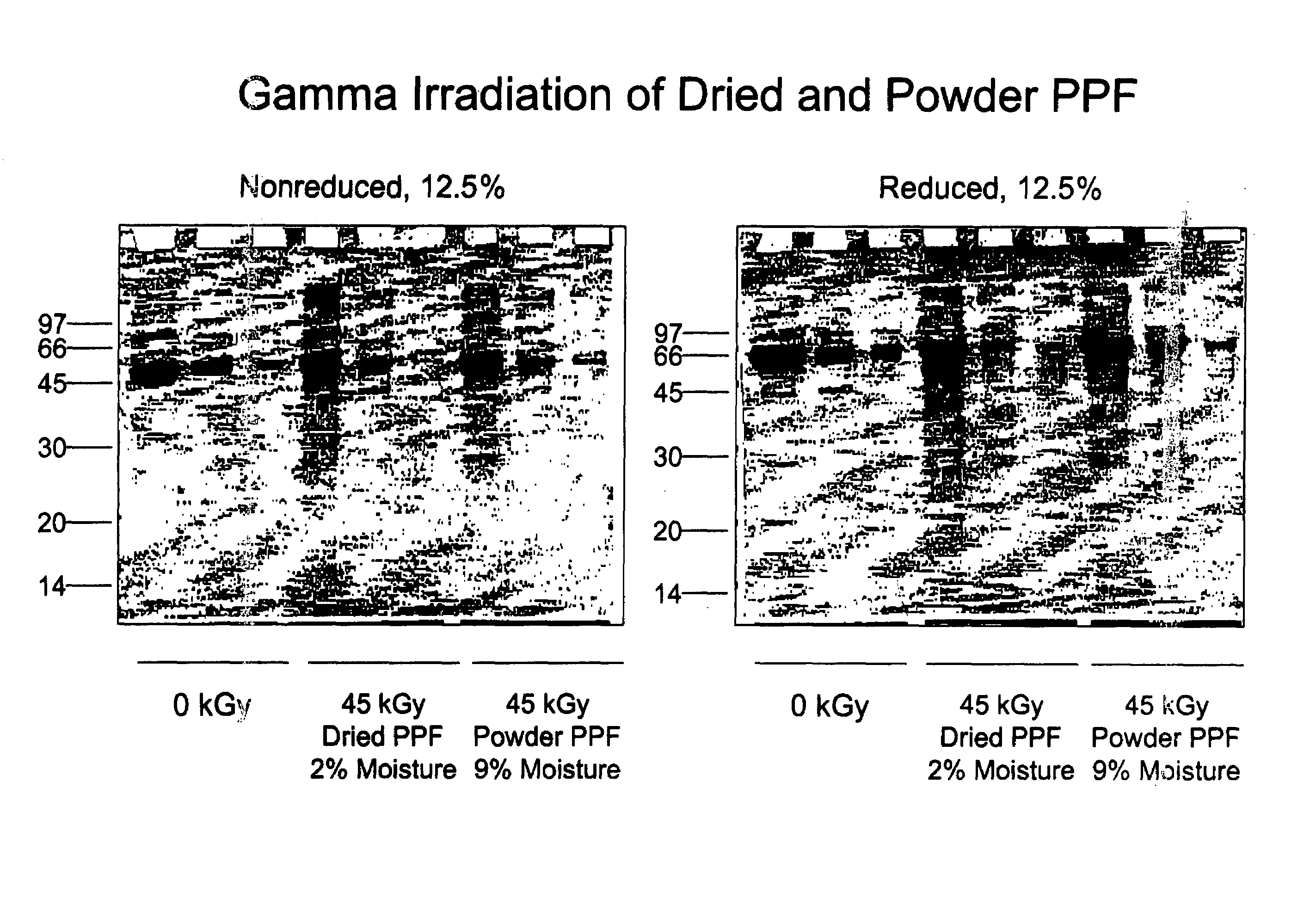
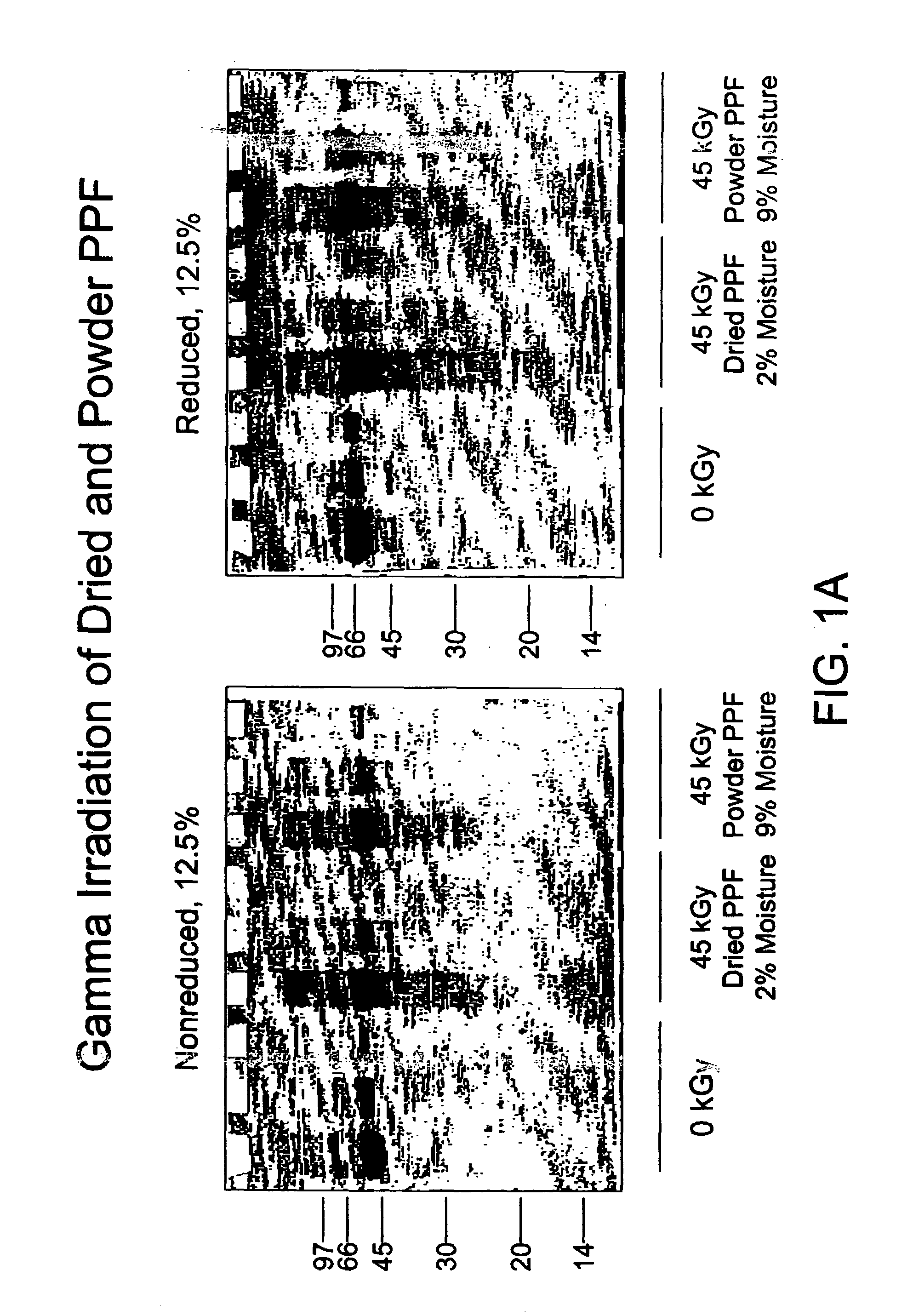
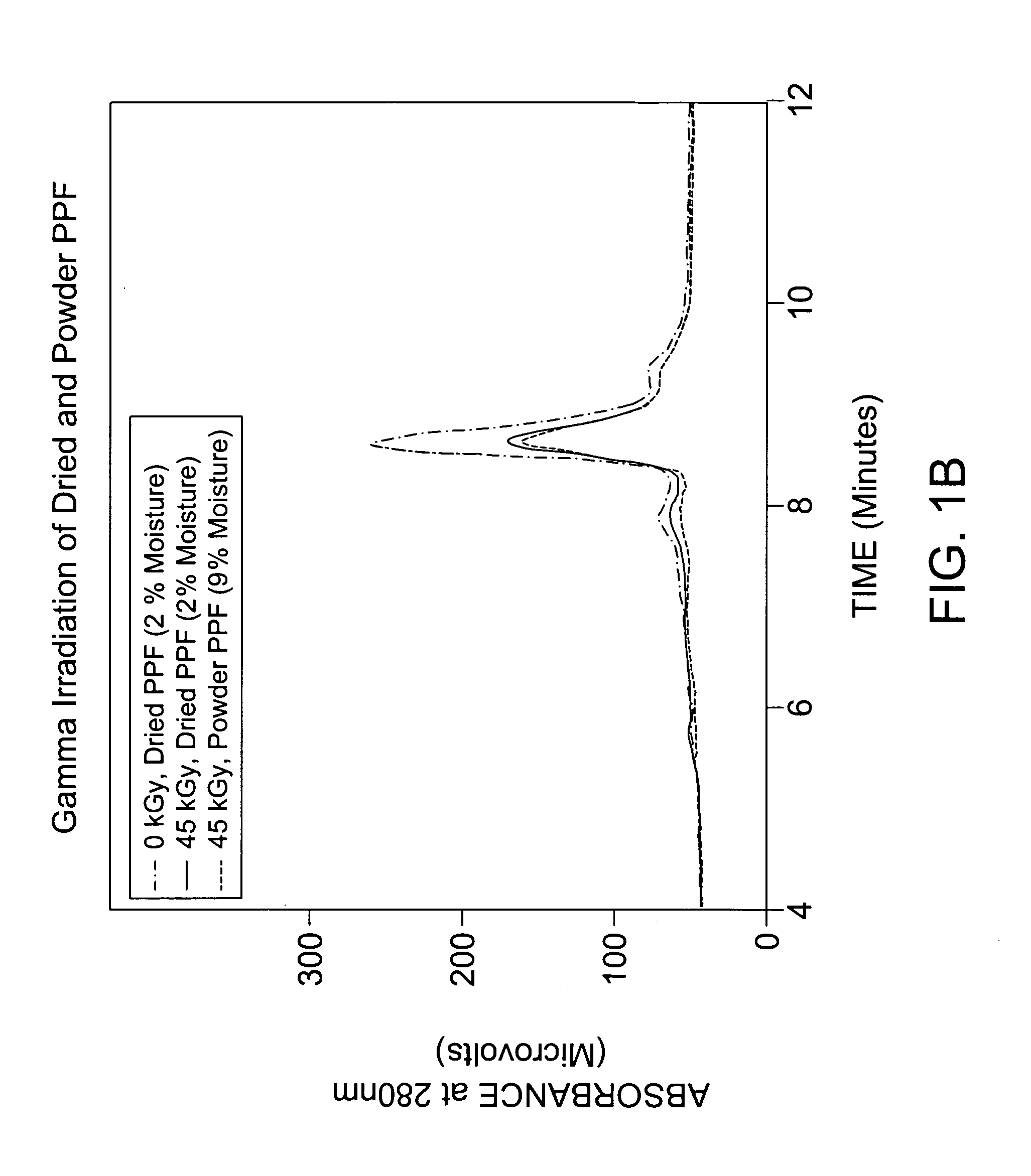
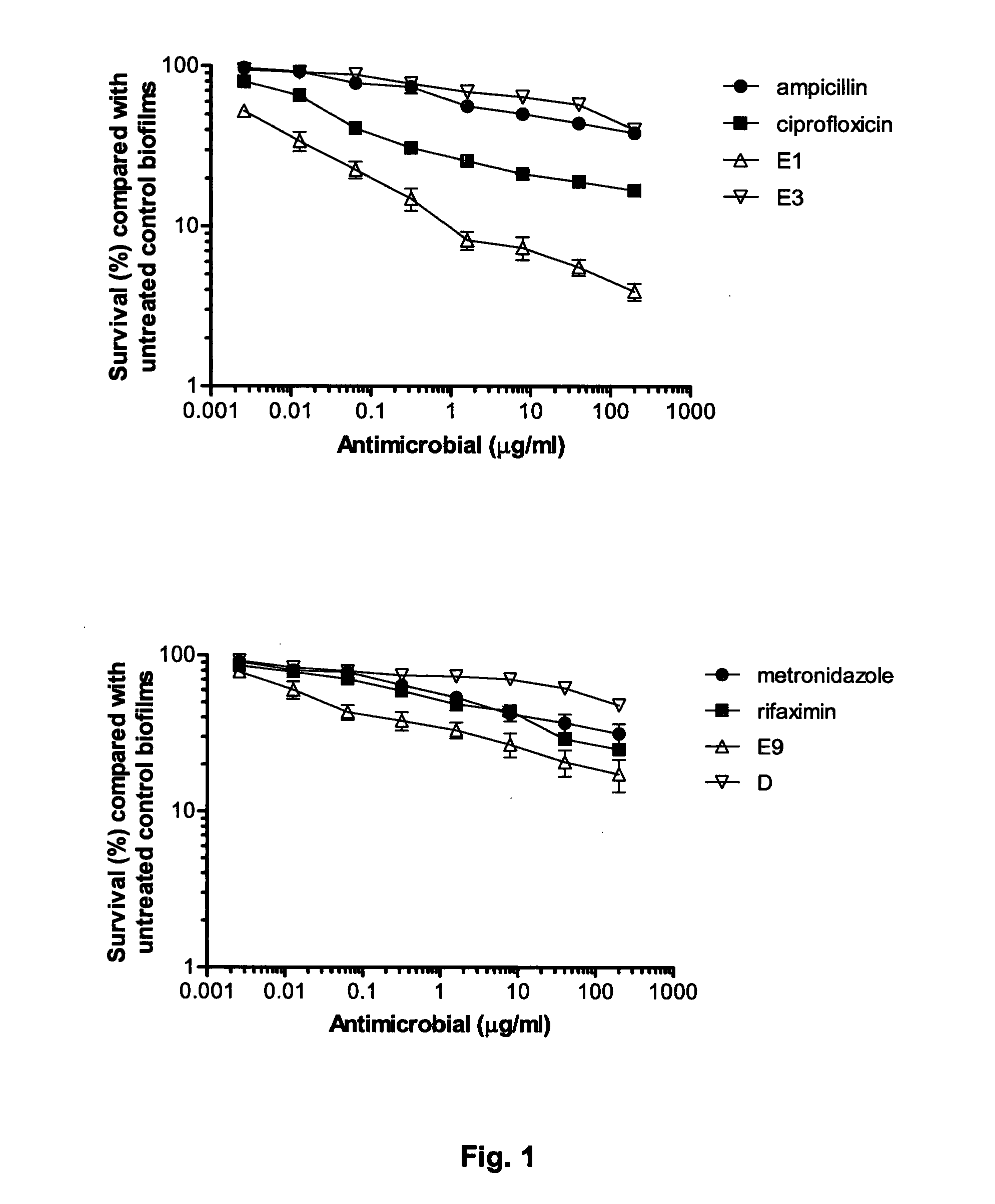
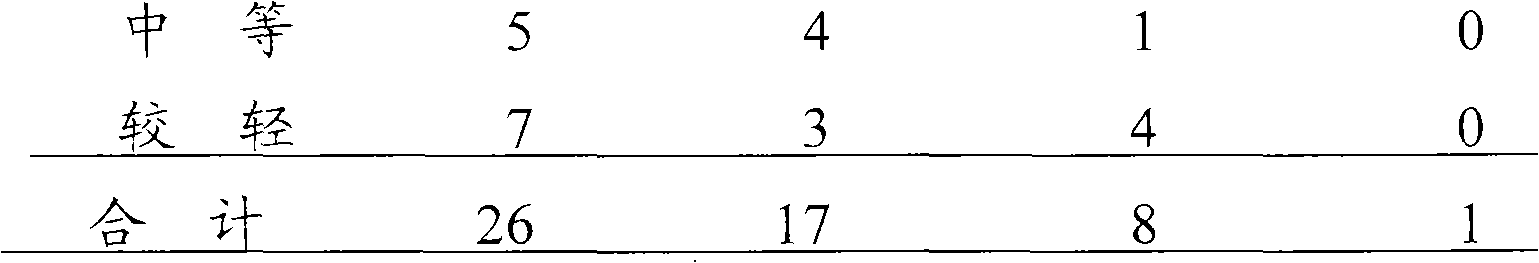Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Intracellular bacterium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Intracellular bacteria are pathogenic bacteria which always cause disease when they enter the human body, in contrast with conditional bacteria, which can cause infections and disease in certain circumstances.
