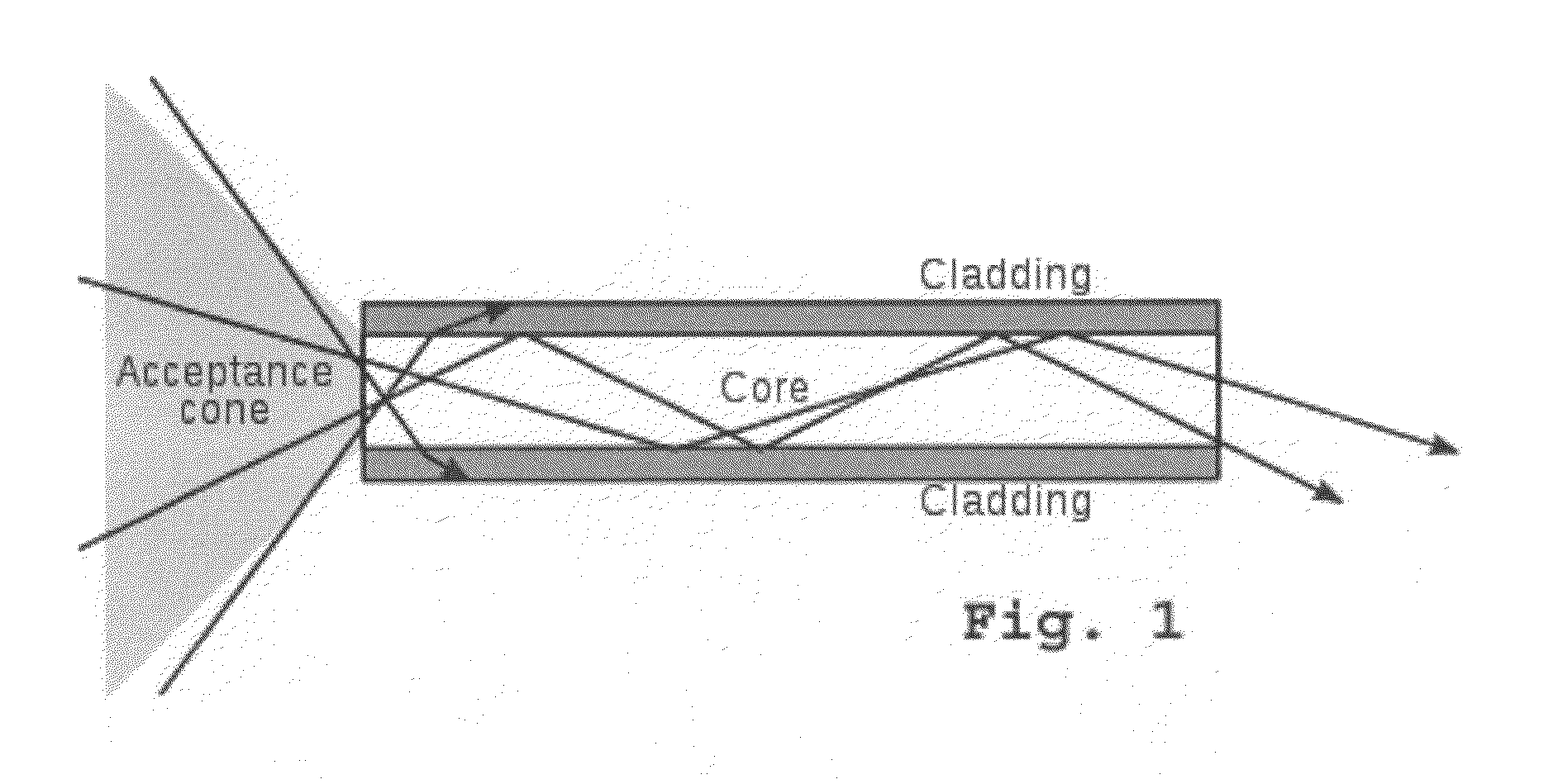
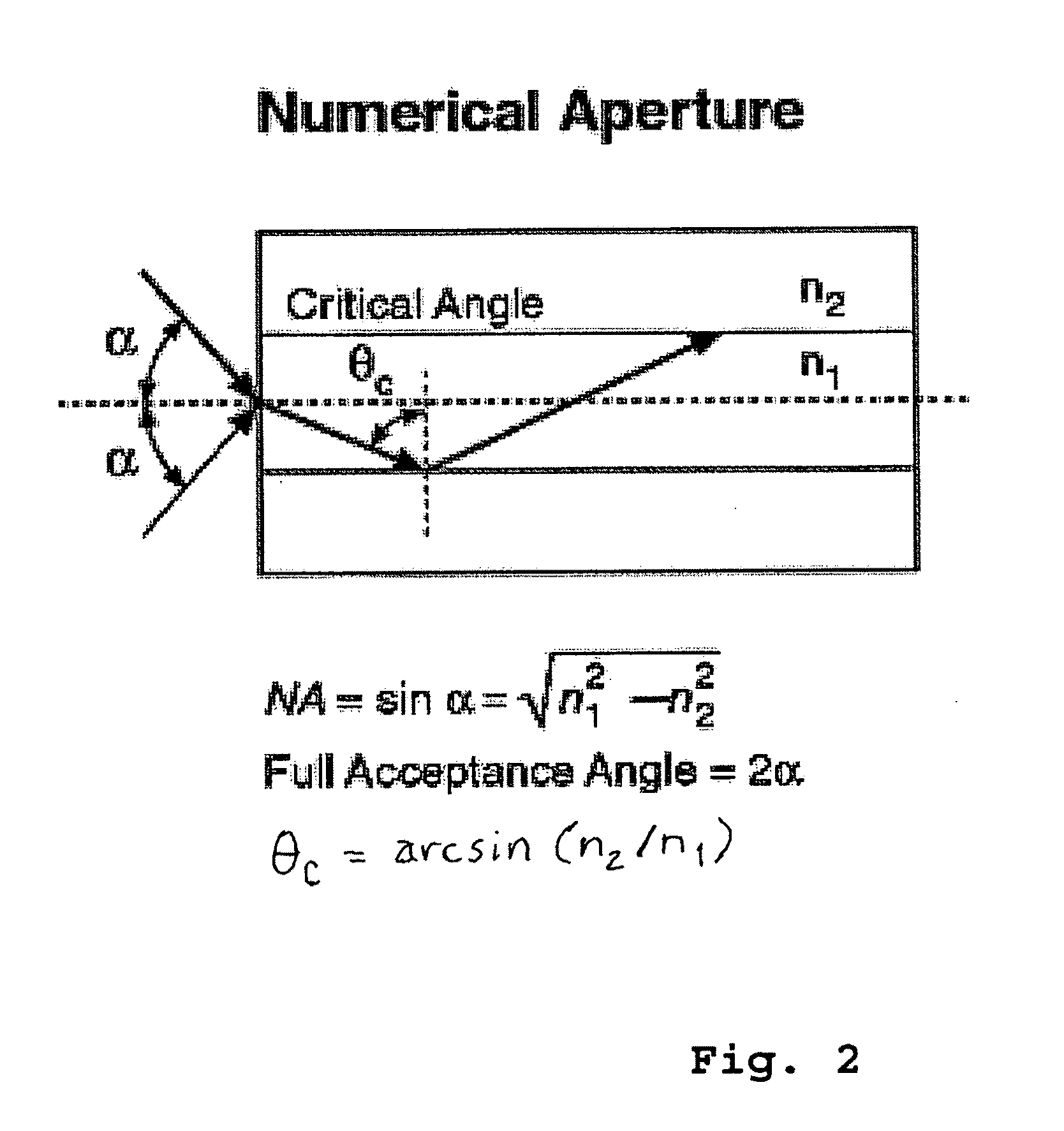
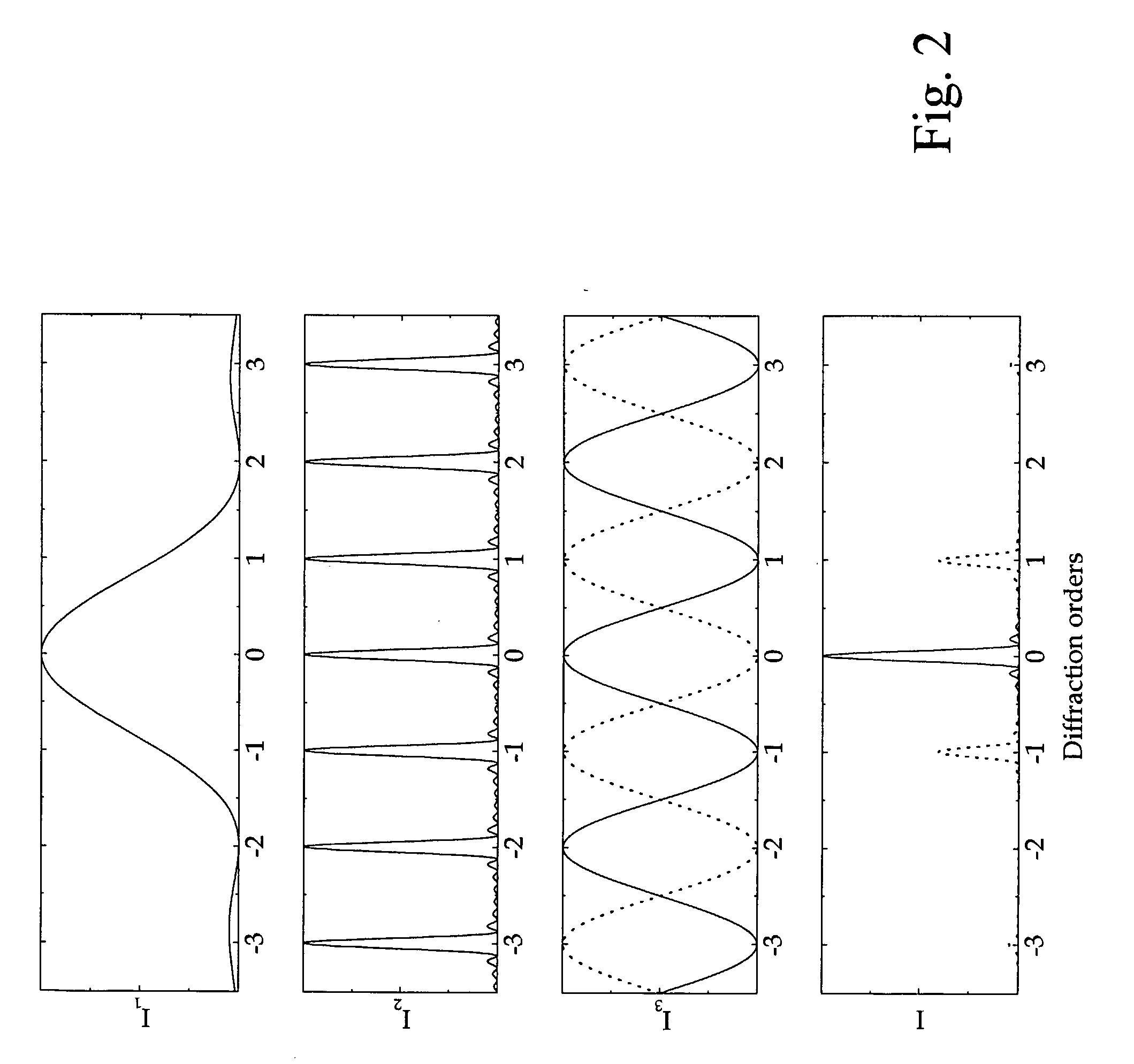
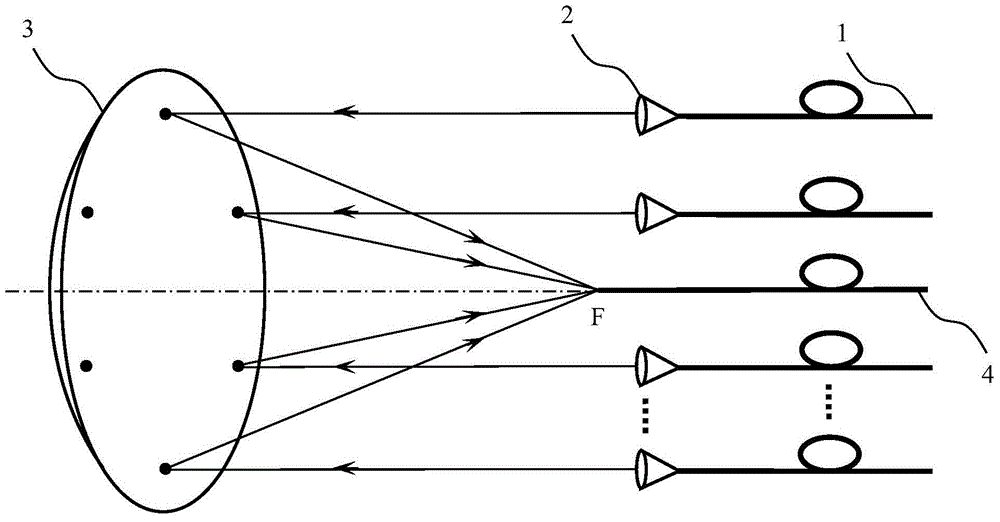
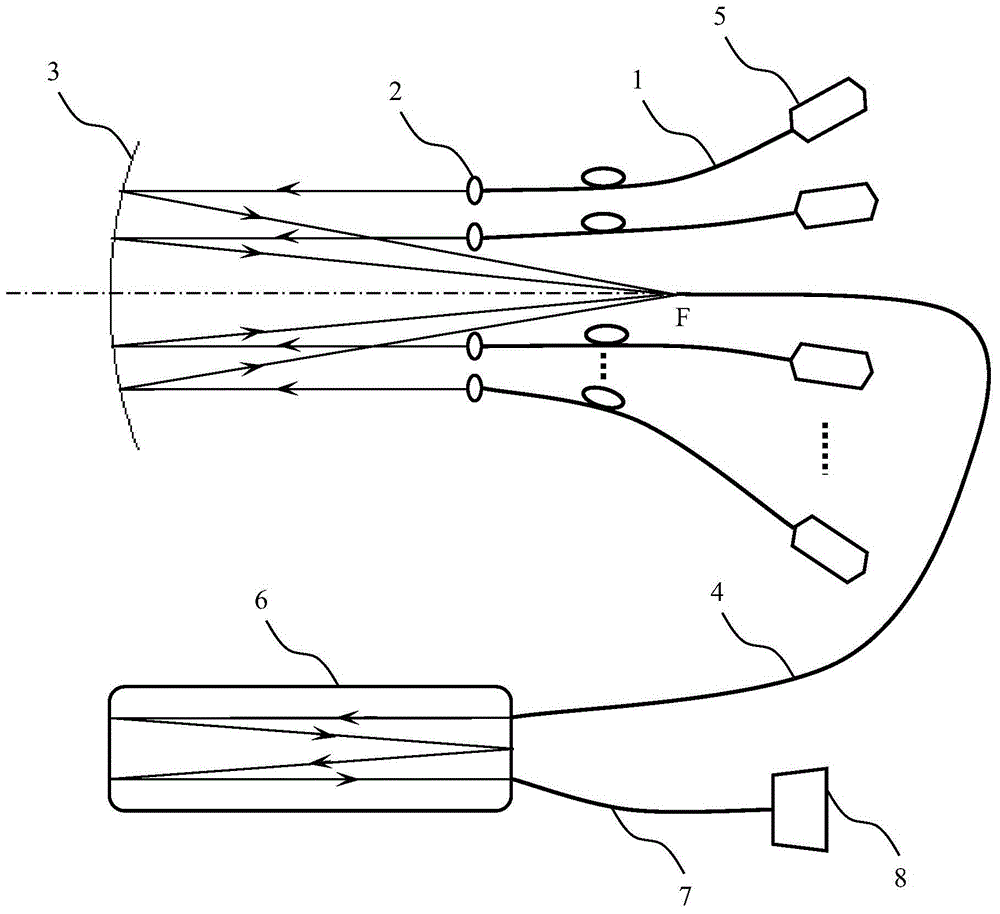
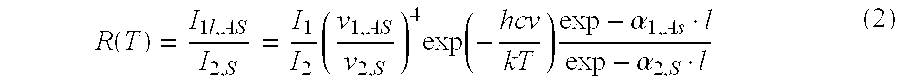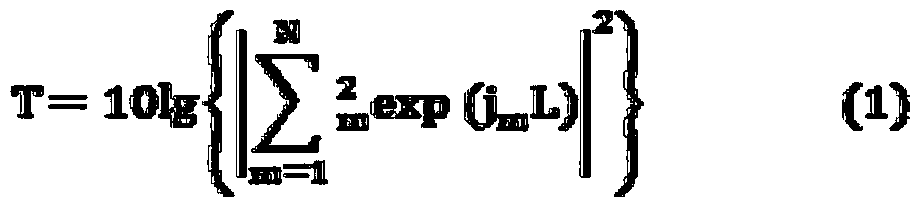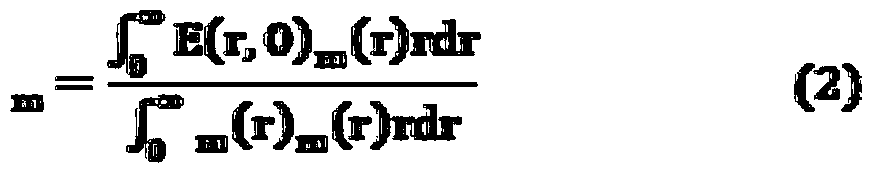Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
416 results about "Multimode fibre" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Multi-Mode Fiber. Definition - What does Multi-Mode Fiber mean? Multi-mode fiber is a type of optical fiber designed to carry multiple light rays or modes simultaneously, each at a marginally different reflection angle inside the optical fiber core.
