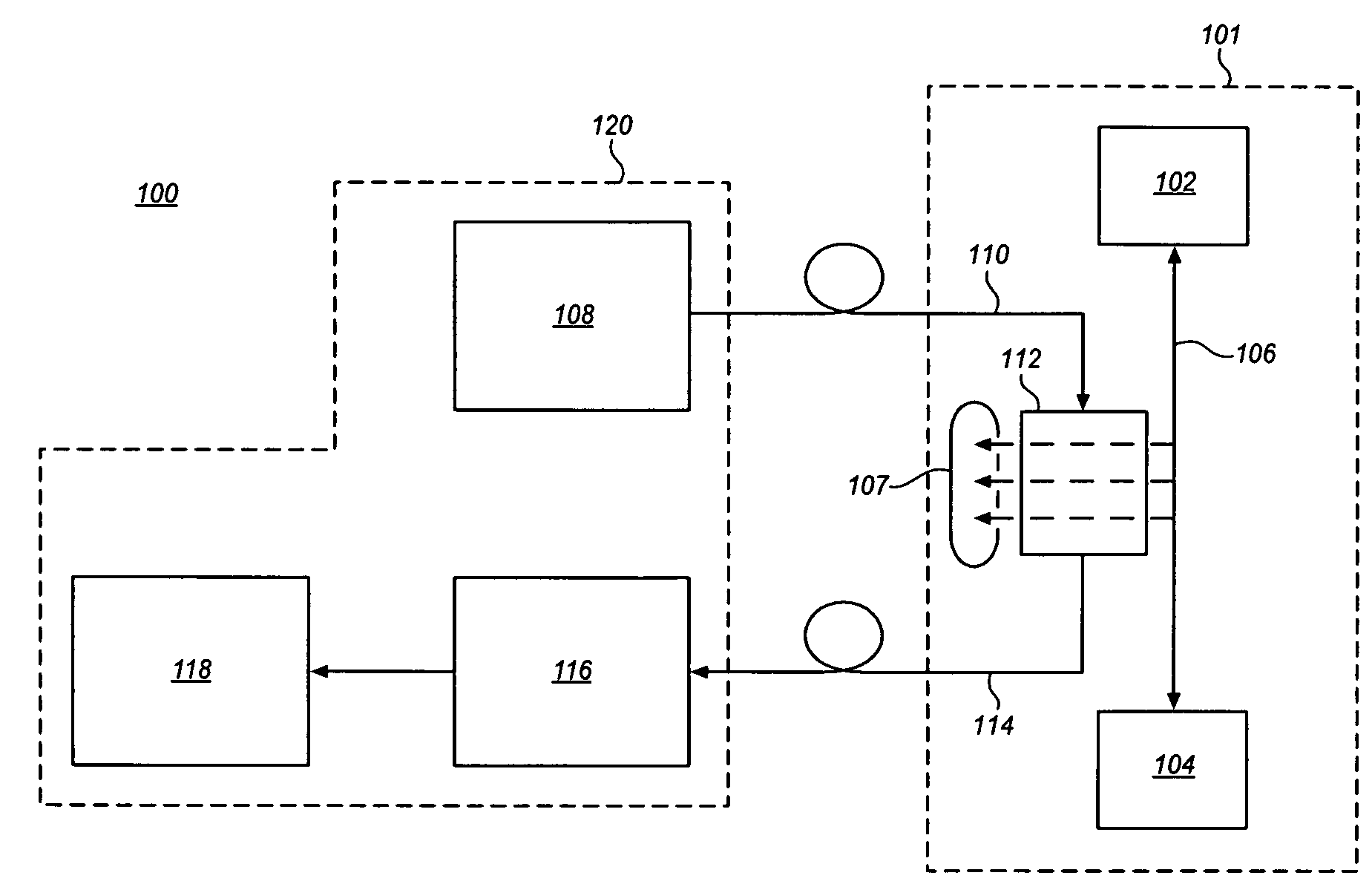
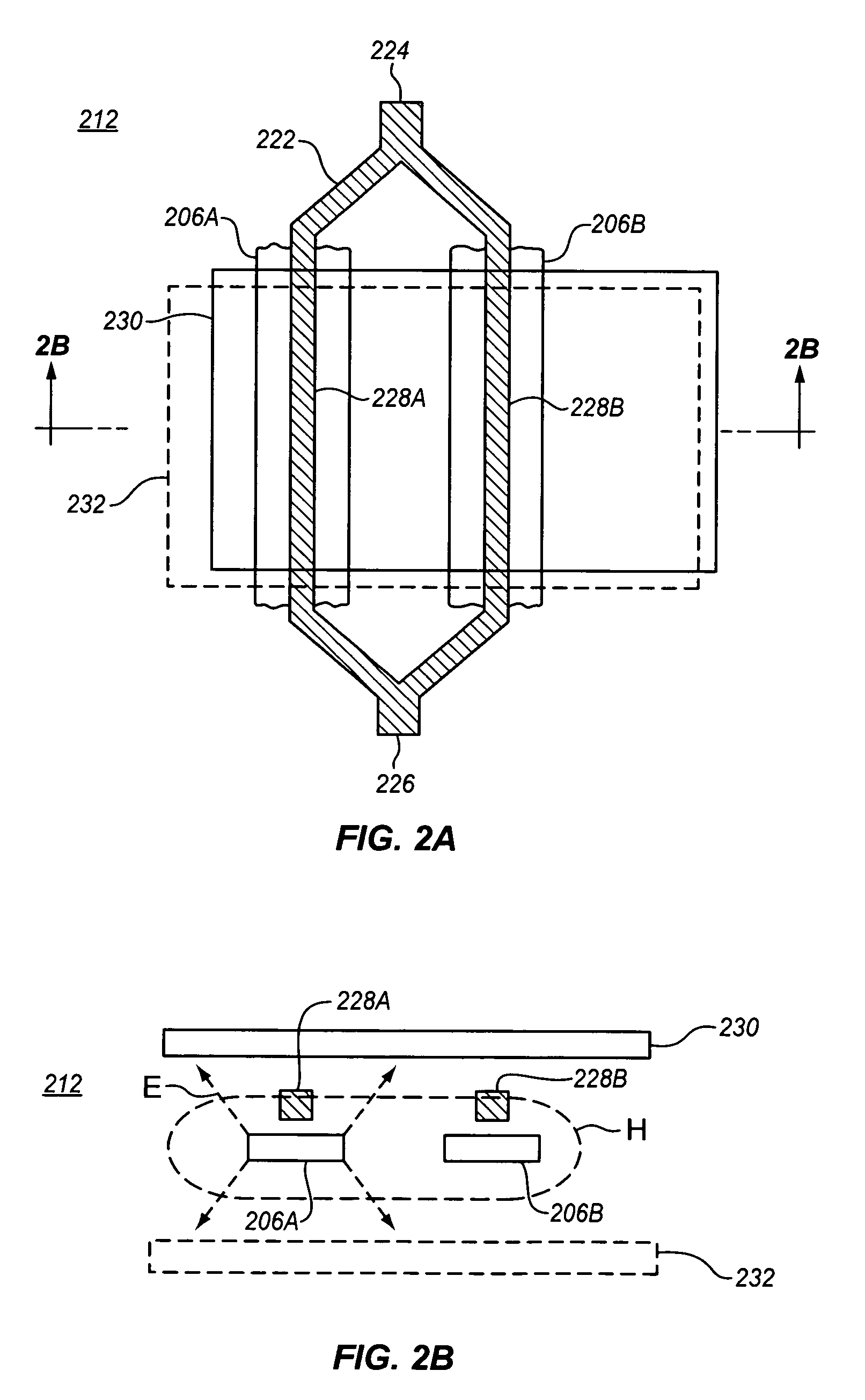
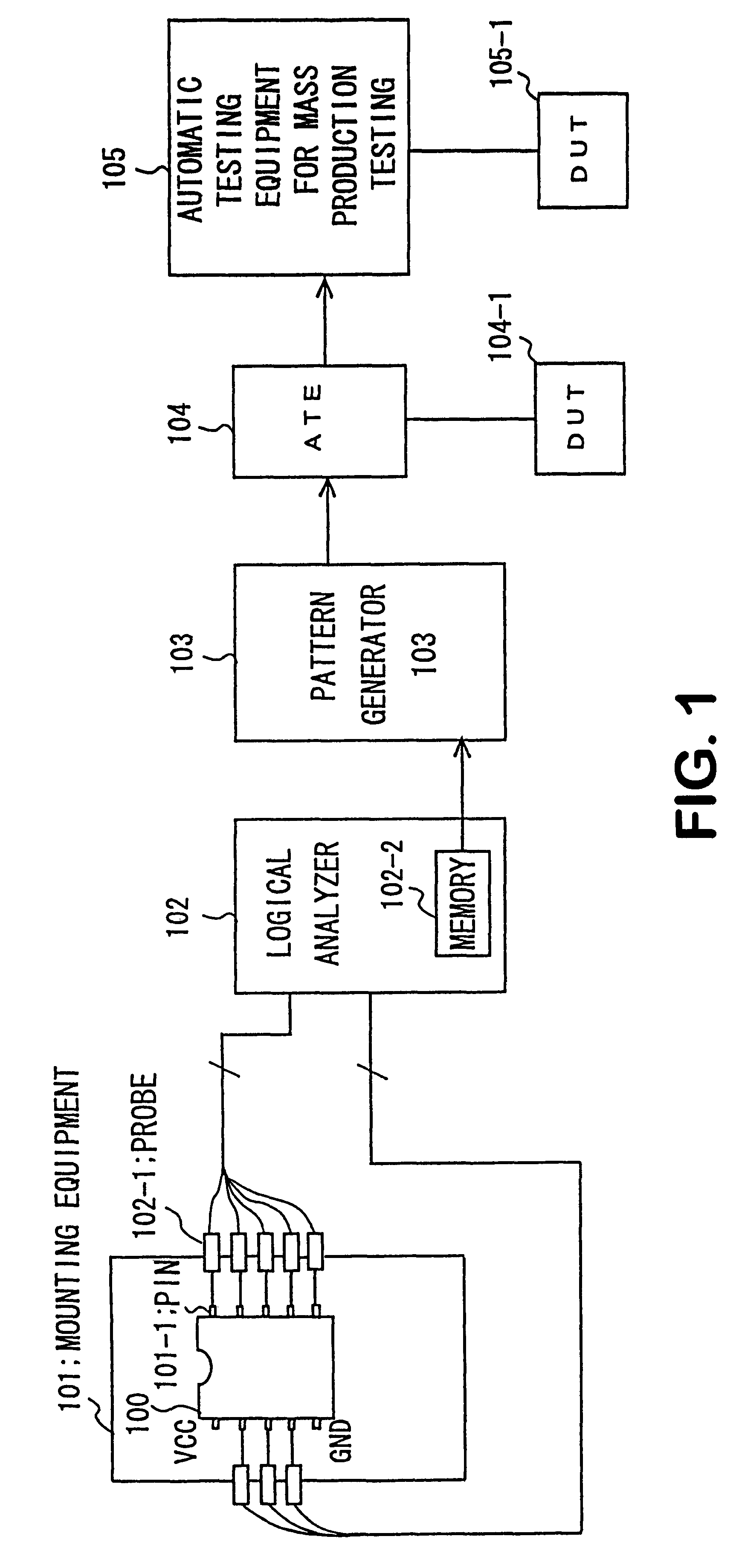
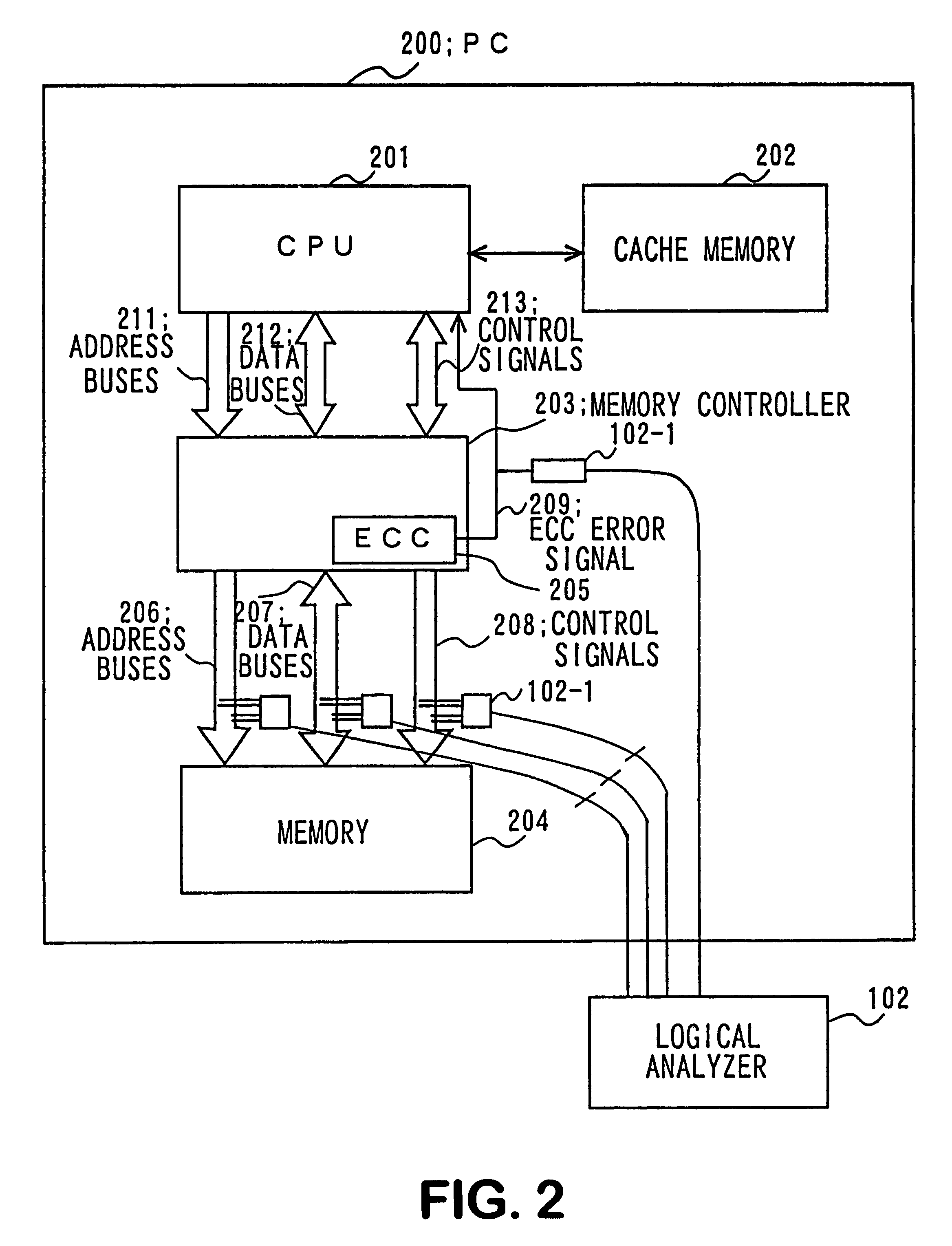
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
280 results about "Logic analyzer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A logic analyzer is an electronic instrument that captures and displays multiple signals from a digital system or digital circuit. A logic analyzer may convert the captured data into timing diagrams, protocol decodes, state machine traces, assembly language, or may correlate assembly with source-level software. Logic analyzers have advanced triggering capabilities, and are useful when a user needs to see the timing relationships between many signals in a digital system.
Adaptive compression and decompression of bandlimited signals
InactiveUS7009533B1Less bandwidthLess storageCode conversionPictoral communicationAdaptive compressionSpectrum analyzer
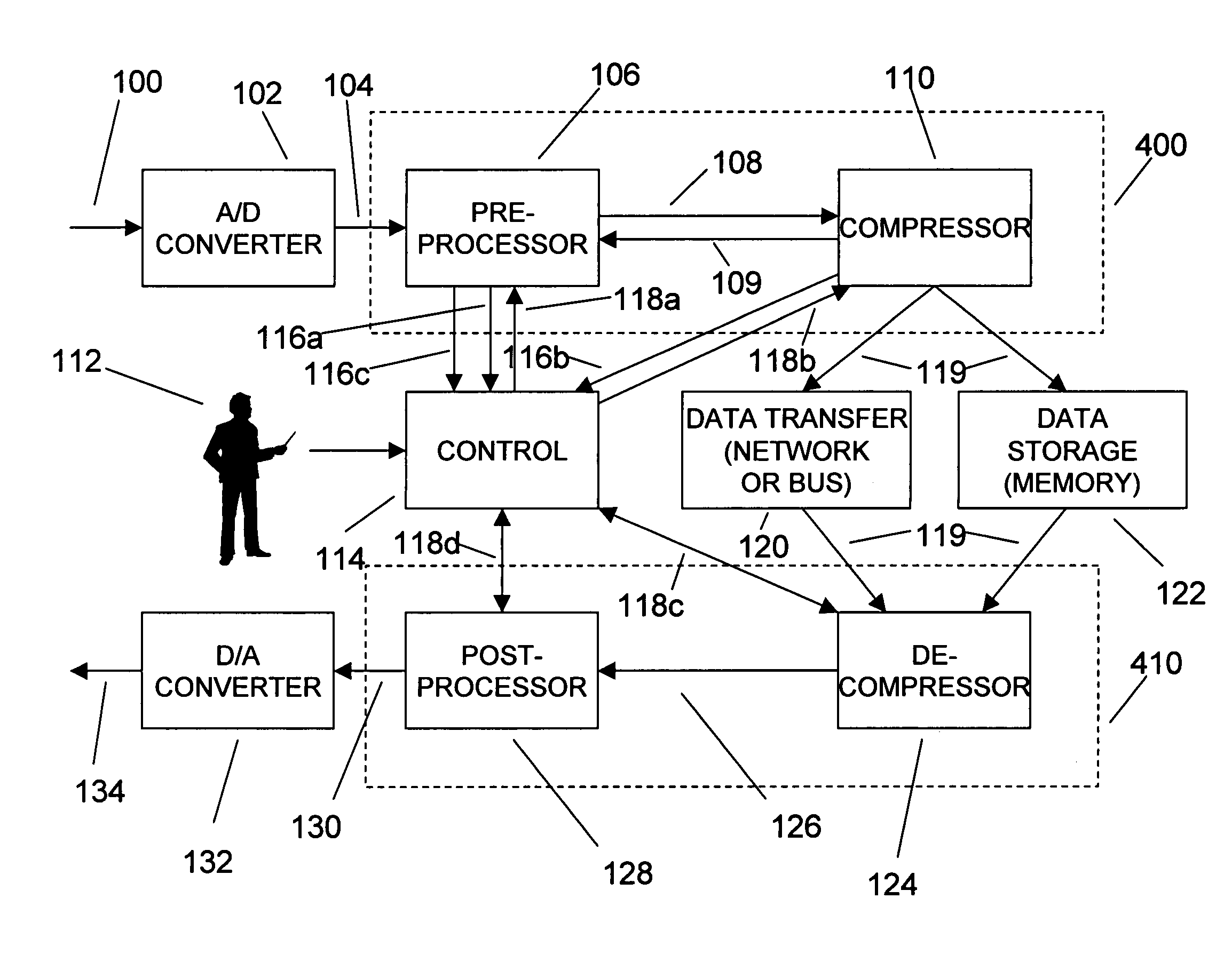
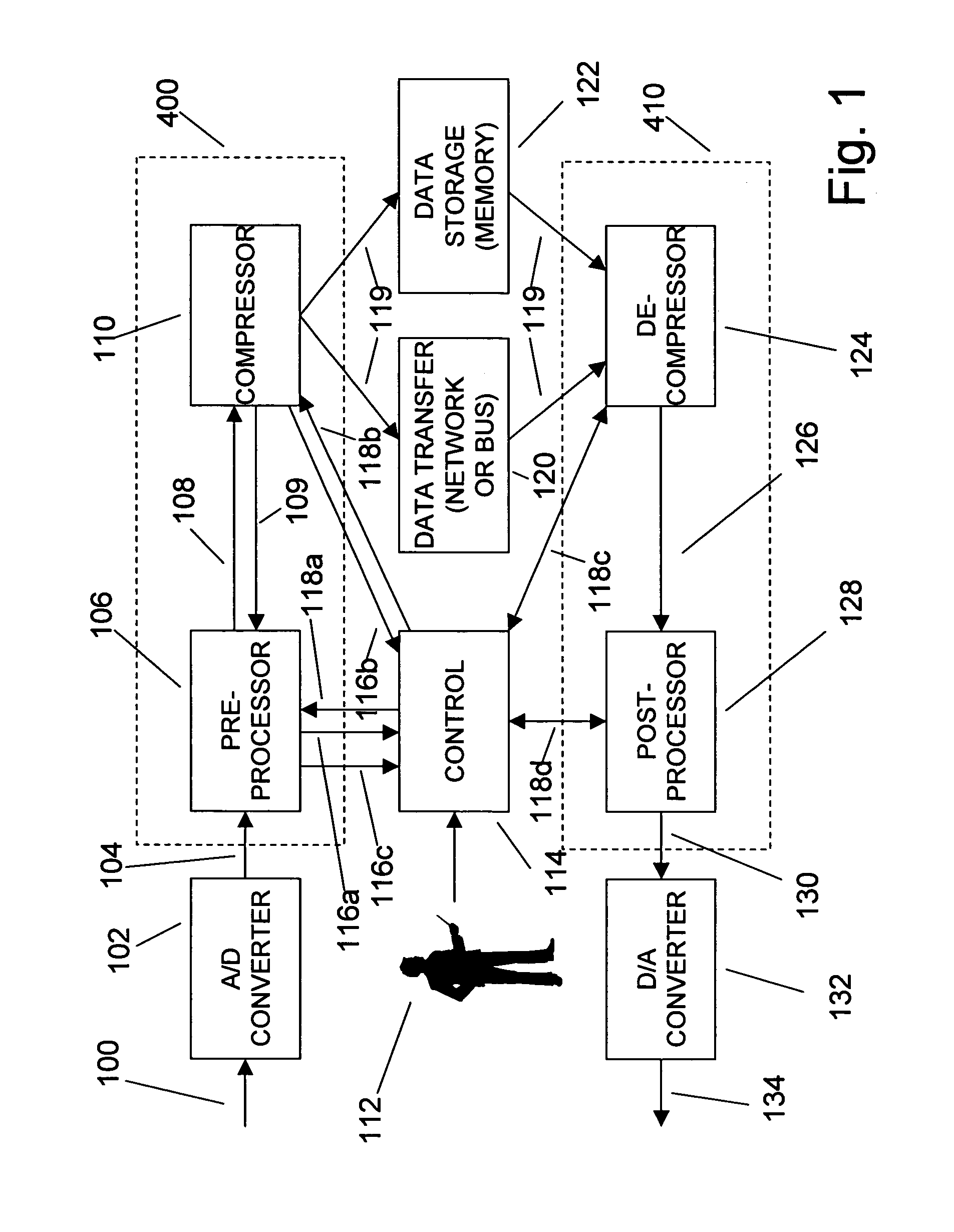
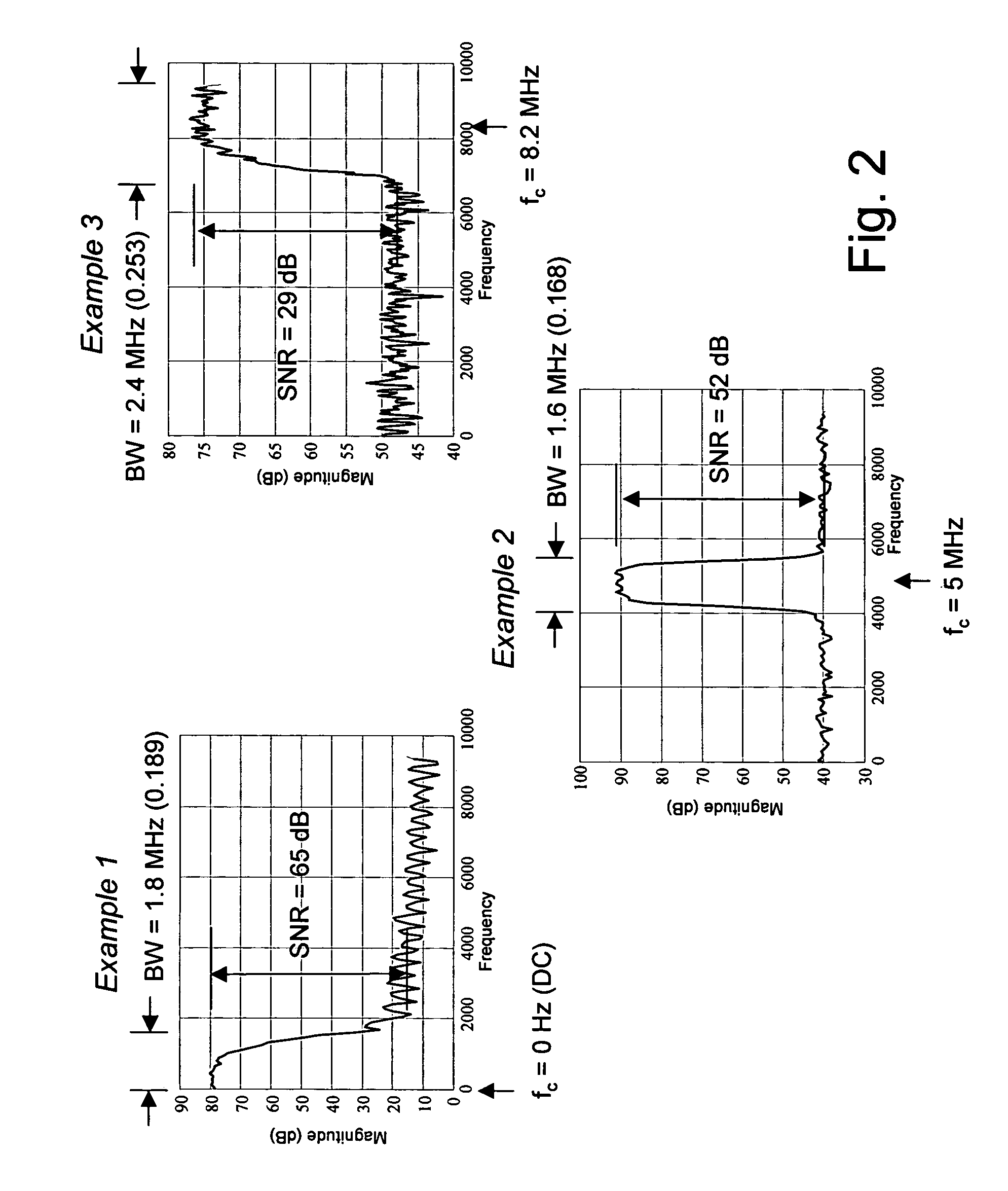
An efficient method for compressing sampled analog signals in real time, without loss, or at a user-specified rate or distortion level, is described. The present invention is particularly effective for compressing and decompressing high-speed, bandlimited analog signals that are not appropriately or effectively compressed by prior art speech, audio, image, and video compression algorithms due to various limitations of such prior art compression solutions. The present invention's preprocessor apparatus measures one or more signal parameters and, under program control, appropriately modifies the preprocessor input signal to create one or more preprocessor output signals that are more effectively compressed by a follow-on compressor. In many instances, the follow-on compressor operates most effectively when its input signal is at baseband. The compressor creates a stream of compressed data tokens and compression control parameters that represent the original sampled input signal using fewer bits. The decompression subsystem uses a decompressor to decompress the stream of compressed data tokens and compression control parameters. After decompression, the decompressor output signal is processed by a post-processor, which reverses the operations of the preprocessor during compression, generating a postprocessed signal that exactly matches (during lossless compression) or approximates (during lossy compression) the original sampled input signal. Parallel processing implementations of both the compression and decompression subsystems are described that can operate at higher sampling rates when compared to the sampling rates of a single compression or decompression subsystem. In addition to providing the benefits of real-time compression and decompression to a new, general class of sampled data users who previously could not obtain benefits from compression, the present invention also enhances the performance of test and measurement equipment (oscilloscopes, signal generators, spectrum analyzers, logic analyzers, etc.), busses and networks carrying sampled data, and data converters (A / D and D / A converters).
