Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Toxigenic strain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Detection of toxigenic strains of clostridium difficile
ActiveUS20090208948A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementClostridium difficileClostridium difficile (bacteria)
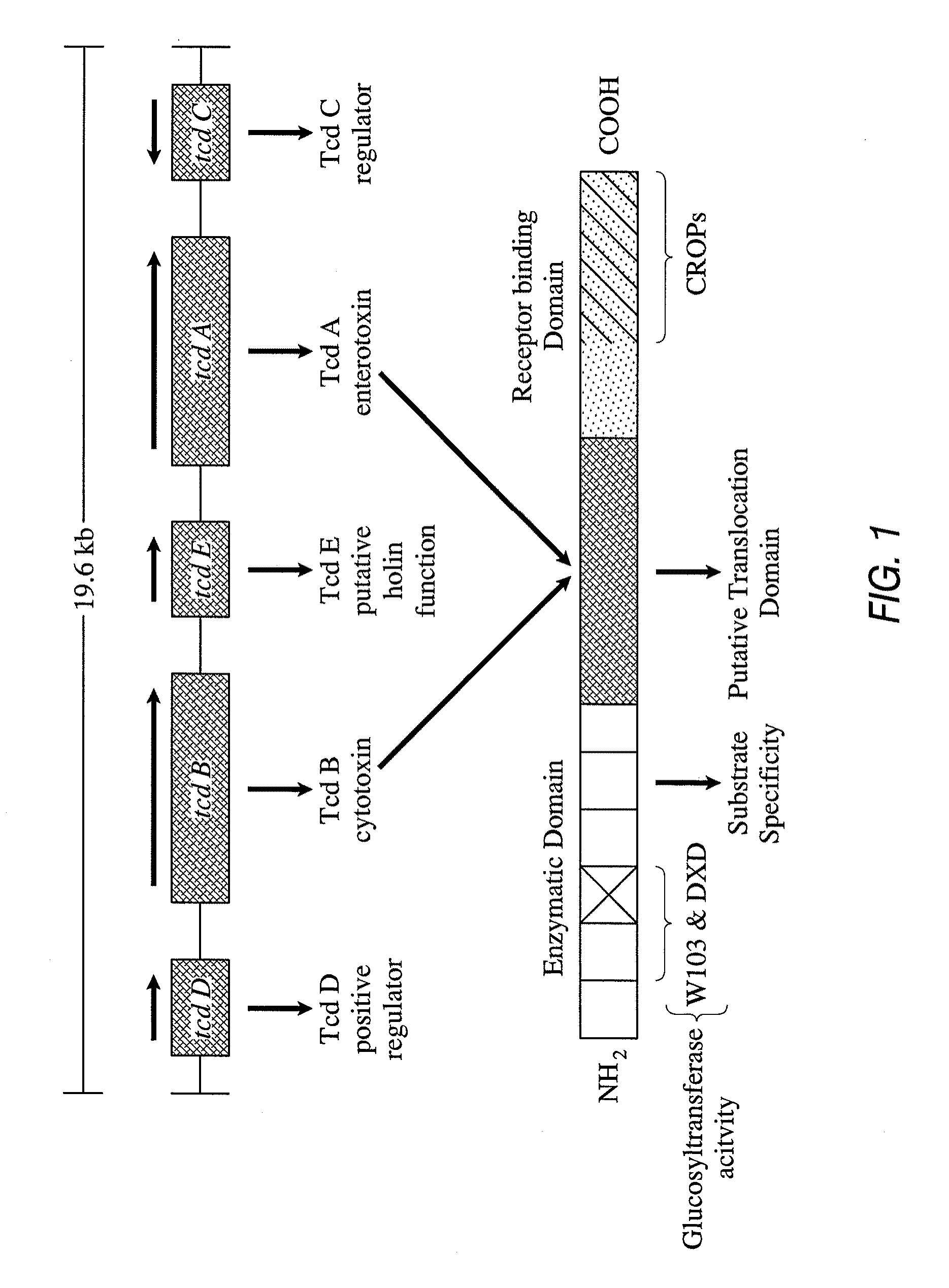
Primers and probes for detection of toxin-producing (toxigenic) strains of Clostridium difficile, and to methods of detecting toxigenic strains using these primers and probes. Toxigenic strains of C. difficile are detected by nucleic acid-based amplification methods using particular primers and probes that bind to the toxin B (TcdB) gene. These primers and probes are used to amplify C. difficile nucleic acids in clinical samples to determine the presence of these toxigenic strains.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
Method for identifying and evaluating toxigenic capability of toxigenic strain of aflatoxin
ActiveCN109557314ARapid virulenceRapid Identification EvaluationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisAflatoxin contaminationPcr method
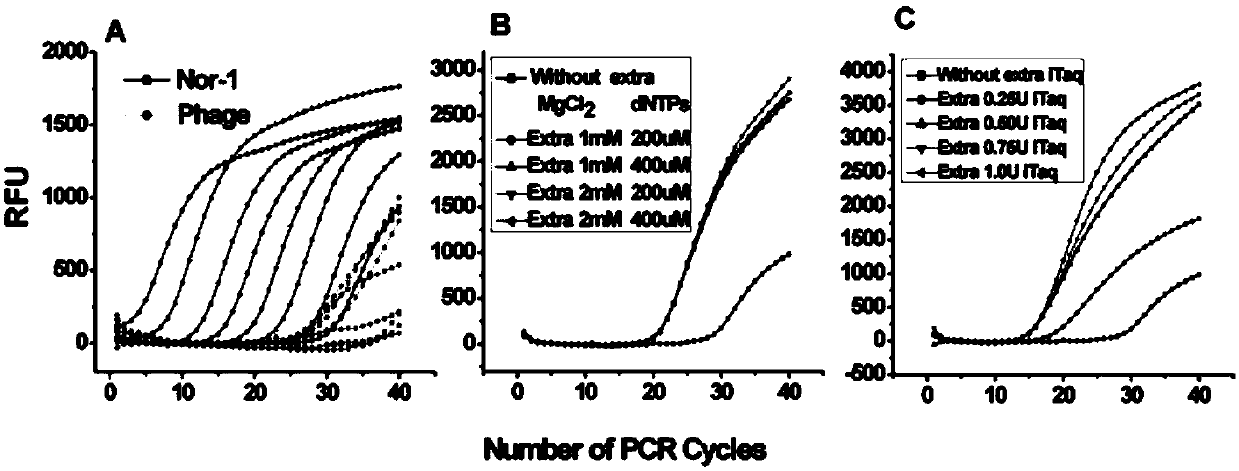
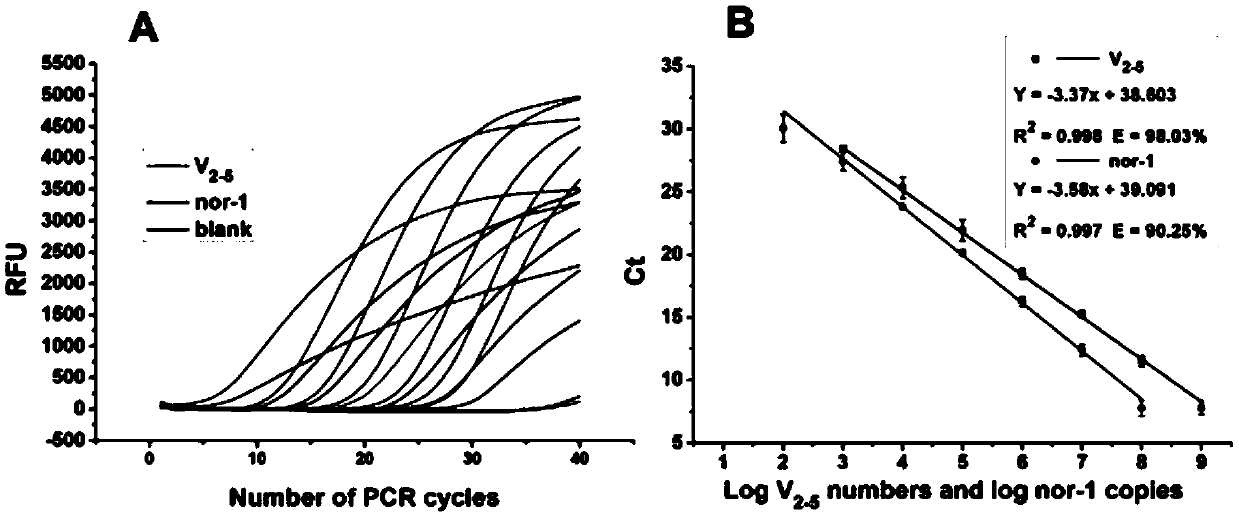
The invention, which belongs to the biological field, particularly relates to a method for identifying and evaluating the toxigenic capability of a toxigenic strain of aflatoxin. A ratio of the aflatoxin yield to the Nor-1 gene transcription amount is determined and the high relative stability is realized. An aflatoxin strain toxigenic capability identification model is established and thus a regression equation between the aspergillus flavus toxigenic capability and the AFT / Nor-1 ratio is obtained. With determination of the AFT / Nor-1 ratio, the toxigenic capability of the aspergillus flavus strain is identified and evaluated rapidly and accurately, so that the method has the important significance in aflatoxin pollution early warning and prevention controlling. Besides, a synchronous detection RT-PCR method for the aflatoxin yield and the nor-1 gene transcription amount is also established; and the AFT / Nor-1 ratio obtained based on the synchronous detection RT-PCR method is reliable and accurate and can be used as the identification index for determining the toxigenic capability of the aspergillus flavus strain.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Multiple fluorescence PCR detection kit and detection method for clostridium difficile toxin genes
ActiveCN103361434AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesClostridium difficile infectionsClostridium difficile toxin B
A provided multiple fluorescence PCR detection kit for clostridium difficile toxin genes mainly comprises specific primers, probes and a PCR reaction reagent, and the specific primers and the probes respectively consist of specific primers and probes of clostridium difficile toxin A (tcdA), toxin B (tcdB), binary toxin A (cdtA) and binary toxinB (cdtB). The beneficial effects of the invention comprise: the fast, sensitive and specific multiple fluorescence PCR detection kit and a detection method are provided for the clostridium difficile toxin genes, and a foundation is provided for distinguishing between toxigenic strains and avirulent strains of clostridium difficile, and early diagnosis on infection of clostridium difficile.
Owner:杭州海基生物技术有限公司
Porcine seneca valley virus strain and application thereof
ActiveCN107513524AGood strain backgroundLay the material foundationSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsPig farmsDisease
