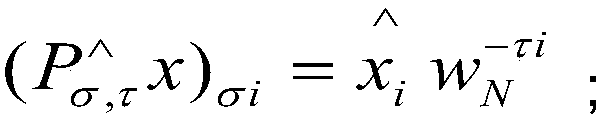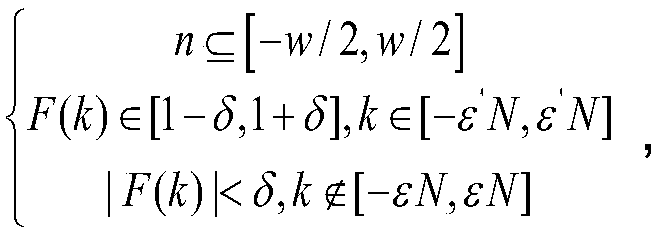Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
68 results about "Polar fourier transform" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
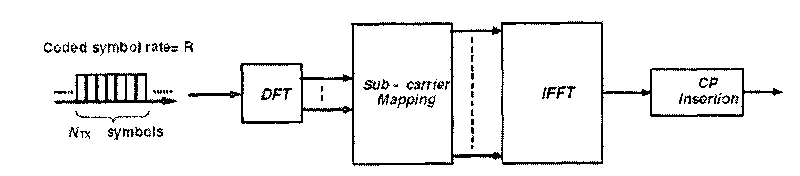
In mathematics, Fourier transform is widely used for transforming the complex valued function into another complex valued function. Fourier transform of the function has both real and complex variables. Polar coordinates are also used in Fourier transform. It is used in signal processing, time domain of the original function.
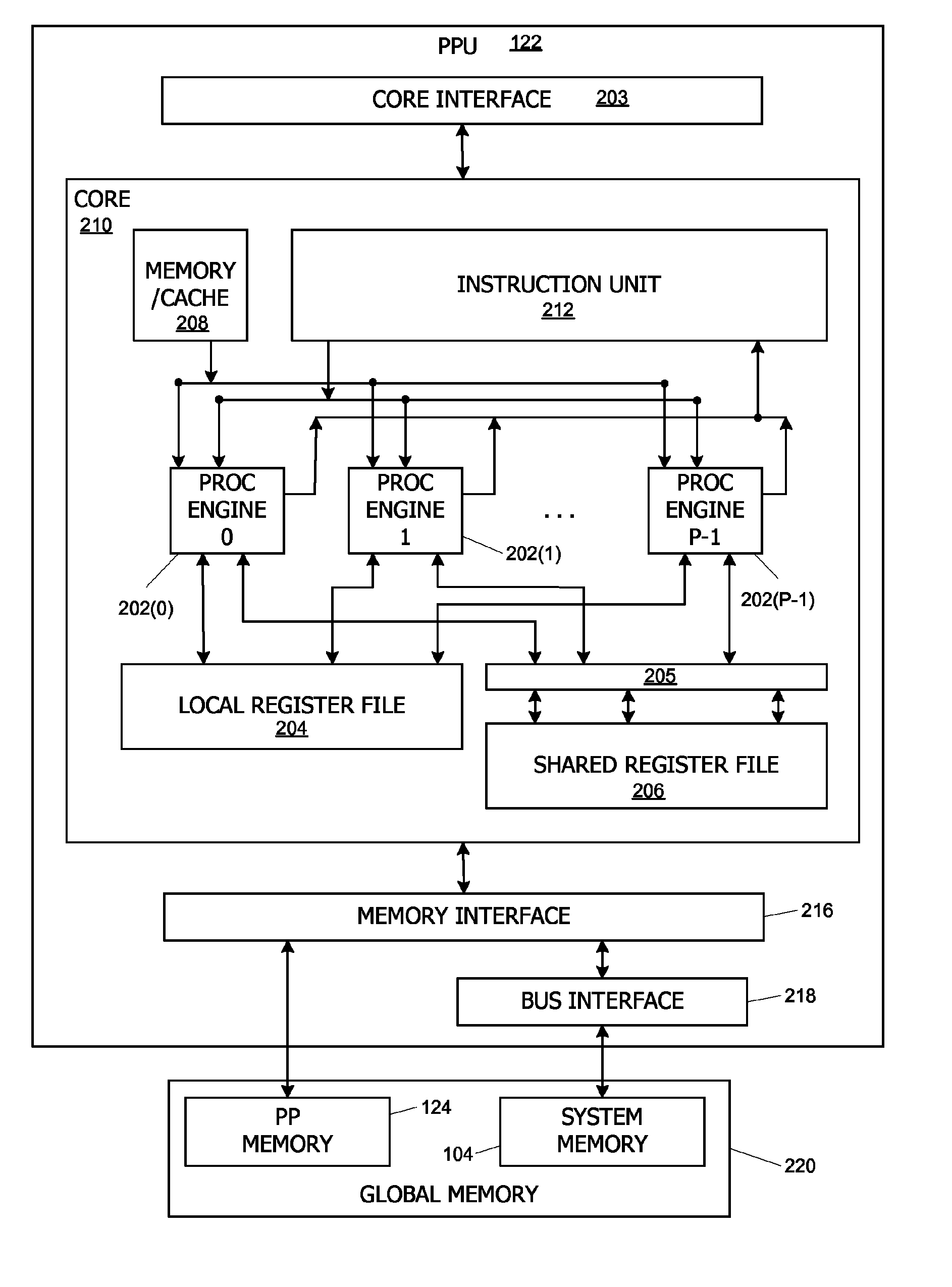
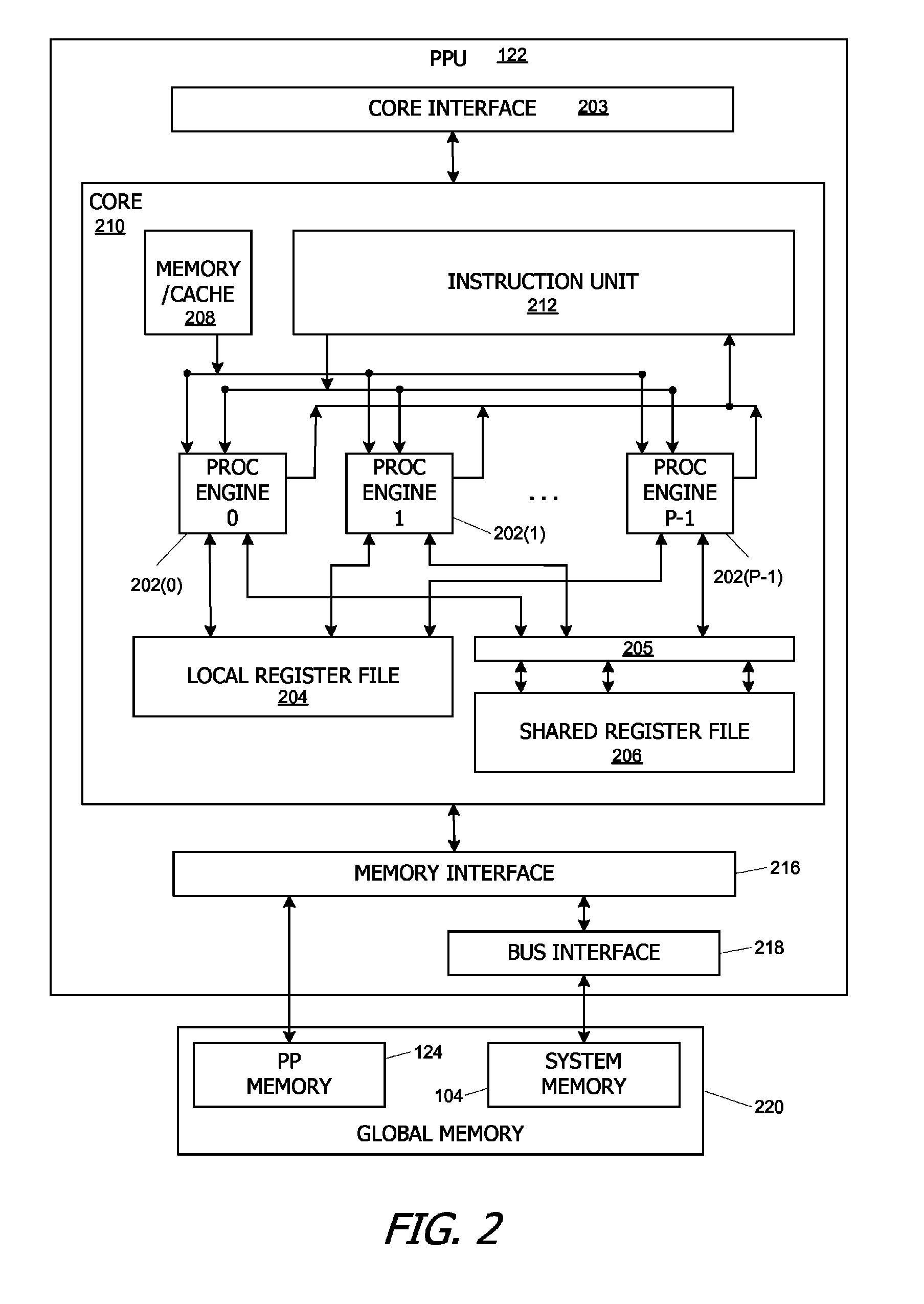
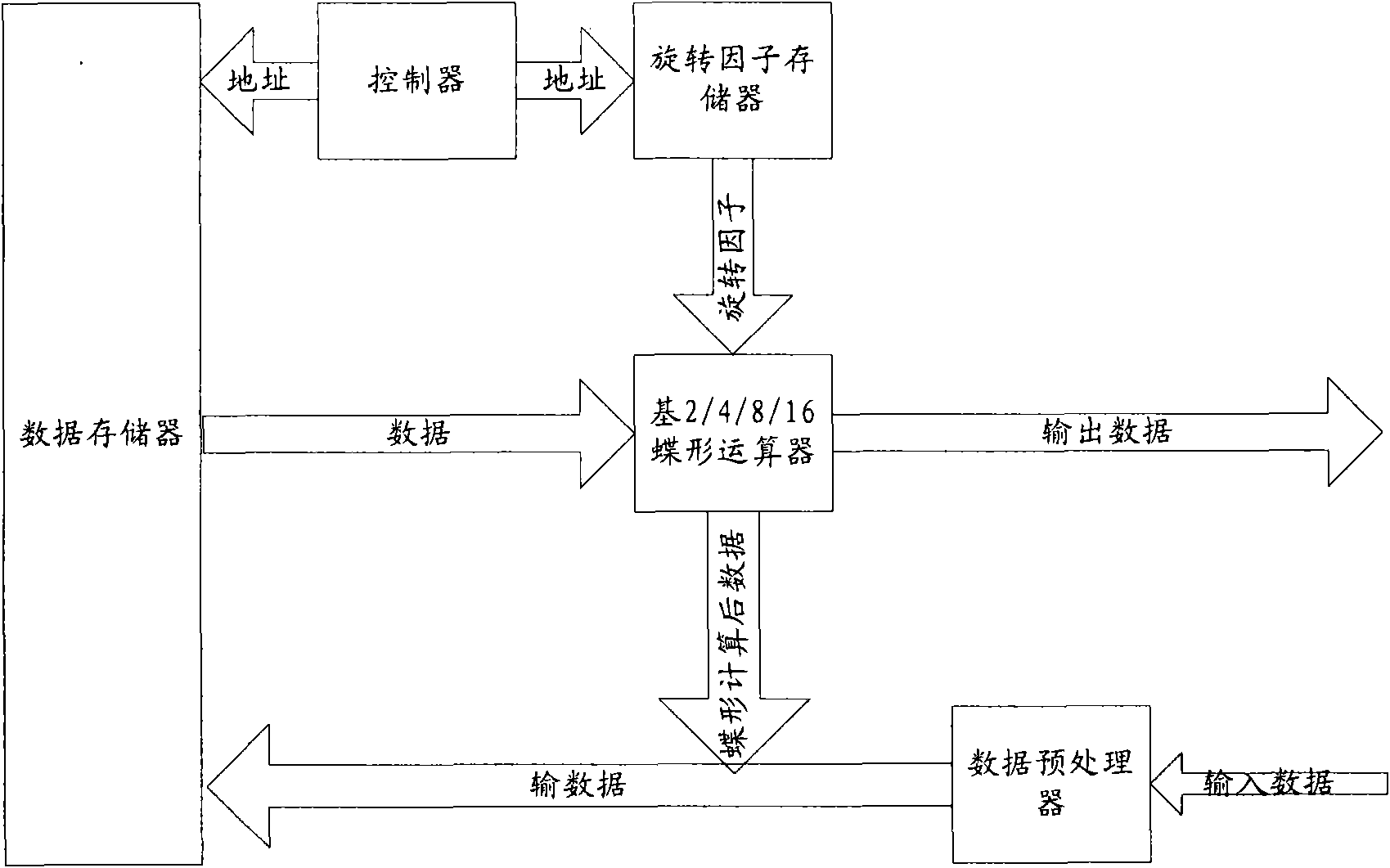
Fast fourier transforms and related transforms using cooperative thread arrays
ActiveUS7836116B1Lower latencyRegister arrangementsDigital computer detailsFast Fourier transformArray data structure
A linear transform such as a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) is performed on an input data set having a number of points using one or more arrays of concurrent threads that are capable of sharing data with each other. Each thread of one thread array reads two or more of the points, performs an appropriate “butterfly” calculation to generate two or more new points, then stores the new points in a memory location that is accessible to other threads of the array. Each thread determines which points it is to read based at least in part on a unique thread identifier assigned thereto. Multiple transform stages can be handled by a single thread array, or different levels can be handled by different thread arrays.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Absolute position encoder including scale with varying spatial characteristic and utilizing fourier transform or other signal processing
ActiveUS20180003524A1Well formedConverting sensor output electrically/magneticallyFast Fourier transformAbsolute measurement
An electronic absolute position encoder is provided including a scale, a detector portion and a signal processing configuration. The scale includes a first scale pattern of signal modulating elements, wherein the first scale pattern includes a spatial characteristic of the signal modulating elements which progressively changes as a function of position along a measuring axis direction and defines an absolute measuring range. The spatial characteristic includes at least one of a spatial wavelength or a spatial frequency of the signal modulating elements and is unique at each unique position in the absolute measuring range. The detector portion includes a group of sensing elements, and the signal processing configuration determines an absolute position of the sensing elements relative to the scale within the absolute measuring range. In various implementations, the signal processing configuration may utilize Fourier transform processing and / or other processing for determining the absolute position.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Fast calculation method and device of discrete Fourier transformation (DFT)/inverse discrete Fourier transform (IDFT)
InactiveCN101751375ACalculation speedReduce computational complexityComplex mathematical operationsFinite fourier transformTime domain
The invention discloses a fast calculation method of discrete Fourier transformation (DFT) / inverse discrete Fourier transform (IDFT). The rapid calculation method comprises the following steps of: carrying out zero fill on a bit sequence to be transformed to enable the sequence length after the zero fill to accord with the processing range of a fast Fourier transform (FFT) / inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT) processor; carrying out FFT / IFFT calculation on the sequence after zero fill by utilizing the FFT / IFFT processor, and resampling time domain / frequency domain of an FFT / IFFT calculation result sequence according to a sampling position determined by the sequence lengths before and after the zero fill; and outputting the resampling result as a DFT / IDFT result sequence. The invention also discloses a fast calculation device of DFT / IDFT. By adopting the invention, the calculation complexity of DFT / IDFT can be reduced, and the calculation speed can be improved.
Owner:POTEVIO INFORMATION TECH
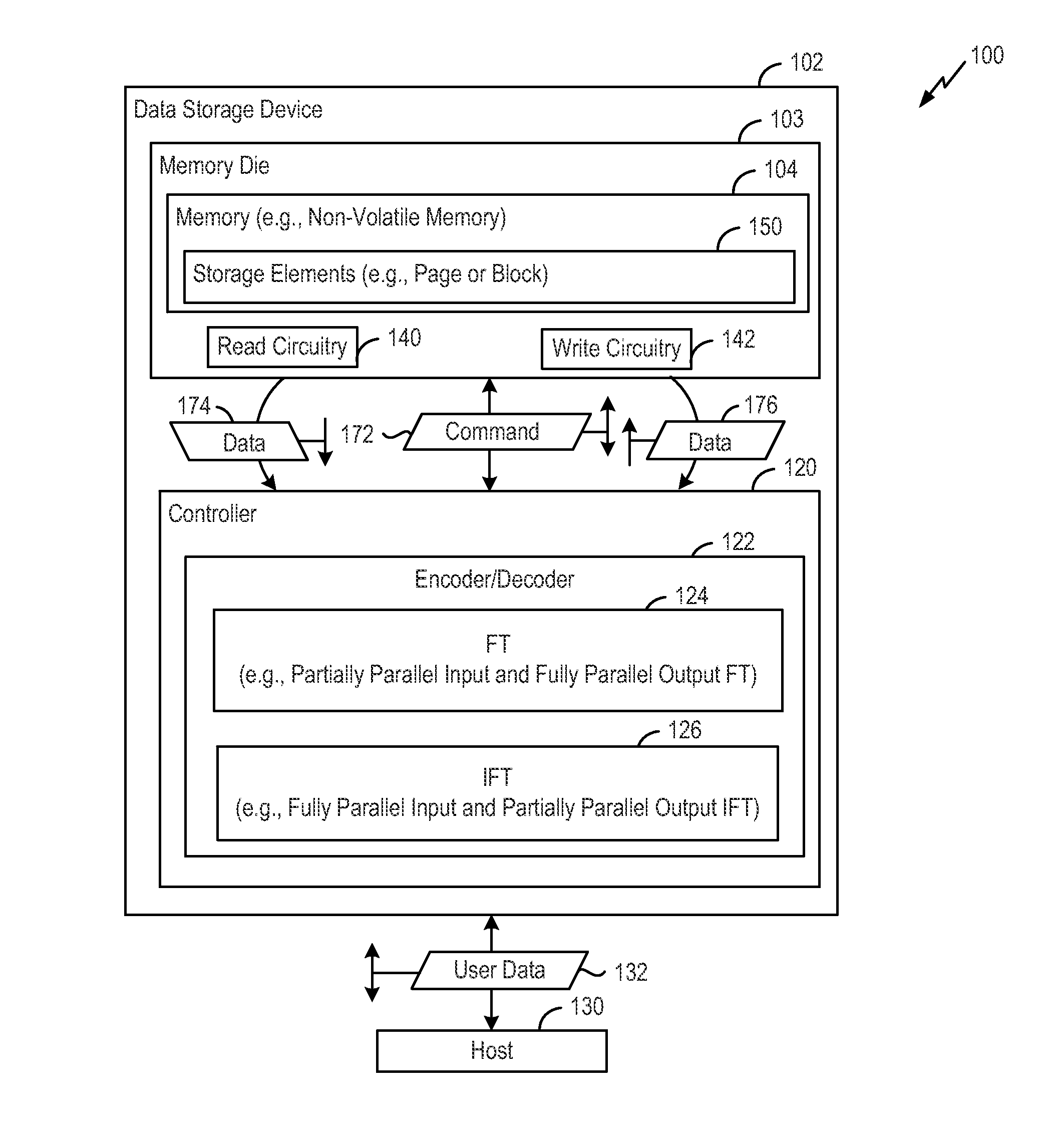
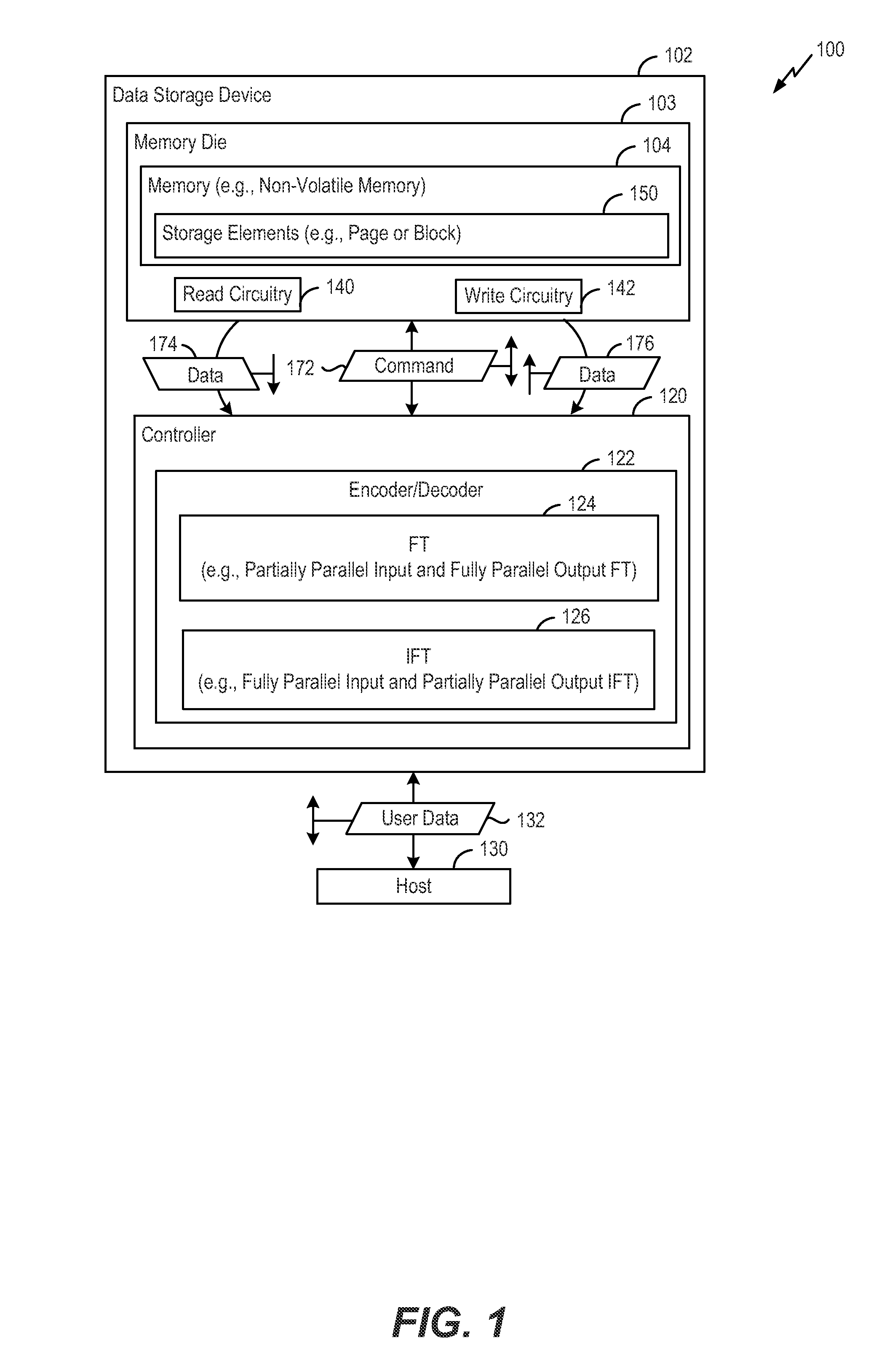
Low complexity partial parallel architectures for fourier transform and inverse fourier transform over subfields of a finite field
InactiveUS20150301985A1Wide applicationReduce complexityDigital computer detailsCode conversionFast Fourier transformFinite fourier transform
Low complexity partial parallel architectures for performing a Fourier transform and an inverse Fourier transform over subfields of a finite field are described. For example, circuits to perform the Fourier transforms and the inverse Fourier transform as described herein may have architectures that have simplified multipliers and / or computational units as compared to traditional Fourier transform circuits and traditional inverse Fourier transform circuits that have partial parallel designs. In a particular embodiment, a method includes, in a data storage device including a controller and a non-volatile memory, the controller includes an inverse Fourier transform circuit having a first number of inputs coupled to multipliers, receiving elements of an input vector and providing the elements to the multipliers. The multipliers are configured to perform calculations associated with an inverse Fourier transform operation. The first number is less than a number of inverse Fourier transform results corresponding to the inverse Fourier transform operation.
