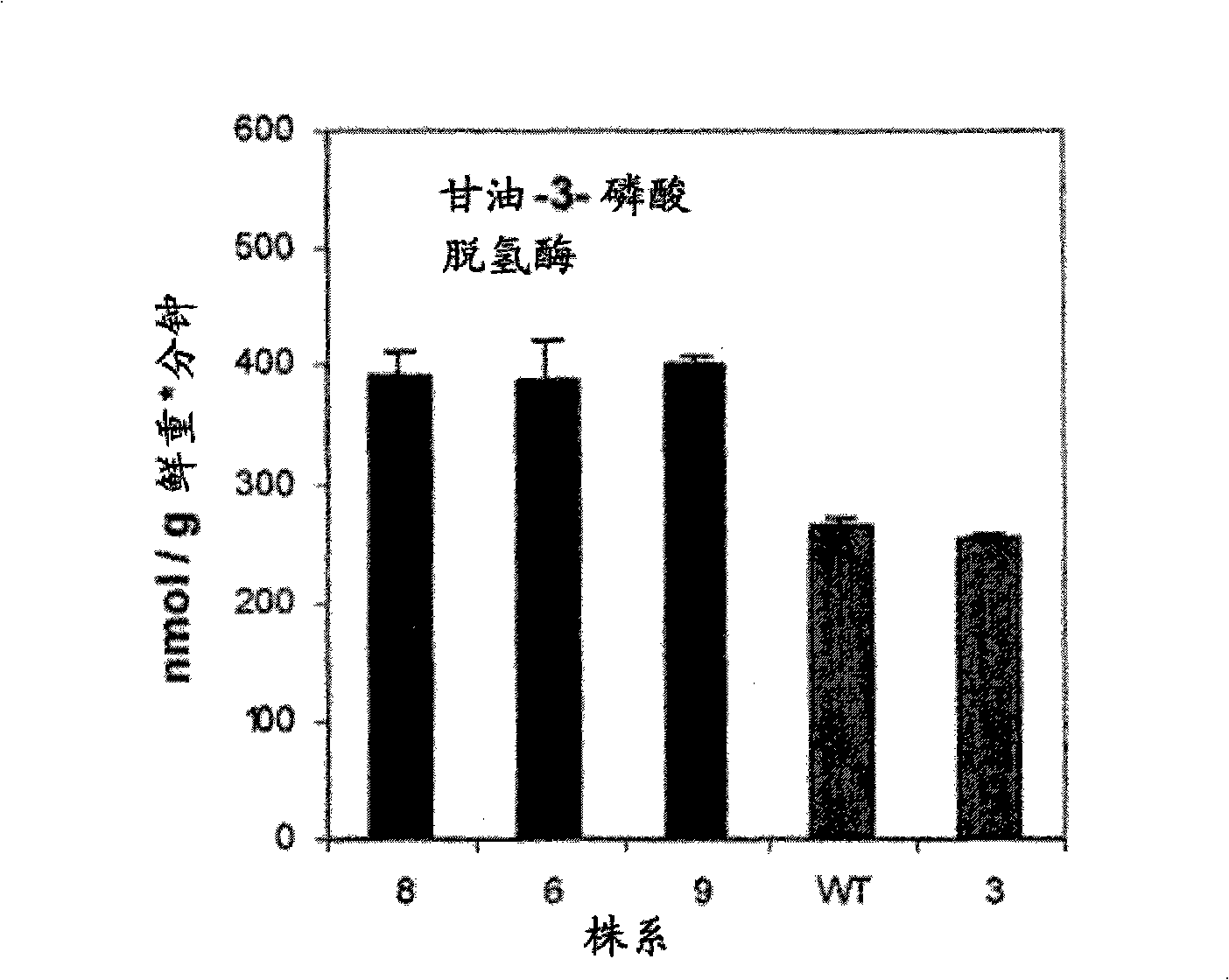
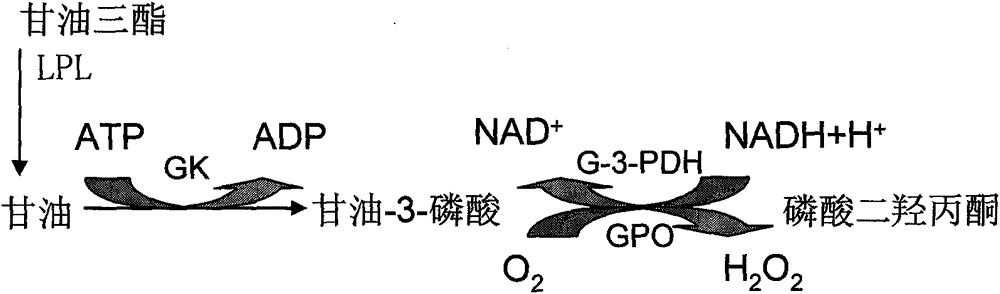
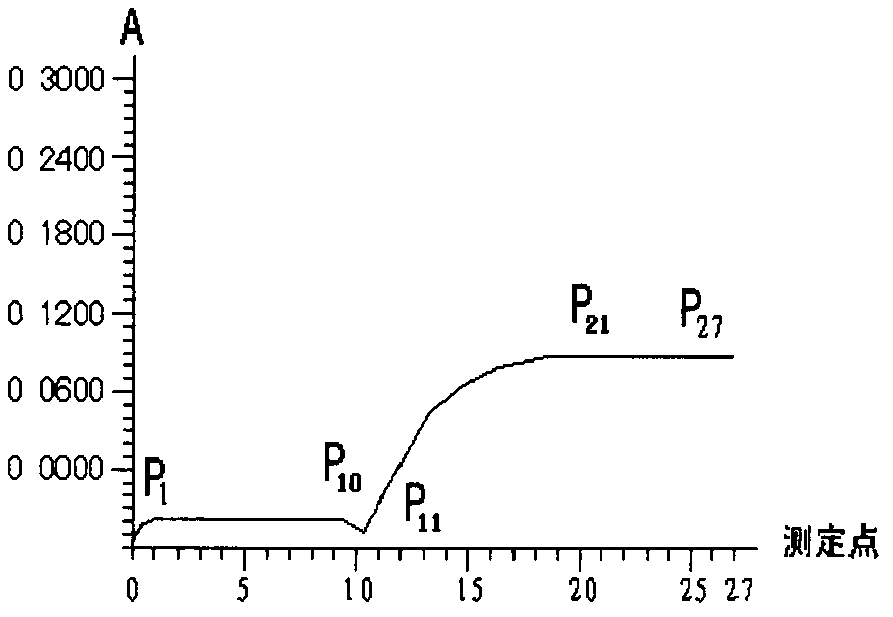
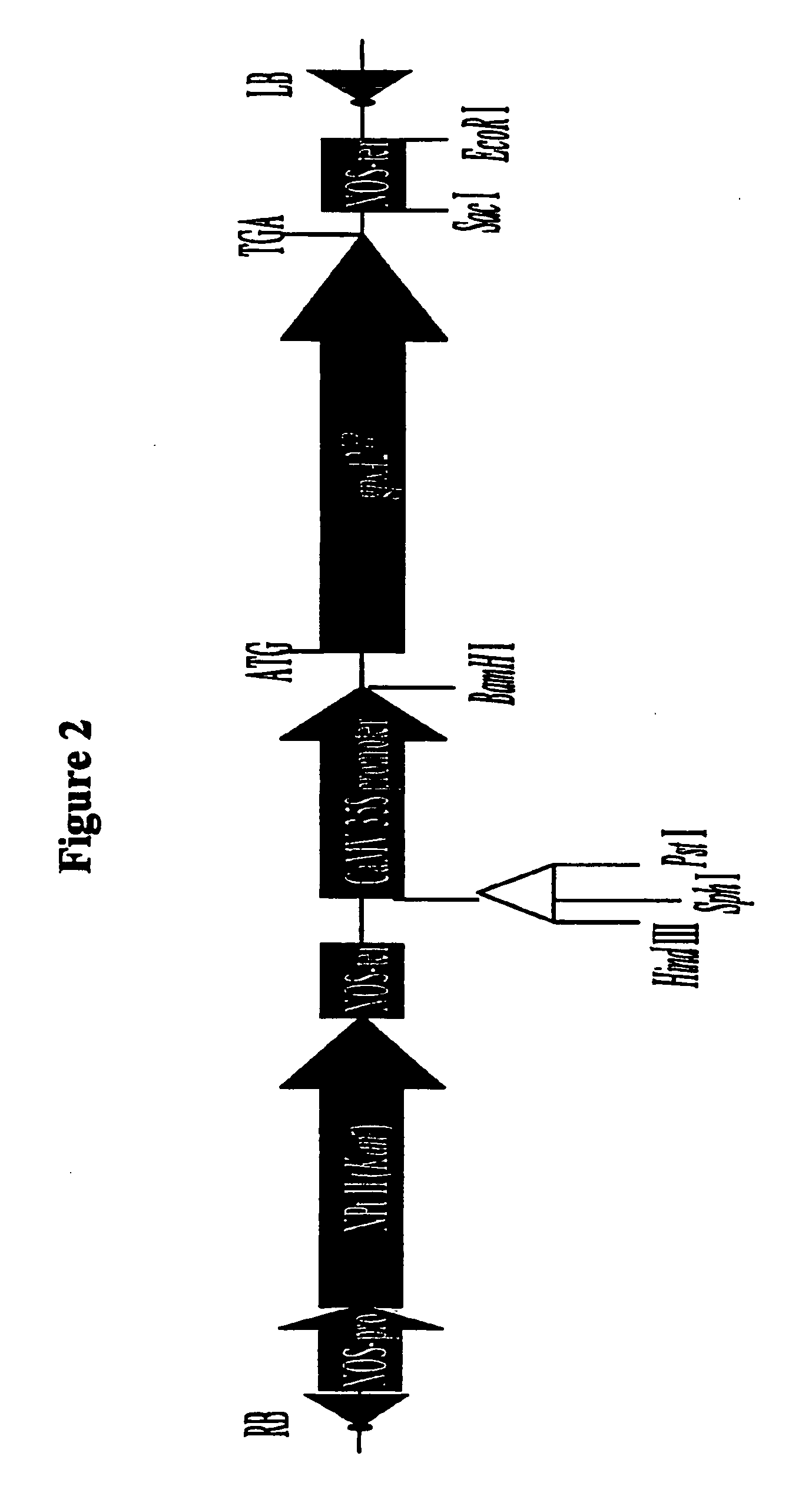
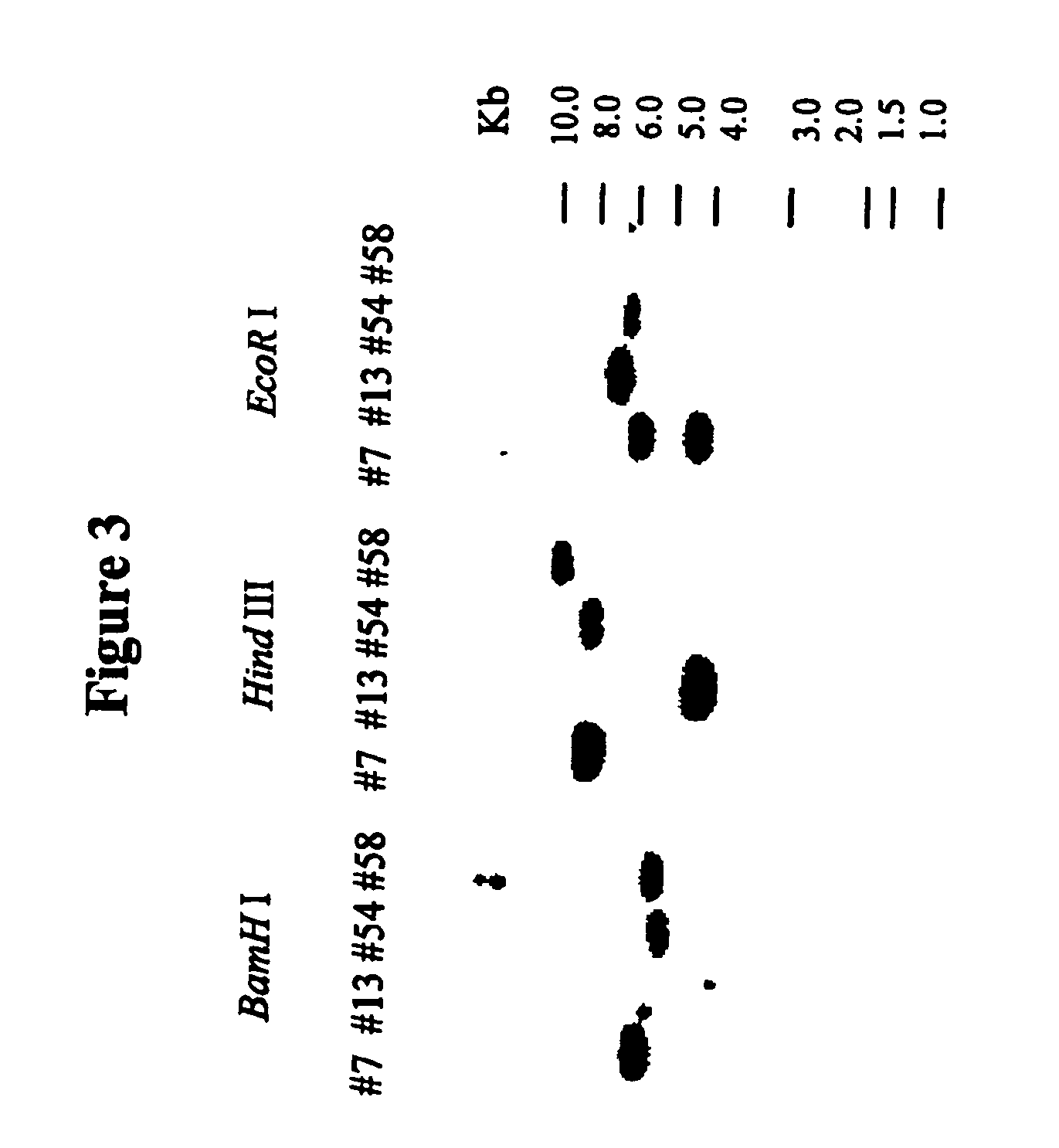
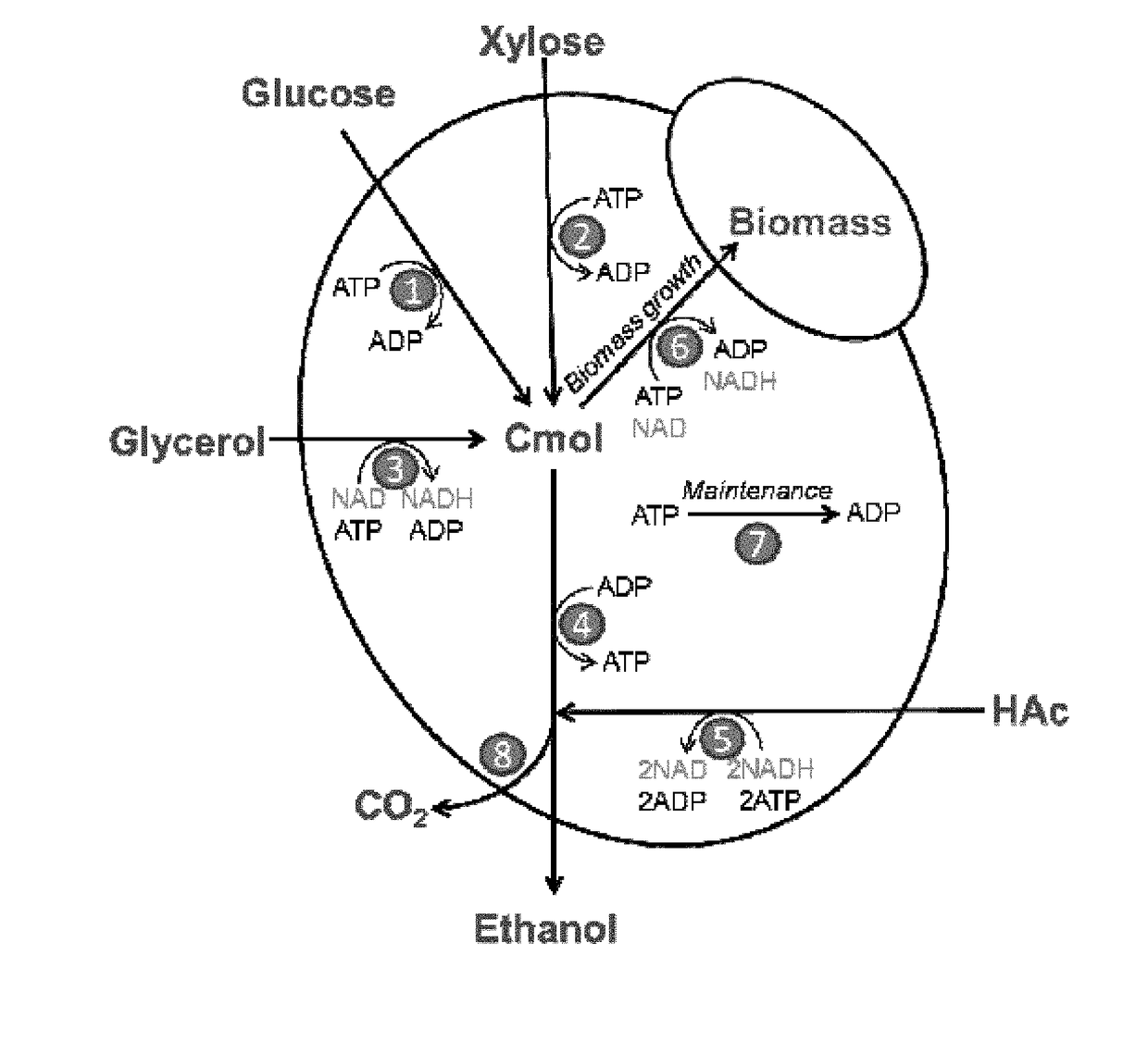
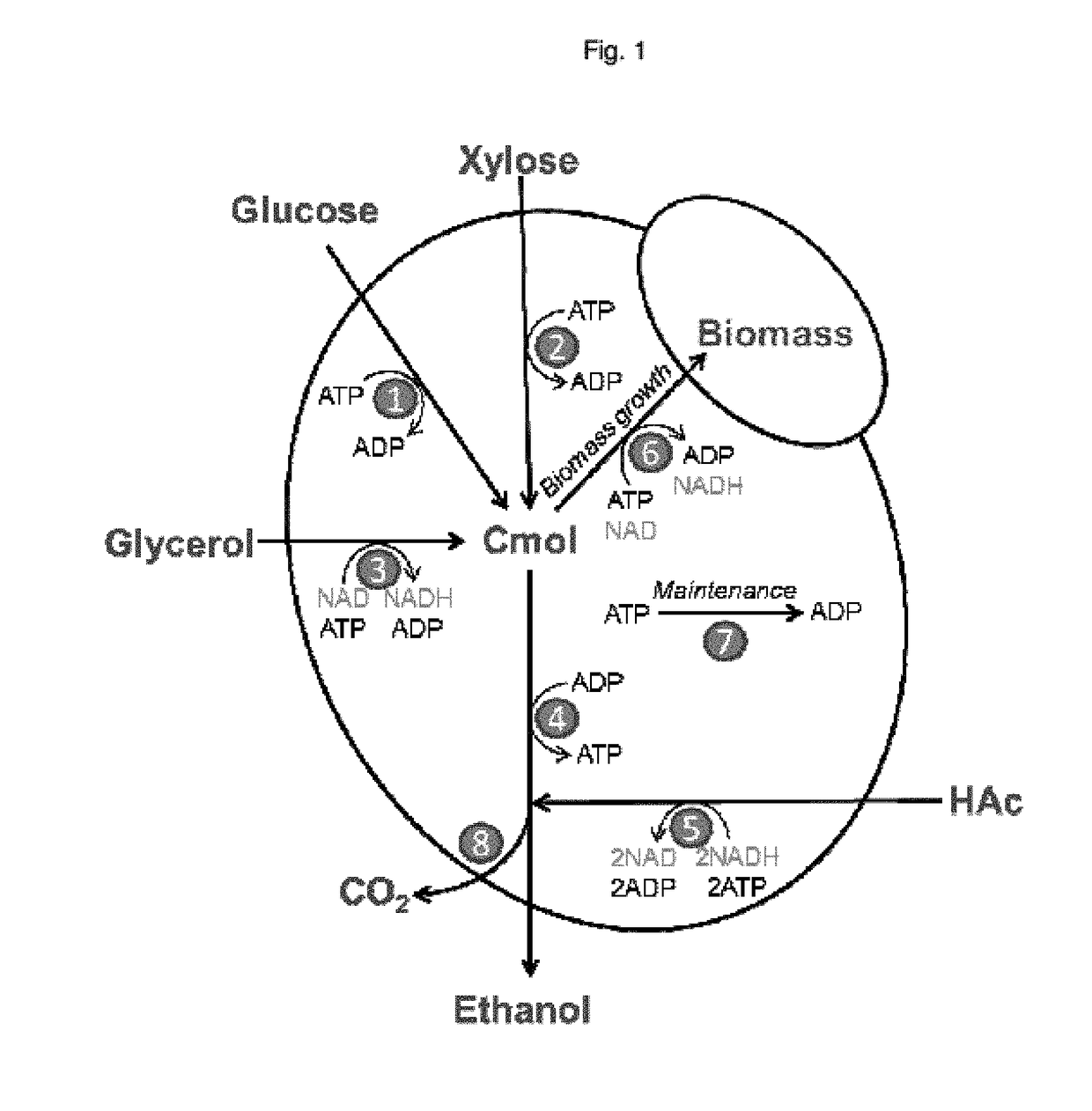
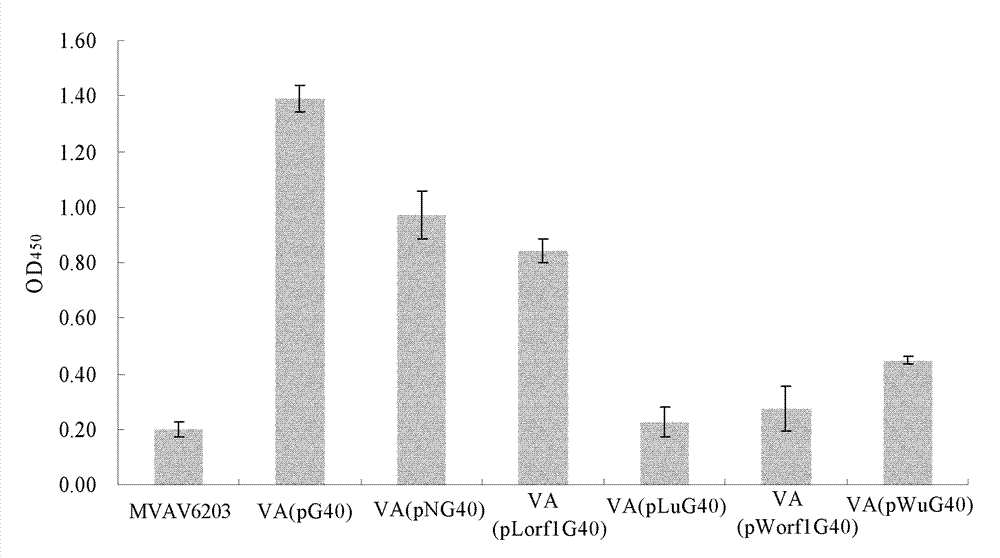
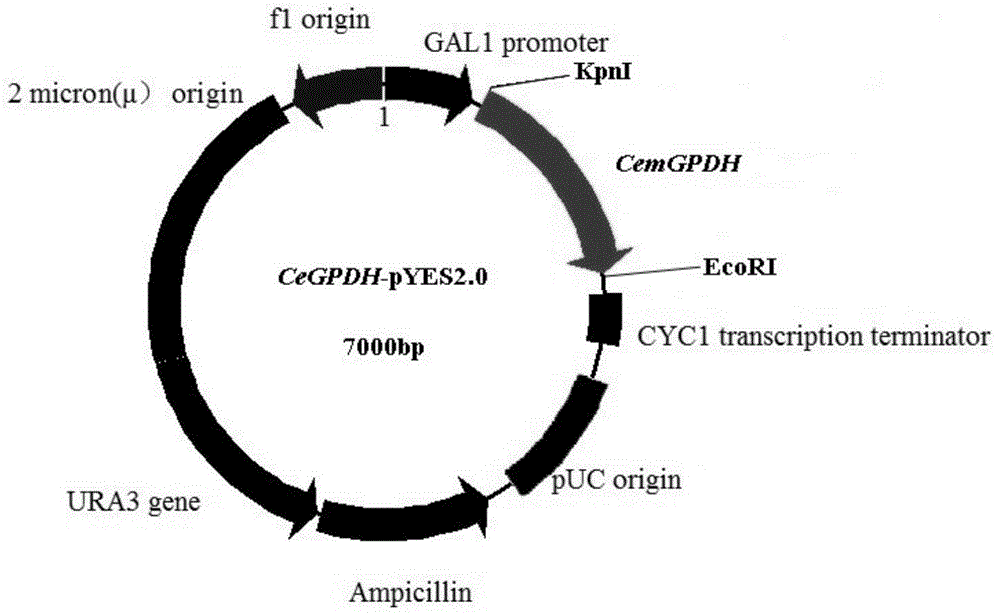
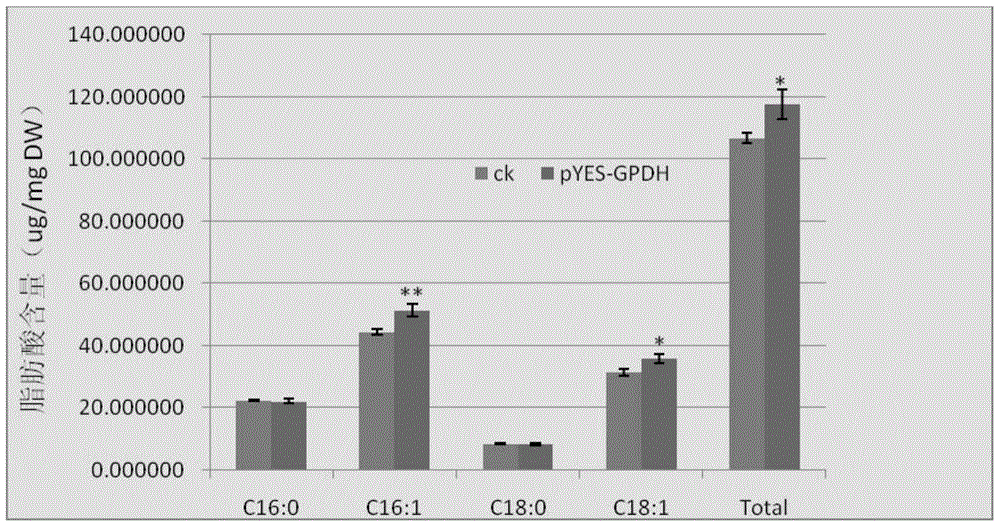
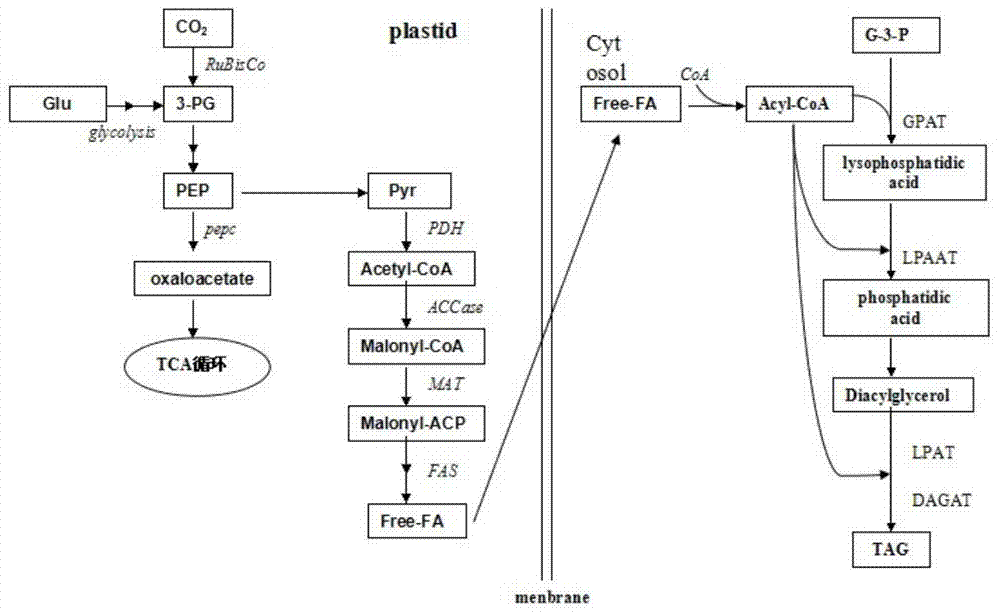
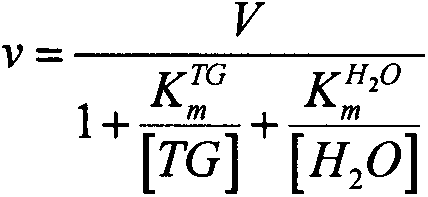Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "Glycerol 3-phosphate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
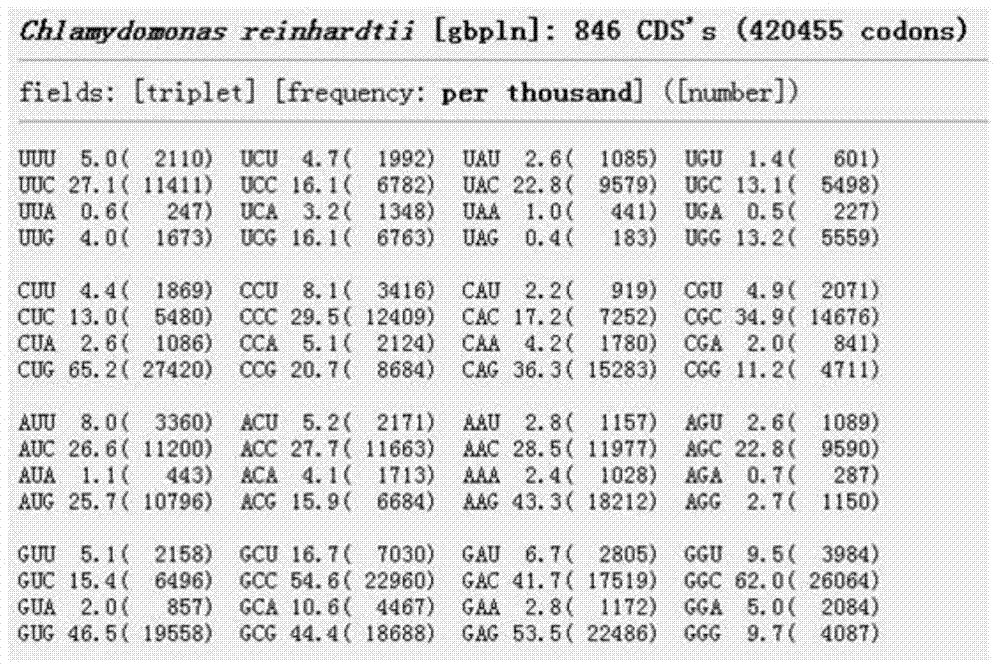
Sn-Glycerol 3-phosphate is a phosphoric ester of glycerol, which is a component of glycerophospholipids. Equally appropriate names in biochemical context include glycero-3-phosphate, 3-O-phosphonoglycerol, 3-phosphoglycerol; and Gro3P. From a historical reason, it is also known as L-glycerol 3-phosphate, D-glycerol 1-phosphate, L-α-glycerophosphoric acid. It should not be confused with the similarly named glycerate 3-phosphate or glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.
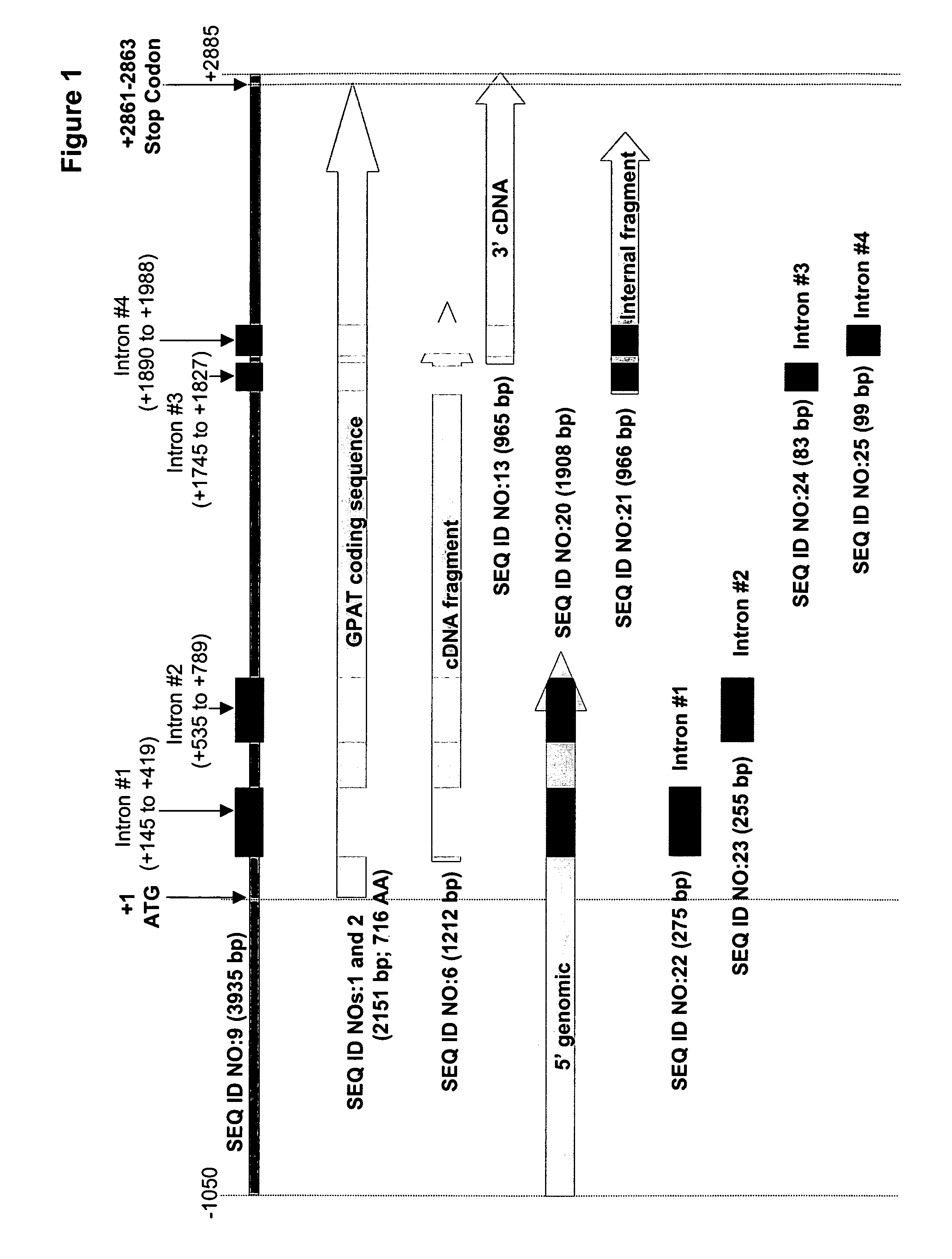
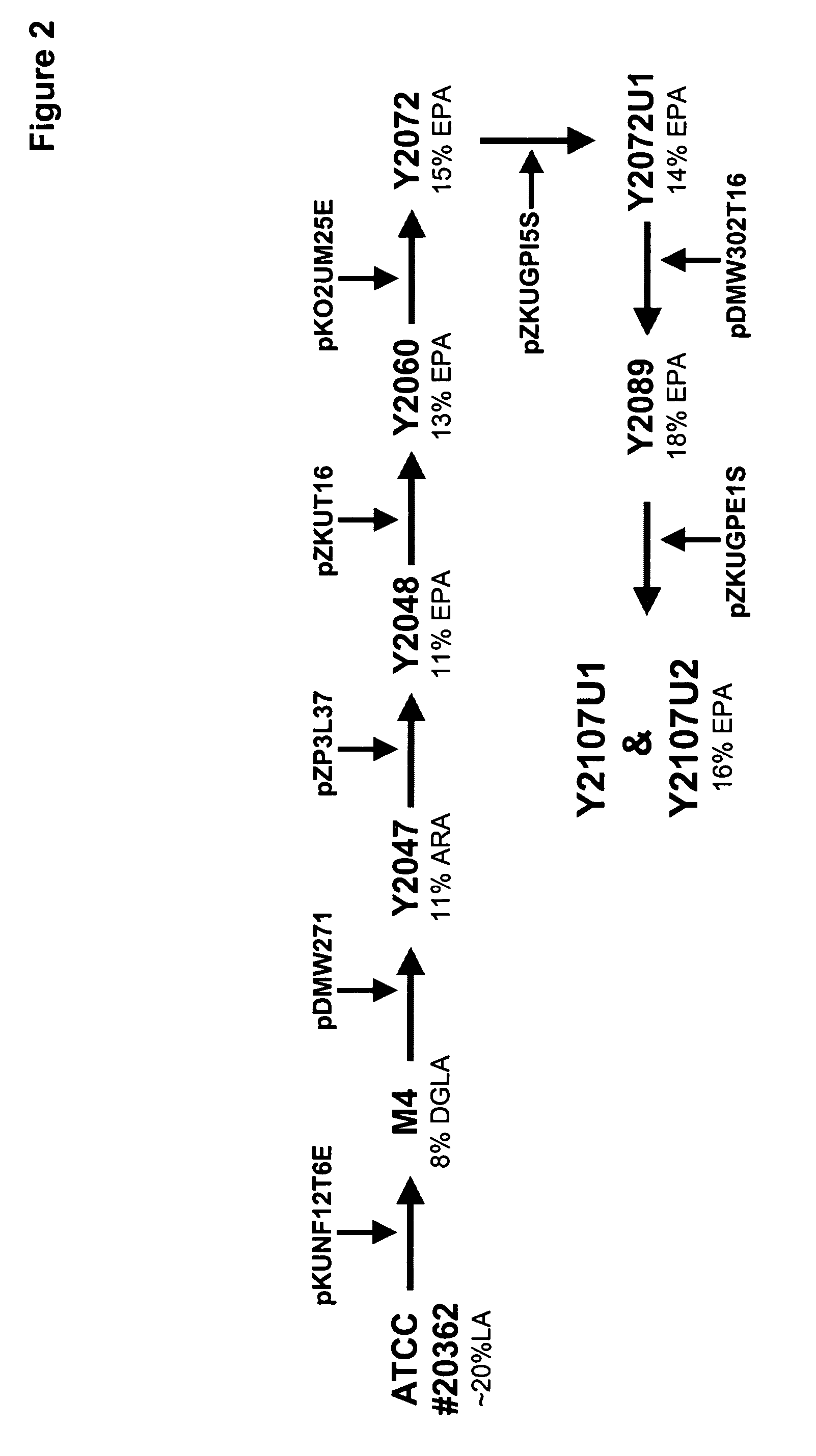
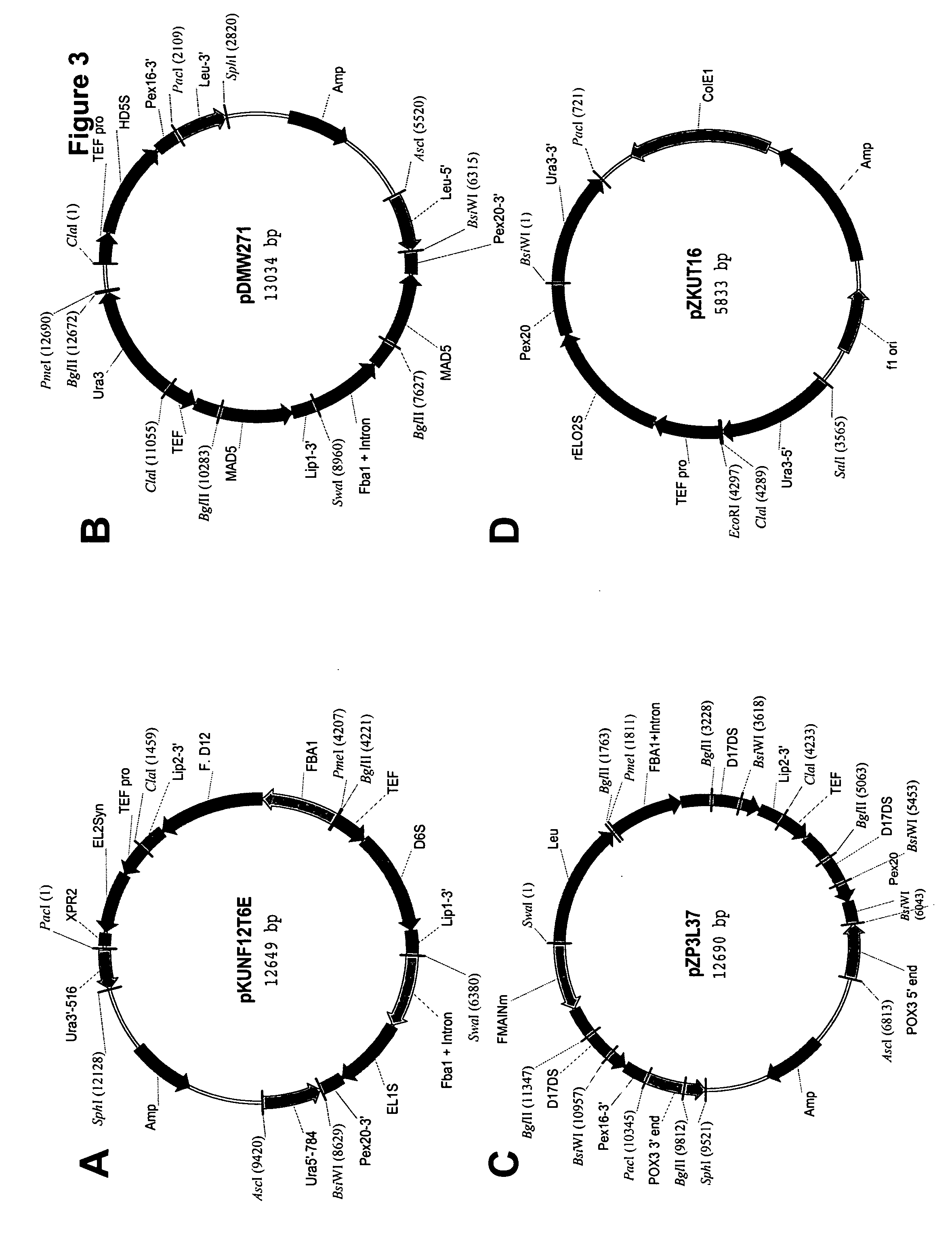
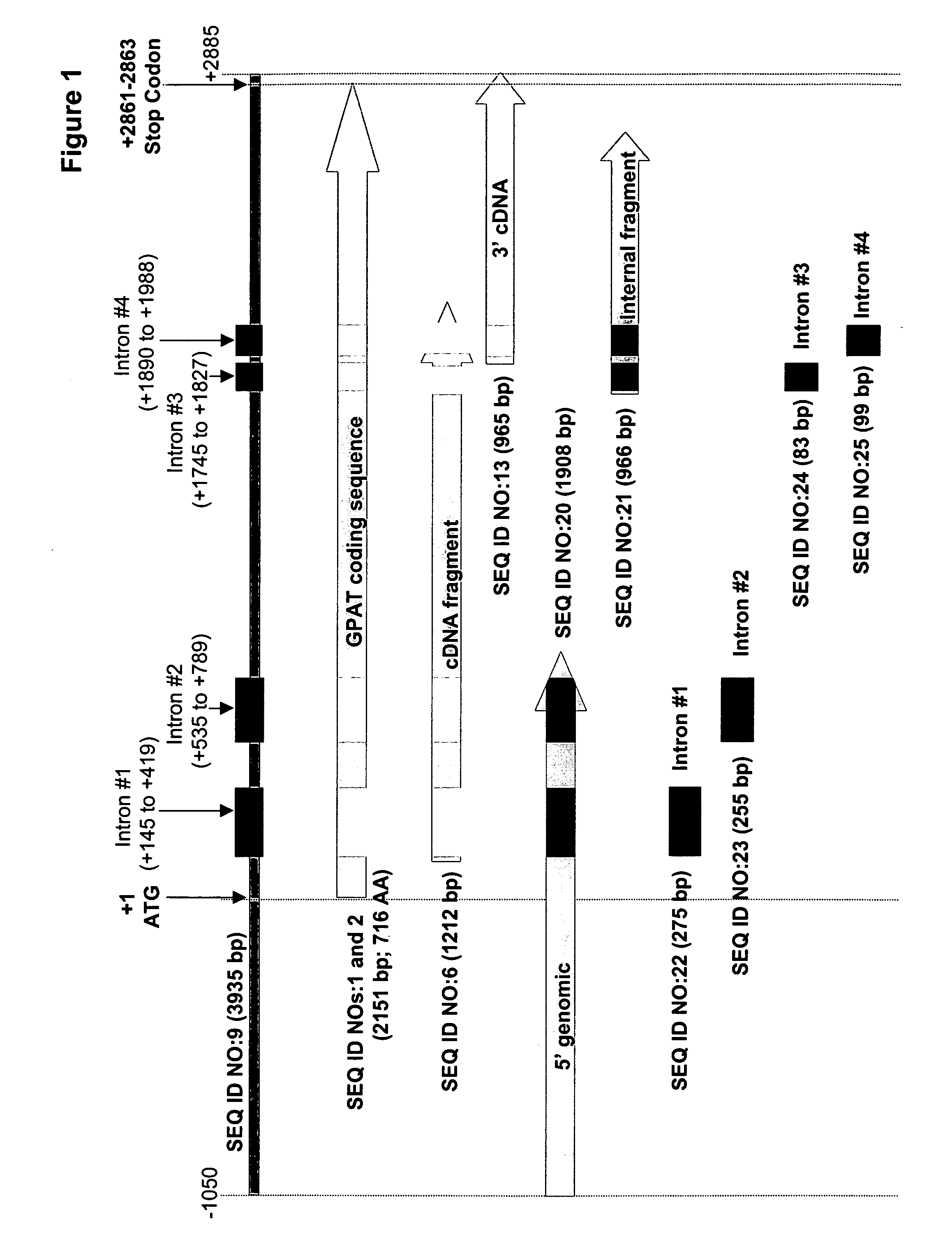
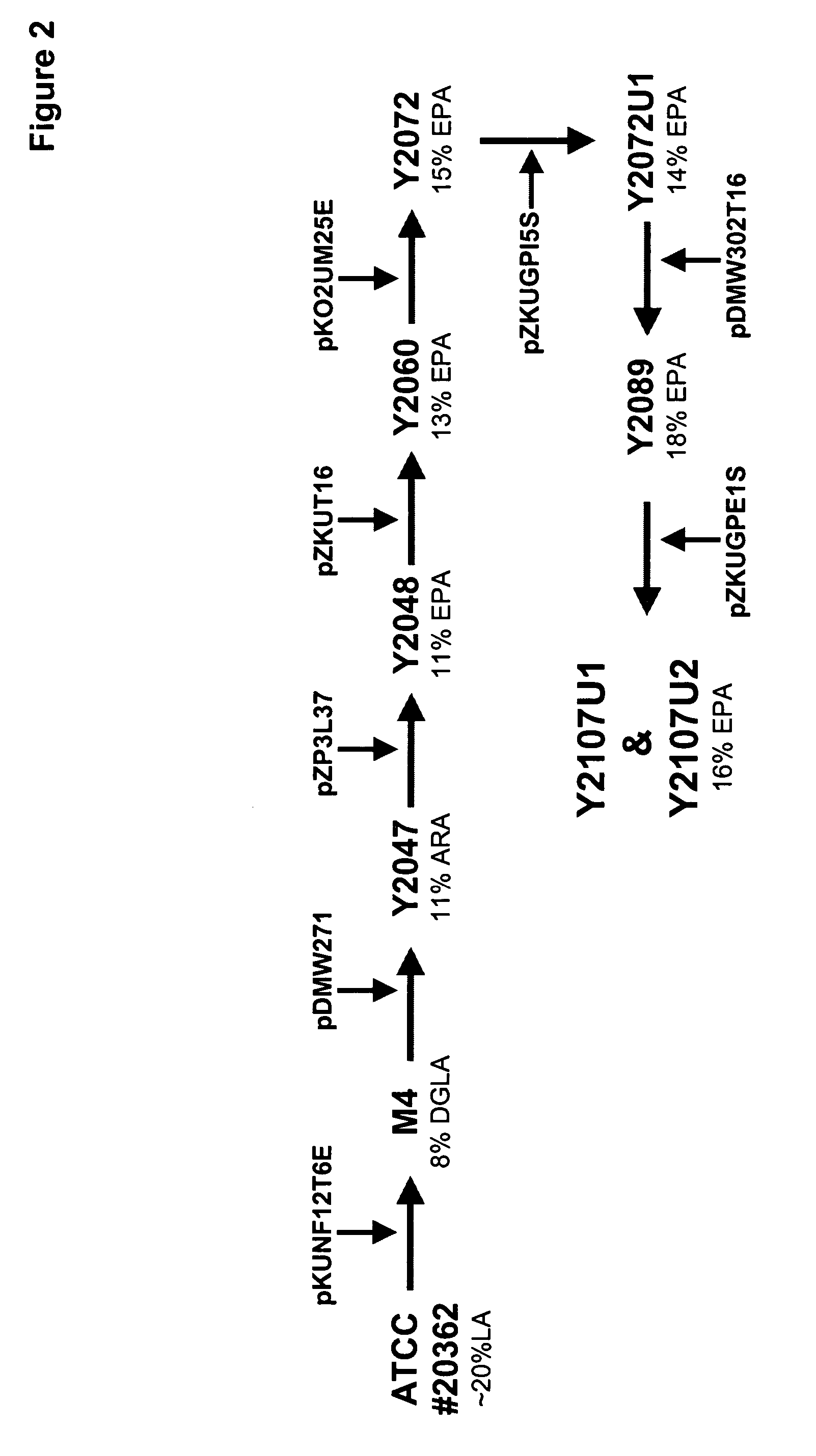
Mortierella alpina glycerol-3-phosphate o-acyltransferase for alteration of polyunsaturated fatty acids and oil content in oleaginous organisms
