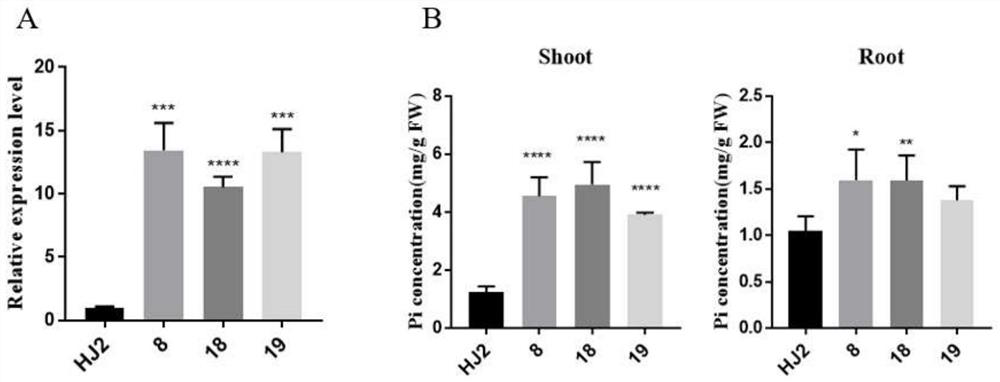
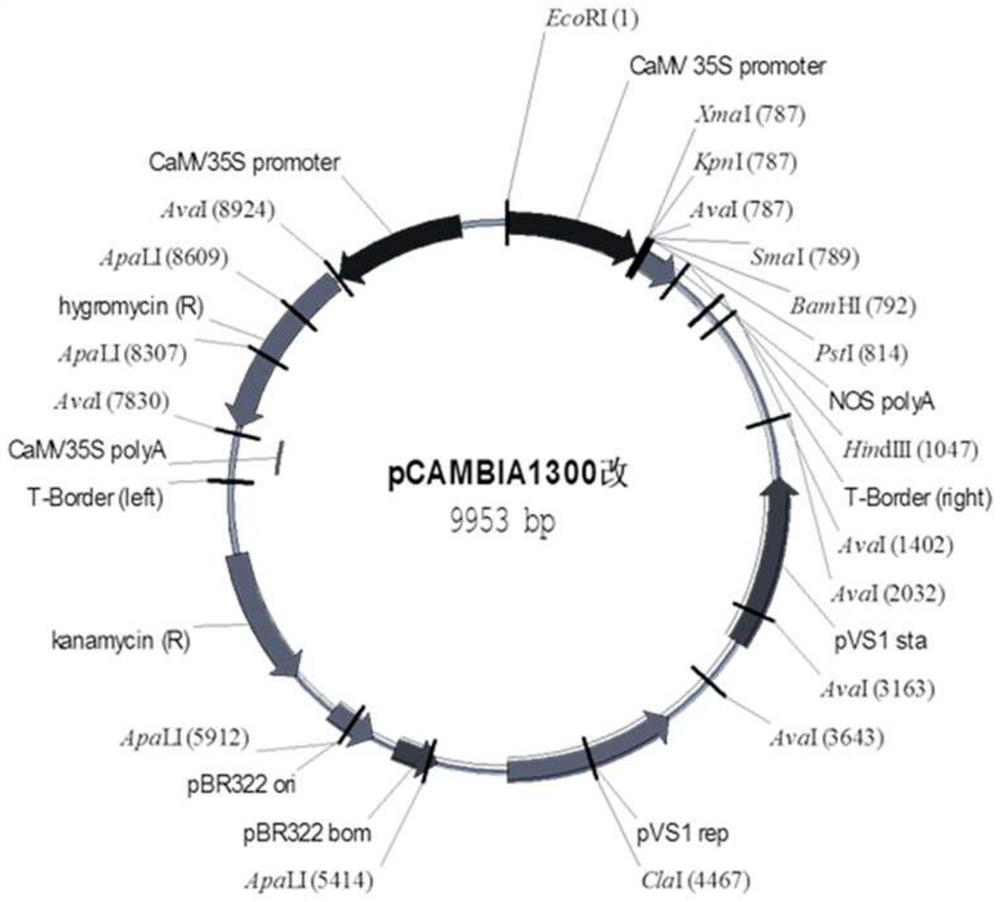
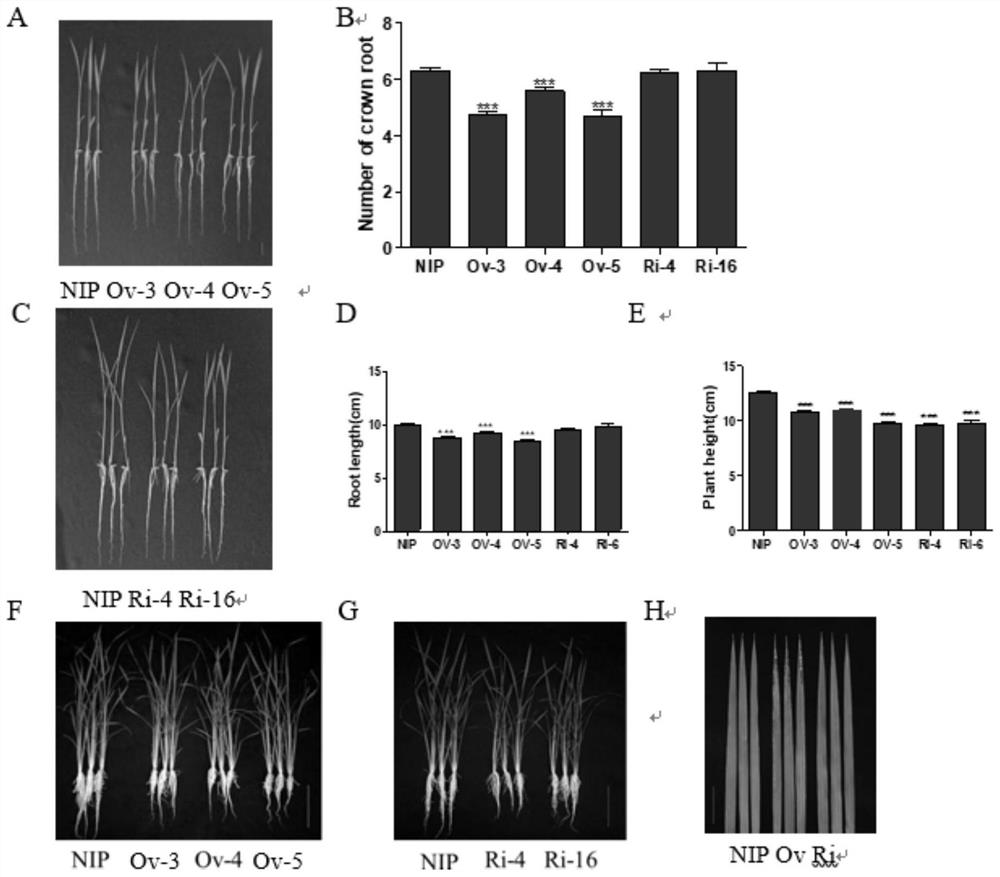
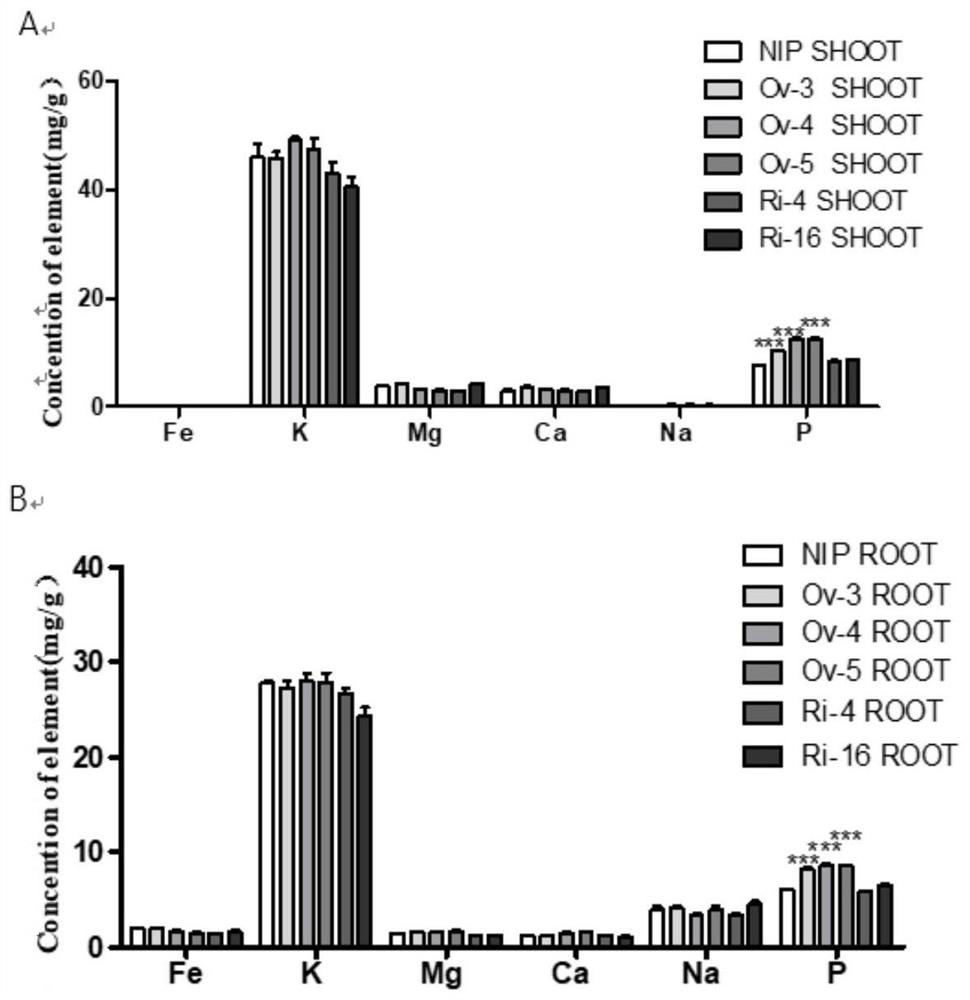
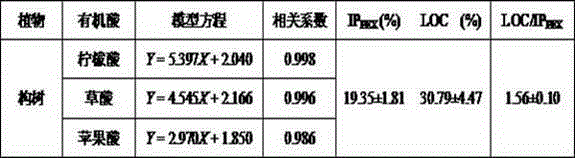
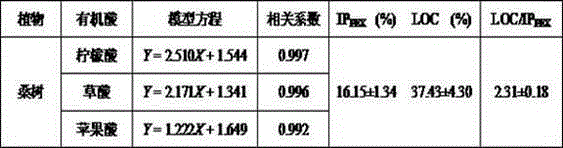
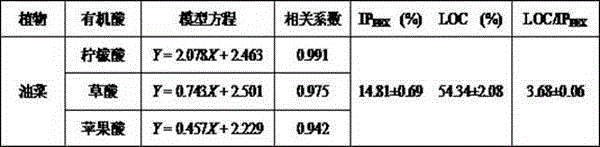
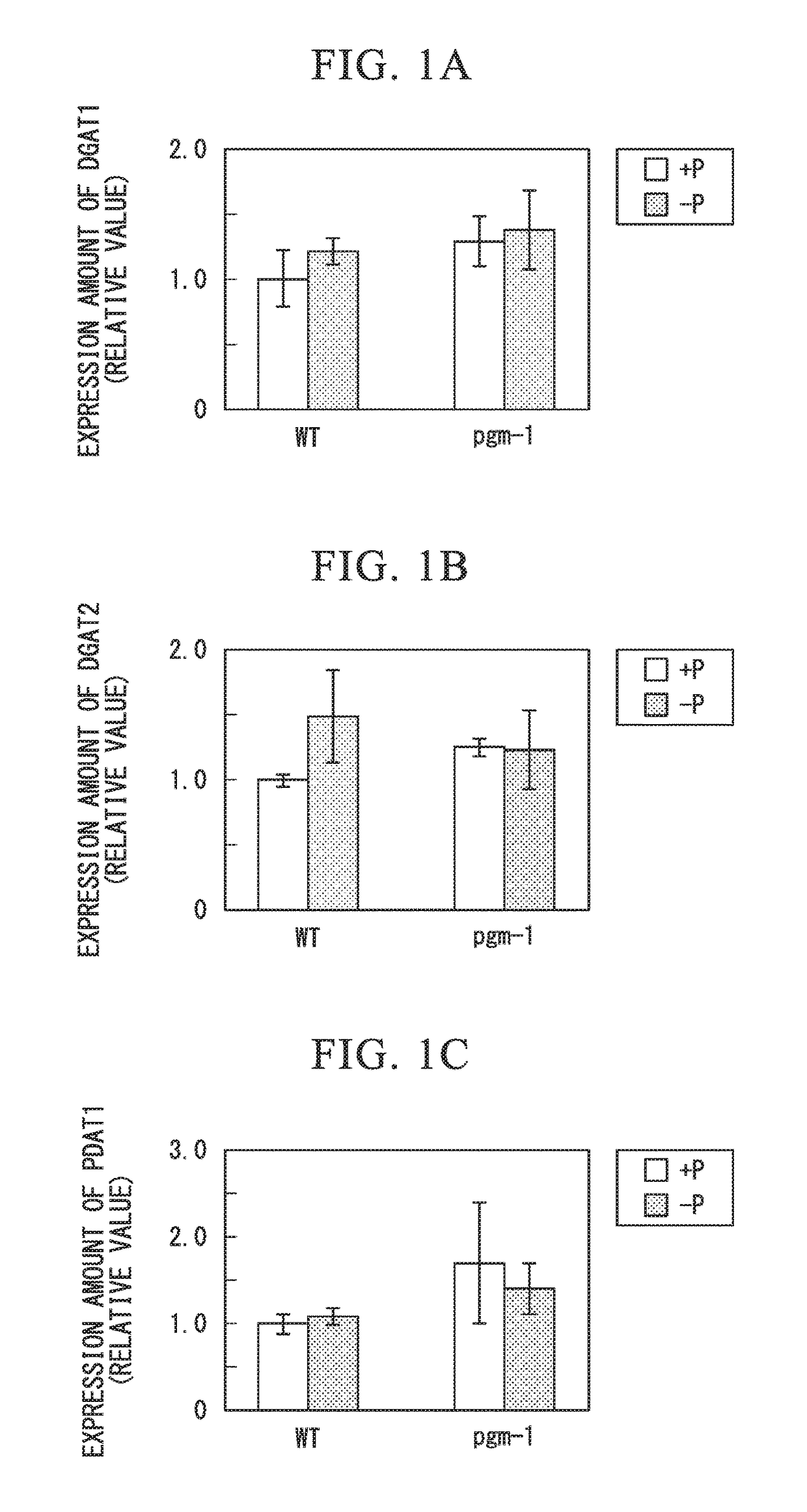
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
64 results about "Phosphorus deficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Phosphorus deficiency is a plant disorder associated with insufficient supply of phosphorus. Phosphorus refers here to salts of phosphates (PO₄³⁻), monohydrogen phosphate (HPO₄²⁻), and dihydrogen phosphate (H₂PO₄⁻). These anions readily interconvert, and the predominant species is determined by the pH of the solution or soil. Phosphates are required for the biosynthesis of genetic material as well as ATP, essential for life. Phosphorus deficiency can be controlled by applying sources of phosphorus such as bone meal, rock phosphate, manure, and phosphate-fertilizers.