The invention discloses a porcine seneca valley virus strain and an application thereof. In the invention, the seneca valley virus strain CH-FJZZ-2017 is isolated from pathological materials of porcine idiopathic vesicular disease in a pig farm in Fujian Province, with the preservation number of CGMCC No. 12160. The isolated porcine seneca valley virus CH-FJZZ-2017 in the invention is isolated from swinery newly suffering from the epidemic disease within Chinese territory, represents the current epidemic predominant virus strain in China, has a good virus strain background, and can be used as an inactivated vaccine production virus strain and a virus seed for testing, thereby providing a material for subsequent relevant experimental study, and laying a material foundation.
Owner:CHINA ANIMAL HUSBANDRY IND
Non-aflatoxigenic Aspergillus flavus isolates
InactiveUS7361499B1Reduce aflatoxin contaminationReduce contaminationBiocideMicroorganismsAflatoxin contaminationToxin
The ability of two Aspergillus flavus Link isolates (CT3 and K49) to reduce aflatoxin contamination of corn was assessed in a four-year field study (2001 to 2004). Soil was treated with six wheat inoculant treatments: toxigenic isolate F3W4; the non-toxigenic isolate K49; the non-aflatoxigenic isolate CT3, two mixtures of CT3 or K49 with F3W4; and an autoclaved wheat control, applied at 20 kg / ha. In 2001, inoculation with the toxigenic isolate increased corn grain aflatoxin levels by 167% compared to the non-inoculated control, while CT3 and K49 inoculation reduced aflatoxin levels in corn grain by 86% & 60%, respectively. In 2002, inoculation of CT3 and K49 reduced aflatoxin levels by 61% and 76% compared to non-inoculated controls, respectively. In 2001 mixtures of toxigenic and non-toxigenic isolates had little effect on aflatoxin levels, but in 2002 inoculation with mixtures of K49 and CT3 reduced aflatoxin levels 68 and 37% compared to non-inoculated controls, respectively. In 2003 and 2004, a low level of natural aflatoxin contamination was observed (8 ng / g). However, inoculation with mixtures of K49+F3W4 and CT3+F3W4, reduced levels of aflatoxin 65 to 94% compared to the toxigenic strain alone. Compared to the non-sclerotia producing CT3, strain K49 produces large sclerotia, has more rapid in vitro radial growth, and a greater ability to colonize corn when artificially inoculated, perhaps indicating greater ecological competence. Results indicate that non-toxigenic, indigenous A. flavus isolates, such as strain K49, have potential use for biocontrol of aflatoxin contamination in southern U.S. corn.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Pharmaceutical compositions for inhibiting metal ion dependent enzymatic activity and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20070027064A1High activityPrevent pathological NO activityBiocideSenses disorderFungal microorganismsCyclooxygenase
Methods for inhibiting metalloprotease activity; treating a pathological condition influenced by the action of MMP; treating a pathological condition influenced by cyclooxygenases, endonucleases, metallopepitidases and 5-epoxigenase; treating a pathological condition for which the presence of a metal ion is required; inhibiting the lethal factor produced by toxigenic strains of anthrax; inhibiting activities of fungi, bacteria or plants that utilize zinc-dependent methionine synthetase; inhibiting the activity of a zinc-dependent enzyme in prokaryotic systems; and inhibiting the activity of zinc-dependent enzymes; and compositions thereof, are disclosed.