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Graphical user interface with logic unifying functions
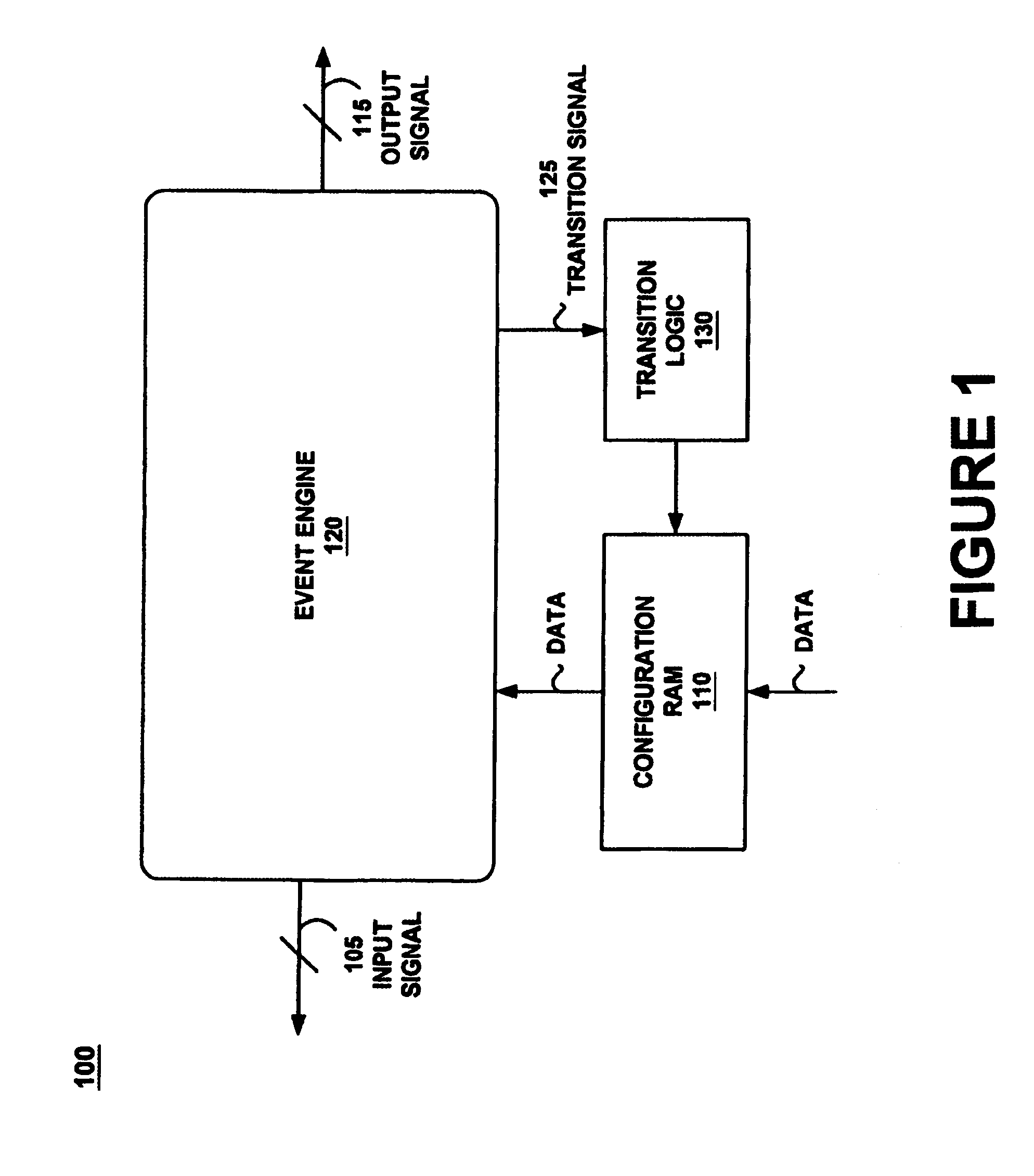
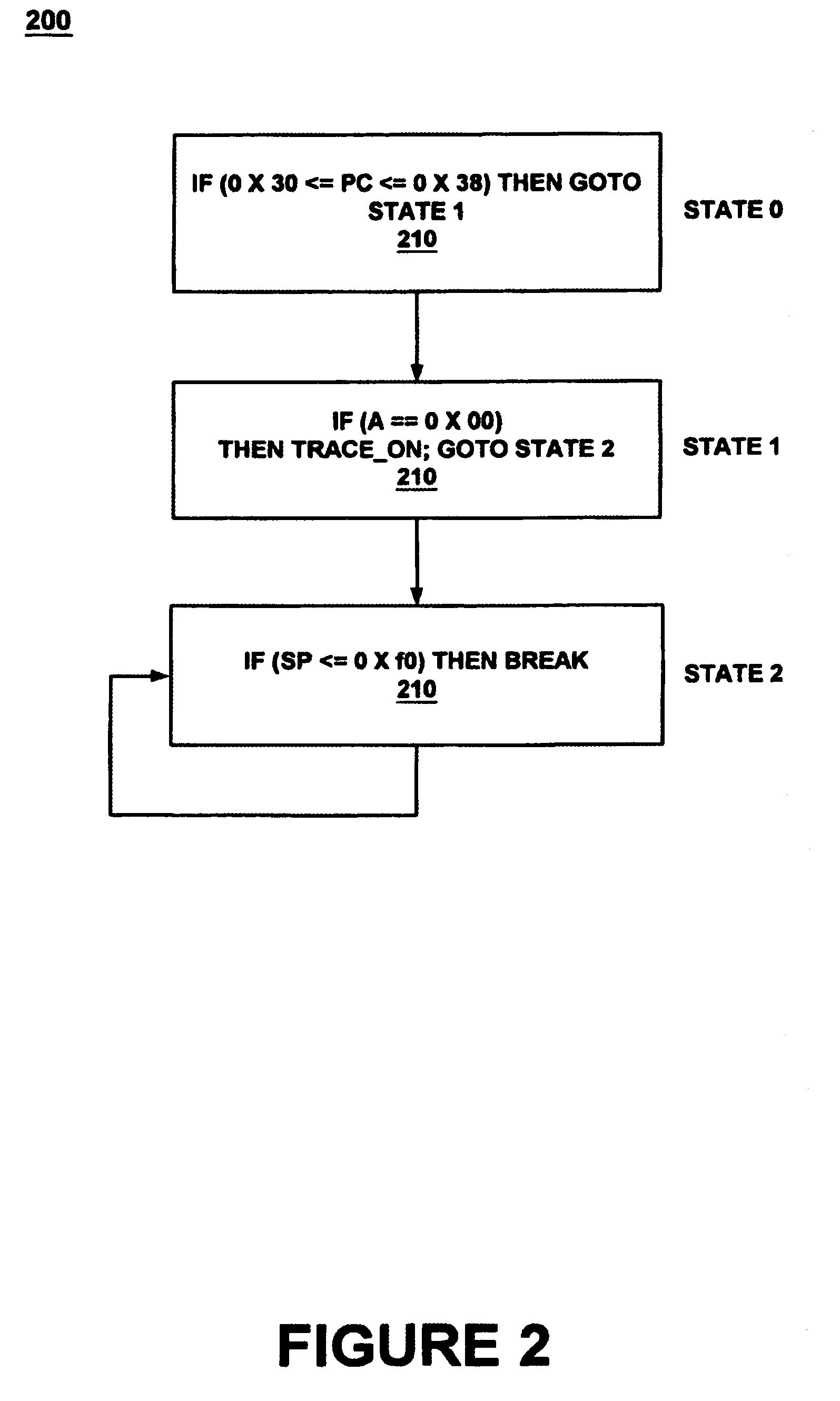
ActiveUS7150002B1Easy programmingError detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsGraphical user interfaceSoftware engineering
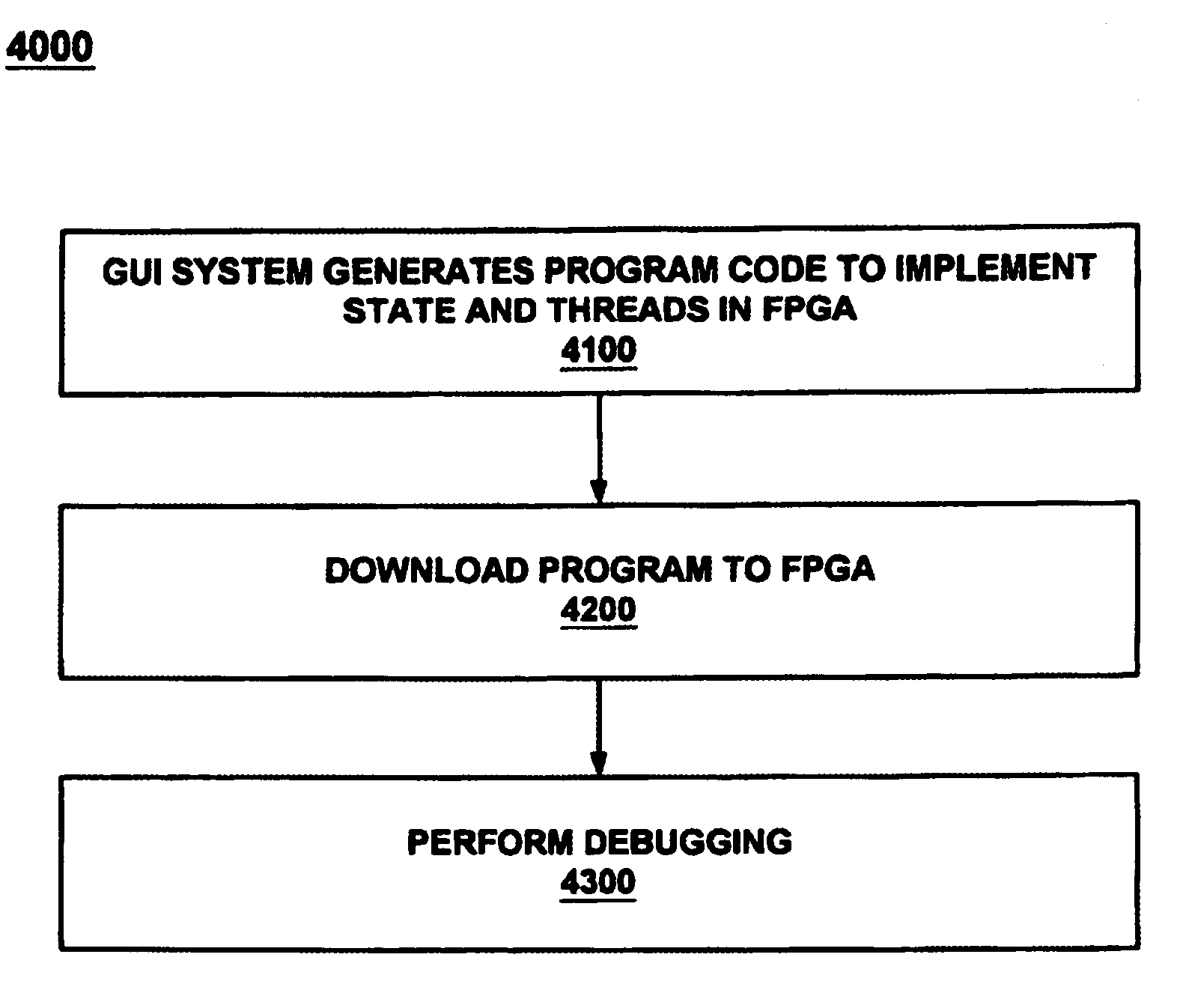
Programming a plurality of states having respective threads is achieved by an event engine and a computer controlled GUI causing the event engine to monitor a signal and execute an action based thereon. The GUI programs an event and several states and causes the event engine to traverse between the states upon reaching the event. The GUI further programs a logic chain which unifies the threads. A method unifies several threads by selecting and executing a logic operation. The method further configures several states and causes traversing between them. The GUI may be deployed co-functionally with debuggers, logic analyzers, scopes, utilities, and software development tools. The results of the GUI are automatically transformed into program code which programs the event engine to operate during debug of a device under test by monitoring for events and taking action based thereon.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Captured synchronous DRAM fails in a working environment
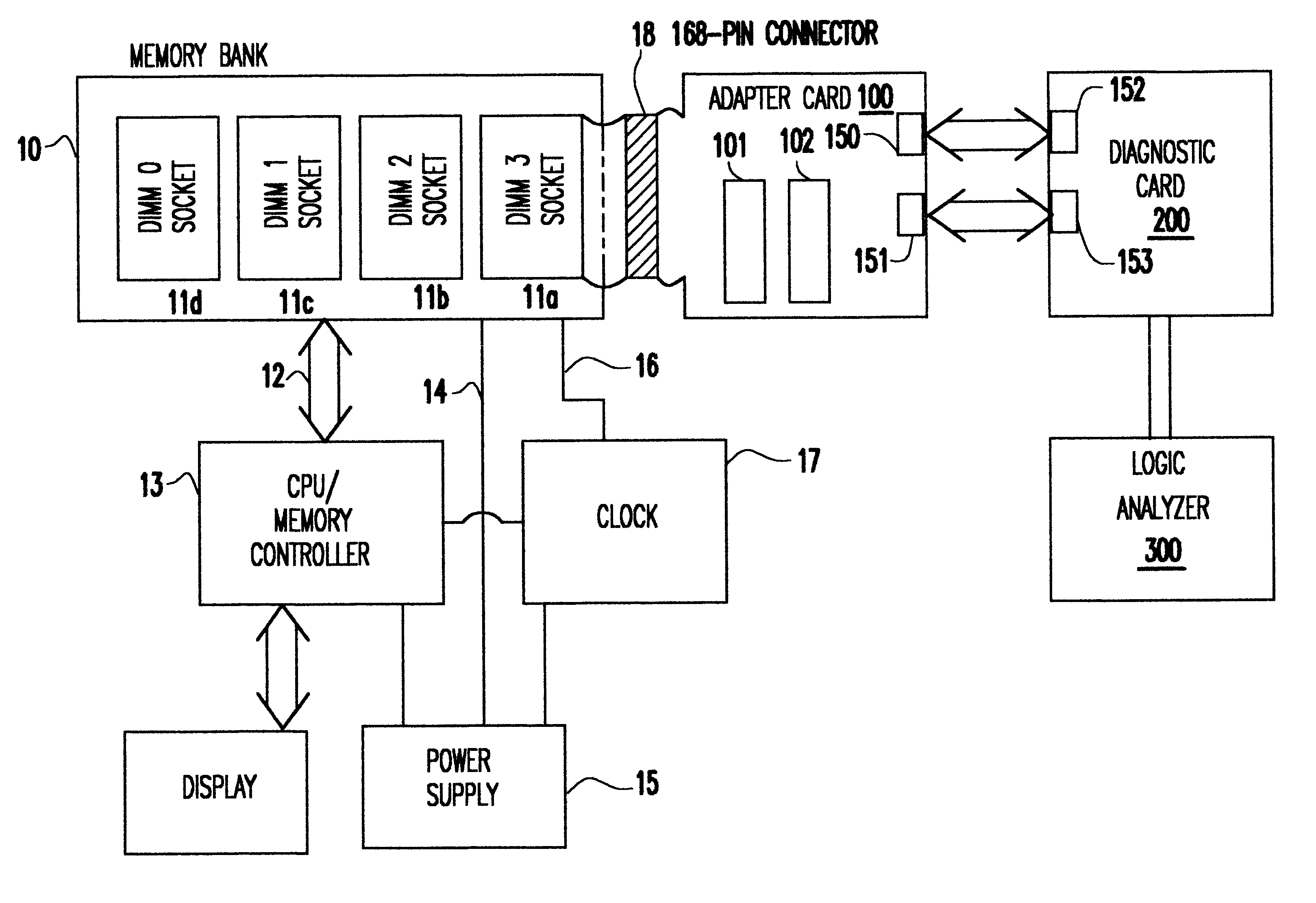
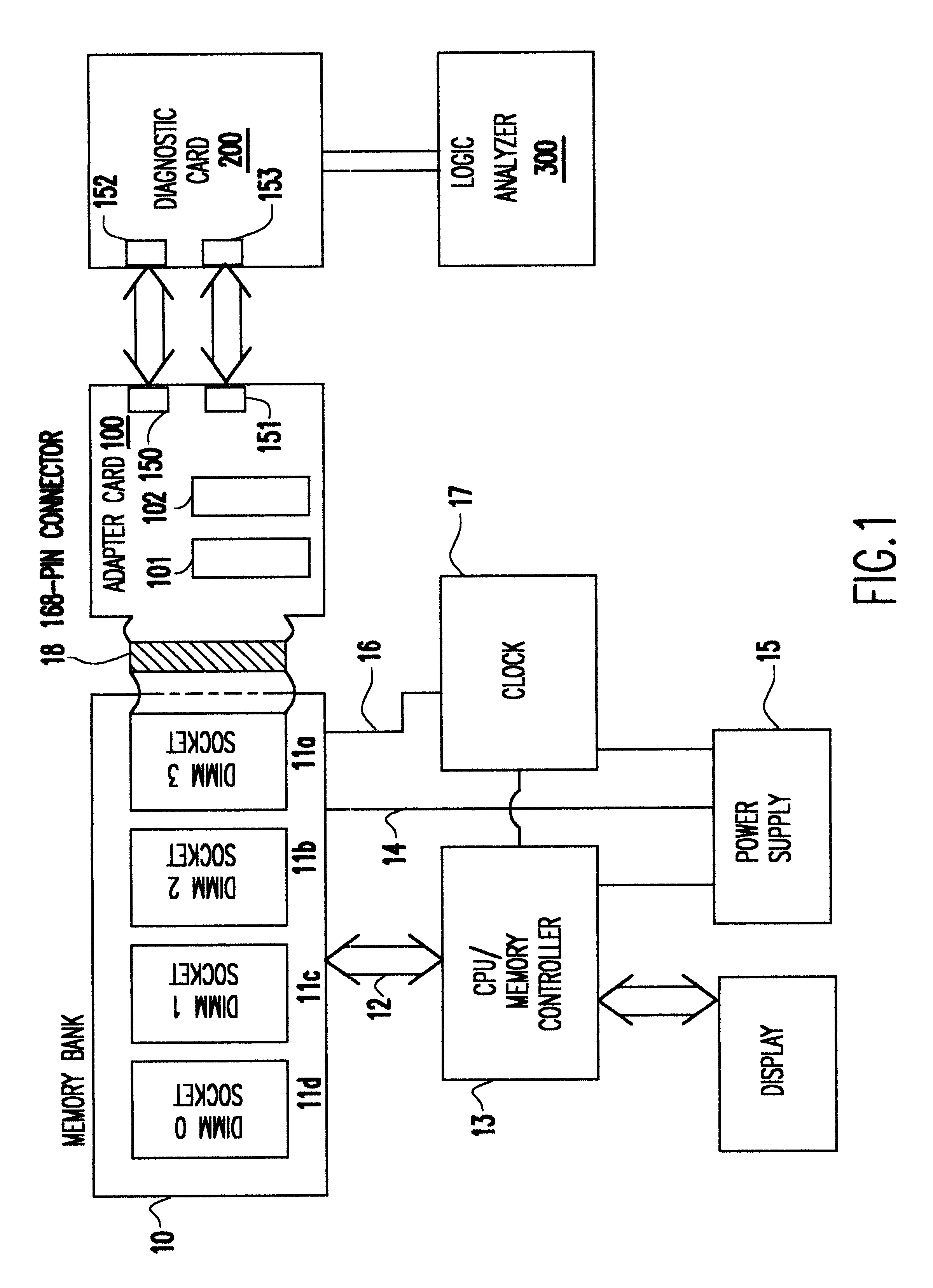
InactiveUS6467053B1Minimize degradationError detection/correctionComponent plug-in assemblagesLength variationDram memory
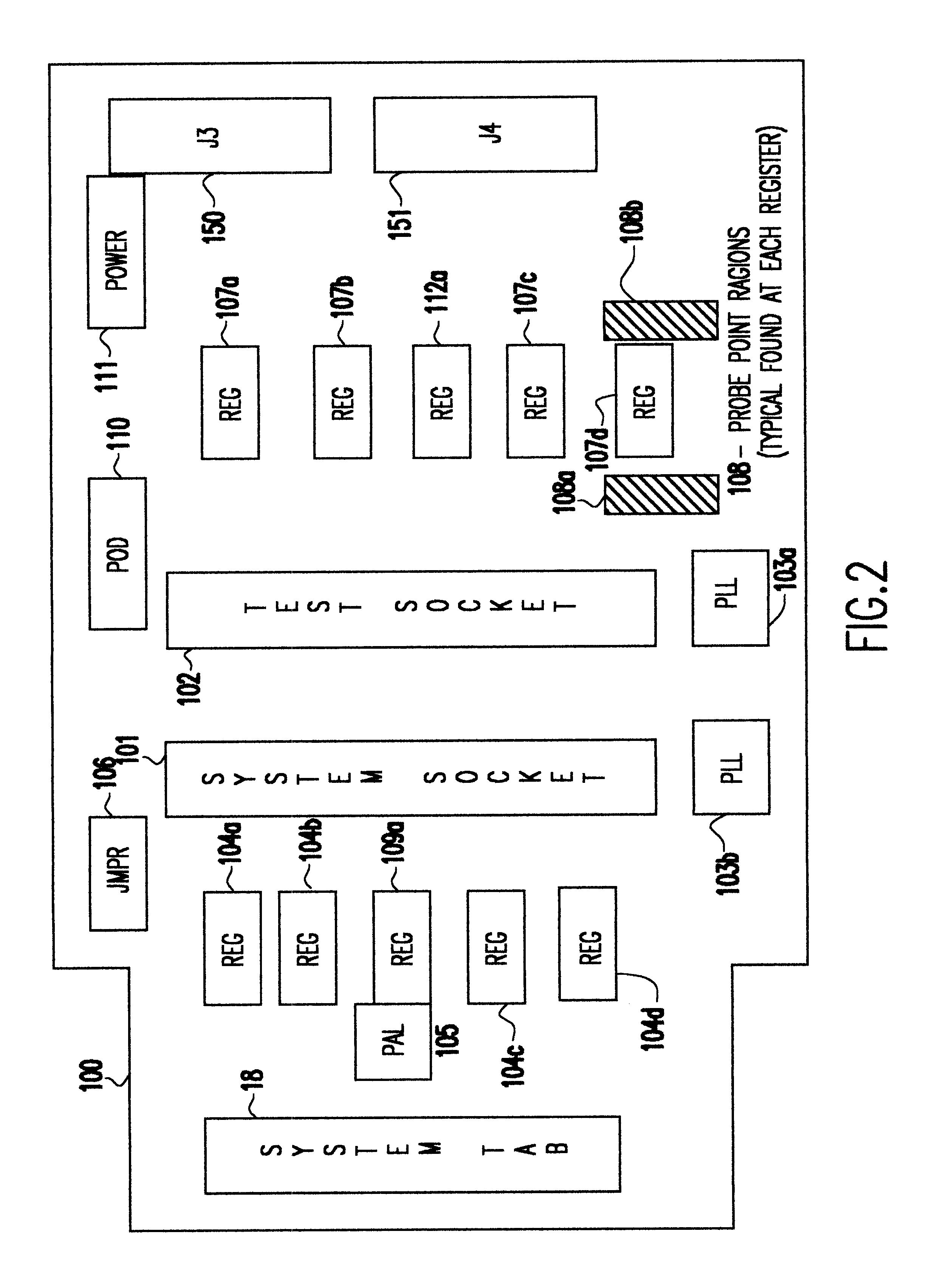
A Synchronous DRAM memory test assembly that converts a normal PC or Workstation with a synchronous bus into a memory tester. The test assembly may be split into two segments: a diagnostic card and an adapter card to limit mechanical load on the system socket as well as permit varying form factors. This test assembly architecture supports memory bus speeds of 66 MHz and above, and provides easy access for a logic analyzer. The test assembly supports Registered and Unbuffered Synchronous DRAM products. The test assembly permits good and questionable synchronous modules to be compared using an external logic analyzer. It permits resolution of in-system fails that occur uniquely in system environments and may be otherwise difficult or impossible to replicate. The test assembly re-drives the system clocks with a phase lock loop (PLL) buffer to a memory module socket on the test assembly to permit timing adjustments to minimize the degradation to the system's memory bus timings due to the additional wire length and loading. The test assembly is programmable to adjust to varying bus timings such as: CAS (column address strobe) Latencies and Burst Length variations. It is designed with Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) to allow for changes internally without modifying the test assembly.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Wide-scan on-chip logic analyzer with global trigger and interleaved SRAM capture buffers
ActiveUS7332929B1Electronic circuit testingError detection/correctionProcessor registerControl register
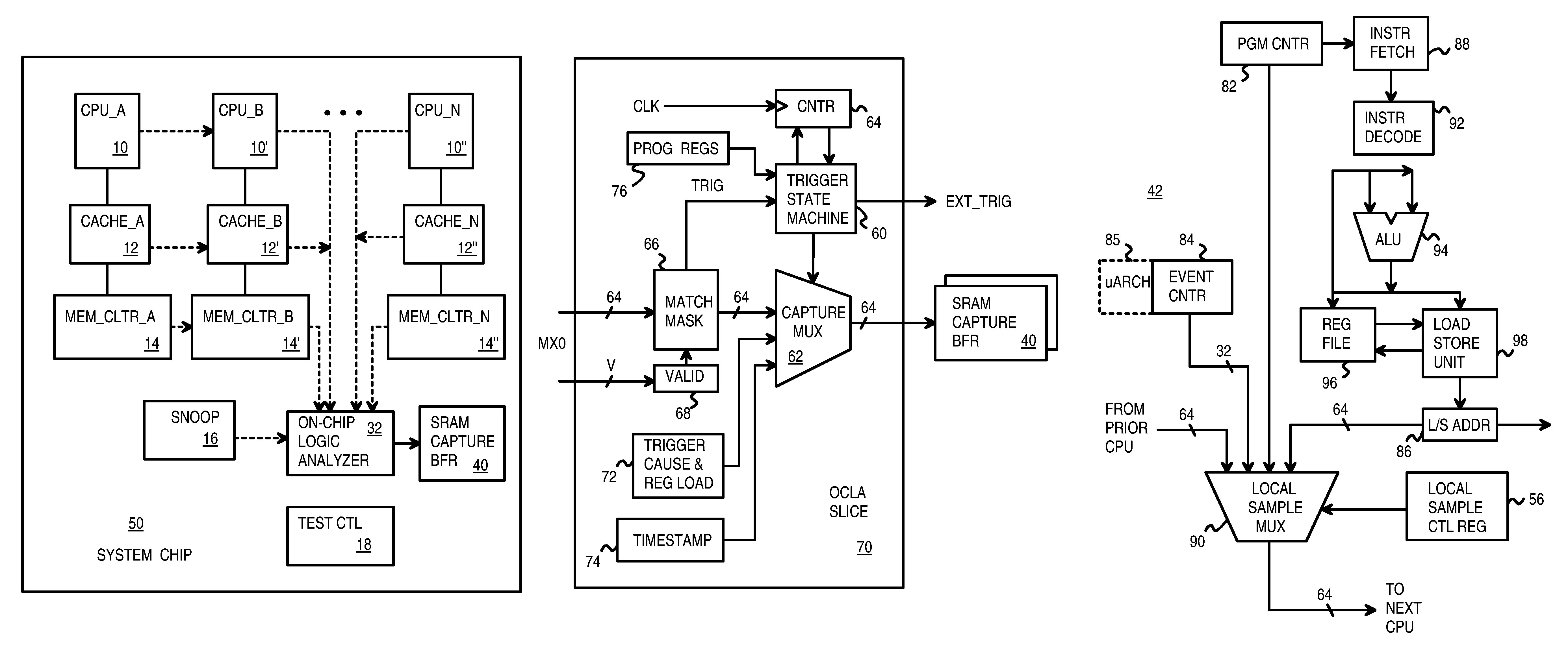
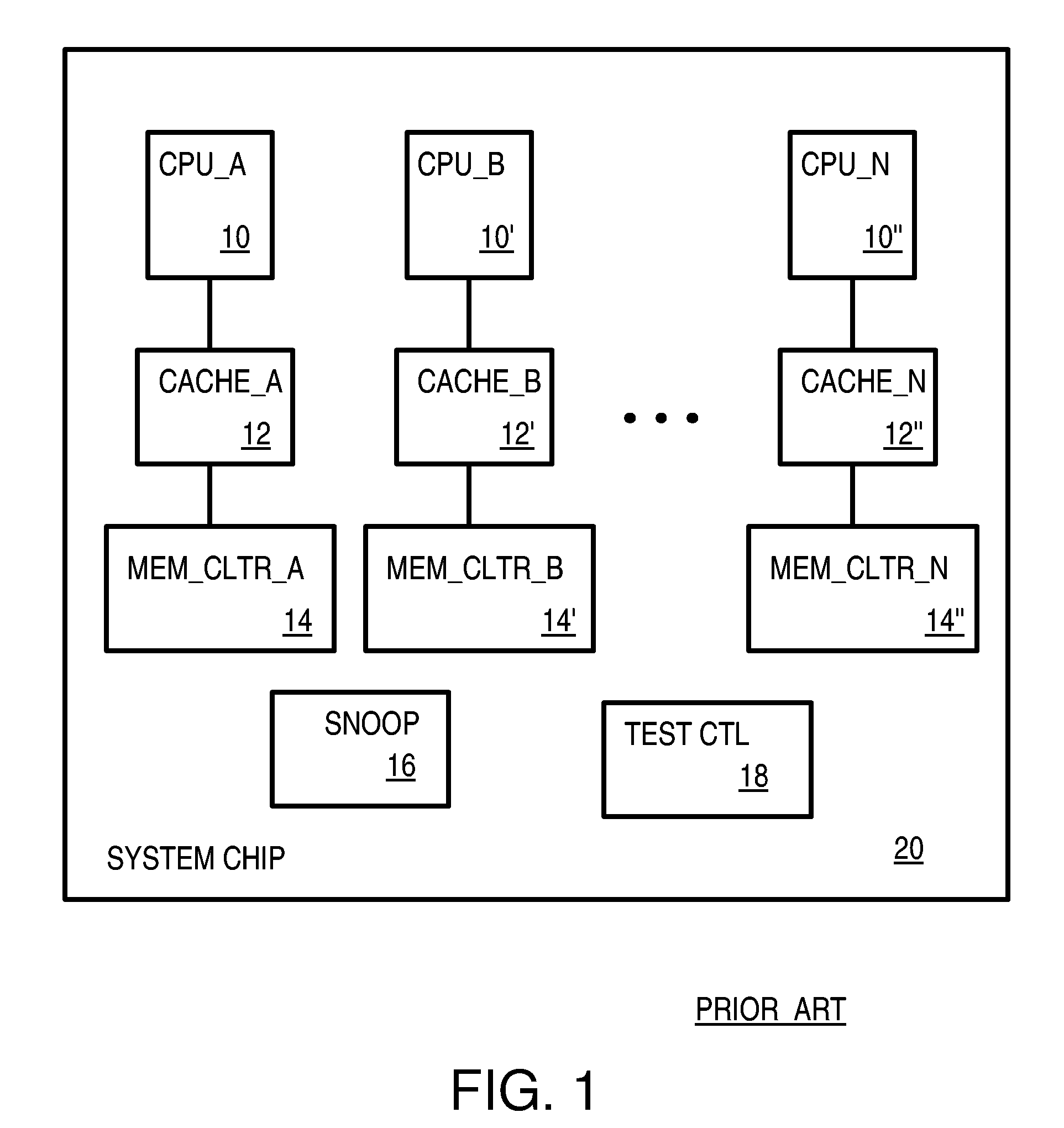
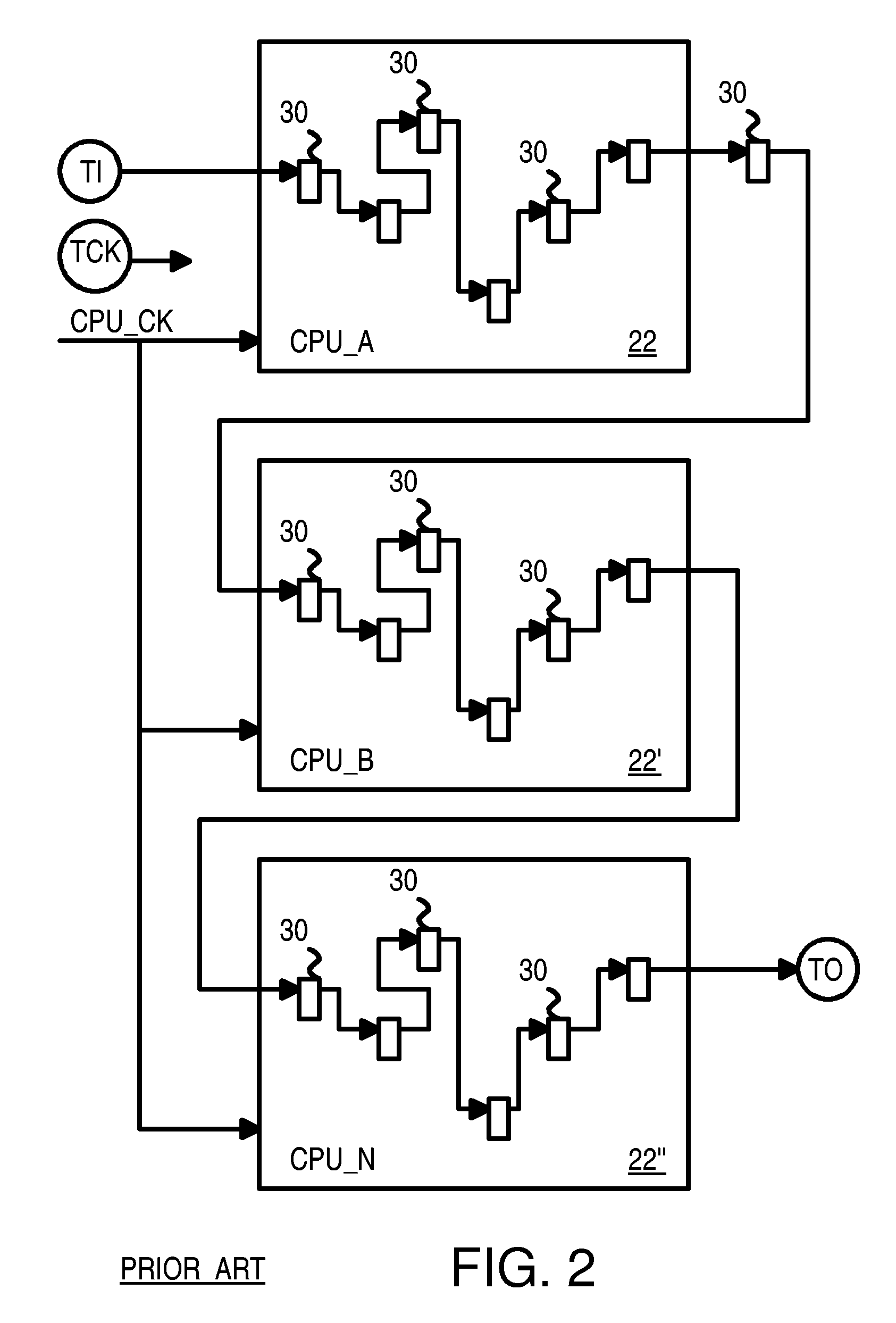
