Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
65 results about "Hemophilia patient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
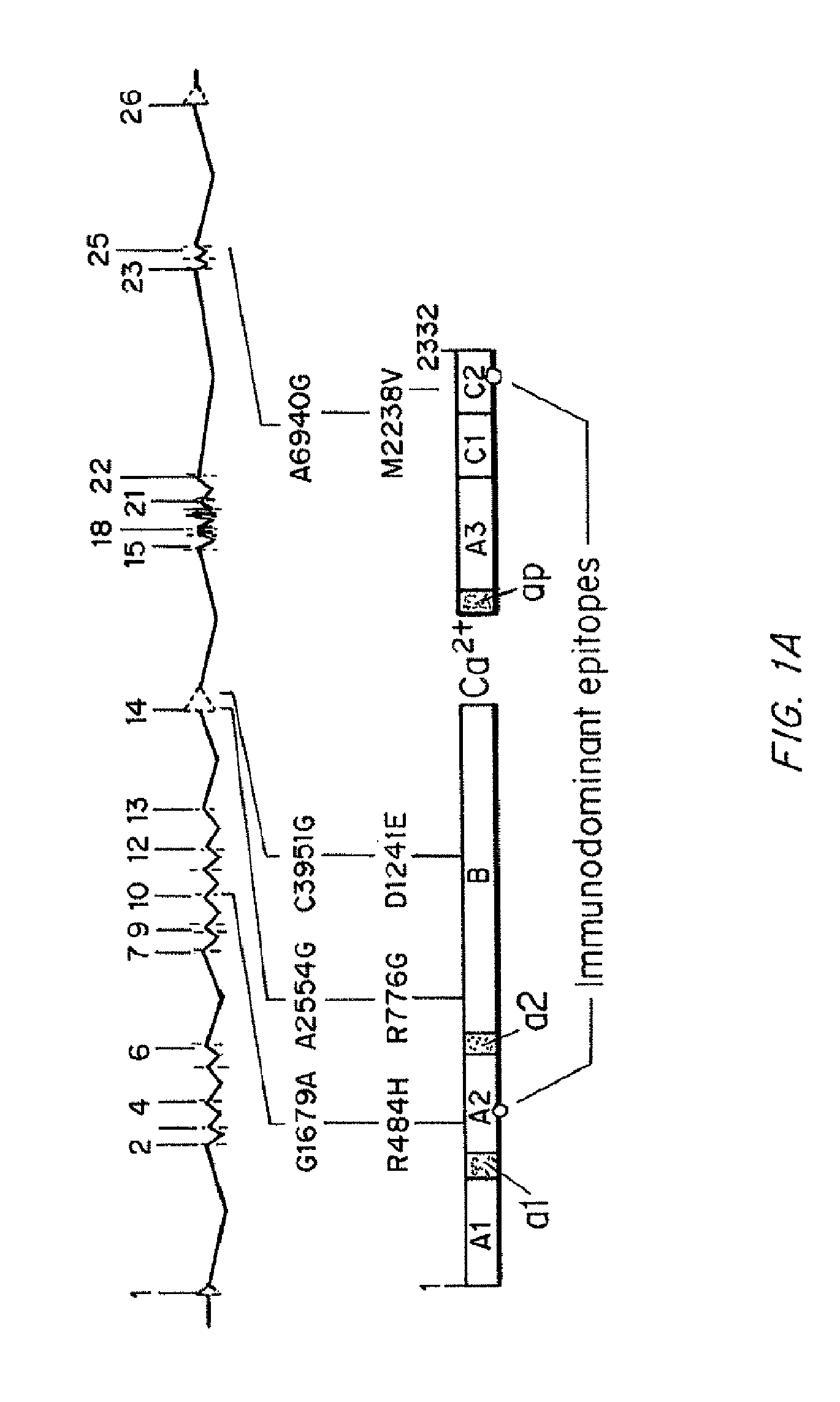
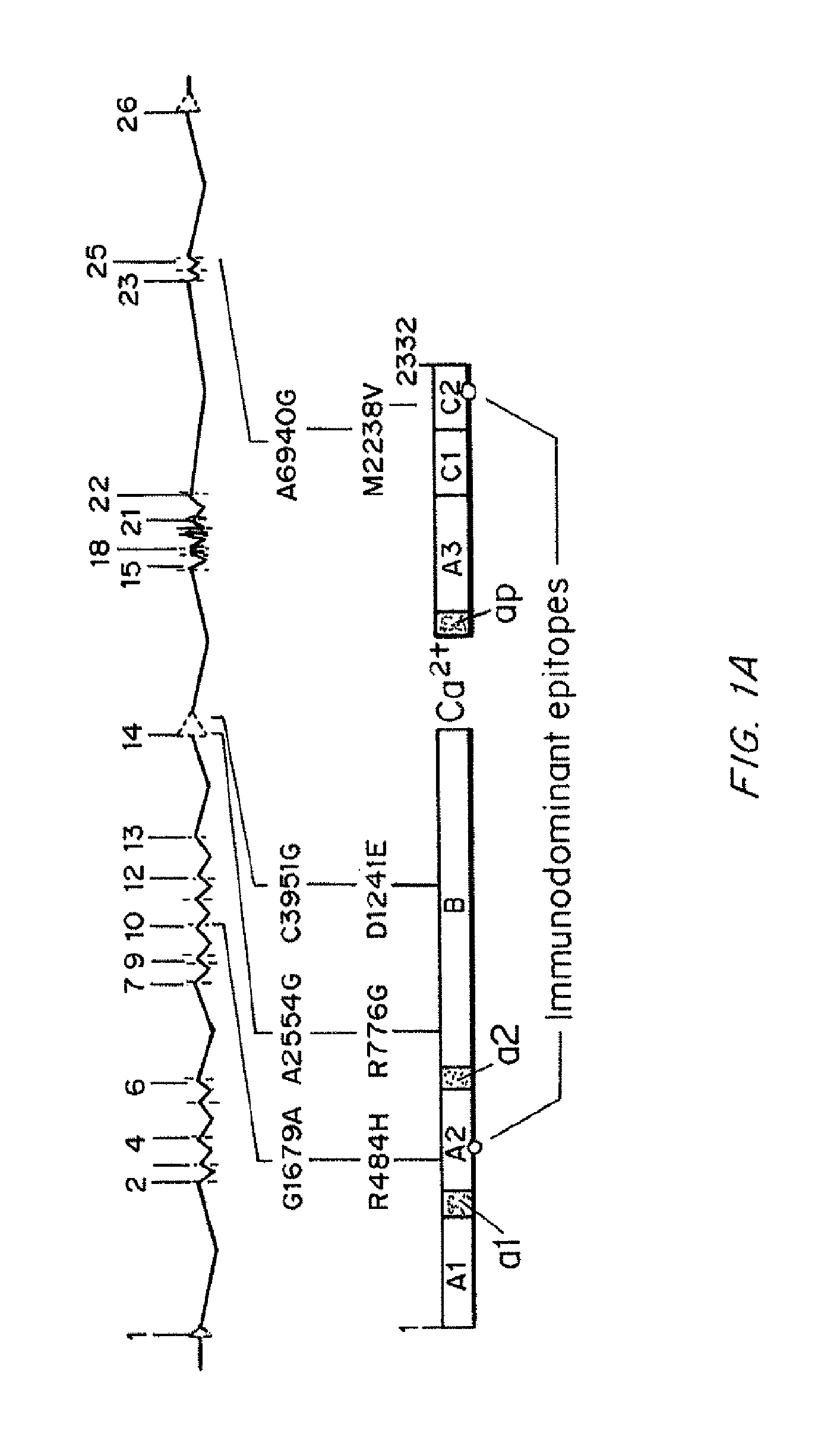
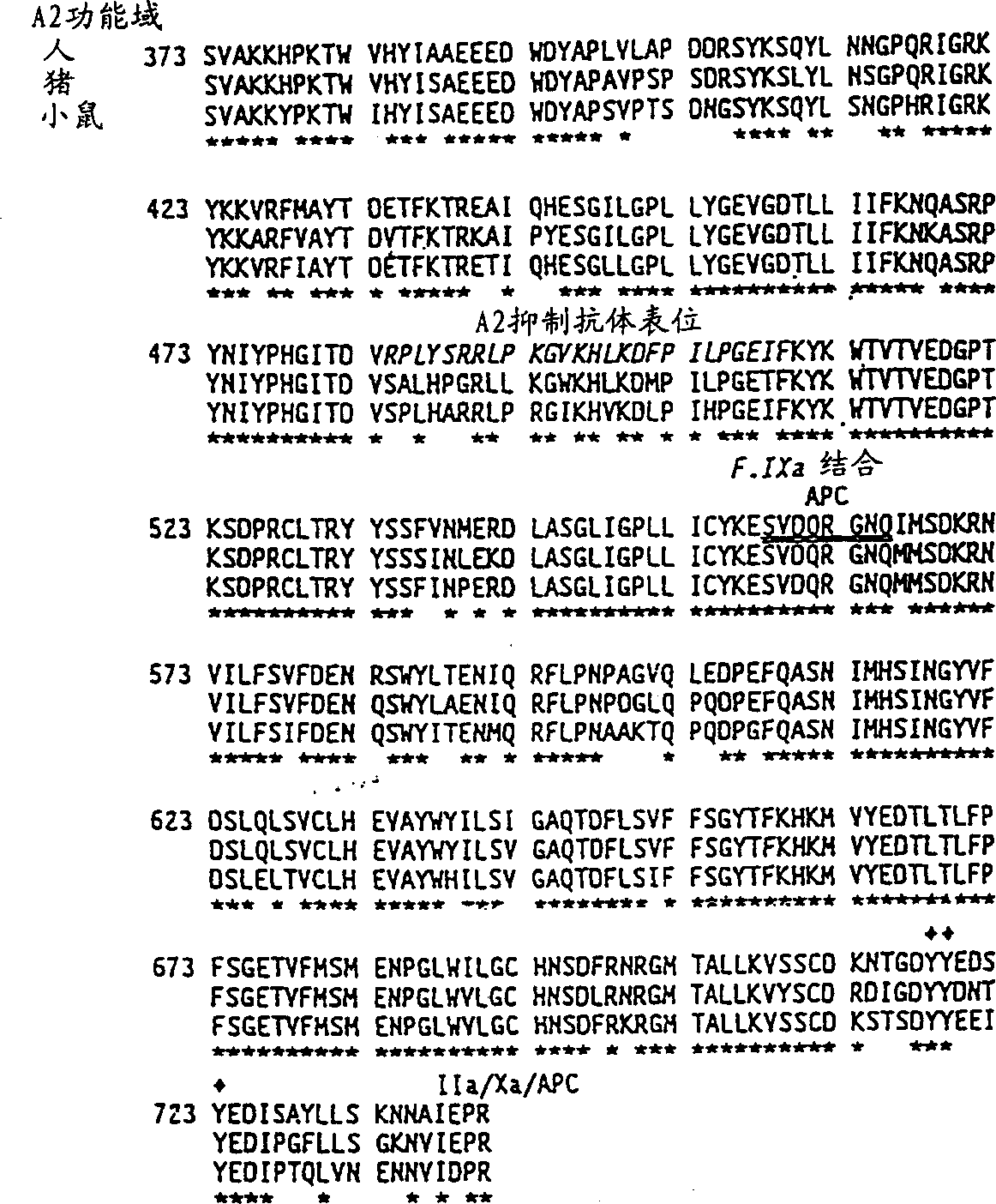
Modified fVIII having reduced immunogenicity through mutagenesis of A2 and C2 epitopes
InactiveUS20050123997A1Low immunogenicityImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsFactor VIIEpitopeVaccine Immunogenicity
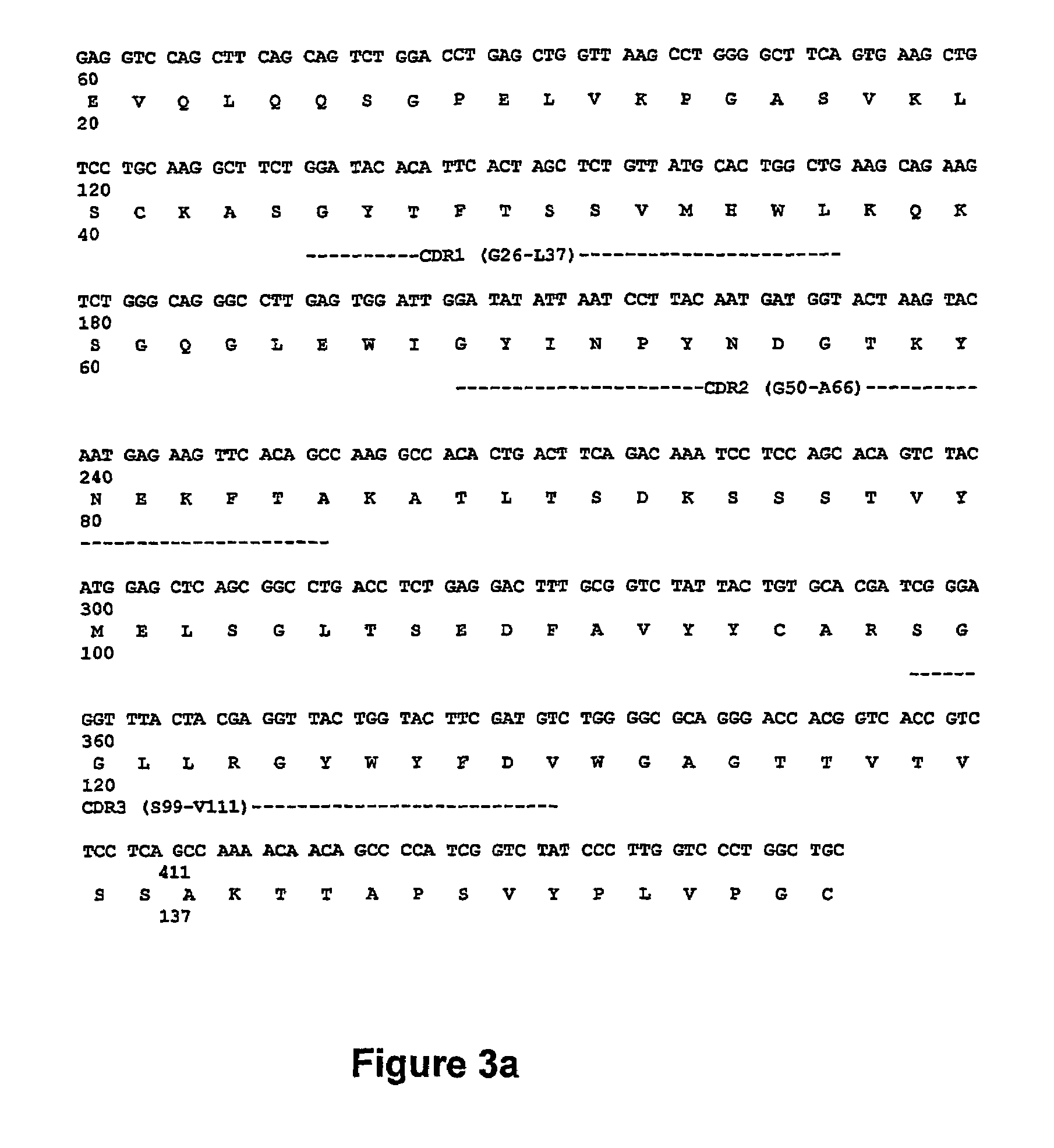
Specific amino acid loci of human fVIII interact with inhibitory antibodies of hemophilia patients after being treated with fVIII. Modified fVIII is disclosed in which the amino acid sequence is changed by multiple substitutions in human fVIII A2 and C2 domains. The modified fVIII is useful for hemophiliacs, either to avoid or prevent the action of inhibitory antibodies.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Modified factor VIII
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Modified factor VIII
Modified porcine factor VIII is disclosed in which most of the B domain has been removed through genetic engineering. This modified factor VIII is particularly useful for treatment of hemophiliacs, especially those undergoing bleeding episodes.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Nucleic acid molecules encoding modified factor VIII proteins, expression products, and methods of making the same
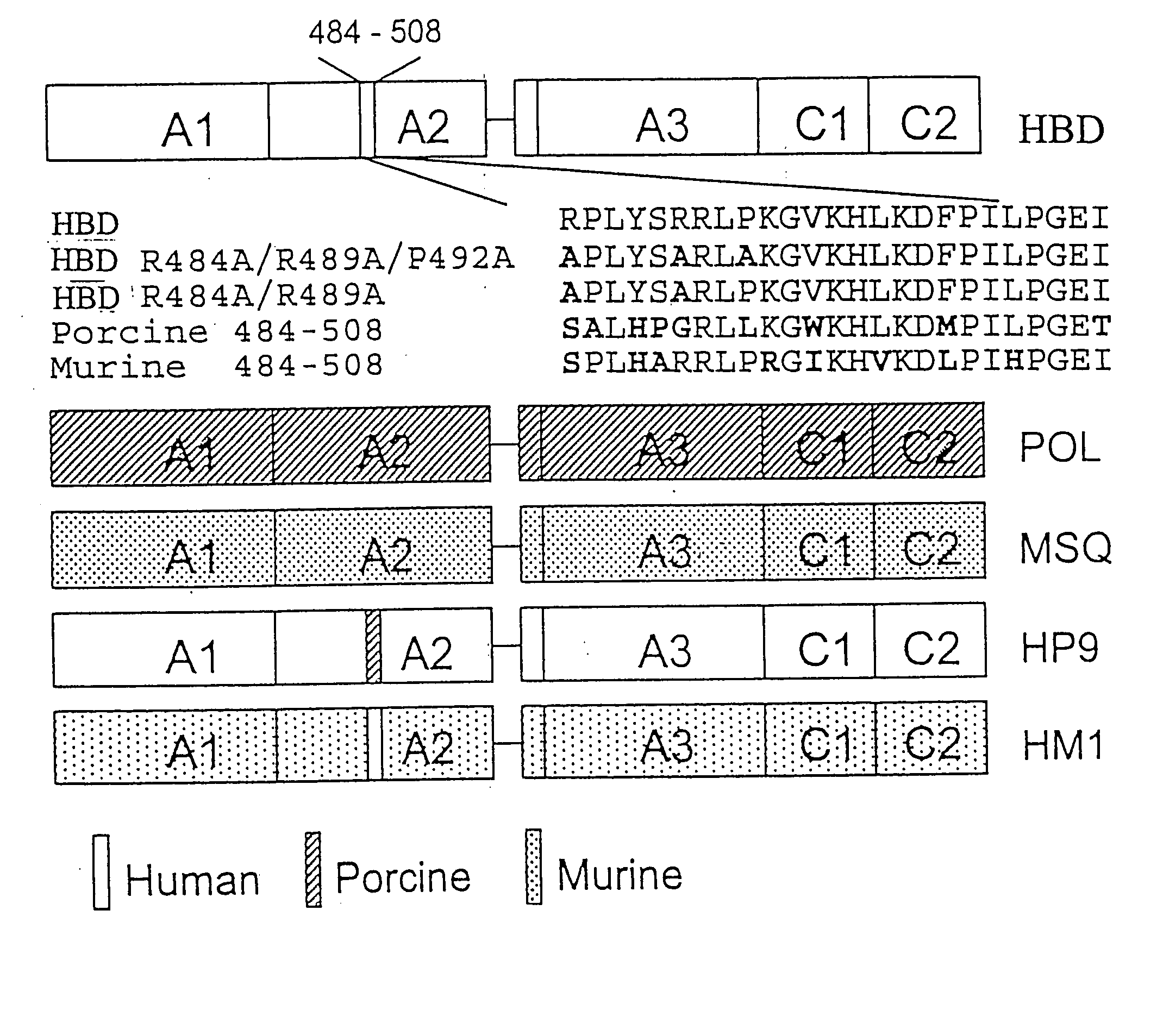
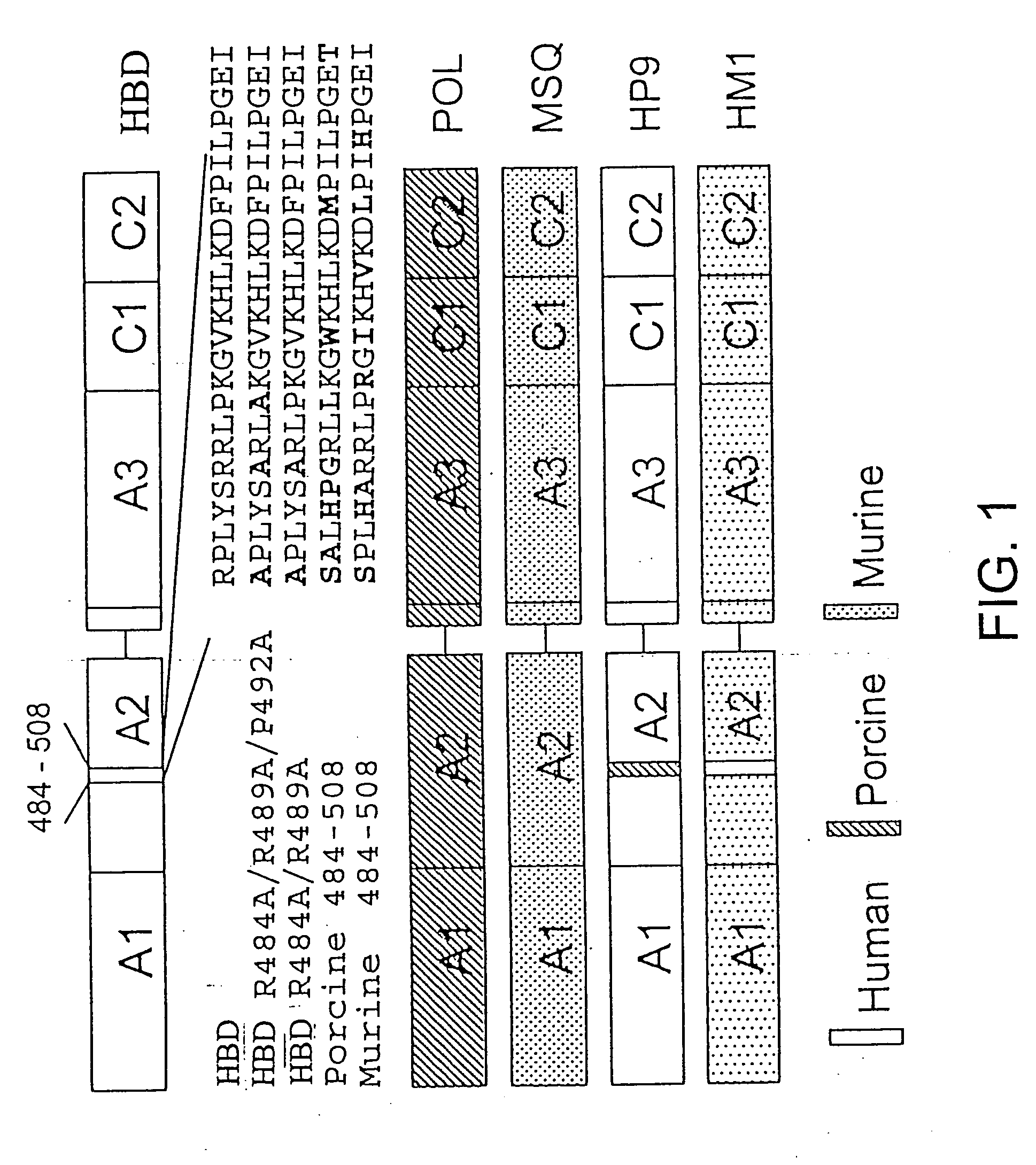
Specific amino acid loci of human factor VIII interact with inhibitory antibodies of hemophilia patients who have developed such antibodies after being treated with factor VIII. Modified factor VIII is disclosed in which the amino acid sequence is changed by a substitution at one or more amino acids of positions 484-508 of the A2 domain. The modified factor VIII is useful as a clotting factor supplement for hemophiliacs.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
Glycosylated, low antigenicity, low immunogenicity factor VIII
InactiveUS20050009148A1Factor VIIMammal material medical ingredientsBlood coagulation factor VIIIVaccine Immunogenicity
The development of inhibitory antibodies to blood coagulation factor VIII (fVIII) results in a severe bleeding tendency. These antibodies arise in patients with hemophilia A (hereditary fVIII deficiency) who have been transfused with fVIII. They also occur in non-hemophiliacs, which produces the condition acquired hemophilia. We describe a method to construct and express novel recombinant fVIII molecules which escape detection by existing inhibitory antibodies (low antigenicity fVIII) and which decrease the likelihood of developing inhibitory antibodies (low immunogenicity fVIII). In this method, fVIII is glycosylated at sites that are known to be antibody recognition sequences (epitopes). This produces the desired properties of low antigenicity fVIII and low immunogenicity fVIII. The mechanism is similar to one used by viruses such as the AIDS virus, which glycosylates its surface proteins to escape detection by the immune system.