Owner:WODEN TECH INC
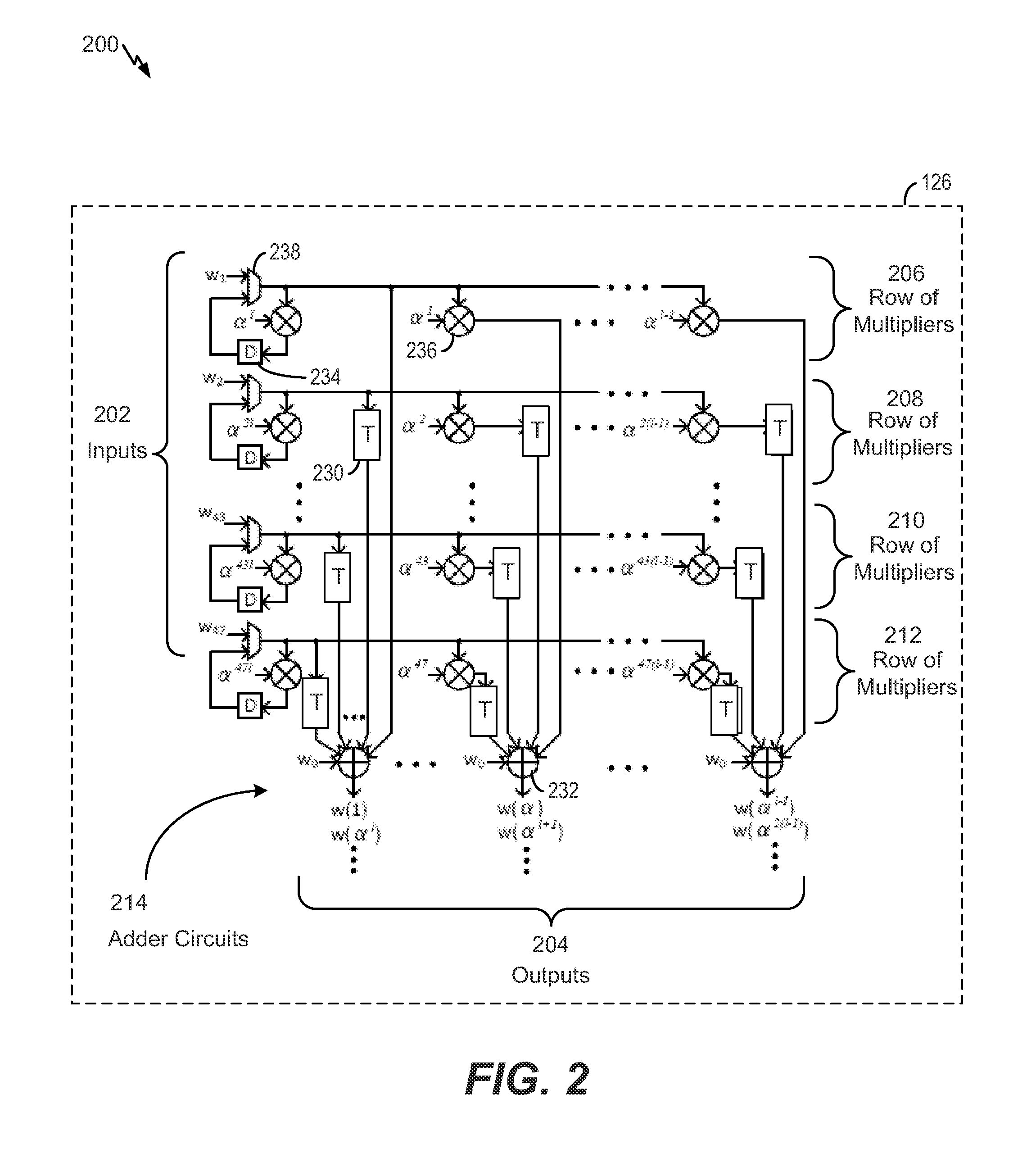
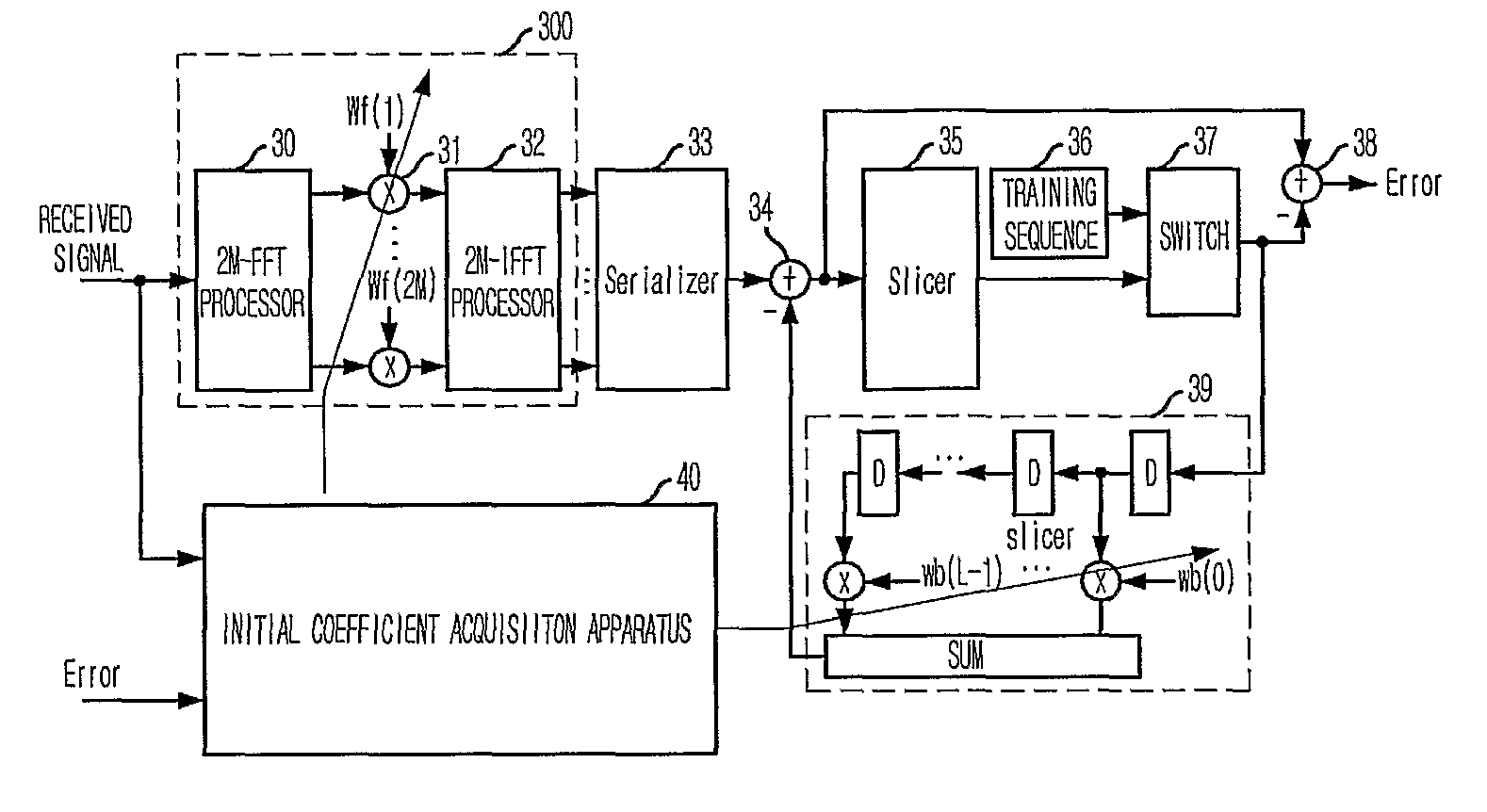
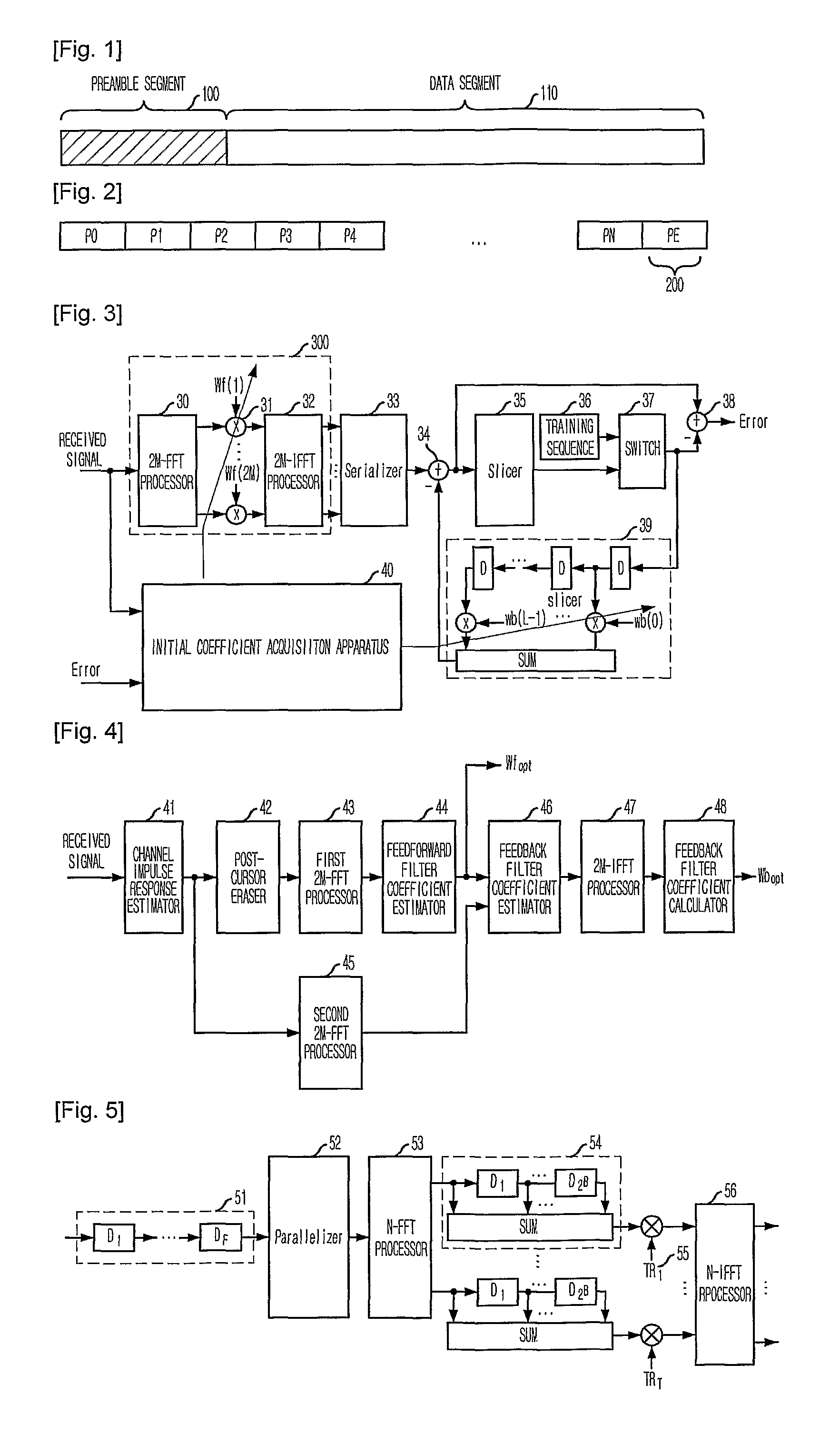
Apparatus and method for acquiring initial coefficient of decision feedback equalizer using fast fourier transform
InactiveUS20100046599A1Small amount of calculationEasy to implementMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsTime domainFast Fourier transform
Provided is an apparatus and method for acquiring an initial coefficient of a DFE using an FFT. The apparatus includes a channel impulse response estimating unit for estimating a non-causal impulse response by delaying a received signal of a time domain and transforming it into frequency domain signals; a feedforward filter coefficient acquisition unit for extracting a predetermined number of signals from the non-causal channel impulse response signals estimated by the channel impulse response estimating unit, and transforming the same into frequency domain signals to acquire an initial coefficient of a feedforward filter; and a feedback filter coefficient acquisition unit for transforming the non-causal channel impulse response signals estimated by the channel impulse response estimating unit into frequency domain signals, multiplying the same by the initial coefficient of the feedforward filter, and transforming the results of multiplication into time domain signals to calculate an initial coefficient of a feedback filter.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
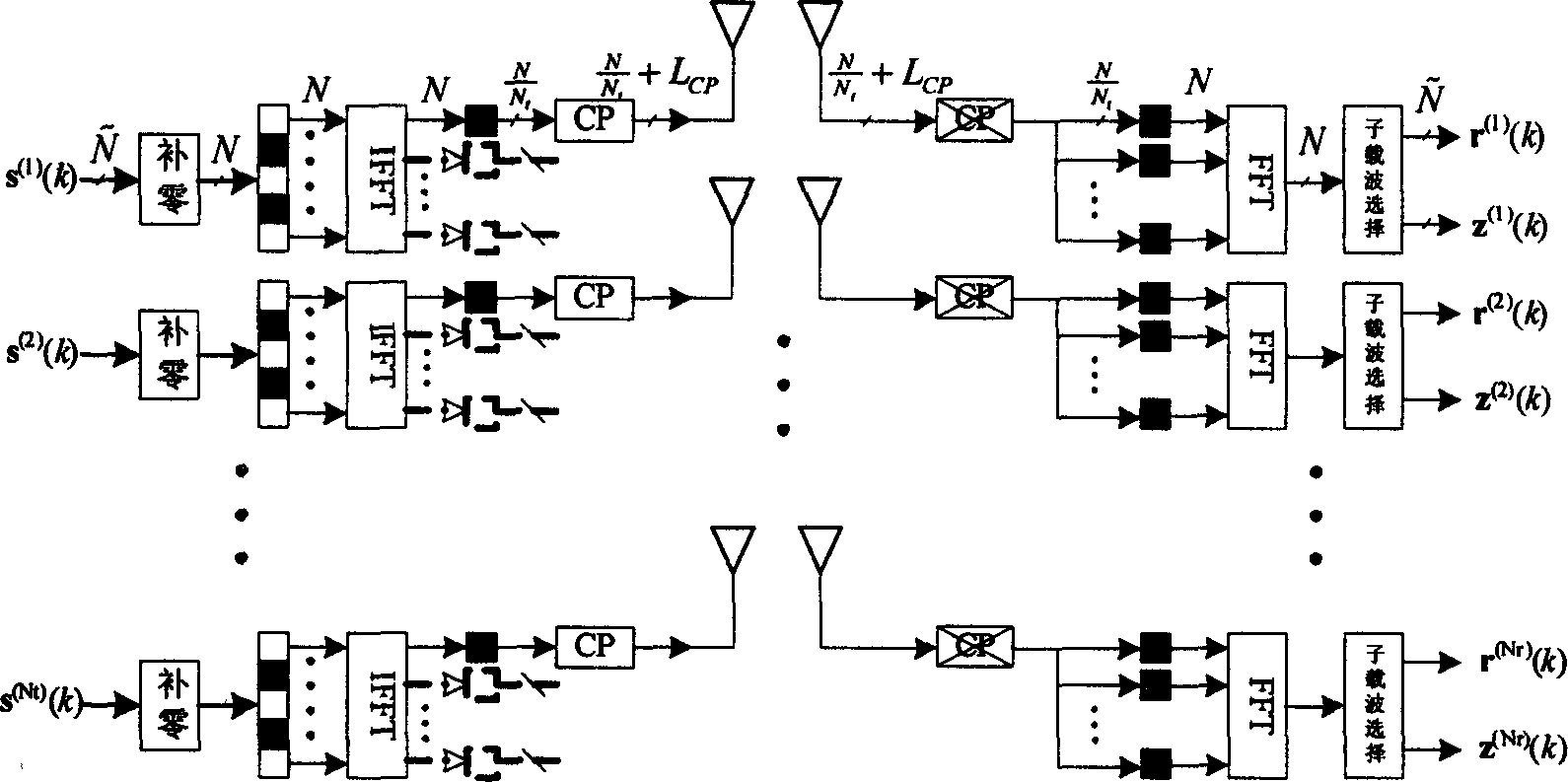
Low complexity channel estimation method based on orthogonal sequence design
InactiveCN1835484AEstimate method is simpleImprove general performanceBaseband system detailsSequence designComputation complexity
The method is used in MIMO-OFDM system having virtual carrier and comprises: the designed orthogonal training sequence is distributed in equal interval in valid sub-carrier on each transmitting antenna; they are pair-wise orthogonal and the rest is filled zero; the transmitting end intercepts a section from the time domain symbol obtained from inverse fast Fourier transform, adds a cycle prefix on it and then transmits it through antenna; the receiving end makes self-copy for the received time domain symbol and then converts it to a frequency domain symbol; the fast Fourier transform, over-sampling and the finite impulse response low-pass interpolating filer are used to make low complexity channel estimation.
Owner:PLA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
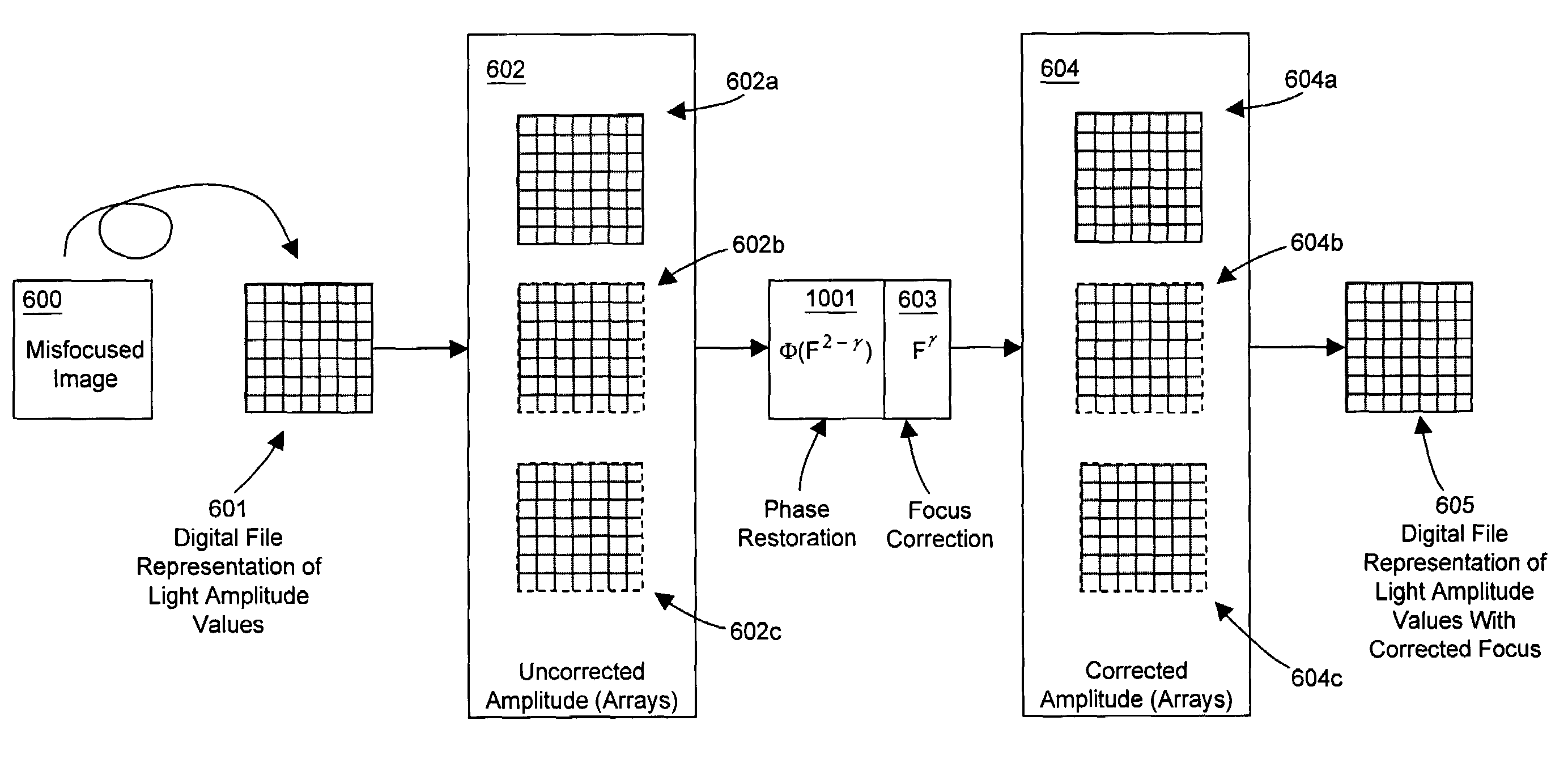
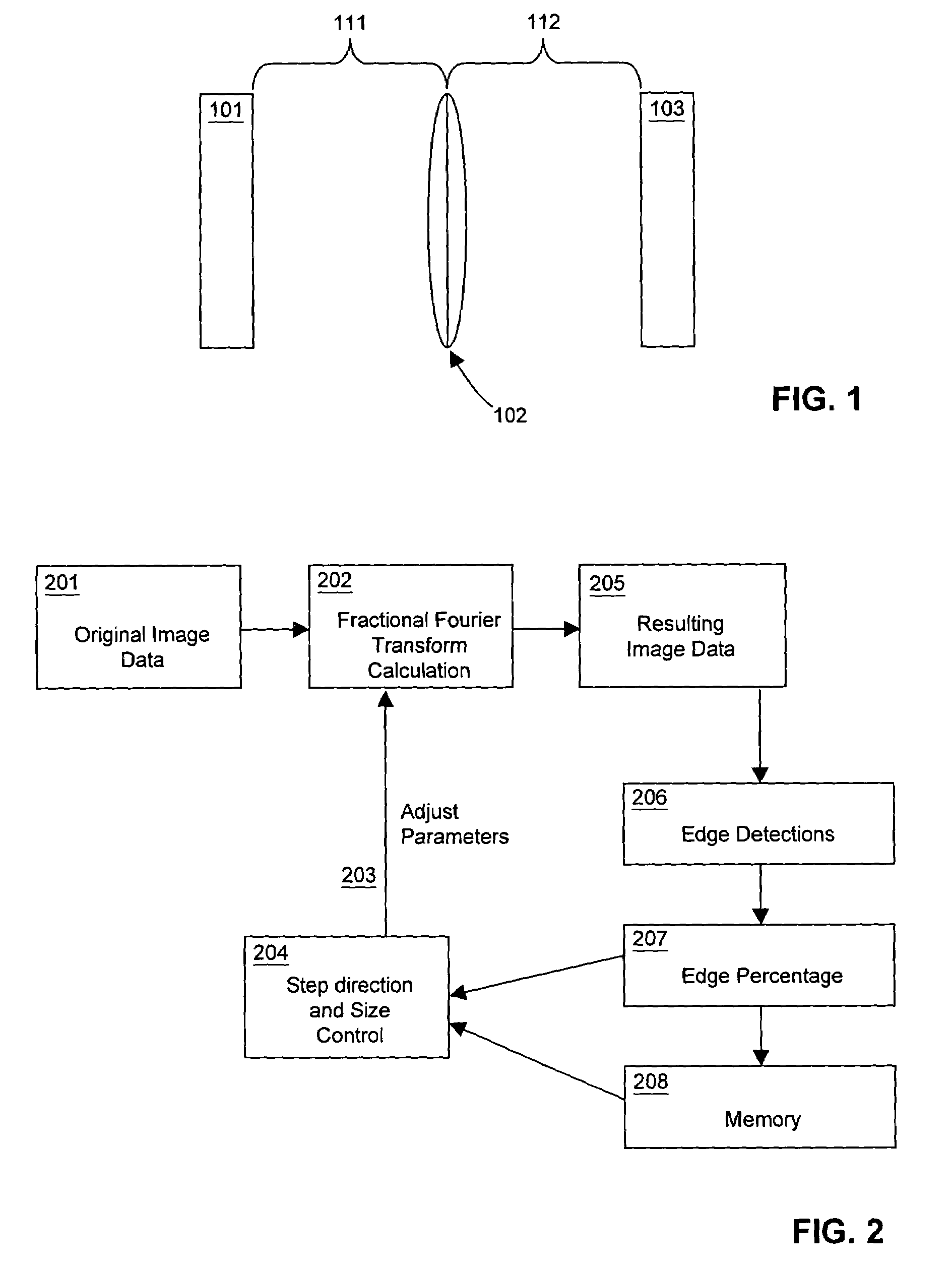
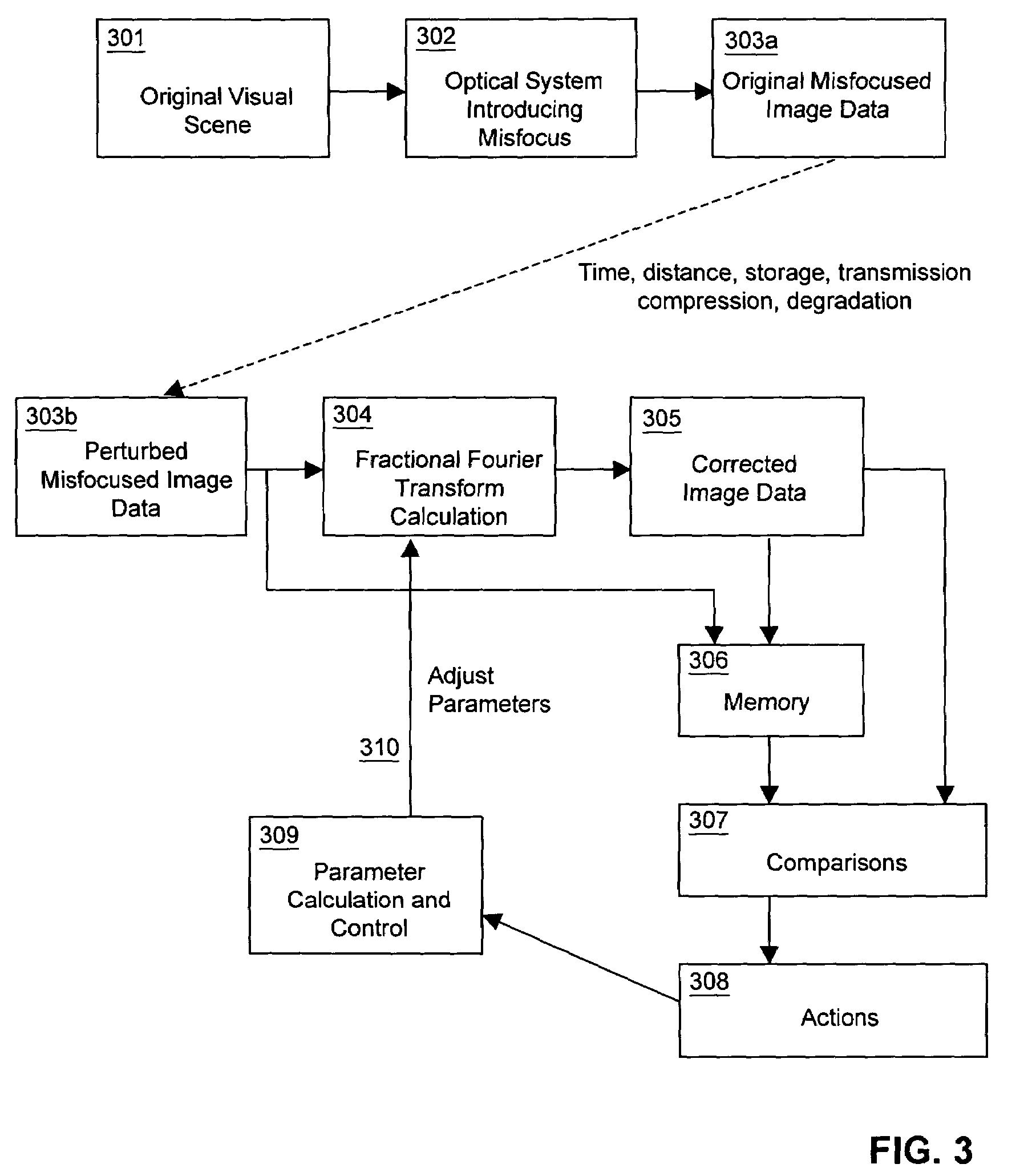
Relative optical path phase reconstruction in the correction of misfocused images using fractional powers of the fourier transform
InactiveUS7054504B2The effect is accurateSimple calculationImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImage correctionElectron
Reconstructing relative phase information in a misfocused image correction process for misfocused image data having image amplitude information, but lacking relative phase information. A suitable automated or human-operated process is utilized to generate an appropriate power value of a fractional Fourier transform correction operation. This power value is then used to simultaneously calculate the Fractional Fourier transform correction operation and back-calculate corresponding phase restoration information in an iterative or non-iterative environment. The phase restoration information and fractional Fourier transform correction operation may be applied to the image data to correct a desired level of misfocus in image data obtained from conventional lens systems or other fractional Fourier environments within integrated optics, optical computing, astronomical observation, and particle beam systems such as accelerators and electron microscopes, and may be incorporated into film processing, photo editing software and web sites, cameras, VCRs, video editing, surveillance, and conferencing video systems.
