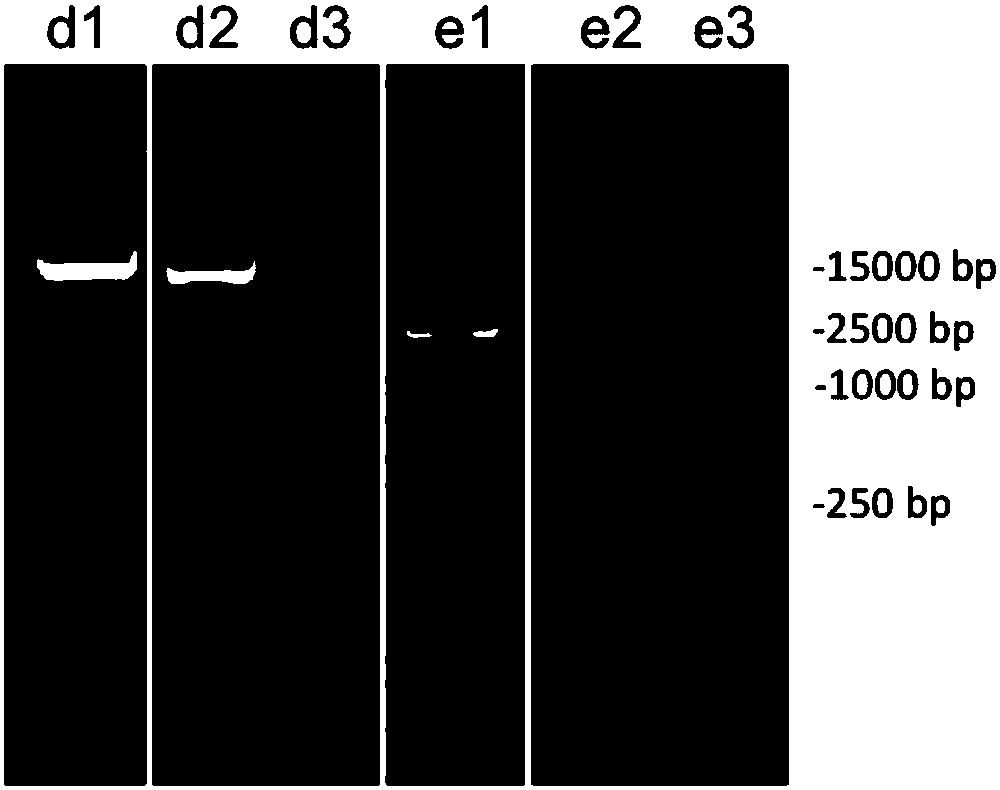
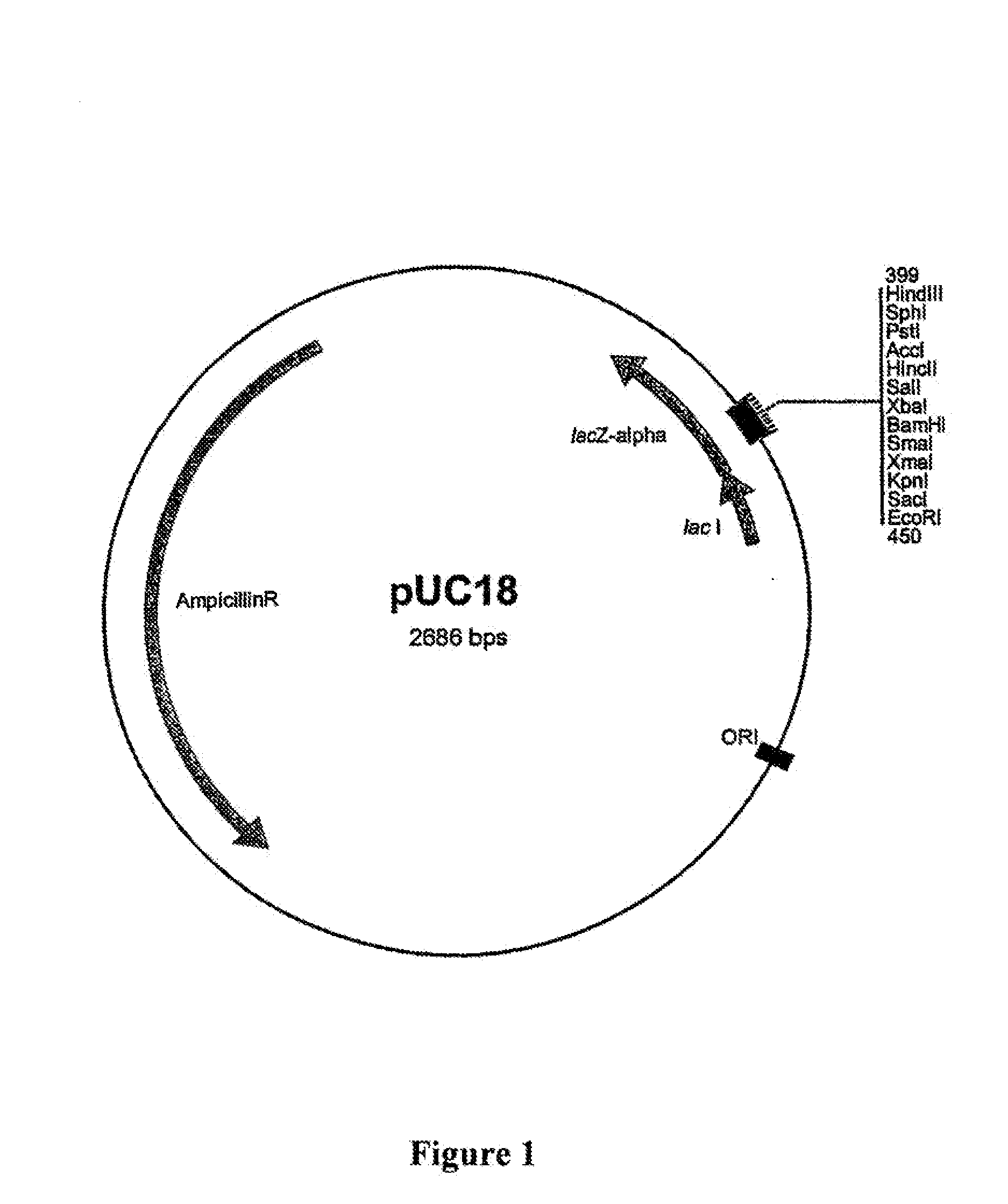
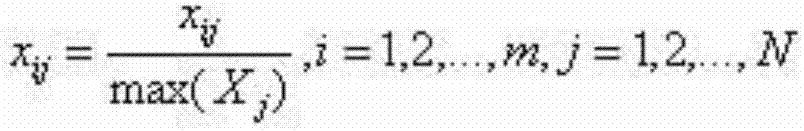Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
39 results about "Metagenomic dna" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Metagenomics is the use of DNA sequencing techniques to study DNA extracted directly from environmental samples. It is a culture-independent tool for studying environmental microorganisms.
Method of simultaneously extracting microorganism macrogenome DNA and total DNA from sea precipitate
A method for simultaneously extracting the macrogenomic DNA and total RNA of microbe from the sea sediment includes such steps as treating the sediment by modifying solution, adding sand, oscillating, adding proteinase and lysozyme, cracking adding SDS and PVPP solution, cracking further, adding extrant, extracting, depositing in isopropanol and purifying by nucleic acid adsortion resin.
Owner:THIRD INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY STATE OCEANIC ADMINISTATION
Glycosyl hydrolases
The invention relates to a new glycosyl hydrolases with an amyloltic activity and nucleic acids coding for said gylcosyl hydrolases, A PCR-based method for identifying and preparing new gylcosyl hydrolases from metagenome DNA and several possible technical uses for such glycosyl hydrolases with an amylolytic activity. Washing and cleaning products containing such enzymes, and methods and possible uses corresponding thereto are particularly interesting.