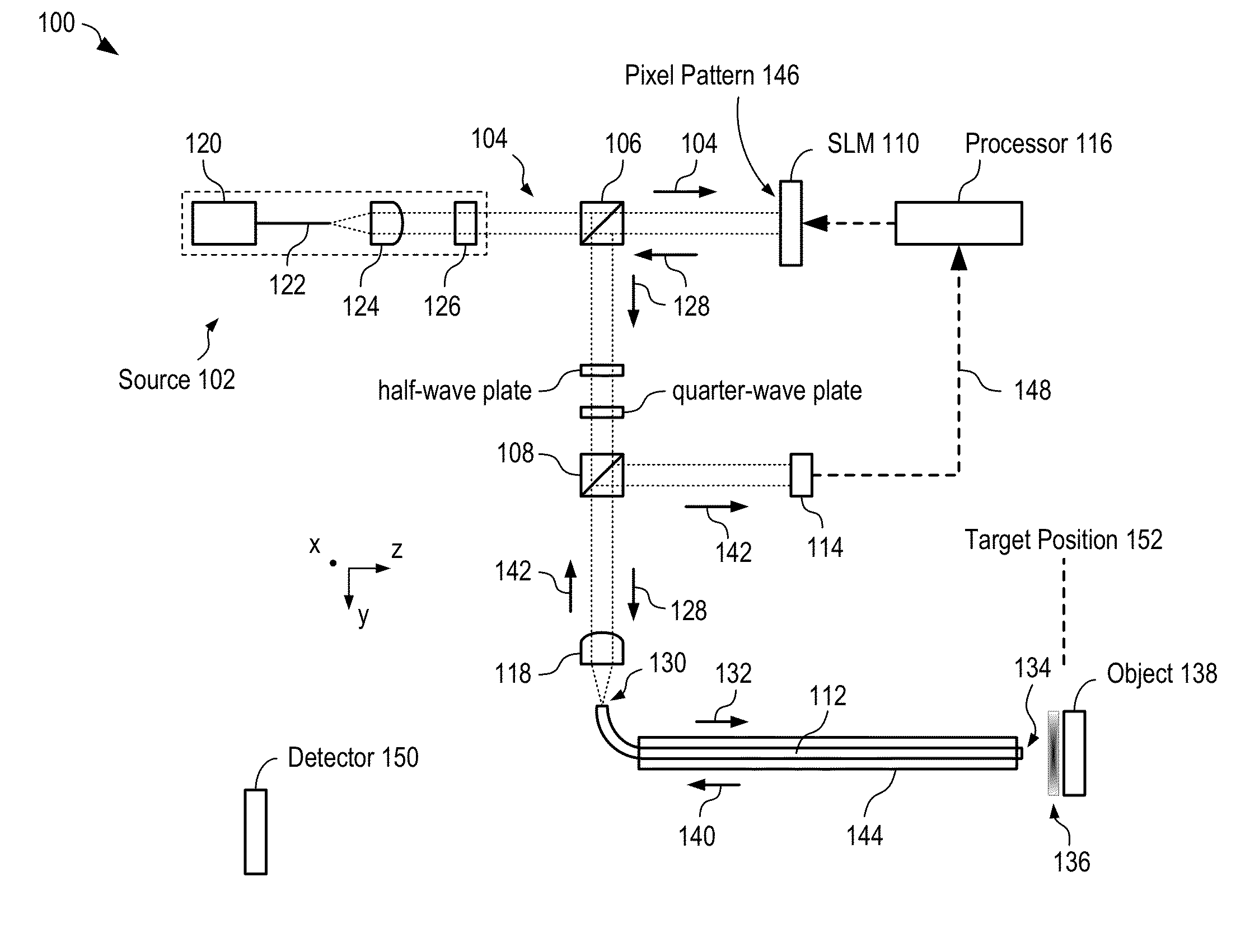
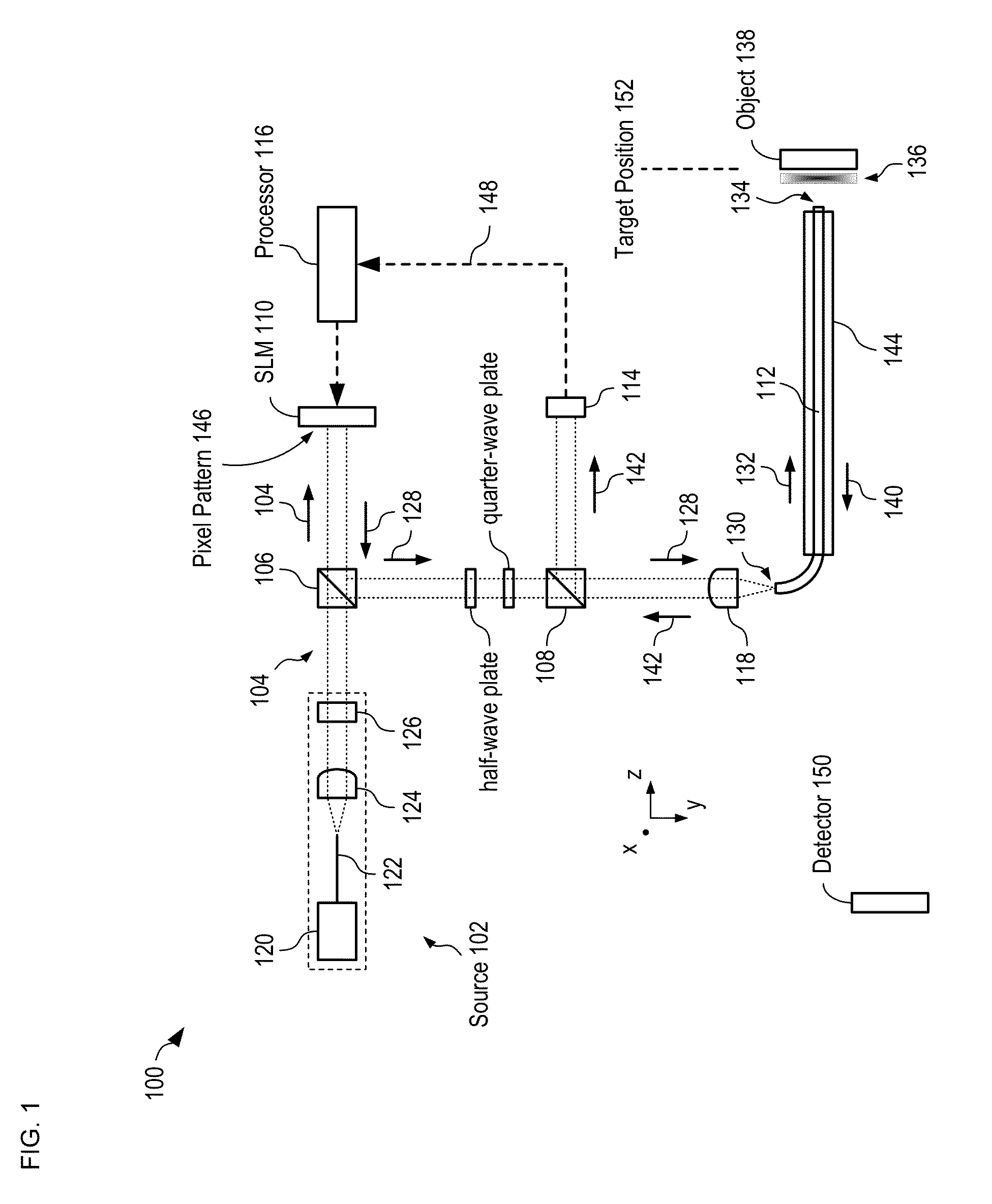
Methods and apparatus for imaging with multimode optical fibers
ActiveUS20150015879A1Radiation pyrometryOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingLight dispersionImage resolution
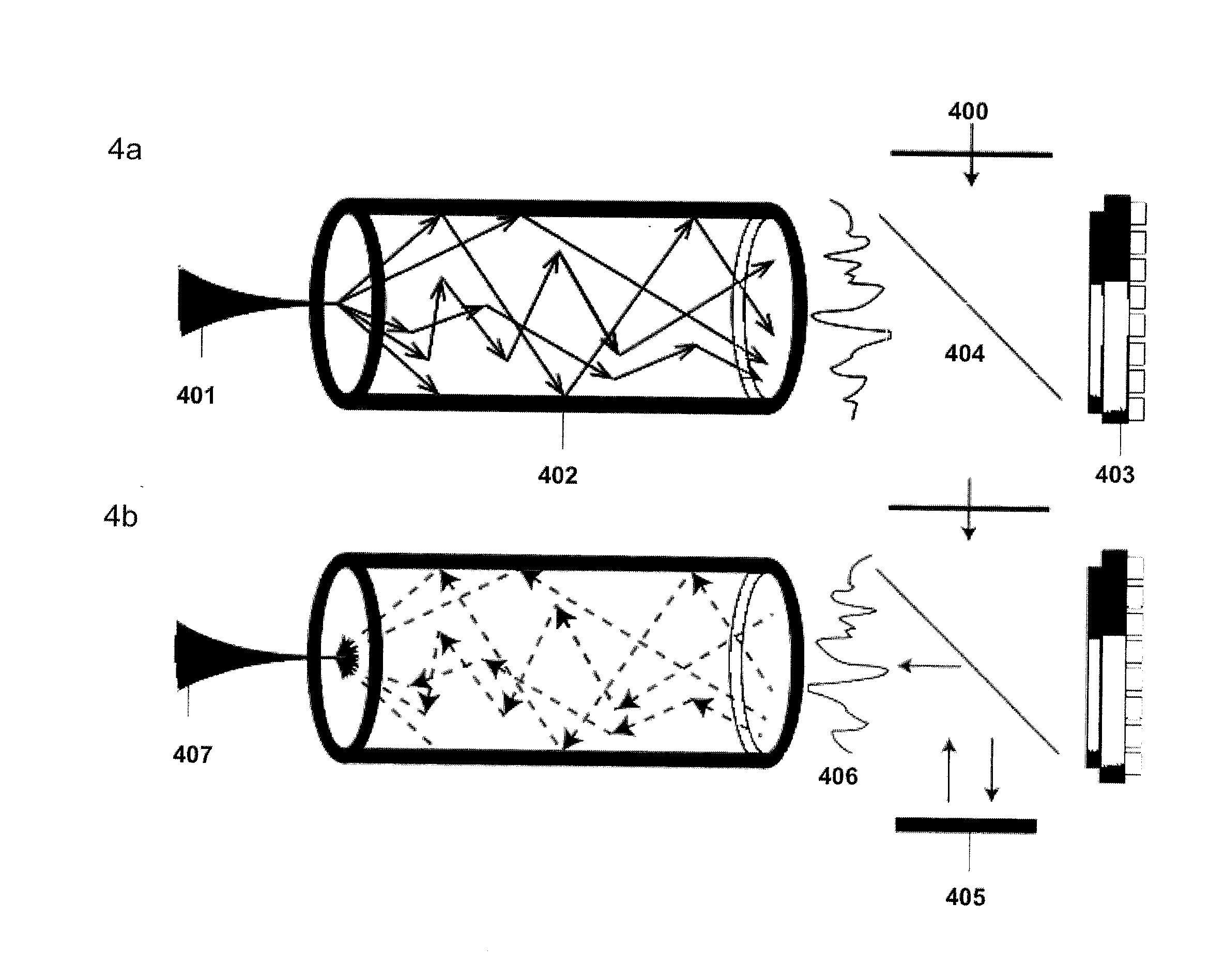
A multimode waveguide illuminator and imager relies on a wave front shaping system that acts to compensate for modal scrambling and light dispersion by the multimode waveguide. A first step consists of calibrating the multimode waveguide and a second step consists in projecting a specific pattern on the waveguide proximal end in order to produce the desire light pattern at its distal end. The illumination pattern can be scanned or changed dynamically only by changing the phase pattern projected at the proximal end of the waveguide. The third and last step consists in collecting the optical information, generated by the sample, through the same waveguide in order to form an image. Known free space microscopy technique can be adapted to endoscopy with multimode waveguide, such as, but not limited to, fluorescence imaging or Raman spectroscopy or imaging, 3D linear scattering imaging or two-photon imaging. Super-resolution, i.e., resolution below the diffraction limit, is achieved for example but not limited to, using the STimulated Emission Depletion microscopy (STED) technique or the Structured Illumination Microscopy (SIM) technique or a stochastic illumination based method (PALM, STORM) in combination with the multimode waveguide imaging method.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Phototherapy mask
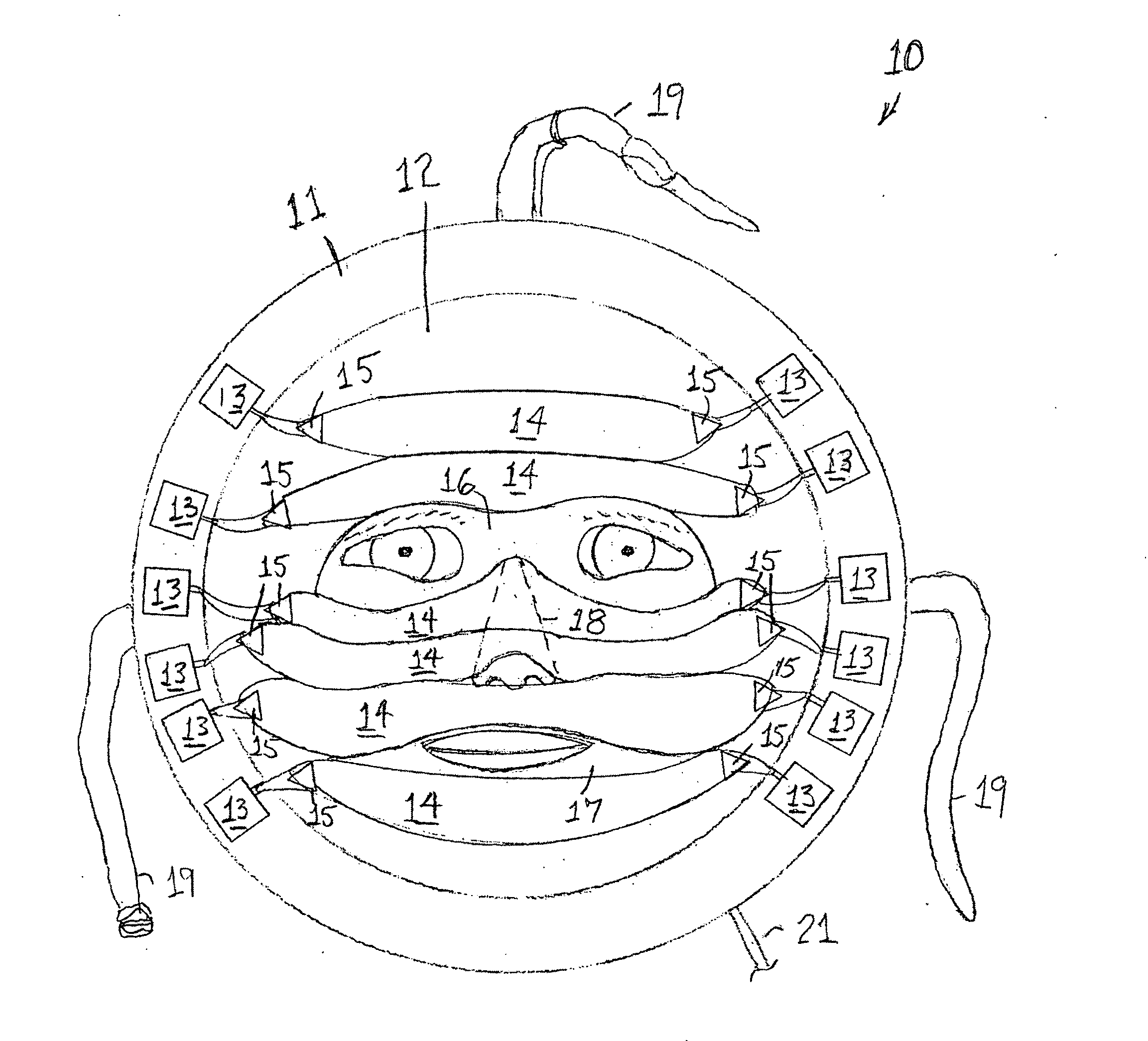
InactiveUS20110040355A1Low refractive indexReduce diffuseLight therapySingle-mode optical fiberMulti-mode optical fiber
A phototherapy mask uses optical fibers coupled to LEDs to irradiate a treated epidermal skin area on or around a person's face with specific wavelengths of light in selected dosages (J / cm2). Peripheral configuration of LEDs on the mask eliminates problems of heat dissipation, and multi-mode optical fiber is employed for diffusion of light uniformly over the treated epidermal skin area.
Owner:FRANCIS STACY
Laser optimized multimode fiber and method for use with laser and LED sources and system employing same
InactiveUS20020197038A1Glass making apparatusOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingFiberHigh power lasers
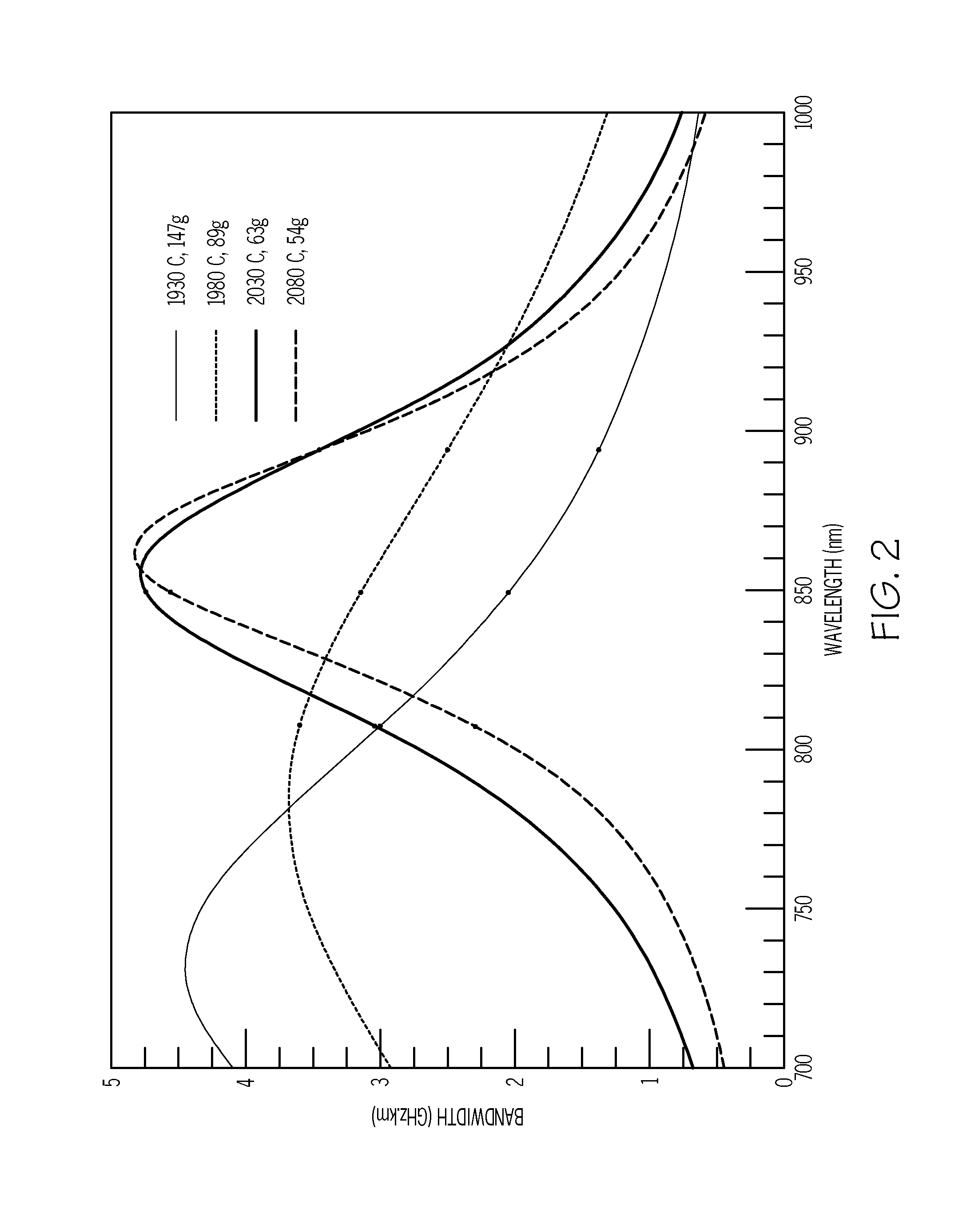
A multimode optical fiber having a first laser bandwidth greater than 220 MHz.km in the 850 nm window, a second laser bandwidth greater than 500 MHz.km in the 1300 nm window, a first OFL bandwidth of at least 160 MHz.km in the 850 nm window, and a second OFL bandwidth of at least 500 MHz.km in the 1300 nm window is disclosed. The multimode fiber is capable of operating in telecommunication systems employing both LED power sources and high power laser sources. Methods of making and testing the multimode optical fiber are also disclosed.
Owner:CORNING INC
Laser optimized multimode fiber and method for use with laser and LED sources and system employing same
InactiveUS6438303B1Optical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingGlass shaping apparatusFiberHigh power lasers
A multimode optical fiber having a first laser bandwidth greater than 220 MHz.km in the 850 nm window, a second laser bandwidth greater than 500 MHz.km in the 1300 nm window, a first OFL bandwidth of at least 160 MHz.km in the 850 nm window, and a second OFL bandwidth of at least 500 MHz.km in the 1300 nm window is disclosed. The multimode fiber is capable of operating in telecommunication systems employing both LED power sources and high power laser sources. Methods of making and testing the multimode optical fiber are also disclosed.
