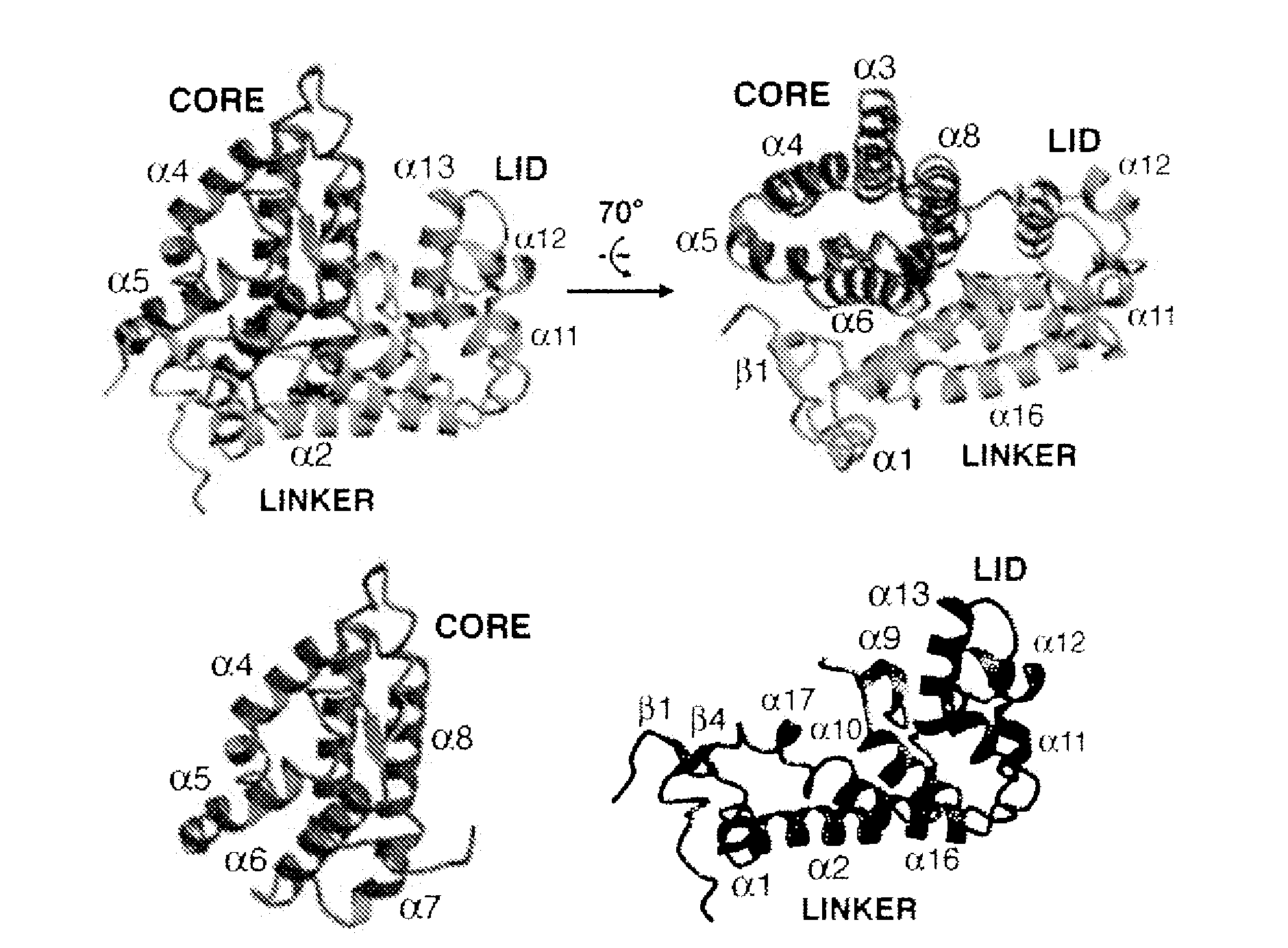
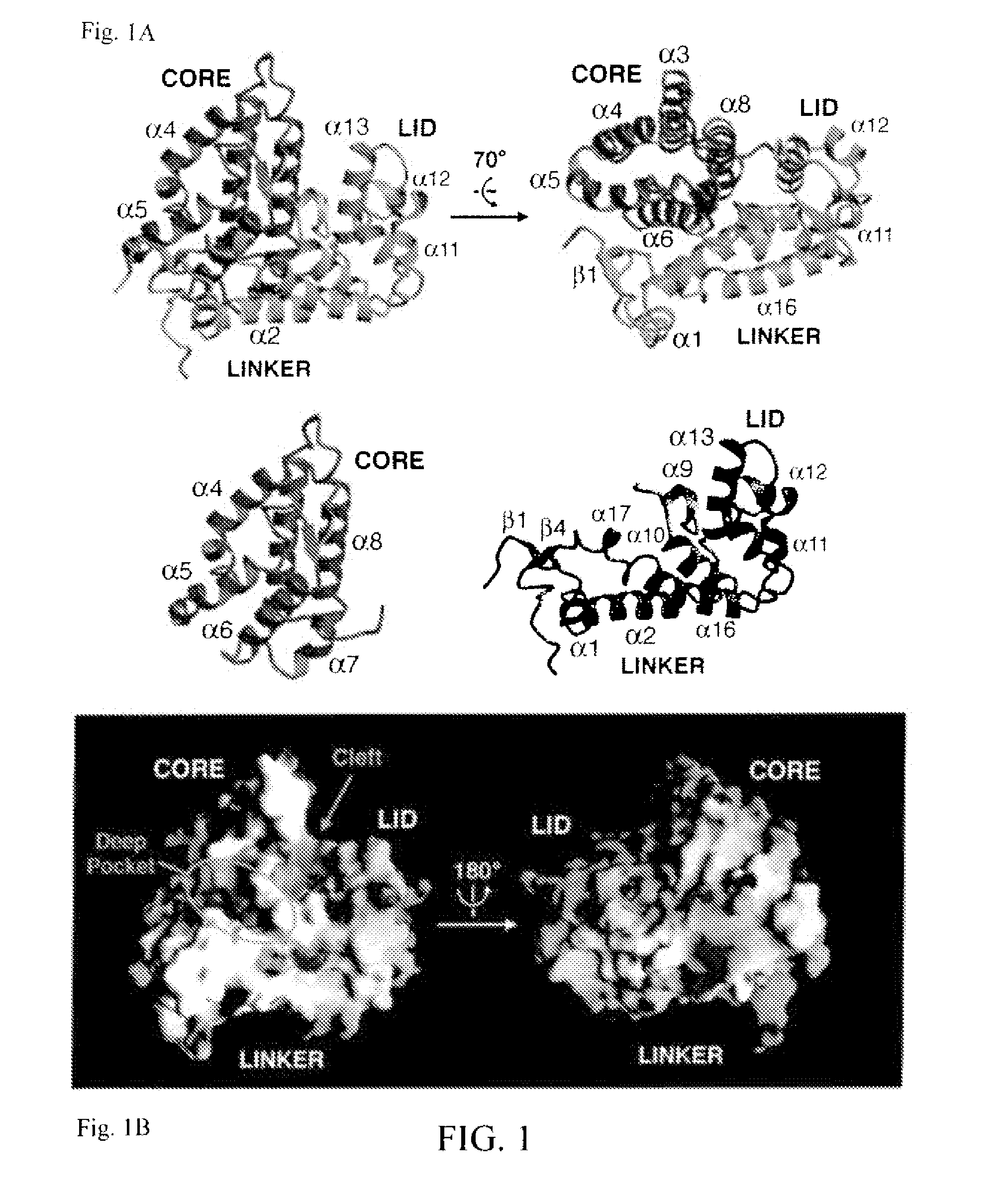
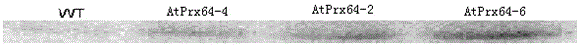Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
76 results about "Atpase activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Pumps have ATPase activity (they hydrolyze ATP). This ATPase activity is generally the easiest way of identifying them. Pumps are membrane-embedded enzymes that couple the hydrolysis of ATP to active translocation of ions across the membrane.
Molecular nanomotor
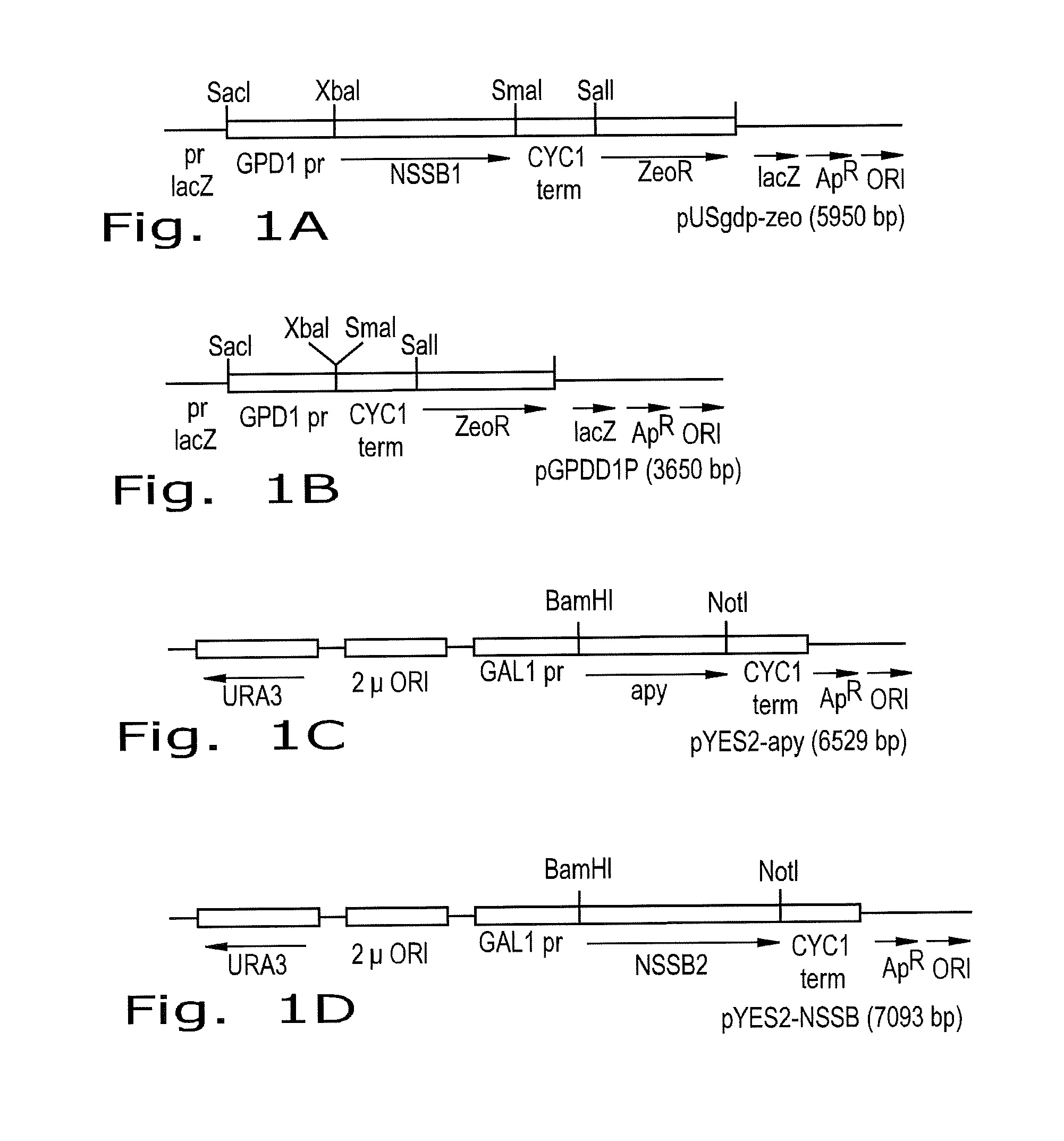
InactiveUS20050266416A1Function increaseImprove hydrophilicityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNanomotorATP hydrolysis
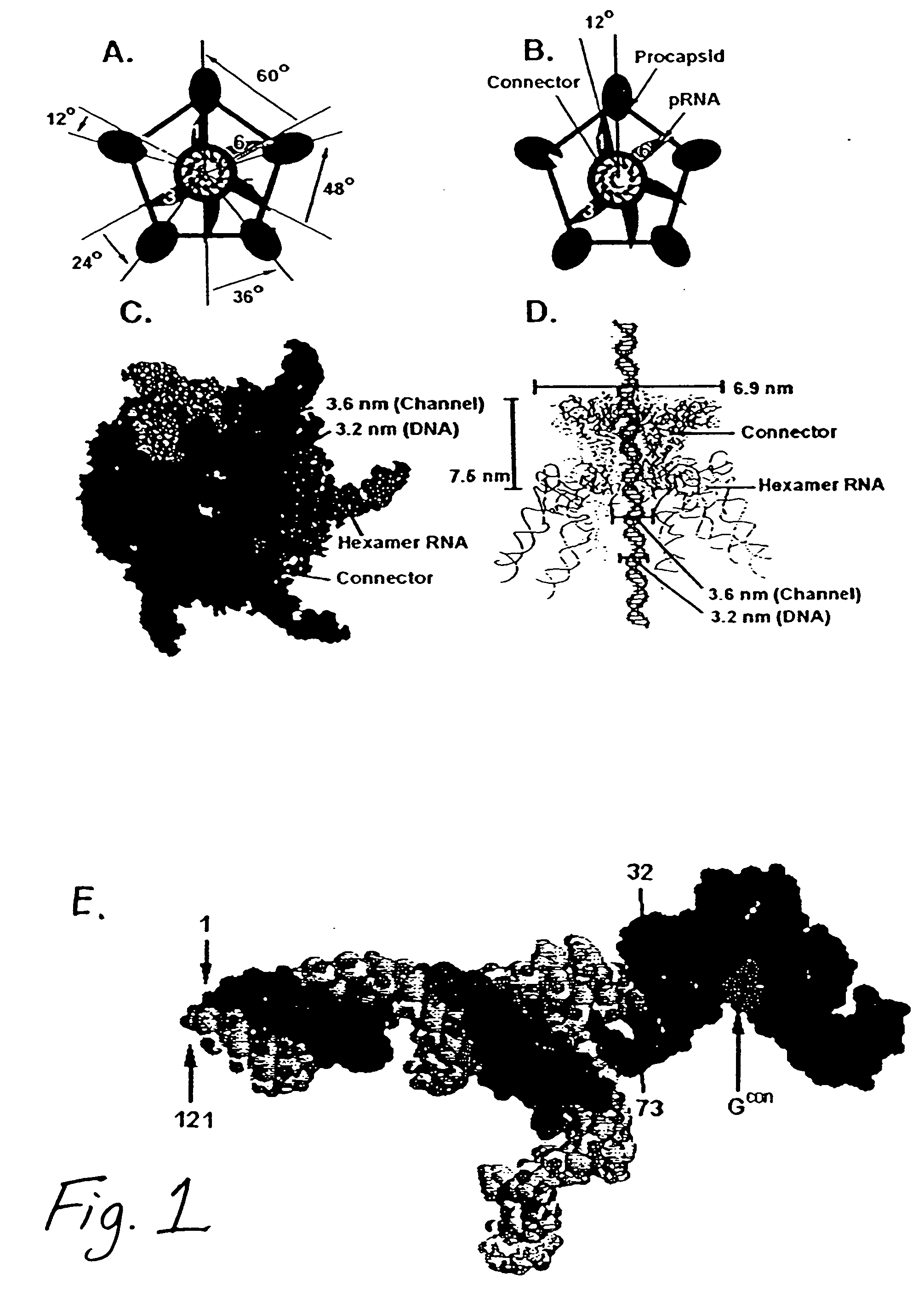
A molecular nanomotor useful for translocating polynucleotides. The nanomotor is a multimolecular complex fueled by ATP hydrolysis. One of the motor components is an ATP-binding RNA molecule that participates in ATPase activity.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Methods and products based on oligomerization of stress proteins
InactiveUS20050221395A1Guaranteed economic efficiencyImproving immunogenicityAntibacterial agentsBiocideHeat shockStress Proteins
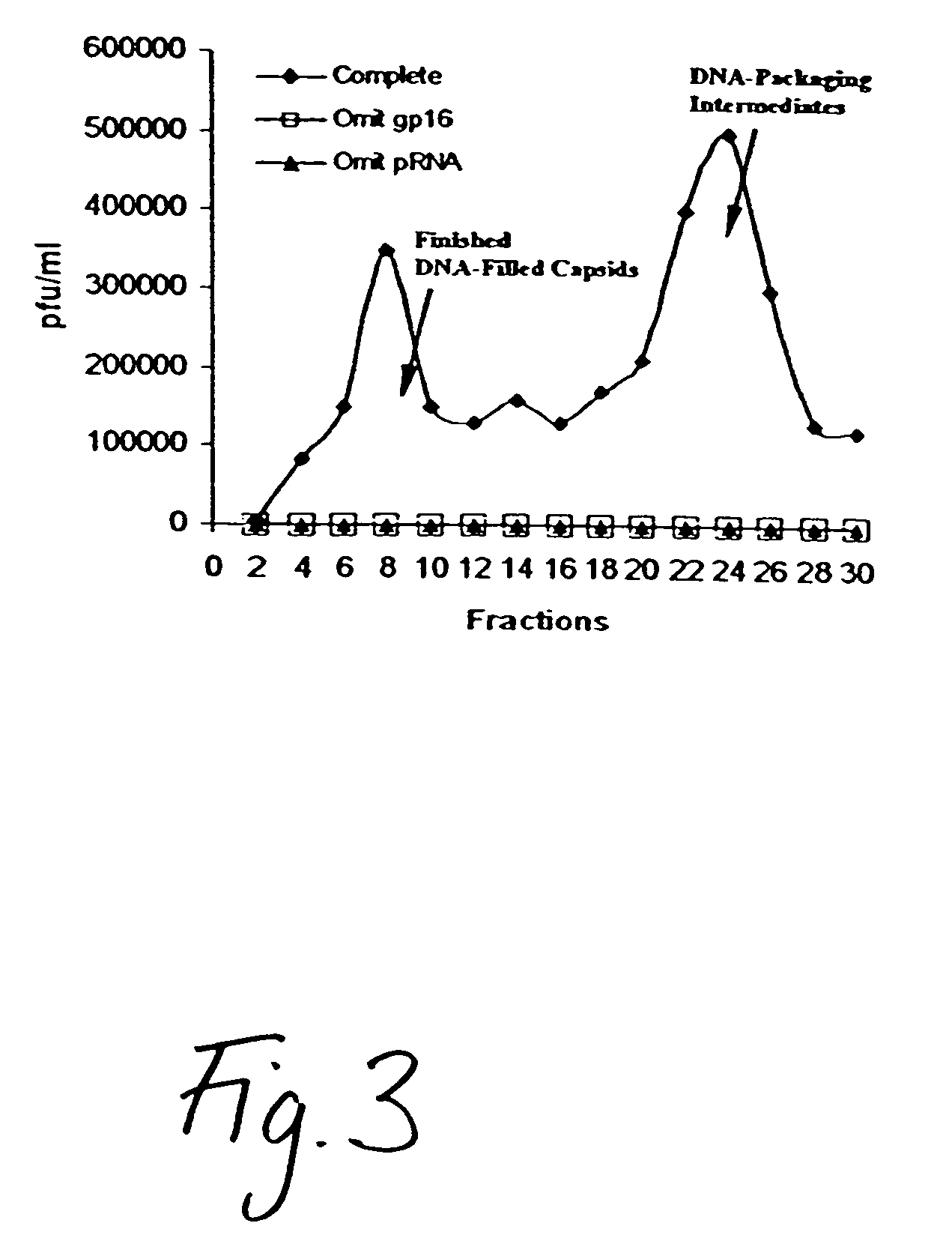
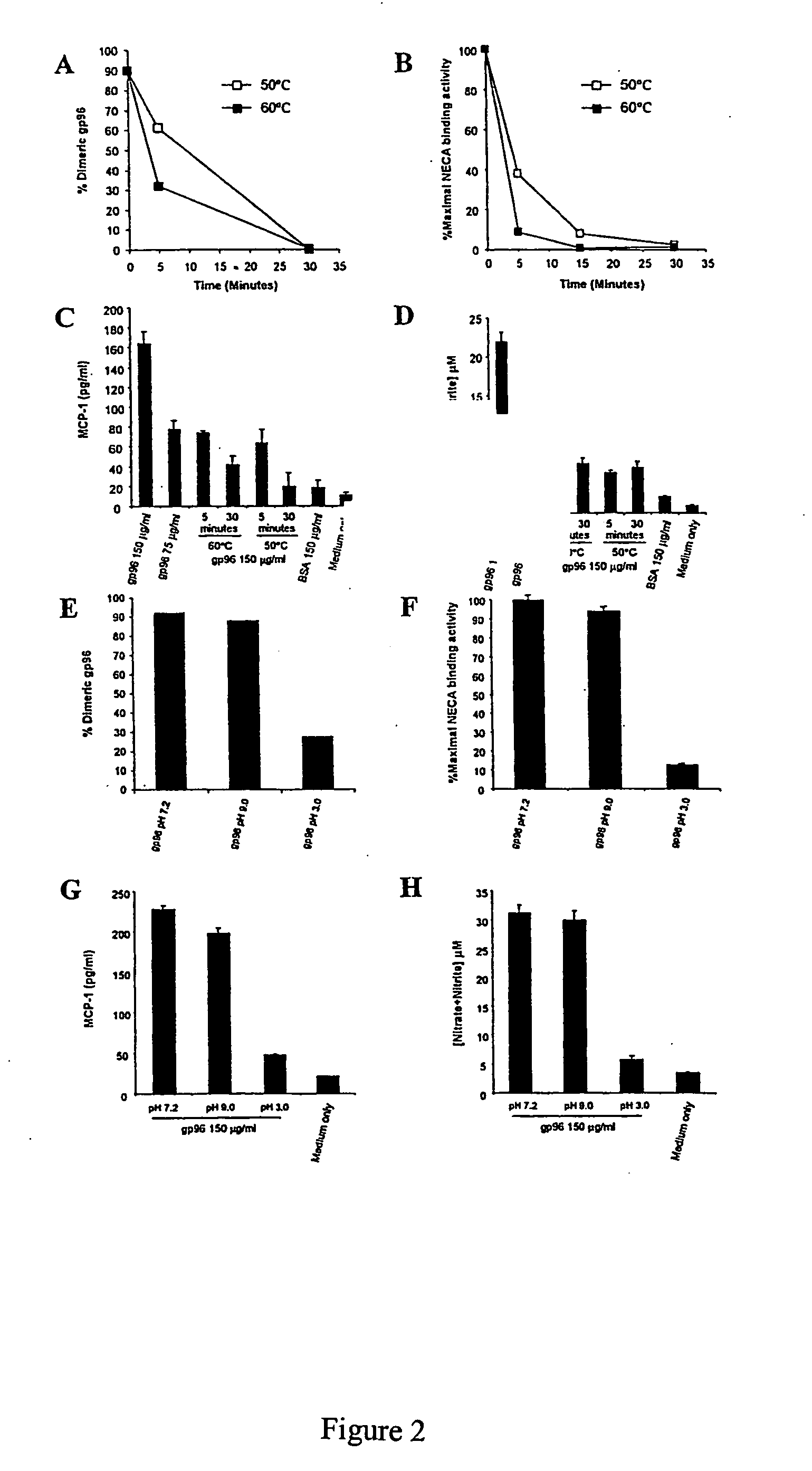
In one aspect, the invention provides methods for determining the biological activity of heat shock proteins or heat shock protein-peptide complexes based on the ATPase activity or the multimeric structure of the heat shock proteins or heal shock protein-peptide complexes, and methods for screening agents that modulate the biological activity of heat shock proteins or heat shock protein-peptide complexes. In another aspect, the invention provides complexes, compositions and methods for enhancing the immunogenicity of a heat shock protein or a complex comprising a heal shock protein and an antigenic molecule.