Method for producing medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates by virtue of excess activated sludge
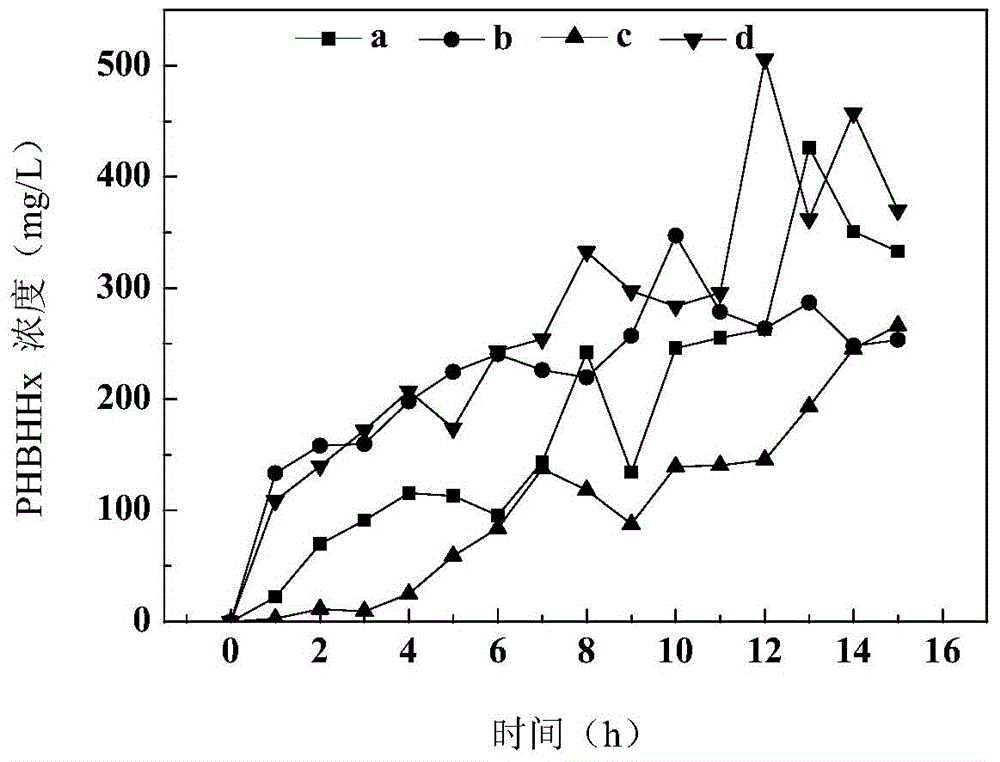
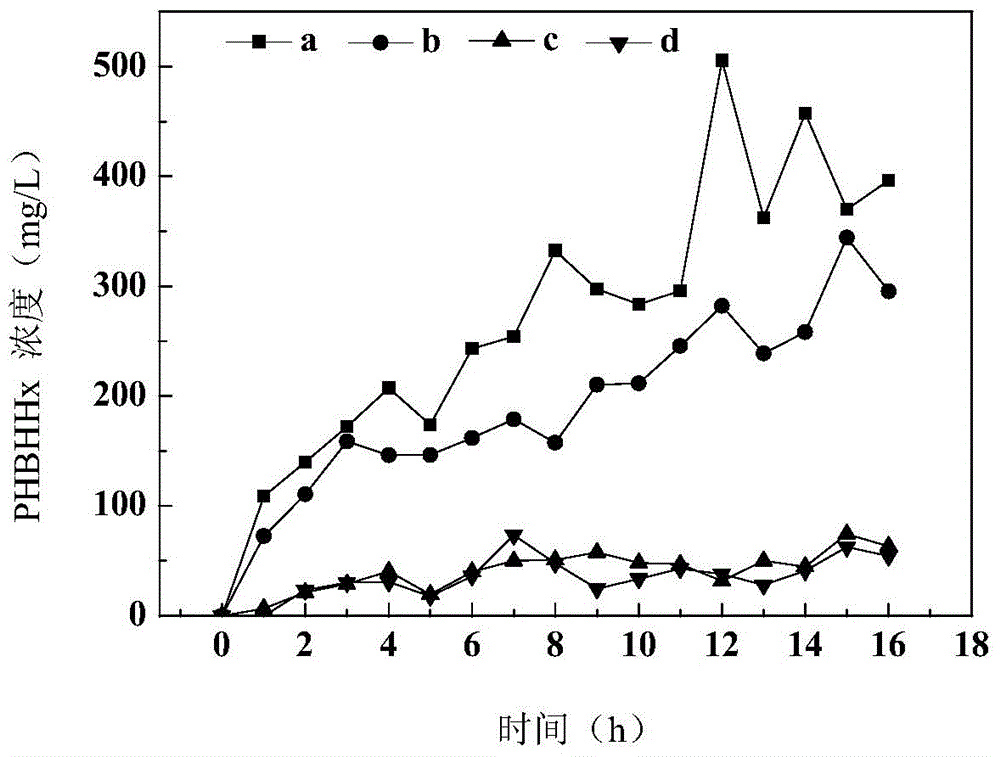
The invention discloses a method for producing medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates by virtue of excess activated sludge, and relates to polyhydroxyalkanoates. The method comprises the following steps: using sodium laurate as a unique substrate carbon source for domesticating original sludge, and synthesising poly-3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate by virtue of the stably-domesticated activated sludge, wherein 1.5g / L sodium laurate is uniformly poured for three times while being used as the unique substrate, and the highest concentration of cumulative PHBHHx of the sludge is 505.5mg / L under a continuous aeration condition and in case of nitrogen deficiency and phosphorus deficiency; the PHBHHx are synthesised by virtue of activated sludge mixed micro-organisms for the first time, and an infrared absorption spectrum and thermogravimetric analysis proves that PHBHHx samples have chemical structures and physical properties similar to those of PHBHHx standard substances synthesised from pure strains. The method is simple in equipment, easy to operate, free from a sterile working condition and rich in excess sludge source, and therefore has a great application prospect in the aspect of producing plastic products needed in the industry and the agriculture.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Rhizobium having high-efficiency phosphate dissolving-capability and application thereof
ActiveCN107881130AIncrease productionStrong nitrogen fixation abilityPlant growth regulatorsBiocidePhosphatePhosphor
The invention discloses rhizobium having high-efficiency phosphate-dissolving capability and an application thereof. The invention firstly discloses the rhizobium having high-efficiency phosphate-dissolving capability, and a microbe preservation number is CGMCC No.14614. The separated rhizobium bacterial strain has strong phosphate-dissolving capability, and has strong nitrogen-fixation capability, and has good nitrogenase activity under drought stress. Under phosphorus deficiency condition, the rhizobium has obvious growth-promoting capability on plant, and can obviously increase the output of medicago sativa. The invention also discloses an application of the rhizobium for increasing the leguminous plants output, increasing the phosphor absorption by the leguminous plants, and increasingthe nitrogen fixation efficiency of the leguminous plants. The invention also discloses an application of the rhizobium in preparation of a phosphate-dissolving bacterial manure or a nitrogen-fixation bacterial manure. The separated rhizobium having high-efficiency phosphate-dissolving capability has an important application prospect for increasing the output of the leguminous plant medicago sativa.
Owner:PRATACULTURE INST HEILONGJIANG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Inorganic phosphorus solubilizing plant growth promoting rhizobacteria strain NG-33 and application thereof
ActiveCN105670961AResistant to high salt concentrationsEffective dissolutionBiocidePlant growth regulatorsAcetic acidGrowth plant
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and particularly relates to inorganic phosphorus solubilizing plant growth promoting rhizobacteria strain NG-33 and application thereof.The inorganic phosphorus solubilizing plant growth promoting rhizobacteria strain NG-33 is taxonomically named as Enterobacter cloacae NG-33 and preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection, and a preservation number of the plant growth promoting rhizobacteria strain NG-33 is CCTCC M 2016056.The plant growth promoting rhizobacteria strain NG-33 is obtained for the first time by screening and separating from soil of the Longgang National Natural Reserve in the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region and is capable of realizing high-yield gluconic acid and acetic acid, dissolving hardly-soluble inorganic phosphorus to increase soluble phosphorus content in soil, relieving phosphorus deficiency of plants and improving soil conditions, and accordingly plant growth is promoted.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Soybean specific response low-phosphorous transcription factor GmPHRLP and application
InactiveCN108728451APromote absorptionIncrease biomassPlant peptidesFermentationBinding sitePhosphate Transporters
