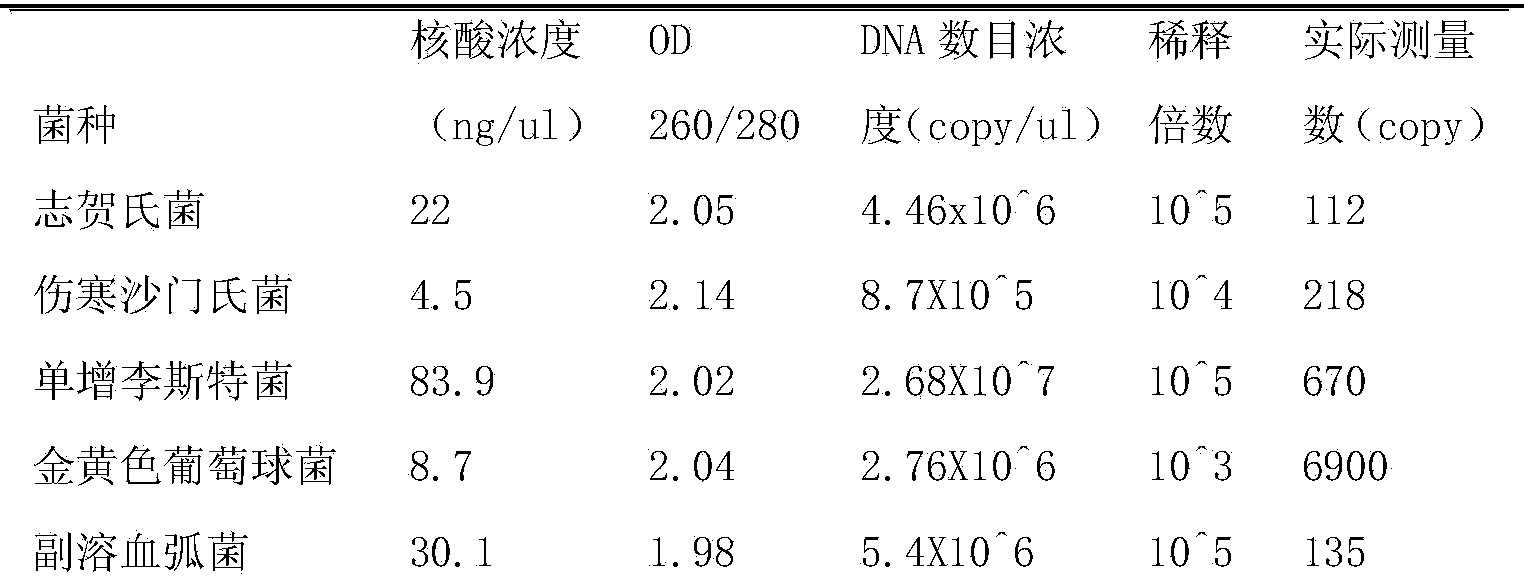
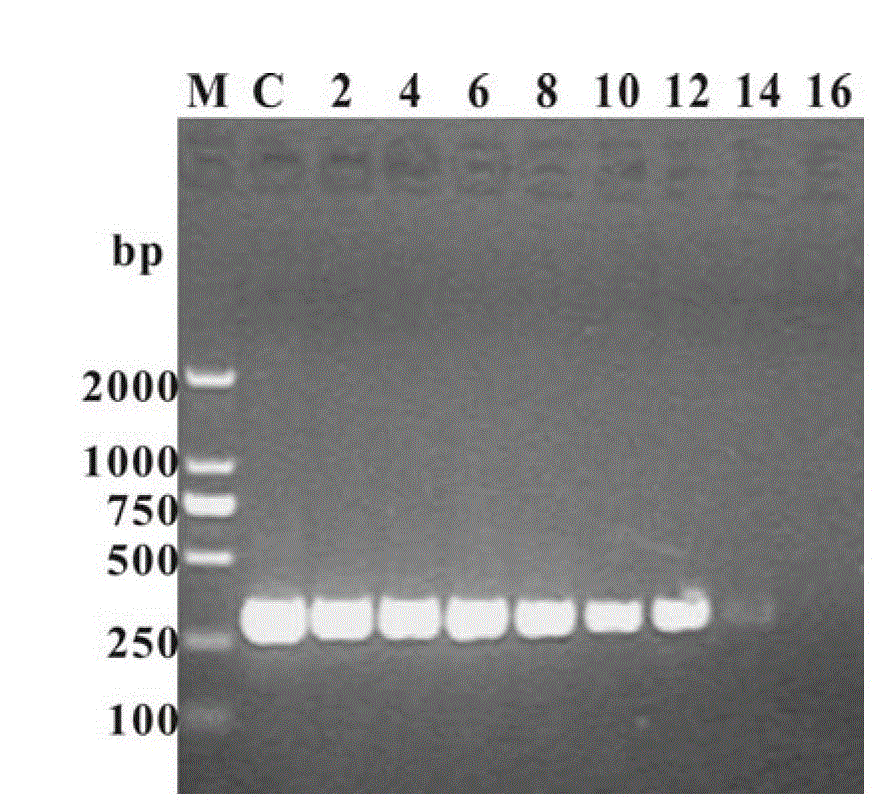
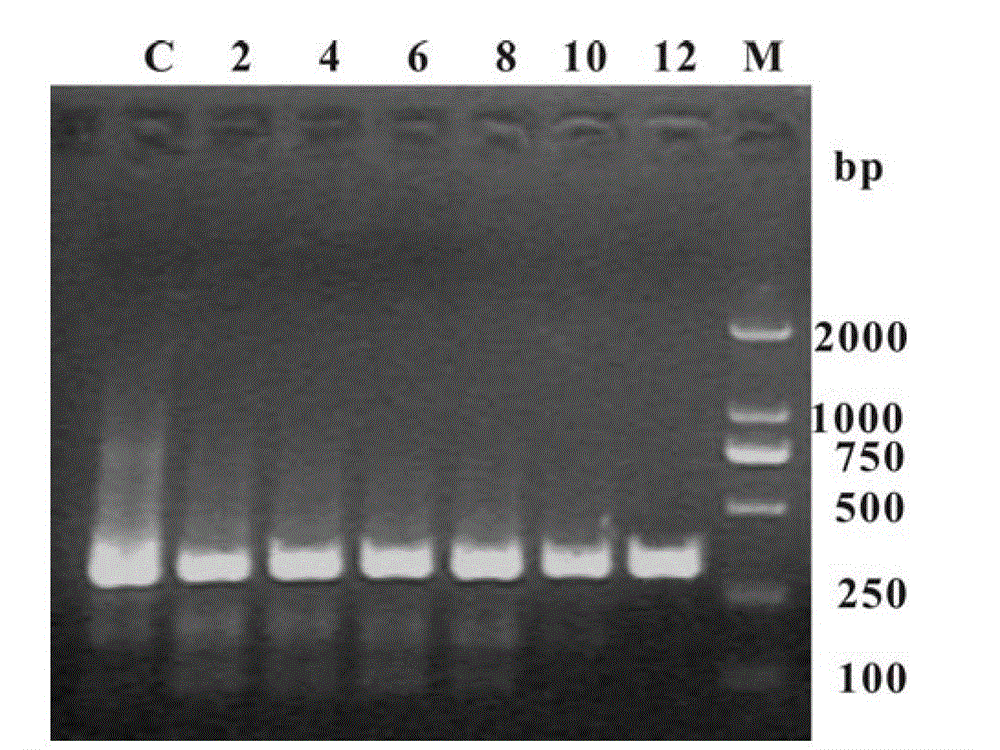
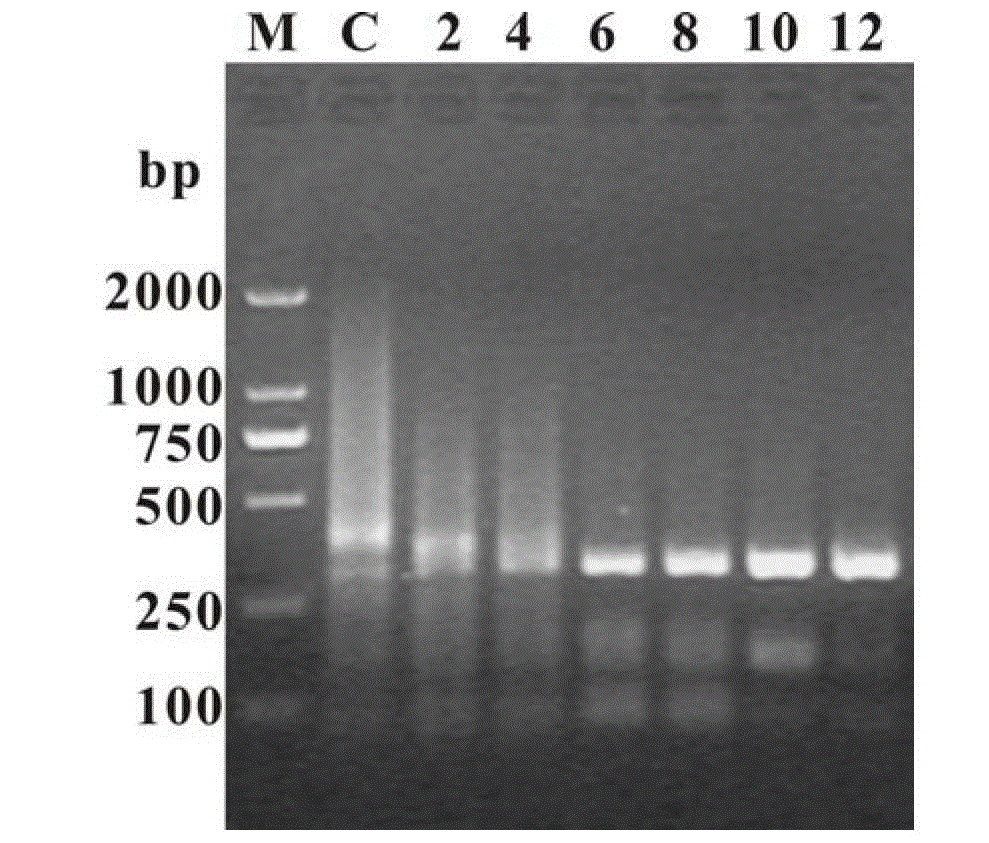
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1006 results about "Nested polymerase chain reaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nested polymerase chain reaction (Nested PCR) is a modification of polymerase chain reaction intended to reduce non-specific binding in products due to the amplification of unexpected primer binding sites.
Method and devices for extremely fast DNA replication by polymerase chain reactions (PCR)
InactiveUS6180372B1Shorten cycle timeHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanotechPolymerase LBiological materials
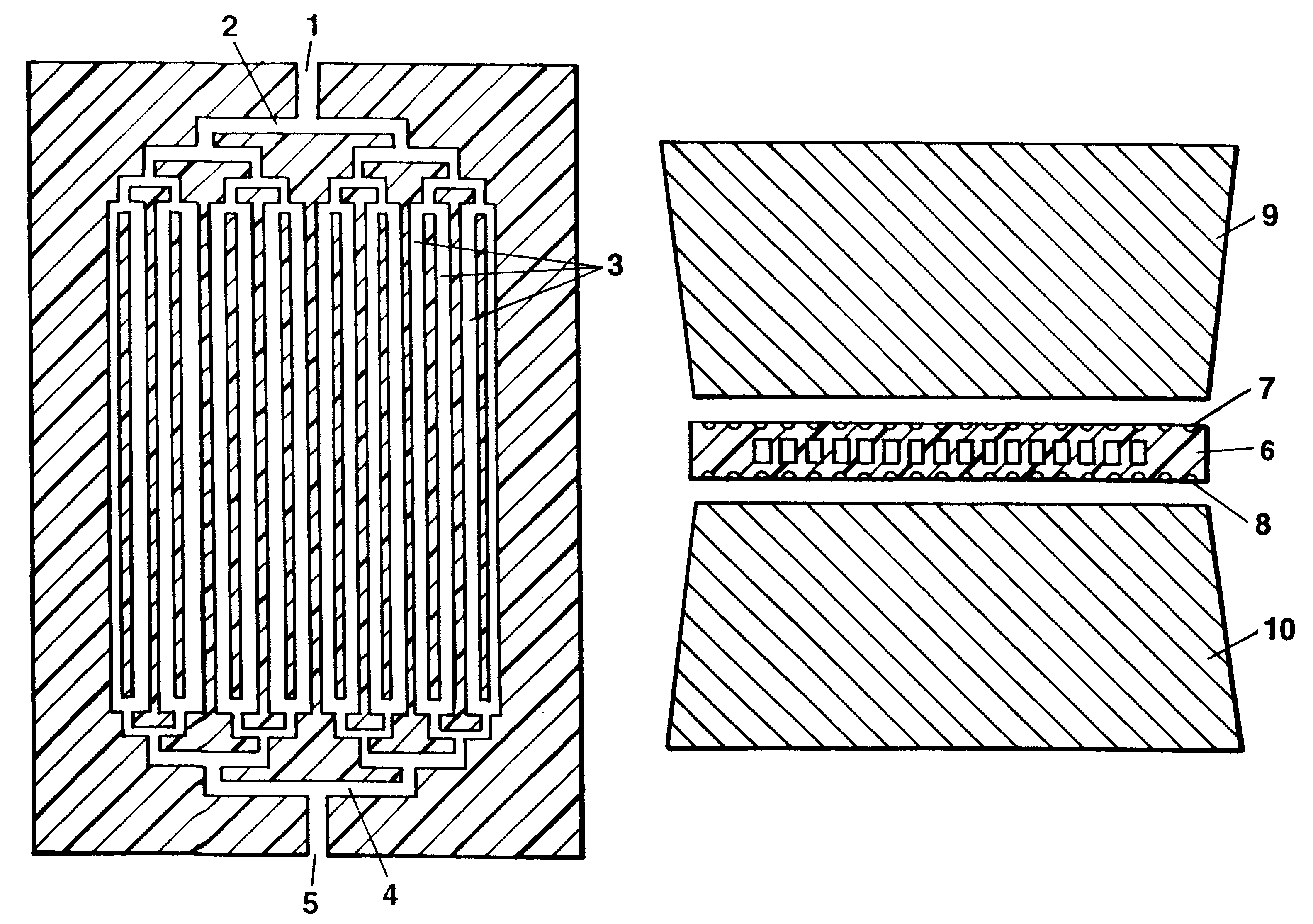
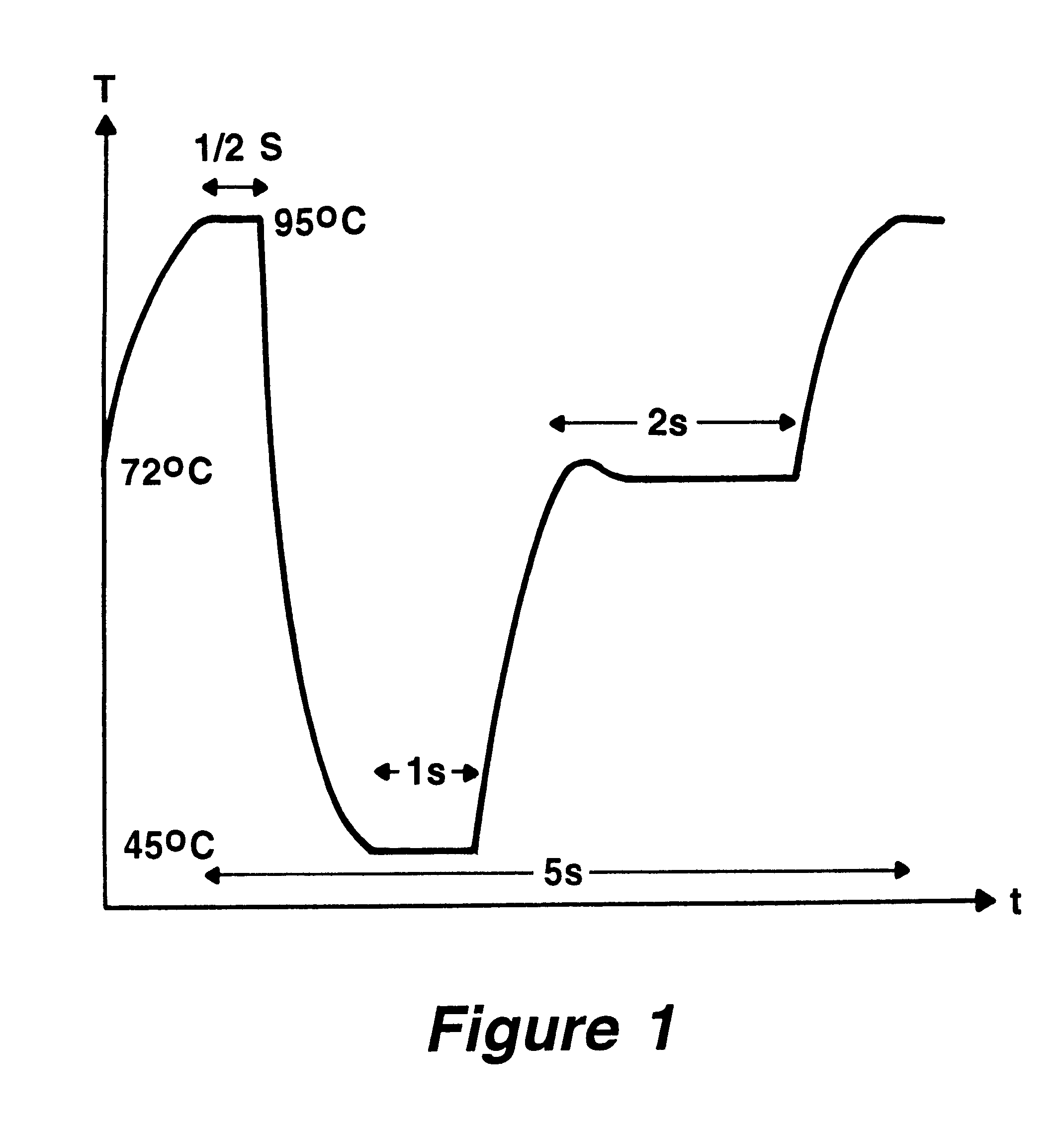
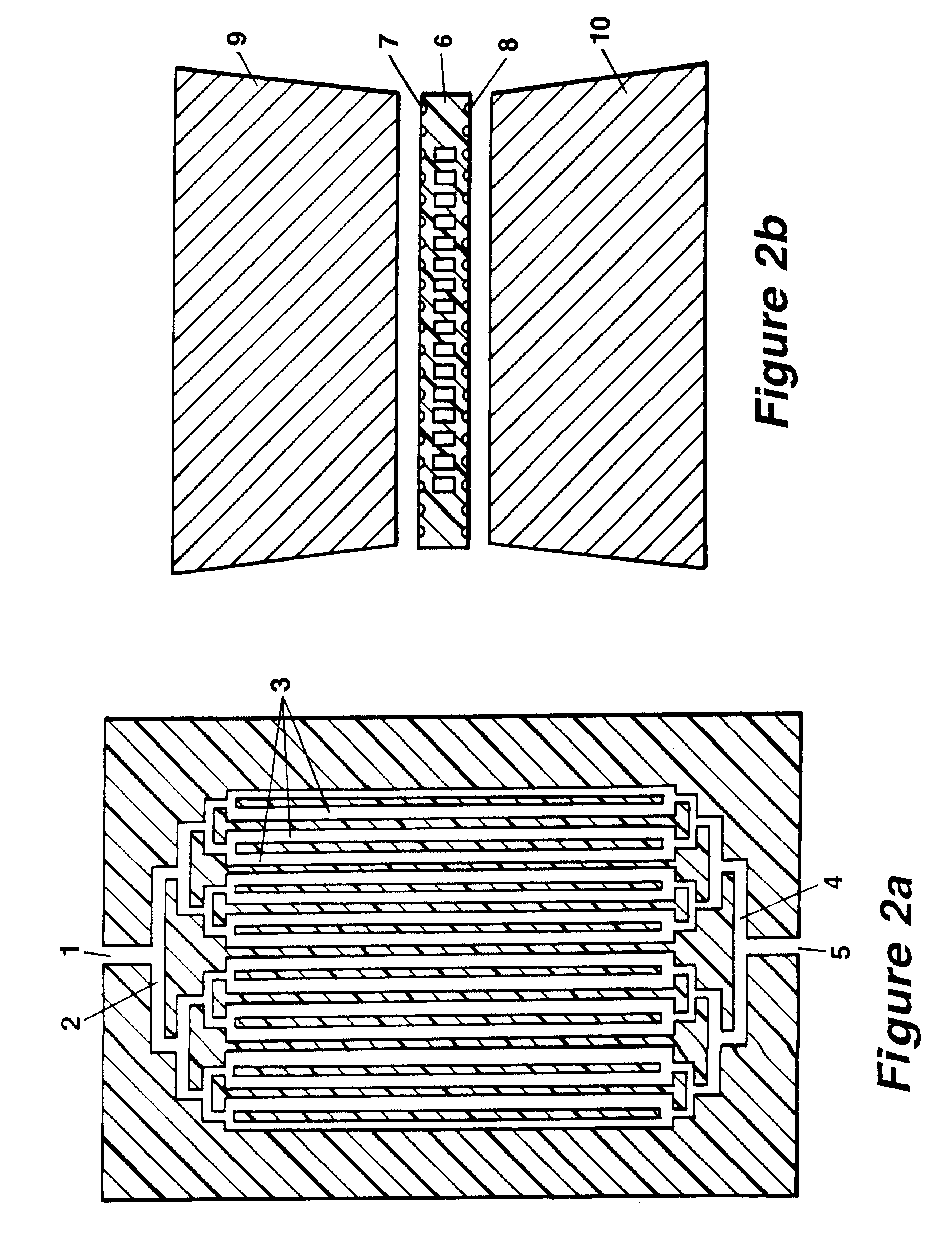
The invention concerns methods and instruments for fast, selective replication of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) from biomaterial through the known polymerase chain reaction (PCR), working in individual duplication thermocycles. The invention consists of extremely brief cycle times of only a few seconds for the PCR reactions, generated, on the one hand, by reaction chambers for the reception of the reaction solution constructed of a pattern of fine capillaries in close proximity to heating and cooling elements in order to optimally accelerate the temperature setting in the reaction solution for the three temperature phases of the PCR duplication cycles and, on the other hand, by keeping the flow rates in the capillaries to a minimum during the amplification phase so that the polymerase reaction is not disturbed. The capillary pattern can be simply produced by means of microsystern technology.
