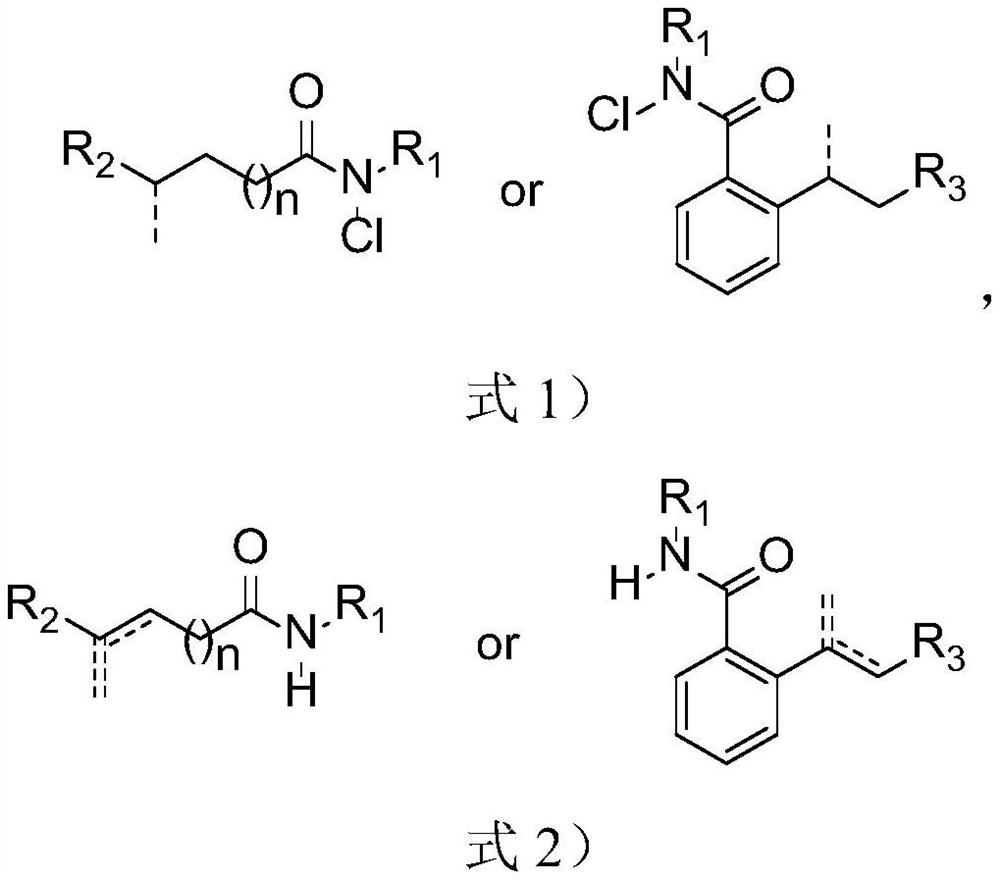
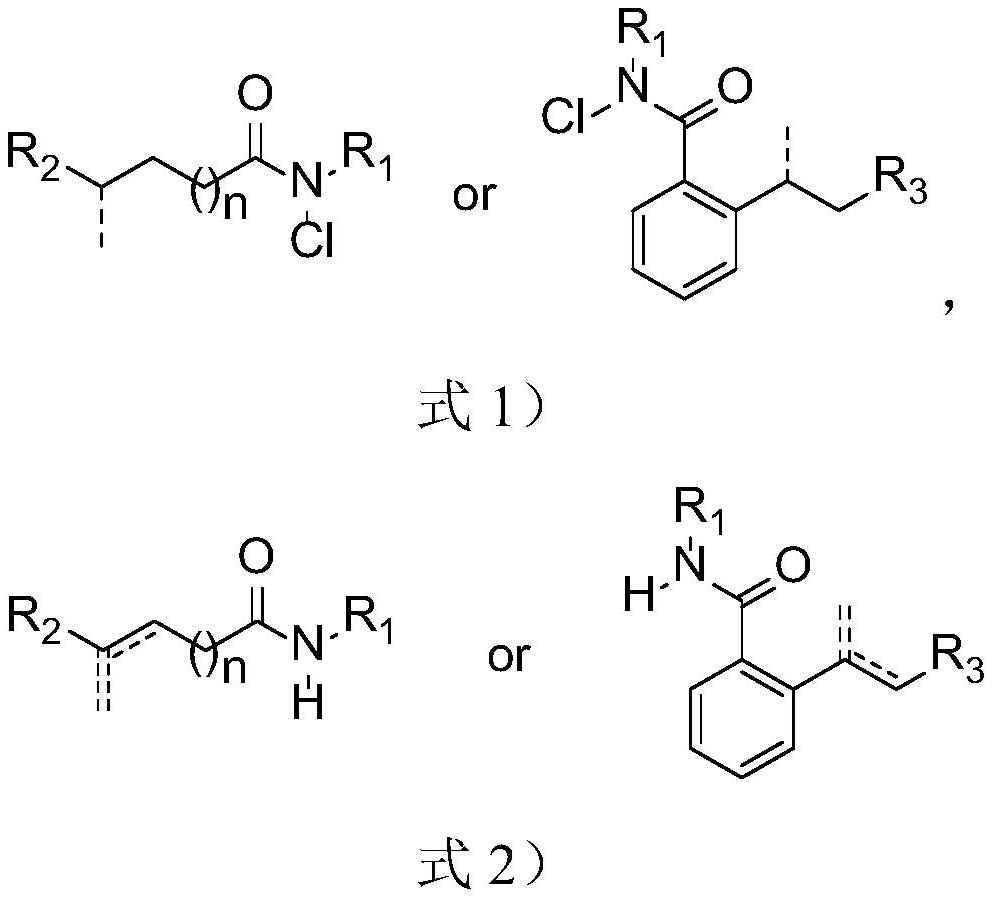
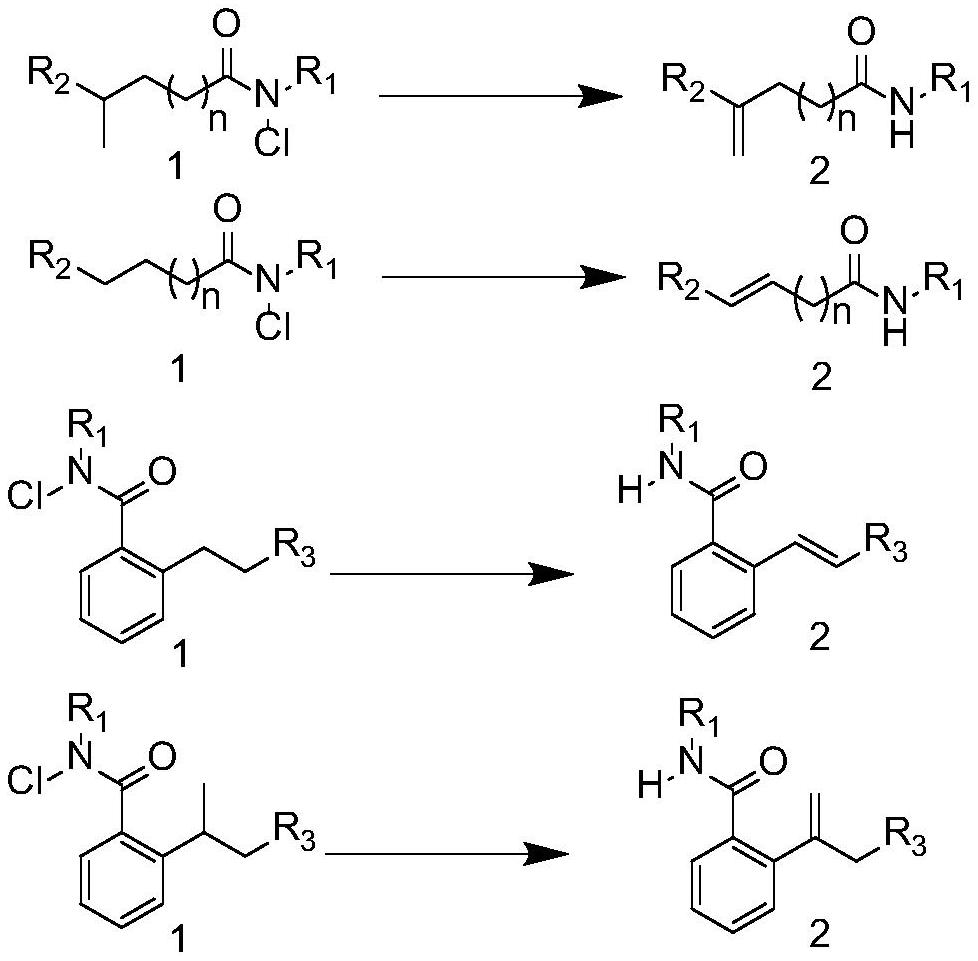
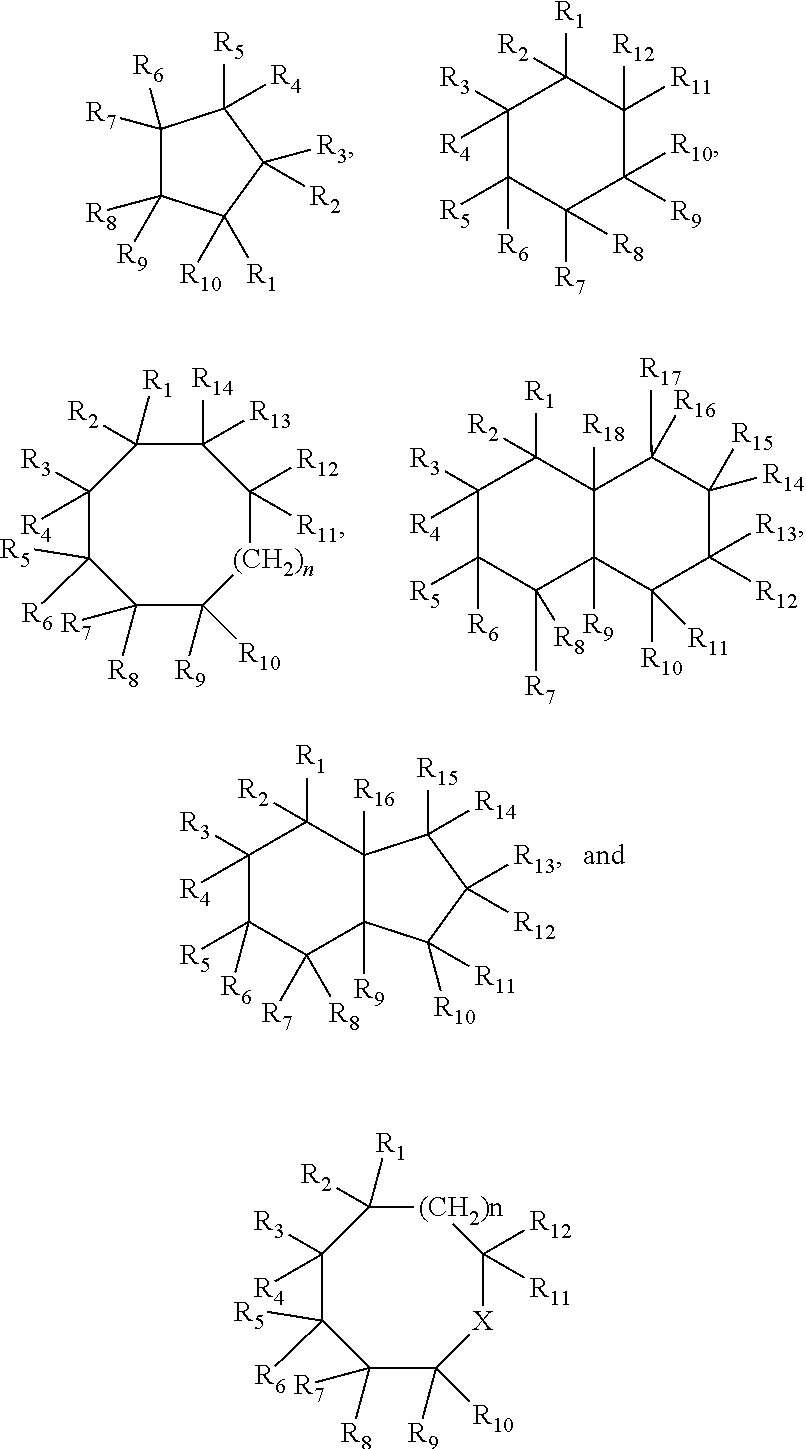
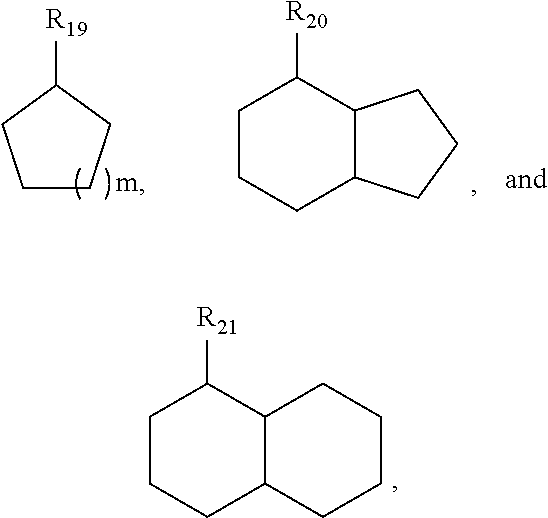
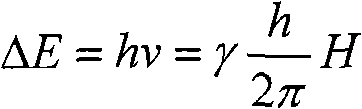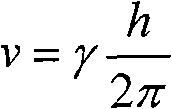Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
51results about "Organic dehydrogenation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
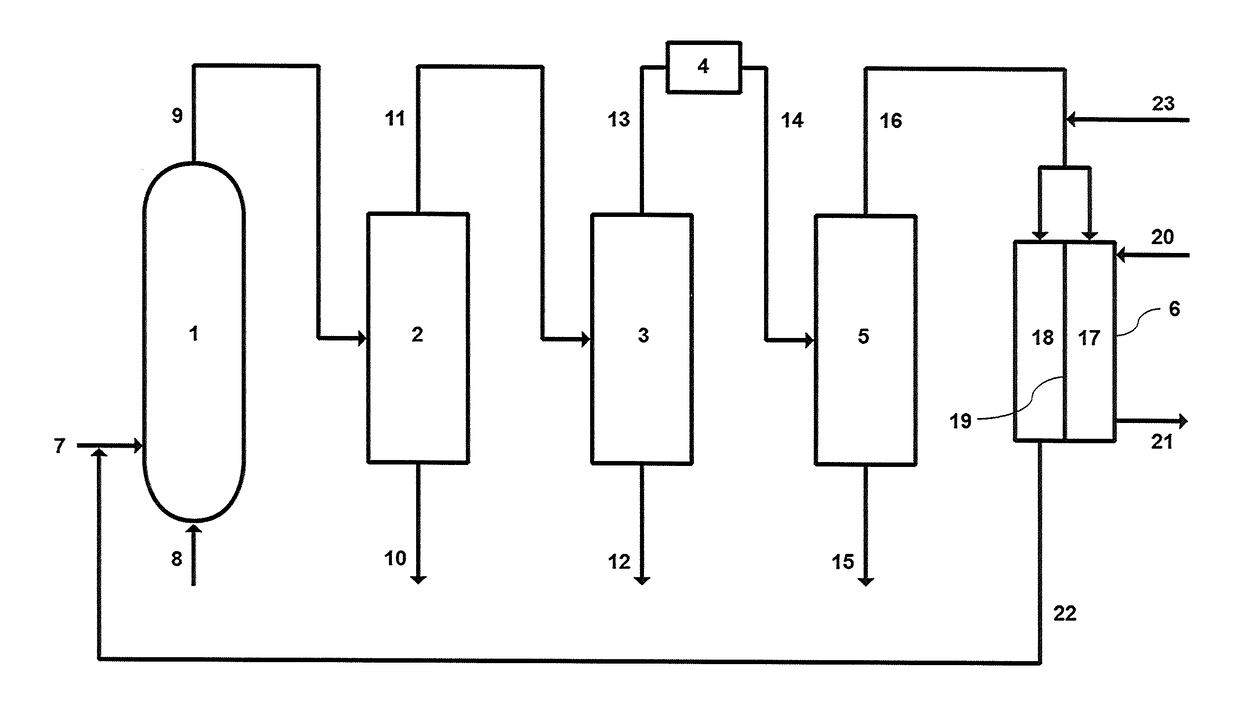
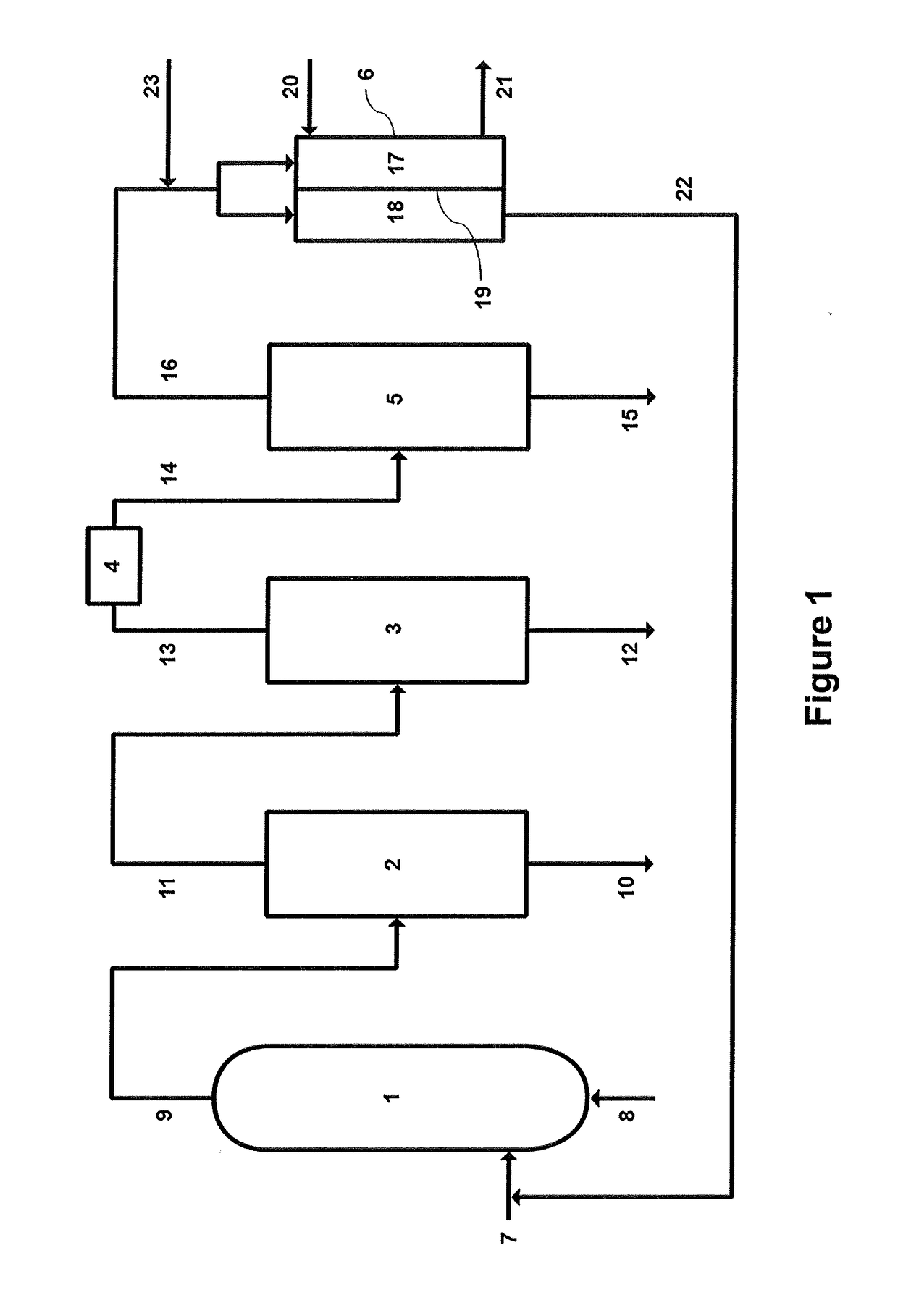
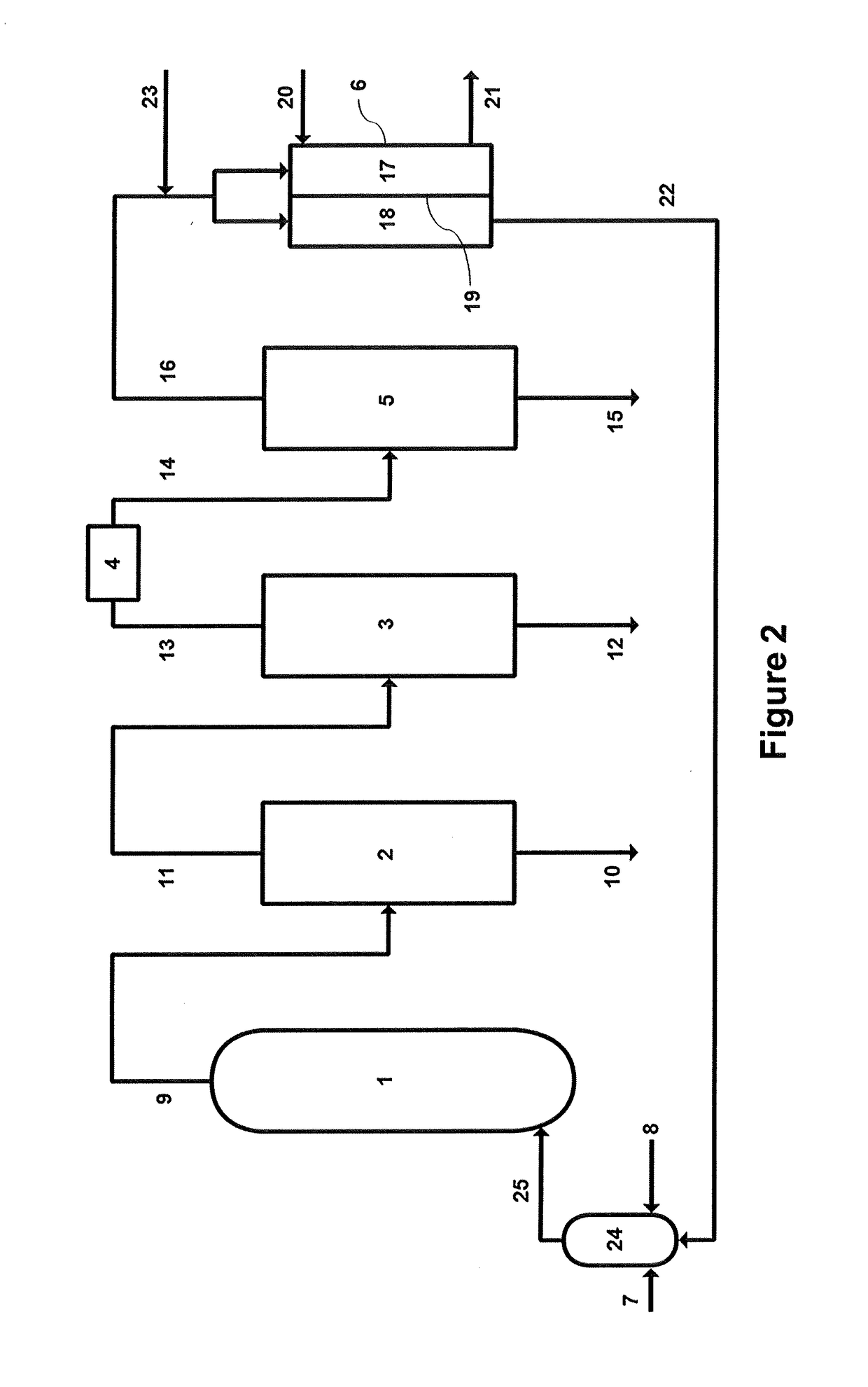
Process for dehydrogenating organic compounds in the presence of a supported bimetallic catalyst with a strong interaction between a group VIII metal and tin
InactiveUS6600082B2Synergistic effectHydrocarbon by dehydrogenationHydrocarbon by hydrogenationPlatinumIsomeric shift
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Process for preparing sorbic acid from sorbic acid polyester
InactiveUS20030065218A1High yieldReduce usageOrganic compound preparationPreparation from carboxylic acid esters/lactonesPolyesterCrotonaldehyde
The invention relates to a process for preparing sorbic acid by cleaving the sorbic acid polyester prepared from crotonaldehyde and ketene, the sorbic acid polyester being distilled and the cleavage being catalyzed by an amine, which comprises separating off the amine from the distillation residue by distillation under reduced pressure and at a temperature which is higher than the temperature of the polyester distillation and recovering it.
