Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
81 results about "Gain measurement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In electronics, gain is a measure of the ability of a two-port circuit (often an amplifier) to increase the power or amplitude of a signal from the input to the output port by adding energy converted from some power supply to the signal.
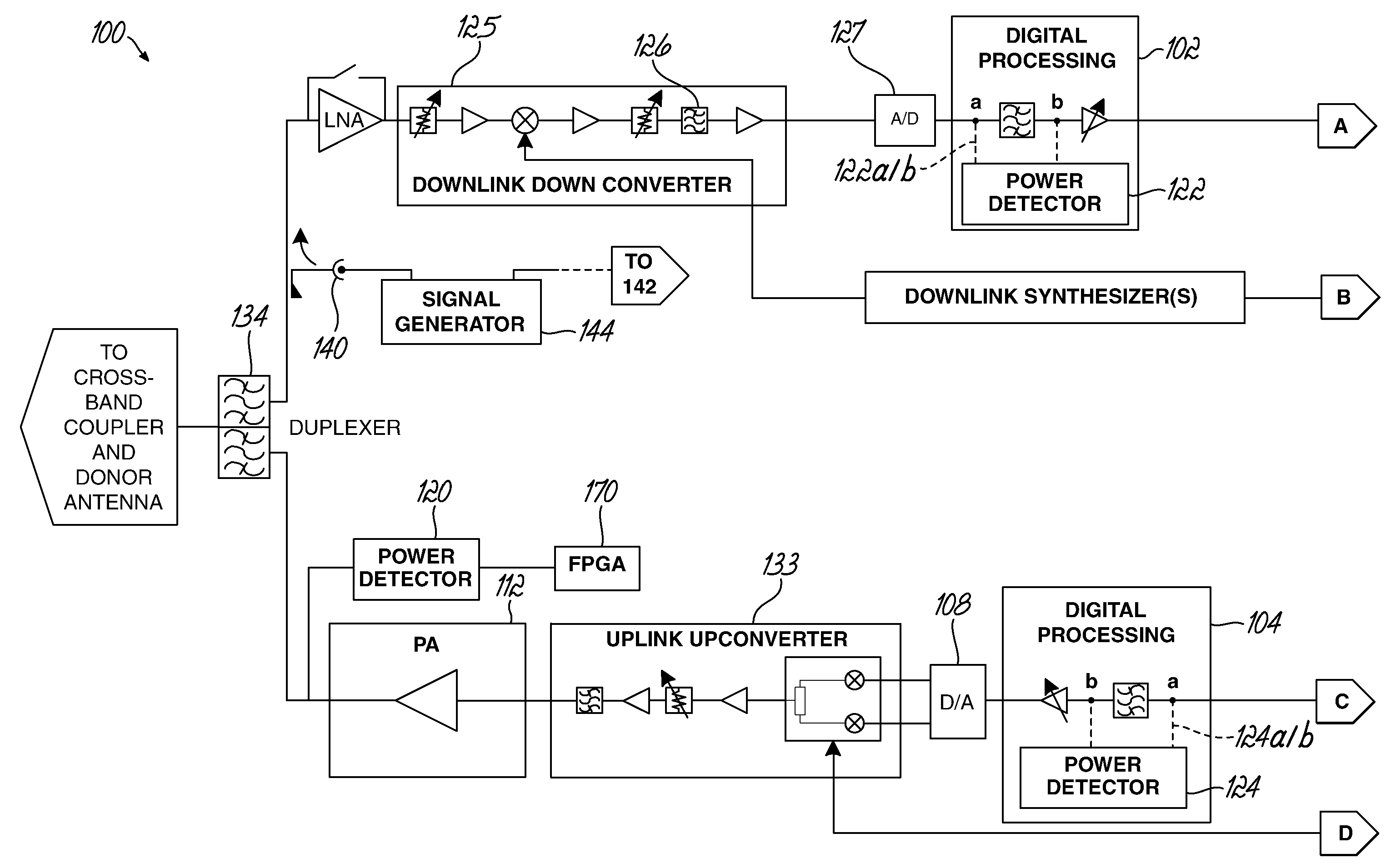
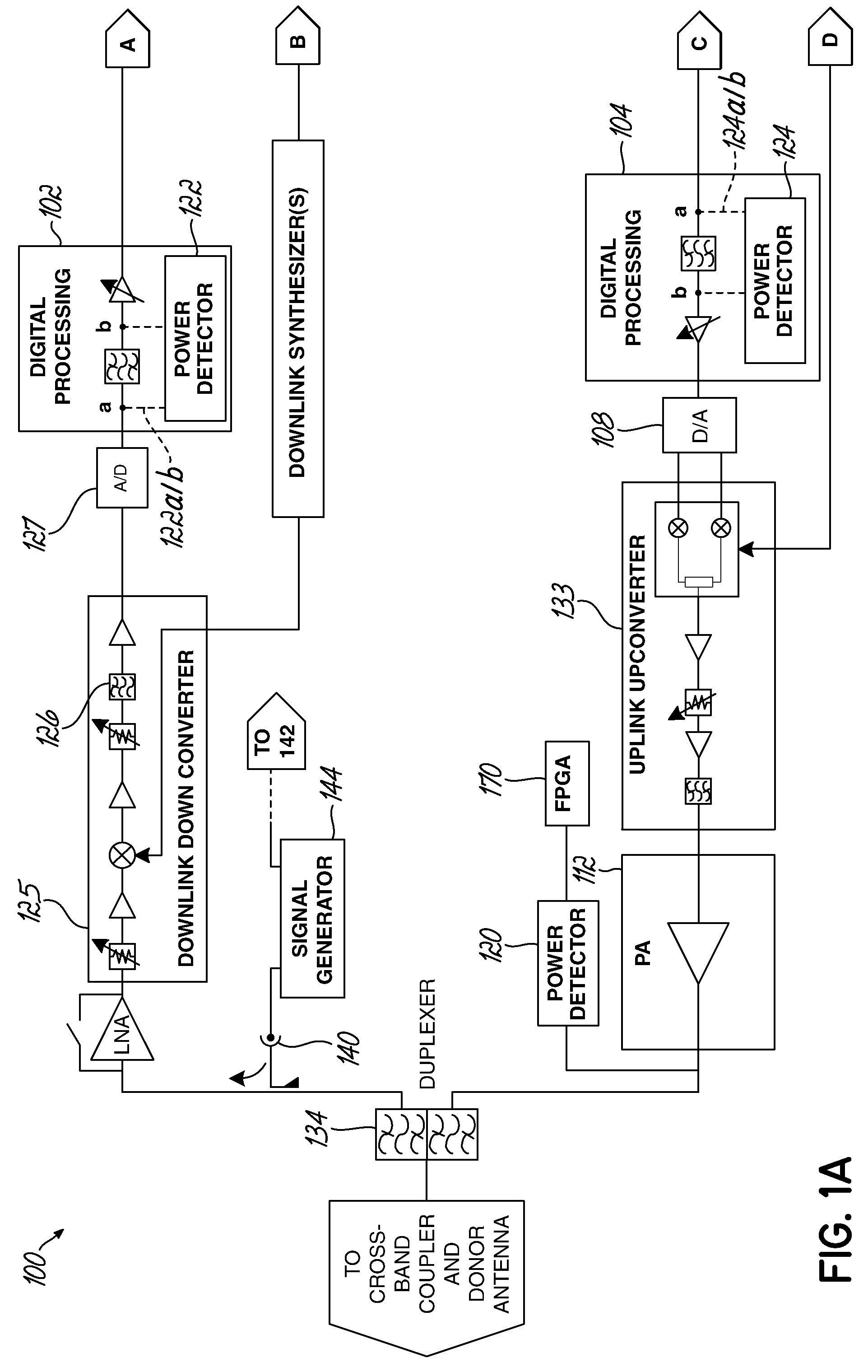
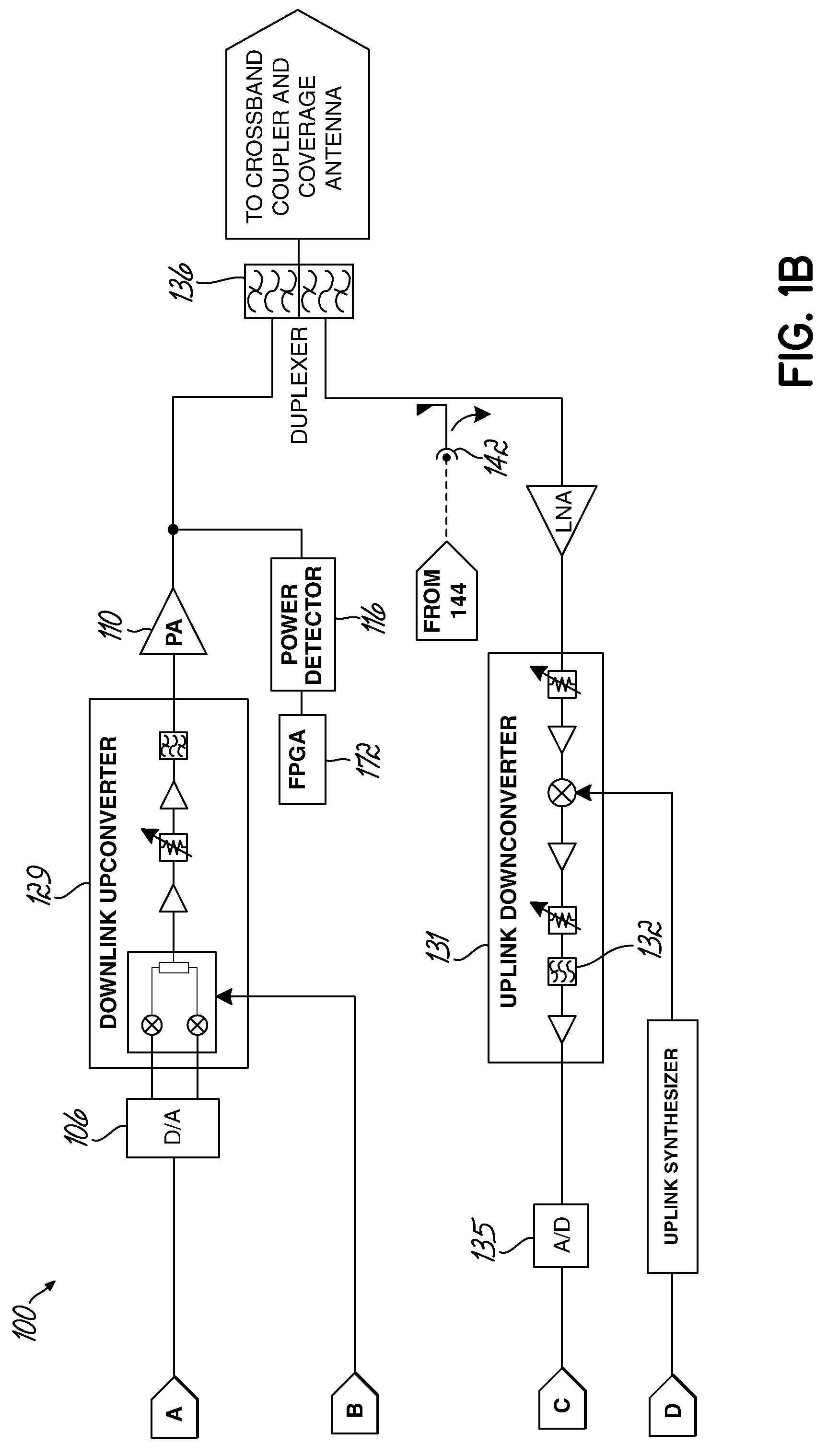
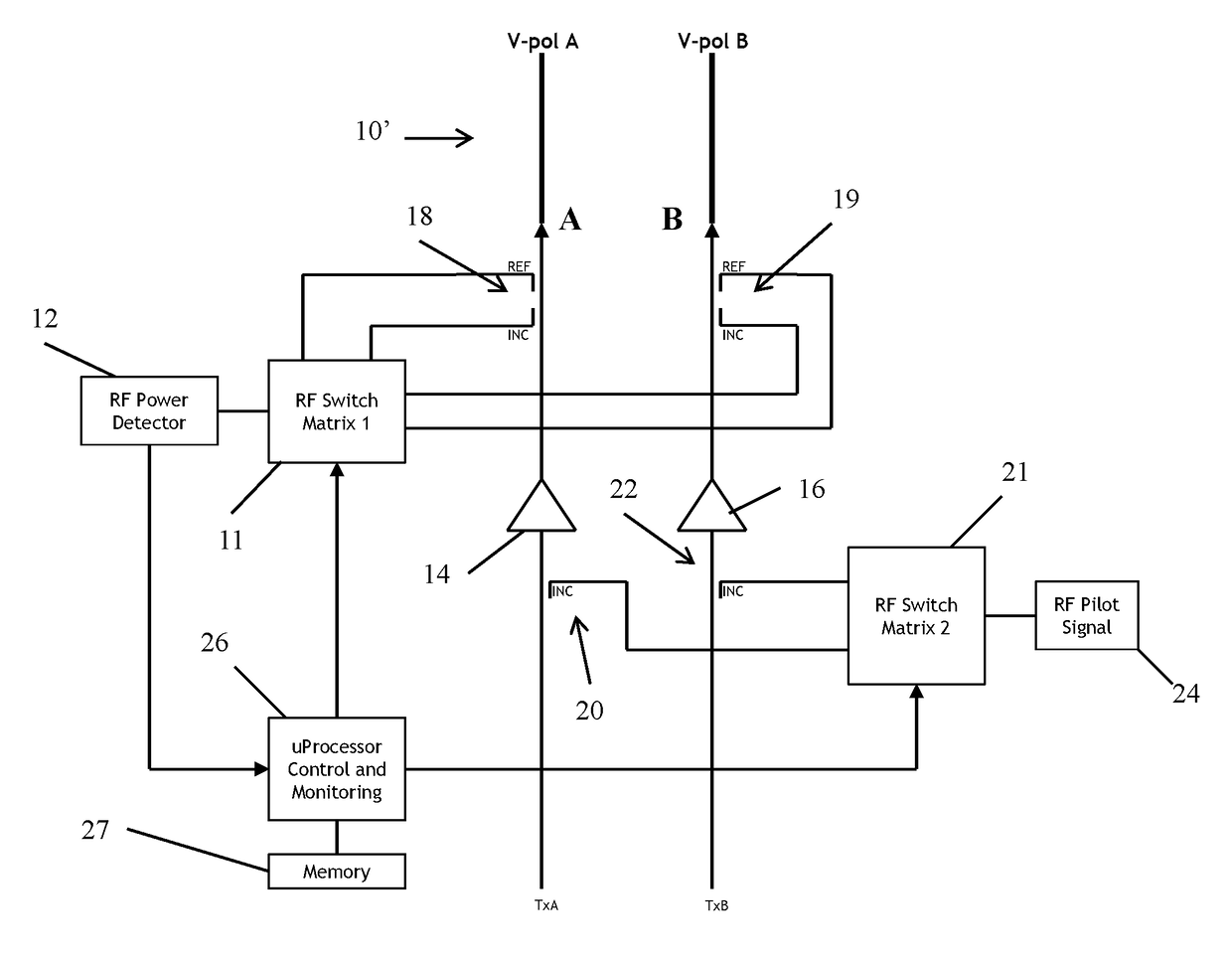
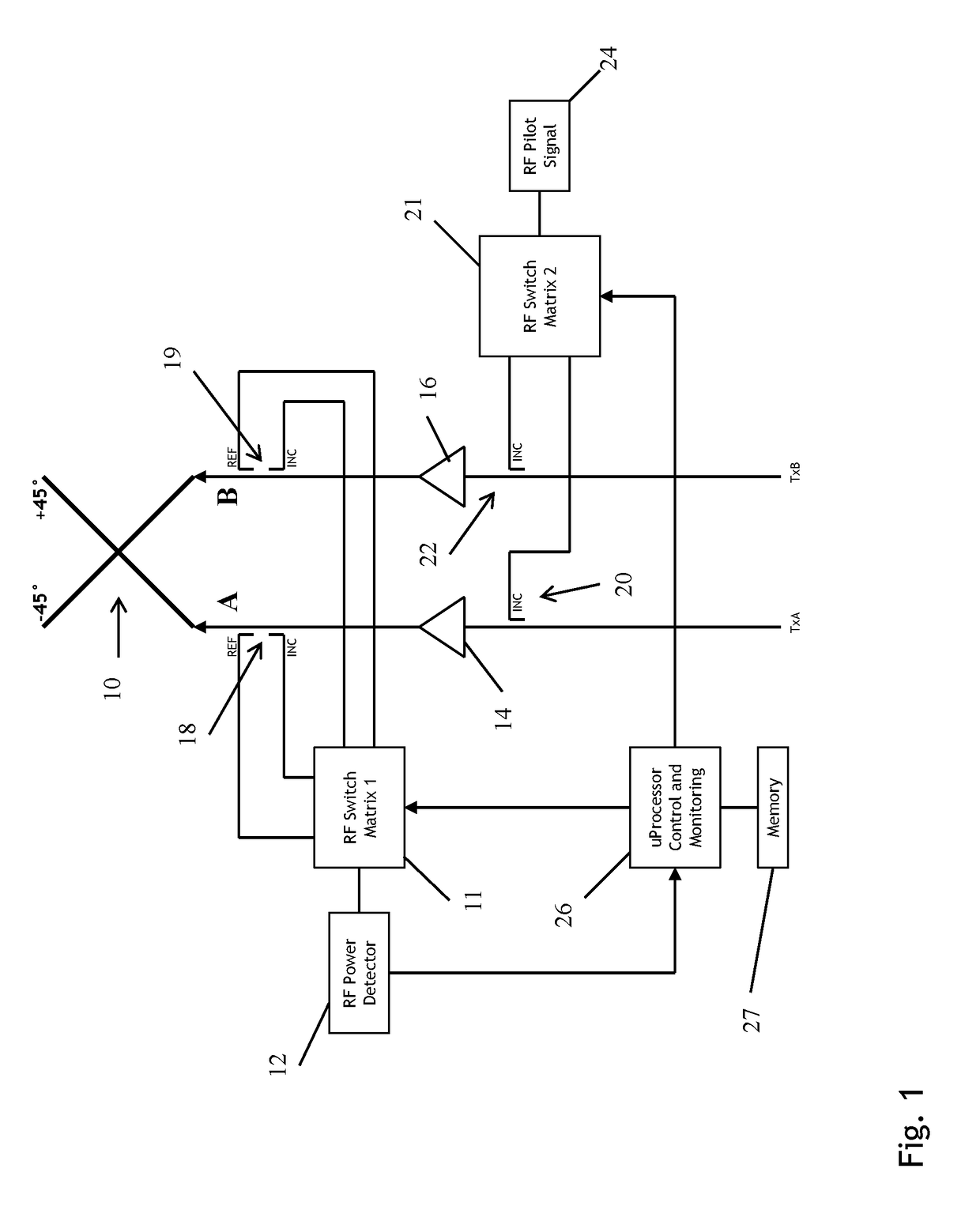
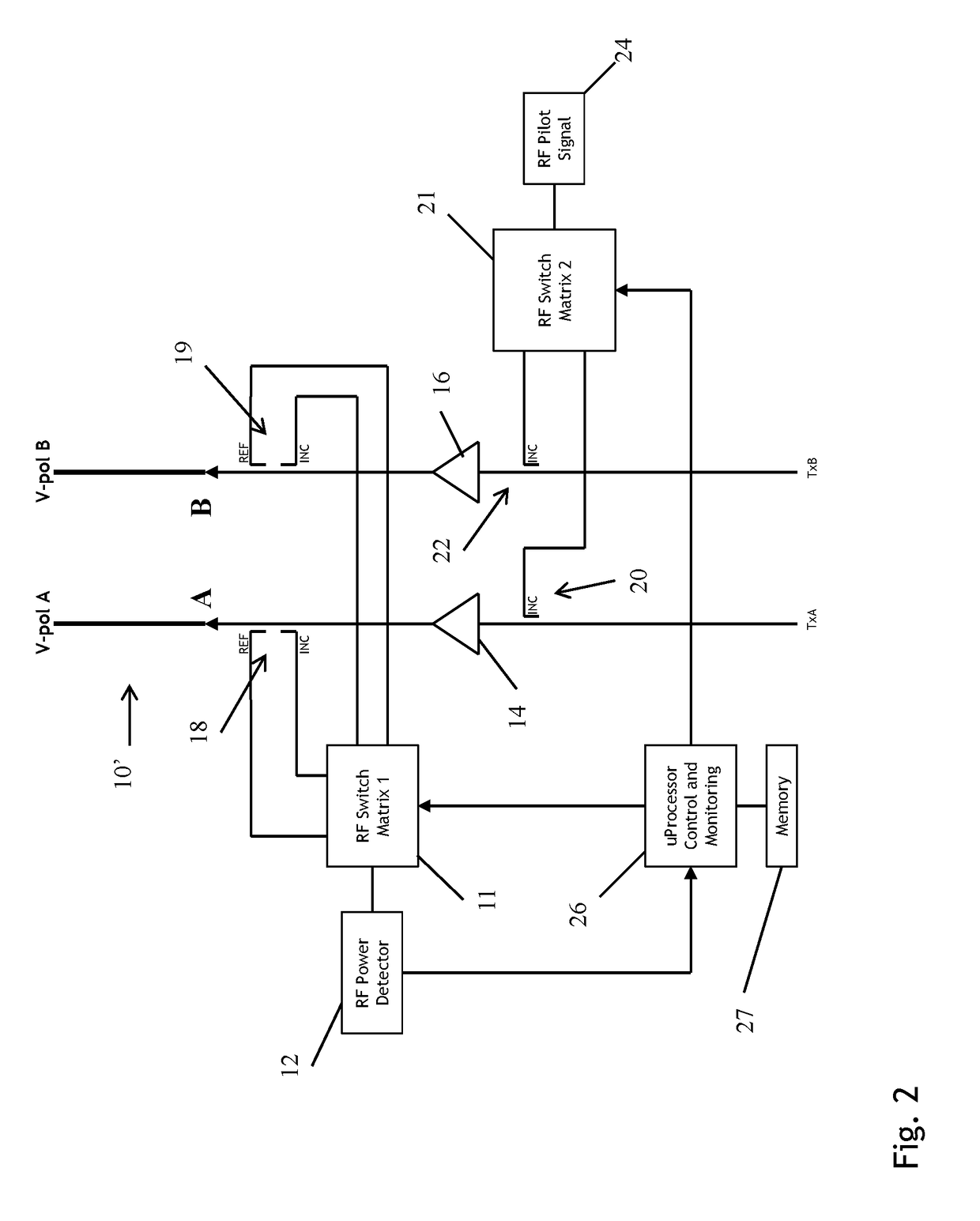
Gain measurement and monitoring for wireless communication systems
A method of monitoring an element in wireless communication system is provided. An operational noise measurement is obtained by measuring a noise value outside of a bandwidth of a first device, but within a bandwidth of a second, subsequent device. The operational noise measurement is alternatively obtained by tuning an input band of the element to shift the input band partially or completely outside of a bandwidth of a first device to create an open band or by suppressing an input of the antenna and measuring noise within the open bandwidth of the element of the wireless communication network. A stored parameter is retrieved and compared to the measured operational noise. Alternatively, a leakage signal of the element may be received at a signal receiver and compared to a reference. The reference is a function of components of the wireless communication system in a leakage path of the leakage signal.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
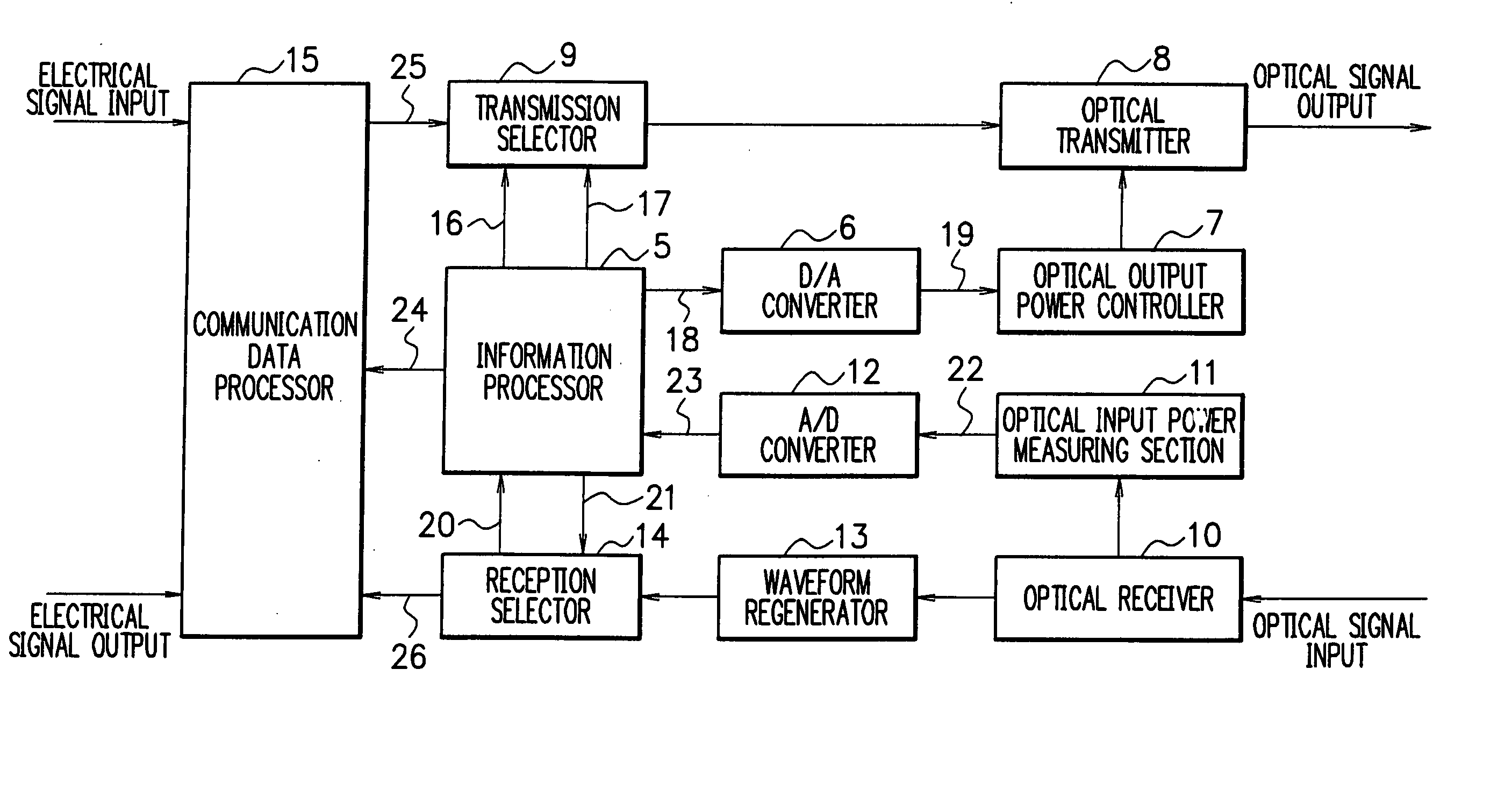
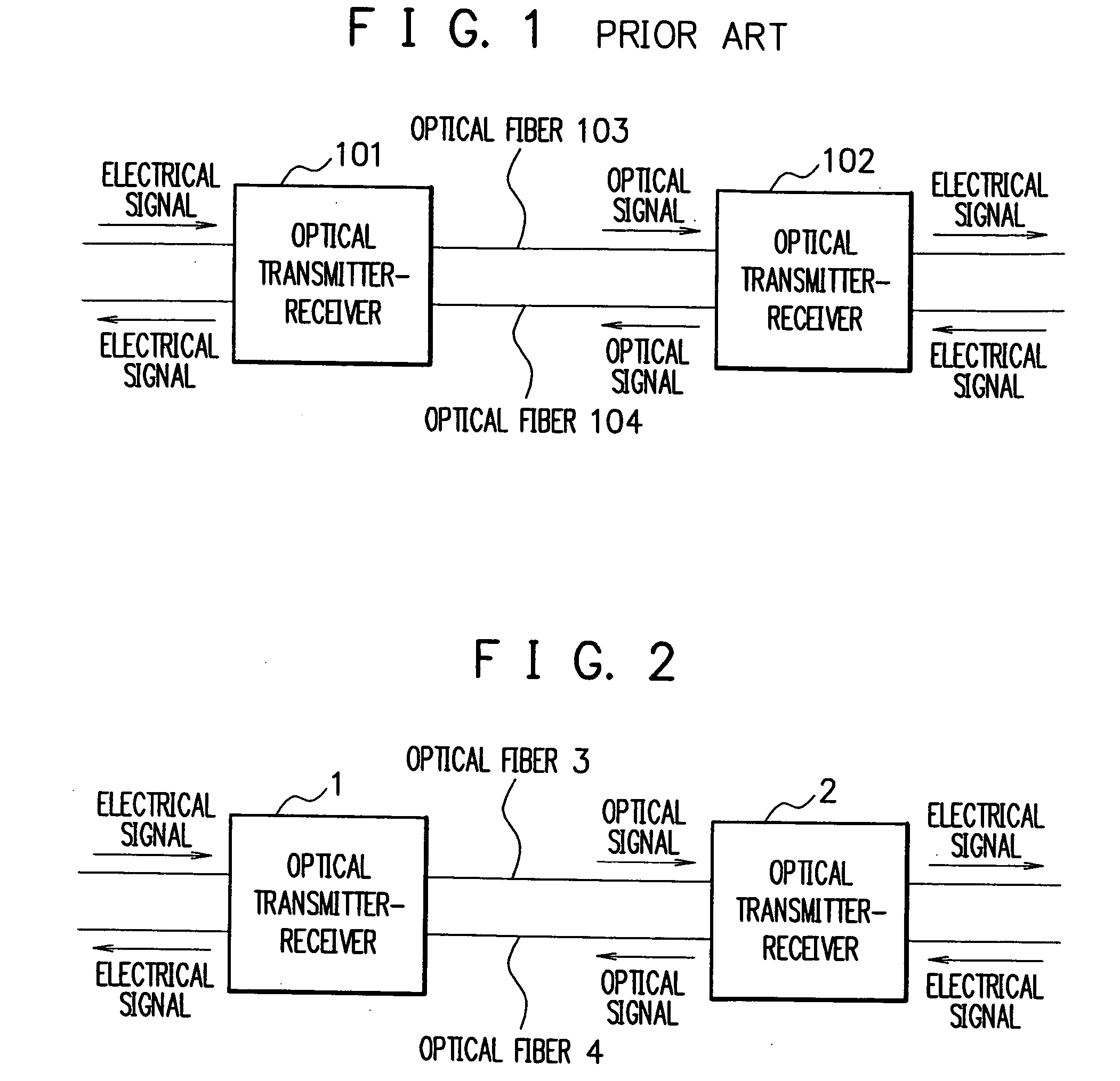
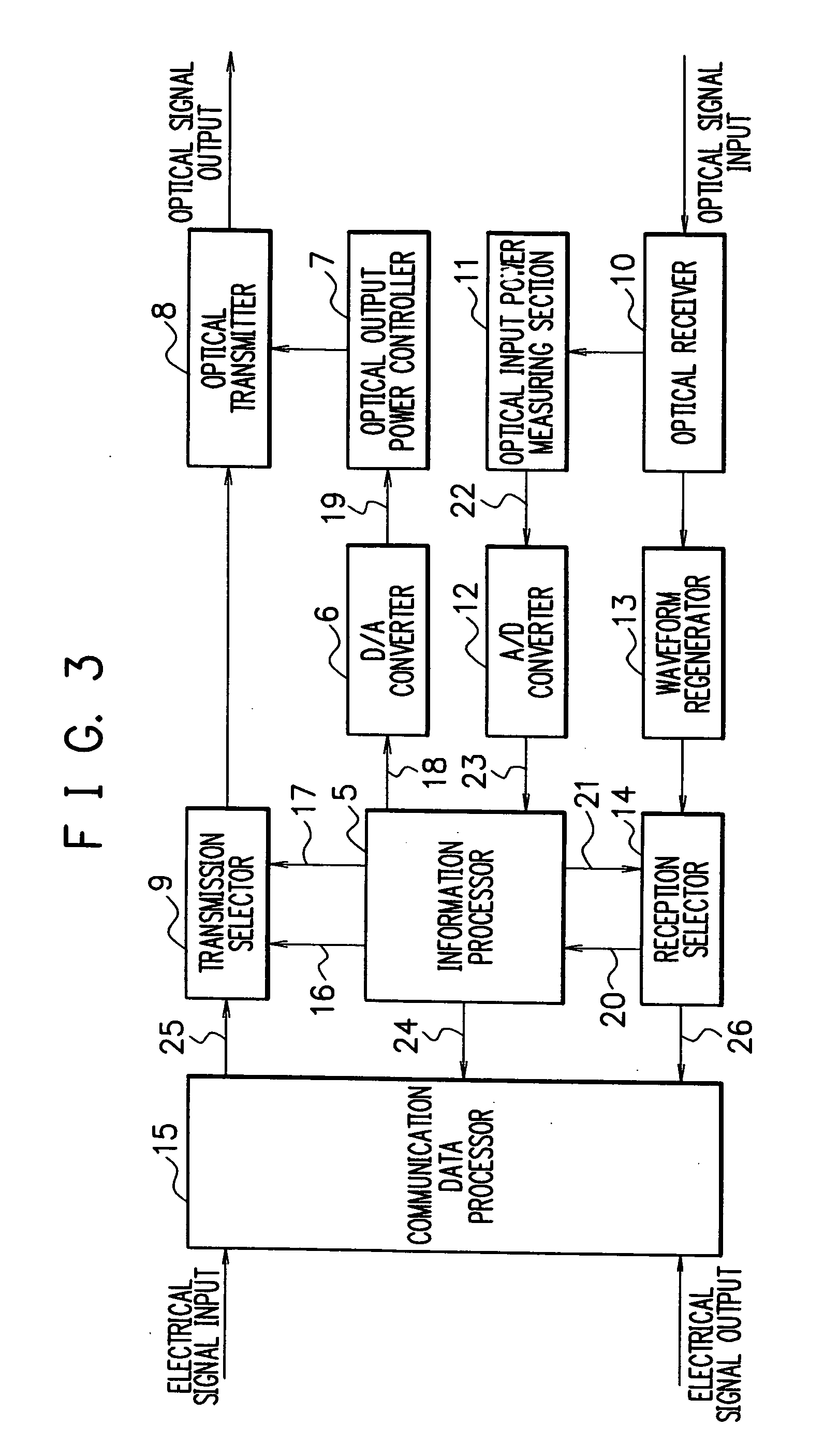
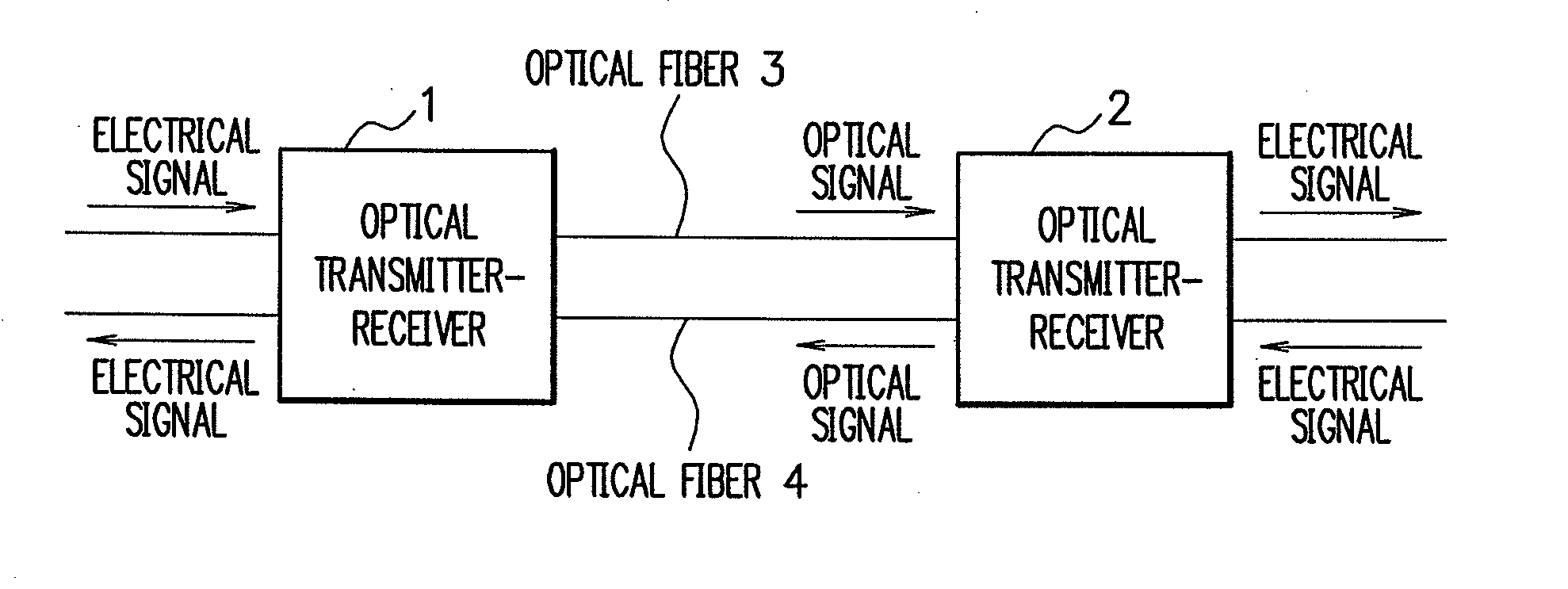
