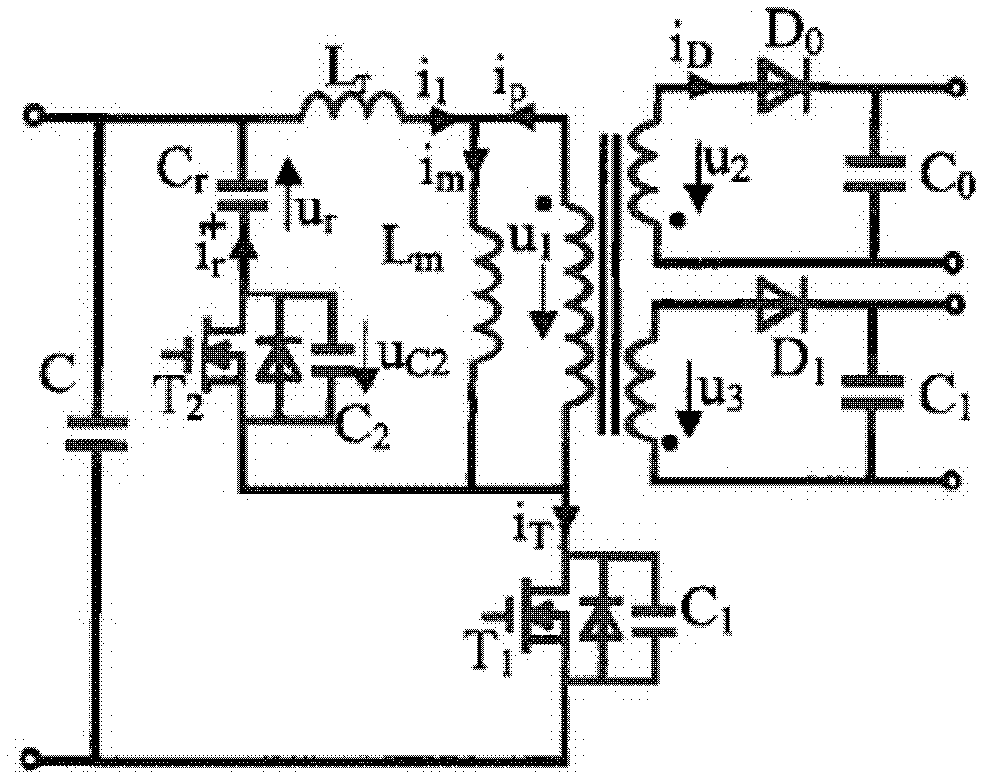
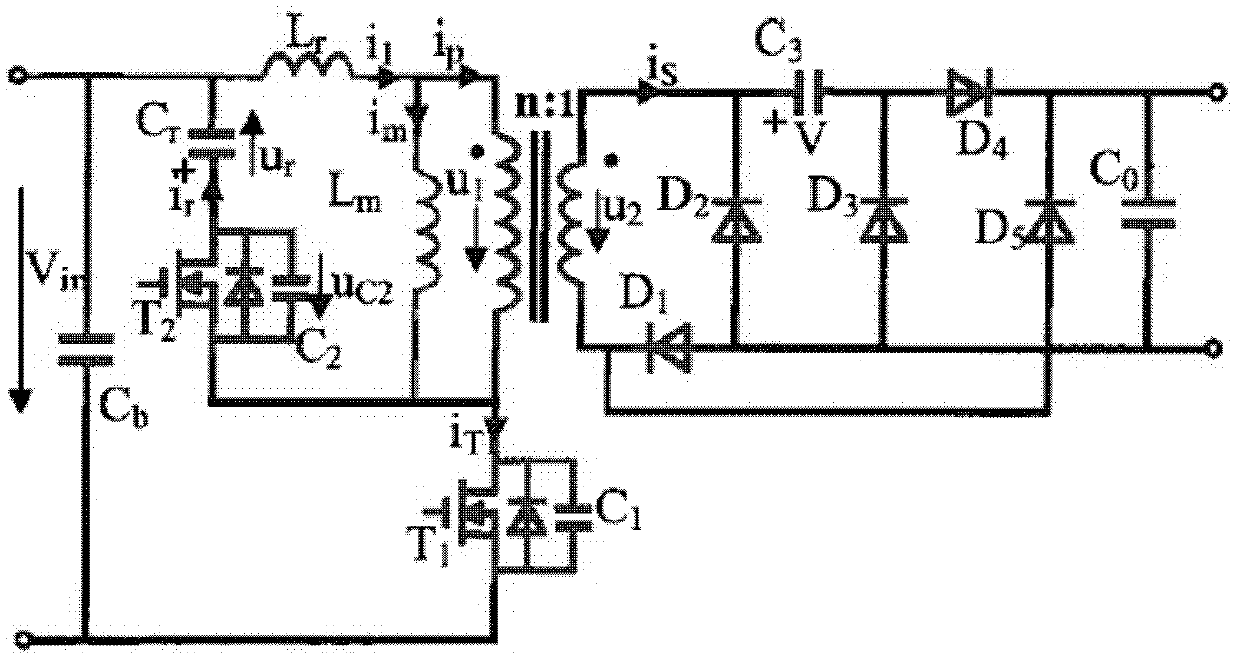
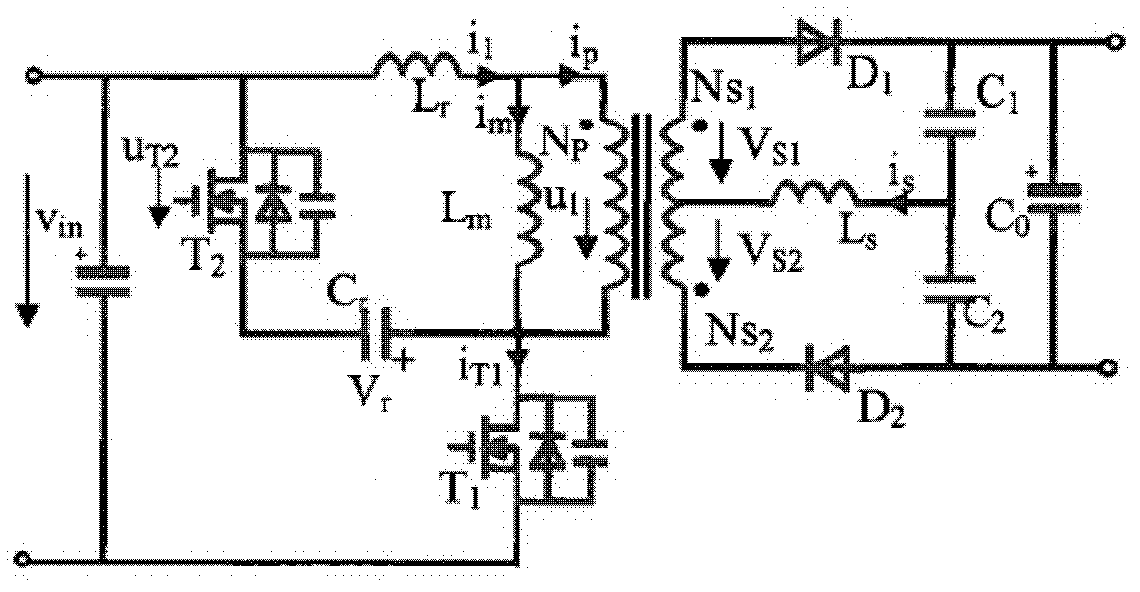
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
434 results about "Lc resonant circuit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An LC resonant circuit is a circuit that is composed of a single inductor and capacitor that can do many powerful and useful things. An LC resonant circuit, as the name implies, achieves resonance.
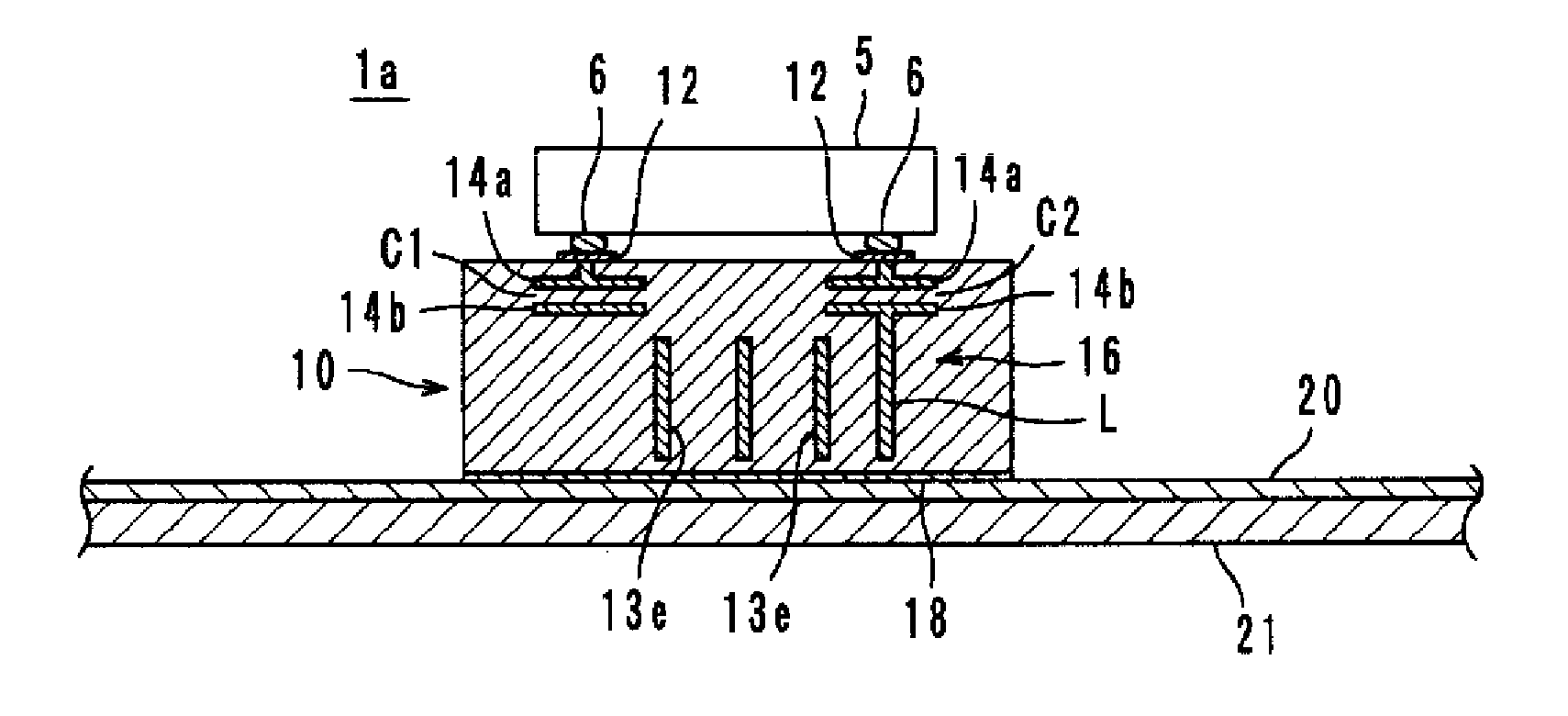
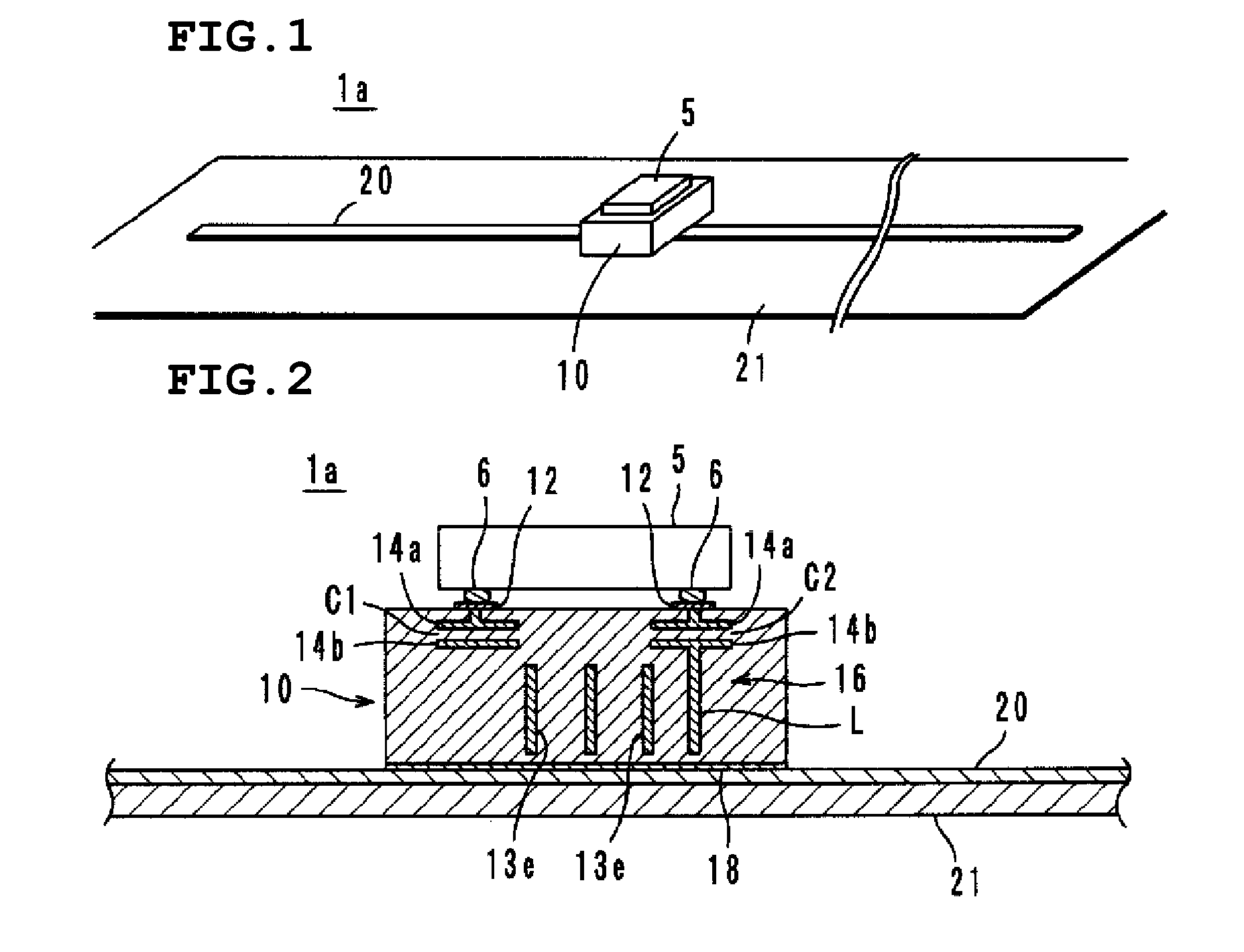
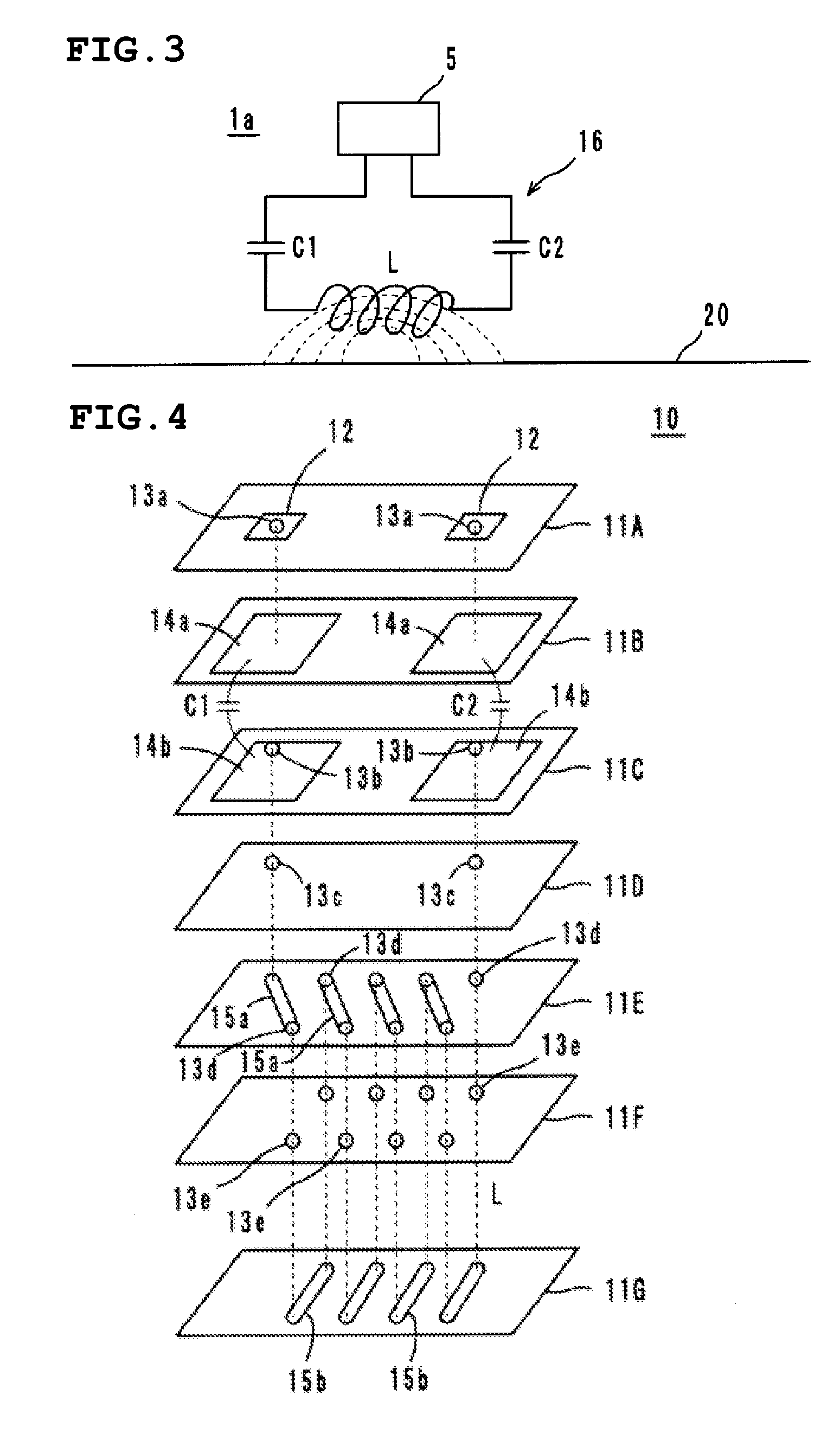
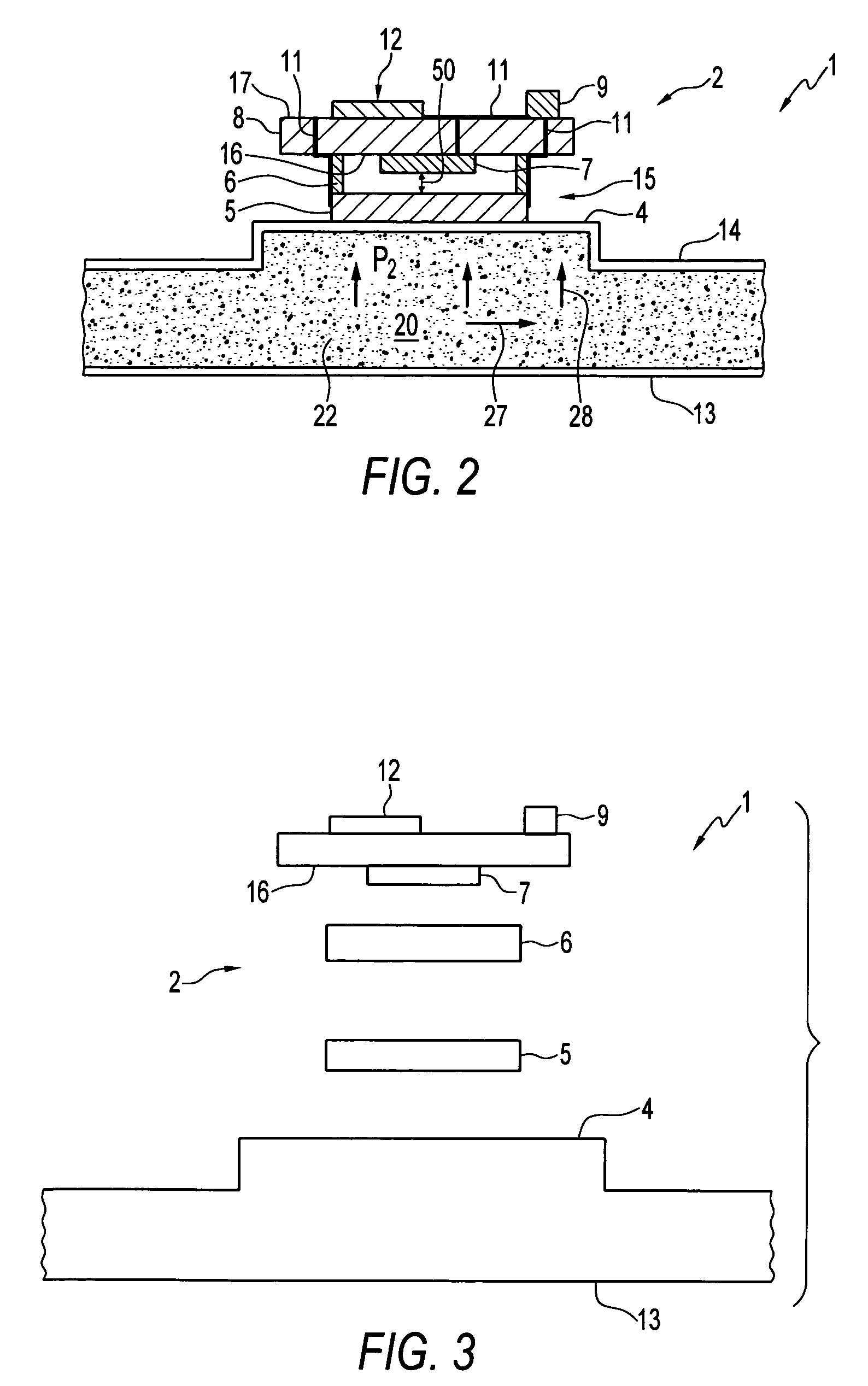
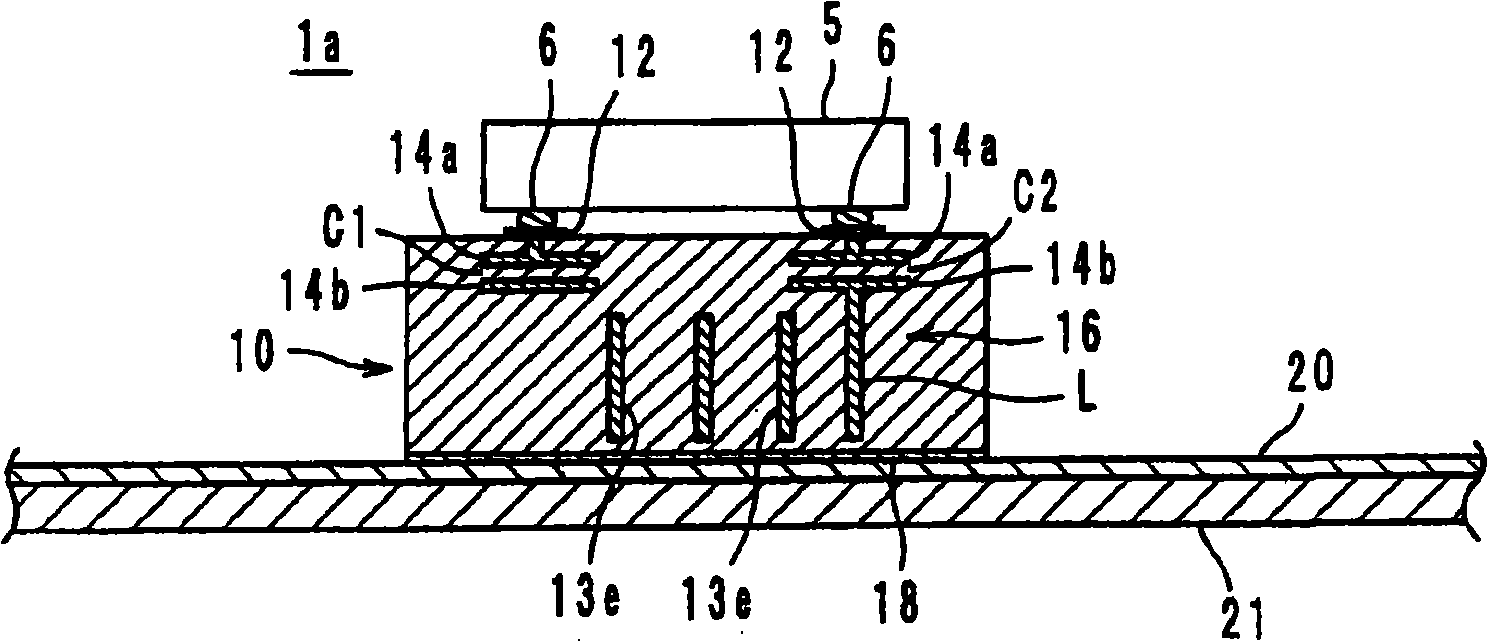
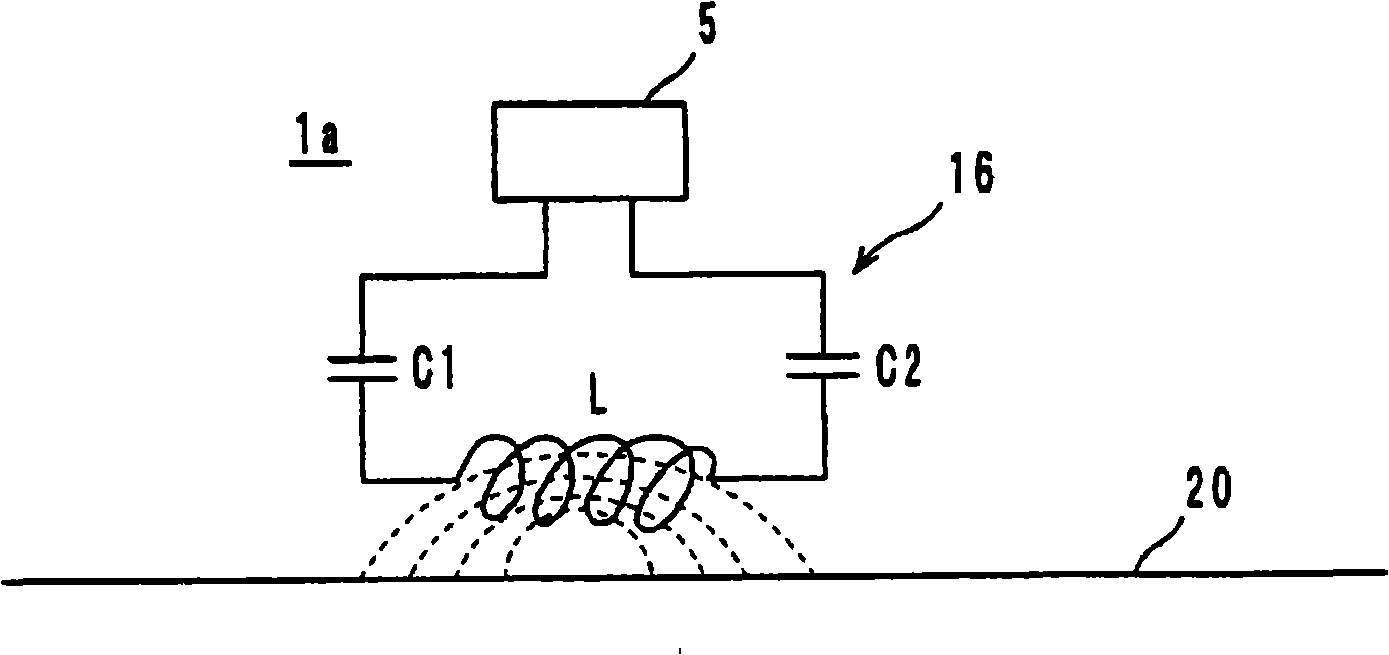
Wireless IC device and component for wireless IC device
ActiveUS20070164414A1Maintain stable propertiesPrevent electromagnetic leakageNear-field transmissionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceCapacitive coupling
A wireless IC device includes a wireless IC chip, a power supply circuit board upon which the wireless IC chip is mounted, and in which a power supply circuit is provided, the power supply circuit includes a resonant circuit having a predetermined resonant frequency, and a radiation pattern, which is adhered to the underside of the power supply circuit board, for radiating a transmission signal supplied from the power supply circuit, and for receiving a reception signal to supply this to the power supply circuit. The resonant circuit is an LC resonant circuit including an inductance device and capacitance devices. The power supply circuit board is a multilayer rigid board or a single-layer rigid board, and between the wireless IC chip and the radiation pattern is connected by DC connection, magnetic coupling, or capacitive coupling.