Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
107 results about "Path width" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
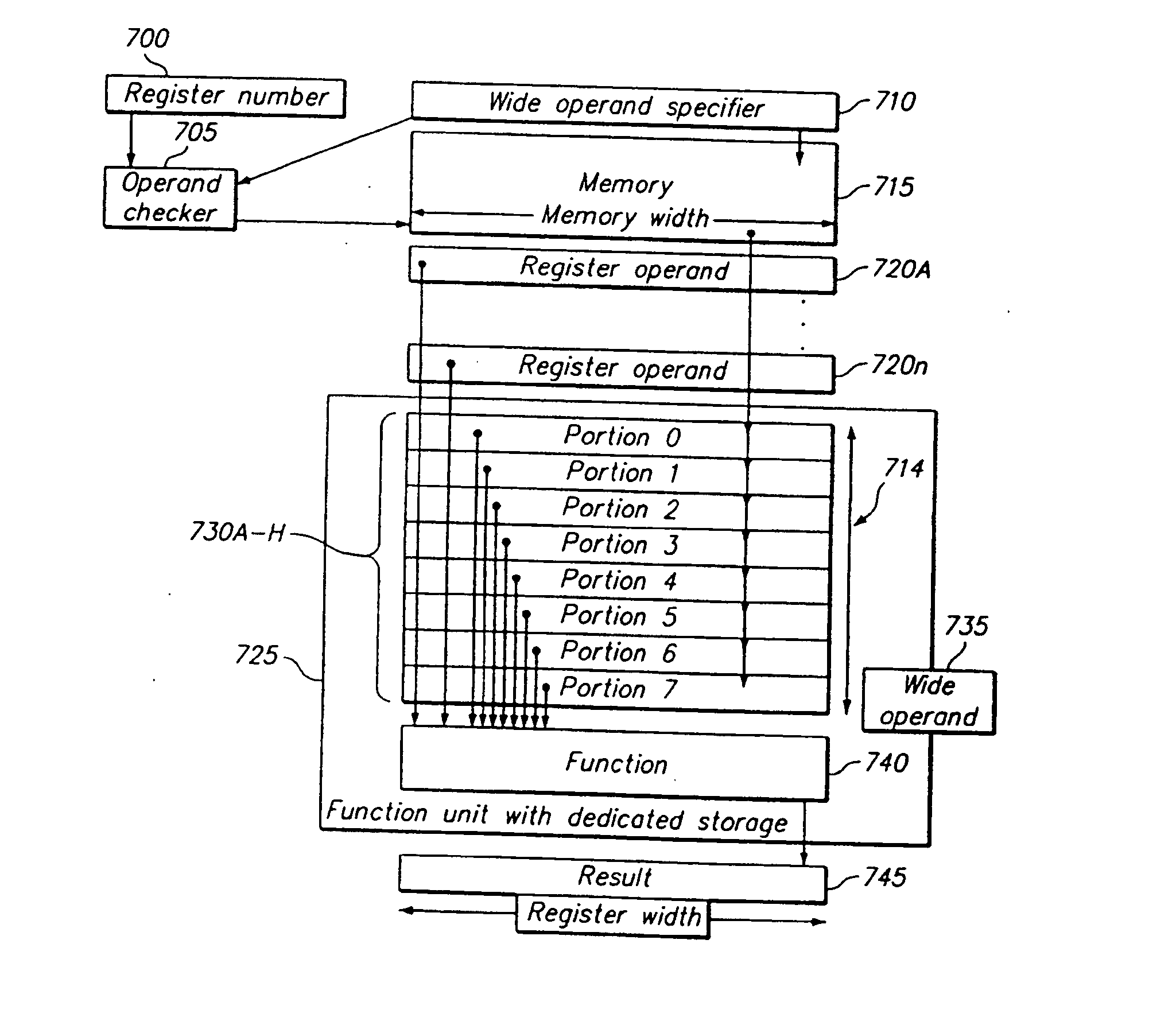
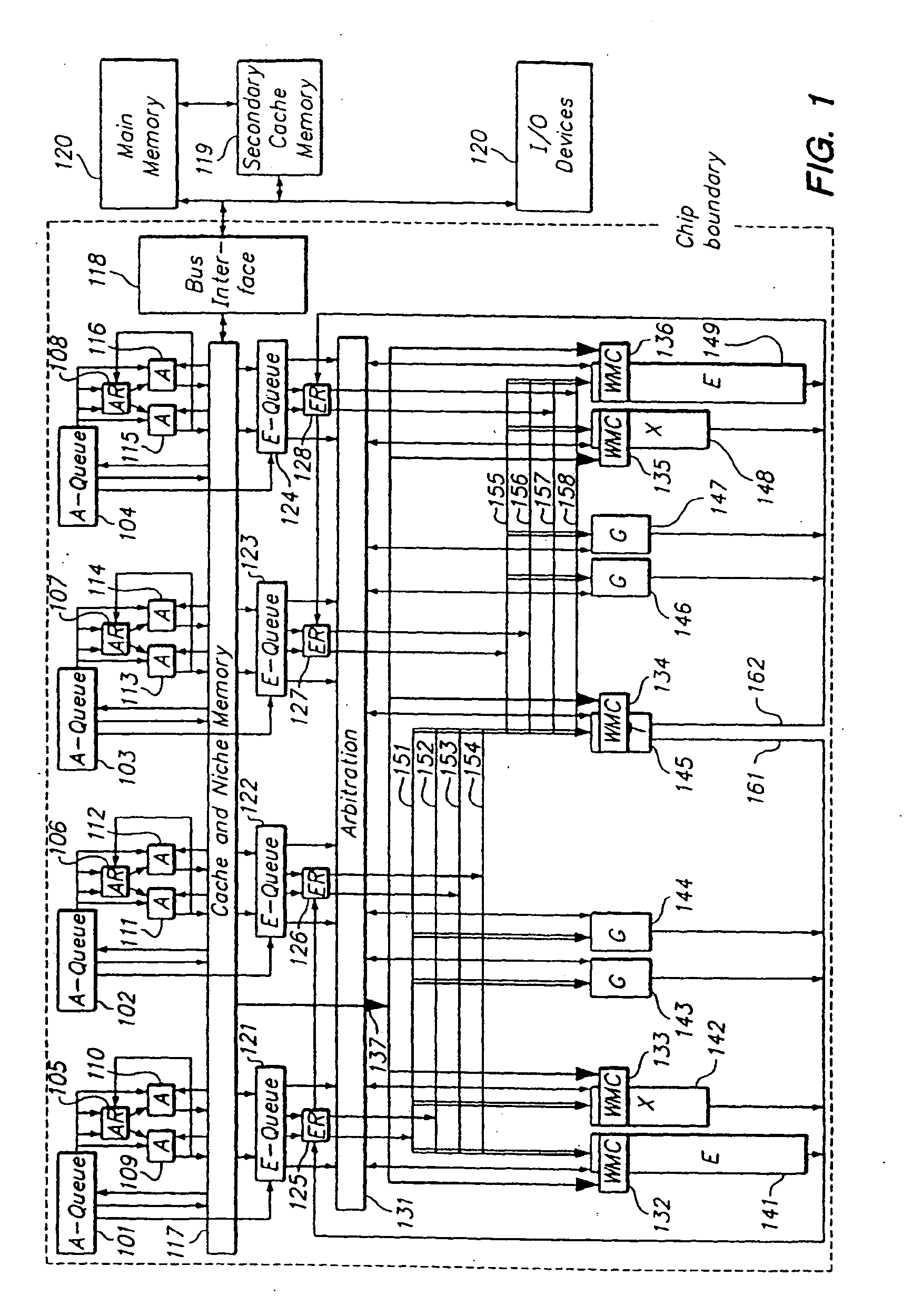
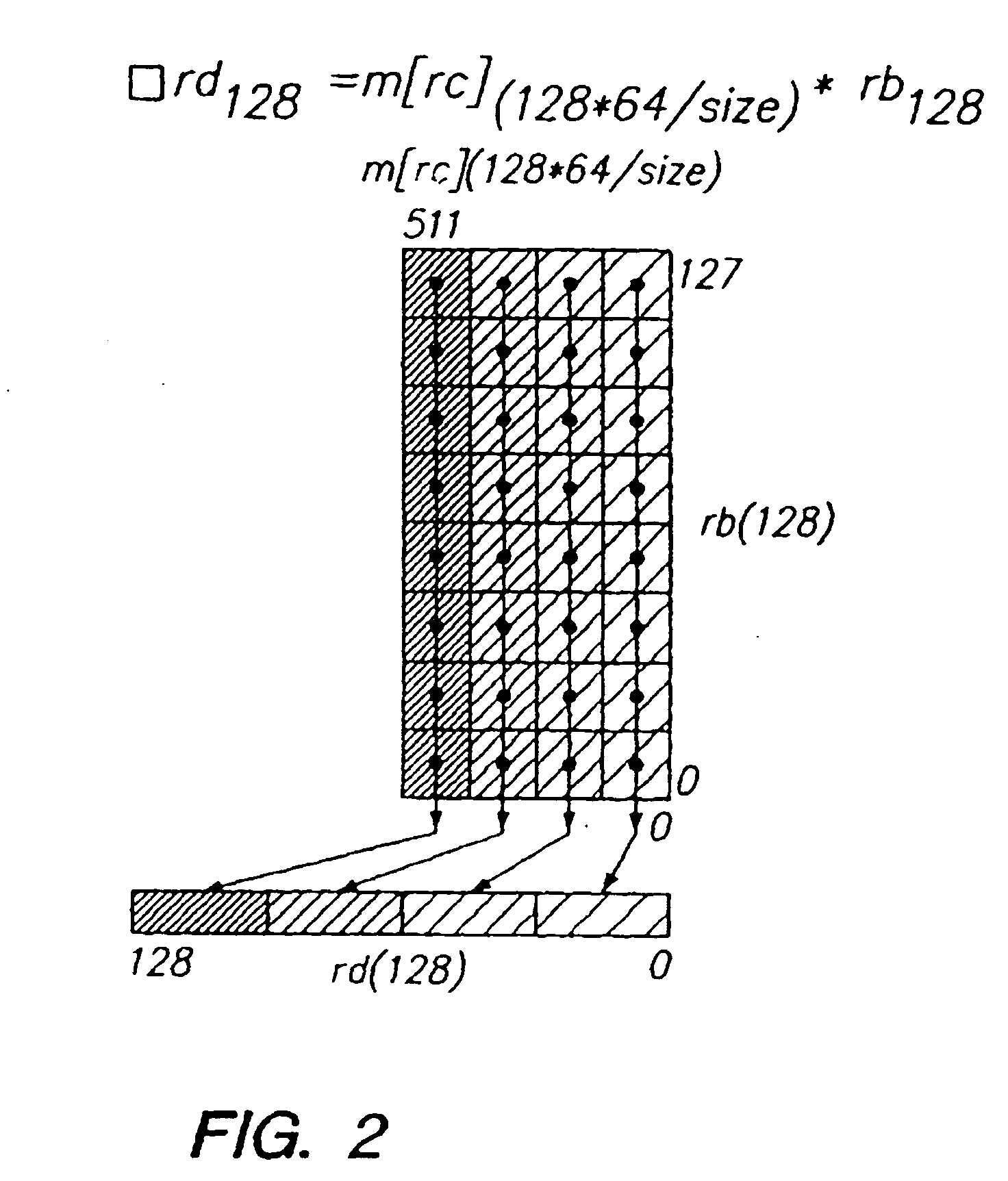
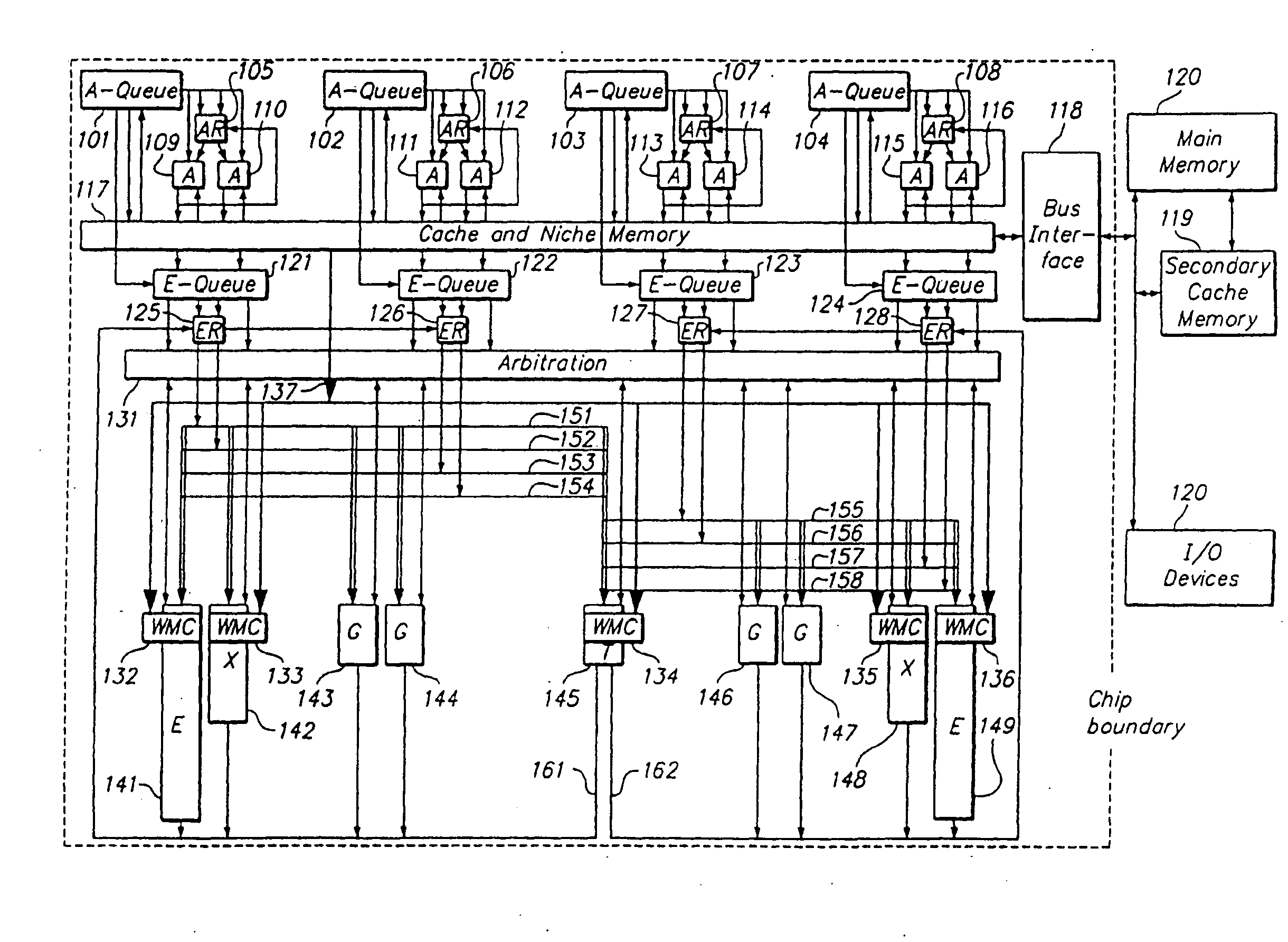
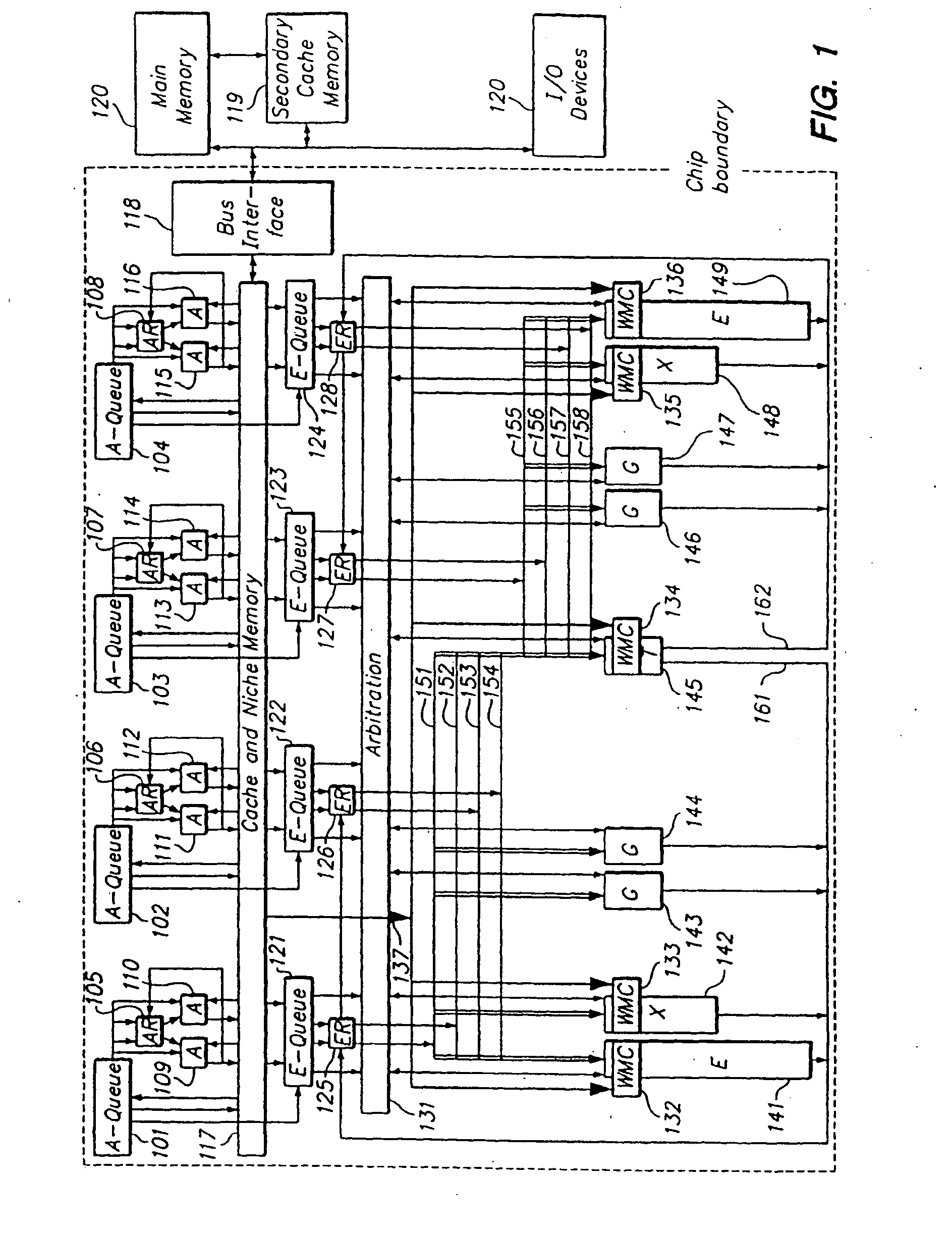
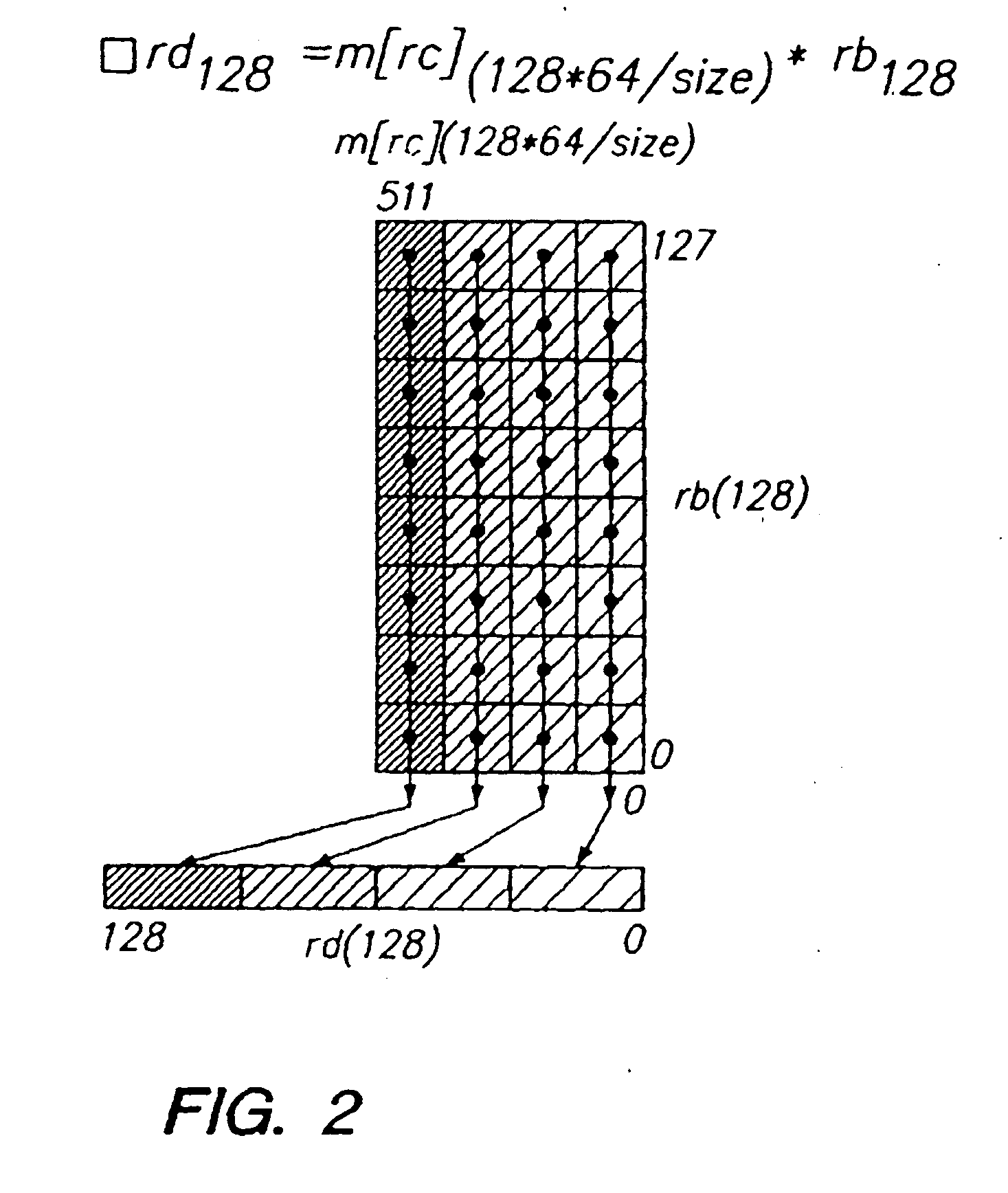
Programmable processor and method with wide operations
InactiveUS7301541B2Improve performanceEnhancing processor flexibilityEnergy efficient ICTCode conversionMemory addressPath width
A programmable processor and method for improving the performance of processors by expanding at least two source operands, or a source and a result operand, to a width greater than the width of either the general purpose register or the data path width. The present invention provides operands which are substantially larger than the data path width of the processor by using the contents of a general purpose register to specify a memory address at which a plurality of data path widths of data can be read or written, as well as the size and shape of the operand. In addition, several instructions and apparatus for implementing these instructions are described which obtain performance advantages if the operands are not limited to the width and accessible number of general purpose registers.
Owner:MICROUNITY
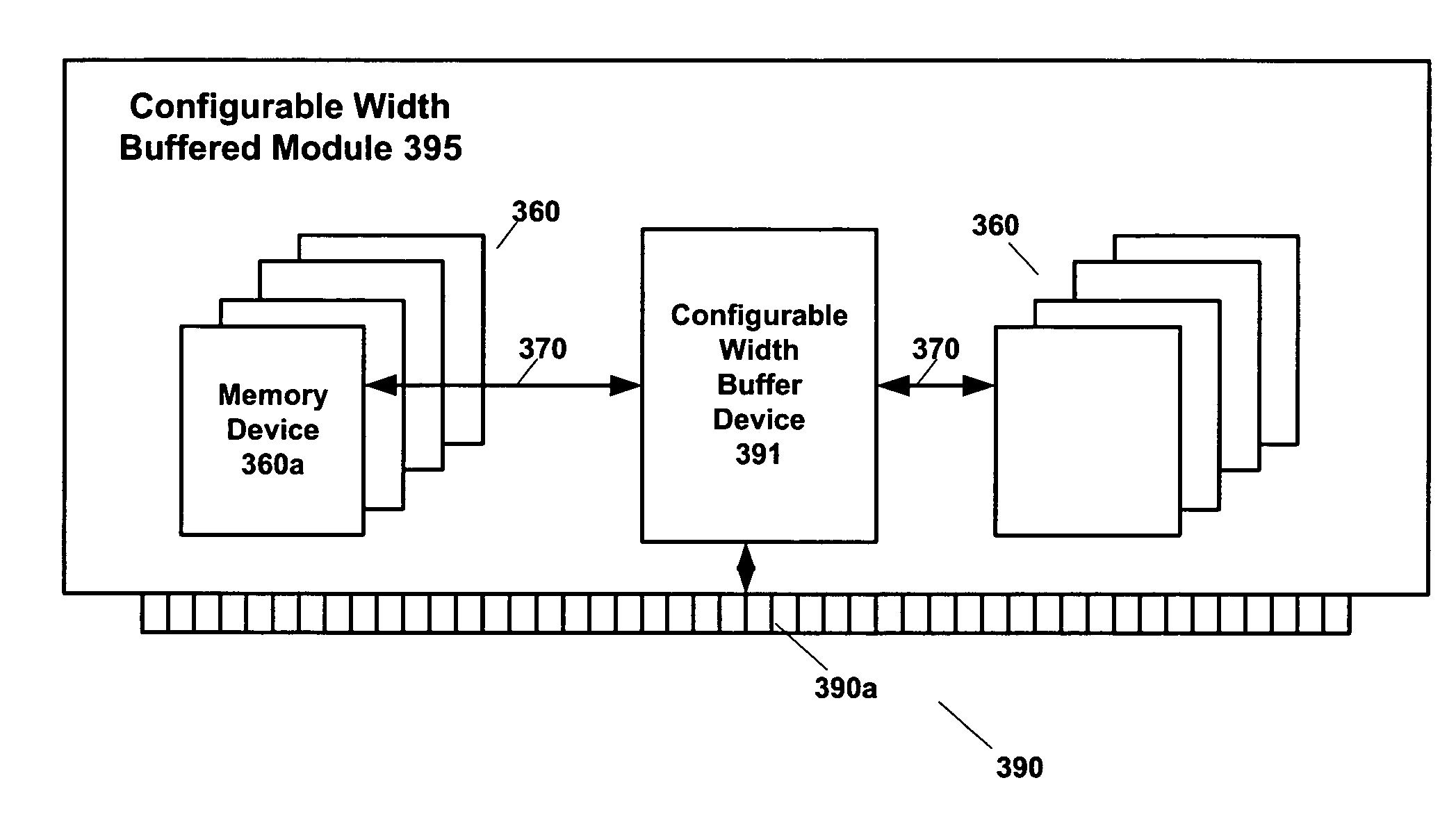
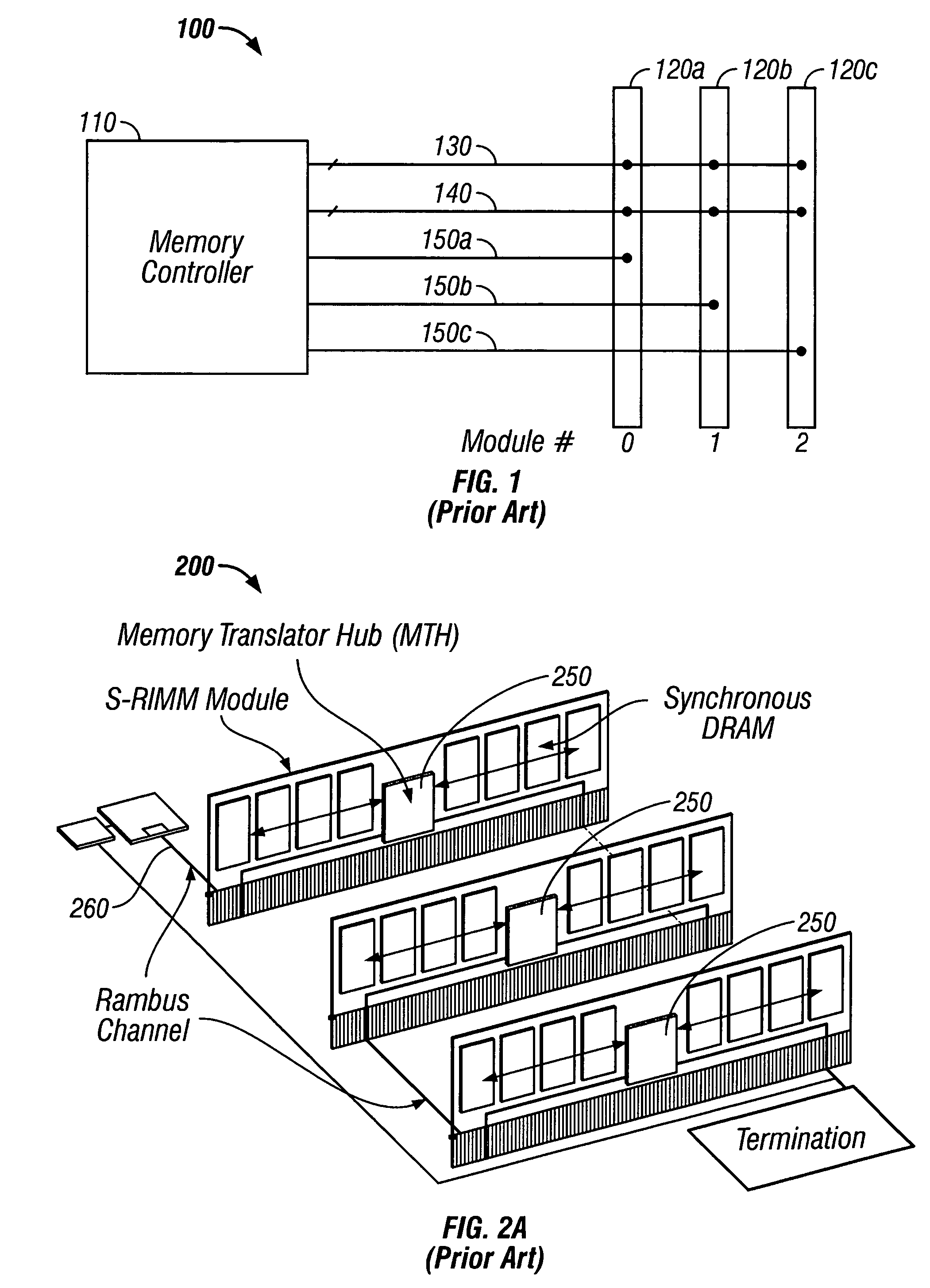
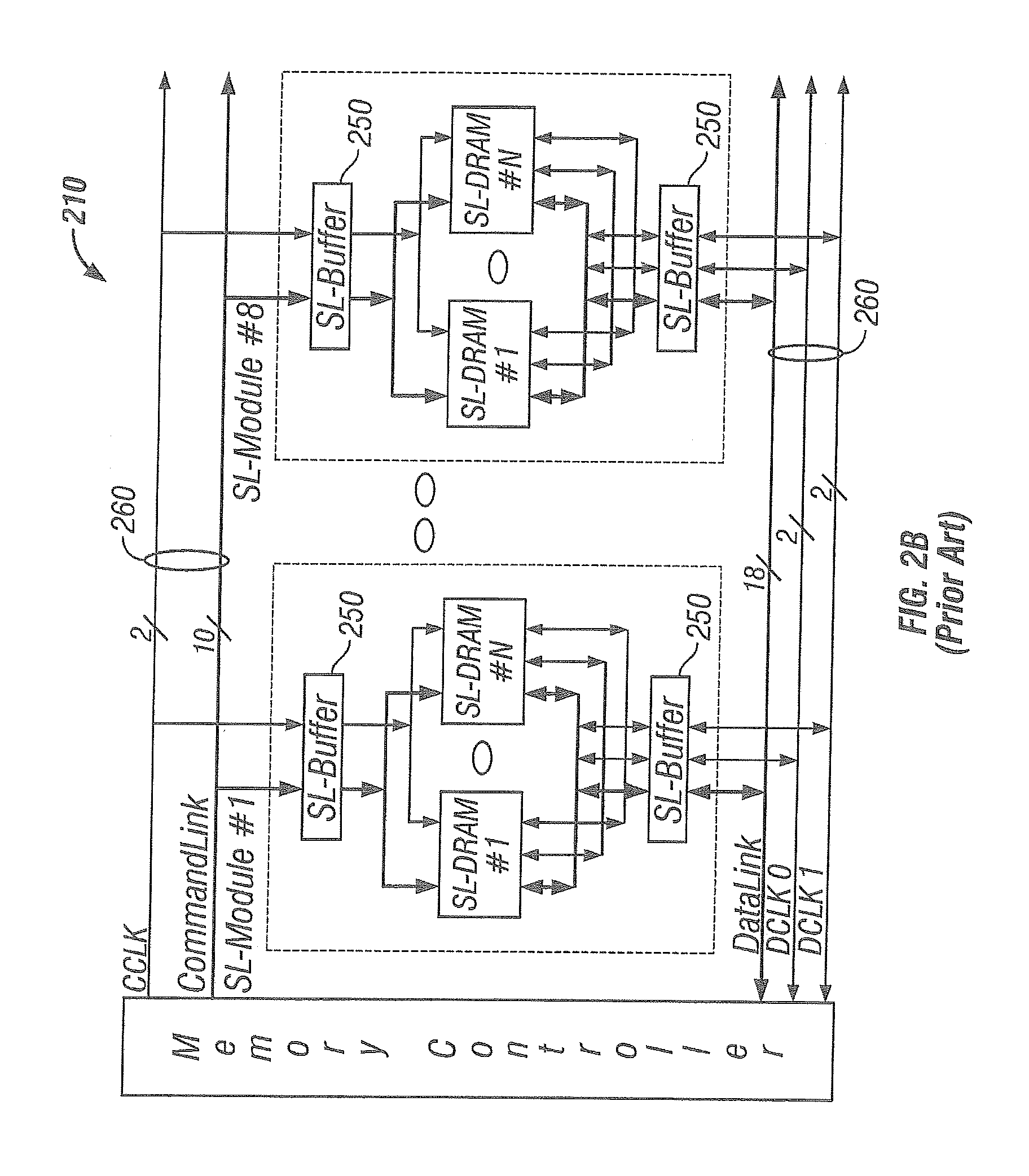
Configurable width buffered module
A memory system architecture / interconnect topology includes a configurable width buffered module having a configurable width buffer device. The configurable width buffer device is coupled to at least one memory device on the configurable width memory module. The configurable width buffer device includes an interface and a configurable serialization circuit capable of varying a data path width or a number of