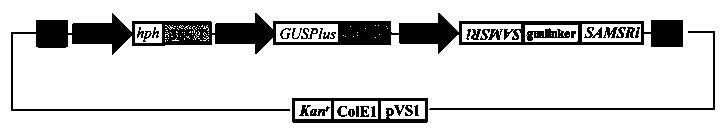
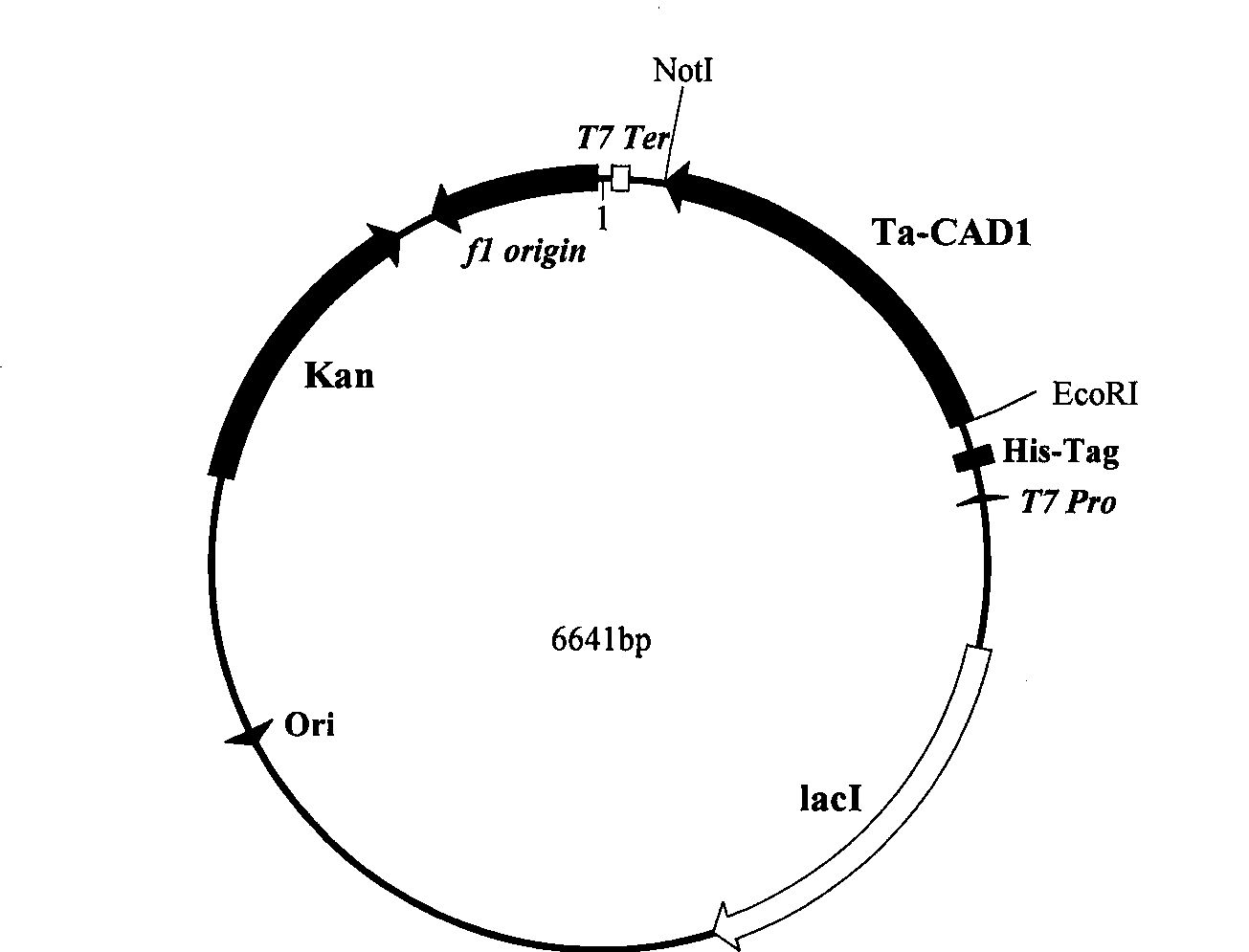
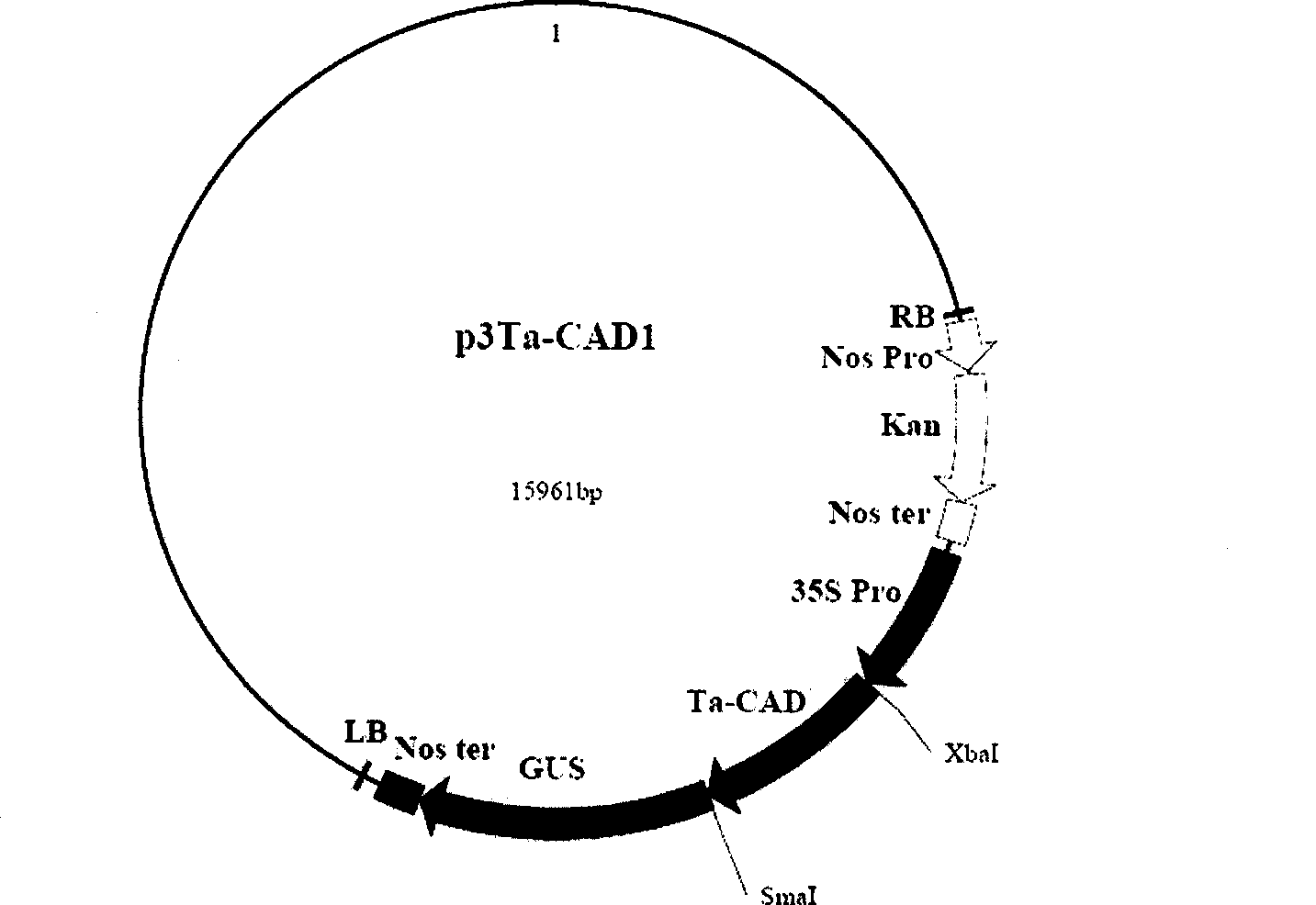
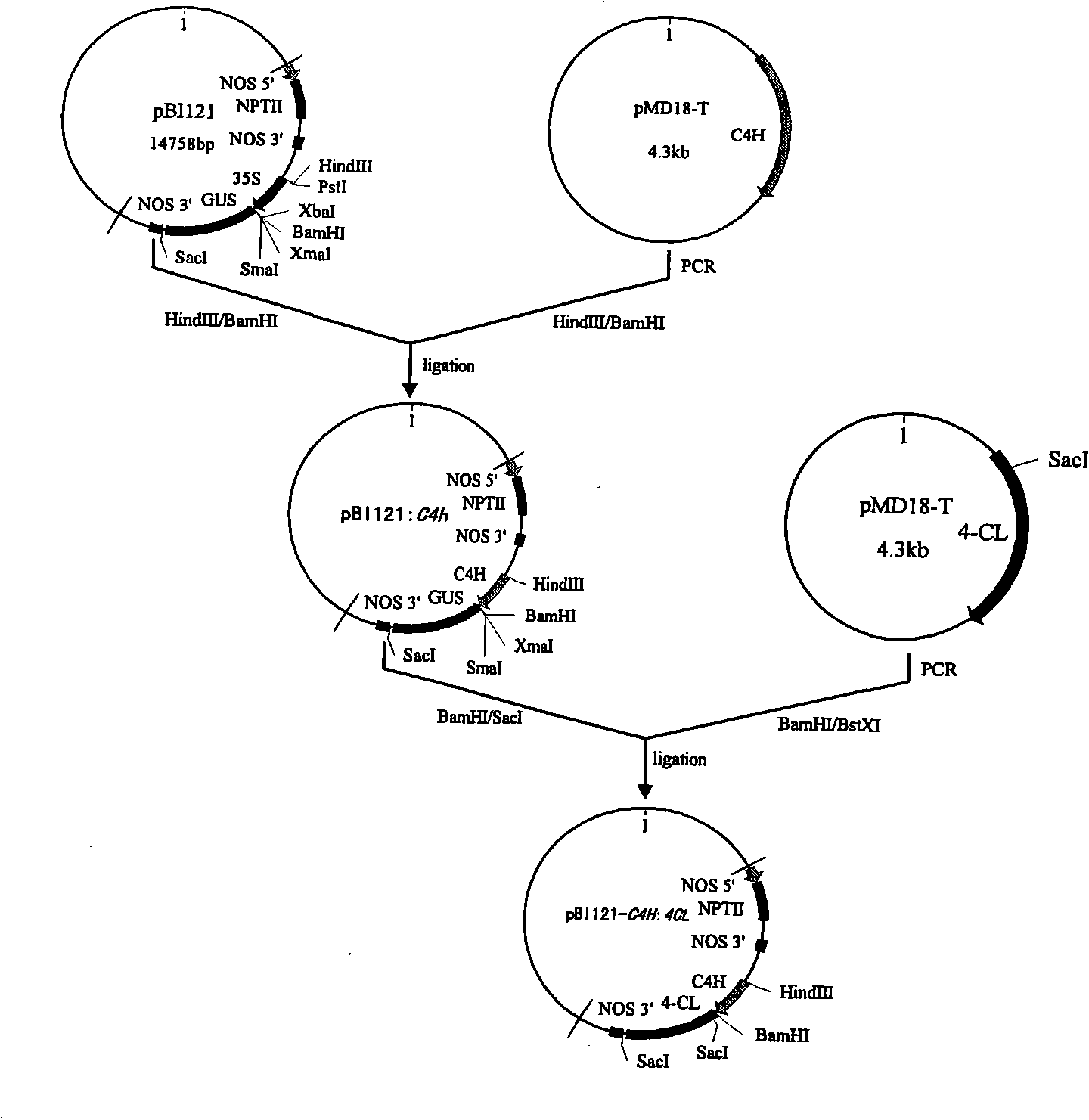
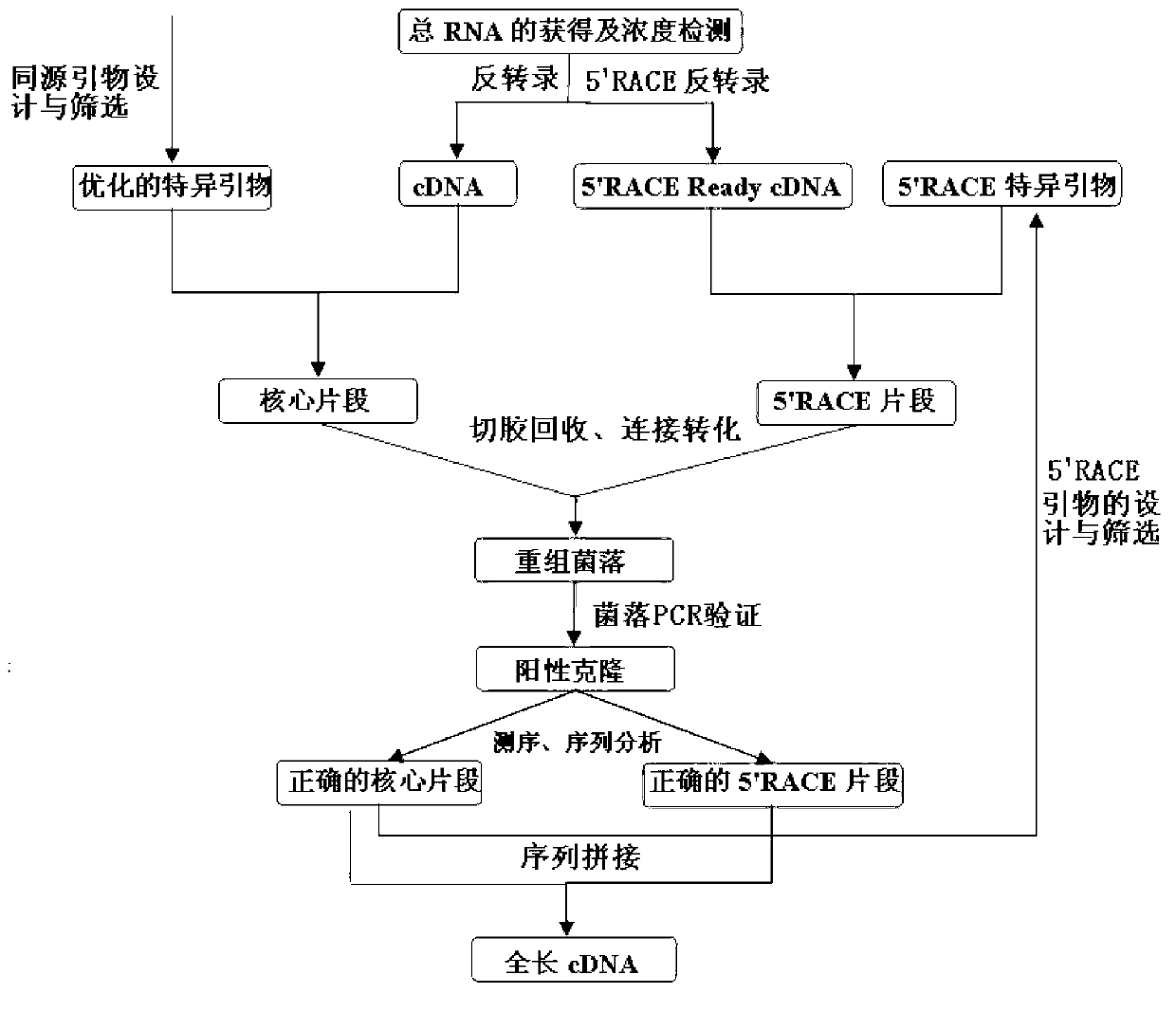
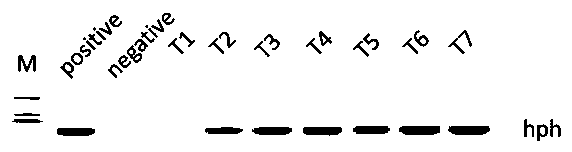Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
84 results about "Lignin synthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
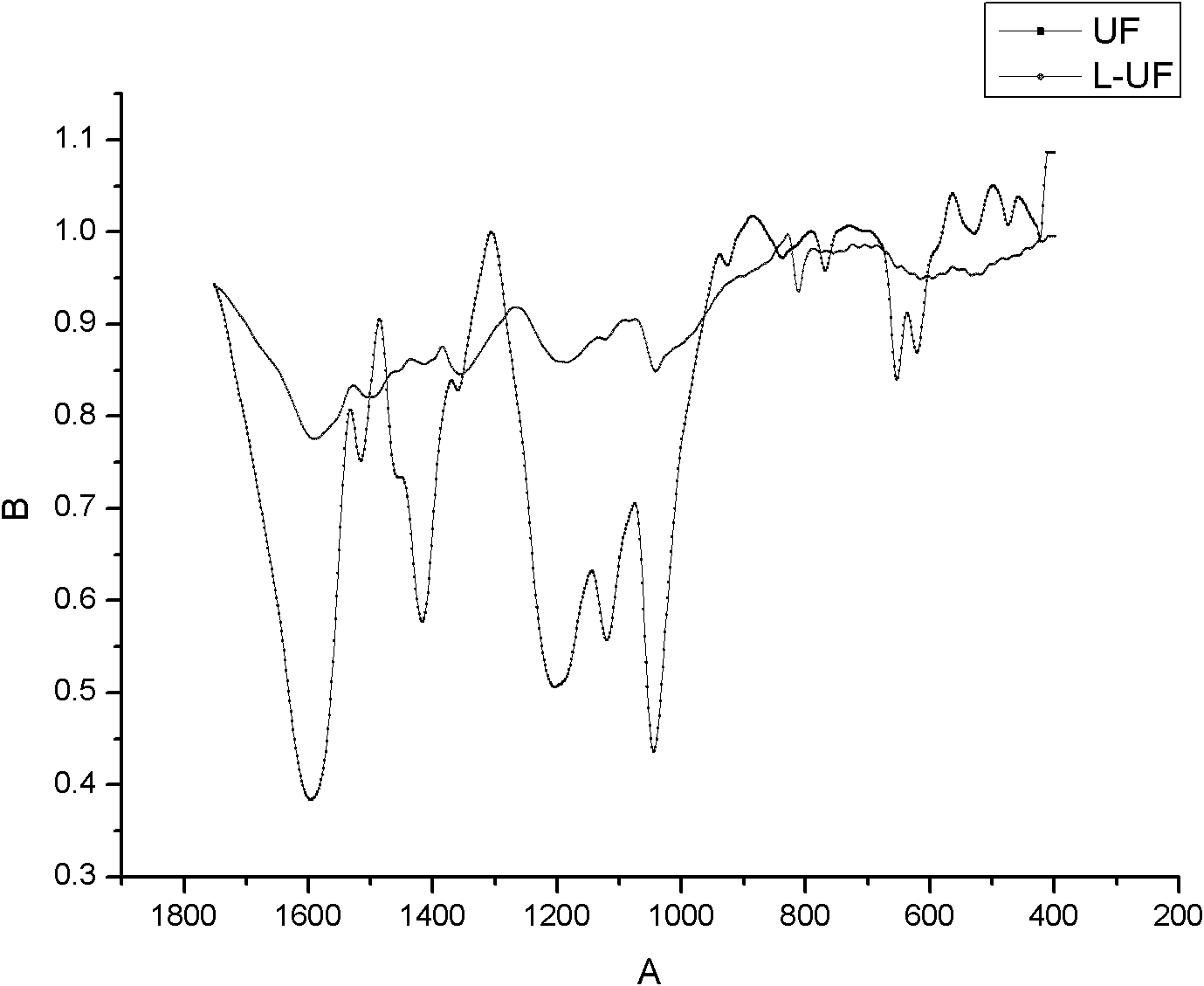
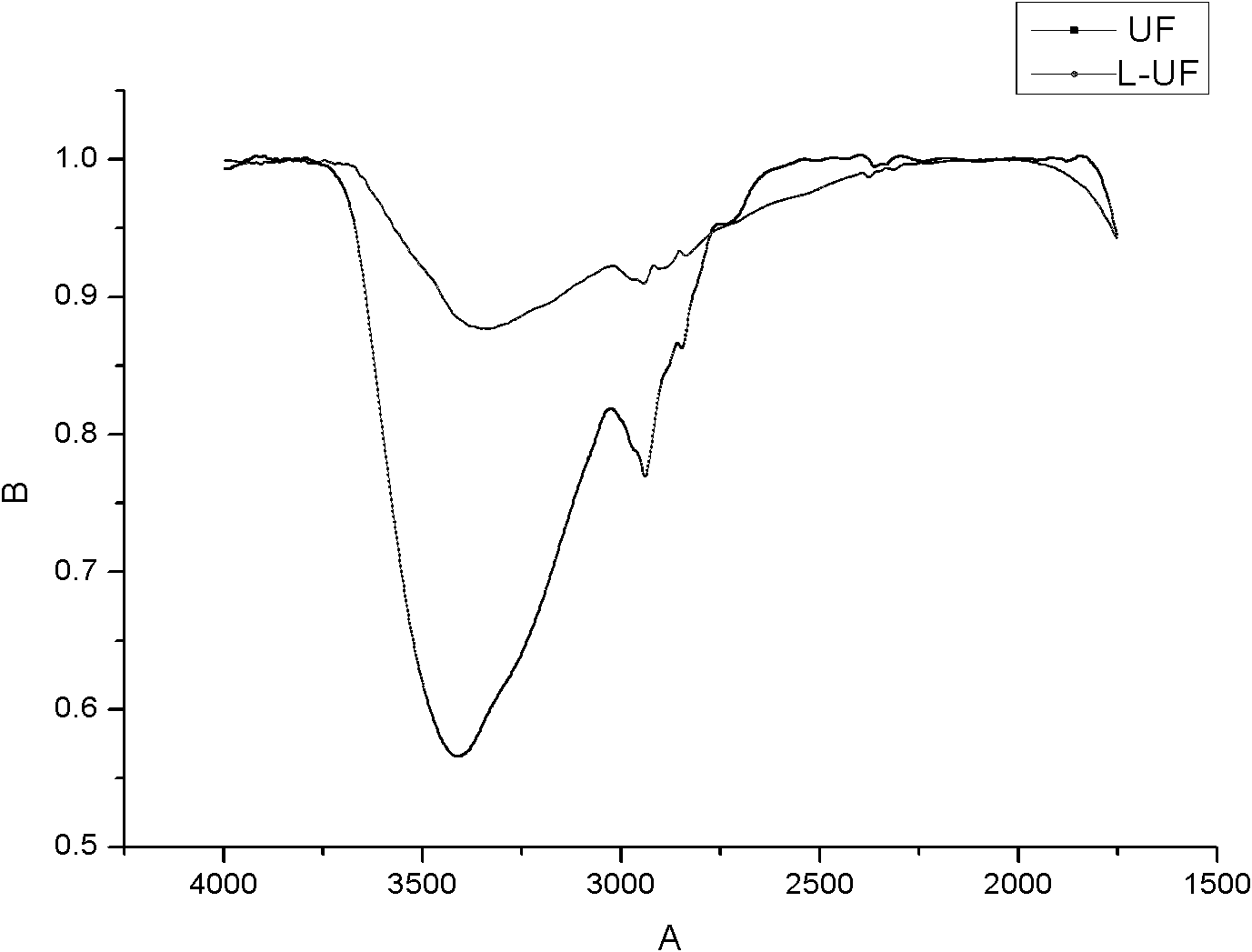
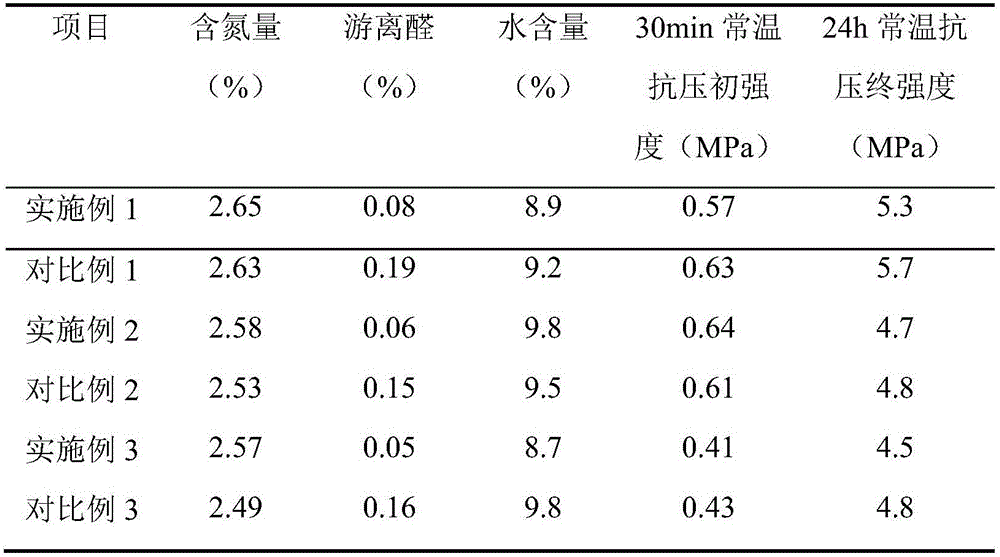
Modified lignin and urea-formaldehyde resin synthesized from same and preparation methods of modified lignin and urea-formaldehyde resin
InactiveCN102241826AHigh bonding strengthReduce formaldehyde emissionAldehyde/ketone condensation polymer adhesivesSynthesis methodsEther
The invention discloses a modified lignin and a urea-formaldehyde resin synthesized from same and preparation methods of the modified lignin and the urea-formaldehyde resin, belonging to the field of bonding agents used in wood processing. A technological synthetic route with weak base-weak acid-weak base is adopted, the molar ratio of formaldehyde to urea is controlled during an addition stage to generate a reasonable structure, the modified lignin as well as residual hydroxymethyl and free formaldehyde are added at the later stage of reaction in order to accomplish reaction, thus the content of methylene ether link (-CH2-O-CH2-) and the content of hydroxymethyl in the resin are reduced to a certain extent, the formaldehyde emission of the resin is lowered, and simultaneously, higher bonding strength and water resistance are ensured. The urea-formaldehyde resin in the invention is simple and brief in process and low in cost, the formaldehyde emission of the plate prepared by adoptingthe bonding agent reaches the E0-level standard and the plate can maintain high bonding strength after being cooked in hot water. The modified lignin is simple in synthesis method and low in cost andis especially suitable for the modification of the urea-formaldehyde resin with low molar ratio.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Perennial ryegrass breeding method based on CRISPR/Cas system
InactiveCN105219799AOther foreign material introduction processesVector-based foreign material introductionGenome editingMutant