Owner:APPELBAUM JERACHMIEL YORI
Porcine pseudorabies virus, and vaccine composition and applications thereof
ActiveCN102952785ARaise antibody levelsLong durationMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsPig farmsAdjuvant
The invention provides a p porcine pseudorabies virus and vaccine composition and applications thereof, belonging to the field of biotechnology. The microbial preservation number of the porcine pseudorabies virus PRV-JS strain is CGMCCNO.6604. The invention further provides a vaccine composition which comprises an inactivated porcine pseudorabies virus PRV-JS strain and adjuvant acceptable on veteriary pharmacy. The vaccine composition further comprises a carrier acceptable on the veterinary pharmacy. The porcine pseudorabies virus PRV-JS strain is screened from porcine pseudorabies prevalent strains separated from all pig farms and has good immunogenicity, and can be used as inactivated vaccine production virus seeds or virus seeds for testing. After being immunized by the vaccine composition, pigs have higher produced antibody level and the lasting period is long. The vaccine composition prepared by adopting the porcine pseudorabies virus PRV-JS strain can be used for preventing the sow abortionbreeding difficulty and mortality syndromeboar infertility caused by the porcine pseudorabies virus, boar infertility and pseudorabies of other pigs.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
LAMP detection method for clostridium difficile AB toxins and special primer and kit thereof
InactiveCN104328204AEasy identification of resultsEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesDiseaseClostridium difficile toxin B
The invention discloses an LAMP detection method for clostridium difficile AB toxins and a special primer and a kit thereof. The LAMP detection method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: designing a primer according to the specific conserved genes tcdA and tcdB of clostridium difficile; then, by taking a genomic DNA of an object to be detected as a template, carrying out LAMP amplification under the guide of the obtained primer; and synchronously and qualitatively detecting toxigenic strains of clostridium difficile in a sample to be detected through the color changes and turbidity changes of a reaction liquid. According to the invention, toxigenic strains of clostridium difficile can be detected in a fast, convenient, synchronous, high efficiency, high specificity and high sensitivity mode under isothermal conditions without using complex instruments, so that a new technical platform is provided for the detection and toxin classification of clostridium difficile, therefore, the LAMP detection method disclosed by the invention can be used for screening and detecting clostridium difficile by grassroots medical health units and various disease prevention and control centers, has a broad market prospect and great economic and social benefits, and is suitable for large-scale popularization and application.
Owner:NANFANG HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
Porcine parvovirus, vaccine composition and application thereof
ActiveCN102965345AImproving immunogenicityImprove securityViral antigen ingredientsMicroorganism based processesAdjuvantVaccine Production
The invention provides porcine parvovirus, vaccine composition and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The microbial preservation number of the porcine parvovirus PPV-JS strain is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.6605. The vaccine composition provided by the invention comprises an inactivated porcine parvovirus PPV-JS strain and veterinary pharmaceutically acceptable adjuvant. The invention also provides the application of the porcine parvovirus PPV-JS strain in preparing medicaments for preventing diseases caused by porcine parvovirus. The porcine parvovirus PPV-JS strain has excellent immunogenicity, and can be used as an activated vaccine production strain and a virus seed for inspection. The vaccine composition (porcine parvovirus inactivated vaccine) provided by the invention is good in safety, high in immune efficacy and long in immunity period, and only requires single dose, so that manpower and side effect of the vaccine to a target animal can be greatly reduced.
