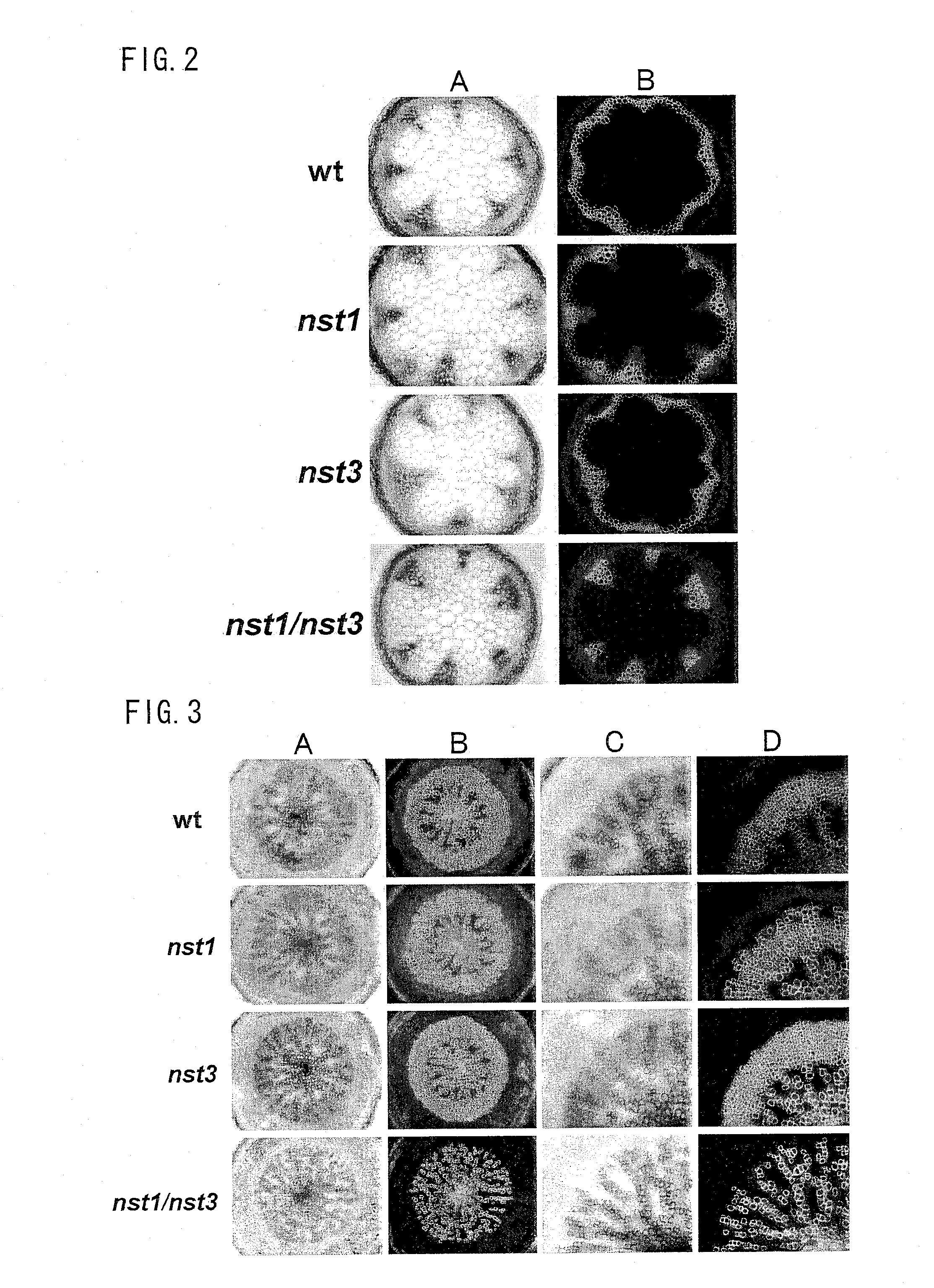
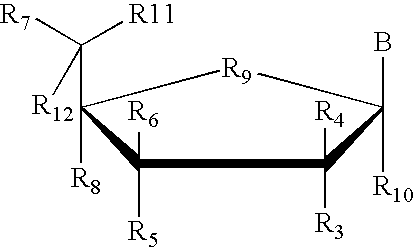
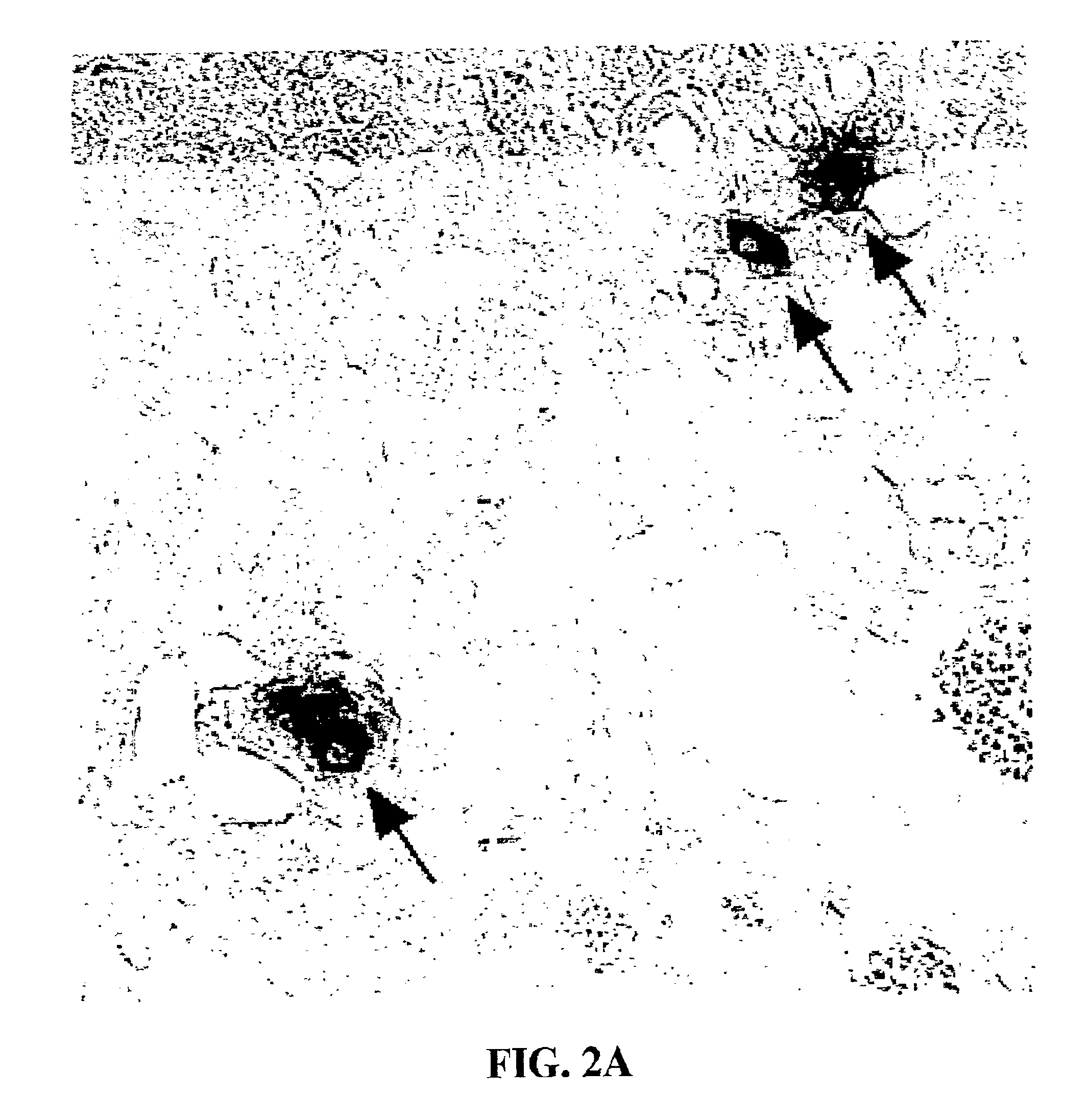
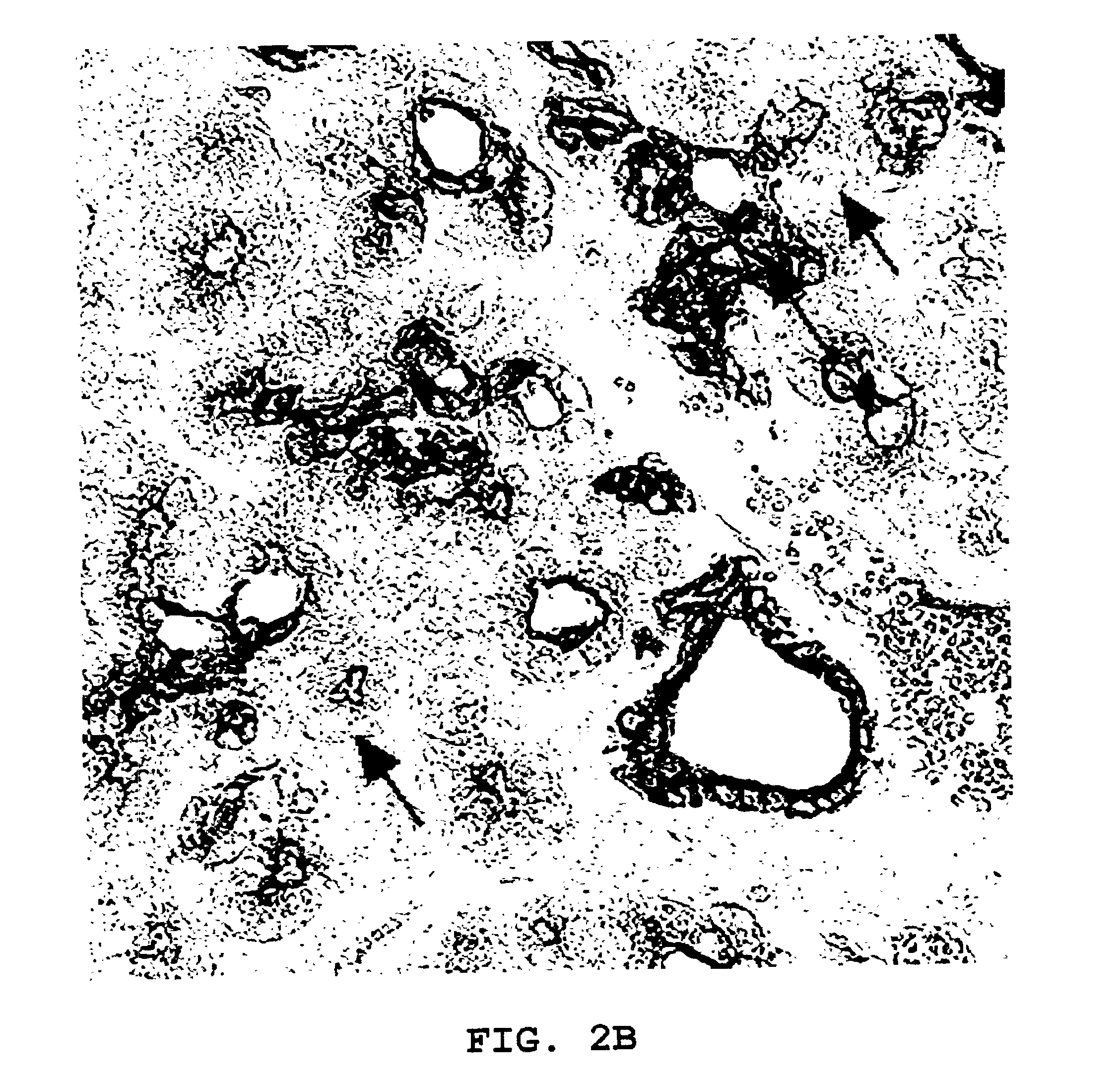
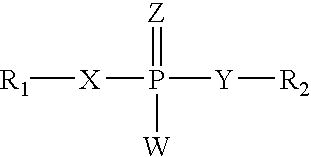Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
415 results about "Transcription Factor Gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
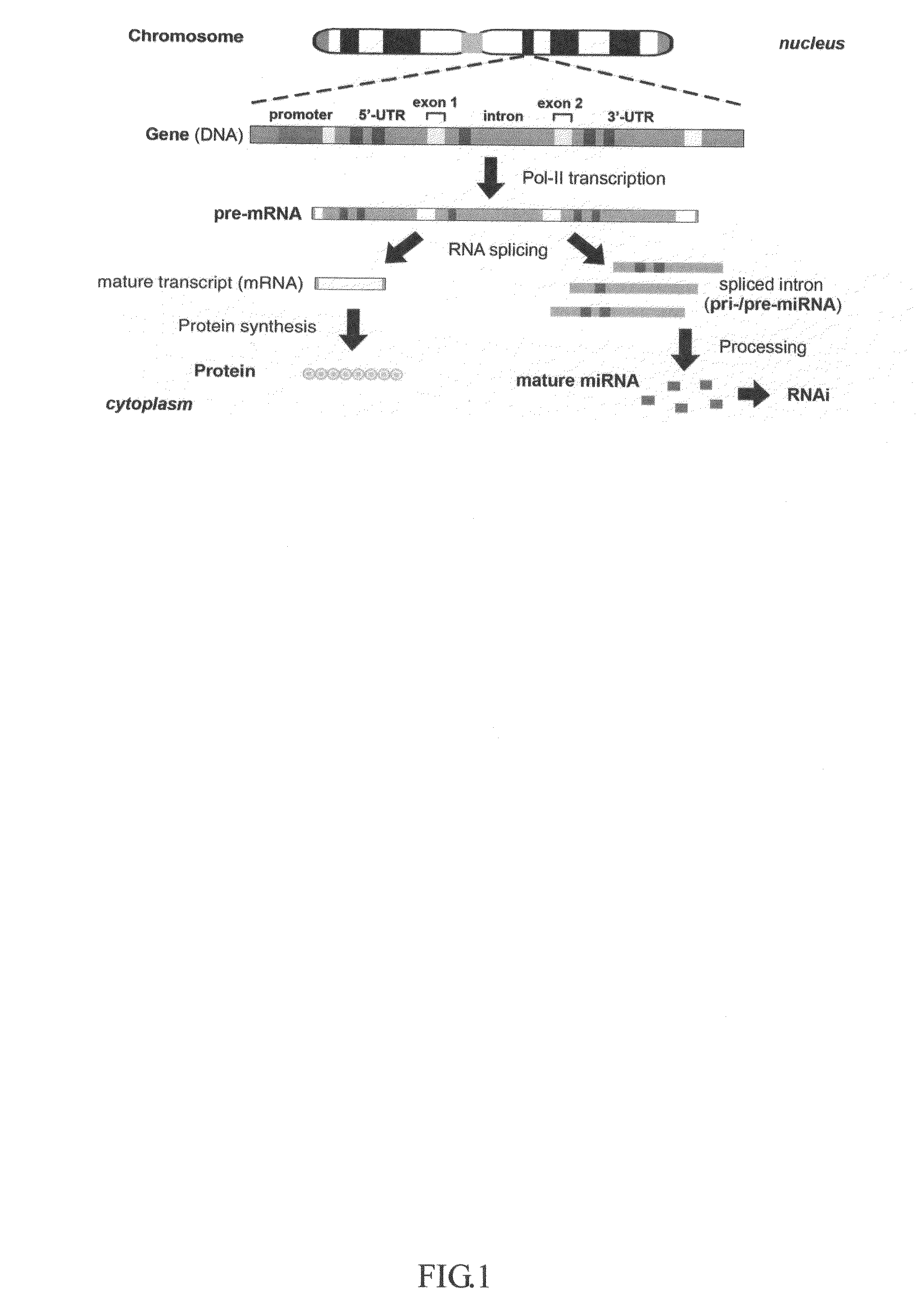
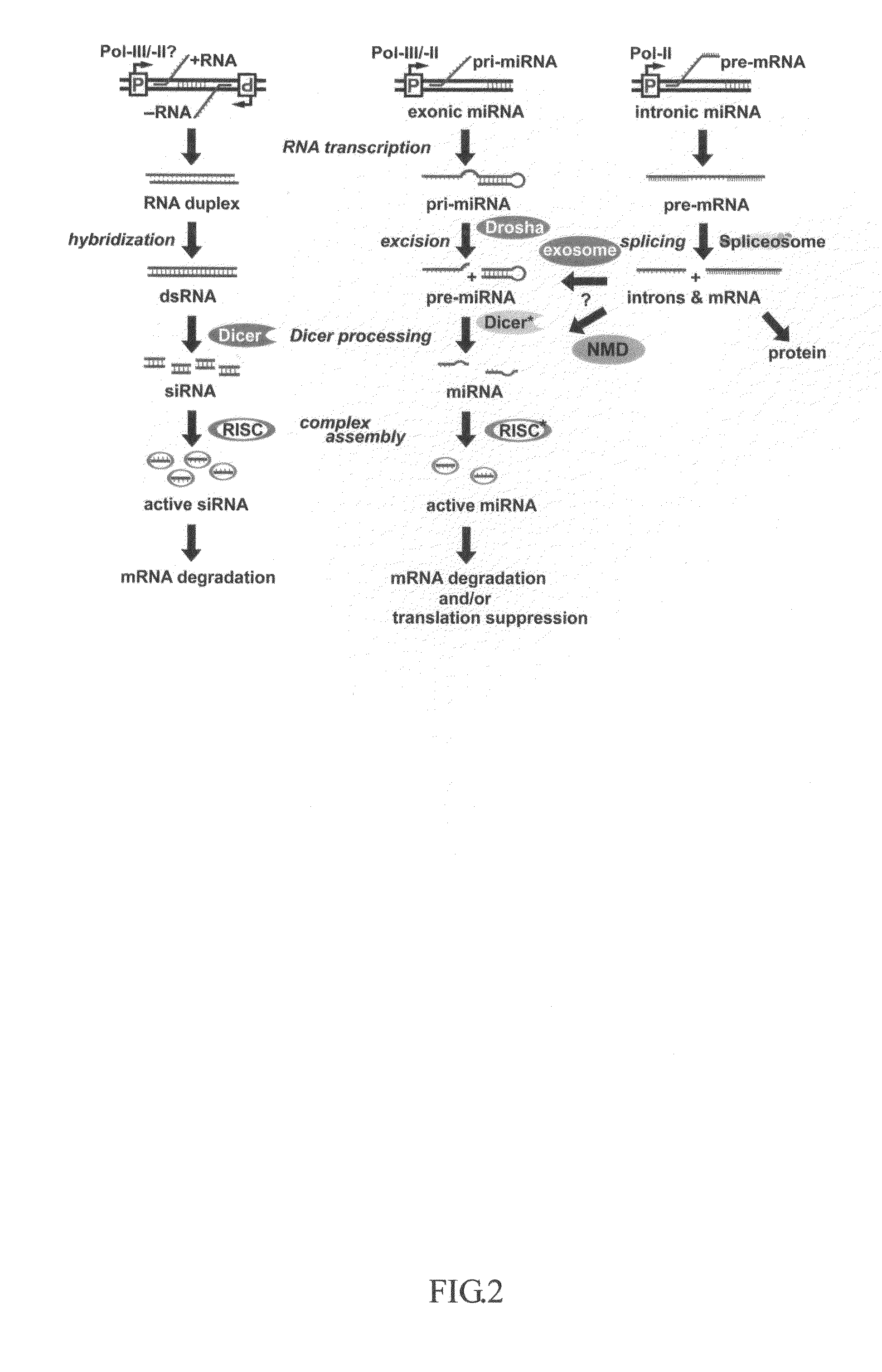
Genes that code for transcription factors.