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
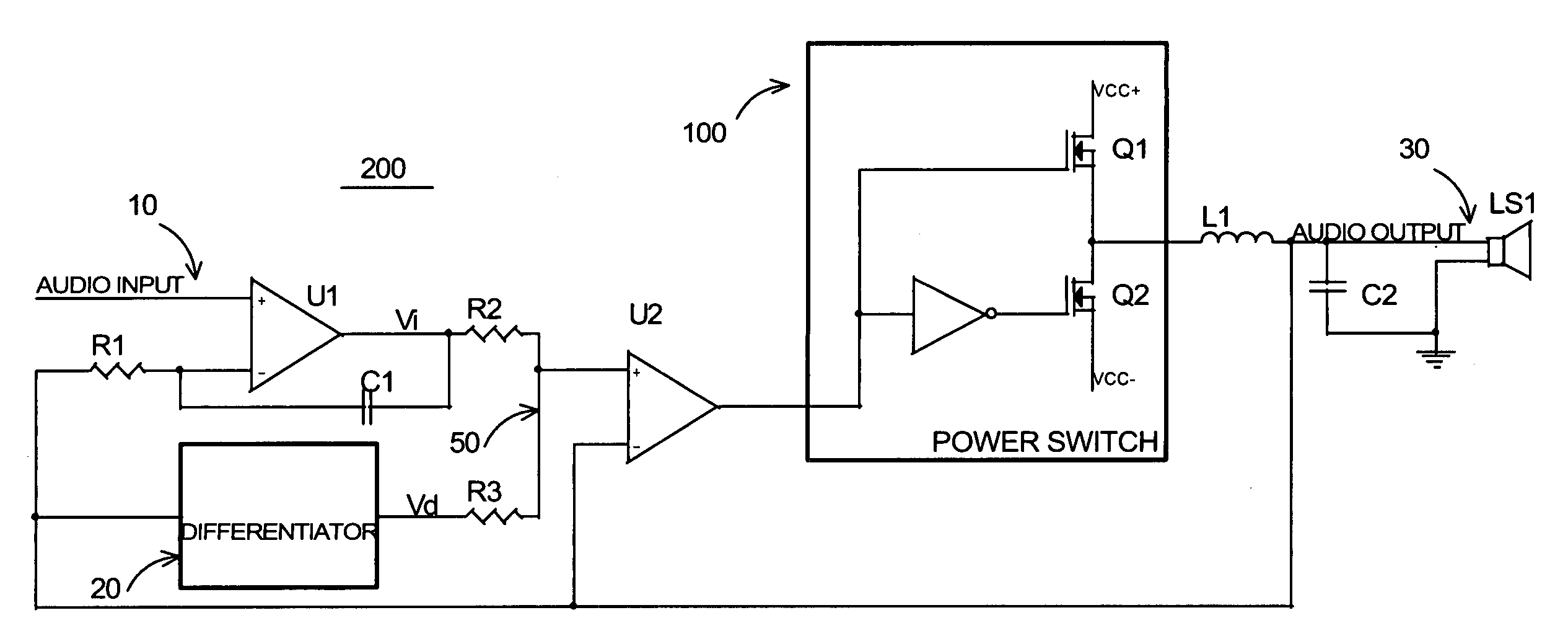
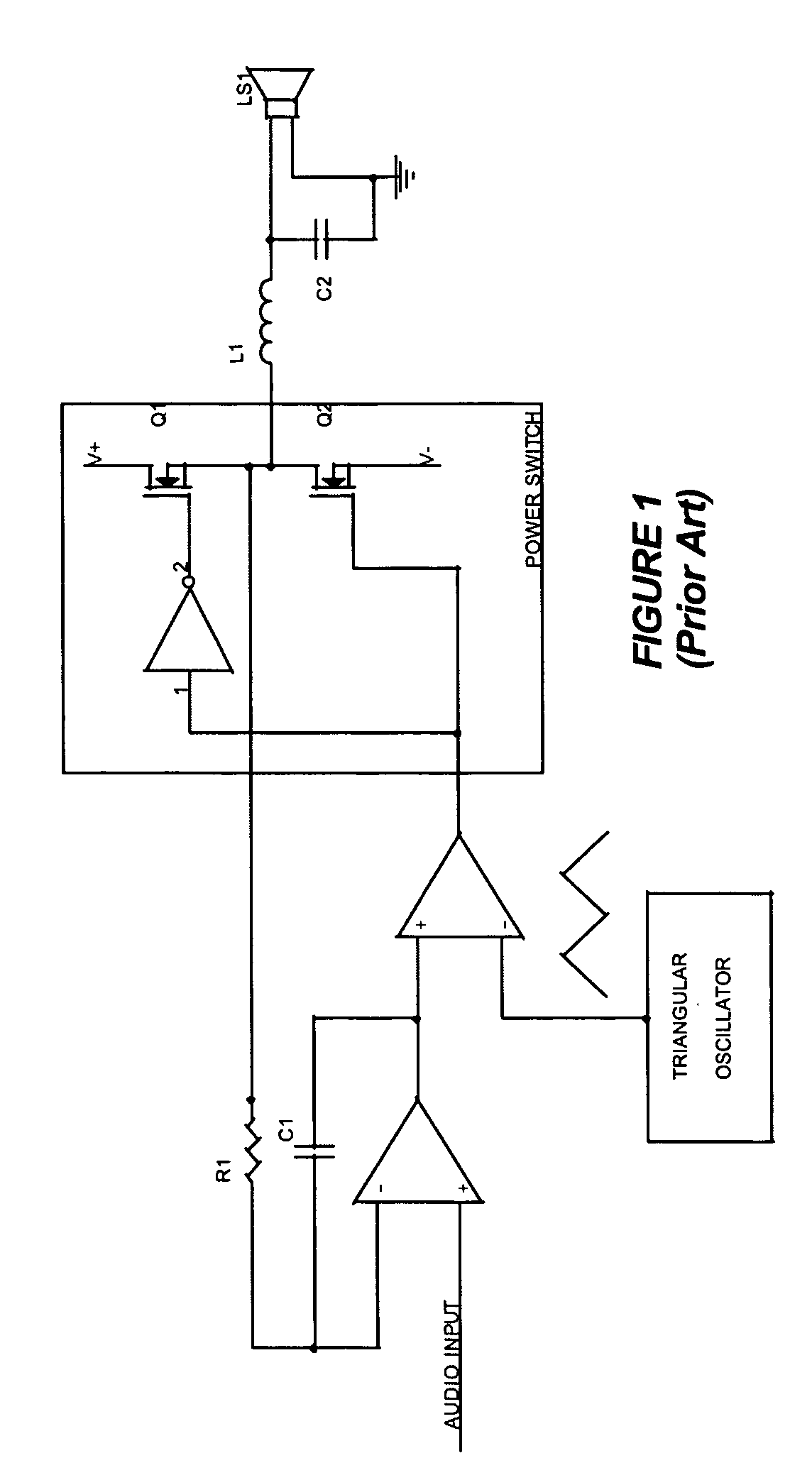
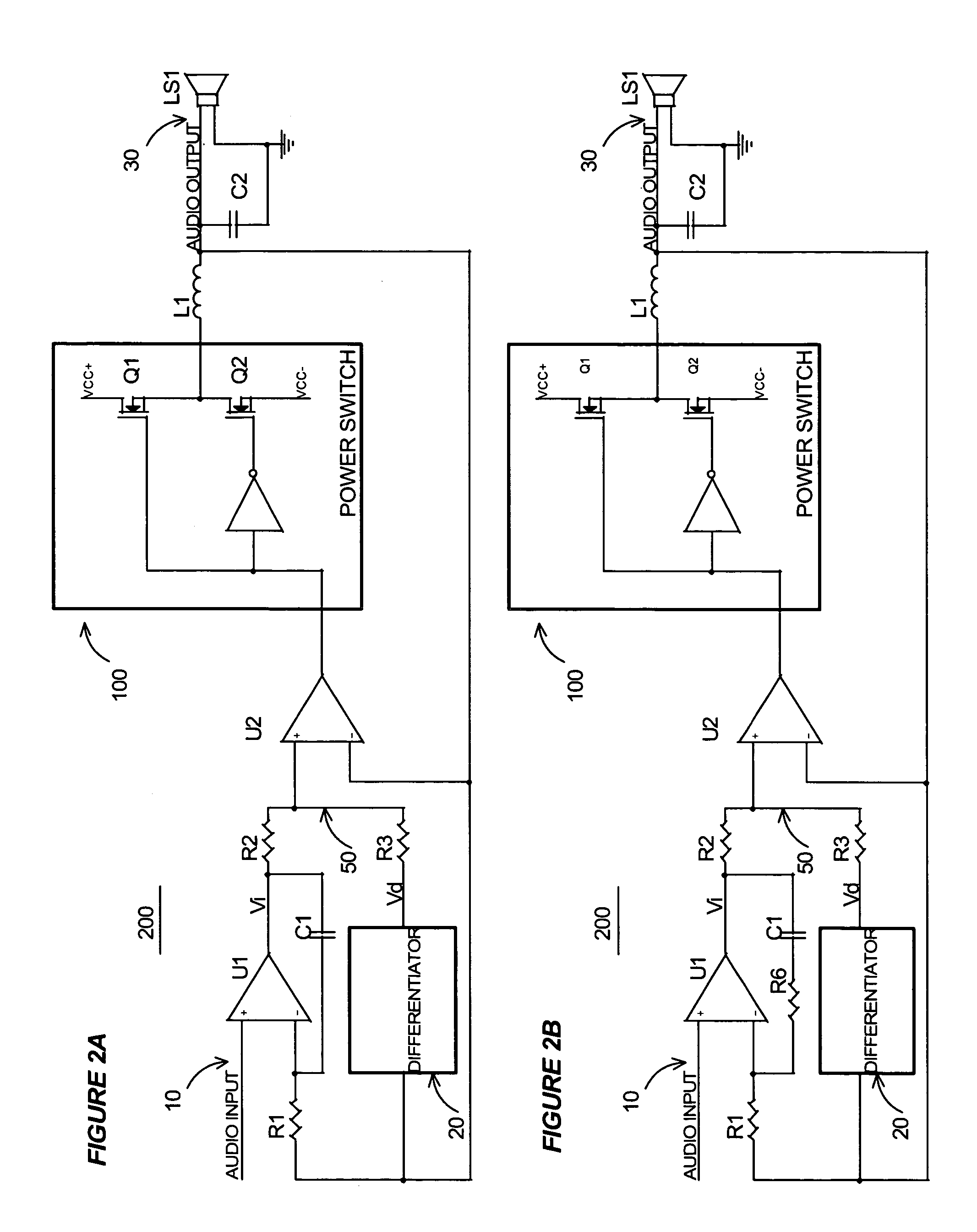
Self-oscillating switching amplifier
InactiveUS7221216B2Improve audio performanceMinimize distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionLow frequency amplifiersDifferentiatorLc resonant circuit
A self-oscillating switching amplifier having an error amplifier output combined with the output of an output signal differentiator according predetermined weighing factors to force a small oscillation around the averaged output signal at a high frequency. The feedback voltage is sensed at the output of the switching amplifier. Additional feedback can be derived from a switching node of the power switch. The switching of the power switch can be dynamically changed from binary switching when the amplitude of the audio signal is low, to ternary switching when the amplitude of the input signal is high to minimize distortion of the output signal. The amplifier can be supplied with a pulsing voltage. In certain embodiments the output signal differentiator is simply a capacitor or a LC resonance circuit coupled directly to an appropriate speaker terminal for the highest possible self-oscillating frequency of the switching amplifier.
