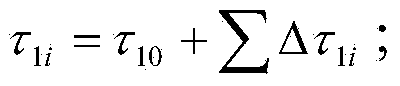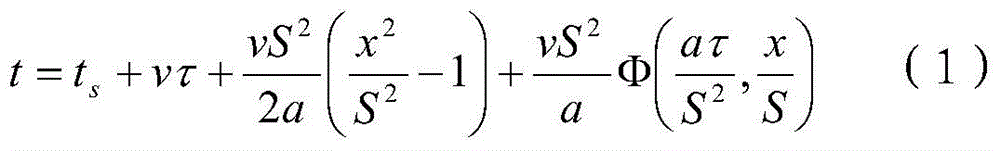Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30results about How to "Achieve practical purposes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
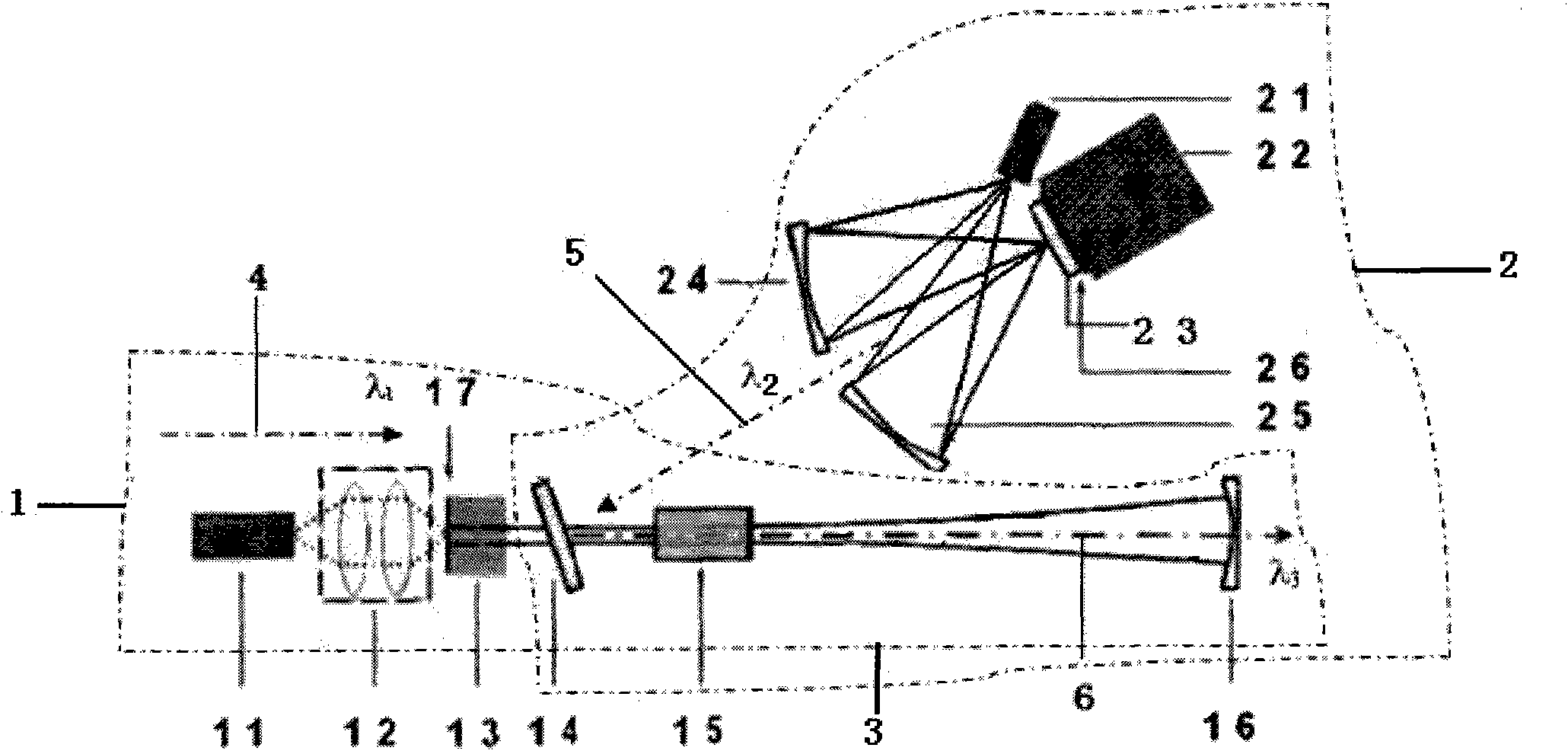
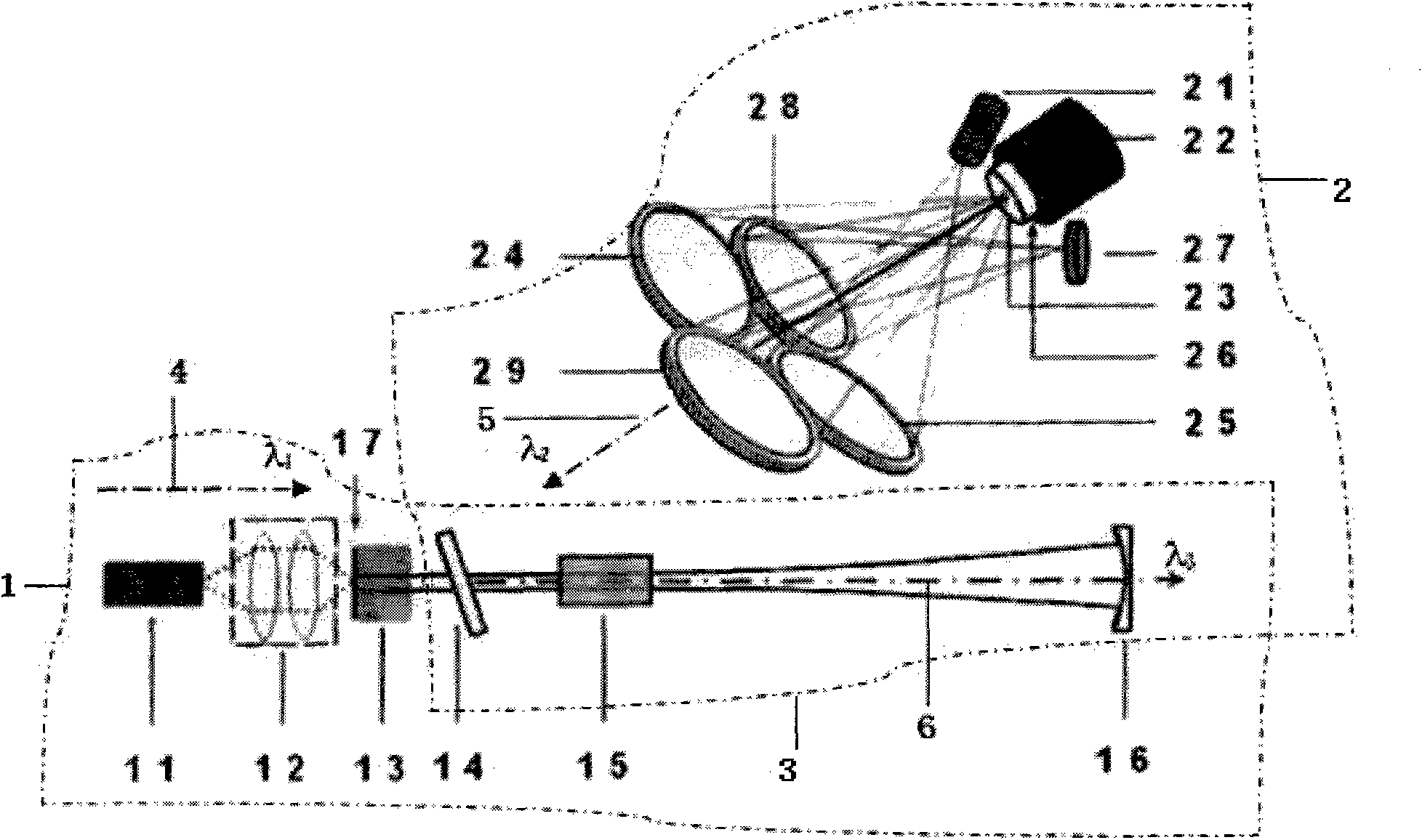
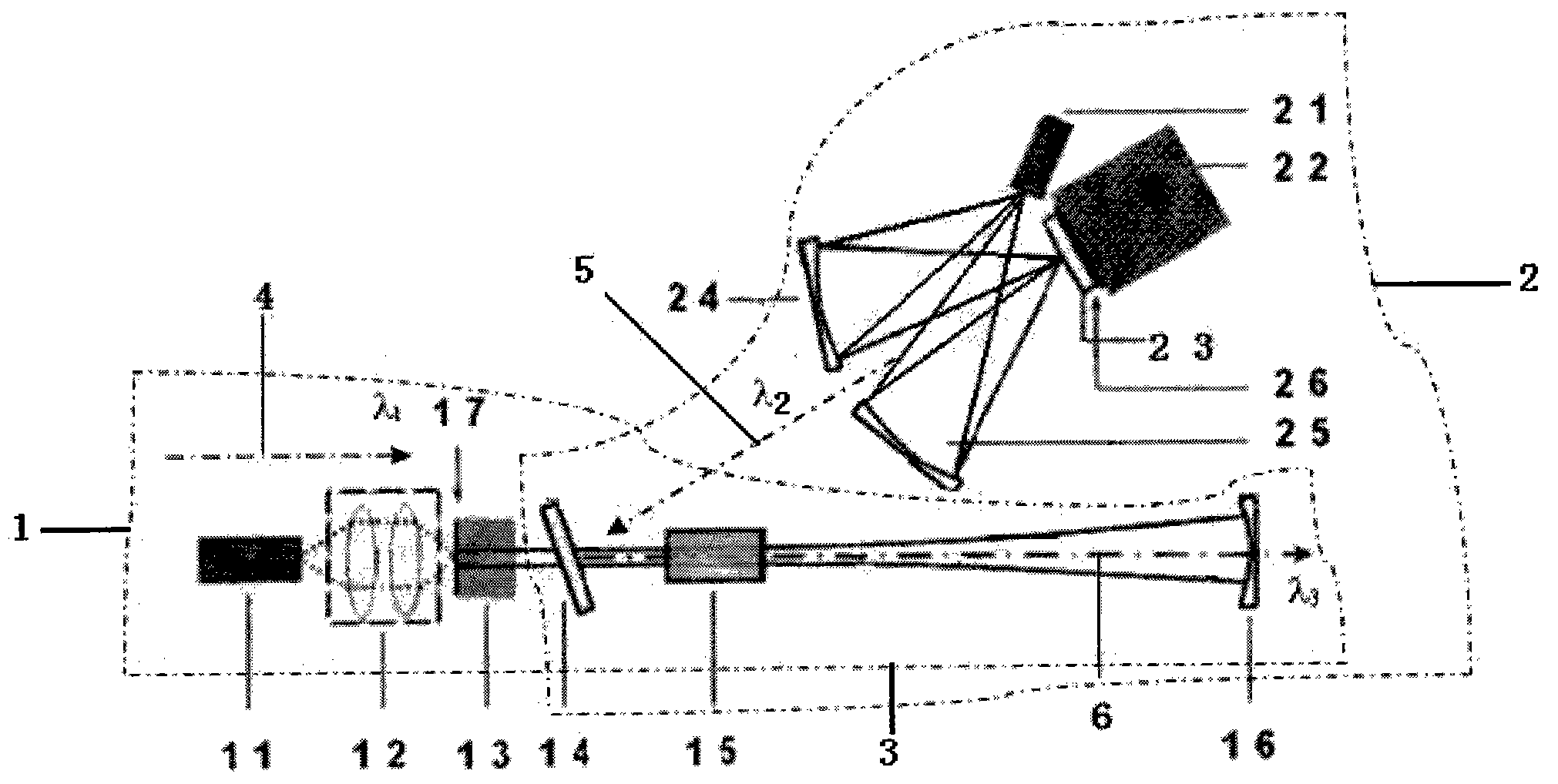
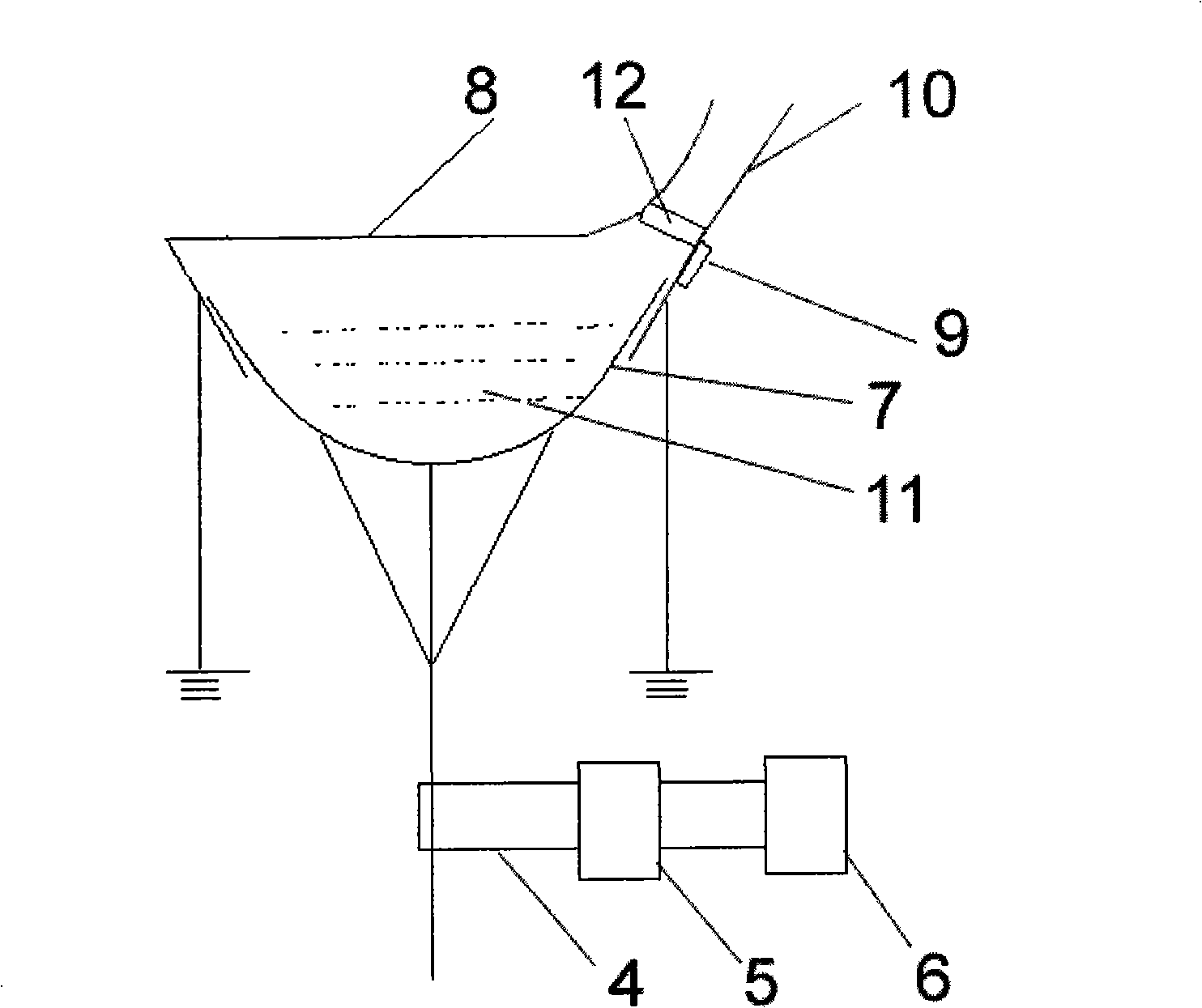
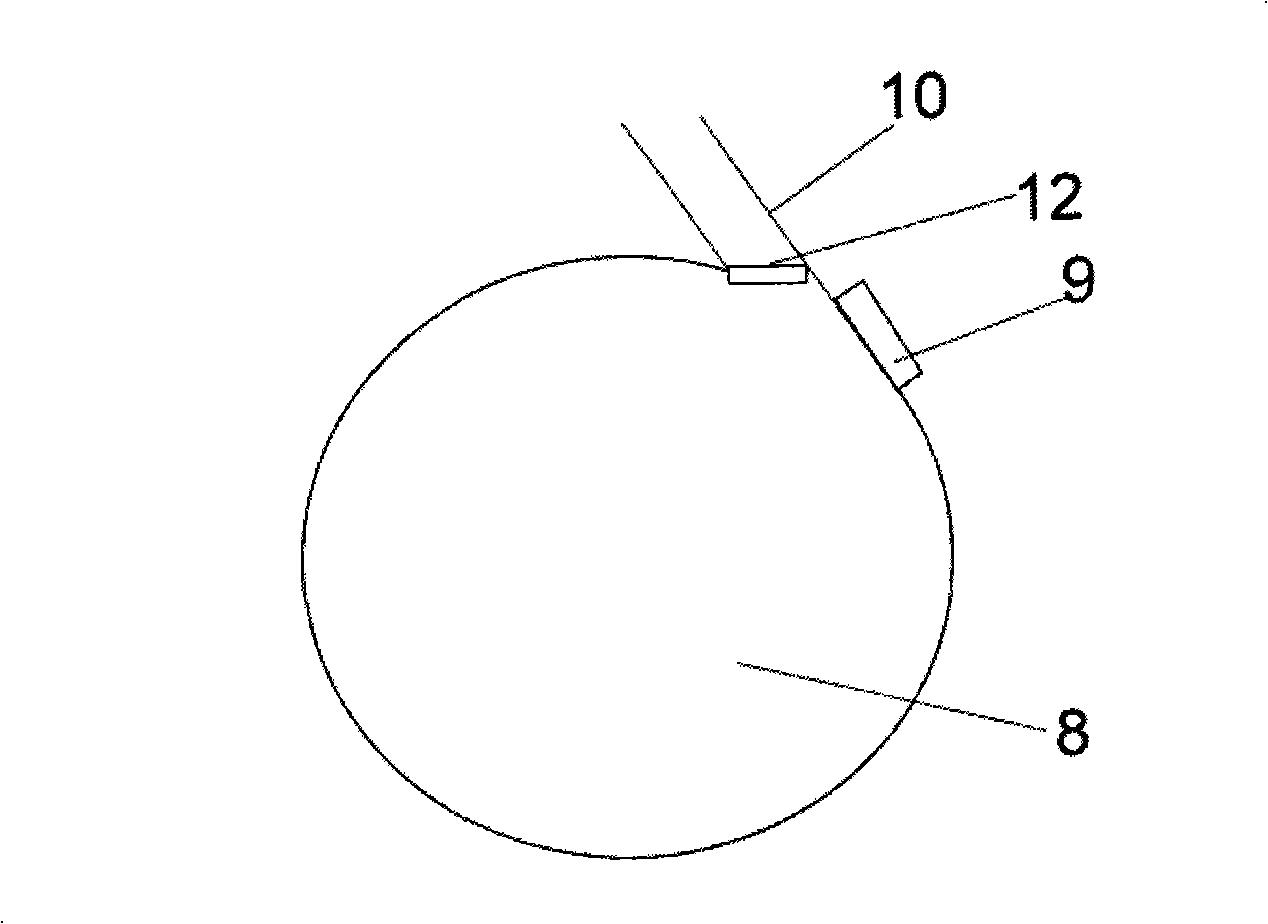
All solid-state medical double resonance intracavity sum frequency yellow light laser
InactiveCN101820132AAchieve practical purposesLaser arrangementsActive medium materialPhysicsLight laser
The invention discloses an all solid-state medical double resonance intracavity sum frequency yellow light laser, comprising a first sub cavity, a second sub cavity and a public cavity shared by the first sub cavity and the second sub cavity; wherein the first sub cavity is used for generating light beam the wavelength of which is lambda1; the second sub cavity is used for generating light beam the wavelength of which is lambda2; and the public cavity is used for polymerizing the light beams the wavelengths of which are lambda1 and lambda2 respectively, then the polymerized light beam is transmitted into the sum frequency crystal of the public cavity, so as to generate light beam the wavelength of which is lambda3, and the light beam the wavelength of which is lambda3 is output from an outputting coupling mirror. The all solid-state yellow light laser of the invention is combined by a slice type structure capable of obtaining 578nm wavelength and intracavity sum frequency, can be used for substituting application of dye laser in the medical field, overcomes the defects of the prior art and achieves the aim of practicability.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH
Emission method and device
InactiveCN101294782AIncrease the distance of the assist phaseSimple structureSling weaponsHigh energyWeapon system
The invention discloses a launching method and a launching device. A method of rotating a rotator is adopted. The launching method is mainly used for launching a carrier aircraft and various spacecrafts; moreover, the launching method can be used for launching various missiles and high-energy weapon systems. The invention manages to overcome the existing problems of various catapults for aircraft carriers based on a novel concept. Meanwhile, compared with an electromagnetic rail gun, the launching device has no need for super-energy launch and manages to solve the power problem which is difficult to overcome for the electromagnetic rail gun, and the power of the launching device far exceeds that of the an electromagnetic rail gun, and creates the future of a novel weapon system.
Owner:孟英志
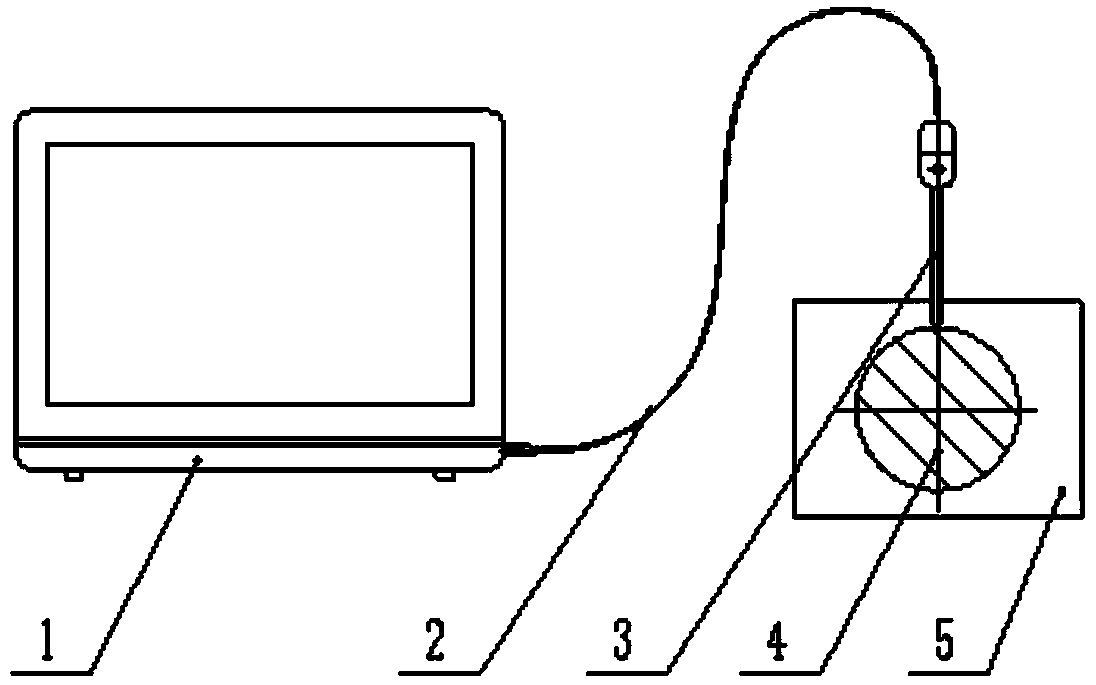
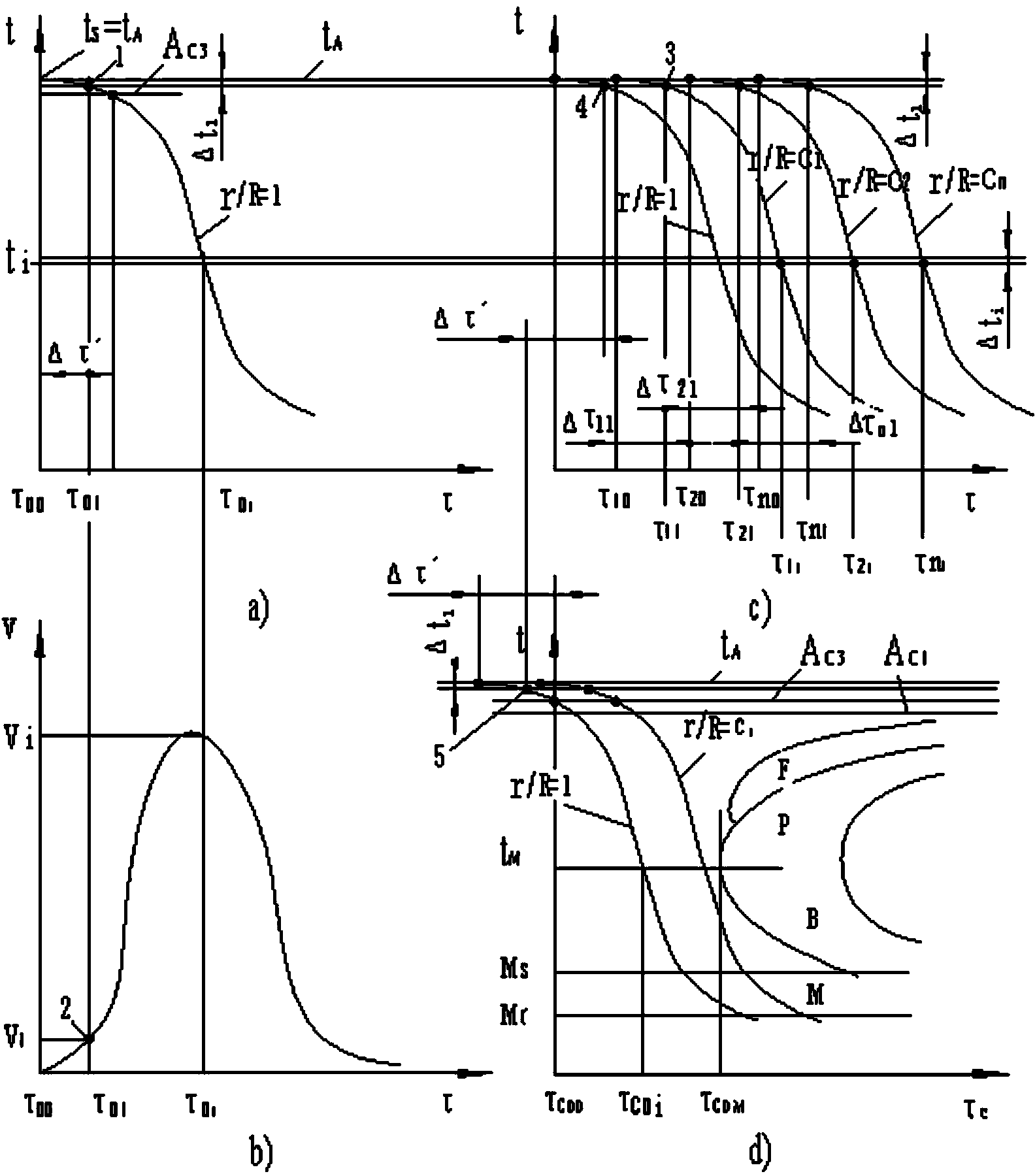
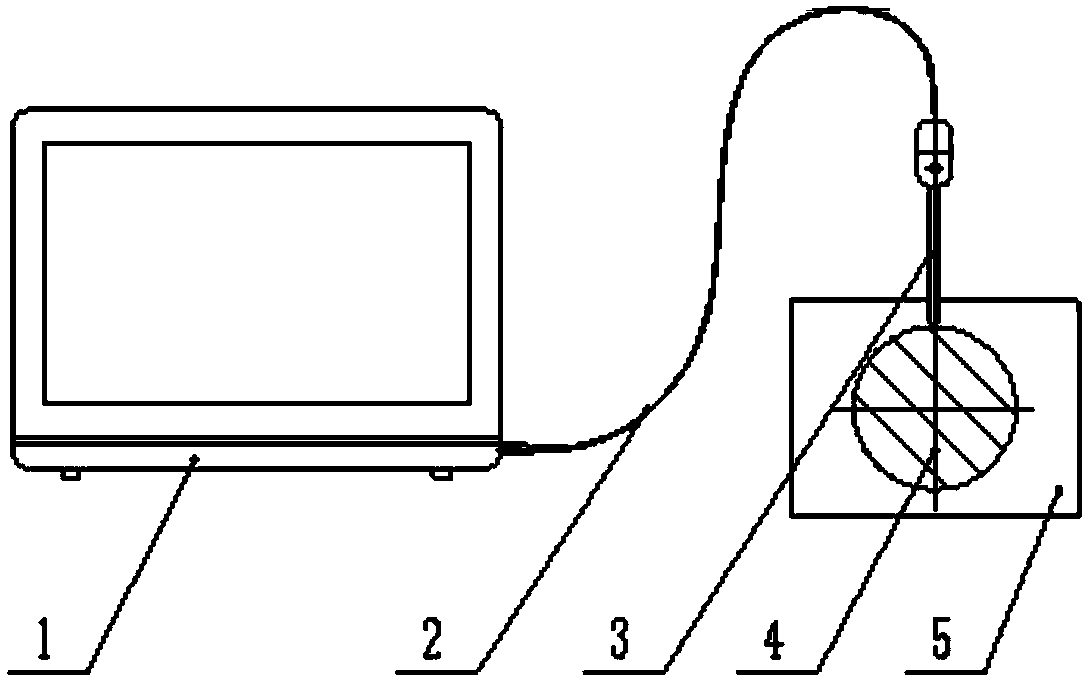
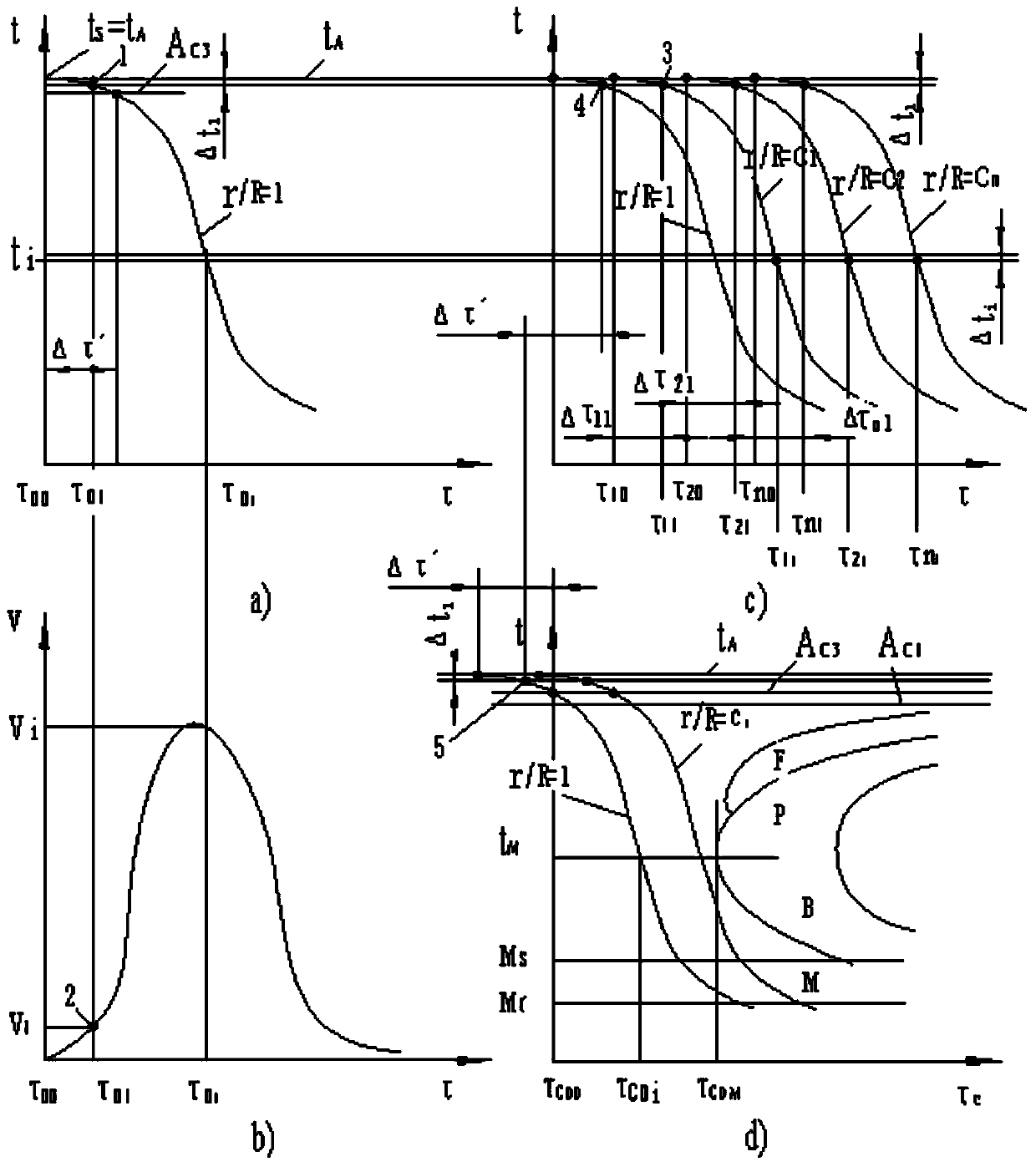
Solid section temperature change measurement system
InactiveCN103413059ASimple calculationNo loss of calculation accuracySpecial data processing applicationsCooling curveEngineering
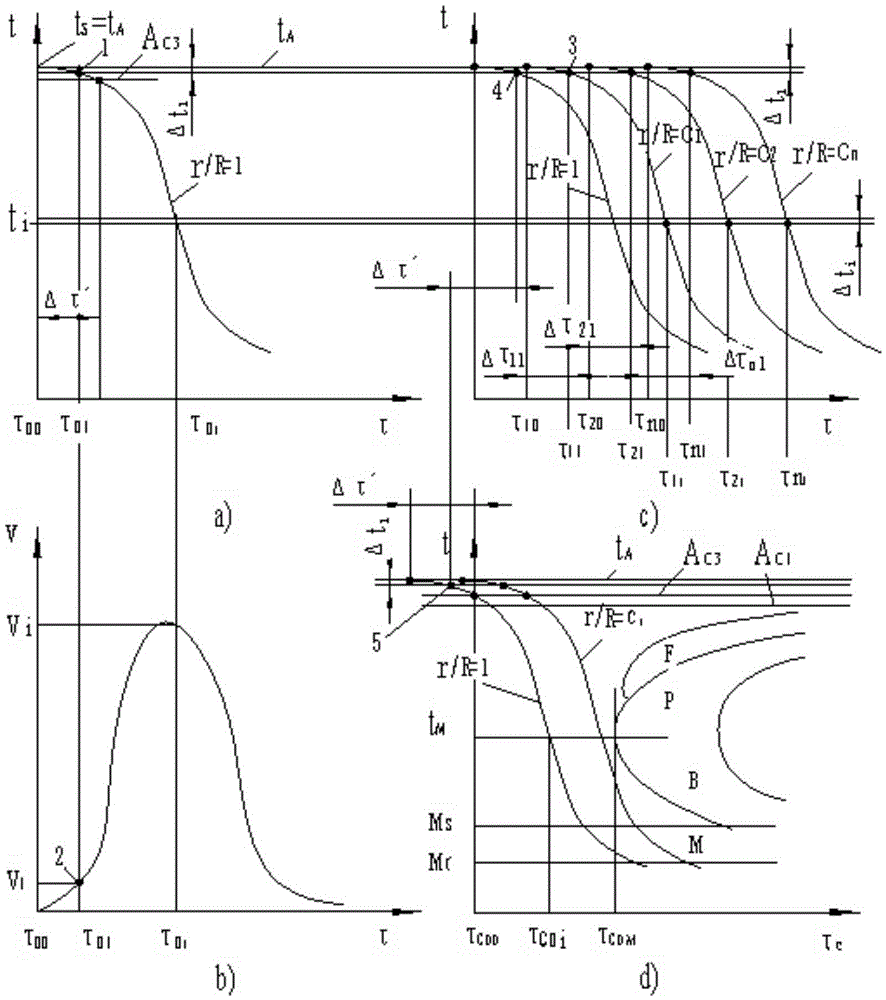
The invention discloses a solid section temperature change measurement system. The solid section temperature change measurement system is characterized by comprising a module for intercepting solid surface temperature and time relations, a data fitting module, a fitting data differential module, a parameter input and calculation module and a CCT (continuous cooling transformation) and TTT (time temperature transformation) curve superposition module. Influences of internal heat sources, quality, physical properties and ingredients of solids on heat transfer are embodied on temperature time curves of the solid surfaces classified according to shape, and different temperature moments form a cooling curve from the measured section center parts of the solids to the random surface positions by measuring surface temperature time curves of to-be-measured objects, obtaining temperature change speeds of the object surfaces and calculating moments with the same temperature as the surfaces from the center parts of the measured solids to the random surface positions. The complex calculation process is simplified while calculation accuracy is not reduced, and the goal of practicality is achieved simultaneously.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