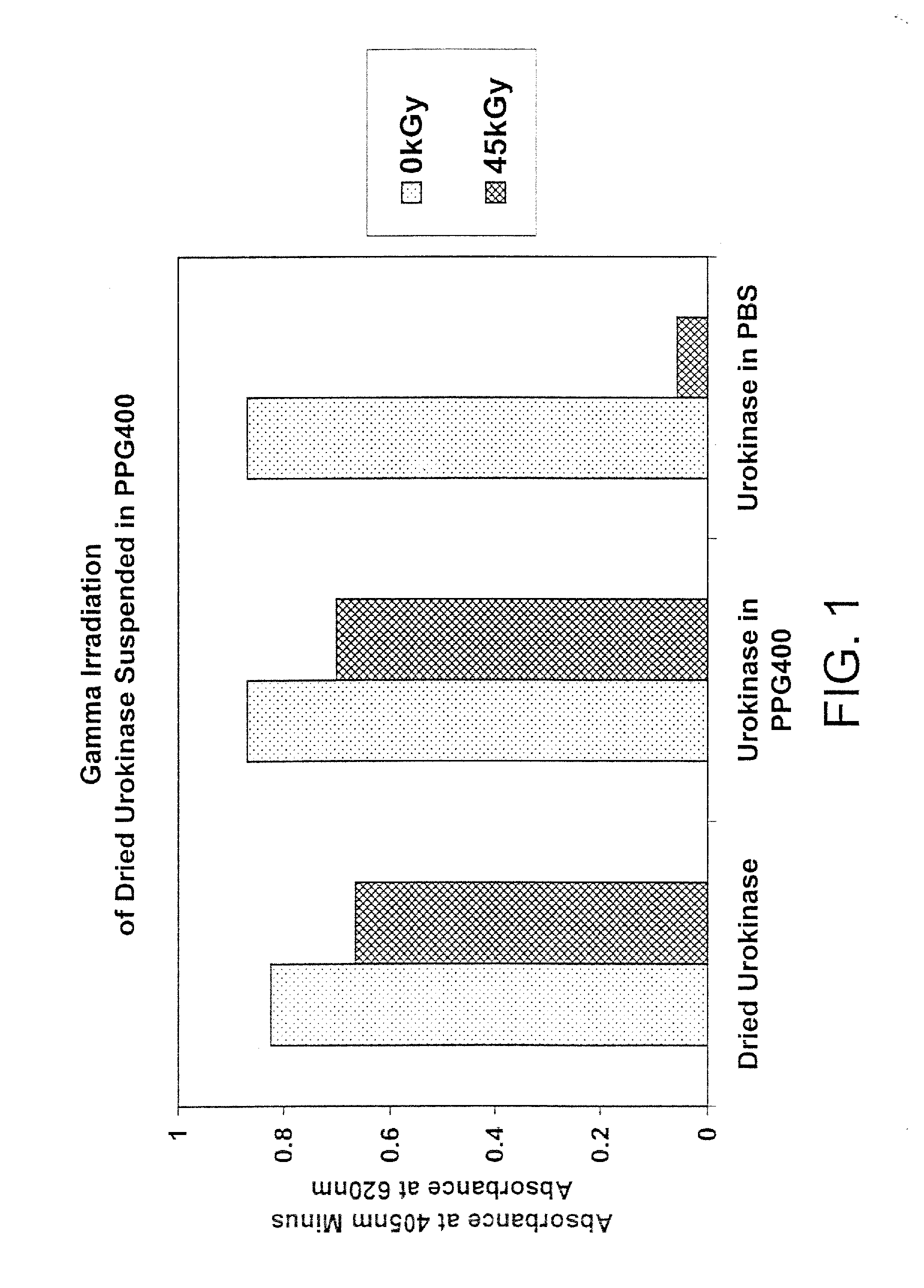
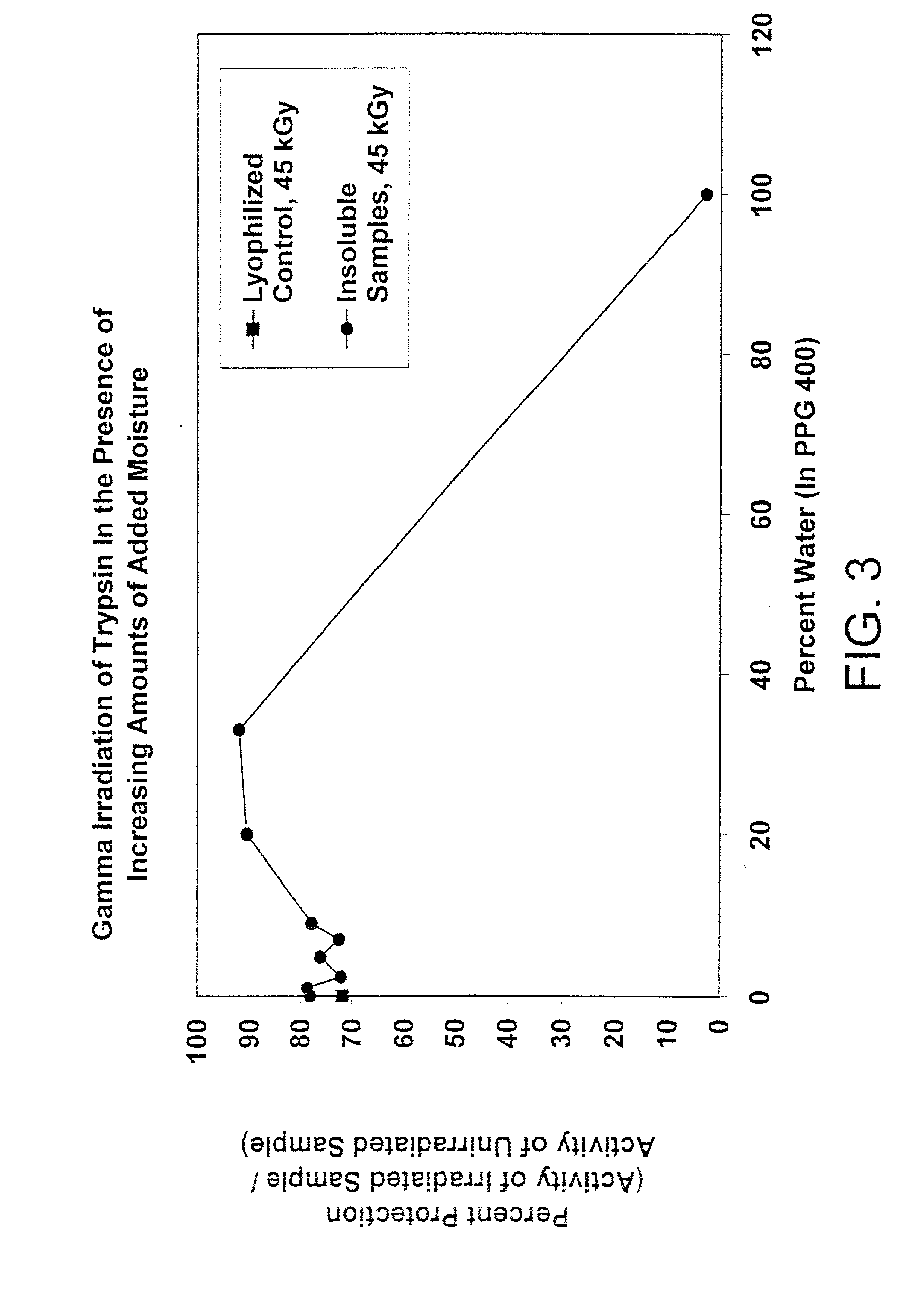
Methods for sterilizing biological materials by irradiation over a temperature gradient
InactiveUS6908591B2Effective sterilizationImprove permeabilityDead animal preservationLavatory sanitoryBiological materialsBiology
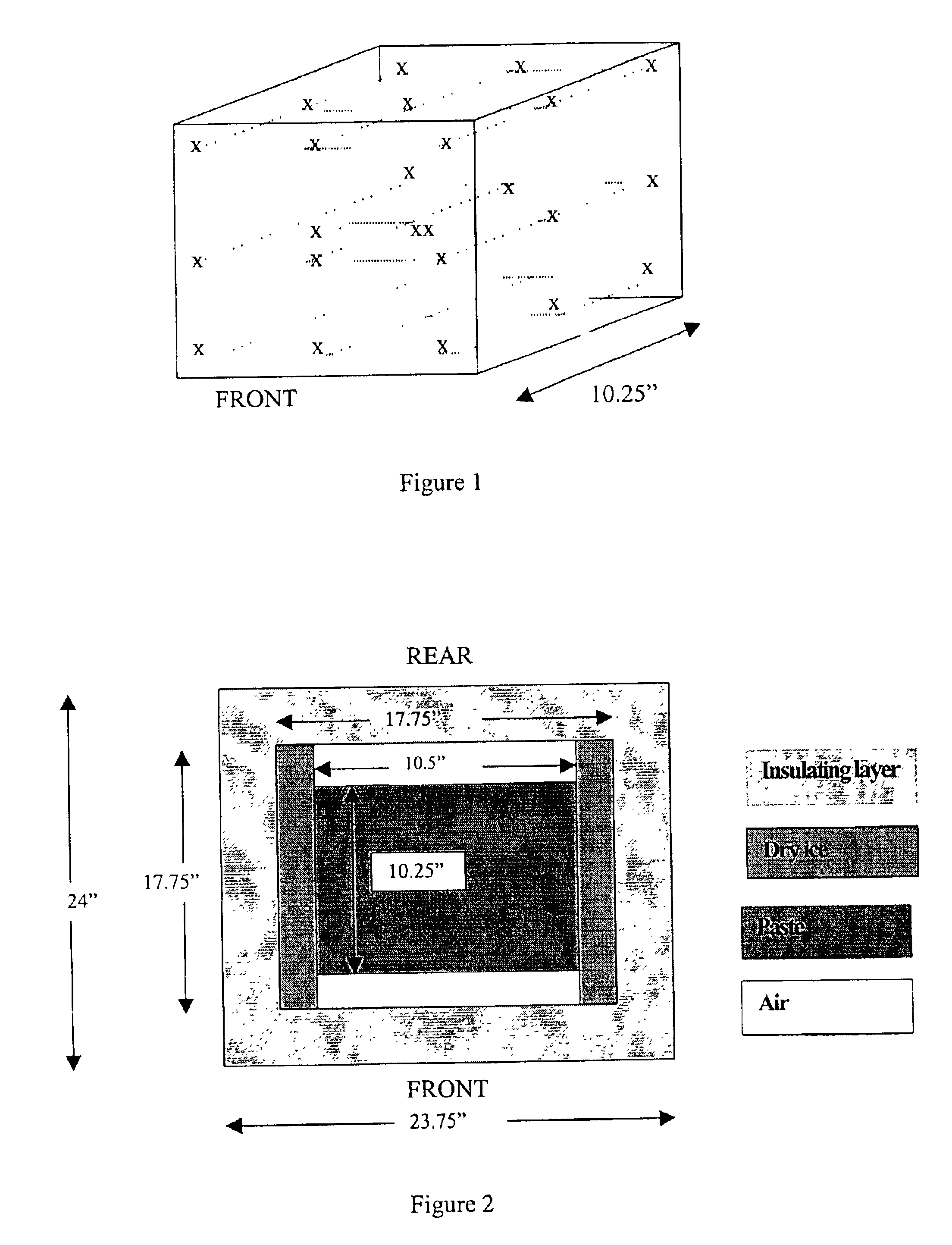
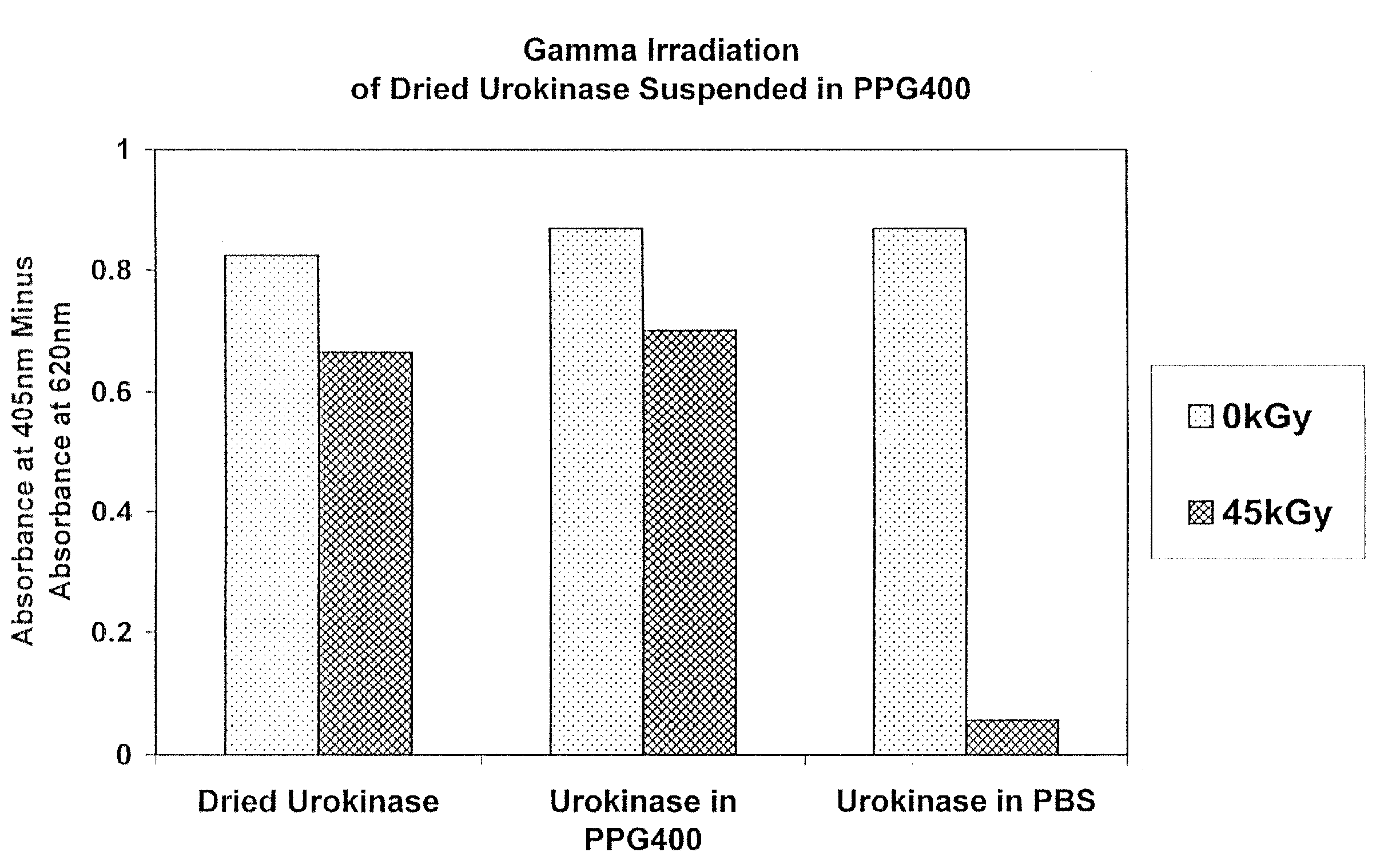
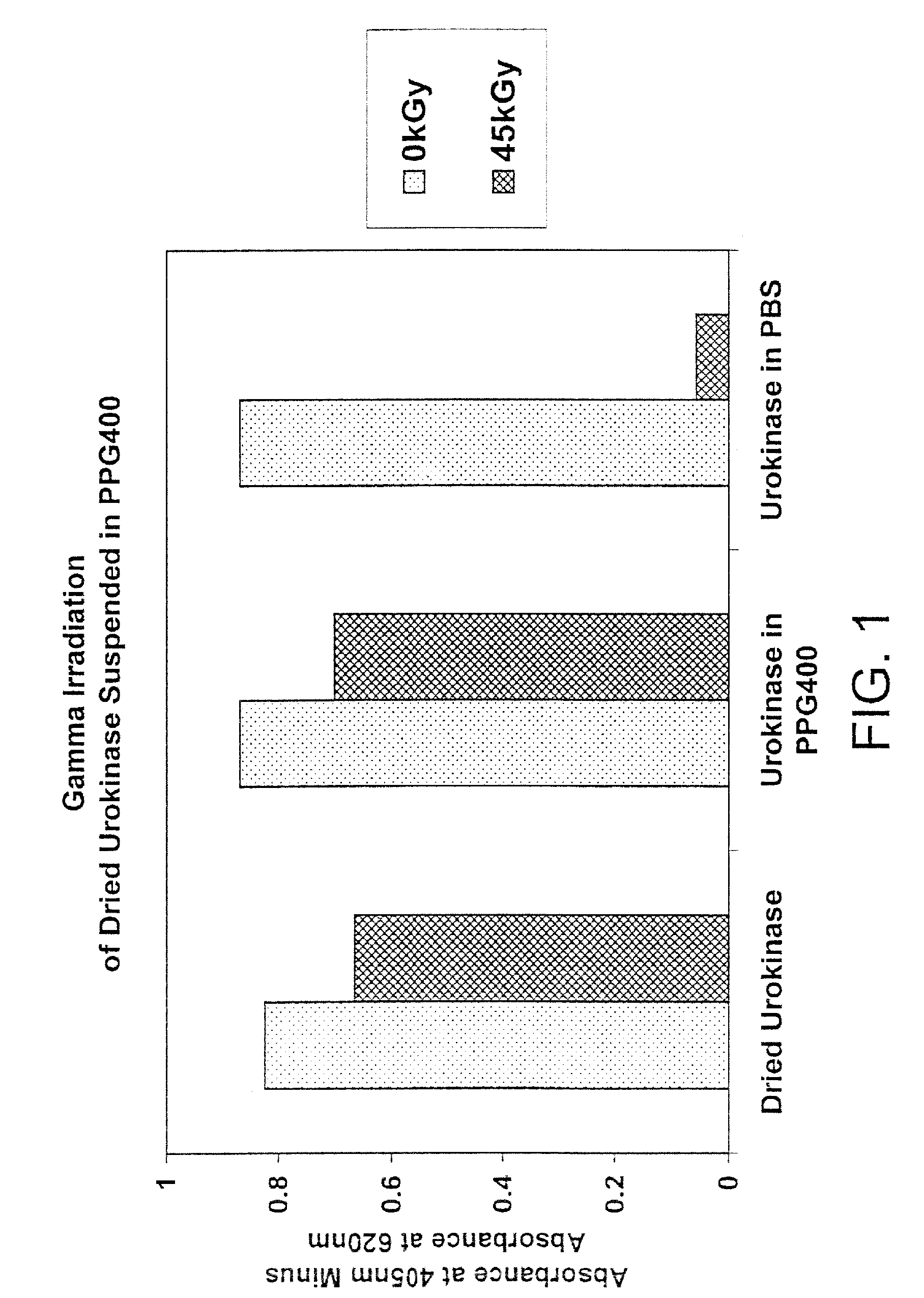
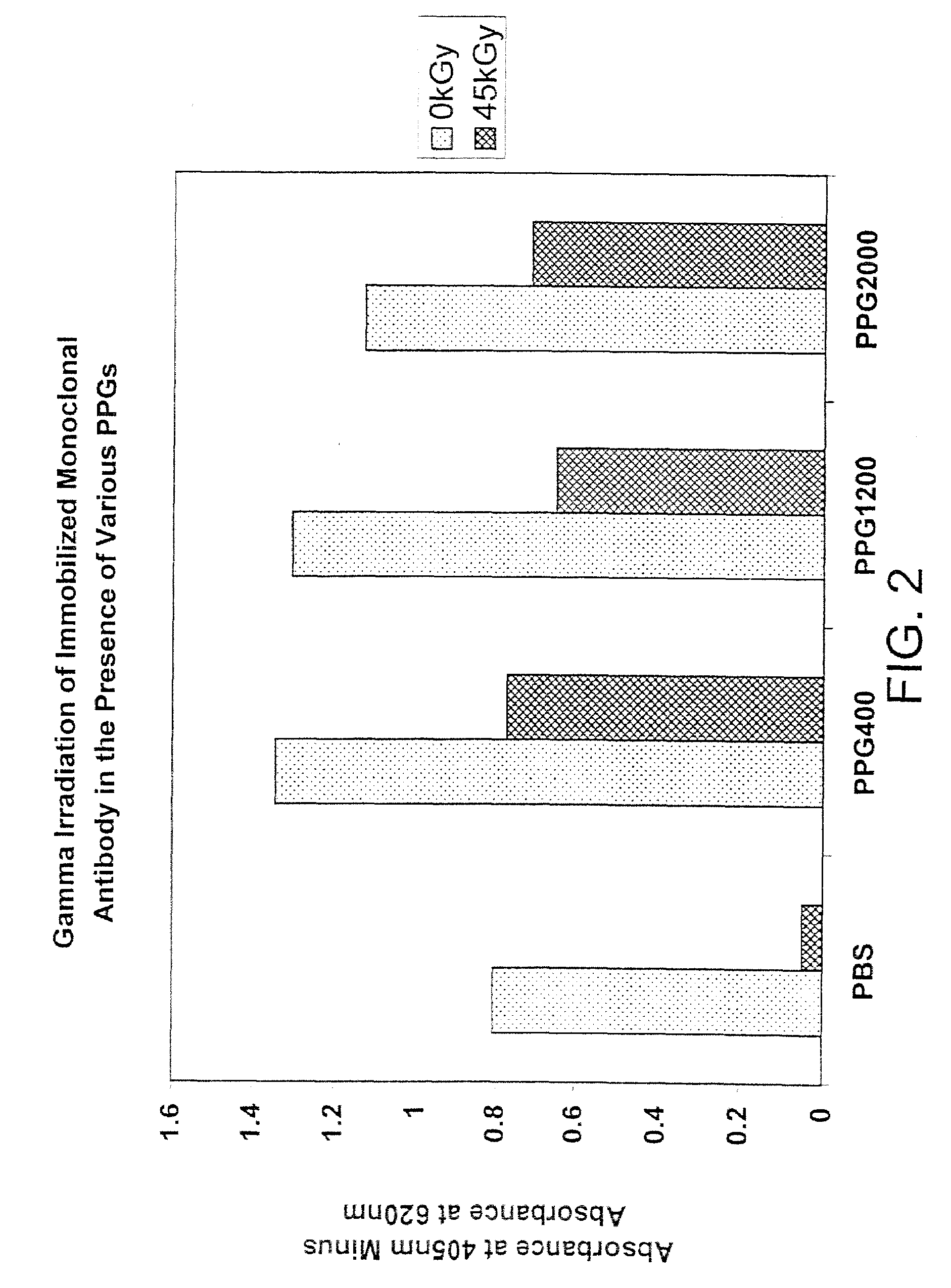
Methods are disclosed for sterilizing tissue to reduce the level of one or more active biological contaminants or pathogens therein, such as viruses, bacteria, (including inter- and intracellular bacteria, such as mycoplasmas, ureaplasmas, nanobacteria, chlamydia, rickettsias), yeasts, molds, fungi, spores, prions or similar agents responsible, alone or in combination, for TSEs and / or single or multicellular parasites. The methods involve sterilizing one or more tissues with irradiation.