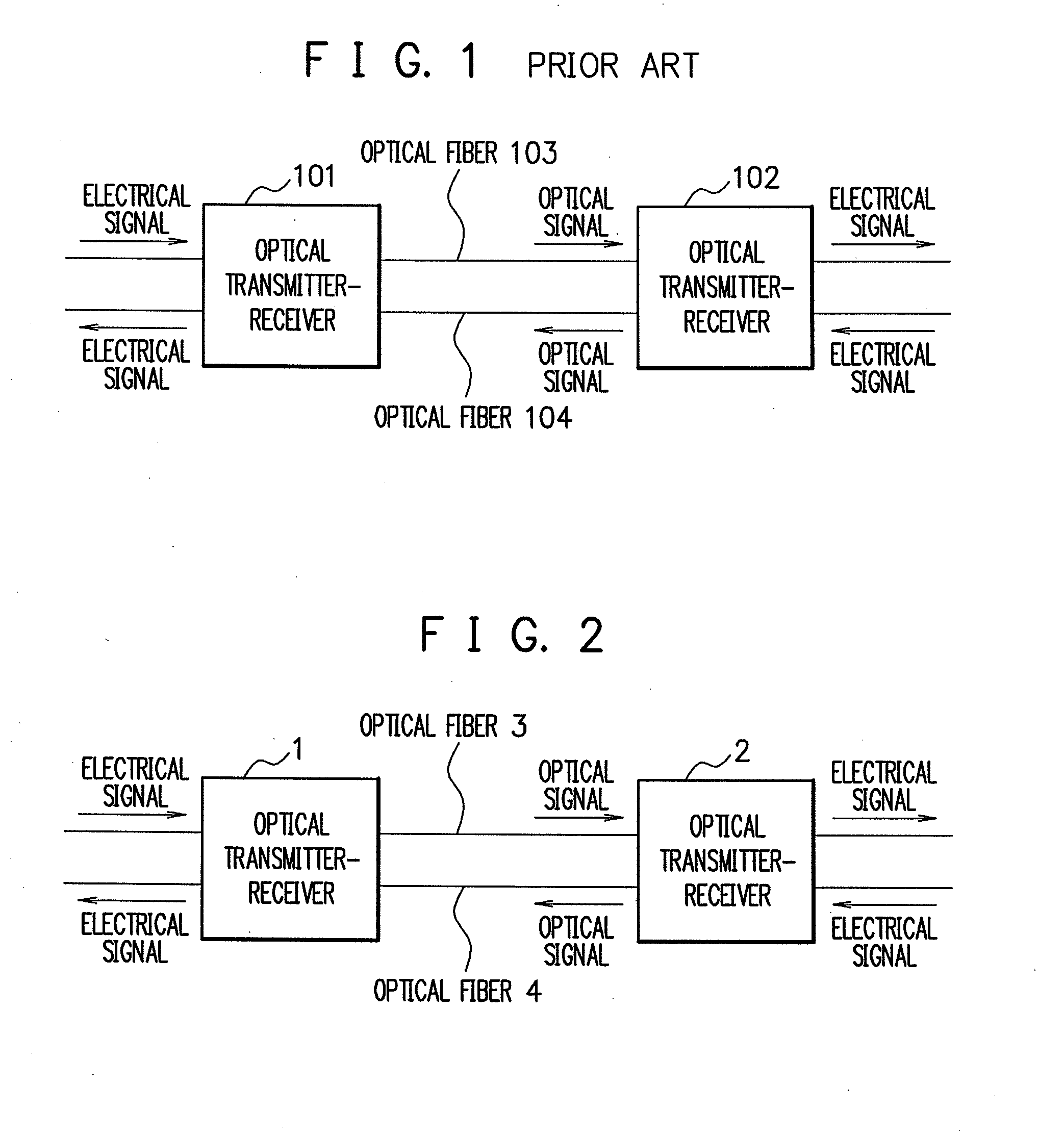
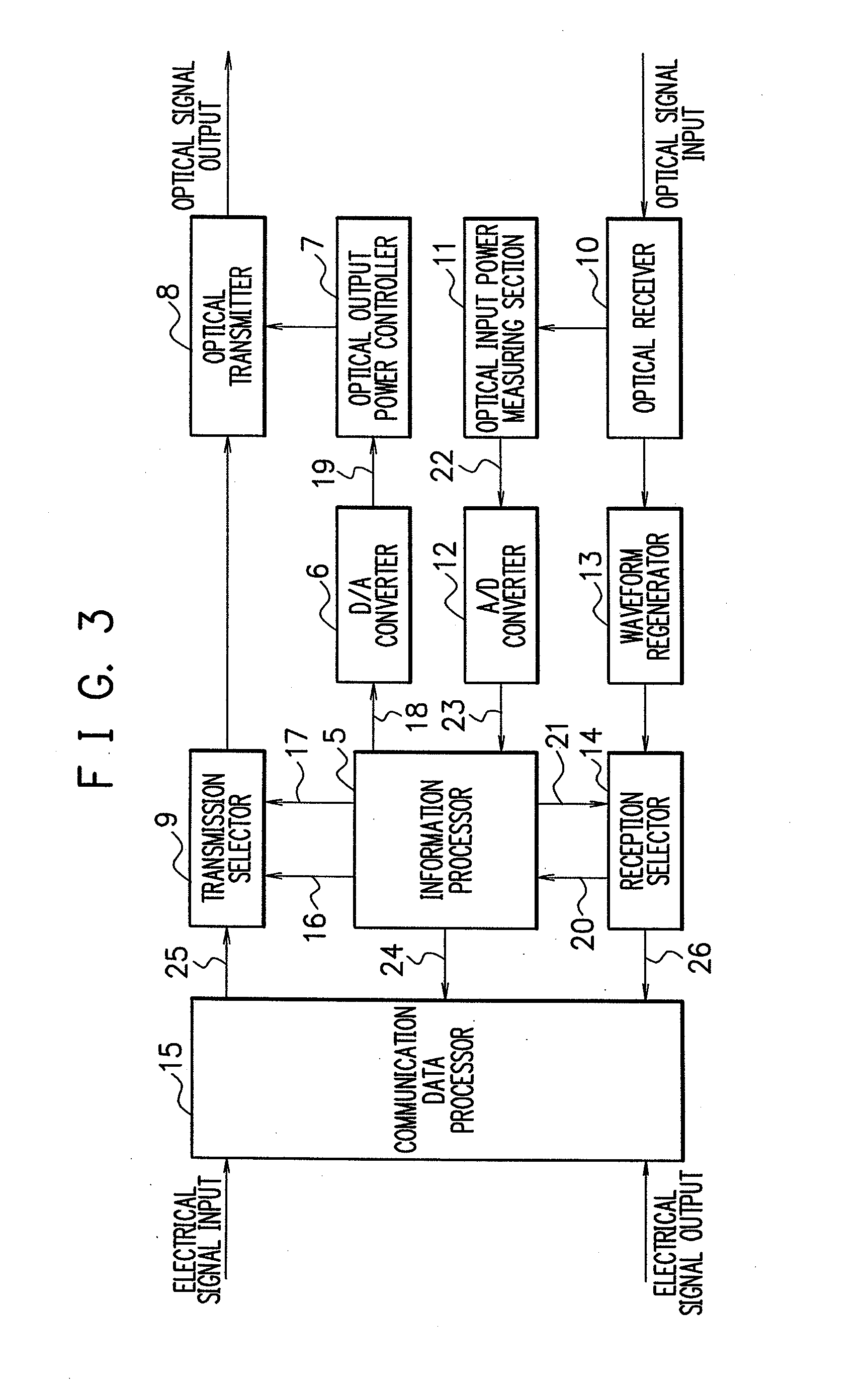
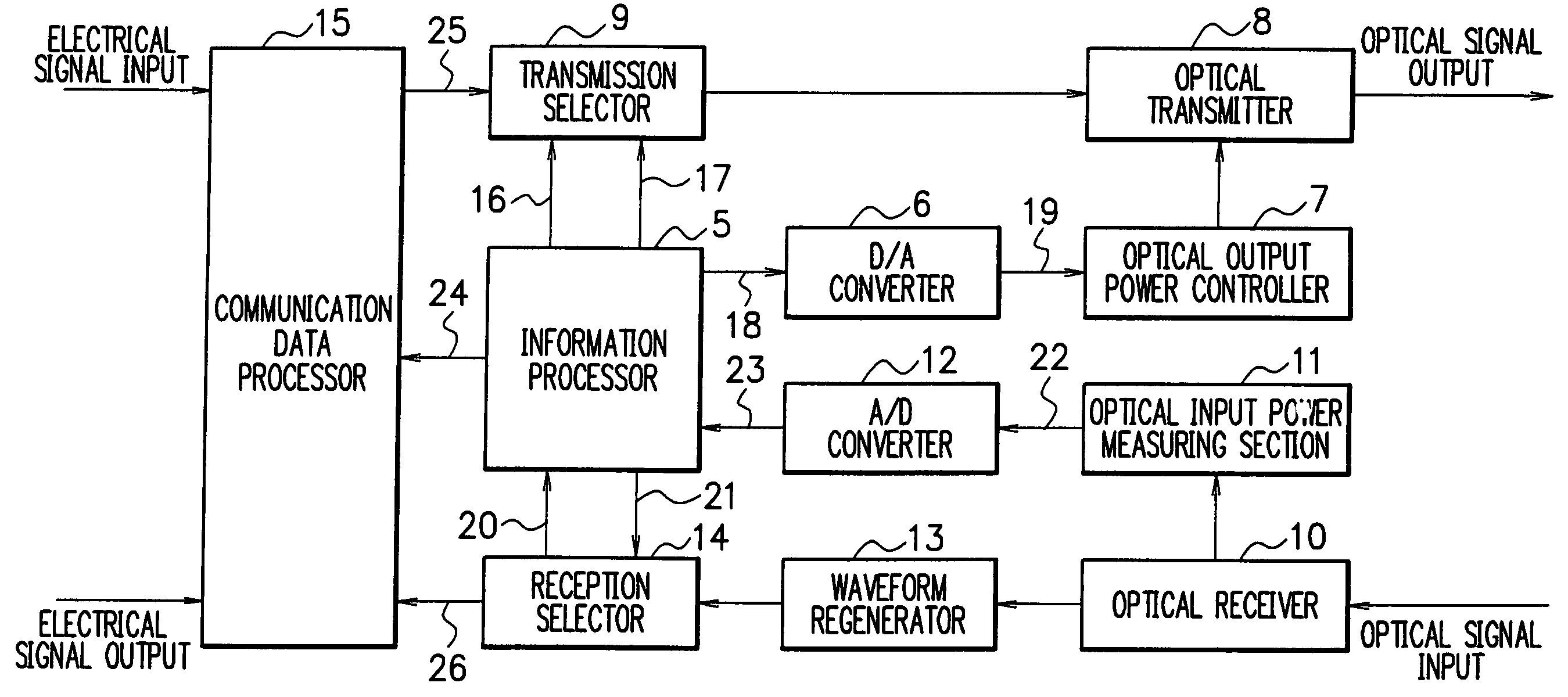
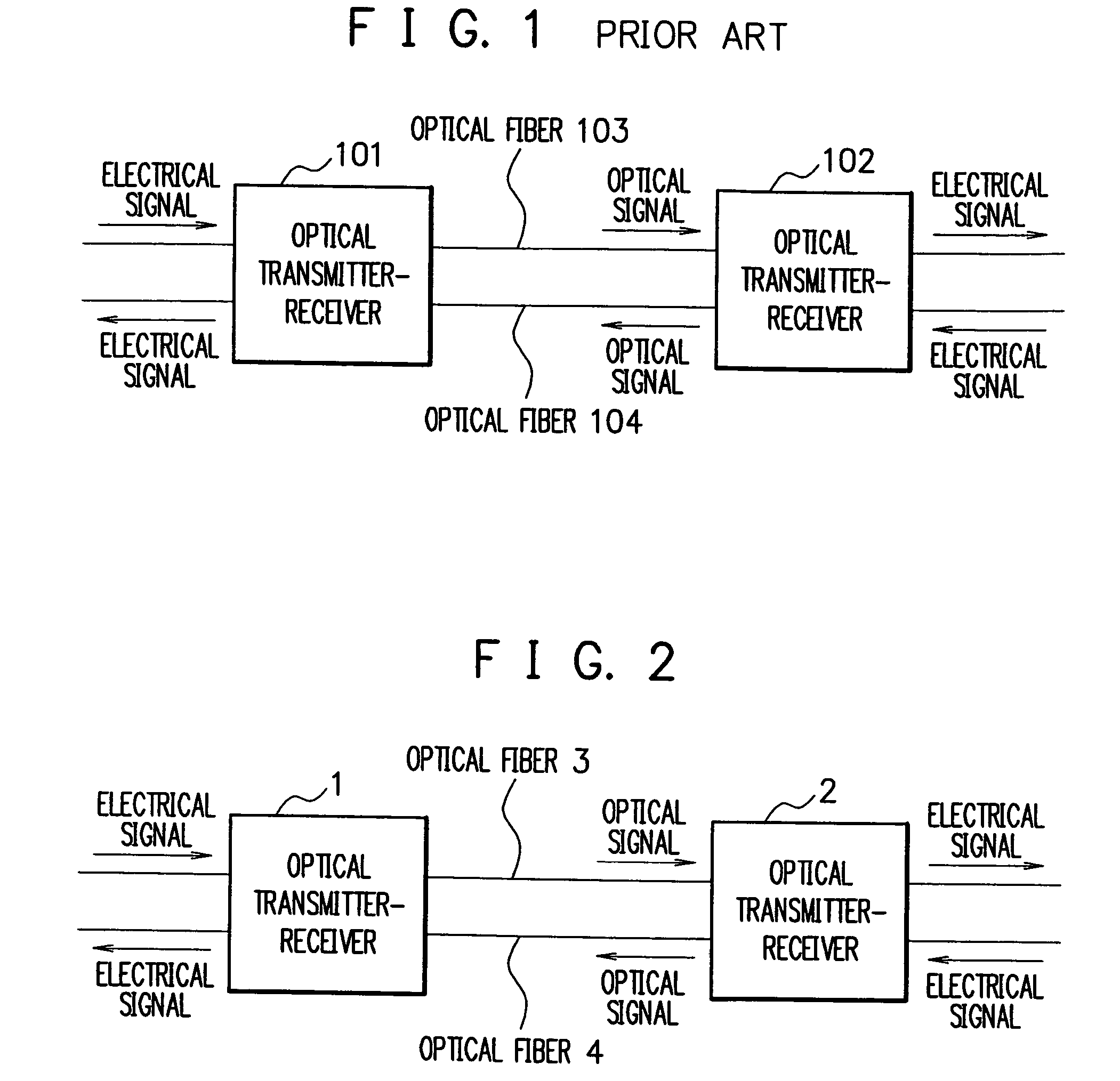
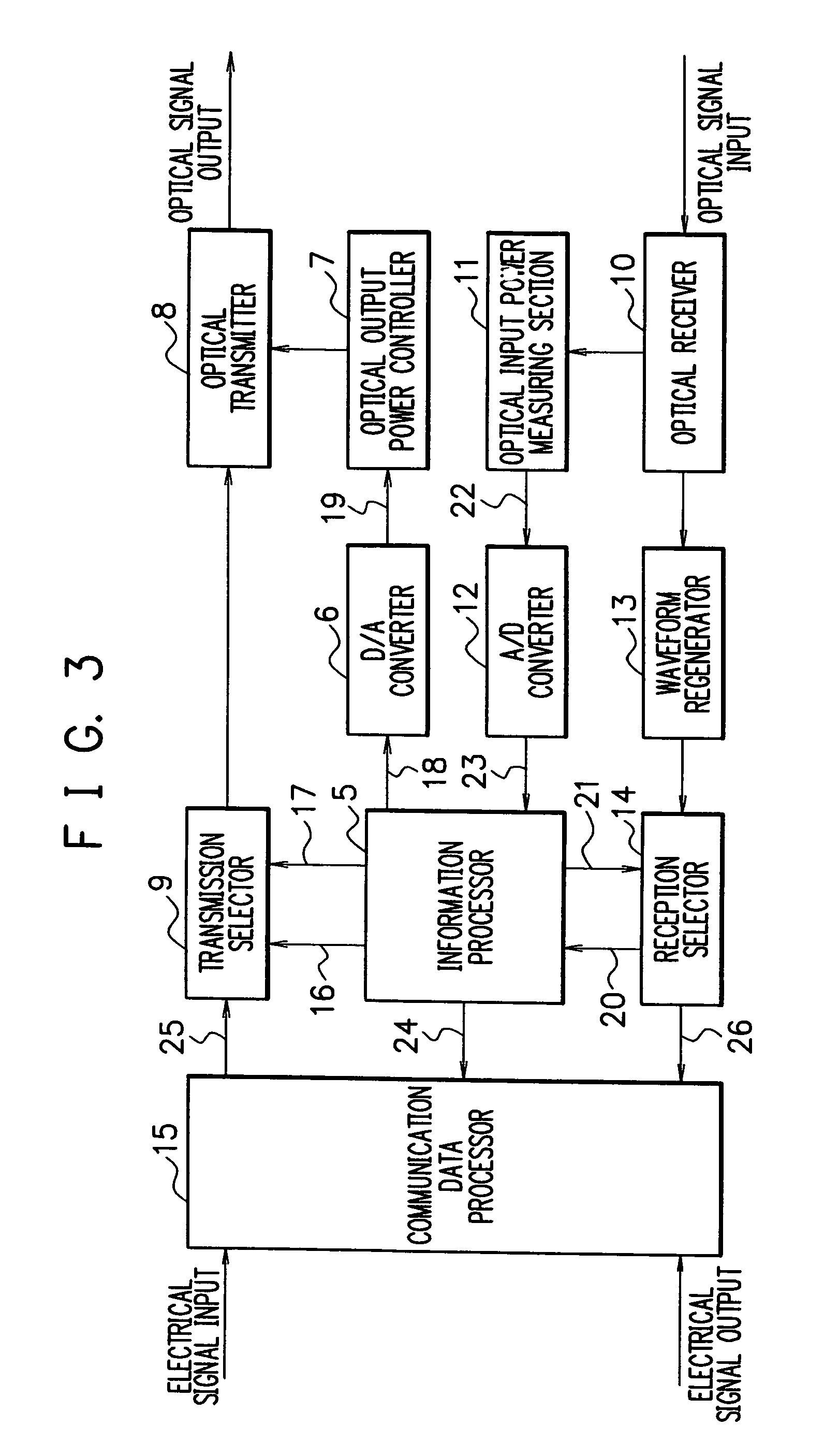
Transmission loss and gain measurement method, transmitter-receiver, and transmitting-receiving system
A transmitter-receiver having, a means for automatically determining the status of transmission medium such as optical fiber, and a means for automatically setting and resetting the transmission rate and / or output power according to the status of the transmission medium, a transmission loss and gain measurement method, and a transmitting-receiving system. A transmitter-receiver comprises at least: an output power controller for controlling the output power of a transmitter; an input power measuring section for measuring the strength of input signals; and an information processor for deriving the loss or gain of a path to change the output power of the transmitter and / or the rate of data transmission according to the derived loss or gain of the path. A transmission loss and gain measurement method applied to a system comprising transmission media and a plurality of the transmitter-receivers connected via the transmission media, comprises the steps of: transmitting information on the output power of a first transmitter-receiver from the first transmitter-receiver to a second transmitter-receiver; measuring reception strength by the second transmitter-receiver when the second transmitter-receiver receives the output power information; reading the output power information by the second transmitter-receiver; and comparing the reception strength with the output power information to calculate a transmission loss or gain by the second transmitter-receiver.