Owner:NUTRINOVA NUTRITION SPECIALTIES & FOOD ENGREDIENTS GMBH
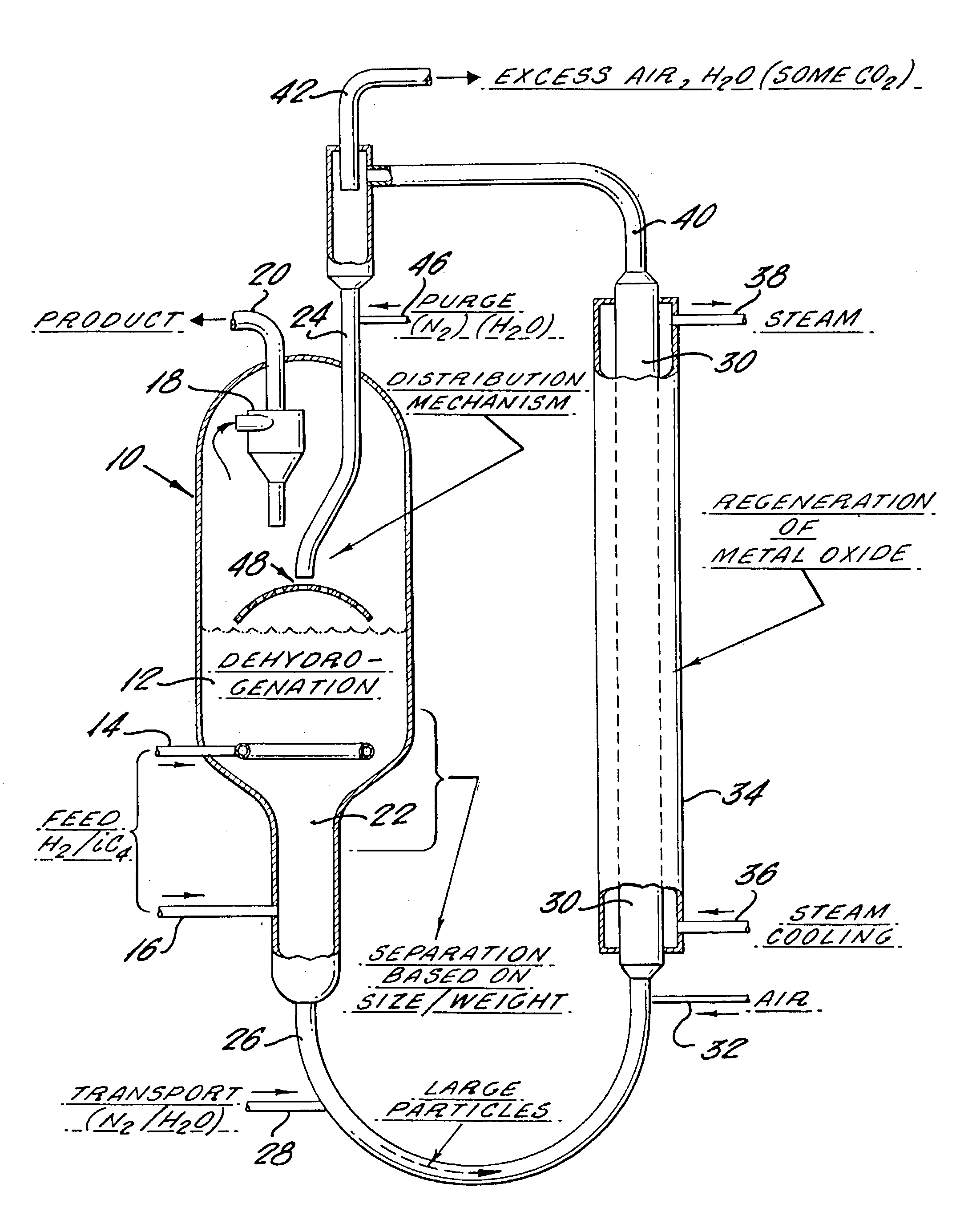
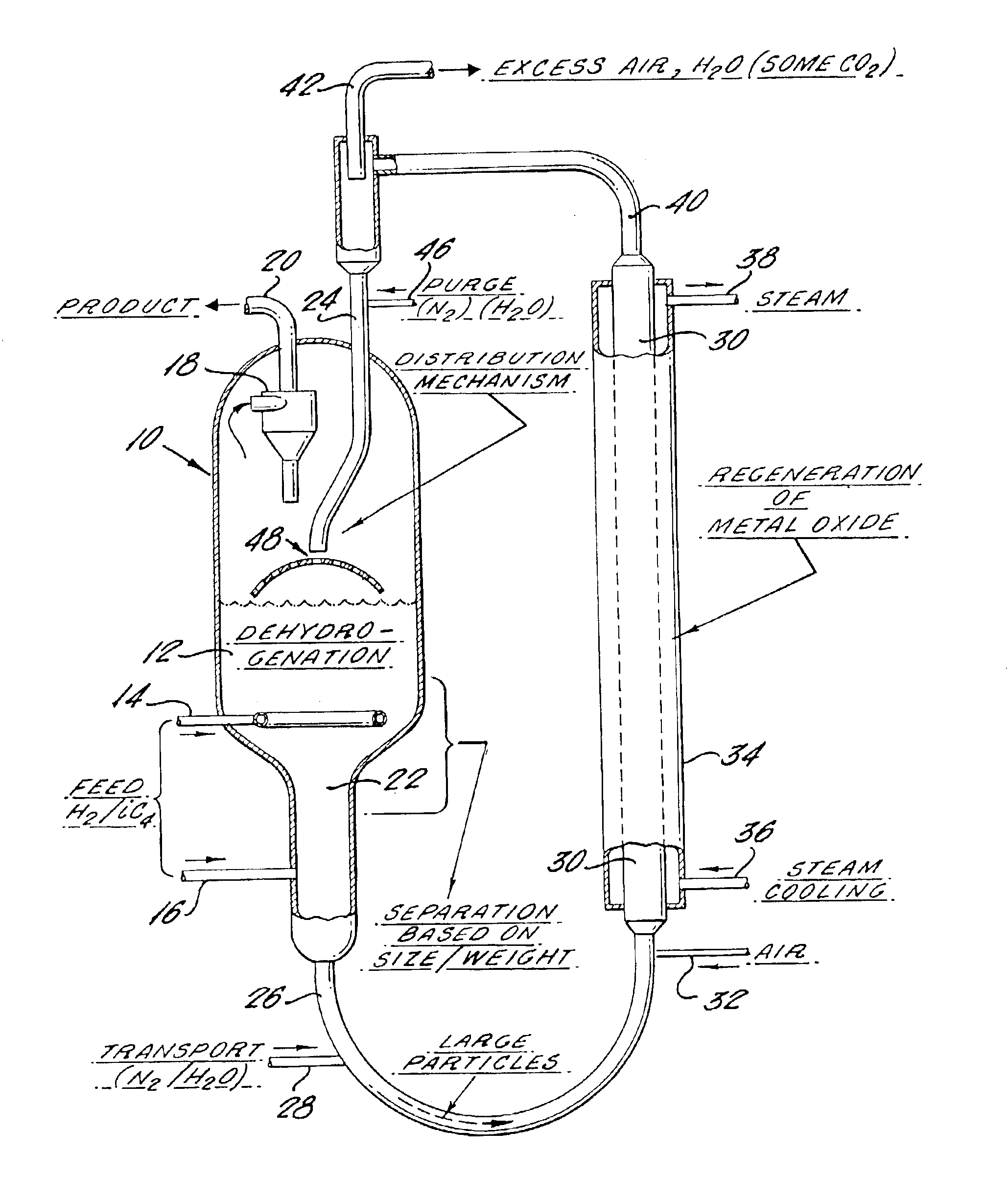
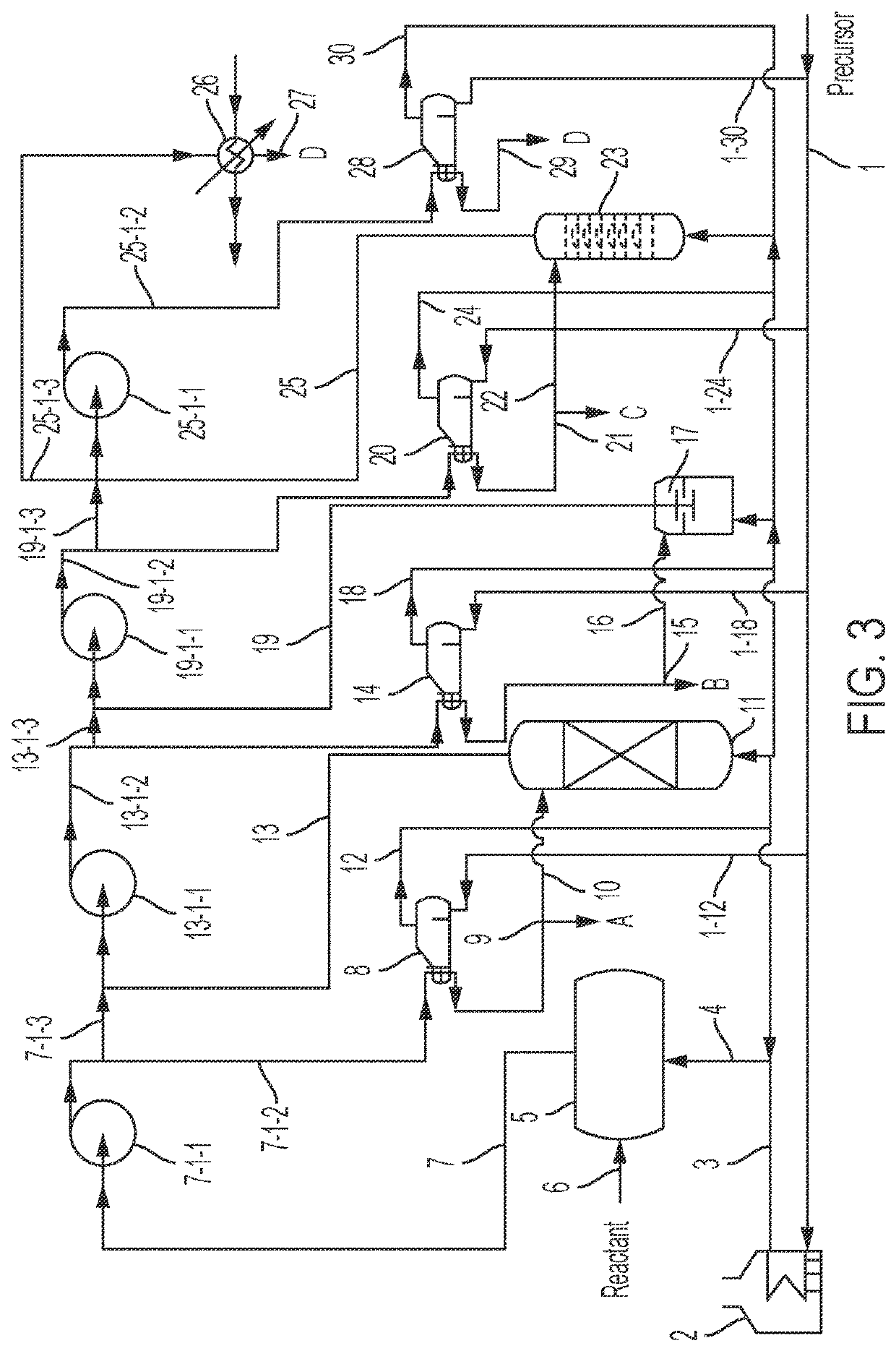
Method and apparatus for endothermic reactions of organic compounds
InactiveUS20030091485A1Good choiceLess explosion hazardMolecular sieve catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationSimple Organic CompoundsPtru catalyst
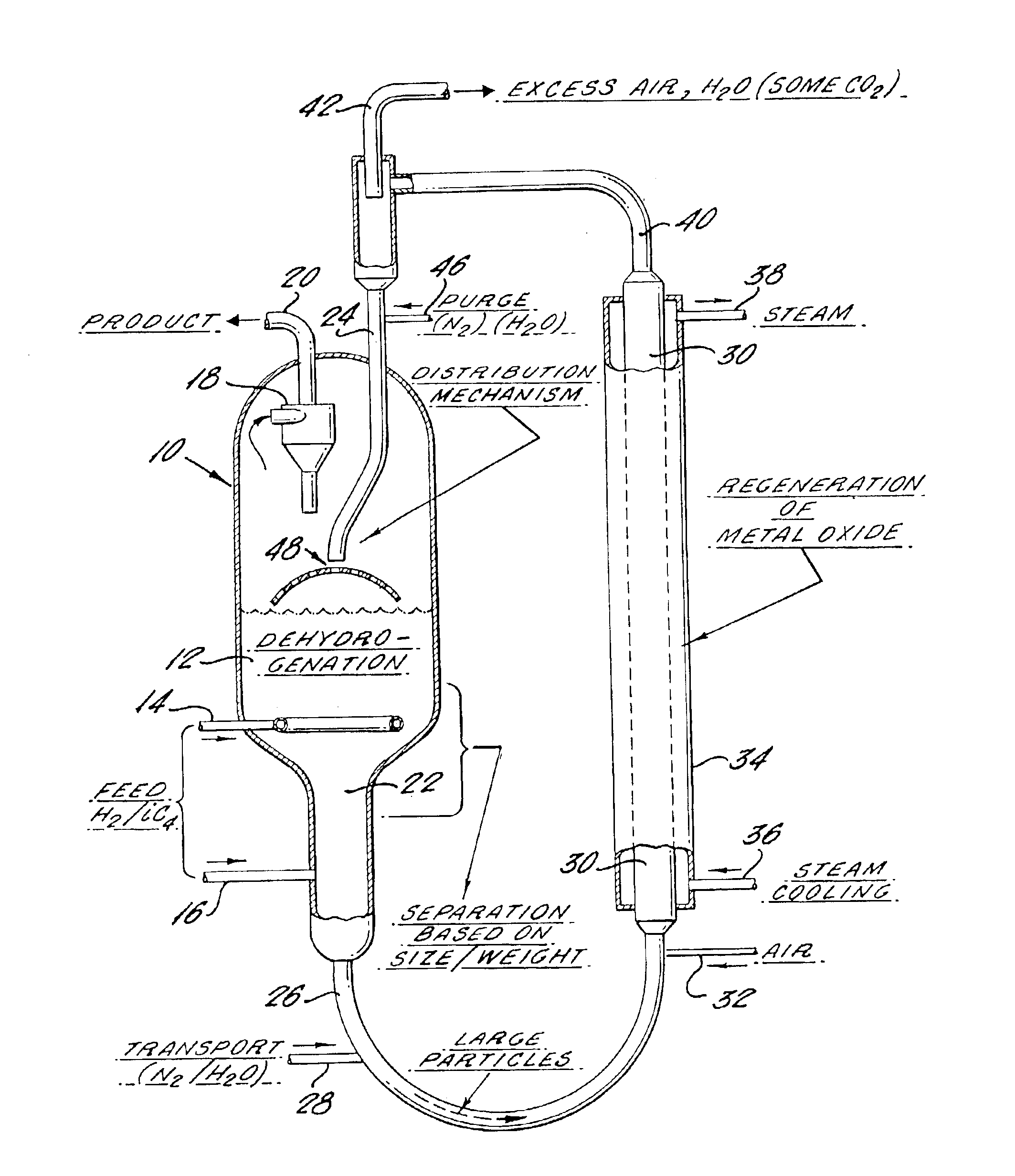
The invention provides process and apparatus for conducting an endothermic reaction of an organic' compound in the presence of molecular hydrogen and of multicomponent solids. The process comprises contacting the compound with a solid catalyst for the endothermic reaction and a hydrogen oxidizing solid reagent intermixed with the solid catalyst. Organic products of the endothermic reaction are produced, with evolution of molecular hydrogen. The solid catalyst becomes gradually deactivated by formation of carbonaceous deposits thereon. The evolved hydrogen undergoes an exothermic reaction with the hydrogen oxidizing solid reagent to form a reduction product which comprises deactivated hydrogen oxidizing solid reagent. The deactivated solid catalyst is reactivated by combustion of carbonaceous deposits thereon and the deactivated hydrogen oxidizing solid reagent is reactivated by contacting the reagent with an oxidizing agent in the absence of substantial quantities of hydrogen and in the absence of substantial quantities of organic compounds other than those on the surface of the reagent. One embodiment of the invention provides apparatus in which an endothermic reaction is carried out in the presence of a fluidized bed of catalyst and in the presence of particles of granular hydrogen oxidizing solid reagent which move downwardly through the fluidized catalyst bed, and in which the solid catalyst and solid reagent are separated prior to reactivation thereof in separate reactivation zones.