Owner:CORNING INC
Quartz capillary tube embedded all-silica fiber Fabry-Perot interferometric sensor and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102374874ALow costHigh degree of miniaturizationConverting sensor output opticallyHigh volume manufacturingInterferometric sensor
The invention discloses a quartz capillary tube embedded all-silica fiber Fabry-Perot interferometric sensor which comprises a single-mode optical fiber, a quartz capillary tube, a reflective optical fiber and a protective film, wherein the reflective optical fiber is a single-mode optical fiber or a multimode optical fiber, the two ends of the quartz capillary tube are respectively connected with one end of the single-mode optical fiber and one end of the reflective optical fiber by way of welding, and the hollow part of the quartz capillary tube is taken as the interferometric cavity of the interferometric sensor. In the interferometric sensor disclosed by the invention, a quartz capillary tube is adopted without plating a film, therefore, the cost for manufacturing the Fabry-Perot interferometric sensor is reduced, and the high contrast of the fiber Fabry-Perot interferometric sensor can be realized. The invention also discloses a method for manufacturing the sensor. The quartz capillary tube embedded all-silica fiber Fabry-Perot interferometric sensor disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of low cost, simple processing method, high miniaturization degree and good mechanical stability, and is convenient for production on large scale; and the practicability of the interferometric sensor is easy to realize, and the interferometric sensor has a potential practical value and a broad market in the field of interferometric sensors.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Illuminator for dark field inspection
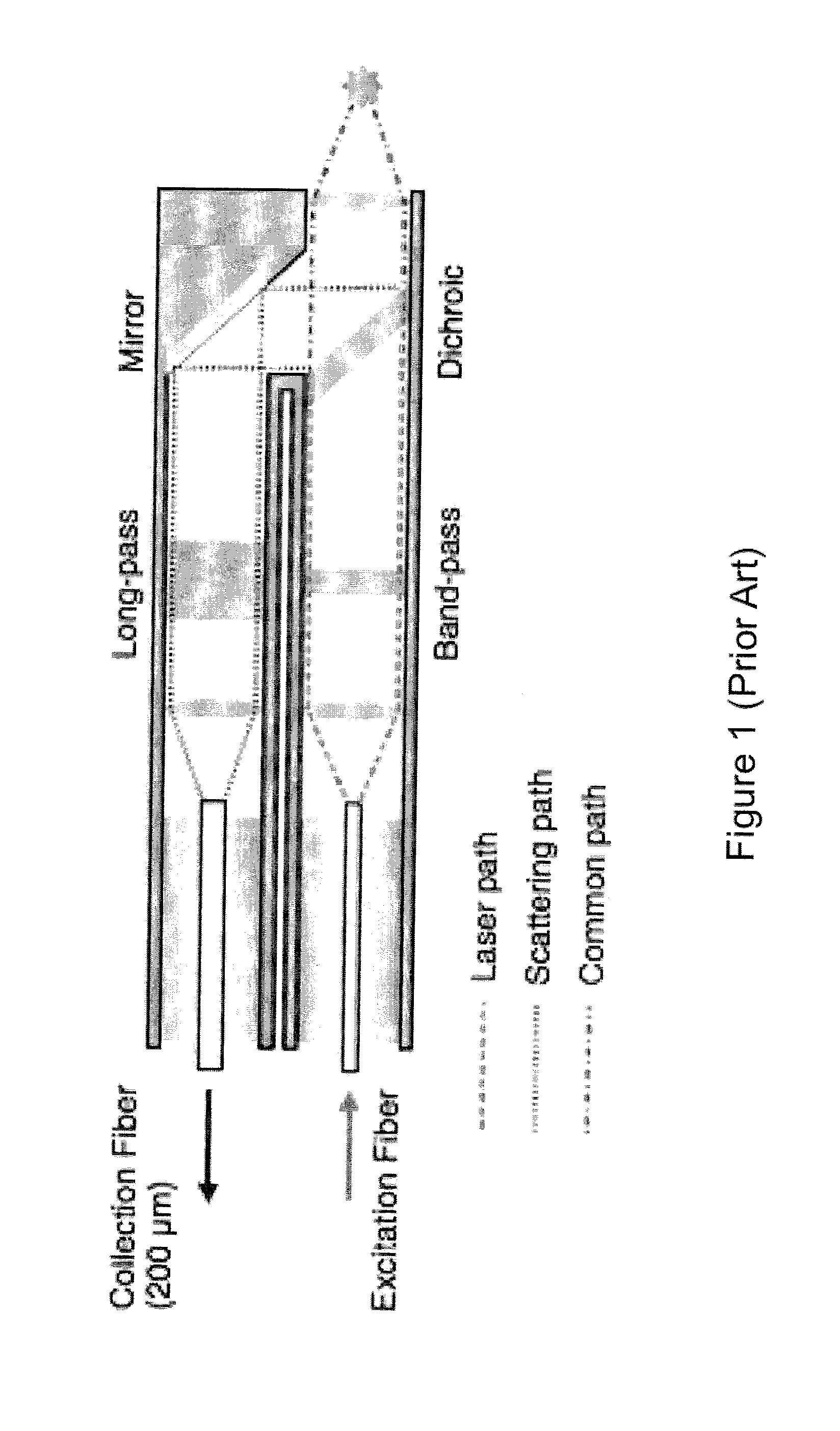
InactiveUS20060012778A1Uniform lightReduce the angle of incidenceOptically investigating flaws/contaminationFiber bundleLight beam
Light from a single source is divided among several illumination arms, each of which directs light via a multimode fiber bundle from the source to the wafer location. The arms are arranged circumferentially around a common illumination region, so that the region is illuminated from several directions. For each arm, light exiting the fiber bundle enters a turning prism, reflects off the hypotenuse of the prism, and is diverged in one dimension by a negative cylindrical surface on the exiting face of the prism. The beam then reflects off an anamorphic mirror and propagates to the illumination region on the wafer. The beam has an asymmetric footprint, so that it illuminates a nearly circular region of the wafer when viewed at normal incidence. The fiber bundle is at the front focal plane in the meridional dimension. The illumination region is at the rear focal plane in both dimensions.
Owner:AUGUST TECH
Laser optimized multimode fiber and method for use with laser and LED sources and system employing same
A multimode optical fiber having a first laser bandwidth greater than 220 MHz.km in the 850 nm window, a second laser bandwidth greater than 500 MHz.km in the 1300 nm window, a first OFL bandwidth of at least 160 MHz.km in the 850 nm window, and a second OFL bandwidth of at least 500 MHz.km in the 1300 nm window is disclosed. The multimode fiber is capable of operating in telecommunication systems employing both LED power sources and high power laser sources. Methods of making and testing the multimode optical fiber are also disclosed.
Owner:CORNING INC
Optical Fiber Gain Medium with Modal Discrimination of Amplification
InactiveUS20080025363A1Easy to controlEasy to adjustLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberRefractive index
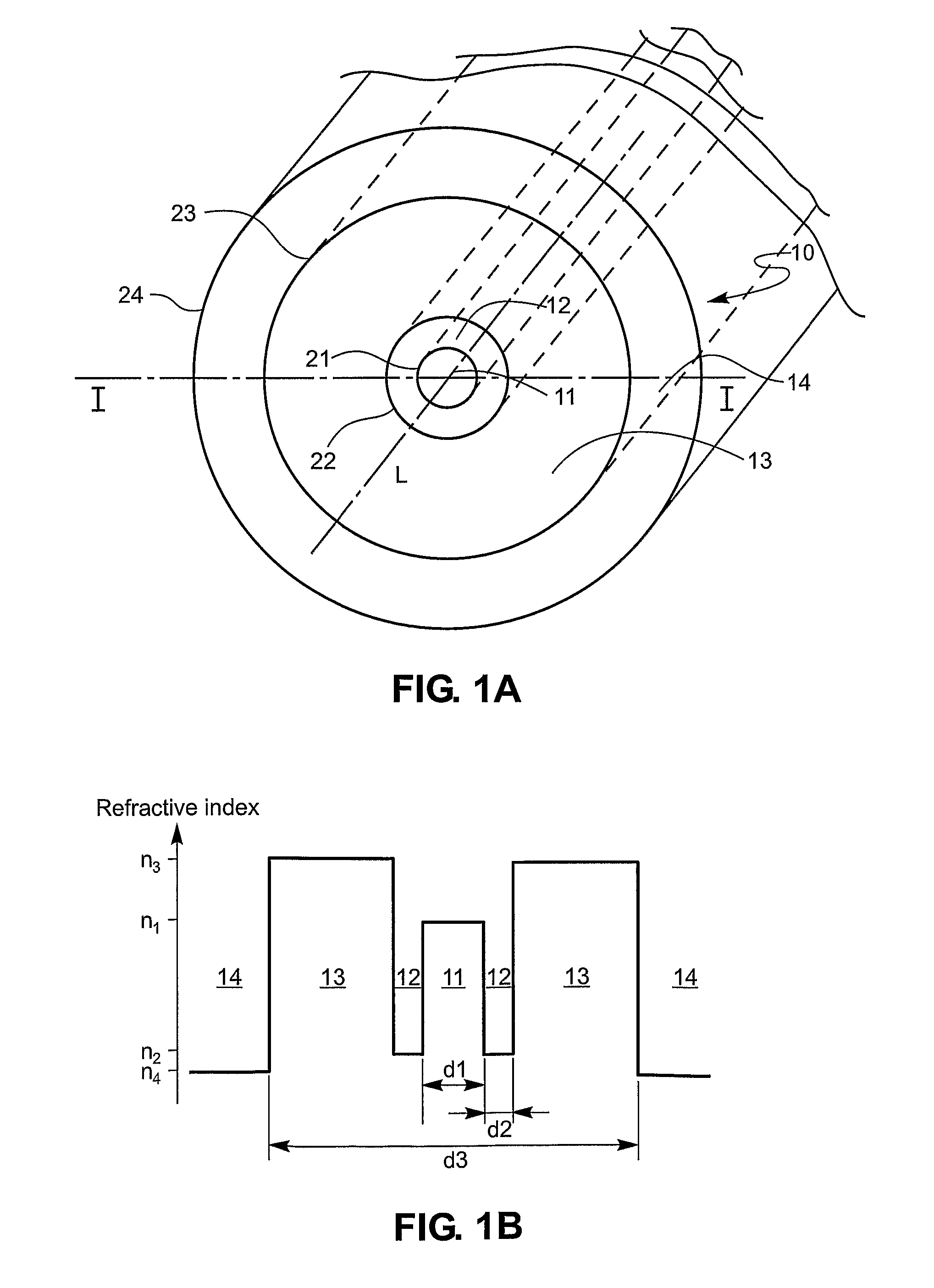
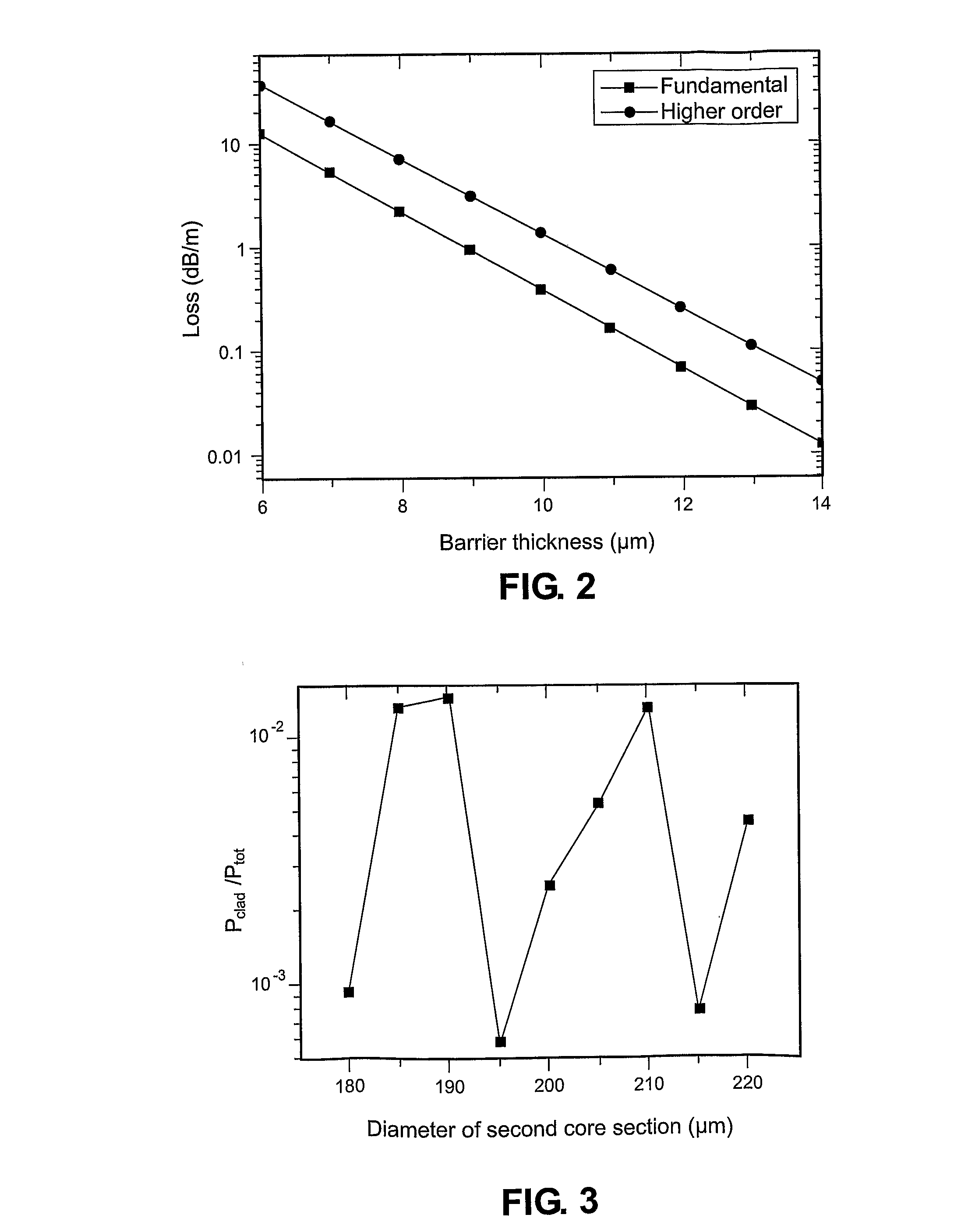
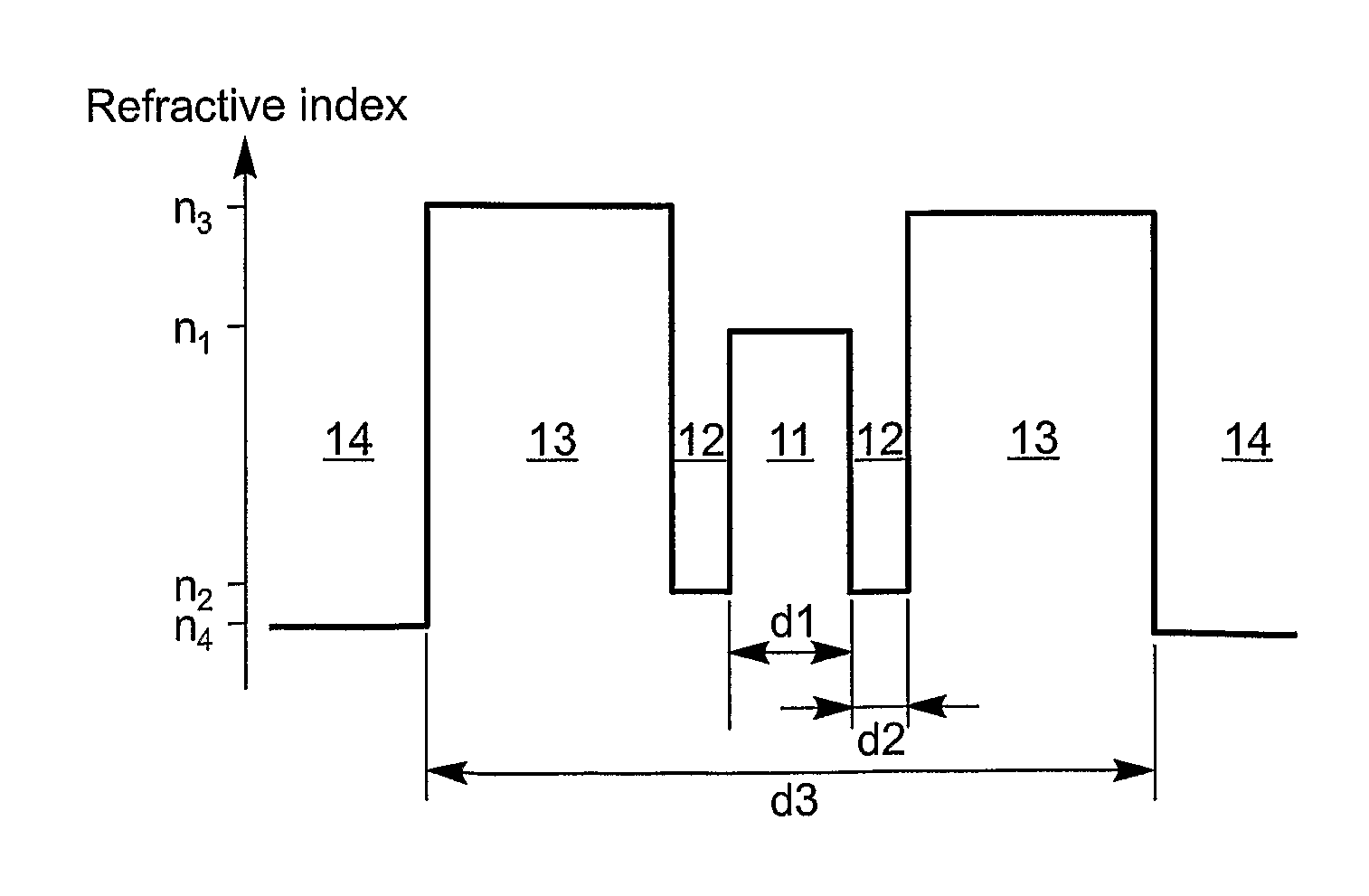
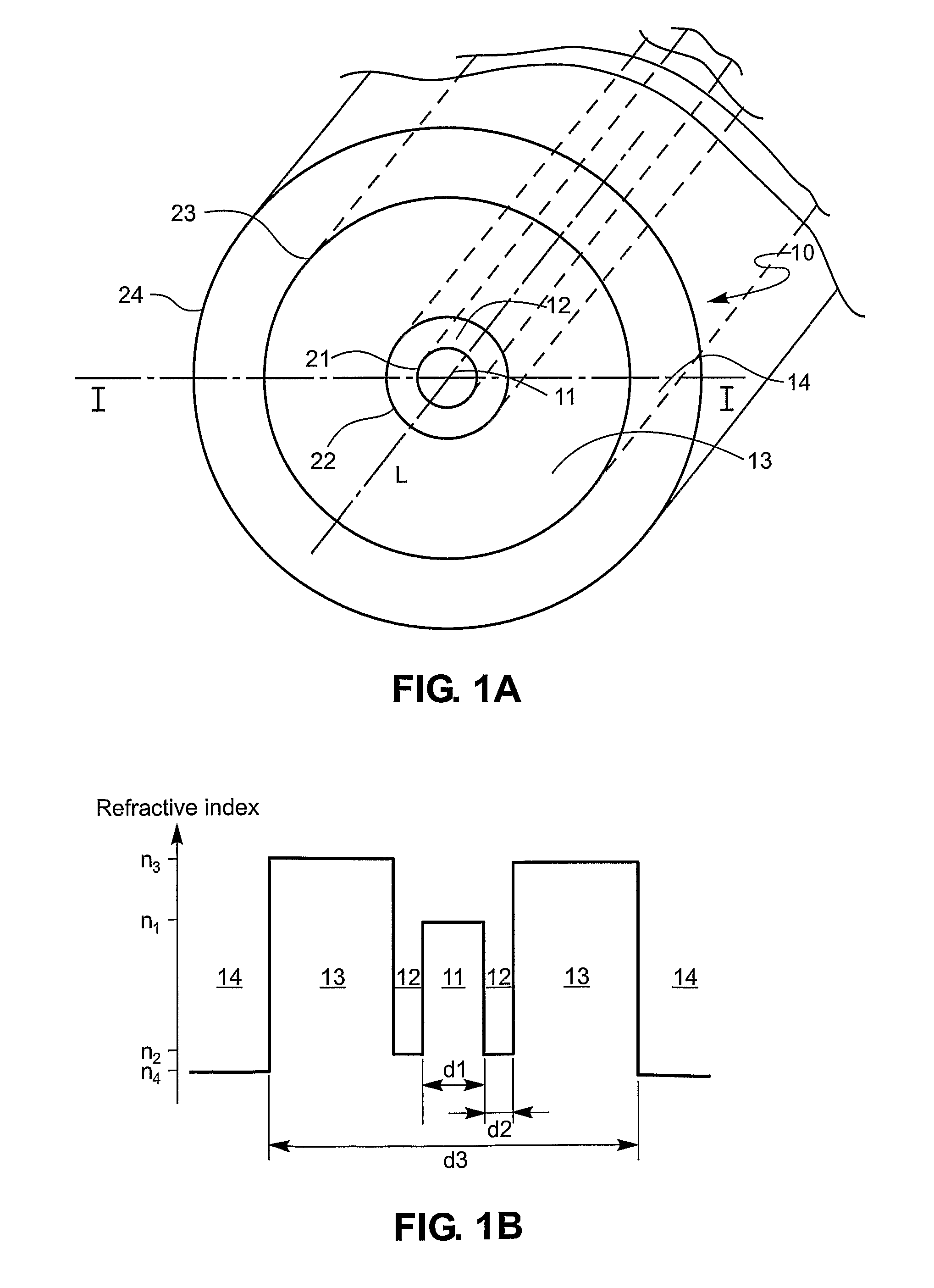
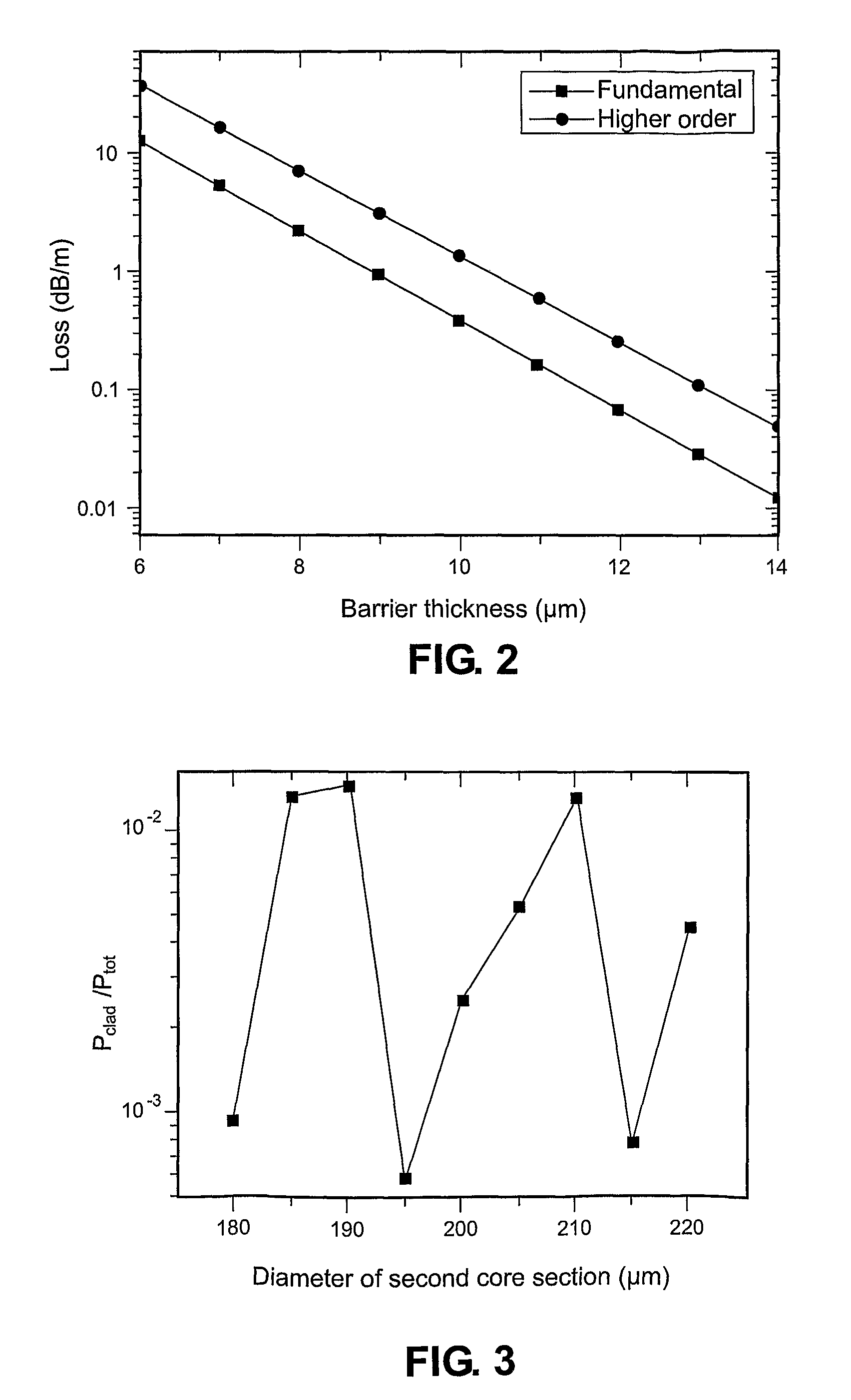
An active multimode optical fiber consisting of a first core section (11), a thin barrier layer (12) material having a thickness (d2) and a lower refractive index than that of the first core section by an index difference (Δn), a second core section (13) having a refrective index equal or higher than that of the first core section, and a cladding (14) having an index lower than that of the first core section. Said index difference and said thickness are selected so that a fundamental core mode couples less strongly with said cladding modes than higher order core modes. A scheme of changing the symmetry of the fiber for reduced sensitivity of the fundamental mode of the first core section to resonance effects.
