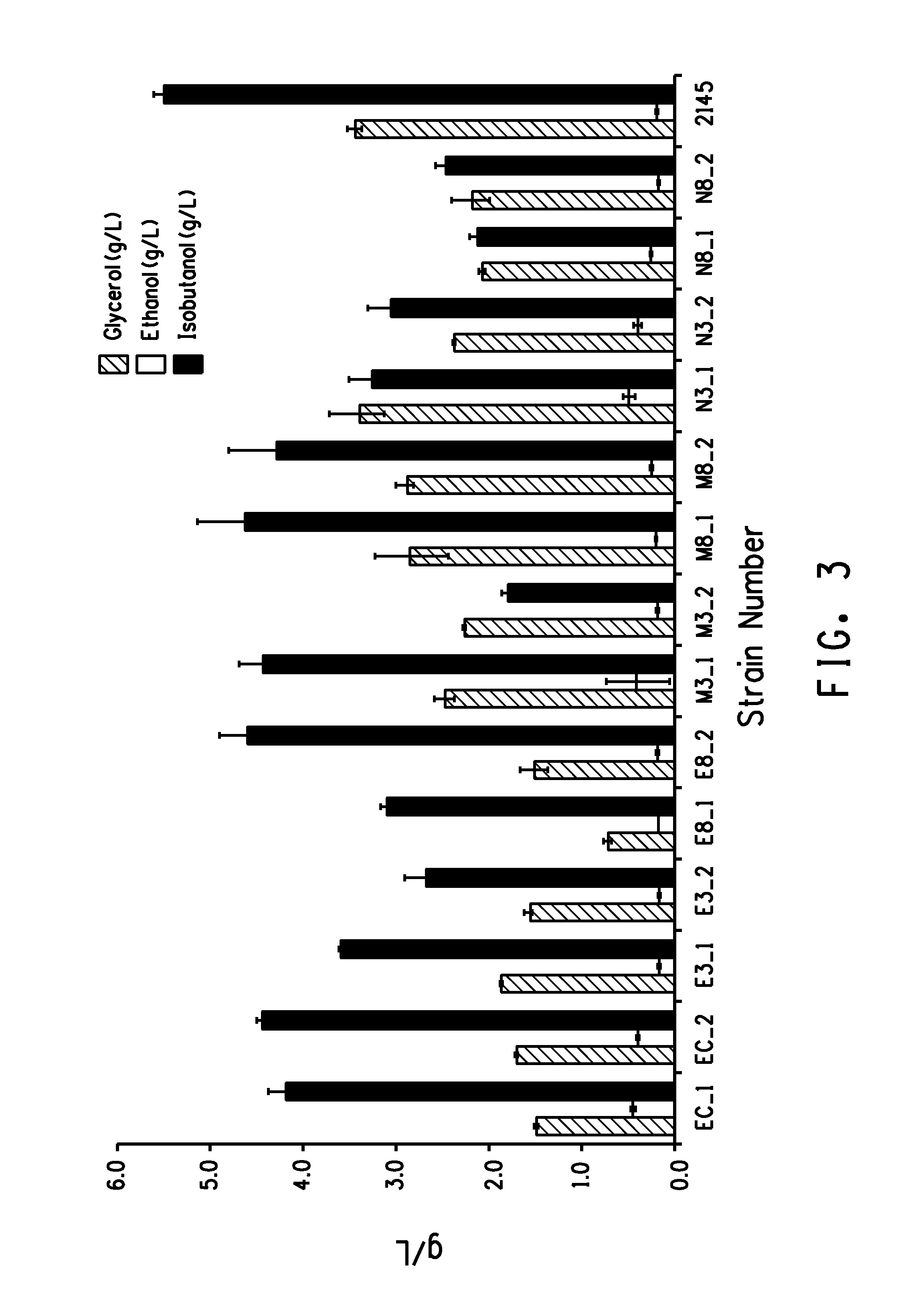
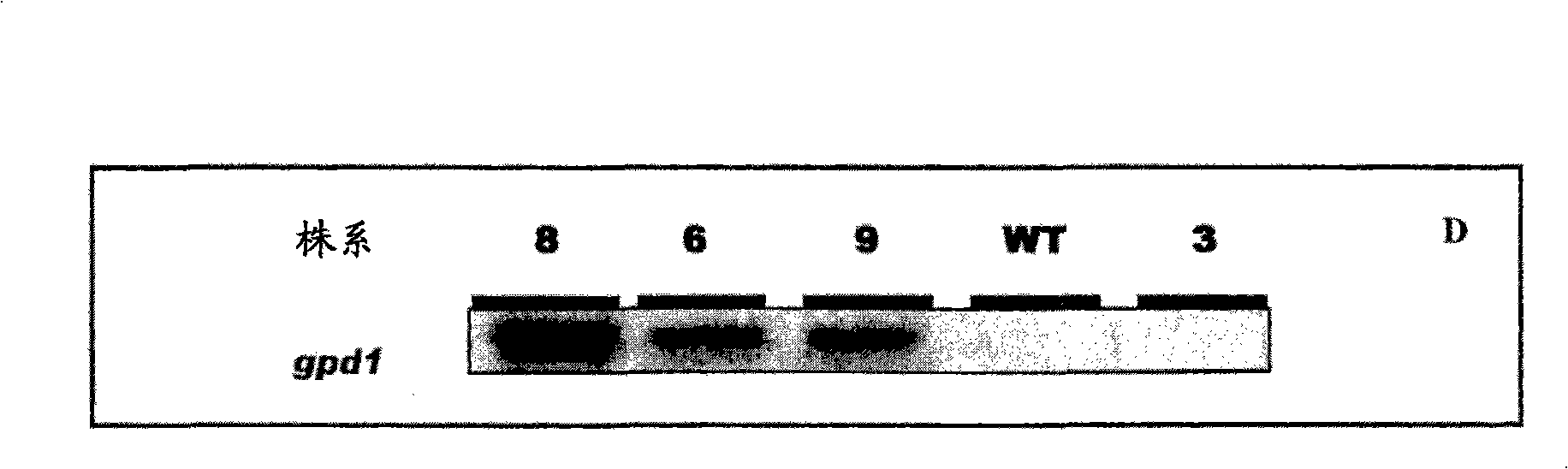
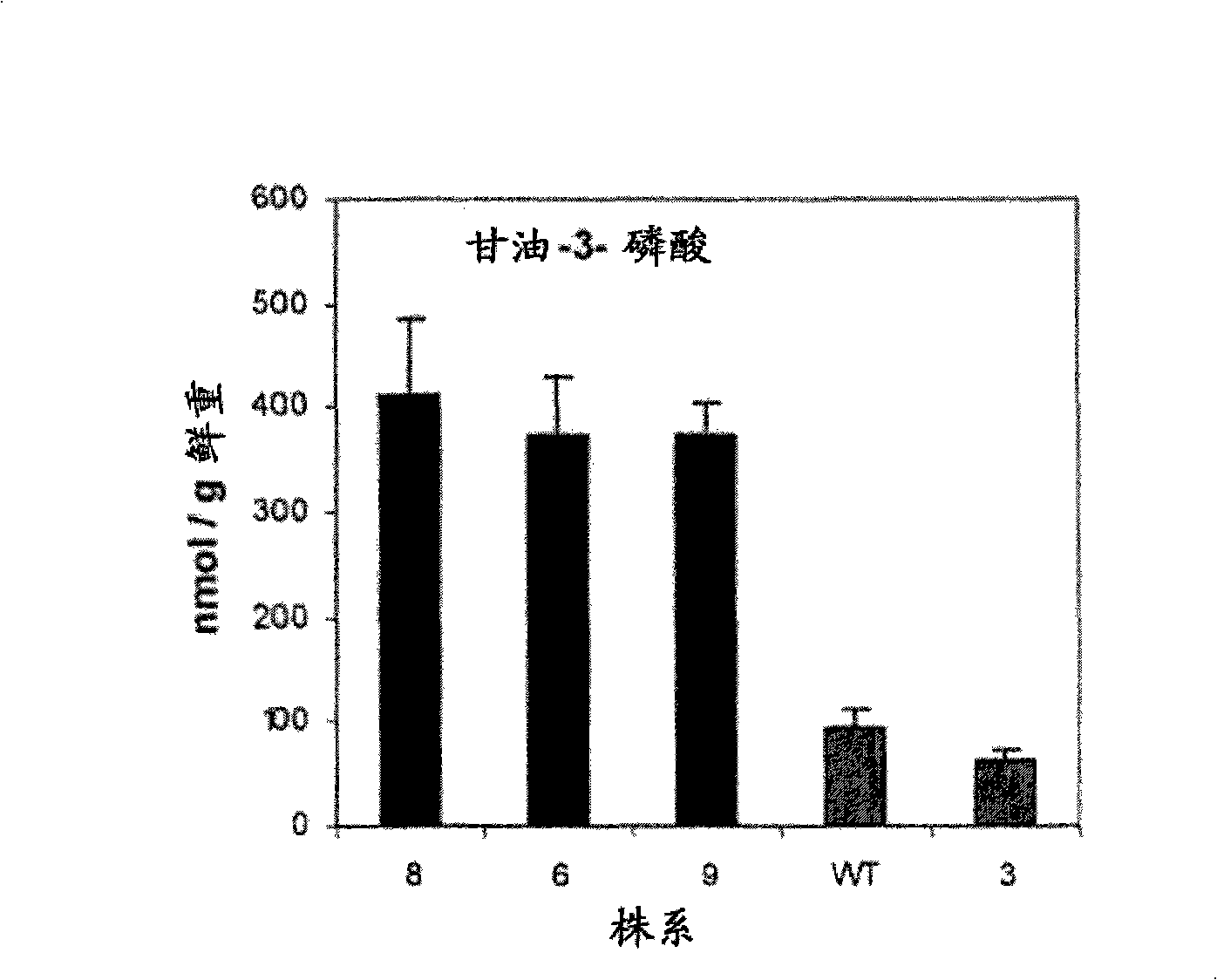
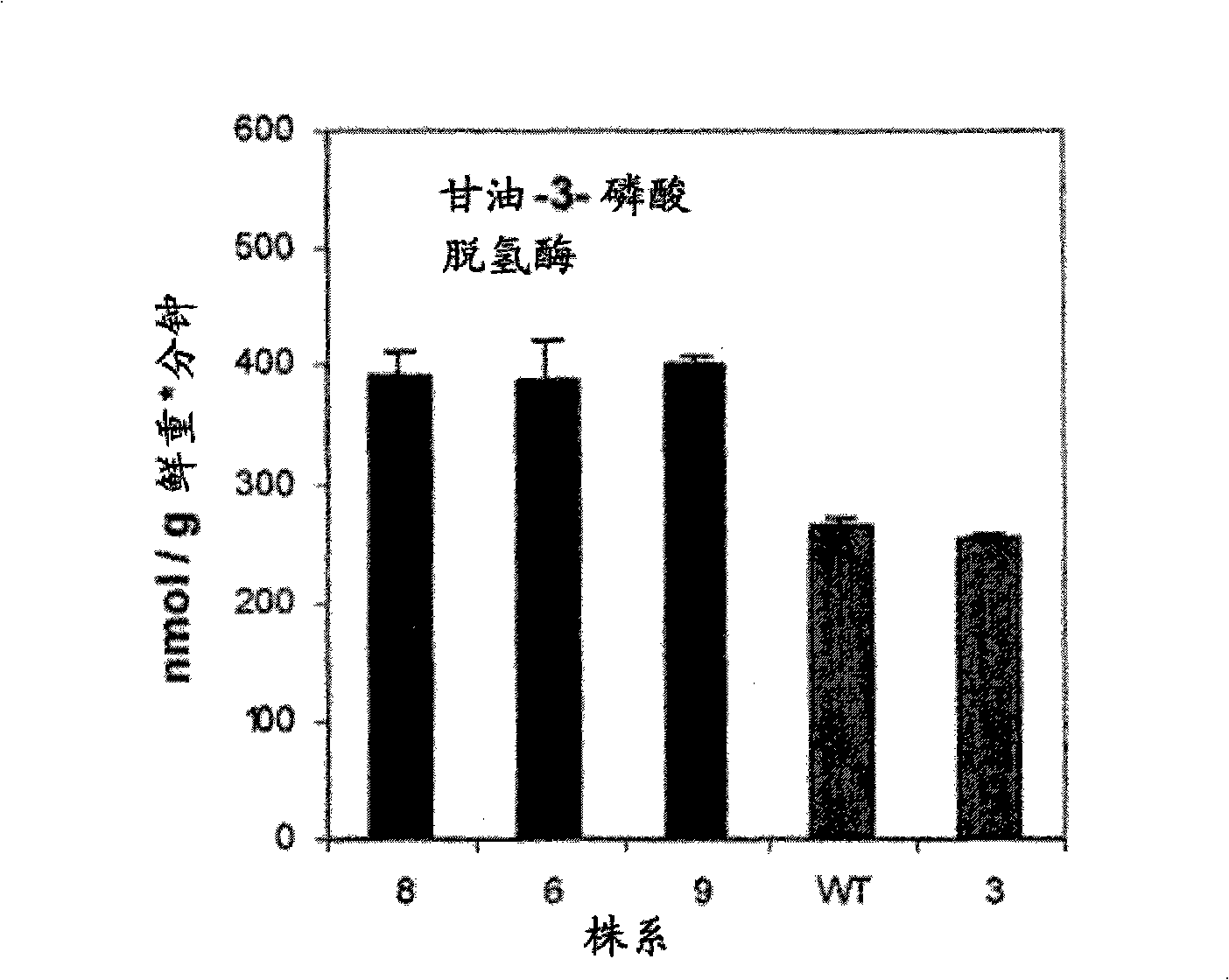
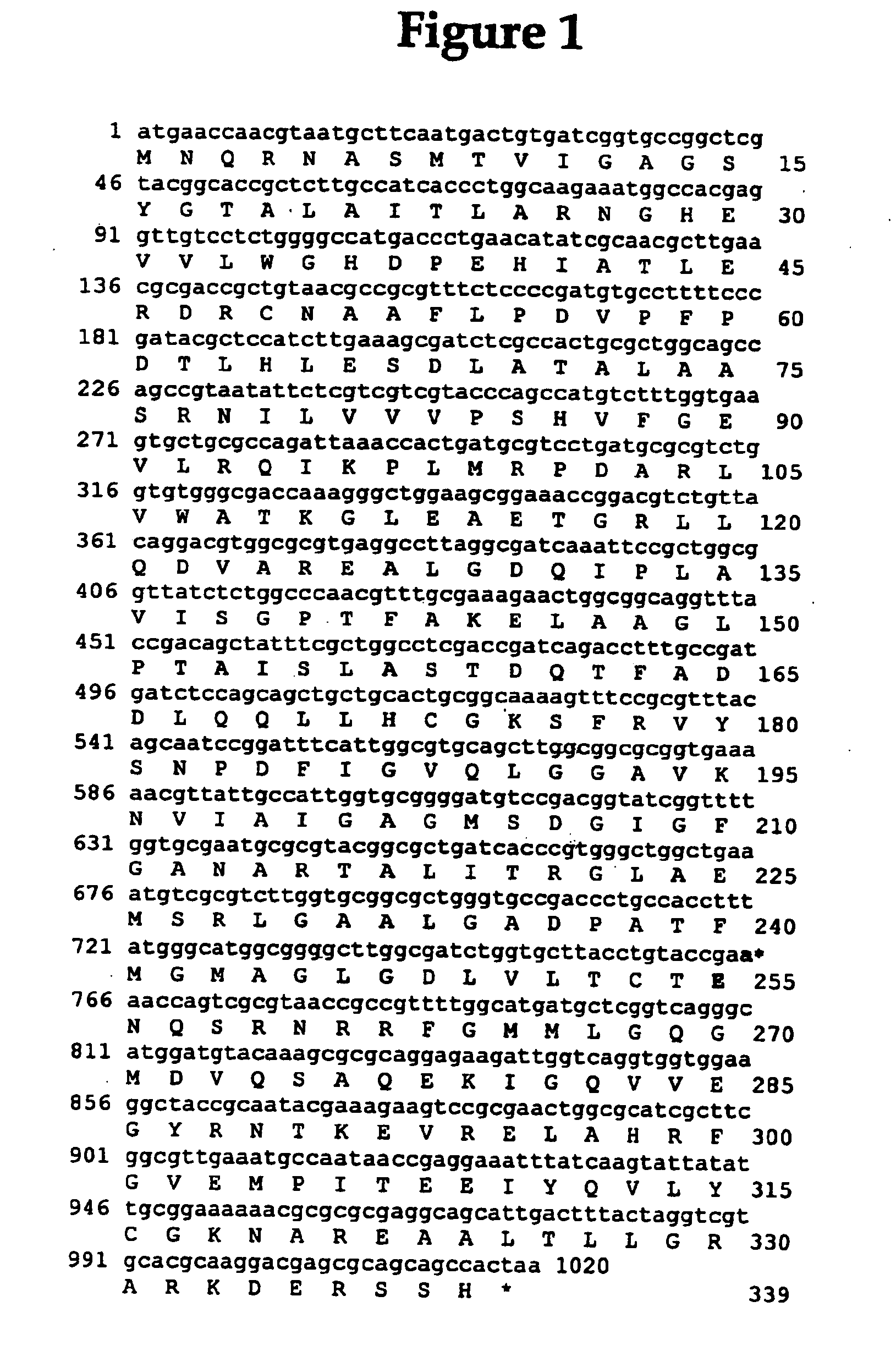
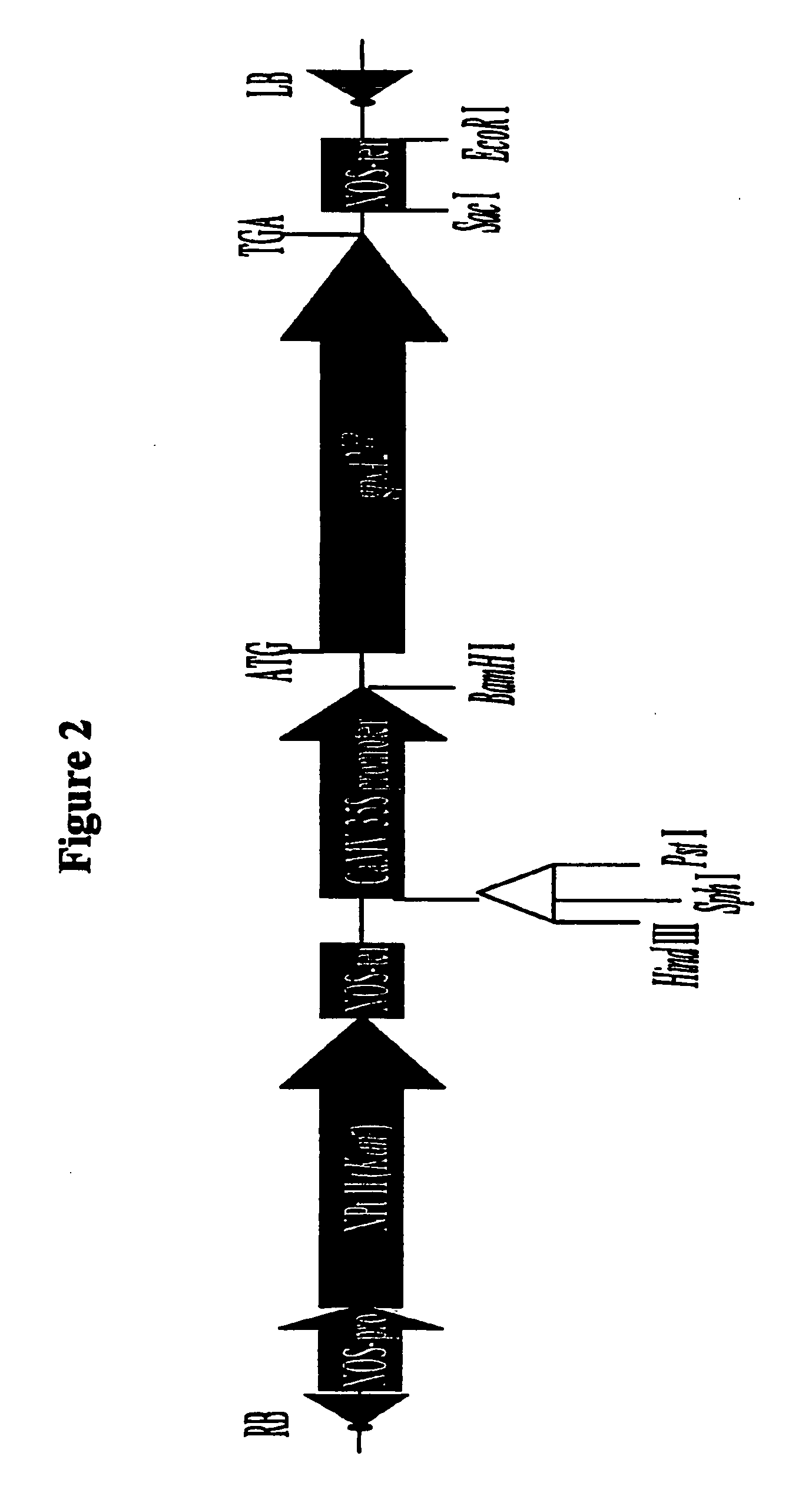
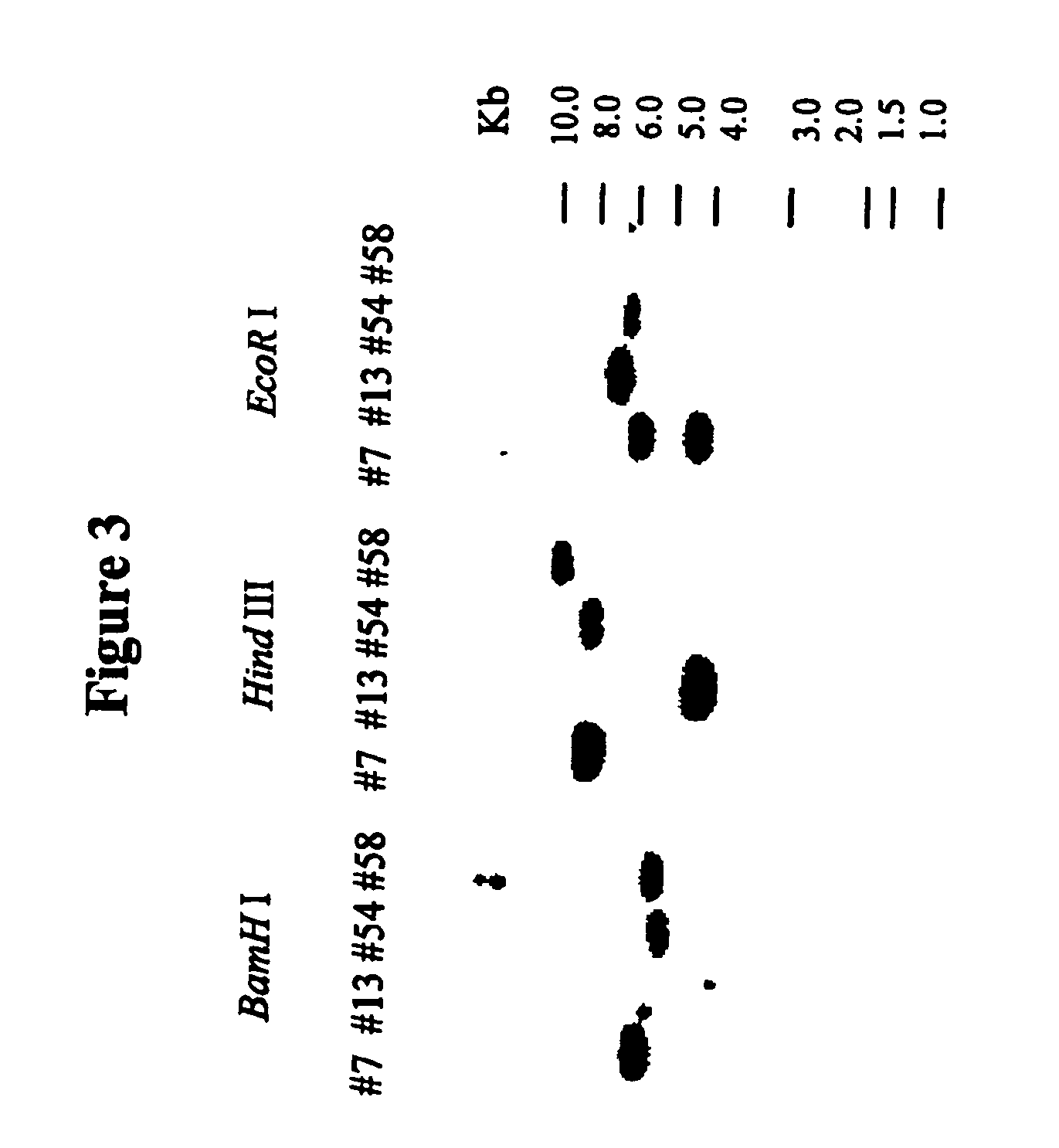
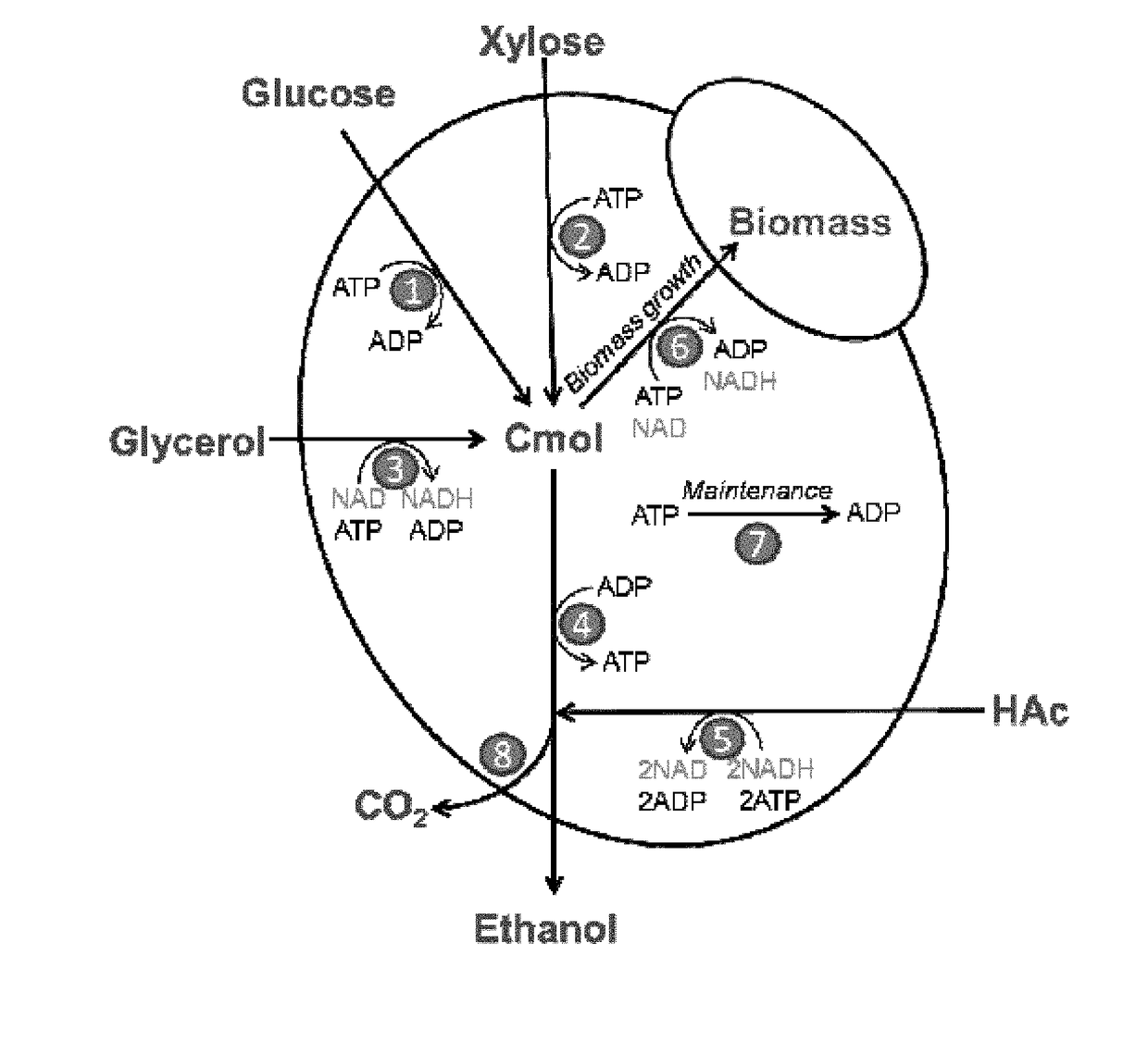