A system chip has many local blocks including processor cores, caches, and memory controllers. Each local block has a local sample-select mux that is controlled by a local selection control register. The mux selects from among hundreds of internal sample nodes in the local block, and can also pass through samples output by an upstream local block. The selected samples from local blocks are sent to a central on-chip logic analyzer that compares the samples to a maskable trigger value. When the trigger value is matched, a trigger state machine advances, and samples are stored into a central capture buffer. A user debugging the chip can later read out the central capture buffer at a slower speed. Thousands of internal nodes from local blocks can be selected for sampling, triggering, and debugging. Local blocks include valid bits in 64-bit-wide samples. Only valid samples are written to the capture buffer.
Owner:AZUL SYSTEMS
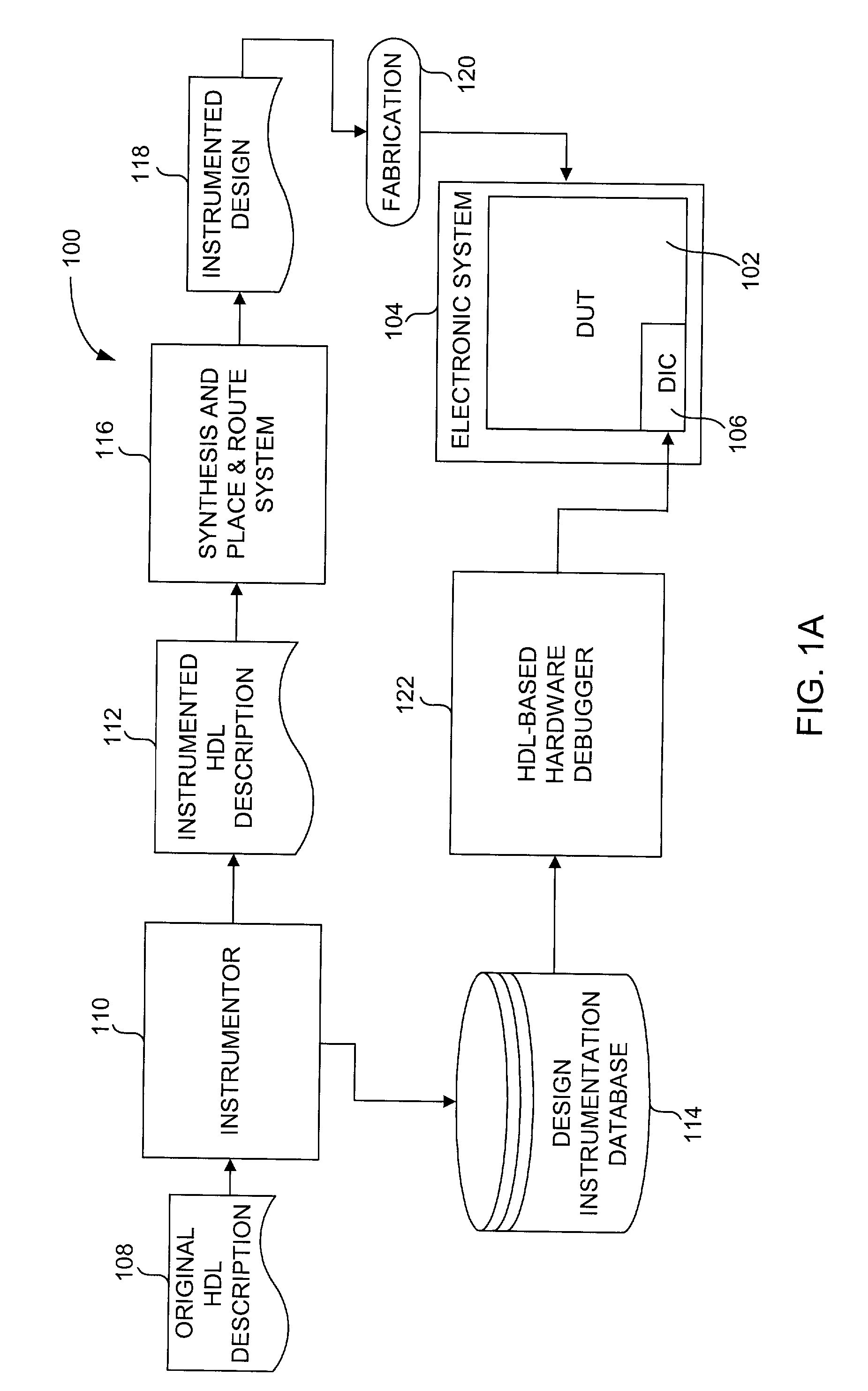
Method and system for debugging an electronic system using instrumentation circuitry and a logic analyzer
InactiveUS7065481B2Facilitates correction and adjustmentSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementAnalogue computers for electric apparatusElectronic systemsLogic analyzer
Techniques and systems for analysis, diagnosis and debugging fabricated hardware designs at a Hardware Description Language (HDL) level are described. Although the hardware designs (which were designed in HDL) have been fabricated in integrated circuit products with limited input / output pins, the techniques and systems enable the hardware designs within the integrated circuit products to be comprehensively analyzed, diagnosed, and debugged at the HDL level at speed. The ability to debug hardware designs at the HDL level facilitates correction or adjustment of the HDL description of the hardware designs.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
System and method for configuring a logic analyzer to trigger on data communications packets and protocols
InactiveUS6850852B1Digital variable displayData processing applicationsGraphicsGraphical user interface
A trigger function display system and methodology for trigger definition development in a signal measurement system having a graphical user interface. The system displays a plurality of graphically selectable icons and an associated protocol profile window. The protocol profile window includes at least a protocol descriptor field and a protocol editors field. The user inputs data into the protocol editors field which causes the system to automatically construct a bit sequence utilizing a plurality of event definitions stored in memory. The event definitions are two bit blocks resulting from the parsing of protocol definition text files. The bit sequence is used to then construct a series of trigger primitives. An optimizing routine is used to consolidate consecutive multiple occurrences of identical bit patterns in the bit sequence into single trigger primitives.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
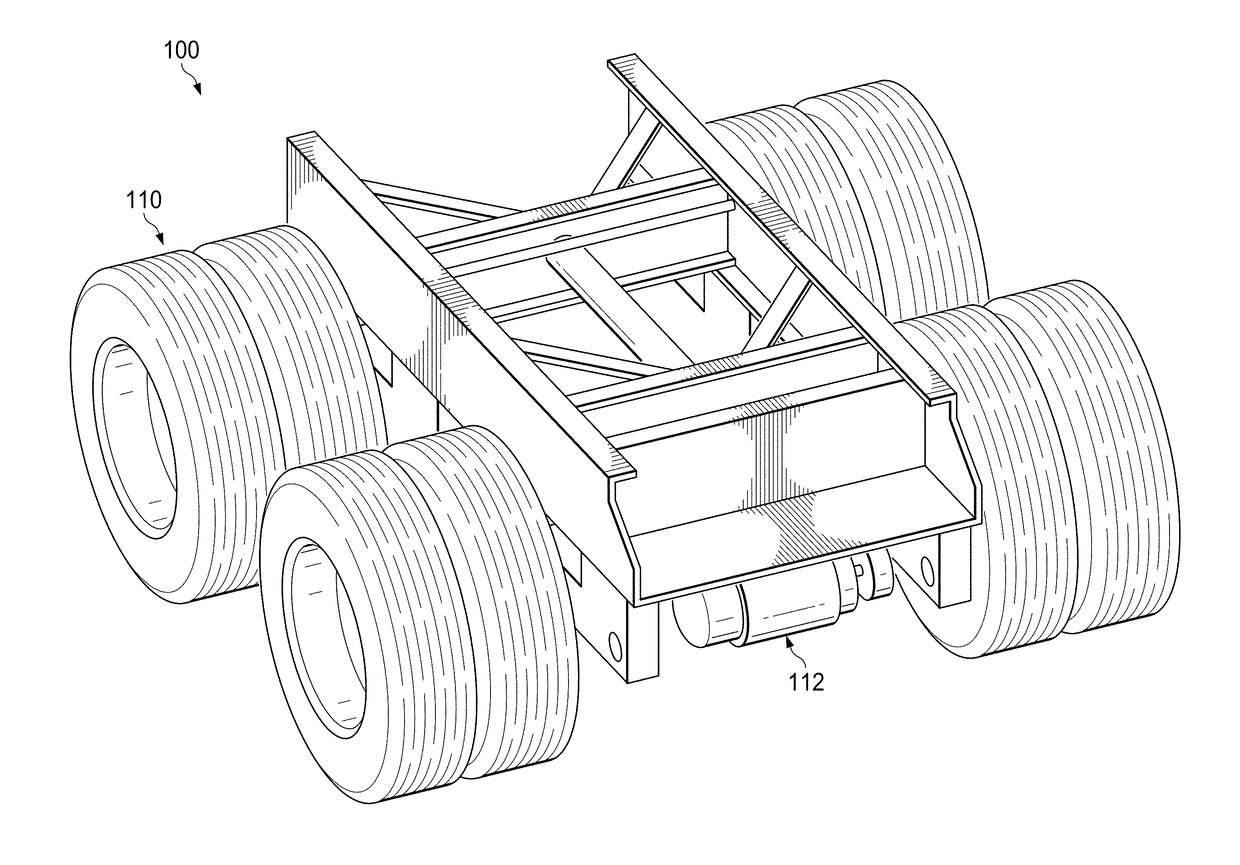
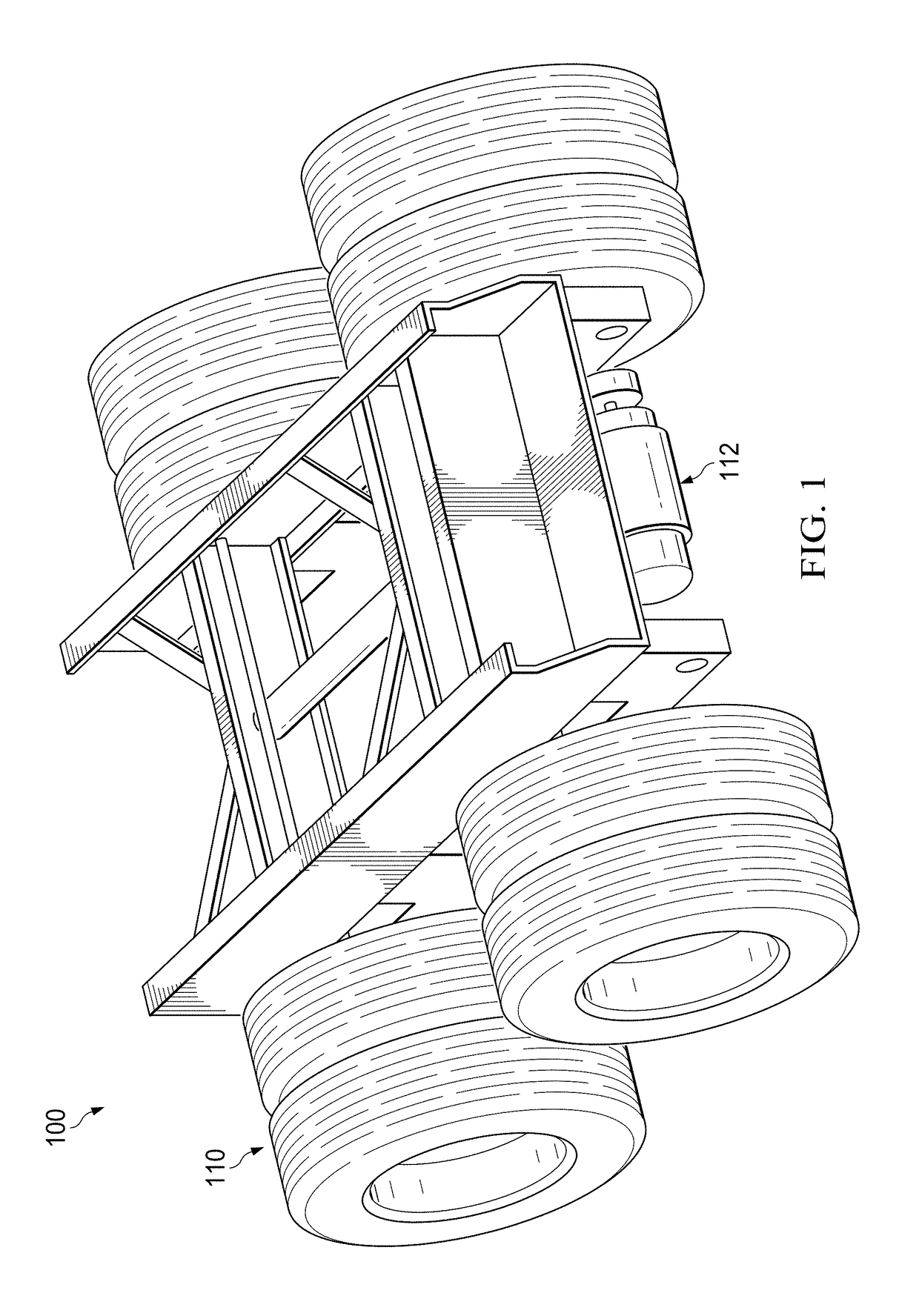
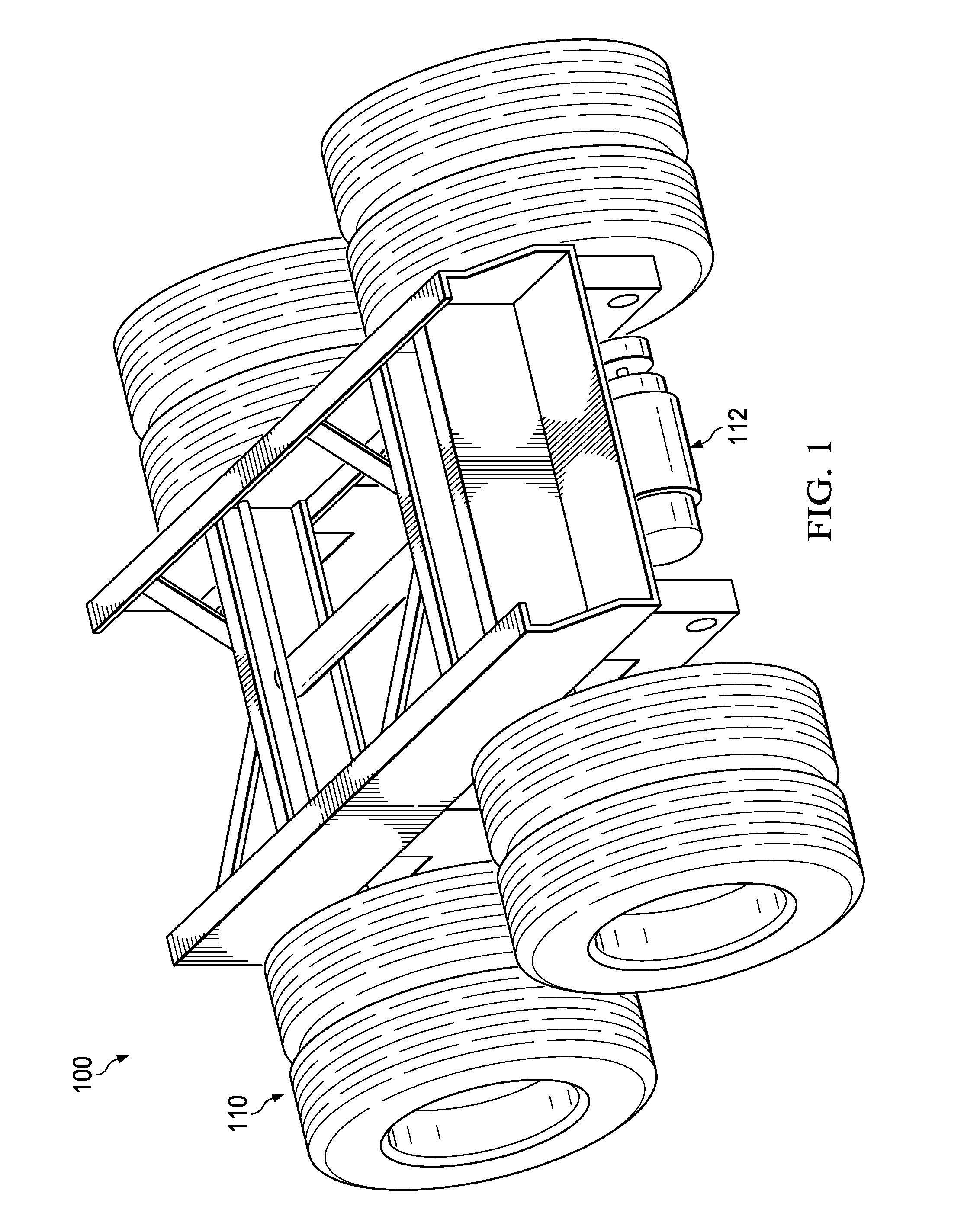
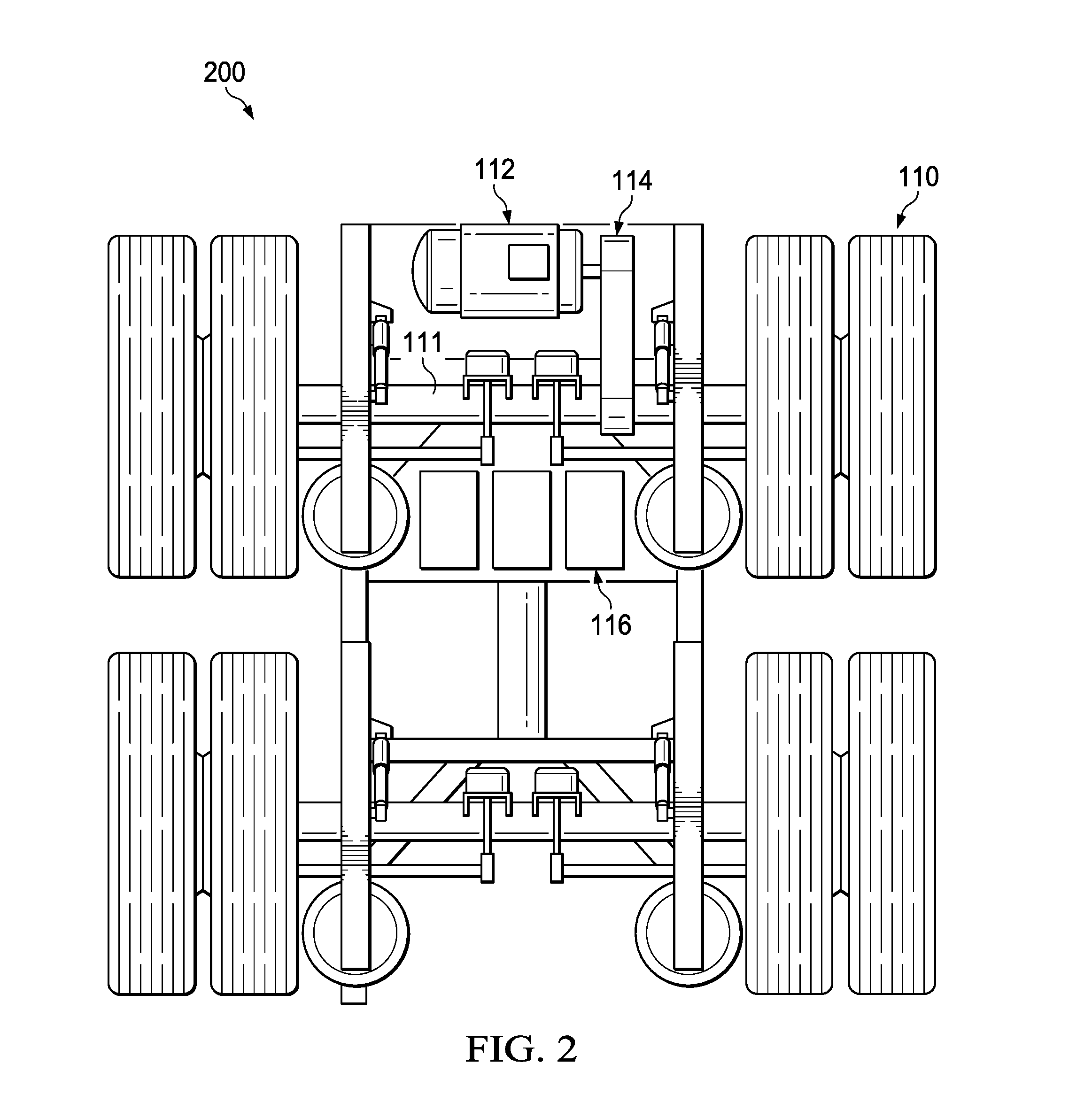
Motor vehicle accessory to increase power supply and reduce fuel requirements
A power control system may include at least one of batteries, a motor, and a data logic analyzer that can interpret certain variable conditions of a transport, such as a tractor trailer, moving along a road or highway. The data can be used to determine when to apply supplemental power to the wheels of a trailer to reduce fuel usage. One example device may include at least one of: a power creation module that generates electrical power, a battery which store the electrical power, a motor affixed to a trailer axle of a trailer which provides a turning force to the trailer axle when enabled to operate from the stored electrical power of the battery, and a motor controller configured to initiate the motor to operate according to a predefined sensor condition.