Owner:BRUKER FRANZEN ANALYTIK
Polymerase chain reaction of DNA of which base sequence is completely unidentified
The present invention relates to a process for amplifying DNA of an organism. More particularly, the present invention is directed to a process for amplifying DNA of an organism through Polymerase Chain Reaction(PCR) without any information regarding a primer needed for amplifying DNA of an organism.
Owner:BIONEER
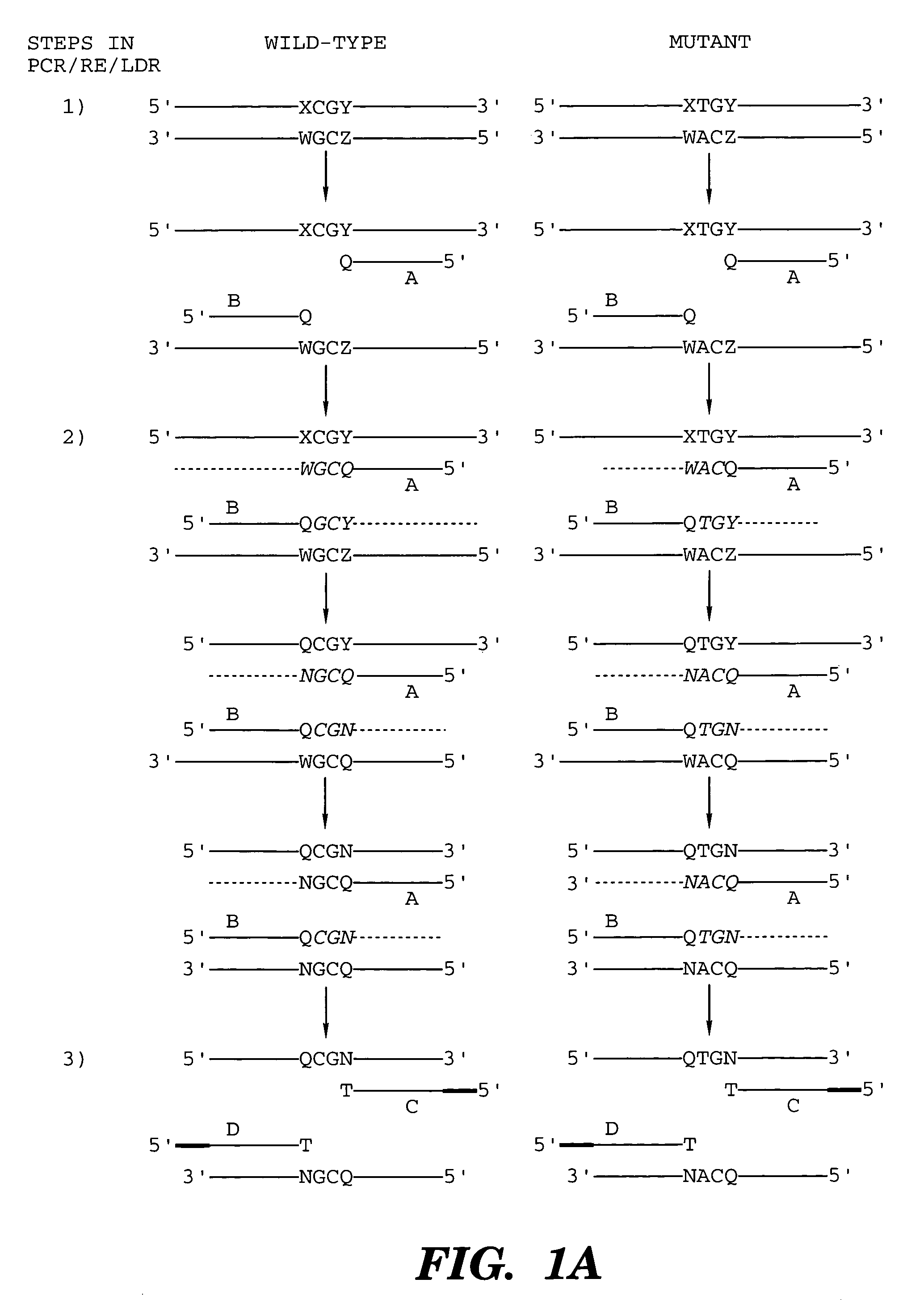
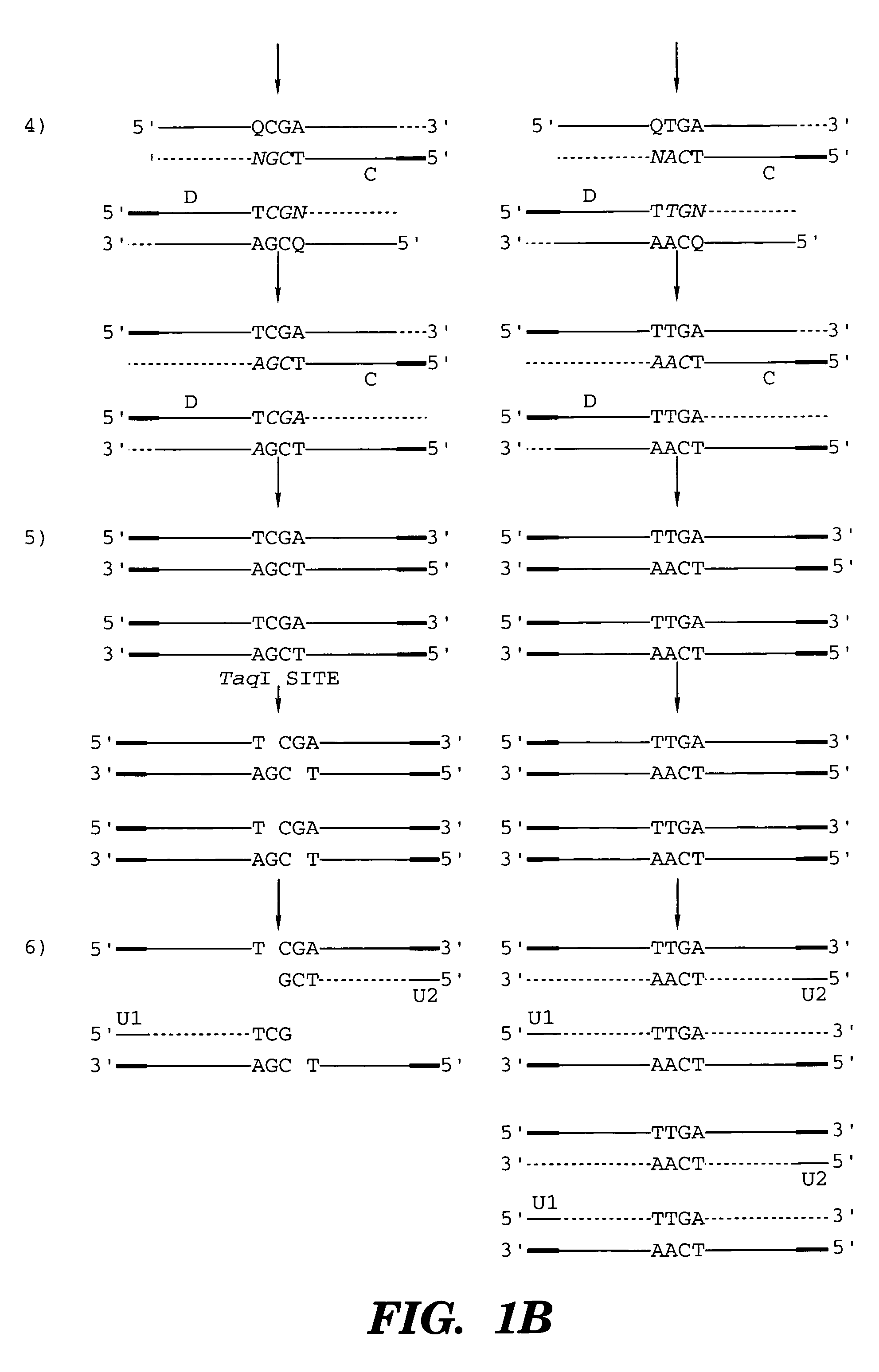
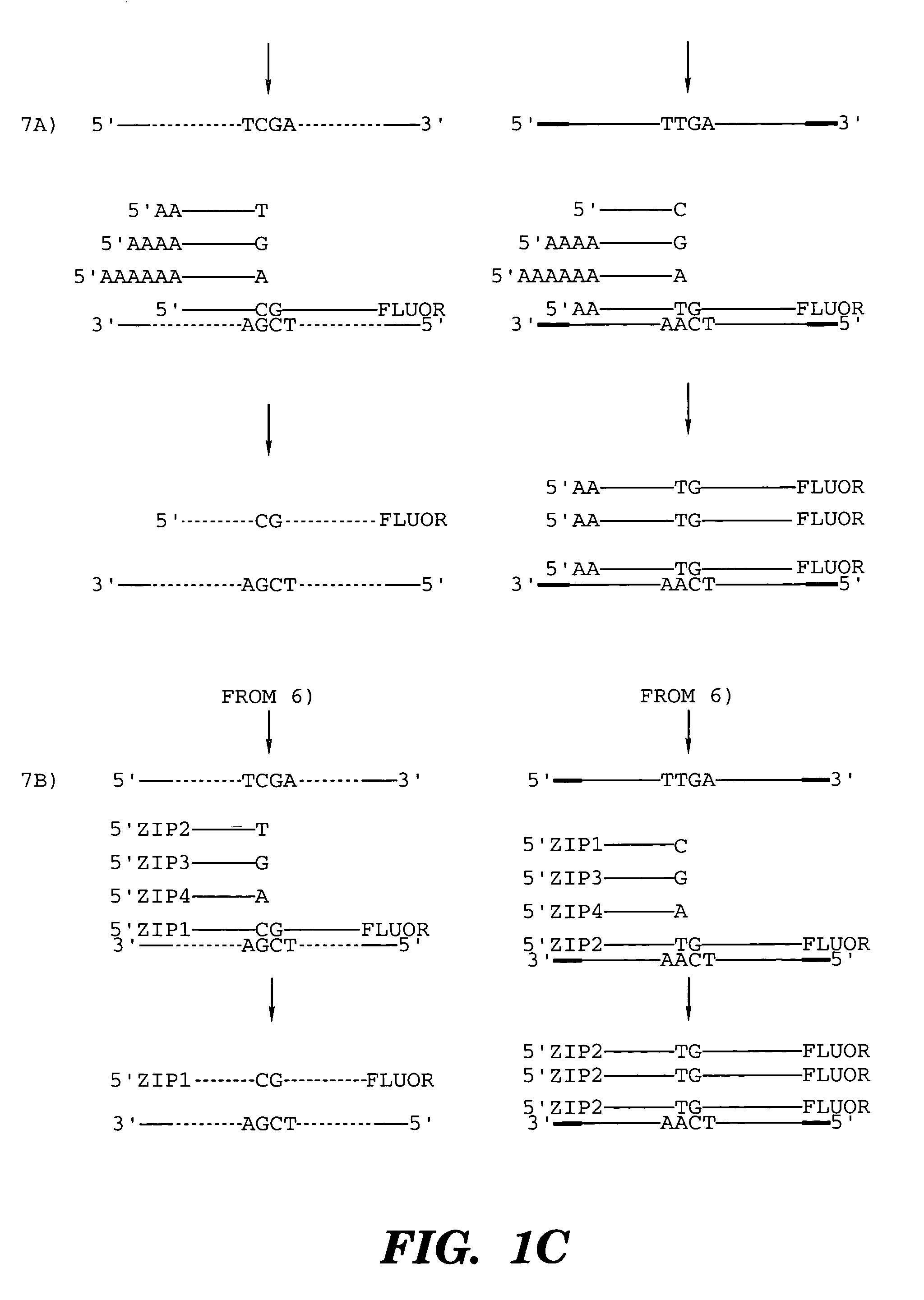
Detection of nucleic acid sequence differences using coupled ligase detection and polymerase chain reactions
InactiveUS7097980B2Maximize productionLess primerMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyNucleotideCoupling
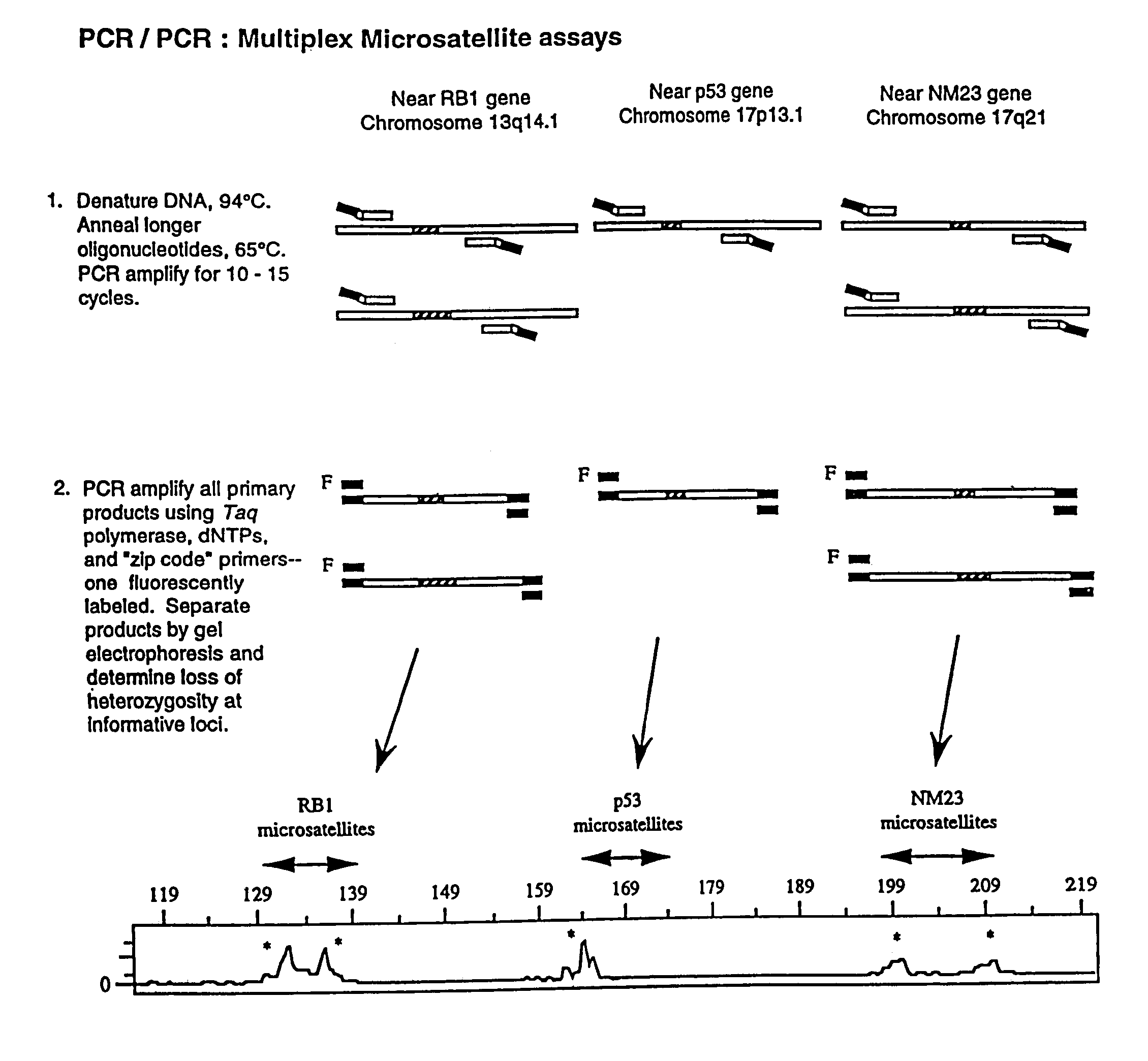
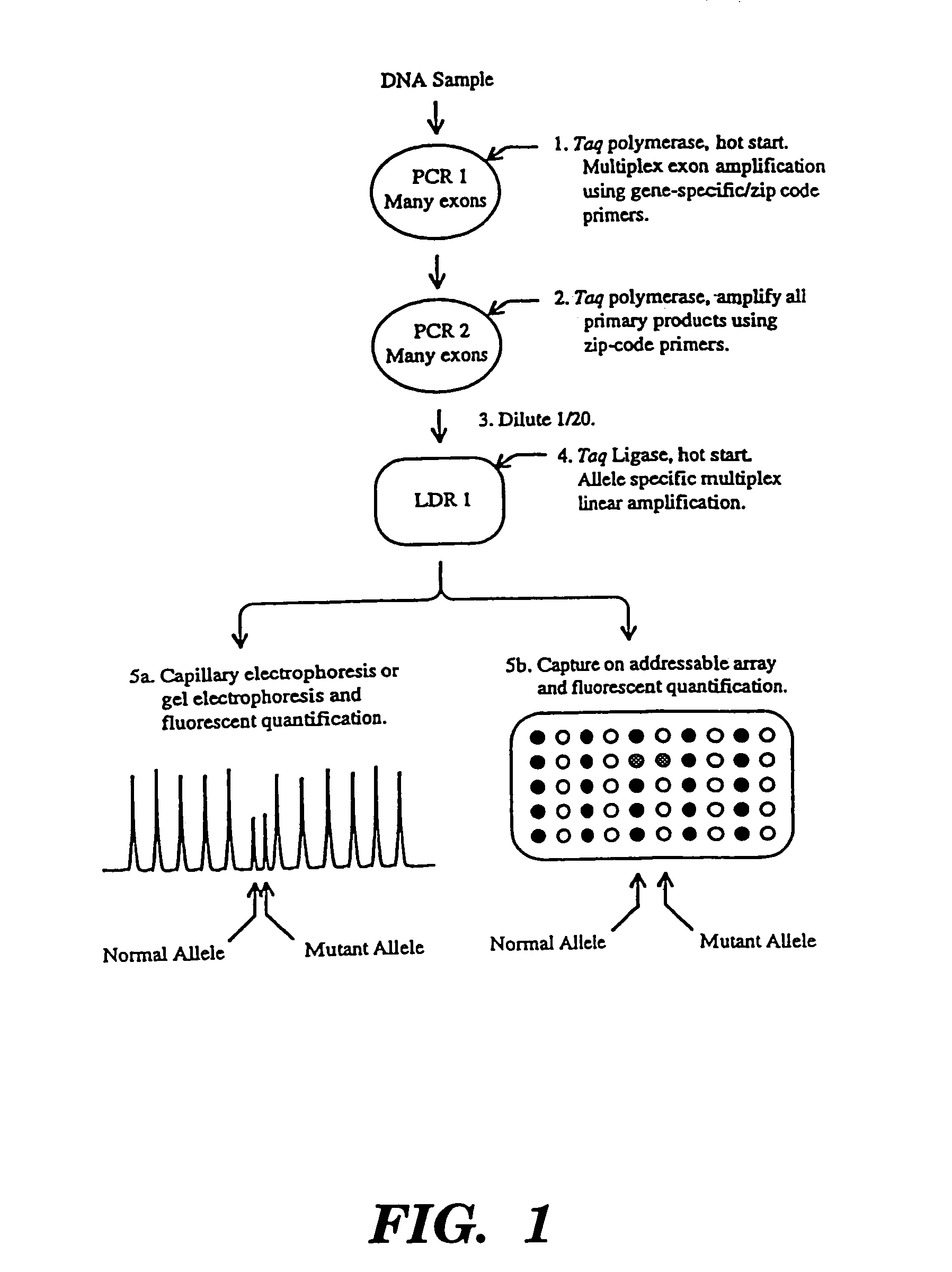
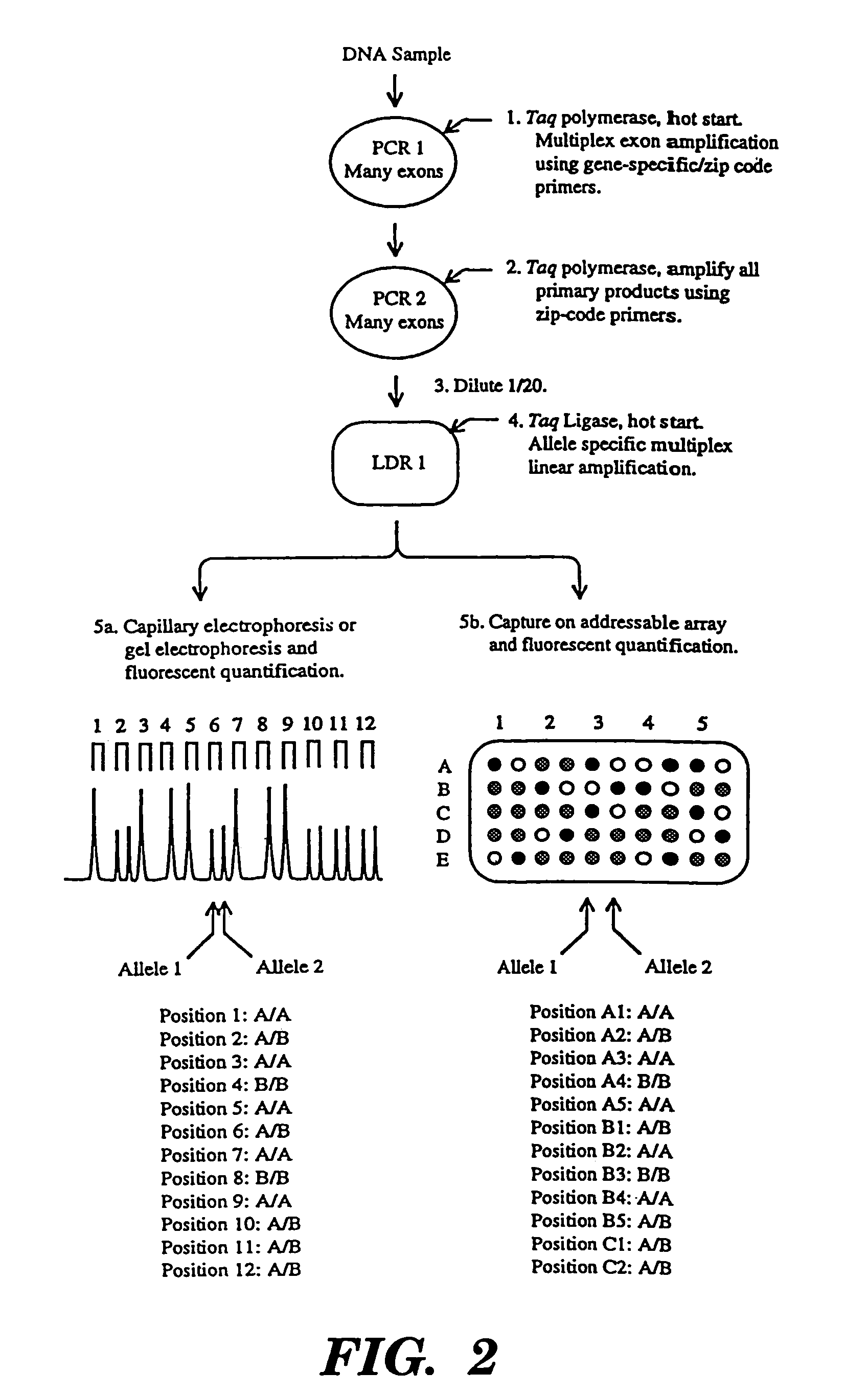
The present invention relates to the detection of nucleic acid sequence differences using coupled ligase detection reaction and polymerase chain reaction. One aspect of the present invention involves use of a ligase detection reaction coupled to a polymerase chain reaction. Another aspect of the present invention relates to the use of a primary polymerase chain reaction coupled to a secondary polymerase chain reaction coupled to a ligase detection reaction. A third aspect of the present invention involves a primary polymerase chain reaction coupled to a secondary polymerase chain reaction. Such coupling of the ligase detection reaction and the polymerase chain reaction permits multiplex detection of nucleic acid sequence differences.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Coupled polymerase chain reaction-restriction-endonuclease digestion-ligase detection reaction process
InactiveUS7014994B1Sensitive highOptimizationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideWild type
The present invention provides a method for identifying one or more low abundance sequences differing by one or more single-base changes, insertions, or deletions, from a high abundance sequence in a plurality of target nucleotide sequences. The high abundance wild-type sequence is selectively removed using high fidelity polymerase chain reaction analog conversion, facilitated by optimal buffer conditions, to create a restriction endonuclease site in the high abundance wild-type gene, but not in the low abundance mutant gene. This allows for digestion of the high abundance DNA. Subsequently the low abundant mutant DNA is amplified and detected by the ligase detection reaction assay. The present invention also relates to a kit for carrying out this procedure.
Owner:LOUISIANA STATE UNIV +1
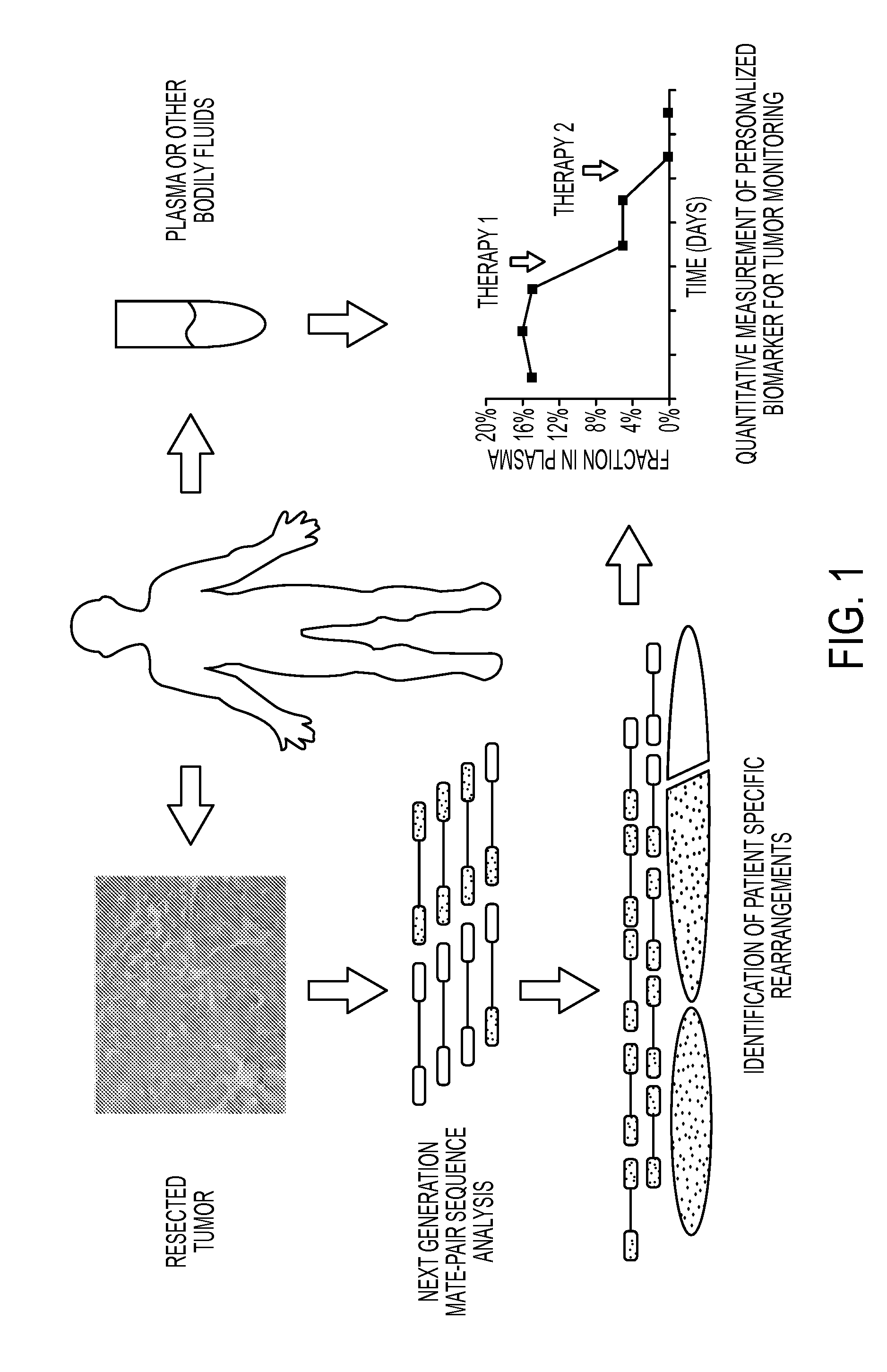
Personalized Tumor Biomarkers
ActiveUS20150344970A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationBlood plasmaWilms' tumor
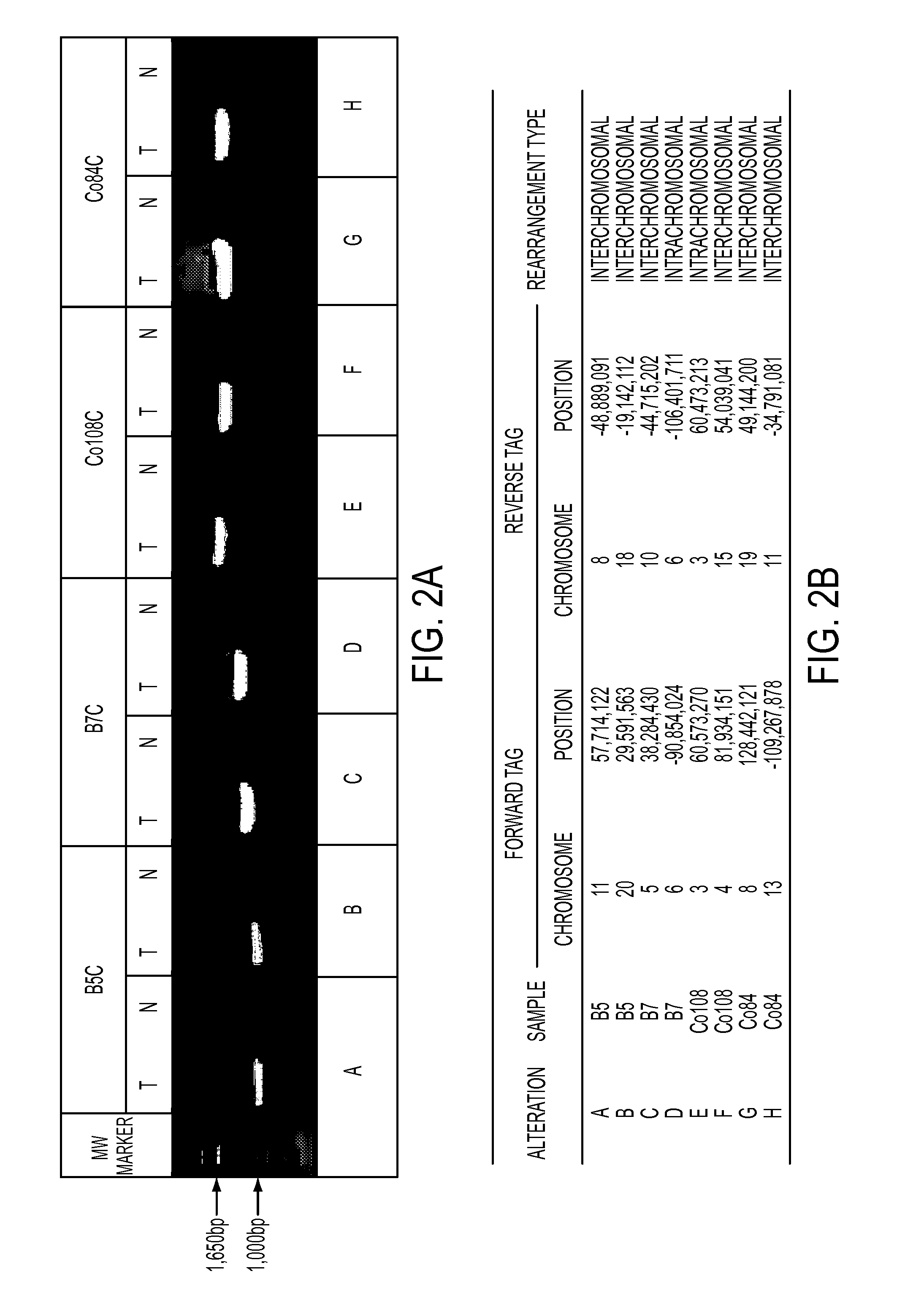