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Mortierella alpina glycerol-3-phosphate o-acyltransferase for alteration of polyunsaturated fatty acids and oil content in oleaginous organisms
Glycerol-3-phosphate o-acyltransferase (GPAT) participates in the first step of oil biosynthesis and is expected to play a key role in altering the quantity of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) produced in oils of oleaginous organisms. The present application provides a nucleic acid fragment isolated from Mortierella alpina encoding a GPAT that is suitable for use in the manufacture of oils enriched in omega fatty acids in oleaginous organisms. Most desirably, the substrate specificity of the instant GPAT will be particularly useful to enable accumulation of long-chain PUFAs having chain lengths equal to or greater than C20 in oleaginous yeast, such as Yarrowia lipolytica.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Glycerol 3- phosphate dehydrogenase for butanol production
ActiveUS20140273129A1Improved and increased production of butanolReduced and decreased production of glycerolBacteriaBiofuelsHeterologousMicroorganism
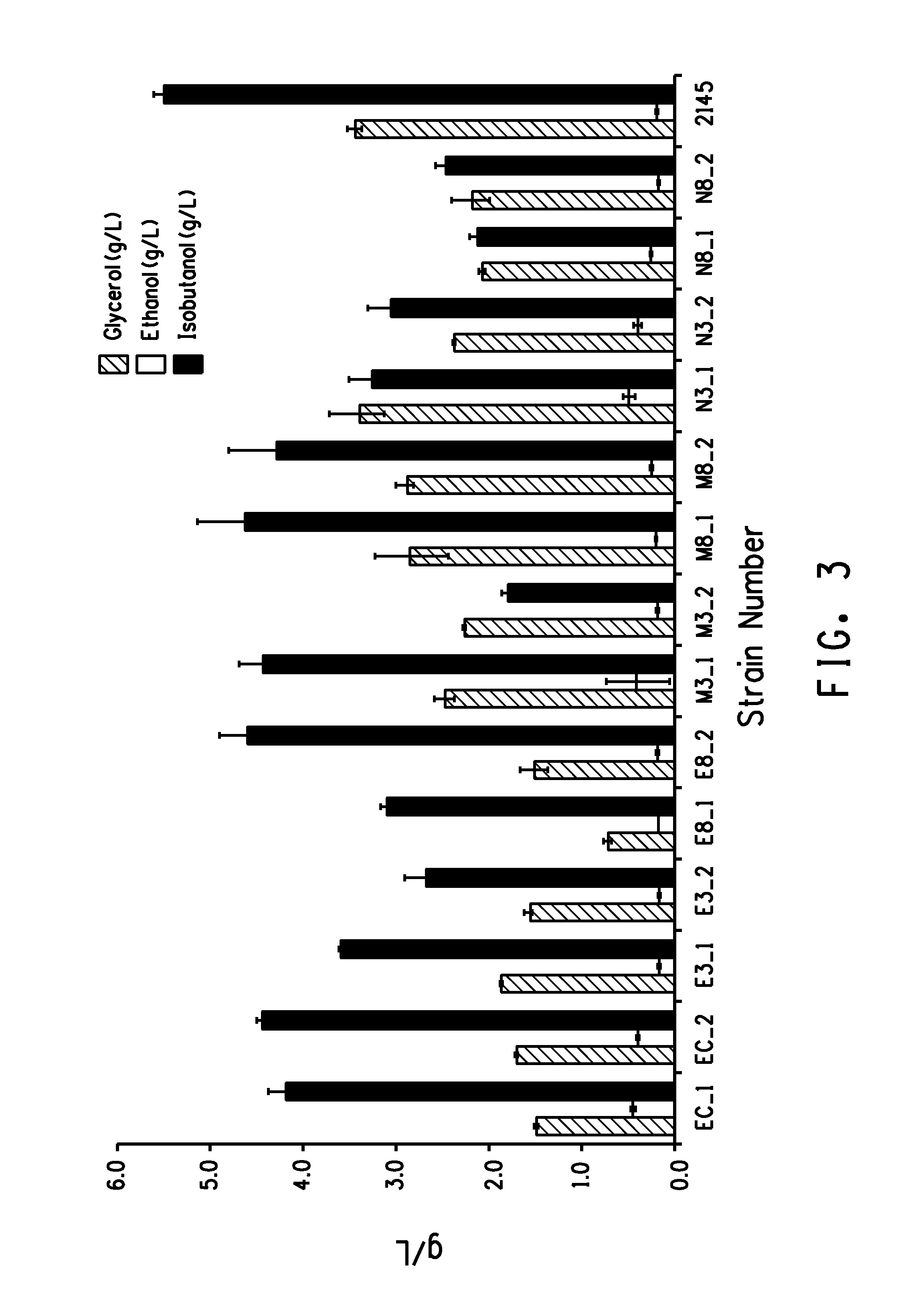
Provided herein are glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GPD) enzymes with increased KM for NADH and GPD enzymes with substantially the same affinity for NADH and NADPH and / or are feedback inhibited by glycerol-3-phosphate. Also provided herein are recombinant microorganisms comprising a heterologous gene encoding GPD and a deletion or disruption in an endogenous gene encoding GPD. Also provided are recombinant microorganisms comprising a heterologous gene encoding GPD and a butanol biosynthetic pathway. Further provided are methods of producing butanol comprising providing the recombinant microorganisms described herein and contacting the recombinant microorganism with at least one fermentable carbon substrate under conditions wherein butanol is produced.
Owner:GEVO INC
Transgenic manipulation of sn-glycerol-3-phosphate and glycerol production with a feedback defective glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenese gene
InactiveUS7112724B1Enhanced production of glycerolIncrease productionOther foreign material introduction processesOxidoreductasesWild typePhosphoric acid
The invention provides a method for genetically transforming a plant so that it expresses a glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase that is feedback-defective. The feedback-defective enzyme raises levels of glycerol and glycerol-3-phosphate in comparison to the wild-type, leading to increased osmotic stress tolerance, and altered fatty acid content in glycerolipids.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Modulators of adp-dependent glucokinase (ADPGK) and glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GPD2) for therapy
Described are compounds capable of modulating (a) the biological activity of ADP-dependent glucokinase (ADPGK) and / or glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GPD2) or (b) the expression of the gene encoding ADPGK or GPD2 for use in treating a disease (a) associated with aberrant cell proliferation, e.g., a neoplasm, or (b) of the immune system, e.g., an autoimmune disease.