The invention provides a perennial ryegrass breeding method based on a CRISPR / Cas system. A CRISPR / Cas genome-editing technique is applied to breed improvement of perennial ryegrass, gene site-directed knock-out is conducted on lignin synthesized key enzyme genes LpCCR and LpCOMT, homozygous and transformation carrier deleted mutants are selected out, the breeding material of the perennial ryegrass of which the lignin content is decreased is bred, and important significance for breeding research and breed improvement of pasture is achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN GENOVO BIOTECH CO LTD
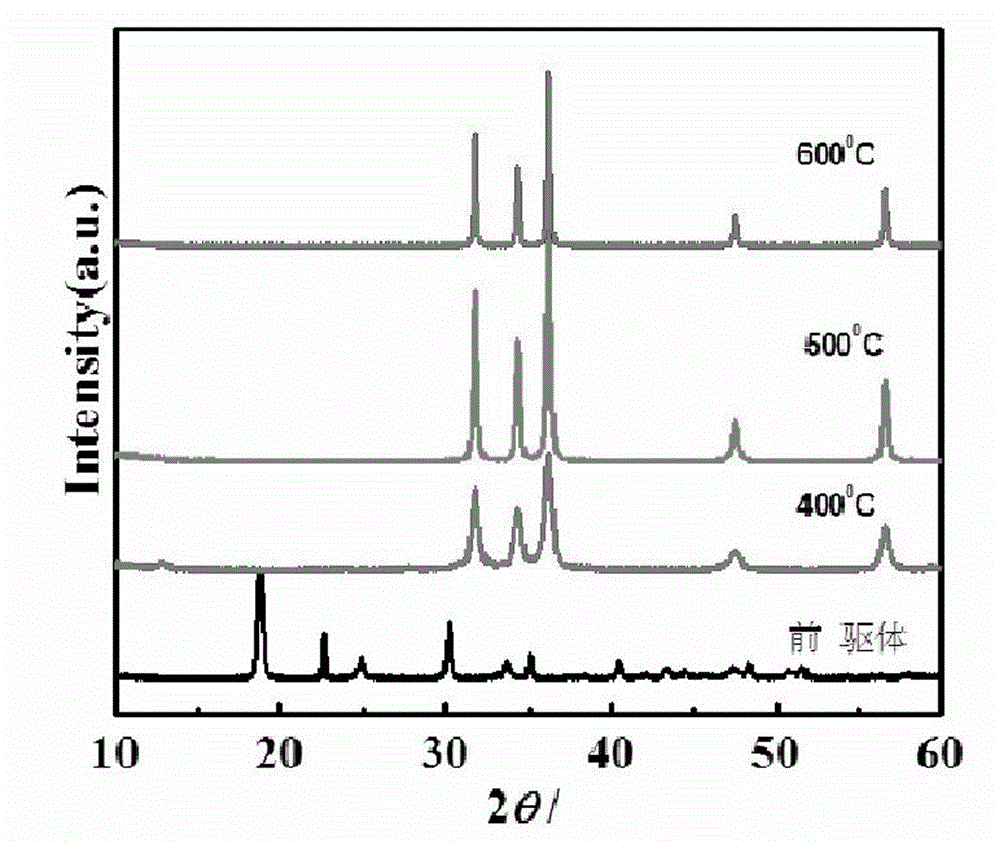
Solid-phase preparation method for nano zinc oxide through template
InactiveCN103183372ALarge specific surface areaHigh yieldMaterial nanotechnologyZinc oxides/hydroxidesMannich reactionNano zinc oxide
The invention discloses a solid-phase preparation method for nano zinc oxide through a template and relates to a solid-phase preparation method for nano zinc oxide. The method comprises the following steps: first, synthesizing lignin into lignin amine; and then, performing solid-phase preparation for nano zinc oxide taking the lignin amine as the template. According to the invention, the reticular lignin amine is prepared from the lignin through Mannick reaction, the advantages of being low in cost, nontoxic, easy to get and the like can be achieved; some base groups of the lignin amine are removed through high-temperature roasting, a pore structure is left, so that the specific surface area of the nano zinc oxide obtained from the lignin amine as a template agent is increased. Therefore, the method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple synthesis process, uniform particle size, controllable dynamics, low cost, easiness in operation, high yield, and low pollution, and reduces the hard aggregation appearance. The product prepared from the method is ice-cream, and adopts the structure of lead zinc ore of hexagonal system, and is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Caragana korshinskii Kom. transcription factor CkMYB4 and its gene
The invention provides a new CkMYB4 transcription factor and its gene. The gene originates from Leguminosae Caragana shrubs Caragana korshinskii Kom., and codes R2R3 MYB transcription factors. The full length cDNA sequence of the gene comprises 1106bps, comprises a 798bp open reading frame, and codes 266 amino acids. The cDNA sequence obtained after cloning is used for constructing a plant expression vector, and the vector is transformed into wild Arabidopis thaliana to obtain a transgenic plant. Transgenic Arabidopis thaliana lignin synthetase gene and lignin content detection results show that the gene provided by the invention can change the expression of the plant lignin synthesis gene and the lignin content.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