Owner:LOLLAR JOHN S
Modified factor VIII
InactiveUS20050079584A1Superior coagulant activityFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsEpitopeInhibitory antibodies
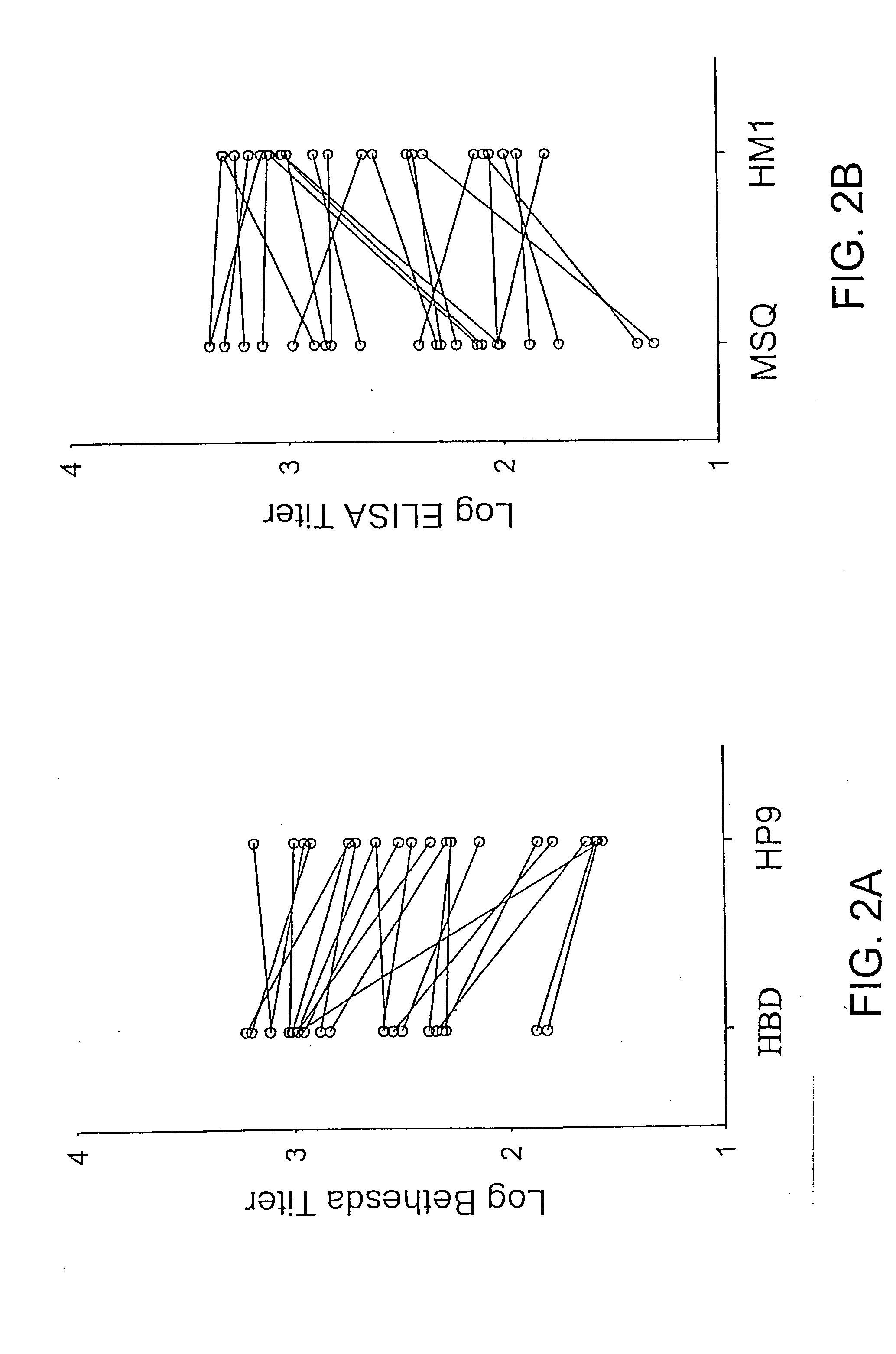
Specific amino acid loci of human factor VIII interact with inhibitory antibodies of hemophilia patients who have developed such antibodies after being treated with factor VIII. Modified factor VIII is disclosed in which the amino acid sequence is changed by a substitution at one or more of the specific loci. The modified factor VIII is not inhibited by inhibitory antibodies against the A2 or C2 domain epitopes. The modified factor VIII is useful for hemophiliacs, either to avoid or prevent the action of inhibitory antibodies.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Methods of using a fixed dose of a clotting factor
ActiveUS20160296607A1Low variabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiseaseDosing regimen
The present invention provides methods of administering a clotting factor by a fixed dosing regimen; methods of reducing, ameliorating, or preventing one or more symptoms of a bleeding disease or disorder; and a kit comprising a dotting factor useful for a fixed dosing regimen. While plasma-derived and recombinant clotting factor products allow hemophilia patients to live longer and healthier, hemophilia still remains one of the most costly and complex conditions to manage.
Owner:BIOVERATIV THERAPEUTICS INC
Freeze-dried tranexamine powder injection and its preparing prcess
InactiveCN1390539AReduce volumeReduce weightPeptide/protein ingredientsBlood disorderFreeze-dryingAngioneurotic oedema
A freeze dried tranexamine acid powder used as antihemorrhagic injection for treating various hemorrhagic diseases contains tranexamine acid (0.05-10 wt. portions), freeze drying supporting agent (0-100) and pH regulator.
Owner:于航
Human blood coagulation factor VIII gene intron 22 inversion mutation in-situ remediation plasmid, kit and method
ActiveCN104762318APrecise point importNo uncertaintyFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionIn situ remediationIntron 22 inversion
The invention discloses a human blood coagulation factor VIII gene intron 22 inversion mutation in-situ remediation plasmid, kit and method. The method constructs specific in-situ remediation treatment and can specifically repair the type of F8 mutation, and the in-situ remediation strategy is verified in hemophilia patient specific iPSCs by combination with a TALEN technology. The in-situ remediation strategy is a first remediation strategy for remediation of intron 22 inversion as common HA mutation. The in-situ remediation strategy utilizes a sequence accurate fixed-point introduction method, is relatively safe and has no nondeterminacy of the prior art.
Owner:SHANGHAI PINPOINT MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Tranexamic acid freeze-dried powder injection and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101744775AReduce volumeReduce weightPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseUrokinase Plasminogen Activator
The invention discloses a tranexamic acid freeze-dried powder injection and a preparation method thereof, comprising the following components in parts by weight: 0.05-10 parts of tranexamic acid, 1-100 parts of freeze-dried powder proppant, and a proper mount of pH regulator. The invention belongs to hemostasis curative, is a freeze-dried powder injection, has stable performance to light, heat, oxygen, water and the like, and has no pollution as well as convenient operation, transportation and storage. The tranexamic acid freeze-dried powder injection is suitable for various haemorrhages caused by acute, chronic, local, systemic and primary fibrinolysis, trauma or operation haemorrhages of organs rich in plasminogen activators, such as prostate and the like and is used as an antagonist of tectotype plasminogen activators (t-PA), streptokinase and urokinase. The tranexamic acid freeze-dried powder injection is also suitable for thrombolytic haemorrhage caused by abortion and amniotic fluid embolism, is used for preventing or lightening haemorrhage of a haemophile after exelcymosis or oral cavity operation, haemorrhage caused by light diseases of nervous centralis pathological changes, and is used for treating hereditary angioneuroticedema and active hemorrhage of haemophile.
Owner:胥祥进
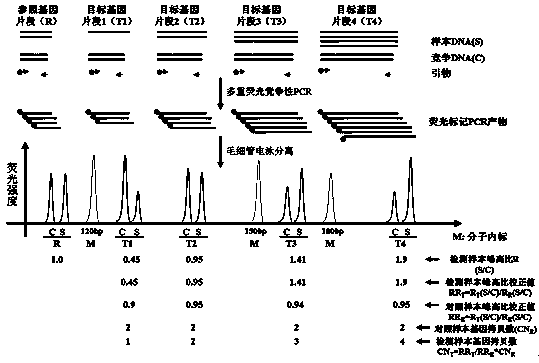
F9 gene copy number variation detection kit
ActiveCN104046699AHigh precisionImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementMedicineHemophilias
The invention discloses an F9 gene copy number variation detection kit which comprises a 2*PCR (Polymerase China Reaction) buffer solution, competitive DNA, PCR primer mixed liquor and Taq DNA polymerase. An AccuCopy technology has high precision, variable coefficient of being less than 5% and high result accuracy. Therefore, according to the F9 gene copy number variation detection kit developed by the AccuCopy technology, about 15 patients suffering hemophilia B with large deletion mutation is detected and found, and the clinical application effect is good.
Owner:RUIJIN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
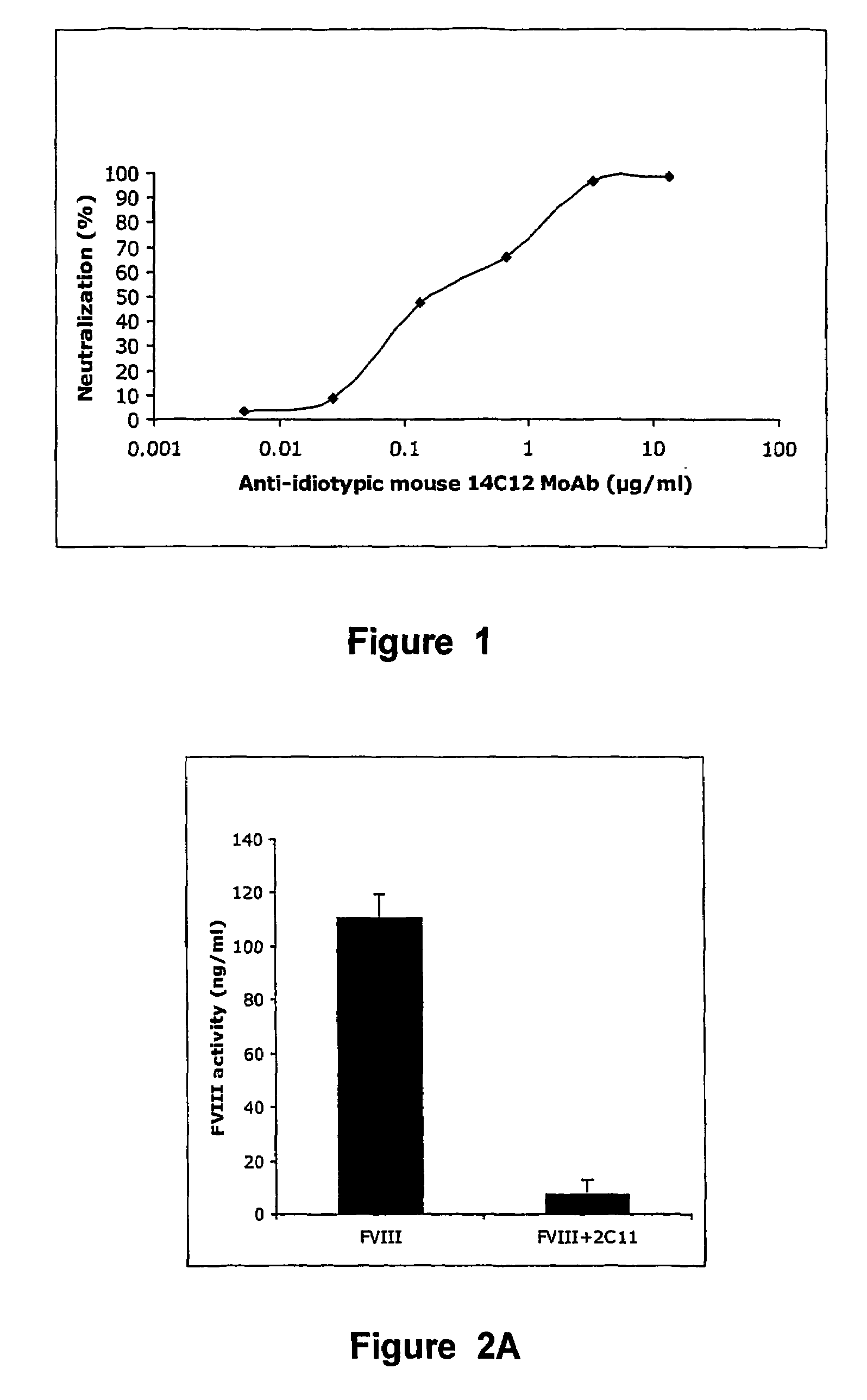
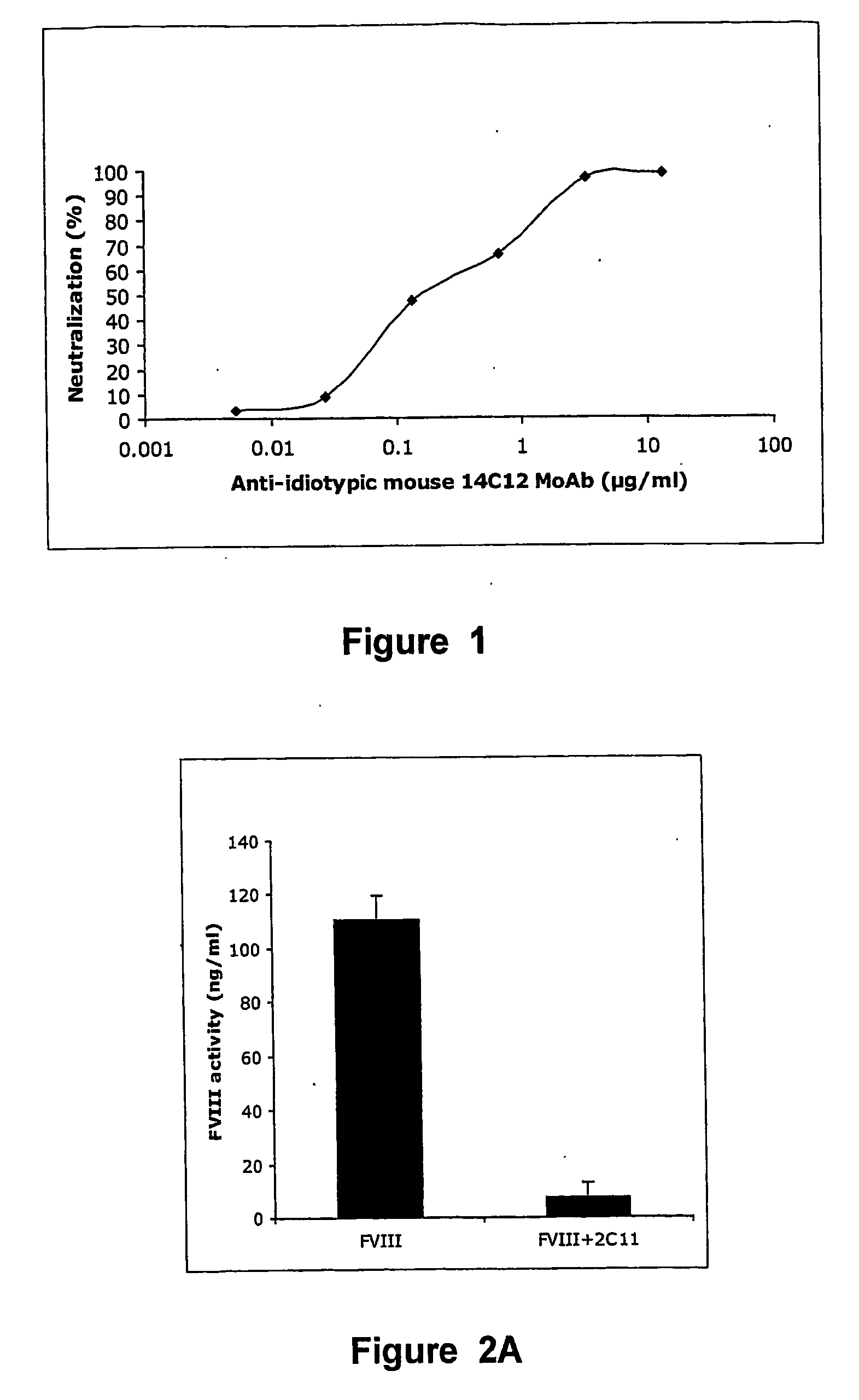
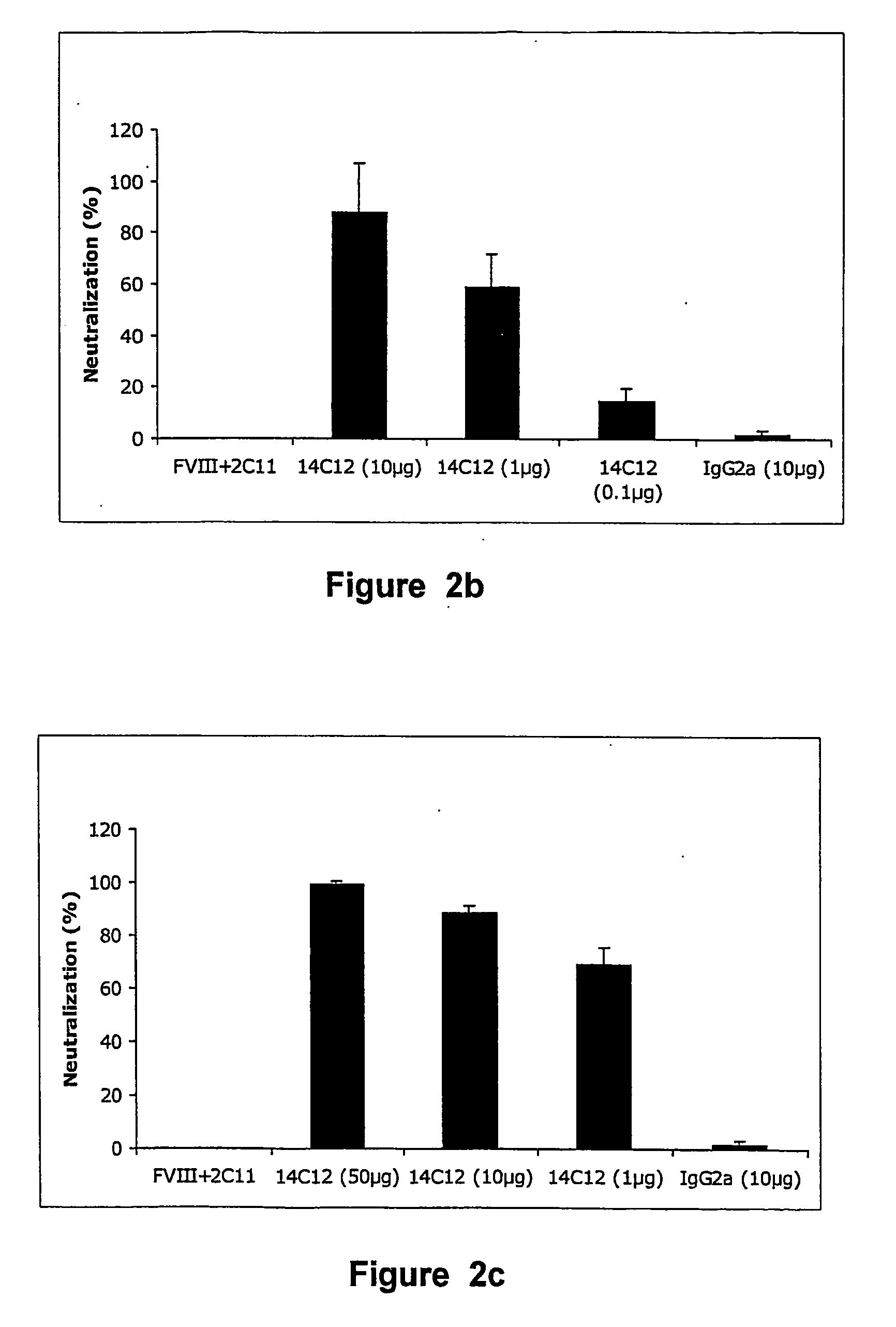
Anti-idiotypic antibodies against factor VIII inhibitor and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060239998A1Increase stability and lifetimeEnhanced inhibitory effectAnimal cellsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsFactor VIII inhibitorIn vivo
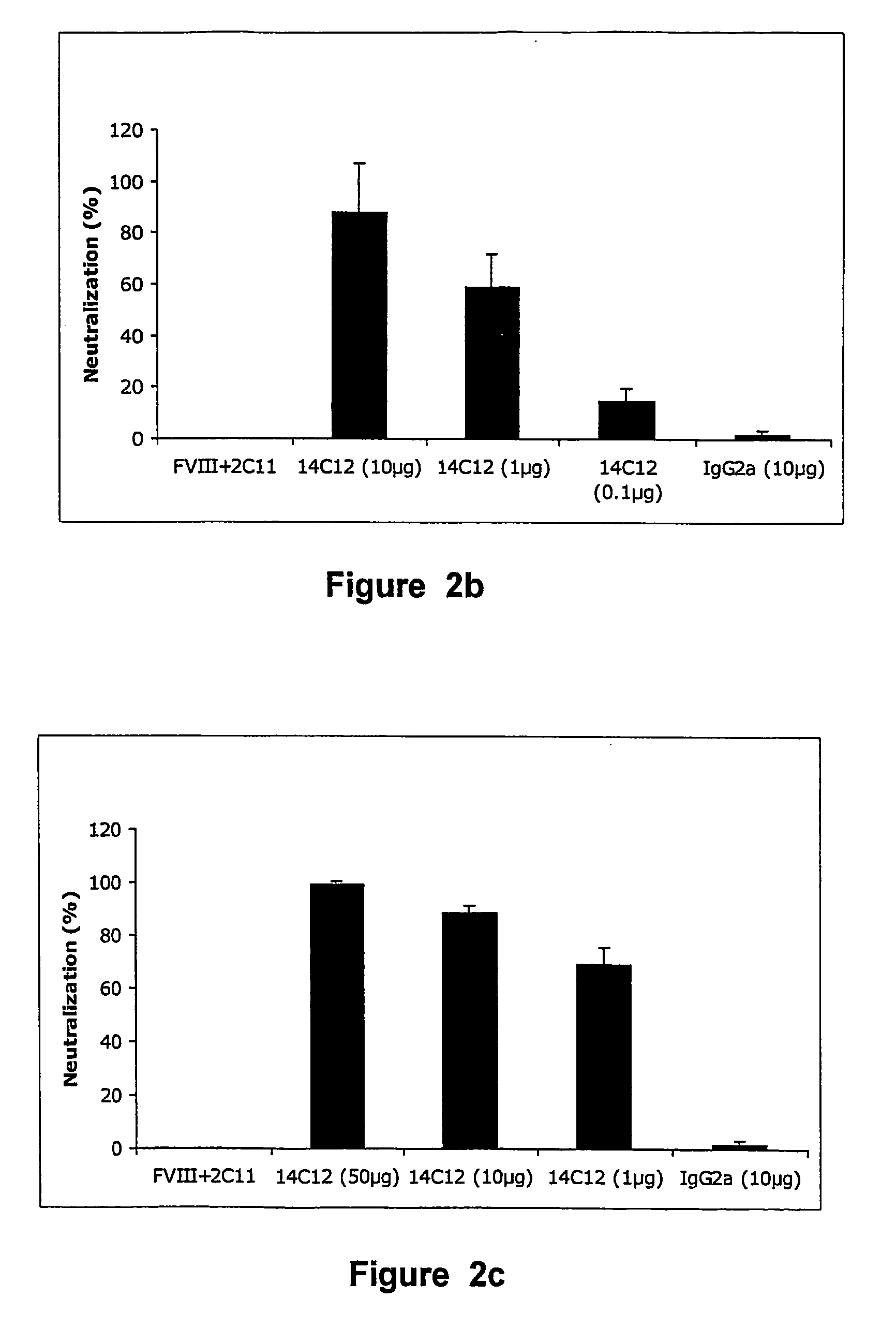
The present invention discloses anti-idiotypic antibodies and fragments thereof against inhibitory Factor VIII anti-bodies, said inhibitory antibodies having an affinity for the C2 domain of Factor VIII. The anti-idiotypic antibodies of the present invention are able to completely neutralise in vitro and in an in vivo mouse model the inhibitory activity of FVIII inhibitors. The anti idiotypic antibodies of the present invention can be applied for the prevention, treatment or reduction of bleeding disorders of hemophilia patients with inhibitory antibody against the C2 domain of Factor VIII.