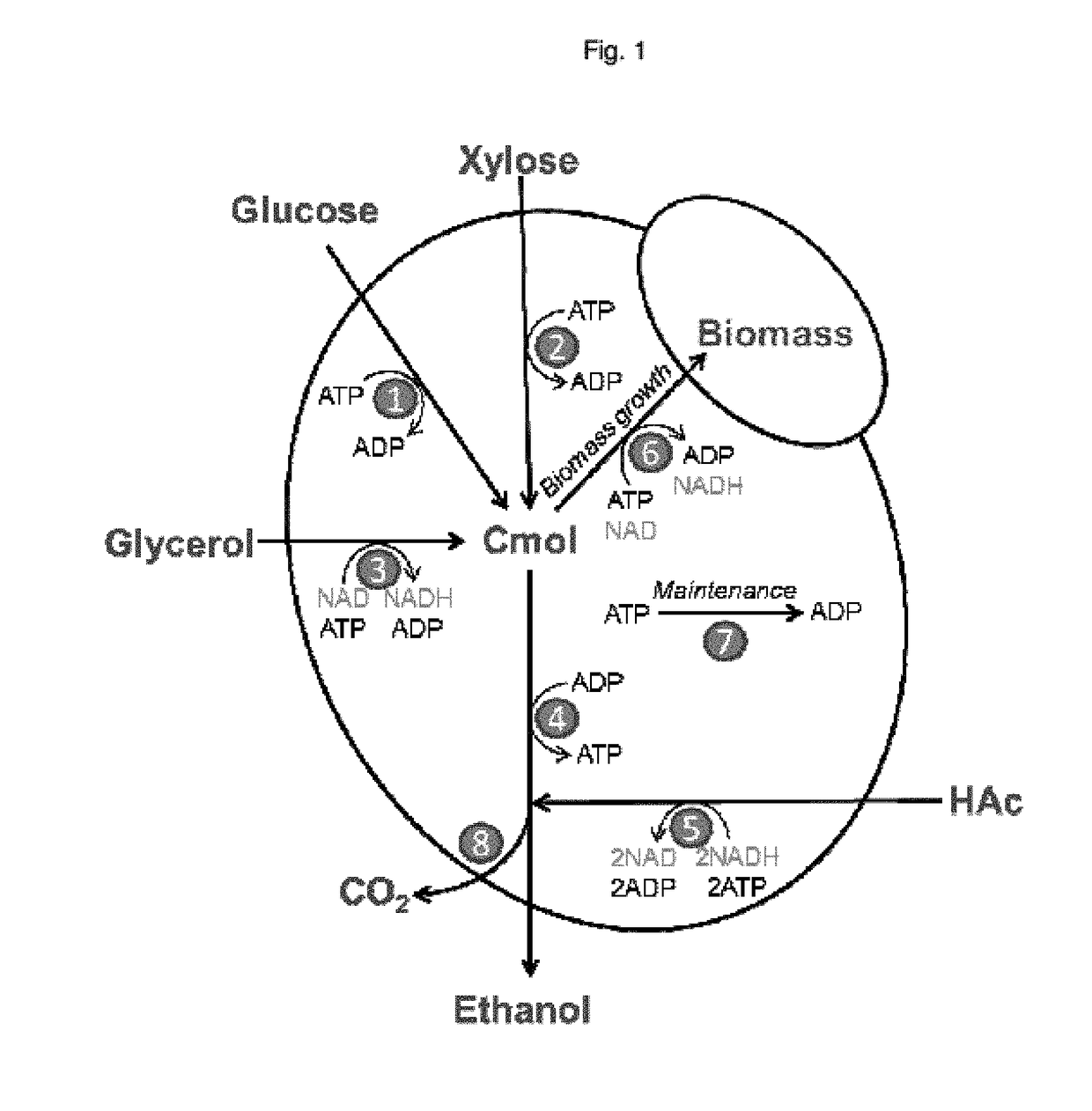
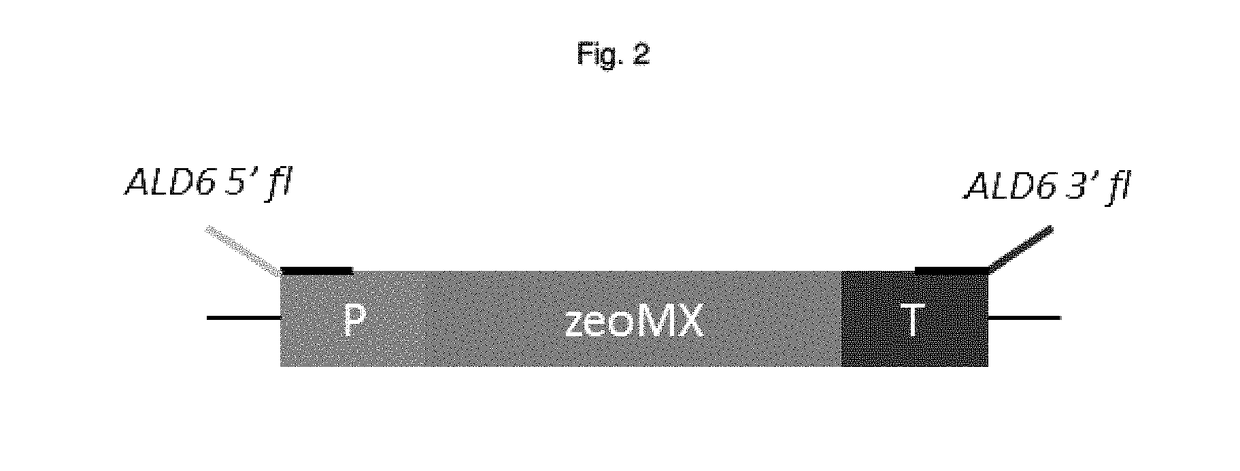
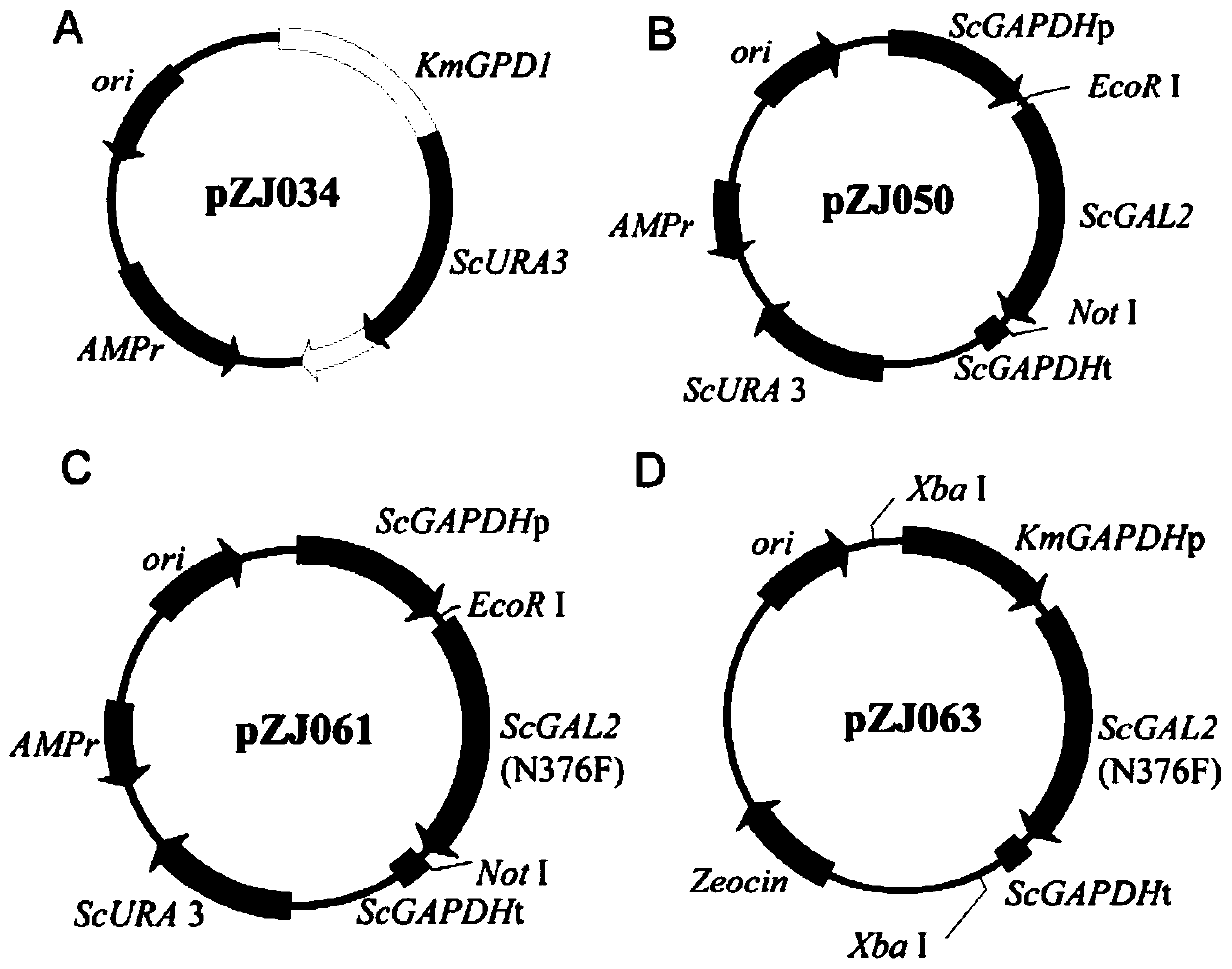
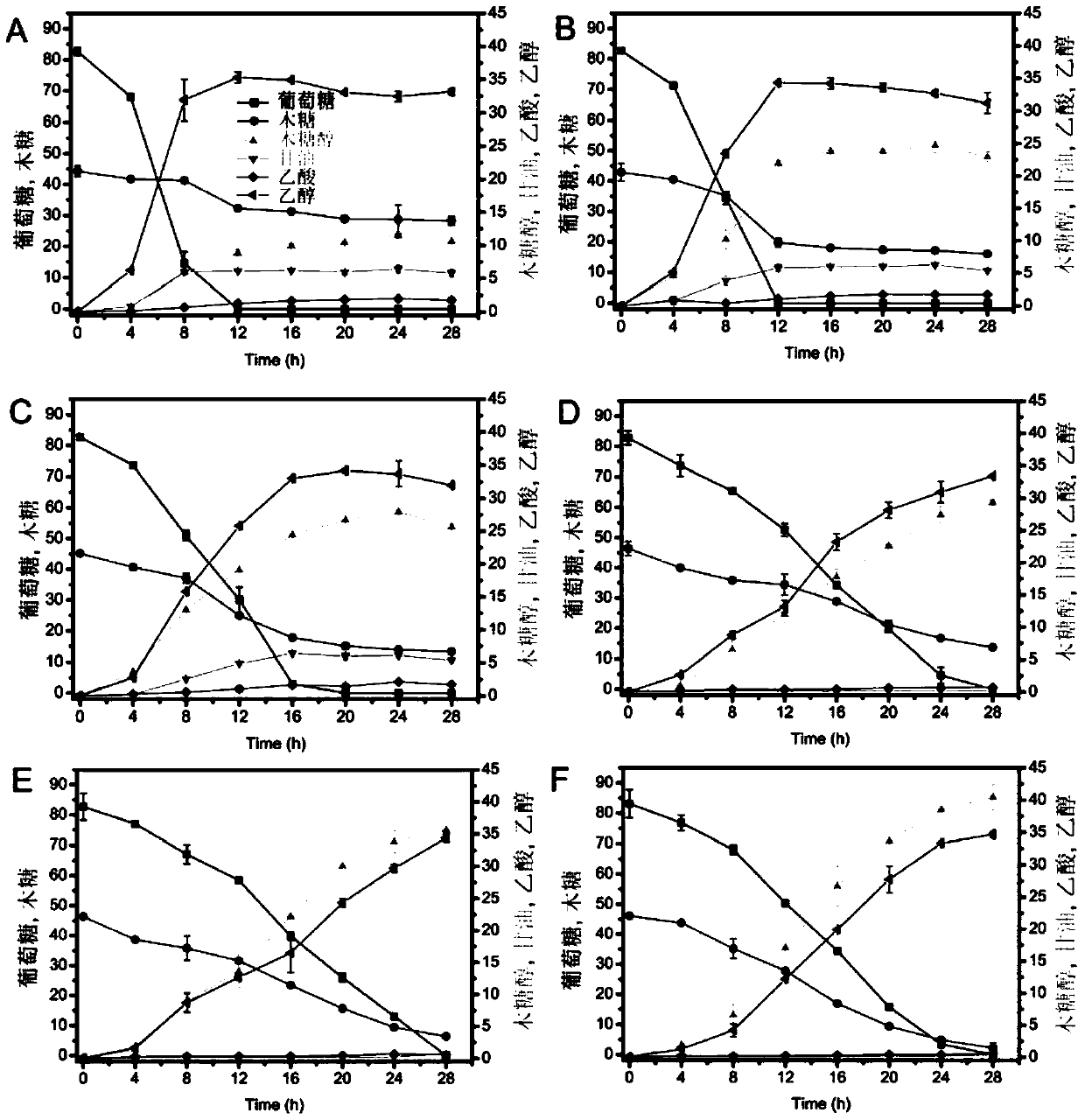
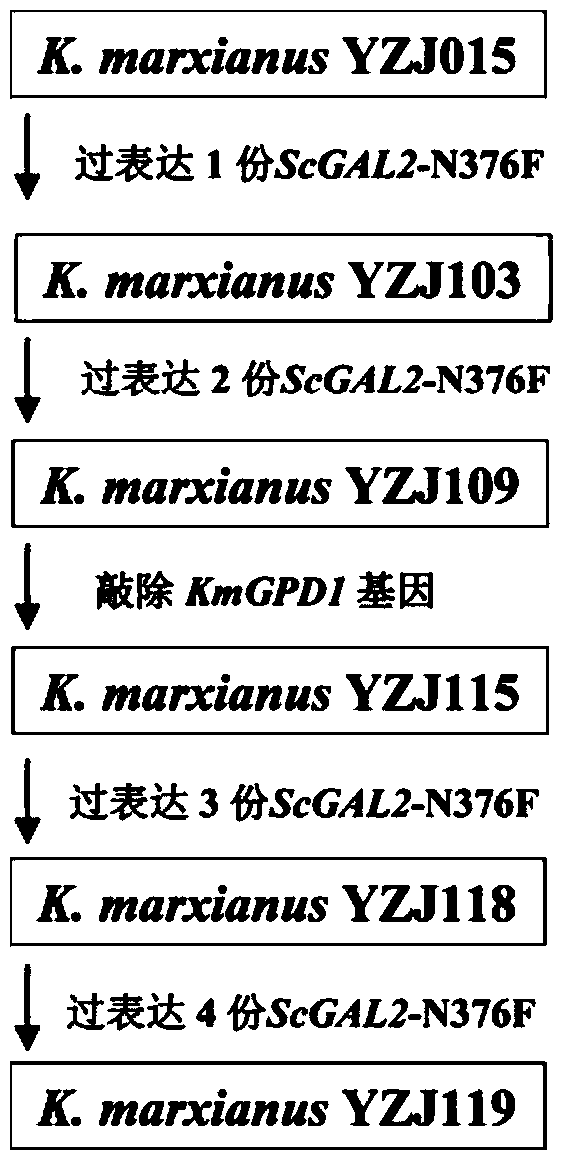
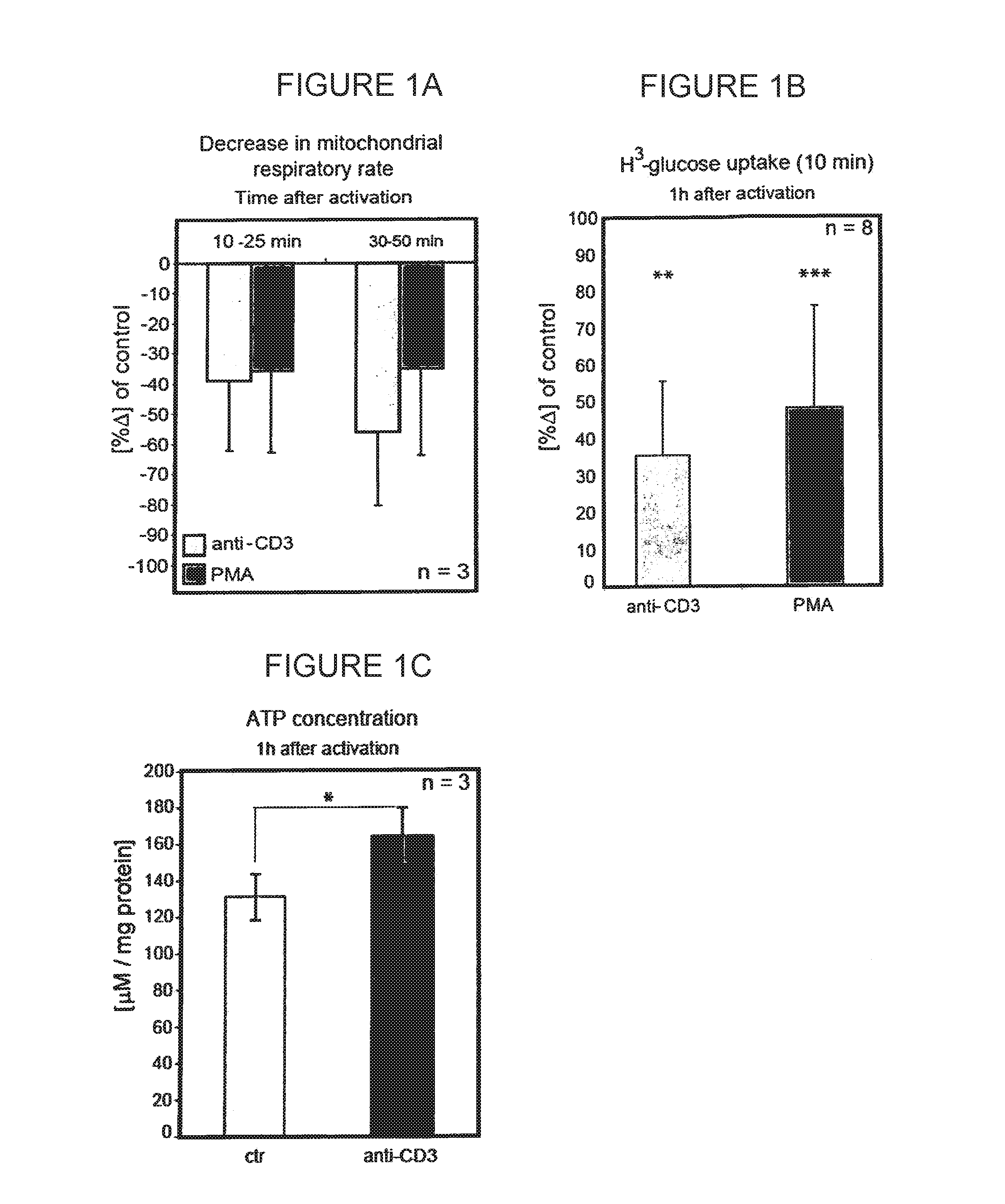
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