Generation of human embryonc stem-like cells using intronic RNA
ActiveUS20080293143A1Stable and relatively long-term effectDelivery stabilityOther foreign material introduction processesElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentReprogrammingMammal
This invention generally relates to a method for developing, generating and selecting human embryonic stem (hES)-like pluripotent cells using transgenic expression of intronic microRNA-like RNA agents. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method and composition for generating a non-naturally occurring intron and its intronic components capable of being processed into mir-302-like RNA molecules in mammalian cells and thus inducing certain specific gene silencing effects on differentiation-related and fate-determinant genes of the cells, resulting in reprogramming the cells into a pluripotent embryonic stem (ES)-cell-like state. The ES-like cells so obtained are strongly express hES cell markers, such as Oct3 / 4, SSEA-3 and SSEA-4, and can be guided into various tissue cell types by treating certain hormones and / or growth factors under a feeder-free cell culture condition in vitro, which may be used for transplantation and gene therapies. Therefore, the present invention offers a simple, effective and safe gene manipulation approach for not only reprogramming somatic cells into ES-like pluripotent cells but also facilitating the maintenance of pluripotent and renewal properties of ES cells under a feeder-free cell culture condition, preventing the tedious retroviral insertion of four large transcription factor genes into one single cell as used in the previous iPS methods.
Owner:MELLO BIOTECH +1
Plant having reduced lignin and cellulose contents without reducing glucan content, method of producing the same and utilization thereof
InactiveUS20090019605A1Reduce the amount of solutionSuppress transcriptionBryophytesSugar derivativesCelluloseNucleotide
By inhibiting the function of a transcription factor that promotes transcription of a gene associated with the amounts of lignin and cellulose, a plant in which the amounts of lignin and cellulose are reduced without reducing the amount of glucan is produced. In this plant, glucan in the obtained cell wall components is in the state of highly easily undergoing saccharification. In this plant, moreover, natural dehiscence of pods is suppressed. A method of inhibiting the transcription factor includes a method in which a chimeric gene between a transcription factor gene and a polynucleotide that encodes a functional peptide capable of converting the transcription factor into a transcription repressor is introduced into a plant cell so that a chimeric protein in which the transcription factor is fused with the functional peptide is produced in a plant cell, and a method of inhibiting the expression of the transcription factor, such as knockout method or RNAi method. Thus, a plant in which the amounts of lignin and cellulose are reduced without reducing the amount of glucan is provided.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Transcription factor RNA interference reagents and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20050197312A1High-efficiency intracellular deliveryInhibit bindingGenetic material ingredientsEnzymesDouble strandGenome
The present invention concerns methods and reagents useful in modulating transcription factor gene expression in a variety of applications, including methods of use in therapeutic, diagnostic, target validation, and genomic discovery applications. Specifically, the invention relates to small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siRNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), and doublestranded RNA (dsRNA) molecules capable of mediating RNA interference (RNAi) against E2F1, NFkB, CREB-1, and / or CDC2A gene expression, useful in the treatment of cell cycle disorders, inflammatory conditions, reproductive disorders, cancers and any other condition that responds to modulation of E2F1, NFkB, CREB-1, and / or CDC2A expression and / or activity.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
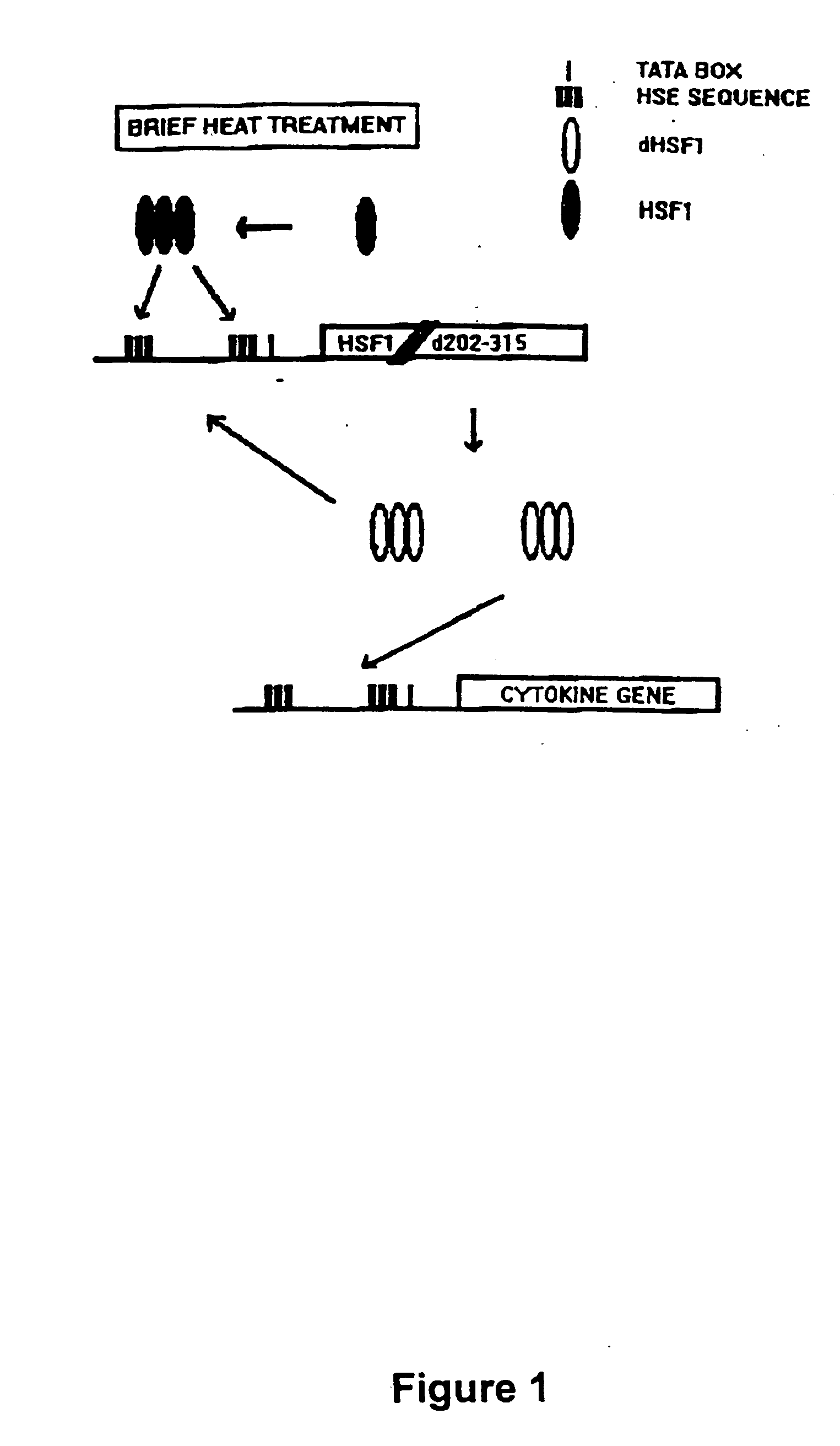
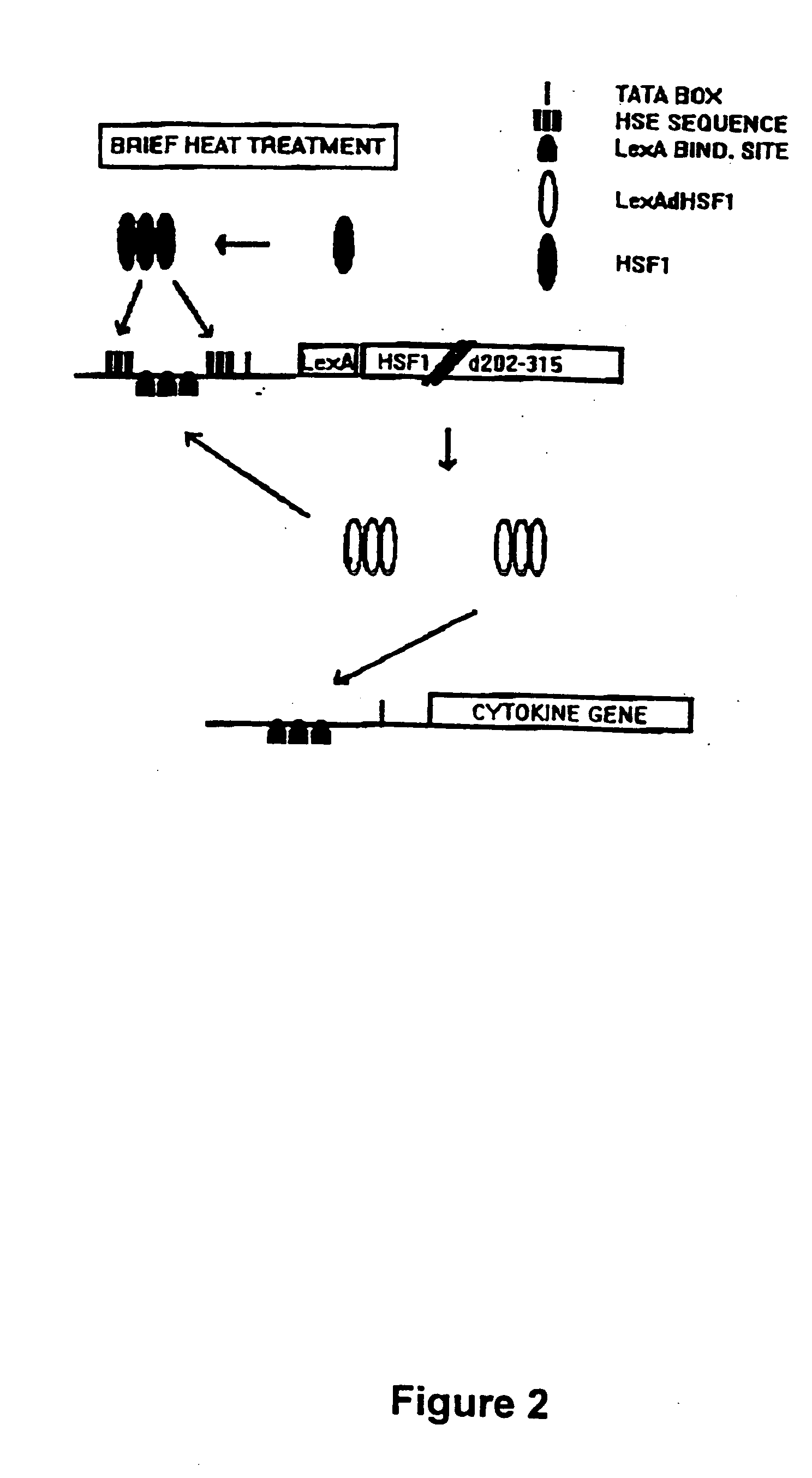
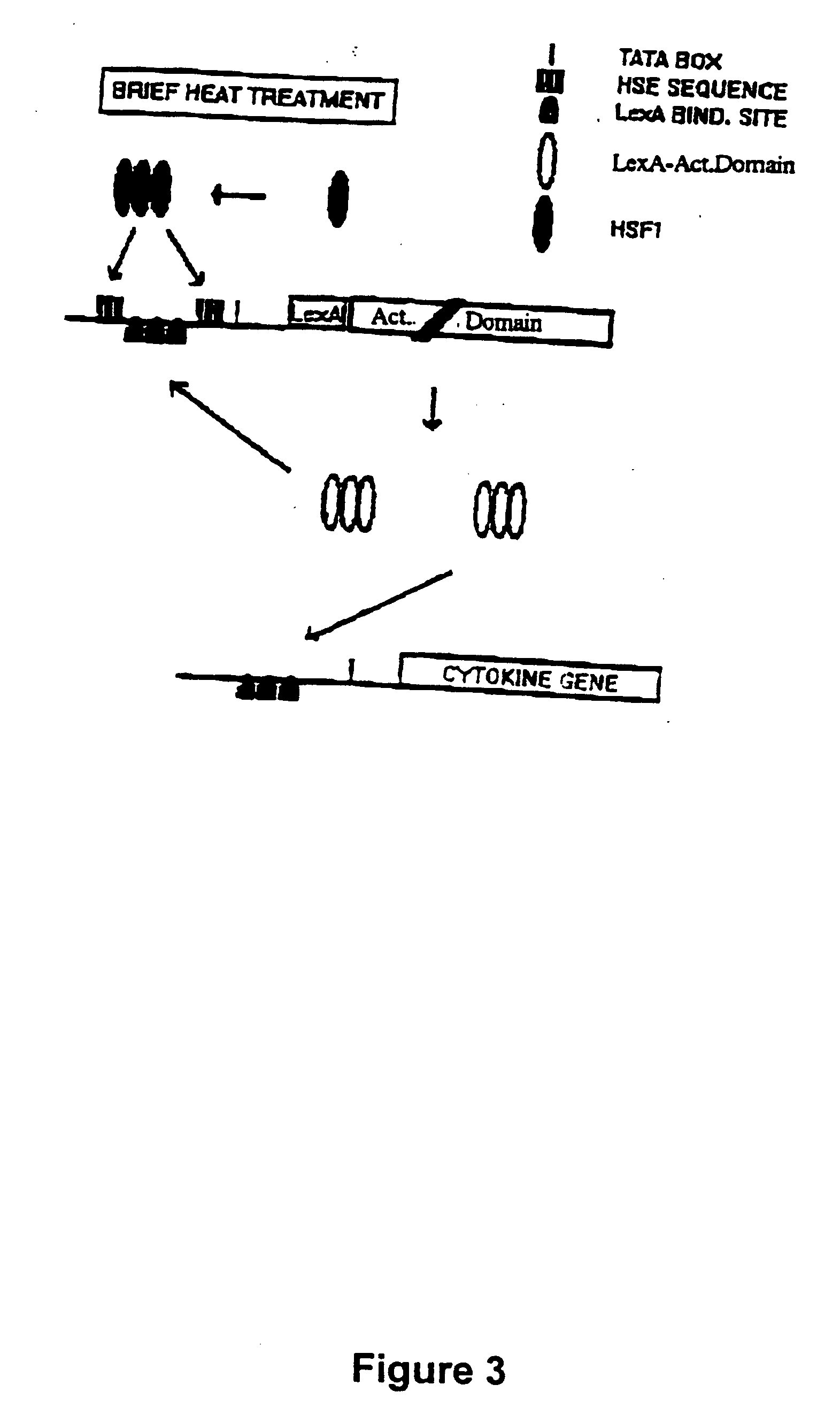
Molecular regulatory circuits to achieve sustained activation of genes of interest by a single stress
The exposure of cells, tissues and organs to “stress,” such as elevated temperature, stimulates production of active heat stress transcription factors (HSF), which in turn, induce expression of genes regulated by stress promoters. Normally, the activity of stress promoters declines after cells, tissues and organs are returned to a normal condition. The present invention relates to molecular circuits that provide for sustained expression of a gene of interest subsequent to a single application of stress. Generally, the molecular circuits of the invention comprise (a) a first nucleic acid molecule that comprises a gene encoding a transcription factor and a first promoter or a combination promoter activatable by stress and by the transcription factor, wherein the first promoter or the combination promoter and the transcription factor gene are operably linked, and (b) a second nucleic acid molecule that comprises a gene of interest and a second promoter activatable by the transcription factor, wherein the second promoter and the gene of interest are operably linked.