Owner:NEC CORP
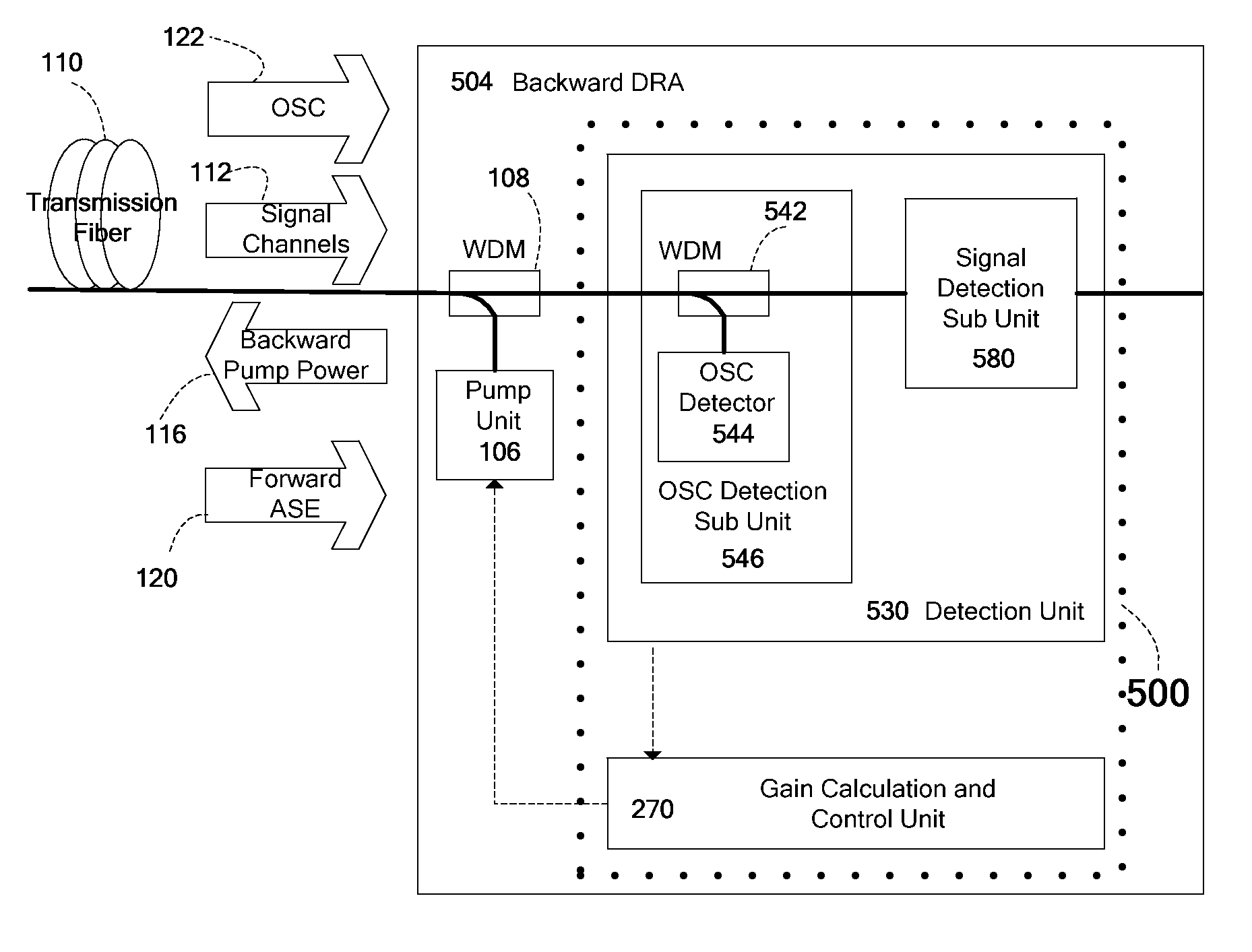
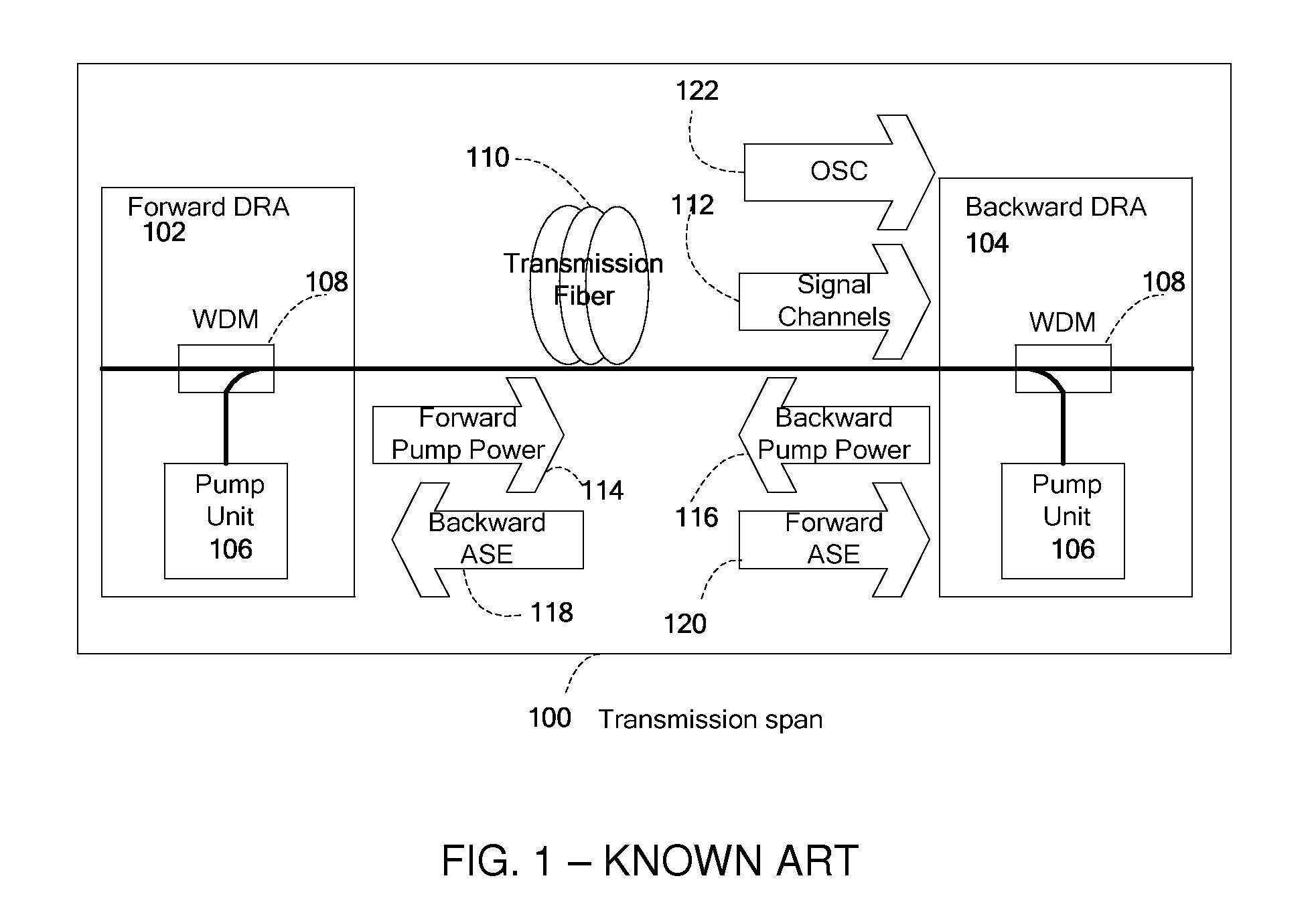
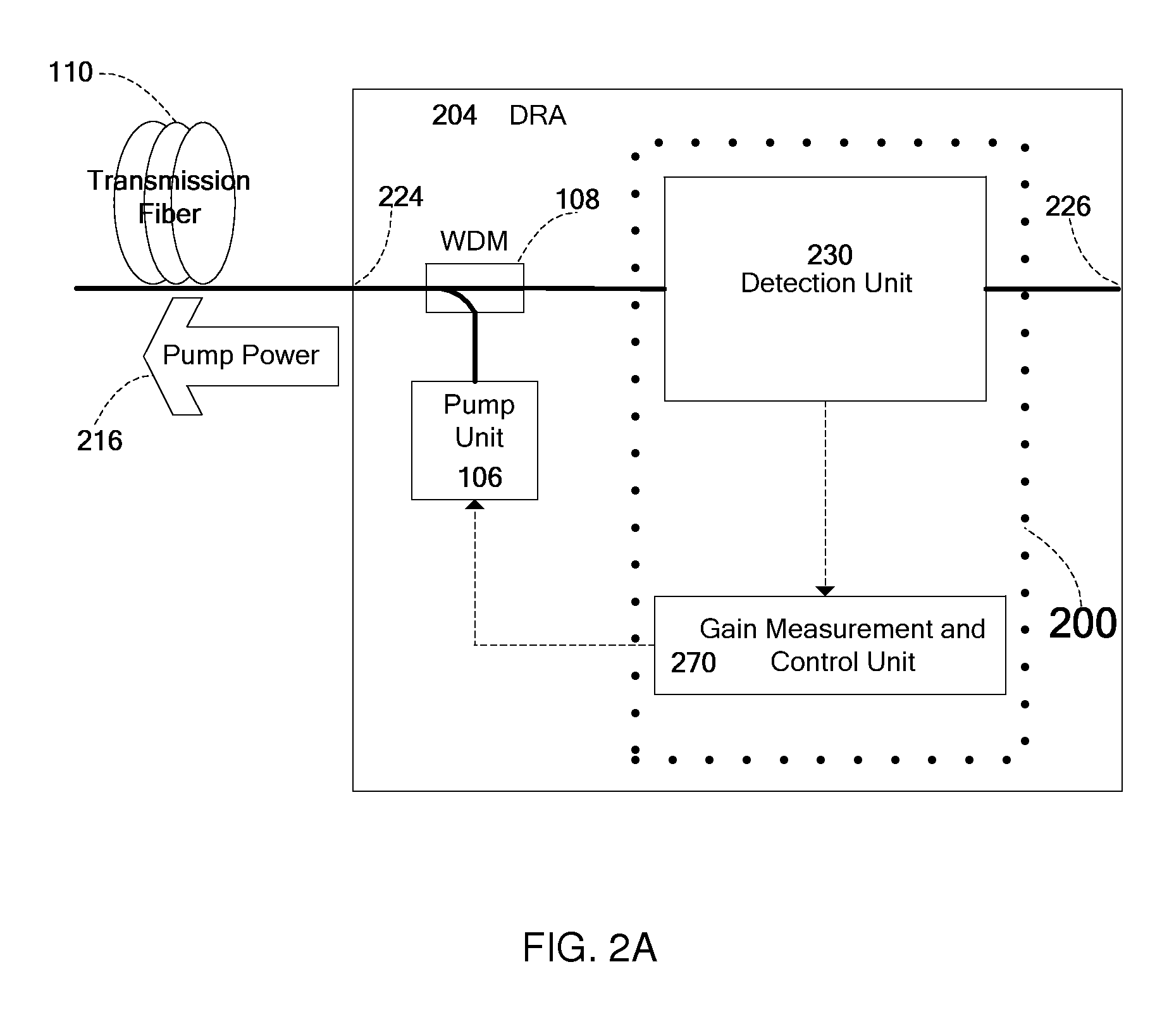
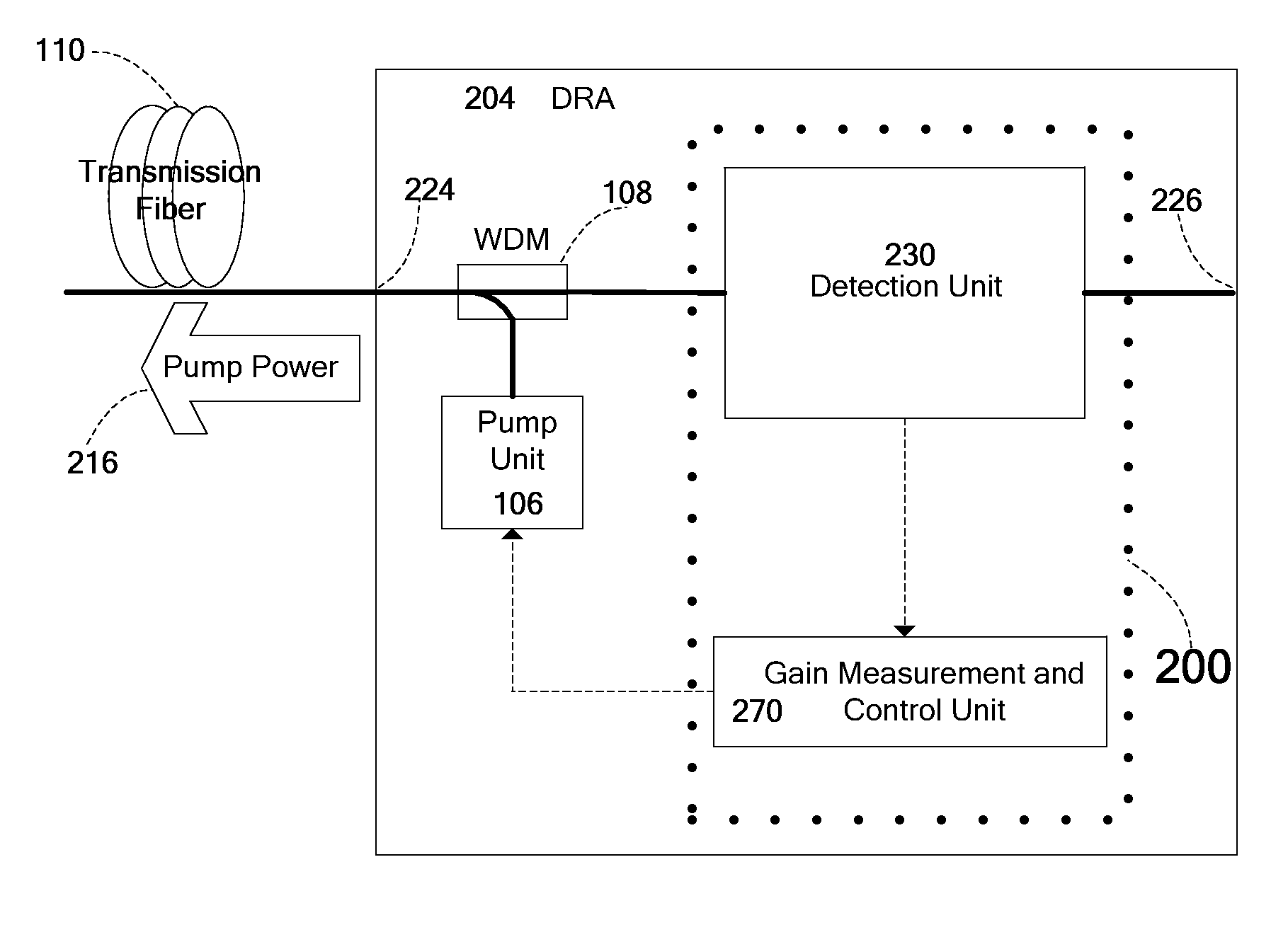
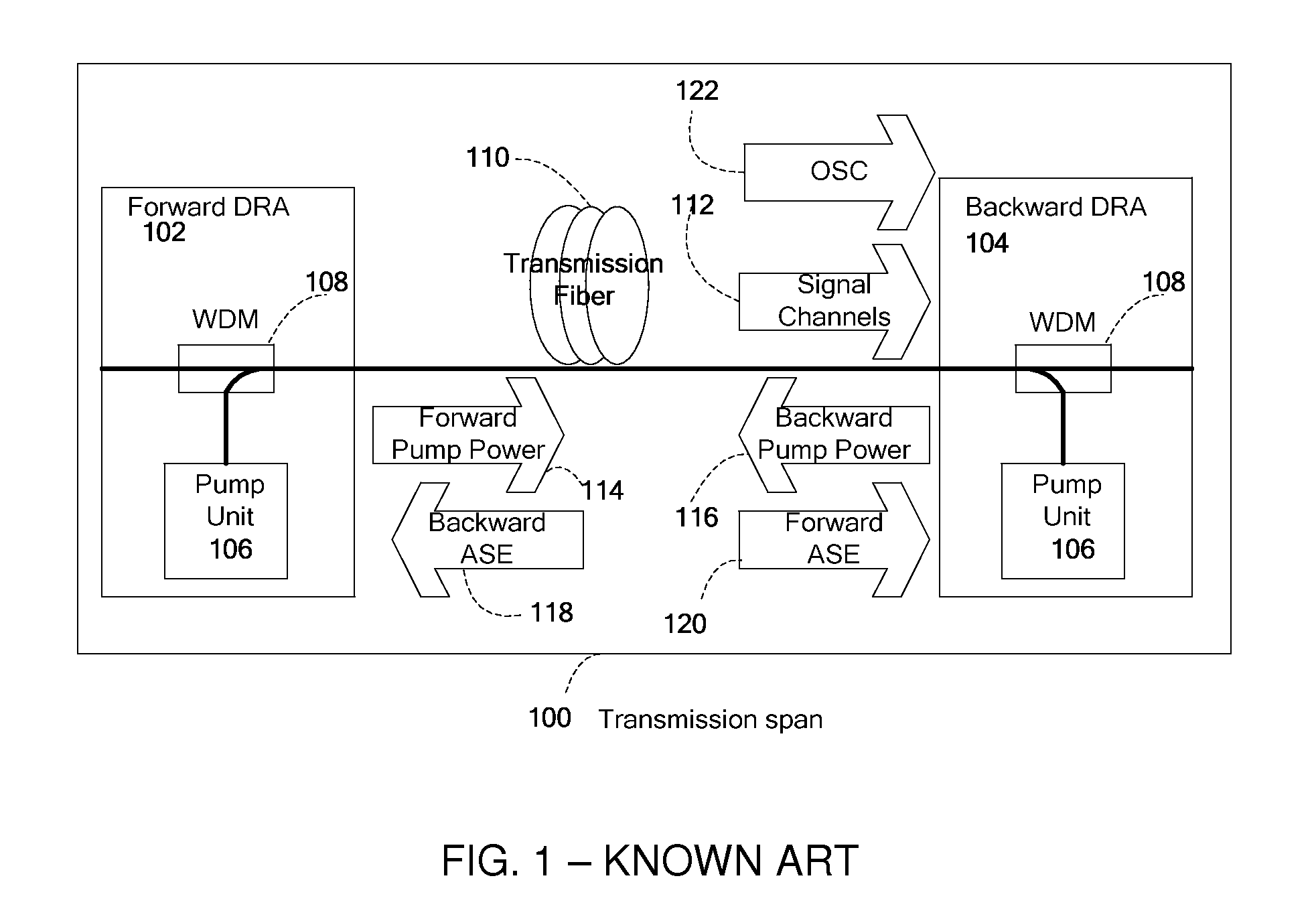
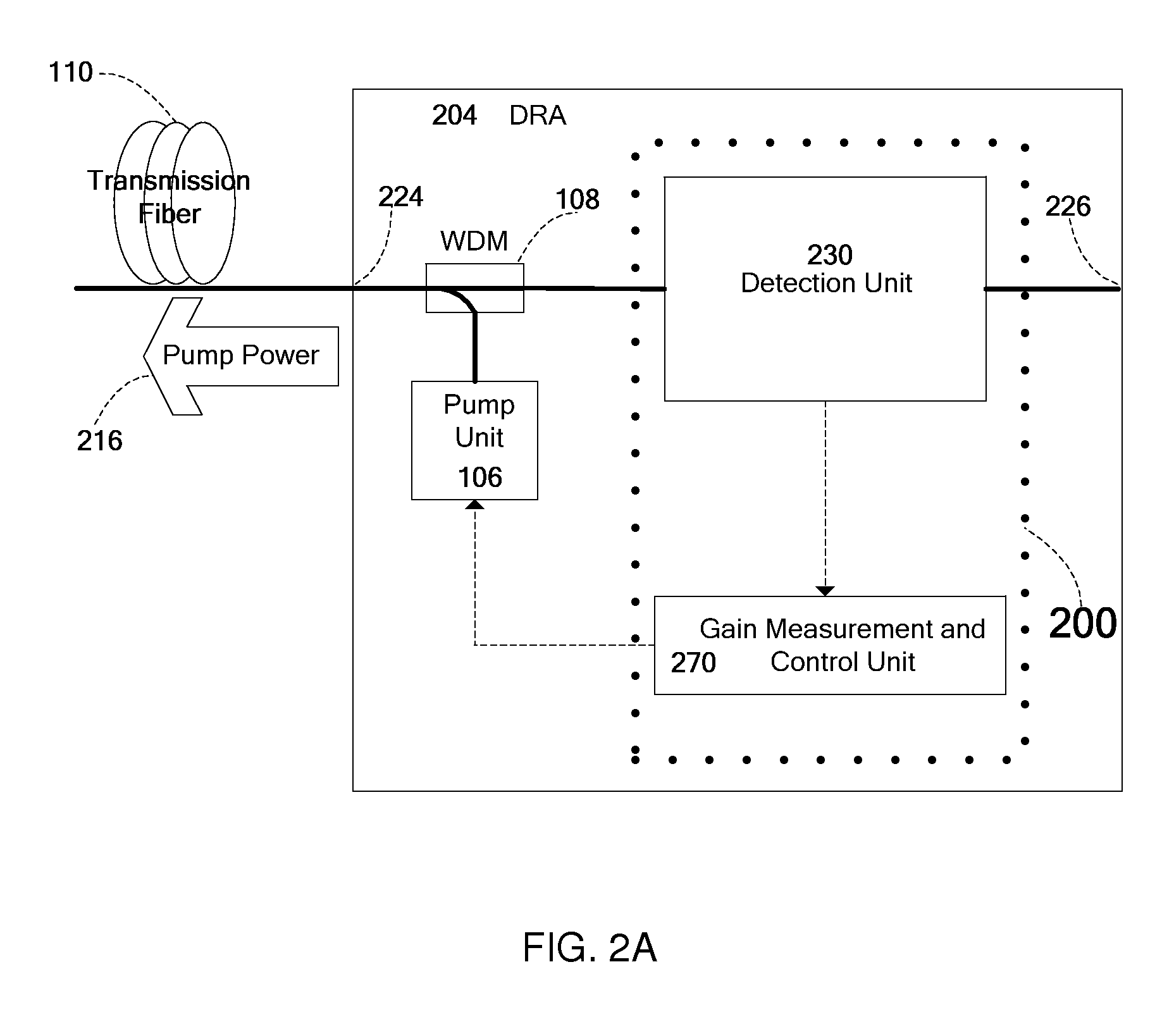
Automatic measurement and gain control of distributed raman amplifiers
ActiveUS20110141552A1Accurate measurementLaser using scattering effectsElectromagnetic transmissionPhysicsGain measurement
Apparatus and method for gain measurement and control of a Distributed Raman Amplifier (DRA). Various embodiments of the apparatus include a detection unit operative to measure, during operation of the DRA, the optical power of a filtered component of the light entering the DRA from the transmission fiber and a gain calculation and control unit coupled to the detection unit and operative to calculate a signal Raman gain property from the measured optical power. The filtered component may exemplarily be a result of passing the light through a band pass filter, a spectral filter with a given spectral shape or a notch filter. The signal Raman gain property may be an average on-off signal Raman gain, an average net signal Raman gain or a signal Raman gain tilt within a communication band. The apparatus and method may be used to operate the DRA in Automatic Gain Control, i.e. to maintain a required constant signal Raman gain and / or signal Raman gain tilt.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC +1
Gain measurement and monitoring for wireless communication systems
A method of monitoring an element in wireless communication system is provided. An operational noise measurement is obtained by measuring a noise value outside of a bandwidth of a first device, but within a bandwidth of a second, subsequent device. The operational noise measurement is alternatively obtained by tuning an input band of the element to shift the input band partially or completely outside of a bandwidth of a first device to create an open band or by suppressing an input of the antenna and measuring noise within the open bandwidth of the element of the wireless communication network. A stored parameter is retrieved and compared to the measured operational noise. Alternatively, a leakage signal of the element may be received at a signal receiver and compared to a reference. The reference is a function of components of the wireless communication system in a leakage path of the leakage signal.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
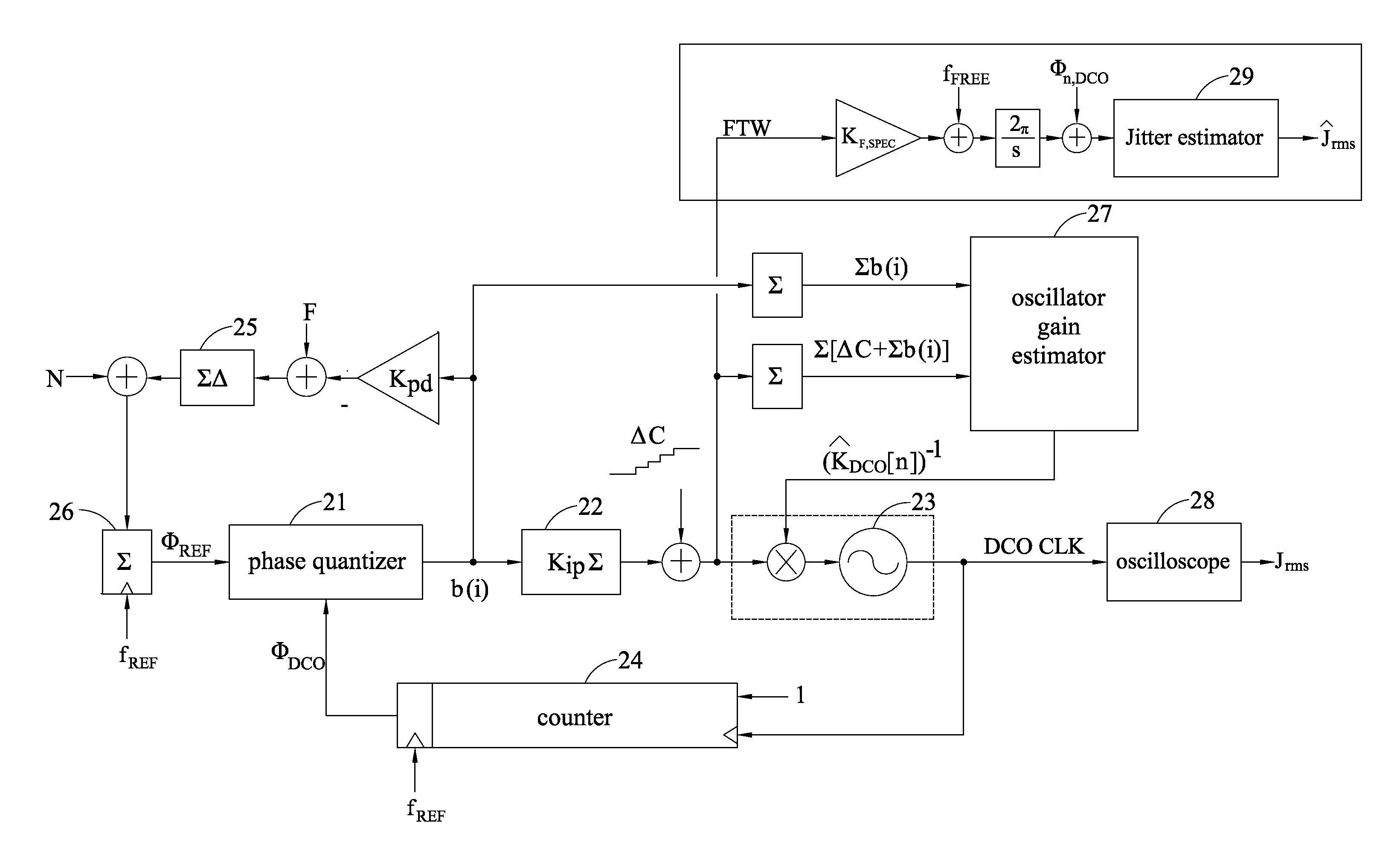
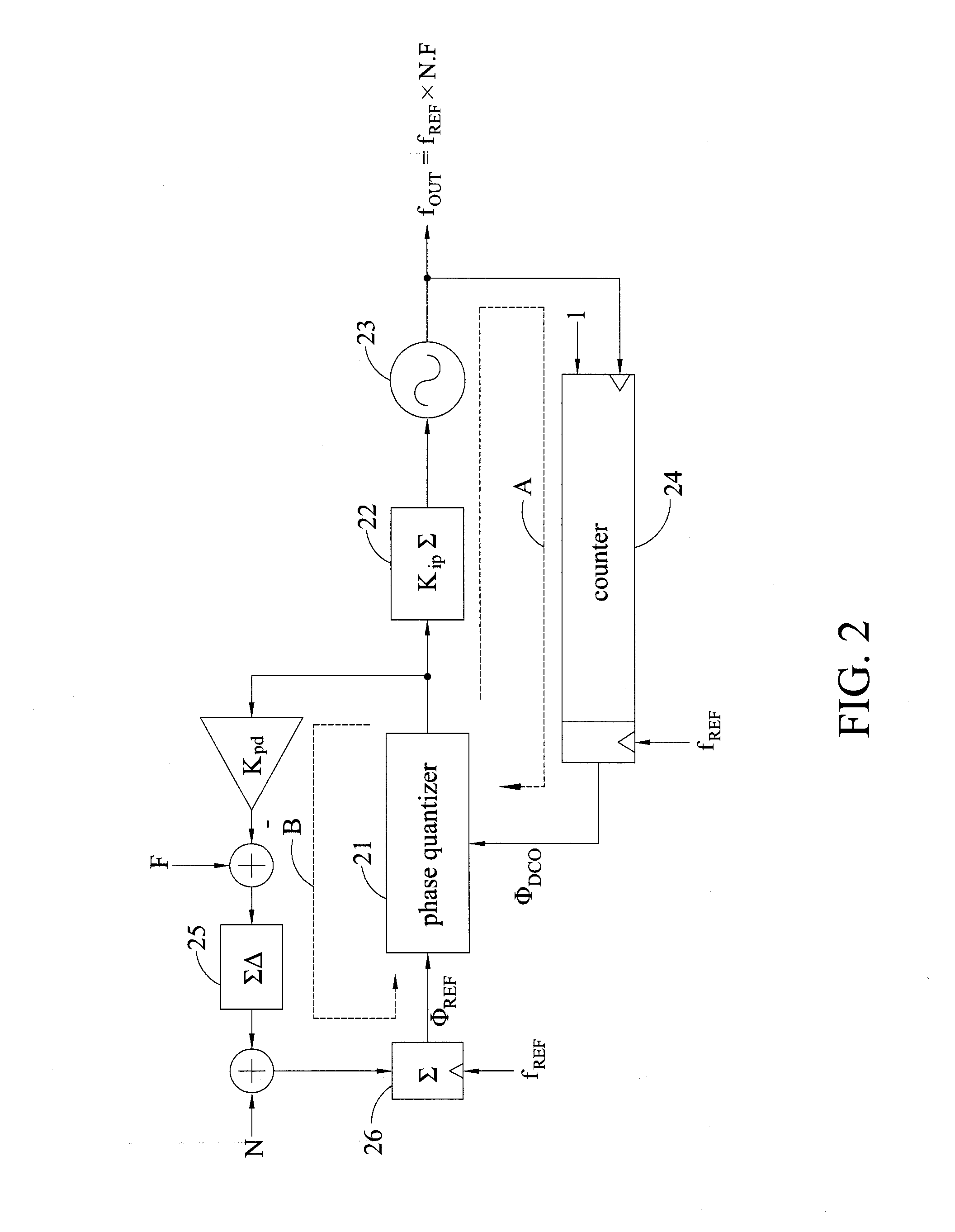
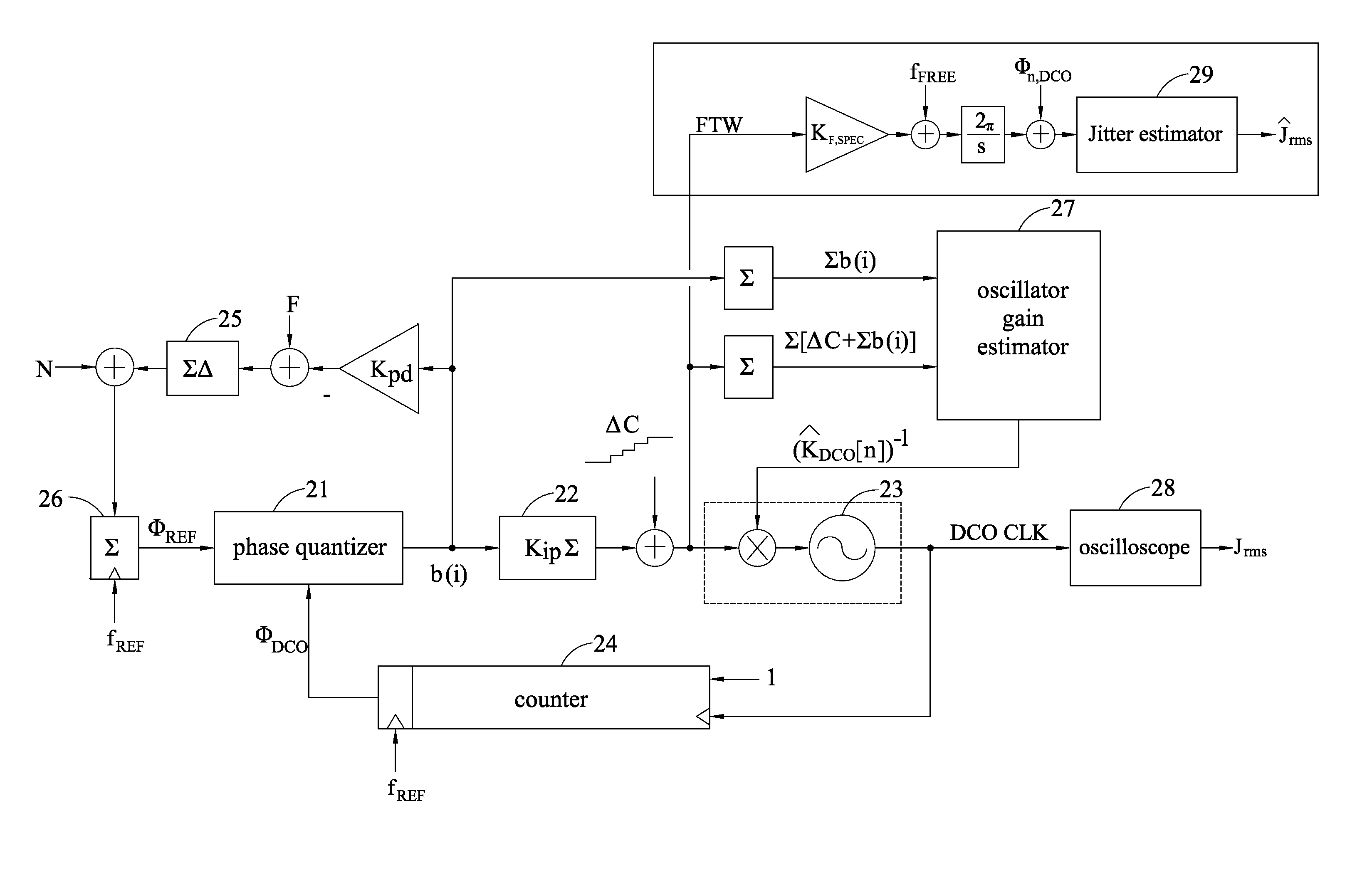
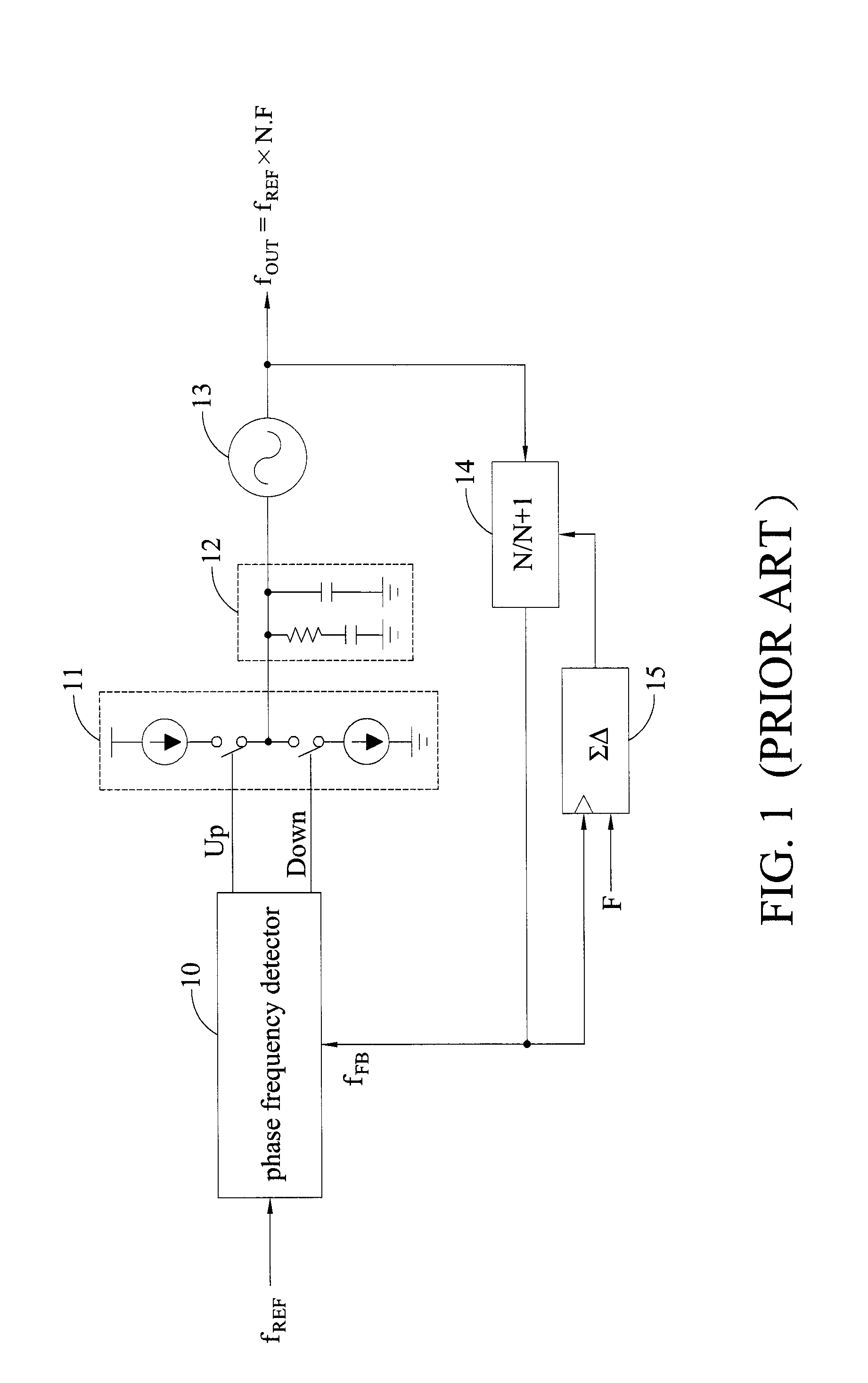
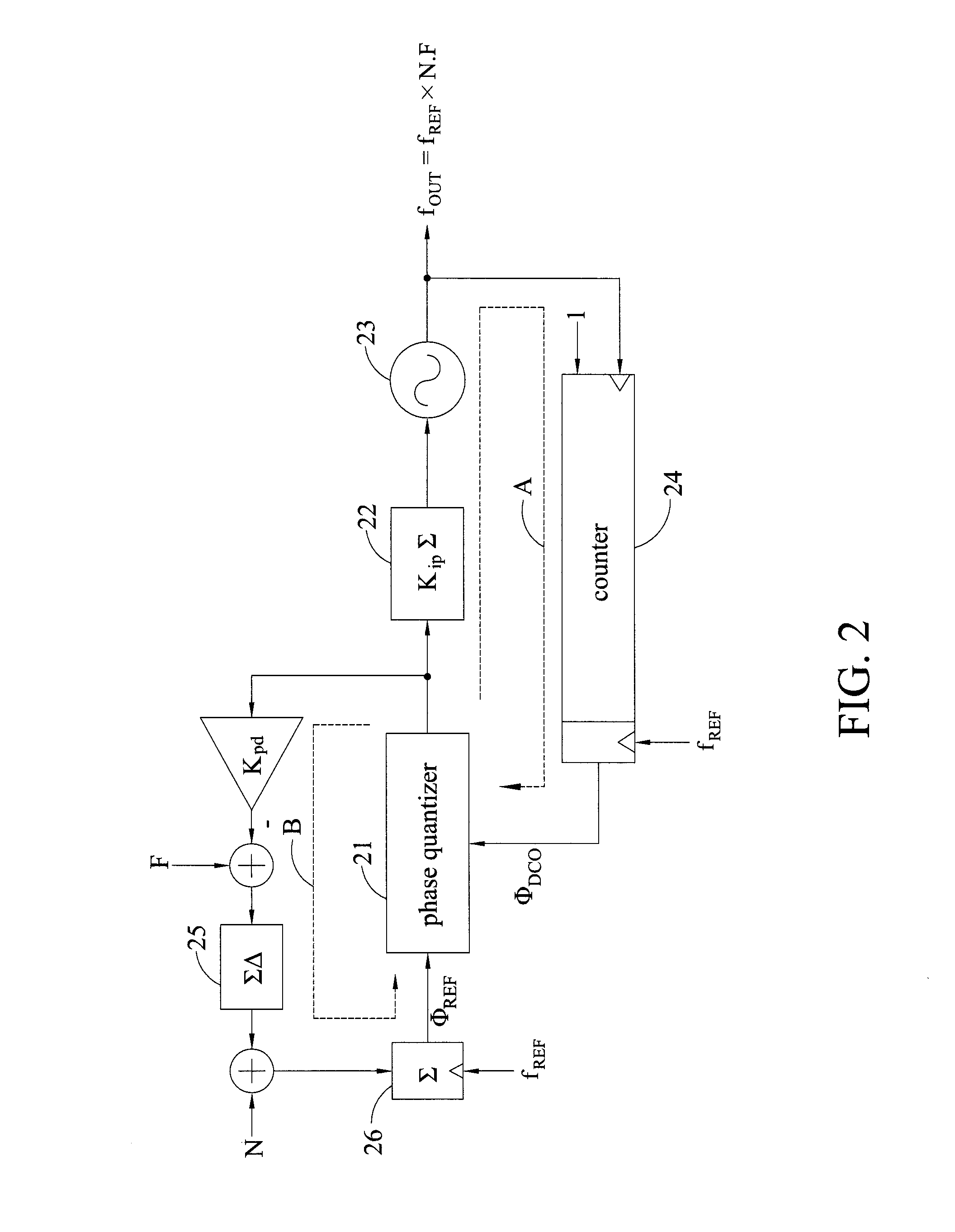
Phase-locked loop with loop gain calibration, gain measurement method, gain calibration method and jitter measurement method for phase-locked loop
InactiveUS20140077849A1Noise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementPulse automatic controlPhase-locked loopGain measurement