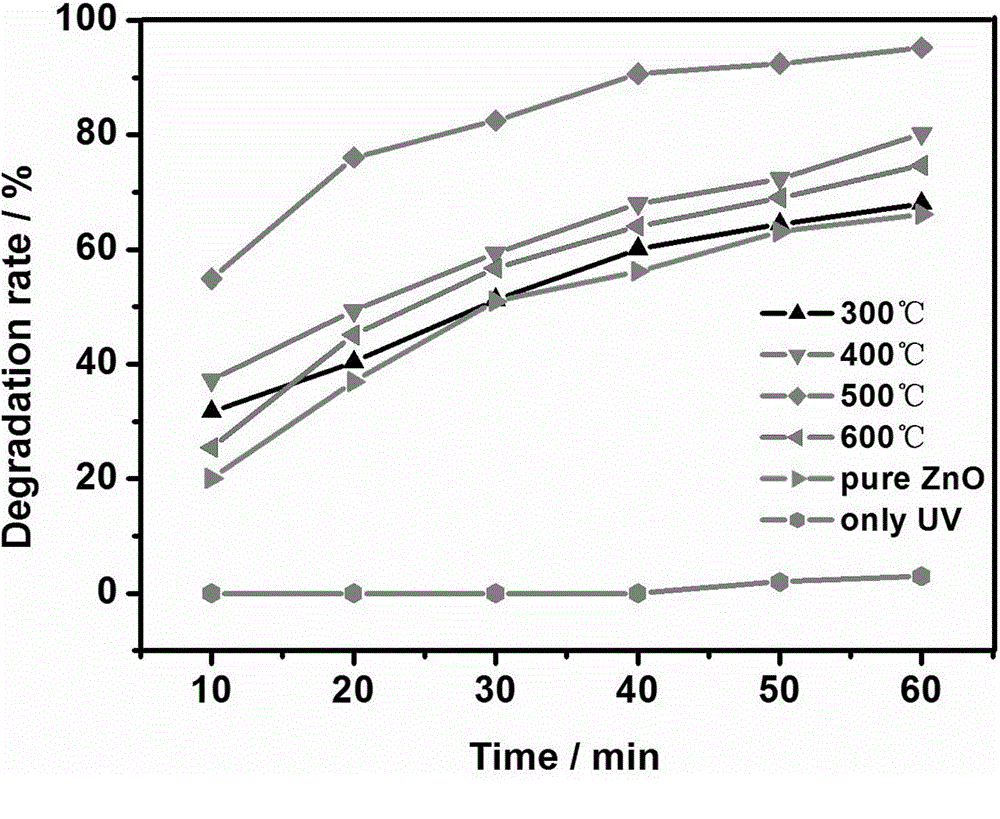
Method of solid phase preparation of nanometer zinc oxide photocatalyst by using lignin amine template method
InactiveCN103058263AImprove photocatalytic performanceLarge specific surface areaWater/sewage treatment by irradiationZinc oxides/hydroxidesNano zinc oxideOrganic chemistry
The invention belongs to the technical field of semiconductor photocatalysis materials, and relates to a method of preparing nanometer zinc oxide photocatalyst by using lignin amine as template molecule, especially to a method of a solid phase preparation of the nanometer zinc oxide photocatalyst by using a lignin amine template method. The method disclosed by the invention firstly synthesizes the lignin into the lignin amine, and then uses the prepared lignin amine as the template for the solid phase preparation of the nanometer zinc oxide photocatalyst. By using the lignin amine derived from the graft-modified lignin, the method is inexpensive, non-toxic, easy to get, etc. Part groups of the lignin amine can be removed after a high-temperature roasting, and pore structures are left, so that the nanometer zinc oxide photocatalyst prepared by using the lignin amine as the template is increased in specific surface area, and shows excellent photocatalysis performance. The method is easy to control, low in cost and simple in technology and flow; the lignin amine is recycled waste, and thus the method is low in cost; and prepared product is milky, has a hexagonal lead-zinc ore structure, and is good in photocatalysis effect and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Furan resin synthesized with modifying lignin and preparing method of furan resin
The invention relates to a furan resin synthesized with modifying lignin. The furan resin is mainly prepared from, by weight, 8-15 parts of lignin, 3-5 parts of maleic anhydride, 1-3 parts of xylitol, 3-8 parts of urea, 80-120 parts of furfuryl alcohol and 8-20 parts of formaldehyde. In the process of synthesizing the furan resin, the modifying lignin serves as an intermediate and is added into a reaction system, the modifying method is simple, and the effect is good. The furan resin modified by the lignin is stable in product performance, low in free formaldehyde content and capable of meeting the performance requirements of most casting resin sand.