Owner:BRAIN AG
Gene encoding beta-glucosidase
InactiveCN101363026AAvoid pollutionSolve the world energy crisisEnzymesGenetic engineeringBeta-glucosidaseNucleotide
The invention provides a gene of coded beta-glucosaccharase, which is called Unbgl1B and is obtained by constructing Metagenome DNA library of uncultured microorganisms of alkality contaminated soil and by the detecting and screening method of the activity of the beta-glucosaccharase of clone library, so as to be one of the following nucleotide sequences: 1) DNA sequences and partial sequence thereof in sequence 1 of a sequence table; 2) DNA sequences having more than 80% of homoeology compared with the DNA sequences defined by the sequence 1 of the sequence table. The DNA in the sequence 1 of a sequence table is DNA sequences of a pGEM-3Zf(+) part of a cloning vector and DNA of exogenetic uncultured microorganisms cloned on the vector, and the exogenetic DNA segment consists of 838 basic groups; the GC content of the gene is 54.3%. The gene is used for producing the beta-glucosaccharase, so as to dissociate cellobiose into single glucose molecule.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Method for screening beta-glucosaccharase gene from mildewed sugarcane leaves based on metagenomic technology
PendingCN105462999AHighly solubleEfficient soluble expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymesBiotechnologyBeta-glucosidase
The invention discloses a beta-glucosaccharase gene, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the beta-glucosaccharase gene is shown as the SEQ ID NO.1. The invention further discloses recombinant beta-glucosaccharase, wherein the amino acid sequence of the recombinant beta-glucosaccharase is shown as the SEQ ID NO.2. The invention also discloses a screening method of the recombinant beta-glucosaccharase. The screening method comprises the following steps: extraction of microbial metagenomic DNA from the mildewed sugarcane leaves; establishment of a metagenomic library; screening of the beta-glucosaccharase gene from the metagenomic library, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the beta-glucosaccharase gene is shown as the SEQ ID NO.1; and cloning and expression for the obtained beta-glucosaccharase gene, thus the recombinant beta-glucosaccharase is obtained, wherein the amino acid sequence of the recombinant beta-glucosaccharase is shown as the SEQ ID NO.2. The recombinant beta-glucosaccharase has extremely high activity and is not sensitive to hydrolysis products under the alkaline condition.
Owner:江西省农业科学院农业应用微生物研究所
Method for scale selection of microorganism alkaliproof related genes
InactiveCN101063174AAchieve high throughputAchieve scaleMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMicroorganismBacillus coli
The invention discloses a method to sieve scale microbe alkali proof relative gene in microbe engineering domain, which is characterized by the following: collecting typical basic environment soil sample; rough-extracting; purifying; getting macro-genom DNA of soil sample; electrization-inverting bacillus coli defect strain E with connecting product between macro-genom DNA part enzyme cutting fragment and carrier; sieving; getting positive colony; proceeding sub-clone and functional appraise for alkali proof related gene of positive clone. This invention can be used to breeding of alkali proof and molecule of microbe.
Owner:RUBBER RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Method for detecting rhizosphere soil prokaryotic microorganisms of various soybeans based on 16SrDNA deep sequencing
InactiveCN105525025AComprehensive detectionImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismSoil microbiology
The invention belongs to the technical field of soil microbiology, and in particular relates to a method for detecting rhizosphere soil prokaryotic microorganisms of various soybeans based on 16SrDNA deep sequencing. The method comprises the following steps: 1. collecting root shook-off soil and rhizosphere soil of various soybeans in different development stages; 2. extracting microorganism metagenome DNA from the soil; 3. performing PCR amplification on a 16S rDNA fourth hypervariable region in the DNA by virtue of a dual-tag primer so as to construct a library; 4. simultaneously synthesizing and sequencing the qualified library by virtue of a Illumina Miseq platform in a mode of 250 nucleotides at dual ends, so that pure READS is obtained; 5. splicing: clustering at least 38000 effective tags generated from each sample into an operable classifying unit; 6. conducting significance analysis on species composition, structure, diversity and relative abundance difference; and 7. by taking the root shook-off soil as a control group of the system, accurately determining the composition, structure, diversity and relative abundance of a rhizosphere soil prokaryotic microorganism colony, and comparing the various soybeans.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Extraction method for soil microorganism metagenome DNA and corresponding kit