Owner:CORETRONIC
Oscillation circuit and a communication semiconductor integrated circuit
InactiveUS6906596B2Reduce parasitic capacitanceWide frequency conversion rangeAngle modulation by variable impedencePulse automatic controlResonance oscillationLc resonant circuit
A voltage controlled LC resonance oscillation circuit has a plurality of capacitive elements connected to an output node. These capacitive elements are applied with voltages at opposing terminals for selecting an oscillating frequency band, so that the oscillating frequency band can be changed step by step in accordance with the selection voltage. The capacitive elements include at least one variable capacitive element such as a MOS capacitor, the capacitance of which is varied in accordance with a voltage applied thereto. The MOS capacitor is similar in structure to a MOS transistor. The variable capacitive element can be supplied at a terminal opposite to the output node with a voltage from a variable voltage source, for example, in place of the selection voltage. The voltage controlled LC resonance oscillation circuit can measure the output amplitude and oscillating frequency without affecting the characteristics thereof, and reduce the parasitic capacitance.
Owner:EPOCH MICROELECTRONICS +1
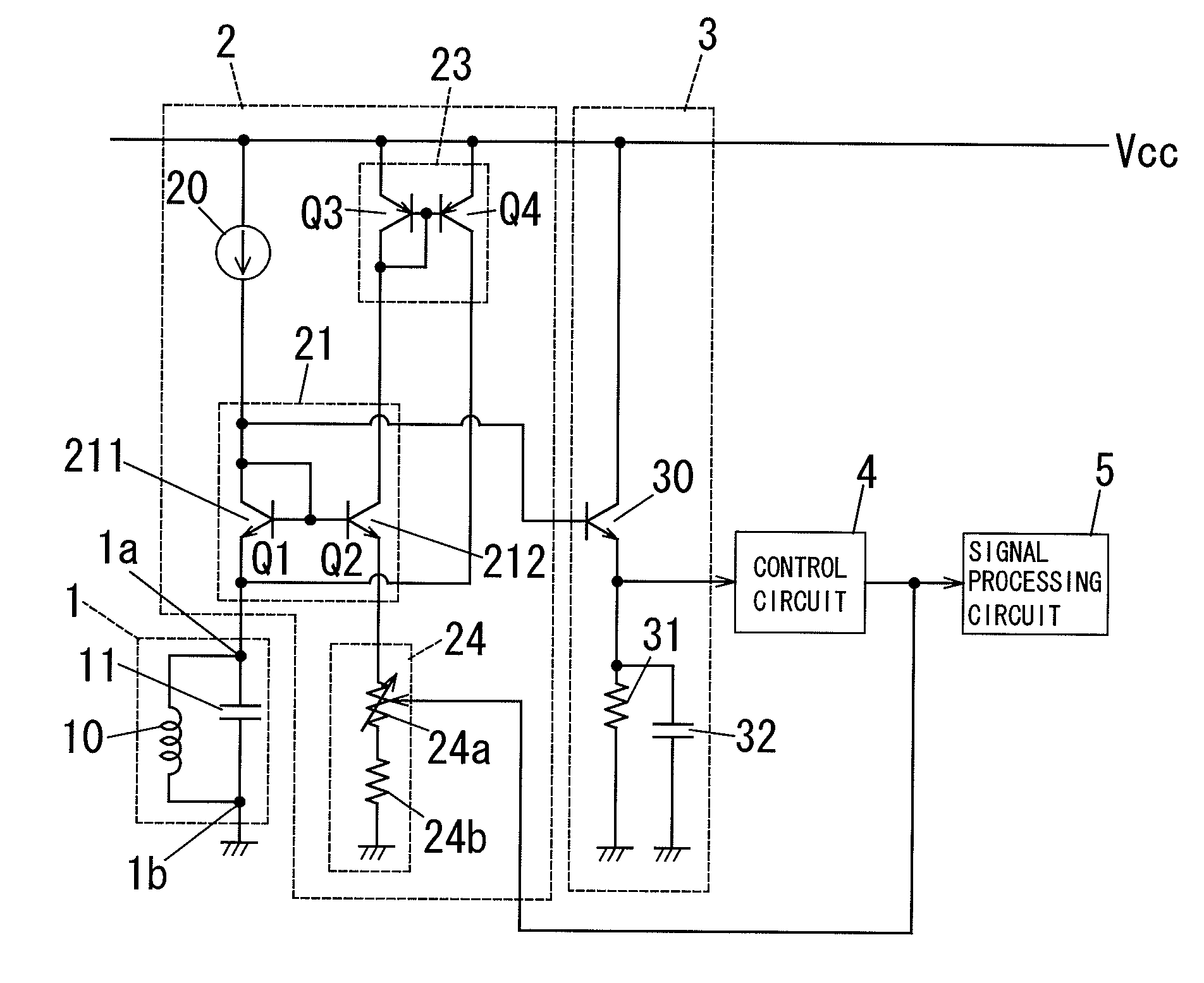
Proximity sensor
InactiveUS20100225332A1Avoid changeImprove sensing accuracyResistance/reactance/impedenceElectronic switchingProximity sensorSignal processing circuits
A proximity sensor has an oscillation circuit, an amplitude measurement circuit, a control circuit and a signal processing circuit. The oscillation circuit has an LC resonant circuit and an oscillation control circuit that is configured to supply an electric current to the LC resonant circuit to generate oscillating voltage across the LC resonant circuit. The amplitude measurement circuit is configured to produce an amplitude signal corresponding to the amplitude of the oscillating voltage. The control circuit is configured to set the negative conductance of the oscillation control circuit to a critical value by which the LC resonant circuit can oscillate based on the amplitude signal. The signal processing circuit is configured to produce a distance signal corresponding to the distance between an object and the sensing coil based on a parameter associated with the negative conductance.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Toroid cavity/coil NMR multi-detector
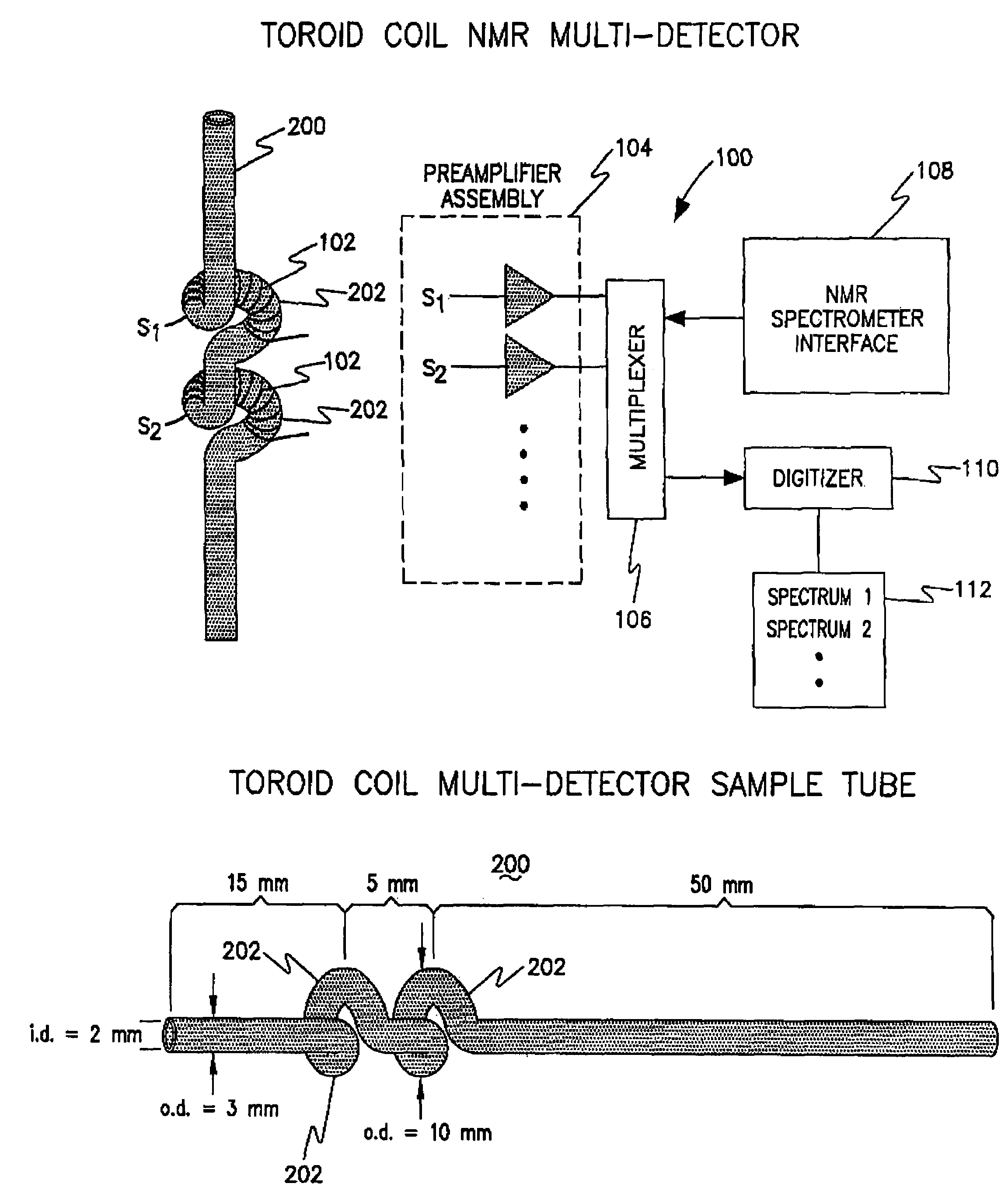
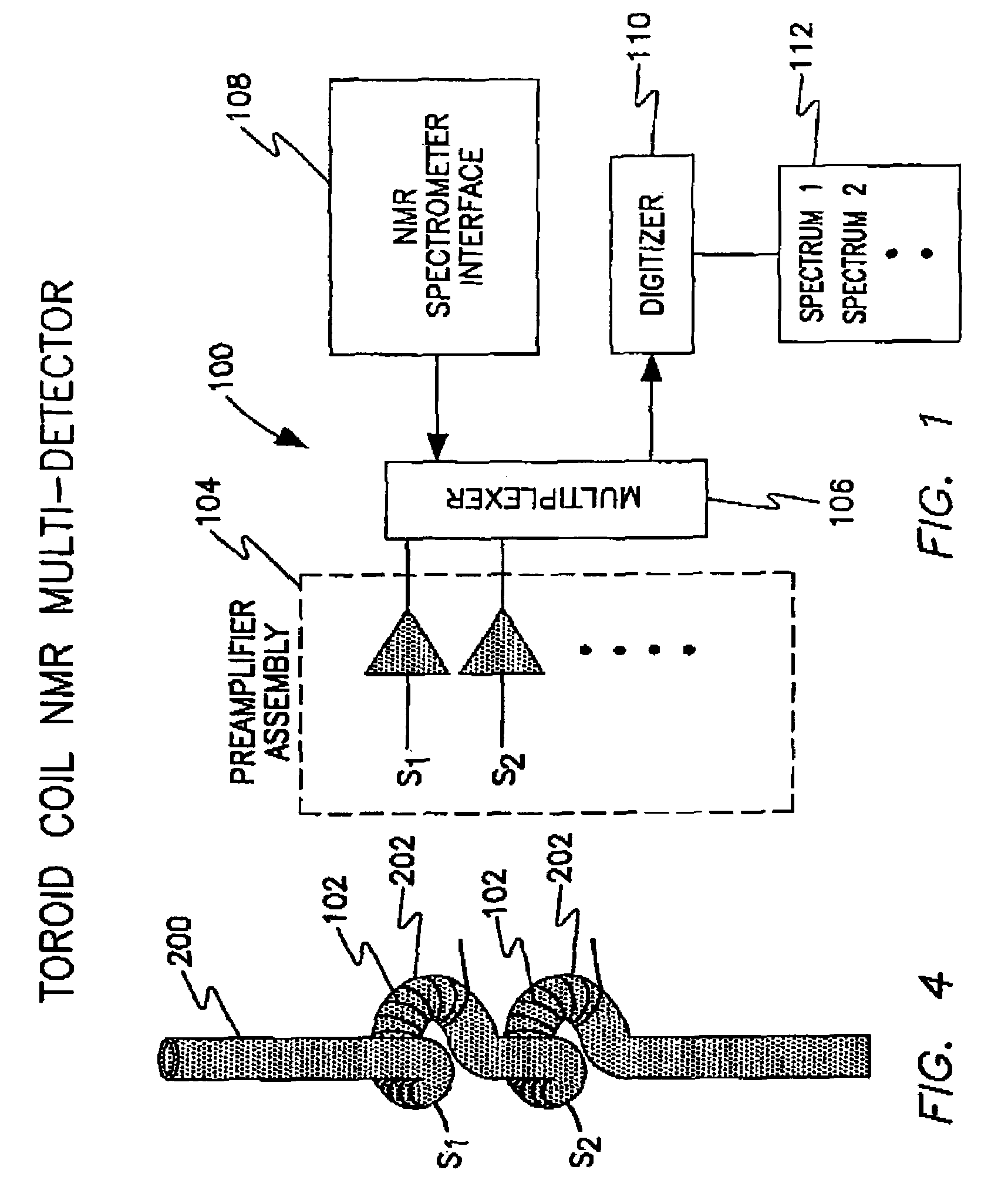
InactiveUS7271592B1Rapid and non-invasive nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopyElimination of poor magnetic field homogeneityMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionElectrical conductorHelmholtz coil
An analytical device for rapid, non-invasive nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy of multiple samples using a single spectrometer is provided. A modified toroid cavity / coil detector (TCD), and methods for conducting the simultaneous acquisition of NMR data for multiple samples including a protocol for testing NMR multi-detectors are provided. One embodiment includes a plurality of LC resonant circuits including spatially separated toroid coil inductors, each toroid coil inductor enveloping its corresponding sample volume, and tuned to resonate at a predefined frequency using a variable capacitor. The toroid coil is formed into a loop, where both ends of the toroid coil are brought into coincidence. Another embodiment includes multiple micro Helmholtz coils arranged on a circular perimeter concentric with a central conductor of the toroid cavity.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Switched-capacitor isolated LED driver
