Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
85results about How to "Large signal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
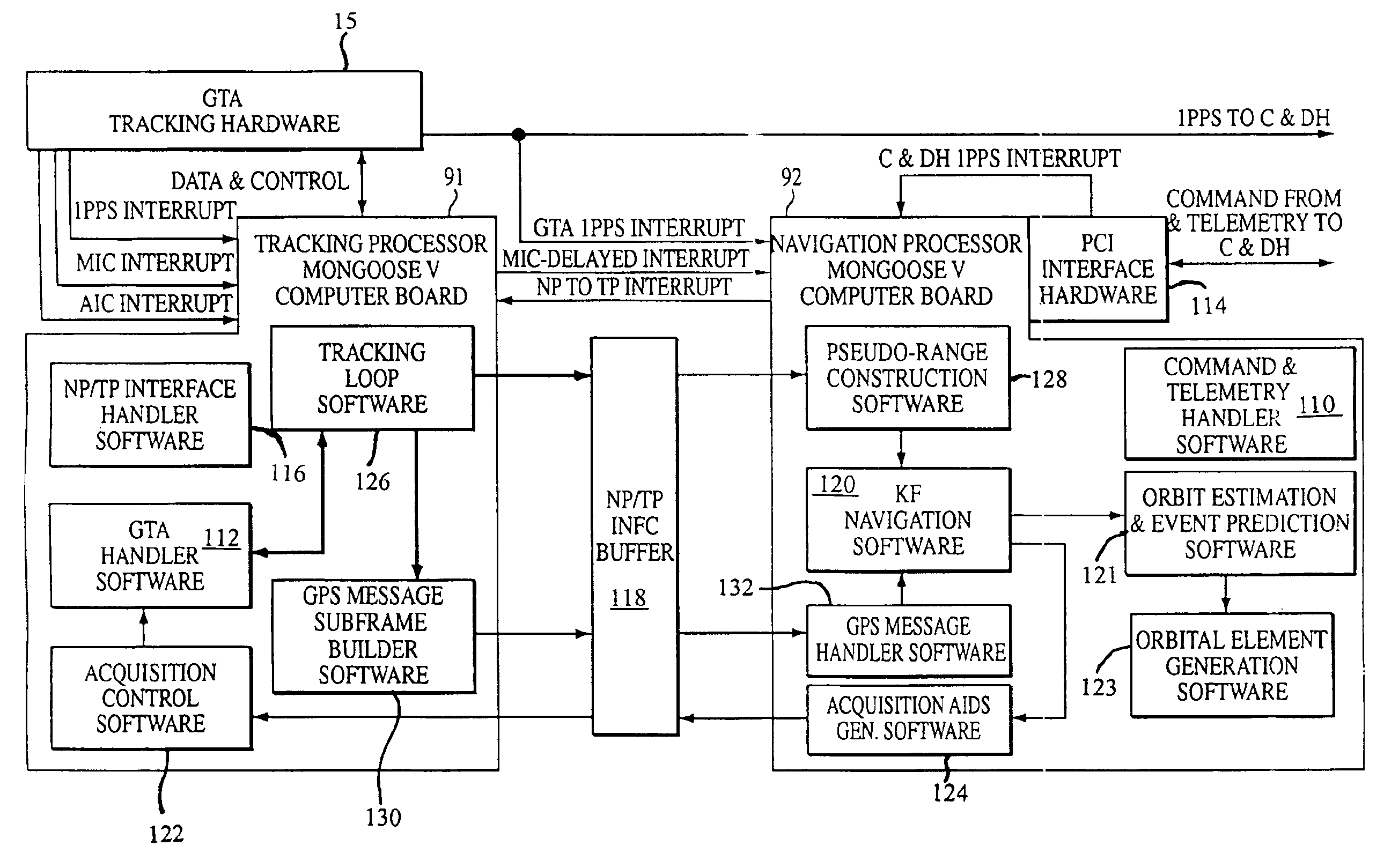
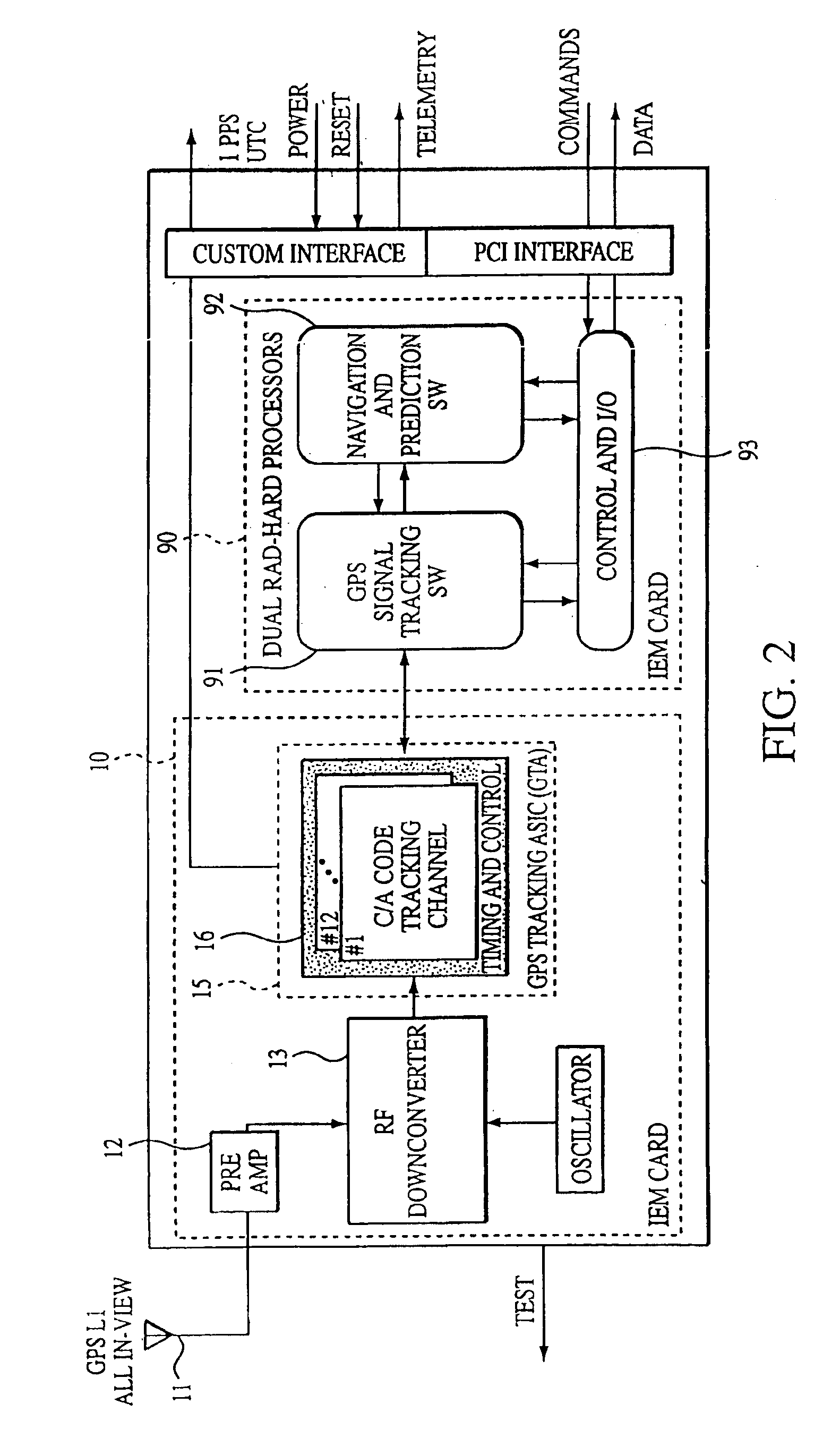
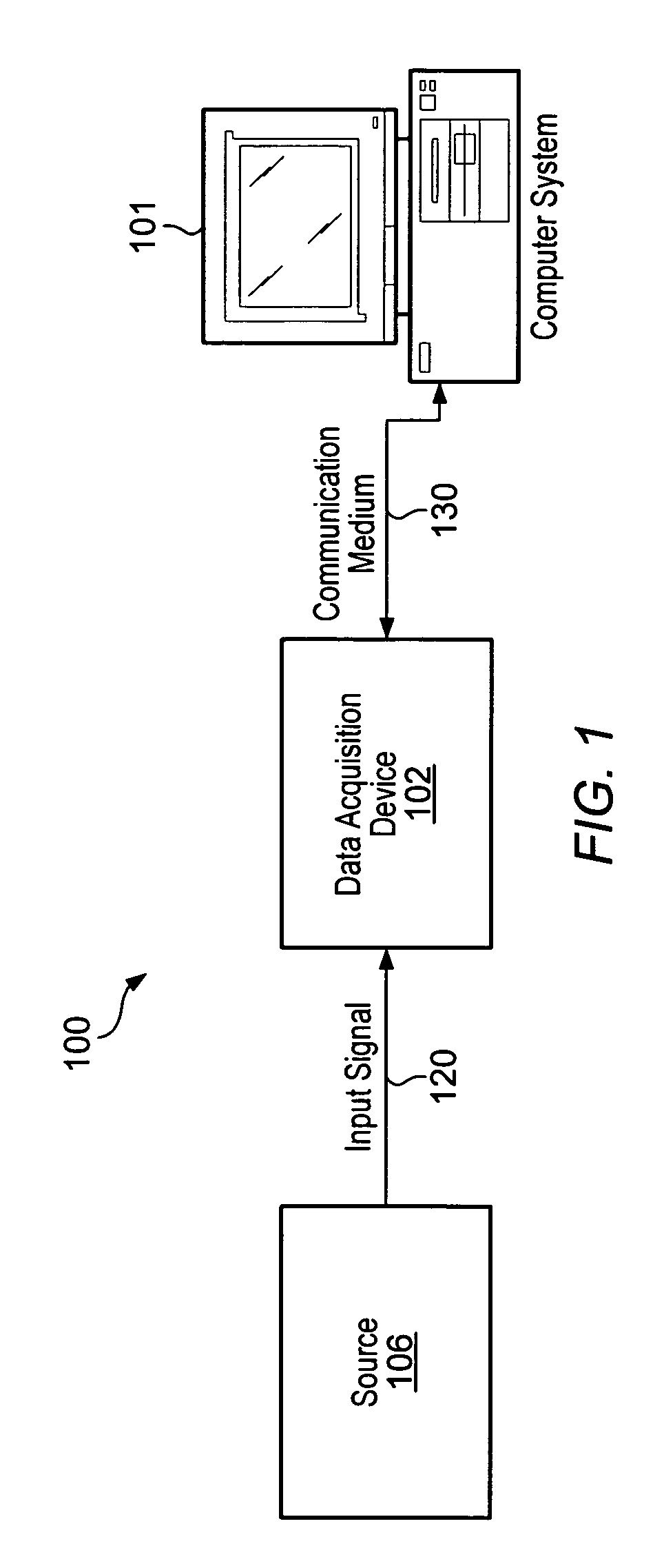
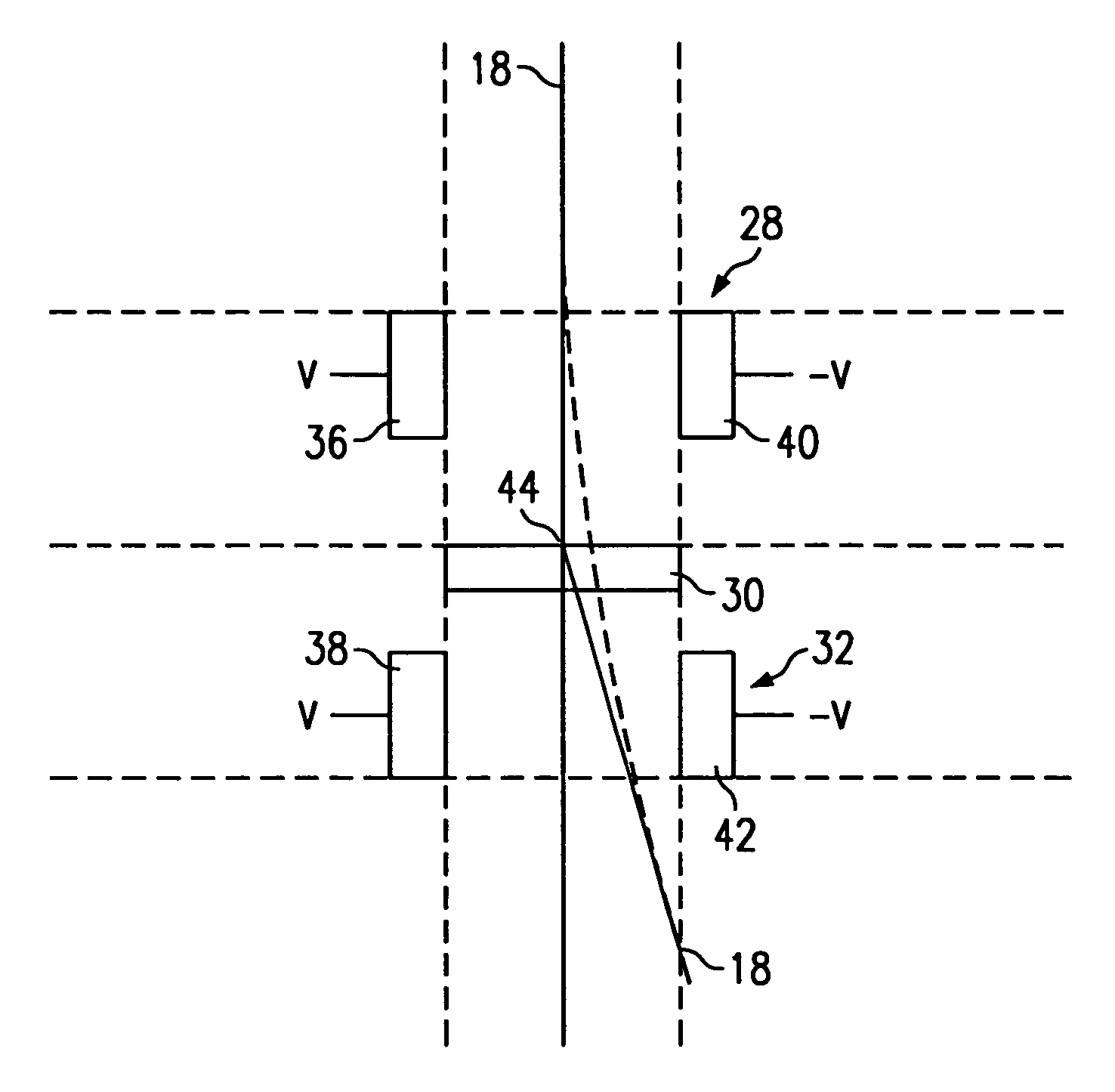
Extended kalman filter for autonomous satellite navigation system
InactiveUS6859170B2Simplify the design processMaximum capabilityInstruments for comonautical navigationArtificial satellitesLow earth orbitMedium Earth orbit
An autonomous navigation system for an orbital platform incorporating a global positioning system based navigation device optimized for low-Earth orbit and medium-Earth orbit applications including a 12 channel, GPS tracking application-specific integrated circuit (15) operating in concert with a computer system (90) implementing an extended Kalman filter and orbit propagator which autonomously generates estimates of position, velocity and time to enable planning, prediction and execution of event-based commanding of mission operations.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
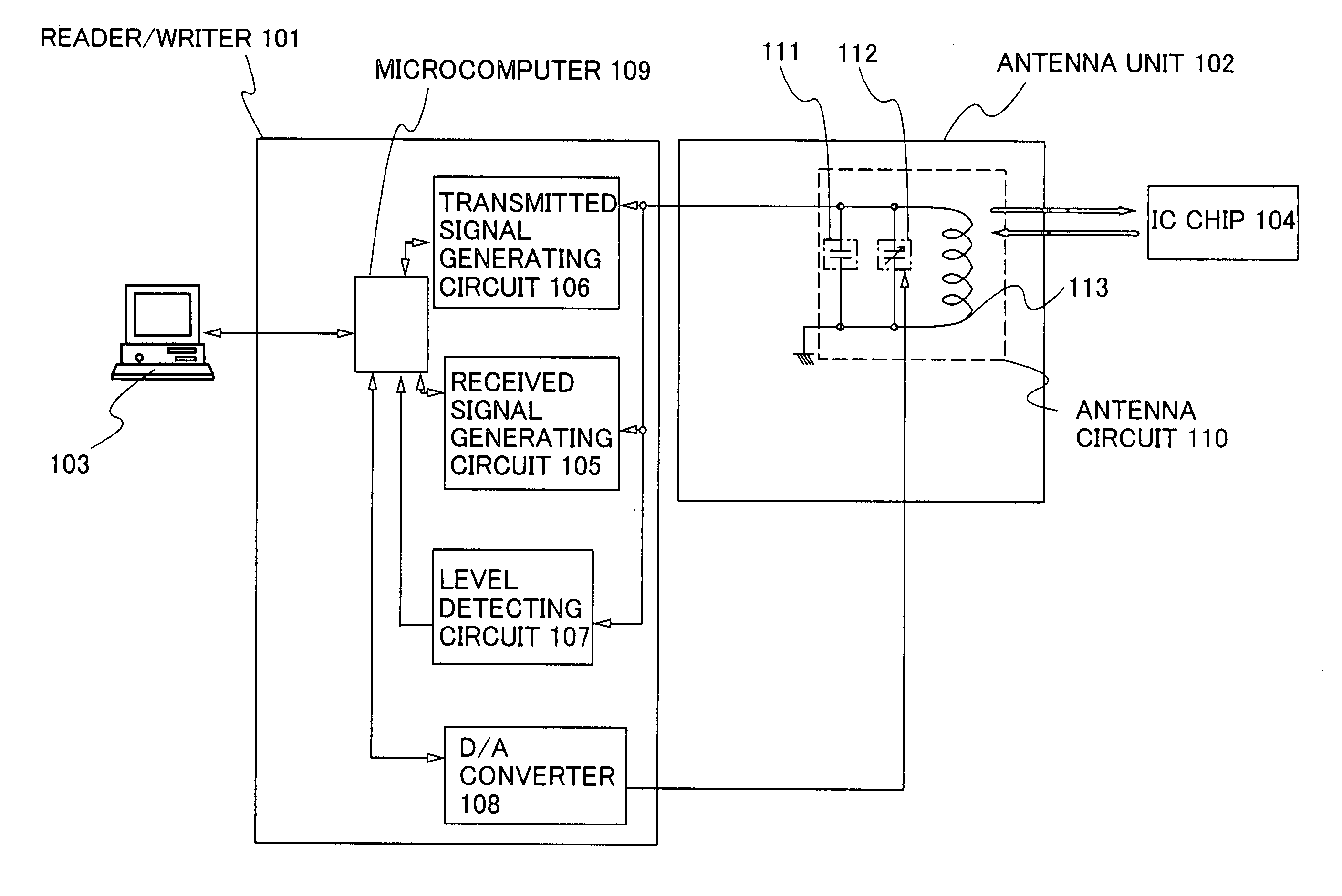
Information processing device
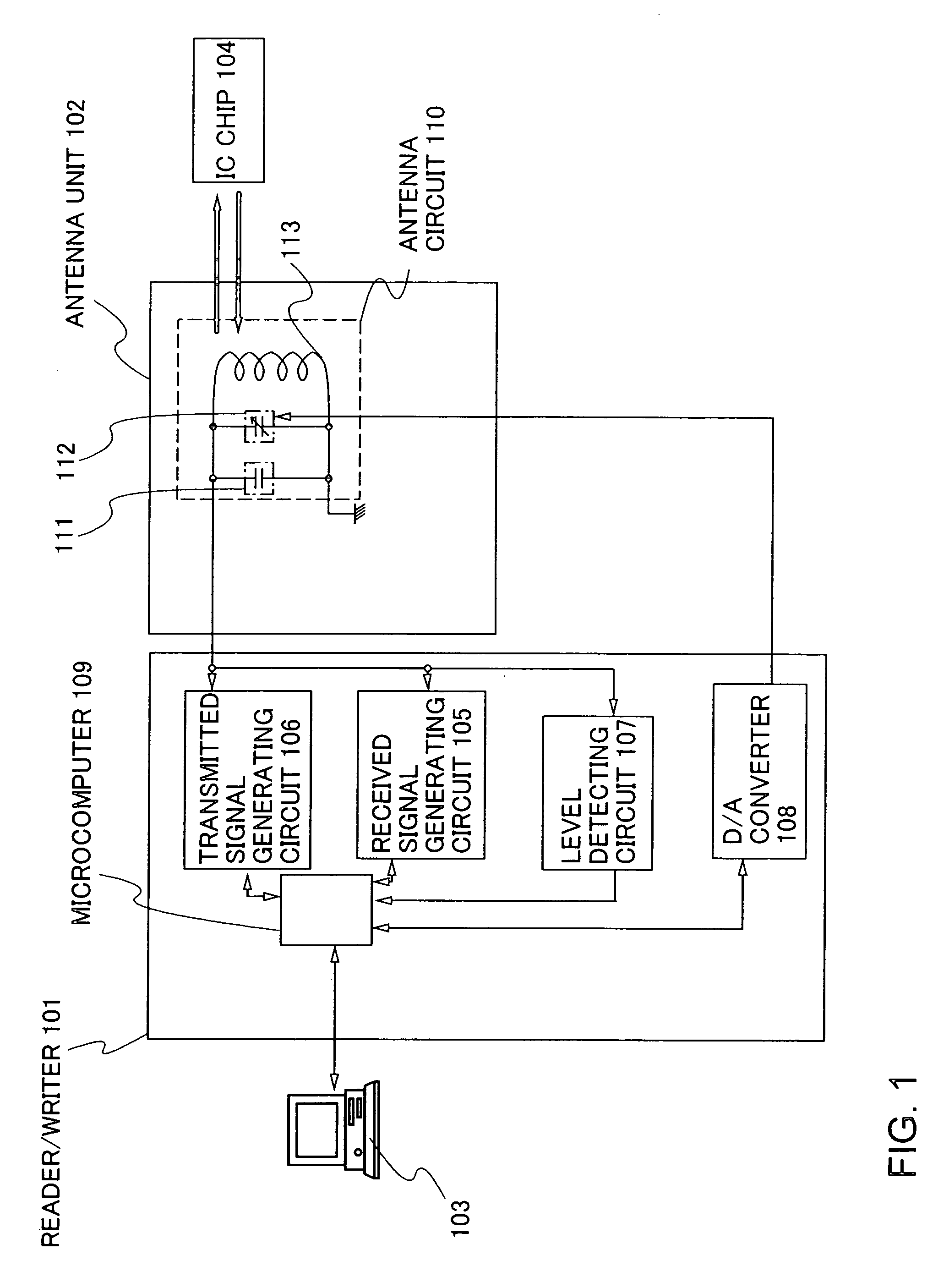
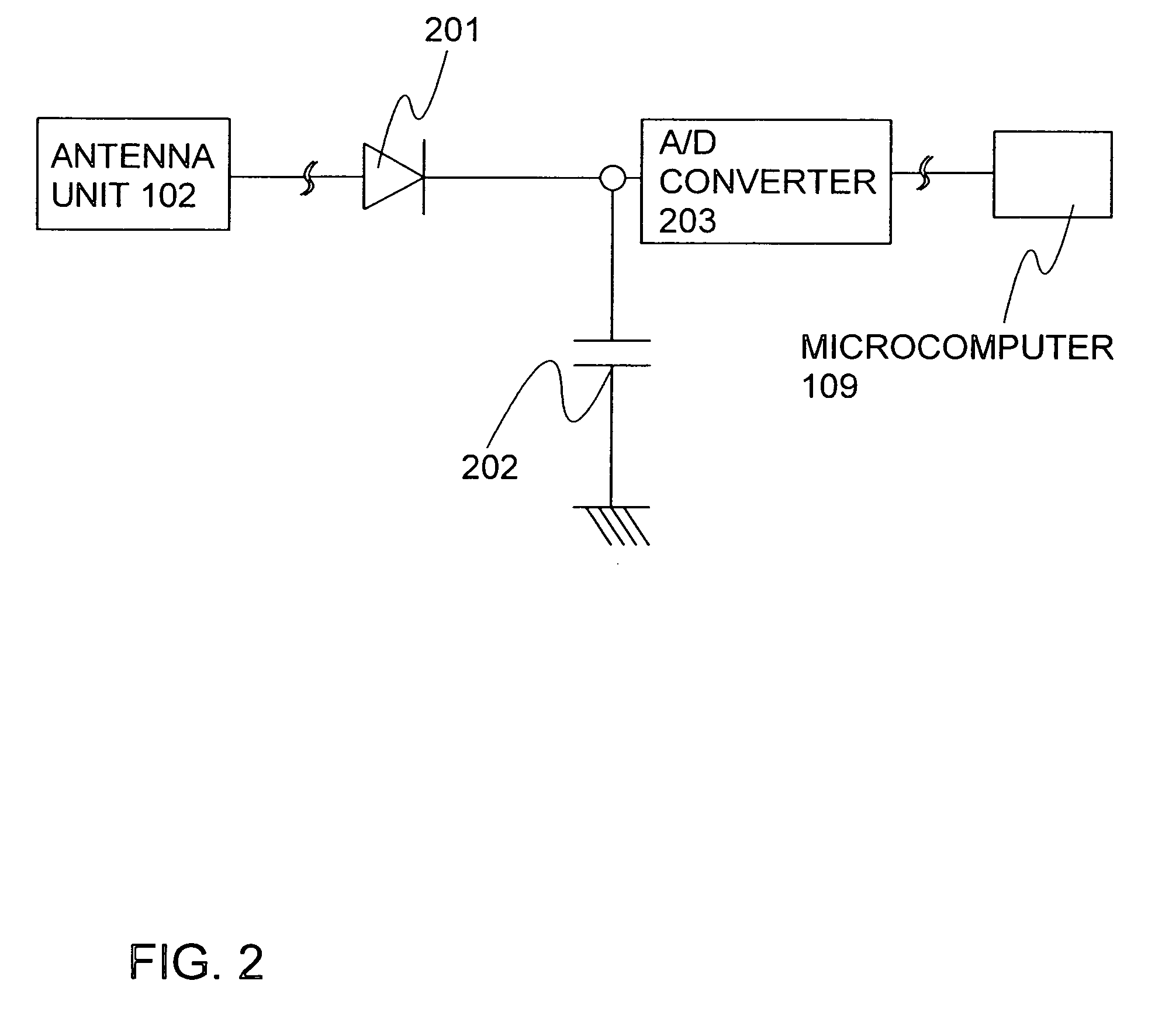
InactiveUS20060220863A1Large signalSubscribers indirect connectionBurglar alarm by hand-portable articles removalInformation processingMicrocomputer
An information processing device of the invention has an antenna circuit, and a reader / writer device provided with a received signal generating circuit, a microcomputer, a transmitted signal generating circuit, a level detecting circuit, and a D / A converter. The received signal generating circuit is connected to the microcomputer and the antenna circuit, the transmitted signal generating circuit is connected to the microcomputer and the antenna circuit, the D / A converter is connected to the microcomputer and the antenna circuit, the level detecting circuit is connected to the microcomputer and the antenna circuit, and the antenna circuit has an antenna, a resonant capacitor, and a variable capacitor.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Microcavity biosensor and uses thereof
InactiveUS7226733B2High sensitivityLarge signalImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPorous semiconductorsCentral layer
A biological sensor which includes: a porous semiconductor structure comprising a central layer interposed between upper and lower layers, each of the upper and lower layers including strata of alternating porosity; and one or more probes coupled to the porous semiconductor structure, the one or more probes binding to a target molecule, whereby a detectable change occurs in a refractive index of the biological sensor upon binding of the one or more probes to the target molecule. Methods of making the biological sensor and methods of using the same are disclosed, as is a detection device which includes such a biological sensor.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
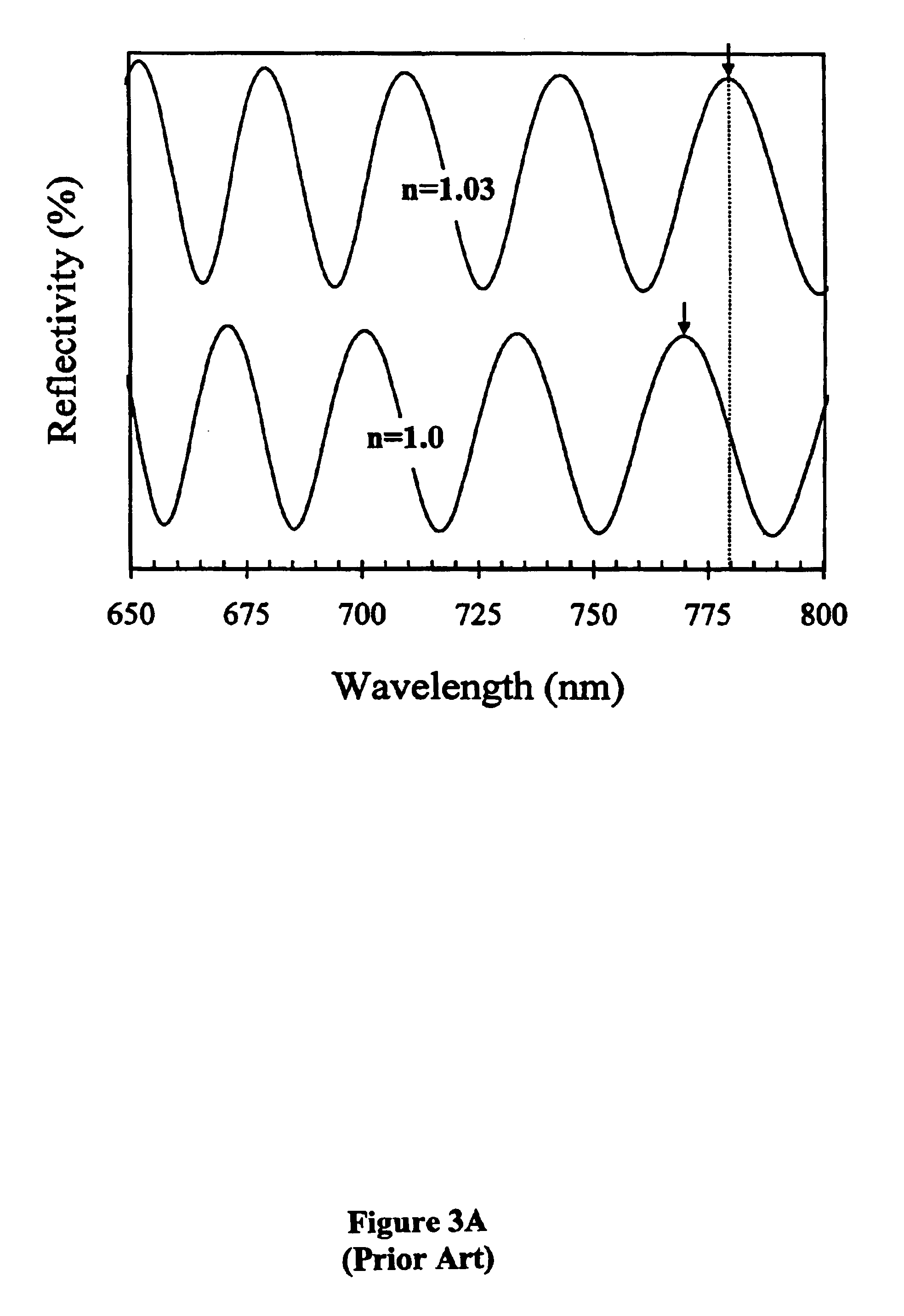
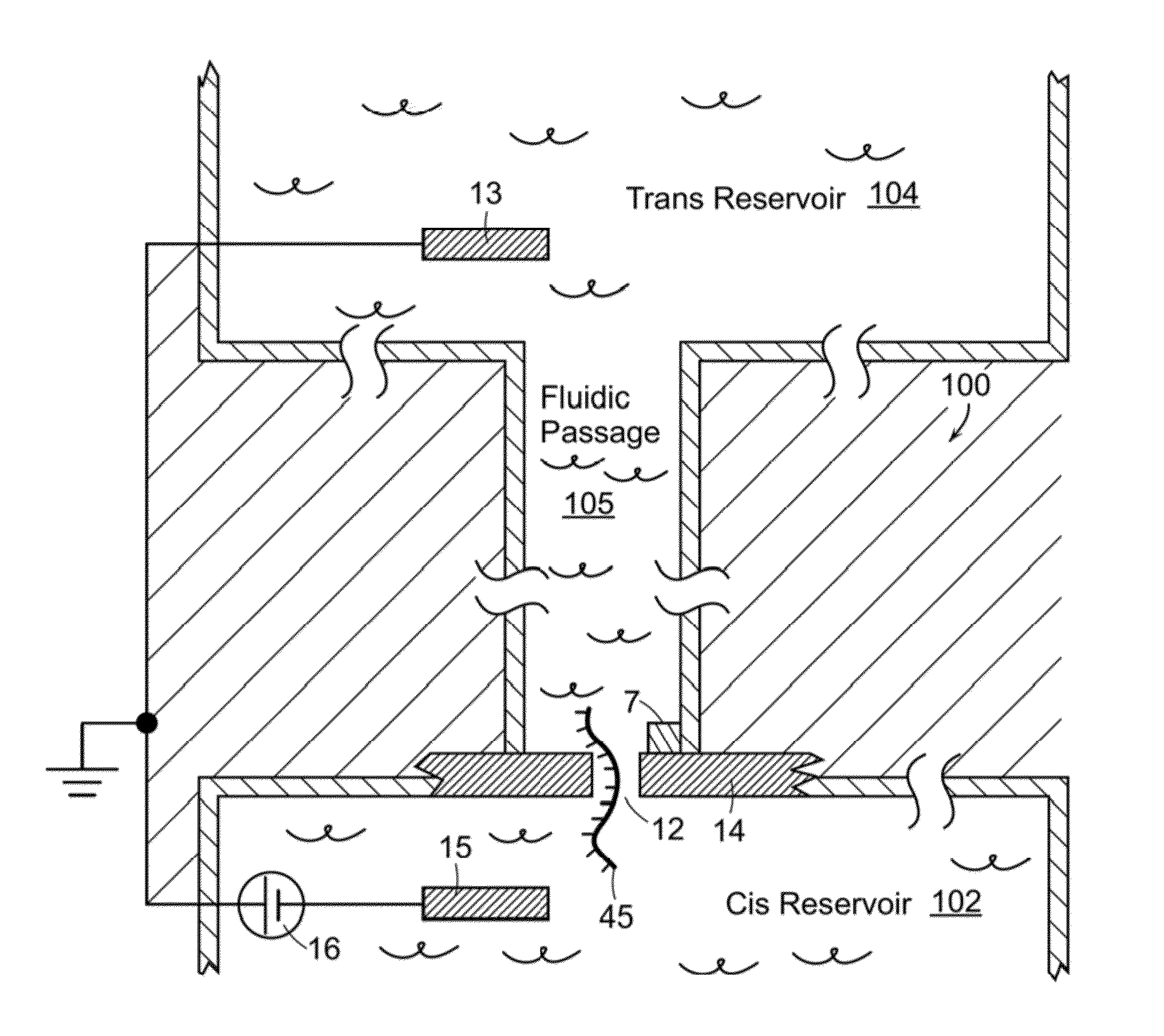