Owner:CLEARANT
Near infrared microbial elimination laser system
InactiveUS20080159345A1Minimal heat depositionWide applicabilityLaser detailsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOptical interactionDual wavelength laser
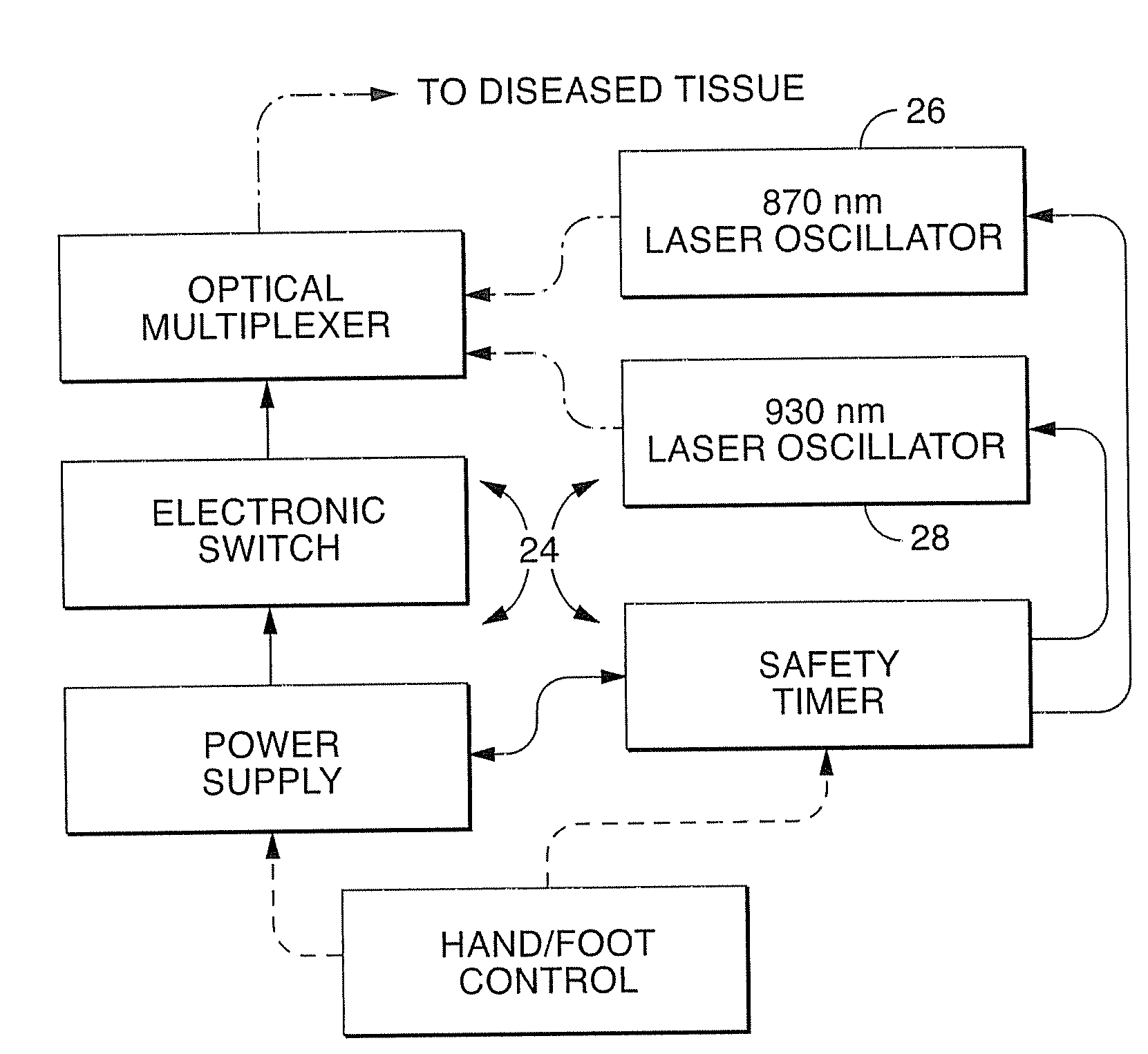
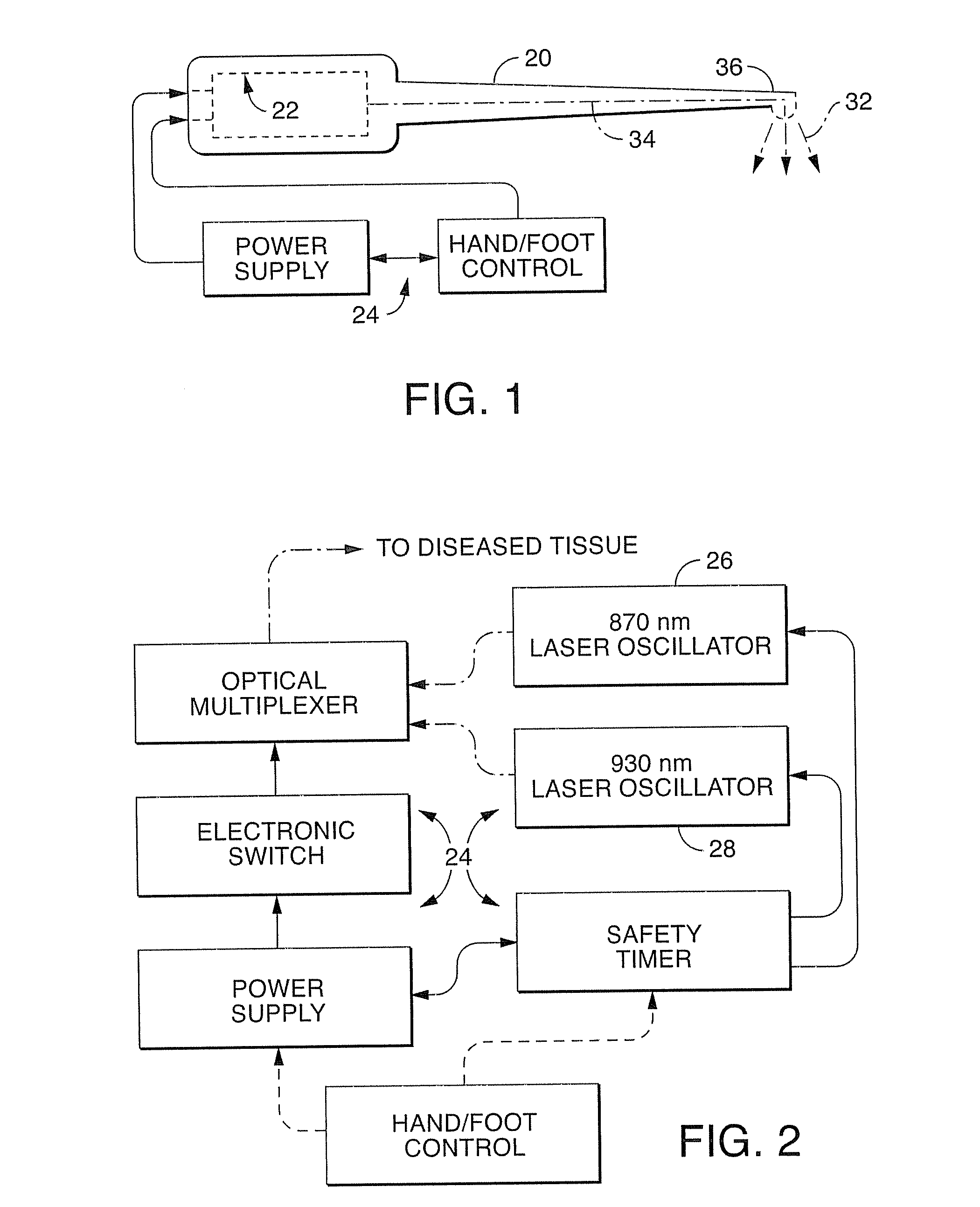
A dual wavelength laser in the low infrared electromagnetic spectrum is disclosed for destruction of bacteria via photo-damage optical interactions through direct selective absorption of optical energy by intracellular bacterial chromophores. The dual wavelength (NIMELS) laser includes an optical assembly and all associated components necessary for the housing of two distinct diode laser arrays (870 nm diode array and 930 nm diode array) that can be emitted through an output connector and wavelength multiplexer as necessary. With this preferred design, the dual wavelengths (870 nm and 930 nm) can be emitted singly, or multiplexed together to be conducted along a common optical pathway, or multiple optical pathways, to achieve maximal bacterial elimination.
Owner:NOMIR MEDICAL TECH
Methods of sterilizing biological materials containing non-aqueous solvents
Methods are disclosed for sterilizing biological materials to reduce the level of one or more active biological contaminants or pathogens therein, such as viruses, bacteria (including inter- and intracellular bacteria, such as mycoplasmas, ureaplasmas, nanobacteria, chlamydia, rickettsias), yeasts, molds, fungi, prions or similar agents responsible, alone or in combination, for TSEs and / or single or multicellular parasites. The methods involve sterilizing biological materials containing one or more non-aqueous solvents with irradiation.
Owner:CRILLANT CORP
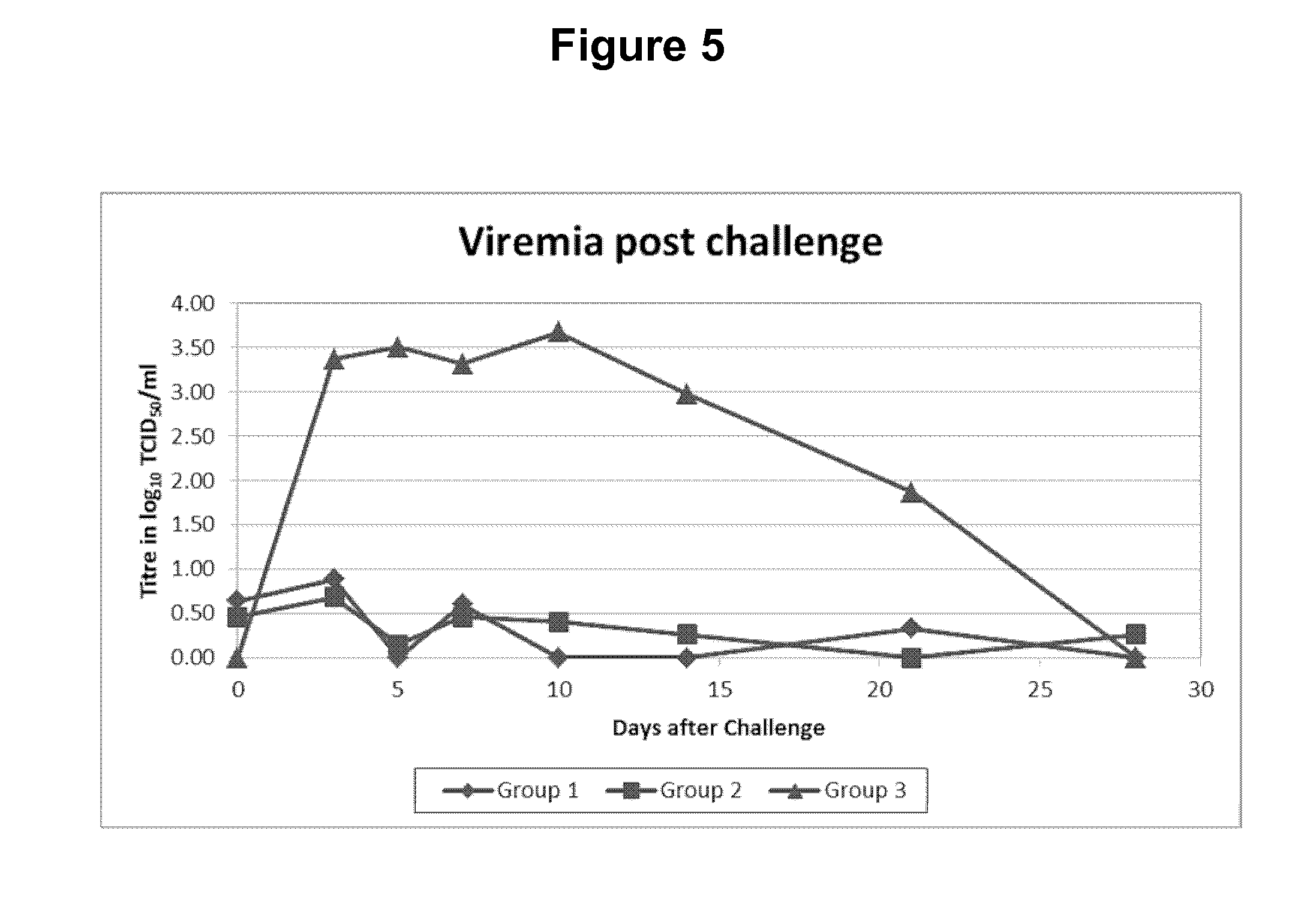
Vaccination of horses against lawsonia intracellularis
The present invention is broadly concerned with vaccination of horses against proliferative enteritis, preferably equine proliferative ileitis, which is caused by an obligate intracellular bacterium Lawsonia Intracellularis (L. intracellularis). Specifically, the invention provides for a method of providing immune protection against L. intracellularis by vaccinating horses, preferably foals starting from one (1) week of age. Preferably the foals are vaccinated with about 4.9 log 10 to about 6.9 log 10 of a live modified L. intracellularis bacteria per dose.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEM VETMADICA INC
Methods for sterilizing biological materials containing non-aqueous solvents
InactiveUS7848487B2Reduce contentLowered residual solventAntibody ingredientsLavatory sanitorySolventBiological materials
Methods are disclosed for sterilizing biological materials to reduce the level of one or more active biological contaminants or pathogens therein, such as viruses, bacteria (including inter- and intracellular bacteria, such as mycoplasmas, ureaplasmas, nanobacteria, chlamydia, rickettsias), yeasts, molds, fungi, prions or similar agents responsible, alone or in combination, for TSEs and / or single or multicellular parasites. The methods involve sterilizing biological materials containing one or more non-aqueous solvents with irradiation.
Owner:CLEARANT
Methods and Compositions Using Immunomodulatory Compounds for the Treatment and Management of Spirochete and Other Obligate Intracellular Bacterial Diseases
Methods of treating, preventing and / or managing a spirochete and / or other obligate intracellular bacterial disease or disorder are disclosed. Specific methods encompass the administration of an immunomodulatory compound alone or in combination with a second active agent.
Owner:CELGENE CORP
Methods for Sterilizing Biological Materials Containing Non-Aqueous Solvents
InactiveUS20090202039A1Reduce contentLowered residual solventLavatory sanitoryAntibody ingredientsSolventBiological materials
Methods are disclosed for sterilizing biological materials to reduce the level of one or more active biological contaminants or pathogens therein, such as viruses, bacteria (including inter- and intracellular bacteria, such as mycoplasmas, ureaplasmas, nanobacteria, chlamydia, rickettsias), yeasts, molds, fungi, prions or similar agents responsible, alone or in combination, for TSEs and / or single or multicellular parasites. The methods involve sterilizing biological materials containing one or more non-aqueous solvents with irradiation.