Owner:CONNECTICUT HEALTH CENT UNIV OF +1
Method of improving biomass yield of lactic acid bacterial cultures
InactiveUS6610530B2Increased biomass productionReduce contentBacteriaUnicellular algaeQuinoneMitochondrial electron transport
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
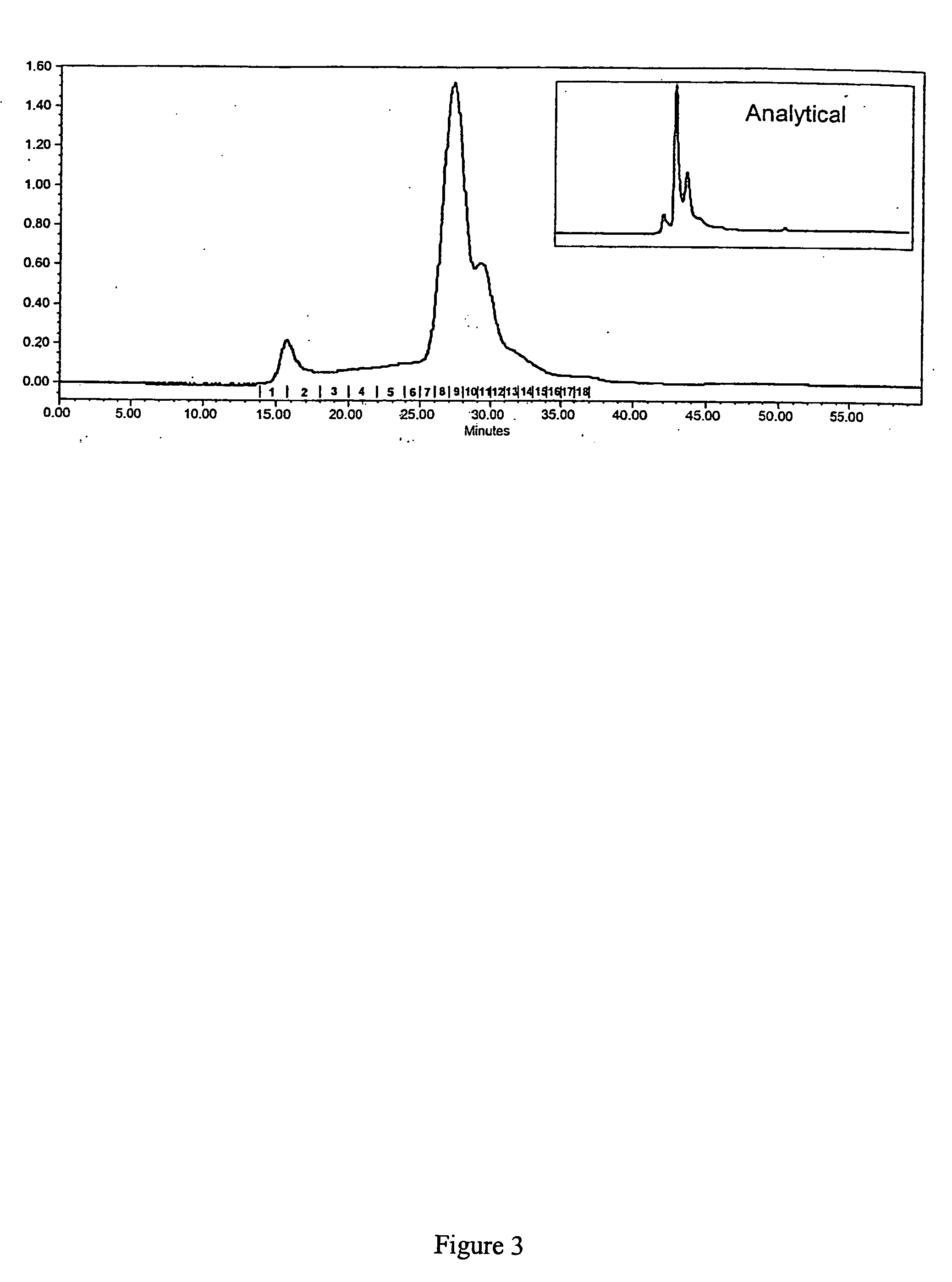
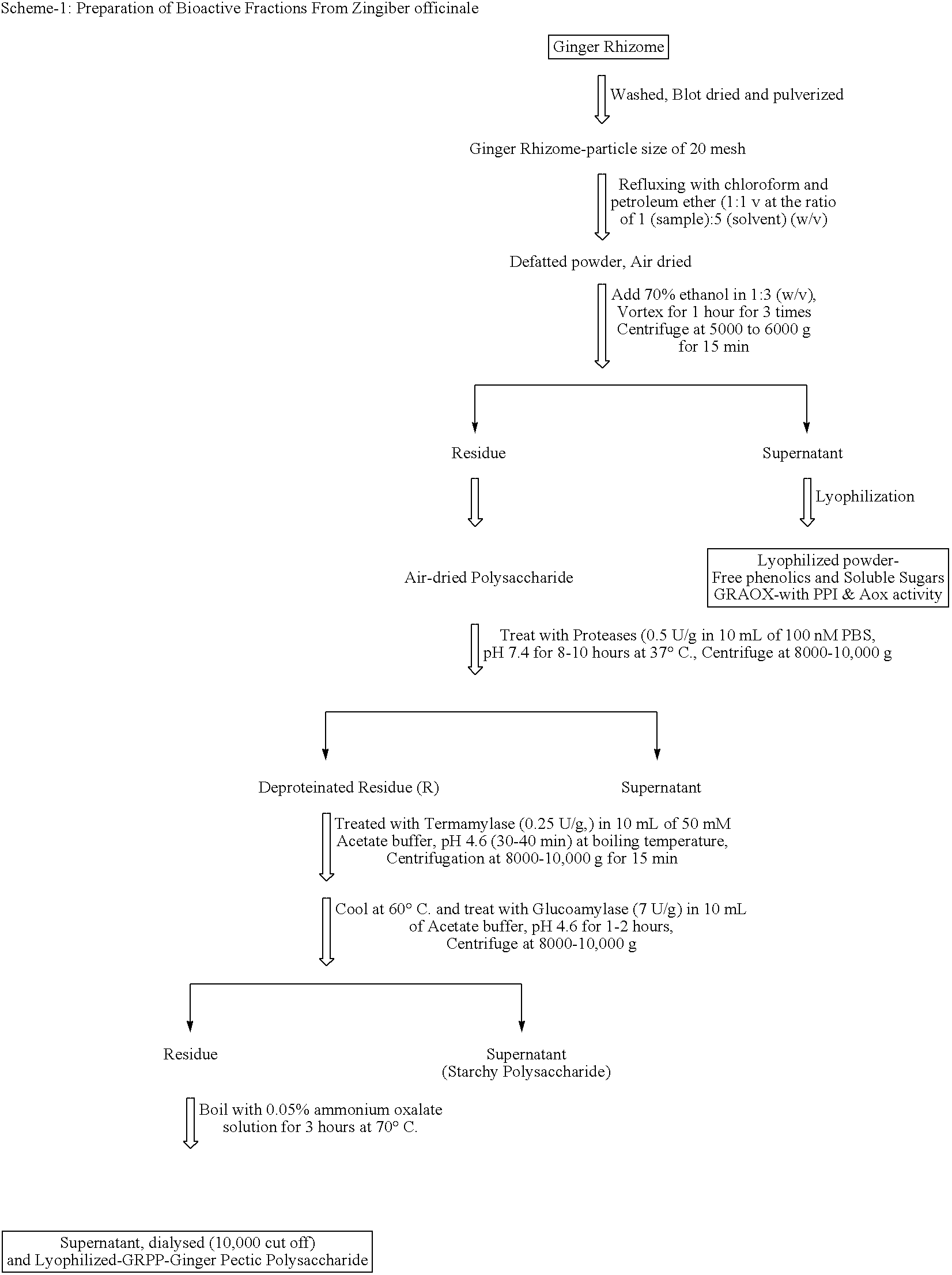
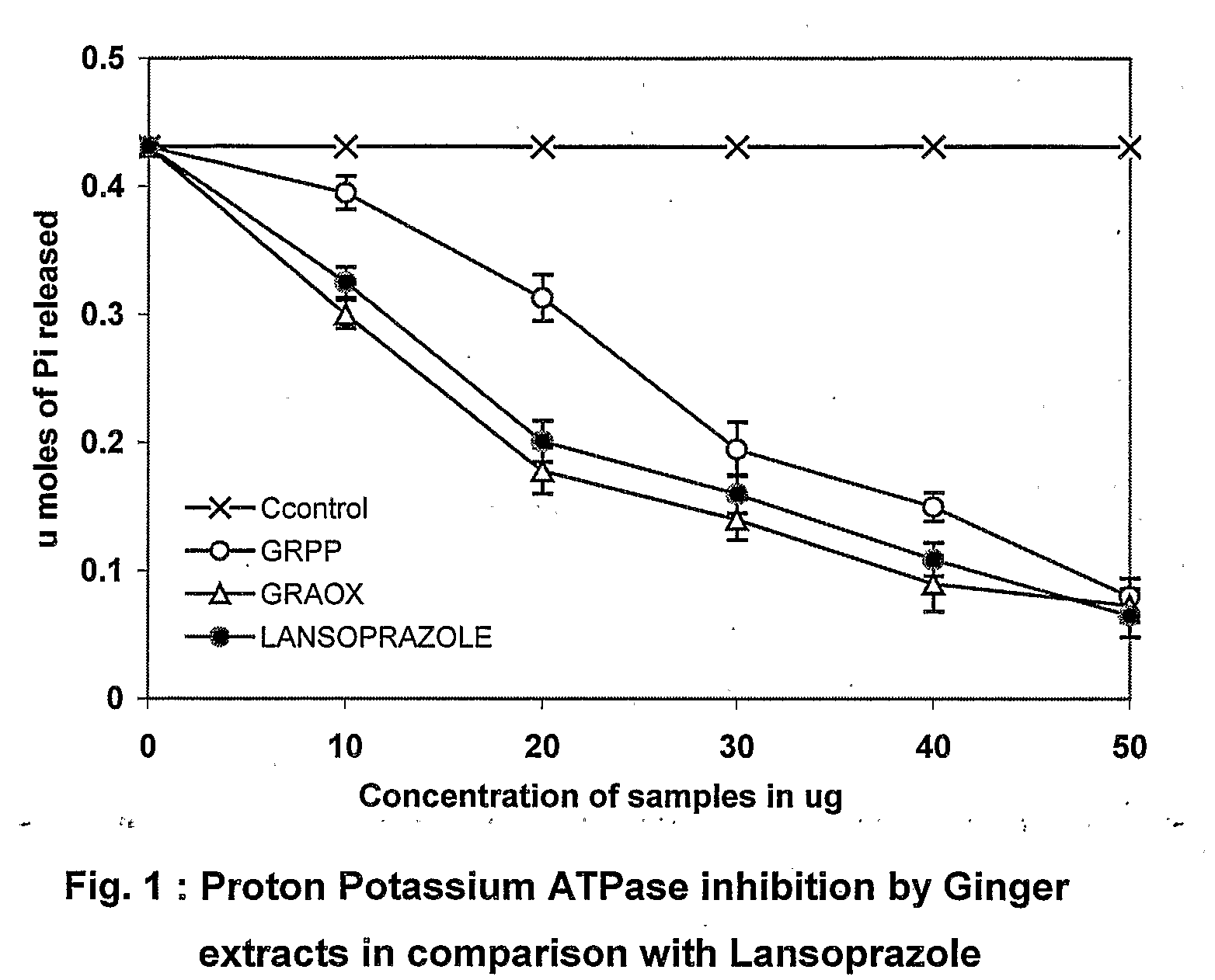
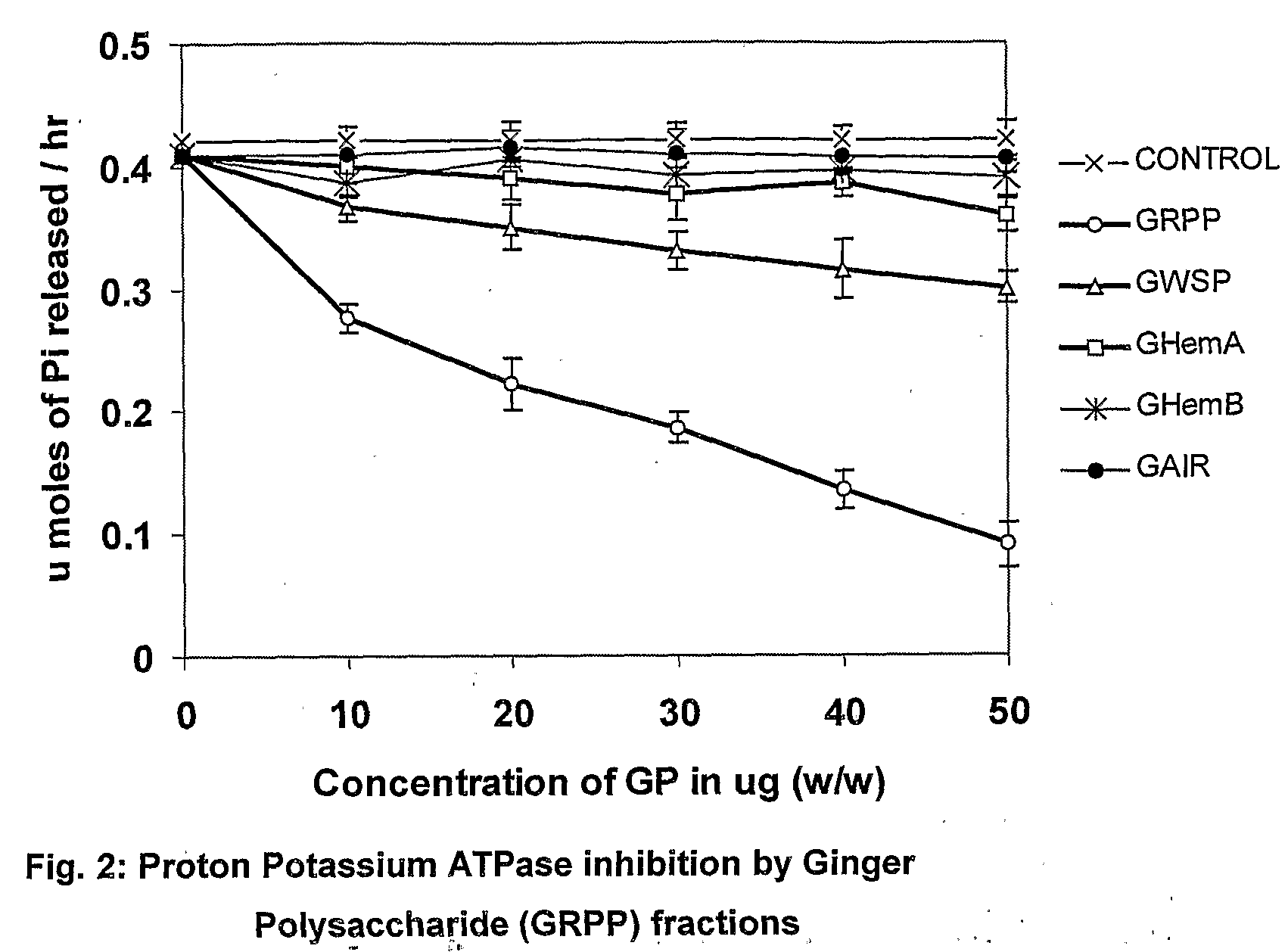
Bioactive fraction from zingier officinale and a process for the preparation thereof
Ulcer is a serious oxidative stress induced disease with complex pathologic events including upregulation of H+K+ ATPase of parietal cell (PC) membrane, damage of mucin layer around PC, PC-DNA damage etc. The polysaccharide (GRPP) fraction and antioxidant extract (GRAOX) of ginger was examined for their ability to inhibit H+ K+ ATPase. Results indicated that the inhibition of H+ K+ ATPase activity which causes acidity in the lumen of the stomach, also exhibited better H+K+ ATPase inhibition (PPI) at the IC50 of 27.2 μg (GRPP) and 16.5 μg GAE (AOX) respectively than the known antiulcer proton pump blocker Lansoprazole (19.3 μg). Further the antioxidant activity in antioxidant extract (GRAOX) by various assay systems was examined such as Reducing power, Free radical scavenging (FRS), DNA and cytoprotection systems etc. GRAOX exhibited concentration dependent reducing power ability at 5-25 g equivalent of phenol. FRS activity with IC50 of 6.8 μg equivalent of phenol etc. At 0.3 μg level GRAOX offered >80% protection to DNA and against FeSO4-Asc'orbate induced oxidation. The major active phenolic components were identified as Gallic acid / Tannic acid (46%), and Cinnamic acid (51%).
