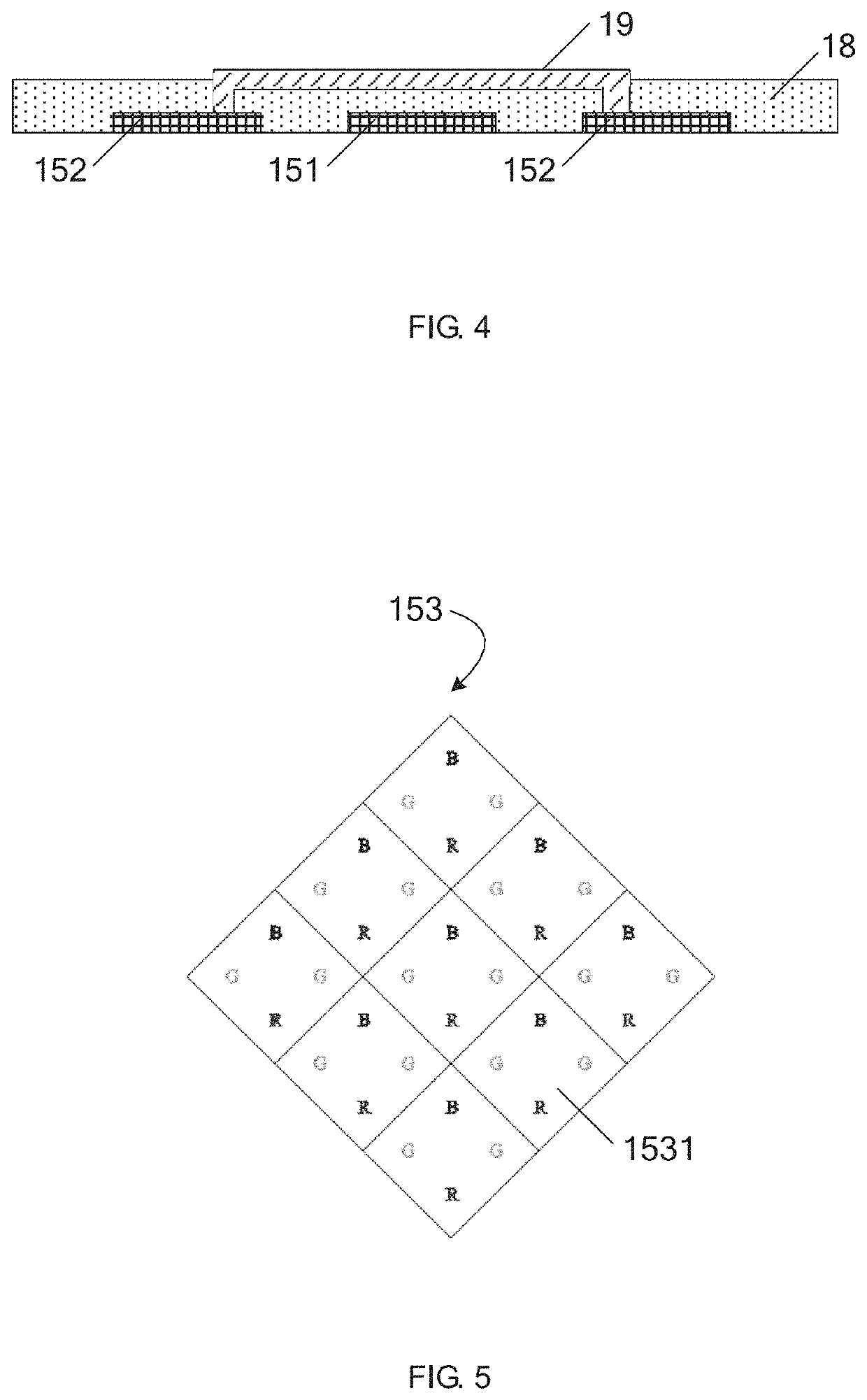
Disclosed is a flexible display panel, comprising a flexible substrate; an organic light emitting diode layer, disposed on the flexible substrate, wherein the organic light emitting diode layer comprises a plurality of sub pixels arranged at intervals; a metal mesh, disposed on the organic light emitting diode layer, wherein metal traces of the metal mesh are correspondingly arranged in gaps among the plurality of sub pixels disposed at intervals, and the metal traces of the metal mesh surround to form a plurality of touch electrodes, and at least one of the touch electrodes comprises at least one first touch area, and the first touch area is correspondingly arranged with at least two of the sub pixels. The flexible display panel can improve the display effect of the flexible display panel by reducing the arrangement density of the metal traces of the metal mesh.