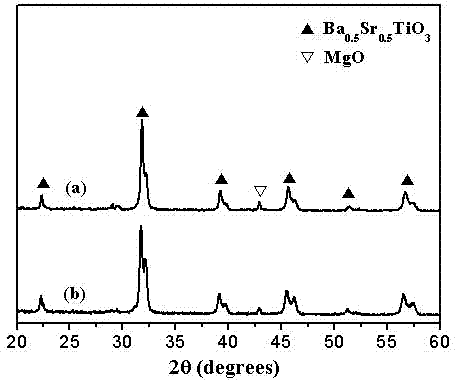
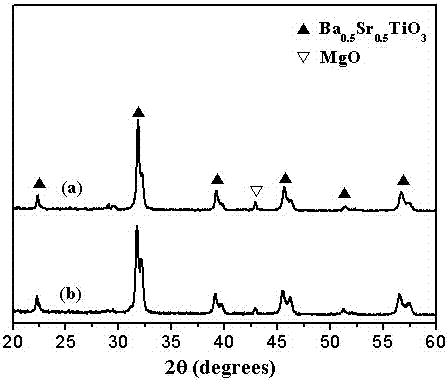
Method for preparing nano barium strontium titanate/magnesium oxide complex-phase powder in situ by coprecipitation
ActiveCN104311003AGood dispersionUniform particle sizeMaterial nanotechnologyAlkaline earth titanatesOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATEStrontium titanate
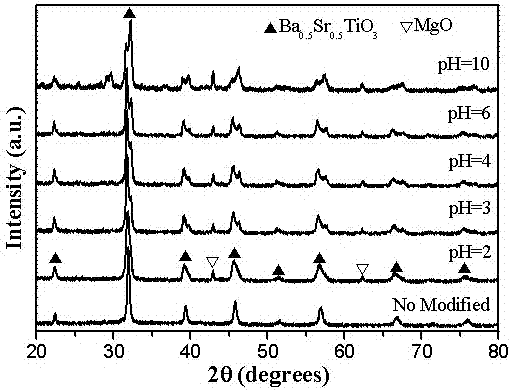
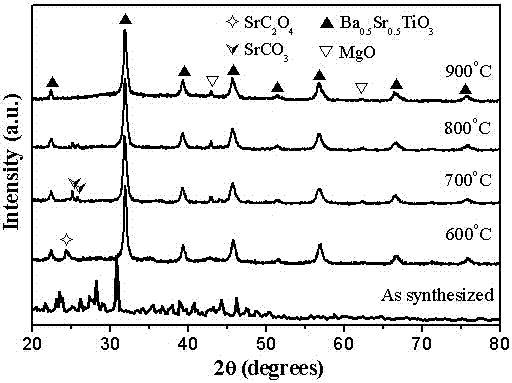
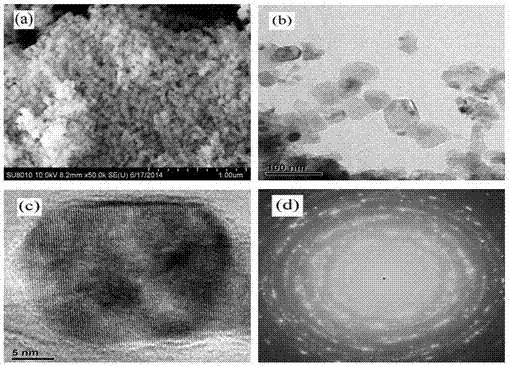
The invention relates to a method for preparing nano (1-x)Ba1-nSrnTiO3-xMgO complex-phase powder in situ by coprecipitation. A preparation flow comprises the following steps: weighing nitrates of barium, strontium and magnesium into water according to an accurate stoichiometric ratio to prepare a solution A; weighing butyl titanate according toan accurate stoichiometric ratio and dissolving into an ethanol-oxalic acid solution to prepare a solution B; slowly dropwise adding ammonia water into a mixed solution of the solution A and the solution B and carrying out a coprecipitation reaction; controlling the pH value of the reaction system to be 2-10; and carrying out filtering, washing, heat treatment and grinding on precipitate to obtain the nano (1-x)Ba1-nSrnTiO3-xMgO complex-phase powder. The preparation process is simple, short in period and low in cost; and the obtained nano complex-phase powder has good dispersity, uniform grain diameter and high degree of crystallization and can be put into practice.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
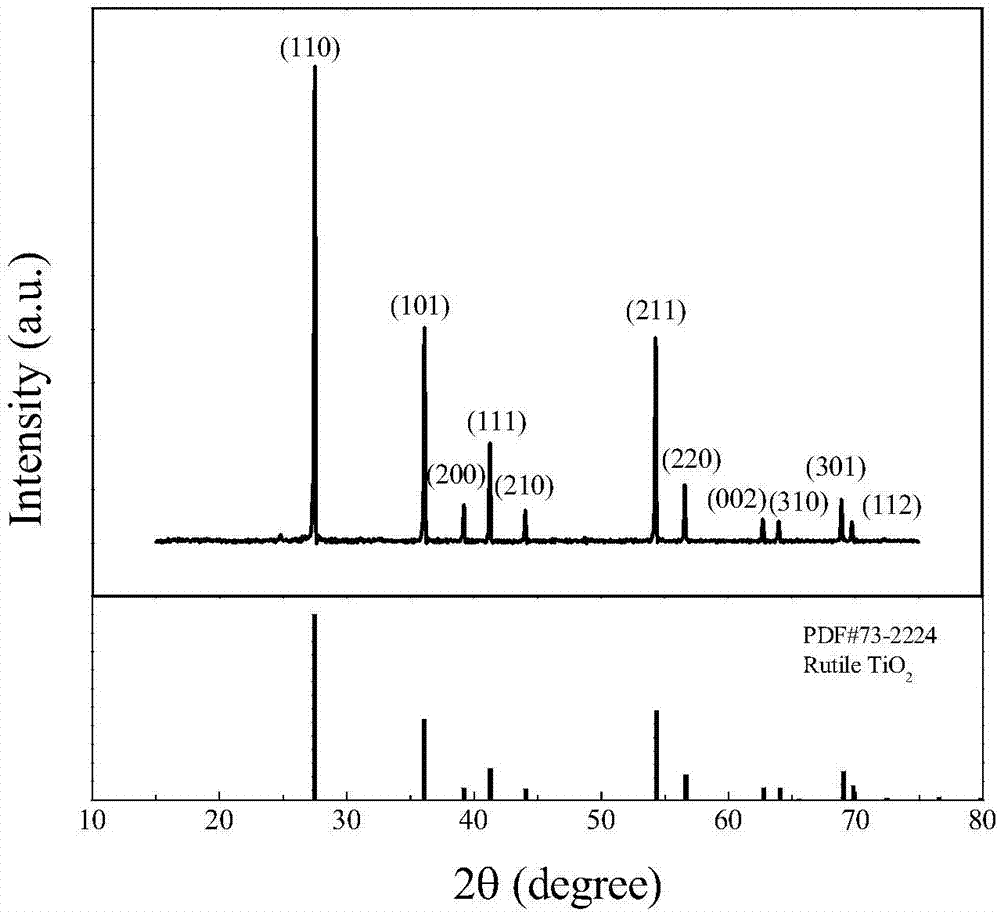
Method for preparing indium niobium co-doped titanium dioxide powder through co-precipitation method
ActiveCN106865612ANarrow particle size distributionRegular shapeTitanium dioxideNiobium compoundsIndiumAlcohol
The invention relates to a method for preparing indium niobium co-doped titanium dioxide powder through a co-precipitation method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a solution, weighting InCl3.4H2O and NbCl and respectively dissolving in absolute ethyl alcohol, thereby obtaining an InCl3 solution and a NbCl5 solution; (2) weighting TiCl4 and dissolving in absolute ethyl alcohol, thereby obtaining a TiCl4 absolute ethyl alcohol solution; (3) dropwise adding the InCl3 solution into the NbCl5 solution, thereby obtaining a mixed solution A; (4) dropwise adding the TiCl4 absolute ethyl alcohol solution into the mixed solution A, thereby obtaining a mixed solution B; (5) using ammonium hydroxide for adjusting pH of the mixed solution B till pH is more than or equal to 11, thereby forming a suspension; (6) performing suction filtration on the suspension, drying the obtained precipitate, grinding and sieving, thereby obtaining precursor powder; (7) roasting the precursor powder prepared in the step (6) at 1100-1200 DEG C, thereby obtaining the indium niobium co-doped titanium dioxide powder.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
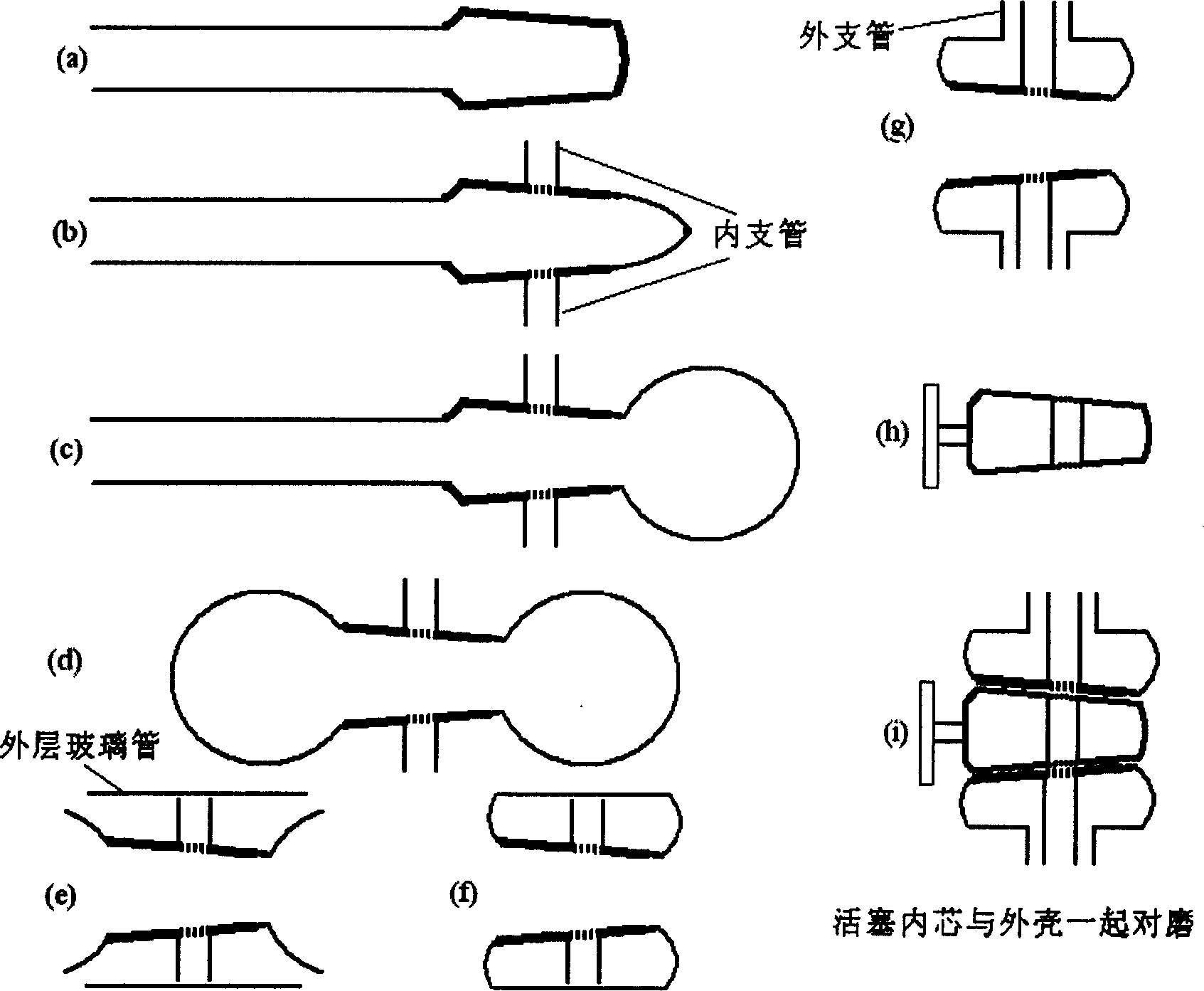
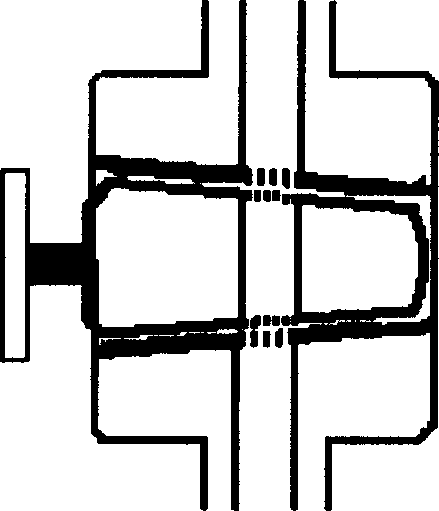
Jacket type glass piston preparation process
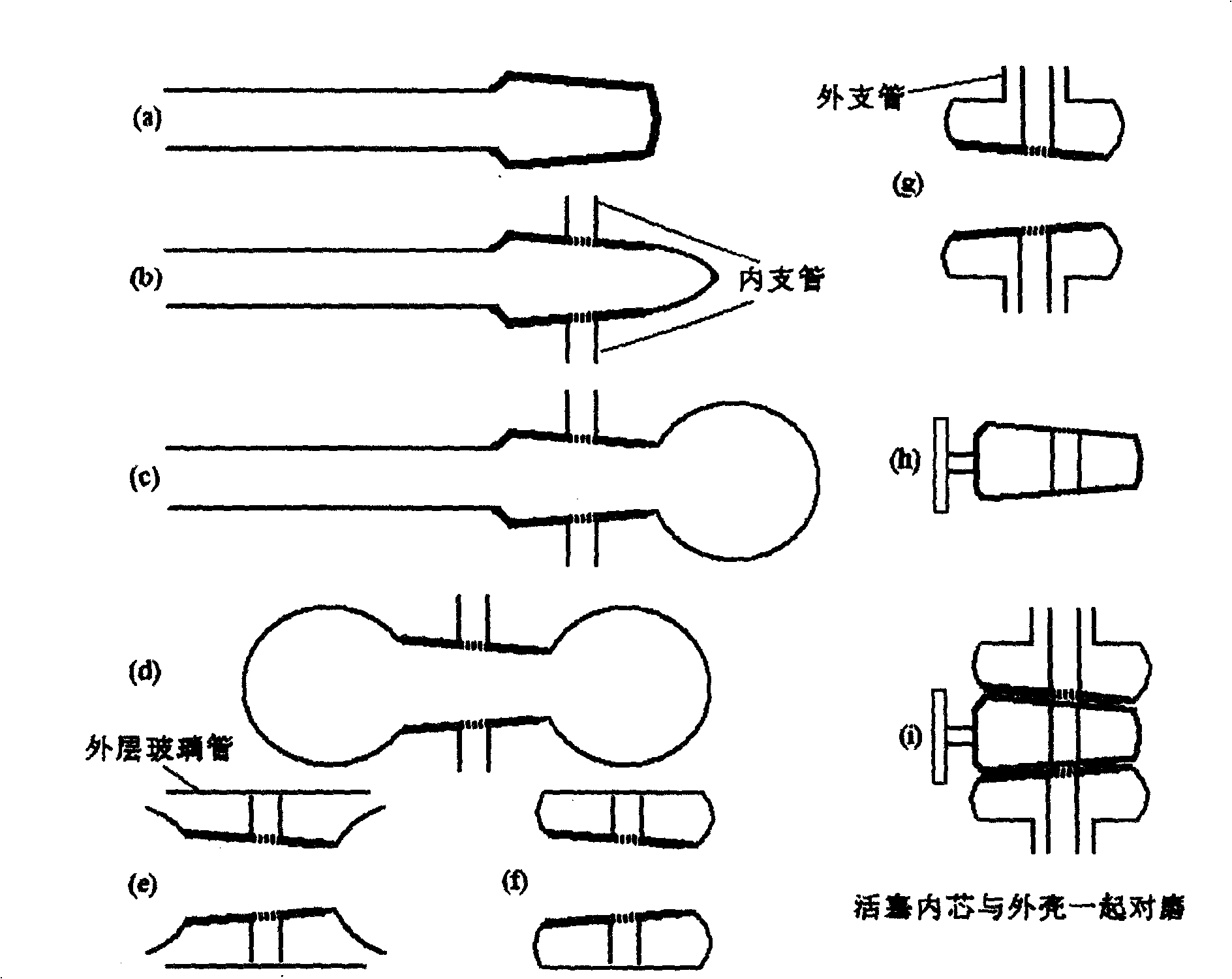
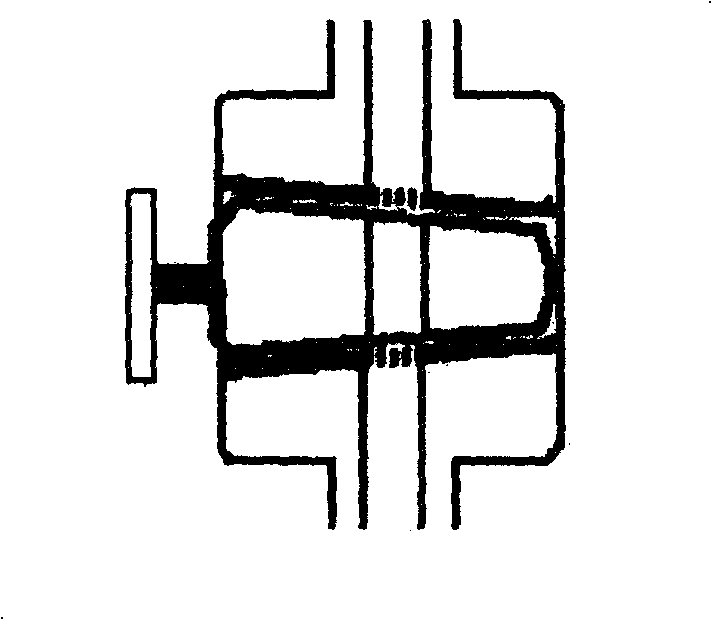
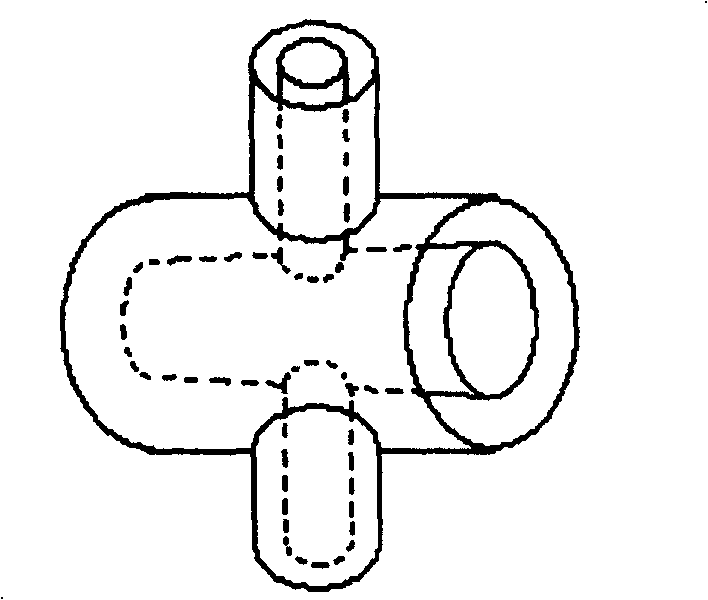
InactiveCN1807296AStress reliefAvoid the pitfalls of contaminating the liquid to be testedGlass blowing apparatusGlass reforming apparatusGlass ballEngineering