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
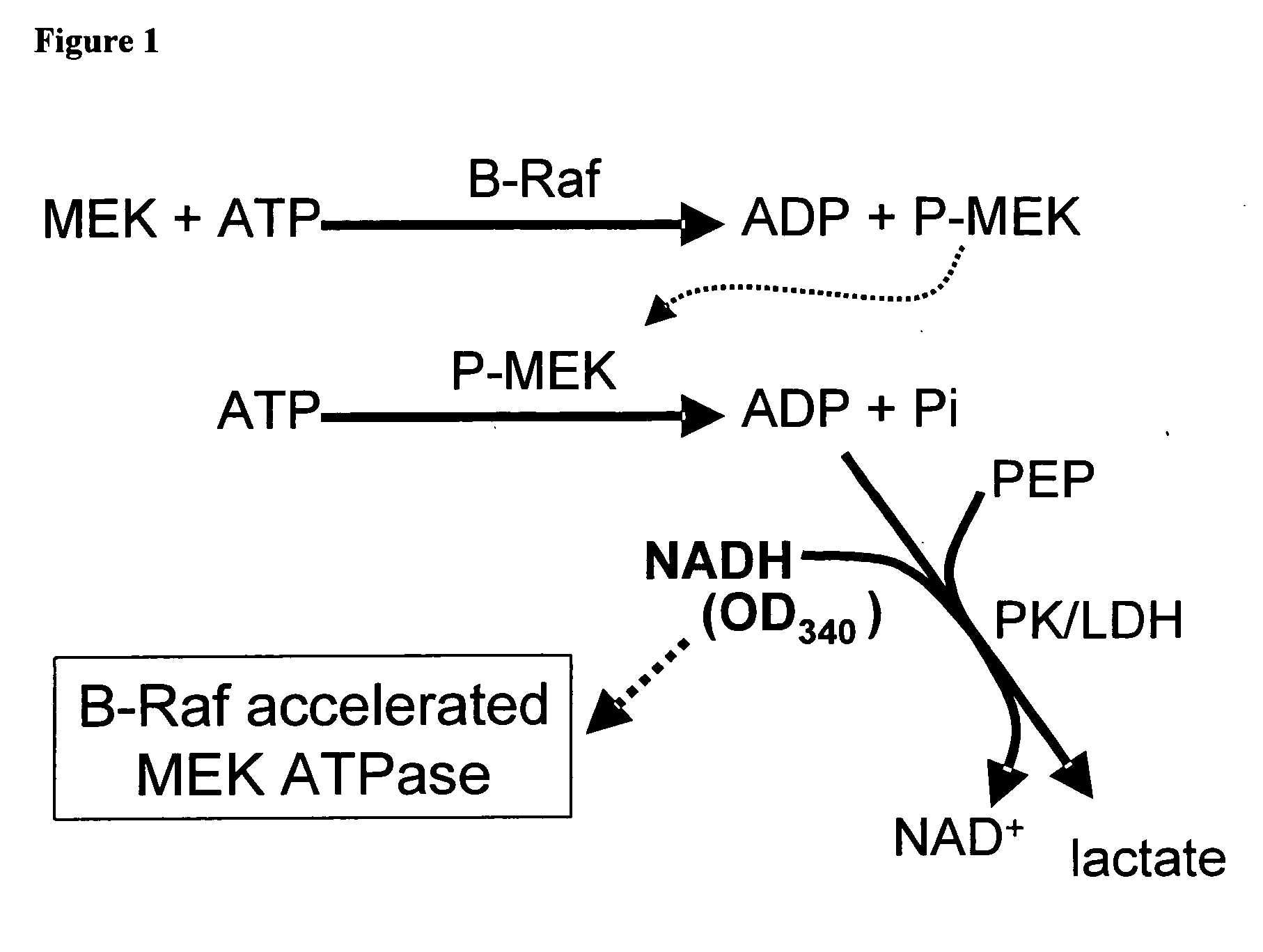
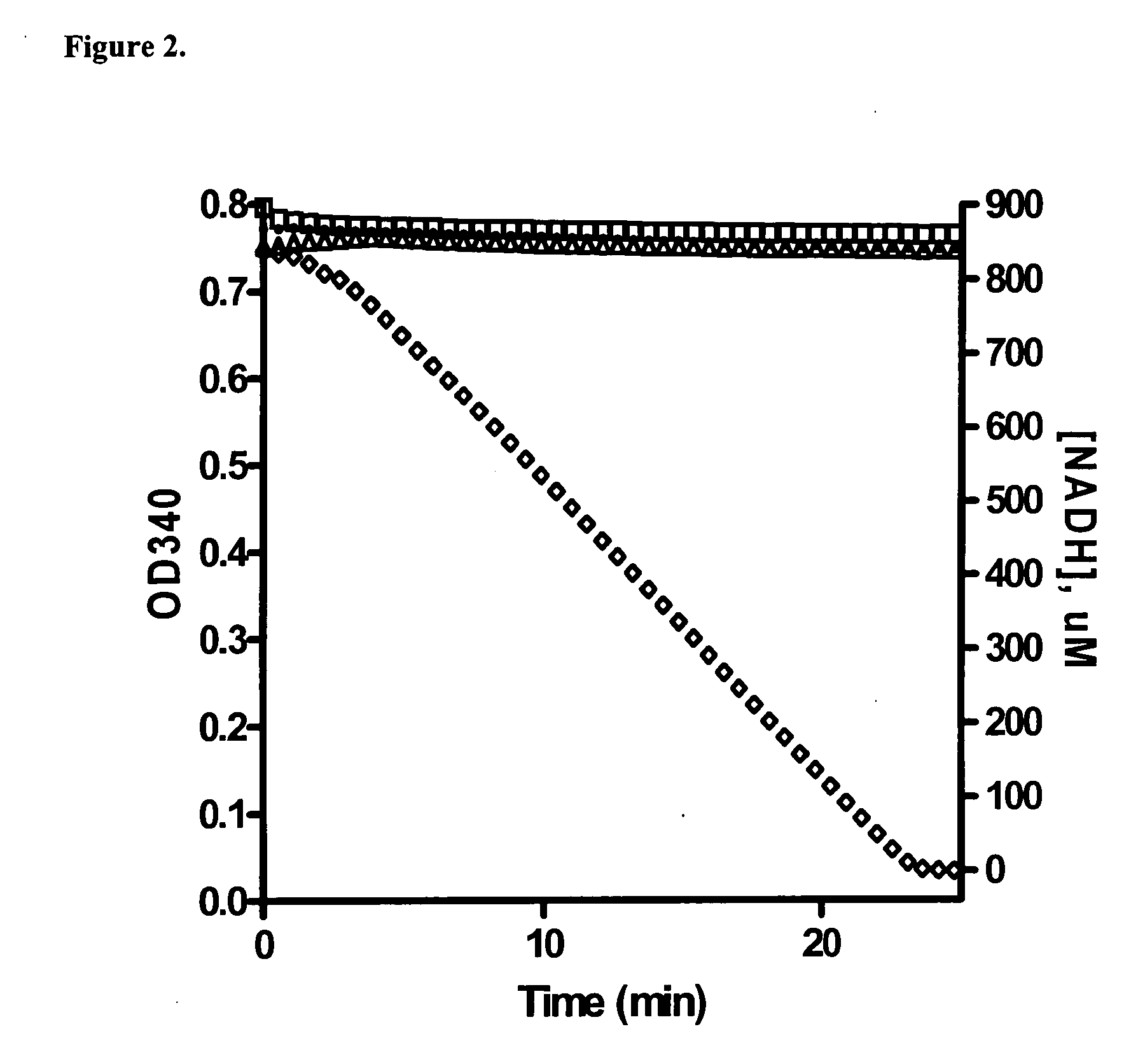
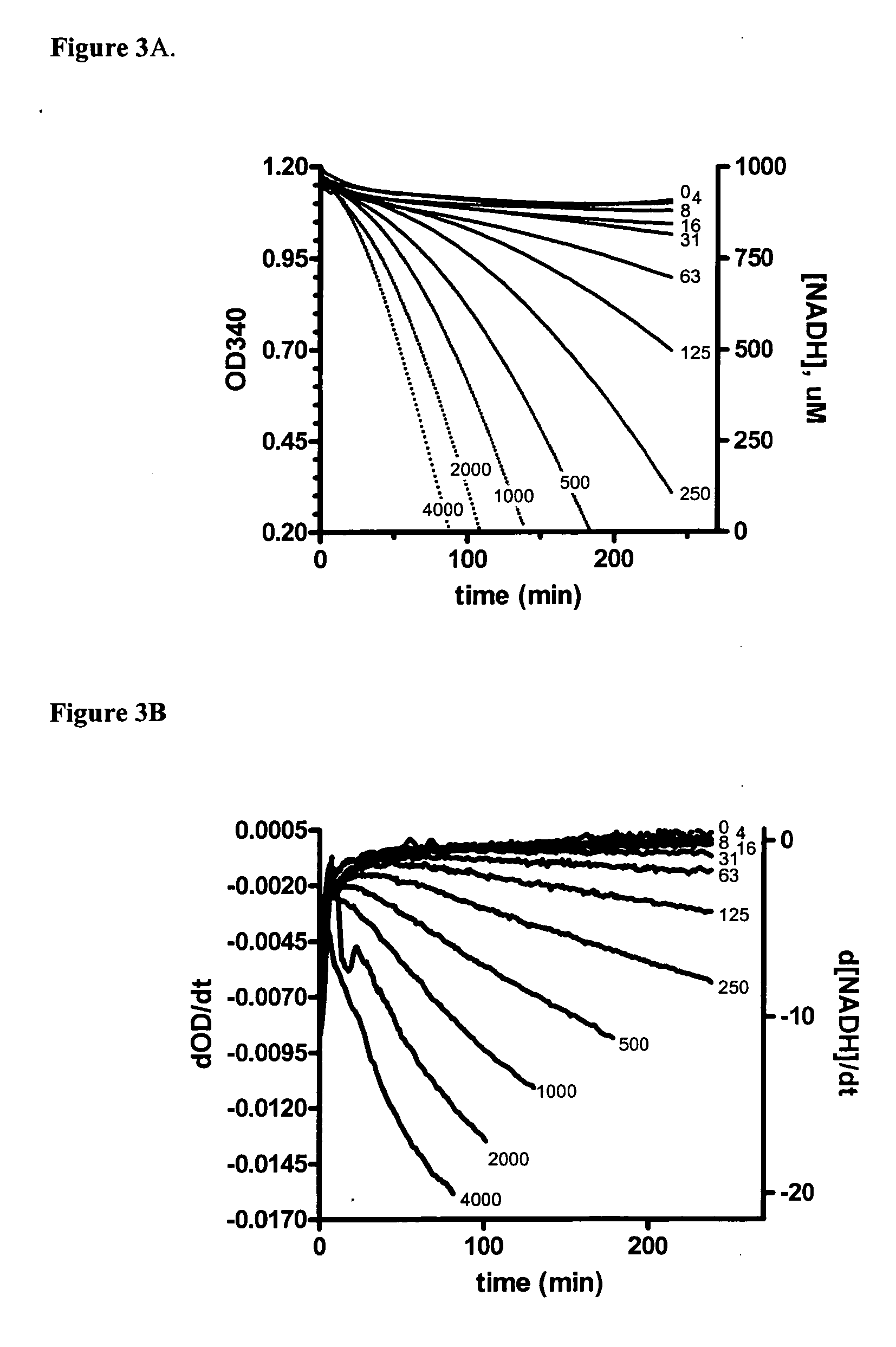
Assay for B-Raf activity based on intrinsic MEK ATPase activity
The present invention provides a convenient assay to identify compounds with B-Raf inhibitory activity, referred to as the BRAMA (B-Raf Accelerated MEK ATPase) assay. The BRAMA assay is based on the discovery of ATPase activity of MEK, and utilizes changes in NADH concentration over time as an indicator of the production of ADP by activated MEK ATPase, where the MEK ATPase activity is activated by B-Raf. NADH concentration may conveniently be measured by Optical Density.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
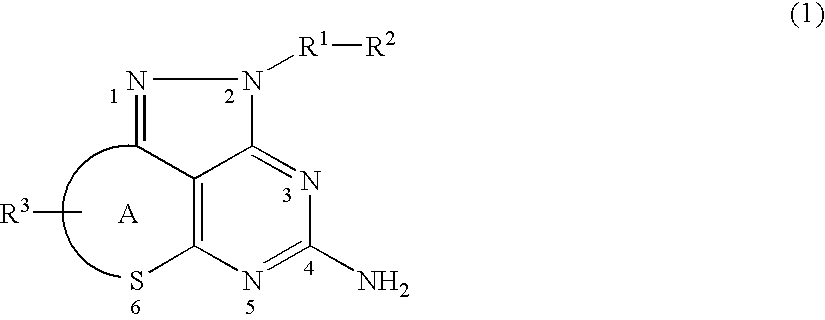
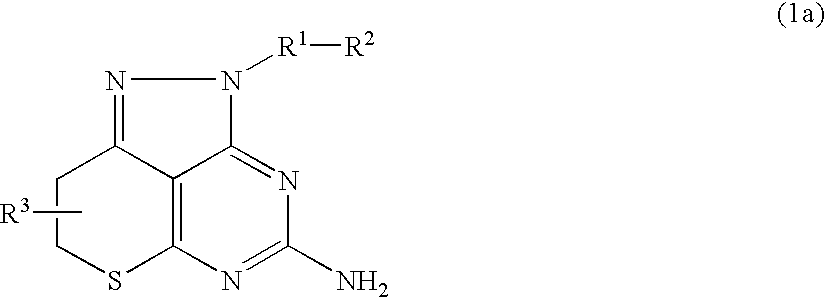
Pyrazolopyrimidine derivative
Problem to be SolvedTo provide a novel compound inhibiting the effect of HSP90, in particular a novel compound inhibiting the function of HSP90 as a chaperone protein and having antitumor activity.SolutionThe present invention provides a pyrazolopyrimidine compound represented by the formula (1) having various substituents which inhibits the ATPase activity of HSP90 and which has antitumor activity, an HSP90 inhibitor comprising the compound represented by the formula (1), a medicament comprising the compound represented by the formula (1), an anticancer agent comprising the compound represented by the formula (1), a pharmaceutical composition comprising the compound represented by the formula (1) and a method for treating cancer using the compound represented by the formula (1).
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
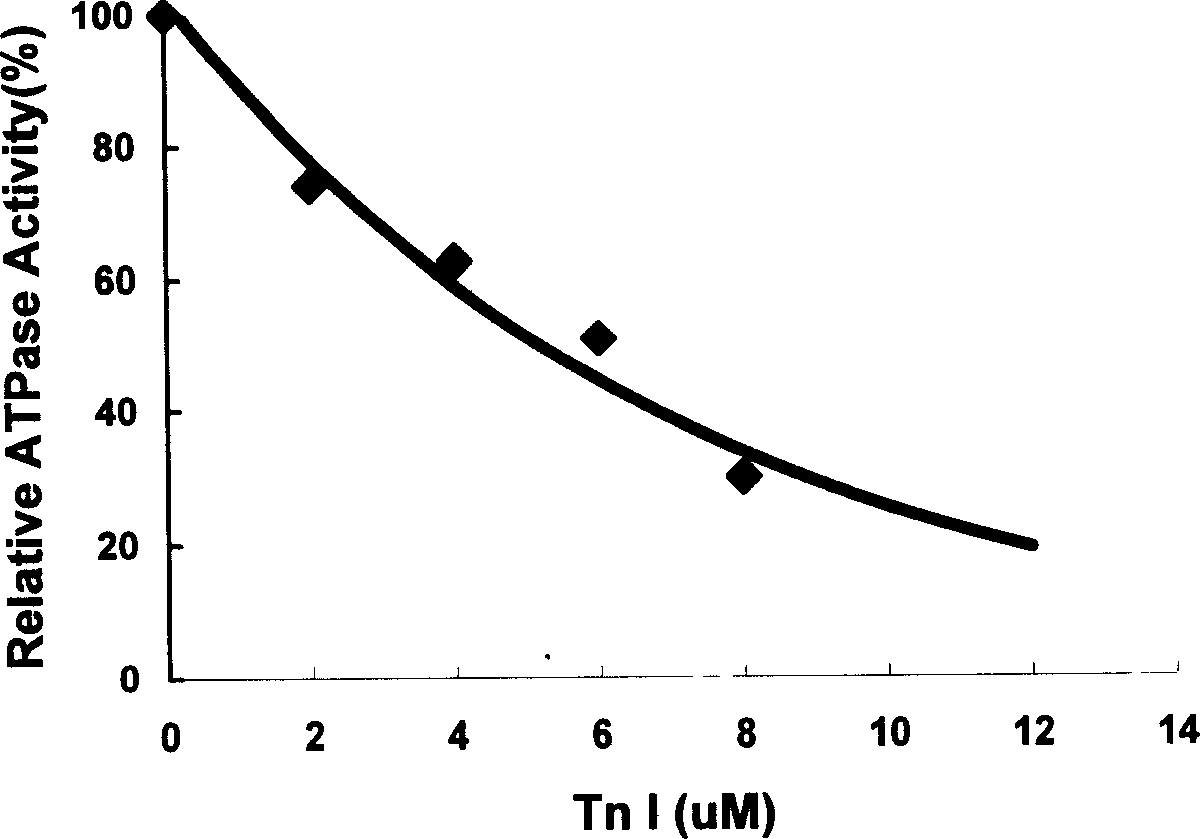
Human rapid contraction of skeletal muscle troponin I production and activity detection method
InactiveCN1570105AInhibition of newbornsThe process is simple and convenientPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsDiseaseAbnormal tissue growth
The invention belongs to gene engineering field. The invention establish a production method of human skeletal muscle troponin I for quick contract: recombing DNA to construct expression plasmid, refining expression products with inclusion bodies, cation exchange resin column chromatography, cation exchange resin column chromatography, renaturing inclusion bodies, at last purifying and obtaining recombinant human troponin I for suppressing blood vessel endothelial cell propagation and angiogenesis. The invention also establishes a method for determing the biological activity index of troponin I by suppressing Acto-S1 Mg-ATPase activity. The troponin I can prepare drugs of the tumor and angiogenesis related disease
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Anti-neoplastic compositions comprising extracts of black cohosh
InactiveUS20090186837A1Treating and preventing neoplasiaPrevent tumorOrganic active ingredientsBiocideBlack Cohosh ExtractIn vivo
A method for treating, preventing or ameliorating breast cancer is provided by administering a synergistic amount of digitoxin and either actein or an extract of black cohosh comprising triterpene glycosides, and optionally another chemopreventive agent which may be paclitaxel. Methods for treating or preventing a neoplasia using a synergistic combination, and compositions of a synergistic combination of a cardiac glycoside and either actein or an extract of black cohosh comprising triterpene glycosides, and optionally another chemopreventive agent which may be a taxane are also provided. The compositions may also be used in a method for modulating Na+K+ATPase activity. In addition, a method for inhibiting the progression or development of breast cancer in vivo by administering either actein or an extract of black cohosh comprising triterpene glycosides and optionally at least one other chemoprotective agent is provided.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
High-throughput screening assay for Na, K-ATPase using atomic absorption spectroscopy
InactiveUS20070092970A1Determine therapeutic effectAnalysis by thermal excitationBiological testingHigh-Throughput Screening AssaysHigh flux
A method of chemical analysis involving Flame Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (FAAS) and Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (GFAAS) in combination with flux assays to directly measure intracellular or extracellular ion concentration to analyze Na+,K+-ATPase activity.