The invention discloses a method for extracting soil microbial metagenomic DNA and a corresponding kit. The method for extracting soil microbial metagenomic DNA of the present invention is to pre-treat the soil sample to be tested, effectively avoid the influence of heavy metals, high salinity and low pH on lysozyme, and then lyse the cells twice by adding lysozyme and combining CTAB and SDS , further freeze-thaw treatment breaks up more microbial cell walls, and the DNA molecules in it are dissolved to the maximum extent, ensuring the abundance, fragment integrity and purity of DNA. The extraction method of the invention is simple in operation and strong in practicability, and the extracted DNA can be directly applied to analyze the structure and function of the soil microbial community. The extraction method of the present invention is particularly suitable for extracting soil microbial metagenomic DNA in extreme environments and with extremely low biomass, and a corresponding DNA extraction kit can be prepared according to the extraction method of the present invention, which has good application prospects.
Owner:广东美格基因科技有限公司
Petroleum pollution marine ecological environment evaluation method based on metagenome technology
InactiveCN104715165ABig amount of dataShort cycleSpecial data processing applicationsEcological environmentStructure analysis
The invention provides a petroleum pollution marine ecological environment evaluation method based on a metagenome technology. The method comprises the steps that seawater samples are collected; extraction and sequencing of metagenome DNA are carried out on the samples; effective sequence data statistical analysis and optimal sequence data statistical analysis are carried out on the sequenced data; OTU-based analysis is carried out through mothur and chopseq software; Alpha-diversity analysis is carried out and comprises analysis on the flora abundance, flora diversity and sequencing coverage rate; the dilution curve analysis is carried out; taxonomic analysis and community structure analysis are carried out; Heatmap clustering analysis is carried out, and the sample microflora structure and the population quantity parameter value are obtained and used for evaluating pollution similarity and perniciousness in different samples. The method can objectively evaluate the extent of damage to an ecological system from spilling oil pollutants and the response changes of the ecological system to the spilling oil pollutants.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Extraction method for metagenome
InactiveCN103060309AEfficient enrichmentReduce high background distractionsDNA preparationConserved sequenceStreptavidin
The present invention discloses an extraction method for metagenome, and a method of probe hybridization-bead capture is used to reduce the host DNA content in a host metagenomic DNA sample. According to the method, the Alu repeat sequence of the host DNA sequences and conserved sequence at both ends thereof are used as templates to design one-way or two-way probes, wherein the 5 'end of each probe is modified with biotin, streptavidin coated beads are used to capture host DNA hybridized with probes, in order to achieve aims of weakening host DNA background in a metagenome, and enhancing sequencing data efficiency.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION +1
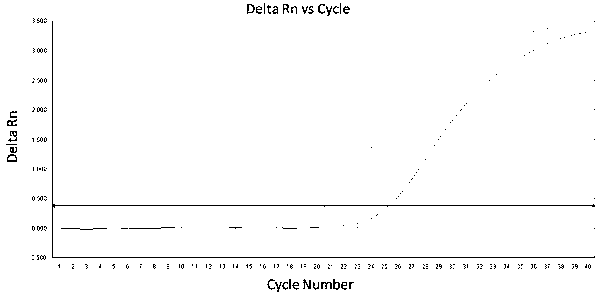
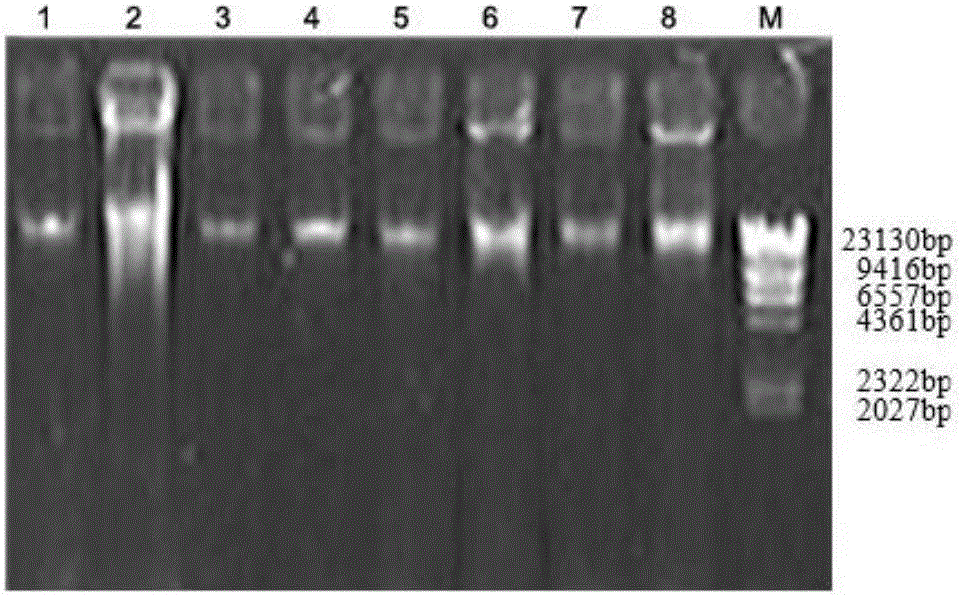
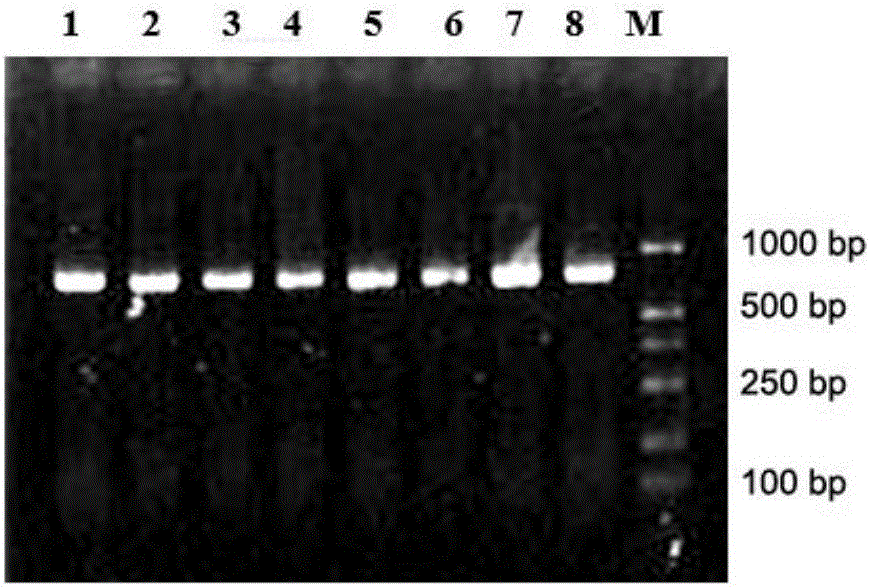
Key microbial functional genome detection method in pepper peeling process
InactiveCN106434914AAccurate analysisAvoid systematic biasMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroecosystemMicroorganism
The invention discloses a key microbial functional genome detection method in a pepper peeling process. According to the key microbial functional genome detection method in the pepper peeling process, from the perspective of micro-ecosystem, pepper epidermis microorganisms in the peeling process are taken as an object; metagenome DNA of pepper epidermis bacteria is extracted and purified and a variable region sequence is amplified, and then the variable region sequence of the epidermis bacteria is read with the application of a high-throughput sequencing technology; by virtue of a bioinformatics platform, the sequence is subjected to quality control and species annotation and function prediction are completed, and on the basis, a microorganism species, which plays a vital role in the pepper peeling process, in fresh fruit epidermis and a core metabolic pathway thereof are comprehensively and objectively revealed depending on a statistical method. The detection method provided by the invention simplifies experimental operations and improves a sequencing efficiency, so that the development of metagenomics is greatly promoted.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
Method for extracting microbial metagenome DNA from intestinal tract content
ActiveCN107653243AEasy extractionReduce species preferenceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationMicroorganismFeces
The invention discloses a method for extracting a microbial metagenome DNA from intestinal tract content. Themethod for extracting the microbial metagenome DNA from the intestinal tract content comprises the following steps that 1, the intestinal tract content or excrement of an animal is subjected to differential centrifugation; 2, microbial cells are combined and are broken by using a liquid nitrogen repeated freezing and thawing cracking method, a glass bead grinding method and a lysate high-temperature cracking method to obtain broken cells; 3, genomes DNA of the broken cells are firstly extracted and then are purified. By adding the steps of washing and enriching microbial cells, the pollution of host and food DNA is reduced. By combining the multiple microbial cell cracking and breaking methods, and the speciespreference of the metagenome DNA is reduced. By adding a purifying step, the purity of the DNA is ensured, and the DNA requirements for establishing second generation of high-throughput sequencing libraries can be met.