Owner:HYLIION INC
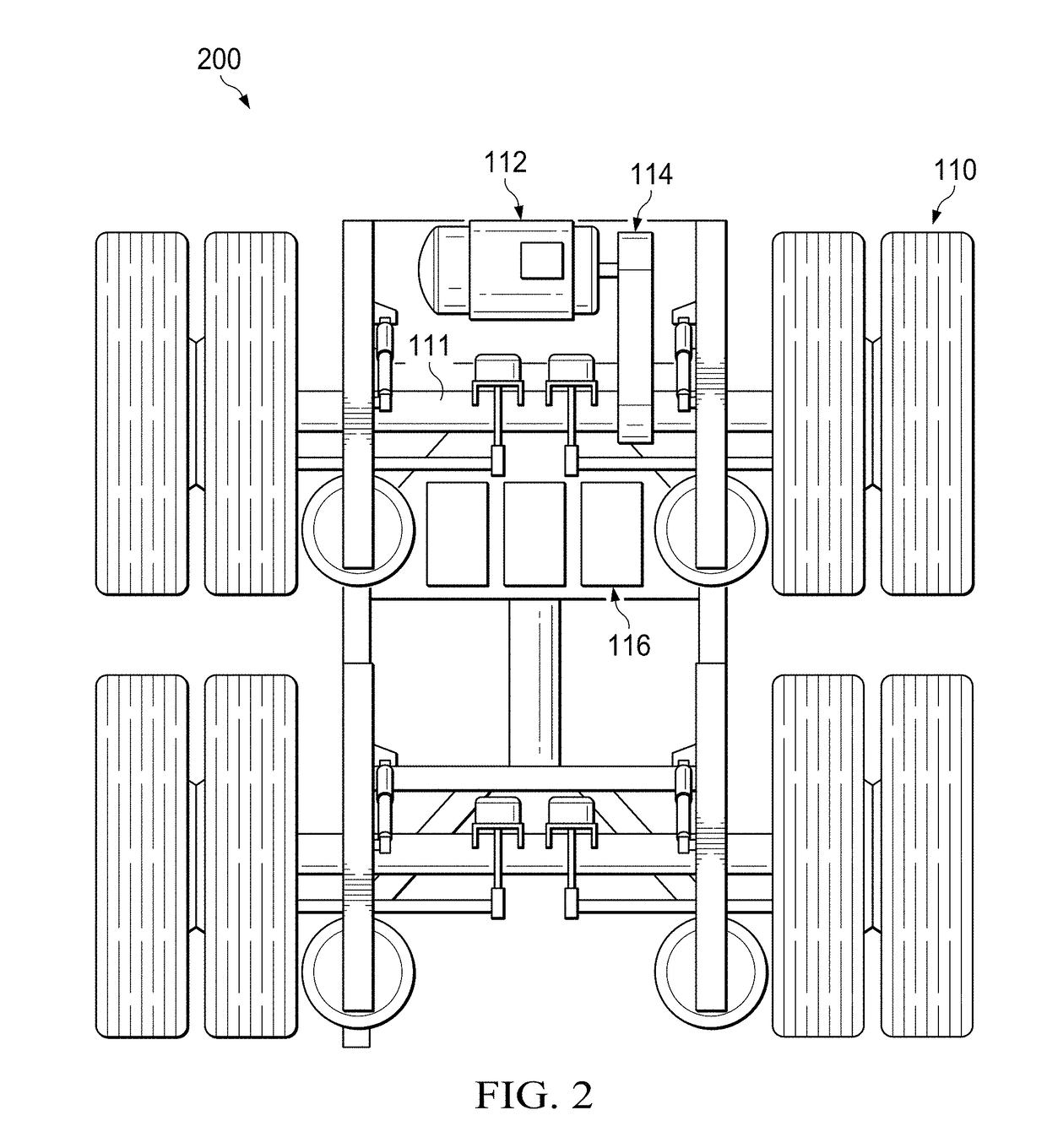
Motor vehicle accessory to increase power supply and reduce fuel requirements
ActiveUS20160318421A1Vehicle sub-unit featuresPropulsion by batteries/cellsPower control systemControl system
A power control system may include at least one of batteries, a motor, and a data logic analyzer that can interpret certain variable conditions of a transport, such as a tractor trailer, moving along a road or highway. The data can be used to determine when to apply supplemental power to the wheels of a trailer to reduce fuel usage. One example device may include at least one of a power source affixed to a trailer to capture energy from movement of an axle of the trailer, and a motor powered by the power source to operate and provide movement assistance to the axle.
Owner:HYLIION INC
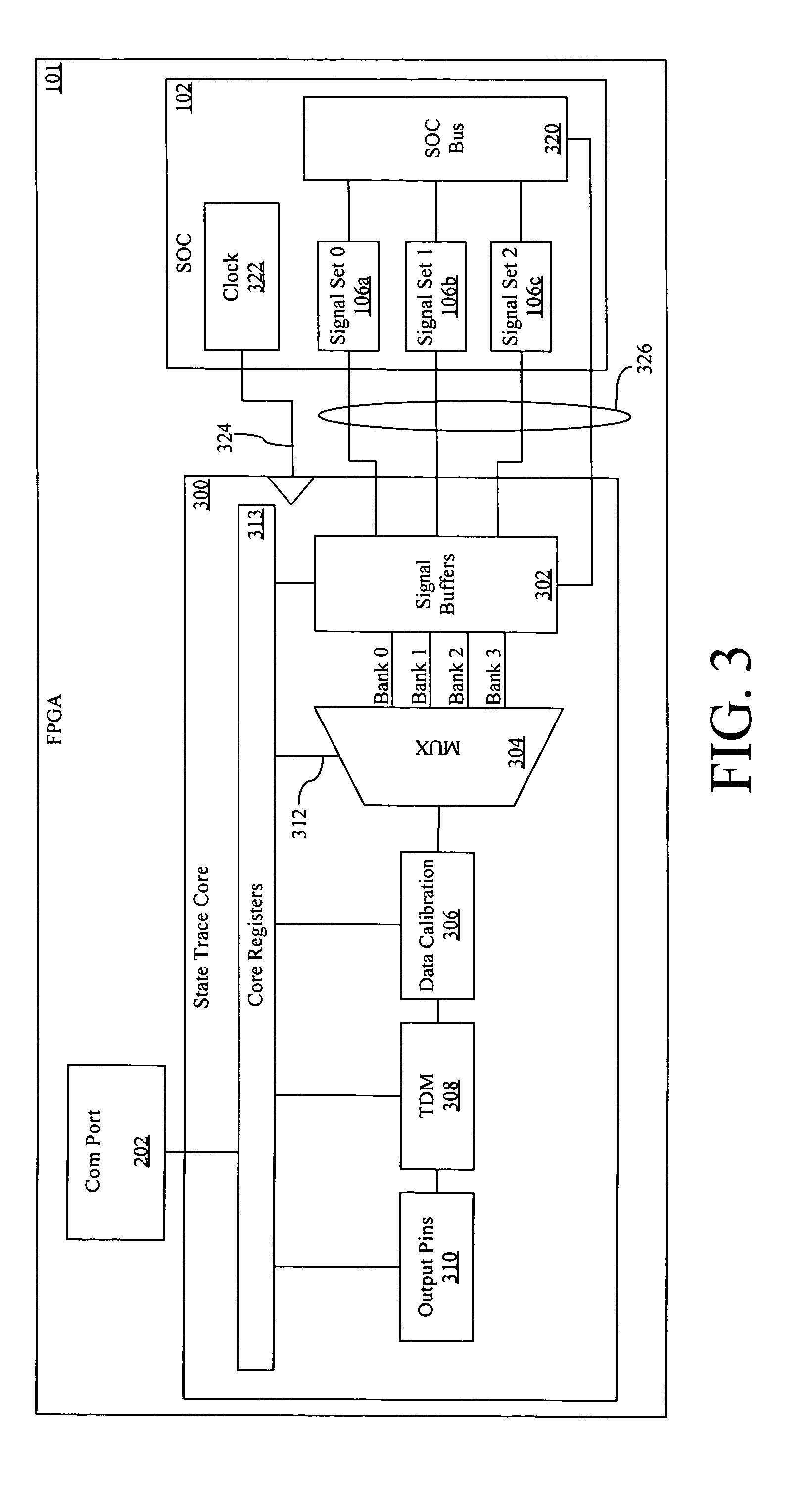
Apparatus and method for dynamic in-circuit probing of field programmable gate arrays
A dynamic probe system for probing a FPGA with at least one core. A trace core is added to the FPGA, the trace core in communication with a plurality of signal banks, each signal bank comprising a plurality of signals in the at least one core. A logic analyzer, in communication with the trace core and selecting the bank of signal to be sent from the trace core to the logic analyzer.
Owner:KEYSIGHT TECH
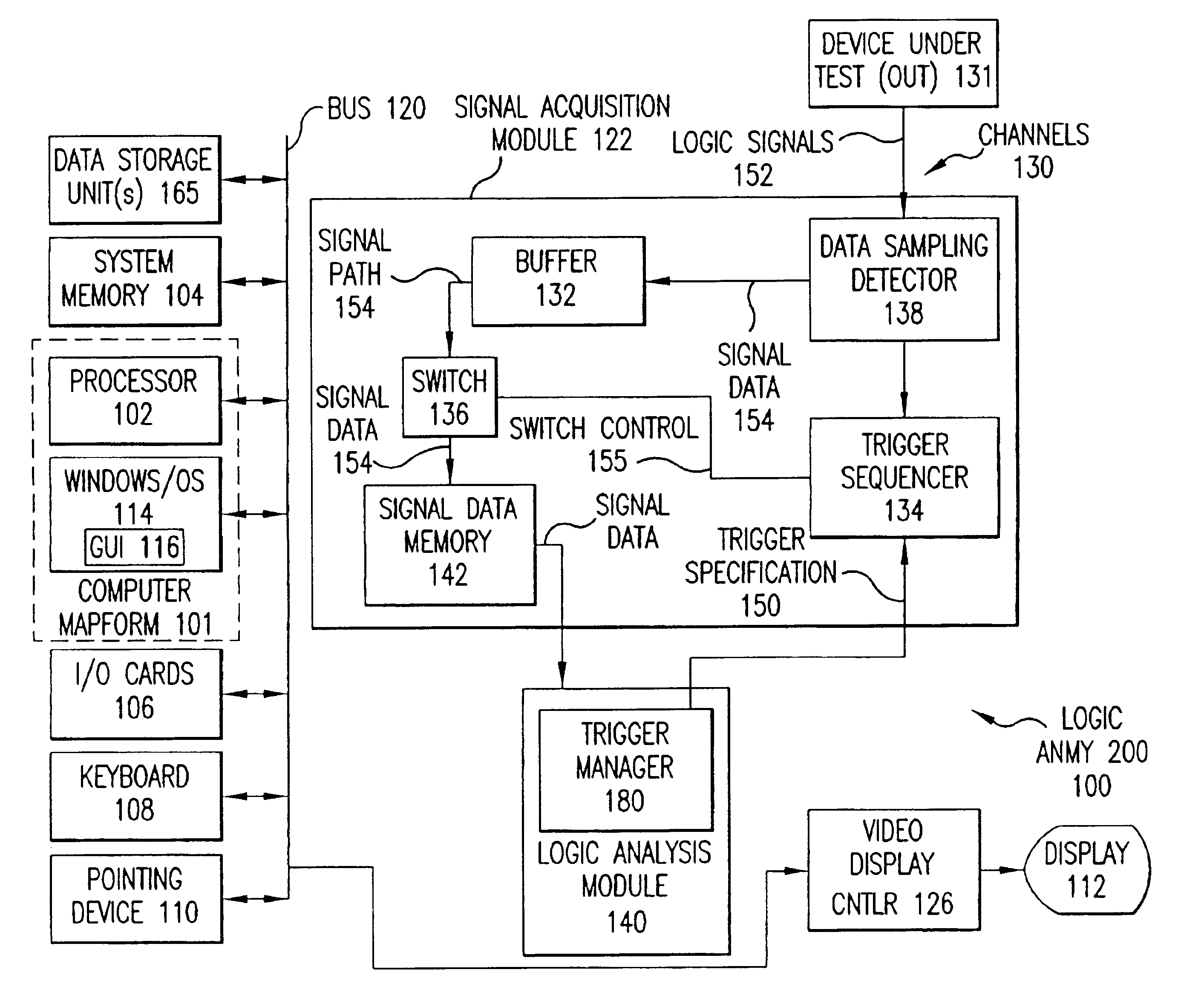
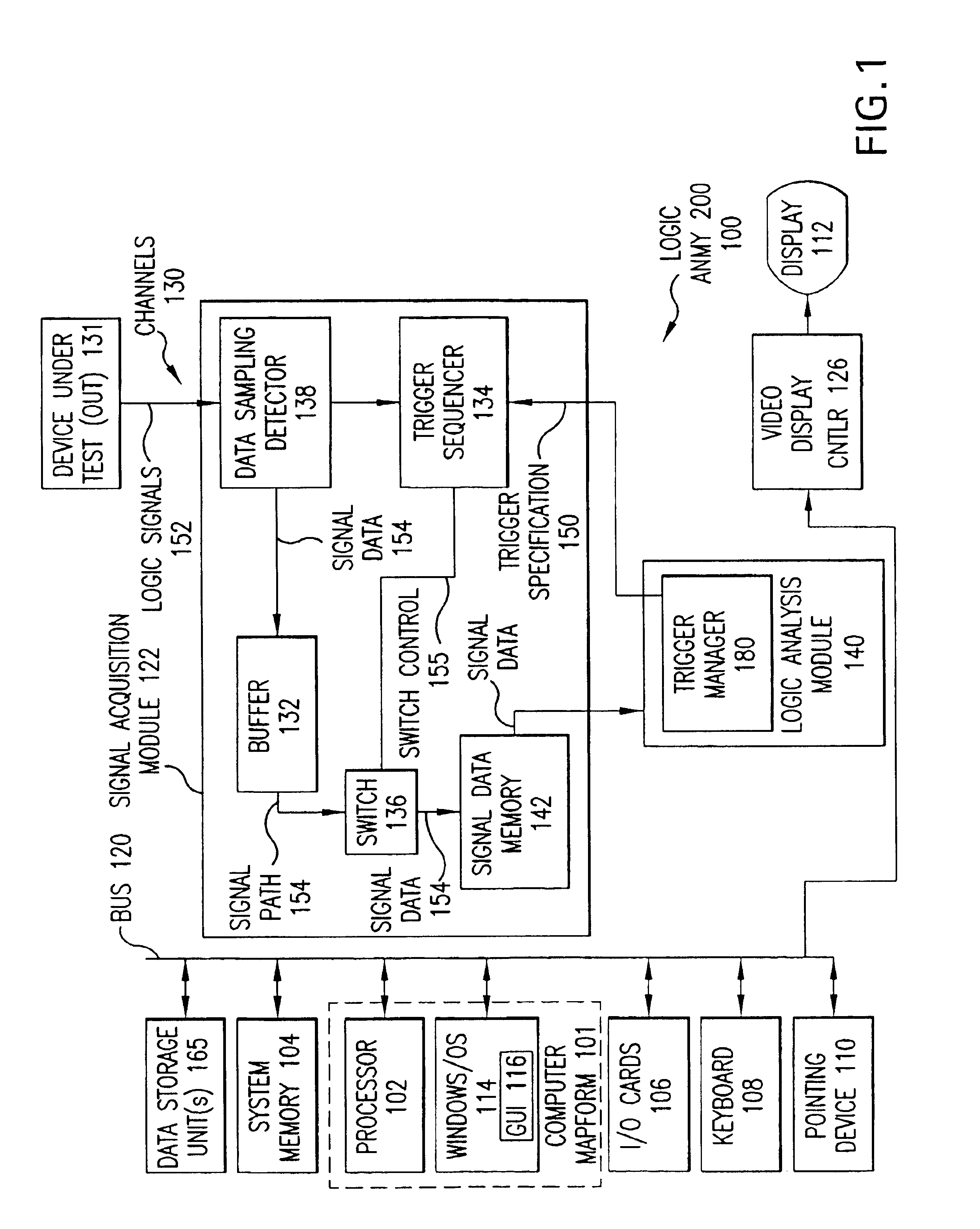
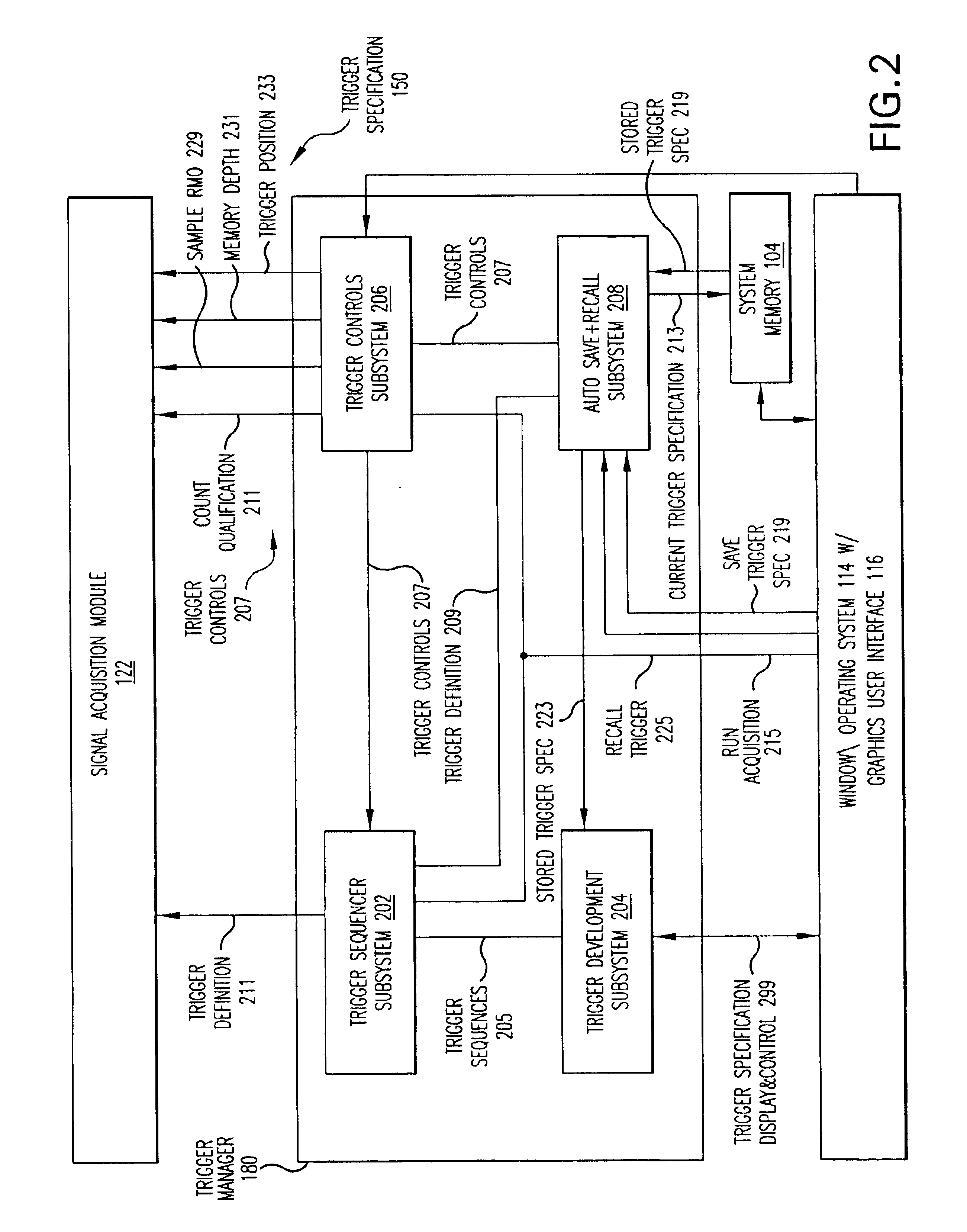
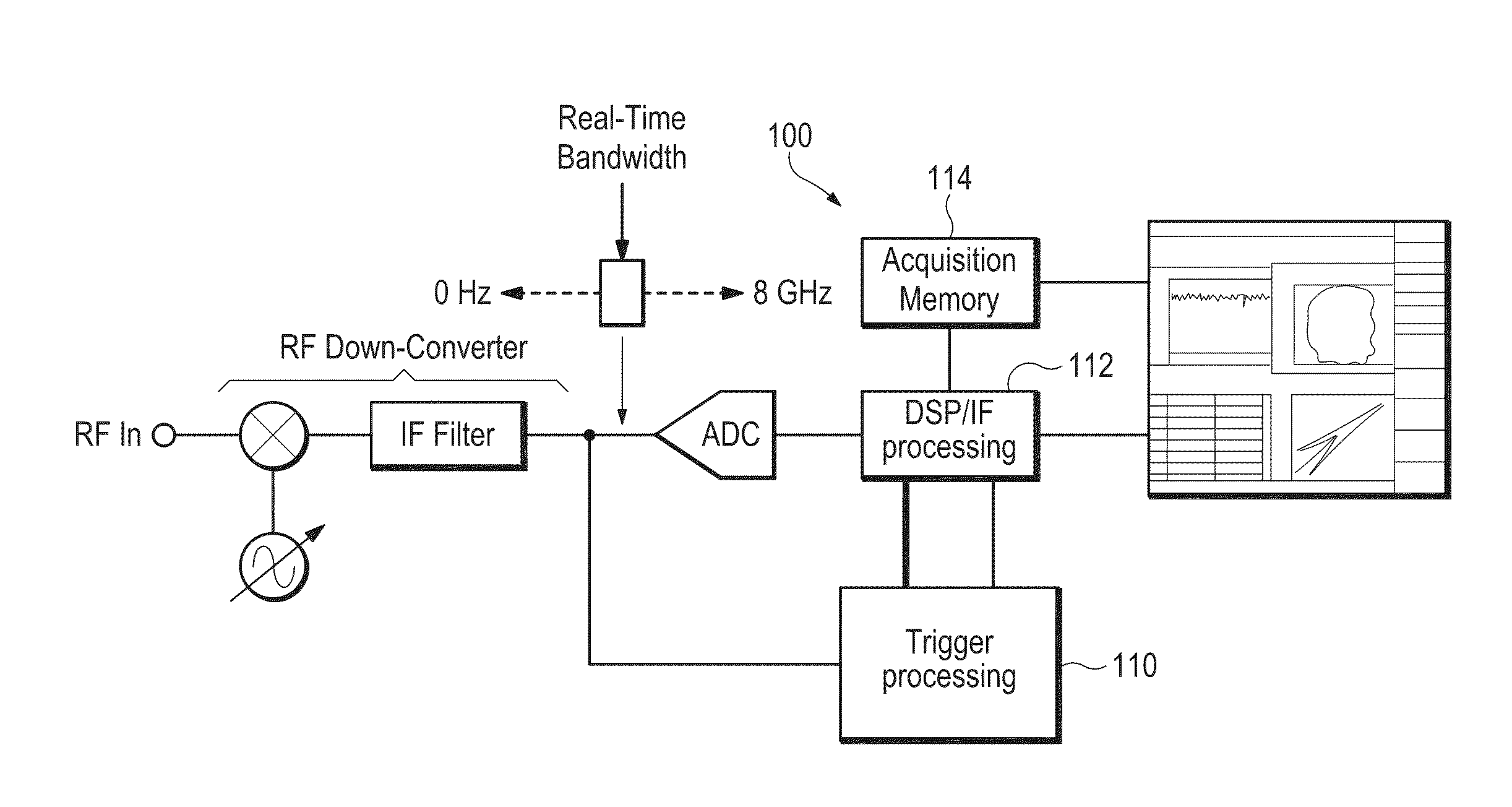
Real Time Statistical Triggers on Data Streams
InactiveUS20110246134A1Digital computer detailsLogical operation testingData streamSpectrum analyzer
Logic analyzers and real-time spectrum analyzers use real-time statistical processes as a basis for creating a trigger. The statistical displays within a test and measurement system such as a Logic Analyzer (LA) or Spectrum Analyzer (SA) or other instrument are used in a user interface to define a trigger based on the statistical event itself. In brief, the invention is a Real Time Statistical trigger established by the user through a direct interaction with the Real Time Statistics displays. This interaction can be via a graphical user interface, or the user interface can employ a non-visible display (e.g., a speaker) or input device (e.g., a microphone).