The invention relates to a preparation technique for jacket-type glass piston. Wherein, using the blown piston-core shell as the jacket inner layer, fused sealing the broken small end with a glass tube; connecting a glass tube on the shell opening as a inner branch tube, blasting one end of glass tube and the large end into a glass ball; cutting part of the ball on blaze to cover a glass tube as the jacket outer layer; connecting and fused sealing two ends and the necked glass balls on ends of inner layer; connecting a out branch tube on outer glass tube; lengthening the inner branch tube; annealing and grinding the piston inner core and shell. This invention improves precision and reduces cost.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Solid state electrolyte and solid state battery
InactiveCN110098430AGood chemical stabilityAchieve practical purposesSolid electrolytesFinal product manufactureSolid state electrolyteChemical composition
A solid state electrolyte having a garnet type crystal structure is provided. The chemical composition of the solid state electrolyte includes lithium, lanthanum, zirconium, oxygen, and sulfur. The content of sulfur in the solid state electrolyte is between 5 mol % and 35 mol % based on the content of oxygen in the solid state electrolyte. A solid state battery including a positive electrode layer, a negative electrode layer, and a solid state electrolyte layer is also provided. The solid state electrolyte layer is disposed between the positive electrode layer and the negative electrode layer.The solid state electrolyte layer includes the solid state electrolyte.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
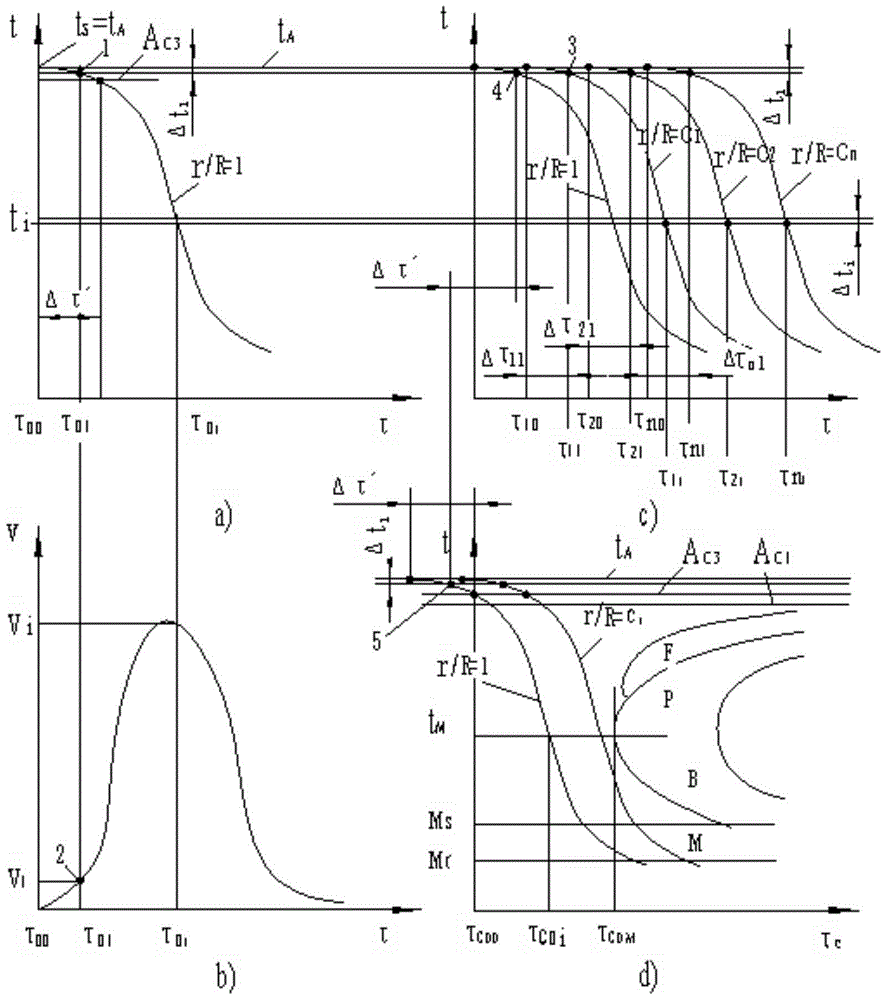
Solid section temperature variation determination method
InactiveCN103439358ASimple calculationReduce calculation precisionMaterial heat developmentCooling curveComputational physics
The invention discloses a solid section temperature variation determination method, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: 1, measuring a change curve of surface temperatures of a solid along with time in a known environment by a determinator, and fitting the measuring curve to a continuous curve to avoid breakpoints during measuring; 2, carrying out differentiation on the fitted measuring curve to obtain a cooling velocity curve; 3, calculating a temperature-time curve of a random location of the measured section of the solid; 4, calculating the start point of a cooling curve of the random location on the measured section; 5, calculating all points at the temperature interval delta ti; 6, superposing overcooling austenite continuous isothermal cooling transition curves of steel and iron materials; and 7, calculating the depth of a through hardening layer. The solid section temperature variation determination method simplifies a complex calculation process without reducing the calculation accuracy, and achieves the purpose of practicability.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
Surfactant assisted in situ co-precipitation method for preparing core-shell structure nano powder
The invention discloses a surfactant assisted in situ co-precipitation method for preparing a core-shell structure nano powder. The preparation process is as follows: weighing nitrate of strontium, barium and magnesium according to the precise stoichiometric ratio, and dissolving the three in water to prepare a solution A; weighing butyl titanate according to precise stoichiometric ratio and dissolving the butyl titanate in an ethanol-oxalic acid solution to prepare a solution B; weighing a certain amount of a surfactant and dissolving the surfactant in hot water-alcohol to prepare a solution C; slowly dropwise adding ammonia into a mixed solution of A, B and C for a co-precipitation reaction; controlling the pH value of the reaction system at 2; and subjecting the precipitate to filtering, washing, heat treatment and grinding to obtain a Ba1-nSrnTiO3 @ MgO core-shell structure nano powder with high degree of crystallinity. The invention has the advantages of simple preparation process, short cycle and low cost, and the obtained nano composite powder has good dispersibility, uniform particle size, high degree of crystallinity and coating structure, so as to meet the purpose of practicality.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