The invention provides a phase-locked loop with loop gain calibration and methods for measuring an oscillator gain, gain calibration and jitter measurement for a phase-locked loop. The method for measuring an oscillator gain of a phase-locked loop includes the steps of providing a varying code at an input end of the oscillator; outputting excess reference phase information by a reference phase integral path and outputting excess feedback phase information based on the varying code by a feedback phase integral path; and obtaining an estimated gain information of the oscillator based on the excess reference phase information and the excess feedback phase information.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
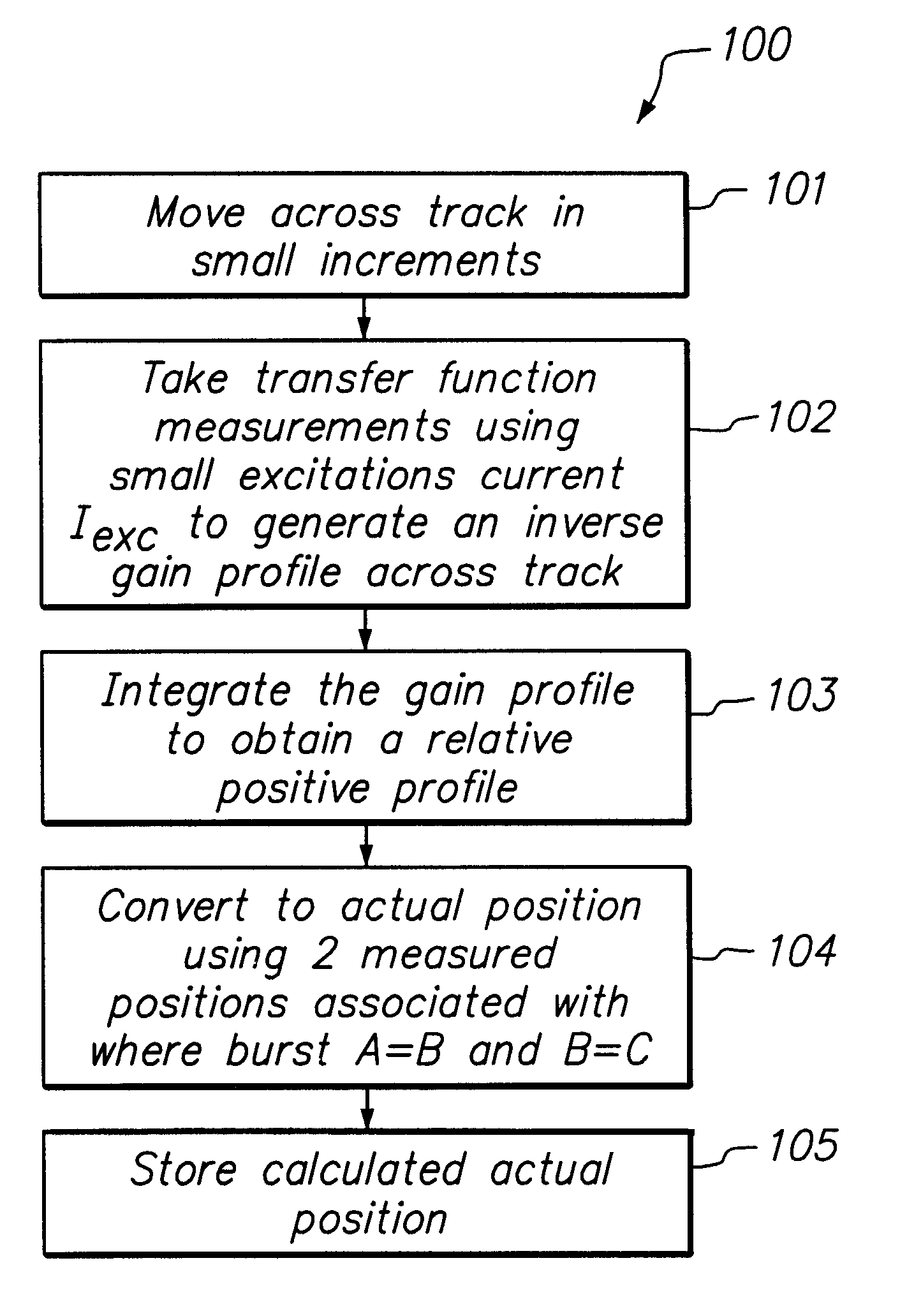
PES linearization scheme for disk drive servo using small excitation bode measurements
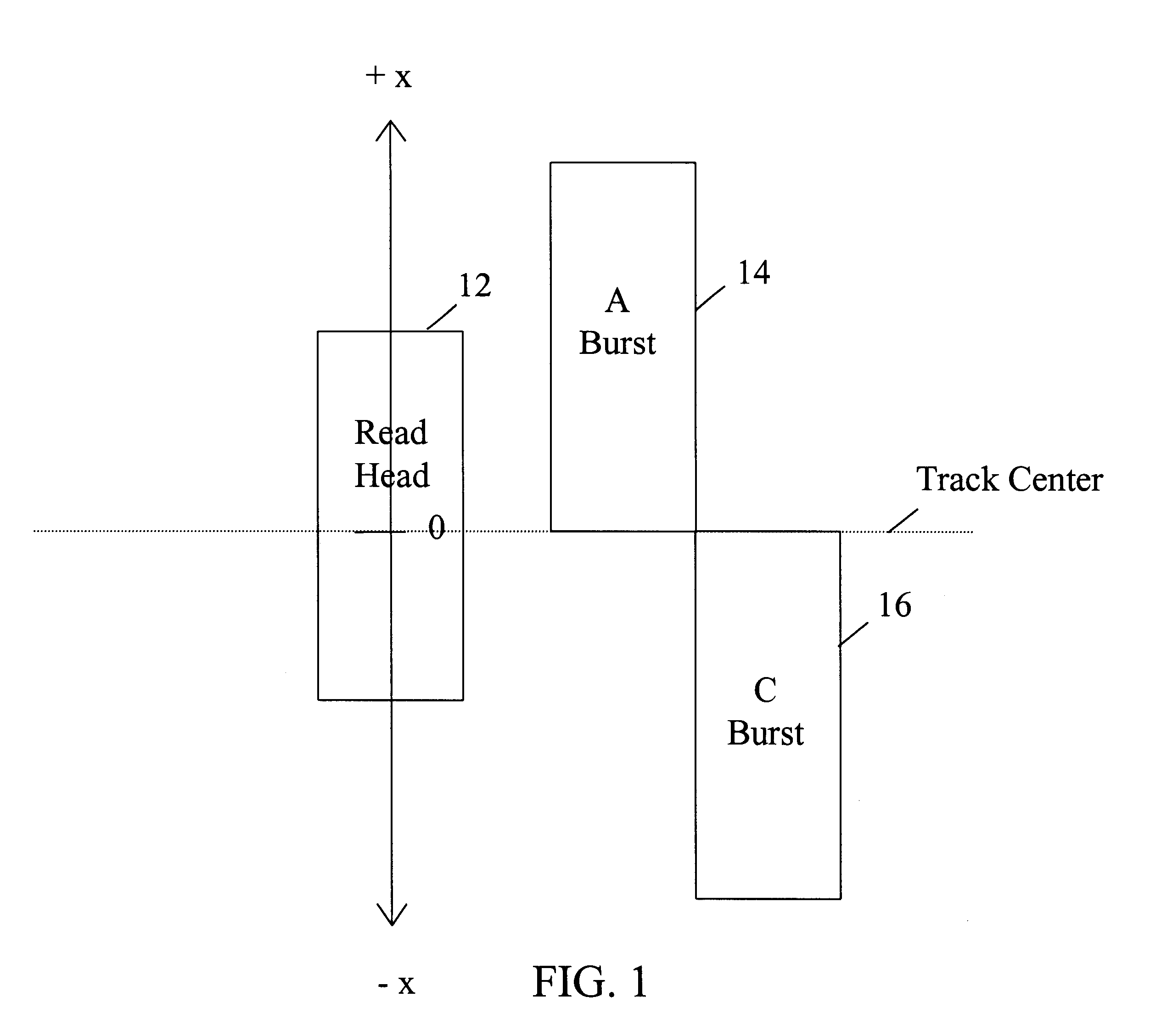
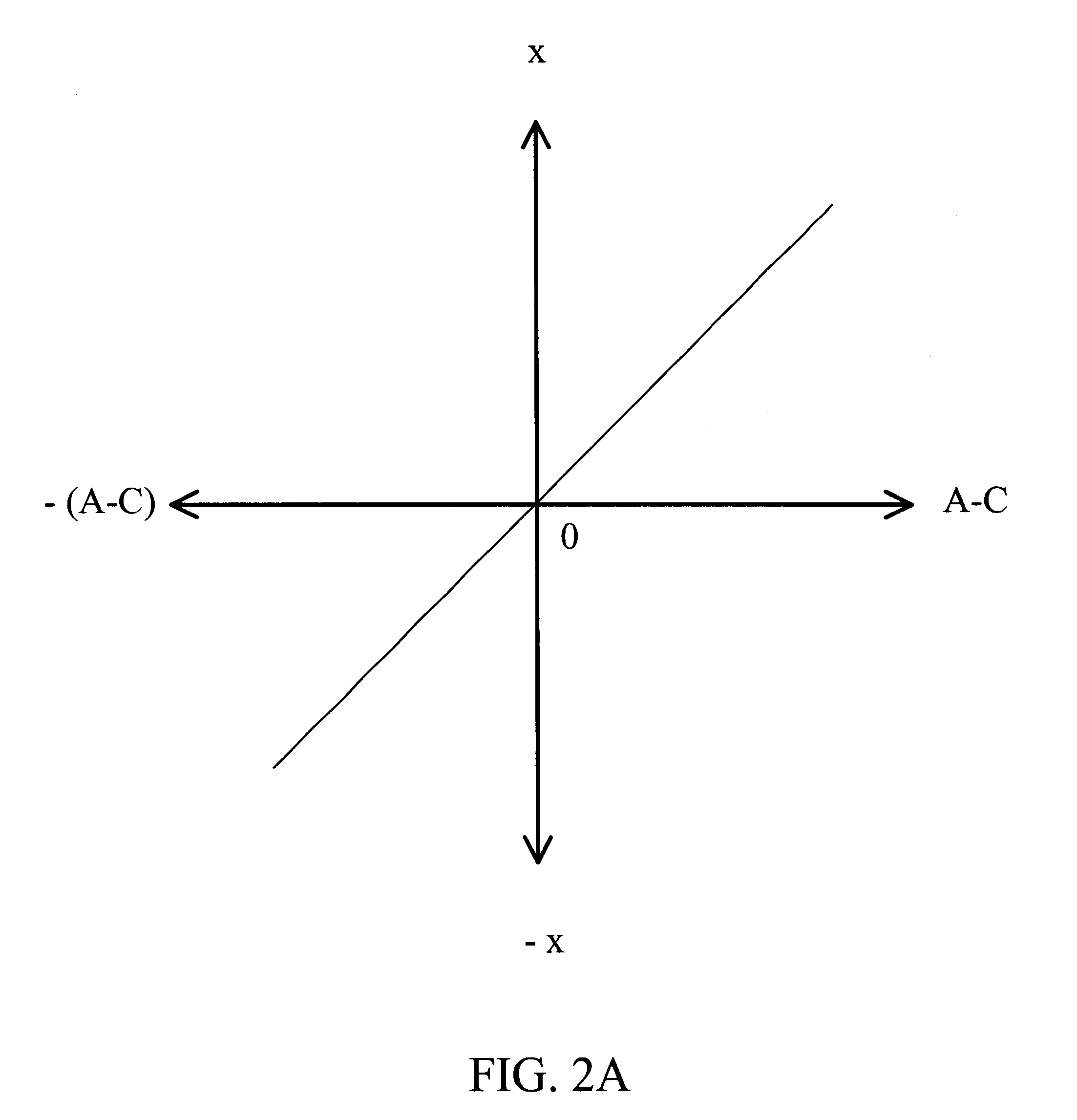
InactiveUS6369971B1Accurate read operationAccurate write operationRecord information storageAlignment for track following on disksEngineeringLinearization
A PES linearization scheme using small excitation bode measurements is provided to account for non-linearity characteristics during measurements of head element positions so to generate a more accurate read and write operation by a head element of a disk drive assembly. The PES linearization scheme of this invention provides making gain measurements as the head element moves across the track, and then integrating the result to get a relative PES profile. By then finding two points on the profile a known distance apart, we can multiply the profile by the appropriate gain factor to get an absolute PES profile. This profile can be then be used as a look up table to convert raw PES numbers into actual position.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
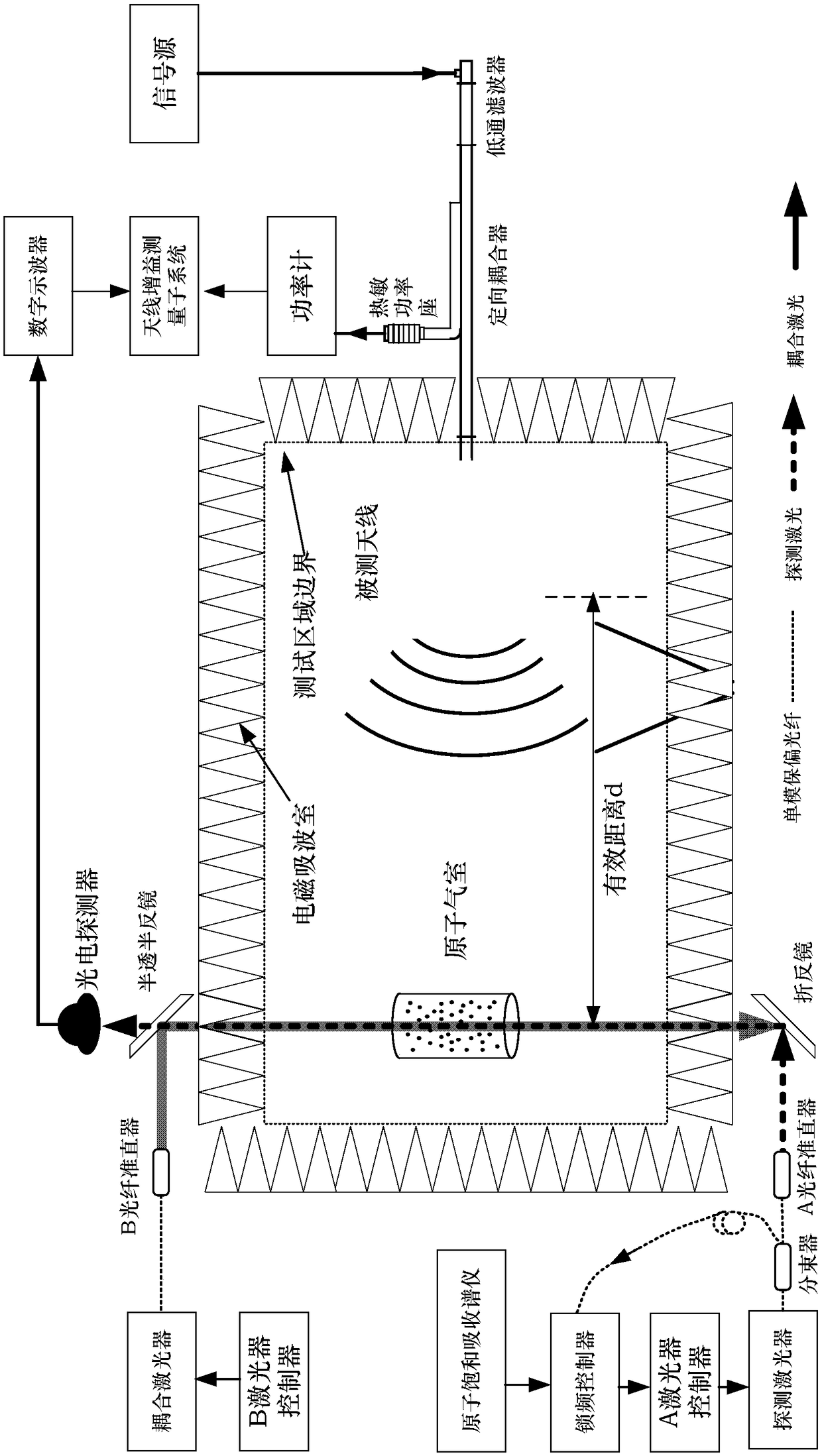
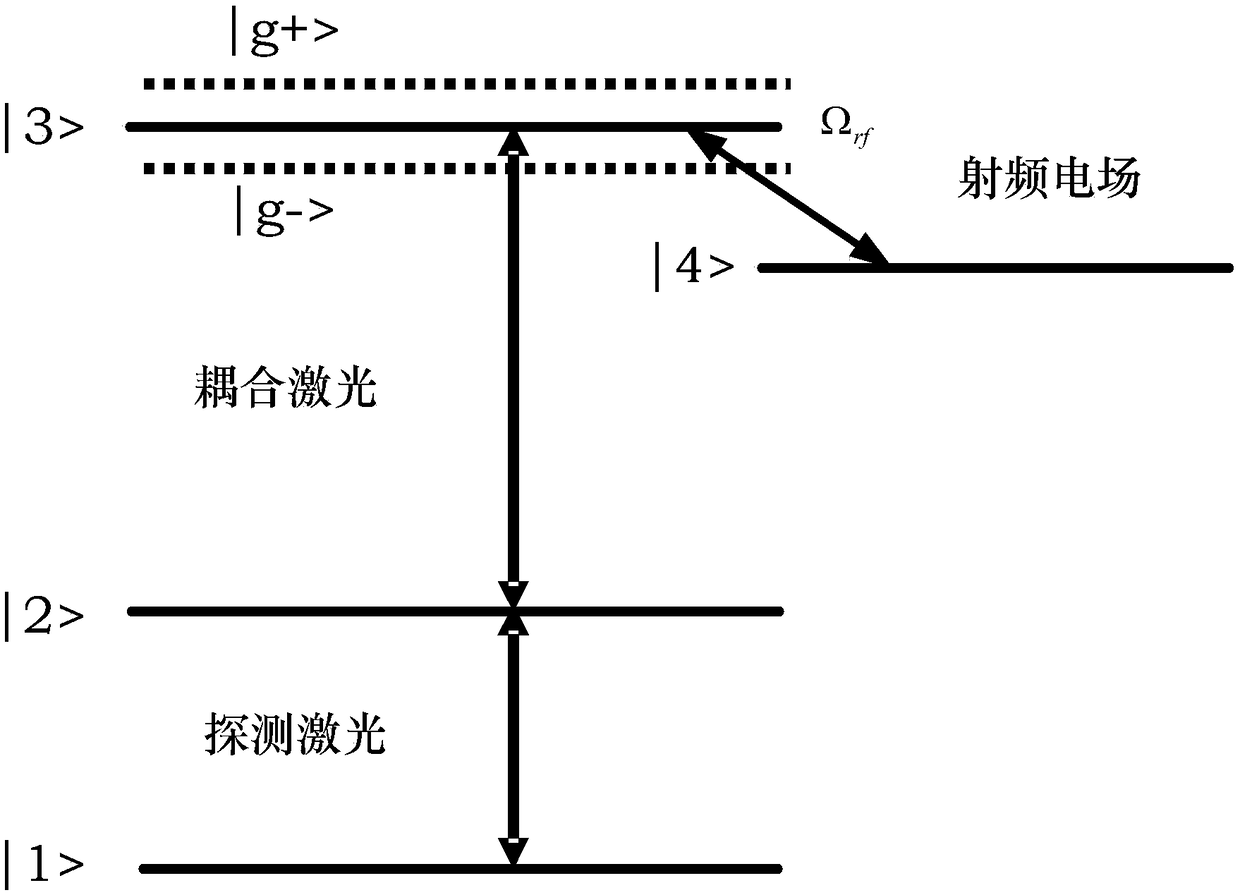
Quantum coherence effect-based antenna gain measuring device
ActiveCN108152602AHigh measurement accuracySimple procedureAntenna radiation diagramsAntenna gainData acquisition
The invention discloses a quantum coherence effect-based antenna gain measuring device. The device comprises an electromagnetic wave absorbing chamber, an atomic gas chamber, a laser light source subsystem, a spectral signal measurement subsystem, a power measurement subsystem, an antenna gain measurement subsystem and a plurality of support platforms. According to the device disclosed by the invention, an optical device is used for triggering an energy spectrum, so that atoms are induced. An energy spectrum is obtained through photoelectric detection. Meanwhile, the wave-absorbing material isadopted to prevent an electromagnetic scattering body from affecting the measurement. Through measuring the feed-in net power of a measurement antenna and the net power of the coupling port of a directional coupler, the data acquisition of the transmitted spectrum of the detection light is completed. A power meter is connected with a computer through a GPIB bus, so that the reading of the feed-inpower value of the antenna is completed. Through an antenna gain measurement model (img file = 'DDA 0001510521350000011.T'wi = '355 'he = '170 '), the gain measurement is completed. Compared with a traditional antenna measuring system, the device has the advantages of high measurement precision, low construction cost, small occupied area and the like.
