Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40results about How to "Large imaging area" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
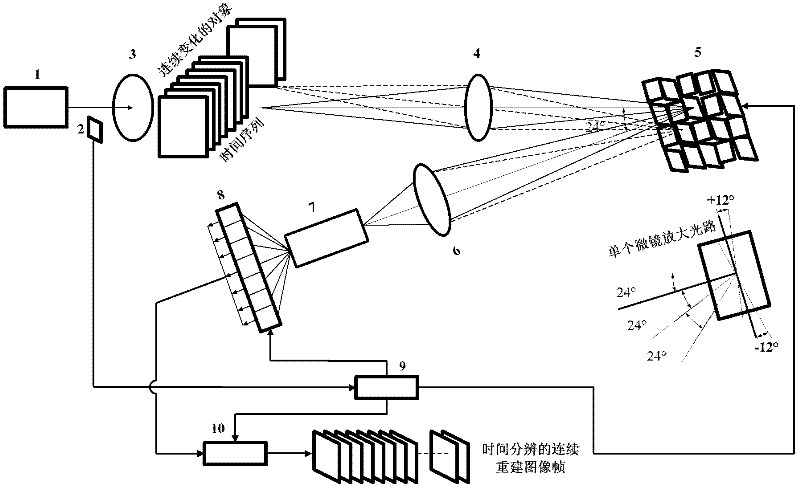
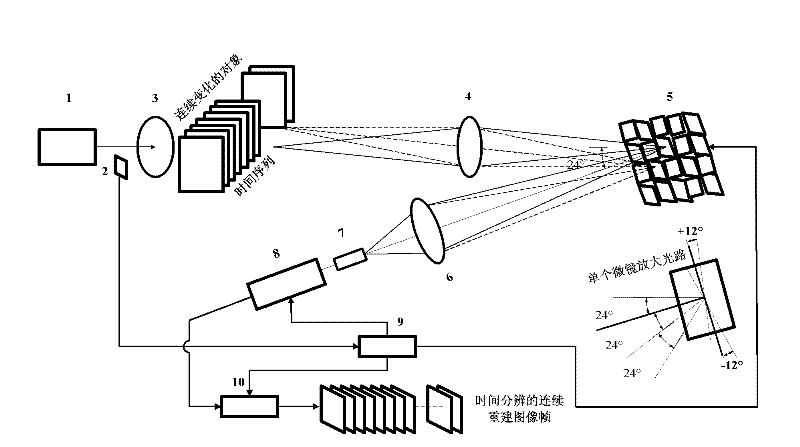
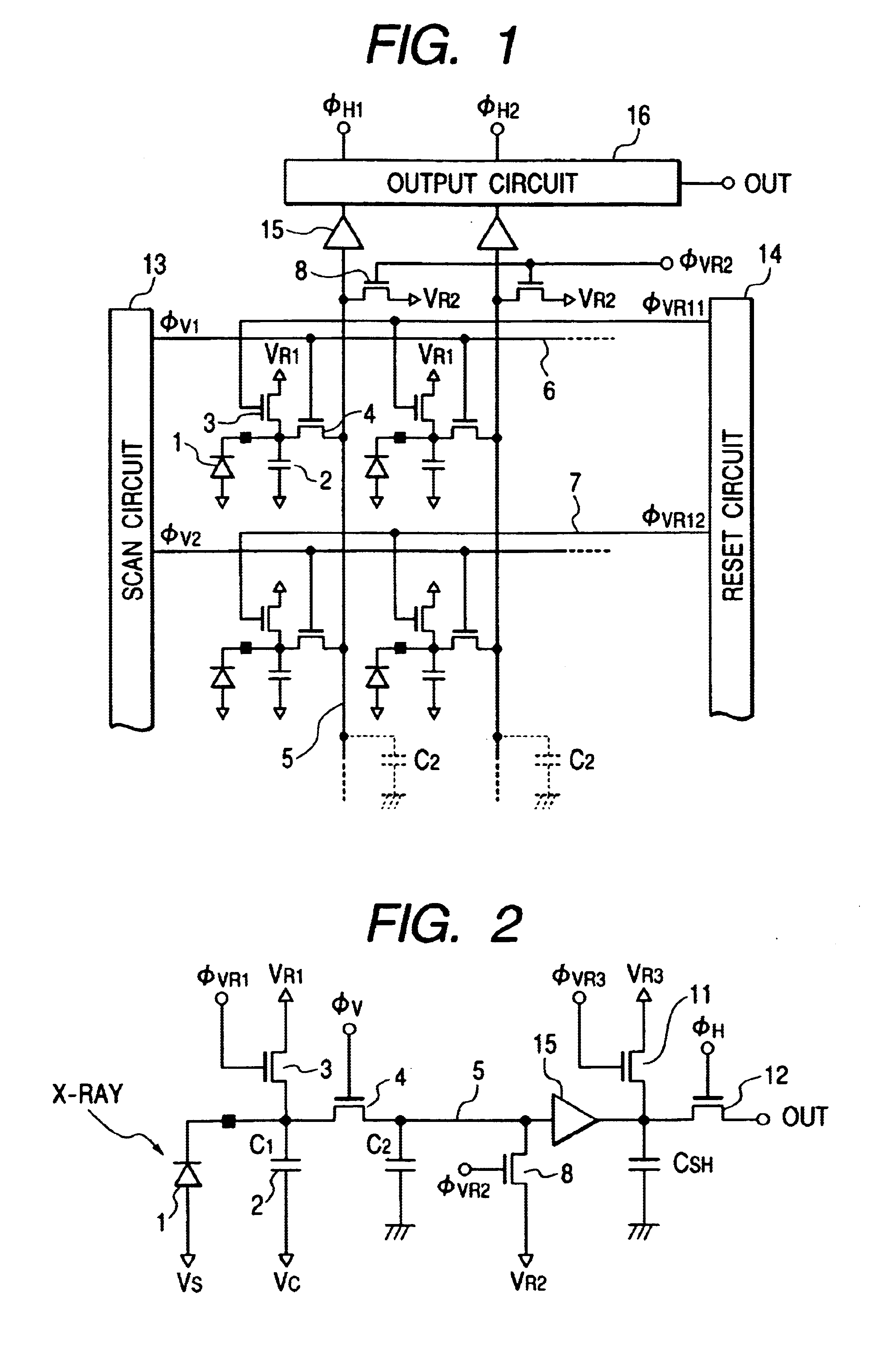
Time-resolved extreme-low-light multispectral imaging system and method
ActiveCN102393248AResolve time resolutionSolve the time resolution by using single photon counter line arraySpectrum investigationPhysicsHyperspectral imaging
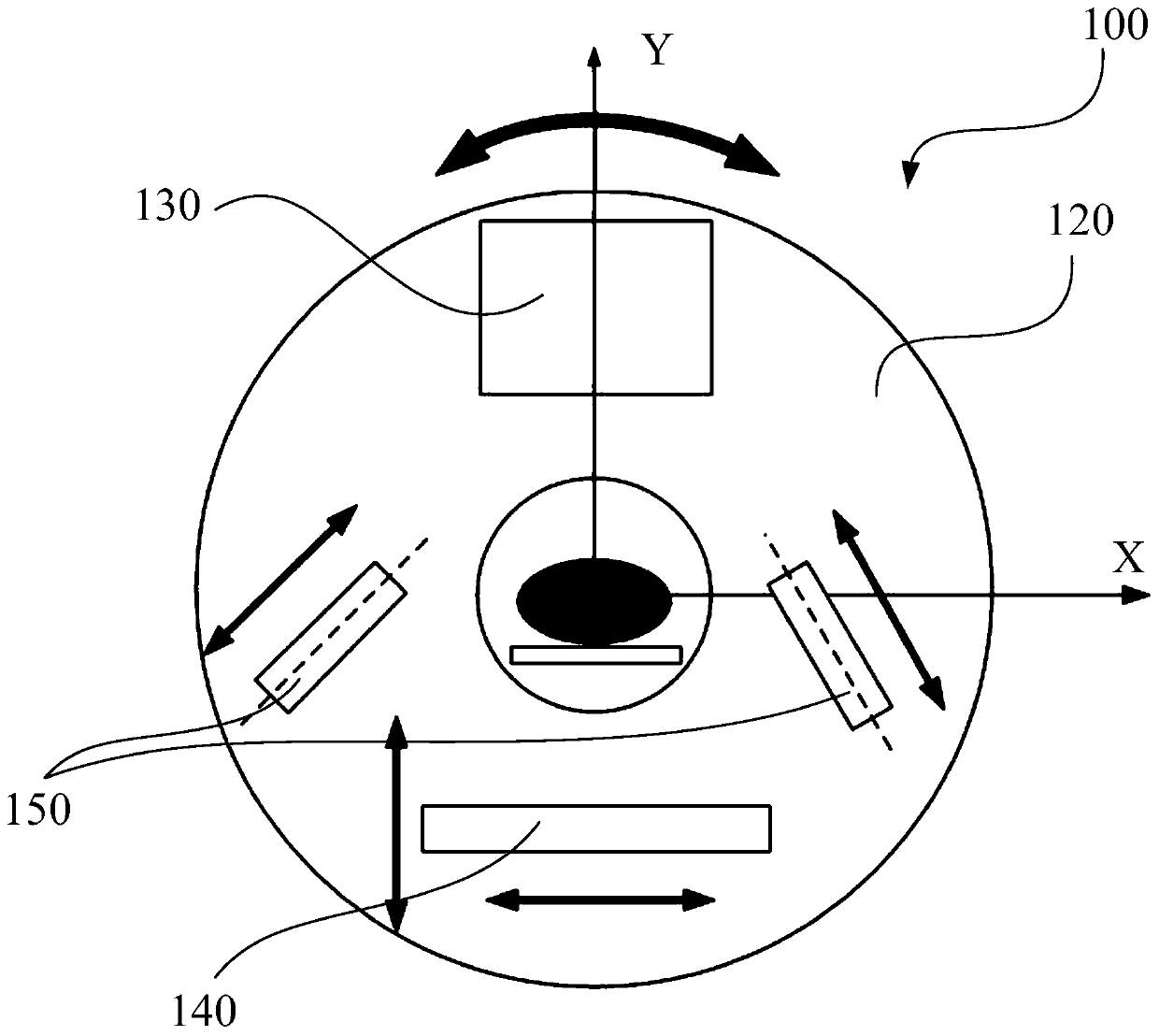
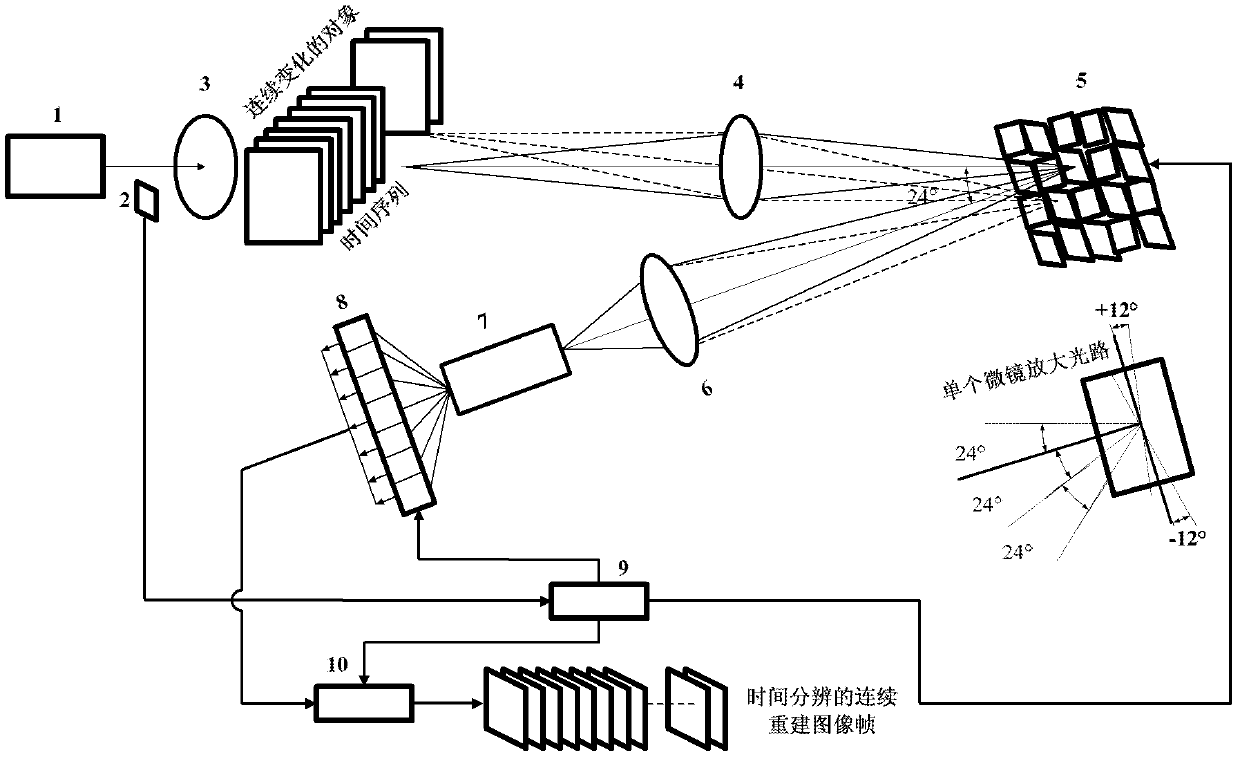
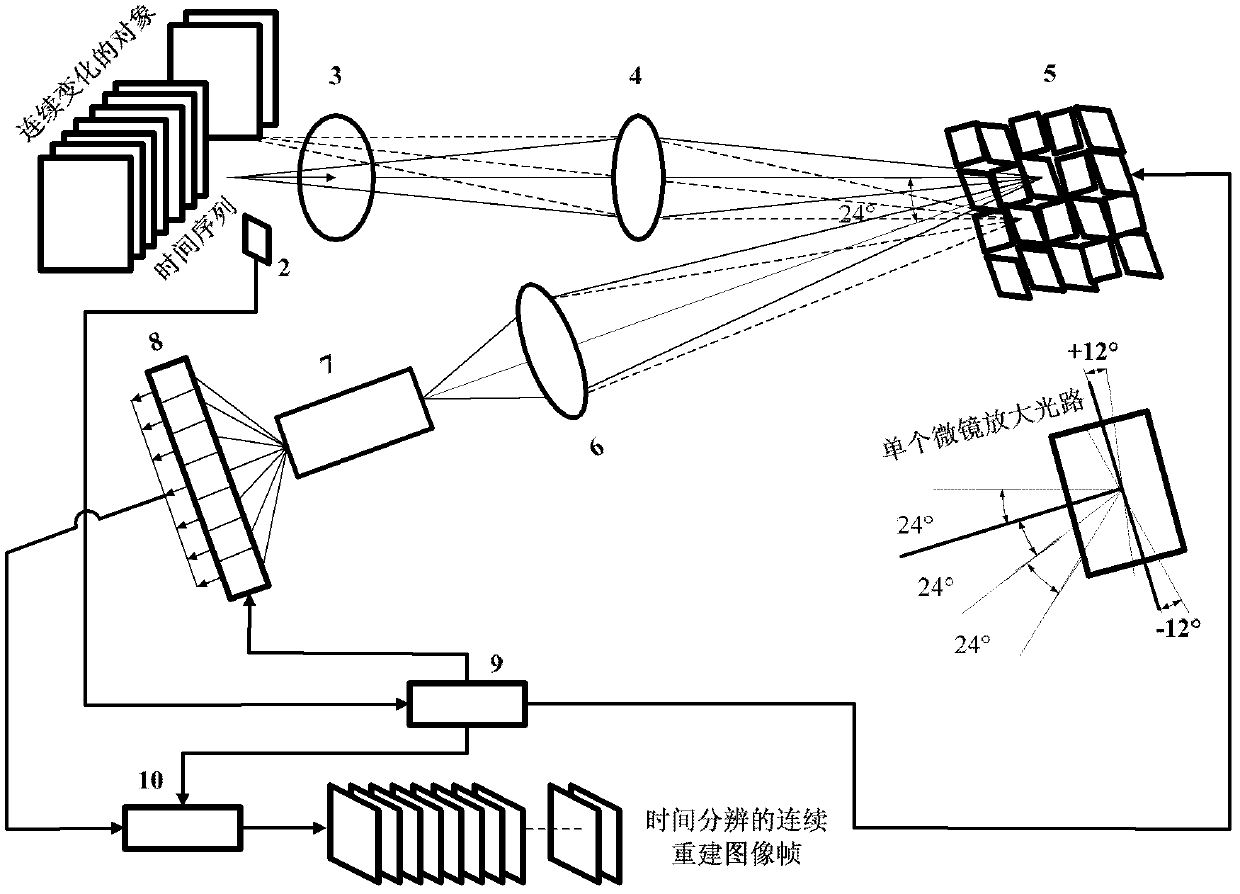
The invention provides a time-resolved extreme-low-light multispectral imaging system and method and belongs to the field of extreme-low-light multispectral imaging, wherein the system is triggered through a trigger to ensure the time-resolved property, and the multispectral high-resolution two-dimensional color imaging for extreme-low-light objects is realized by combining a triggering technology of the trigger, the compressive sensing theory, a DLP (digital light processing) technology, a spectrum-dividing technology, an optical fiber coupling technology and a photon counter linear array detection technology; the system is composed of an extreme-low-light light source or self-luminous organisms, the trigger, an optical filter, an optical imaging system, a DMD (digital mirror device) micromirror array, an optical focussing and collecting system, a spectrophotometer, a photo counter lineary array consisting of a plurality of photon counters with different wavelengths, a driving control module and an optimization algorithm module; the sensitivity of the system can reach the level of a photon, and can be widely applied to the fields of self-luminous organism detection, medical treatment imaging, data acquisition, communication, astronomy, military, hyperspectral imaging, measurement in quantum mechanics and the like.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