A method for preparing indium-niobium co-doped titanium dioxide powder by co-precipitation
ActiveCN106865612BNarrow particle size distributionRegular shapeTitanium dioxideNiobium compoundsIndiumAlcohol
The invention relates to a method for preparing indium niobium co-doped titanium dioxide powder through a co-precipitation method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a solution, weighting InCl3.4H2O and NbCl and respectively dissolving in absolute ethyl alcohol, thereby obtaining an InCl3 solution and a NbCl5 solution; (2) weighting TiCl4 and dissolving in absolute ethyl alcohol, thereby obtaining a TiCl4 absolute ethyl alcohol solution; (3) dropwise adding the InCl3 solution into the NbCl5 solution, thereby obtaining a mixed solution A; (4) dropwise adding the TiCl4 absolute ethyl alcohol solution into the mixed solution A, thereby obtaining a mixed solution B; (5) using ammonium hydroxide for adjusting pH of the mixed solution B till pH is more than or equal to 11, thereby forming a suspension; (6) performing suction filtration on the suspension, drying the obtained precipitate, grinding and sieving, thereby obtaining precursor powder; (7) roasting the precursor powder prepared in the step (6) at 1100-1200 DEG C, thereby obtaining the indium niobium co-doped titanium dioxide powder.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
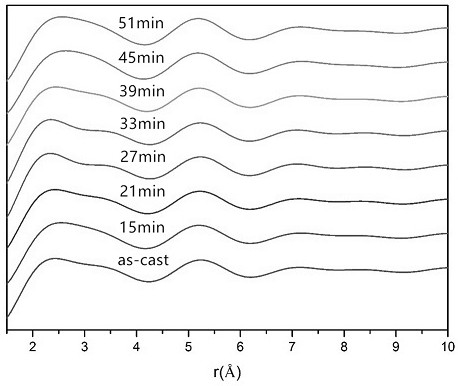
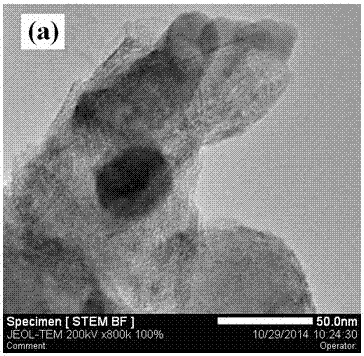
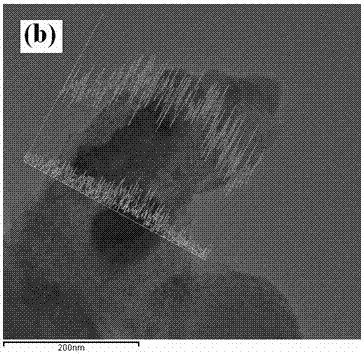
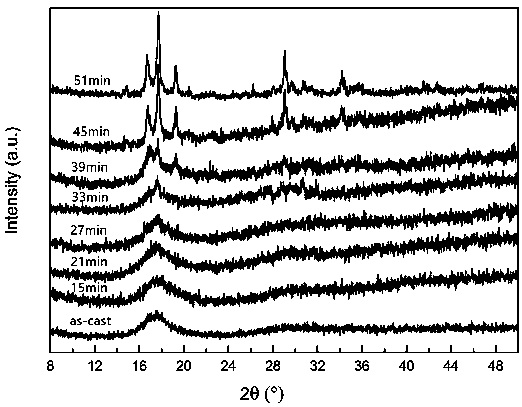
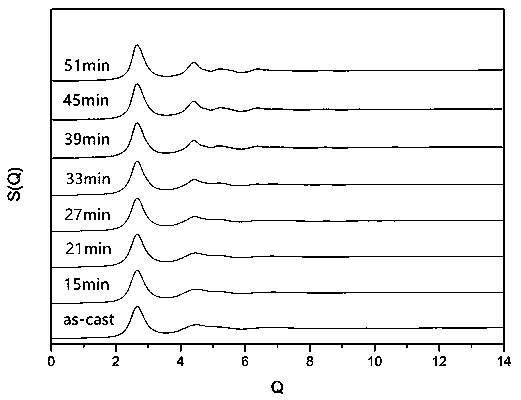
In situ exafs characterization method for crystallization kinetics of amorphous alloys
ActiveCN110702711BAccurate analysisAccurate dynamic characteristicsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationCrystallization kineticsAmorphism
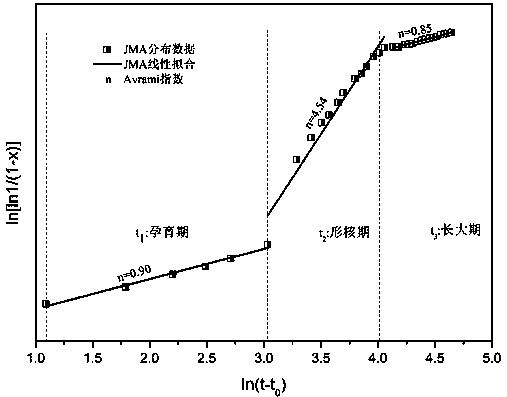
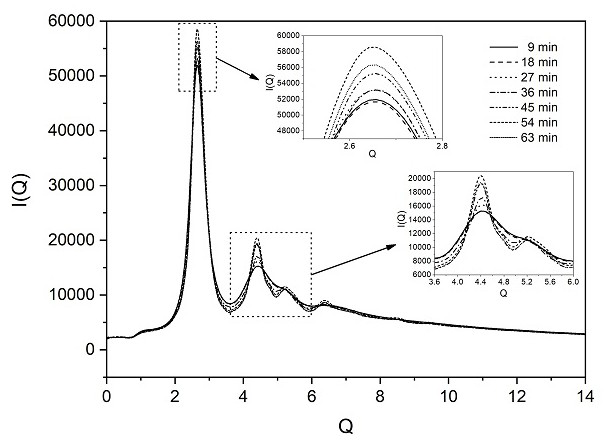
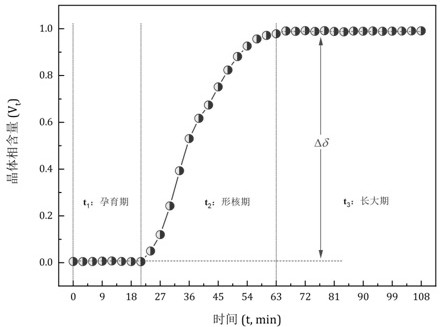
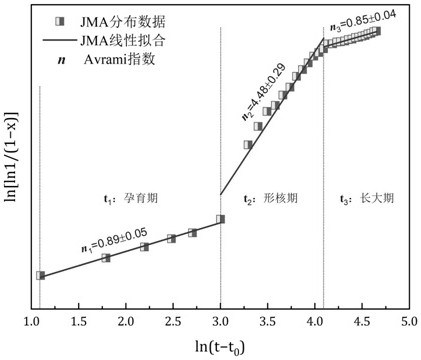
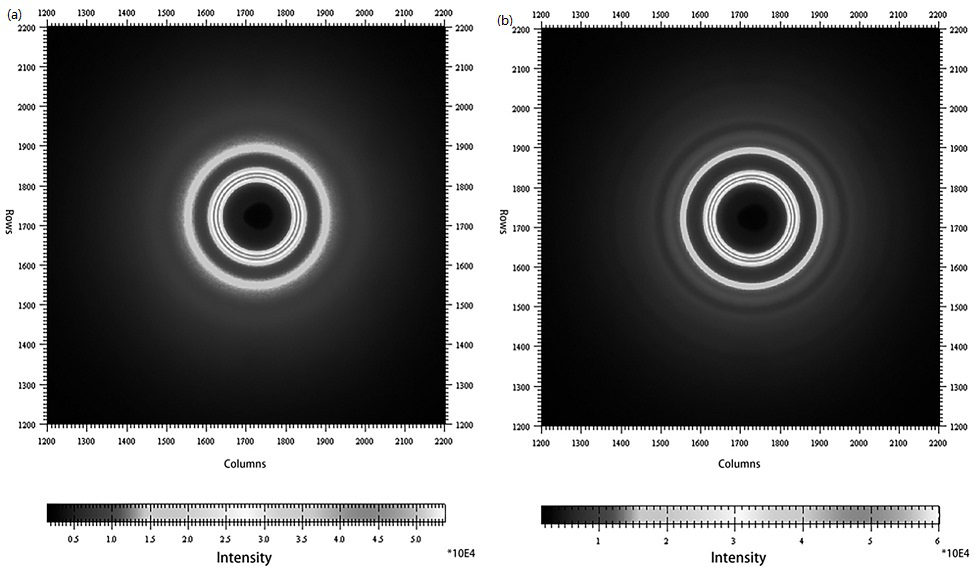
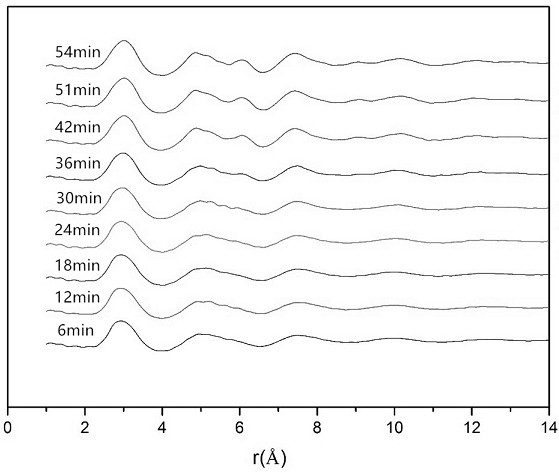
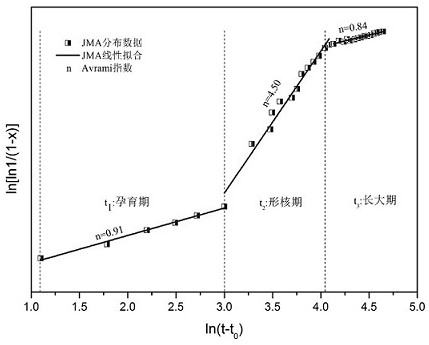
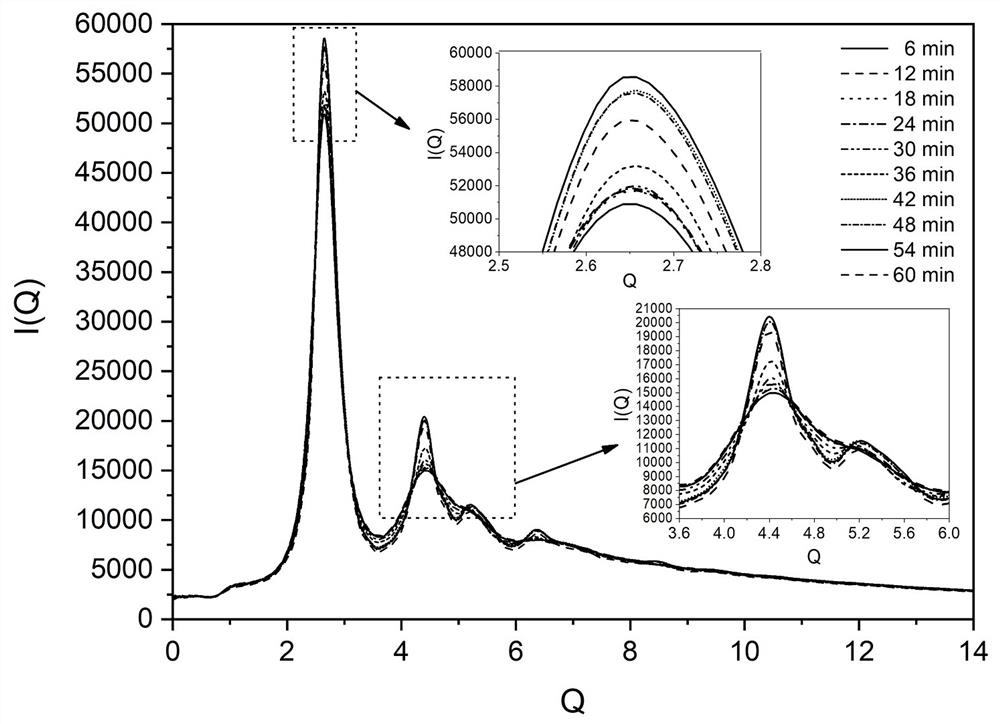
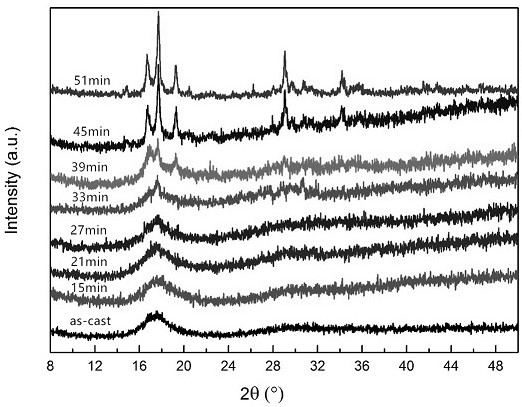
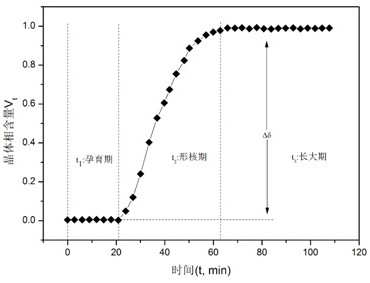
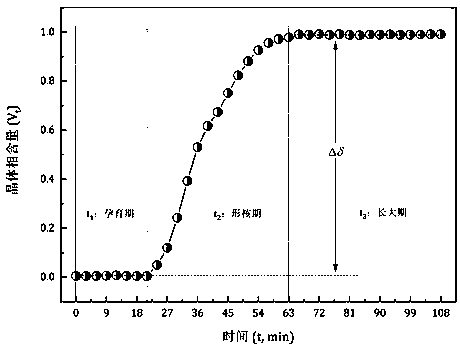
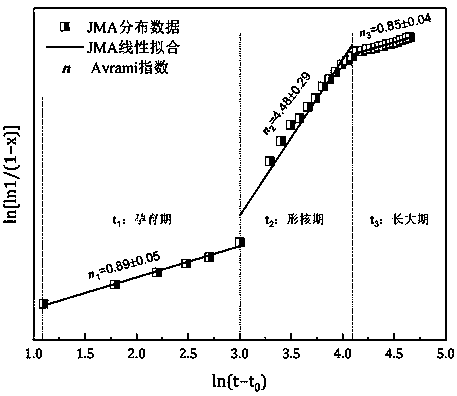
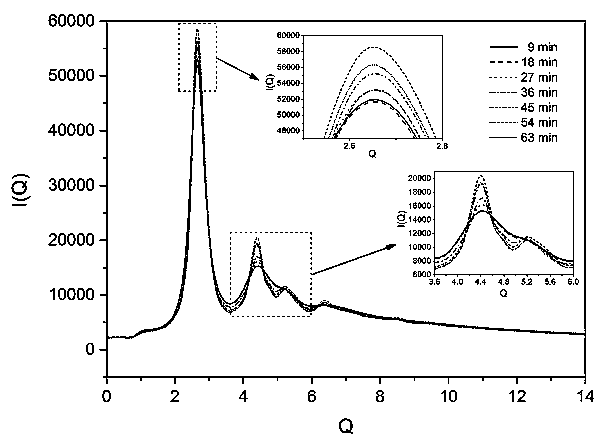
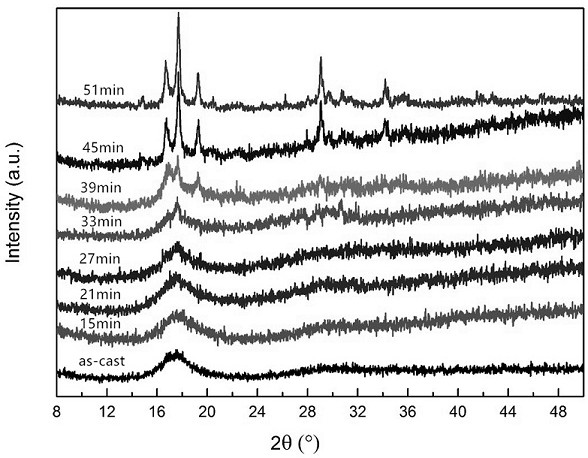
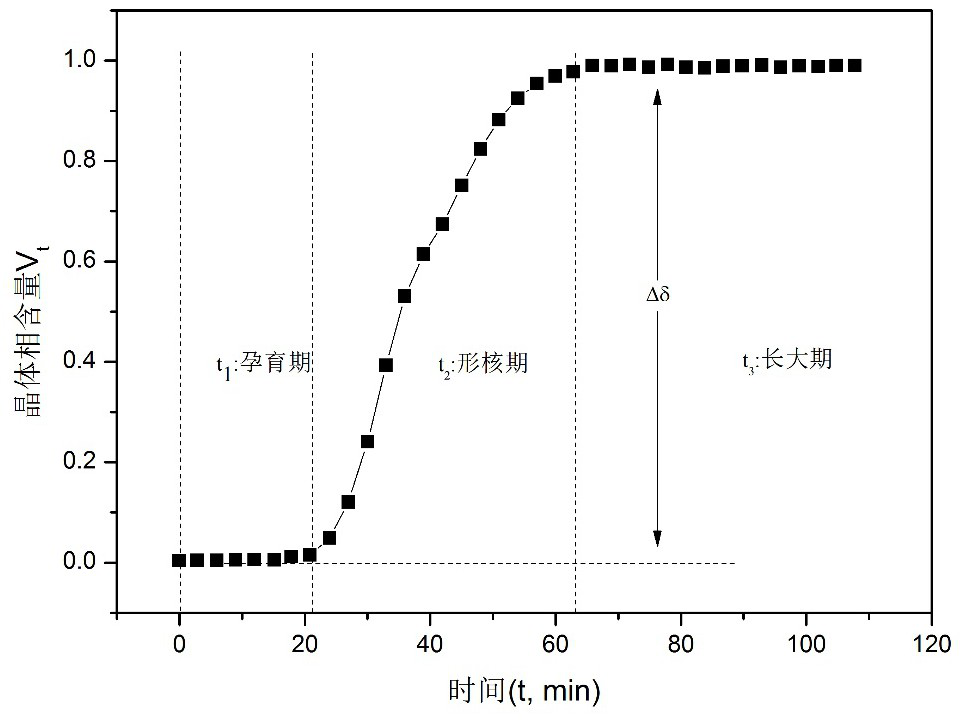
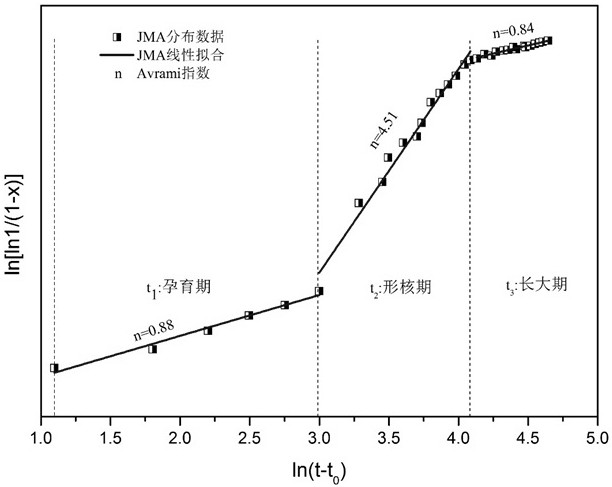
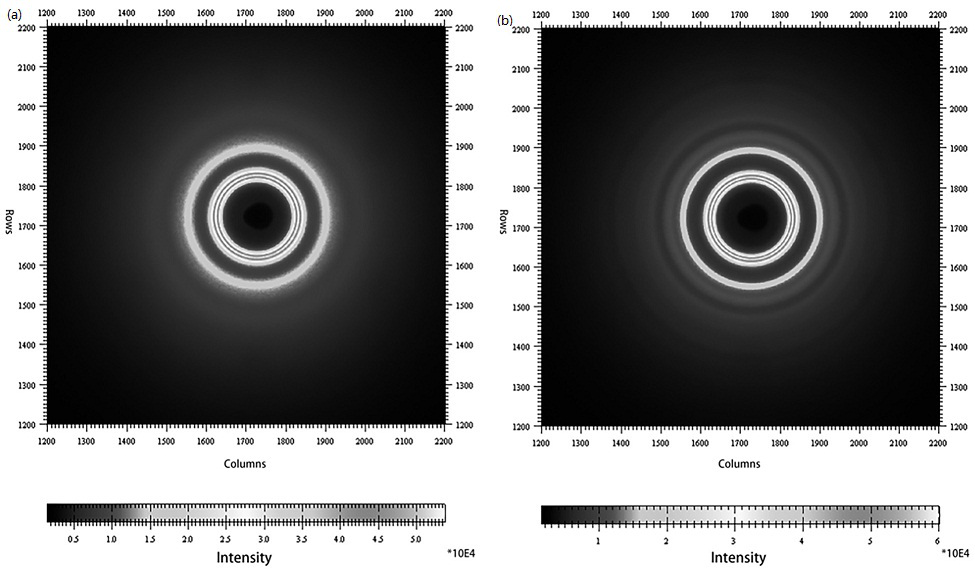
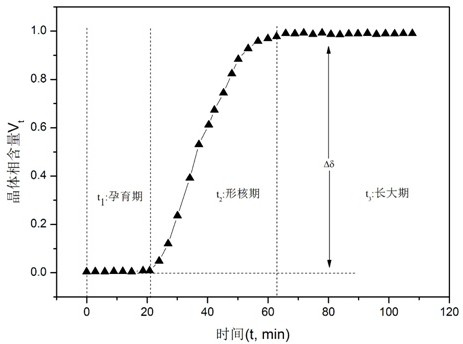
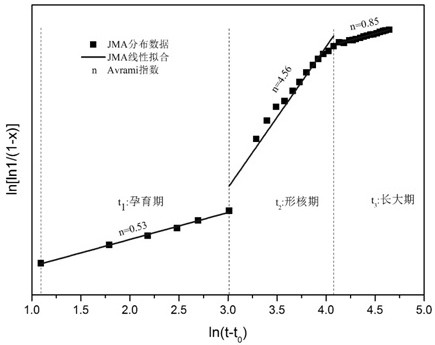
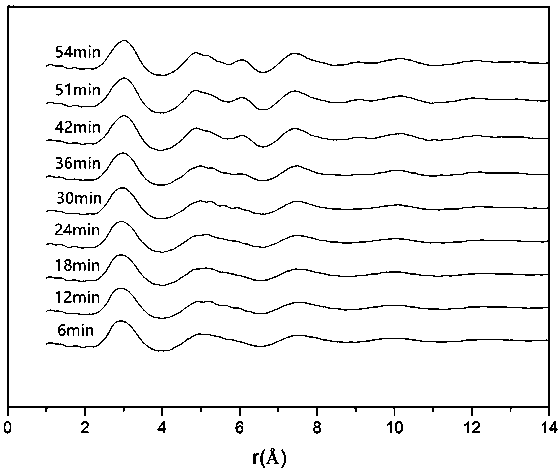
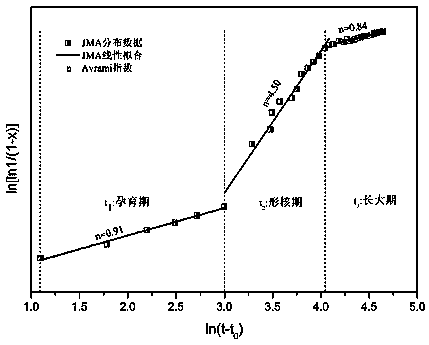
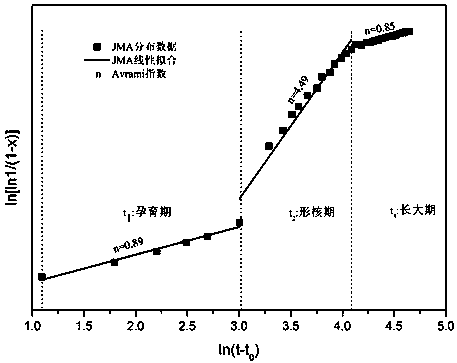
An in-situ EXAFS characterization method for the crystallization kinetics of amorphous alloys belongs to the field of nanocrystalline material preparation technology. It uses Fourier transform and structural function derivation, and uses a specific JMA equation for segmental fitting to analyze crystals. Kinetics, making the analysis more accurate and reliable.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
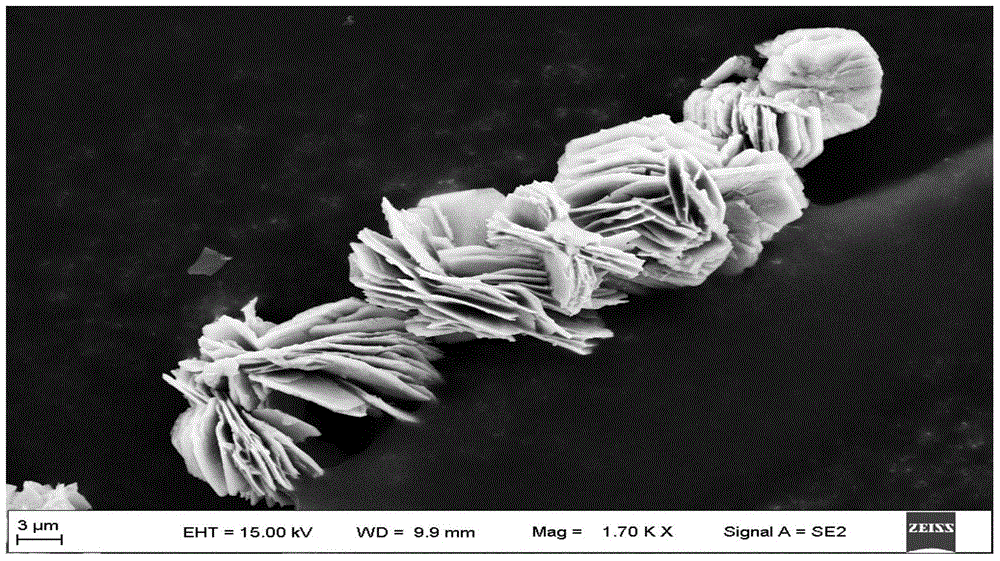
Synthesis method of copper-rare earth nano petal-shaped metal oxide
InactiveCN104108737BAchieve hybridAvoid mismatchMaterial nanotechnologyCopper compoundsRare earthMixed materials
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing copper-rare earth nanometer petal-shaped metal oxides, which comprises: weighing copper and rare earth soluble salt compounds in deionized water according to a molar ratio of 0.3 to 2:1, and dissolving them in deionized water at 0 to 90 Stir at ℃ for 10-90 minutes; add coordination solvent, continue to stir, and let the solution stand for 30-120 minutes to obtain an acidic precursor; add a neutralizing precipitant to the acidic precursor solution to make the solution If stratification occurs, add the coordination solvent again, and repeat the operation from the beginning of stirring to the end of standing until the solution appears stratified; After 3-5 hours, a metal oxide material with a petal-like lamellar structure is obtained. The invention realizes the mixing of materials at the atomic size, and can accurately control the atomic ratio; after low-temperature sintering, a copper-rare earth nano-petal-like sheet structure with high purity and uniform sheets composed of nanoparticles is prepared.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