Owner:ROFIN SINAR LASER
Vital signs fiber optic sensor systems and methods
ActiveCN107072565AHigh sensitivityLow costForce measurementEvaluation of blood vesselsEngineeringVital sign monitoring
An intensity-based, micro-bending optical fiber sensor is disclosed herein, which is configured to acquire clean, stable, and reliable vital sign signals. Related systems and methods for vital sign monitoring are also provided herein. The sensor of various embodiments includes a multi-mode optical fiber, an LED light source, an LED driver, a receiver, and a single layer deformer structure. In various embodiments, the optical fiber and single layer deformer structure of the sensor are selected to meet specific parameters necessary to achieve a level of reliability and sensitivity needed to successfully monitor vital signs. In some embodiments, a specific sizing relationship exists between the optical fiber and the single layer deformer structure. In some embodiments, the sensor is configured to acquire ballistocardiograph waveforms.
Owner:SHENZHEN DARMA TECH CO LTD
Micro-nano fiber grating laser writing method and device
InactiveCN102540322AReduce splice lossHigh core energyCladded optical fibrePhotomechanical exposure apparatusFiberMicro nano
The invention discloses a micro-nano fiber grating laser writing method and a micro-nano fiber grating laser writing device. The method comprises the following steps of: tapering normal multi-mode fibers; manufacturing micro-nano fibers; and then taking 193 nm ultraviolet laser as a scribing means. The device comprises a fiber clamp, and an ArF excimer laser, a 45-degree full power reflector, a cylindrical lens and a phase mask plate which are sequentially arranged, wherein the ArF excimer laser is used for emitting 193 nm ultraviolet laser; the tapered fiber is fixed on the fiber clamp; micro-nano fiber regions of the fibers are arranged in front of the phase mask plate in parallel; the 193 nm ultraviolet laser emitted by the ArF excimer laser is reflected through the 45-degree full power reflector and then vertically emitted to the cylindrical lens; and the phase mask plate is arranged in front of the cylindrical lens. According to the method and the device, extra processing for the fibers is not required, the mechanical strength and the toughness of the fibers are kept, the cost is low, the scribing efficiency is high, the bandwidth is narrow, the mode is controllable and the repeatability is high.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Dispersion and loss spectrum auto-correction distributed optical fiber raman temperature sensor
InactiveUS20130028289A1Stable structureSimple structureThermometers using physical/chemical changesRayleigh scatteringFiber chromatic dispersion
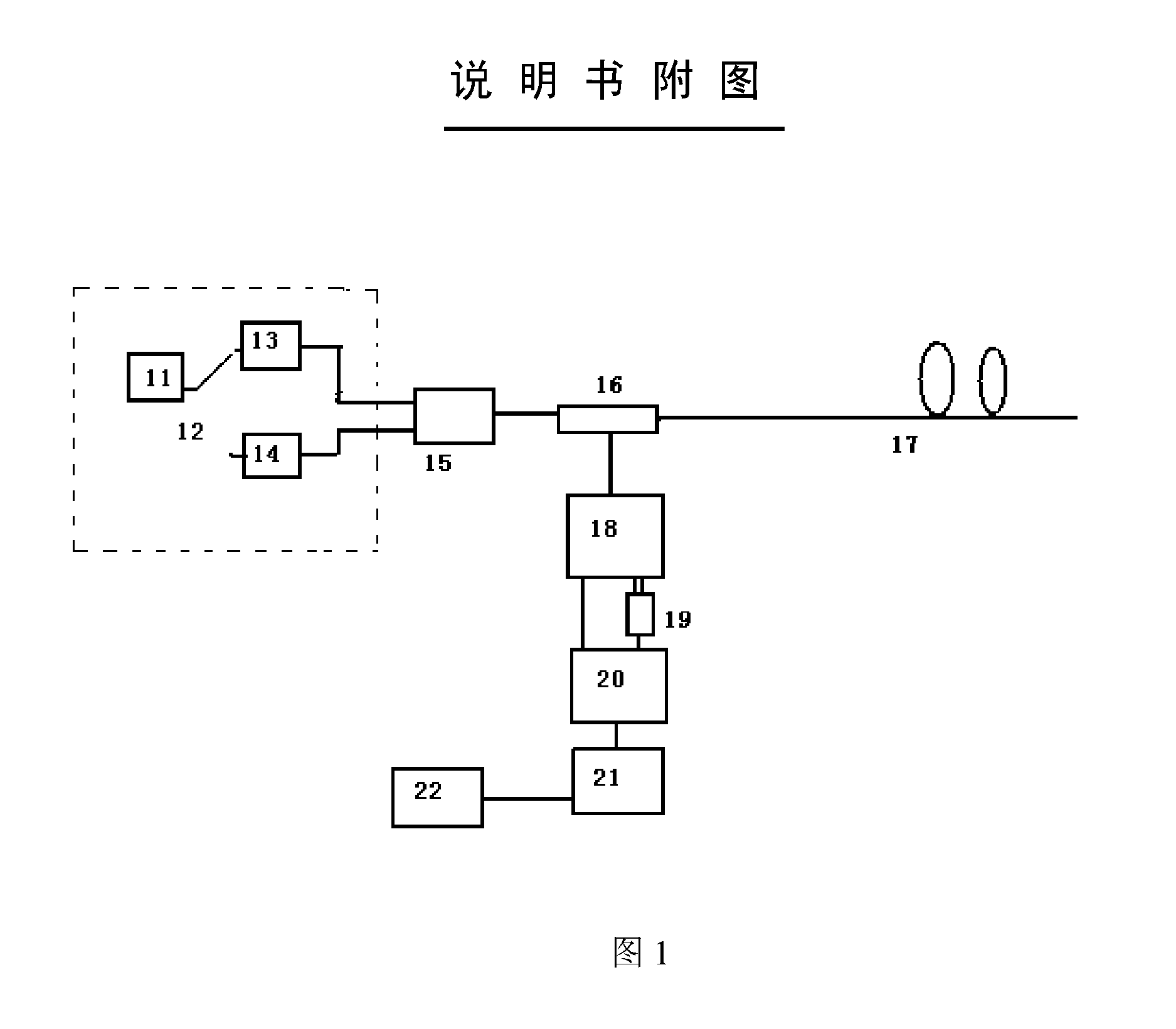
A dispersion and loss spectrum auto-correction distributed optical fiber Raman temperature sensor has a dual fiber pulsed laser module with dual Raman wavelength shifts. The laser module is composed of a power supply (11), an electronic switch (12), a primary laser (13) and a secondary laser (14), a first combiner (15), a bidirectional coupler (16), a multimode fiber (17), an integrated optical fiber wavelength division multiplexer (18), a second combiner (19), a direct detection system (20), a signal collection and processing system (21) and a display (22). The sensor uses two light sources that have two Raman wavelength shifts, wherein the central wavelength of backward anti-Stokes Raman scattering peak of the primary light source coincides with that of the backward Stokes scattering peak centre wavelength of the secondary light source, and the time domain reflection signal of the one-way optical fiber Rayleigh scattering is deducted. Based on the optical fiber Raman scattering temperature measurement principle, the dispersion and loss spectrum auto-correction method and the optical time domain reflection principle, the optical fiber dispersion and the loss spectrum can be self-corrected, and the random power loss caused by bending and stretching in installation can also be auto-corrected.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Optical fiber gain medium with modal discrimination of amplification
InactiveUS7760771B2Precise adjustment and controlHigh gainLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberRefractive index
An active multimode optical fiber consisting of a first core section (11), a thin barrier layer (12) material having a thickness (d2) and a lower refractive index than that of the first core section by an index difference (Δn), a second core section (13) having a refractive index equal or higher than that of the first core section, and a cladding (14) having an index lower than that of the first core section. Said index difference and said thickness are selected so that a fundamental core mode couples less strongly with said cladding modes than higher order core modes. A scheme of changing the symmetry of the fiber for reduced sensitivity of the fundamental mode of the first core section to resonance effects.
Owner:ROFIN SINAR LASER
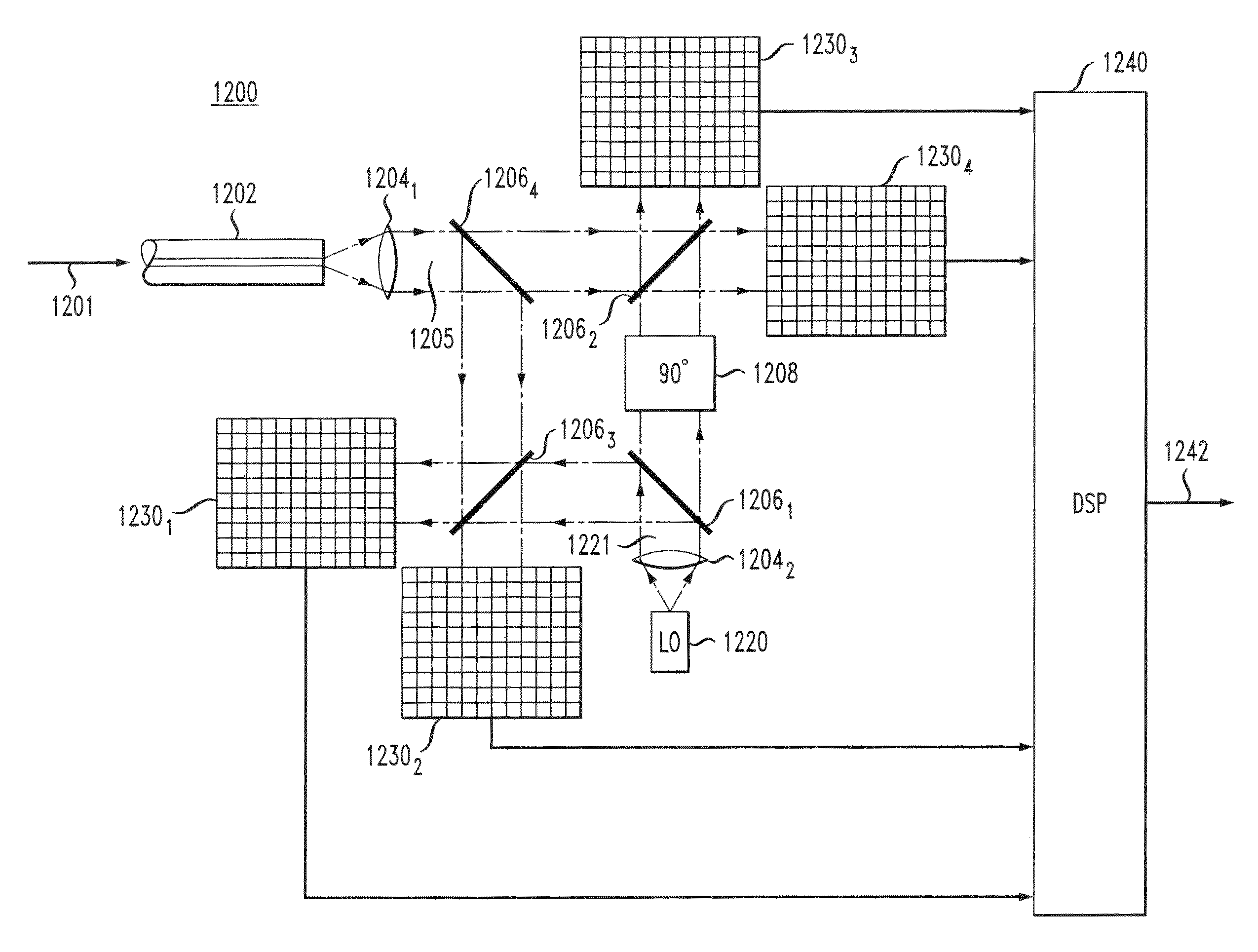
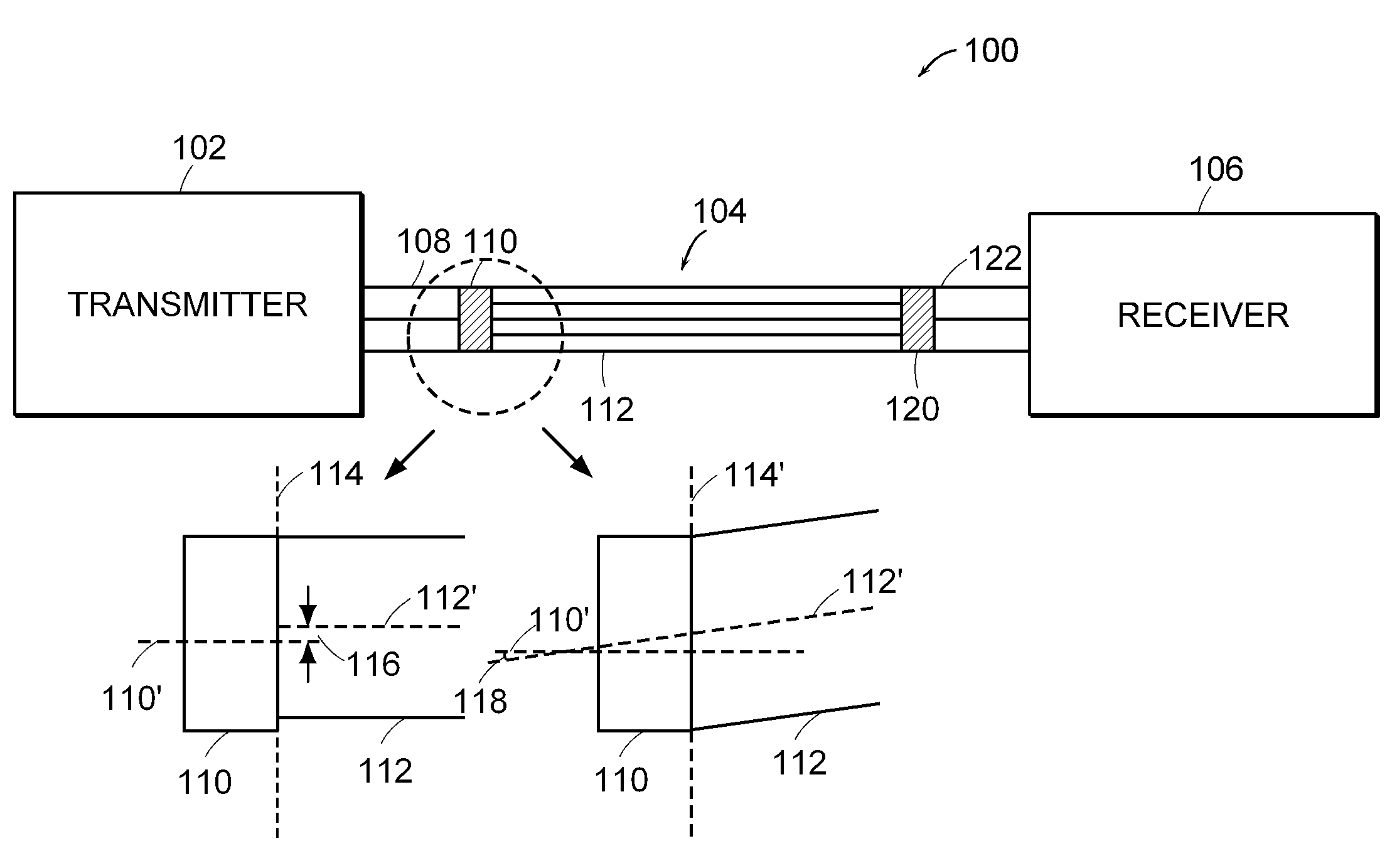
Receiver for optical transverse-mode-multiplexed signals
ActiveUS8355638B2Polarisation multiplex systemsOptical mode multiplex systemsTransverse modeOptical detector
A representative optical receiver of the invention receives an optical transverse-mode-multiplexed (TMM) signal through a multimode fiber that supports a plurality of transverse modes. The optical receiver has a plurality of optical detectors operatively coupled to a digital signal processor configured to process the TMM signal to determine its modal composition. Based on the determined modal composition, the optical receiver demodulates each of the independently modulated components of the TMM signal to recover the data encoded onto the TMM signal at the remote transmitter.