Owner:VOELLMY RICHARD
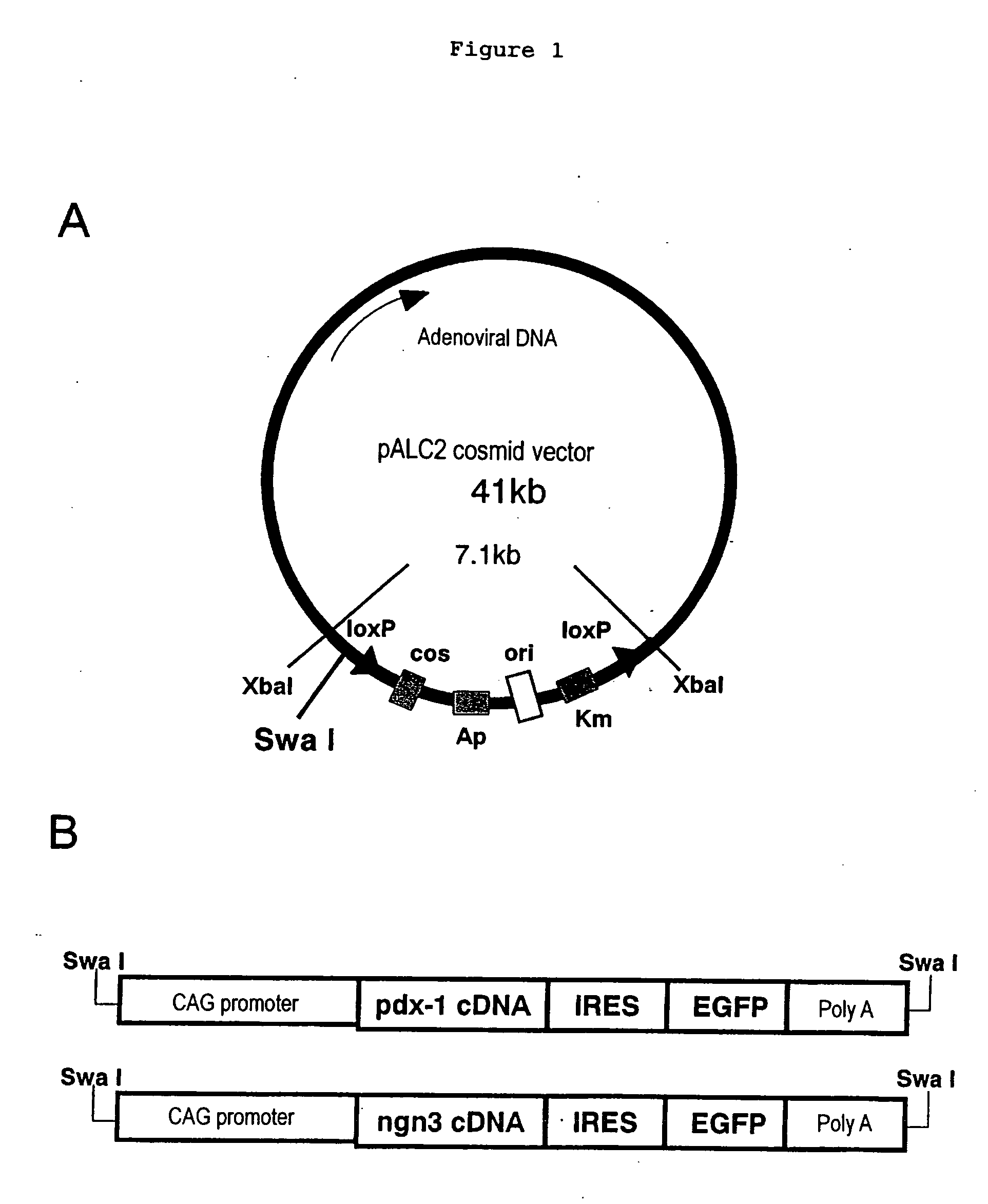
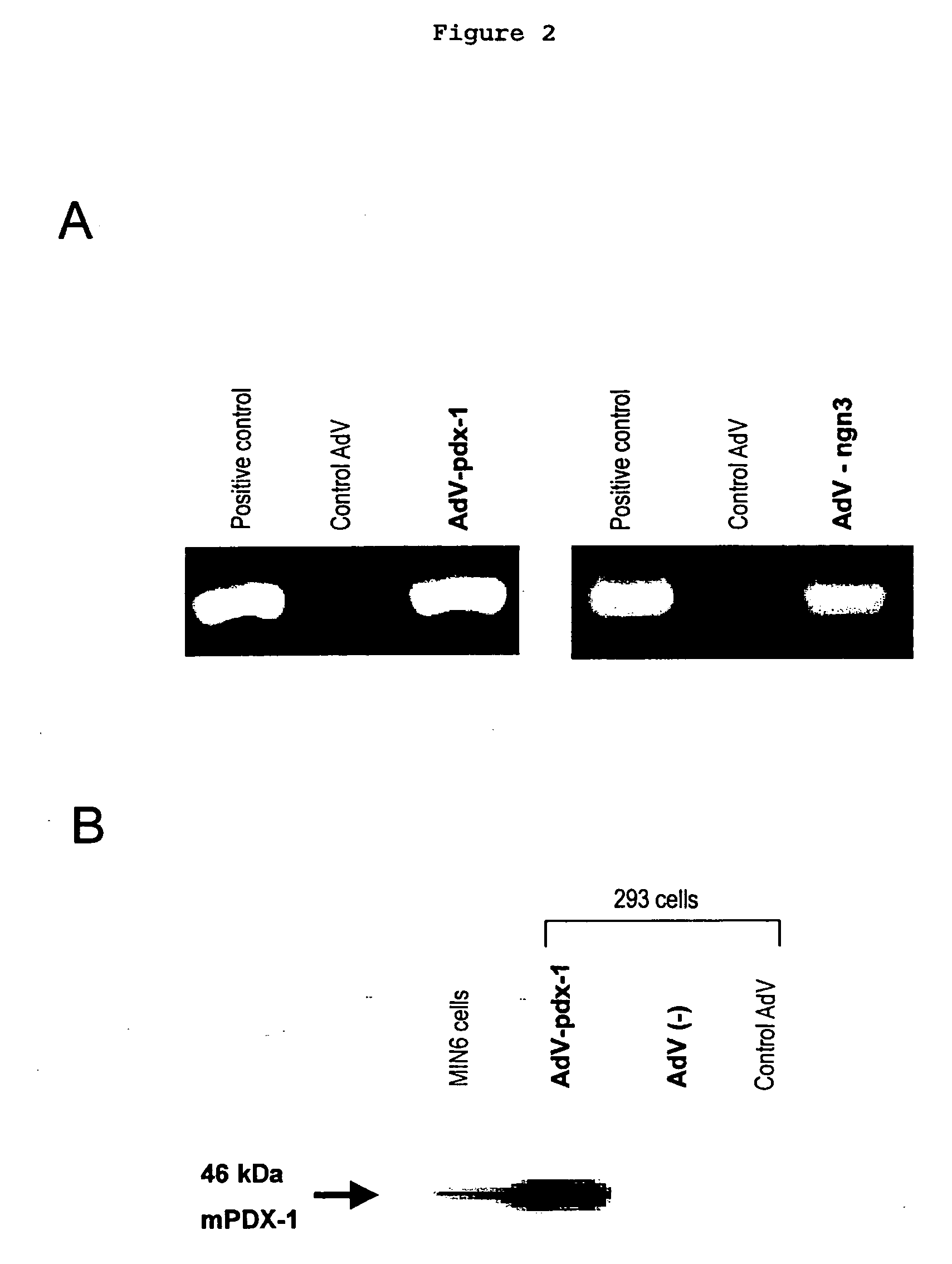
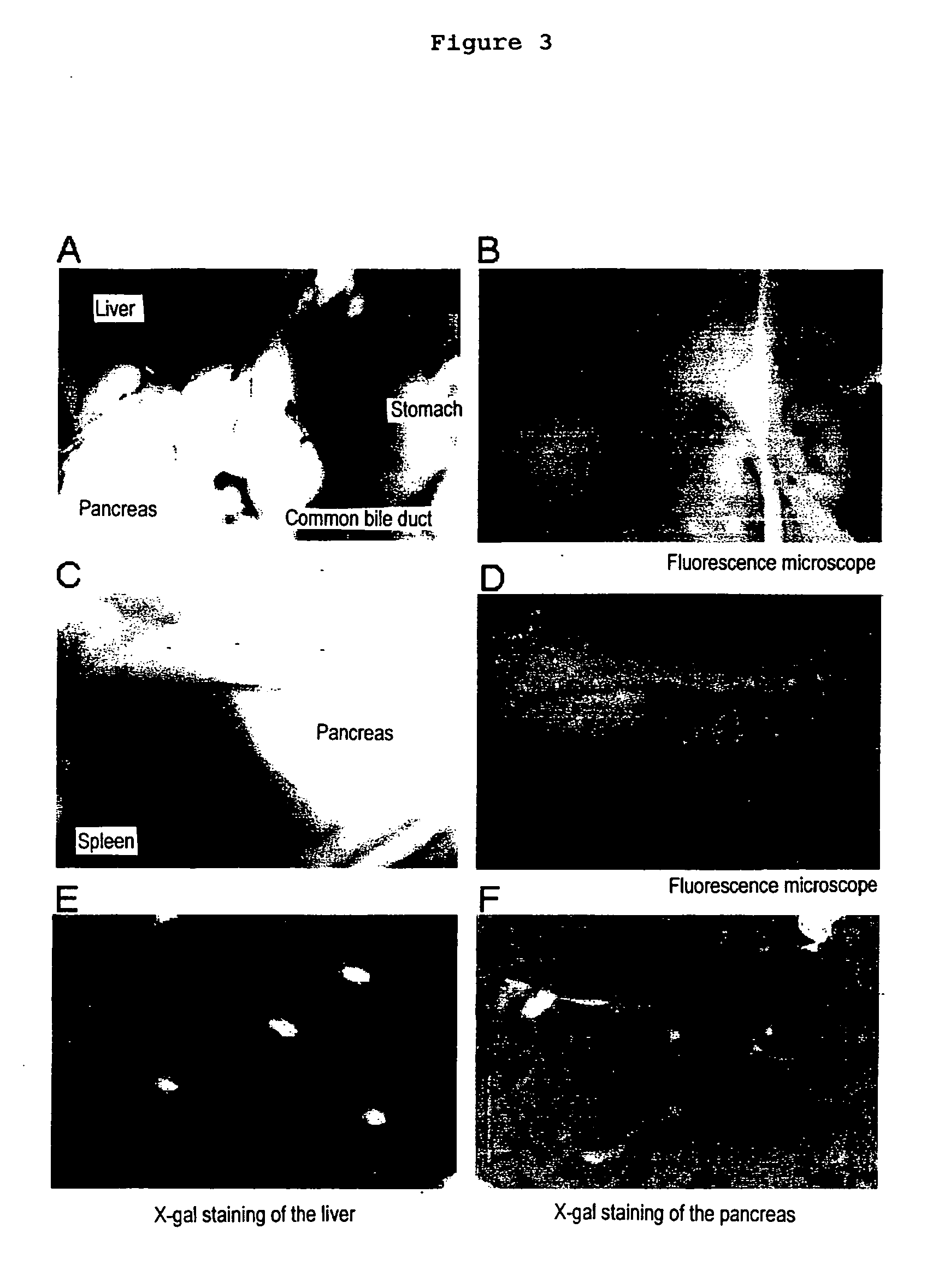
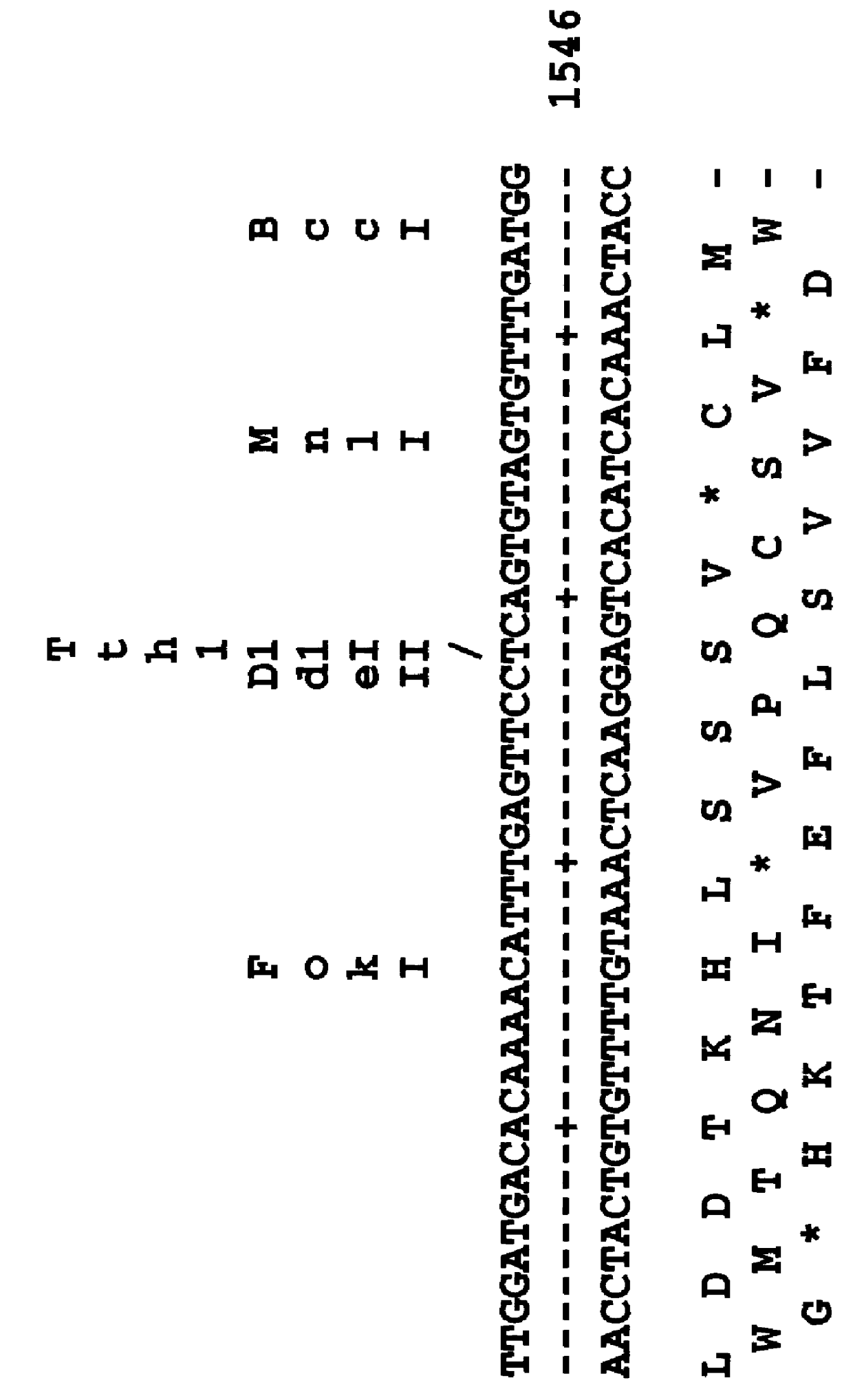
Induction of the formation of insulin-producing cells via gene transfer of pancreatic beta-cell-associated transcriptional factor
The present invention provides a method of inducing the formation of insulin-producing cells which comprises transferring a pancreatic β-cell associated transcriptional factor gene into the pancreas to induce the formation of insulin-producing cells. The pancreatic β-cell associated transcriptional factor gene is transferred into the pancreatic tissue stem cells by the ICBD injection without ligating the common bile ducts and thus the formation of insulin-producing cells is induced. In the present invention, pdx-1, neurogenin3, etc. are used as such pancreatic β-cell associated transcriptional factor gene and an adenoviral vector with the use of the Cre-loxP recombination system, etc. is used as a vector for transferring the pancreatic β-cell associated transcriptional factor gene into the pancreas. The method of the invention enables regeneration therapy for diabetes mellitus by inducing the formation of insulin-producing cells.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Modification of seed crops with transcription factors
InactiveUS6160202AReduce degradationReduce in quantitySugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesPhaseolin7s globulin
The present invention relates to an isolated transcription factor gene which is expressed in a maturing dicot seed and which encodes a transcription factor protein which targets a promoter of a gene encoding seed storage proteins. One group of such genes binds to 7S globulin (b-phaseolin) or lectin (PHA-L) promoters. Transcription factors identified as Pv Seed Factor-1 (PvSF1) and Vicilin-box Binding Protein-1 (VBP1) have been isolated. There is also disclosed a method for enhancing or reducing expression of seed storage protein, lectin or oil-protein genes in dicot seed crops comprising transforming a seed crop plant with the transcription factor gene of the invention.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY
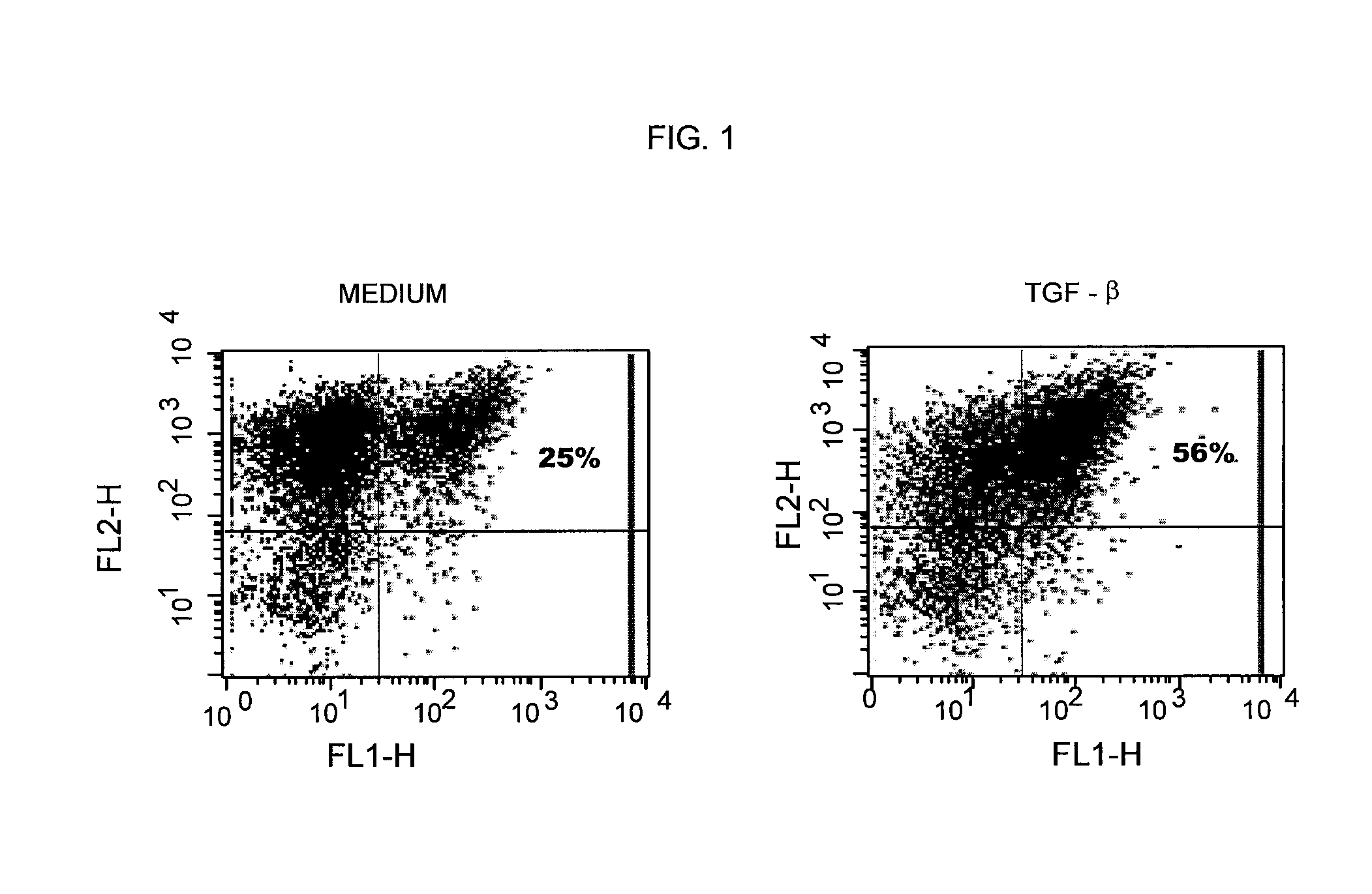
Methods and compositions for accelerating the generation of regulatory t cells ex vivo
The present invention is directed to generating regulatory T cells by treating a cell culture that includes non-regulatory T cells with a regulatory composition. The invention encompasses methods utilizing a regulatory composition that includes agents that prevent methylation of the locus for the FOXP3 transcription factor, agents that accelerate differentiation of T cells into suppressor cells, and agents that are histone deacetylase inhibitors. The invention also encompasses compositions of regulatory T cells generated by culturing non-regulatory T cells with a regulatory composition as well as the use of such regulatory T cells in the treatment of autoimmune diseases and aberrant immune responses.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Gene promoter of ginseng PgPDR3 responded by methyl jasmonate and application thereof
InactiveCN103103194AVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsNicotiana tabacumSalicylic acid
The invention discloses a gene promoter of ginseng PgPDR3 responded by methyl jasmonate and an application thereof. The sequences of the gene promoter of the ginseng PgPDR3 are shown in SEQ ID NO.1, or are the DNA sequences of which the homology with SEQ ID NO.1 is over 99%. According to the invention, a Genomewalker technology is adopted to clone, later the sequences of the gene promoter of the PDR transport protein is obtained, and then the expression vector Pcambia1301-ProPDR3::GUS of the promoter is built; if the promoter in the transgenic tobacco drives the GUS to express, and can be controlled by ginsenoside, salicylic acid, gibberellins and abscisic acid, the promoter participates in the transport and accumulation of the ginsenoside, which provides a basis for cloning the gene of key control recording factor in the ginsenoside transport signal pathway and controlling the transport and accumulation of the terpenoid, such as ginsenoside; and fine plants containing rich ginsenoside can be obtained by using a method for controlling or improving the ginseng and other plants via the promoter or the derivative thereof.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Application of panax japonicus transcription factor gene PjWRKY1
ActiveCN105087601AIncrease contentHigh expressionGenetic engineeringFermentationBiotechnologyGenomics