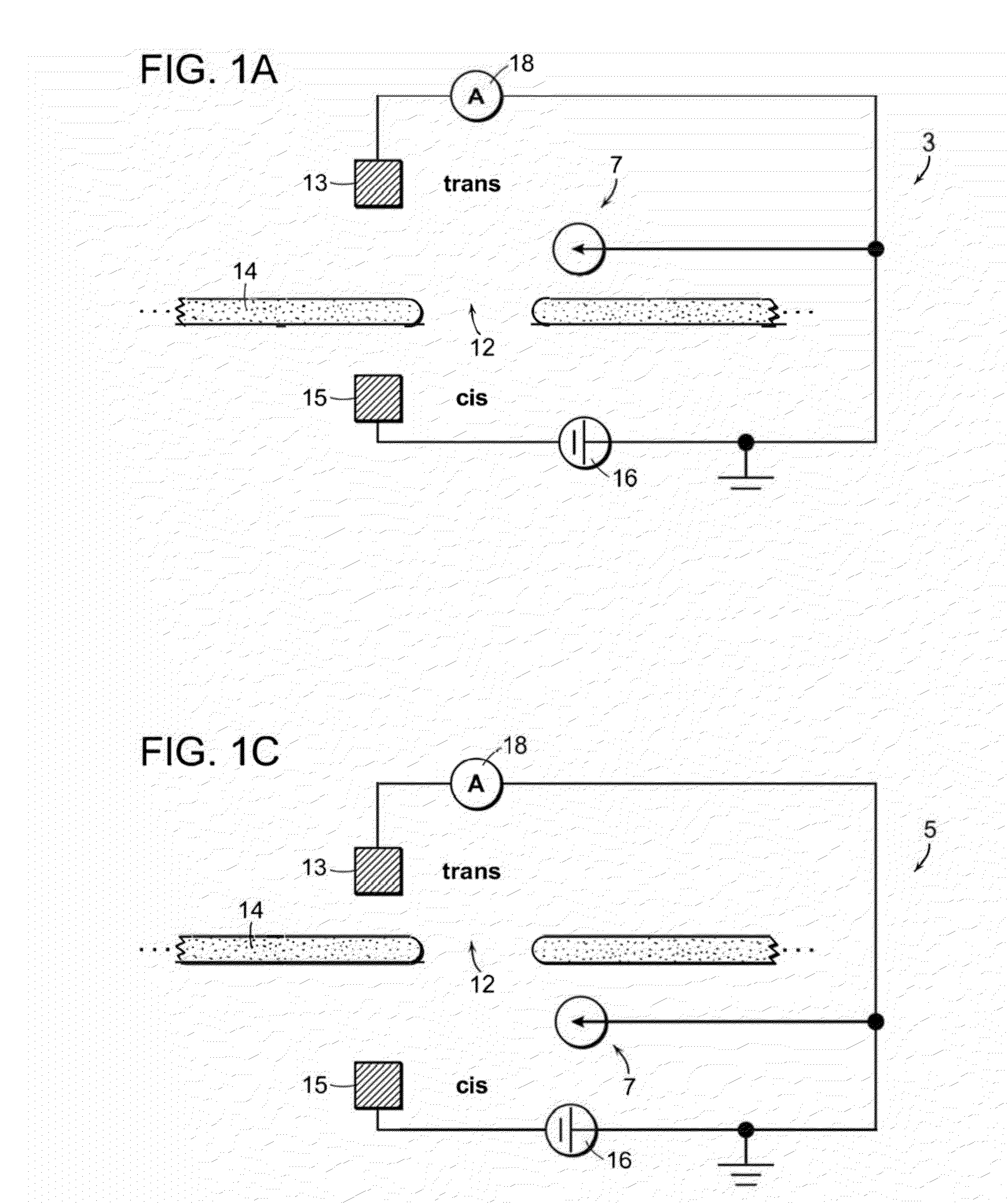
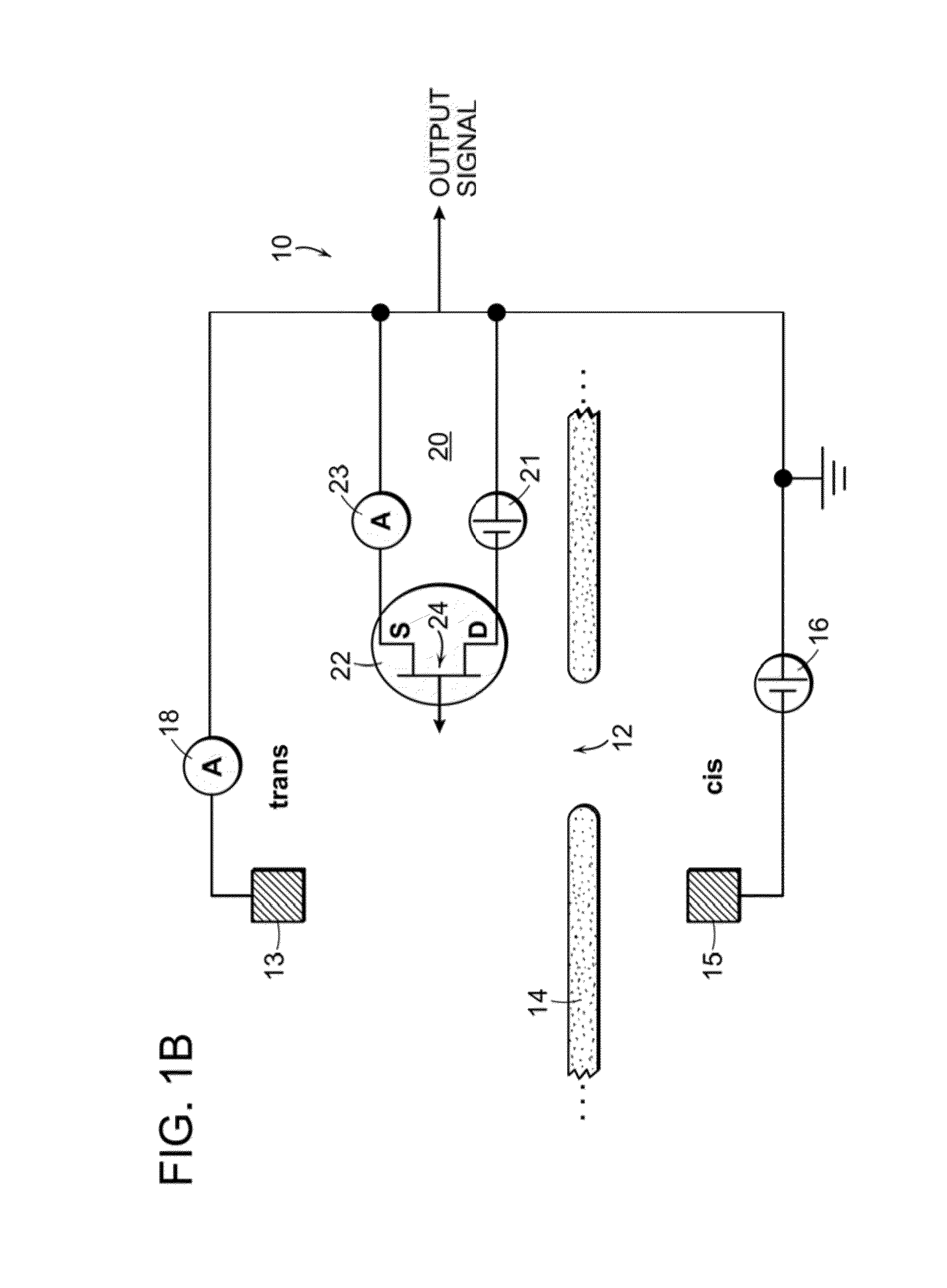
Nanopore Sensor Including Fluidic Passage
ActiveUS20160231307A1Overcome limitationsHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEngineeringNanopore
A nanopore sensor is provided, including a nanopore disposed in a support structure. A fluidic passage is disposed between a first fluidic reservoir and the nanopore to fluidically connect the first fluidic reservoir to the nanopore through the fluidic passage. The fluidic passage has a passage length that is greater than the passage width. A second fluidic reservoir is fluidically connected to the nanopore, with the nanopore providing fluidic communication between the fluidic passage the second reservoir. Electrodes are connected to impose an electrical potential difference across the nanopore. At least one electrical transduction element is disposed in the nanopore sensor with a connection to measure the electrical potential that is local to the fluidic passage.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Switching power supply device and switching power supply control circuit
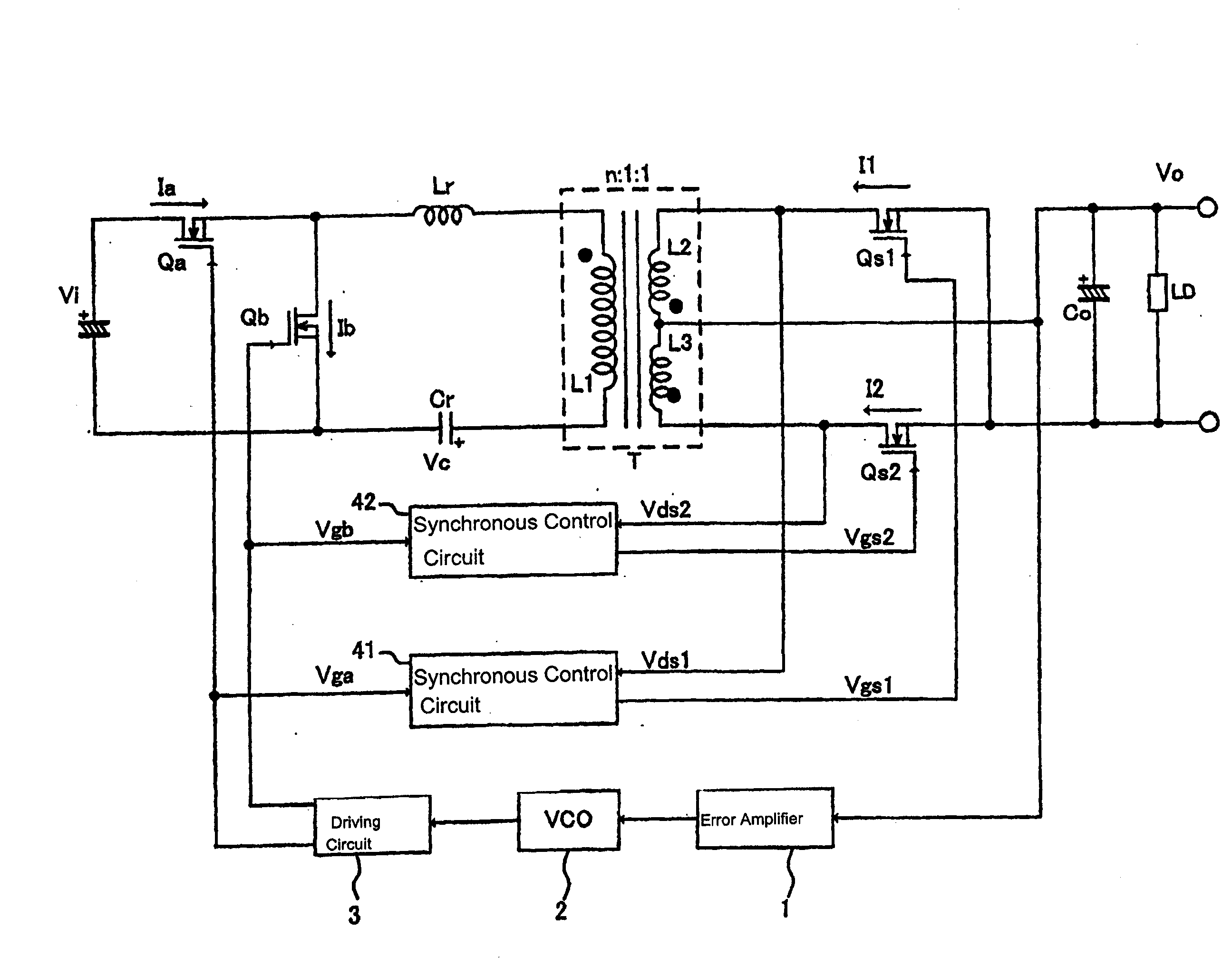
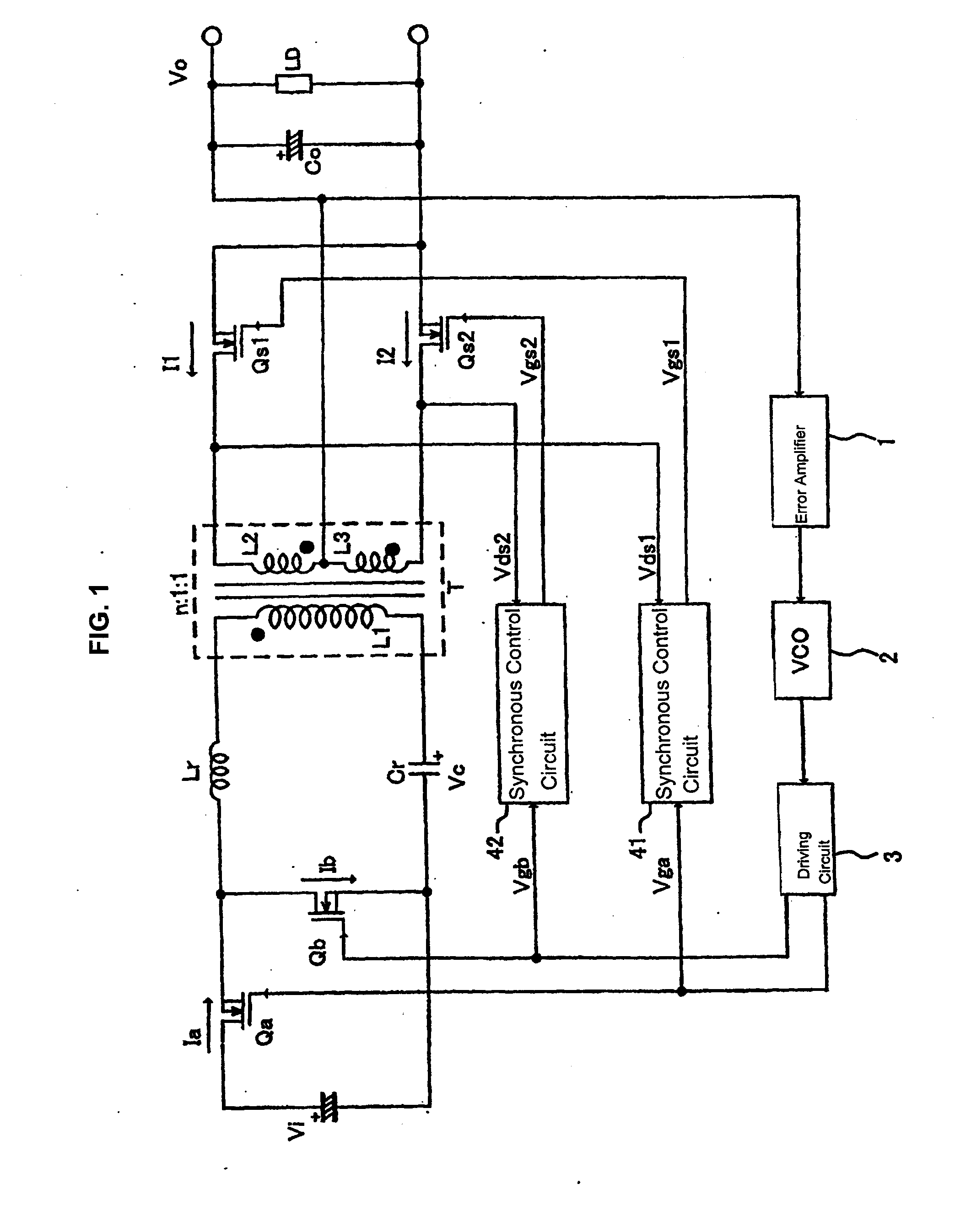
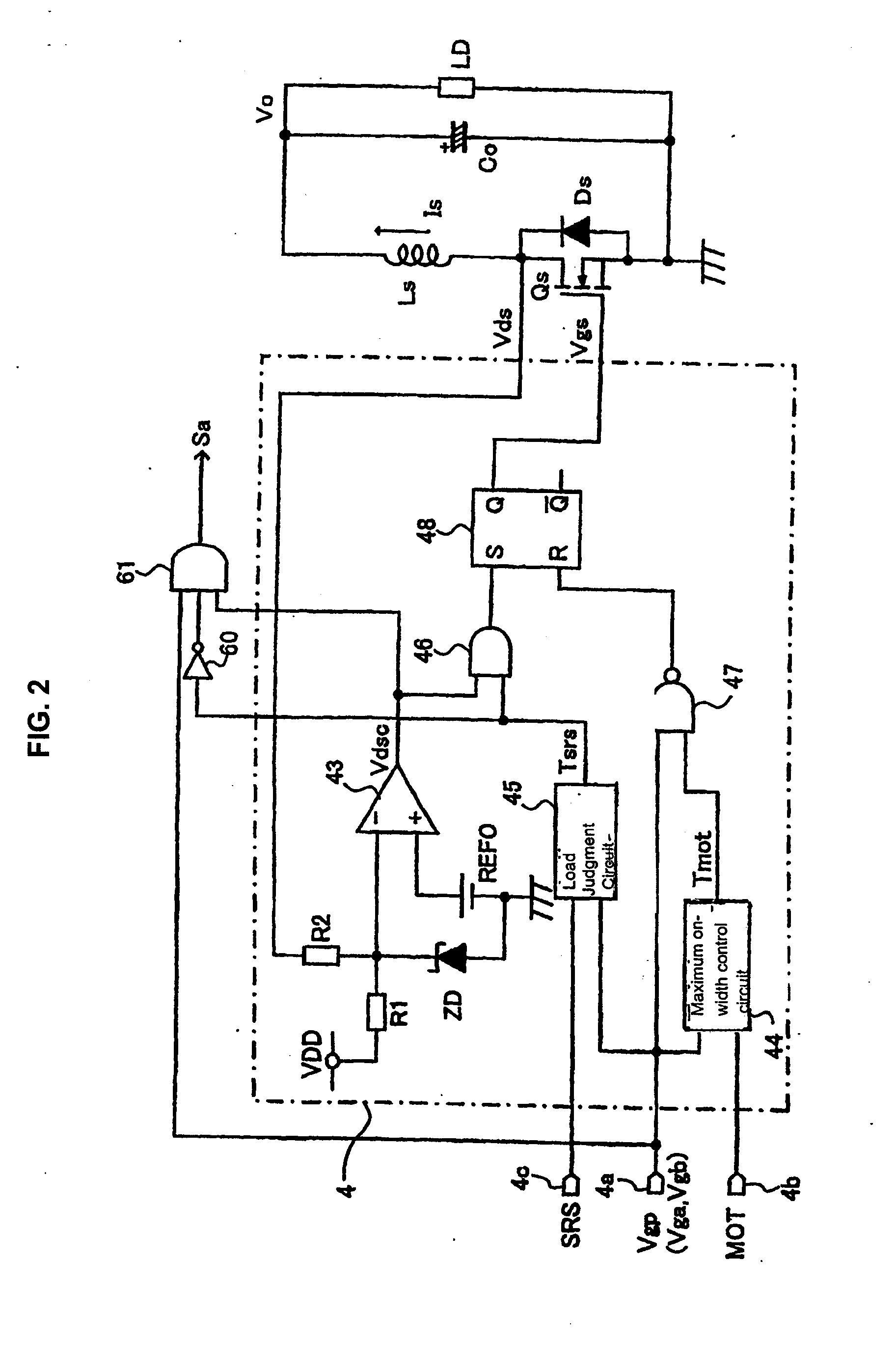
ActiveUS20100172157A1Remove noiseLarge signalEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionMOSFETDelayed time
The invention provides a switching power supply device which can detect a light load state on a pulse-by-pulse basis without worsening power efficiency. In a synchronous control circuit, for each timing of the turning-on of main switching elements, the delay time Tdif of the conduction timing of internal diodes Ds determined according to the magnitude of the load LD is detected by a comparator, a reference time pulse Tsrs having a prescribed time width is generated by a load judgment circuit, and the logical product of the two is generated by an AND circuit. By this means, the load is regarded as being a light load when the delay time Tdif is longer than the reference time pulse Tsrs, and the synchronous rectification MOSFETs Qs are not turned on.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
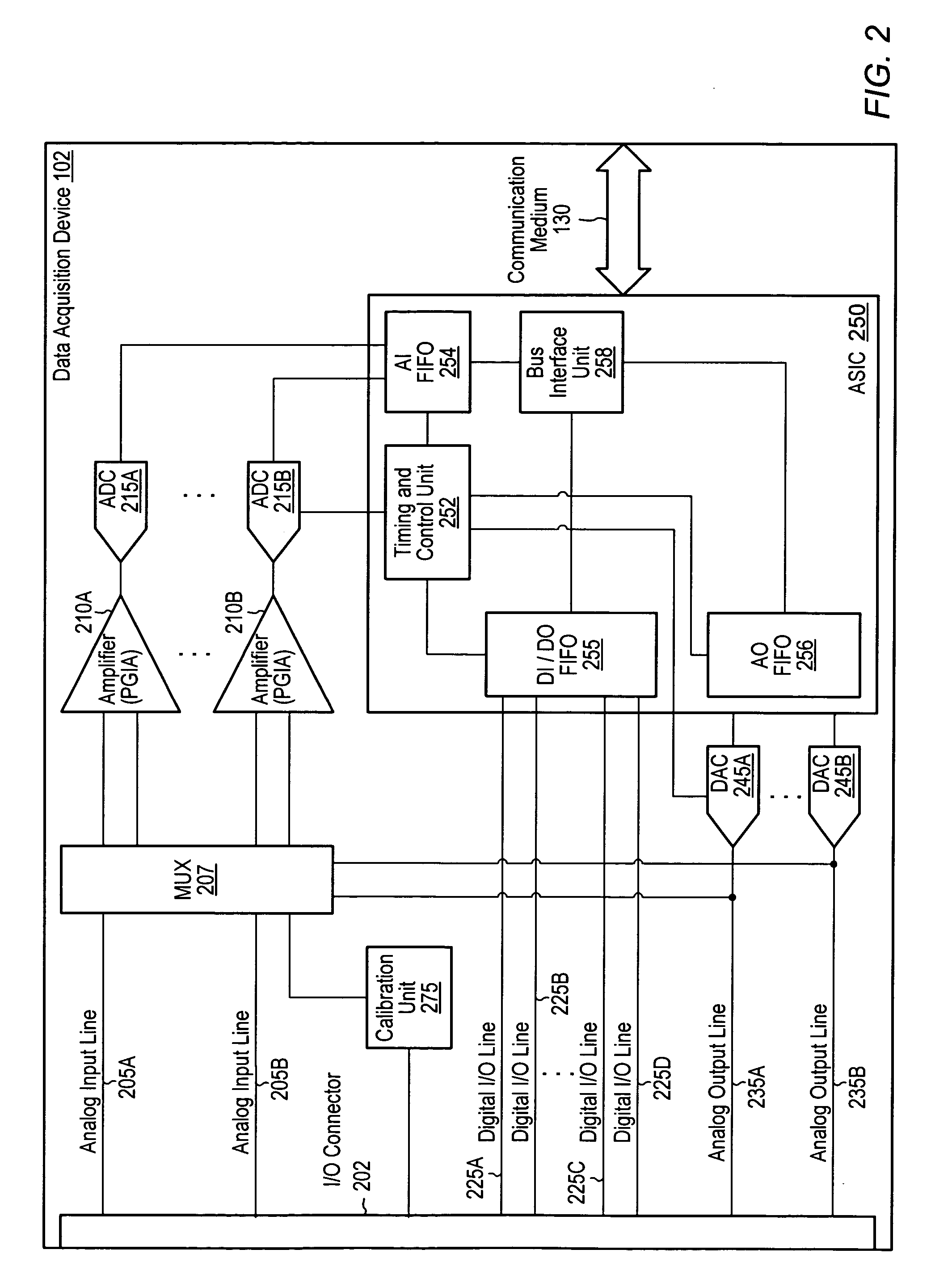
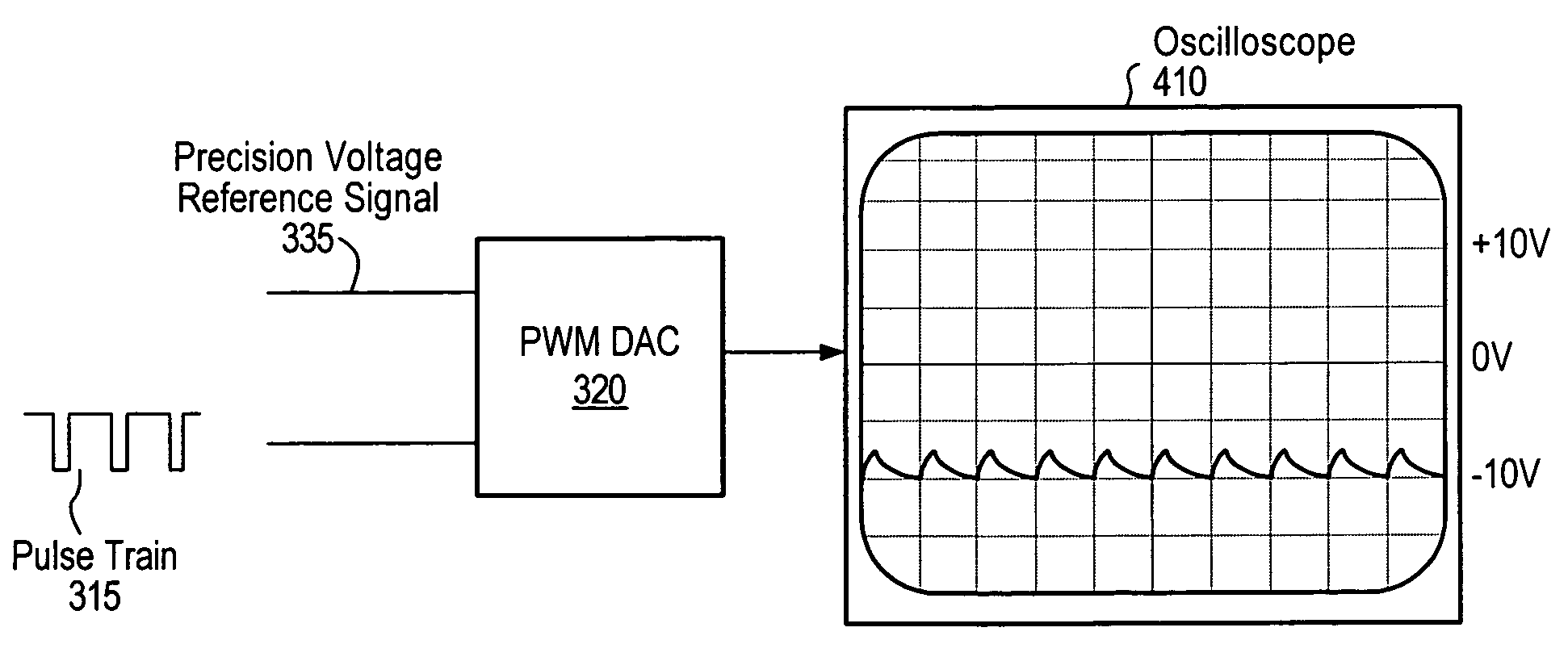
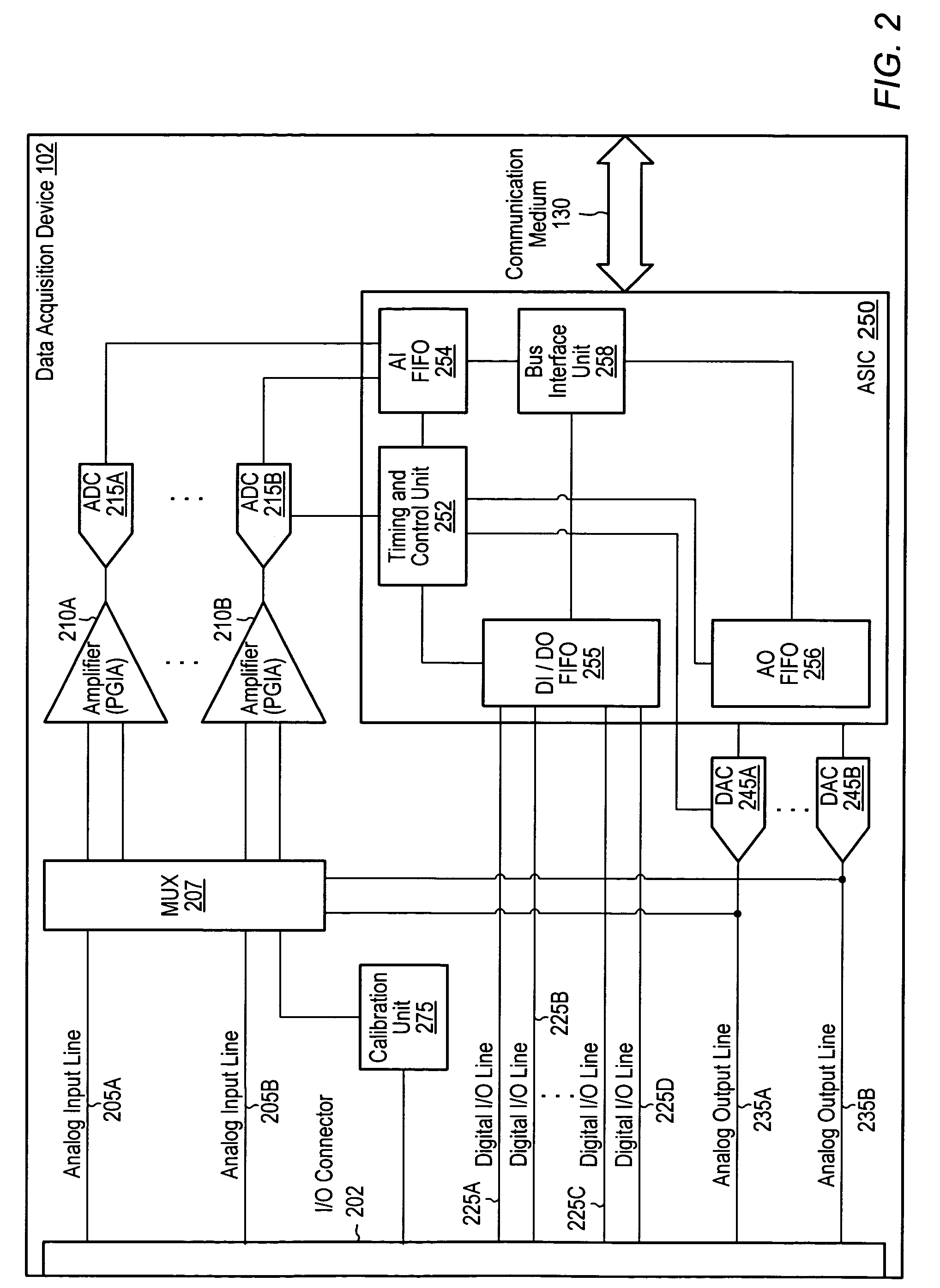
Calibrating analog-to-digital systems using a precision reference and a pulse-width modulation circuit to reduce local and large signal nonlinearities
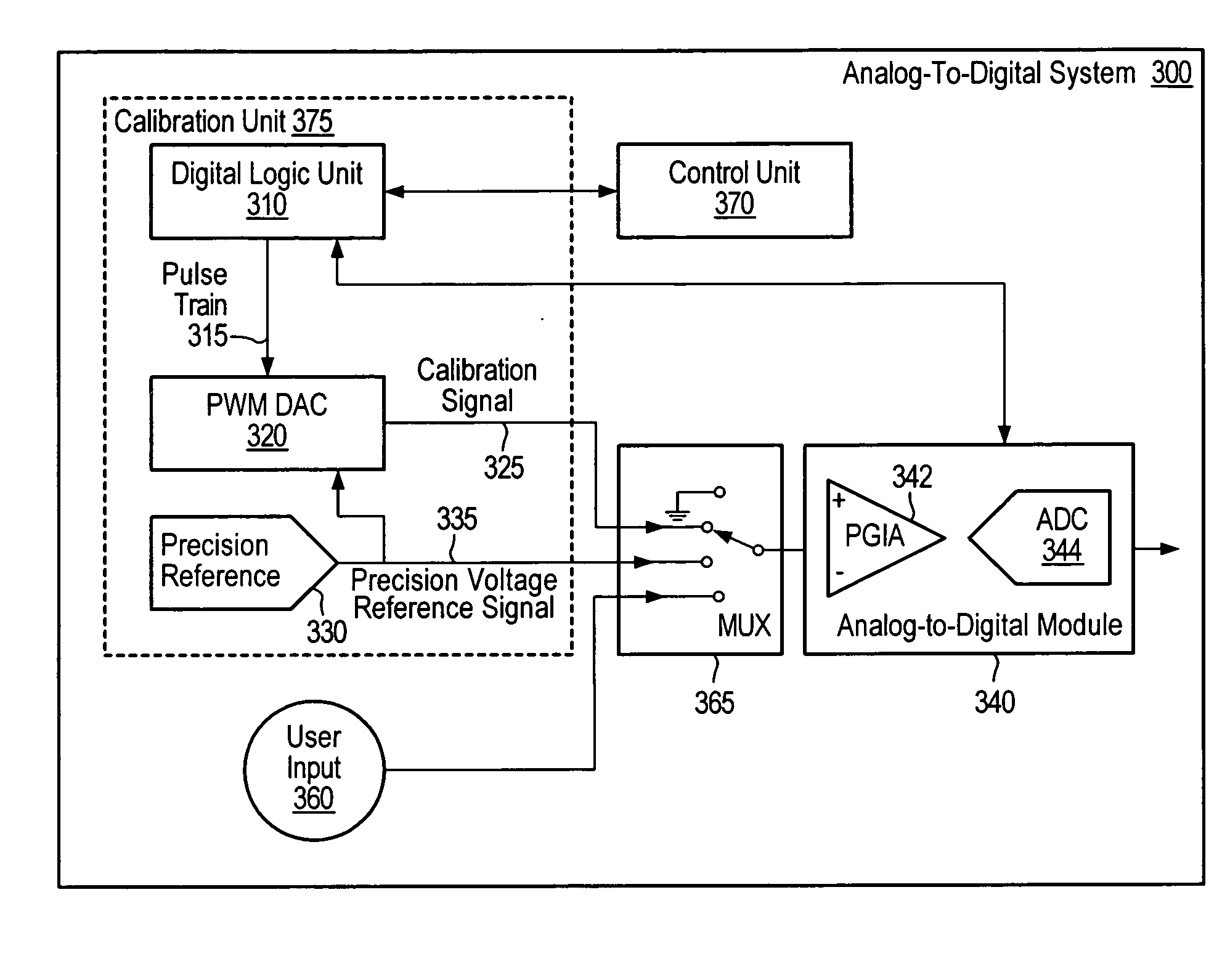
ActiveUS20050197796A1Reduce measurementReduce large signal nonlinearitiesElectric signal transmission systemsVoltage-current phase angleElectrical resistance and conductanceData acquisition