Owner:AGRI GENOMICS INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Quantification method for denitrifying microorganisms in aquaculture environment sediments
InactiveCN105132553AShorten the timeGood effectMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceEcological study
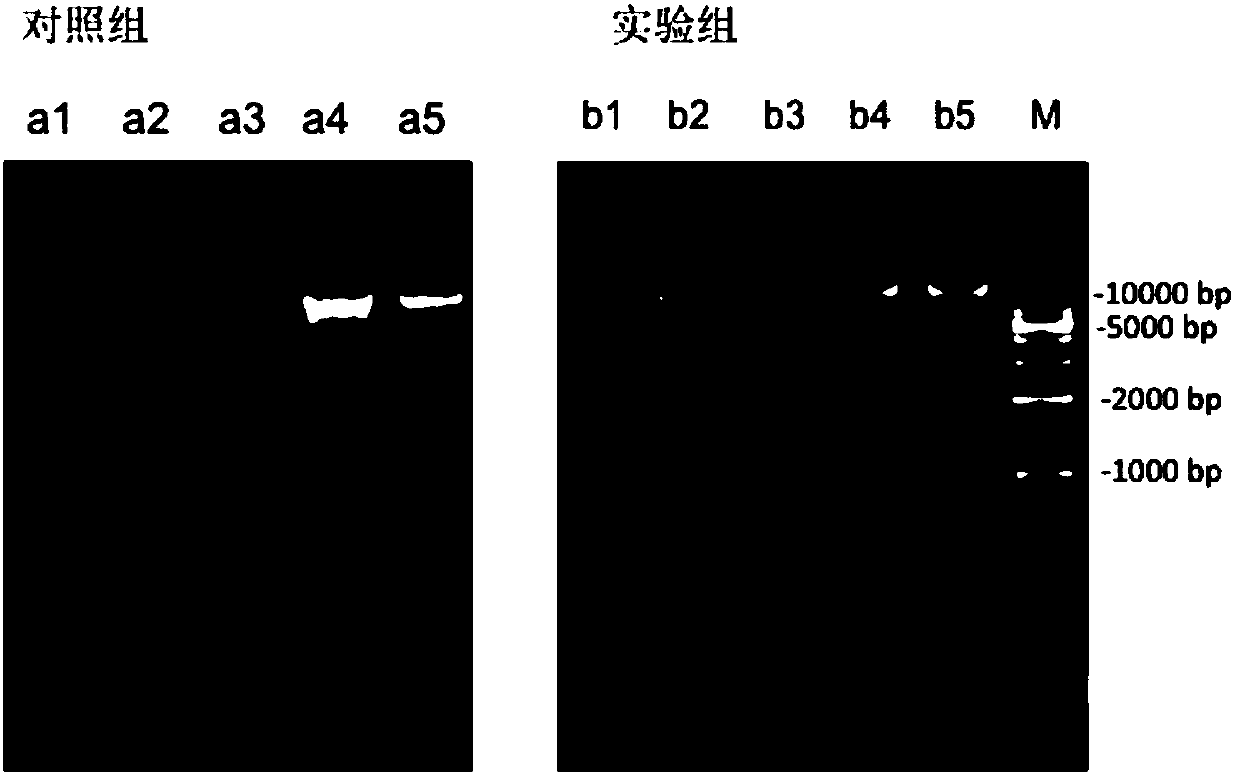
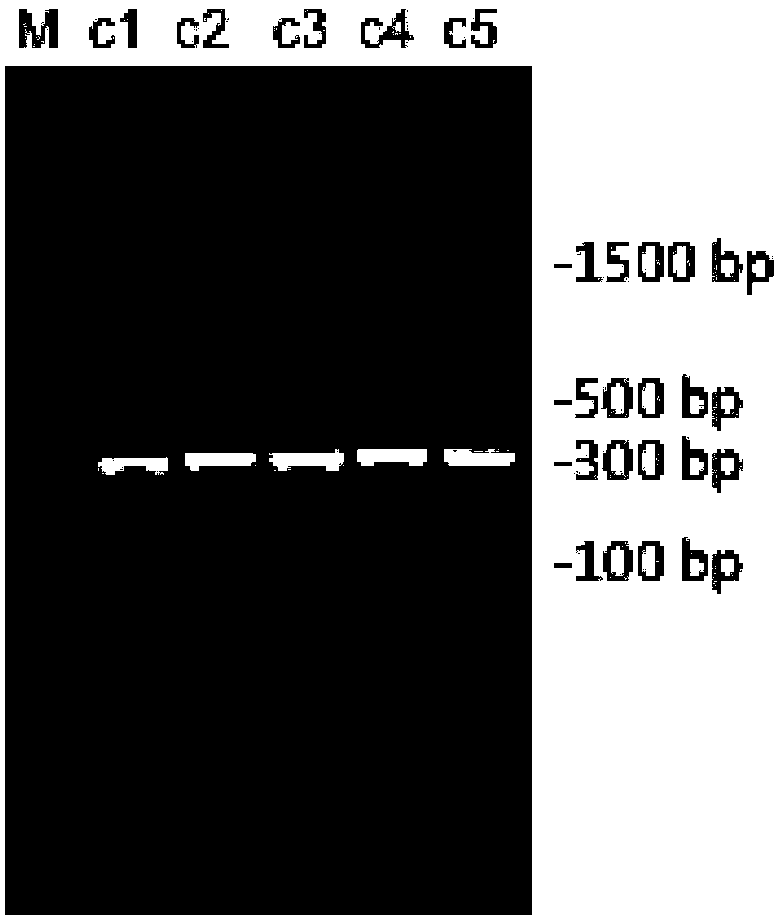
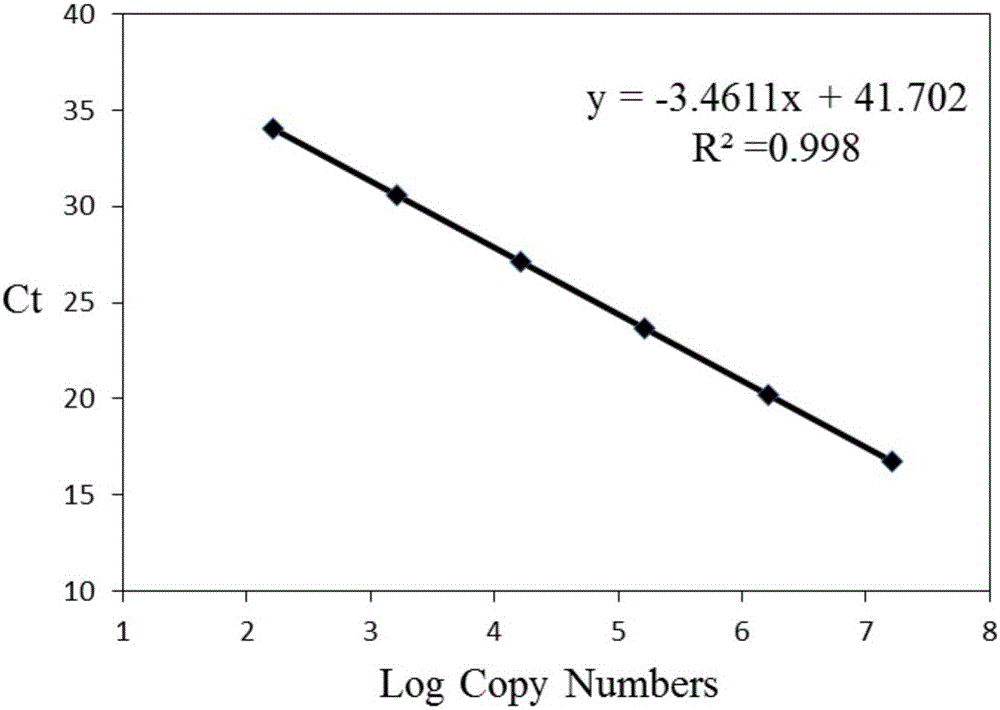
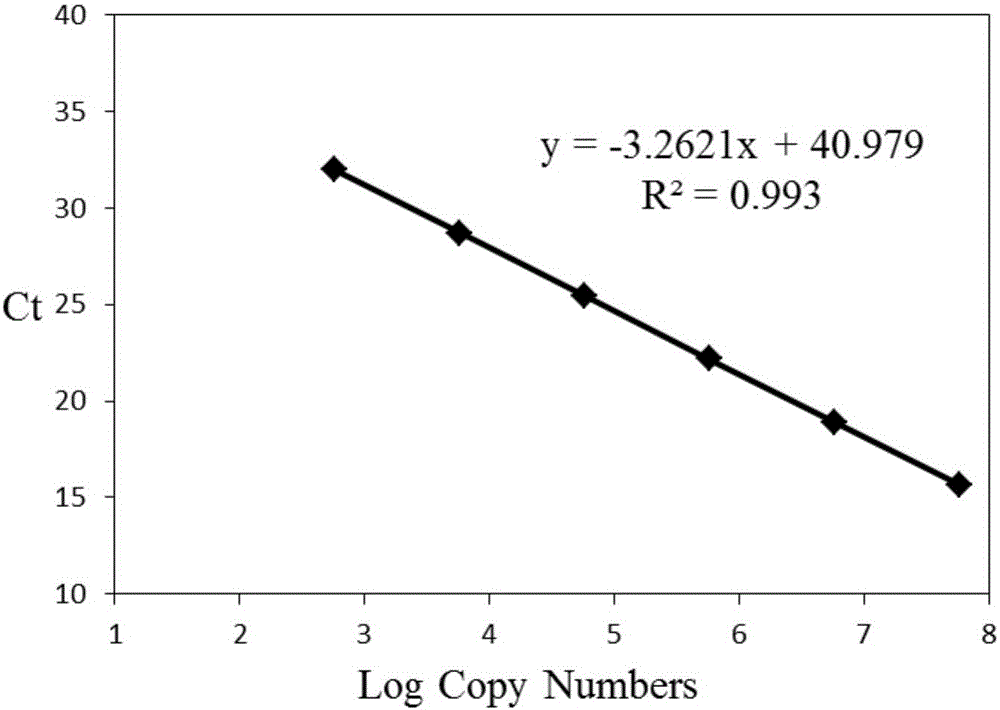
The invention discloses a method for real-time fluorescence quantification PCR (qPCR) detection of denitrifying microorganisms in aquaculture environment sediments, and belongs to the technical field of environmental microbial ecology. The method comprises the following contents: metagenome DNA extraction and concentration determination of sediment samples in various stations, PCR amplification of nirK and nirS genes, construction of a standard plasmid, preparation of a standard curve, qPCR amplification and calculation of the number of denitrifying microorganisms in the samples according to a qPCR result in accordance with the standard curve. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for determining the number of the denitrifying microorganisms in an aquaculture environment through quantitative analysis on two genes, namely nirK and nirS, so as to overcome the shortcoming that 16S rRNA gene cannot be used in the quantification of the denitrifying microorganisms as well as the shortcoming that the prior art, which focuses on some functional gene only, is incomplete in quantification; and the provided method for detecting the number of the denitrifying microorganisms in the aquaculture environment is good in specificity, high in repeatability and high in accuracy. According to the method disclosed by the invention, logarithm values of nirK and nirS gene copy numbers keep a good linear relation with Ct value of a luminescence threshold, and the regression coefficient of the standard curve is above 0.99.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Method for obtaining natural variant of enzyme and super thermostable cellobiohydrolase
InactiveUS20150259659A1Efficiently obtainedIncrease enzyme activityMicroorganismsLibrary screeningGenome databaseEnzyme
A method for selectively obtaining a natural variant of an enzyme having activity includes (1) a step of detecting an ORF sequence of a protein having enzyme activity from a genome database including base sequences of metagenomic DNA of environmental microbiota; (2) a step of obtaining at least one PCR clone including the ORF sequence having a full length, a partial sequence of the ORF sequence, or a base sequence encoding an amino acid sequence which is formed by deletion, substitution, or addition of at least one amino acid residue in an amino acid sequence encoded by the ORF sequence, by performing PCR cloning on at least one metagenomic DNA of the environmental microbiota by using a primer designed based on the ORF sequence; (3) a step of determining a base sequence and an amino acid sequence which is encoded by the base sequence for each PCR clone obtained in the step (2); and (4) a step of selecting a natural variant of an enzyme having activity by measuring enzyme activity of proteins encoded by each PCR clone obtained in the step (2).