Owner:FUJIAN AONONG BIOLOGICAL TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Corn and composite PCR detecting method of fumonisin toxigenic strain in corn products
InactiveCN101418337AImprove accuracyShorten detection timeMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisSerine
The invention relates to a composite PCR detection method for fumonisin toxicogenic strains in corn and corn products, wherein a plurality of pairs of primers are designed by application of DNAman sequence analysis software respectively on the basis of polyketide synthetase genes FUM1, serine-hexadecanoyl transferase genes FUM8 and longevity guarantee factor genes FUM17 required for biosynthesis of fumonisin, and primer matched groups with optimized specificity are obtained through experimental comparison of the primers and fusarium specific primers IstF / IstR; the fumonisin toxicogenic strains are simultaneously detected in the same reaction system; and the plurality of pairs of primers are subjected to amplification simultaneously in the same reaction system by the composite PCR technology. The composite PCR detection method comprises the following detection steps: template DNA is directly extracted from a sample to be detected by the improved SDS method; and the template DNA is subjected to composite PCR reaction, electrophoresis, dyeing and rinsing, a gel imaging device is used for observing the result and taking a picture, and finally the detection result is obtained after spectrogram analysis. The composite PCR detection method improves the detection accuracy, saves the detection time and can be massively promoted by means of a reagent kit.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Specific multiple PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection method and kit for toxigenic microcystis and kit therefor
InactiveCN102952876AImprove detection accuracySimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrophoresisMicrocystis
Aiming at overcoming the technical problems of complex toxigenic microcystis detection method, high instrument requirement and the like in the prior art, the invention provides a specific multiple PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection method and kit for toxigenic microcystis. The specific multiple PCR detection method for the toxigenic microcystis comprises the following steps of: (1) sampling microcystis from a detected site, and extracting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of genome; (2) designing and synthesizing the microcystis which comprises seven pairs of primers, i.e. toxigenic and non-toxigenic strain ropC1 gene, toxigenic microcystis mcyA, mcyB, mcyD, mcyE, mcyI and mcyJ gene sections; and (3) respectively carrying out PCR amplification reaction by the designed specific primers, and carrying out electrophoresis gel detection. According to the invention, a plurality of genes are taken as molecular indexes, so that the detection precision can be improved, the method is simple and convenient to operate, and easy to grasp, the microcystis in water body can be quickly detected, and the toxigenic strain can be effectively identified.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Detection of toxigenic strains of Clostridium difficile
ActiveUS9096638B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementClostridium difficileClostridium difficile (bacteria)
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
Method for detecting fumonisin toxigenic strain in asparagus using composite PCR technique
InactiveCN101418338AImprove detection accuracyImprove detection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrobiologyPcr ctpp
The invention relates to a method for detecting fumonisin toxicogenic strains in asparaguses by the composite PCR technology, which uses primer pairs rp32 / rp33 and primer pairs rp679 / rp680 which are designed according to polyketide synthetase genes FUM1 and serine-hexadecanoyl transferase genes FUM8 required for biosynthesis of fumonisin, and fusarium specific primers IstF / IstR respectively. The method simultaneously detects the fumonisin toxicogenic strains in the same reaction system, and not only can detect unknown fumonisin toxicogenic strains but also can identify whether the detected strains belong to fusarium. Moreover, a plurality of pairs of primers are subjected to amplification in the same reaction system simultaneously by the composite PCR technology, so that the method improves the detection accuracy, saves the detection time, is a simple, quick and effective composite PCR detection method for the fumonisin toxicogenic strains in the asparaguses, and can be massively promoted by means of a kit.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Water dispersible formulation for delivery of biocontrol fungi to reduce aflatoxin
InactiveUS9011891B2Avoid contaminationPrevent proliferationPowder deliveryBiocideAspergillus flavusToxin
A formulation containing conidia of non-toxigenic strains of fungi is a useful biocontrol agent for preventing toxin contamination in agricultural commodities, especially those for human and animal consumption such as peanuts, corn, cotton and tree nuts. The formulation of the invention is a water dispersible granule formulation suitable for spraying and includes non-toxigenic and / or non-aflatoxigenic Aspergillus flavus strains capable of inhibiting growth of fungi which produce aflatoxin and further capable of suppressing production of aflatoxin by the toxigenic fungi. A method of preparing the formulation is shown.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
A Porcine Circovirus Type 2 Virus Strain and Its Application
ActiveCN109825480BGood strain backgroundImproving immunogenicityViral antigen ingredientsSerum immunoglobulinsPorcine CircovirusesVirus strain
The invention discloses a porcine circovirus II virus strain and application thereof. The name of the porcine circovirus II virus strain is porcine circovirus II ZM-PCV3-13, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.17291. The virus strain is separated from swinery in which the porcine circovirus II newly breaks out and is endemic and represents a current domestic epidemic predominant virus strain,the virus strain has a good virus strain background, can be used as a inactivated vaccine to produce virus strains and virus seeds for inspection, a material is provided for subsequent related experiment research, and a material basis is laid.
Owner:CHINA ANIMAL HUSBANDRY IND
Clostridium difficile specific antigen peptide
The invention relates to a clostridium difficile specific antigen peptide, in particular to a specific antigen peptide for a high-poison-yield clostridium difficile RT027. The clostridium difficile specific antigen peptide comprises an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.1. A specific peptide fragment and a specific antibody thereof are used, a novel clostridium difficile high-poison-yield strain detection kit and a clostridium difficile vaccine can be developed, and the clostridium difficile specific antigen peptide has an important significance on detection and treatment of clostridium difficile high-poison-yield strain infection.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG HIPRO BIOTECH
Plate kit for identifying vibrio parahemolyticus toxigenic strain, and preparation and using methods for plate kit
InactiveCN102703566ASolve the problems of difficult identification and detectionSmall individual differencesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesHemolysisYeast extract
The invention relates to a kit for identifying a vibrio parahemolyticus toxigenic strain by using the hemolysis of the vibrio parahemolyticus toxigenic strain, and preparation and using methods for the kit, and mainly solves the problems that the technical problems that the conventional methods for identifying the vibrio parahemolyticus toxigenic strain are complex and cannot be unified easily, and the vibrio parahemolyticus toxigenic strain cannot be used as the conventional detection target to be used. According to technical scheme, the ready-to-use vibrio parahemolyticus toxigenic strain identification plate kit is characterized by comprising a vibrio parahemolyticus toxigenic strain identification culture medium which comprises 3.0g of yeast extract, 10.0g of peptone, 80.0g of sodium chloride, 30.0g of disodium hydrogen phosphate, 10.0g of glucose, 15.0g of agar, 1000.0ml of distilled water, and 50ml of fresh rabbit blood; and the pH of the culture medium is adjusted to be 8.0+ / -0.2; and the rabbit blood contains 0.3 volume percent of anticoagulant of sodium citrate. A blood plate is prepared by using the hemolysis characteristic of the vibrio parahemolyticus toxigenic strain, the hemolysis of vibrio parahemolyticus is observed by a one-step inoculation-culturing method, and the effects of quickly identifying the toxigenic strain quickly and easily can be achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Preparation method and application of attenuated strain of contagious pustular dermatitis virus
PendingCN114350623AGood immune protectionImprove protectionMicrobiological testing/measurementInactivation/attenuationPustular dermatitisImpetigo contagiosa
The invention provides a preparation method of a contagious pustular dermatitis virus attenuated strain, which is characterized in that virulence genes of contagious pustular dermatitis virus are mutated and inactivated, and the virulence genes are mutated into ORFs 120 / 121 double-gene mutation. After the ORFs 120 / 121 gene is deleted, the pathogenicity of the ORFV is obviously reduced. According to the present invention, the ORFs 120 / 121 gene of the ORFV-SY17 strain is knocked out to obtain the double-gene-deleted contagious pustular dermatitis virus attenuated strain, and the double-gene-deleted contagious pustular dermatitis virus attenuated strain has potential application value in preparation of the contagious pustular dermatitis gene-deleted attenuated live vaccine production strain. The deleted ORFs 120 / 121 gene can also be used as a marker gene to establish a differential diagnosis method for ORFV vaccine virus and wild virus detection.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Clostridium difficile-specific antigenic peptide
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG HIPRO BIOTECH
Porcine parvovirus, vaccine composition and application thereof
ActiveCN102965345BImproving immunogenicityImprove securityViral antigen ingredientsMicroorganism based processesAdjuvantVaccine Production
The invention provides porcine parvovirus, vaccine composition and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The microbial preservation number of the porcine parvovirus PPV-JS strain is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.6605. The vaccine composition provided by the invention comprises an inactivated porcine parvovirus PPV-JS strain and veterinary pharmaceutically acceptable adjuvant. The invention also provides the application of the porcine parvovirus PPV-JS strain in preparing medicaments for preventing diseases caused by porcine parvovirus. The porcine parvovirus PPV-JS strain has excellent immunogenicity, and can be used as an activated vaccine production strain and a virus seed for inspection. The vaccine composition (porcine parvovirus inactivated vaccine) provided by the invention is good in safety, high in immune efficacy and long in immunity period, and only requires single dose, so that manpower and side effect of the vaccine to a target animal can be greatly reduced.