Owner:SUZHOU XINGYE MATERIALS TECH
Gene engineering method for raising plant useful secondary substance content
InactiveCN1513986AIncrease contentReduce biosynthesisMicroinjection basedHorticulture methodsPlant cellIsoflavones
A gene engineering method for increasing the content of useful secondary substance in plant, such as isoflavone, polyphenol and taxol, includes configuring chimeric gene, introducing it to plant cell to generate, the transgenic plant cell, making it grow in the condition benefiting expression, screening and discriminating the transgenic plant cell, and further derivative culture.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Pear laccase gene PbLAC1 and vector, host cell and application thereof
ActiveCN109207493AImprove inner qualityImprove appearance qualityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCell wall
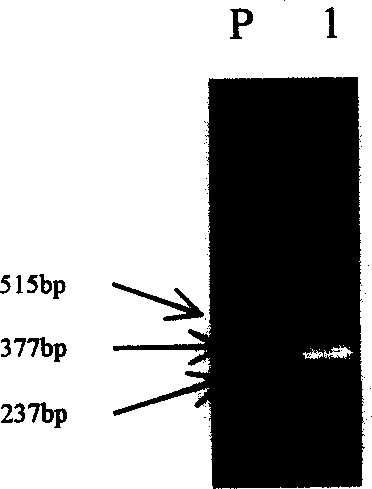
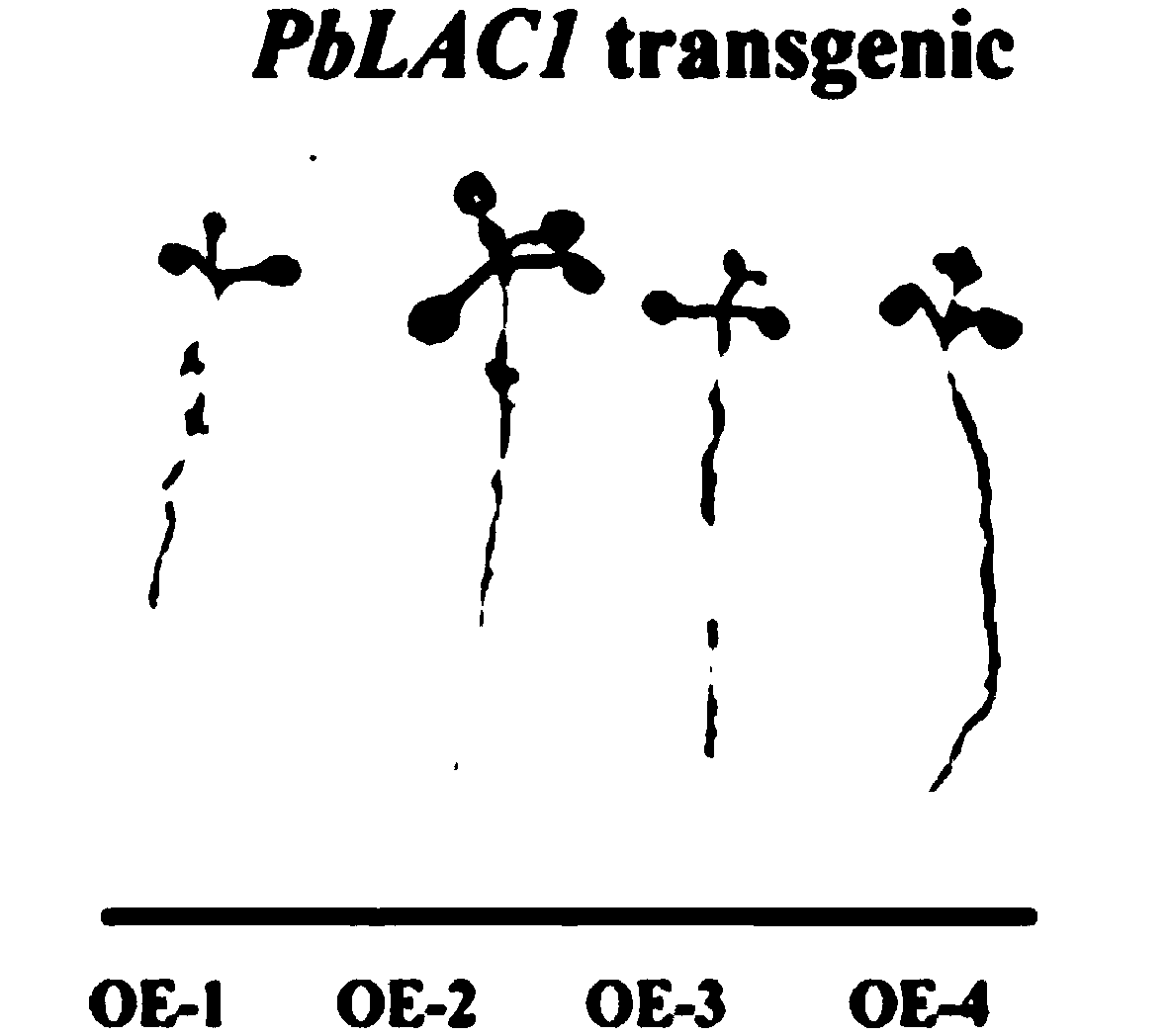
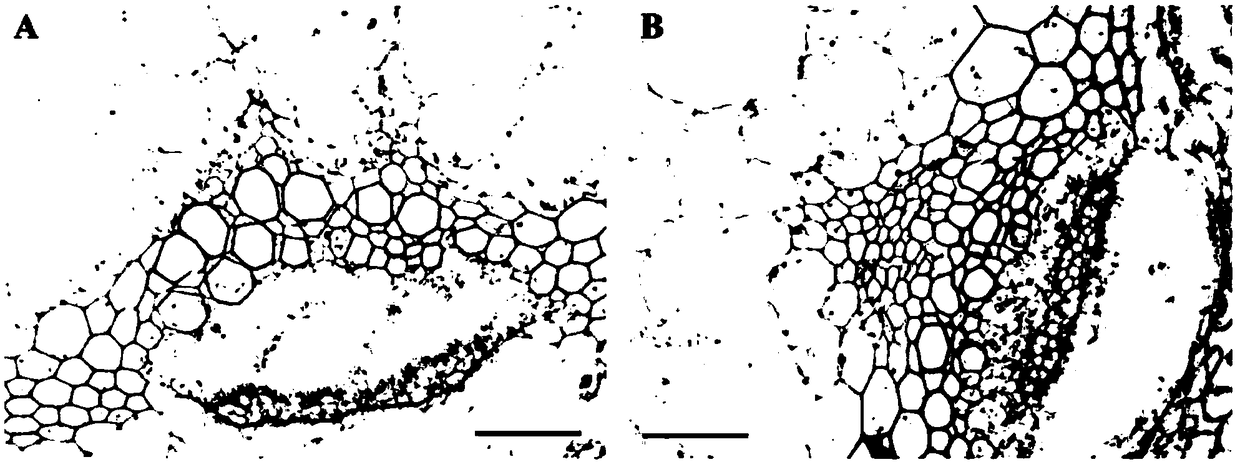
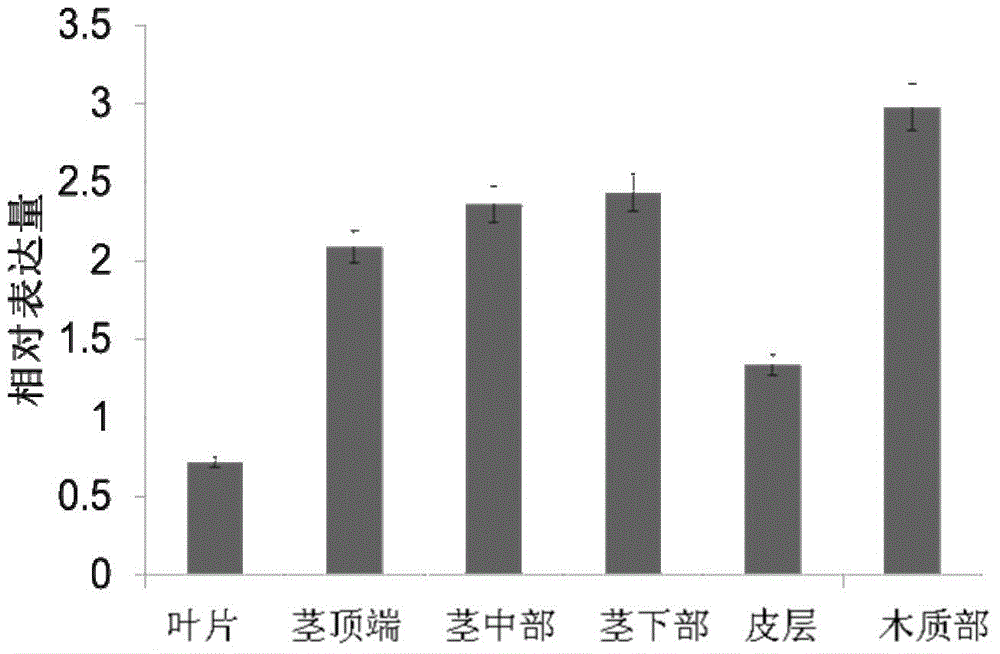
The invention relates to the technical fields of plant molecular biology and genetic engineering, and provides a pear laccase gene PbLAC1, the nucleotide sequence of which is shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. The invention also provides a plant over-expression vector, wherein the plant over-expression vector comprises pMD-18T-PbLAC1 plasmid constructed by PbLAC1. The invention also provides a genetically engineered host cell comprising a PbLAC1 gene sequence. The invention also provides the application of the pear laccase gene PbLAC1 in regulating plant lignin synthesis and cell wall development. The pear laccase gene PbLAC1 of the present invention provides new evidence for perfecting the plant lignin synthesis pathway, has important theoretical and practical significance for improving fruit qualityand other key agronomic characteristics of crops, and also provides a new way for regulating the content of pear stone cells by genetic engineering.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
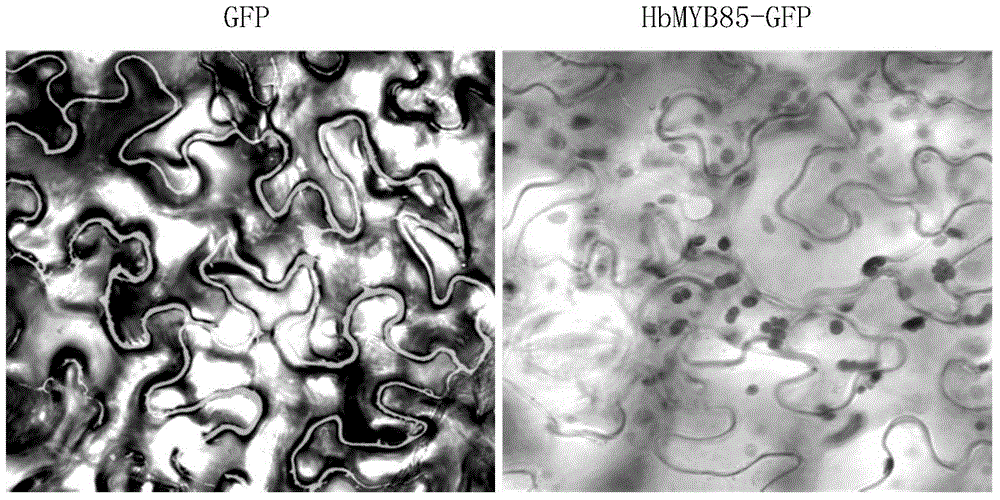
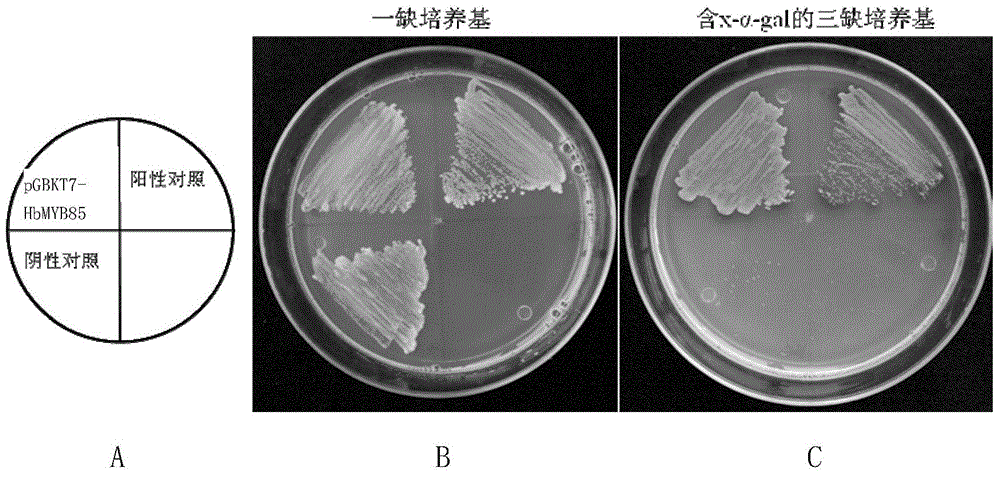
Regulatory protein HbMYB85 synthesized by virtue of rubber tree lignin as well as encoding gene and application of regulatory protein HbMYB85
InactiveCN104829702ASignificant application valueGood thickeningPlant peptidesFermentationBiologyGMO Plants
The invention discloses a regulatory protein HbMYB85 synthesized by virtue of rubber tree lignin as well as an encoding gene and application of the regulatory protein HbMYB85. The protein is named HbMYB85 protein and is shown as follows (a) or (b): (a) a protein formed by amino acid sequences shown by a sequence 1; and (b) a regulatory protein which is derivated by the sequence 1 and formed by replacement and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues on the amino acid sequences shown by a sequence 1 and synthesis of thickness of a plant secondary cell wall and / or lignin. An HbMYB85 gen also belongs to the protection range of the invention. The invention also protects a method of cultivating a transgenic plant. The method comprises the following steps: introducing the HbMYB85 gene into a target plant to obtain the transgenic plant with the thickness of the plant secondary cell wall and / or the content of the lignin higher than that or those of the target plant. The regulatory protein HbMYB85 has important significance of promoting thickness increase of the plant secondary cell wall and accumulation of the lignin and particularly quality genetic improvement of rubber woods and cultivation of a new wind-resistant variety.