Owner:LIFE SCI RES PARTNERS VZW
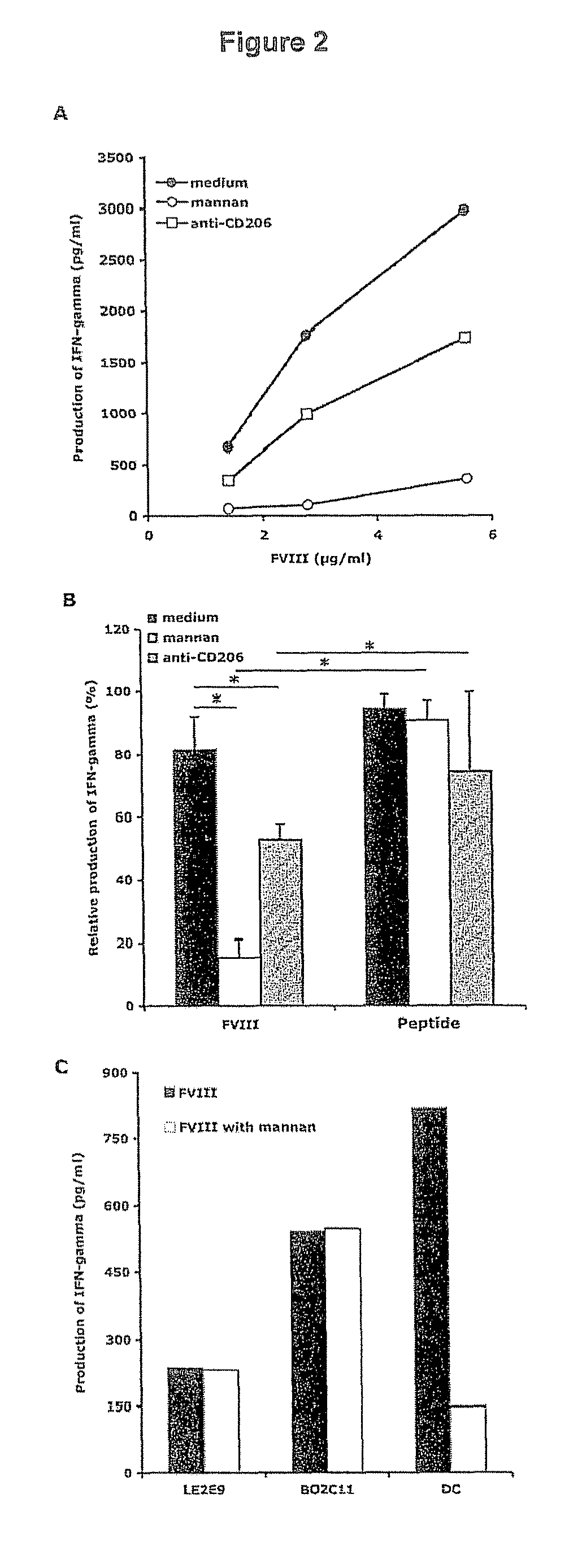
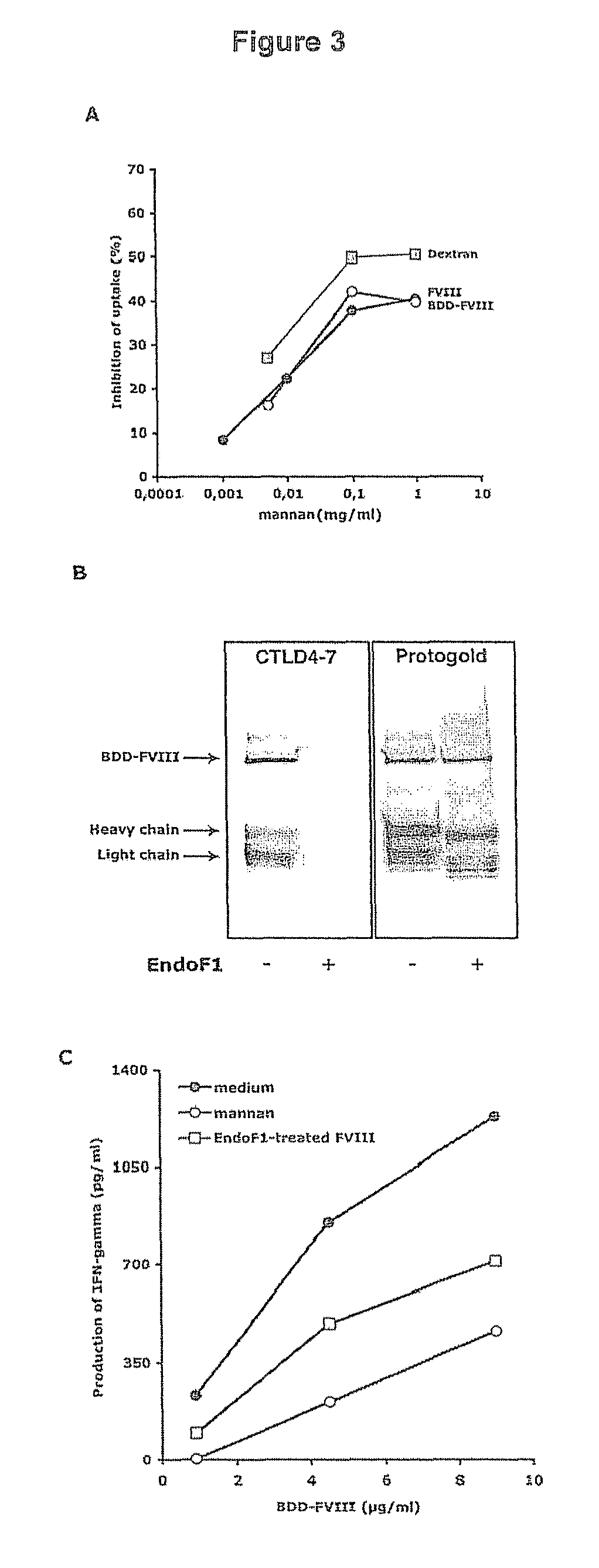
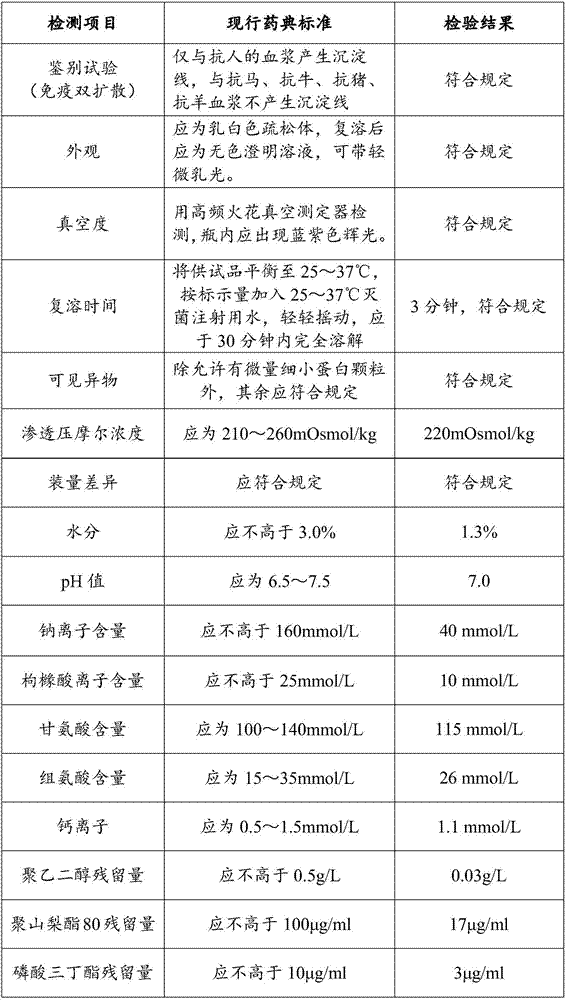
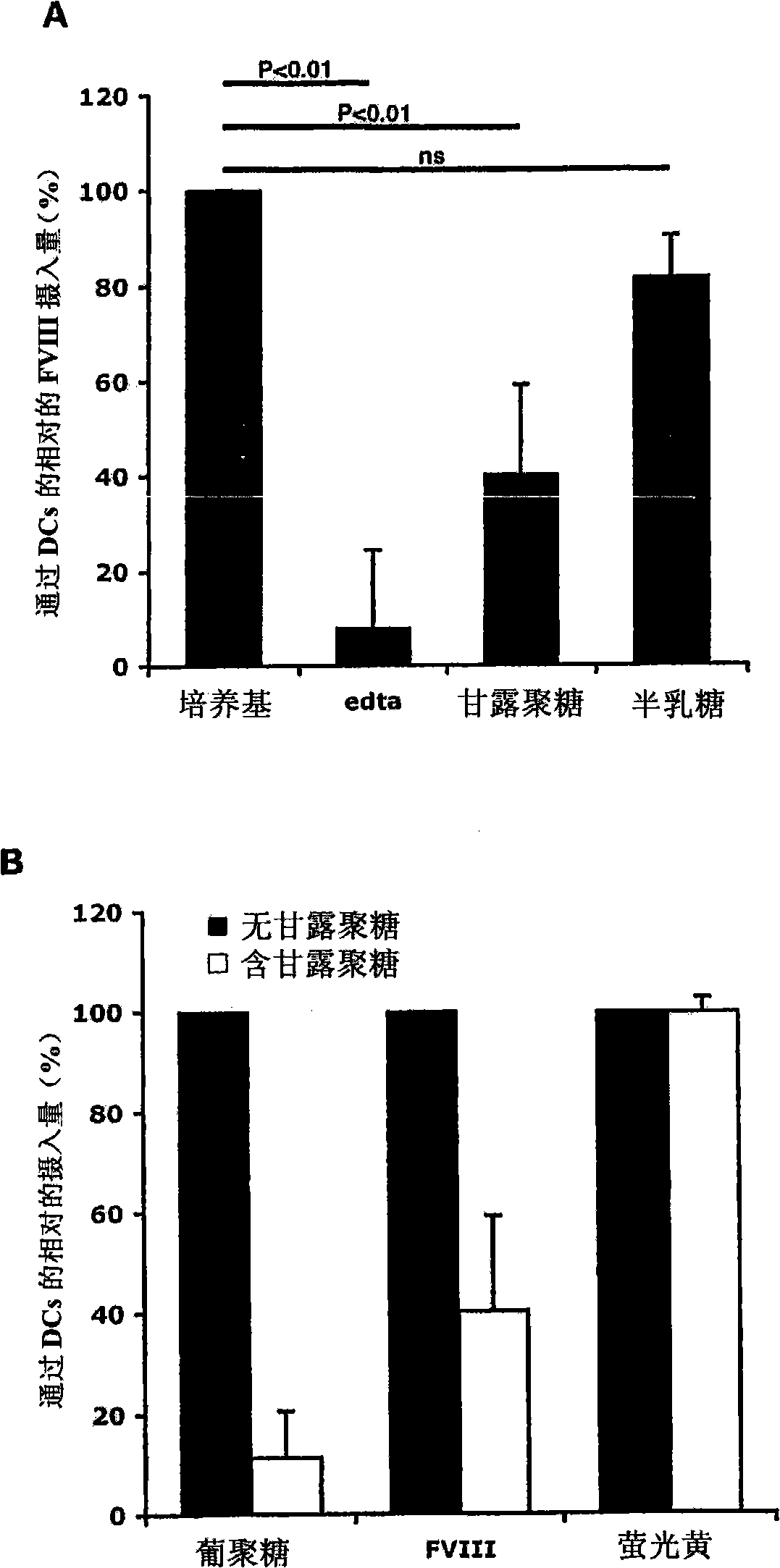
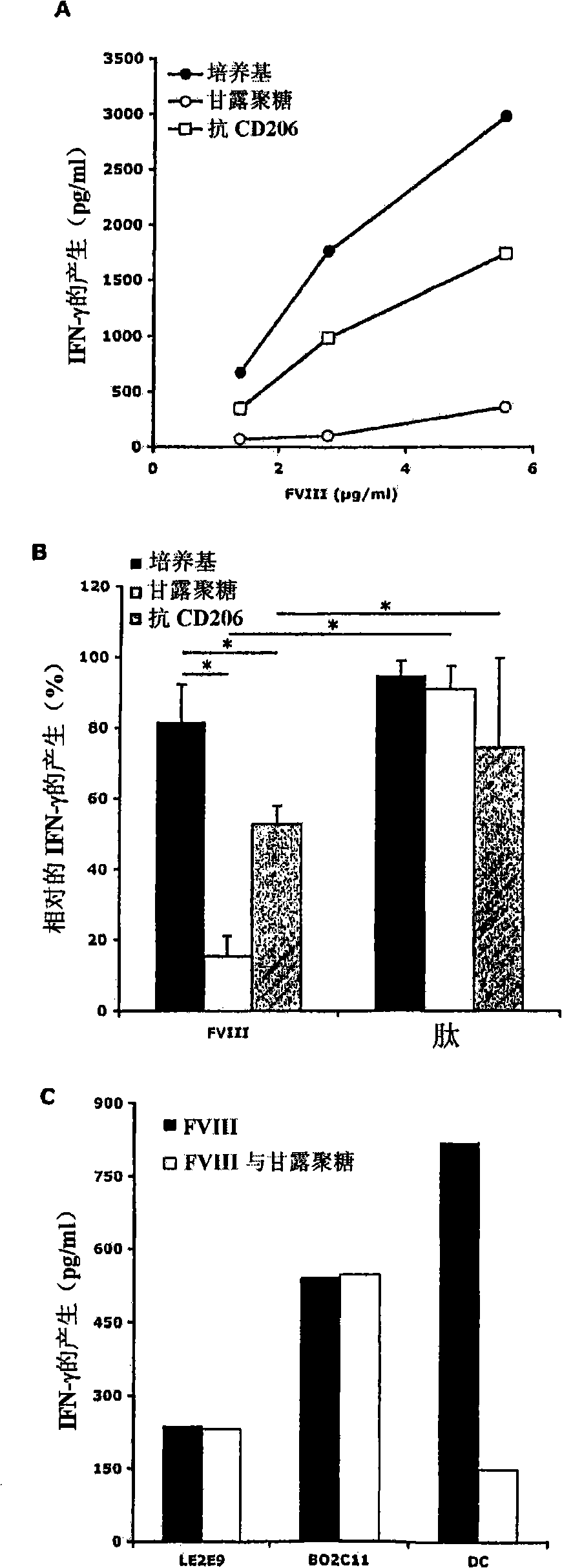
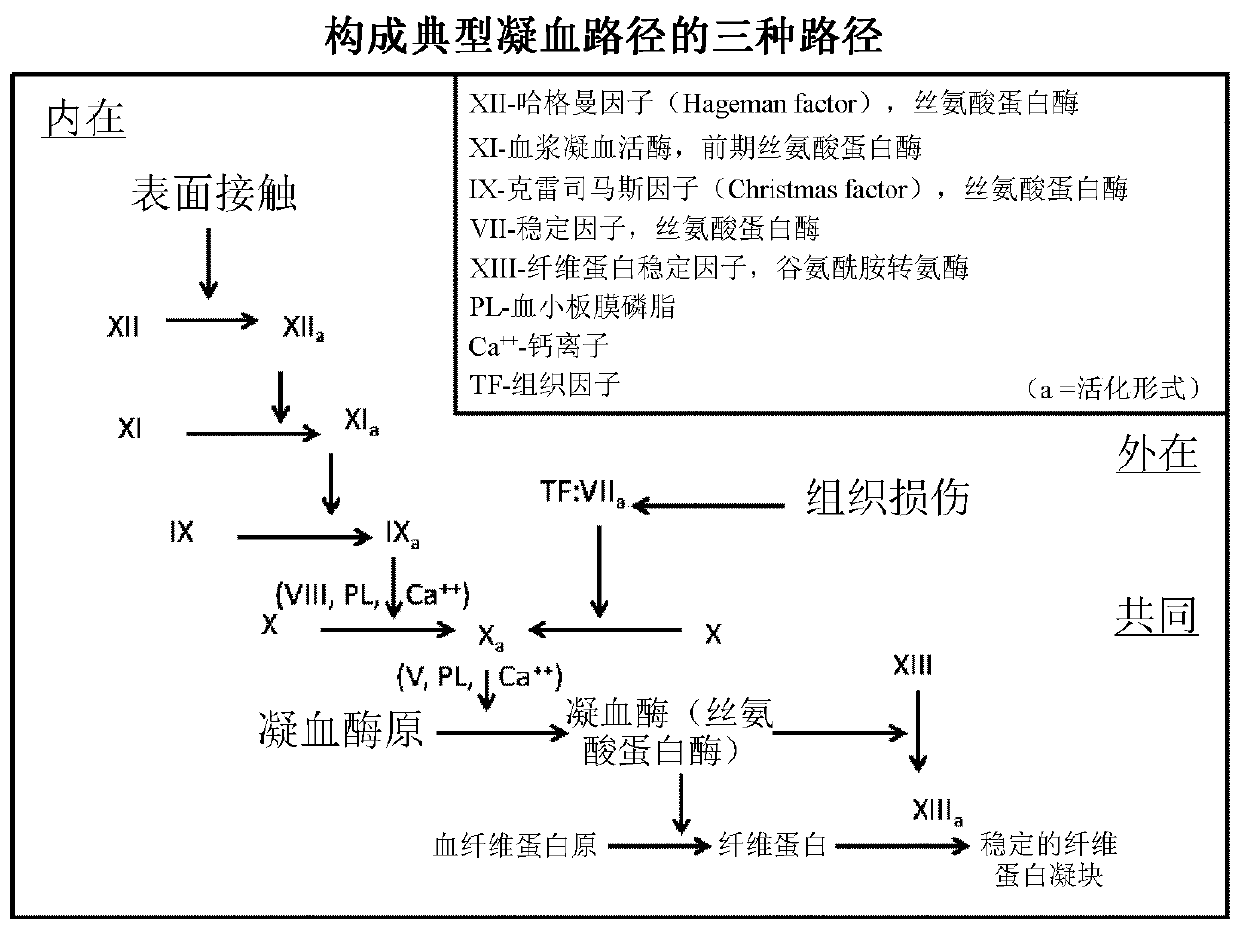
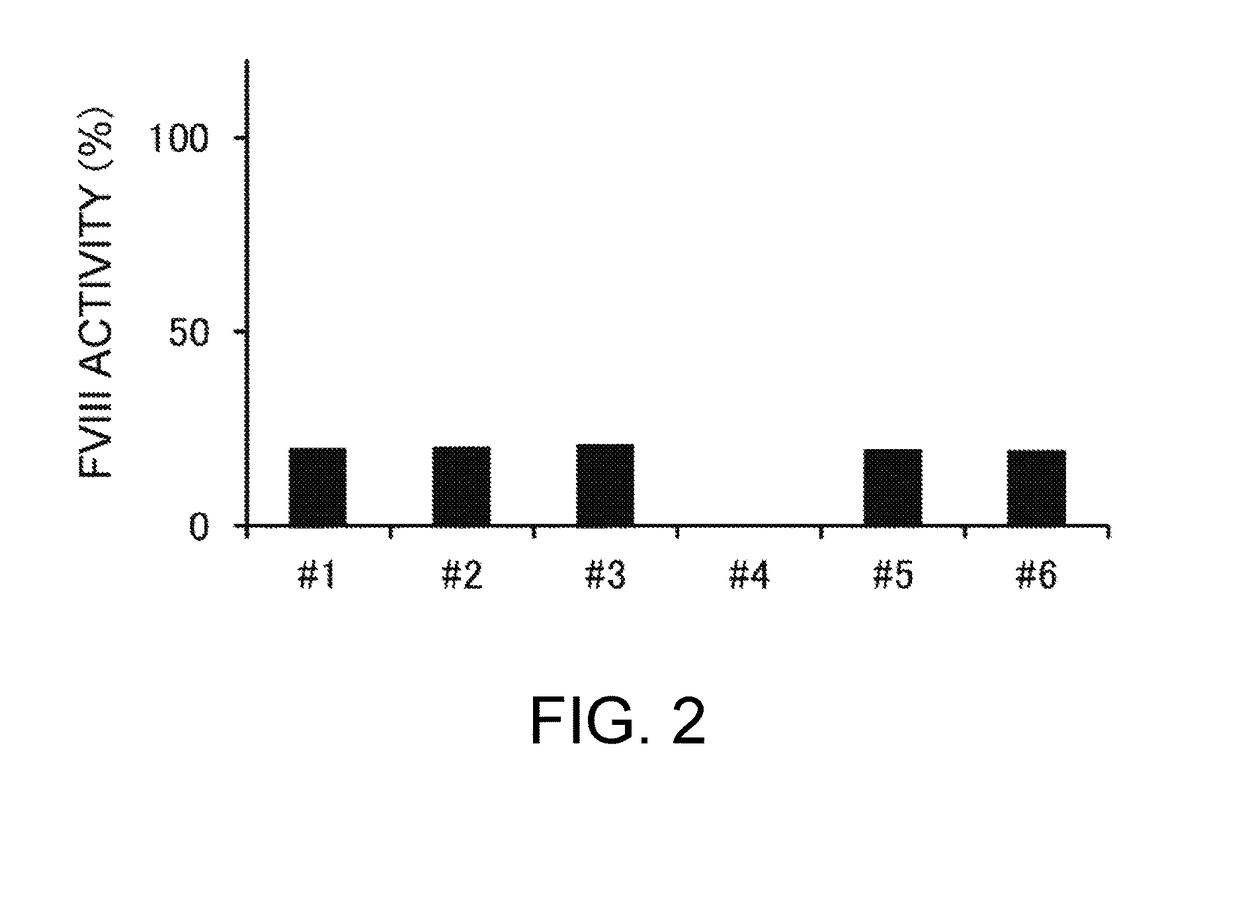
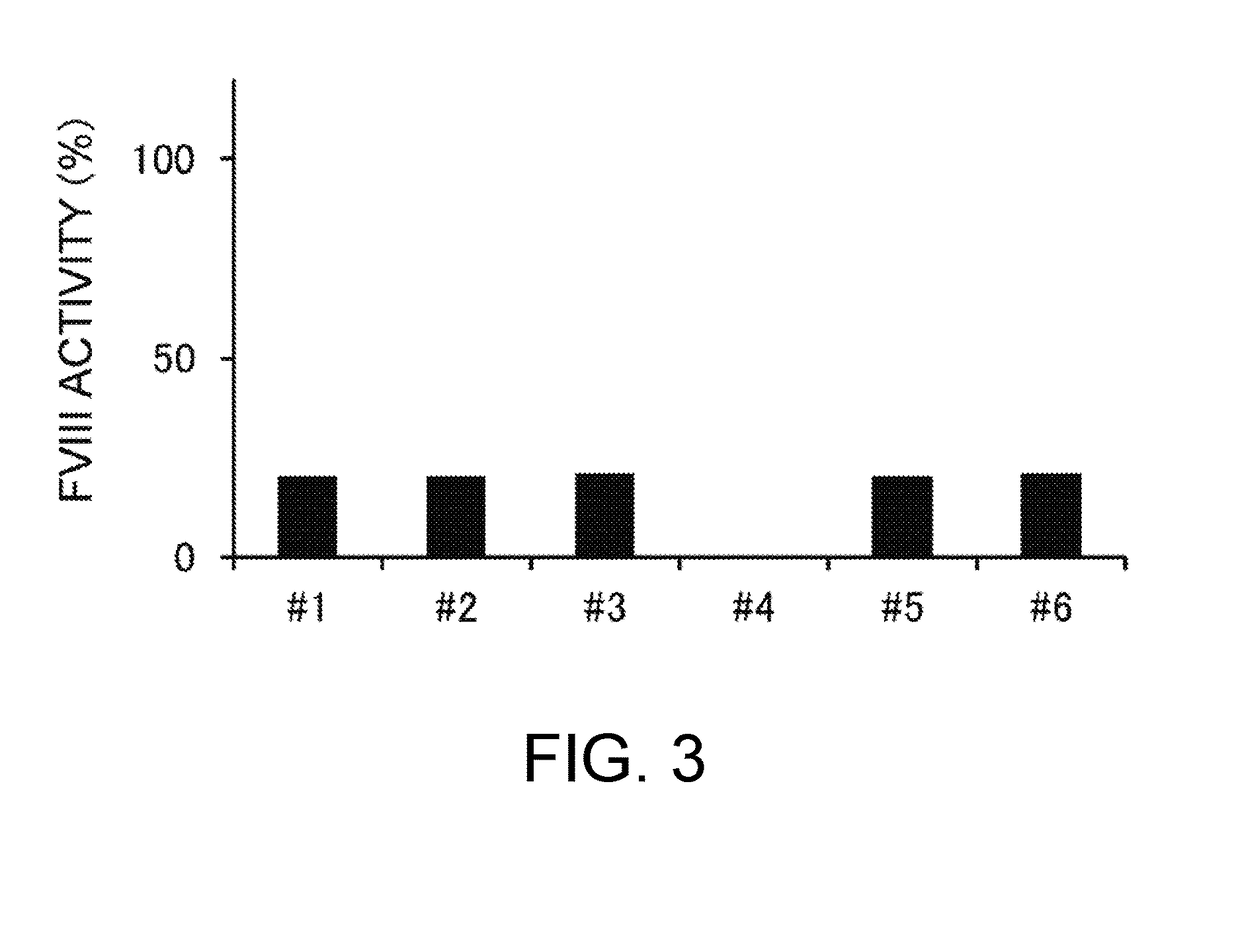
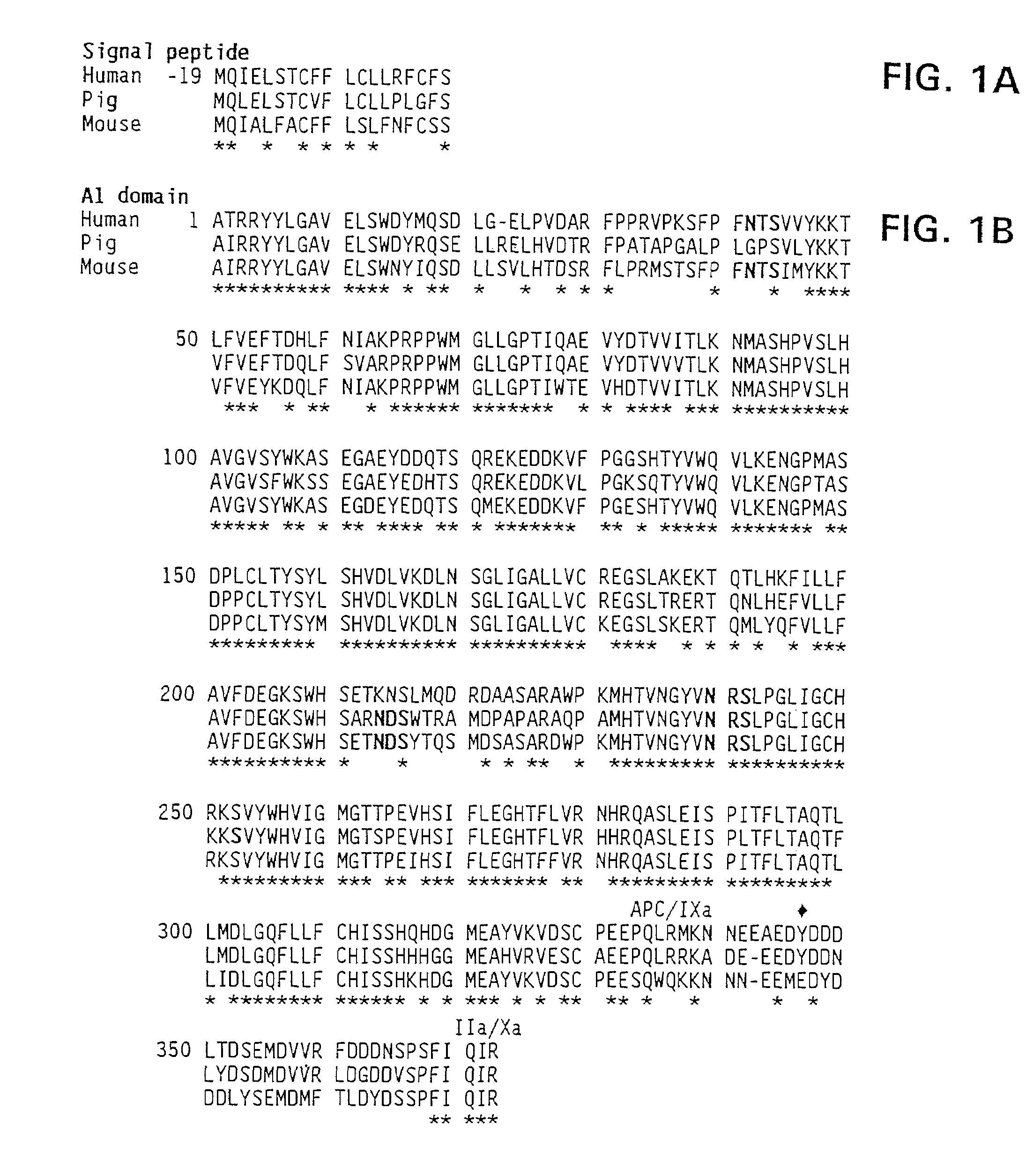
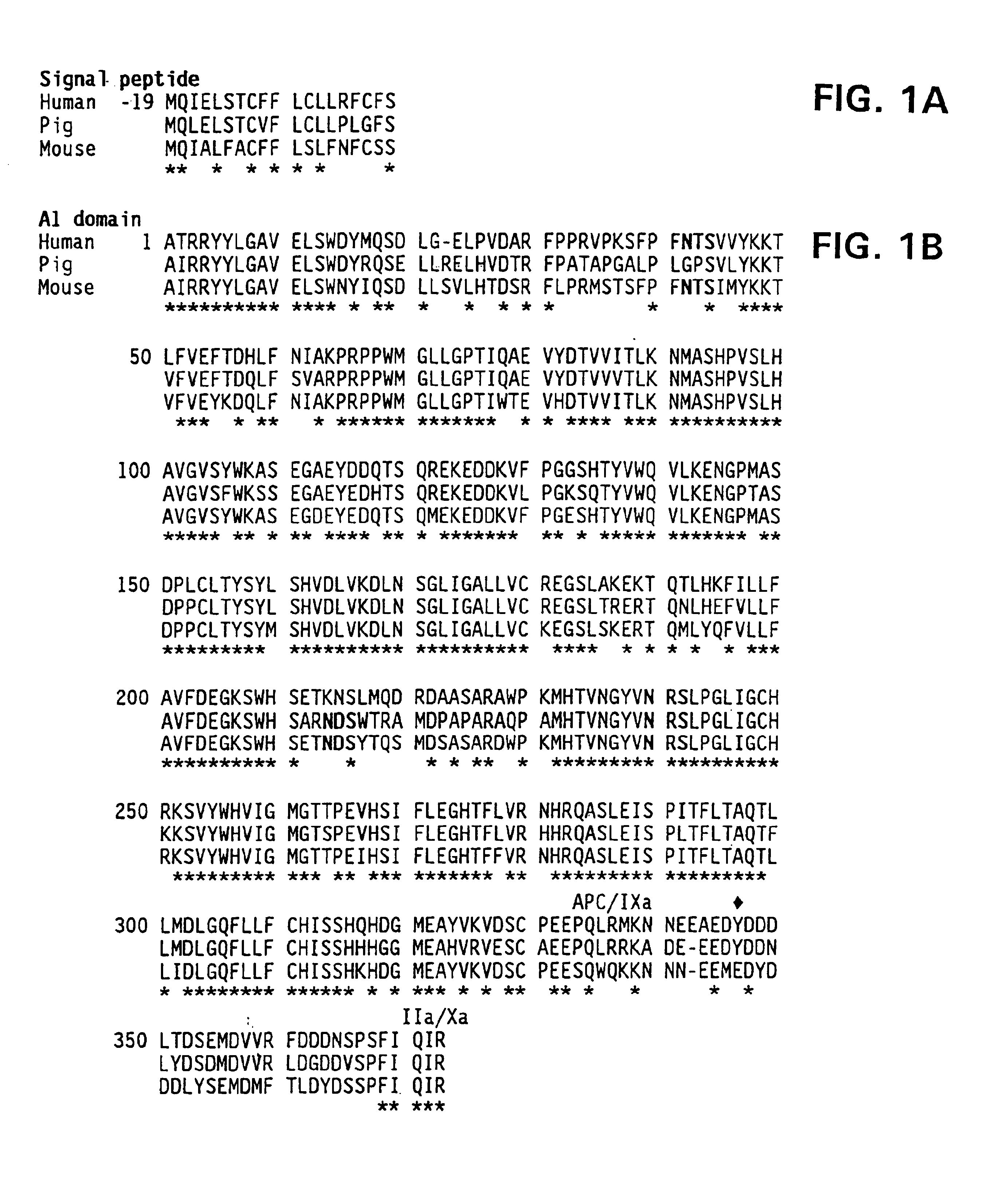
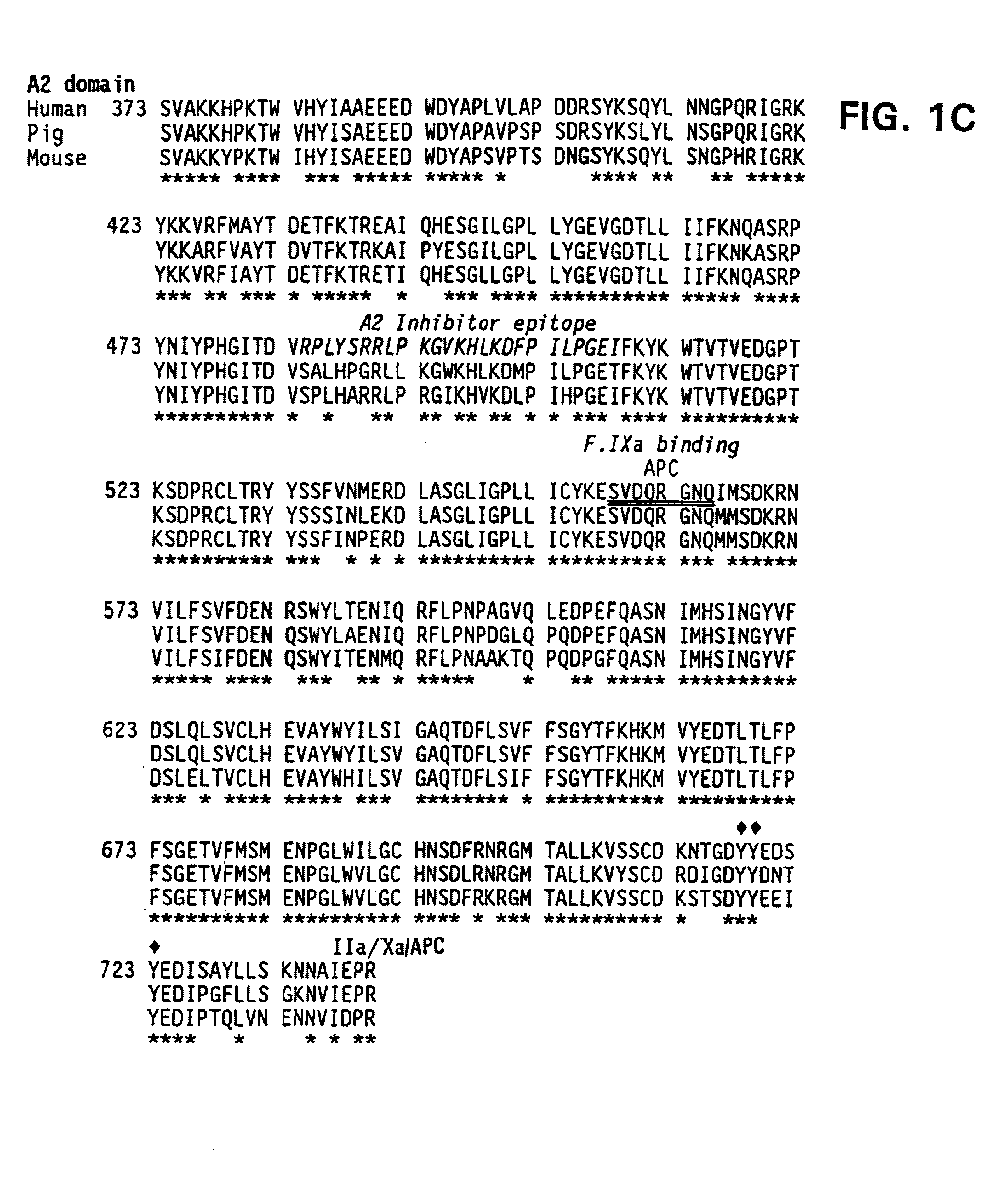
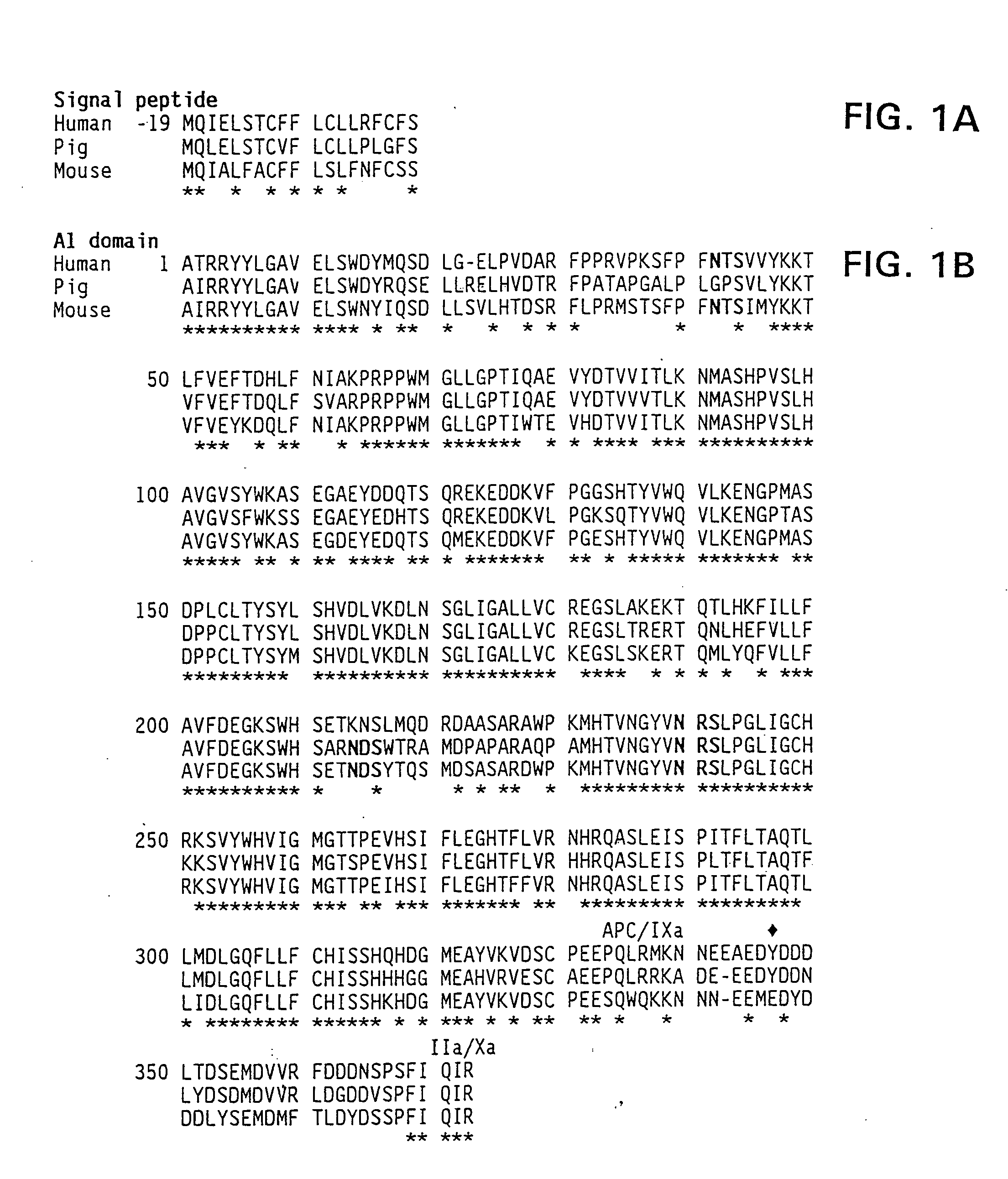
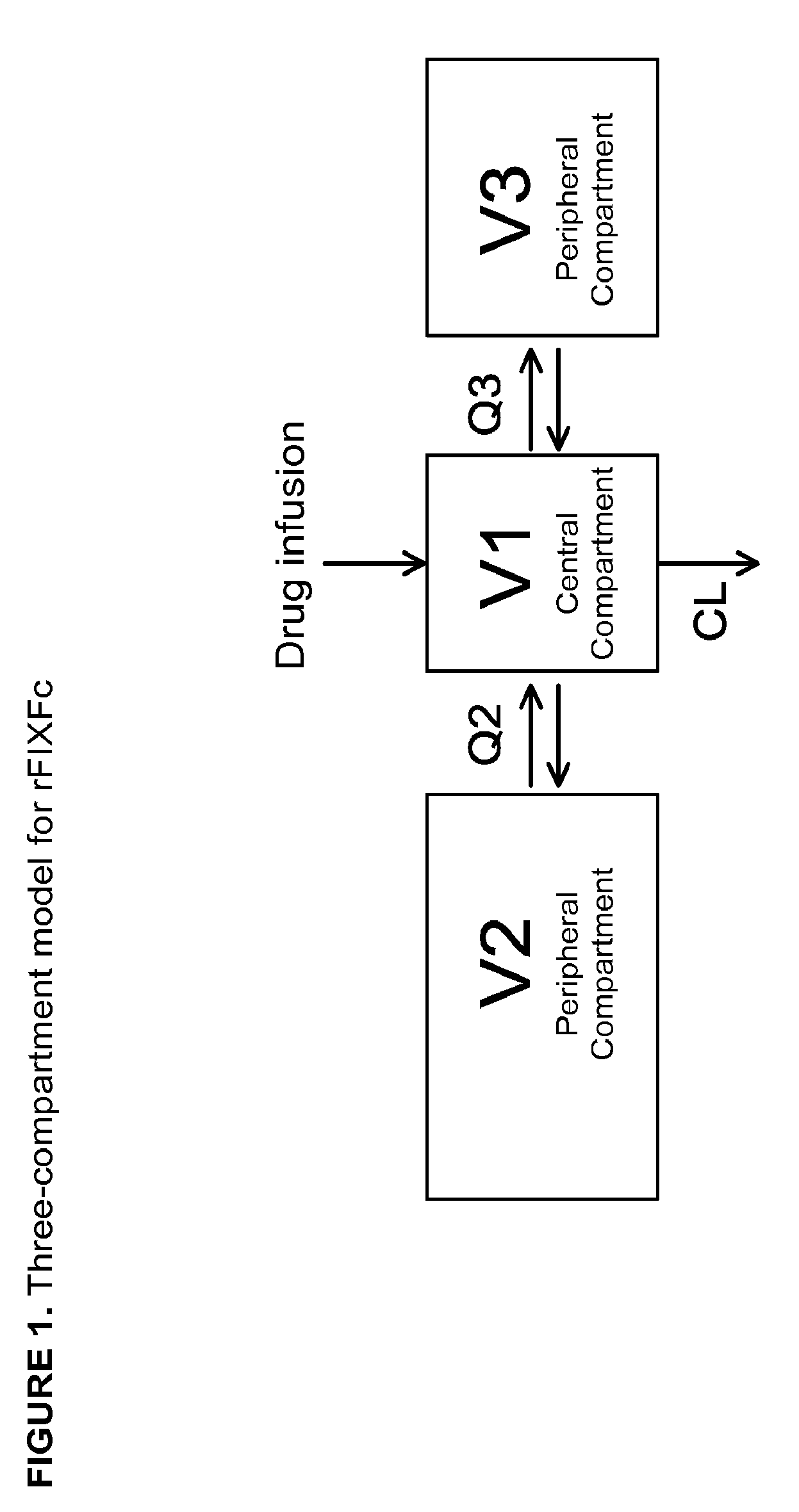
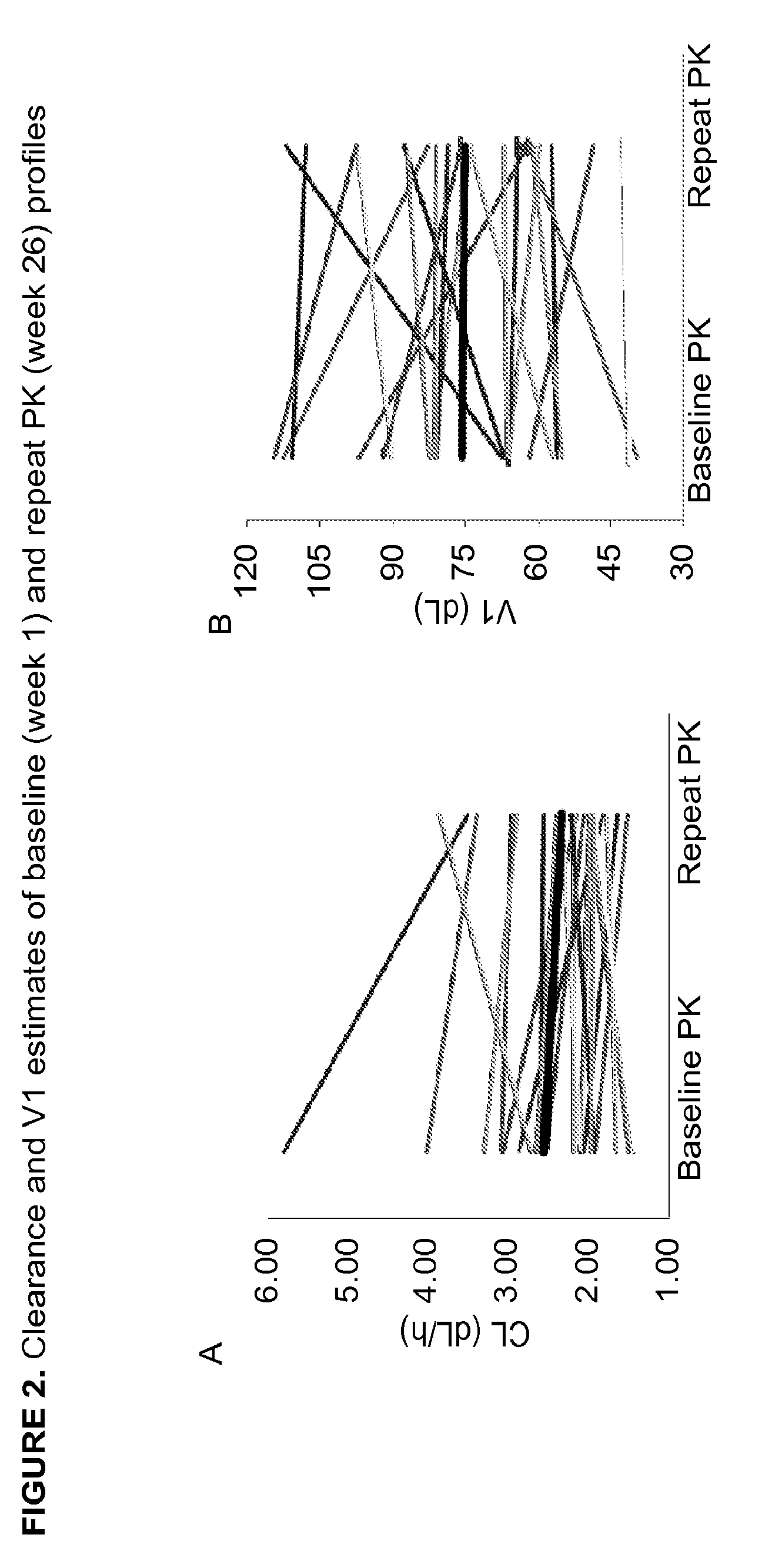
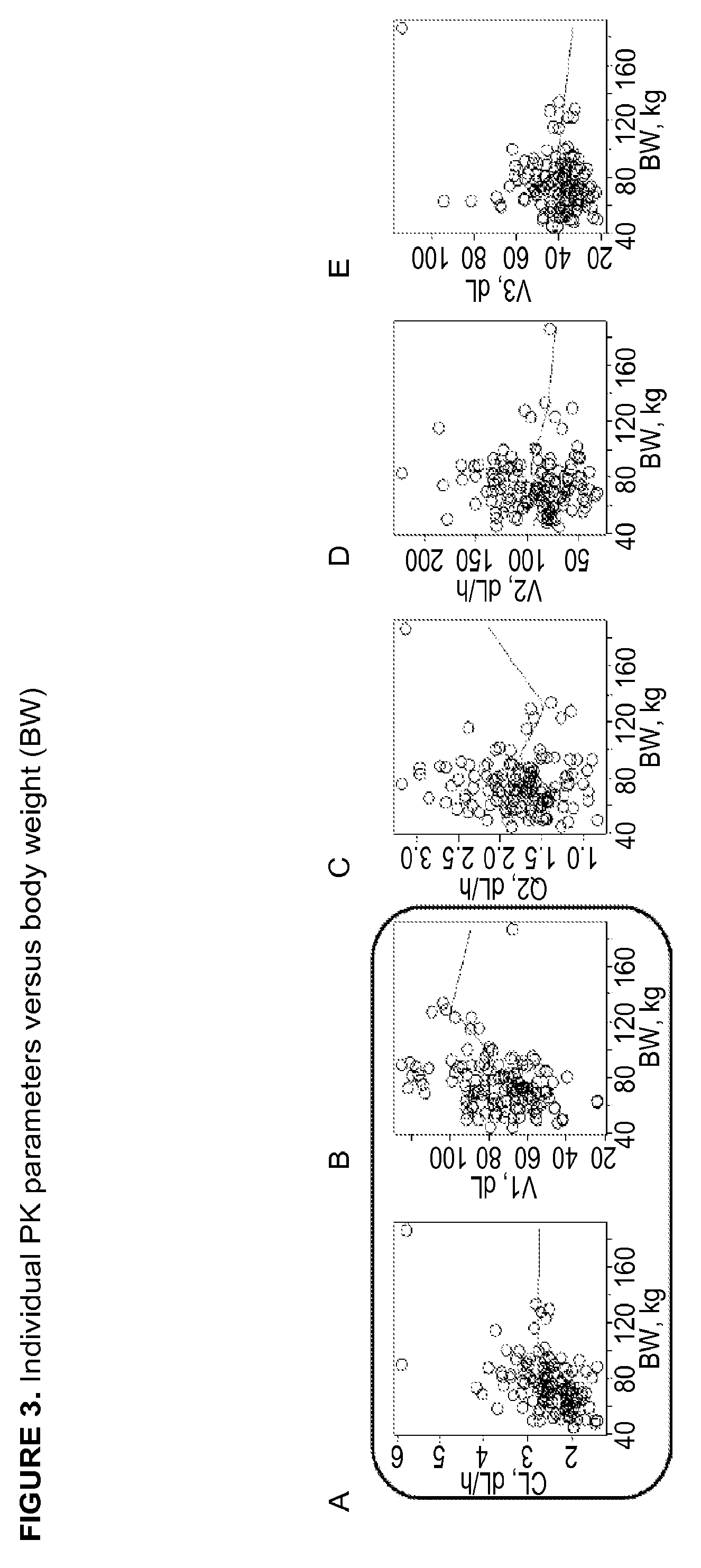
Demannosylated recombinant factor viii [[vii]] for the treatment of patients with haemophilia a
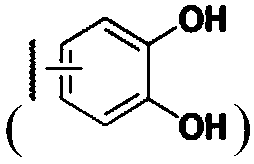
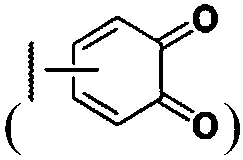
There is provided in accordance with the practice of this invention a demannosylated Factor VIII, the immunogenicity of which is substantially decreased or abolished in Human. The modified factor VIII is disclosed together with the modified amino acid sequence, changed by at least one substitution. The modified factor VIII is useful for hemophiliacs, either to avoid or prevent the action of inhibitory anti-FVIII antibodies.
Owner:LFB BIOTECH +1
Demannosylated recombinant factor VIII for the treatment of patients with haemophilia A
There is provided in accordance with the practice of this invention a demannosylated Factor VIII, the immunogenicity of which is substantially decreased or abolished in Human. The modified factor VIII is disclosed together with the modified amino acid sequence, changed by at least one substitution. The modified factor VIII is useful for hemophiliacs, either to avoid or prevent the action of inhibitory anti-FVIII antibodies.