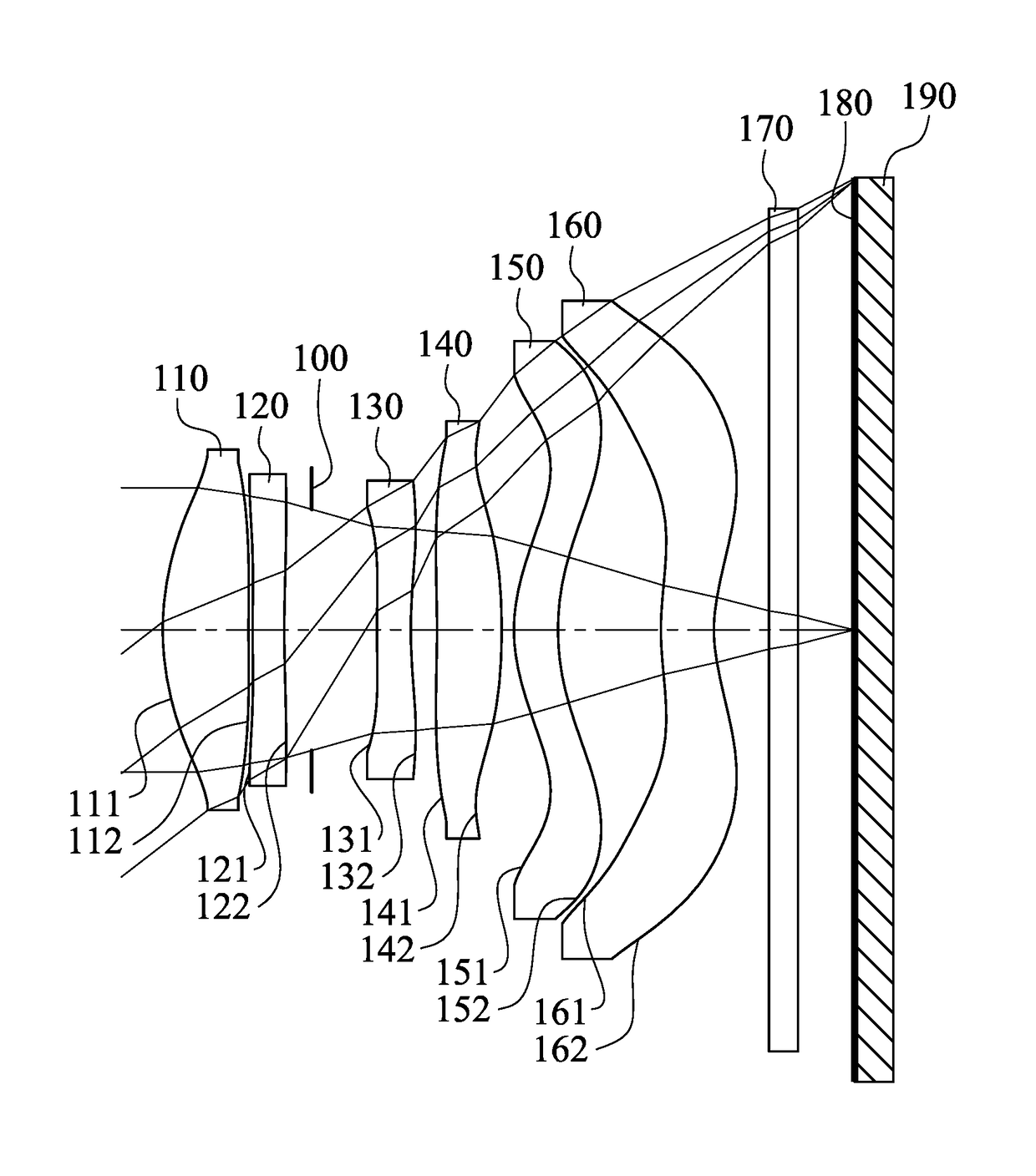
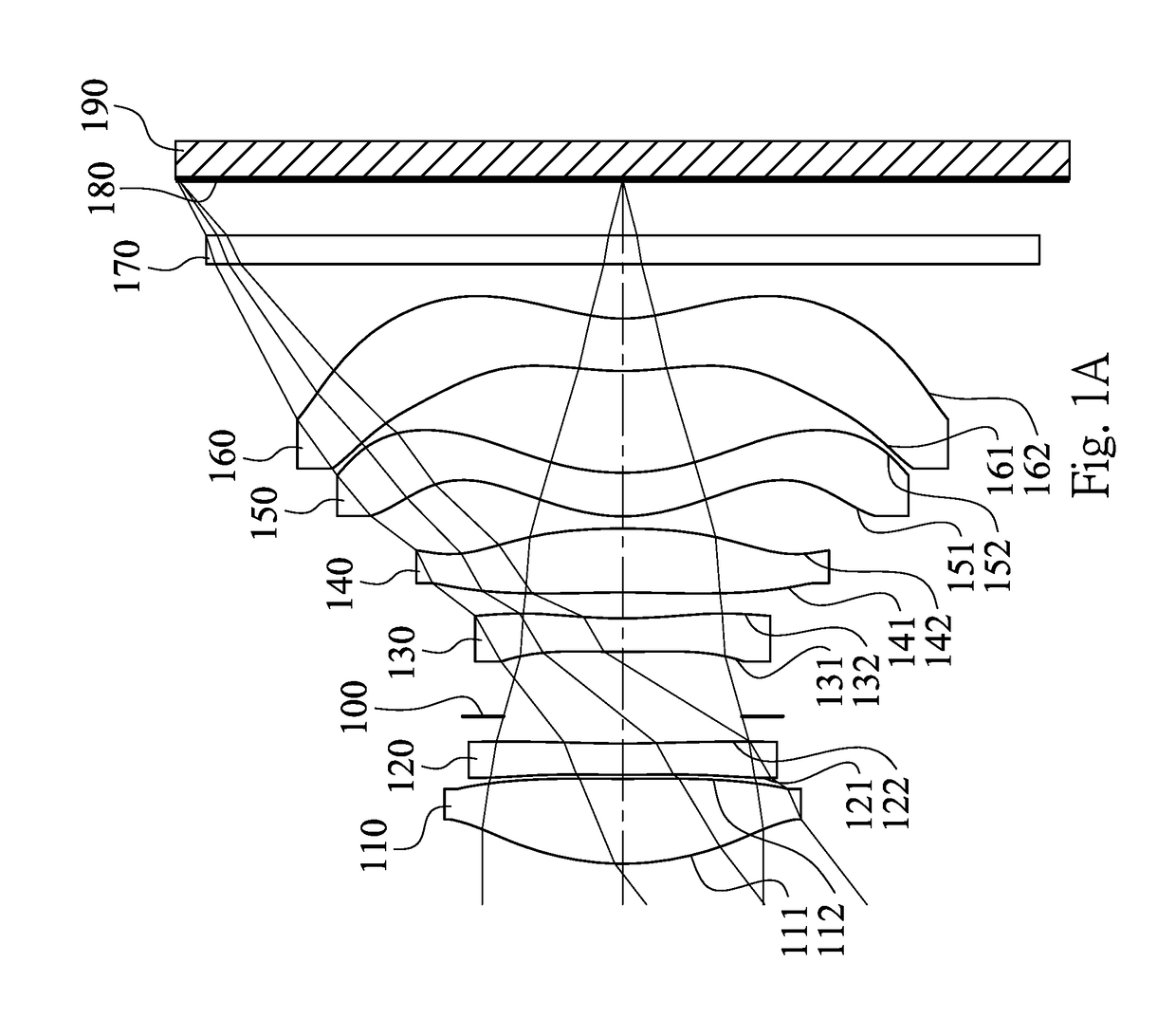
Imaging optical lens system, image capturing apparatus and electronic device
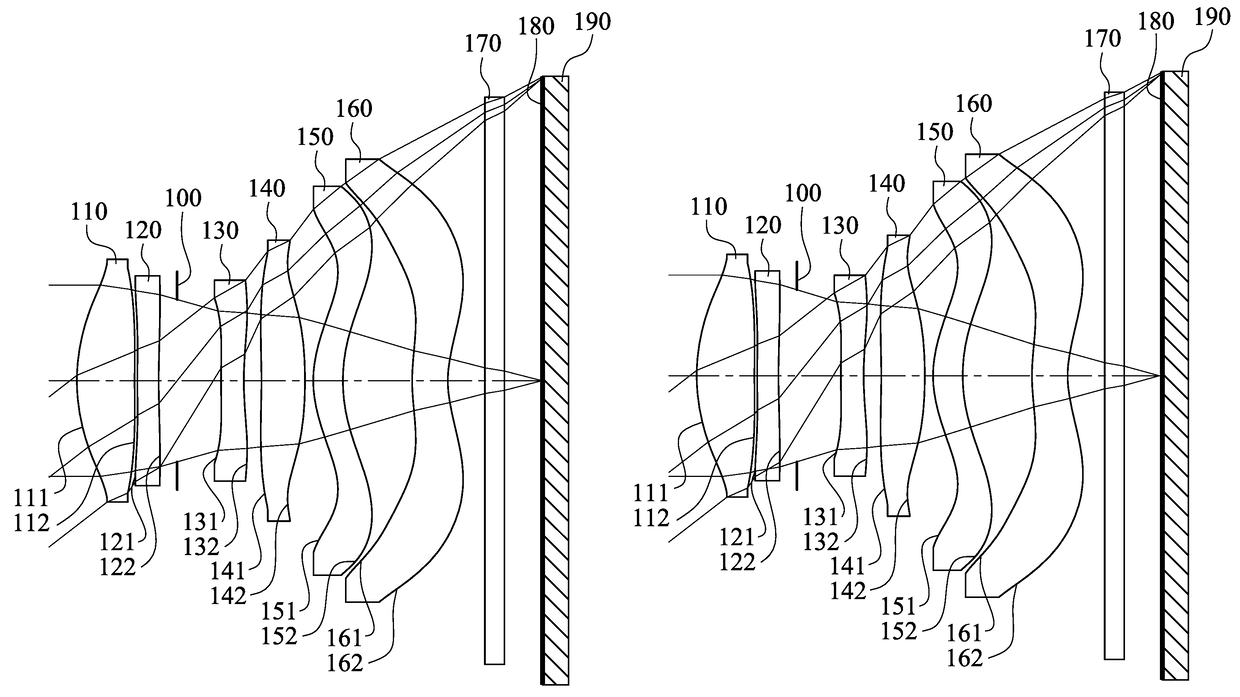
An imaging optical lens system includes six lens elements, the six lens elements being, in order from an object side to an image side, a first lens element, a second lens element, a third lens element, a fourth lens element, a fifth lens element and a sixth lens element. The first lens element has positive refractive power. The third lens element has an image-side surface being concave in a paraxial region thereof. The fifth lens element has an object-side surface and an image-side surface being both aspheric. The sixth lens element has an image-side surface being concave in a paraxial region thereof, wherein an object-side surface and the image-side surface of the sixth lens element are both aspheric, and the image-side surface of the sixth lens element includes at least one convex critical point in an off-axial region thereof.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
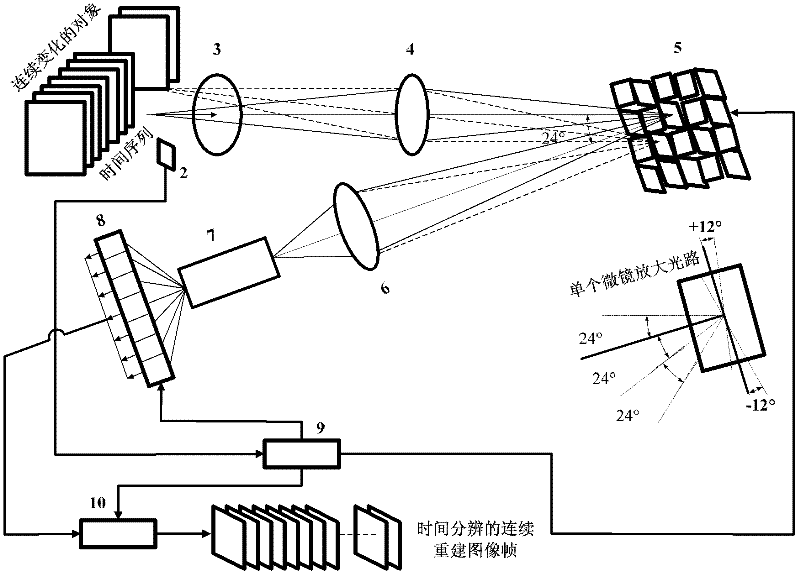
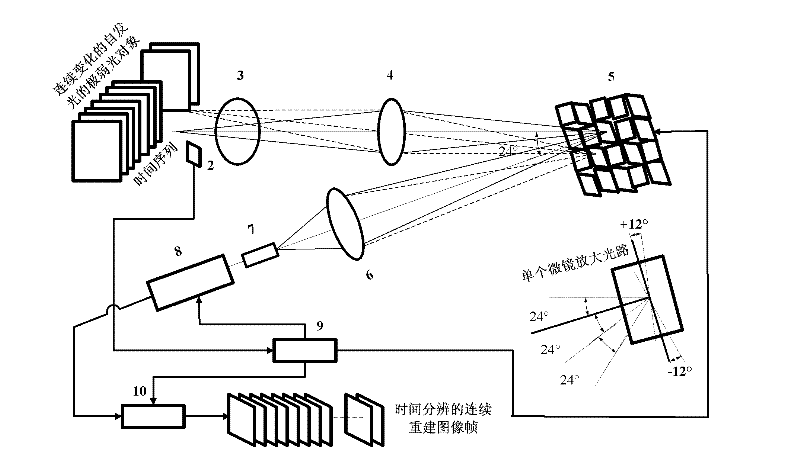
Time-resolved single-photon counting two-dimensional imaging system and method
ActiveCN102510282AResolve SensitivitySolve the small size of the arrayPulse techniqueDigital micro mirror deviceData acquisition
The invention provides a time-resolved single-photon counting two-dimensional imaging system and a time-resolved single-photon counting two-dimensional imaging method and belongs to the technical field of extremely-weak light detection. A trigger 2 is triggered to start sampling, centralized sampling is performed at t time intervals, and measurement and counting are performed if light comes at the intervals, so that time resolving of an extremely-weak light object is realized, and a time sequence image is generated. Imaging is performed on the basis of a compressive sensing (CS) theory, a digital micro-mirror