Owner:CLEARANT
Methods for Sterilizing Tissue
InactiveUS20110091353A1Effective sterilizationAvoid radiationLavatory sanitoryChemicalsYeastIrradiation
Methods are disclosed for sterilizing tissue to reduce the level of one or more active biological contaminants or pathogens therein, such as viruses, bacteria, (including inter- and intracellular bacteria, such as mycoplasmas, ureaplasmas, nanobacteria, chlamydia, rickettsias), yeasts, molds, fungi, prions or similar agents responsible, alone or in combination, for TSEs and / or single or multicellular parasites. The methods involve sterilizing one or more tissues with irradiation.
Owner:BURGESS WILSON +3
Methods for sterilizing preparations containing albumin
InactiveUS7252799B2Reduce contentLow preparation temperaturePeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticYeastBlood plasma
Methods are disclosed for sterilizing preparations containing albumin to reduce the level of one or more active biological contaminants or pathogens therein, such as viruses, bacteria (including inter- and intracellular bacteria, such as mycoplasmas, ureaplasmas, nanobacteria, chlamydia, rickettsias), yeasts, molds, fungi, prions or similar agents responsible, alone or in combination, for TSEs and / or single or multicellular parasites. These methods involve sterilizing preparations containing albumin, such as plasma protein fractions, with irradiation.
Owner:CLEARANT
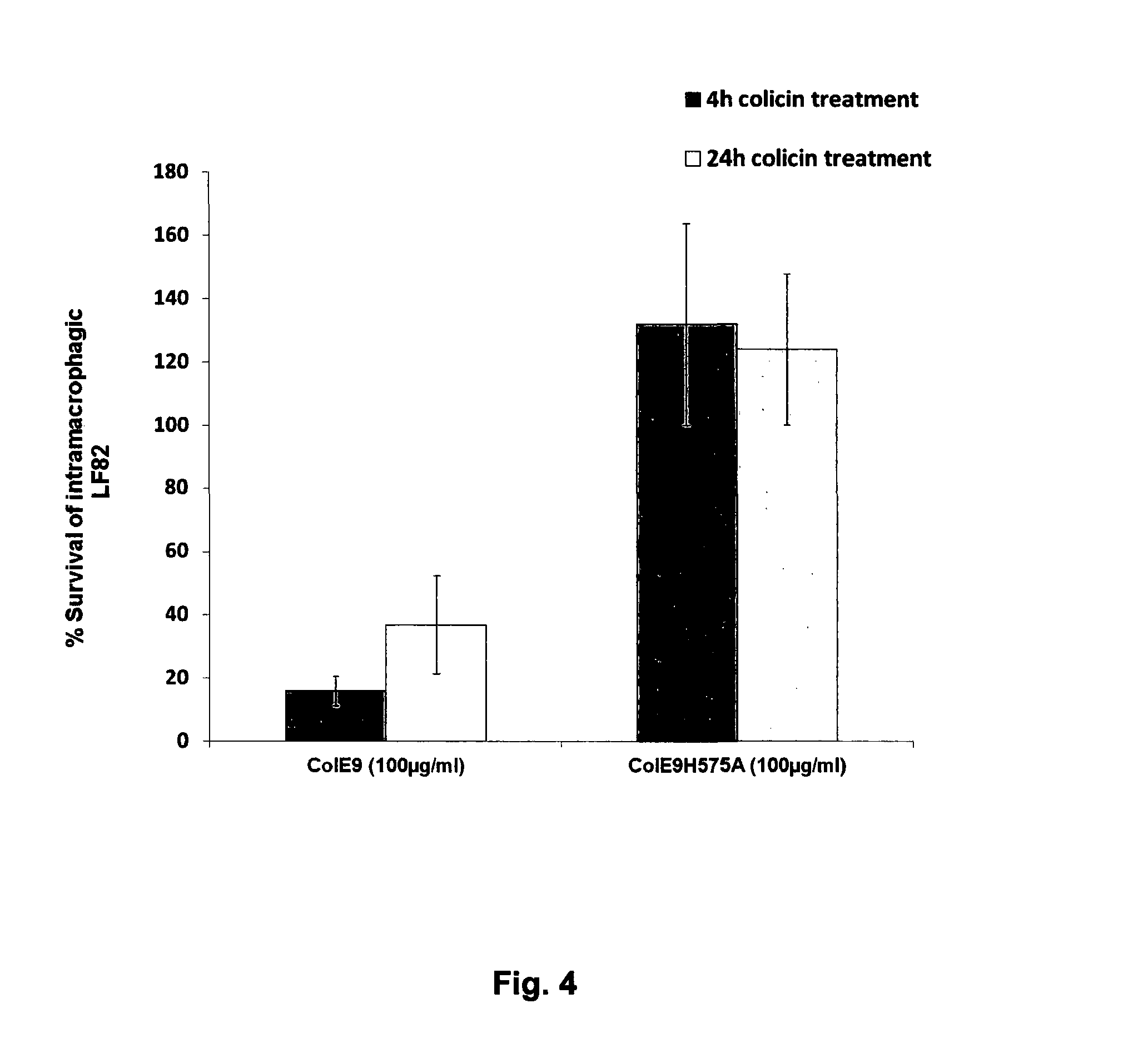
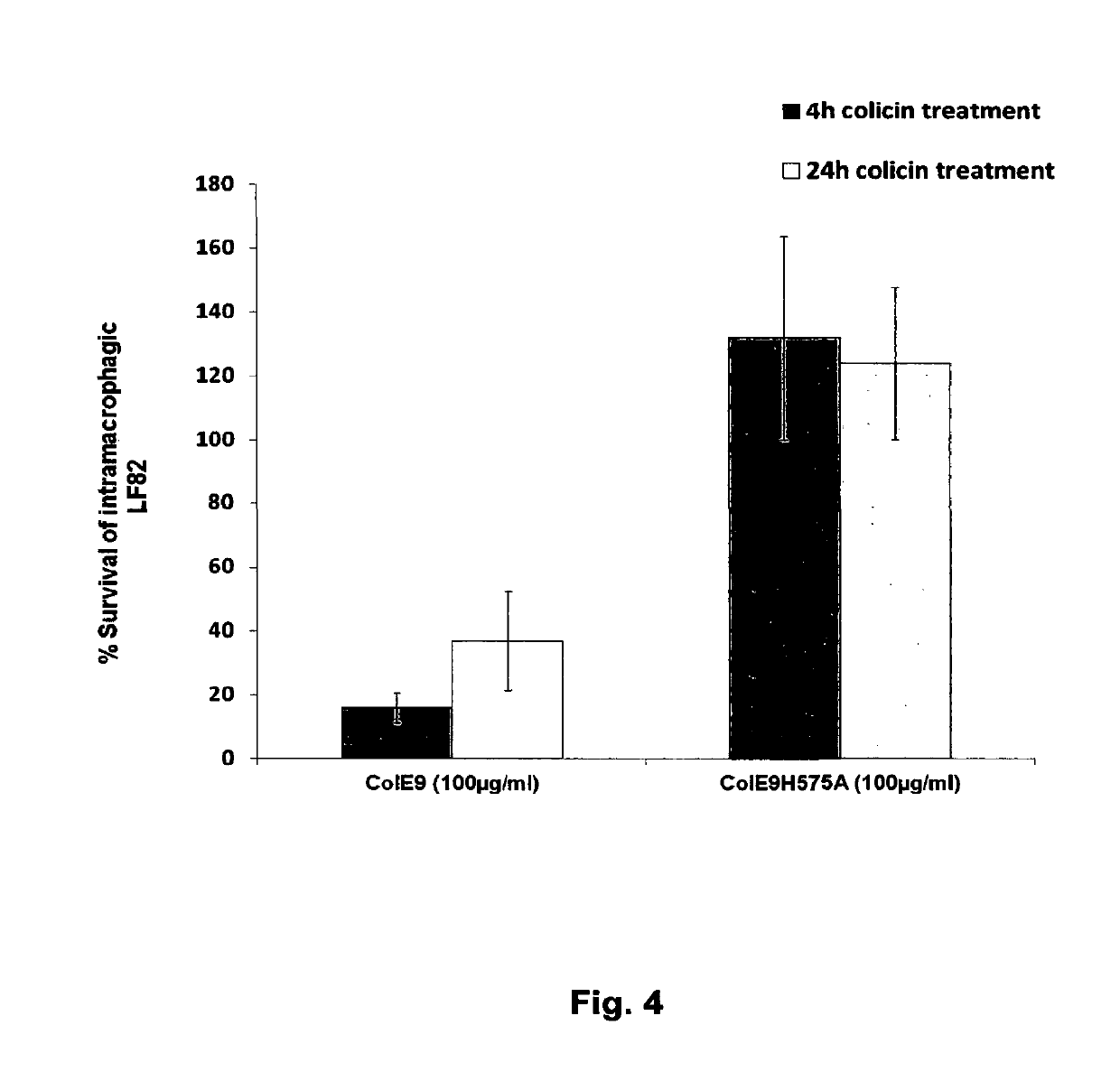
Colicins for Treating Bacterial Infections
InactiveUS20150164984A1Highly active andUsing treatment methodAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseEscherichia coli
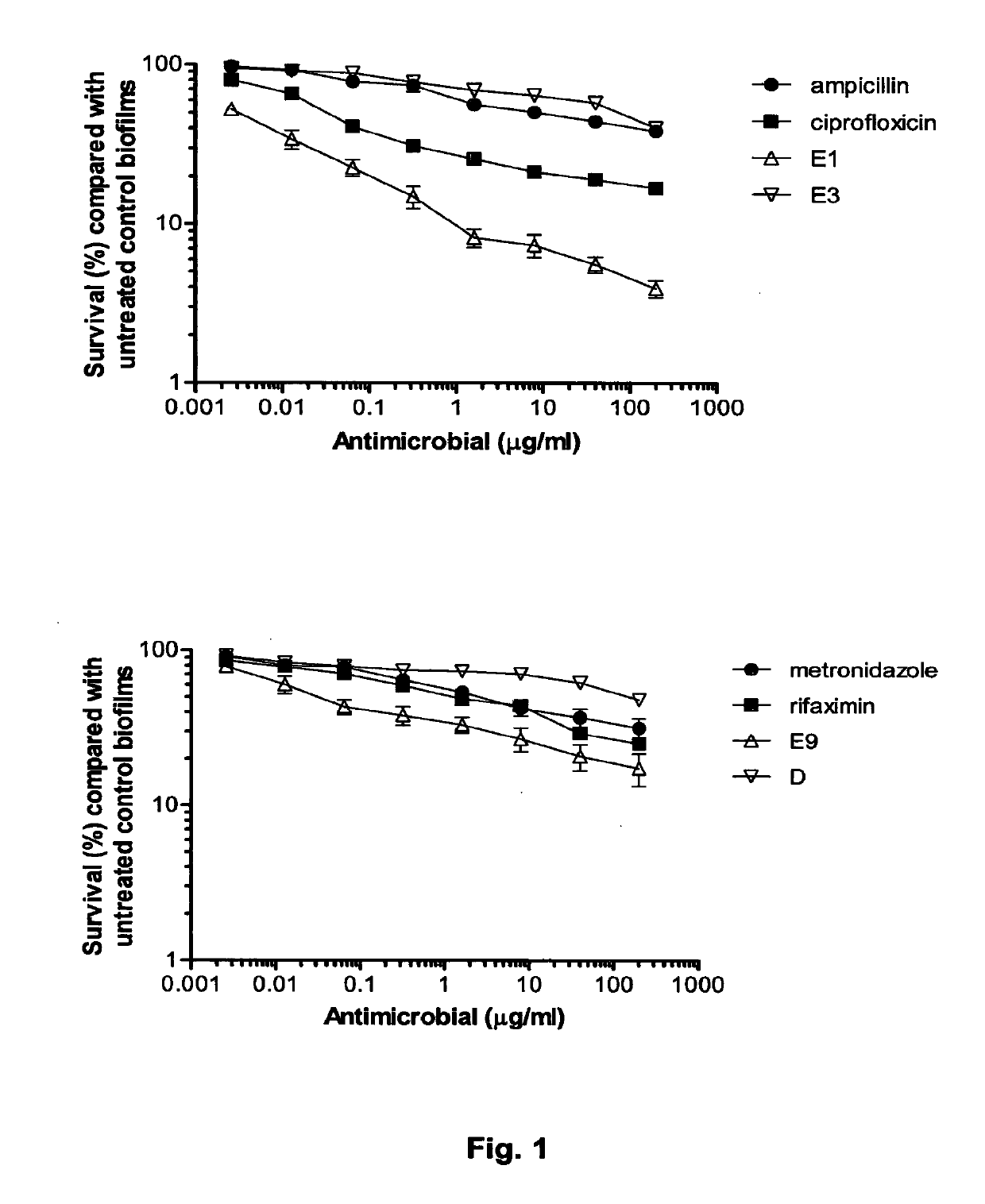
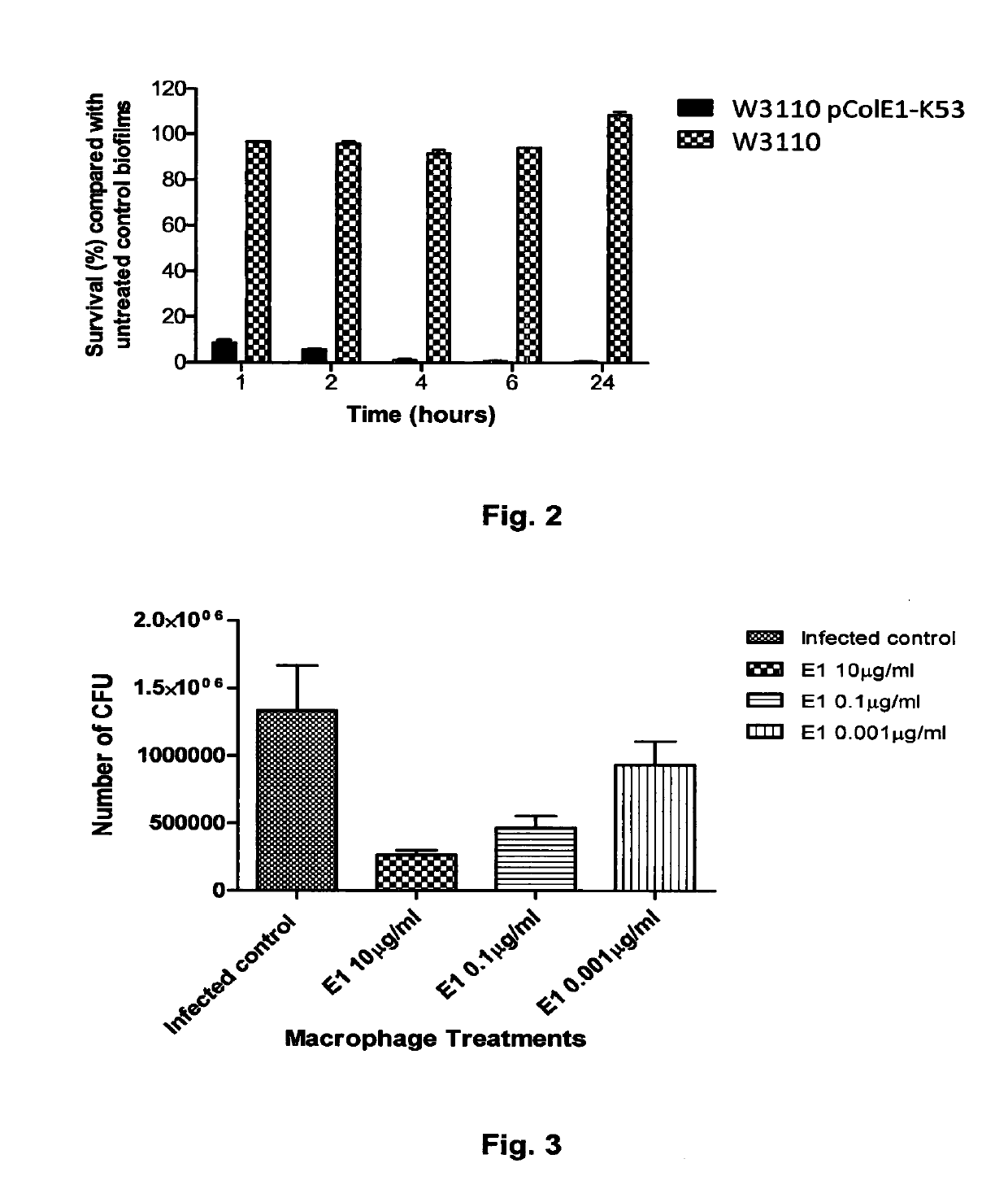
The Invention relates to materials and methods for the treatment of conditions associated with bacterial biofilms, intracellular bacterial infections and / or adherent-invasive Escherichia coli infections, including Crohns' disease. In particular, the invention relates to the use of colicins and bacteria producing colicins, for the treatment of such conditions.
Owner:UNIV OF GLASGOW THE UNIV COURT OF
Treatment of intracellular bacterial infection
An intracellular bacterial infection in a plant or animal is treated by administration to a plant cell or animal cell of a particle to which an infectious bacteriophage is covalently attached, wherein the particle is internalised by the cell. Particles with phage attached and compositions comprising the particles are provided. A formulation, for treatment of a bacterial infection, comprises bacteriophage, liquid carrier and adhesive, which dries so that the adhesive adheres the bacteriophage to a surface, one such formulation comprising liquid carrier: 85%-99.98% by weight; bacteriophage: 0.01%-5% by weight; and adhesive: 0.01%-10% by weight.
Owner:FIXED PHAGE
Treatment of intracellular bacterial infection
An intracellular bacterial infection in a plant or animal is treated by administration to a plant cell or animal cell of a particle to which an infectious bacteriophage is covalently attached, wherein the particle is internalized by the cell. Particles with phage attached and compositions comprising the particles are provided. A formulation, for treatment of a bacterial infection, comprises bacteriophage, liquid carrier and adhesive, which dries so that the adhesive adheres the bacteriophage to a surface, one such formulation comprising liquid carrier: 85%-99.98% by weight; bacteriophage: 0.01%-5% by weight; and adhesive: 0.01%-10% by weight.