Owner:NRI R&D PATENT LICENSING LLC
Harmonic analysis algorithm combining fast Fourier transform (FFT) and nonlinear least square
InactiveCN102636693AHigh-resolutionHigh frequency resolutionSpectral/fourier analysisFast Fourier transformImage resolution
The invention discloses a harmonic analysis algorithm combining fast Fourier transform (FFT) and nonlinear least square. The harmonic analysis algorithm is applied in the field of harmonic analysis of power grids, and can realize accurate calculation of frequency, amplitude and phase of power grid signals. The technical scheme (1) provides a method for calculating initial parameters of harmonic by using FFT and establishing a harmonic model, and (2) provides a nonlinear least square method for solving the parameters of the harmonic model. The algorithm has the advantages that influence of data length in no-parameter harmonic analysis on resolution is avoided, and the frequency resolution is improved; the structure and the initial parameters of the model are provided by the FFT, the parameter modeling problem of the least square is solved, and the initial values of the parameters are provided; by proper initial value selection, the initial value sensitivity of the iterative algorithm is reduced, and the iteration step is greatly reduced, so that the calculation efficiency is improved; and the parameter calculation precision of the nonlinear least square algorithm is further higher than that of a Hanning window interpolation method.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Fourier transform infrared spectrum distortion identifying and processing method
The invention discloses a Fourier transform infrared spectrum distortion identifying and processing method. Aiming at the problem of inaccurate analysis result caused by spectrum distortion due to the factors of environment change and the like in a Fourier transform infrared spectrum analysis-based gas online analysis process, the method comprises the following steps of: aiming at a specific application situation, determining possible components in the gas to be analyzed, searching spectral lines nearly insensitive to all the components in the whole spectrum wave number range according to the spectrum of the gas components, and correcting base line rule distortion in the spectrum by adopting a spectrogram sectioned rotation and translation method according to the spectrum values of the spectral lines; performing gas concentration quantitative analysis by using the corrected spectrum, and performing spectrum reconstruction according to the analysis result; and judging whether the spectrum has local irregular distortion according to the difference between the reconstructed spectrum and the actual spectrum, if so, abandoning the analysis result, and if the local irregular distortion is continuously caused, rescanning the background to eliminate the deviation of the spectrum distortion to the analysis result.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for realizing 3780-point fast Fourier transform/inverse fast Fourier transform (FFT/IFFT) and processor thereof
InactiveCN102214159AGuaranteed real-timeSave storage resourcesComplex mathematical operationsRotation factorFast Fourier transform
The invention relates to a method for realizing 3780-point fast Fourier transform / inverse fast Fourier transform (FFT / IFFT) and a processor thereof. The processor consists of a top layer, an intermediate layer and a bottom layer, wherein the top layer resolves 3780-point by using a mixed based number algorithm, the intermediate layer resolves 63-point and 60-point FFT by using a prime factor algorithm, and the bottom layer complete 7-point, 9-point, 3-point, 4-point and 5-point FFT calculation by using a winograd fourier transform algorithm (WFTA) algorithm. The method realizes 3780-point FFT by combining the mixed base number algorithm, the prime factor algorithm and the WFTA algorithm, avoids errors caused by calculating 4096-point by using an interpolation method, and reduces rotation factors and a chaotic unit in the mixed base number algorithm. Furthermore, an index structure completed by a multiplex memory in the design has a simple circuit, is easy to realize, and can save chip resources.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Hypersonic speed target detecting method for polynomial Radon-polynomial Fourier transform
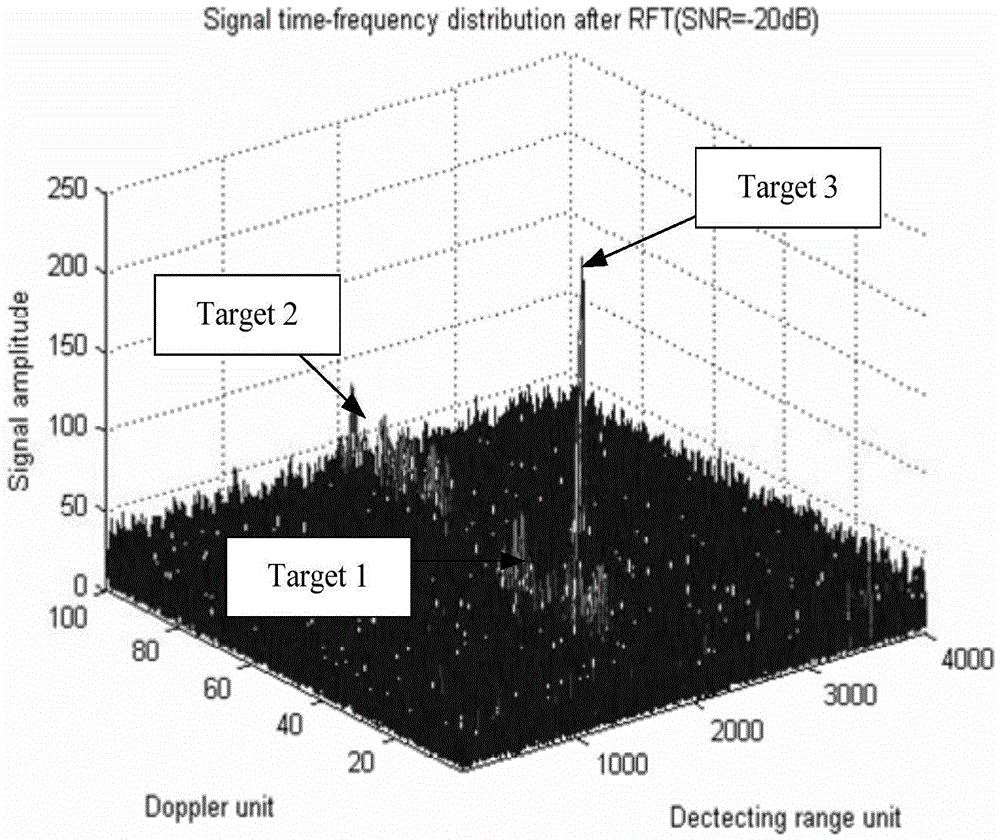
ActiveCN105652258AImprove discoveryCoherent accumulation implementationWave based measurement systemsParametric searchRadar signal processing
The invention relates to a hypersonic speed target detecting method for polynomial Radon-polynomial Fourier transform, and belongs to the technical field of radar signal processing and detecting. The method comprises the steps that N periodic signals to be accumulated are sampled, a slow time-fast time target observed value is extracted, and pulse compression is performed on the sampled signals separately; initialization parameters of polynomial Radon-polynomial Fourier transform are determined; search, compensation and accumulation are performed in a parameter space through polynomial Radon-polynomial Fourier transform to obtain a range-Doppler distribution diagram subjected to phase-coherent accumulation; constant false-alarm detection and target motion parameter estimation are performed on the range-Doppler distribution diagram. According to the method, model building is performed on target motion through polynomial, range walk and Doppler spread of the signals are compensated through parameter search of the polynomial, and therefore effective accumulation detection on a high-speed high-mobility target can be achieved under a low signal-to-noise ratio background; in addition, effective search on the multi-dimensional parameter space is achieved in a multi-resolution search mode, and therefore the search real-time performance is improved.
Owner:NAVAL AVIATION UNIV
Method and system for performing a fast-Fourier transform
InactiveUS7024443B2Much-reduced storageImprove calculation accuracyDigital computer detailsComplex mathematical operationsTransformation algorithmFourier transform on finite groups
In a method for performing a fast-Fourier transform (FFT), input data samples are written to a storage instance in a data input step, then subjected to a processing step in which the stored input samples are read out of the storage instance and processed in accordance with a transformation algorithm. The resulting output data samples are written back to the storage instance and, in a transformed data output step, read out of the storage instance, successively received batches of the input data samples being fed cyclically to a plurality of such multiple-function storage instances. Each batch is fed to a respective storage instance such that, at any given time during performance of the method, the input, processing and output steps are being performed simultaneously in respect of different batches using different respective storage instances. For each received data input batch, the processing step comprises a plurality of calculation passes creating intermediate data values which are stored between passes in both the respective multiple function storage instance and a further storage instance which is substantially dedicated for use in such processing steps. The invention also includes a related method for performing an inverse fast-Fourier transform (IFFT), as well as FFT and IFFT systems.