Owner:LFB BIOTECH +1
Preparation method of human blood coagulation factor VIII and human blood coagulation factor VIII product
ActiveCN107880112AHigh recovery rateTaller than aliveFactor VIIPeptide preparation methodsWhole blood productIon chromatography
The invention discloses a preparation method of a human blood coagulation factor VIII and a human blood coagulation factor VIII product and relates to the field of blood products. The preparation method of the human blood coagulation factor VIII comprises the following steps: dissolving a cryoprecipitate with a 0.015-0.025mol / L tromethamine solution in a mass ratio of (3-5): 1 by reasonably processing the cryoprecipitate; and carrying out separation and purification by means of a polyethylene glycol precipitating method combined with ion exchange chromatography, wherein the recovery ratio of the human blood coagulation factor VIII and the specific activity of a final product can be improved effectively, the yield reaches 180-240IU / L plasma, and the specific activity is not lower than 100IU / mg proteins. The prepared human blood coagulation factor VIII product is rich in vWF factors and the proportion of the vWF factors and the human blood coagulation factor VIII is close to 1: 1. Besides treating hemophiliac A, the human blood coagulation factor VIII can be also used for treating patients with angiohemophilia, and the human blood coagulation factor VIII has good stability and heat resistance.
Owner:HUALAN BIOLOGICAL ENG INC +2
Demannosylated recombinant factor viii for the treatment of patients with hemophiila a
Owner:LFB BIOTECH +1
Bispecific antibodies for factor ix and factor x
PendingCN110753704AReduce dosing frequencyEasy for subcutaneous injectionImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsHybrid immunoglobulinsAntiendomysial antibodiesBispecific antibody
Bispecific antigen binding molecules (e.g., antibodies) that bind blood clotting factors, factor IXa (FIXa) and factor X (FX), and enhance the FIXa-catalysed activation of FX to FXa. Use of the bispecific antigen binding molecules is to control bleeding, by replacing natural cofactor FVIIIa which is deficient in patients with haemophilia A.
Owner:KIMAB LTD
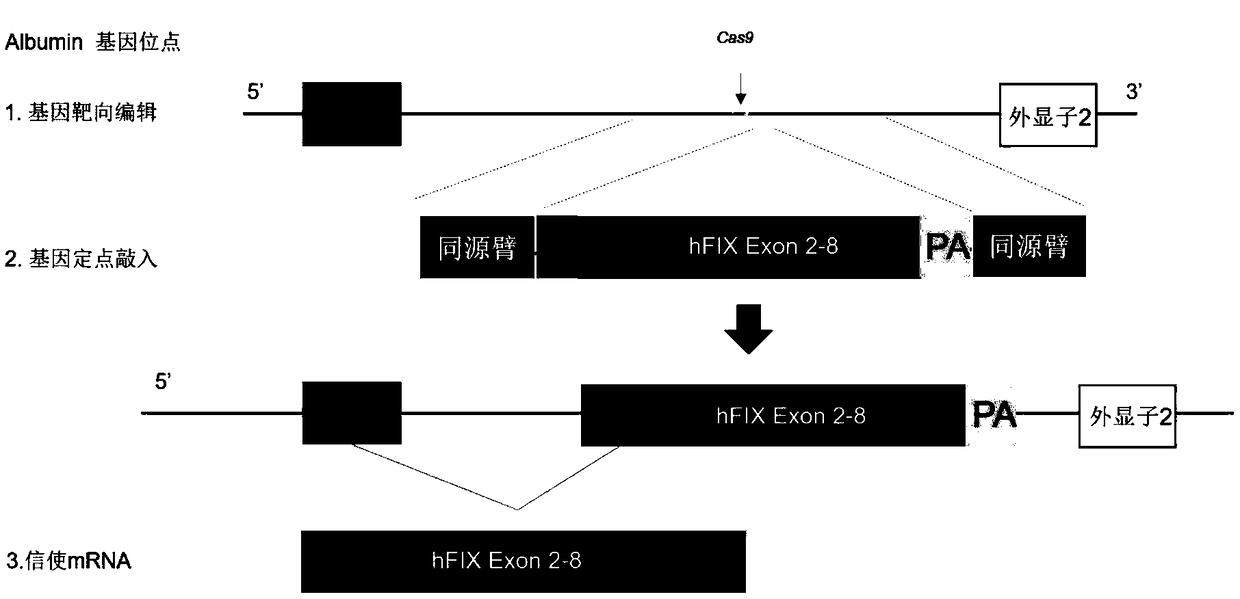
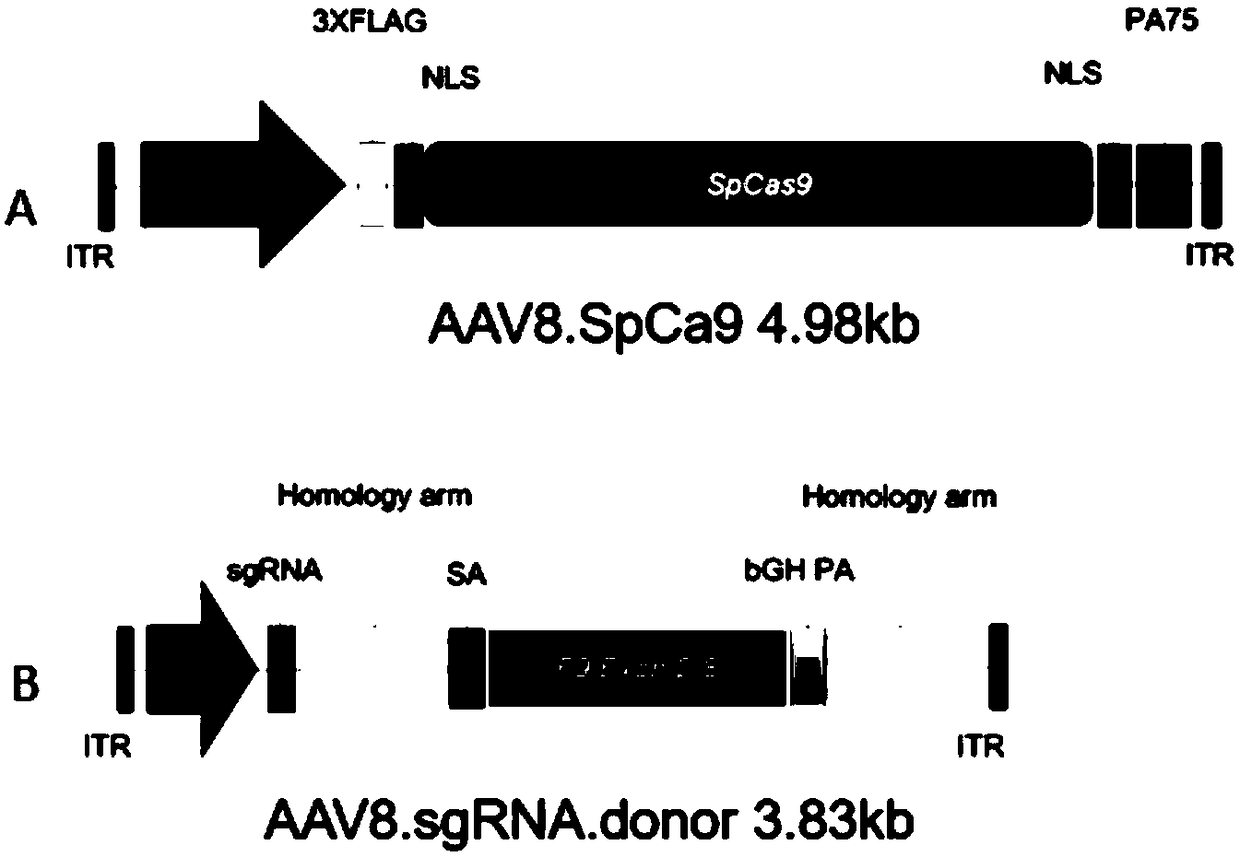
Composition for improving coagulation activity of patient with type B hemophilia, medicine and sgRNA (small guide Ribonucleic Acid)
ActiveCN108977464APeptide/protein ingredientsStable introduction of DNAB hemophiliaHemophilia patient
The invention discloses a composition for improving the coagulation activity of a patient with type B hemophilia, a medicine and sgRNA (small guide Ribonucleic Acid), and relates to the field of genetreatment of hemophilia. The composition comprises a first AAV (Adeno-associated Virus) vector and a second AAV vector for expressing the sgRNA; a core sequence of the sgRNA is selected from SEQ ID NO. 6 to SEQ ID NO. 9. The composition can be used for treating the type B hemophilia and recovering the coagulation activity.