Owner:LIANG DONG CUAN +2
Inhibition of vacuolar proton ATPase activity and/or the modulation of acidic organelle function sensitizes cells to radiation, chemotherapy and biological agents
InactiveUS6982252B2Reduced dosDiminishes unwanted damageBiocideCompound screeningSensitized cellCancer cell
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for inhibiting cell survival and / or promoting cell death following exposure to cytotoxic agents and stress such as radiation or chemotherapy exposure through inhibition of V-H+-ATPase. In particular, the formation and / or acidification of acidic vesicular organelles (AVOs) may be prevented or decreased by inhibiting the activity of vacuolar proton ATPase (“V-H+-ATPase”). The methods and compositions of the invention are based on the observation that (i) following irradiation surviving cancer cells accumulate AVOs and that their acidification is mediated by V-H+-ATPase; (ii) surviving colonies of cells contain higher levels of AVOs; and (iii) inhibition of V-H+-ATPase decreases the clonogenic survival of cells irradiated or exposed to chemotherapeutic agents. These observations led to the conclusion that V-H+-ATPase activity and AVO function serve to protect cells from radiation and chemotherapy damage. In addition, agents such as bFGF, TNF-α, PMA, rapamycin and tamoxifen were shown to be inducers of acidic organelle formation. Therefore signal transduction pathways mediated by these agents provide targets for drug screening assays designed to identify inhibitors of V-H+-ATPase activity and AVO formation / acidification. The present invention may be used to treat cancer subjects through sensitization of neoplastic cells to the toxic effects of radiation and chemotherapy.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
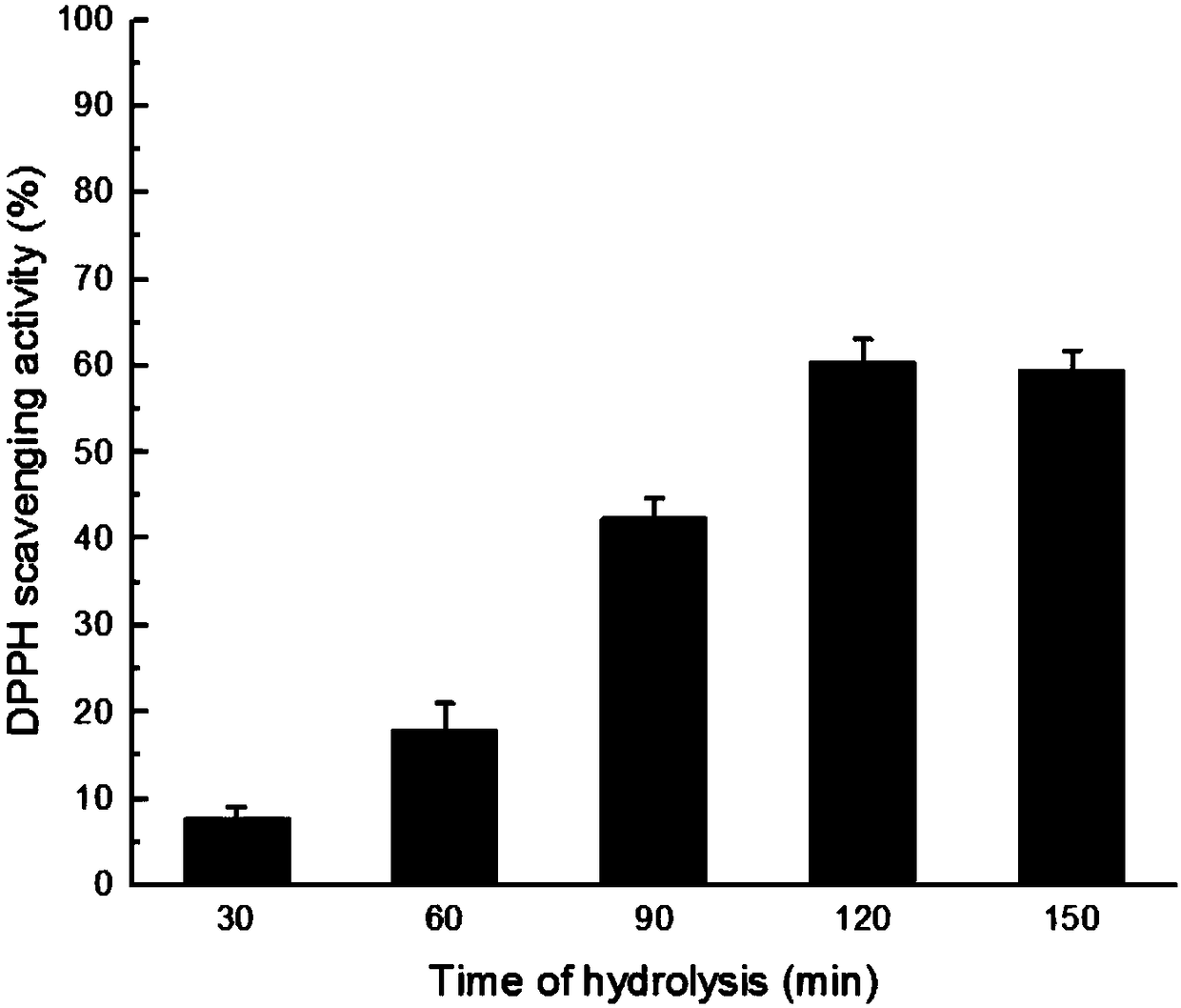
Process for preparing antioxidative peptide and antifreeze peptide through enzymatic hydrolysis of salmon collagens
InactiveCN108118077ADifferent biological activitiesLow costConnective tissue peptidesHydrolasesOxygen radical absorbance capacityFiltration
The invention discloses a process for simultaneously preparing an antioxidative peptide and an antifreeze peptide through enzymolysis of collagens. The method comprises the following steps: extractingcollagens by taking salmon skin as a raw material, hydrolyzing the collagens into a short peptide solution by utilizing crude enzymes of extracellaluar protease obtained by fermentation of Vibrio sp.SQS2-3, performing centrifugal ultrafiltration by a 3000 Da ultrafiltration tube 4500*g for 45 minutes so as to obtain the antifreeze peptide with effects of protecting myosin and relieving decreaseof Ca<2+>-ATPase activity in multigelation, performing Sephadex LH-20 gel filtration chromatography to separate lower ultrafiltration components so as to obtain the antioxidative peptide which has effects of scavenging DPPH free radicals and hydroxyl radicals and a certain ability of inhibiting DNA oxidative damage and shows concentration-dependent antioxidant activity in oxygen radical absorptioncapacity detection. The LC-MS technology shows that the antioxidant component contains 19 polypeptides.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
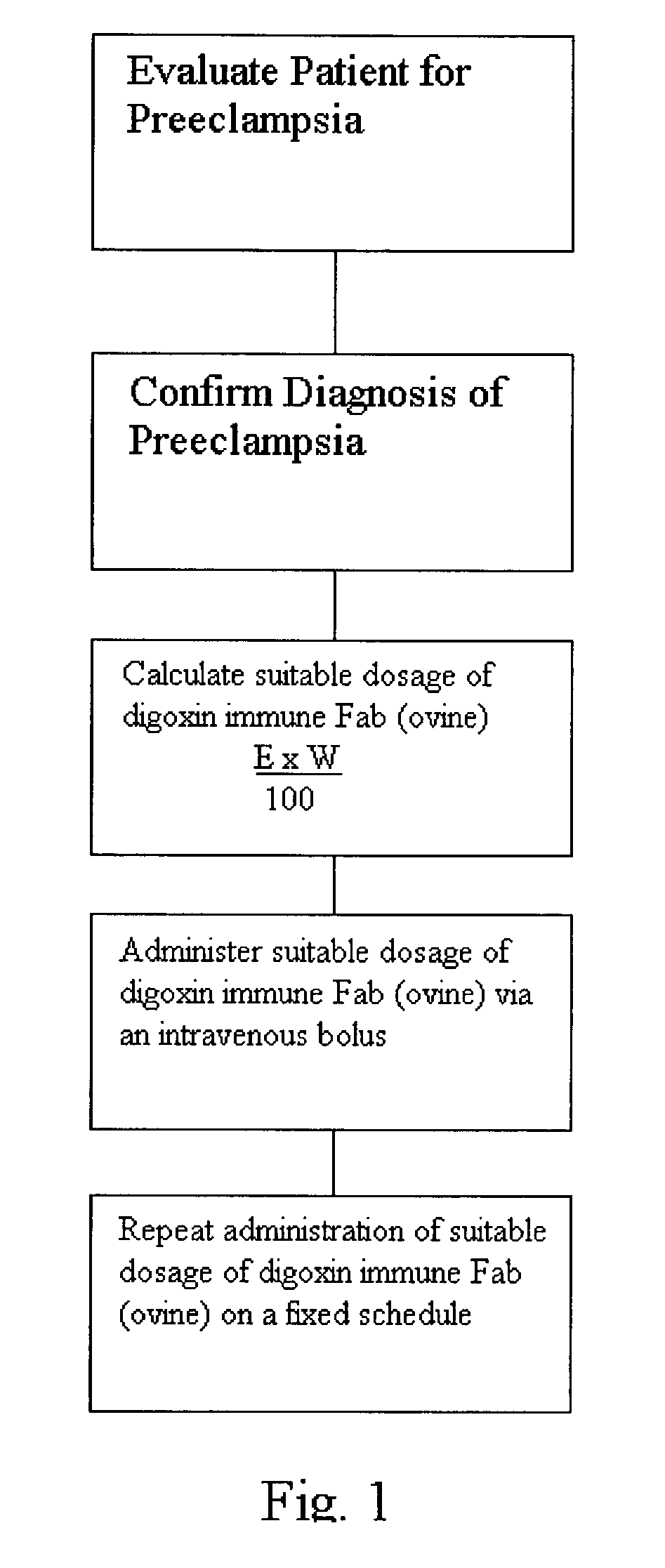
Use of digoxin immune Fab (ovine) for the regulation of sodium/potassium ATPase activity in preeclamptic and eclamptic patients