Owner:SUNOCO INC (R&M)
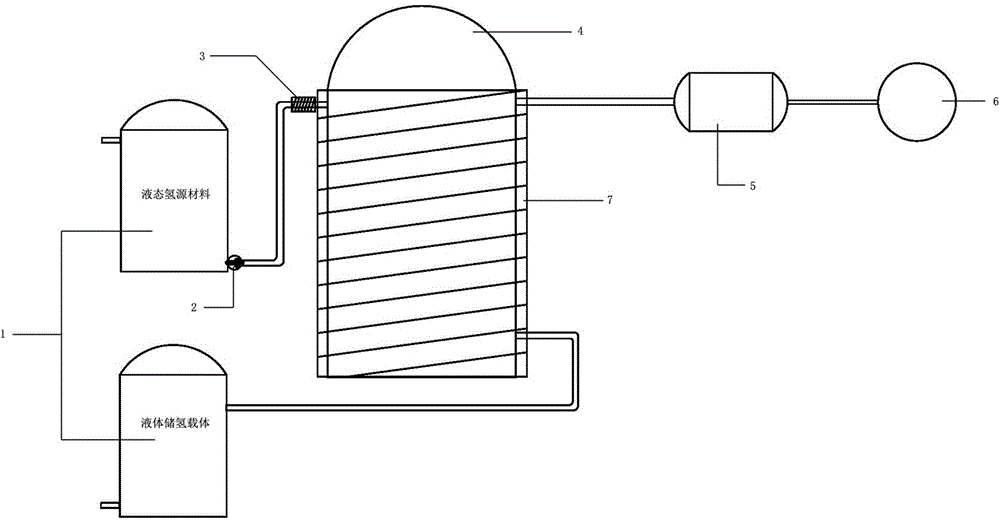
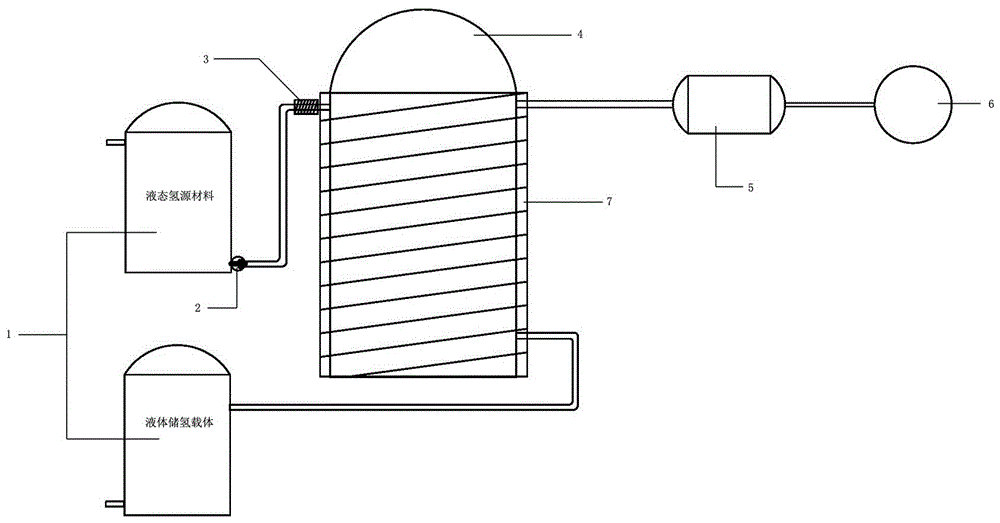
Liquid hydrogen source material dehydrogenation reaction system and application method thereof
The invention discloses a liquid hydrogen source material dehydrogenation reaction system and an application method thereof. The dehydrogenation system comprises a storage device used for storing a liquid hydrogen source material and a liquid hydrogen-storage carrier, a reaction kettle used for dehydrogenating the liquid hydrogen source material, a buffering tank used for storing hydrogen gas, and a heating device arranged outside the reaction kettle and used for heating the reaction kettle. According to the invention, the liquid hydrogen source material is delivered into the reaction kettle through a pump; the liquid hydrogen source material is dehydrogenated in the reaction kettle; produced hydrogen gas is delivered to the buffering tank; and residual liquid hydrogen-storage carrier is delivered back to the hydrogen storage tank. The normal-temperature normal-pressure liquid hydrogen source material dehydrogenation system provided by the invention is used for carrying out a dehydrogenation reaction upon the liquid hydrogen source material. The produced hydrogen gas is supplied for a fuel cell or an internal combustion engine. The hydrogen gas is converted into electrical energy or mechanical energy which can be applied in various industrial and civil fields such as automobiles, electrical power, energy storage, chemical engineering, pharmacy, and mobile devices.