Owner:成都金唯科生物科技有限公司
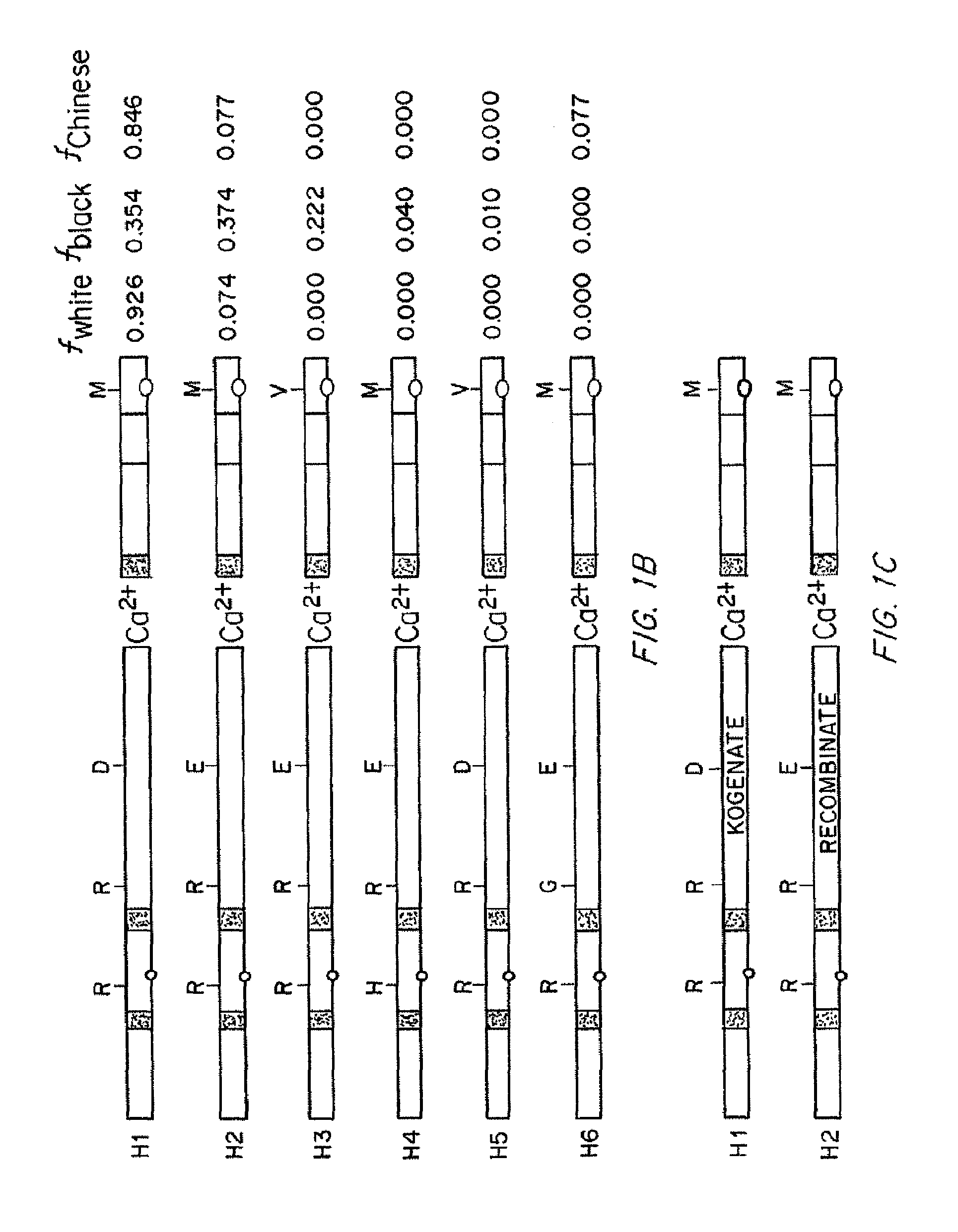
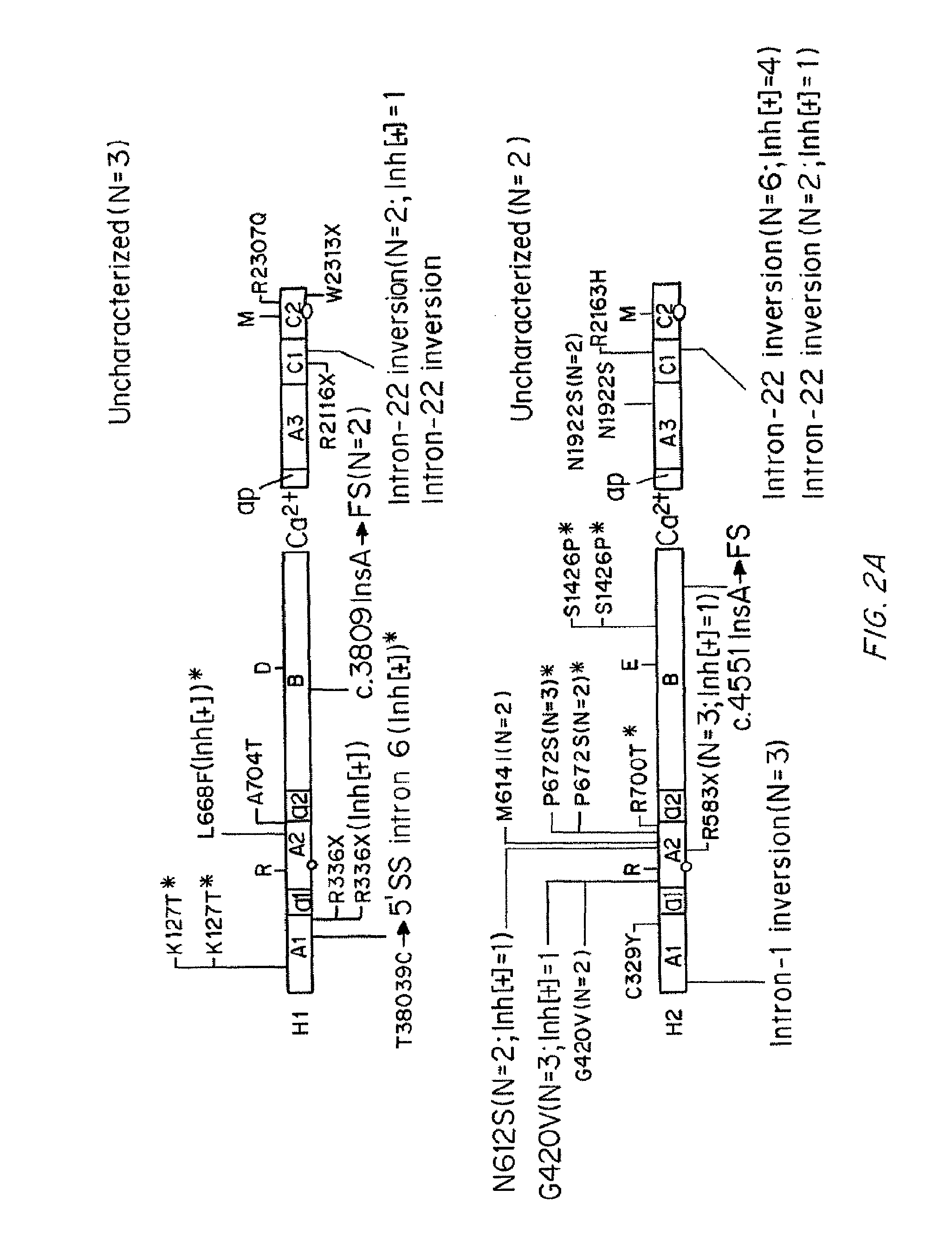
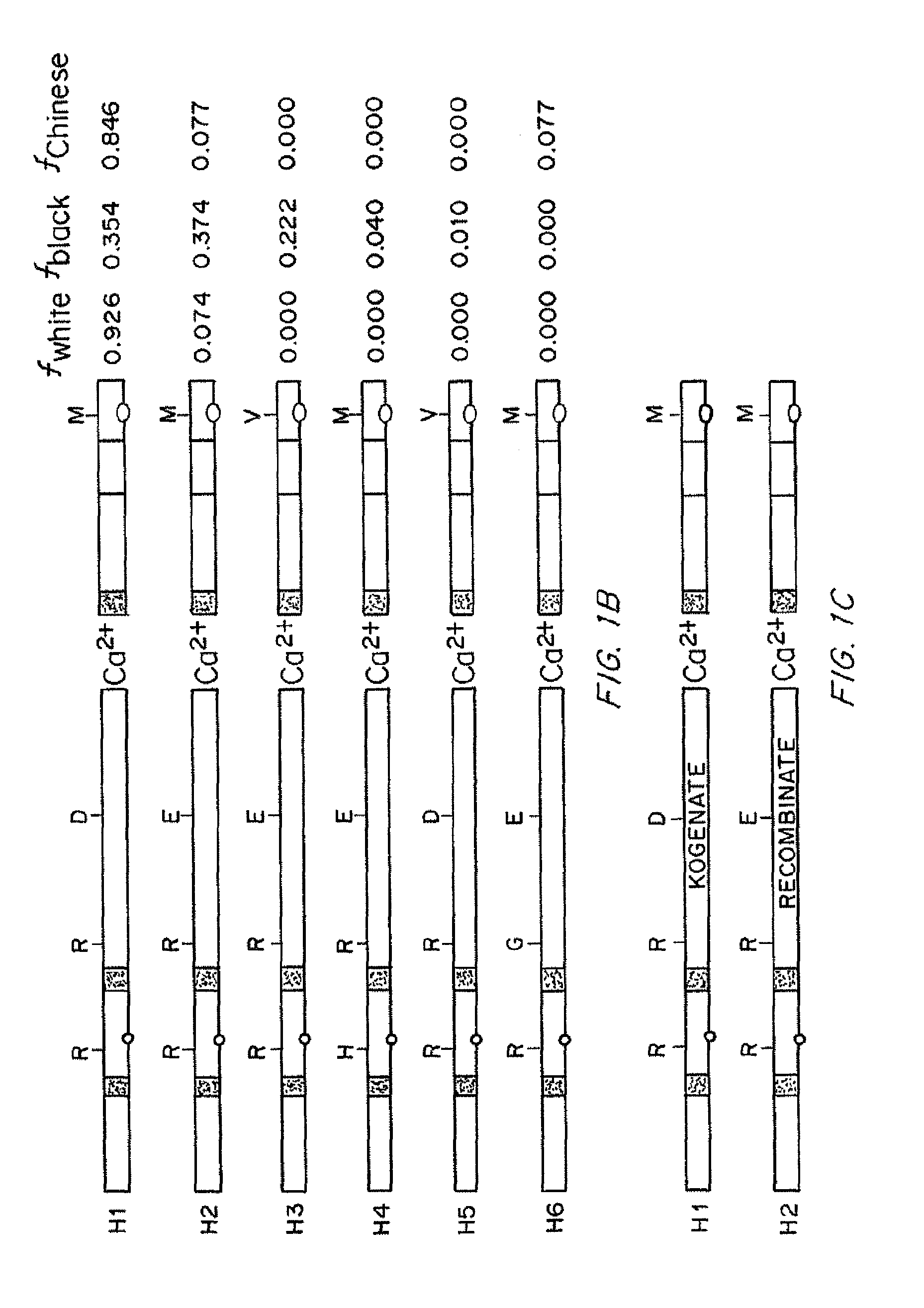
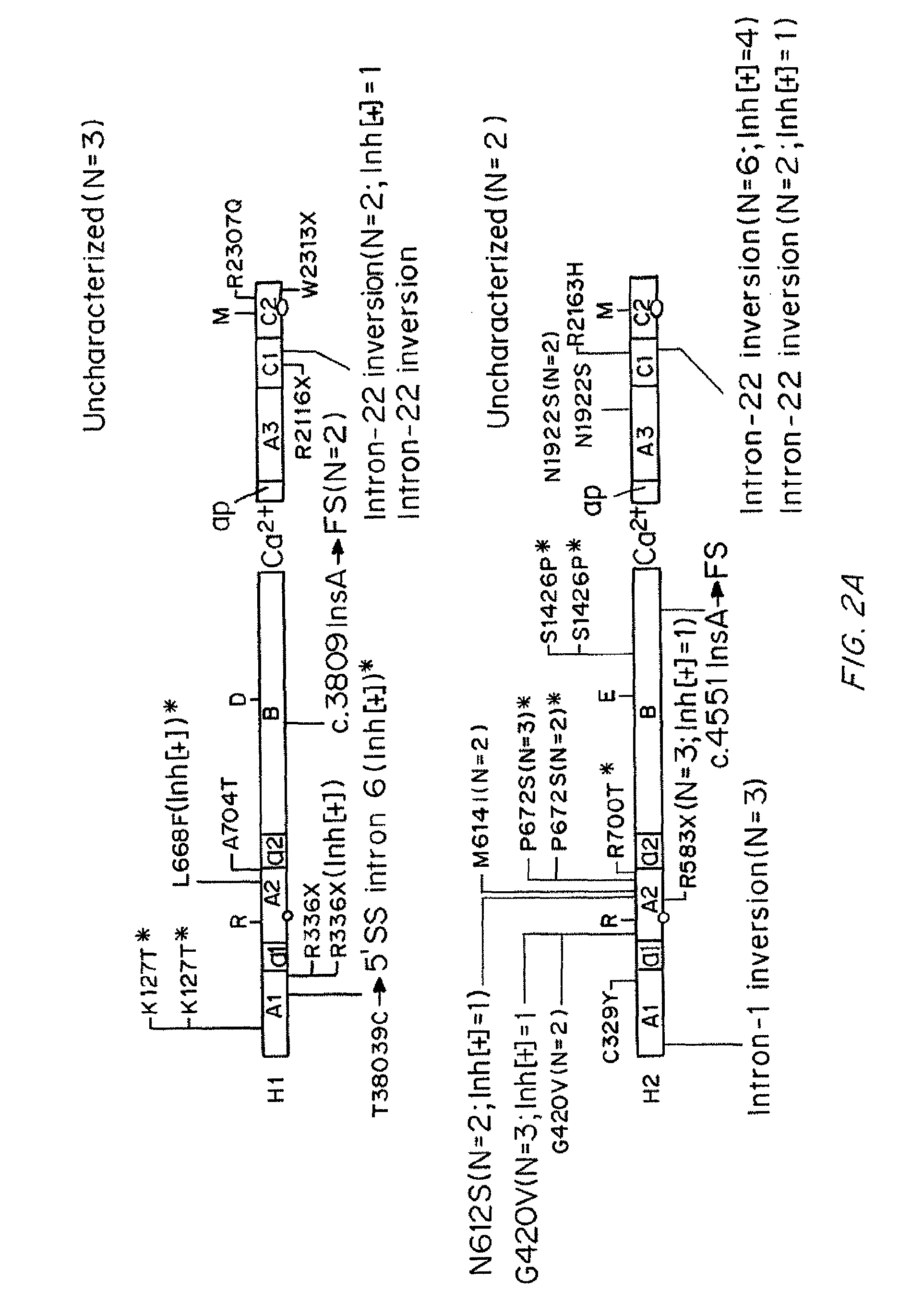
Compositions and Methods of Treatment of Black Hemophiliac Patients
InactiveUS20150197552A1High oddsFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsHaplotypeSignificant difference
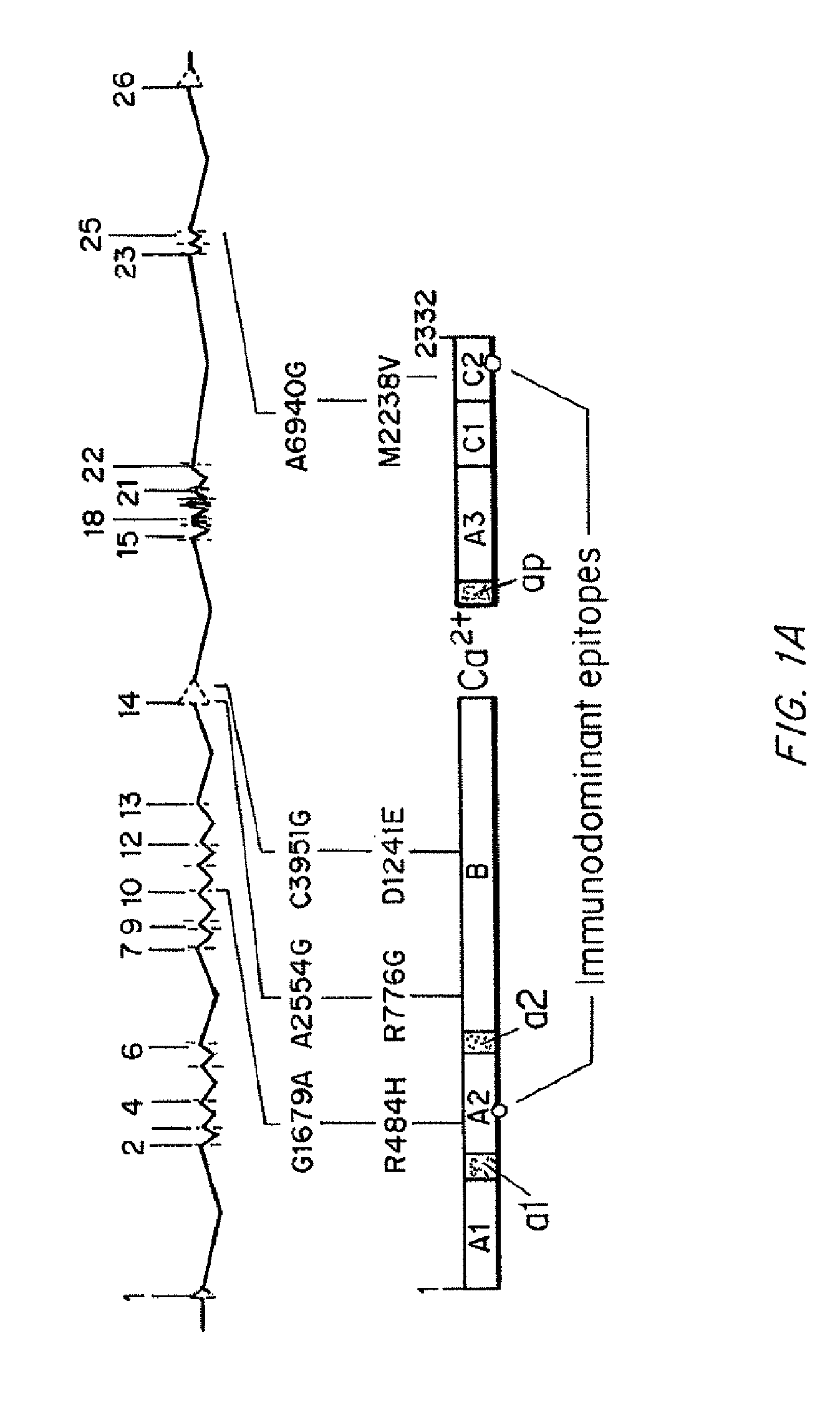
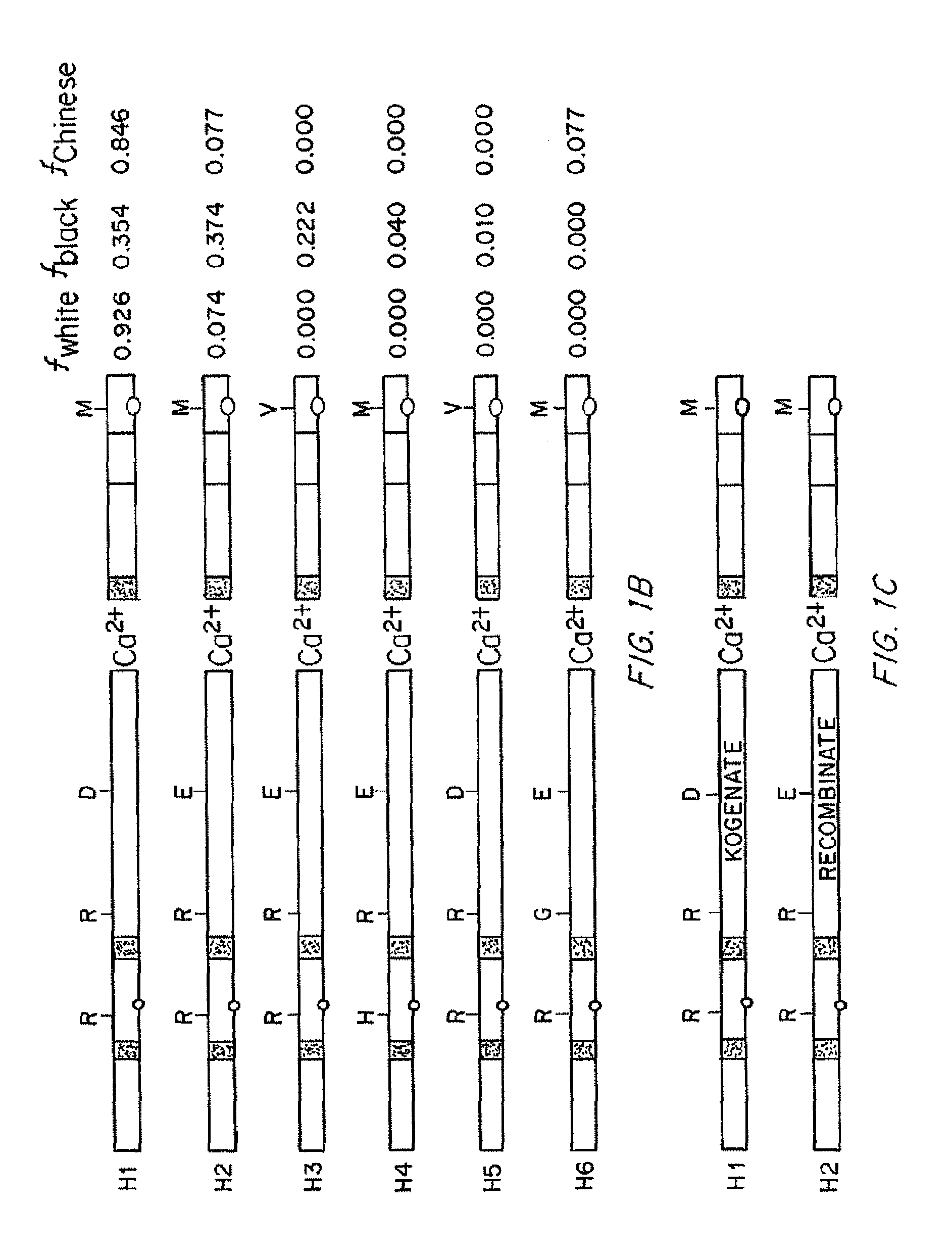
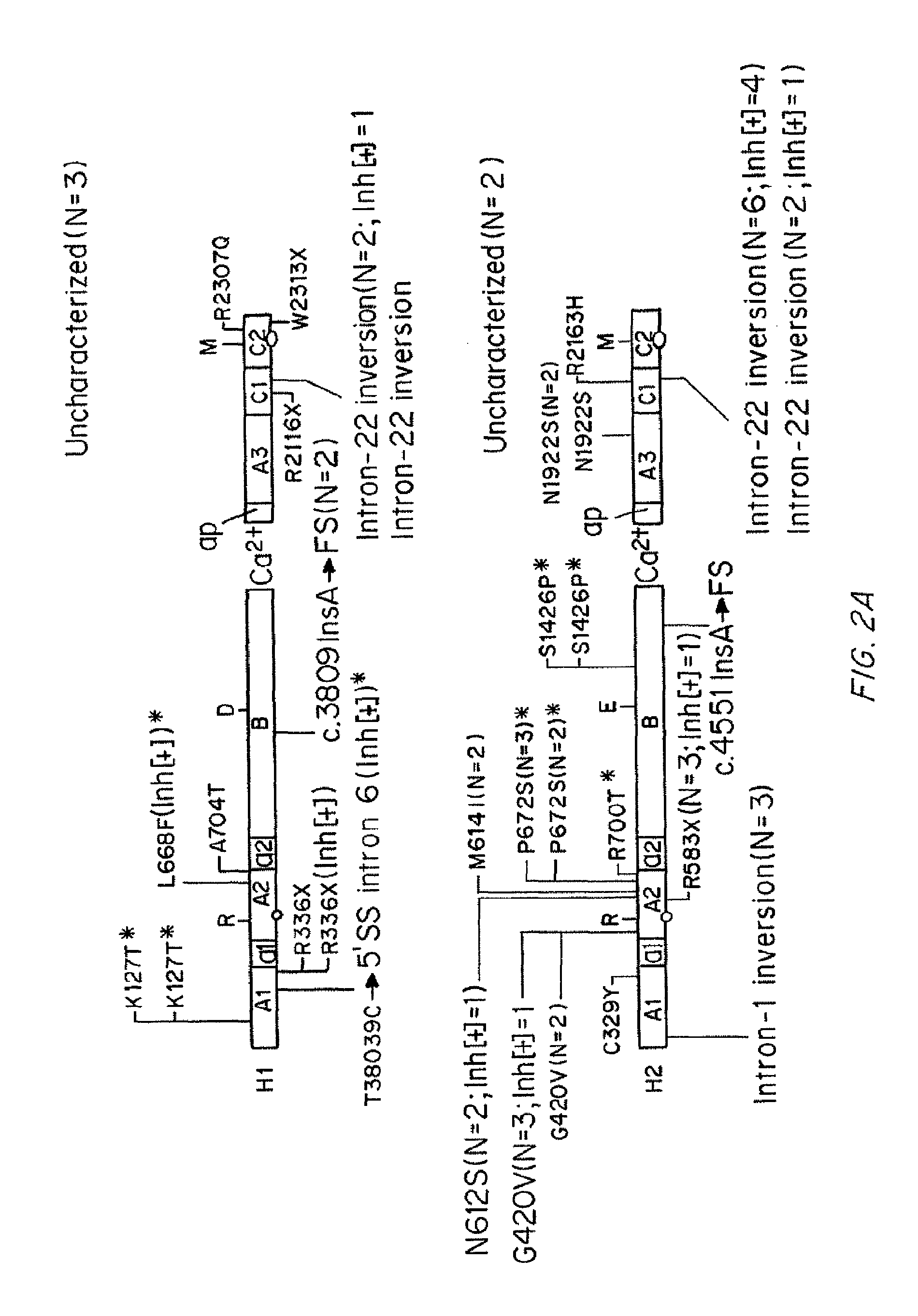
It has been determined that most mutations in factor VIII occur in multiple haplotypes, not primarily in one haplotype. The frequencies of mild, moderate, and severe hemophilia did not differ significantly according to the background haplotype. The odds of having inhibitor were significantly higher among patients in the H3+H4 haplotype groups as compared to H1+H2 haplotype groups. This association appears to be independent of the mutation. The results indicate that white hemophiliacs should be treated with Kogenate®. However, it would clearly be of benefit to assess the haplotype of black hemophiliacs prior to prescribing the recombinant FVIII to be used for treatment. It is not essential to determine the actual mutations responsible for the hemophilia prior to prescribing the recombinant FVIII. Also described are transgenic human FVIII animal models.
