Cell penetrating antibacterial peptide and application thereof
A technology of antimicrobial peptides and cells, which is applied in the direction of application, antibacterial drugs, peptides, etc., can solve the problems of difficult intracellular bacteria to play a role, and achieve the effect of less drug resistance, low cytotoxicity, and broad-spectrum antibacterial activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
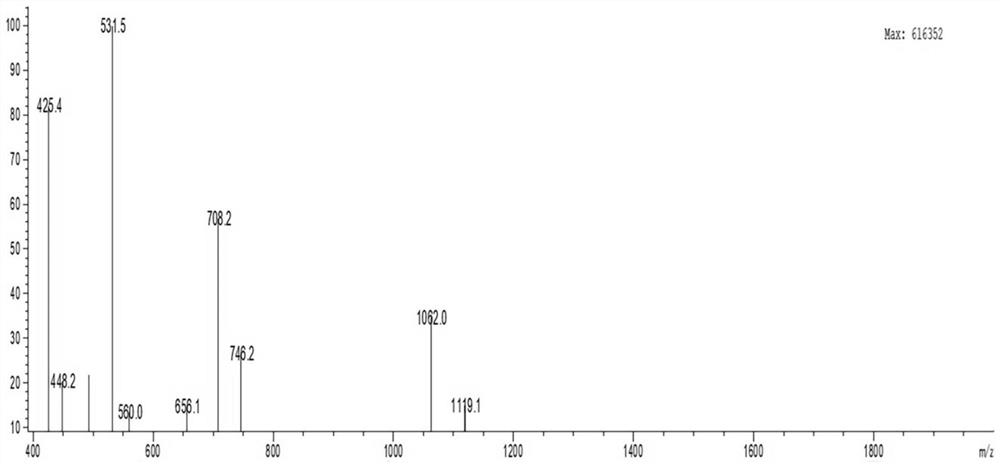
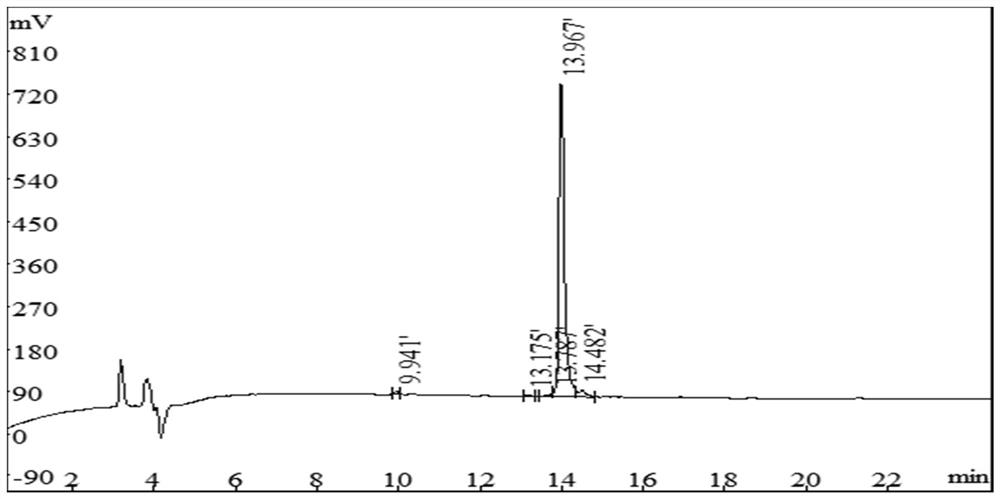
[0046] Embodiment 1 solid phase chemical synthesis method synthetic antimicrobial peptide
[0047] In this example, the antimicrobial peptide was synthesized by solid-phase chemical synthesis. The amino acid sequence of the antimicrobial peptide is shown in SEQ ID NO.3. The specific method is as follows:
[0048] 1. The preparation of antimicrobial peptides is carried out one by one from the C-terminal to the N-terminal, and is completed by a peptide synthesizer. First, Fmoc-X (X is the first amino acid at the C-terminal of each antimicrobial peptide) is inserted into Wang resin, and then the Fmoc group is removed to obtain X-Wang resin; then Fmoc-Y-Trt-OH (9 - Fmoxy-trimethyl-Y deprotection group, Y is the second amino acid at the C-terminus of each antimicrobial peptide); according to this procedure, it is synthesized from the C-terminus to the N-terminus until the synthesis is completed, and the Fmoc Group side chain protected resin;
[0049]2. Add a cleavage reagent to t...