Owner:WUHAN HYNERTECH CO LTD
Method of improving a dehydrogenation process
The invention relates to a method of improving a dehydrogenation process comprising: removing a volume of a first dehydrogenation catalyst from a radial dehydrogenation reactor; loading the reactor with a volume of a second dehydrogenation catalyst that has a lower decline rate than the first dehydrogenation catalyst; and passing a dehydrogenatable hydrocarbon through the reactor wherein the volume of the second catalyst is at most 90% of the volume of the removed catalyst.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Dehydrogenation catalyst
ActiveUS20110263416A1High activityHigh selectivityCatalystsHydrocarbon preparation catalystsPlatinumActivity concentration
This invention relates to a dehydrogenation catalyst having a macropore size and a high active density of platinum, suitable for use in dehydrogenation of a hydrocarbon gas. This dehydrogenation catalyst having a macropore size and a high active density of platinum is highly active, has high active density per unit catalytic surface area, facilitates material transfer of reactants and products, delays deactivation due to coke formation, keeps the initial activity constant after being regenerated thanks to the disposal of coke, has high strength and so is resistant to external impact, and undergoes neither structural changes due to heat nor changes in the properties of active materials.
Owner:HYOSUNG CHEM CORP
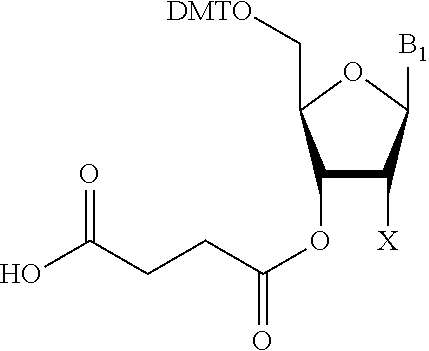
Solid-phase support for oligonucleotide synthesis and oligonucleotide synthesis method
ActiveUS9045573B2A large amountReduce loadSugar derivativesOrganic free radical generationPolyethylene glycolOligonucleotide synthesis
The present invention provides a solid-phase support for oligonucleotide synthesis for synthesizing long chain oligonucleotide, RNA oligonucleotide and modified oligonucleotide at high synthetic quantity and high purity with a low loading amount of a linker. Provided is a solid-phase support for oligonucleotide synthesis comprising a porous resin bead having a monovinyl monomer unit, a crosslinkable vinyl monomer unit and a polyethylene glycol unit and a cleavable linker loaded on its surface,the porous resin bead having a group capable of binding to a carboxy group by a dehydration condensation reaction on its surface, the cleavable linker having a carboxy group, wherein the carboxy group of the cleavable linker is bound to the group capable of binding to a carboxy group, by a dehydration condensation reaction, anda loading amount of the cleavable linker is 1 to 80 μmol / g relative to the weight of the porous resin bead.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Dehydrogenation catalyst
ActiveUS8993474B2High activityHigh selectivityCatalystsHydrocarbon preparation catalystsPlatinumDehydrogenation
Owner:HYOSUNG CHEM CORP
Process for the dehydrogenation of a hydrocarbon feed stock
Process for the dehydrogenation of a hydrocarbon feed comprising a step of dehydrogenating the hydrocarbon feed and a step of removing hydrogen being formed by dehydrogenation reactions, wherein the dehydrogenation and hydrogen removal steps are performed simultaneously in presence of a dehydrogenation catalyst being combined with a metal compound being reduced in presence of hydrogen.
Owner:HALDOR TOPSOE AS
Supported Catalyst, Its Activated Form, and their Preparation and Use
InactiveUS20150231612A1Simple methodLess impuritiesHydroxy compound preparationOrganic reductionDehydrogenationAlloy
A supported catalyst and preparation method thereof, the catalyst comprising an organic polymer material carrier and Raney alloy particles supported on the organic polymer material carrier, wherein substantially all of the Raney alloy particles are partially embedded in the organic polymer material carrier. The catalyst can be used in hydrogenation, dehydrogenation, amination, dehalogenation or desulfuration reactions.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
Complex comprising odh unit with integrated oxygen separation module
ActiveUS20180305278A1Large scaleHydrocarbon by dehydrogenationDistillation purification/separationAlkaneInstability
Oxidative dehydrogenation is an alternative to the energy extensive steam cracking process presently used for the production of olefins from paraffins, but has not been implemented commercially partially due to the unstable nature of hydrocarbon / oxygen mixtures, and partially due to the cost involved in the construction of new facilities. An oxidative dehydrogenation chemical complex designed to reduce costs by including integration of an oxygen separation module that also addresses safety concerns and reduces emission of greenhouse gases is described.
Owner:NOVA CHEM (INT) SA
Apparatus for endothermic reactions of organic compounds
InactiveUS6872364B2Good choiceLess explosion hazardMolecular sieve catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationSimple Organic CompoundsPtru catalyst
An apparatus for conducting an endothermic reaction of an organic' compound in the presence of molecular hydrogen and of multicomponent solids is described. The process of operating the apparatus comprises contacting the compound with a solid catalyst for the endothermic reaction and a hydrogen oxidizing solid reagent intermixed with the solid catalyst. Organic products of the endothermic reaction are produced, with evolution of molecular hydrogen. The solid catalyst becomes gradually deactivated by formation of carbonaceous deposits thereon. The evolved hydrogen undergoes an exothermic reaction with the hydrogen oxidizing solid reagent to form a reduction product which comprises deactivated hydrogen oxidizing solid reagent. The deactivated solid catalyst is reactivated by combustion of carbonaceous deposits thereon and the deactivated hydrogen oxidizing solid reagent is reactivated by contacting the reagent with an oxidizing agent in the absence of substantial quantities of hydrogen and in the absence of substantial quantities of organic compounds other than those on the surface of the reagent. The apparatus provides an endothermic reaction which is carried out in the presence of a fluidized bed of catalyst and in the presence of particles of granular hydrogen oxidizing solid reagent which move downwardly through the fluidized catalyst bed, and in which the solid catalyst and solid reagent are separated prior to reactivation thereof in separate reactivation zones.
Owner:SUNOCO INC (R&M)
Complex comprising ODH unit with integrated oxygen separation module
ActiveUS10343957B2Large scaleHydrocarbon by dehydrogenationDistillation purification/separationAlkaneDehydrogenation
Oxidative dehydrogenation is an alternative to the energy extensive steam cracking process presently used for the production of olefins from paraffins, but has not been implemented commercially partially due to the unstable nature of hydrocarbon / oxygen mixtures, and partially due to the cost involved in the construction of new facilities. An oxidative dehydrogenation chemical complex designed to reduce costs by including integration of an oxygen separation module that also addresses safety concerns and reduces emission of greenhouse gases is described.
Owner:NOVA CHEM (INT) SA
A method of improving a dehydrogenation process
The invention relates to a method of improving a dehydrogenation process comprising: removing a volume of a first dehydrogenation catalyst from a radial dehydrogenation reactor; loading the reactor with a volume of a second dehydrogenation catalyst that has a lower decline rate than the first dehydrogenation catalyst; and passing a dehydrogenatable hydrocarbon through the reactor wherein the volume of the second catalyst is at most 90% of the volume of the removed catalyst.