Surfactant-assisted in-situ co-precipitation method for preparing nano-powder with core-shell structure
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
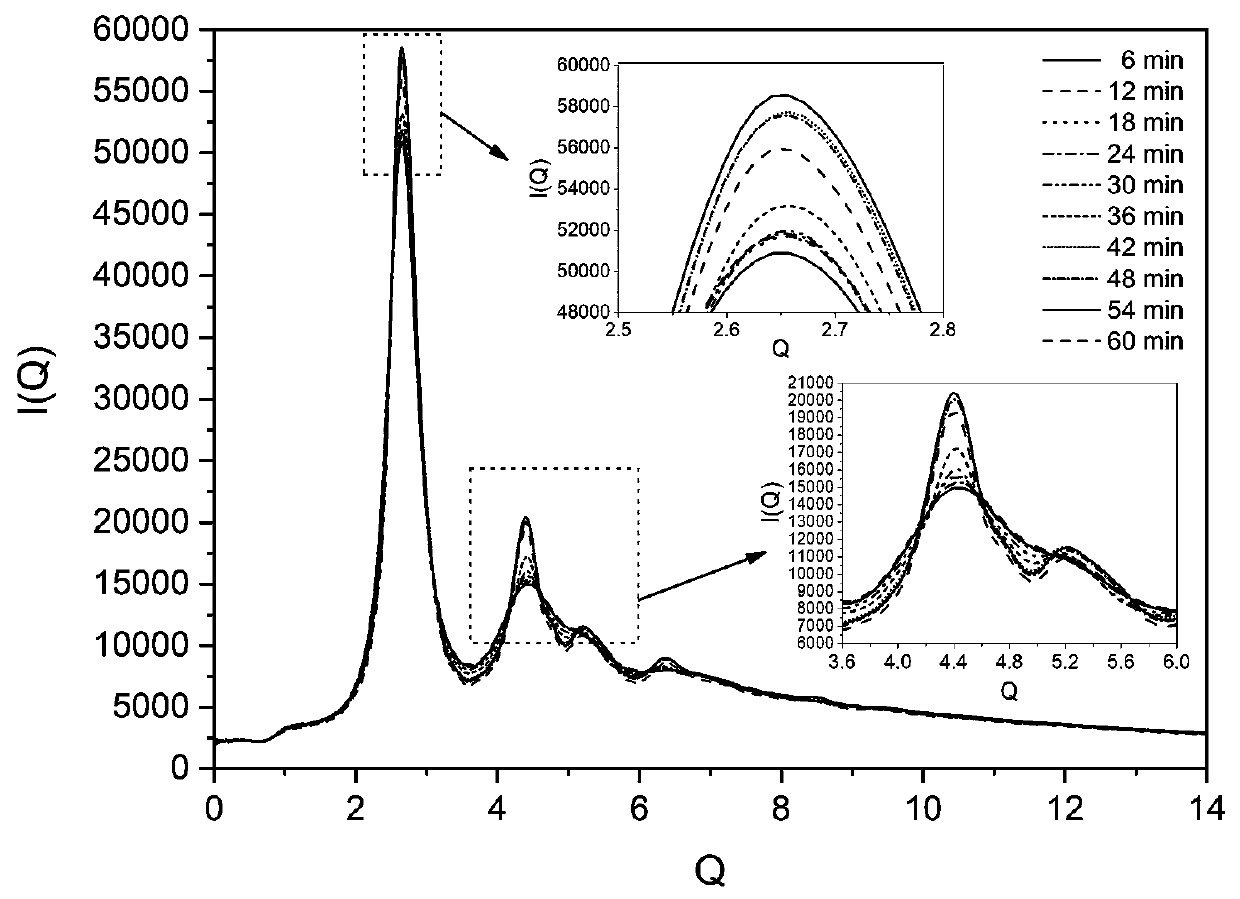
Method for characterizing amorphous-crystal transformation kinetic characteristics by using high-energy X-rays
ActiveCN110793988AAccurate analysisAccurate measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial heat developmentChemical physicsRay
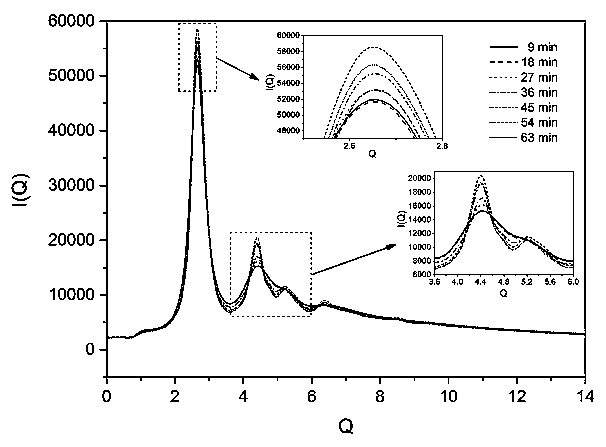
The invention, which belongs to the technical field of nanocrystalline alloy preparation, relates to a method for characterizing amorphous-crystal transformation kinetic characteristics by using high-energy X-rays. Fourier transform and structural function derivation are carried out on diffraction data to obtain distribution data of atoms in a matrix under different time conditions; segmented fitting is carried out by using a specific JMA equation to obtain an Avrami index; and then amorphous-crystal transformation kinetic analysis is carried out according to the Avrami index. Therefore, the analysis method is simpler, more convenient and more accurate.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
Jacket type glass piston preparation process
InactiveCN100427416CStress reliefAvoid the pitfalls of contaminating the liquid to be testedGlass blowing apparatusGlass reforming apparatusGlass ballEngineering
The invention relates to a preparation technique for jacket-type glass piston. Wherein, using the blown piston-core shell as the jacket inner layer, fused sealing the broken small end with a glass tube; connecting a glass tube on the shell opening as a inner branch tube, blasting one end of glass tube and the large end into a glass ball; cutting part of the ball on blaze to cover a glass tube as the jacket outer layer; connecting and fused sealing two ends and the necked glass balls on ends of inner layer; connecting a out branch tube on outer glass tube; lengthening the inner branch tube; annealing and grinding the piston inner core and shell. This invention improves precision and reduces cost.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Synchrotron Radiation In Situ Measurement of Kinetic Curves of Metallic Glass Ordering Process
ActiveCN110793983BAccurate analysisAccurate measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial heat developmentChemical physicsPhysical chemistry
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
A method for measuring temperature change of solid cross-section
InactiveCN103439358BSimple calculationNo loss of calculation accuracyMaterial heat developmentCooling curveComputational physics
The invention discloses a solid section temperature variation determination method, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: 1, measuring a change curve of surface temperatures of a solid along with time in a known environment by a determinator, and fitting the measuring curve to a continuous curve to avoid breakpoints during measuring; 2, carrying out differentiation on the fitted measuring curve to obtain a cooling velocity curve; 3, calculating a temperature-time curve of a random location of the measured section of the solid; 4, calculating the start point of a cooling curve of the random location on the measured section; 5, calculating all points at the temperature interval delta ti; 6, superposing overcooling austenite continuous isothermal cooling transition curves of steel and iron materials; and 7, calculating the depth of a through hardening layer. The solid section temperature variation determination method simplifies a complex calculation process without reducing the calculation accuracy, and achieves the purpose of practicability.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