Owner:FUJIAN AONONG BIOLOGICAL TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Early warning method before occurrence of aflatoxin contamination
PendingUS20220120722A1Improve classification accuracyAccurate identificationComponent separationTesting foodBiotechnologyMass spectrometric
The present invention relates to an early warning method before the occurrence of aflatoxin contamination. The steps are as follows: extracting toxins from the sample to obtain a sample extract, and subjecting the sample extract to detection and analysis by liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometer, performing qualitative analysis based on the mass spectrometry information to obtain qualitative results, performing quantitative analysis based on a standard curve of the chromatographic peak area of each warning molecule / the peak area of the internal standard-warning molecule concentration to obtain quantitative results of these warning molecules, wherein a risk of aflatoxin contamination of the sample is assessed to obtain a classification prediction model, inputting the quantitative results of the warning molecules for a toxigenic strain of Aspergillus flavus, and outputting a risk assessment result based on the classification prediction model, thereby achieving the early warning before aflatoxin contamination occurs.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
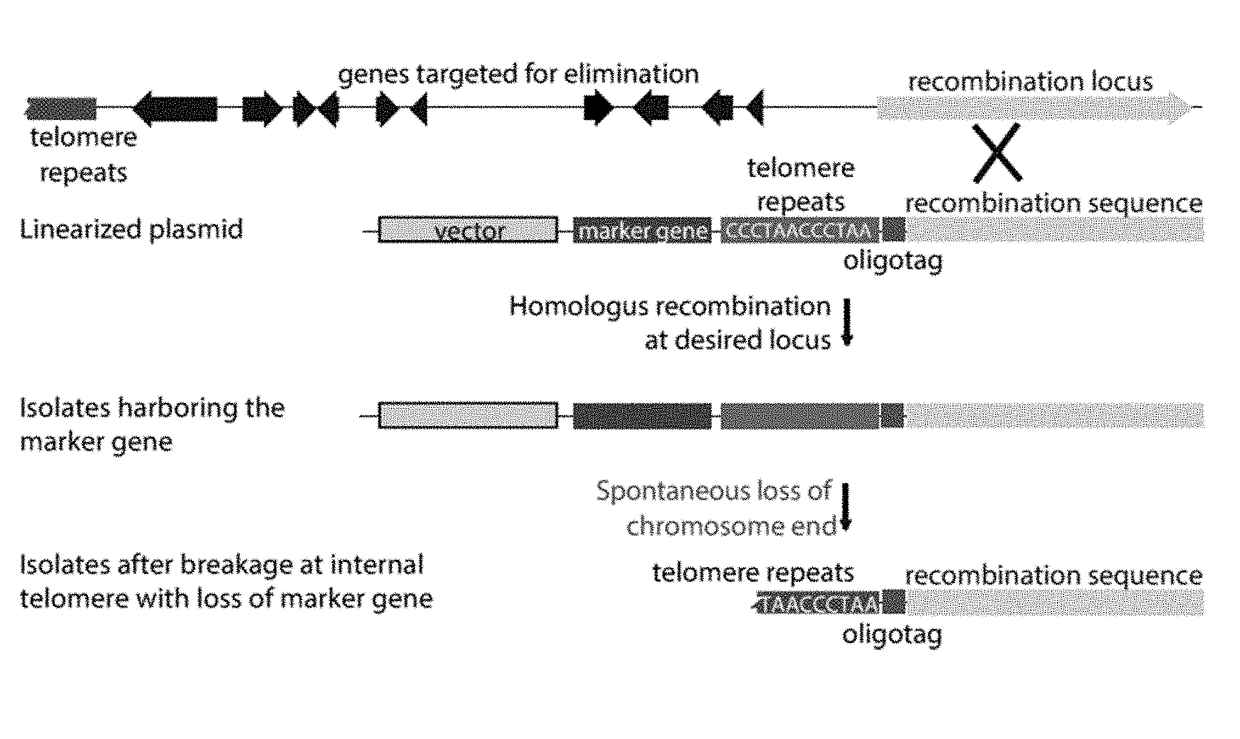
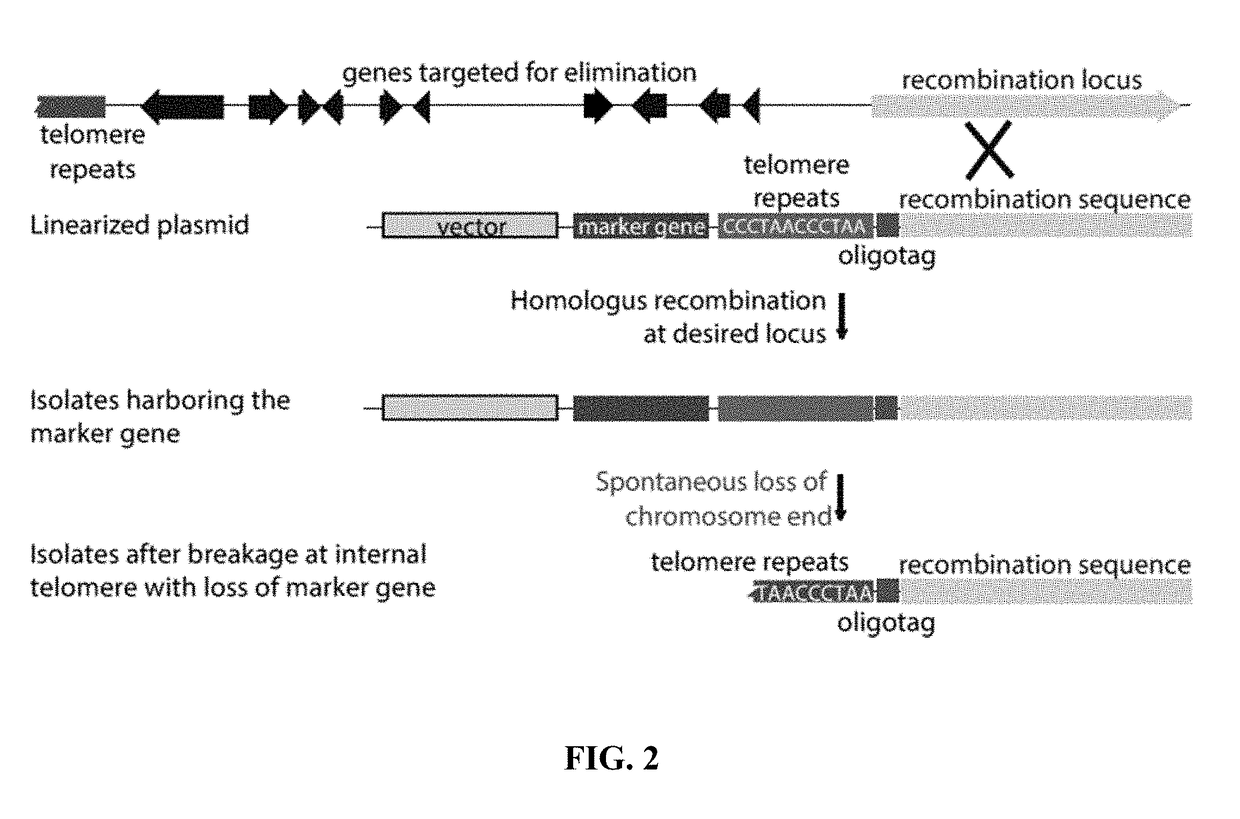
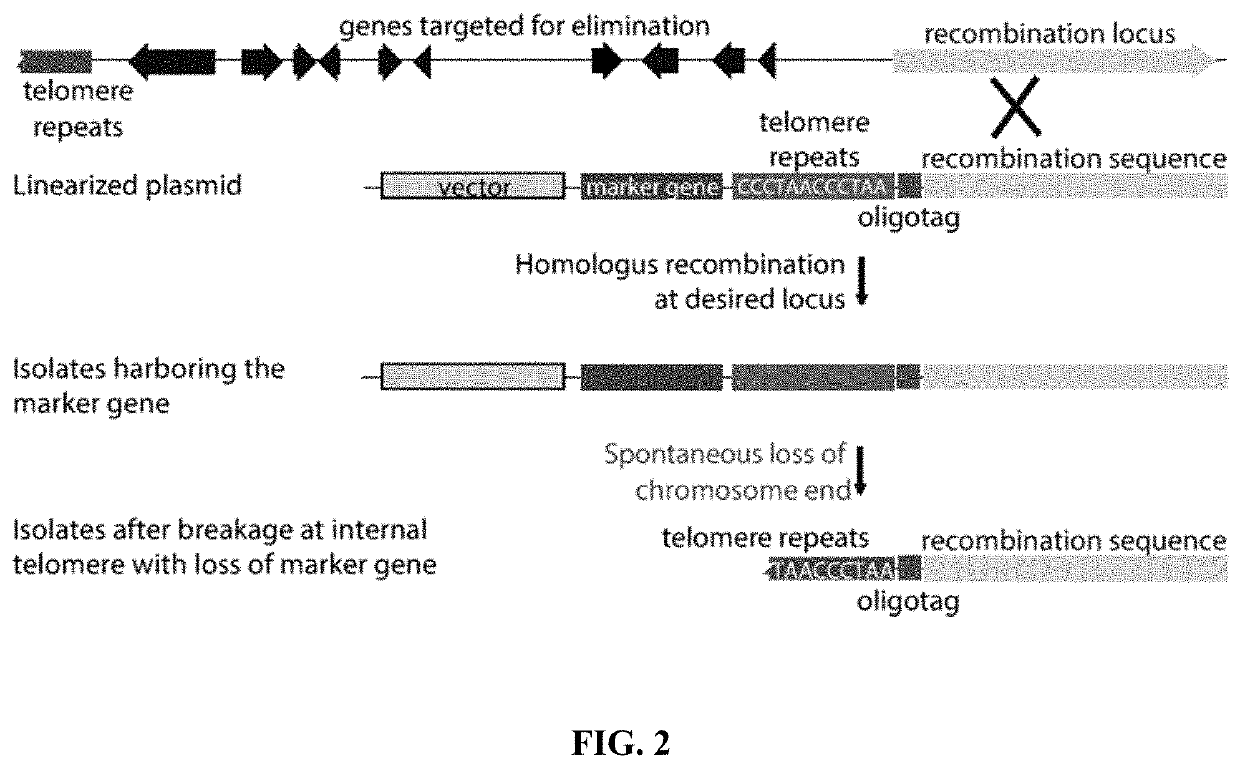
Fungal chromosome-end knockoff strategy
ActiveUS11021760B2Reduce expressionAffect expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyMicrobiology
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Lamp detection method of Clostridium difficile ab toxin and its special primers and kit
InactiveCN104328204BStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesSocial benefitsClostridium difficile toxin B
The invention discloses an LAMP detection method for clostridium difficile AB toxins and a special primer and a kit thereof. The LAMP detection method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: designing a primer according to the specific conserved genes tcdA and tcdB of clostridium difficile; then, by taking a genomic DNA of an object to be detected as a template, carrying out LAMP amplification under the guide of the obtained primer; and synchronously and qualitatively detecting toxigenic strains of clostridium difficile in a sample to be detected through the color changes and turbidity changes of a reaction liquid. According to the invention, toxigenic strains of clostridium difficile can be detected in a fast, convenient, synchronous, high efficiency, high specificity and high sensitivity mode under isothermal conditions without using complex instruments, so that a new technical platform is provided for the detection and toxin classification of clostridium difficile, therefore, the LAMP detection method disclosed by the invention can be used for screening and detecting clostridium difficile by grassroots medical health units and various disease prevention and control centers, has a broad market prospect and great economic and social benefits, and is suitable for large-scale popularization and application.