The invention discloses application of panax japonicus transcription factor gene PjWRKY1, namely, application in improving the expression quantity of key enzyme genes in the biological synthesis of panax japonicus saponins, and increasing the content of saponins in panax japonicus callus. The nucleotide sequence of the PjWRKY1 gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, and WRKY transcription factors are coded. Through the adoption of functional genomics and techniques related to metabolic engineering, a panax japonicus PjWRKY1 transcription factor is proved to have the effect of positively regulating the biological synthesis of panax japonicus saponins; when the panax japonicus PjWRKY1 transcription factor gene disclosed by the invention is established on a plant expression vector and transferred into the panax japonicus callus for over expression, the expression quantity of the key enzyme genes in the synthetic route of panax japonicus saponins is increased, and the yield of panax japonicus saponins is increased.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
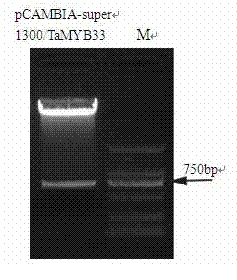
Salt-tolerant and drought-resistant gene TaMYB33 of wheat and coding protein as well as application thereof
InactiveCN102234653AImprove salt toleranceImprove drought resistanceFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyResistant genes
The invention particularly relates to a salt-tolerant and drought-resistant gene TaMYB33 of wheat and coding protein as well as application thereof, belonging to the technical field of biological gene engineering. The salt-tolerant and drought-resistant gene TaMYB33 of wheat is a nucleotide sequence SEQ ID No.1 in a sequence table. The invention has the beneficial effects that an MYB transcription factor gene TaMYB33 of wheat is obtained by cloning for the first time, and a mediation method of agrobacterium tumefaciens is used for transferring the gene into arabidopsis. The comparative analysis proves that compared with a wild arabidopsis plant, the salt tolerance and drought resistance of a transgenic arabidopsis plant containing the gene TaMYB33 provided by the invention are obviously improved.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN +1
Gingko MADS-box transcription factor gene GbMADS9 for controlling blossoming of plants and encoding protein and application of Gingko MADS-box transcription factor gene GbMADS9
InactiveCN106591322AShortened childhoodImprove tolerancePlant peptidesGenetic engineeringTotal rnaPcr method
The invention provides Gingko MADS-box transcription factor gene GbMADS9 for controlling blossoming of plants; the gene is acquired by subjecting cDNA as a template to PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification, wherein the cDNA is acquired by reverse transcription of total RNA of gingko female flowers. The gene has the advantages that the gene GbMADS9 is capable of controlling blossoming of plants and shortening juvenile phase of plants, and under induction of GA3, ABA, salt stress, drought stress and cold damage stress, the overexpressed gene GbMADS9 is capable of enhancing plant tolerance to osmotic stress; the gene is applicable to controlling the blossoming phase of plants.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
Soybean holy bean 9# NAC transcription factor gene GmST1 and application thereof
ActiveCN102660554AImprove salt/drought toleranceImproves salt/drought toleranceFermentationGenetic engineeringTransgeneGenetic engineering
The invention discloses a soybean holy bean 9# NAC transcription factor gene GmST1 and a plant expression vector of the gene GmST1 and further discloses application of the gene GmST1 in improving salt / drought resistance of arabidopsis thaliana and soybean plants. An experiment proves that compared with a non-transgenic plant, the salt / drought resistance of a transgenic plant is greatly improved. Therefore, the theory basis and the practice foundation are provided for improving the salt / drought resistance of plants through genetic engineering means. The soybean holy bean 9# NAC transcription factor gene GmST1 can be widely used for cultivating salt / drought resistant plant varieties.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Nitrogen-Regulated Sugar Sensing Gene and Protein and Modulation Thereof
InactiveUS20070250956A1Increased and decreased resistanceEnhanced diminished requirementSugar derivativesClimate change adaptationNitrogenSugar