Neutron Diffraction Characterization of Crystallization Kinetic Properties of Bulk Amorphous Alloys
ActiveCN110793990BAccurate measurementDetermination is accurate and reliableMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial heat developmentCrystallization kineticsParticle physics
The neutron diffraction characterization method for the crystallization kinetics of bulk amorphous alloys, through Fourier transform and structure function derivation of the diffraction data, obtains the distribution data of atoms in nanocrystals under different time conditions, and uses specific JMA equations Segmented fitting, based on which the crystallization kinetics analysis was carried out. The present invention starts from the most fundamental atomic structure, accurately and reliably measures and analyzes the kinetic characteristics of nanocrystal formation, and achieves the purpose of practical application.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
An In Situ Synchrotron Radiation Characterization Method for Crystallization Kinetics of Amorphous Alloys
ActiveCN110749573BAccurate analysisAccurate dynamic characteristicsScattering properties measurementsCrystallographyAmorphism
An in-situ synchrotron radiation characterization method for the crystallization kinetics of amorphous alloys belongs to the technical field of nanocrystalline material preparation. Starting from the most fundamental atomic structure, the nanocrystalline formation process is combined with macroscopic production and preparation conditions, so that The analysis is more accurate and reliable.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
A Method for Characterizing Amorphous-Crystal Transition Dynamics Using High Energy X-rays
ActiveCN110793988BAccurate analysisAccurate measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial heat developmentCondensed matter physicsRay
A method for characterizing the kinetic properties of amorphous-crystal transitions with high-energy X-rays, belonging to the technical field of nanocrystalline alloy preparation, by performing Fourier transform and structure function derivation on diffraction data to obtain the distribution of atoms in the matrix under different time conditions Data, and use a specific JMA equation for segmental fitting to obtain the Avrami index, based on which the amorphous-to-crystal transition kinetics analysis is performed, making the analysis method more convenient and accurate.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
A method for characterizing the ordering process of metallic glasses using exafs
ActiveCN110763708BAccurate analysisAccurate measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPreparing sample for investigationChemical physicsPhysical chemistry
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
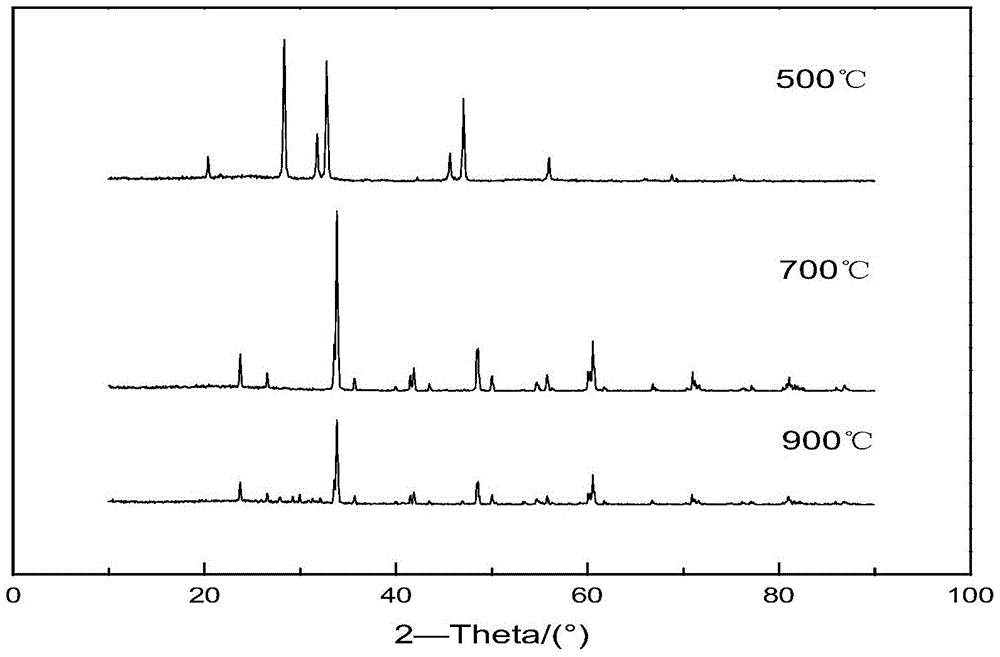
Composite preparation method for fine crystal titanium alloy
InactiveCN102121078BGive full play to high temperature plasticityHigh densityDehydrogenationTitanium alloy
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method for in-situ determination of kinetic curve of metallic glass ordering process by synchrotron radiation
ActiveCN110793983AAccurate analysisAccurate measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial heat developmentSynchrotron radiationMaterials science
The invention, which belongs to the technical field of nanocrystalline preparation, relates to a method for in-situ determination of a kinetic curve of a metallic glass ordering process by synchrotronradiation, thereby solving a problem of kinetic characteristics of the metallic glass ordering process. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out in-situ synchrotron radiation determination of metallic glass ordering; calculating atomic structure distribution; carrying out kinetic fitting of data; and performing ordered kinetic characteristic analysis. With the provided method, the kinetic characteristics of the ordering process can be measured and analyzed accurately and reliably to guide the production and preparation process of the nanocrystalline material, so that the purposeof practical industrialization is achieved.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