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Pretreatment method for extracting metagenome DNA of intestinal contents
ActiveCN107475250AHigh purityPracticalMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationOmnivorePretreatment method
The invention discloses a pretreatment method for extracting metagenome DNA of intestinal contents. The pretreatment method comprises the following steps of: adding a necrotic-tissue removing agent into the intestinal contents to wash for twice, then adding nuclease eliminating solution for washing, cracking cells by adopting a freezing-thawing method and a cracking method, fully releasing DNA in the cells, finally adding protease K, SDS and RNA enzyme to remove protein, fiber and RNA in the cells, and treating products by adopting a conventional method to obtain the metagenome DNA of the intestinal contents. The pretreatment method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the effect for extracting the DNA of the metagenome DNA of the intestinal contents of omnivorous animals is obvious, and both the extracting purity and the extracting amount can meet downstream experiments such as PCR augmentation and high-throughput sequencing and the like, so that the practicability is very strong.
Owner:广东美格基因科技有限公司
An extracting method of an alveolar lavage fluid metagenome
ActiveCN106244580AEliminate distractionsHigh precisionDNA preparationAlveolar lavage fluidDna adsorption
A safe, simple, convenient, low-pollution and good-repeatability extracting method of alveolar lavage fluid metagenome DNAs is provided. The method includes steps of liquefying a sample, crushing cells, isolating target DNAs, removing impurity proteins and salt ions, performing DNA adsorption and performing DNA elution. The method can increase the yield and purity of the metagenome DNAs and can meet PCR, DNA library construction, gene sequencing, and other molecular biological experiments.
Owner:厦门基源医疗科技有限公司
Method for constructing molecular map of bactrocera dorsalis intestinal bacteria colony
InactiveCN104450917AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBacteroidesForward primer
The invention relates to a method for constructing a molecular map of a bactrocera dorsalis intestinal bacteria colony. The method comprises the following steps: extracting metagenomic DNA of bactrocera dorsalis intestinal bacteria as a template, amplifying V6-V8 hypervariable regions of 16S rDNA gene by using primer pairs 968GC and L1401, recovering an amplification product to obtain a DNA fragment library, connecting with a pMD19-T vector to obtain a recombinant plasmid library, amplifying the recombinant plasmid by using a primer pair comprising a forward primer RV-M and a reverse primer M13-47, amplifying a positive recombinant plasmid by 968GC and L1401 to obtain V6-V8 hypervariable regions of the positive recombinant plasmid 16S rDNA gene, and performing denaturing gel gradient electrophoresis to obtain the molecular map. The method is simple and practical and used for constructing the bacteria colony 16S rDNA library, and has important meaning on definition of the structure, inheritance and functional diversity of the bactrocera dorsalis intestinal bacteria colony.