Owner:RIM SEMICON
Ground penetrating radar signal denoising method based on mixed Fourier-wavelet analysis
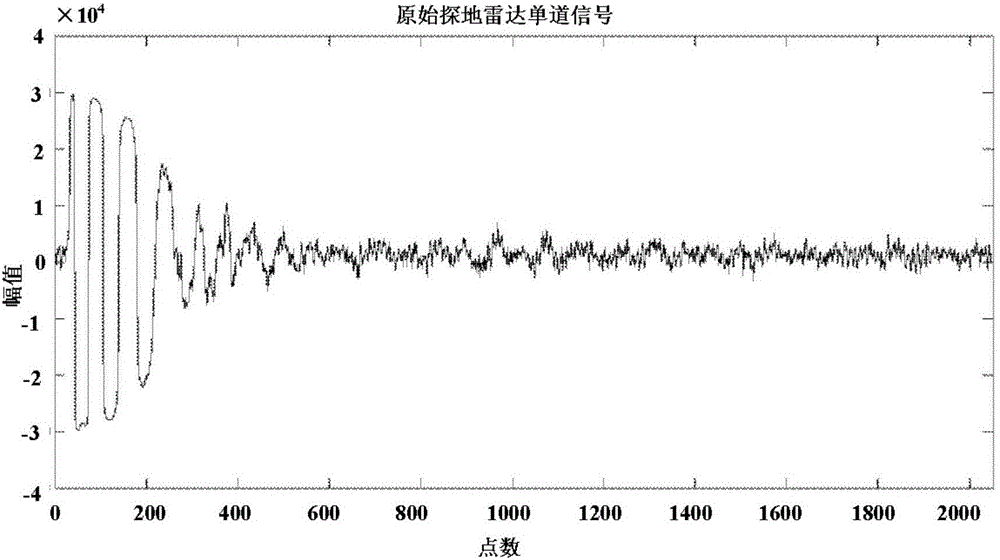
ActiveCN106199532AMake up for the defect that the low-frequency noise removal effect is not goodSimple and fast operationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFast Fourier transformWavelet decomposition
The invention provides a ground penetrating radar signal denoising method based on mixed Fourier-wavelet analysis. Through carrying out multi-scale wavelet decomposition on a ground penetrating radar echo signal, a threshold function is used for updating a wavelet coefficient, the advantage of high resolution in the frequency domain of Fourier transform is inherited, defects that the Fourier transform is not applied to a non-stationary signal, and frequency feature information of a local time segment can not be extracted are overcome, advantages of wavelet transform localization and automatic focusing are made full use of, the defect that the wavelet transform has poor effects on removing low-frequency noise is remedied, particular features of the ground penetrating radar are fully considered, a specific formula in each step during the using process is given, parameters such as a sampling rate, a central frequency and a bandwidth can be directly substituted for denoising processing as for different ground penetrating radars in actual use, and the operation is simple and convenient.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
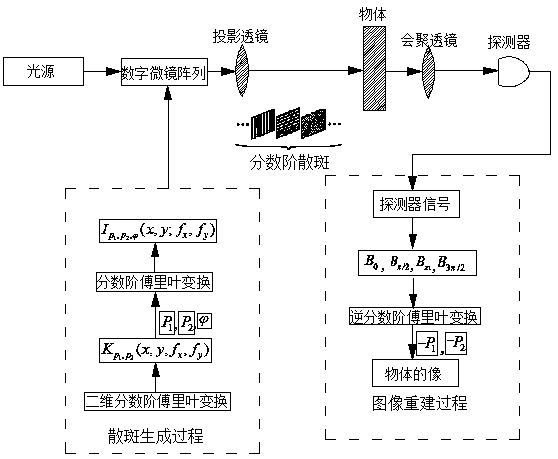
A correlation imaging method based on fractional Fourier transform
ActiveCN109242808AImprove image qualityReduce noiseImage enhancementImage analysisFast Fourier transformImage resolution
The invention discloses a correlation imaging method based on fractional Fourier transform, by irradiating the generated specific fractional speckle onto the object, then using a barrel detector without spatial resolution to receive the light transmitted or reflected by the object to be imaged, and finally using the inverse fractional Fourier transform to obtain the image of the object to be imaged in the case of obtaining the order of speckle design. The invention introduces the sparsity of the fractional-order Fourier transform in the transform domain into the correlation imaging, which canimprove the imaging quality of the correlation imaging. At the same time, fractional order is introduced into correlation imaging, and the order set when fractional order speckle is designed is used as the key to recover the object. Only when the correct key is obtained, the correct recovered object can be obtained, and the security of correlation imaging can be effectively improved by this scheme. The invention has the advantages of simple structure and convenient realization, is suitable for the situation of high requirements on imaging quality and safety, and has great application prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Adaptive Frequency Domain Filtering For Phase Plane Correlation
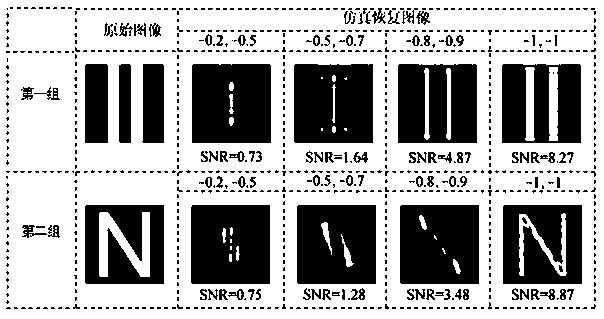
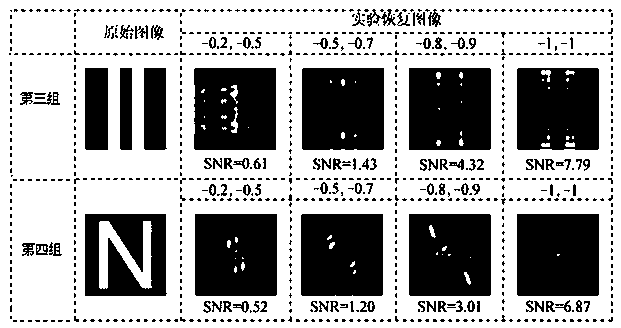
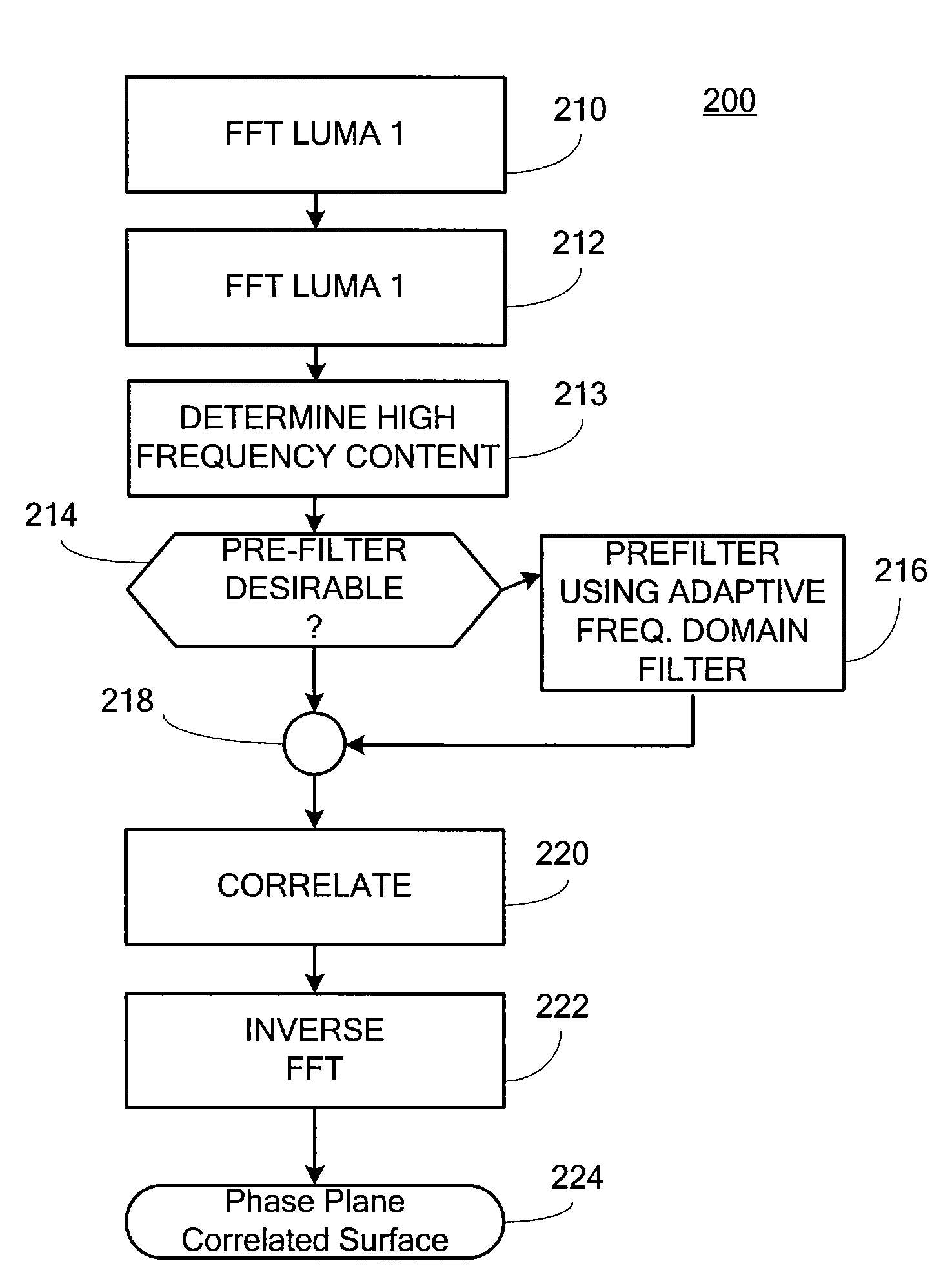
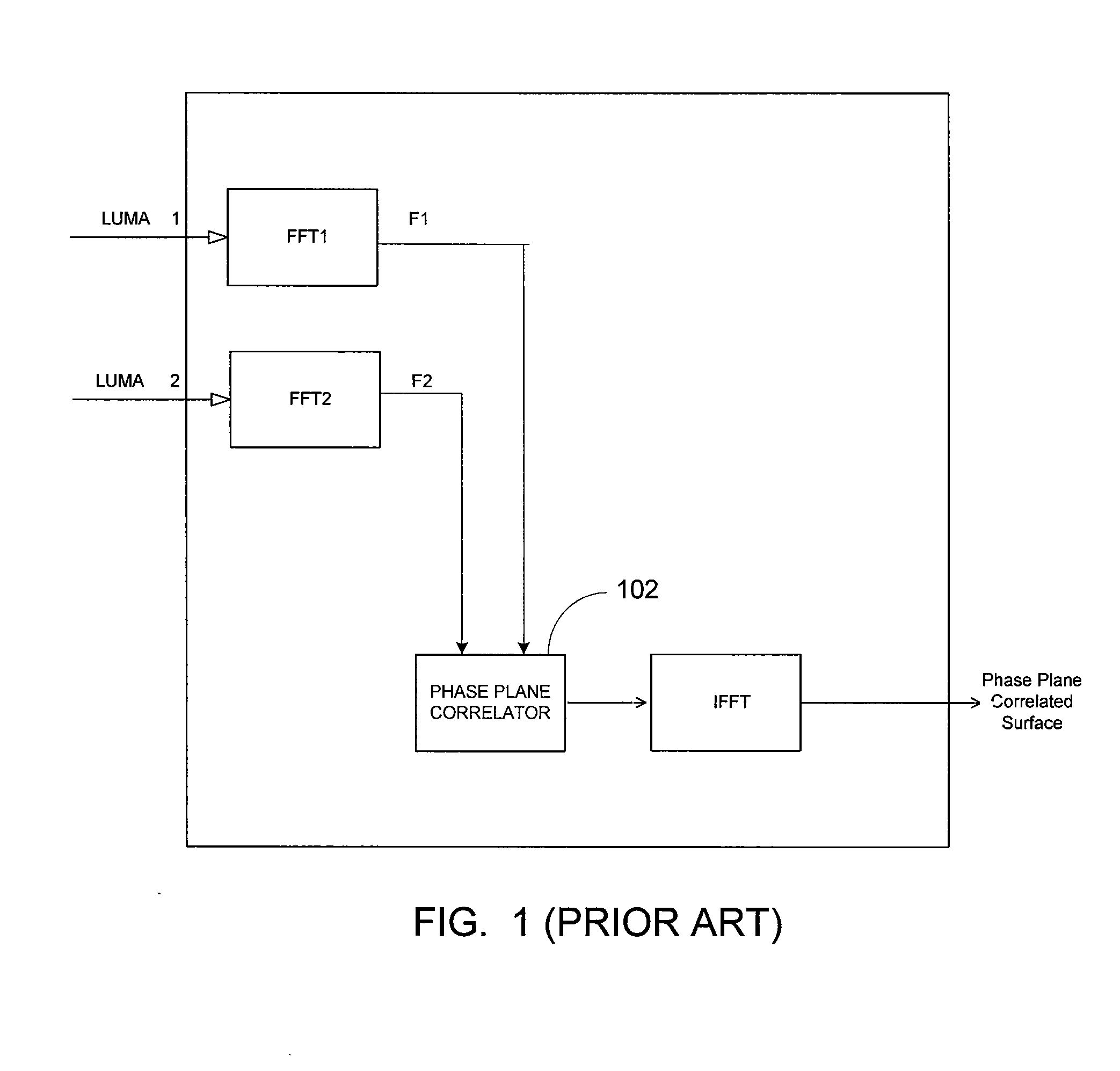
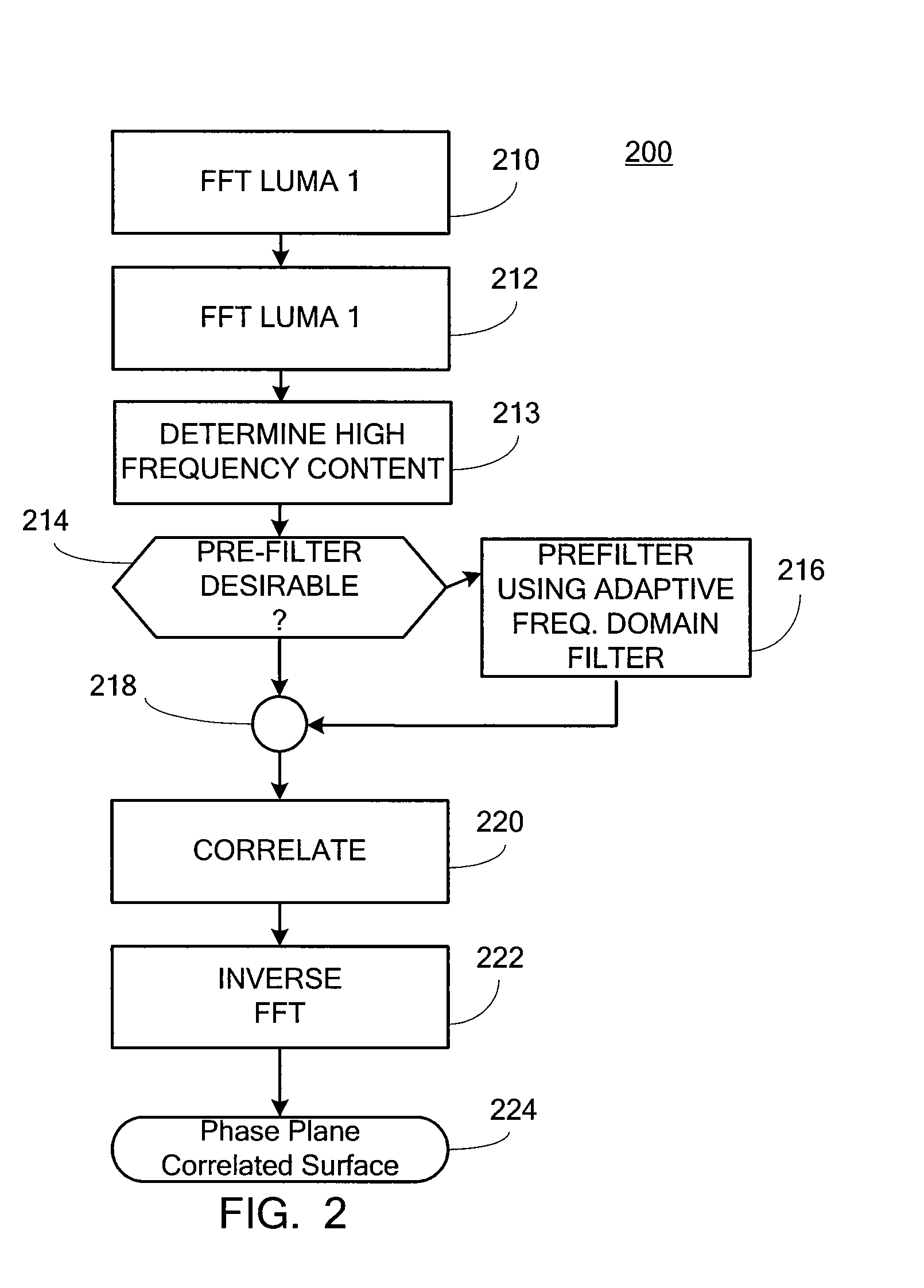
ActiveUS20100150225A1Reliable and consistent PPCImage enhancementImage analysisPhase correlationHigh frequency content measure
In a Phase Plane Correlation (PPC) process, using adaptive frequency domain filtering to aid in generating candidate motion vectors. It is determined when it is beneficial to pre-filter an input image, prior to a PPC process. This results in more reliable and consistent PPC surfaces than otherwise. The filter is applied in the frequency domain where time-domain convolution becomes a much more efficient component-wise multiplication with an in-place window. An energy measure of the high-frequency content in the computed Fourier surfaces gauges the degree of high frequency content in the image. First, the Fourier transform of the two images is computed. Then, the high-frequency content is estimated from the Fourier surfaces. A window function is computed as a function of the high-frequency energy. The window is applied to the Fourier surfaces. Then, the modified Fourier surfaces are fed into the PPC process.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
Method for computing external illuminator radar cross-ambiguity function utilizing sparse Fourier transform
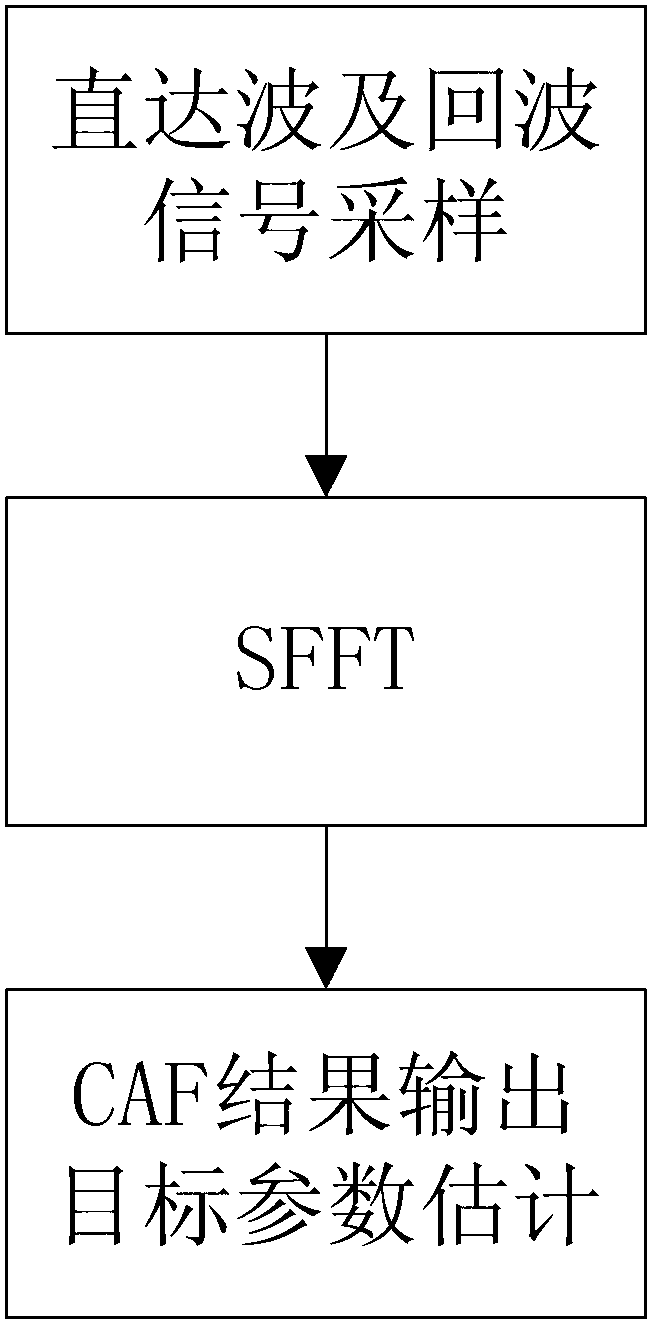
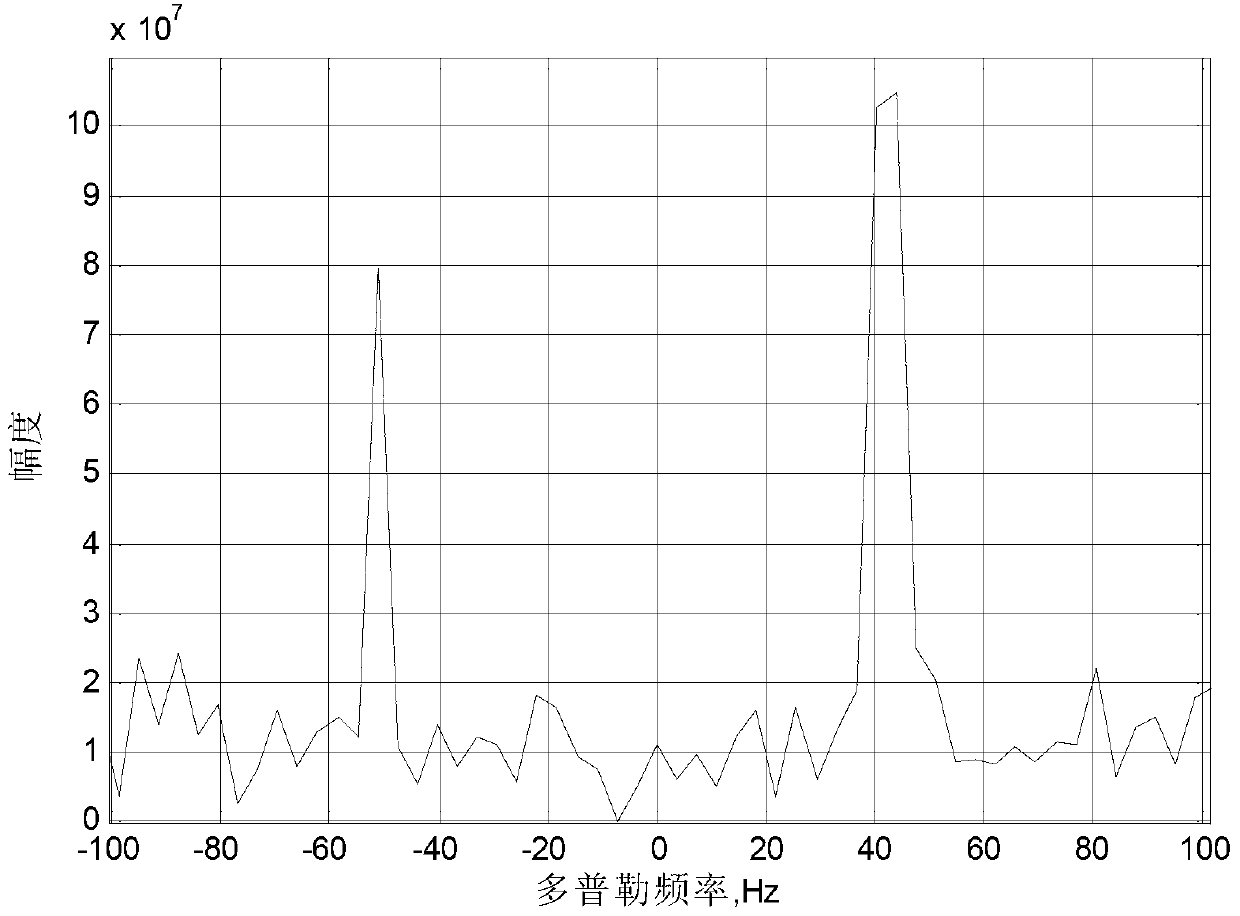
The invention relates to a method for computing an external illuminator radar cross-ambiguity function utilizing the sparse Fourier transform and belongs to the field of radar target acquisition processing. Firstly, point multiplication is carried out on direct wave signals and echo delay signals to construct a new vector, wherein the direct wave signals are received by an external illuminator radar antenna, and filtering and down extraction are carried out on the direct wave signals. Secondly, the sparse Fourier transform is carried out on the new vector, and therefore a Doppler tangent plane result of the cross-ambiguity function on the delay point is obtained. Lastly, parameters like target Doppler frequency shift can be estimated through the sparse Fourier transform results. Compared with a traditional method that cross-ambiguity function operation is carried out on the external illuminator radar through the Fourier transform, the method utilizes the sparse Fourier transform to solve the cross-ambiguity function and can greatly reduce operand of the cross-ambiguity function under the condition of long-time accumulation according to the characteristics that the number of targets appearing in the air in reality is limited and the targets have sparsity.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
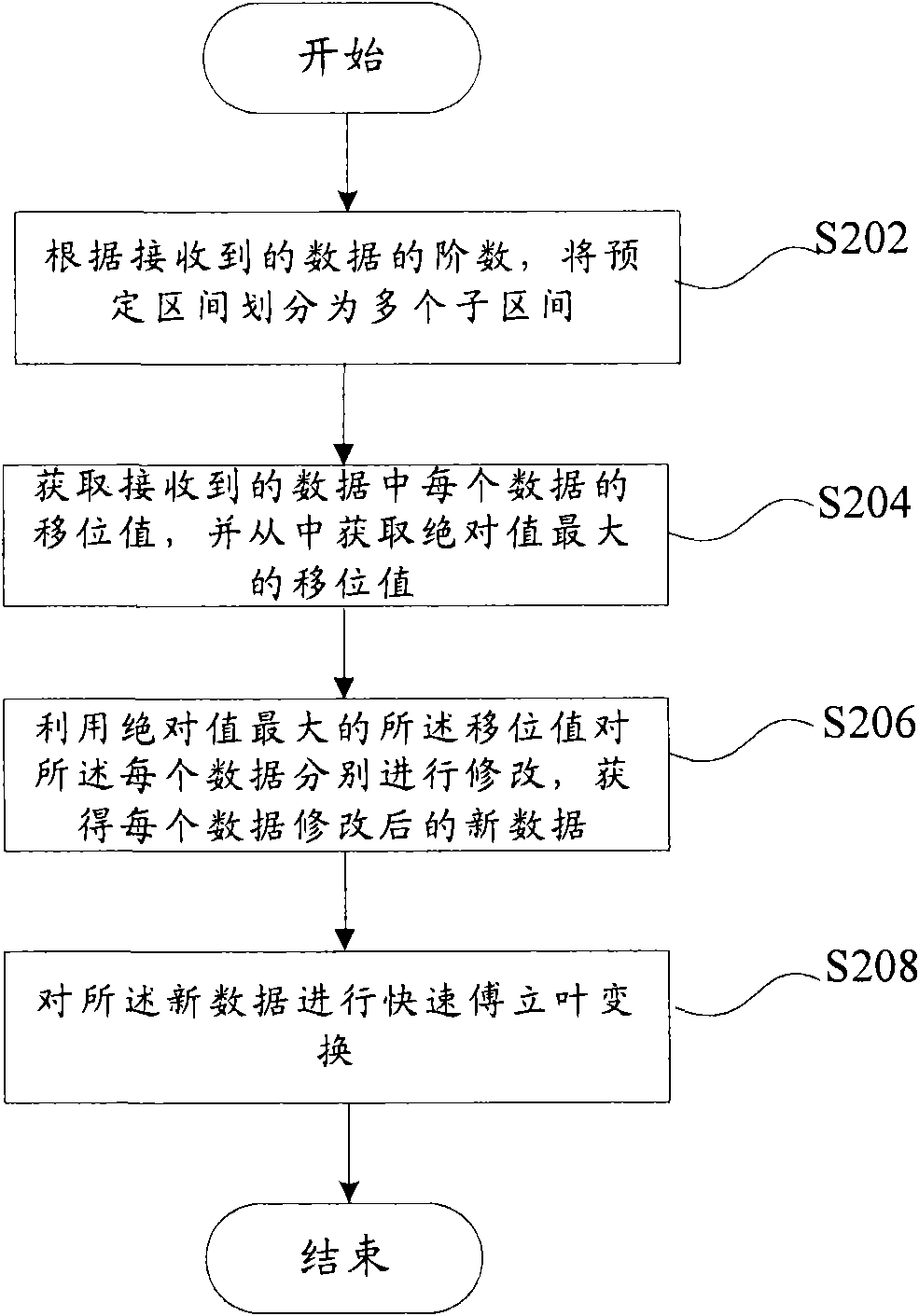
Realizing method and device of fast Fourier transform
ActiveCN101551790AReduce usageLow costComplex mathematical operationsFourier transform on finite groupsComputer science
The invention provides a realizing method of fast Fourier transform, which is used for controlling the overflow of received data and then carrying out the Fourier transform. The realizing method of the fast Fourier transform comprises the following steps: dividing a predetermined area into a plurality of sub-areas according to the exponent number of received data; obtaining a shifting value of each datum of the received data and also obtaining a shifting value with a maximal absolute value from the obtained shifting values; utilizing the shifting value with the maximal absolute value to respectively modify each datum and obtaining new modified data corresponding to each datum; and carrying out the fast Fourier transform for the new data, wherein the shifting values express the position relation of the sub-area where the data locating relative to a pointed sub-area of the sub-areas. Besides, the invention also provides a realizing device of the fast Fourier transform. The invention can ensure the calculation precision under the precondition of overflow control and can also reduce the utilization of circuit resources, lower the circuit cost and enhance the qualification rate of circuits.