Owner:DEUTES KREBSFORSCHUNGSZENT STIFTUNG DES OFFENTLICHEN RECHTS
Method for preparing 1-deoxy-D-xylulose with chemical method-enzymatic method
InactiveCN101748170AHigh yieldImprove conversion rateSugar derivativesFermentationPhosphoric acidReaction step
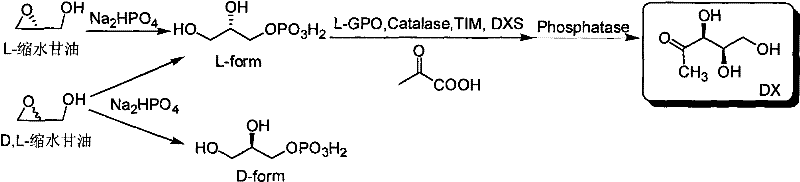
The invention relates to a method for preparing 1-deoxy-D-xylulose with the combination of a chemical method and an enzymatic method, which comprises the steps as follows: in a water phase system under certain temperature, the glycidol can form glycerol 3-phosphate by inorganic phosphate through ring opening, then the generated L-glycerol 3-phosphate is oxidized by L-GPO to form DHAP under the existence of catalase, the DHAP is converted into DXP under the existence of pyruvic acid, TIM enzyme and DXS, and target molecule DX can be obtained by hydrolyzing the compound through phosphatase. The method organically couples the simple method for preparing the DHAP by taking the stable, cheap and easily available compound as raw material with the method for preparing the DX by using the enzymatic method, the target molecule DX can be obtained through one-step reaction, the yield is high, the purification step is simple and feasible, the DX with high purity (more than 95%) can be obtained, the price of the raw material is low, the nature is stable, and the technical problems of expensive and unstable reaction material, complicated reaction steps, longer time consuming and lower overall yield of the method for preparing DX in the background technology are solved.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Anticancer agent sensitivity-determining marker
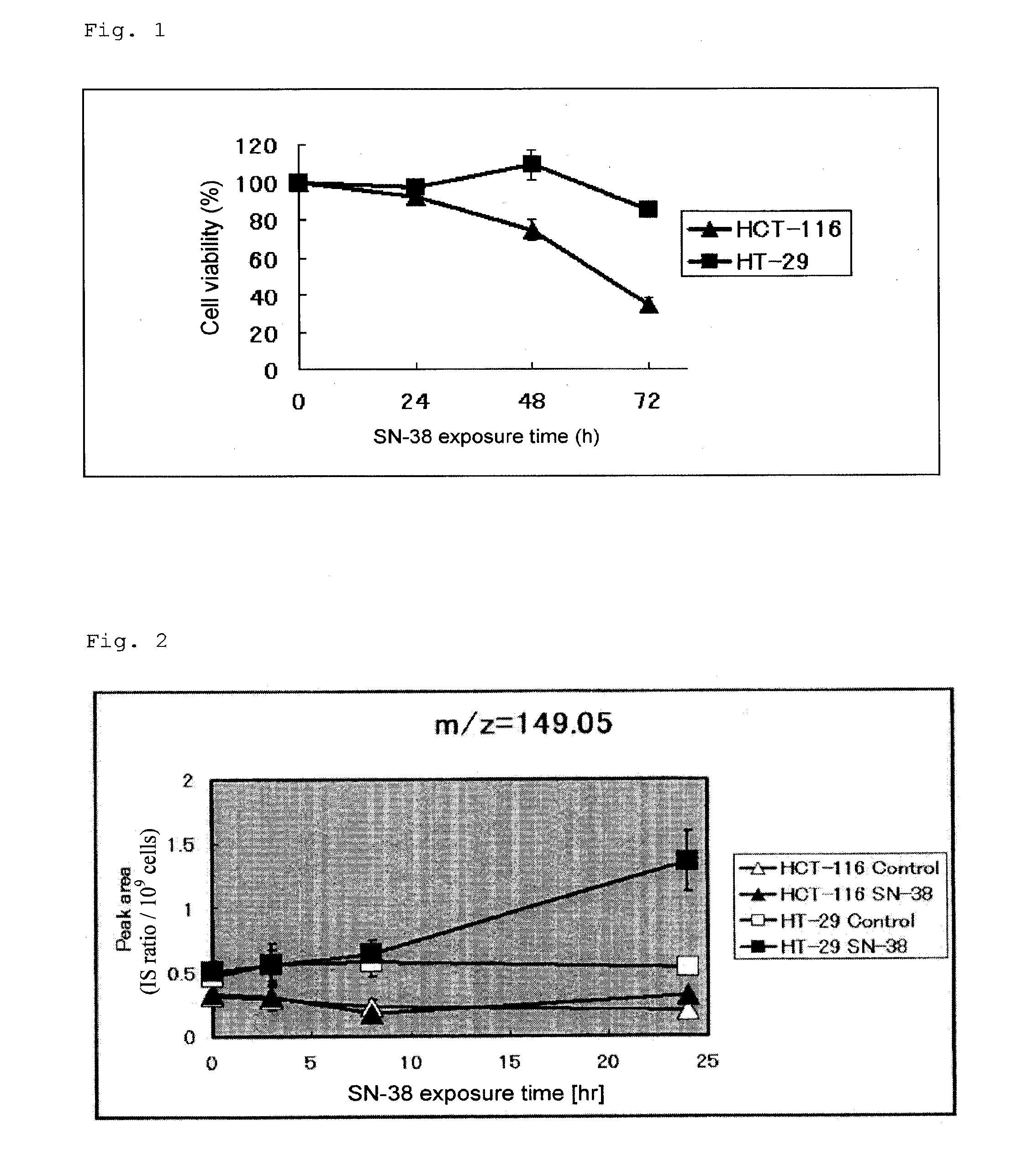
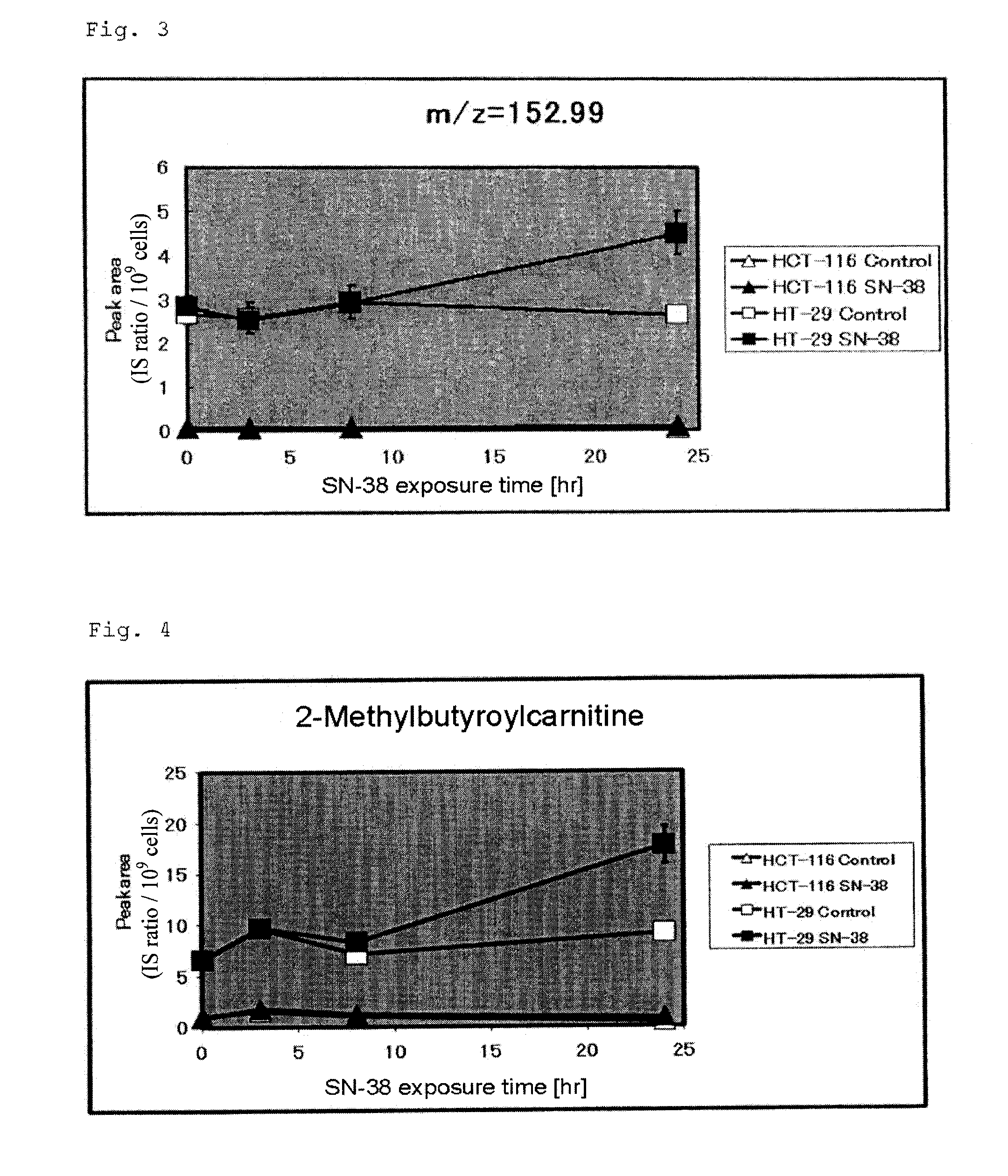
ActiveUS20120220618A1High therapeutic effectPromote anti-cancer agent sensitivityBiocideCompound screeningAnticarcinogenDiglycerol phosphate
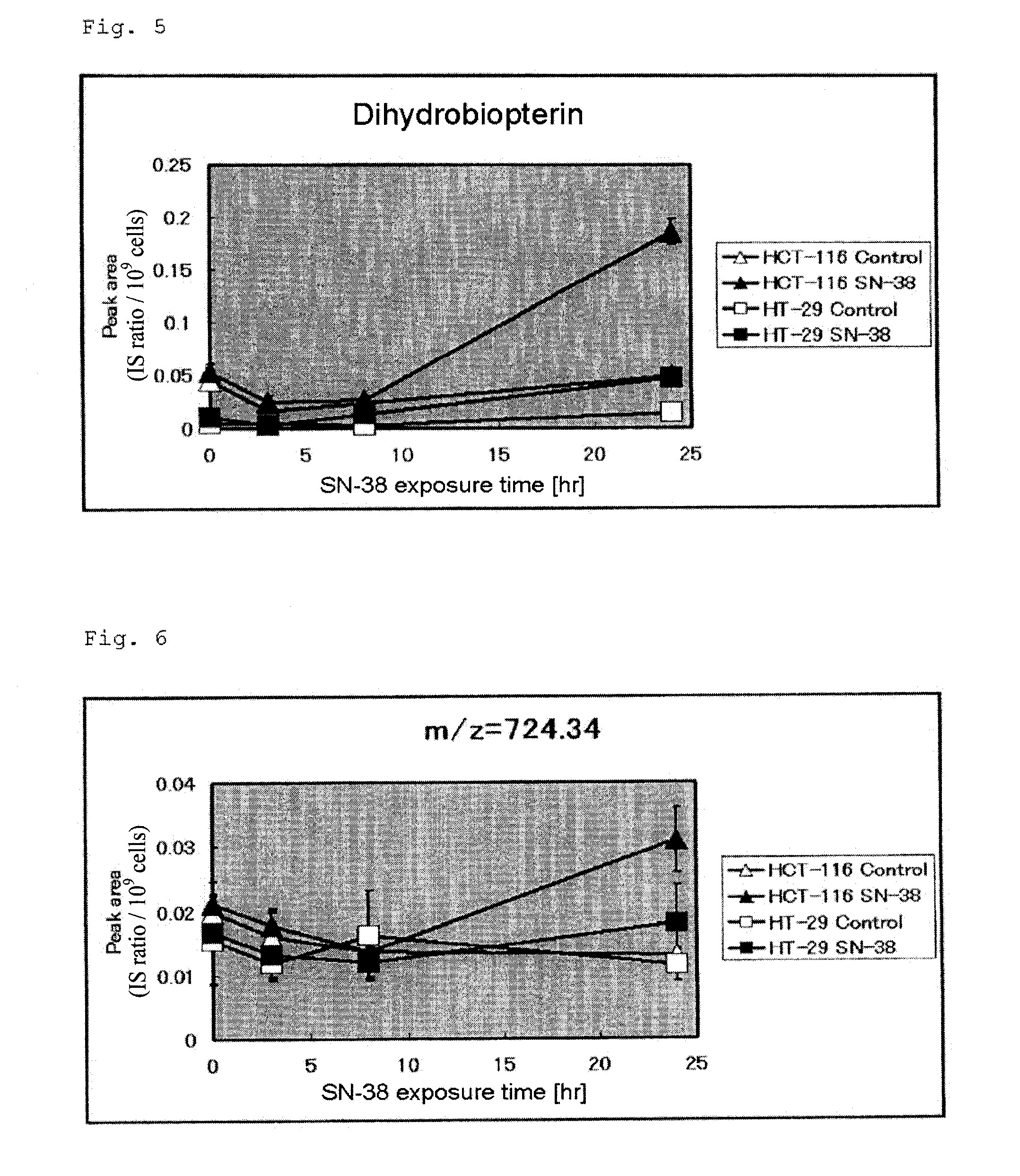
To provide a marker for determining sensitivity of a patient to an anti-cancer agent, and novel cancer therapeutic means employing the marker.The marker for determining sensitivity to an anti-cancer agent is formed of one or more substances selected from the group consisting of a substance or a fragment thereof detected as an anion at m / z of 149.05 to 149.06, a substance or a fragment thereof detected as an anion at m / z of 152.99 to 153.00, a substance or a fragment thereof detected as a cation at m / z of 724.34 to 724.35, the peaks being determined by means of a mass spectrometer, glycerol 3-phosphate, dihydrobiopterin, GABA, lactic acid, asparagine, aspartic acid, 2-methylbutyroylcarnitine, 1-methyladenosine, and glutathione, and a substance involved in a metabolic pathway of any of these substances.
