Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
211 results about "Hydrogen absorbing alloy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
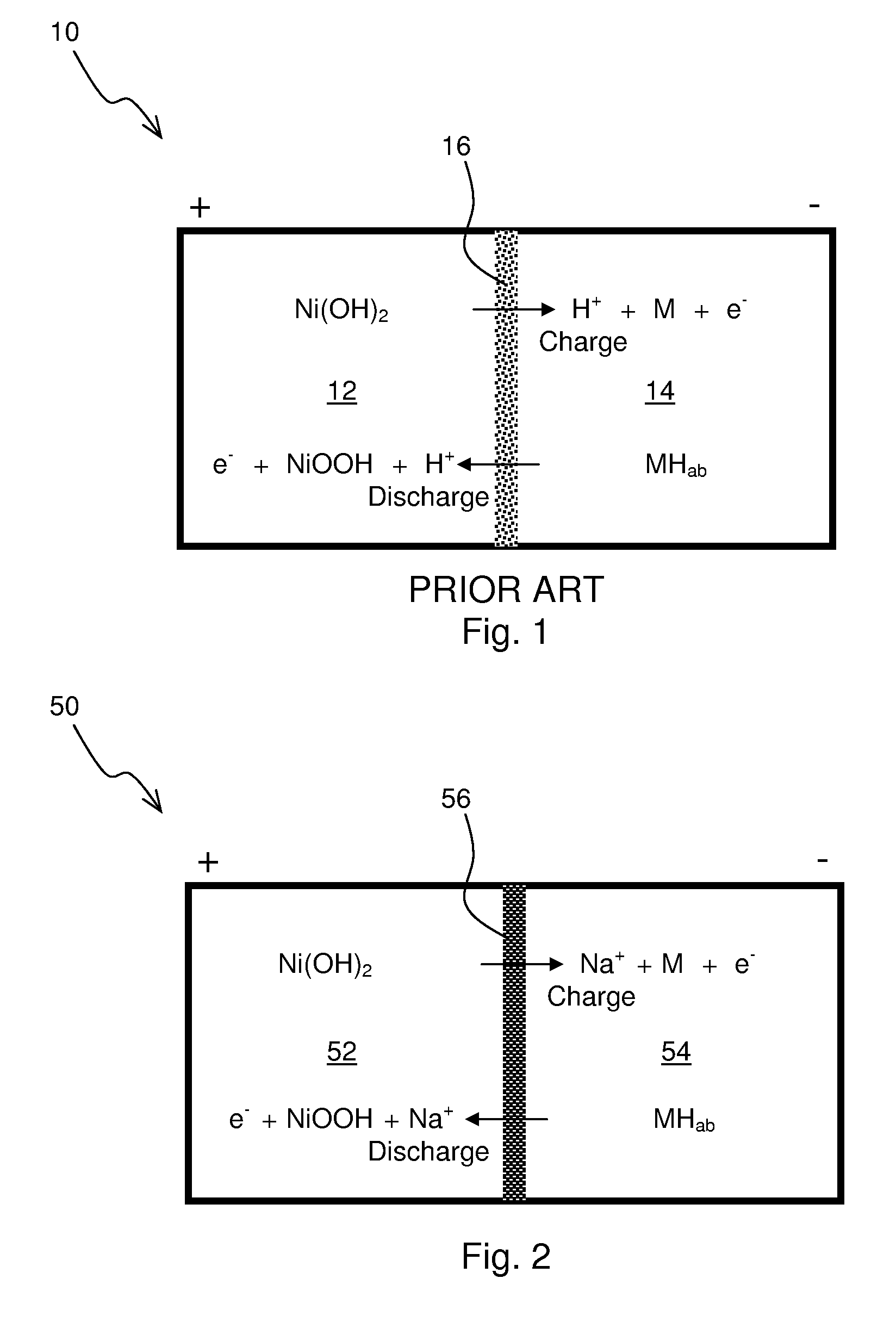
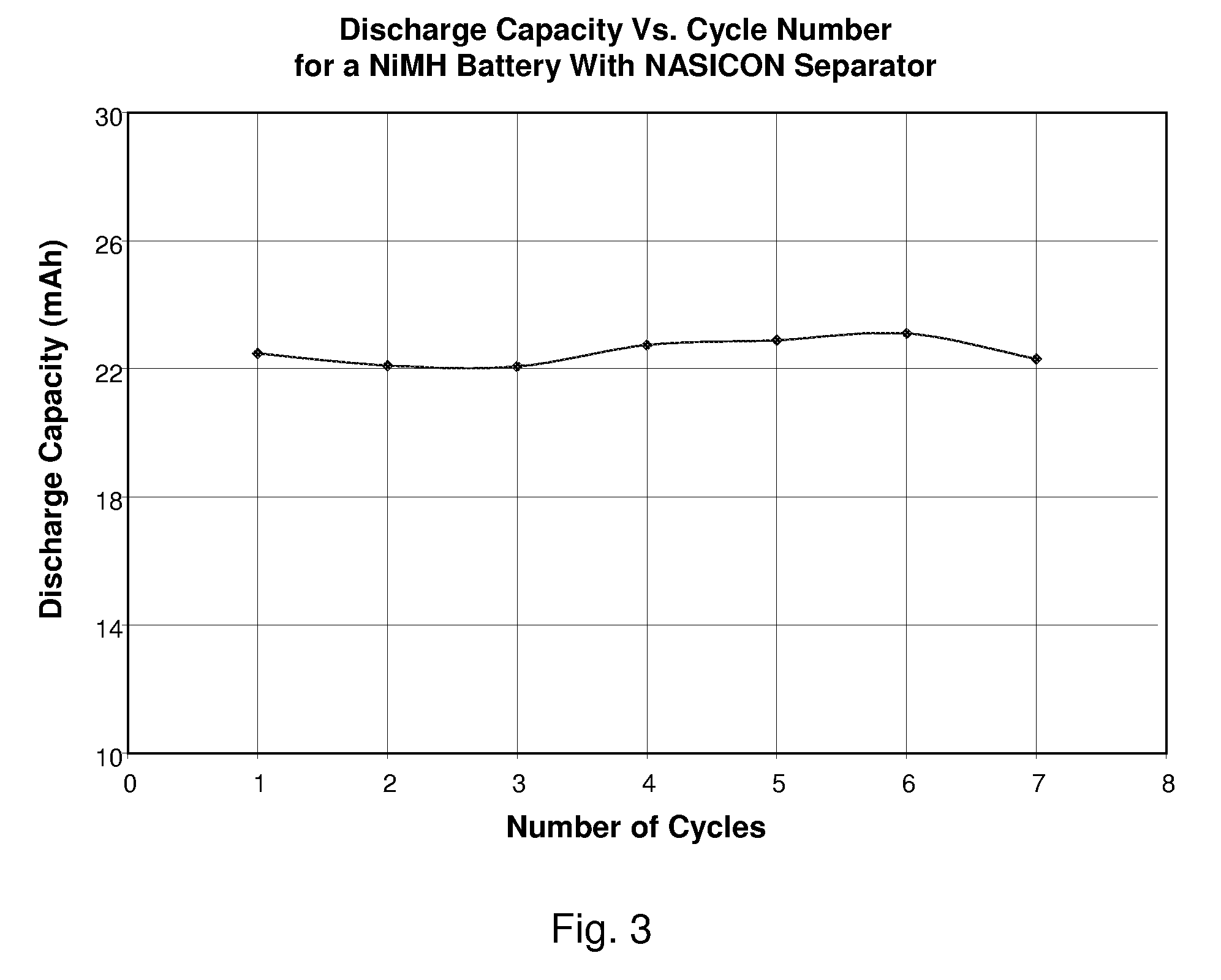
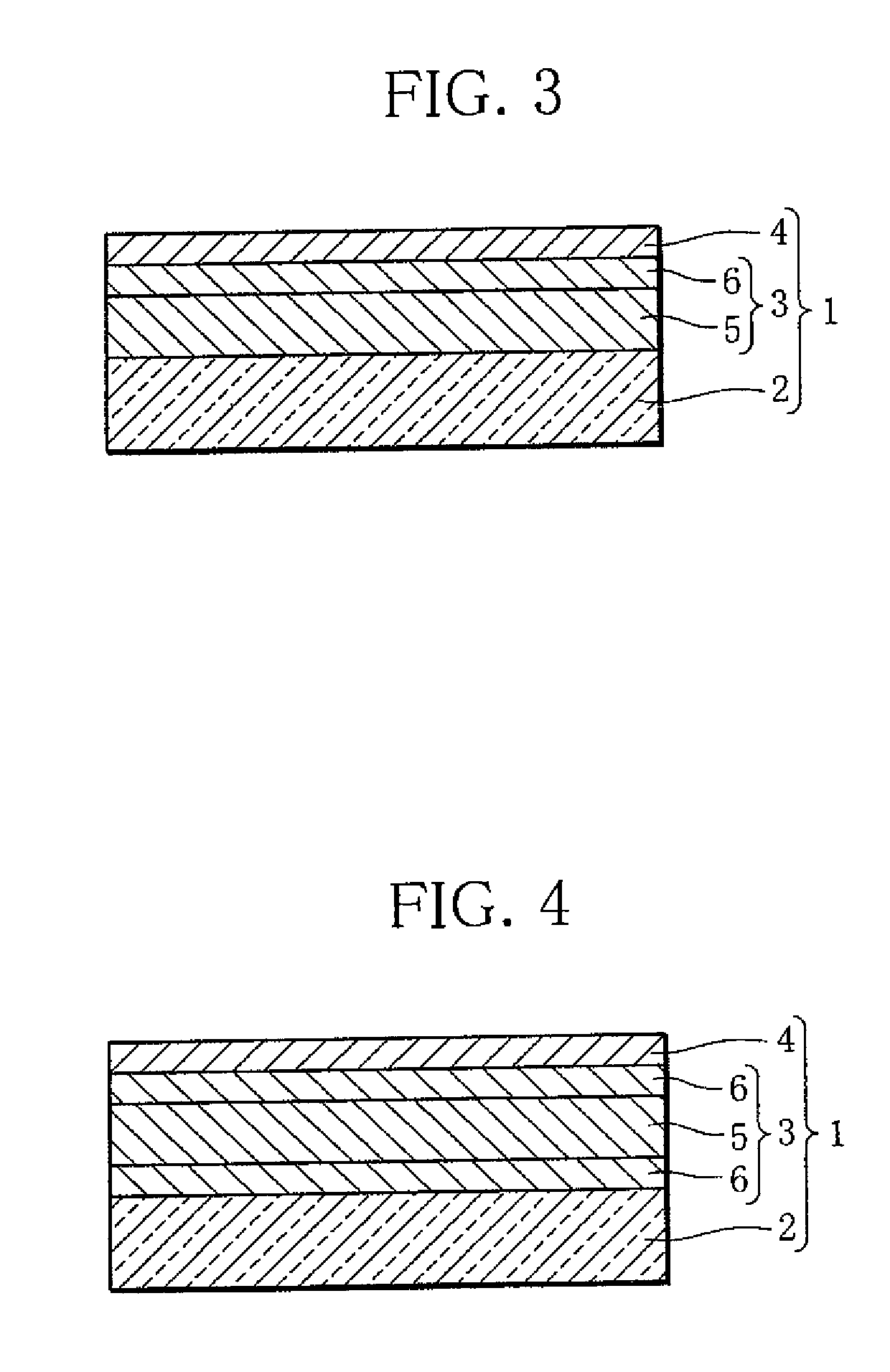
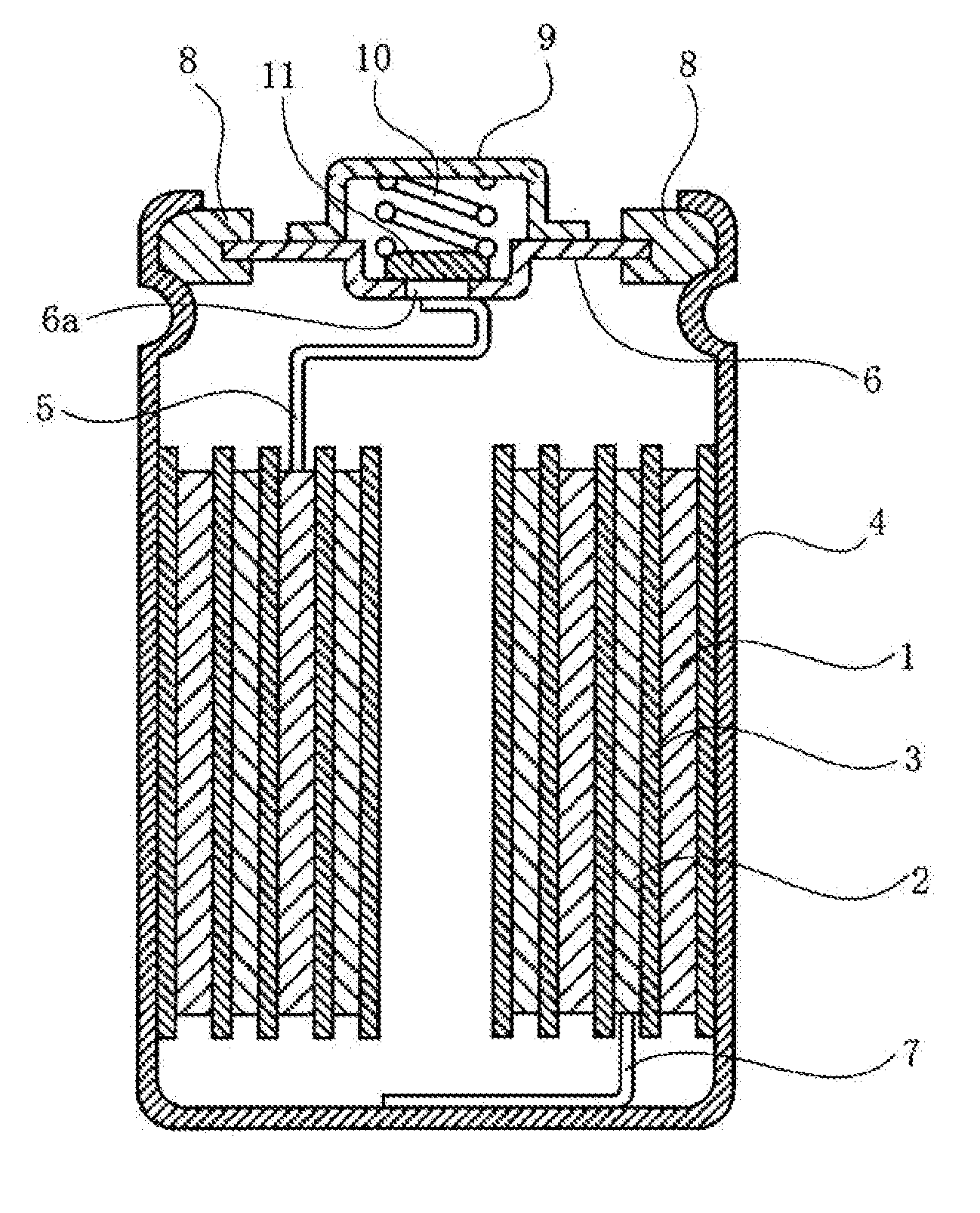
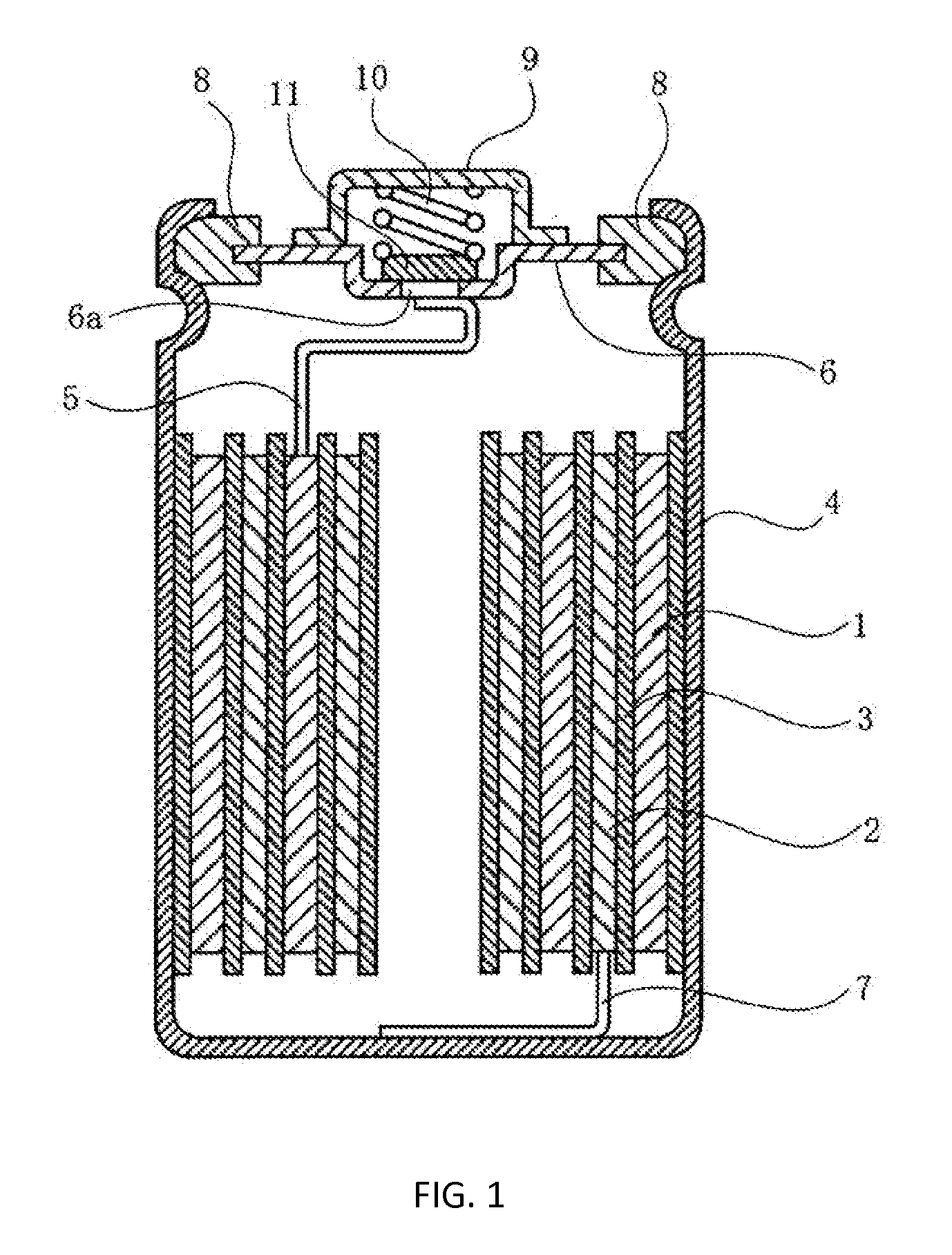
Nickel-Metal Hydride Battery Using Alkali Ion Conducting Separator
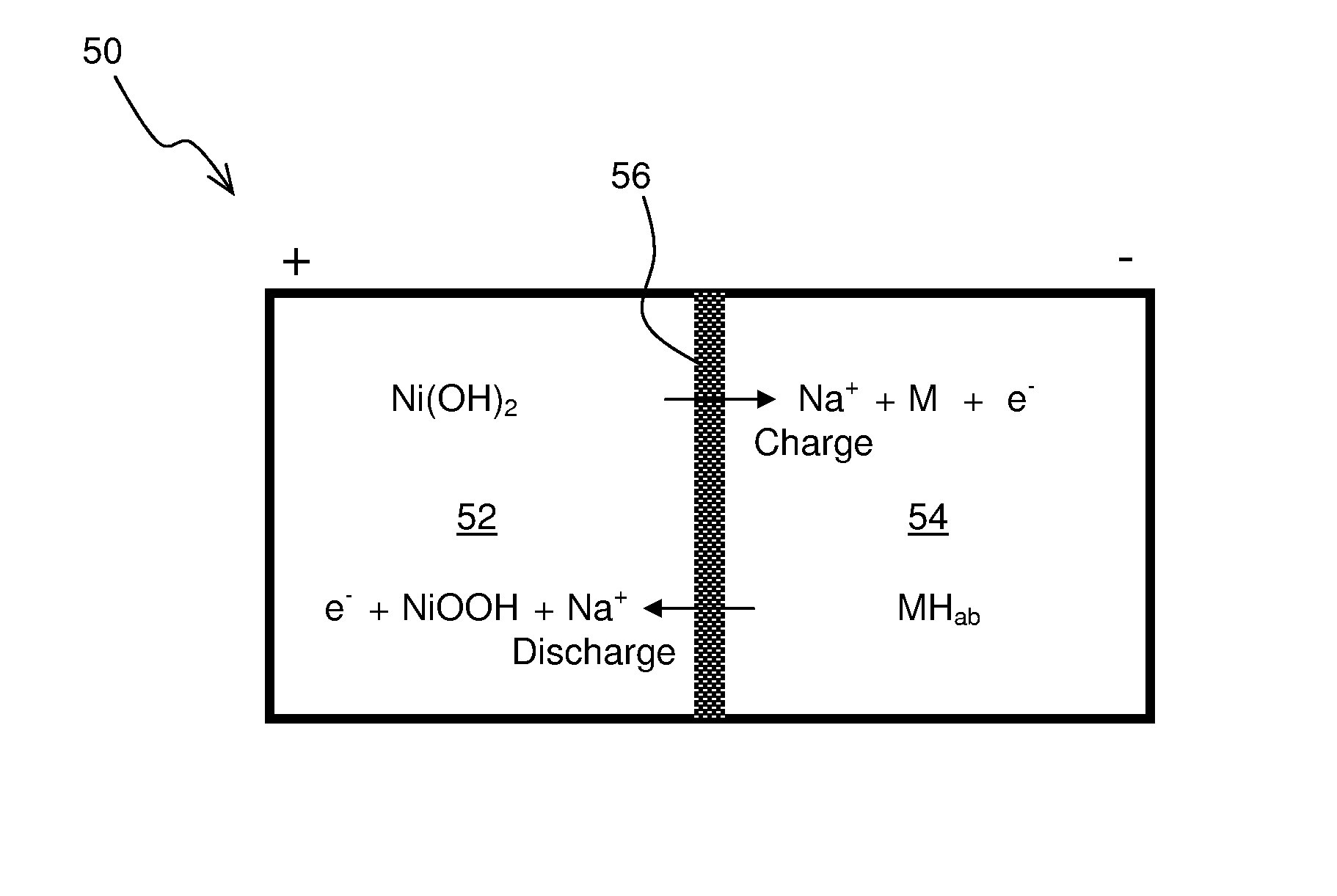
ActiveUS20090134842A1Eliminates capacity lossEliminates self dischargeBatteries circuit arrangementsAlkaline accumulatorsAlkali ionsNickel oxide hydroxide
A nickel-metal hydride storage battery comprising a positive electrode containing nickel hydroxide, a negative electrode containing a hydrogen absorbing alloy, an alkaline electrolyte, and an alkali conducting separator provided between the positive electrode and the negative electrode. The alkali conducting separator may be a solid alkali metal ion super ion conducting material, wherein the alkali metal is Na, K, or Li
Owner:FIELD UPGRADING USA INC
Hydrogen absorbing alloy for alkaline storage battery
ActiveUS20040134569A1Improve cycle lifeReduce capacityElectrode thermal treatmentAlkaline accumulator electrodesRare-earth elementHydrogen absorbing alloy
A hydrogen absorbing alloy represented by the formula Ln1-xMgxNiy-aAla (where Ln is at least one element selected from rare earth elements, 0.05<=x<0.20, 2.8<=y<=3.9 and 0.10<=a<=0.25) which is used for an alkaline storage battery.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Hydrogen storage material and hydrogen storage apparatus
InactiveUS7094276B2Increase volumeEfficiently adsorb hydrogen moleculesMaterial nanotechnologyHydrogenPorous carbonChemistry
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC
Nickel-metal hydride battery using alkali ion conducting separator
ActiveUS8012621B2Reduce capacityEliminate dischargeFinal product manufactureAlkaline accumulator electrodesAlkali ionsElectrolyte
A nickel-metal hydride storage battery comprising a positive electrode containing nickel hydroxide, a negative electrode containing a hydrogen absorbing alloy, an alkaline electrolyte, and an alkali conducting separator provided between the positive electrode and the negative electrode. The alkali conducting separator may be a solid alkali metal ion super ion conducting material, wherein the alkali metal is Na, K, or Li.