Owner:RPX CORP
Flow cytometer
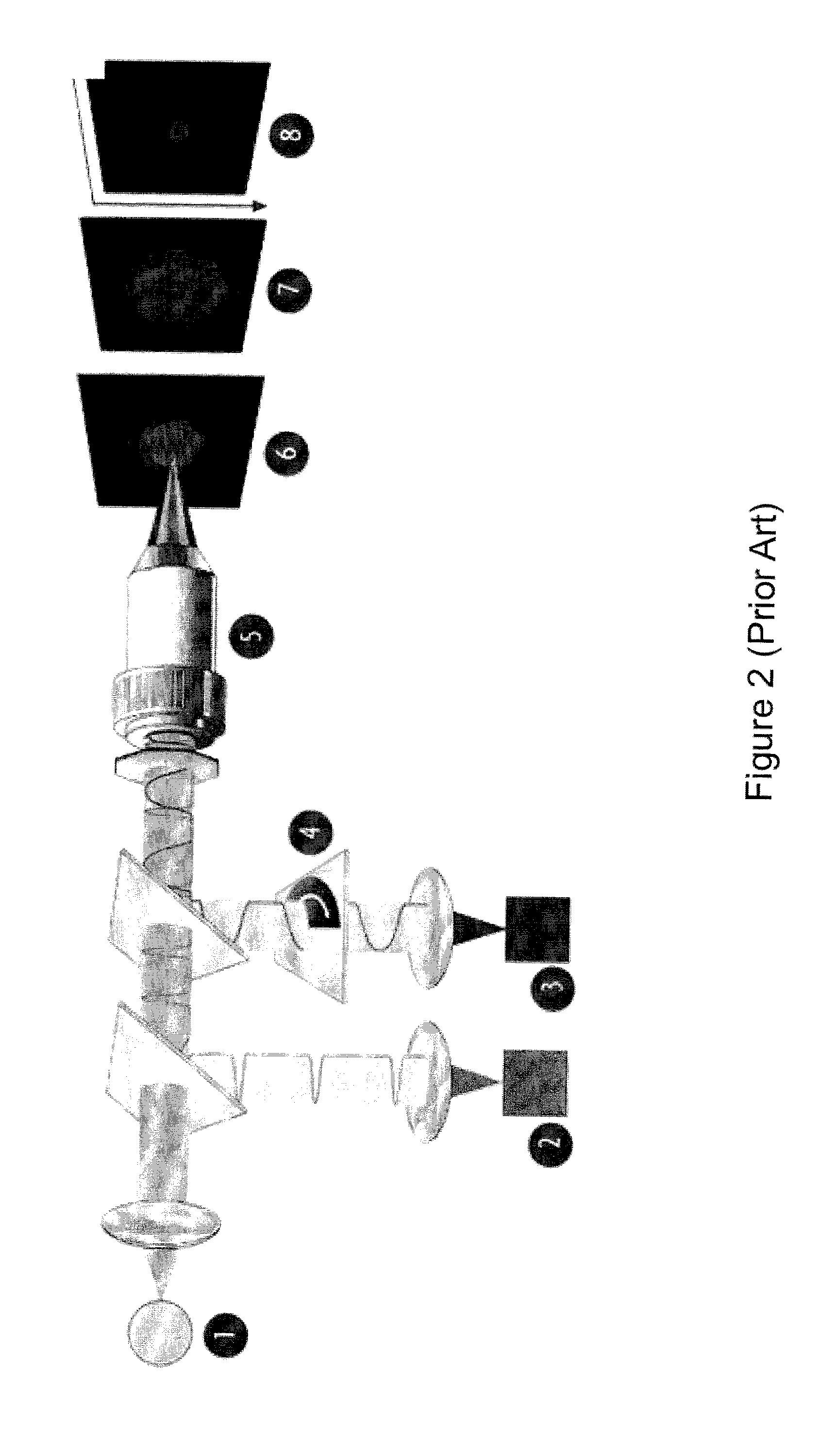
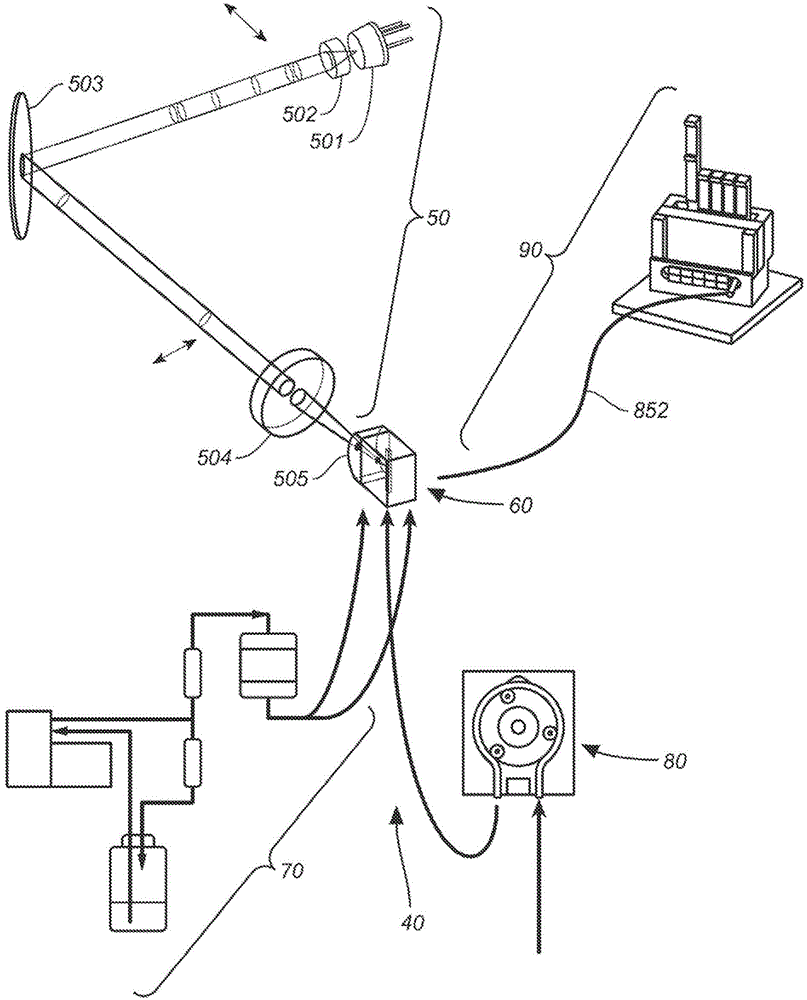
The disclosed flow cytometer (40) includes; 1. a laser diode ("LD") based optical subsystem (50) for impinging a beam of light upon particles passing through a viewing zone; 2. a composite microscope objective (60) for gathering and imaging light scattered from or fluoresced by particles passing through the viewing zone; 3. a fluidic subsystem (70) for supplying a liquid sheath flow to the viewing zone; 4. a peristaltic pump (80) for injecting into the liquid sheath flow a liquid sample flow carrying particles that passes together with the liquid sheath flow through the viewing zone; 5. a multimode optical fiber (852) that receives scattered and fluoresced light from the viewing zone that the composite microscope objective (60) gathers and images; and 6. a wavelength division multiplexer (90) for optically separating into color bands light received via the optical fiber (852).
Owner:IRIS INT
Manufacturing process for optical fiber coupler
InactiveCN102520485AReduce sensitivityStable temperature characteristicsCoupling light guidesPolarization-maintaining optical fiberOptical fiber coupler
The invention discloses a manufacturing process for an optical fiber coupler, which includes: firstly, respectively grinding two optical fibers; secondly, combining two grinded surfaces; fusing the grinded surfaces by a high-temperature heating source; and finally, precisely controlling the splitting ratio of the coupler by the process of continuous fusing or biconical taper. The manufacturing process can be used for manufacturing a high-performance polarization maintaining optical fiber coupler, a single-mode optical fiber coupler, a multi-mode optical fiber coupler and a multi-mode coupler with a splitting ratio unrelated to an input wavelength and an activation pattern, the polarization maintaining optical fiber coupler and the single-mode optical fiber coupler manufactured by the manufacturing process have the advantages of short coupled area, high reliability, fine temperature property, polarization independence, wavelength independence and the like, and the multi-mode optical fiber coupler manufactured by the manufacturing process has quite high reliability besides quite low added loss.
Owner:COMCORE OPTICAL TECH
Inner wall-silver plated and liquid crystal-filled hollow optical fiber surface plasmon resonance temperature sensor
InactiveCN105371981ASimple structureSimple processThermometers using physical/chemical changesSilver platePlasma resonance
The invention provides an inner wall-silver plated and liquid crystal-filled hollow optical fiber surface plasmon resonance temperature sensor and belongs to the optical fiber sensing technical field. According to the structure of the sensor, the interior of a hollow glass optical fiber is plated with silver, and the silver-plated hollow glass optical fiber is filled with liquid crystal; the inner diameter of the hollow glass optical fiber ranges from 300 microns to 500 microns, the numerical aperture of the hollow glass optical fiber is not lower than 0.27, and the length of the hollow glass optical fiber ranges from 30 mm to 50 mm; sensitization treatment is performed on the inner wall of the hollow glass optical fiber, and a 45nm-to 80nm uniform silver film is formed in the optical fiber through adopting a liquid phase chemical deposition method, and therefore, a sensing layer of surface plasmon resonance can be formed; and the hollow optical fiber is filled with thermotropic nematic liquid crystal, and plastic-clad multimode optical fibers are coupled to the ports of the optical fiber respectively, and end sealing processing is realized. With the inner wall-silver plated and liquid crystal-filled hollow optical fiber surface plasmon resonance temperature sensor adopted, subtle temperature changes can be dynamically monitored in real time. The inner wall-silver plated and liquid crystal-filled hollow optical fiber surface plasmon resonance temperature sensor is suitable for long-distance transmission. According to the inner wall-silver plated and liquid crystal-filled hollow optical fiber surface plasmon resonance temperature sensor, special inner wall silver plating technology is adopted, and the hollow optical fiber is filled with the thermotropic liquid crystal, and therefore, the oxidation of the external silver layer of the solid optical fiber surface plasma resonance sensor can be avoided.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Multimode optical fiber and system incorporating such
ActiveUS20130077926A1Optical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideFiberRefractive index
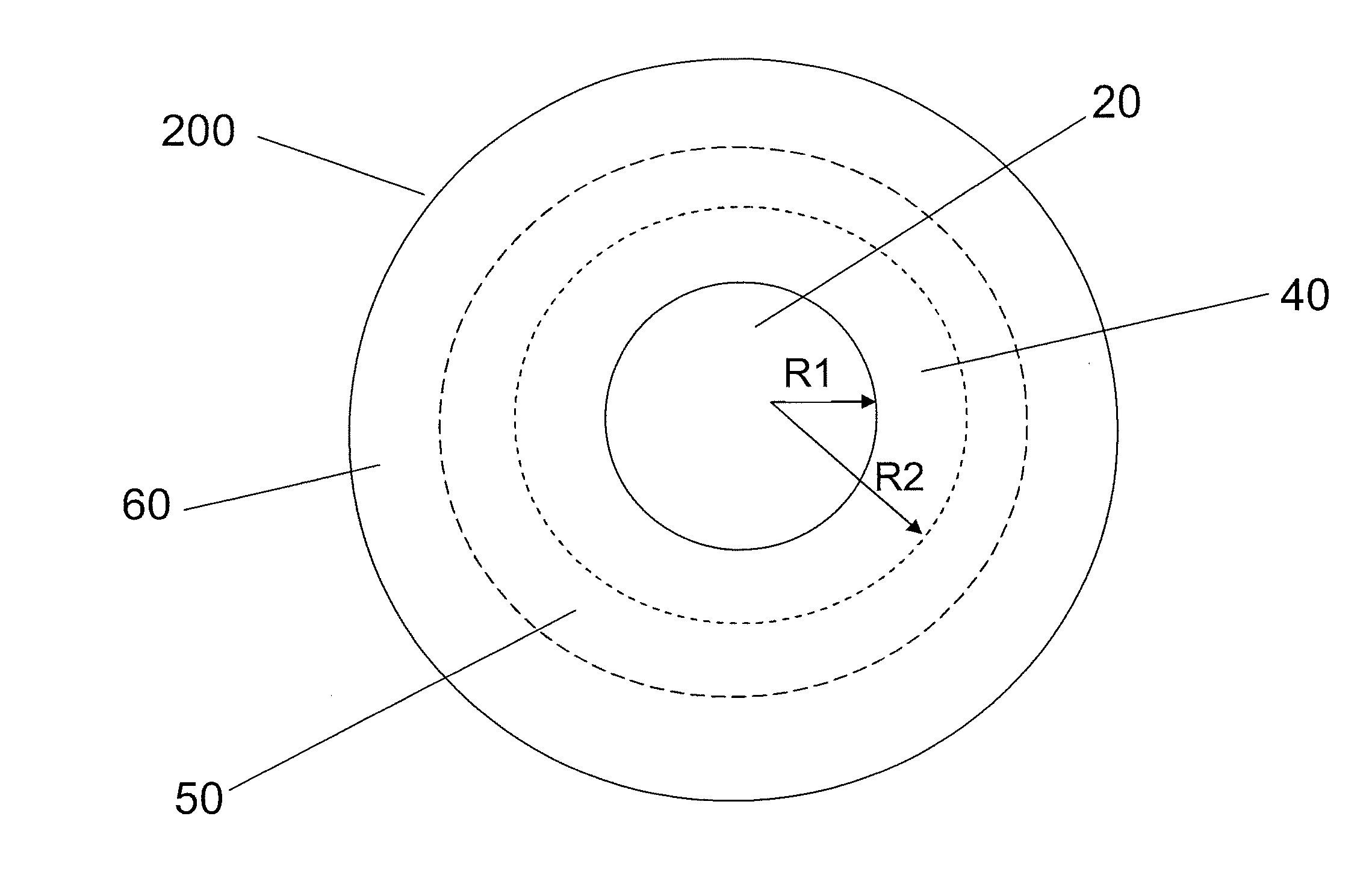
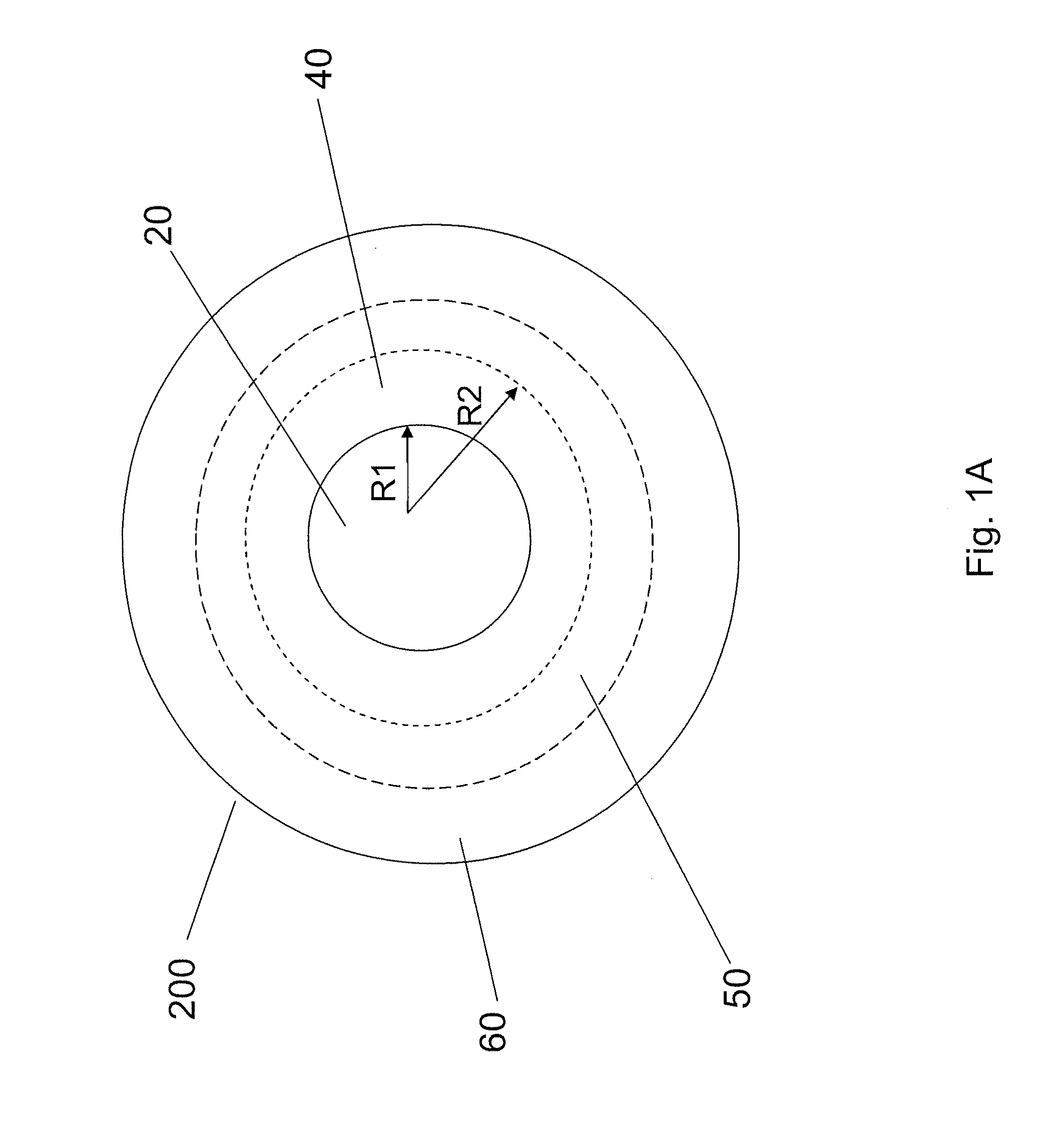
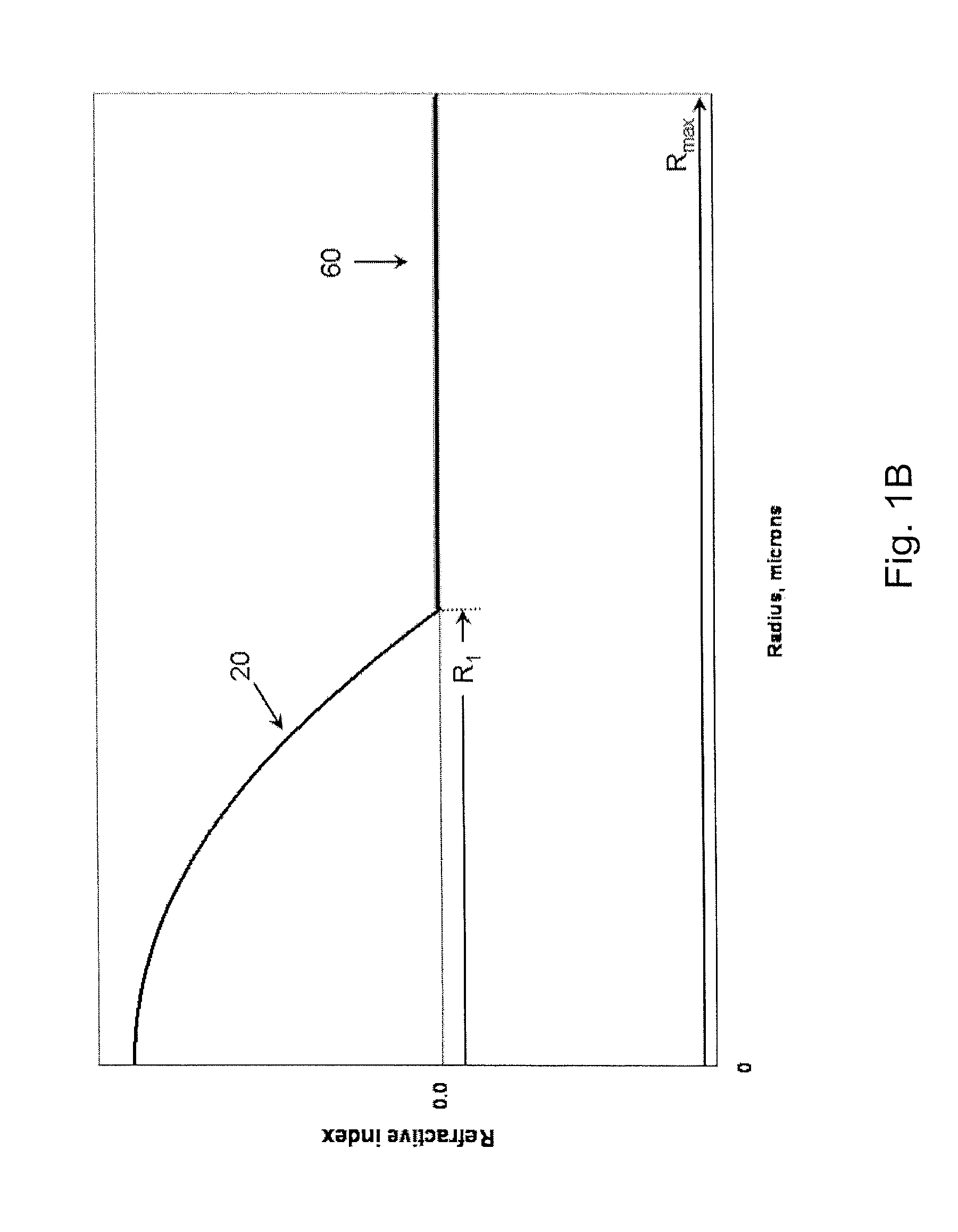
According to some embodiments, a multimode optical fiber comprises a graded index glass core with refractive index Δ1, a maximum refractive index delta Δ1MAX, and a core radius between 10 and 40 microns; and cladding region surrounding the core comprising refractive index Δ4, wherein the fiber exhibits an overfilled bandwidth at an operating wavelength in a 900 to 1250 nm wavelength range of greater than 2.5 GHz-km. According to some embodiments the fiber exhibits an overfilled bandwidth at a wavelength between 950 and 1100 nm which is greater than 4 GHz-km. According to some embodiments the fiber exhibits an overfilled bandwidth at a wavelength between 950 and 1100 nm which is greater than 10 GHz-km.