A calibration unit and technique for calibrating A / D systems (e.g., data acquisition devices) using a pulse-width modulation (PWM) circuit to reduce nonlinearity. The calibration unit may be coupled to an analog-to-digital module (ADM) of the A / D system. The PWM circuit may generate a calibration signal with intentional ripple, which may exercise a region of a transfer curve of the ADM to reduce local nonlinearities in measurements associated with the calibration of the system. Pulse trains of varying frequency and duty cycle may be generated to sweep the PWM circuit through an ADM range and to calculate an ADM linearity correction function, which may be used to perform gain and offset correction with respect to a best-fit line through an ADM transfer curve to reduce large signal nonlinearities. The PWM circuit may include a resistor divider circuit including a plurality of taps to improve the ability to calibrate small input ranges.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
Touch panel and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20140182894A1Reduce signalIncrease in wire areaElectric switchesSelector switchesTouch panelEngineering
A touch panel is partitioned into a sensing region and a circuit region and the circuit region is positioned around the edges of the sensing region. The touch panel comprises an electrode layer, a first wire layer, a second wire layer and an insulating layer. The electrode layer is disposed in the sensing region. The first wire layer is disposed in the circuit region and electrically connects to the electrode layer. The second wire layer electrically connects to the first wire layer in the circuit region. The insulating layer has a portion being disposed between the first wire layer and the second wire layer in the circuit, and has a plurality of first through holes wherein the first wire layer electrically connects to the second wire layer through the first through holes. The present disclosure also provides a method of manufacturing a touch panel.
Owner:TRENDON TOUCH TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
Method and apparatus for detecting marine deposits
InactiveUS20110013481A1High sensitivityAccurate detectionMagnetic gradient measurementsSeismology for water-covered areasMagnetic gradientMagnetic measurements
Noise compensation in controlled source electromagnetics (CSEM) comprises measuring time-varying magnetic gradients of the marine environment subjected to CSEM. From the measured magnetic gradients, oceanographic electric and magnetic field noise is determined and used for noise compensation of CSEM measurements of electric and magnetic fields. Selection of magnetic gradient measurement provides improved measurement of oceanographic magnetic noise as other electromagnetic noise sources produce negligible magnetic gradients in the marine environment. Electric field noise is then predicted from the magnetic measurements.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
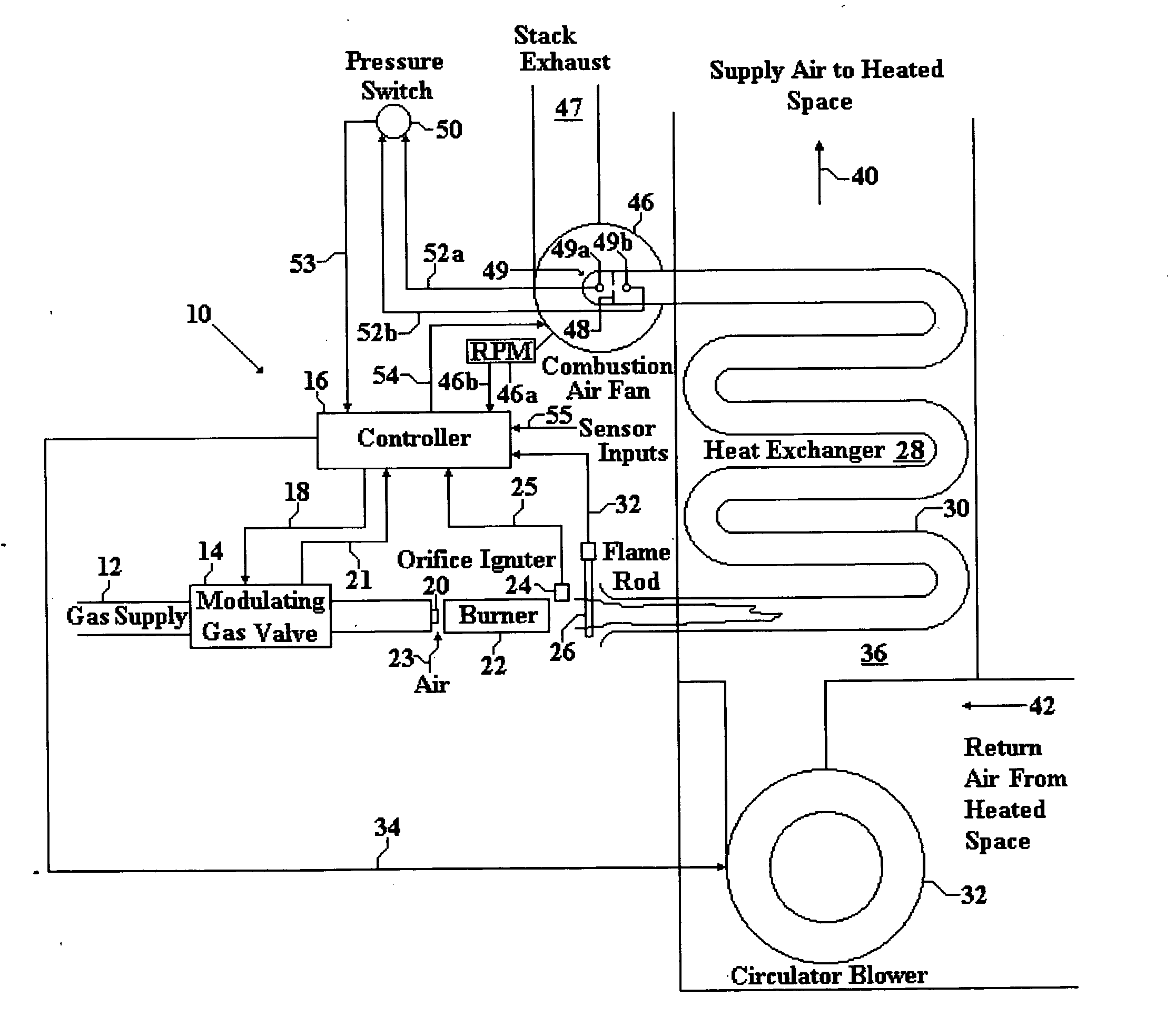
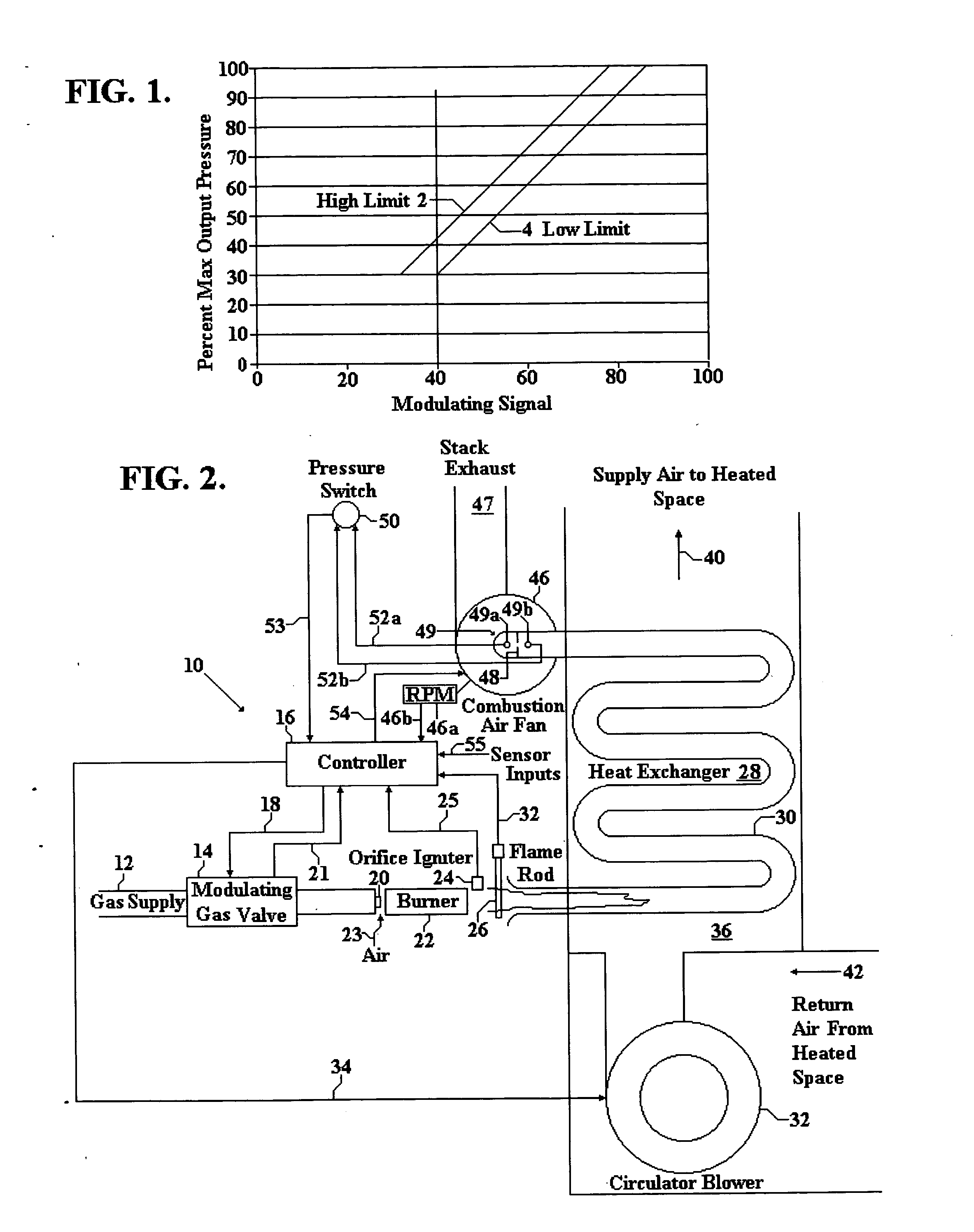
Feedback control for modulating gas burner
ActiveUS20060105279A1Maintain accuracyLarge signalFuel supply regulationCombustion ventilatorsClosed loop feedbackControl system
A modulating gas burner control system using closed loop feedback from a flame rod which provides a signal that varies with gas pressure and which provides combustion air fan control to accurately control the heat from the system without use of expensive control valves.