The present invention relates to a nitrogen-regulated GATA transcription factor gene required for sugar sensing and the modulation of the expression of this gene to modulate a characteristic in a plant. The GATA transcription factor of the present invention is involved in regulating sugar sensing in plants and its expression is influenced by nitrogen status. Increased expression of this or substantially similar genes can produce plants with improved nitrogen utilization and increased yield.
Owner:GUELPH UNIV OF
Rice SBP-box transcription factor genes and application thereof
ActiveCN104450744AImproved salt stress resistanceRaw materials are simpleMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologySalt resistance
The invention provides rice SBP-box transcription factor genes and application thereof. The rice SBP-box transcription factor genes comprise SEQ ID No.1 nucleotide sequences and SEQ ID No. 2 amino acid sequences, coding sequences with the transcription factors and carriers or hosts containing the coding sequences. The invention further relates to a method of improving salt resistance of plants and a method of choosing plants with high salt resistance. The invention provides a new method of improving and searching salt resistance of plants; and the new method has wide application prospects.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
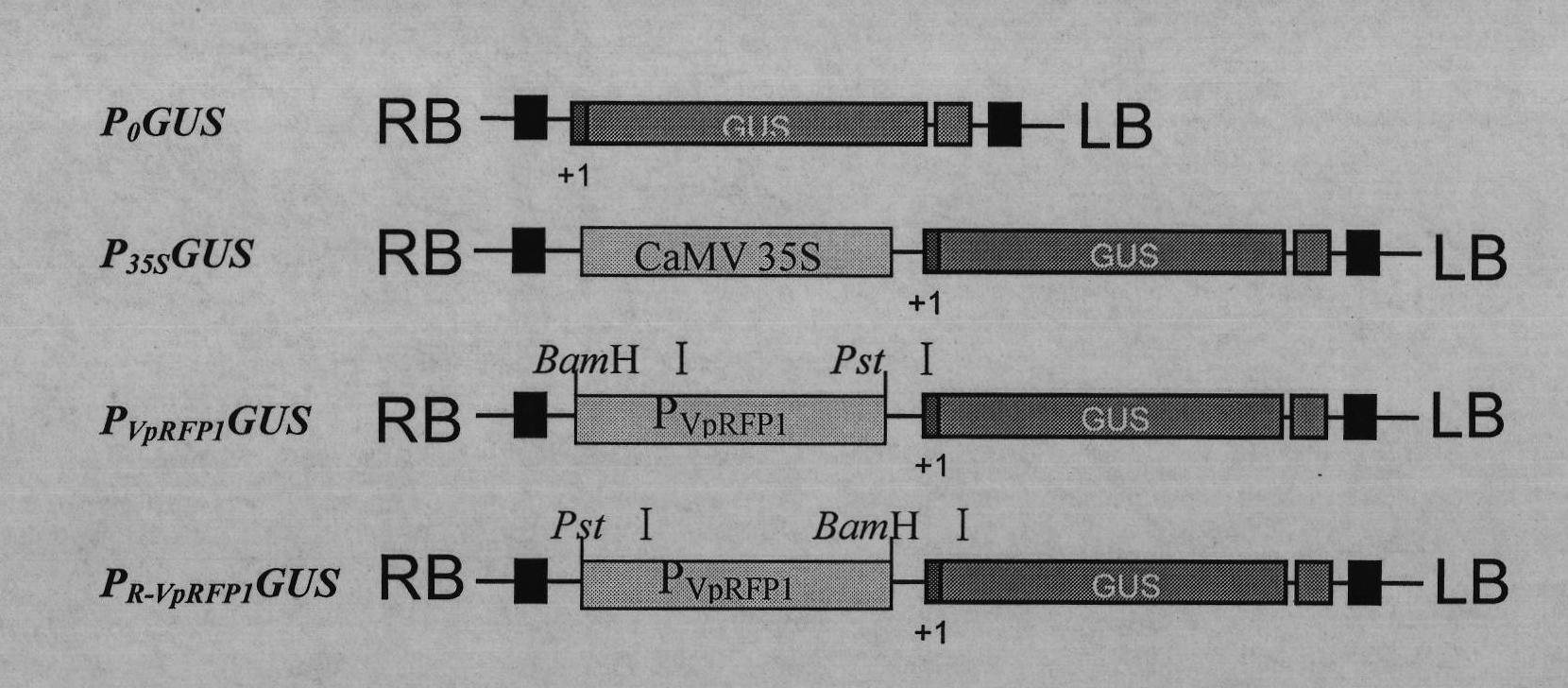
Grapevine powdery mildew resistance transcription factor gene VpRFP1 promoter sequence and application thereof
InactiveCN102121005AMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionPlant hormoneDisease
The invention relates to a grapevine powdery mildew resistance transcription factor gene VpRFP1 promoter sequence and application thereof. In the sequence, a full-length 1249bp promoter sequence of a Chinese wild vitis pseudoreticulata powdery mildew transcription factor gene VpRFP1 is cloned by adopting chromosomal walking in combination with a nested polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technology, wherein the sequence comprises 103 TATA-boxes and 27 CAAT-boxes, has 8 elements related to plant defense reaction, 14 photoreaction elements, 5 plant hormone response elements, and 14 other unknown elements. By adopting an agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated instantaneously converted nicotiana benthamiana leaves analyzing method, the function of the Chinese wild vitis pseudoreticulata powdery mildew transcription factor gene VpRFP1 promoter proves that: the promoter has stronger promotion activity, can actively respond to pathogen invasion and disease resistant signal substances, and can improve the disease resistance and high temperature resistance of wheat, rice, potato, corn, soybean, rape and other plants through a transgenic method.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
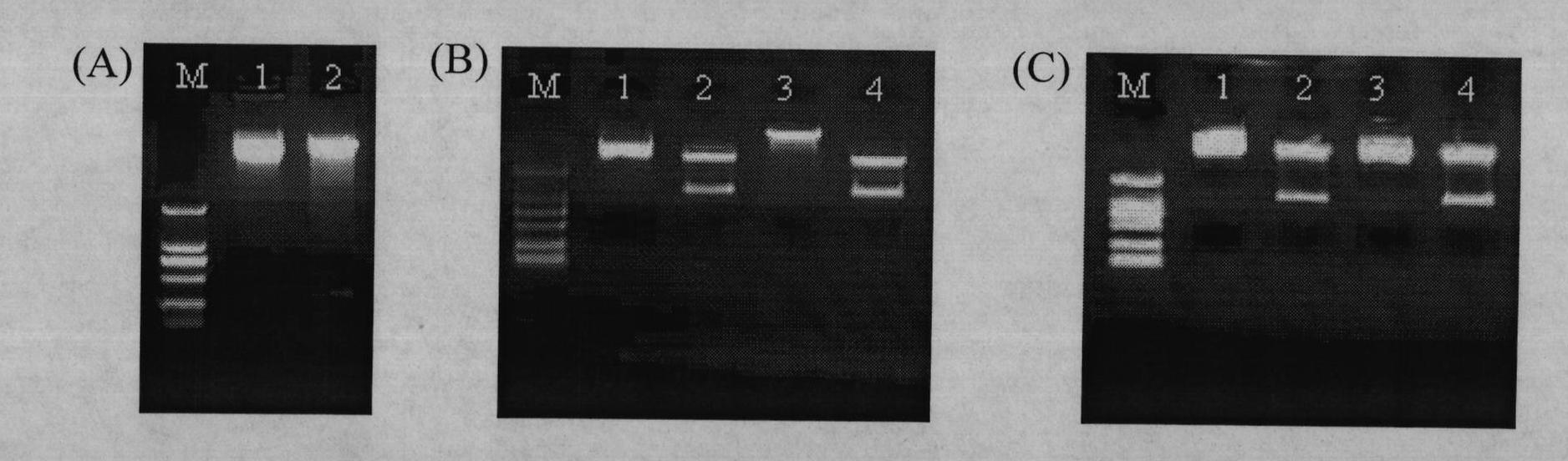
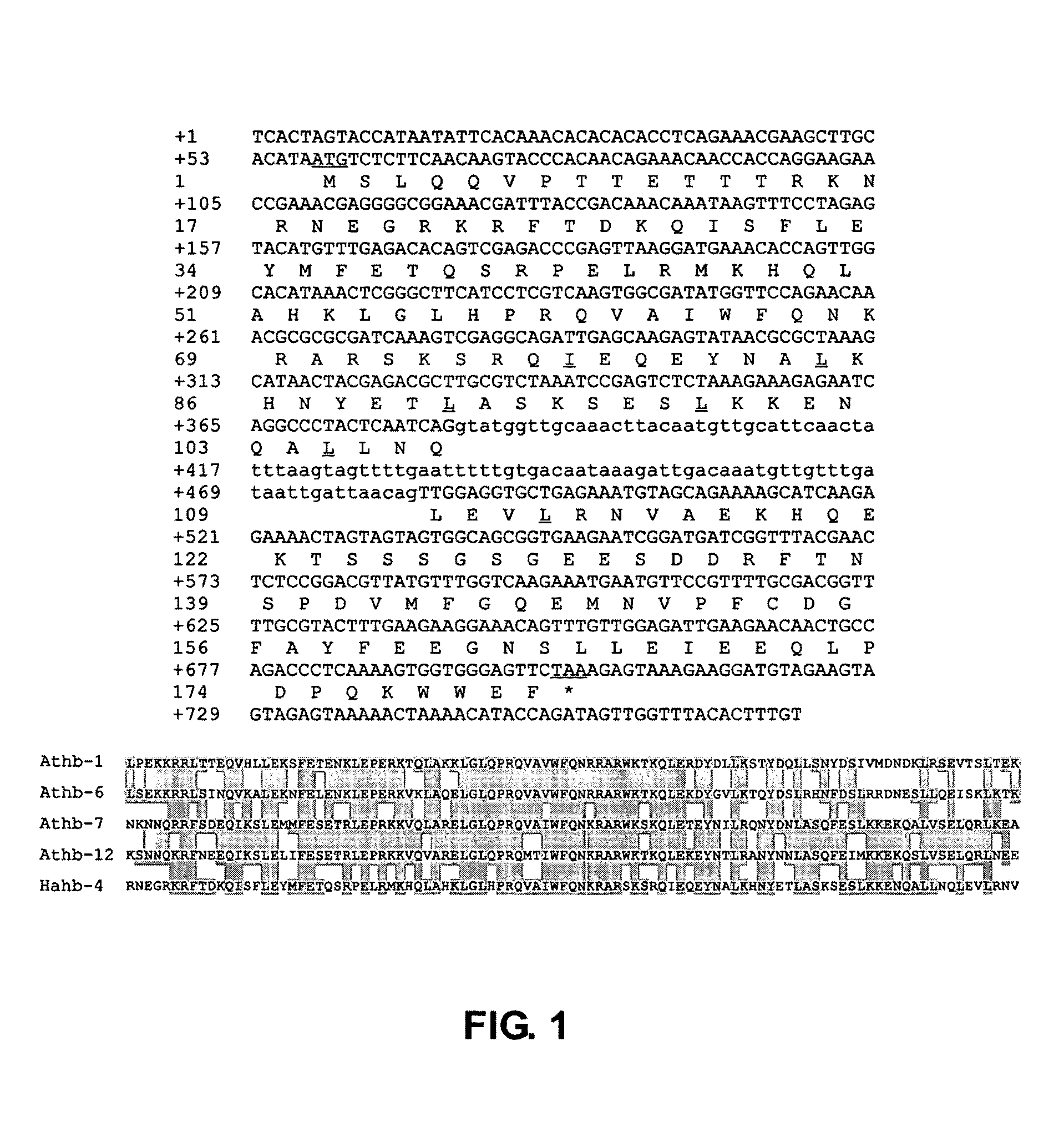
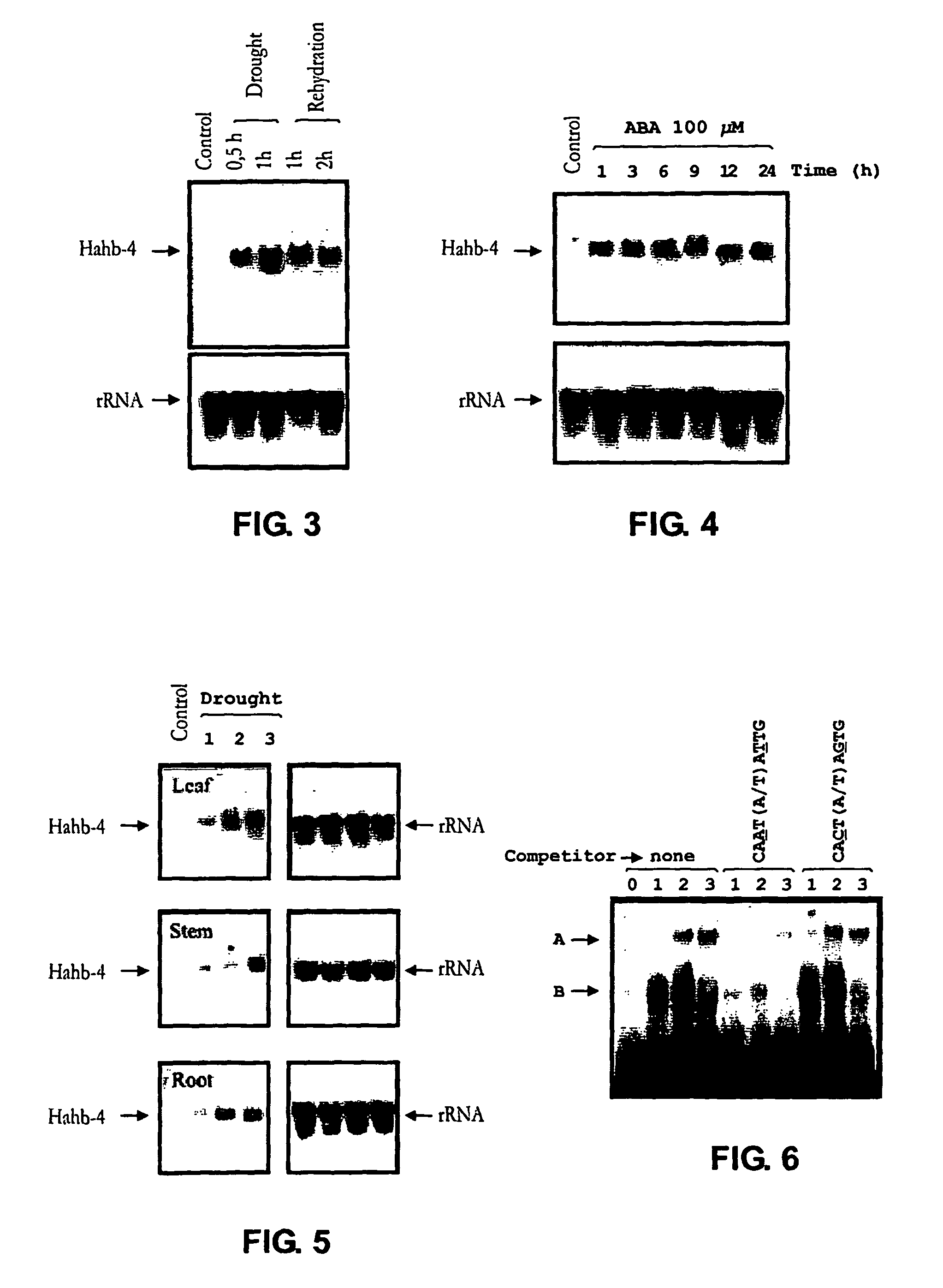
Transcription factor gene induced by water deficit conditions and abscisic acid from Helianthus annuus, promoter and transgenic plants
A new transcription factor coding gene induced by water deficit or abscisic acid of Helianthus annuus, having a homeodomain associated to a leucine zipper, was characterized. The transcription factor is useful to be cloned in DNA constructions for transforming host cells and plants. The transgenic plants comprising the transcription factor gene are tolerant and resistant to harmful environmental conditions such as water stress and high salinity. A nucleic acid promoting sequence is also provided wherein the sequence is induced by water deficit or abscisic acid. Constructions, host cells and transgenic plants that comprise the transcription factor gene are provided.
Owner:BIOCERES
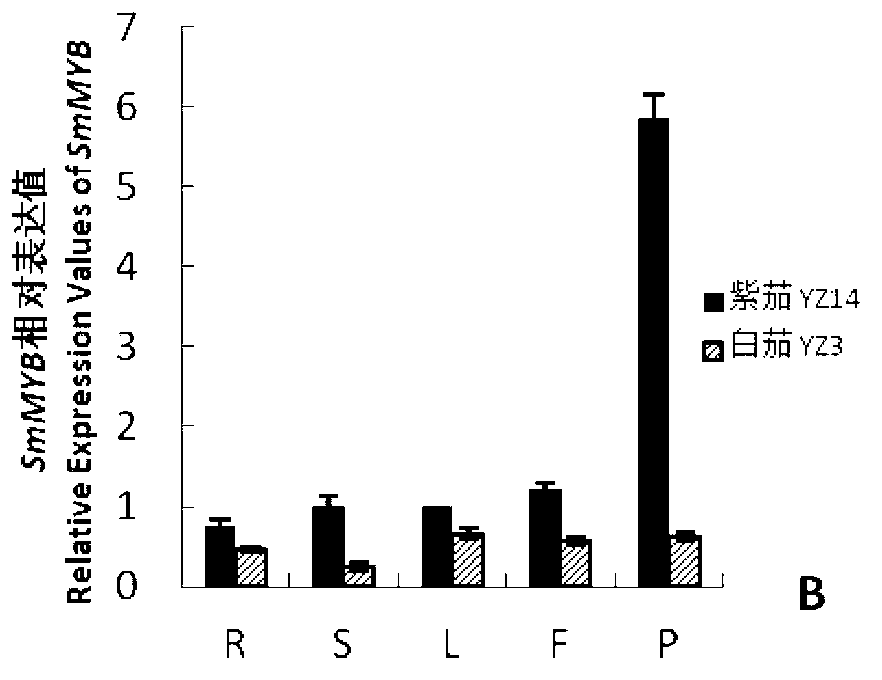
Gene sequence for synthesizing relative transcription factor SmMYB by eggplant anthocyanidin
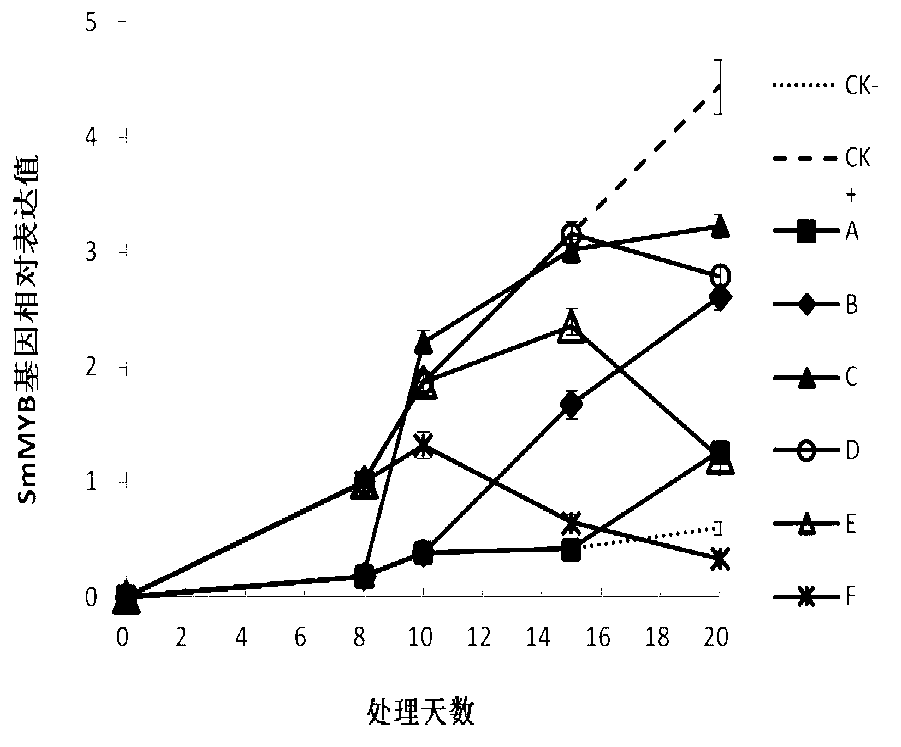
The invention discloses a gene sequence for synthesizing a relative transcription factor SmMYB by eggplant anthocyanidin, comprising a nucleotide sequence shown in 1st-1035th nucleotides in SEQ ID NO.1, wherein a polypeptide coded by the gene sequence comprises an amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The gene sequence in the invention is a key regulation and control gene for synthesizing eggplant anthocyanidin, the relative transcription factor SmMYB is synthesized by eggplant anthocyanidin. A downstream gene which is regulated and controlled by the gene sequence and is closely related to anthocyanidin synthesis, and other transcription factor genes manually acting with the gene sequence, are screened. The gene sequence in the invention is applied to obtain an eggplant kind with high anthocyanidin content and excellent resistance quality.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Maize water-logging tolerance-related transcription factor gene zm-bRLZ, molecular marker and application