Owner:TEKTRONIX INC
Delay test method for video image processing system
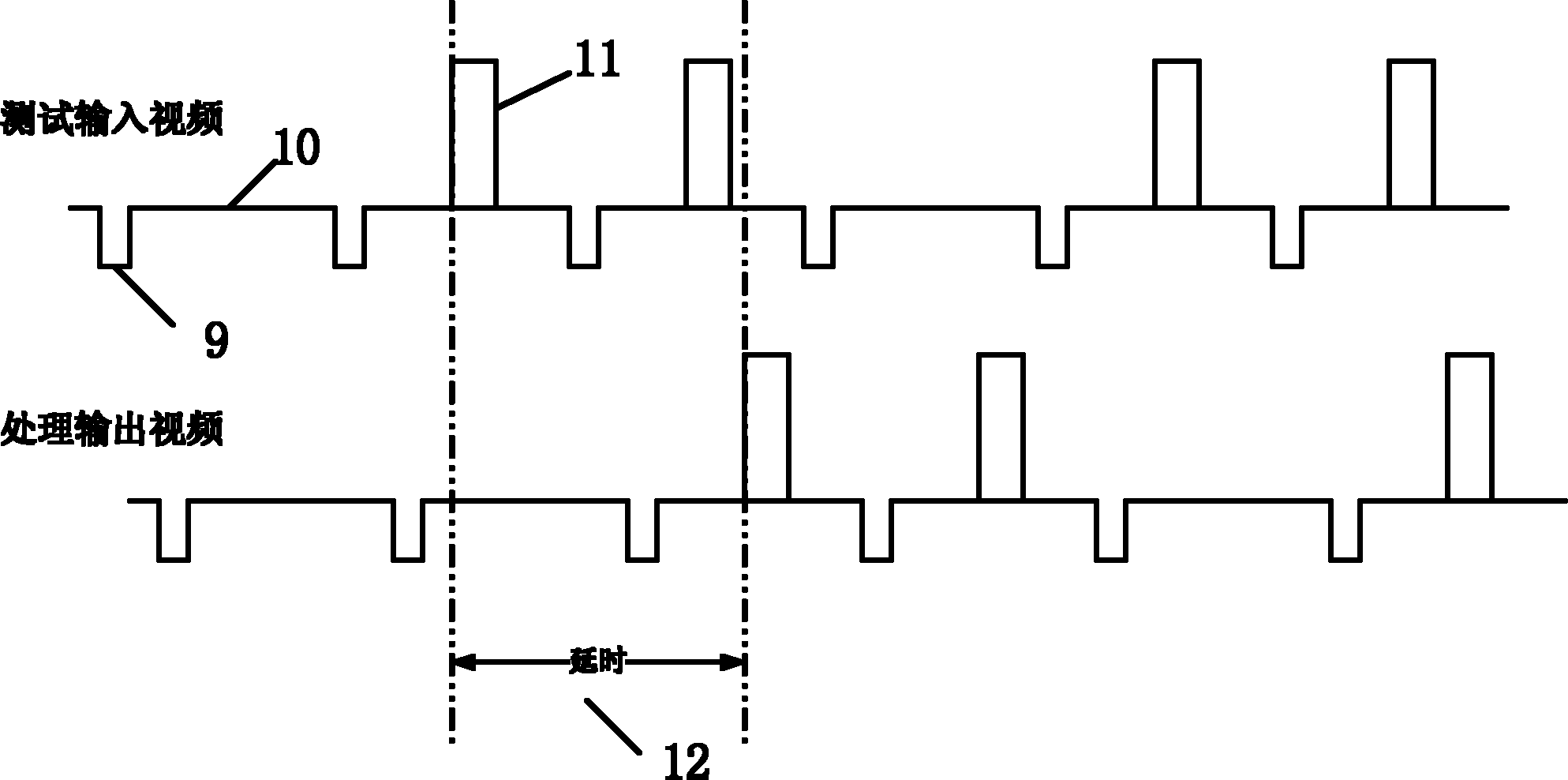
The invention relates to a delay test method for a video image processing system, which comprises the following steps: 1) editing a to-be-tested image by the using of a PC (personal computer), sending the to-be-tested image to a tested video generator, storing the to-be-tested image in a flash by the tested video generator, and standing by; 2) at the moment of testing, selecting the to-be-tested image by an upper computer according to a video standard of tested system and testing the specific sequence form and video format; 3) sending a to-be-tested video into the tested system; and 4) sending the to-be-tested video generated from the step 2) and the video outputted by the tested system to an oscilloscope or logic analysis meter, and reading the time difference of input and output, namely acquiring the system delayed volume. The tested images in the tested video are continuously outputted at intervals. The invention provides a simple, direct and practical method, which can be used for accurately testing the delay of the video image processing system.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Embedded time domain analyzer for high speed circuits
InactiveUS20080183409A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime informationTime transformation
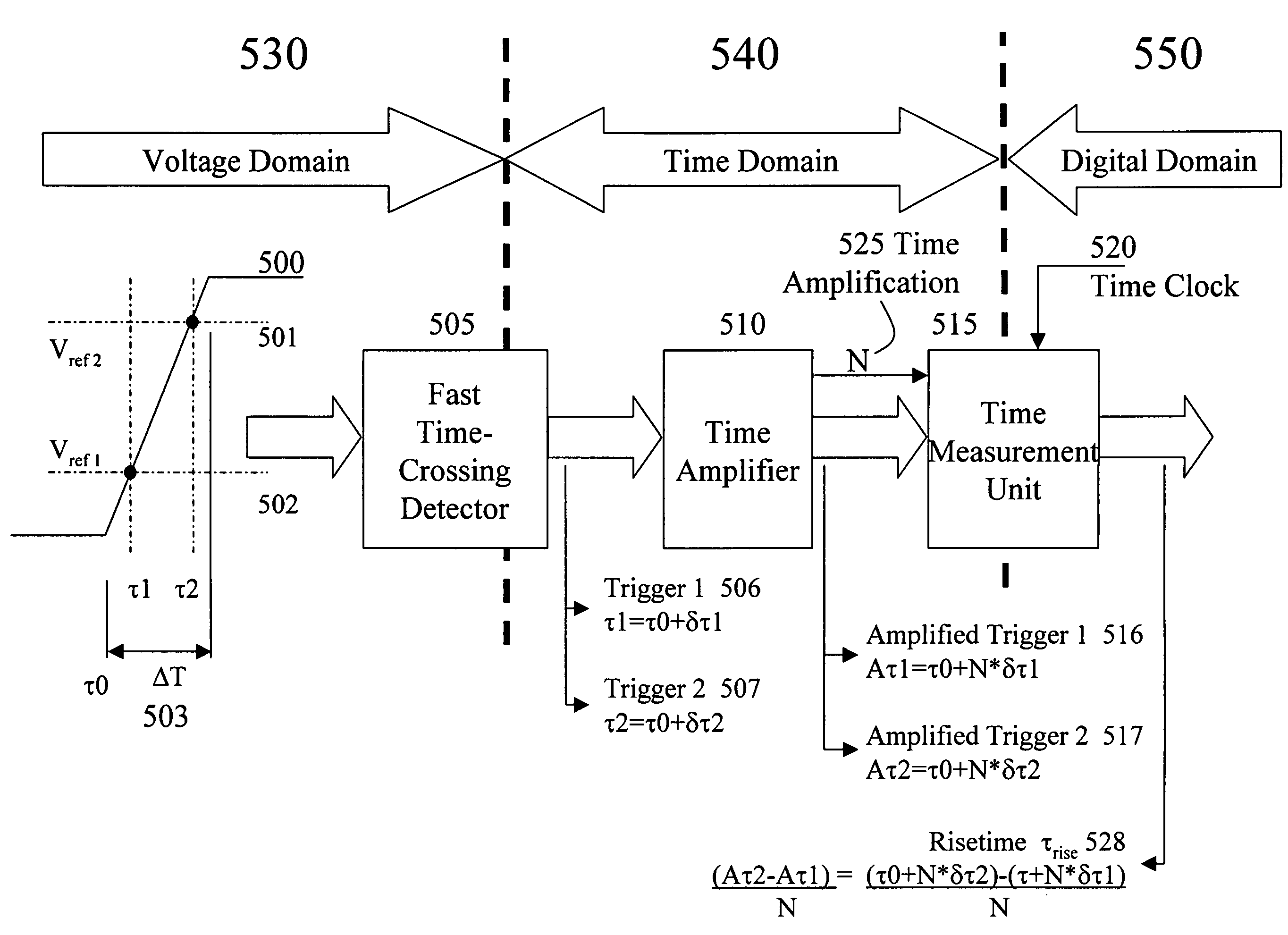
A method of providing an on-chip high-speed time domain digital analyzer for the characterization and analysis of signals within an integrated circuit is provided. The method involves processing the signal being characterized / analyzed in the digital domain irrespective of it's starting format. The approach performs a voltage-to-time conversion using predetermined voltage thresholds, applying a time amplification to the digital time information, measuring the amplified time difference between events and converting the amplified time difference as required by the characterization / analysis. The method allows the capture of very high-speed signals with high resolution without the requirements of complex and high-speed electronics. As such the on-chip high-speed time domain digital analyzer can function as an oscilloscope, pulse width analyzer, rise time analyzer and even logic analyzer. Further the method allows the capture and analysis of single and non-repetitive signal events unlike prior art approaches to time domain oscilloscopes.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
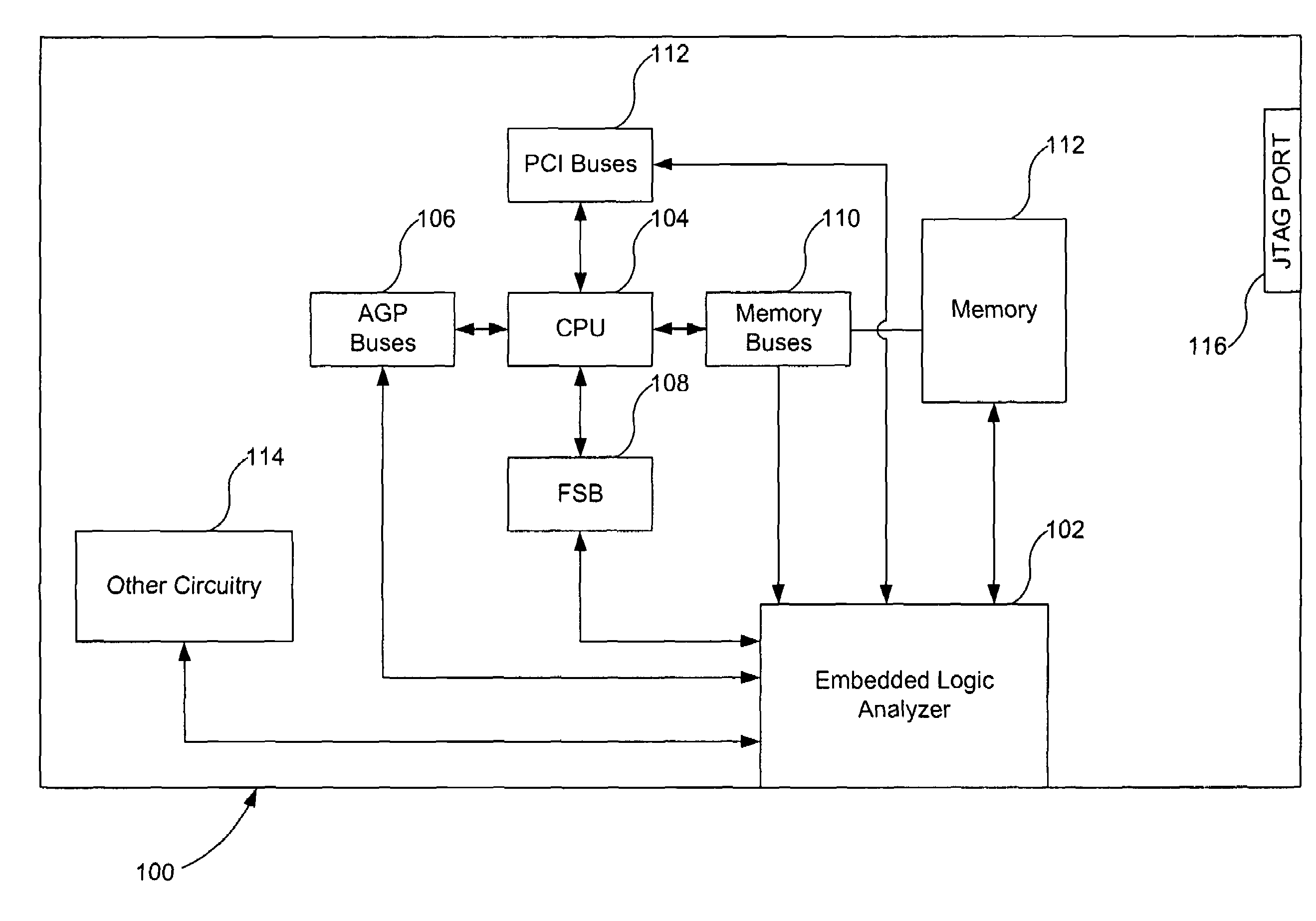
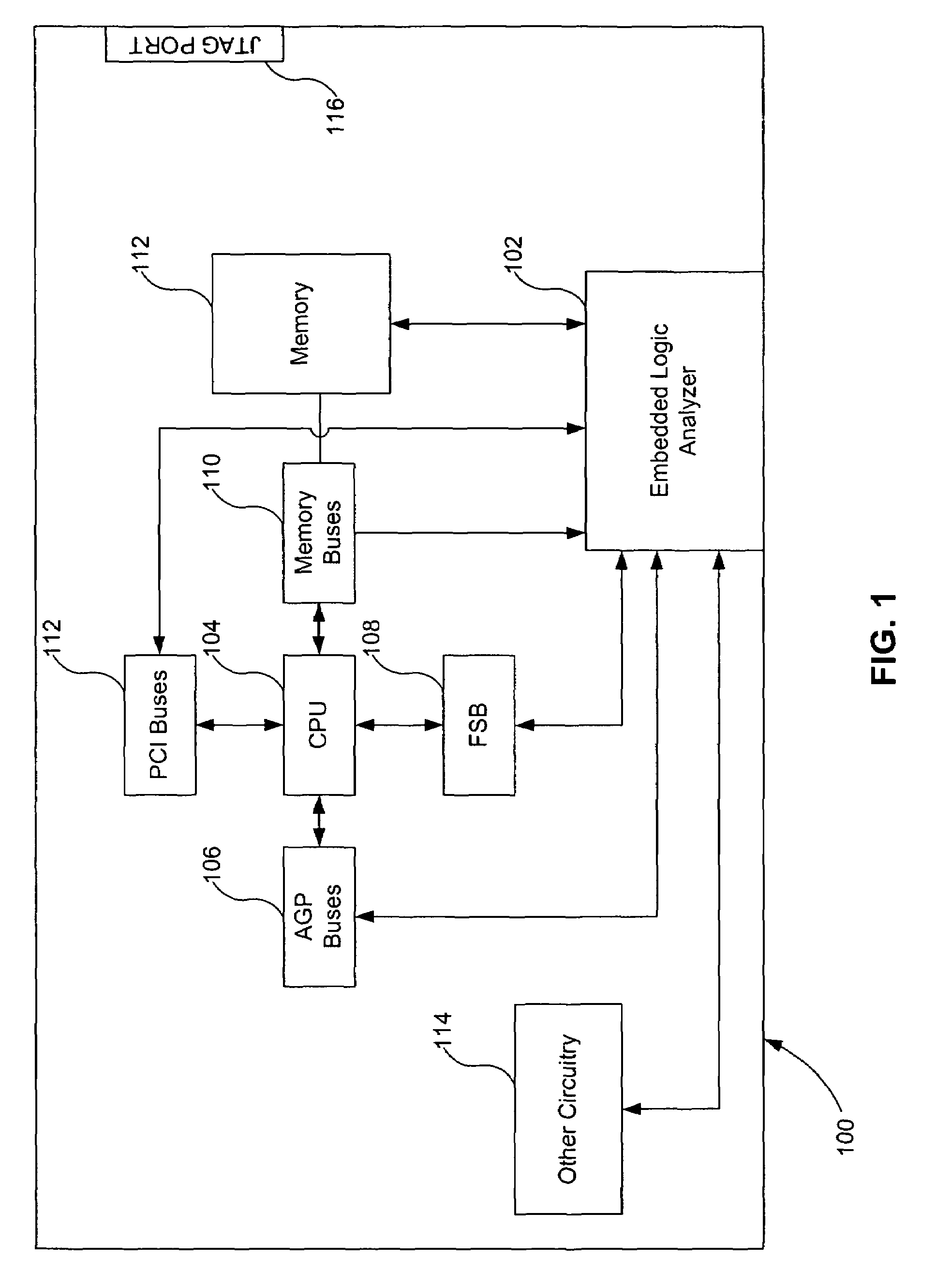
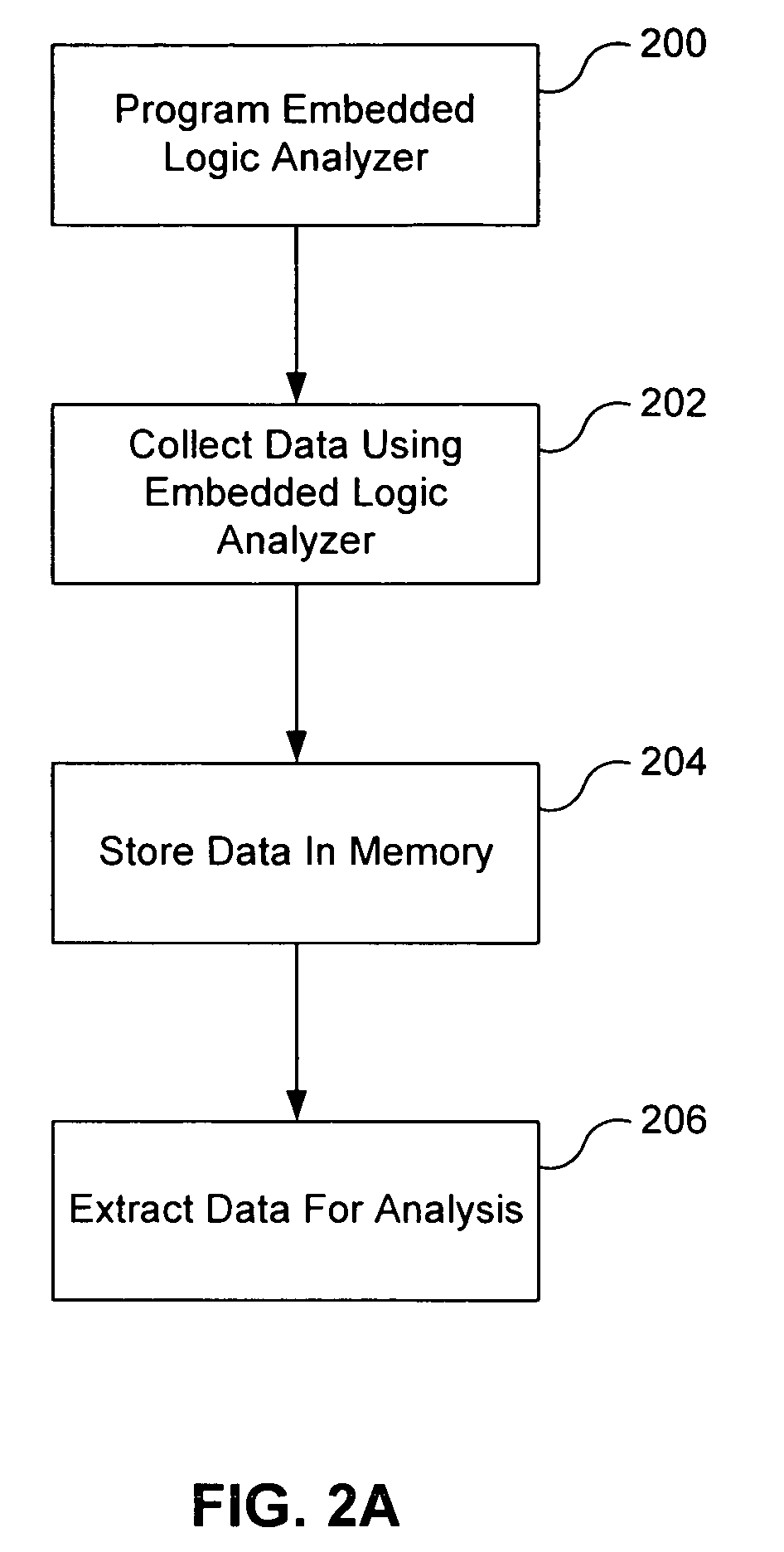
Programmable embedded logic analyzer in an integrated circuit
A logic analyzer having internal access to the test buses, clocks and events of a chip is used to debug the chip. The logic analyzer is designed with the capability to share existing memory in the chip during the debug process. Additionally, the configuration of the logic analyzer and observation of the acquired results in the shared memory can be accessed through normal control interfaces of the chip and does not require special test cards. The logic analyzer includes a clocking function, a trigger function, a signal multiplexer, and a memory block. The clocking function is configured to select as the sample clock for the function any of the clocks in the integrated circuit. In addition, the clocking function may provide a means to decimate these clocks by some factor to sample over larger intervals.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Secure cloud computing system
InactiveUS20120185692A1Comprehensive understandingDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationElectronic systemsProtection system
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for securing electronic systems, including computers, information appliances and communication devices. The invention in question addresses the problem of preventing compromise by severe attacks directed at the protected systems. A severe attack could mean any of the following: low level debugging, use of in-circuit emulators or logic analyzers, removal of silicon dice and inspection including by lapping and micro-photography, and other well-known methods of attack such as distributed denial of service. In order to protect systems and data from such severe attacks, a mechanism is required whose operation is irreparably altered by the attempt to understand its operation through such attacks. Moreover, the mechanism must cease operation instantly upon detection of any intrusion associated with an attack, whether by software or by hardware based means.