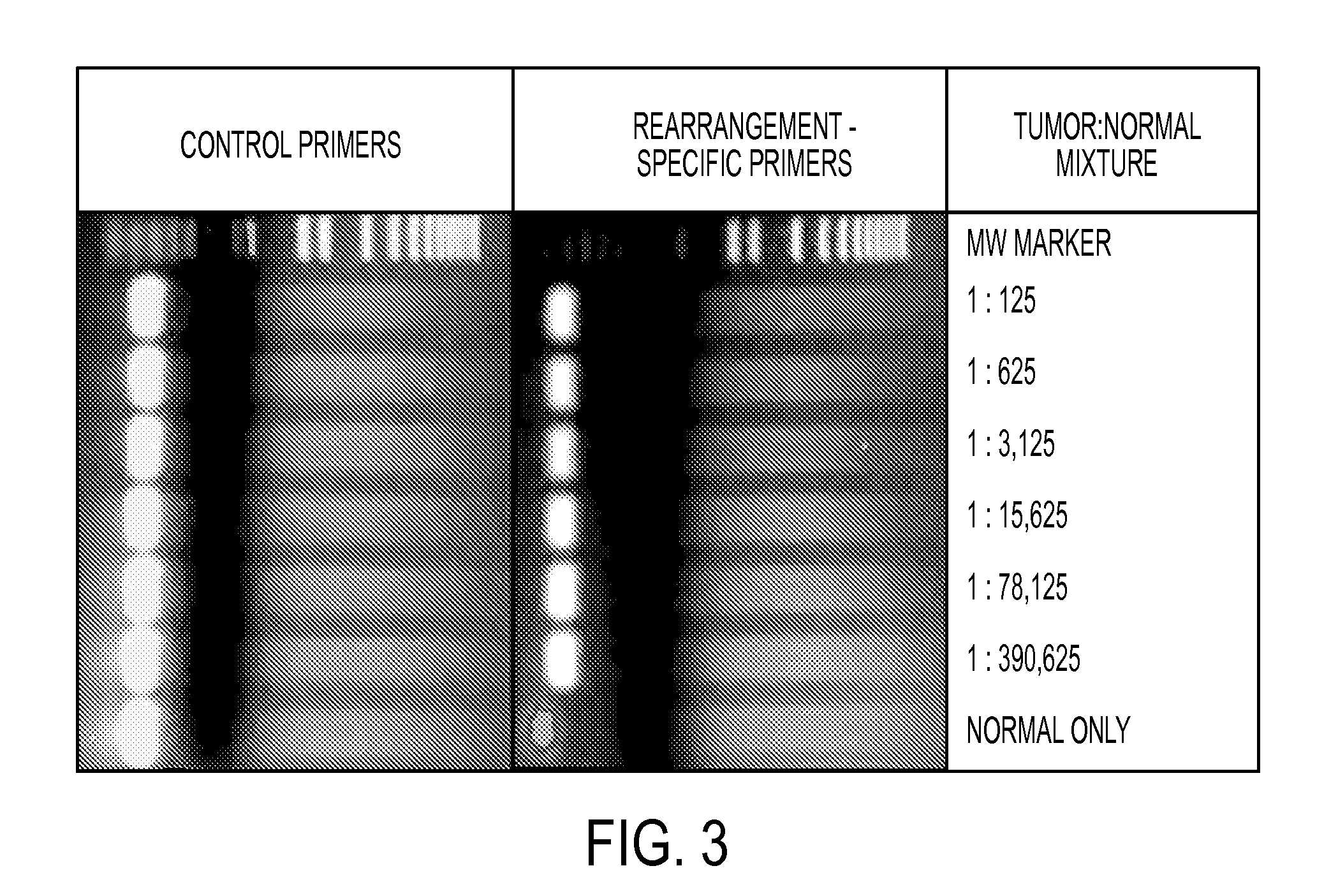
Clinical management of human cancer is dependent on the accurate monitoring of residual and recurrent tumors. We have developed a method, called personalized analysis of rearranged ends (PARE), which can identify translocations in solid tumors. Analysis of four colorectal and two breast cancers revealed an average of nine rearranged sequences (range 4 to 15) per tumor. Polymerase chain reaction with primers spanning the breakpoints were able to detect mutant DNA molecules present at levels lower than 0.001% and readily identified mutated circulating DNA in patient plasma samples. This approach provides an exquisitely sensitive and broadly applicable approach for the development of personalized biomarkers to enhance the clinical management of cancer patients.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Dual phase multiplex polymerase chain reaction
ActiveUS7432055B2Further amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationGenomic DNASingle pair
Highly specific and sensitive methods were developed for multiplex amplification of nucleic acids on supports such as microarrays. Based on a specific primer design, methods include five types of amplification that proceed in a reaction chamber simultaneously. These relate to four types of multiplex amplification of a target DNA on a solid support, directed by forward and reverse complex primers immobilized to the support and a fifth type—pseudo-monoplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of multiple targets in solution, directed by a single pair of unbound universal primers. The addition of the universal primers in the reaction mixture increases the yield over the traditional “bridge” amplification on a solid support by approximately ten times. Methods that provide multitarget amplification and detection of as little as 0.45-4.5×10−12 g (equivalent to 102-103 genomes) of a bacterial genomic DNA are disclosed.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC +1
DNA amplification of a single cell
InactiveUS6673541B1Improve accuracyImprove comprehensive applicabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-strand conformation polymorphismComparative genomic hybridization
The present invention relates to a novel method for the amplification of DNA, this method being particularly useful for the amplification of the DNA or the whole genome of a single cell, chromosomes or fragments thereof. Described is also the use of the method in DNA analysis for medical, forensic, diagnostic or scientific purposes, like comparative genomic hybridization (CGH)-, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)-, polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-, single strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP)-, DNA sequence-, "loss of heterozygosity" (LOH)-, fingerprint- and / or restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP)-analysis.