InactiveCN101974537AMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleotideCandidate Gene Association Study
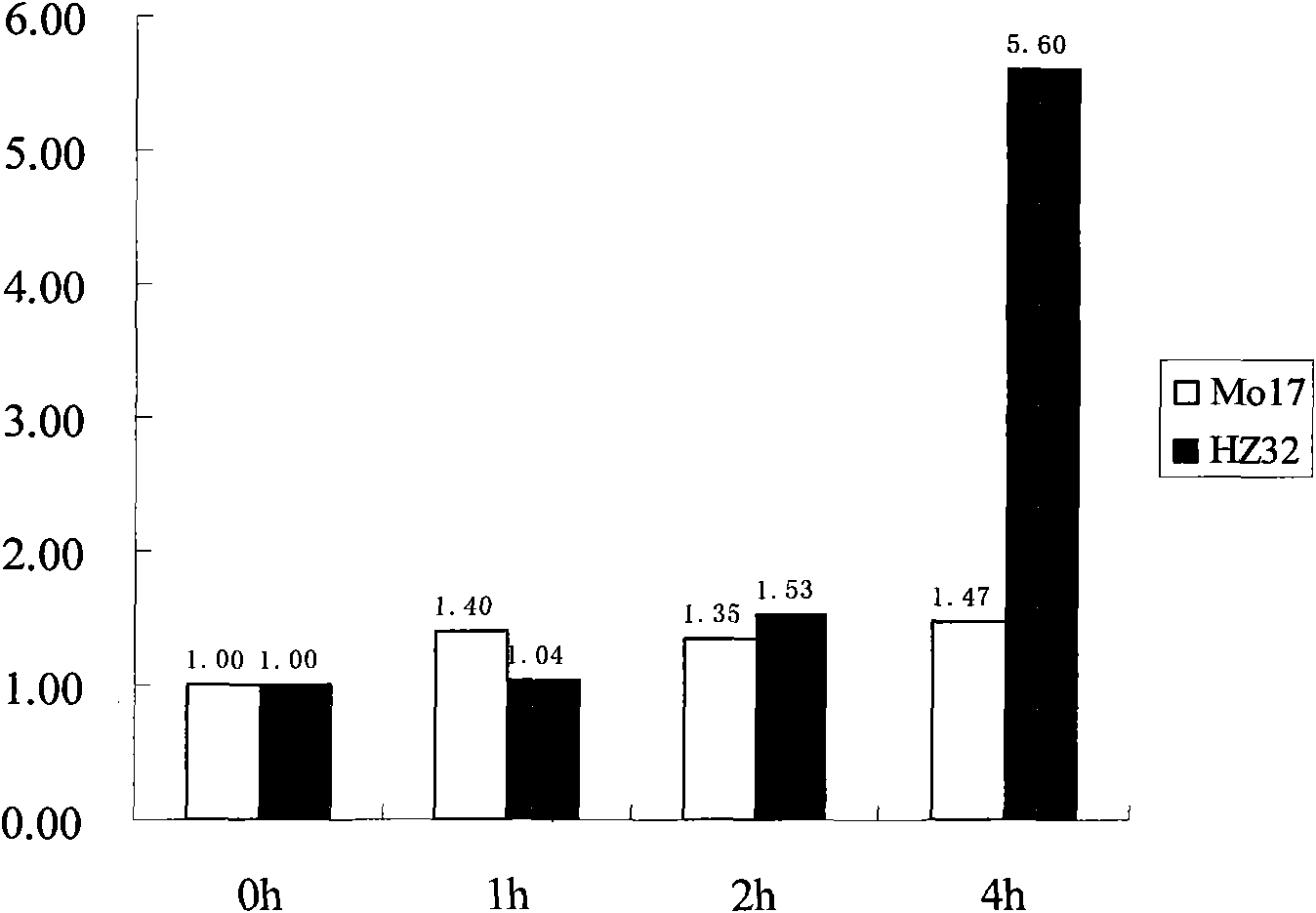
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant gene engineering, and relates to clone and application of a maize water-logging tolerance-related transcription factor gene zm-bRLZ. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID No. 1, and the gene has a total length of 4,027bp and comprises 6 exons. The cDNA sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID No. 2, and 282 amino acids are encoded on the gene. In flooding stress, the expression of the gene in maize inbred line Hz32 seedling roots is up-regulated and the expression level of the gene in the Mo17 is kept unchanged. The in-vitro combination of a gene protein product and an antidiuretic hormone (ADH) promoter anaerobic response factor shows that the zm-bRLZ gene has a regulation and control effect on an anaerobic induced gene. A pair of cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence (CAPS) markers is developed by utilizing zm-bRLZ gene sequence difference of the maize water-logging tolerance inbred line Hz32 and high-sensitivity K12. The gene is positioned at a water-logging tolerance quantitative trait locus (QTL) peak part of 9.04bin by utilizing K12*Hz32 F2 group. A candidate gene correlation analysis proves that a zm-bRLZ gene promoter region and a plurality of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) sites at a 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR) are all obviously associated with a plurality of water-logging tolerance indexes.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Application of panax japonicus transcription factor gene PjERF1
ActiveCN105087599AIncrease contentHigh expressionFermentationGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyEnzyme Gene
The invention discloses application of panax japonicus transcription factor gene PjERF1, namely, application in improving the expression quantity of key enzyme genes in the biological synthesis of panax japonicus saponins, and increasing the content of saponins in panax japonicus callus. The nucleotide sequence of the PjERF1 gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, and AP2 / ERF transcription factors are coded. Through the adoption of functional genomics and techniques related to metabolic engineering, a panax japonicus PjERF1 transcription factor is proved to have the effect of positively regulating the biological synthesis of panax japonicus saponins; when the panax japonicus PjERF1 transcription factor gene disclosed by the invention is established on a plant expression vector and transferred into the panax japonicus callus for over expression, the expression quantity of the key enzyme genes in the synthetic route of panax japonicus saponins is increased, and the yield of panax japonicus saponins is increased.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Stress resistance ERF transcription factor gene derived from Brassica napus
InactiveCN101736012AImprove low temperature resistanceStrong frost resistancePlant peptidesFermentationBrassicaPolymerase L
The invention provides a stress resistance ERF transcription factor gene derived from Brassica napus, a preparation method and usage thereof. The Brassica napus stress resistance ERF transcription factor gene is BnaERFB1-2-Hy15, the base sequence thereof is shown as SEQ ID No1. In the invention, the gene sequence of Brassica napus stress resistance ERF transcription factor is cloned from Brassica napus seedling by polymerase amplification technology, the obtained ERF transcription factor gene can be used in plant transformation to improve stress resistance of plants.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
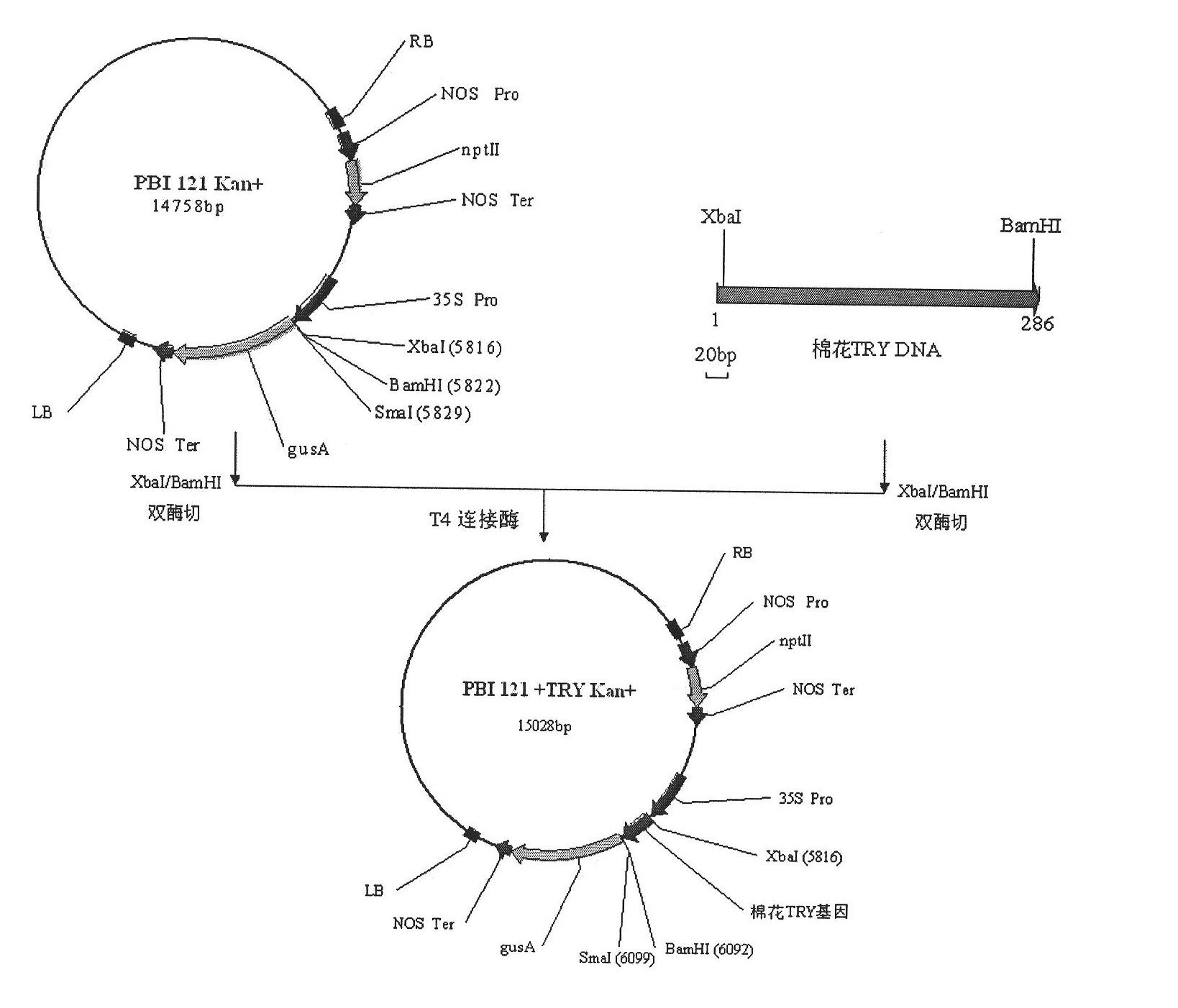
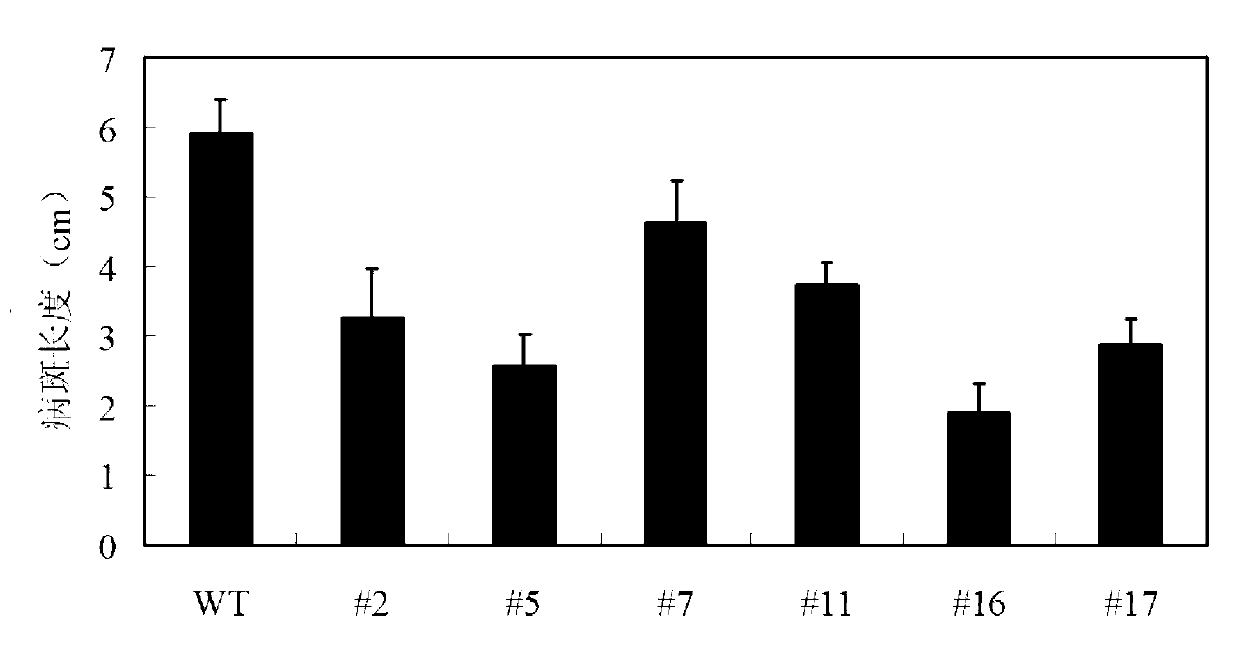
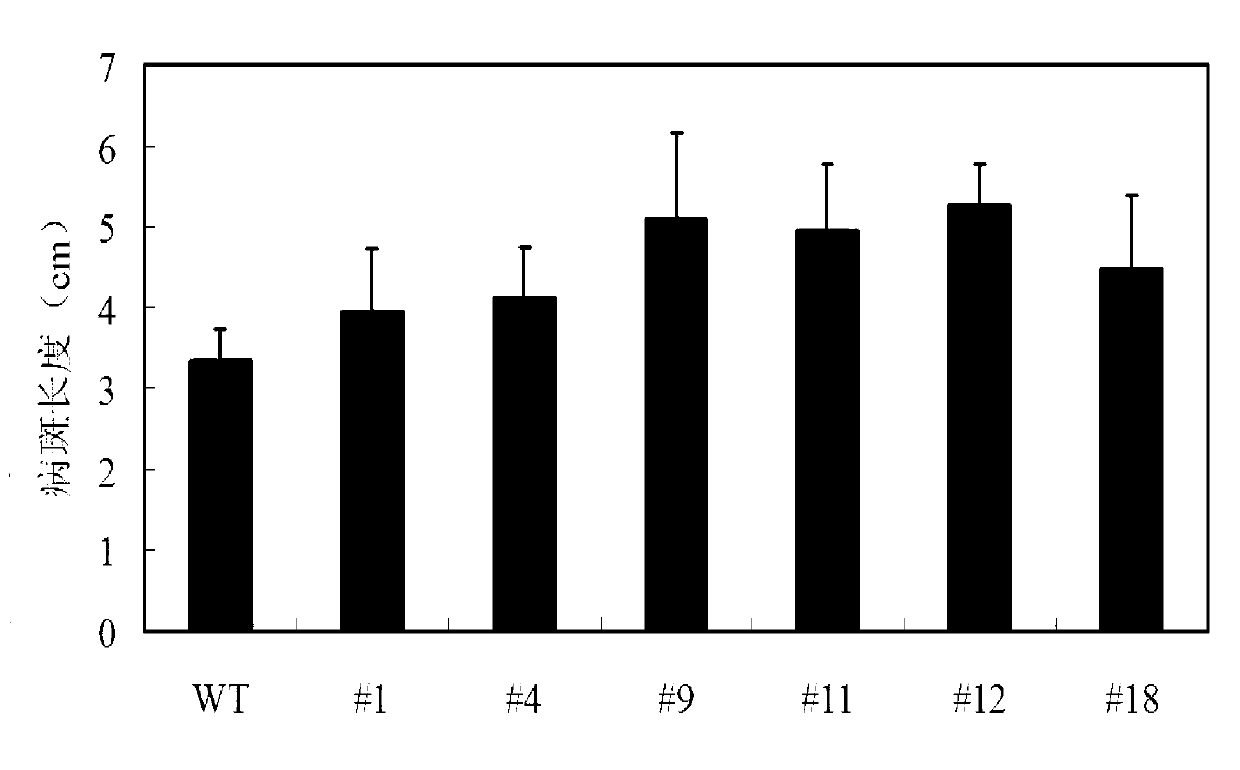
Cotton TRY gene
The invention relates to the field of plant genetic engineering and provides a TRY transcription factor gene of cotton. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO:1. TRY transgenic cotton is obtained by constructing a pBI121-CRY expression vector and transforming tobacco by using agrobactrium tumefaciens. The TRY gene of the cotton is expressed in transgenic tobacco and inhibits the development of leaf indumentums and root hairs of the transgenic tobacco.