Owner:BLACKRIDGE TECH HLDG
Configurable IC with trace buffer and/or logic analyzer functionality
InactiveUS20080191733A1Quick configurationEasy to operateReliability increasing modificationsFail-safe circuitsHemt circuitsLogic analyzer
Some embodiments of the invention provide a configurable integrated circuit (IC) that includes several configurable circuits for configurably performing different operations and several user design state (UDS) circuits for storing user-design state values. The IC further includes a trace buffer for storing user-design state values associated with an operational trigger event of the IC. In some embodiments, the configurable circuits, UDS circuits, and tracer buffer are on a single IC die.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
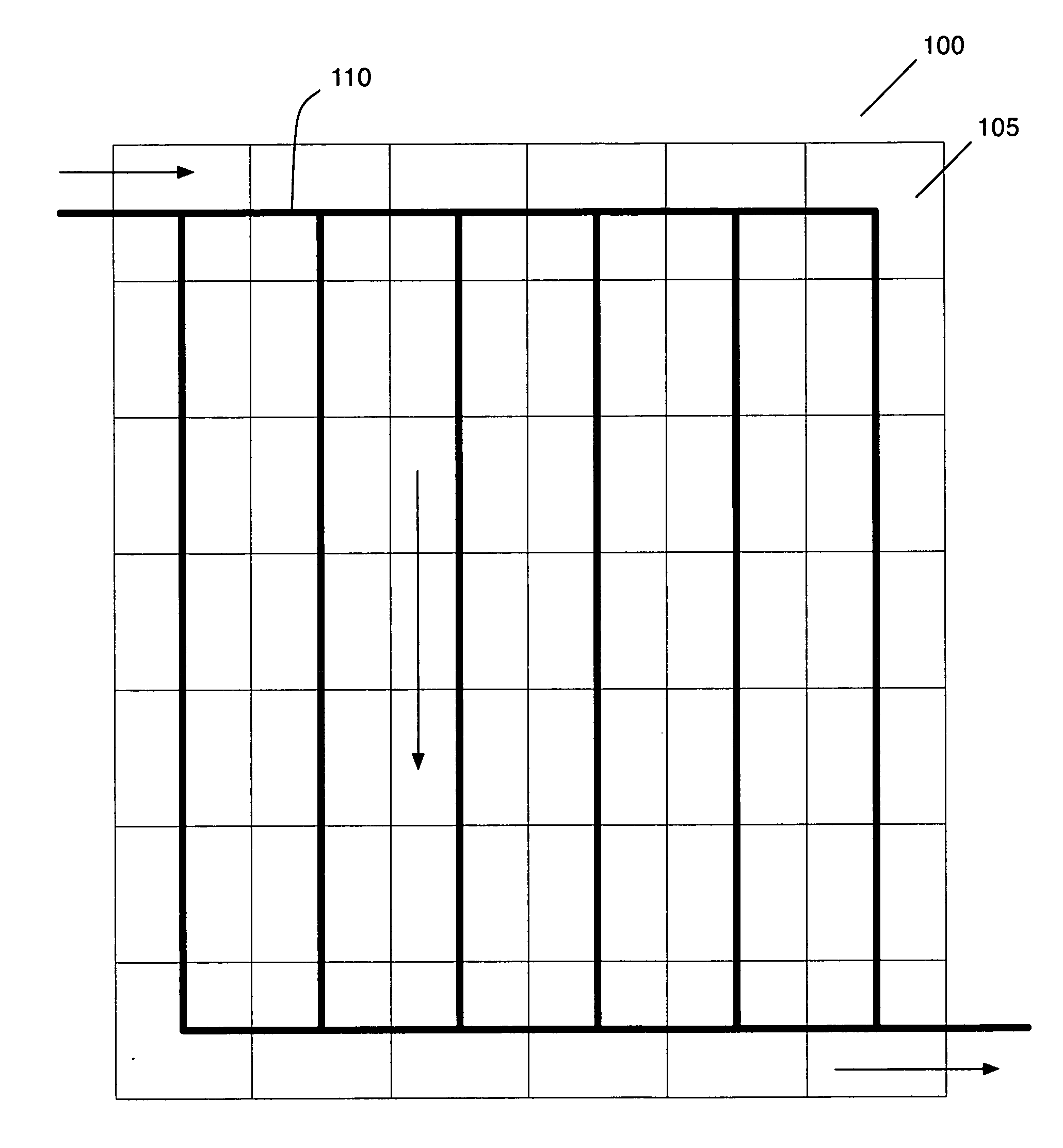
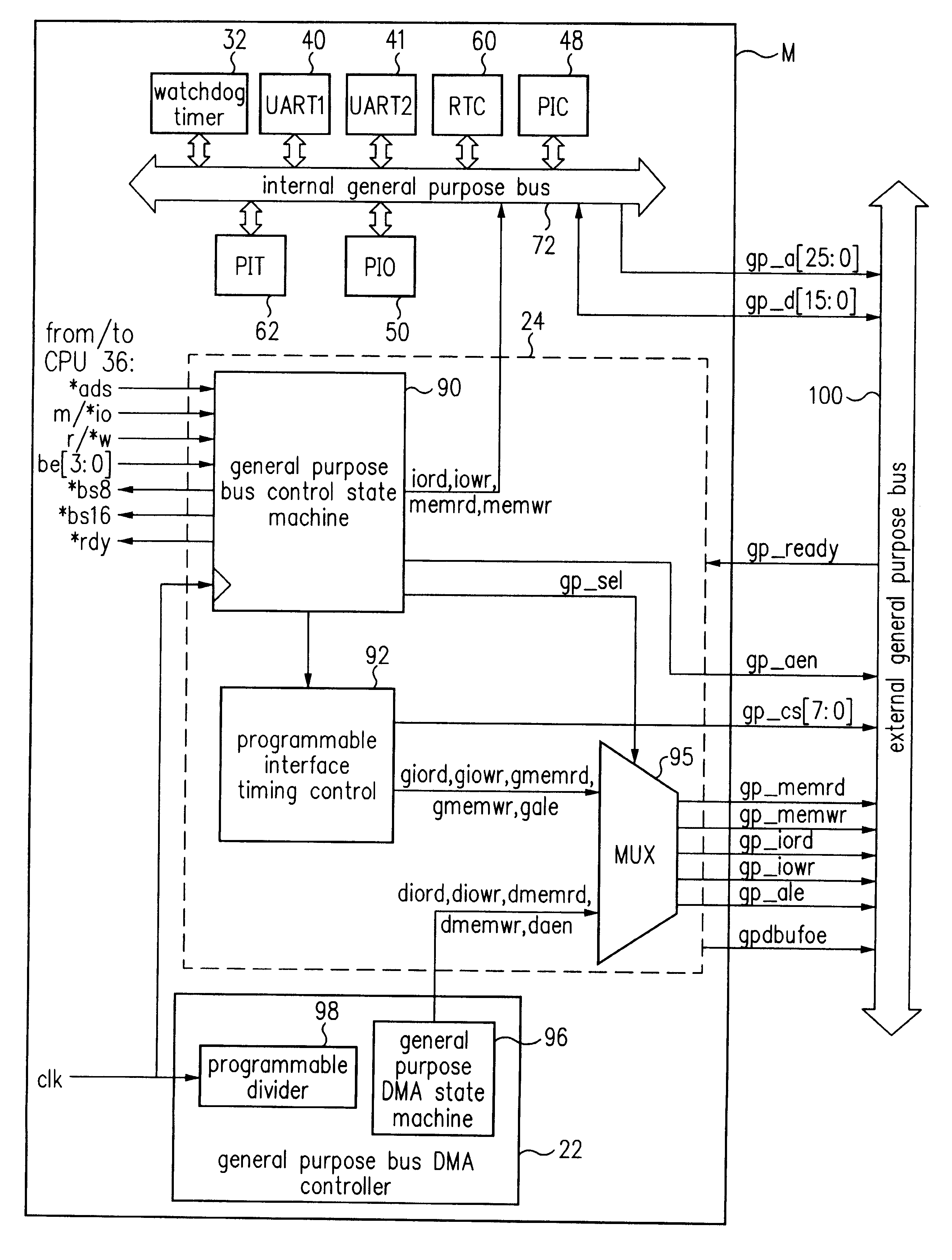
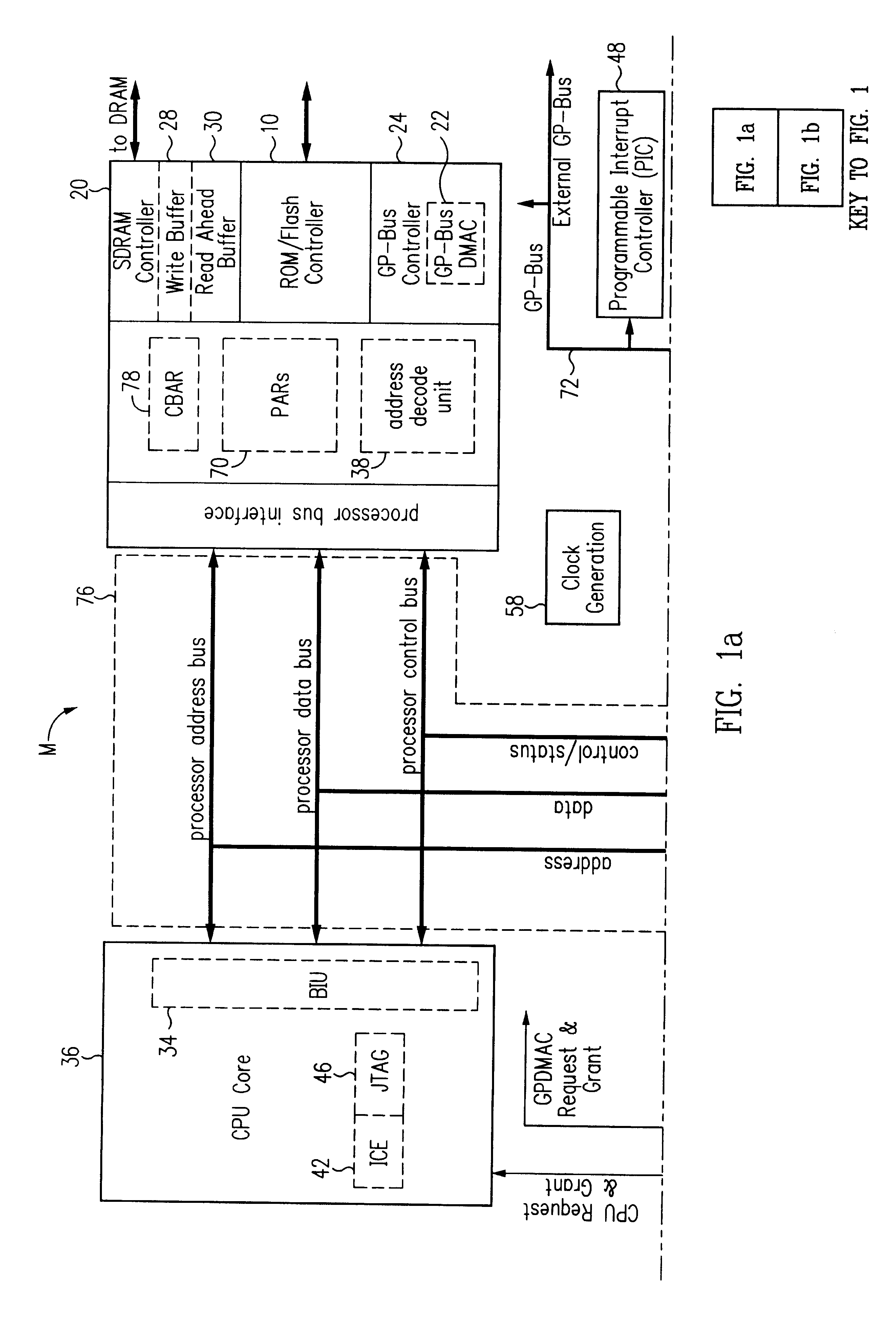
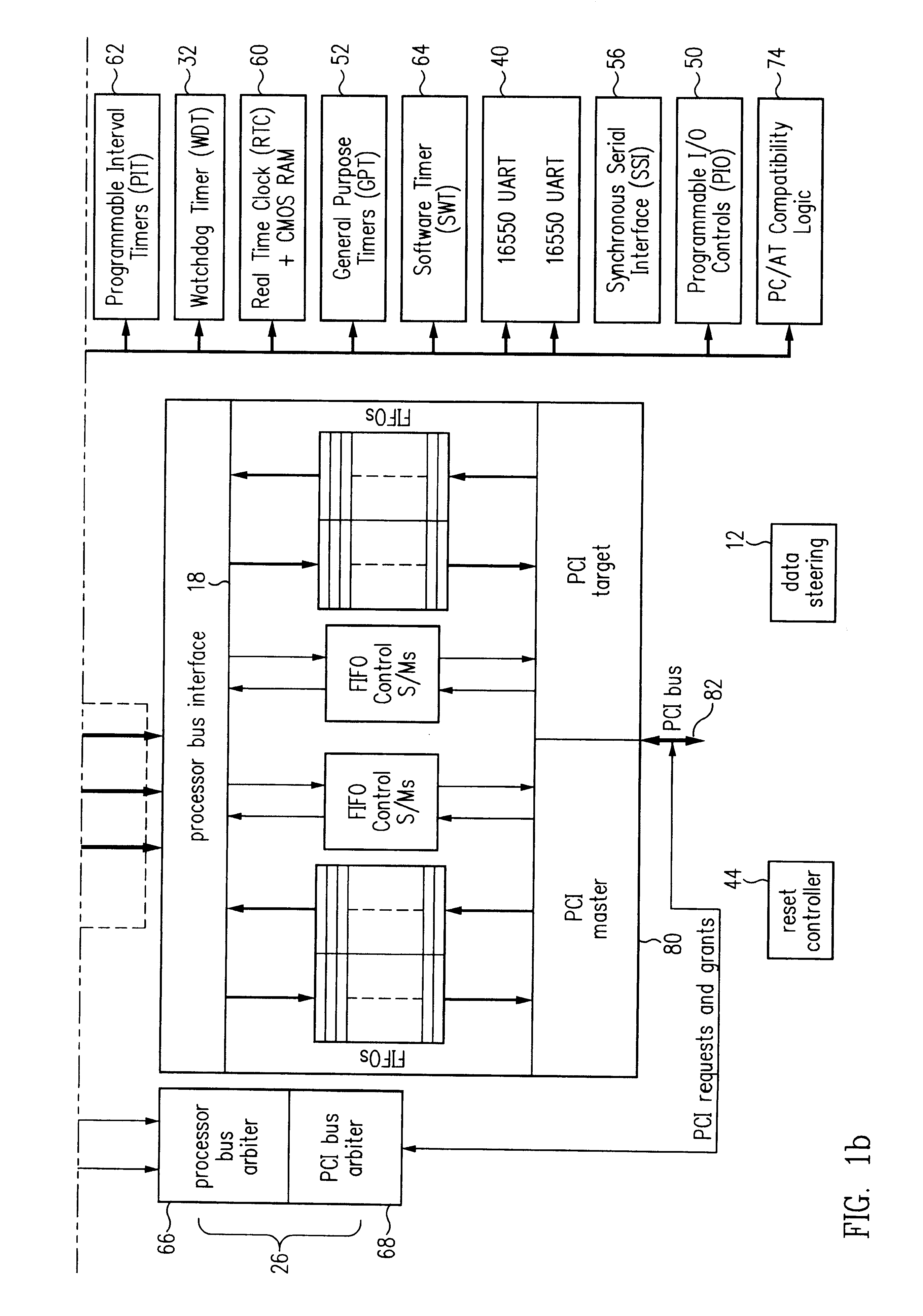
General purpose bus with programmable timing
InactiveUS6490638B1Generating/distributing signalsInput/output processes for data processingGeneral purposeMicrocontroller
A system provides a general purpose bus with programmable timing capability. As part of a microcontroller, this general purpose bus provides a mechanism for communication between general purpose peripherals connected to the bus and enables external devices to be connected with proper timing to the microcontroller. The general purpose bus controller includes programmable interface timing control logic which allows the bus cycle length for commands from a processor or other bus master to be programmed. Accordingly, memory and I / O read and write commands are customized to suit the timing requirements of peripheral devices connected externally to the microcontroller. A significant variety of peripheral devices may thus be coupled to the microcontroller without requiring additional glue logic. The general purpose bus controller further includes an echo mode which permits accesses to internal peripheral devices to be interpreted by a logic analyzer or other debugging equipment.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
PCI bus utilization diagnostic monitor
The present invention provides a PCI Bus Diagnostic Monitor which eliminates the need to hook up a logic analyzer and manually analyze the data passing on the PCI Bus. The present invention provides an accurate analysis of the PCI Bus master's utilization and / or latency time to acquire the PCI Bus by controlling a 12-bit counter and analyzing count values at appropriate times, e.g., between the time the PCI Bus request is output and the time that the data transfer begins, and the time between when the data transfer begins and when the data transfer ends. The data corresponding to a large number of data transfers may be buffered and analyzed to provide performance statistics relating to the PCI Bus. The analysis can be performed in lightly loaded, typically loaded, and heavily loaded PCI bus situations to fully and accurately test real-world capabilities of new peripherals, particular combinations of peripherals, and statistics relating to customized usage of a host system. The accurate statistics relating to the performance of the PCI Bus will also allow a system designer to assign and / or reassign PCI Bus priorities for various bus agents or peripherals.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
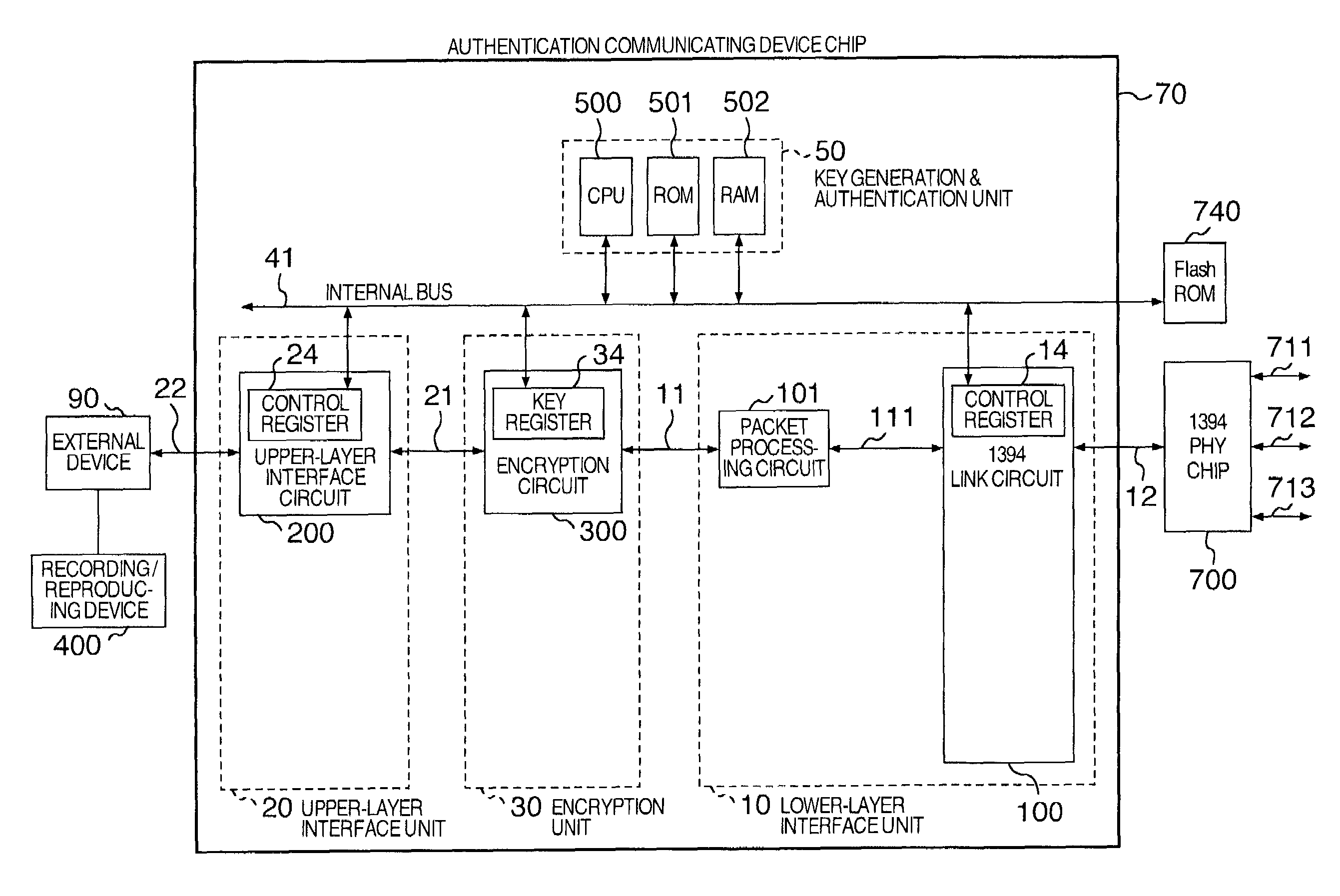
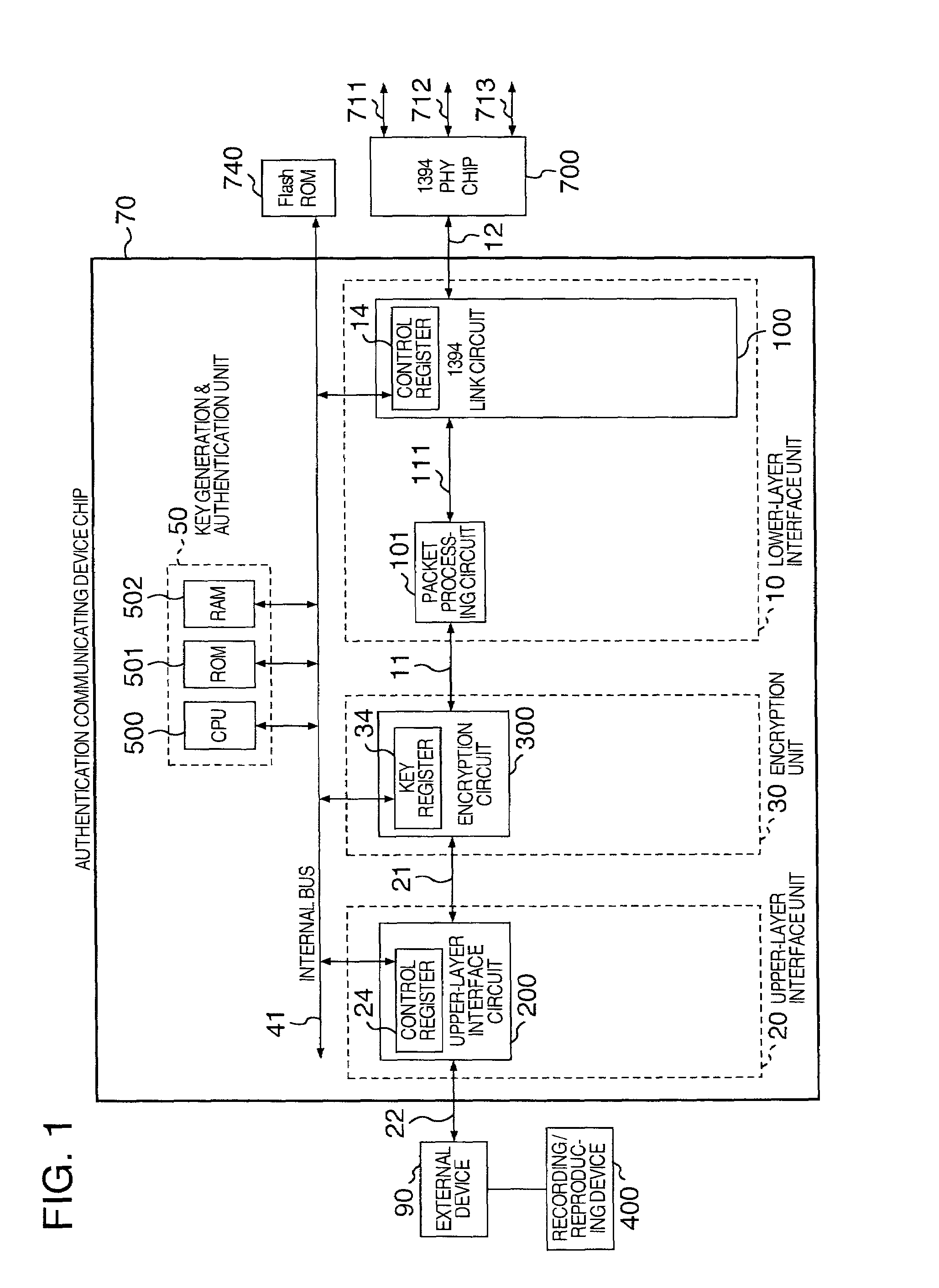
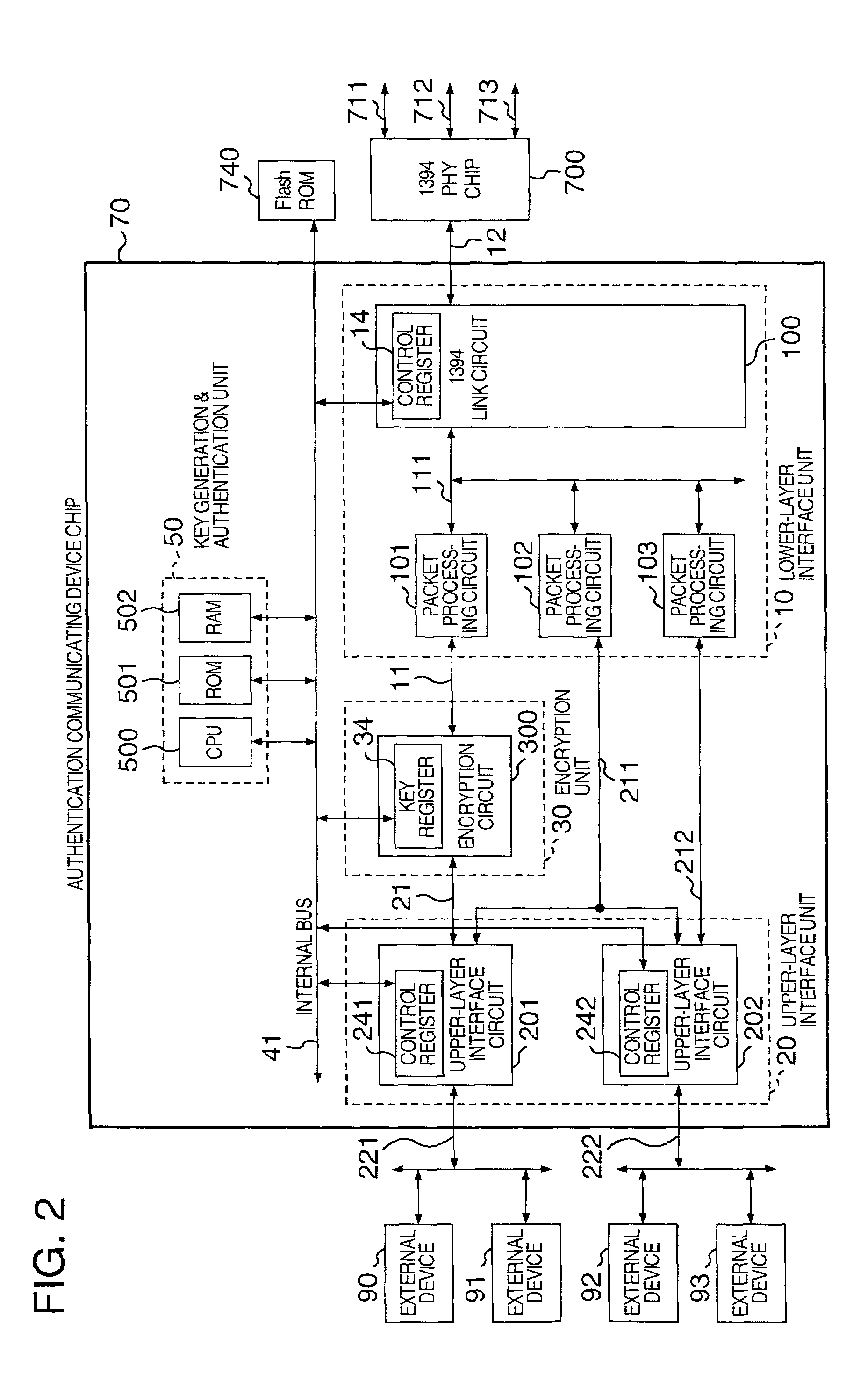
Authentication communicating semiconductor device
InactiveUS7107458B2Improve securityLow costTelevision system detailsDigital data processing detailsMain processing unitControl communications
In an authentication communicating semiconductor device to enhance protection against illegal copying, a logic analyzer probe or the like is connected to a CPU bus to suppress possibility in which the authentication process is intercepted and is analyzed to break the mechanism of illegal copy protection and the electronic device is modified to set a tampered encryption key to the CPU bus. The authentication communicating semiconductor device includes a semiconductor chip, a main processing unit formed on the chip for generating a key code according to a predetermined algorithm, for determining approval / non-approval of communication of data with an external device, and for controlling the communication; an encryption unit formed on the chip for encrypting and decoding communication data using the key code generated by the main processing unit, and an interface unit formed on the chip for conducting communication with an upper-layer or a lower-layer according to a predetermined protocol.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
System for integrating event-related information and trace information
InactiveUS7103530B1Error detection/correctionSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationMicrocontrollerDisplay device
An emulation and debugging system that includes an in-circuit emulator couplable to a microcontroller. The in-circuit emulator is adapted to execute an event thread in lock-step with the microcontroller. Event information generated as a result of executing the event thread is sampled at selected points and the sampled event information is stored in memory. Trace information is also recorded at the selected points. The sampled event information and the recorded trace information are time-stamped. In one embodiment, a display device is coupled to the in-circuit emulator. The display device is used for displaying analog and / or digital waveforms representing the sampled event information and the recorded trace information. Accordingly, an in-circuit emulator system can also function as an oscilloscope and / or as a logic analyzer, allowing a user to view event and trace information, along with other information, that are generated as part of the debugging process.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
