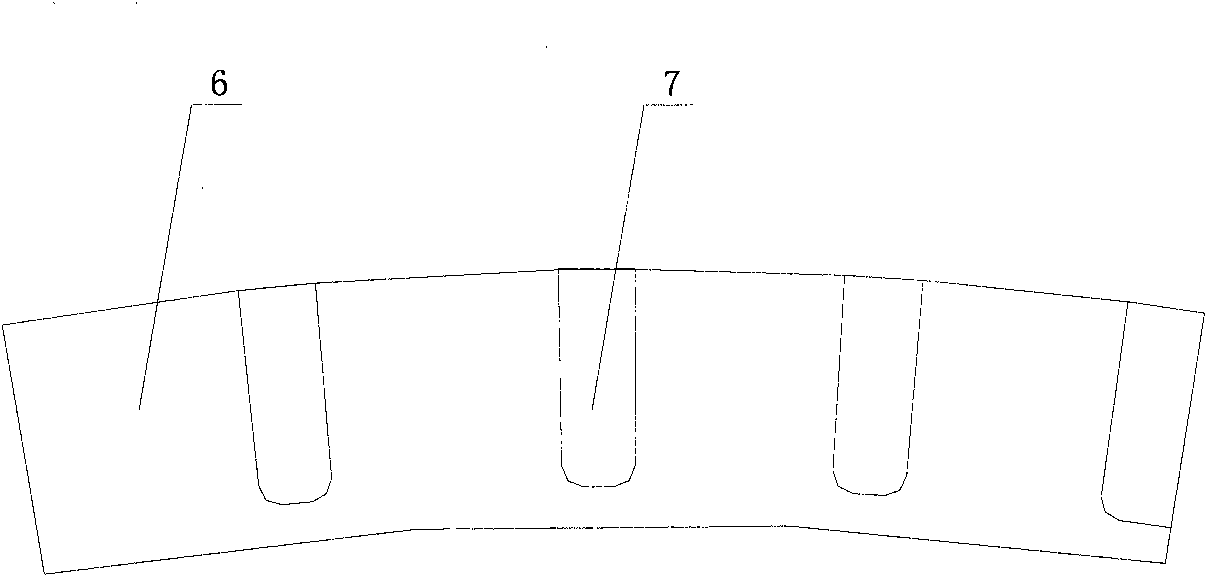Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
70 results about "Mixed pattern" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
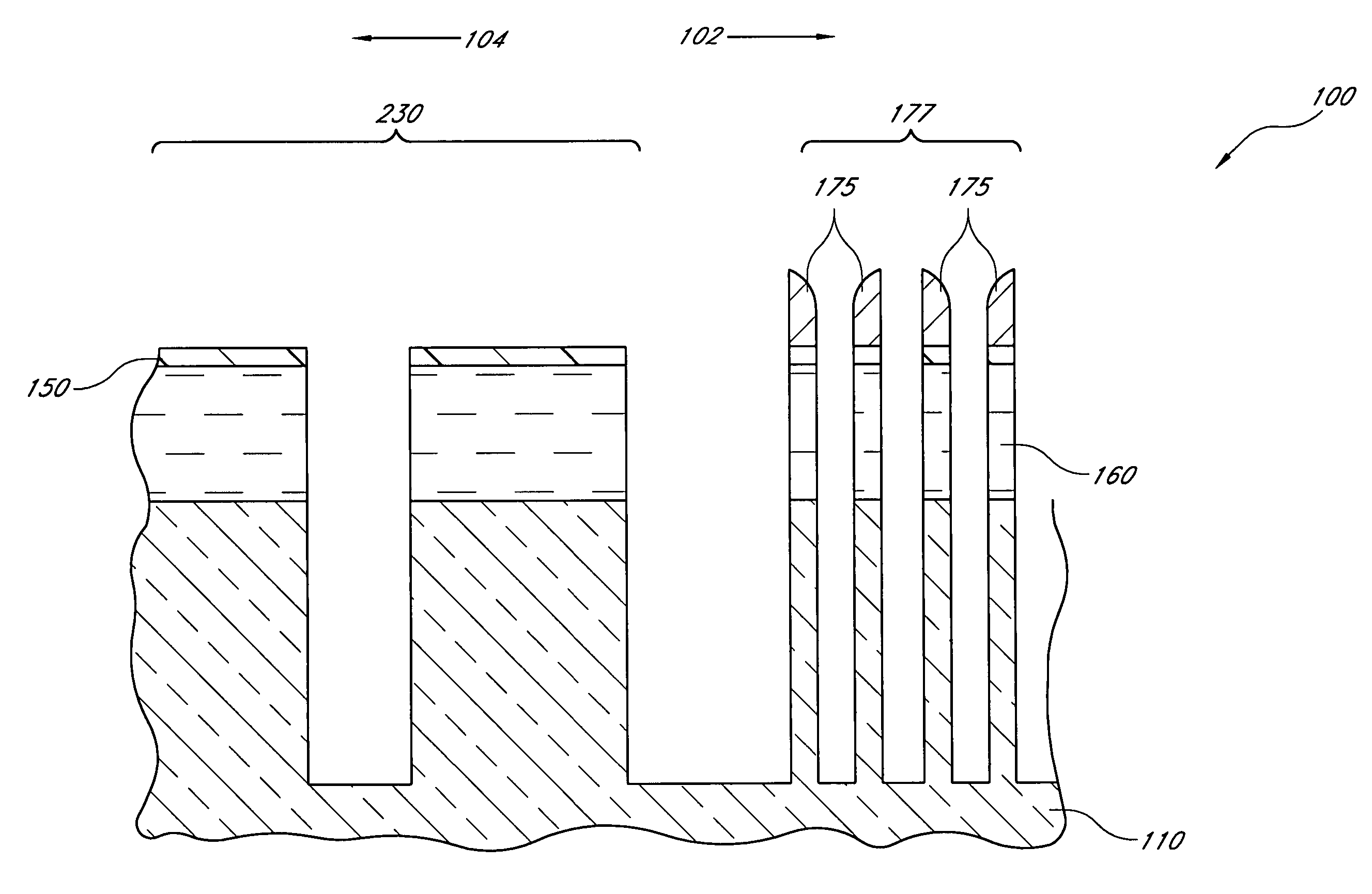
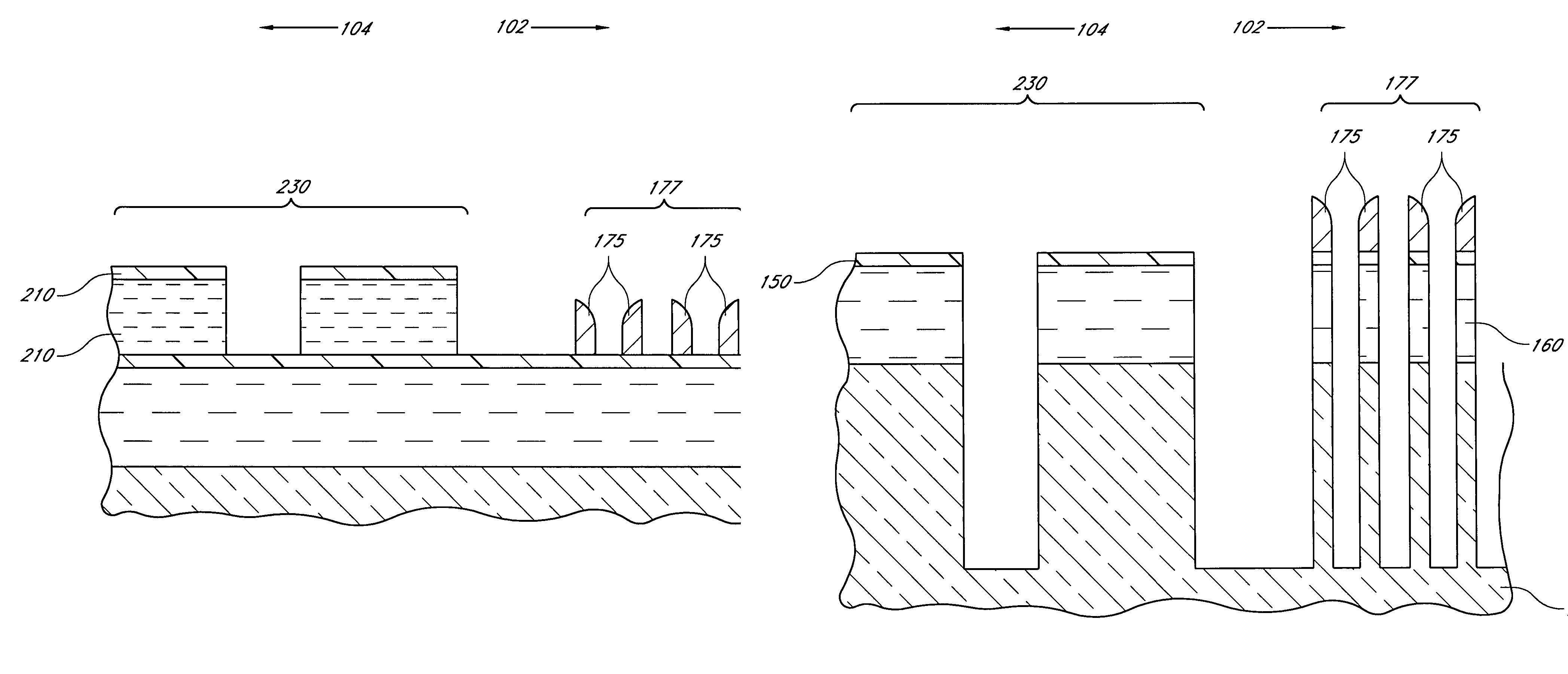
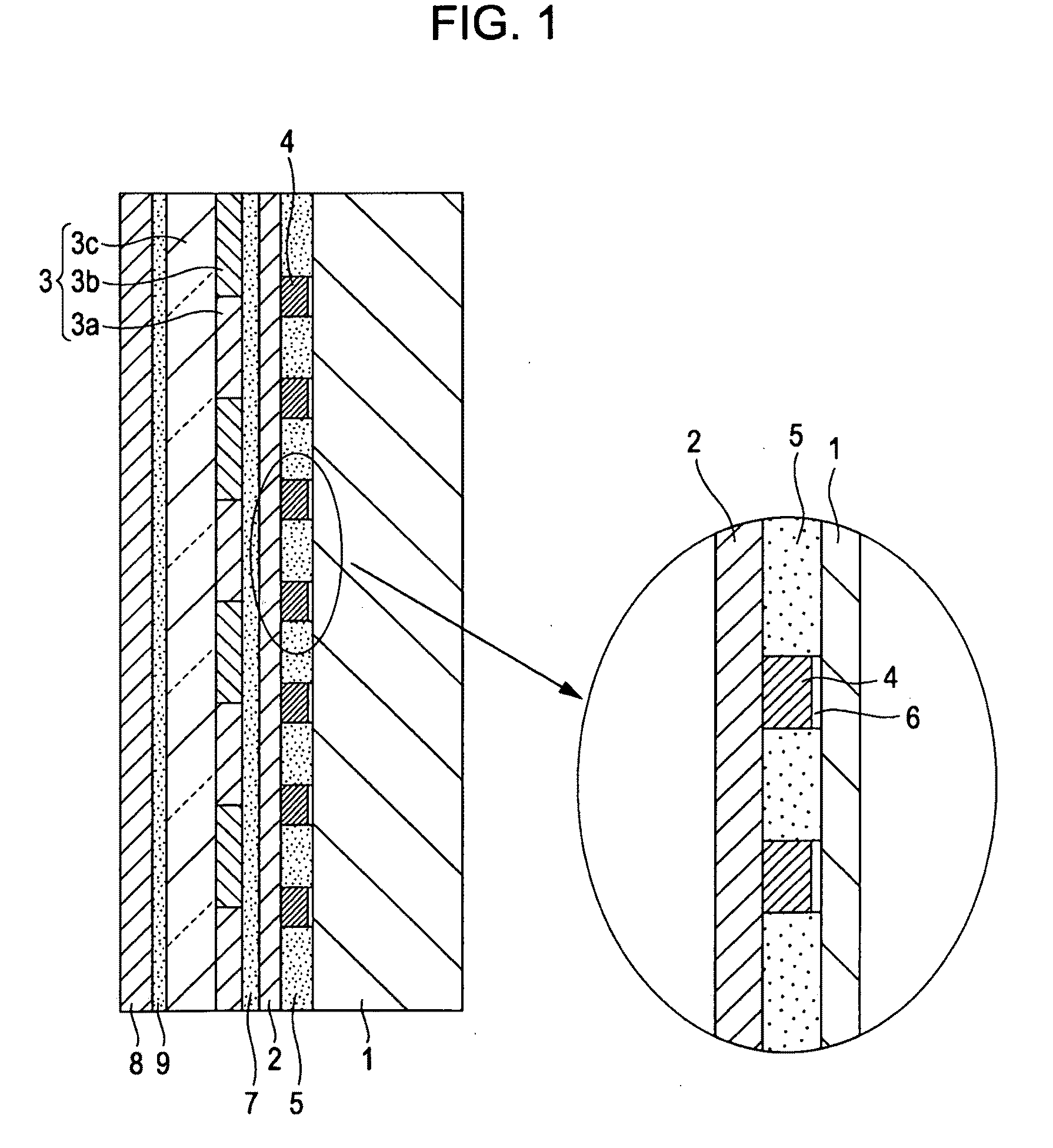
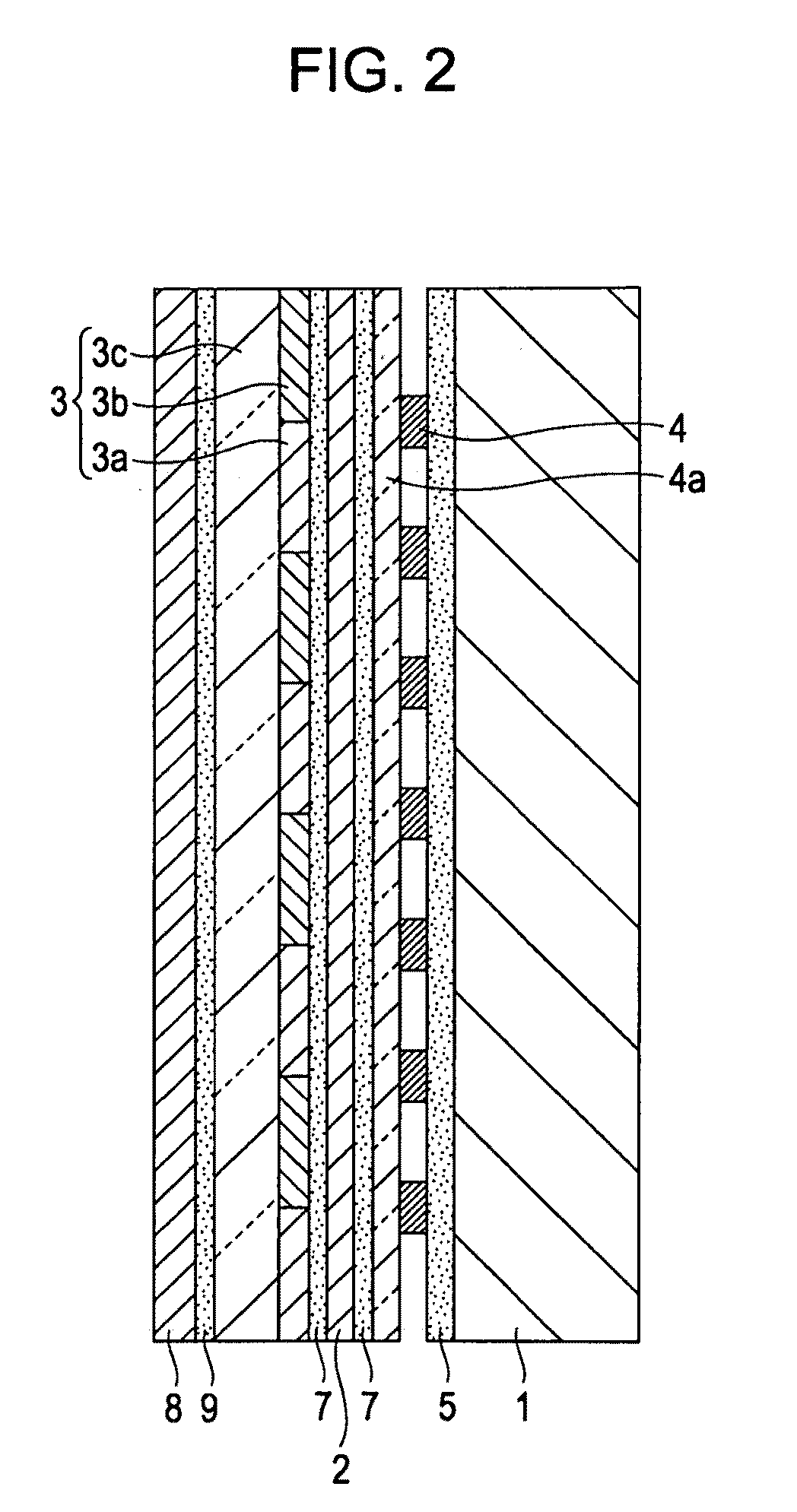
Method for integrated circuit fabrication using pitch multiplication
InactiveUS7115525B2Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistEngineering
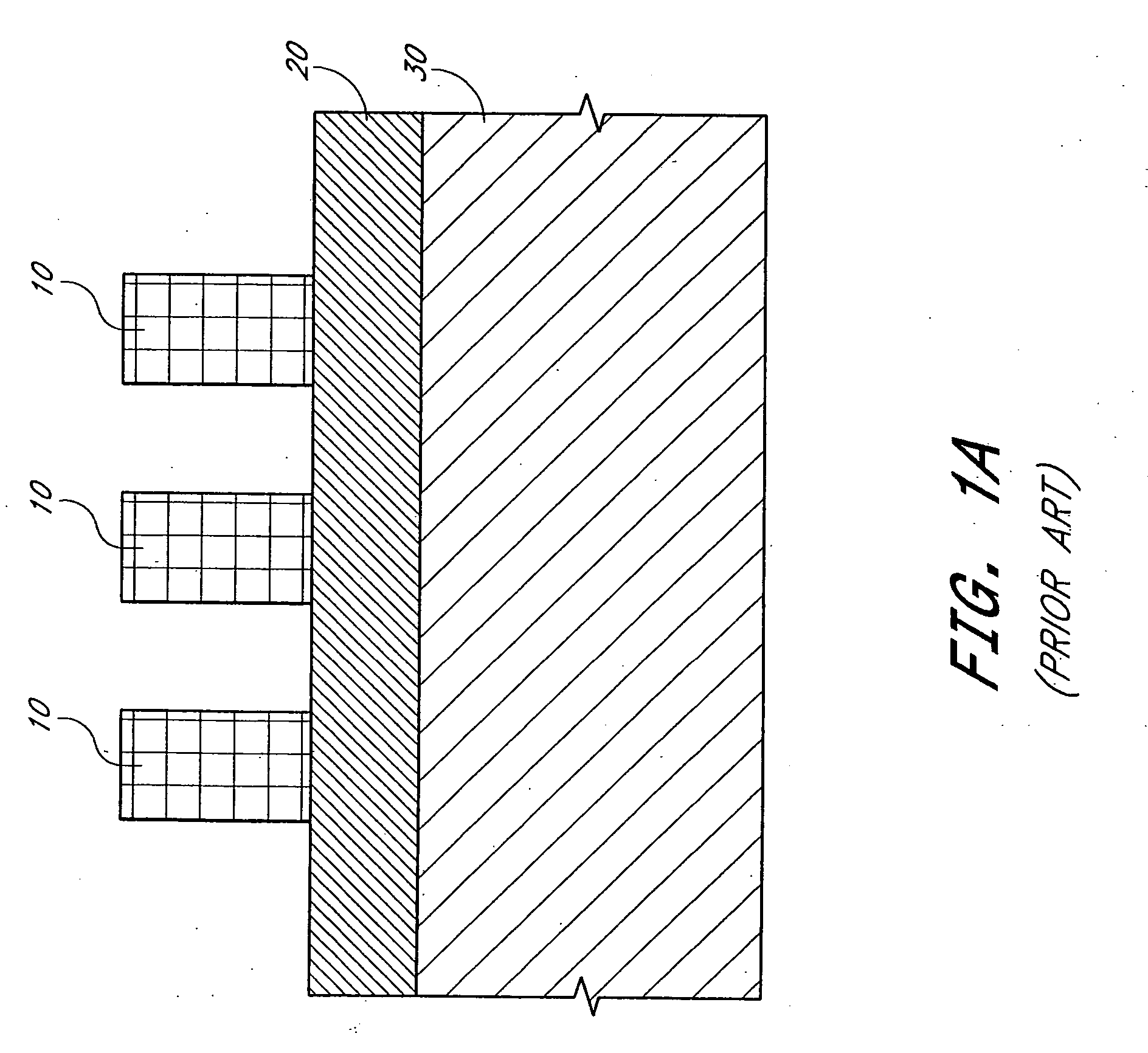
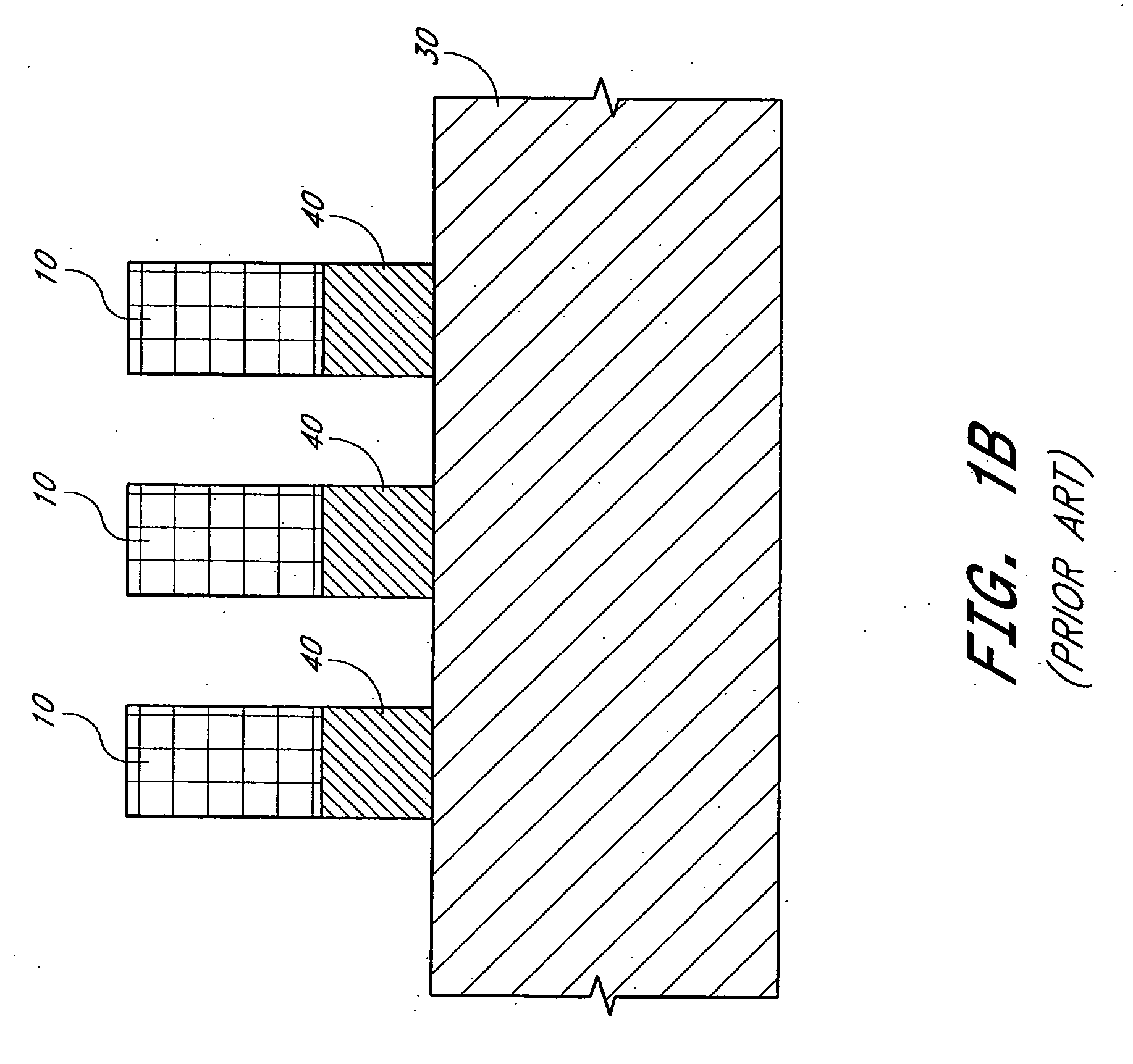
Different sized features in the array and in the periphery of an integrated circuit are patterned on a substrate in a single step. In particular, a mixed pattern, combining two separately formed patterns, is formed on a single mask layer and then transferred to the underlying substrate. The first of the separately formed patterns is formed by pitch multiplication and the second of the separately formed patterns is formed by conventional photolithography. The first of the separately formed patterns includes lines that are below the resolution of the photolithographic process used to form the second of the separately formed patterns. These lines are made by forming a pattern on photoresist and then etching that pattern into an amorphous carbon layer. Sidewall pacers having widths less than the widths of the un-etched parts of the amorphous carbon are formed on the sidewalls of the amorphous carbon. The amorphous carbon is then removed, leaving behind the sidewall spacers as a mask pattern. Thus, the spacers form a mask having feature sizes less than the resolution of the photolithography process used to form the pattern on the photoresist. A protective material is deposited around the spacers. The spacers are further protected using a hard mask and then photoresist is formed and patterned over the hard mask. The photoresist pattern is transferred through the hard mask to the protective material. The pattern made out by the spacers and the temporary material is then transferred to an underlying amorphous carbon hard mask layer. The pattern, having features of difference sizes, is then transferred to the underlying substrate.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Method for integrated circuit fabrication using pitch multiplication
InactiveUS20060046484A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingImage resolutionDifferences size
Different sized features in the array and in the periphery of an integrated circuit are patterned on a substrate in a single step. In particular, a mixed pattern, combining two separately formed patterns, is formed on a single mask layer and then transferred to the underlying substrate. The first of the separately formed patterns is formed by pitch multiplication and the second of the separately formed patterns is formed by conventional photolithography. The first of the separately formed patterns includes lines that are below the resolution of the photolithographic process used to form the second of the separately formed patterns. These lines are made by forming a pattern on photoresist and then etching that pattern into an amorphous carbon layer. Sidewall pacers having widths less than the widths of the un-etched parts of the amorphous carbon are formed on the sidewalls of the amorphous carbon. The amorphous carbon is then removed, leaving behind the sidewall spacers as a mask pattern. Thus, the spacers form a mask having feature sizes less than the resolution of the photolithography process used to form the pattern on the photoresist. A protective material is deposited around the spacers. The spacers are further protected using a hard mask and then photoresist is formed and patterned over the hard mask. The photoresist pattern is transferred through the hard mask to the protective material. The pattern made out by the spacers and the temporary material is then transferred to an underlying amorphous carbon hard mask layer. The pattern, having features of difference sizes, is then transferred to the underlying substrate.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
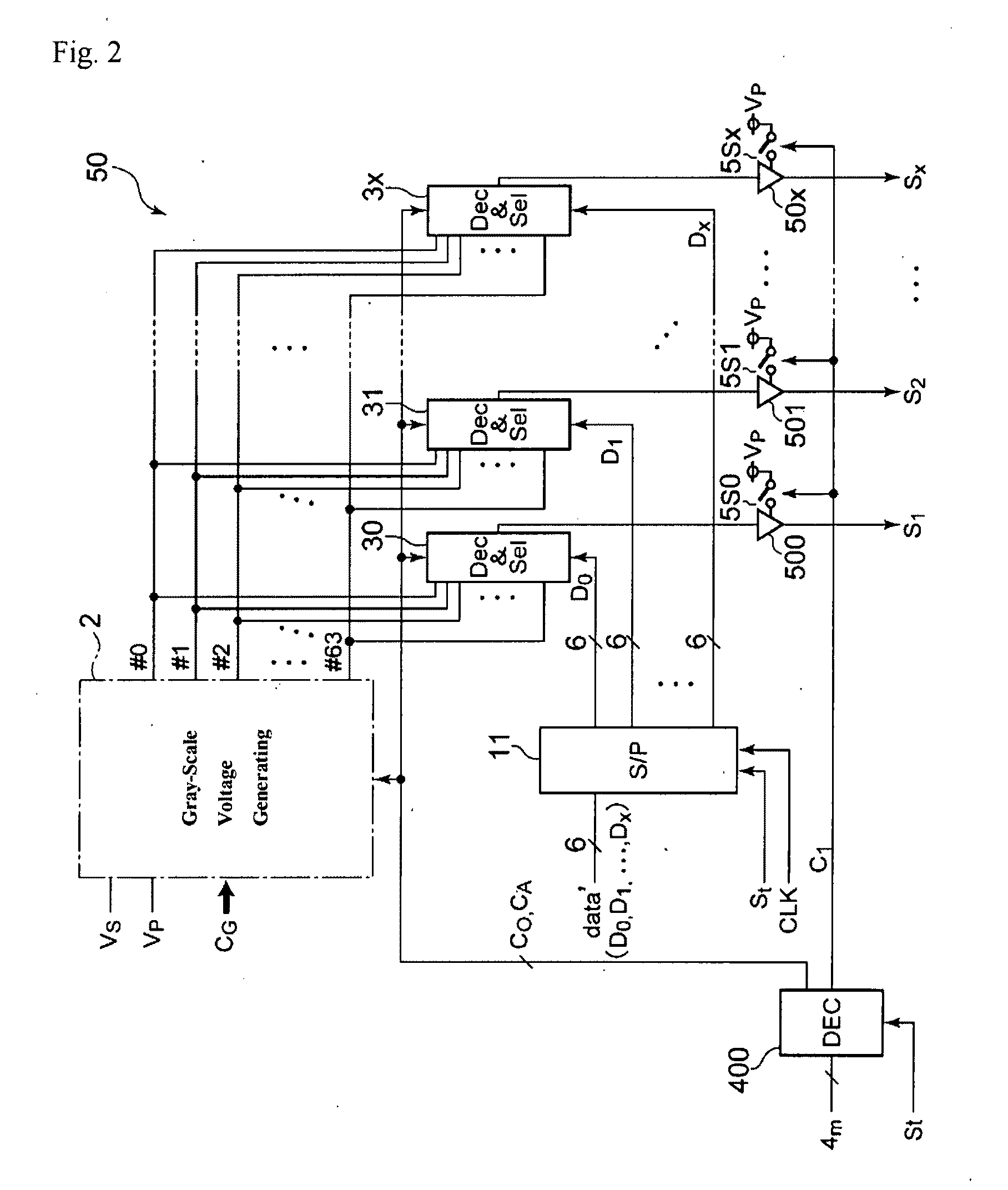