Owner:KEIO UNIV +1
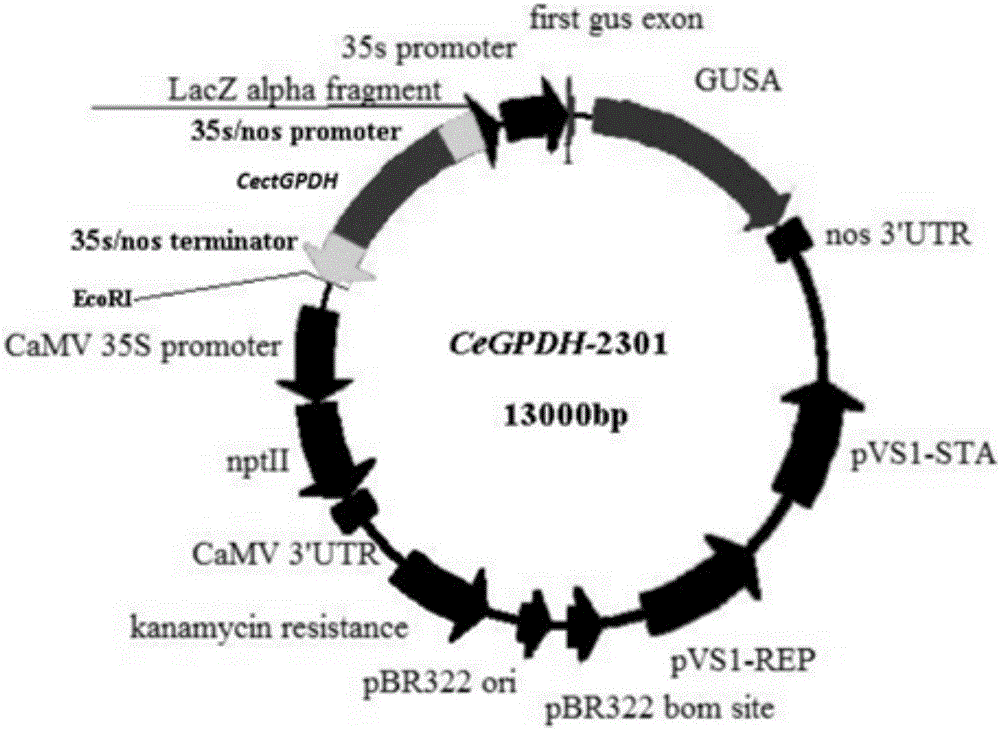
CectGPDH2 (cytosolic glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 2) gene and application thereof
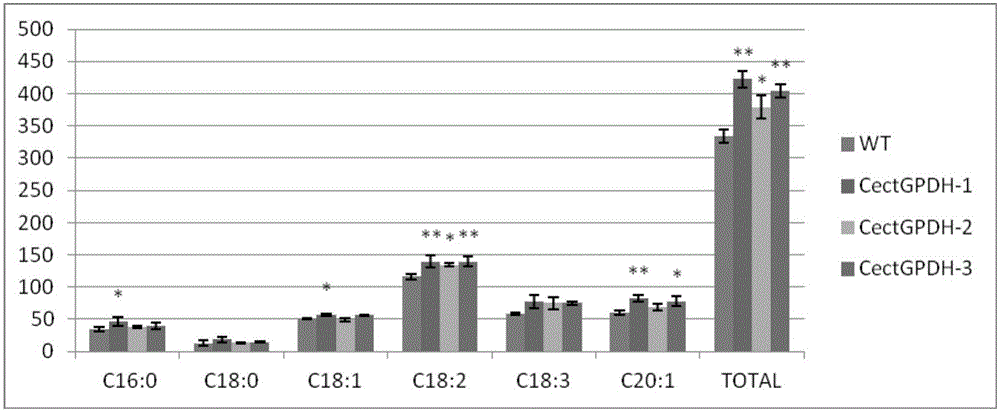
The invention provides a CectGPDH2 gene and an application thereof in increase of fatty acid content. The nucleotide sequence of the CectGPDH2 gene is shown as SEQ NO.1. The gene comes from Chlorella ellipsoidea and encodes GPDH, wherein the GPDH participates in shuttle of the mitochondrion G3P (glycerol-3-phosphate), provides electrons for respiratory chains, is a key enzyme for G3P synthesis, is one of the key enzymes for connecting glucose metabolism with lipid metabolism and plays an important role in lipid synthesis and energy metabolism in plants. The total fatty acid content of seeds of Arabidopsis thaliana and rape genetically modified with the gene can be increased obviously, and the gene can be used for increasing the oil content of plant cells and the content of linoleic acid (C18:2) and eicosenoic acid (C20:1) in the plants and has good application prospect.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
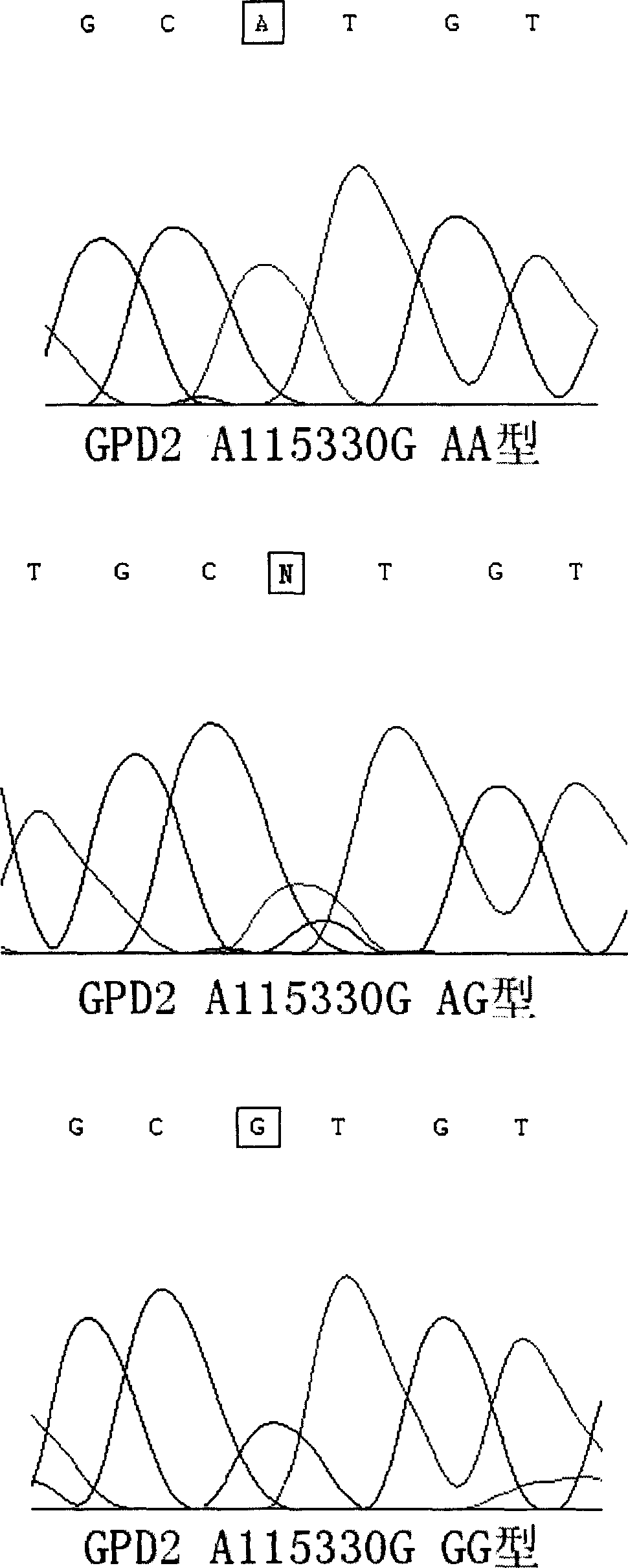
Relativity of glycerotriphosphate dehydrogenase gene with primary hypertension
InactiveCN1861805AEarly preventionEarly benefitMicrobiological testing/measurementMedicineDiglycerol phosphate
This invention discloses a method to check primary hypertension which is easy to infect, it includes the detection of individual glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogonase's gene (GPD2), whether the transcript or protein is changed as normal lever, if there is difference, it shows that the individual is apt to infect the primary hypertension than the normal. This invention also discloses corresponding measuring reagent box.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF HYPERTENSION +1
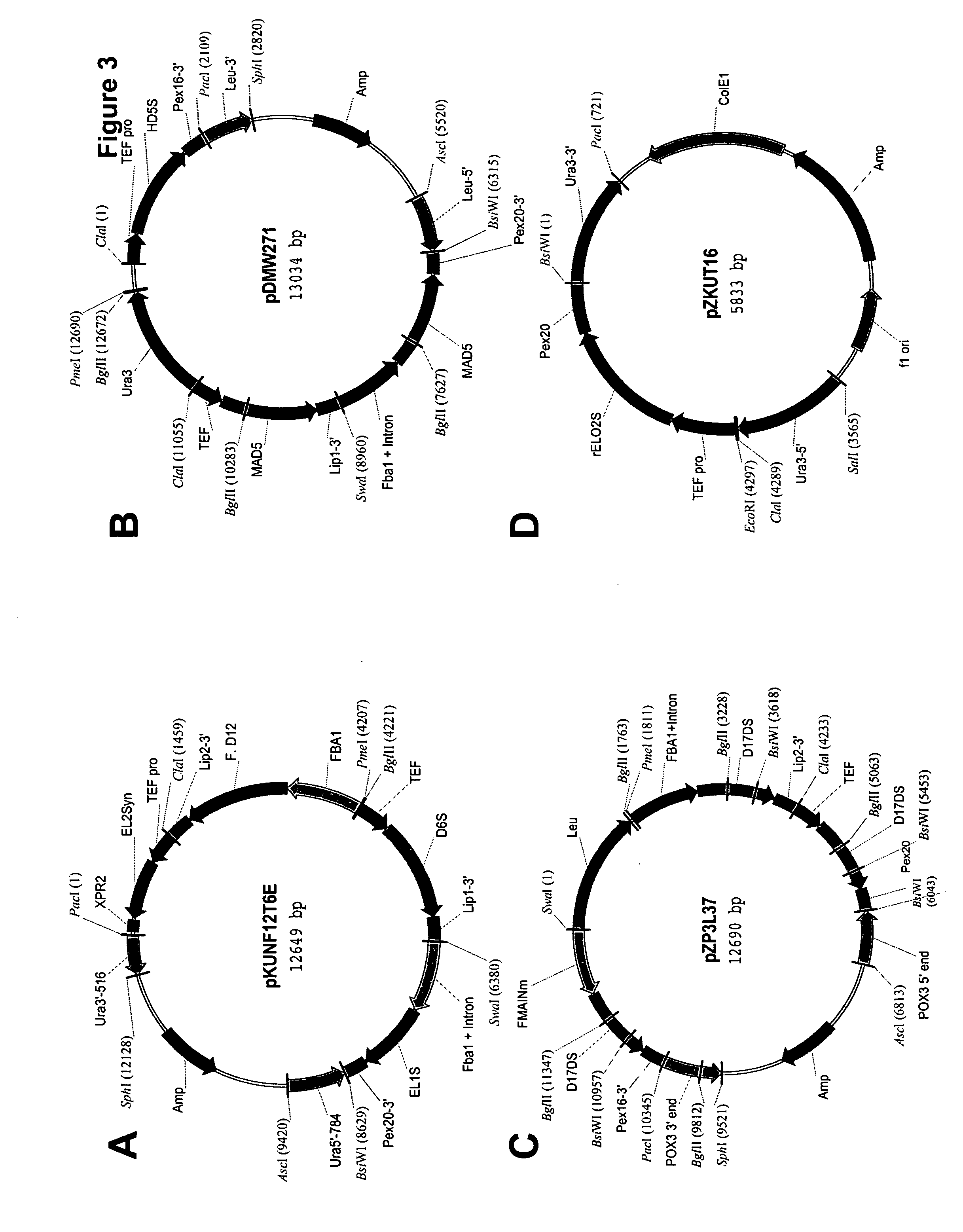
Higher plant cytosolic er-based glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase genes
InactiveUS20060206960A1Modifying lipid metabolismChange outputSugar derivativesTransferasesBiotechnologyHeterologous
Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase is the initial enzyme of the glycerolipid biosynthetic pathway. Biochemical analyses indicated that the reaction mediated by glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase represents a potential rate-limiting step for the synthesis of phospholipids and storage neutralipid, triacylglycerol. The present invention relates to the cloning of genes encoding extraplastidic membrane-bound glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferases. Heterologous expression of the genes, GPAT1, GPAT2, and GPAT3 in a yeast glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase mutant demonstrated that the encoded products could efficiently utilize glycerol-3-phosphate to mediate sn-1 stereo-specific fatty acid acylation. The invention encompasses the glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase peptides disclosed and fragments and homologues thereof, the corresponding gene sequences and fragments and homologues thereof, as well as the use of the peptide and gene sequences of the present invention for use in generating recombinant proteins, and transgenic plants with altered lipid metabolism. In this way, the present invention also encompasses the use of such recombinant peptides and transgenic plants for the production of lipid products for use, for example, in pharmaceutical and nutritional applications.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
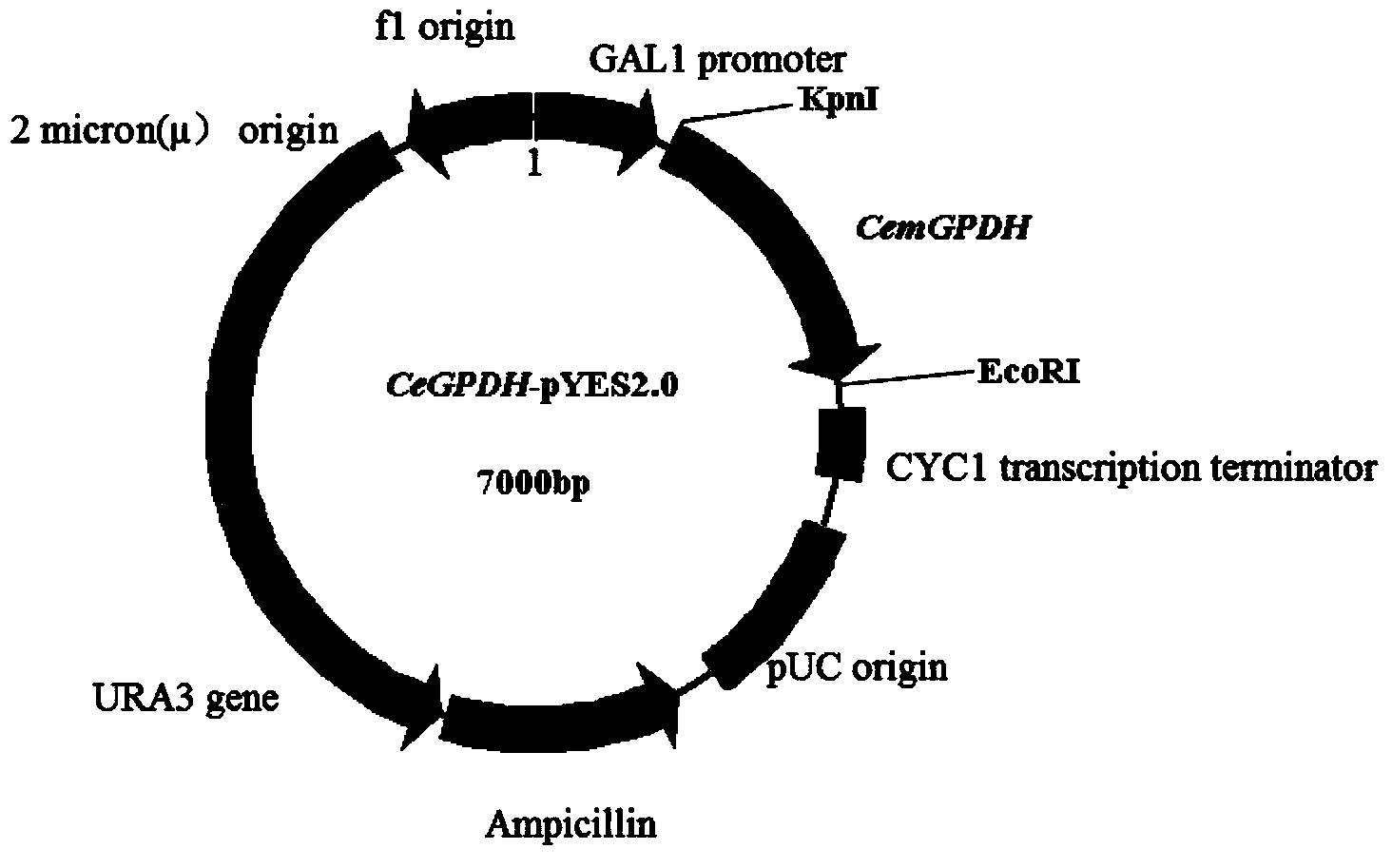
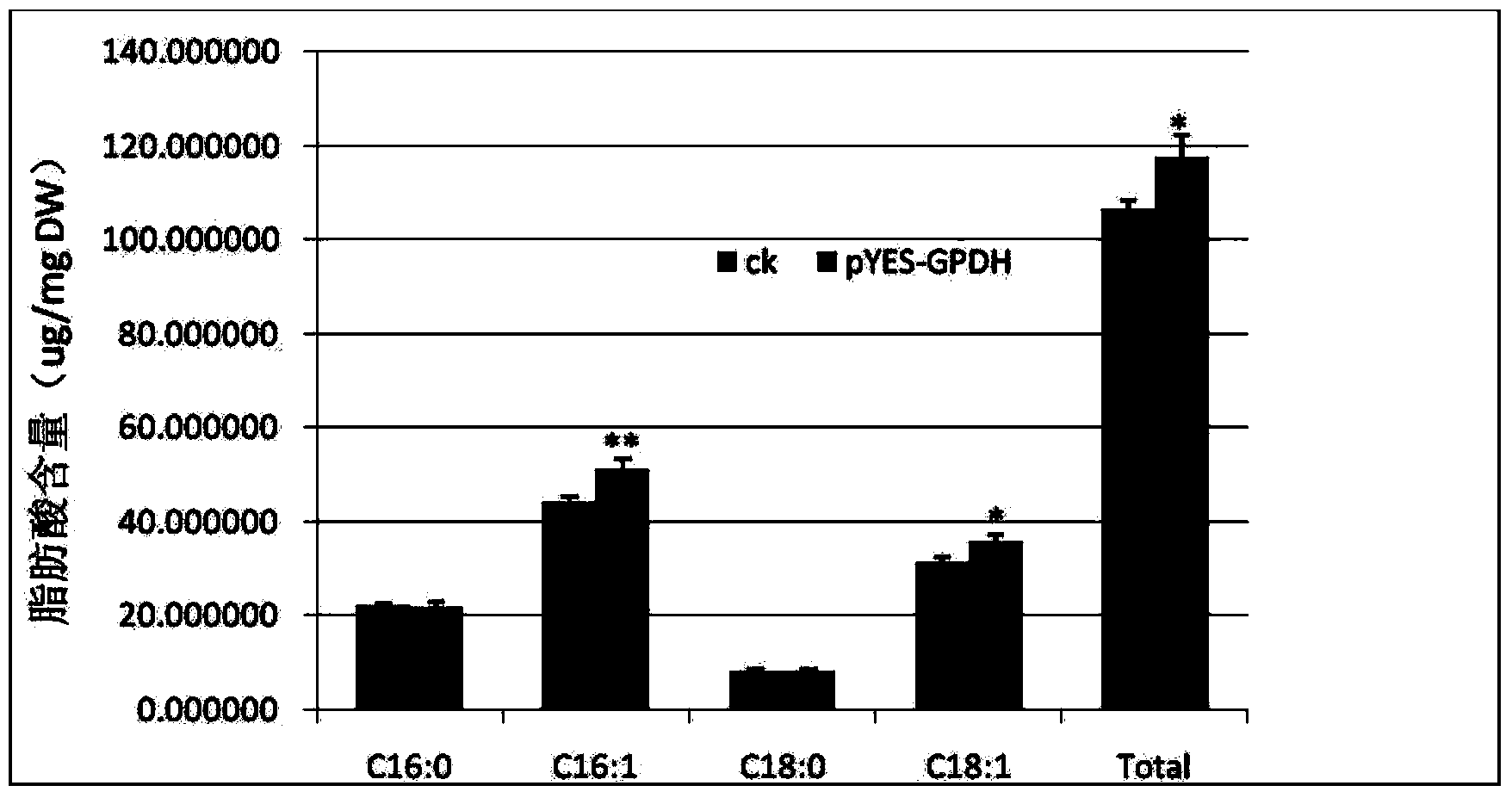
Cem GPDH (Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) gene and application thereof
