Composition and method for new antimicrobial agents with secondary mode of action
A technology of antibiotics and conjugates, applied to medical preparations with non-active ingredients, medical preparations containing active ingredients, antibodies, etc., can solve problems such as inability to deal with drug-resistant pathogens, slow bactericidal action mode, and chronic infection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
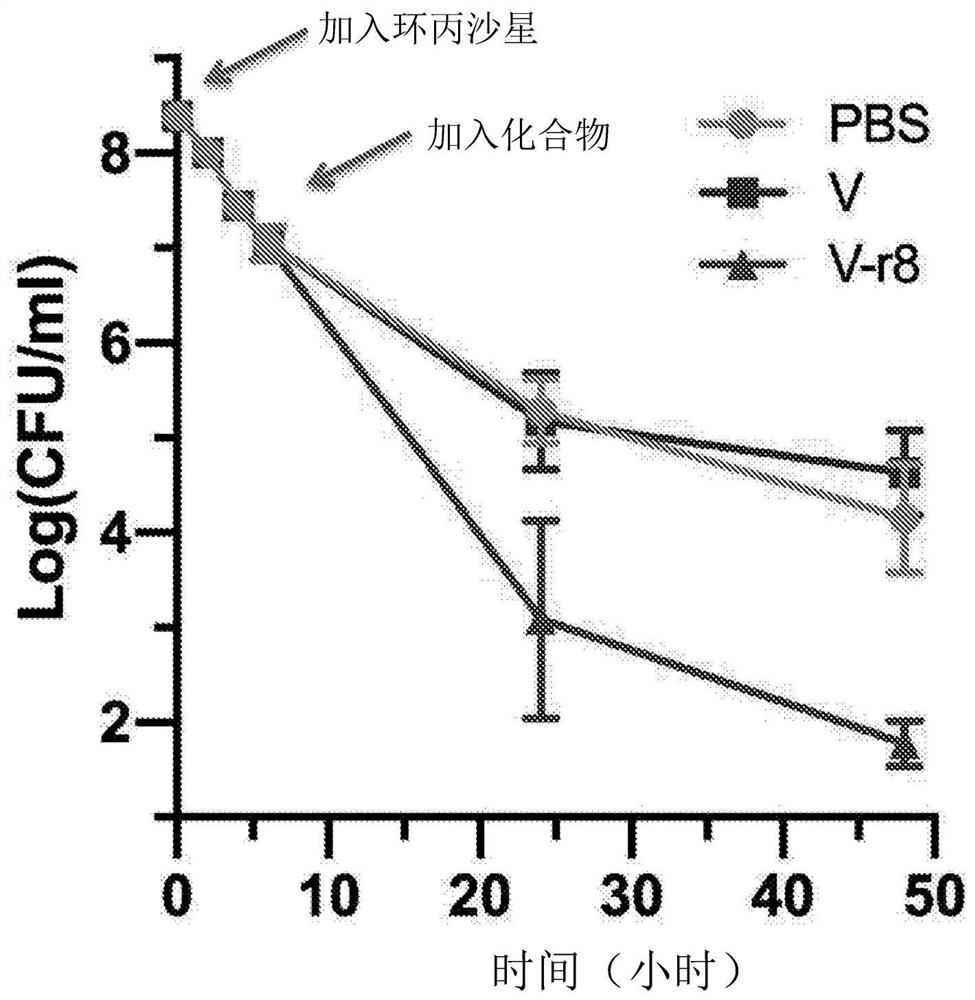
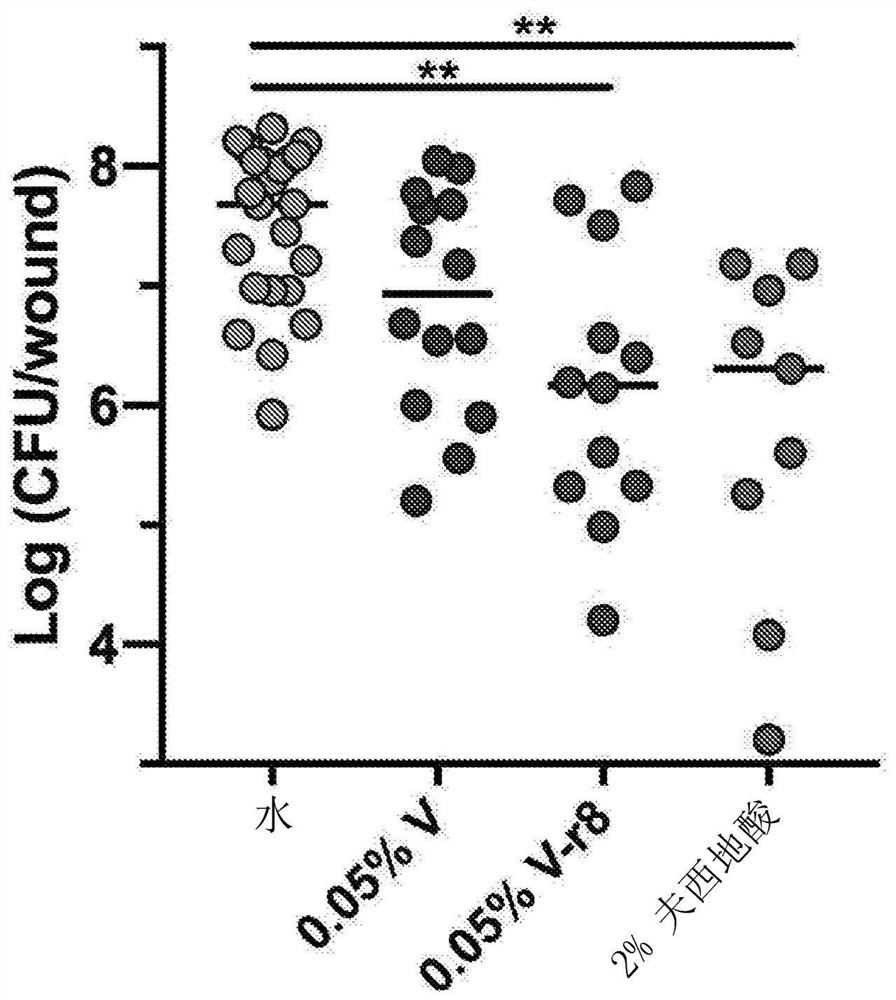
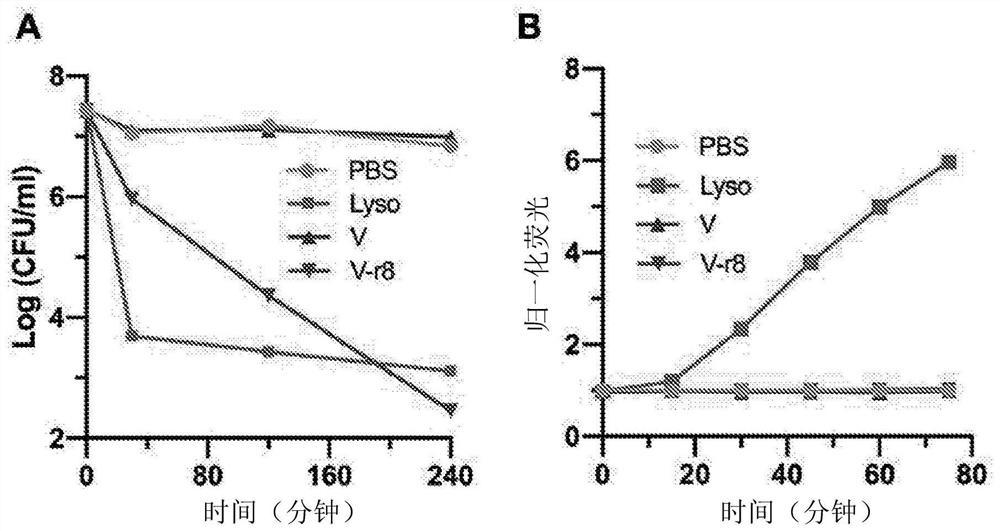
[0175] Activity on Gram-negative cells
[0176] In Pseudomonas aeruginosa, H. pylori, and Acinetobacter baumannii, neither V-r8 nor vancomycin (V) was effective at therapeutically relevant concentrations (Table 5, data not shown for the latter two strains, but MIC >32 μM). Interestingly, V-r8 exhibited antimicrobial activity against Vibrio cholerae, a pathogenic Gram-negative strain that causes cholera disease, and moderately in a pathogenic E. coli strain that causes urinary tract infections active. However, in E. coli strains, the MIC of V-r8 correlated strongly with that of pure r8 as well as a 1:1 noncovalent mixture of V and r8, suggesting that the activity of V-r8 is due to the r8 moiety of V-r8 caused by. The activity of V-r8 in V. cholerae was far superior to that of pure r8 or vancomycin (even non-covalent V+r8), suggesting that covalent association of the two molecules could enhance activity. Thus, V-r8 appears to have selective antimicrobial activity against V. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com