Owner:FIXED PHAGE
Swine Vaccine Against PRRS and Lawsonia Intracellularis
InactiveUS20160303219A1Less-safe and effectiveComplicate safetyAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsAntigenLawsonia intracellularis
The present invention pertains to a swine vaccine, in particular a vaccine comprising in combination live attenuated PRRS virus and inactivated Lawsonia intracellularis antigen, for the protection of a swine against an infection with PRRS virus and Lawsonia intracellularis bacteria. The invention also pertains to a method to protect a swine against an infection with PRRS virus and Lawsonia intracellularis bacteria using this vaccine.
Owner:INTERVET INC
Use Of 5,6-Dimethylxanthenone-4-Acetic Acid as an Antimicrobial Agent
The invention relates to the areas of therapeutics, pharmaceuticals, drug discovery, and immunotherapy. More specifically, the present invention relates to methods of stimulating the immune system through the administration of flavone acetic acid [FAA] analogues, and in particular, the flavone acetic acid analogue, 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid (DMXAA) so as to comprise an antimicrobial therapeutic agent for the treatment of viral, fungal, bacterial or parasitic infections in humans and non-human animals. The invention is especially suitable for use in a process of treating and preventing infection by viruses (for example, rhinoviruses, enteroviruses, and influenza viruses, etc.) and bacteria (especially intracellular bacterial pathogens such as Francisella tularensis).
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Pro-apoptotic bacterial vaccines to enhance cellular immune responses
InactiveUS8021671B2Improves vaccine efficacyDiminishing intracellular survivalAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesApoptosis
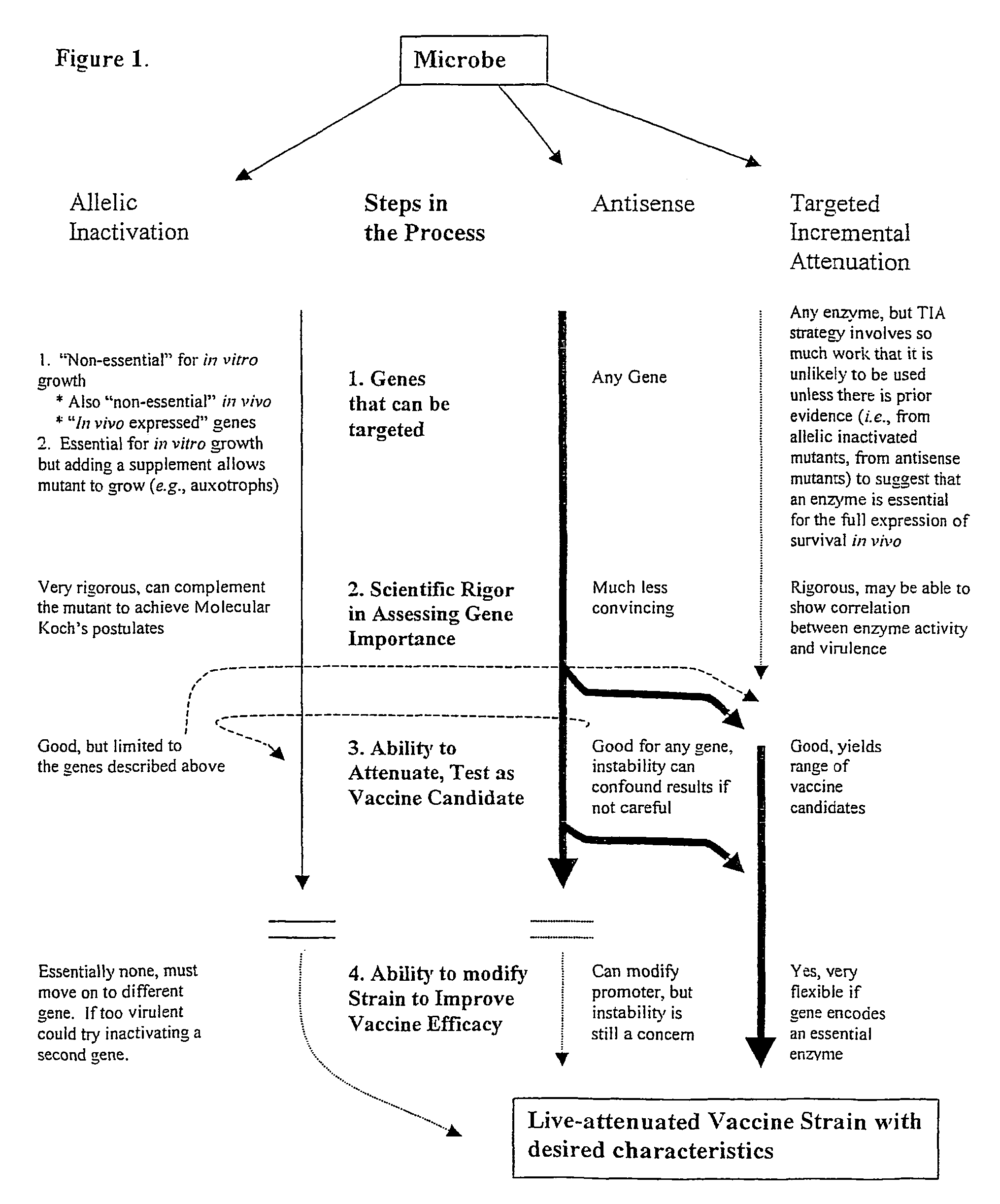
Whole-cell vaccines and methods for their use in producing protective immune responses in vertebrate hosts subsequently exposed to pathogenic bacteria. The present invention involves a method of enhancing antigen presentation by intracellular bacteria in a manner that improves vaccine efficacy. After identifying an enzyme that has an anti-apoptotic effect upon host cells infected by an intracellular microbe, the activity of the enzyme is reduced, thereby modifying the microbe so that it increases immunogenicity. Also, the present invention provides a method of incrementally modifying enzyme activity to produce incrementally attenuated mutants of the microbe from which an effective vaccine candidate can be selected.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV +1
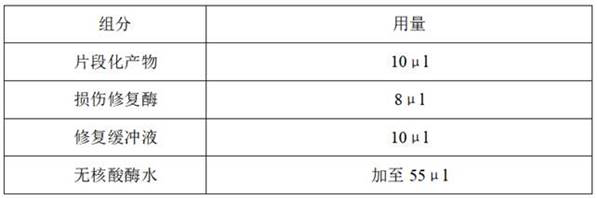
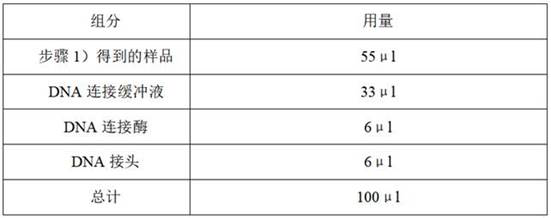
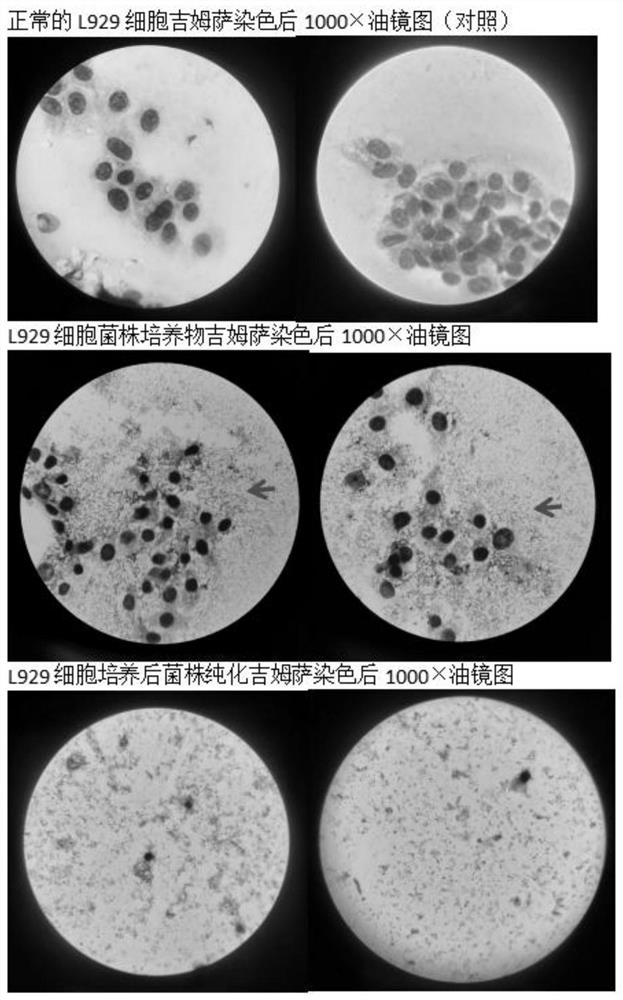
Method and kit for synchronously cultivating bacterium group
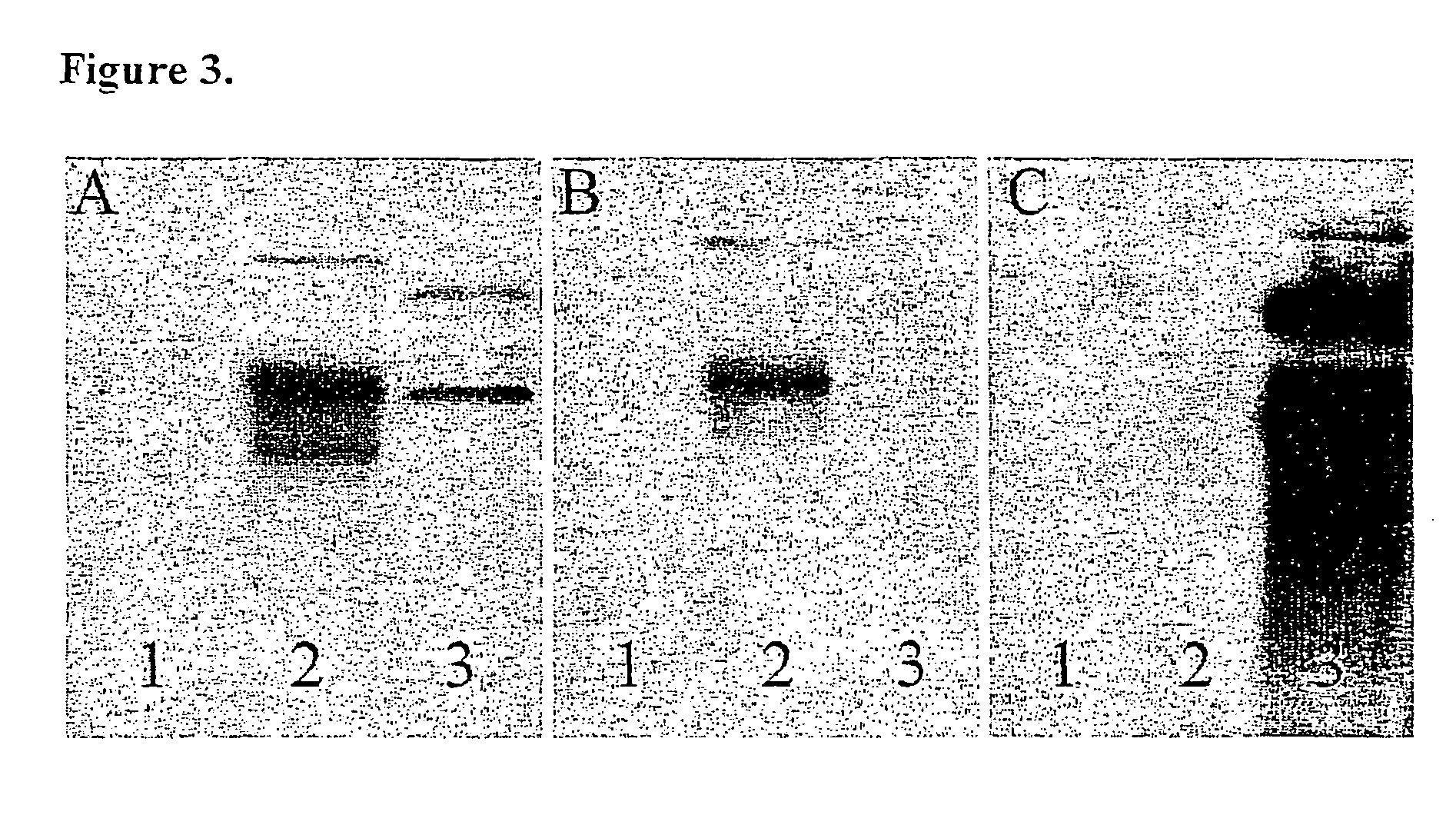
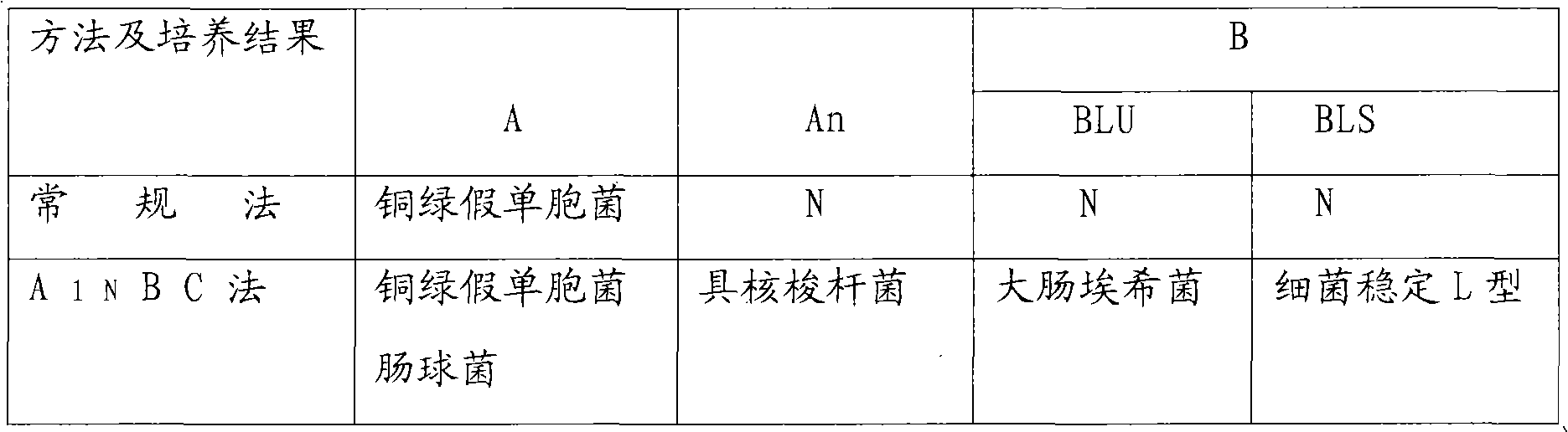
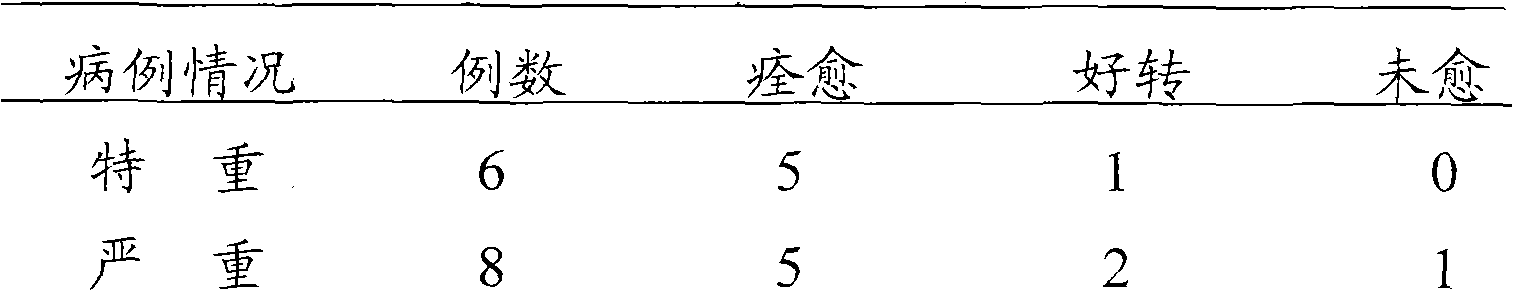
The invention relates to the field of medicaments, in particular to a method for synchronously cultivating a bacterium group and a kit for synchronously cultivating the bacterium group. The kit of the invention comprises aerobe group cultivation proliferation solution, anaerobe group cultivation proliferation solution, bacteria L-form group cultivation proliferation solution and cell bacterium group cultivation proliferation solution. The method and the kit of the invention have the advantages of necessary sample amount for cultivating bacteria of only 1 to 2 percent of an ordinary using amount, positive detection rate of over 95 percent, capacity of judging a result within 6 to 8 hours of bacterium cultivation, obtainment of pathogenic bacterium group medicament sensitive data within 24 hours, accordance with the basic rule of evidence-based diagnosis of evidence-based medicament and wide clinical application prospect.