Owner:NAT INST OF METROLOGY CHINA
Photonic circuit device with on-chip optical gain measurement structures
ActiveUS20160252692A1Laser active region structureExcitation process/apparatusPhotonicsGain measurement
The present invention is directed to a photonic circuit device for optical gain measurement, including: a substrate with a photonic circuit; an active gain section; at least two light couplers arranged such that at least a part of the active gain section is between the light couplers; and a partial reflector arranged to reflect light propagating along the same direction back to a center of the gain section, and wherein the device does not include any other reflector opposite to the partial reflector with respect to the active gain section and configured to reflect light back to the center of the gain section. The present invention is further directed to related gain measurement methods.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for monitoring the influence of ambient noise on stochastic gradient algorithms during identification of linear time-invariant systems
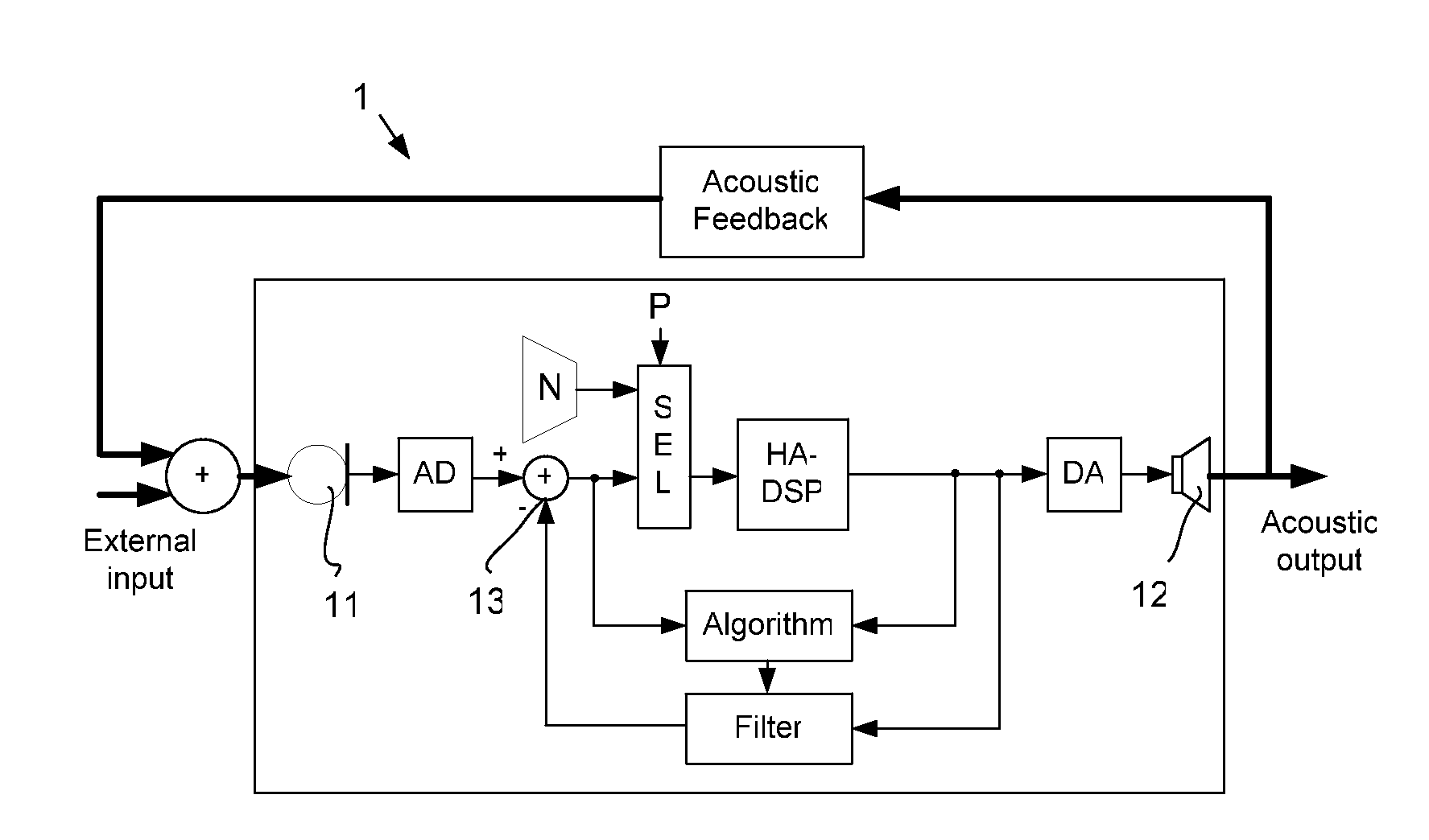
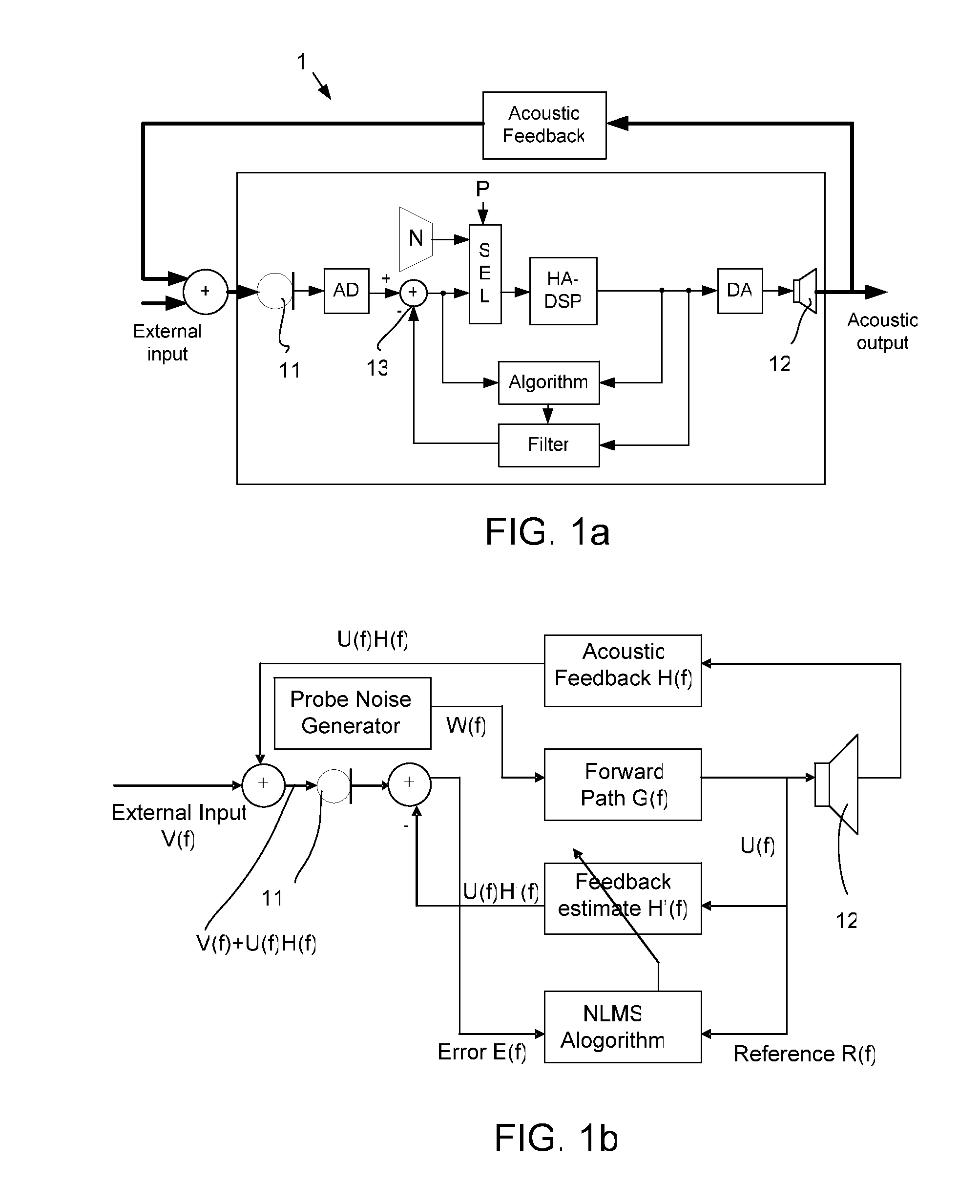
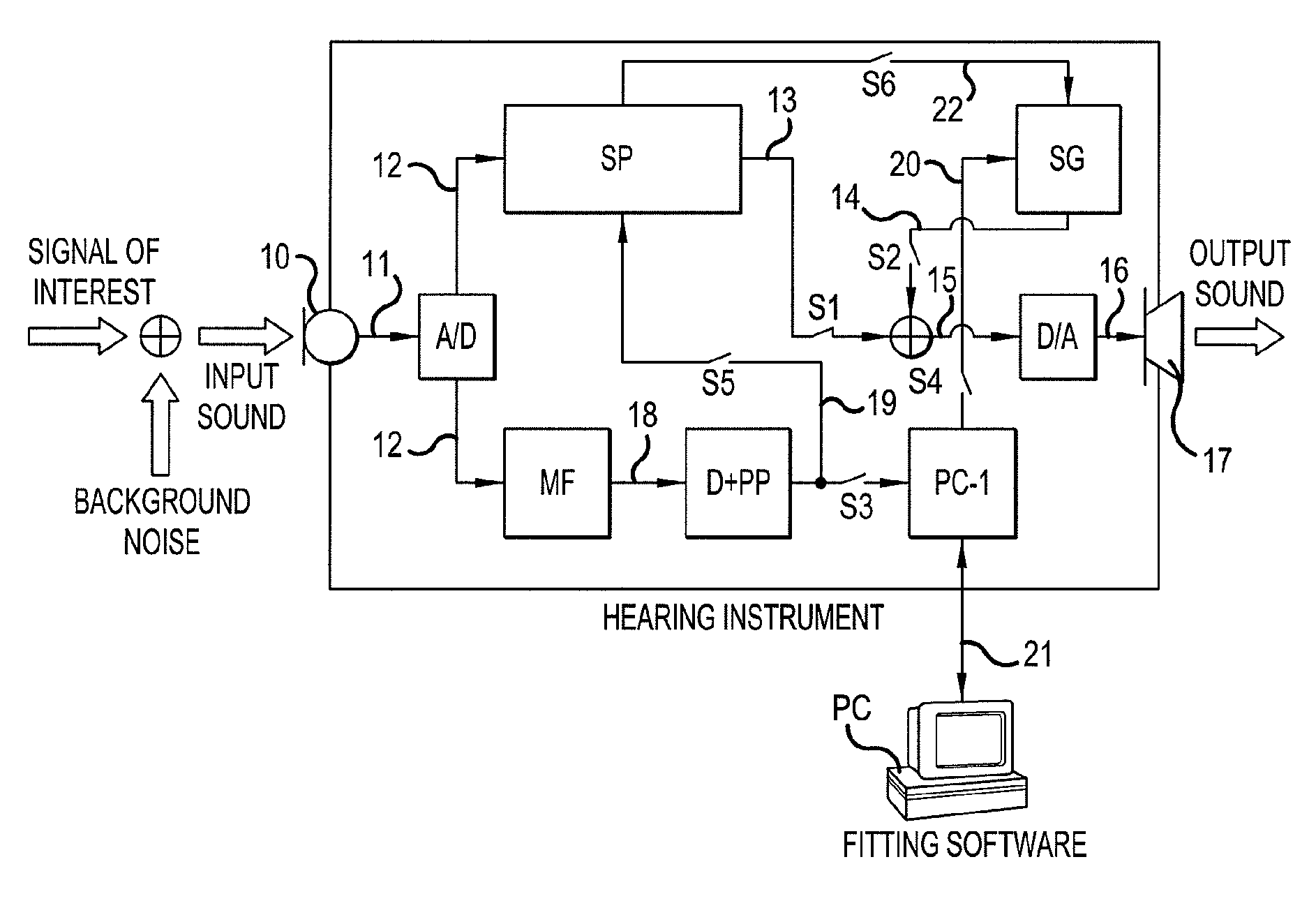
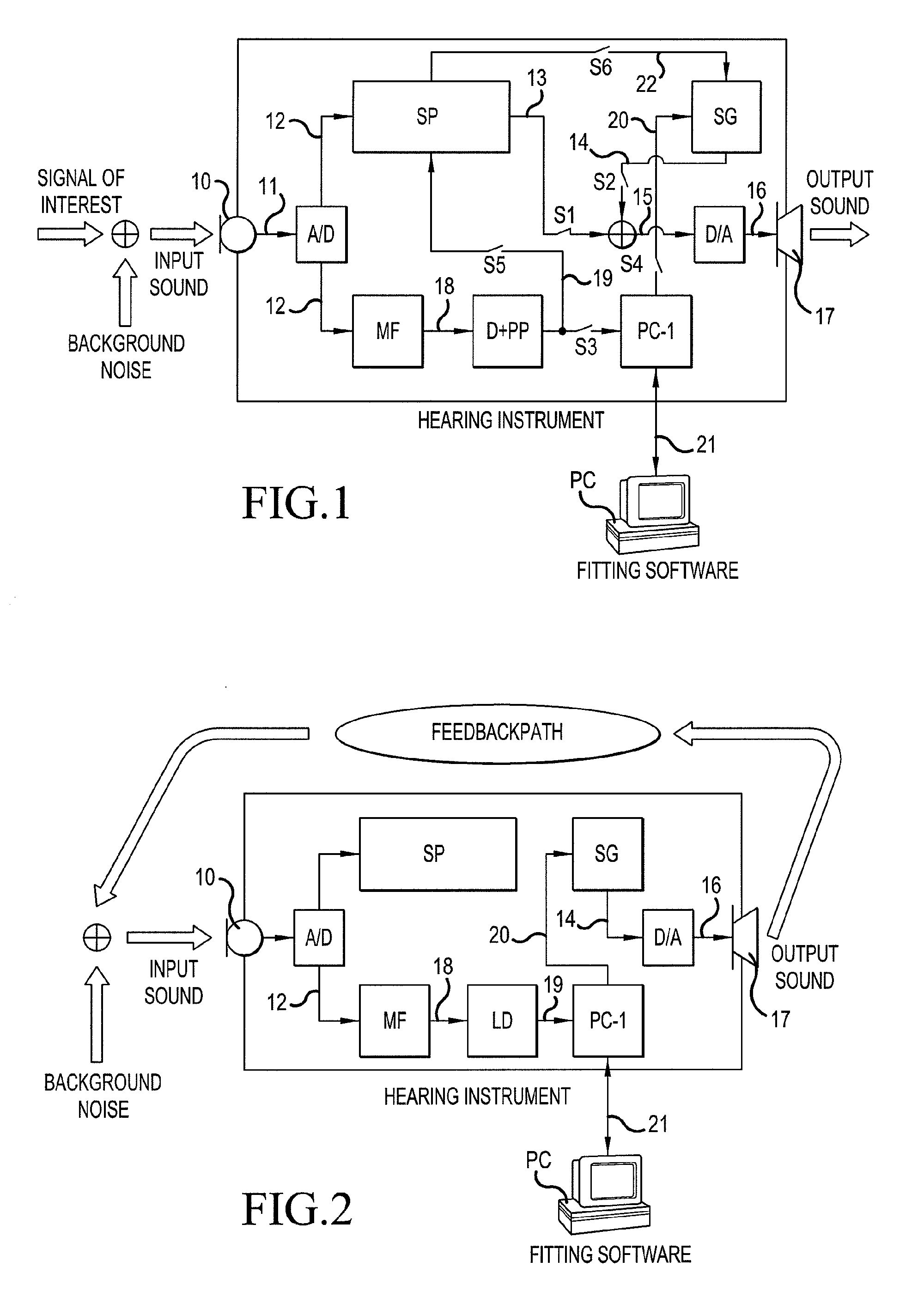
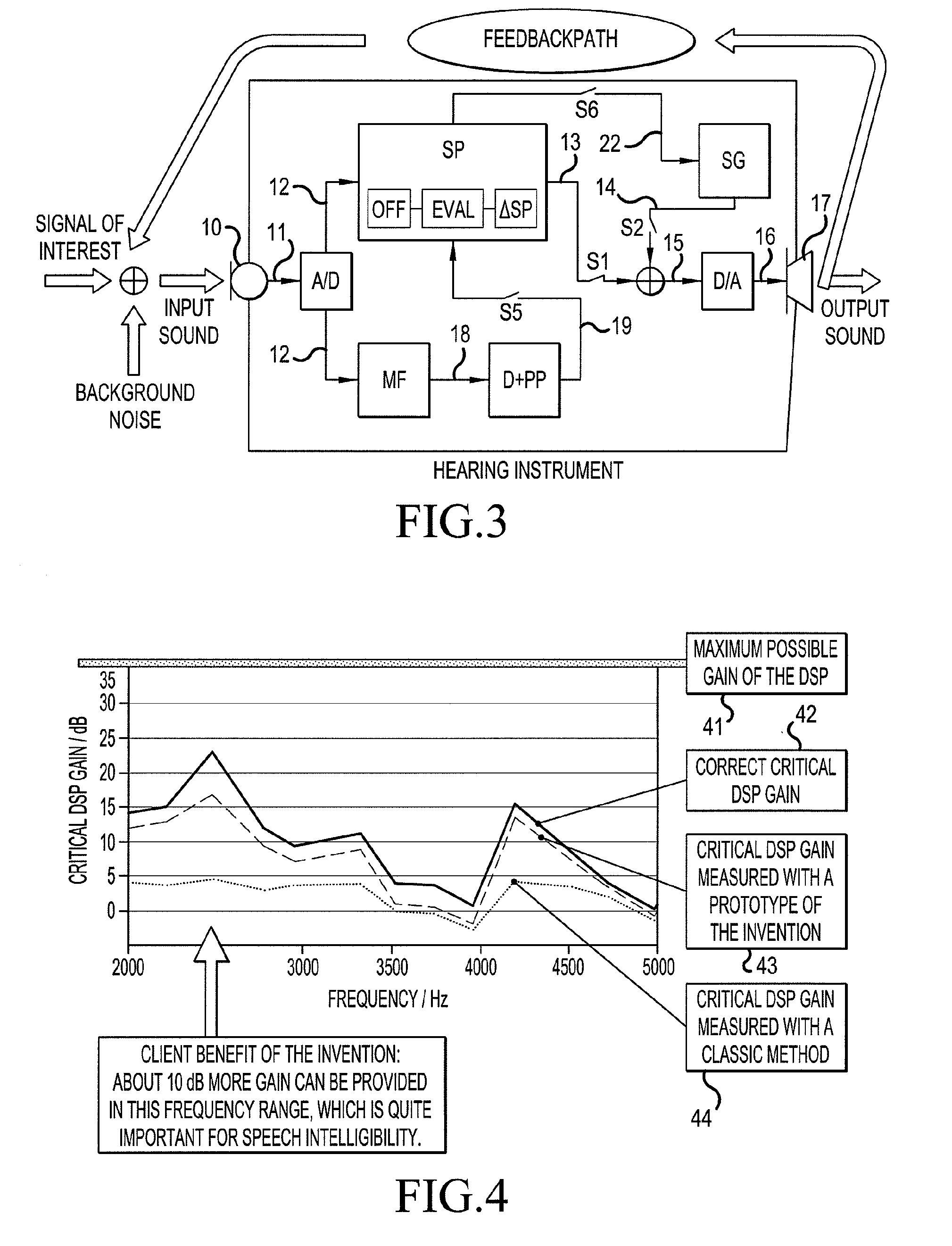
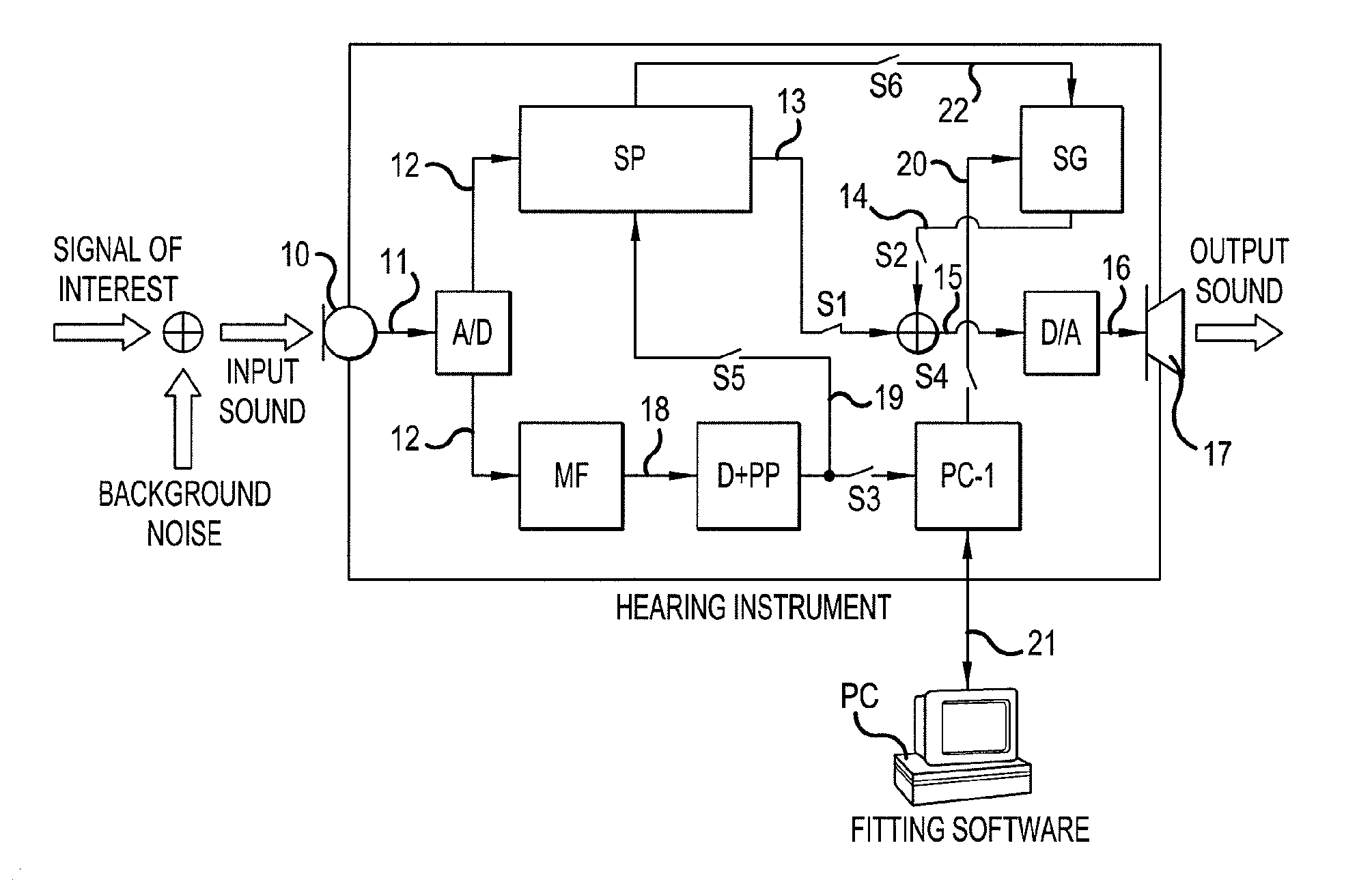
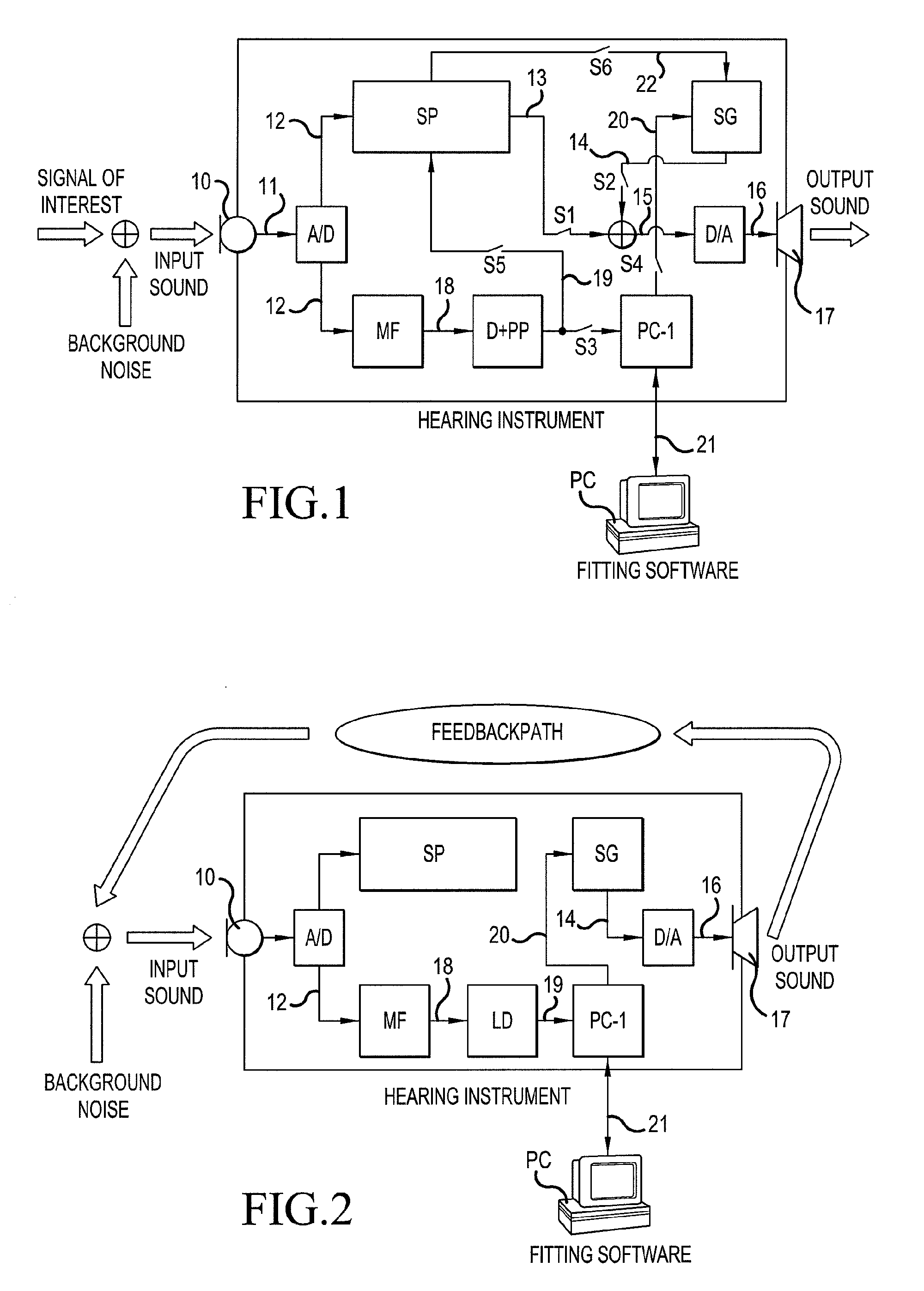
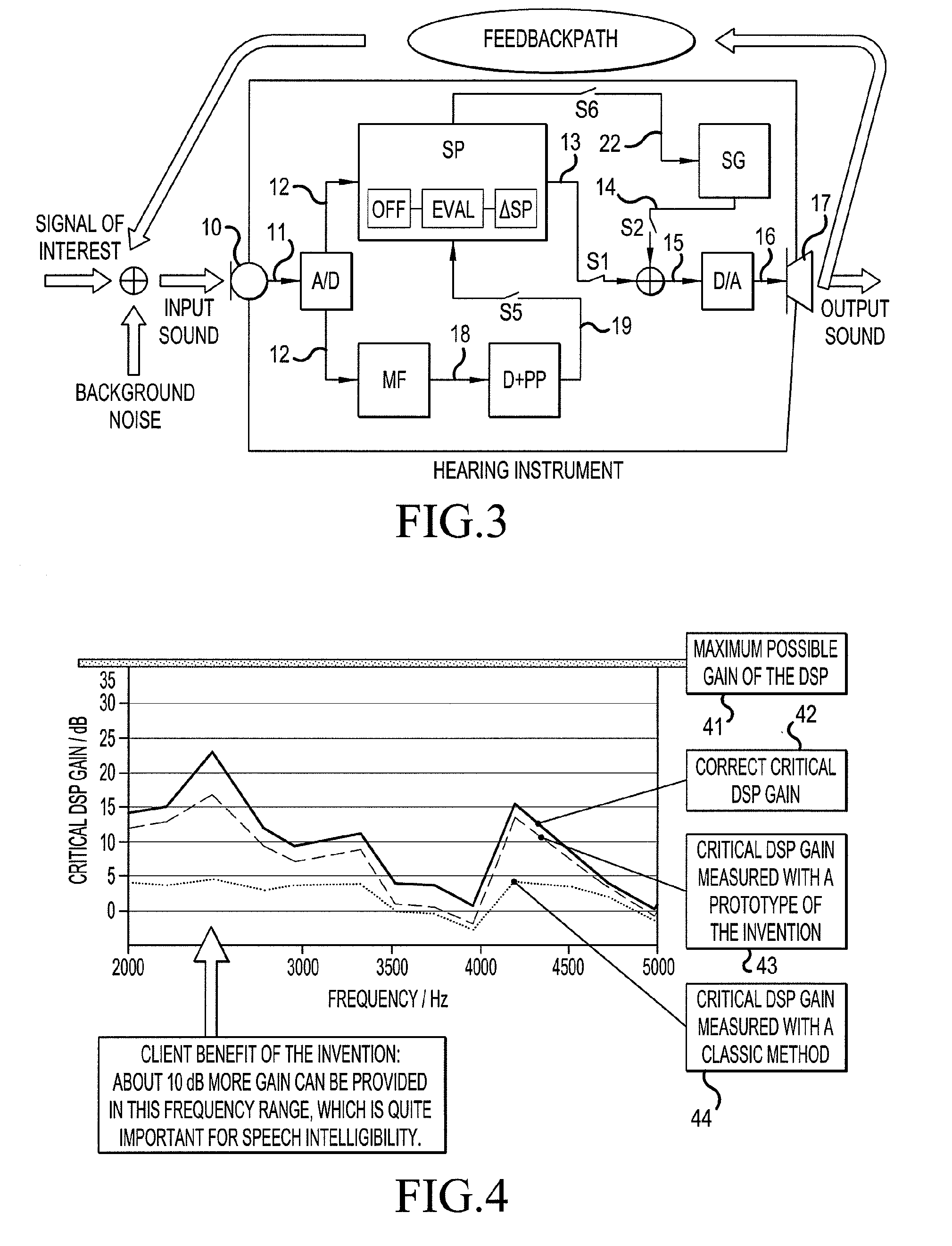
A hearing aid system and a method of estimating ambient noise in a listening device includes an input transducer and an output transducer, an electrical forward path between the input transducer and the output transducer providing a forward gain, an electrical feedback path comprising an adaptive filter for estimating the acoustic feedback gain from the output transducer to the input transducer. A method determines the quality of a critical gain measurement for a listening device. The method comprises a) monitoring the energy of the first-difference of the filter coefficients of the adaptive filter over time and b) applying a predefined threshold criterion to the change in energy content from one time instance to another to determine an acceptable impact of the ambient noise. This technique may e.g. be used for the fitting of hearing instruments where background noise is variable.
Owner:OTICON
Manufacturing method for semiconductor device and rapid thermal annealing apparatus
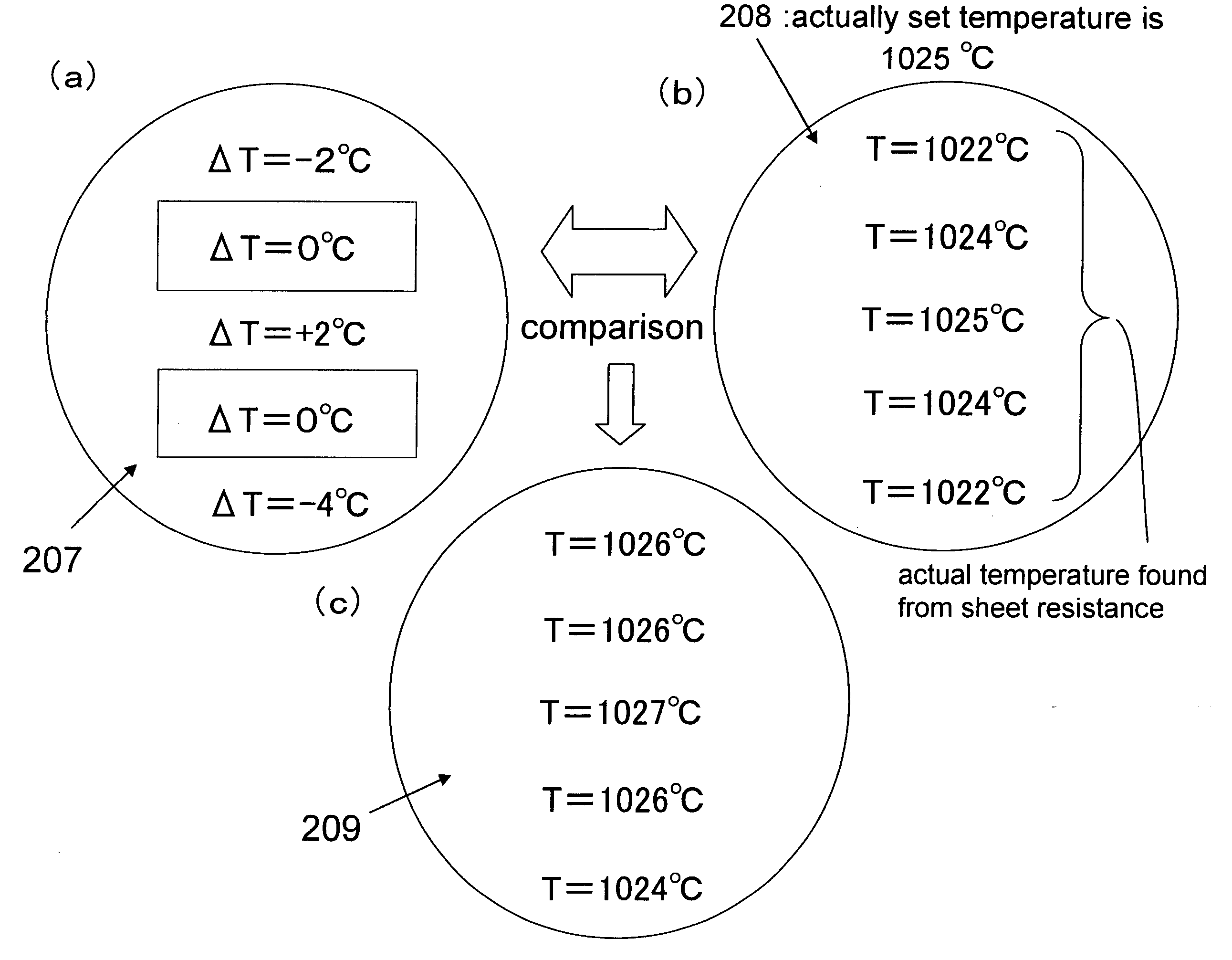
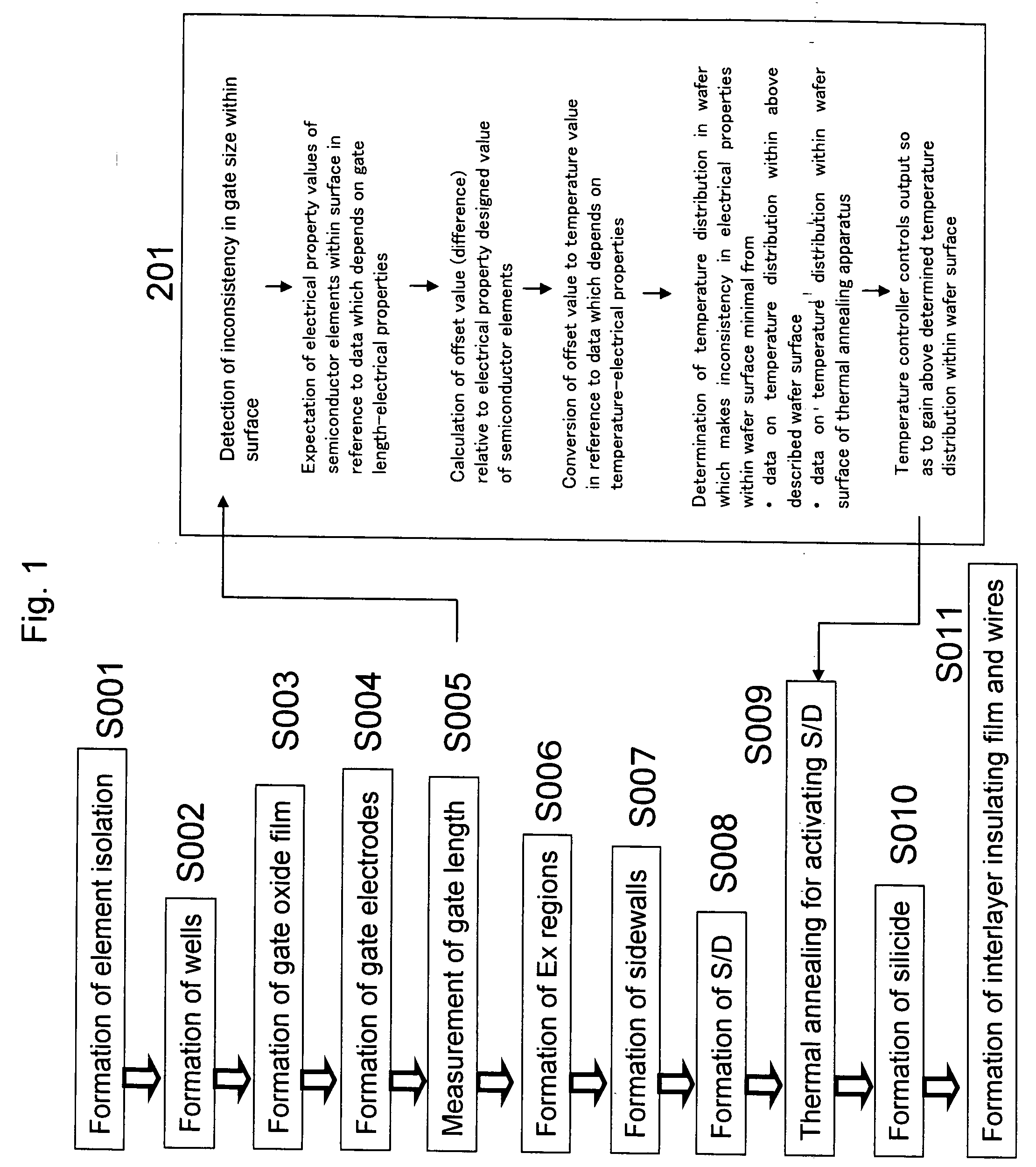
InactiveUS20060183290A1Rapid thermal annealingUniform qualitySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesElectricityDevice material