contacts used at the interface of the configurable width buffer device in accessing the at least one memory device. In an alternate embodiment of the present invention, a multiplexer / demultiplexer circuit is provided. A state storage provides a data width for the configurable width buffer and a SPD provides the configurable width buffer and / or module capabilities to the memory system.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Acoustic touchscreen having waveguided reflector arrays
InactiveUS6636201B1Acoustic energy concentrationCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingTransducerTouchscreen
An acoustic touchscreen (1a) has transmitting transducers (23a, 23b) for generating acoustic signals which are deflected across a touch-sensitive area (2) by an array 13 of partially acoustically reflective elements 14. A touch on the touch-sensitive area causes a perturbation in the acoustic signals. After traversing the touch-sensitive area, the acoustic signals are redirected by another array 13 of partially acoustically reflective elements 14, towards receiving transducers (26a, 26b), where the signals (and any perturbations) are sensed. To accommodate touchscreens having narrow border regions (15a), the acoustic signals are propagated across the border regions using acoustic waveguides (18). The waveguide confines the acoustic signals to traveling along a narrow path width, but yet permit them to be deflected across the touch-sensitive area. In this manner, the transducers and reflective elements can in turn be of narrower construction and can fit within narrow border regions.
Owner:ELO TOUCH SOLUTIONS INC
Tag-use antenna and tag using the same
ActiveUS20070252770A1Little changeRadiating elements structural formsAntenna feed intermediatesDielectricResonance wavelength
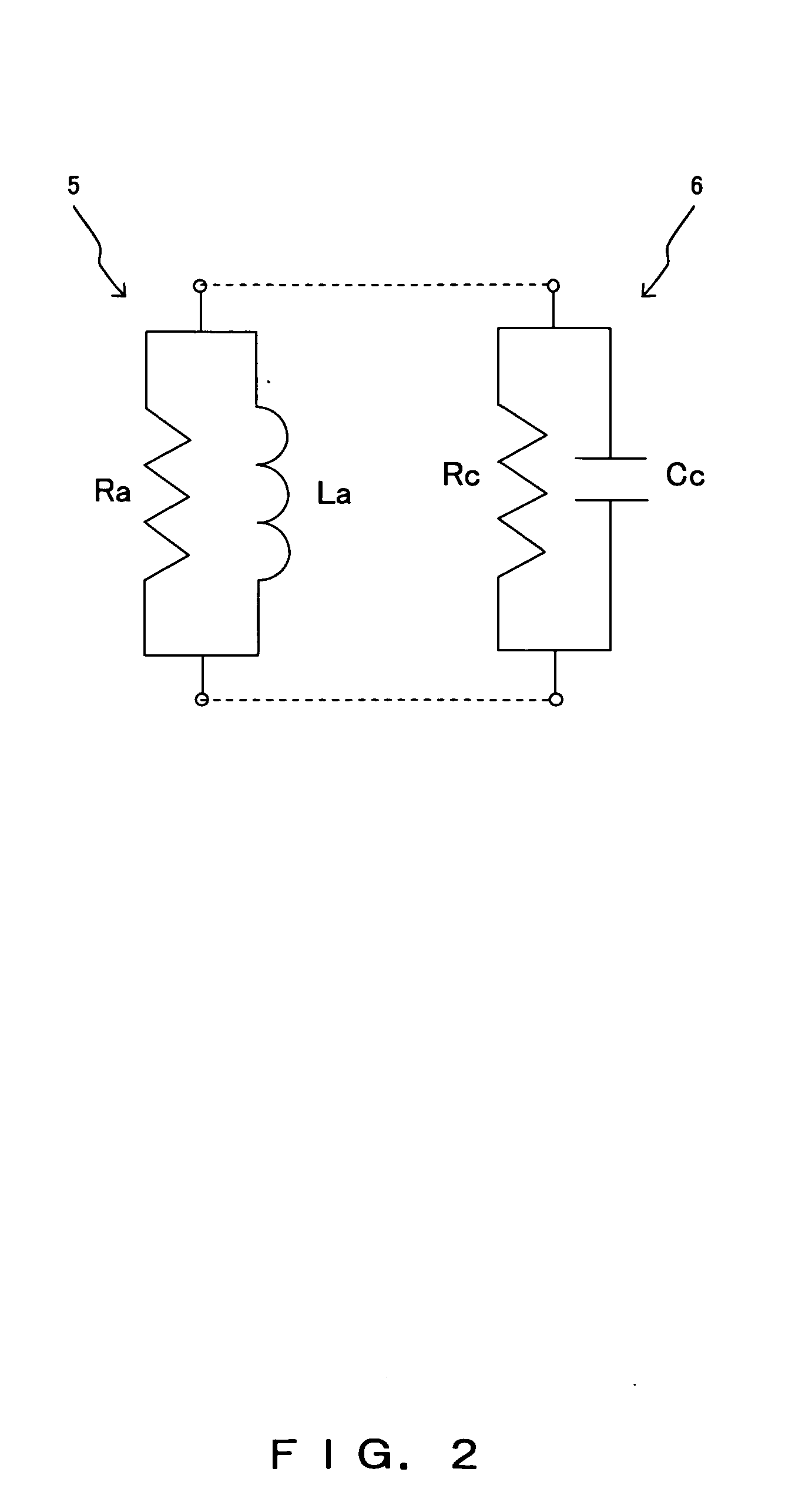