device (DMD5) performs linear random projection on a compressible two-dimensional image, the compressible two-dimensional image is optically modulated and then synchronously detected by using a single-photon counter, and a high-resolution extremely-weak light image can be reconstructed by a small amount of sampling operation. The measurement process is linear and non-adaptive, the reconstruction process is non-linear, and the invention has the advantages of high generality, robustness, expandability, superposition and computation asymmetry, and can be widely applied to the fields of life science, medical imaging, data acquisition, communication, astronomy, military affairs, hyper-spectral imaging and quantum measurement.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
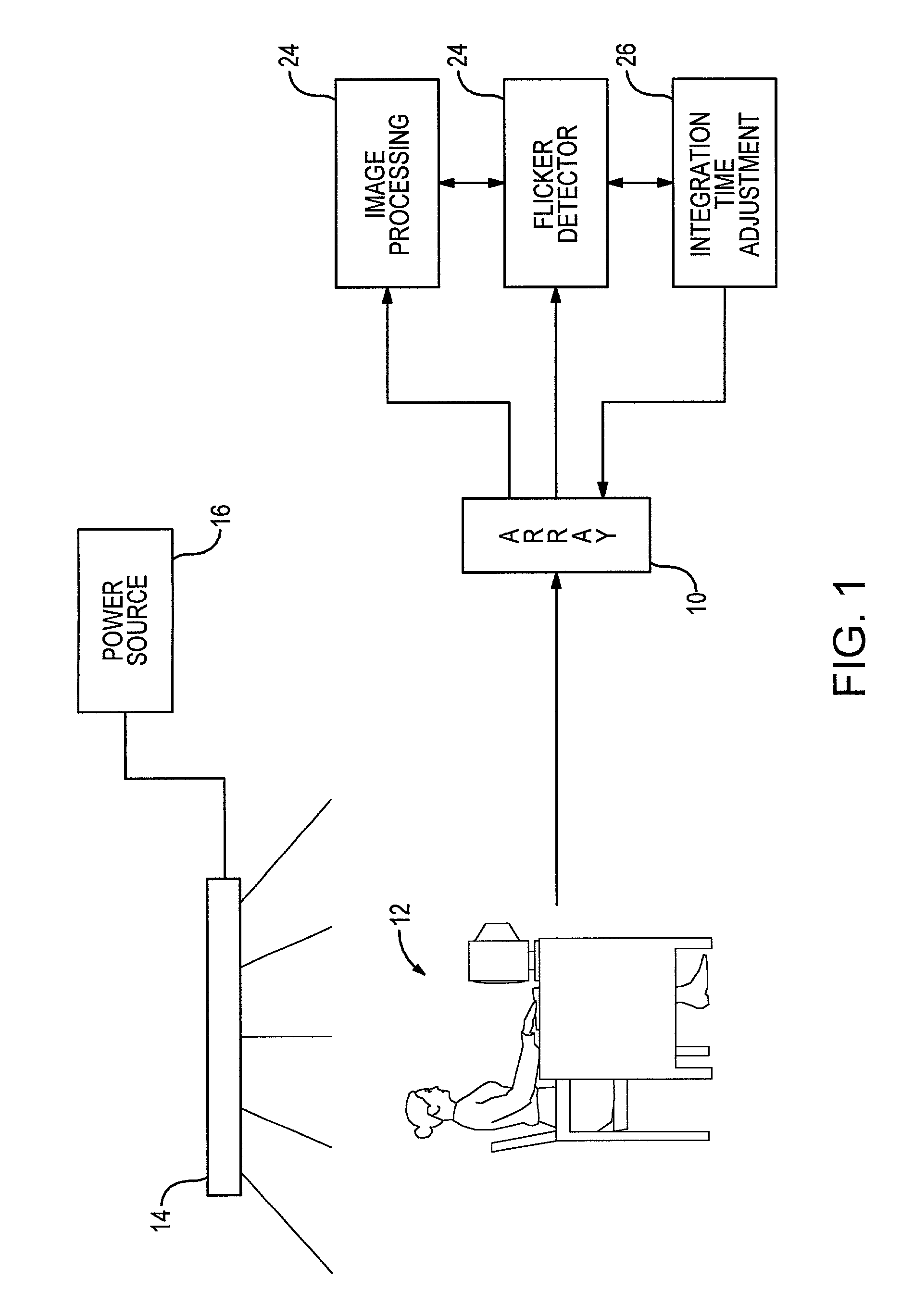
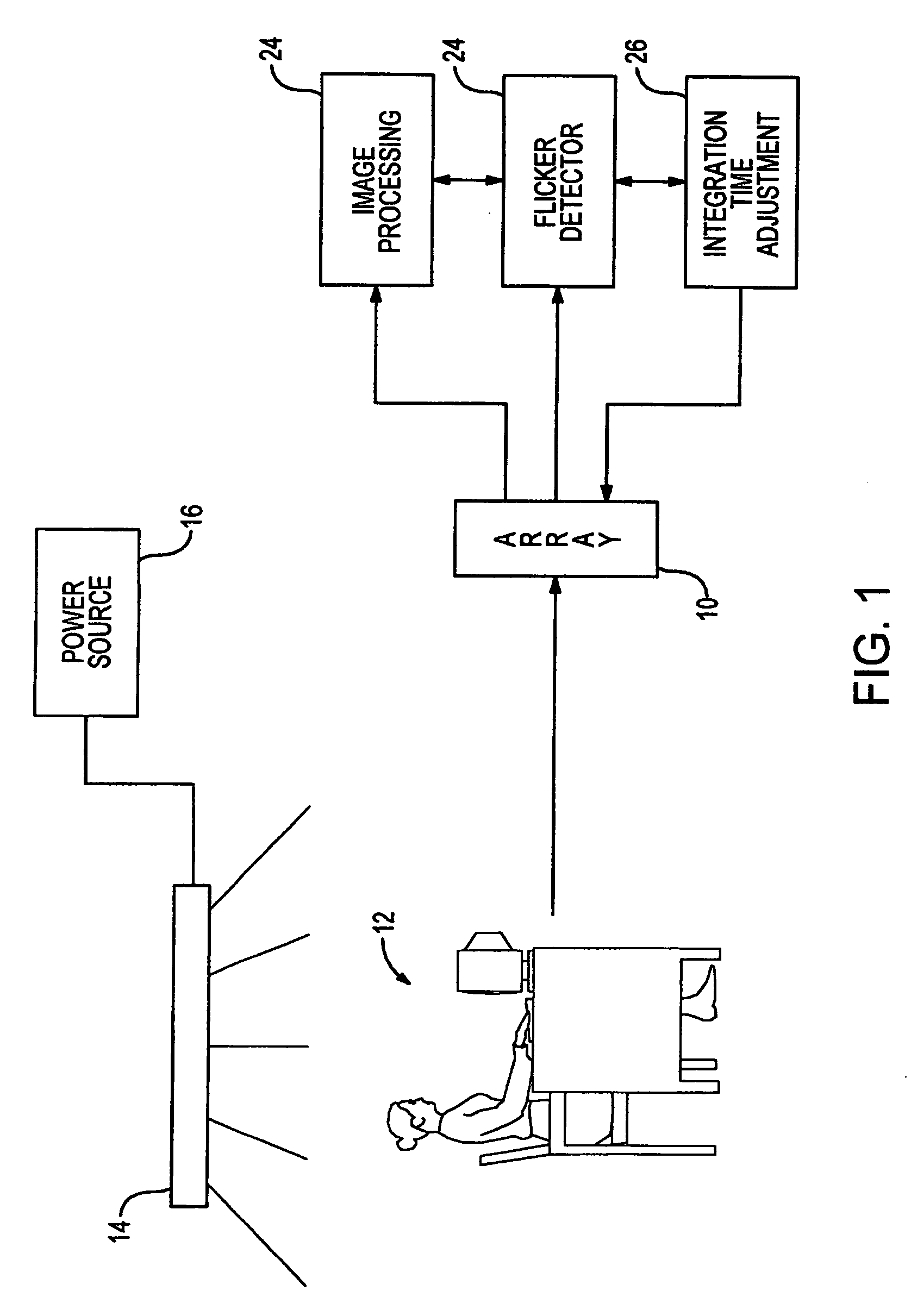
Automatic flicker frequency detection device and method
ActiveUS7187405B2Made robustReliable identificationTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsSensor arrayDigital camera
An image device, such as a digital camera, detects specific repeating patterns of signal variations by processing columnar information from the device's two-dimensional sensor array used to generate images. In one embodiment, the columnar information is derived from calculating row averages for two image frames, with each row average being a computed average of the multiple signal intensities generated from some or all of the sensors within a particular row. After the columnar information is determined for each of the two frames, a difference signal is generated as a sequence of the differences between the row averages for the first frame and the row averages for the second frame. This row averaging and frame differencing removes a large percentage of the signal energy that is not a result of the artifact of interest, such as the flicker generated by illumination having intensity fluctuations at 100 Hz or at 120 Hz. In some embodiments of the invention, the row averaging and / or the frame-to-frame comparison are deleted.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