ActiveUS20140346962A1Improve cooling effectElectroluminescent light sourcesDc-dc conversionCapacitanceLc resonant circuit
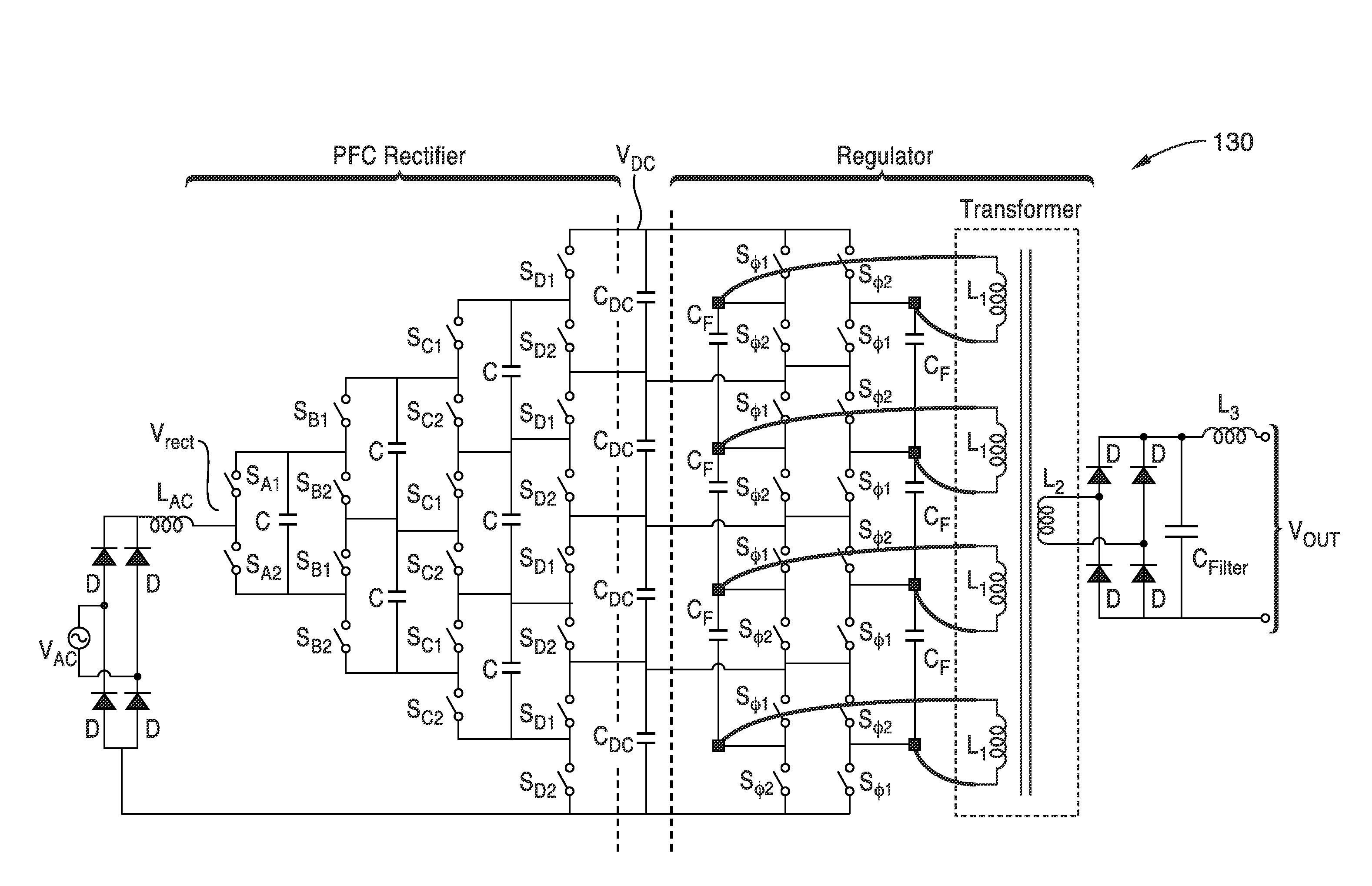
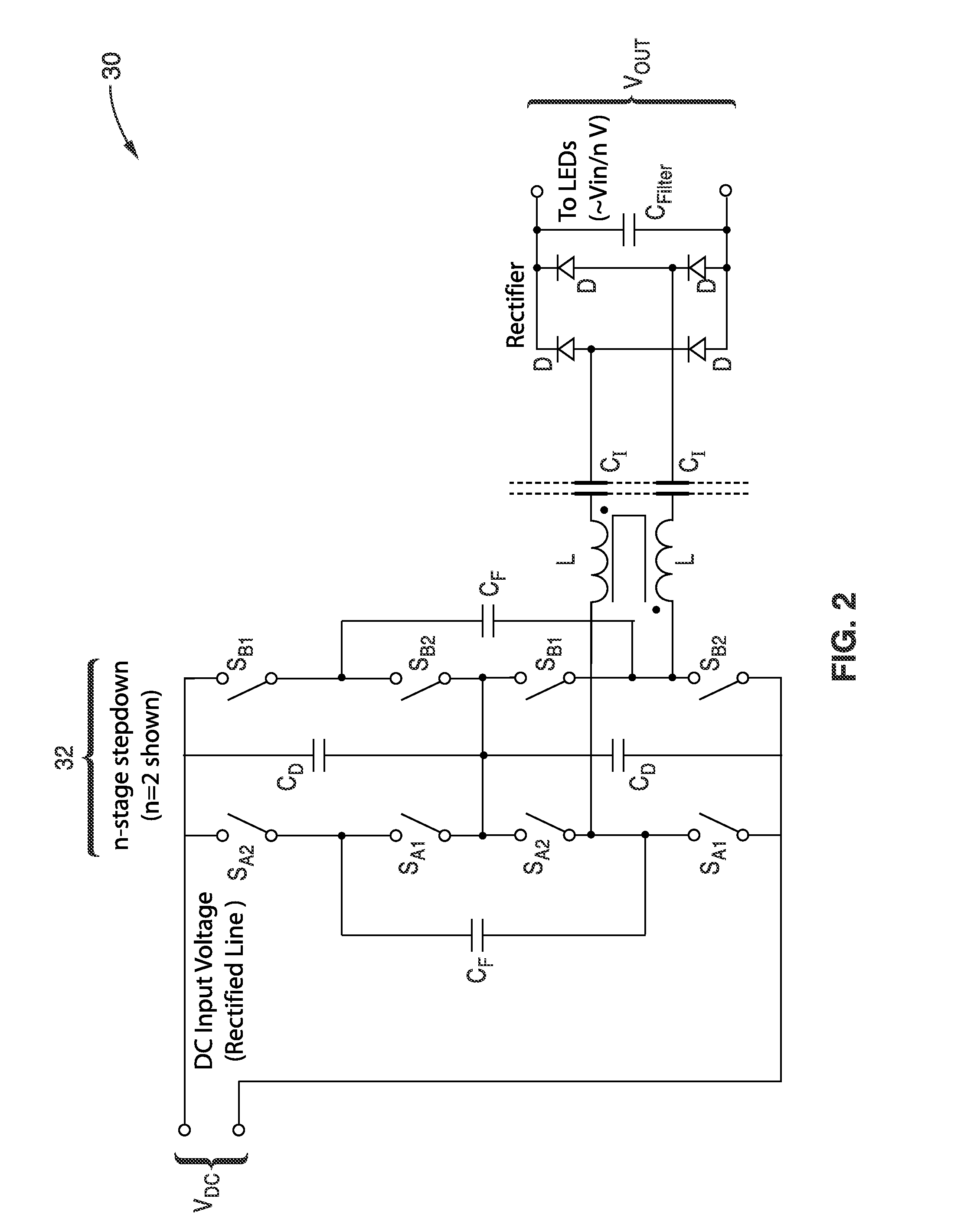
A switched-capacitor voltage converter which is particularly well-suited for receiving a line voltage from which to drive current through a series of light emitting diodes (LEDs). Input voltage is rectified in a multi-level rectifier network having switched capacitors in an ascending-bank configuration for passing voltages in uniform steps between zero volts up to full received voltage VDC. A regulator section, operating on VDC, comprises switched-capacitor stages of H-bridge switching and flying capacitors. A current controlled oscillator drives the states of the switched-capacitor stages and changes its frequency to maintain a constant current to the load. Embodiments are described for isolating the load from the mains, utilizing an LC tank circuit or a multi-primary-winding transformer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Stylus without active components and an associated touch panel
InactiveUS20150199035A1Low costReduce power consumptionInput/output processes for data processingActive componentLc resonant circuit
A stylus without active components includes a housing, and a resonant circuit, such as an LC resonant circuit, disposed in the housing. The resonant circuit is operatively configured to one of a plurality of resonant frequencies respectively associated with a plurality of function modes.
Owner:HIMAX TECH LTD
Synchronous Rectifier Type Series Resonant Converter for Operating in Intermittence Mode
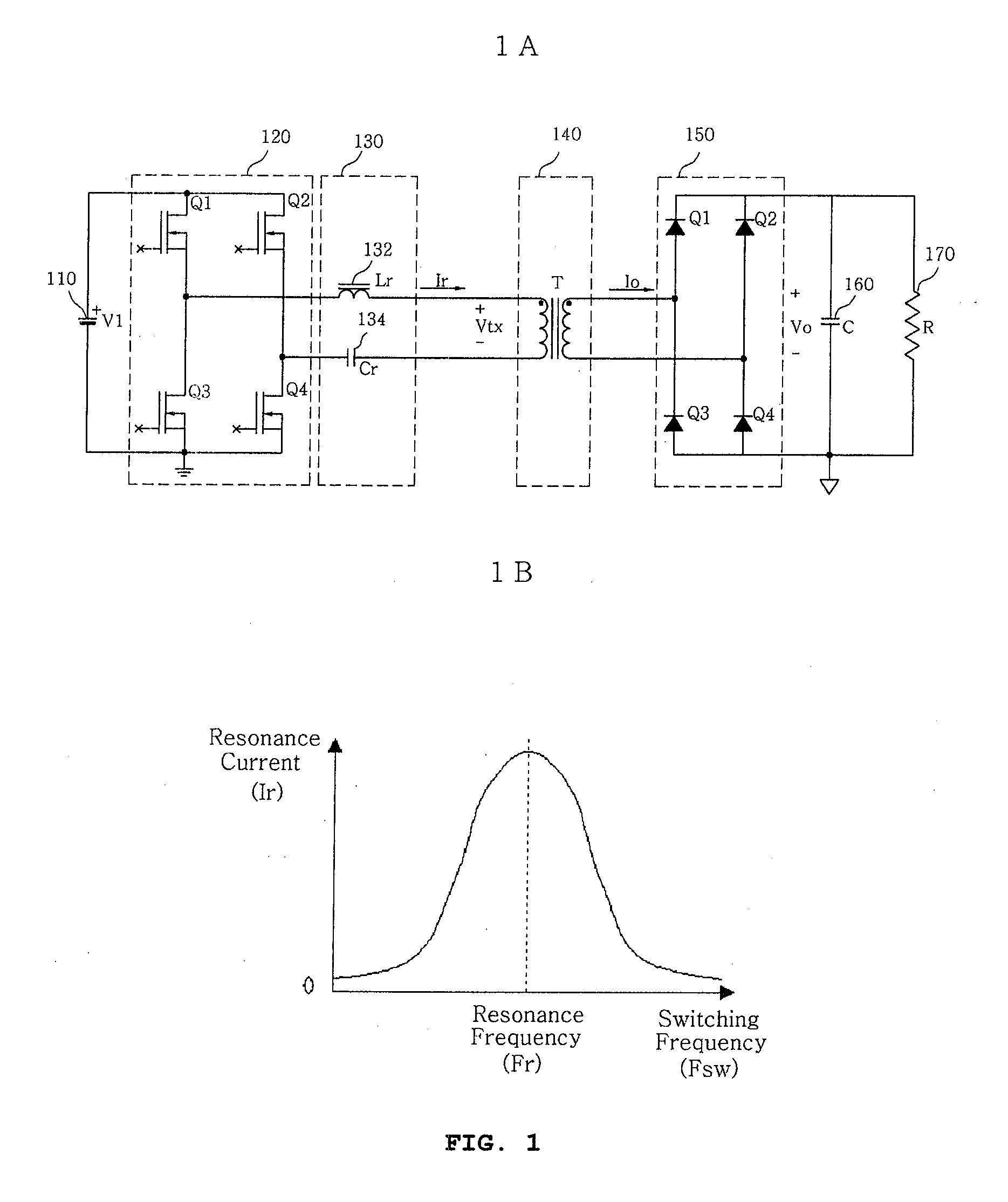
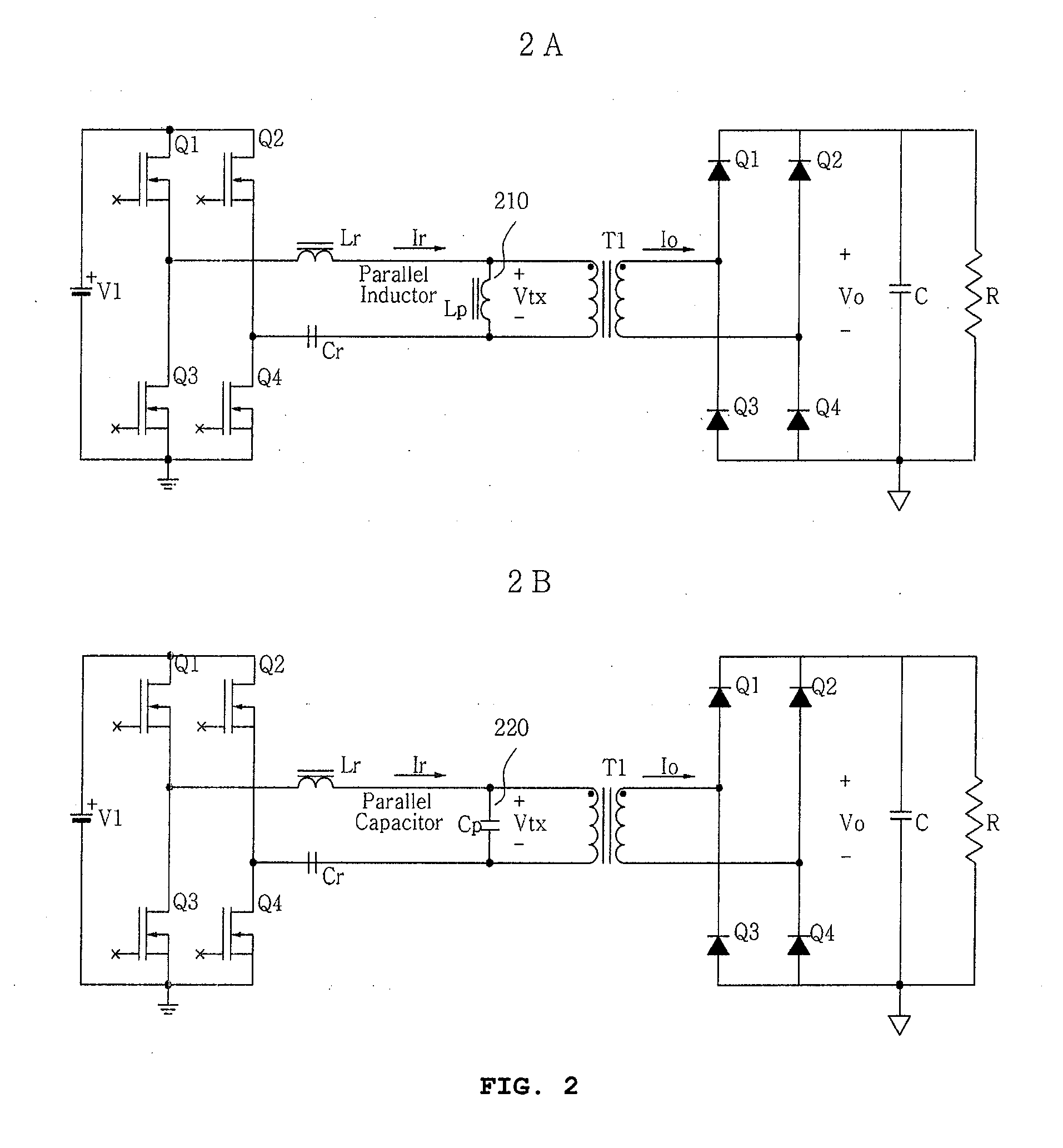
InactiveUS20080186742A1Reduce switching lossesMaximize conversion efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionLc resonant circuitResonance
Disclosed is a synchronous rectifier type SRC for operating in an intermittence mode, which includes: an input power for supplying the input DC voltage; an input-side switching unit for switching four input-side switching devices to convert the input DC voltage to AC voltage, the input-side switching unit being connected to the input power, an LC resonance circuit for storing energy in a resonance inductor and a resonance capacitor by means of LC resonance, and outputting resonance voltage, the LC resonance circuit being connected to the input-side switching unit; a transformer with a primary winding and a secondary winding for converting the resonance voltage to voltage of a predetermined level according to a turn ratio to generate secondary voltage, and transferring the secondary voltage through the secondary winding, the primary winding being connected to the LC resonance circuit; an output-side switching unit for switching four output-side switching devices to convert the secondary voltage to the output DC voltage, the output-side switching unit being connected to the secondary winding of the transformer; and a gate driving circuit for detecting a polarity of secondary current flowing in the secondary winding, generating dead time, generating driving signals for driving the output-side switching device of the output-side switching unit according to the polarity, and then controlling turn-on or turn-off of the output-side switching devices, the gate driving circuit being connected to both the secondary winding of the transformer and the output-side switching unit. According to the synchronous rectifier type SRC, a no-load characteristic can be controlled with an easy scheme and a simple construction. In addition, a simple resistor is added, and thus dead time can be generated. Consequently, it is possible to simply reduce switching loss that may occur in zero voltage switching.