Owner:SANECHIPS TECH CO LTD
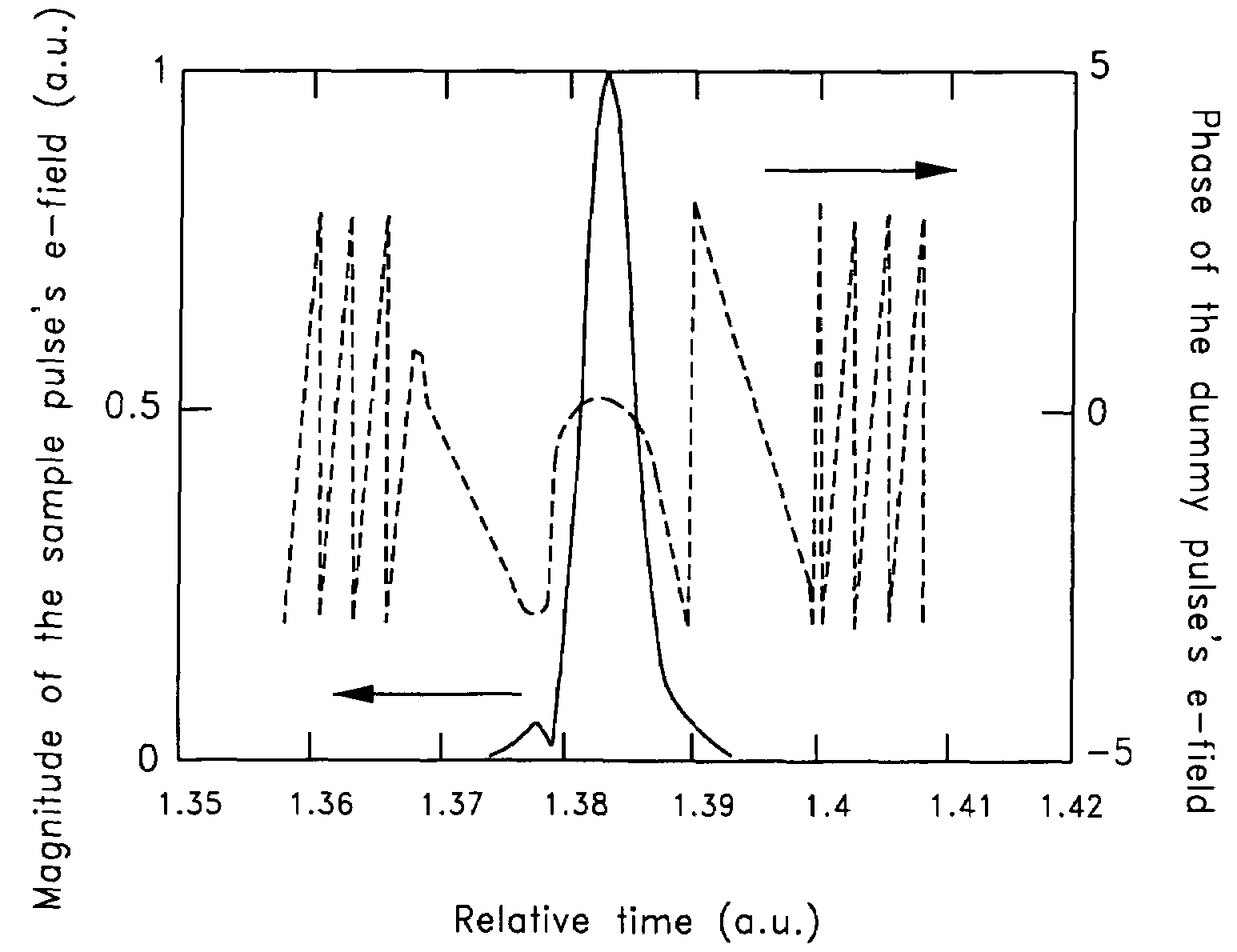
Femtosecond spectroscopy using minimum phase functions
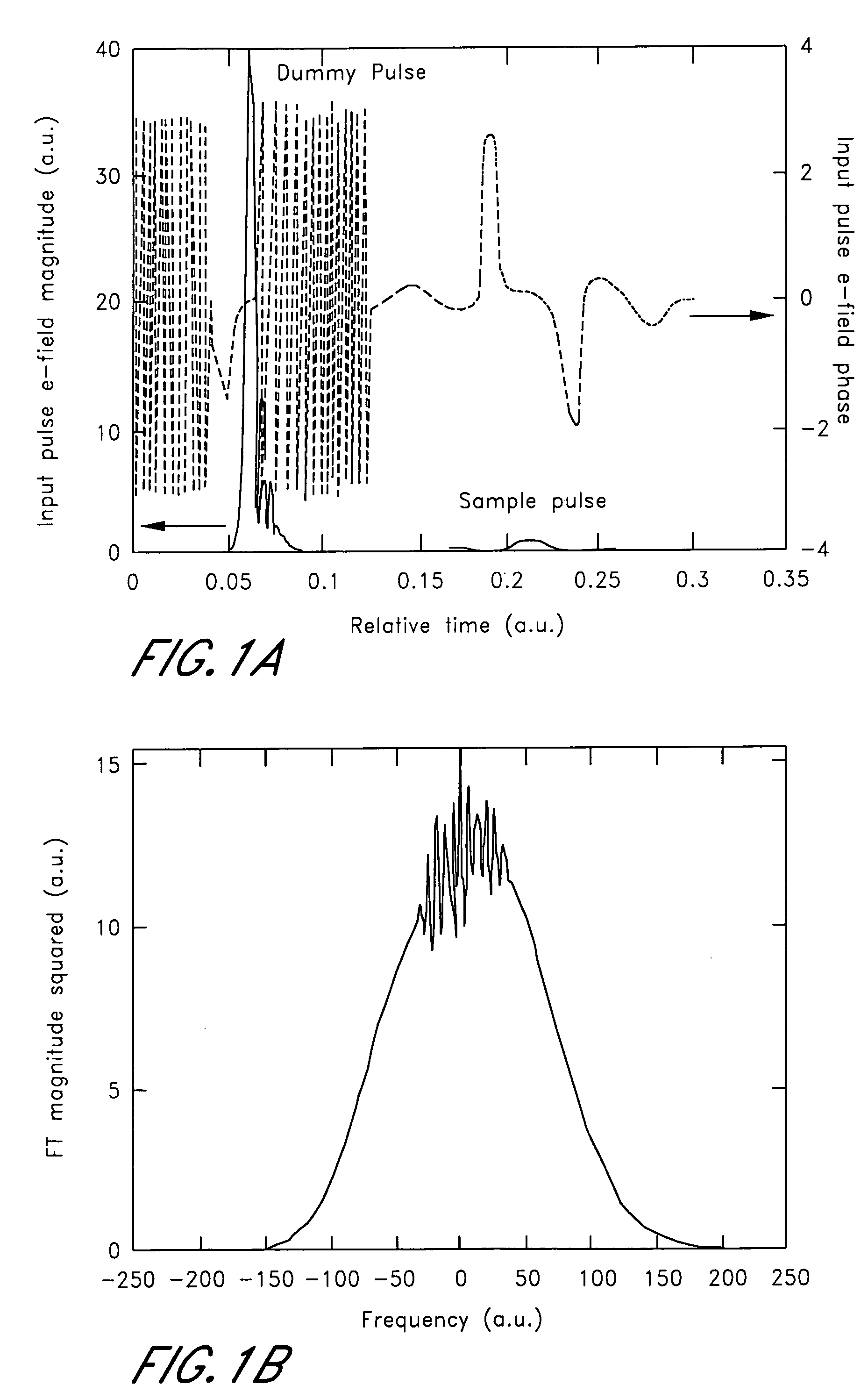
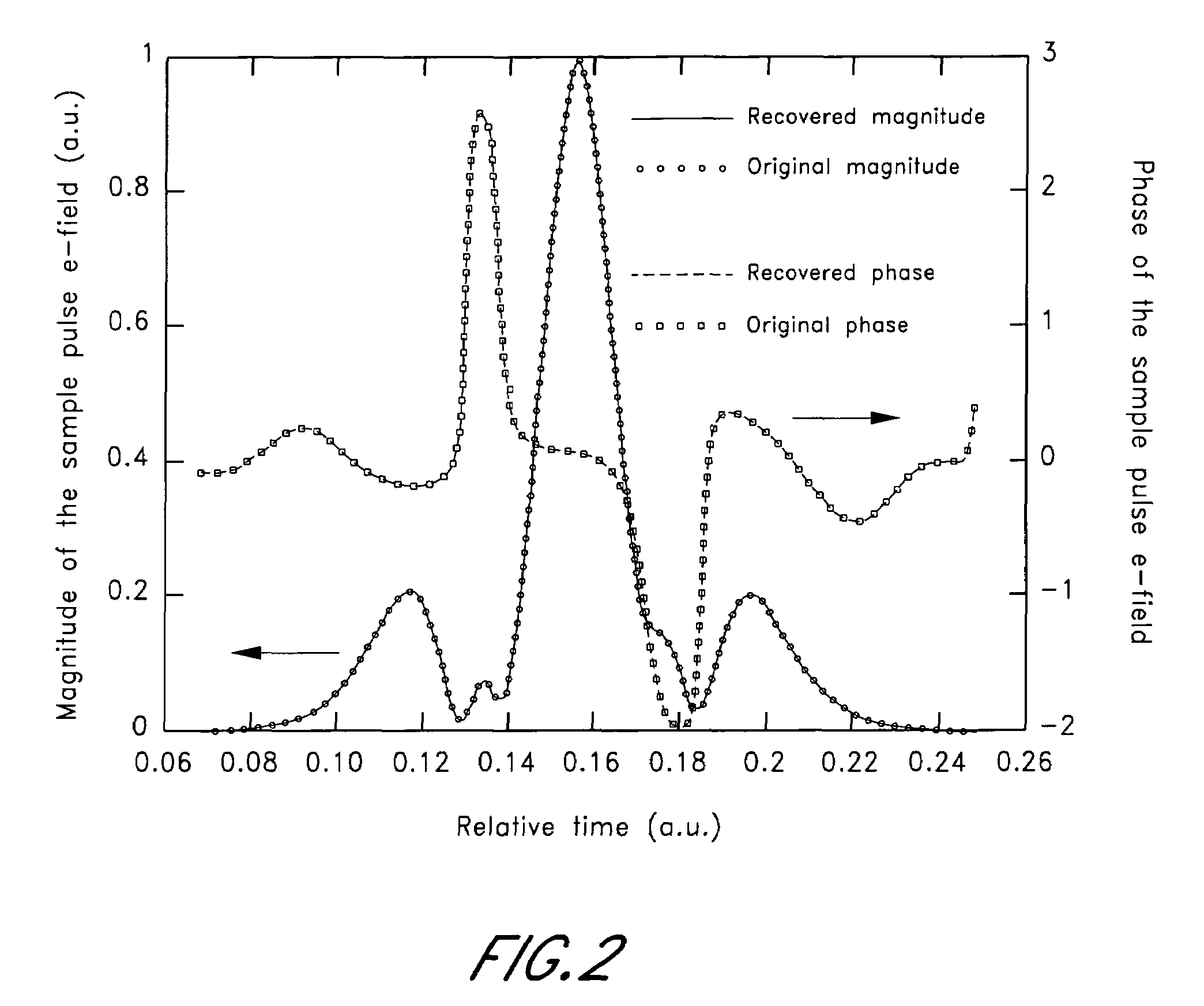
ActiveUS7369953B2Spectral/fourier analysisAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceFast Fourier transformPhase function
A method determining a transient response includes providing a measured magnitude of the Fourier transform of a complex electric field temporal profile of a pulse sequence comprising a probe pulse and a dummy pulse, wherein the probe pulse is indicative of the transient response of a sample. The method further includes providing an estimated phase term of the Fourier transform of the complex electric field temporal profile of the pulse sequence and multiplying the measured magnitude and the estimated phase term to generate an estimated Fourier transform of the complex electric field temporal profile of the pulse sequence. The method further includes calculating an inverse Fourier transform of the estimated Fourier transform, wherein the inverse Fourier transform is a function of time, and calculating an estimated complex electric field temporal profile of the pulse sequence by applying at least one constraint to the inverse Fourier transform.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Fast Fourier transform-based blind frequency spectrum sensing method and apparatus
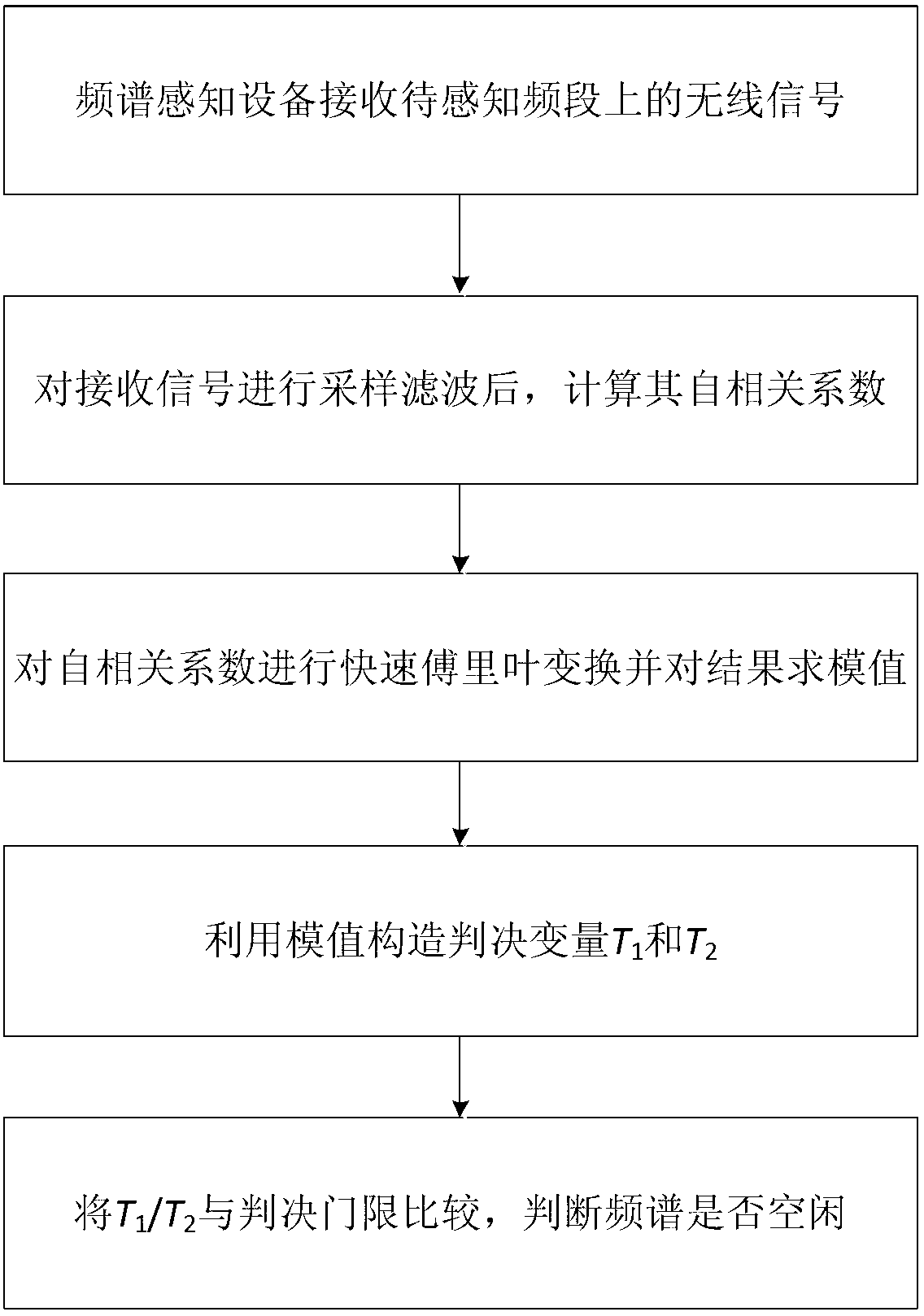
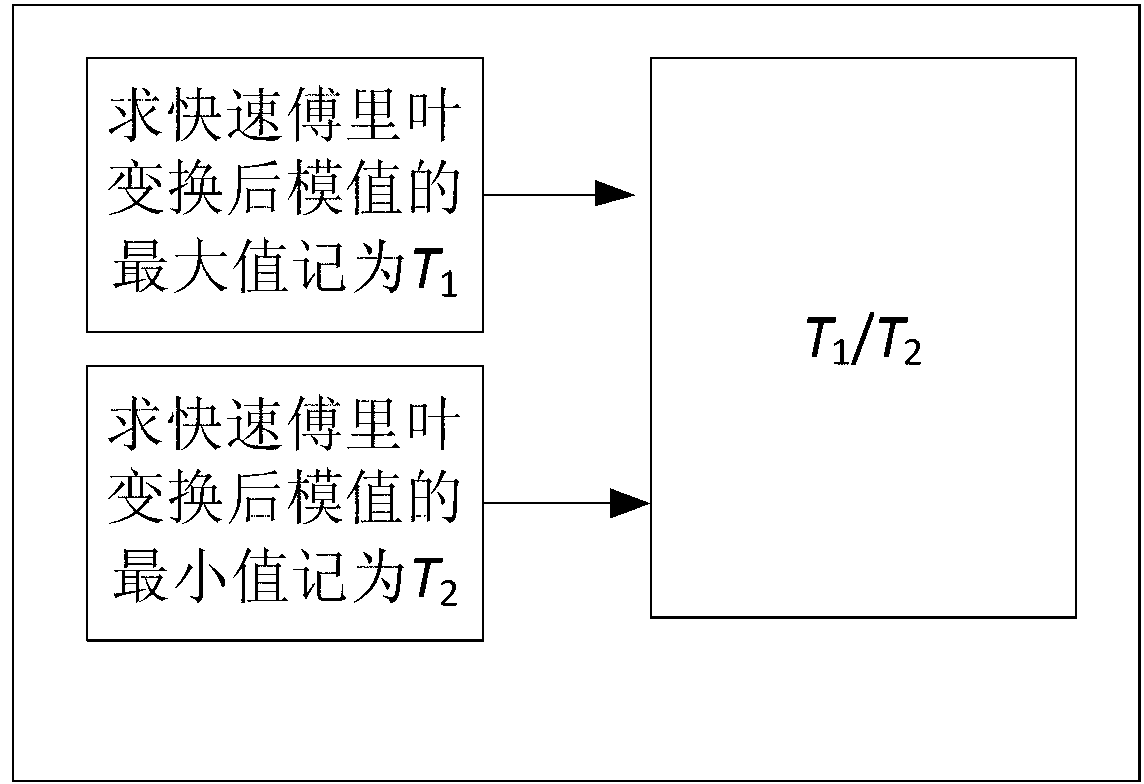
InactiveCN103346845AReduce complexitySpectral gaps assessmentTransmission monitoringFast Fourier transformFrequency spectrum
The invention, which relates to the frequency spectrum sensing technology in a radio system, discloses a fast Fourier transform-based blind frequency spectrum sensing method and apparatus. The method comprises the following steps that: a frequency spectrum sensing device receives a signal at an authorized frequency range; after sampling and filtering are carried out on a received signal; an autocorrelation coefficient of the signal is calculated; fast Fourier transform is carried out on the autocorrelation coefficient and a module value is solved for a conversion result; a decision variable is constructed according to the module value and whether a signal of an authorized user exists is determined. According to the invention, the provided method and apparatus have the advantages of having low calculating complexity, not needing an authorized signal characteristic, being uncertain of and not sensitive of noises and the like and have excellent performances.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
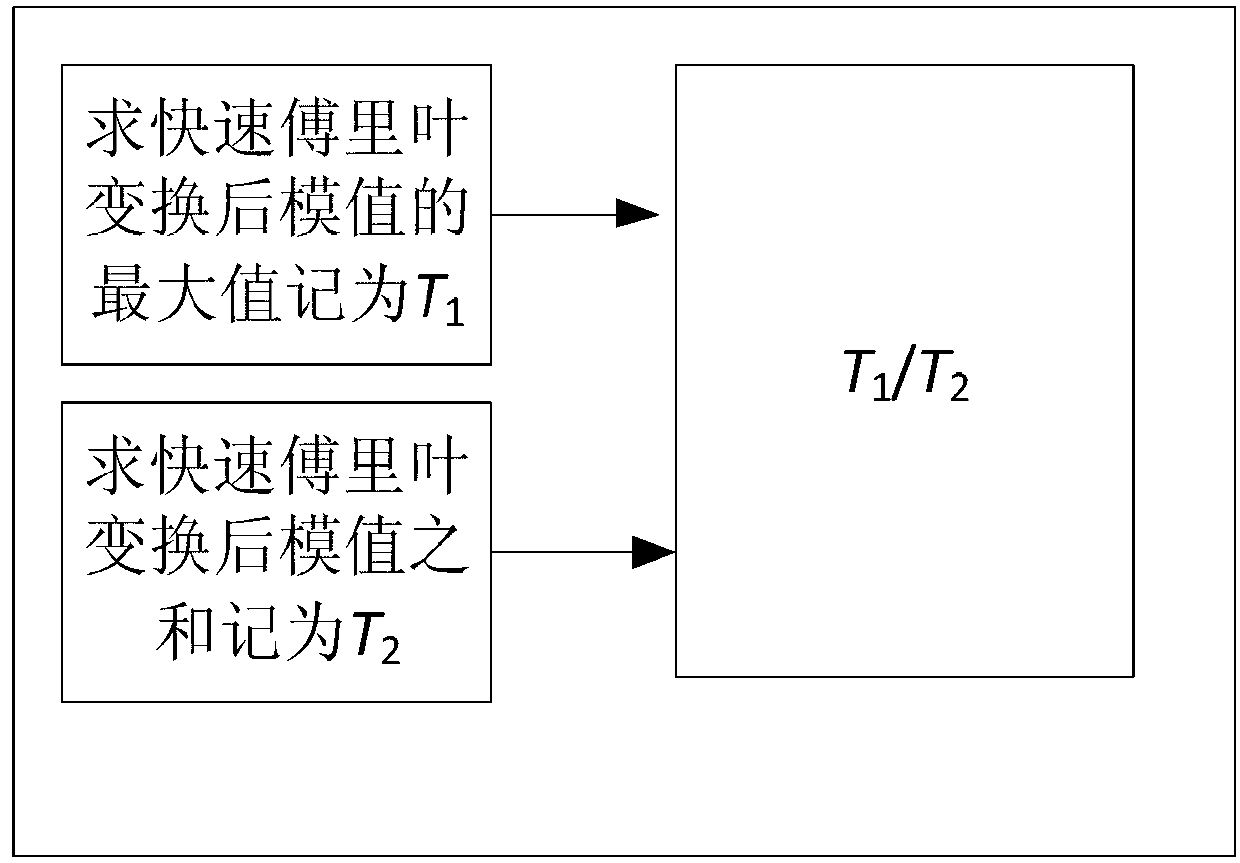
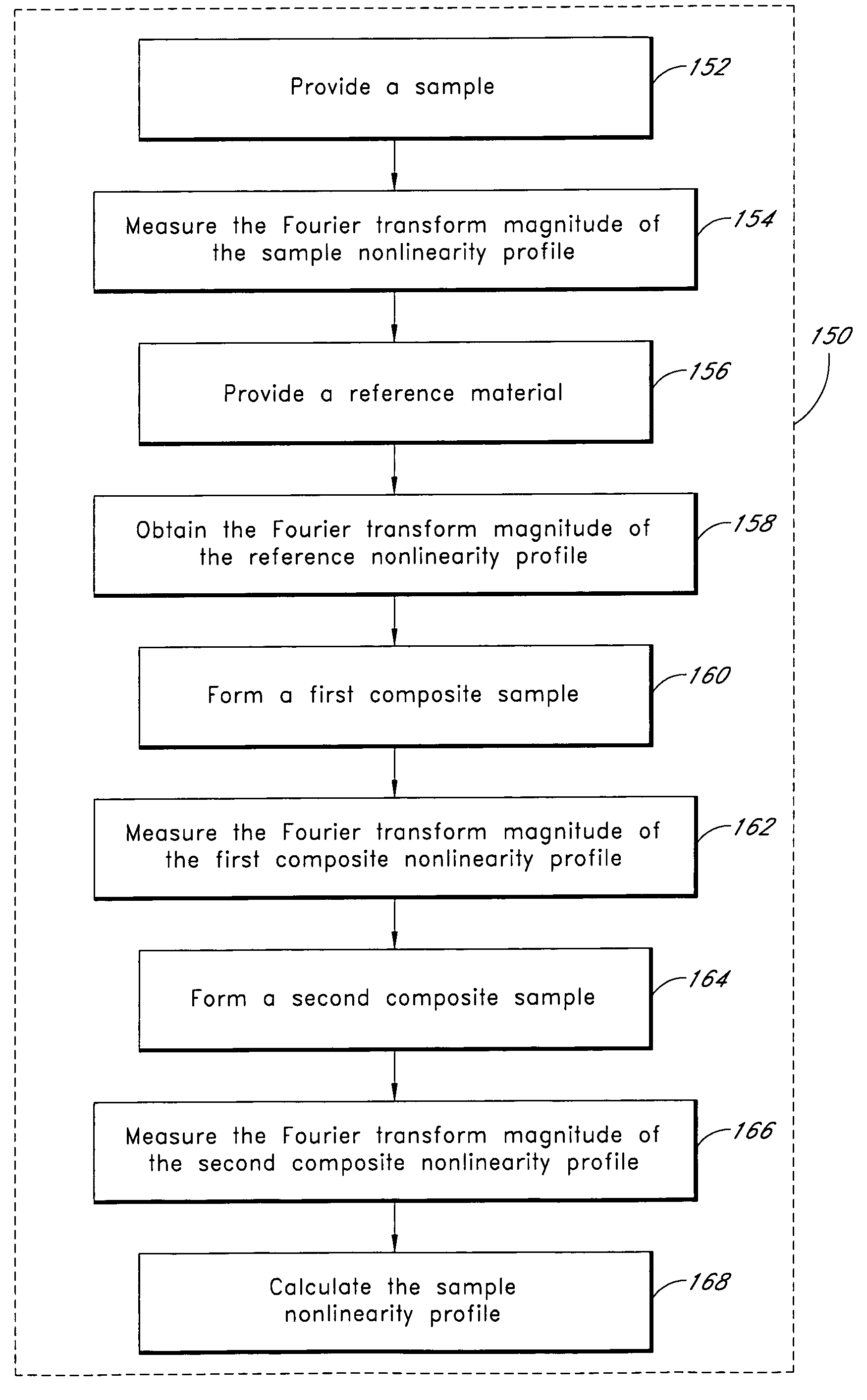
Method of measuring a physical function using a composite function which includes the physical function and an arbitrary reference function
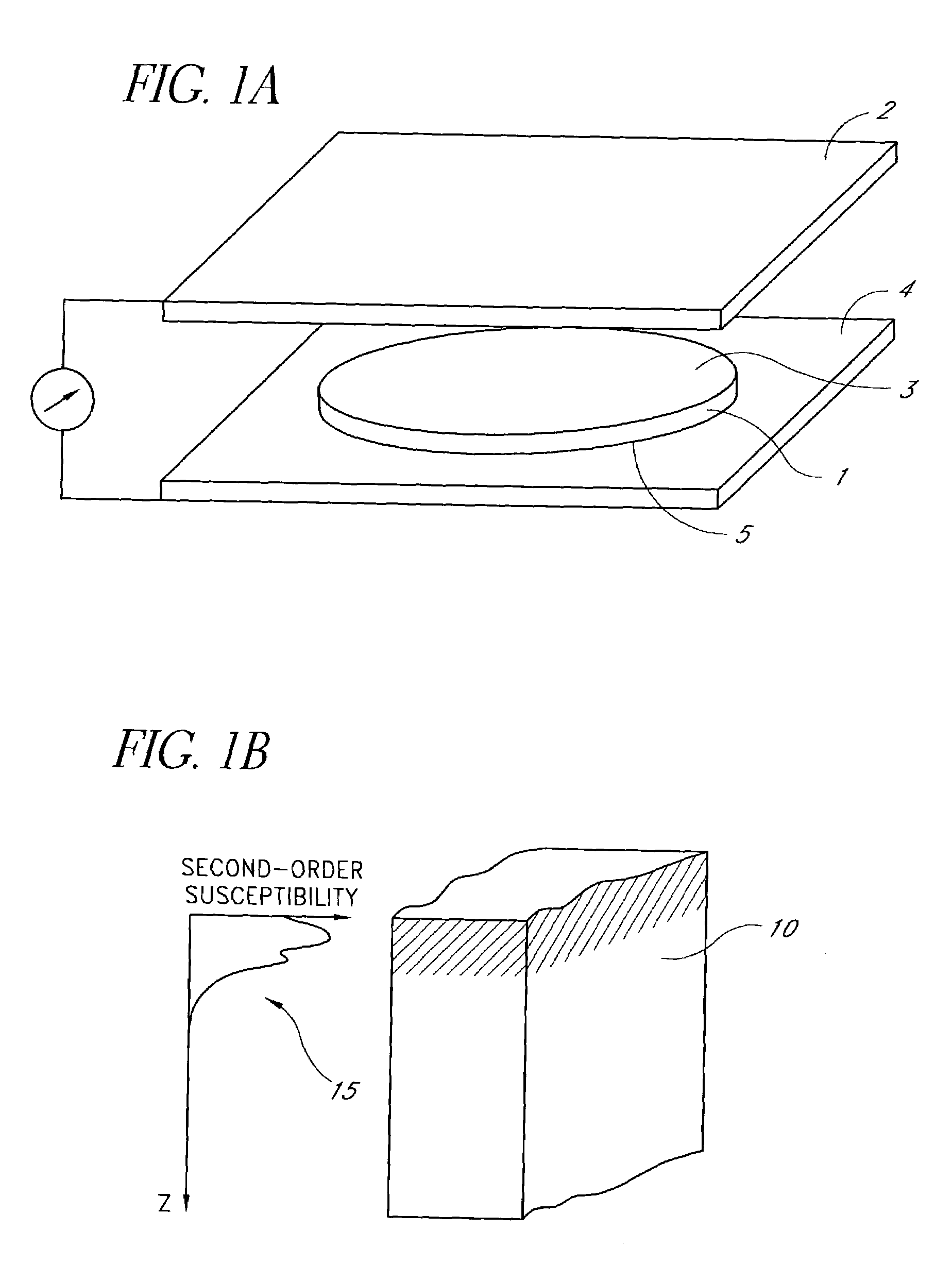
InactiveUS7050169B2MirrorsPolarisation-affecting propertiesFast Fourier transformFourier transform on finite groups
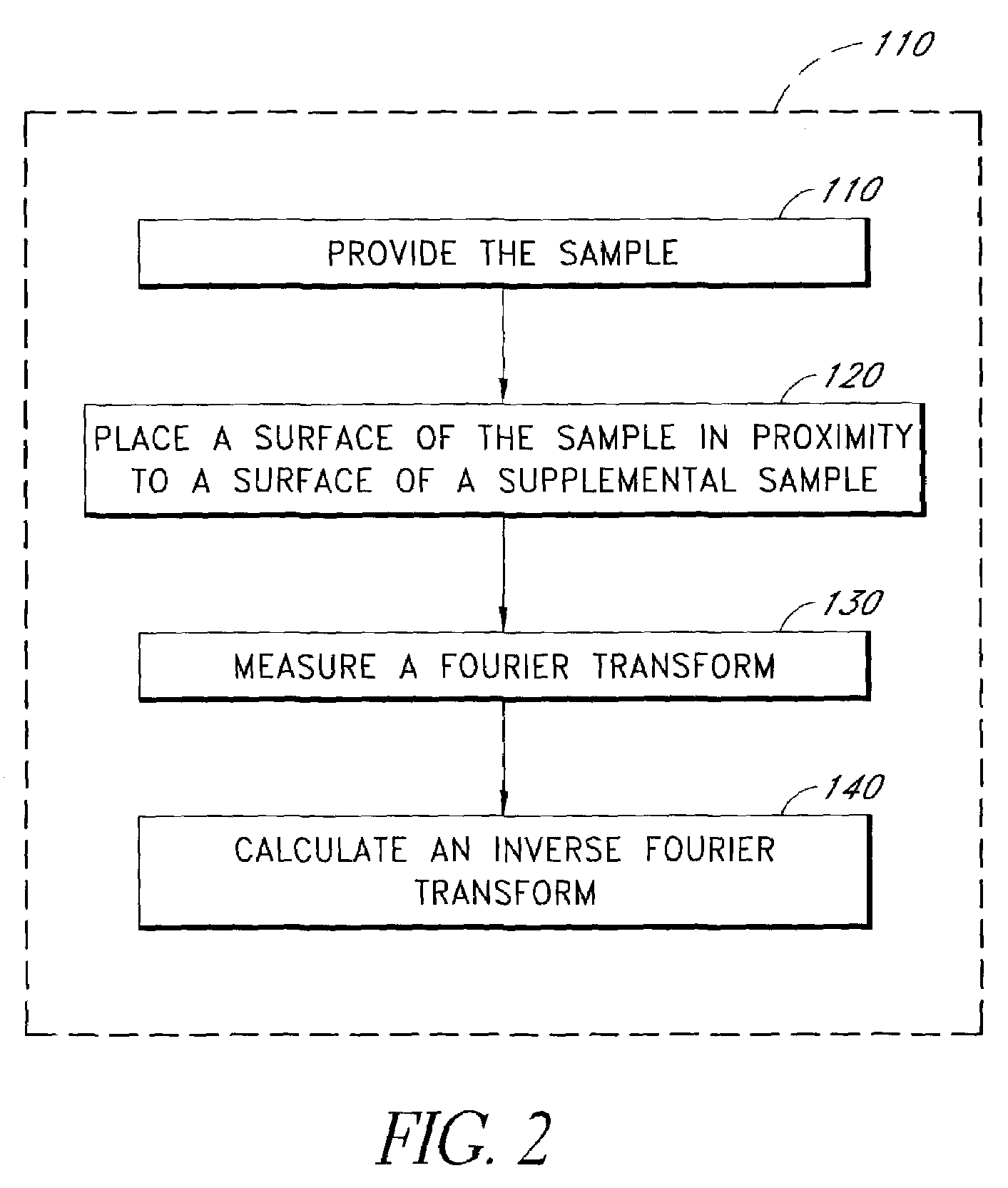
A method for measuring a physical function forms a symmetric composite function by combining the physical function with a reference function. The method obtains a Fourier transform of the symmetric composite function. The method calculates an inverse Fourier transform of the obtained Fourier transform, wherein the calculated inverse Fourier transform provides information regarding the physical function. The physical function can be a nonlinearity profile of a sample with at least one sample surface. The physical function can alternatively by a sample temporal waveform of a sample optical pulse.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
64-point fast fourier transform (FFT) calculator
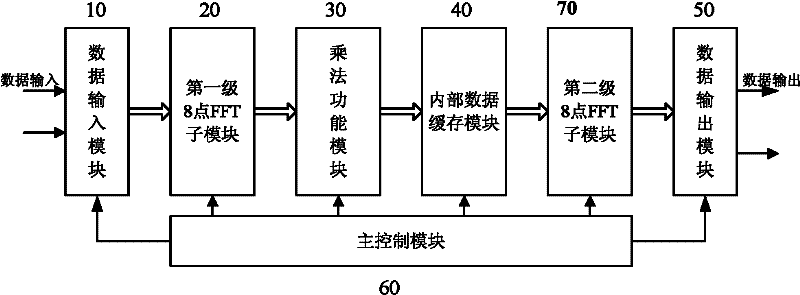
InactiveCN102364456ASave storage spaceReduce areaComplex mathematical operationsRotation factorFast Fourier transform