Owner:FIELD UPGRADING USA INC
Hydrogen absorbing alloy electrode, electrode producing method and alkali storage battery
InactiveUS6660431B1Alkaline accumulator electrodesSecondary cell gas removalCrystal structureLarge capacity
The present invention relates to a hydrogen storage alloy electrode composed of a hydrogen storage alloy having a CaCu5 region and a Ce2Ni7 region in the crystal structure and satisfies the relational formula: p:q=1:(4+a), where p is the sum of the mole fraction of an element occupying the Ca site of the CaCu5 region and the mole fraction of an element occupying the Ce site of the Ce2Ni7 region, q is the sum of the mole fraction of an element occupying the Cu site of the CaCu5 region and the mole fraction of an element occupying the Ni site of the Ce2Ni7 region, and -0.2<=a<=0.4. Accordingly, although the hydrogen storage alloy electrode contains a little or no Co, it is possible to obtain an electrode having little deterioration due to pulverization of the alloy and a high capacity.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Solid filling tank
InactiveUS20050051294A1Reduced heat exchange capacityAvoid problemsReversible hydrogen uptakeHeat storage plantsHeat exchangerHeat transfer
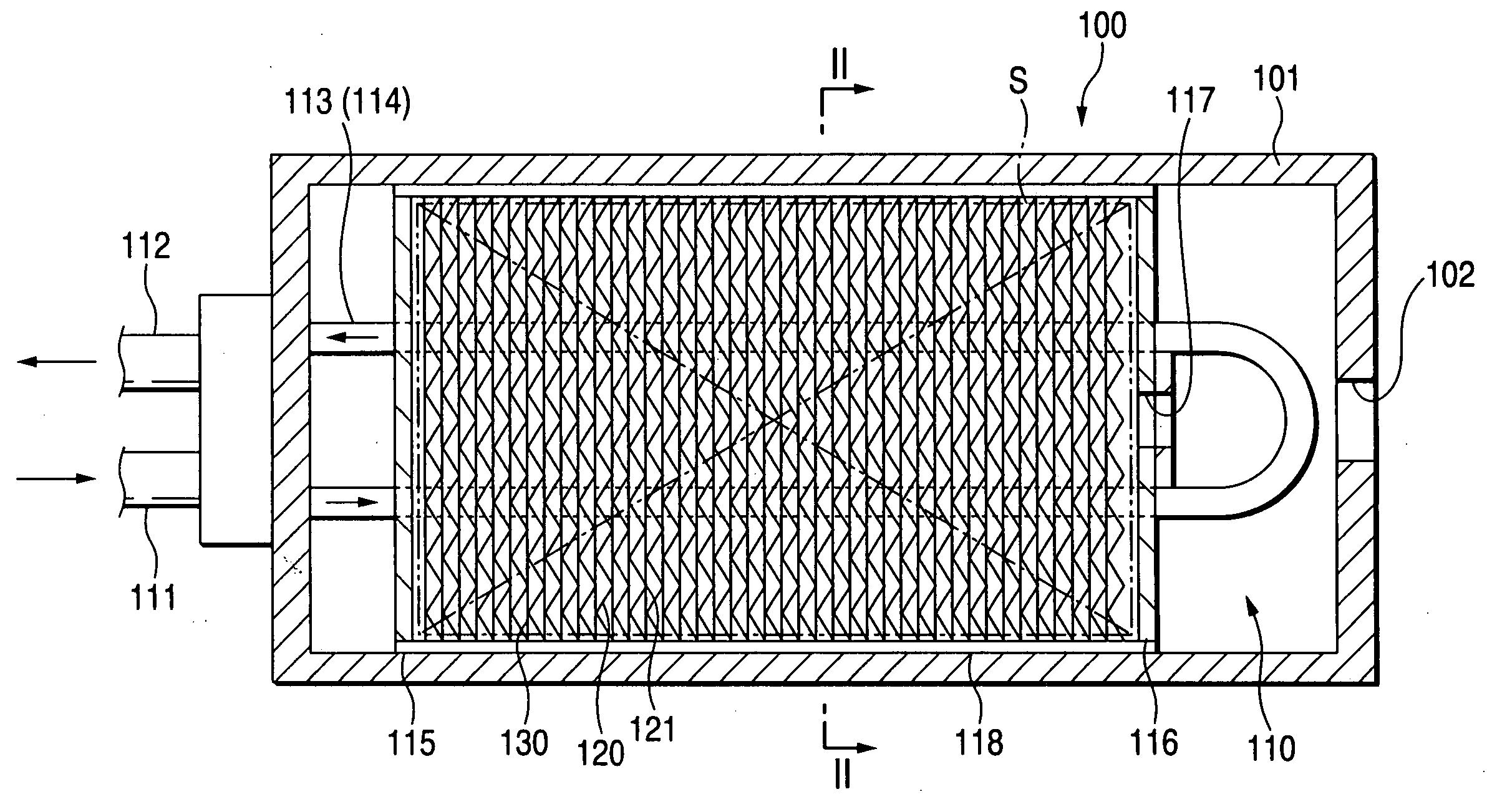
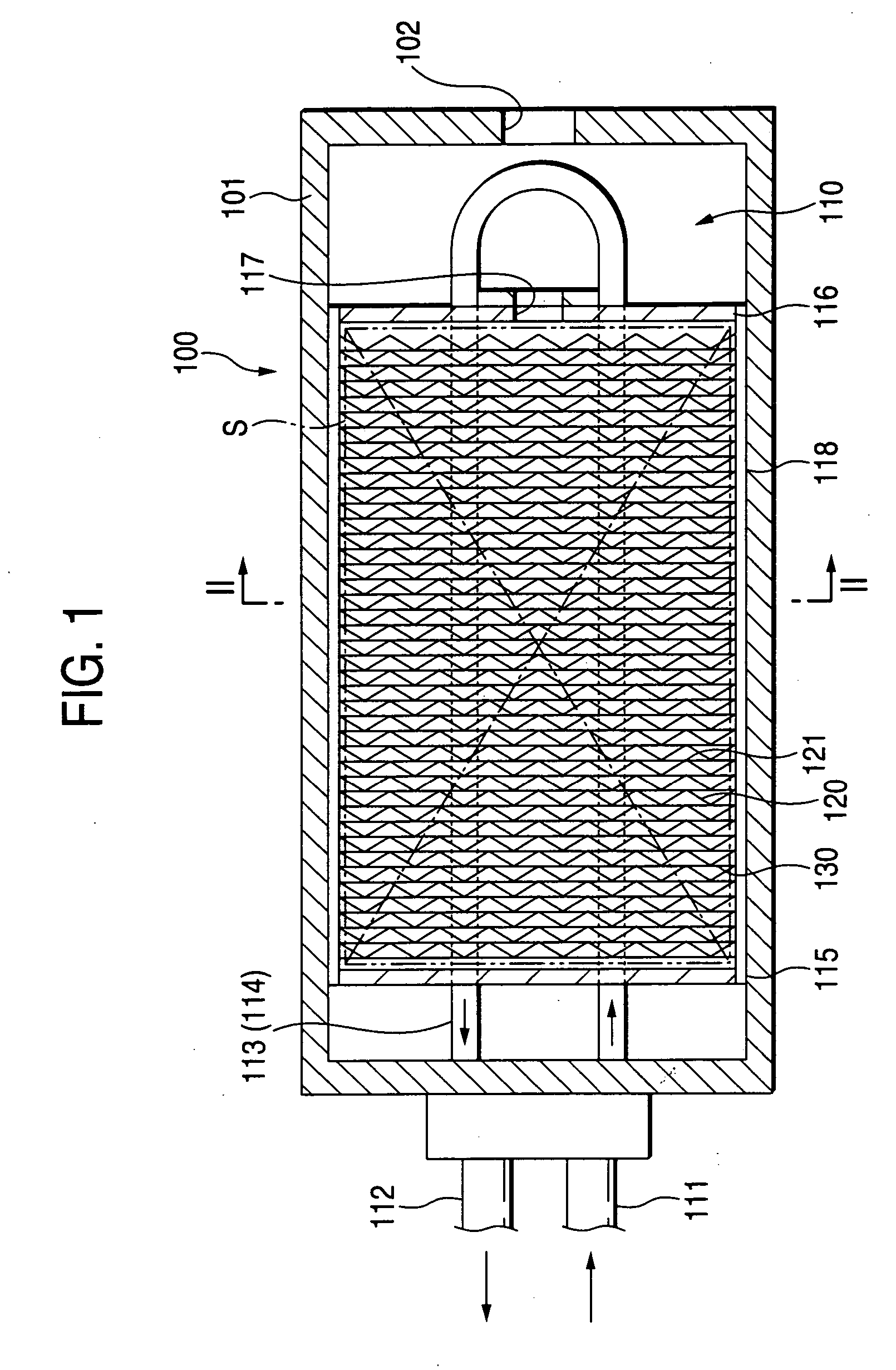
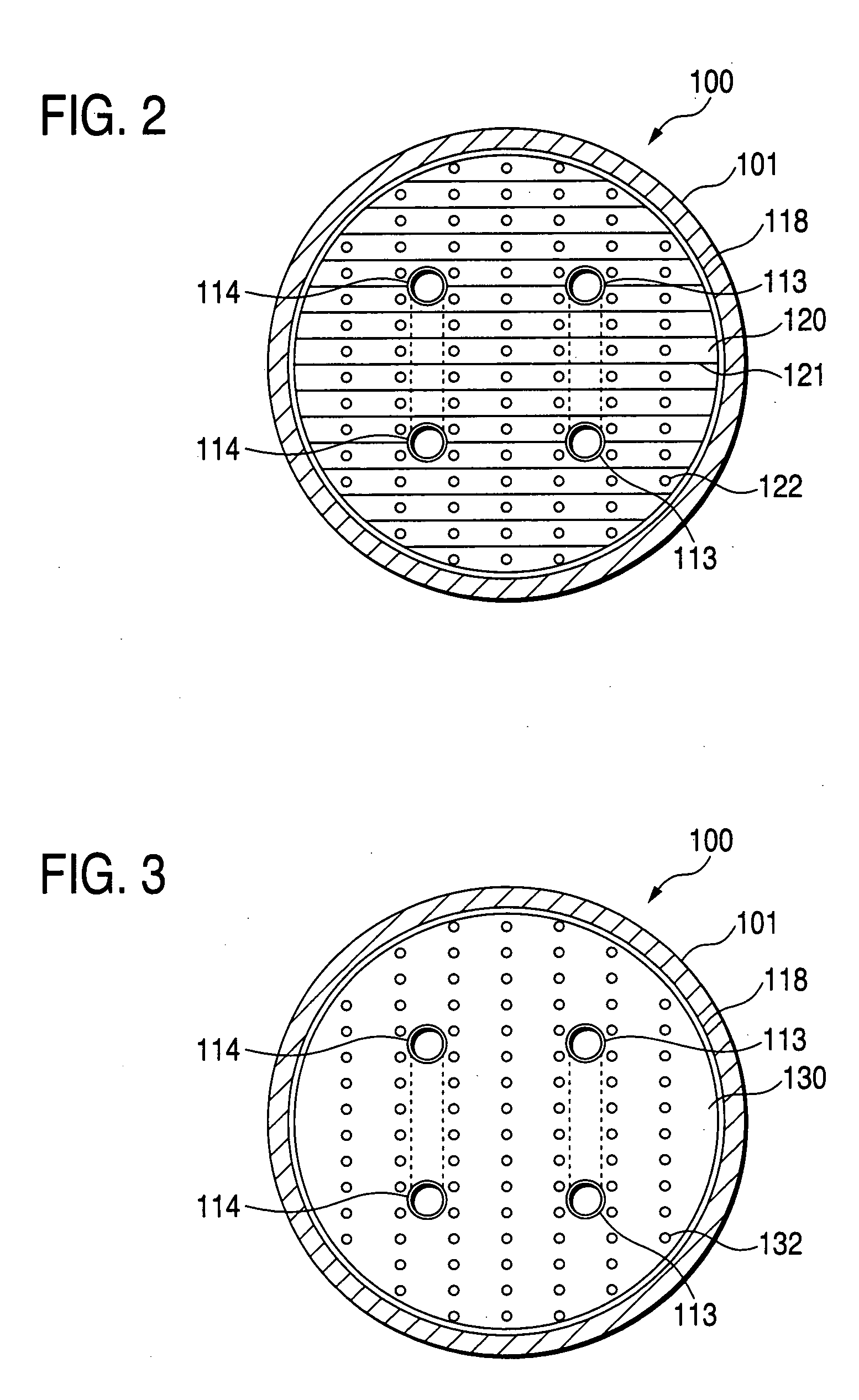
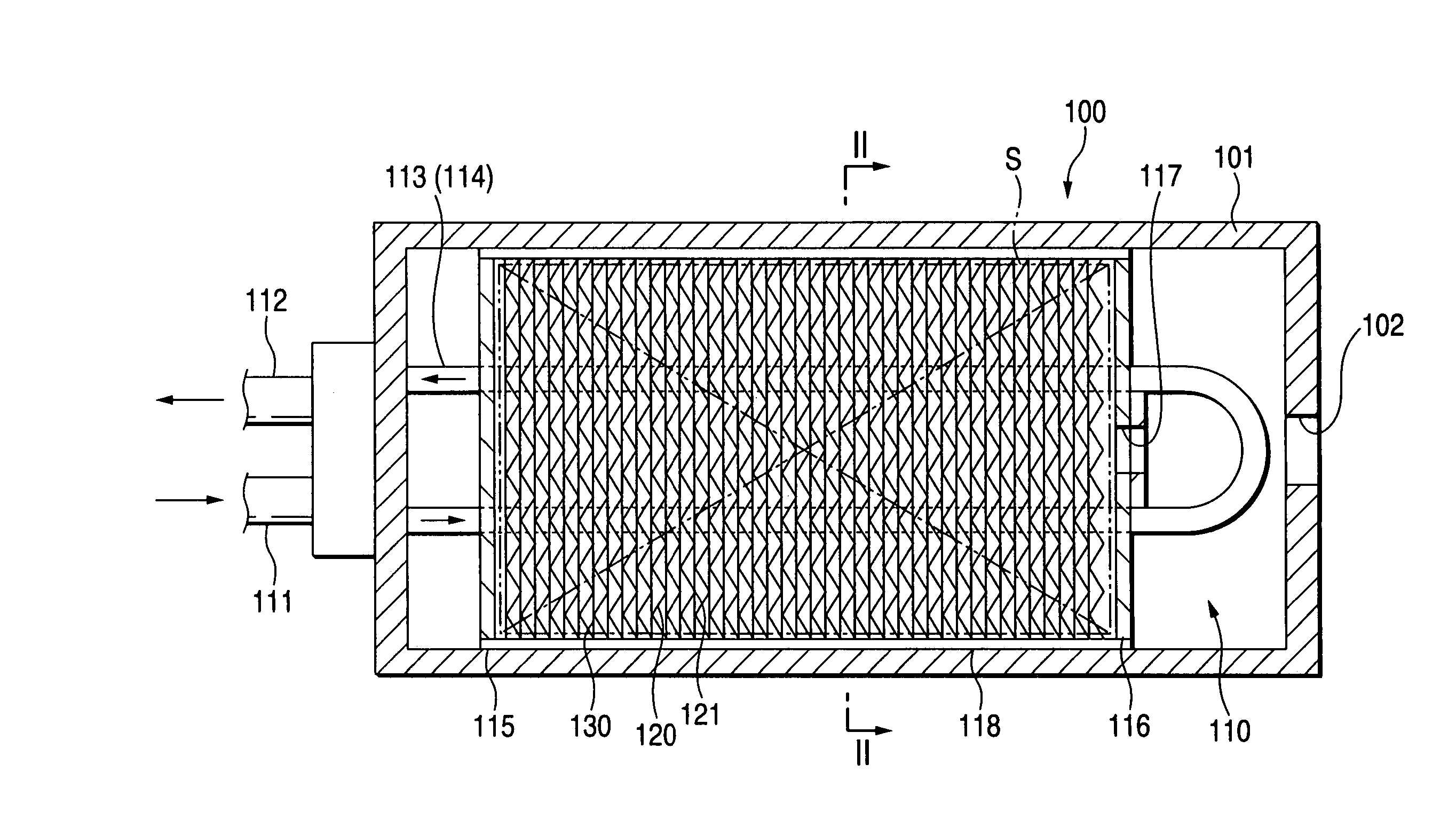
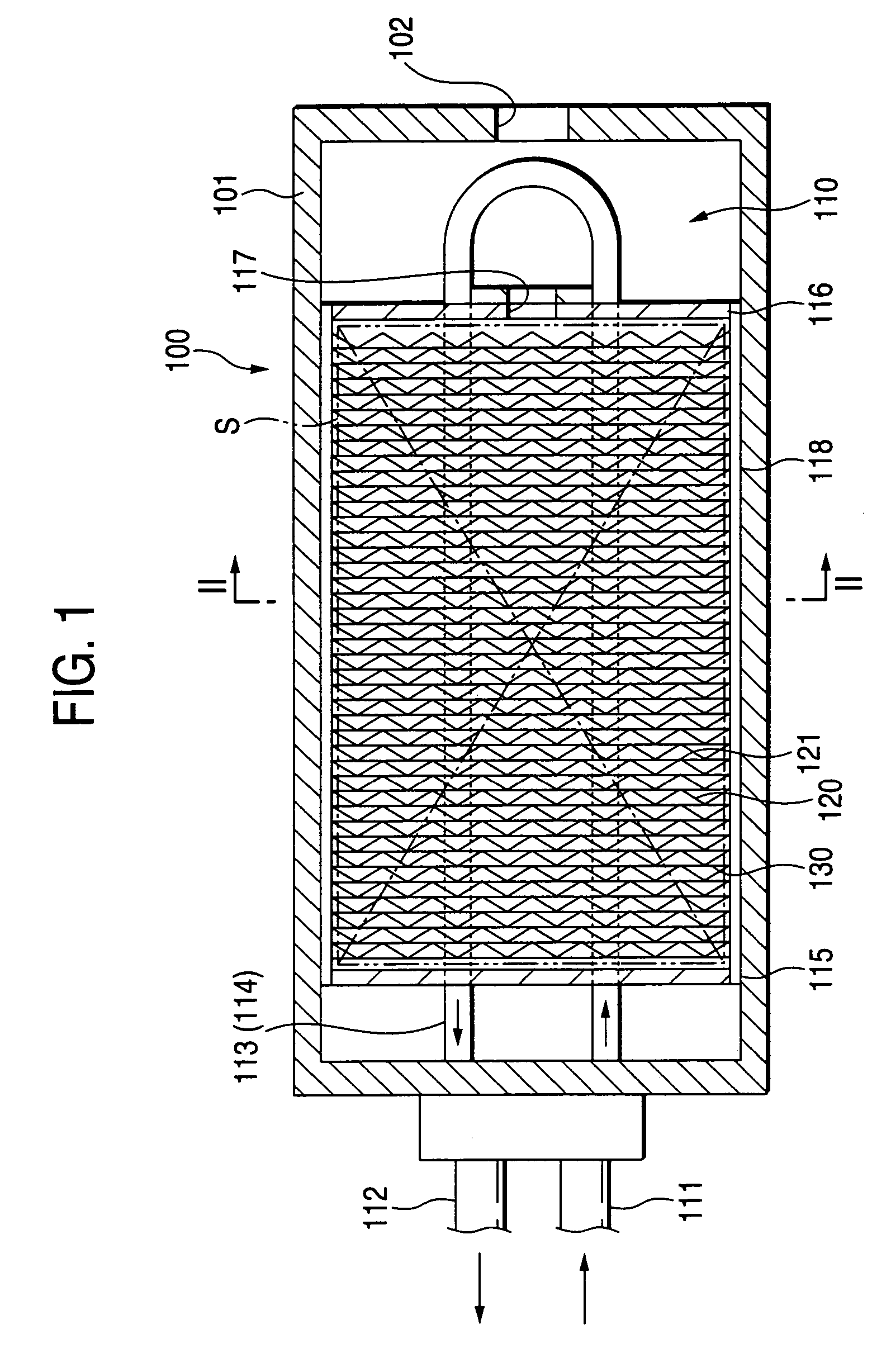
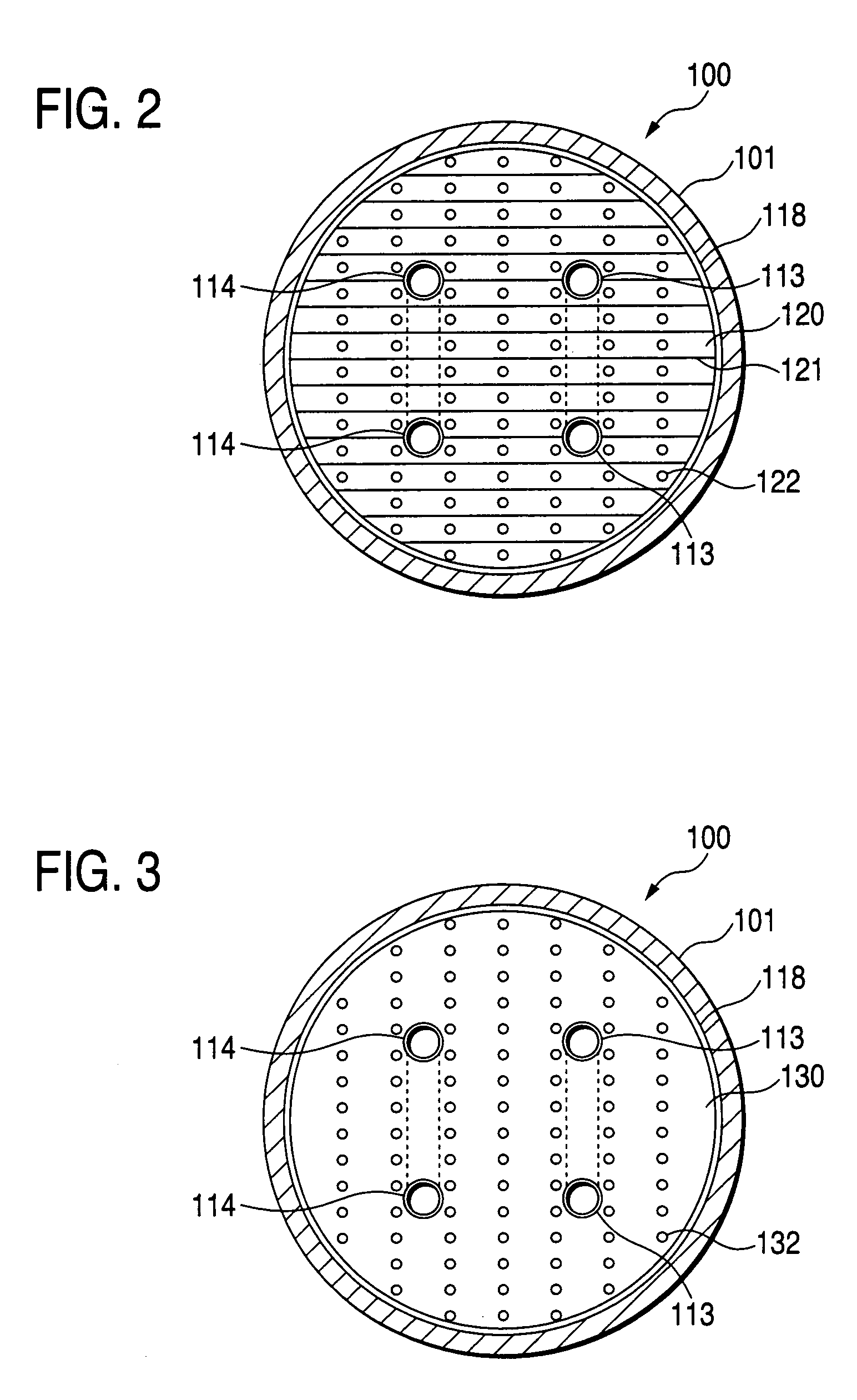
In a hydrogen storing tank (solid filling tank) in which a hydrogen absorbing alloy (solid) is filled, a heat exchanger for executing heat exchange with the hydrogen absorbing alloy is constructed by laminating alternately a first heat-transferring fins formed in corrugated plate shape and a second heat-transferring fins formed in flat plate shape. Partitioned portions that are partitioned by the first heat-transferring fins and the second heat-transferring fins restrict movement of hydrogen absorbing alloy powders (MH powders) in a subsiding direction. Therefore, movement of the MH powders can surely be prevented by not using members that has no concern with the heat exchange and reduces an amount of filled MH powders and a volume in which the heat exchanger is provided.