Owner:上海康元科技发展股份有限公司
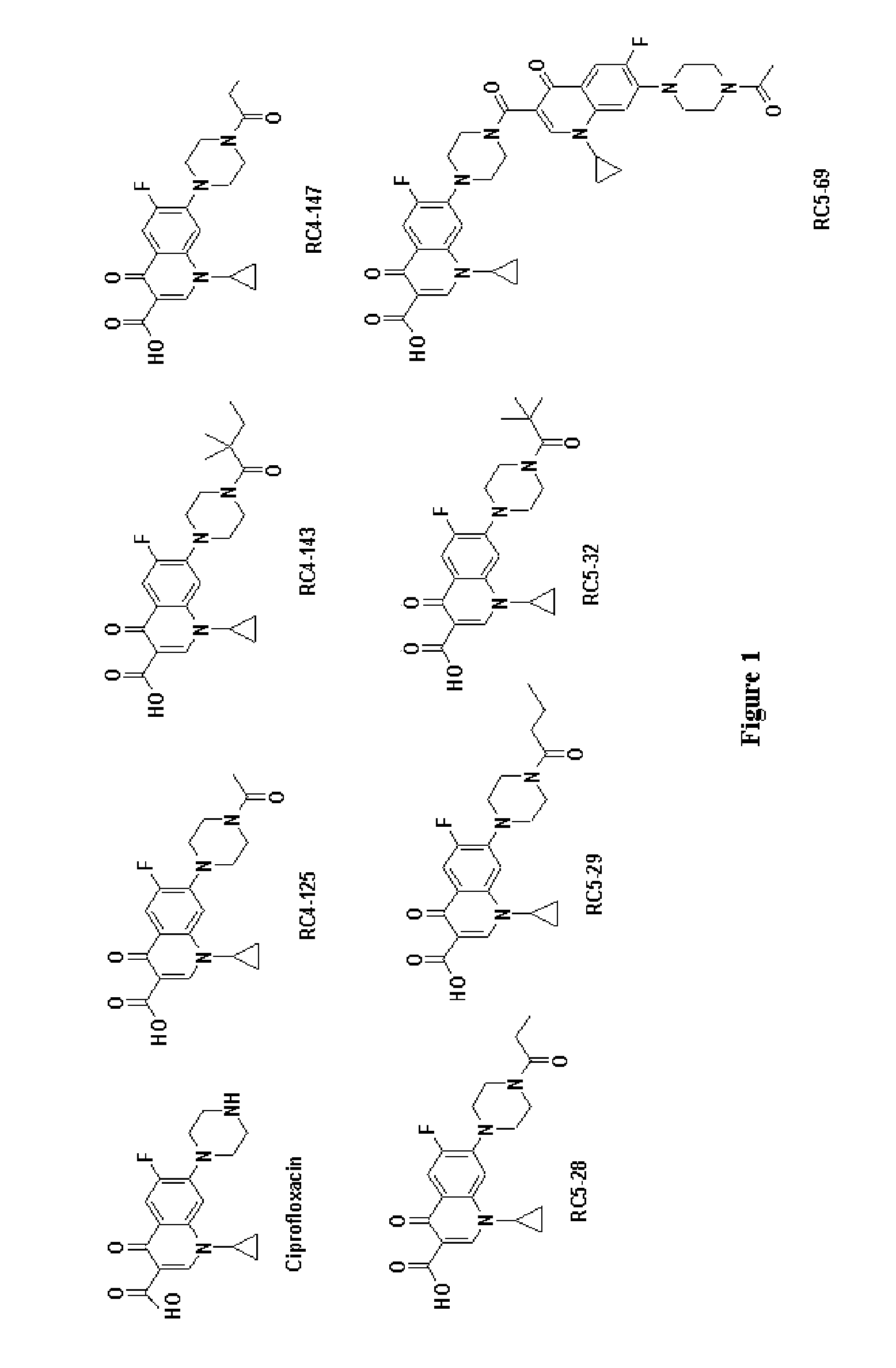
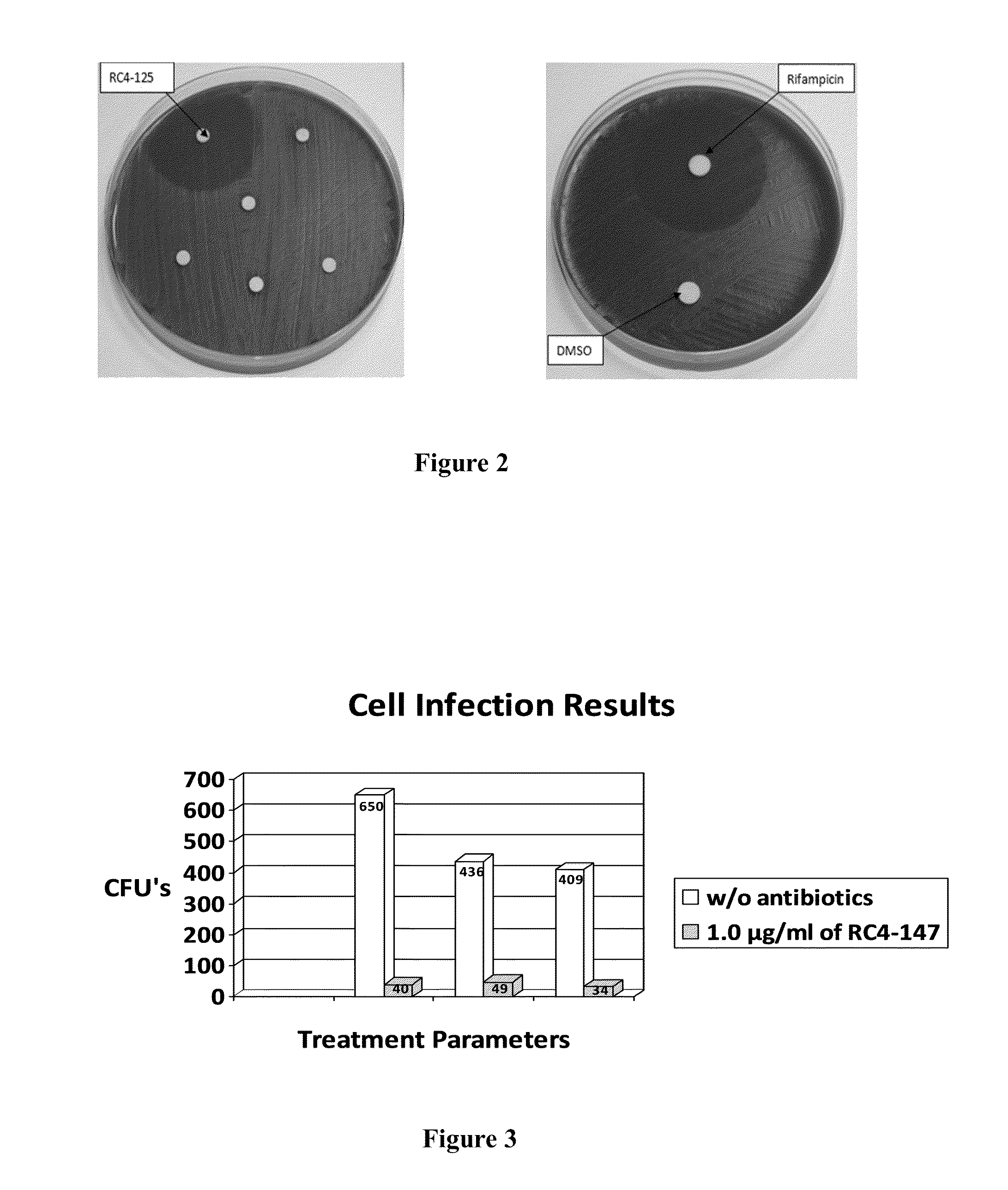
Activity of new N-acylated ciprofloxacin derivatives against faculative intracellular bacteria
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Novel immune stimulating compound
ActiveUS20200010499A1Direct effectAvoid developmentAntibacterial agentsSugar derivativesProtozoaMacrocyclic lactone
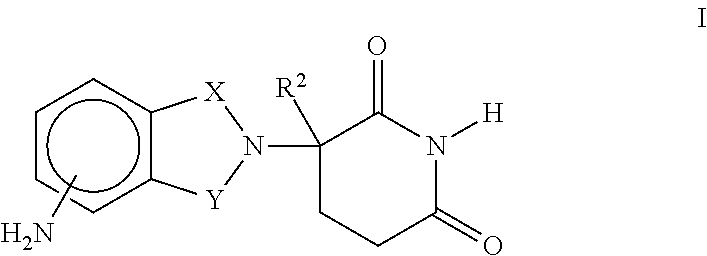
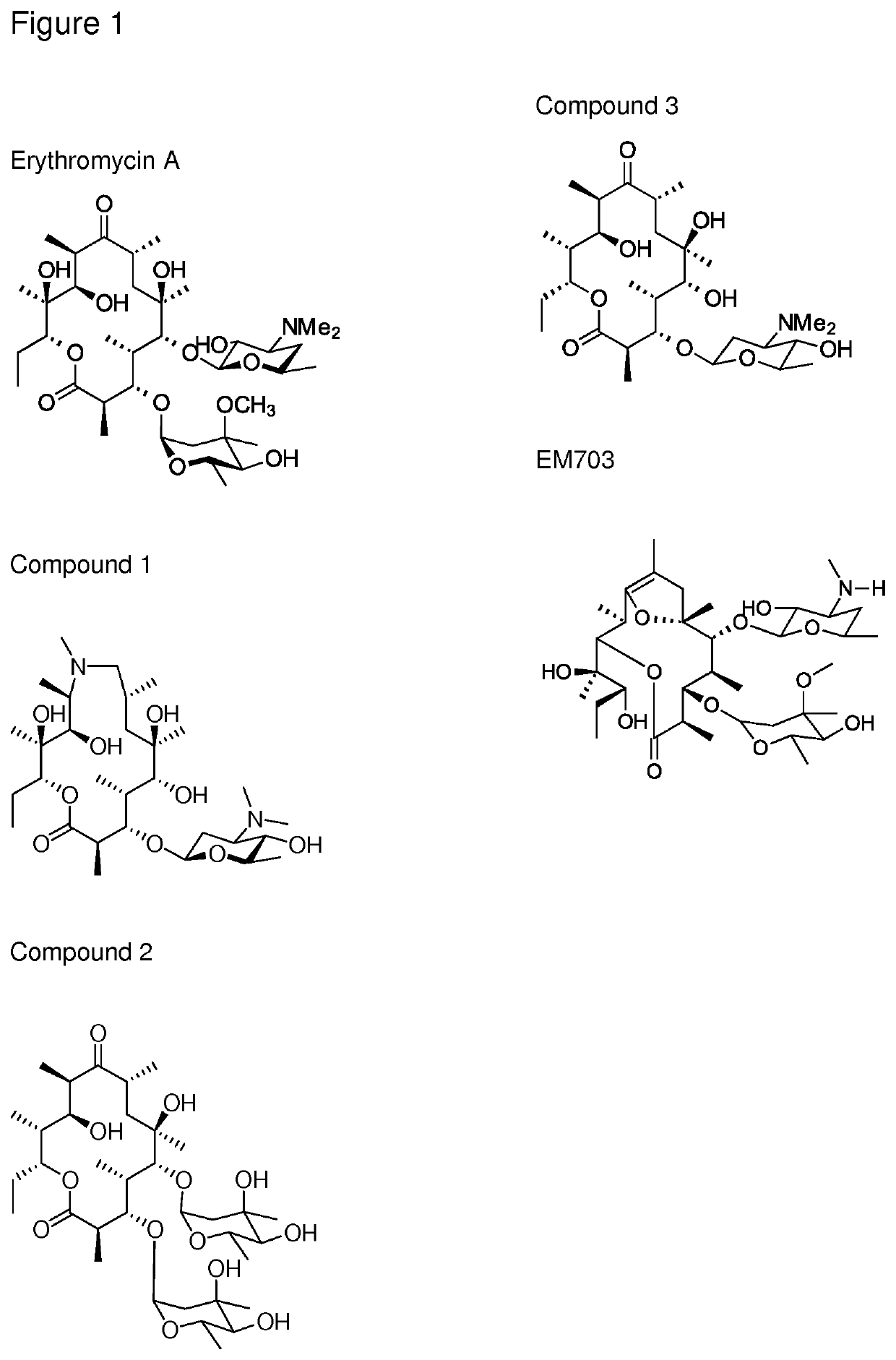
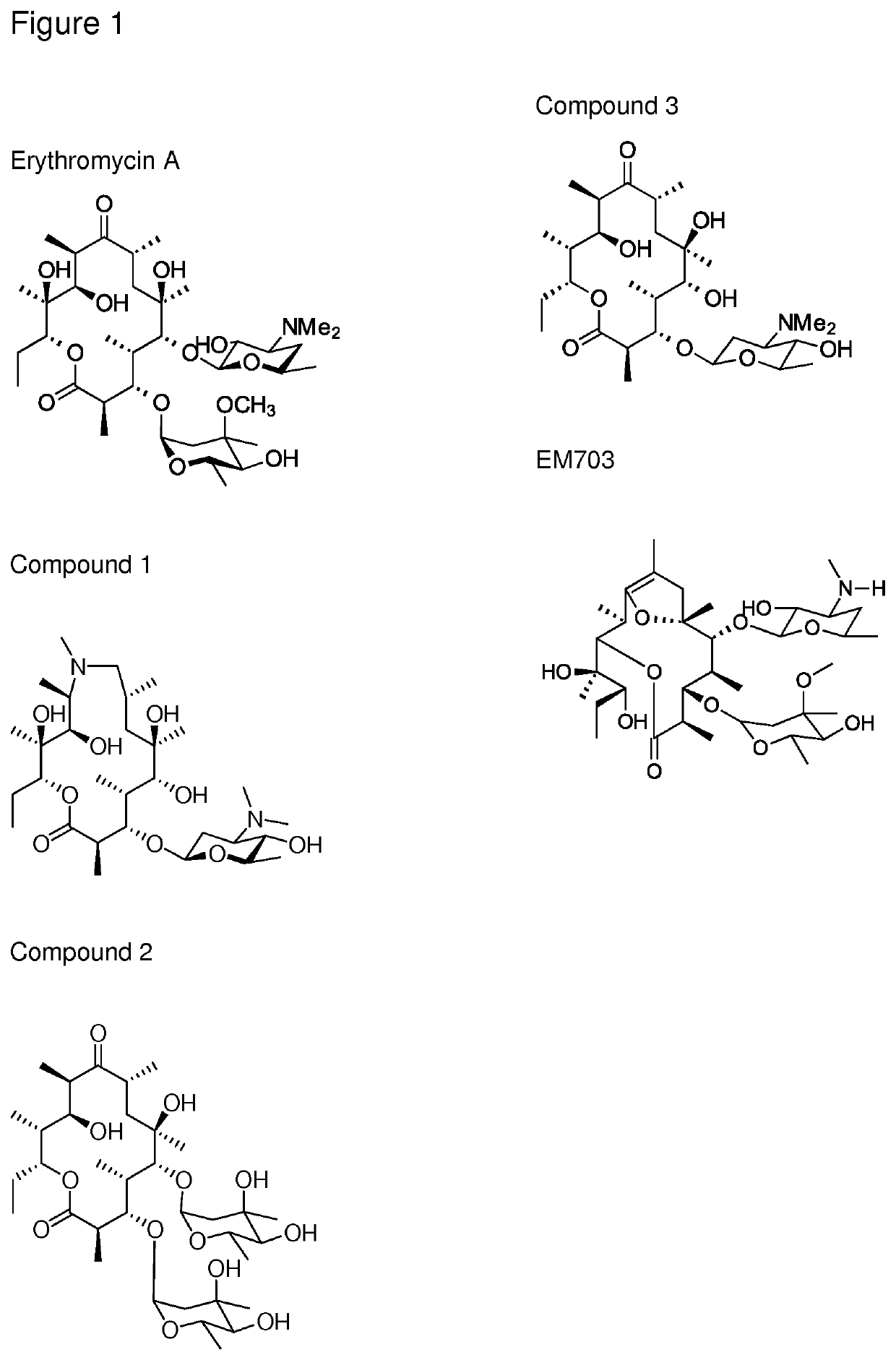
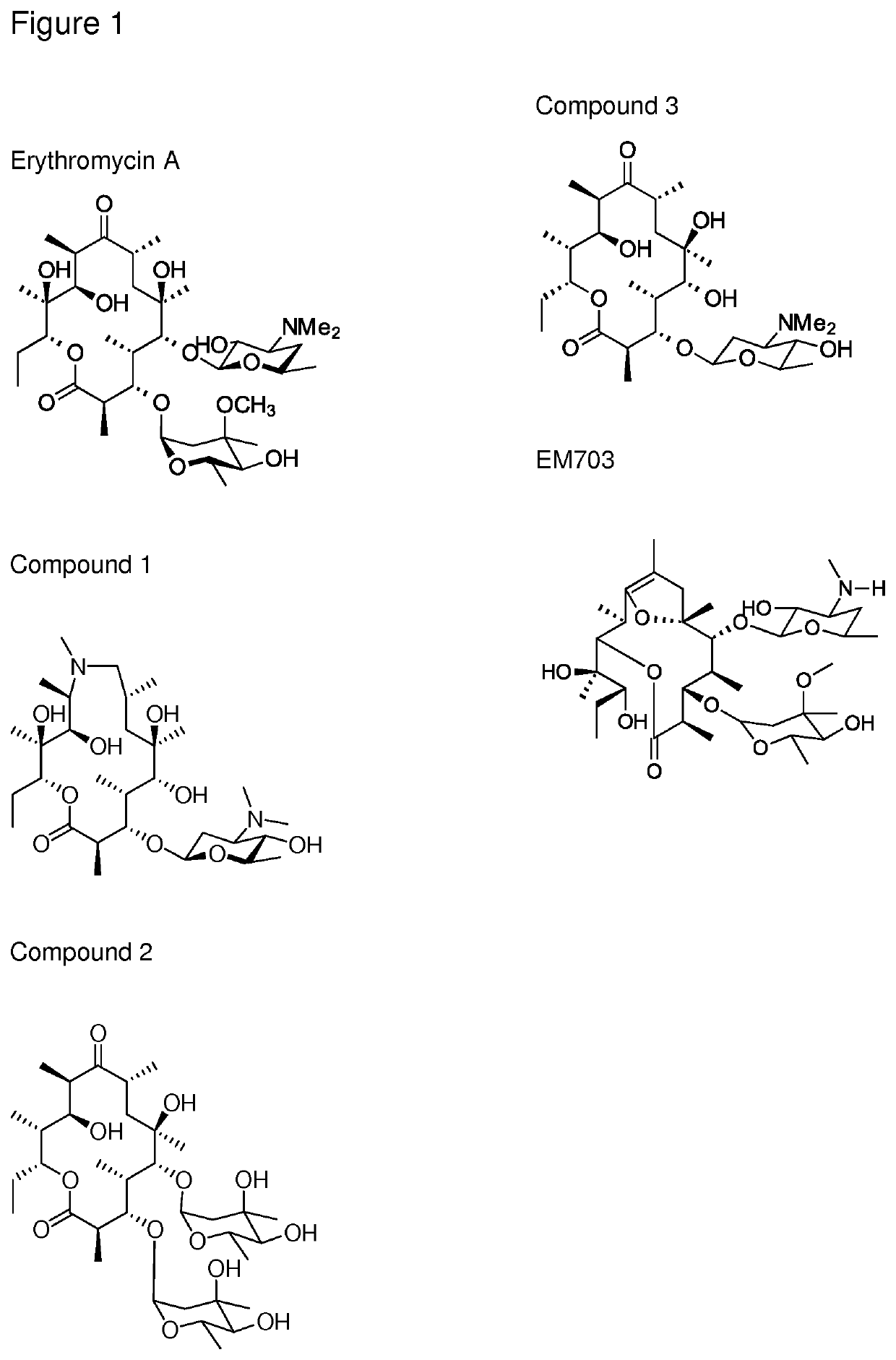
The present invention provides immune stimulating macrolide of formula (I). The macrolide has utility in treating intracellular bacterial, fungal, and protozoal infections.