The invention provides a soybean specific response low-phosphorous transcription factor GmPHRLP and an application. A soybean variety 'BX10' serves as a material, a transcription factor is discoveredby RNA-seq, the expression level of the transcription factor is remarkably improved under the condition of phosphorus deficiency, a specific primer of a gene is designed by a sequencing joint sequence, cloned and subjected to homologous analysis, a result discovers that the transcription factor belongs to an MYB-CC family, the transcription factor and a phosphorous signal center regulating factorof model plant Arabidopsis and rice have high protein homology, P1BS (PHR1 Binding Sites) can be combined, expression of the transcription level of the transcription factor is affected by low-phosphorus specific induction, expression of a phosphate transporter protein can be induced, and absorption and transport of phosphorus are increased under low phosphorus. The gene is over-expressed in soybean hair roots, so that phosphorus absorption of soybeans can be improved, and biomass of the soybeans is remarkably improved under low-phosphorus culture conditions.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Phosphorus deficiency response regulatory protein and coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN101928336AIncrease phosphorus uptake capacityReduce fertilizationFungiBacteriaWAS PROTEINNutrition
The invention discloses a phosphorus deficiency response regulatory protein and a coding gene and application thereof. The protein provided by the invention is protein (a) or protein (b), wherein the protein (a) has amino acid sequences shown as a sequence 1 in a sequence table; and the protein (b) has an amino acid sequence which is derived from the sequence 1 by substituting and / or losing and / or adding one or more amino acid residues and is related with the phosphorus absorption of plants. By transforming the coding gene of the protein into the plants, the phosphorus absorbed by the transgenic plants is increased, so the phosphorus content of the transgenic plants is greatly increased, the phosphorus nutrition condition is improved, and both the plant height and the root length of the plants are obviously increased. Under the condition of same soil fertility, particularly low phosphorous, the transgenic plants can require less fertilizer application, so soil environmental pollution is reduced and resources are saved. The regulatory protein plays an important role in improving breeds of plants, particularly food crops and commercial crops such as wheat, rice, cotton and the like, and has a broad prospect.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Promoter for expressing phosphor deficiency speciality induction in root and use thereof
The invention discloses a phosphorus deficiency specific inducement root-expression promoter and applications thereof. The promoter can be a DNA molecule as the following 1), 2) or 3): (1) the ribonucleotide sequence thereof is a DNA molecule in the 1st-serial in a sequence list; (2) a DNA molecule which can be hybridized with the DNA molecule of the 1st-serial in the sequence list under a strict condition and can drive targeted genes to be expressed specially in root in case of phosphorus deficiency; (3) a DNA molecule which has the homeology with the DNA by more than 90 percent and can drive targeted genes to be expressed specially in root in case of phosphorus deficiency. The promoter of the invention can be applied to the construction of carriers with economic value and the constructed carriers can be used for breeding transgenic plants with economic value.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
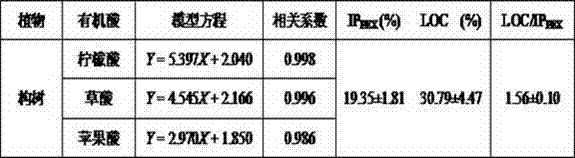
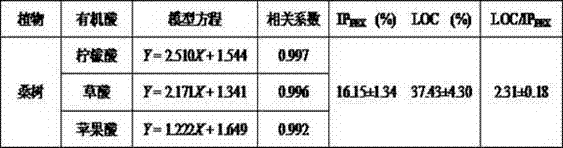
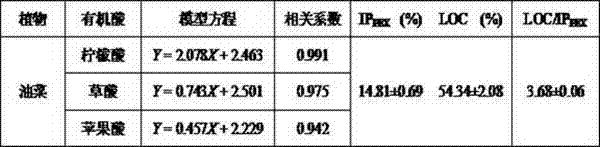
Method of using organic acid secretion characteristics to detect phosphorus deficiency stress resistance ability of plants
The invention discloses a method of using organic acid secretion characteristics to detect phosphorus deficiency stress resistance ability of plants. Detected organic acid standard solution is added into air drying rhizosphere soil samples to establish a relationship model between the concentration of the organic acid standard solution and the effective phosphorus content; a phosphorus extraction ability of the organic acid secreted by a root system on the rhizosphere soil is calculated according to the relational model; an increasing proportion between a phosphorus extraction ability of organic acid secreted by a plant root system cultured in the nutrient solution prepared in a phosphorus deficiency formula on the rhizosphere soil and the phosphorus extraction ability of organic acid secreted by a plant root system cultured in the nutrient solution prepared in a normal formula on the rhizosphere soil is calculated. Then extraction cost of the organic acids secreted by the root system on the phosphorus is calculated, and the size of the phosphorus deficiency stress resistance ability of different plants is judged. The method can quantitatively detect the phosphorus deficiency stress resistance ability of the plants, and detected results of the different plants are comparable; the method is not influenced by any time and space geographical factors, and can dynamically monitor physiological change characteristics in plants for a long term.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