Owner:RUBBER RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
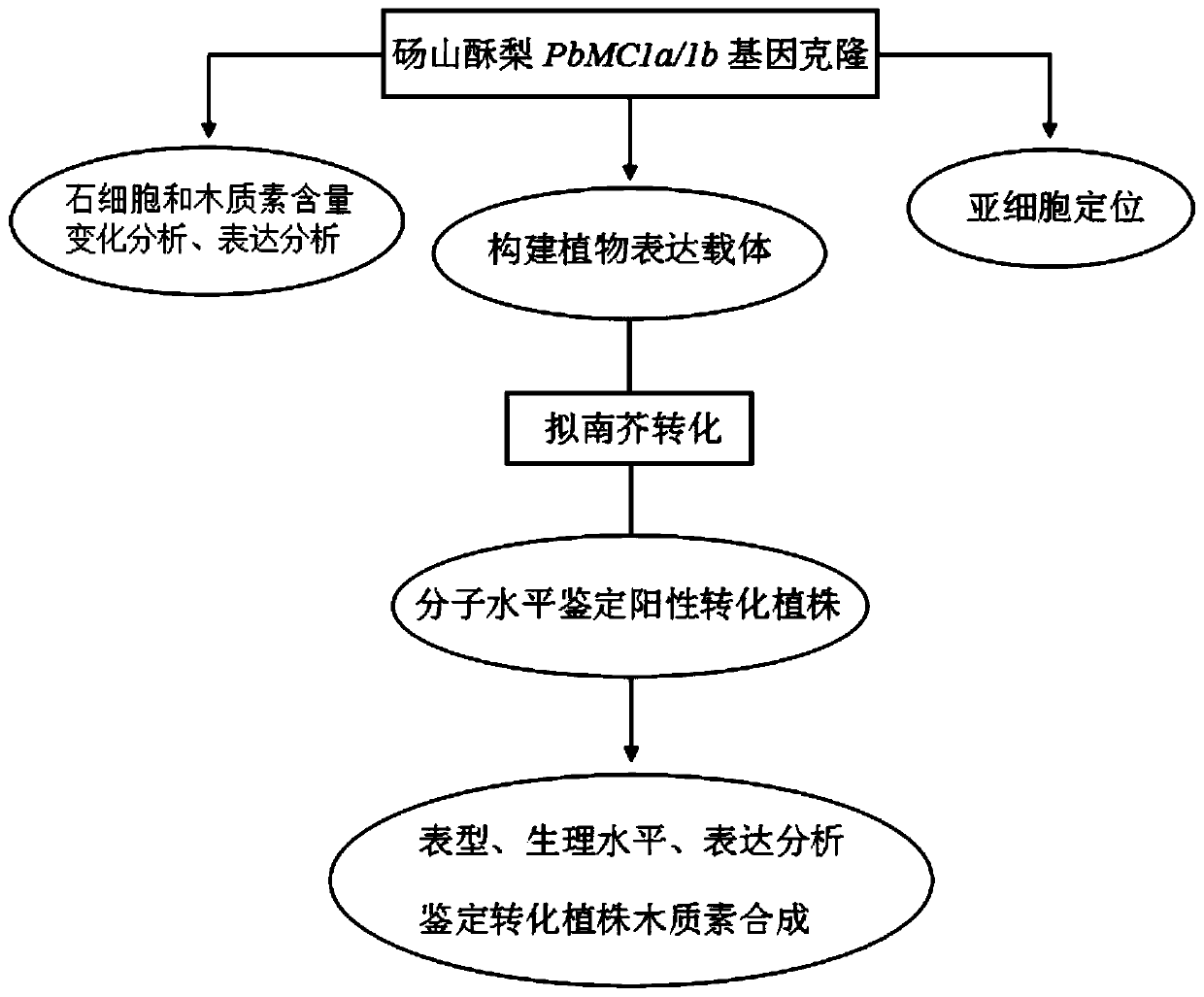
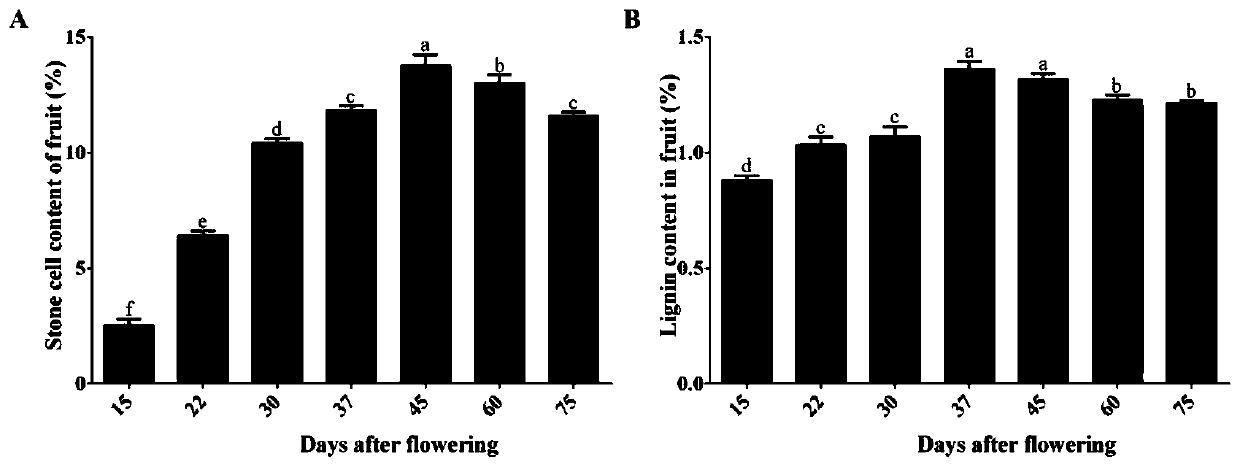
Pear lignin synthesis gene PbMC1a/1b and application of pear lignin synthesis gene PbMC1a/1b in genetic improvement of fruit quality
ActiveCN110577960AHigh expressionReduced Breeding ResearchHydrolasesFermentationBiotechnologyVascular bundle
The invention discloses a pear lignin synthesis gene PbMC1a / 1b and application of the pear lignin synthesis gene PbMC1a / 1b in genetic improvement of fruit quality. The PbMC1a / 1b gene is a cysteine-like protease isolated and cloned from Dangshansu pear with high lignin content, an applicant names the gene as PbMC1a / 1b, the sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and the corresponding amino acid sequenceis shown as SEQ ID NO.2. A gene construction over-expression vector is introduced into arabidopsis thaliana, obtained transgenic plants are verified by a biological function, the cloned PbMC1a / 1b genecan promote the cell walls of fibers between ducts, lignocellulosic fibers and vascular bundles to be obviously thickened, lignin accumulation in stems is promoted and plant growth is inhibited, theexpression of genes related to lignin biosynthesis is increased, new genetic resources is provided for molecular design and breeding of fruit quality, and the PbMC1a / 1b gene is an important candidategene for future genetic engineering to improve fruit quality breeding.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
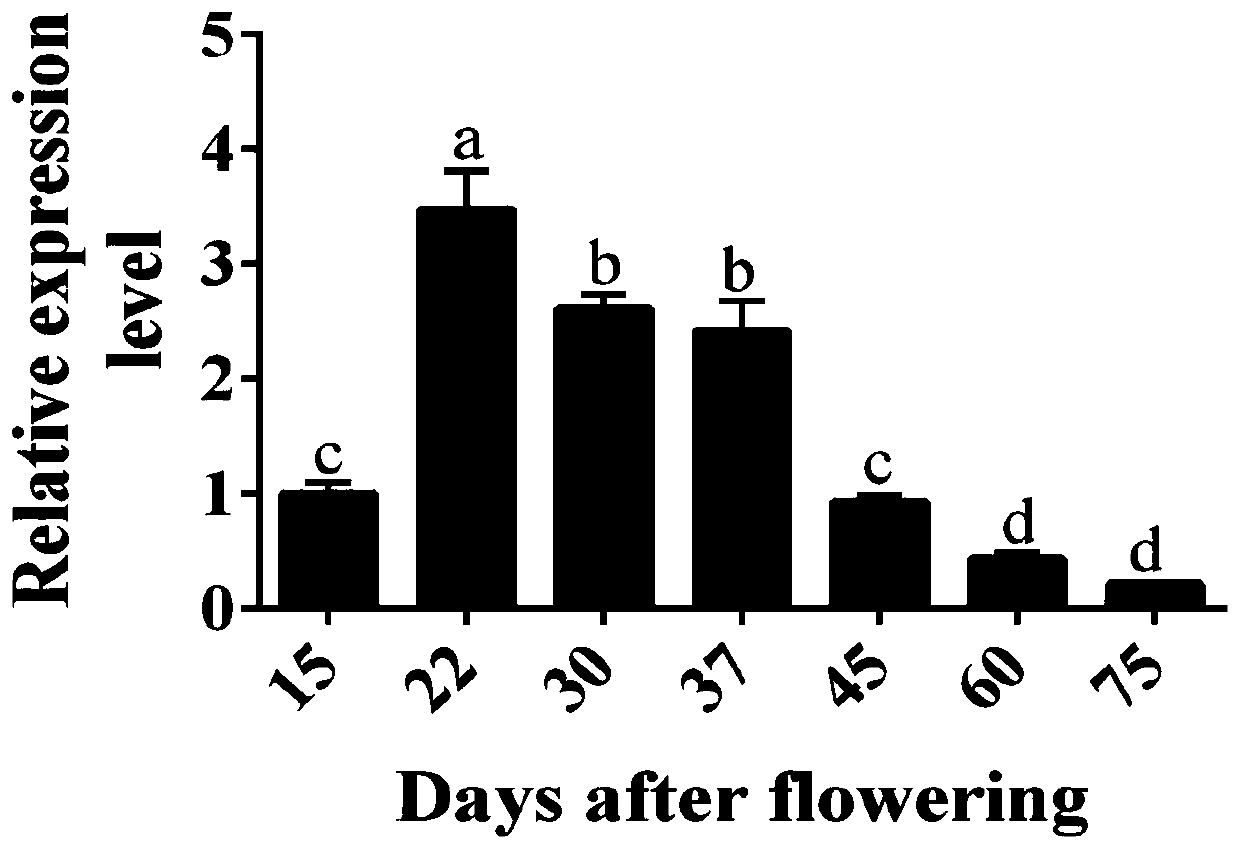
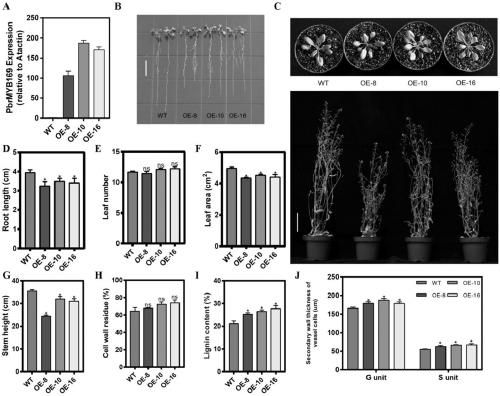
Pear transcription factor PbrMYB169 and application thereof
ActiveCN109609514AAchieve friendlyReduce the cost of farmingBacteriaPlant peptidesAgricultural scienceSclereid
The invention discloses a pear transcription factor PbrMYB169 and an application thereof. The pear transcription factor PbrMYB169 is separated from Dangshan crisp pears, and has MYB family member PbrMYB169 genes capable of adjusting and controlling development of sclereid of pear fruits, the nucleotide sequence of the pear transcription factor PbrMYB169 is as shown in SEQID No.1, and the coding amino acid sequence of the pear transcription factor PbrMYB169 is as shown in a sequence table SEQID No.2. Through an agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated heredity conversion method, PbrMYB169 transcription factors are converted into arabidopsis thaliana, and transgenic plants are obtained; biological function verification indicates that the PbrMYB169 gene cloned through the pear transcription factorPbrMYB169 has the function of promoting synthesis of arabidopsis thaliana inflorescence stem lignin, besides, the PbrMYB169 transcription factor has the advantage of being capable of adjusting and controlling a plurality of genes, and an efficient way is provided for molecular breeding. New genetic resources are provided for reduction of molecular breeding of synthesis of organism lignin, new heredity resources are provided for implementing green agriculture, and reduction of the agriculture cost and realization of an environmental-friendly purpose can be facilitated through development and utilization of the heredity resources.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Plant RNA (Ribose Nucleic Acid) interference vector for inhibiting lignin from synthesizing, and construction method and application of plant RNA interference vector
The invention relates to a plant RNA (Ribose Nucleic Acid) interference vector for inhibiting lignin from synthesizing, and a construction method and application of the plant RNA interference vector. The plant RNA interference vector is that some nucleotide sequences (serving as forward nucleic acid fragments) of alfalfa CCoAOMT as shown in a sequence table SEQ ID No.1 and some nucleotide sequences (serving as reverse nucleic acid fragments) of the alfalfa CCoAOMT as shown in a sequence table SEQ ID No.2 are inserted into a plant expression vector pFGC5941, thus constructing the plant RNA interference vector pFGC5941-CCoAOMTi. The obtained interference vector is used for transforming agrobacterium tumefaciens EHA105 competent cells, so as to obtain agrobacterium engineering bacteria containing the interference vector. The agrobacterium engineering bacteria containing the interference vector is utilized for transforming the plant, and therefore, the plant with low lignin content can be cultivated. By adopting the method, a transgenic plant with normal growth and low lignin content can be gained, and germplasm resources are provided for cultivating low-lignin grass and papermaking plant and the like.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
White birch CCoAOMT gene for lowering lignin and encoded protein thereof
InactiveCN105624129AImproved plant lignin contentImproved lignin contentTransferasesGenetic engineeringNicotiana tabacumGene technology
The invention relates to a white birch CCoAOMT gene for lowering lignin synthesis and an encoded protein thereof, belonging to the technical field of genes in molecular biology. The white birch CCoAOMT gene is characterized in lowering lignin synthesis. The sequence of the white birch CCoAOMT gene is disclosed as SEQ ID NO:1 in the sequence table; and the amino acid sequence of the protein encoded by the white birch CCoAOMT gene is disclosed as SEQ ID NO:2 in the sequence table. The invention provides a white birch lignin synthesis gene CCoAOMT and a plant expression vector for establishing the white birch CCoAOMT gene. According to the established plant expression vector, a tobacco plant and a white birch plant are infected by agrobacterium to obtain the transgenic tobacco plant, in the stem of which the lignin content is lowered, which indicates that the gene has the function of lowering the tobacco stem lignin content and can regulate the changes of the lignin monomer components. The analysis on the fiber morphology and chemical components of the heptaennial white birch individual plant with 16 reverse transformed CCoAOMT genes is utilized to screen out four (1, 4, 12 and 16) dominant transgenic individual plants for paper pulp. The white birch CCoAOMT gene provides gene resources and theoretical references for lowering the white birch lignin content by using the gene engineering technique, thereby having high application value.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY +3
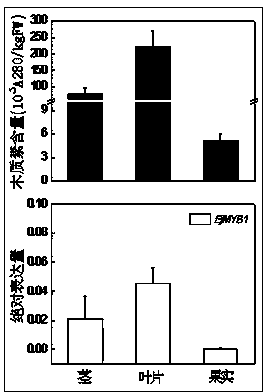
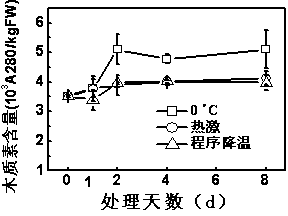
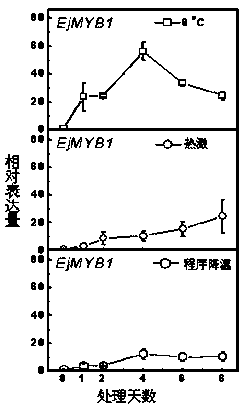
Transcription factor EjMYB1 participating in control on synthesis of loquat fruit lignin and application thereof
InactiveCN104031922AReduce synthesisInhibit synthesisFermentationPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyPromoter activity