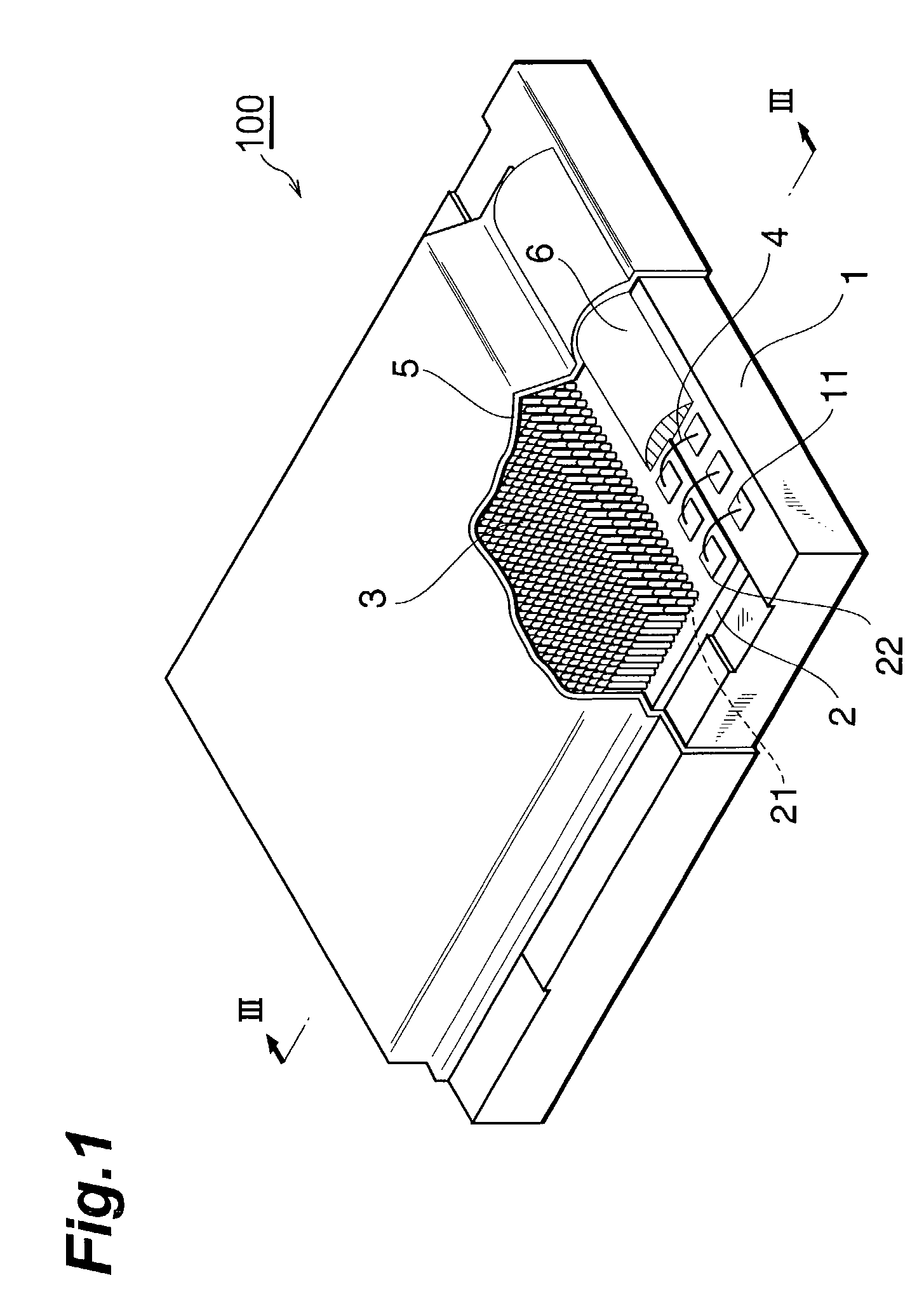
Radiation detector and method of manufacture thereof
InactiveUS6919569B2Thin and small structureLarge imaging areaTelevision system detailsPhotometryEngineeringPhotoelectric conversion
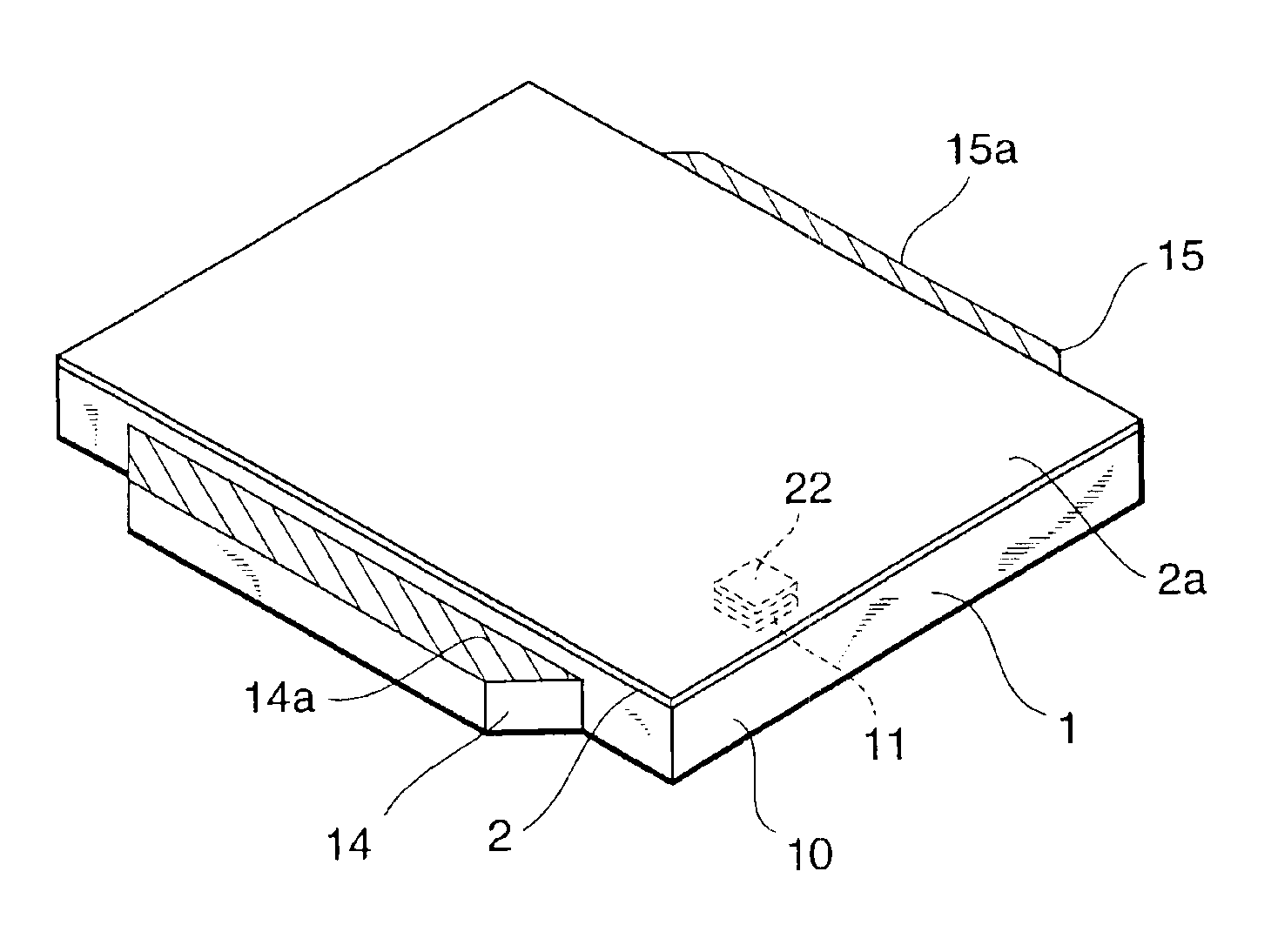
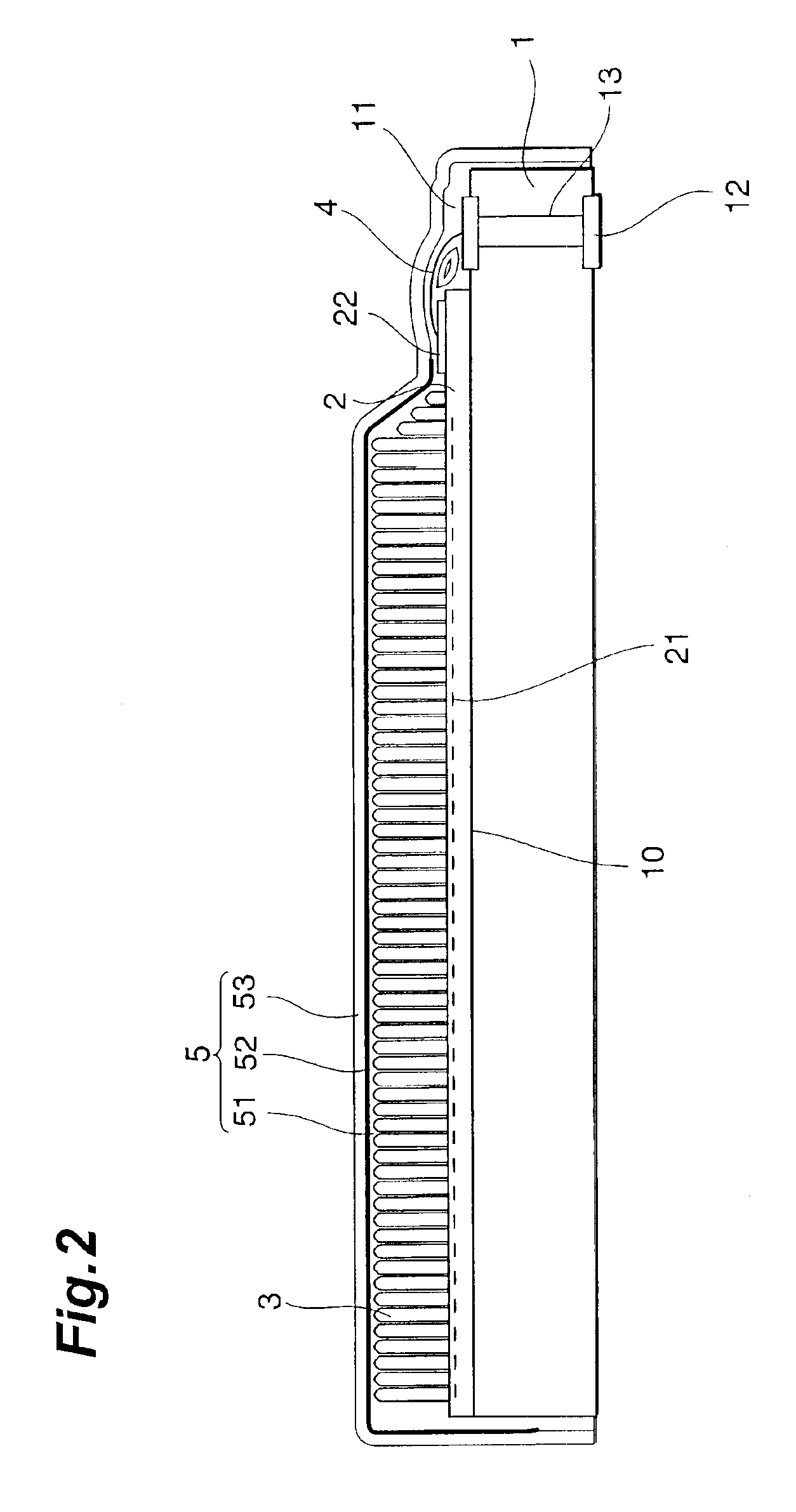
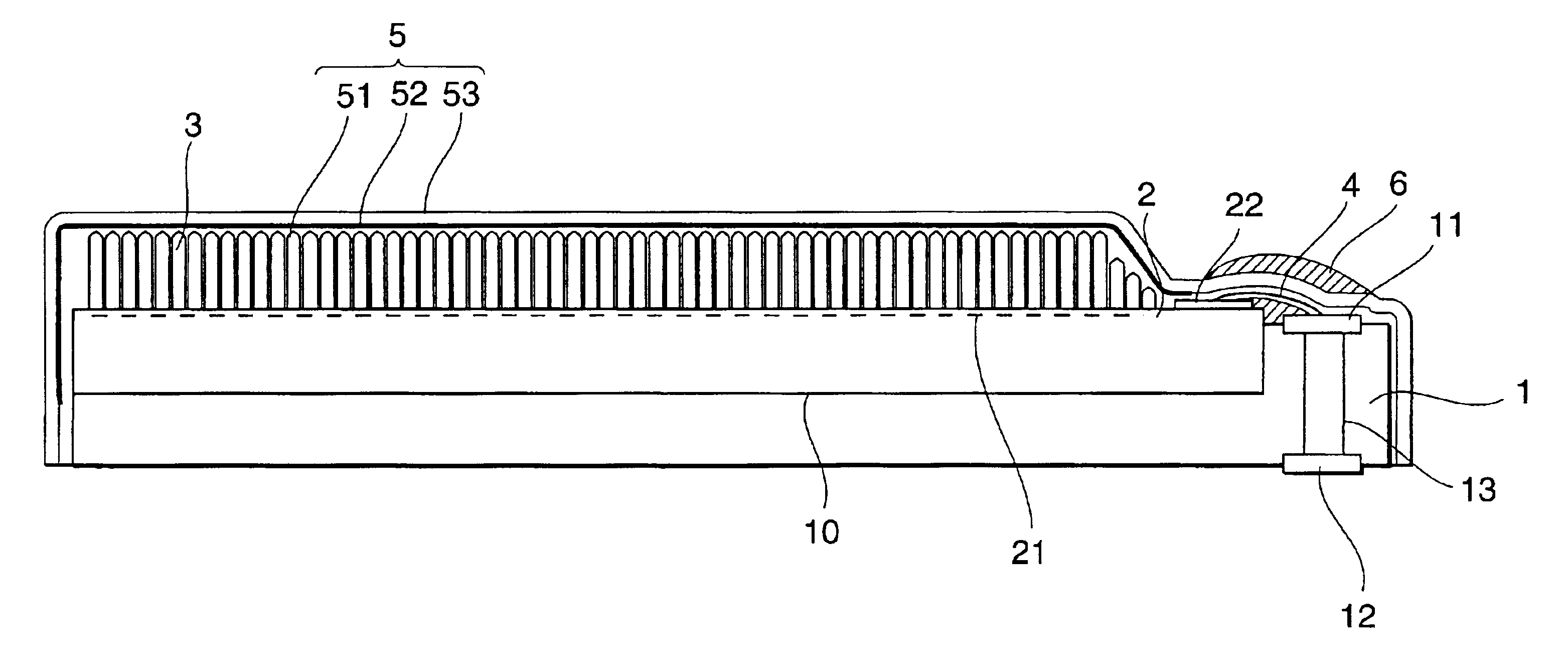
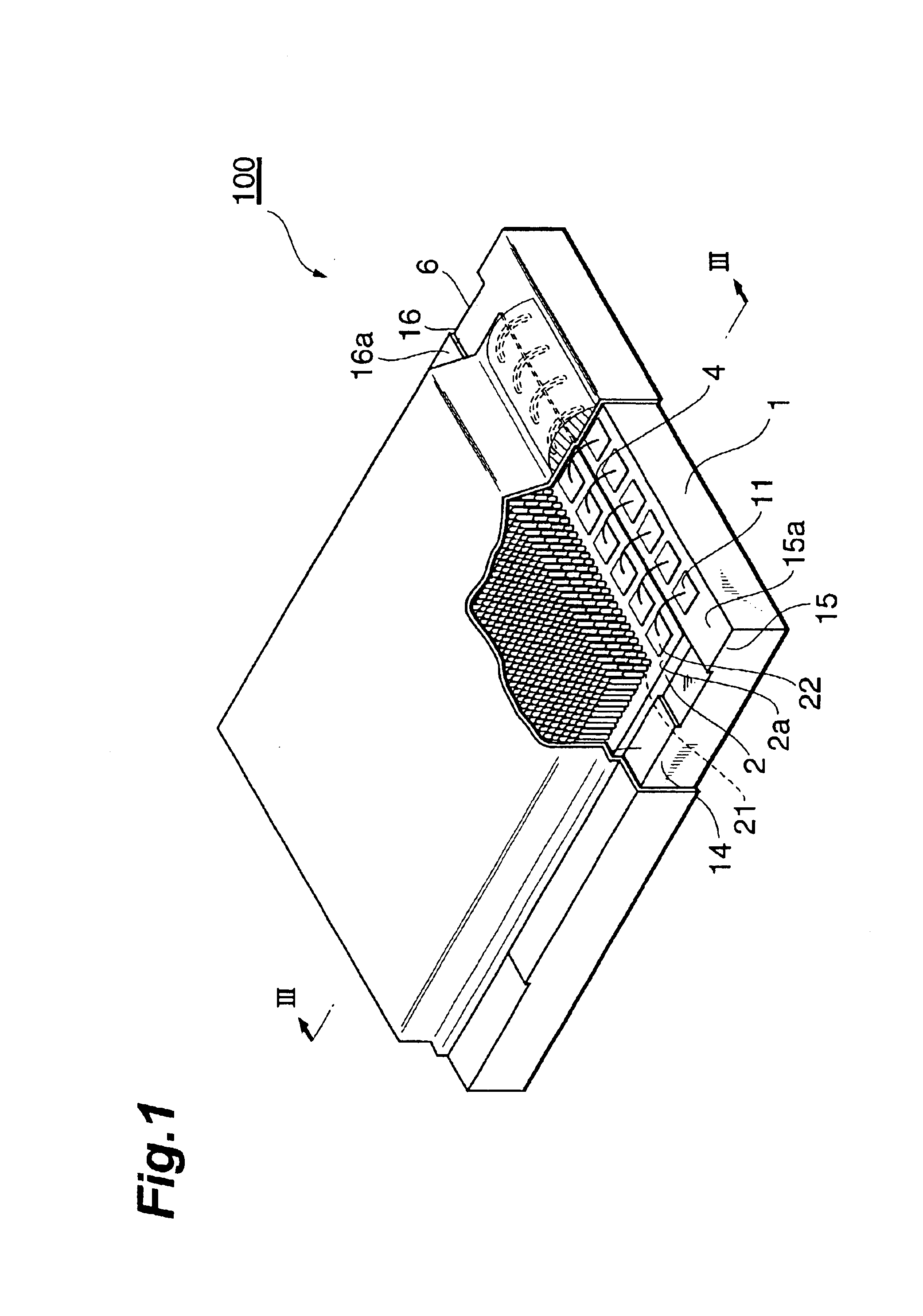
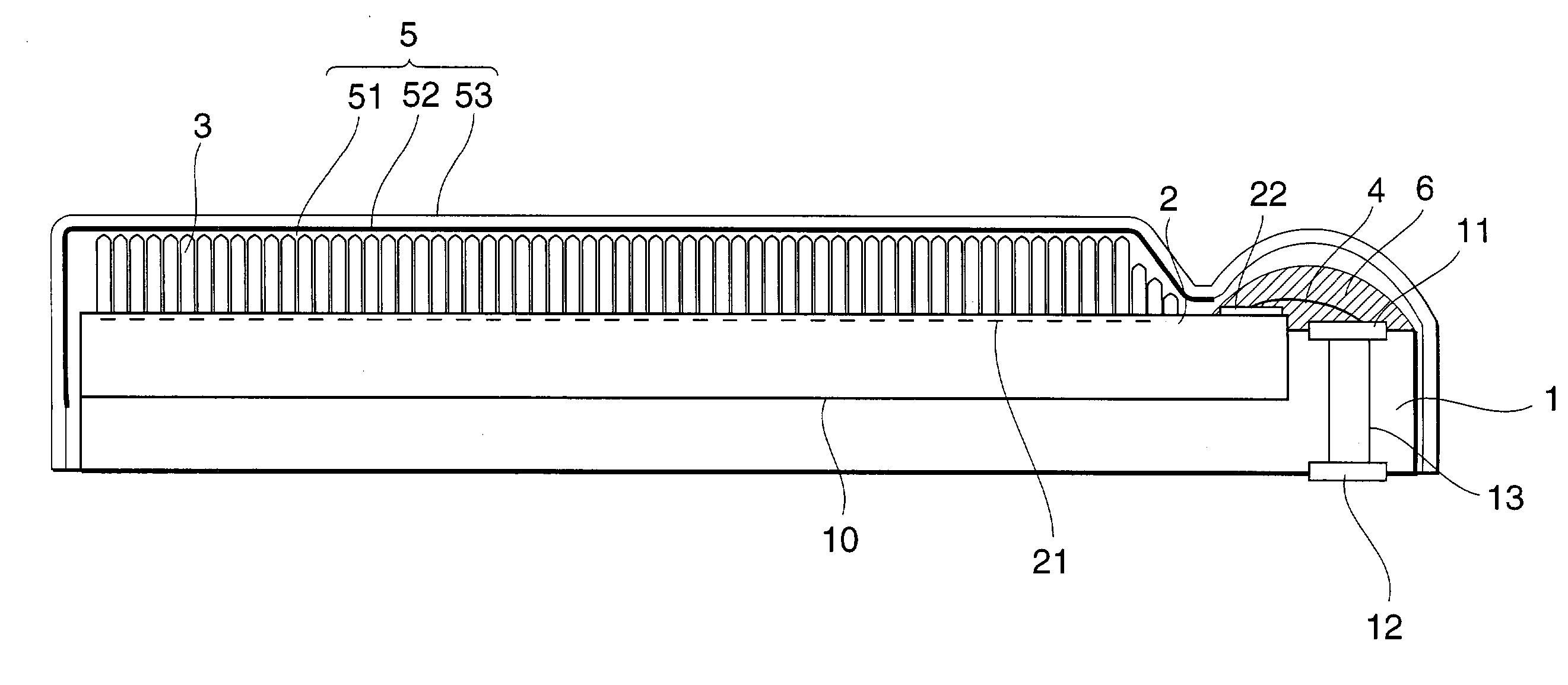
A solid-state imaging element 2 having a light-receiving portion where a plurality of photoelectric conversion elements 21 are arranged, and electrode pads 22 electrically connected to the photoelectric conversion elements 21 is mounted on a substrate 1. A scintillator 3 is formed on the surface of the light-receiving portion of the solid-state imaging element. Around a support surface 10 where the solid-state imaging element 2 of the substrate 1 is mounted, holding portions 14 and 15 are formed on opposing side walls to hold and project the surface of the light-receiving portion from a vapor deposition holder toward a vapor deposition chamber in forming the scintillator 3.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
High resolution surveillance camera
InactiveUS20070126867A1Large imaging areaTelevision system scanning detailsPicture taking arrangementsSurveillance cameraReference image
A surveillance device makes use of a fixed point in space such as a stabilized blimp, and a downward-looking high-resolution scanning camera. One or more line scan devices are arranged in a radial fashion on a rotating disk, together with associated lenses, so as to repeatedly scan an area of interest. To allow for manageable data bandwidth and to focus on objects of interest, the data from successive scans is compared so as to show primarily the moving objects, with occasional full-scan reference images included.