42 results about "Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
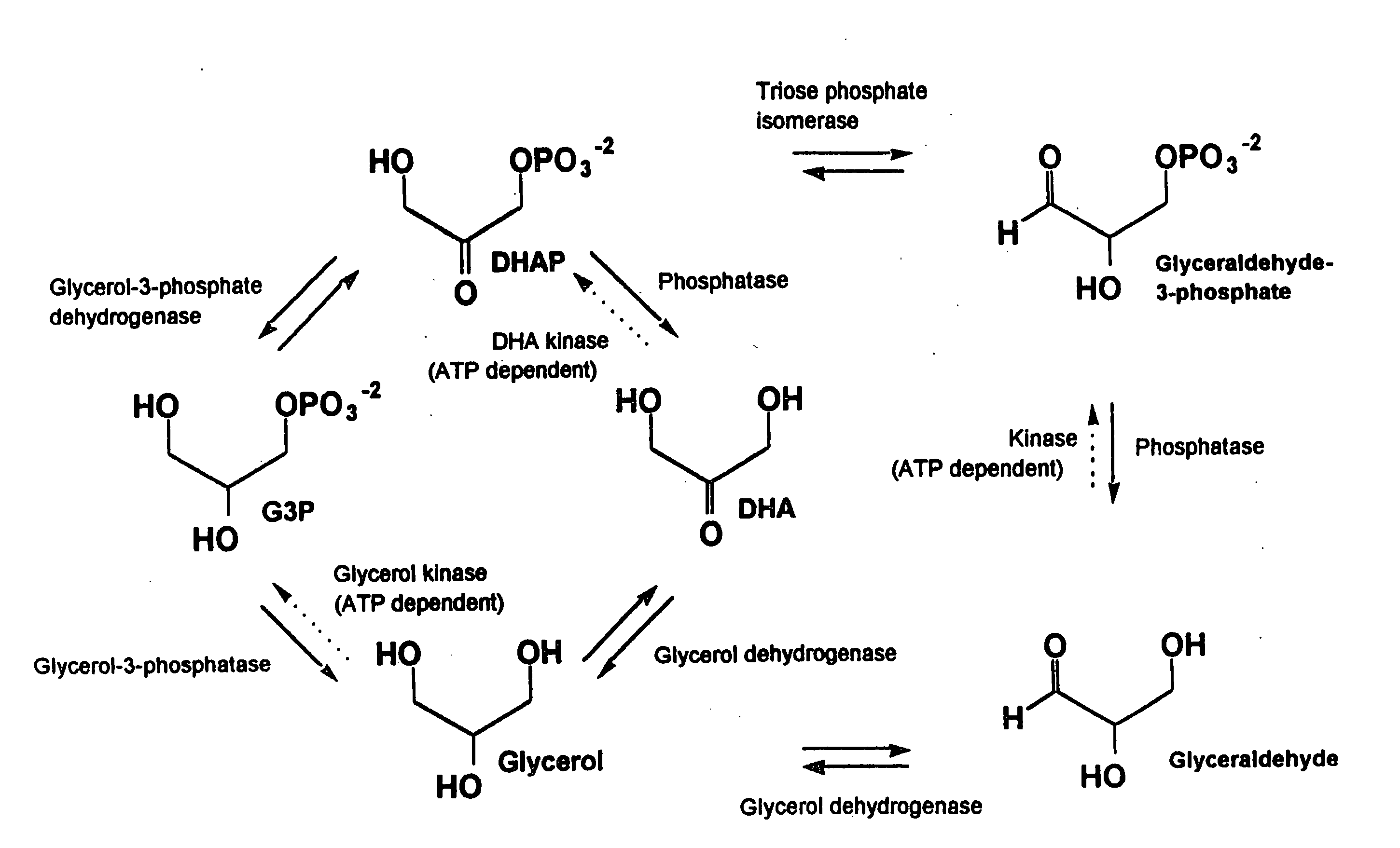
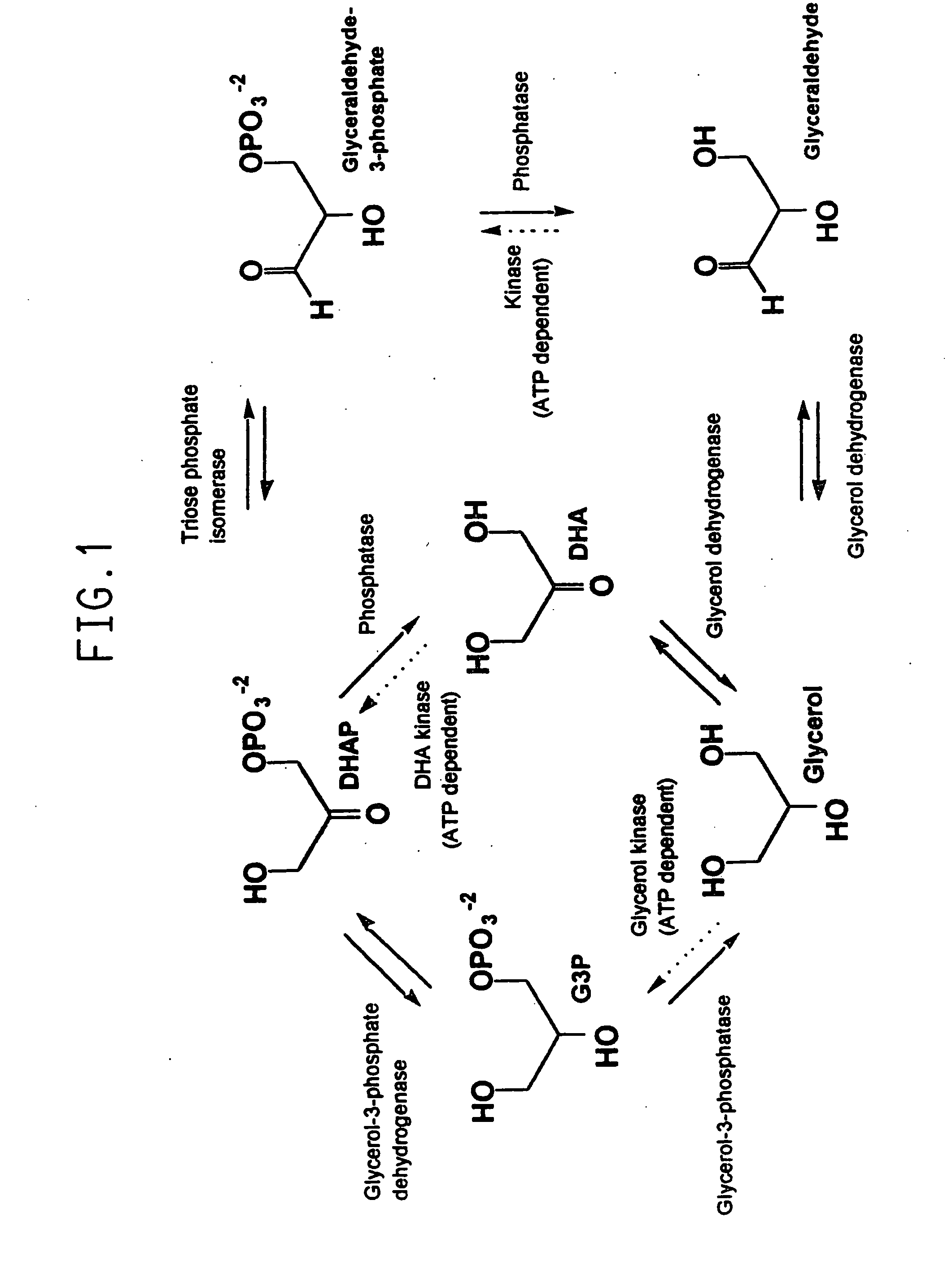
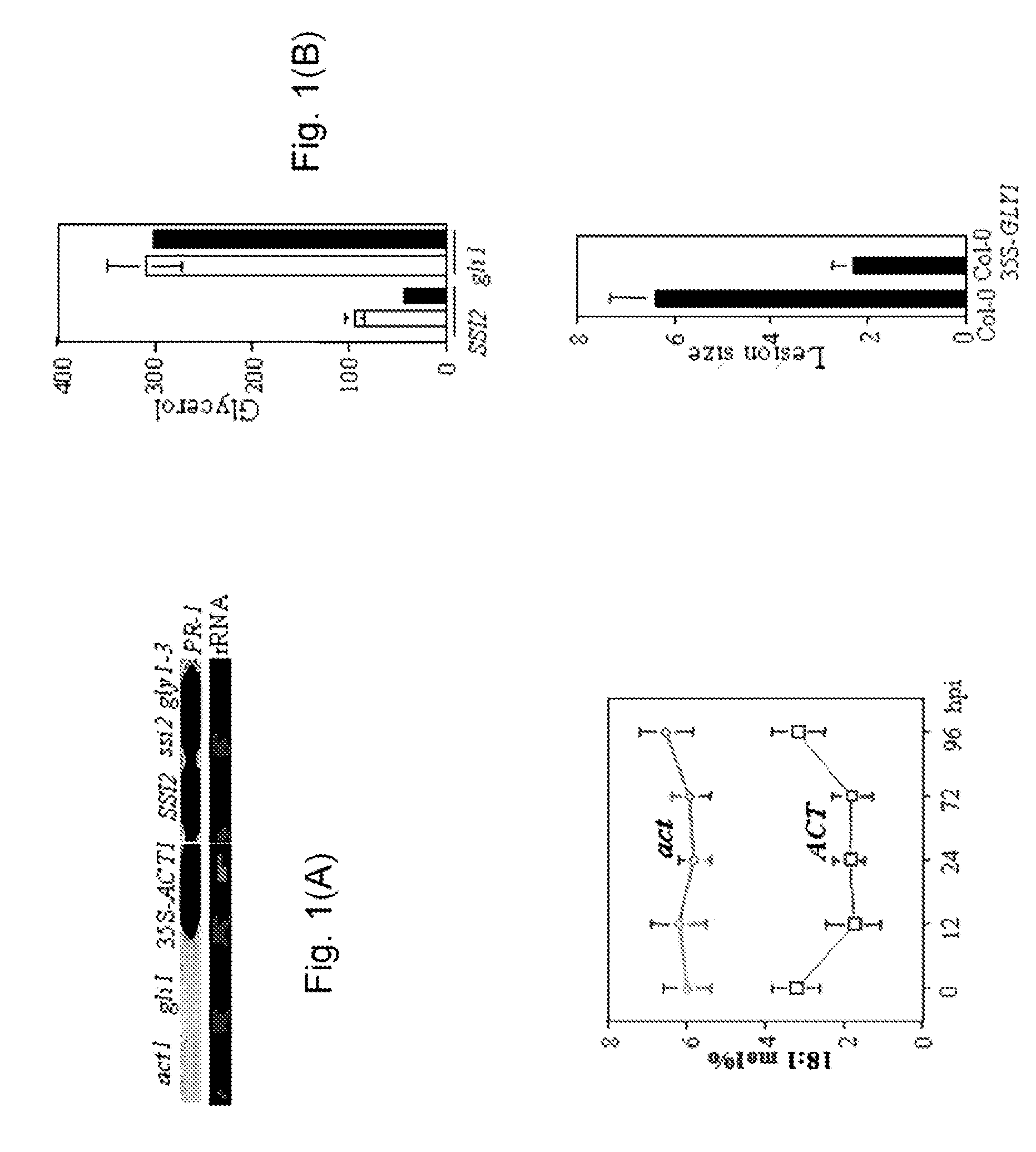
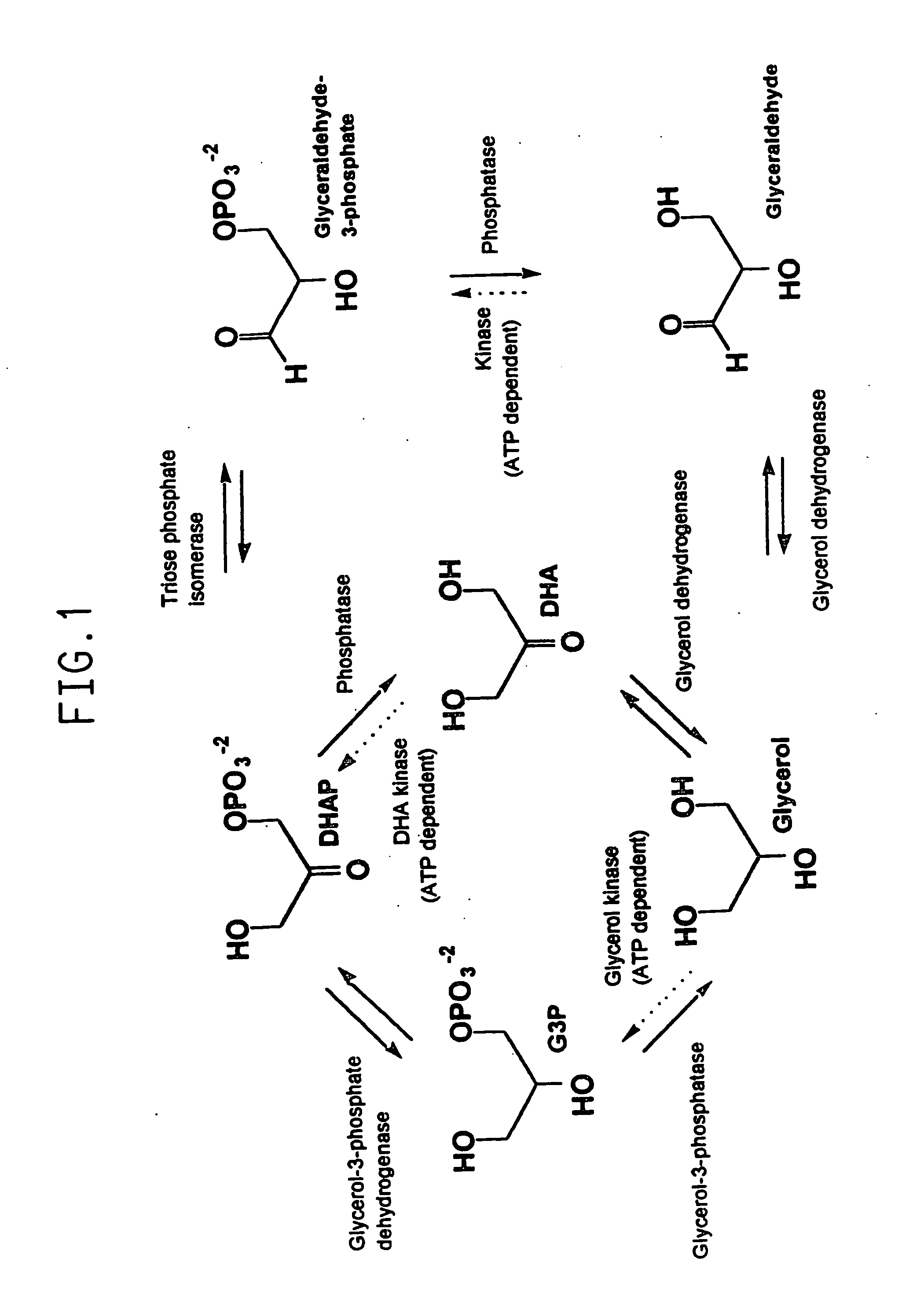
Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GPDH) is an enzyme that catalyzes the reversible redox conversion of dihydroxyacetone phosphate (a.k.a. glycerone phosphate, outdated) to sn-glycerol 3-phosphate. Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase serves as a major link between carbohydrate metabolism and lipid metabolism. It is also a major contributor of electrons to the electron transport chain in the mitochondria.