The invention provides a transcription factor EjMYB1 participating in control on synthesis of loquat fruit lignin. By using AtMYB58 amino acid sequence for specifically controlling the lignin synthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana as the reference sequence, homologous cloning is performed according to the rose family database to obtain the transcription factor EjMYB1. The expression level of the EjMYB1 is positively related to the accumulation of the lignin in different tissues and different treatment processes of the loquat. The EjMYB1 can positively control the promoter activity of the lignin synthesis genes EjPAL1, Ej4CL1 and Ej4CL5. The EjMYB1 can obviously enhance the leaf lignin content when being instantaneously overexpressed in tobacco.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
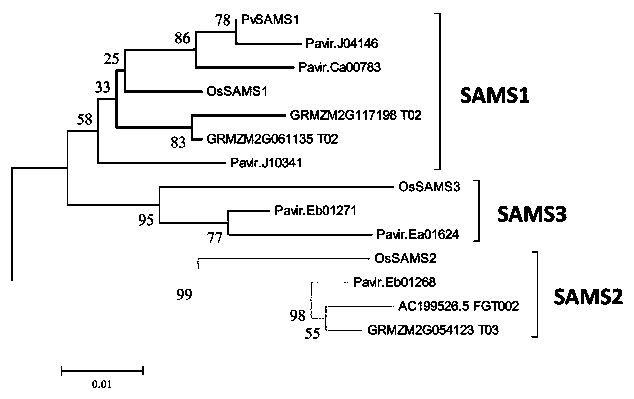
Application of panicum virgatum L. S-adenosylmethionine synthase gene SAMS1 to regulation and control of lignin synthesis
ActiveCN108130334AReduced expression levelGood effectTransferasesFermentationS-Adenosyl-l-methionineWild type
The invention discloses application of a panicum virgatum L. S-adenosylmethionine synthase gene SAMS1 to change of the lignin content and further improvement on the saccharification efficiency, and belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering. The application comprises the following main contents: performing cloning and sequence determination on the panicum virgatum L. SAMS1 gene; constructing an interference expression vector (pANIC8B-PvSAMS1-RNAi) of the PvSAMS1 gene; transforming a panicum virgatum L. callus by an agrobacterium mediated method, and transforming an interference fragment of a target gene into lowland-type Alamo wild-type panicum virgatum L. to obtain a transgenic plant with reduced total lignin content. The expression quantity of the PvSAMS1 in the obtainedtransgenic plant is significantly reduced, the lignin content is significantly reduced, and the saccharification efficiency is significantly improved. Through regulation and control of lignin metabolism by the identified panicum virgatum L. SAMS1, a novel target can be provided for molecular breeding in future.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Wheat cinnamyl alcohol desaturase, encoding gene and uses thereof
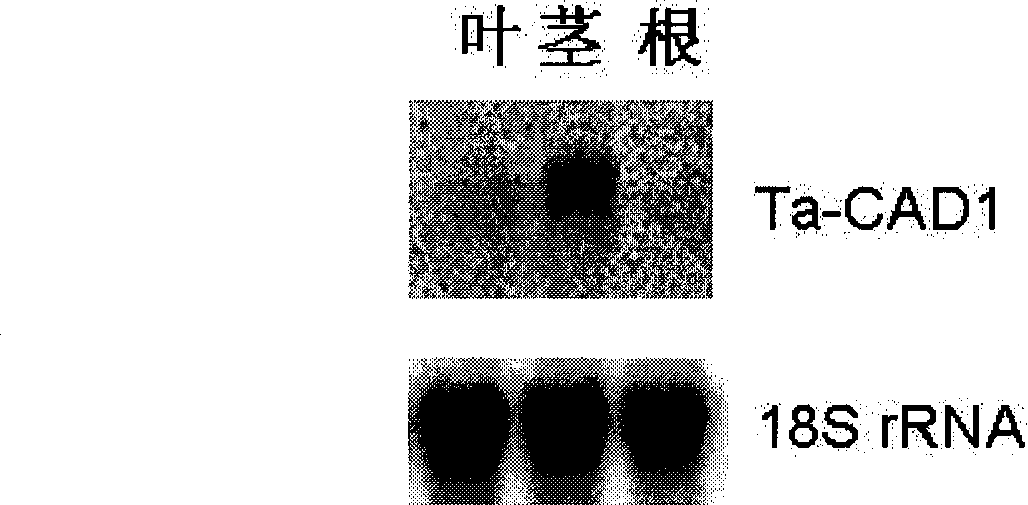
The invention discloses a cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase of wheat and an encoding gene and application thereof; the cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase is the protein of the following a) or b): a) the protein composed of the amino acid sequences represented by the sequences 2 in the sequence table; b) the protein derived from a) and related to the cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase function by substituting and / or deleting and / or adding one or more amine acid in the amino acid sequences represented by the sequences 2 in the sequence table. The invention further provides the encoding gene of the cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase, and application of the encoding gene in culturing lodging-resistant plants. The encoding gene is introduced in the plants; and the transformed plant hosts can be wheat. The protein in the invention utilizes coniferyl aldehyde as base materials and has enzyme activities of 94.49 nmol / sec / mg, showing that the protein can control the lignin synthesis of the wheat. Northern hybridization is carried out on the Ta-CADI genes of the stems of easily-lodging and lodging-resistant wheat, which shows that the Ta-CADI genes not only control the lignin synthesis of the wheat, but also are closely related to the lodging-resistant characteristics of the stems of the wheat.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cryptomeria fortunei CfCCR gene and application thereof
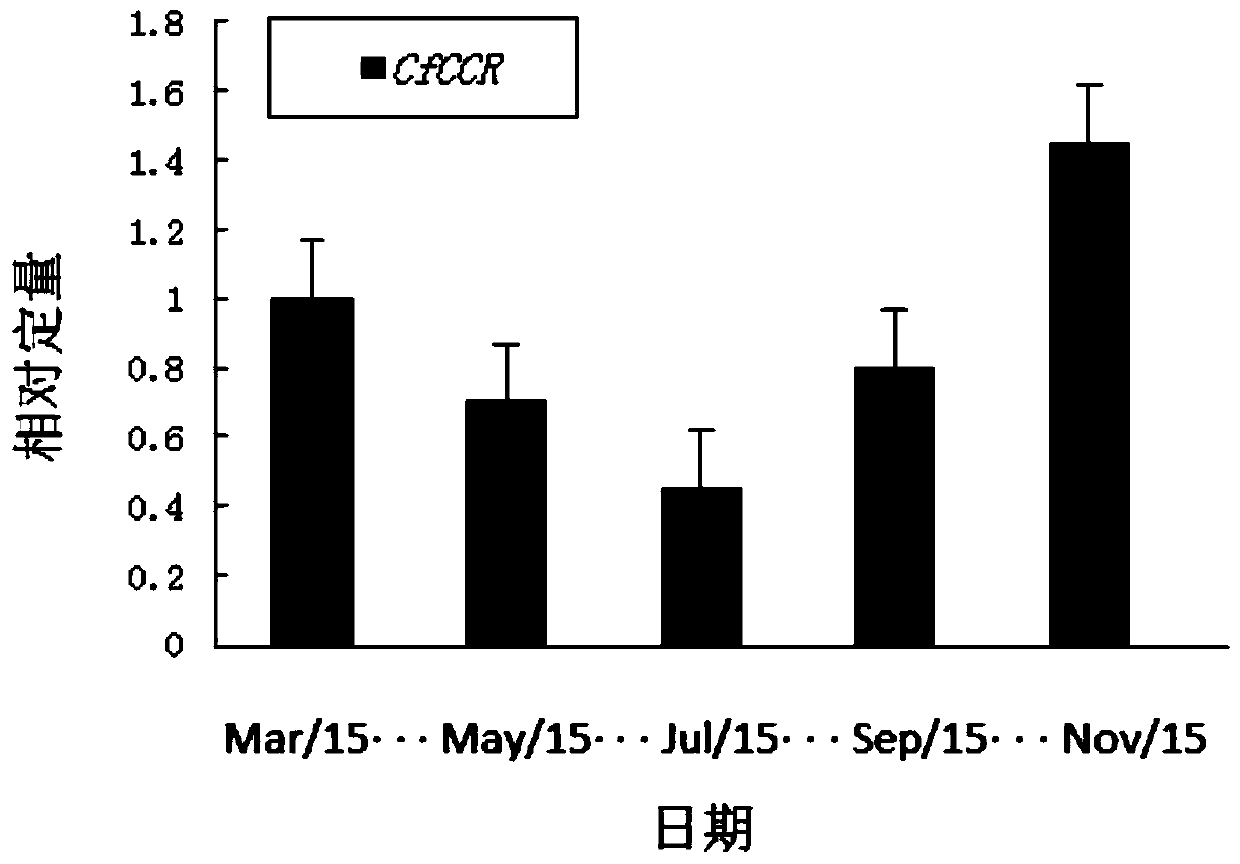
ActiveCN111139253AImprove stress resistanceImprove qualityBacteriaOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a cryptomeria fortunei CfCCR gene and an application thereof, belonging to the technical fields of plant molecular biology and gene engineering. The cryptomeria fortunei ligninsynthesis regulation CfCCR gene provided by the invention has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1, and the amino acid sequence of an expression protein of the cryptomeria fortunei lignin synthesis regulation CfCCR gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. The CfCCR gene is a key rate-limiting enzyme of a lignin synthesis specific pathway, regulates the expression of related genes for synthesizing lignin in plants through encoding protein, and plays an important role in biosynthesis and stress resistance of lignin. The tobacco transformed with the CfCCR gene is increased in lignin expression and developed in cell walls. Thus, the thickness of xylem cell walls in plant stems like cryptomeria fortunei can be changed by expressing the CfCCR gene, so the wood density is increased, and the wood quality and plant stress resistance are improved.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Metabolic pathway reconstruction method for reducing lignin content and use thereof
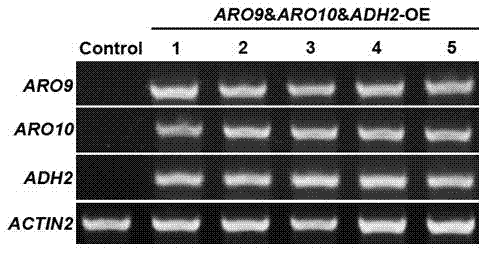
InactiveCN104212731ALow lignin contentNormal growth is not affectedFungiVector-based foreign material introductionFiberEthanol dehydrogenase
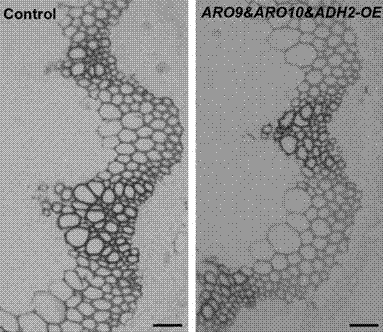
The invention relates to the field of gene engineering and discloses a metabolic pathway reconstruction method for reducing lignin content and a use thereof. The metabolic pathway reconstruction method can construct a 2-phenylethyl alcohol synthesis pathway in the plant so that lignin synthesis is reduced and thus fiber biomass conversion efficiency is improved. The 2-phenylethyl alcohol synthesis pathway is from yeast and comprises three key genes of amino acid transaminase gene ARO9, pyruvate decarboxylase gene ARO10 and ethanol dehydrogenase gene ADH2. The 2-phenylethyl alcohol synthesis pathway is constructed in arabidopsis thaliana, and through competition between 2-phenylethyl alcohol synthesis and lignin synthesis in initial substrate phenylalanine use, carbon metabolism shunting is caused and synthesis of lignin in the transgenic plant is reduced. The method provided by the invention can reduce fiber biomass pretreatment difficulty by reducing plant lignin synthesis. At present, the method can reduce lignin synthesis in arabidopsis thaliana and can improve glucose release efficiency of stem cell wall extract enzymolysis.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Lignin synthesis related protein and its coding gene and uses
The invention discloses a lignin-related protein as well as its gene encoding and application. The lignin-associated protein has one of the following amino acid residues sequences: (1) SEQ ID No. : 2 in the sequence table, and (2) lignin-related protein after SEQ ID No. : 2 one or several amino acid residues replaced and / or deleted and / or added in the sequence table. The lignin-related protein gene can regulate the content and composition of rice lignin without influences on plant growth and development, and improve the values as feed and industrial raw material of paper. In addition, the lignin-related protein gene also has important theoretical value in revealing the mechanism of plant lignin biosynthesis.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Gene 4-CL for Chinese white poplar lignose monomer synthesis and application thereof