Owner:ISR IMMUNE SYST REGULATION HLDG AB PUBL
Novel uses of parapoxvirus preparations
The present invention related to use of Parapoxvirus preparations for the treatment of conditions related to infections with strictly intracellular bacteria
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV +1
Determination of intracellular bacteria
InactiveUS20160138090A1Reduce riskHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesBacilli
This application pertains to methods for the whole-cell analysis of intracellular bacteria. The methods are capable of making a determination of whether or not a sample (e.g. a clinical sample) comprises one or more select bacteria within host cells, for example, predatory host cells such as phagocytic cells. The method is performed on substantial intact bacteria and may be performed without the use of permeabilising or lysis reagents and using PNA probes. Furthermore, the application pertains to in situ hybridization methods for Gram-positive bacteria performed using buffered saline for hybridization.
Owner:STENDER DIAGNOSTICS
Use of unsaturated sphingosine compounds as chemotherapeutic agents for the treatment of cancer
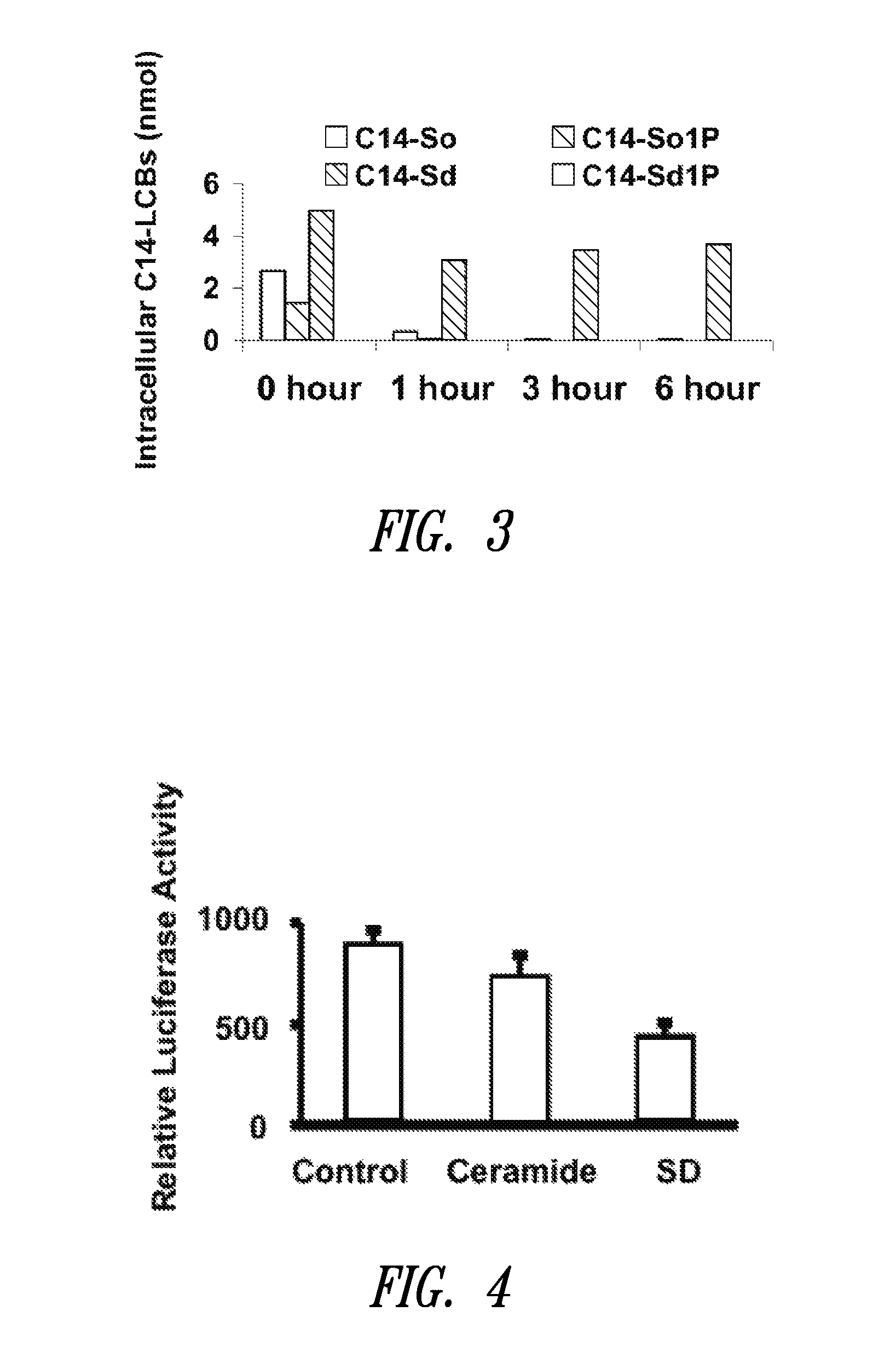
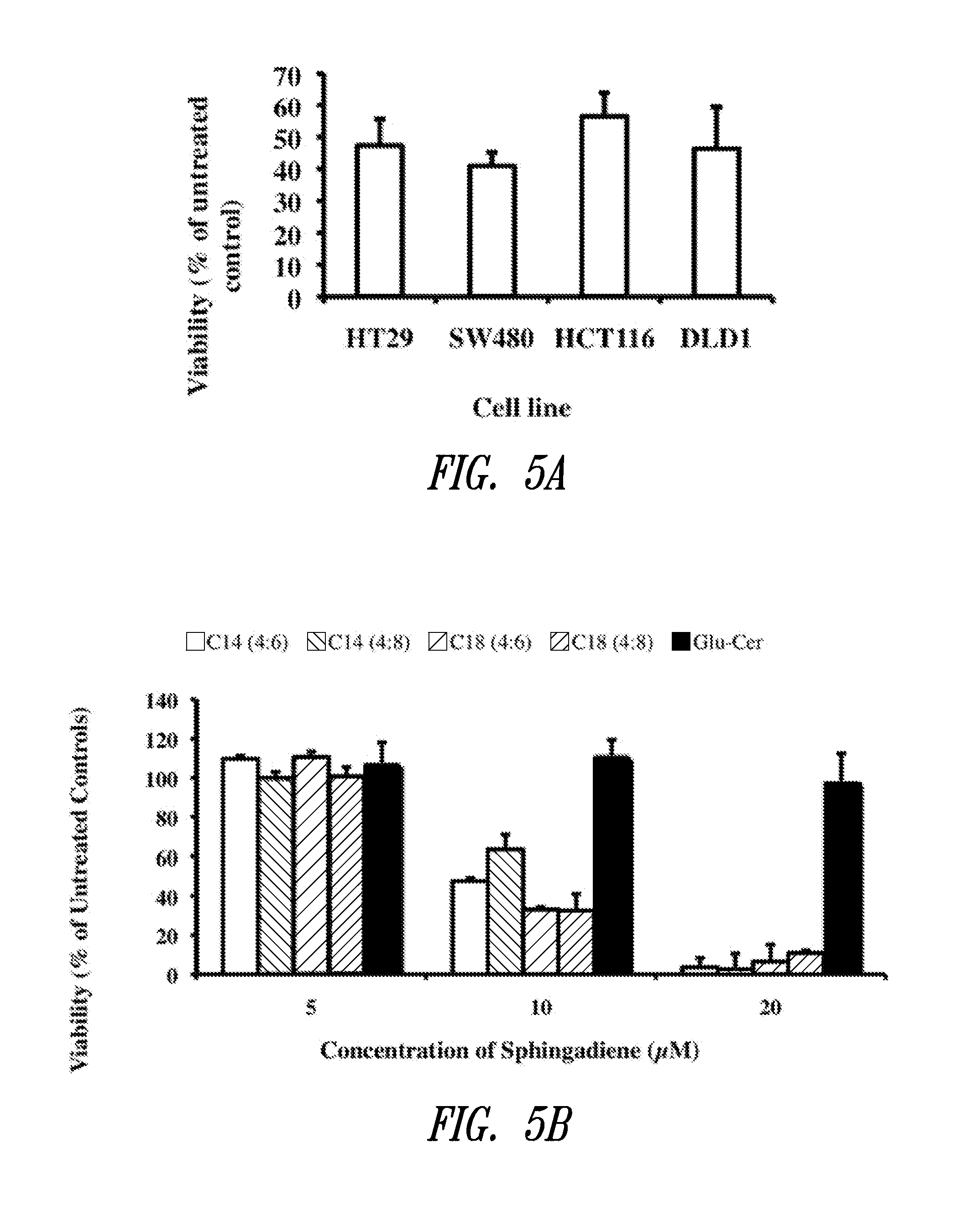
The present invention is directed to unsaturated sphingosine compounds which are useful as therapeutic agents for the treatment of cancer and for the treatment of other diseases including diabetes and infection with intracellular bacteria. This invention is also directed to methods of using the compounds and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds in treating these diseases.
Owner:CHILDREN S HOSPITAL &RES CENT AT OAKLAN +1
Colicins for treating bacterial infections
The Invention relates to materials and methods for the treatment of conditions associated with bacterial biofilms, intracellular bacterial infections and / or adherent-invasive Escherichia coli infections, including Crohns' disease. In particular, the invention relates to the use of colicins and bacteria producing colicins, for the treatment of such conditions.
Owner:THE UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF GLASGOW
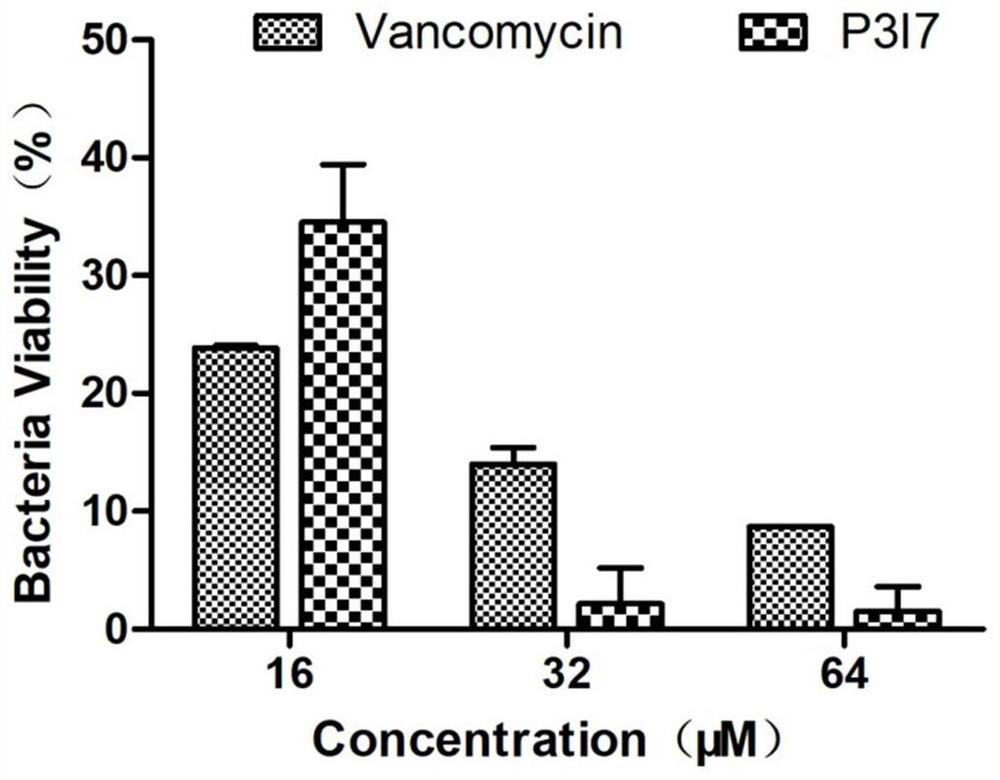
Cell penetrating antibacterial peptide and application thereof
ActiveCN113754784ABroad-spectrum antimicrobial activityLow cytotoxicityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifAntibacterial agentsEscherichia coliCytotoxicity
The invention relates to the technical field of antibacterial peptides, in particular to a cell penetrating antibacterial peptide and application thereof. The antibacterial peptide provided by the invention is a chimeric peptide formed by a polypeptide with an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and a polypeptide with an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The antibacterial peptide has cell penetrating and antibacterial functions, has a broad-spectrum antibacterial effect, has good antibacterial activity on escherichia coli, staphylococcus aureus, salmonella and the like, can enter cells and has a strong inhibition effect on intracellular bacteria; and meanwhile, the antibacterial peptide disclosed by the invention has relatively low cytotoxicity, good biocompatibility and wide application prospect.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Immune stimulating macrolides
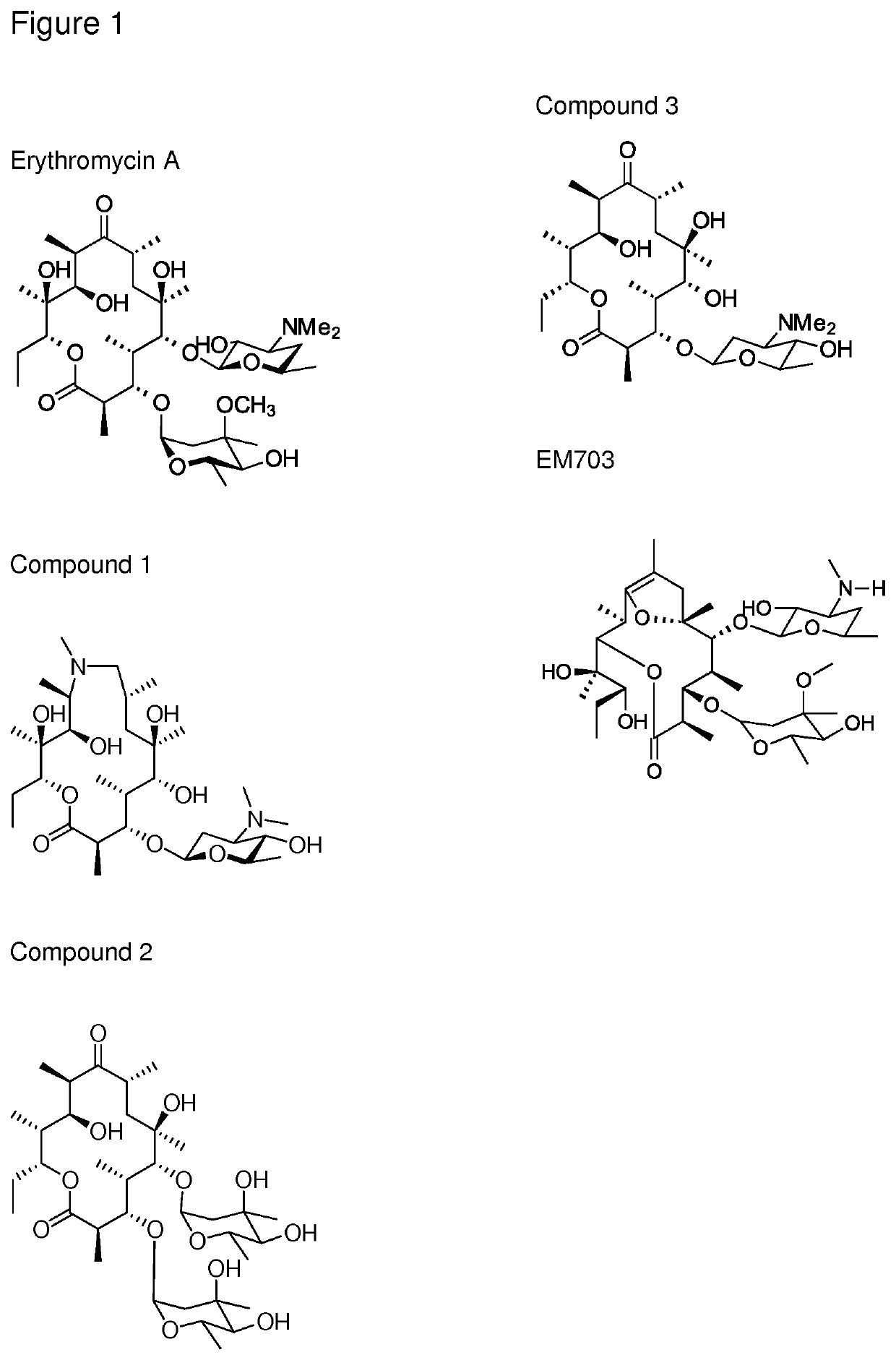
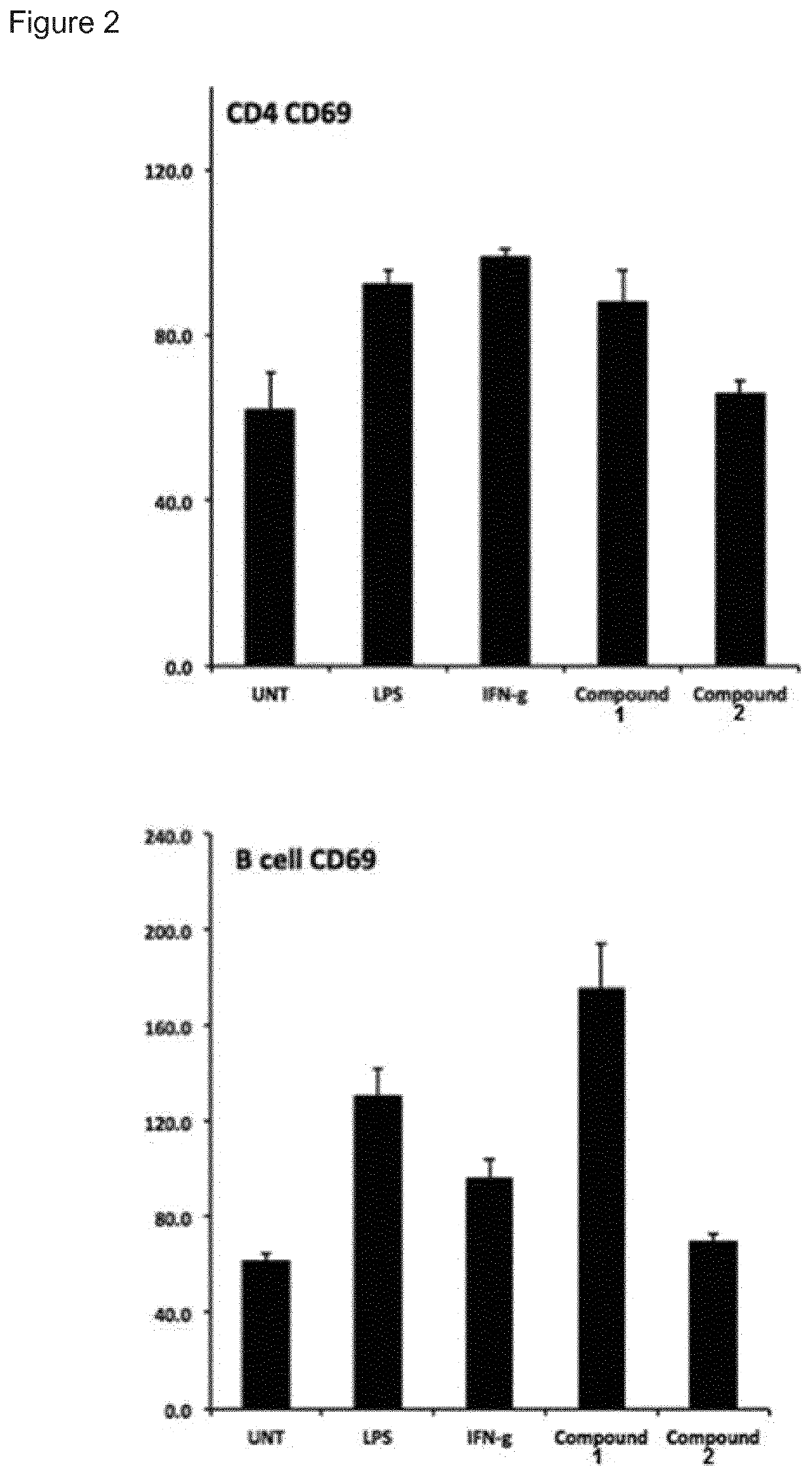
ActiveUS11059845B2Direct effectAvoid developmentBiocideSugar derivativesProtozoaMacrolide resistance
The present invention provides immune stimulating macrolides of formula (I), wherein the substituents are as defined in claim 1. The macrolides have utility in treating intracellular bacterial, fungal, and protozoal infections.