Owner:PS TECH CO LTD
Frequency adjustment techniques in coupled LC tank circuits
CMOS LC tank circuits and flux linkage between inductors can be used to distribute and propagate clock signals over the surface of a VLSI chip or μprocessor. The tank circuit offers an adiabatic behavior that recycles the energy between the reactive elements and minimizes losses in a conventional sense. Flux linkage can be used to orchestrate a number of seemingly individual and distributed CMOS LC tank circuits to behave as one unit. Several frequency-adjusting techniques are presented which can be used in an distributed clock network environment which includes an array of oscillators. A passive flux linkage, mechanical, and finite state machine technique of frequency adjustment of oscillators are described.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HOLDING 81 LLC
Pressure flow sensor systems and pressure flow sensors for use therein
ActiveUS7290454B2Low costFluid pressure measurement using inductance variationCatheterElectricityLc resonant circuit
A differential pressure flow sensor system comprises a disposable flow sensor which has upstream and downstream pressure sensing devices for detecting a differential pressure in a flow channel. Each sensing device comprises a diaphragm, a capacitor and an inductor electrically coupled to the capacitor so as to form an LC tank circuit. The capacitor and / or inductor can be mechanically coupled to the diaphragm such that a deflection of the diaphragm in response to fluid pressure applied thereto causes a change in the resonant frequency of the LC tank. The differential pressure and flow rate can be determined by detecting changes in the resonant frequency using interrogation electronics which can wirelessly interrogate the devices. A calibration capacitor and / or inductor can be formed on each sensing device and trimmed thereon for calibration purposes. Such pressure flow systems can be implemented in medical applications.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Wireless IC device and component for wireless IC device
ActiveUS7519328B2Maintain stable propertiesPrevent electromagnetic leakageNear-field transmissionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceLc resonant circuit
A wireless IC device includes a wireless IC chip, a power supply circuit board upon which the wireless IC chip is mounted, and in which a power supply circuit is provided, the power supply circuit includes a resonant circuit having a predetermined resonant frequency, and a radiation pattern, which is adhered to the underside of the power supply circuit board, for radiating a transmission signal supplied from the power supply circuit, and for receiving a reception signal to supply this to the power supply circuit. The resonant circuit is an LC resonant circuit including an inductance device and capacitance devices. The power supply circuit board is a multilayer rigid board or a single-layer rigid board, and between the wireless IC chip and the radiation pattern is connected by DC connection, magnetic coupling, or capacitive coupling.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Passive Wireless Gastroesophageal Sensor
ActiveUS20080234599A1More compactMore untetheredDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRefluxLc resonant circuit
A passive wireless gastroesophageal sensor includes a LC resonance circuit, two or more electrodes and a passive batteryless Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) circuit connected to the LC resonance circuit and the one or more electrodes. The electrodes are configured to measure an impedance within a gastroesophageal tract. The passive batteryless RFID circuit transmits a frequency modulated signal using the LC resonance circuit that varies between a first frequency corresponding to a non-acid reflux condition and a second frequency corresponding to an acid reflux condition based on the measured impedance in response to a signal received from a detector.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
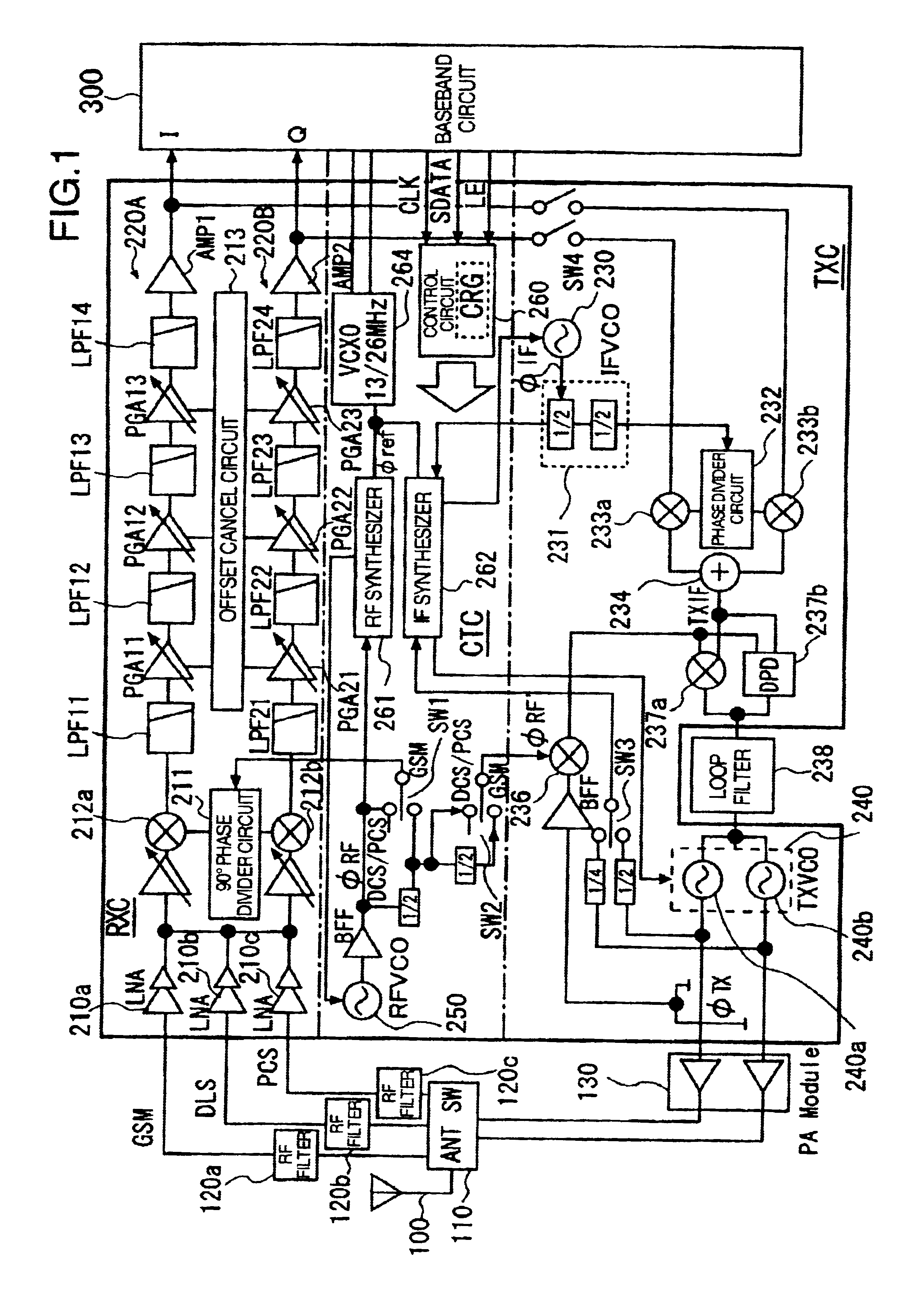
Semiconductor integrated circuit for communication
InactiveUS20050014476A1Deterioration in noise figure can be avoidedPreventing deterioration of noise characteristicResonant long antennasFrequency-modulated carrier systemsQuadrature modulationLc resonant circuit
An orthogonal modulating circuit for modulating signals of two oscillation frequencies differing in phase by 90° with transmission data (I and Q) is used in common for a plurality of bands, an LC resonance circuit comprising inductances L and a capacitor C is used as the output load on the orthogonal modulating circuit instead of resistors commonly used according to the prior art, and the values of L or C constituting the resonance circuit are switched over between each other according to the transmission band.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
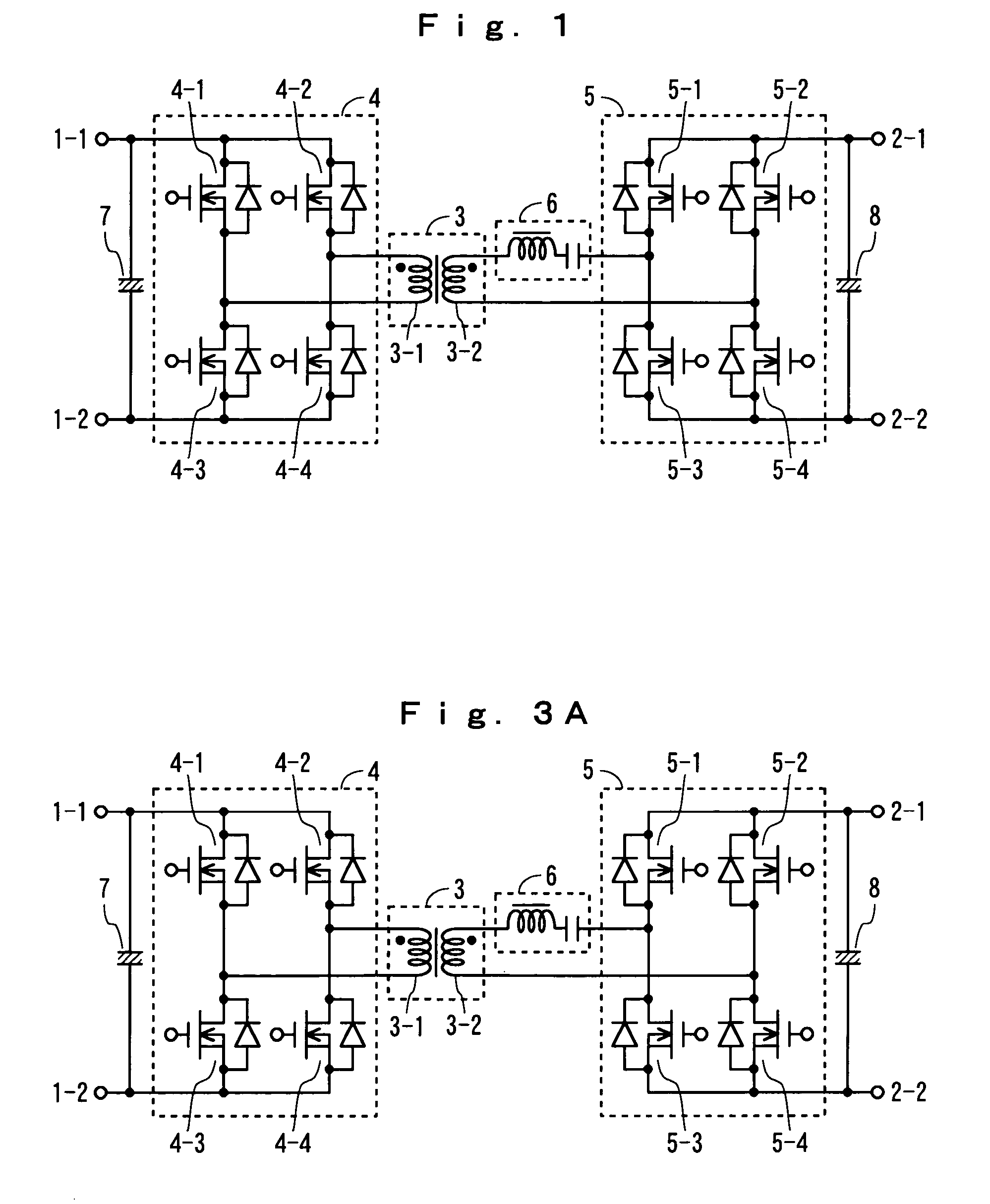
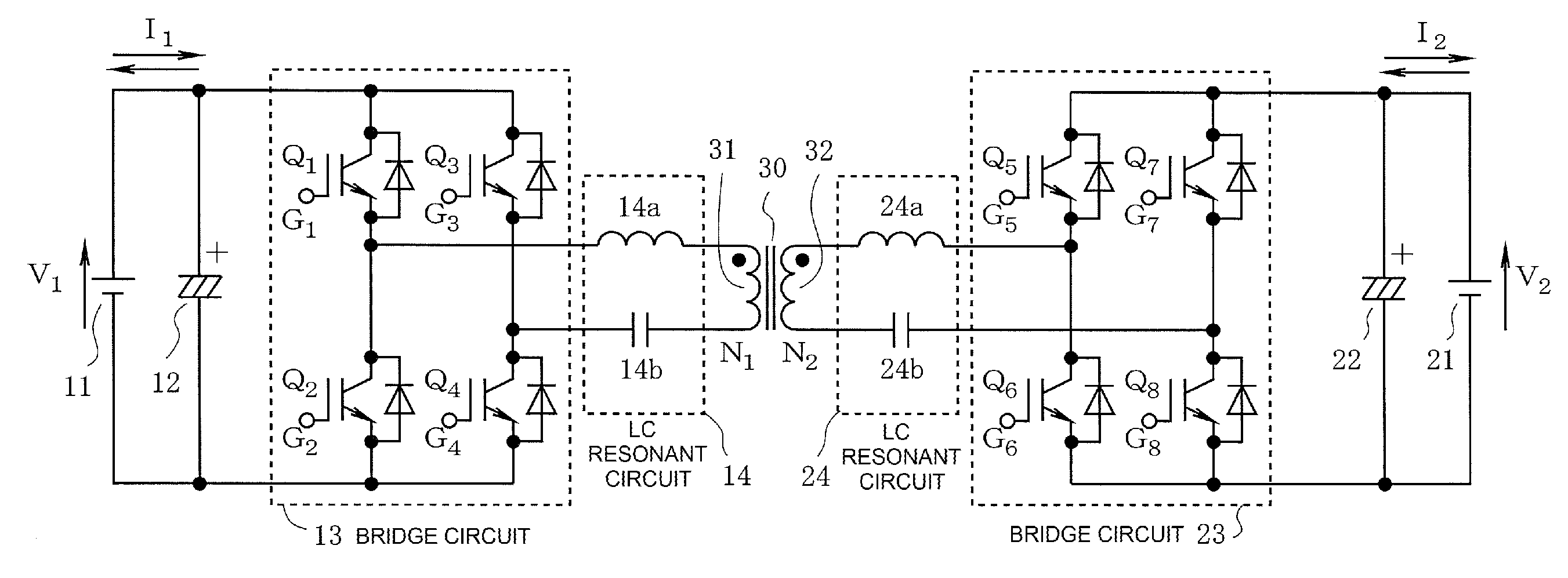
Two-way DC-DC converter
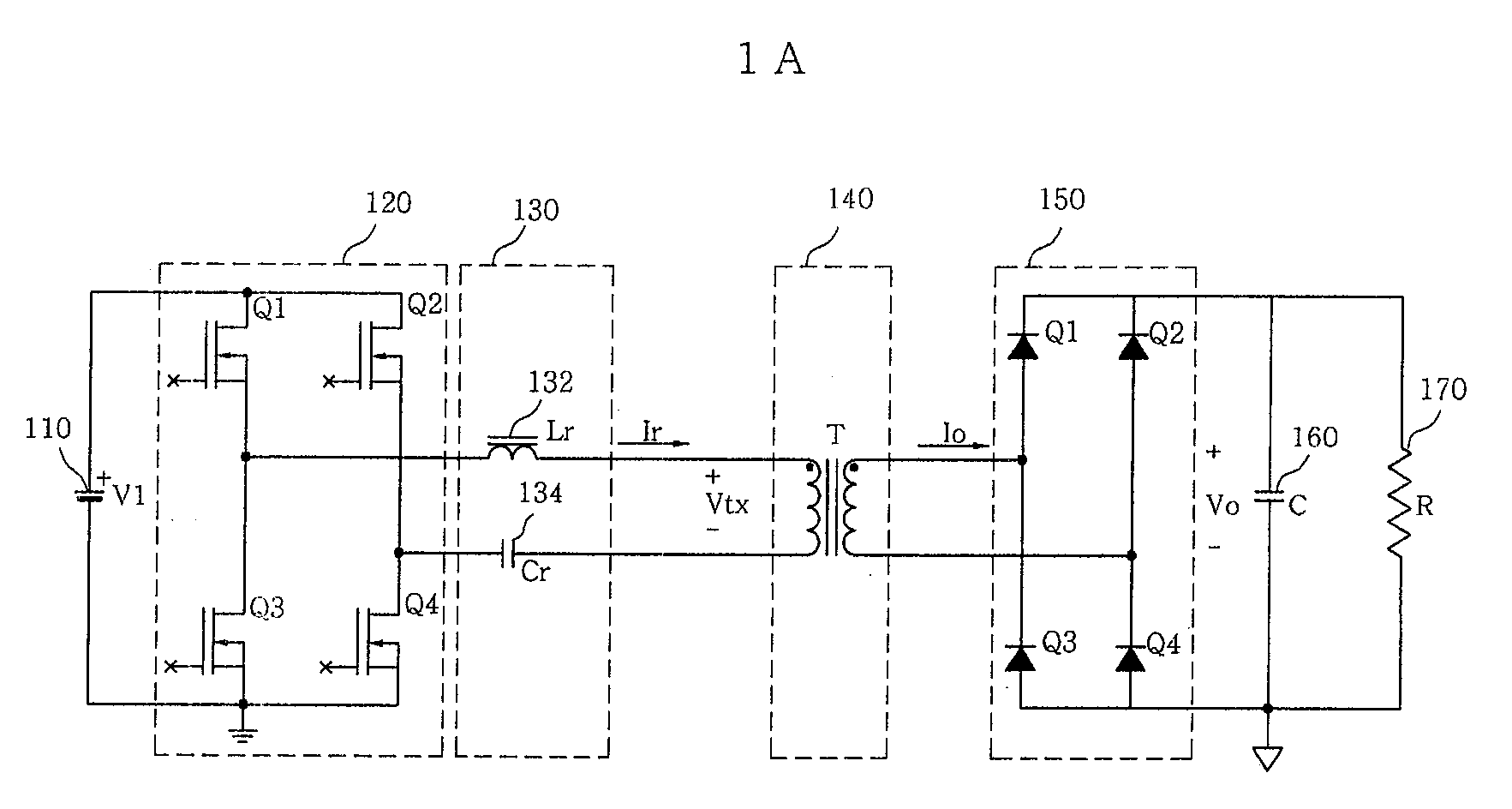
ActiveUS7177163B2Reduce switching lossesSimple configurationAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionDc dc converterLc resonant circuit
Rectifying elements are connected in parallel with switching elements 4-1 through 4-4 in a switching section 4 for the lower voltage side and rectifying elements are connected in parallel with switching elements 5-1 through 5-4 in a switching section 5 for the higher voltage side. An LC resonant circuit 6 is provided between the winding wire 3-2 for the high-voltage side in the transformer 3 and the switching section 5 for the higher voltage side; currents which flows on the primary side and the secondary side is changed into a sinusoidal one; and switching is executed in the vicinity of the zero crossing points of the currents.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Tag having patterned circuit elements and a process for making same
InactiveUS7116227B2Line/current collector detailsElectronic circuit testingLc resonant circuitAdhesive
A tag having a substrate having a surface with a preformed first patterned adhesive disposed over the surface thereof and a first layer of electrically conductive material having a shape corresponding to a desired final pattern for a first electrically conductive trace secured to the surface of the substrate. The preformed first patterned adhesive corresponds to the desired final pattern. A second patterned adhesive is disposed over a portion of a surface area of the tag. An electrically conductive trace is disposed over the second patterned adhesive to adhere the second electrically conductive trace thereto. An electrical connection is provided for electrically coupling portions of the first and second electrically conductive traces to form a tag circuit. The tag circuit can be an LC resonant circuit. The preformed first patterned adhesive can be a flexographic printed layer.