Owner:TOYOTA IND CORP +1
Air-hydrogen cell
InactiveUS20030143457A1Increase profitExcellent cycle characteristicsElectrode manufacturing processesFuel and secondary cellsHigh energyIon-exchange membranes
An air-hydrogen battery with high energy density and satisfactory cycle characteristics is provided. The air-hydrogen battery includes: a positive electrode made of an air electrode; a negative electrode provided with a hydrogen-absorbing alloy; and a cation-exchange film or an anion-exchange film formed as an electrolyte between the positive electrode and the negative electrode, wherein a periphery of the hydrogen-absorbing alloy of the negative electrode is covered with an anion-exchange resin, whereby the contact area between the anion-exchange resin that functions as an electrolyte and the hydrogen-absorbing alloy is increased, and the utilization factor and resistance to corrosion of the hydrogen-absorbing alloy are enhanced.
Owner:HITACHI MAXELL ENERGY LTD
Hydrogen-absorbing alloy
InactiveUS6258184B1Excellent hydrogen absorptionExcellent desorption characteristicHydrogenCell electrodesFine structureLattice constant
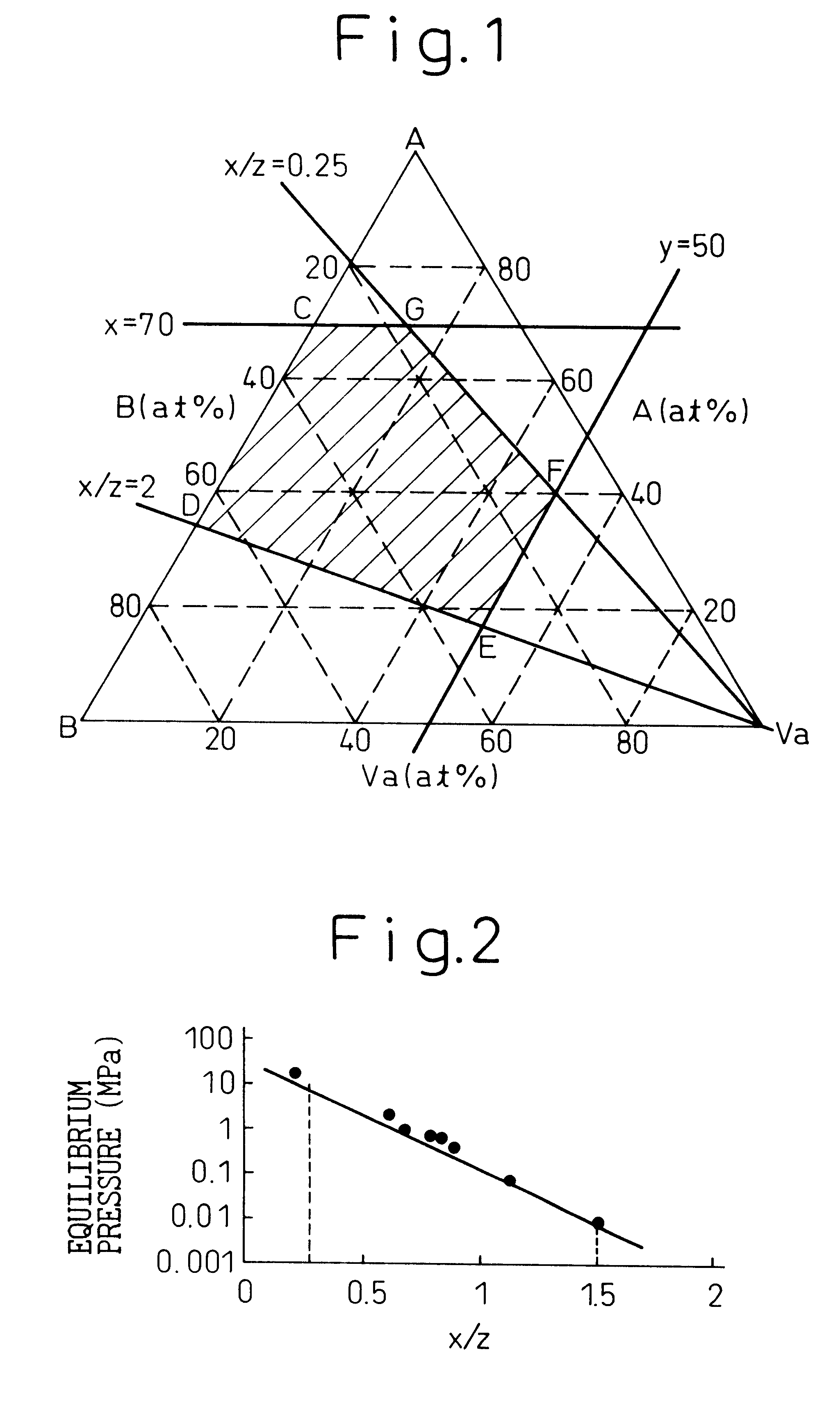
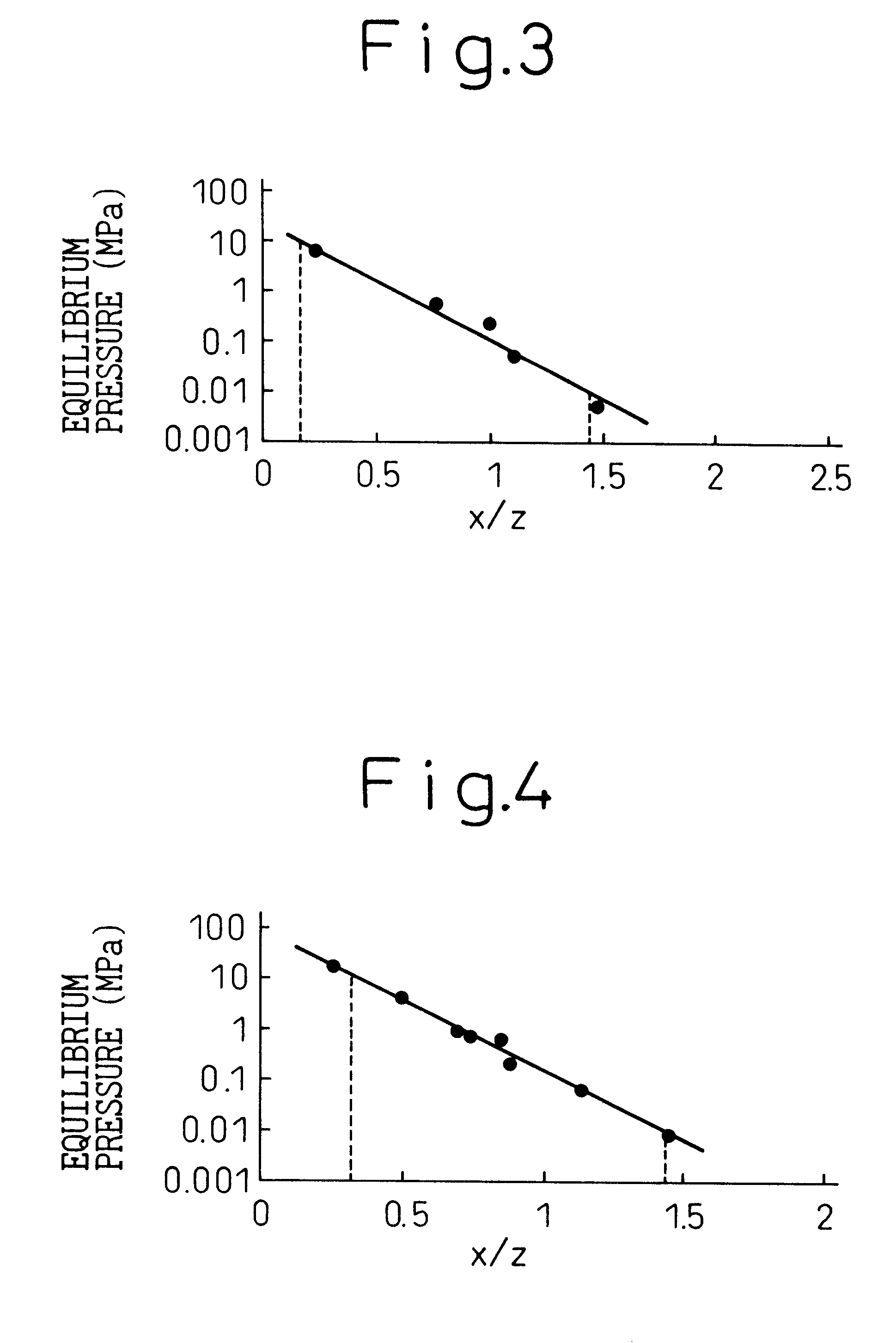
A BCC type hydrogen-absorbing alloy, which uses a ferroalloy, is advantageous from the aspect of the production cost and exhibits excellent hydrogen absorption and desorption characteristics due to a fine structure constituted by spinodal decomposition even when the iron component is increased. The hydrogen-absorbing alloy is expressed by the general formula AxVayBz, where A is at least one of Ti and Zr, Va is at least one member of the Group Va elements of the Periodic Table consisting of V, Nb and Ta, and B contains at least Fe and is at least one member selected from the group consisting of Cr, Mn, Co, Ni, Cu, Al, Mo and W, each of x, y and z satisfies the relation, in terms of of the atomic number ratio, 0<=x<=70, 0<=y<=50, x+y+z=100, and x / z=0.25 to 2.0, the phase of the body-centered cubic structure is at least 50% in terms of the phase fraction and its lattice constant is at least 0.2950 nm but not greater than 0.3100 nm.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Hydrogen storage container and mixture therein
InactiveUS20060081483A1Increase surface areaLong movementGas treatmentDispersed particle separationNetwork structureMetal fibers
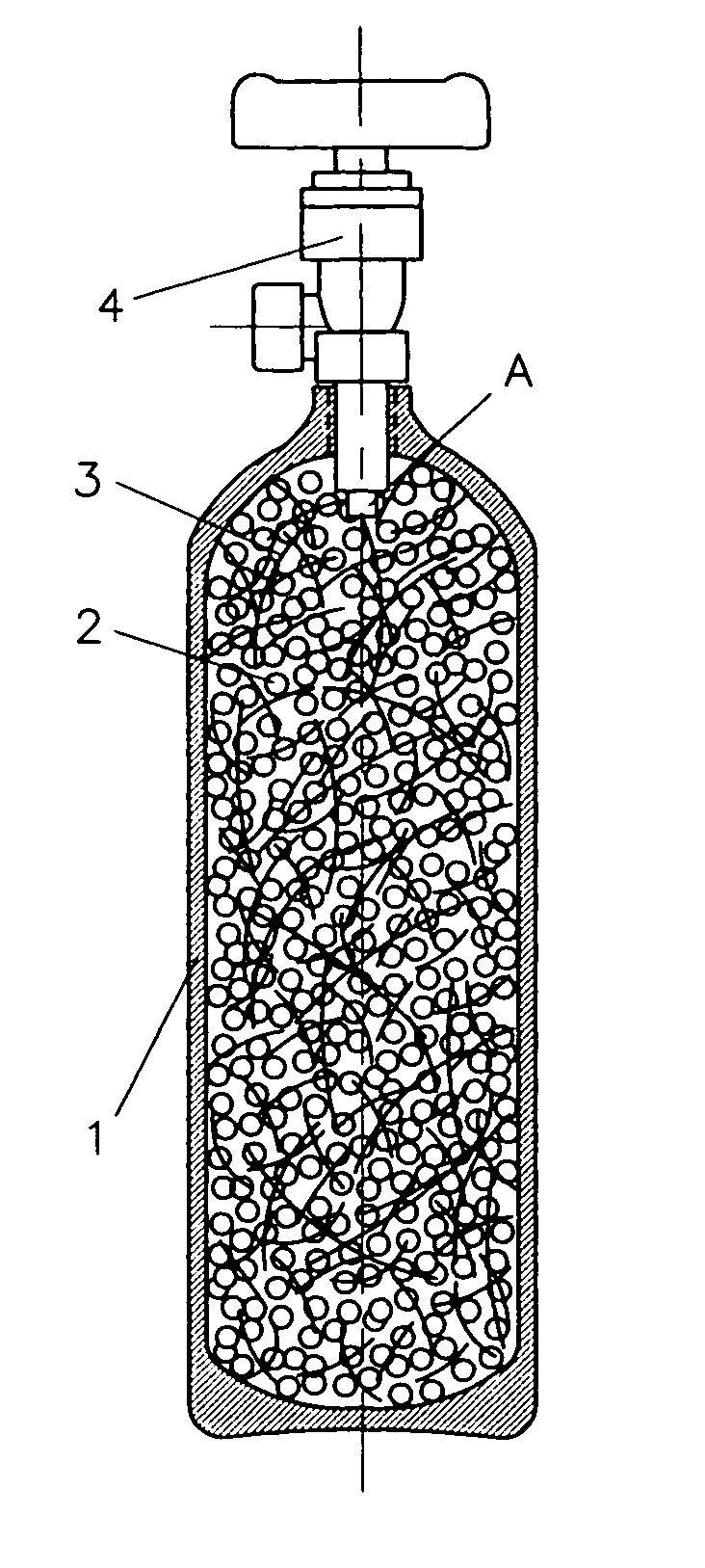
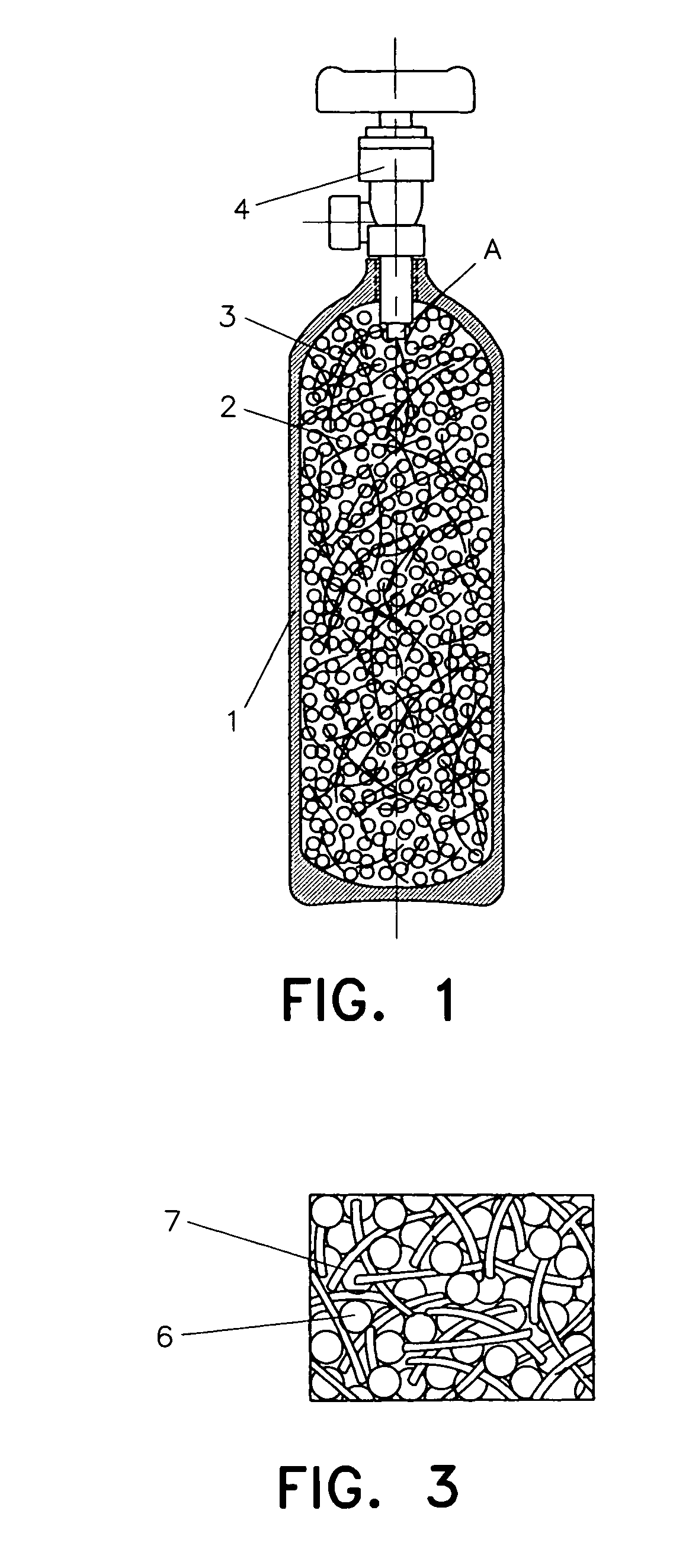
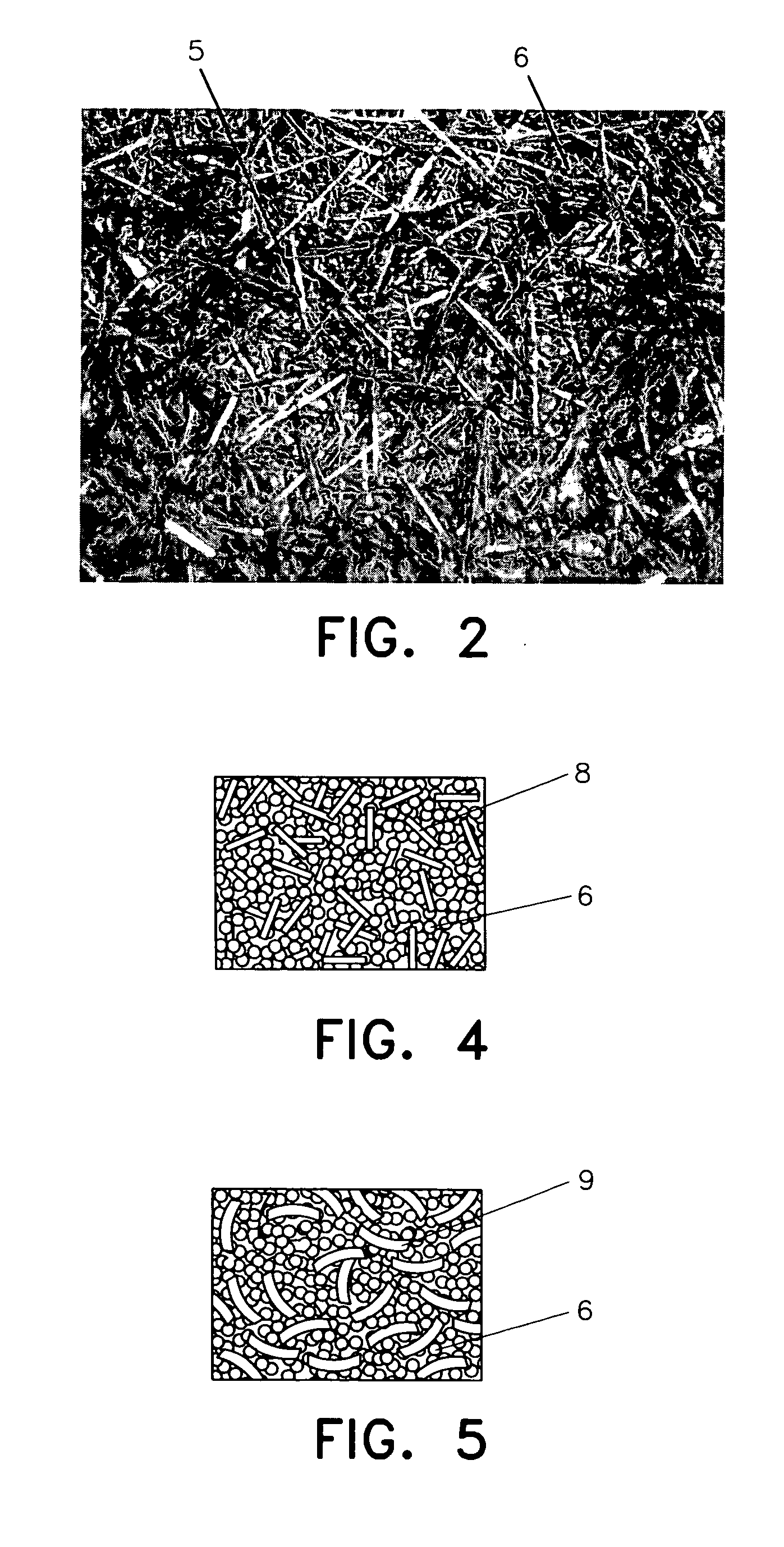
This invention relates to a new kind of hydrogen storage mixture and container thereof. This hydrogen storage container consists of a container casing, a hydrogen storage mixture and a valve. The hydrogen storage mixture loaded inside the container is made of hydrogen storage alloy granules and metal fibers and / or non-hydrogen-absorbing alloy fibers that do not absorb hydrogen. The non-hydrogen-absorbing fibers are dispersed among the hydrogen storage alloy granules and form a network structure. The non-hydrogen-absorbing fibers include non-hydrogen-absorbing metal fibers and / or non-hydrogen-absorbing alloy fibers, or their mixture. In the hydrogen storage mixture, the weight ratio of the non-hydrogen-absorbing fibers to the hydrogen storage alloys is about 0.01˜0.1. The hydrogen storage installation adopting the technology of this invention can effectively prevent the metal hydride granules from moving over a comparatively long distance and accumulating in some locations in the container during hydriding and dehydriding, and also can improve the thermal conductivity of the hydrogen storage mixture inside the container. The hydrogen storage container of this invention is easy to manufacture, safe to use, and low in cost. This invention can be used for the manufacture of hydrogen storage containers for hydrogen storage, transport, compression and purification.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Hydrogen storage material and hydrogen storage apparatus
