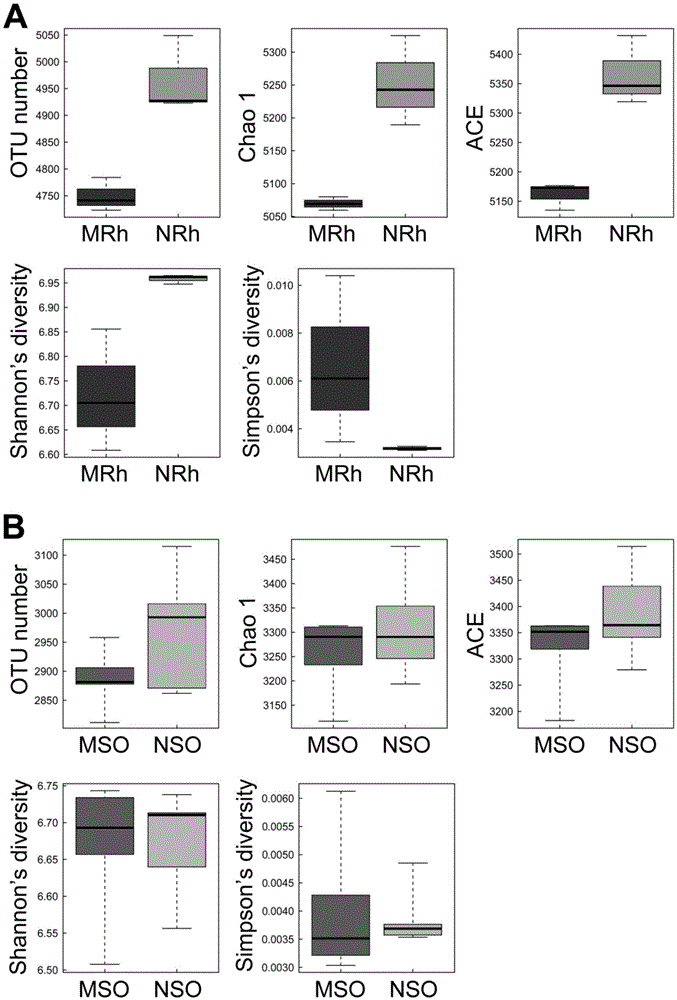
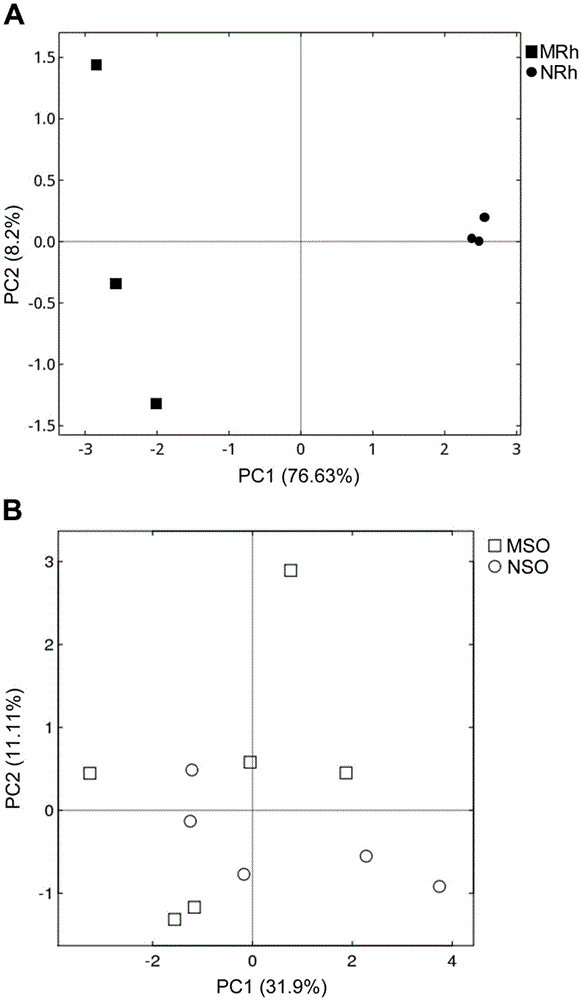
Method for detecting rhizosphere soil prokaryotic microorganisms of various soybeans based on 16SrDNA deep sequencing
A technology of prokaryotic microorganisms and deep sequencing, which is applied in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc. It can solve the problems of low detection throughput, small scale, and low coverage of non-culturable microorganisms, and achieve low cost and low cost. Low, reliable results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026] 1. Soybean material: Mengdou 12; NZL06-698 contains EPSPS herbicide tolerance gene.
[0027] 2. Field trial design:
[0028] The field test site is in Gongzhuling City, Jilin Province, and each genotype soybean is planted in three or more plots, and the area of each plot is not less than 12m 2 (4m×3m). Each plot has two sampling points, and each sampling point takes two or more plants.
[0029] 3. Sample collection
[0030] First remove ground weeds and litter, remove about 1cm of topsoil on the surface of the field soil, and then take out the soybean plants in the blooming stage (or seedling stage, bulging stage, and mature stage) from the soil and shake it off. Method to take root shaking soil as a system control, mix well and remove root hairs, etc., and store at minus 70°C (at least minus 20°C); then use stroke method to remove the rhizosphere soil that is tightly attached to soybean roots, mix well and remove Root hair, etc., and store at minus 70°C.
[0031] 4. Extract...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com