Owner:WUHAN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS SEMICON DISPLAY TECH CO LTD
Display control method, display control device and display system
ActiveUS20170206858A1Reduce intensityLight transmittanceInstrument arrangements/adaptationsCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay deviceComputer science
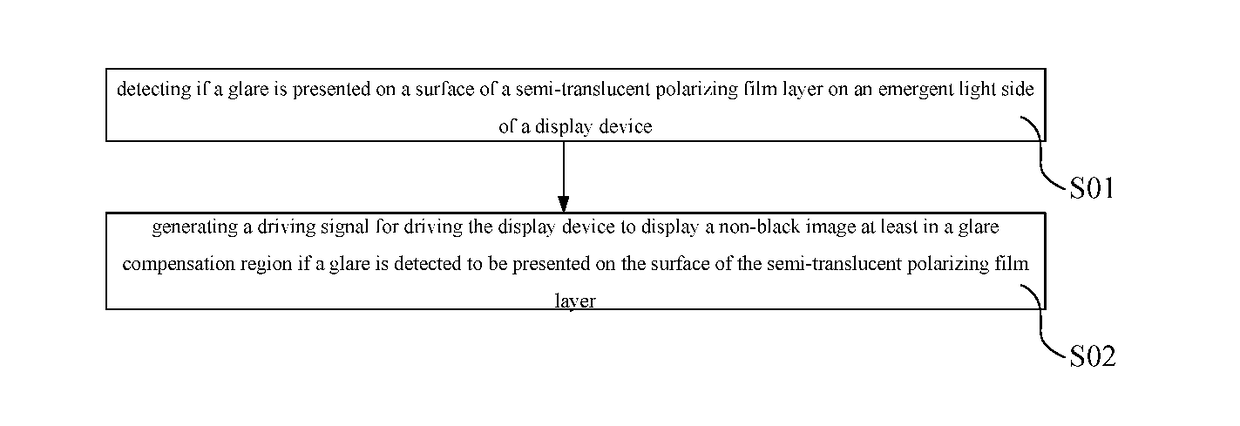
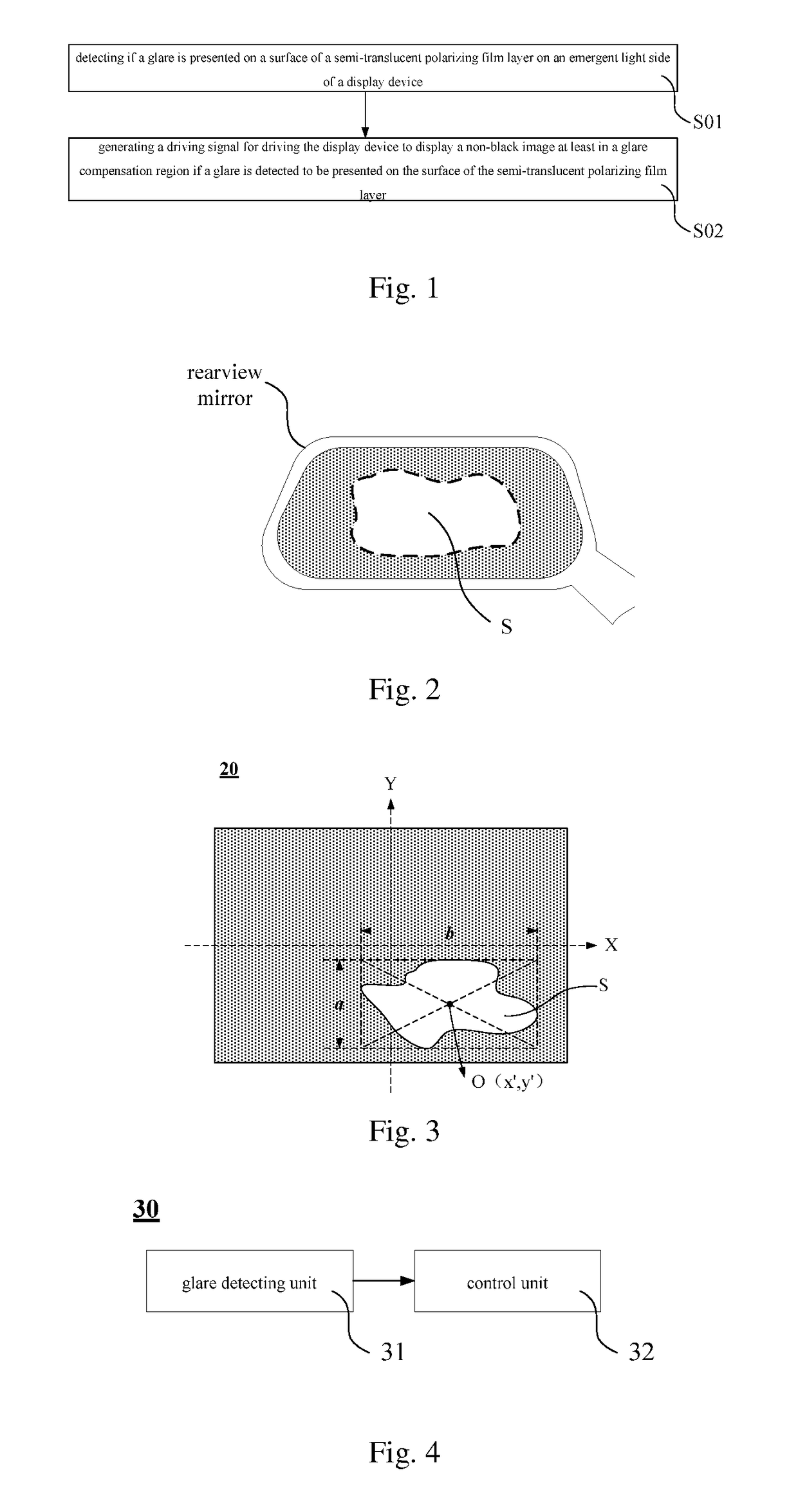
The embodiments of the present disclosure relate to the display technology field, and provide a display control method, a display control device and a display system. The display control method includes: detecting if a glare is presented on the surface of the semi-translucent polarizing film layer on the emergent light side of the display device; generating a driving signal for driving the display device to display a non-black image in a glare compensation region if a glare is detected to be presented on the surface of the semi-translucent polarizing film layer; in which the glare compensation region corresponds to a glare region in the semi-translucent polarizing film layer and the glare region is an region in which a glare is presented. The display control method of the present disclosure may reduce glare intensity when a glare is created on a mirror surface such as a rearview mirror.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Active matrix substrate and method for producing same
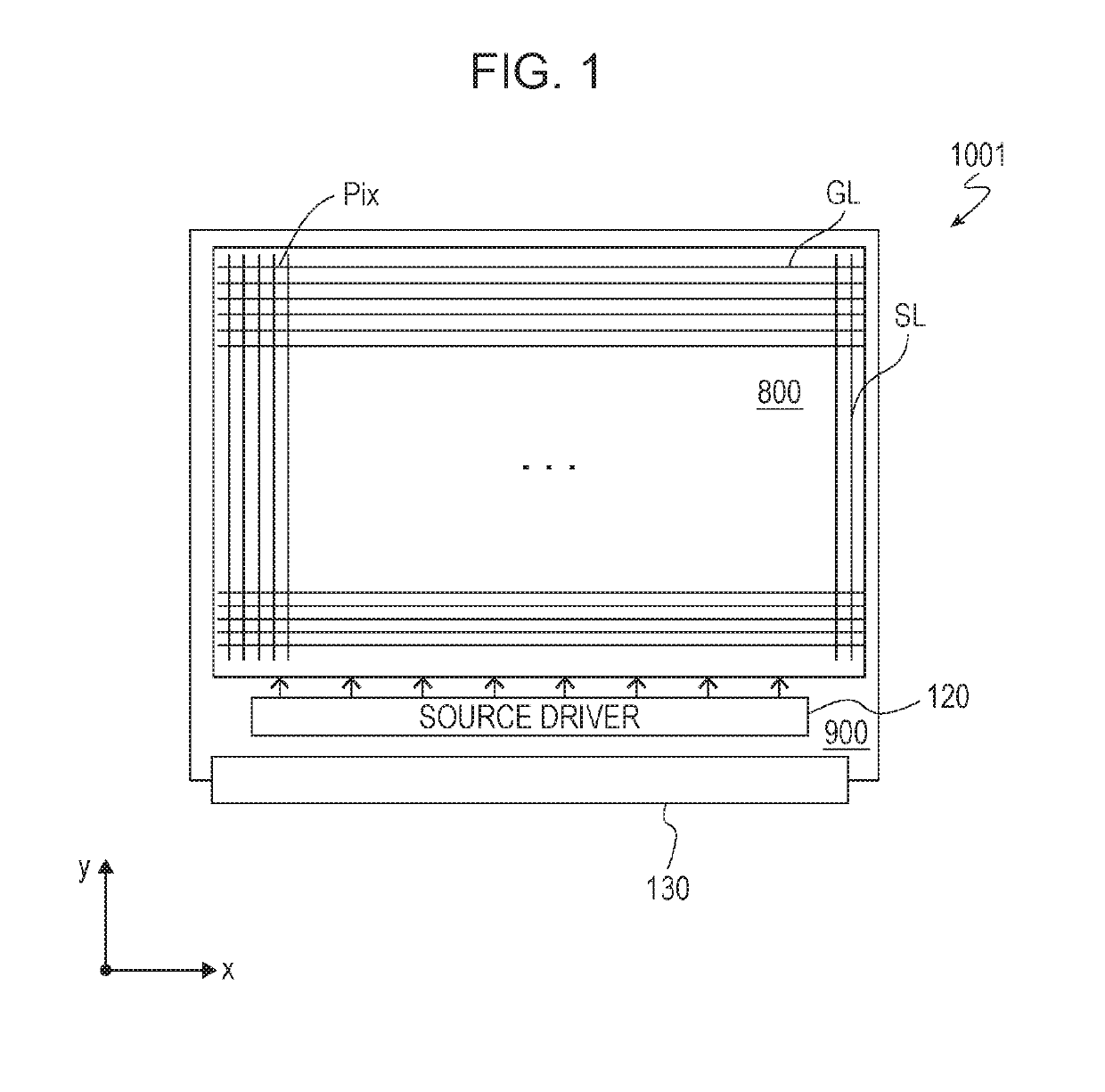
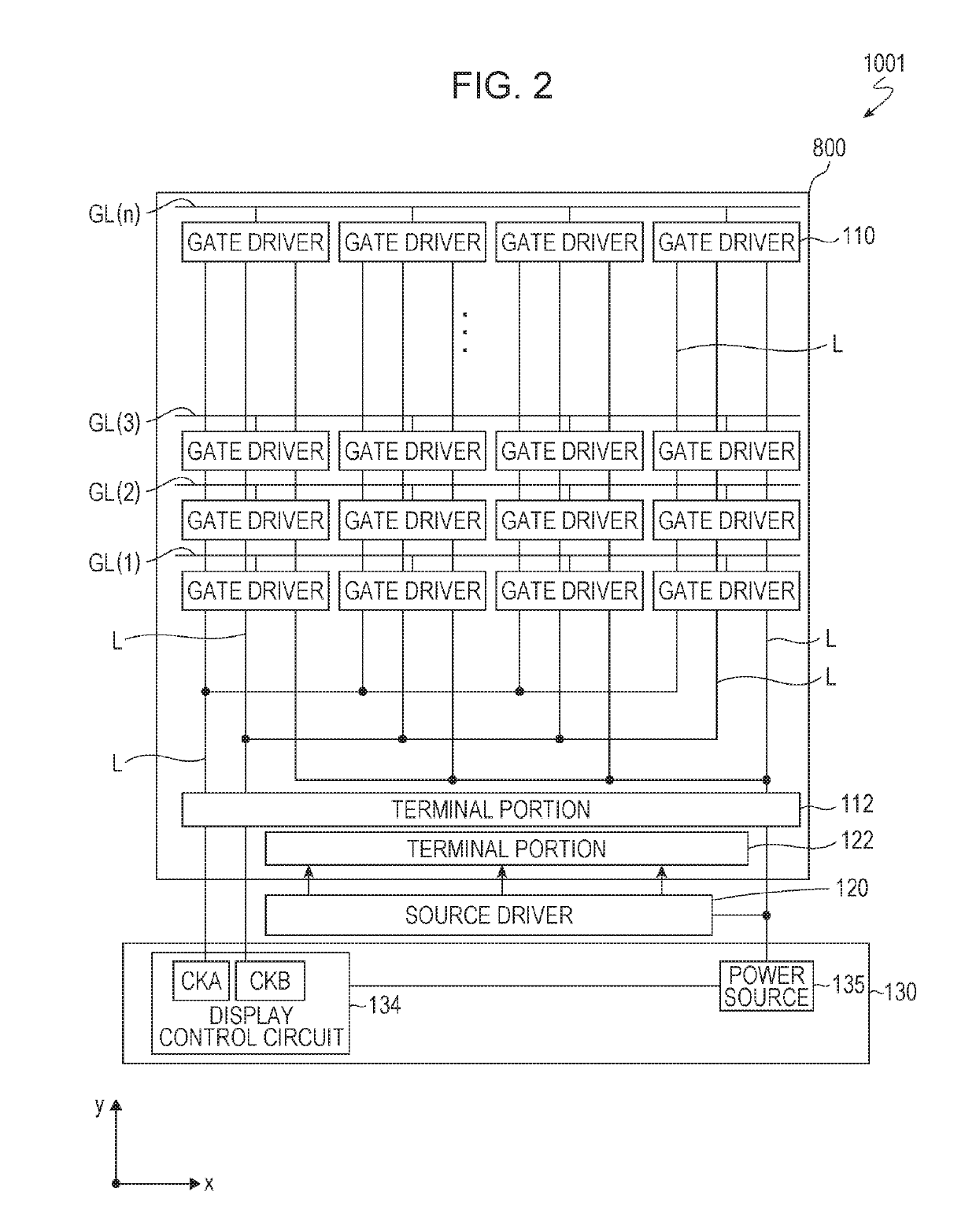
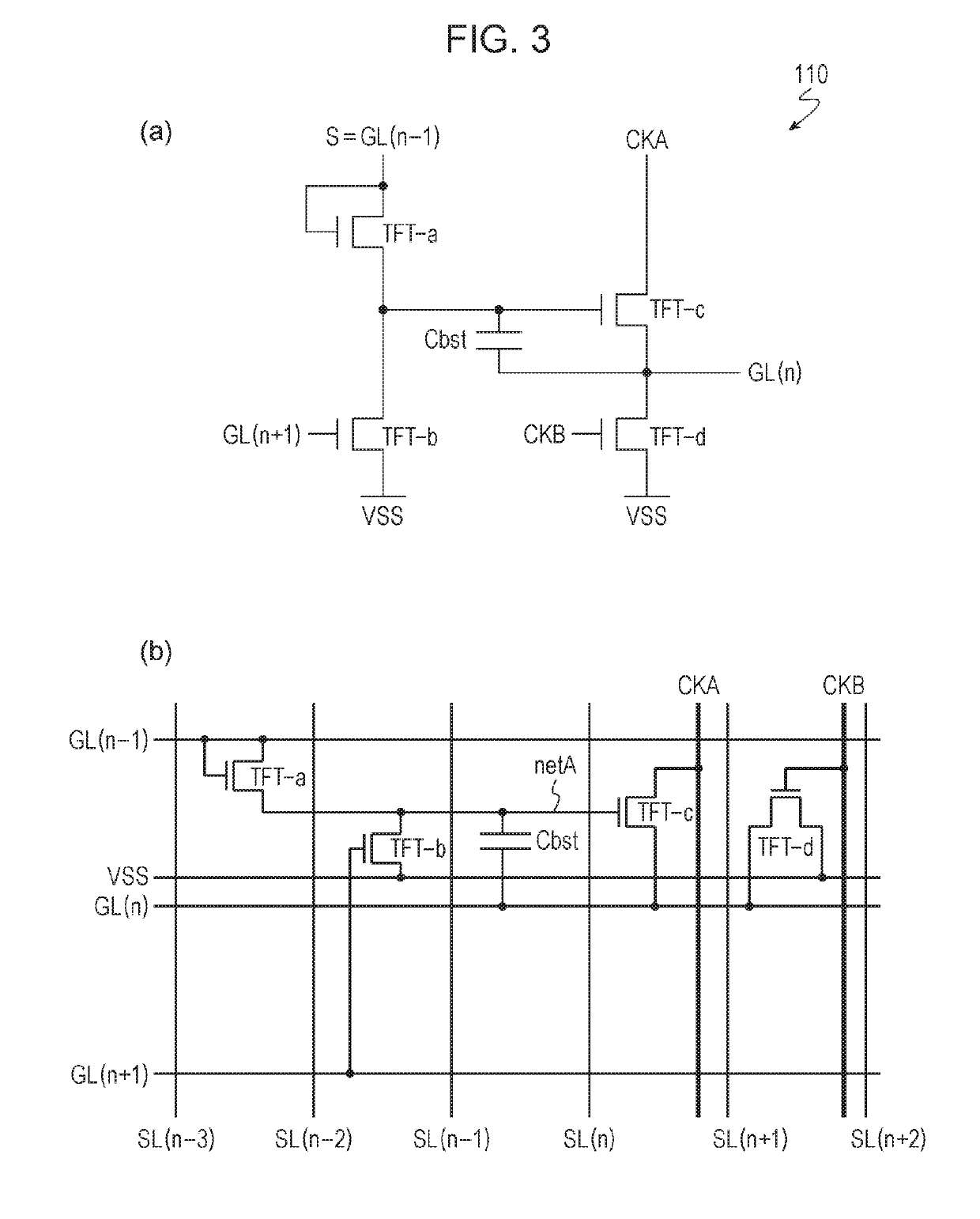
ActiveUS20190237489A1Pixel aperture ratioLight transmittanceStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesActive matrixEngineering
An active matrix substrate (1001) has multiple pixel areas. At least one pixel area includes a pixel TFT (20), a pixel electrode (15), a first circuit TFT (10), and drive circuit wiring lines (L1 to L3) that are connected to the first circuit TFT. The pixel TFT (20) and the first circuit TFT (10) are oxide semiconductor TFTs. The pixel electrode (15) is formed from an upper transparent conductive film. The drive circuit wiring line includes a transparent wiring line portion (L1 and L2) that is formed from a lower transparent conductive film which is positioned closer to a substrate 1 than the upper transparent conductive film. At least one of a source electrode (8) and a drain electrode (9) of the first circuit TFT (10) is formed from the lower transparent conductive film.