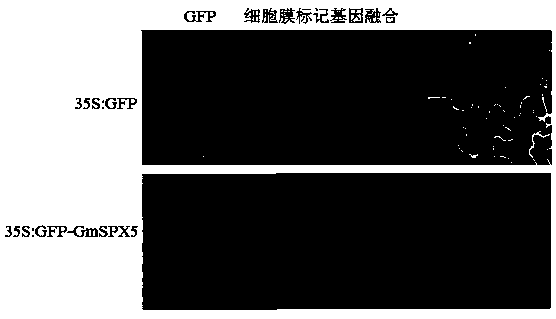
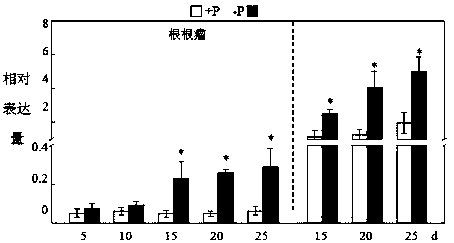
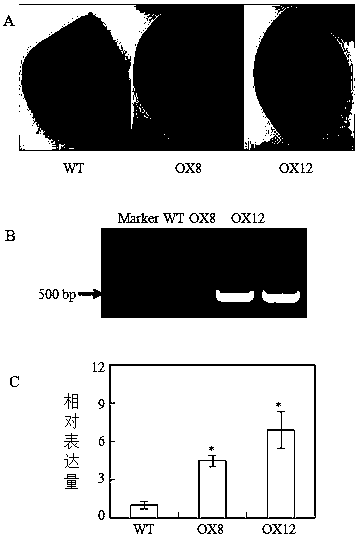
Gene GmSPX5 for regulating and controlling growth of leguminosae root nodules, and application of gene GmSPX5
ActiveCN108624596AGenetic improvementIncrease the number of nodulesPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyPlant nodule
The invention discloses a gene GmSPX5 for regulating and controlling growth of leguminosae root nodules, and the application of gene GmSPX5. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and the coding amino acid sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The research shows that excessive expression of the GmSPX5 can increase the number of the leguminosae root nodules and the density ofroot nodules infecting cells under high phosphorus treatment; furthermore, the nitrogen phosphorus content and the yield of soybeans can be remarkably increased. Therefore, the GmSPX5 can regulae andcontrol the growth and development of the root nodules and has important effects of improving the nitrogen phosphorus nitration of plants and increasing the yield; and the gene GmSPX5 can be used forregulating and controlling the adaptability on phosphorus deficiency and nitrogen deficiency in soil by the plants through a transgenic technology, also can be applied to leguminous crop nitrogen phosphorus synergistic and efficient genetic improvement and has a very important market prospect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Iron-essential for flora and fauna
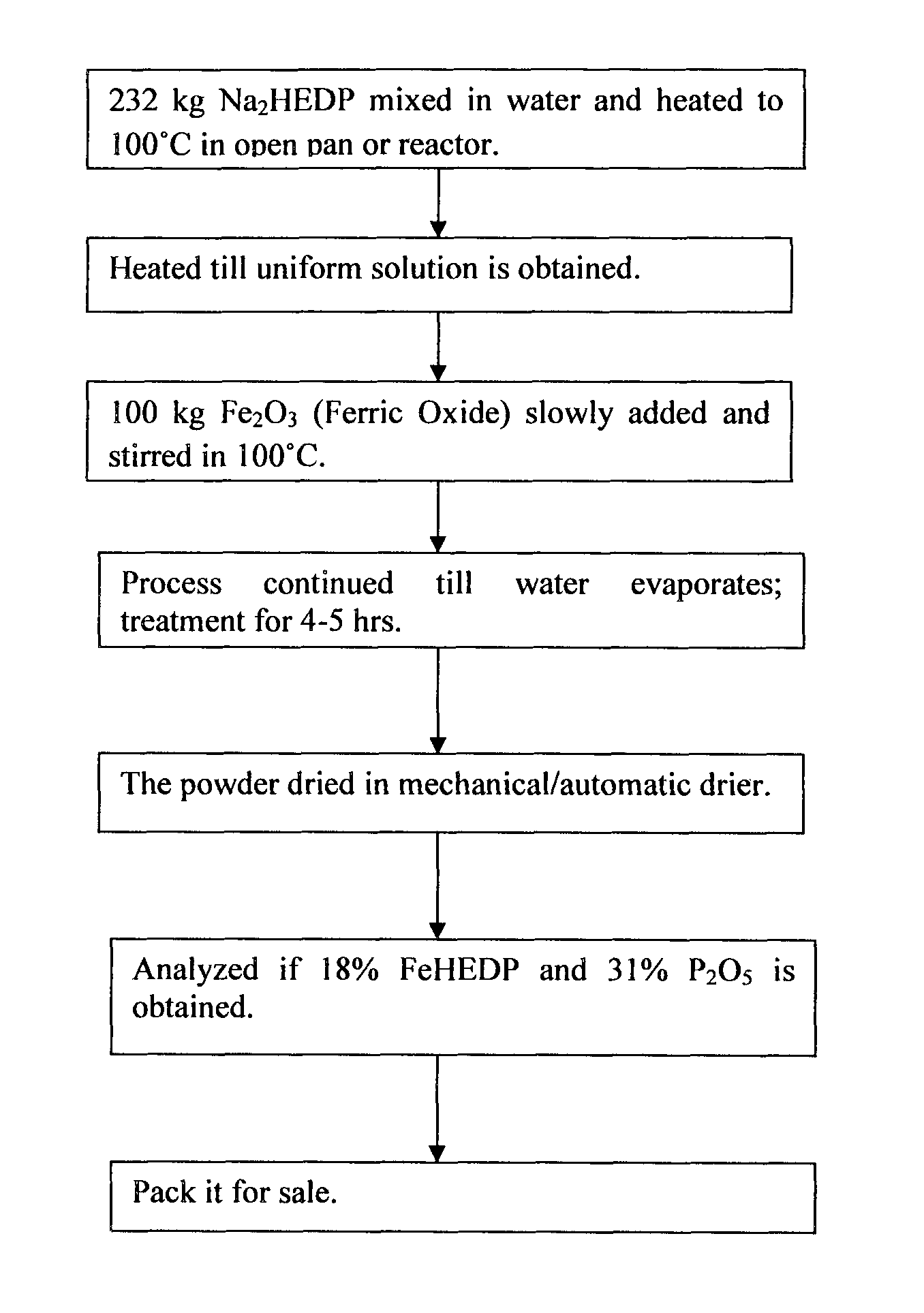
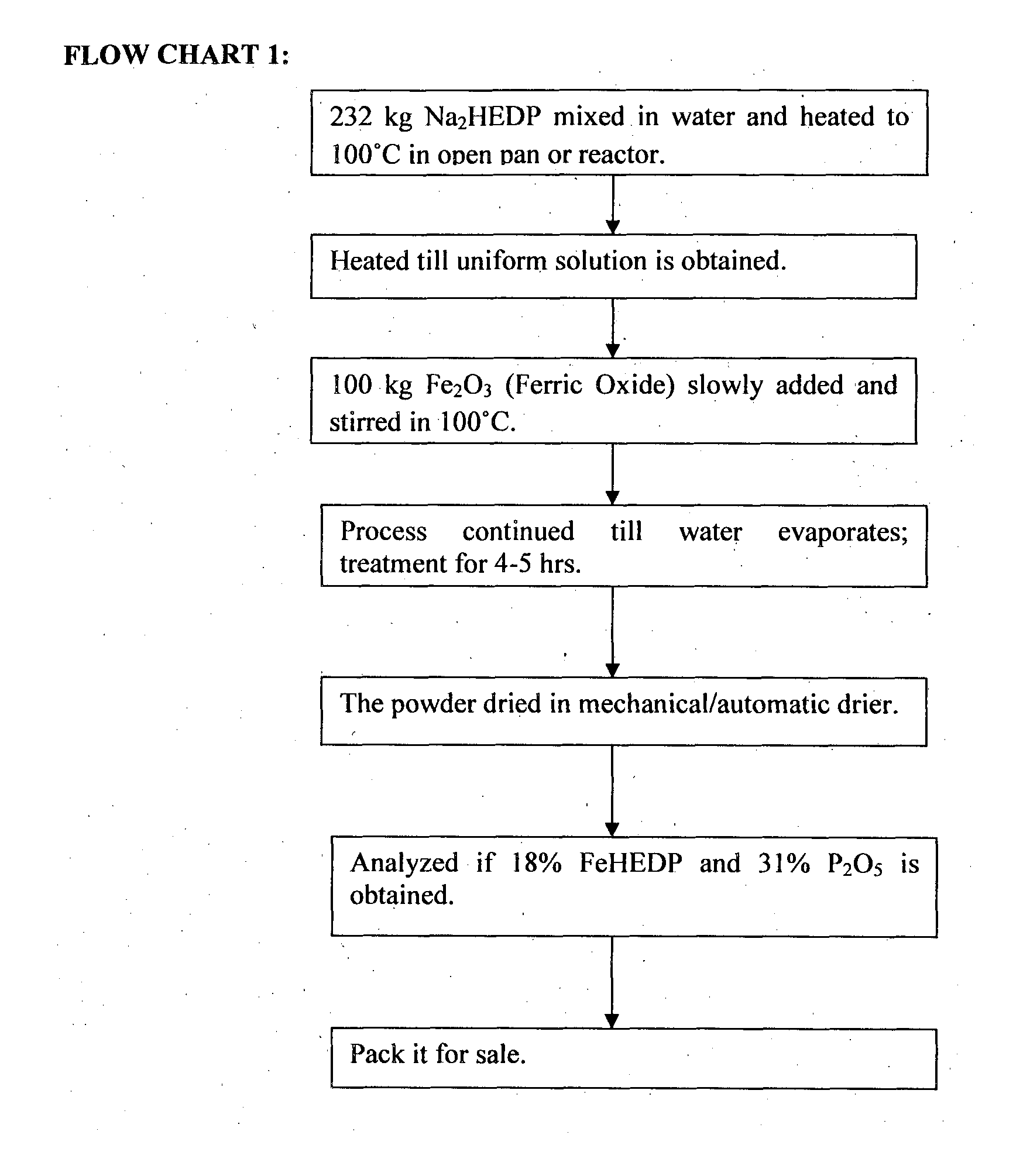
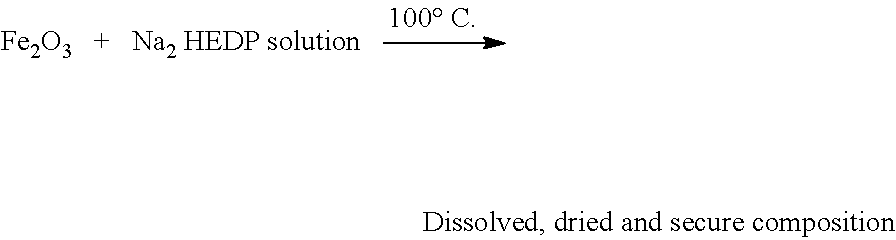
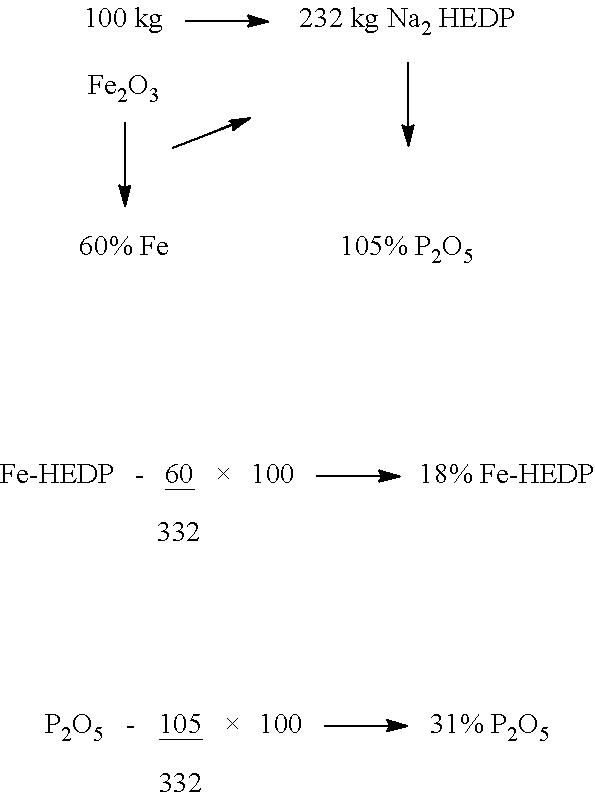
The present invention relates to a chelated fertilizer composition for enriching Iron and Phosphorus content in agriculture / horticulture crops and plants through foliar application. The fertilizer composition is prepared using compounds comprising chelating agents and Ferric Oxide (Fe2O3). The chelation of Fe by disodium salt of Hydroxy Ethylidene Di Phosphonic Acid (Na2 HEDP) developed 17% to 18% Fe-HEDP and 31% Phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5). The final chelated fertilizer composition obtained is in powder form and is 100% water-soluble concentrate. The chelated fertilizer composition can be used to cure Iron and Phosphorus deficiency in crops and plants, increase yield with more Iron and Phosphorus content, thus reducing the risk of Iron and Phosphorus deficiency in humans.
Owner:SUBRAMANYAM SUNDARESAN
Acid soil conditioner
InactiveCN105967935AImprove organic levelIncrease available phosphorus contentCalcareous fertilisersMagnesium fertilisersAlkaline earth metalApatite
The invention discloses an acid soil conditioner, which is made from the following raw materials, by weight part, 9-11 of plant ash, 2.6-2.8 of apatite powder, 10-12 of golden needle mushroom residue, 5-6 of pod powder, 30-34 of bagasse, 1.6-1.8 of magnesium sulfate, 4-5 of potassium nitrate, 3-4 of lime powder, 65-70 of polluted pig dung and urine, 12-15 of a black liquor from papermaking, 3.6-3.8 of a nitric acid solution with the concentration being 10%, 11-13 of a thick alum liquid and a proper amount of water. In the soil conditioner, alkaline raw materials, such as plant ash, are adopted and match thoroughly-decomposed materials including processed pig dung and urine and bagasse, and therefore salt in the soil can be well neutralized. Alkaline-earth metal, such as magnesium sulfate, is added and matches golden needle mushroom residue for prompting activity of rhizosphere microorganisms, prompting insoluble mineral elements in the soil to change into soluble nutrients, and preventing manganese and aluminum damage to the soil. The available phosphorus content is the soil is further increased, and the obstacle of phosphorus deficiency is overcome under the function of application of apatite powder, and the problem that acid soil is low in planting yield is solved.
Owner:HANSHAN COUNTY FENGHUA SUPPLY & MARKETING COOP CO LTD
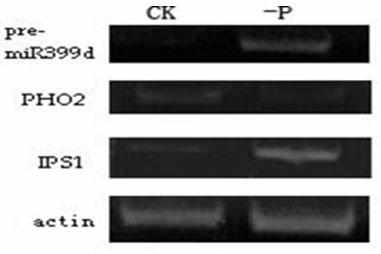
Paddy rice miR399d and application thereof
InactiveCN102676525AMicrobiological testing/measurementAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyGenetically modified rice