InactiveUS20040018202A1Exaggerated myocardial functionOrganic active ingredientsBiocideAtpase activityIntracellular sodium
A method of regulating a preeclamptic / eclamptic patient's sodium / potassium ATPase activity includes the administration of digoxin immune Fab (ovine). It is theorized that an endogenous digitalis-like factor present in preeclamptic and eclamptic patients inhibits the functioning of sodium / potassium ATPase, resulting in elevated level of intracellular sodium and calcium levels. These elevated intracellular sodium and calcium levels lead to intravascular volume contraction and vasoconstriction. Digoxin immune Fab (ovine) binds with the endogenous digitalis-like factor to prevent it from interfering with the functioning of the sodium / potassium ATPase, thereby allowing the patient's intracellular sodium and calcium to return to a more normal level.
Owner:VELO BIO
Assay of micro-organisms in cell cultures
InactiveUS6951723B2Convenient and easy screeningImprove the level ofBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatments3D cell cultureAbsolute level
Micro-organisms which over-produce ATPase, especially mycoplasmas in a sample of a cell culture, are detected by making use of the ATPase activity to convert cellular or externally added ATP to ADP. The decrease in ATP externally added or the increase or absolute level of ADP produced from cellular ATP can then be detected or measured. For example, if a reagent such as phosphenol pyruvate / pyruvate kinase is added to convert that ADP back to ATP, the resulting high level of ATP can be detected bioluminescently using the reaction: Luciferin+luciferase enzyme+ATP→hv+products.
Owner:LUMITECH UK
Method of improving the production of biomass or a desired product from a cell
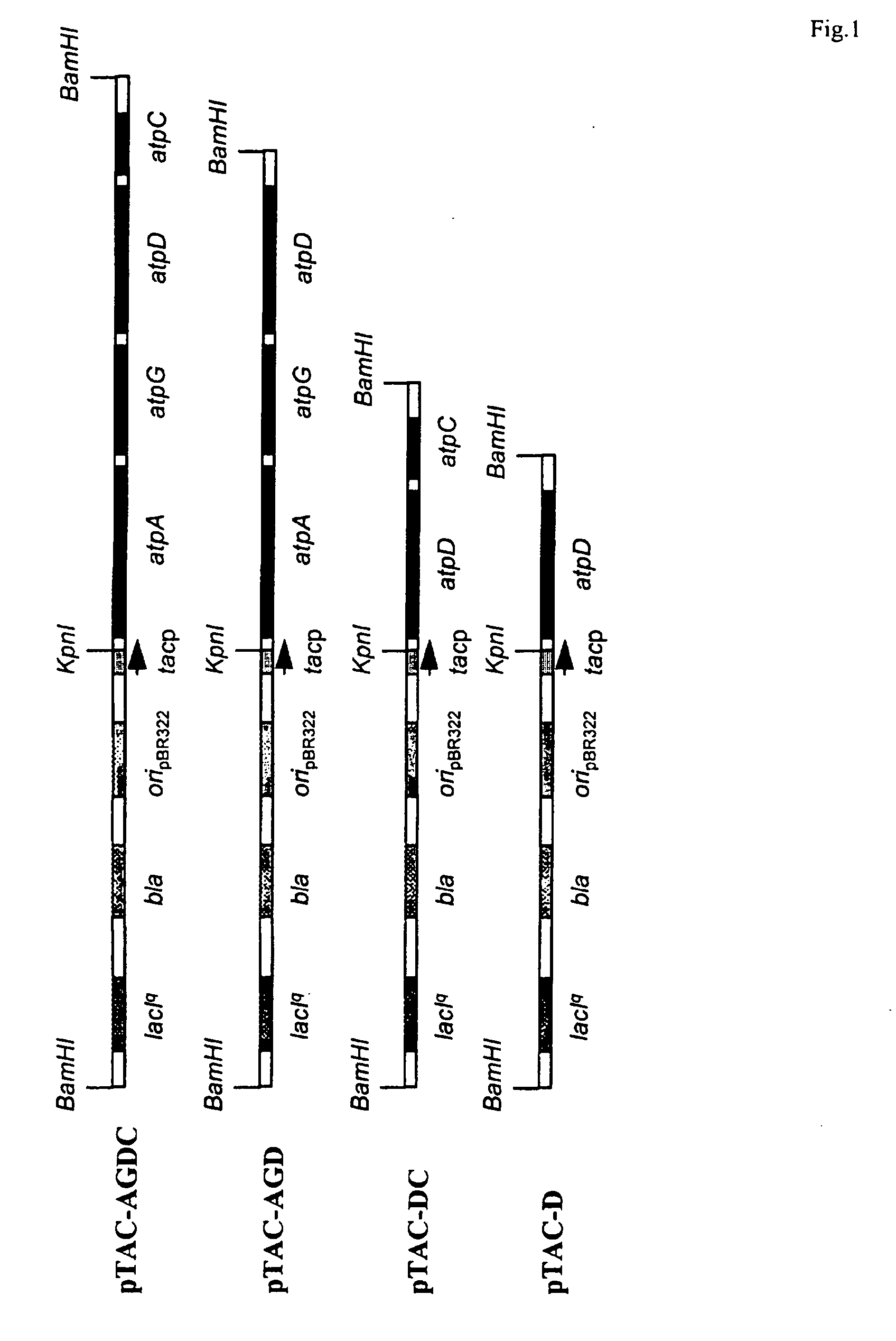
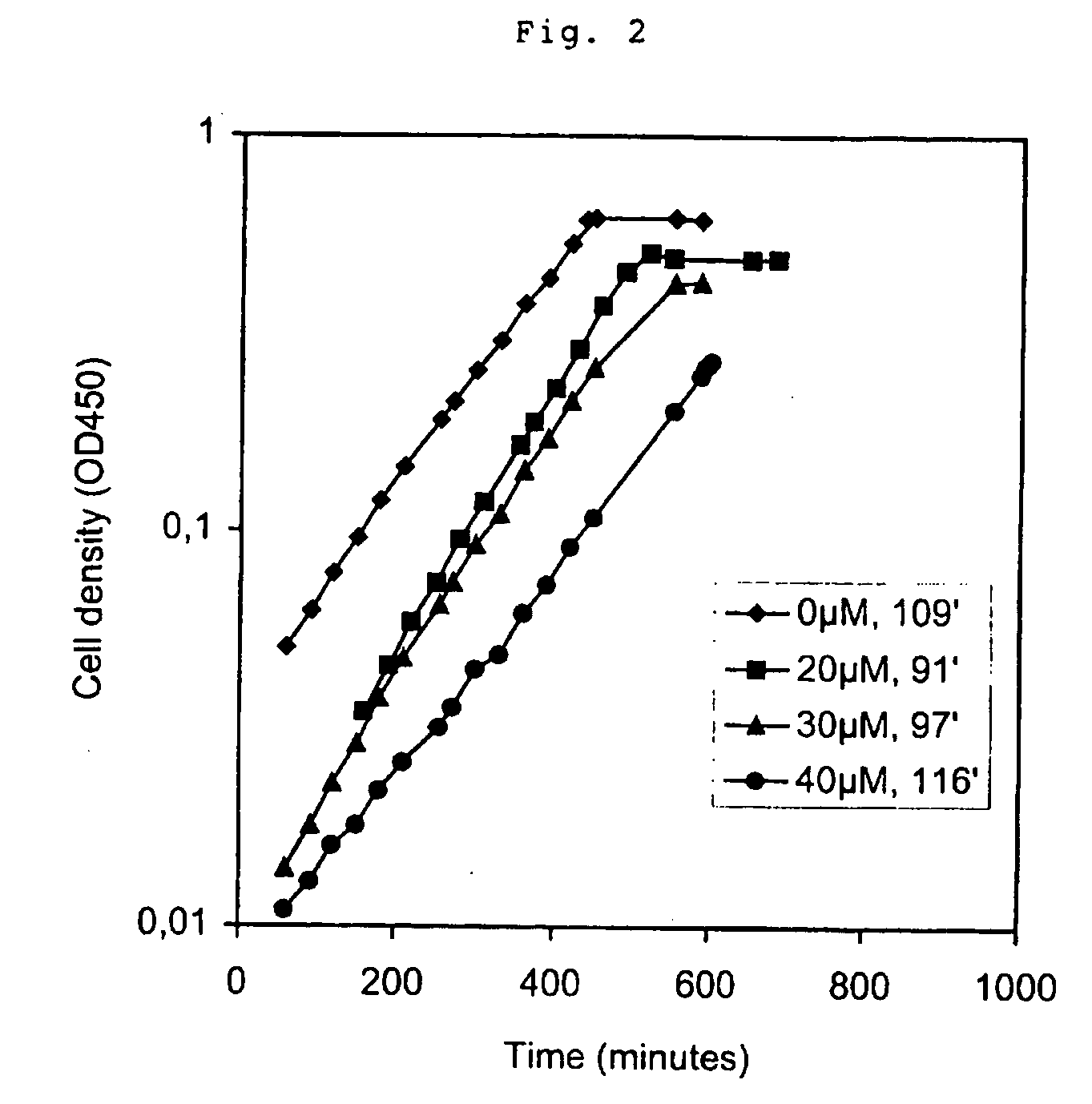
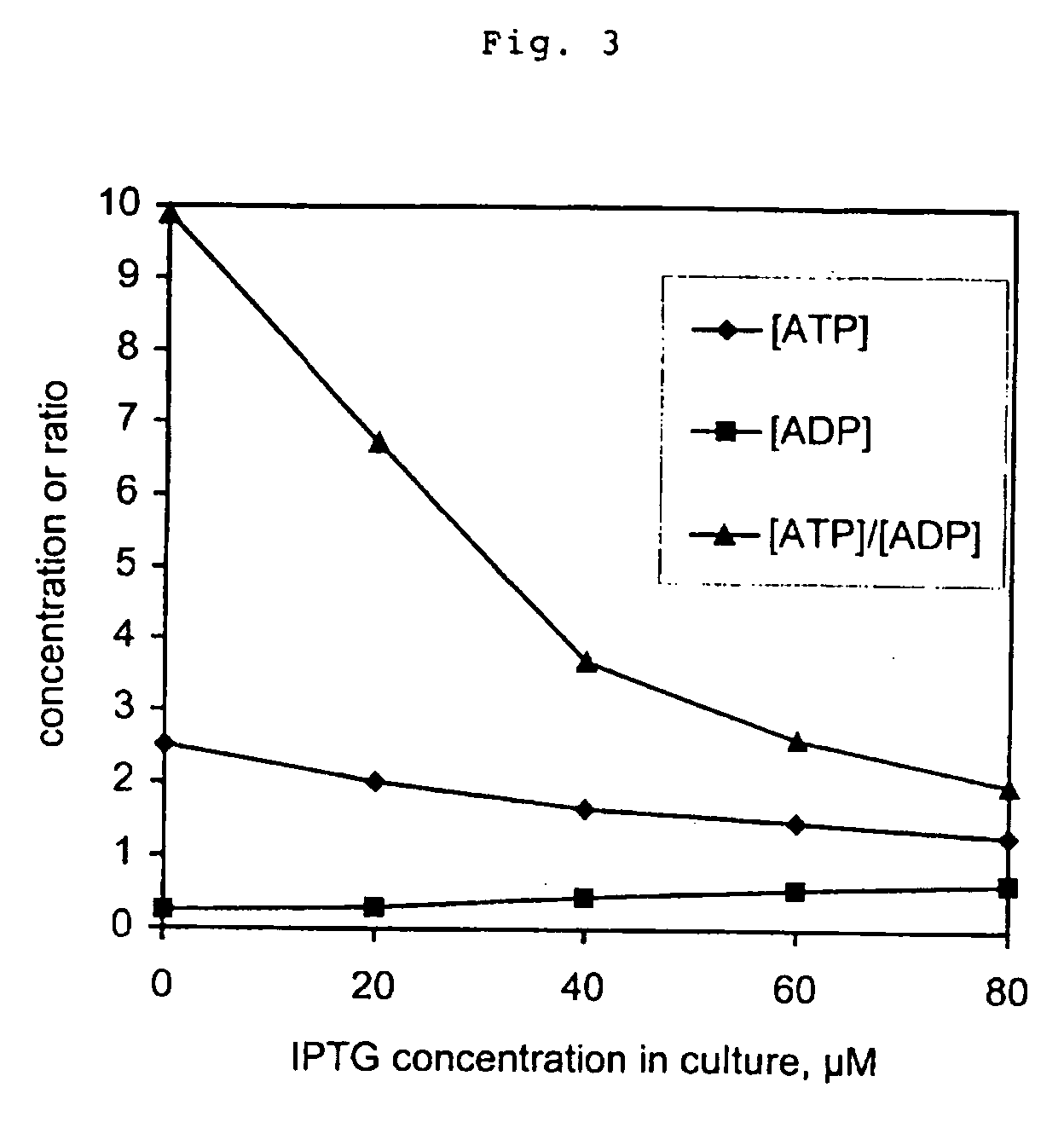
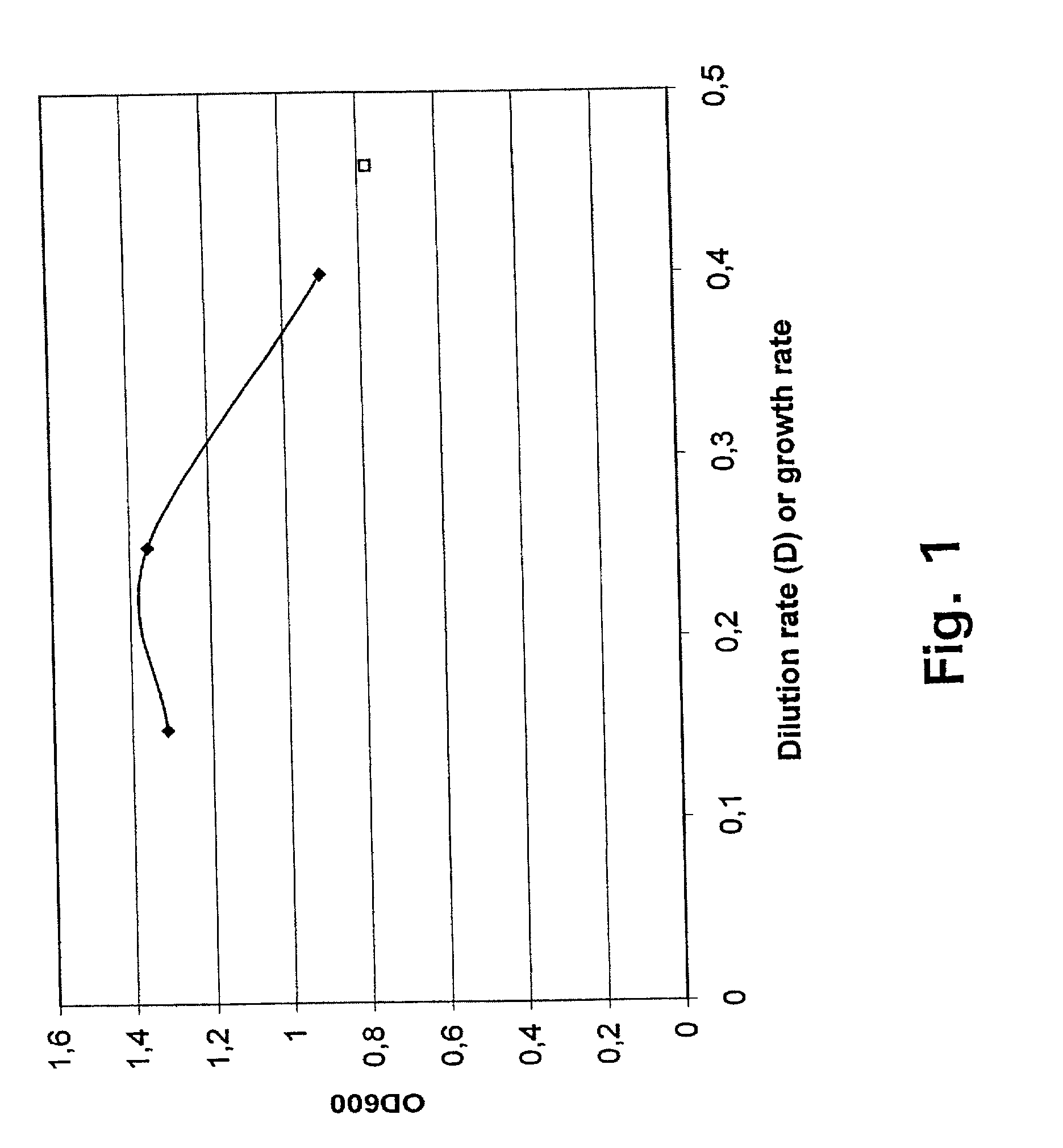
The production of biomass or a desired product from a cell can be improved by inducing conversion of ATP to ADP without primary effects on other cellular metabolites or functions which is achieved by expressing an uncoupled ATPase activity in said cell and incubating the cell with a suitable substrate to produce said biomass or product. This is conveniently done by expressing in said cell the soluble part (F1) of the membrane bound (F0F1 type) H+-ATPase or a portion of F1 exhibiting ATPase activity. The organism from which the F1 ATPase or portions thereof is derived, or in which the F1 ATPase or portions thereof is expressed, may be selected from prokaryotes and eukaryotes. In particular, the DNA encoding F1 or a portion thereof may be derived from bacteria and eukaryotic microorganisms such as yeast, other fungi and cell lines of higher organisms and be selected from the group consisting of the gene encoding the F1 subunit beta or a portion thereof and various combinations of said gene or portion with the genes encoding the other F1 subunits or portions thereof. The method can be used i.a. for optimizing the formation of biomass or a desired product by a cell by expressing different levels of uncoupled ATPase activity in the cell, incubating the cell on a suitable substrate, measuring the conversion rate of substrate into biomass or the desired product at each level of ATPase expression, and choosing a level of ATPase expression at which the conversion rate is optimized.