Owner:HAPLOMICS
Compositions and methods of treatment of black hemophiliac patients
It has been determined that most mutations in factor VIII occur in multiple haplotypes, not primarily in one haplo-type. The frequencies of mild, moderate, and severe hemophilia did not differ significantly according to the background haplo-type. The odds of having inhibitor were significantly higher among patients in the H3+H4 haplotype groups as compared to H1+H2 haplotype groups. This association appears to be independent of the mutation. The results indicate that white hemophiliacs should be treated with Kogenate®. However, it would clearly be of benefit to assess the haplotype of black hemophiliacs prior to prescribing the recombinant FVIII to be used for treatment. It is not essential to determine the actual mutations responsible for the hemophilia prior to prescribing the recombinant FVIII. Also described are transgenic human FVIII animal models.
Owner:HOWARD TOMMY EUGENE
Modified factor VIII
Specific amino acid loci of human factor VIII interact with inhibitory antibodies of hemophilia patients who have developed such antibodies after being treated with factor VIII. Modified factor VIII is disclosed in which the amino acid sequence is changed by a substitution at one or more of the specific loci. The modified factor VIII is not inhibited by inhibitory antibodies against the A2 or C2 domain epitopes. The modified factor VIII is useful for hemophiliacs, either to avoid or prevent the action of inhibitory antibodies.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Anti-idiotypic antibodies against factor VIII inhibitor and uses thereof
InactiveUS7582296B2Increase stability and lifetimeEnhanced inhibitory effectAnimal cellsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsFactor VIII inhibitorIn vivo
The present invention discloses anti-idiotypic antibodies and fragments thereof against inhibitory Factor VIII anti-bodies, said inhibitory antibodies having an affinity for the C2 domain of Factor VIII. The anti-idiotypic antibodies of the present invention are able to completely neutralise in vitro and in an in vivo mouse model the inhibitory activity of FVIII inhibitors. The anti idiotypic antibodies of the present invention can be applied for the prevention, treatment or reduction of bleeding disorders of hemophilia patients with inhibitory antibody against the C2 domain of Factor VIII.
Owner:LIFE SCI RES PARTNERS VZW
Compositions and Methods of Treatment of Black Hemophiliac Patients
InactiveUS20150196017A1High oddsFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsHaplotypeSignificant difference
It has been determined that most mutations in factor VIII occur in multiple haplotypes, not primarily in one haplotype. The frequencies of mild, moderate, and severe hemophilia did not differ significantly according to the background haplotype. The odds of having inhibitor were significantly higher among patients in the H3+H4 haplotype groups as compared to H1+H2 haplotype groups. This association appears to be independent of the mutation. The results indicate that white hemophiliacs should be treated with Kogenate®. However, it would clearly be of benefit to assess the haplotype of black hemophiliacs prior to prescribing the recombinant FVIII to be used for treatment. It is not essential to determine the actual mutations responsible for the hemophilia prior to prescribing the recombinant FVIII. Also described are transgenic human FVIII animal models.
Owner:HAPLOMICS
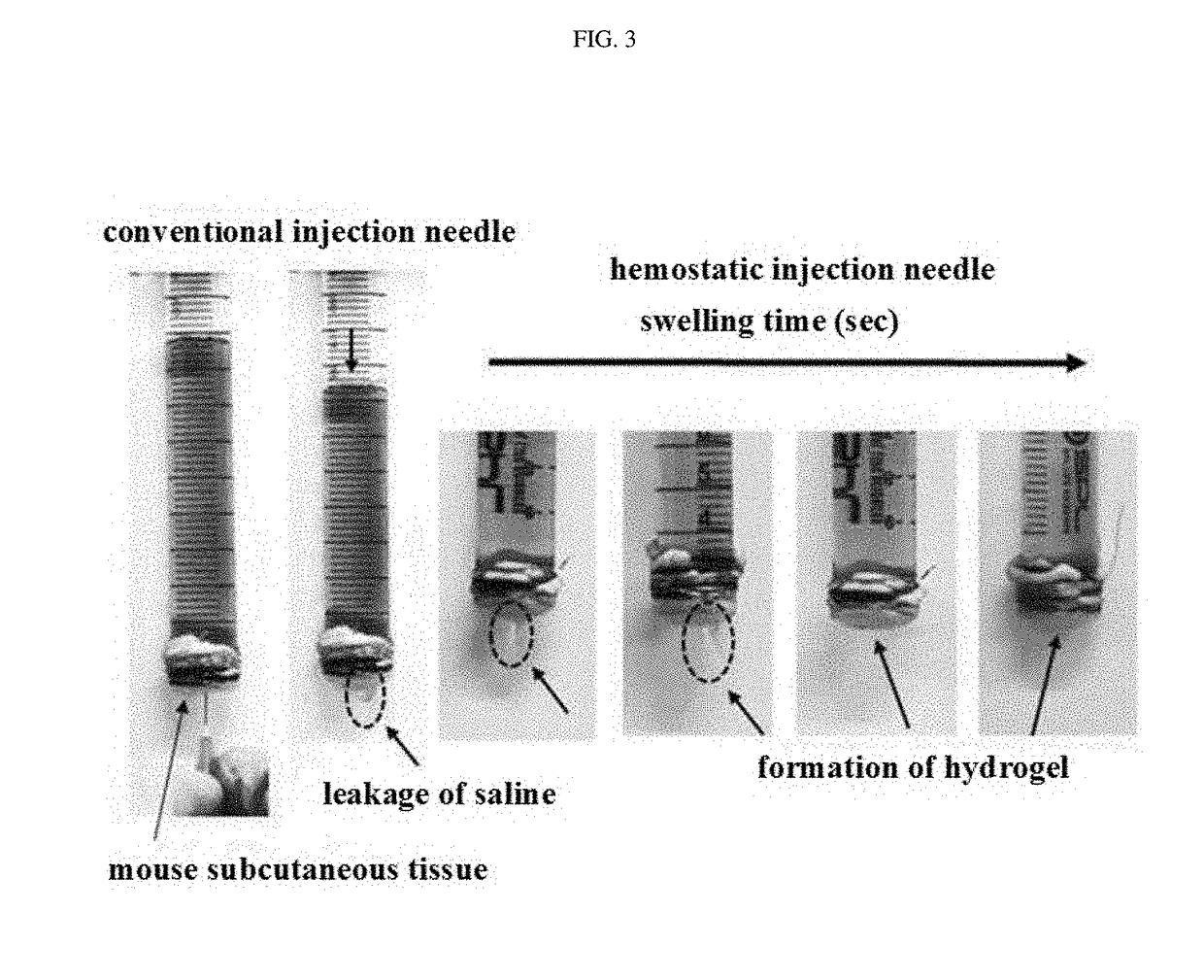
Bleed-free injection needle coated with crosslinked chitosan having introduced catechol group and oxidized catechol group
InactiveCN107530477AAvoid bleedingSurgical adhesivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCrosslinked chitosanEstrogens catechol
The present invention relates to a bleed-free injection needle coated with crosslinked chitosan having an introduced catechol group and oxidized catechol group, and the bleed-free injection needle according to the present invention is advantageous in that said needle can suppress the bleeding that occurs during an injection and hence can beneficially be used not only in patients having reduced hemostatic capacity such as diabetic patients, anticancer therapy patients and haemophilia patients but also in patients exhibiting blood rejection reactions and in injections to children as well.
Owner:INNO THERAPY INC
Method for measuring reactivity of fviii
ActiveUS20180011114A1Immunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsDisease diagnosisTiterPhases of clinical research
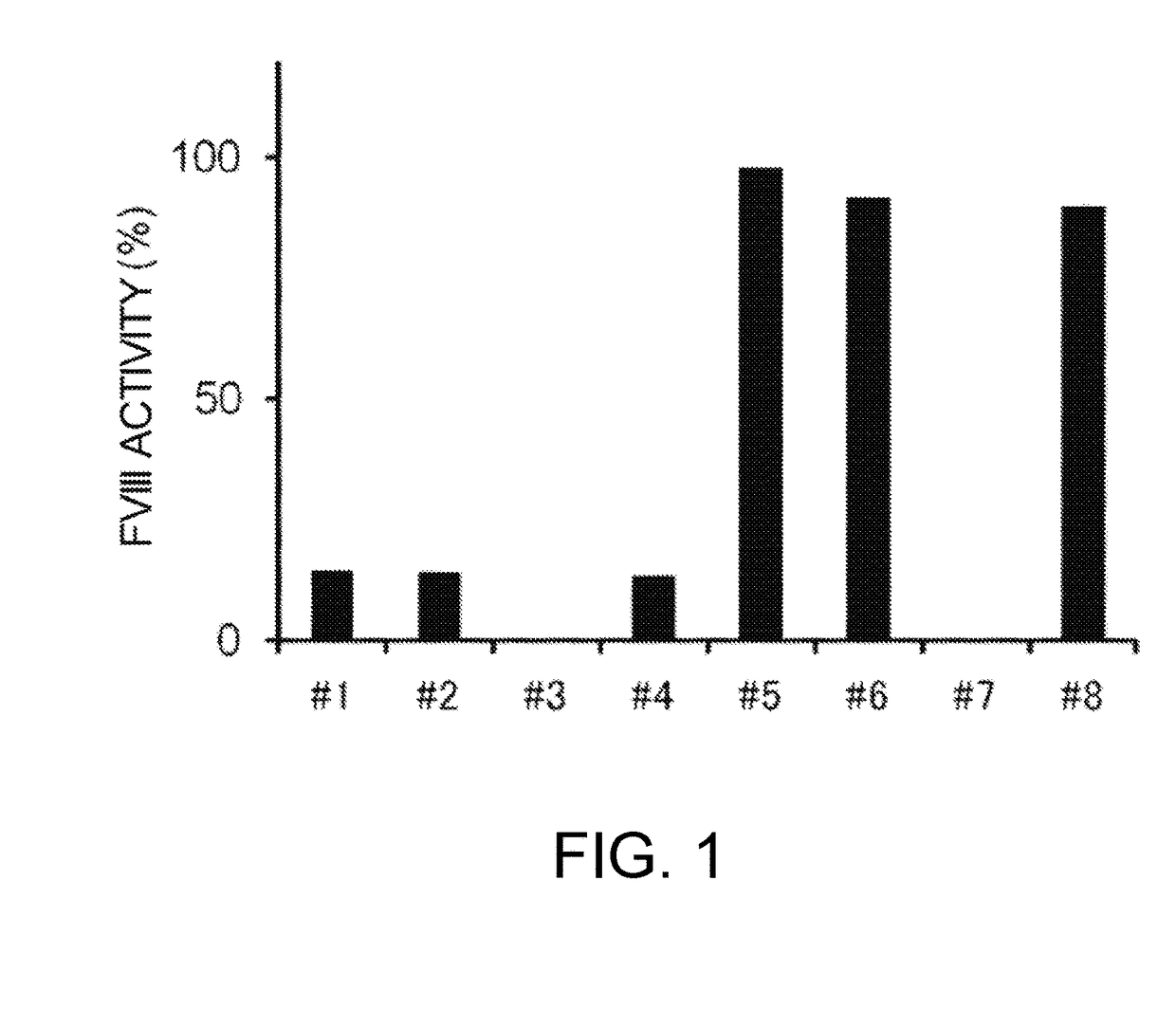
The inventors produced substances that neutralize the activity of a bispecific antibody having an activity of functionally substituting for FVIII, and undertook the construction of methods for measuring the reactivity of FVIII that can ensure accuracy even in the presence of this bispecific antibody. As a result, the inventors discovered that in APTT-based one-stage clotting assay, FVIII activity in the plasma of a hemophilia A patient can be evaluated accurately, and also that in APTT-based Bethesda assay, FVIII inhibitor titer in the plasma of a hemophilia A patient carrying a FVIII inhibitor can be evaluated accurately.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Hemostatic injection needle coated with crosslinked chitosan having catechol group and oxidized catechol group
ActiveUS20180085500A1Avoid bleedingSurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCrosslinked chitosanCross-link