The invention provides a Cem GPDH (Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) gene and an application of the Cem GPDH gene in the aspect of increase of cellular fatty acid content. A nucleotide sequence of the Cem GPDH gene is represented as SEQ ID NO: 1. The gene is derived from Chlorella ellipsoidea, and GPDH is coded. G3P (Glycerol-3-phosphate) synthesized through catalysis by GPDH is an important raw material for synthesis of TAG (triacylglycerol), the enzyme participates in mitochondria G3P shuttle, provides electrons for a respiratory chain, is a key enzyme for G3P synthesis, is one of key enzymes for connecting glycometabolism and lipid metabolism and has an important effect on lipid synthesis and energy metabolism in plants; and besides, the gene can remarkably increase the total fatty acid content of cells when utilized to convert yeast cells, plant cells and microalgae cells.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Glycerol 3- phosphate dehydrogenase for butanol production
ActiveUS9441250B2Improved and increased production of butanolReduced and decreased production of glycerolBacteriaBiofuelsHeterologousMicroorganism
Owner:GEVO INC
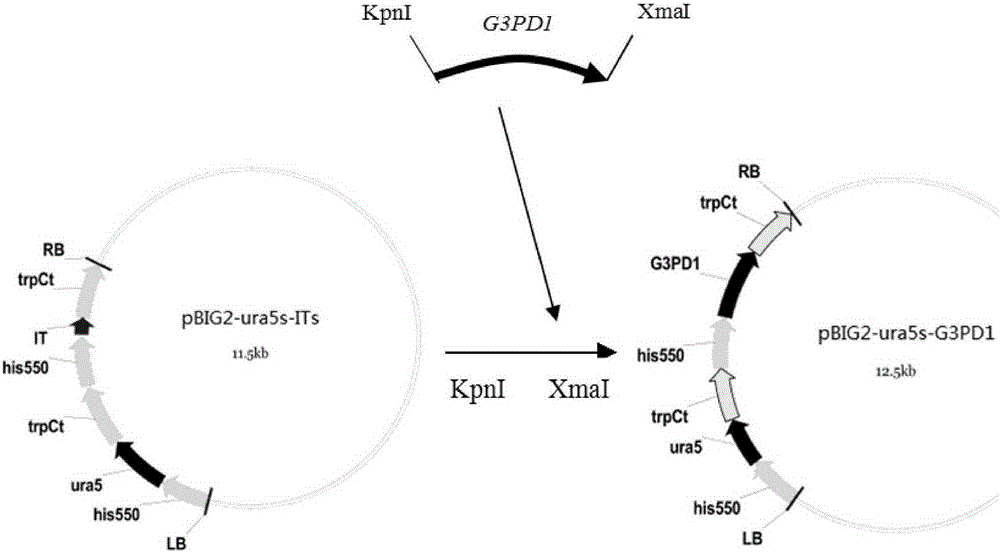
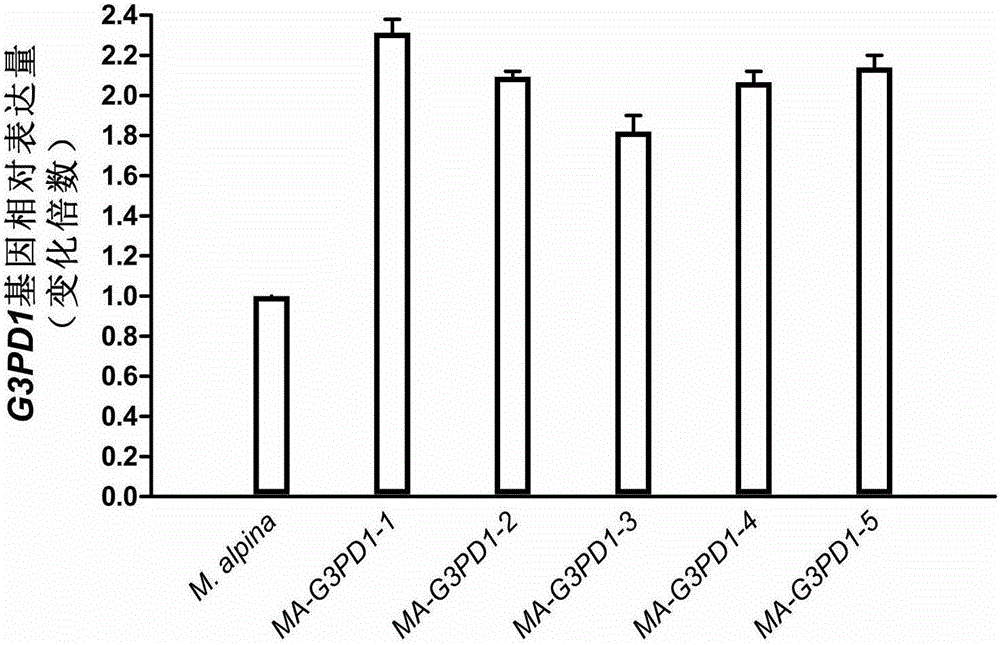
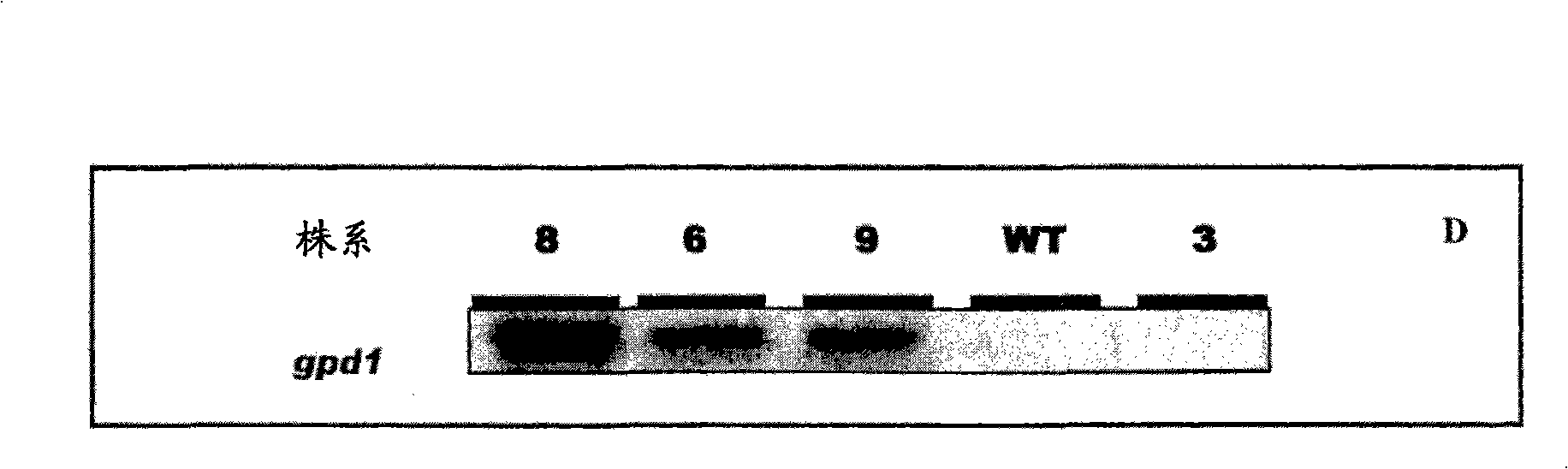
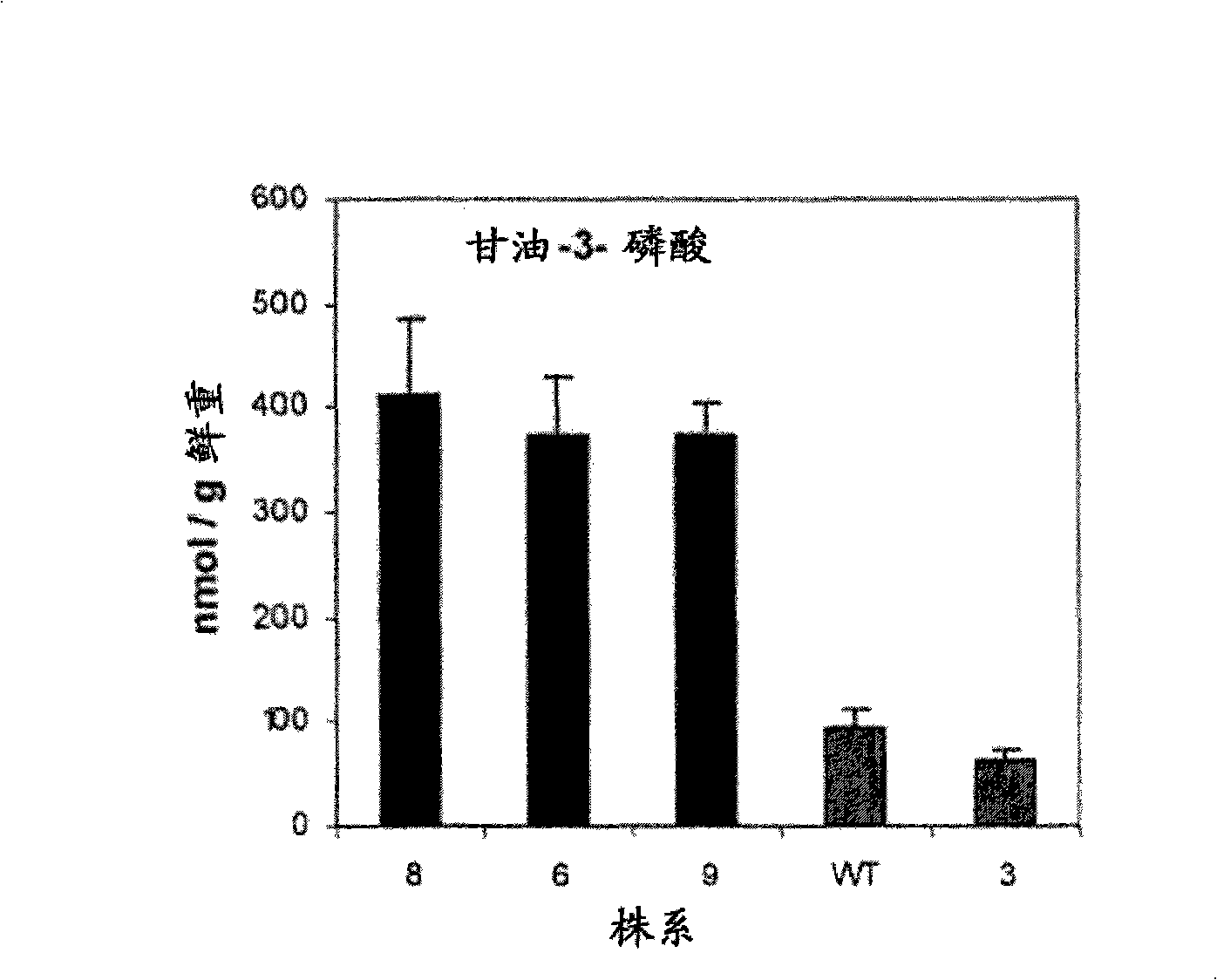
Mortierella alpine strain overexpressing 3-phosphoglycerol dehydrogenase gene(G3PD1), and construction method and application thereof
The invention relates to a recombinant Mortierella alpine strain GPD-1 overexpressing G3PD1 and a construction method. According to the invention, uracil-auxotrophic Mortierella alpine MAU1 is used as a material, Agrobacterium tumefaciens is used for mediation, and a G3PD1-overexpressing recombinant strain with obviously increased lipid content is obtained. Compared with wild Mortierella alpine, the total lipid content of the strain provided in the invention is increased by about 50%, and the transcription amount of G3PD1 is increased by about 2 times; so theoretical and application foundations are laid for subsequent industrial application.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for increasing the total oil content in oil plants
InactiveCN101356278AOxidoreductasesVector-based foreign material introductionPlanting seedPhosphoric acid
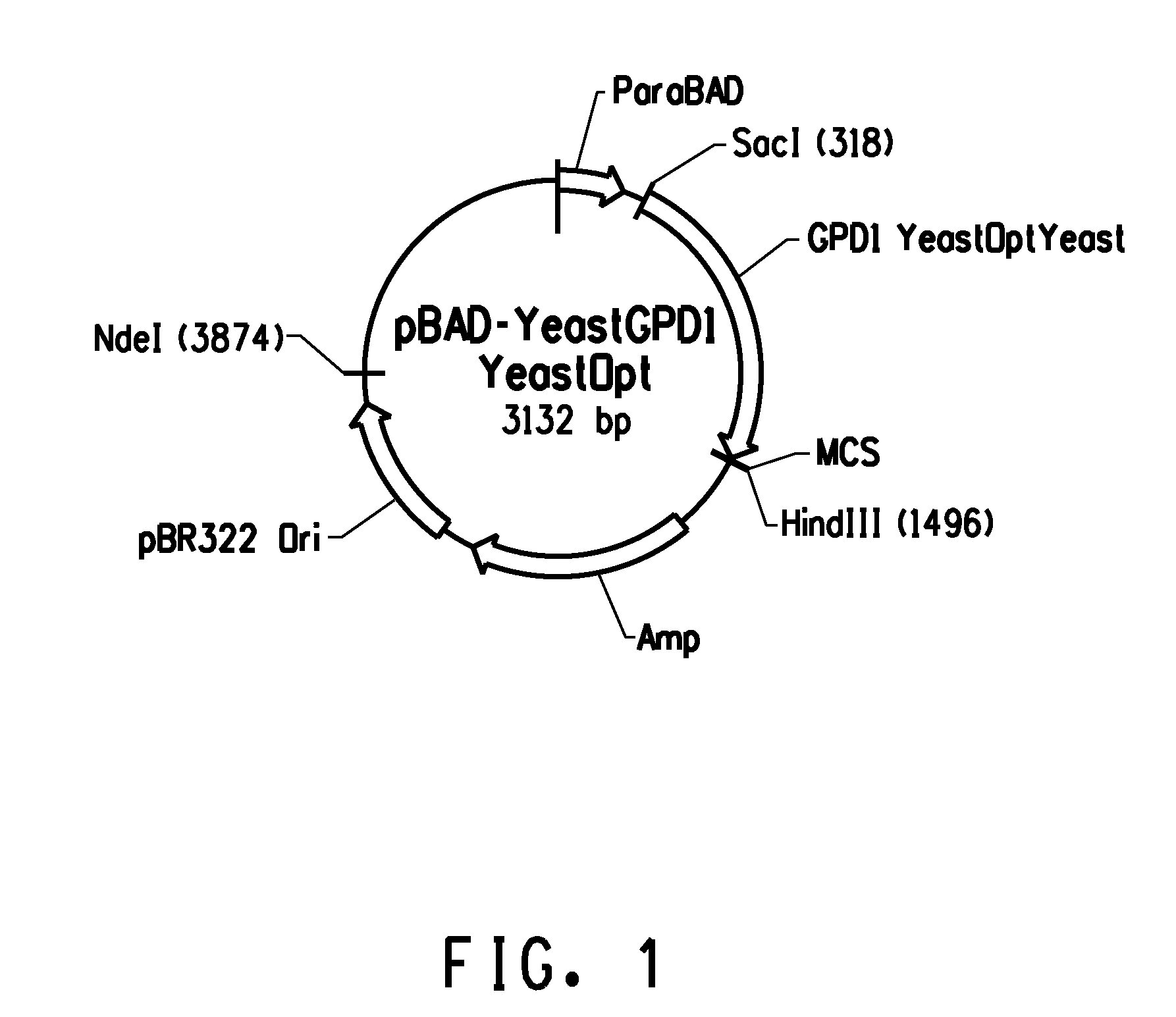
The invention relates to methods for increasing the total oil content and / or the content of glycerol-3-phosphate in transgenic oil plants, which contain at least 20 wt.-% oleic acid in relation to the total fatty acid content, preferably in plant seeds, by the expression of glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenases (G3PDH) from yeasts, preferably from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Advantageously, the oil obtained by this method and / or the free fatty acids are added to polymers, foodstuffs and feedstuffs, cosmetics, pharmaceutical products or products with industrial applications.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV +1
Cyclophorase determination method for triglyceride in serum
InactiveCN103913581AWill not increase the burdenLow costComponent separationBiological material analysisPeroxidaseGlycerol kinase
The invention discloses a cyclophorase determination method for triglyceride in serum, and belongs to a method for measuring materials by measuring color change generated by reactions. A technical solution lies in that a reagent I contains effective components of glycerol kinase, 3-phosphoglycerol dehydrogenase, phosphoglycerol oxidase, peroxidase, adenosine triphosphate, NADH, 4-aminoantipyrine and 2,4-dichlorophen; and a reagent II only contains an effective component of lipoprotein lipase. Free glycerol in the serum is subjected to circular reactions with adenosine triphosphate, NADH, 4-aminoantipyrine and 2,4-dichlorophen in the reagent I under catalysis of glycerol kinase, 3-phosphoglycerol dehydrogenase, phosphoglycerol oxidase and peroxidase to generate quinoneimine; and after the reagent II is added, triglyceride is hydrolyzed to generate glycerol, and then the circular reaction is carried out. The content of triglyceride is calculated by an instrument based on quinoneimine generated by reactions in the reagent II, by using quinoneimine generated by reactions in the reagent I as a blank.