Owner:JENSEN PETER RUHDAL
Method of improving biomass yield of lactic acid bacterial cultures
InactiveUS20020034815A1Increased biomass productionReduce contentBacteriaUnicellular algaeBiotechnologyQuinone
A method of enhancing biomass yield of a lactic acid bacterial species cell culture, comprising cultivating the cells in a process comprising the steps of providing conditions that results in a reduced glycolytic flux and providing conditions that enable the cells to have, under aerobic conditions, a respiratory metabolism. The increased yield of biomass may be the result of an increased yield of ATP which can be obtained by activating the native ATP synthase activity of the H+-ATPase complex by lowering the ATP / ADP ratio, e.g. by carbon source limitation, and / or by increasing the proton gradient (membrane potential) of the cells, e.g. by enhancing or establishing an electron transport chain which can be achieved by enhancing expression of dehydrogenases or electron transport chain components, by adding to the medium a quinone or porphyrin compound or by enhancing the expression of the H+-ATPase activity.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
A kind of myosin ATP enzyme activity micro-assay method and its application
InactiveCN102288601AOrganic active ingredientsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMyosinAssay
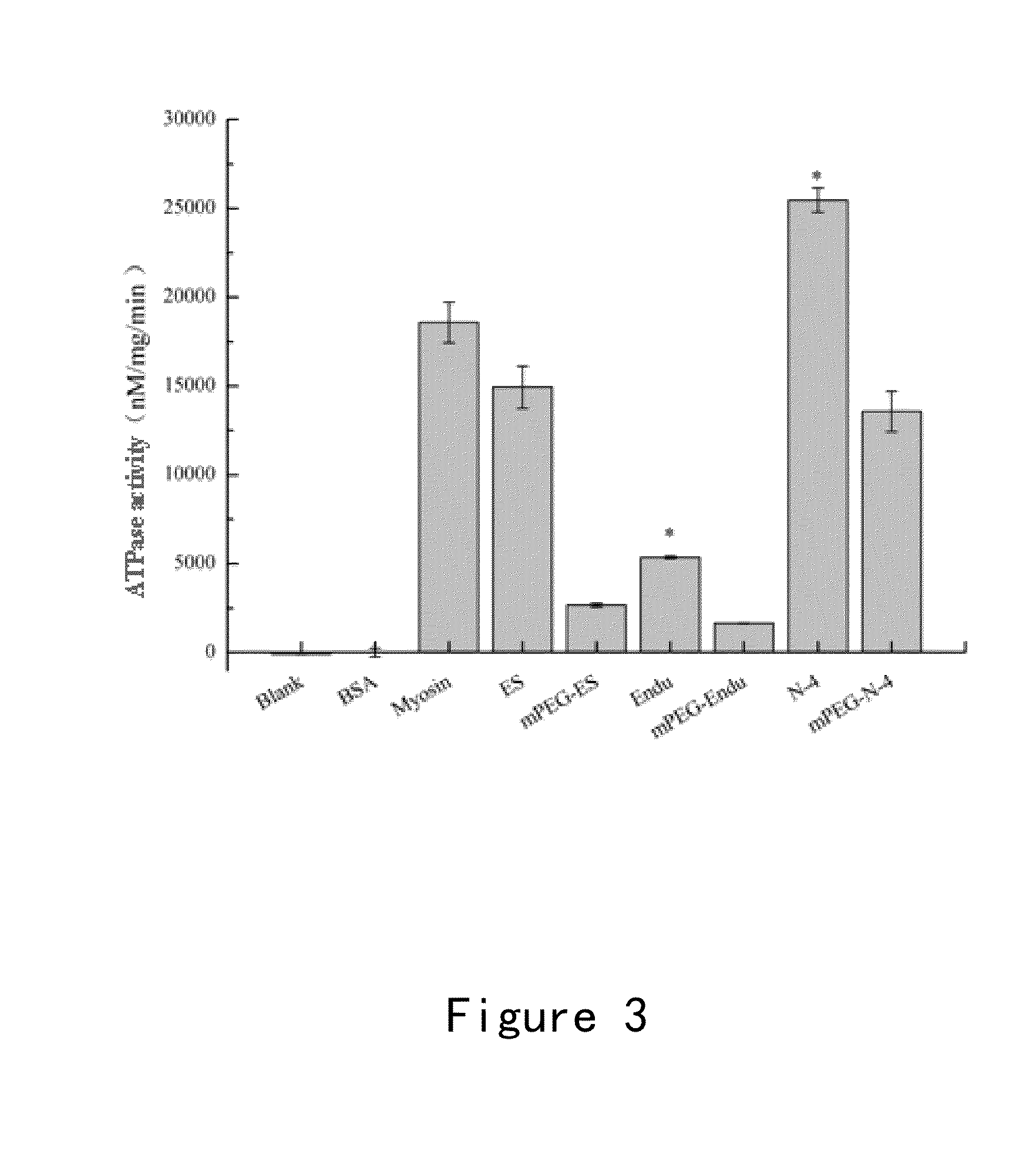
The invention relates to a method for the microdetermination of ATPase activity of myoglobulin, and the method is characterized in that based on the reaction method of a classic molybdenum blue method, the molar ratio of ATP (adenosine-triphosphate) to myoglobulin is controlled at 2000:1 and the molar ratio of ammonium molybdate to stannous chloride is controlled at 5.5:1. The determination method provided by the invention is simple, convenient, fast, high in response value and wide in linear range, and can be applied to the screening of inhibitors. The invention discloses an application of Ruscogenin in inhibiting the ATPase activity of the myoglobulin.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
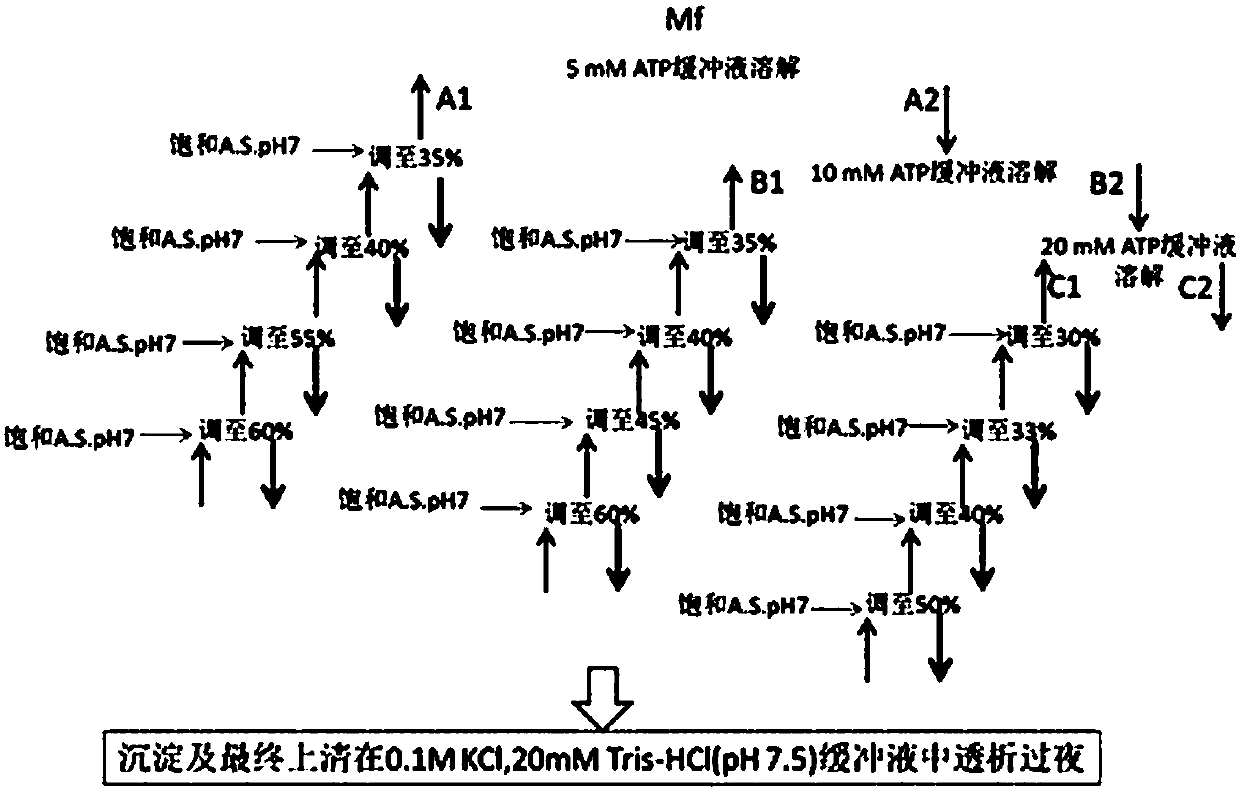
Muscle protein purifying method
InactiveCN109942692ALow denaturationEfficient purificationPeptide preparation methodsAnimals/human peptidesSmooth muscleMyofibril
A muscle protein purifying method adjusts the concentrations of KCl, ATP and ammonium sulfate (A.S.) through the influences of different solution mediums on separation and purification and analyzes the dissociation and precipitation law of all fibrillin components and determines the separation and purification conditions of actin, myoballs and paramyosin with the ATPase activity as the protein denaturation indicating parameter. The method has the advantages that compared with a traditional protein purifying method, the novel method is low in purified protein denaturation degree and simple in purifying process, the actin, myoballs and paramyosin in smooth muscles of aquatic invertebrates are efficiently obtained through purification, and the purifying cost is saved to the maximum extent.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Use of MDA-5 as an antiviral and antiproliferative agent