During a manufacturing process for a semiconductor device, the size of gate electrodes is measured within the wafer surface. The gained measurement data is compared with the data which depends on the gate length-electrical properties of the semiconductor elements, and thus, distribution in the electrical properties within the wafer surface is expected. Next, the difference between the expected data on the electrical properties and the designed value is calculated, and this difference is compared with the data which depends on the temperature-electrical properties, so that the electrical property values a reconverted to temperature values. Next, the temperature distribution within the surface which makes inconsistency in said electrical properties within the surface minimal is determined from the gained data on the temperature distribution within the surface and the data on the temperature distribution within the surface which is gained from the equipment management data of the thermal annealing apparatus.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Automatic measurement and gain control of distributed Raman amplifiers
ActiveUS8643941B2Laser using scattering effectsFibre transmissionOptical power meterRaman amplifiers
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC +1
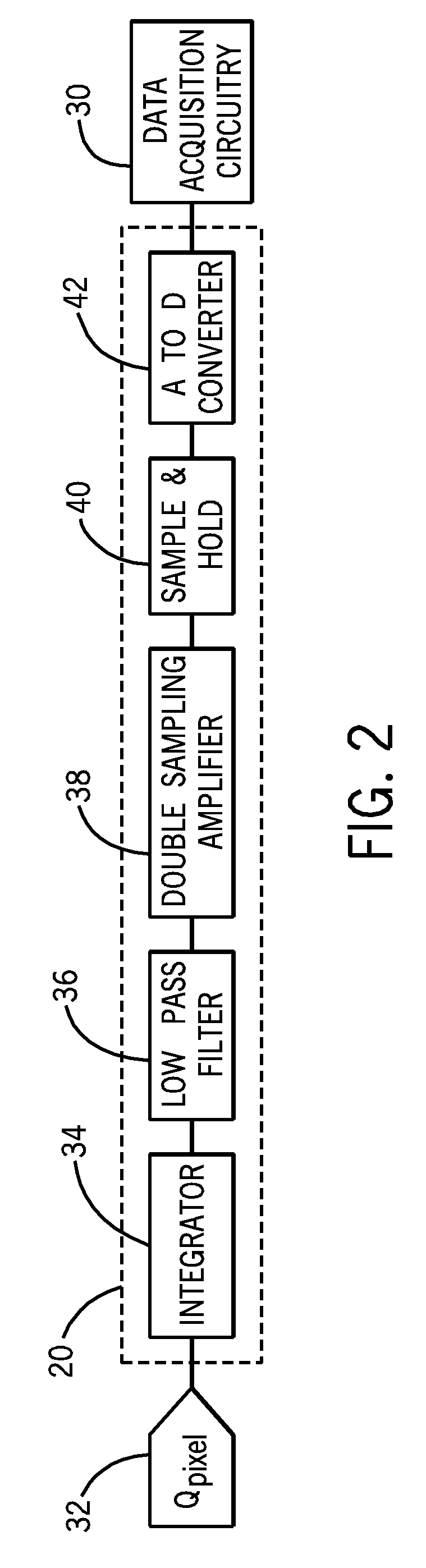
Low-noise data acquisition system for medical imaging
ActiveUS20100215146A1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersLow noiseIntegrator
According to embodiments of the present technique, a system and a method for obtaining low-noise measurements for a wide range of analog signal strengths is provided. According to aspects of the present technique, a low-gain measurement of an input pixel charge is performed, wherein the input pixel charge is distributed to two feedback capacitors, which together provide a relatively low integrator gain. After the low-gain measurement, a high-gain measurement is performed, wherein one of the capacitors is remove from the feedback loop and the charge is redistributed to the remaining capacitor.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Hearing aid system comprising a matched filter and a measurement method
ActiveUS20090147977A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioDeaf aid adaptationStereophonic arrangmentsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Transducer
The invention relates to a hearing aid system comprising an input transducer for converting an input sound signal comprising an information signal part of a known waveform and a background noise part to an electrical analogue input signal, optionally an A / D converter for converting the electrical input signal to a digital input signal. The invention further relates to a method of making a critical gain measurement. The object of the present invention is to improve the signal-to-noise ratio of a signal to be measured or detected in a hearing instrument compared to prior art solutions. The problem is solved in that a matched filter receiving said analogue or digital input signal and optimized to improve the identification of the information signal part from the noisy input signal. An advantage of the invention is that it provides an alternative scheme for improving signal to noise ratio of a hearing aid. The invention may e.g. be used for the customization of hearing aid parameters in cooperation with fitting software and / or for improving signal to noise ratio of a detected or measured signal.