Owner:ADEMCO INC +1
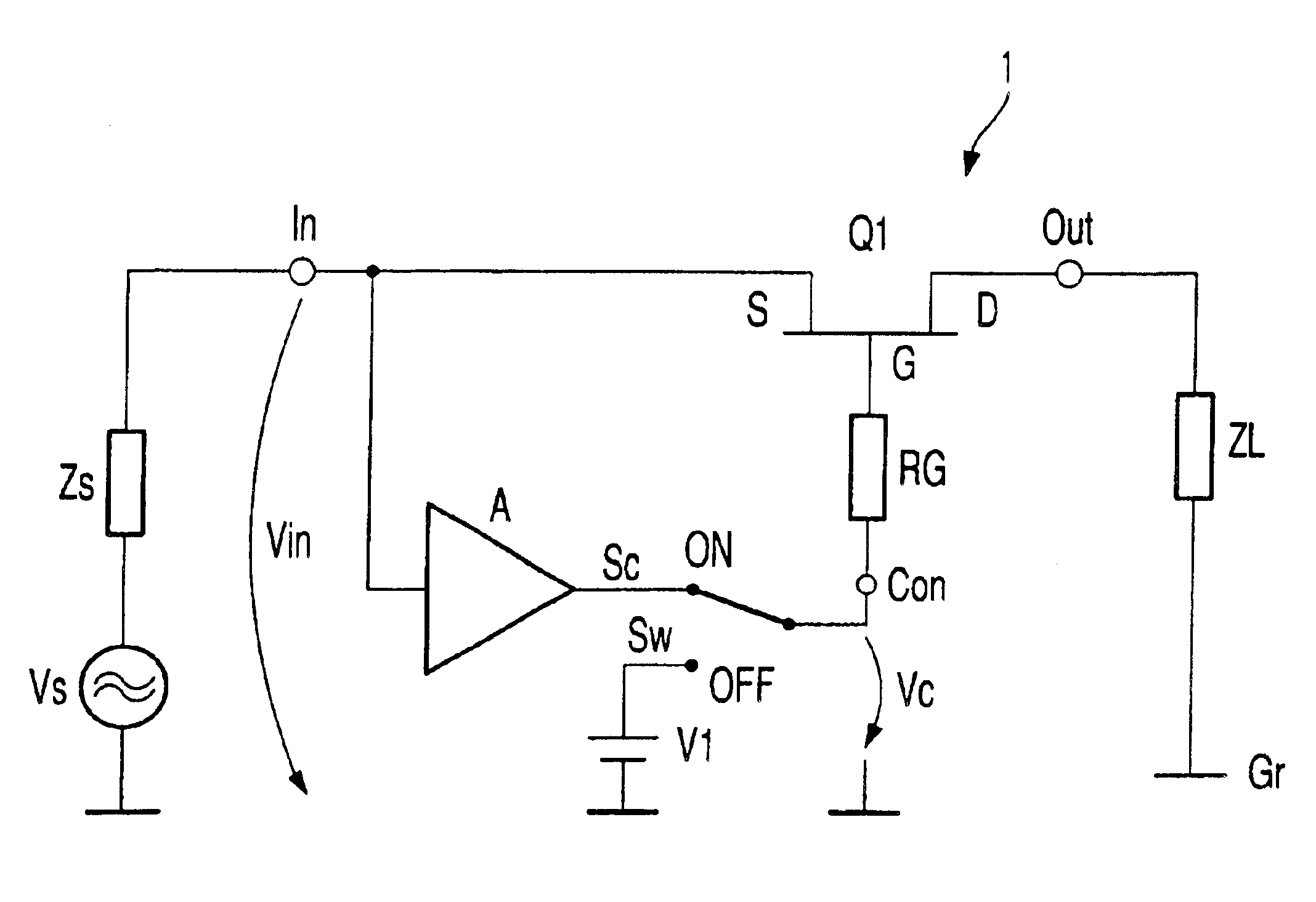
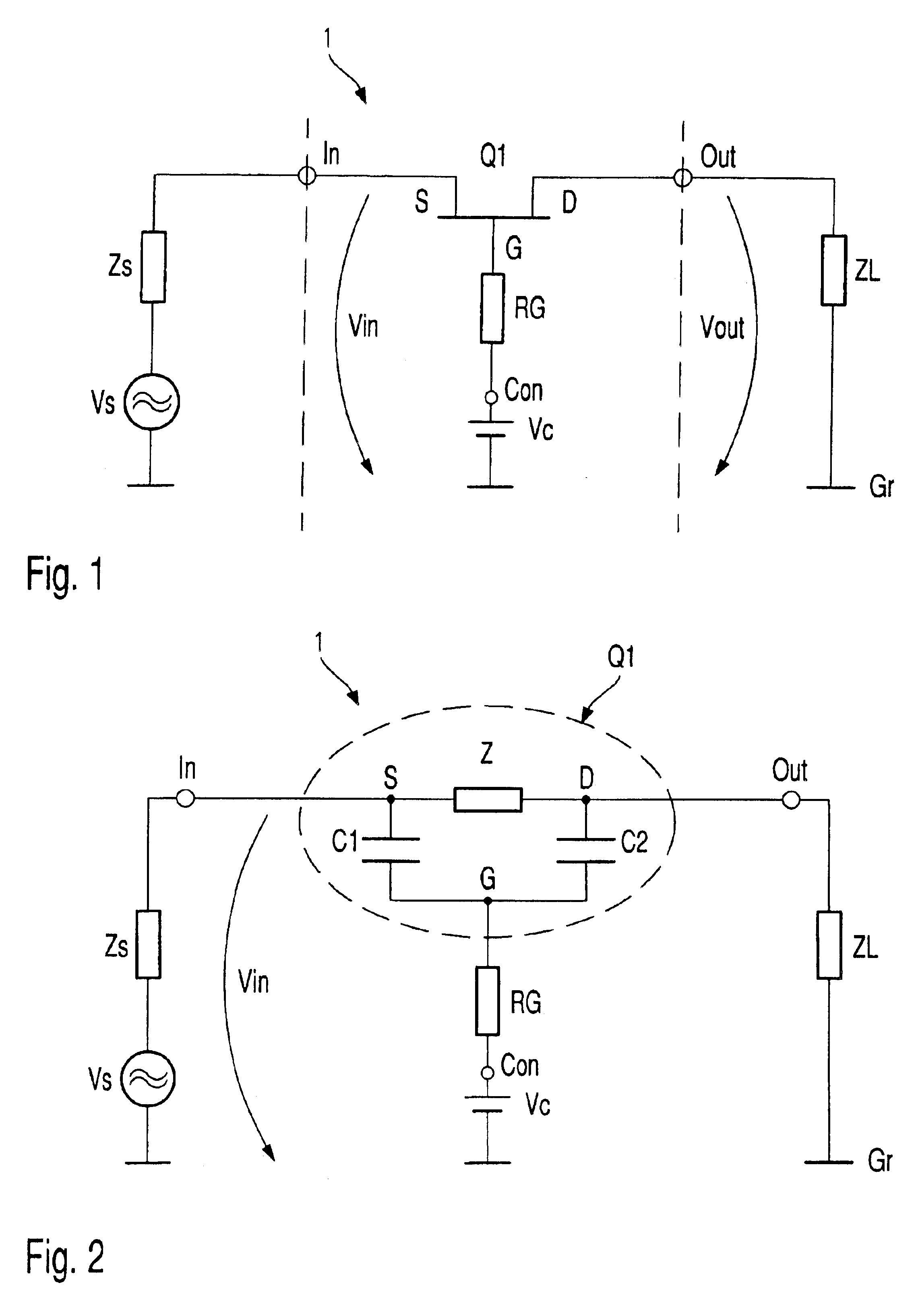
Electronic switch
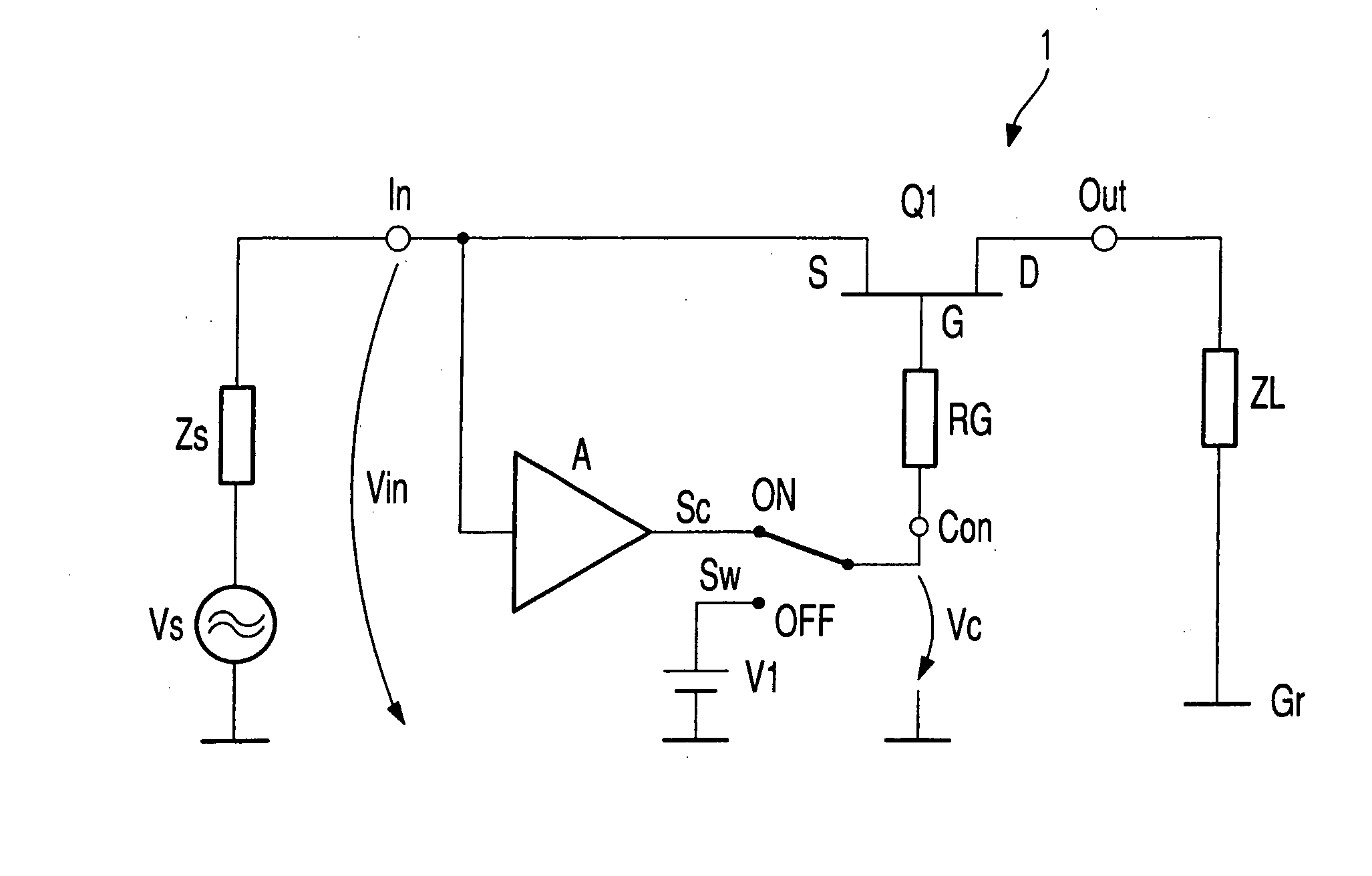
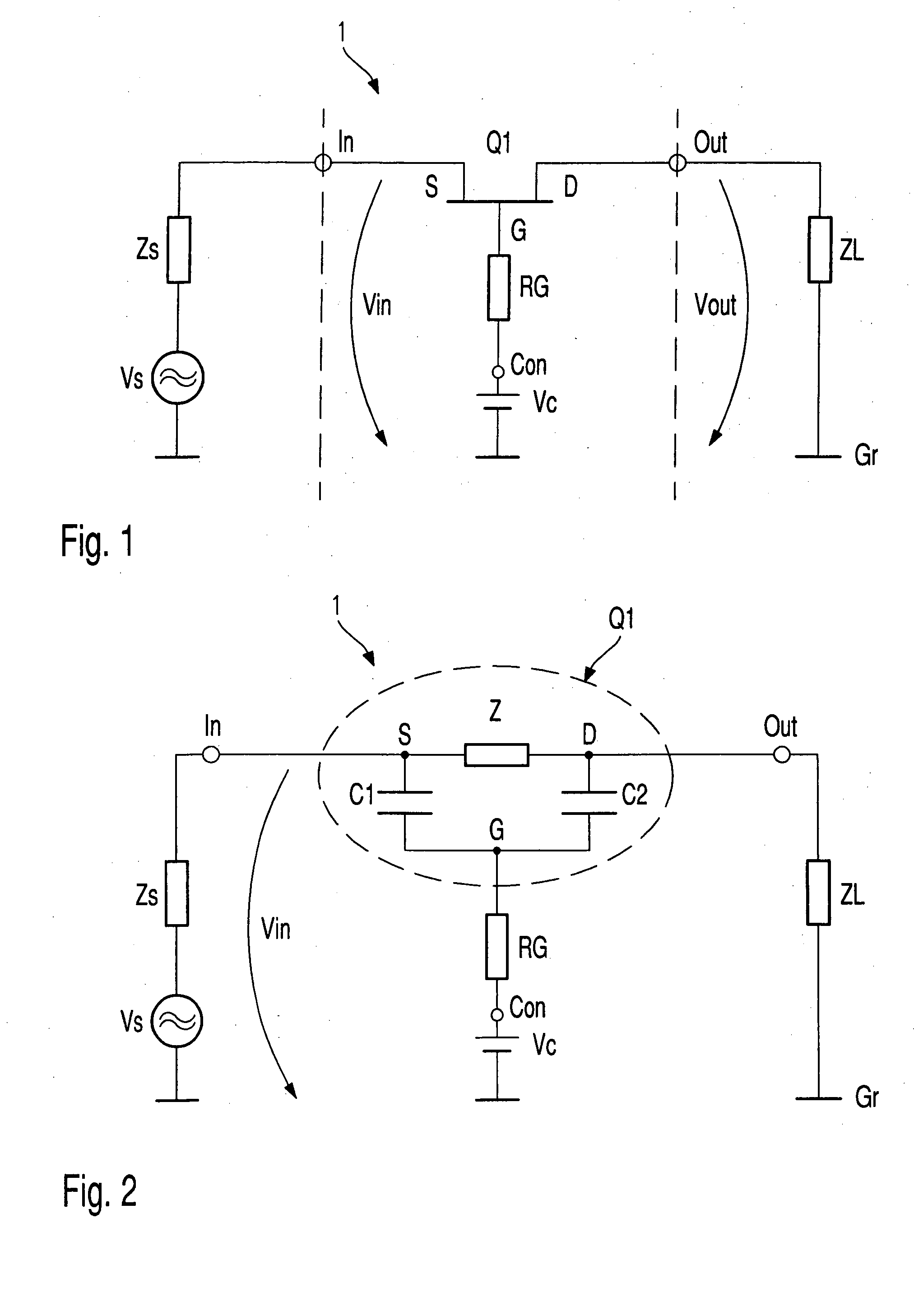
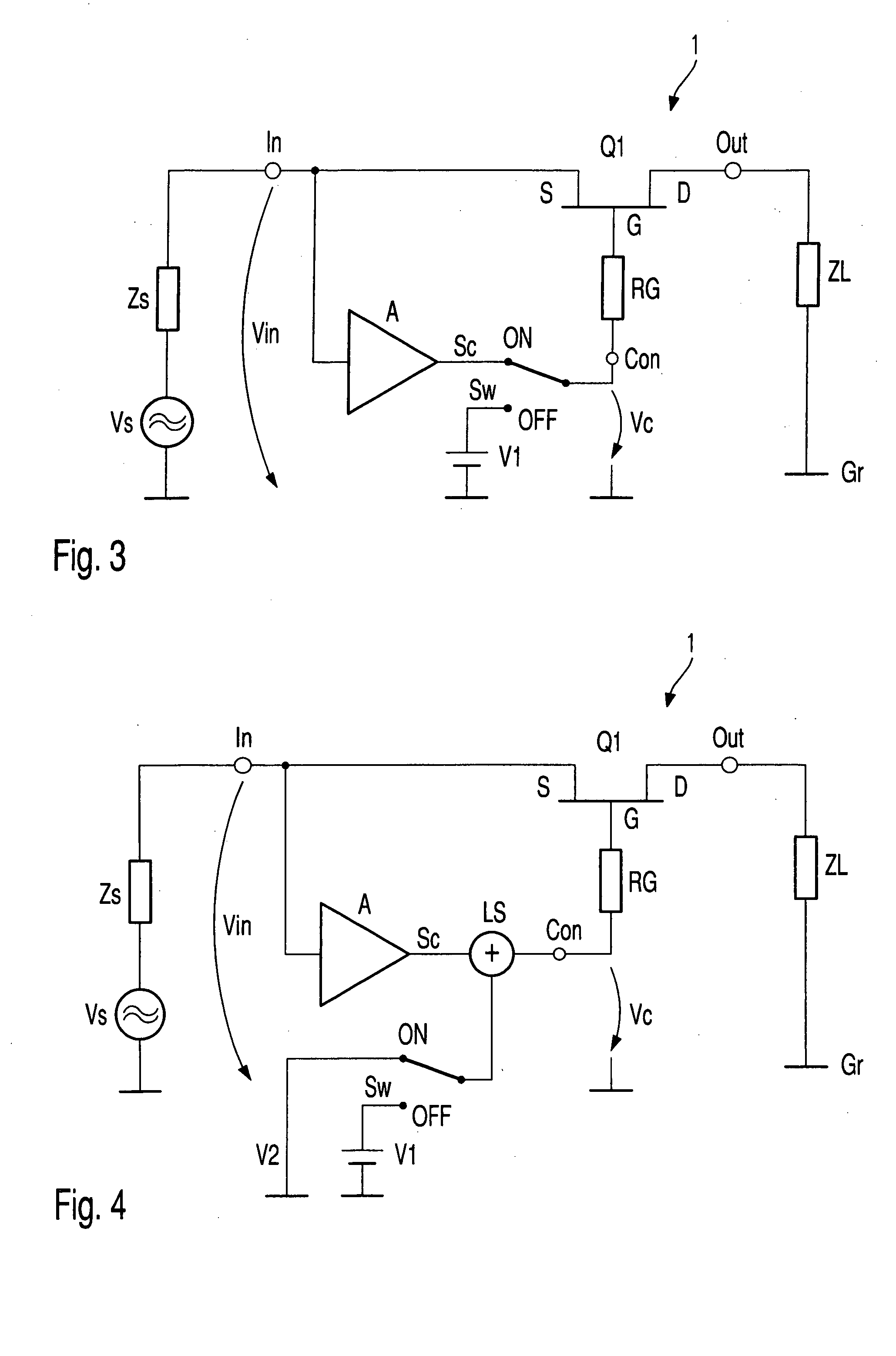
InactiveUS6873200B2Shorten the switching timeLarge low-frequencyTransistorMultiple-port networksControl signalSwitching signal
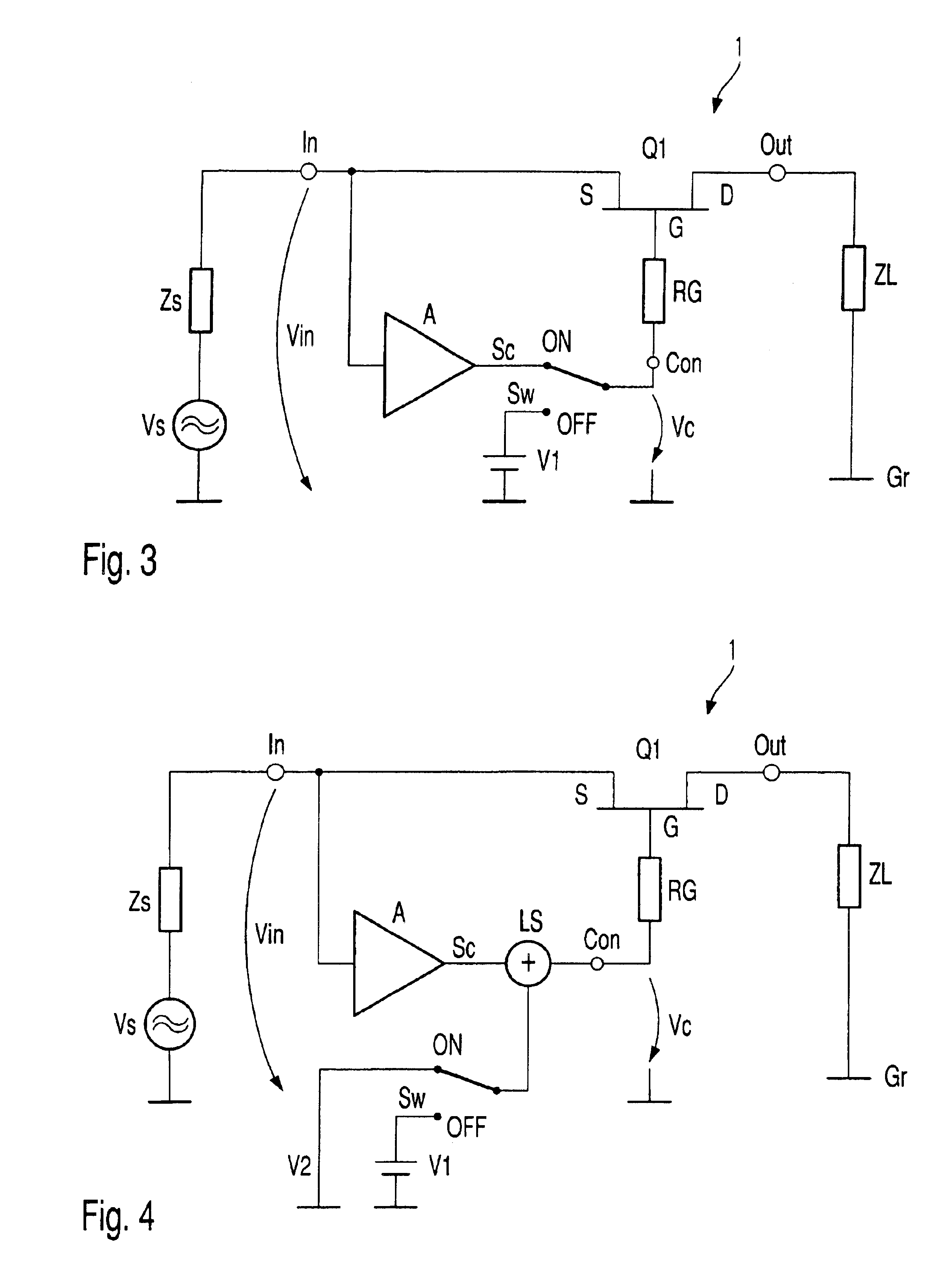
Electronic switch (1) with two switching states (ON, OFF) possesses at least one field effect switching transistor (Q1), input port (In) connected with source terminal (S), on which input signal (Vin) is present, output port (Out) connected with drain terminal, on which switched signal (Vout) is present, control port (Con) connected to gate terminal (G), on which is present signal (Vc) for controlling electronic switch (1) and switch apparatus (Sw), which creates the two switching states (ON, OFF) by means of a changing of control signal (Vc). Controlling signal (Vc), during at least one of the two switching states (ON, OFF) is, at least partially, formed by correction signal (Sc), which in turn is produced from input signal (Vin), so that the frequency dependent drop in voltage between the drain-source channel and the gate electrode of the field effect switching transistor (Q1) is at least partially compensated.
Owner:ROHDE & SCHWARZ GMBH & CO KG
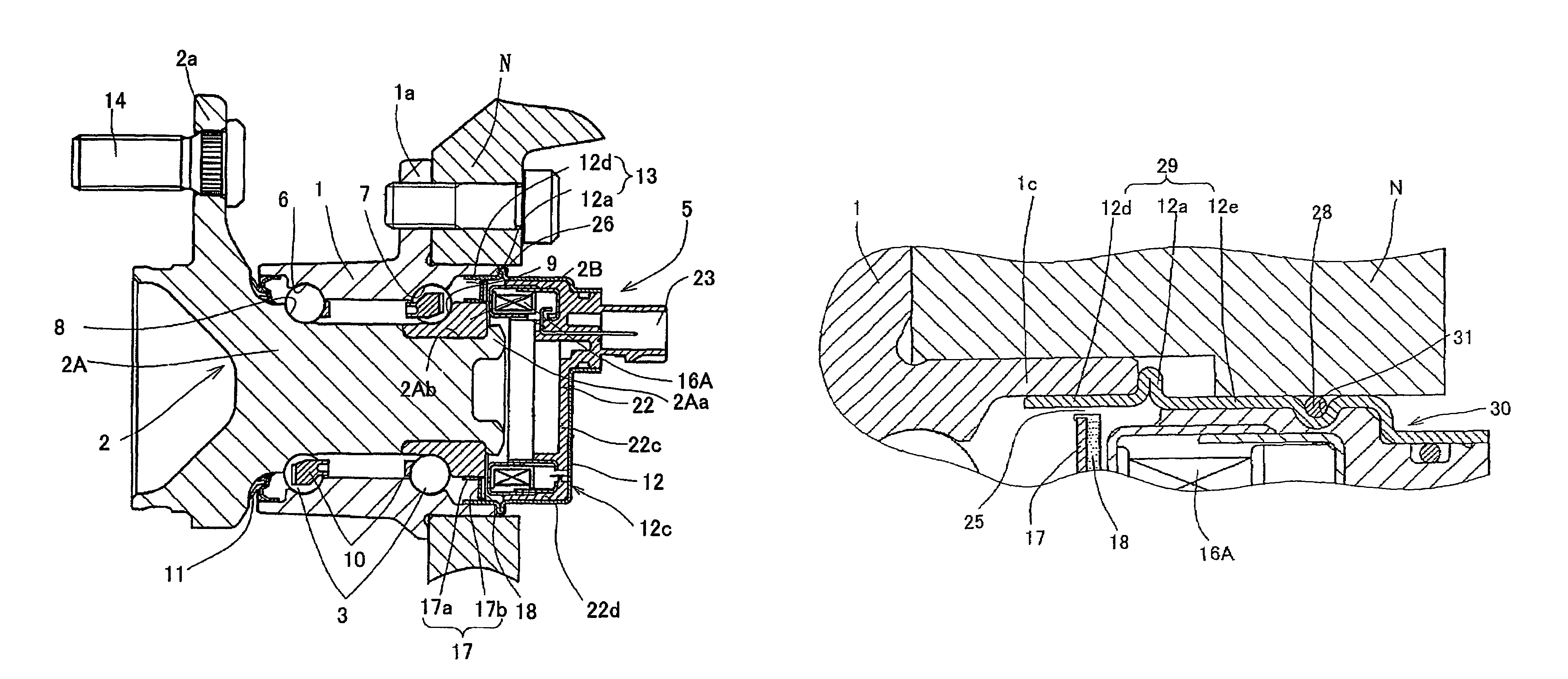
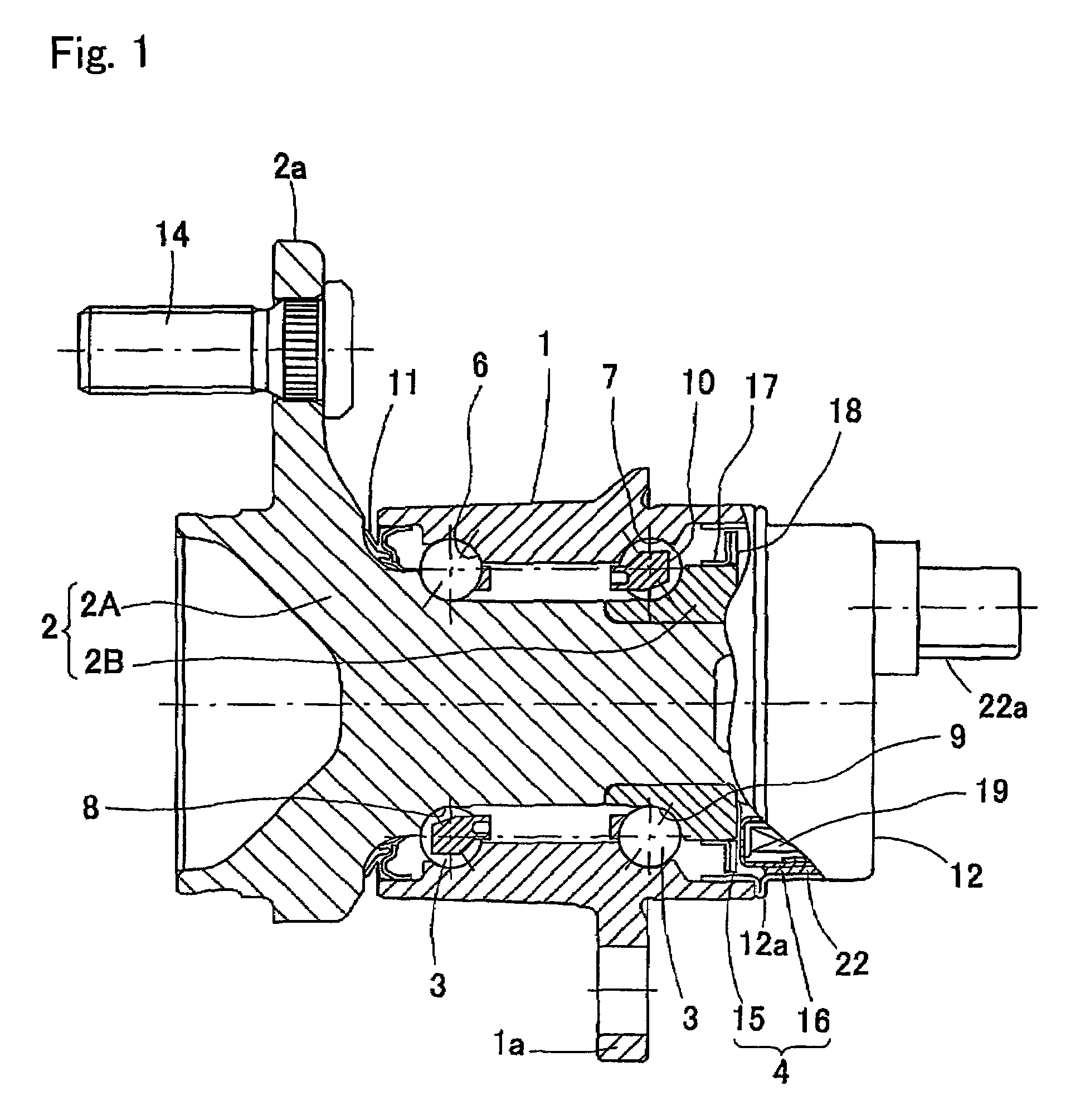
Bearing Assembly with Rotation Sensor
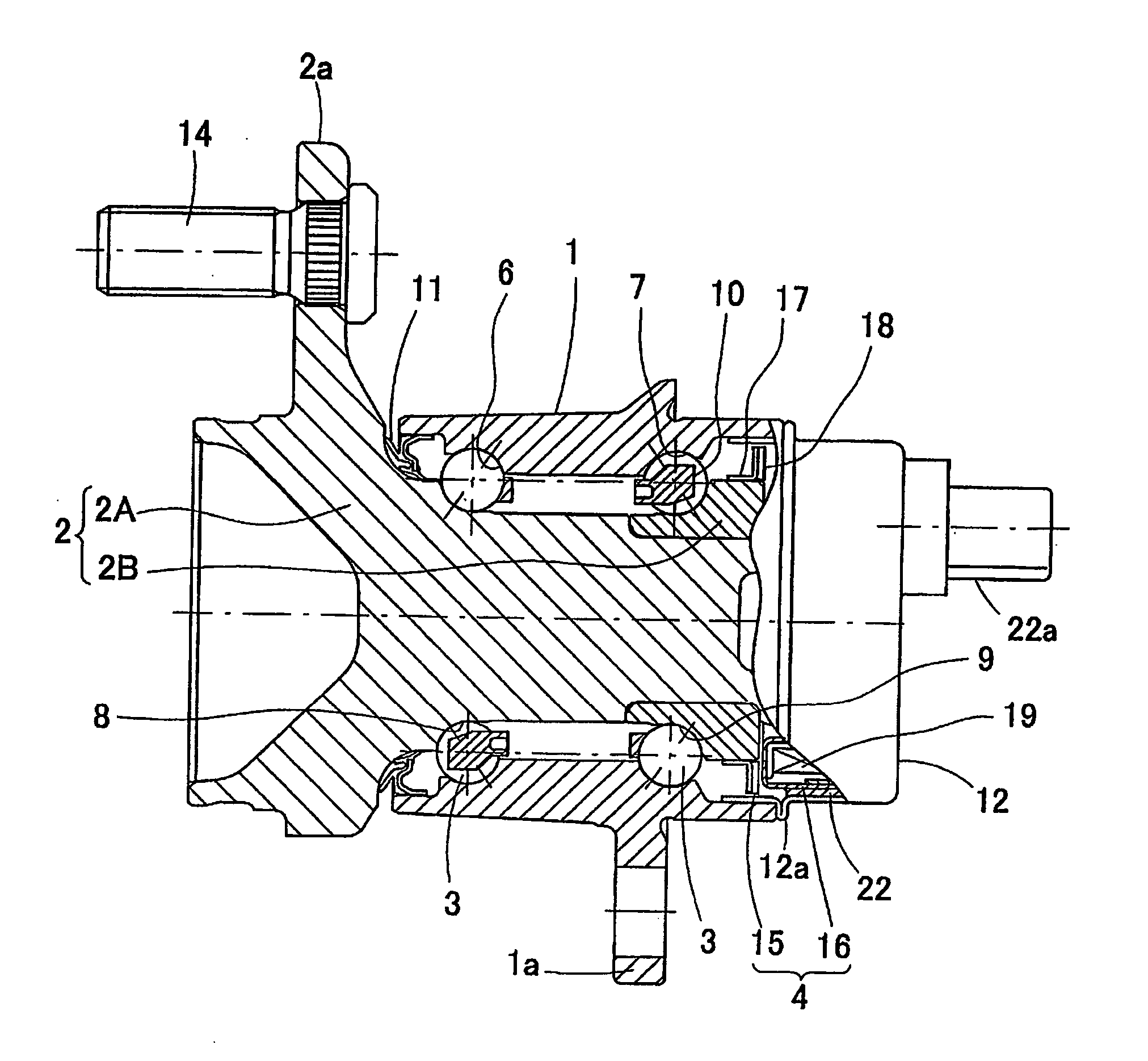
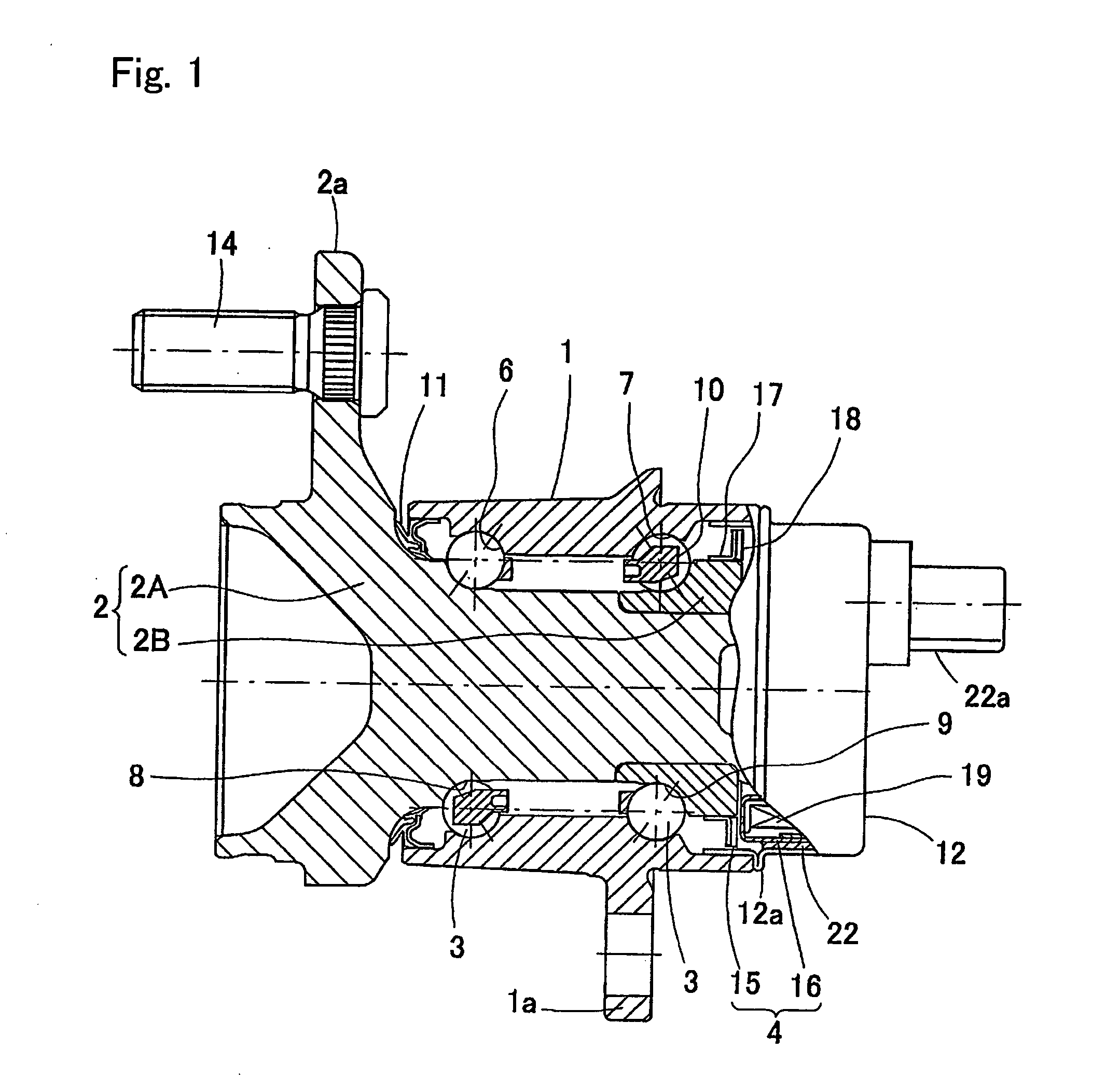
InactiveUS20070268013A1Inhibit deteriorationSimple structureRolling contact bearingsBearing assemblyEngineeringRotation sensor
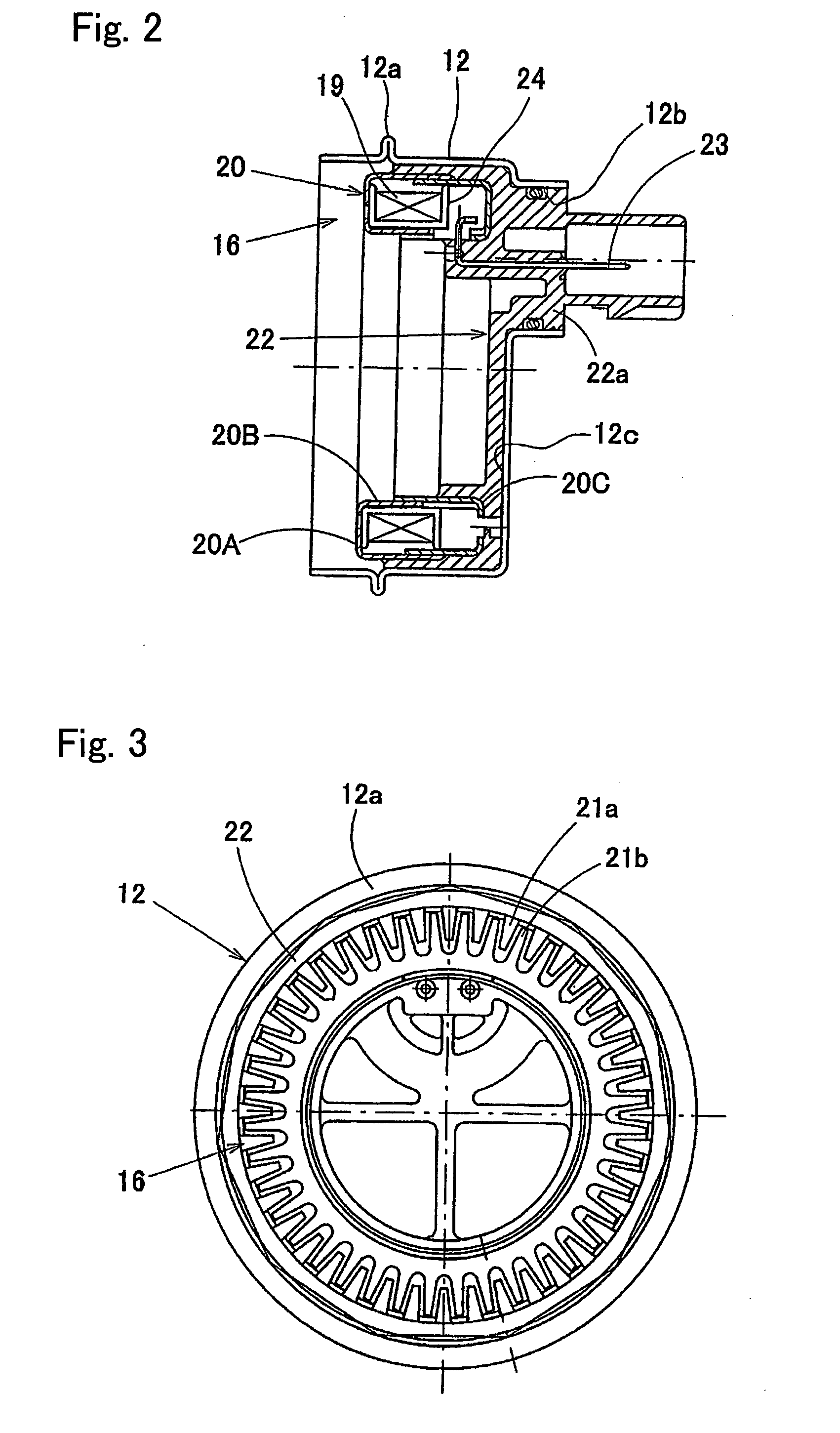
A bearing assembly with a rotation sensor, comprising an outer member (1), an inner member (2), a plurality of rolling elements (3) interposed between the opposed raceway surfaces, and a rotation sensor (4). The rotation sensor (4) includes an annular magnetic encoder (15) and an annular magnetic sensor (16) fitted to the outer member (1) through a sensor cap (12) and a sensor connector (22). The sensor cap (12) is formed in a cylindrical shape having a bottom shape, and has an opening end fitted to an inner periphery or outer periphery of the outer member (1) The sensor connector (22) is formed integrally with the magnetic sensor (16), formed in a polygonal shape on its outer periphery, and fitted to the inner periphery of the sensor cap (12) by a press-fitting.