The present invention relates to a tag-use antenna allowing a miniaturization while maintaining a constant minimal change of a communication distance. The tag-use antenna has a feed part of a folded dipole antenna of a size of 53 mm long and 7 mm wide being connected to, and equipped with, an LSI chip of Rc=500 ohms and Cc=1.4 pF and is covered with plastic resin 13 of the dielectric constant εr=3 and thickness of t=0.75 mm on both sides of the antenna. The dipole part of 1 mm wire path width of the tag-use antenna is formed in a rectangular spiral by being bent inward from both ends at bending parts at four places. The entire length of the dipole antenna when extending the four bending parts straight is featured so as to be shorter than one half of a resonance wavelength of the antenna. An inductance part is featured in the intermediate part of the both dipole parts in the neighborhood of the center of the antenna. The inductance part is connected to the chip equipment part in parallel with the both dipole parts.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Programmable processor and method with wide operations
InactiveUS20080104375A1Reduce in quantityImprove performanceEnergy efficient ICTCode conversionMemory addressGeneral purpose
A programmable processor and method for improving the performance of processors by expanding at least two source operands, or a source and a result operand, to a width greater than the width of either the general purpose register or the data path width. The present invention provides operands which are substantially larger than the data path width of the processor by using the contents of a general purpose register to specify a memory address at which a plurality of data path widths of data can be read or written, as well as the size and shape of the operand. In addition, several instructions and apparatus for implementing these instructions are described which obtain performance advantages if the operands are not limited to the width and accessible number of general purpose registers.