Owner:AMGEN RES (MUNICH) GMBH
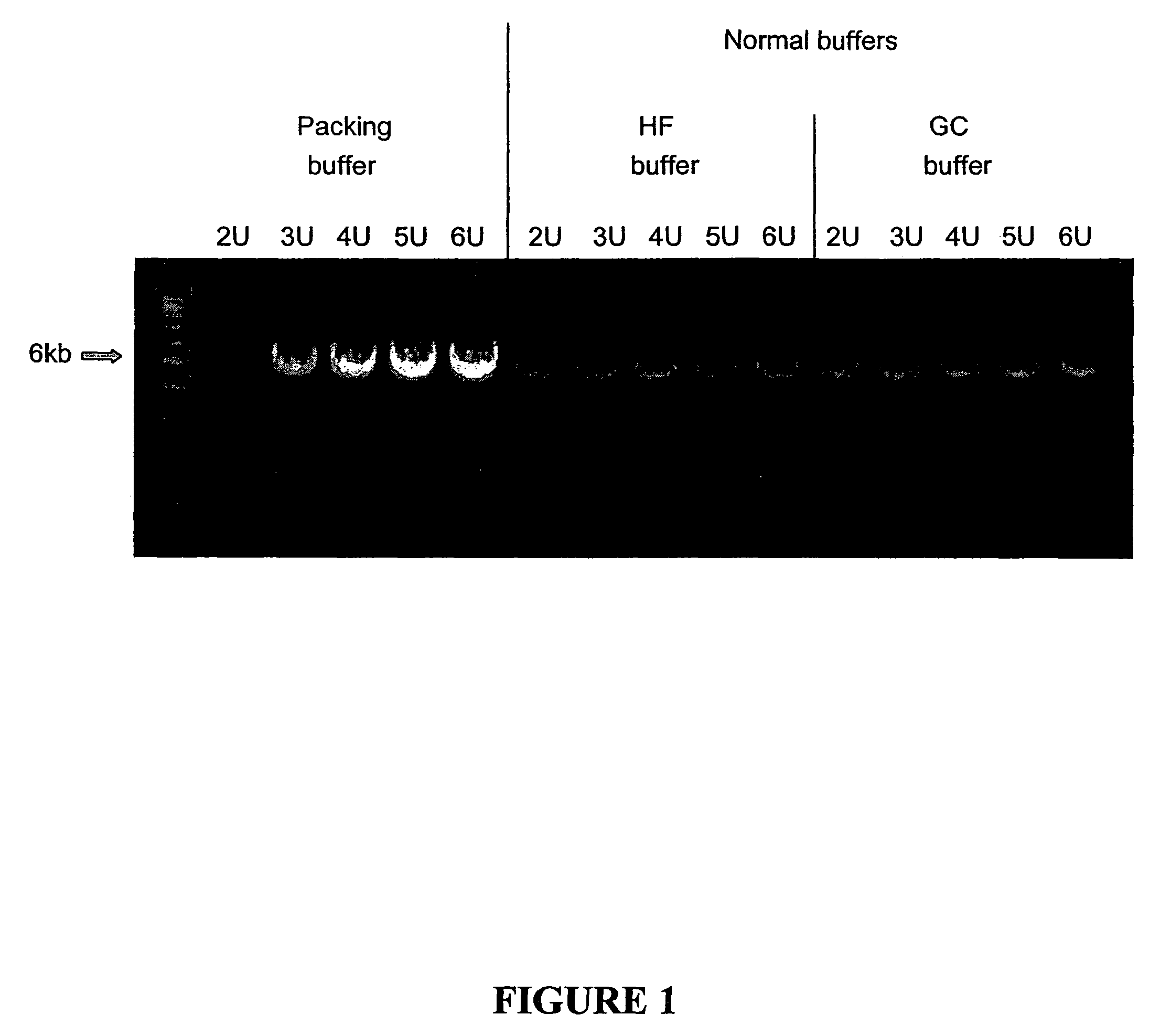
Reaction buffer composition for nucleic acid replication with packed DNA polymerases
The invention relates to compositions, methods, and kits for nucleic acid replication, including polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and mutagenesis reactions. A buffer composition is provided which allows higher concentrations of DNA polymerase to be used, resulting in greater yield of amplified product and faster reaction kinetics.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Method for carrying out high-throughput sequencing on TCR (T cell receptor) or BCR (B cell receptor) and method for correcting multiplex PCR (polymerase chain reaction) primer deviation by utilizing tag sequences
InactiveCN103710454AFully functionalReduce sequencing errorsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationV regionPcr ctpp
The invention provides a method for carrying out high-throughput sequencing on a TCR (T cell receptor) or a BCR (B cell receptor). The method is characterized by designing upstream primers according to gene features of a V region of the TCR or the BCR and designing downstream primers according to gene features of a C region or a J region of the TCR or the BCR and obtaining sequences of the of the TCR or the BCR in combination with the multiplex PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technology and high-throughput sequencing, thus analyzing the rearrangement information of the TCR or the BCR. Compared with 25-30 cycles of existing multiplex PCR, two cycles of the multiplex PCR technology provided by the invention can conduce to greatly reducing the sequencing errors caused by primer amplification preference. Besides, the invention also provides a method for correcting multiplex PCR (polymerase chain reaction) primer deviation by utilizing DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) tag sequences, thus further reducing the sequencing errors caused by primer amplification preference and intrinsic sequencing errors of high-throughput sequencing.
Owner:SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY OF CHINA +1
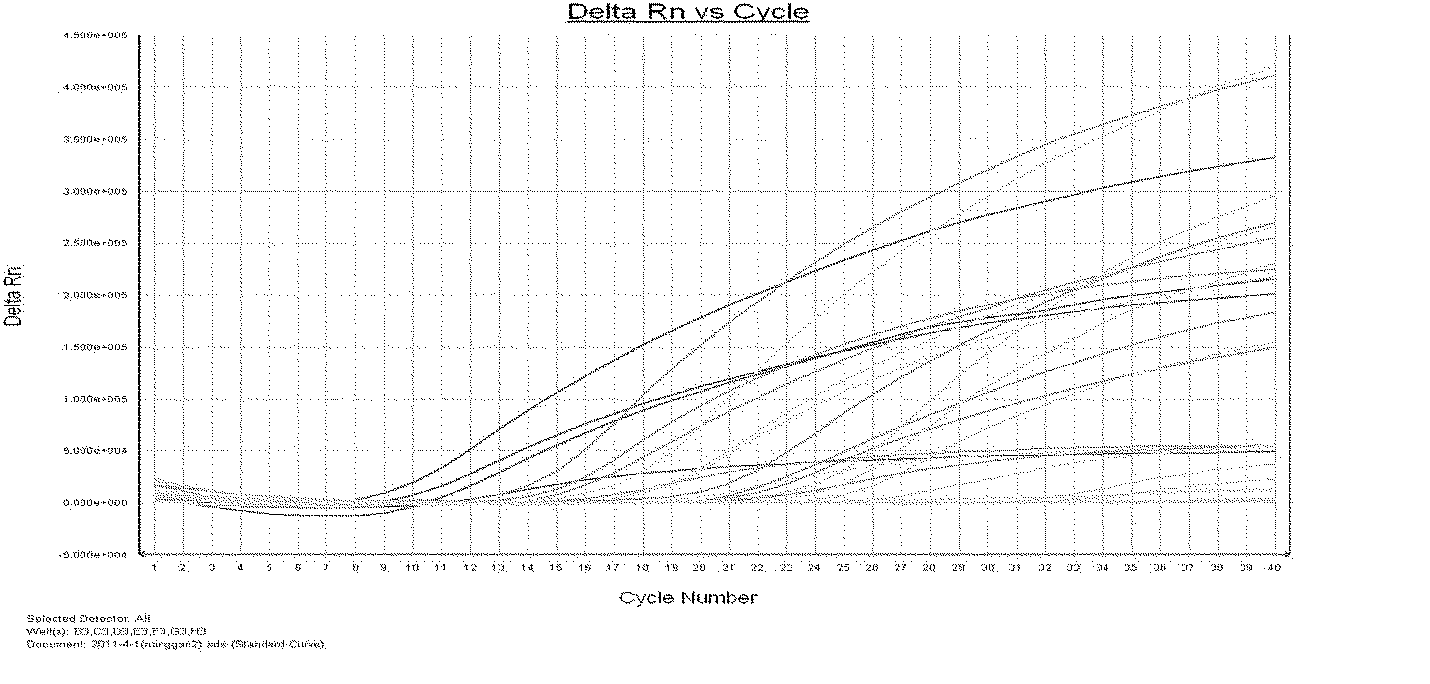
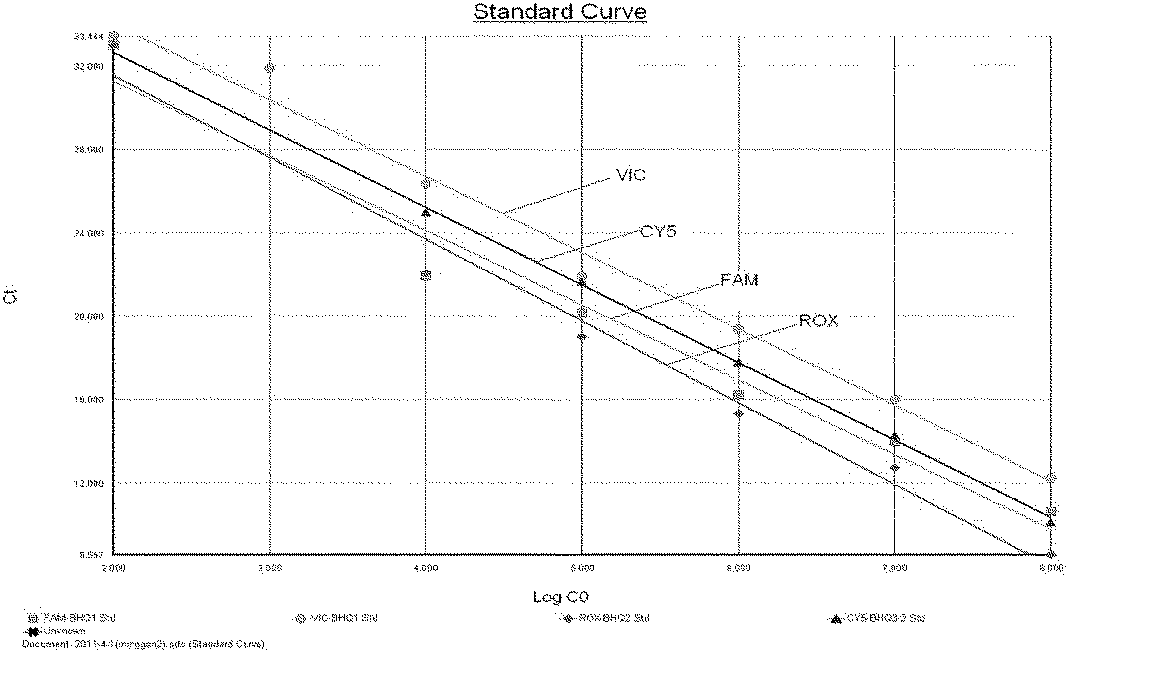
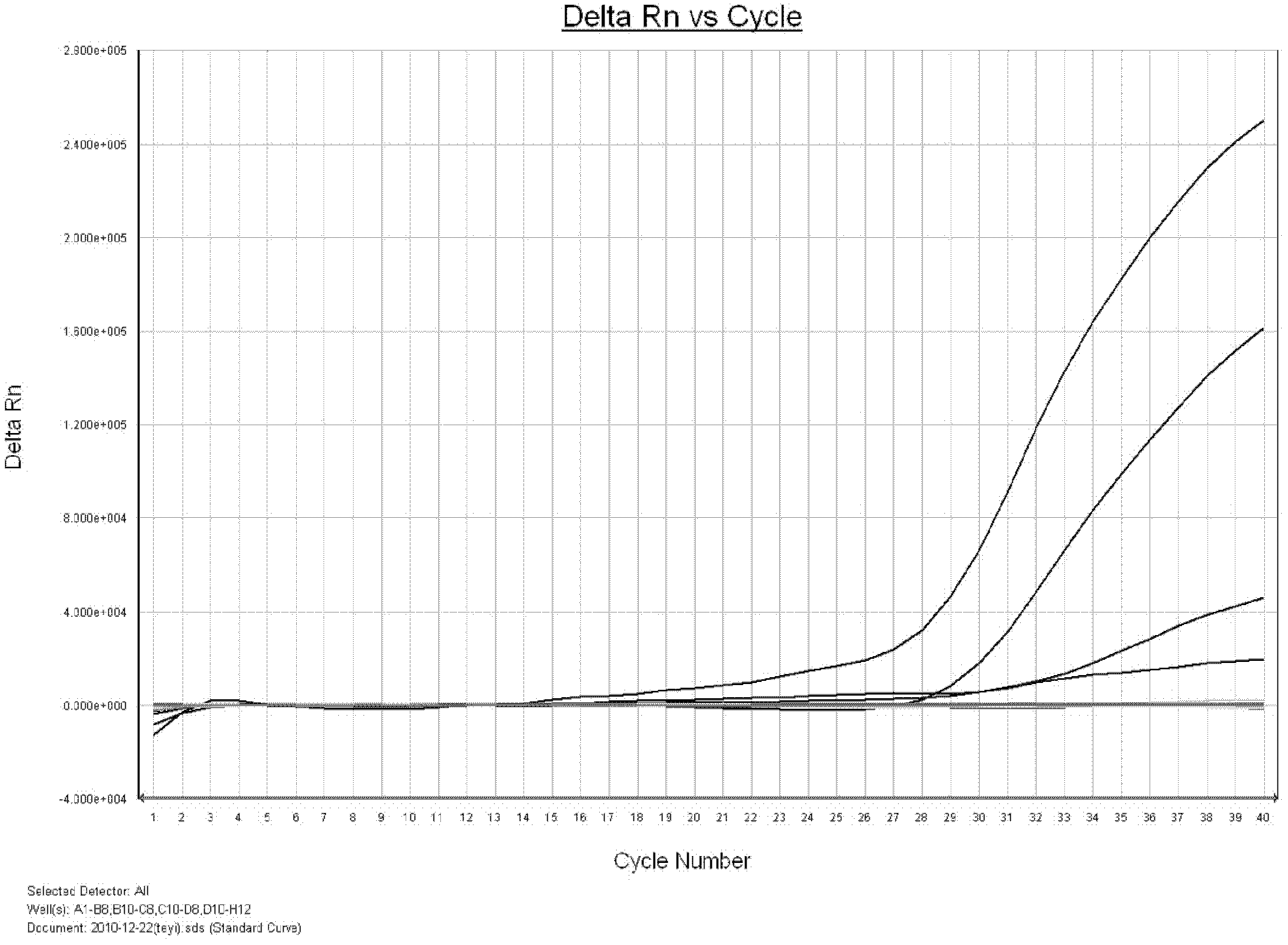
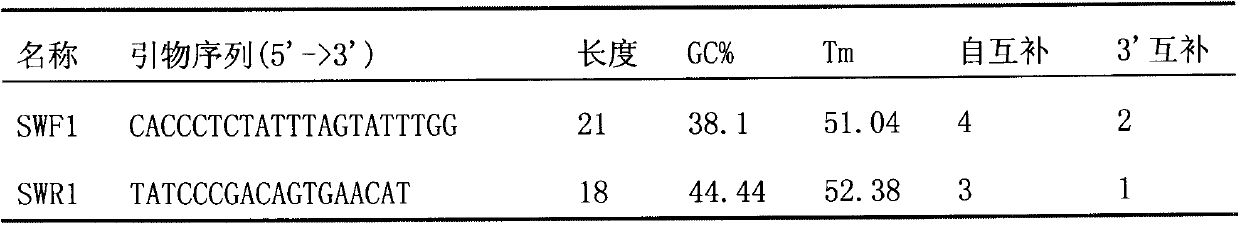
Primer set for detecting functional genes of wheat on basis of KASP [competitive allele specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction)] technology and application of set primer
ActiveCN105112546AImprove throughputImprove detection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceNucleotide sequencing
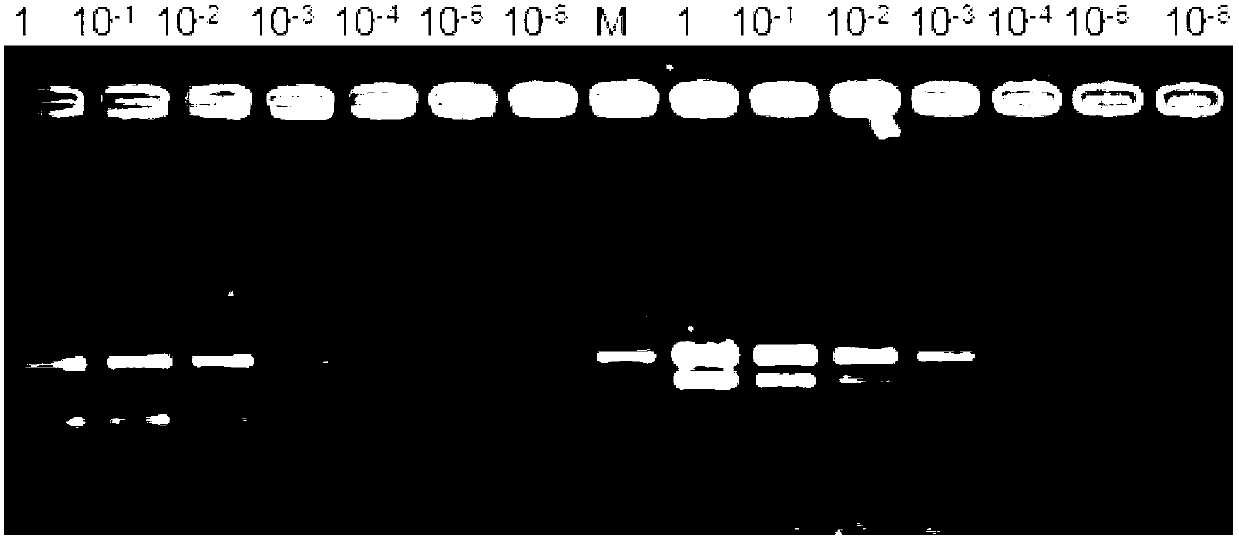
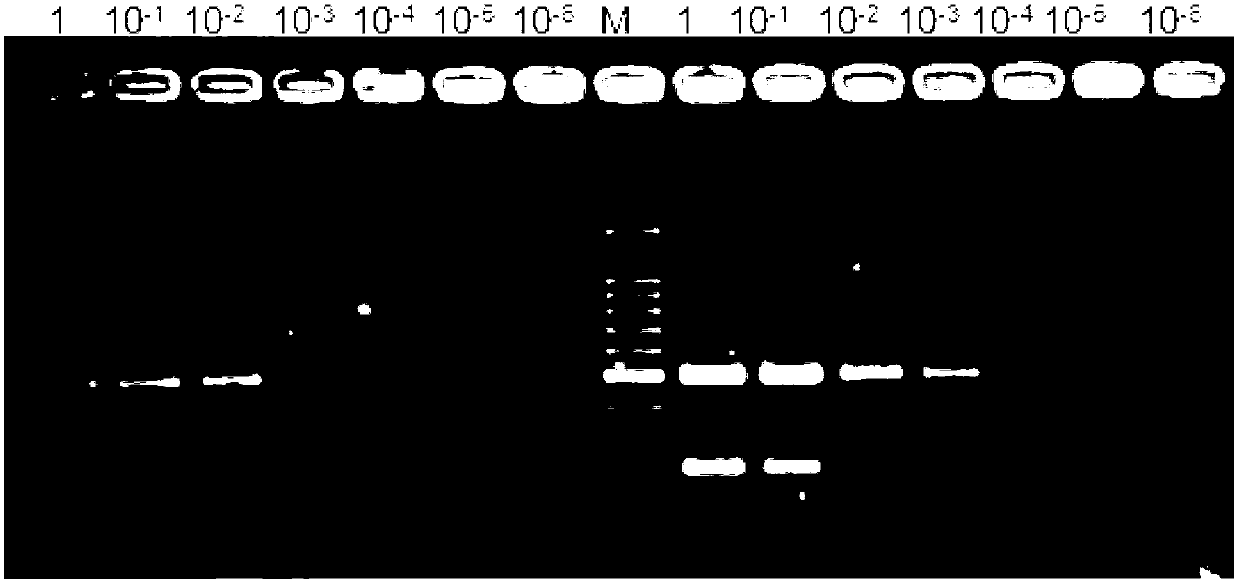
The invention discloses a primer set for detecting functional genes of wheat on the basis of a KASP [competitive allele specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction)] technology and application of the set primer. The primer set comprises totally 14 groups of KASP primers. The KASP primers are respectively designed for the 14 functional genes of the wheat, and particular nucleotide sequences of the KASP primers are sequences 1-42 in sequence tables. The primer set and the application have the advantages that the functional genes of different wheat varieties can be quickly detected by the aid of the KASP primer set, methods for detecting the functional genes of the wheat are simple, convenient and speedy, and detection results are accurate and reliable; the primer set has an important theoretical significance and important economic value in assistant selection of the wheat varieties by the aid of molecular markers.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Reaction buffer composition for nucleic acid replication with packed DNA polymerases