InactiveCN101280315AIncrease expansionSmall lesion expansionVector-based foreign material introductionPlant genotype modificationDiseaseBiotechnology
The invention discloses a Chinese white poplar lignin monomer synthesis gene 4-CL and an application thereof. The gene is responsible to catalyzing each cinnamic acid and each corresponding coenzyme A ester generated by derivative thereof, the synthesis of each downstream secondary product is participated, and the gene is the essential gene of controlling the lignin synthesis. The findings indicates that the infection of the plant resistance pathogen is reinforced through the increase of the lignin content, the rape stem strength is enhanced, and thus the lodging resistance is obviously enhanced. The concrete result shows that the lignin content of the transgenic rape increases over 10 percents than the acceptor compared with the lignin content; the transgenic plant leaf reduces about 30 percents than the acceptor compared with the disease spots expanding area; and the cane strength of the transgenic plant comparably increases about 20 percents.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Full-length cDNA (complementary Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) of switchgrass lignin biosynthetic enzyme gene PvCCoAOMT and cloning method of full-length cDNA
The invention discloses a full-length cDNA (complementary Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) of a switchgrass lignin biosynthetic enzyme gene PvCCoAOMT. The full-length cDNA has a nucleotide sequence as shown in (1) or (2): (1) a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No.1, and (2) a nucleotide sequence with the same function and formed by replacing, missing or adding one or more nucleotide to the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.1. The invention also provides a cloning method of the full-length cDNA of the switchgrass lignin biosynthetic enzyme gene PvCCoAOMT. The cloning method provides convenience for the subsequent study on primer design, vector construction and genetic transformation by utilizing the sequence of the full-length cDNA of the switchgrass lignin biosynthetic enzyme gene PvCCoAOMT, and also provides the foundation for developing the study on fluorescence quantitative expression, transgenosis, gene function identification and the like in switchgrass in future.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Pear PbrmiR397a and application thereof
ActiveCN107236740AAchieve friendlyReduce the cost of farmingVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsPEARBiotechnology
The invention discloses pear PbrmiR397a and application thereof. The microRNA gene (PbrmiR397a) is separated from Dangshan pear and has a function of regulating pear fruit sclereid development, and a precursor nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID No.1. PbrmiR397a is converted into tobacco through an agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation method to obtain a transgenic plant, biological function verification shoes that the cloned PbrmiR397a gene has a function of reducing lignin synthesis. A new gene resource is provided for molecular breeding with lignin synthesis reduced by the finding of the PbrmiR397a. The PbrmiR397a gene has the advantage of targeting and regulating multiple genes at the same time, so that a more efficient approach is provided for molecular breeding.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
CAD gene of eucalyptus urophylla and application thereof
InactiveCN108588098AStrong inhibition of synthesisTargeted regulation of lignin contentBacteriaFermentationNucleotide sequencingGenetic engineering
The invention discloses a CAD gene of eucalyptus urophylla and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the CAD gene of the eucalyptus urophylla is as shown in SEQ ID No.1, the gene can be applied to transgenic plants, and it is proved that the gene has the function of adjusting and controlling lignin synthesis. The study of the function of the CAD gene of the eucalyptus urophylla is conducive to promoting the genetic engineering breeding of transgenic directional adjustment and control of lignin synthesis by the eucalyptus caudate.
Owner:GUANGXI FORESTRY RES INST
Modified lignin and urea-formaldehyde resin synthesized from same and preparation methods of modified lignin and urea-formaldehyde resin
InactiveCN102241826BLow free formaldehyde contentModerate shelf lifeAldehyde/ketone condensation polymer adhesivesPolymer scienceEther
The invention discloses a modified lignin and a urea-formaldehyde resin synthesized from same and preparation methods of the modified lignin and the urea-formaldehyde resin, belonging to the field of bonding agents used in wood processing. A technological synthetic route with weak base-weak acid-weak base is adopted, the molar ratio of formaldehyde to urea is controlled during an addition stage to generate a reasonable structure, the modified lignin as well as residual hydroxymethyl and free formaldehyde are added at the later stage of reaction in order to accomplish reaction, thus the content of methylene ether link (-CH2-O-CH2-) and the content of hydroxymethyl in the resin are reduced to a certain extent, the formaldehyde emission of the resin is lowered, and simultaneously, higher bonding strength and water resistance are ensured. The urea-formaldehyde resin in the invention is simple and brief in process and low in cost, the formaldehyde emission of the plate prepared by adoptingthe bonding agent reaches the E0-level standard and the plate can maintain high bonding strength after being cooked in hot water. The modified lignin is simple in synthesis method and low in cost andis especially suitable for the modification of the urea-formaldehyde resin with low molar ratio.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Eucalyptus urophylla COMT (catechol-O-methyltransferase) gene and application thereof
InactiveCN108342403AEasy to synthesizePlay a regulatory roleBacteriaTransferasesNucleotide sequencingTransgene
The invention discloses a eucalyptus urophylla COMT (catechol-O-methyltransferase) gene and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the eucalyptus urophylla COMT gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The gene can be applied to transgenic plants, and the gene is proven to have the effect of improving G lignin synthesis. The research on the functions of the eucalyptus urophylla COMT gene is favorable for promoting genetic engineering breeding for transgenic directional adjustment and control of lignin synthesis by eucalyptus urophylla.
Owner:GUANGXI FORESTRY RES INST
Key gene regulating plant cell wall recalcitrance
ActiveUS9994998B2High and low expressionIncreased S/GVector-based foreign material introductionNon-woody plant/crop pulpBiofuelPlant cell