Owner:CORNING INC
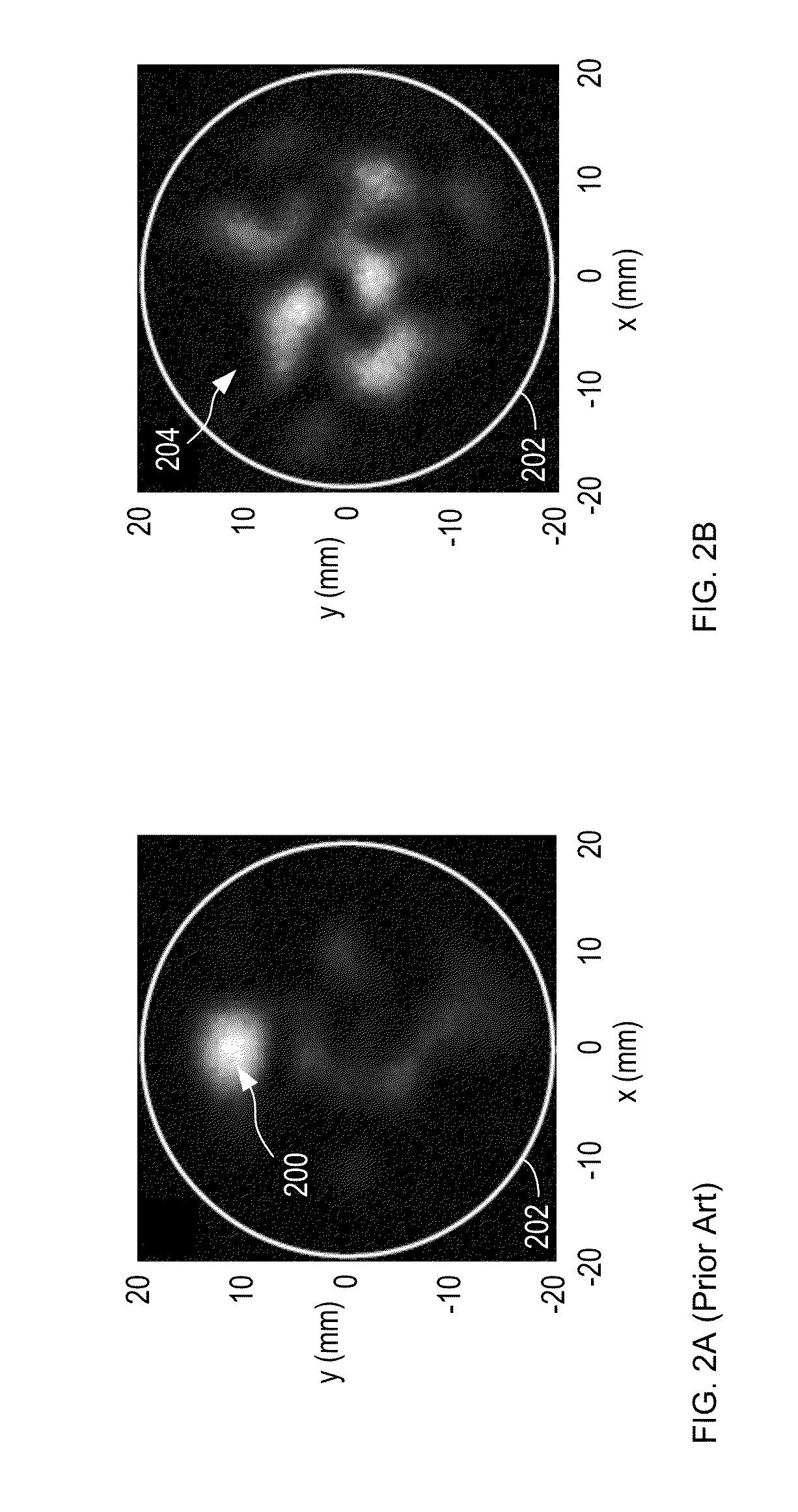
Method for single-fiber microscopy using intensity-pattern sampling and optimization-based reconstruction
InactiveUS20140235948A1Image resolutionIncrease the number ofSurgeryEndoscopesImage resolutionSingle fiber
A method for imaging an object with resolution that exceeds the number of spatial modes per polarization in a multimode fiber is disclosed. In some embodiments, the object is interrogated with a plurality of non-spot-sized intensity patterns and the optical power reflected by the object is detected for each intensity pattern. The plurality of optical power values is then used in a non-local reconstruction based on an optimization approach to reconstruct an image of the object, where the image has resolution up to four times greater than provided by prior-art multimode fiber-based imaging methods.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Optical fiber transmission system with increased effective modal bandwidth transmission
A multi-mode optical fiber link is described that includes a single-mode optical fiber having an input that receives an optical signal for transmission through the multi-mode optical fiber link. A first spatial mode converter is coupled to the single-mode optical fiber. The first spatial mode converter conditions a modal profile of the optical signal for propagation through a multi-mode optical fiber. A multi-mode optical fiber is coupled to an output of the first spatial mode converter. A second spatial mode converter is coupled to an output of the multi-mode optical fiber. The second spatial mode converter reduces a number of optical modes in the optical signal. Both the first and the second spatial mode converters increase an effective modal bandwidth of the optical signal propagating through an output of the second spatial mode converter.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Miniature Lamellar Grating Interferometer Based on Silicon Technology
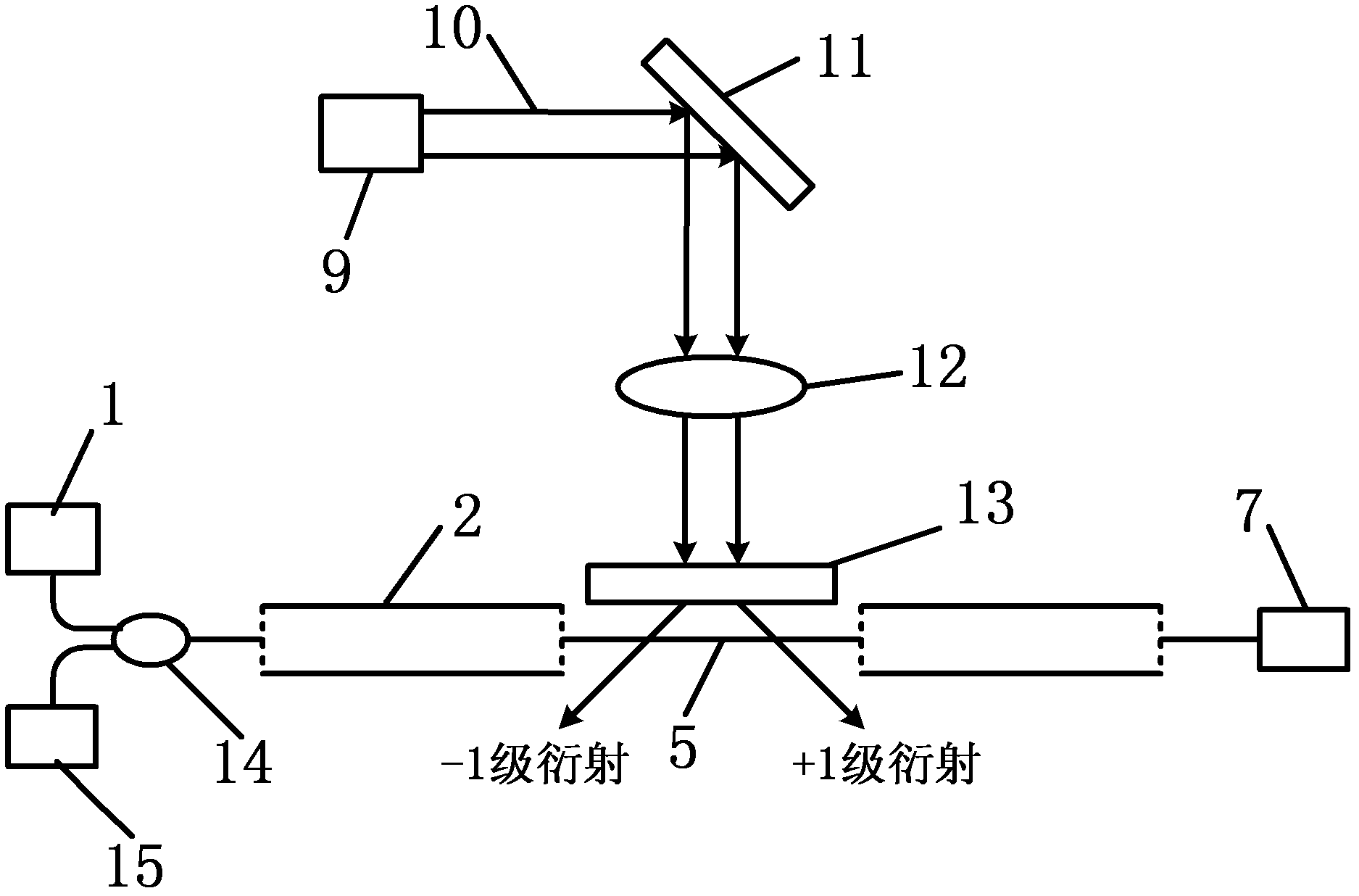
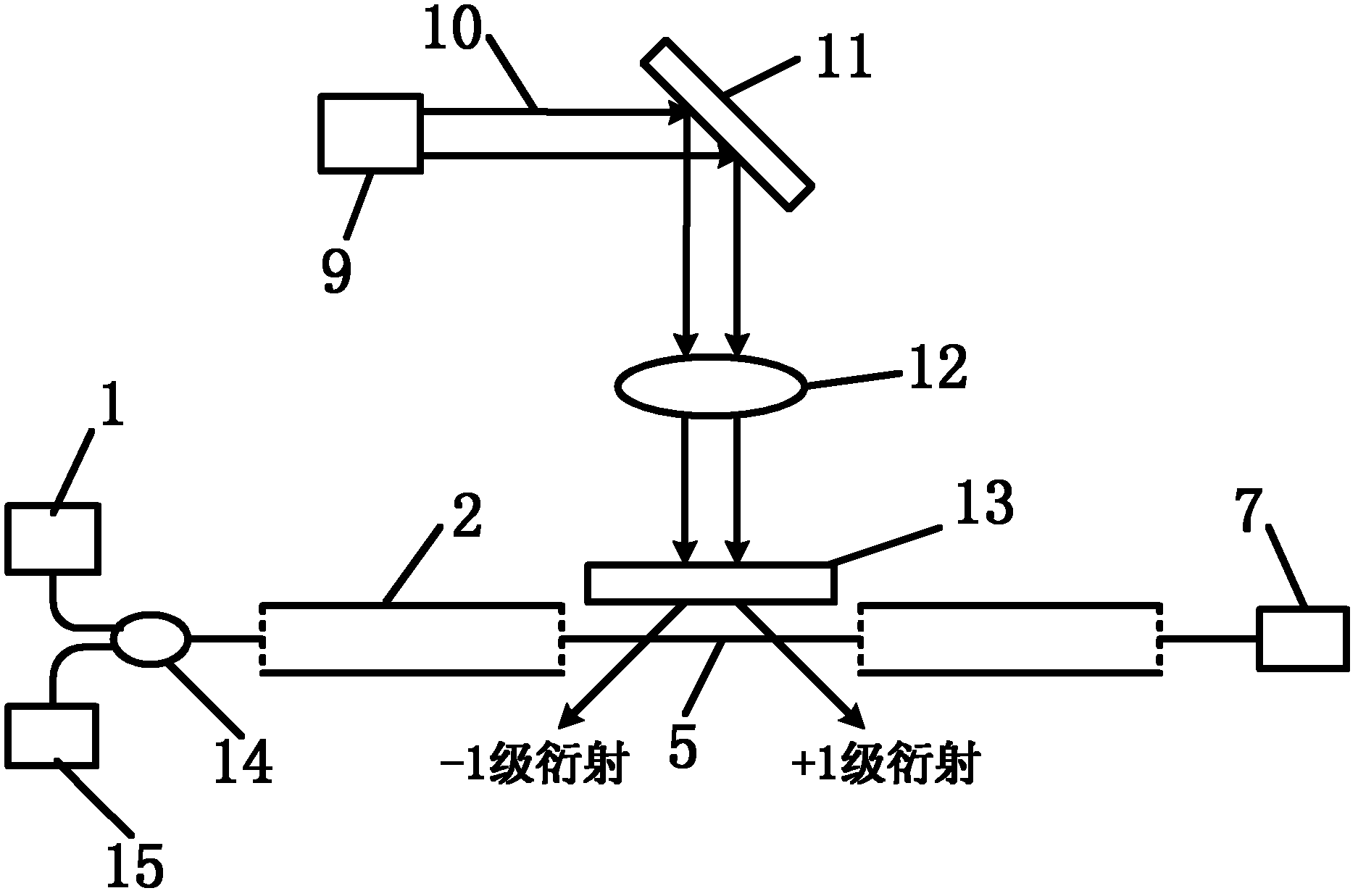
InactiveUS20080204879A1Conducive to lightweightImprove reliabilityRadiation pyrometryDiffraction gratingsFiberGrating interferometer
A lamellar grating interferometer is described, in which the light beams are collimated and focused onto the grating by means of mirror 9, which at the same time serves for collecting the light reflected from the grating. In this case, the light beam of a white light source 1 is first collimated by means of first lens 2, and subsequently passed through a sample cuvette 3. The transmitted light beam is subsequentlyy focused and coupled by another lens 2 into a fibre 17. The light to this fibre 17 is subsequentlyy directed towards a mirror 9, reflected from this mirror 9 onto a grating 11, which forms part of a lamellar grating interferometer which is realised by means of a micro electro mechanical device MEMS 7, which is mounted on a MEMS holder 6, as is the fibre 17. The light reflected from this grating 11 is reflected onto the same mirror 9, and focused and coupled by this same mirror 9 into a second multimode fibre 18, which is also fastened to the holder 6. The light guided by this second multimode fibre 18 is subsequently fed into a detection device 4.
Owner:CARAG AG
Bend-insensitive multimode fiber
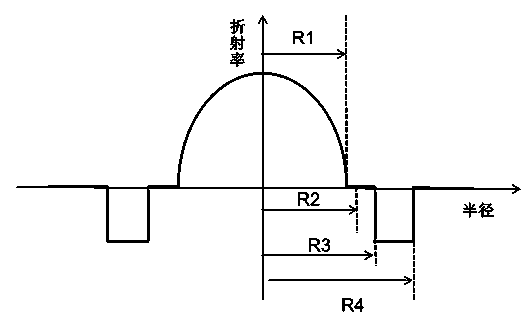
InactiveCN104360435AReduced bend sensitivityGood for stress reliefOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRelative refractive indexDistributed index
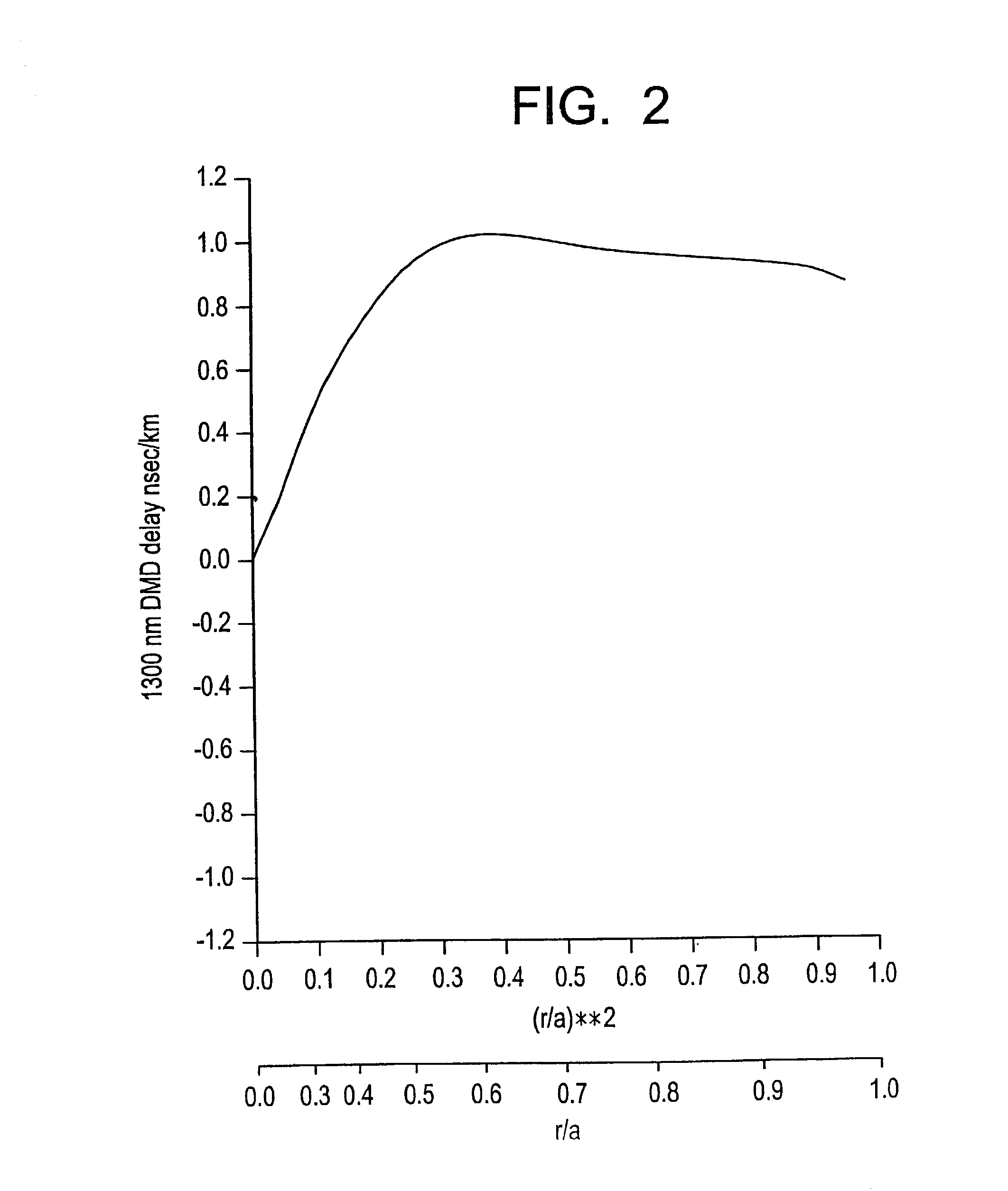
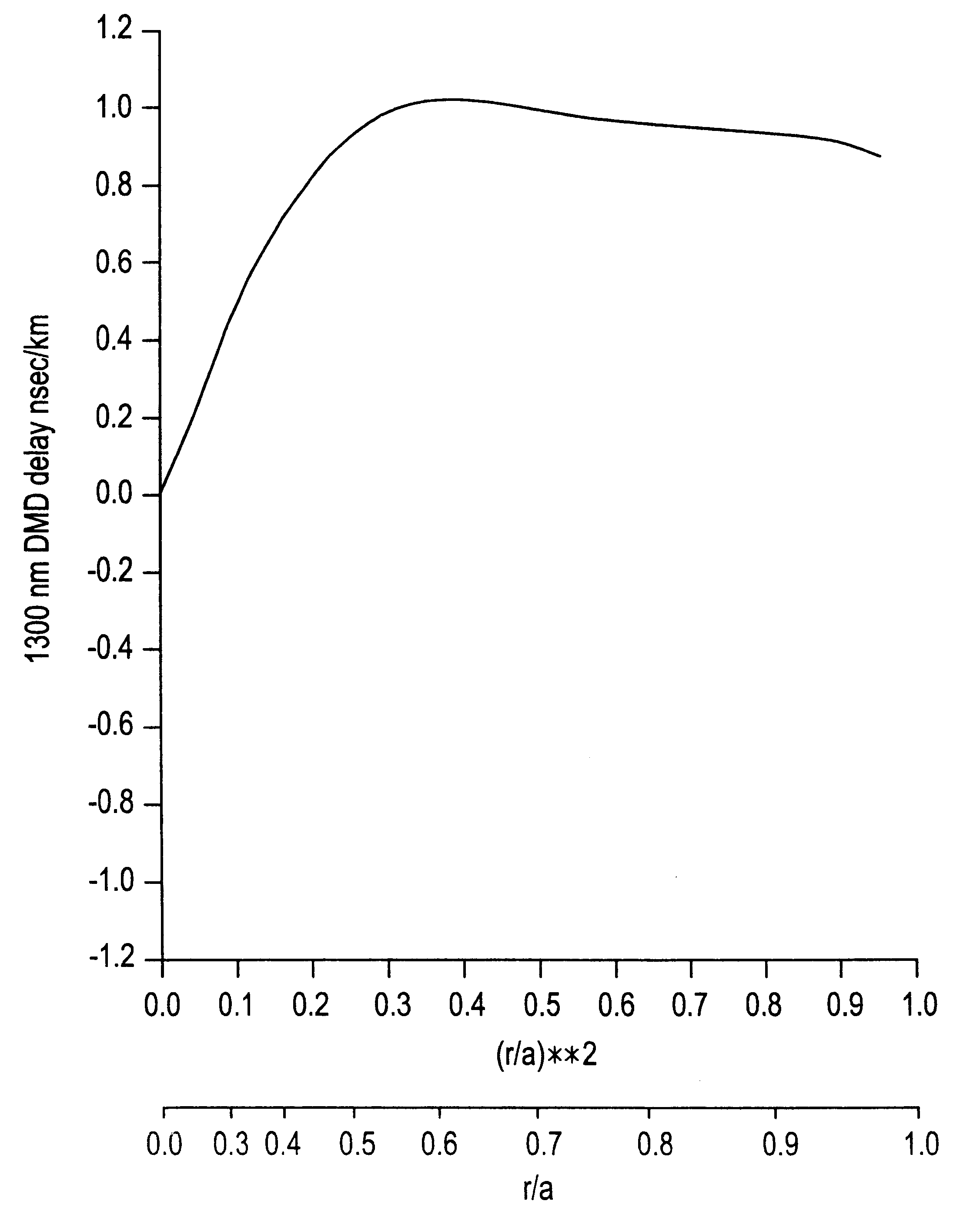
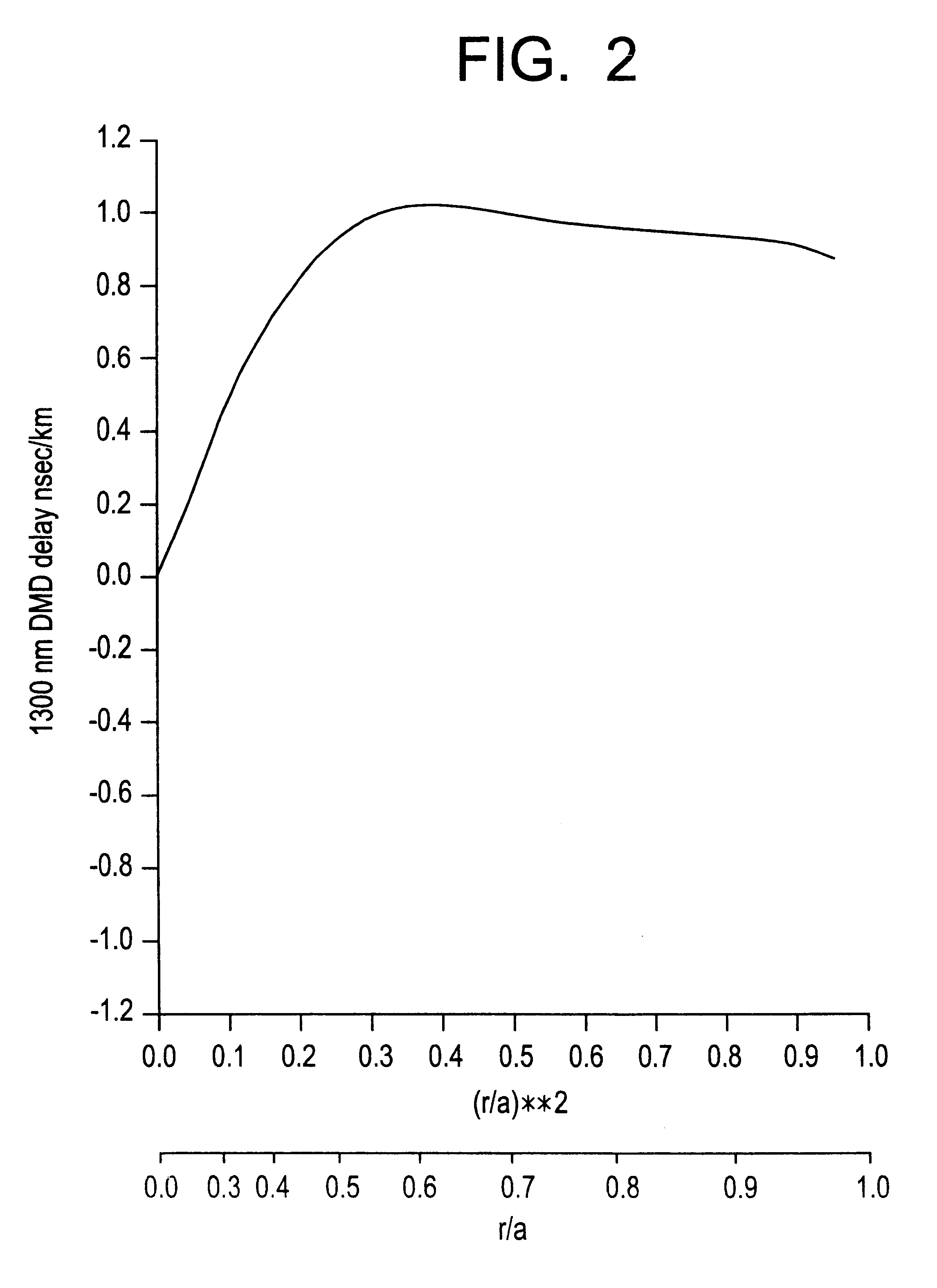
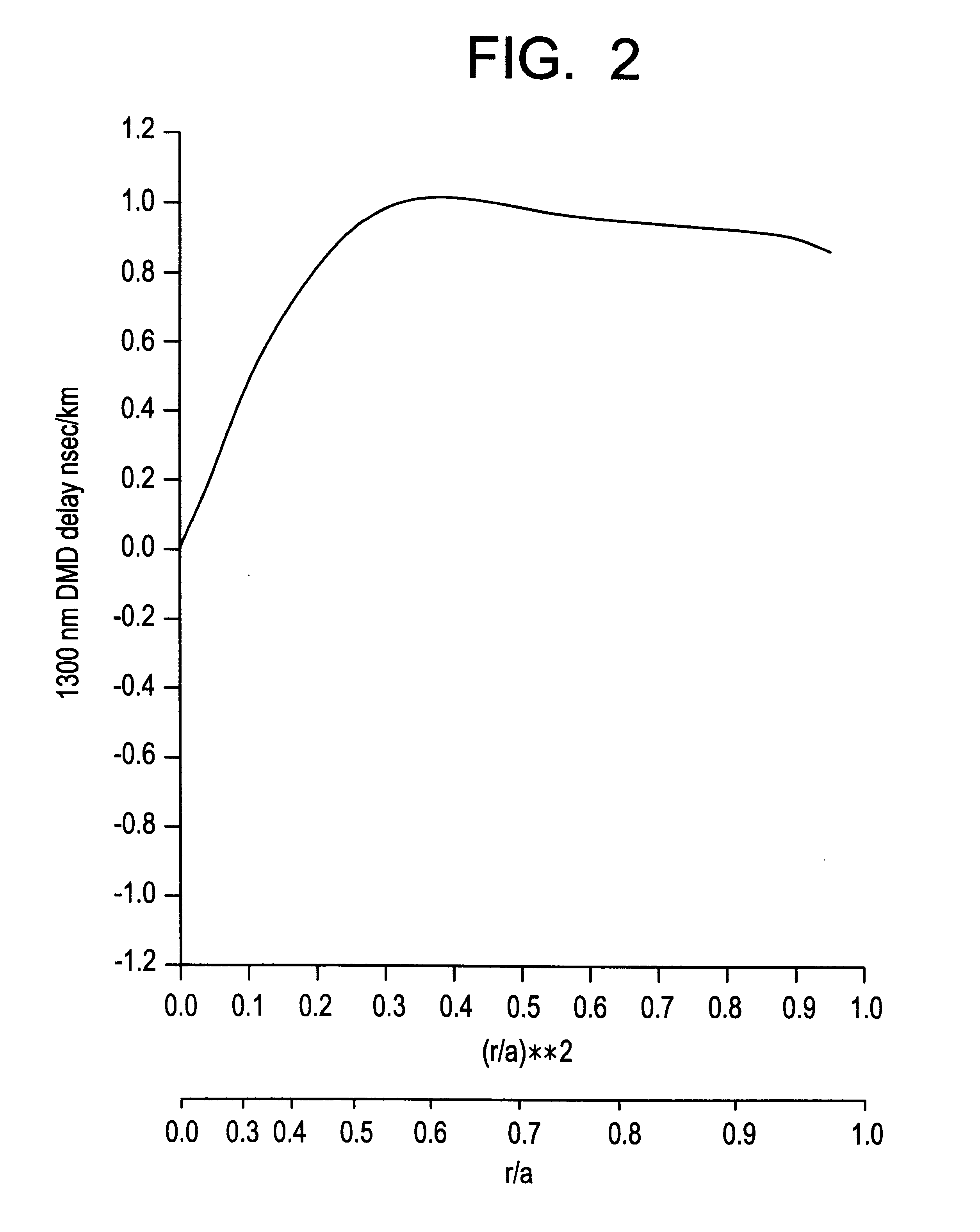
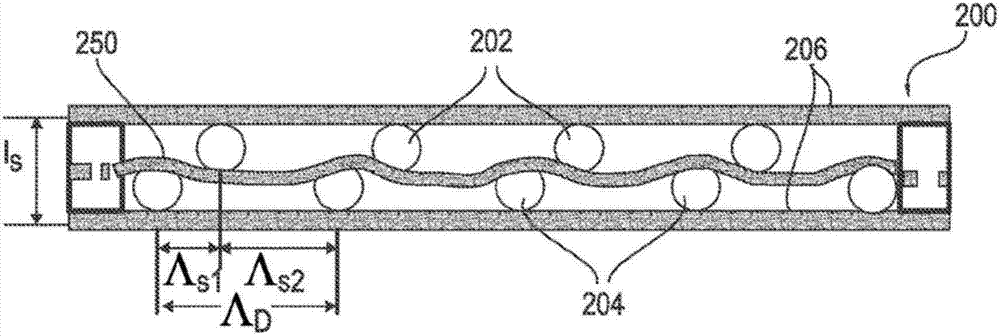
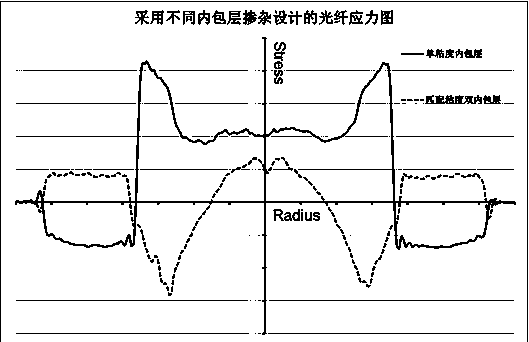
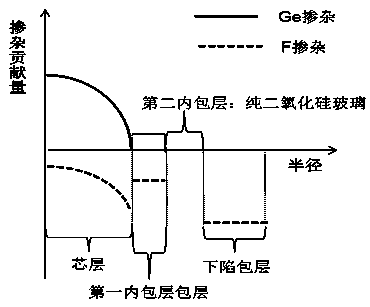
The invention relates to a bend-insensitive multimode fiber comprising a core layer, inner sheath layers and an outer sheath layer. The bend-insensitive multimode fiber is characterized in that the radius R1 of the core layer is 23-26 micrometers, the refractivity section of the core layer is parabolic, the distribution index Alpha thereof is 1.9-2.2, a maximum relative refractive index difference Delta1 thereof is 0.9-1.2%, the first inner sheath layer, the second inner sheath layer and a recessed sheath layer are provided in order from inside to outside, the unilateral width of the first inner sheath layer is 1-3 micrometers, a relative refractive index difference Delta2 of the first inner sheath layer is -0.02-0.02%, the second inner sheath layer is an all-carbon dioxide layer 2-6 micrometers in unilateral width, the recessed sheath layer is an F-doped silica glass layer, and the recessed sheath layer is an all-silica glass layer. The double-inner-sheath structure of matching viscosity is used, the influence of drawing tension upon the core layer is reduced in terms of viscosity, and bend sensitiveness of the fiber is reduced; the width of the inner sheath layers and the size of the recessed sheath layer are reasonably optimized and designed, matching of the width and the size is achieved, and optimal width and size are acquired; meanwhile, excellent bend resistance and DMD (differential mode delay) performance are achieved.
Owner:YANGTZE OPTICAL FIBRE & CABLE CO LTD
Optical transmitting antenna system and beam control method thereof
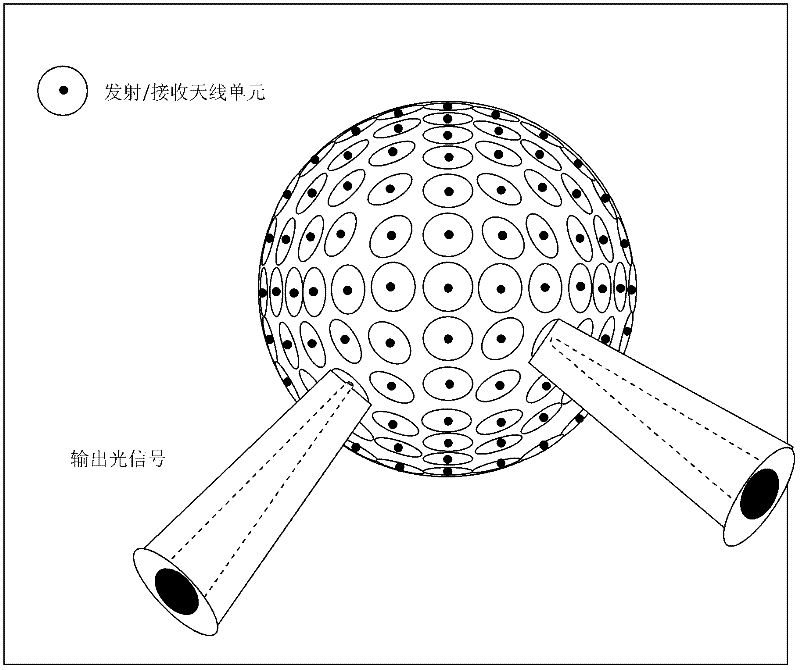
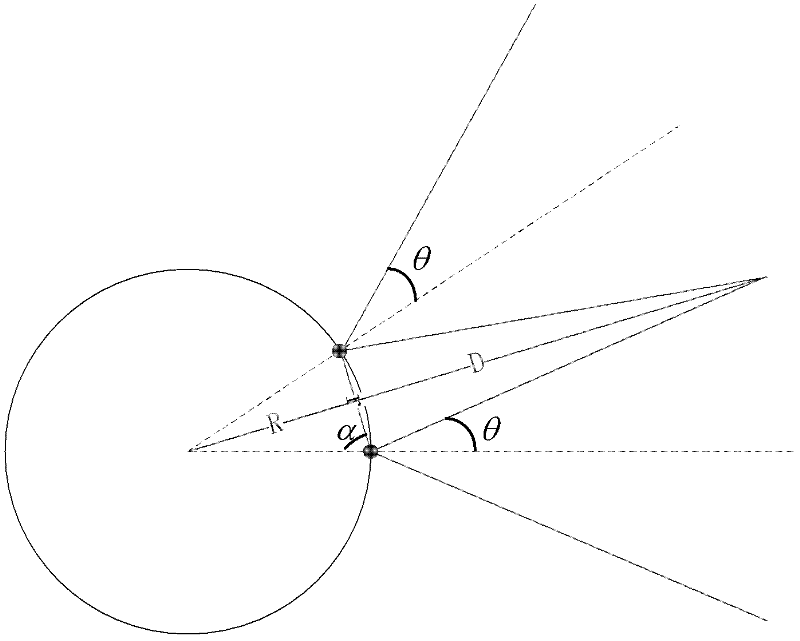
InactiveCN102571204AEffective coverageBroken beam scanning speed fastCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmissionFiberOptical antenna