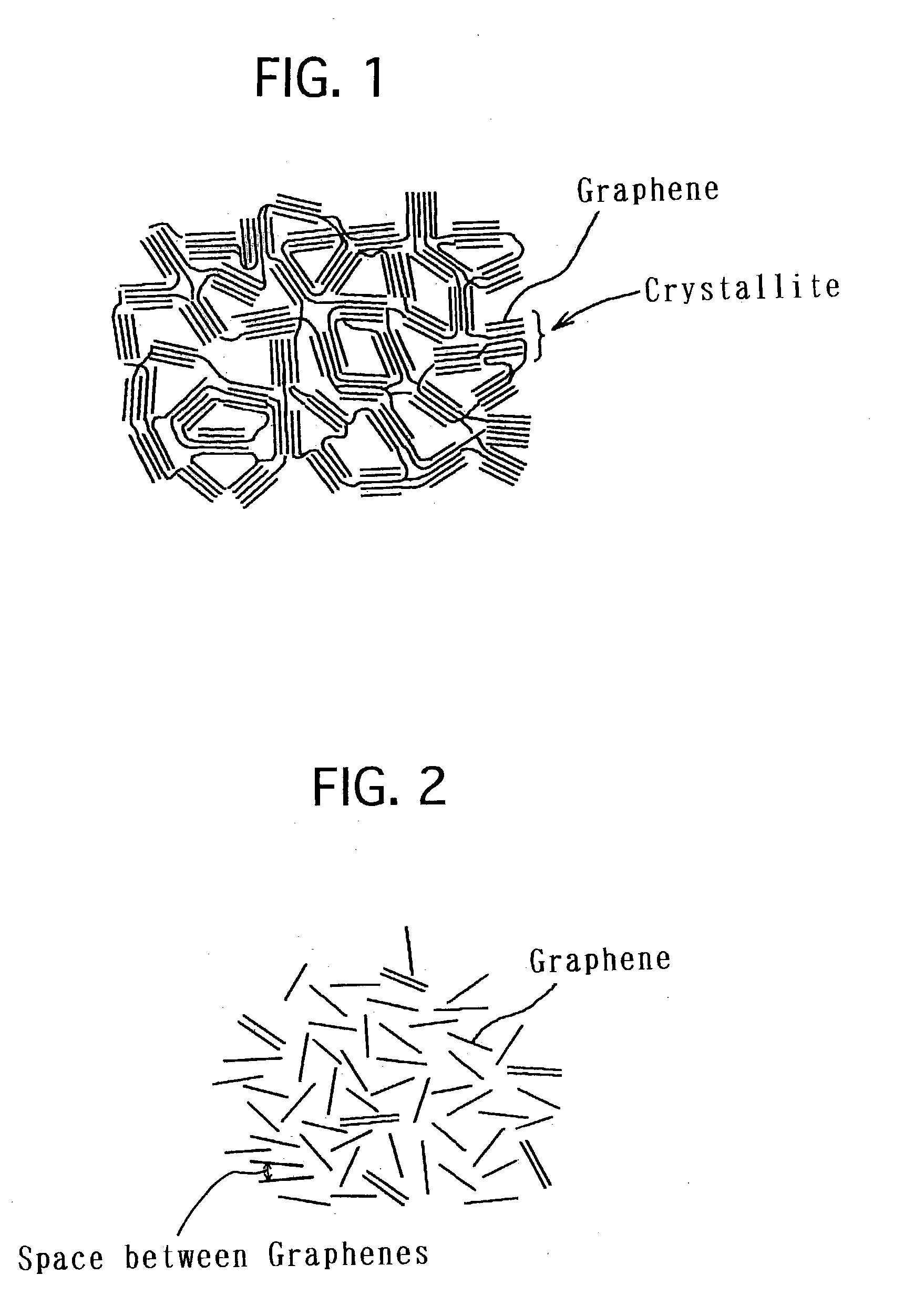
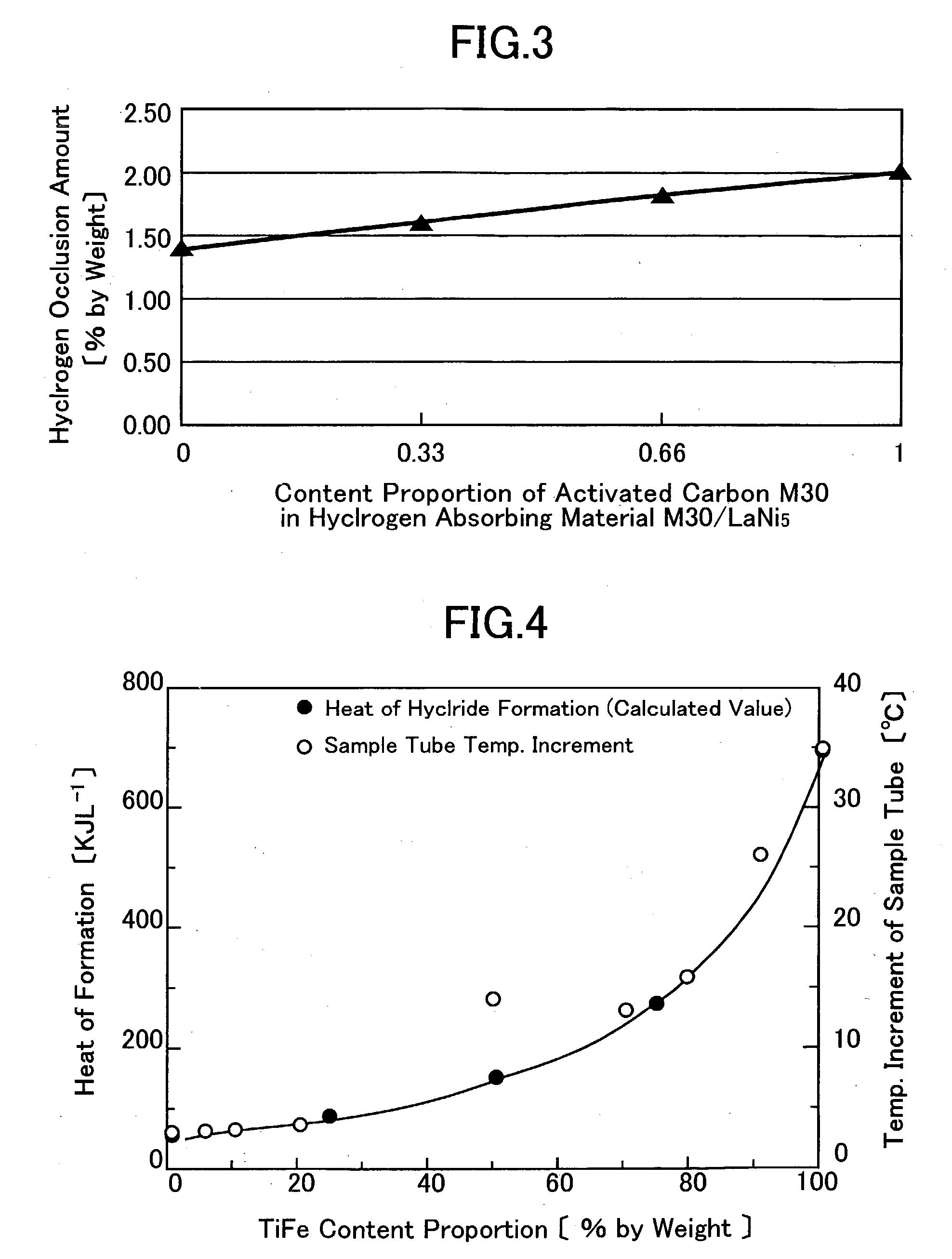
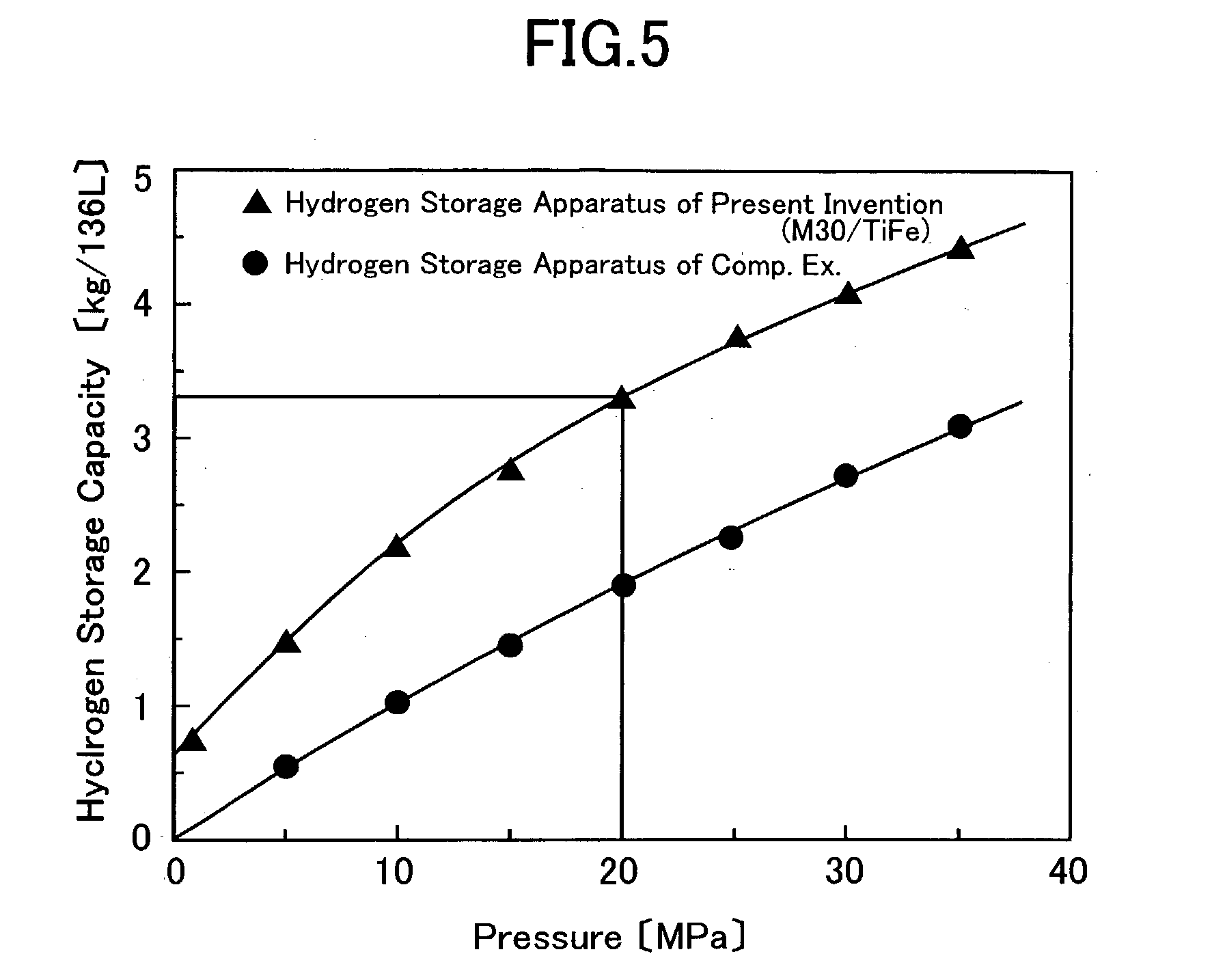
Two types of less expensive and lightweight hydrogen storage materials are provided. One of them is a carbon material for absorbing hydrogen, exhibiting a specific surface area being 3,000 m2 / g or more, and having pores, a pore mode diameter of the pores, measured by the BJH method, being from 1 nm to 2 nm. The present carbon material for absorbing hydrogen is such that the hydrogen storage capacity at ordinary temperature is large. The other one of the hydrogen storage materials is a carbon-based hydrogen storage material which includes a carbon material, exhibiting a specific surface area, being 1,000 m2 / g or more, and a bulk density, being from 0.4 g / cm3 or more to 1 g / cm3 or less. The present carbon-based hydrogen storage material is such that the hydrogen storage capacity per unit volume, is large. Moreover, to provide a hydrogen storage apparatus whose hydrogen storage capacity per unit volume is large. The hydrogen storage apparatus is constituted so as to include a container and a hydrogen absorbing material accommodated in the container, and the hydrogen absorbing material is arranged to be one which includes a porous carbon material whose specific surface area is 1,000 m2 / g or more, and a hydrogen absorbing alloy.
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC
Solid filling tank
InactiveUS7115159B2Prevent movementWithout lowering the heat exchanging performanceReversible hydrogen uptakeHeat storage plantsMicro heat exchangerFlat panel
In a hydrogen storing tank (solid filling tank) in which a hydrogen absorbing alloy (solid) is filled, a heat exchanger for executing heat exchange with the hydrogen absorbing alloy is constructed by laminating alternately first heat-transferring fins formed in corrugated plate shape and second heat-transferring fins formed in flat plate shape. Partitioned portions that are partitioned by the first heat-transferring fins and the second heat-transferring fins restrict movement of hydrogen absorbing alloy powders (MH powders) in a subsiding direction. Therefore, movement of the MH powders can surely be prevented by not using members that has no concern with the heat exchange and reduces an amount of filled MH powders and a volume in which the heat exchanger is provided.
Owner:TOYOTA IND CORP +1
Hydrogen absorbing alloy for battery application
InactiveUS6013387ALarge exchange current densityImprove responseAlkaline accumulatorsSecondary cell gas removalRare-earth elementMischmetal
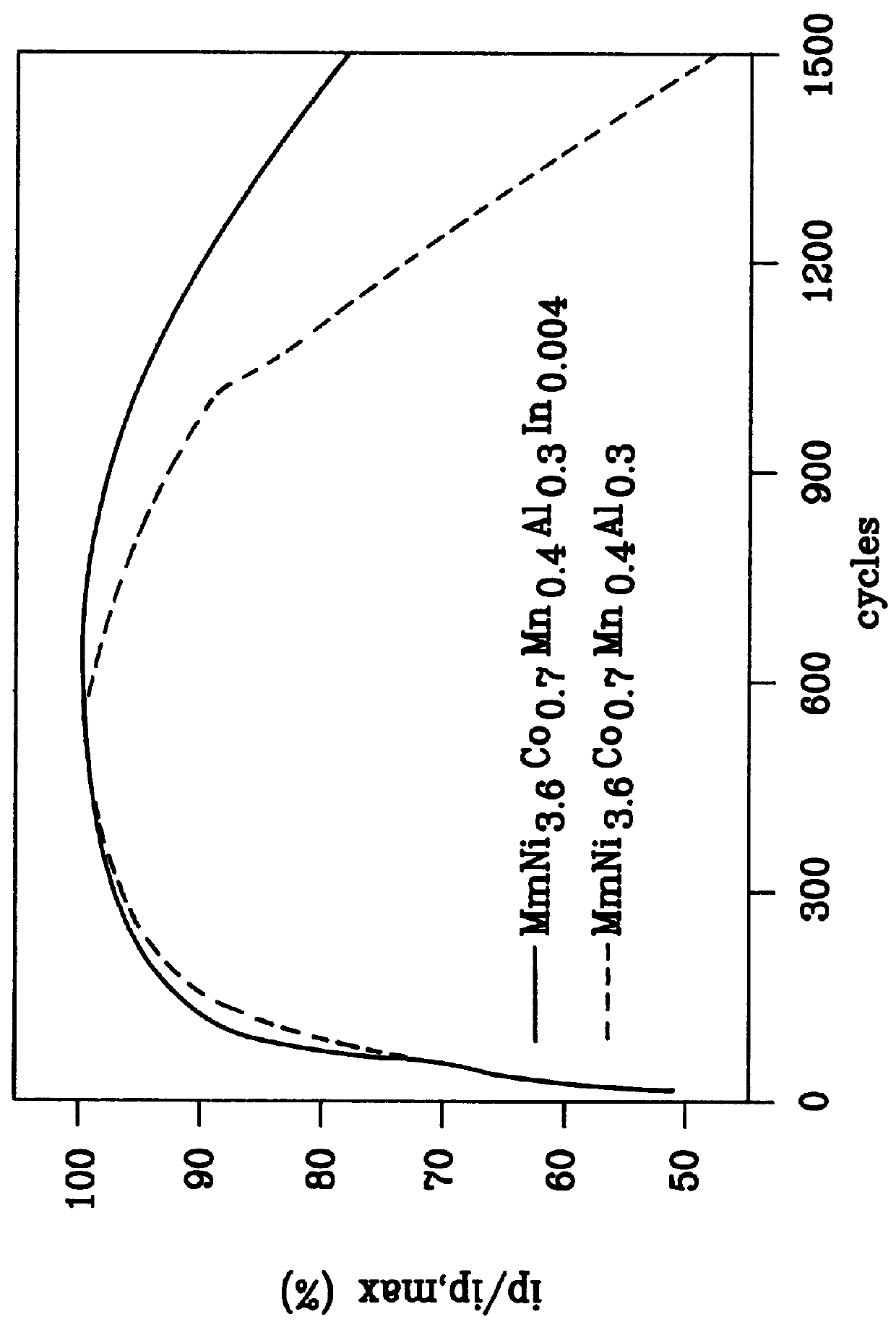
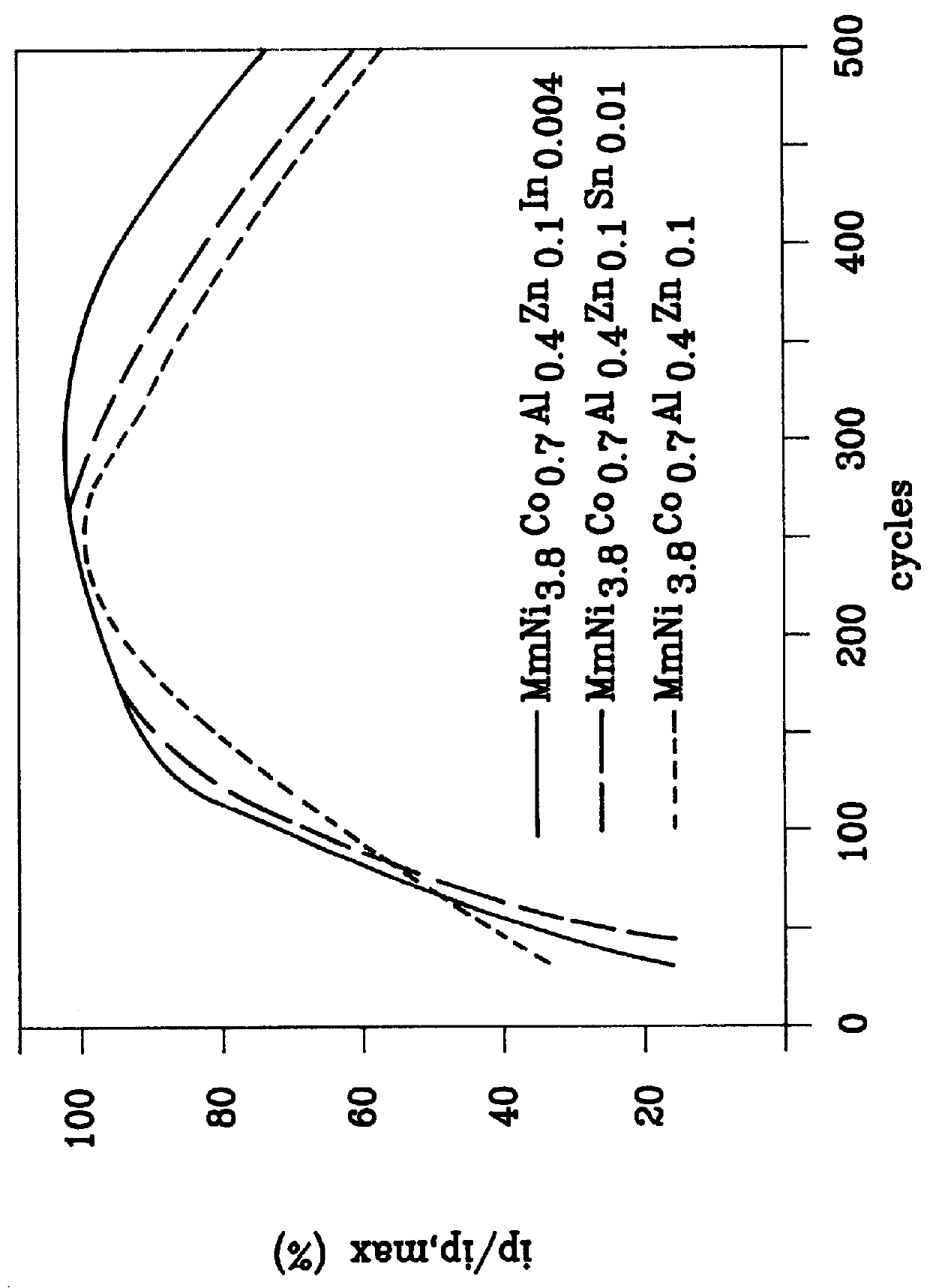
A hydrogen absorbing alloy is disclosed for use as the negative electrode in alkaline batteries. The general formula of the alloy is ABxMy, wherein A is selected from the rare earth element La or a mischmetal thereof; B is selected from the group consisting of Ni, Fe, Mn, Cr, Cu, Co, and mixtures thereof; M is selected from the group consisting of Al, In, Zn, Sn, Ga, Si, Ge, Bi, and mixtures thereof; 4.5< / =x< / =5.5; and 0.3<y< / =0.6. This alloy has a longer cycle life, along with larger capacity and better reactivity.