Owner:NANFANG HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
Porcine pseudorabies virus, and vaccine composition and applications thereof
ActiveCN102952785BRaise antibody levelsLong durationMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsPig farmsAdjuvant
The invention provides a p porcine pseudorabies virus and vaccine composition and applications thereof, belonging to the field of biotechnology. The microbial preservation number of the porcine pseudorabies virus PRV-JS strain is CGMCCNO.6604. The invention further provides a vaccine composition which comprises an inactivated porcine pseudorabies virus PRV-JS strain and adjuvant acceptable on veteriary pharmacy. The vaccine composition further comprises a carrier acceptable on the veterinary pharmacy. The porcine pseudorabies virus PRV-JS strain is screened from porcine pseudorabies prevalent strains separated from all pig farms and has good immunogenicity, and can be used as inactivated vaccine production virus seeds or virus seeds for testing. After being immunized by the vaccine composition, pigs have higher produced antibody level and the lasting period is long. The vaccine composition prepared by adopting the porcine pseudorabies virus PRV-JS strain can be used for preventing the sow abortionbreeding difficulty and mortality syndromeboar infertility caused by the porcine pseudorabies virus, boar infertility and pseudorabies of other pigs.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Multiple fluorescence PCR detection kit and detection method for clostridium difficile toxin genes
ActiveCN103361434BMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesClostridium difficile infectionsFluorescence
Owner:杭州海基生物技术有限公司
Aflatoxin contamination risk warning molecule and use thereof
PendingUS20220120725A1Improve classification accuracyAccurate identificationMolecular entity identificationComponent separationAflatoxin contaminationToxicology
The present invention relates to an aflatoxin contamination risk warning molecule and use thereof. The steps are as follows: weighing a quantitative sample, extracting the aflatoxin contamination risk warning molecule to obtain a sample extract, and detecting and analyzing the sample extract to obtain a quantitative result of the aflatoxin contamination risk warning molecule; performing modeling with a chemometrics method using the content of one or more of the aflatoxin contamination risk warning molecules as a variable to obtain a classification prediction model, and performing risk assessment on aflatoxin contamination risk of the sample based on the classification prediction model, wherein a warning molecule of an aflatoxin toxigenic strain is one or a combination of more than one of versiconol (VOH), versicolorin B (Ver B), and 5-methoxysterigmatocystin (5-MST).
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Simultaneous quantitative multiple primer detection of Clostridium difficile