Owner:江西省农业科学院农业应用微生物研究所
Method for simultaneously extracting microbial genome deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and total ribonucleic acid (RNA) in mining area environmental sample
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously extracting microbial genome deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and total ribonucleic acid (RNA) in a mining area environmental sample. The method comprises the following steps: S1, pretreatment of an environmental sample: collecting microorganisms in a liquid sample by a centrifuging method, or removing impurities out of a solid sample by a filtering method; S2, crushing cells: mixing the sample pretreated in the step S1 with quartz sand, adding liquid nitrogen, grinding for three times, adding PIPES extraction buffer of which the pH value is 7.0 and a sodium dodecyl sulfate solution, splitting cells at 65 DEG C for 1 hour; S3, purifying and participating nucleic acid: collecting supernate by the centrifuging method at the end of splitting of cells, adding an extraction agent to the supernate to centrifugally extract protein and lipids, participating the supernate by using isopropanol, and centrifuging so as to obtain the total ribonucleic acid; separating the total ribonucleic acid, so as to obtain the metagenome DNA and the total RNA. The method is low in cost and is capable of simultaneously extracting the metagenome DNA and the total RNA with high purity and good integrity from the mining area environmental sample.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for constructing metagenomic Fosmid library of soil microorganisms in tropical rainforest
InactiveCN107475244AEasy to digEfficient use ofBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFosmidLow voltage
The invention belongs to the field of microorganisms, and discloses a method for constructing a metagenomic Fosmid library of soil microorganisms in a tropical rainforest. The method comprises the following steps: washing by using cross-linked polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVPP), removing impurities, and then adopting a lysozyme-protease K-SDS-CTAB lysis method to extract and purify deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) in large fragments of soil microbial genomes; carrying out agarose gel low-voltage electrophoresis detection and pulsed electrophoresis detection; carrying out tail end repairing on the metagenomic DNA, cutting off a marker and a small sample, and using ligase to enable a recycled product to be ligated with pCC1FOS of a Fosmid carrier; carrying out a ligation reaction within 2h; packing a ligation product with a lambda packaging extract, carrying out transfection by using an EPI300-T1R strain, coating an LB flat plate, which contains 12.5mu g / ml of chloramphenicol, with a product of the transfection, and culturing overnight at the temperature of 37 DEG C. The method provided by the invention reflects that in the extreme environment of the tropical rainforest, the microorganisms and genetic resources thereof are extremely rich and abundant; the method is beneficial to the excavation and utilization of functional genes of the microorganisms.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION HAINAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
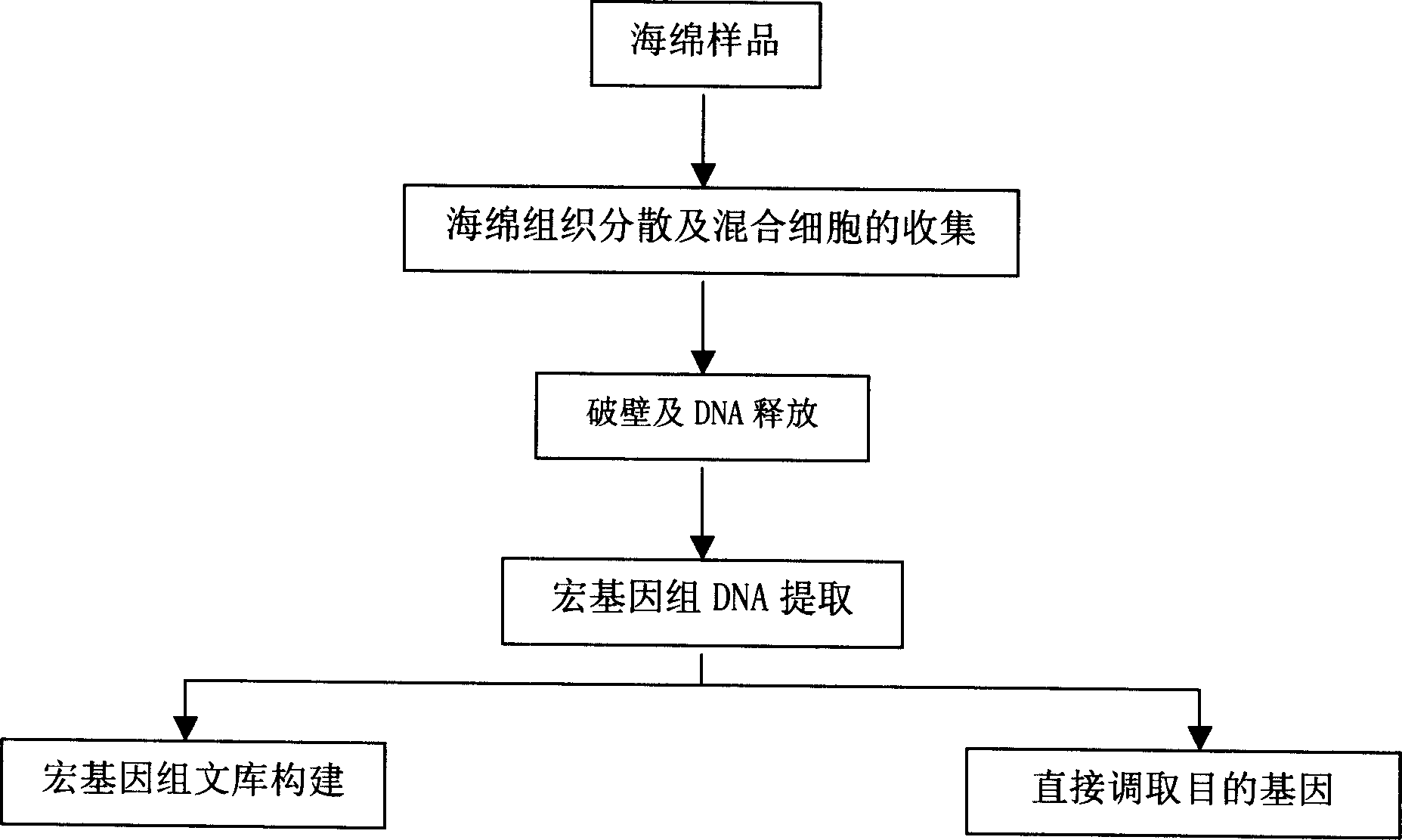
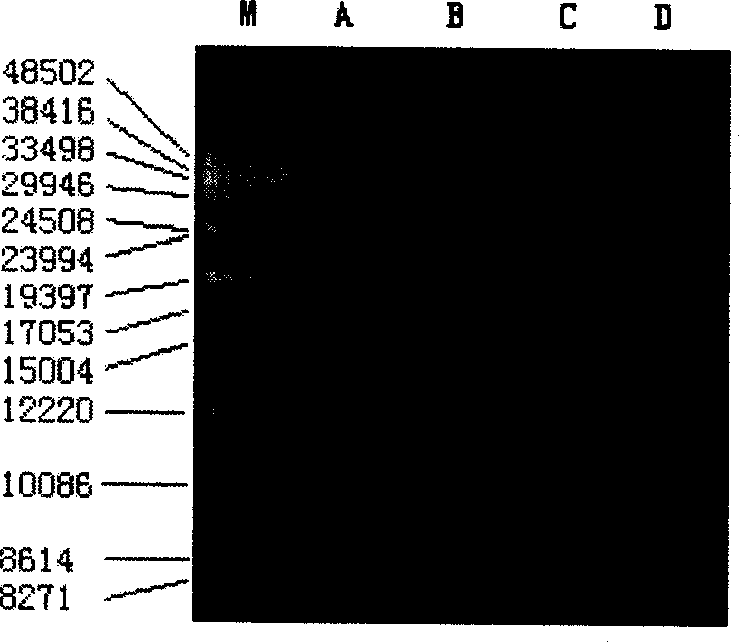
Quick extracting method for large fragment sponge macro genome DNA
InactiveCN1821402AMeet research needsSimple methodFermentationPlant genotype modificationSodium acetateEthylenediamine
The quick extracting process of large fragment sponge macro genome DNA includes the following steps: soaking sponge in artificial sea water without Ca and Mg, tearing the sponge into small blocks of 1-3 cu mm, soaking to disperse sponge cell and epicole microbes inside the solution, stilling, taking the mixed cell suspension from the upper layer; adding alkali wall-breaking buffer solution comprising EDTA and sodium dodecyl sarcosinate and Ca2+ containing proteinase K solution to digest cell wall; extracting DNA with the mixed solution of Tris-saturated phenol, chloroform and isoamyl alcohol and mixed solution of chloroform and isoamyl alcohol; adding sodium acetate to obtain DNA precipitate, washing with 70-75 % concentration alcohol ethanol solution, drying, dissolving in TE buffer solution, slaking RNA with RNase enzyme and detecting DNA in agar-sugar gel electrophoresis. The present invention is simple, fast and suitable for extracting sponge macro genome DNA with over 40000 bases.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Metagenome fragment attribute reduction and classification method based on neighbourhood rough set
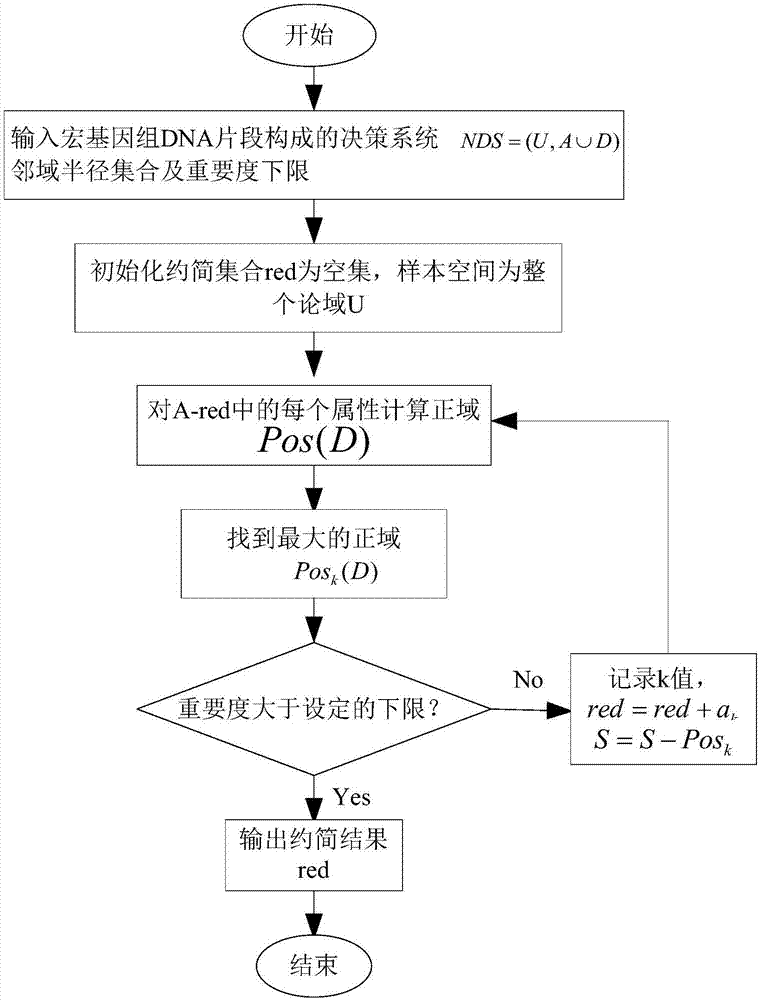
InactiveCN107423580AEffective classificationReduce data volumeBiostatisticsProteomicsLower limitGenomic Segment
The invention relates to a metagenome fragment attribute reduction and classification method based on a neighbourhood rough set. The method comprises the following steps that: A: randomly obtaining the whole genome sequence of microbial flora, taking the amount and the dimension of each DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) fragment as condition attributes, and randomly selecting a line and a row as corresponding identification for representing each DNA fragment to serve as a decision attribute so as to form a decision table; B: taking an initial reduction set as an empty set, taking a sample as a whole domain of discourse, calculating the attribute importance degrees of all residual attributes each time, and adding the attribute with the highest attribute importance degree into the reduction set until the attribute importance degrees of all residual attributes are smaller than the lower limit of the set attribute importance degree; and C: classifying the low-dimension genes of the reduced metagenome DNA fragment in the B. Under a situation that the metagenome fragment is not assembled, the metagenome fragment is reduced to obtain classification accuracy which is the same with or higher than classification accuracy before reduction is carried out.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Extracting method for metagenome DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