Owner:YAO LI HO
Fuel Cell System
InactiveUS20080044704A1Stable driving stateClose the hydrogen passage of the fuel cellFuel cell heat exchangeReactant parameters controlEngineeringHydrogen supply
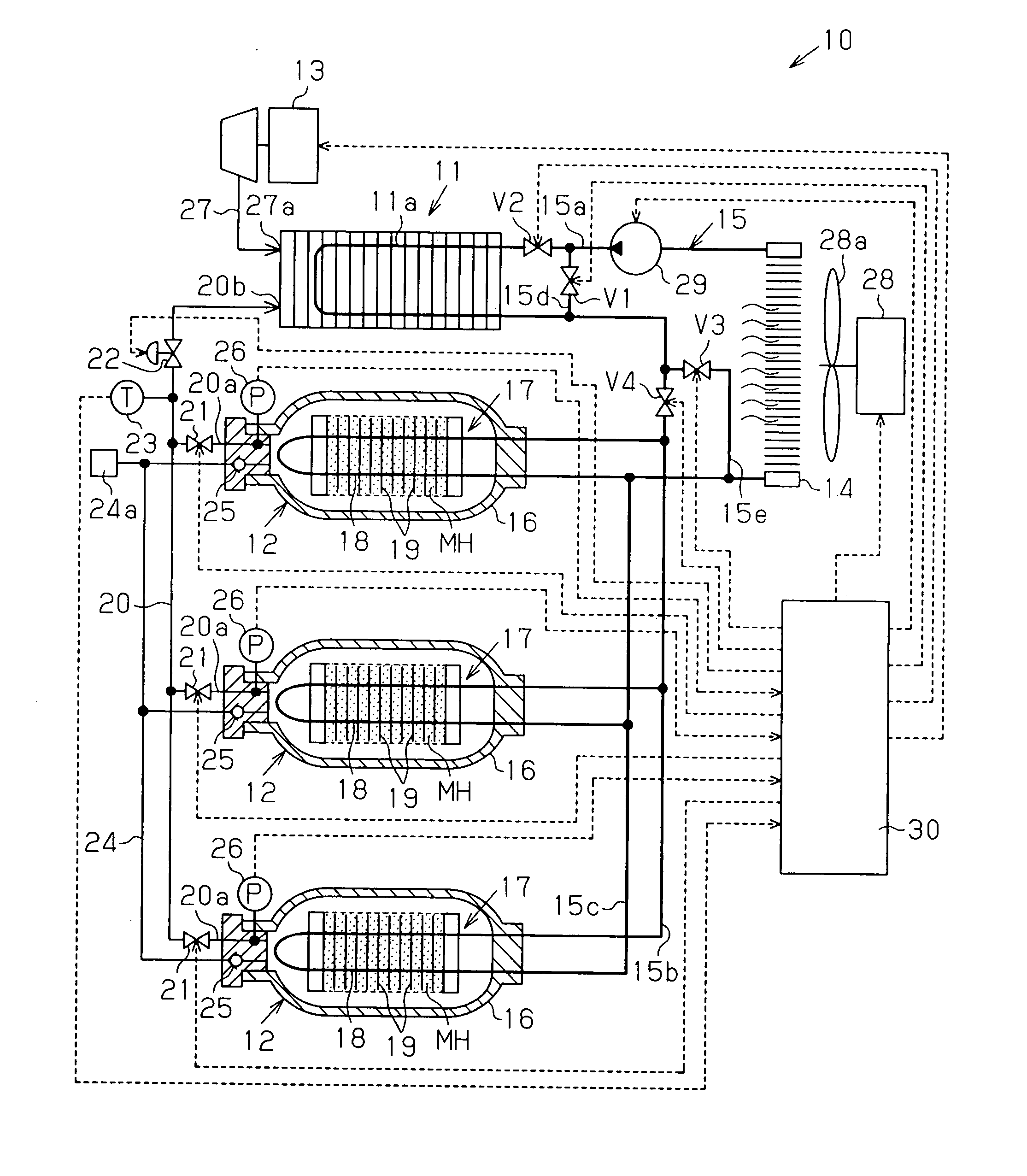
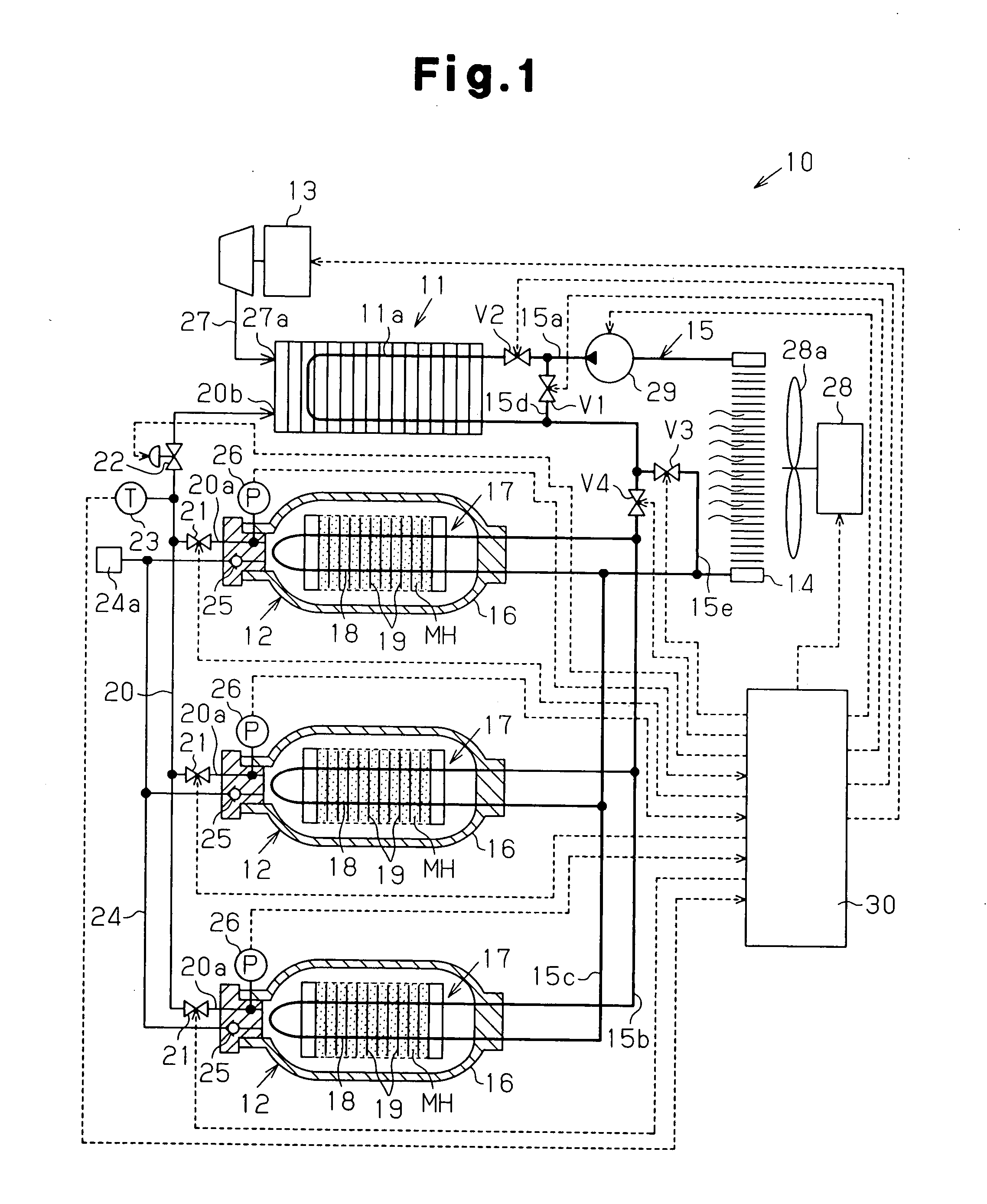
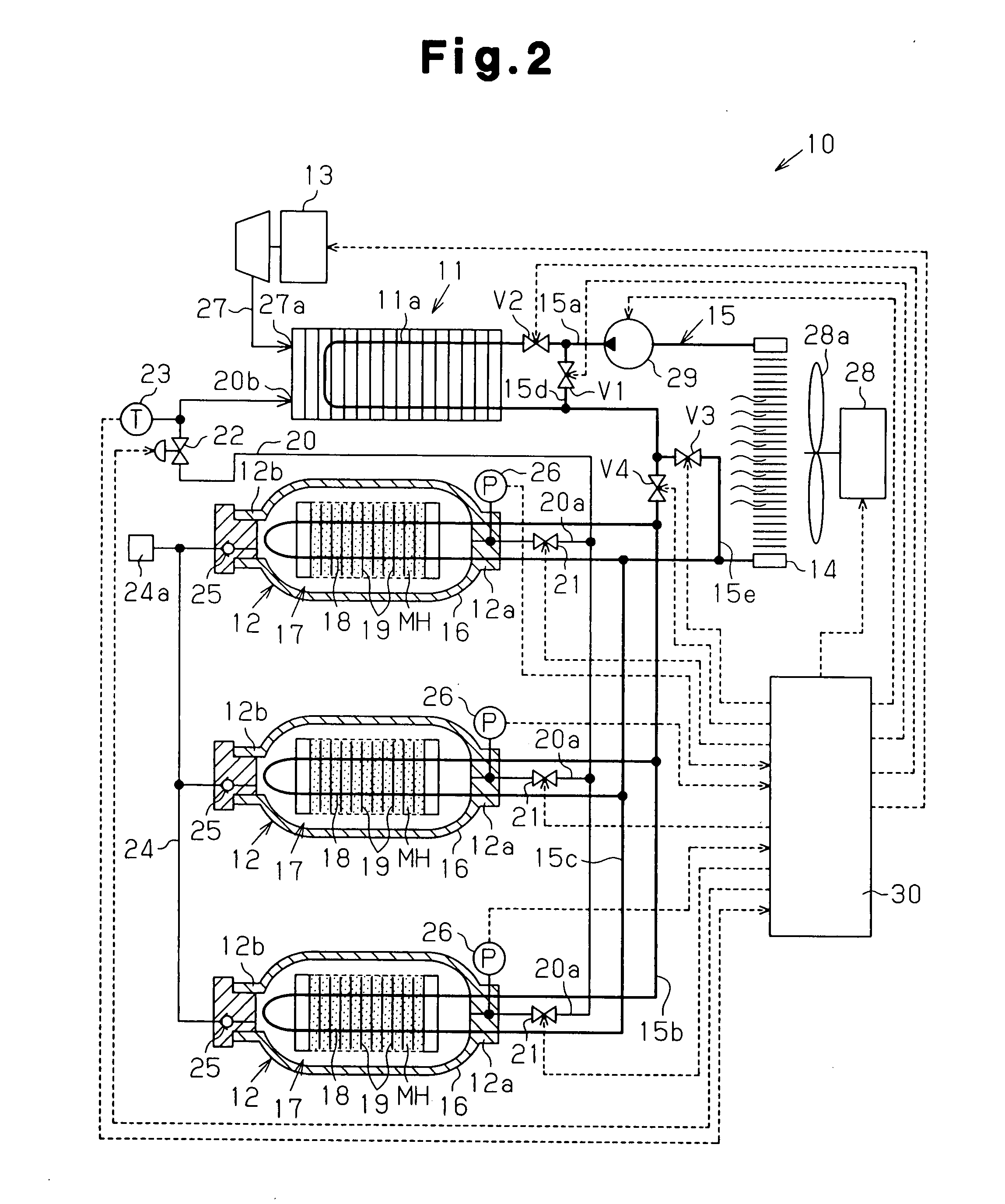
In a fuel cell system 10, hydrogen is supplied to a fuel cell 11 from a hydrogen storage tank 12 provided with a hydrogen-absorbing alloy MH and a heat exchanger 18. In this process, the pressure in the hydrogen storage tank 12 is held at a level equal to or higher than a predetermined pressure by using a heat medium that cooled the fuel cell 11. When the temperature of the hydrogen supplied to the fuel cell 11 is at the predetermined temperature or below, a control device 30 controls, based on a detection signal provided from a temperature sensor 23, first to fourth electromagnetic valves V1 to V4 so that the heat medium after having cooled the fuel cell 11 is supplied to the heat exchanger 18.
Owner:TOYOTA IND CORP +1
Nickel-metal hydride secondary battery module and secondary battery module manufacturing method
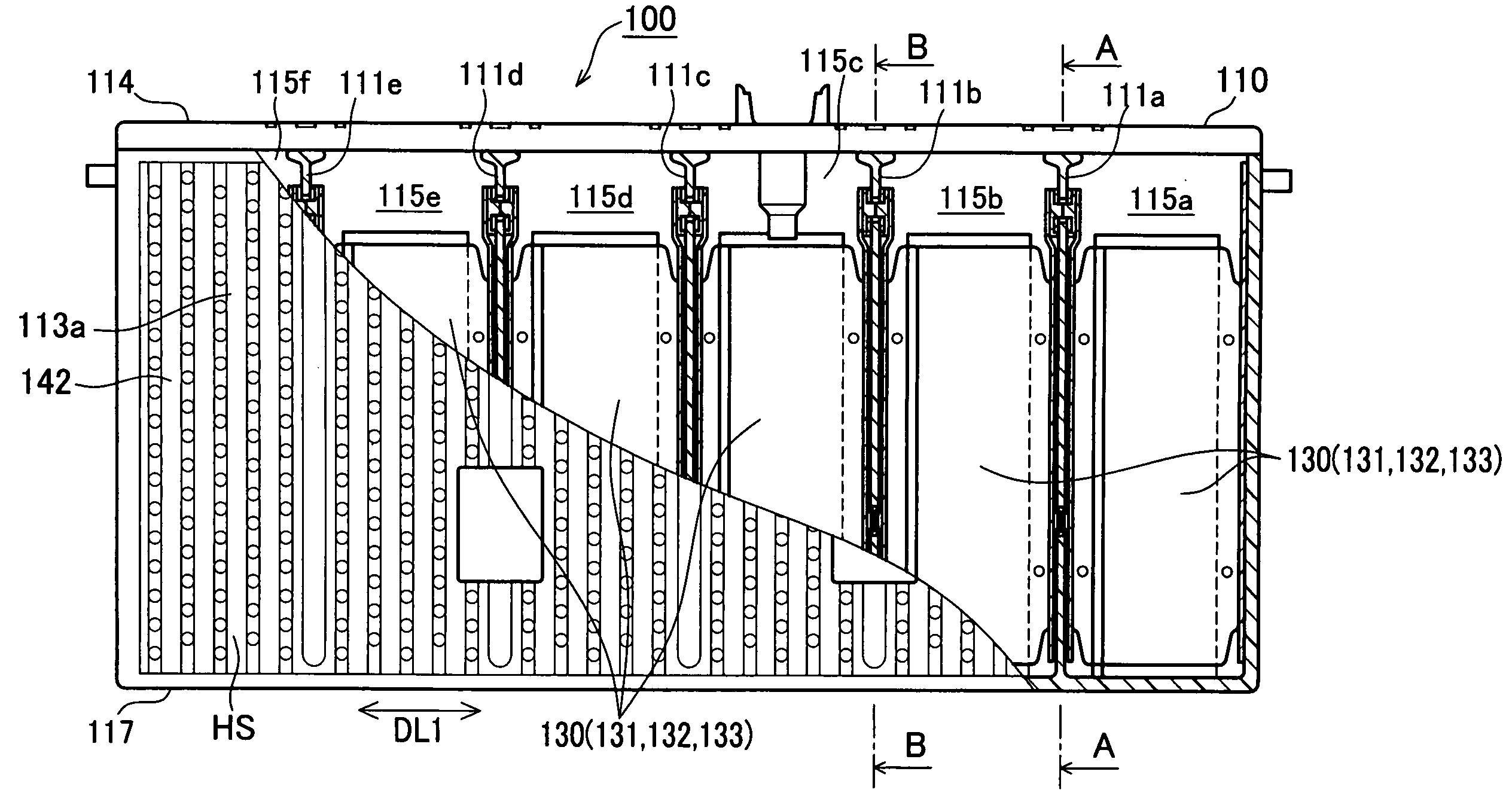
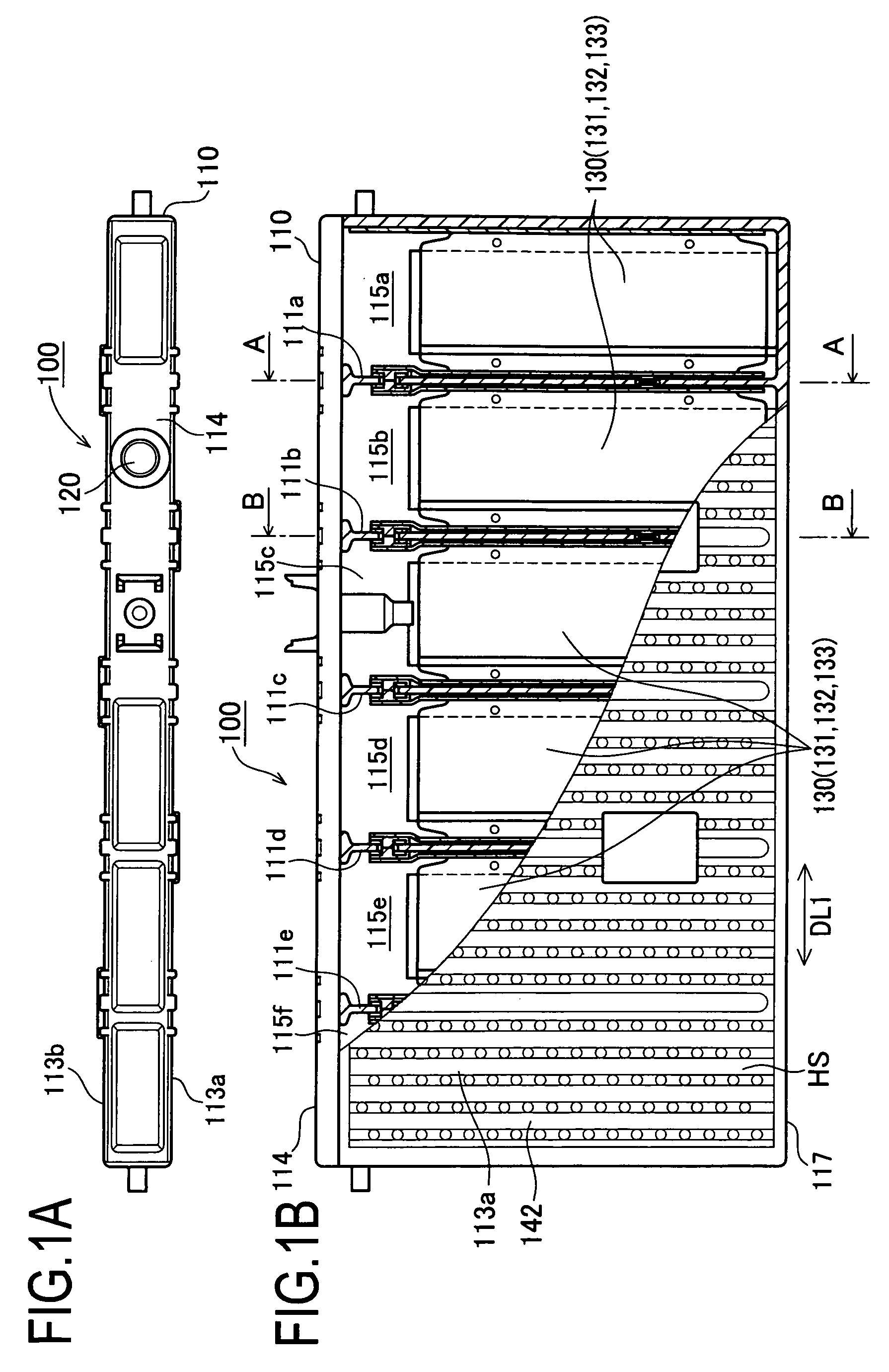
InactiveUS20090068549A1FillReliable formingFinal product manufacturePrimary cellsEngineeringSafety valve
A nickel-metal hydride secondary battery includes: a plurality of power generating elements each having a negative plate containing hydrogen absorbing alloy; a battery case provided with partition walls and a plurality of compartments arranged adjacently on both sides of each partition wall, each of the compartments accommodating each power generating element, and the compartments allowing gas intercommunication between compartments through communication holes formed in the partition walls; and at least one of safety valves placed on the battery case, the safety valves being less in number than the number of the compartments; wherein each of the communication holes has a hole sectional area per battery module capacity in a range 0.03 to 0.30 mm2 / Ah.
Owner:PANASONIC EV ENERGY CO LTD
Battery separator and manufacturing method thereof, and alkali secondary battery having the separator incorporated therein
InactiveUS20030138701A1Improve hydrophilicityPrimary cellsElectrode carriers/collectorsFiberEngineering
There is provided a battery separator comprising synthetic resin fibers, wherein hydrophilization treatment, preferably plasma treatment is applied, and a contact angle to pure water indicates a value of 0 to 100 degrees; an alkali secondary battery in which a electrode group having the separator between a positive electrode and a negative electrode is sealed in a battery case together with an alkali electrolyte, in particular, a nickel-metal hydride secondary battery whose positive electrode is a nickel electrode and whose negative electrode is a hydrogen absorbing alloy electrode, wherein active substances of said nickel electrode comprising powders consisting essentially of nickel hydroxides and higher-order cobalt hydroxides formed a surface of a part or whole thereof are employed, thereby providing its superiority in both of self-discharge properties and charge and discharge cycle life performance.
Owner:TOSHIBA BATTERY
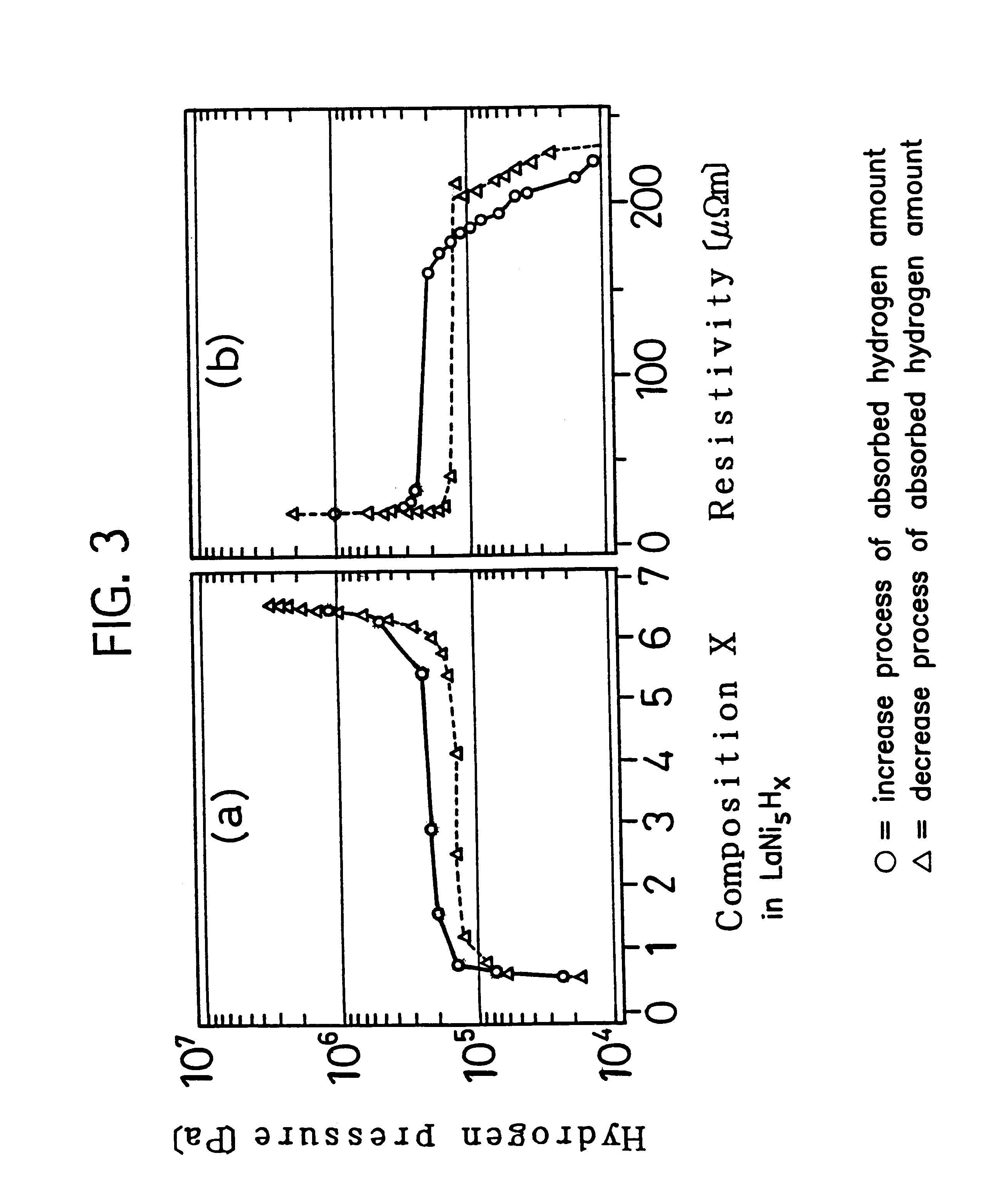
Detecting apparatus and detecting method of absorbed hydrogen amount in hydrogen absorbing tank
InactiveUS6285179B1Reversible hydrogen uptakeResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical resistance and conductanceDesorption
This invention relates to a detecting method and a detecting apparatus for detecting an absorbed hydrogen amount in a hydrogen absorbing tank. An object of the present invention is to to provide a detecting method and a detecting apparatus of absorbed hydrogen amount in a hydrogen absorbing tank, which can detect a hydrogen occlude condition in the hydrogen absorbing tank accurately, irrespective of repeating the absorption and desorption of the hydrogen to and from the hydrogen absorbing tank. In order to achieve the above object, the detecting method in the hydrogen absorbing tank comprises a contain step for containing a hydrogen absorbing alloy powder of a predetermined amount in a hydrogen absorbing tank so that a hydrogen gas comes in the hydrogen absorbing tank from external and goes out therefrom to the external, in the predetermined amount of the hydrogen absorbing alloy powder a contact condition between adjacent hydrogen absorbing alloy powders changing due to a volume expansion of the hydrogen absorbing alloy powder in occluding a hydrogen; a measure step for measuring an electrical resistance value between a pair of detect electrodes provided in the hydrogen absorbing tank; and a determine step for determining an absorbed hydrogen amount in the hydrogen absorbing tank based on a change of the electrical resistance value.