Owner:CHECKPOINT SYST INC
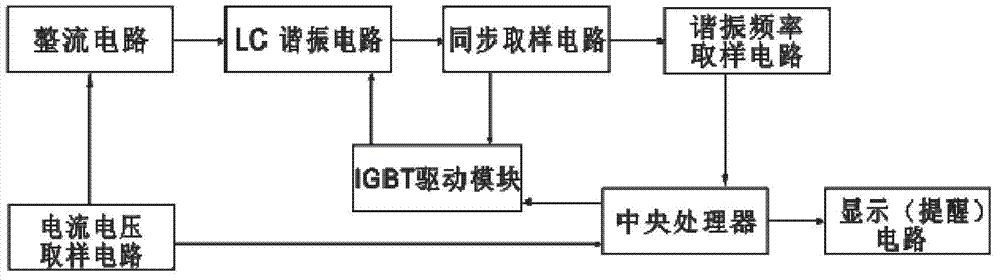
Induction cooker control circuit suitable for cookers of different materials and power control method
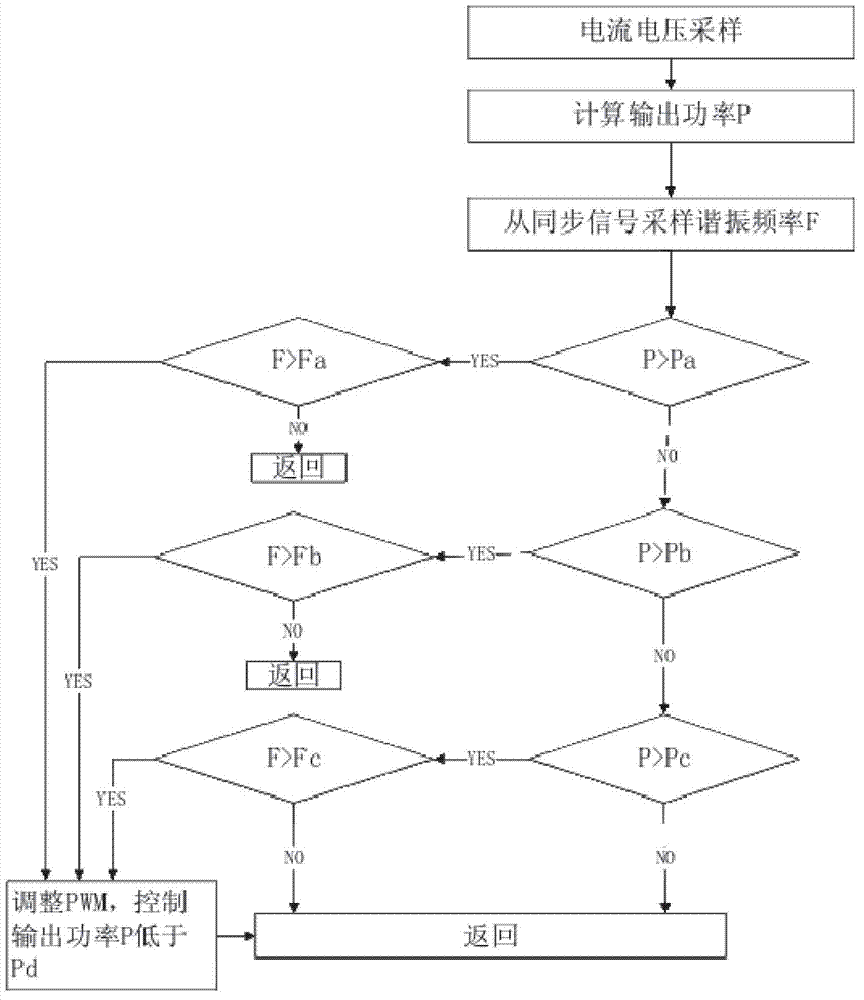
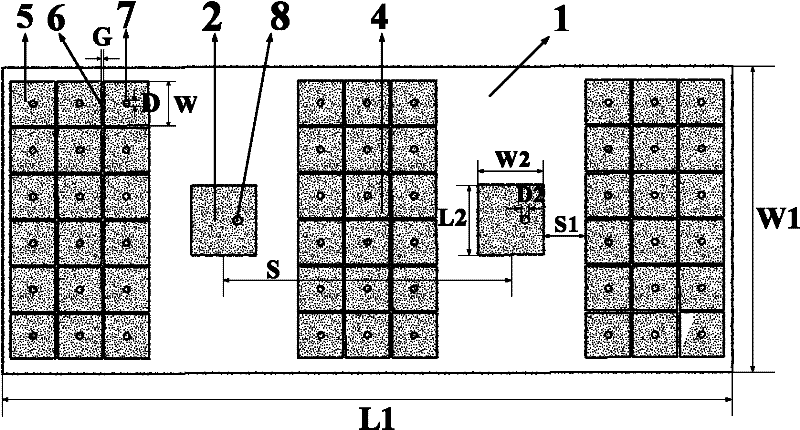
ActiveCN102821501AEasy to useOutput power adjustmentInduction heating controlLc resonant circuitEngineering
The invention relates to an induction cooker control circuit suitable for cookers of different materials. The induction cooker control circuit comprises an IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Translator), an IGBT driving module, an LC (Launch Control) resonance circuit, a central processing unit, a synchronous sampling circuit and a sampling circuit, wherein the LC resonance circuit is connected with the IGBT, and the central processing unit is connected with the IGBT driving module; the synchronous sampling circuit is electrically connected with the LC resonance circuit; and the sampling circuit is connected with the central processing unit and provides current and voltage signals. The control circuit also comprises a resonance frequency sampling circuit which is used for sampling a resonance frequency generated when the cookers of different materials work. The sampling point of the resonance frequency sampling circuit is arranged at the output end of the synchronous sampling circuit, and the output end of the resonance frequency sampling circuit is connected with the central processing unit. The output power and a power preset value are compared and the collected resonance frequency and a resonance frequency preset value are compared to judge whether the resonance frequency is beyond the resonance frequency range of safe working of an induction cooker or not. The output power of an electromagnetic coil is adjusted through the IGBT, so that a main loop working current works in a rated range, and therefore the safe working of the induction cooker is protected.
Owner:JOYOUNG CO LTD
Antenna for reducing radar scattering cross section
InactiveCN102176537ASimple structureEasy to processRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsCapacitanceScattering cross-section
The invention discloses an antenna for reducing a radar scattering cross section, aiming to solve the problem of large radar scattering cross section of the traditional microstrip antenna. The antenna comprises a dielectric slab (1), a microstrip radiating unit (2) and an earth plate (3), wherein the microstrip radiating unit is arranged at the upper surface of the dielectric slab, and the earth plate is arranged at the lower surface of the dielectric slab; both sides of the microstrip radiating unit are provided with a high impedance surface array (4) respectively; each high impedance surface array is formed by arranging a plurality of metal chips into a rectangle, a gap is arranged between the adjacent metal chips to form a capacitor C; the center of each metal chip is provided with a metal via hole which penetrates through the dielectric slab; a current path connected by the via holes can form an inductor L, and the capacitor and the inductor form an LC resonant circuit; the frequency of the resonant circuit can be adjusted to be coincident with the working frequency of the antenna, thus realizing scattered field compensation of the high impedance surface array and the antenna. The invention has stable performance of reducing radar scattering cross section within and outside the frequency band of the antenna, and also has no effect on the size, weight and cost of the antenna.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
High-efficiency and low-cost forward-flyback DC-DC (direct current-direct current) converter topology
InactiveCN102891608AAvoid voltage spikesAvoid lossEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionClamp capacitorDc dc converter
The invention relates to a high-efficiency and low-cost forward-flyback DC-DC (direct current-direct current) converter topology. The forward-flyback DC-DC converter topology comprises a transformer, a main switch tube, a clamp circuit, a first rectification switch tube, a second rectification switch tube, an LC resonance circuit and an output capacitor, wherein a primary winding of the transformer is connected in series with the main switch tube between a first input end and a second input end; the clamp circuit consisting of a clamp capacitor and a clamp switch tube which are connected in series is connected in parallel with the primary winding or the main switch tube; a secondary winding of the transformer comprises a forward winding and a flyback winding; one end making the current flow into the primary winding is a dotted end of the primary winding; the secondary side of the transformer is connected in a manner that: the dotted end of the forward winding is connected to the first output terminal through the first rectification switch tube, and the dotted end of the flyback winding is connected to the second output terminal through the second rectification switch tube; the LC resonance circuit is connected to the first output terminal and the second output terminal and the unlike ends of the forward winding and the flyback winding so as to switch on or switch off the first rectification switch tube and the second rectification switch tube at zero current; and the output capacitor is connected between the first output terminal and the second output terminal.
Owner:SANTAK ELECTRONICS SHENZHEN
Radio IC device and radio IC device part
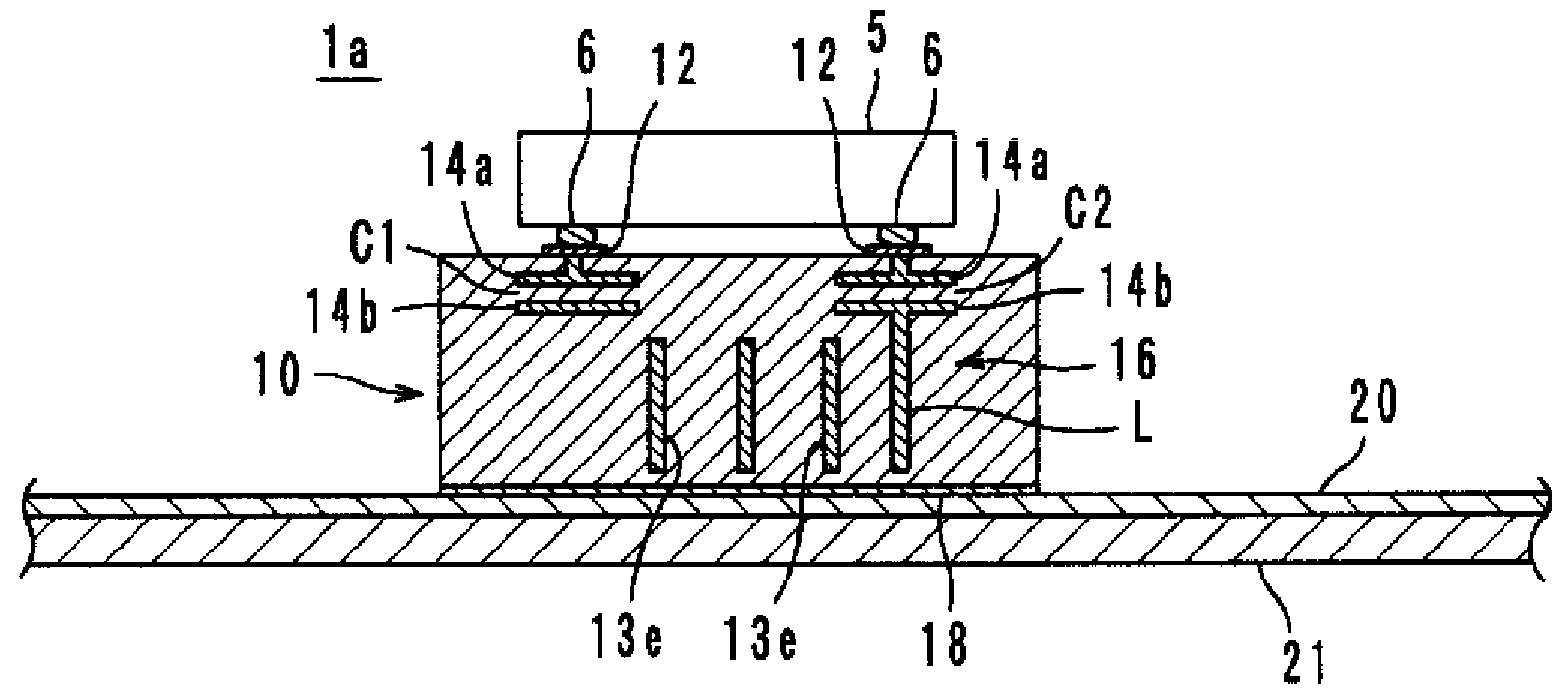
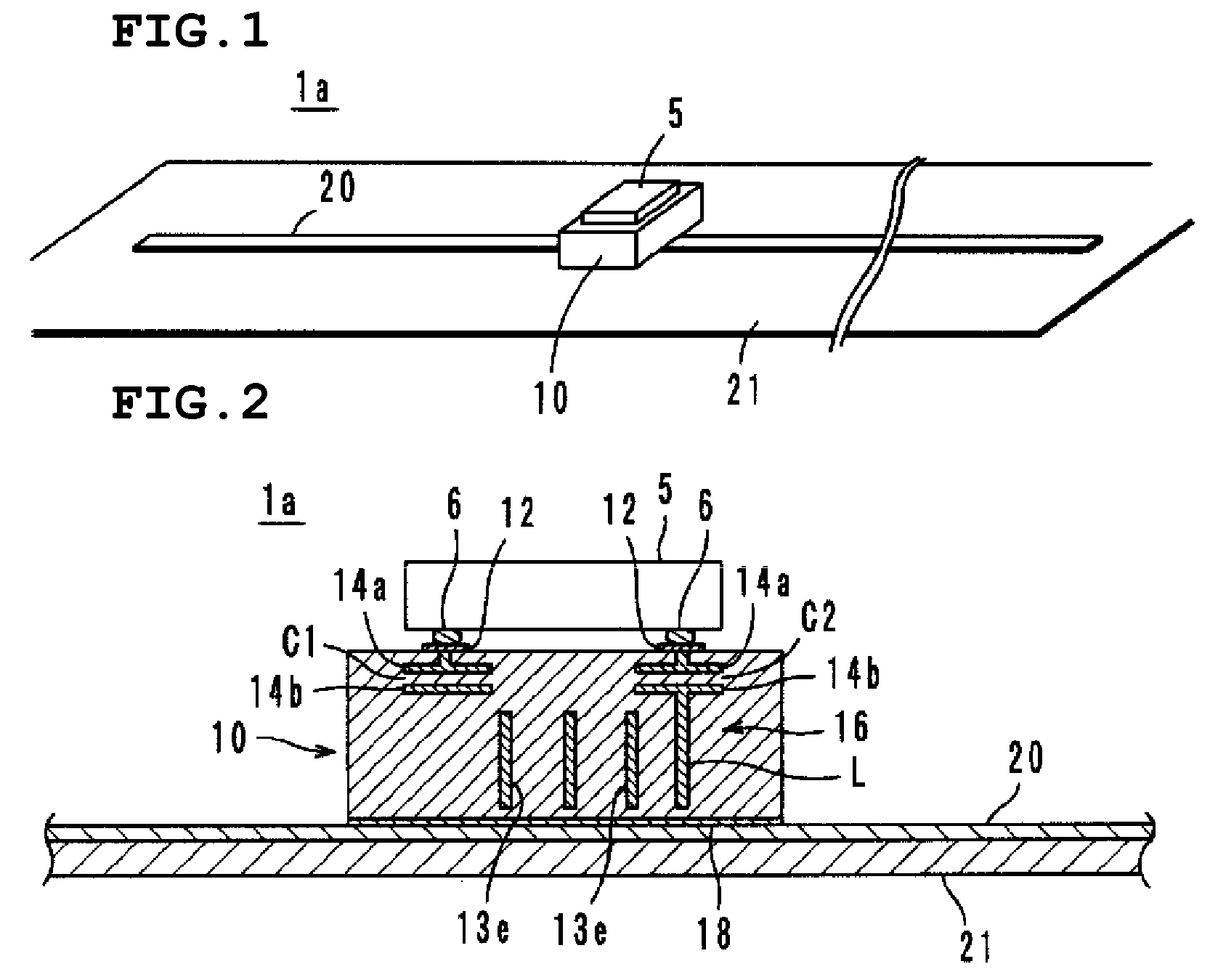
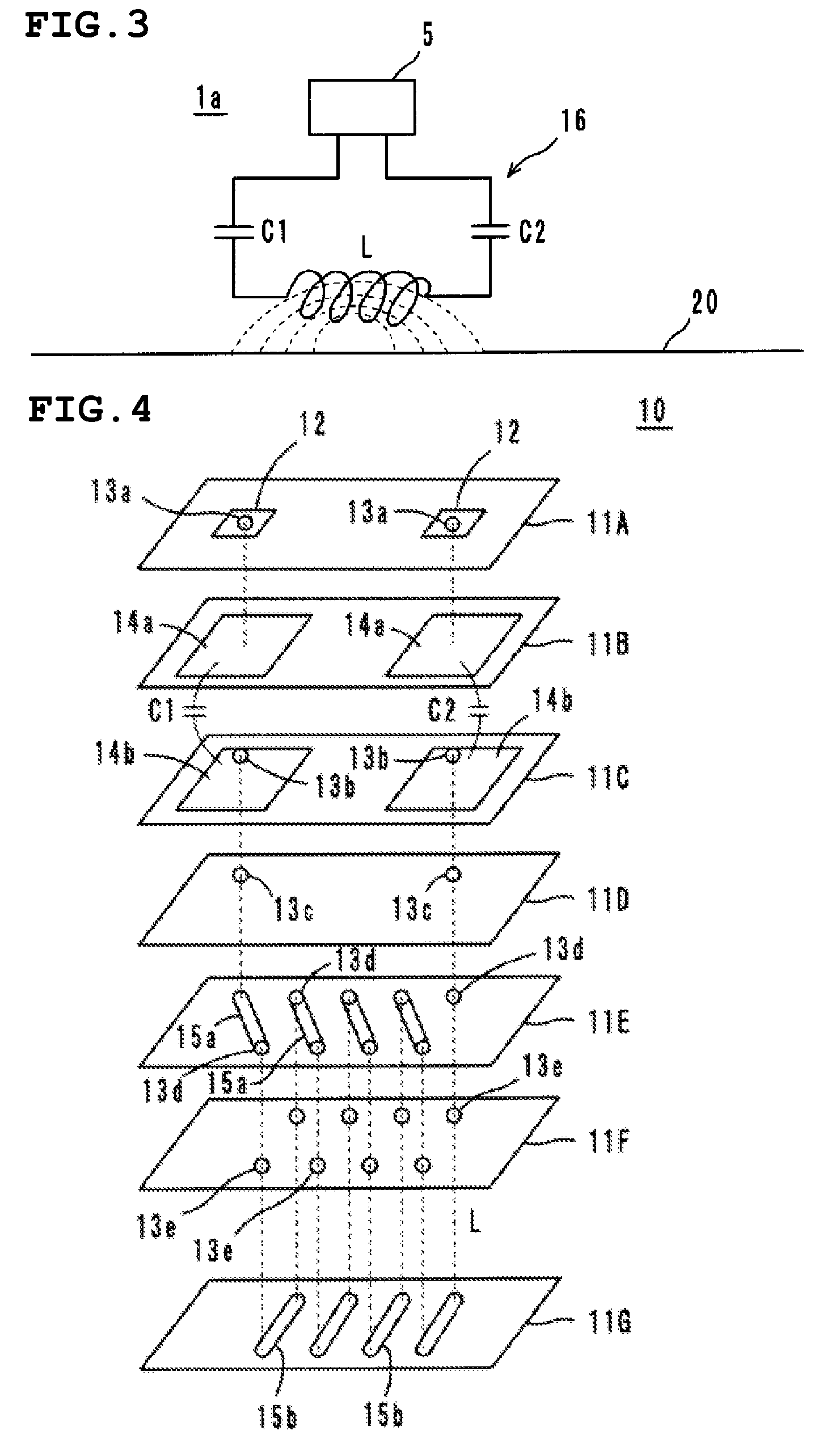
InactiveCN101351924AFrequency characteristics do not changeStable Frequency CharacteristicsSolid-state devicesRadiating elements structural formsCapacitanceLc resonant circuit
It is possible to provide a radio IC device and a radio IC device part having stable frequency characteristic. The radio IC device includes: a radio IC chip (5); a feed circuit substrate (10) having the radio IC chip (5) mounted thereon and a feed circuit (16) containing a resonance circuit having a predetermined resonance frequency; and an emission plate (20) bonded to the lower surface of the feed circuit substrate (10) for emitting the transmission signal supplied from the feed circuit (16) and supplying the reception signal to the feed circuit (16). The resonance circuit is formed by an LC resonance circuit having an inductance element (L) and capacitance elements (C1, C2). The feed circuit substrate (10) is a multi-layer or single-layer rigid substrate and connected to the radio IC chip (5) and the emission plate (20) by DC coupling, magnetic coupling, or capacity coupling.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Tag having patterned circuit elements and a process for making same
InactiveUS20050184873A1Line/current collector detailsElectronic circuit testingAdhesiveLc resonant circuit
A tag having a substrate having a surface with a preformed first patterned adhesive disposed over the surface thereof and a first layer of electrically conductive material having a shape corresponding to a desired final pattern for a first electrically conductive trace secured to the surface of the substrate. The preformed first patterned adhesive corresponds to the desired final pattern. A second patterned adhesive is disposed over a portion of a surface area of the tag. An electrically conductive trace is disposed over the second patterned adhesive to adhere the second electrically conductive trace thereto. An electrical connection is provided for electrically coupling portions of the first and second electrically conductive traces to form a tag circuit. The tag circuit can be an LC resonant circuit. The preformed first patterned adhesive can be a flexographic printed layer.