The invention discloses an optical transmitting antenna system and a beam control method thereof. An optical antenna has an array structure which is formed by uniformly arranging a plurality of laser transmitting antennae and a plurality of receiving antennae. The array structure is arranged on a cambered surface (a hemispherical surface or a spherical surface). Each laser transmitting antenna comprises a transmitting multimode fiber and a transmitting micro-lens. Each receiving antenna comprises a receiving multimode fiber and a receiving micro-lens. A transmitting micro-lens is positioned in the center of each receiving micro-lens. By the optical transmitting antenna system and the beam control method thereof, the mobile communication of a near-earth atmospheric laser system is well realized, dependence on a complex acquisition pointing and tracking (APT) system is reduced, and communication reliability is improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
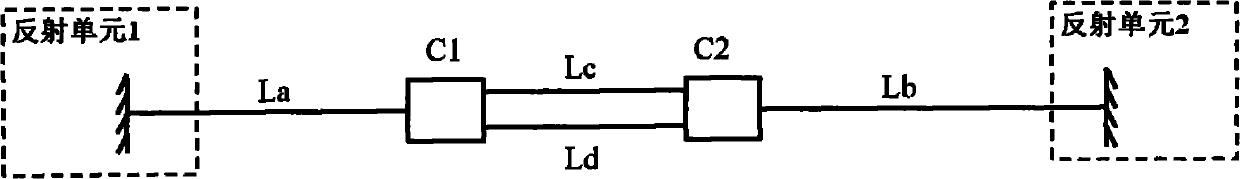
All-fiber high accuracy sensor based on optical fiber multi-mode interference and application thereof
InactiveCN103940455ALow costHigh precisionMachines/enginesLevel indicatorsAccuracy and precisionHigher order mode
The invention discloses an all-fiber high accuracy sensor based on optical fiber multi-mode interference and an application thereof. The all-fiber high accuracy sensor is composed of a first single-mode optical fiber, a multi-mode optical fiber, a coreless optical fiber and a second single-mode optical fiber. The first single-mode optical fiber, the multi-mode optical fiber, the coreless optical fiber and the second single-mode optical fiber are sequentially combined to be subjected to butt fusion. The specification of the first single-mode optical fiber is the same as the specification of the second single-mode optical fiber, the diameter of a core layer of the single-mode optical fiber is smaller than the diameter of a core layer of the multi-mode optical fiber, and the first single-mode optical fiber and the second single-mode optical fiber are used as the incidence end and the transmission end of a light source respectively. The multi-mode optical fiber is used as a mode coupler, the excitation efficiency of a high order mode in the coreless optical fiber is improved, and the coreless optical fiber serves as a measurement zone. The all-fiber sensor has the advantages of being low in cost, high in precision, small in size and compact in structure. A section of multi-mode optical fiber is used as the mode coupler, so that the measurement accuracy of the all-fiber high accuracy sensor is further optimized.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Laser beam combiner for simultaneously detecting various types of gas of TDLAS (Tunable Diode Laser Absorption Spectroscopy)
InactiveCN103604773AConcentrated light intensity distributionUniform distribution of light intensityColor/spectral properties measurementsUltrasound attenuationOptical axis
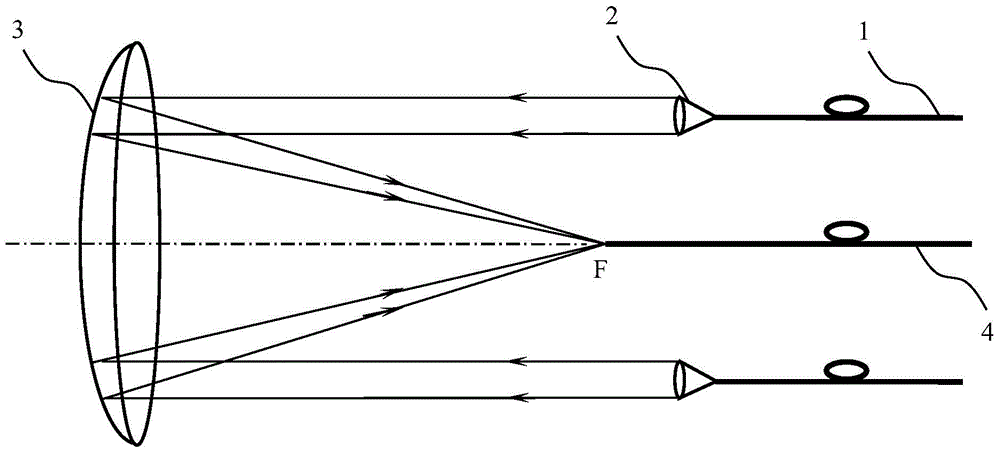
The invention provides a laser beam combiner for simultaneously detecting various types of gas of a TDLAS (Tunable Diode Laser Absorption Spectroscopy) and belongs to the technical field of laser gas detection. In the prior art, the attenuation is high, the work wavelength range is narrow and the construction cost of a beam combining part is high. The laser beam combiner is characterized by being provided with a plurality of paths of incidence optical fibers; an emergent end of each path of the incidence optical fiber is connected with a collimating mirror and each incidence optical fiber is a single-core and single-mode optical fiber; mutually-parallel optical axes of the plurality of collimating mirrors of the plurality of paths of incidence optical fibers are parallel to the optical axis of a concave spherical surface reflection mirror; the mutually-parallel optical axes of the plurality of collimating mirrors intersect with a reflection surface of the concave spherical surface reflection mirror; an incidence end face of an emergent optical fiber is located on a reflection surface focus point F of the concave spherical surface reflection mirror and is vertical to the optical axis of the concave spherical surface reflection mirror; the emergent optical fiber is a single-core and multi-mode optical fiber; the numerical aperture of the concave spherical surface reflection mirror is less than that of the emergent optical fiber.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Symmetrical all-fiber Fabry-Perot sensor and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN105180980AStructural symmetryCompact structureConverting sensor output opticallyButt jointFourier transform on finite groups
The invention discloses a symmetrical all-fiber Fabry-Perot sensor, a first single-mode fiber is welded with a first multi-mode fiber, and a second single-mode fiber is welded with a second multi-mode fiber; tail ends of the first multi-mode fiber and the second multi-mode fiber are provided with concave cavities; the concave cavities of the first multi-mode fiber and the second multi-mode fiber are in butt joint with each other to form an FP cavity. According to the symmetrical all-fiber Fabry-Perot sensor and the manufacturing method thereof provided by the invention, the structure is small and exquisite, manufacture is easy and cost is low, the fiber sensor can utilize a chemical corrosion method to obtain a long Fabry-Perot cavity, is symmetrical in structure and low in stripe fineness, is little affected by temperature, and can utilize a phase method based on Fourier transform to realize measurement of pressure and strain under high temperature.