The invention provides a method for extracting metagenomic DNA. The extraction method comprises the following steps: firstly, adding a buffer solution and proteinase K to a sample to be tested to obtain a mixed solution, and heating the mixed solution so that the buffer solution and proteinase K are cracked. The host cells in the test sample are further heated to inactivate proteinase K, and then the microbes are broken by beating, and then the DNA is extracted to obtain the metagenomic DNA. In the invention, the lysate is firstly added to suspend the host cell, and then proteinase K is added to degrade the protein of the host cell and free the DNA. Due to the absence of lysozyme and external force, bacterial microorganisms can maintain a complete form. In the process of beating to break the microbial wall, on the one hand, the bacteria and microorganisms are broken, and on the other hand, the host DNA is broken into small fragments or even degraded. Finally, the metagenomic DNA is extracted according to the conventional method, which can reduce the background interference of the host DNA .
Owner:SHANGHAI MAJORBIO BIO PHARM TECH
Method for obtaining biomass conversion related genes from anaerobic fermentation system
InactiveCN102146368AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationMicroorganismDNA fragmentation
The invention relates to a method for obtaining biomass conversion related genes from an anaerobic fermentation system. The method comprises the steps of extracting a metagenomic DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) from an anaerobic microbial community, collecting DNA fragments, connecting the DNA fragments into a carrier, packaging and transfecting into cells to obtain cell clones carrying the DNA fragments; screening cell clones with biomass conversion characters from the obtained cell clones, wherein the clones carry biomass conversion related genes; and identifying or separating the biomass conversion related genes in the obtained clones with the biomass conversion characters. In the invention, without culturing of microbes in the anaerobic microbial community, the metagenomic DNA in the anaerobic microbial community is directly used for screening gene resources of biomass conversion related enzymes. The method is also specific to all microbes in the anaerobic fermentation community and has the advantages of culture deprivation, high pass and low cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for obtaining natural variant of enzyme and super thermostable cellobiohydrolase
InactiveUS9944914B2Efficiently obtainedIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaLibrary screeningGenome databasePcr cloning
A method for selectively obtaining a natural variant of an enzyme having activity includes (1) a step of detecting an ORF sequence of a protein having enzyme activity from a genome database including base sequences of metagenomic DNA of environmental microbiota; (2) a step of obtaining at least one PCR clone including the ORF sequence having a full length, a partial sequence of the ORF sequence, or a base sequence encoding an amino acid sequence which is formed by deletion, substitution, or addition of at least one amino acid residue in an amino acid sequence encoded by the ORF sequence, by performing PCR cloning on at least one metagenomic DNA of the environmental microbiota by using a primer designed based on the ORF sequence; (3) a step of determining a base sequence and an amino acid sequence which is encoded by the base sequence for each PCR clone obtained in the step (2); and (4) a step of selecting a natural variant of an enzyme having activity by measuring enzyme activity of proteins encoded by each PCR clone obtained in the step (2).
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Method for directionally and rapidly screening lactobacillus plantarum capable of producing bile salt hydrolase
InactiveCN108148773AReduce blindnessReduce workloadBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMolecular identificationBile salt hydrolase
The invention discloses a method for directionally and rapidly screening lactobacillus plantarum capable of producing bile salt hydrolase, and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The invention comprises the following steps: (1) taking metagenome DNA of a sample as a template, performing PCR amplification on BSHL / BSHR by utilizing a primer, and screening to obtain the sample with a BSH gene; (2) taking the sample as a separating object, and purifying to obtain a suspected plant lactobacillus strain; (3) taking the strain genome DNA as a template, performing PCR amplification on the BSHL / BSHR by utilizing the primer, and screening to obtain a suspected strain with the BSH gene; (4) performing molecular identification on the strain and screening to obtain the lactobacillus plantarum capable of producing bile salt hydrolase. According to the method, most samples which do not contain the lactobacillus plantarum capable of producing the BSH can be filtered out through the firststep of amplification of metagenome-specific fragments, so that blind screening is avoided, the screening range is greatly reduced, and the method has the advantages of directionality, rapidness, easiness, convenience, low workload and the like.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Oral throat swab bacterial metagenome DNA extraction method
ActiveCN106047868AEfficient extractionQuick extractionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationGenomic DNAMetagenomic dna
The present invention provides an oral throat swab bacterial metagenome DNA extraction method, which comprises five steps such as oral throat swab pretreatment, bacterial lysis, DNA separation and hybrid protein removing, adsorption of DNA through a silica gel membrane purification column and impurity removal, and elution of DNA so as to extract the oral throat swab bacterial genome DNA. According to the present invention, with the special sample treatment method, the yield can be substantially increased; the combination of ultrasonic wave crack cleavage and enzyme cleavage is used, and the appropriate wall breaking time and the mild conditions are used, such that the gram-negative bacteria, the gram-positive bacteria and other bacteria are subjected to appropriate wall breaking, and the breaking of the genomic DNA due to the excessive strong physical factors can not be produced; and the oral throat swab bacterial metagenome DNA can be extracted only in 1.5 h, and the bacterial metagenome yield is high.