The invention relates to compositions, methods, and kits for nucleic acid replication, including polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and mutagenesis reactions. A buffer composition is provided which allows higher concentrations of DNA polymerase to be used, resulting in greater yield of amplified product and faster reaction kinetics.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
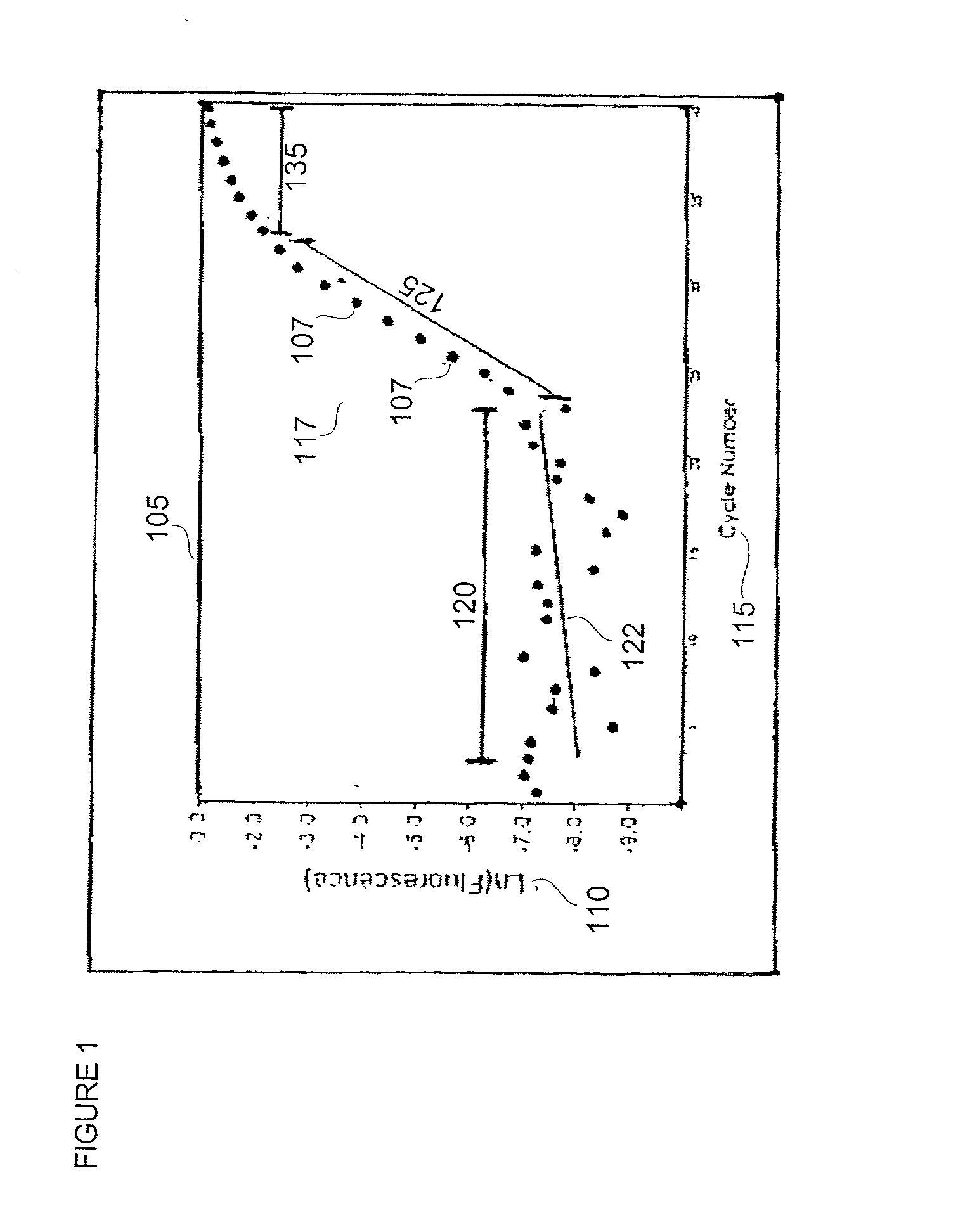
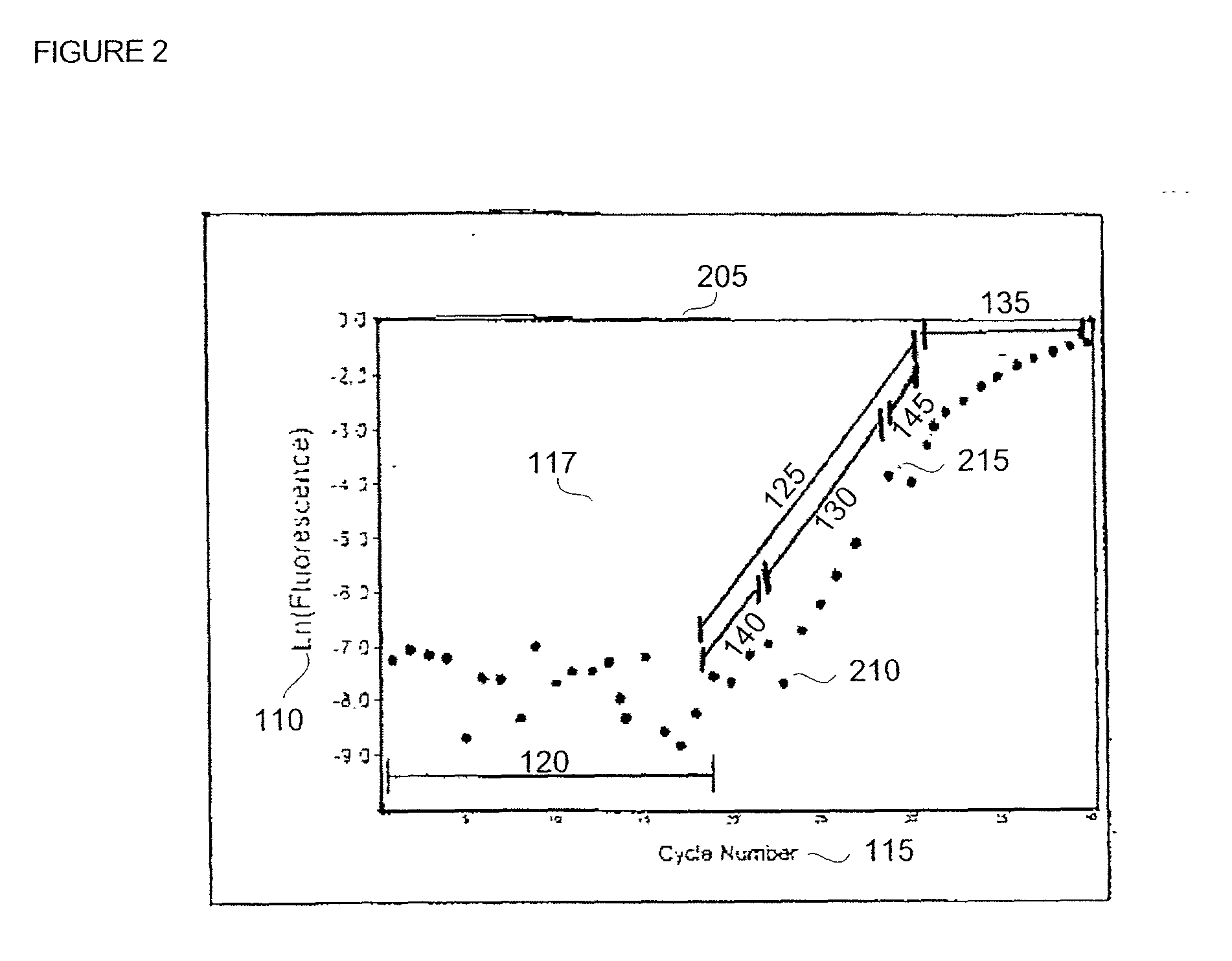
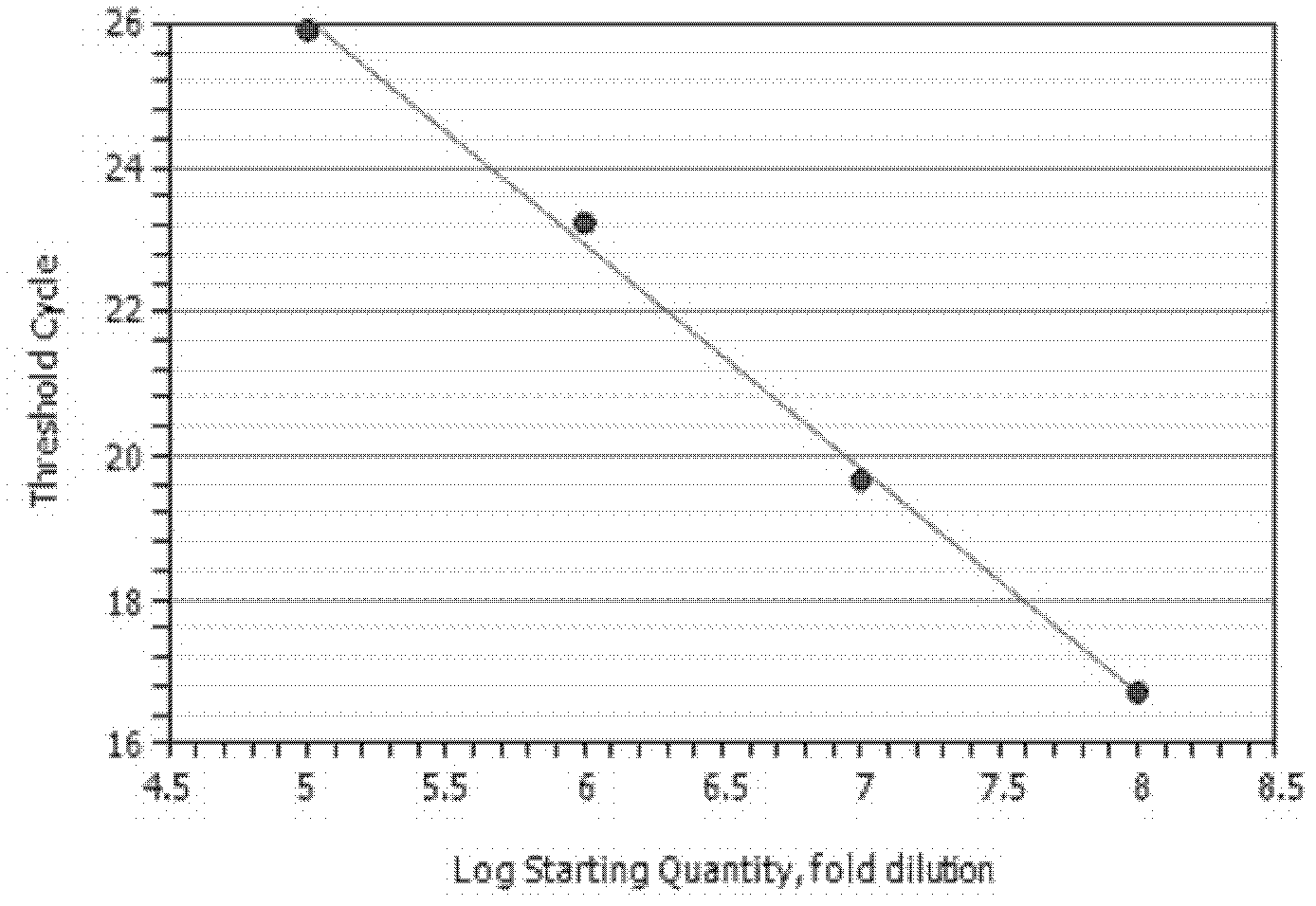
Automatic threshold setting for quantitative polymerase chain reaction
InactiveUS20030044826A1Microbiological testing/measurementRecognisation of pattern in signalsFluorescenceBiology
Disclosed are systems and methods for identifying and quantitating the presence of one or more DNA species in a sample population through PCR amplification. DNA species quantitation includes a determination of a threshold fluorescence value used in the assessment of the PCR amplification reaction. Various embodiments of the present invention incorporate an enhancement function useful in selecting appropriate threshold fluorescence values and facilitate the determination of DNA concentrations by quantitative PCR based methodologies.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
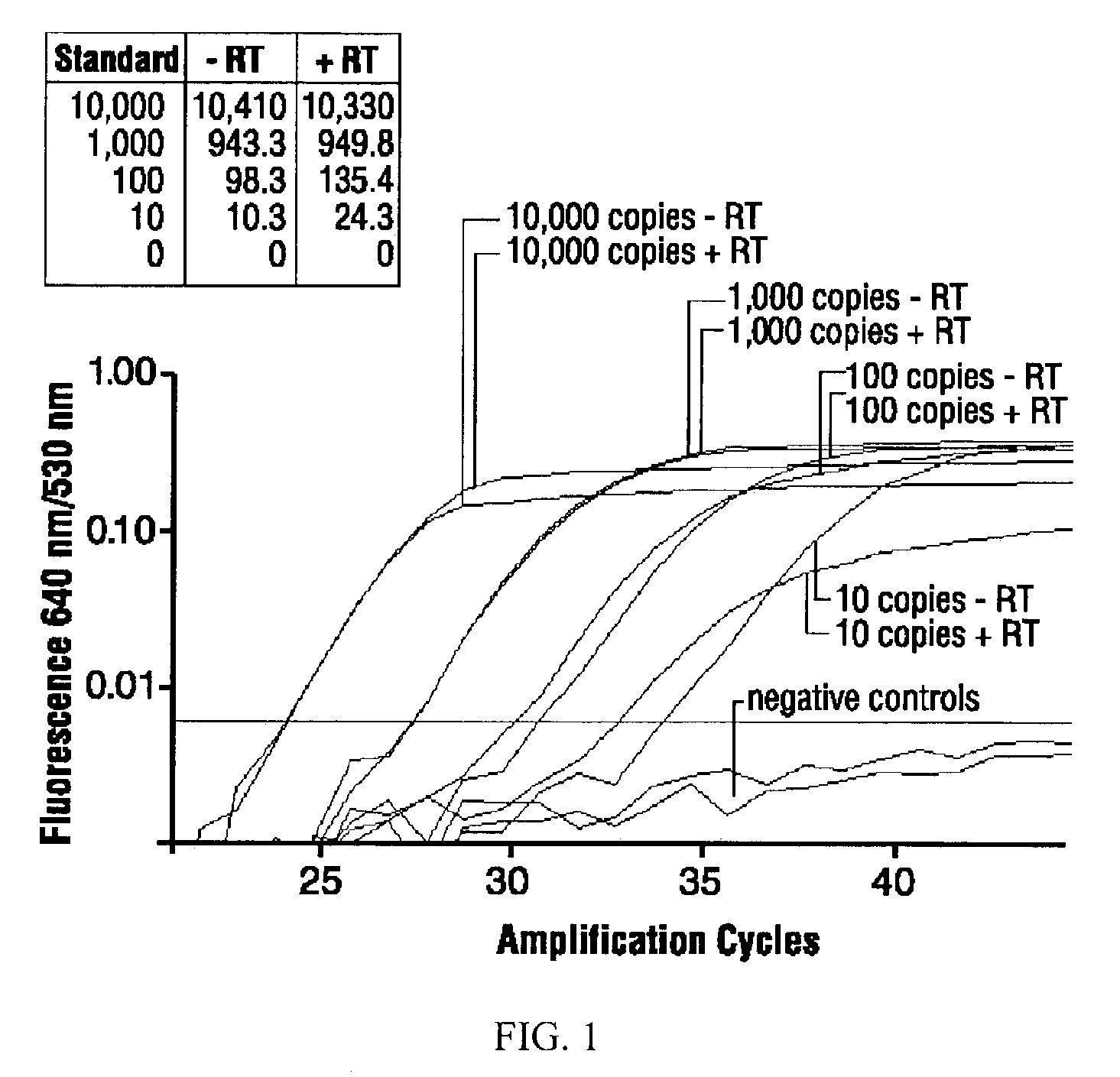
High-sensitivity real-time polymerase chain reaction for detection of nucleic acids
InactiveUS7252937B2Easy extractionImprove stabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementClinical settingsHybridization probe
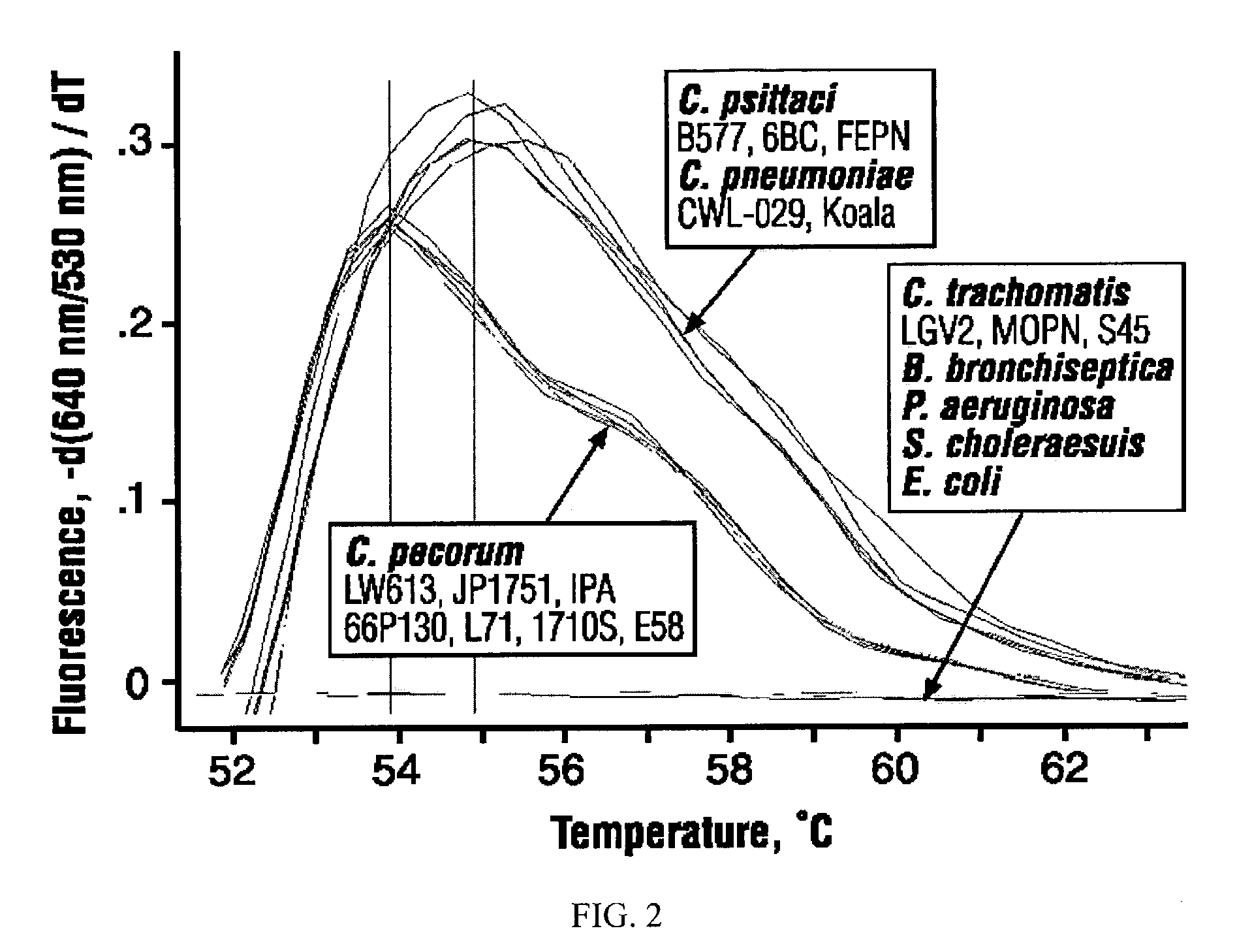
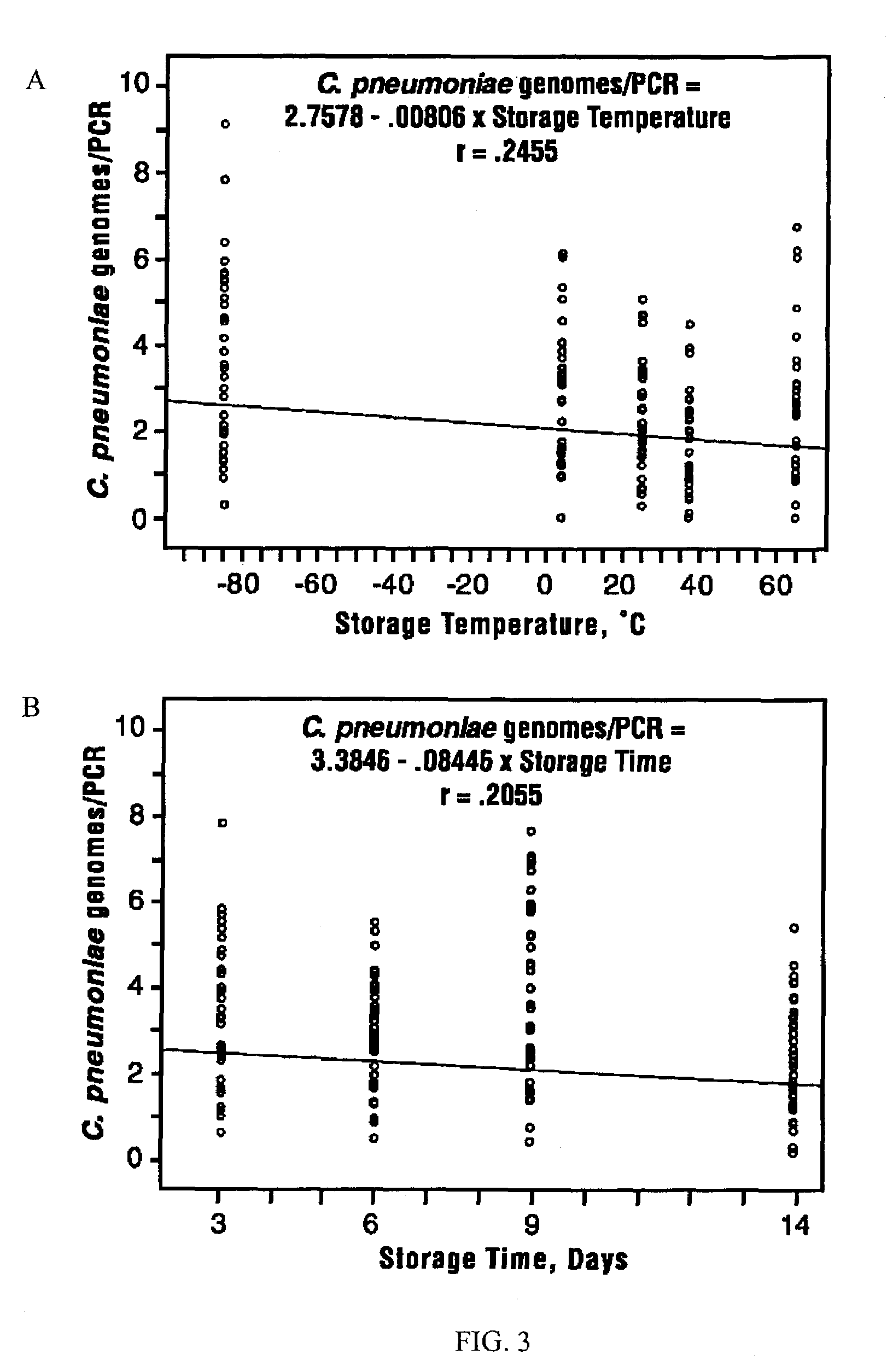
The invention features methods that are capable of detecting single target molecules in a sample input volume of, e.g., 5 μl, and of quantifying organismal, e.g., chiamydial, DNA. Desirably, these methods employ a single tube format coupled with fluorescent detection of amplicons. This approach facilitates the application of quantitative PCR (qPCR) to microbiological diagnosis in clinical settings. The invention also features primers and probes for the detection of Chlamydia. The use of specific hybridization probes with qPCR amplification provides the ability for identification of individual species or strains of microorganisms.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
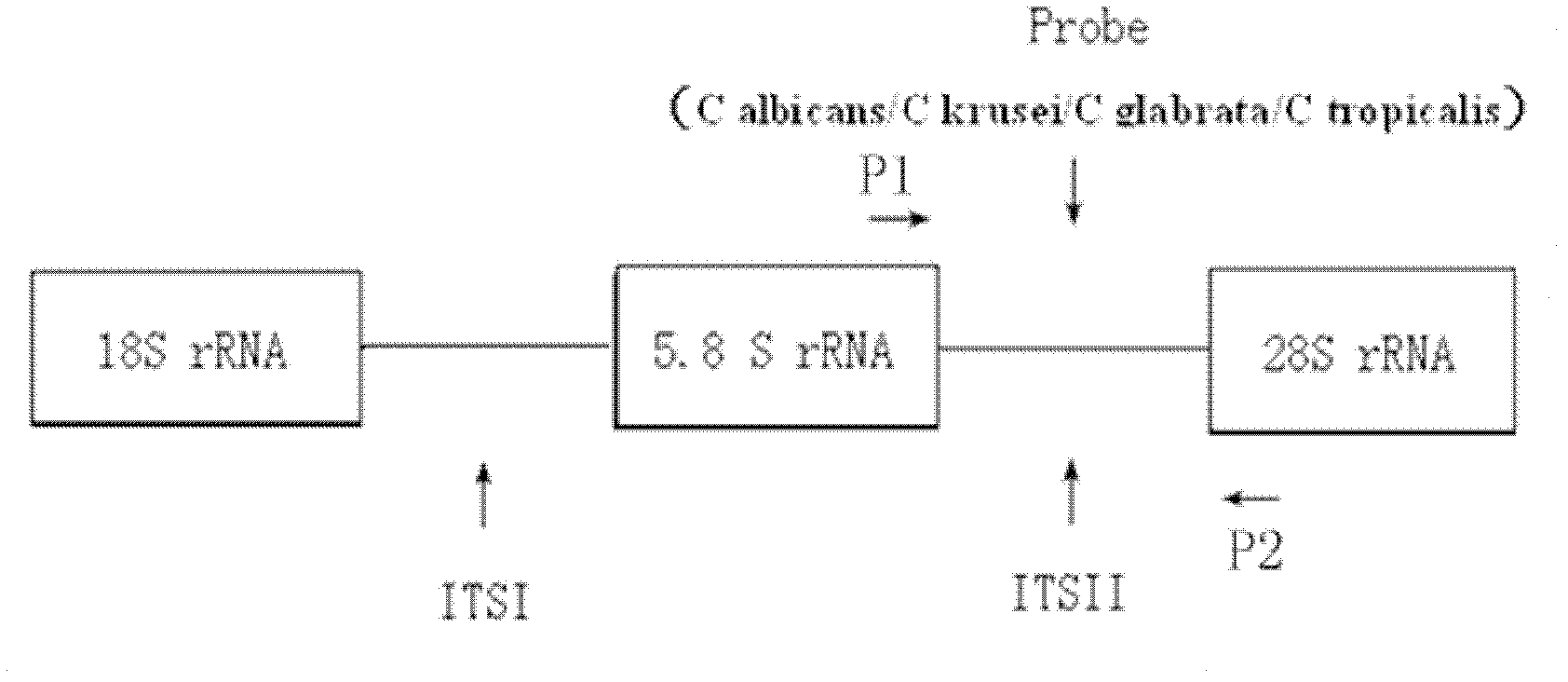
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method for diagnosing human papillomavirus (HPV) and reagent kit thereof
InactiveCN101017141AEfficient, systematic, economical and simpleShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceHuman bodyHuman papillomavirus
This invention relates to one polymer enzyme linkage reaction fluorescence test method to dialogue dangerous human body nipple shape virus and to isolate DNA sample HPV gene type to test one set of dangerous HPV infection from patient by the method, wherein, it belongs to life science and biological technique. This invention agent case comprises one fluorescence meter PCR technique as base of multi-layer polymer enzyme reaction composed of multiple HPV positive lead object, reaction lead object and fluorescence detector.
Owner:GENETEL PHARMA SHENZHEN
Multiplex quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection kit for vibrio parahaemolyticus and detection method
InactiveCN102605055AMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFood poisoningSaxitoxin