Owner:IMMERSIVE VENTURES
Structured light source
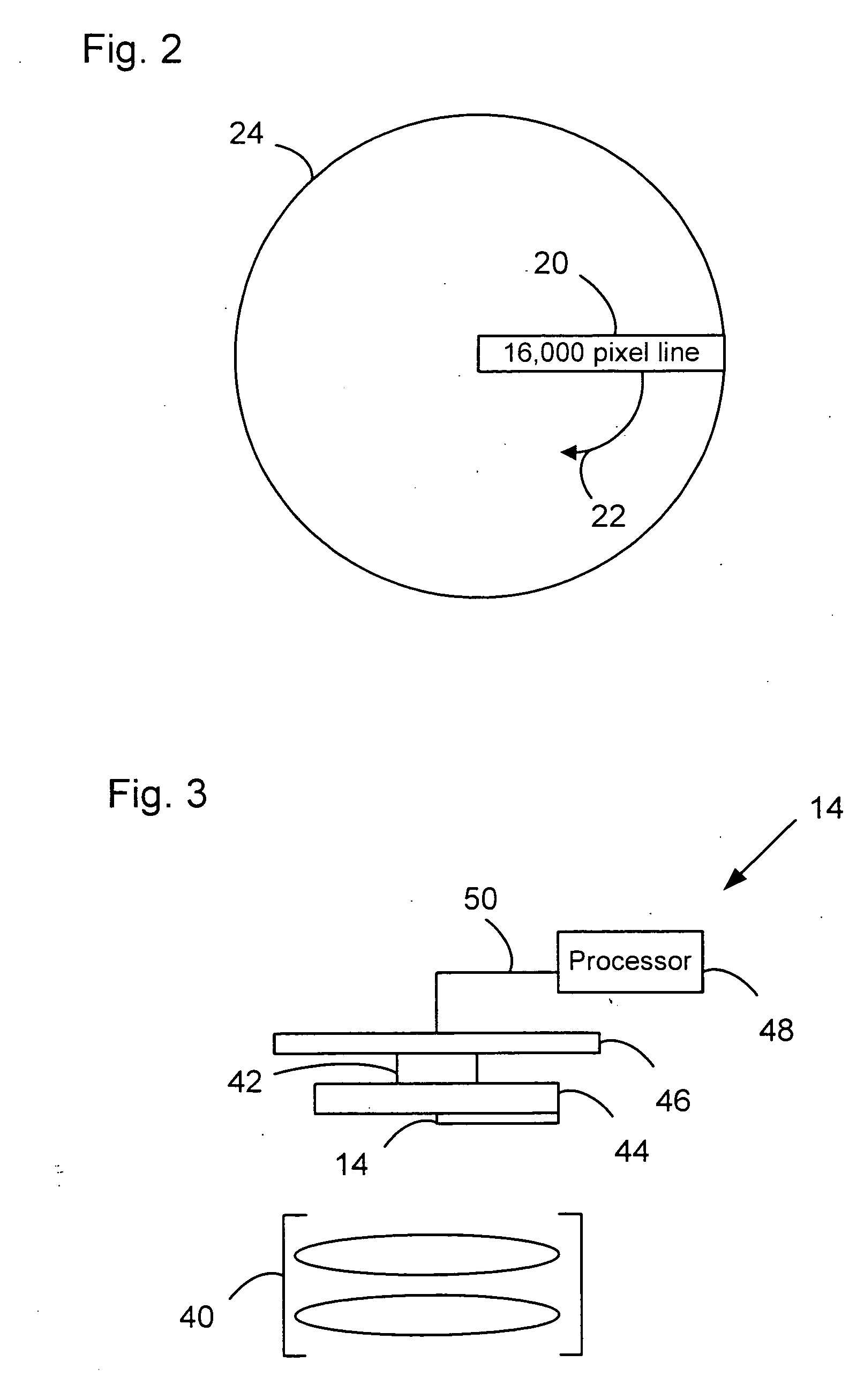
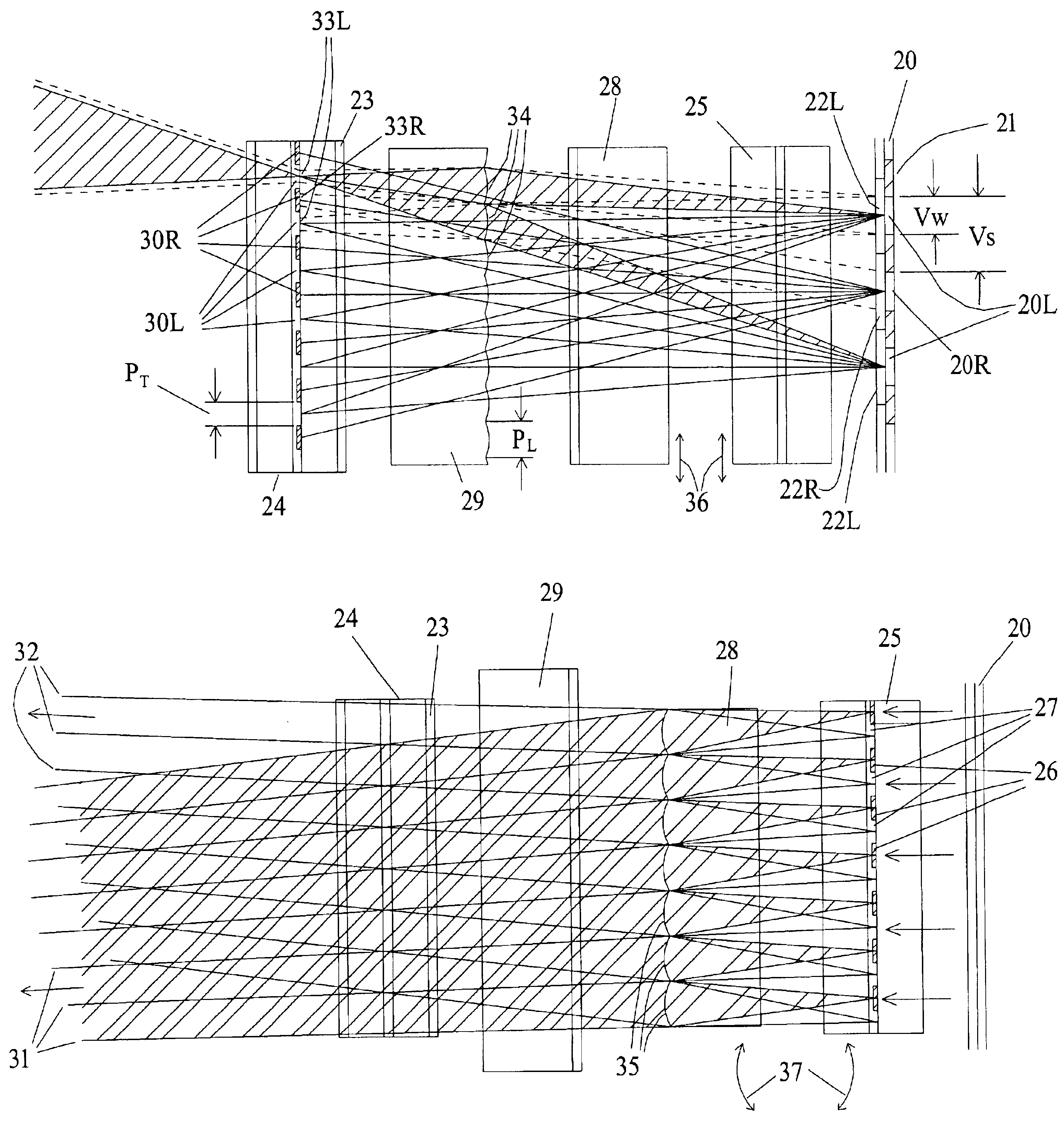
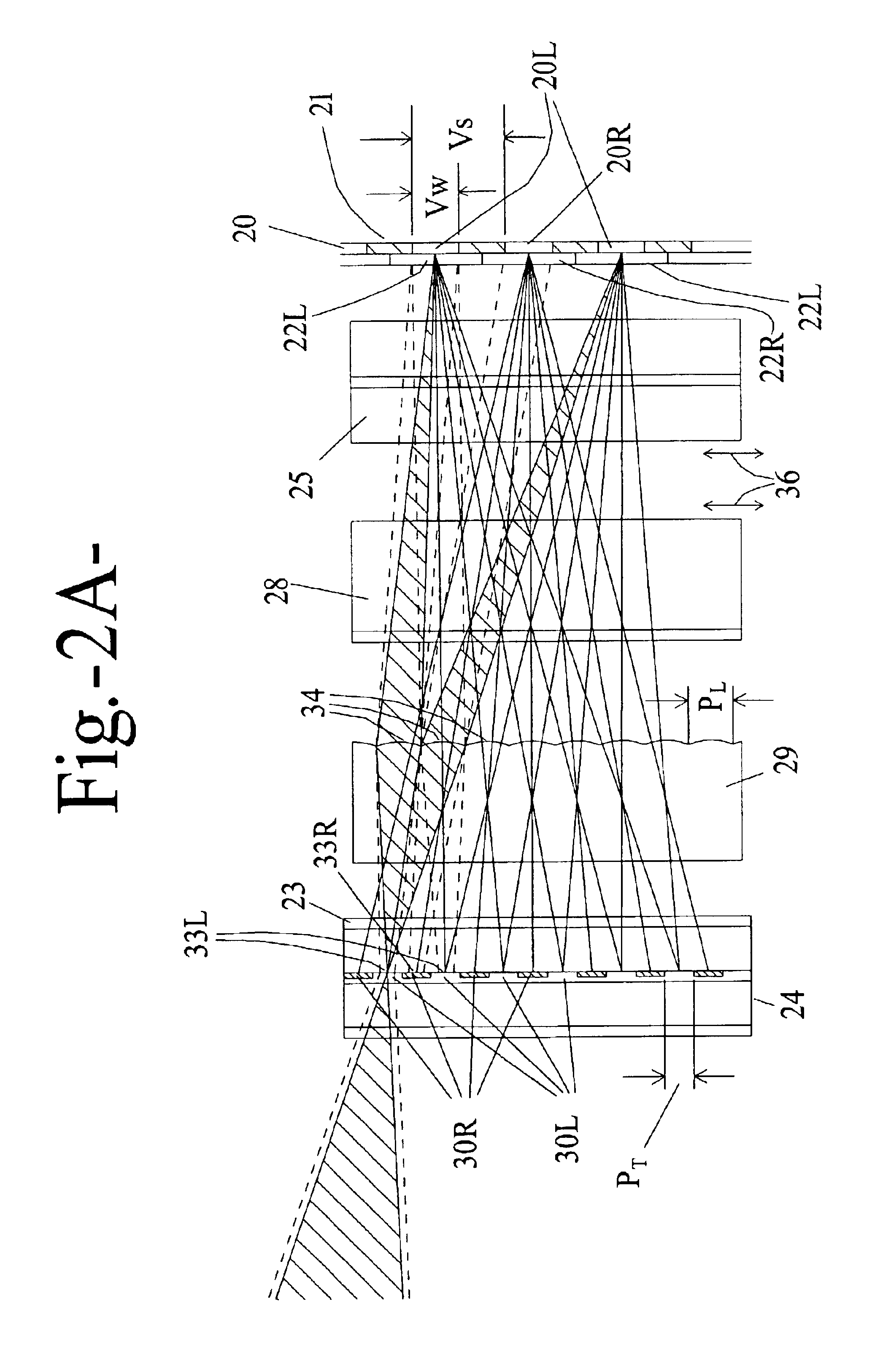
InactiveUS6876495B2Improve efficiencyLarge imaging areaSteroscopic systemsNon-linear opticsImage resolutionDisplay device
Apparatus and method for the display of autostereoscopic images, in which two or more perspective views are generated by a single transmissive display screen is provided. A structured light source behind the screen directs light through different sets of display elements to correspondingly different viewing zones. The structured light source includes two crossed arrays of cylindrical convergent optical elements, two linear arrays of polarisation altering elements which, in conjunction with the convergent arrays and the first polariser of the LCD, prevent light from passing through a particular set of display elements and reaching the wrong viewing zone. In some variations, one or both of the polarisation altering arrays may be programmed. Observer co-ordinate data permits the correct viewing zone to be co-located with each of the observer's corresponding eyes and includes devices for accommodating changes in the observer's distance from the display. The displayed image adapts to the observer's location. All or part of the display may provide conventional two-dimensional images at the screen's full resolution.
Owner:STREET GRAHAM STEWART BRANDON
Radiation detector and method of producing the same
InactiveUS6833548B2Easy to manufactureLarge imaging areaTelevision system detailsPhotometryElectricityEngineering
A solid-state imaging element 2 having a light-receiving portion where a plurality of photoelectric conversion elements 21 are arranged, and electrode pads 22 electrically connected to the photoelectric conversion elements 21 is mounted on a substrate 1. A scintillator 3 is formed on the surface of the light-receiving portion of the solid-state imaging element. Around a support surface wherein the solid-state imaging element 2 of the substrate 1 is mounted, positioning portions 14 to 16 are formed, which project higher than the support surface and position the solid-state imaging element 2 with side walls. The top surfaces of these positioning portions are formed such that a light-receiving surface 2a of the solid-state imaging element 2 is higher than the top surfaces.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Radiation detector and method of manufacture thereof
InactiveUS20030116716A1Large imaging areaDecreasing manufacturing operabilityMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementOrganic filmEngineering
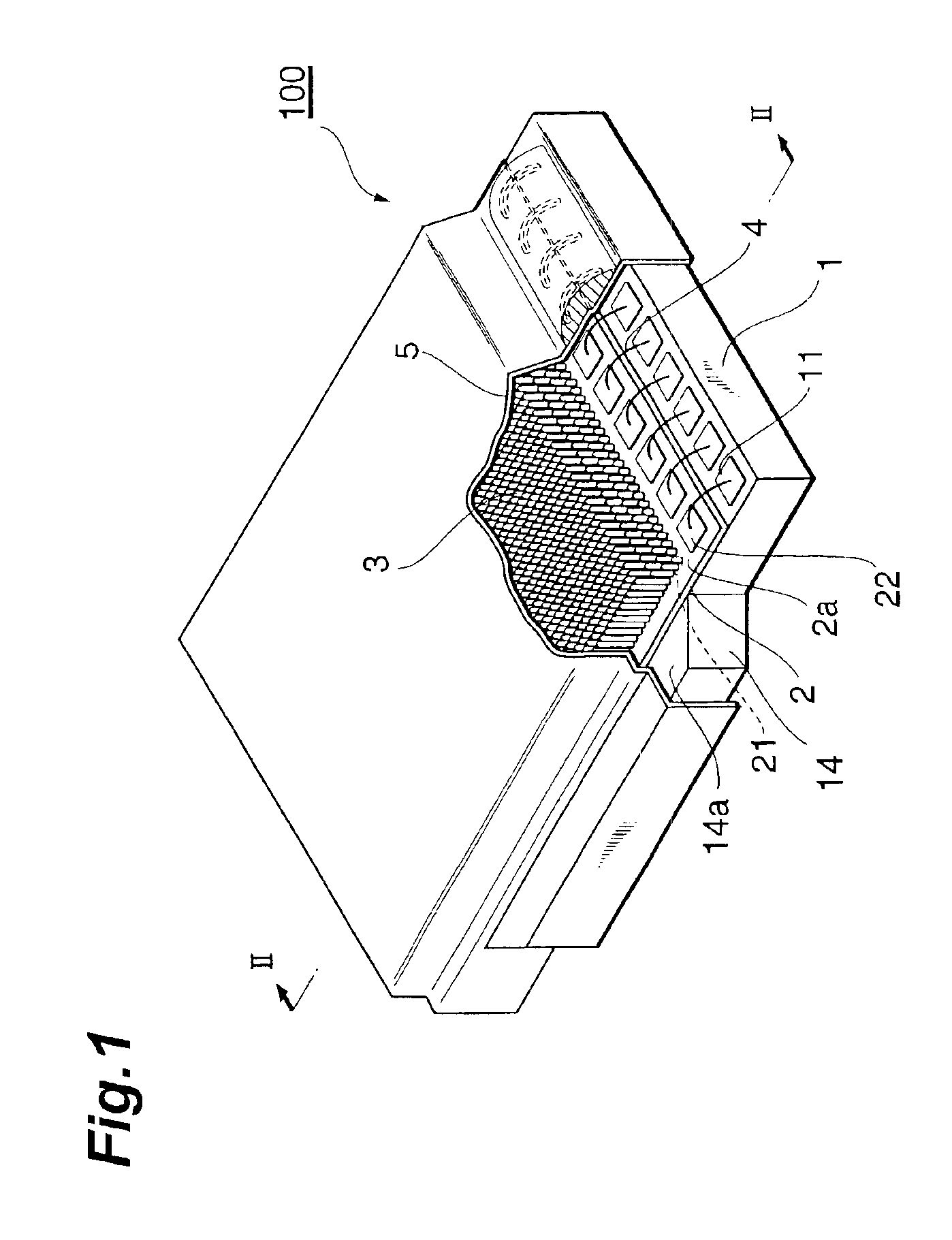
A solid-state imaging element 2 having a light-receiving portion where a plurality of photoelectric conversion elements 21 are arranged, and electrode pads 22 electrically connected to the photoelectric conversion elements 21 is mounted on a substrate 1 having external connection electrodes 12 and electrode pads 11 electrically connected to them. A scintillator 3 is formed on the surface of the light-receiving portion of the solid-state imaging element 2. The electrodes pads 11 and 22 are electrically connected by wiring lines 4. An electrical insulating organic film 51 tightly seals the scintillator 3 and covers the electrode pads 11 and 22 and the wiring lines 4. A metal thin film 52 is formed on the organic film 51.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
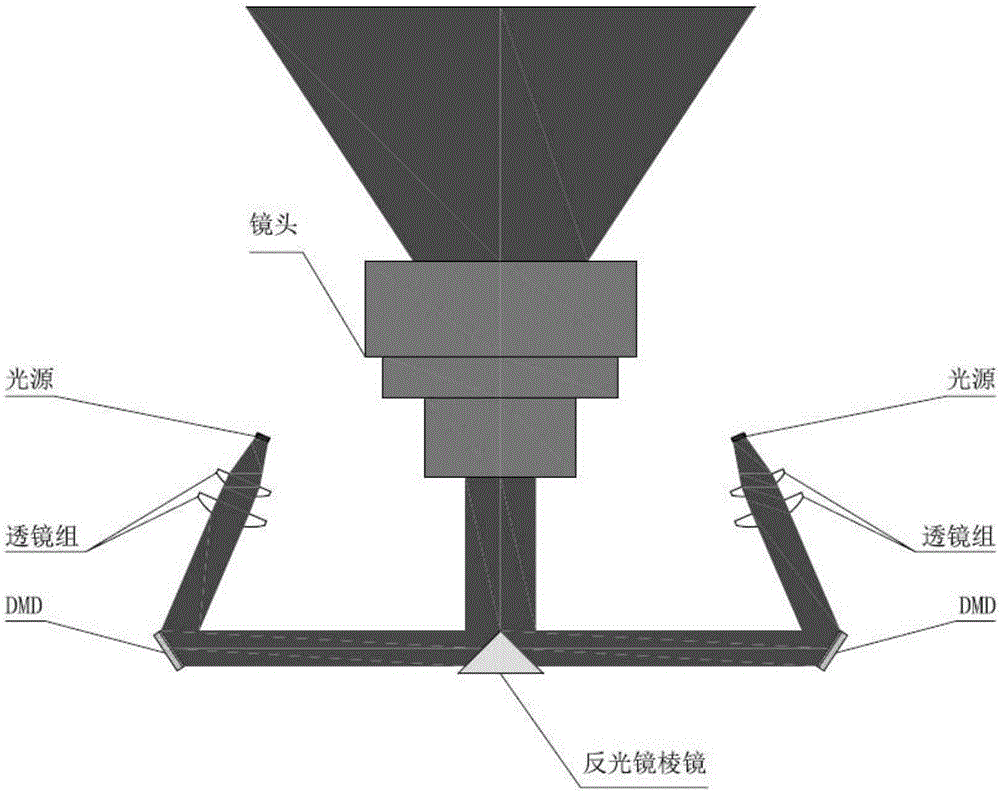
Method for improving resolution of projection picture by multi-disc DMD common imaging
The invention relates to a method for raising the resolution of projected pictures through common imaging of multiple DMDs. The ultraviolet light source, the lens group and the DMD are placed symmetrically in pairs with respect to the projected lens, the reflective prism is placed vertically with the projected lens, and the projected picture information is divided into two parts. The information is collected separately by two DMDs, and the beams are reflected and spliced completely at the prism, and then projected and imaged uniformly, so that a larger imaging area can be obtained in the case of a higher resolution.