Owner:MICROUNITY
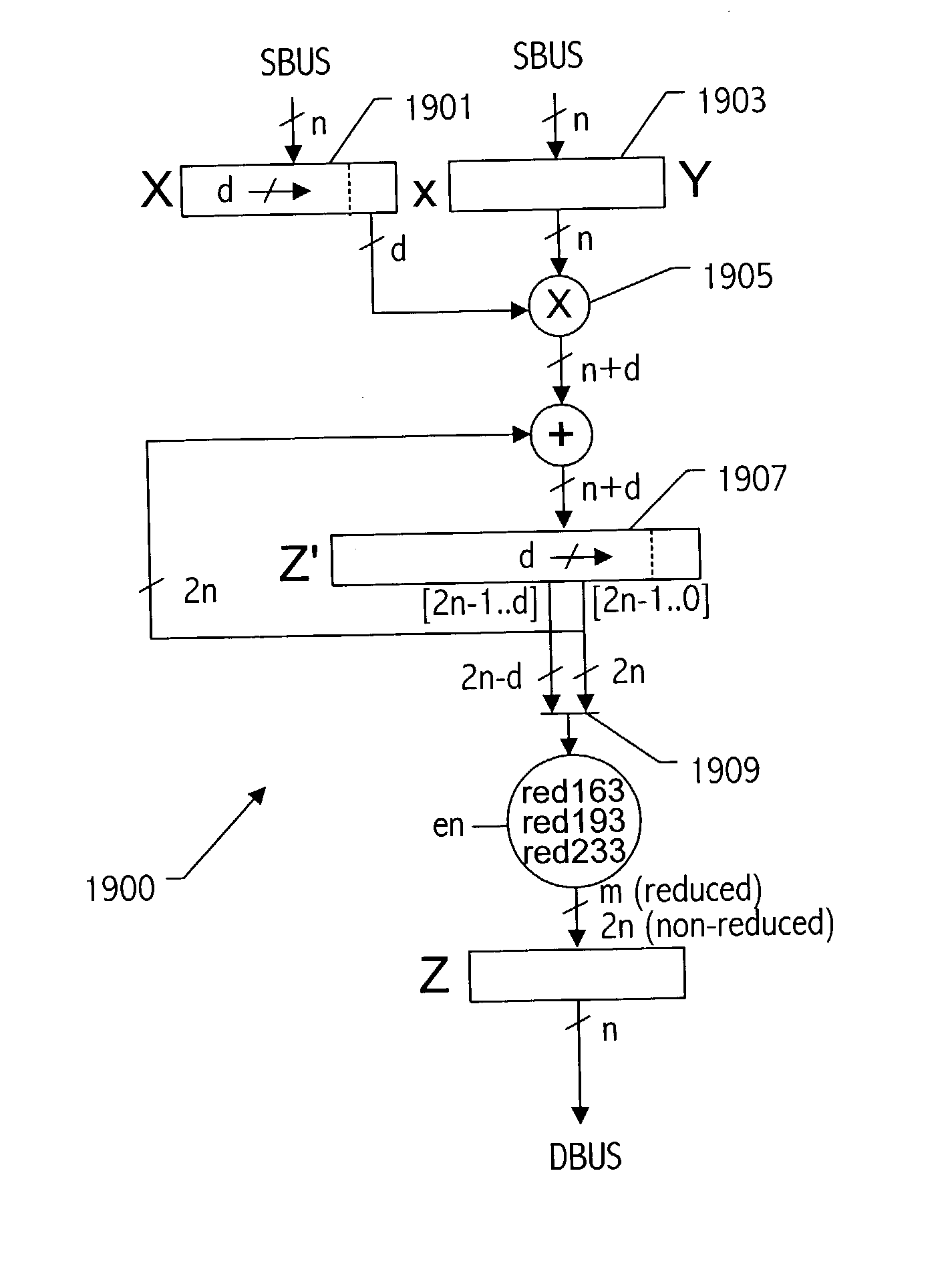
Generic implementations of ellipitic curve cryptography using partial reduction
ActiveUS20030208518A1Digital computer detailsComputations using residue arithmeticBinary multiplierOperand
A reduction operation is utilized in an arithmetic operation on two binary polynomials X(t) and Y(t) over GF(2), where an irreducible polynomial Mm(t)=t<m>+am-1t<m-1>+am-2t<m-2>+ . . . +a1t+a0, where the coefficients as are equal to either 1 or 0, and m is a field degree. The reduction operation includes partially reducing a result of the arithmetic operation on the two binary polynomials to produce a congruent polynomial of degree less than a chosen integer n, with m<=n. The partial reduction includes using a polynomial M'=(Mm(t)-t<m>)*t<n-m>, or a polynomial M''=Mm(t)*t<n-m >as part of reducing the result to the degree less than n and greater than or equal to m. The integer n can be the data path width of an arithmetic unit performing the arithmetic operation, a multiple of a digit size of a multiplier performing the arithmetic operation, a word size of a storage location, such as a register, or a maximum operand size of a functional unit in which the arithmetic operation is performed.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Buffered Memory Having A Control Bus And Dedicated Data Lines
InactiveUS20080034130A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital storageInterconnect topologyMultiplexer
A memory system architecture / interconnect topology includes a configurable width buffered module having a configurable width buffer device. The configurable width buffer device is coupled to at least one memory device on the configurable width memory module. The configurable width buffer device includes an interface and a configurable serialization circuit capable of varying a data path width or a number of contacts used at the interface of the configurable width buffer device in accessing the at least one memory device. In an alternate embodiment of the present invention, a multiplexer / demultiplexer circuit is provided. A state storage provides a data width for the configurable width buffer and a SPD provides the configurable width buffer and / or module capabilities to the memory system.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
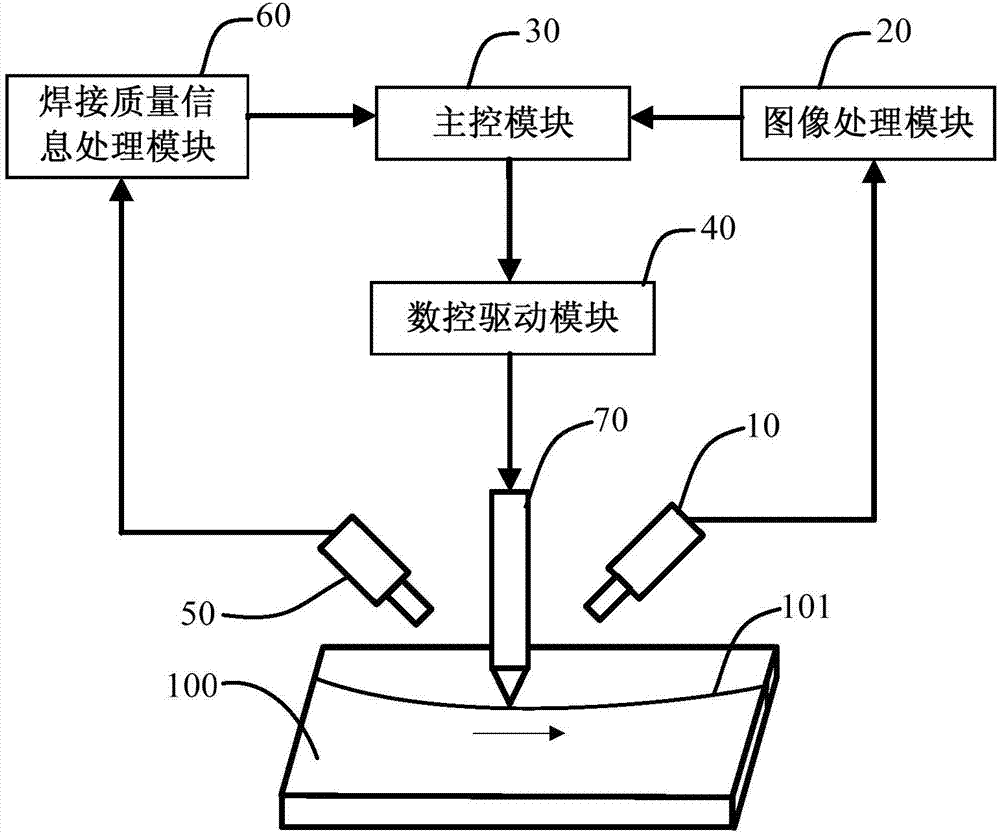
Welding seam tracking system and method of laser welding machine
ActiveCN103753015AImprove the level ofThe workload is reduced or even ignoredLaser beam welding apparatusNumerical controlSimulation
The invention discloses a welding seam tracking system of a laser welding machine. A CCD (Charge Coupled Device) visual sensor is used for converting collected light signals into image data which is output in a serial mode according to the time sequence to obtain a welding seam path image; an image processing module is used for preprocessing the welding seam path image, calculating the actual welding seam path width and tracking direction and combining with the obtained workpiece height through detection to output actual welding track data; a main control module is used for processing the actual welding track data and sending out a control instruction according to the processing result; a numerical control driving module is used for executing the control instruction of the main control module to drive a lase welding head, adjusting the position of the laser welding head and controlling the welding action of the welding head. According to the welding seam tracking system and method of the laser welding machine, the automatic laser welding is achieved, the deviation is small, the accuracy is high, the welding quality is good, and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN GDLASER TECH CO LTD
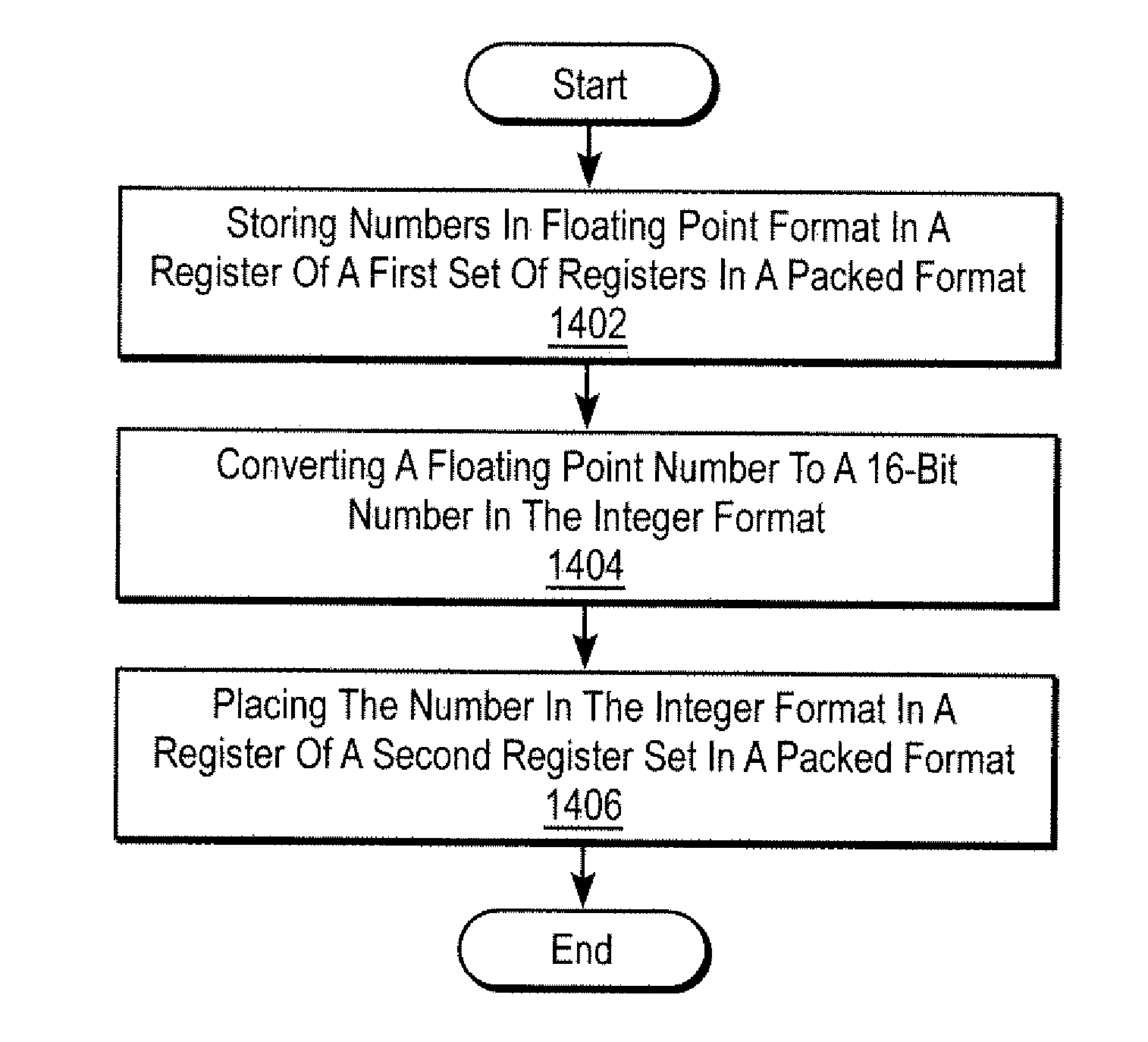
Method and apparatus for floating point operations and format conversion operations
A method and apparatus are described for converting a number from a floating point format to an integer format or from an integer format to a floating point format responsive to a control signal of a control signal format.Numbers are stored in the floating point format in a register of a first set of architectural registers in a packed format. One or more numbers in the floating point format are converted to the integer format and placed in a register of a second set of architectural registers in a packed format. Conversion from integer format to floating point format is performed in a similar manner.A floating point arithmetic apparatus is described that provides for converting a plurality of numbers between integer formats and a floating point formats, further providing for conversion operations that require a greater data path width than floating-point arithmetic operations.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Buffered memory having a control bus and dedicated data lines
InactiveUS7526597B2Memory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital storageParallel computingControl bus
A memory system architecture / interconnect topology includes a configurable width buffered module having a configurable width buffer device. The configurable width buffer device is coupled to at least one memory device on the configurable width memory module. The configurable width buffer device includes an interface and a configurable serialization circuit capable of varying a data path width or a number of contacts used at the interface of the configurable width buffer device in accessing the at least one memory device. In an alternate embodiment of the present invention, a multiplexer / demultiplexer circuit is provided. A state storage provides a data width for the configurable width buffer and a SPD provides the configurable width buffer and / or module capabilities to the memory system.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Processor architecture for executing transfers between wide operand memories
InactiveUS20090089540A1Improve performanceEnhancing processor flexibilityInstruction analysisProgram control using wired connectionsMemory addressGeneral purpose
A programmable processor and method for improving the performance of processors by expanding at least two source operands, or a source and a result operand, to a width greater than the width of either the general purpose register or the data path width. The present invention provides operands which are substantially larger than the data path width of the processor by using the contents of a general purpose register to specify a memory address at which a plurality of data path widths of data can be read or written, as well as the size and shape of the operand. In addition, several instructions and apparatus for implementing these instructions are described which obtain performance advantages if the operands are not limited to the width and accessible number of general purpose registers.