The invention discloses a 64-point fast Fourier transform (FFT) calculator, which comprises a data input module for inputting cache of data and preparing required data for the next module, a first-stage 8-point FFT operation sub module for sequentially performing 8-point FFT operation on the data output by the data input module for the first time, a multiplication functional module for multiplying a processed result of the first-stage 8-point FFT operation with a corresponding rotation factor, an inner data cache module for caching the data operated by the multiplication functional module, adjusting the sequence and preparing the required data for the next module, a second-stage 8-point FFT operation sub module for performing 8-point FFT operation on the data output by the inner data cache module again, a data output module for adjusting the sequence of the data output by the second-stage 8-point FFT operation sub module and outputting the data, and a main control module for generating enabling signal of the functional modules and controlling data transmission and signal transmission of the functional modules.
Owner:GUANGZHOU KINGRAY INFORMATION TECH
Fourier transform algorithm for reducing time loss
PendingCN109101462AEnsuring Efficiency in Time-Frequency AnalysisImprove computing efficiencyComplex mathematical operationsFast Fourier transformTime–frequency analysis
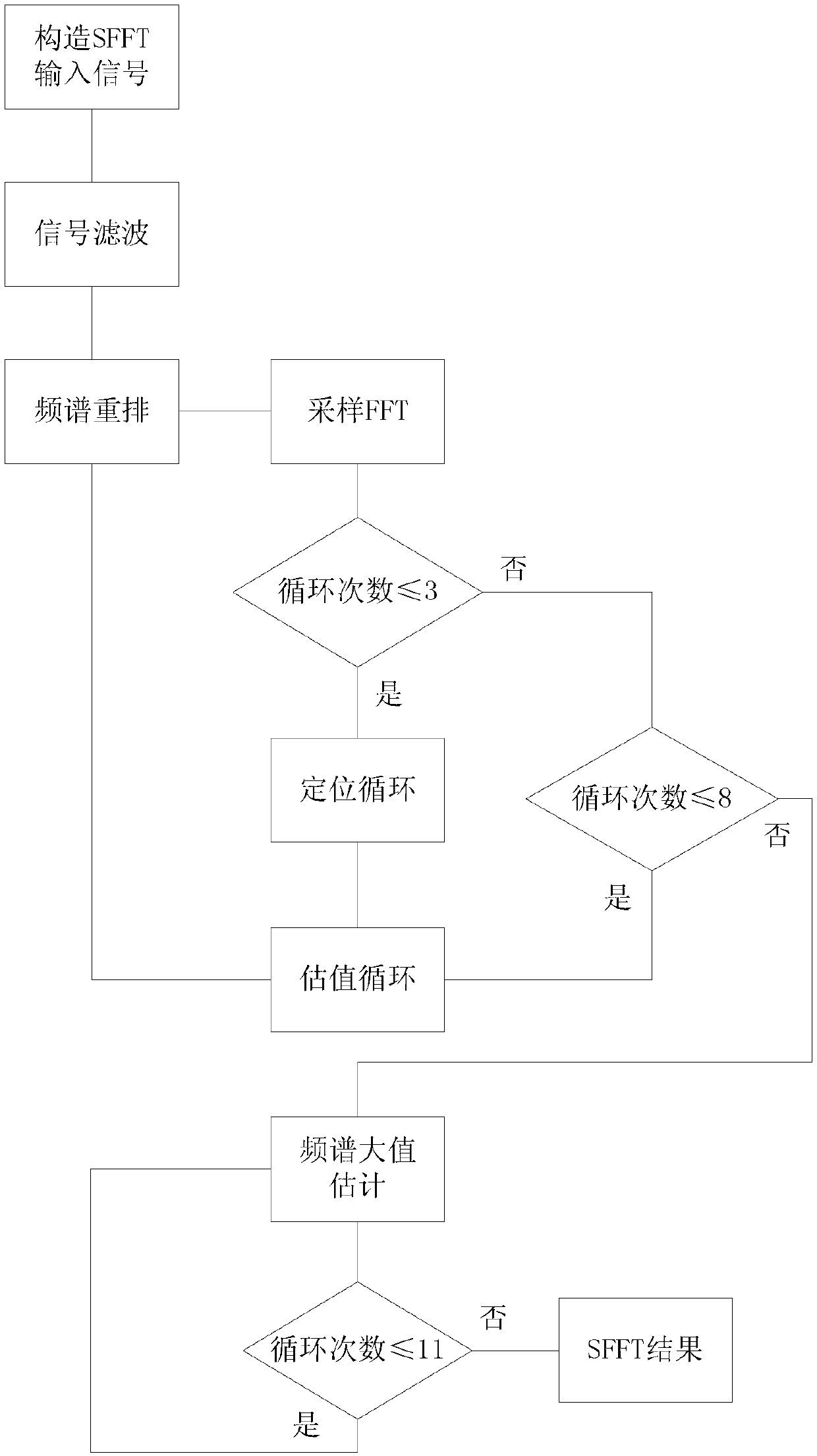
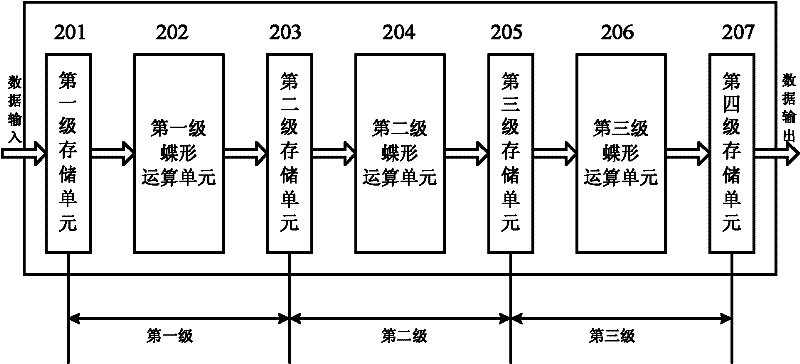
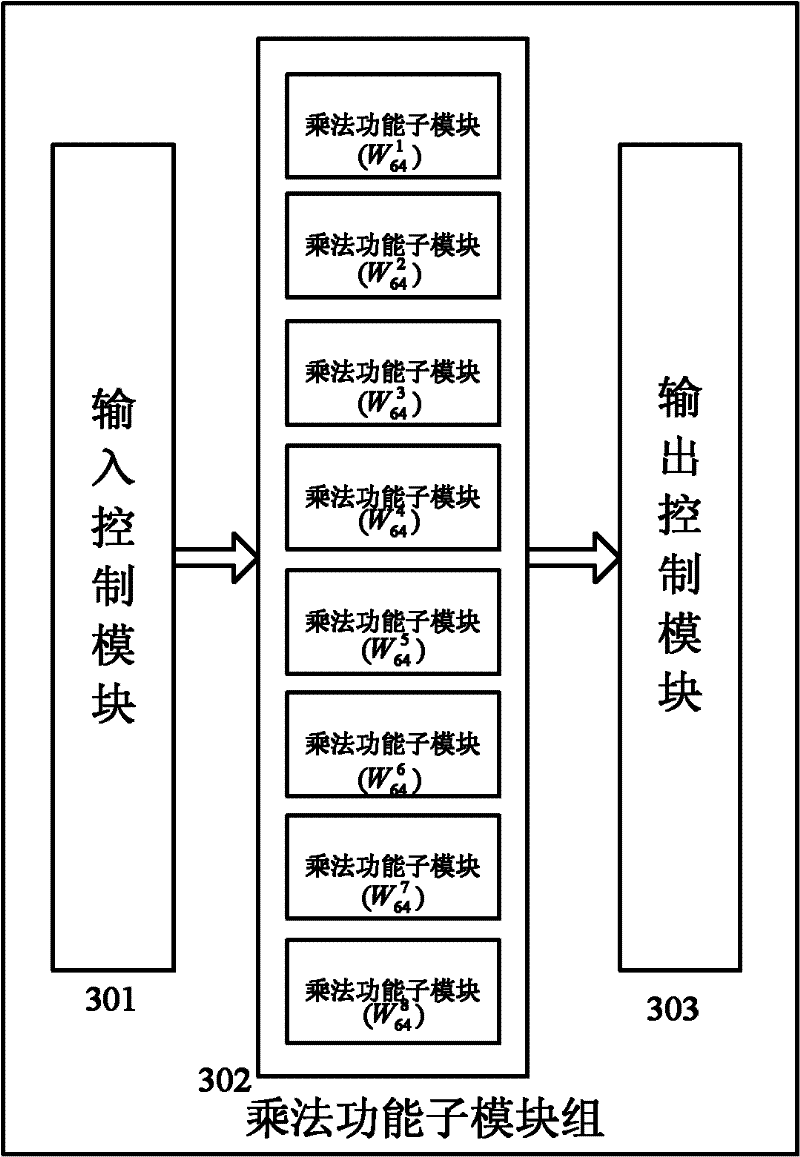
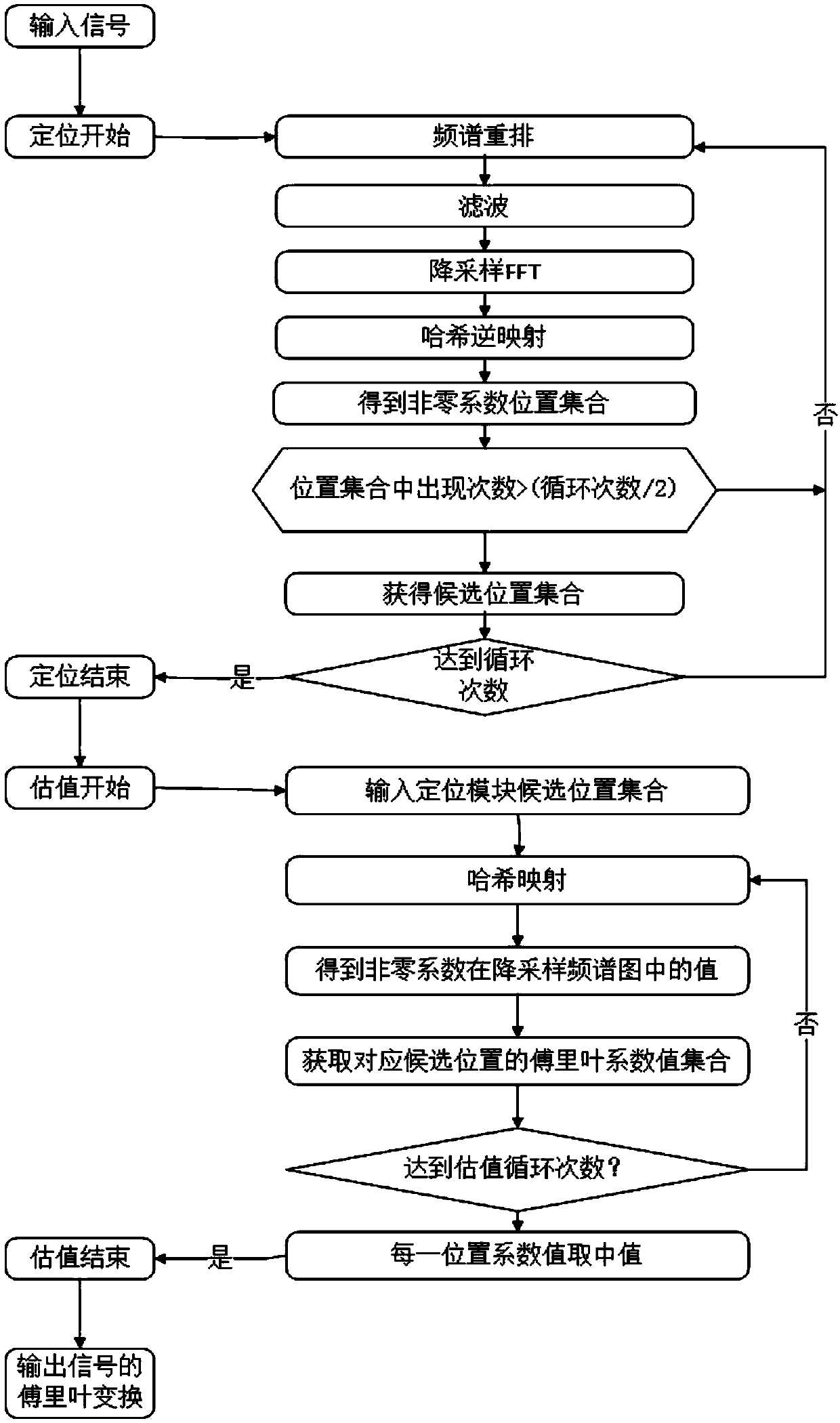
The invention discloses a Fourier transform algorithm capable of reducing time loss, comprising the following steps: S1, a positioning step of estimating the position of a non-zero Fourier coefficientor an important coefficient of a signal in the frequency domain through a plurality of cyclic iterations to obtain position data; S2, an estimation step of estimating a coefficient value corresponding to the position data through a plurality of cycles of iteration according to the obtained position data; S3, a conversion step of setting in the all-zero output sequence according to the obtained position data and the corresponding coefficient value, completing the Fourier transform of the signal, and outputting the result. The invention adopts a sparse fast Fourier transform method realized byusing a hash algorithm and an adaptive sparse fast Fourier transform method suitable for sparse unknown signals as basic components of a time-frequency analysis technology, the computational efficiency is significantly improved, the time loss is reduced, and the efficiency of signal time-frequency analysis is ensured.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
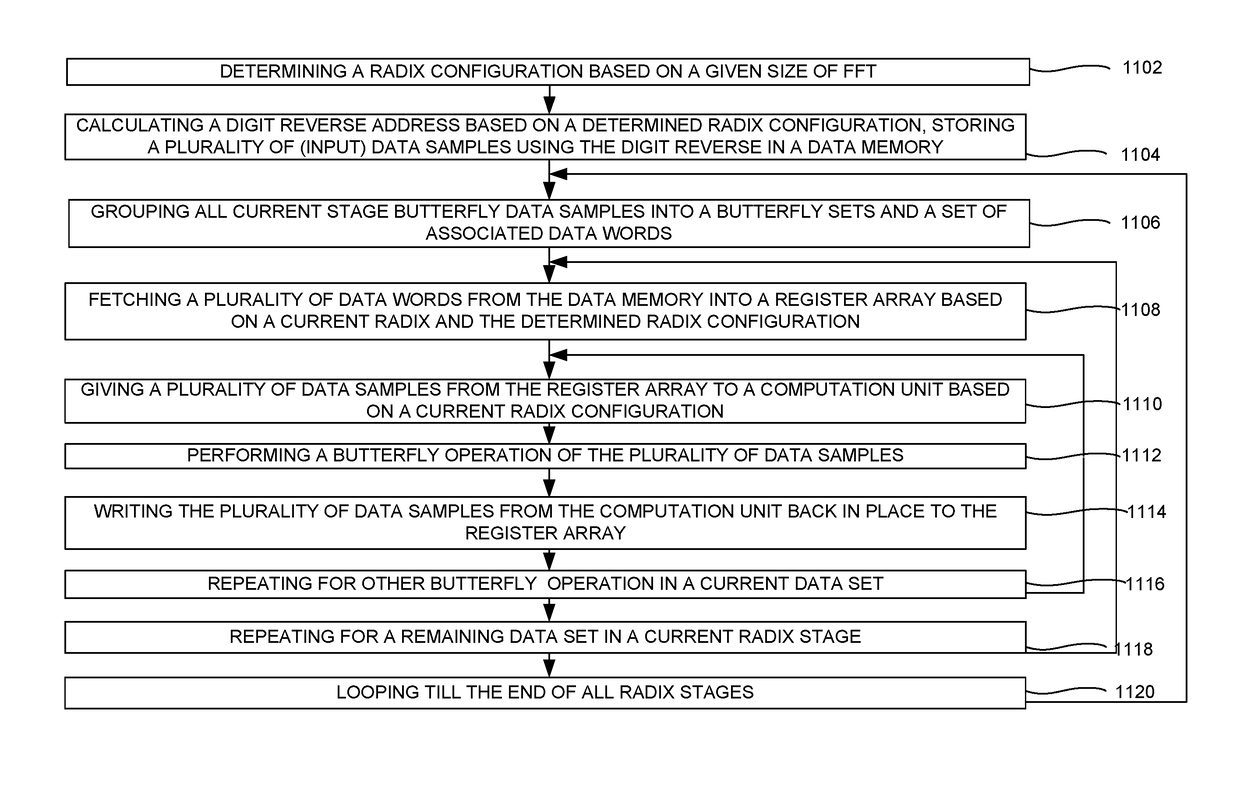
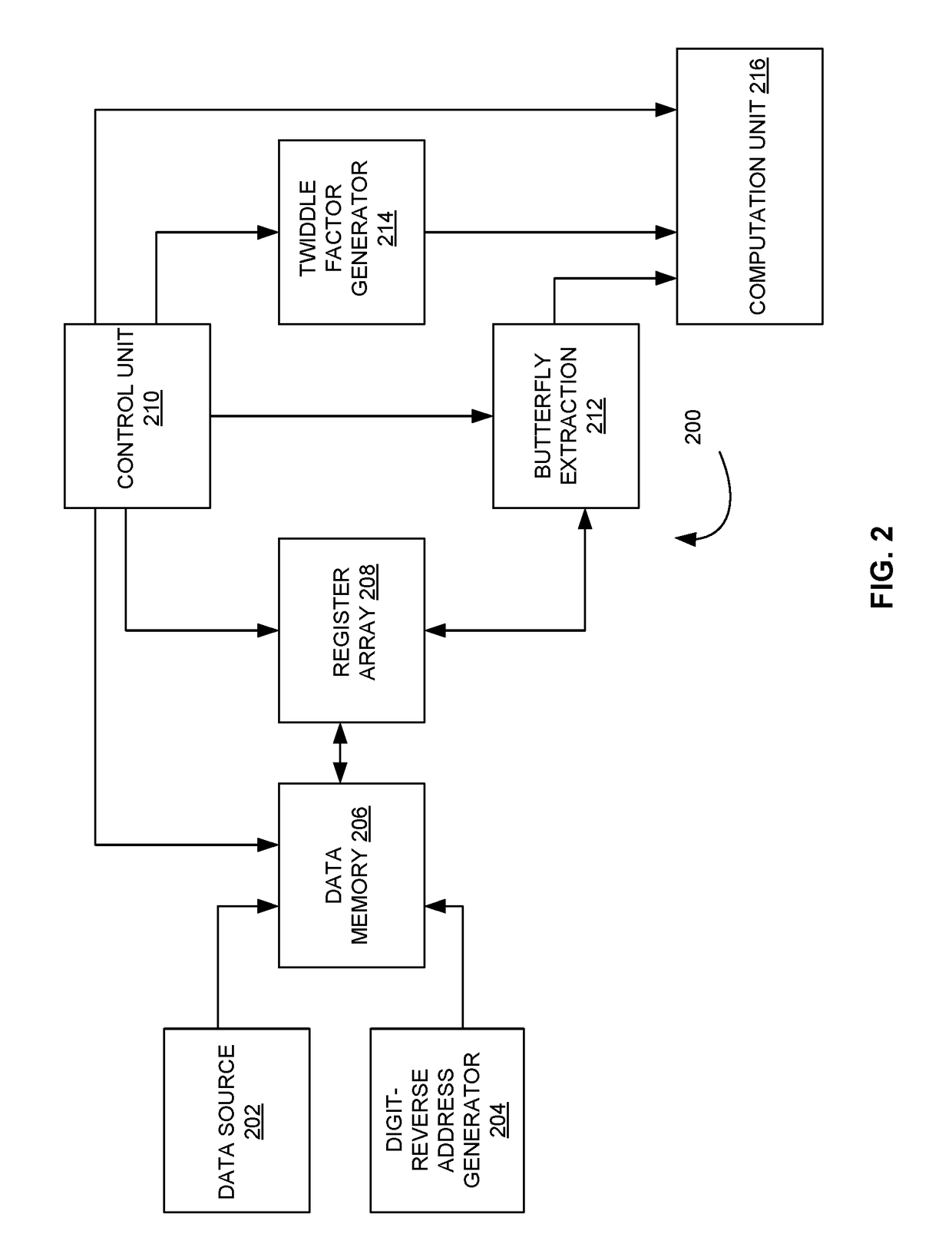
System and method for optimizing mixed radix fast fourier transform and inverse fast fourier transform
ActiveUS20170103042A1Maximize Bandwidth UtilizationComplex mathematical operationsProcessor registerAddress generator
A system for implementing a mixed radix fast fourier transformation is disclosed. The system includes a data source 202, a digit-reverse address generator 204, a data memory 206, a register array 208, a control unit 210, a butterfly extraction unit 212, a twiddle factor generator 214, and a computation unit 216. The data source 202 provides input data. The digit reverse address generator 204 processes the input data (i) to generate a digit reverse index and performs a digits reverse address calculation. The data memory 206 stores the input data. The register array 208 includes one or more registers that are configured to cache multiple data words. The control unit 210 includes of identifying butterfly operations and generate addresses for fetching / storing data. The butterfly extraction unit 212 extracts data samples. The twiddle factor generator 214 generates and outputs a twiddle factors based on the current radix and radix configuration. The computation unit 216 performs twiddle factor multiplications and the butterfly operations for current radix.