Polyhydroxyalkanoate production from polyols
InactiveUS20050239179A1Promote recoveryProduct can be usedBacteriaMicroorganism based processes3-Hydroxypropionic acidPropanoic acid
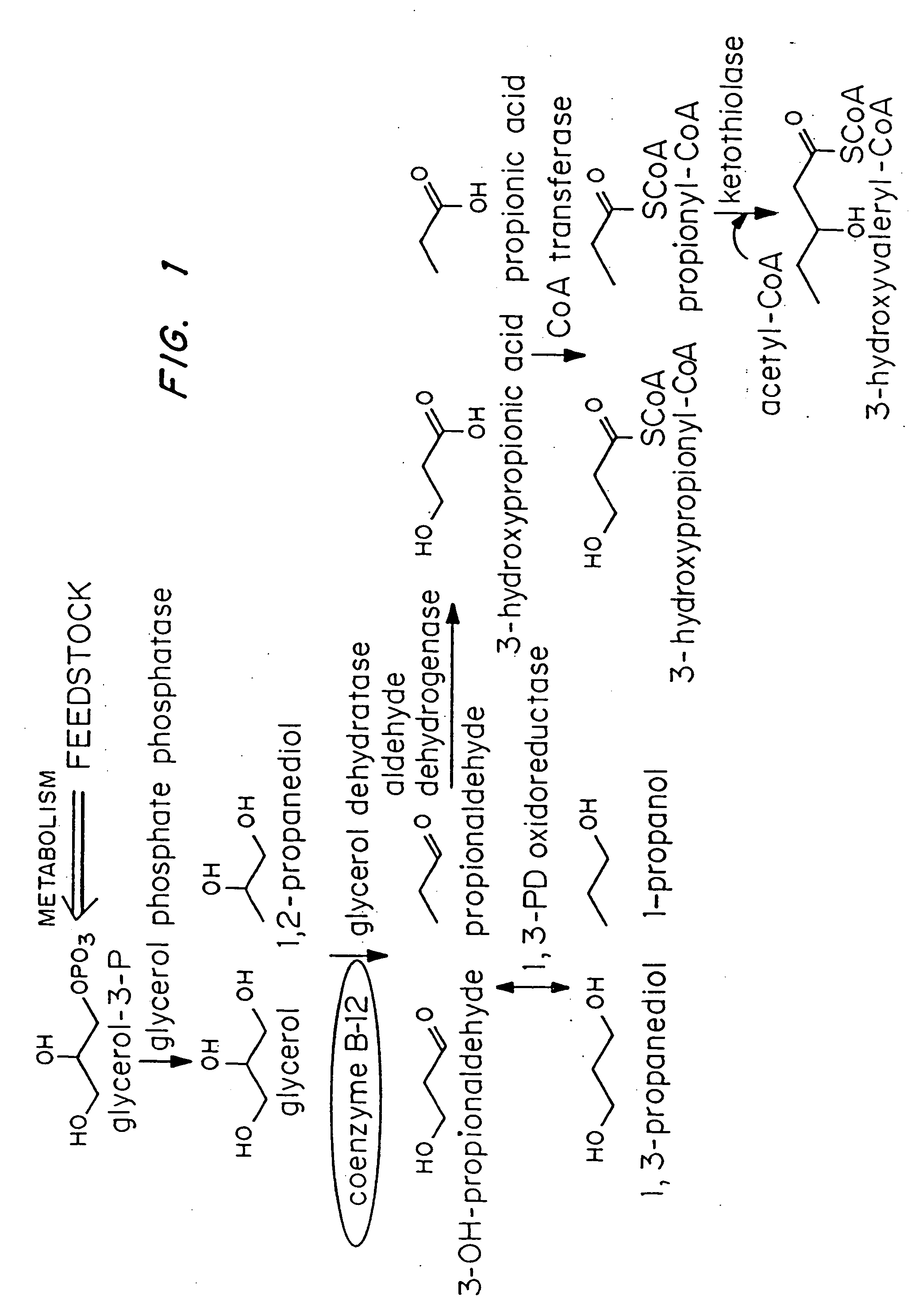
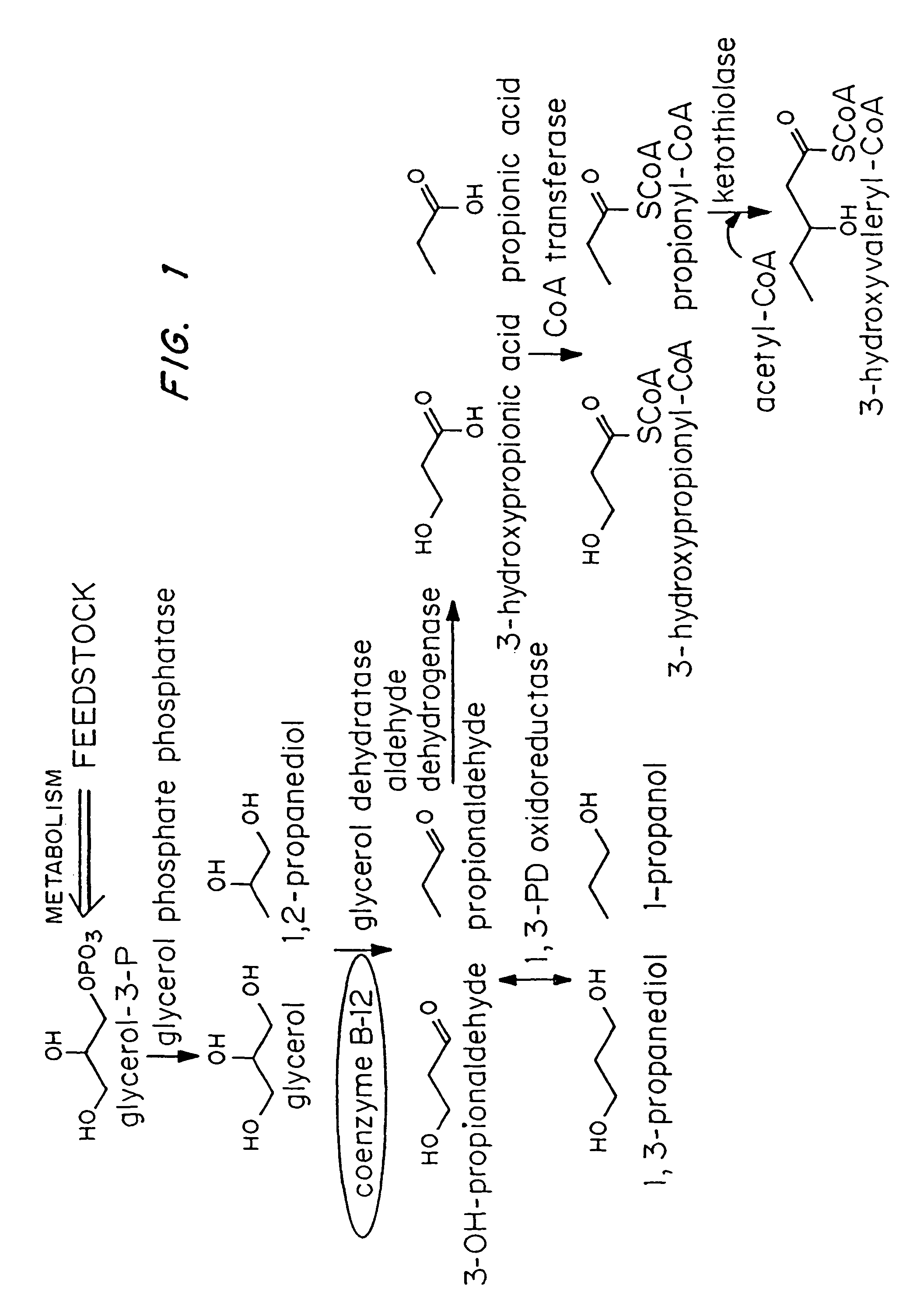
Organisms are provided which express enzymes such as glycerol dehydratase, diol dehydratase, acyl-CoA transferase, acyl-CoA synthetase β-ketothiolase, acetoacetyl-CoA reductase, PHA synthase, glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and glycerol-3-phosphatase, which are useful for the production of PHAs. In some cases one or more of these genes are native to the host organism and the remainder are provided from transgenes. These organisms produce poly (3-hydroxyalkanoate) homopolymers or co-polymers incorporating 3-hydroxypropionate or 3-hydroxyvalerate monomers wherein the 3-hydroxypropionate and 3-hydroxyvalreate units are derived from the enzyme catalysed conversion of diols. Suitable diols that can be used include 1,2-propanediol, 1,3 propanediol and glycerol. Biochemical pathways for obtaining the glycerol from normal cellular metabolites are also described. The PHA polymers are readily recovered and industrially useful as polymers or as starting materials for a range of chemical intermediates including 1,3-propanediol, 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde, acrylics, malonic acid, esters and amines.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Transformed microorganisms and genes useful in the production of glycerol and 1,3-propanediol
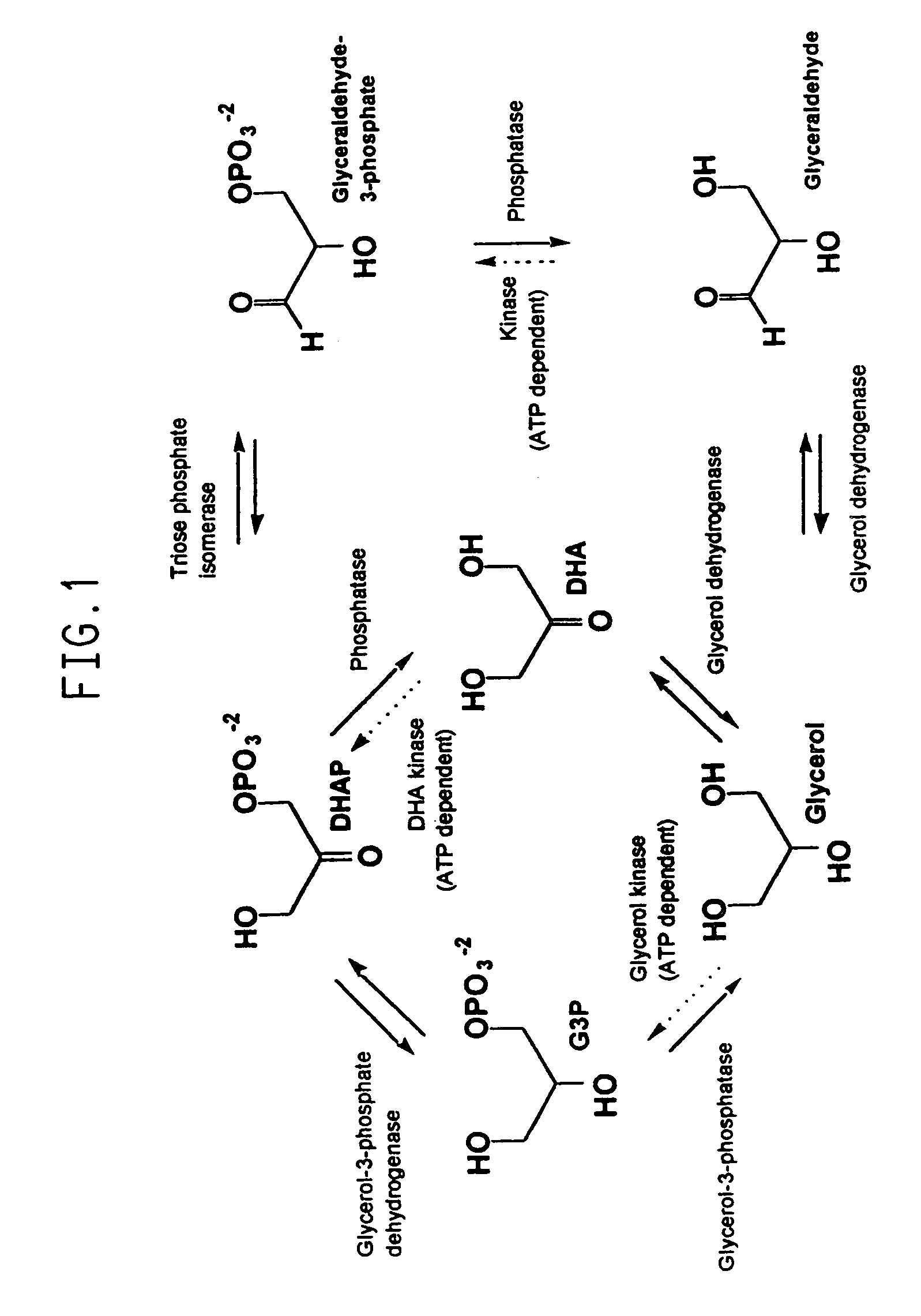
Recombinant organisms are provided comprising genes encoding a glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and / or a glycerol-3-phosphatase activity useful for the production of glycerol from a variety of carbon substrates. The organisms further contain disruptions in the endogenous genes encoding proteins having glycerol kinase and glycerol dehydrogenase activities.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO +1
Glycerol 3- phosphate dehydrogenase for butanol production
ActiveUS20140273129A1Improved and increased production of butanolReduced and decreased production of glycerolBacteriaBiofuelsHeterologousMicroorganism
Provided herein are glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GPD) enzymes with increased KM for NADH and GPD enzymes with substantially the same affinity for NADH and NADPH and / or are feedback inhibited by glycerol-3-phosphate. Also provided herein are recombinant microorganisms comprising a heterologous gene encoding GPD and a deletion or disruption in an endogenous gene encoding GPD. Also provided are recombinant microorganisms comprising a heterologous gene encoding GPD and a butanol biosynthetic pathway. Further provided are methods of producing butanol comprising providing the recombinant microorganisms described herein and contacting the recombinant microorganism with at least one fermentable carbon substrate under conditions wherein butanol is produced.