This disclosure provides plants having desirable levels of lignin synthesis, sugar release, S / G ratio, and resistance to stress and pathogens; methods of selecting plants with such desirable levels of lignin synthesis, sugar release, S / G ratio, and resistance to stress and pathogens; methods of genetically modifying plants to modulate lignin synthesis, sugar release, S / G ratio, and resistance to stress and pathogens; and uses of such plants. The inventors have determined that the expression and / or activity of POPTR_0014s08530, a gene encoding an Angustifolia / CtBP transcription factor, modulates lignin synthesis, sugar release, S / G ratio, and resistance to stress and pathogens in plants. Plants with lignin synthesis, sugar release, S / G ratio, and resistance to stress and pathogens, based on modulation of the expression or activity of the POPTR_0014s08530 gene, have divergent uses including pulp and paper production, and ethanol / biofuel production.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND +1
Rice seedling culture solution added with exogenous salicylic acid and application of rice seedling culture solution
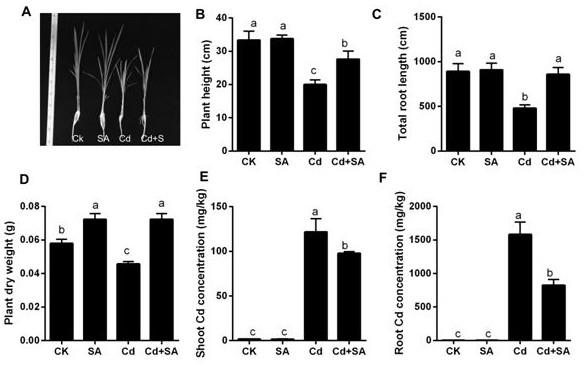
ActiveCN113105293AReduce absorptionReduce accumulationCalcareous fertilisersMagnesium fertilisersSalicylic acidNutrient solution
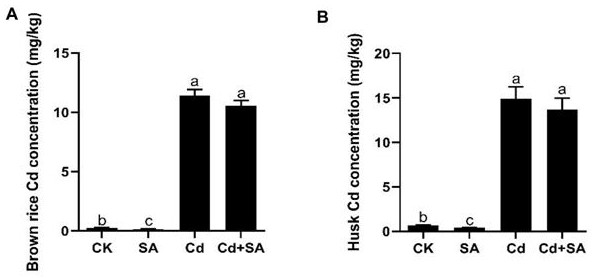
The invention discloses a rice seedling culture solution added with exogenous salicylic acid and application of the rice seedling culture solution. According to the rice seedling culture solution added with the exogenous salicylic acid, the exogenous salicylic acid is added on the basis of a rice nutrient solution formula, and the addition amount is 100 [mu]mol / L<-1>. The cadmium content of root systems and overground parts of rice seedlings is reduced; the rice seedling culture solution is used for regulating pectin synthesis, deesterification and lignin synthesis to reduce cadmium accumulation of rice plants and relieve poison of cadmium stress to rice seedlings; the rice seedlings are cultured in the rice seedling culture solution for 10 days, the pectin content and deesterification degree of roots are increased, free carboxyl in pectin is increased, and the adsorption and combination capacity of cell walls to cadmium is enhanced; meanwhile, root lignin content is increased, the cell walls are thickened, and cadmium ions are prevented from entering cells. The invention discloses and verifies an important rice Cd regulation mechanism, and provides theoretical guidance and a feasible scheme for safe production of cadmium-polluted rice field soil.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
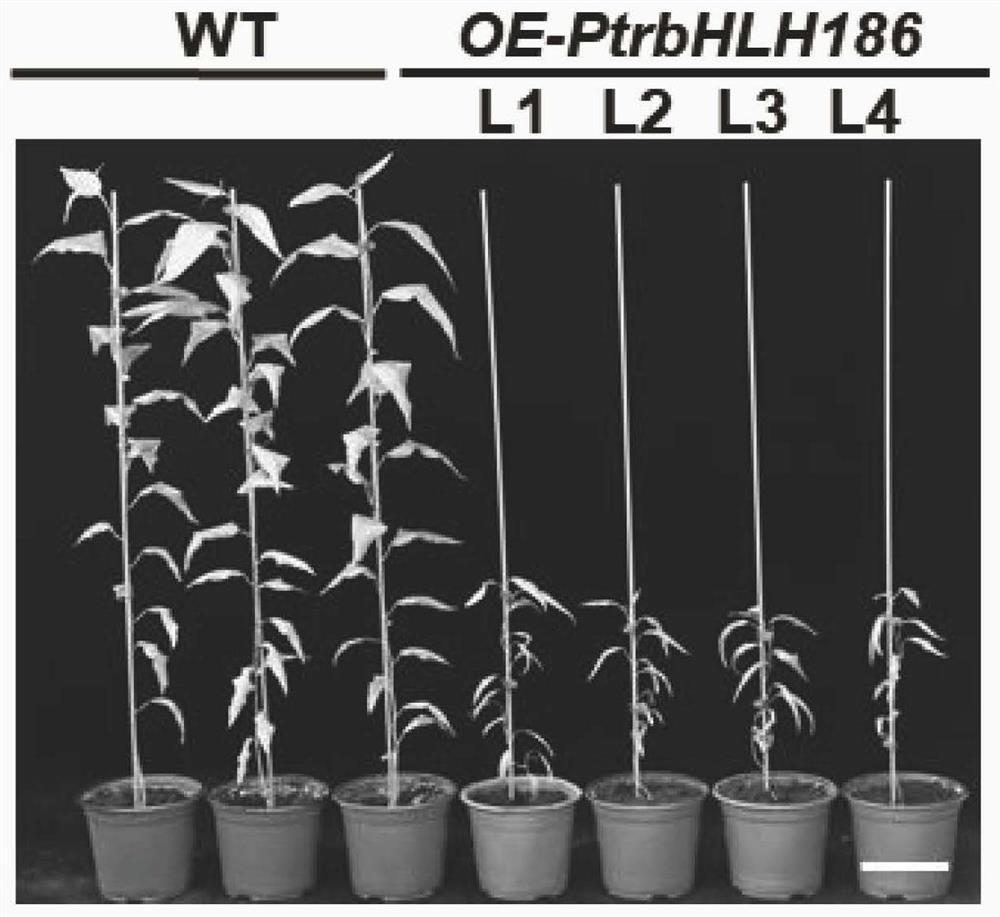
Application of populus trichocarpa PtrbHLH186 gene in regulation and control of secondary xylem development of trees
ActiveCN114195873AGrowth retardationIncrease the occupied areaPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyPopulus trichocarpa
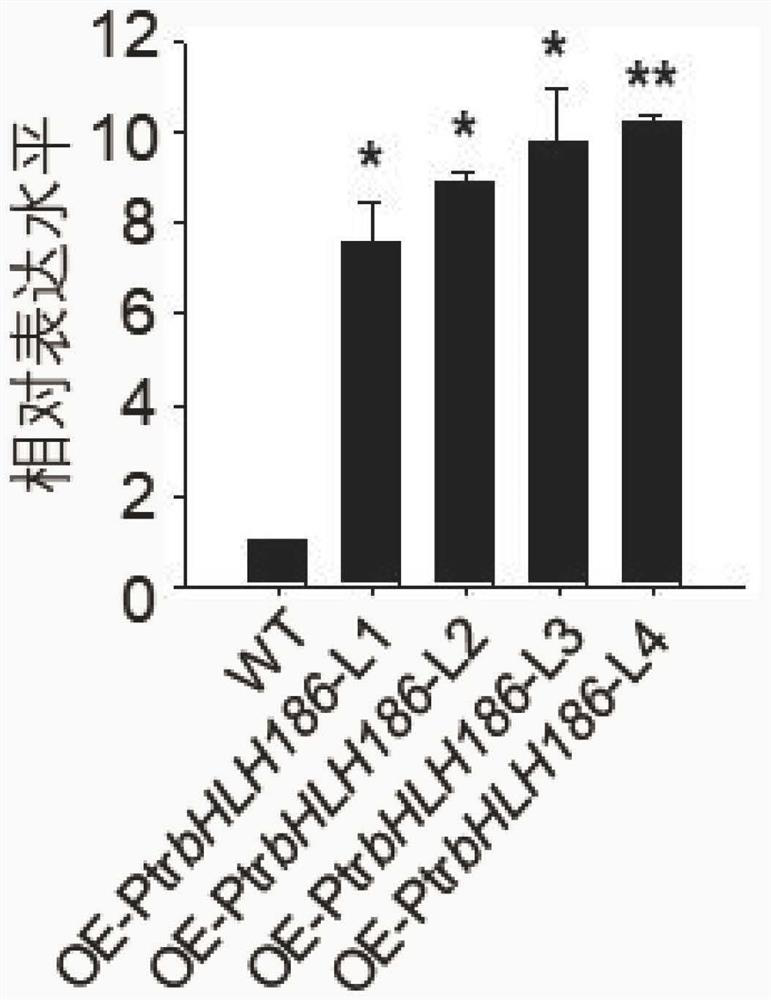
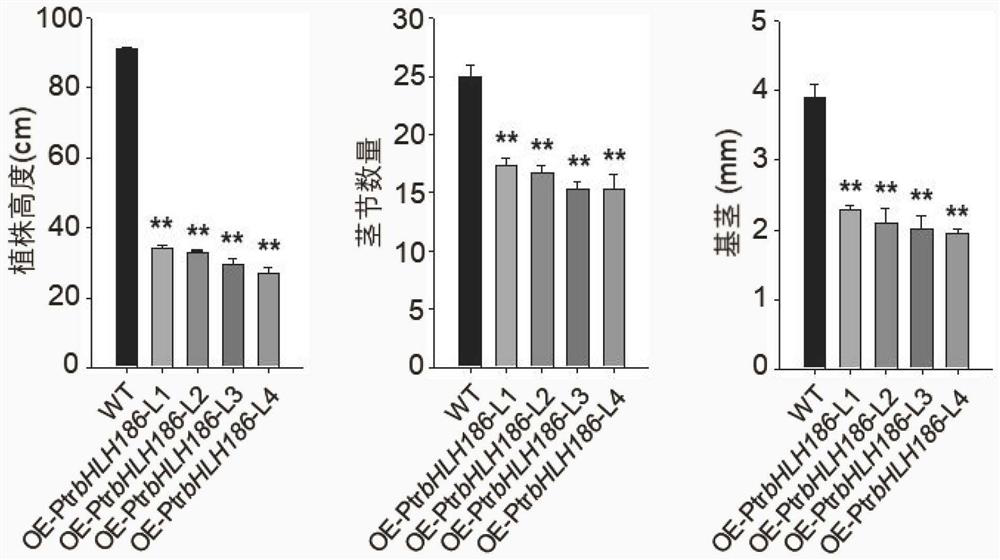
The invention relates to application of a populus trichocarpa PtrbHLH186 gene in regulation and control of secondary xylem development of trees, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. In order to solve the problems that the need for wood quantity and quality is increased day by day and the biological function of the PtrbHLH186 transcription factor is unknown, a PtrbHLH186 overexpressed populus trichocarpa transgenic plant is obtained through an agrobacterium-mediated populus trichocarpa genetic transformation system, and then a series of technical means are utilized for analysis and discovery that the PtrbHLH186 overexpressed populus trichocarpa transgenic plant is found to have the advantages that the PtrbHLH186 overexpressed populus trichocarpa transgenic plant; the overexpression of the PtrbHLH186 transcription factor affects the growth and development of plants and the formation of wood, which is mainly embodied in that the lignin synthase gene is regulated by the gene to affect the deposition of lignin in the secondary cell wall of a tree, so that the morphological structure and distribution of xylem cells are changed; the results show that the PtrbHLH186 transcription factor has a certain regulation effect on the development of the secondary xylem of the tree. The research content provided by the invention has important theoretical guiding significance for cultivating new varieties of high-quality woods and forests.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
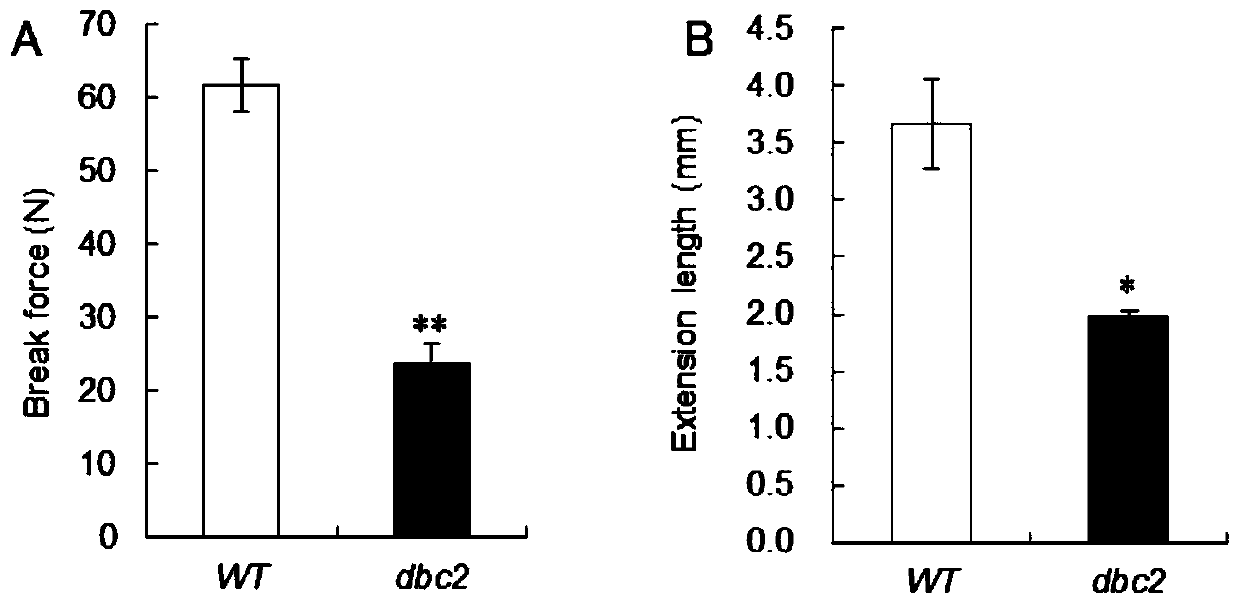
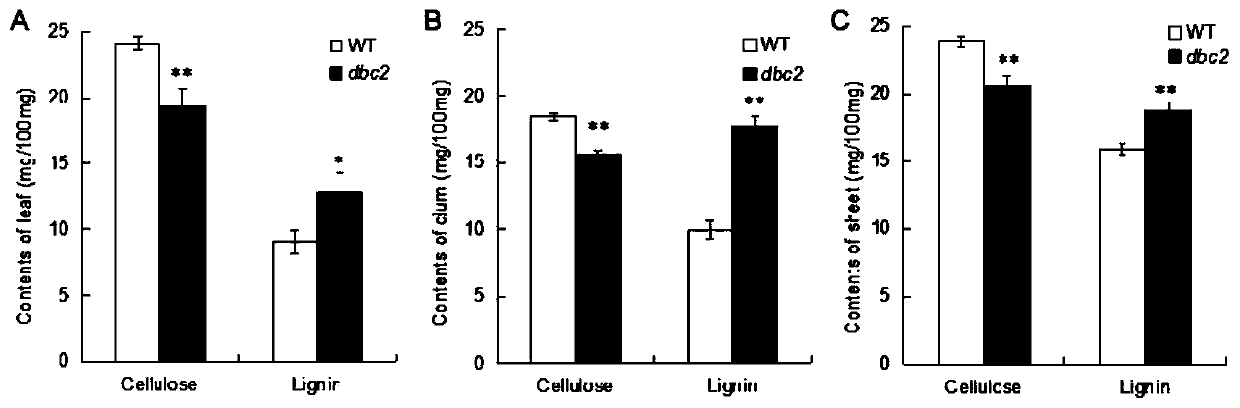
Rice brittle stem regulatory gene DBC2 and application thereof
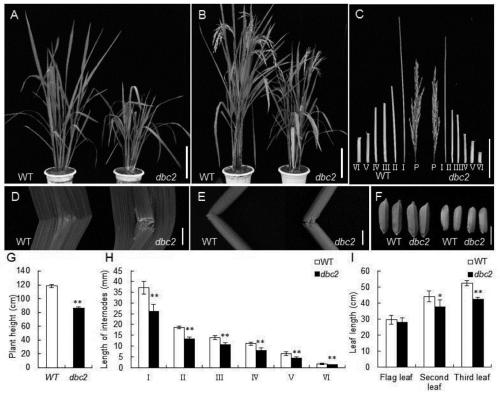
The invention belongs to the technical field of rice breeding, and particularly relates to a rice brittle stem regulatory gene DBC2 and application thereof. The invention discloses the rice brittle stem regulatory gene DBC2, the nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID No.1, and a protein encoded by the gene is glucoside hydrolase OsGH9A3 with an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No.2.The rice brittle stem regulatory gene DBC2 disclosed by the invention regulates rice brittle stem traits and dwarfing traits by directly or indirectly influencing the expression quantity of celluloseand lignin synthesis genes and secondary cell wall growth related transcription factor genes, and the regulation of the expression of the brittle stem traits is also regulated by temperature. The rice brittle stem regulatory gene DBC2 is applied to rice improvement, rice with brittle and tender stems is expected to be modified, the brittle and tender stems can be used for feed production, and theproblem that existing rice stems are inconvenient to treat is solved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Refreshing method for preventing picked phyllostachys pracecox shoots from flesh lignification
ActiveCN102960431APrevent lignificationDelays the development of lignification decay symptomsFruits/vegetable preservation by freezing/coolingShootDistilled water
The invention discloses a refreshing method for preventing picked phyllostachys pracecox shoots from flesh lignification. The refreshing method comprises the following steps of: (1) pre-cooling: selecting the picked phyllostachys pracecox shoots, removing the hard stumps and shells, cleaning, horizontally spreading, and cooling by the air until reaching temperature of about 20 DEG C; (2) processing by BTH (Benzo-thiadiazole-7-carbothioic acid S-methyl ester): dissolving BTH powder into sterile distilled water at 20 DEG C, so as to obtain the BTH solution with concentration of 30 to 50mg / L; putting the phyllostachys pracecox shoots processed in the step (1) into a sealed cylinder for soaking in the BTH solution for 10 to 20 minutes at negative pressure of -0.1 to -0.01MPa; and (3) packaging and storing: airing the phyllostachys pracecox shoots processed in the (2) for 1 hour; sub-packaging; and refrigerating. By adopting the refreshing method, the picked phyllostachys pracecox shoots can be effectively prevented from lignin combining and the quality deterioration during the storage period, and therefore, the storage period of the phyllostachys pracecox shoots can be prolonged to more than 40 days.
Owner:重庆汇达柠檬科技集团有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com