Owner:SIGNALCHIP INNOVATIONS
An astronomical image fusion method based on Fourier transform
ActiveCN109949256AGood imaging effectImprove data utilizationImage enhancementGeometric image transformationFast Fourier transformAstronomical image processing
The invention relates to an astronomical image fusion method based on Fourier transform, and belongs to the field of astronomical image processing. The method comprises the steps of reading a firmwarefile, performing background deduction processing on each frame of image, removing cosmic rays, performing mean filtering, finding out a maximum value of pixels in the image, performing cutting by taking a point where the maximum value is located as a coordinate center to obtain a cut picture, and completing registration of the picture to obtain a pre-processed file; Grouping the pre-processed files, and carrying out data processing to obtain a frequency domain reconstructed image of each group; And superposing the processing results of each group, calculating an average value, carrying out Fourier inverse transformation on the final result image, and carrying out enhancement processing on the reconstructed high-resolution image to obtain a final high-resolution image. The imaging effect of the method is superior to that of a classic airspace lucky imaging algorithm, and for processing picture data observed by a telescope without an adaptive optical system, the imaging effect is also very good, and the data utilization rate is higher.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method of measuring a physical function using a symmetric composite function
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Borehole Log Data Processing Methods
ActiveUS20140292764A1Reduce impactDynamic range of the image logImage enhancementElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingFast Fourier transformFourier transform on finite groups
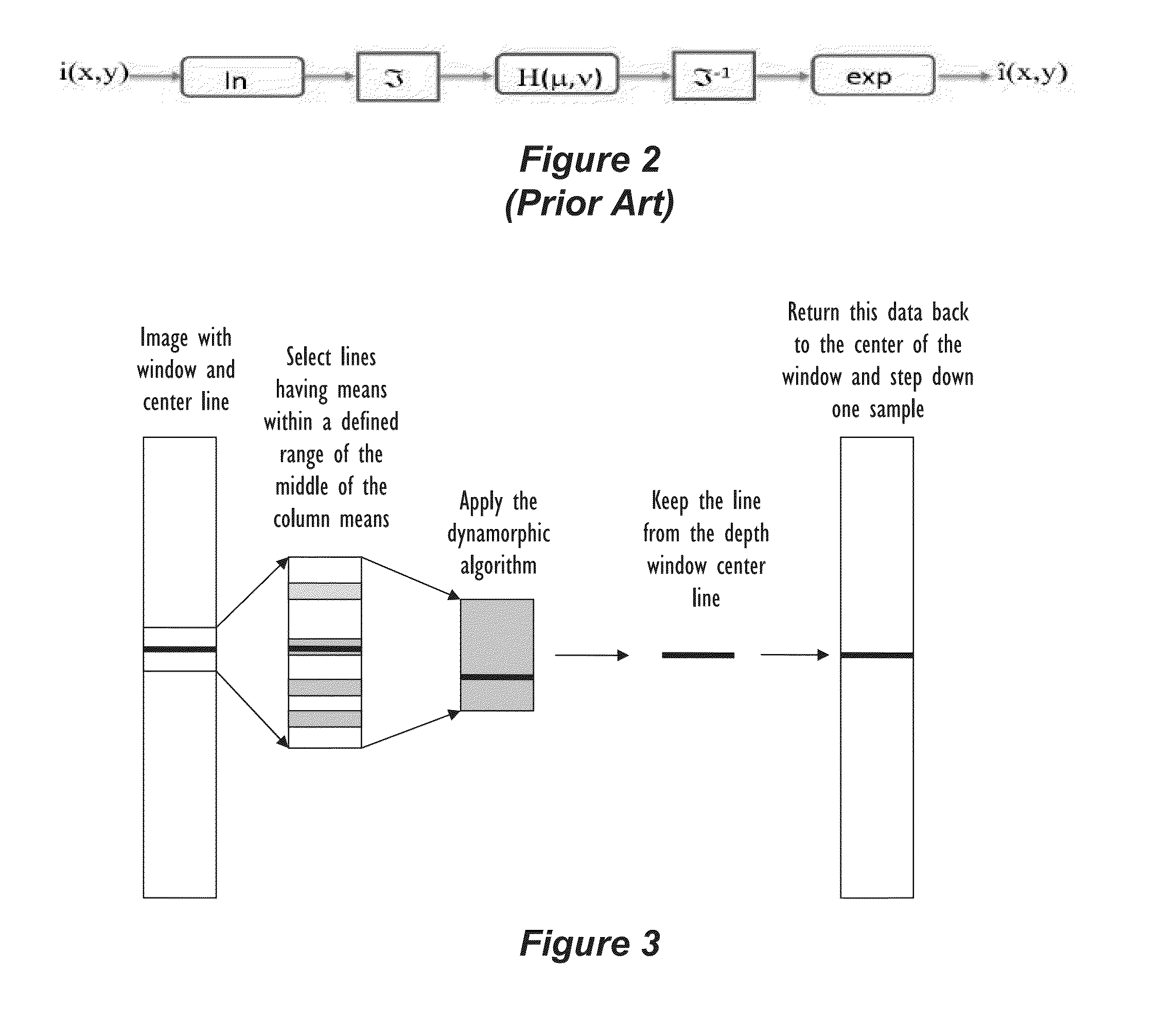
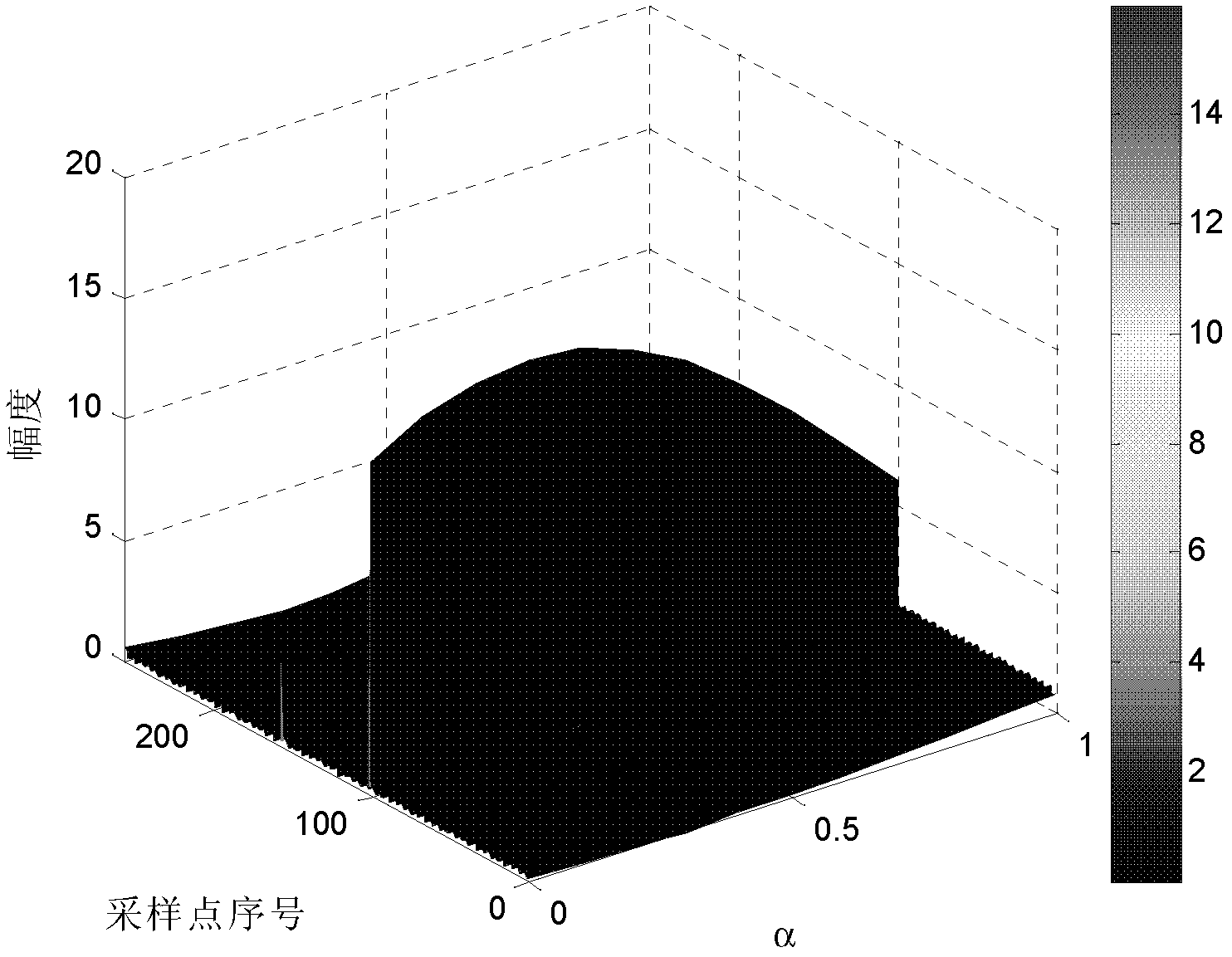
A method of processing borehole log data to create one or more image logs involve modeling the log data as components of an image in the form i(x, y)=l(x, y)×r(x, y) (1), in which i(x, y) is an image representative of the log data, l(x, y) denotes an illumination value of the image at two-dimensional spatial co-ordinates x, y, and r(x, y) denotes a surface reflectance value at the co-ordinates x, y. Equation (1) is transformed to a logarithmic domain, and a Fourier transform is obtained of the resulting logarithmic domain expression to obtain a Fourier domain expression. The Fourier domain expression is high-pass filtered, and an inverse Fourier transform is obtained of the resulting filtered Fourier domain expression. An exponential operation is performed on the result of inverse Fourier transform to obtain a filtered image model expression. Values of the filtered image model expression are mapped to respective color values across the range of the filtered image model expression values. The mapped color values can then be displayed, printed, saved and / or transmitted as one or more image logs.
Owner:REEVES WIRELINE TECH
Narrowband interference suppression method based on weighted score Fourier transform domain
InactiveCN102611672AFor the purpose of anti-interferenceEffectively compatibleMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksDigital signal processingFast Fourier transform
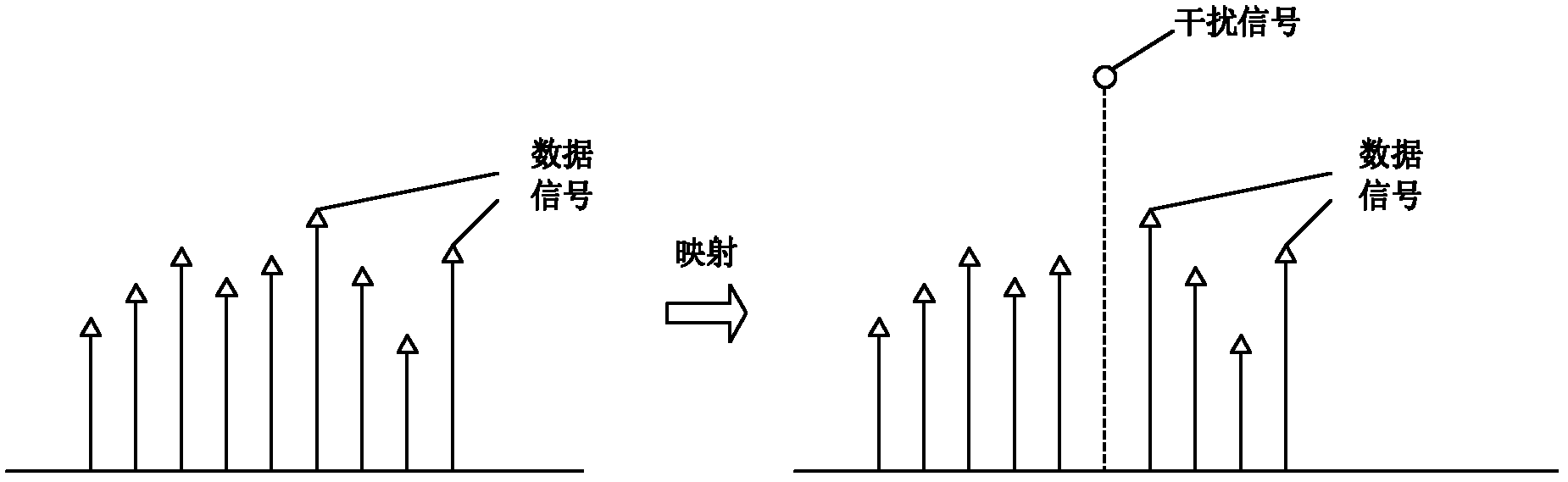
The invention relates to a narrowband interference suppression method based on a weighted score Fourier transform domain, which belongs to the technical field of digital signal processing. The invention aims at solving the problem that the conventional frequency-based multi-address way has a certain limitation on resistance to burst interference. The narrowband interference suppression method comprises the following steps of: performing serial / parallel conversion; performing alpha-order weighted score Fourier transform; performing data mapping: performing the data mapping on data after the transform to get L data after mapping; mapping data signals into positions with small interference or no interference and writing 0 into the positions without the data at data points with strong interference by adopting an avoidance way in the mapping process on the premise that a system can effectively detect the positions with the interference; performing minus alpha-order weighted score Fourier transform; performing parallel / serial conversion; and performing receiving-end multi-address access pretreatment by matching with the data sending process of a sending end. The data points with the interference can be well avoided by adopting the transform domain multi-address way based on weighted score Fourier transform and an anti-interference purpose can be realized.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