Matrix Addressing Method and Circuitry and Display Device Using the Same
ActiveUS20090213042A1Reduced legibilitySave powerCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDisplay deviceComputer science
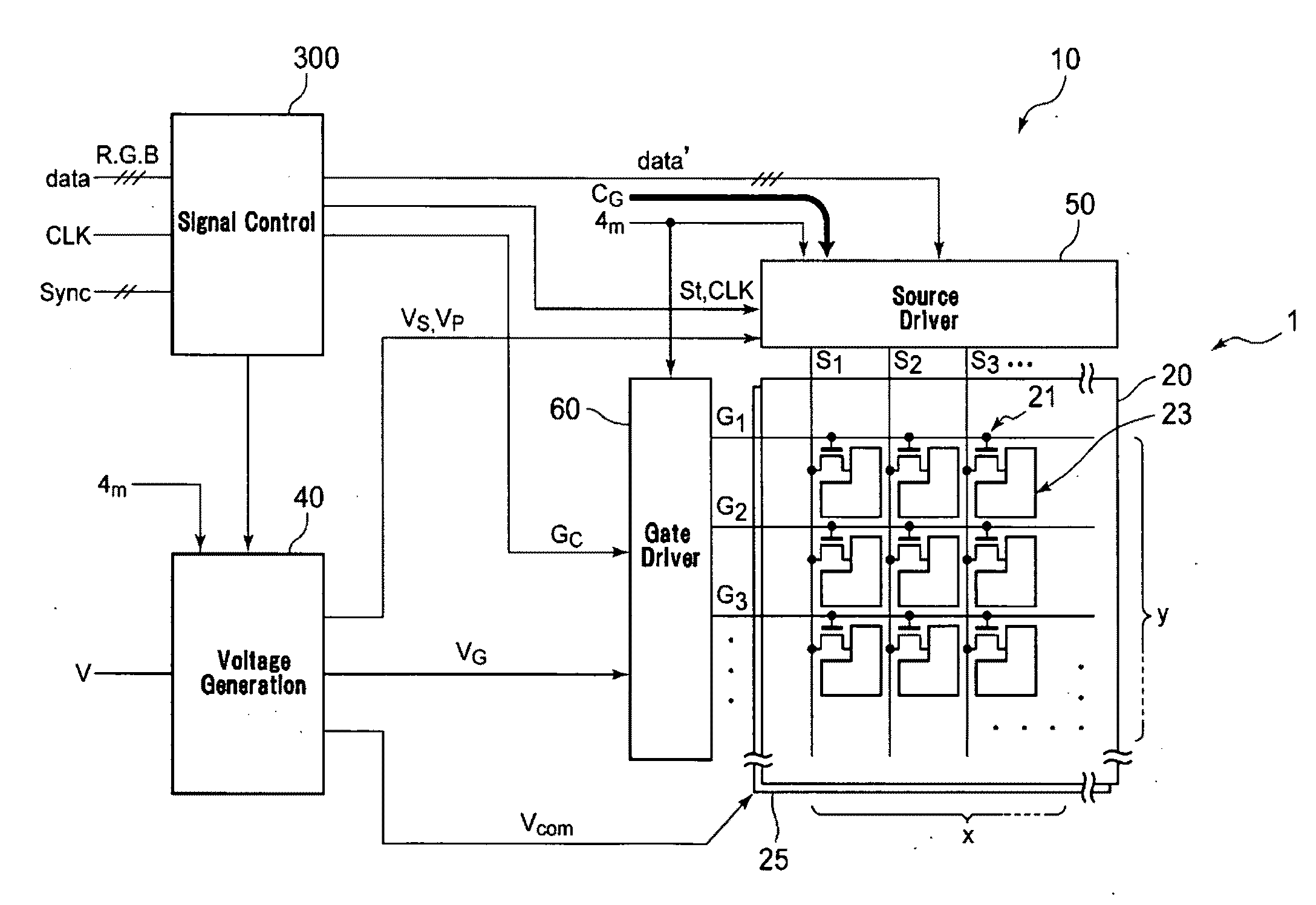
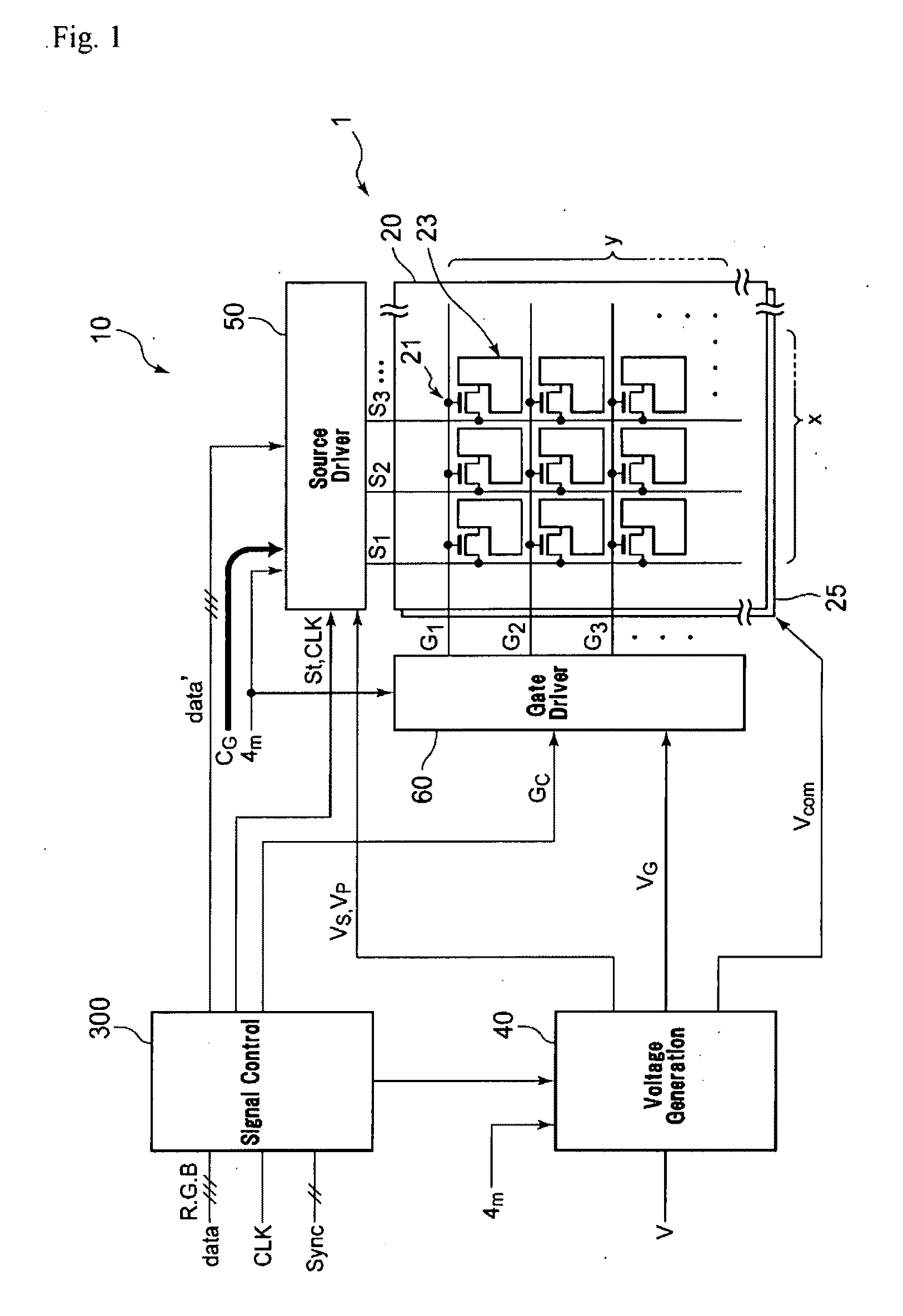
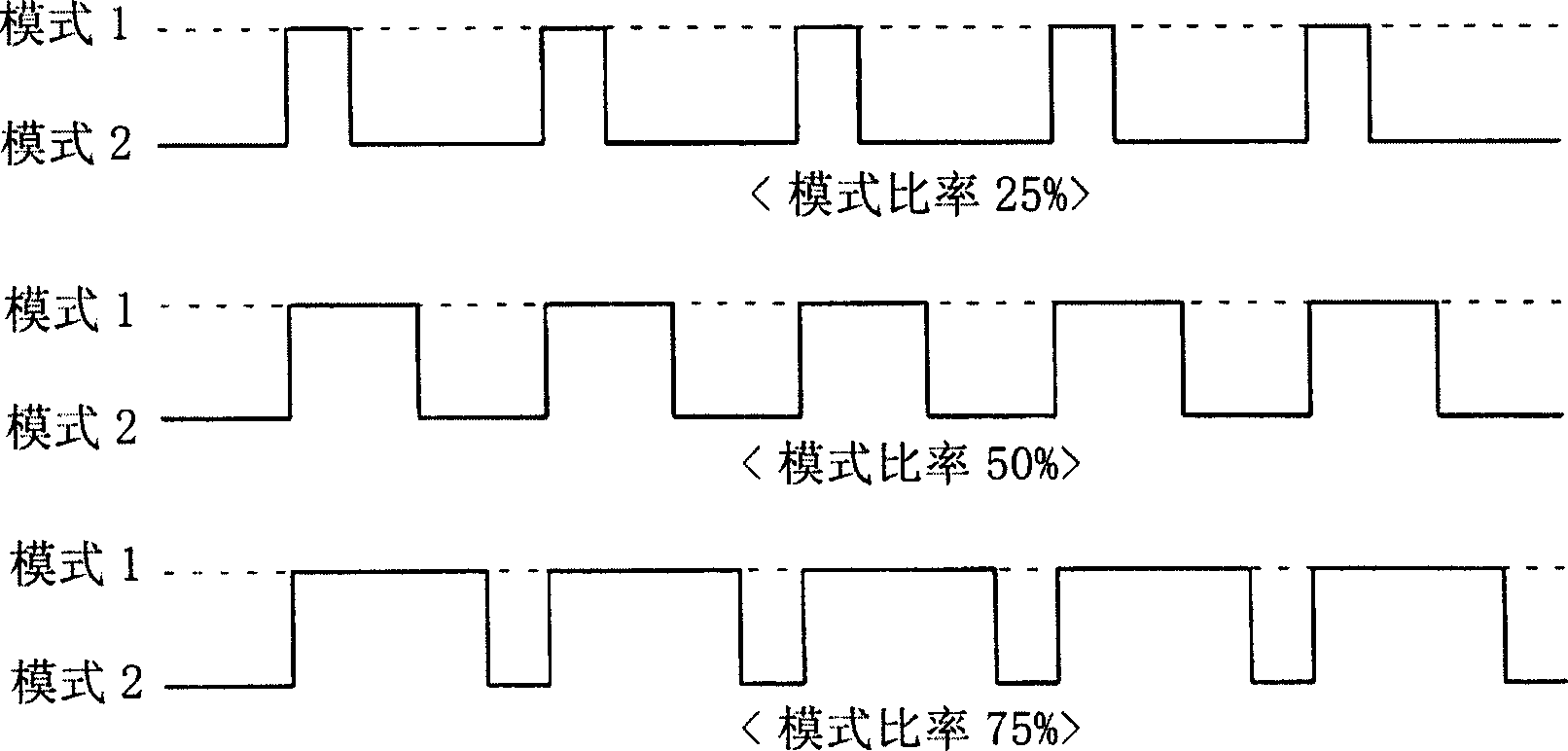
The invention aims at providing a matrix addressing method and circuitry and display device, which enable power savings without as little degrading the legibility of content of an image as possible. A matrix addressing method for driving pixels arranged over a display area by signals supplied to row electrodes and column electrodes arranged to cross one another. Rich-gray-scale pixel information signals (#0 to #63) are generated in a predetermined number of levels of gray scale according to original pixel information signals, while poor-gray-scale pixel information signals (#0 and #63) are generated in a smaller number of levels of gray scale than the maximum number of levels of gray scale, according to original pixel information signals, and rich-gray-scale pixels driven by the rich-gray-scale pixel information signals (#0 to #63) and poor-gray-scale pixels driven by the poor-gray-scale pixel information signals (#0 and #63) are mixed and coexist discretely in at least a part of the display area in a predetermined mixing pattern to display the same image object in a predetermined mode.
Owner:INNOLUX CORP
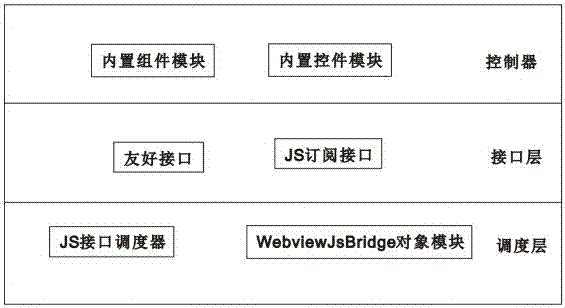
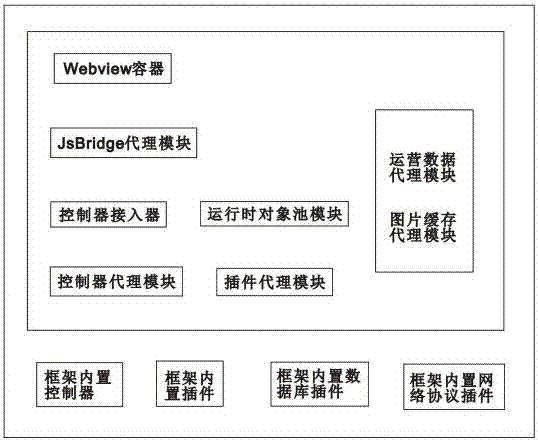
Hybrid-mode smartphone application development framework
ActiveCN106951233AIncrease flexibilityAchieve decouplingSoftware engineeringSpecific program execution arrangementsControl layerApplication software
The invention discloses a hybrid-mode smartphone application development framework. The development framework comprises a JS SDK framework, a client framework and a server framework; the JS SDK framework comprises a control layer, an interface layer and a scheduling layer; the control layer comprises a built-in component module and a built-in control module; the interface layer comprises a friendly interface and a JS subscription interface; the scheduling layer comprises a JS interface scheduler and a WebviewJsBridge object module; the client framework is used for providing an operating environment for a web page of a Hybrid APP in an offline package page mode; the server framework comprises a server control layer, a service layer and a data access layer; the server control layer is used for connection and interaction between operation on the page and a bottom layer; the service layer is connected into a kernel in a plug-in form to provide support for the server control layer; and the data access layer is connected into the kernel in a plug-in form to provide a network request and sqlite data operation. The development framework provides a whole set of solution for rapid iterative development, online deployment and building block type integration of application programs according to functional requirements.
Owner:GUANGZHOU TIANGAO SOFTWARE TECH CO LTD
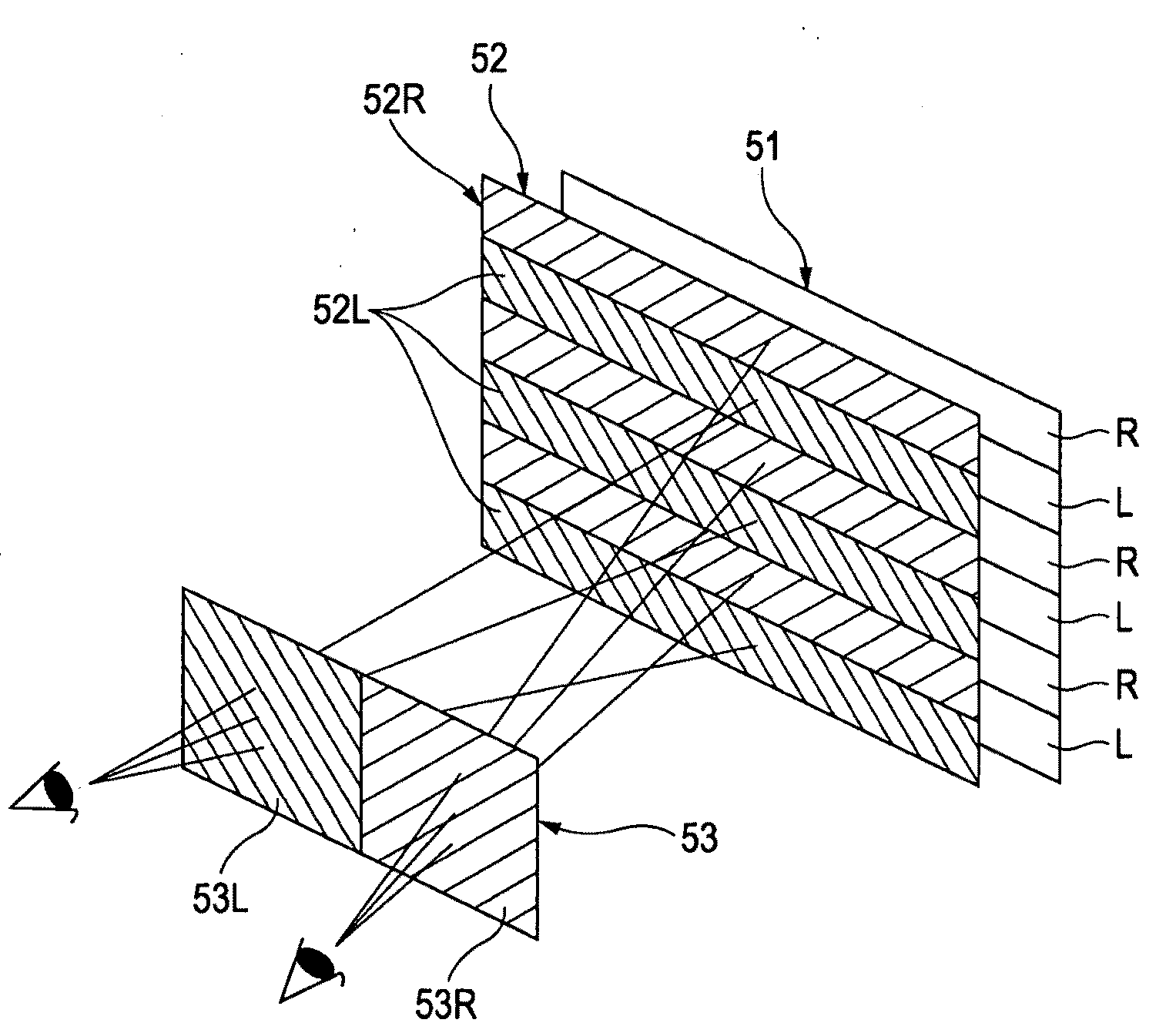
Stereoscopic image display and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20100033557A1Avoid crosstalkWidth of pattern smallVessels or leading-in conductors manufactureColor television detailsComputer graphics (images)Display device
A stereoscopic image display includes an image display panel that displays right-eye images and left-eye images in a regularly mixed pattern in a plane; a retarder disposed on an image output side of the image display panel and including right-eye-image display portions, corresponding to the right-eye images, and left-eye-image display portions, corresponding to the left-eye images, that cause polarization so that the right-eye images and the left-eye images have different polarization states; a polarizer disposed between the image display panel and the retarder; and a light-shielding layer disposed between the image display panel and the polarizer so as to correspond to regions including boundaries between the right-eye-image display portions and the left-eye-image display portions of the retarder.