Owner:CHECKPOINT SYST INC
Bidirectional dc/dc converter
ActiveUS20150381064A1Wide inputIncrease working frequencyEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionPhase shift controlLc resonant circuit
A bidirectional DC / DC converter includes first and second control circuits, and first and second bridge circuits respectively connected to first and second direct current voltage supplies. In one embodiment variant, when power is supplied from the first direct current voltage supply to the second direct current voltage supply, the first control circuit carries out PFM control of the first bridge circuit at a frequency equal to or lower than the resonance frequency of an LC resonant circuit in accordance with a control amount based on the voltage and current of the second direct current voltage supply. When power is supplied in the other direction, the second control circuit carries out fixed frequency control of the second bridge circuit, using phase shift control or the like, in accordance with a control amount based on the voltage and current of the first direct current voltage supply.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
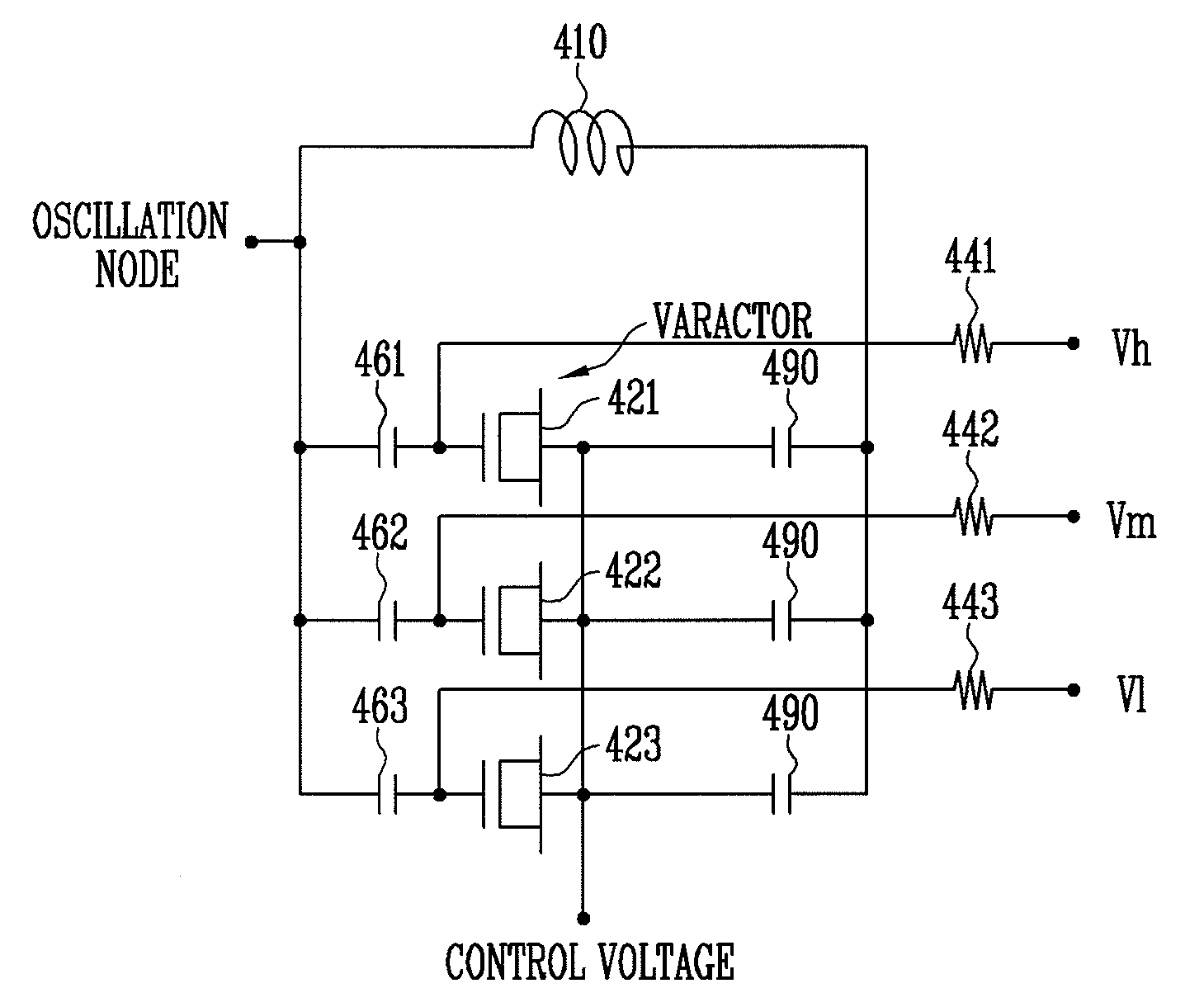
Linearized variable-capacitance module and lc resonance circuit using the same
InactiveUS20080012654A1Angle modulation by variable impedenceMultiple-port networksInput controlLc resonant circuit
Provided are a linearized variable-capacitance module for a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) and an LC resonance circuit using the same. The VCO is a circuit for outputting a certain frequency in response to an input control signal (voltage or current). The VCO includes an inductor, a variable capacitor (or a varactor), and an active device for compensating for loss of energy caused by the inductor and varactor. The frequency of the VCO is varied by changing inductance or capacitance. In general, the VCO includes a variable-capacitance device (i.e., the varactor) so that the frequency of the VCO may be varies by changing the capacitance via a control voltage. In most cases, the frequency of the VCO varies nonlinearly with respect to the control voltage. The nonlinear variation in the frequency of the VCO results in a great variation in a VCO gain within a certain control voltage range. When a phase locked loop (PLL) includes the VCO, the variation in the VCO gain leads to a variation in the entire loop gain, thus causing a variation in output phase noise. To solve this problem, a varactor designed to have a capacitance that varies linearly with a control voltage is provided so that a VCO gain can be held constant. The variable-capacitance module includes a plurality of variable-capacitance devices with respectively different linear variation regions on an application voltage axis. Also, the variable-capacitance devices are coupled in common and receive a control voltage at one end while each receiving a different fixed voltage at the other end.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Proximity sensor
InactiveUS8432169B2High resolutionLow costResistance/reactance/impedenceElectronic switchingProximity sensorPower flow
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
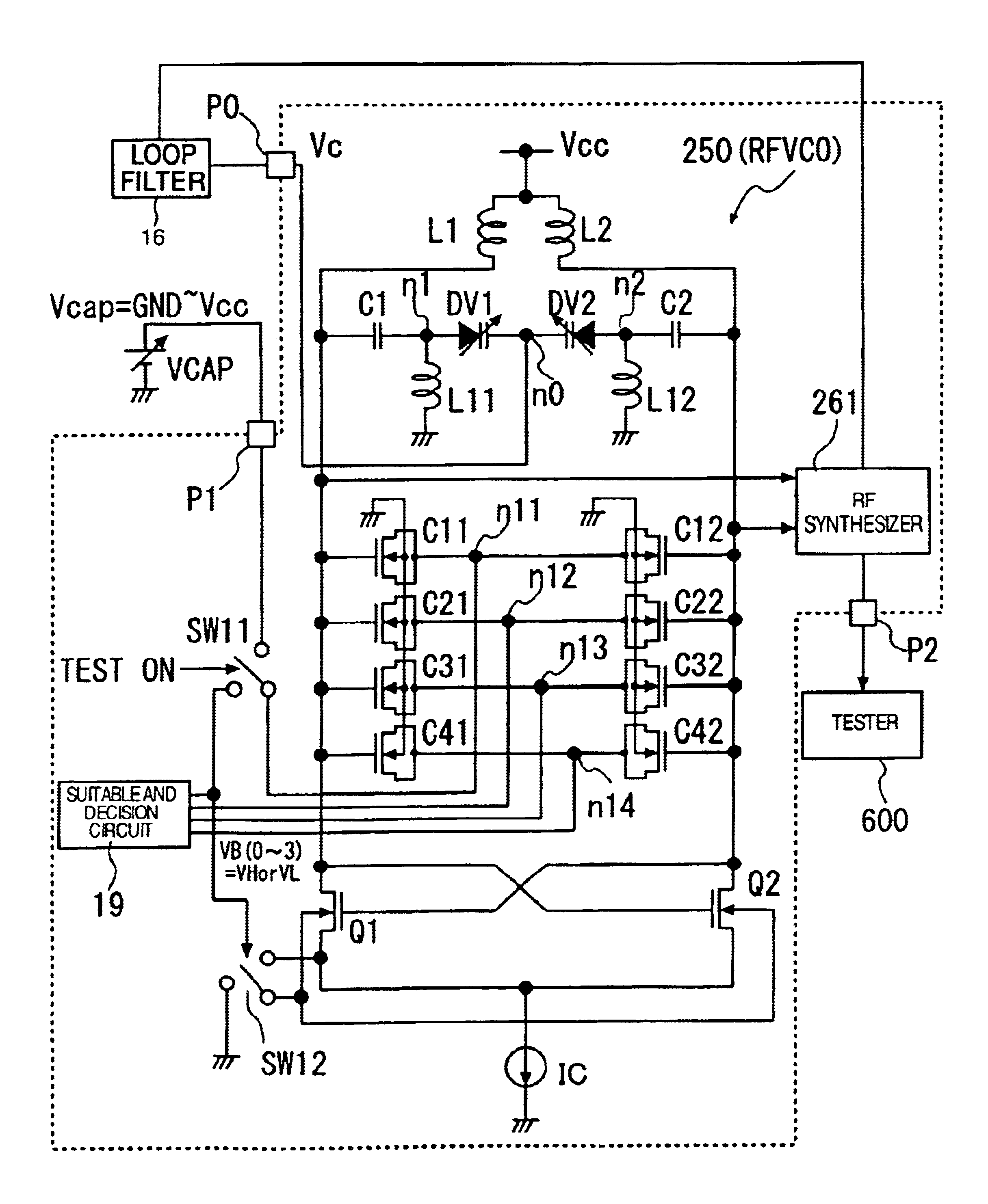
Voltage controlled oscillator having reduced phase noise
ActiveUS8102216B1Less time transitioningImprove signal-to-noise ratioElectric pulse generatorOscillations generatorsLc resonatorPhase noise
A VCO comprises an LC tank circuit coupled to a plurality of cross-coupled transistor devices. A first resonance frequency of a waveform output of the VCO is dependent upon the values of a first capacitor and a first inductor of the LC tank. The VCO further comprises a first series LC resonator comprising a second capacitor and a second inductor in parallel to the first capacitor and the first inductor. The values of the second capacitor and second inductor are selected to produce a second resonance frequency that is a third harmonic of the first resonance frequency, thereby increasing a slope of the voltage controlled oscillator output. The increased slope reduces phase noise, which leads to improved signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
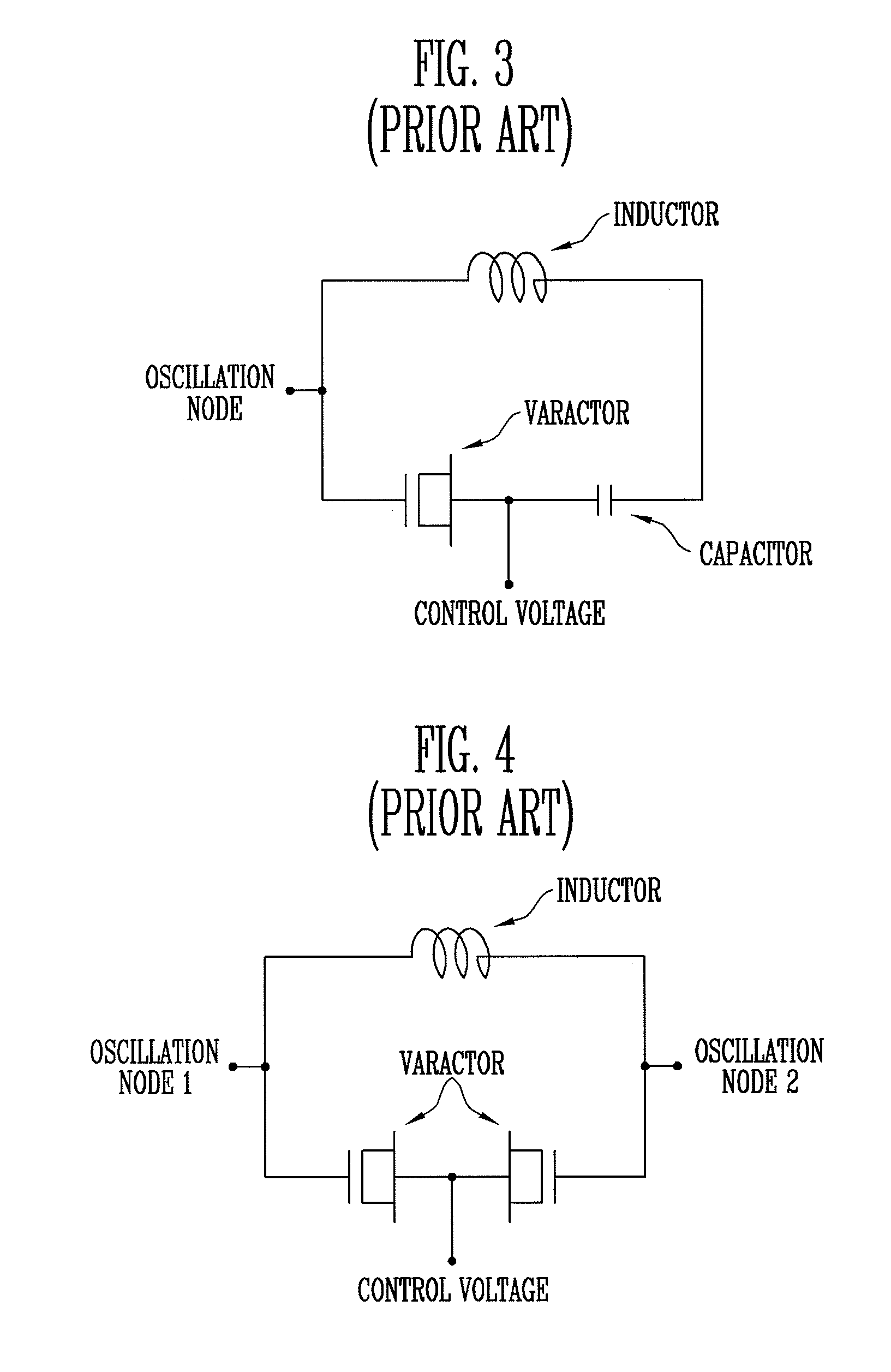
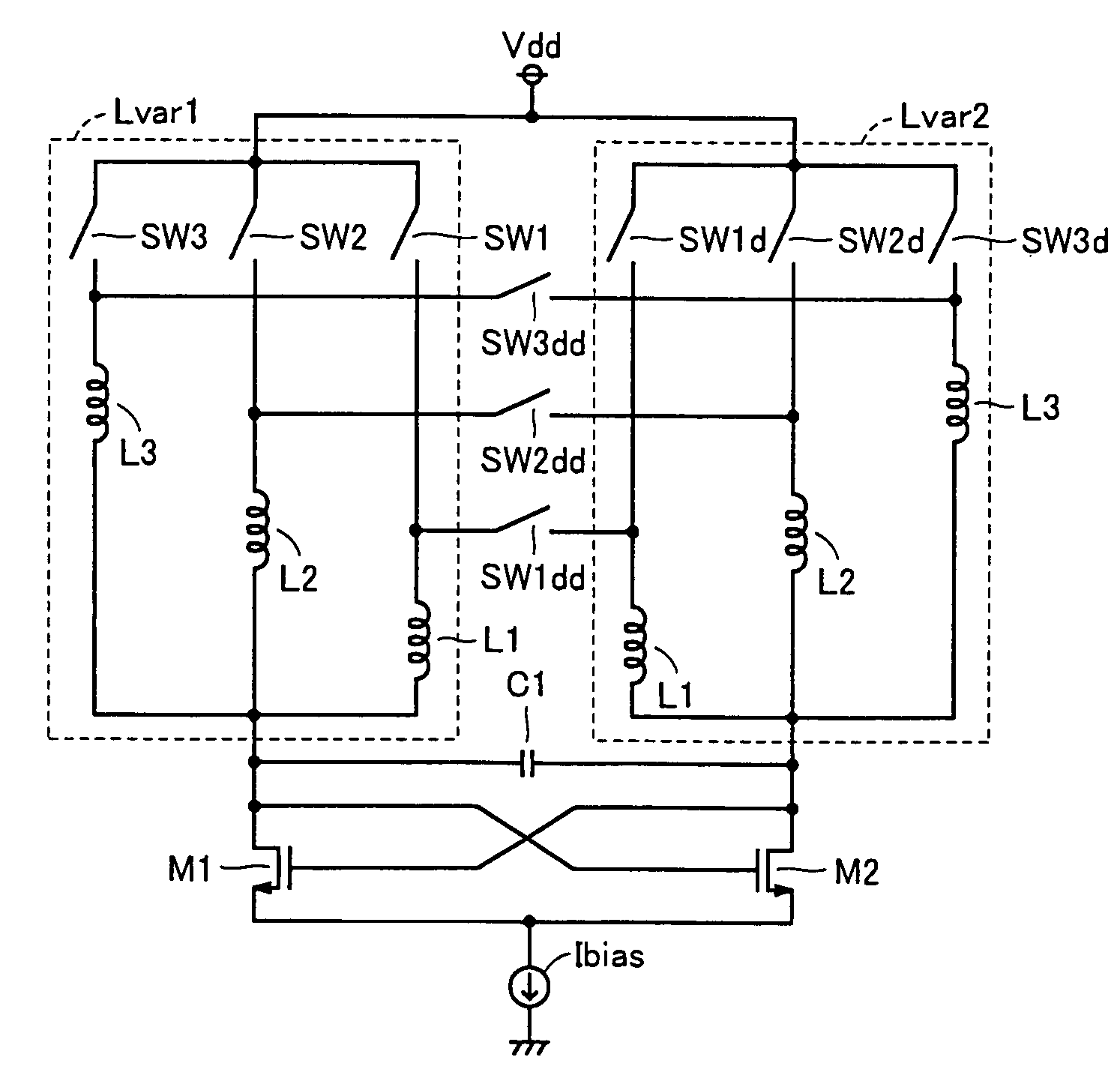
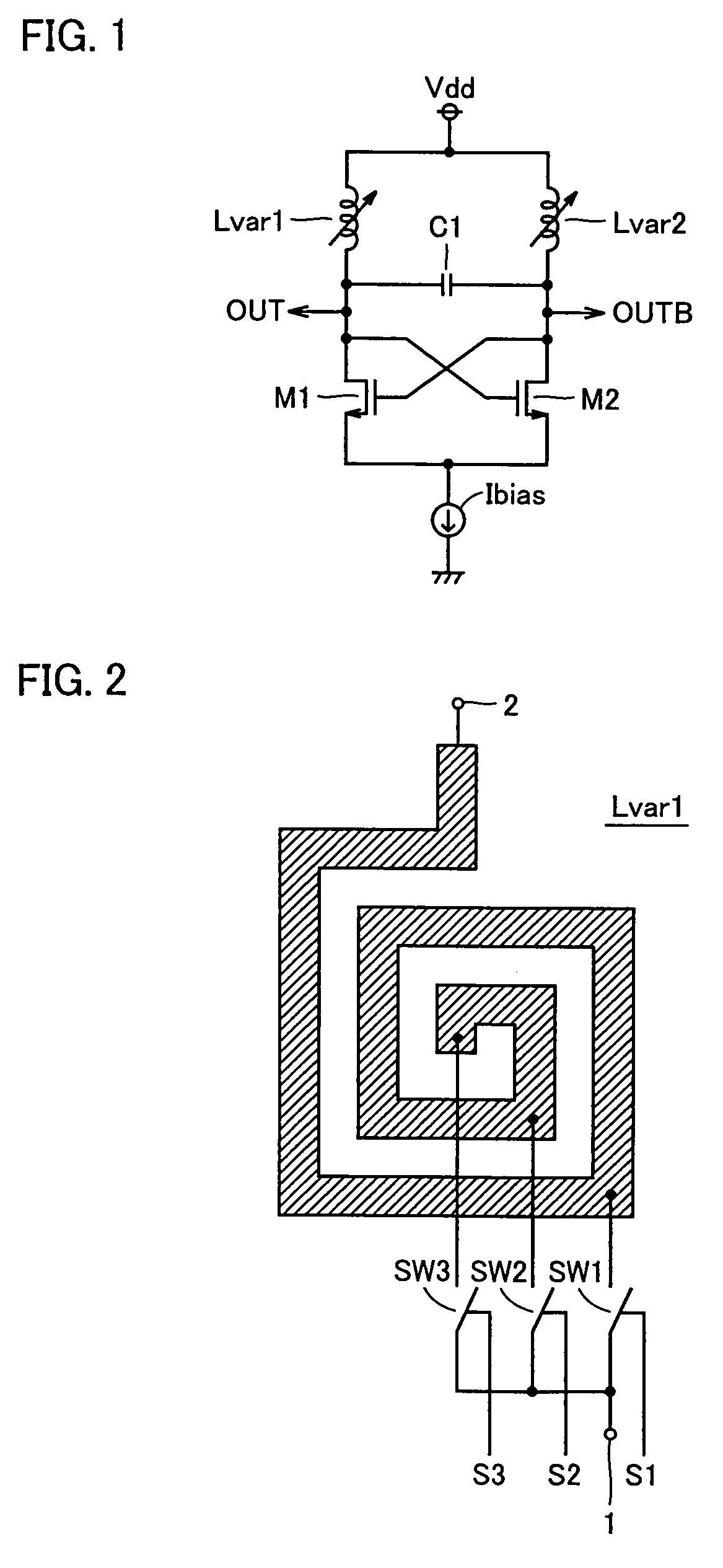
Voltage-controlled oscillator with LC resonant circuit
InactiveUS6861913B1Pulse automatic controlSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPhase noiseLc resonant circuit
A voltage-controlled oscillator device with an LC-resonant circuit, in particular for implementing integrated voltage-controlled oscillators for the lower GHz range, is disclosed. The device achieves continuous frequency tunability in a wide range in particular with a low level of phase noise and phase jitter. In the voltage-controlled oscillator, a second inductor can be periodically switched in parallel and / or in series with at least one first inductor of the LC-resonant circuit by way of a switching means actuated with the oscillator frequency. A control input of the switching means is connected to a variable dc voltage. In that respect the relationship of the duration of the conducting state and the duration of the non-conducting state of the switching means is variable within an oscillation period of the oscillator in dependence on the value of the control voltage. In accordance with the relationship of the duration of the conducting state and the duration of the non-conducting state of the switching means within an oscillation period of the oscillator the time-averaged effective inductance is variable in dependence on the value of the control voltage.