ActiveUS9234248B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementClostridium difficile toxin AMicrobiology
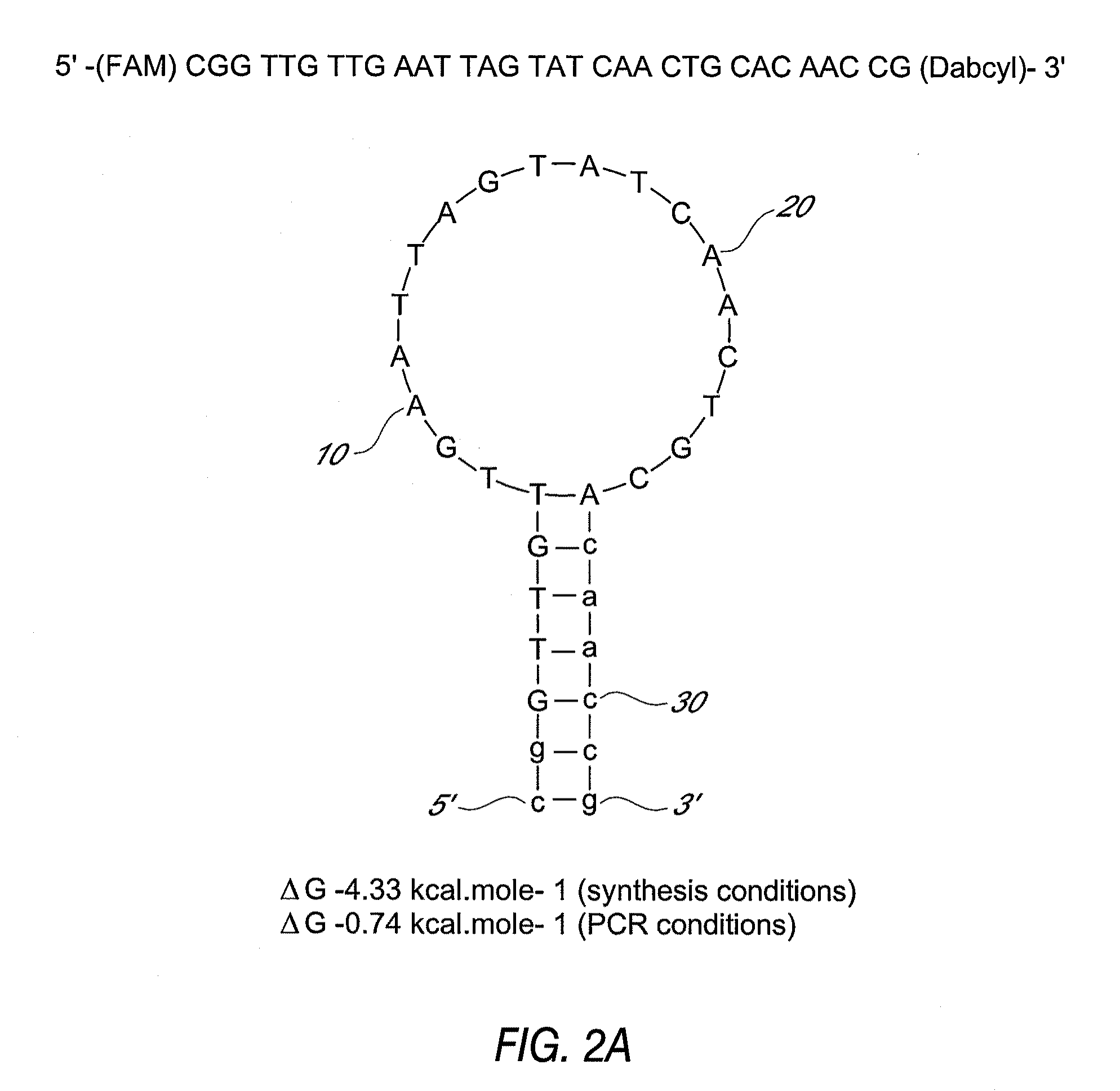
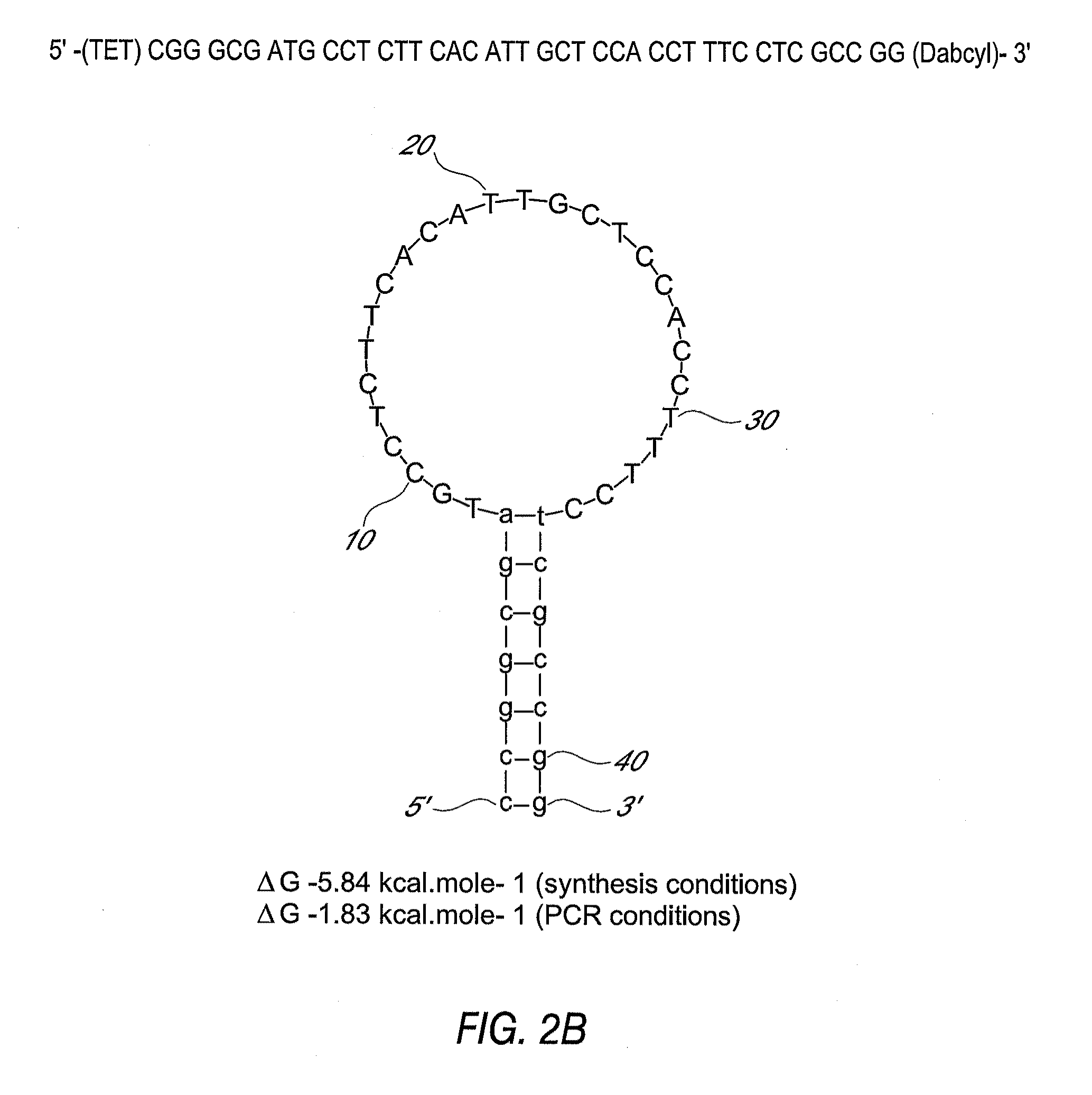
This invention comprises a multiplex-capable oligonucleotide which is capable of hybridizing to at least one of the C. difficile tcdB, tcdC, or cdtB genes, wherein, wherein said primer consists of a sequence selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NOS: 1 through 9, or a sequence that exhibits no more than one substitution of a base to a sequence selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NOS: 1 through 9 and method for polymerase chain reaction (PCR) determining of the presence of a toxigenic strain of C. difficile in a biological sample utilizing said probes.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
Simultaneous quantitative multiple primer detection of clostridium difficile
ActiveUS20120252029A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementClostridium difficile toxin BOligonucleotide
This invention comprises a multiplex-capable oligonucleotide which is capable of hybridizing to at least one of the C. difficile tcdB, tcdC, or cdtB genes, wherein, wherein said primer consists of a sequence selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NOS: 1 through 9, or a sequence that exhibits no more than one substitution of a base to a sequence selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NOS: 1 through 9 and method for polymerase chain reaction (PCR) determining of the presence of a toxigenic strain of C. difficile in a biological sample utilizing said probes.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
Cytology detection kit for discriminating cholera toxin and detection method
InactiveCN102533926AHigh sensitivityRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementCytologyCell culture media
The invention provides a cytology detection kit for discriminating cholera toxin and a detection method. The kit mainly comprises Y1 adrenocortical cells, anti-cholera toxin neutralizing antibody, polylysine, 96-E-plate and cell culture medium for the adrenocortical cells. The invention provides the cytology detection kit for discriminating the cholera toxin and the detection method, and with respect to the specific cellular reaction of the cholera toxin, a system capable of dynamically and sensitively detecting the cholera toxin in real time is established, therefore, the cholera toxin can be fast and accurately identified with high specificity, strains producing toxin can be effectively discriminated from strains producing no toxin, the monitoring and control of the strains producing toxin are strengthened, and effects and benefits of prevention can be greatly improved. The invention has important significance for preventing and controlling cholera.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com