Owner:SHARP KK
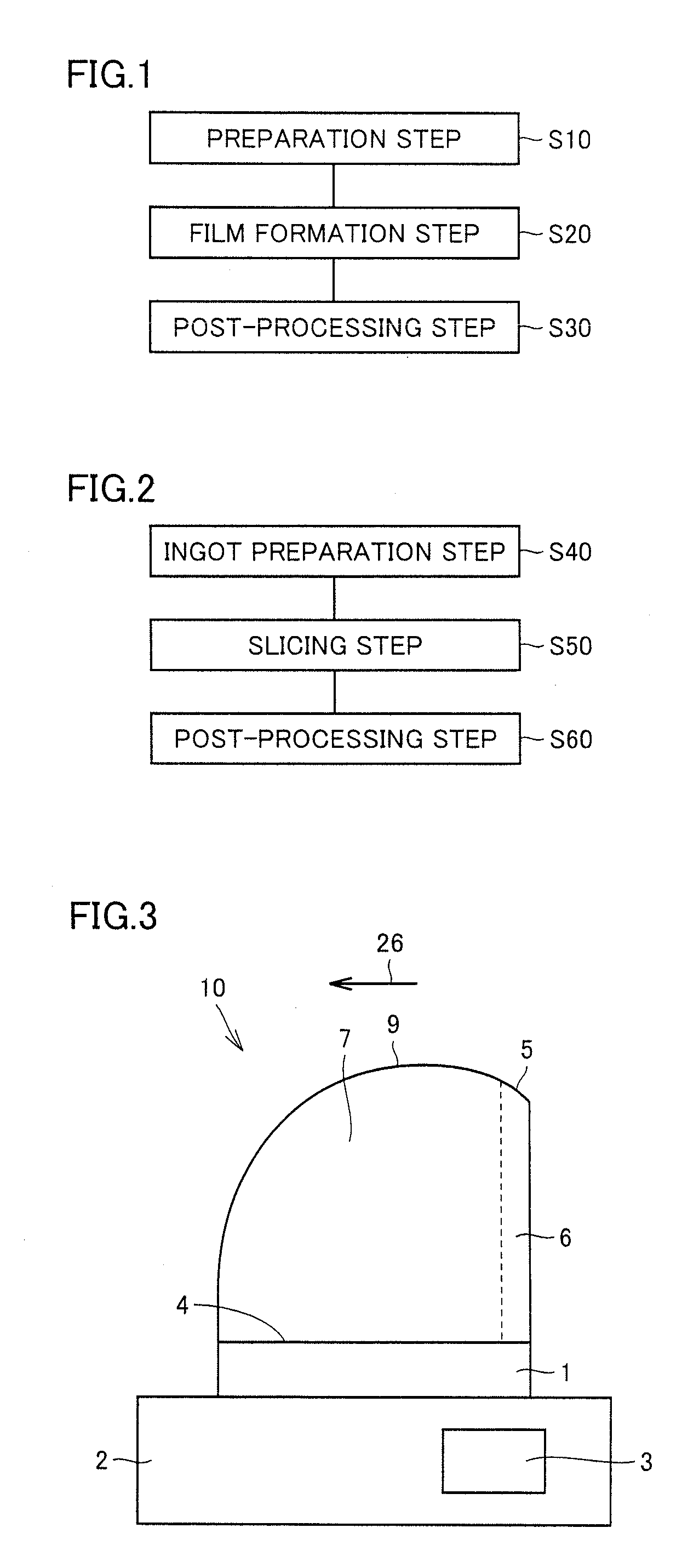
Silicon carbide substrate, silicon carbide ingot, and methods for manufacturing silicon carbide substrate and silicon carbide ingot
InactiveUS20120294790A1High light transmittanceEasy to getPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesAcute angleCarbide
A method of manufacturing a silicon carbide ingot having highly uniform characteristics includes a preparation step of preparing a base substrate made of single crystal silicon carbide and having an off angle of 0.1° or more and 10° or less in an off angle direction which is either a <11-20> direction or a <1-100> direction relative to a (0001) plane, and a film formation step of growing a silicon carbide layer on a surface of the base substrate. In the film formation step, a region having a (0001) facet 5 is formed on a surface of the grown silicon carbide layer at an end portion on an upstream side, the upstream side being a side where an angle of intersection between a <0001> direction axis of the base substrate and the surface of the base substrate in the off angle direction is an acute angle.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Phosphor-dispersed glass
ActiveUS9434876B2Improve moisture resistanceHigh production costLuminescent compositionsSemiconductor devicesPhosphorMaterials science
Owner:CENT GLASS CO LTD
Photomask and Method of Fabricating the Same
InactiveUS20090253052A1Increase light transmittanceLight transmittanceOriginals for photomechanical treatmentOptical transmittancePhotomask
A photomask comprises: a light transmitting substrate; patterns disposed over the light transmitting substrate to define a light transmitting region; and a light transmittance control layer disposed between the light transmitting substrate and the patterns having a relatively high light transmittance in a first control layer region overlapping a first portion of the light transmitting region adjacent to a poor pattern having a size larger than a normal size than in a second control layer region overlapping a second portion of the light transmitting region between normal patterns having a normal size.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Photomask and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS7901849B2Light transmittanceHigh light transmittanceOriginals for photomechanical treatmentControl layerOptical transmittance
A photomask comprises: a light transmitting substrate; patterns disposed over the light transmitting substrate to define a light transmitting region; and a light transmittance control layer disposed between the light transmitting substrate and the patterns having a relatively high light transmittance in a first control layer region overlapping a first portion of the light transmitting region adjacent to a poor pattern having a size larger than a normal size than in a second control layer region overlapping a second portion of the light transmitting region between normal patterns having a normal size.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Phosphor-Dispersed Glass
ActiveUS20160115379A1Improve moisture resistanceHigh production costLuminescent compositionsSemiconductor devicesPhosphorMaterials science
Disclosed is a phosphor-dispersed glass, including: a glass material; and a phosphor dispersed in the glass material, wherein the glass material is substantially free of Nb2O5 and contains: 15 to 40 mass % of SiO2; 10 to 30 mass % of B2O3; 1 to 35 mass % of ZnO; 0 to 20 mass % of Al2O3; 2 to 30 mass % in total of at least one kind selected from the group consisting of BaO, CaO and SrO; 0 to 1 mass % of MgO; 5 to 35 mass % in total of R2O (at least one selected from the group consisting of Li2O, Na2O and K2O); and 0 to 15 mass % in total of at least one of antimony oxide and tin oxide.