The invention provides a multiplex quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction detection kit for vibrio parahaemolyticus toxin gene and a detection method. The kit mainly comprises specific primers, probes and PCR reaction reagent, wherein the specific primers and the probes consist of specific primers and probes of vibrio parahaemolyticus thermostable direct hemolysin gene (tdh), thermolabile hemomysin gene (tlh), toxin expression regulating protein gene (toxR) and thermostable related hemolysin gene (trh). The invention provides the quick, sensitive and specific multiplex fluorescent quantitative PCR detection kit and the detection method aiming at the vibrio parahaemolyticus toxin gene, and provides basis for controlling food poisoning caused by the vibrio parahaemolyticus in time and early diagnosis of the food poisoning caused by the vibrio parahaemolyticus.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Nucleic acid releasing agent, nucleic acid PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification method and PCR amplification kit
ActiveCN109402240AGuaranteed amplification efficiencyAvoid degradationMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptidasesPotassiumPolyethylene glycol
Owner:SANSURE BIOTECH INC
Molecular identification method of atlantic salmon
ActiveCN103122386ALower requirementEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular identificationEnzyme digestion
The invention discloses a molecular identification method of an atlantic salmon. The molecular identification method comprises the following steps of 1, extraction of fish DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid); 2, PCR (polymerase chain reaction) augmentation; 3, enzyme digestion and electrophoresis detection; and 4, identification. The atlantic salmon can be accurately determined in four steps. The molecular identification method of the atlantic salmon has the characteristics of being simple to operate, rapid and accurate, low in price, low in requirement on an instrument and equipment, and the like.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Polymerase chain reaction-sequence based typing (PCR-SBT) method for ABO blood type genotyping and reagent
ActiveCN101921834ASolve the recombination phenomenonThe result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementSodium acetateHuman DNA sequencing
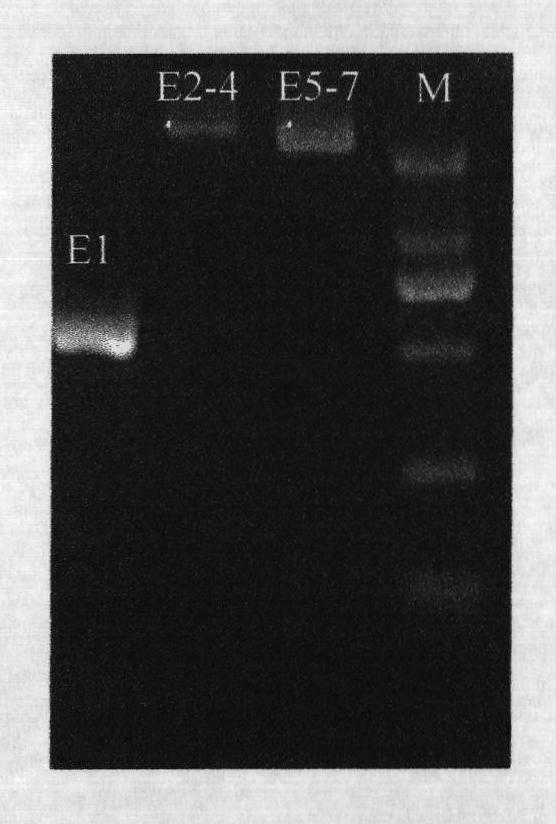
The invention provides a polymerase chain reaction-sequence based typing (PCR-SBT) method for ABO blood type genotyping. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing human genome DNA; amplifying segments of ABO gene exon 1, exons 2-4 and exons 5-7; performing double enzyme digestion purification on the obtained amplified products; performing a sequencing PCR reaction on the purified products; purifying the sequenced products by a sodium acetate-ethanol precipitation method and performing capillary electrophoresis sequencing; and analyzing the obtained sequences by using software to determine the genotype. The method has the advantages of solving the problems of identification of an ABO subtype, judgment of difficult blood types, discovery of a new mutational site, gene recombination among genes, genetic polymorphism detection and the like, exerting the characteristics of high flux and result accuracy of ABO genotyping operation by PCR-SBT, achieving great importance for the relative application in the fields of clinical transfusion medicinal research, genetics and the like and having important practical significance for medicinal research units, pharmic research and reagent development units.