Owner:NTN CORP
System for auralizing a loudspeaker in a monitoring room for any type of input signals
InactiveUS7783054B2Large signalExtension of timeGain controlTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsEngineeringLoudspeaker
The system comprises a loudspeaker simulation unit for simulating the transmission behavior of the loudspeaker and comprises a room simulation unit, which is connected in outgoing circuit to the loudspeaker simulation unit and which is provided for simulating the transmission behavior of a given monitoring room. The room simulation unit is followed by a presentation unit, which generates an acoustic signal that corresponds to the auditory impression of the loudspeaker in the monitoring room, and / or is followed by an evaluation unit that evaluates the signal, which is provided by the room simulation unit, with regard to at least one psychoacoustic measured quantity, and the evaluation unit outputs a corresponding measurement signal. This measurement signal corresponds to a measurement signal that occurs inside the monitoring room during the presentation of the input signals.
Owner:HARMAN AUDIO ELECTRONICS SYST
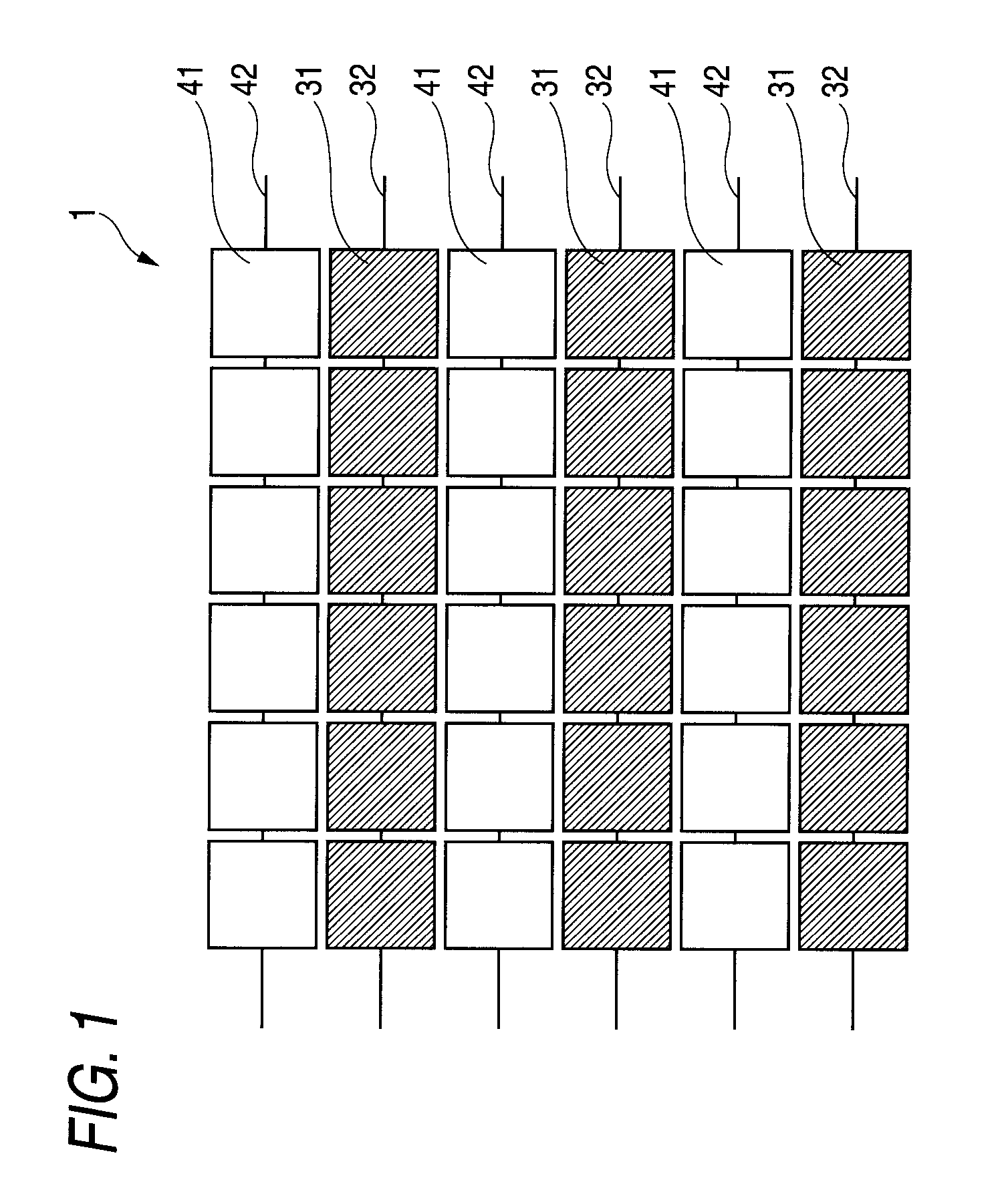
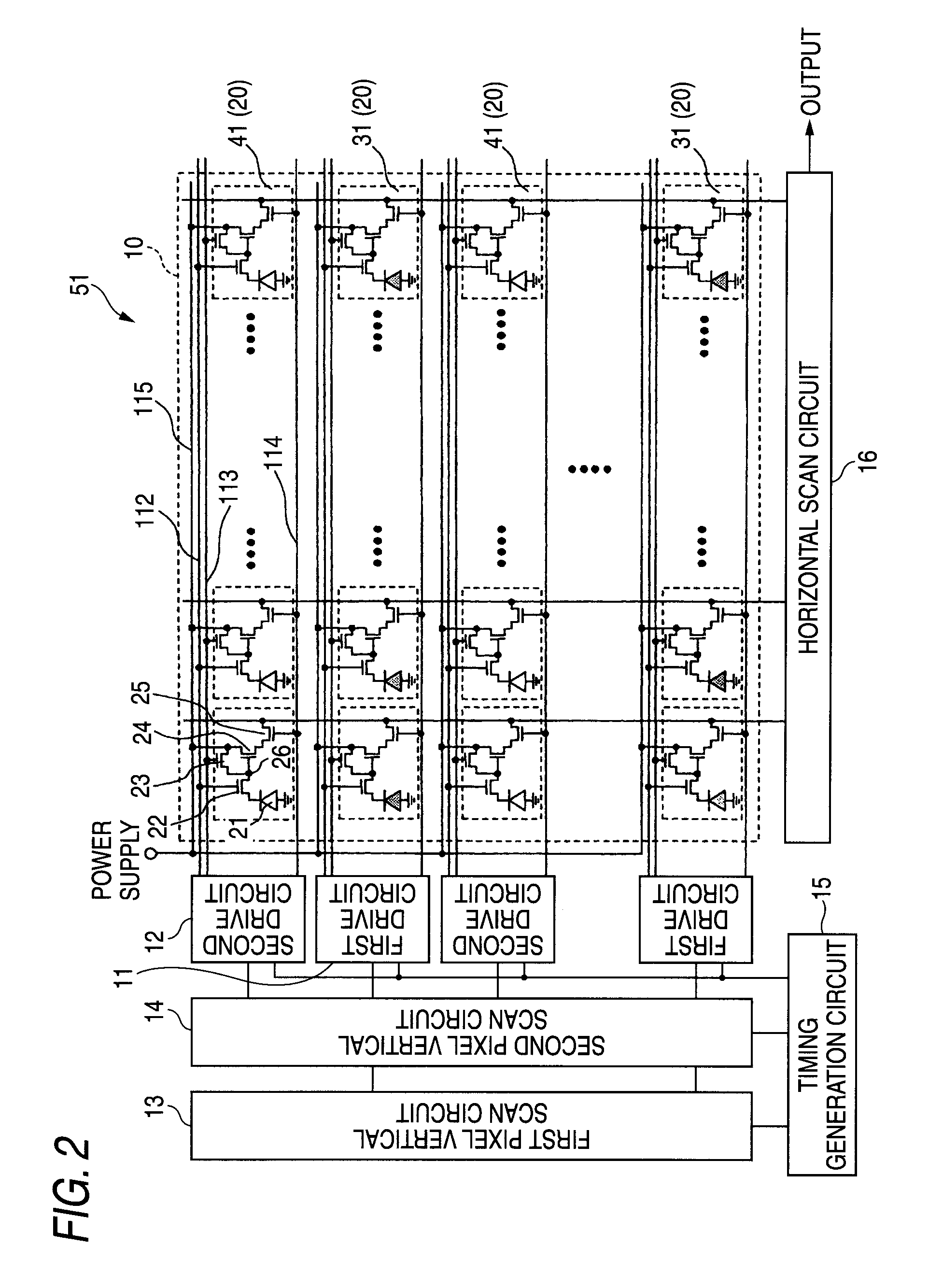
Solid-state imaging device, method for driving solid-state imaging device and camera
ActiveUS7750278B2Reduce signal to noise ratioReduce sensitivityTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometryControl signalEngineering
A solid-state imaging device including an array of a plurality of first pixels and a plurality of second pixels with higher sensitivity than the first pixels, a first control signal line that controls the first pixels, and a second control signal line that controls the second pixels, wherein the first control signal line and the second control signal line are driven independent of each other.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
Bearing assembly having rotation sensor and mounting structure to support sensor cap and connector
InactiveUS7692422B2Large signalStable and accurate outputBearing assemblyMeasurement apparatus componentsEngineeringRotation sensor
A wheel support bearing assembly includes an outer member inserted in a knuckle, an inner member made up of a hub axle, double rows of rolling elements, and a cover closing an opening of one end of the outer member. The cover includes a sensor connector and a sensor cap. A pulsar ring is mounted on the inner race and a rotation sensor is opposed to the pulsar ring and embedded in the sensor connector. The cover extends over an outer surface of the sensor connector. The cover has a cylindrical portion mounted in an inner peripheral surface of one end of the outer member, which end forms a pilot portion for the knuckle. The cylindrical portion of the cover has an outer periphery provided with an annular elastic member held in contact with an inner peripheral surface of the knuckle.
Owner:NTN CORP
Electronic switch
ActiveUS20050024122A1Improvement of low frequency large signal behaviorHigh input impedanceTransistorElectronic switchingControl signalElectronic switch
Electronic switch (1) with two switching states (ON, OFF) possesses at least one field effect switching transistor (Q1), input port (In) connected with source terminal (S), on which input signal (Vin) is present, output port (Out) connected with drain terminal, on which switched signal (Vout) is present, control port (Con) connected to gate terminal (G), on which is present signal (Vc) for controlling electronic switch (1) and switch apparatus (Sw), which creates the two switching states (ON, OFF) by means of a changing of control signal (Vc). Controlling signal (Vc), during at least one of the two switching states (ON, OFF) is, at least partially, formed by correction signal (Sc), which in turn is produced from input signal (Vin), so that the frequency dependent drop in voltage between the drain-source channel and the gate electrode of the field effect switching transistor (Q1) is at least partially compensated.
Owner:ROHDE & SCHWARZ GMBH & CO KG
Method and system for calibrating the scan amplitude of an electron beam lithography instrument
InactiveUS6941006B1Effective positioningControlling signalElectric discharge tubesNanoinformaticsLight beamElectron-beam lithography