Owner:广州顶盛益电子科技有限公司
Single-pixel camera system based on multi-mode optical fiber
ActiveCN107817641ASave the step of adjusting the photosensitive surfaceImprove signal-to-noise ratioCamera body detailsEnvironmental noiseObservation matrix
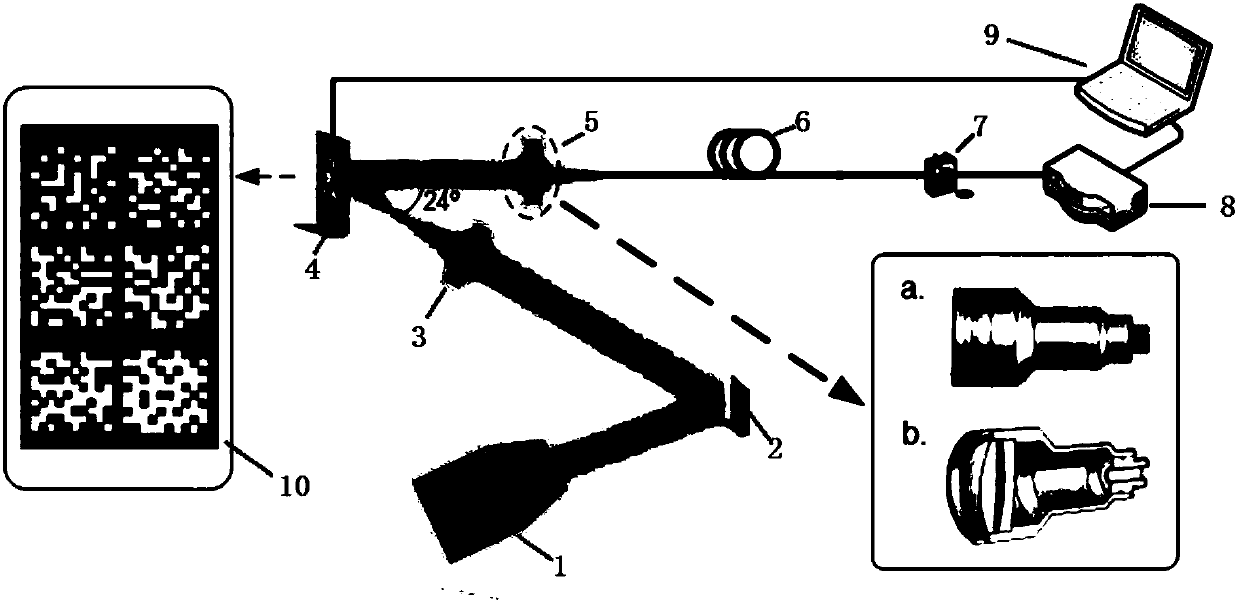
The invention provides a single-pixel camera system based on a multi-mode optical fiber, which has the advantages of high signal-to-noise ratio, simple optical path structure and high expansibility. The single-pixel camera system mainly comprises a DMD modulation portion, a data acquisition portion and an algorithm recovery portion. Specifically, the traditional single-pixel camera system converges light modulated by a DMD to a light sensitive surface of a unit detector by using a lens, then the light is converted into a corresponding light intensity value through A / D conversion, and imaging can be performed by inputting the light intensity value into a recovery algorithm by combining an observation matrix. The method utilizing the general lens often brings great noise interference to an experiment result, and the signal-to-noise ratio of the system is reduced by influences of the aberration generated by convergence of the lens for the space light, the dispersion of light and the ambient light in the light propagation process in addition to system noise and environmental noise. The utilization of the multi-mode optical fiber on the basis not only can reduce the loss of light transmission in the space, but also can realize single-pixel imaging in a specific band. Only an optical fiber with a specific transmission wavelength is required to be replaced.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Methods for modifying multi-mode optical fiber manufacturing processes
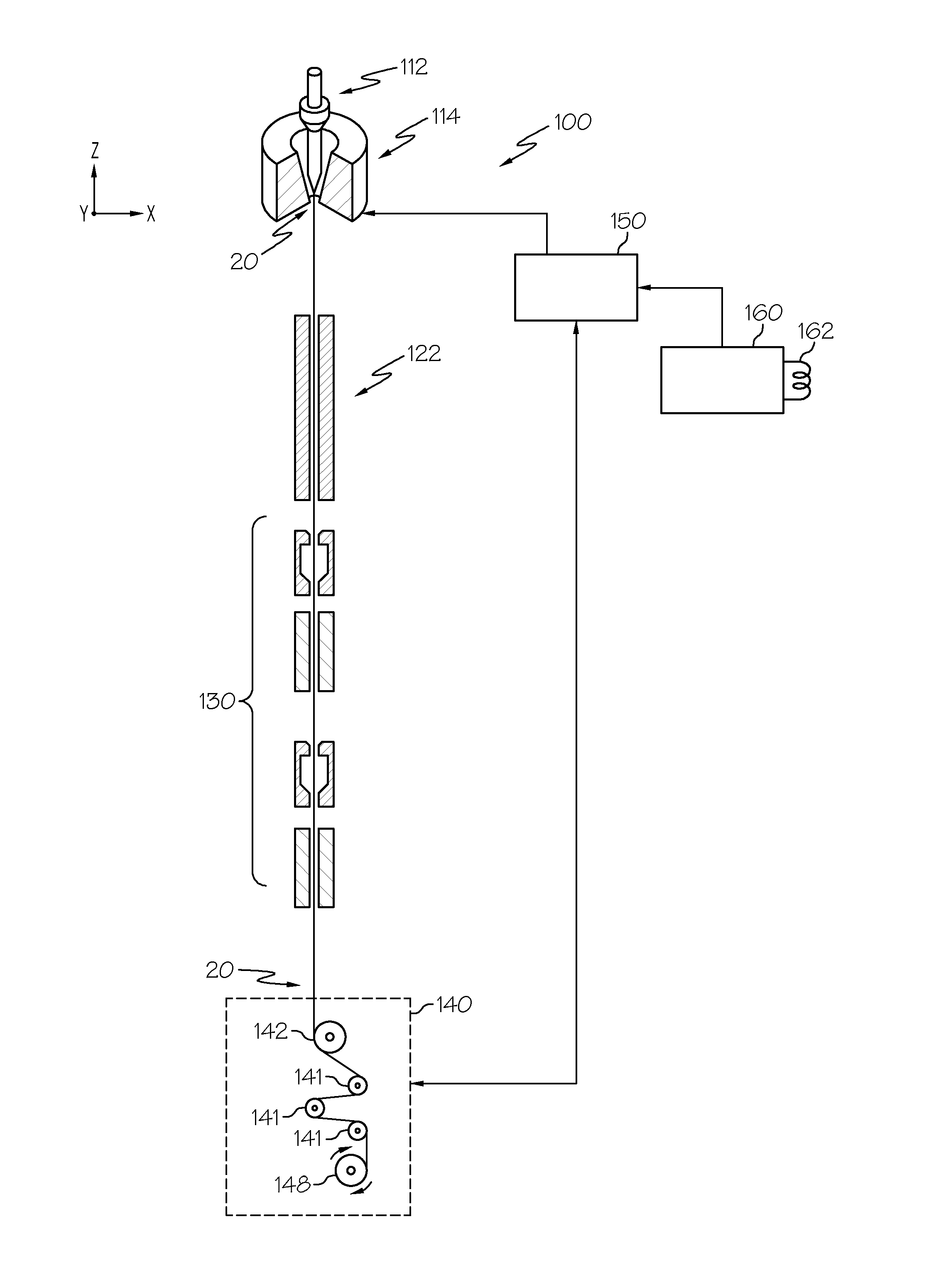
ActiveUS20140318188A1Maximizes bandwidth functionAttenuation bandwidthMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationGlass fibre drawing apparatusLength waveModal bandwidth
Methods for modifying multi-mode optical fiber manufacturing processes are disclosed. In one embodiment, a method for modifying a process for manufacturing multi-mode optical fiber includes measuring at least one characteristic of a multi-mode optical fiber. The at least one characteristic is a modal bandwidth or a differential mode delay at one or more wavelengths. The method further includes determining a measured peak wavelength of the multi-mode optical fiber based on the measured characteristic, determining a difference between the target peak wavelength and the measured peak wavelength, and modifying the process for manufacturing multi-mode optical fiber based on the difference between the target peak wavelength and the measured peak wavelength.
Owner:CORNING INC
Line cavity laser with super-narrow line width based on parallel feedback
InactiveCN102005697AAchieve laser outputSimple structureLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionLine widthOptoelectronics
The invention provides a line cavity laser with super-narrow line width based on parallel feedback, which comprises a DFB (Distributed Feedback) laser, a 90:10 coupler, a reflection unit, multiple sections of single mode optical fibers and multiple mold optical fibers, wherein the DFB laser and the 90:10 coupler as well as the 90:10 coupler and the reflection unit are respectively coupled through an optical fiber structure composed of the single mode optical fibers and the multiple mold optical fibers.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
OCT imaging compound micro probe integrated with optical fiber sensing multi-parameter measuring and preparation method thereof
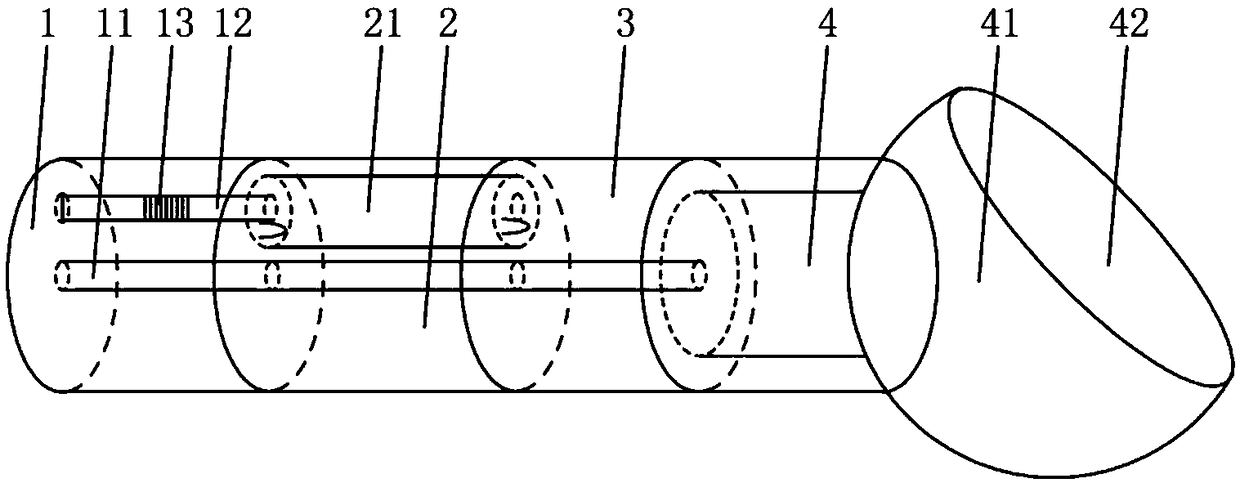
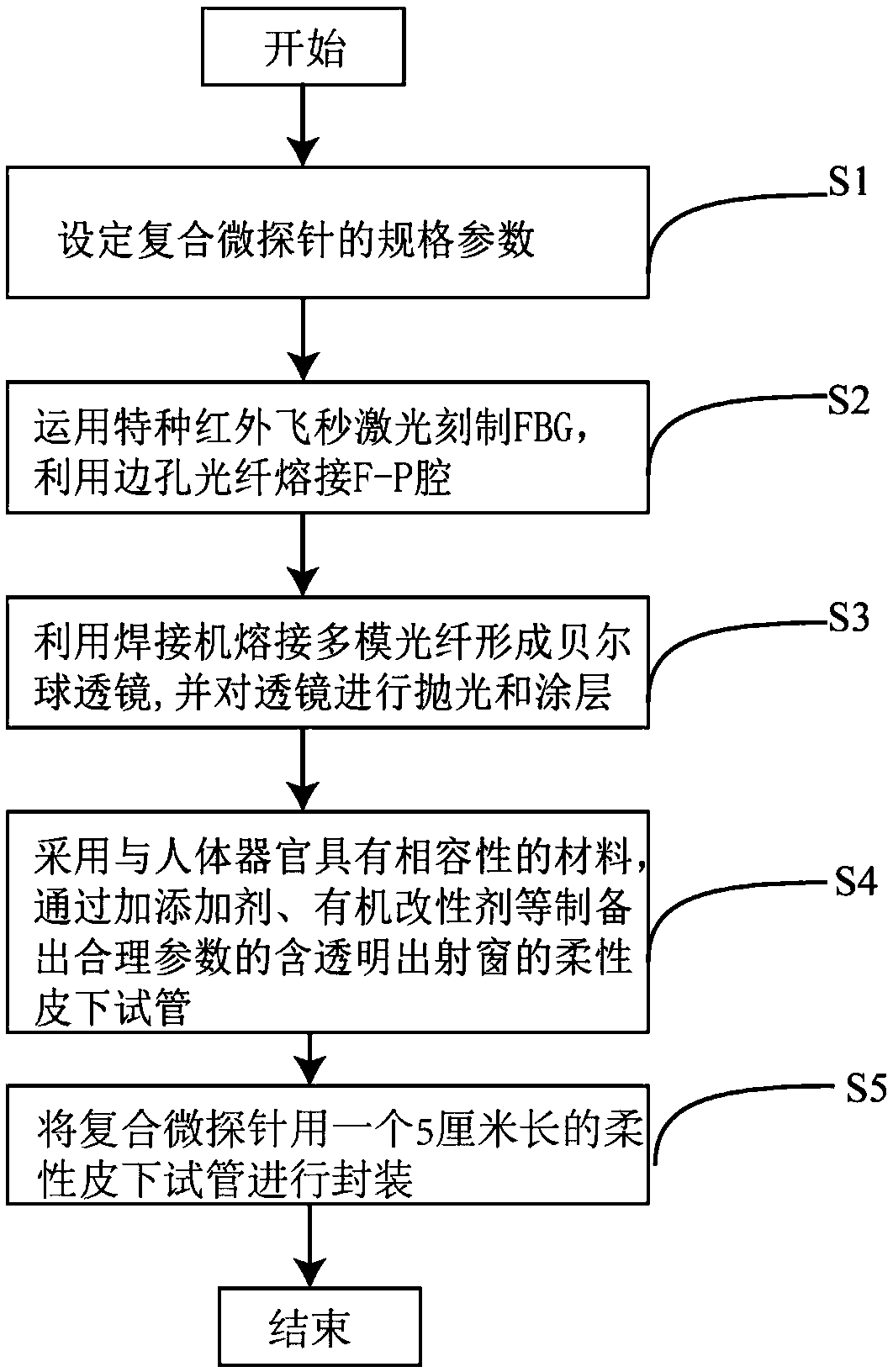
The invention relates to the technical field of optical fiber sensor medical devices, in particular to an OCT imaging compound micro probe integrated with optical fiber sensing multi-parameter measuring, and discloses a preparation method of the composite micro probe. The probe comprises a multi-core optical fiber, a side-hole optical fiber, a single-mode optical fiber and a multi-mode optical fiber which are sequentially welded, the multi-mode optical fiber comprises a central axis fiber core and an eccentric fiber core, the central axis fiber core and the fiber core of the single-mode optical fiber are welded at two ends of the fiber core of the side-hole optical fiber, photoetching FBG optical grating is arranged on the eccentric fiber core, and the front end of the eccentric fiber coreand the rear end of a side-hole air cavity on the side-hole optical fiber are aligned to further form an F-P air cavity; the front end of the multi-mode optical fiber is fused with a Bell ball. The structure of the probe is reasonable, sensitive units of FBG grating, F-P air cavity are integrated, a Bell ball focusing lens is fused through the multi-mode optical fiber, the definition of an OCT imaging observing image can be effectively improved, body tissue detecting imaging is conducted while measuring of parameters of temperature, pressure and the like is conducted, the overall structure iscompact, the size is small, and the probe has significant meaning in in vivo microvessel disease diagnosis and the like.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Demodulating device and method for optical fiber Young interference optical path difference based on low coherent interference
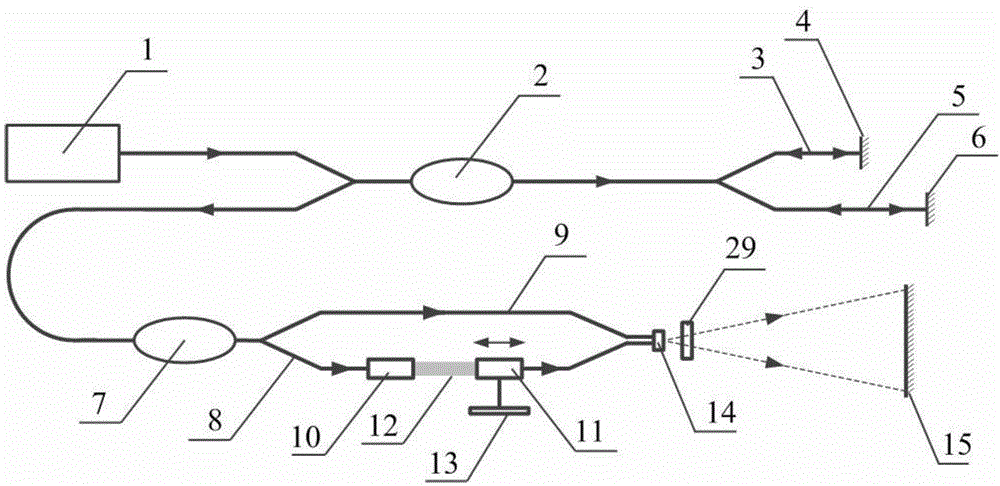
ActiveCN102980601ANo mechanical movementImprove stabilityConverting sensor output opticallyLine arrayOptical pathlength
The invention discloses a demodulating device for an optical fiber Young interference optical path difference based on low coherent interference. The demodulating device comprises a wideband light source, a 3dB coupler, a sensing interferometer, a demodulating interferometer, a calibration interferometer and a line array camera, wherein a multimode optical fiber is adopted in a light path formed by the components in sequence for optical signal transmission. A demodulating method mainly comprises the steps of optical path difference sensing, optical path difference demodulating and optical path difference calibration. Compared with the prior art, the demodulating device and the method integrate modes of space scanning and time scanning to conduct low coherent interference optical path difference demodulating; no mechanical movement is available; the stability is high; compared with the time scanning, the demodulating precision is not affected by moving precision of a scanning motor; the nano-level high precision demodulating can be realized; the optical path difference calibration of an overall system is realized by adjusting the optical path difference; in addition, a nano displacement platform is adopted to control the output optical path difference effectively; an optical path difference demodulating interval of the overall system is amended; and with the adoption of an optical fiber interferometer structural form, the system adjustment is facilitated and the working stability is high.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com