Owner:TOYOTA IND CORP
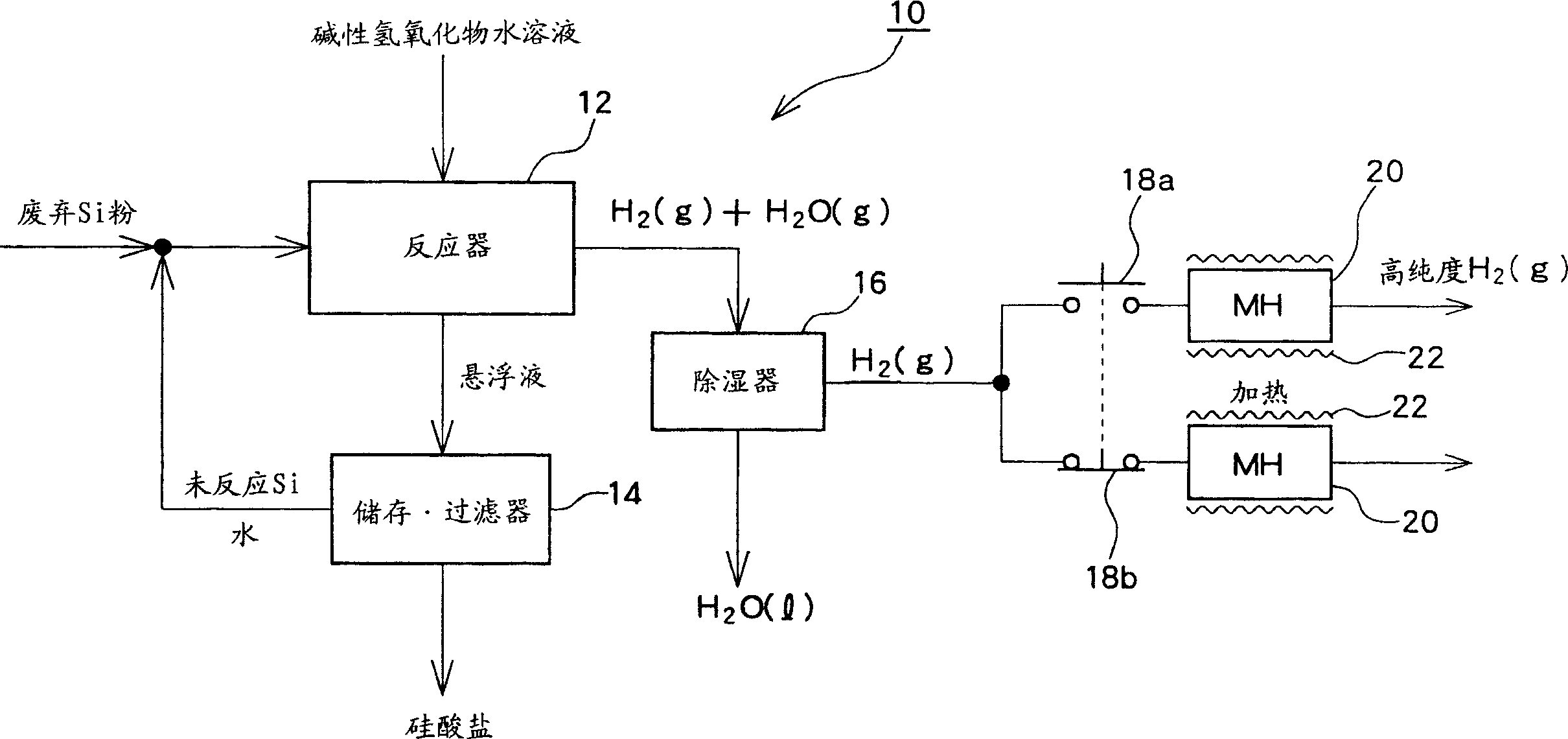
Hydrogen production method and apparatus and engine employing hydrogen production apparatus
InactiveCN1673068ALower fuel costsEnergy recovery in ventilation and heatingReversible hydrogen uptakeLiquid productAqueous solution
There is provided a hydrogen production apparatus having a simple structure for efficiently producing hydrogen. The hydrogen production apparatus 10 comprises a reactor 12 for reacting silicon (which may be waste silicon) and an aqueous basic hydroxide solution, a hydrogen absorbing alloy 20 for storing hydrogen produced by the reaction, and a reservoir / filter 14 which retains a solid or liquid product generated in the reactor 12 and filters a solution or suspension containing the solid or liquid product so as to separate the product from water.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD +3
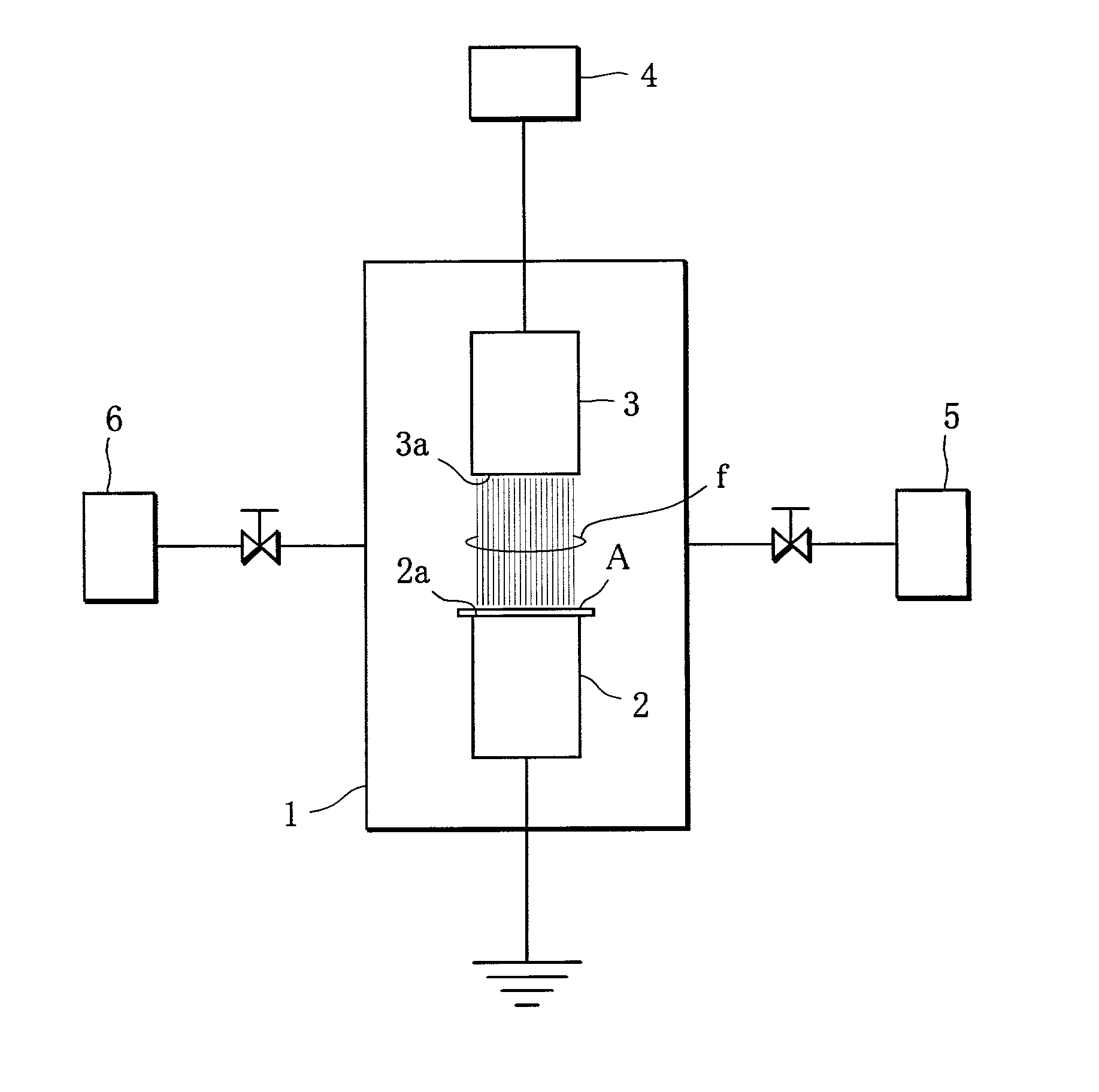
Hydrogen sensor
InactiveUS20050067281A1Thermal interferenceAvoid thermal interferenceUsing mechanical meansGas analyser construction detailsHydrogen sensorStrain gauge
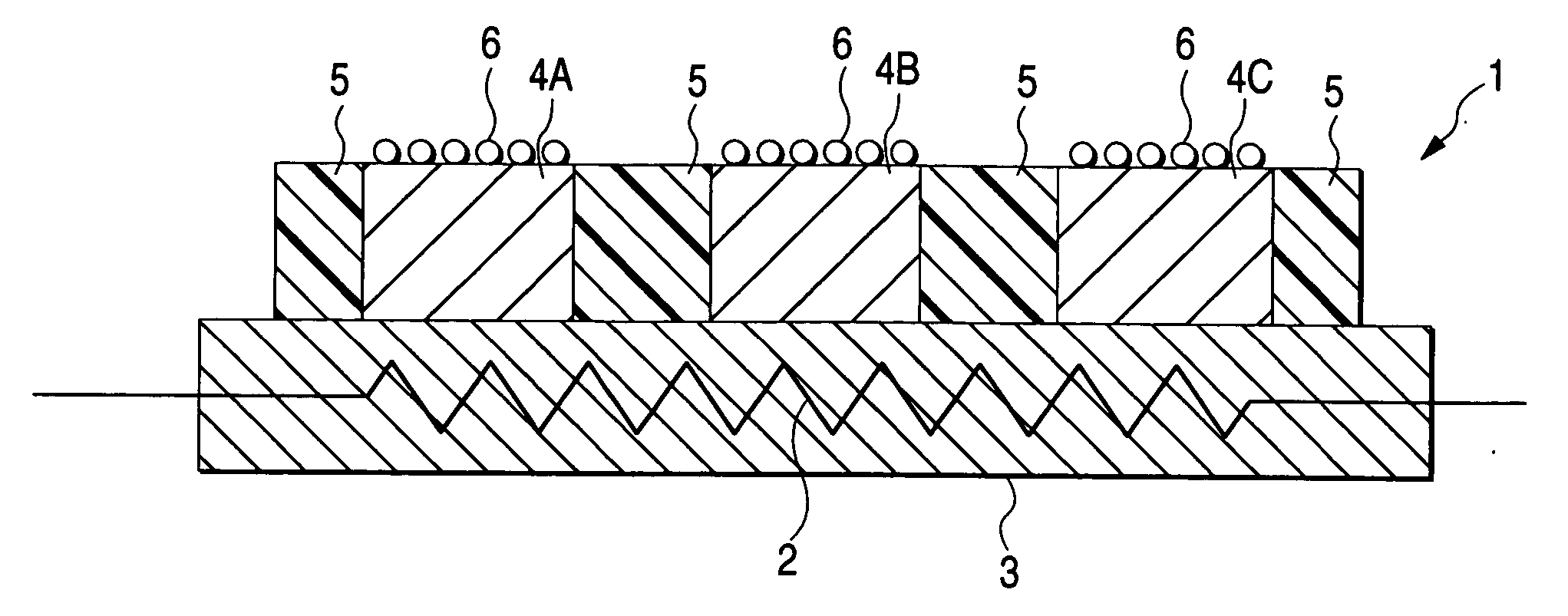
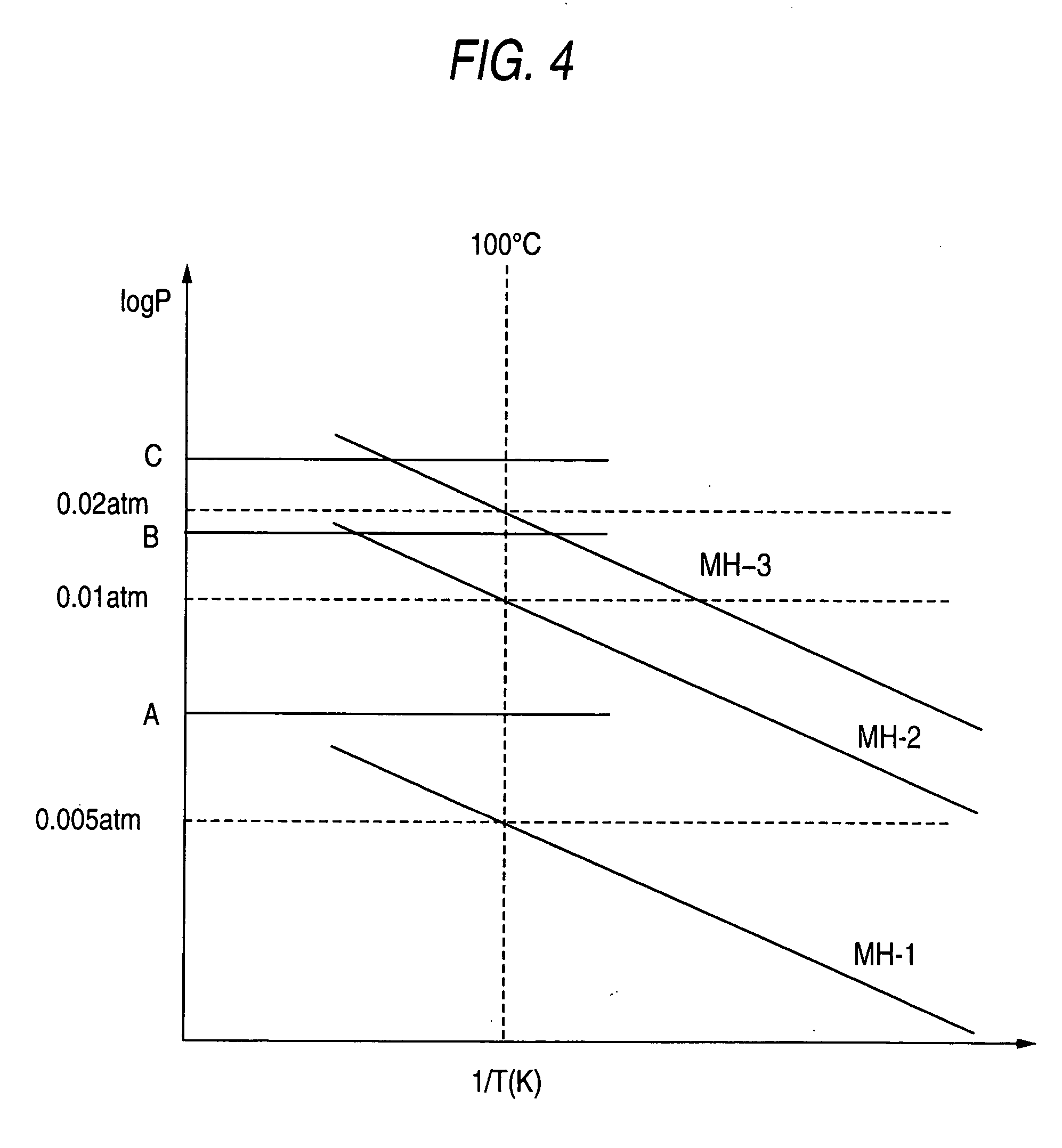
A hydrogen sensor 1 includes detection elements 4A, 4B, 4C formed from hydrogen-absorbing alloys which exhibit different hydrogen-absorbing pressures at a given temperature; a strain gauge 6 which detects changes in volume upon absorbing of hydrogen by the detection elements 4A, 4B, 4C; a micro-heater 2 which controls the temperatures of all the detection elements 4A, 4B, 4C to approximate equal values; and a substrate 3.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Nickel hydrogen secondary battery
ActiveCN1505197ASolve the problem of reduced capacityHydrogenAlkaline accumulator electrodesLanthanideElectrolyte
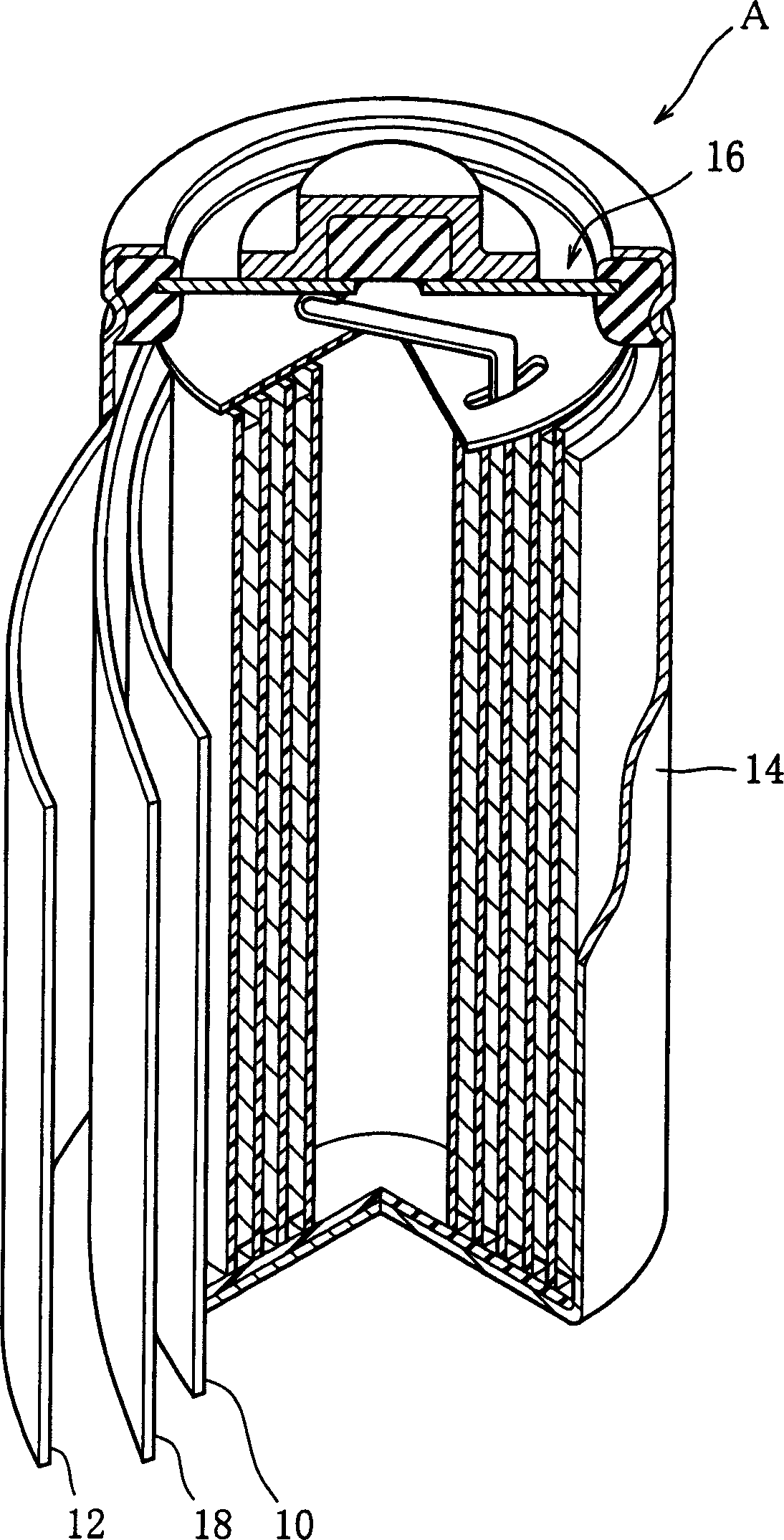
A nickel-hydrogen secondary battery comprises a positive electrode (10) and a negative electrode (12) opposite each other with a separator (18) between, and contained in a container (14) with an alkaline electrolyte. The positive electrode (10) contains nickel hydroxide and at least one element selected from a group consisting of Y, Yb, Er, Ca, Sr, Ba, Nb, Ti, W, Mo and Ta. The negative electrode (12) contains a hydrogen-absorbing alloy having composition represented by a general formula Ln1-xMgx(Ni1-yTy)s, where Ln is at least one element selected from a group consisting of the lanthanoids, Ca, Sr, Sc, Y, Ti, Zr and Hf, T is at least one element selected from a group consisting of V, Nb, Ta, Cr, Mo, Mn, Fe, Co, Al, Ga, Zn, Sn, In, Cu, Si, P and B, and x, y and z are numerical values satisfying the requirements 0 H01M 10 / 30 H01M 4 / 32 H01M 4 / 38 H01M 4 / 52 1 15 1 2003 / 11 / 27 1505197 2004 / 6 / 16 1237648 2006 / 1 / 18 2006 / 1 / 18 2006 / 1 / 18 Sanyo Electric Co., Ltd. Japan Kibara Suguri wang huimin 11021 The Patent Agency of the Chinese Academy of Sciences Inside the Chinese Academy of Sciences, No.52 Sanlihe Road, Fuwai, Beijing 100864 Japan 2002 / 11 / 28 2002-345997
Owner:FDK CORP
Hydrogen-absorbing alloy electrode, alkaline storage battery, and method of manufacturing the alkaline storage battery
InactiveUS8053114B2Reduce discharge capacityImprove rate discharge performanceMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureRare-earth elementHigh rate
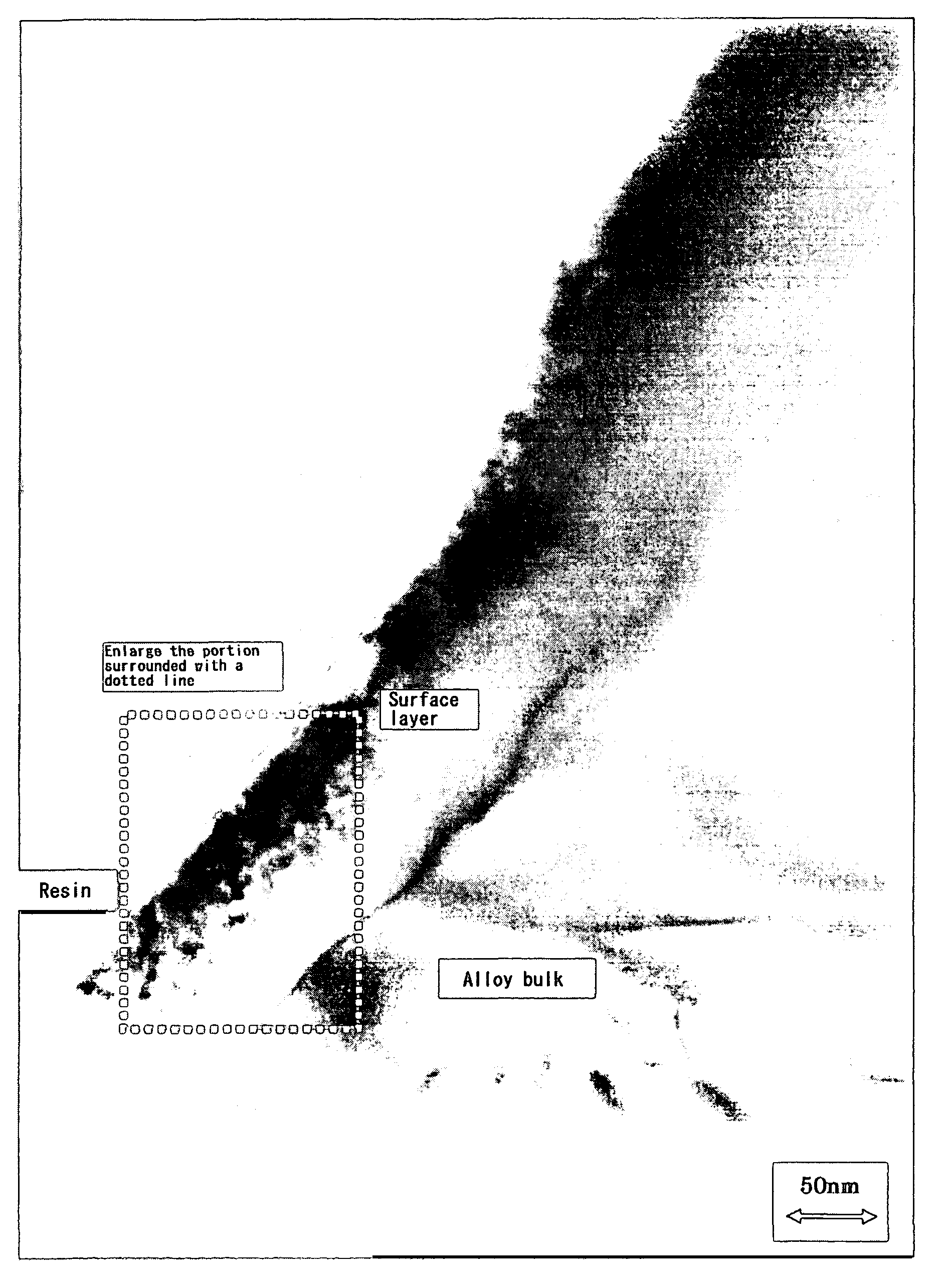
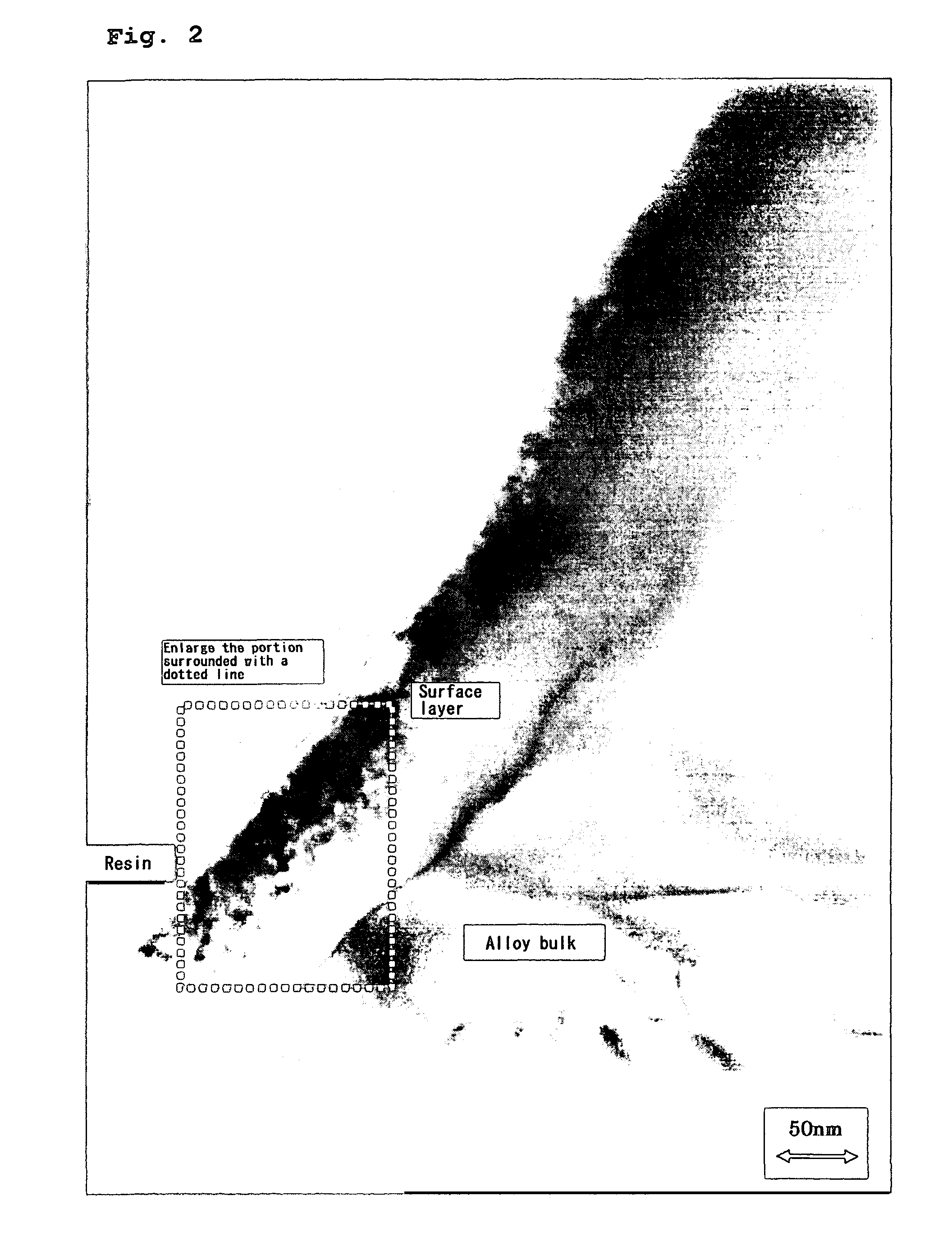
Low temperature discharge capability and high rate discharge capability are improved in an alkaline storage battery that uses as its negative electrode a hydrogen-absorbing alloy electrode employing hydrogen-absorbing alloy particles containing at least nickel and a rare-earth element. An alkaline storage battery uses as the negative electrode a hydrogen-absorbing alloy electrode employing hydrogen-absorbing alloy particles containing at least nickel and a rare-earth element. The hydrogen-absorbing alloy particles have a surface layer and an interior portion, the surface layer having a nickel content greater than that of the interior portion, and nickel particles having a particle size within a range of from 10 nm to 50 nm are present in the surface layer.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Nickel metal hydride storage battery