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, in particular to paddy rice miR399d and application thereof. Functions of a paddy rice miR399d gene are verified through overexpression of transgenic rice plants of the paddy rice miR399d (short for OsmiR399d). The paddy rice miR399d comprises a clone of a paddy rice miR399d precursor gene, construction of an expression carrier containing the gene, a primer sequence, an Osmir399d overexpression plant, response of the gene OsmiR399d on low phosphorus stress and salt stress, and verification of a target gene of the gene OsmiR399d. Semiquantitative and quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection results show that the expression of phosphorus deficiency treatment and salt treatment in roots and stem leaves can be improved. The target gene of the OsmiR399d is proved to be OsPHO2 through 5'RACE. The invention also discloses the application of the paddy rice miR399d, which is characterized in that the content of phosphorus in the stem leaves of the transgenic plants can be obviously improved after the gene OsmiR399d is overexpressed in the paddy rice, so that the plants are shown as phosphorus poisoning. The gene OsmiR399d can be used for variety improving of plants.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
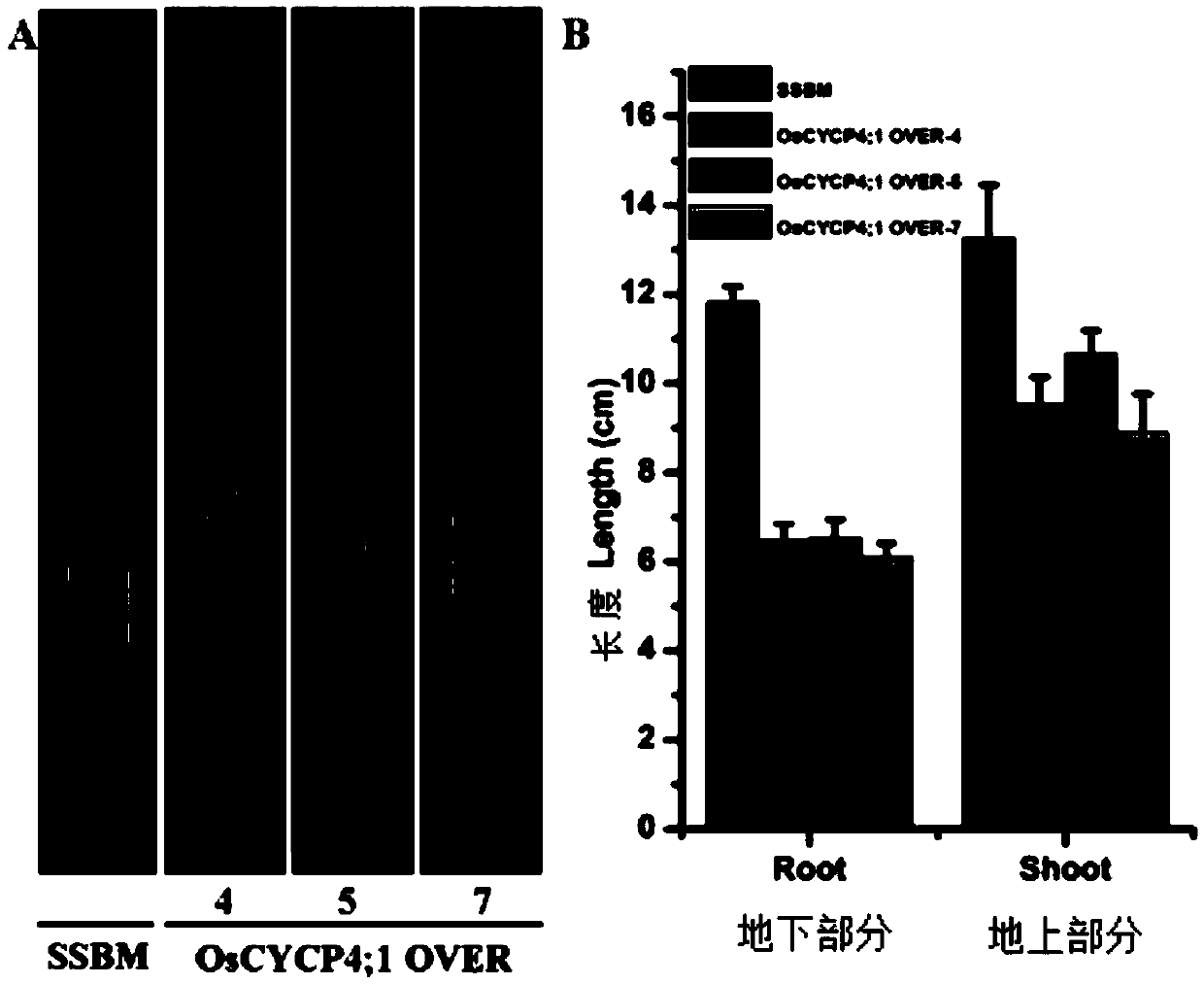
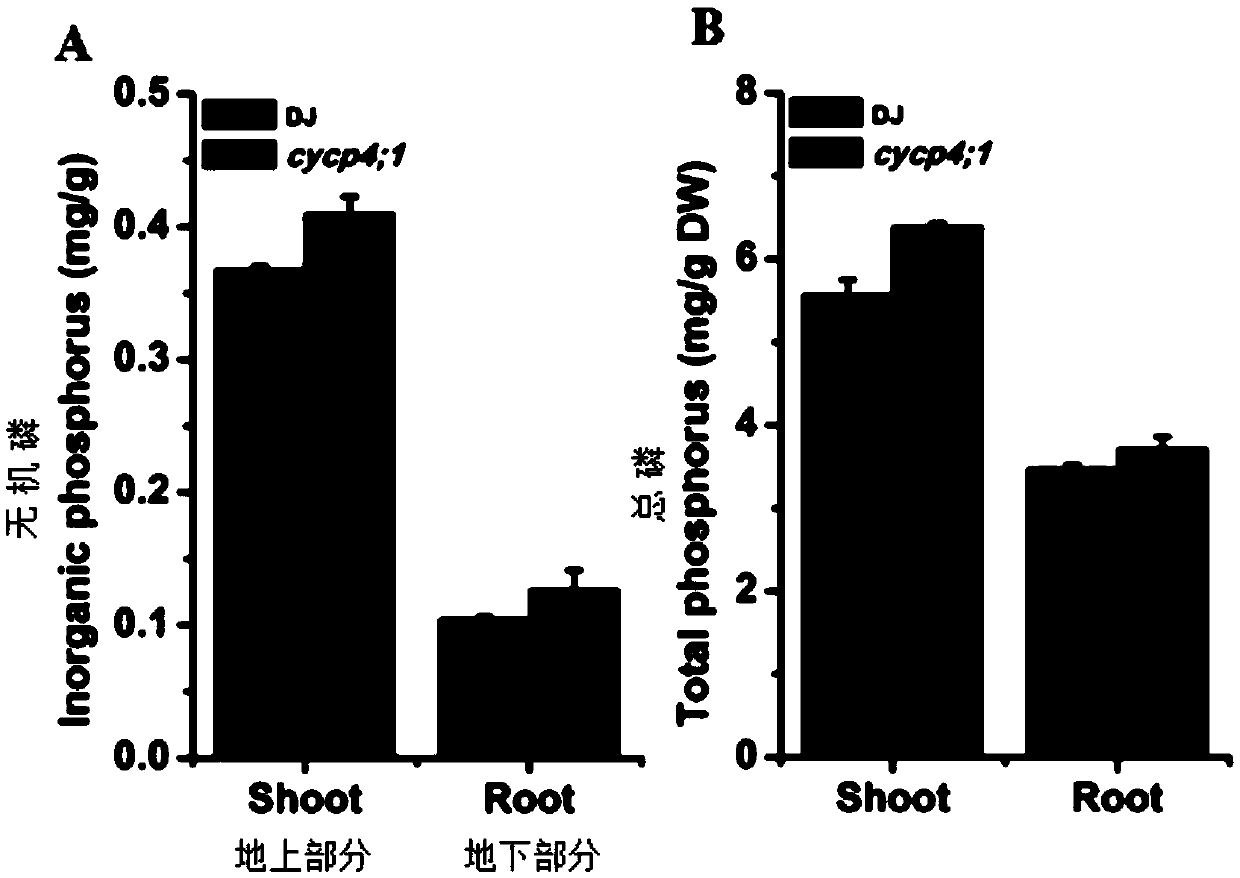
Application of rice cell cycle protein OsCYCP4;1 and method for improving deficient phosphorus stress resistance of rice
ActiveCN105504033AImprove toleranceImprove low phosphorus toleranceNucleic acid vectorPlant peptidesWild typePhosphorus deficiency
The invention discloses application of a rice cell cycle protein OsCYCP4;1 and a method for improving deficient phosphorus stress resistance of rice. Expression of OsCYCP4;1 is induced by deficient phosphorus stress on both the transcription level and the translation level. An over-expressed OsCYCP4;1 gene restrains rice growth, and it is proved that rice growth is negatively adjusted by the over-expressed OsCYCP4;1 gene. Under the normal cultivation conditions, compared with wild type mutants, OsCYCP4;1 afunction mutants have no remarkable phenotypic difference but have remarkably higher phosphorus content. Under the phosphorus deficiency conditions, OsCYCP4;1 afunction mutants reduce the sensitivity of low-phosphorus inhibit aboveground growth. Guarantees are provided for improving the low phosphorus tolerance of plants and cultivating rice new species suitable for phosphorus deficient soil.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Rapid plant phosphorus nutrition diagnosis and visual dynamic monitoring method and application of recombinant expression vector
ActiveCN103509821AConserved regulatory functionSo as not to damageColor/spectral properties measurementsFermentationDynamic monitoringAnthocyanin synthesis
The invention discloses a rapid plant phosphorus nutrition diagnosis and visual dynamic monitoring method and application of a recombinant expression vector. A promoter which specifically responds to a phosphorus deficiency signal is used for regulating and controlling a recombinant expression vector for plant anthocyanin synthetic route gene expression to be converted into a plant so as to obtain a transgenic plant; when sufficient phosphorus is supplied, the leaves of the transgenic plant are maintained to be original green; when the plant is lack of the phosphorus, the promoter specifically drives overexpression of the anthocyanin synthesis gene, the anthocyanin is greatly accumulated on the leaves of the transgenic plant, and then the leaves of the plant are turned into dark pulp; when sufficient phosphorus is supplied again, the transgenic plant can be recovered to be green within a short time, so that the purpose of visual dynamic monitoring of the phosphorus of the plant is achieved. Due to the adoption of the method, the dynamic change of the phosphorus inside the plant can be sensitively and specifically monitored, and meanwhile with the application of the remote sensing technique, the supply state of the plant phosphorus supply condition can be rapidly monitored in large area, so that instruction of rational application of fertilizers in the field can be realized.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Genetic engineering chlamydomonas having increased hydrogen producing capacity and application thereof
InactiveCN102181369AIncrease hydrogen productionUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesGas phaseWild type