Owner:MICROUNITY
Deviation detection in mobile transit systems
ActiveUS20140200805A1Instruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsTransit systemBias detection
In one embodiment, a mobile device or a network device is configured to identify when a transit vehicle deviates from a transit path. The mobile device is configured to perform a positioning technique to generate data indicative of the location of a mobile device. Based on the location of the mobile device, a path is identified. The path is associated with an estimated path width based on the classification of the path and / or the accuracy of the positioning technique. A target route is calculated using the estimated path width. As the transit vehicle travels, the target route is compared to the location of the mobile device. If the mobile device and or transit vehicle deviates from the target route, a message is generated. The message may indicate that the transit vehicle is being re-routed and / or recommends the computation of a new path.
Owner:HERE GLOBAL BV
Processor for executing switch and translate instructions requiring wide operands
InactiveUS20080189512A1Improve performanceEnhancing processor flexibilityInstruction analysisMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory addressGeneral purpose
A programmable processor and method for improving the performance of processors by expanding at least two source operands, or a source and a result operand, to a width greater than the width of either the general purpose register or the data path width. The present invention provides operands which are substantially larger than the data path width of the processor by using the contents of a general purpose register to specify a memory address at which a plurality of data path widths of data can be read or written, as well as the size and shape of the operand. In addition, several instructions and apparatus for implementing these instructions are described which obtain performance advantages if the operands are not limited to the width and accessible number of general purpose registers.
Owner:MICROUNITY
Laser additive manufacturing method applied to large-sized metal part
ActiveCN106513679AAvoid deformationAvoid crackingAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyLoad distributionLaser additive manufacturing
The invention provides a laser additive manufacturing method applied to a large-sized metal part. The laser additive manufacturing method comprises the following steps: according to the configuration characteristics and load distribution characteristics of the integral structure of the part, dividing the part into a plurality of sub-blocks; according to the shape structure characteristics of all the sub-blocks, separately dividing the sub-blocks into a plurality of scanning areas: wed plate scanning areas, edge strip scanning areas, T-shaped block scanning areas and ear plate scanning areas, and then setting the scanning sequence according to the principle that priority is given to the farthest scanning area; adopting a short-edge reciprocating scanning mode in the scanning areas, guaranteeing the consistent widths of scanning paths in the scanning areas, and completing the manufacturing of all the sub-blocks; assembling, clamping and positioning the manufactured sub-blocks according to the position relation determined when the part is divided into the sub-blocks, guaranteeing that deformation allowance is left at the seam between two adjacent sub-blocks, and adopting a deformation mapping mode for positioning between two adjacent sub-blocks; and subjecting all the positioned sub-blocks to laser additive connection till all the sub-blocks are connected together to form a whole, thereby completing the manufacturing of the part.
Owner:SHENYANG AEROSPACE UNIVERSITY
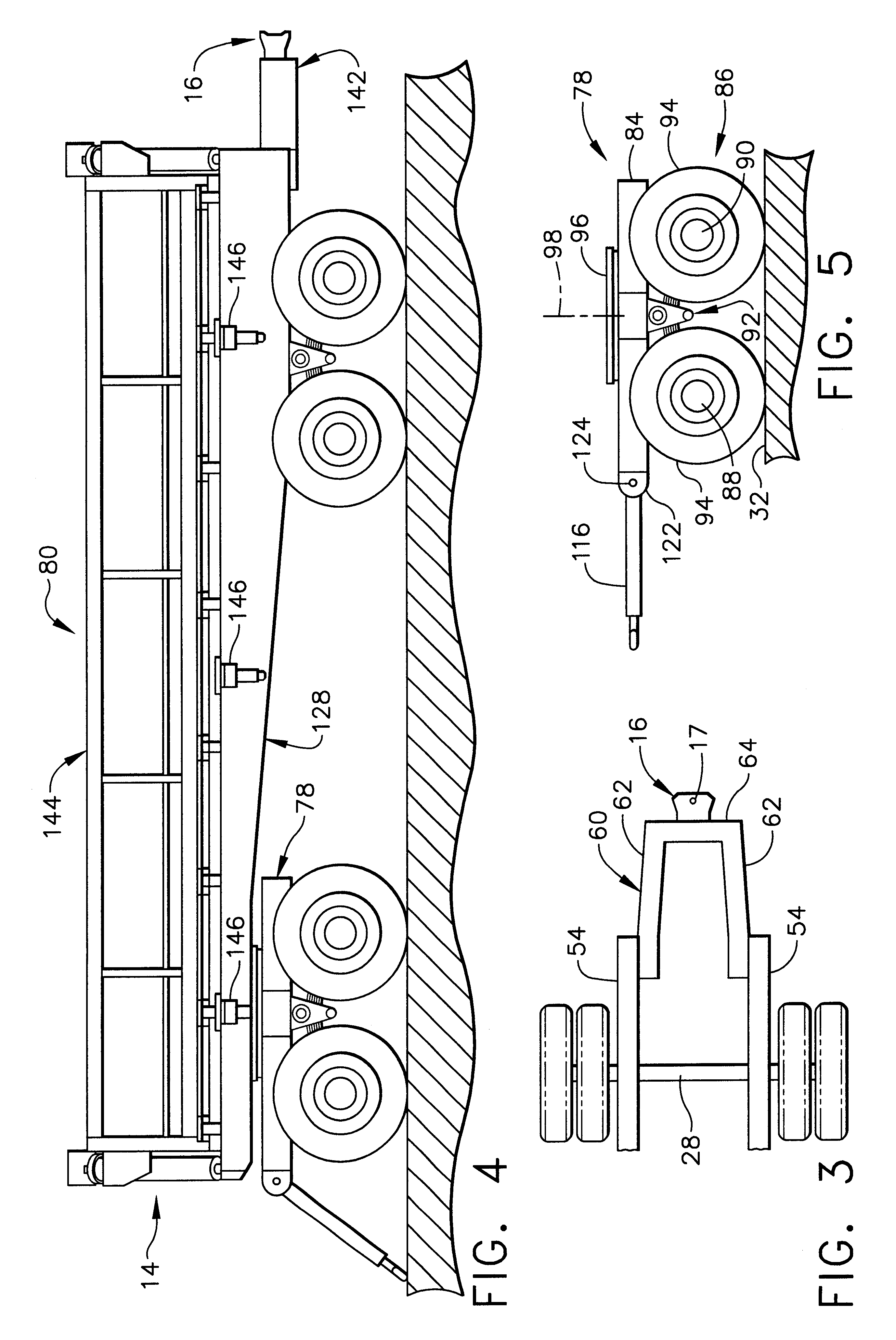
Multicombination vehicle and method for transporting a payload in an underground mine
A multicombination vehicle and method are provided for transporting a payload, such as a mined metal ore, over the roadways existing in an underground mine. The multicombination vehicle includes a powered towing unit, which may comprise a rigid body truck, and at least one towed unit mechanically coupled to the rigid body truck. The vehicle may also include a plurality of the towed units, with a forward most one of the units coupled to the rigid body truck and each adjacent pair of the towed units being coupled to one another. Each of the units includes a chassis, a plurality of wheeled axles connected to the chassis for supporting the respective unit as the vehicle travels over the roadways of the mine, and a draw frame attached to and extending rearwardly from the corresponding chassis, with a coupling attached to a rear end of the draw frame. Each towed unit may comprise a semi-trailer mounted on a dolly, with a drawbar attached to and extending forwardly from the dolly and connected with the coupling of the immediately forward unit of the vehicle. The multicombination vehicle is configured so as to minimize the swept path width of the vehicle as the vehicle negotiates turns. This is accomplished by providing each of the towed units with a dolly drawbar length having a value of less than 3.0 meters and establishing a ratio of the coupling overhang-to-wheelbase, for each of the units, of at least 0.5.
Owner:COOPER JAMES W
Method and apparatus for monitoring and control of suck back level in a photoresist dispense system
ActiveUS20080035666A1Improve system stabilityEasy to monitorPower operated devicesScattering properties measurementsLight beamMonitoring and control
An apparatus for monitoring a position of a semiconductor process fluid interface in a dispense nozzle includes an extended optical source adapted to provide an optical beam propagating along an optical path. The optical beam is characterized by a path width measured in a first direction aligned with a dispense direction. The apparatus also includes an optical detector coupled to the optical path and adapted to detect at least a portion of the optical beam and a dispense nozzle disposed along the optical path at a location between the extended optical source and the optical detector. The apparatus further includes a nozzle positioning member coupled to the dispense nozzle and adapted to translate the dispense nozzle in the first direction.
Owner:SCREEN SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
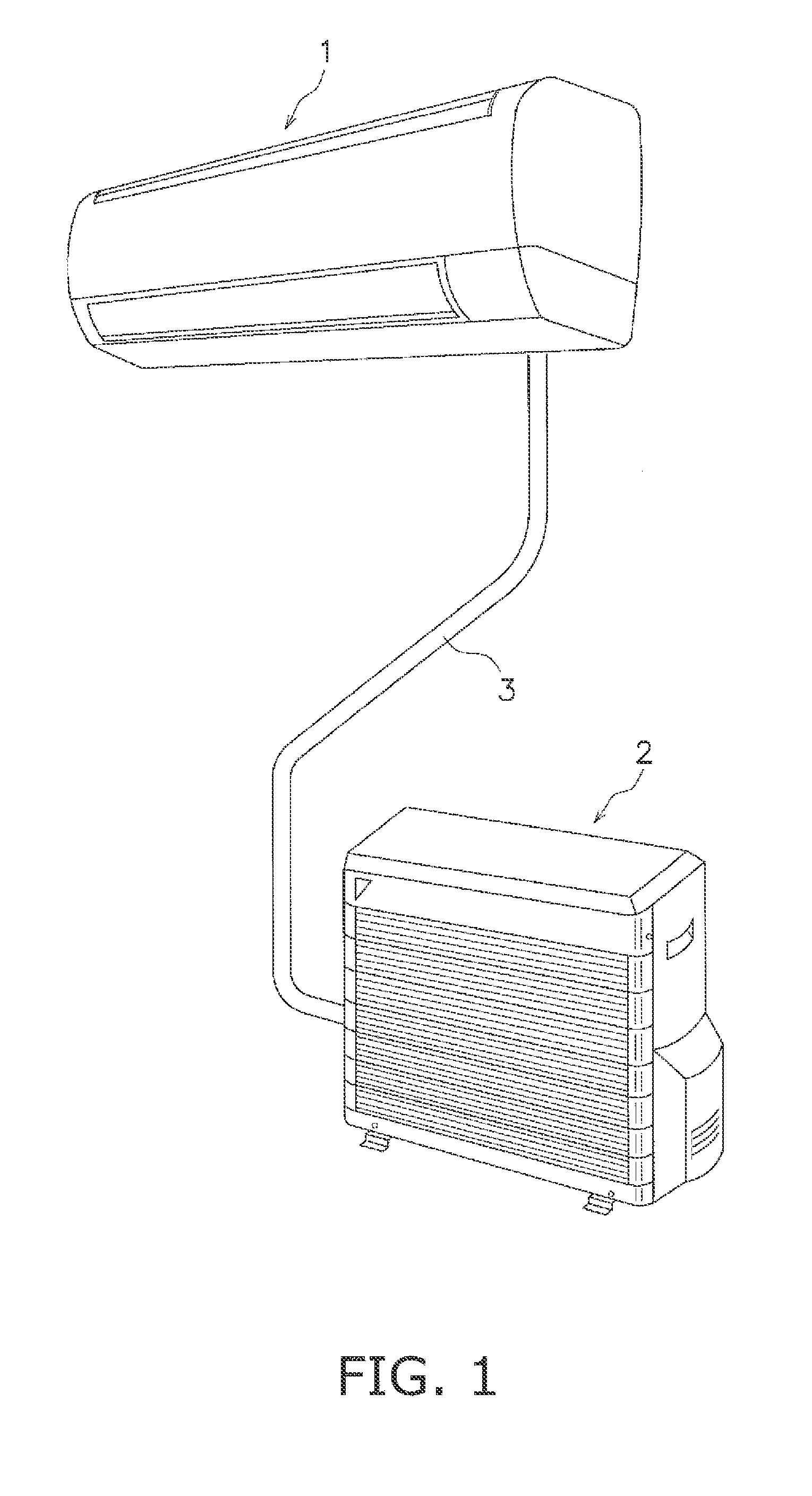
Induction motor, compressor and refrigerating cycle apparatus
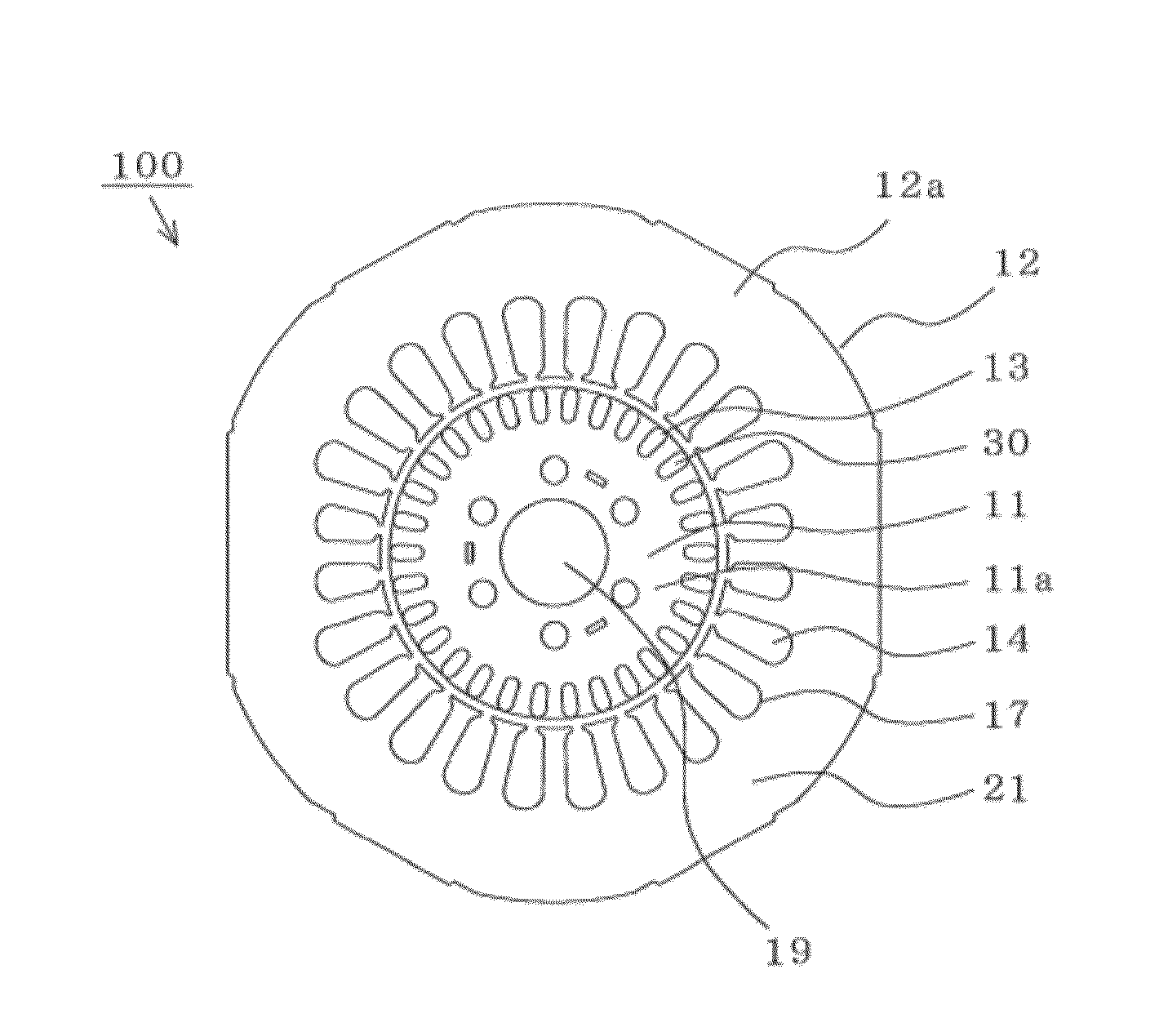
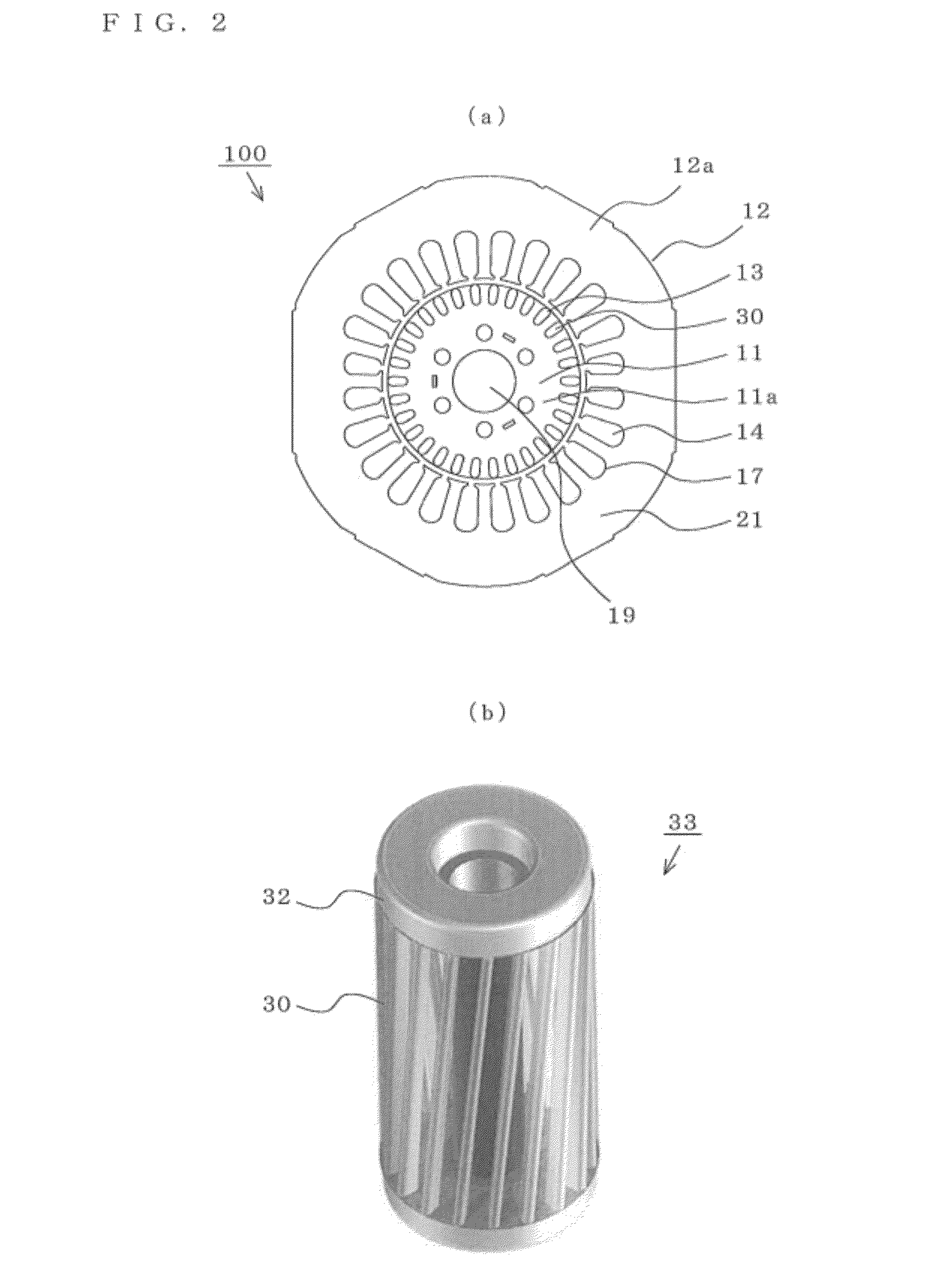
ActiveUS20120159983A1Improve efficiencyIncrease widthRotary/oscillating piston combinations for elastic fluidsCompressorInduction motorMagnetic flux
The efficiency of an induction motor is improved while suppressing the generation of magnetic flux saturation of a rotor core. In an induction motor, “a magnetic path width of a rotor” which is the product of a circumferential width of a rotor tooth formed in the rotor and the number of rotor teeth is equal to or larger than “a magnetic path width of a stator” which is the product of a circumferential width of a stator tooth formed in the stator and the number of stator teeth.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Flat cable