A high-energy x-ray characterization method for nanocrystallization kinetics
ActiveCN110793982BAccurate measurementDetermination is accurate and reliableMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial heat developmentCrystallization kineticsHigh energy
A high-energy X-ray characterization method for the kinetic process of nanocrystallization. Through Fourier transform and structure function derivation of radiation data, the distribution density data of atoms in nanocrystals at different time conditions are obtained, and the specific JMA equation is used for analysis. The Avrami index is obtained by segment fitting, and the crystallization kinetics analysis is performed based on this, which makes the analysis more accurate and reliable.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
A Method for Characterizing the Ordering Process of Bulk Metallic Glasses Using In Situ Neutron Diffraction
ActiveCN110793989BAccurate analysisAccurate measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial heat developmentMacroscopic scaleMetallurgy
A method for characterizing the ordering process of bulk metallic glasses using in-situ neutron diffraction, including: in-situ neutron diffraction measurement of ordering of metallic glasses; calculation of atomic structure distribution; data dynamic fitting; ordering kinetic characteristics analyze. The present invention starts from the disorder-to-order transition of atomic stacking, combines the ordering process with macroscopic production and preparation conditions, accurately and reliably measures and analyzes the kinetic characteristics of the ordering process, and guides nanocrystalline The production and preparation process of materials achieves the purpose of practical industrialization.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
In-situ synchrotron radiation characterization method for crystallization kinetic characteristics of amorphous alloy
ActiveCN110749573AAccurate analysisAccurate dynamic characteristicsScattering properties measurementsCrystallographyMacroscopic scale
The invention relats to an in-situ synchrotron radiation characterization method for crystalline kinetic characteristics of an amorphous alloy, belonging to the technical field of nanocrystalline material preparation. Starting from the most fundamental atomic structure, a nanocrystalline formation process is combined with macroscopic production and preparation conditions, so that the analysis is more accurate and reliable.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
A system for measuring temperature change of solid cross section
InactiveCN103413059BSimple calculationNo loss of calculation accuracySpecial data processing applicationsCooling curveComputer module
The invention discloses a solid section temperature change measurement system. The solid section temperature change measurement system is characterized by comprising a module for intercepting solid surface temperature and time relations, a data fitting module, a fitting data differential module, a parameter input and calculation module and a CCT (continuous cooling transformation) and TTT (time temperature transformation) curve superposition module. Influences of internal heat sources, quality, physical properties and ingredients of solids on heat transfer are embodied on temperature time curves of the solid surfaces classified according to shape, and different temperature moments form a cooling curve from the measured section center parts of the solids to the random surface positions by measuring surface temperature time curves of to-be-measured objects, obtaining temperature change speeds of the object surfaces and calculating moments with the same temperature as the surfaces from the center parts of the measured solids to the random surface positions. The complex calculation process is simplified while calculation accuracy is not reduced, and the goal of practicality is achieved simultaneously.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