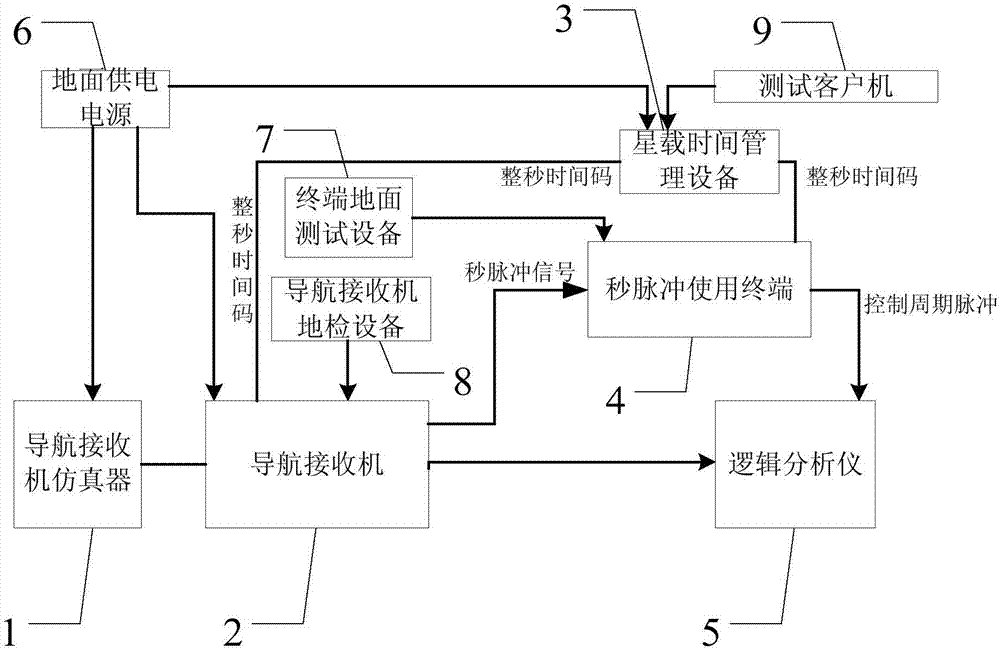
Spacecraft synchronization precision test system and spacecraft synchronization precision test method based on second pulse
ActiveCN106909071ARealize computingImplement testElectric unknown time interval measurementRadio-controlled time-piecesTime managementEngineering
A spacecraft synchronization precision test system and a spacecraft synchronization precision test method based on second pulse are disclosed. The system comprises a navigation receiver simulator, a navigation receiver, a satellite-borne time management device, a second pulse using terminal, a logic analyzer, a ground power supply, a terminal ground test device, a navigation receiver ground inspection device, and a test client. The logic analyzer compares the control cycle pulse of the second pulse using terminal with a hardware second pulse signal provided by the navigation receiver to get the second pulse synchronization precision between the terminal and the navigation receiver. The system can acquire the actual parameter value of the control cycle pulse quickly by using a telemetry signal recorded by the second pulse using terminal. The second pulse synchronization precision can be calculated and tested conveniently and quickly according to the output value of hardware second pulse read by the logic analyzer.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
Testing microelectronic devices using electro-optic modulator probes
InactiveUS20080122463A1Electrical measurement instrument detailsUsing optical meansTransducerOpto electronic
Testing microelectronic devices using electro-optic modulator probes is disclosed. In one aspect, a testing apparatus may include an electrical signaling medium to exchange electrical signals with a microelectronic device. The testing apparatus may include an electro-optic modulator probe to provide optical signals that are modulated by the electrical signals. An optoelectronic transducer may be included to convert the modulated optical signals to modulated electrical signals. The testing apparatus may further include a logic analyzer module to receive and analyze the modulated electrical signals. Other testing apparatus are disclosed, as well as systems incorporating such apparatus, and various methods of testing microelectronic devices.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Semiconductor device testing method and system employing trace data
InactiveUS6617842B2Electronic circuit testingDetecting faulty computer hardwareSignal waveAutomatic test equipment
Owner:PS4 LUXCO SARL
Communications chip having a plurality of logic analysers
ActiveUS7680142B1Time-division multiplexStore-and-forward switching systemsTraffic capacityLogic analyzer
A communications chip having a plurality of ports. Each port is provided with an interface for attachment to an external communications facility to exchange data traffic. There is also a switching matrix for routing data traffic on the chip between the ports. The chip further includes a plurality of logic analyzers. Each logic analyzer is associated with a corresponding one of the ports. Each logic analyzers is operable to monitor data traffic passing through its corresponding port and to trigger on one or more predetermined conditions relating to the monitored data traffic. The chip further includes a control interface to allow reconfiguration of the predetermined conditions for at least one of the logic analyzers.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
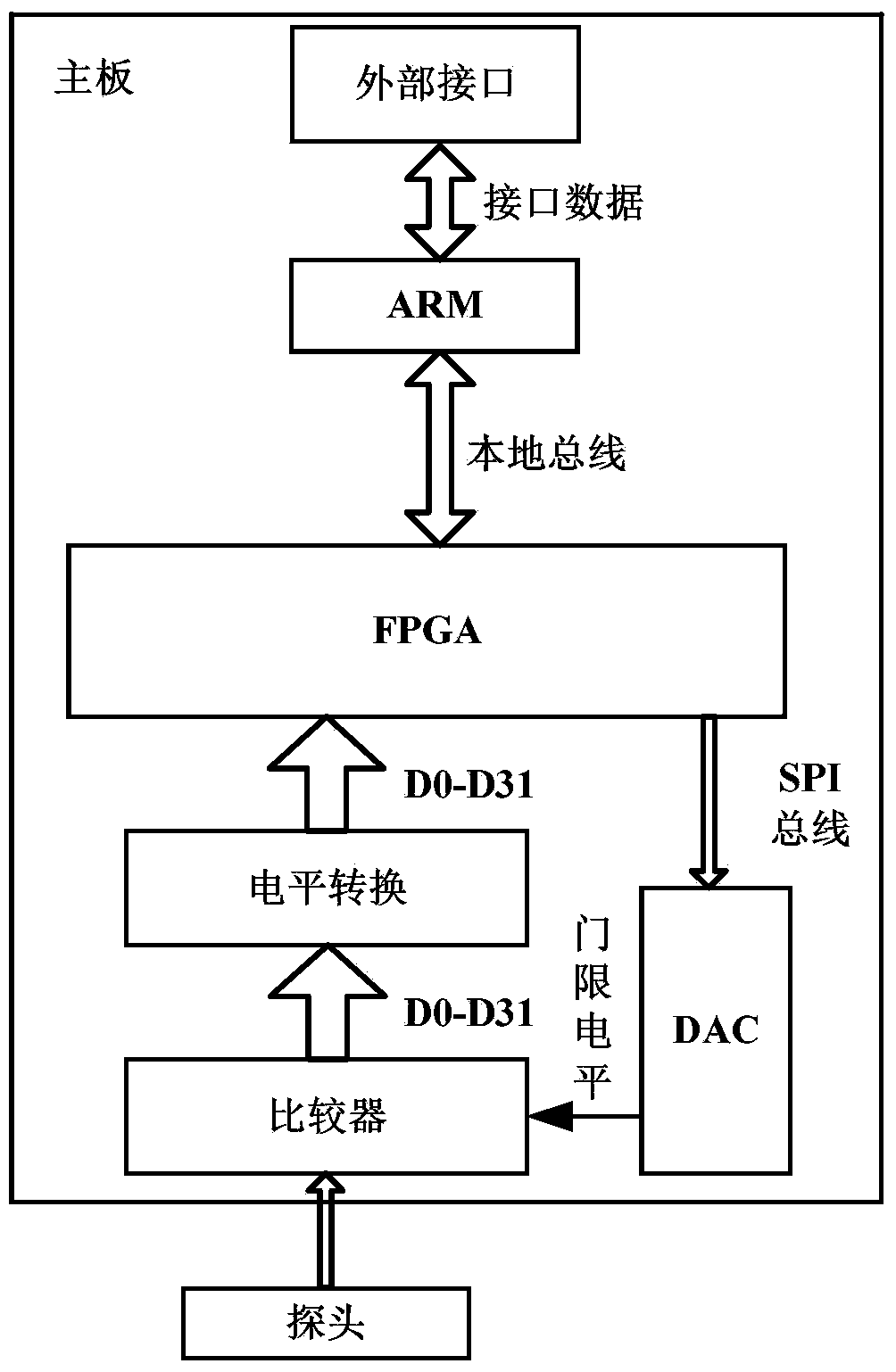
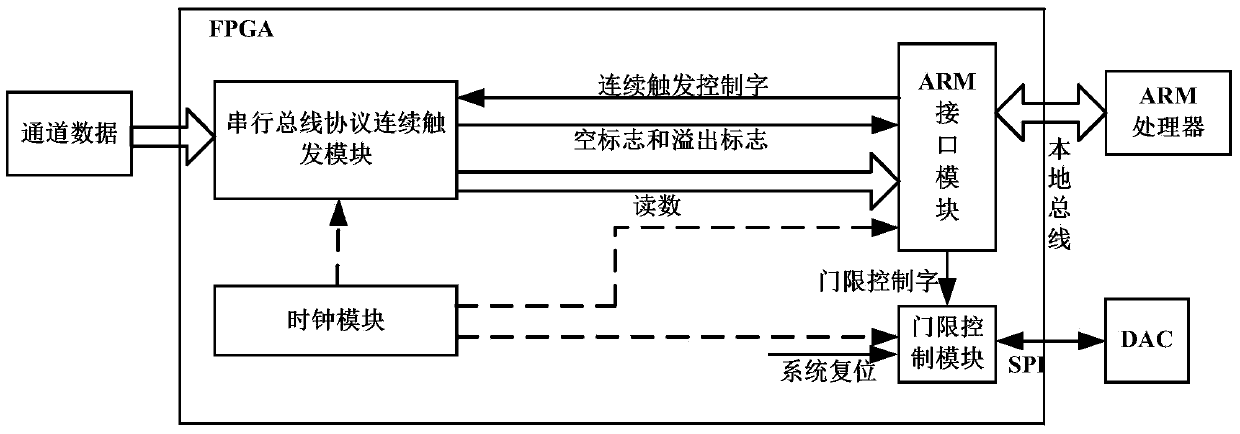
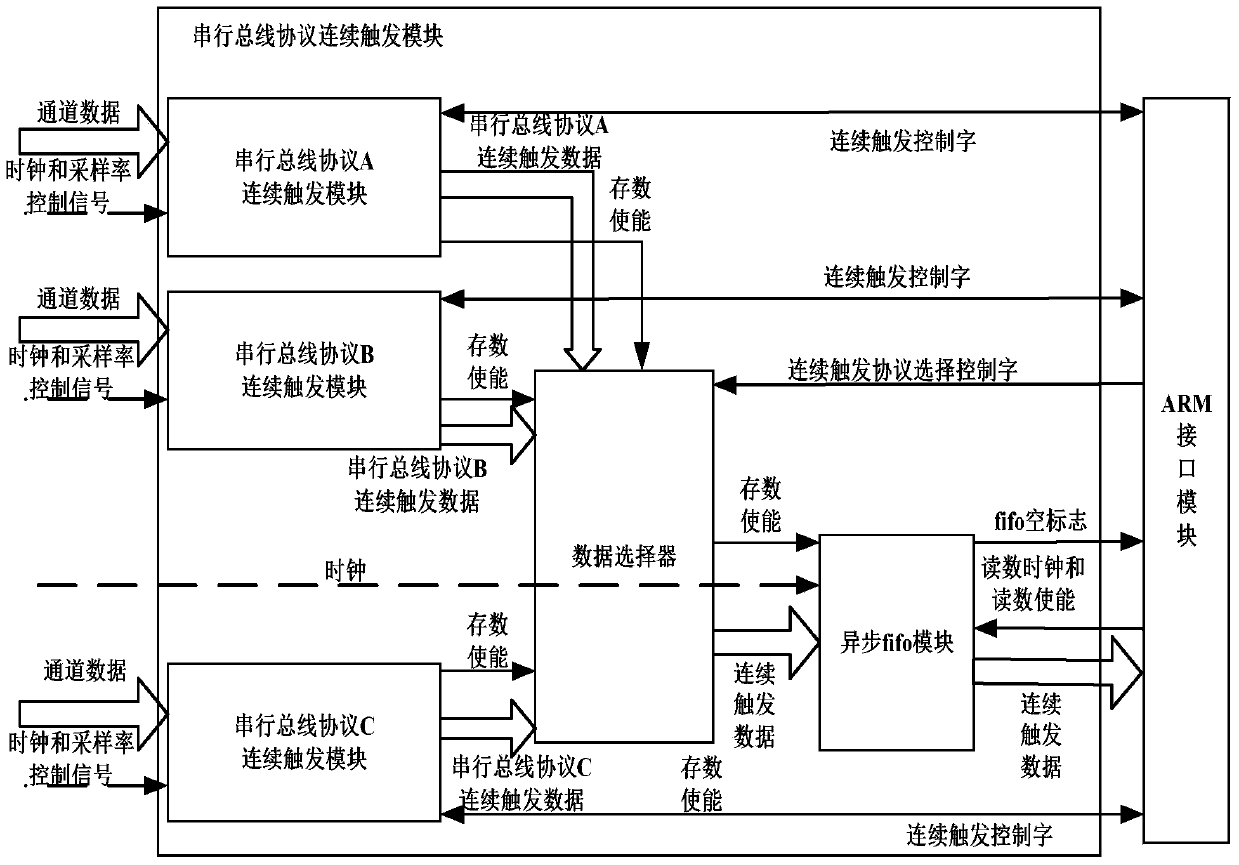
Logic analyzer with serial bus protocol continuous triggering function
InactiveCN103995764ARealize long-term continuous monitoringTargetedLogical operation testingChannel dataMultiplexer
The invention discloses a logic analyzer with a serial bus protocol continuous triggering function. Each continuous triggering module in an FPGA corresponds to a serial bus protocol. A clock timer in each continuous triggering module provides a clock overflow mark and clock data. Each continuous triggering state machine corresponds to a triggering mode. Channel data are received, and continuous triggering data collecting is triggered according to continuous triggering control words. In a next cycle after data collecting is completed, data storing enable signals are enabled to be effective. A data selector is triggered to select continuous triggering data to be output to a data splicing module. The data storing enable signals are selected to be output to the data selector. The data splicing module combines the clock data and the continuous triggering data and then output the data to the data selector. The data selector in the FPGA outputs corresponding continuous triggering data and data storing enable signals to an asynchronization FIFO module according to triggering type control words. The asynchronization FIFO module stores the continuous triggering data which are provided for an ARM processor to read. According to the logic analyzer, hardware is used for achieving continuous triggering of the serial bus protocol.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Efficient emulation and logic analysis
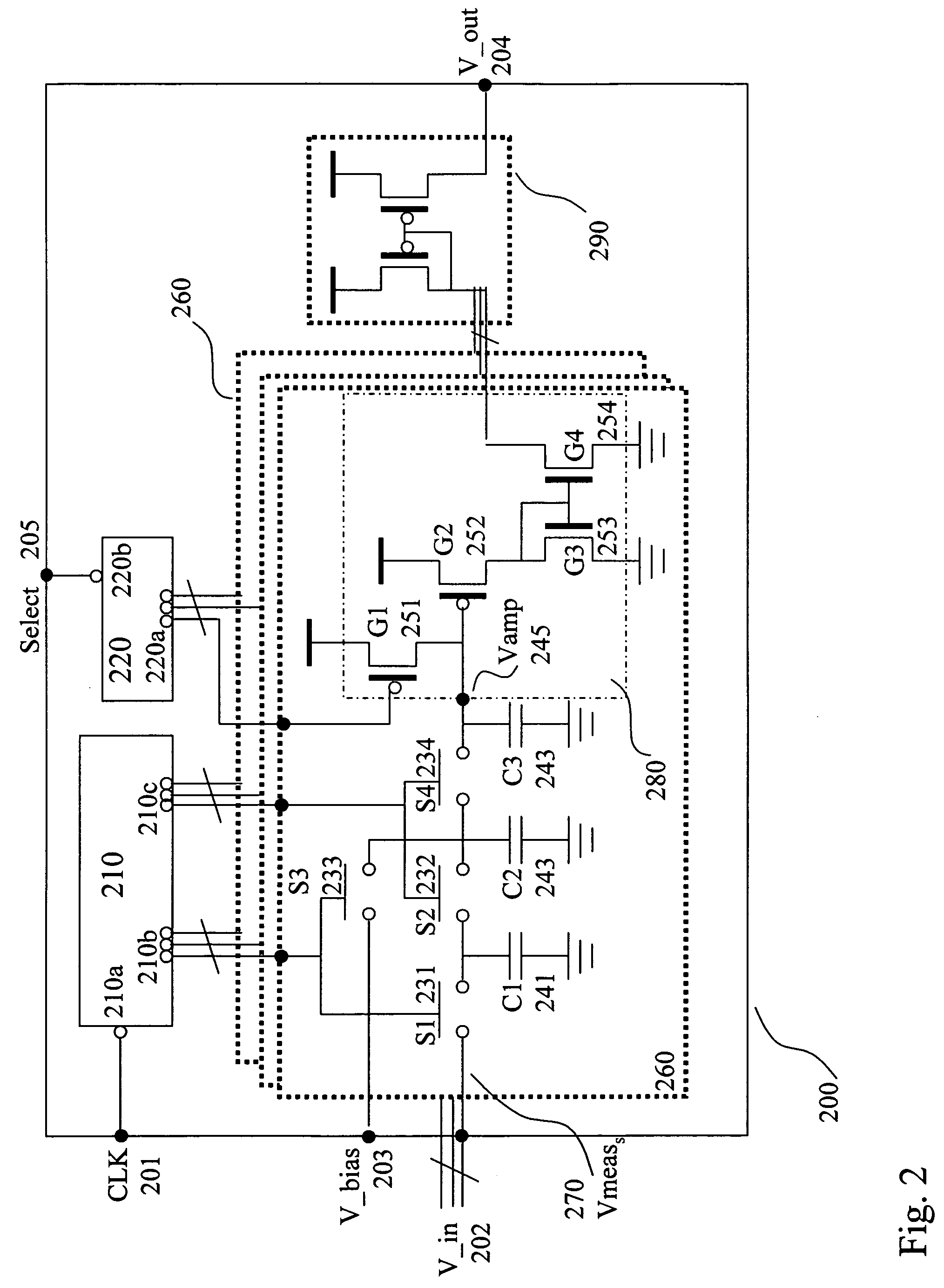
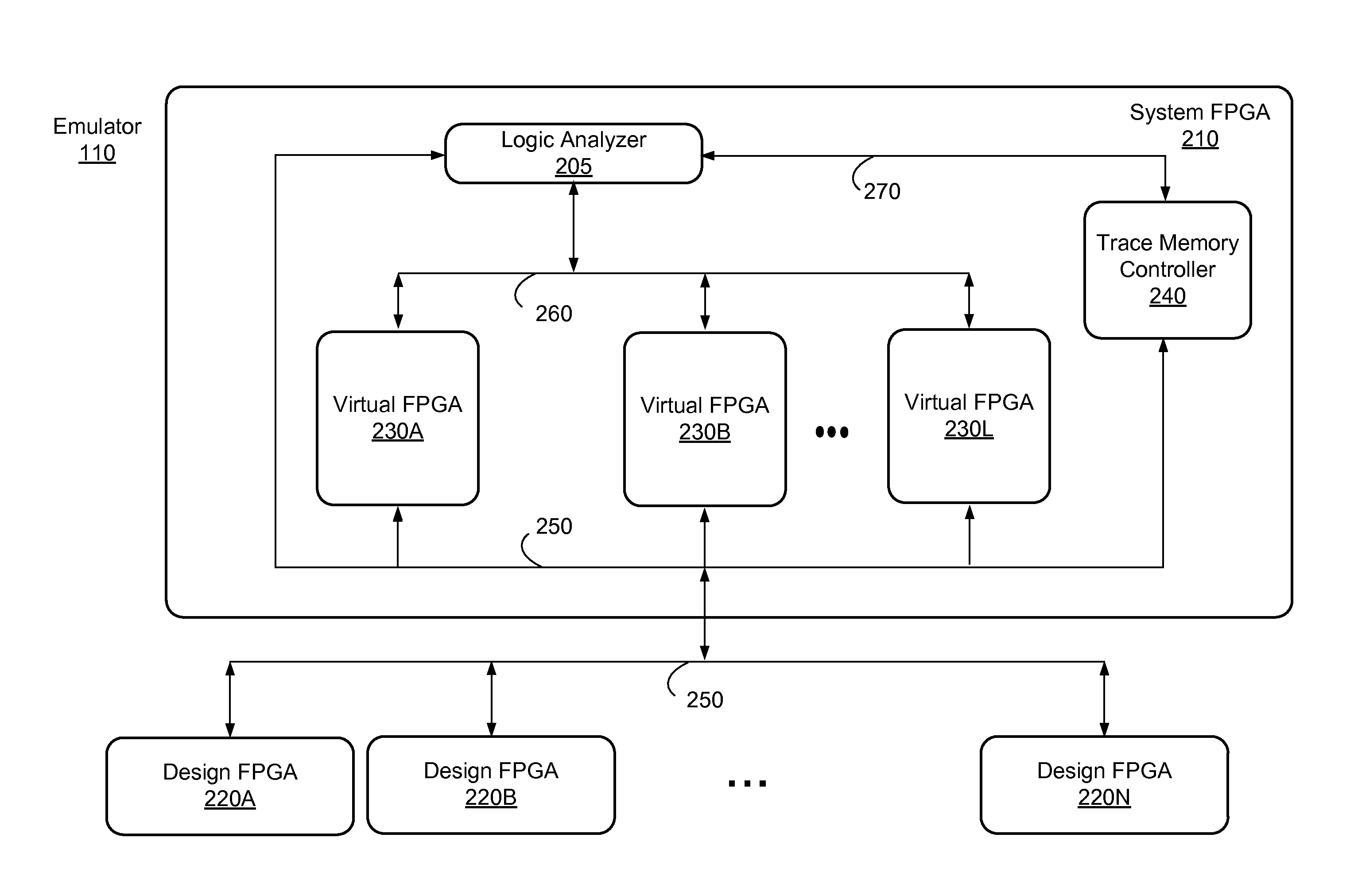
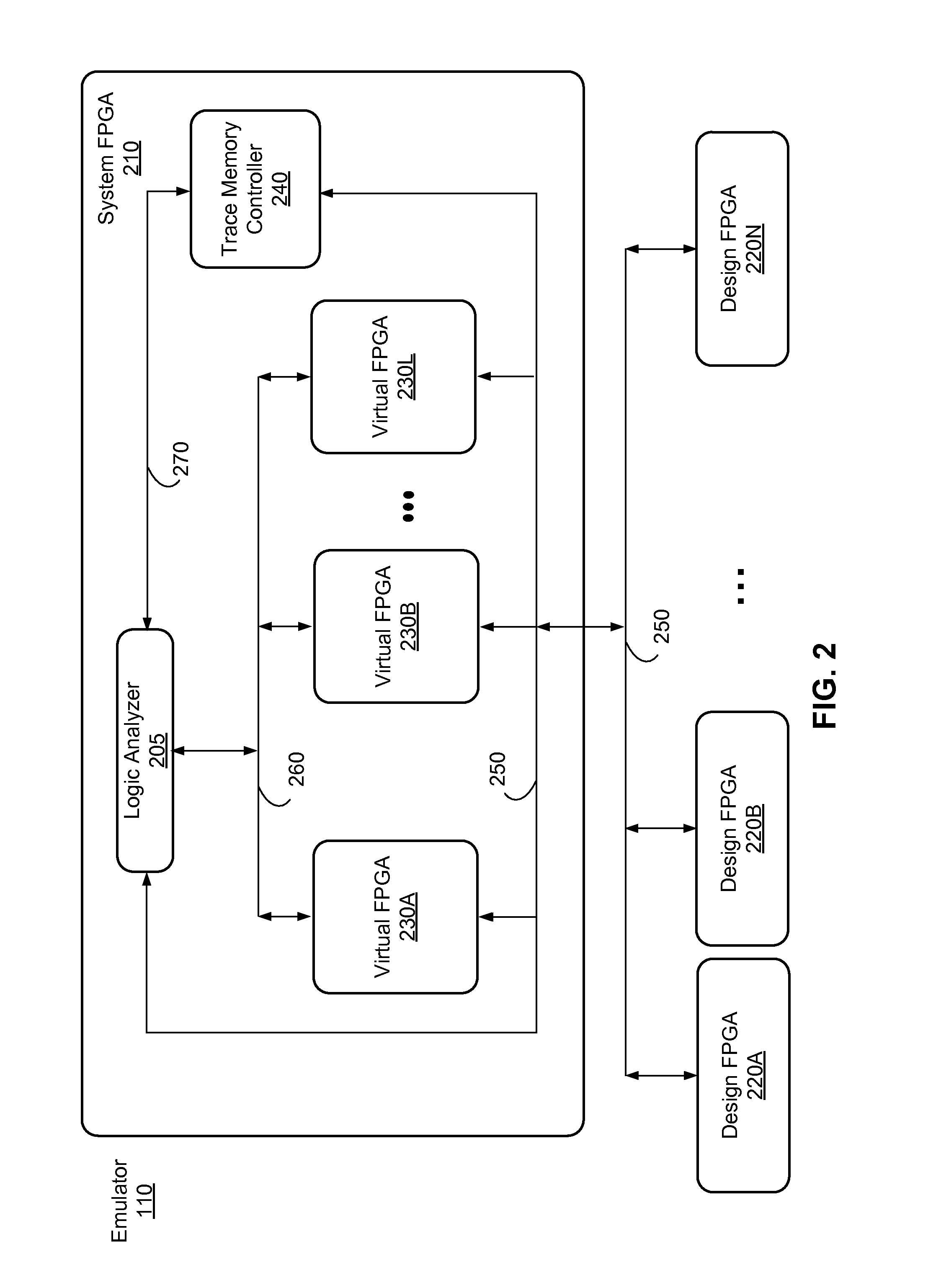
ActiveUS20160098505A1Computer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsParallel computingLogic analyzer