A method for calibrating the scan amplitude of an electron beam lithography instrument by determining the position of a feature within the scan. The method is effective at the operating frequency of the scan and using a limited bandwidth video signal including the steps of determining the reference feature to be an edge over which the video signal rises abruptly from a background level to a white level. The method turns the beam on only over a short region of the scan and represents the degree of overlap between the beam on portion of the scan and the white part of the feature as the total video signal accumulated in that scan.
Owner:DUPONT PHOTOMASKS
Calibrating analog-to-digital systems using a precision reference and a pulse-width modulation circuit to reduce local and large signal nonlinearities
ActiveUS7146283B2Reduce measurementLarge signalElectric signal transmission systemsVoltage-current phase angleComputer moduleData acquisition
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
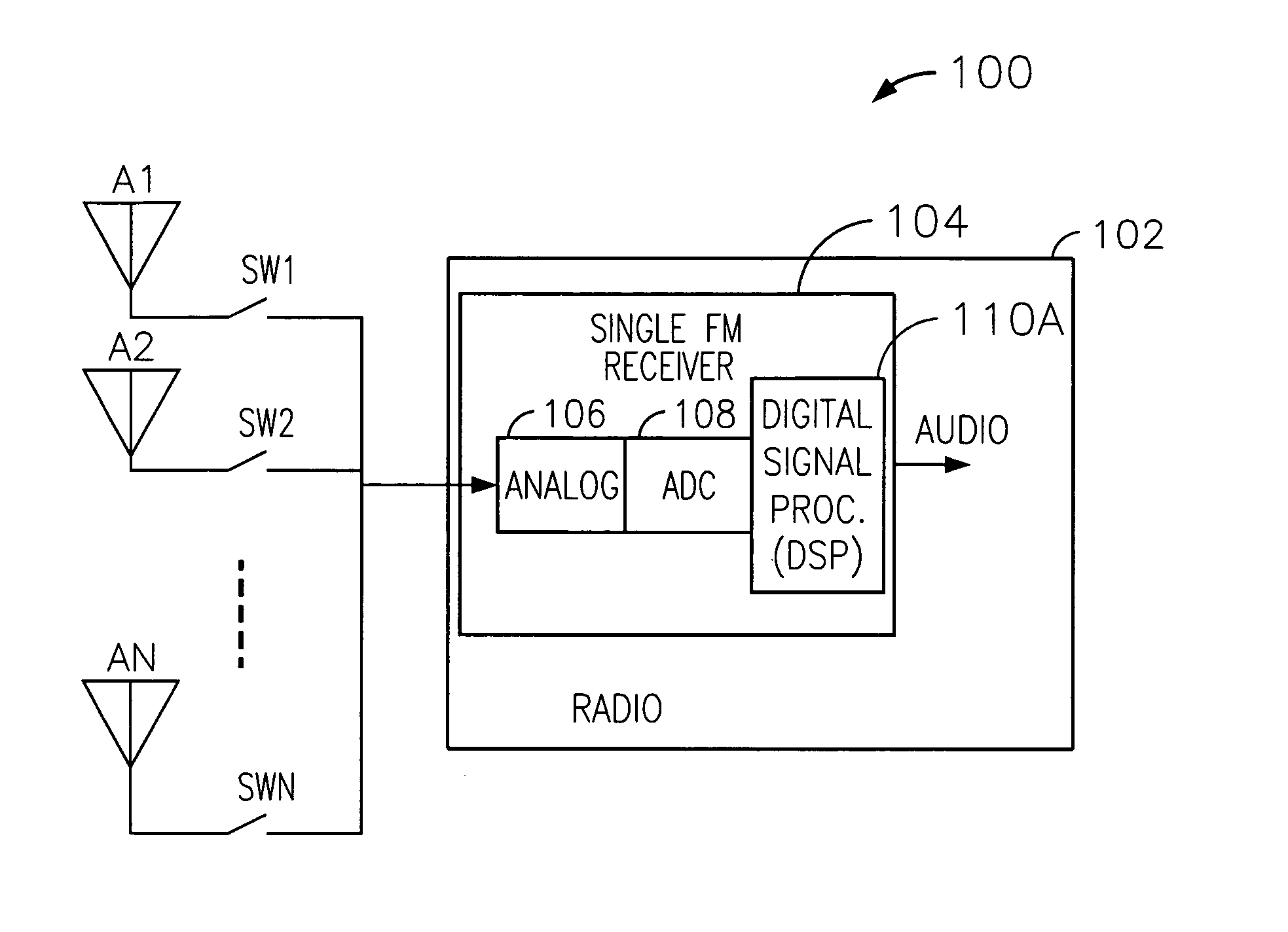
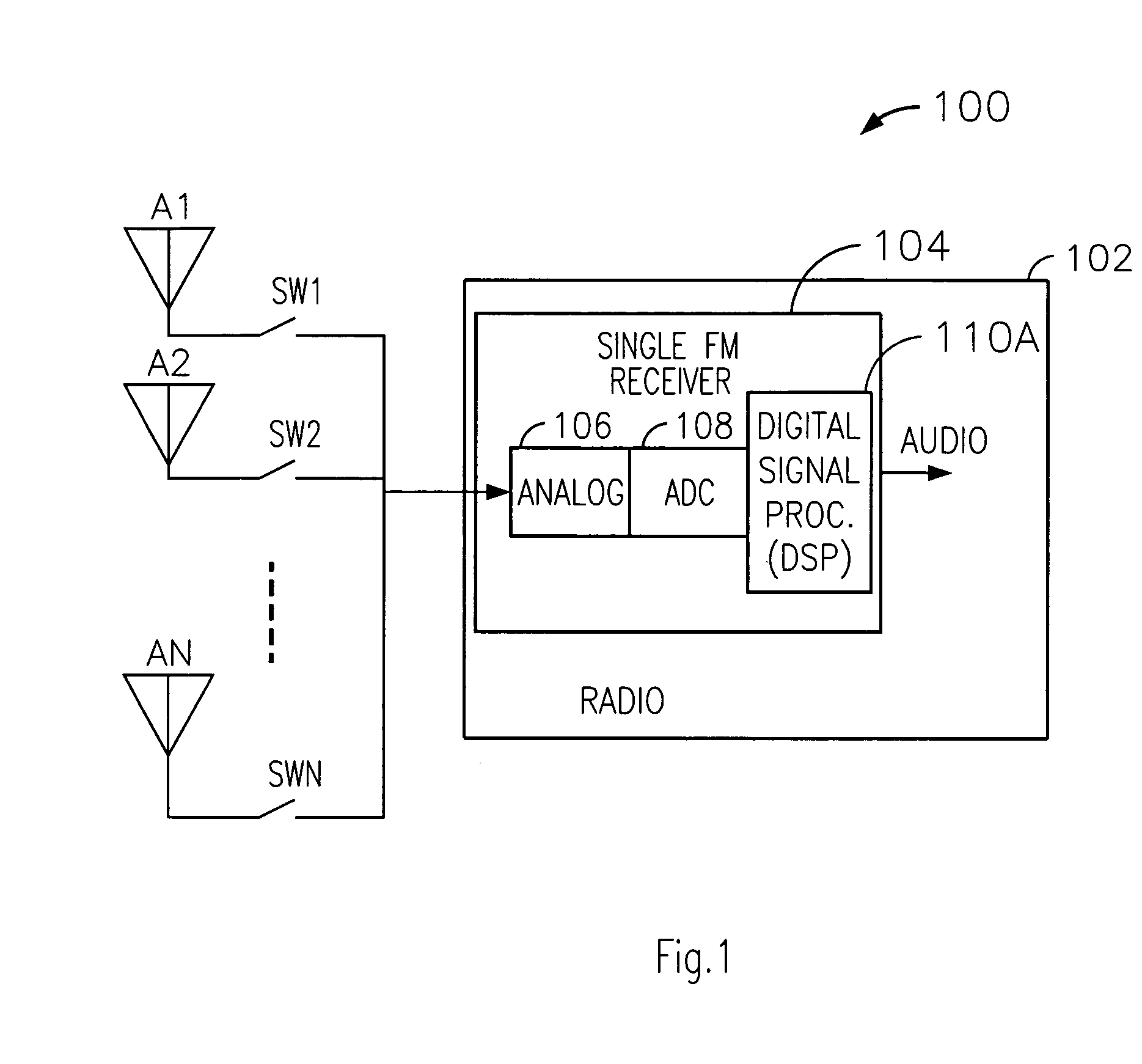
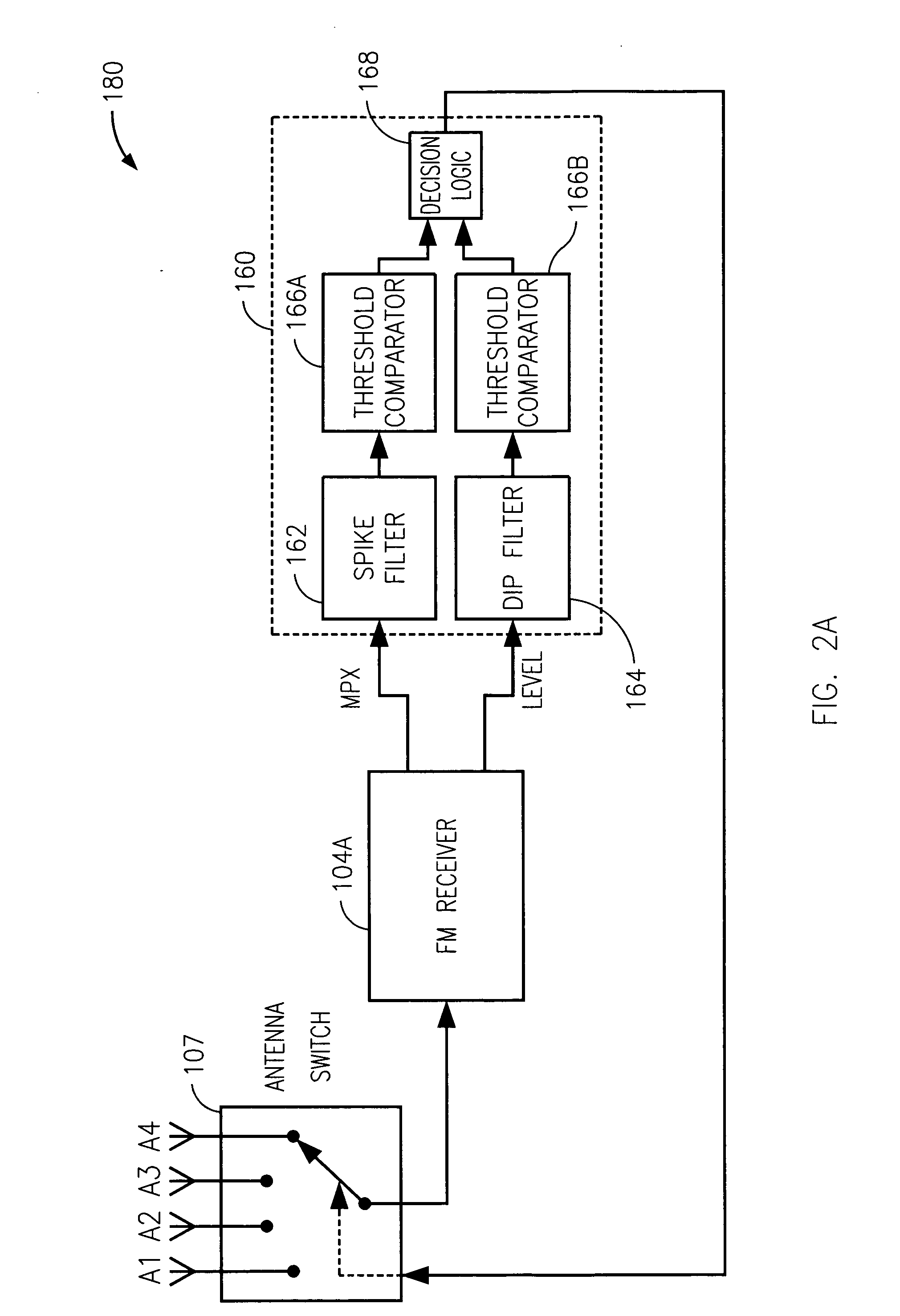
Technique for reducing multipath interference in an FM receiver
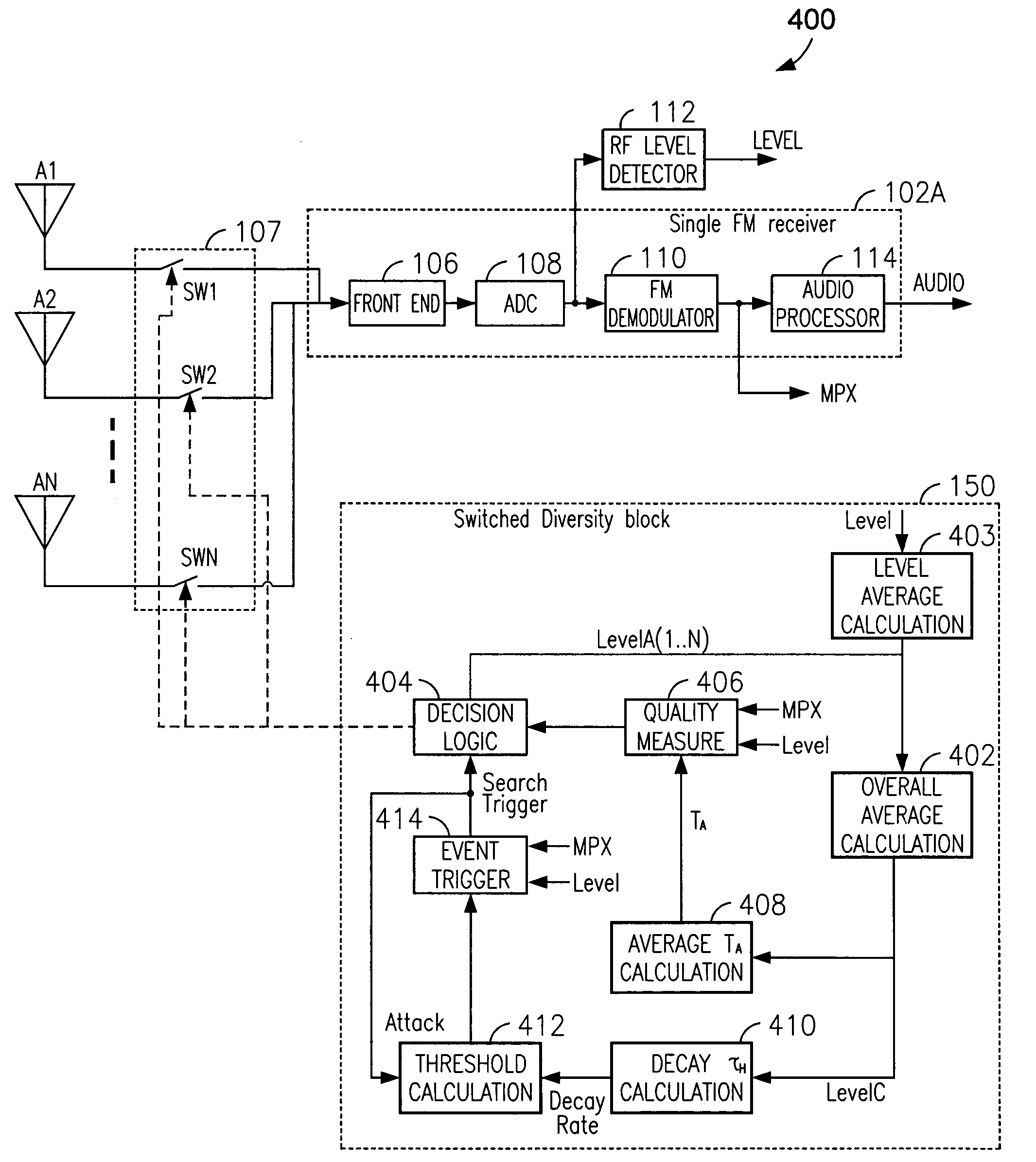
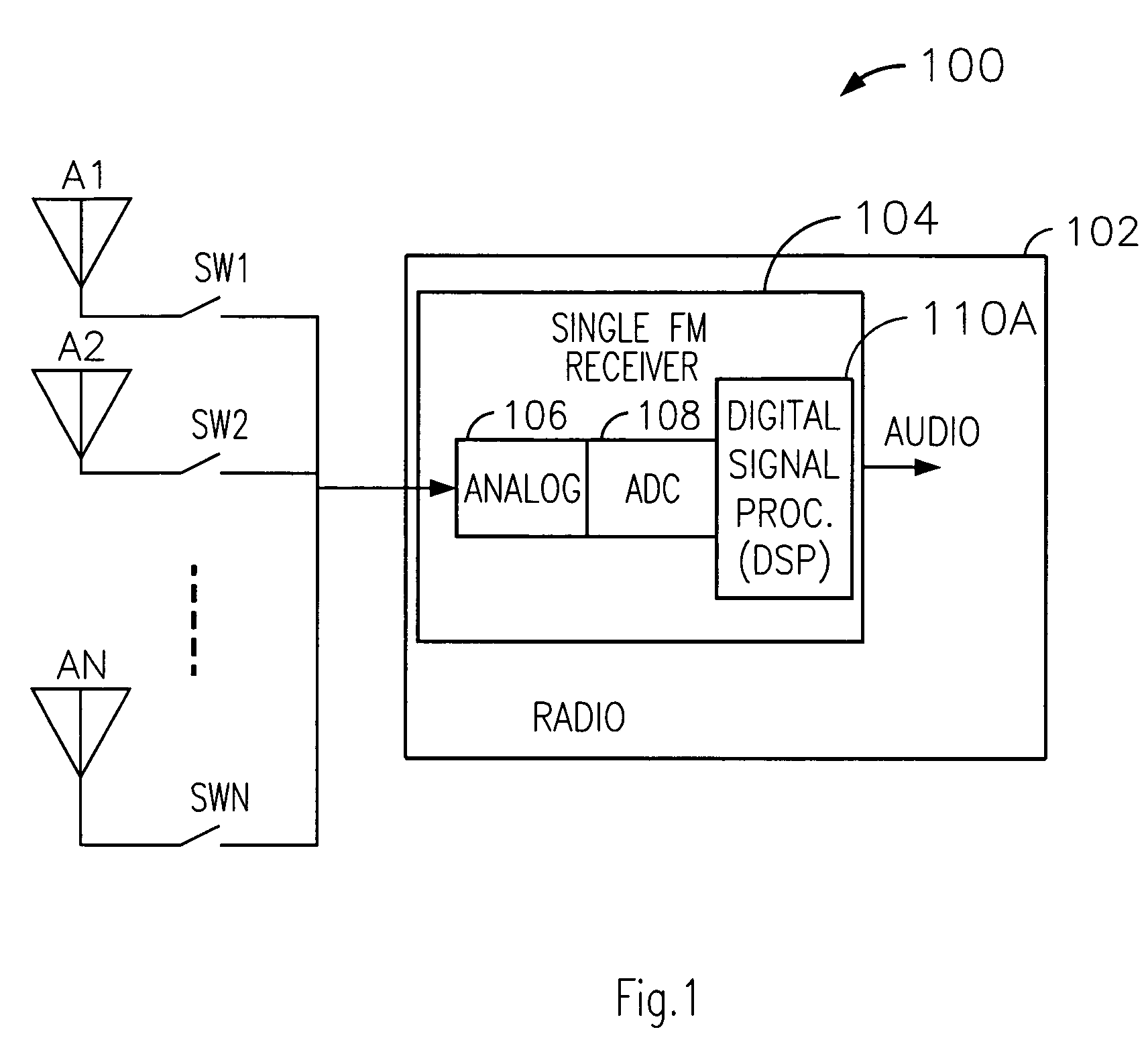
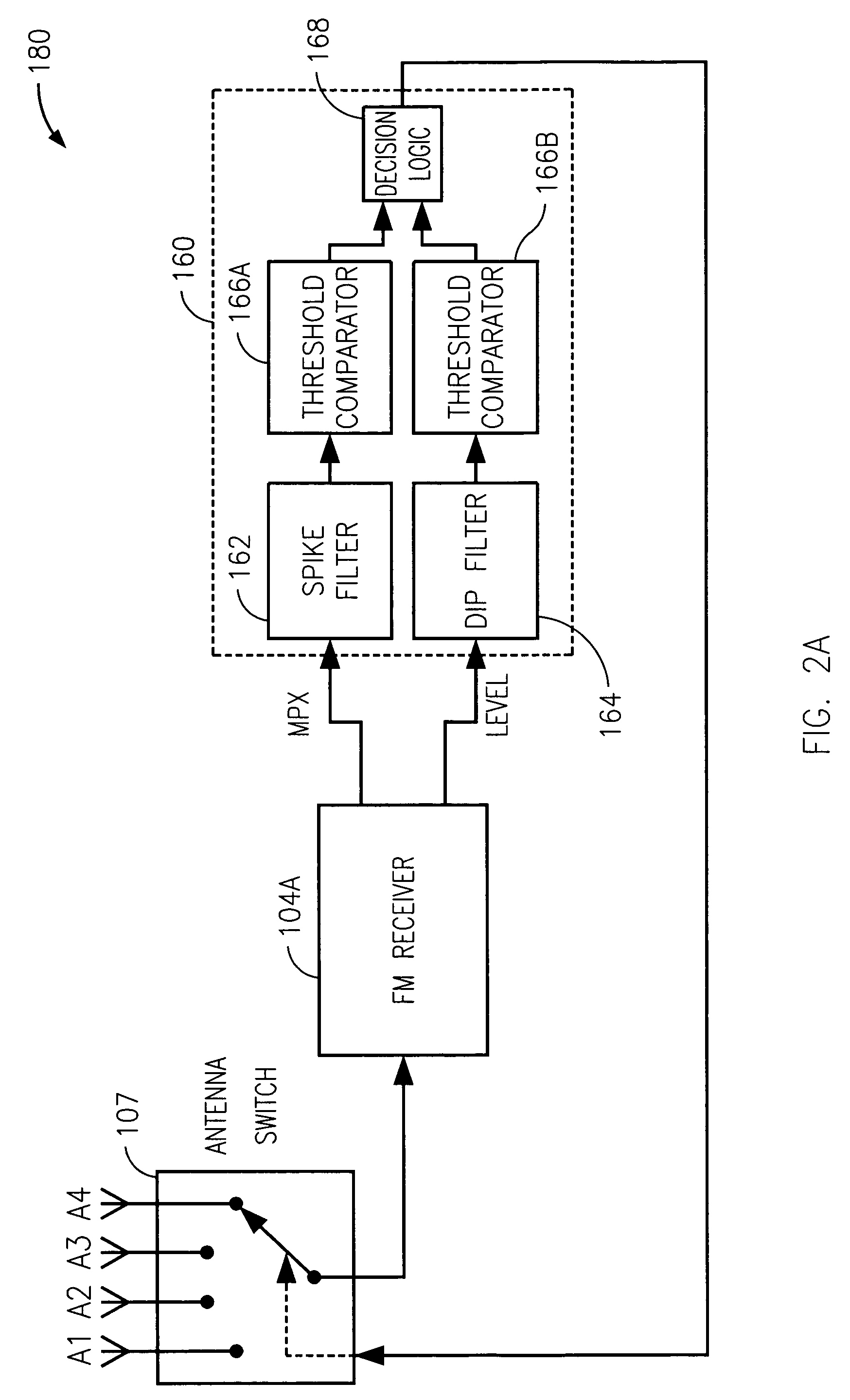
ActiveUS20070037538A1Minimize antenna switchingLarge signalReceivers monitoringRadio transmissionLow distortionSignal quality
A technique for reducing multipath distortion in an FM receiver, with a plurality of switchable antennas, provides a fast distortion detector that monitors a received signal for significant distortion events of less than about 15 microseconds in duration. In response to a multipath event, the output of the fast distortion detector initiates a search for a lower distortion (better quality) antenna. To prevent frequent antenna searches from causing an audible disturbance, a threshold is introduced to desensitize the fast distortion detector. Threshold decay is a function of an overall received RF signal level. A slow distortion detector is also provided that measures distortions of the received signal relating to signal quality.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
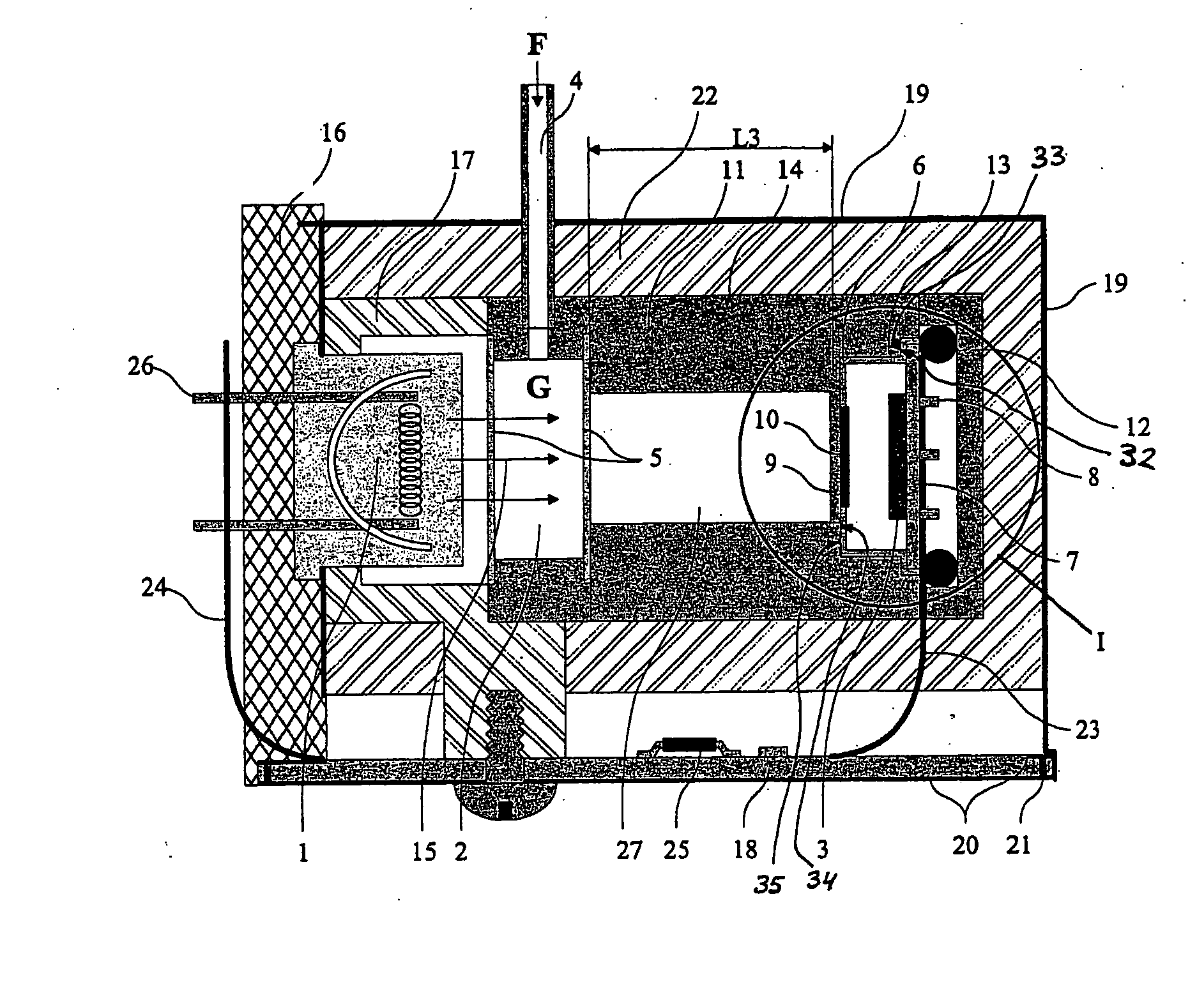
Method and apparatus for eliminating and compensating thermal transients in gas analyzer
ActiveUS20050268690A1Improve thermal conductivityFunction increaseAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBandpass filteringLight beam
The invention concerns a gas analyzer comprising: a measuring volume (2), a radiation source (1) for providing a beam to pass said measuring volume; a heat sink (16) for said radiation source; at least one thermal detector (3) having a hot junction within a support structure and receiving the radiation and a cold junction for reference within the same support structure and protected from said radiation; at least one optical bandpass filter (9) between said hot junction and said radiation source; and a thermal mass (11), which is formed of a material having high thermal conductance. The thermal mass has a cavity with a bottom step (34) and a rim (32), and a first length therebetween. The support structure has a frontal edge (35) and a base plate lip (33), and a second length therebetween. There is a radial gap between the thermal mass and the support structure. Press means urge said support structure in the cavity, whereupon a more efficient thermal contact is either between said frontal edge and said bottom step, or between said base plate lip and said rim. A first thermal barrier (17) is between the heat sink and the thermal mass, and a second thermal barrier (22) surrounds the thermal mass. A shield (19) formed of a material having high thermal conductance covers said second thermal barrier and is in thermal contact with said heat sink.
Owner:INSTRUMENTARIUM CORP
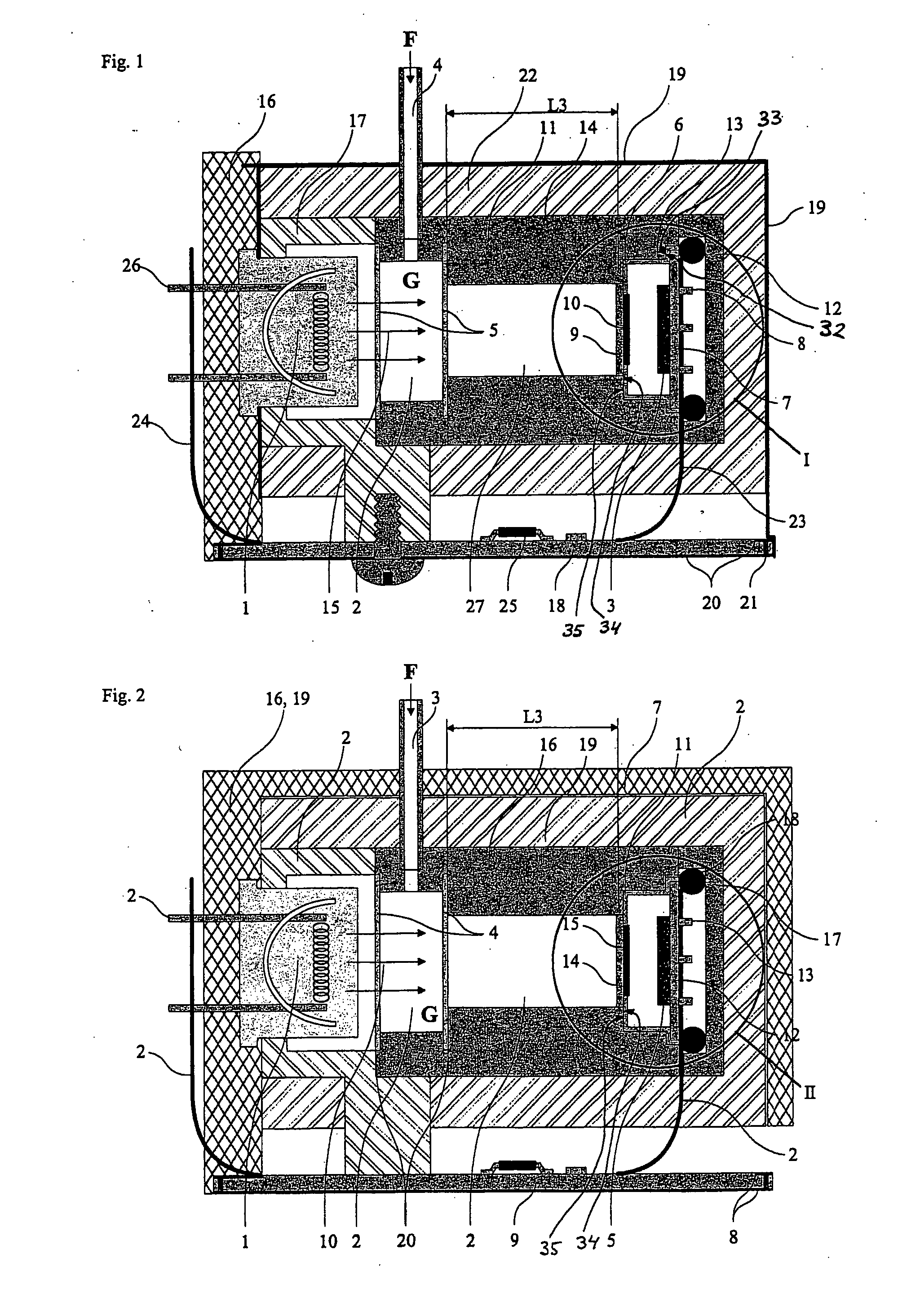
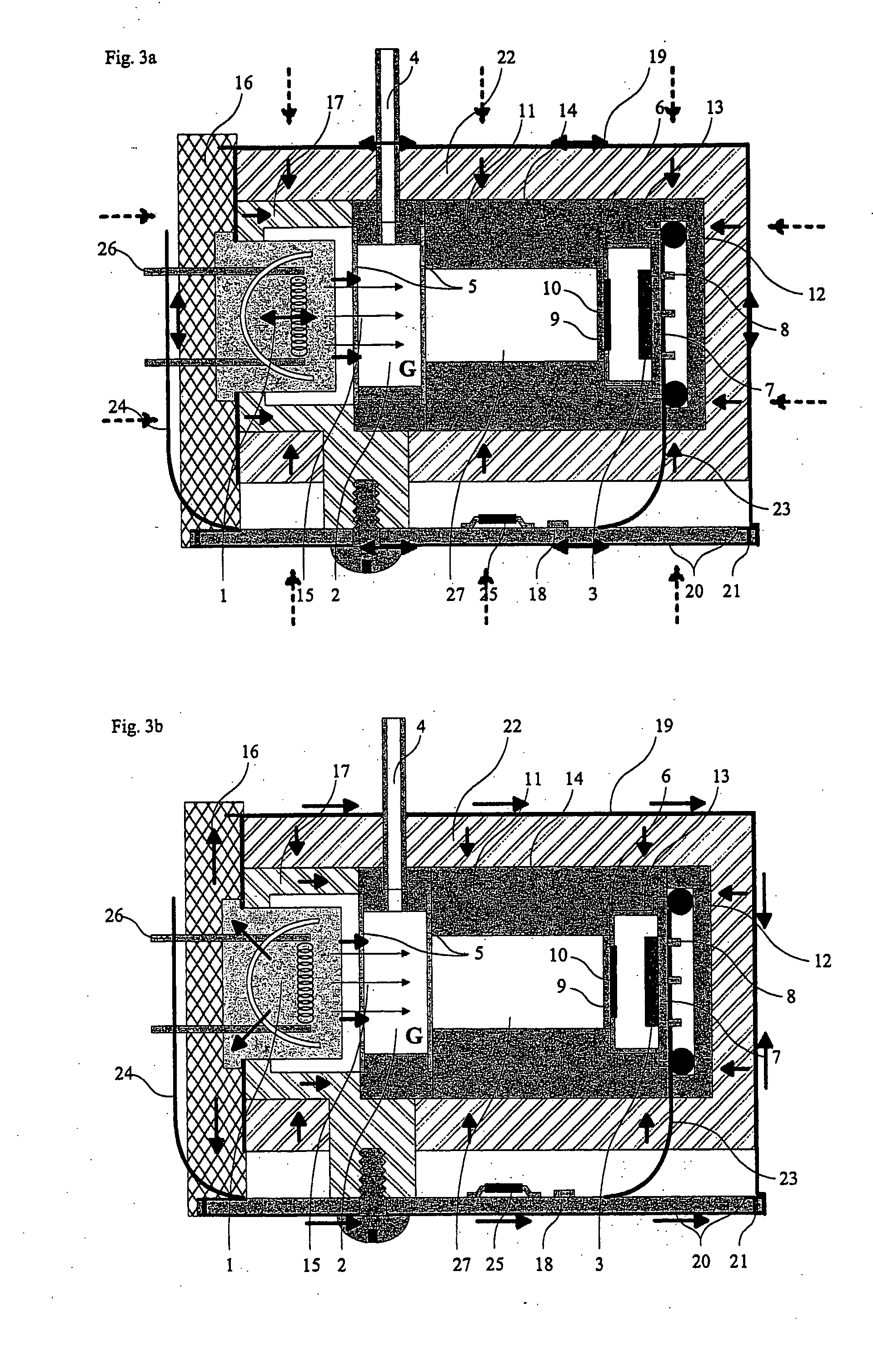
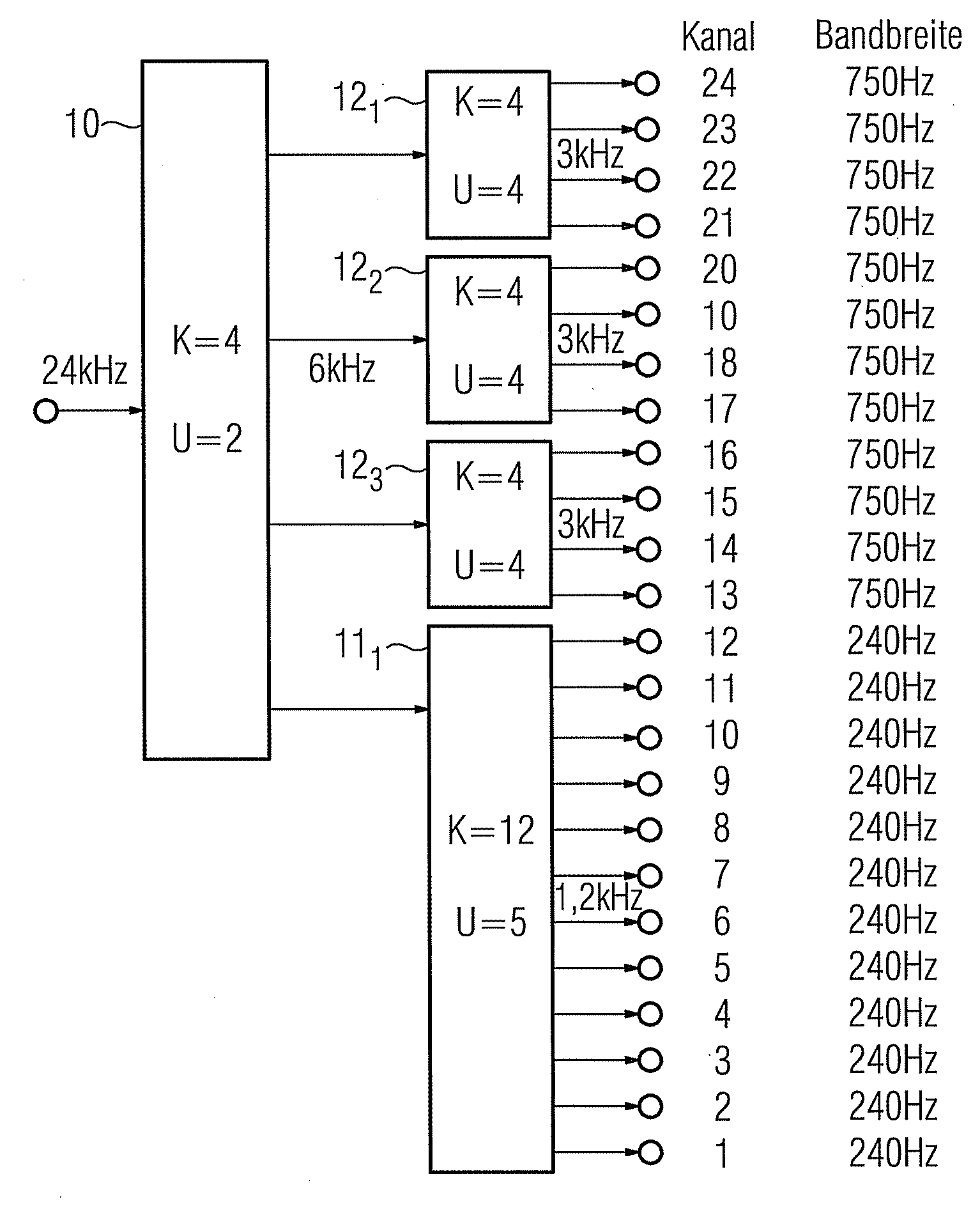
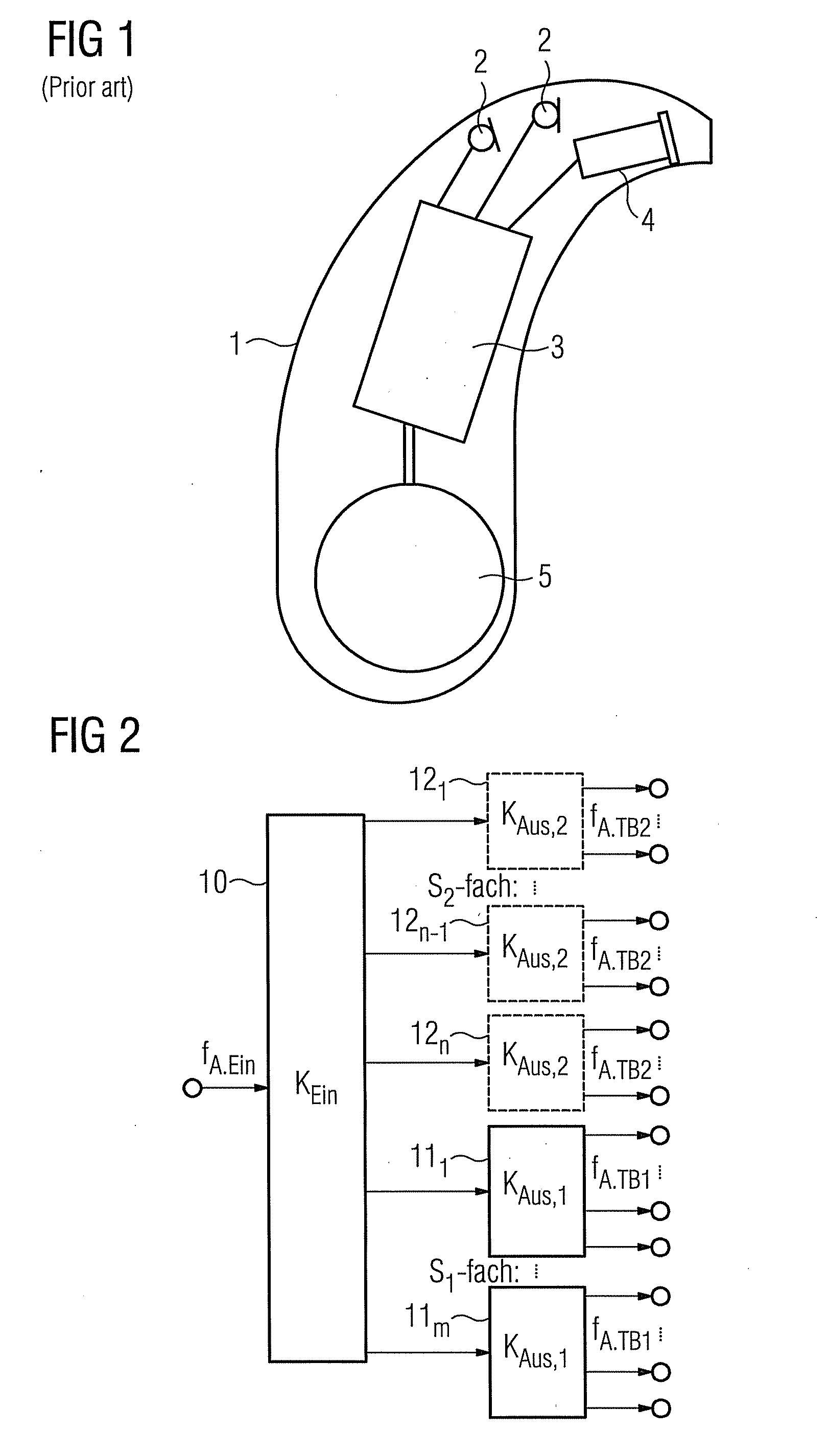
Method for optimizing a multilevel filter bank and corresponding filter bank and hearing apparatus
ActiveUS20090290737A1High resolutionIncrease the number ofDigital technique networkDeaf-aid setsHearing apparatusFilter bank
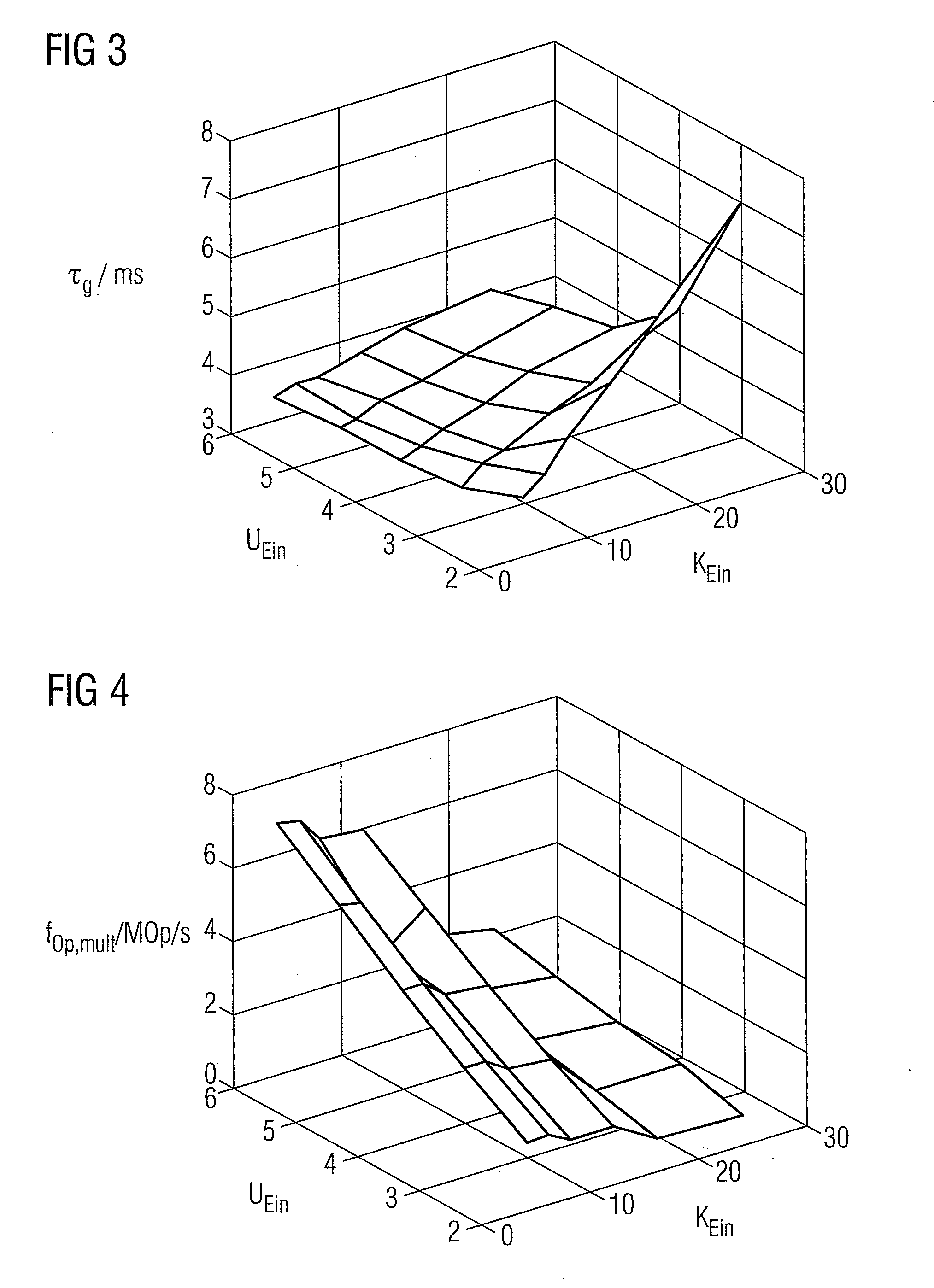