Owner:深圳晗竣雅科技有限公司
Electromagnetic wave detector
InactiveUS6855935B2High energyEffectively and efficiently detectingTransistorTelevision system detailsHigh energyCapacitor
An electromagnetic wave detector includes a conversion element for converting incident electromagnetic waves or high energy radiations into an electric charge, a storage capacitor for storing the electric charge produced by the conversion element, a thin film read transistor connected to the storage capacitor, and a thin film reset transistor also connected to the storage capacitor. To the gates of the read and reset thin film transistors are applied ON and OFF voltages at predetermined timings and these voltages are set to values such that any excessive electric charge produced in the storage period is discharged by way of the thin film reset transistor, not by way of the thin film read transistor, in the same storage period.
Owner:CANON KK
Automatic flicker frequency detection device and method
InactiveUS20070109425A1Large imaging areaEasy to detectTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsSensor arrayRepeat pattern
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
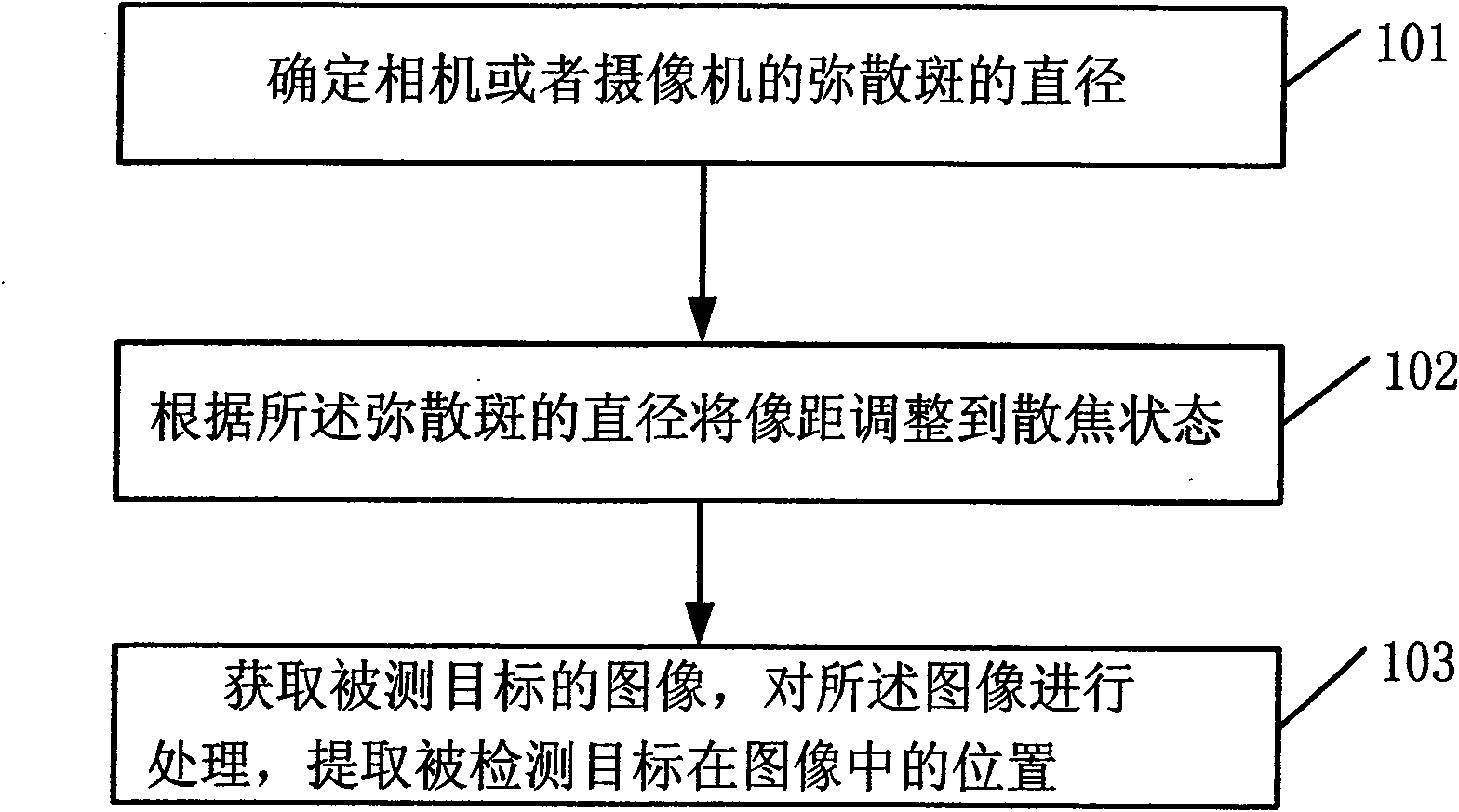
Object detection method, system and stereoscopic vision system
ActiveCN101571953ALarge imaging areaExpand the scope of detectionTelevision system detailsImage analysisVisual perceptionObject detection
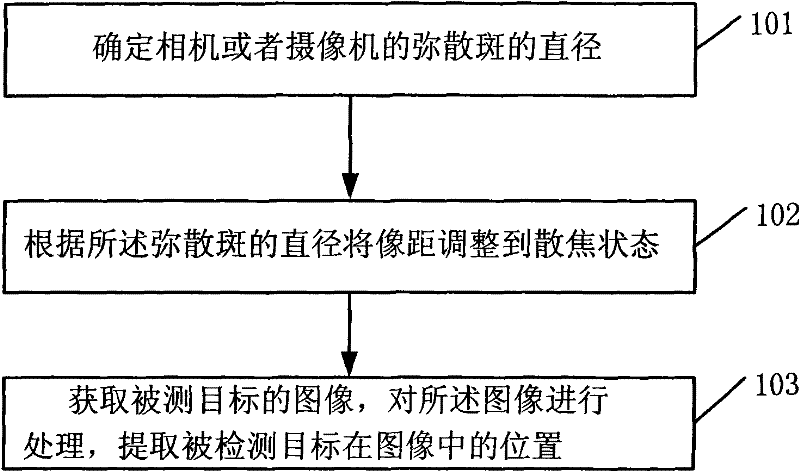
The invention provides an object detection method, a system and a stereoscopic vision system; wherein the method comprises the following steps: determining the diameter of the dispersed spot of a lens; adjusting image distance to a defocusing state according to the diameter of the dispersed spot; adjusting image distance of the lens, increasing imaging area of the object, increasing detection range of the object to facilitate the camera to collect images under the state of dispersed spot; as the dispersed spot facilitates recognition area to rise and pixel to increase, as a result, influence of interfering pixel is reduced, meanwhile, precision of calculated sub-pixel level areal coordinate is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN TAISHAN SPORTS TECH CO LTD
Device and method for rapid scanning and imaging of two-dimensional distribution of pollutant gases
InactiveCN109187396AOptimize locationFlexible accessColor/spectral properties measurementsSpectroscopyDifferential absorption
The invention relates to a device and method for rapid scanning and imaging of two-dimensional distribution of pollutant gases. A front optical system receives a sun scattered light passing through the pollutant gases, and the sun scattered light is coupled through an introduction optical system, and then enters an imaging spectrometer, and is received by an area array CCD detector after being dispersed by the imaging spectrometer; the area array CCD detector completes the spectrum acquisition work of a spectral dimension and a spatial dimension, and transmits to a computer through a USB afterdigitization; the computer uses a differential absorption spectroscopy analysis method to performing inversion, so as to obtain detected slant column concentration of the pollutant gases in differentspatial dimensions; and the concentration information is matched with pixels on the spatial dimension according to a geometric model of an observation angle and sequentially reconstructed according to the scanning direction, so that the two-dimensional concentration field distribution of the pollutant gas is quickly scanned and imaged without an interval. The invention realizes the rapid imagingof the two-dimensional distribution information of conventional pollutant gases in the area without the interval, which is beneficial for determining the position information and conveying situation of each scattered source in the area, and provides technical support for the environmental protection department to grasp the position situation of each scattered source in the area.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Radiation detector and method of manufacture thereof
InactiveUS7151263B2Large imaging areaEasy to operatePhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansOrganic filmPhotoelectric conversion
A solid-state imaging element 2 having a light-receiving portion where a plurality of photoelectric conversion elements 21 are arranged, and electrode pads 22 electrically connected to the photoelectric conversion elements 21 is mounted on a substrate 1 having external connection electrodes 12 and electrode pads 11 electrically connected to them. A scintillator 3 is formed on the surface of the light-receiving portion of the solid-state imaging element 2. The electrodes pads 11 and 22 are electrically connected by wiring lines 4. An electrical insulating organic film 51 tightly seals the scintillator 3 and covers the electrode pads 11 and 22 and the wiring lines 4. A metal thin film 52 is formed on the organic film 51.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Image pickup apparatus and radiation image pickup system
InactiveUS20110073750A1Increase in imaging areaLarge image areaTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesElectricityElectrical connection