The present invention relates to a hemostatic injection needle coated with a chitosan in which a catechol group and an oxidized catechol group are introduced and cross-linked. The hemostatic injection needle according to the present invention can suppress bleeding during and after injection, and thus can be effectively used for injection not only into coagulopathy patients, including diabetic patients, patients under anticancer treatment, and haemophilia patients, who have a low hemostatic ability, but also into patients showing blood rejection responses, and children.
Owner:INNOTHERAPY
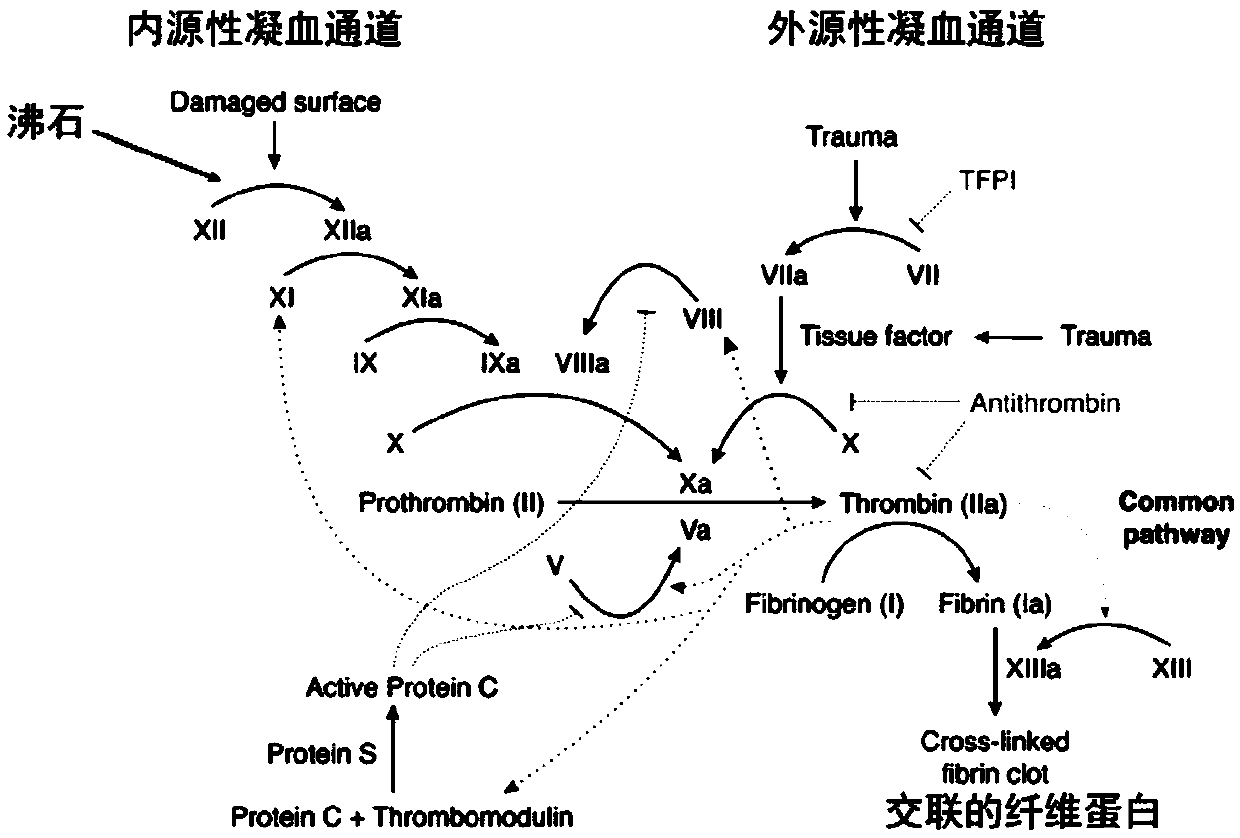
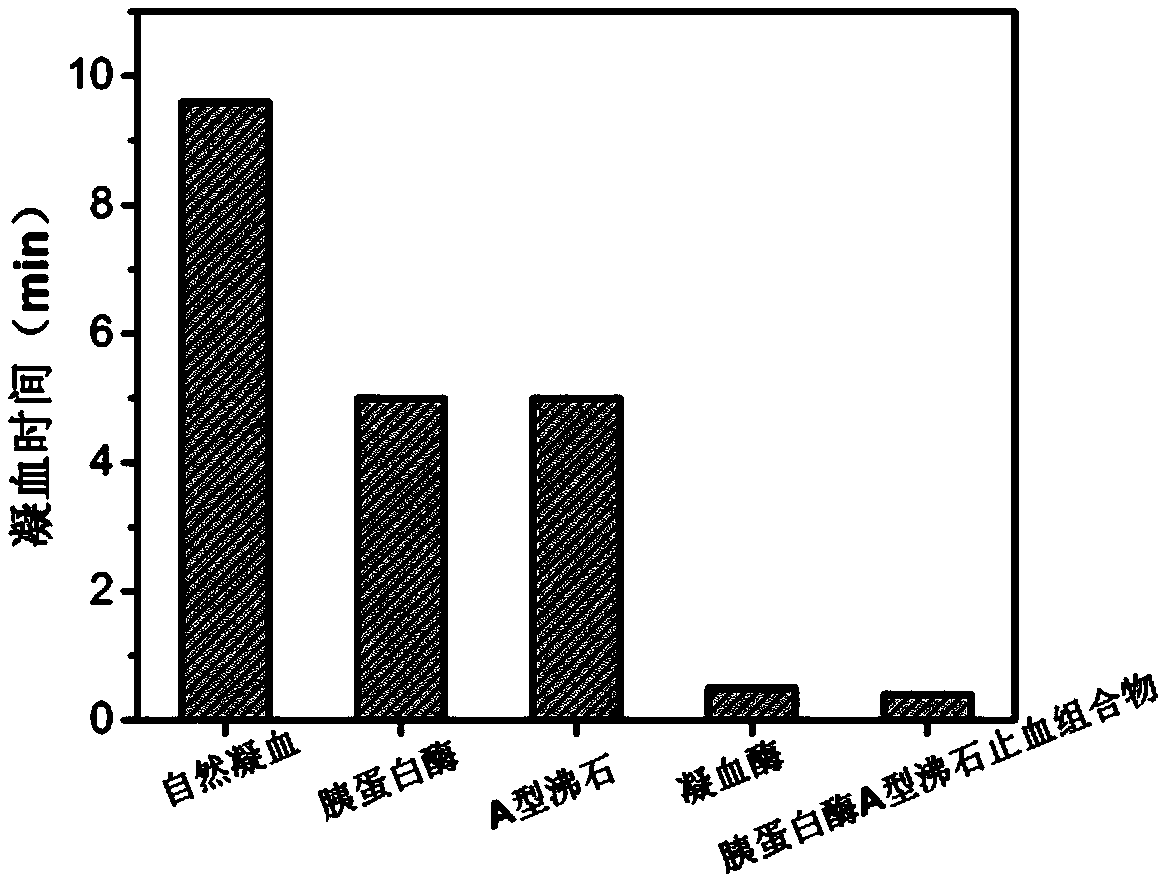
Hemostasis composition and preparation method therefor
ActiveCN111249518AReduced risk of bleeding to deathAvoid damageSurgical adhesivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismSurgical HemostasisDivalent metal
The invention provides a hemostasis composition. The hemostasis composition comprises trypsin and zeolite; pore channels of the zeolite are micropores; the zeolite includes divalent metal positive ions; the mass ratio of the trypsin to the zeolite is 1:200-4:10. According to the hemostasis composition, the trypsin and the zeolite are specifically bound, so that the trypsin keeps a certain conformation on the surface of the zeolite, and higher procoagulant activity is obtained, and thereby, the hemostasis composition with an excellent blood coagulation effect is obtained. The hemostasis composition provided by the invention has a simple preparation method, is low in cost, and convenient to use, can be widely used for traumas and surgical hemostasis, and is especially suitable for emergencyhemostasis of hemophilia patients.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Compositions and methods for suppression of inhibitor formation against coagulation factors in hemophilia patients
ActiveUS20160289277A1Reduce formationSuppress formationFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsTherapeutic proteinPlant cell
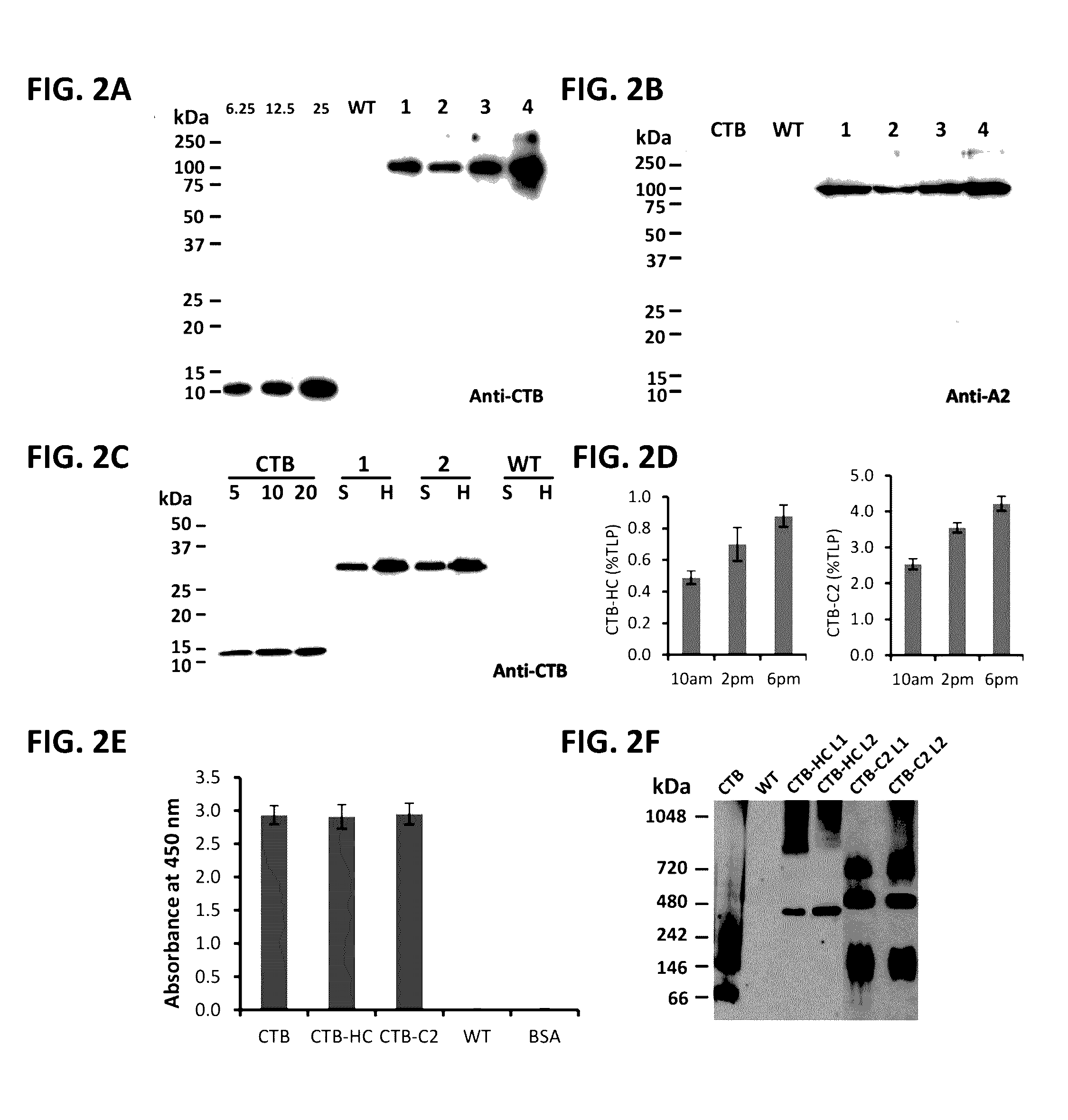
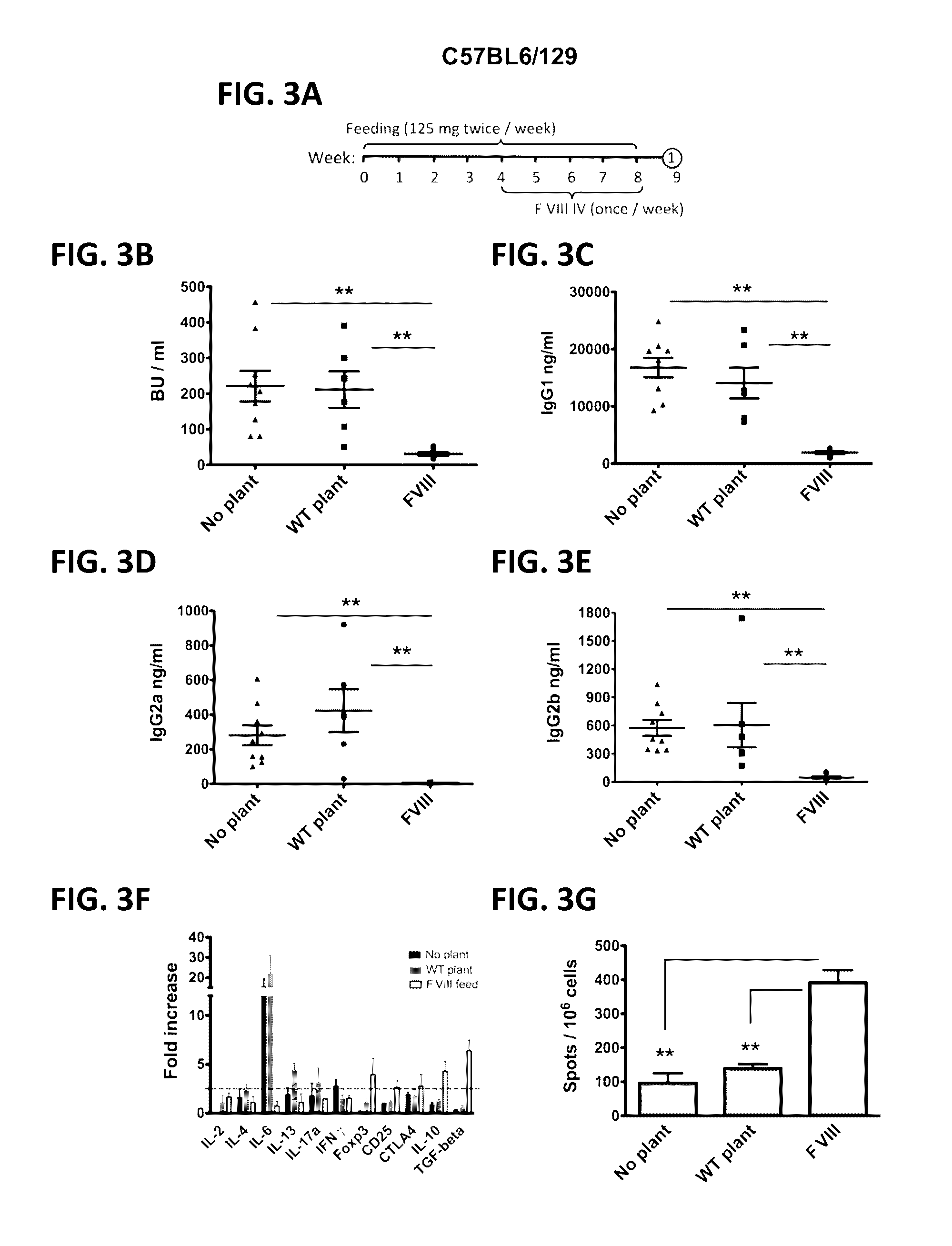
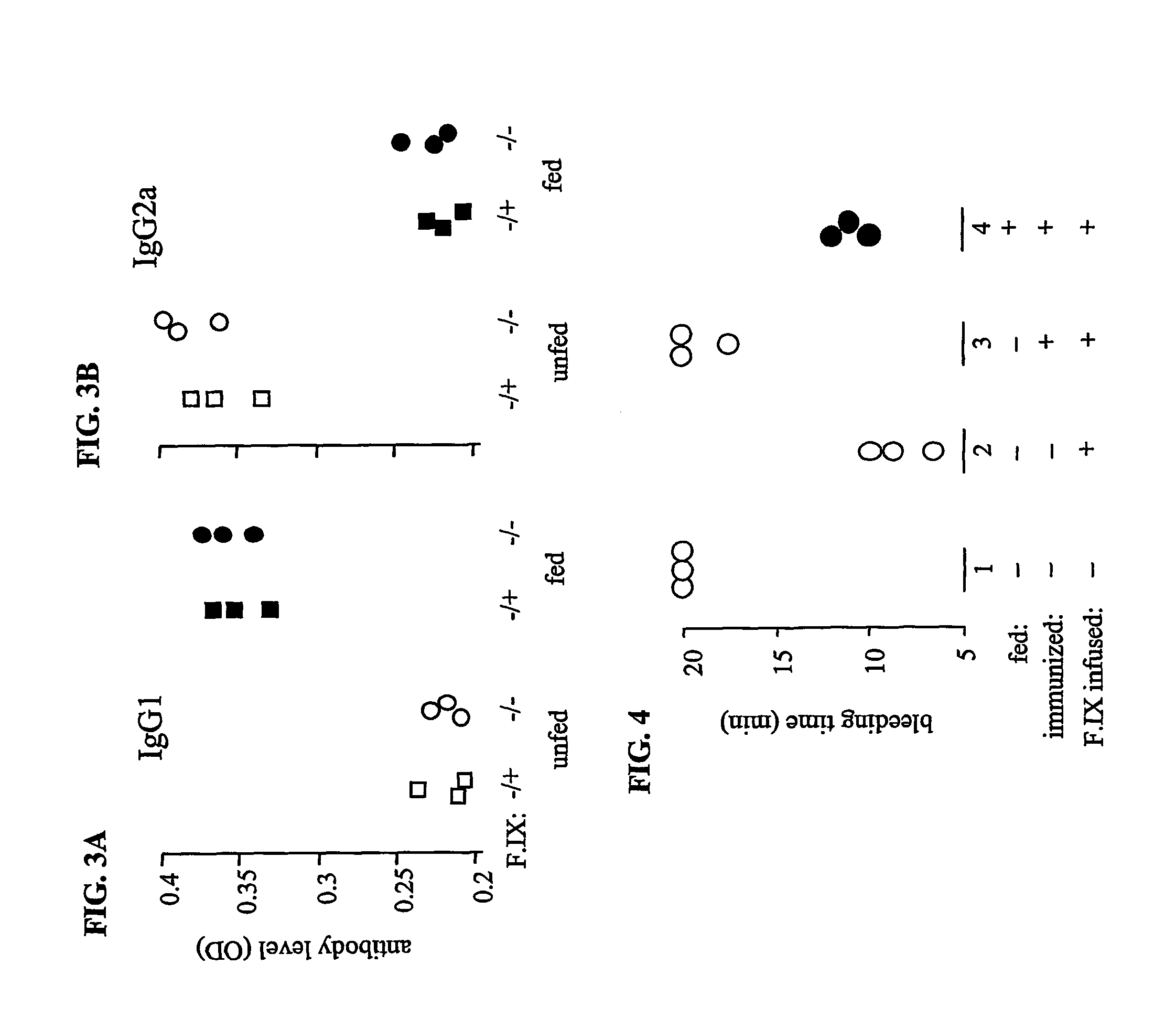
Protein replacement therapy for patients with hemophilia or other inherited protein deficiencies is often complicated by pathogenic antibody responses, including antibodies that neutralize the therapeutic protein or that predispose to potentially life-threatening anaphylactic reactions by formation of IgE. Using murine and canine hemophilia as a model, we have developed a prophylactic protocol against such responses that is non-invasive and does not include immune suppression or genetic manipulation of the patient's cells. Oral delivery of a coagulation factor expressed in chloroplasts, bioencapsulated in plant cells, effectively blocked formation of inhibitory antibodies in protein replacement therapy. Inhibitor titers were mostly undetectable and up to 100-fold lower in treated subjects when compared to controls. Moreover, this treatment eliminated fatal anaphylactic reactions that occurred after four to six exposures to intravenous coagulation factor protein. Finally, the method can effectively be used to reverse or reduce undesirable pre-existing inhibitor titers.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
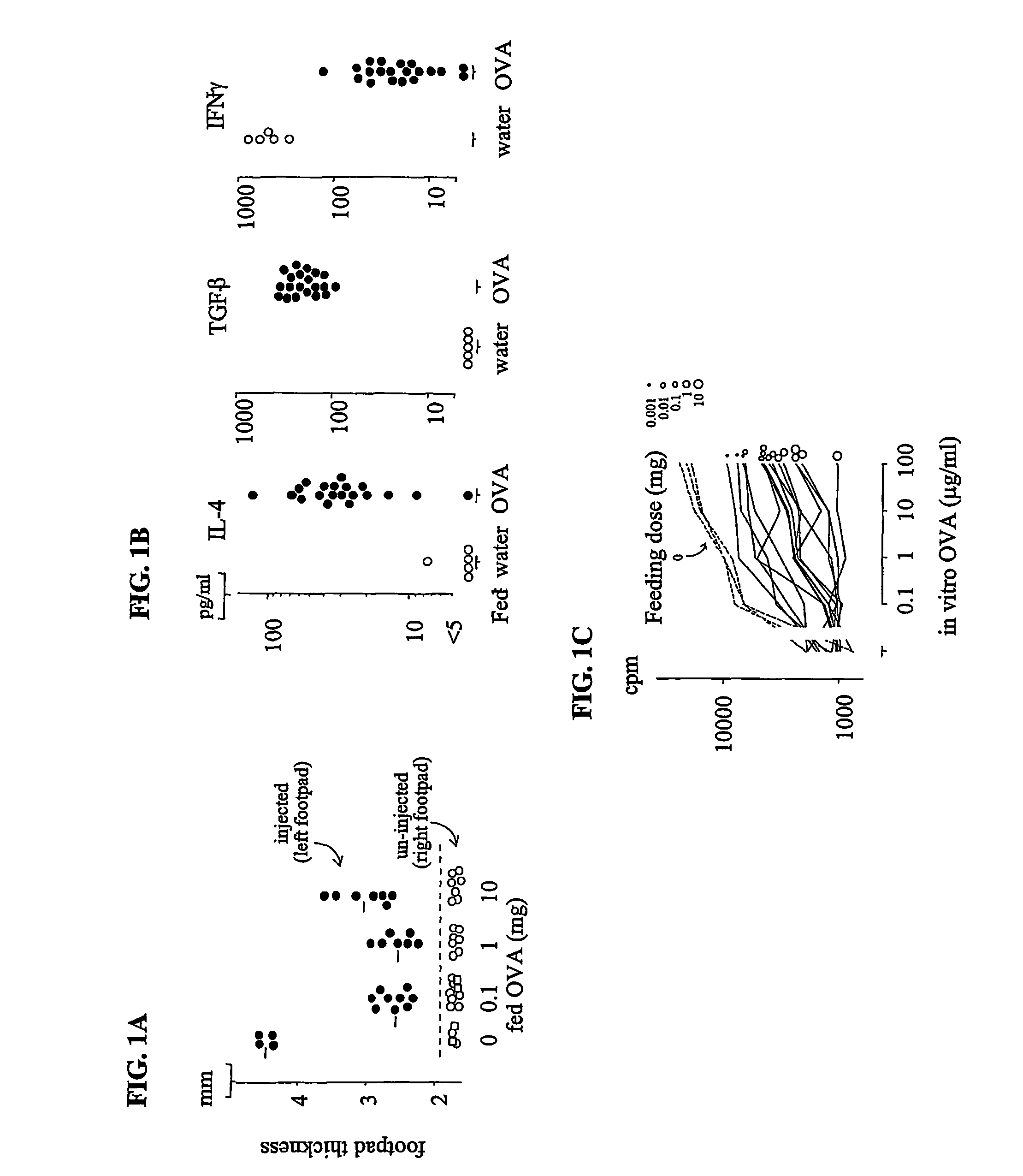
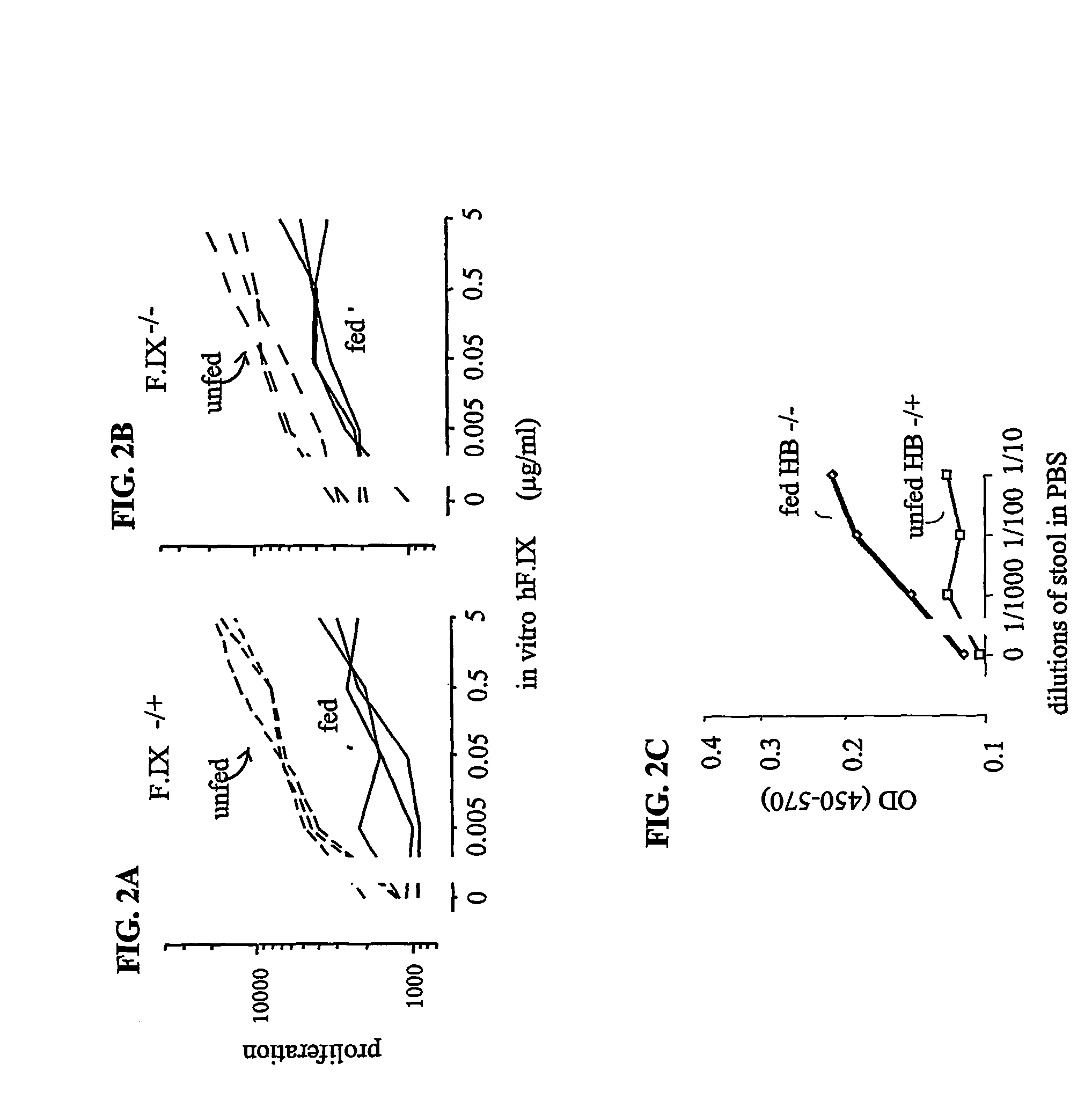
Oral treatment of hemophilia
InactiveUS7220718B2Eliminate needEasy to handleVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsOral treatmentFactor ii
Disclosed herein is a simple method for the treatment of antigen-deficiency diseases, by orally administering to a subject a therapeutically effective amount of the deficient antigen, wherein the antigen is not present in a liposome. In one embodiment, the method increases hemostasis in a subject having hemophilia A or B, by orally administering to the hemophiliac a therapeutically effective amount of the appropriate clotting factor other than in a liposome, sufficient to induce oral tolerance and supply exogenous clotting factor to the subject.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC +1
Novel antibody binding to tfpi and composition comprising the same
The invention discloses a novel antibody binding to TFPI and a composition comprising the same. The present invention relates to an antibody that binds specifically to a tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI), a nucleic acid encoding the antibody, a vector comprising the nucleic acid, a host cell transformed with the vector, a method for producing the antibody, and a pharmaceutical composition for treating hemophilia, which comprises the antibody as an active ingredient. The antibody of the present invention, which binds specifically to TFPI, can activate the extrinsic pathway of blood coagulation by inhibiting TFPI. Thus, the antibody of the present invention can be effectively used for the treatment of antibody-induced hemophilia patients and for the prevention of blood coagulation disease in hemophilia-A or hemophilia-B patients.
Owner:MOGAM INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com












![Demannosylated recombinant factor viii [[vii]] for the treatment of patients with haemophilia a Demannosylated recombinant factor viii [[vii]] for the treatment of patients with haemophilia a](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/de8b7244-99c8-43b2-81e4-d70e4ac6493c/US20100197578A1-20100805-D00001.png)
![Demannosylated recombinant factor viii [[vii]] for the treatment of patients with haemophilia a Demannosylated recombinant factor viii [[vii]] for the treatment of patients with haemophilia a](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/de8b7244-99c8-43b2-81e4-d70e4ac6493c/US20100197578A1-20100805-D00002.png)
![Demannosylated recombinant factor viii [[vii]] for the treatment of patients with haemophilia a Demannosylated recombinant factor viii [[vii]] for the treatment of patients with haemophilia a](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/de8b7244-99c8-43b2-81e4-d70e4ac6493c/US20100197578A1-20100805-D00003.png)