Complex phase powder and preparation method thereof
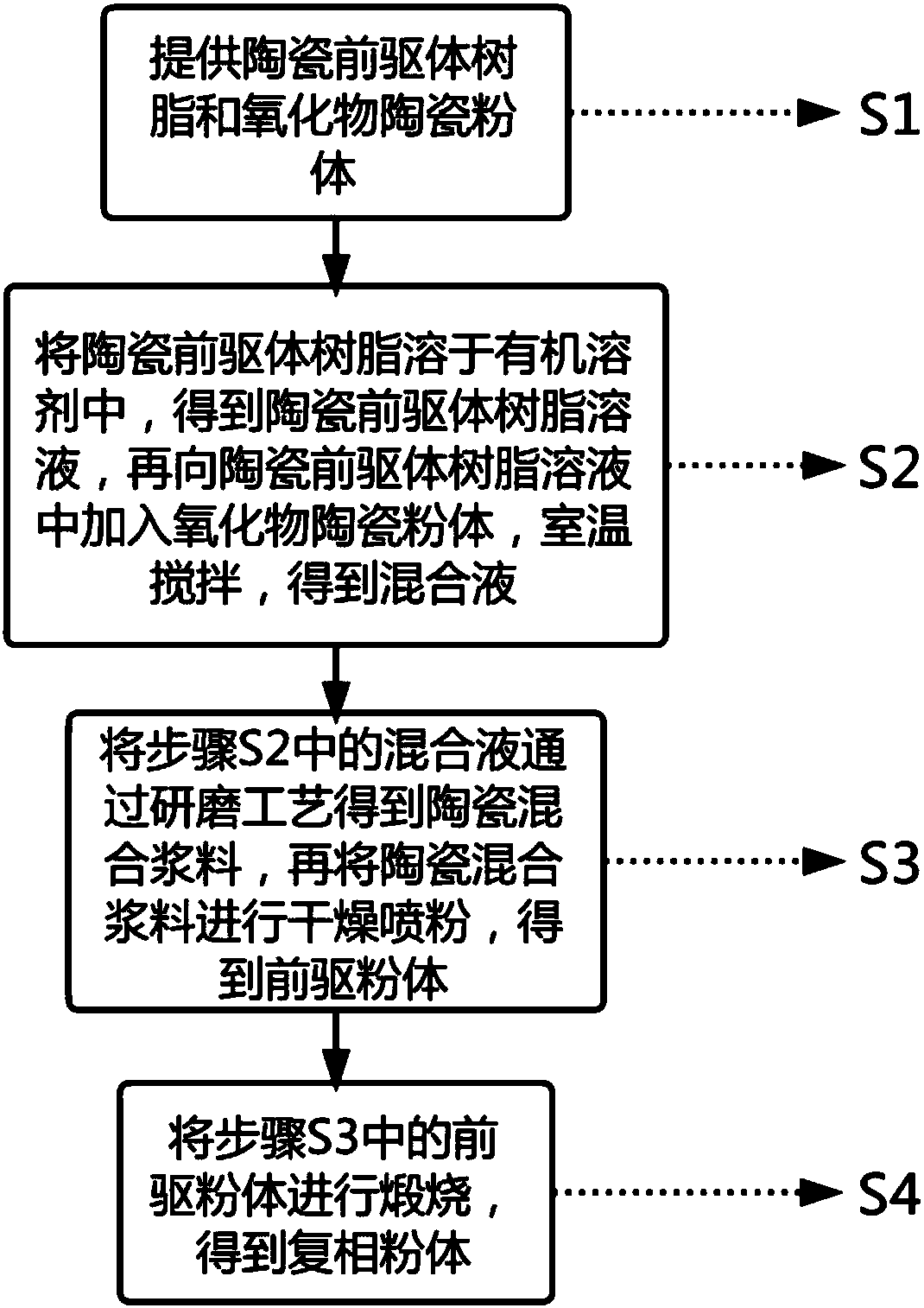
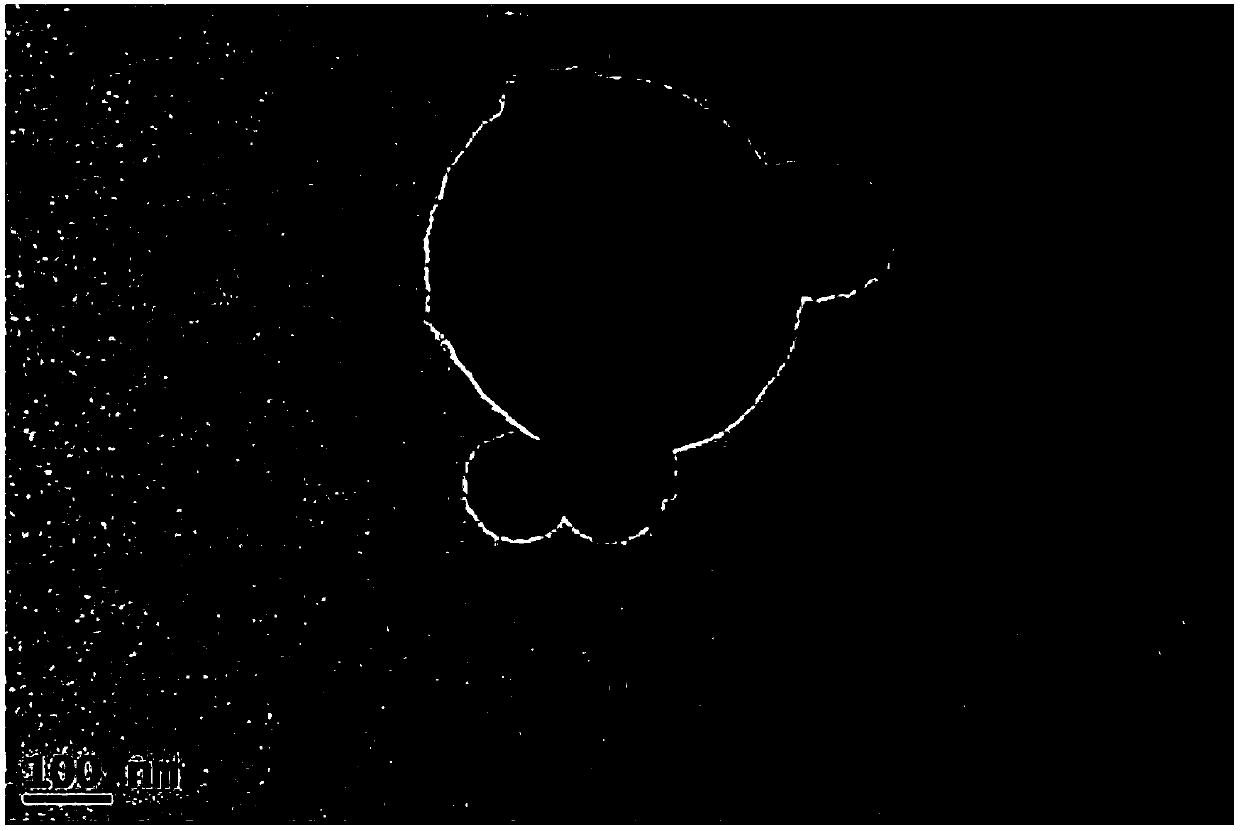
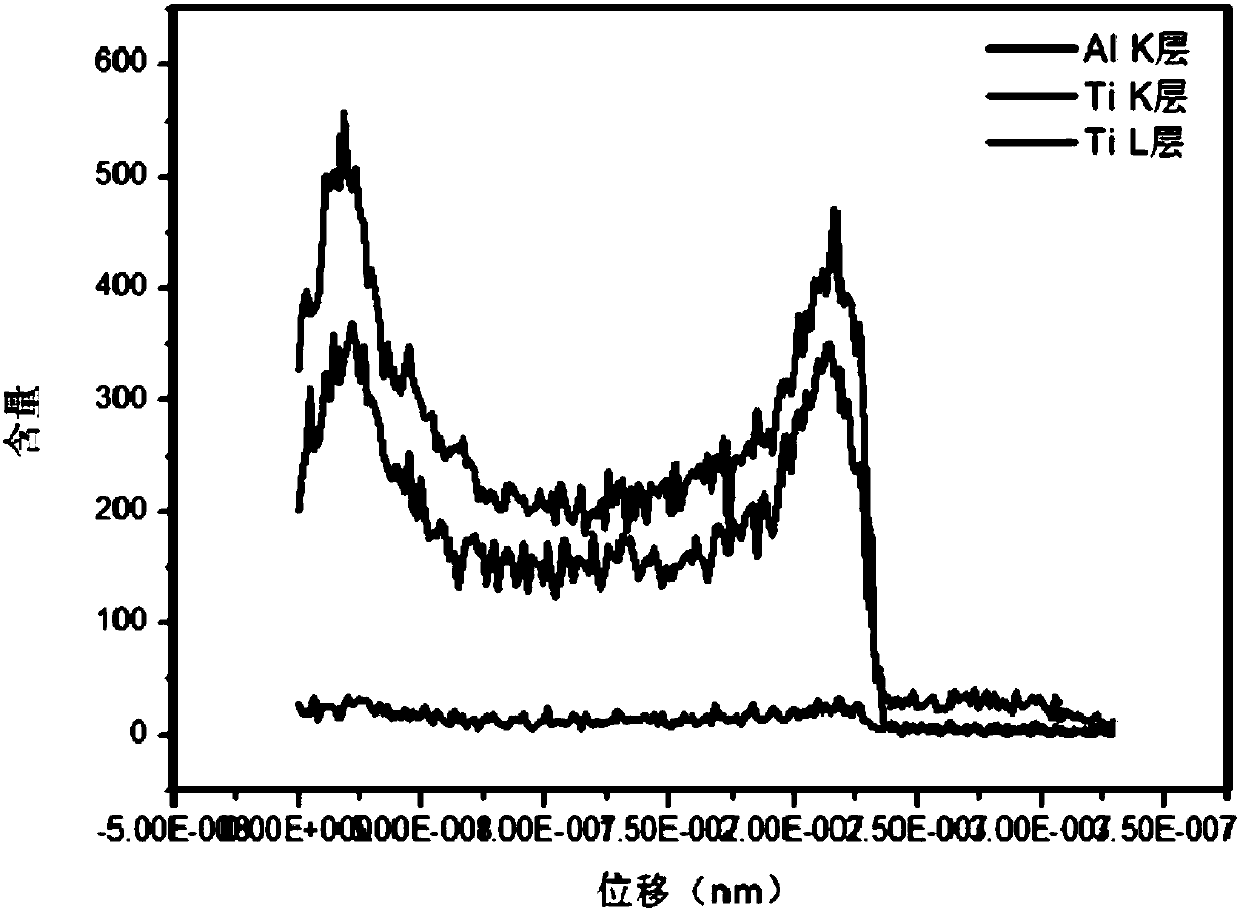
The invention relates to complex phase powder and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises steps as follows: S1, providing ceramic precursor resin and oxide ceramic powder; S2, dissolving the ceramic precursor resin in an organic solvent to obtain a ceramic precursor resin solution, adding the oxide ceramic powder to the ceramic precursor resin solution, and performing stirring at the room temperature to obtain a mixed liquid; S3, grinding the mixed liquid with a grinding process to obtain mixed ceramic slurry, drying the mixed ceramic slurry, and performing powder spraying to obtain the precursor powder; S4, calcining the precursor powder to obtain the complex phase powder. The preparation method adopts a simple process, is low in energy consumption, low in cost andfree from environmental pollution and can be adapted to production and industrial application of large-scale spherical complex phase sub-micron powder. The prepared complex phase powder has good dispersity, uniform particle size, high purity and crystallinity, contains uniform ingredients, has a spherical cladding structure and can achieve the practical purpose.
Owner:SUZHOU TUNABLE MATERIALS TECH CO LTD
Co-precipitation in situ preparation of nano-strontium barium titanate/magnesia composite powder
ActiveCN104311003BGood dispersionUniform particle sizeMaterial nanotechnologyAlkaline earth titanatesDispersityBarium titanate
The invention relates to a method for preparing nano (1-x)Ba1-nSrnTiO3-xMgO complex-phase powder in situ by coprecipitation. A preparation flow comprises the following steps: weighing nitrates of barium, strontium and magnesium into water according to an accurate stoichiometric ratio to prepare a solution A; weighing butyl titanate according toan accurate stoichiometric ratio and dissolving into an ethanol-oxalic acid solution to prepare a solution B; slowly dropwise adding ammonia water into a mixed solution of the solution A and the solution B and carrying out a coprecipitation reaction; controlling the pH value of the reaction system to be 2-10; and carrying out filtering, washing, heat treatment and grinding on precipitate to obtain the nano (1-x)Ba1-nSrnTiO3-xMgO complex-phase powder. The preparation process is simple, short in period and low in cost; and the obtained nano complex-phase powder has good dispersity, uniform grain diameter and high degree of crystallization and can be put into practice.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Neutron diffraction characterization method for crystallization kinetic characteristics of bulk amorphous alloy
ActiveCN110793990ASolve the macroSolve the characteristicsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial heat developmentCrystallization kineticsParticle physics
The invention relates to a neutron diffraction characterization method for the crystallization kinetic characteristics of bulk amorphous alloy. Fourier transform and structural function derivation arecarried out on diffraction data to obtain distribution data of atoms in nanocrystals under different time conditions; and segmented fitting is carried out by using a specific JMA equation and crystallization kinetic analysis is carried out based on the segmented fitting. According to the invention, the dynamic characteristics of nanocrystalline formation can be measured and analyzed accurately and reliably by starting with the most fundamental atomic structure, so that high practicability is realized.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com