Owner:CENT GLASS CO LTD
Thermoplastic resin composition and formed article using the same
InactiveUS8075984B2Good shading effectLight transmittanceLiquid crystal compositionsOrganic active ingredientsBlock effectPolyresin
The present invention provides a thermoplastic resin composition characterized by comprising (A) a thermoplastic resin and (B) a white pigment in a mass ratio of 50:50 to 90:10 and further comprising (C) a black coloring material and a blue coloring material; and provides a formed article using the resin composition. The above thermoplastic resin composition is an improvement of the conventional technique for preventing the permeation of light from a thin part of the formed article while securing a satisfactory reflectance, and can markedly improve the light blocking effect of a thermoplastic resin composition, without the increase of the number of parts, the employment of a more complicated process, or the like.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
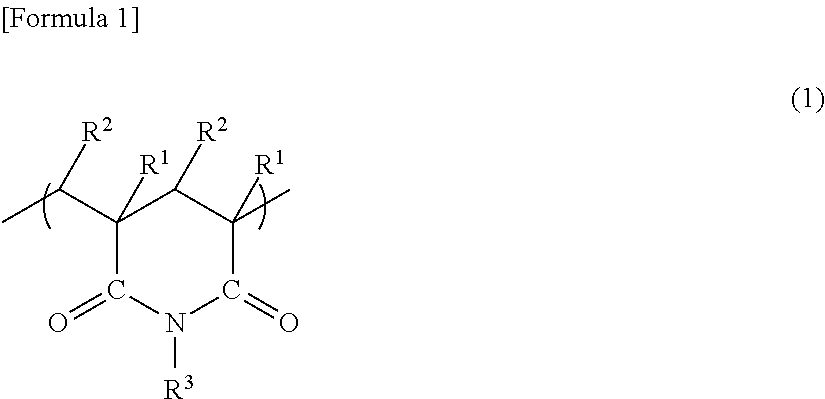
Polarizing plate and liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS9739910B2Good effectIncreased durabilityAntifouling/underwater paintsPolarising elementsTectorial membraneAcrylic resin
A polarizing plate includes: a polyvinyl alcohol-based polarizer; and transparent protective films provided on both surfaces of the polyvinyl alcohol-based polarizer with an adhesive layer interposed between each of the transparent protective films and the polyvinyl alcohol-based polarizer. A first transparent protective film contains a (meth)acrylic resin and an ultraviolet absorber, the (meth)acrylic resin having an unsaturated carboxylic acid alkyl ester unit and a glutarimide unit represented by the general formula (1), having an imidization ratio of 2.5 to 5.0% and an acid value of 0.10 to 0.50 mmol / g, and having an acrylic ester unit of less than 1% by weight. A second transparent protective film contains a cycloolefin-based resin.R1 and R2 each independently represent hydrogen or an alkyl group; and R3 represents an alkyl group, a cycloalkyl group, or an aryl group.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Reflective polarizer and backlight unit including same
ActiveUS20180172887A1Excellent and uniform brightnessLight transmittancePolarising elementsOptical light guidesPolarizerReflectivity
The present invention relates to a reflective polarizer and a backlight unit including same and, more particularly, to a reflective polarizer and a backlight unit including same which can display excellent and uniform brightness throughout the visible light wavelength range in the following manner. Regardless of the incident angle of incident light, a discordance in the refractive index in one particular direction is minimized, and the transmissivity of polarized light targeted within the visible light wavelength range is uniform. Thus, light transmitted through the reflective polarizer is not biased toward a particular wavelength range, and the exterior is not colorful or a particular color due to rainbow-colored light. Because the reflectivity of polarized light not targeted within the visible light wavelength range is significantly large, the light is not biased toward a particular wavelength range.