InactiveUS20050100789A1Sufficient cycle lifeReduce the amount requiredHydrogenAlkaline accumulator electrodesRare-earth elementManganese
A nickel metal hydride storage battery including a positive electrode, a negative electrode including a hydrogen absorbing alloy, and an alkaline electrolyte, the hydrogen absorbing alloy containing at least a rare-earth element, magnesium, nickel and aluminum, and having an intensity ratio (IA / IB) of not smaller than 0.1 (where IA represents an intensity of the highest peak in a range of 2θ=30°˜34° in an X-ray diffraction pattern using CuKα-radiation as the X-ray source and IB represents the intensity of the highest peak in a range of 2θ=40°˜44° in an X-ray diffraction pattern using CuKα-radiation as the X-ray source), and the battery containing manganese in an amount of not greater than 1.0 wt % relative to the hydrogen absorbing alloy.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Hydrogen supply method
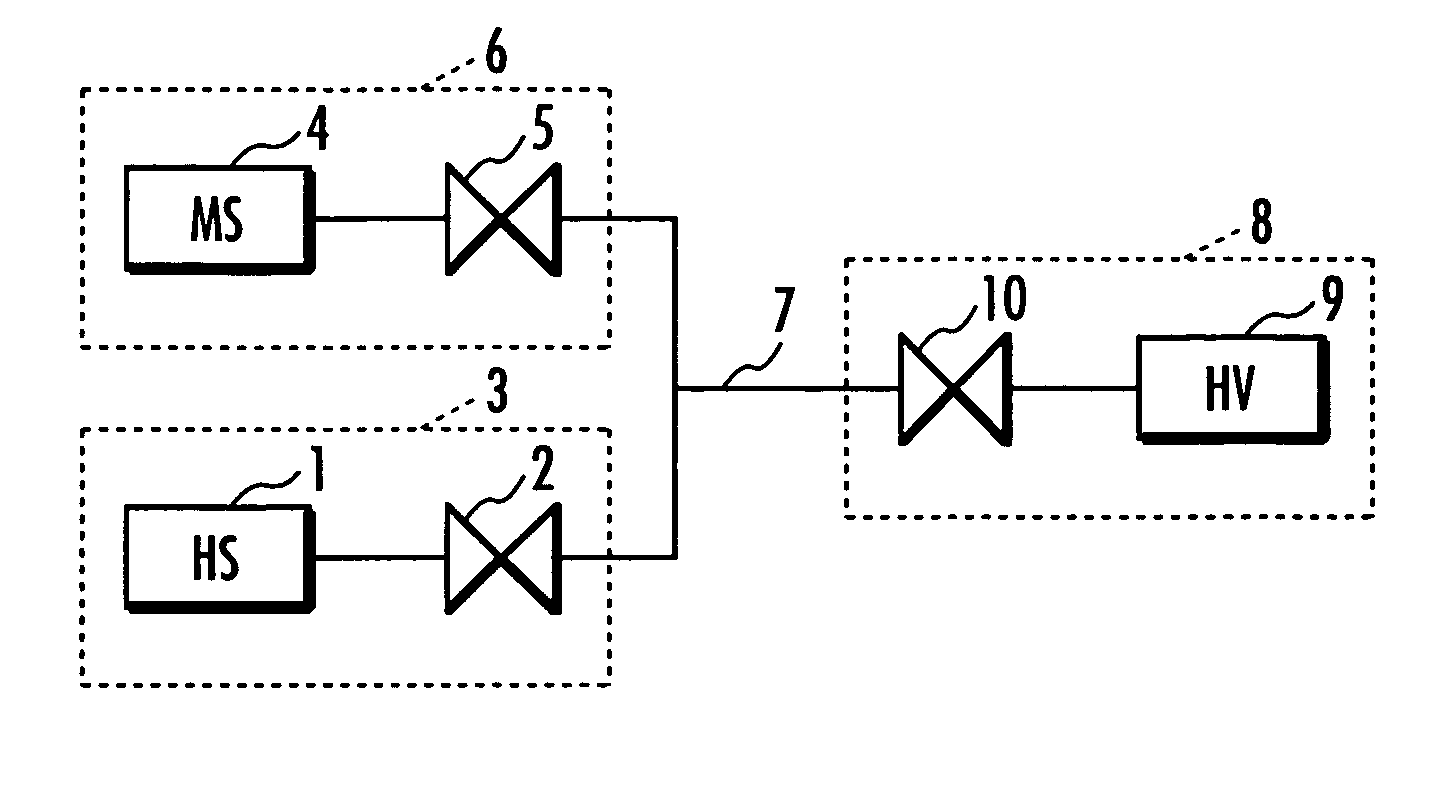
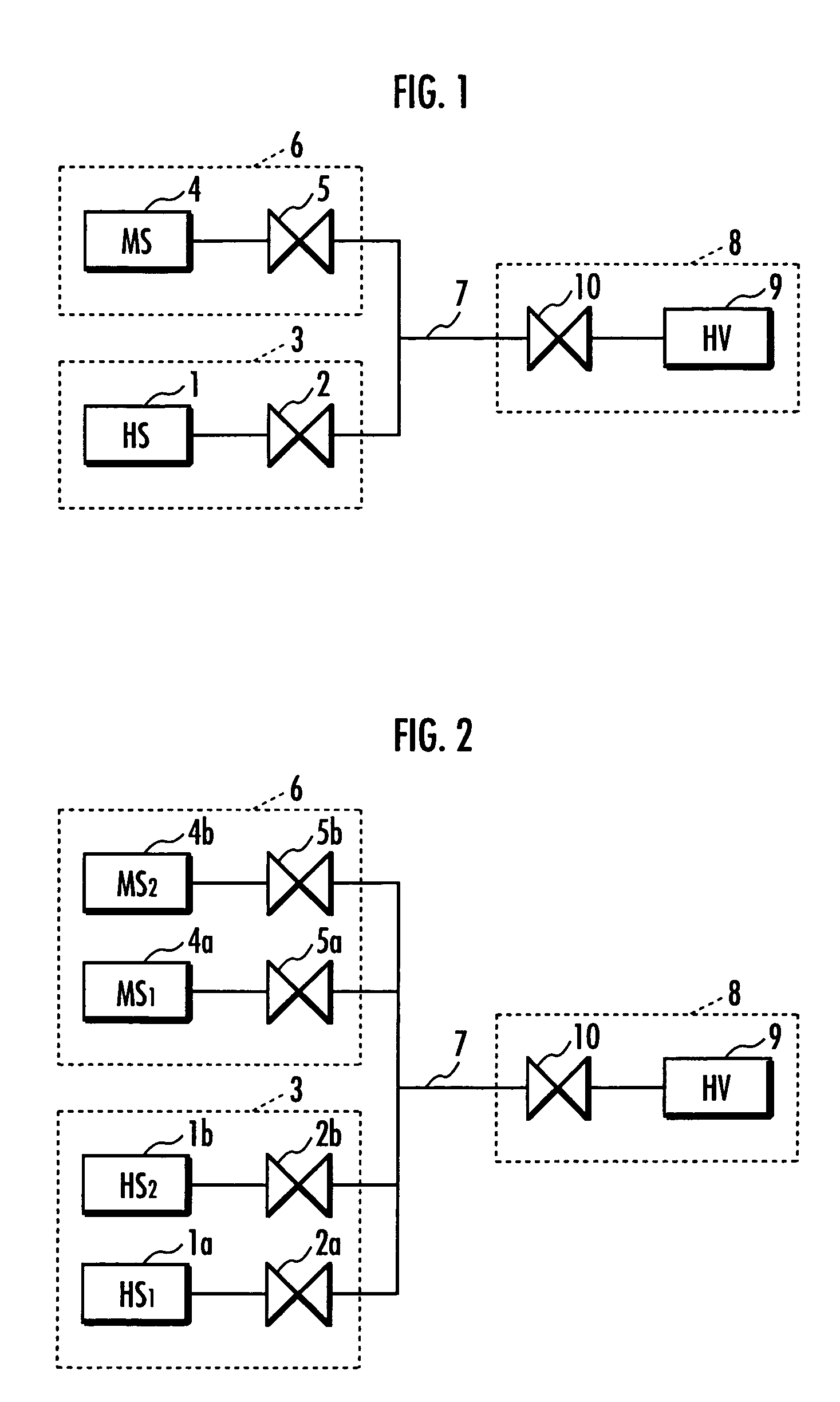
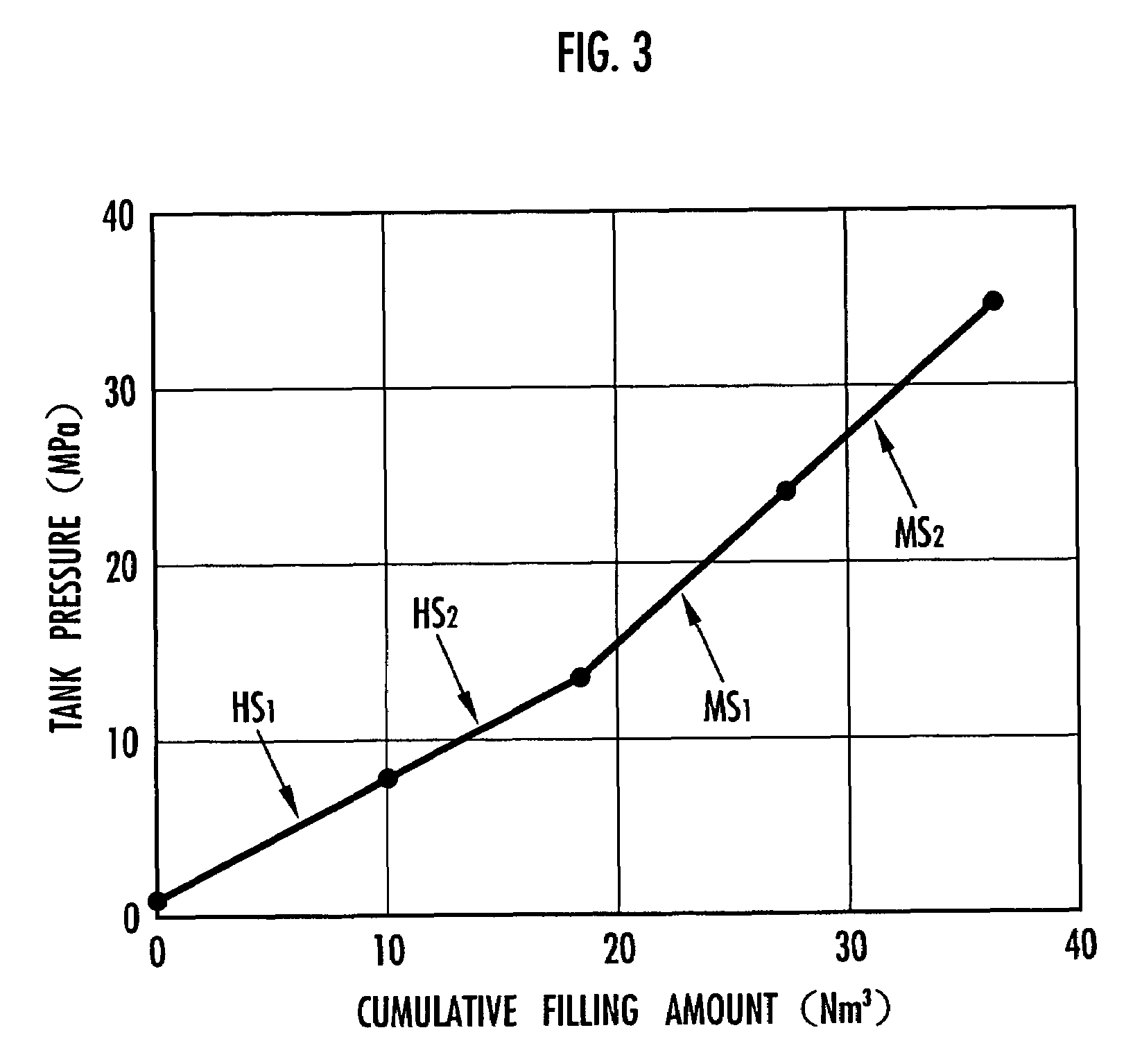
InactiveUS7314056B2Efficient supplyReduce pressureAuxillary drivesReactant parameters controlHigh pressure hydrogenHydrogen supply
A hydrogen supply method using an inexpensive and compact hydrogen supply means to reduce a pressure of hydrogen stored in the hydrogen supply means and to supply efficiently hydrogen to a high pressure hydrogen storage means. Hydrogen is supplied under high pressure from first hydrogen supply means and from second hydrogen supply means containing a hydrogen absorbing alloy to a hydrogen storage means for storing hydrogen under high pressure. Hydrogen is supplied from the first hydrogen supply means to the hydrogen storage means until the pressure in the hydrogen storage means reaches a predetermined pressure. Thereafter, hydrogen is supplied from the second hydrogen supply means to the hydrogen storage means until the pressure in the hydrogen storage means reaches a maximum filling pressure. A plurality of the first hydrogen supply means or a plurality of the second hydrogen supply means may be used.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Hydrogen absorbing alloy powder and hydrogen storing tank for mounting in a vehicle
InactiveUS7060120B1Shorten milling timeLong milling timeHydrogenTransportation and packagingMetalHydrogen absorbing alloy
To produce a hydrogen absorbing alloy powder which is an aggregate of alloy particles each including a metal matrix and added-components, an aggregate of metal matrix particles and an aggregate of added-component particles are used, and mechanical alloying is carried out. In this case, the relationship between the particle size D of the metal matrix particles and the particle size d of the added-component particles is set at d≦D / 6. Thus, the milling time can be shortened remarkably.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Cylindrical alkaline storage battery
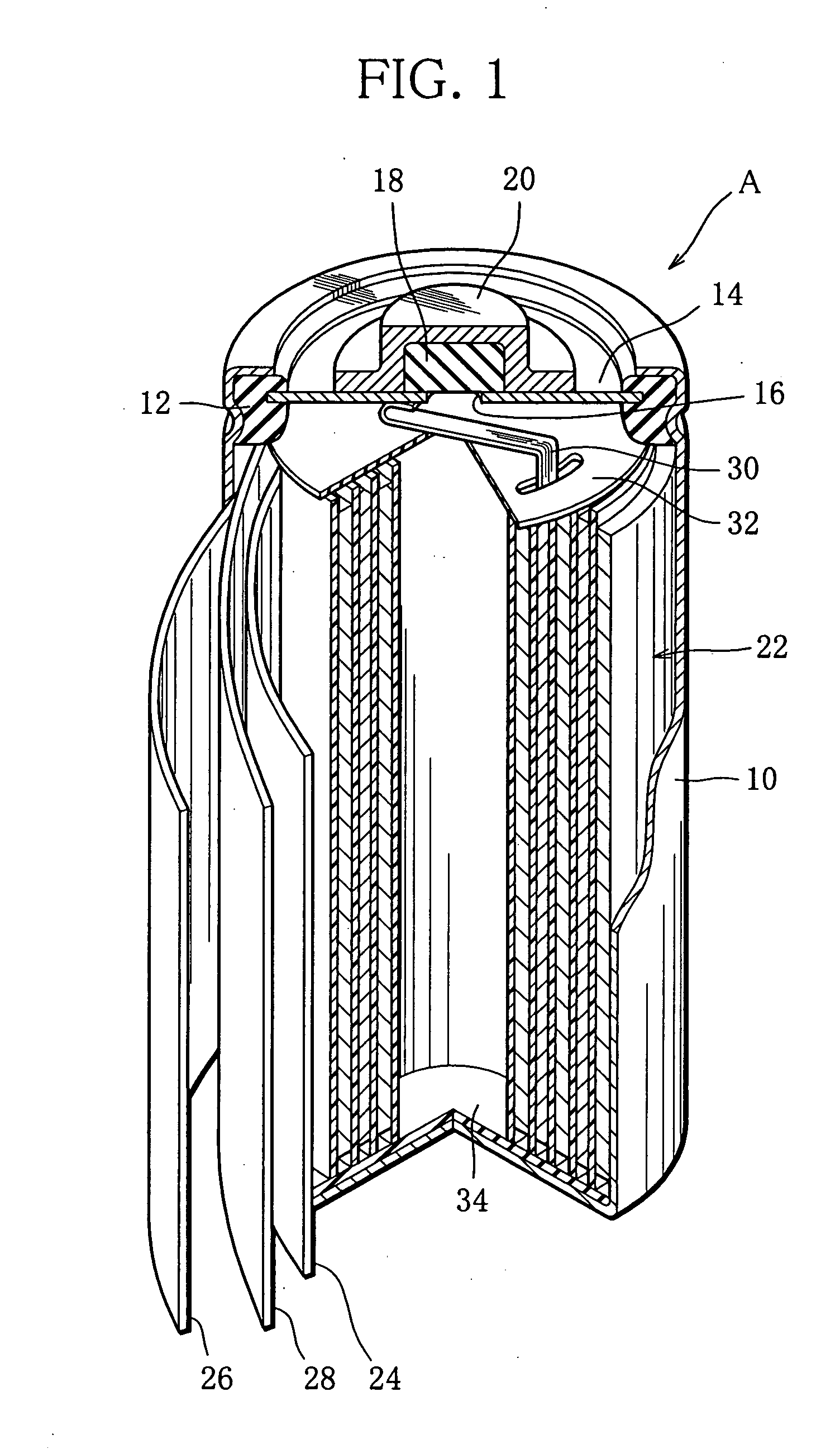
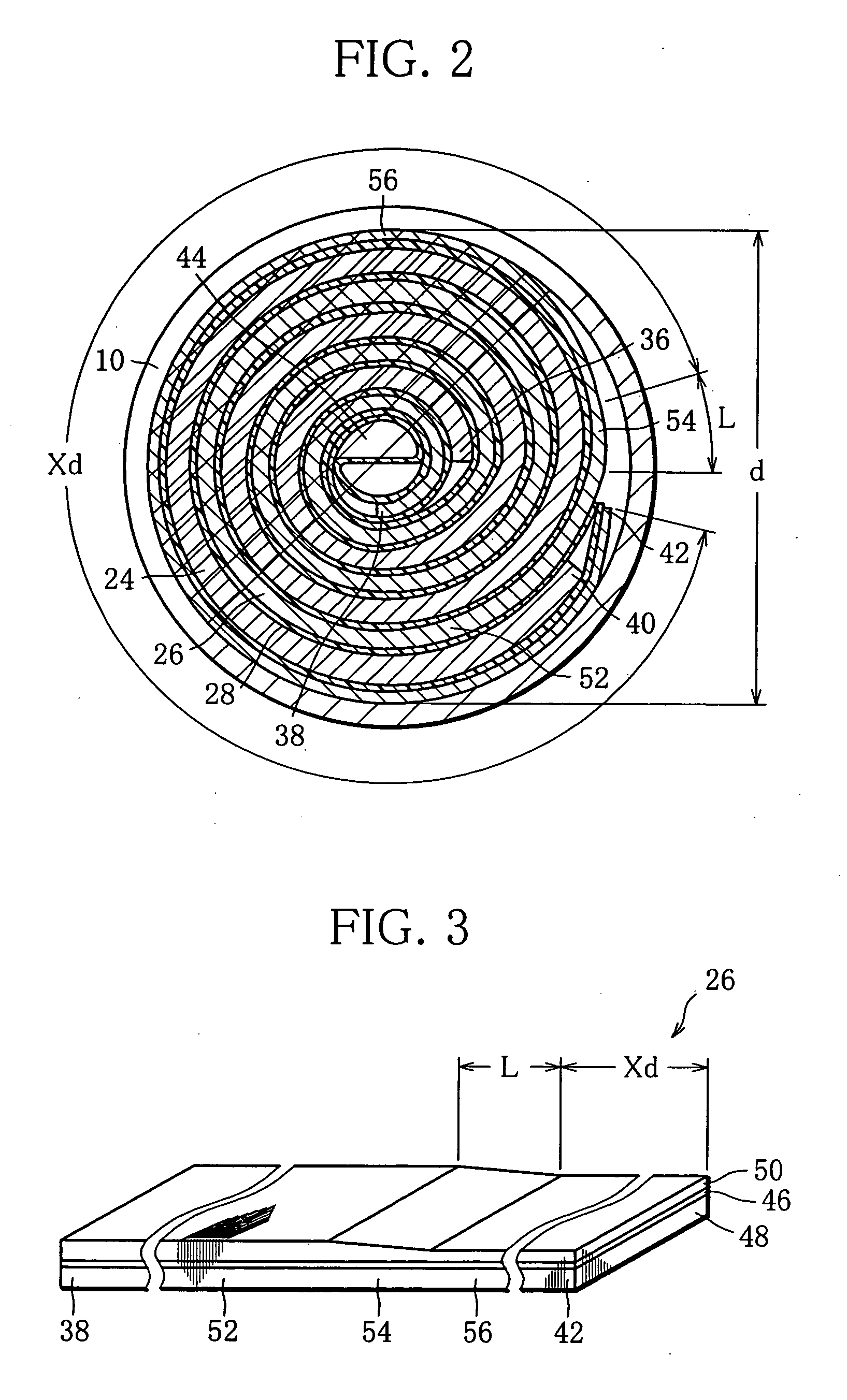
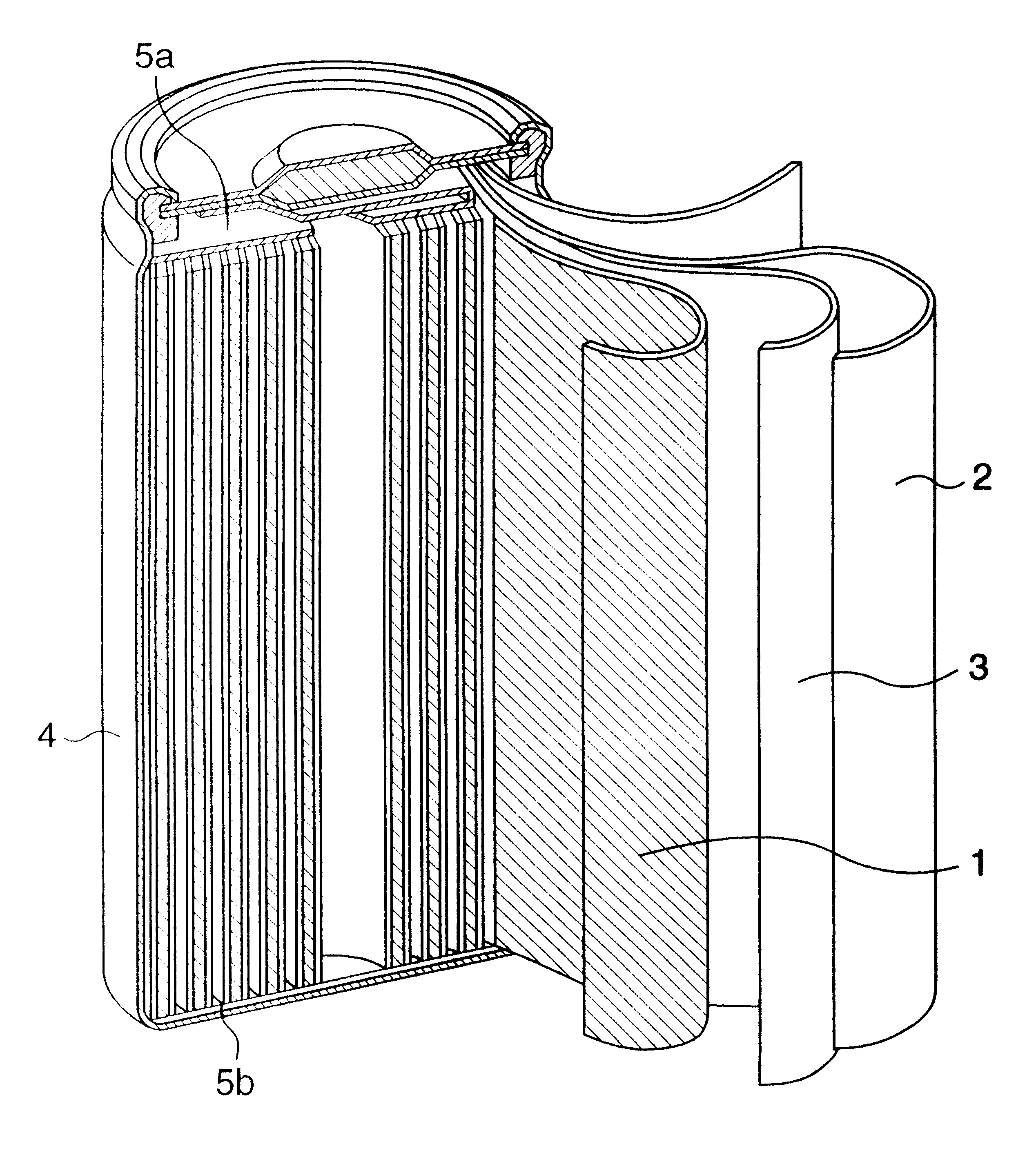
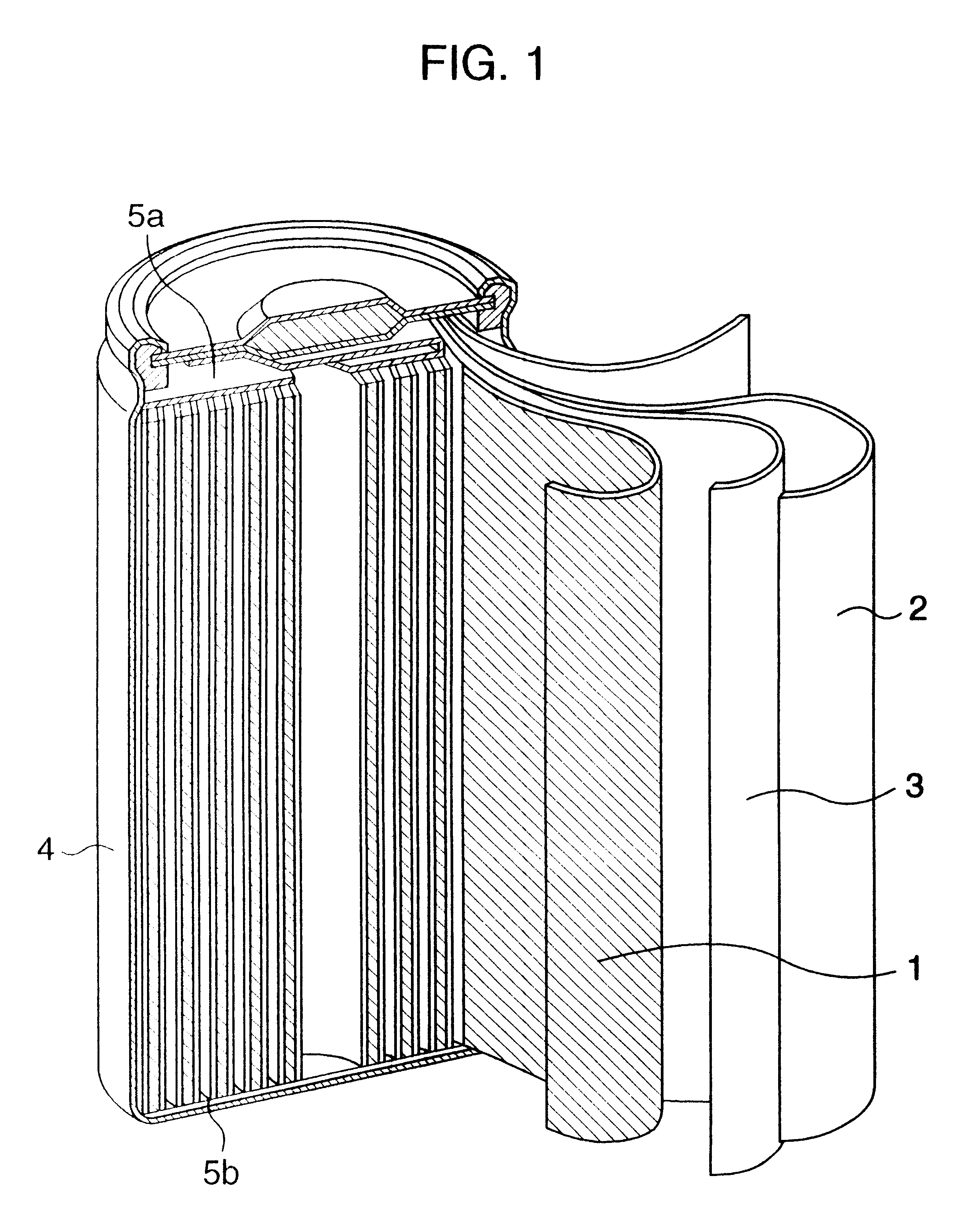
ActiveUS20050031939A1Lower internal resistanceIncrease internal resistanceFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsInternal resistanceLayer thickness
A cylindrical alkaline storage battery suitable to increase its capacity and arranged to prevent a short circuit and internal resistance increase, including an electrode group held in an outer can and formed by rolling up together a negative electrode having a negative-electrode core body and a hydrogen-absorbing alloy layer supported thereon, a positive electrode, and a separator. The negative electrode includes a main part forming inside part of the electrode group, a thin part smaller than the main part in the thickness of the hydrogen-absorbing alloy layer and the amount of a hydrogen-absorbing alloy contained in unit volume of that layer, and a boundary part formed between the main and thin parts and having a hydrogen-absorbing alloy layer thickness varying along the length of the negative-electrode core body. The positive electrode outer end and the negative electrode boundary part are at different positions circumferentially of the electrode group.