Owner:SONY CORP
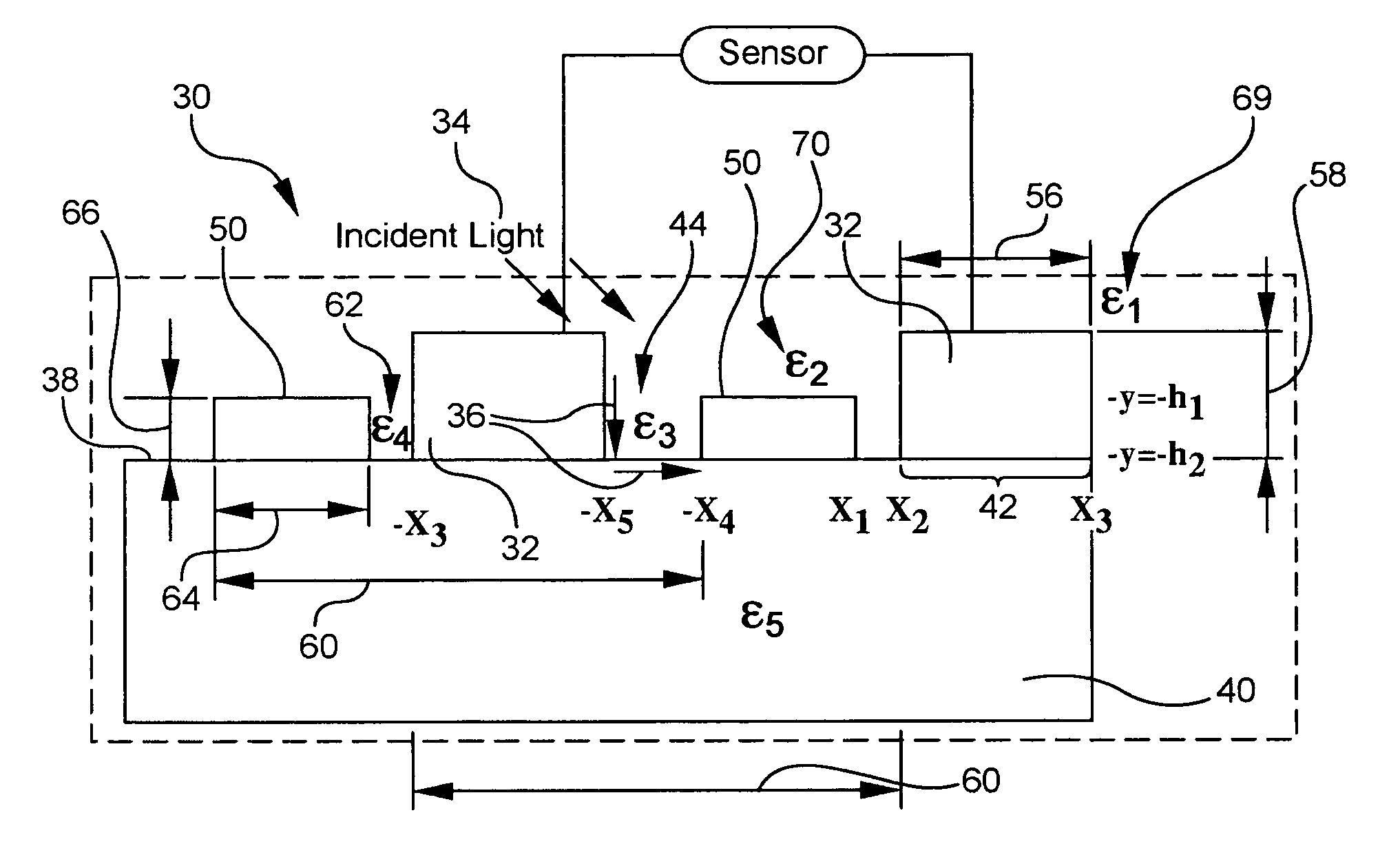
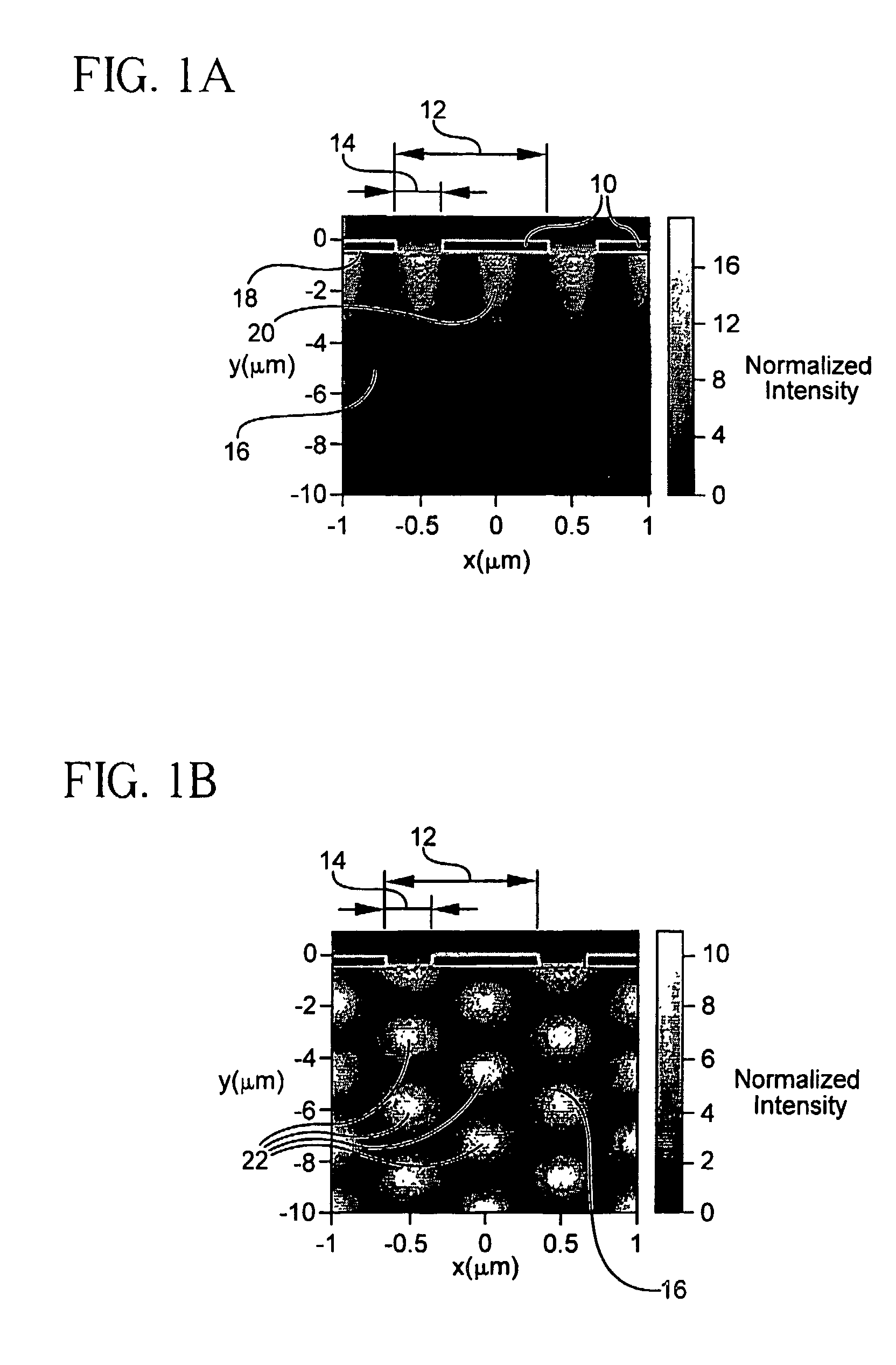
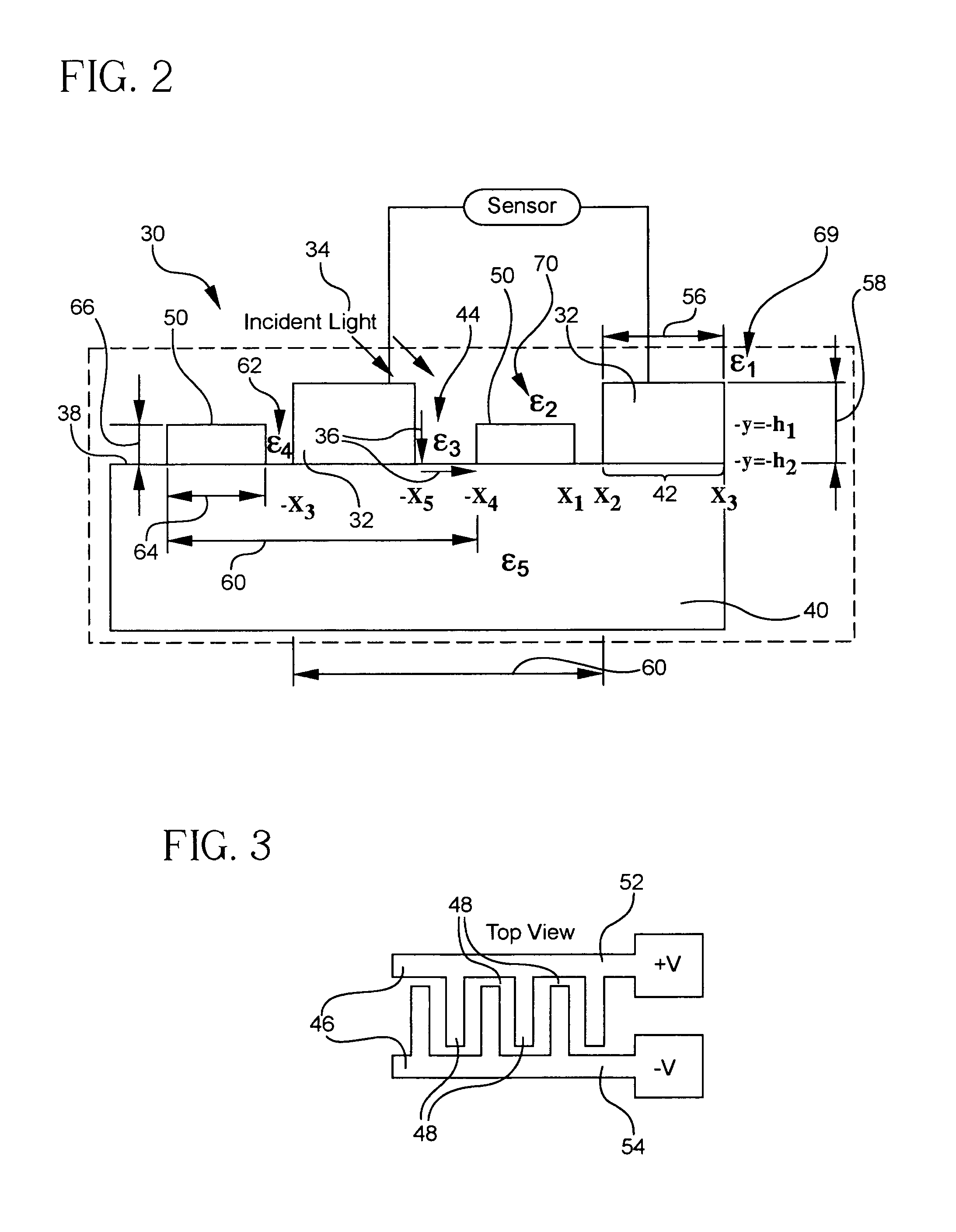
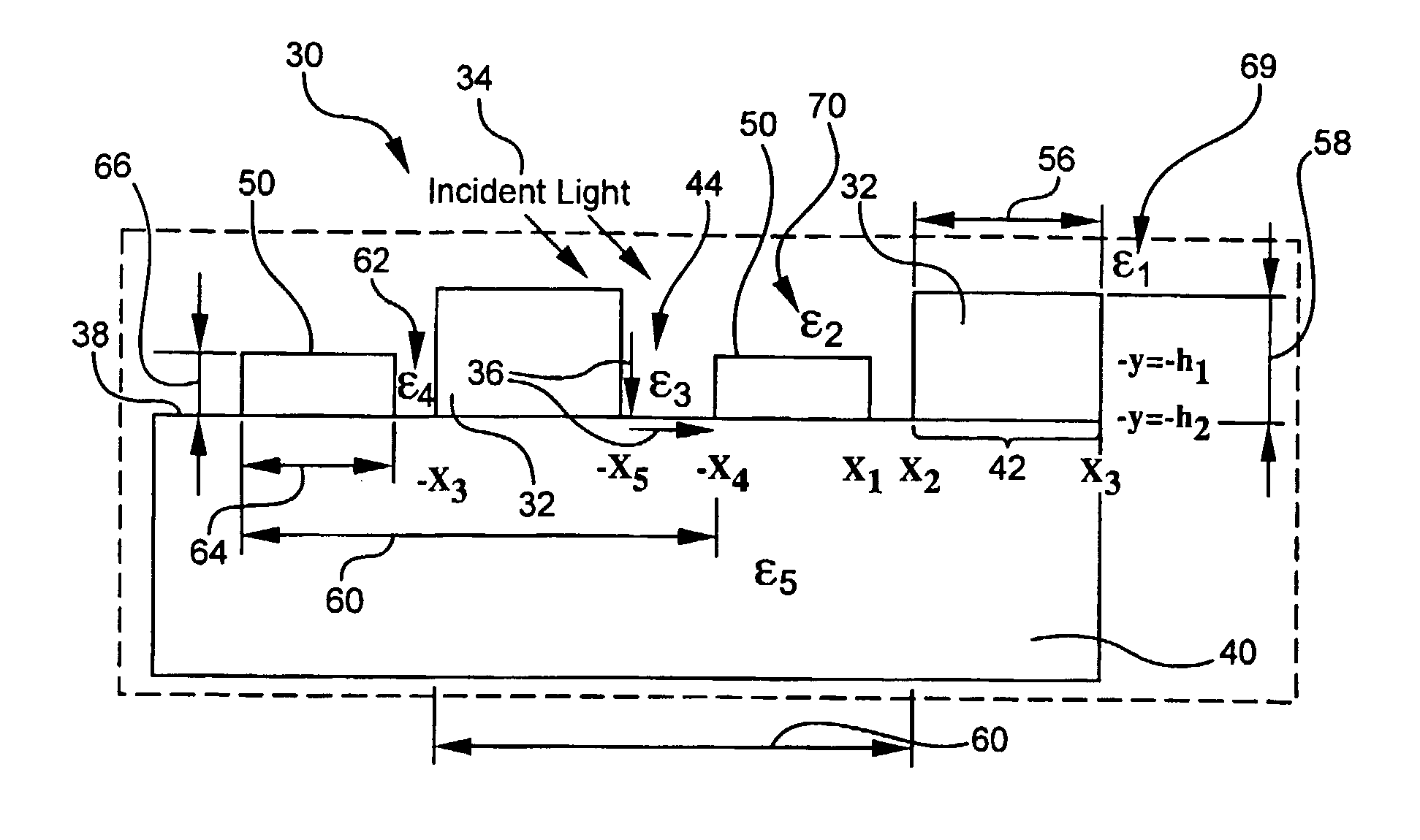
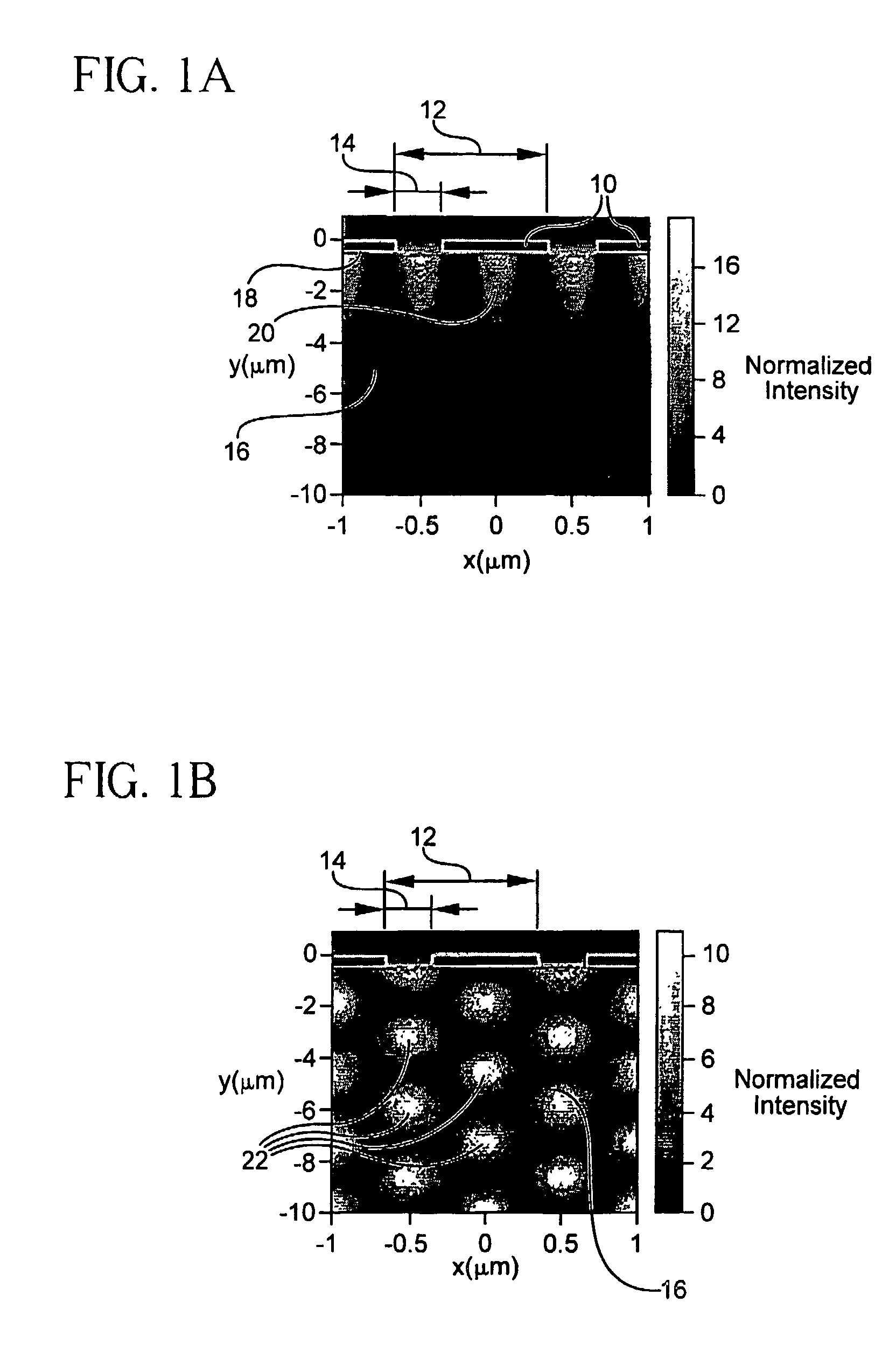
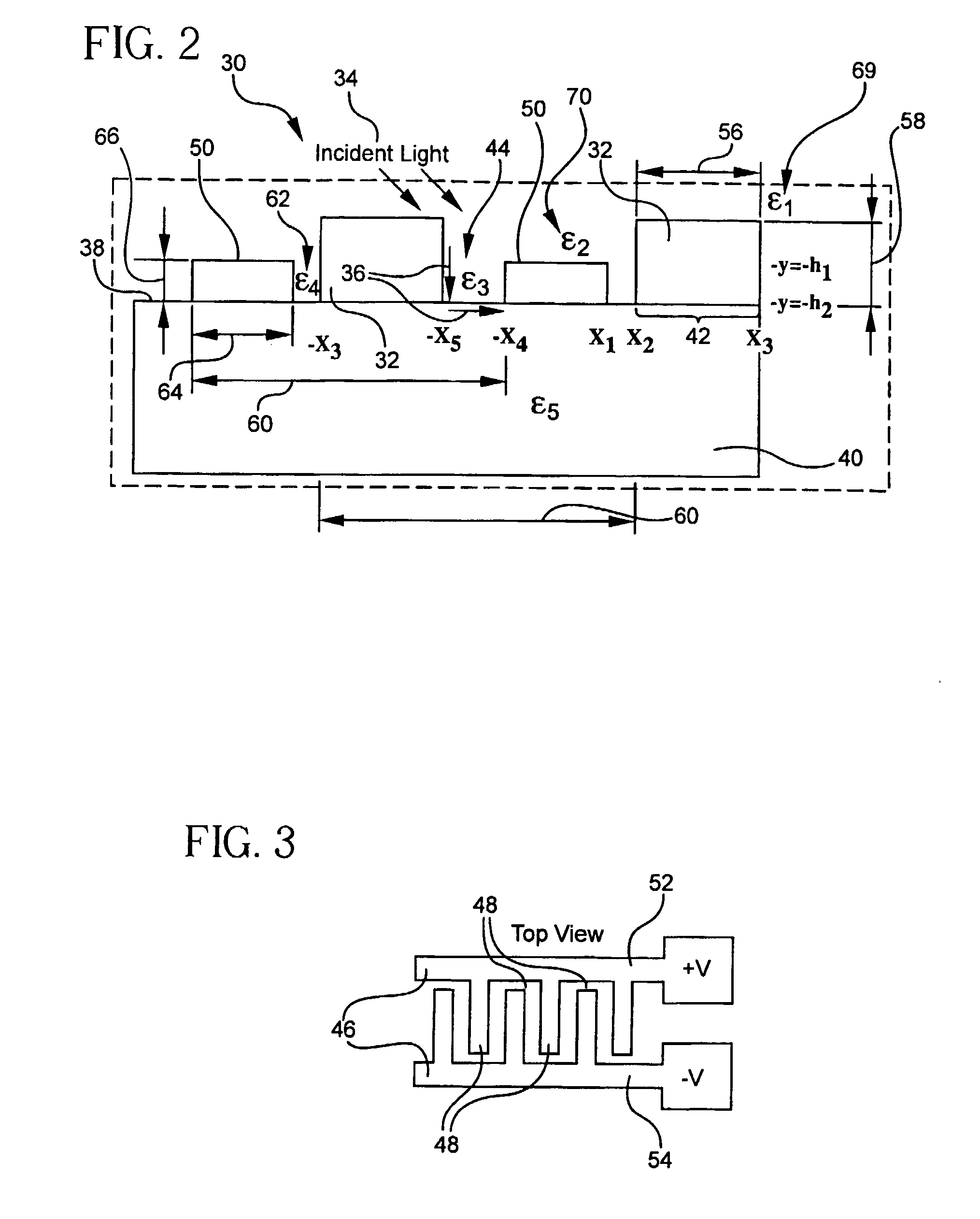
High responsivity high bandwidth metal-semiconductor-metal optoelectronic device
InactiveUS7423254B2Improve responsivenessSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansDielectricSilicon oxide
An optical device for sensing an incident optical wave within a wavelength range includes a first array and a second array of electrodes superposed on a substrate, and a sensor connected to the contacts. The arrays are interdigitated. Each array includes its own parameters: contact width, contact thickness, groove width, and a groove dielectric constant. A structure associated with the arrays resonantly couples the incident wave and a local electromagnetic resonance or hybrid mode including at least a surface plasmon cavity mode (CM). For coupling the CM, an aspect ratio of contact thickness to spacing between electrodes is at least 1. A preferred structure for coupling a hybrid mode for high bandwidth and responsivity includes a higher dielectric constant in alternating grooves. The substrate may include silicon, including silicon-on-insulator (SOI). An SOI device having a alternating grooves with a higher dielectric, e.g., silicon oxide, provides 0.25 A / W and 30 GHz bandwidth.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
Stereoscopic image display and method for producing the same
InactiveCN101639617AReduce brightnessSmall pattern widthStereoscopic photographySteroscopic systemsComputer graphics (images)Display device
The present invention provides a stereoscopic image display and a method for producing the same. A stereoscopic image display includes an image display panel that displays right-eye images and left-eye images in a regularly mixed pattern in a plane; a retarder disposed on an image output side of the image display panel and including right-eye-image display portions, corresponding to the right-eyeimages, and left-eye-image display portions, corresponding to the left-eye images, that cause polarization so that the right-eye images and the left-eye images have different polarization states; a polarizer disposed between the image display panel and the retarder; and a light-shielding layer disposed between the image display panel and the polarizer so as to correspond to regions including boundaries between the right-eye-image display portions and the left-eye-image display portions of the retarder.
Owner:SONY CORP
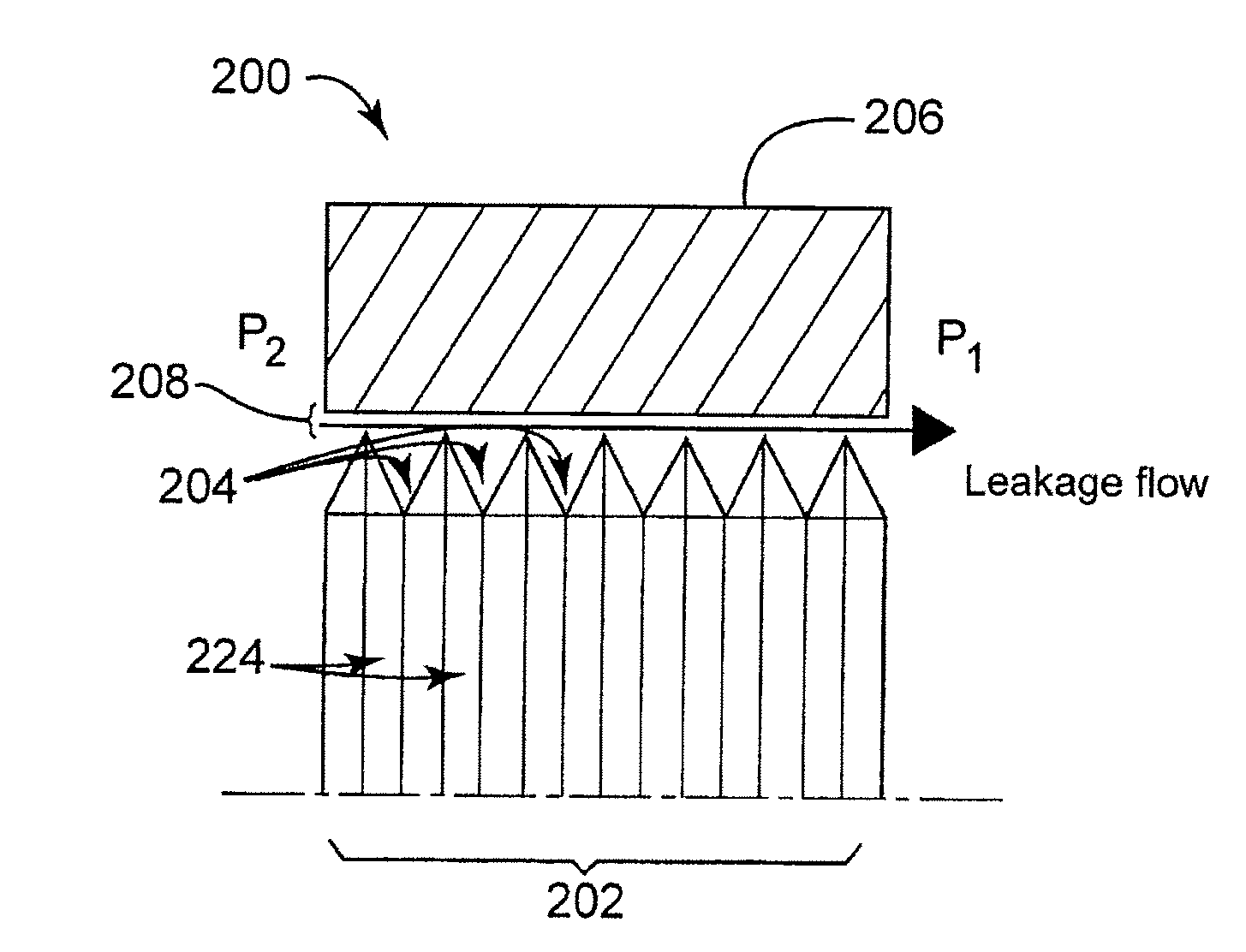
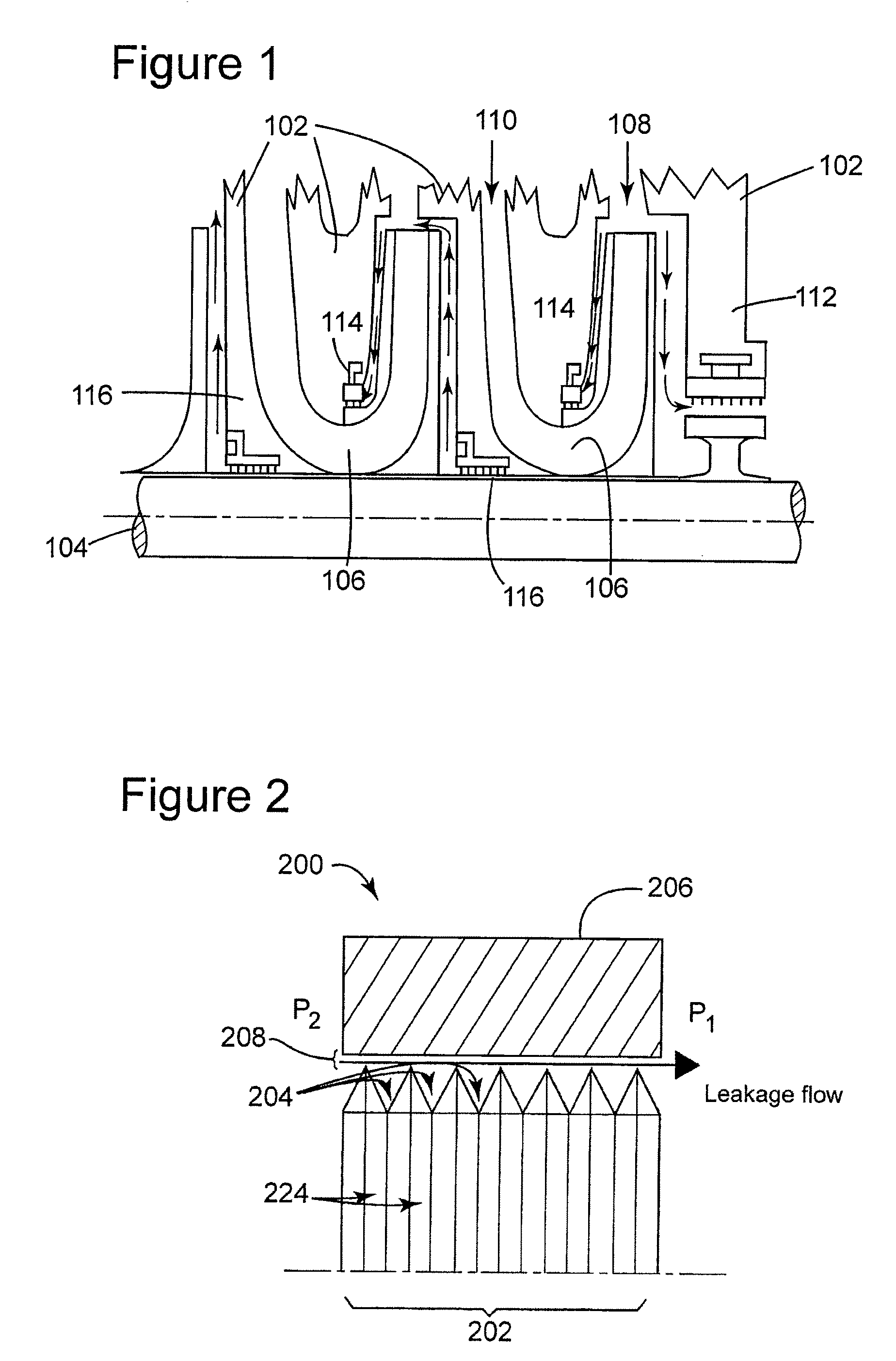
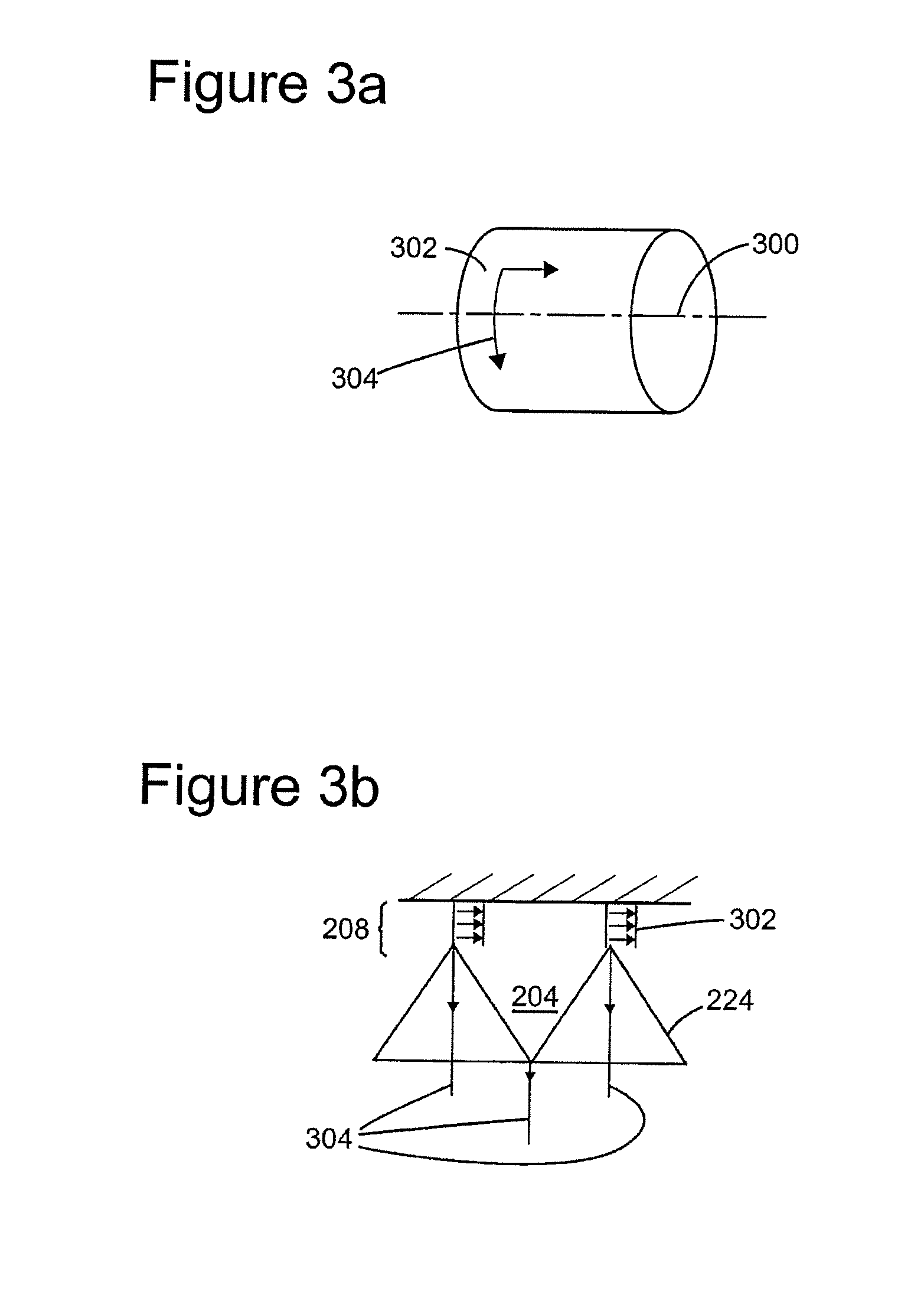
High damping labyrinth seal with helicoidal and helicoidal-cylindrical mixed pattern
A device for sealing a high pressure region in a turbomachine from a low pressure region; the turbomachine has one or more statoric parts and one or more rotoric parts; the device comprises a labyrinth seal having a first plurality of grooves and a second plurality of grooves; the first plurality of grooves is disposed in a helical pattern and the second plurality of grooves is disposed in a cylindrical pattern; the labyrinth seal is disposed between at least one of the one or more rotoric parts of the turbomachine and at least one of the one or more statoric parts of the turbomachine between the high pressure region and the low pressure region of the turbomachine; the helical pattern has a helix angle less than or equal to 10°, wherein a stabilization effect of the turbomachine is obtained and leakage due to the second plurality of grooves is negligible.