The invention discloses a genetic engineering chlamydomonas having increased hydrogen producing capacity and application thereof. The genetic engineering chlamydomonas provided by the invention is a genetic engineering chlamydomonas which is obtained by inhibiting an expression level of ferredoxin-NADP (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate) reductase coding genes in a starting chlamydomonas. It is determined by gas chromatography that the hydrogen producing capacity of the genetic engineering chlamydomonas is increased by 6-10 times compared with a wild strain after phosphorus deficiency treatment is carried out for 48 hours. The mutant strain is obtained to lay the basis for industrialization of a microalgal photosynthetic hydrogen production technology.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
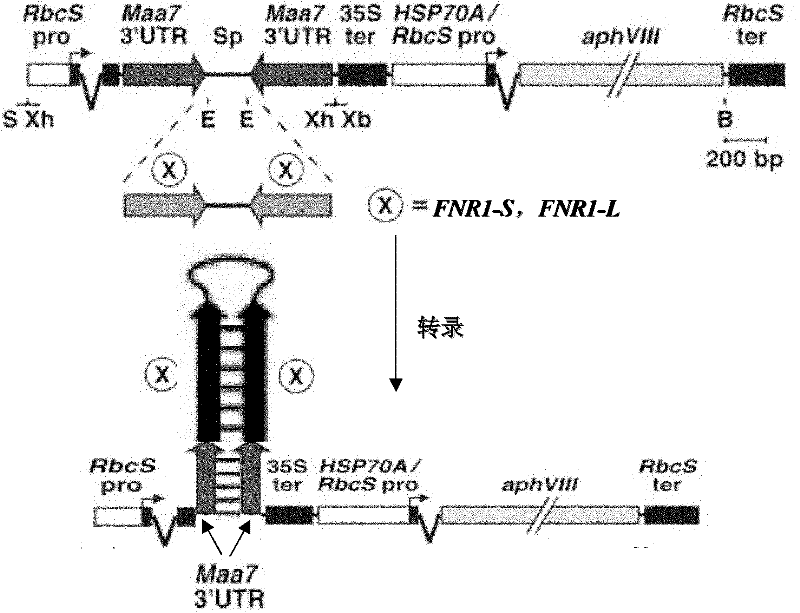
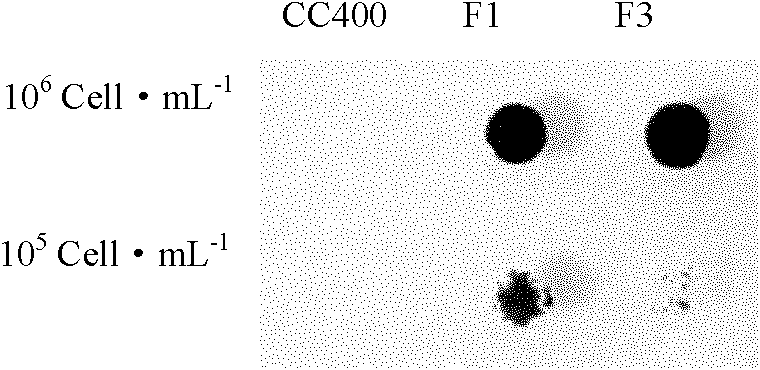
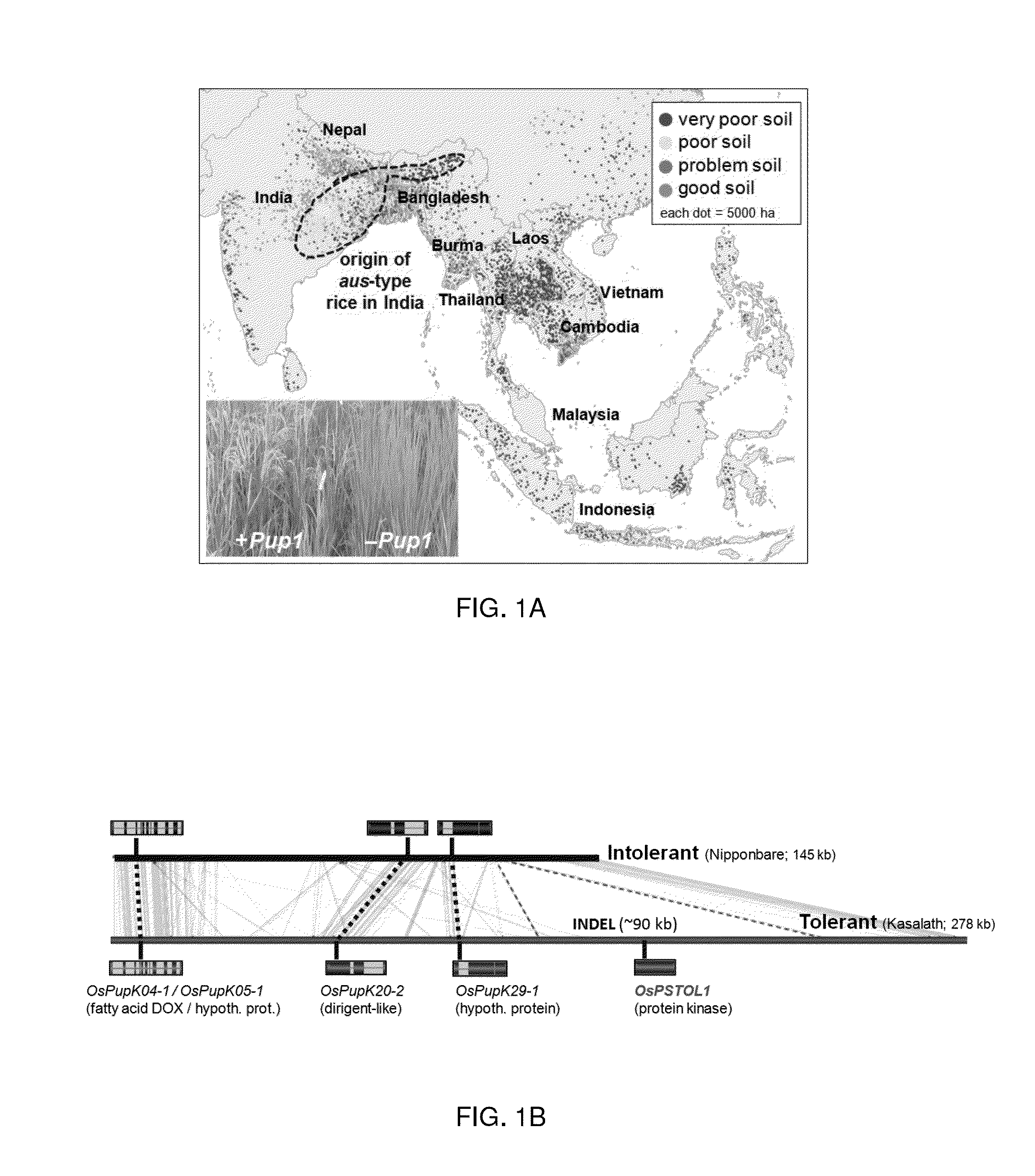
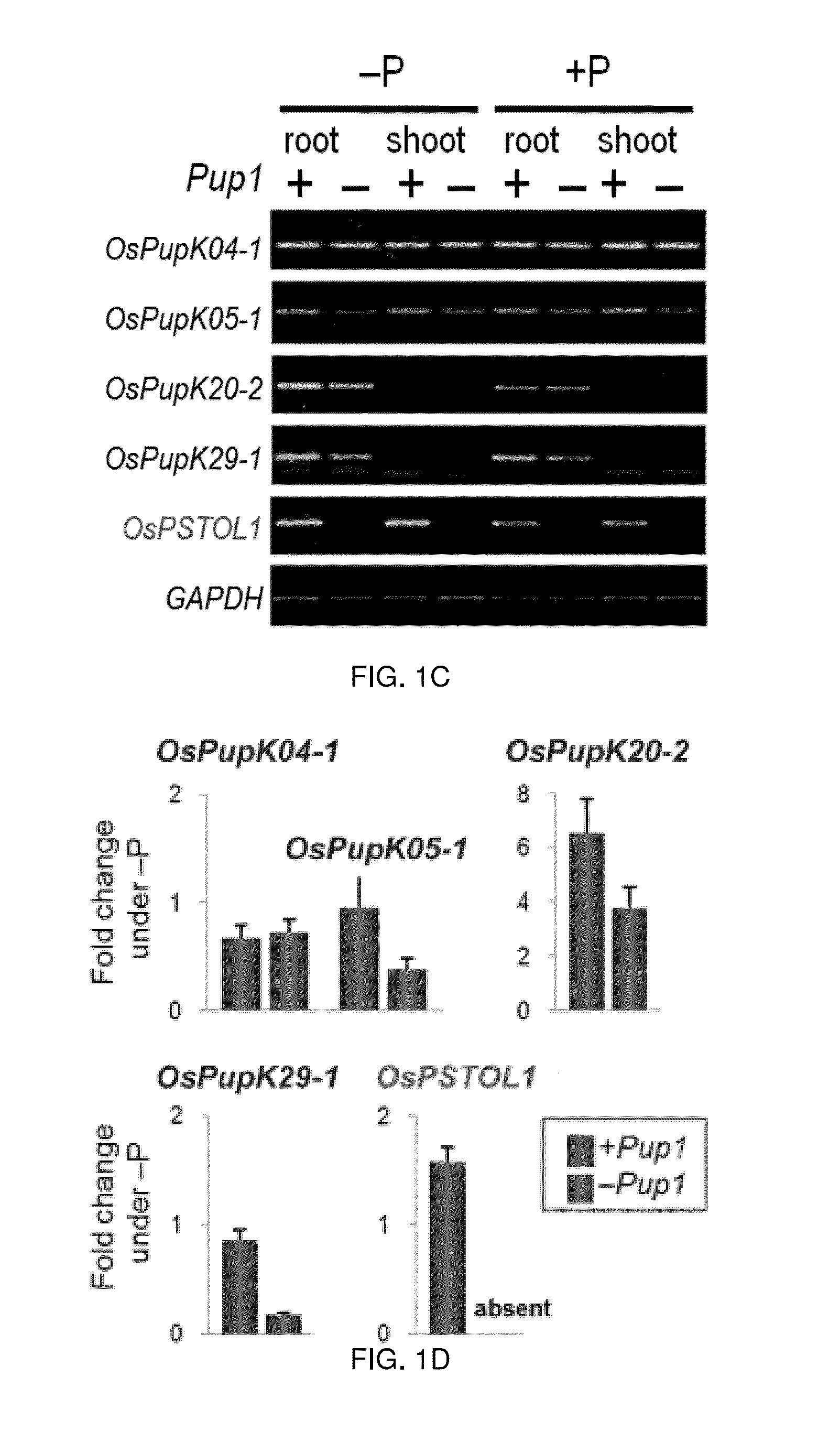
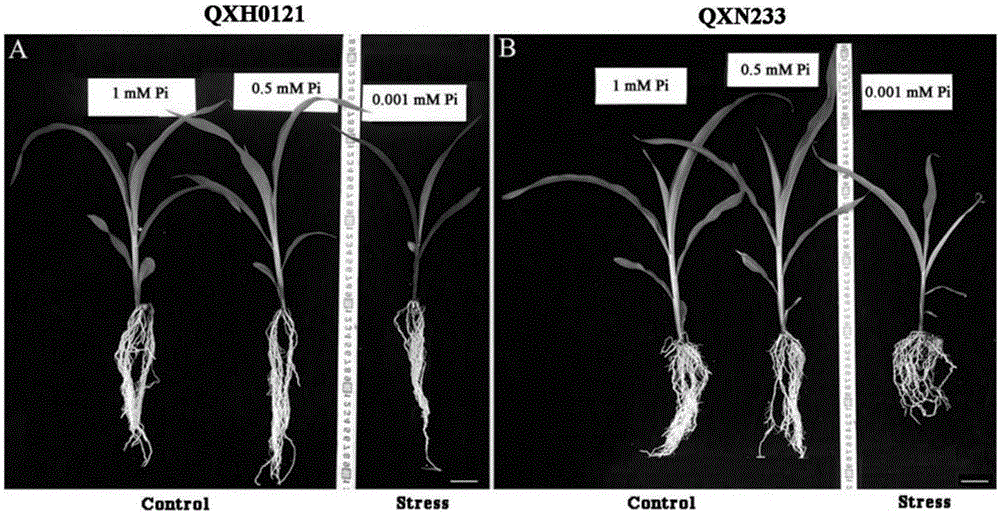
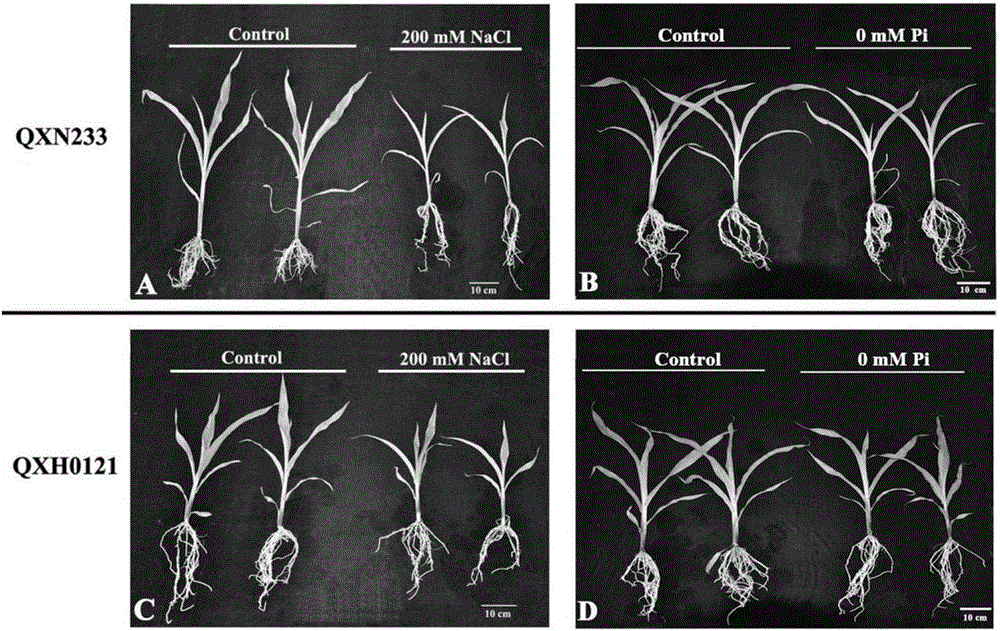
Root Growth, Nutrient Uptake, and Tolerance of Phosphorus Deficiency in Plants and Related Materials and Methods
InactiveUS20150082475A1Increased root growthPromote absorptionMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationMarker-assisted selectionRoot growth
Described herein are methods and materials useful for improving root growth and nutrient uptake in cereal grasses. In particular, present disclosure provides methods for increasing root growth and nutrient uptake in a cereal grass involving marker assisted selection and backcrossing. The present disclosure also provides recombinant DNA for the generation of transgenic plants, transgenic plant cells, and methods of producing the same. The present disclosure also provides materials and methods useful for improving the tolerance of a cereal grass to phosphorus-deficiency The present disclosure further provides methods for generating transgenic seed that can be used to produce a transgenic plant having increased root growth, nutrient uptake, and phosphorus-deficiency tolerance.
Owner:INDEPENDENT ADMINISTRATIVE INST JAPAN INT RES CENT FOR AGRI SCI +1
Iron-essential for flora and fauna
The present invention relates to a chelated fertilizer composition for enriching Iron and Phosphorus content in agriculture / horticulture crops and plants through foliar application. The fertilizer composition is prepared using compounds comprising chelating agents and Ferric Oxide (Fe2O3). The chelation of Fe by disodium salt of Hydroxy Ethylidene Di Phosphonic Acid (Na2 HEDP) developed 17% to 18% Fe-HEDP and 31% Phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5). The final chelated fertilizer composition obtained is in powder form and is 100% water-soluble concentrate. The chelated fertilizer composition can be used to cure Iron and Phosphorus deficiency in crops and plants, increase yield with more Iron and Phosphorus content, thus reducing the risk of Iron and Phosphorus deficiency in humans.
Owner:SUBRAMANYAM SUNDARESAN
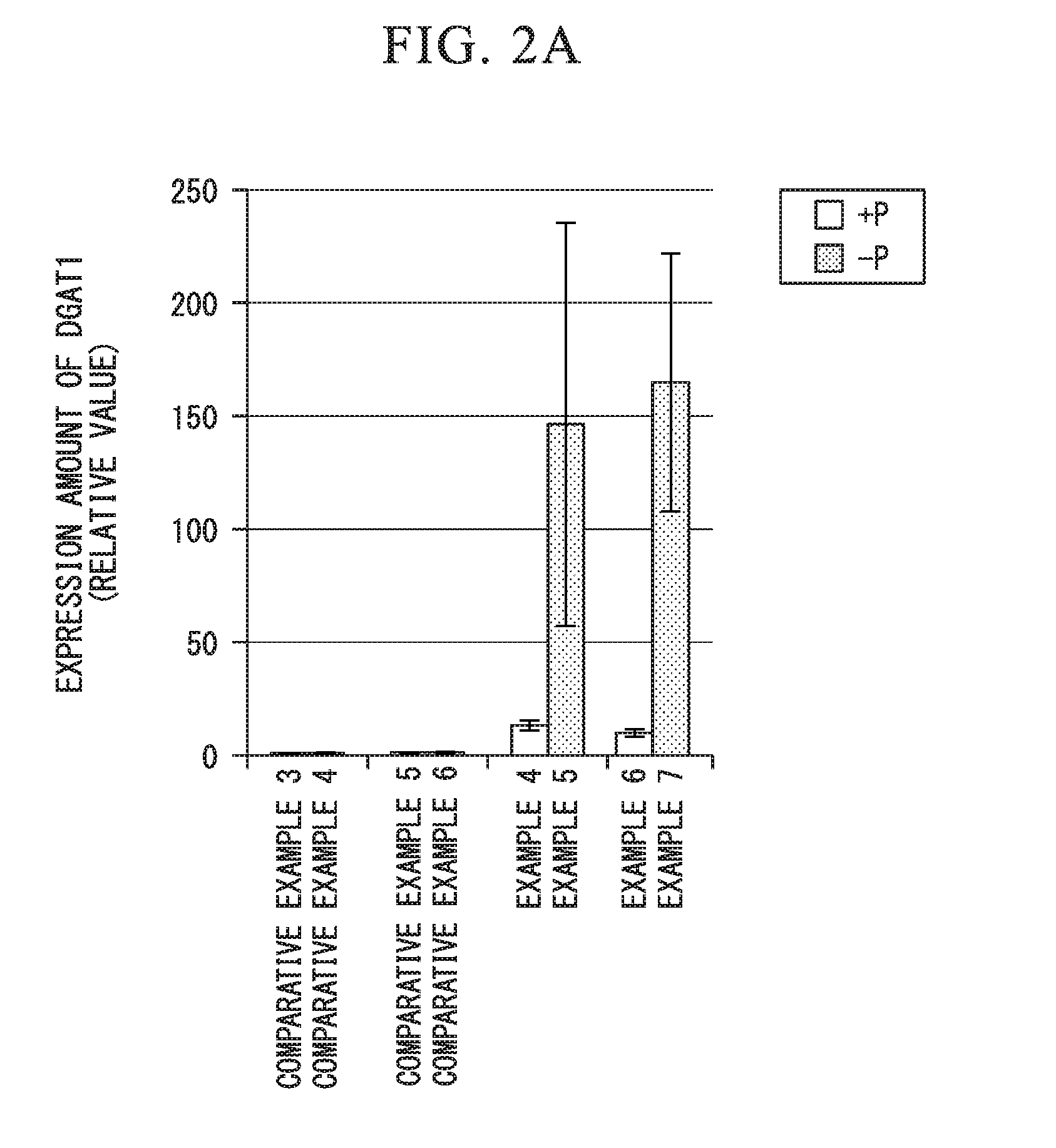
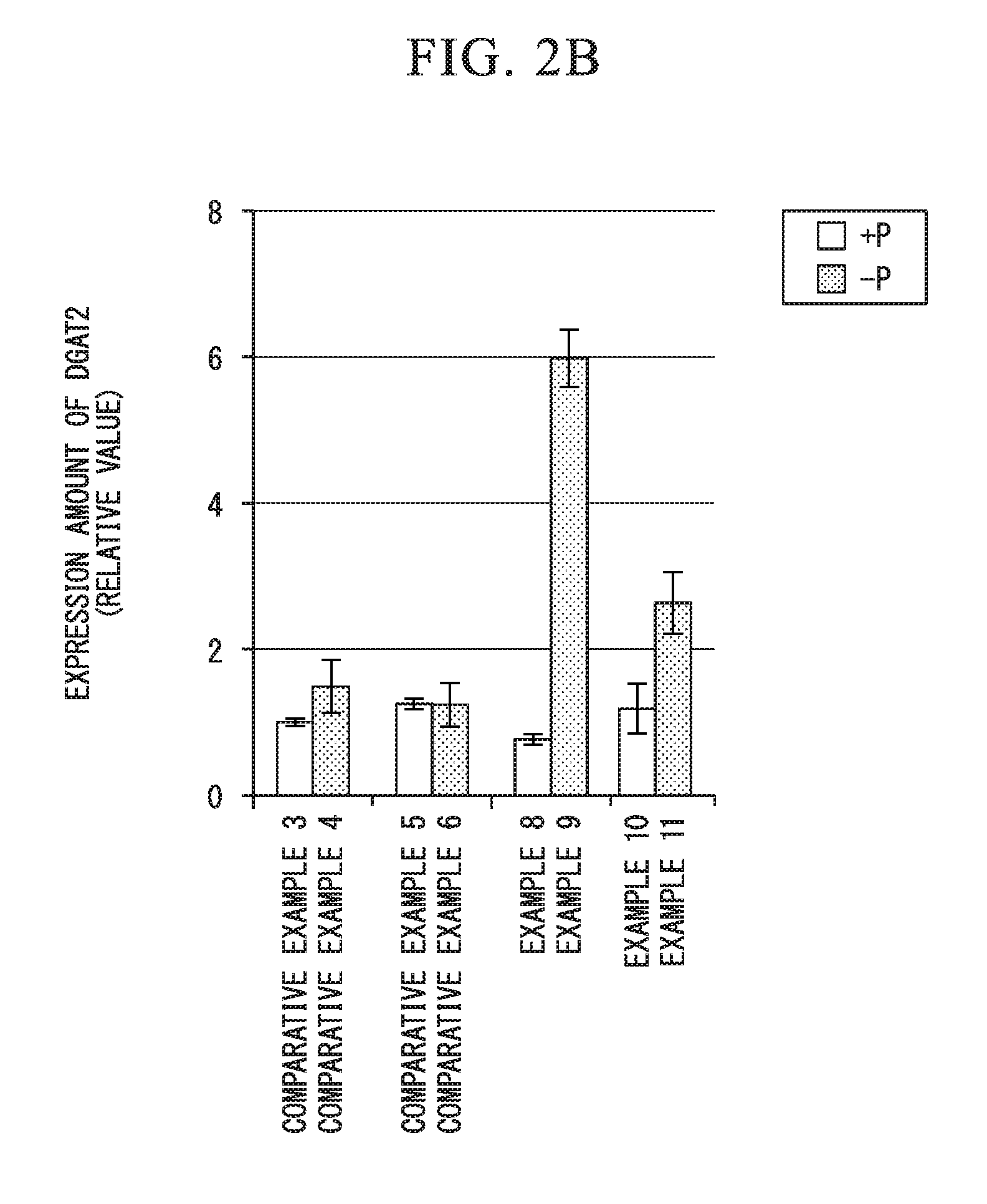
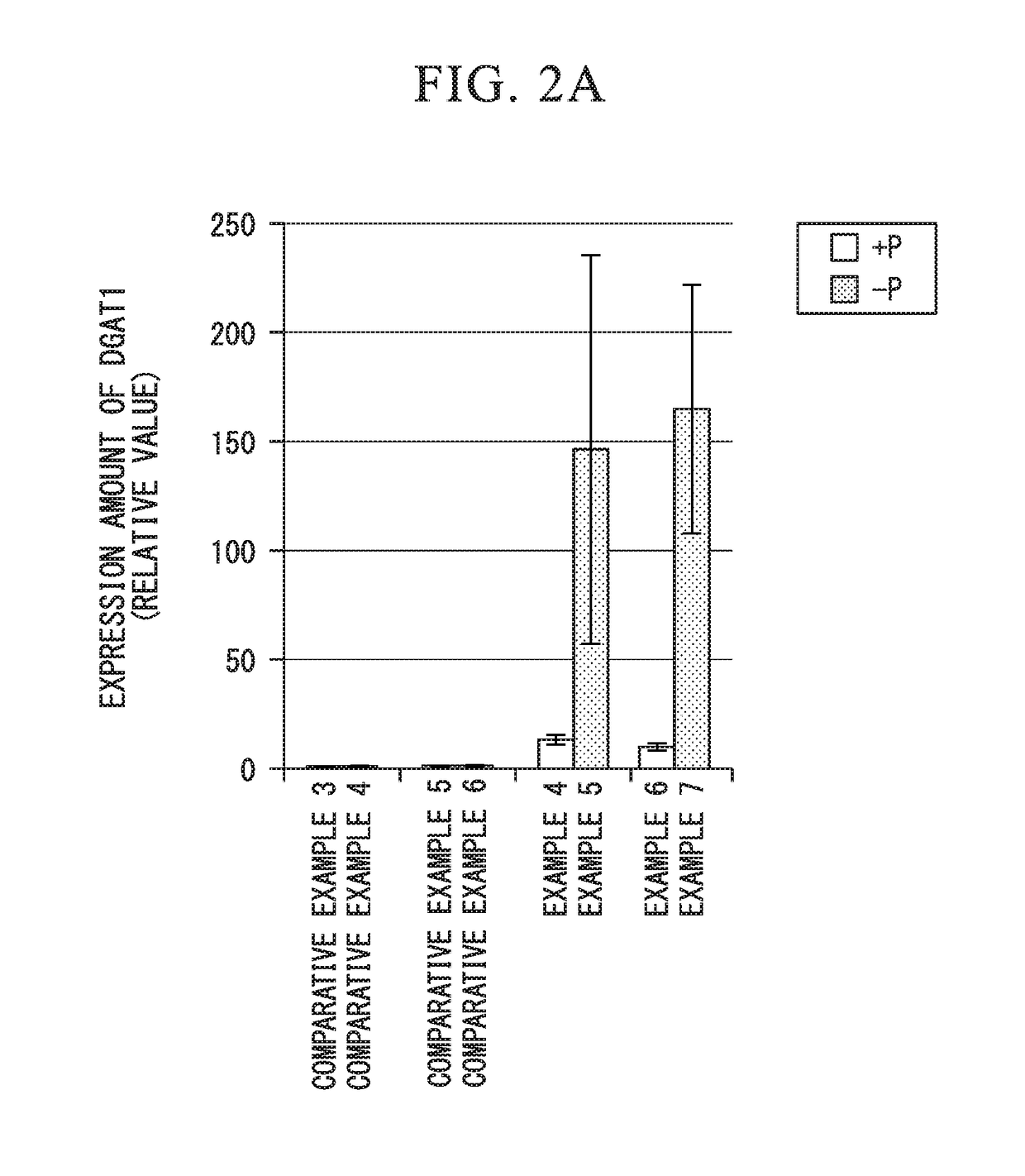
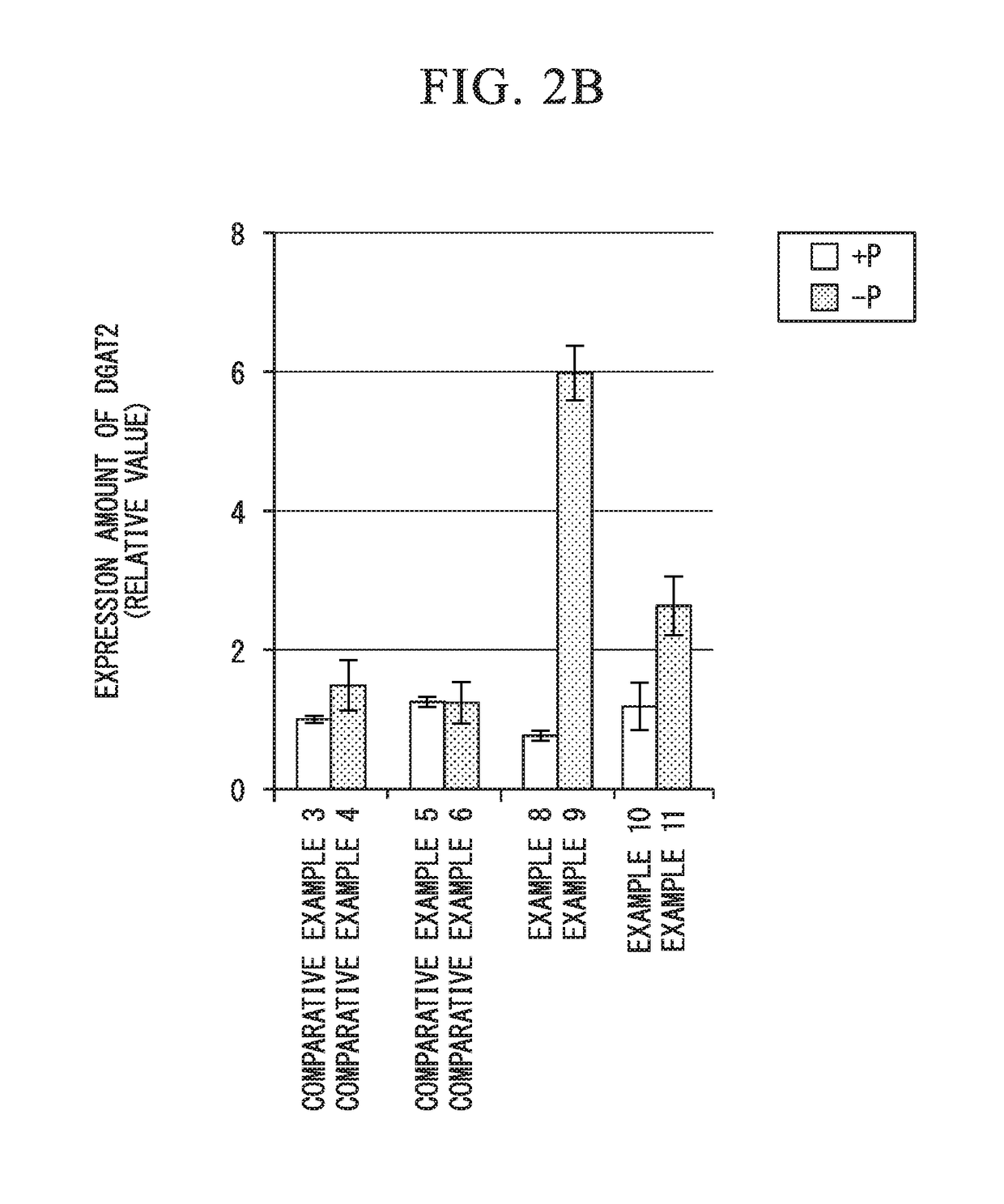
Fused gene, vector, transgenic plant, method for manufacturing vegetable fat or oil, method for constructing transgenic plant, and kit for constructing transgenic plant
ActiveUS20160244772A1Efficient preparationEfficient methodVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyNucleic acid sequencing
1) A fused gene including a nucleic acid sequence which affects the biosynthesis or accumulation of neutral lipid and a phosphorus deficiency-responsive expression control sequence which is operably linked to the nucleic acid sequence and controls the expression of the nucleic acid sequence, 2) a transgenic plant which contains the fused gene, 3) a method for manufacturing vegetable fat or oil, including a cultivation step of cultivating the transgenic plant, and 4) a method for manufacturing vegetable fat or oil in which the cultivation step is a step of cultivating the transgenic plant in a phosphorus-deficient state are provided.
Owner:TOKYO INST OF TECH
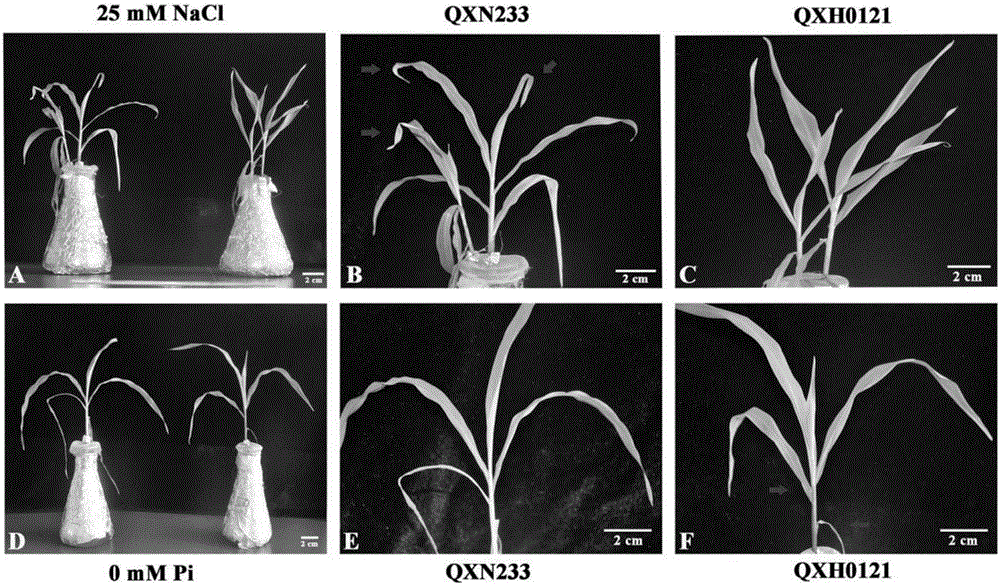
Screening and identification method of salt tolerance of corns at seedling stage
ActiveCN106416773ANon-toxicNo pollution in the processMagnesium fertilisersAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserSalt-tolerant cropsZinc stress
Owner:MAIZE RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
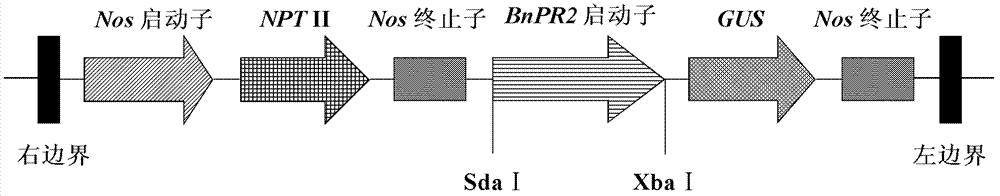
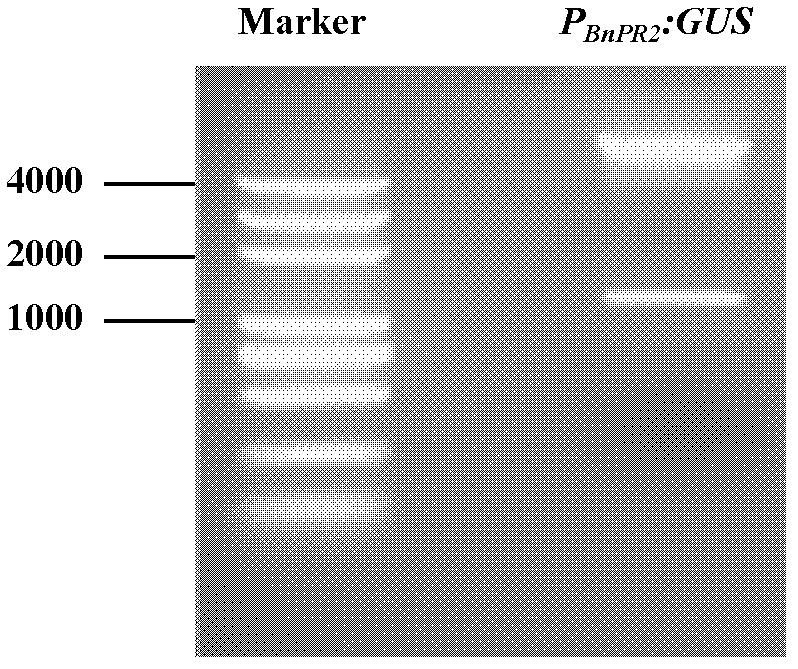
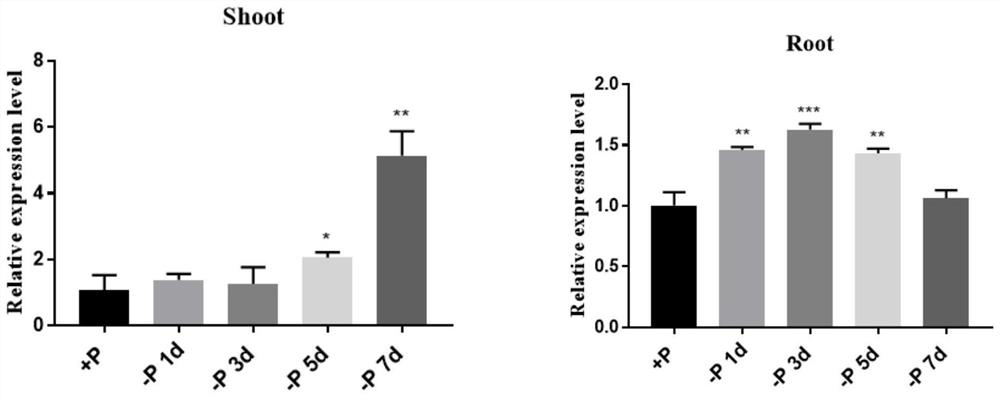
Brassica napus phosphorus deficiency inducible expression promoter