An emulation environment includes a host system and an emulator. The host system configures the emulator to load a design under test (DUT) and the emulator emulates the DUT. The emulator includes one or more design field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) that emulate the DUT. In addition, the emulator includes at least one system FPGA with a logic analyzer and multiple virtual FPGA. The virtual FPGAs emulate sections of the DUT. By the virtual FPGAs emulating sections of the DUT, the logic analyzer is able to obtain for performing logic analysis certain signals from the virtual FPGAs, rather than from the design FPGAs.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
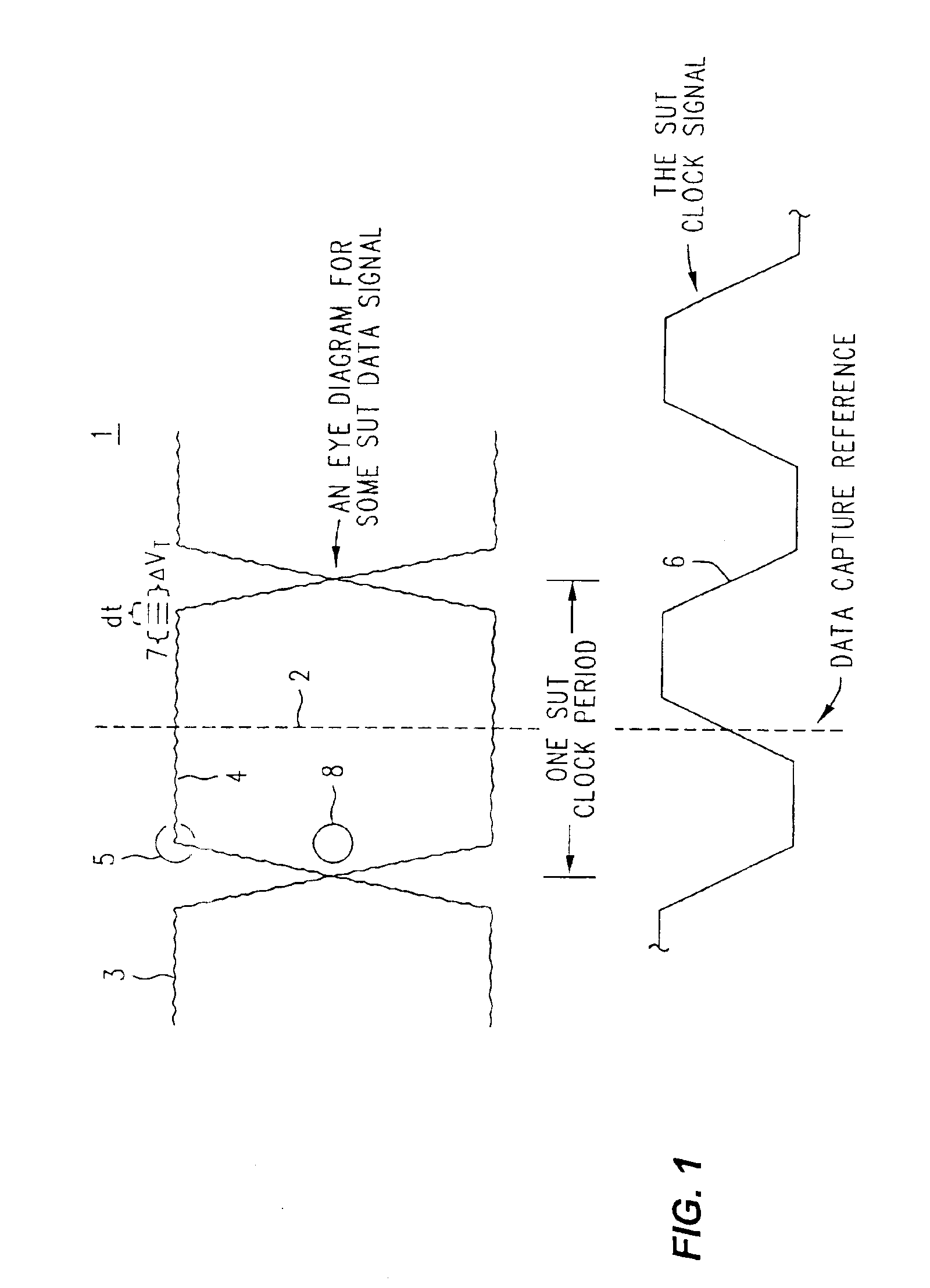
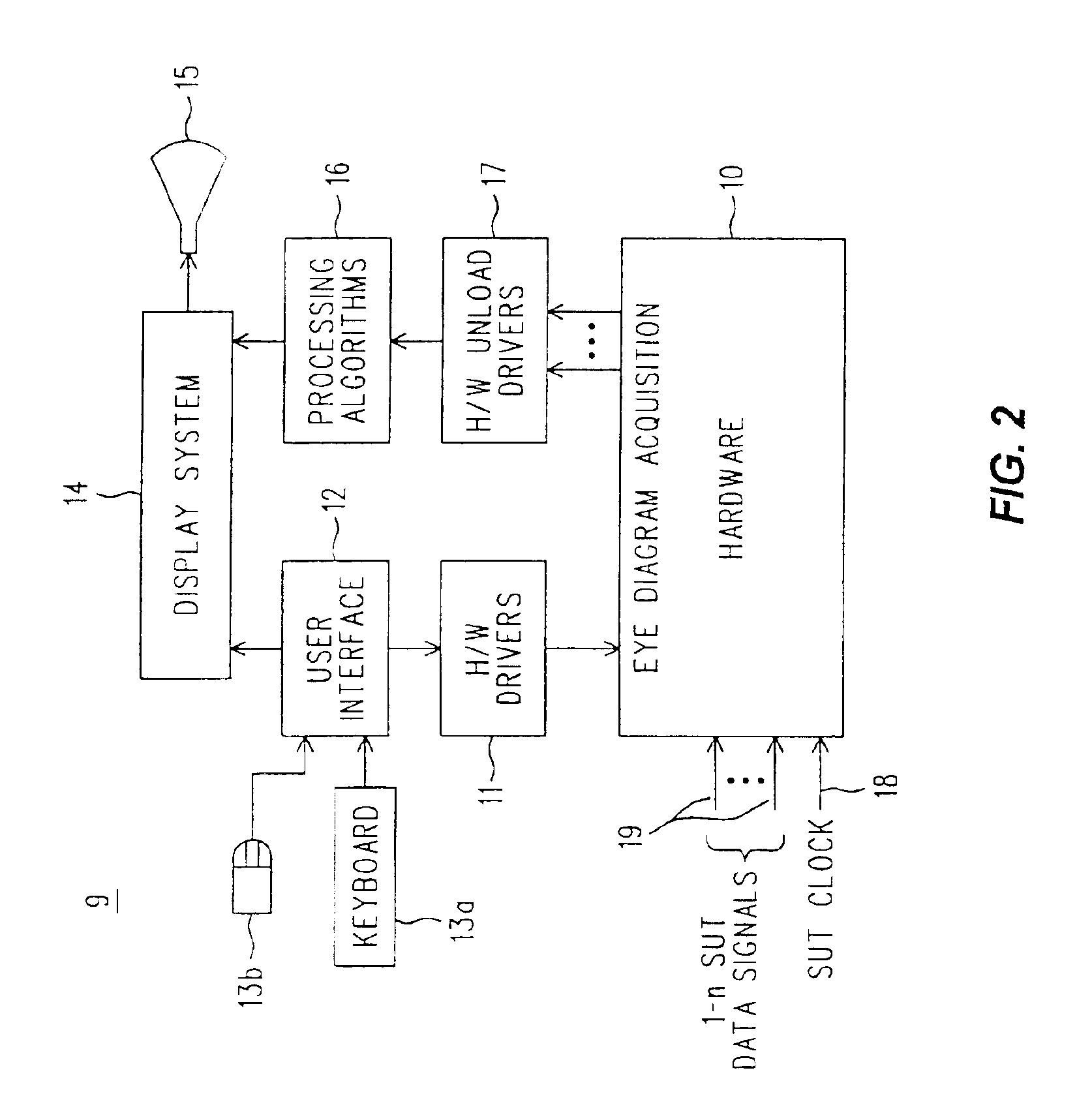
Method and apparatus for performing eye diagram measurements
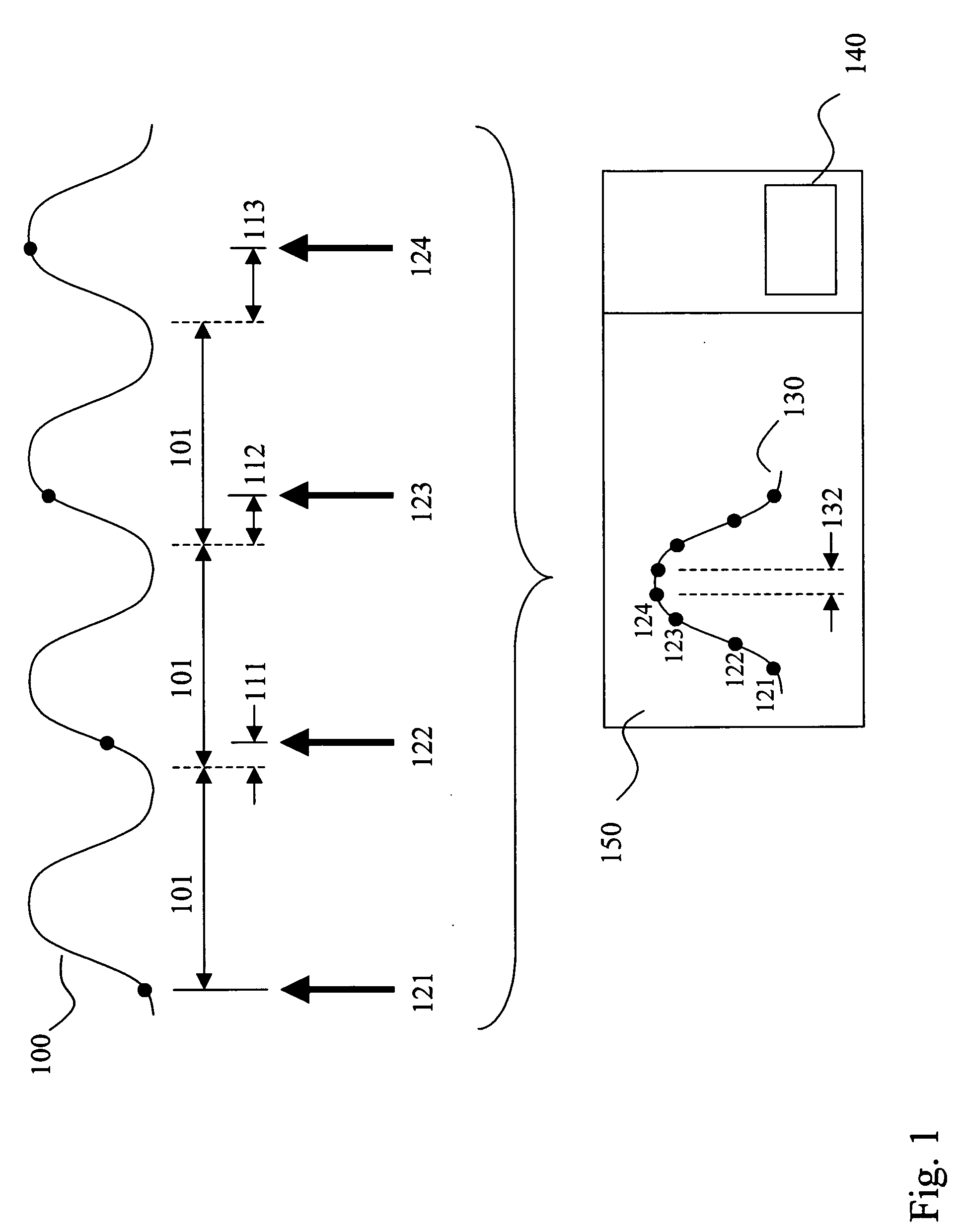
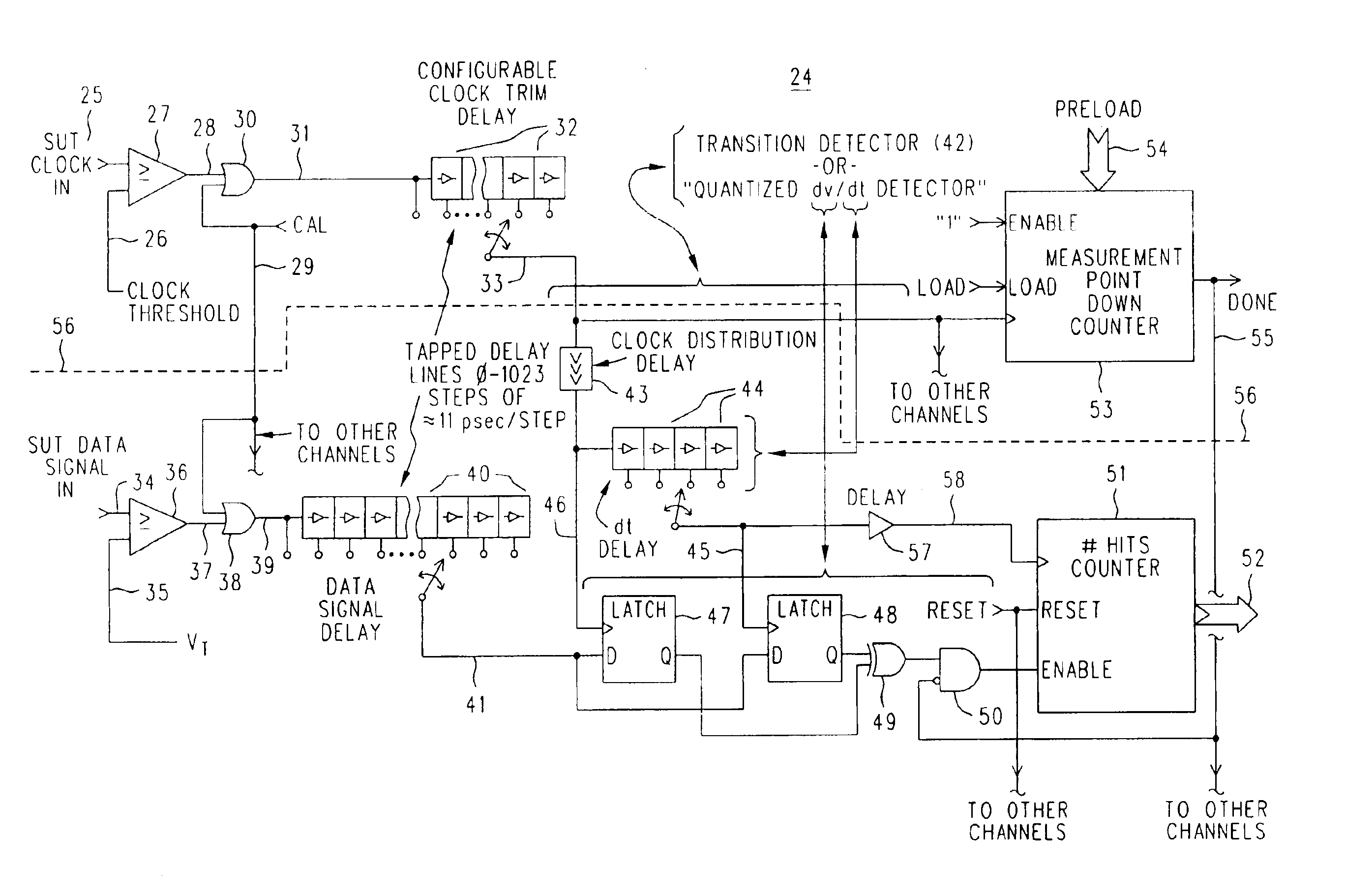
An eye diagram analyzer equips each SUT data and clock signal input channel with individually variable delays in their respective paths. For a range of signal delay of n-many SUT clock cycles, the SUT clock signal delay might be set at about n / 2. For each data channel there is specified a point in time relative to an instance of the delayed clock signal (data signal delay) and a voltage threshold. The specified combination (data signal delay, threshold and which channel) is a location on an eye diagram, although the trace may or may not ever go through that location. A counter counts the number of SUT clock cycles used as instances of the reference for the eye diagram, and another counter counts the number of times the specified combination of conditions was met (“hits”). After watching a specified combination for the requisite length of time or number of events, the number of SUT clock cycles involved and the associated number of hits are stored in memory using a data structure indexed by the components of the specified combination (data signal delay, threshold). Next, a new combination of data signal delay and threshold is specified and a measurement taken and recorded in the data structure. The process is repeated until all possible combinations within a stated range of data signal delay and threshold voltage (using specified resolution / step sizes for delay and voltage) have been investigated. As this process proceeds under the control of firmware within the logic analyzer, other firmware can be examining the data structure and generating a partial eye diagram visible on a display, and that will be complete soon after the measurement itself is finished.” has been changed to “An eye diagram analyzer equips each SUT data and clock signal input channel with individually variable delays in their respective paths. For a range of signal delay of n-many SUT clock cycles, the SUT clock signal delay might be set at about n / 2. For each data channel there is specified a point in time relative to an instance of the delayed clock signal (data signal delay) and a voltage threshold. The specified combination (data signal delay, threshold and which channel) is a location on an eye diagram, although the trace may or may not ever go through that location.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Motor vehicle accessory to increase power supply and reduce fuel requirements
ActiveUS20160318406A1Vehicle sub-unit featuresPropulsion by batteries/cellsElectrical batteryPower control system
Owner:HYLIION INC
Integrated Circuit Including a Programmable Logic Analyzer with Enhanced Analyzing and Debugging Capabilities and a Method Therefor
InactiveUS20110047427A1Efficient testingEffectively test and debugElectronic circuit testingDetecting faulty hardware by remote testLogic analyzerComputer science
An integrated circuit including a logic analyzer with enhanced analyzing and debugging capabilities and a method therefor. In one embodiment, an integrated circuit includes a logic analyzer having a first input receiving a plurality of signals and an output for providing an indication of a detection, by the logic analyzer, of at least one trigger event; and a built in self test block having a first input for receiving one or more of the signals appearing at the first input of the logic analyzer, a second input coupled to the output of the logic analyzer for selectively enabling the BIST block, the BIST block generating and maintaining a signature based upon the first and second inputs thereof.
Owner:LEXMARK INT INC
Apparatus and method for dynamic in-circuit probing of field programmable gate arrays
A dynamic probe system for probing a FPGA with at least one core. A trace core is added to the FPGA, the trace core in communication with a plurality of signal banks, each signal bank comprising a plurality of signals in the at least one core. A logic analyzer, in communication with the trace core and selecting the bank of signal to be sent from the trace core to the logic analyzer.
Owner:KEYSIGHT TECH
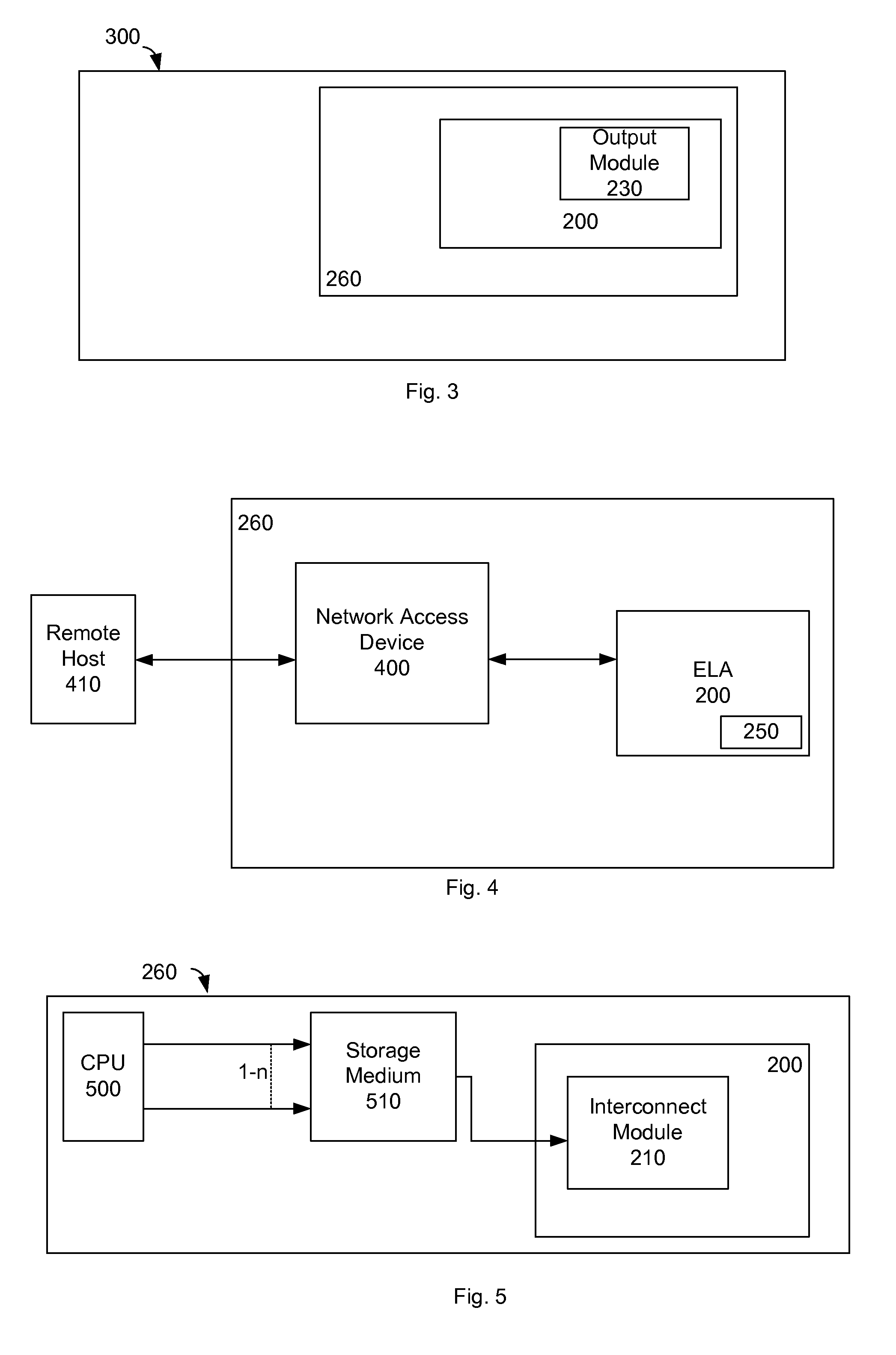
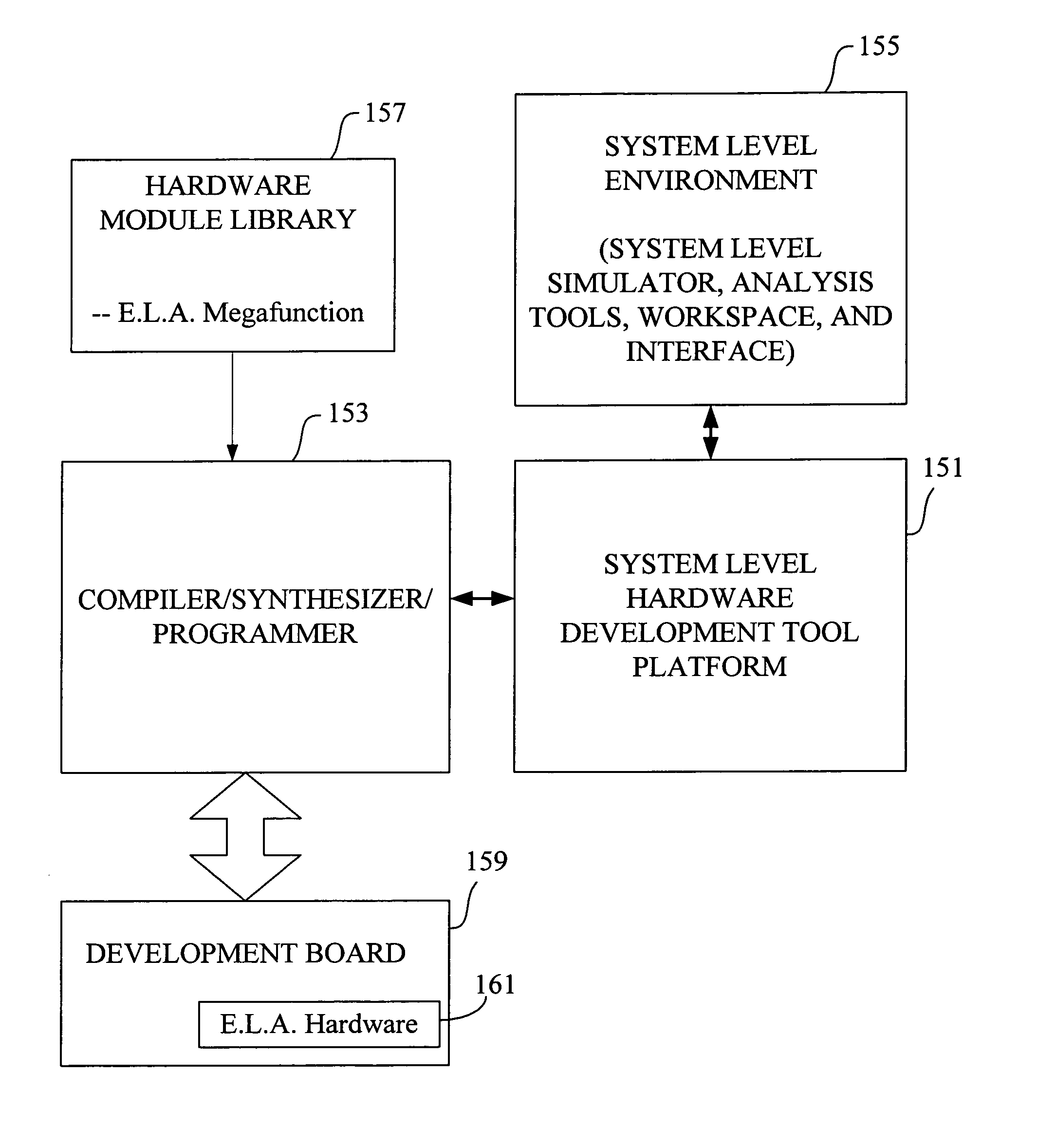
Embedded logic analyzer functionality for system level environments
ActiveUS7991606B1CAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationLogic analyzerElectronic design automation
An electronic design automation system merges embedded logic analyzer technology with system level design and analysis technology. Embedded logic analyzers provide hardware to allow board-level signal capture and subsequent analysis of test devices programmed with a hardware design generated using electronic design automation. System level environments provide interactive tools for entering, modeling, simulating and analyzing multi-domain systems such as DSP designs. Typically, a user enters a system level design as a block diagram, including embedded logic analyzer blocks. The user inserts such blocks at nodes in the design where he or she wishes to capture signals to verify the design.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com