Owner:SHELL INT RES MAATSCHAPPIJ BV
Process for dehydrogenating organic compounds in the presence of a supported bimetallic catalyst with a strong interaction between a group VIII metal and tin
InactiveUS20020045787A1Synergistic effectHydrocarbon by dehydrogenationHydrocarbon by hydrogenationAlkaneSimple Organic Compounds
A process for dehydrogenating organic compounds, in particular paraffins and naphthenes, is carried out in the presence of a supported catalyst comprising a group VIII metal such as platinum, and tin, at least a portion of which interacts strongly with the group VIII metal in the catalyst in the reduced state. In the partially oxidised state, the catalyst contains at least 10% of tin in the form of a reduced tin species with oxidation state 0, said species having an isomer shift in the range 0.80 to 2.60 mm / s and a quadrupolar splitting in the range 0.65 to 2.00 mm / s.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
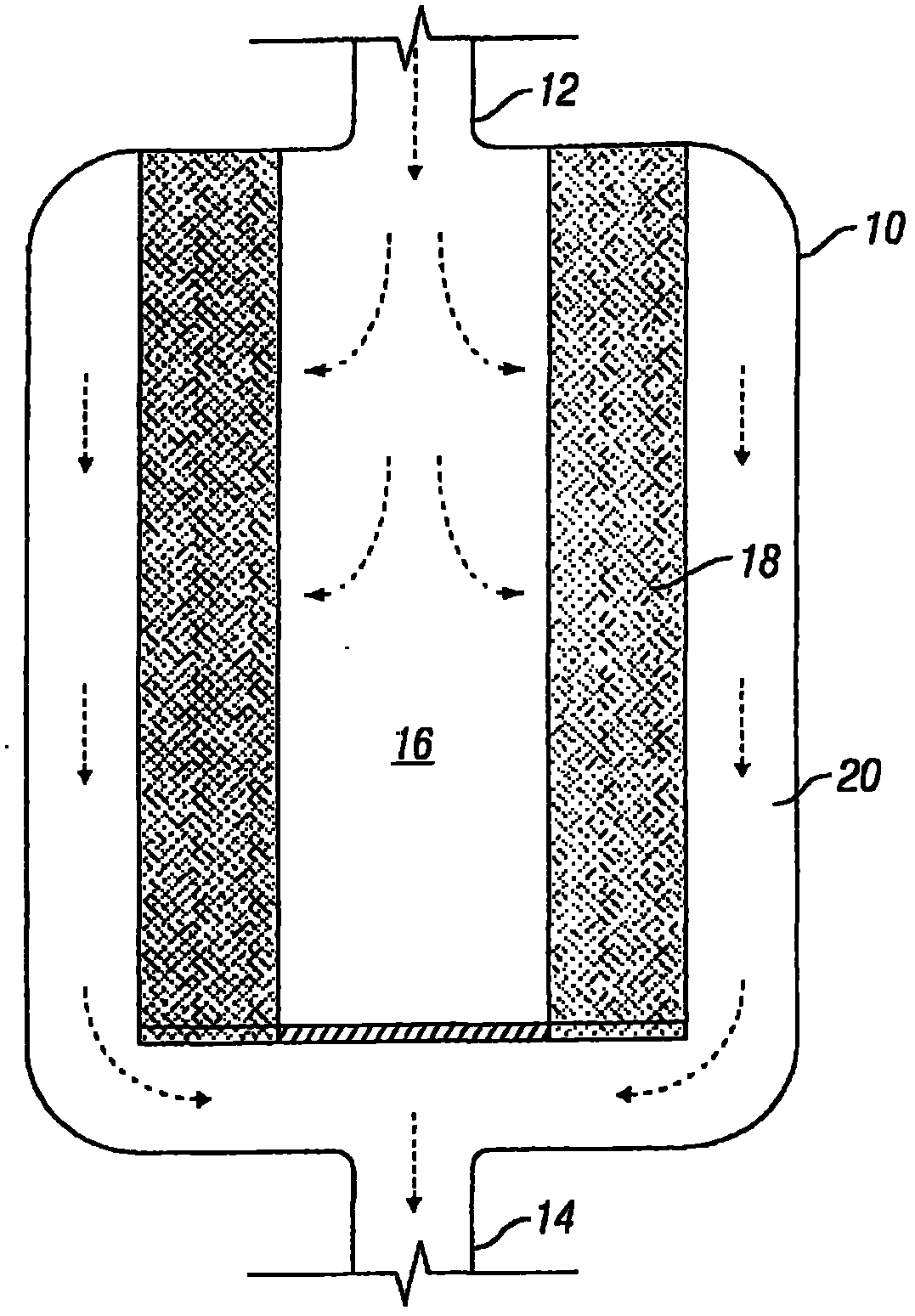
Method for dehydrogenation by positioning through nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention discloses a method for dehydrogenation by positioning through nuclear magnetic resonance, and belongs to the technical field of organic chemical reactions. The method is expected to open a new way for the organic chemical reactions, new substance discoveries and new medicament synthesis. The adopted technical scheme is that: the method for dehydrogenation by positioning through the nuclear magnetic resonance comprises the following steps of: firstly, accurately measuring a Delta H or Delta C of a known organic compound so as to obtain a correct 1H-NMR or 13C-NMR spectrum; secondly, finding a position of an atom to be dehydrogenated according to the 1H-NMR or 13C-NMR spectrum so as to determine a corresponding electromagnetic radiation frequency v and a corresponding external magnetic field H0; thirdly, adding the known organic compound and a dehydrogenation catalyst in a sample tube so as to fully enhance the irradiation according to the determined electromagnetic radiation v and the corresponding fixed external magnetic field H0; and, fourthly, separating and purifying the dehydrogenated organic compound. The method is applied to the technical field of the organic chemical reactions.
Owner:张建旺
Dehydrogenation process
Processes comprising: providing a dehydrogenatable compound; and subjecting the dehydrogenatable compound to a dehydrogenation reaction at a temperature of from 150 to 400° C., in the presence of oxygen, and at a temperature profile of the dehydrogenation reaction which does not differ substantially from the temperature profile of the dehydrogenation reaction in the absence of oxygen under otherwise identical conditions.
Owner:BASF AG
Circular economy methods of preparing unsaturated compounds
ActiveUS10435345B2Organic compound preparationHydrocarbon by hydrogenationDehydrogenationCircular economy
Methods of preparing unsaturated compounds or analogs through dehydrogenation of corresponding saturated compounds and / or hydrogenation of aromatic compounds are disclosed.
Owner:INTERNATIONAL FLAVORS & FRAGRANCES
Unsaturated carbonyl compounds as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109896918ATypical high functional group structureThe reaction process is safe and controllableCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationAntioxidantDehydrogenation
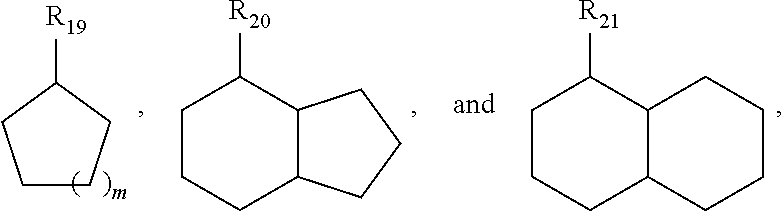
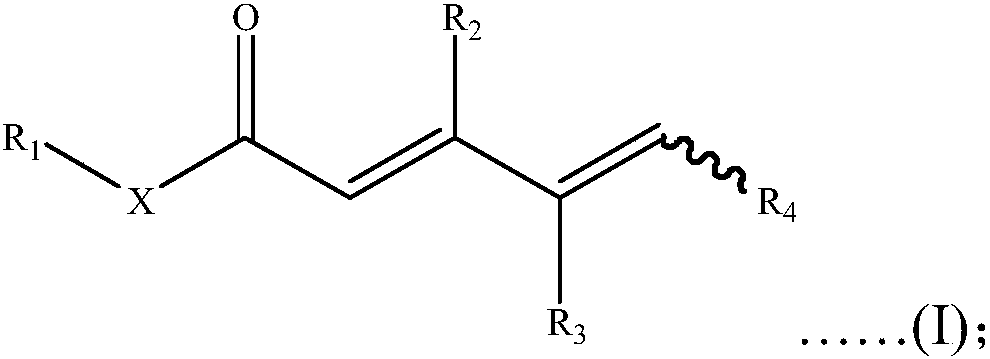
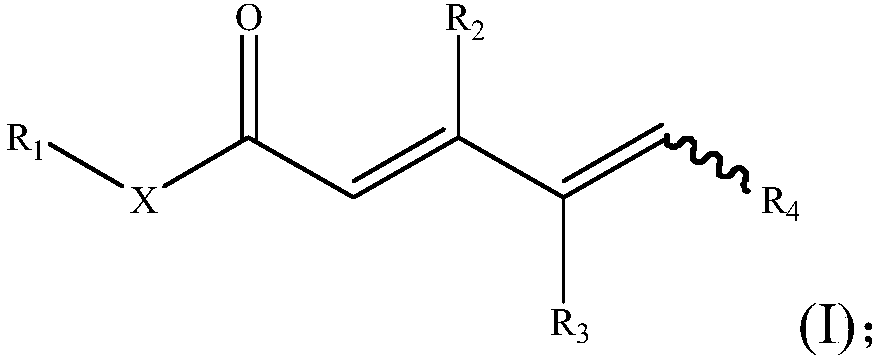
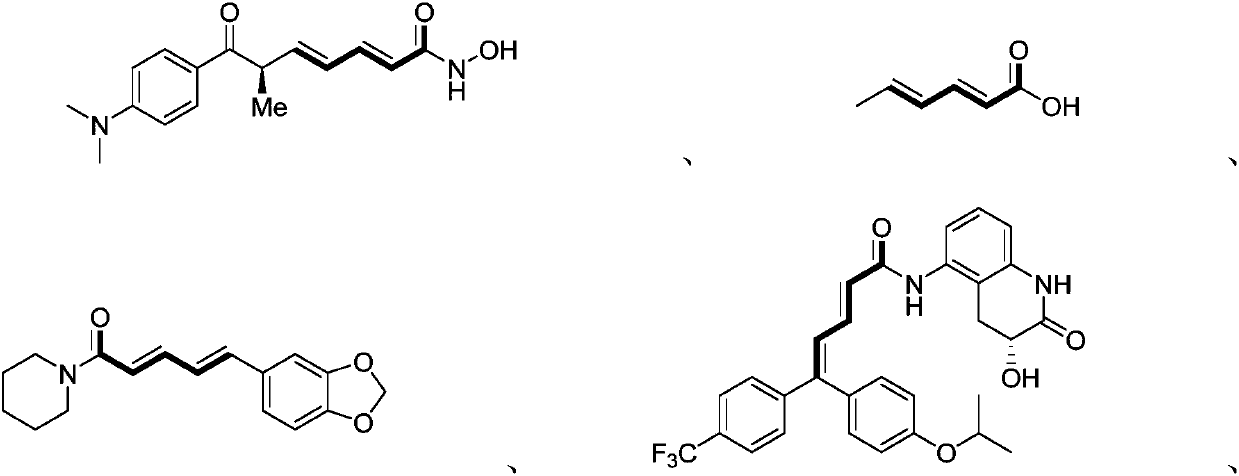
The invention discloses unsaturated carbonyl compounds as well as a preparation method and application thereof. A general formula of the molecular structures of the unsaturated carbonyl compounds is shown in a formula (I); the preparation method of the unsaturated carbonyl compounds comprises the steps of adding a gamma, delta-unsaturated carbonyl compound A into a reaction system containing a transition metal catalyst, an additive and an antioxidant to react and the like. The unsaturated carbonyl compounds disclosed by the invention have two continuous double bonds and carbonyl functional groups; a large quantity of compounds having a special functionalization center can be obtained through simple chemical conversion; the preparation method of the compounds is simple in technology, low inreaction condition requirements, safe and controllable in reaction process, and high in utilization ratio of atoms and production efficiency; meanwhile, the regioselectivity of a product is efficiently ensured; the environmental pollution pressure of a methodology is low through the introduction of a concept of direct dehydrogenation by oxidation of carbonyl compounds with air; and the method iswidely applicable to the preparation of natural products and drug molecular intermediates.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
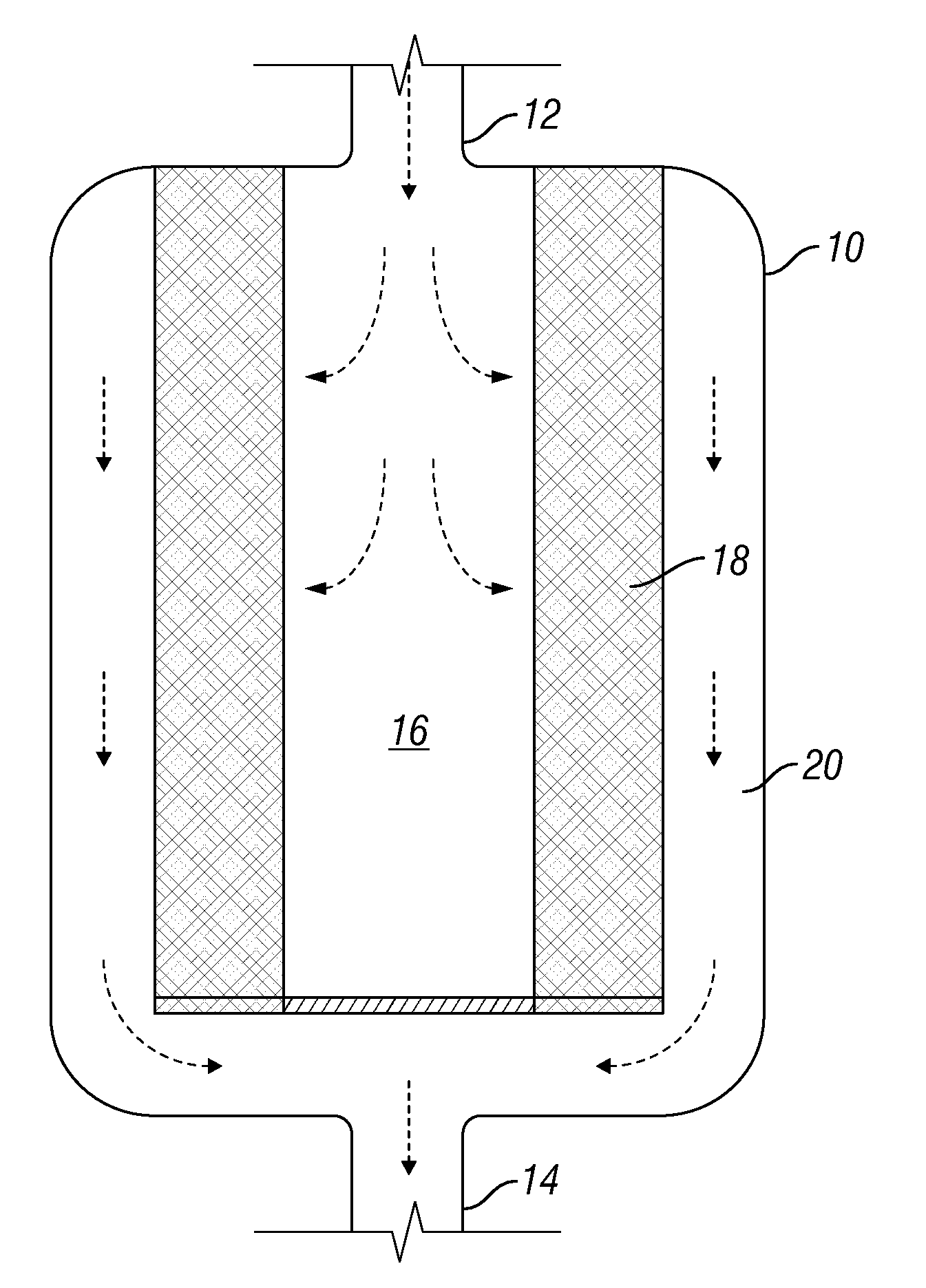
Reactor for carrying out a continuous oxide hydrogenation, and method
InactiveCN101563148AUniform air temperaturePromote regenerationHydrocarbon by dehydrogenationFlow mixersProduct gasOxygen
The invention relates to a reactor (1) for carrying out a continuous oxide hydrogenation of a feed gas flow (2) of saturated hydrocarbons, which has been previously mixed with a gas flow (3) containing oxygen, on a moving catalyst bed (4) arranged between two concentric cylindrical holding devices (5, 6) in the longitudinal direction of the reactor, leaving a central inner space (7) and an intermediate space (8) between the moving catalyst bed (4) and the inner envelope of the reactor, in order to obtain a reaction gas mixture. Said reactor (1) is characterised in that it comprises at least two reactor sections which are separated from each other and split into sub-sections by means of alternating disk-type deflector plates (10) arranged in the central inner space (7) and annular deflector plates (11) arranged in the intermediate space between the moving catalyst bed (4) and the inner envelope of the reactor. The reactor sections each comprise a mixing device (12) which is arranged in the direction of flow of the reaction gas mixture upstream of the moving catalyst bed (4), said mixing device being formed from the following elements: two or three successively arranged rows of tubes (13) comprising turbulence generators on the outer side thereof, which narrow the cross-section for the passage of the feed gas flow (2) to between 1 / 2 and 1 / 10 of the free cross-section, the oxygen-containing gas flow (3) being guided through the tubes and sprayed into the feed gas flow (2) through holes (14) in the tubes (13); in addition to a perforated plate (17) mounted upstream of the tubes (13); and a perforated plate (18) mounted downstream of the tubes (13).