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant gene engineering. A phosphorus deficiency inducible expression promoter is cloned from Brassica napus, and has a nucleotide sequence shown as 1-1459th base group in a SEQ ID NO.1 in the sequence table; the promoter is fused with a report gene GUS and transferred into Arabidopsis; and GUS histochemical analysis shows that the promoter only has activity under phosphorus deficiency conditions, and is lack of activity under normal, nitrogen deficiency, potassium deficiency, sulfur deficiency and iron deficiency conditions. In addition to application to cultivation of low phosphorus tolerant or phosphorus efficiency tolerant crop, the promoter can also be applied to research on regulation mechanism of phosphorus deficiency induced expression gene.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
OsWRKY12 and application thereof in efficient phosphorus breeding of rice
The invention belongs to the field of plant genetic engineering, and particularly relates to a rice OsWRKY12 gene identified by a reverse genetics approach. The gene is induced by phosphorus deficiency at the overground part, and the root is induced by phosphorus deficiency and then recovered; and the phosphorus absorption efficiency of rice can be significantly improved by over-expression of the gene. The invention further relates to improvement of the phosphorus absorption efficiency of the rice by using the gene product. The invention discloses a protein OsWRKY12 for regulating phosphorus absorption of the rice, wherein the amino acid sequence of the protein OsWRKY12 is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2; and the nucleotide sequence of the gene for encoding the protein is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
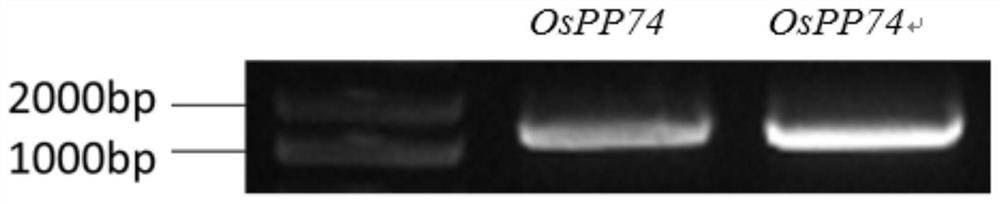
Application of protein phosphatase OsPP74 in improvement of phosphorus absorption of rice
ActiveCN113667658AImprove absorption efficiencyImprove utilization efficiencyHydrolasesGenetic engineeringMolecular breedingPhosphorus deficiency
The invention discloses an application of protein phosphatase OsPP74 in improvement of phosphorus absorption of rice. The amino acid sequence of the protein phosphatase OsPP74 is shown as SEQ ID NO:2. The protein phosphatase OsPP74 is found to participate in rice phosphorus absorption regulation and control for the first time, the expression of the protein phosphatase OsPP74 gene is increased in a plant body, and the phosphorus absorption and utilization efficiency of rice is improved. The research on phosphorus absorption and transport regulation and control mechanisms is enriched, a reference mechanism is provided for corresponding phosphorus deficiency stress of rice, and great application potential in molecular breeding is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
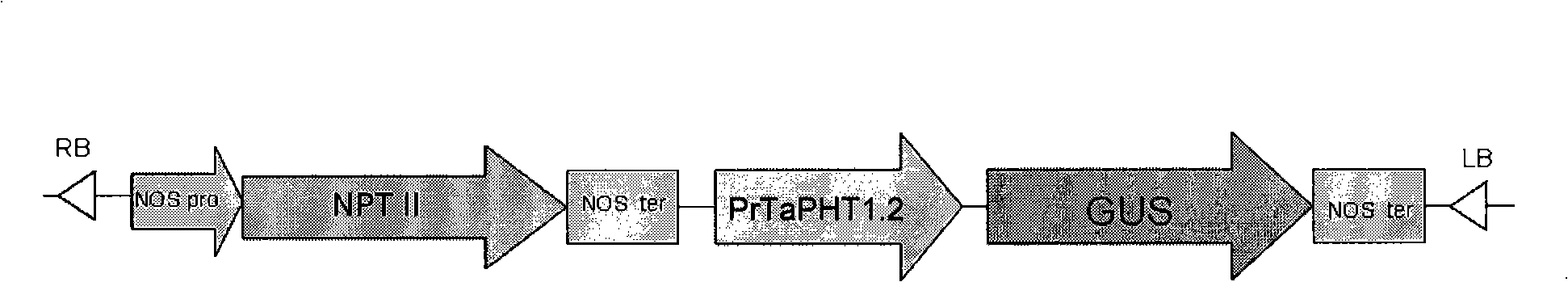
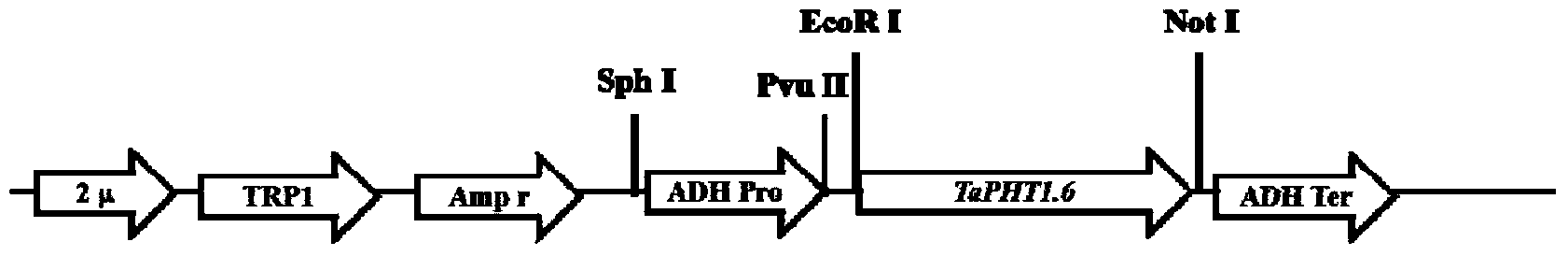
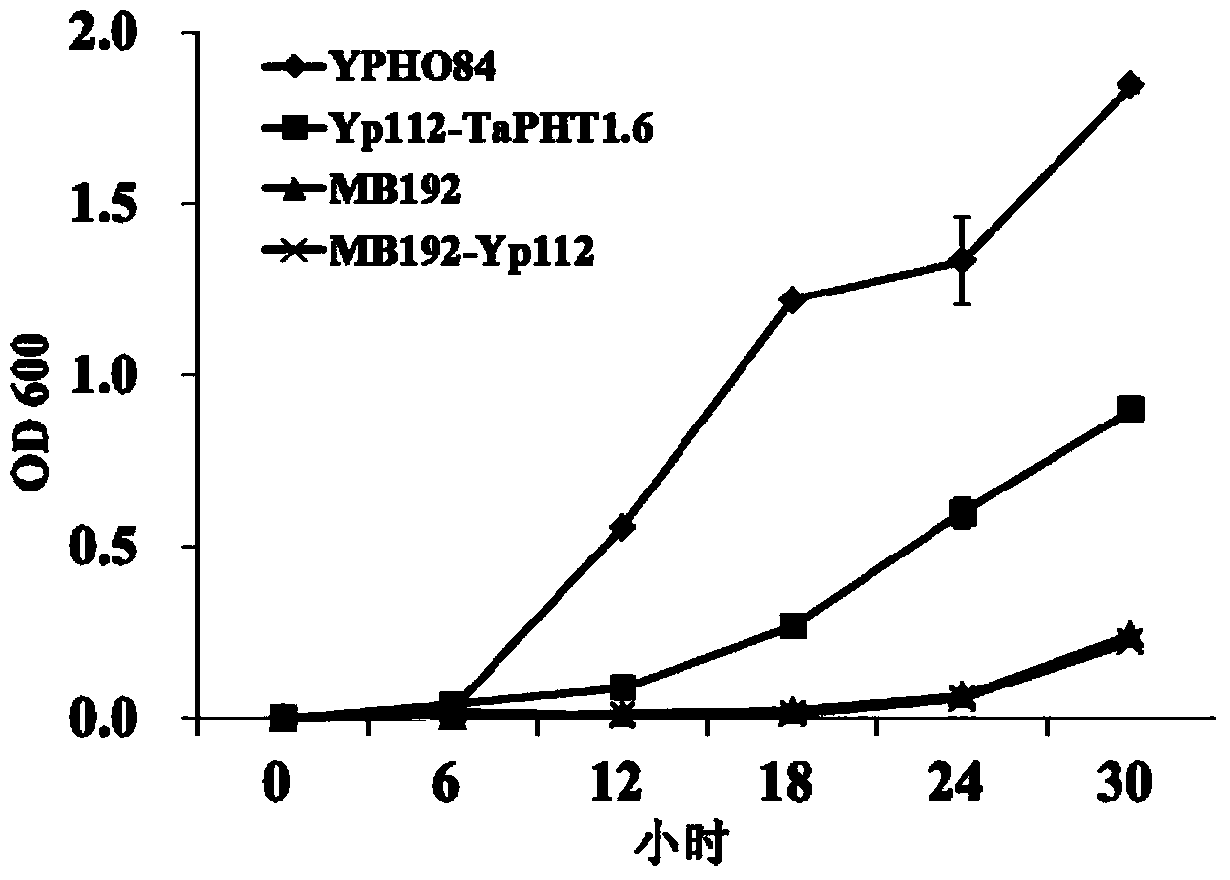
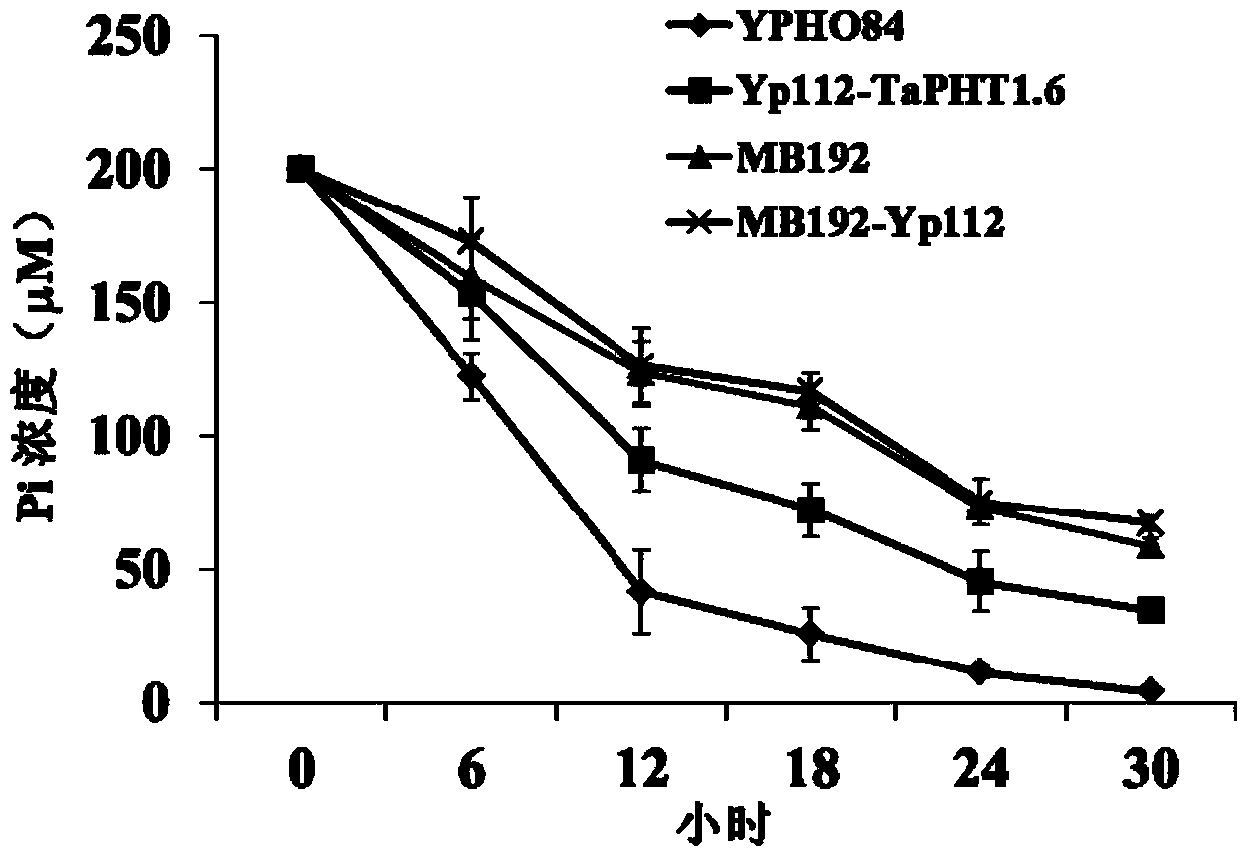
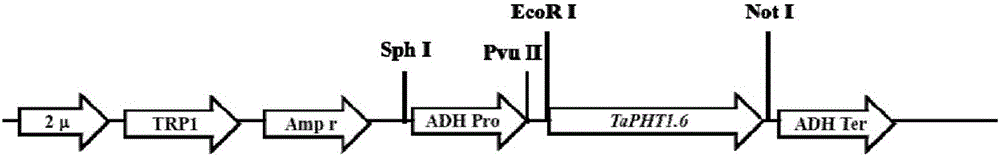
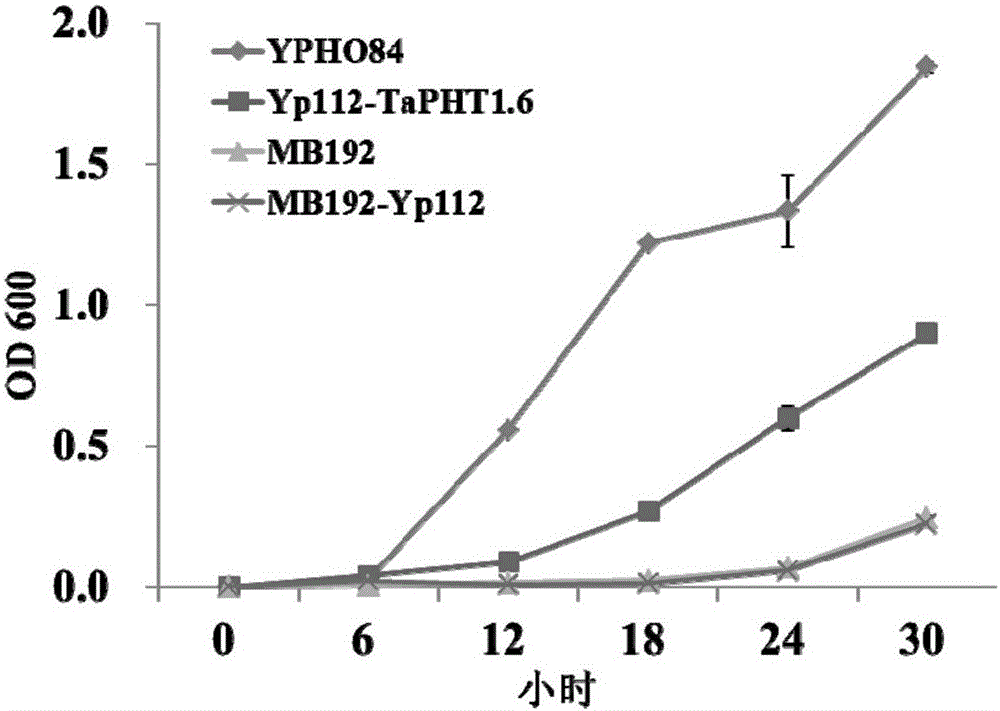
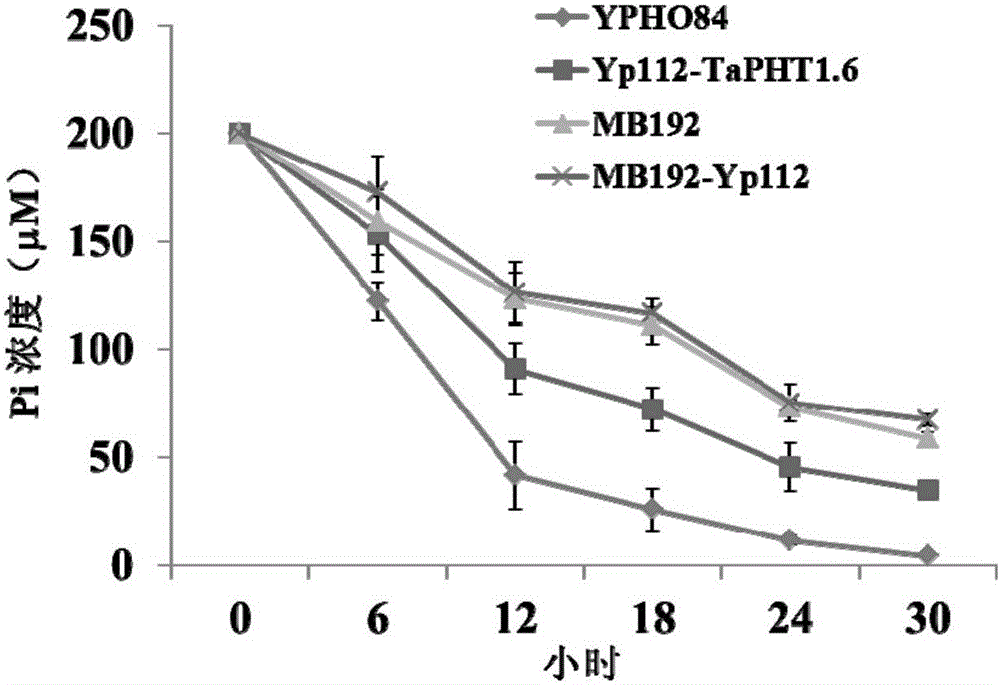
Phosphate radical transport protein TaPHT1.6 with phosphorus deficiency response as well as coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN103864909AIncrease phosphorus uptake capacityPromote absorptionFungiPlant peptidesNutritional statusMutant
The invention discloses a phosphate radical transport protein TaPHT1.6 with phosphorus deficiency response as well as a coding gene and application thereof. The protein provided by the invention is (a) or (b) as follows: (a), protein consisting of amino acid sequences as shown in a sequence 2 in a sequence table; and (b), protein obtained by substituting and / or deleting and / or adding one or more amino acid residues of the amino acid sequence of the sequence 2, having the same function as the protein a and derived from the sequence 2. Experiments prove that absorption of yeast to phosphor is increased and phosphor nutritional status of the protein is improved by inducing a coding gene of the protein into a yeast phosphor absorption mutant, so that growth velocity of the protein is obviously increased.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Corn base fertilizer for phosphorus deficiency soil
InactiveCN109020722AThe effect of increasing production and income is obviousSignificant effect of increasing incomeAmmonium salt fertilisersOrganic fertilisersSulfatePotassium
The invention discloses a corn base fertilizer for phosphorus deficiency soil, and relates to the technical field of fertilizers. The corn base fertilizer is prepared from the following raw materialsin parts by weight: 4-6 parts of nitrogen, 10-15 parts of phosphorus, 3-5 parts of potassium, 0.1-0.2 part of zinc sulfate, 1-3 parts of water-soluble organic substances, 1-3 parts of humic acid, 1-3parts of fulvic acid, 0.1-0.3 part of a synergistic factor and 0.1-0.3 part of a gamma-SIPF soil factor. The corn base fertilizer is good in corn yield-increasing effect, does not cause negative effect on soil, does not burn seeds, is high in emergence rate, is safe to use, and is good in growth vigor.