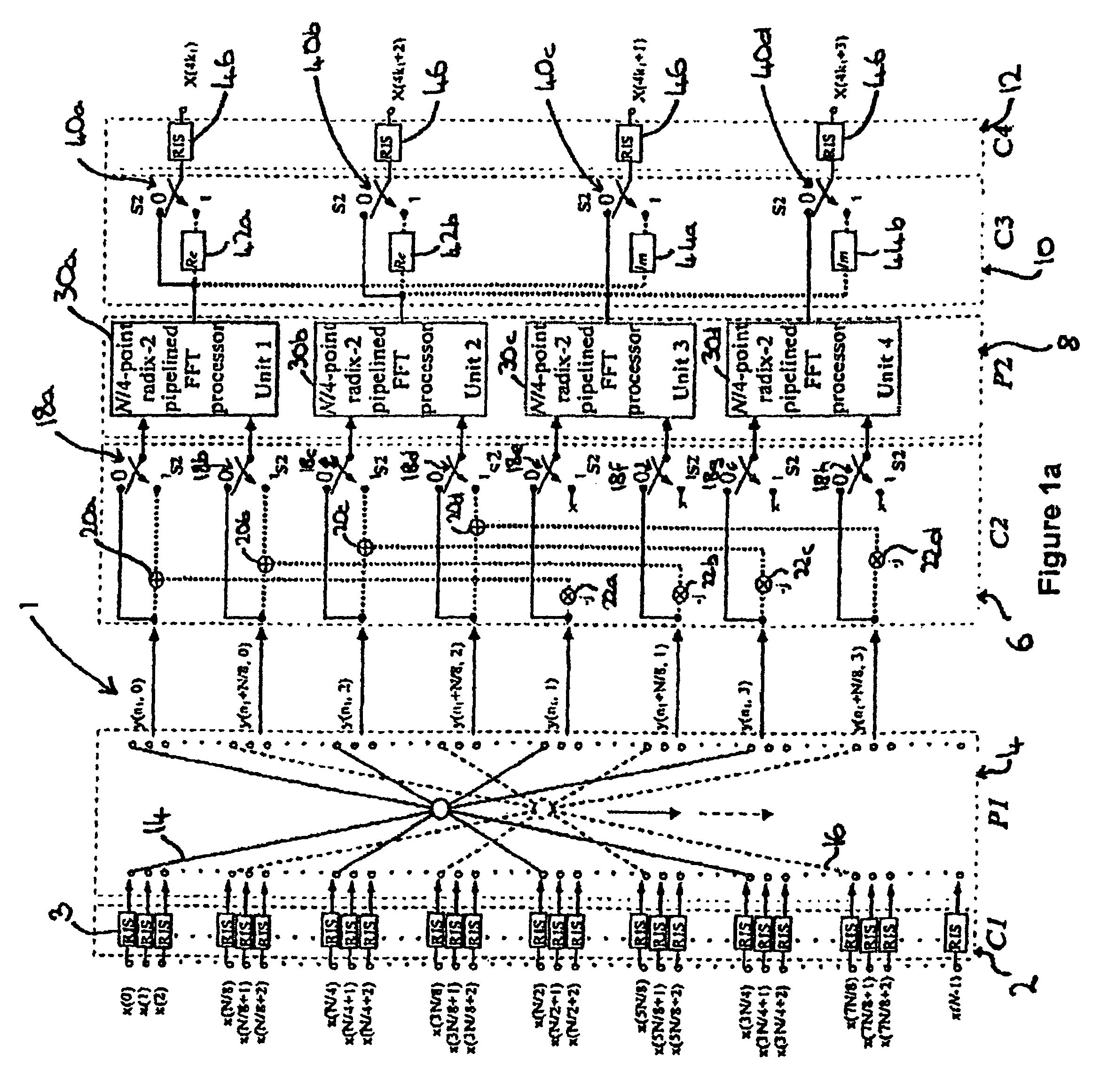
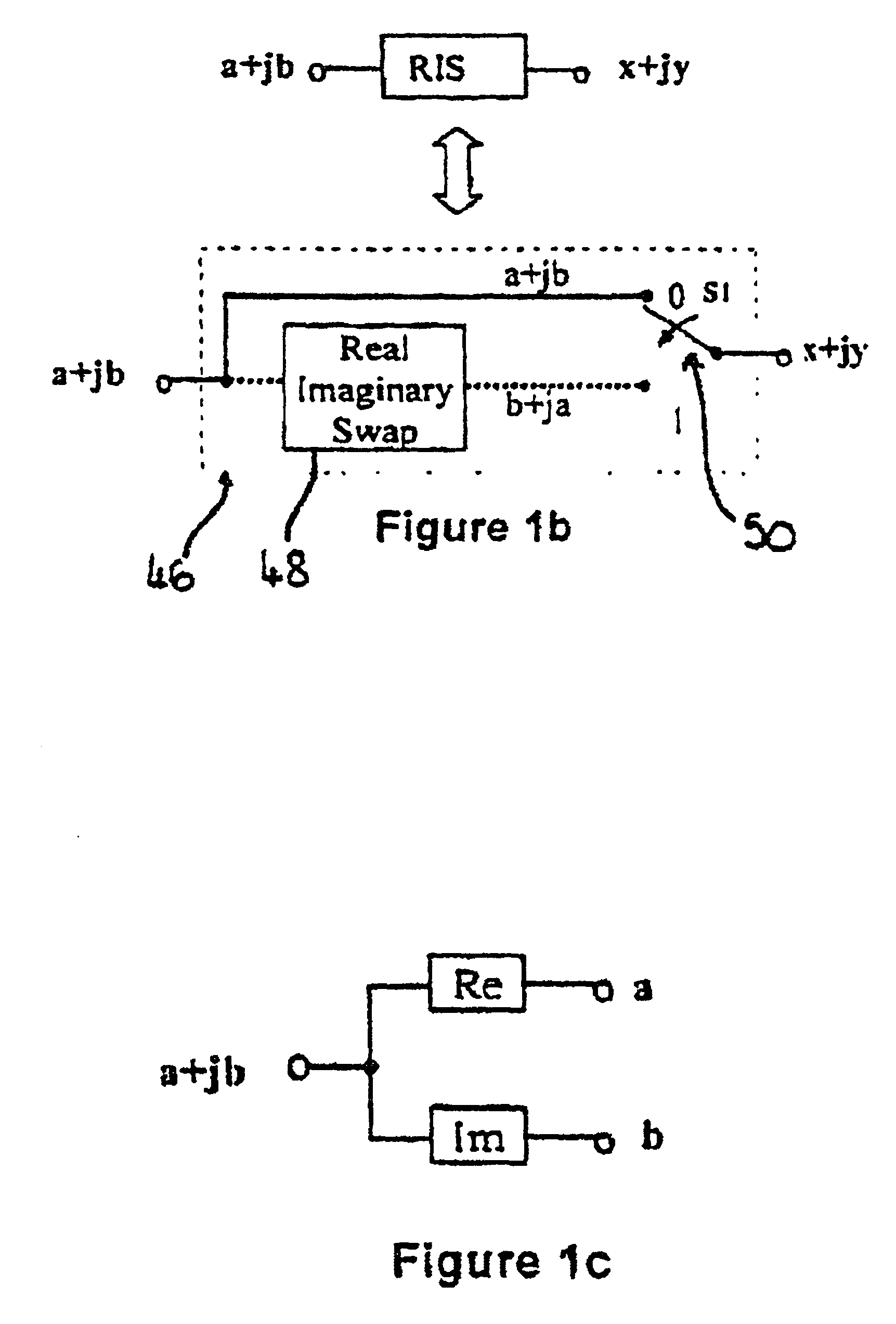
Processor and method for performing a fast fourier transform and/or an inverse fast fourier transform of a complex input signal
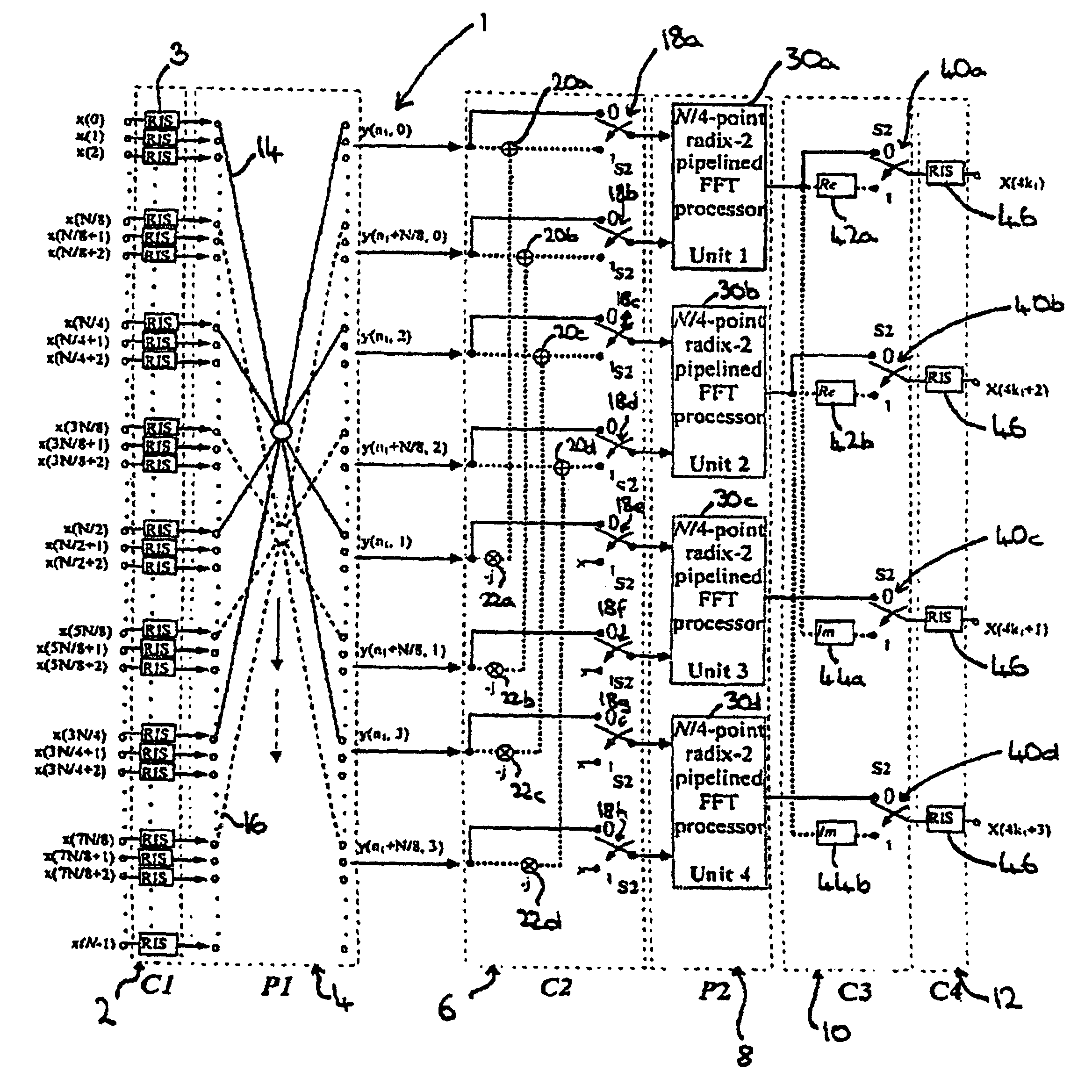
ActiveUS7818360B2Highly parallelHighly pipelinedModulated-carrier systemsDigital computer detailsFinite fourier transformInverse discrete fourier transform
A processor for performing a Fast Fourier Transform and / or an Inverse Fast Fourier Transform of a complex input signal comprises a first stage for passing the input signal to a second stage when a Fast Fourier Transform procedure is to be performed and for swapping the real and imaginary components of the complex input signal before passing the signal to the second stage if an Inverse Fast Fourier Transform procedure is to be performed. The second stage has first and second radix-4 butterfly elements. A third stage is arranged to switch between first and second operating modes, the second operating mode being for processing a complex conjugate symmetrical input signal. A fourth stage has a plurality of processing units, one or more of the processing units comprising a radix-2 pipelined Fast Fourier Transform processor. The first and second radix-4 butterfly elements are arranged to perform a butterfly operation on the complex input signal to generate and deliver one or more components of a processed signal to the fourth stage. The fourth stage is arranged to process the processed signal received from the first stage according to a Fast Fourier Transform processing procedure to produce an output signal. There is also disclosed a method for performing a Fast Fourier Transform and / or Inverse Fast Fourier Transform of a complex input signal.
Owner:WIPRO LTD
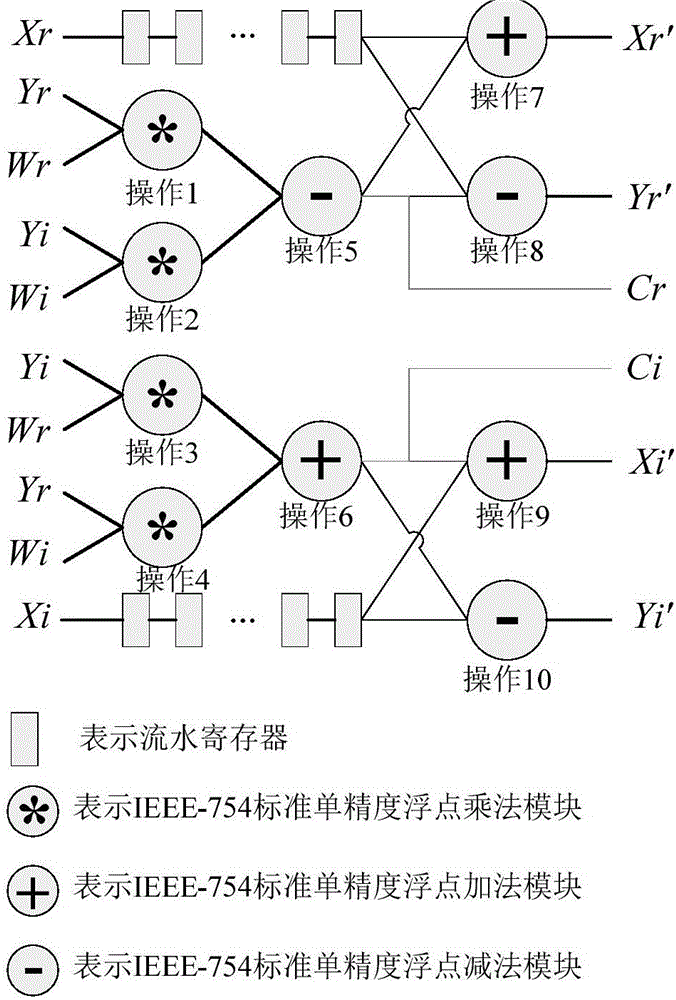
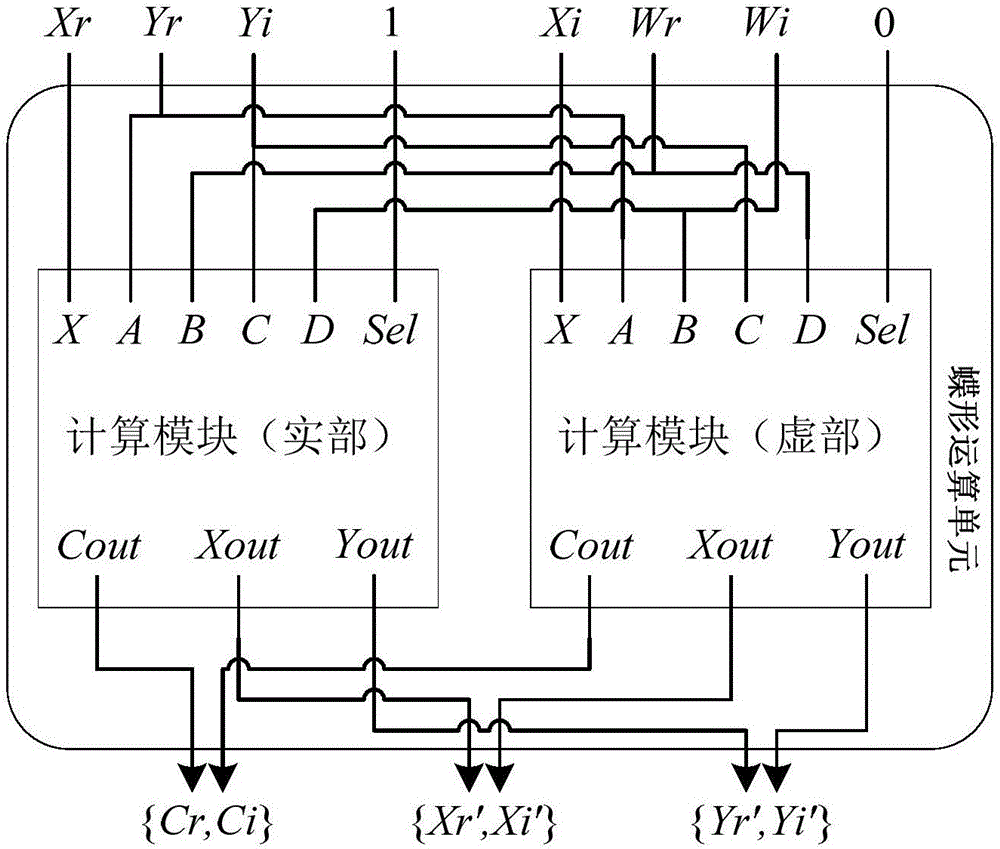
FFT (fast Fourier transform) butterfly operation hardware implementation circuit supporting complex multiplication
ActiveCN106168941AReduce overheadReduce normalizationComplex mathematical operationsFast Fourier transformHardware implementations
The invention discloses an FFT (fast Fourier transform) butterfly operation hardware implementation circuit supporting complex multiplication. The circuit comprises a real part calculation module and an imaginary part calculation module, wherein the real part calculation module is used for calculating a real part in complex multiplication and calculating real parts of X and Y in butterfly operation, and the imaginary part calculation module is used for calculating an imaginary part in complex multiplication and calculating imaginary parts of X and Y in butterfly operation. The circuit has the advantages of capabilities of reducing hardware cost, decreasing calculation delay and improving calculation accuracy and the like.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Upsampling technology-based fast Fourier transform/inverse fast Fourier transform (FFT/IFFT) approximate calculation method and device
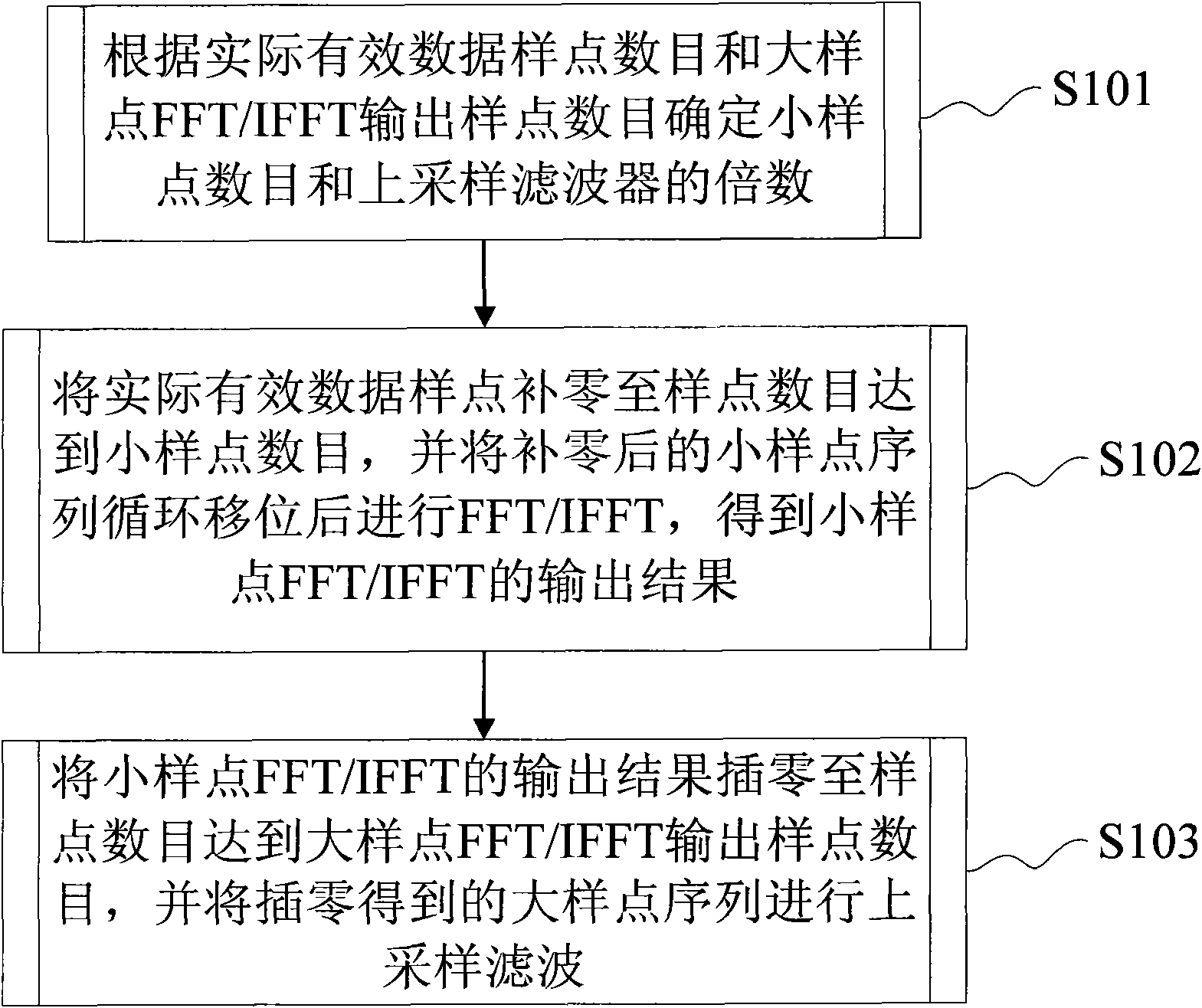
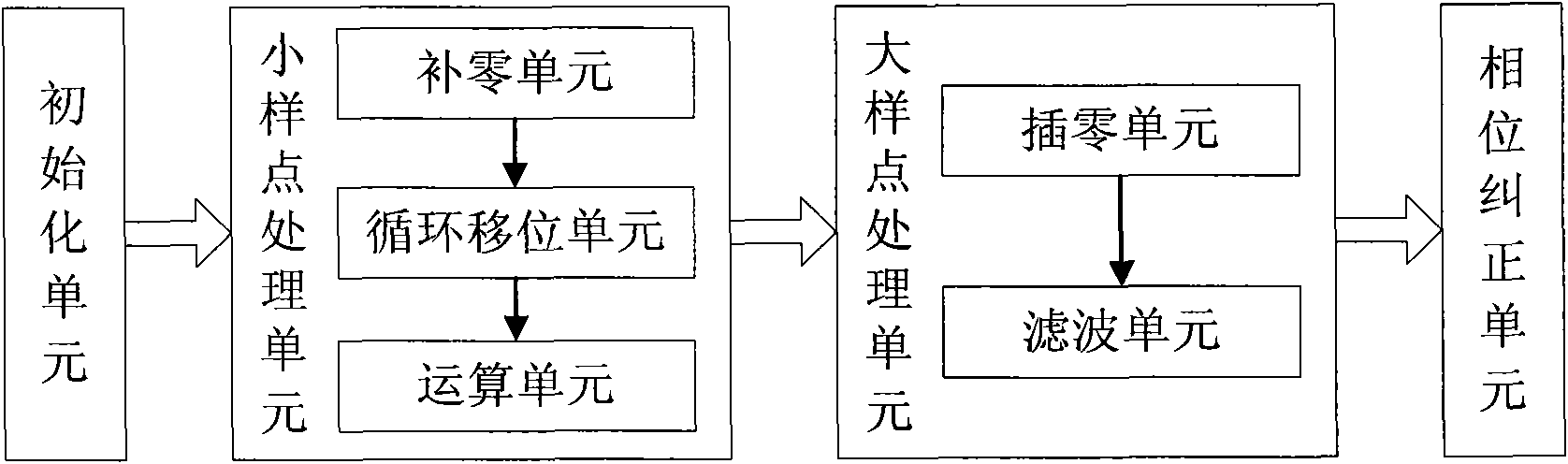
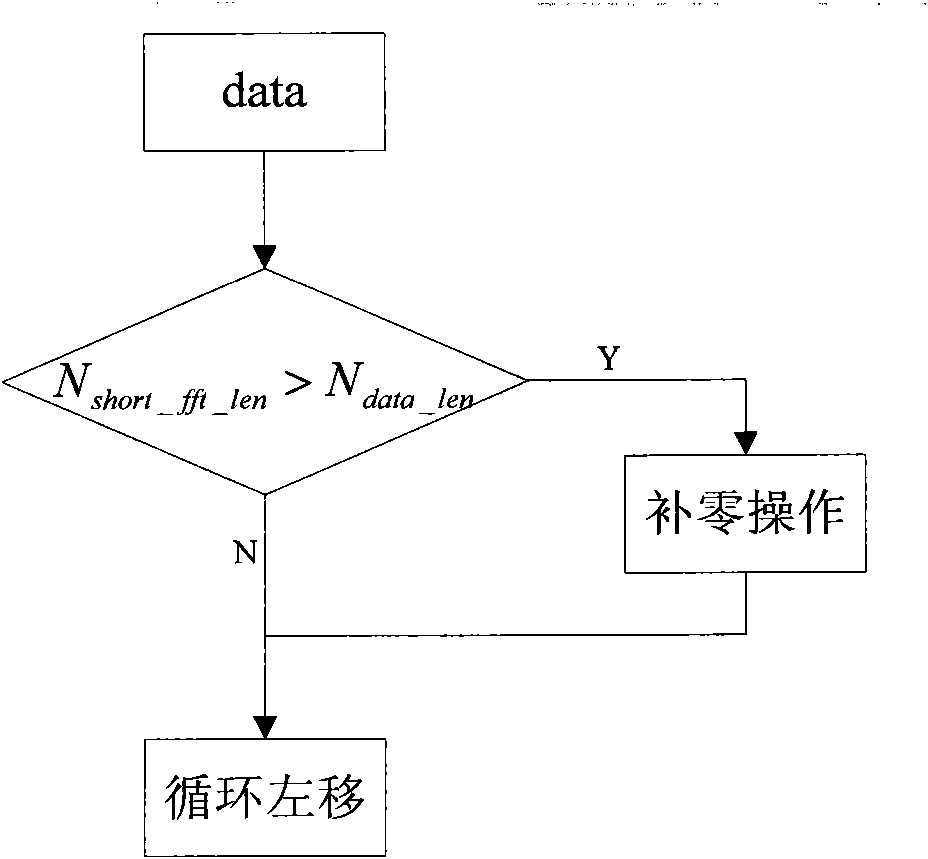
InactiveCN102339273ASolve the problem of large calculation and resource consumptionComplex mathematical operationsFast Fourier transformZero padding
The invention discloses an upsampling technology-based fast Fourier transform / inverse fast Fourier transform (FFT / IFFT) approximate calculation method and an upsampling technology-based FFT / IFFT approximate calculation device. The method comprises the following steps of: determining the number of small sampling points and the multiple of an upsampling filter according to the number of actual valid data sampling points and the number of large FFT / IFFT output sampling points; performing zero padding on the actual valid data sampling points until the number of the sampling points reaches the number of the small sampling points, and performing cyclic shift and FFT / IFFT on a small sampling point sequence obtained through zero padding to obtain an FFT / IFFT output result of the small sampling points; and performing zero insertion on the FFT / IFFT output result of the small sampling points until the number of the sampling points reaches the number of the large FFT / IFFT output sampling points, and performing upsampling filtering on a large sampling point sequence obtained through zero insertion. By the method and the device for realizing the FFT / IFFT of the large sampling points through the FFT / IFFT of the small sampling points and the upsampling filter, the problems of large calculated amount and high resource consumption when a system processes the FFT / IFFT process of the large sampling points are solved.
Owner:NANJING ZHONGXING SOFTWARE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com