Owner:TIANJIN BAODI HOSPITAL
Methods of producing and growing plants having improved phosphorus utilization
InactiveUS7759547B2Low costIncrease capacityBryophytesOther foreign material introduction processesPhosphorus utilizationWild type
The invention discloses methods for genetically transforming a plant so that it expresses a glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. The method raises levels glycerol-3-phosphate in comparison to the wild type, leading to increased stress tolerance, and altered fatty acid content in glycerolipids. The method also produces plants having improved phosphorus utilization.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Use for glycolipoprotein gintonin, isolated and identified from ginseng, as a natural medical-plant derived ligand
InactiveUS20140234868A1Trouble growingPromoting various calcium-dependent biologicalNervous disorderAntipyreticLPA ReceptorsNervous system
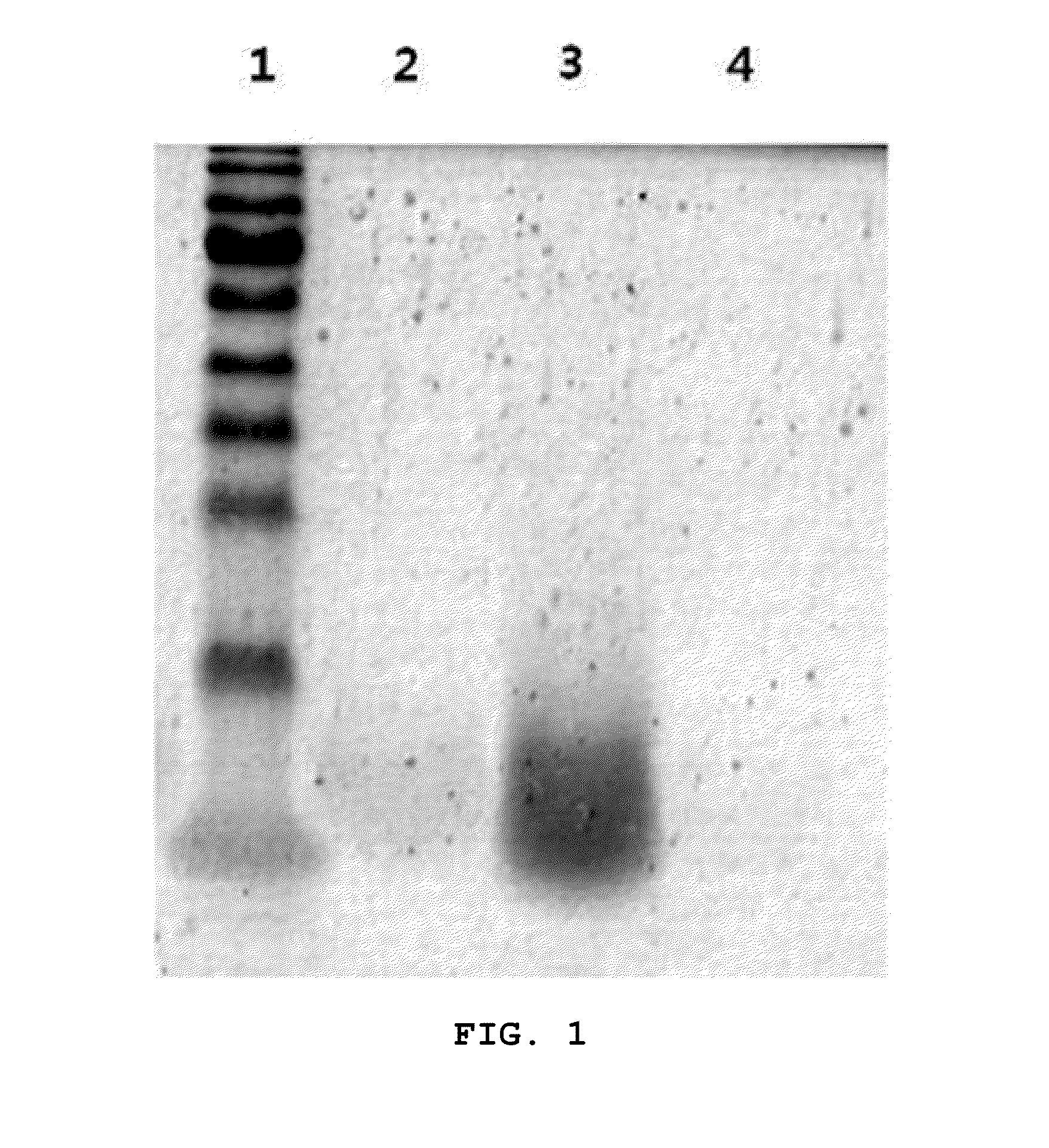
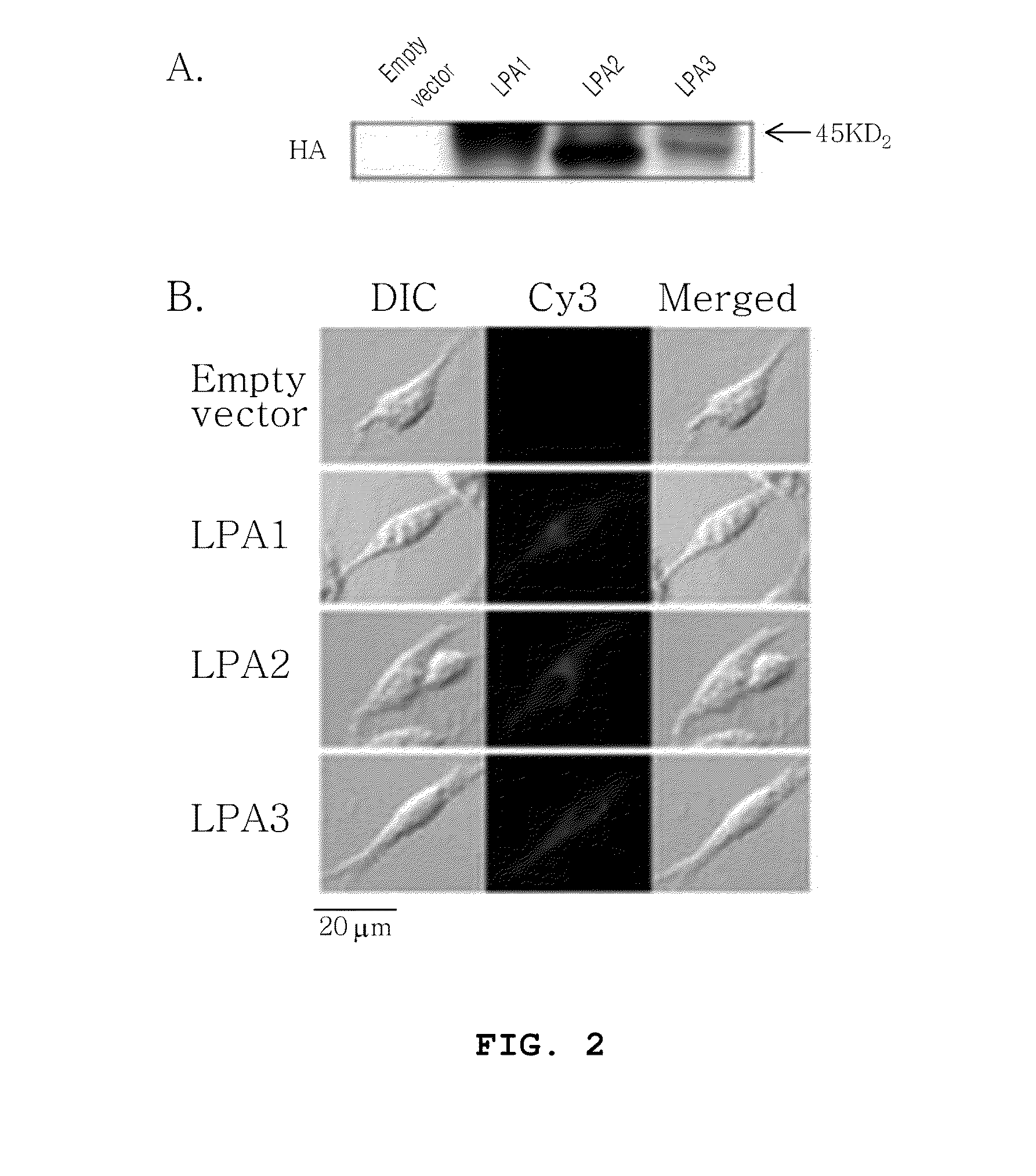
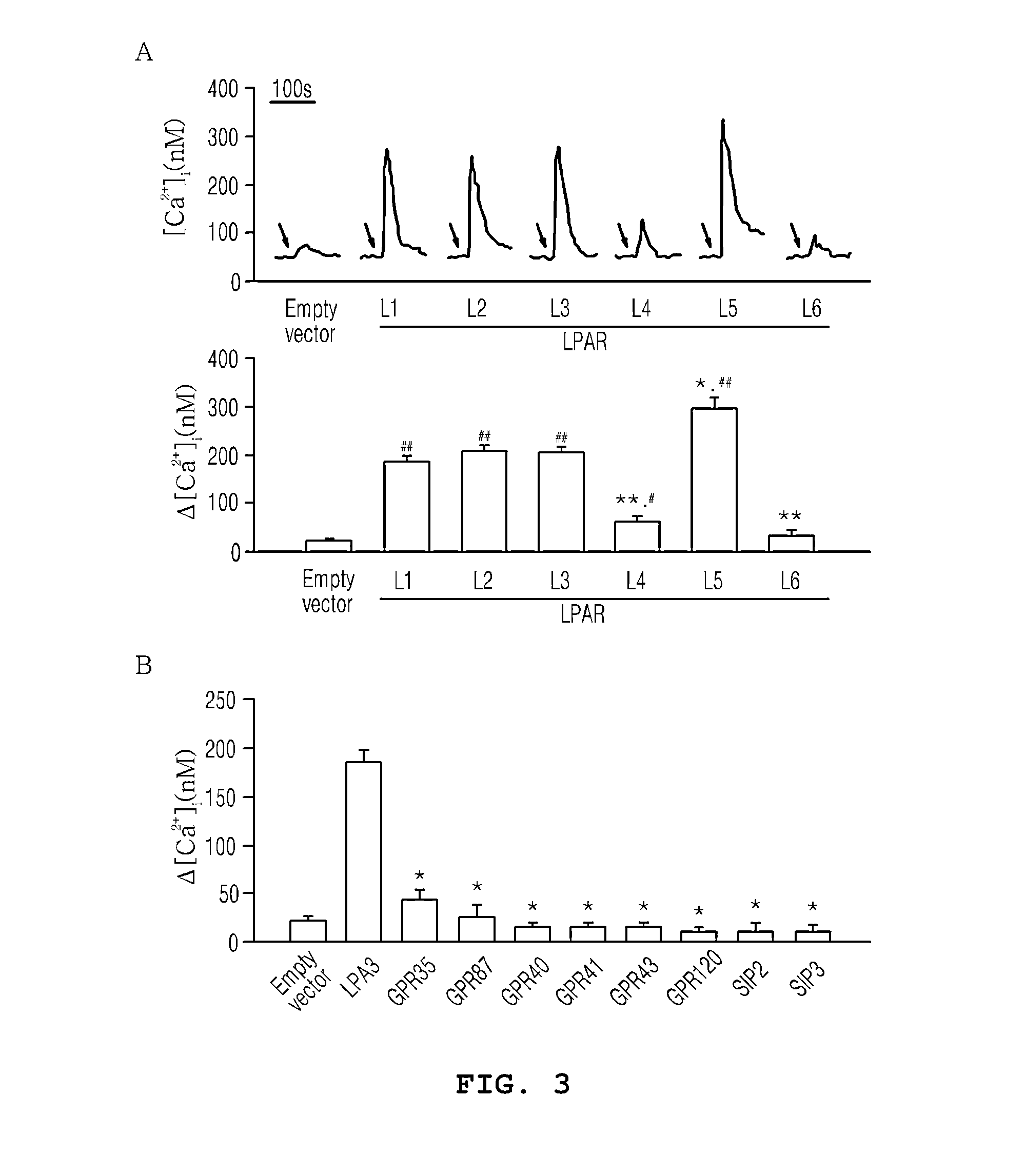
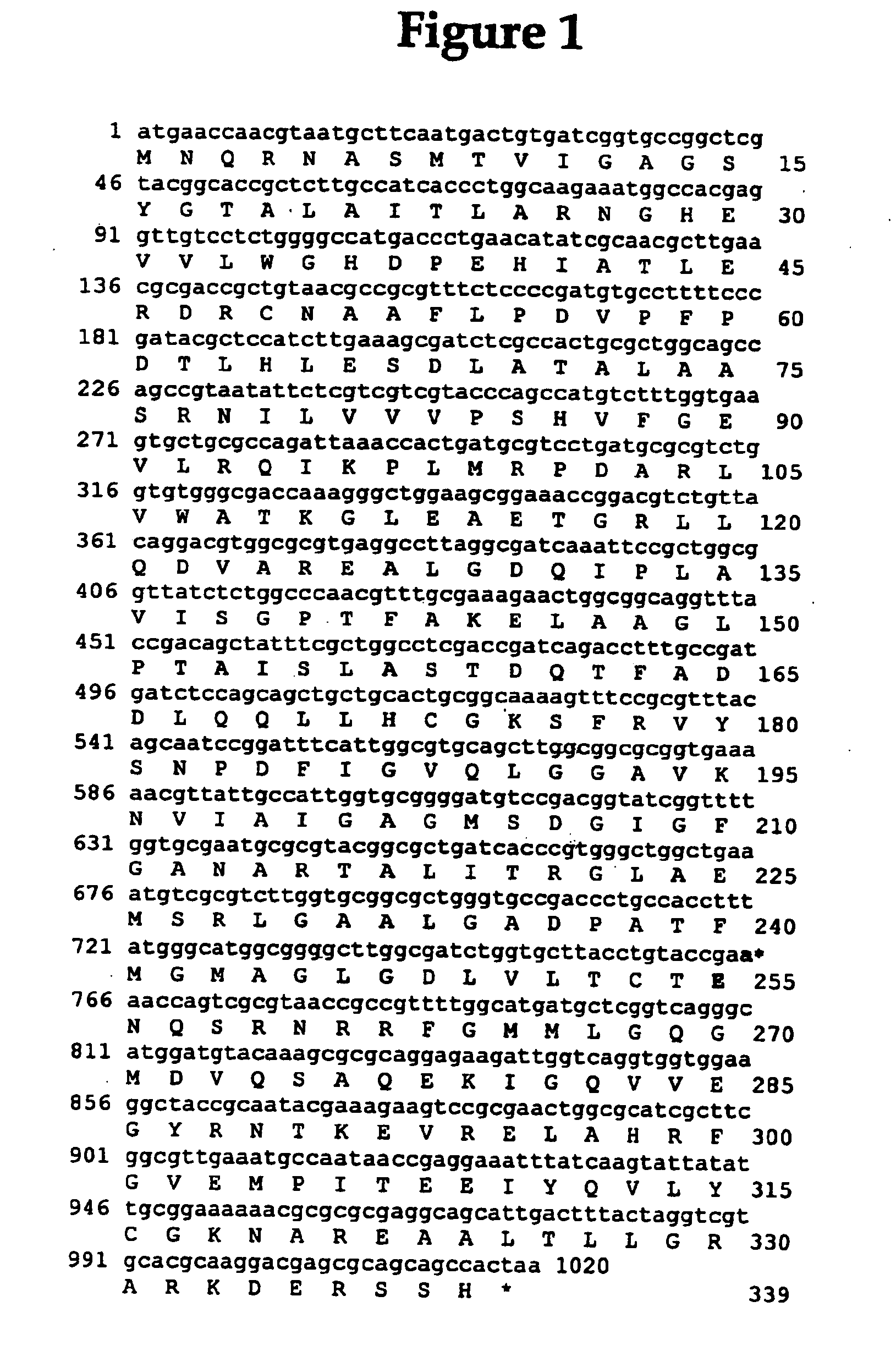
The present invention relates to glycolipoprotein gintonin, isolated and identified from ginseng, as a natural medicinal-plant-derived ligand acting on LPA1 (lysophosphatidic acid; 1- or 2-acyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphate), LPA2, LPA3, LPA4 and LPA5 receptors whose efficacy is exhibited physiologically / pharmaceutically via an interaction with subset receptors [LPA1(edg-2), LPA2(edg-4), LPA3(edg-7), LPA4, PLA5] in the EDG (endothelial differentiation gene) family in G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) present in the cell membranes of animals including humans. The gintonin of the present invention can be used to advantage in the prevention and treatment of various diseases arising from reduced calcium concentration and various physiological activities and pharmaceutical activities dependent on calcium, since the gintonin of the present invention interacts with LPA receptors so as to activate a series of signal transmission processes and temporarily induce an increase in free Ca2+ in the cytoplasm, and a temporary increase in the intracellular calcium concentration gives rise to a temporary increase in the intracellular calcium concentration in various organs including, inter alia, those of the nervous system, cardiovascular system, endocrine system, reproductive system, digestive system and immune system when the LPA receptors are expressed, with physiological activity being exhibited.
Owner:KONKUK UNIV IND COOP CORP
Methods of producing and growing plants having improved phosphorus utilization
InactiveUS20050204423A1Enhanced production of glycerolLow costBryophytesOther foreign material introduction processesGlycerol 3-phosphateGlycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
The invention discloses methods for genetically transforming a plant so that it expresses a glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. The method raises levels glycerol-3-phosphate in comparison to the wild type, leading to increased stress tolerance, and altered fatty acid content in glycerolipids. The method also produces plants having improved phosphorus utilization.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Acetate consuming yeast cell
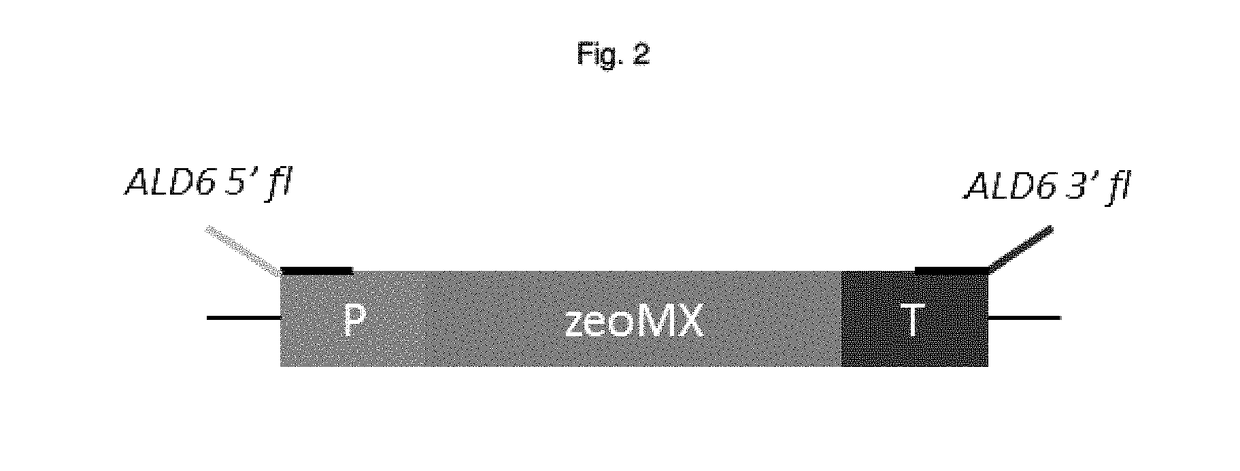
ActiveUS20180127763A1Shorten fermentation timeIncrease productionHydrolasesTransferasesNucleotideBiology
The present invention relates to a yeast cell that is genetically modified comprising:a) a disruption of one or more aldehyde dehydrogenase (E.C:1.2.1.4) native to the yeast;b) one or more nucleotide sequence encoding a heterologous NAD+-dependent acetylating acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (E.C. 1.2.1.10);c) one or more nucleotide sequence encoding a homologous or heterologous acetyl-CoA synthetase (E.C. 6.2.1.1); andd) a modification that leads to reduction of glycerol 3-phosphate phosphohydrolase (E.C. 3.1.3.21) and / or glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (E.C. 1.1.1.8 or E.C. 1.1.5.3) activity, native to the yeast.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
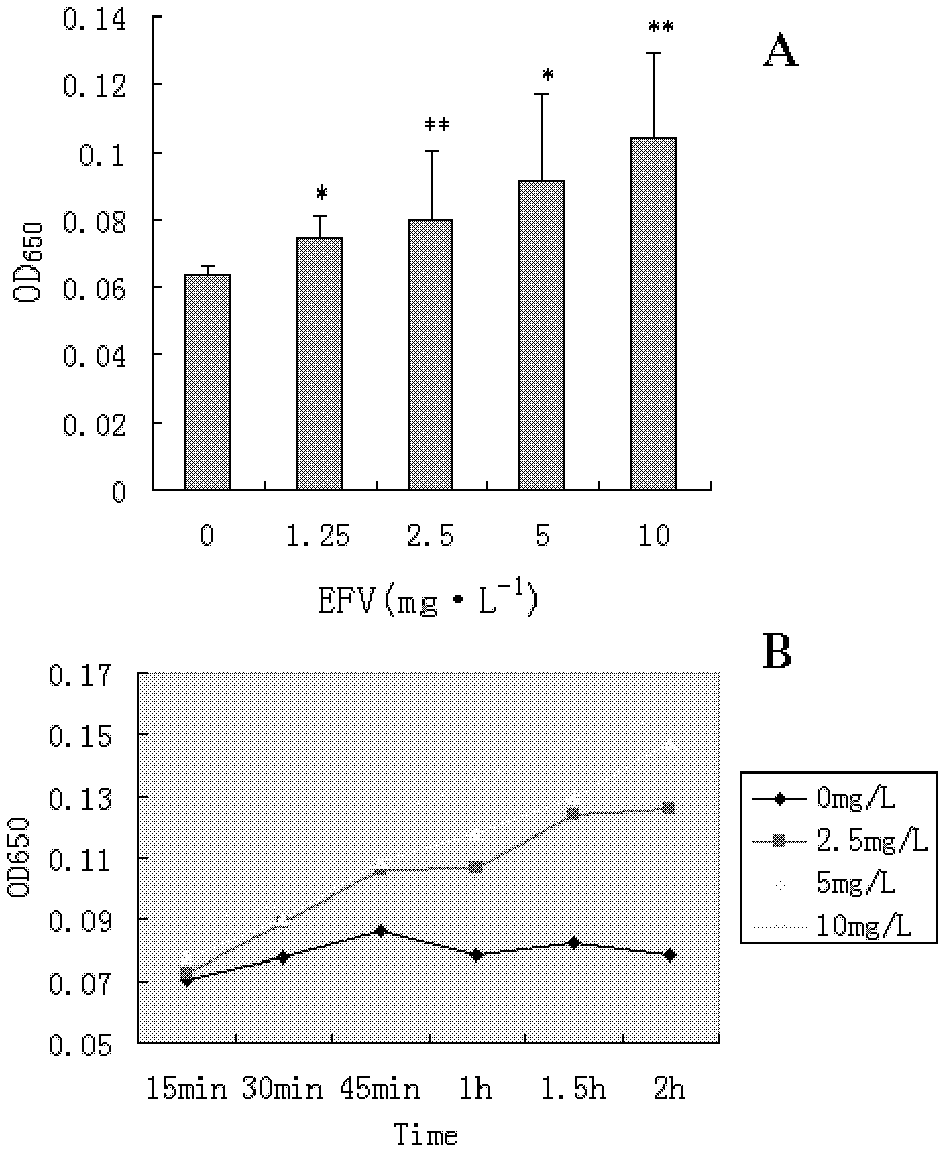
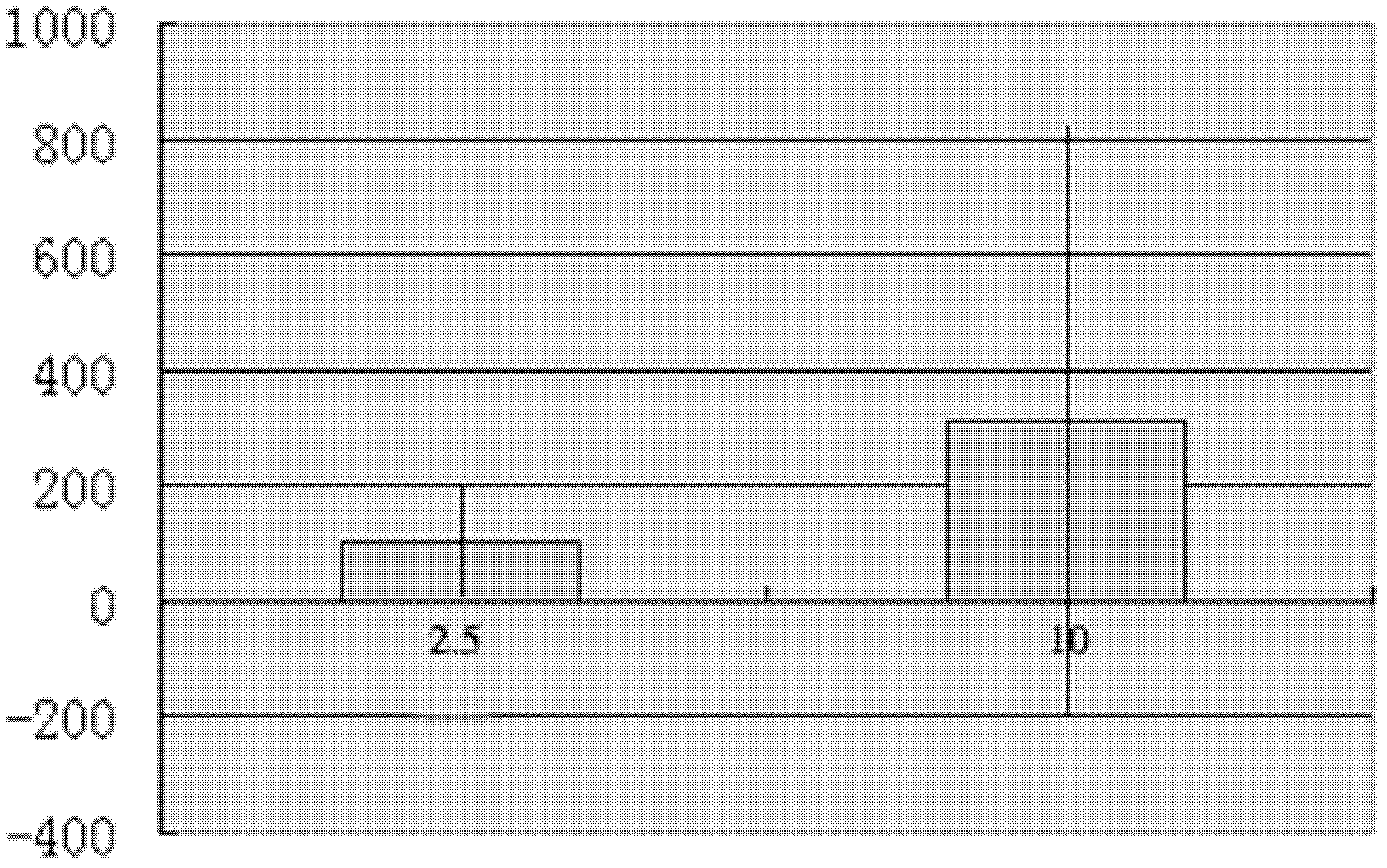
Efavirenz hepatotoxicity molecular marker and application thereof
InactiveCN103215341AMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisProteomics methodsCytotoxicity
The invention belongs to the biology technical field, and relates to an efavirenz hepatotoxicity molecular marker and an application, and especially relates to an application of D-3-phosphoglycerol dehydrogenase in preparation of the molecular marker for detecting hepatotoxicity. A cell model of hepatotoxicity, a proteomics method used for screening, fluorescent quantitation PCR and immunoblotting experiments are used to obtain the D-3-phosphoglycerol dehydrogenase which is positively related to the hepatotoxicity. The protein in EFV processed groups with different concentrations enables high expression by comparing with unprocessed protein, and the D-3-phosphoglycerol dehydrogenase is positively related to the EFV hepatotoxicity. The result shows that a transcript of protein can be taken as one molecular marker to perform quantitative determination on transcriptional level, so that the EFV hepatotoxicity can be detected. The specific primers and antibody of the D-3-phosphoglycerol dehydrogenase can be used for preparing a preparation to detect EFV hepatotoxicity, and can be used to prepare a kit for detecting the EFV hepatotoxicity.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Acyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphate compound and application thereof
InactiveCN110283198AObvious weight loss effectWide variety of sourcesOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderNatural sourceAcyl residue
The invention discloses an acyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphate compound and application thereof. The structural formula of the acyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphate compound is shown in the description, wherein R1 and R2 are independently selected from H and a fatty acid chain acyl residue, and R3 is a phosphate group; the application refers to application of the acyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphate compound in controlling the body weight and the blood lipid level. The acyl-sn-glycerol-phosphate compound has a significant weight reducing effect, has wide sources which can be natural sources such as animals and plants, has high safety and has potential high market value.