Owner:NUOVO PIGNONE TECH SRL
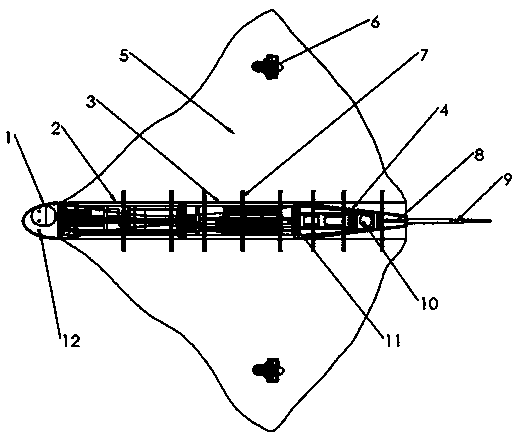
A novel large-span hybrid-driven unmanned underwater vehicle
ActiveCN109018271AImprove stabilityIncrease the voyageUnderwater vesselsUnderwater equipmentBuoyancy regulationControl system
The invention relates to a novel large-span hybrid-driven unmanned underwater vehicle, which comprises a shell structure, a large-span structure, an antenna, a gliding wing, a propeller and a tail fin. The invention is characterized in that: a buoyancy adjusting system, a pitch adjusting system, a control system, a throwing device, a sensor and a communication antenna are arranged in the shell structure; The underwater vehicle can realize the switching of three motion modes according to different tasks and work requirements, and achieve the requirements of saving energy and completing tasks. Mixed gliding and propulsion modes can be used when accelerated diving and descent are required; By controlling the different differential speeds of the two wing-end thrusters, the spatial spiral motion with different radii of gyration can be realized. By adjusting the wing structure and the overall layout of the glider, the anti-disturbance flow performance during gliding is optimized, and the stability of the unmanned aerial vehicle is improved. The underwater vehicle realizes the combination of the advantages of the glider and the AUV, and has the advantages of long range, sufficient space,powerful function, high stability, and strong maneuverability.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV +1
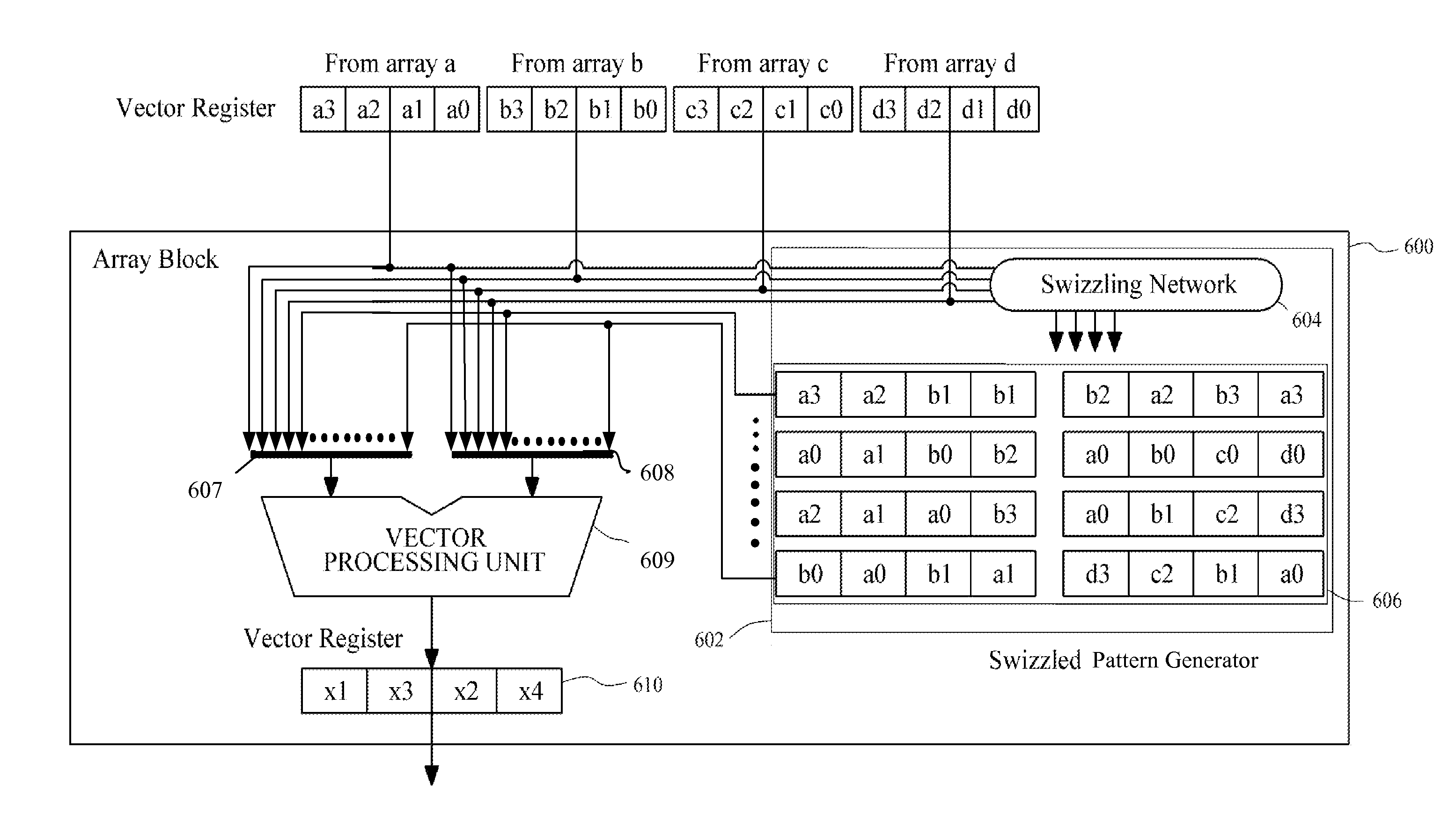
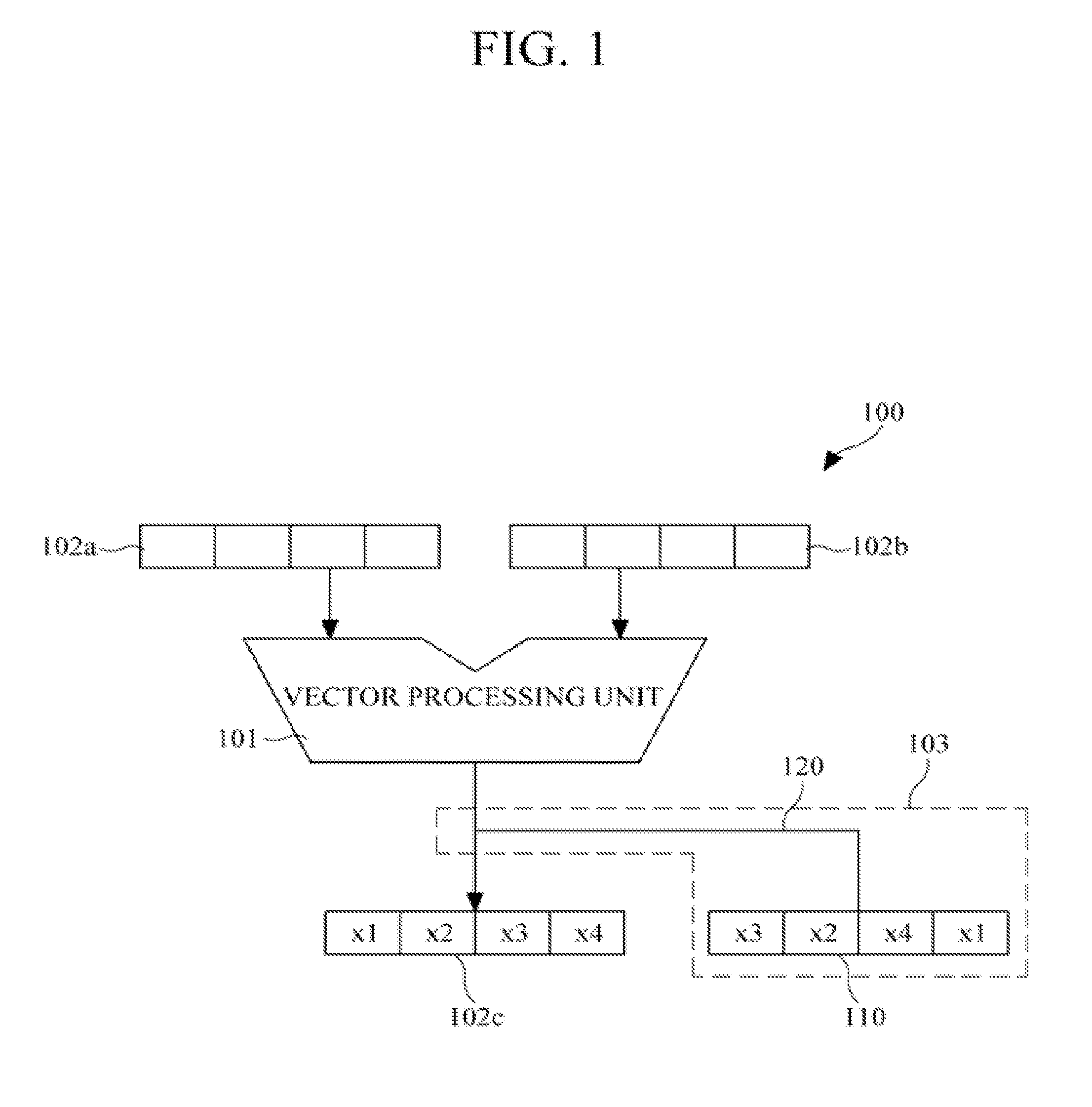
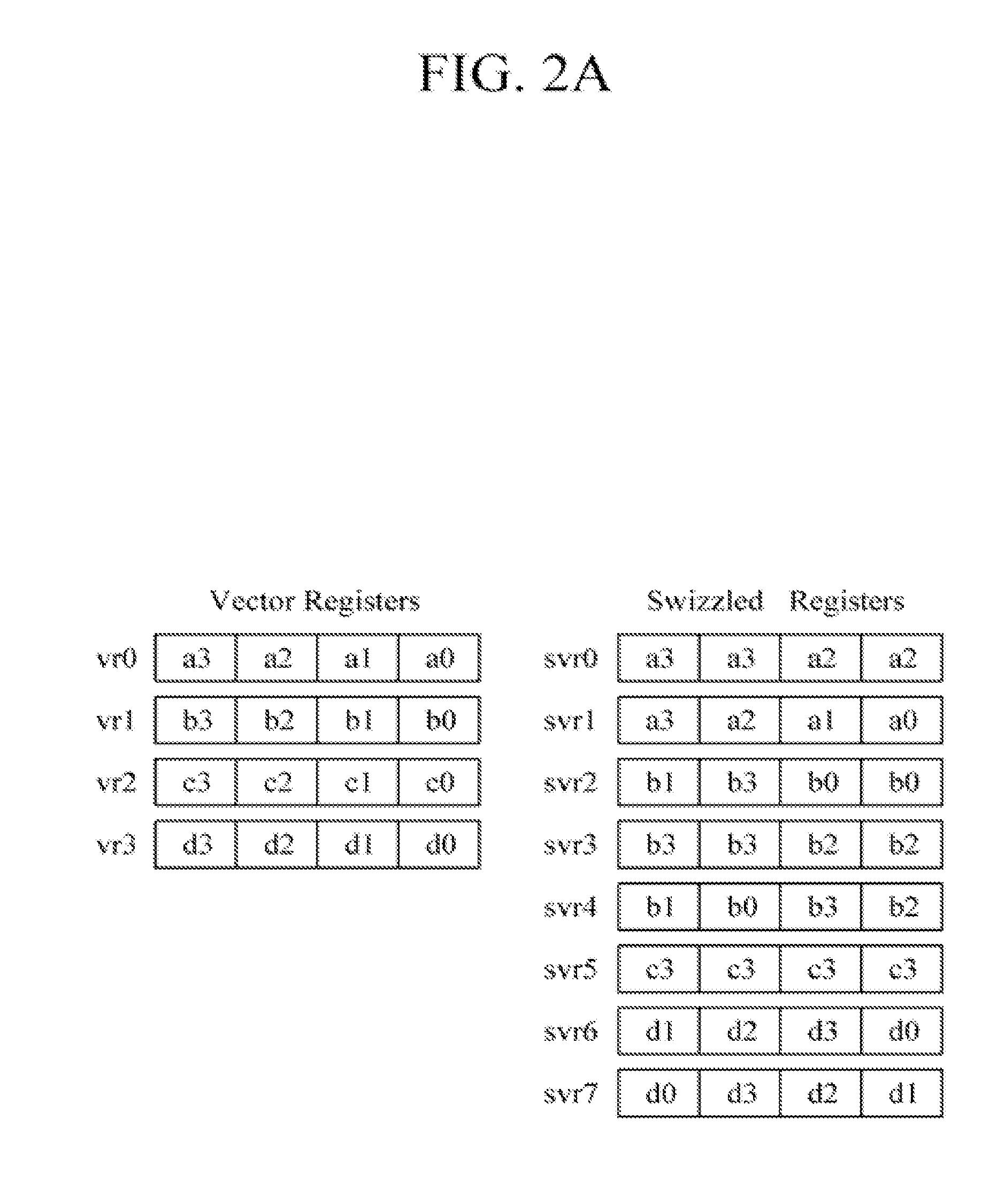
Processing device and a swizzle pattern generator
InactiveUS20130067203A1Program control using stored programsDigital computer detailsData setPattern generation
A swizzle pattern generator is provided to reduce an overhead due to execution of a swizzle instruction in vector processing. The swizzle pattern generator is configured to provide swizzle patterns with respect to data sets of at least one vector register or vector processing unit. The swizzle pattern generator may be reconfigurable to generate various swizzle patterns for different vector operations.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
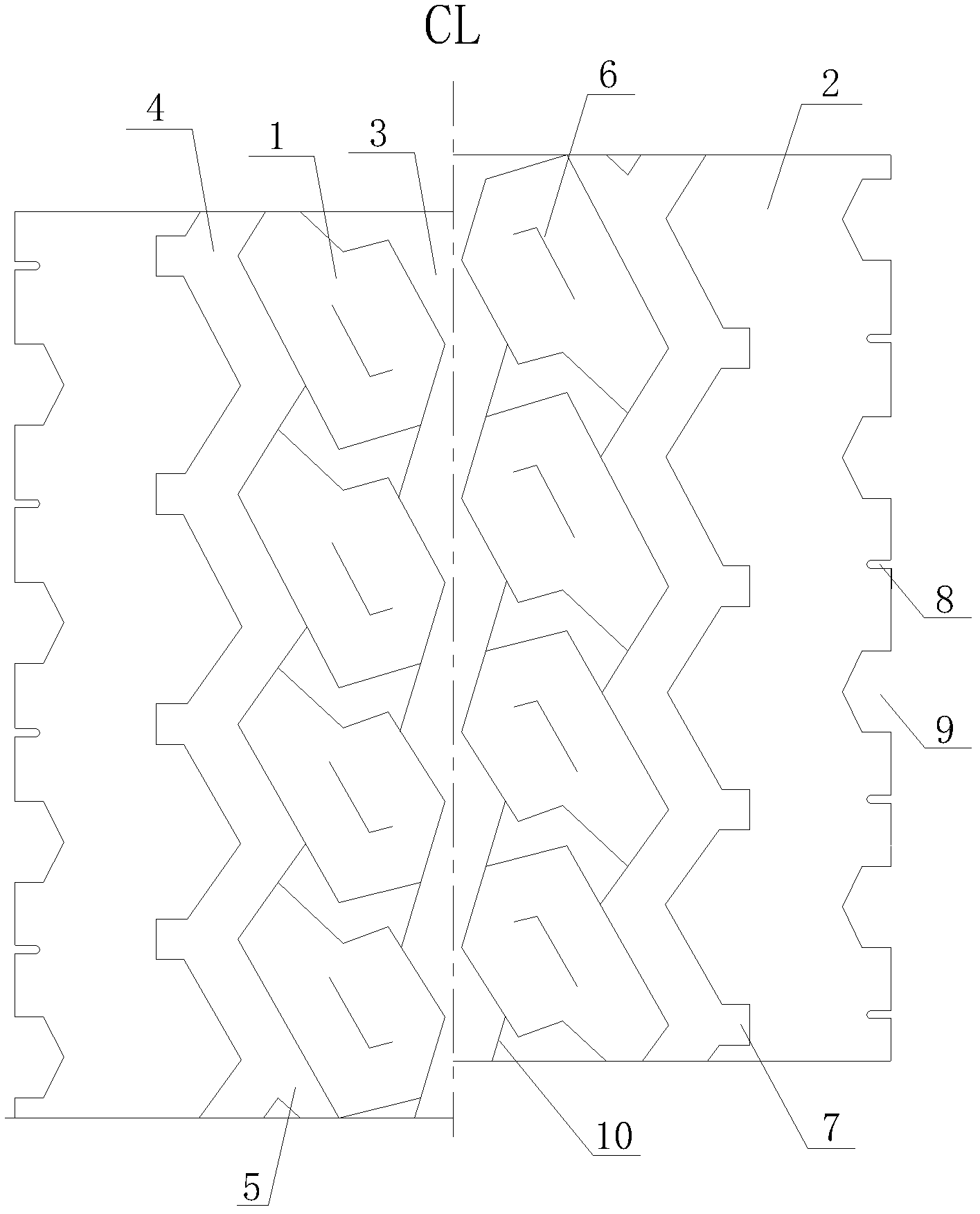
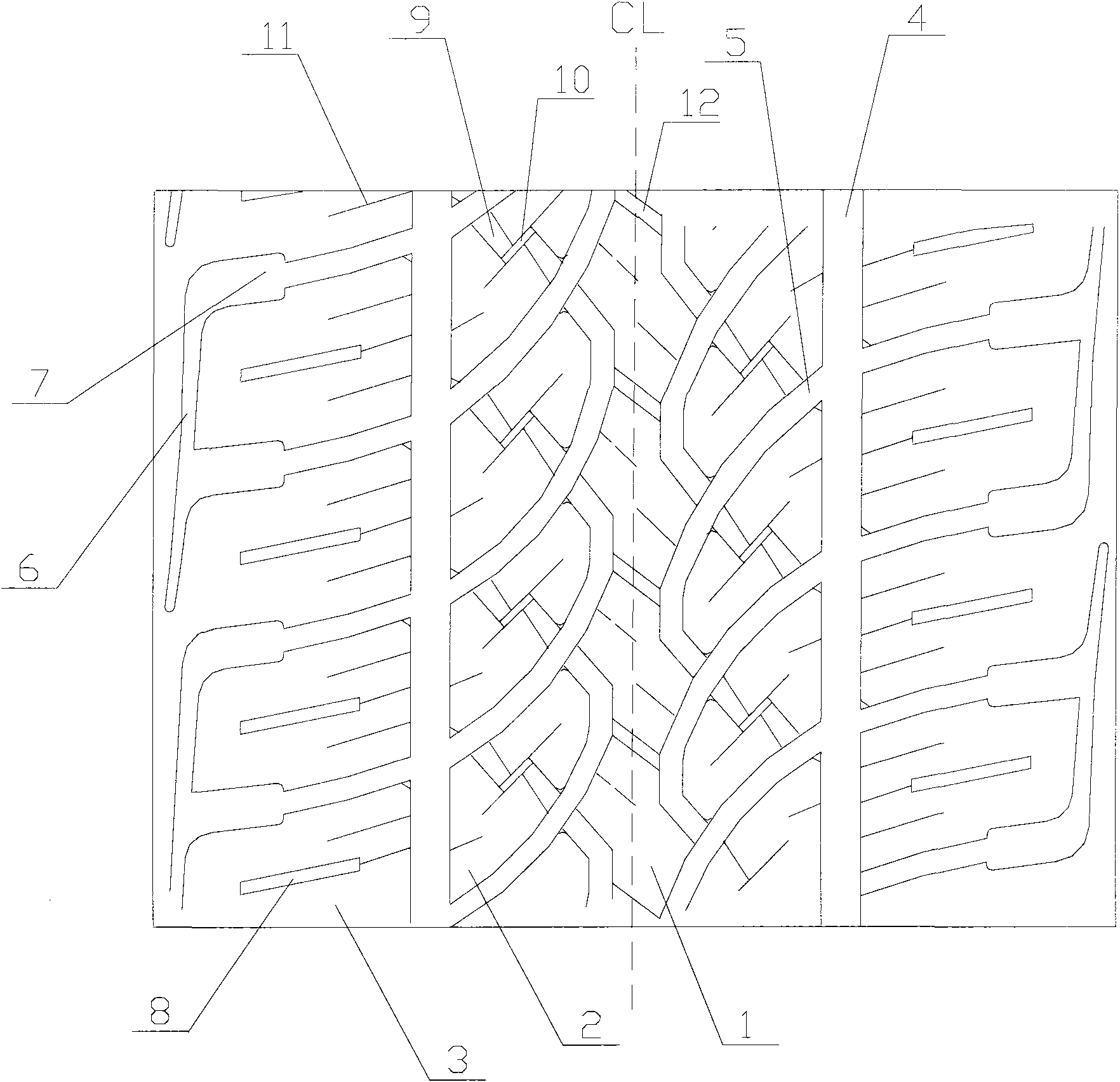
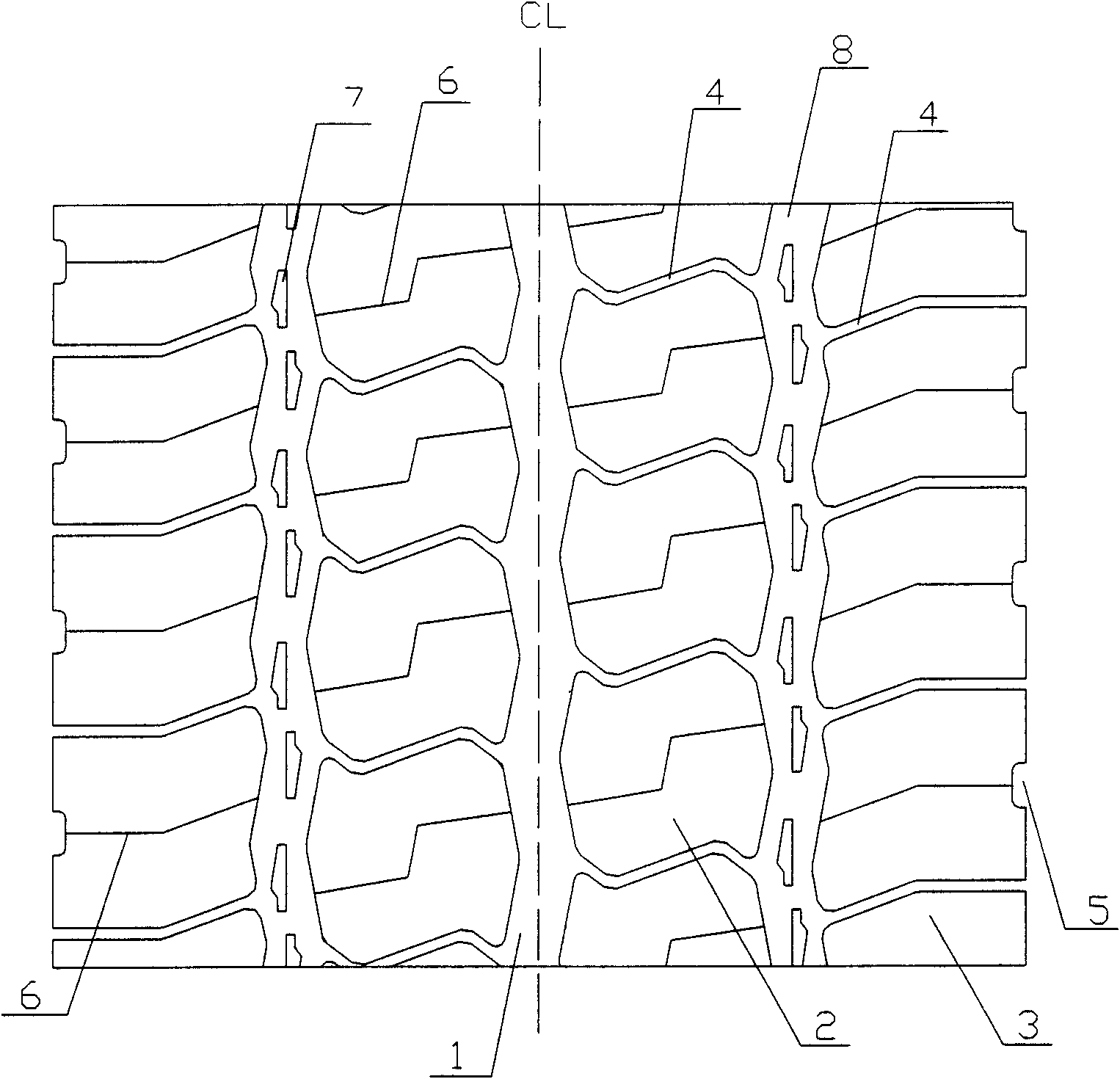
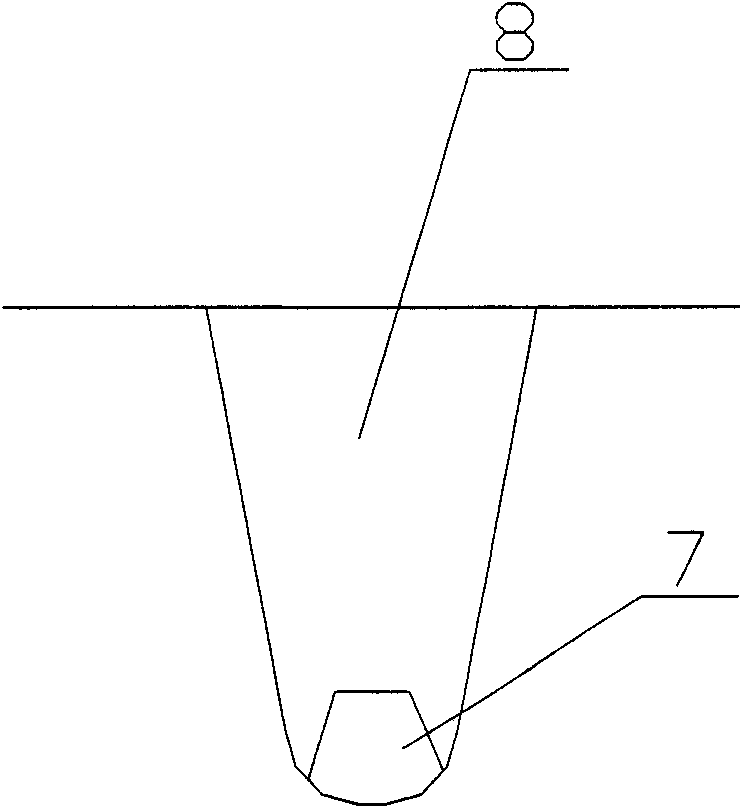
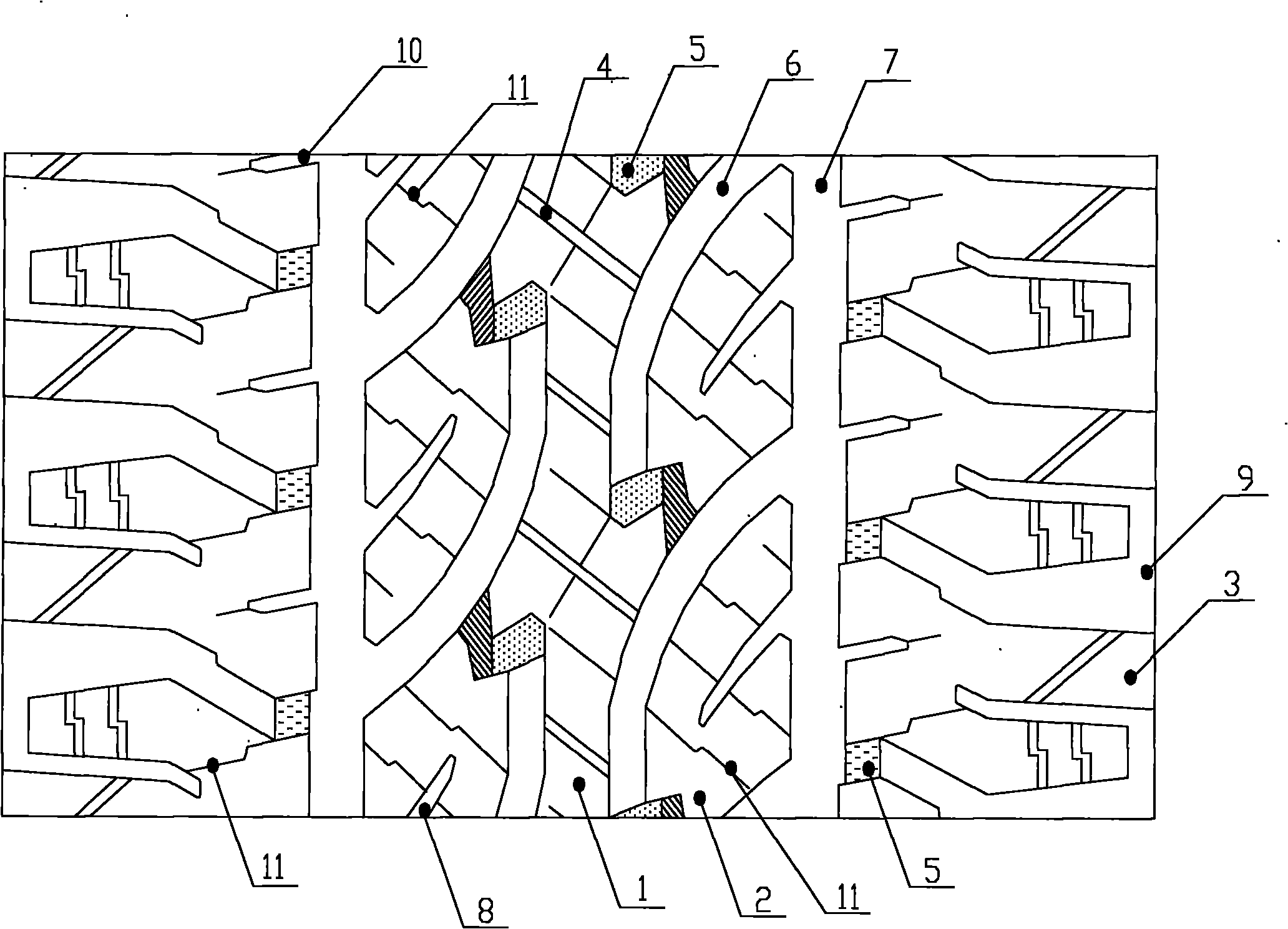
Tire tread of cargo truck
InactiveCN103158444ASufficient braking forceImprove maneuverabilityTyre tread bands/patternsWave shapePoint symmetry
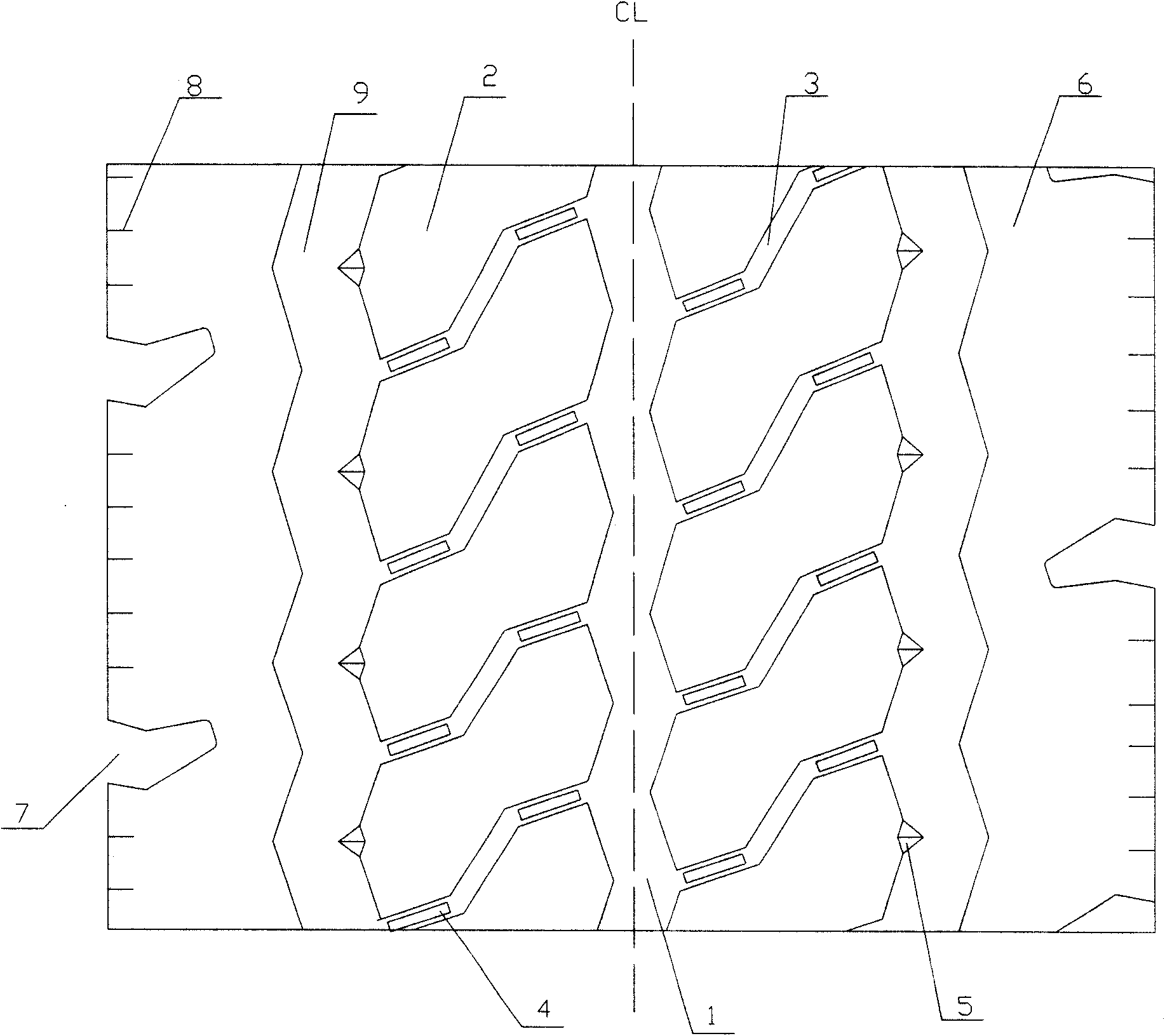
The invention relates to a truck tire, in particular to a tire tread pattern structure of a truck tire. A tire tread of a cargo truck comprises a central longitudinal circumferential pattern groove which is arranged at the position of a longitudinal center line of the tire tread and enables the tire tread to be evenly divided into two symmetrical parts in a left-right mode. Side part pattern blocks and tire shoulder pattern blocks are sequentially arranged on two sides of the central longitudinal circumferential pattern groove form interior to exterior. The side part pattern blocks and the tire shoulder pattern blocks are separated by an auxiliary longitudinal circumferential pattern groove. Each two adjacent side part pattern blocks along the circumferential direction are separated by an