Owner:陈全家 +1
Application of OsWRKY28 transcription factor gene of rice in improvement of plant disease resistance
ActiveCN102816773AIncrease resistanceFermentationGenetic engineeringDiseaseGenetically modified rice
The invention belongs to the field of plant genetic engineering and discloses application of OsWRKY28 transcription factor gene of rice in improvement of plant disease resistance. In research of functions of the WRKY transcription factor gene OsWRKY28 of rice as shown inthe SEQ ID NO.1 by means of a reverse genetics method, the OsWRKY28 transcription factor gene is found to have positive regulation function for resistance to rice banded sclerotial blight. The OsWRKY28 transcription factor gene is planted on a proper plant expressing carrier to convert cells or rice, and resistance of obtained rice with OsWRKY28 excessive-expression transcription factor to the banded sclerotial blight is evidently improved. Accordingly, disease resistance of rice and other crops can be improved by the OsWRKY28 gene, and new varieties of transgenosis plants resistant to the banded sclerotial blight can be cultured.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
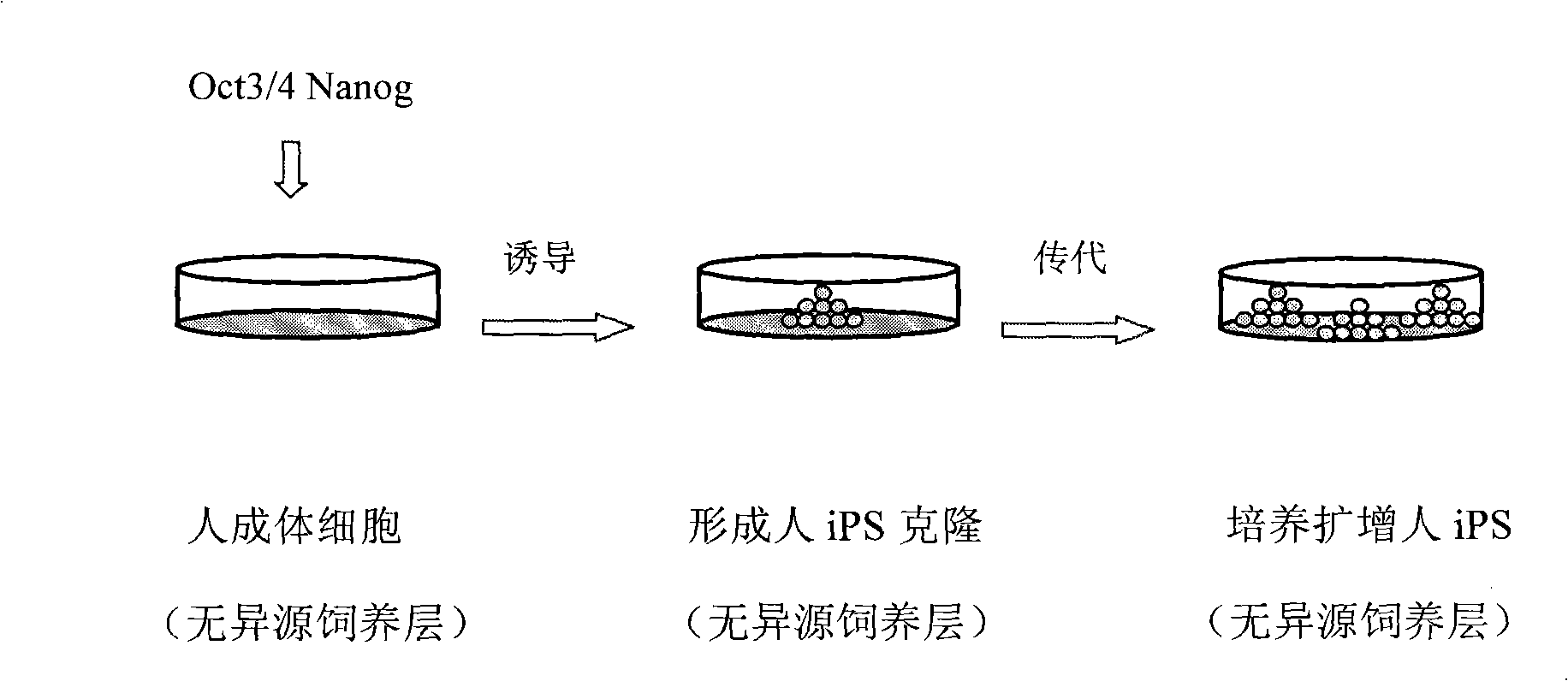
Method for in vitro abduction and cultivation of multi-potentiality stem cell
The invention discloses a method for inducing and culturing in vitro multi-potential stem cells, comprising the following steps: two transcription factors, i.e., Oct3 / 4 and Nanog, are transferred into audult cells, cultivated in cell induction culture solution under the condition of non-heterologous feeder cells, to induce and clone multi-potential stem cells; and the induced multi-potential stem cells are cloned in embryo stem cell culture solution, cultured and amplified under the condition of heterologous feeder cells, and the multipotentiality thereof is maintained. The multi-potential stem cells generated by the invention can avoid transplant rejection; the multi-potential stem cells induced by non-heterologous feeder cells has better clinical application value; the technology of adopting Oct3 / 4 and Nanog transcription factor genes or direct transfer of relevant protein is concise and has higher biological safety.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN OPHTHALMIC CENT SUN YAT SEN UNIV
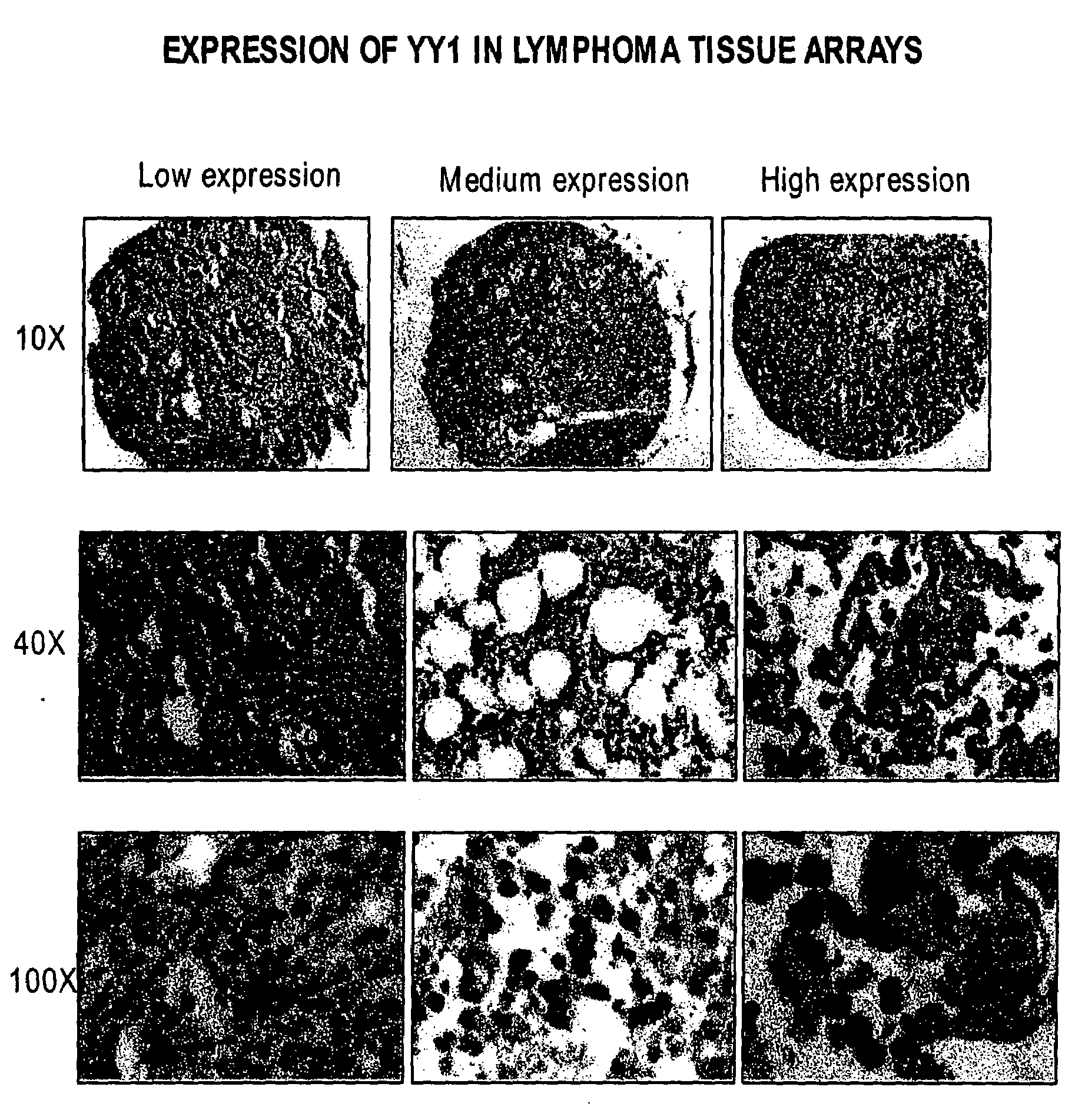
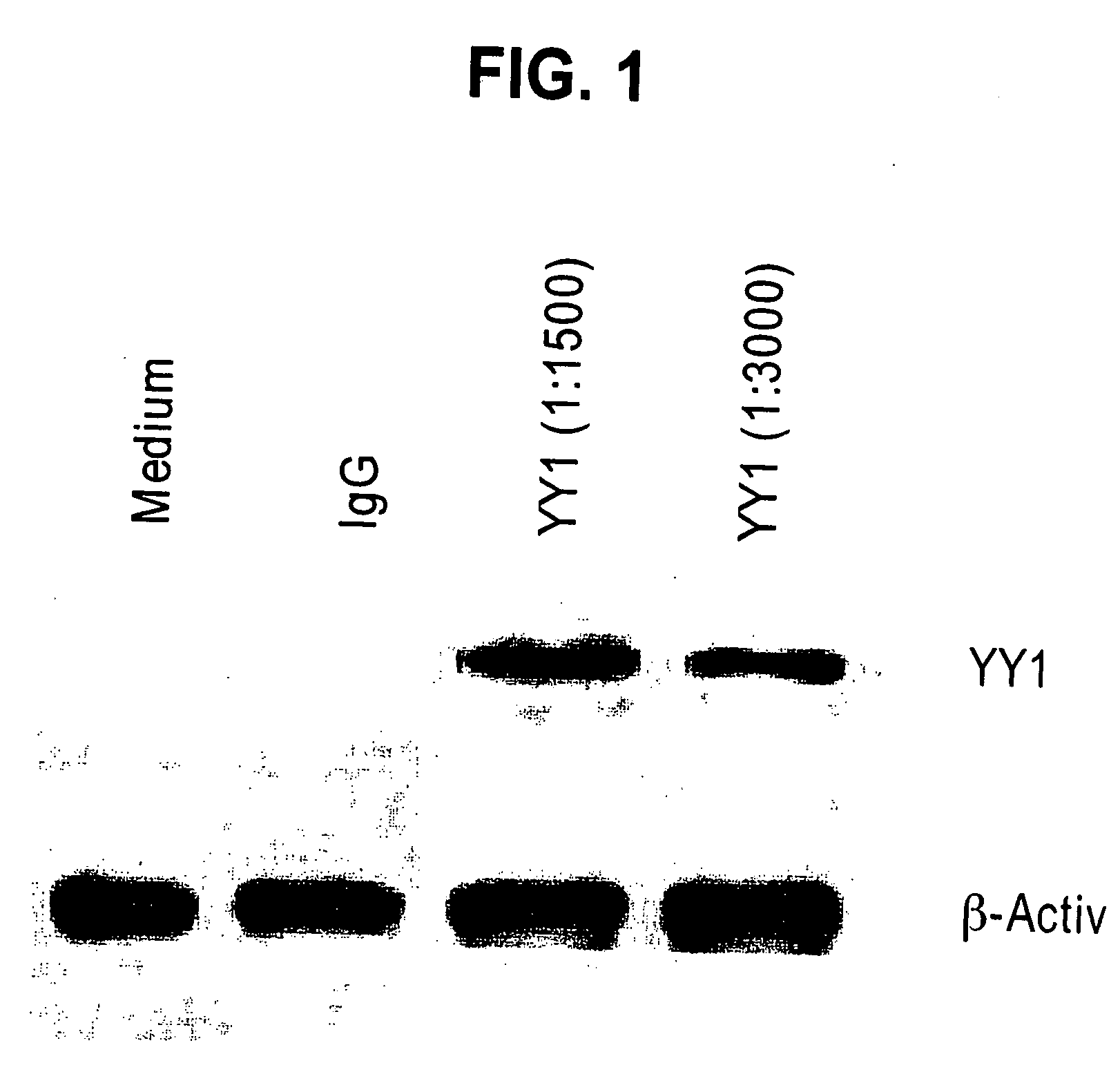
Therapeutic and Prognostic Factor Yy1 in Human Cancer
The present invention provides for the first time YY1, a transcription factor gene over-expressed and / or functionally overactive in human cancer. The present invention provides methods of diagnosing and providing a prognosis for cancer such as prostate cancer, as well as methods of drug discovery. YY1 is also a therapeutic target for treatment of cancer resistant to conventional and experimental cancer therapeutics. Inhibition of YY1 expression and / or activity sensitizes resistant tumor cells to cytotoxic treatments, including chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormonal therapy, and immunotherapy.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
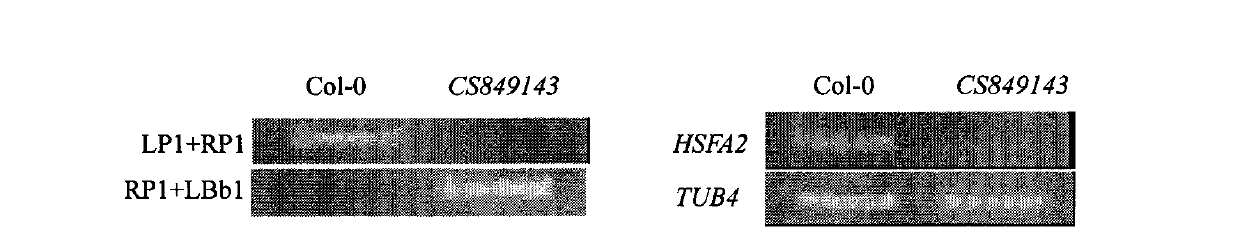
Arabidopis thaliana heat shock transcription factor gene HSFA 2 and coding protein and application thereof
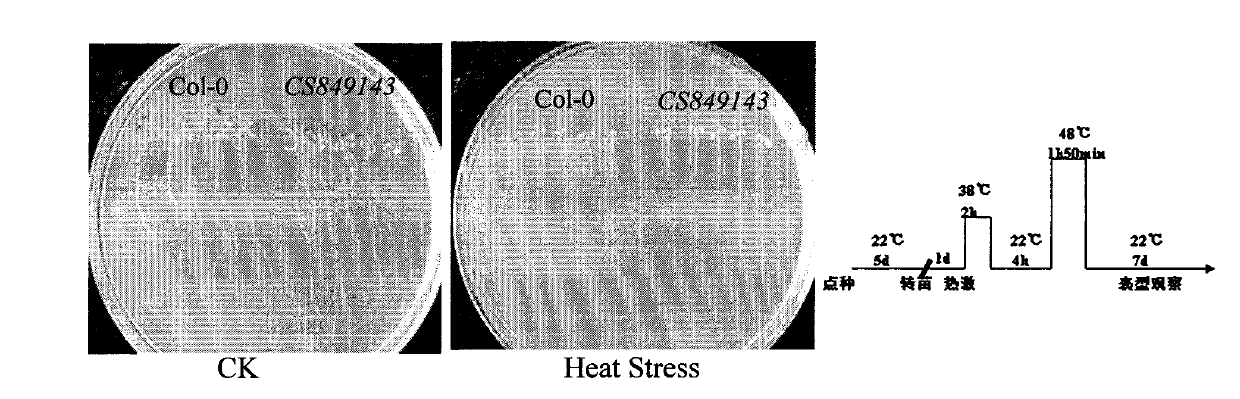
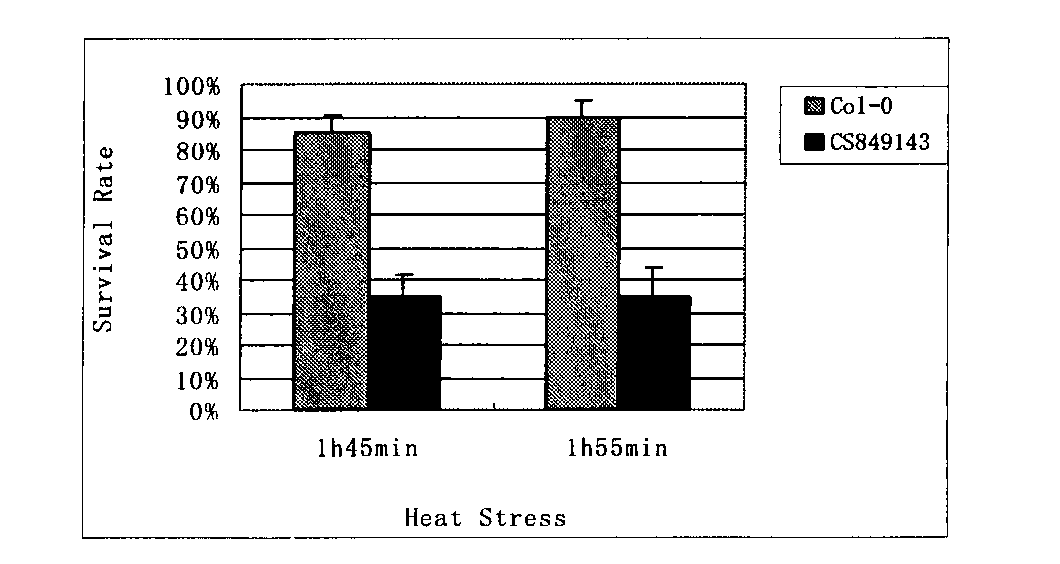
The invention belongs to the field of technology related to plant molecular biology and transgenosis. Concretely, the invention relates to verification of high temperature resistance function of the Arabidopis thaliana heat shock transcription factor gene HSFA 2, and the application of the gene in high temperature resistance plant new species cultivation. According to the invention, a model plant Arabidopis thaliana is used as material, and a HSFA gene T-DNA is inserted into a homozygous mutant lines CSS 849143 for researching high temperature resistance function of the HSFA2 gene in plants. The experiment result displays that the HSFA2 gene knock-out mutant appears a sensitive phenotype with heat shock stress, and survival rate, conductivity and osmotic pressure and other physiological indexes are significantly or highly significantly different from those of the wild type; The invention instructs that the HSFA2 gene plays an important effect in the signal transduction pathway of plant response low nitrogen stress, and predicts that the excessive expression of the gene can improve the heat resistance capability of plant and has a larger economic value in the plant stress-resistance molecular breeding.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
NAC transcription factor gene GmST2 of soybean holy bean No.9 and application of NAC transcription factor gene GmST2
ActiveCN102676541AImprove salt/drought toleranceImproves salt/drought toleranceGenetic engineeringFermentationSalt resistanceArabidopsis