Owner:IHP GMBH INNOVATIONS FOR HIGH PERFORMANCE MICROELECTRONICS LEIBNIZ INST FUR INNOVATIVE
Oscillator circuit and L load differential circuit achieving a wide oscillation frequency range and low phase noise characteristics
InactiveUS7202754B2Inhibit deteriorationWide frequency rangeElectric pulse generatorOscillations generatorsCapacitancePhase noise
An oscillator circuit is formed of a differential LC resonant circuit formed of an L load differential circuit including inductance-variable portions and a capacitive element, and a positive feedback circuit formed of N-channel MOS transistors. The inductance-variable portion is configured to vary the inductance by selecting a plurality of switch circuits arranged between a plurality of arbitrary positions on a spiral interconnection layer and the input / output terminal, and thereby can control an oscillation frequency. The inductance-variable portions form an inductor pair when the switch circuit among the switch circuits coupled between the first input / output terminals is turned on together with the switch circuit.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Antenna, radio device, method of designing antenna, and method of measuring operating frequency of antenna
ActiveUS7330161B2Simple designBandwidthAntenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsRadio equipmentLc resonant circuit
Owner:DENSO CORP
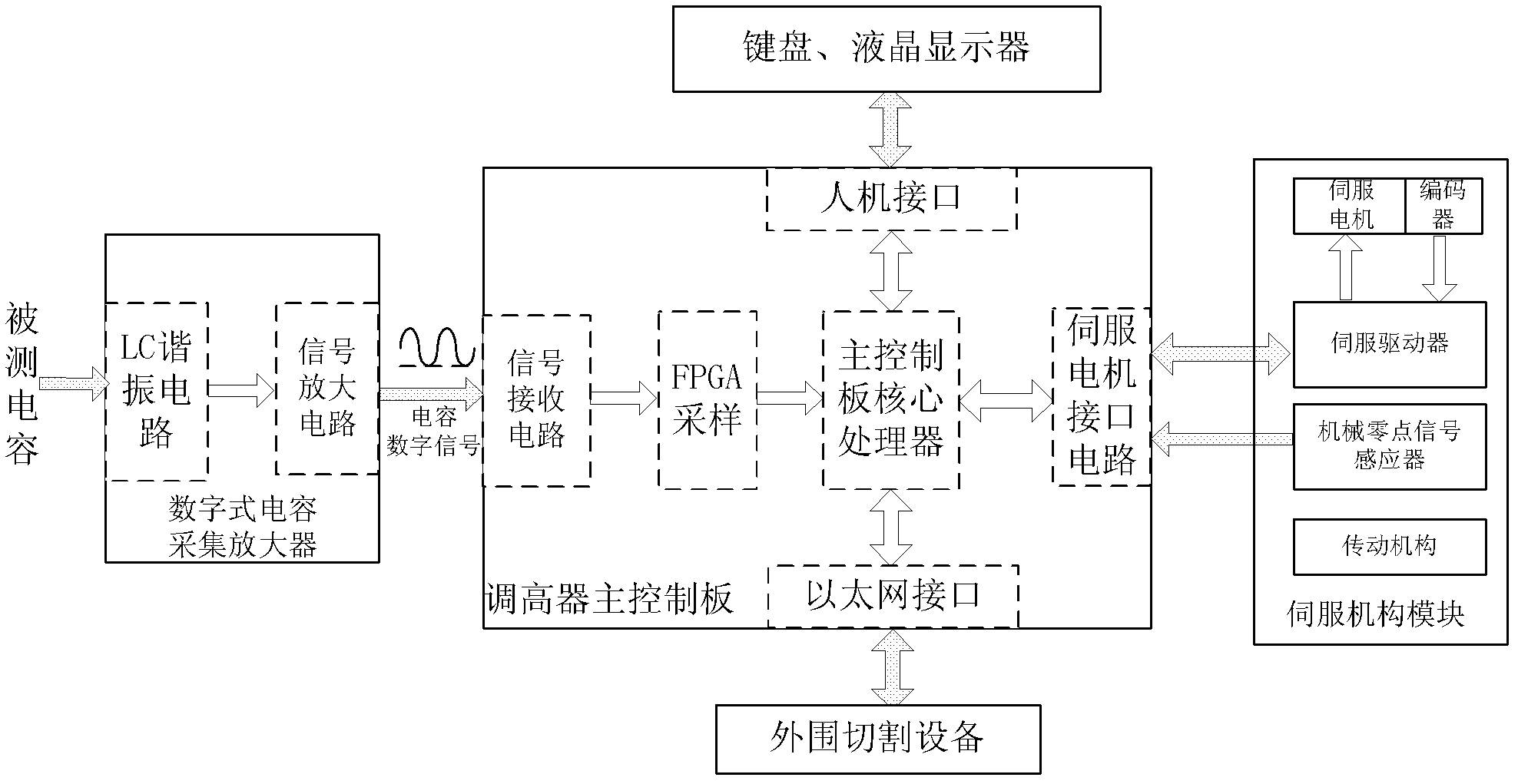
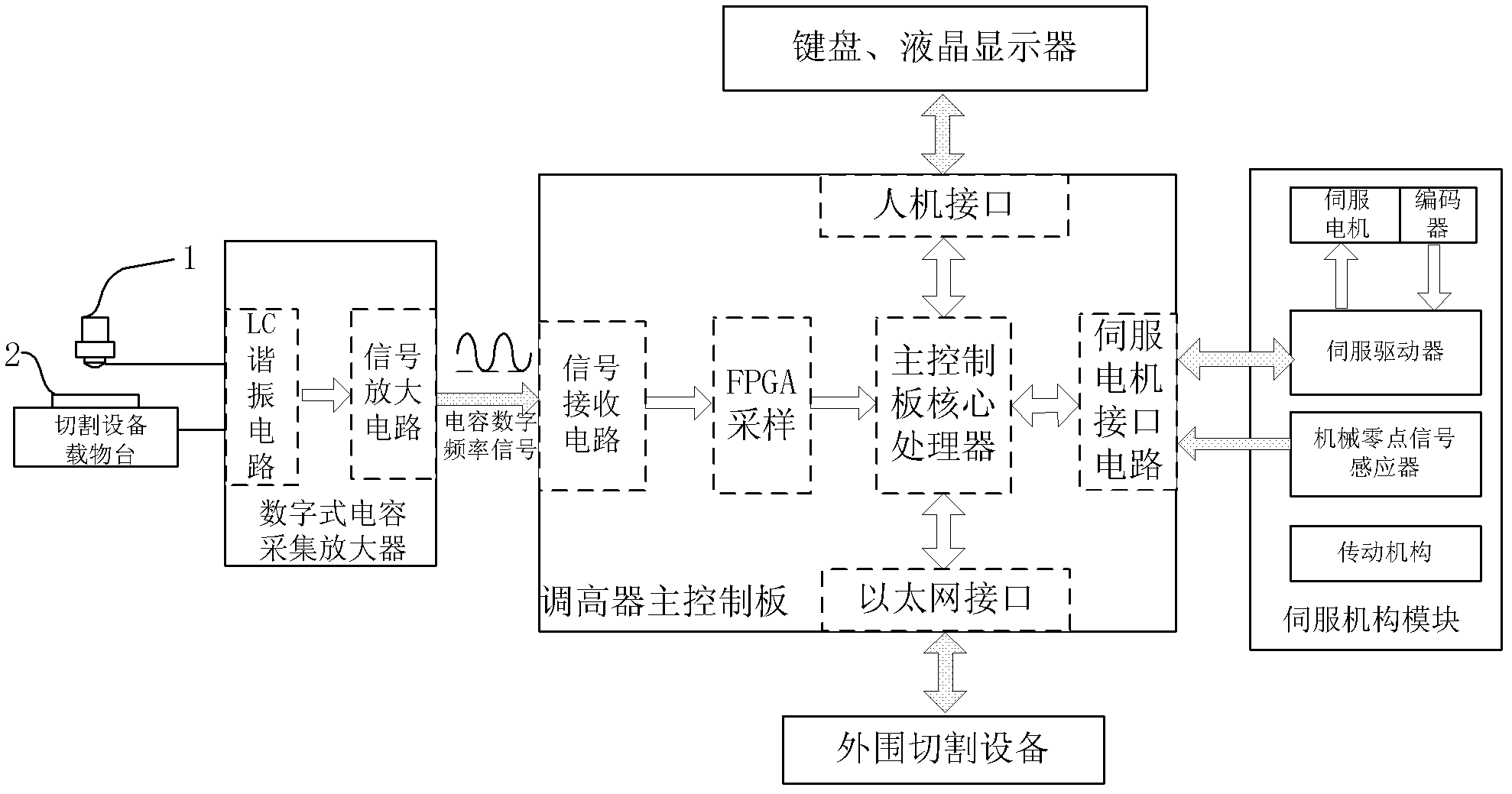
Method for digital closed-loop control capacitance raising system
ActiveCN102528288ALower requirementImprove anti-interference abilityNumerical controlLaser beam welding apparatusNumerical controlCapacitance
The invention relates to the technical field of numerical control, in particular to a method for a digital closed-loop control capacitance raising system. In a capacitance acquisition amplifier, the output end of an inductance-capacitance (LC) resonance circuit is connected with the input end of a signal amplifying circuit; in a raiser main control board, the output end of a signal receiving circuit is sequentially connected with the signal input end of a field programmable gate array (FPGA) chip, one input end of a main control board core processor and the other signal end of a servo motor interface circuit; the other two signal ends of the main control board core processor are respectively connected with one end of a human-machine interface and one end of an Ethernet interface in a bidirectional mode; the output end of the signal amplifying circuit is connected with the input end of the signal receiving circuit; and the output end of a magneto-electric conversion circuit of the signal receiving circuit is connected with the signal input end of the FPGA chip. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that: after board capacitance is converted into digital frequency signals, the digital frequency signals are transmitted and measured, so that the method is strong in anti-jamming capability, is not limited by the transmission distance and is high in measurement precision.
Owner:上海柏楚电子科技股份有限公司
Antenna, radio device, method of designing antenna, and nethod of measuring operating frequency of antenna
ActiveUS20070075903A1Simple designBandwidthAntenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsRadio equipmentLc resonant circuit
An antenna comprises a first conductive layer, a second conductive layer and an LC resonance circuit. The first conductive layer has plural elements and is disposed adjacently to each other. The second conductive layer is disposed at a predetermined distance from the first conductive layer via a dielectric substrate. The LC resonance circuit comprises connection for electrically connecting the elements and the second conductive layer. The LC resonance circuit takes a resonance state in which impedance becomes high in the operating frequency of the antenna. Of the plural elements, a power feeding section is provided in each of any two adjacent elements. Power is fed to the power feeding sections during transmission so that signals of the operating frequency are opposite in phase, and signals of the operating frequency inputted to the antenna are outputted in opposite phase from the power feeding sections during reception.
Owner:DENSO CORP
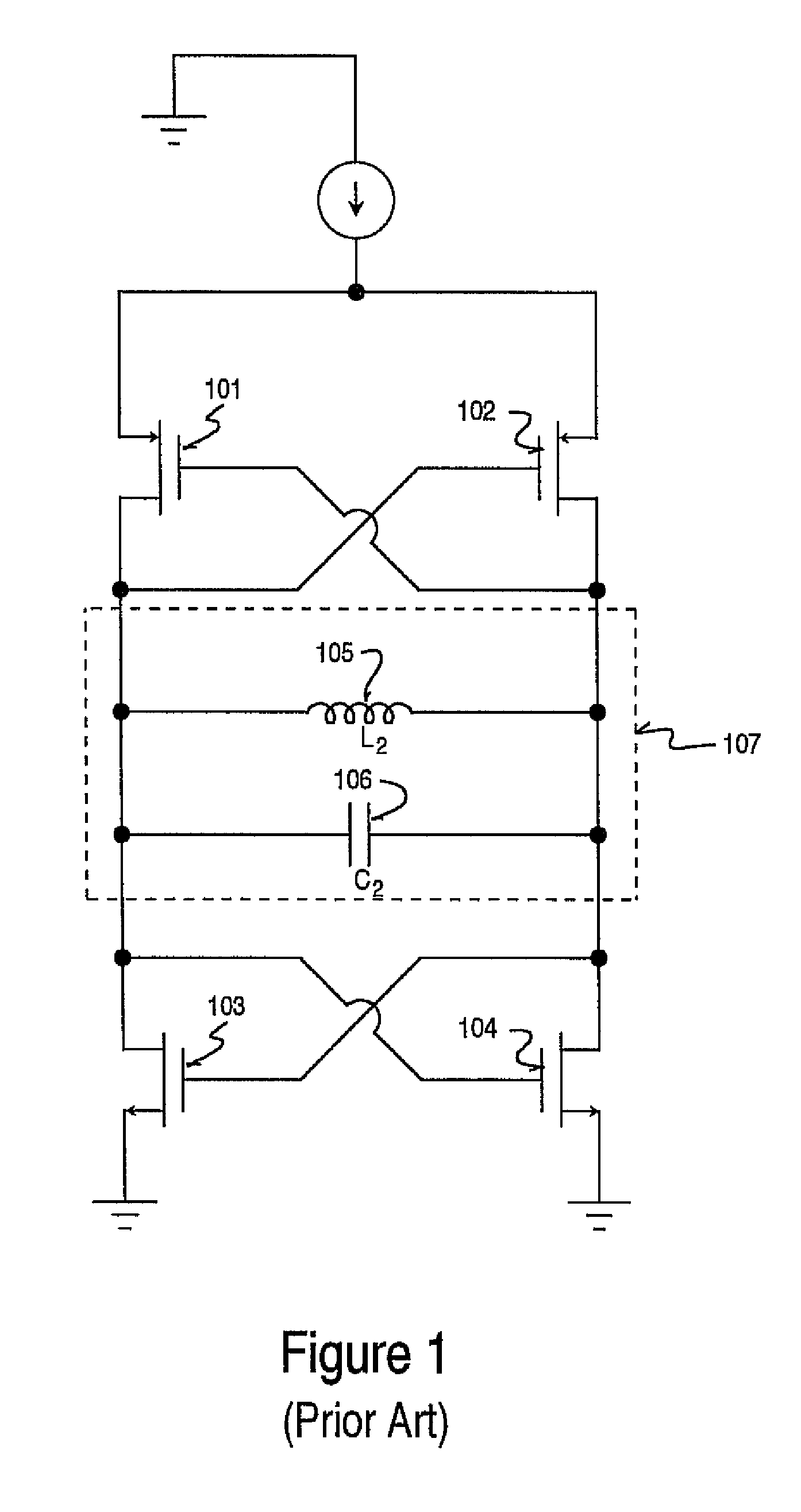
System and method for extending vco output voltage swing
InactiveUS20120001699A1Increased output voltage swingElectric pulse generatorOscillations generatorsPhase noiseLinear region
Voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) has been widely used in radio frequency communication systems. In a typical VCO implementation, a pair of directly cross-coupled MOS transistors is used as a switching device and an LC resonant circuit is used to tune the desired frequency. The direct cross coupling of the MOS transistor pair will result in limited output voltage swing since a large swing may cause the MOS transistors into a linear region to increase phase noise. The VCO system to increase the output voltage swing according to one embodiment of the present invention includes DC-blocking capacitors to avoid direct cross coupling of the MOS pair. The VCO further includes circuit to provide bias for the gate voltage of the MOS pair. A method for increasing the output voltage swing is disclosed for a VCO system having LC resonant circuit. The method includes providing DC-blocked cross coupling from the drains of the cross-coupled transistor pair to the gates of the cross-coupled transistor pair. The method also includes providing an offset voltage to the gates of the cross-coupled transistor pair to reduce the maximum gate-to-drain voltage of a cross-coupled NMOS transistor pair or maximum drain-to-gate voltage of a cross-coupled PMOS transistor pair so that the cross-coupled transistor pair will work in a saturation region when the output voltage swing is increased.
Owner:QUINTIC MICROELECTRONICS WUXI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com