auxiliary pattern groove. The central longitudinal circumferential pattern groove and the auxiliary longitudinal circumferential pattern groove are respectively in a wave shape. Two ends of each auxiliary pattern groove are respectively communicated with the central longitudinal circumferential pattern groove and the auxiliary longitudinal circumferential pattern groove. The side part pattern blocks on two sides of the central longitudinal circumferential pattern groove are in point symmetry and arranged in a vertically staggered mode. The tire shoulder pattern blocks are integral pattern blocks. According to the tire tread of the cargo truck, mixed patterns are adopted. The tire tread of the cargo truck has sufficient braking force and good operational properties, and is attractive.
Owner:QINGDAO YELLOWSEA RUBBER
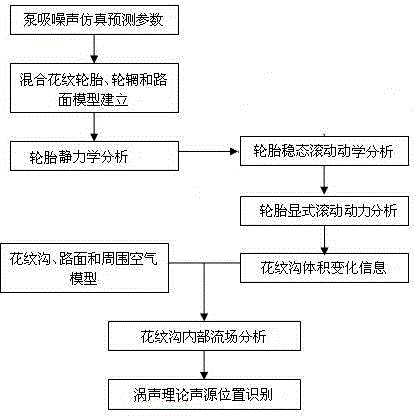
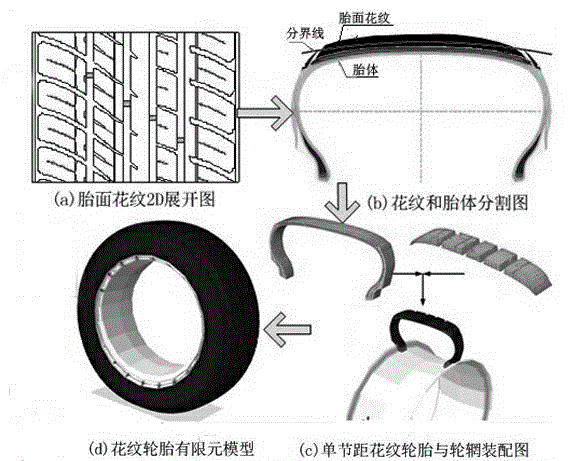
Tread pattern groove pumping noise source recognition method
ActiveCN104344967AReduce noiseSustainable transportationSpecial data processing applicationsStable stateLow noise
The invention discloses a tread pattern groove pumping noise source recognition method which comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a tire-road surface finite element model with mixed patterns, calculating tire static load and carrying out mechanical analysis; (2) carrying out kinetic analysis under the stable state and the transient rolling state of a tire; (3) establishing a pattern groove noise numerical model at the ground connection area; (4) analyzing the flow field characteristics in the patter groove; (5) establishing the relation between the flow field and the sound field by adopting a vortex sound theory, and solving Lamb vector to obtain the distribution position of a pattern groove pumping noise source. The tread pattern groove structure is improved at the position where the noise is produced, and tread pattern groove pumping noise source recognition is carried out again until the design requirements of the noise are reached. The distribution position of the pattern groove noise source is recognized on the basis of the vortex sound theory in the rolling process of the tire, so that the aim of reducing the tread pattern groove noise can be achieved by controlling the sound source, and a guidance is provided for the design of the low-noise tread pattern.
Owner:AEOLUS TIRE
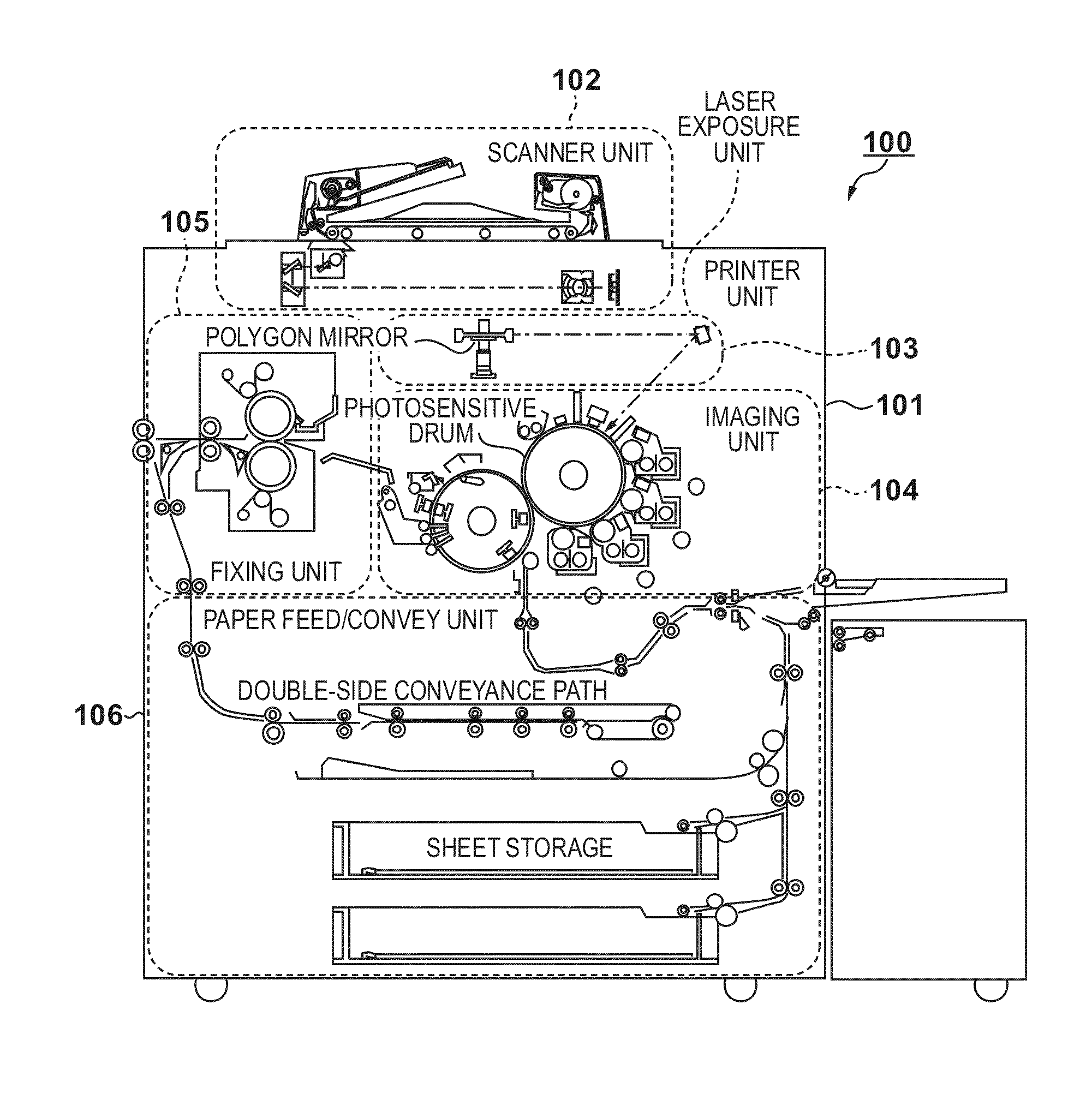
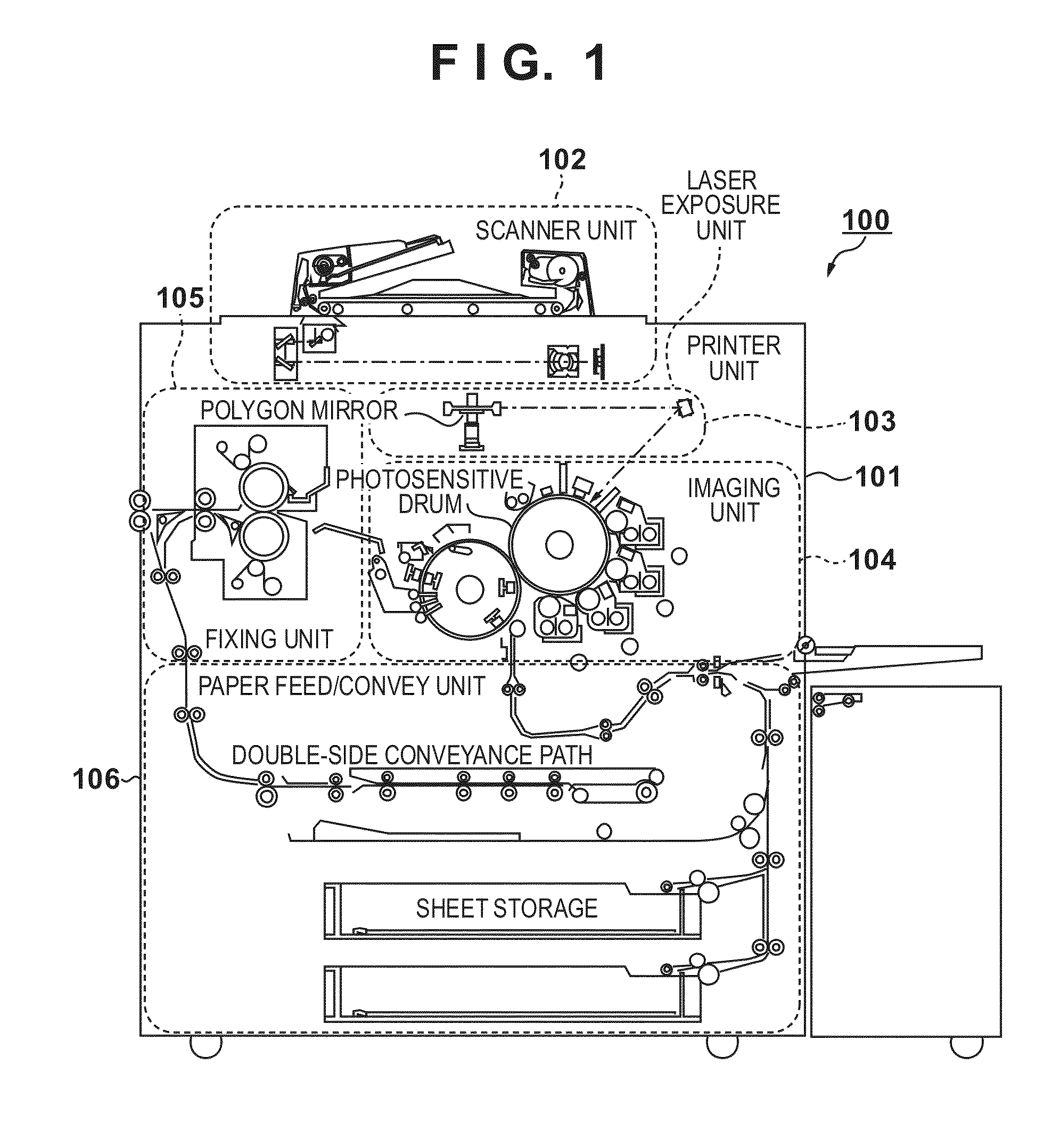
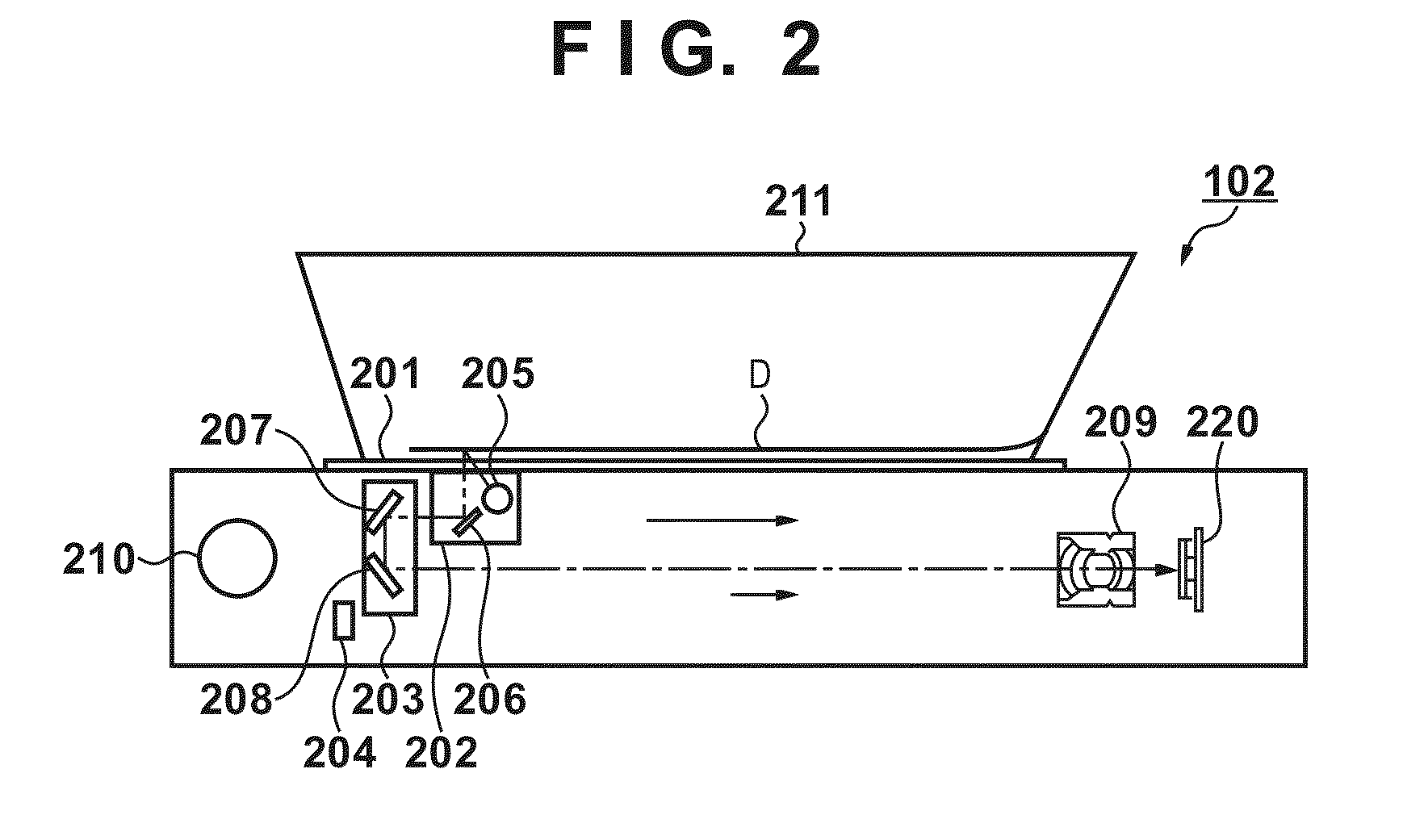
Image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20130094036A1Good colorPrevent image defectsDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsPattern recognitionGranularity
The present invention provides an image forming apparatus that forms a test pattern for controlling the amount of color material, suppresses increase of the color material amount, and prevents image defects such as spattering, poor fixation due to granularity, or the like. To accomplish this, the image forming apparatus forms a test pattern on printing material using color material of a plurality of colors, reads the formed test pattern, and controls the color material amount of each color by changing an image forming condition in accordance with a result of the reading. Note that the image forming apparatus forms a mixed pattern image using color material of a plurality of chromatic colors, and controls the amount of color material of a single color based on the mixed pattern image.