Owner:浙江省血液中心
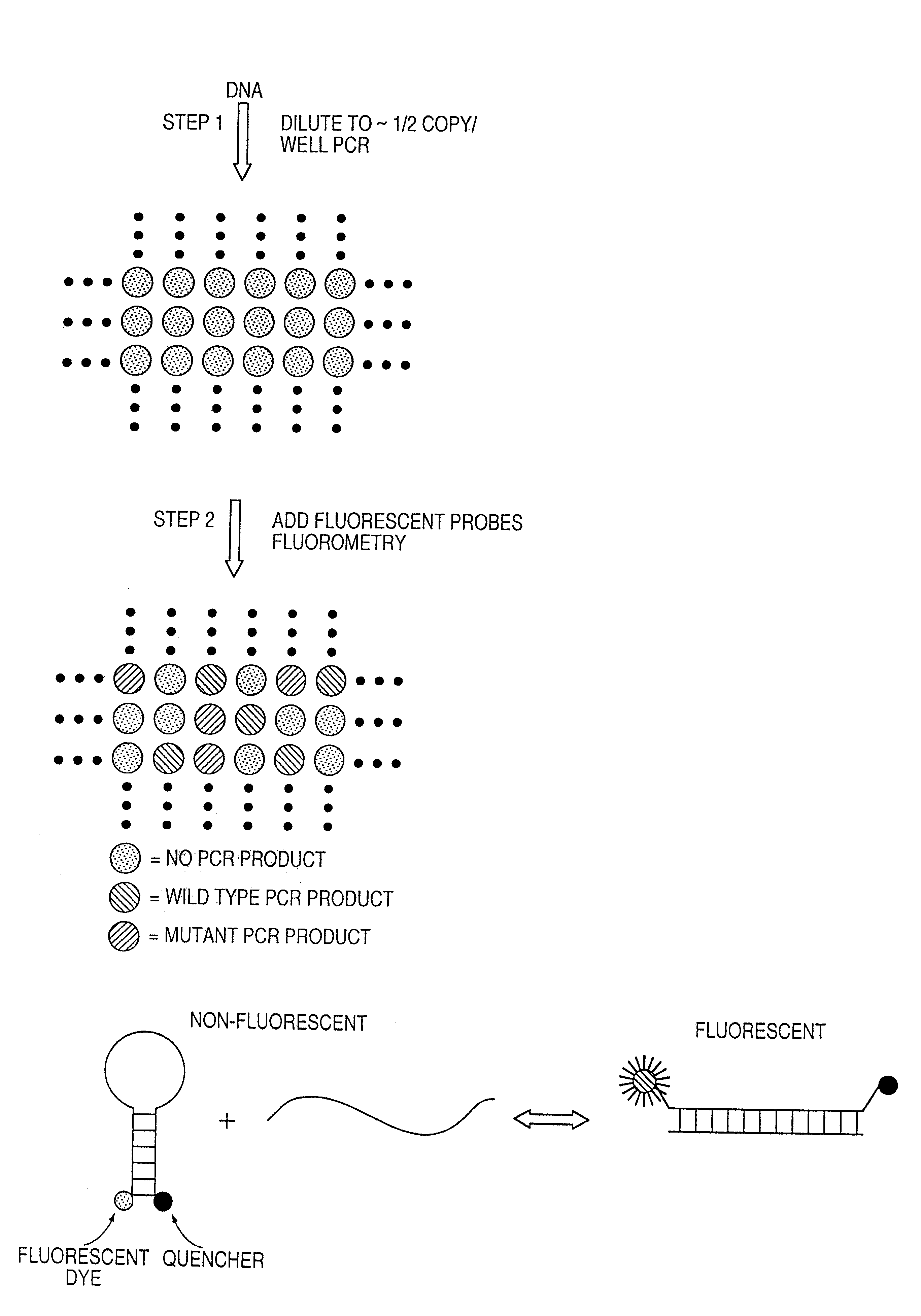
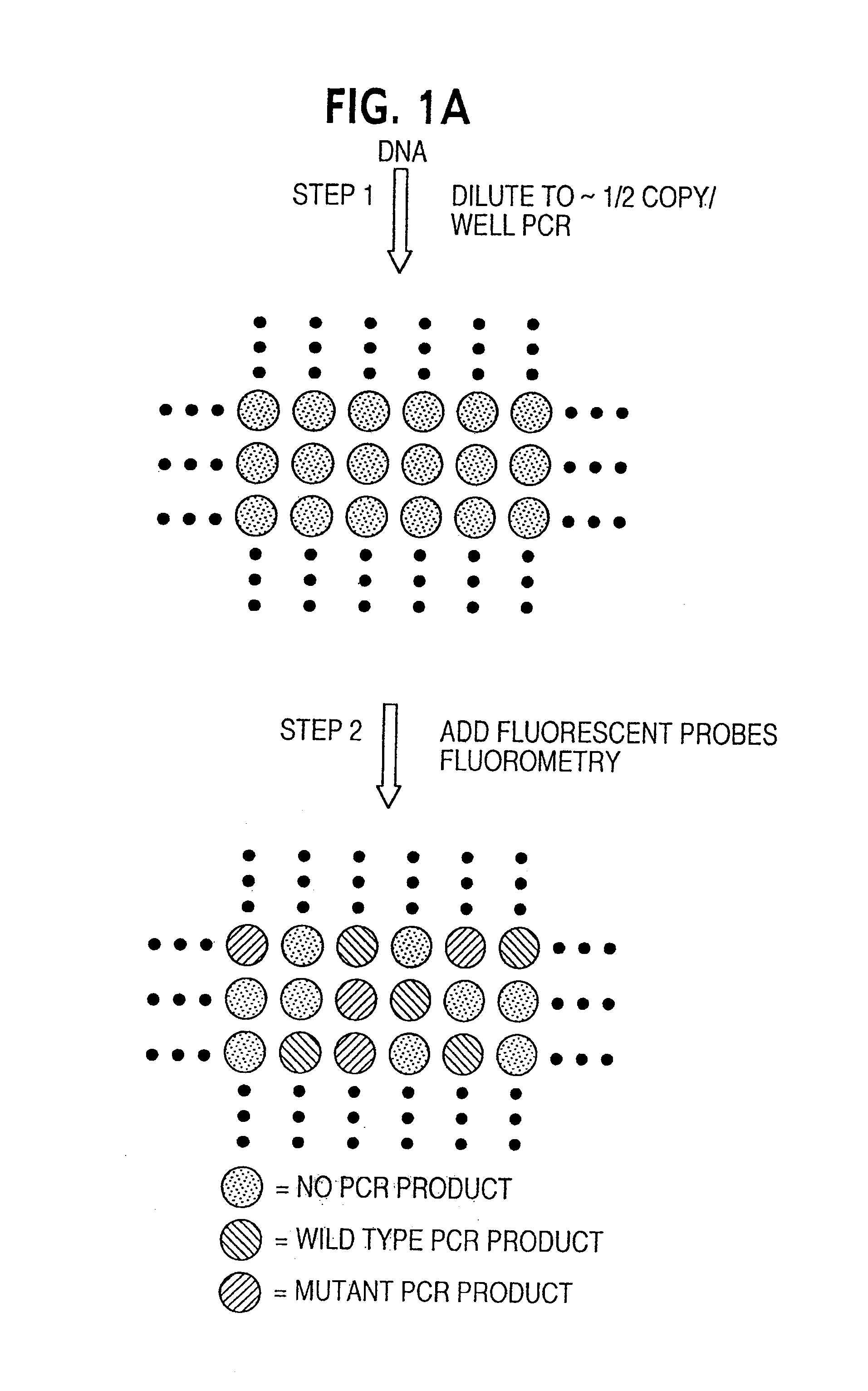
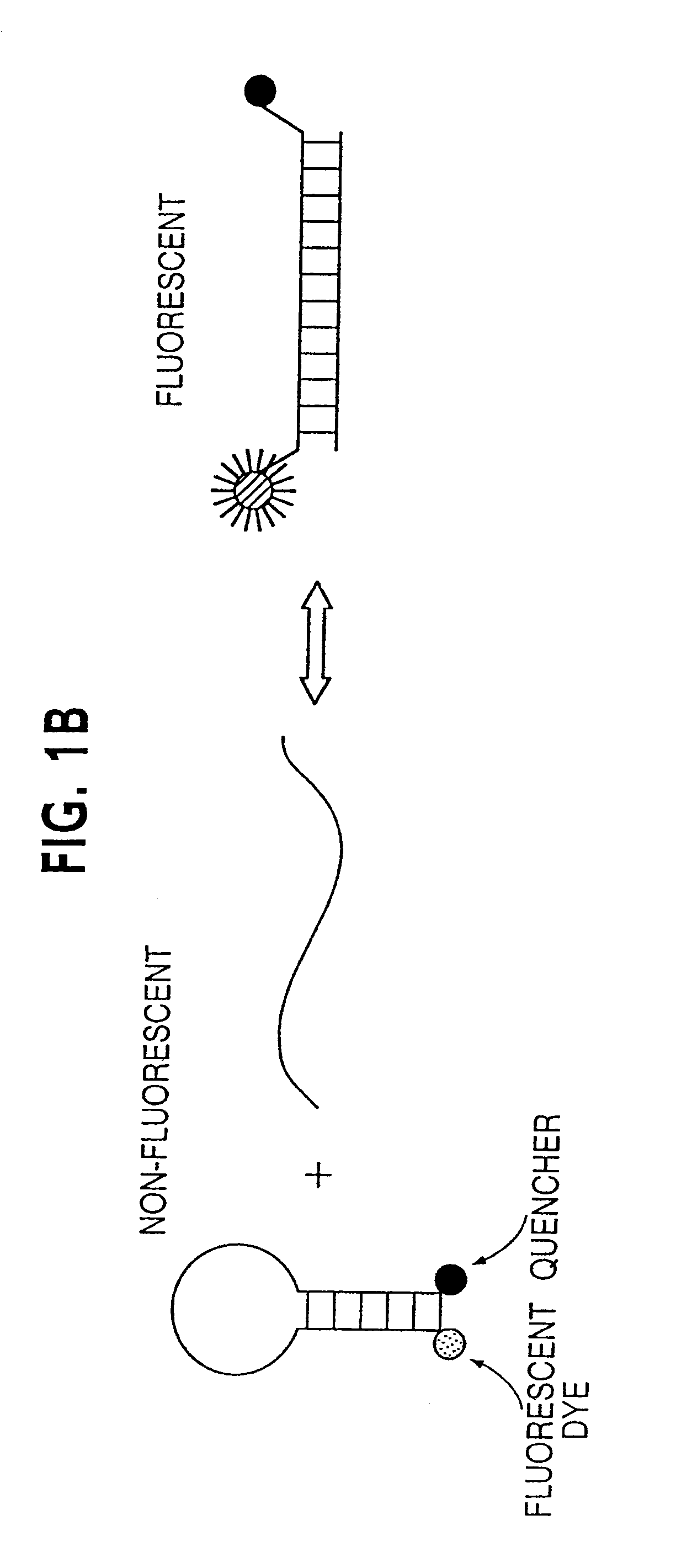
Digital amplification
The identification of pre-defined mutations expected to be present in a minor fraction of a cell population is important for a variety of basic research and clinical applications. The exponential, analog nature of the polymerase chain reaction is transformed into a linear, digital signal suitable for this purpose. Single molecules can be isolated by dilution and individually amplified; each product is then separately analyzed for the presence of pre-defined mutations. The process provides a reliable and quantitative measure of the proportion of variant sequences within a DNA sample.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Detection of Fusarium species infecting corn using the polymerase chain reaction
InactiveUS6846631B2Detailed informationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFungal isolateMultiplex polymerase chain reaction
The present invention relates to the use of primers in polymerase chain reaction assays for the detection of a Fusarium proliferatum, F. verticillioides and F. subglutinans. Specific primers are identified as being useful for the identification of fungal isolates using PCR based techniques.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Microsatellite colorectal cancer instability amplification system and detection kit thereof
InactiveCN103555843AAvoid cumbersomeReduce competitionMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceInstability
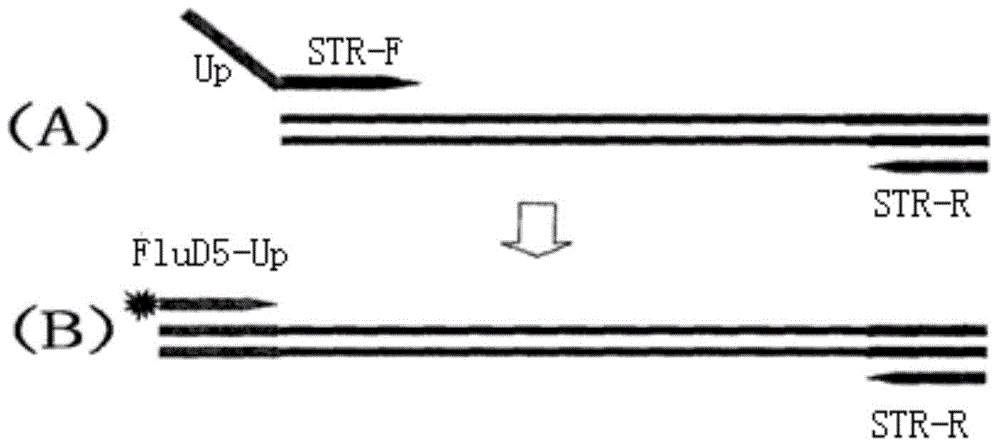
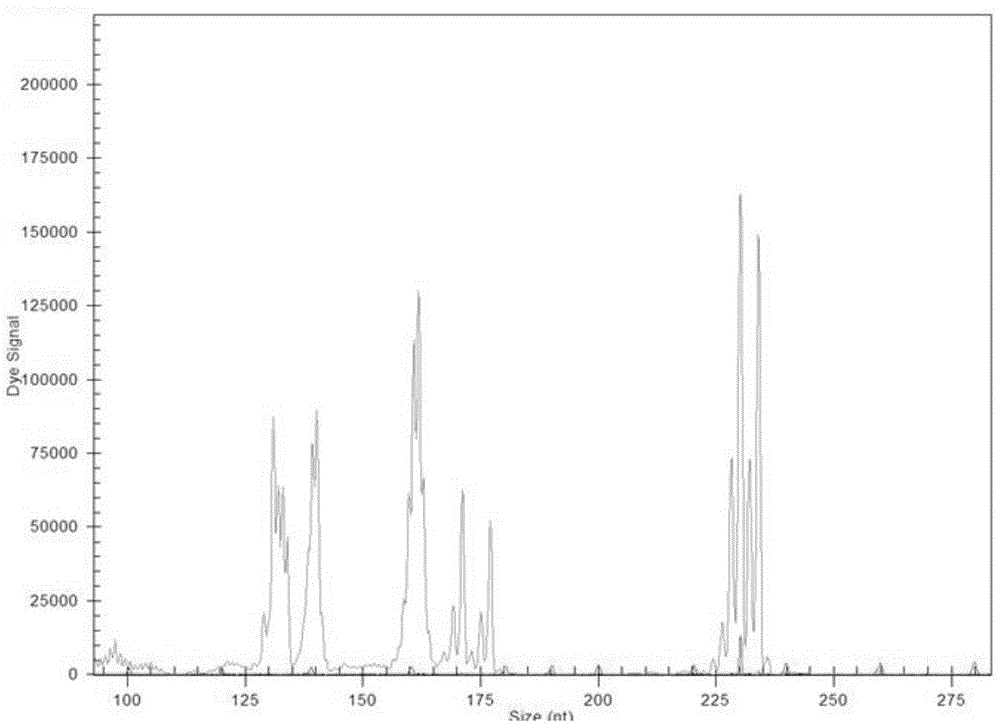
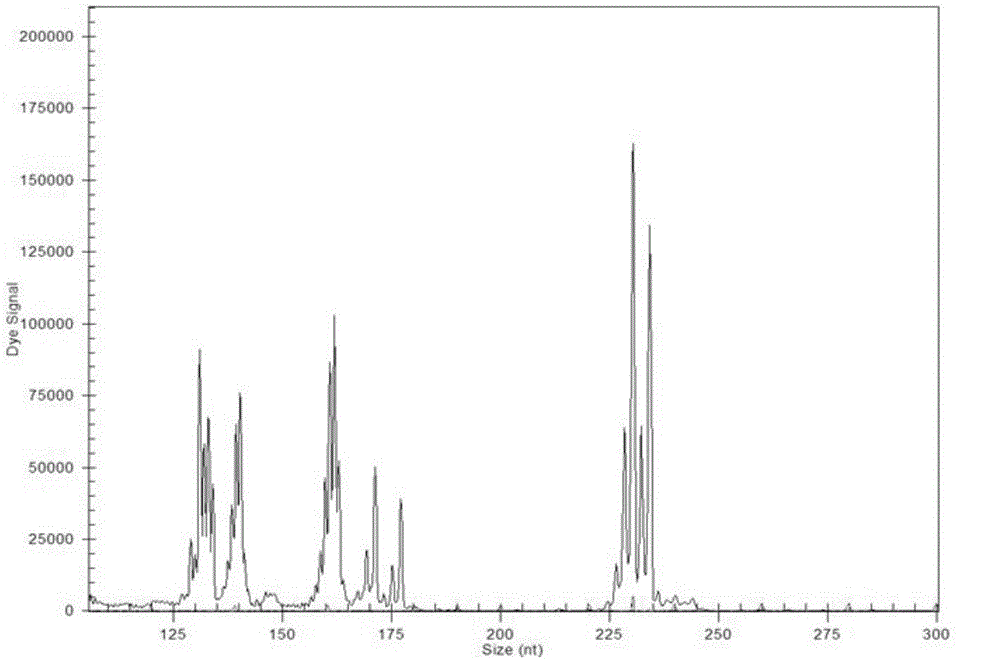
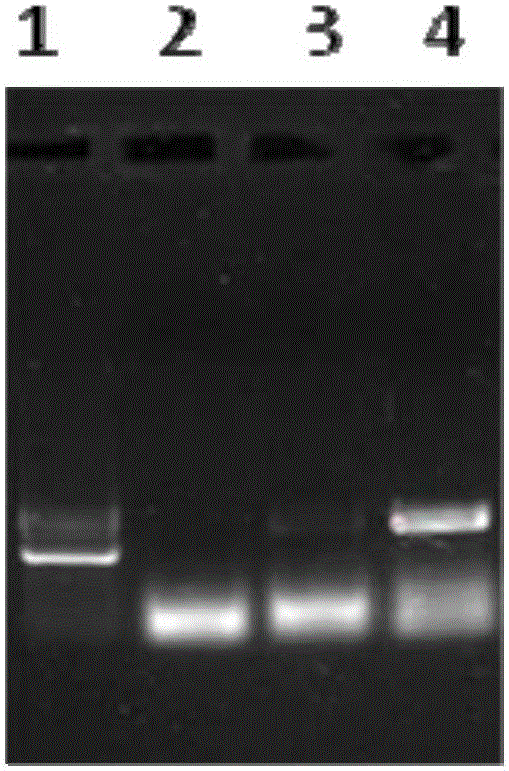
The invention relates to a microsatellite colorectal cancer instability amplification system and a detection kit thereof. The amplification system disclosed by the invention comprises a general-specific chimeric primer pair and a mixture of general primers, wherein the general-specific chimeric primer pair respectively aims at microsatellite sites BAT25, BAT26, D2S123, D5S346 and D17S250; the general primer is FluD5-Up; respective positive primer 5' ends in the general-specific chimeric primer pair are provided with a sequence of the FluD5-Up; the FluD5-Up is a fluorescent-labeled primer. The amplification system and the detection kit thereof which are disclosed by the invention overcome the shortcoming that different primers require for multiple fluorescent labels; five microsatellite gene sites are detected in the same PCR (polymerase chain reaction) system, so that a result is intuitive and reliable; the time can be saved, and the efficiency is high; MSI (medium-scale integration) gene sites can be effectively detected and analyzed.