Owner:BASF AG
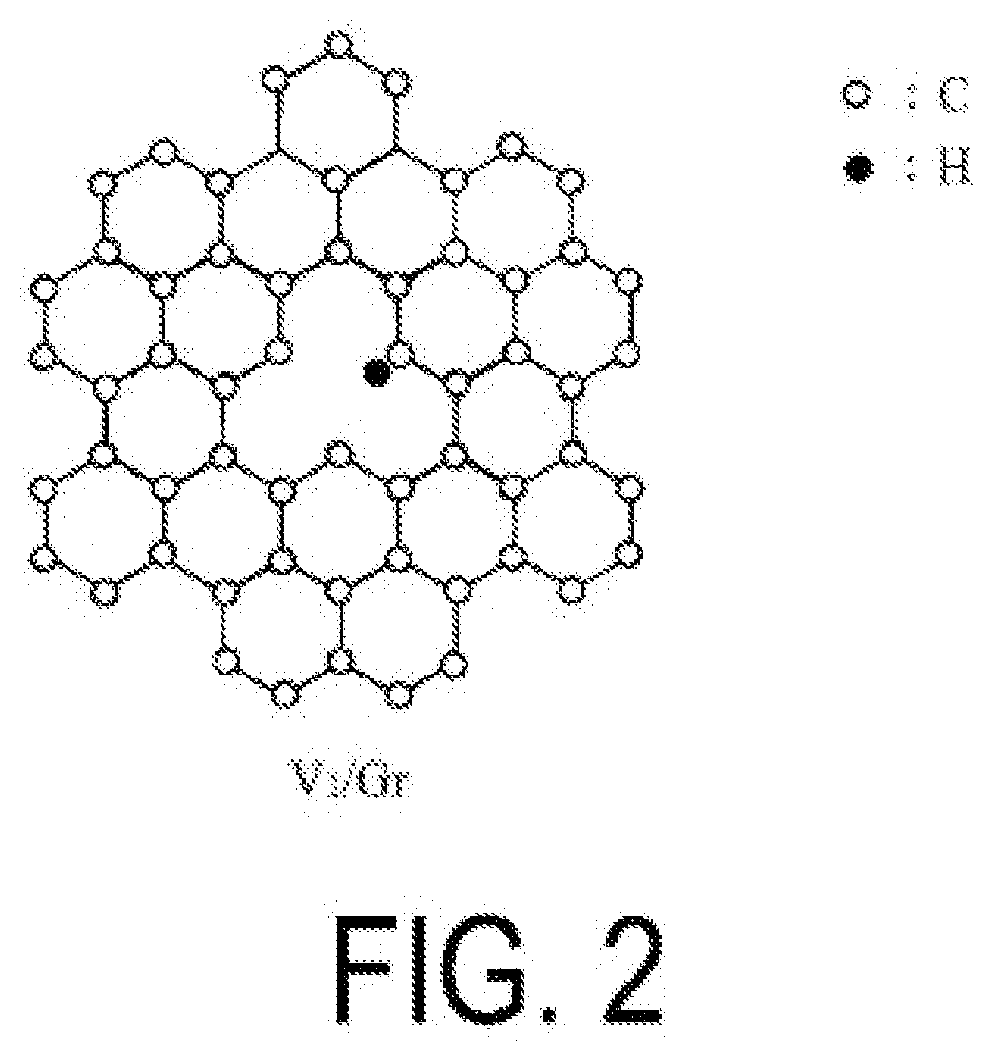
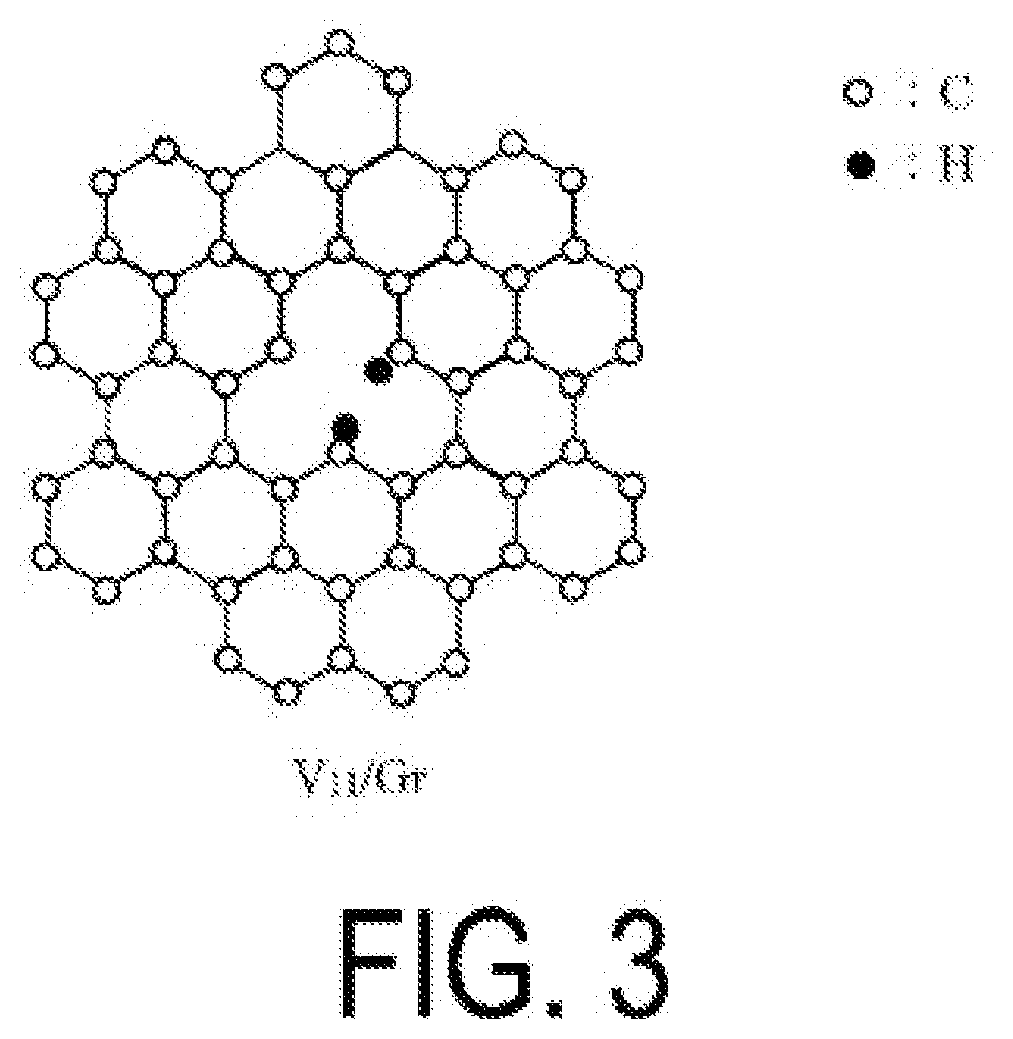
Alkane dehydrogenation catalyst, and hydrogen production method using same
Provided are: a catalyst that is used in a reaction for producing hydrogen from an alkane without emitting CO2; a method of producing hydrogen without emitting CO2 by using the catalyst; and a method of producing ammonia using, as a reducing agent, hydrogen produced using the catalyst. The alkane dehydrogenation catalyst according to the present disclosure contains a graphene having at least one type of structure selected from an atomic vacancy structure, a singly hydrogenated vacancy structure, a doubly hydrogenated vacancy structure, a triply hydrogenated vacancy structure, and a nitrogen-substituted vacancy structure. The graphene preferably has from 2 to 200 of the structure approximately per 100 nm2 of the atomic film of the graphene. In addition, the hydrogen production method according to the present disclosure includes extracting hydrogen from an alkane by using the alkane dehydrogenation catalyst.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV +2
Hybrid catalyst systems and hybrid process for converting alkanes to alkenes and to their corresponding oxygenated products
InactiveCN1781597ASmall sizeEliminate integration stepsMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic compound preparationContact timeAlkene
Alkenes, unsaturated carboxylic acids, saturated carboxylic acids and their higher homologues are produced cumulatively from the corresponding alkanes by using a mixed catalyst system and a hybrid process comprising steam cracking of alkanes to the corresponding alkenes and using one or more oxidation catalyst, thereby further catalytically converting the corresponding olefin to the corresponding oxidation product under short contact time reactor conditions.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO
Supported catalyst, its activated form, and their preparation and use
ActiveUS20180169632A1Simple methodLess impuritiesHydroxy compound preparationOrganic reductionDehydrogenationAlloy
A supported catalyst and preparation method thereof, the catalyst comprising an organic polymer material carrier and Raney alloy particles supported on the organic polymer material carrier, wherein substantially all of the Raney alloy particles are partially embedded in the organic polymer material carrier. The catalyst can be used in hydrogenation, dehydrogenation, amination, dehalogenation or desulfuration reactions.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
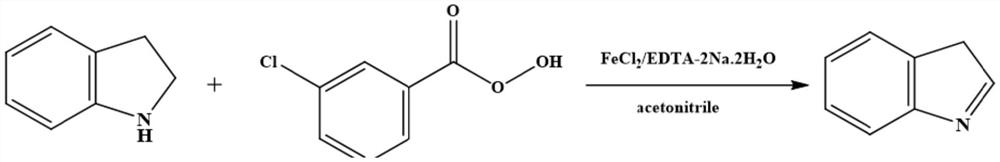
Aromatization method of nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compound
PendingCN113788778AHigh yieldImprove biological activityOrganic dehydrogenationBulk chemical productionPtru catalystNitrogenous heterocyclic compound
The invention relates to the technical field of organic synthesis, and particularly discloses an aromatization method of a nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compound. The aromatization method of the nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compound comprises the following step: by taking the nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compound as a reaction substrate, a transition metal salt or a complex formed by the transition metal salt and an organic compound as a catalyst and peroxide as an oxidant, carrying out reacting in a solvent to obtain a reaction solution containing an aromatization product of the nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compound. The aromatization method of the nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compound provided by the invention has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, small catalyst dosage, simple post-treatment process and high yield and purity of reaction products, is simple to operate, and has extremely high application value.
Owner:HEBEI VEYONG BIO CHEM
Methods and systems for optimizing mechanical vapor compression and/or thermal vapor compression within multiple-stage processes
ActiveUS20220016542A1Increase pressureIncrease temperatureThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingThermodynamicsVapor quality
The present invention utilizes mechanical vapor compression and / or thermal vapor compression integrating compression loops across multiple process stages. A sequential network of compressors is utilized to increase the pressure and condensing temperature of the vapors within each process stage, as intra-vapor flow, and branching between process stages, as inter-vapor flow. Because the vapors available are shared among and between compressor stages, the number of compressors can be reduced, improving economics. Balancing vapor mass flow through incremental compressor stages which traverse multiple process stages by splitting vapors between compressor stages enables the overall vapor-compression system to be tailored to individual process energy requirements and to accommodate dynamic fluctuations in process conditions.
Owner:ENERGY INTEGRATION INC
Solid-phase support for oligonucleotide synthesis and oligonucleotide synthesis method