The present invention relates to mda-5 nucleic acids, MDA-5 proteins, the mda-5 promoter, and related molecules, and the use of each of these elements in protecting against or limiting viral infection, controlling cell proliferation, and promoting apoptosis. It is based upon the discovery that, contrary to earlier hypotheses based on the amino acid sequence of MDA-5, the protein is not a defective ATPase but rather exhibits ATPase activity. This supports the role of MDA-5 as a RNA helicase protein and consequently its use in promoting RNA degradation, for example in the context of antiviral defense, limitation of cell proliferation, or induction of apoptosis.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
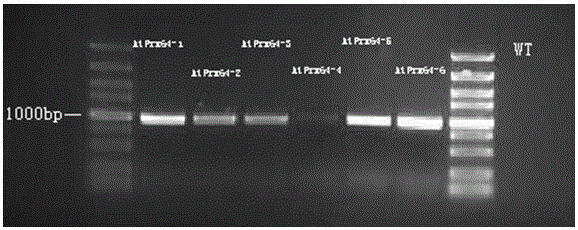
Application of AtPrx64 gene in improving aluminum tolerance of plants
ActiveCN105861459AImprove toleranceEasy to storeEnzymesGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyReduction rate
The invention discloses application of an AtPrx64 gene in improving aluminum tolerance of plants. According to the application, the AtPrx64 gene is recombined into a plant expression vector, wild tobacco is transformed, and transgenic AtPrx64 tobacco can be screened; the experimental result shows that under the condition of aluminum stress, the relative growth rate and the soluble protein content of roots of the transgenic tobacco are gradually reduced along with increase of aluminum concentration, and the reduction rate of the transgenic tobacco is lower than that of wild tobacco; the contents of H2O2 and MDA of the transgenic tobacco are gradually increased along with increase of the aluminum concentration, and the increase rate of the transgenic tobacco is lower than that of the wild tobacco; no matter whether aluminum stress acts or not, the activity of plasmalemmas H<+>-ATPase and the secretion of citric acid of the transgenic tobacco are both higher than those of the wild tobacco; the test on the aluminum content in the roots under aluminum stress of different concentrations shows that the aluminum content in the roots of the transgenic tobacco is remarkably lower than that of the wild tobacco; the tolerance of the transgenic AtPrx64 tobacco to aluminum stress can be remarkably improved.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
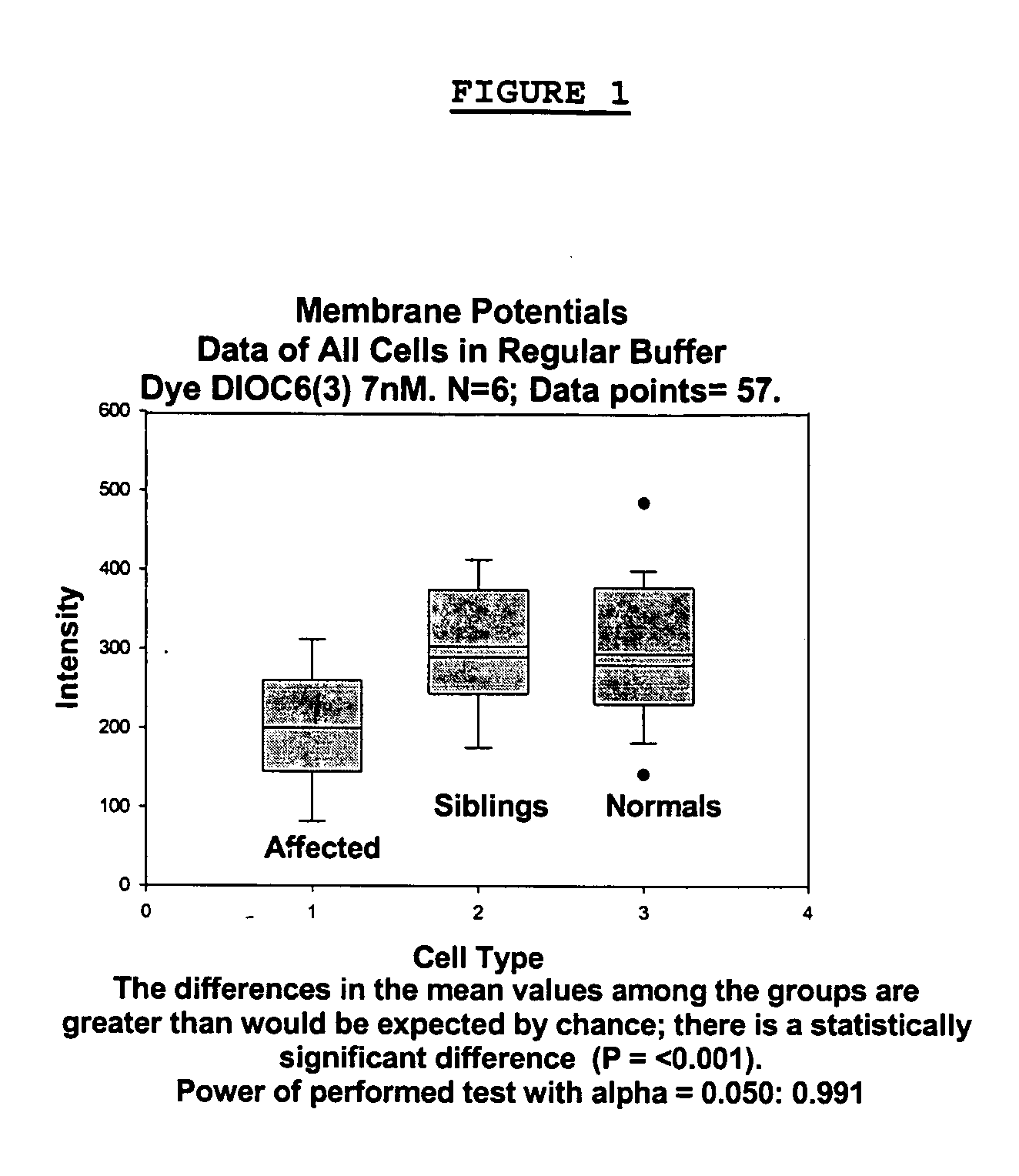
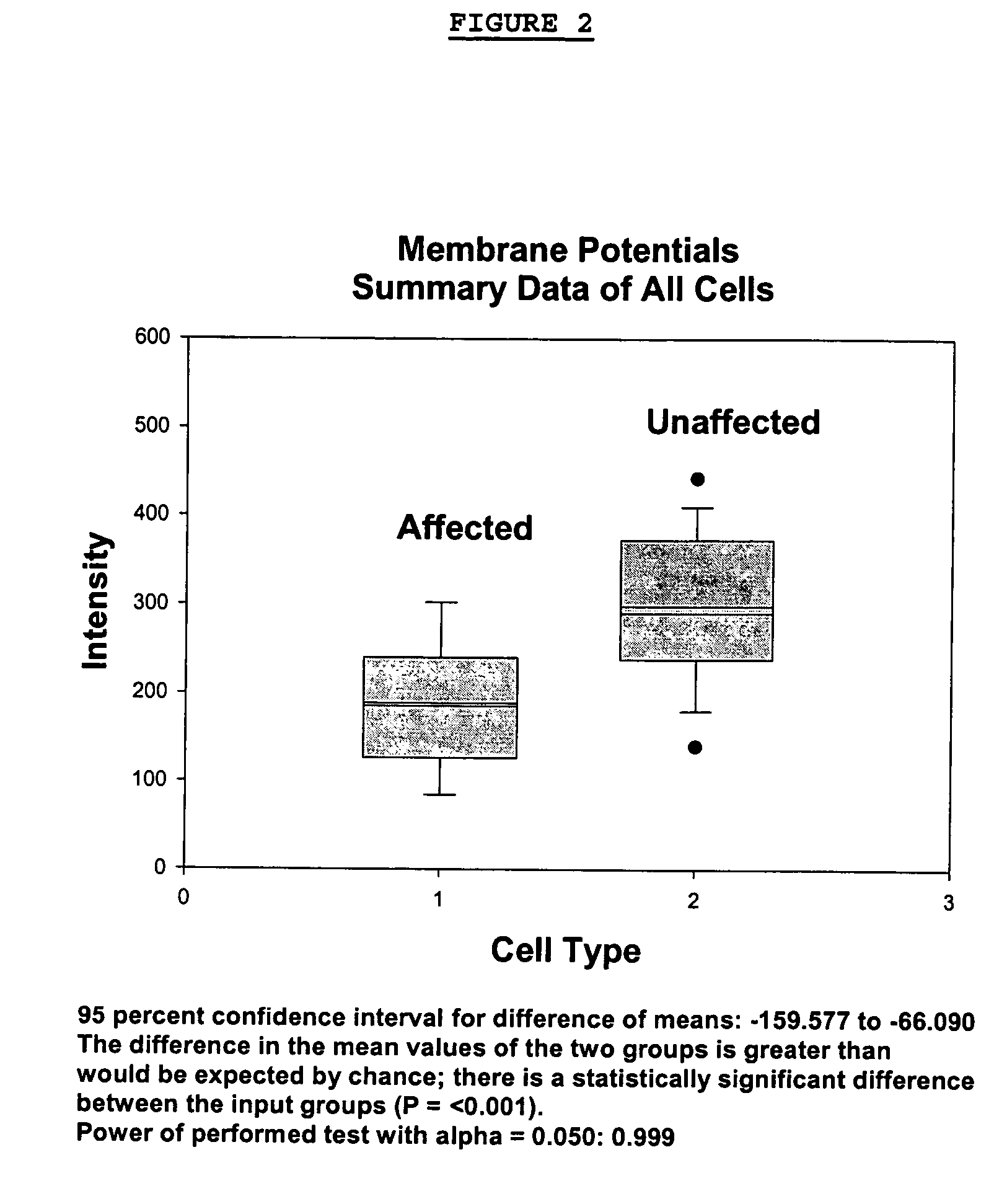
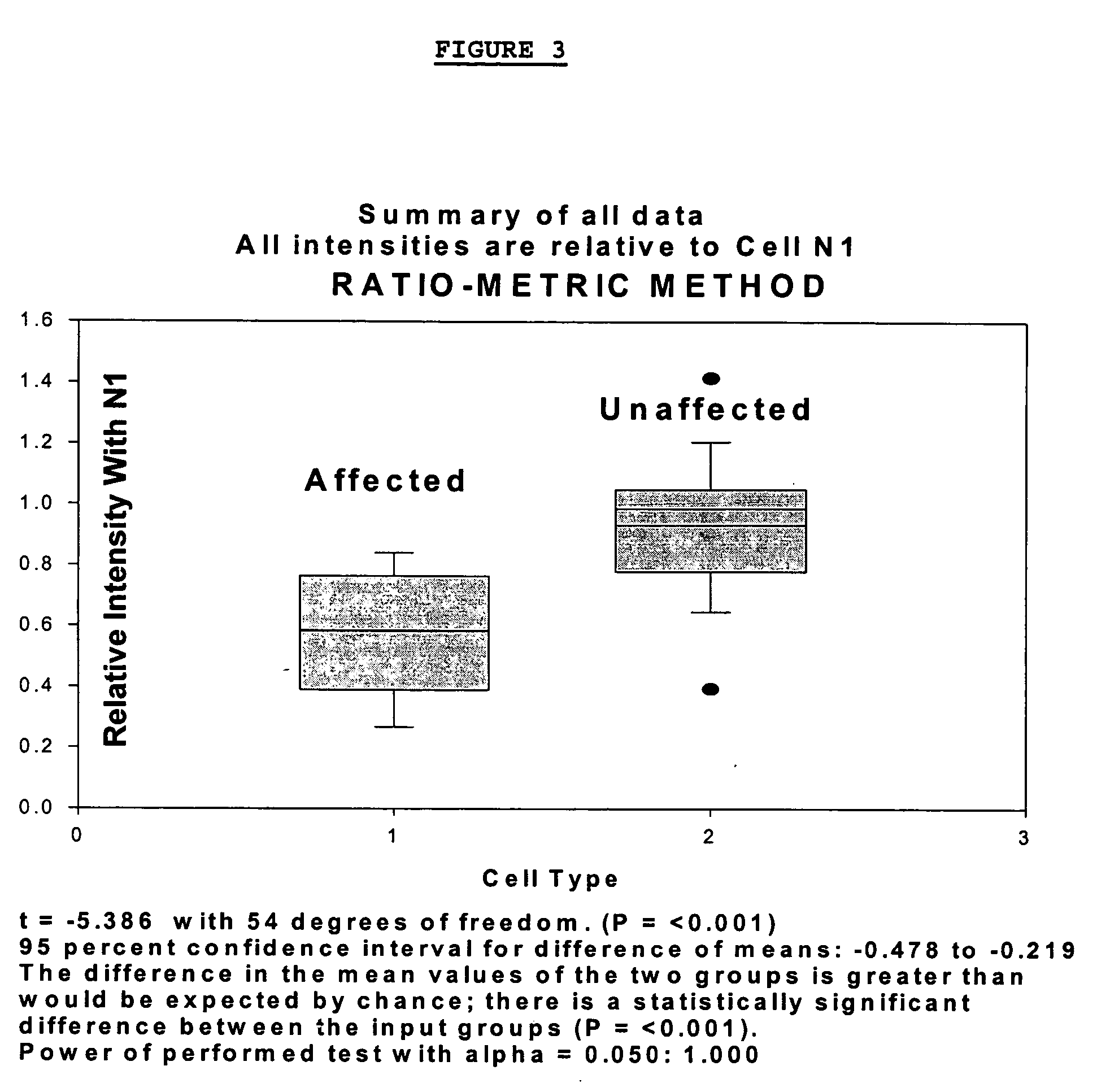
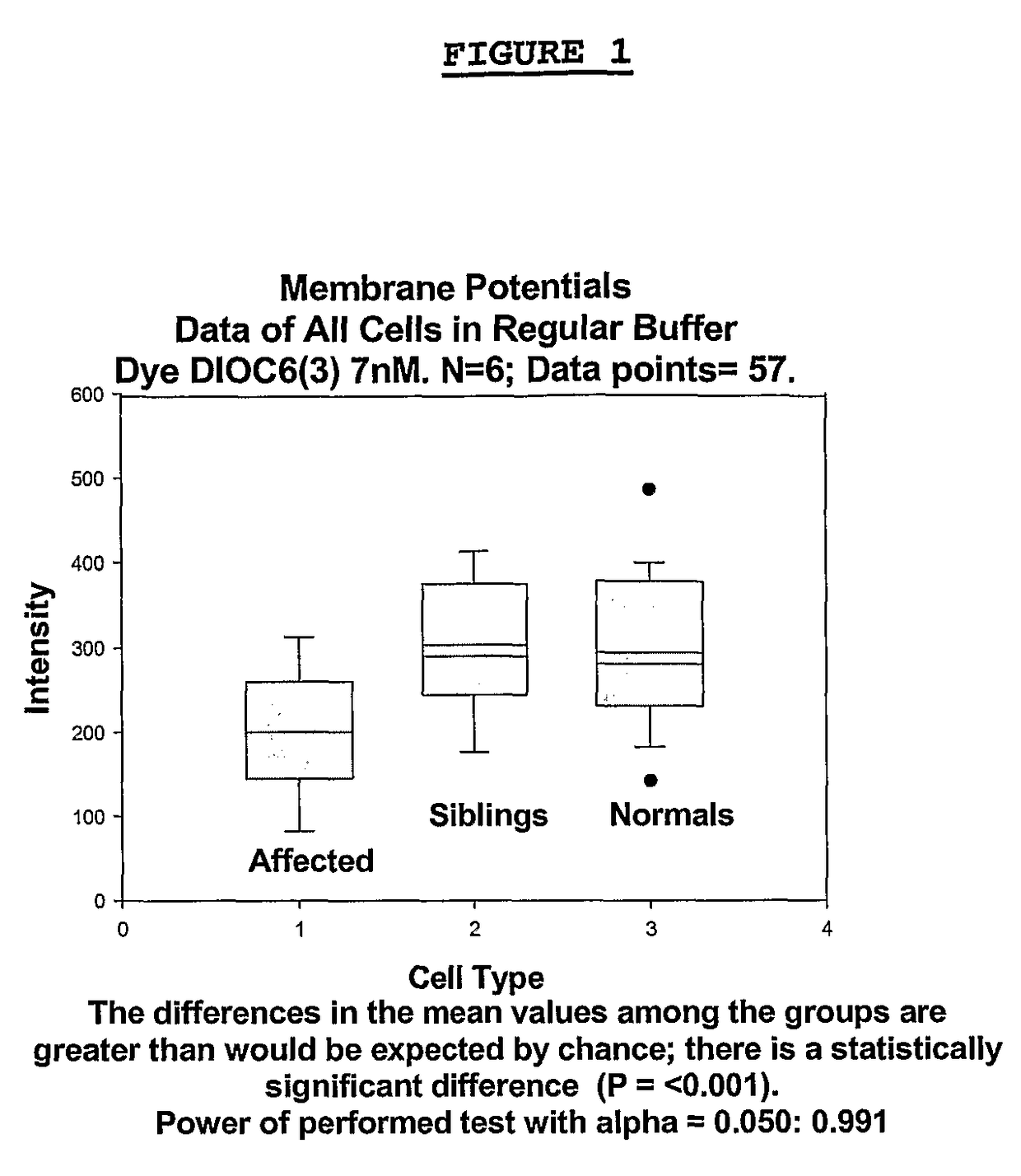
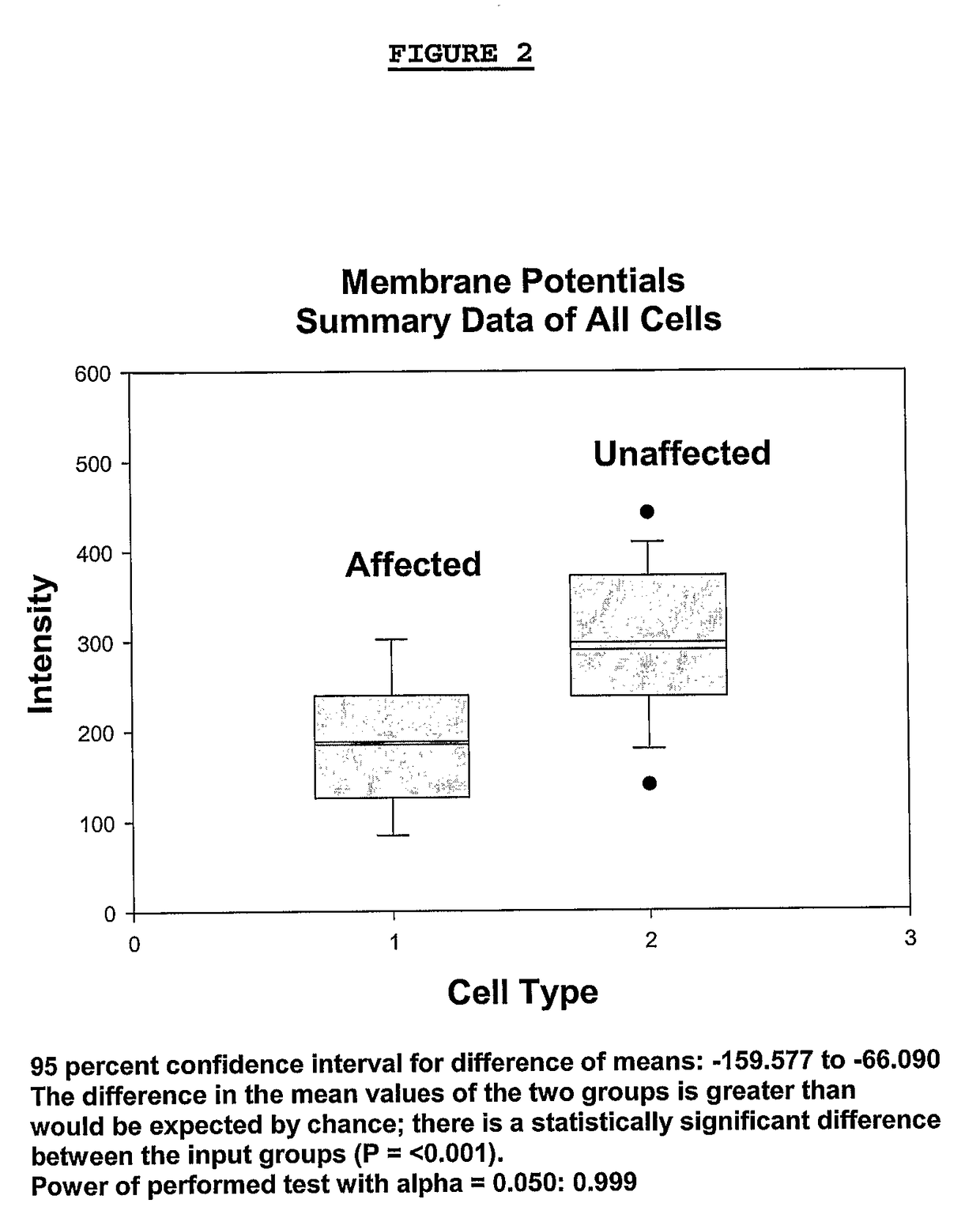
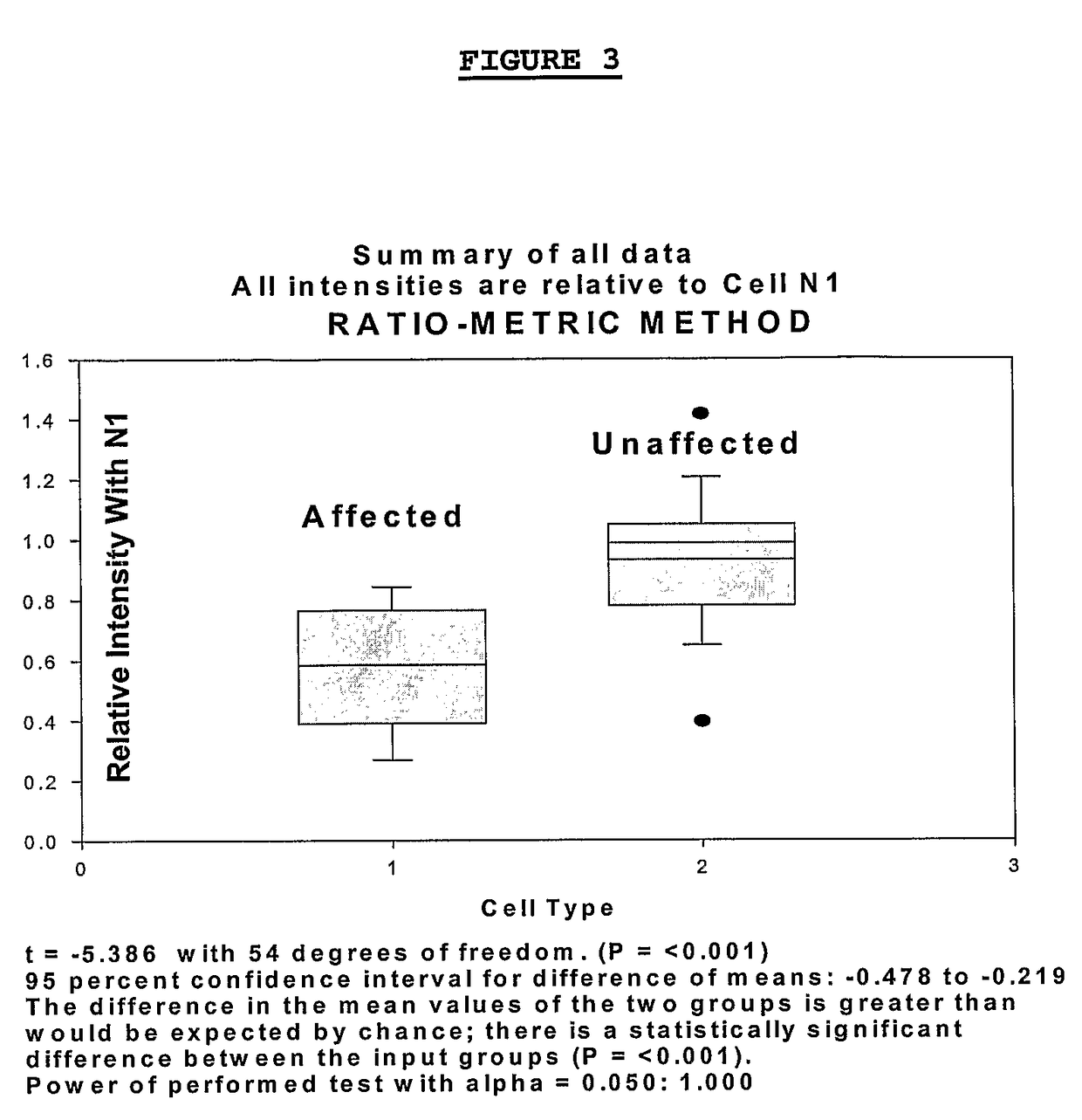
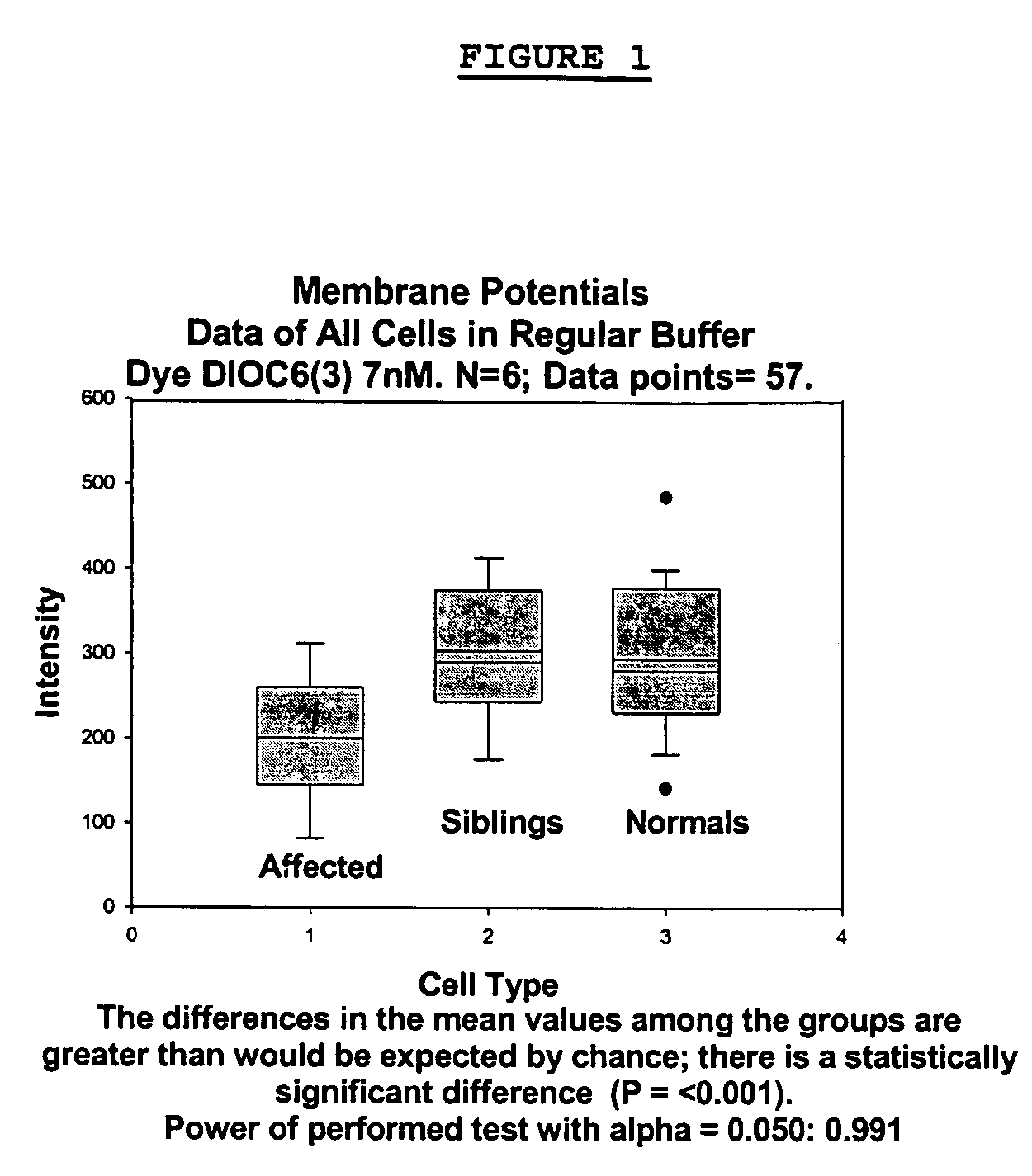
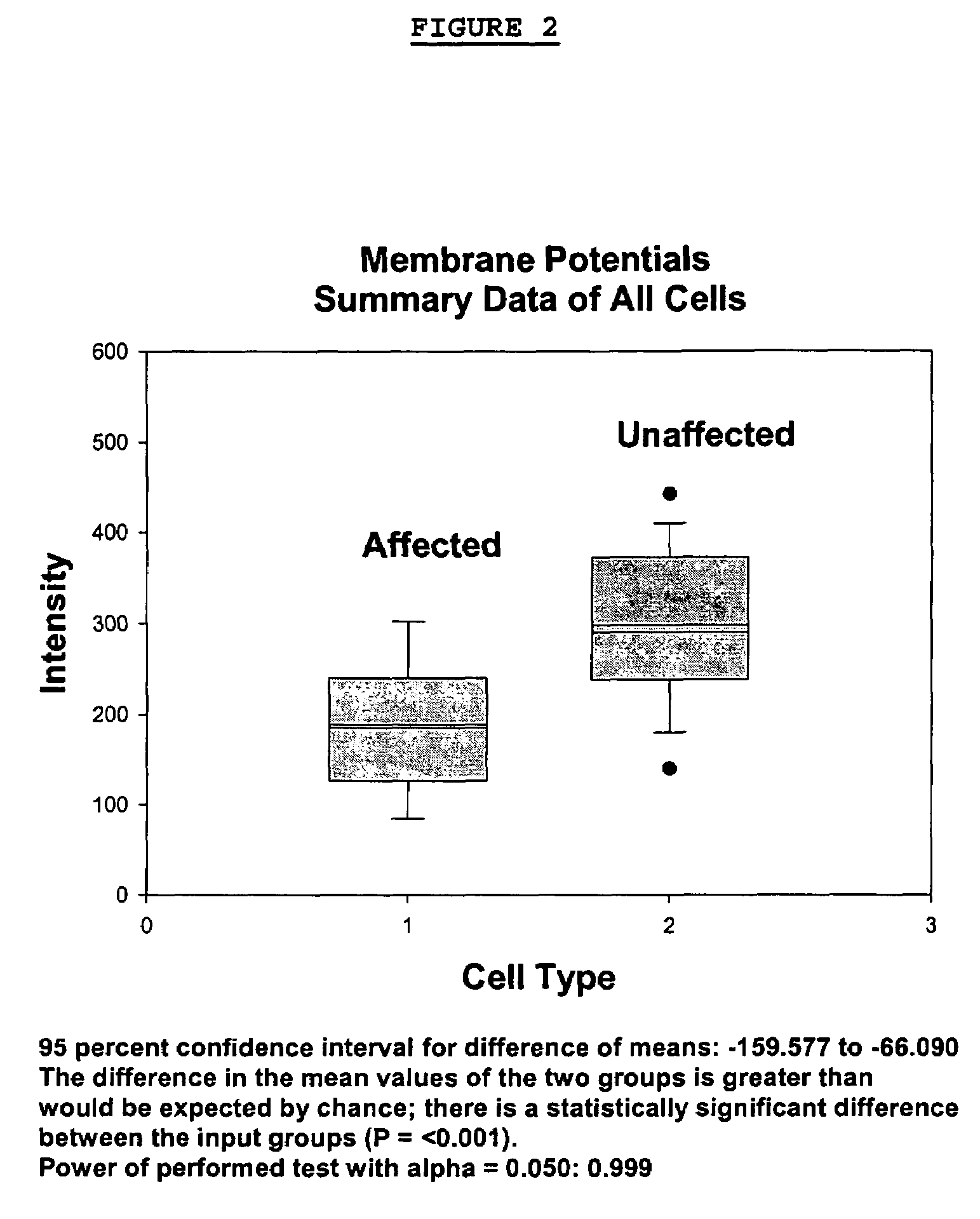
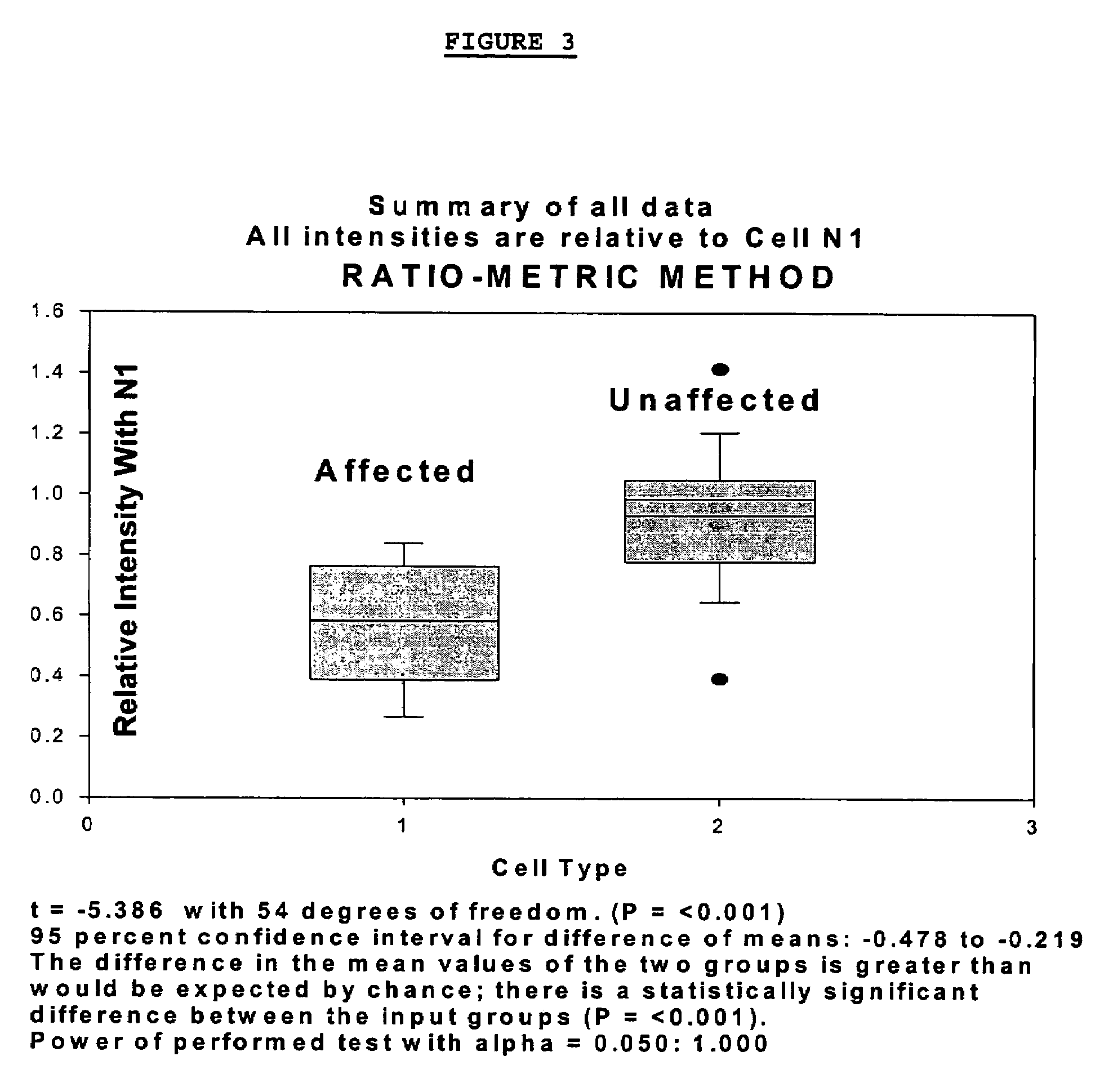
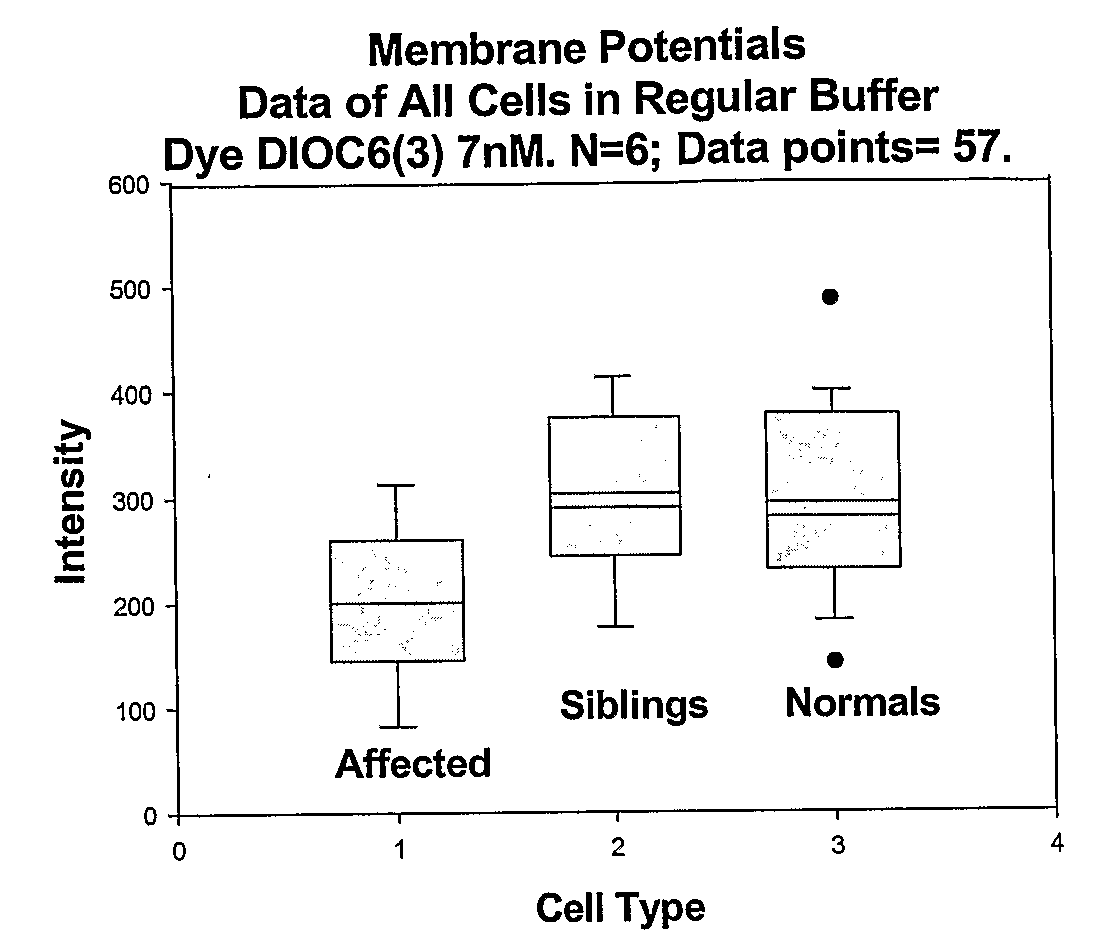
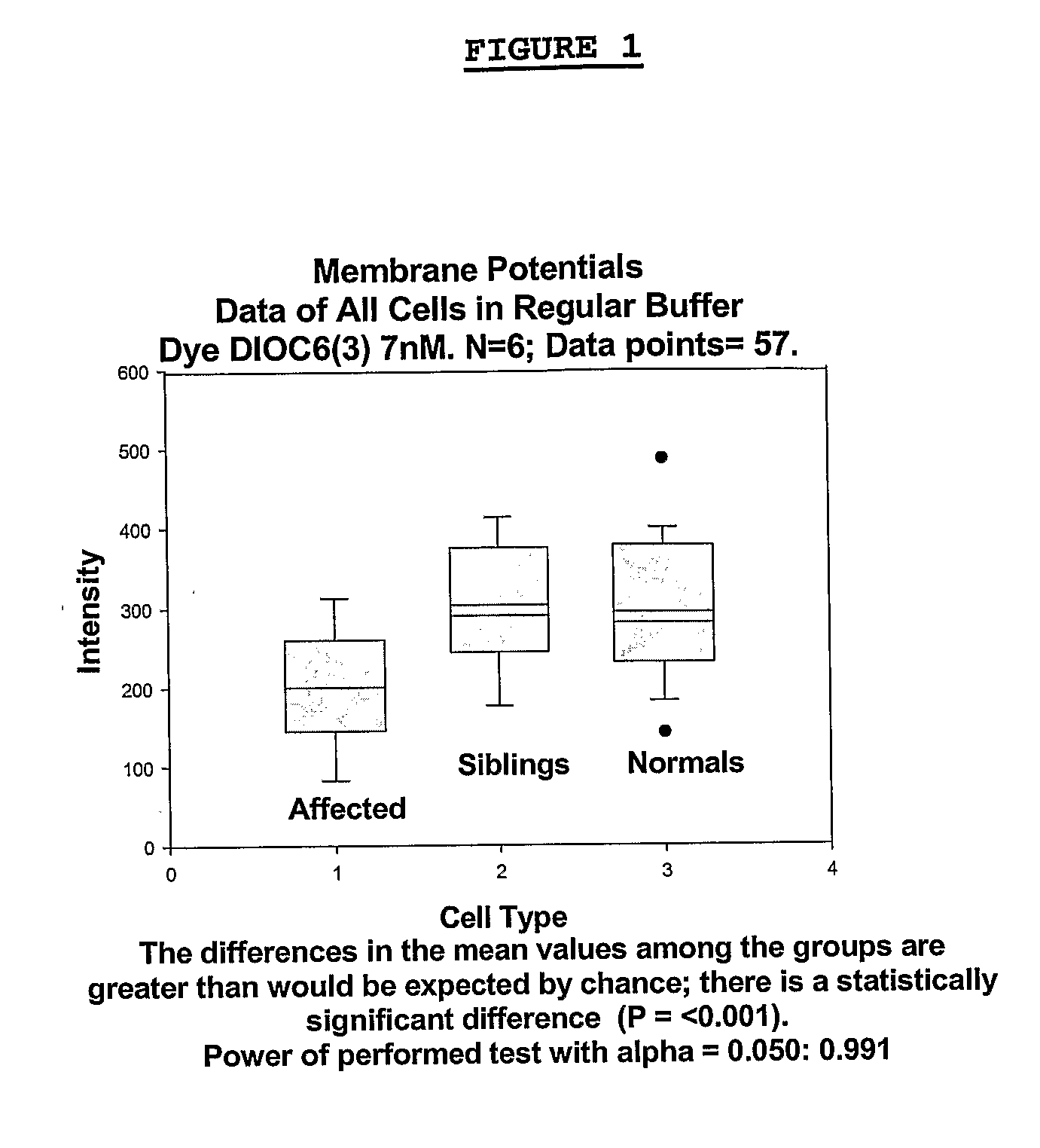
Methods for diagnosing bipolar and unipolar disorder
Changes that occur in Na+K+ ATPase regulation and therefore in the membrane potential in cells from bipolar individuals, as compared to cells from unaffected control individuals, are utilized to provide a diagnostic assay for bipolar disorder. The diagnostic assay may also or instead exploit the similarity of cells from bipolar patients to those of people already known to have bipolar disorder. A similar diagnostic assay is provided for diagnosing unipolar disorder. The diagnostic assays may further involve manipulation of membrane potential by incubation of cells in K+-free buffer and / or incubation with one or more compounds that alter Na+K+ ATPase activity. Although a variety of cells may be used, the diagnostic assays preferably employ lymphoblasts or whole blood cells.