ActiveCN101647072APremium FlexibilityExcellent bending resistanceCommunication cablesFlat/ribbon cablesElectrical conductorEngineering
Provided is a thin flexible flat cable which can exhibit an excellent flexibility and bending resistance without degrading excellent electric characteristic based on a strip structure and improve thecost performance. The flexible flat cable (1) includes: an air-containing layer which has a width substantially identical to a transmission path width of a cable body (10) having a plurality of conductors (11) arranged at a predetermined pitch and which serves as an insulating member arranged to sandwich the cable body (10) from both sides; and a shield member (23, 24) which covers the surface ofthe air-containing layer and is electrically connected to a ground layer at terminal portions at both ends of the cable body (10). The air-containing layer is formed by nonwoven fabric pieces (14, 15)cut with a width substantially identical to the transmission path width of the cable body (10).
Owner:DEXERIALS CORP
Right-turning lane design method by considering turning characteristic of large vehicle
The invention belongs to the field of traffic safety designs and lane designs. Aiming at the maximum sweeping path width and a difference of a radius between front inner wheels and a radius between rear inner wheels during right turning of a large vehicle, the invention provides a right-turning lane design method by considering a turning characteristic of the large vehicle. Compared with the conventional design method, the design method has the advantage that the safety, the efficiency and the land utilization are improved greatly. According to the technical scheme, the right-turning lane design method by considering the turning characteristic of the large vehicle comprises the following step of: calculating deflection of traces of a dragging articulated vehicle and a small coach, wherein (1) the width of a diversion lane is required to be equal to a sum of a wheel trace inner displacement, namely the maximum sweeping path width, and a lateral clearance, and (2) the right-turning trace of the large vehicle is fit by an asymmetric three-center composite curve with a relatively small curve radius of an entrance lane and a relatively large curve radius of an exit lane; and under the condition that the width of the diversion lane and an inner-arc radius are known, drawing the three-center composite curve of a right-turning lane. The method is mainly applied to lane design.
Owner:TIANJIN MUNICIPAL ENG DESIGN & RES INST
Liquid ejection head and liquid ejection device
A flow path structure includes a heating element, a barrier layer, a liquid chamber formed by a part of the barrier layer and a pair of walls confronting each other to hold the heating element therebetween and a first individual flow path and a second individual flow path disposed on both the sides of the liquid chamber to communicate with the liquid chamber, a liquid is supplied to the liquid chamber from at least one of first and second individual flow paths, and the distance U between the walls in the liquid chamber and the flow path width W of the first individual flow path are set to satisfy U>W. With this arrangement, a flow path structure can be provided in which a failure in flow paths due to dusts is unlike to occur and which minimizes the influence of bubbles and has almost no uneven ejection.
Owner:SONY CORP
Generic implementations of elliptic curve cryptography using partial reduction
ActiveUS7240084B2Digital computer detailsComputations using residue arithmeticDatapathComputer science
A reduction operation is utilized in an arithmetic operation on two binary polynomials X(t) and Y(t) over GF(2), where an irreducible polynomial Mm(t)=tm+am−1tm−1+am−2tm−2+ . . . +a1t+a0, where the coefficients ai are equal to either 1 or 0, and m is a field degree. The reduction operation includes partially reducing a result of the arithmetic operation on the two binary polynomials to produce a congruent polynomial of degree less than a chosen integer n, with m≦n. The partial reduction includes using a polynomial M′=(Mm(t)−tm)*tn−m, or a polynomial M″=Mm(t)*tn−m as part of reducing the result to the degree less than n and greater than or equal to m. The integer n can be the data path width of an arithmetic unit performing the arithmetic operation, a multiple of a digit size of a multiplier performing the arithmetic operation, a word size of a storage location, such as a register, or a maximum operand size of a functional unit in which the arithmetic operation is performed.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
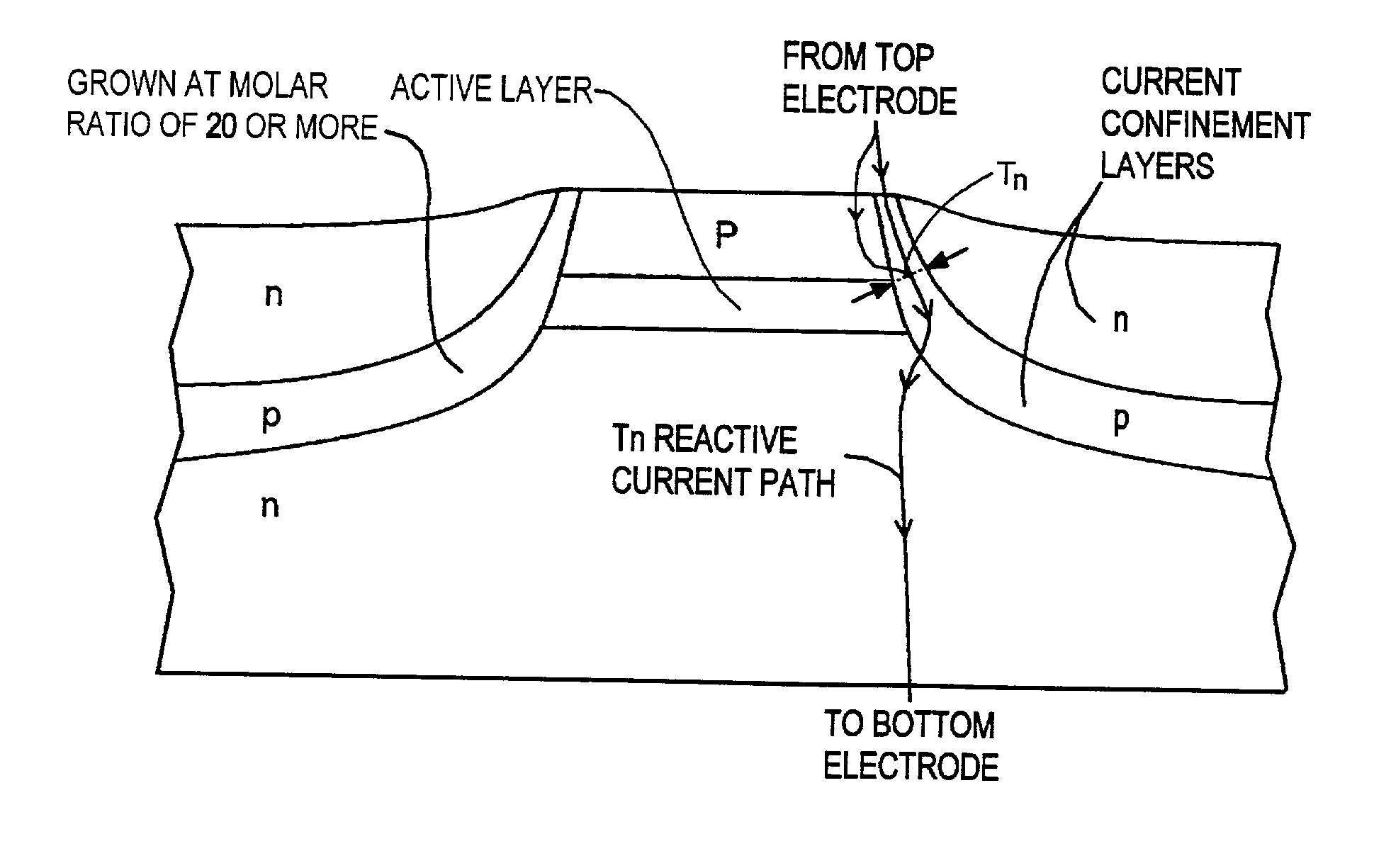
Semiconductor laser device and method for fabricating the same
A method for fabricating a buried semiconductor laser device including the steps of: forming a mesa structure including a bottom cladding layer, an active layer and a top cladding layer overlying an n-type semiconductor substrate; and forming a current confinement structure by growing a p-type current blocking layer and an n-type current blocking layer on each side surface of the mesa structure and on a skirt portion extending from the each side surface, the p-type current blocking layer being fabricated by using a raw material gas containing a group III element gas and a group V element gas at a molar ratio between 60 and 350 inclusive. In this method, the semiconductor laser device including the current confinement structure with the specified leakage current path width can be fabricated with the excellent reproducibility.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Lawn mower towing device
InactiveUS7347036B1Quick and easy disconnectionQuick and easy to disassembleSpadesHarvestersTerrainEngineering
An assembly is provided for towing first and second push-type lawn mowers behind a riding mower. A base plate attachable to the rear of the riding mower releasably holds a tow bar. First and second tow arms are releasably coupled to the tow bar and are each adapted for pivoting motion relative to and in an arc defined by the tow bar. The first and second tow arms are received in respective first and second couplers that are attachable to the first and second push-type mowers, respectively. The first and second couplers allow releasable attachment of the respective first and second tow arms. Each coupler is configured to allow rotational movement thereof relative to the tow arm such that respective first and second mowers to which the first and second couplers are attached can follow the contours of the terrain, thereby providing an even cut. The towing assembly is easily disassembled and re-connectable. Likewise, each push-type mower is easily removed from the towing assembly for quick use. A mowing path width gauge may be provided on the riding mower.