Owner:厦门基源医疗科技有限公司
Extraction method for metagenome
InactiveCN103060309BEfficient enrichmentReduce high background distractionsDNA preparationConserved sequenceStreptavidin
The present invention discloses an extraction method for metagenome, and a method of probe hybridization-bead capture is used to reduce the host DNA content in a host metagenomic DNA sample. According to the method, the Alu repeat sequence of the host DNA sequences and conserved sequence at both ends thereof are used as templates to design one-way or two-way probes, wherein the 5 'end of each probe is modified with biotin, streptavidin coated beads are used to capture host DNA hybridized with probes, in order to achieve aims of weakening host DNA background in a metagenome, and enhancing sequencing data efficiency.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION +1
Method for separating metagenome deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and total ribonucleic acid (RNA) of microorganism
InactiveCN103642799AEfficient separationQuality improvementDNA preparationLithium chlorideOrganic solvent
The invention relates to the technical field of separation of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) and discloses a method for separating metagenome DNA and total RNA of a microorganism. The method comprises the following steps: S1, extracting total ribonucleic acid, namely preparing cell lysis buffer, removing protein and lipids from the cell lysis buffer by using an organic solvent; S2, separating total RNA, namely adding a lithium chloride solution to the total ribonucleic acid in the step S1, separating out the total RNA by adopting a centrifuging method after standing at a low temperature, and transferring and placing the metagenome DNA in supernate; S3, participating the metagenome DNA, namely taking out the supernate transferred and placed in the step S2, participating the metagenome DNA in the supernate by using pre-cooled isopropanol or ethanol, and separating out the metagenome DNA by adopting the centrifuging method after stewing at low temperature; S4, purifying the metagenome DNA and the total RNA, washing and purifying the total RNA and the metagenome DNA obtained in the steps S2 and S3 by adopting ethanol, and obtaining the purified total RNA and metagenome DNA by adopting the centrifuging method. The method has the advantages of being good in separation effect, high in recovery rate, low in cost, and simple in operation.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
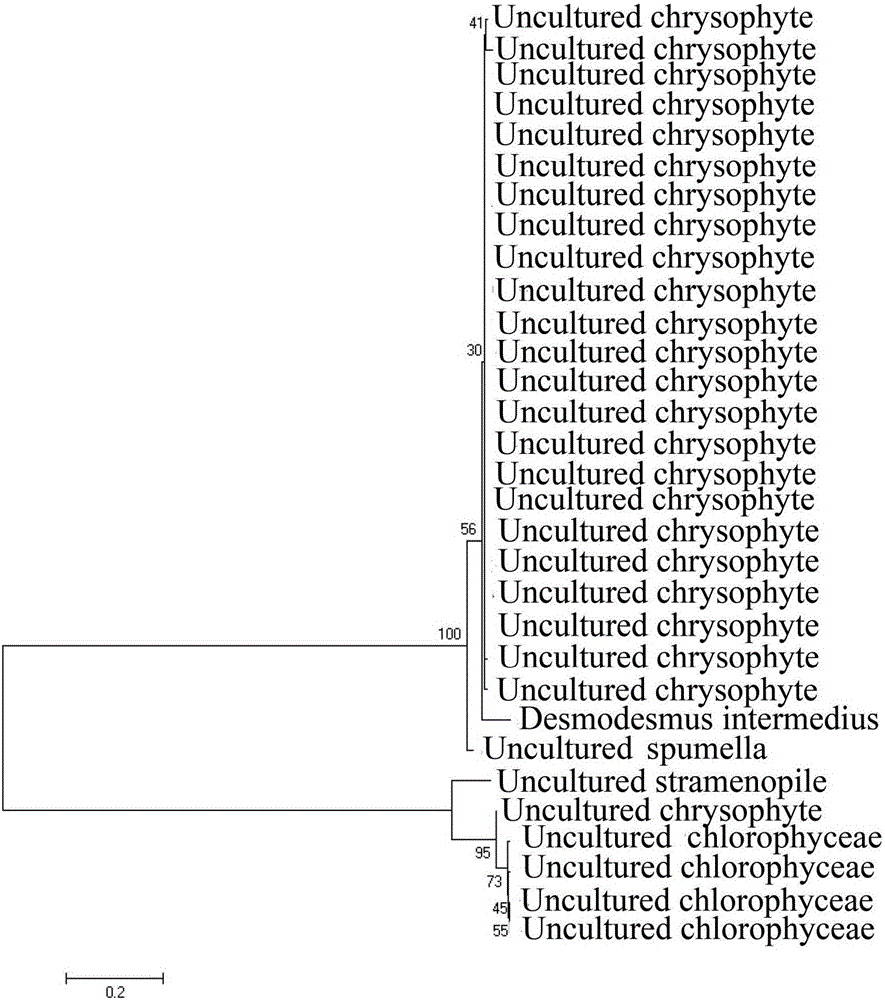
Primers and method for identifying diversity of eukaryotic algae in activated sludge of epoxypropane saponified wastewater
InactiveCN106048058AEffective separation and identificationSimple stepsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationActivated sludgeNucleotide
The invention relates to primers and a method for identifying the diversity of eukaryotic algae in activated sludge of epoxypropane saponified wastewater. There is a pair of the primers. The upstream primer nucleotide sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1, and the downstream primer nucleotide sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. The invention also relates to a method for identifying the diversity of eukaryotic algae in activated sludge of epoxypropane saponified wastewater. By the design of the eukaryotic algae-specific primers, metagenome DNA of the activated sludge of epoxypropane saponified wastewater can undergo specific amplification to obtain different eukaryotic algae. Then, eukaryotic algae species in the activated sludge can be identified.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Method for extracting metagenome DNA from endosymbiotic bacterium mycetocyte of bemisia tabaci
The invention discloses a method for extracting metagenome DNA from endosymbiotic bacterium mycetocyte of bemisia tabaci. The method comprises the following steps: treating a mycetocyte extract containing the endosymbiotic bacteria of the bemisia tabaci by using a denaturing solution, adding protease and lysozyme to crack, adding an SDS solution to treat, adding an extraction agent, precipitating the extracted supernate by using isopropanol and finally purifying by using a nucleic acid adsorption resin to obtain the DNA. The method for directly extracting the metagenome DNA, disclosed by the invention, is simple in whole process, needs no valuable drugs and is relatively economic and practical; by means of the method, high-purity microbiological metagenome DNA with the molecular size above 30kb can be extracted from the endosymbiotic bacterium mycetocyte of the bemisia tabaci; and the method is particularly suitable for the extraction of the metagenome DNA from endosymbiotic bacterium extracts of insects and is also suitable for the extraction of the metagenome DNA from some other microbiological samples at the same time.
Owner:YANAN UNIV
A method for extracting bacterial metagenomic DNA from oral and pharyngeal swabs
ActiveCN106047868BEfficient extractionQuick extractionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationGenomic DNAHybrid protein
The present invention provides an oral throat swab bacterial metagenome DNA extraction method, which comprises five steps such as oral throat swab pretreatment, bacterial lysis, DNA separation and hybrid protein removing, adsorption of DNA through a silica gel membrane purification column and impurity removal, and elution of DNA so as to extract the oral throat swab bacterial genome DNA. According to the present invention, with the special sample treatment method, the yield can be substantially increased; the combination of ultrasonic wave crack cleavage and enzyme cleavage is used, and the appropriate wall breaking time and the mild conditions are used, such that the gram-negative bacteria, the gram-positive bacteria and other bacteria are subjected to appropriate wall breaking, and the breaking of the genomic DNA due to the excessive strong physical factors can not be produced; and the oral throat swab bacterial metagenome DNA can be extracted only in 1.5 h, and the bacterial metagenome yield is high.
Owner:厦门基源医疗科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com