Owner:KUNMING NONGJIALE COMPOUND FERTILIZER CO LTD
Method for determining two-dimensional distribution of available phosphorus content
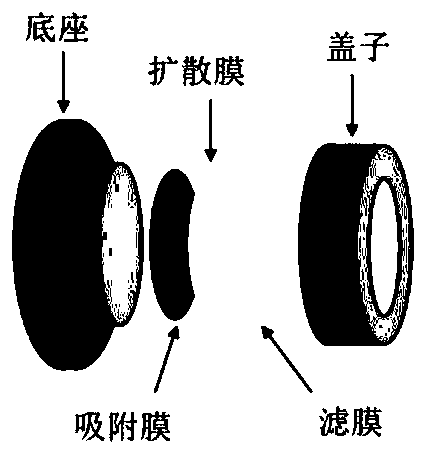
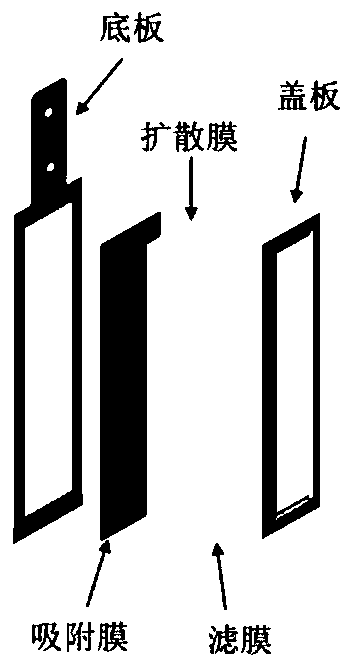
PendingCN111504988AImprove adsorption capacityNot easy to curlMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorAdsorptive membraneSoil science
The invention relates to a method for determining the two-dimensional distribution of available phosphorus content. A DGT device assembled with a precipitated adsorption film into a sediment or soil medium to absorb available phosphorus in the longitudinal section of the medium; the precipitated adsorption film in the DGT device is taken out, is soaked in a color developing agent so as to be subjected to a color developing reaction; the surface gray value of the precipitated adsorption film is obtained by using a CID method; according to the established standard curve of the phosphorus adsorption capacity per unit surface area of the precipitated adsorption film and the gray value, the gray value is converted into a phosphorus adsorption capacity; and the two-dimensional distribution of the available phosphorus content in the sediment or the soil medium is calculated through a formula; the precipitated zirconium oxide adsorption film with high adsorption capacity is used for representing phosphorus, so that the method is suitable for being applied to various environment scenes of phosphorus deficiency, phosphorus application and the like, particularly under the condition of strongphosphorus content spatial distribution heterogeneity; the front and back surfaces of the adsorption film do not need to be distinguished when the adsorption film is used for loading different amountsof phosphorus to prepare mark lines; and only the adsorption film is used instead of the complete DGT device, so that operation complexity is avoided.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
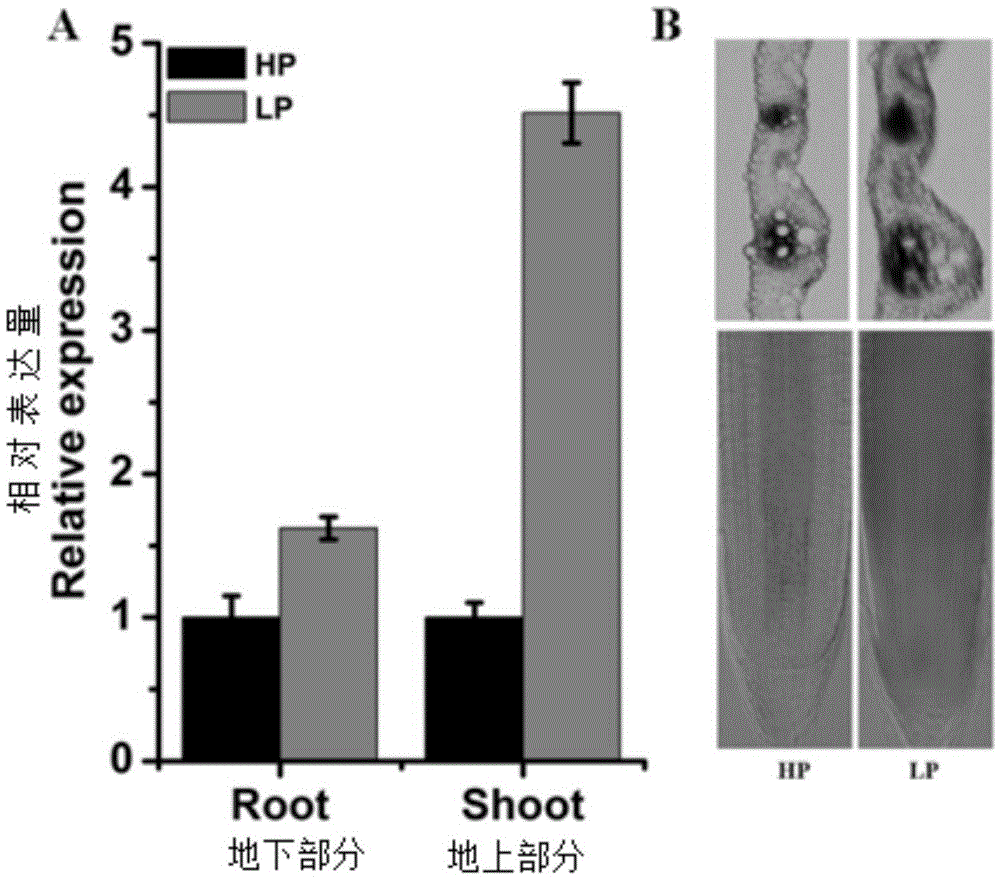
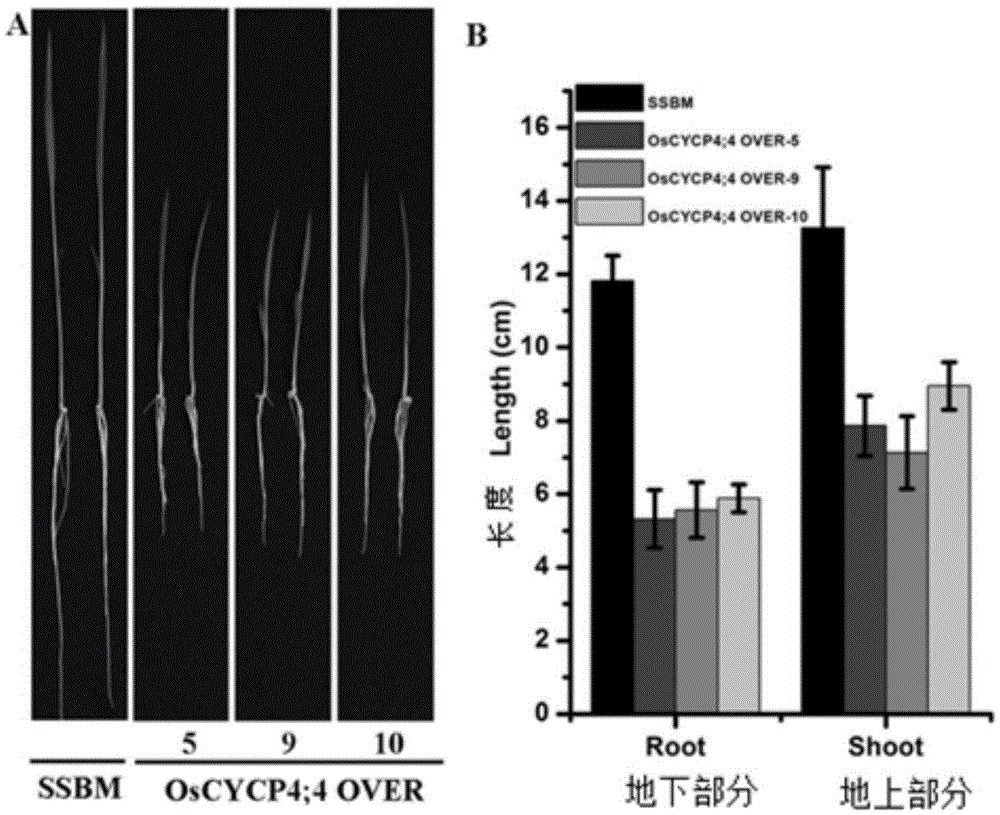
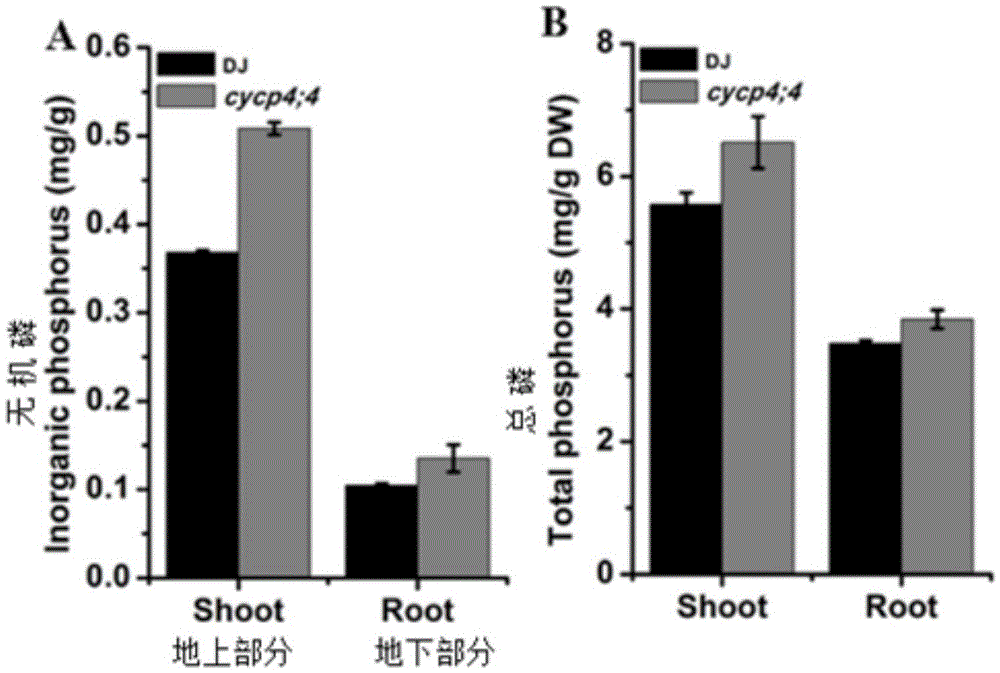
Rice cyclin OsCYCP4 ; 4 application and method for improving rice tolerance to low phosphate stress
ActiveCN105524153AImprove toleranceImprove low phosphorus tolerancePlant peptidesFermentationAgricultural sciencePhosphate
The present invention discloses rice cyclin OsCYCP4 ; 4 application and a method for improving rice tolerance to low phosphate stress, and OsCYCP4 ; 4 transcription level expression and OsCYCP4 ; 4 translation level expression are both induced by phosphorus starvation stress. Inhibition of overexpression of OsCYCP4; 4 gene on the growth of rice proves that the overexpression of OsCYCP4; 4 gene negatively regulates the growth of rice. Under normal culture conditions, and compared with a wild type, an OsCYCP4; 4 functional deletion mutant has no obvious phenotypic differences, but the phosphorus content of the mutant is significantly higher than that of the wild type. Under phosphorus deficiency conditions, the OsCYCP4; 4 functional deletion mutant reduces sensitivity of low-phosphorus inhibition on growth of overground parts. A guarantee for improvement of plant tolerance to low phosphorus and cultivation of new rice varieties suitable for phosphorus poor soils is provided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Health-care composition capable of increasing bone mineral density and preparation method thereof
PendingCN111631397AEasy to losePrevent secretionVitamin food ingredientsNatural extract food ingredientsPuerarinSynthetic bone
The invention discloses a health-care composition capable of increasing bone mineral density. The composition is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage: 45 to 75 percent of bone meal,1 to 3 percent of soy isoflavone, 13 to 27 percent of shrimp meal, 0.1 to 1.2 percent of herba epimedii extract, 18 to 35 percent of glucosamine salt, 2 to 5 percent of vitamin D, 0.1 to 0.5 percentof radix salviae miltiorrhizae aqueous extract and 0.15 to 0.3 percent of puerarin. The bone meal includes different bones, can be absorbed by different people conveniently when in use, and supplements the required calcium. Phosphorus in the shrimp meal is an element necessary for a human body, and the phosphorus and the calcium are combined into osteogenic mineral. Phosphorus deficiency caused bypoor phosphorus absorption can cause bone mass reduction, and osteoporosis is finally developed. The level of vitamin D is related to bone mineral density and muscle strength density, the vitamin D is a main adjusting factor for calcium absorption and can help a human body to absorb calcium, the bone mineral density of the human body can be effectively increased, and the peak value of bone mineral density can be maintained by long-time calcium intake.
Owner:夏新兴
A phosphorous deficiency responsive phosphate transporter tapht1.6 and its coding gene and application
ActiveCN103864909BIncrease phosphorus uptake capacityPromote absorptionFungiPlant peptidesNutritional statusPhosphate Transporters
The invention discloses a phosphate radical transport protein TaPHT1.6 with phosphorus deficiency response as well as a coding gene and application thereof. The protein provided by the invention is (a) or (b) as follows: (a), protein consisting of amino acid sequences as shown in a sequence 2 in a sequence table; and (b), protein obtained by substituting and / or deleting and / or adding one or more amino acid residues of the amino acid sequence of the sequence 2, having the same function as the protein a and derived from the sequence 2. Experiments prove that absorption of yeast to phosphor is increased and phosphor nutritional status of the protein is improved by inducing a coding gene of the protein into a yeast phosphor absorption mutant, so that growth velocity of the protein is obviously increased.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A method for detecting the ability of plants to resist phosphorus deficiency stress by using the characteristics of root organic acid secretion
The invention discloses a method for detecting the ability of plants to resist phosphorus deficiency stress by using the secretion characteristics of organic acids in roots. According to the relational model, the phosphorus extraction capacity of the organic acids secreted by the roots to the rhizosphere soil is calculated, and the ratio of the organic acids secreted by the roots of plants cultivated in the nutrient solution of the phosphorus deficiency formula to the phosphorus extraction capacity of the rhizosphere soil is calculated. The increase ratio of the organic acids secreted by the roots of plants cultured in the nutrient solution of the normal formula to the phosphorus extraction capacity of the rhizosphere soil, and then by calculating the cost of the phosphorus extraction by the organic acids secreted by the roots, the ability of different plants to resist phosphorus deficiency stress can be judged. size. The invention can quantitatively detect the ability of plants to resist phosphorus deficiency stress, the detection results of different plants are comparable, not affected by any time and space geographical factors, and can dynamically monitor the physiological change characteristics of plants for a long time.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Fused gene, vector, transgenic plant, method for manufacturing vegetable fat or oil, method for constructing transgenic plant, and kit for constructing transgenic plant
ActiveUS10174333B2Efficient preparationEfficient methodVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyNucleic acid sequencing
1) A fused gene including a nucleic acid sequence which affects the biosynthesis or accumulation of neutral lipid and a phosphorus deficiency-responsive expression control sequence which is operably linked to the nucleic acid sequence and controls the expression of the nucleic acid sequence, 2) a transgenic plant which contains the fused gene, 3) a method for manufacturing vegetable fat or oil, including a cultivation step of cultivating the transgenic plant, and 4) a method for manufacturing vegetable fat or oil in which the cultivation step is a step of cultivating the transgenic plant in a phosphorus-deficient state are provided.
Owner:TOKYO INST OF TECH
Use method of reagent kit of Hoagland phosphorus deficiency plant nutrient solution
InactiveCN105294203ASimple and fast operationGuaranteed effectFertilizer mixturesAdditive ingredientNutrient solution
Provided is a use method of a reagent kit of a Hoagland phosphorus deficiency plant nutrient solution. A plurality of premix ingredient pockets of the Hoagland phosphorus deficiency plant nutrient solution are contained in the reagent kit of the Hoagland phosphorus deficiency plant nutrient solution, various reagents in the pockets are matched according to the proportion of the reagents in the Hoagland phosphorus deficiency plant nutrient solution, and the reagents are charged into the pockets separately according to the ingredient quantity needed by the preparation quantity of the nutrient solution of a certain volume. It is very easy and convenient to prepare the nutrient solution through the reagent kit, it is only needed to pour the reagents in the premix ingredient pockets into water according to the solute quantity needed by the preparation quantity of the nutrient solution and stir the reagents till dissolution, and the tedious and complex process of repeated weighing, mother liquor preparation, storage, separated taking and the like in nutrient solution preparation in the prior art is omitted. In this way, under the condition of guaranteeing the original effect, labor consumption is reduced, and working efficiency is substantially improved. Thus, the use method has broad popularization prospects.
Owner:有限会社林平
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com