Owner:OTICON
Transmission method, transmitter-receiver, and transmitting-receiving system
InactiveUS20090279897A1Distortion/dispersion eliminationTransmission monitoringPower controllerTransmission loss
A transmitter-receiver having a means for automatically determining the status of transmission medium such as optical fiber, and a means for automatically setting and resetting the transmission rate and / or output power according to the status of the transmission medium, a transmission loss and gain measurement method, and a transmitting-receiving system. A transmitter-receiver comprises at least: an output power controller for controlling the output power of a transmitter; an input power measuring section for measuring the strength of input signals; and an information processor for deriving the loss or gain of a path to change the output power of the transmitter and / or the rate of data transmission according to the derived loss or gain of the path. A transmission loss and gain measurement method applied to a system comprising transmission media and a plurality of the transmitter-receivers connected via the transmission media, comprises the steps of: transmitting information on the output power of a first transmitter-receiver from the first transmitter-receiver to a second transmitter-receiver; measuring reception strength by the second transmitter-receiver when the second transmitter-receiver receives the output power information; reading the output power information by the second transmitter-receiver; and comparing the reception strength with the output power information to calculate a transmission loss or gain by the second transmitter-receiver.
Owner:NEC CORP
Transmission method, transmitter-receiver, and transmitting-receiving system
ActiveUS7580634B2Transmission monitoringDistortion/dispersion eliminationPower controllerTransmission loss
Owner:NEC CORP
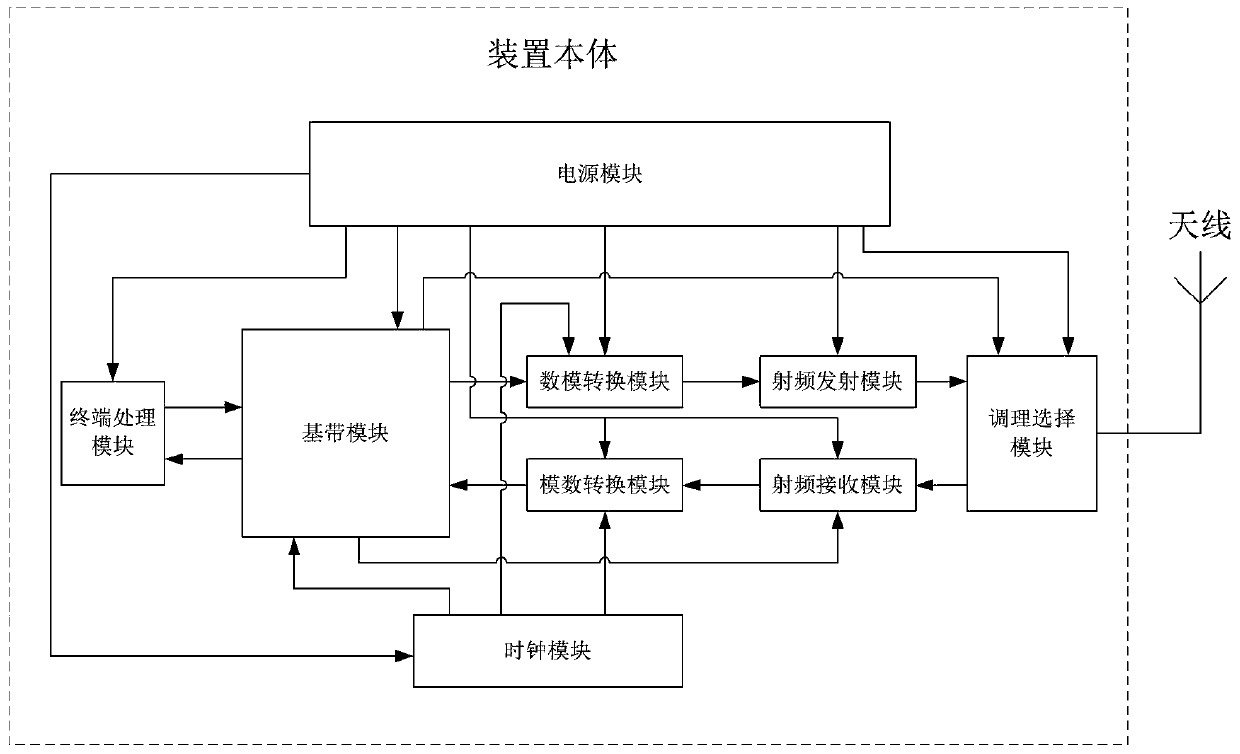
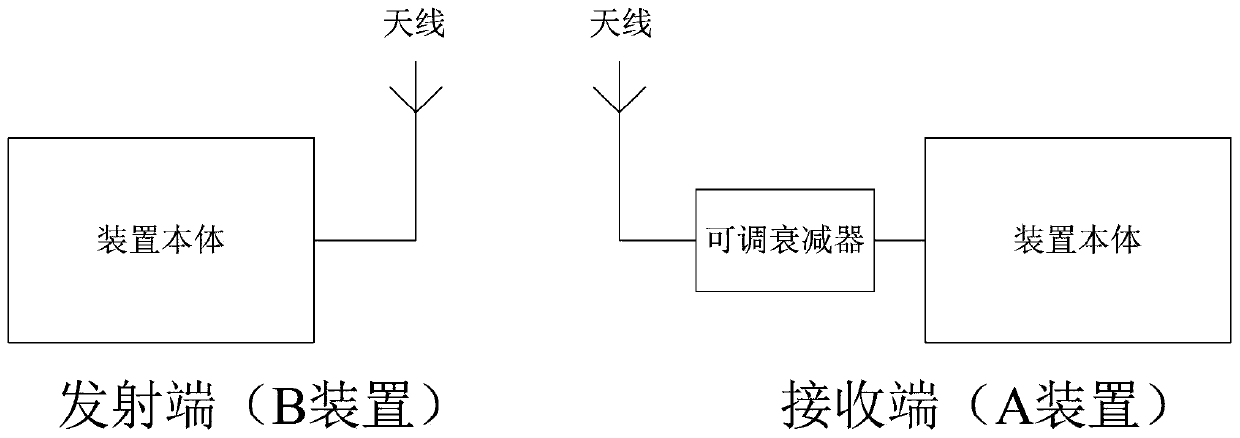
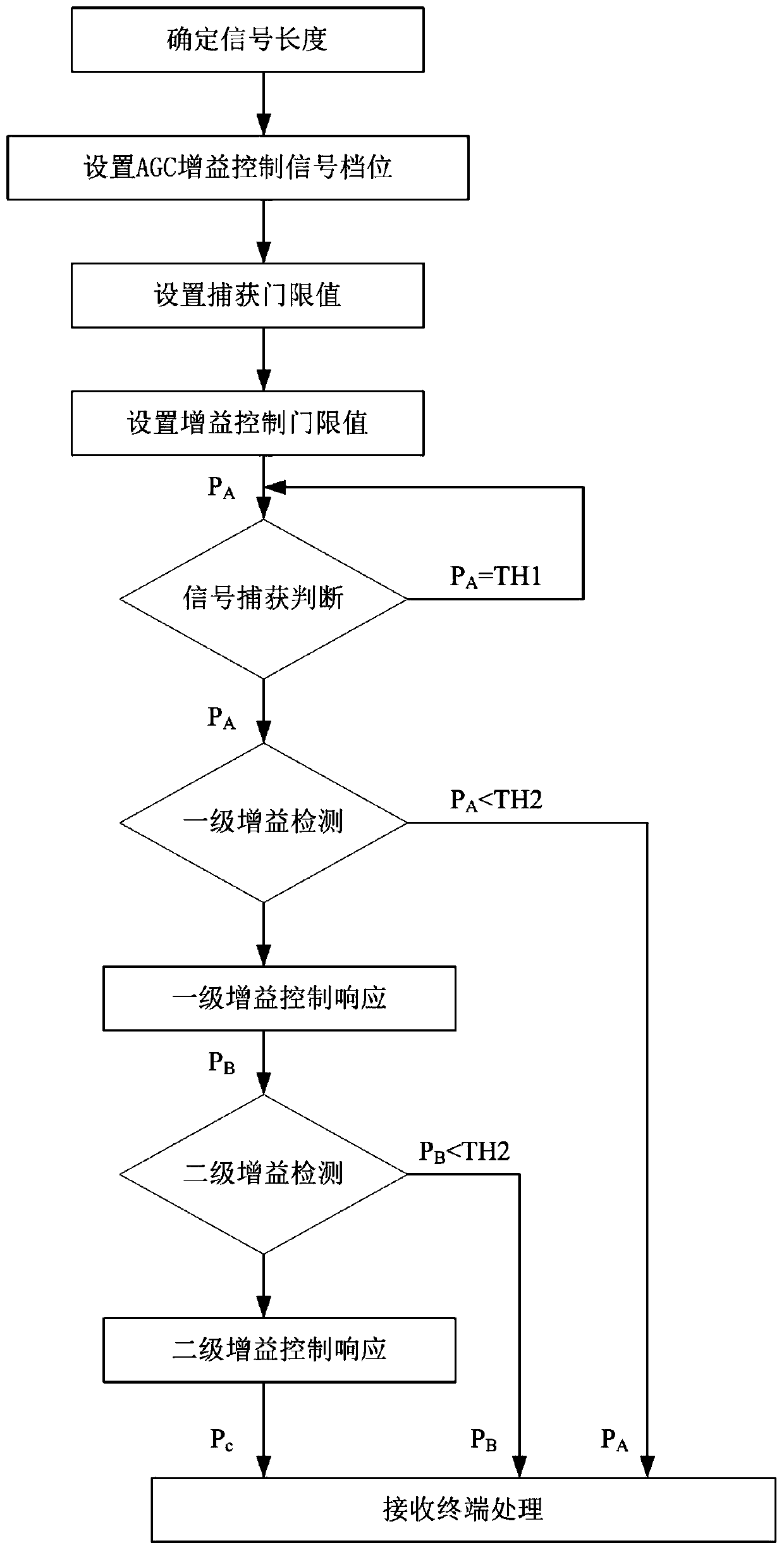
Automatic gain control method and device of communication system
ActiveCN110365302AImprove data processing capabilitiesAvoid interferenceAnalog signal digital controlHigh level techniquesCommunications systemRadio frequency
The invention relates to an automatic gain control device of a communication system. The automatic gain control device comprises a device body and an antenna, and is characterized in that the device body is connected with the antenna through a radio-frequency cable; and the device body comprises a clock module, a radio frequency receiving module, an analog-to-digital conversion module, a basebandmodule, a digital-to-analog conversion module, a radio frequency transmitting module, a conditioning selection module, a terminal processing module and a power supply module. The invention further comprises a gain measurement method and corresponding equipment in the automatic gain control device of the communication system. According to the invention, the receiving of signals in a large dynamic range is realized; the interference of instantaneous noise generated in the receiving process on demodulation is effectively avoided; the bit error rate is greatly reduced; the baseband data processingperformance is better improved; and the automatic gain control device of the invention has the advantages of higher flexibility, high control precision and wide application.
Owner:AIR FORCE UNIV PLA
Apparatus for measuring foam wet weight gain for low temperature insulation
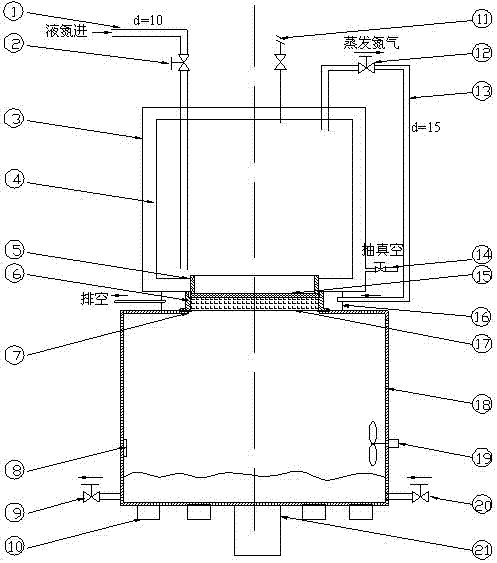
InactiveCN102288510AEasy to disassembleEasy to installWeighing by absorbing componentMeasurement deviceWater discharge
The invention discloses a hygroscopic weight increment measuring device for low-temperature and heat-insulating foam plastic. A constant-temperature high-humidity box, a sample sleeve, a liquid nitrogen trough, an external liquid nitrogen tank and an internal liquid nitrogen tank are connected in sequence; a flow guiding cover is sleeved outside the sample sleeve; a groove is arranged at the upper end of the constant-temperature high-humidity box; a G-10 washer is arranged in the groove; the inner wall of the constant-temperature high-humidity box is provided with a PTC (positive temperature coefficient) heating resistor and a fan; a water inlet system and a water discharging pipeline are arranged at the lower part of the constant-temperature high-humidity box; an ultrasonic generator anda miniature lifter is arranged at the bottom of the constant-temperature high-humidity box; a sample is mounted in the sample sleeve; a liquid nitrogen inlet pipe, a safety valve and an outlet shutoff valve are arranged at the top of the external liquid nitrogen tank; the liquid nitrogen inlet pipe is provided with a manual shutoff valve; the external liquid nitrogen tank and the internal liquid nitrogen tank are connected with the liquid nitrogen trough; a copper disc is welded at the bottom of the liquid nitrogen trough; the lower part of the external liquid nitrogen tank is provided with avacuumizing opening; and the outlet shutoff valve is connected with the flow guiding cover through a pipeline. By using the measuring device, the hygroscopic weight increment measurement of the sample is achieved in a high-humidity extreme environment with one side at a super-low temperature and the other side at a room temperature, and furthermore, the sample can be conveniently moved away and mounted.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Gain measuring device and method of cascaded micro channel plate
ActiveCN105372572ASolve measurement problemsEasy to operateVacuum tube testingGain measurementPhysics
The invention discloses a gain measuring device and method of a cascaded micro channel plate (MCP). The method comprises the following steps that: step (1) after being attenuated, ultraviolet light is emitted to a quartz window, and an ultraviolet Au photocathode is excited to emit photoelectrons; step (2) under the action of electric fields, the photoelectrons are emitted to the input end of the cascaded MCP, and are multiplied by the cascaded MCP, and the multiplied photoelectrons are outputted from the output end of the cascaded MCP, and the multiplied photoelectrons bombard a fluorescent screen under the action of the electric fields, so that bright spots can be generated; step (3) the bright spots on the fluorescent screen are imaged by a CCD or CMOS camera, and a computer acquires the output signals of the CCD or CMOS camera so as to measure the number of the bright spots; and (4) after the number of the bright spots is measured, a circuit is switched to the output current loop of the cascaded MCP, and a nanoammeter is connected in series in the loop so as to measure the output current of the cascaded micro channel plate (MCP), and the gain of the cascaded micro channel plate (MCP) is calculated according to the number of the bright spots and the output current of the cascaded micro channel plate (MCP). The gain measuring method of the cascaded micro channel plate (MCP) provided by the invention has the advantages of simple operation and high accuracy.
Owner:NORTH NIGHT VISION TECH
Phase-locked loop with loop gain calibration, gain measurement method, gain calibration method and jitter measurement method for phase-locked loop
The invention provides a phase-locked loop with loop gain calibration and methods for measuring an oscillator gain, gain calibration and jitter measurement for a phase-locked loop. The method for measuring an oscillator gain of a phase-locked loop includes the steps of providing a varying code at an input end of the oscillator; outputting excess reference phase information by a reference phase integral path and outputting excess feedback phase information based on the varying code by a feedback phase integral path; and obtaining an estimated gain information of the oscillator based on the excess reference phase information and the excess feedback phase information.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
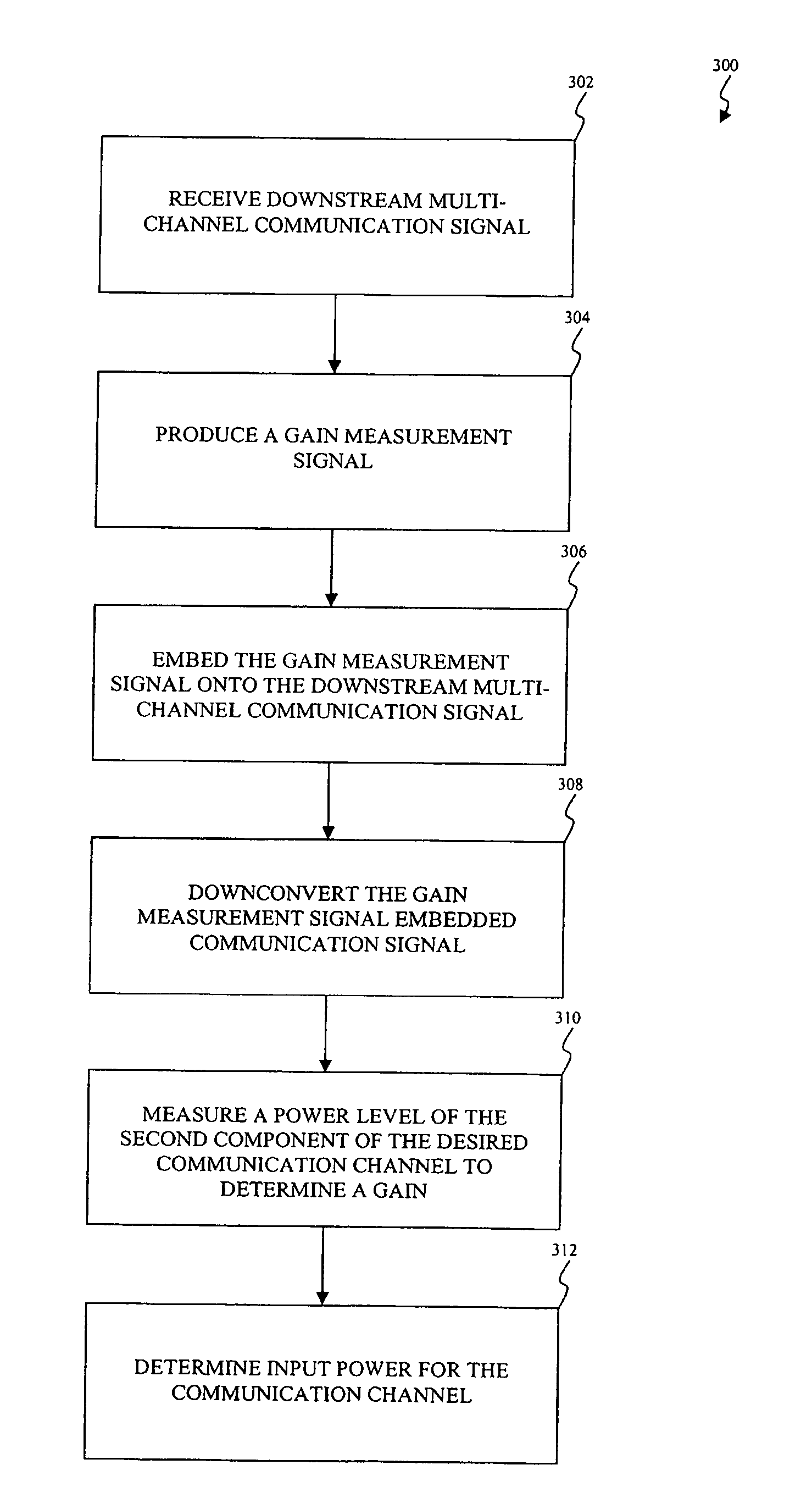