Embodiment 2
[0053] The mensuration of the antibacterial activity of embodiment 2 peptide
[0054] Utilize the microdilution method to measure the antibacterial peptide (P3I7) that embodiment 1 prepares to the minimum inhibitory concentration of bacteria, specifically as follows:
[0055] Add 0.2% fetal bovine serum albumin containing 0.01% acetic acid as a diluent into a 96-well plate, and sequentially prepare a series of gradient antimicrobial peptide solutions using the doubling dilution method, so that the volume of the solution in each well is 50 μL. Then add 50 μL of the bacteria solution to be tested (~10 5 CFU / mL) in each well, the medium is MHB (pH=7.0). Positive controls (containing bacterial fluid but not antimicrobial peptides) and negative controls (neither bacterial fluid nor peptides) were set up. Incubate at a constant temperature of 37°C for 18 hours, then measure the light absorption value at 492nm with a microplate reader, and use the value greater than 0.1 as the judg...
Embodiment 3
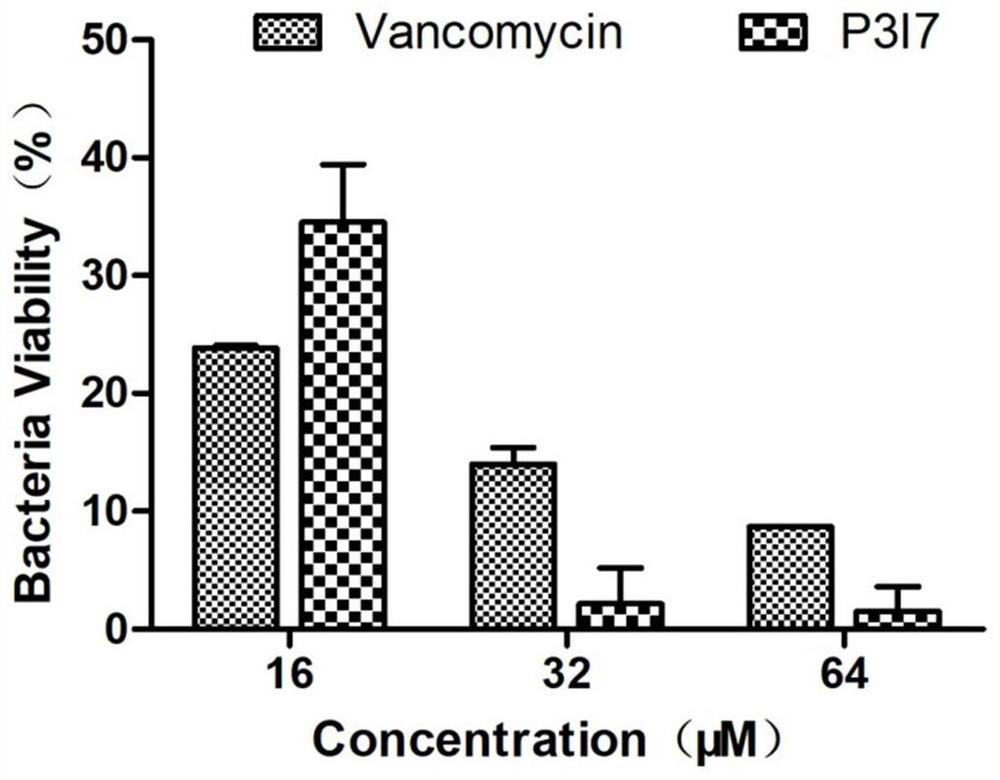
[0059] Intracellular bacteriostatic activity assay of embodiment 3 peptide
[0060] The intracellular bacteriostatic activity of the antimicrobial peptide prepared in Example 1 is determined, specifically as follows:
[0061] The S.aureus 6538 strain was grown in culture medium for 4 hours, centrifuged at 3000×g for 10 minutes, bacterial cells were collected, washed three times with PBS, and resuspended in culture medium without fetal bovine serum. Concentration is 10 5 The macrophages of each cell / well were spread evenly in a 96-well plate, and S.aureus6538 (10 7 CFU / well), co-cultivate at 37°C for 1 hour, aspirate the culture supernatant and wash with PBS, add complete medium containing 100 μg / mL gentamicin at 37°C for 2 hours to kill extracellular bacteria, and wash the cells with PBS . Afterwards, 100 μL of doubly diluted antimicrobial peptides and vancomycin (Vancomycin) were added to treat for 6 hours, and then incubated with 0.1% TritonX-100 for 15 minutes to lyse th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com