Owner:EASLEY JR J ALEXANDER
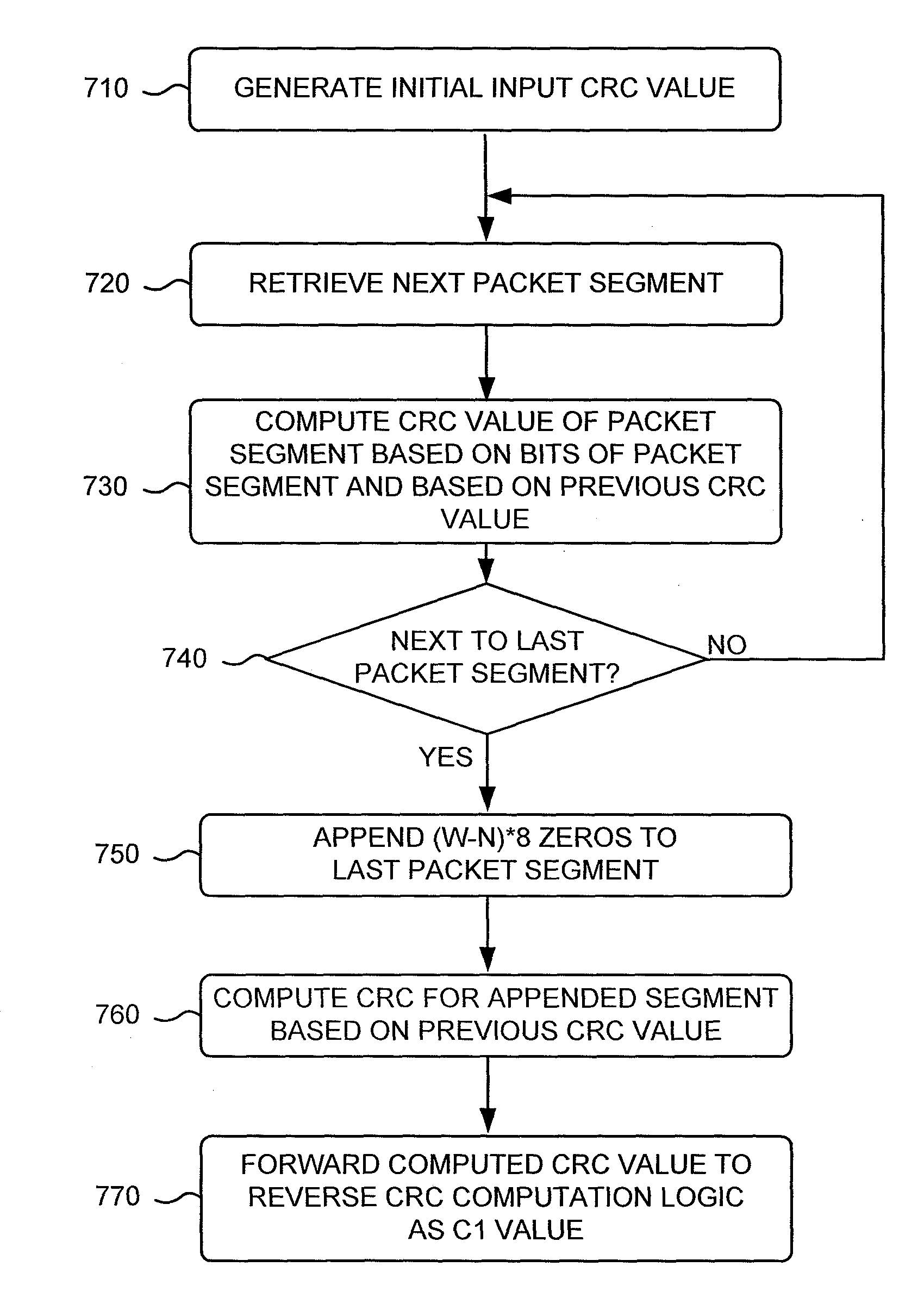
CRC computation for packet length not multiple of data path width
A communication device may include a cyclic redundancy check (CRC) calculator. The CRC calculator may determine a packet remainder of a packet based on a data path width associated with the communication device; append zeros to the packet remainder to generate an appended packet remainder equal in size to the data path width; compute a first CRC value for the appended packet; reverse bits of the computed first CRC value to obtain a reversed CRC value; multiply the bit reversed CRC value with a value based on a reciprocal CRC polynomial to generate a multiplication product; compute a second CRC value for the generated multiplication product based on the reciprocal CRC polynomial; and reverse bits of the second CRC value to generate a CRC for the packet.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
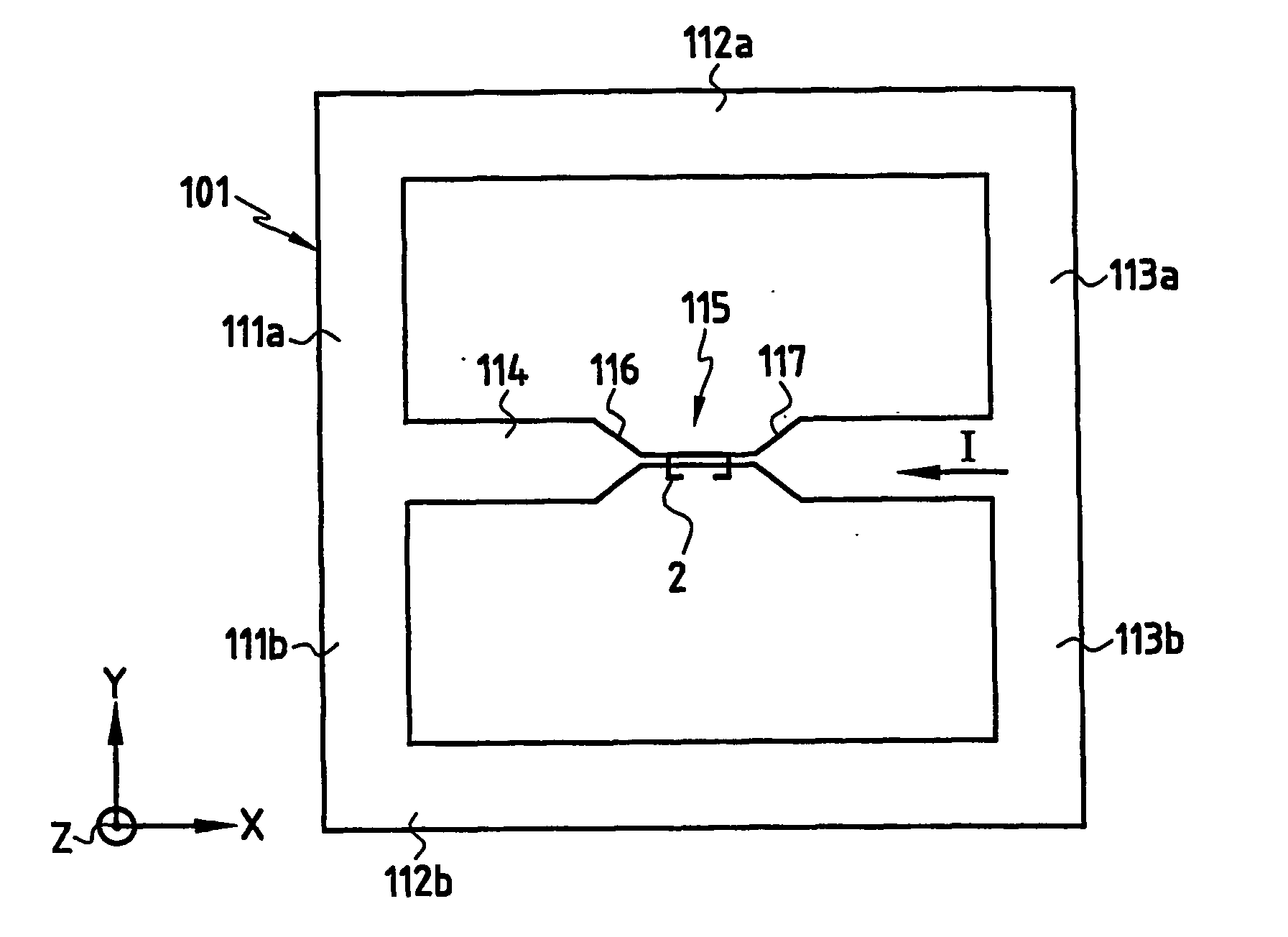
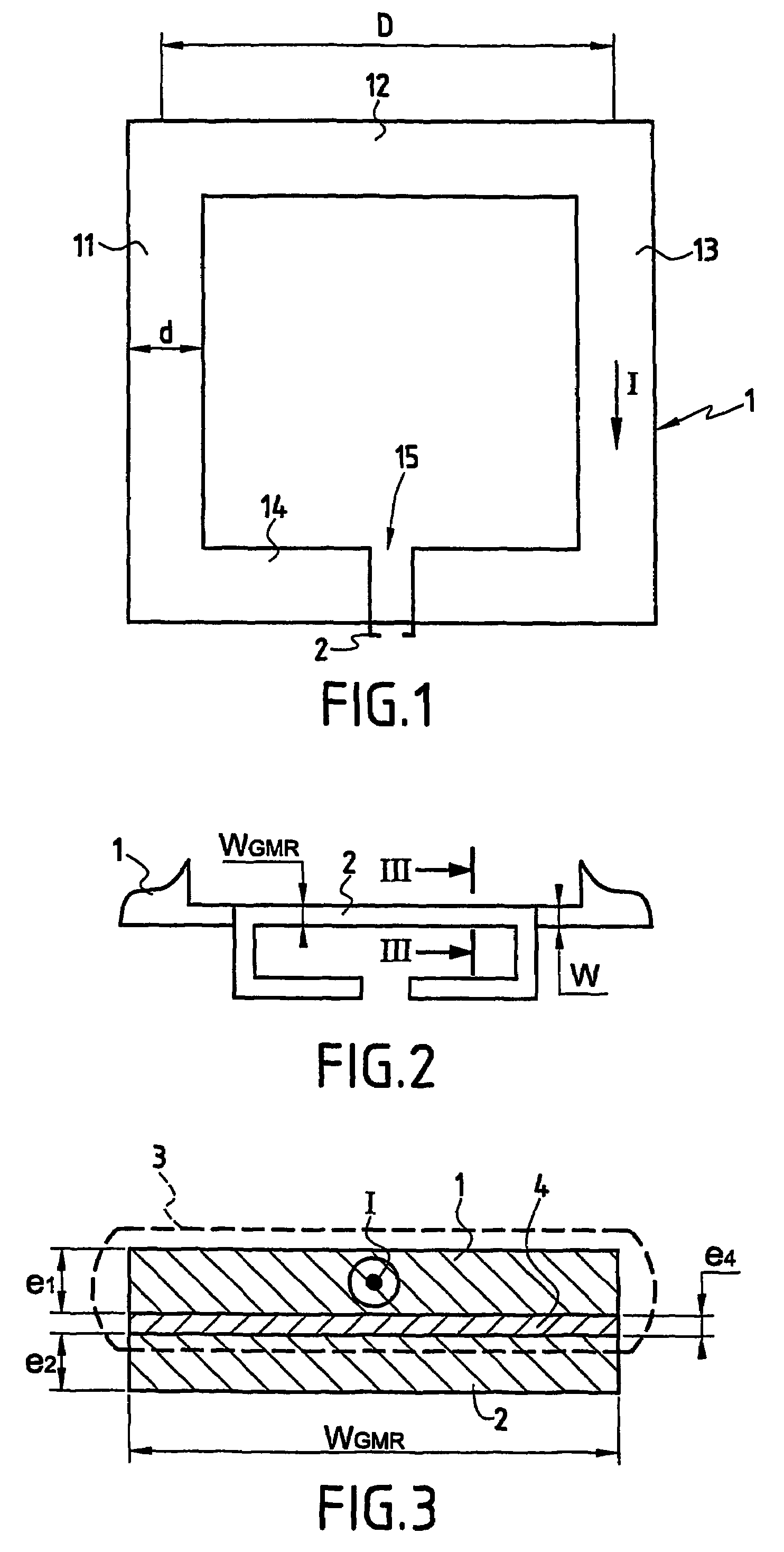
Device for sensing a magnetic field
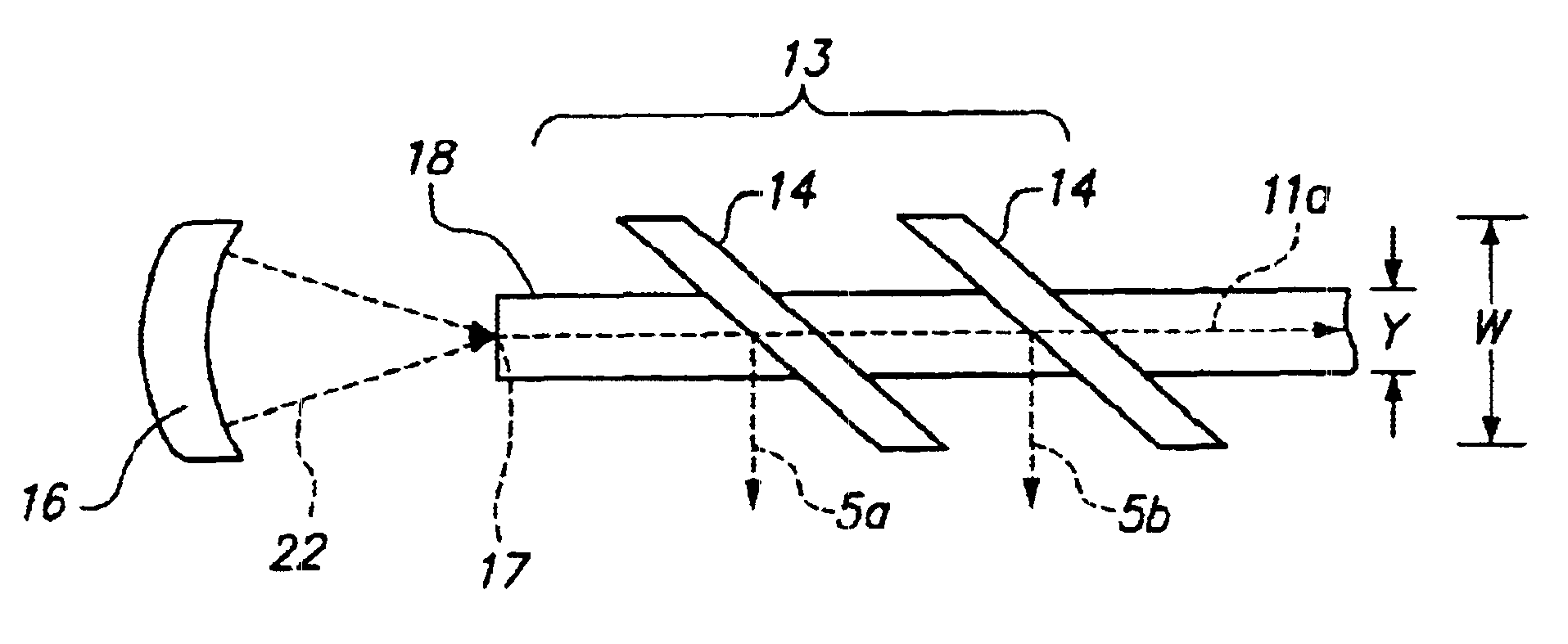
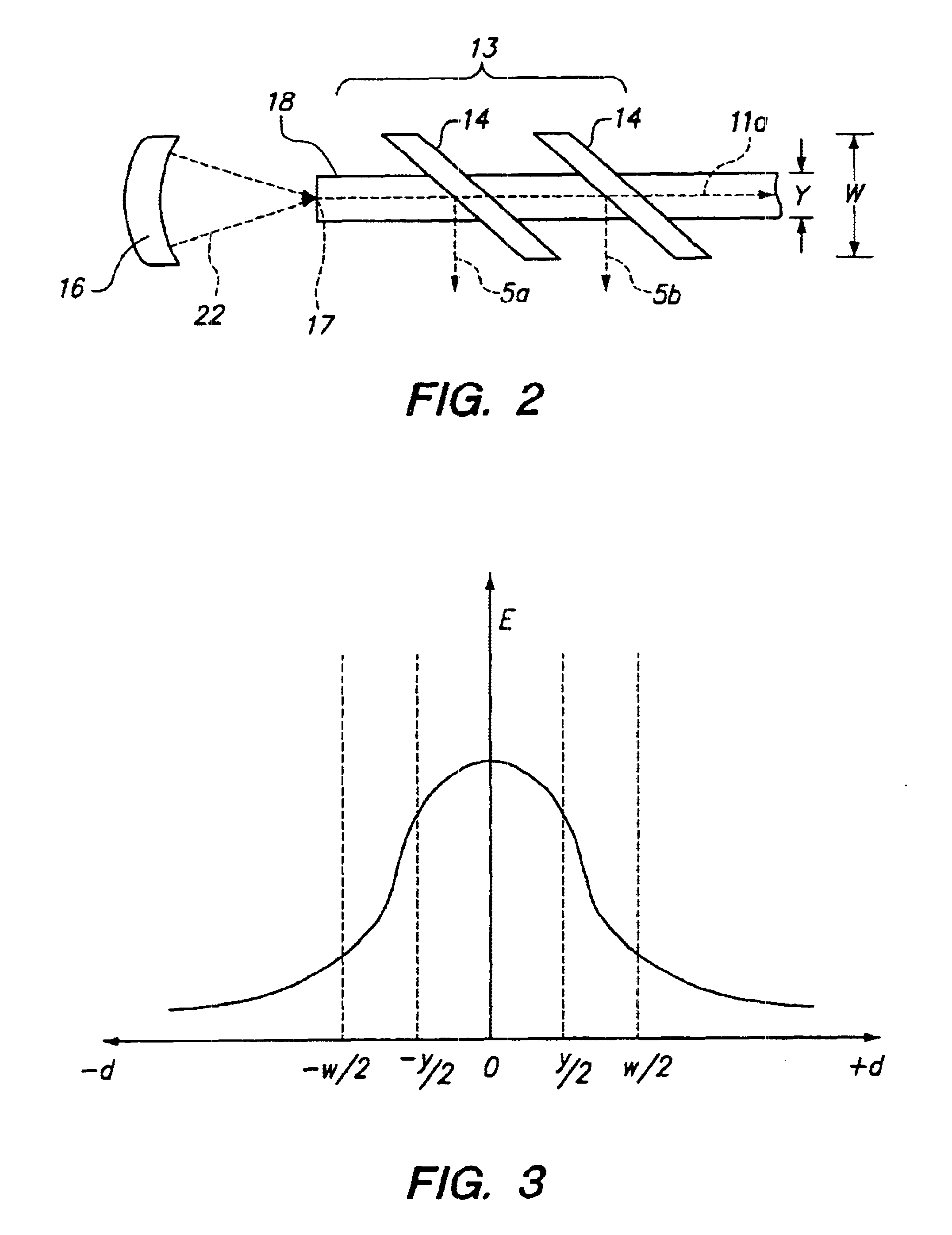
InactiveUS20060220641A1Comparable and good performanceEasy to produceMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesElectrical currentPath width
The device for sensing a magnetic field comprises a closed superconducting pick-up loop (1) having a path width (d) etched out of a single layer superconducting thin film and provided with a constriction (15) having a width (w) of narrow dimension smaller than the path width (d). The closed superconducting pick-up loop (1) constitutes a flux-to-field transformer (FFDT). At least one magnetoresistive element (2) is placed on top of or below the superconducting thin film, is isolated from the superconducting thin film by a thin insulating layer and is located so that an active part of the magnetoresistive element (2) is at the location of the constriction (15) and has a width equal to or less than the width of the constriction (15). The active part of the magnetoresistive element (2) is oriented so that the bias current in this active part is directed essentially along the constriction (15), orthogonally to the width of narrow dimension.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
Liquid ejection head and liquid ejection device
A flow path structure includes a heating element, a barrier layer, a liquid chamber formed by a part of the barrier layer and a pair of walls confronting each other to hold the heating element therebetween and a first individual flow path and a second individual flow path disposed on both the sides of the liquid chamber to communicate with the liquid chamber, a liquid is supplied to the liquid chamber from at least one of first and second individual flow paths, and the distance U between the walls in the liquid chamber and the flow path width W of the first individual flow path are set to satisfy U>W. With this arrangement, a flow path structure can be provided in which a failure in flow paths due to dusts is unlike to occur and which minimizes the influence of bubbles and has almost no uneven ejection.
Owner:SONY CORP
Impedance Compensation For A Differential Pair Of Conductive Paths
InactiveUS20130097577A1Computer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsPath lengthElectrical conductor
Methods, apparatus, and products for impedance compensation for a differential pair of conductive paths, including: determining the differential impedance and conductor geometry for the differential pair of conductive paths; determining the path length differential between the conductive paths in the differential pair of conductive paths; determining a centerline path to follow for a shorter conductive path in the differential pair of conductive paths, wherein the centerline path lengths the shorter conductive path such that the length of each conductive path in the differential pair of conductive paths is identical within a predetermined threshold; determining a number of subdivisions of one or more serpentine segments on one of the conductive paths in the differential pair; and determining, in dependence upon the differential impedance at each of the subdivisions of the one or more serpentine segments, a serpentine segment path width for the serpentine segment.