Owner:CANON KK
Investment casting method
InactiveCN103861998AHigh dimensional accuracyPrecise DimensionsFoundry mouldsFoundry coresInvestment castingTurpentine
The invention discloses an investment casting method. The investment casting method mainly comprises the following steps: configuring pattern materials; pressing the pattern materials: painting a compression surface with a layer of turpentine oil and pouring the mixed pattern materials obtained in the step A so as to press the pattern materials; drying a fired mold; combining the fired mold with a gating system so as to manufacture a shell; roasting the shell. According to the method provided by the invention, a prepared fired mold product is high in dimensional accuracy, small in number of casting flaws and reliable in product quality, castings obtained through pouring by utilizing the method are precious in sizes and high in surface quality, and the method is even suitable for casting fired molds and castings which are complicated in casting shapes, resistant to high temperature and not easy to process. According to the method provided by the invention, the production cycle is shortened, the production efficiency is improved, the production cost is reduced, and the method has the guiding significance on practical production.
Owner:SUZHOU JIEDERUI PRECISION MACHINERY
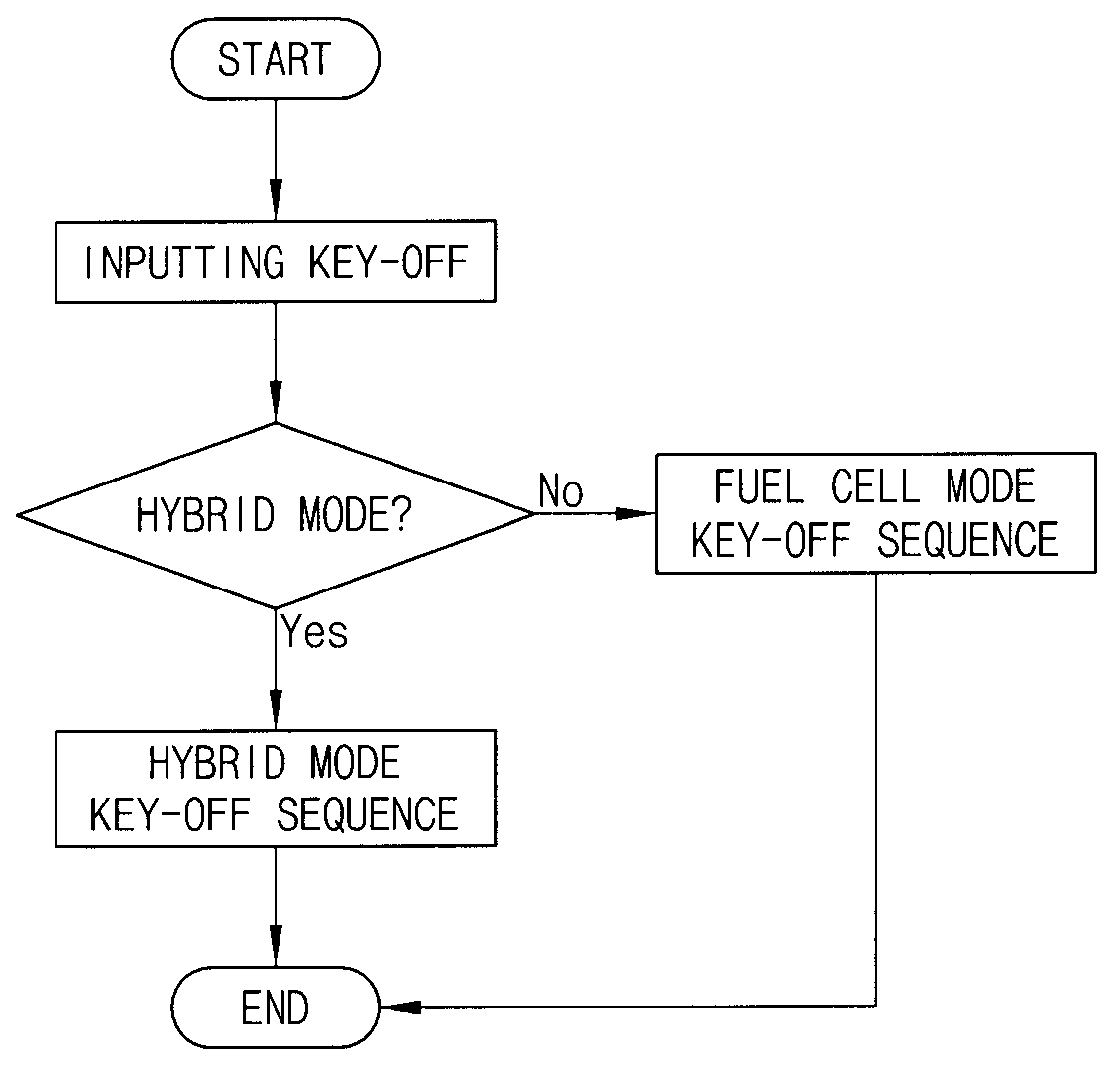
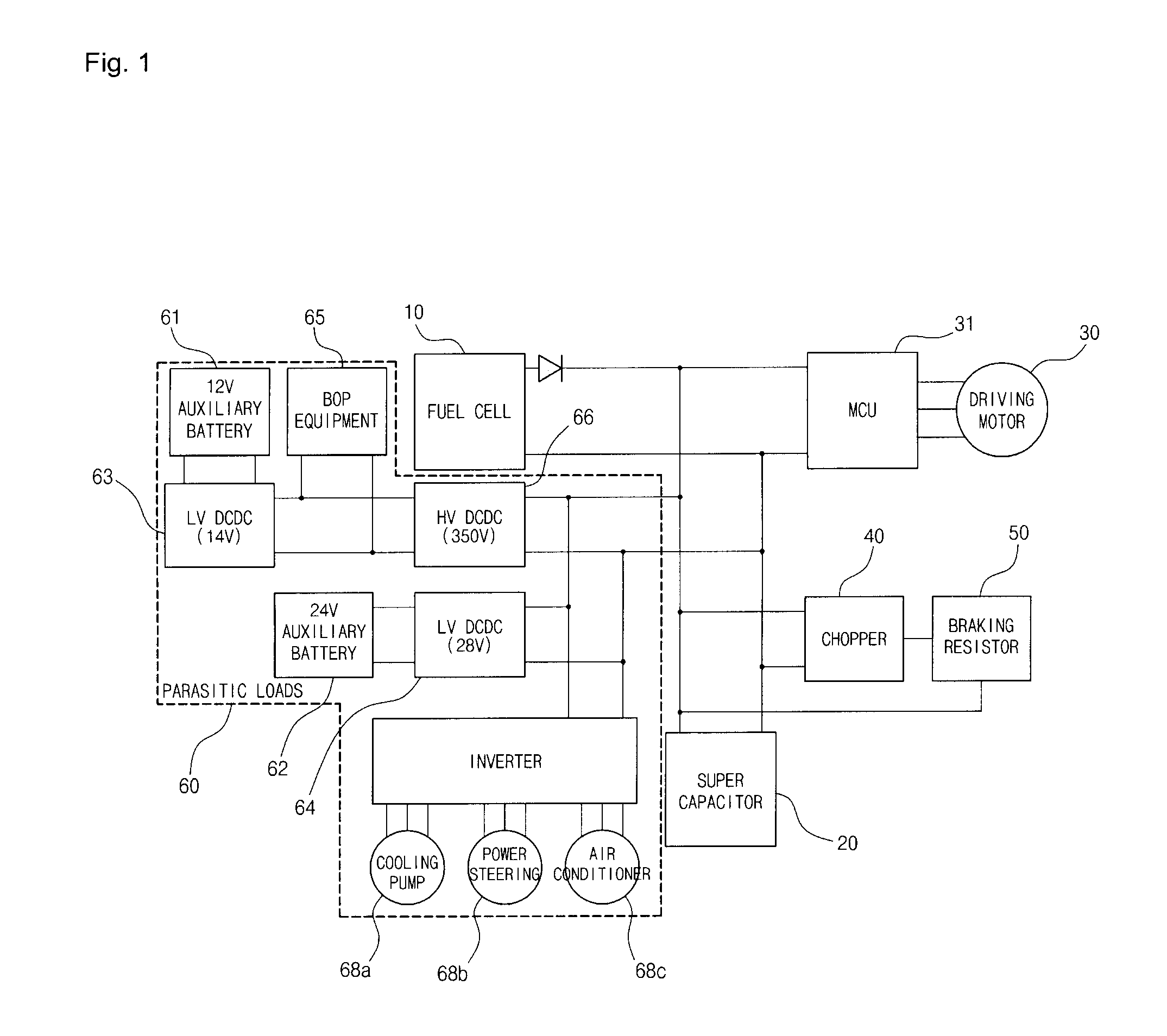
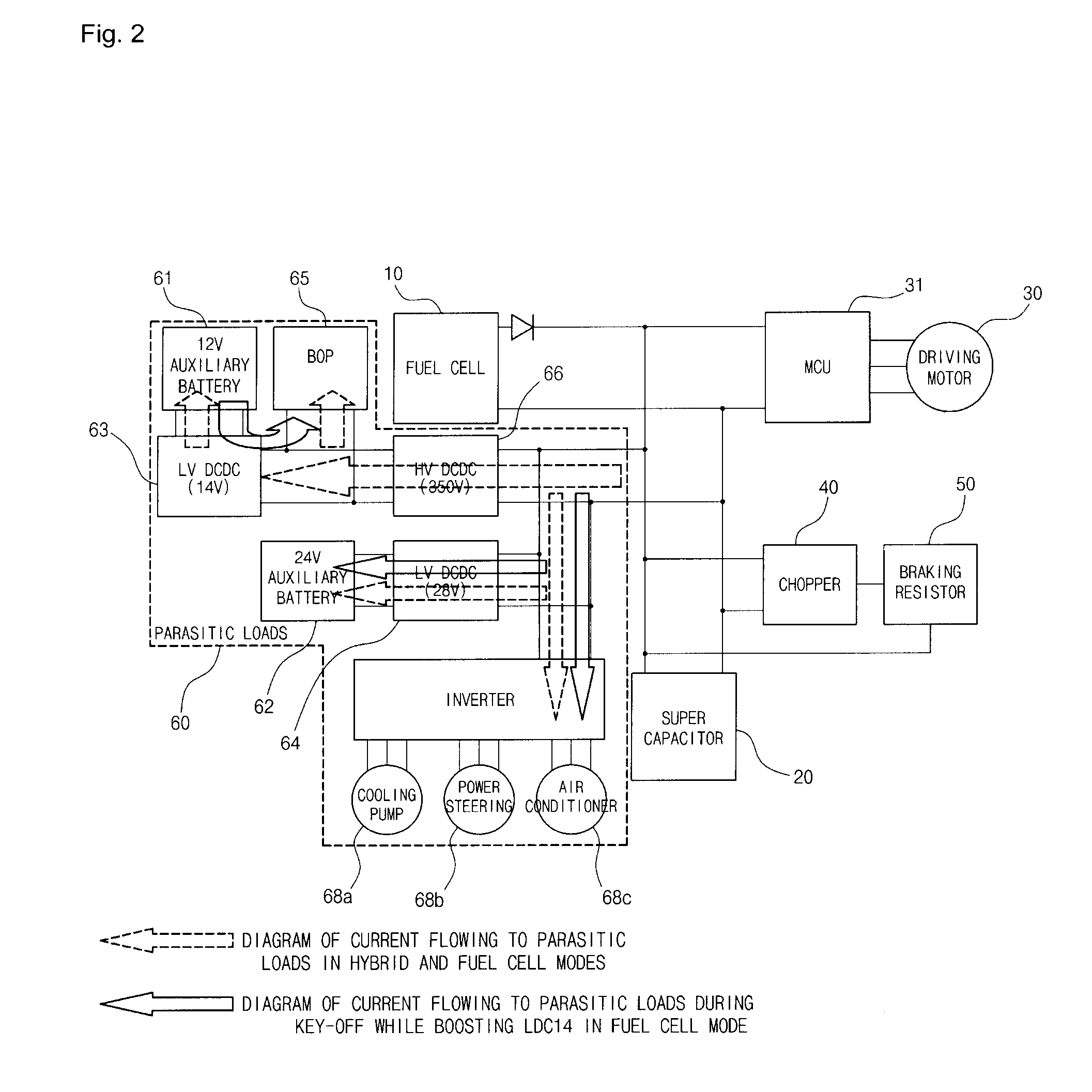
Power-down control method of fuel cell hybrid electric vehicle
ActiveUS20080140275A1Digital data processing detailsVehicle sub-unit featuresDc dc converterFuel cells
A power-down control method of a fuel cell hybrid vehicle includes determining an operation mode when a key-off command is input. If the mode is a fuel cell mode, the method includes: converting a low voltage DC-DC converter connected to an auxiliary battery to a boost mode; maintaining a driving state of a high voltage part, powered by voltage from the auxiliary battery and boosted by the low voltage DC-DC converter; subsequently stopping operation of a fuel cell stack and turning off the high voltage part; and subsequently turning off the low voltage DC-DC converter. If the mode is a hybrid mode, the method includes: maintaining a driving state of the high voltage part, powered by voltage from a super capacitor; subsequently stopping operation of the fuel cell stack and turning off the high voltage part; subsequently turning off the DC-DC converters; and subsequently cutting power of the super capacitor.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
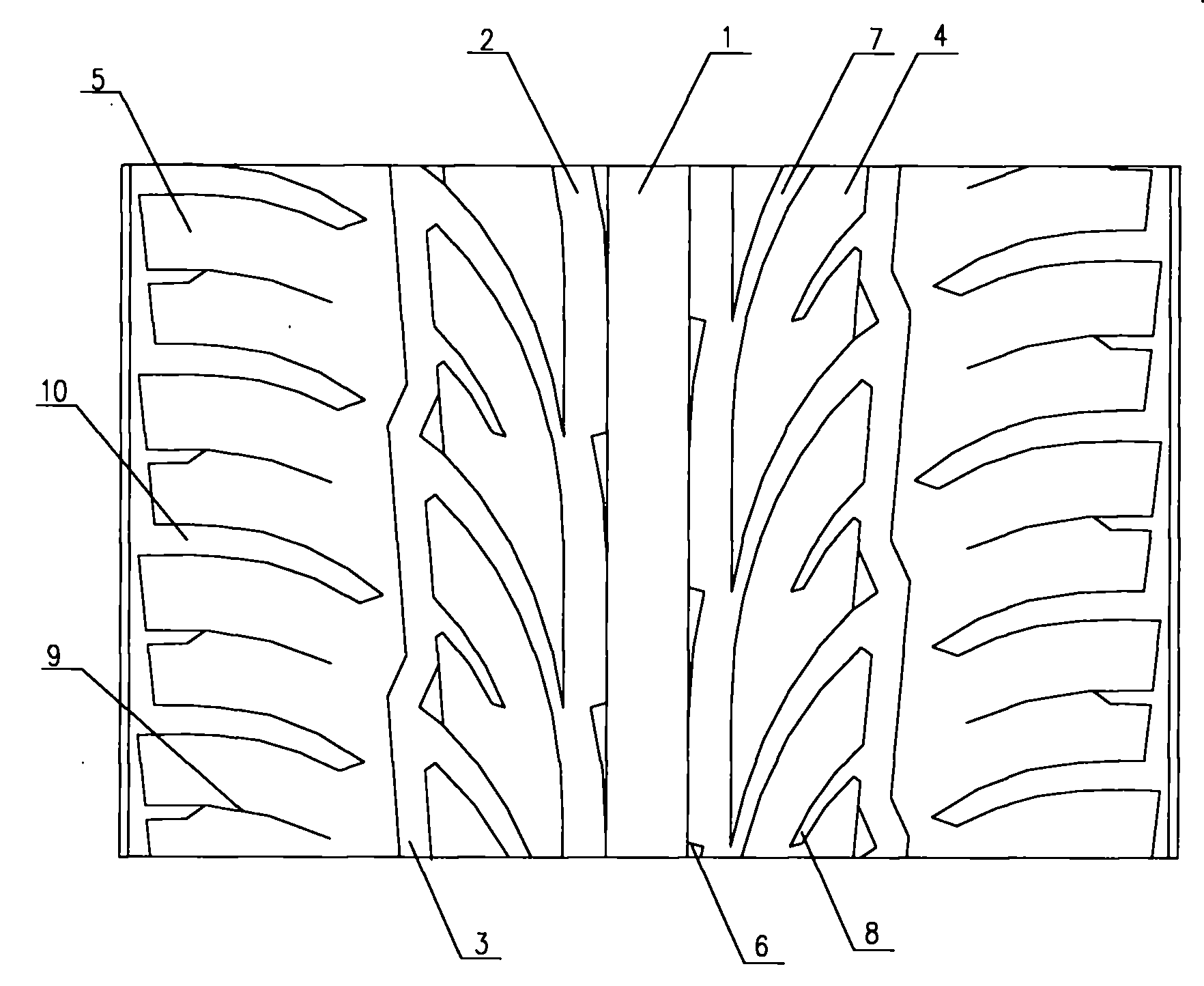
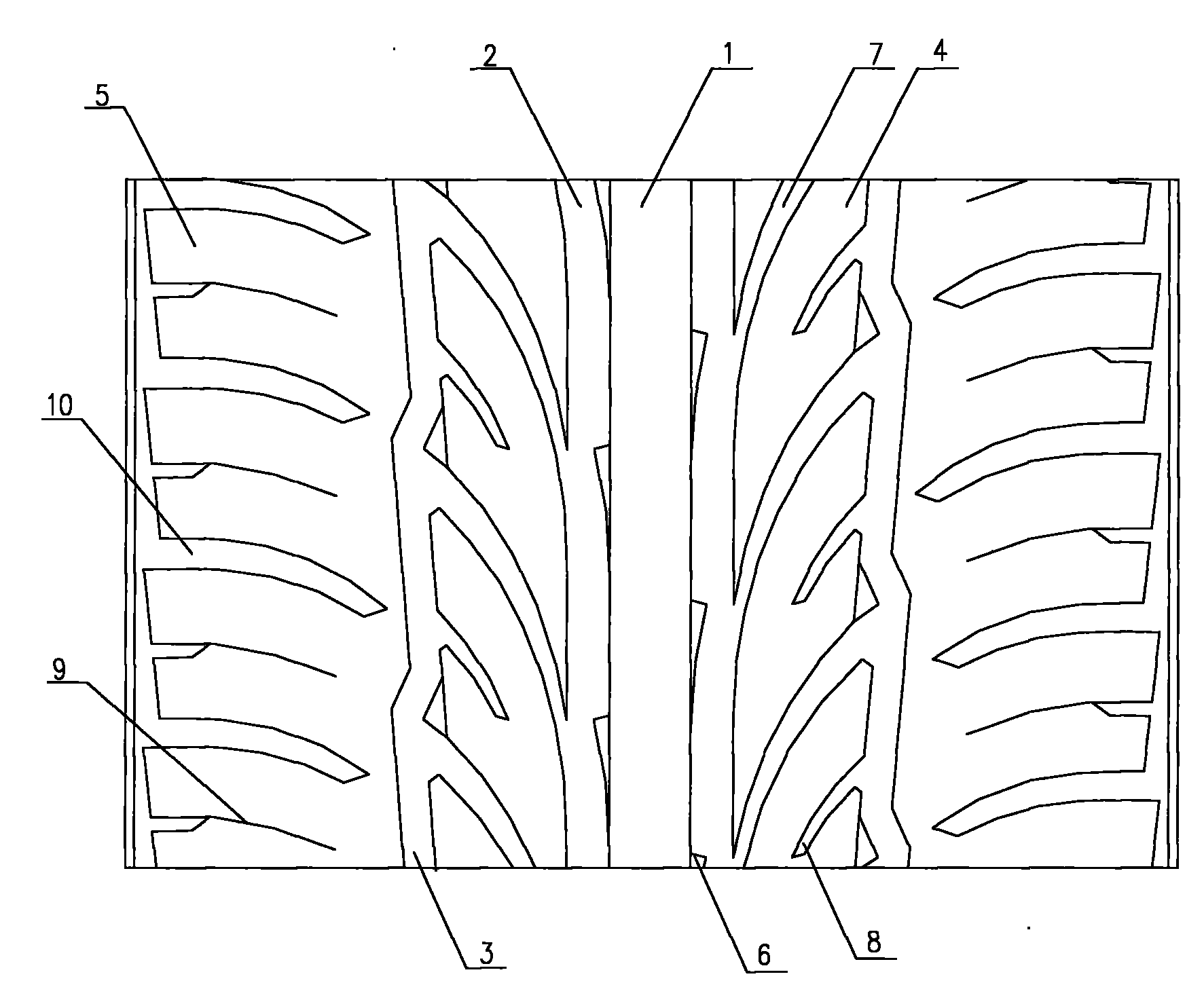
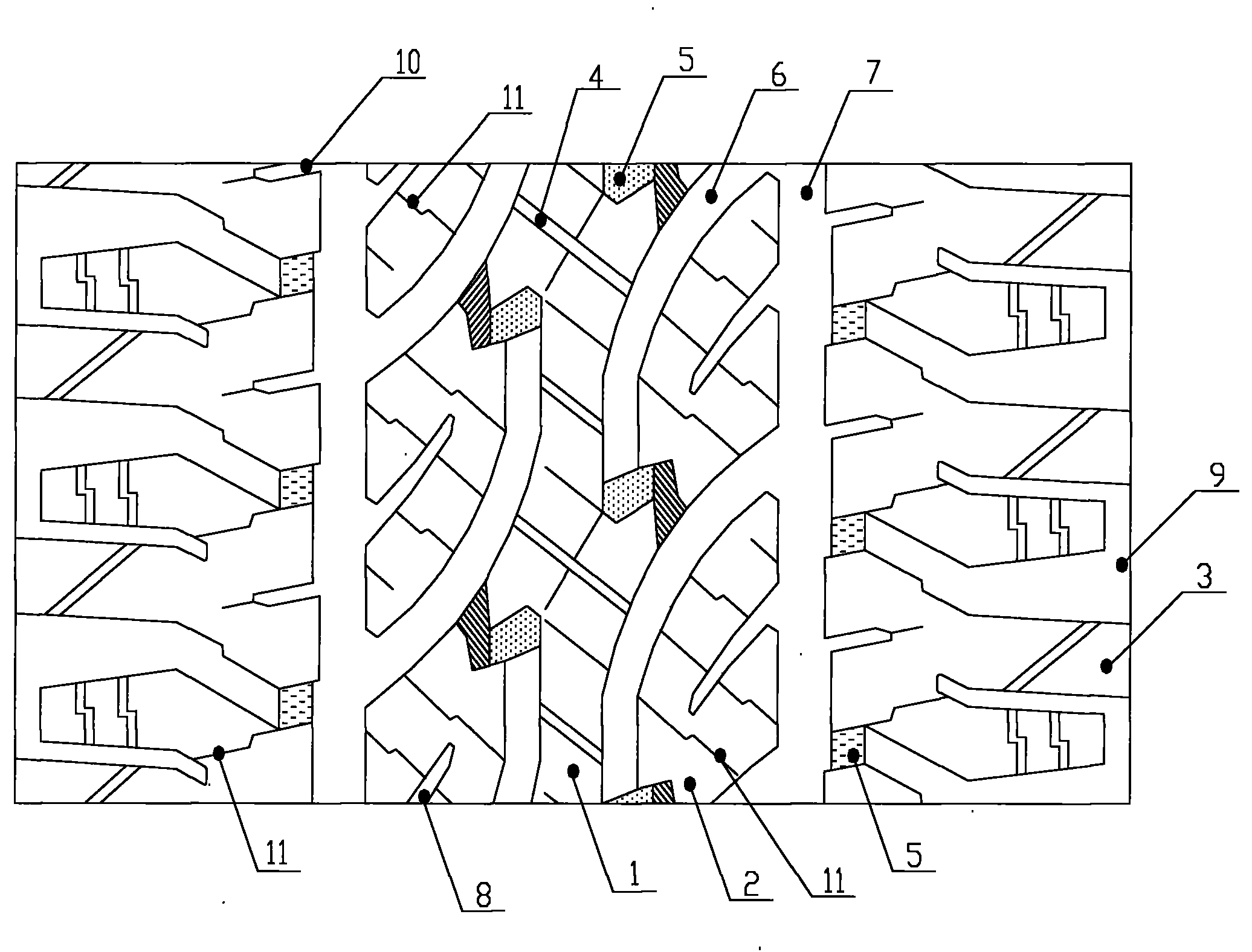
Tire tread of sedan meridian tire
ActiveCN101607512ASufficient braking forceImprove maneuverabilityTyre tread bands/patternsTire beadCentral line placement
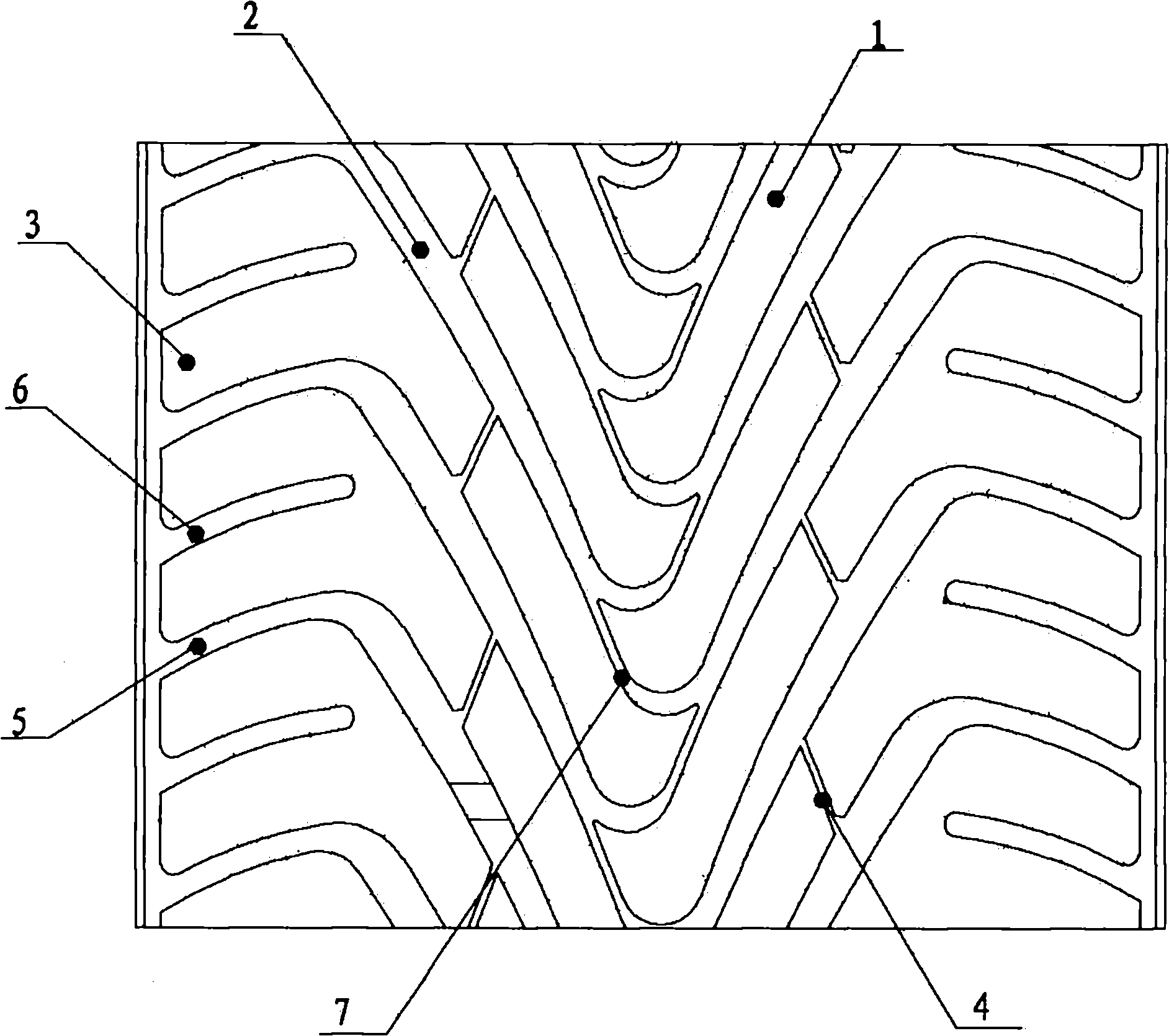
The invention relates to a sedan tire structure, in particular to a tire tread pattern structure of a sedan tire. The tire tread of the sedan meridian tire comprises central pattern blocks, lateral pattern blocks and tire shoulder pattern blocks, wherein the central pattern blocks are the longitudinal pattern blocks; the lateral pattern blocks and the tire shoulder pattern blocks are regularly arranged on the left side and the right side of the central pattern blocks from inside to outside in sequence; the central pattern blocks are positioned on the central line position of the tire tread; the same arched pattern ditch is spaced between the central pattern blocks and the lateral pattern blocks, between the two adjacent lateral pattern blocks, and between the two adjacent tire shoulder pattern blocks respectively; an inclined lateral pattern ditch is spaced between the two adjacent central pattern blocks; and a longitudinal circumferential pattern ditch is spaced between the lateral pattern blocks and the tire shoulder pattern blocks. The tire tread of the tire adopts mixed patterns, and has the advantages of sufficient braking force, good control performance and elegant appearance.