An image pickup apparatus includes an insulating substrate, and a plurality of pixels each including a conversion element configured to convert incident light or radiation into a charge and also including a switch element configured to transfer an electric signal corresponding to the charge generated by the conversion element. Gate wiring is configured to drive the switch element to transfer the electric signal through signal wiring. The plurality of pixels, the signal wiring, and the gate wiring are disposed on one surface of the insulating substrate. The insulating substrate has vias that provide electrical connections between the one surface and an opposite surface of the insulating substrate.
Owner:CANON KK
Spaceborne multi-baseline holographic SAR imaging method
InactiveCN110488294ASolution rangeSolve the limited detection areaRadio wave reradiation/reflectionGeosynchronous orbitHolographic imaging
The invention discloses a spaceborne multi-baseline holographic SAR imaging method, which realizes 360-degree omnibearing imaging based on multiple navigation geosynchronous orbit baselines. The method comprises the following steps: S1, an orbit model for geosynchronous orbit spaceborne holographic SAR imaging is constructed; S2, based on the orbit model and an imaging geometric model of the geosynchronous orbit spaceborne holographic SAR imaging, a geosynchronous orbit spaceborne holographic SAR echo signal model is constructed; S3, two-dimensional holographic imaging is carried out; S4, a three-dimensional imaging sparse basis is constructed through constructing an altitude sparse basis; S5, the altitude of a ground target is reconstructed by using a compressed sensing reconstruction algorithm; and S6, a holographic image is displayed. The problems that the airborne platform has a small detection range, the detection area is limited, and the holographic imaging quality is affected bythe movement of a carrier and the like can be solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
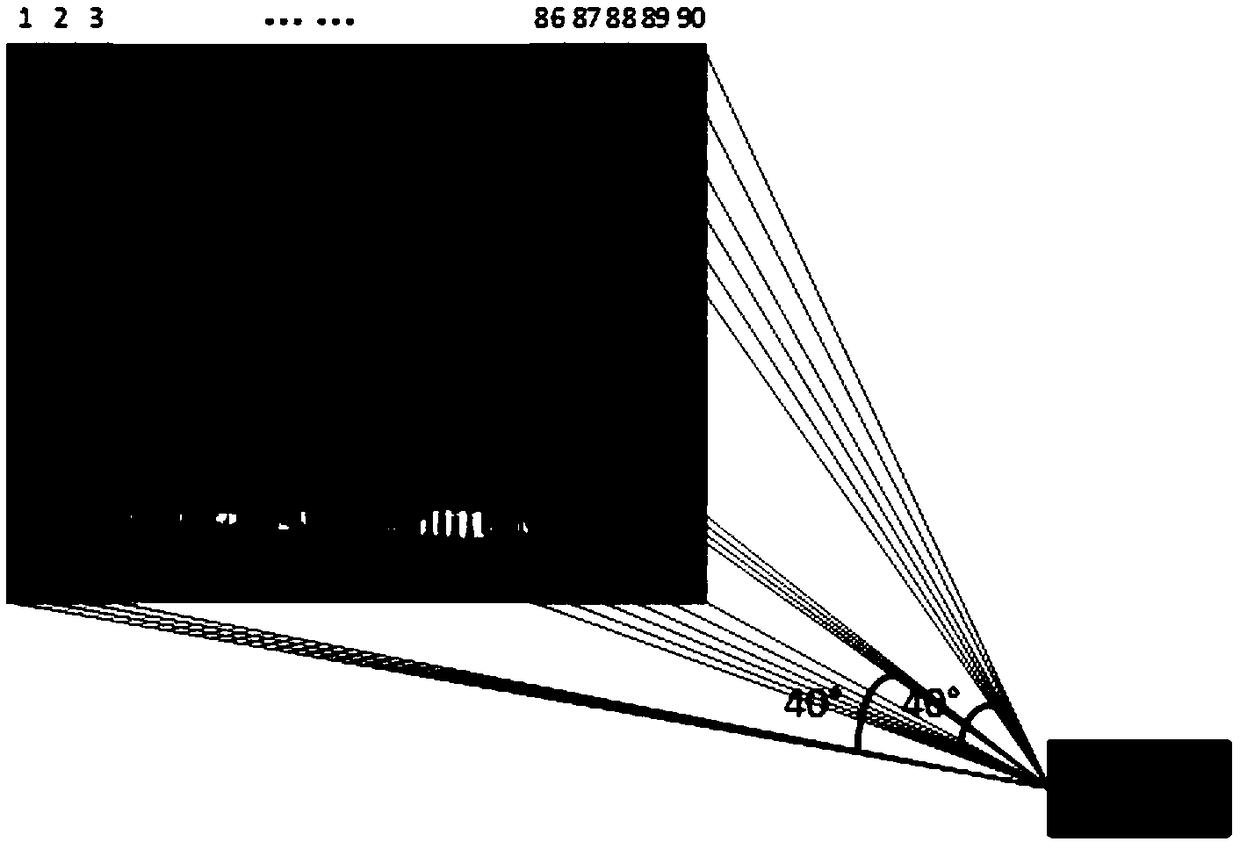
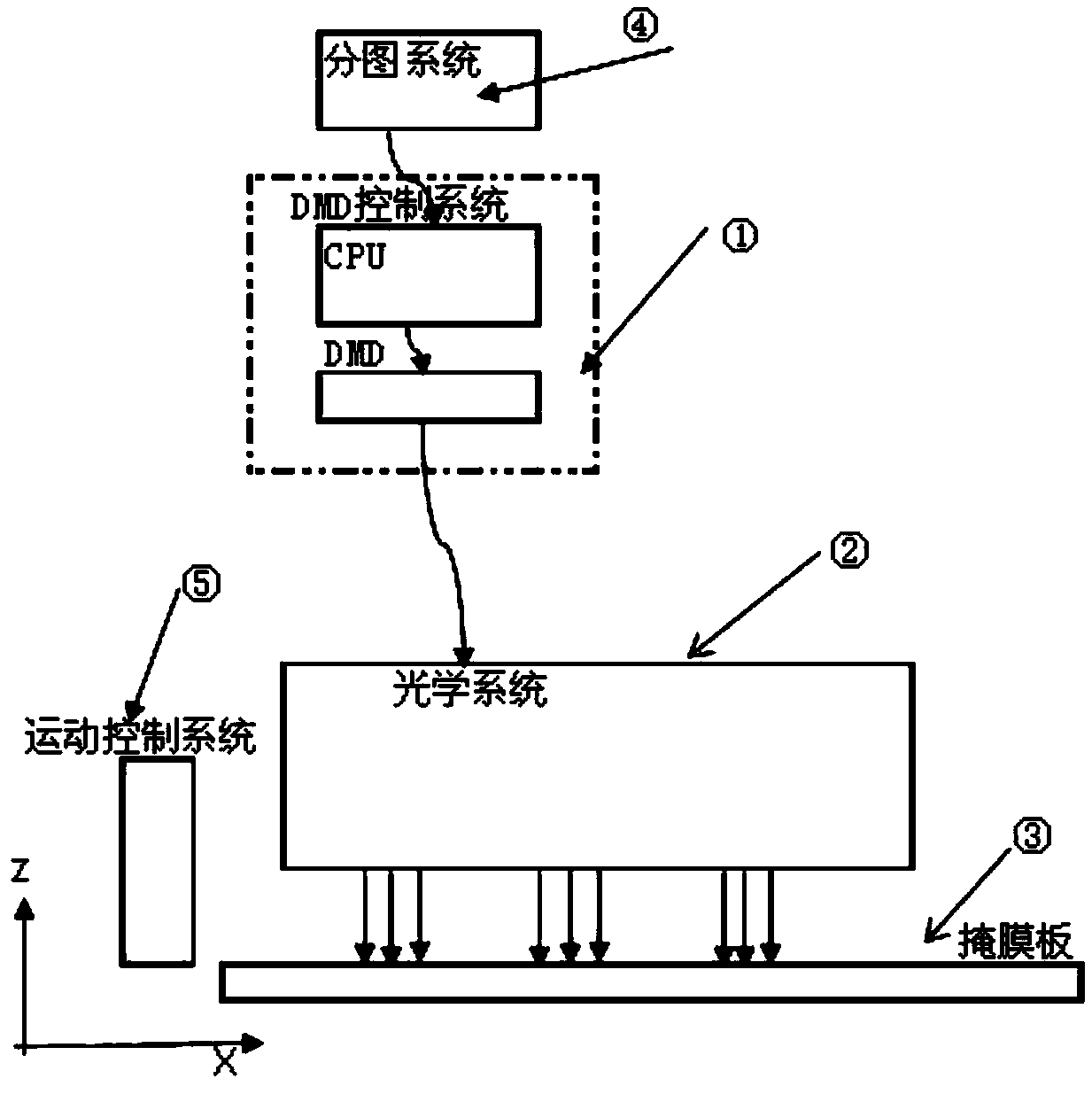
A DMD multi-region laser projection system and exposure method
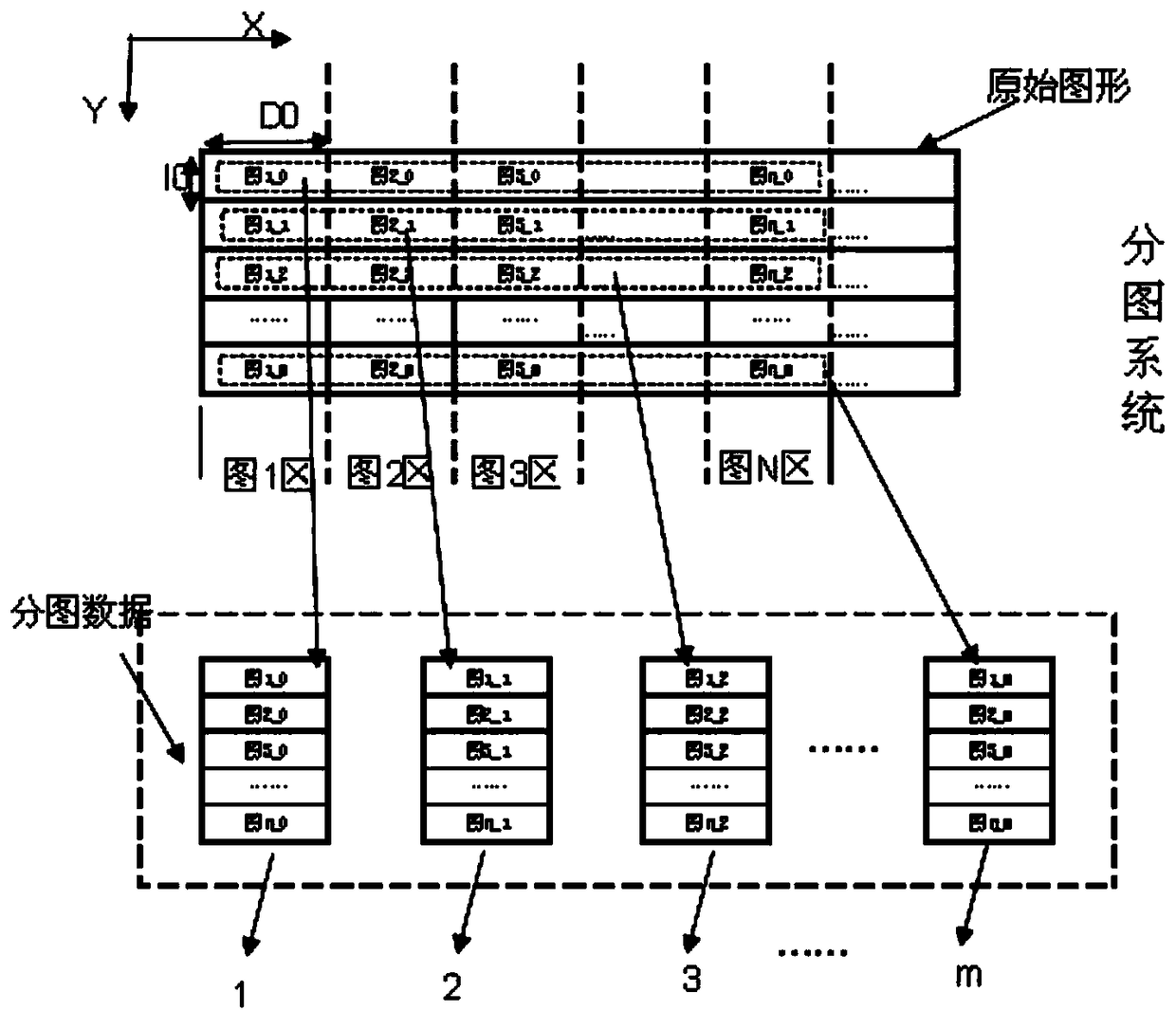
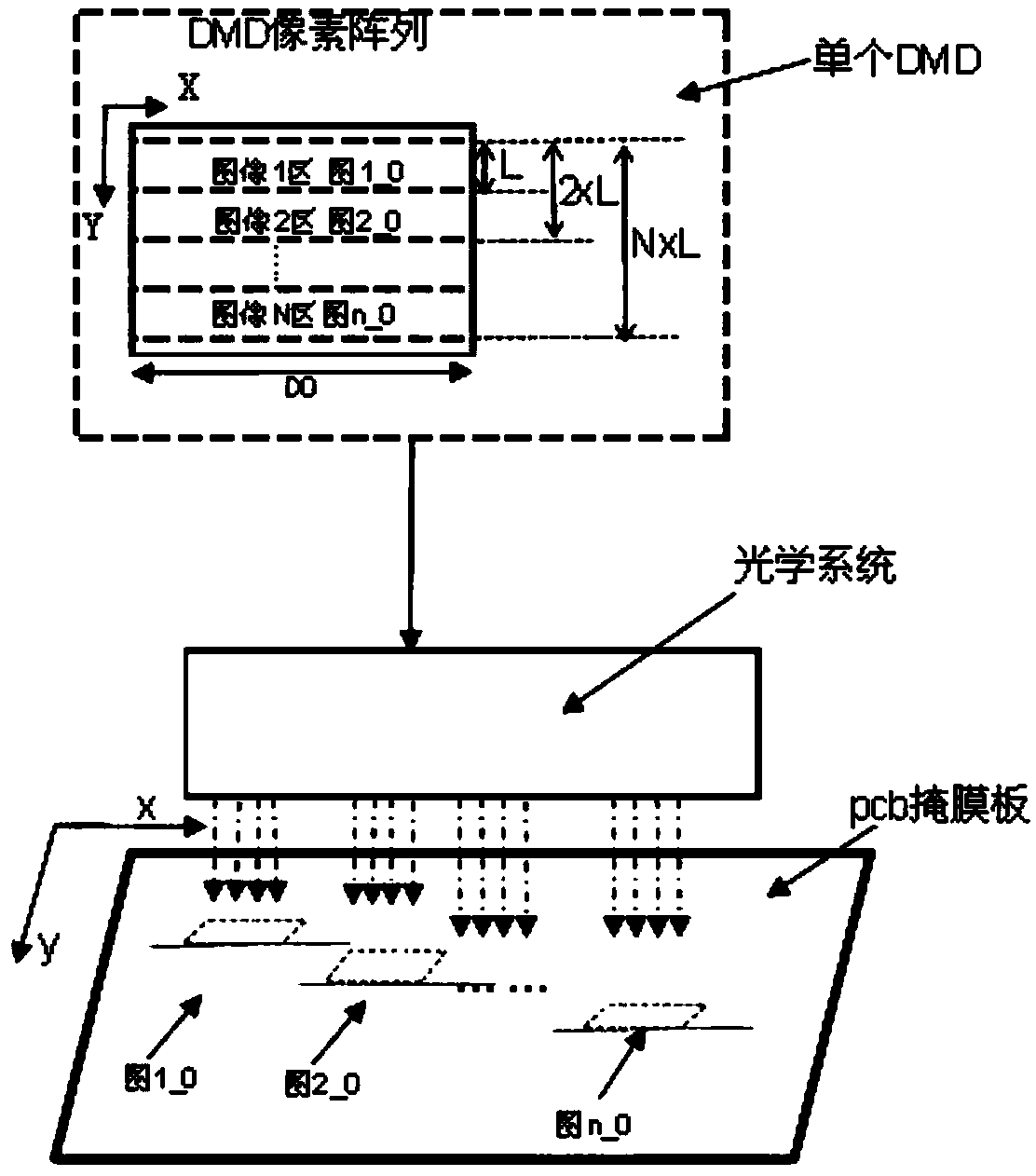
ActiveCN109116686AIncrease exposure timeLarge imaging areaPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusEngineeringWhole systems
A DMD multi-region laser projection system and exposure method are disclosed, the system includes a DMD control system, an optical system, a mask, a graph division system and a motion control system,a plurality of exposure patterns are displayed on a single DMD, combined with the optical system, the plurality of exposure patterns are mapped to different exposure areas of the mask for exposure, and the whole system can use a single DMD or a plurality of DMDs for simultaneous exposure, and exposure according to the method of the invention can rapidly increase the overall exposure time and savethe material cost of the DMD at the same time.
Owner:SUZHOU YUANZHUO OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Zoom lens
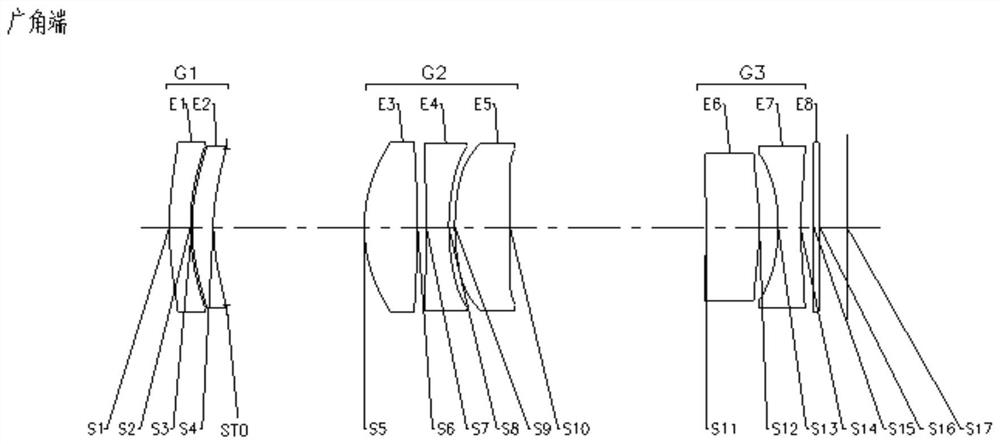
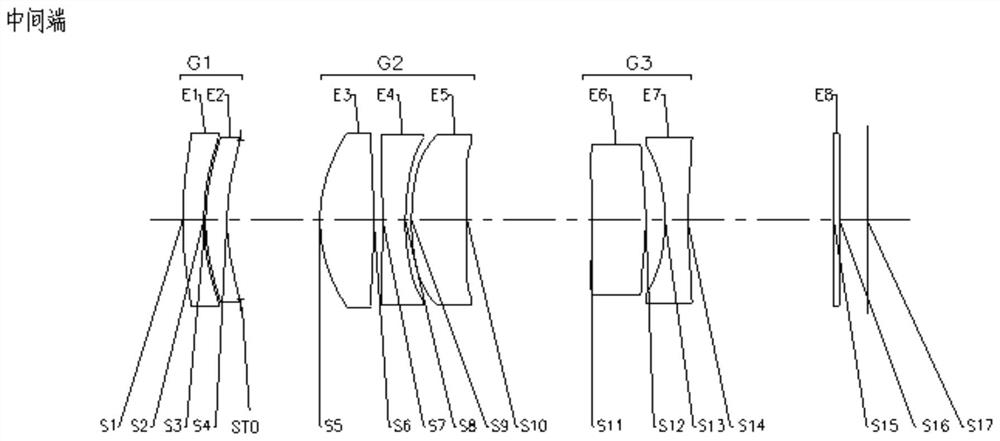
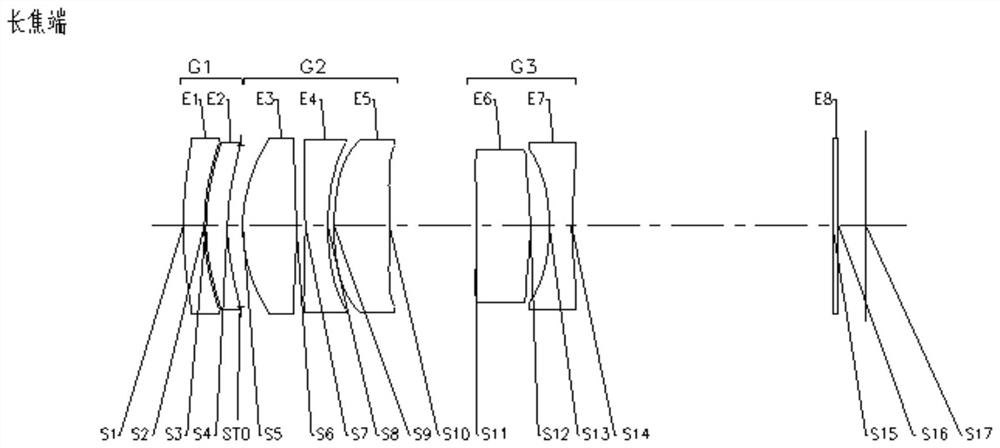
The invention provides a zoom lens. The zoom lens sequentially comprises the following lens groups from the object side to the image side along the optical axis of the zoom lens: a first lens group, wherein a plurality of lenses in the first lens group are arranged at intervals; a second lens group which has positive focal power, wherein a plurality of lenses in the second lens group are arrangedat intervals; a third lens group which has negative focal power, wherein a plurality of lenses in the third lens group are arranged at intervals, the second lens group and the third lens group move along the optical axis to realize continuous zooming, and the zoom lens has a wide-angle end position, a middle end position and a long-focus end position; wherein the entrance pupil diameter (EPD) of the zoom lens, half ImgH of the diagonal length of an effective pixel area on the imaging surface of the zoom lens and the maximum value DTmax in the effective radiuses of the lenses in the first lensgroup, the second lens group and the third lens group meet the following formula: EPD * ImgH / DTmax > 6.5 mm. The zoom lens solves the problem that a zoom lens in the prior art is poor in imaging quality.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SUNNY OPTICAL CO LTD
Imaging optical lens system, image capturing apparatus and electronic device
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Method for improving resolution of projection picture by multiple times of imaging through reflection mirror swinging
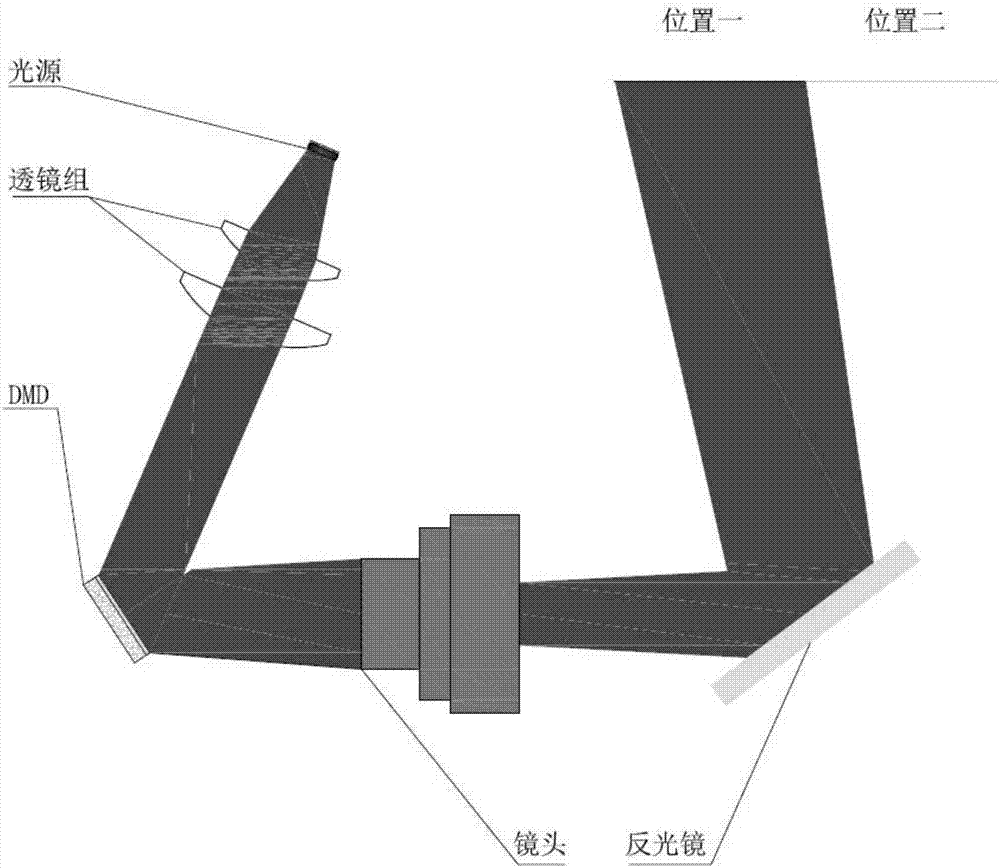
The invention relates to a method for improving resolution of a projection picture by multiple times of imaging through reflection mirror swinging. When picture information is input to DMD, half of the picture information just covers all micro-mirrors of the DMD, the DMD projects a light beam which carries half of the picture information into a lens, and then the lens performs imaging and shots in the first imaging position through reflection of the reflection mirror; next, the other half of the picture information is input to the DMD, and the light beam performs imaging through the same path; only through strict mathematical calculation, the reflection mirror rotates for a proper angle, and the projection picture in the second time is formed in the second position; and the two imaged pictures are seamlessly spliced in the first position and the second position. Therefore, relatively high resolution is obtained while a relatively large imaging area is obtained.