Owner:江苏中酶生物科技有限公司
Modulators of adp-dependent glucokinase (ADPGK) and glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GPD2) for therapy
Owner:DEUTES KREBSFORSCHUNGSZENT STIFTUNG DES OFFENTLICHEN RECHTS
Vibrio anguillarum and edwardsiella tarda-resistant multi-valence live vaccine, correlative expression vector and application
ActiveCN102154348BPrevention of polyvalent functionGood immune protectionAntiviralsBacteria peptidesDiseaseVibrio anguillarum
The invention provides a vibrio anguillarum and edwardsiella tarda-resistant multi-valence live vaccine which is obtained by transferring a vibro anguillarum attenuated strain through a constructed recombinant expression vector, wherein a 3-phosphoglycerol dehydrogenase is displayed on the surface of a vibrio anguillarum attenuated strain cell by an ice nucleus protein outer membrane positioning element of the recombinant expression vector-expressed pseudomonas syringae and the fusion protein of the 3-phosphoglycerol dehydrogenase of the edwardsiella tarda through the ice nucleus protein outer membrane positioning element. The invention further provides a correlative expression vector and application. The vibrio anguillarum and edwardsiella tarda-resistant multi-valence live vaccine is unique and ingenious in design, vibrio anguillarum and edwardsiella tarda-resistant, good in immune protection effect, simple in use, safe, and low in cost. The invention provides a safe, efficient and ecumenical mode to the diseases for preventing the cultured fishes, has practical business development and application value, and is suitable for the large-scale popularization and application.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Yeast engineering bacterium of high productive glycerin
The invention has supplied a yeast germ for producing glycerine with high productivity and its preparing method and application. In the yeast germ, the Dunaliella salina glycerol phosphate dehydrogenize is introduced, so that the glycerine with good quality can be produced with high productivity and low cost.
Owner:SI CHUAN HEBEN BIOTIC ENG
cemgpdh gene and its application
The invention provides a Cem GPDH (Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) gene and an application of the Cem GPDH gene in the aspect of increase of cellular fatty acid content. A nucleotide sequence of the Cem GPDH gene is represented as SEQ ID NO: 1. The gene is derived from Chlorella ellipsoidea, and GPDH is coded. G3P (Glycerol-3-phosphate) synthesized through catalysis by GPDH is an important raw material for synthesis of TAG (triacylglycerol), the enzyme participates in mitochondria G3P shuttle, provides electrons for a respiratory chain, is a key enzyme for G3P synthesis, is one of key enzymes for connecting glycometabolism and lipid metabolism and has an important effect on lipid synthesis and energy metabolism in plants; and besides, the gene can remarkably increase the total fatty acid content of cells when utilized to convert yeast cells, plant cells and microalgae cells.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
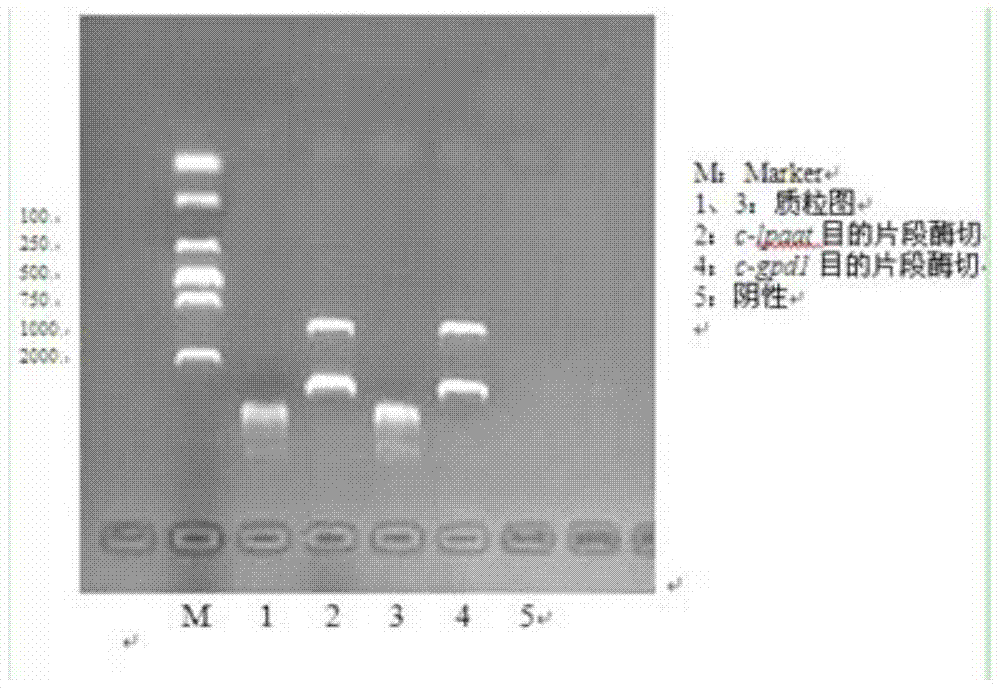
A kind of transgenic Chlamydomonas for improving fatty acid content of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, construction method and use thereof
ActiveCN104651236BIncrease oil productionDoes not affect normal growthUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesBiodieselChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention discloses a transgenic Chlamydomonas for improving fatty acid content of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, as well as a construction method and application thereof. The construction method comprises the following steps: respectively constructing a lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase gene recombination expression vector and a glycerol 3-phosphate acyl transferase gene recombination expression vector; and respectively or jointly converting the lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase gene recombination expression vector and the glycerol 3-phosphate acyl transferase gene recombination expression vector to the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cell, thereby obtaining converted lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase gene and / or glycerol 3-phosphate acyl transferase gene Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. According to the method, exogenous genes are converted into the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, thus, oil production of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii is increased, compared with the physicochemical methods, such as mutagenesis, effects of the method provided by the invention are more remarkable, and the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii has genetic stability; the obtained transgenic Chlamydomonas has increased oil production and lowered polyunsaturated fatty acids proportion, and saturation and modification steps in a biodiesel production process are reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
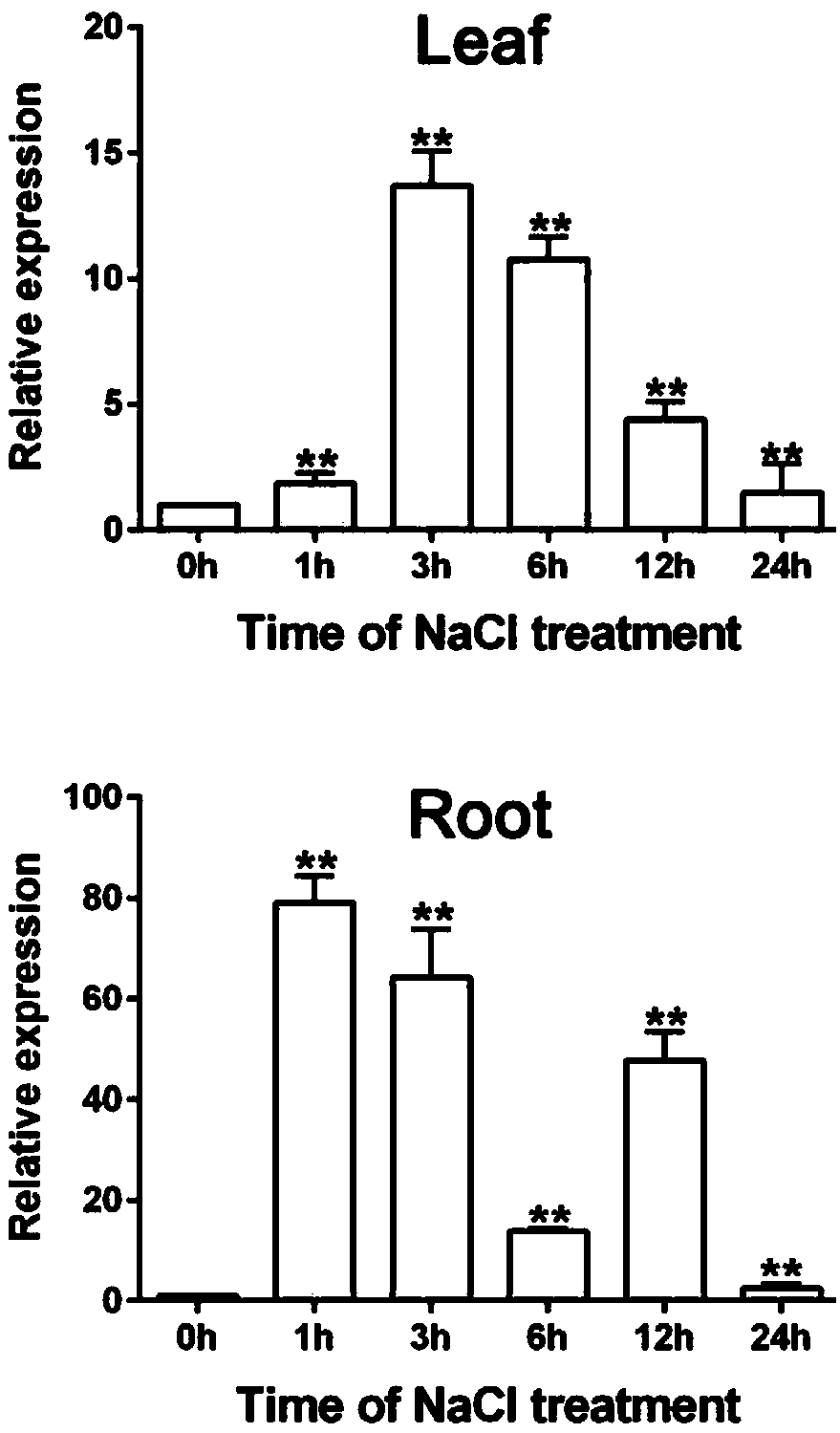
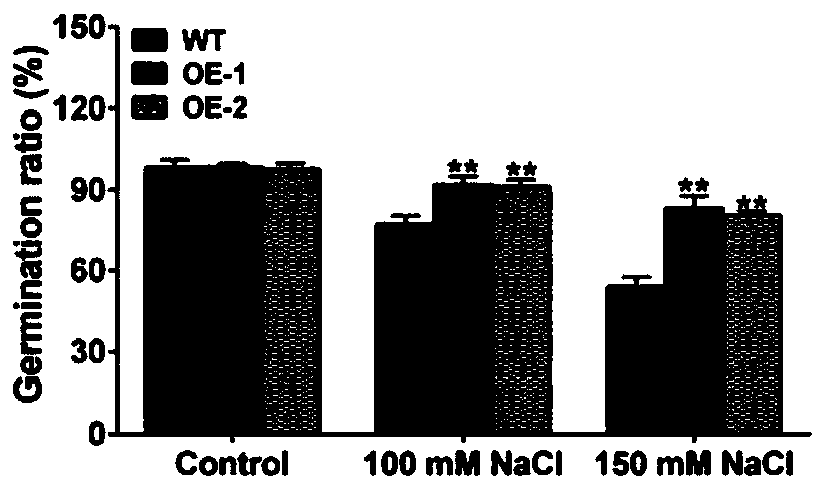
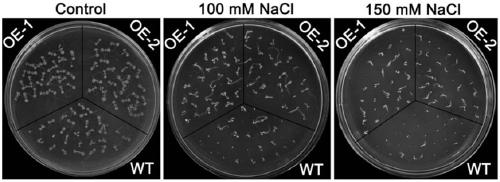
ZmGPDH5 (Zea Mays Glycerol-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase 5) and application of encoding gene thereof in regulating stress tolerance of plant
ActiveCN109576289AGen ChangyouImprove salt toleranceOxidoreductasesFermentationResearch ObjectWild type
The invention discloses ZmGPDH5 (Zea Mays Glycerol-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase 5) and application of an encoding gene thereof in regulating the stress tolerance of a plant. A member ZmGPDH5 of a ZmGPDHgene family is used as a study object, and is transferred into wild type Arabidopsis to obtain T3-generation homozygous transformants; two transformants of OE-1 and OE-2 in the T3-generation homozygous transformants are selected for identifying the salt-tolerant function; taking the wild type Arabidopsis as a control, the germination rate, the root length and the fresh weight change of ZmGPDH5 transgenic Arabidopsis under salt stress can be studied; a result shows that under the treatment condition of the salt stress, the seed germination rate of the ZmGPDH5 transgenic Arabidopsis is remarkably higher than that of the wild type Arabidopsis, and the root length, the fresh weight and the growth vigor of the ZmGPDH5 transgenic Arabidopsis are remarkably superior to those of the control; the result shows that the ZmGPDH5 is capable of remarkably increasing the salt tolerance of a transgenic plant, and the ZmGPDH5 as a salt-tolerant gene can be applied to breeding of stress-tolerant varieties of zea mays.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG BAYI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Glycerol-3-phosphate acyl transferase
InactiveCN102753685BIncrease productivityEfficient manufacturingCosmetic preparationsMetabolism disorderNucleotideDiglycerol phosphate
The present invention relates to glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferases, polynucleotides encoding the same, etc. The present invention provides a polynucleotide comprising the nucleotide sequence of, e.g., SEQ ID NO: 1 or 4, a polynucleotide encoding a protein consisting of the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 2, an expression vector and transformant comprising the polynucleotide, a method for producing food, etc. using the transformant, food, etc. produced by the method, and so on.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Expression system used for the antibiotic-free production of polypeptides
InactiveCN101952439AHigh yieldOxidoreductasesVector-based foreign material introductionResistant genesPhosphate
The invention relates to an expression system for the production of one or several target polypeptide(s), comprising a host cell, in whose genome the DNA sequence coding the glycerine-3-phosphate dehydrogenase is inactivated or partially or fully deleted and which is transformed with an extrachromosomal element that comprises a DNA Sequence coding the target polypeptide(s) and the glycerine-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. According to the invention, both the host cell genome and the extrachromosomal element do not carry any antibiotic-resistant gene.
Owner:AB多酶两合公司
Inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) diagnostic and measuring kit and method for measuring inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) concentration
InactiveCN101609036AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsPhosphateGlycerol kinase
The invention relates to an inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) diagnostic and measuring kit utilizing technologies of an enzymatic-colorimetric method and an enzyme-link method, also relates to a method and a principle of measuring inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) concentration and compositions and components of reagents, and belongs to the technical field of testing and measuring of medical science, food, and environment. The kit mainly comprises the following compositions: buffer solution, coenzyme, glutamine, adenosine diphosphate, glycerin, magnesium chloride, glutamine synthetase, glycerol kinase, glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrigebase and stabilizer; samples are mixed with the reagents in certain volume ratio to perform a series of enzymatic reactions; then reactants are placed under a UV / visible analyzer; and the ascending level of absorbance is tested at the position where dominant wave length is 340nm so as to measure and calculate the inorganic phosphorus (phosphate radical) concentration.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com