Owner:TORAY ADVANCED MATERIALS KOREA
Multilayer optical recording medium and optical recording method
InactiveUS20090155514A1Storage stability be excellentEnhance record performanceLayered productsPhotomechanical apparatusPhysicsOxide
A multilayer optical recording medium including at least multiple information layers having at least a phase change recording layer capable of recording information by laser irradiation and a reflection layer, wherein information layer as seen from a side of the laser irradiation has at least a lower protection layer, the phase change recording layer, an upper protection layer, the reflection layer and an optical transmission layer, the upper protection layer and the optical transmission layer in each information layer other than the innermost one are composed of an Sn oxide-containing material and a thickness of the upper protection layer in each information layer other than the innermost one as seen from the side of the laser irradiation is 2 nm to 15 nm is provided.
Owner:RICOH KK
Transparent film
ActiveUS8007895B2Good flexibilityHigh transparencySemi-permeable membranesMembranesHigh resistancePolymer science
The present invention provides a novel technology and a novel transparent material having high thermal stability, excellent pliability, surface smoothness, dimensional stability and gas barrier properties, for the technical fields of packaging materials, sealing materials and display materials, and the invention relates to an inorganic layered compound film having oriented inorganic layered compound particles, exhibiting high surface smoothness, high dimensional stability, high transparency, excellent pliability, excellent gas barrier properties and high heat resistance, that is obtained by dispersing an inorganic layered compound of high transparency and a small amount of water-soluble polymer of high transparency in water or a liquid having water as a main component thereof, to thereby obtain a homogenous dispersion containing no agglomerates, applying thereafter this dispersion onto a support having a flat and water-layered compound particles, and separating the liquid, as a dispersion medium, according to any of various solid-liquid separation methods, for example, centrifugation, filtration, vacuum drying, vacuum freeze drying, evaporation by heating or the like to thereby attain formation into a film shape, and optionally followed by methods such as drying / heating / cooling to thereby effect detachment from the support.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Display device and protective cover window
InactiveUS20200139672A1Good flexibilitySimple processDigital data processing detailsSynthetic resin layered productsDisplay deviceStructural engineering
The present disclosure proposes a display device and a protective cover window. The display device includes a display panel comprising a bending area and a non-bending area, an adhesive layer arranged on a surface of the display panel, and a protective cover window attached onto the display panel through the adhesive layer. The protective cover window includes a first portion and a second portion. The first portion corresponds to the non-bending area. The second portion corresponds to the bending area. A hardness of the first portion is greater than a hardness of the second portion.
Owner:WUHAN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS SEMICON DISPLAY TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com