Owner:FREE STATE DIAGNOSTICS
Methods for diagnosing an attention-deficit/Hyperactivity disorder
Changes that occur in Na+K+ ATPase regulation and therefore in the membrane potential in cells from bipolar individuals, as compared to cells from unaffected control individuals, are utilized to provide a diagnostic assay for bipolar I and bipolar II disorders. The diagnostic assay may also or instead exploit the similarity of cells from new patients to those of people already known to have bipolar I or bipolar II disorder. A similar diagnostic assay is provided for diagnosing attention-deficit / hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and unipolar disorder. The diagnostic assays may further involve manipulation of membrane potential by incubation of cells in K+-free buffer and / or incubation with one or more compounds that alter Na+K+ ATPase activity. Although a variety of cells may be used, the diagnostic assays preferably employ lymphoblasts or whole blood cells.
Owner:PSYCHNOSTICS
Use of purine nucleosides to stimulate Na/K ATPase and to treat or prevent shock
InactiveUS20050187181A1Preventing and treating septic shockHigh activityBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsInosineMedicine
This invention relates to methods of treating or preventing hemorrhagic and septic shock in an animal by administering inosine, guanosine, deoxyinosine, deoxyguanosine or a mixture thereof. Other purine nucleosides or analogs are described that have therapeutic use in treating or preventing shock. The invention also describes methods for increasing Na / K ATPase activity in erythrocytes or other cells in an animal having below normal activity of this enzyme by administering inosine, guanosine, deoxyinosine, deoxyguanosine or a mixture thereof.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Methods for diagnosing a bipolar disorder and unipolar disorder
Changes that occur in Na+K+ ATPase regulation and therefore in the membrane potential in cells from bipolar individuals, as compared to cells from unaffected control individuals, are utilized to provide a diagnostic assay for a bipolar disorder. The diagnostic assay may also or instead exploit the similarity of cells from bipolar patients to those of people already known to have a bipolar disorder. A similar diagnostic assay is provided for diagnosing unipolar disorder. The diagnostic assays may further involve manipulation of membrane potential by incubation of cells in K+-free buffer and / or incubation with one or more compounds that alter Na+K+ ATPase activity. Although a variety of cells may be used, the diagnostic assays preferably employ lymphoblasts or whole blood cells.
Owner:FREE STATE DIAGNOSTICS
Use of mda-5 as an antiviral and antiproliferative agent
The present invention relates to mda-5 nucleic acids, MDA-5 proteins, the mda-5 promoter, and related molecules, and the use of each of these elements in protecting against or limiting viral infection, controlling cell proliferation, and promoting apoptosis. It is based upon the discovery that, contrary to earlier hypotheses based on the amino acid sequence of MDA-5, the protein is not a defective ATPase but rather exhibits ATPase activity. This supports the role of MDA-5 as a RNA helicase protein and consequently its use in promoting RNA degradation, for example in the context of antiviral defense, limitation of cell proliferation, or induction of apoptosis.
Owner:FISHER PAUL +2
Modulators of phosphotyrosyl phosphatase activator
InactiveUS20080153773A1Inhibiting ATPase activityPreventing modulationBiocideSugar derivativesPhosphoprotein phosphatasePHOSPHOTYROSYL PHOSPHATASE ACTIVATOR
Atomic coordinates for human phosphotyrosyl phosphatase activator (PTPA) and ATPγS bound by PTPA, as well as methods for using these atomic coordinates to prepare ATPase inhibitors of PTPA and ATPase inhibitors prepared using such methods are provided herein. Comprehensive biochemical analyses of the interactions of PTPA with ATP and protein phosphatase 2A are also provided. Compositions including mimetics and small molecules of the invention and, optionally, secondary agents may be used to treat disorders in which PTPA ATPase activity plays a contributing role.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Methods For Diagnosing Bipolar Disorders and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
InactiveUS20080160554A1Microbiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsBipolar mood disorderLymphoblast
Changes that occur in Na+K+ ATPase regulation and therefore in the membrane potential in cells from bipolar individuals, as compared to cells from unaffected control individuals, are utilized to provide a diagnostic assay for bipolar I and bipolar II disorders. The diagnostic assay may also or instead exploit the similarity of cells from new patients to those of people already known to have bipolar I or bipolar II disorder. A similar diagnostic assay is provided for diagnosing attention-deficit / hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and unipolar disorder. The diagnostic assays may further involve manipulation of membrane potential by incubation of cells in K+-free buffer and / or incubation with one or more compounds that alter Na+K+ ATPase activity. Although a variety of cells may be used, the diagnostic assays preferably employ lymphoblasts or whole blood cells.
Owner:PSYCHNOSTICS
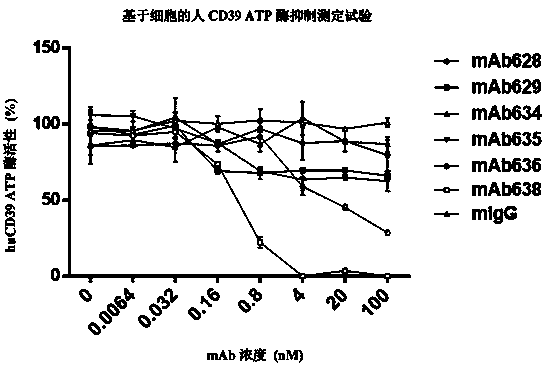
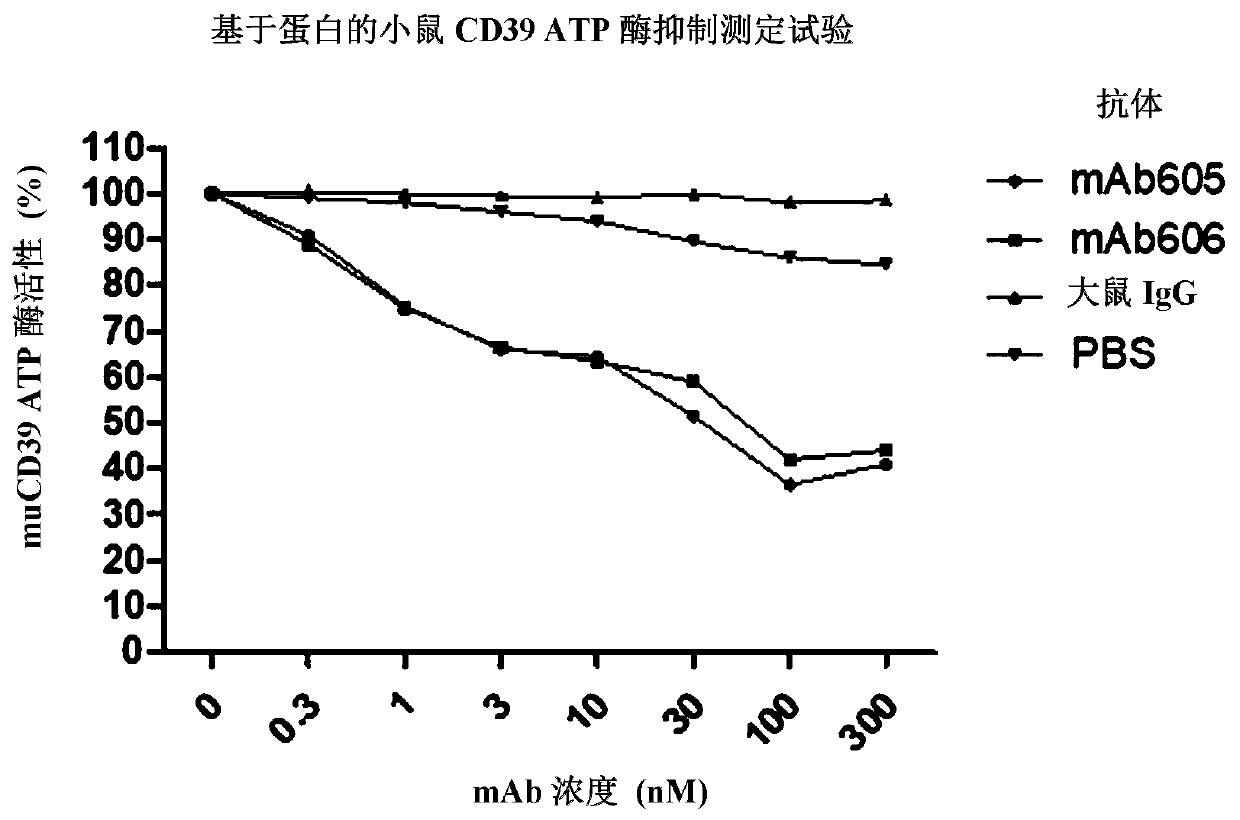
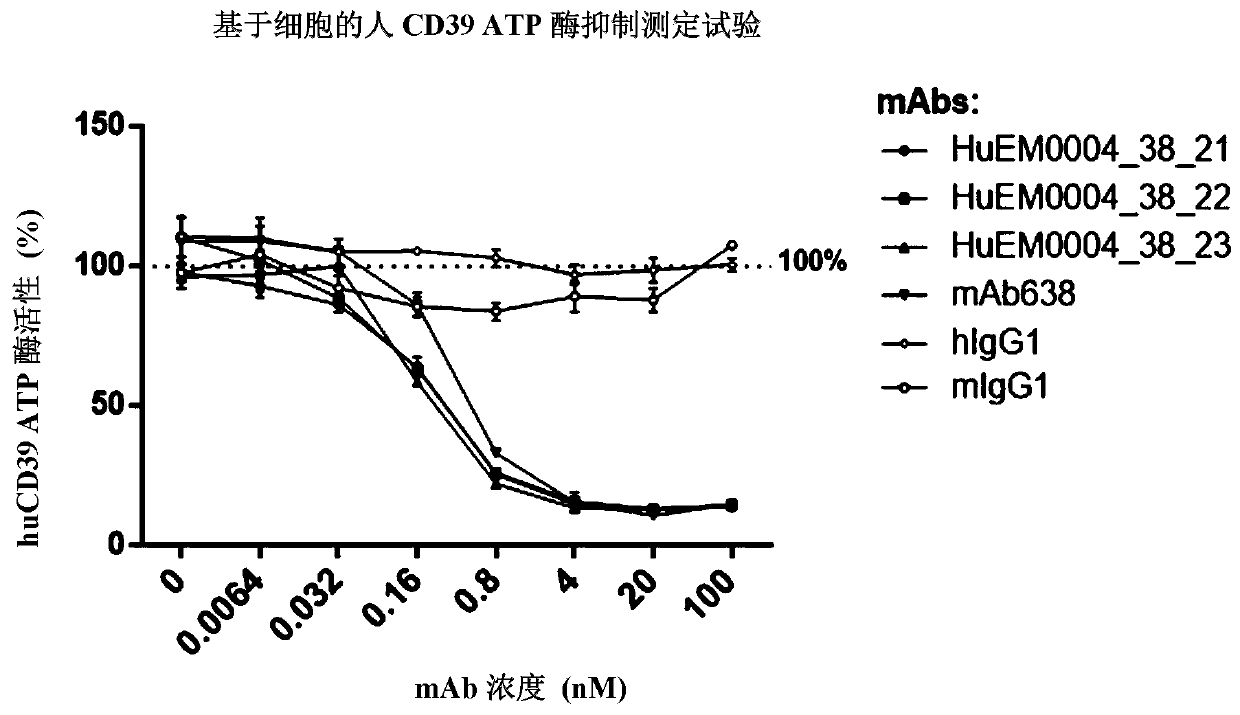
CD39 high-affinity antibody and use thereof
ActiveCN110407941AGrowth inhibitionInhibitory activityImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsDiseaseHigh affinity antibody
Owner:EPIMAB BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Endostatin mutants with mutations at atp binding sites
ActiveUS20140308263A1Easy to operateGood reproducibilityHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsBinding siteEndostatin
The present invention discloses a new anti-tumor medicament comprising a mutant of endostatin. The mutant comprises a mutation in the ATP-binding site of endostatin and has a decreased ATPase activity and an increased anti-angiogenesis activity.
Owner:BEIJING PROTGEN +1
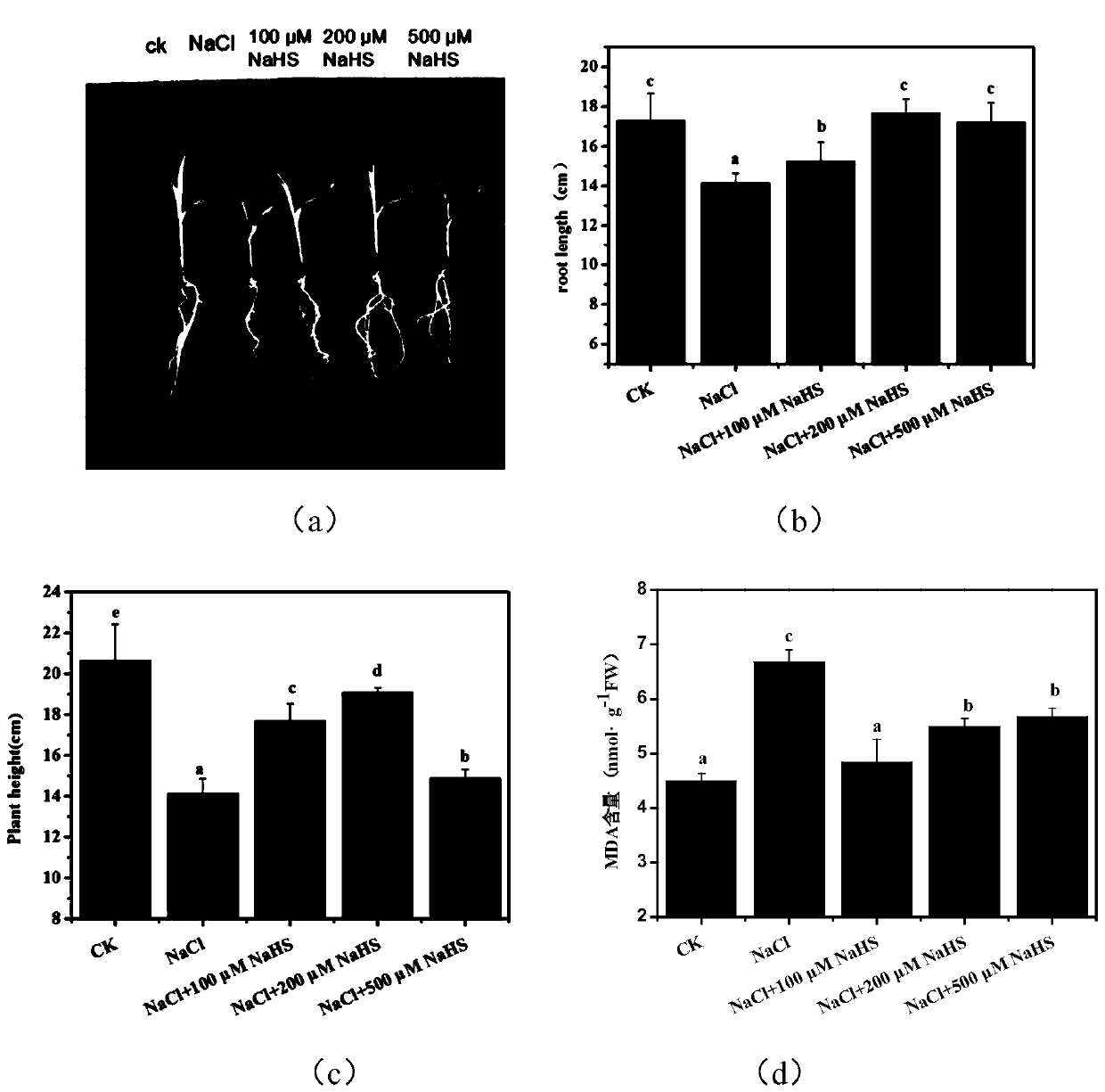
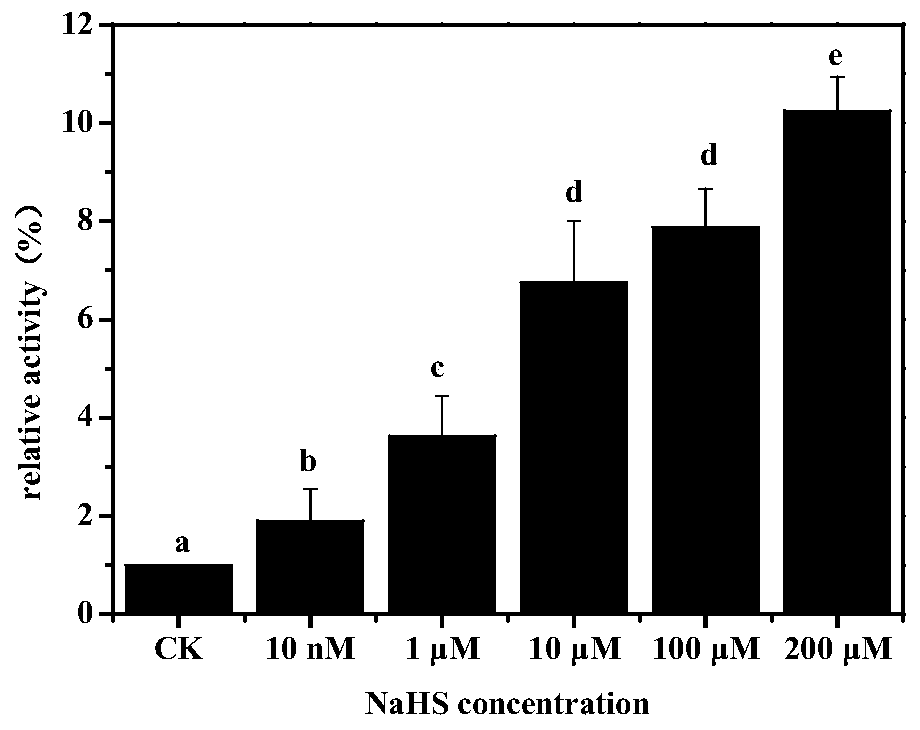
Application of sodium hydrosulfide in improvement of salt resistance of corn seedlings
InactiveCN110447658AImprove PMH
<sup>+</sup>
-ATPase activityImprove salt resistancePlant growth regulatorsBiocideSalt resistanceAgricultural science
The invention discloses application of sodium hydrosulfide in improvement of the salt resistance of corn seedlings and belongs to the field of plant stress resistance. According to application of thesodium hydrosulfide in improvement of the salt resistance of the corn seedlings, by improving the activity of PM H+-ATPase of the corn seedlings, conveying of related ions of salt stress is improved to improve the salt resistance of corn, and growth of corn plants can be promoted. The operation is easily and conveniently conducted, a certain basis is provided for research on the salt resistance ofplants, and the sodium hydrosulfide has great economic benefits and social value. According to the application, the sodium hydrosulfide is adopted as a donor of hydrogen sulfide, double distilled water is directly used for being prepared into a mother solution, and the operation is conducted easily and quickly.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com