Owner:上海赛安生物医药科技股份有限公司
Method and PCR (polymerase chain reaction) reagent kit for identifying DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) barcodes of animal medicinal materials
InactiveCN105112525AGuarantee the success rate of amplificationEfficient amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementBetainePolyethylene glycol
The invention provides a method and a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) reagent kit for identifying DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) barcodes of animal medicinal materials. The PCR reagent kit comprises PCR enhancers. The PCR enhancers comprise bovine serum albumin, dithiothreitol, betaine and nonidet p40. The method and the PCR reagent kit for identifying the DNA barcodes of the animal medicinal materials have the advantages that low-abundance traditional Chinese medicine samples with difficulty in amplification, particularly, samples with difficulty in identifying DNA barcodes, such as samples of buffalo horns, antelope horns, tortoise shells, carapax trionycis, pangolins and snake slough, can be effectively amplified, accordingly, the amplification success rate which is close to 100%, of DNA barcode identification techniques can be guaranteed, and DNA barcode techniques can be widely applied.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Fluorescence quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) universal premier for detecting pathogenic aspergillus, detection probe and kit
InactiveCN102321738AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceAspergillus fumigatusFluorescence
The invention discloses a fluorescence quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) universal premier for detecting aspergillus, detection probes and a detection kit, wherein the detection kit comprises universal premiers displayed by base compositions such as SEQ ID. NO: 1 and SEQ ID. NO: 2; and the detection probe is CY5-TAAAGTTGGGTGTCGGCTGG-BHQ aiming at aspergillus fumigatus, the detection probe is FAM-TTGATTTGCGTTCGGCAAGC-BHQ aiming at aspergillus flavus, the detection probe is HEX-ACAAGTTGCAAATAAATGCGTCG-BHQ aiming at aspergillus, and / or the detection probe is ROX-ATGGTTGGAAAACGTCGGCA-BHQ aiming at aspergillus Niger. The multiple PCR detection method, premier, the probes and the kit thereof provided by the invention aim at four main pathogenic aspergilli and have high specificity and sensitivity; and the detection method is rapid, simple and convenient, and can be used for detecting and identifying the strain of pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF RESPIRATORY DISEASE
Multiplex-PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection method and kit for BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutation
The invention provides a method and a kit for detecting BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutation. The method and the kit utilize two sets of PCR (polymerase chain reaction) primers, wherein a first set of PCR primers comprises 189 pairs of PCR primers and is divided into two groups, a first group comprises 95 pairs of primers with sequences represented as SEQ ID NO.5-SEQ ID NO.194, a second group comprises 94 pairs of primers with sequences represented as SEQ ID NO.195-SEQ ID NO.382, a sequence represented as SEQ ID NO.1 is added to the 5' end of each upstream primer, and a sequence represented as SEQ ID NO.2 is added to the 5' end of each downstream primer; sequences of upstream and downstream primers of a second set of PCR primers are represented as SEQ ID NO.3 and SEQ ID NO.4.
Owner:艾吉泰康(嘉兴)生物科技有限公司
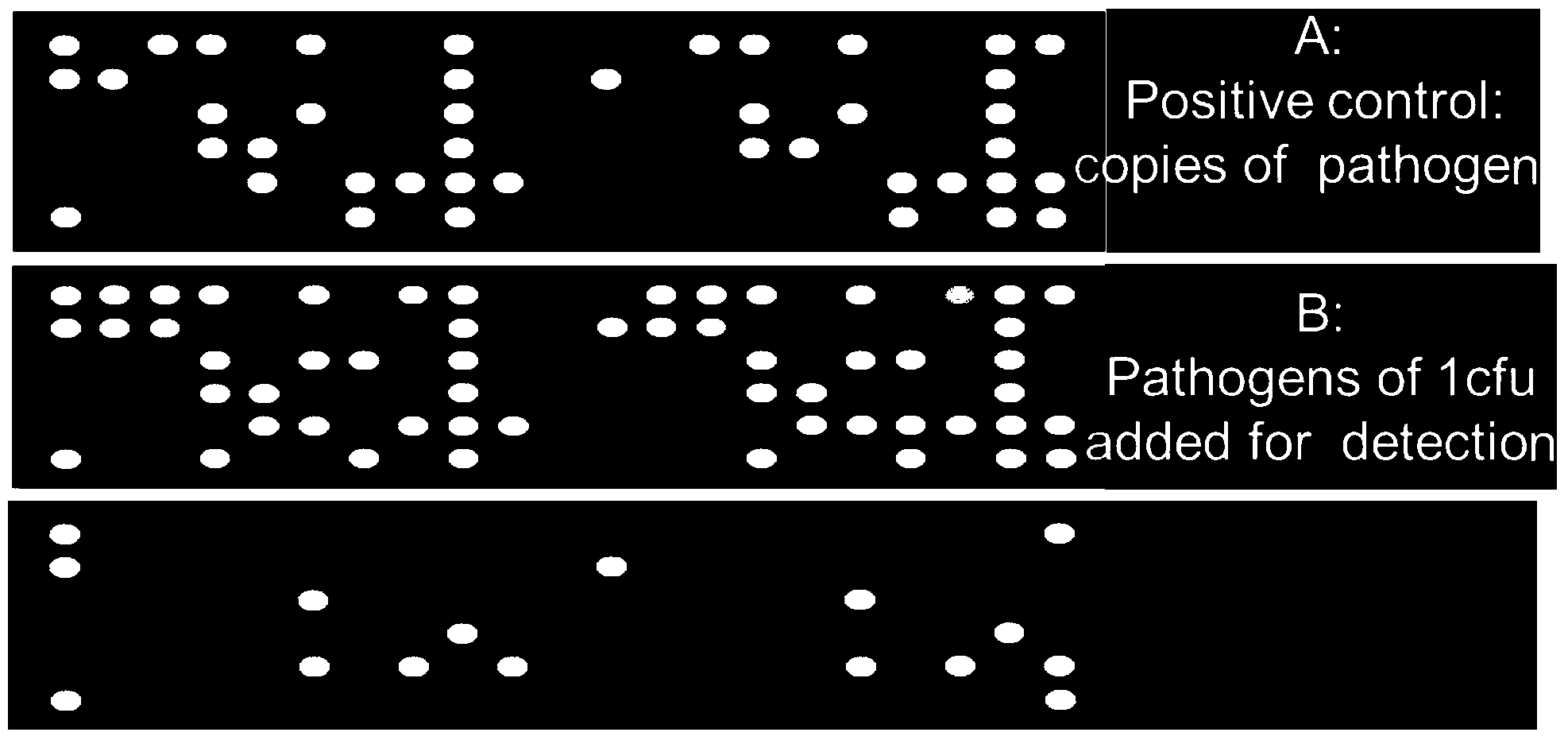
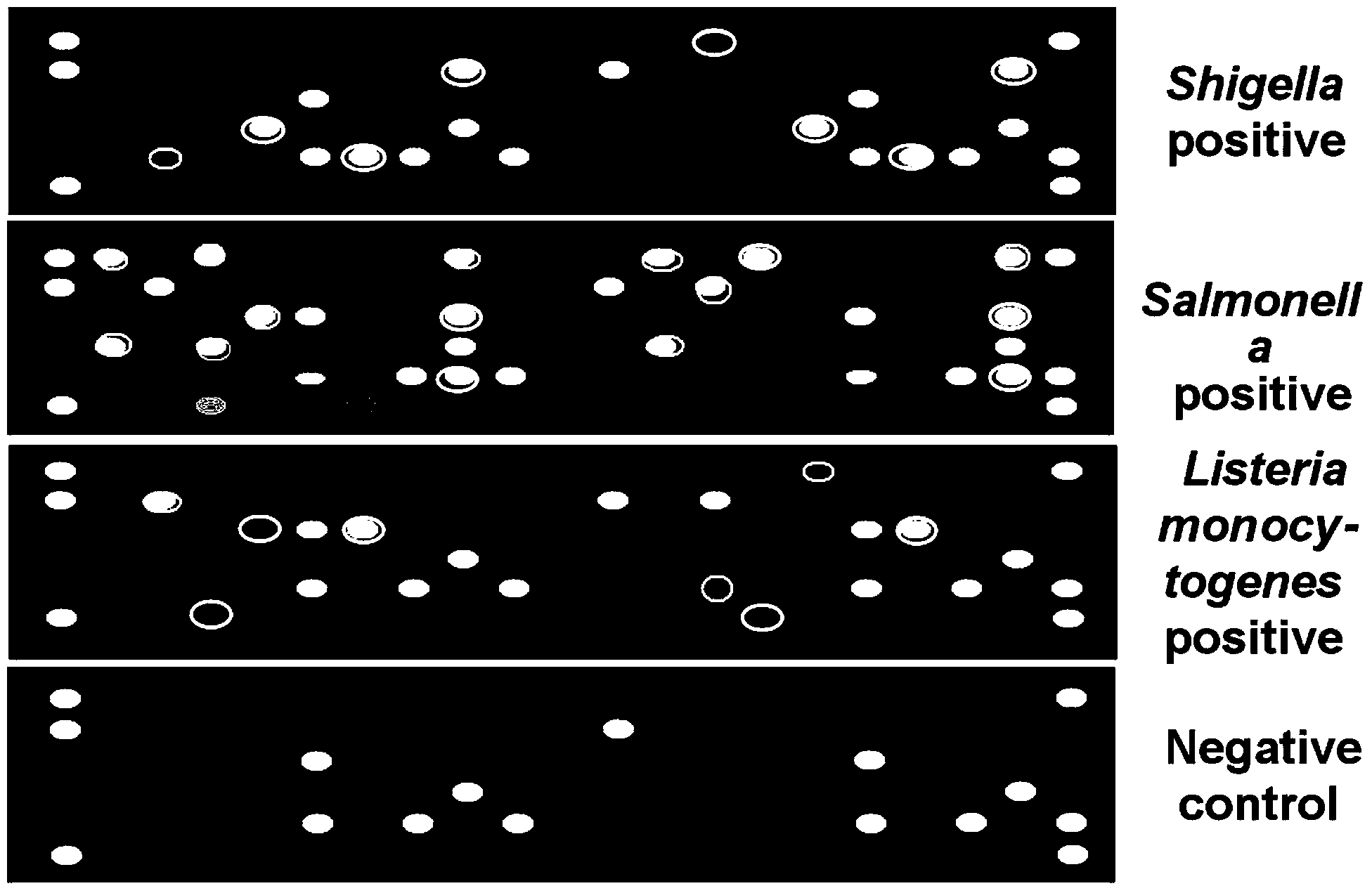
Quick high-throughput intestines source pathogenic bacterium detection method
InactiveCN103898208AMeet the requirements of safety testingMeet the testing requirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesStaphylococcus aureusA-DNA
The invention relates to a quick, sensitive and high-throughput intestines source pathogenic bacterium detection method. The detection method provided by the invention integrates two powerful molecular biological techniques: polymerase chain reaction PCR and a micro-array, and directly fixes a probe of PCR hybridization in a hybridization cabin of the micro-array on a same chip with a PCR reaction chamber. The detection method comprises the following steps of enriching bacteria; extracting a DNA solution; carrying out PCR amplification; hybridizing; cleaning; and judging the result. The method provided by the invention can quickly detect genes of vibrio parahaemolyticus, Shigella, staphylococcus aureus, listeria monocytogenes and salmonella in high throughput, and the detection efficiency of front-line inspection and quarantine personnel of import and export ports can be greatly improved, thereby not only reducing the workload, but also solving the undetected positive result problem probably caused by conventional detection method to the maximum extent. Therefore, food safety incidents are prevented to the maximum extent.
Owner:SHANGHAI ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU OF P R C
Real-time polymerase chain reaction using large target amplicons
InactiveUS20040170981A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleic acid sequencingBiological materials
The present invention relates to methods for analyzing a target nucleic acid sequence in a biological material. More particularly, the present invention relates to methods for analyzing a target nucleic acid sequence by real time polymerase chain reaction using nucleic acid primers that are separated by at least about 750 nucleic acid residues in the target sequence.
Owner:CLEARANT
Application of graphene in polymerase chain reaction as reinforcing agent
An application of graphene in polymerase chain reaction as a reinforcing agent relates to a graphene material. An improved Hummers method is utilized to synthesize graphite oxide, and hydrazine hydrate is utilized to synthesize graphene. A plasmid is used as a template to carry out polymerase chain reaction and multi-round polymerase chain reaction, the graphene can increase the specificity of the polymerase chain reaction within 14 mu gmL-1, and a target product with strong specificity can even be obtained through 8-round polymerase chain reaction. A clinical blood sample deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is taken as a template to carry out the polymerase chain reaction, and a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) reaction system which is added with the graphene can obtain a product with single specificity and can still obtain the target product with the strong specificity within a scope between 25 DEG C and primer annealing temperature. The amplification products which are added with the graphene do not influence the primer sequence and length through sequencing tests, and the graphene can be used as a polymerase chain reaction reinforcing agent with good performance for polymerase chain reaction.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Methods for high level multiplexed polymerase chain reactions and homogeneous mass extension reactions
ActiveUS8003317B2Improve throughputLow costSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LSequence variation
Provided herein are optimized methods for performing multiplexed detection of a plurality of sequence variations. Also provided are methods for performing multiplexed amplification of target nucleic acid.
Owner:AGENA BIOSCI
DNA polymerase
The present invention relates to a DNA polymerase possesses the properties of 1) exhibiting higher polymerase activity when assayed by using as a substrate a complex resulting from primer annealing to a single stranded template DNA, as compared to the case where an activated DNA is used as a substrate; 2) possessing a 3'->5' exonuclease activity; 3) being capable of amplifying a DNA fragment of about 20 kbp, in the case where polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is carried out using lambd-DNA as a template. It also relates to a DNA polymerase-constituting protein; a DNA containing the base sequence encoding thereof; and a method for producing the DNA polymerase. The present invention provides a novel DNA polymerase possessing both a high primer extensibility and a 3'->5' exonuclease activity.
Owner:TAKARA HOLDINGS
Multiple PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method for identifying salmonella enteritidis, salmonella typhimurium, salmonella pullorum and salmonella gallinarum
InactiveCN103131784AShorten diagnostic timeMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesSerotype
The invention relates to a multiple PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method for identifying salmonella enteritidis, salmonella typhimurium, salmonella pullorum and salmonella gallinarum. The multi-PCR method comprises the following steps of: with the extracted DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of a bacterium to be detected as a template, carrying out mPCR (multiple polymerase chain reaction) amplification on five pairs of primers as shown in SEQ ID NO.1-10; and carrying out agarose gel electrophoresis on mPCR amplification products, and then determining according to electrophoresis results. According to the multiple PCR method, the synthesized primers are used for carrying out PCR amplification, a diseased material can be directly ground and amplified by adopting the established multiple PCR, different salmonella serotypes can be detected in one system, serum glass plate agglutination is completed in only about six hours compared with three days for the traditional serum glass plate agglutination after separation pure culture in clinical detection, the diagnosis time is greatly shortened, and a basis is provided for clinical diagnosis.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com




![Primer set for detecting functional genes of wheat on basis of KASP [competitive allele specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction)] technology and application of set primer Primer set for detecting functional genes of wheat on basis of KASP [competitive allele specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction)] technology and application of set primer](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/935db461-2e79-4d64-a703-4ba19d999536/HDA0000809386820000011.PNG)
![Primer set for detecting functional genes of wheat on basis of KASP [competitive allele specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction)] technology and application of set primer Primer set for detecting functional genes of wheat on basis of KASP [competitive allele specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction)] technology and application of set primer](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/935db461-2e79-4d64-a703-4ba19d999536/HDA0000809386820000012.PNG)
![Primer set for detecting functional genes of wheat on basis of KASP [competitive allele specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction)] technology and application of set primer Primer set for detecting functional genes of wheat on basis of KASP [competitive allele specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction)] technology and application of set primer](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/935db461-2e79-4d64-a703-4ba19d999536/HDA0000809386820000013.PNG)