A filter bank system that is optimized with respect to group delay and power consumption is provided. The filter bank system has multiple levels and has an input-side and an output-side filter bank based on a defined filter type. The input-side filter bank has input channels as a variable first parameter, and an oversampling factor as a variable second parameter. For optimizing the multilevel filter bank, a group delay and an operation rate are now respectively determined for each of a plurality of value pairs of the first and second parameters. The value pair for which the associated group delay and the associated operation rate satisfy a defined criterion, in particular for which they are as low as possible, is selected from the value pairs. The input-side filter bank is subsequently configured with the number of channels and the oversampling factor corresponding to the selected value pair.
Owner:SIVANTOS PTE LTD
Pseudomorphic high electron mobility field effect transistor with high device linearity
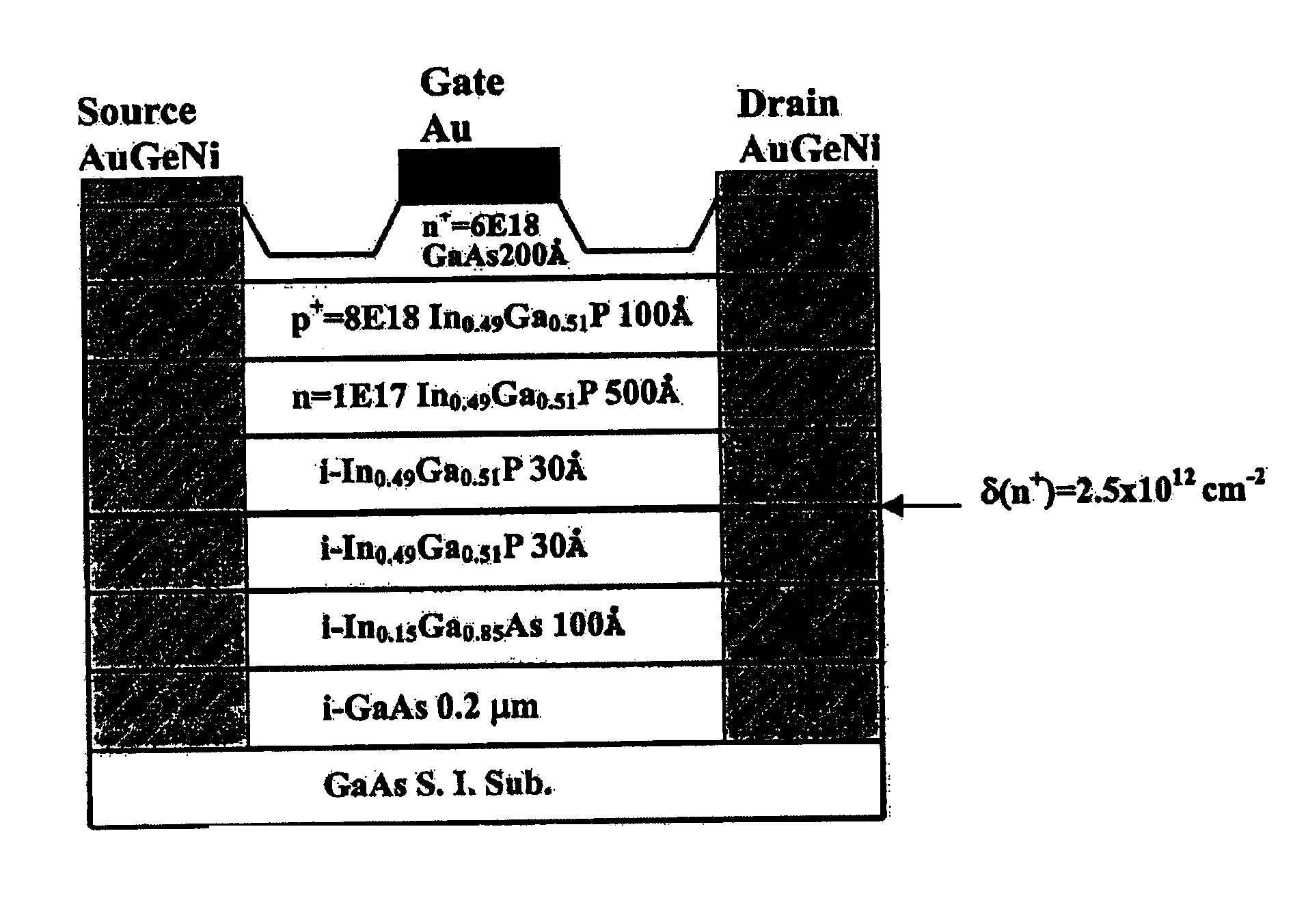
InactiveUS20040262626A1Additional drawbackSmall saturation voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesField-effect transistorGate voltage
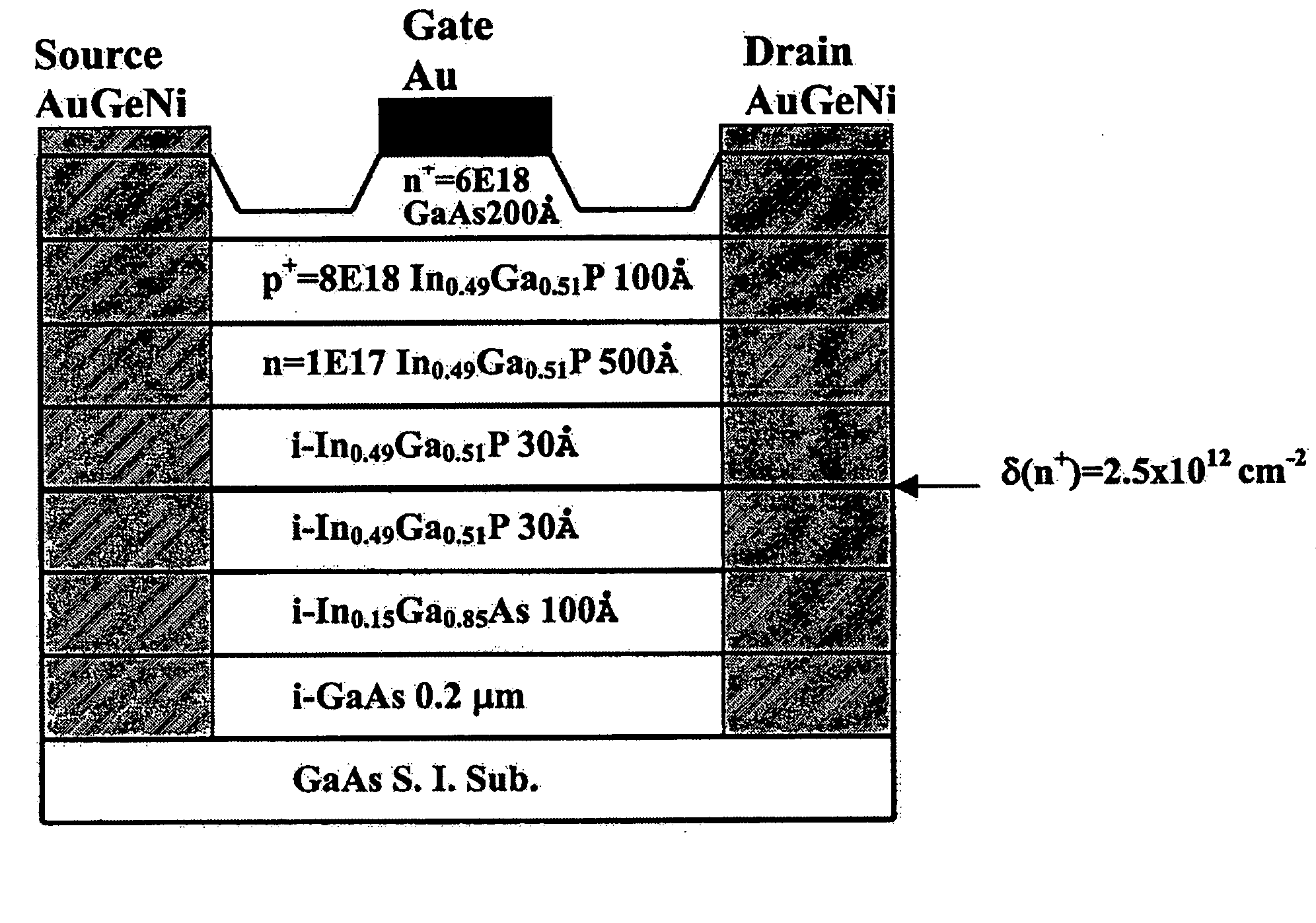
New pseudomorphic high electron mobility transistors (pHEMT's) with extremely high device linearity having an n.sup.+ / p.sup.+ / n camel-gate heterostructure and .delta.-doped sheet structure is disclosed. For the example of InGaP / InGaAs / GaAs .delta.-doped pHEMT's with an n.sup.+-GaAs / p.sup.+-InGaP / n-InGaP camel-gate structure, due to the p-n depletion from p.sup.+-InGaP gate to channel region and the presence of large conduction band discontinuity (.DELTA.Ec) at InGaP / InGaAs heterostructure, the turn-on voltage of gate is larger than 1.7 V. Attributed to the applied gate voltage partly lying on the camel gate and influence of the carrier modulation, the change of total depletion thickness under gate bias is relatively small, and high drain current and linear transconductance can be achieved, simultaneously. The excellent device performances provide a promise for linear and large signal amplifiers and high-frequency circuit applications.
Owner:NAT KAOHSIUNG NORMAL UNIV
Technique for reducing multipath interference in an FM receiver
ActiveUS7590399B2Minimize antenna switchingLarge signalReceivers monitoringRadio transmissionSignal qualityLow distortion
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Method and system for dynamic range power control
InactiveUS20060068727A1Wide bandwidthMinimize distortionResonant long antennasGain controlRadio frequencyPower control
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
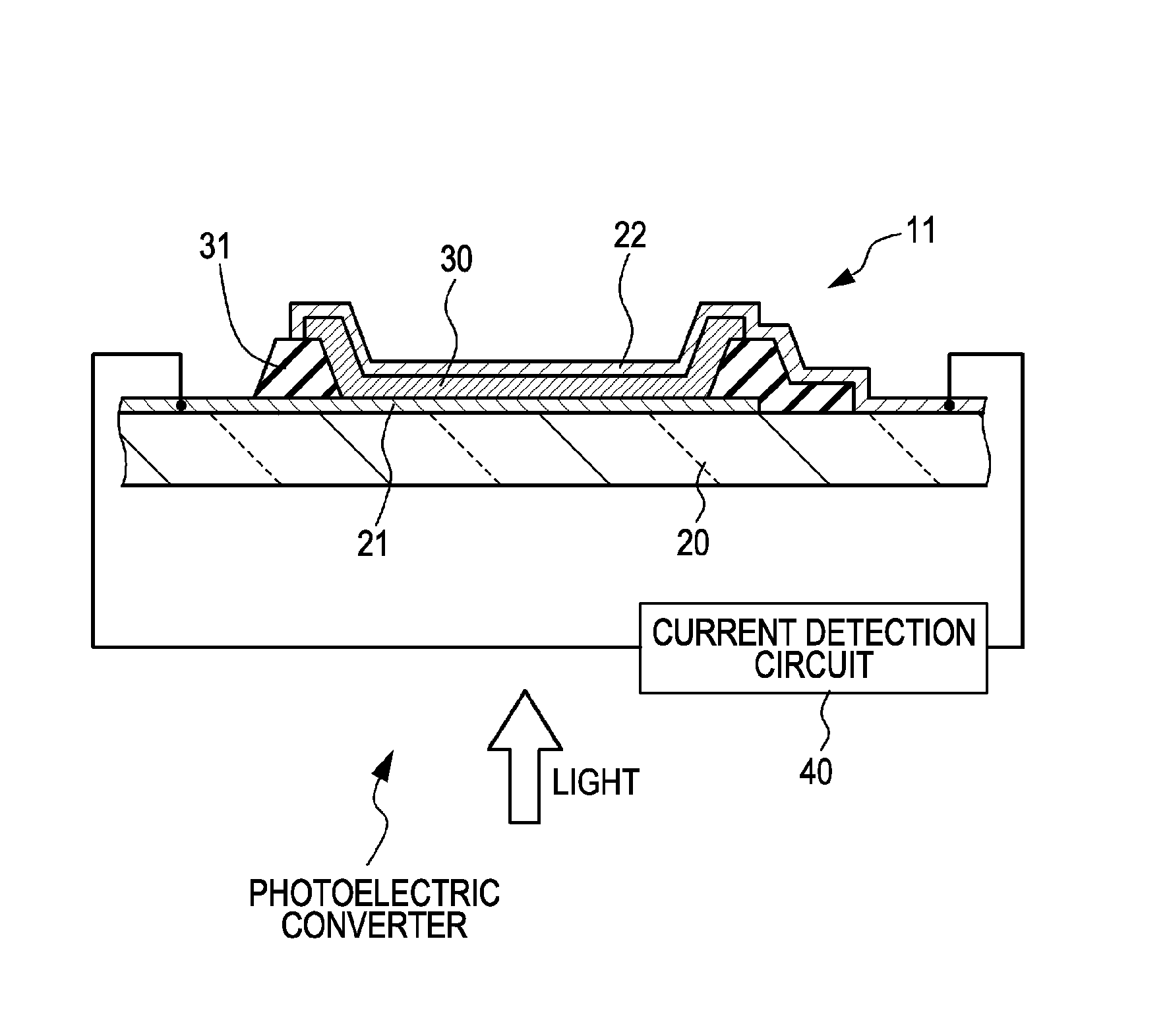
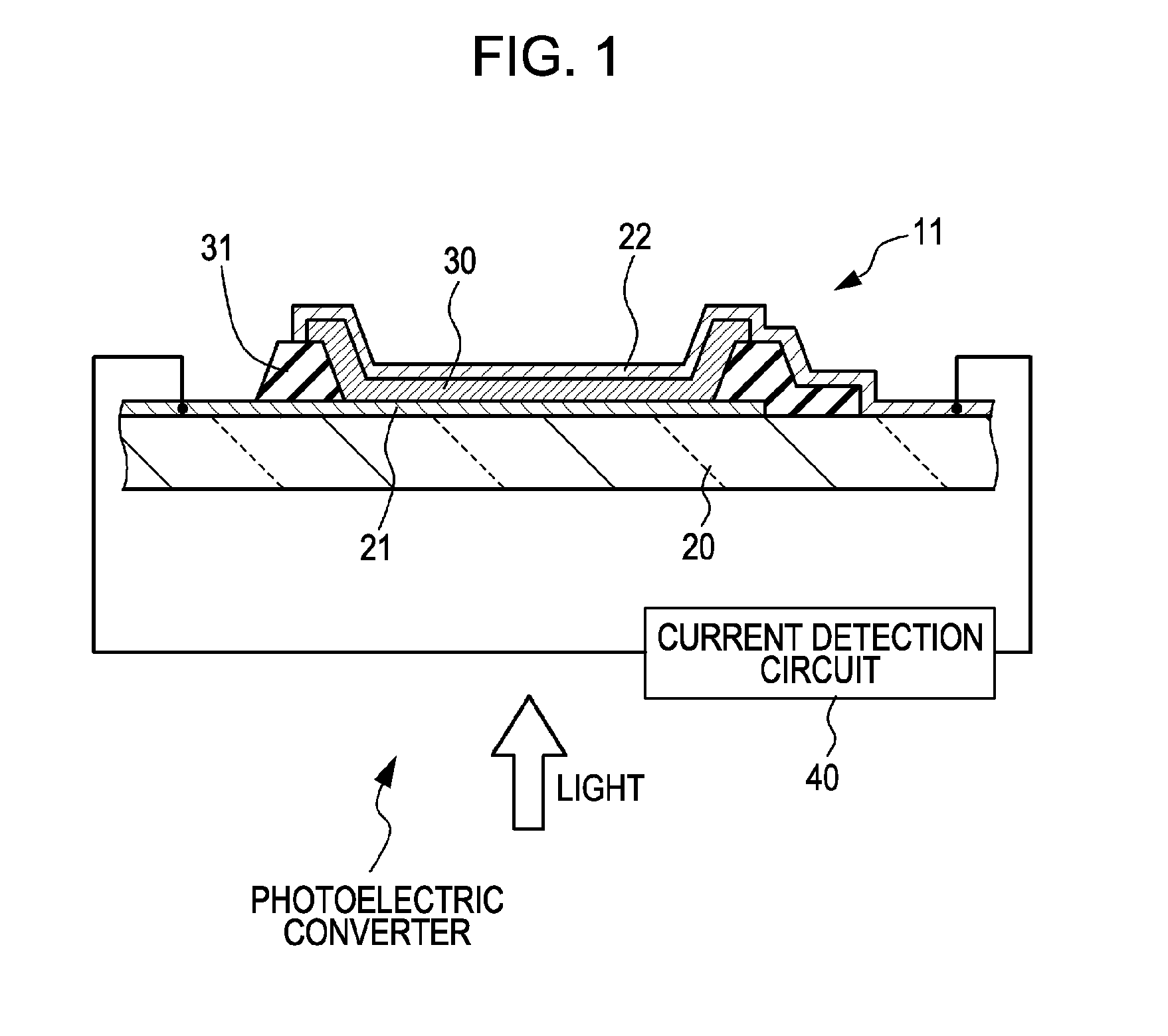
Photoelectric converter and photoelectric conversion element
ActiveUS8212201B2High sensitivityImprove signal-to-noise ratioSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansPower flowPhotoelectric conversion
A photoelectric converter includes a photoelectric conversion element, which includes a first electrode and a second electrode disposed discretely and a photoelectric conversion material layer disposed between the first electrode and the second electrode and in which a current generated in the photoelectric conversion material layer changes with the lapse of an application time, where a constant amount of light is applied to the photoelectric conversion material layer while a voltage is applied between the first electrode and the second electrode, and a current detection circuit to detect the change in the current.
Owner:SONY CORP
Switch-Off Time Regulation System for an Inverter for Driving a Lamp
InactiveUS20090295299A1Optimized switch-on timeConvenient timeDc-dc conversionElectric light circuit arrangementConvertersElectrical ballast
The present invention relates to an electronic ballast for operating a lamp (L) which has a Class E converter (T1, L1). When a lamp (L) is connected, the output current of the Class E converter (T1, L1) once a switching element (T1) of the Class E converter (T1, L1) has been switched off has a first and a second half-cycle of opposite polarity. The electronic ballast has a measurement apparatus for measuring the output current and a regulating apparatus for adjusting a switch-on time of the switching element. In this case, the measurement apparatus is designed to determine a first output current value of the first half-cycle and a second output current value of the second half-cycle, wherein the regulating apparatus for adjusting the switch-on time is fed a control variable based on the discrepancy between the two output current values.