Owner:QINGDAO YELLOWSEA RUBBER
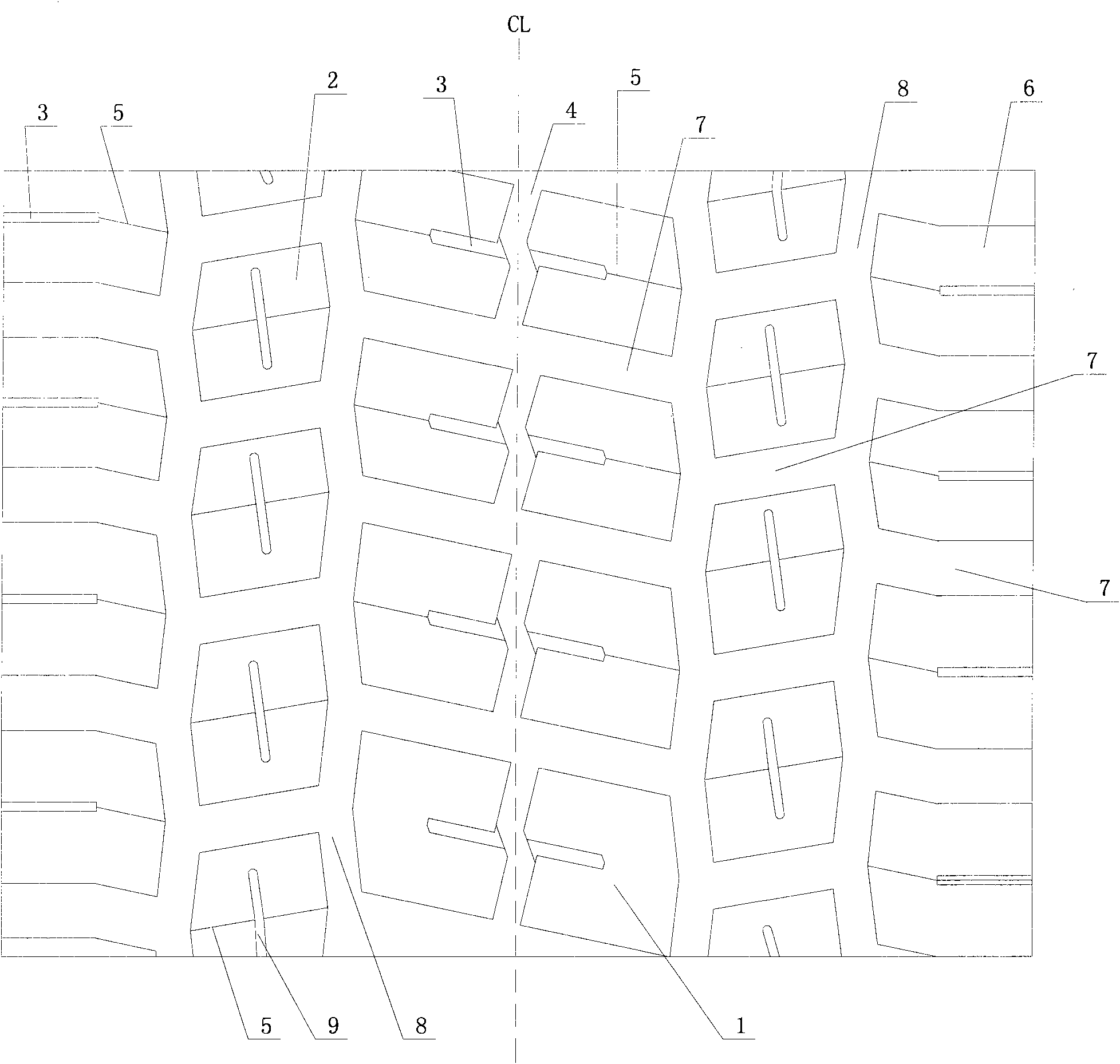
Truck tyre tread
ActiveCN101618664AAvoid eccentric wearImprove maneuverabilityTyre tread bands/patternsEngineeringTruck
The invention relates to an auto tyre structure, in particular to a tread pattern structure for a tyre of a truck. The truck tyre tread comprises a central vertical circumferential pattern groove arranged on the center position of the tyre tread, namely the center line of the tyre tread, wherein the central vertical circumferential pattern groove equally divides the tyre tread into two eudipleural parts, the left side and the right side of the central vertical circumferential pattern groove are provided with lateral pattern blocks and shoulder pattern blocks in turn regularly from inside to the outside, the lateral pattern blocks and the shoulder pattern blocks are spaced by the vertical circumferential pattern groove, and the groove bottom of the vertical circumferential pattern groove is provided with a bulge which is connected with the two side walls of the circumferential pattern groove; and two adjacent lateral pattern blocks and two adjacent shoulder pattern blocks are spaced by a transverse pattern groove respectively. The tyre tread of the truck tyre adopts mixed patterns and has sufficient braking force, good maneuverability, and elegant appearance.
Owner:QINGDAO YELLOWSEA RUBBER
Tread of meridian tire for car
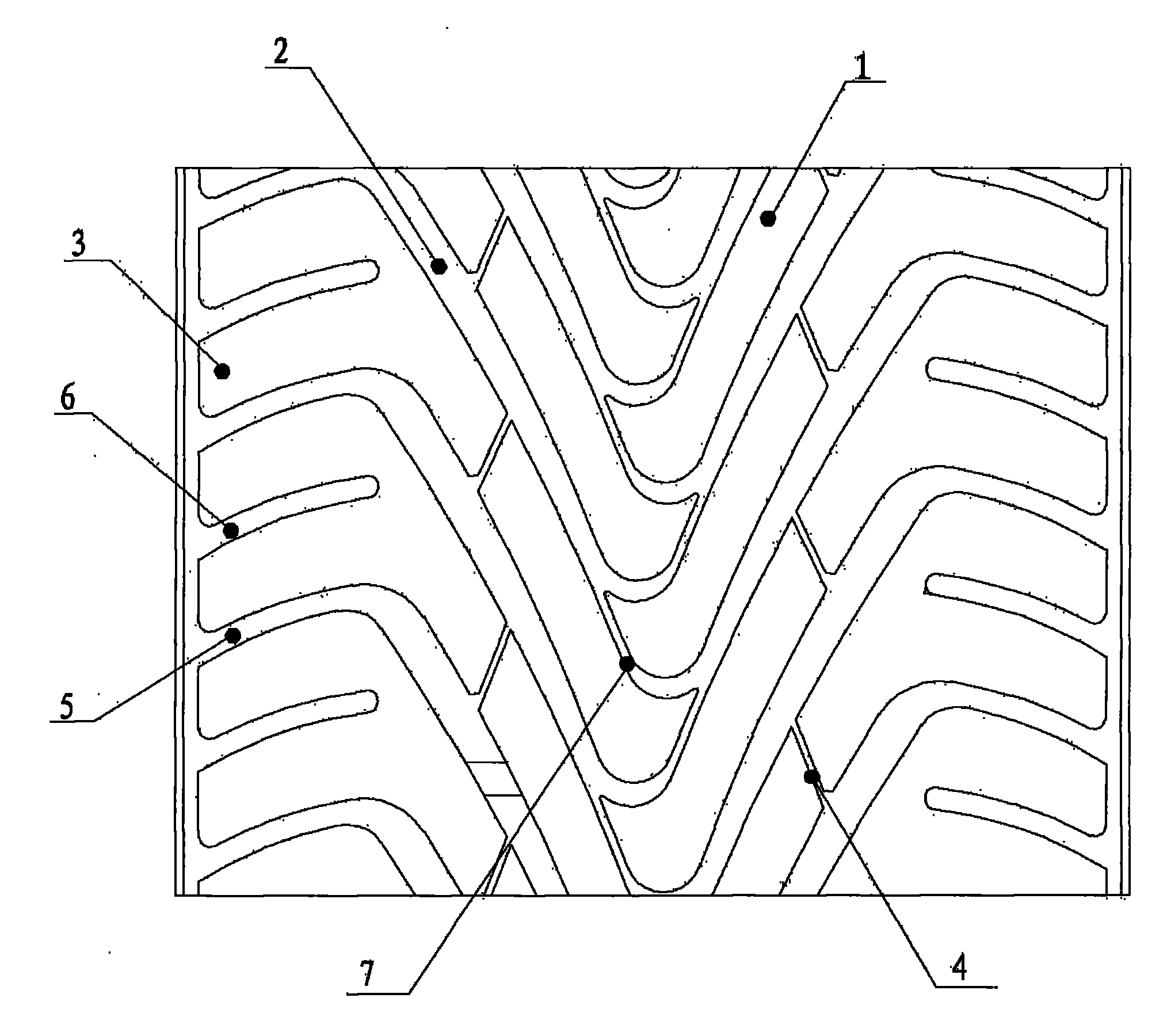
InactiveCN102248868ASufficient braking forceImprove maneuverabilityTyre tread bands/patternsEngineeringMixed pattern
The invention relates to a tire structure for a vehicle, in particular to a tread of a meridian tire for a car. The tread of the meridian tire for the car comprises a central pattern block, lateral pattern blocks and a tire shoulder pattern block; the central pattern block is an integrative longitudinal pattern block, and the lateral pattern blocks are regularly arranged at left and right sides of the central pattern block sequentially from inside to outside; the central pattern block is located in the centre of the tread; the central pattern block is spaced from the lateral pattern blocks via main longitudinal circumferential pattern grooves; the lateral pattern blocks are spaced from the tire shoulder pattern block via auxiliary longitudinal circumferential pattern grooves; two adjacent lateral pattern blocks are spaced from each other via an inclined lateral pattern groove, and two ends of the lateral pattern blocks are respectively communicated with the main longitudinal circumferential pattern grooves and the auxiliary longitudinal circumferential pattern grooves; and the tire shoulder pattern block is an integrative longitudinal pattern block. The tread of the tire has the characteristics of adoption of mixed patterns, enough braking force, good maneuvering performance and elegant appearance.
Owner:克劳斯玛菲股份有限公司
High Responsivity High Bandwidth Metal-Semiconductor-Metal Optoelectronic Device
InactiveUS20070235635A1Improve responsivenessSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansDielectricSilicon oxide
An optical device for sensing an incident optical wave within a wavelength range includes a first array and a second array of electrodes superposed on a substrate, and a sensor connected to the contacts. The arrays are interdigitated. Each array includes its own parameters: contact width, contact thickness, groove width, and a groove dielectric constant. A structure associated with the arrays resonantly couples the incident wave and a local electromagnetic resonance or hybrid mode including at least a surface plasmon cavity mode (CM). For coupling the CM, an aspect ratio of contact thickness to spacing between electrodes is at least 1. A preferred structure for coupling a hybrid mode for high bandwidth and responsivity includes a higher dielectric constant in alternating grooves. The substrate may include silicon, including silicon-on-insulator (SOI). An SOI device having a alternating grooves with a higher dielectric, e.g., silicon oxide, provides 0.25 A / W and 30 GHz bandwidth.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
Method suitable for treating plateau stony desertification under photovoltaic panels
InactiveCN106386094AReduce churnReduce degradationSuperphosphatesClimate change adaptationPlateauFestuca ovina
The invention discloses a method suitable for treating plateau stony desertification under photovoltaic panels. Festuca ovina l. is planted within the scope 10m away from the photovoltaic panels and under the photovoltaic panels; the plantation mode of festuca ovina l. is seed sowing; sweet osmanthus or tea trees are planted in the scope from 10 to 20m away from the photovoltaic panels, wherein the plantation mode of sweet osmanthus or tea trees is seedling planting, and Betula platyphylla is planted at the place 20m beyond the photovoltaic panels; before seed sowing or seedling growing, 80 to 600g / m2 fertilizer is applied on the soil surface; before seed sowing or seedling growing, the seed sowing and seedling growing areas are watered. According to the method of the invention, fertilizer is applied before planting, well-adapted and drought tolerant sweet osmanthus or tea trees, festuca ovina l. and Betula platyphylla are selected and forestation modes of directed seeding or seedling growing are adopted to recover the land surface vegetation, reduce soil loss and land degeneration, increase survival rate of seedlings, and block fierce wind and severe cold; multiple tree species three-dimensional mixed pattern is formed to treat the plateau stony desertification under photovoltaic panels; the method is suitable for large-scale promotion.
Owner:云南云创数字生态科技有限公司
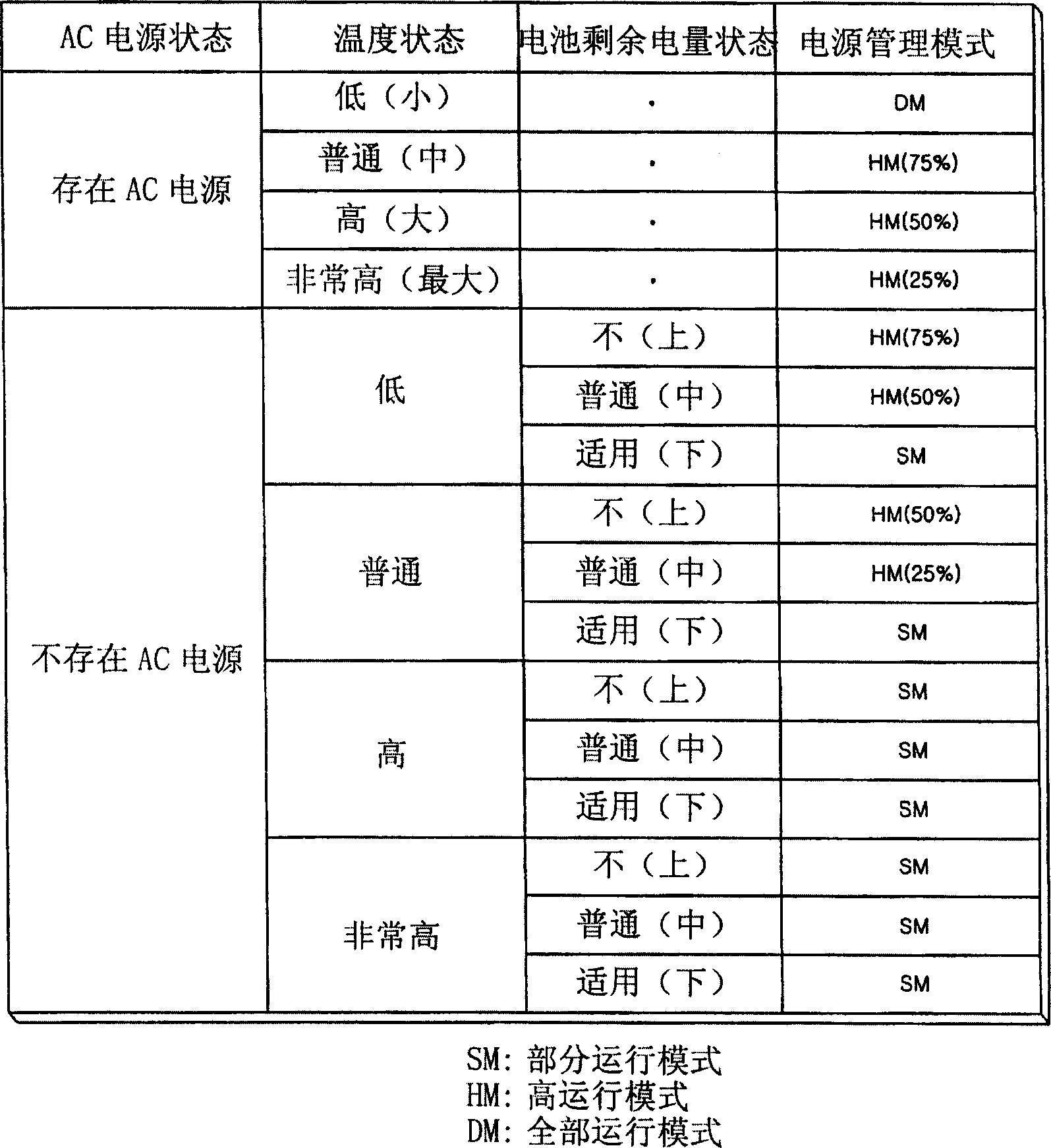
Method and apparatus for implementing a hybrid mode for a multi-core processor and powder supply manage mode setting method
InactiveCN1877491AAutomatically change mode ratioImprove performanceEnergy efficient ICTMultiprogramming arrangementsEngineeringSingle-core
A method of implementing a hybrid mode of a multi-core processor includes setting a hybrid mode as a power management mode of the multi-core processor. The hybrid mode includes operating more than one core of the processor and alternately operating only a single core of the processor. The hybrid mode includes operating a first core of the processor and alternately operating a second core of the processor. The hybrid mode of a method, apparatus or computer readable medium includes alternate operation between two or more processor cores of a multi-core processor according to a preset or adjustable operating ratio.
Owner:LEJIN ELECTRONICS KUNSHAN COMPUTER CO LTD
Tire tread of motortruck
InactiveCN101618663ASufficient braking forceImprove maneuverabilityTyre tread bands/patternsMixed patternTread
The invention relates to a tire tread of a motortruck, in particular to a tread pattern structure of a motortruck tire. The tire tread of the motortruck comprises a central longitudinal circumferential pattern groove which is arranged on the center of the tire tread, namely the center line of the tire tread, wherein, the central longitudinal circumferential pattern groove equally divides the tire tread into a left part and a right part which are symmetrical to each other; lateral pattern blocks and tire shoulder pattern blocks are sequentially arranged on both sides of the central longitudinal circumferential pattern groove from the inside out and are partitioned by the longitudinal circumferential pattern groove, and every two adjacent lateral pattern blocks are partitioned by an auxiliary pattern groove; and the tire shoulder pattern blocks form an integral structure along the circumferential direction of the tire tread. The tire tread of the tire adopts the mixed patterns, and has enough braking force, favorable maneuvering performance and shapely configuration.
Owner:克劳斯玛菲股份有限公司
Tread pattern for radial ply tire of sedan
InactiveCN102248867ASufficient braking forceImprove maneuverabilityTyre tread bands/patternsEngineeringMixed pattern
The invention relates to an automobile tire structure, in particular to a tread pattern structure of a load-carrying automobile tire. In a tread pattern for a radial ply tire of a sedan, V-shaped pattern grooves are formed at the central position of a tire tread along the circumferential direction at intervals; central pattern blocks and tire shoulder pattern blocks are arranged in the groove wall directions of the V-shaped pattern grooves from groove bottoms to groove tops sequentially; the central pattern blocks are spaced from the tire shoulder pattern blocks through lateral pattern grooves; the two ends of the lateral pattern grooves are communicated with two adjacent V-shaped pattern grooves; the central pattern blocks are arranged in a sequentially superposed and staggered way along the circumferential direction; the inclined directions of the two adjacent central pattern blocks are symmetrical to each other relative to the central position; every two adjacent tire shoulder pattern blocks are spaced from each other through a transverse pattern groove; and the transverse pattern grooves are communicated with the V-shaped pattern grooves and are smoothly transitioned. Mixed patterns are used for the tread of the tire, and have sufficient braking force, high maneuvering performance and aesthetic and elegant appearance.
Owner:克劳斯玛菲股份有限公司
Radial ply tire tread
InactiveCN102248866ASufficient braking forceImprove maneuverabilityTyre tread bands/patternsEngineeringTruck
The invention relates to an auto tire structure, in particular to a tread pattern structure of a truck tire. The radial ply tire tread disclosed in the invention comprises central pattern blocks, lateral pattern blocks and shoulder pattern blocks, wherein, the central pattern blocks are vertical pattern blocks, the lateral pattern blocks and the shoulder pattern blocks are successively arranged from in to outside at the two side of the central pattern blocks, the central pattern blocks are positioned at the central position of the tread, the spacing between the central pattern blocks and the lateral pattern blocks and the spacing between the two neighboring lateral pattern blocks are realized by arched tread grooves, the spacing between the two neighboring central pattern blocks is realized by tilted lateral tread grooves, the communication of the neighboring arched tread grooves is realized by auxiliary tread grooves, the spacing between the lateral pattern blocks and the shoulder pattern blocks is realized by vertical circle tread grooves, and the arched tread grooves are communicated with the vertical circle tread grooves. The tread of the tire uses mixed patterns, and has enough braking force, good maneuvering performance and nice figure.
Owner:克劳斯玛菲股份有限公司
Heavy-duty truck tyre tread
The invention relates to a truck tyre structure, in particular to a tread pattern structure of heavy-duty truck tyre tread. The heavy-duty truck tyre tread comprises a central pattern block, a lateral small pattern block and a tyre shoulder pattern block, wherein the central pattern block is of a transverse pattern block, the lateral small pattern block and the tyre shoulder pattern block are regularly arranged at the left side and the right side of the central pattern block from interior to exterior, the central position of the central pattern block, namely, a central line of the tread is provided with a central longitudinal circumferential pattern groove, and the central pattern block is evenly divided into a left part and a right part which are symmetrical by the central longitudinal circumferential pattern groove; the central pattern block and the lateral small pattern block as well as the lateral small pattern block and the tyre shoulder pattern block are separated by a longitudinal circumferential pattern groove; and the two adjacent central blocks, the two adjacent lateral small pattern blocks and the two adjacent tyre shoulder pattern blocks are separated by a transverse pattern groove. The tyre tread adopts mixed patterns and has enough braking force, favorable maneuvering performance as well as attractive and elegant appearance.