Owner:GEVO INC
Transgenic manipulation of sn-glycerol-3-phosphate and glycerol production with a feedback defective glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenese gene
InactiveUS7112724B1Enhanced production of glycerolIncrease productionOther foreign material introduction processesOxidoreductasesWild typePhosphoric acid
The invention provides a method for genetically transforming a plant so that it expresses a glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase that is feedback-defective. The feedback-defective enzyme raises levels of glycerol and glycerol-3-phosphate in comparison to the wild-type, leading to increased osmotic stress tolerance, and altered fatty acid content in glycerolipids.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Polyhydroxyalkanoate production from polyols
Organisms are provided which express enzymes such as glycerol dehydratase, diol dehydratase, acyl-CoA transferase, acyl-CoA synthetase β-ketothiolase, acetoacetyl-CoA reductase, PHA synthase, glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and glycerol-3-phosphatase, which are useful for the production of PHAs. In some cases one or more of these genes are native to the host organism and the remainder are provided from transgenes. These organisms produce poly (3-hydroxyalkanoate) homopolymers or co-polymers incorporating 3-hydroxypropionate or 3-hydroxyvalerate monomers wherein the 3-hydroxypropionate and 3-hydroxyvalerate units are derived from the enzyme catalysed conversion of diols. Suitable diols that can be used include 1,2-propanediol, 1,3 propanediol and glycerol. Biochemical pathways for obtaining the glycerol from normal cellular metabolites are also described. The PHA polymers are readily recovered and industrially useful as polymers or as starting materials for a range of chemical intermediates including 1,3-propanediol, 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde, acrylics, malonic acid, esters and amines.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Recombinant Escherichia coli and application of recombinant Escherichia coli in synthesizing 3-hydroxypropionic acid
ActiveCN105567622AIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coli3-Hydroxypropionic acid
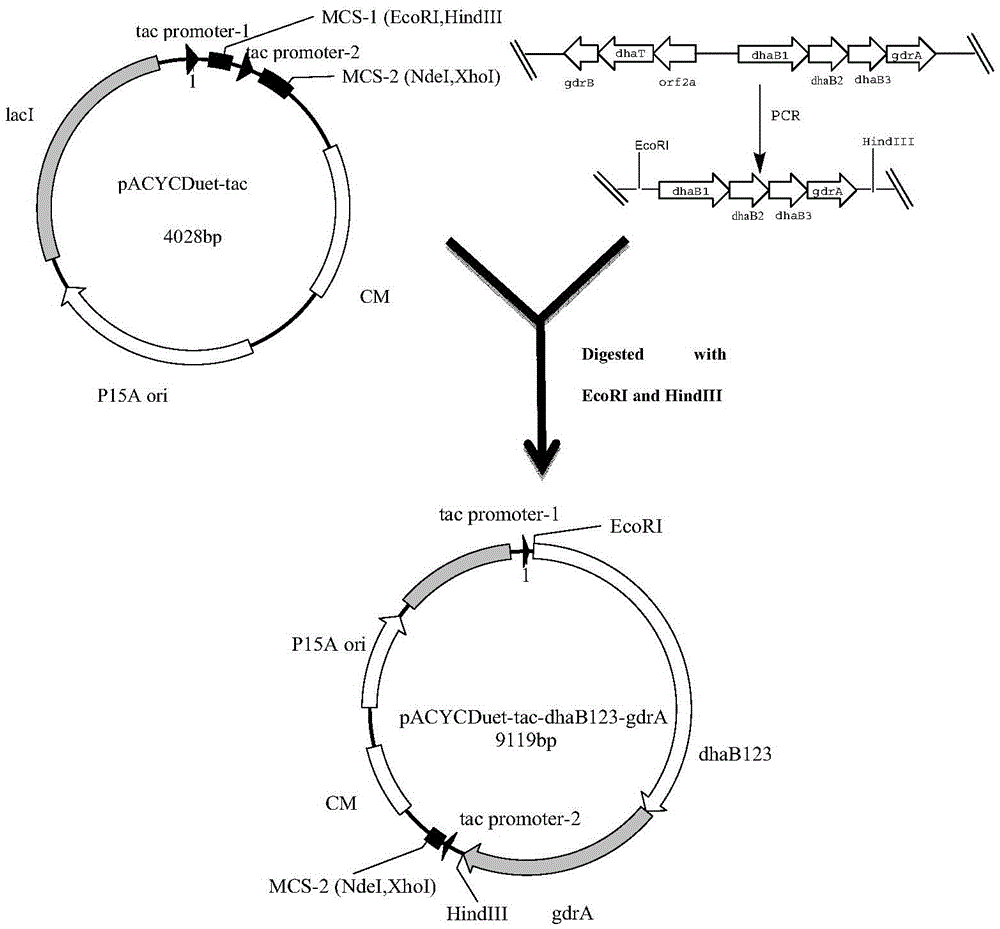
The invention discloses recombinant Escherichia coli and application of the recombinant Escherichia coli in synthesizing 3-hydroxypropionic acid. The recombinant Escherichia coli is formed by glycerol dehydratase genes dhaB123, glycerol dehydratase reactivating factor genes gdrA, alpha-oxoglutarate semialdehyde dehydrogenase mutant coding genes TUkgsadh and glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase coding genes gpdl which are guided into host bacteria. By means of the gene knockout technique, the yield of byproduct 1,3-propylene glycol is reduced, and meanwhile, cofactors NAD+ of aldehyde dehydrogenase are regenerated. Thus, the yield of the 3-hydroxypropionic acid is improved by 1.5 times.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Identification of compositions, compositions, and methods of treatment of obesity and overweight conditions
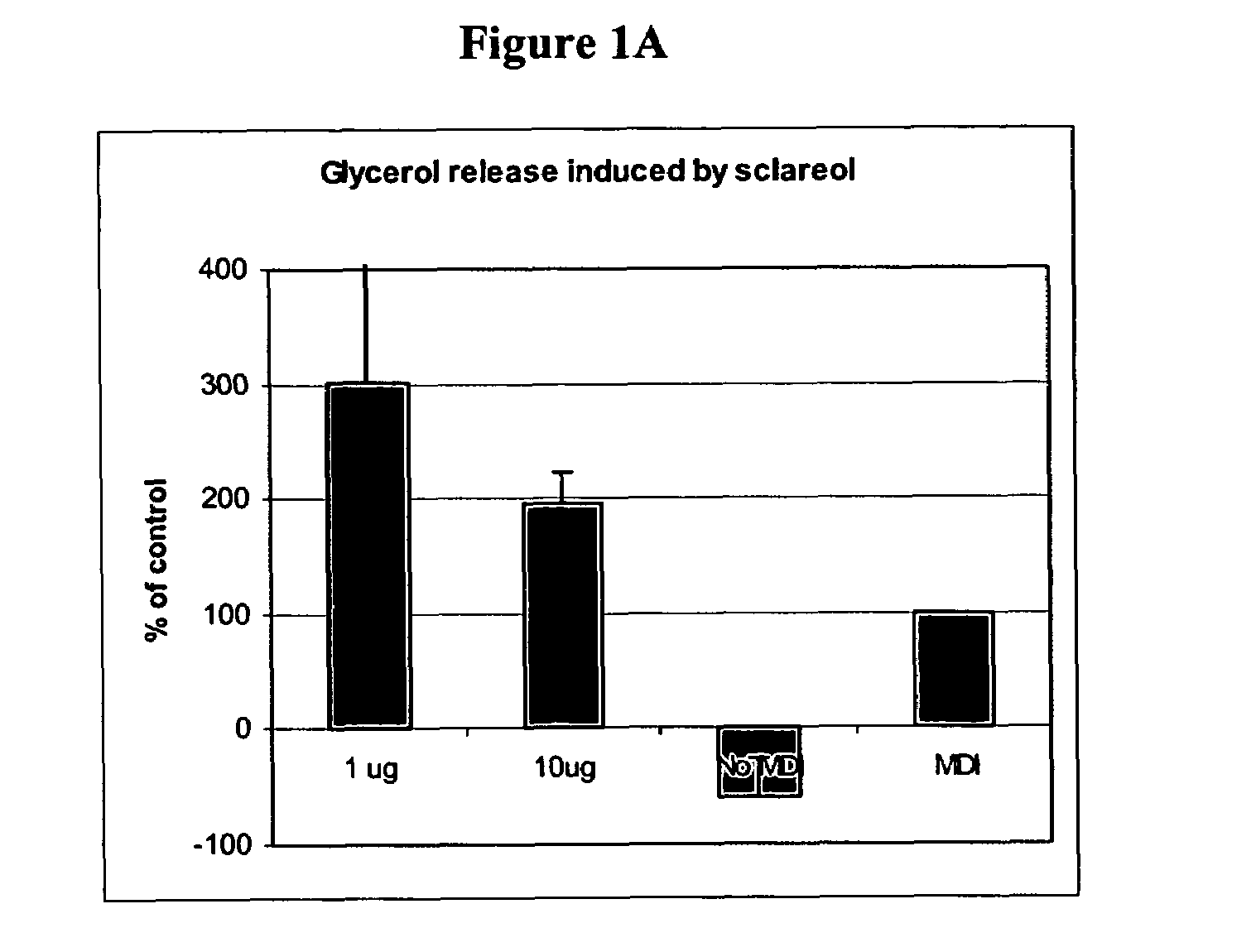
A method for the identification of a composition useful in the treatment of an overweight or obese person to reduce the person's body mass index is provided which comprises obtaining an extract of an ethnobotanical plant, and evaluating the activity of the extract in an assay selected from the group consisting of a lipolysis assay, an assay that measures the amount of glycerol introduced by a cell into a suspension medium of the cell, an adipocyte differentiation assay, an assay that measures the level of the enzyme glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, an assay that measures the inhibition of differentiation of preadipocytes to adipocytes, an assay that measures the accumulation of lipid in an adipocyte, an assay that measures the de-differentiation of adipocytes into preadipocytes, and combinations thereof. Sclareol and sclareol-like compounds and sclareolide and sclareolide-like compounds are identified as useful in the treatment of overweight and obese conditions and disorders and conditions associated with adipose tissue abnormalities. These compounds can be formulated for oral administration.
Owner:PHYTOMYCO RES CORP
Modulators of adp-dependent glucokinase (ADPGK) and glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GPD2) for therapy
Described are compounds capable of modulating (a) the biological activity of ADP-dependent glucokinase (ADPGK) and / or glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GPD2) or (b) the expression of the gene encoding ADPGK or GPD2 for use in treating a disease (a) associated with aberrant cell proliferation, e.g., a neoplasm, or (b) of the immune system, e.g., an autoimmune disease.
Owner:DEUTES KREBSFORSCHUNGSZENT STIFTUNG DES OFFENTLICHEN RECHTS
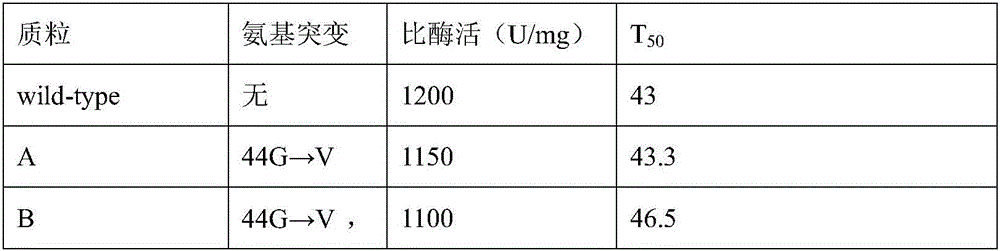
Glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase mutant
ActiveCN106190996AIncreased specific enzyme activityImprove thermal stabilityBiological material analysisOxidoreductasesMutantSorbitol-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
The invention relates to a glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase mutant. The mutant is obtained by mutating 44th-site glycine into valine and 319th-site glycine into valine in a glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase of which the amino acid sequence is disclosed as SEQ ID No.1; and compared with the glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase of which the amino acid sequence is disclosed as SEQ ID No.1 before mutation, the mutant has higher heat stability. The glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase mutant has the advantages of high heat stability and high inhibition rate; and the mutant enzyme can be used as a raw material for multiple small molecule detection kits, so that the obtained kit has higher stability and sensitivity.