ActiveUS20130317206A1A large amountLow loading amountSugar derivativesOrganic free radical generationPolyethylene glycolOligonucleotide synthesis
The present invention provides a solid-phase support for oligonucleotide synthesis for synthesizing long chain oligonucleotide, RNA oligonucleotide and modified oligonucleotide at high synthetic quantity and high purity with a low loading amount of a linker. Provided is a solid-phase support for oligonucleotide synthesis comprising a porous resin bead having a monovinyl monomer unit, a crosslinkable vinyl monomer unit and a polyethylene glycol unit and a cleavable linker loaded on its surface, the porous resin bead having a group capable of binding to a carboxy group by a dehydration condensation reaction on its surface, the cleavable linker having a carboxy group, wherein the carboxy group of the cleavable linker is bound to the group capable of binding to a carboxy group, by a dehydration condensation reaction, and a loading amount of the cleavable linker is 1 to 80 μmol / g relative to the weight of the porous resin bead.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
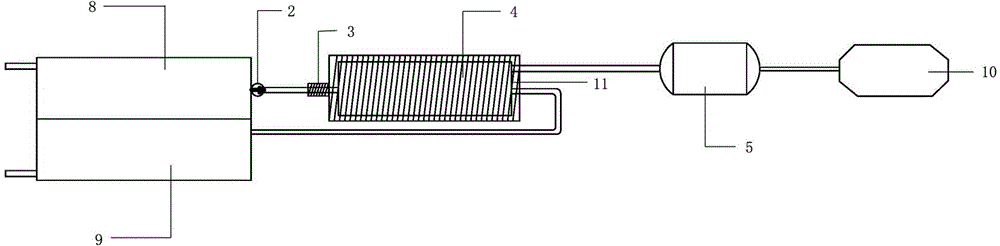
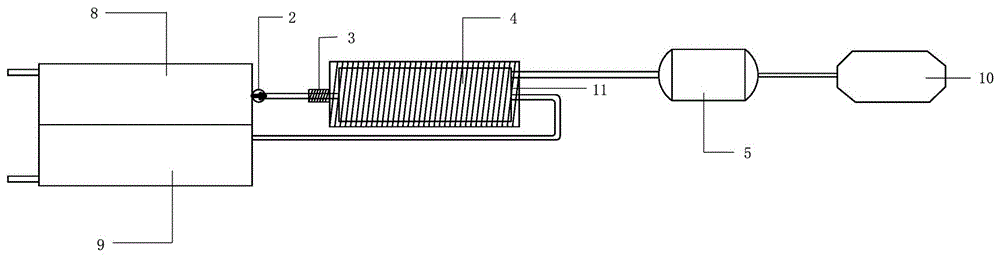
A dehydrogenation reaction system of liquid hydrogen source material and its application method
The invention discloses a liquid hydrogen source material dehydrogenation reaction system and an application method thereof. The dehydrogenation system comprises a storage device used for storing a liquid hydrogen source material and a liquid hydrogen-storage carrier, a reaction kettle used for dehydrogenating the liquid hydrogen source material, a buffering tank used for storing hydrogen gas, and a heating device arranged outside the reaction kettle and used for heating the reaction kettle. According to the invention, the liquid hydrogen source material is delivered into the reaction kettle through a pump; the liquid hydrogen source material is dehydrogenated in the reaction kettle; produced hydrogen gas is delivered to the buffering tank; and residual liquid hydrogen-storage carrier is delivered back to the hydrogen storage tank. The normal-temperature normal-pressure liquid hydrogen source material dehydrogenation system provided by the invention is used for carrying out a dehydrogenation reaction upon the liquid hydrogen source material. The produced hydrogen gas is supplied for a fuel cell or an internal combustion engine. The hydrogen gas is converted into electrical energy or mechanical energy which can be applied in various industrial and civil fields such as automobiles, electrical power, energy storage, chemical engineering, pharmacy, and mobile devices.
Owner:WUHAN HYNERTECH CO LTD
Conversion Of Alcohols To Linear And Branched Functionalized Alkanes
Embodiments herein concerns the eco-friendly conversion of simple alcohols to linear or branched functionalized alkanes, by integrated catalysis. The alcohols are firstlyoxidized either chemically or enzymatically to the corresponding aldehydes or ketones, followed by aldol condensations using a catalyst to give the corresponding enals or enones. The enals or enones are subsequently and selectively hydrogenated using a recyclable heterogeneous metal catalyst, organocatalyst or an enzyme to provide linear or branched functionalized alkanes with an aldehyde, keto- or alcohol functionality. The process is also iterative and can be further extended by repeating the above integrated catalysis for producing long-chain functionalized alkanes from simple alcohols.
Owner:ORGANOFUEL SWEDEN AB
Method for synthesizing olefin through selective desaturation of inert carbon-carbon bonds
ActiveCN113173862AHigh stereoselectivityEasy to retouchOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationPtru catalystDouble bond
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing olefin by selective desaturation of inert carbon-carbon bonds. The method comprises the following steps of: synthesizing a chlorinated amide compound serving as a raw material in the presence of visible light, a ruthenium catalyst and a ligand, and post-treating reaction liquid to obtain a remote alkenyl amide compound. In the presence of the ruthenium catalyst and the phenylpyridine ligand, intramolecular carbon-hydrogen bond activation of the amide compound is successfully realized, and the remote olefin compound is synthesized; according to the method, chloro-amide which is simple and easy to obtain is used as a raw material, the substrate application range is wide, and the reaction efficiency is high; in the free radical migration process, 1, 5 migration occurs all the time along with beta-H elimination, terminal alkene and conjugated double bonds are used as main products, and high regioselectivity is achieved; and the maximum E / Z value of the obtained olefin compound is greater than 20: 1, and the stereoselectivity is good. The double bond of the compound can be further converted into other functional groups, the conversion process is simple in one step, and the obtained derivative can be used as a medical intermediate and has high potential application value.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Circular economy methods of preparing unsaturated compounds
ActiveUS20190389791A1Organic compound preparationHydrocarbon by hydrogenationDehydrogenationCombinatorial chemistry
Methods of preparing unsaturated compounds or analogs through dehydrogenation of corresponding saturated compounds and / or hydrogenation of aromatic compounds are disclosed.
Owner:INTERNATIONAL FLAVORS & FRAGRANCES
Popular searches
Metal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalysts Hydrocarbon by hydrocarbon cracking Carboxylic compound separation/purification Fluidised-bed furnaces Chemical recycling Hydrocarbon preparation Hydrocarbon from carbon oxides Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalysts Organic decomposition Catalytic reactions
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com