Owner:QINGDAO YELLOWSEA RUBBER
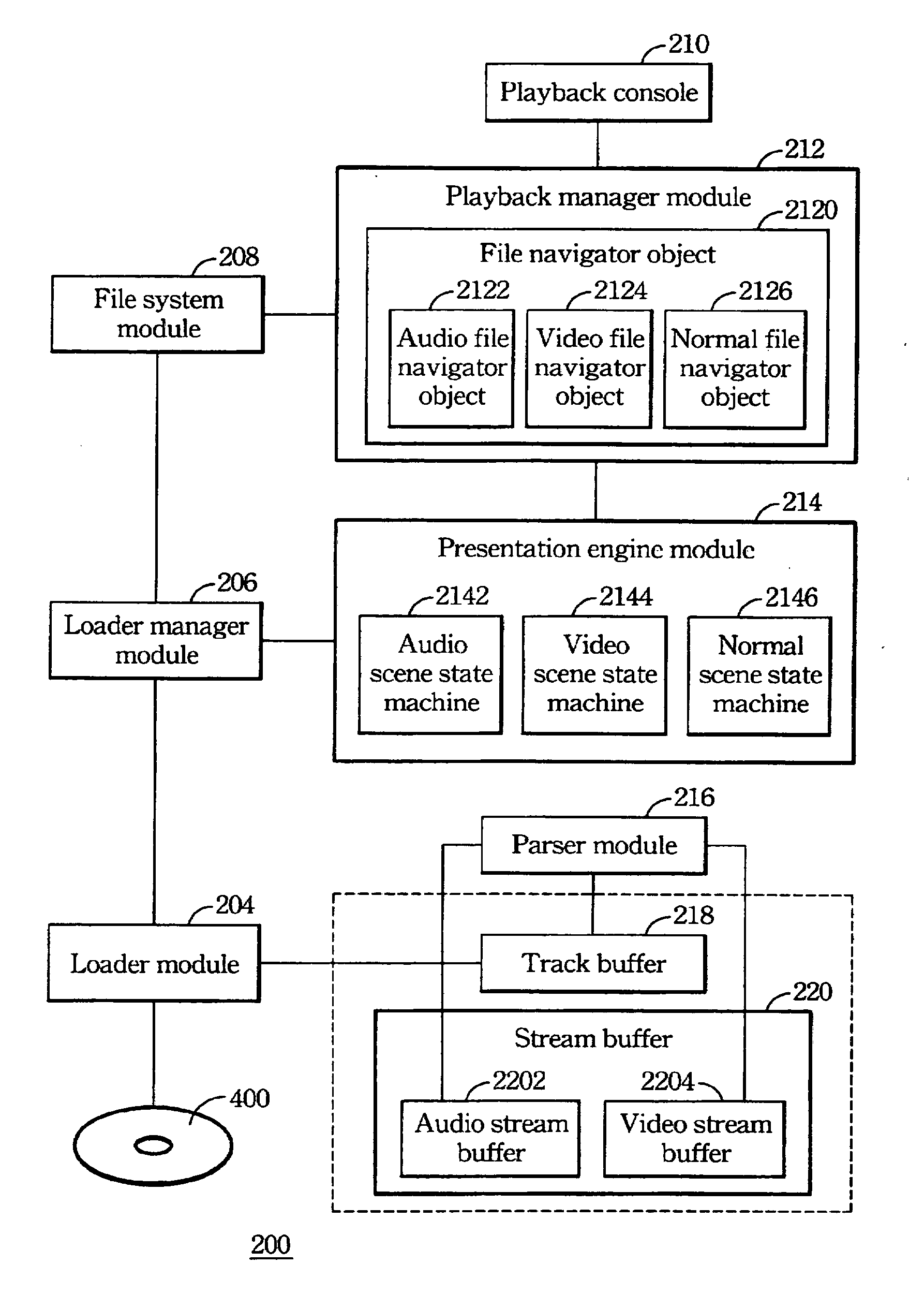
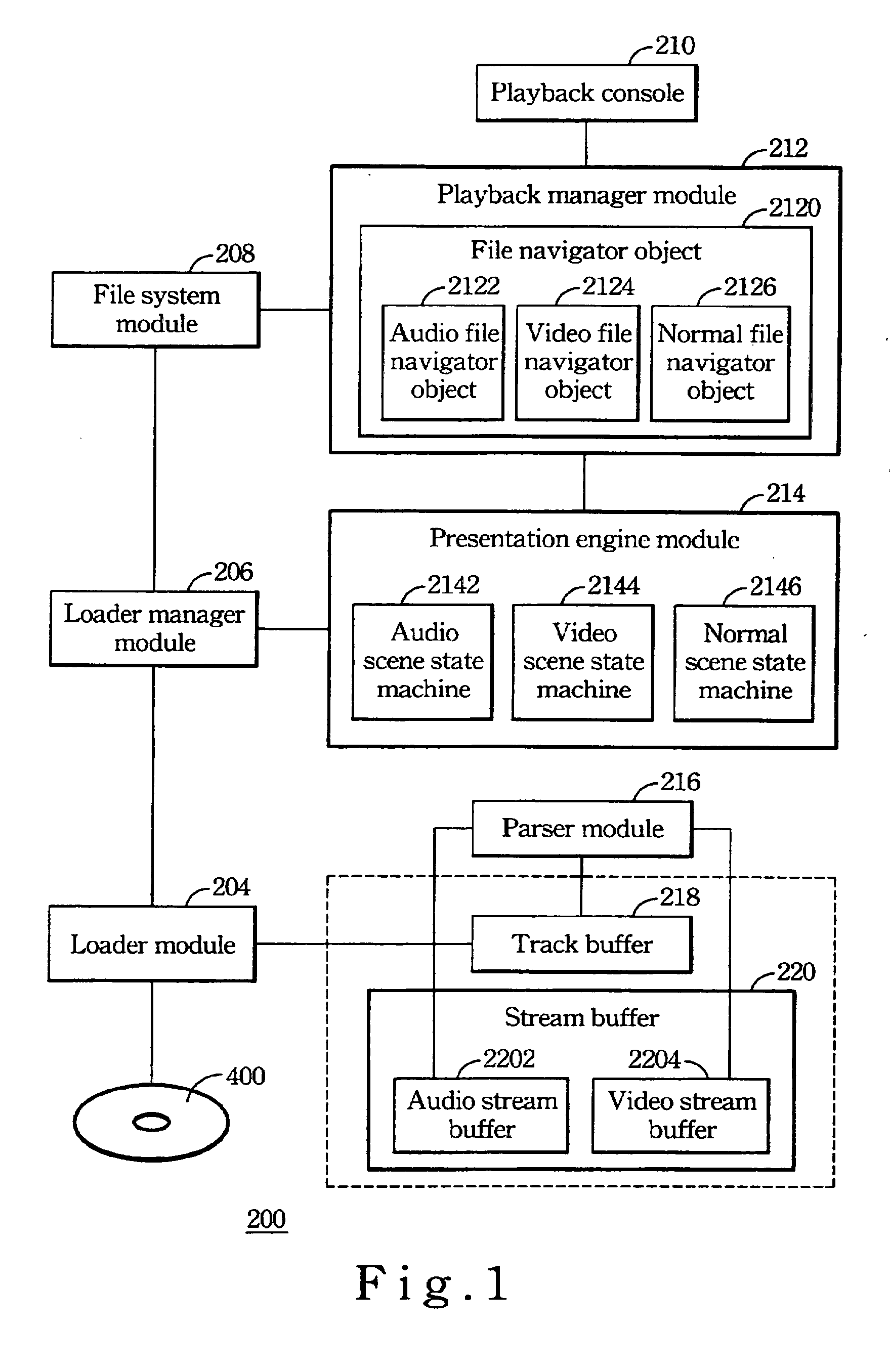
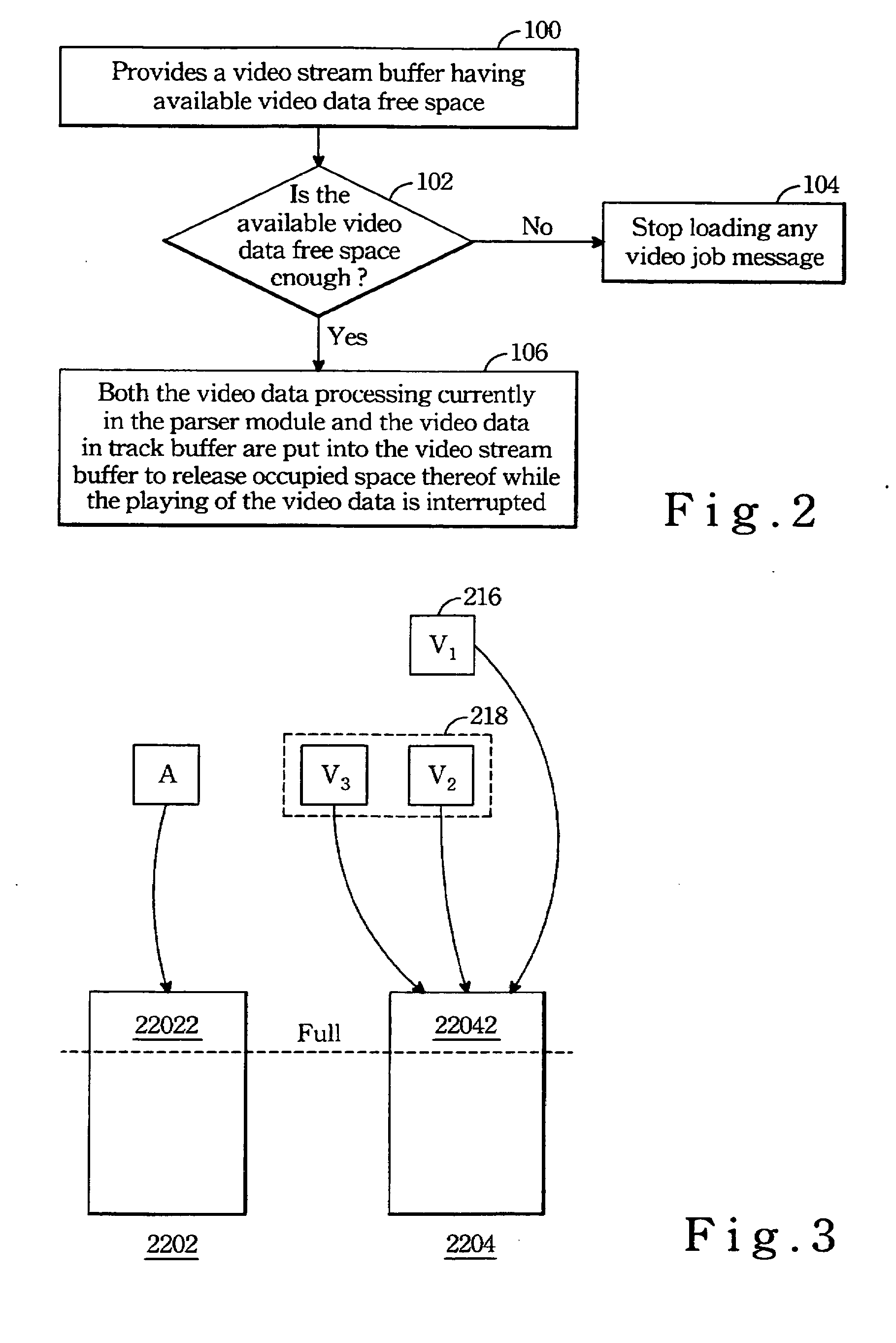
Method of preventing audio or video from interruption due to the other for a mix mode multimedia player
ActiveUS20060257121A1Television system detailsColor television signals processingComputer hardwareComputer science
A method of preventing playing of audio or video data from being interrupted for a mix mode multimedia playback system comprises the following steps: a video stream buffer, a audio stream buffer, and a parser module is provided; then amount of free space in the video stream buffer is checked so as to ensure the amount of the free space is larger than a sum of a track buffer and video data being processed by the parser module. Whenever the playing of an audio scene state machine is paused or stopped, audio data processed by the parser module and audio data in the track buffer are pushed into the free space of the audio stream buffer so as to release entire space of the track buffer for video data to be loaded. On the other hand, whenever the playing of a video scene state machine is paused or stopped, the video data processed by the parser module and video data in the track buffer are pushed into the free space of the video stream buffer so as to release entire space of the track buffer for audio data to be loaded.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Method and apparatus for implementing a hybrid mode for a multi-core processor and powder supply manage mode setting method
InactiveCN100461071CImprove performanceManagement consumptionEnergy efficient ICTMultiprogramming arrangementsEngineeringSingle-core
A method of implementing a hybrid mode of a multi-core processor includes setting a hybrid mode as a power management mode of the multi-core processor. The hybrid mode includes operating more than one core of the processor and alternately operating only a single core of the processor. The hybrid mode includes operating a first core of the processor and alternately operating a second core of the processor. The hybrid mode of a method, apparatus or computer readable medium includes alternate operation between two or more processor cores of a multi-core processor according to a preset or adjustable operating ratio.
Owner:LEJIN ELECTRONICS KUNSHAN COMPUTER CO LTD
Mixed slip-casting ceramics
Mixed slip-casting ceramics includes the following steps: preparing materials and forming. The preparing step includes preparing ceramic clay slurry. The forming step includes placing a prepared ceramic mold on a rotating plate to allow regular or irregular texture to be formed on the ceramic mold under the rotating action of the rotating plate; or directly injecting the ceramic clay slurry into the ceramic mold, and simultaneously shaking a slurry injecting tube or a slurry injecting barrel to allow the texture to be formed on the ceramic mold during slurry injecting; or injecting few single-color ceramic clay slurry into the ceramic mold, and then using ceramic clay slurry with the other color or multiple colors to form patterns and the texture on the surface of the single-color ceramic clay slurry injected previously to allow the ceramic mold to have mixed patterns with different colors as well as the texture. The mixed slip-casting ceramics has the advantages that forming preparation is simple, the texture and the patterns of ceramic products are clear, vivid and bright, the ceramic products are less prone to fading, and the like.
Owner:涂瑞漫
Resolution plate used for evaluating quality of aerial photogrammetry and application method thereof
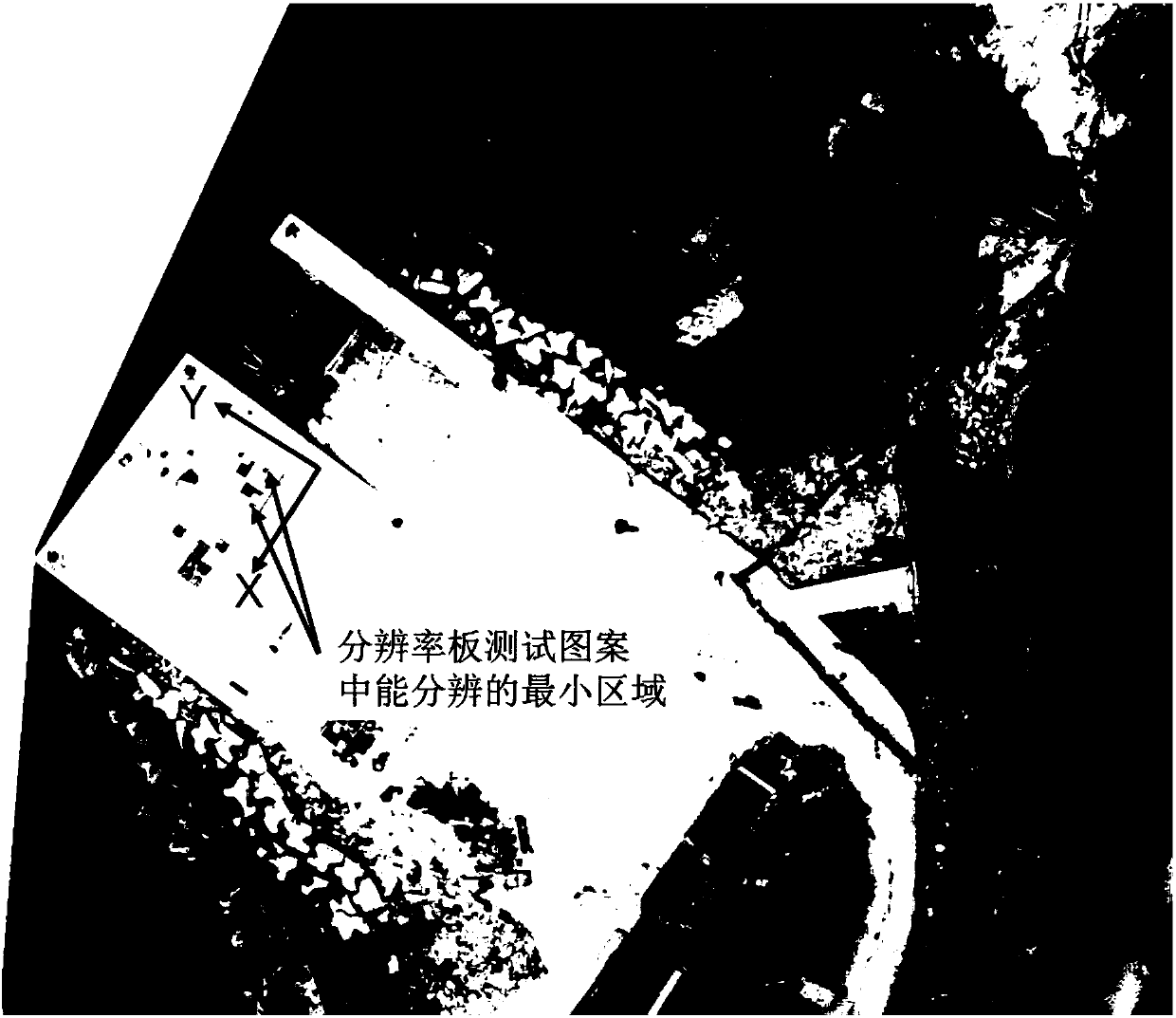
ActiveCN107941241AEase of quality evaluationExpand the resolution rangeMeasurement devicesAviationVisual field loss
The invention relates to a resolution plate used for evaluating quality of aerial photogrammetry and an application method thereof. A printing or painting technology is employed for making a resolution test pattern and a visual field indication frame on a substrate; the visual field indication frame is used for indicating a visual field size of the resolution plate; the resolution test pattern istransversely and vertically mixed patterns, which are symmetrical along an inclined diagonal and spliced by n types of square patterns; transverse and vertical resolutions of an aerial ortho-photo mapare obtained by analyzing the resolution test patterns, and a short-line size corresponding to a minimum group of patterns which can be clearly seen is the resolution of the ortho-photo map. The resolution plate uses the autonomously designed resolution plate as a test tool, the resolution plate pattern in a finally synthesized three-dimensional model is analyzed, and the resolution of the imageis calculated, internal and external parameters of a camera are calculated through the characteristic corners in the resolution plate, distortion rectification of the camera is carried out, and imaging quality is increased. The resolution plate and the application method are capable of simultaneously inversing the imaging resolution and rectifying the camera.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Package substrate, method for manufacturing the same, and package on package substrate
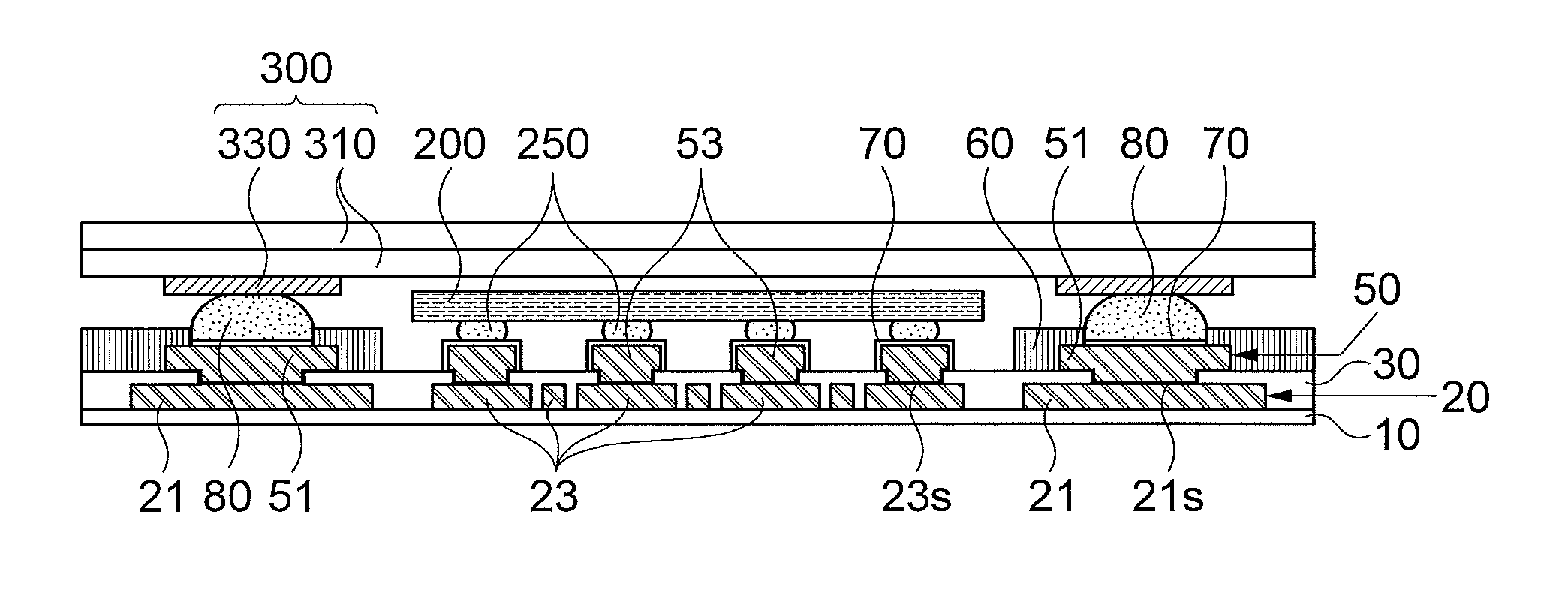
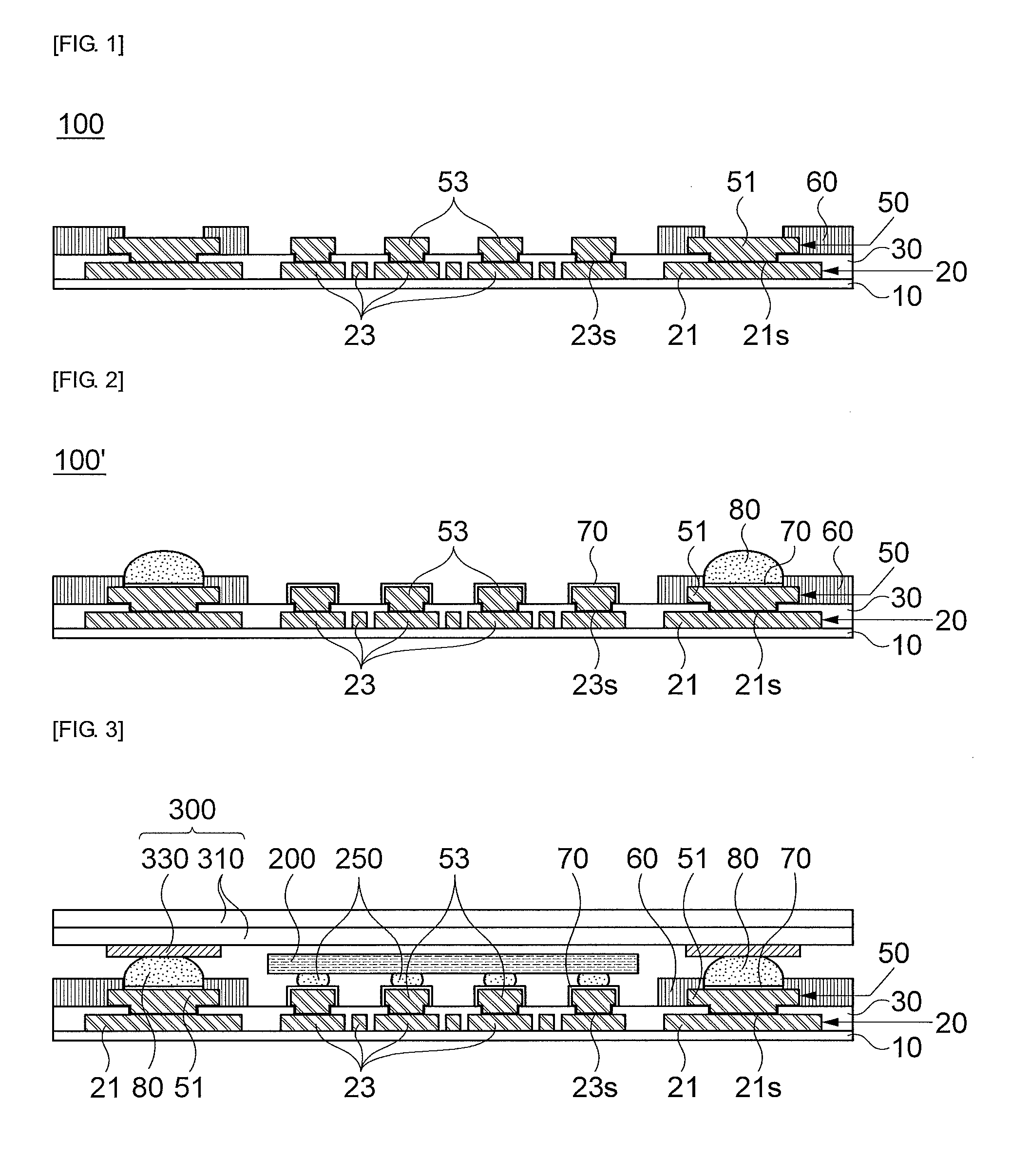
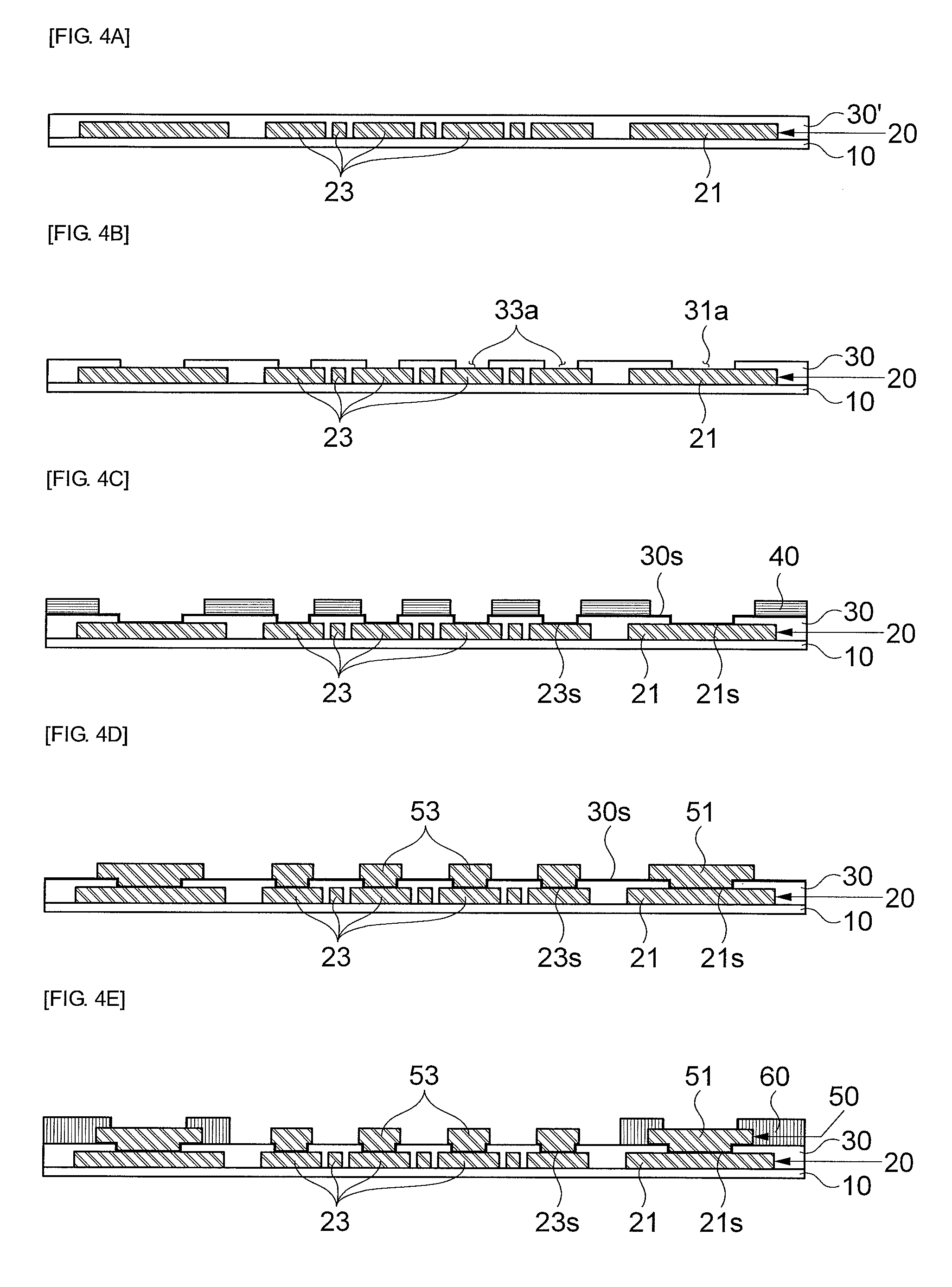
InactiveUS20140183726A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesResistMixed pattern
The present invention relates to a package substrate, a method for manufacturing the same, and a package on package substrate. In accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, a package substrate including: an inner insulating layer; a circuit pattern layer formed on the inner insulating layer; an outer insulating layer formed on the inner insulating layer to protect the circuit pattern layer and expose portions of external and internal patterns of the circuit pattern layer; a mixed pattern layer consisting of post bumps and outermost layer patterns formed on the portions of the internal and external patterns exposed by the outer insulating layer; and a resist layer formed on the outer insulating layer to protect the outermost layer patterns of the mixed pattern layer and expose the outermost layer patterns by an open region.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com