Owner:IBM CORP
Cross flow fan
ActiveUS20140301825A1Reduce flow rateSlow changePump componentsCircumferential flow pumpsImpellerSuction surface
A cross flow fan includes a support plate and an impeller with a plurality of blades disposed on the support plate at predetermined intervals. On each blade, a radius of a pressure surface arc is greater than a radius of a suction surface arc, a radius of an inner peripheral side arc is greater than a radius of an outer peripheral side arc, and a region of maximum thickness is located 40% to 60% from the inner peripheral side arc in the lengthwise direction. The blades are disposed such that the inner peripheral side arcs are positioned on an inner peripheral side of the support plate and the outer peripheral side arcs are positioned on an outer peripheral side of the support plate. A flow path width between the plurality of blades gradually decreases from the inner peripheral side toward the outer peripheral side of the support plate.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
Device for sensing a magnetic field
InactiveUS7342396B2Comparable and good performanceEasy to produceMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesElectrical currentSuperconducting thin films
The device for sensing a magnetic field comprises a closed superconducting pick-up loop (1) having a path width (d) etched out of a single layer superconducting thin film and provided with a constriction (15) having a width (w) of narrow dimension smaller than the path width (d). The closed superconducting pick-up loop (1) constitutes a flux-to-field transformer (FFDT). At least one magnetoresistive element (2) is placed on top of or below the superconducting thin film, is isolated from the superconducting thin film by a thin insulating layer and is located so that an active part of the magnetoresistive element (2) is at the location of the constriction (15) and has a width equal to or less than the width of the constriction (15). The active part of the magnetoresistive element (2) is oriented so that the bias current in this active part is directed essentially along the constriction (15), orthogonally to the width of narrow dimension.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
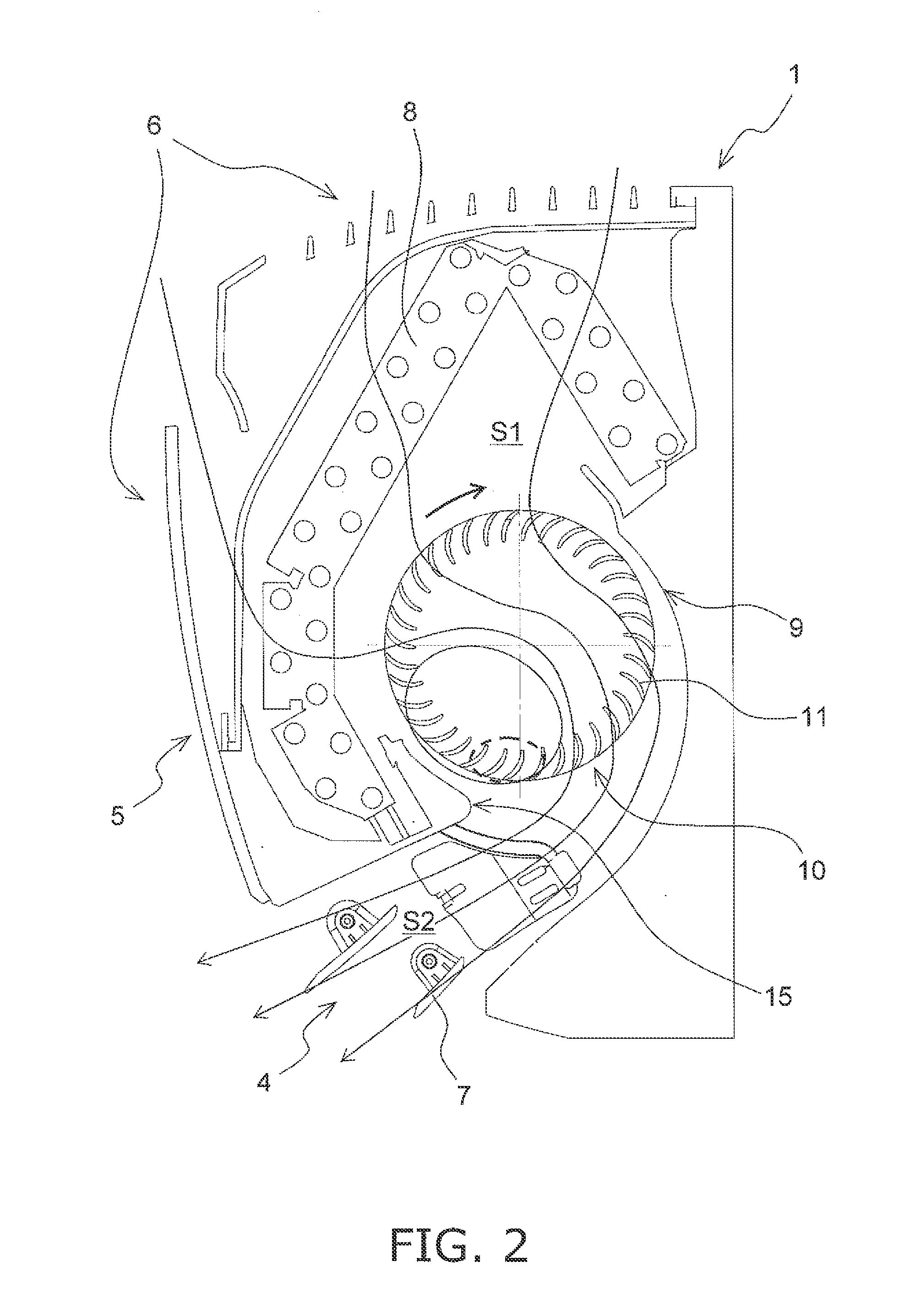
Centrifugal compressor
In order to reduce the rotating stall onset flowrate, this centrifugal compressor comprises: a vaneless diffuser (12) provided on a discharge outlet (6B) side of an impeller (6); and a fluid circulation flow path (21) having an inlet (21A) that opens into a first wall section (22) of a hub casing (2B) forming the vaneless diffuser (12) and also having an outlet (21B) that opens into a second wall section (23) of the hub casing (2B) facing a hub disk (6C) rear surface in the impeller (6). As a result of causing the first wall section (22) to protrude on to a wall section (31) side of the shroud casing (2A), the flow path width (D) of the vaneless diffuser (12) is smaller than the width (W) of the discharge outlet (6B) in the impeller (6). In addition, the hub casing (2B) comprises an inclined wall section (24) having a protruding end (24A) between the discharge outlet (6B) of the impeller (6) and the inlet of the vaneless diffuser (12), said inclined wall section (24) connecting the second wall section (23) and the first wall section (22).
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com