Owner:FDK CORP
Hydrogen Absorbing Alloy, Hydrogen Absorbing Alloy Electrode, Secondary Battery and Production Method of Hydrogen Absorbing Alloy
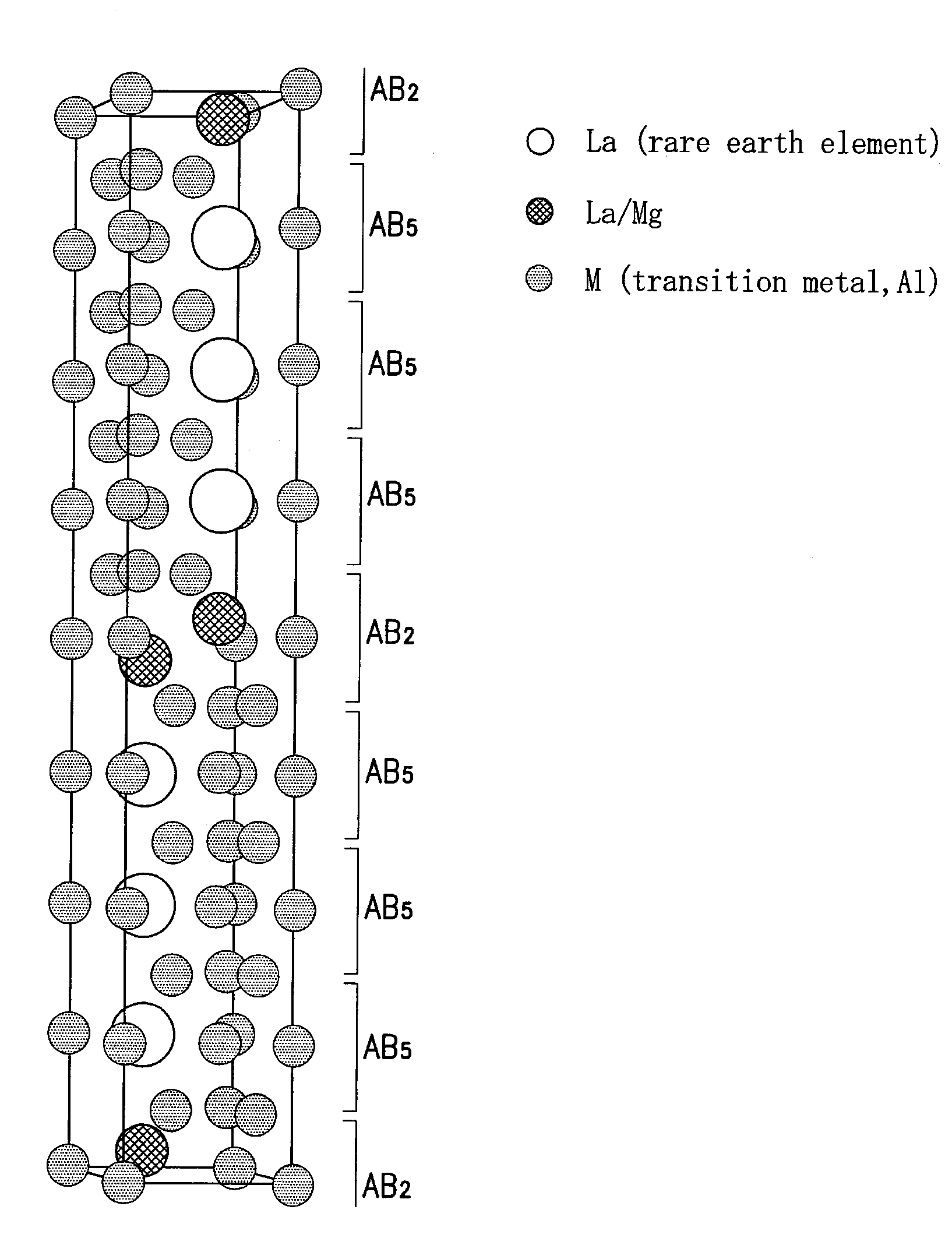
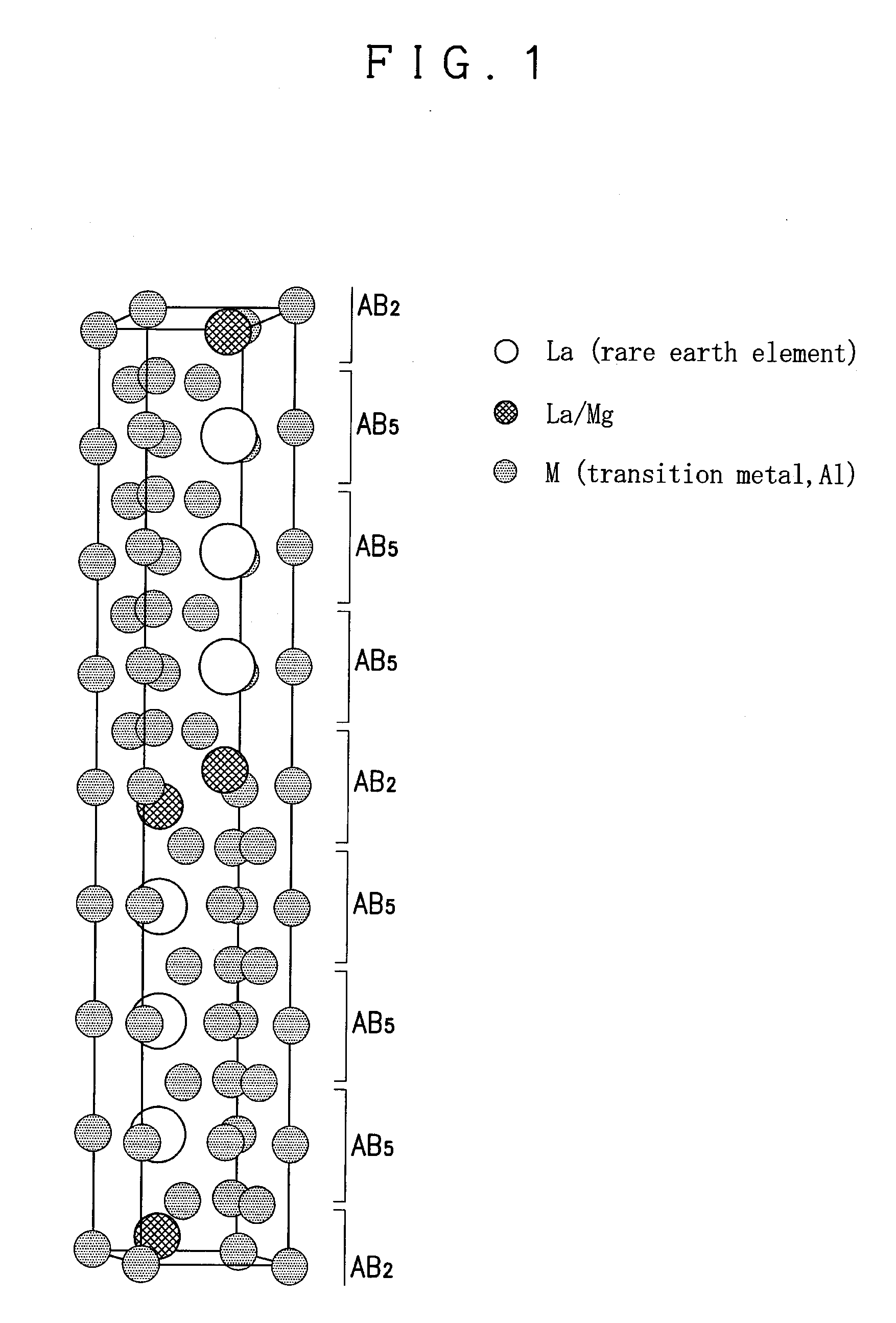
ActiveUS20090226342A1Improve hydrogen storage performanceIncreased durabilityReactant parameters controlCell electrodesRare-earth elementCrystal structure
The present invention provides a hydrogen absorbing alloy containing a phase of a Pr5Co19 type crystal structure having a composition defined by a general formula A(4−w)B(1+w)C19 (A denotes one or more element(s) selected from rare earth elements including Y (yttrium); B denotes an Mg element; C denotes one or more element(s) selected from a group consisting of Ni, Co, Mn, and Al; and w denotes a numeral in a range from −0.1 to 0.8) and having a composition as a whole defined by a general formula R1xR2yR3z (15.8≦x≦17.8, 3.4≦y≦5.0, 78.8≦z≦79.6, and x+y+z=100; R1 denotes one or more element(s) selected from rare earth elements including Y (yttrium); R2 denotes an Mg element, R3 denotes one or more element(s) selected from a group consisting of Ni, Co, Mn, and Al; the numeral of Mn+Al in the z is 0.5 or higher; and the numeral of Al in the z is 4.1 or lower).
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
A yttrium-nickel rare earth hydrogen storage alloy and a secondary battery containing the hydrogen storage alloy
ActiveCN104513925BStructural stress reliefImprove mechanical propertiesAlkaline accumulator electrodesDesorptionGas phase
A yttrium-nickel rare earth hydrogen storage alloy and a secondary battery containing the hydrogen storage alloy of the present invention relate to an AB3 type RExYyNiz-a-bMnaAlb hydrogen storage electrode alloy. The alloy has good activation performance, rate discharge capability, cycle stability of charging and discharging or hydrogen absorption and desorption, can be used in a wide temperature range, has small self-discharge, and its maximum electrochemical capacity can reach more than 360mAh·g-1 . The electrochemical performance of the alloy as a hydrogen storage electrode and the gas-phase hydrogen absorption and desorption performance as a hydrogen storage material are superior to those of the traditional LaNi5 type hydrogen storage alloy. In comparison, the fabrication method is simple and safe.
Owner:BAOTOU RES INST OF RARE EARTHS +2
Nickel Metal-Hydride Battery
ActiveUS20090130551A1Improved output power performanceImprove cycle performanceHydrogenFinal product manufactureRare-earth elementNickel electrode
A sealed nickel metal-hydride battery shows a high output density and an excellent cycle performance particularly in a cold atmosphere. In a nickel metal-hydride battery having a nickel electrode and a hydrogen absorbing electrode respectively as positive electrode and negative electrode, the hydrogen absorbing electrode is formed by making an conductive support carry hydrogen absorbing alloy powder of rare earth elements and non-rare earth elements including nickel and the saturation mass susceptibility of the hydrogen absorbing alloy powder is 2 to 6 emu / g while the rate at which the hydrogen absorbing electrode carries hydrogen absorbing alloy powder per unit area is 0.06 to 0.15 g / cm2.
Owner:GS YUASA INT LTD
Alkaline storage battery
InactiveUS6268083B1Alkaline accumulator electrodesNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesElectrical resistance and conductanceHigh rate
The invention relates to an improvement of an alkaline storage battery and provides an alkaline storage battery excellent in high-rate discharge characteristic at low temperatures particularly by suppressing the increase of electrode resistance. The alkaline storage battery includes a positive electrode which includes a metal oxide as the main constituent material, a negative electrode which includes a hydrogen absorbing alloy, a separator, and an alkaline electrolyte, wherein the negative electrode has a capacity per unit area of 10-40 mAh / cm2.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Hydrogen-absorbing alloy and hydrogen sensor using the alloy
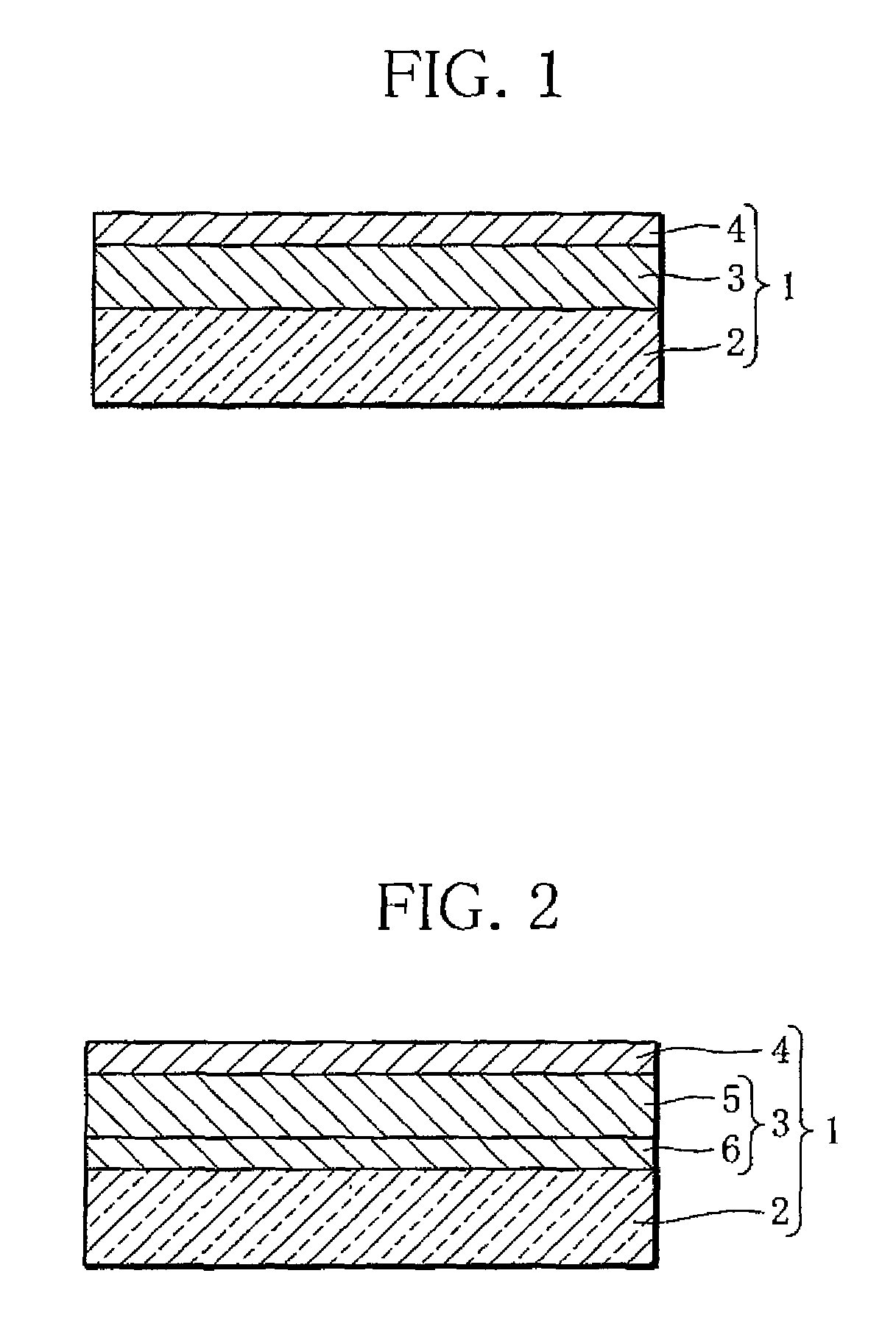
ActiveUS8758691B2Dehydrogenation and additionQuick releaseAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWeather/light/corrosion resistanceReaction layerHydrogen sensor
A hydrogen sensor using a hydrogen-absorbing alloy containing an Mg—Ni-based alloy and a Zr—Ti-based alloy includes a substrate (2), a hydrogen reaction layer (3) formed on the substrate (2) and containing the Mg—Ni-based alloy and the Zr—Ti-based alloy, and a first catalyst layer (4) formed on the hydrogen reaction layer (3) and capable of accelerating hydrogenation of the Mg—Ni-based alloy.
Owner:ATSUMITEC CO LTD
Negative electrode for alkaline storage battery and alkaline storage battery
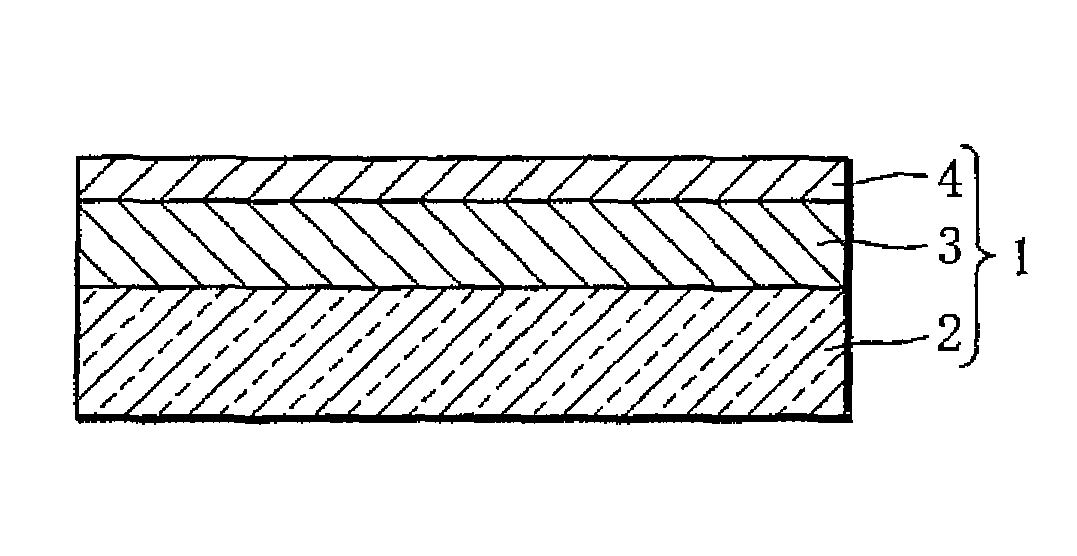
InactiveUS20110052983A1Low costSignificantly improvedActive material electrodesSecondary cellsRare-earth elementElectrolyte
An alkaline storage battery having a positive electrode (1), a negative electrode (2), and an alkaline electrolyte solution, and the negative electrode having fluorinated oil being present on the surface thereof. The negative electrode includes a hydrogen-absorbing alloy represented by the general formula Ln1-xMgxNiy-a-bAlaMb, where Ln is at least one element selected from Zr, Ti, and a rare-earth element including Y; M is at least one element selected from the group consisting of V, Nb, Ta, Cr, Mo, Mn, Fe, Co, Ga, Zn, Sn, In, Cu, Si, P, and B; 0.05≦x≦0.30; 0.05≦a≦0.30; 0≦b≦0.50; and 2.8≦y≦3.9.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com