Owner:NINGBO MEDICAL SYSTEM BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
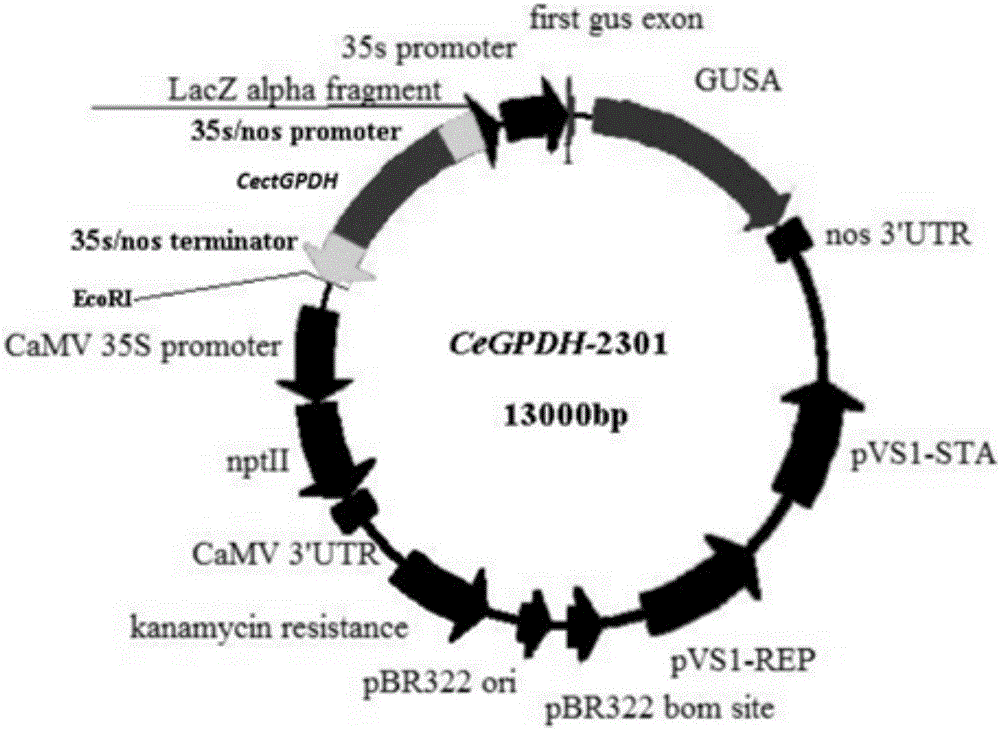
CectGPDH2 (cytosolic glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 2) gene and application thereof
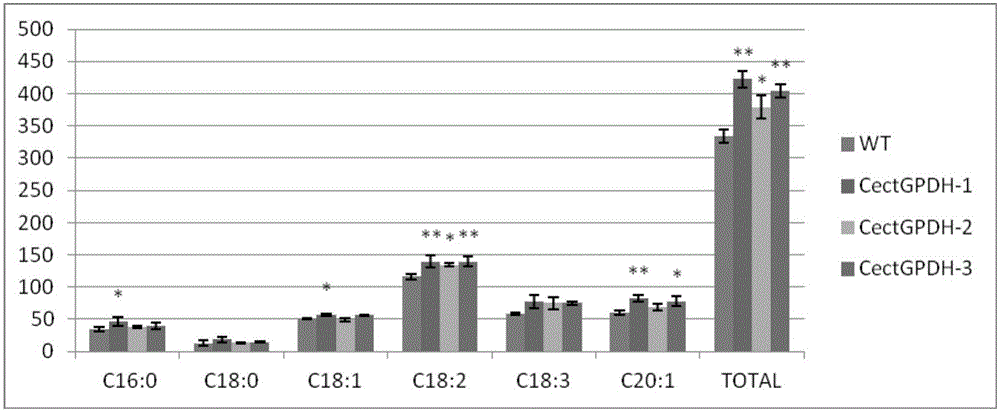
The invention provides a CectGPDH2 gene and an application thereof in increase of fatty acid content. The nucleotide sequence of the CectGPDH2 gene is shown as SEQ NO.1. The gene comes from Chlorella ellipsoidea and encodes GPDH, wherein the GPDH participates in shuttle of the mitochondrion G3P (glycerol-3-phosphate), provides electrons for respiratory chains, is a key enzyme for G3P synthesis, is one of the key enzymes for connecting glucose metabolism with lipid metabolism and plays an important role in lipid synthesis and energy metabolism in plants. The total fatty acid content of seeds of Arabidopsis thaliana and rape genetically modified with the gene can be increased obviously, and the gene can be used for increasing the oil content of plant cells and the content of linoleic acid (C18:2) and eicosenoic acid (C20:1) in the plants and has good application prospect.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Yeast having improved ethanol yield
InactiveUS20110250664A1Reduced activityReduce expressionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFungiBiotechnologyWild type
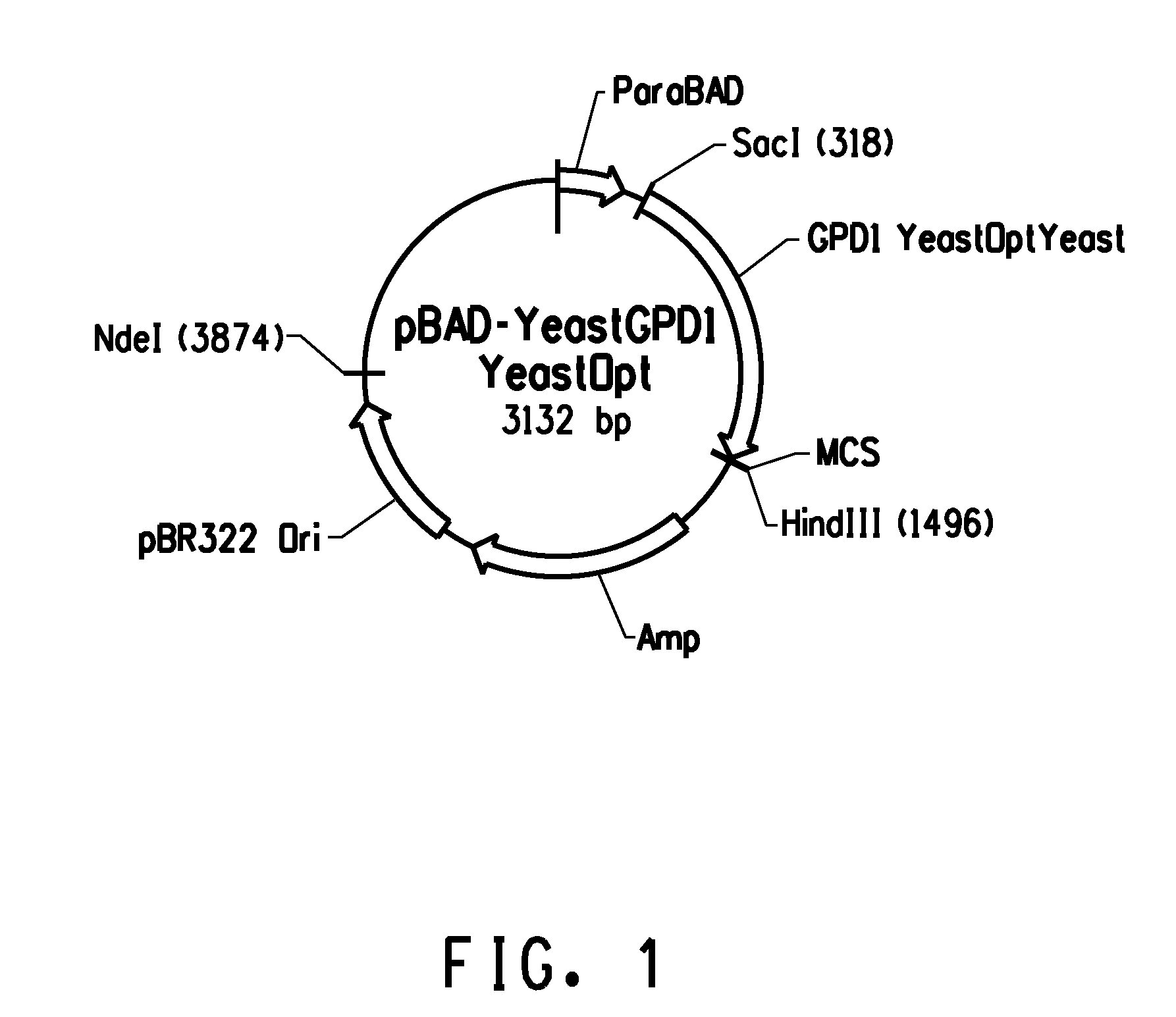
The present invention provides for a genetically-altered haploid yeast cell characterized by reduced activity or expression of FPS1, reduced activity or expression of glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase-1 (GPD1), reduced activity or expression of glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase-2 (GPD2), and increased expression of glutamate synthase (GLT1), wherein the reduced activity or expression, and the increased expression, is relative to expression or activity in a wildtype yeast strain, e.g., S. cervisiae strain S288C.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Pyruvate high-temperature and high-yield engineered strain and application thereof
ActiveCN106318879AReduce pollutionReduce cooling energy consumptionFungiTransferasesCelluloseBiotechnology
The invention uses Kluyveromyces marxianus yeast as a platform to construct a strain of knockout pyruvate decarboxylase and glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase by means of genetic engineering, metabolic engineering, molecular biology and synthetic biology. The strain's growth is restored by metabolic regulation in order to improve the yield and production rate of pyruvate, and then the strain's xylose metabolism is improved, so that it has the ability to produce pyruvate with xylose. Eventually the glucose effect of the engineering strain is removed so that the engineered strain is capable of simultaneously saccharifying lignocellulose, using glucose and xylose and fermenting at high temperature to produce pyruvate. The Kluyveromyces marxianus strain YZB058 obtained by the present invention can produce pyruvate at the same time using glucose and xylose at 42 DEG C. At 42 DEG C, YZB058 is able to produce 29.21 g / l of pyruvate with 40.97 g / l of glucose and 20.37 g / l of xylose for 36 h, the production rate is at a rate of 0.81 g / l / h, and the total yield is at 0.48 g / g.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Identification of compositions, compositions, and methods of treatment of obesity and overweight conditions
A method for the identification of a composition useful in the treatment of an overweight or obese person to reduce the person's body mass index is provided which comprises obtaining an extract of an ethnobotanical plant, and evaluating the activity of the extract in an assay selected from the group consisting of a lipolysis assay, an assay that measures the amount of glycerol introduced by a cell into a suspension medium of the cell, an adipocyte differentiation assay, an assay that measures the level of the enzyme glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, an assay that measures the inhibition of differentiation of preadipocytes to adipocytes, an assay that measures the accumulation of lipid in an adipocyte, an assay that measures the de-differentiation of adipocytes into preadipocytes, and combinations thereof. Sclareol and sclareol-like compounds and sclareolide and sclareolide-like compounds are identified as useful in the treatment of overweight and obese conditions and disorders and conditions associated with adipose tissue abnormalities. These compounds can be formulated for oral administration.