The invention discloses an NAC (N-acetyl-L-Cysteine) transcription factor gene GmST2 of soybean holy bean No.9 and a plant expression vector of the GmST2. The invention further discloses application of the gene GmST2 in improvement on the salt resistant / drought tolerance in arabidopsis thaliana and soybean plants. Provided by tests, the salt resistance / drought tolerance of a transgenic plant is greatly improved compared with that of a non transgenic plant and theoretical base and practice foundation for improving the salt resistance / drought tolerance of crops through genetic engineering means are provided. The NAC transcription factor gene GmST2 can be widely applied to cultivation of salt-resisting / drought tolerant plant varieties.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Production of pancreatic islet cells and delivery of insulin
The present invention relates to the production of islet cells and insulin in a subject by providing for expression of an islet transcription factors in the pancreas of the subject, by for example, introduction of nucleic acid encoding the transcription factor neurogenin3 or a factor that induces neuorgenin3 expression. The present invention also relates to methods for using a islet transcription factor gene and the islet transcription factor polypeptide to alter cellular differentiation in culture or in vivo to produce new β-cells to treat patients with diabetes mellitus.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
ERF transcription factor related to plant stress resistance and encoding gene and application thereof
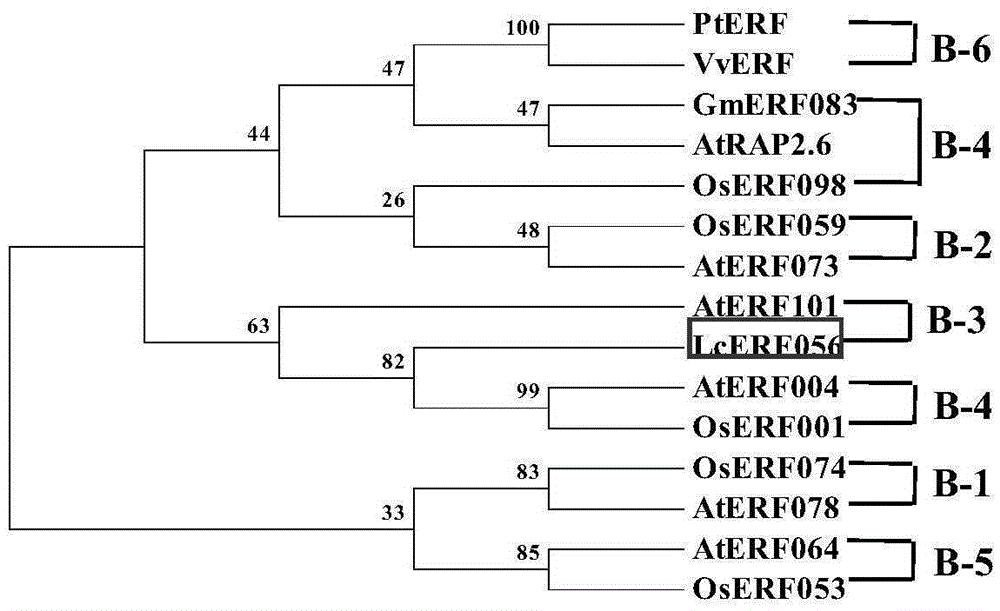
The invention discloses an ERF transcription factor related to the plant stress resistance and an encoding gene and application thereof. The invention firstly provides an ERF transcription factor gene LcERF056 separated from lotus japonicas, the amino acid sequence of the gene LcERF056 is shown as SEQ ID No.1, and the nucleotide sequence of the encoding transcription factor is shown as SEQ ID No.2. The invention further provides an ERF transcription factor structure domain which can be combined with a cis-acting element to start stress resistance response gene expression and is shown as SEQ ID No.3. Function analysis experiments prove that the resistance of a plant to high salt stress can be effectively enhanced or improved by overexpressing the LcERF056 gene in the plant, and therefore the protein encoded by the LcERF056 gene has the functions of the EFR transcription factor. The invention further provides application of the ERF transcription factor and the encoding gene on the aspects of enhancing the adversity stress resistance of the plant, breeding new transgenic plant varieties with the adversity stress resistance and the like.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Panax notoginseng transcription factor gene PnMYB1 and application thereof
ActiveCN106497939AIncrease contentHigh expressionPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyPANAX NOTOGINSENG ROOT
The invention discloses a panax notoginseng transcription factor gene PnMYB1 and application thereof. The PnMYB1 gene has a base sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:1, and encodes MYB transcription factor. The invention adopts functional genomics and metabolic engineering related technologies to prove that panax notoginseng PnMYB1 transcription factor has the function of regulating the biosynthesis of saponins of panax notoginseng. The panax notoginseng PnMYB1 transcription factor gene is constructed on a plant expression vector and is transferred into panax notoginseng callus for overexpression, thus enhancing the expression level of key enzyme gene in the synthetic route of saponins of panax notoginseng and PnbHLH1 transcription factor in panax notoginseng, and increasing the content of total saponins of panax notoginseng and part of monomer saponin.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
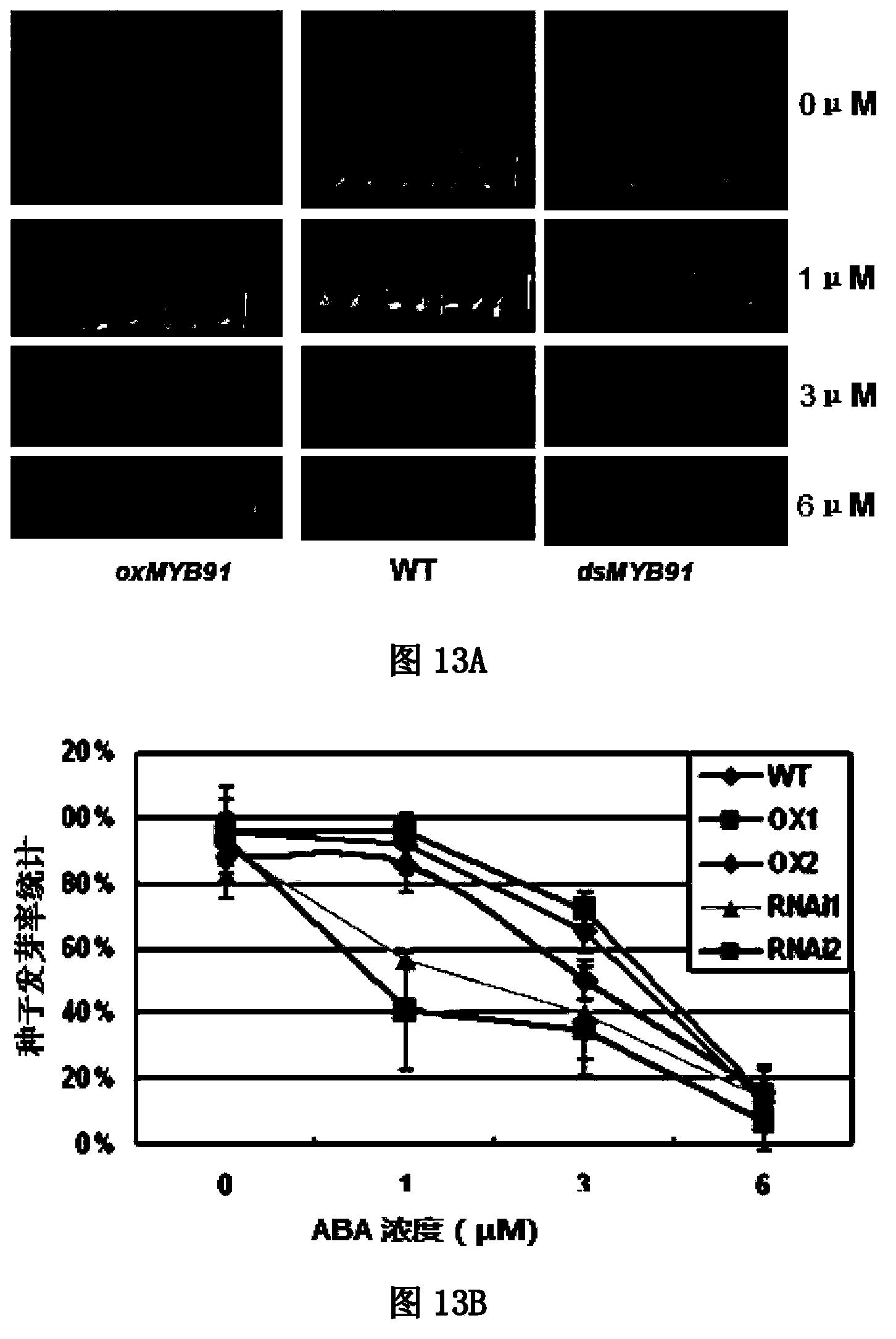
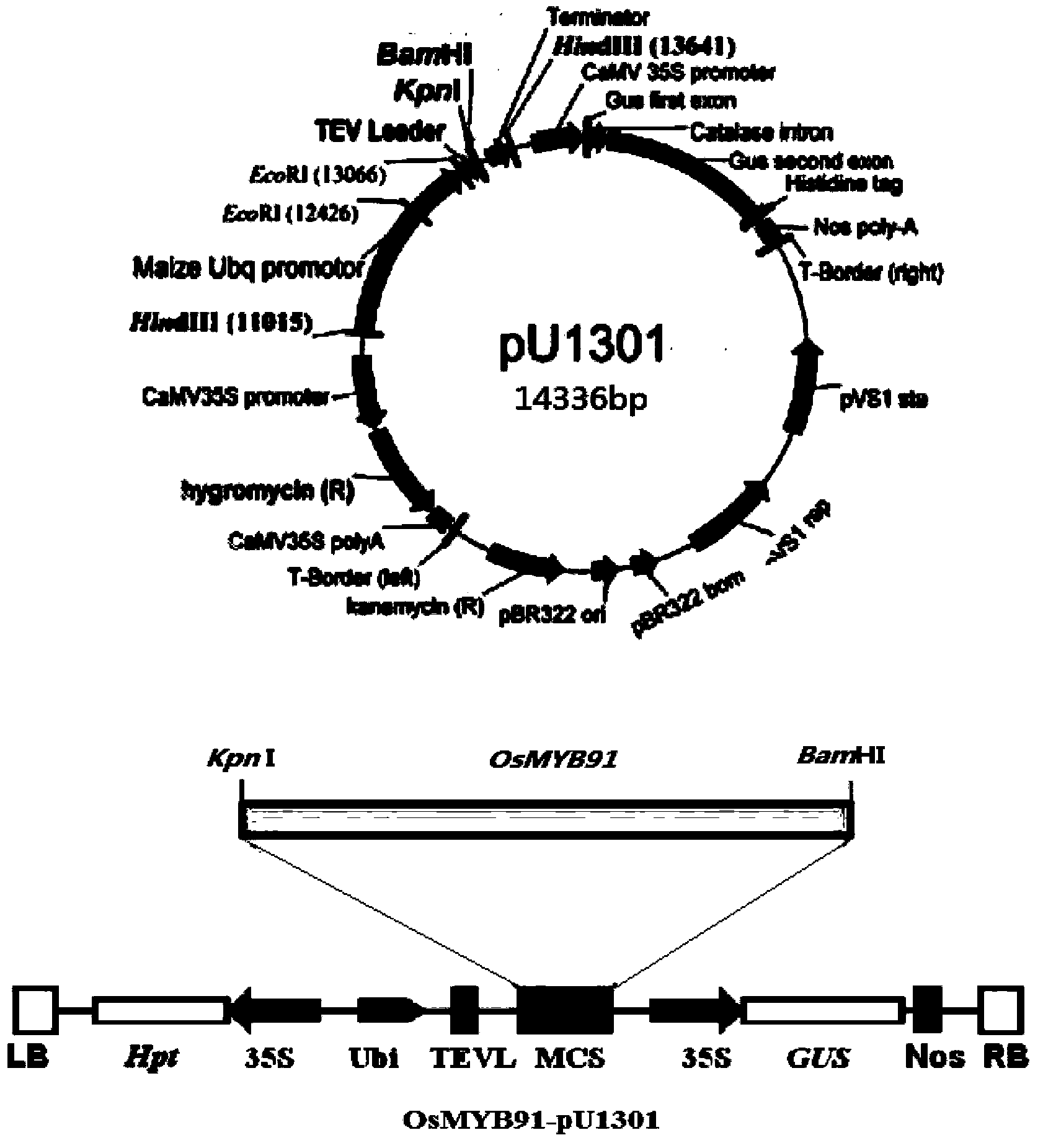
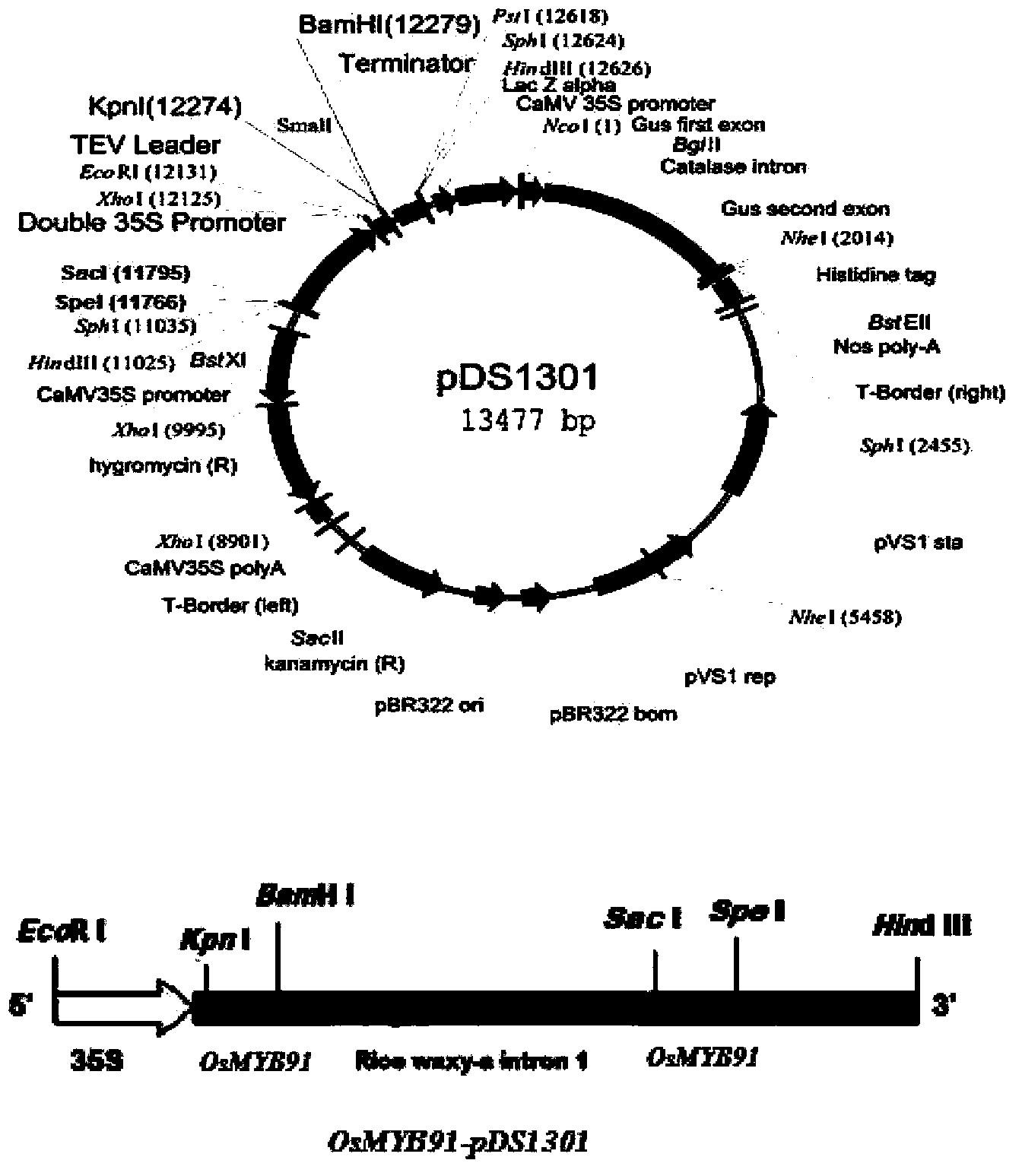
Application of OsMYB91 transcription factor in rice growth and stress-tolerance
InactiveCN103421807AIncrease productionImprove qualityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionPlant hormoneWild type
The invention belongs to the technical field of rice genetic engineering, and in particular relates to functions and application of a transcription factor gene OsMYB91 in an MYB family relevant to stress-tolerance. The gene has the nucleotide sequence length of 990 bp, and is induced by various stress conditions such as drought simulation, cold, salt, heat shock, and plant hormones including ABA, ACC, NAA, 6-BA, JA, SA and the like; under the natural growing condition, the plant height of an over-expression pant of the gene is obviously lowered than that of a wild plant and an inhibited plant; when a rooting culture medium containing mannitol and ABA is used for treating the seedlings of over-expression, RNAi and wild plants, the over-expression of the gene is discovered to be capable of increasing the resistance to mannitol, and meanwhile, the growth and the germination rate of the transgenic plant are both influenced by an exogenous ABA; measurement of physiological indexes relevant to stress-tolerance of different transgenic plants after the NaCl treatment shows that the gene has the function of reinforcing the resistance of the rice.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com