Owner:深圳晗竣雅科技有限公司
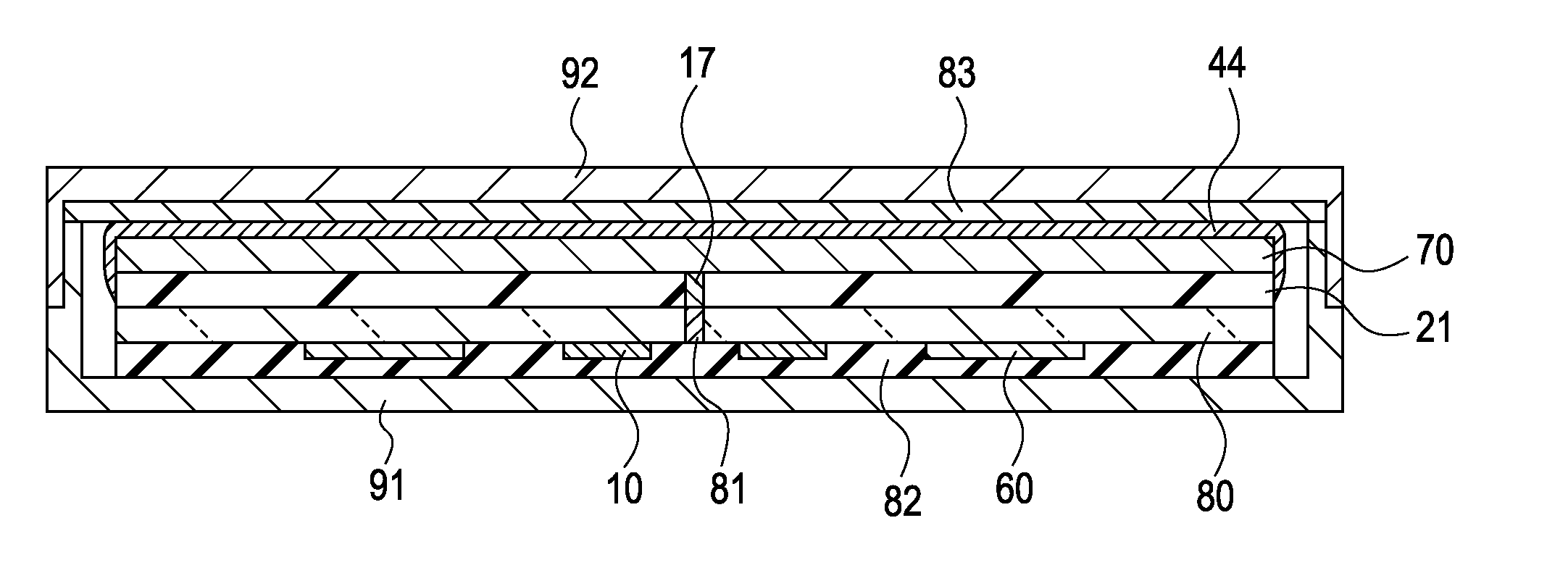
Detector capable of conducting double-sided incidence, detector array, imaging system and imaging method
PendingCN112083468ALarge imaging areaIncrease the imaging area areaRadiation intensity measurementRadiation diagnosticsDetector arrayImage system
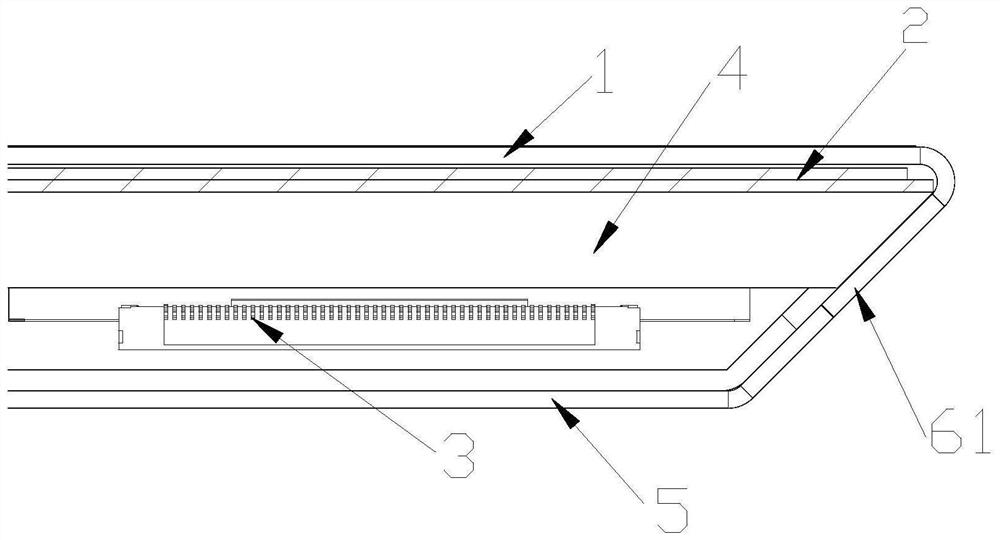
The invention discloses a detector capable of conducting double-sided incidence, a detector array, an imaging system and an imaging method. The detector comprises an upper cover plate, a lower cover plate, and an imaging part, a supporting frame and a circuit board which are arranged between the upper cover plate and the lower cover plate, wherein the supporting frame is used for supporting the imaging part, the circuit board is electrically connected with the imaging part, the imaging part is used for converting a ray signal into a charge signal, and the circuit board is used for converting the charge signal into a digital signal; the upper cover plate, the supporting frame and the lower cover plate are all made of materials capable of allowing rays to penetrate through; and the circuit board is arranged in an edge area inside the detector, and the circuit board is not arranged opposite to a main imaging area of the imaging part. The detector provided by the invention can realize front-side or back-side incident imaging. The invention further provides a technical scheme for realizing cooperative work and seamless splicing imaging of a plurality of detectors in the detector array.
Owner:CARERAY DIGITAL MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Near-eye optical system
ActiveUS20210141230A1Decrease of optical thicknessMitigate issueMechanical apparatusMirrorsLight beamOptic system
A near-eye optical system receiving an image beam including a first optical waveguide is provided. The first optical waveguide expands the image beam in a first direction and includes first and second surfaces, first and second beam-splitting surfaces, and a plurality of first and second reflective inclined surfaces. The first and second beam-splitting surfaces are located in the first optical waveguide and disposed in a tilted manner relative to the first and second surfaces. The first and second beam-splitting surfaces have opposite tilt directions. The first and second beam-splitting surfaces receive an image beam incident from the first surface so that a first portion of the image beam passes through and a second portion of the image beam is reflected. The near-eye optical system further reduces a thickness of the optical waveguide and alleviates the issue that the image beam is not completely projected to the optical waveguide.
Owner:CORETRONIC
Splicable detector array, imaging system and imaging method
PendingCN112147665AIncrease the imaging area areaImprove adaptabilityMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationRadiation intensity measurementFlat panel detectorDetector array
The invention discloses a splicable detector array, an imaging system and an imaging method. The detector array comprises at least two flat panel detectors, wherein each flat panel detector comprisesan upper cover plate, a lower cover plate, an imaging part and a circuit board; the imaging part and the circuit board are arranged between the upper cover plate and the lower cover plate; the circuitboard is electrically connected with the imaging part; the imaging part is used for converting a ray signal into a charge signal; the circuit board converts the charge signal into a digital signal; the first flat panel detector is provided with a first inclined side surface inwards inclining from the upper cover plate to the lower cover plate; the second flat panel detector is provided with a second inclined side surface outwards inclining from the upper cover plate to the lower cover plate; the imaging part of the second flat panel detector is provided with a flexible substrate; the imagingpart of the second flat panel detector extends to the second inclined side surface from the upper cover plate; the two flat panel detectors are spliced in the forward direction; and the imaging partsof the two flat panel detectors are arranged at the splicing part of the two inclined side surfaces in an up-and-down way. The detector array has the advantage that the cooperative work and the seamless splicing imaging of a plurality of detectors are realized.
Owner:CARERAY DIGITAL MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Computational holographic 3D display system and method based on spliced array of spatial light modulators
Owner:杭州辰景光电科技有限公司
Automatic balancing device, tomography equipment and automatic balancing method
PendingCN111528887AIncrease the scanning field of viewLarge imaging areaComputerised tomographsTomographyPhysicsTomography
The invention provides an automatic balancing device, tomography equipment and an automatic balancing method. The automatic balancing device comprises a base, a rotary substrate, a ray emission assembly, a ray detection assembly and two counterweight assemblies, the rotary substrate has a radial direction and a tangential direction perpendicular to the radial direction, the ray emission assembly and the ray detection assemblies are oppositely installed on the rotary substrate in the radial direction, the ray detection assembly can move in the tangential direction, the two counterweight assemblies are symmetrically arranged on the rotary substrate with the radial direction as a symmetric line, and the counterweight assemblies are obliquely arranged relative to the radial direction. The detection assembly has a plurality of scanning view fields in the process of moving along the tangential direction, and a plurality of scanning view fields can be superposed and fused to obtain the overall image information of a scanned object so as to expand the scanning view field of the automatic balancing device and increase the imaging area of the scanned object.
Owner:武汉中科医疗科技工业技术研究院有限公司
Time-resolved extreme-low-light multispectral imaging system and method
ActiveCN102393248BResolve time resolutionSolve the time resolution by using single photon counter line arraySpectrum investigationColor imageData acquisition
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Super-definition large-area-array day and night zoom lens
ActiveCN114355595AReasonable designLarge amount of lightOptical elementsOphthalmologyImaging quality
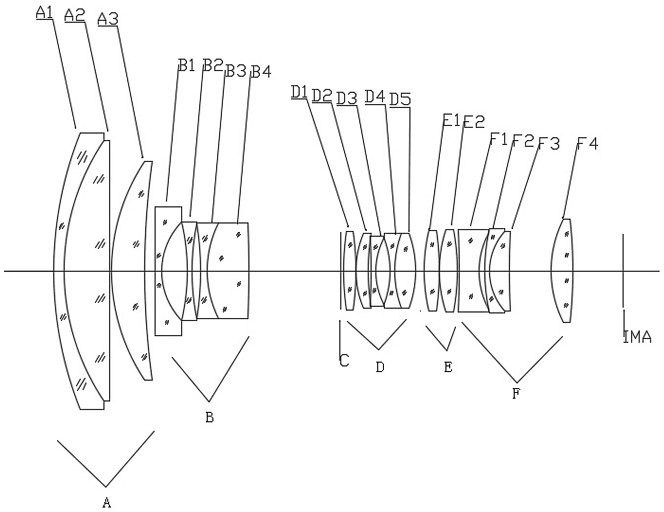
The invention relates to a super-definition large-area-array day and night dual-purpose zoom lens, which comprises a front fixing group, a zoom group, an iris diaphragm, a middle fixing group, a compensation group and a rear fixing group which are arranged along a light incidence direction, and is characterized in that the front fixing group comprises a meniscus negative lens A1, a biconvex positive lens A2 and a meniscus positive lens A3; the zoom group comprises a biconcave negative lens B1, a biconcave negative lens B2, a biconcave negative lens B3 and a biconvex positive lens B4; the middle fixed group D comprises a biconvex positive lens D1, a meniscus positive lens D2, a biconcave negative lens D3, a biconcave negative lens D4 and a biconvex positive lens D5; the compensation group comprises a biconvex positive lens E1 and a biconvex positive lens E2; and the rear fixed group comprises a biconcave negative lens F1, a meniscus negative lens F2, a meniscus positive lens F3 and a biconvex positive lens F4. The lens adopts a five-group zoom structural form, various aberrations of a large-aperture large-image-plane lens can be fully balanced, through reasonable material selection and focal power ratio, the sensitivity of the lens is reduced, the imaging quality of the lens is improved, and the lens has productivity.
Owner:FUJIAN FORECAM OPTICS CO LTD
Object detection method, system and stereoscopic vision system
ActiveCN101571953BLarge imaging areaExpand the scope of detectionTelevision system detailsImage analysisVisual perceptionObject detection
The invention provides an object detection method, a system and a stereoscopic vision system; wherein the method comprises the following steps: determining the diameter of the dispersed spot of a lens; adjusting image distance to a defocusing state according to the diameter of the dispersed spot; adjusting image distance of the lens, increasing imaging area of the object, increasing detection range of the object to facilitate the camera to collect images under the state of dispersed spot; as the dispersed spot facilitates recognition area to rise and pixel to increase, as a result, influence of interfering pixel is reduced, meanwhile, precision of calculated sub-pixel level areal coordinate is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN TAISHAN SPORTS TECH CO LTD
Plant root system fine matrix image online observation system
PendingCN111263040AConvenient researchHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsBatteries circuit arrangementsMicrocontrollerHigh resolution imaging
The invention discloses a plant root system fine matrix image online observation system. The system comprises an image acquisition device, a data acquisition and remote wireless transmission device and a solar power supply device. The image acquisition device comprises a micro-root observation window, a matrix camera module and a handle with scales; the data acquisition and wireless transmission device comprises a microcontroller, a data storage module, a wireless communication module and a power supply management module; a light supplement lamp and a matrix camera module power line in the image acquisition device are connected with the power supply management module; the power supply is supplied by the solar power supply device; and the matrix camera module is connected with the data storage module in the data acquisition and wireless transmission device through a data line. The online observation system further comprises a data cloud platform. The system not only has all the advantages of an existing micro-root canal method, but also has the advantages of being high in resolution, large in imaging area and free of curved surface correction, integrates a wireless transmission module and a field power supply module , and realizes field unattended automatic online observation.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com