Owner:ISR IMMUNE SYST REGULATION HLDG AB (PUBL)
Novel immune stimulating macrolides
ActiveUS20190389896A1Direct effectAvoid developmentSugar derivativesAntiviralsMacrolide resistanceProtozoal Infection
The present invention provides immune stimulating macrolides of formula (I), wherein the substituents are as defined in claim 1. The macrolides have utility in treating intracellular bacterial, fungal, and protozoal infections.
Owner:ISR IMMUNE SYST REGULATION HLDG AB PUBL
System and method for the detection and treatment of infection by a microbial agent associated with HIV infection
InactiveUS9580758B2Reduce loadReduce oxidative stressSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsBacteroidesMicrobial agent
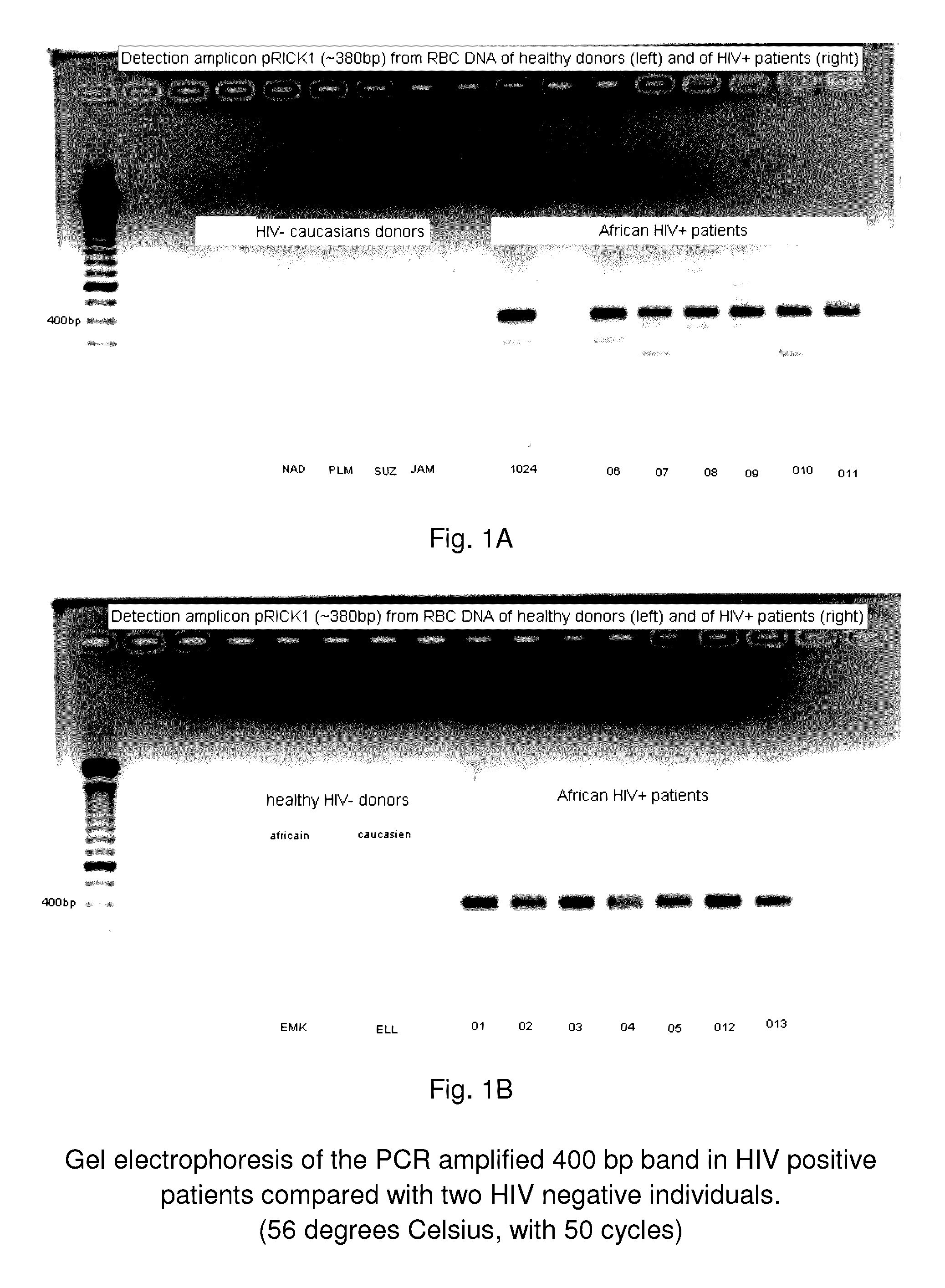
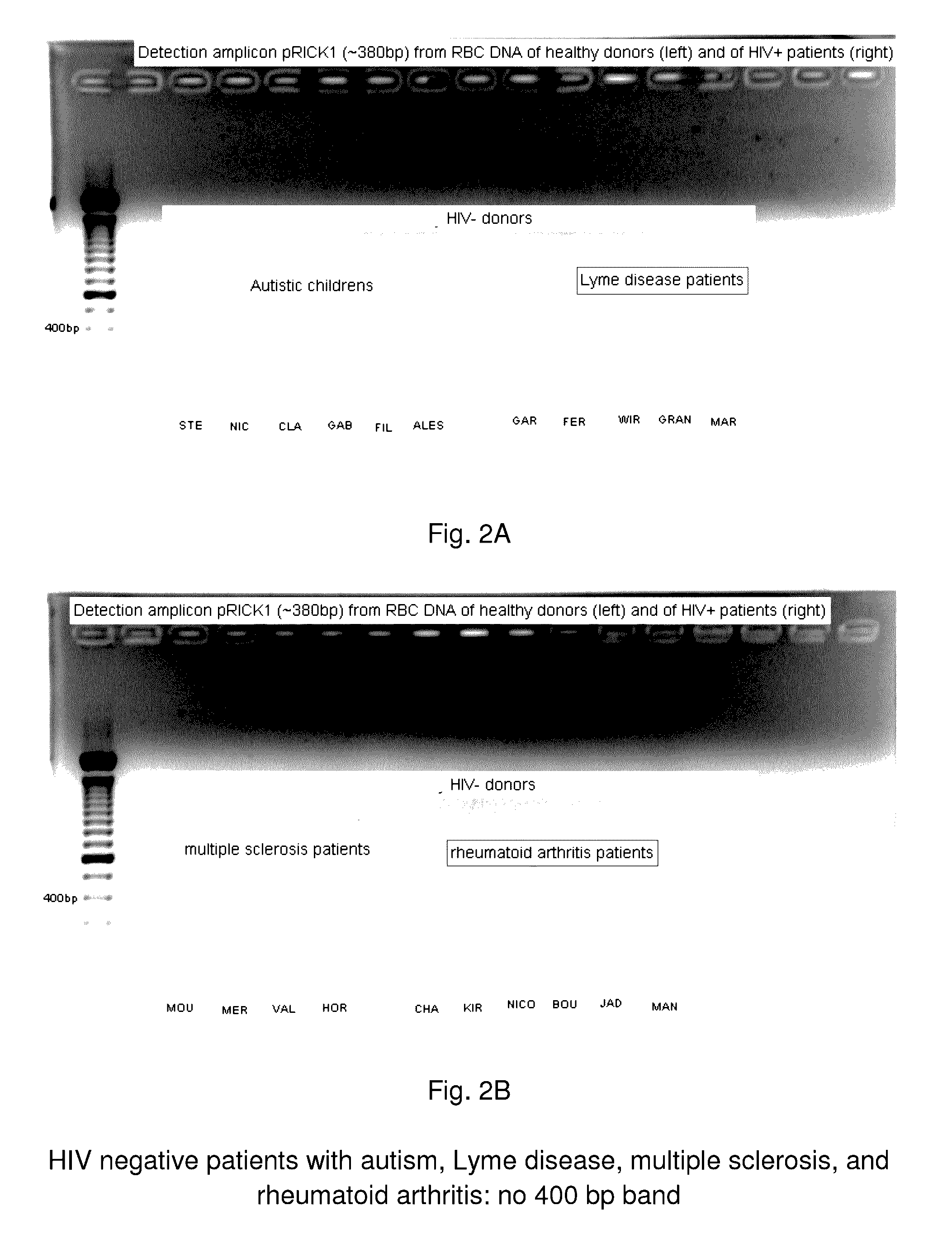
A method of treating a patient, comprising administering at least one antibiotic, e.g., doxycycline and ciprofloxacin, sufficient to substantially treat an intracellular bacterial organism present in at least erythrocytes, e.g., over a course of at least two weeks; and subsequently administering at least one immunostimulant, e.g., which directly or indirectly increases levels of immunostimulatory cytokines in the patient, and at least one antioxidant, e.g., glutathione, to effectively treat a coinfection of the patient with a virus. The intracellular bacterial organism may be a rickettsiales-like organism, and the virus may be HIV.
Owner:MONTAGNIER LUC
Immune stimulating compound
ActiveUS11059846B2Direct effectAvoid developmentAntibacterial agentsBiocideProtozoaMacrocyclic lactone
The present invention provides immune stimulating macrolide of formula (I). The macrolide has utility in treating intracellular bacterial, fungal, and protozoal infections.
Owner:ISR IMMUNE SYST REGULATION HLDG AB (PUBL)
Kit for simultaneously extracting plasma and blood cell pathogenic bacterium DNA and application
InactiveCN113637668AHigh purityComprehensive pathogen detection resultsDNA preparationWhite Blood Cell LysisEnzyme digestion
The invention relates to the technical field of molecular biology, and particularly relates to a kit for simultaneously extracting plasma and blood cell pathogenic bacterium DNA and application. The kit comprises an anticoagulant, red blood cell lysis buffer, white blood cell lysis buffer, RNase A, Proteinase K, bacterial cell lysis buffer and a protein precipitator. Compared with the prior art, the kit has the advantages that plasma and blood cells in a blood sample are separated, DNA of pathogenic bacteria in the blood cells is extracted firstly, then the DNA is combined with the plasma, purification is carried out to obtain all the pathogenic bacterium DNA in the blood sample, and a comprehensive and accurate pathogen detection result is provided for clinic. The kit is suitable for blood of multiple species and whole blood pathogenic bacterium DNA including plasma free DNA and intracellular bacterium DNA; the obtained DNA is high in purity and can be directly used for PCR, enzyme digestion and other experiments, the detection process is simple and rapid, and the DNA of all bacteria in the blood can be obtained within one hour.
Owner:微岩医学科技(北京)有限公司 +1
Separation method of rickettsia intracellular bacteria strain
PendingCN113234595AThe separation method is simpleHigh purityMicroorganism based processesMicroorganism separationBiotechnologyMeglumine diatrizoate
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical microbiology, particularly relates to a separation method of a rickettsia intracellular bacterium strain, and solves the problems that in the prior art, the rickettsia intracellular bacterium strain is difficult to separate, and the separated strain is low in purity and is difficult to culture in cells. The preparation method of the separation method of the rickettsia intracellular bacterium strain comprises the following steps: centrifuging, crushing and centrifuging adherent cells infected by rickettsia to obtain a primary pure strain, adding meglumine diatrizoate for ultracentrifugation to obtain an intra-layer bacterium suspension, and finally centrifuging and fixing the volume to obtain the rickettsia intracellular bacterium strain. The separation method of the rickettsia intracellular bacteria strain is simple and easy to operate, the rickettsia intracellular bacteria are separated from cells, the rickettsia intracellular bacteria strain with high purity is obtained, the method can be used for subsequent research on the pathogenic mechanism and specific clinical manifestation of rickettsia, and the significance is profound.
Owner:李家斌
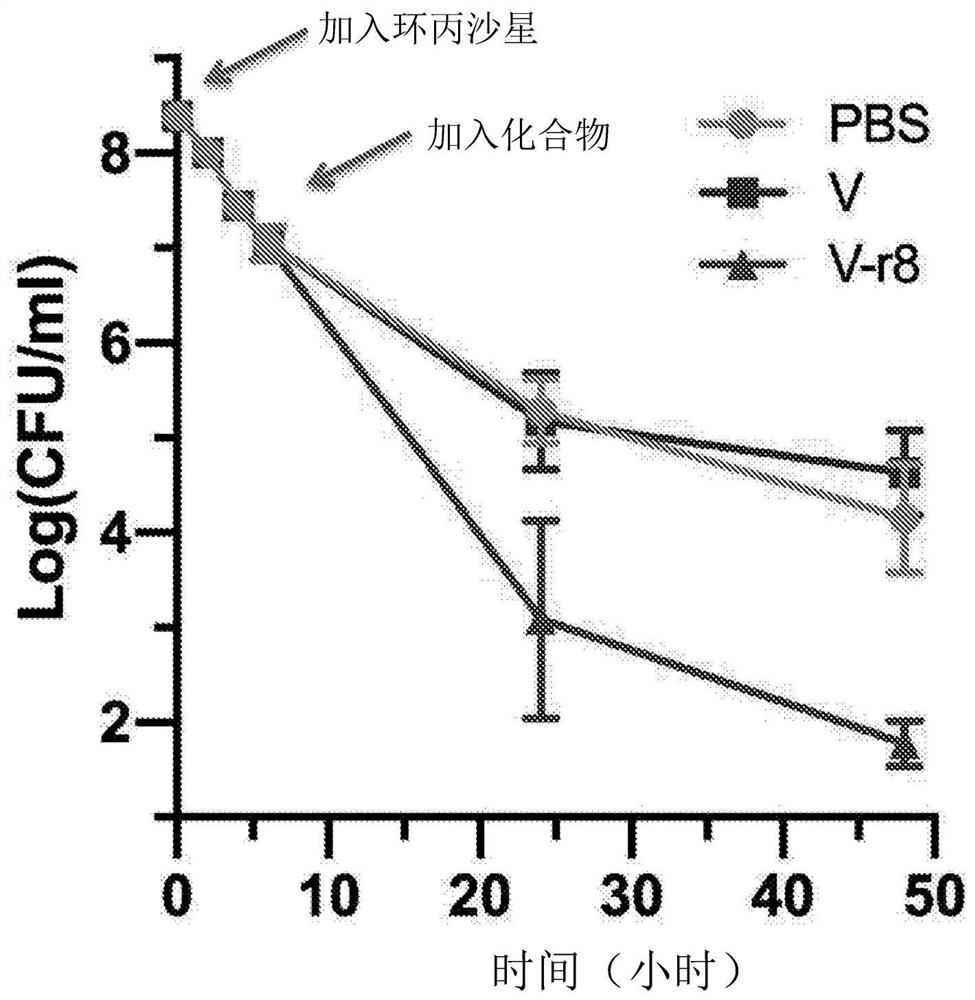
Composition and method for new antimicrobial agents with secondary mode of action
PendingCN111867615AImprove efficacyAntibacterial agentsSaccharide peptide ingredientsMolecular TransportAntibiotic drug
Antibiotic agents conjugated to a guanidinium-rich molecular transporter (GR-MoTr) are provided. The drug conjugates show surprising increases in efficacy compared to the unconjugated drug in difficult-to-treat bacterial infections including biofilms, stationary and persister cells, and multi-drug resistant bacteria, as well as intracellular bacteria.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com