Owner:PHYTOMYCO RES CORP
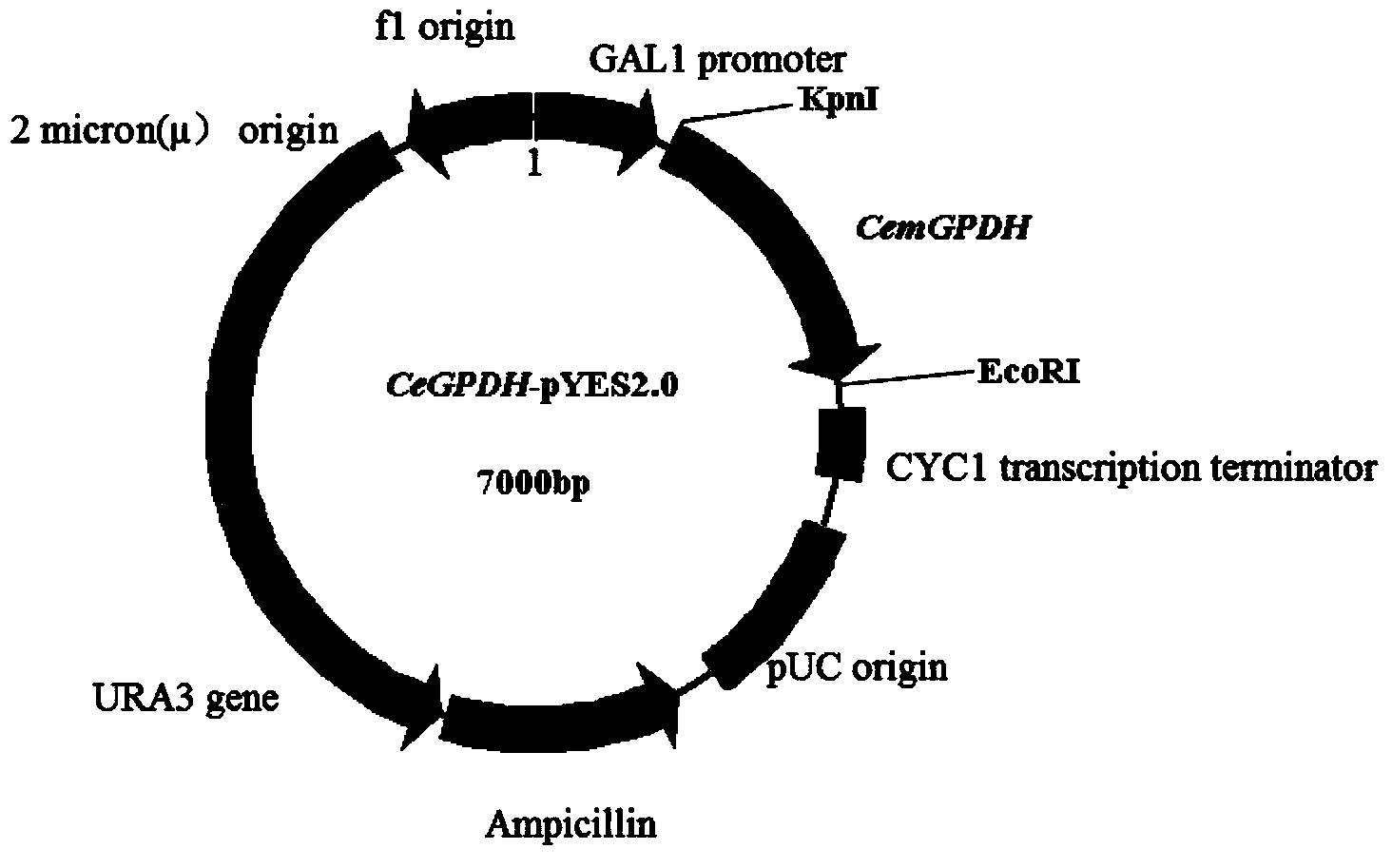
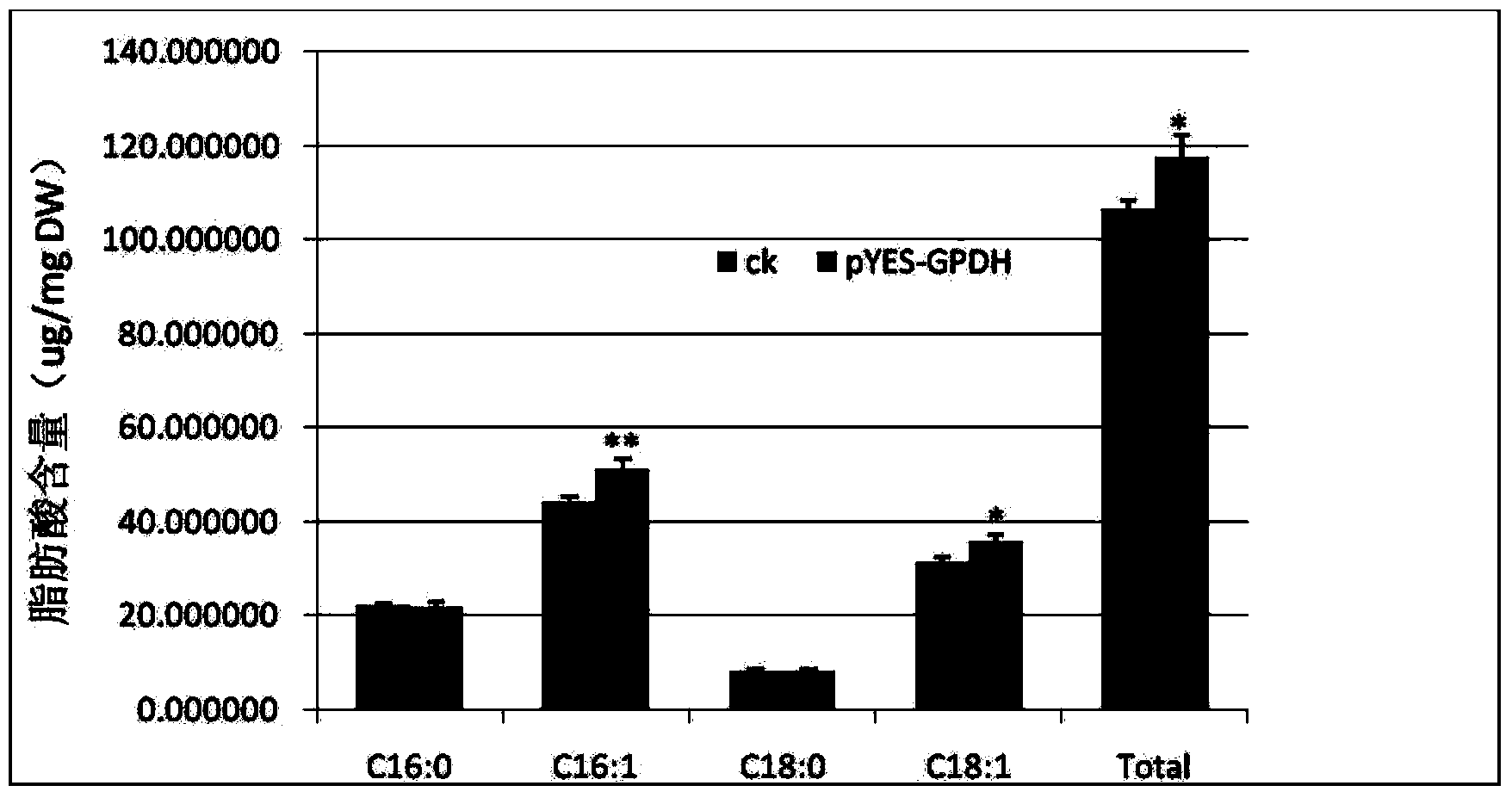
Cem GPDH (Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) gene and application thereof
The invention provides a Cem GPDH (Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) gene and an application of the Cem GPDH gene in the aspect of increase of cellular fatty acid content. A nucleotide sequence of the Cem GPDH gene is represented as SEQ ID NO: 1. The gene is derived from Chlorella ellipsoidea, and GPDH is coded. G3P (Glycerol-3-phosphate) synthesized through catalysis by GPDH is an important raw material for synthesis of TAG (triacylglycerol), the enzyme participates in mitochondria G3P shuttle, provides electrons for a respiratory chain, is a key enzyme for G3P synthesis, is one of key enzymes for connecting glycometabolism and lipid metabolism and has an important effect on lipid synthesis and energy metabolism in plants; and besides, the gene can remarkably increase the total fatty acid content of cells when utilized to convert yeast cells, plant cells and microalgae cells.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Glycerol 3- phosphate dehydrogenase for butanol production
ActiveUS9441250B2Improved and increased production of butanolReduced and decreased production of glycerolBacteriaBiofuelsHeterologousMicroorganism
Owner:GEVO INC
Method for increasing the total oil content in oil plants
InactiveCN101356278AOxidoreductasesVector-based foreign material introductionPlanting seedPhosphoric acid
The invention relates to methods for increasing the total oil content and / or the content of glycerol-3-phosphate in transgenic oil plants, which contain at least 20 wt.-% oleic acid in relation to the total fatty acid content, preferably in plant seeds, by the expression of glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenases (G3PDH) from yeasts, preferably from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Advantageously, the oil obtained by this method and / or the free fatty acids are added to polymers, foodstuffs and feedstuffs, cosmetics, pharmaceutical products or products with industrial applications.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV +1
Compositions and methods for producing lipids and other biomaterials from grain ethanol stillage and stillage derivatives
ActiveUS20180245109A1Increase profit marginDecreasing thin stillage viscosityFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementBio engineeringLysophospholipid Acyltransferase
Lipogenic yeasts bioengineered to overexpress genes for lipid production, and methods of use thereof. The yeasts are modified to express, constitutively express, or overexpress an acetyl-CoA carboxylase, an alpha-amylase, an ATP citrate lyase, a diacylglycerol acyltransferase, a fatty acid synthase, a glycerol kinase, a 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, a glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, a malic enzyme, a fatty acyl-CoA reductase, a delta-9 acyl-CoA desaturase, a glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase, a lysophosphatidate acyltransferase, a glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, a beta-glucosidase, a hexose transporter, a glycerol transporter, a glycoside hydrolase enzyme, an auxiliary activity family 9 enzyme, or combinations thereof. The yeasts in some cases are also modified to reduce or ablate activity of certain proteins. The methods include cultivating the yeast to convert low value soluble organic stillage byproducts into lipids suitable for biodiesel production and other higher value uses.
Owner:XYLOME CORP
Method for the production of glycerol by recombinant organisms
Recombinant organisms are provided comprising genes encoding a glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and / or a glycerol-3-phosphatase activity useful for the production of glycerol from a variety of carbon substrates. The organisms further contain disruptions in the endogenous genes encoding proteins having glycerol kinase and glycerol dehydrogenase activities.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO +1
Ethanol yield and reduction of biomass accumulation in the recombinant strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae overexpressing atpase
Owner:ARCHER DANIELS MIDLAND CO
Methods of producing and growing plants having improved phosphorus utilization
InactiveUS7759547B2Low costIncrease capacityBryophytesOther foreign material introduction processesPhosphorus utilizationWild type
The invention discloses methods for genetically transforming a plant so that it expresses a glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. The method raises levels glycerol-3-phosphate in comparison to the wild type, leading to increased stress tolerance, and altered fatty acid content in glycerolipids. The method also produces plants having improved phosphorus utilization.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Ethanol yield and reduction of biomass accumulation in the recombinant strain of saccharomyces cerevisiae overexpressing atpase
ActiveUS20120088290A1Increased ethanol productionDecreased ATP levelFungiBacteriaAtp degradationGlycerol
A new approach for increase of ethanol yield during alcoholic fermentation via decrease of biomass accumulation by using ATP degrading enzymes is described. The part of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae SSB1 gene coding for cytosolic ATPase domain of ribosome associated chaperon cloned into expression cassette under control of the glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene (GPD1) promoter was introduced into the S. cerevisiae BY4742 strain. The recombinant strains were tested for their ability to grow and produce ethanol during glucose anaerobic and aerobic cultivations. Strains overexpressing ATPase domain of SSB1 possessed decreased concentration of intracellular ATP. They accumulated elevated amounts of ethanol and were characterized by decreased biomass accumulation as compared to the wild-type strain under both anaerobic and aerobic conditions. Similarly, the apyrase gene apy from E. coH encoding ATP / ADP hydrolyzing phosphatase and ATPase domain of SSB1 gene of S. cerevisiae were co-expressed under the control of galactose-inducible GAL1 promoter. The recombinant S. cerevisiae strains revealed slight reduction of biomass accumulation, while specific ATPase activity, ethanol accumulation and yield during alcoholic galactose fermentation under semi anaerobic conditions were increased.
Owner:ARCHER DANIELS MIDLAND CO
Methods of producing and growing plants having improved phosphorus utilization
InactiveUS20050204423A1Enhanced production of glycerolLow costBryophytesOther foreign material introduction processesGlycerol 3-phosphateGlycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
The invention discloses methods for genetically transforming a plant so that it expresses a glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. The method raises levels glycerol-3-phosphate in comparison to the wild type, leading to increased stress tolerance, and altered fatty acid content in glycerolipids. The method also produces plants having improved phosphorus utilization.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Acetate consuming yeast cell
ActiveUS20180127763A1Shorten fermentation timeIncrease productionHydrolasesTransferasesNucleotideBiology
The present invention relates to a yeast cell that is genetically modified comprising:a) a disruption of one or more aldehyde dehydrogenase (E.C:1.2.1.4) native to the yeast;b) one or more nucleotide sequence encoding a heterologous NAD+-dependent acetylating acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (E.C. 1.2.1.10);c) one or more nucleotide sequence encoding a homologous or heterologous acetyl-CoA synthetase (E.C. 6.2.1.1); andd) a modification that leads to reduction of glycerol 3-phosphate phosphohydrolase (E.C. 3.1.3.21) and / or glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (E.C. 1.1.1.8 or E.C. 1.1.5.3) activity, native to the yeast.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Gene chip for detecting hypertension and kit thereof
ActiveCN106192017AImprove detection efficiencyHigh sensitivityNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementEssential hypertensionGene
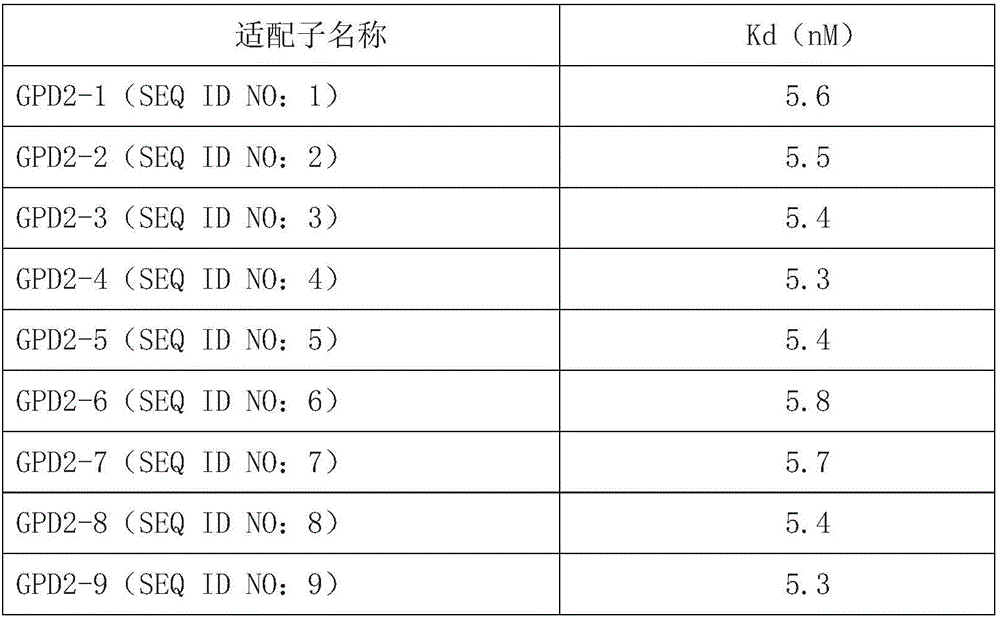
The invention provides a gene chip for detecting hypertension and a kit of the gene chip. The gene chip is provided with an aptamer. The kit can rapidly detect human glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, and whether a sample is essential hypertension is identified by detecting the quantity of the glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. The kit detects in a mode of the chip, the detection with the chip has the effects of high detection efficiency, high sensitivity and wide scope of application, and the chip and the kit can be widely popularized and used.
Owner:GENE CRAB BIOTECH CO
Glycerol-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Gene And Use Thereof
The present invention relates to a gene encoding glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and use thereof, in particular, a brewer's yeast which produces alcoholic beverages with superior body and mellowness, alcoholic beverages produced with said yeast, and a method for producing said beverages. More particularly, the present invention relates to a yeast whose ability of producing glycerol, which contribute to body and mellowness of products, is enhanced by amplifying expression level of GPD1 or GPD2 gene encoding a Gpd1p or Gpd2p which is a glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in brewer's yeast, especially non-ScGPD1 gene or non-ScGPD2 gene specific to a lager brewing yeast and to a method for producing alcoholic beverages with said yeast, etc.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Plants having an enhanced resistance to necrotrophic pathogens and method of making same
InactiveUS20070016978A1Improve the immunitySugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesPresent methodGlycerol
A method for enhancing resistance to necrotrophic and / or hemibiotrophic pathogens by overexpressing glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase using an expression vector in a plant species. For example, the present method can be used to enhance resistance to C. haggansianum by overexpressing glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in a plant such as Arabidopsis plant, using an expression vector in a plant.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Method for the production of glycerol by recombinant organisms
Recombinant organisms are provided comprising genes encoding a glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and / or a glycerol-3-phosphatase activity useful for the production of glycerol from a variety of carbon substrates. The organisms further contain disruptions in the endogenous genes encoding proteins having glycerol kinase and glycerol dehydrogenase activities.
Owner:NAIR RAMESH +3
Construction and application of high-temperature and high-yield engineered strains of xylitol and ethanol at the same time
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Modulators of adp-dependent glucokinase (ADPGK) and glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GPD2) for therapy
Owner:DEUTES KREBSFORSCHUNGSZENT STIFTUNG DES OFFENTLICHEN RECHTS
Inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) diagnosis/determination kit and method for determining inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) concentration
InactiveCN101620147AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsPhosphateGlycerol kinase
The invention relates to an inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) diagnosis / determination kit using the technology of an enzyme colorimetric method and an ELISA method, a method for determining inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) concentration and composition and components of a reagent, and belongs to the technical field of test and determination of medical science, food, and environment. The kit comprises the following main components: buffer solution, coenzyme, adenosine diphosphate, oxaloacetic acid, glycerine, magnesium chloride, pyruvate carboxylase, glycerol kinase, glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and a stabilizer. The method comprises the following steps: mixing a sample and the reagent according to a certain volume ratio to perform a series of enzymic reaction, and then placing reactants under a UV / visible light analyzer to test the ascending speed of absorbance at the position where the dominant wave length is 340nm to determine the inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) concentration.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com