Owner:OSRAM GMBH
Actuator unit having two actuator pins
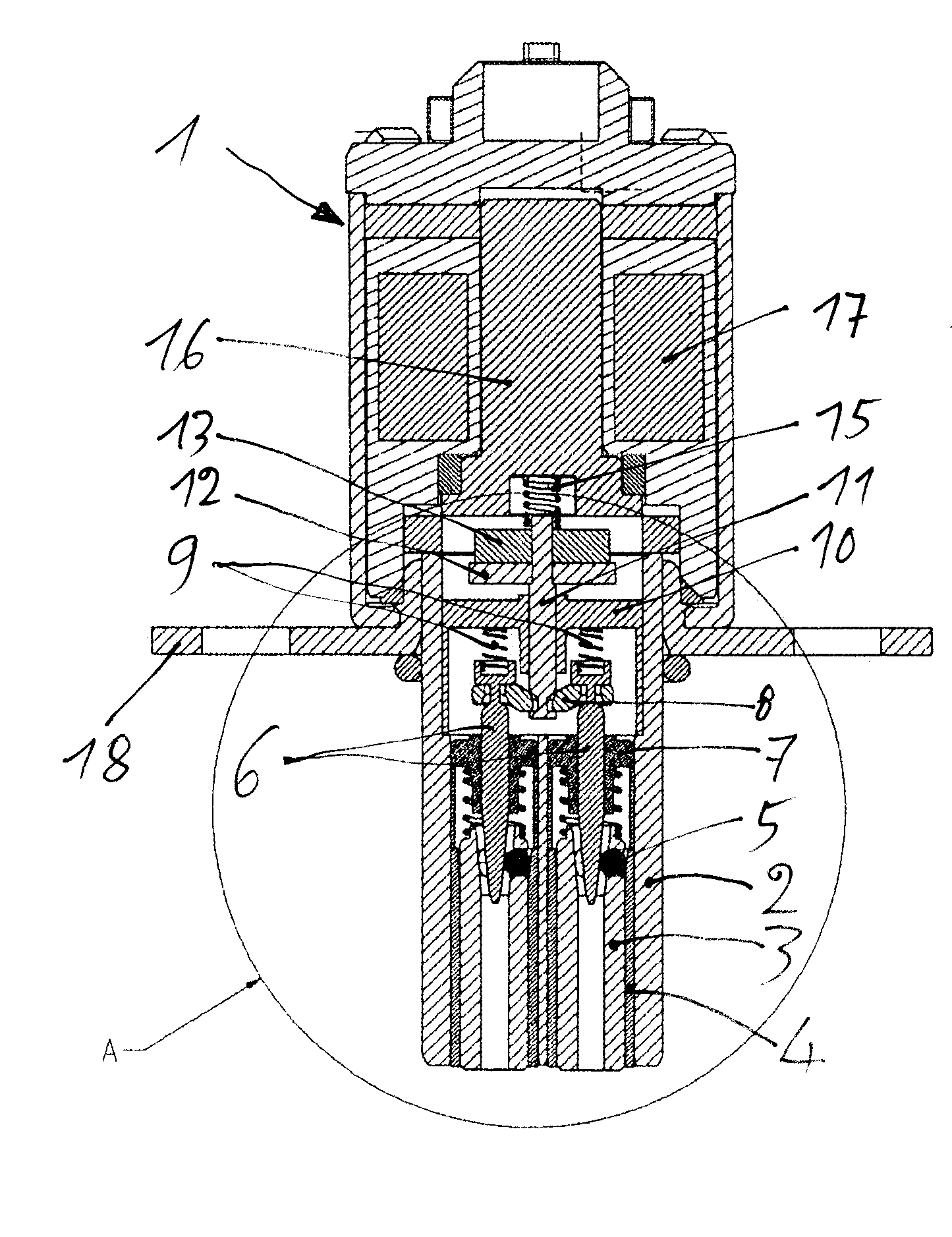
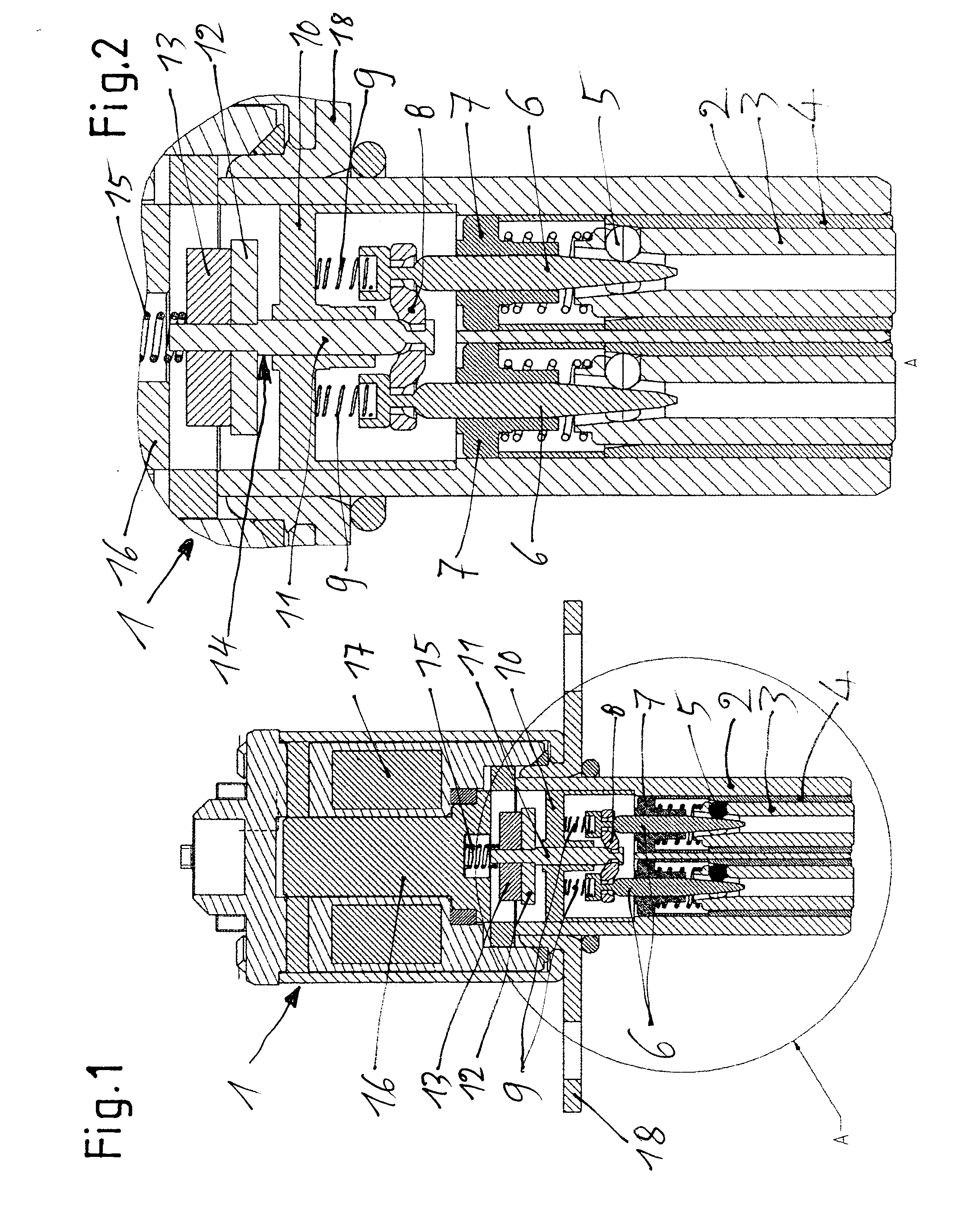
InactiveUS20130000581A1Avoid disadvantagesLarge signalValve drivesMetal-working apparatusEngineeringCam
An internal combustion piston engine having gas exchange valves actuated by cams of a camshaft. The cams are sliding cams having two cams per sliding cam unit situated on a basic shaft in rotationally fixed fashion but axially displaceable. At least one actuator unit has two actuator pins for displacing the sliding cam units into different axial positions using displacement grooves on the circumference of the sliding cam units, the grooves being helical and situated mirror-symmetrically, and having an ejection ramp for the actuator pins. The actuator pins are spring-loaded toward the sliding cam unit and, in retracted positions, can be fixed by arresting devices, which have control needles that correspond to clamping bodies of locking devices. These needles are actuatable by an electromagnet unit, with the control needles being connected with a needle bridge. A pin engages the needle bridge, and the pin is controlled by the electromagnet unit.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
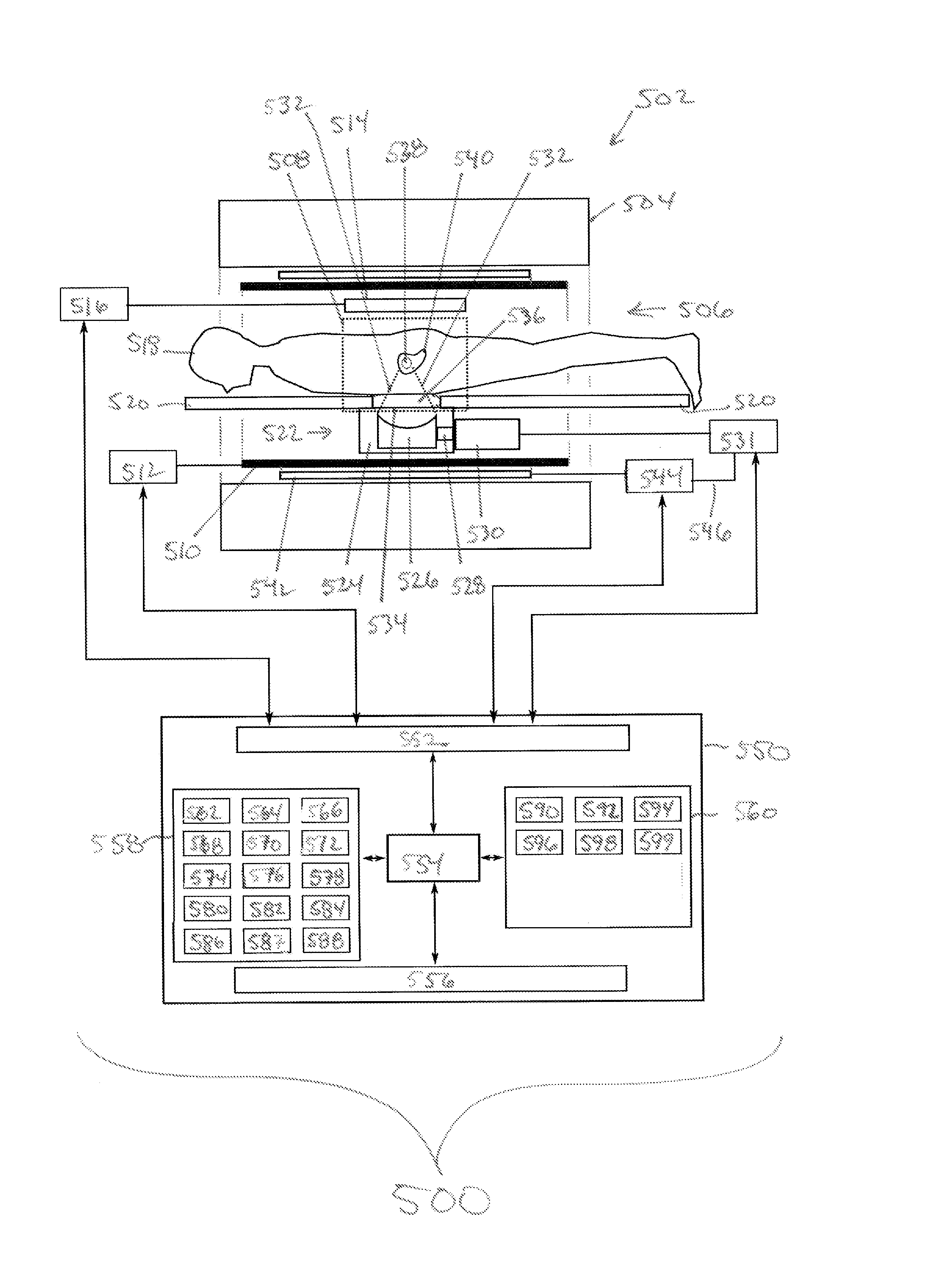
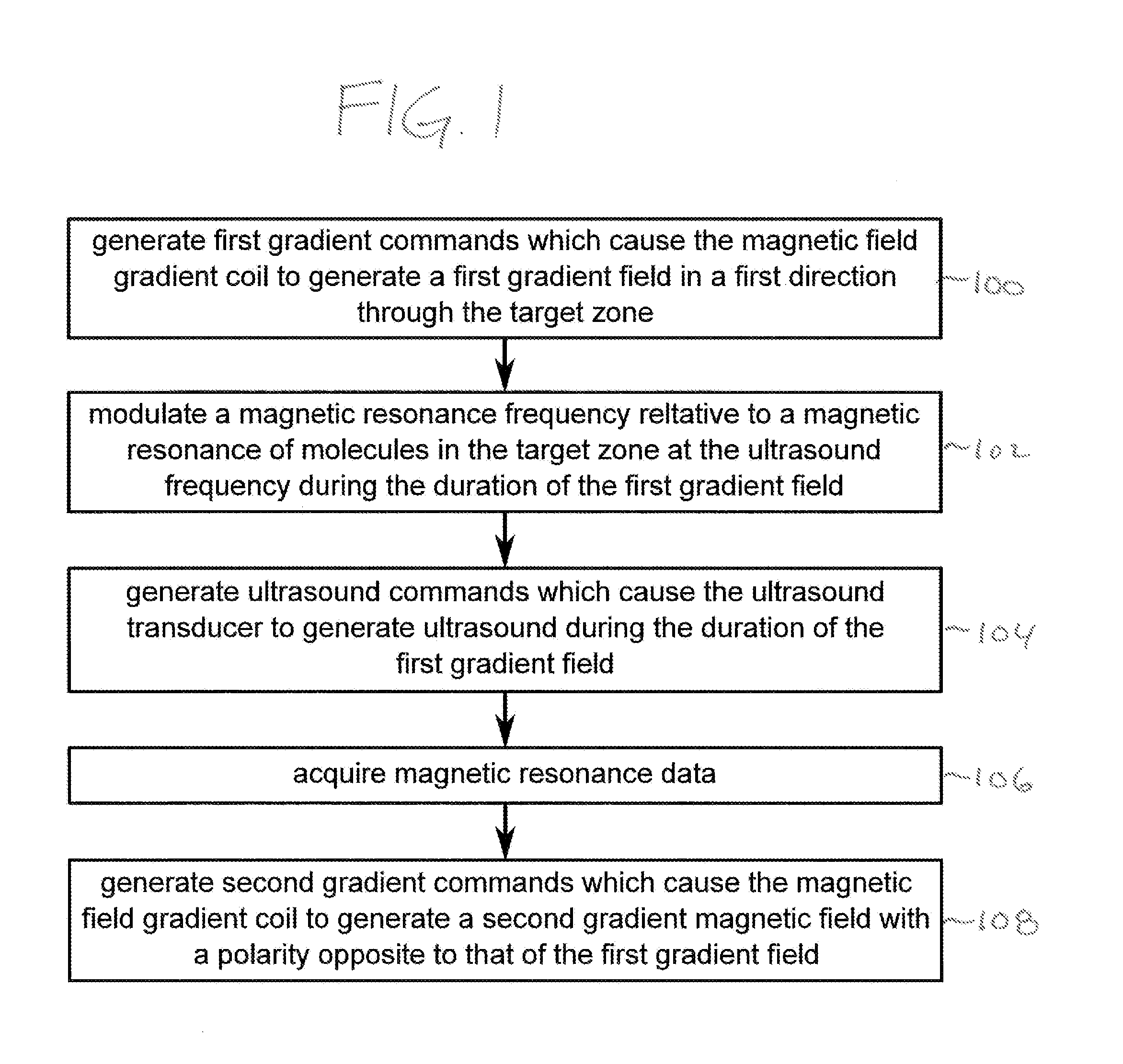
Magnetic resonance measurement of ultrasound properties
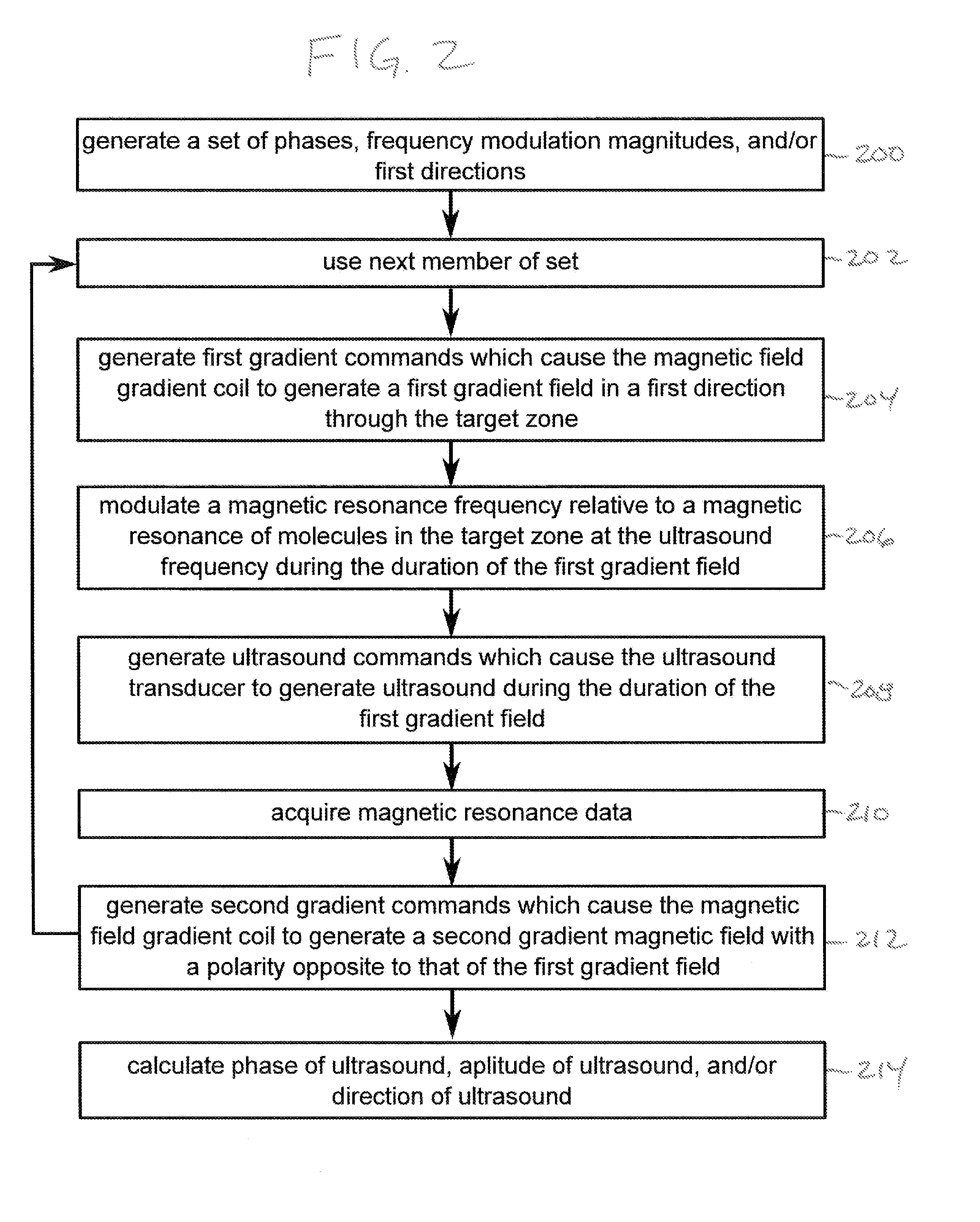
ActiveUS20130345547A1Maximize signalLarge signalUltrasound therapyMagnetic measurementsResonance measurementMagnetic field gradient
An apparatus (500, 600) comprising an ultrasound transducer element (300) for generating an ultrasonic beam (302) through a target zone (308, 538). The ultrasonic beam has an ultrasound frequency. The apparatus comprises a magnetic resonance system (502) with a resonant frequency modulator (542, 544, 516) for modulating a magnetic resonance frequency relative to a magnetic resonance of molecules in the target zone at the ultrasound frequency. Instructions cause a processor to repeatedly generate (100, 204) first gradient commands (562) which cause a magnetic field gradient coil to generate a first gradient magnetic field (710, 810) through the target zone. The gradient magnetic field has field lines directed in a first direction (304). The processor repeatedly modulates (102, 206) the magnetic resonance frequency at the ultrasound frequency, generates (104, 208) ultrasound commands (566), acquires (106, 210) magnetic resonance data from the target zone, and generates (108, 212) second gradient commands (564).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Interferometric technique for measuring upper atmospheric Doppler winds utilizing projections of a satellite's velocity
ActiveUS10184841B1Reduced thermal driftReduce thermal effectsOptical measurementsRadiation pyrometryHorizonControl system
An apparatus on a satellite includes a standard fixed-path Michelson interferometer. The Michelson interferometer includes an input, at least one first output detector, and at least one second output detector. The Michelson interferometer includes a plurality of respective fields of view and a corresponding plurality of scanning azimuthal angles relative to a satellite velocity vector. The plurality of respective fields of view corresponds to a plurality of tangent points with constant tangent point height arranged around an Earth horizon circle. The apparatus includes an attitude determination and control system on the satellite, or an actuator on the satellite. The apparatus includes an input mirror and / or input optics in optical communication with the input of the Michelson interferometer. The attitude determination and control system rotates the satellite or the actuator rotates the input mirror and / or the input optics, so as to sweep through the plurality of respective fields of view around the Earth horizon circle.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Distributed dynamic strain fiber optics measurement by brillouin optical time-domain reflectometry
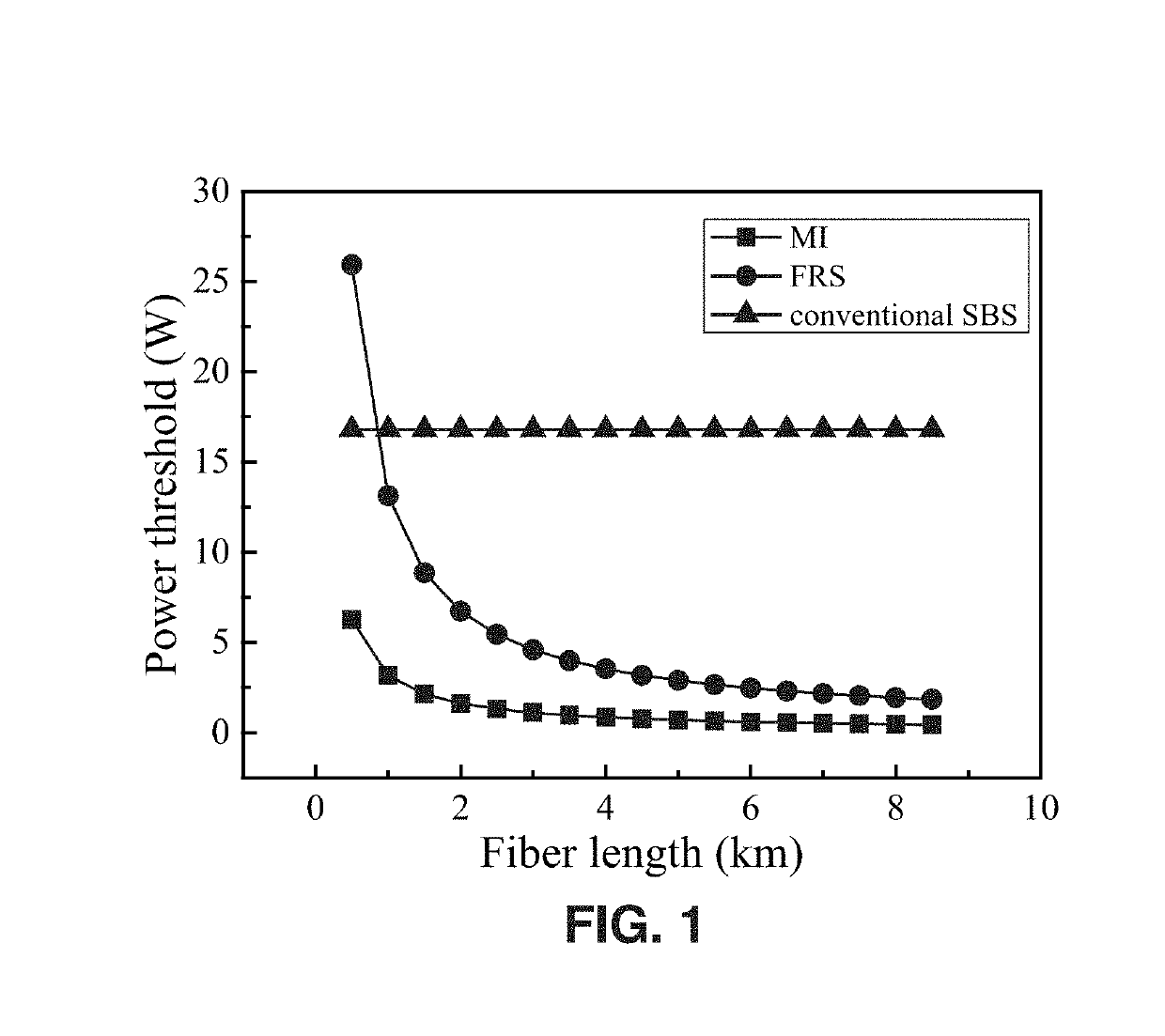
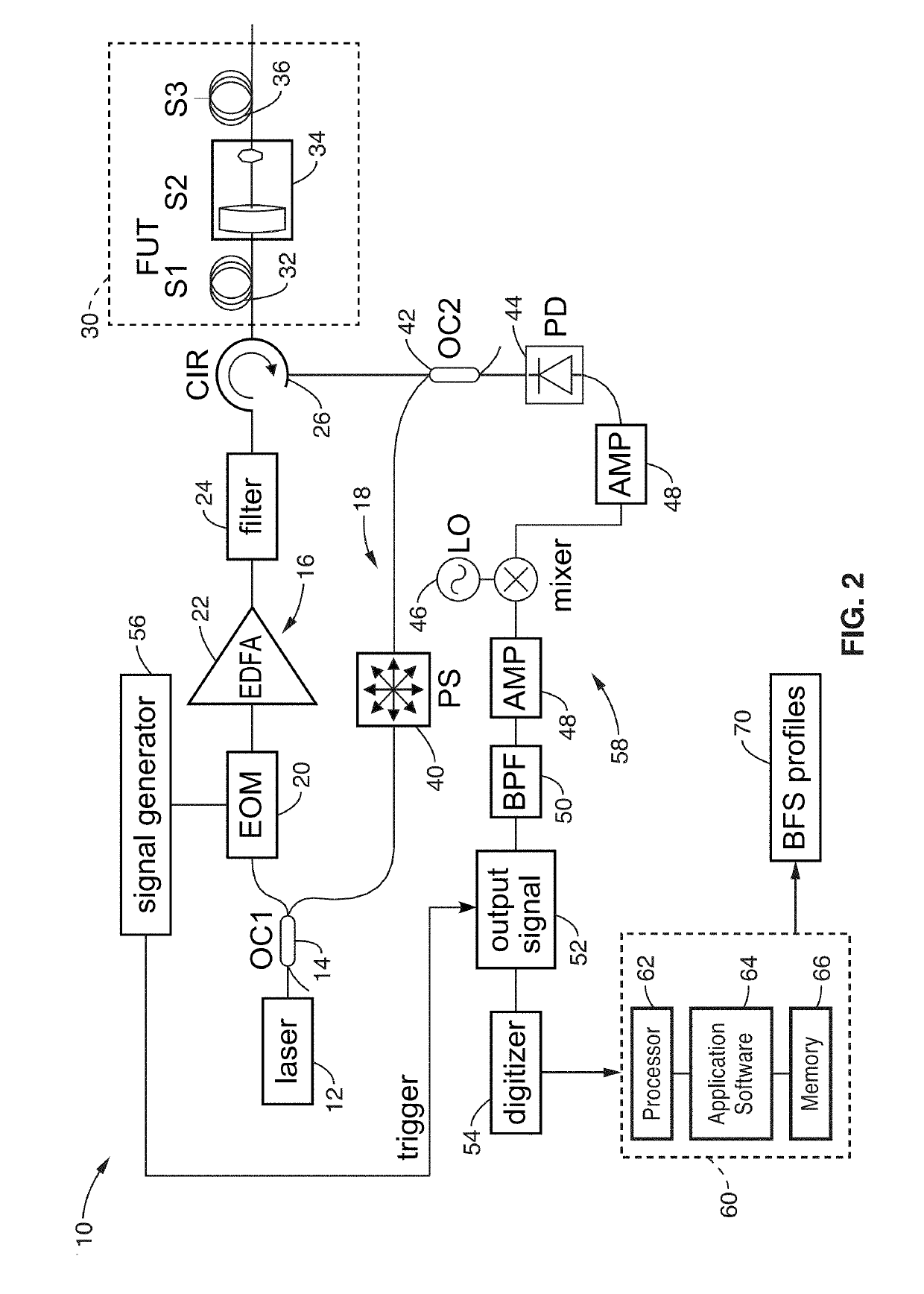
ActiveUS20190195665A1Shorten sensing distanceIncrease powerForce measurement by measuring optical property variationThermometers using physical/chemical changesTime-domain reflectometryShort time fourier transformation
A system and method for distributed dynamic strain measurement using optical fiber that is based on Brillouin optical time-domain reflectometry (BOTDR) with stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS). A short-time Fourier transform (STFT) is used to rebuild the Brillouin frequency shift (BFS) of the SBS scattered signal to perform the dynamic strain measurement.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Pseudomorphic high electron mobility field effect transistor with high device linearity
InactiveUS6943386B2Wide range of operationsImprove linearitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesField-effect transistorLinearity
New pseudomorphic high electron mobility transistors (pHEMT's) with extremely high device linearity having an n+ / p+ / n camel-gate heterostructure and δ-doped sheet structure is disclosed. For the example of InGaP / InGaAs / GaAs δ-doped pHEMT's with an n+-GaAs / p+-InGaP / n-InGaP camel-gate structure, due to the p-n depletion from p+-InGaP gate to channel region and the presence of large conduction band discontinuity (ΔEc) at InGaP / InGaAs heterostructure, the turn-on voltage of gate is larger than 1.7 V. Attributed to the applied gate voltage partly lying on the camel gate and influence of the carrier modulation, the change of total depletion thickness under gate bias is relatively small, and high drain current and linear transconductance can be achieved, simultaneously. The excellent device performances provide a promise for linear and large signal amplifiers and high-frequency circuit applications.
Owner:NAT KAOHSIUNG NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com