Apparatus and method for downstream power management in a cable system
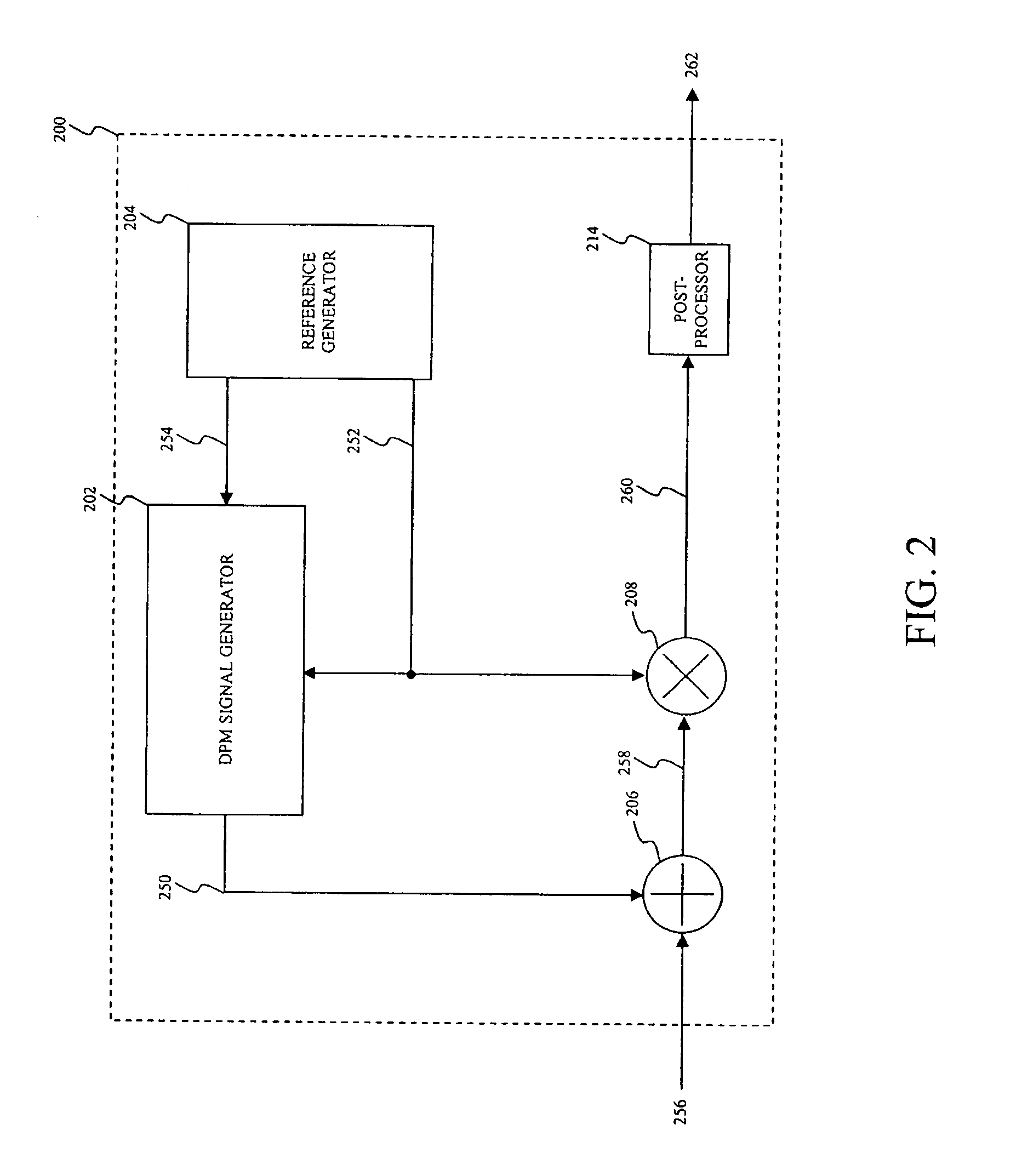
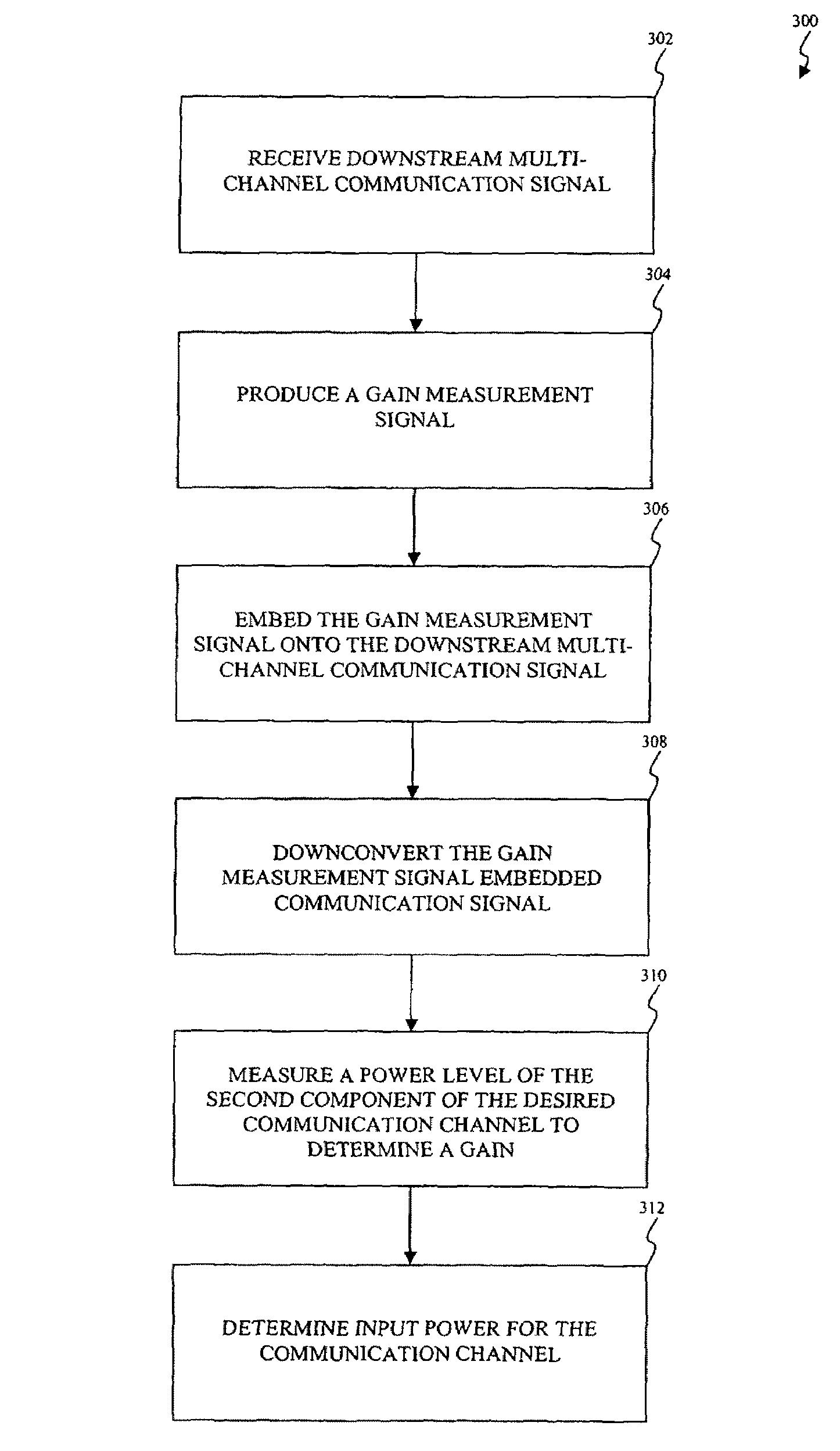
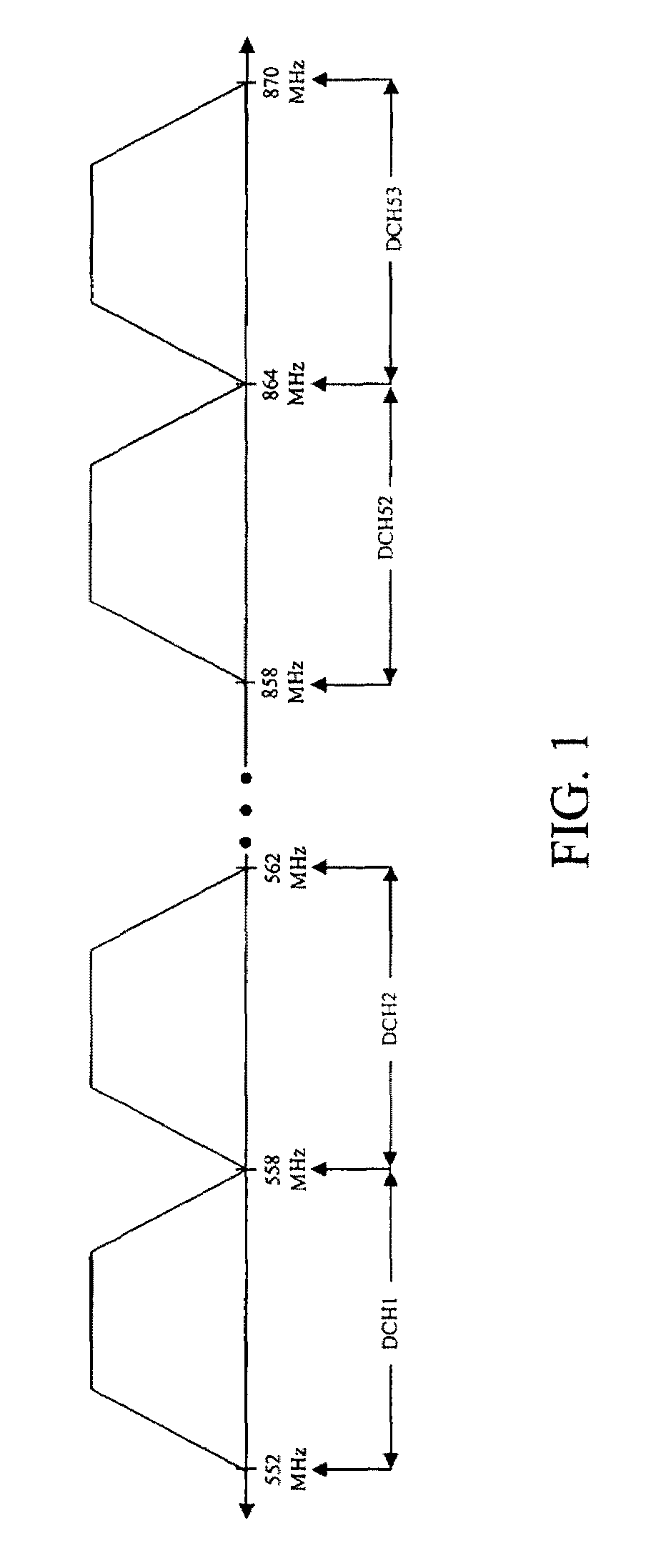
InactiveUS20090141839A1Power managementData switching by path configurationChannel powerTransmitted power
An apparatus and method is disclosed to calculate the actual received desired channel power from the downstream transmit power of a Cable Modem Termination System (CMTS) when operating at the nominal line voltage and / or at the normal room temperature as per the DOCSIS specification. A Set-top Device produces a Downstream Power Management (DPM) gain measurement signal having a known power level. The Set-top Device embeds the DPM gain measurement signal onto a received downstream multi-channel communication signal. After embedding the DPM gain measurement signal onto the downstream multi-channel communication signal, the Set-top Device downconverts the combined DPM gain measurement signal and downstream multi-channel communication signal to recover one or more communication channels containing information of a broadcast. The Set-top Device measures a power level of a representation of the DPM gain measurement signal embedded within the one or more communication channels containing the information of the broadcast to determine a Set-top Device gain. The Set-top Device measures a power level of the one or more communication channels containing the information of the broadcast. The Set-top Device calculates the actual received desired channel power from the downstream transmit power of the CMTS based on the Set-top Device gain and the power level of the one or more communication channels containing the information of the broadcast.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Turbine assembling method, turbine assembling auxiliary system, and recording medium
The invention is directed to maintaining the accuracy in the positional adjustment of a stationary part while shortening a turbine assembly period through the omission of the temporary assembly of a casing. A assembling method includes gaining measurement data on the configuration of a casing upper half part not fastened to a casing lower half part; gaining measurement data on the configuration ofthe casing lower half part in an open state in which the casing upper half part and a rotor are removed and in which a stationary part is mounted; comparing measurement data on the configuration of the casing upper half part and the casing lower half part with simulation data on the configuration of the casing upper half part and the casing lower half part previously obtained to select simulationdata closest to the measurement data on the configuration of the casing upper half part and the casing lower half part; calculating, based on the selected simulation data, a change amount of the configuration of the casing upper half part and the casing lower half part when the casing upper half part is fastened to the casing lower half part in the open state; and adjusting the installation position of the stationary part inside the casing taking into account the calculated change amount.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POWER LTD
Antenna element self-test and monitoring
A method of testing a phased array antenna that includes a plurality of antenna element pairs, each antenna element pair of the plurality of antenna element pairs including a first antenna element and a second antenna element, the method including: for each antenna element pair of the plurality of antenna element pairs, performing a first cross element gain measurement from the first antenna element to the second antenna element of that antenna element pair; and determining whether there is a problem associated with the phased array antenna by examining the first cross element gain measurements for the plurality of antenna element pairs.
Owner:BLUE DANUBE LABS
Multiplication gain fitting measurement method for multiplication CCD
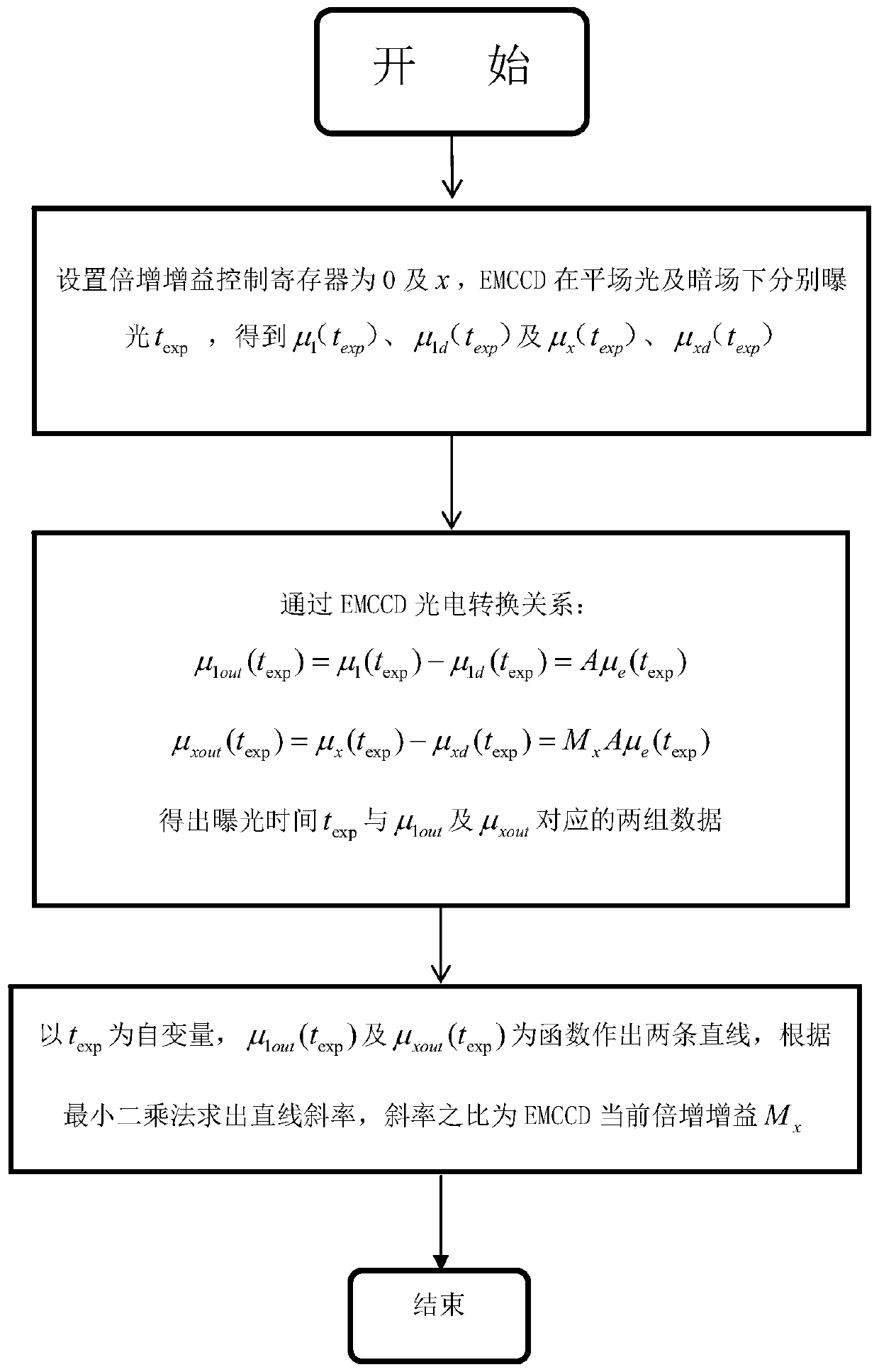
InactiveCN110996095AAccurate multiplier gainSuitable for engineering applicationsTelevision systemsControl registerEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of electronic component testing, in particular to the field of multiplication gain fitting measurement methods for a multiplication CCD (Charge Coupled Device). The method comprises the following steps that a multiplication gain control register is set to be 0, and an EMCCD obtains a set of mean values of image gray scale signals for different exposuretime in a flat field light field and a dark field respectively; a multiplication gain control register is set to be x, and the EMCCD obtains a group of mean values of the image gray signals for different exposure time under the flat field light and the dark field; and fitting two straight lines through a least square method, wherein the ratio of the straight line slope to the straight line slope is the current multiplication gain of the EMCCD. The method has the beneficial effects that the EMCCD multiplication gain measurement method based on multiple groups of data is provided, compared withthe existing method, more accurate multiplication gain can be obtained, and the method is stable, reliable and suitable for engineering application.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Optical transmission systems including optical amplifiers and methods of use therein
InactiveUS20050213985A1Easy to controlIncrease flexibilityLaser using scattering effectsFibre transmissionLength waveWavelength range
Optical transmission systems of the present invention include at least one optical amplifier configured to provide optical amplification of one or more information carrying optical signal wavelengths. At least one optical amplifier is controlled based on an in situ performance characterization of the at least one optical amplifier and the transmission fiber. The in situ, or installed, performance characteristics of the optical amplifier can be characterized based on relative gain measurements over the signal wavelength range as a function of the supplied pump power. The installed characterization allows the optical amplifier performance and gain profiles to be tightly controlled over the signal wavelength range in the transmission system.
Owner:OPTIC153 LLC
Active reflective surface shape adjustment method based on axial gain measurement
ActiveCN109873253AEnsure observation efficiencyProximity CorrectionComplex mathematical operationsAntennasPower detectorAntenna gain
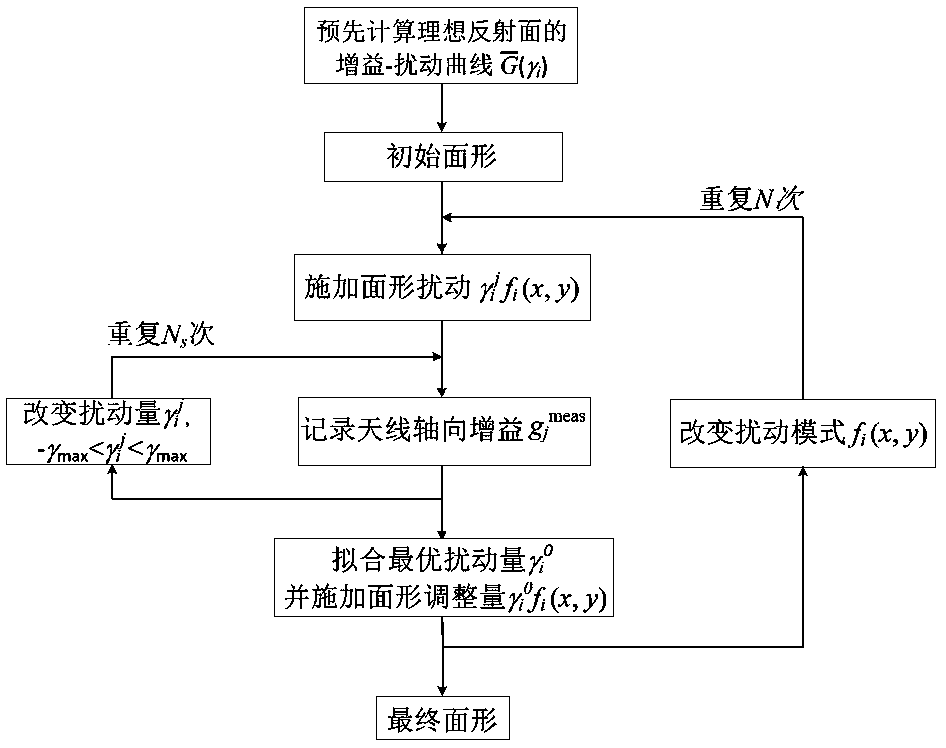
The invention discloses an active reflective surface shape adjustment method based on axial gain measurement. According to the method, a series of micro-disturbance is applied to a reflective surfaceshape through an actuator network in an active surface system, and the change in antenna axial gain is measured in the disturbing process; a group of orthogonal basis functions defined on an antenna port surface are used as disturbance modes to disturb the surface shape one by one, and under each disturbance mode, a curve of the change in the antenna axial gain along with the disturbance quantityis recorded, and the optimal adjustment quantity under each disturbance mode is fitted out of the corresponding curve; and through a series of disturbance, measurement and adjustment processes, finally the antenna gain can reach a maximal value, and the surface shape error can reach a minimal value. The method has a low requirement on a detector, and a single-pixel power detector can be used; in the running process of a telescope, a scientific receiver and an astronomical point source target can be directly utilized to carry out surface shape measurement and adjustment frequently, and therefore the observation efficiency of the telescope in the running process is maintained.
Owner:ZIJINSHAN ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
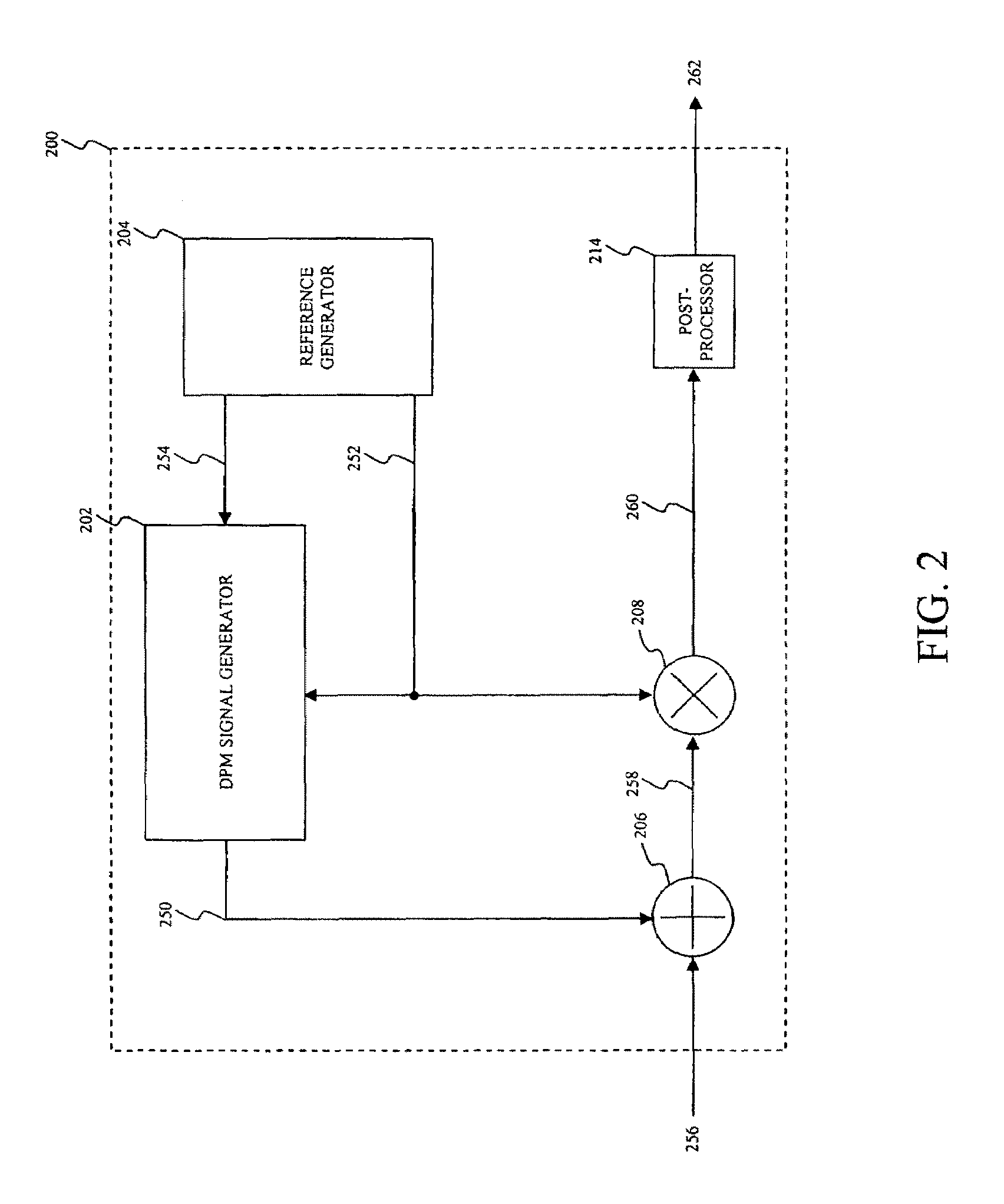
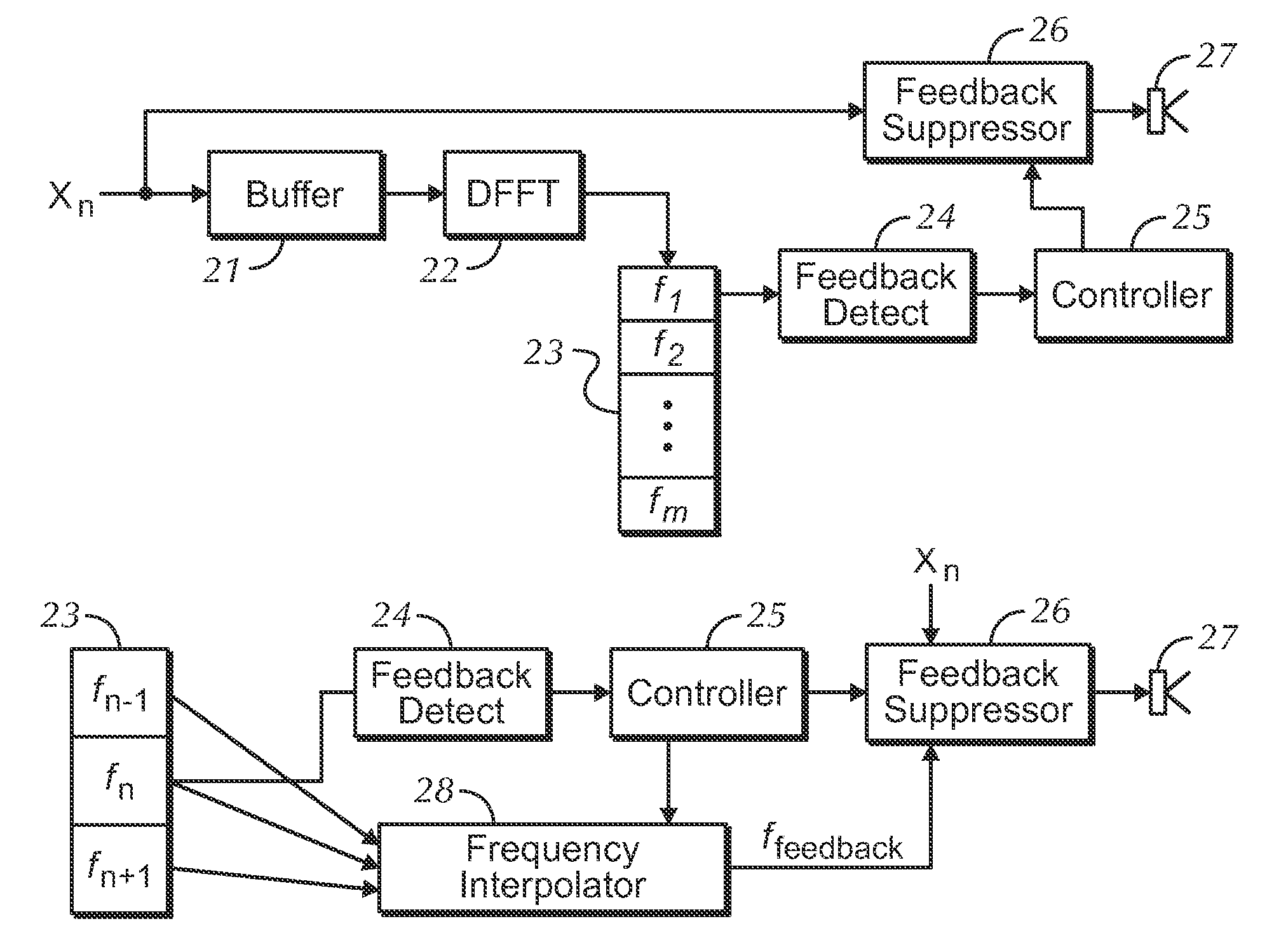
Probabilistic ringing feedback detector with frequency identification enhancement
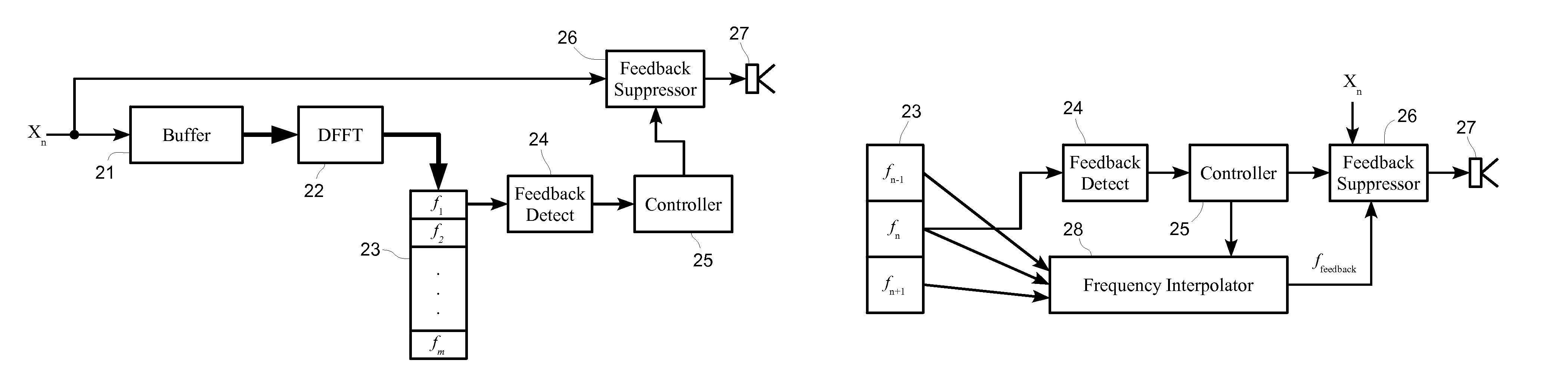
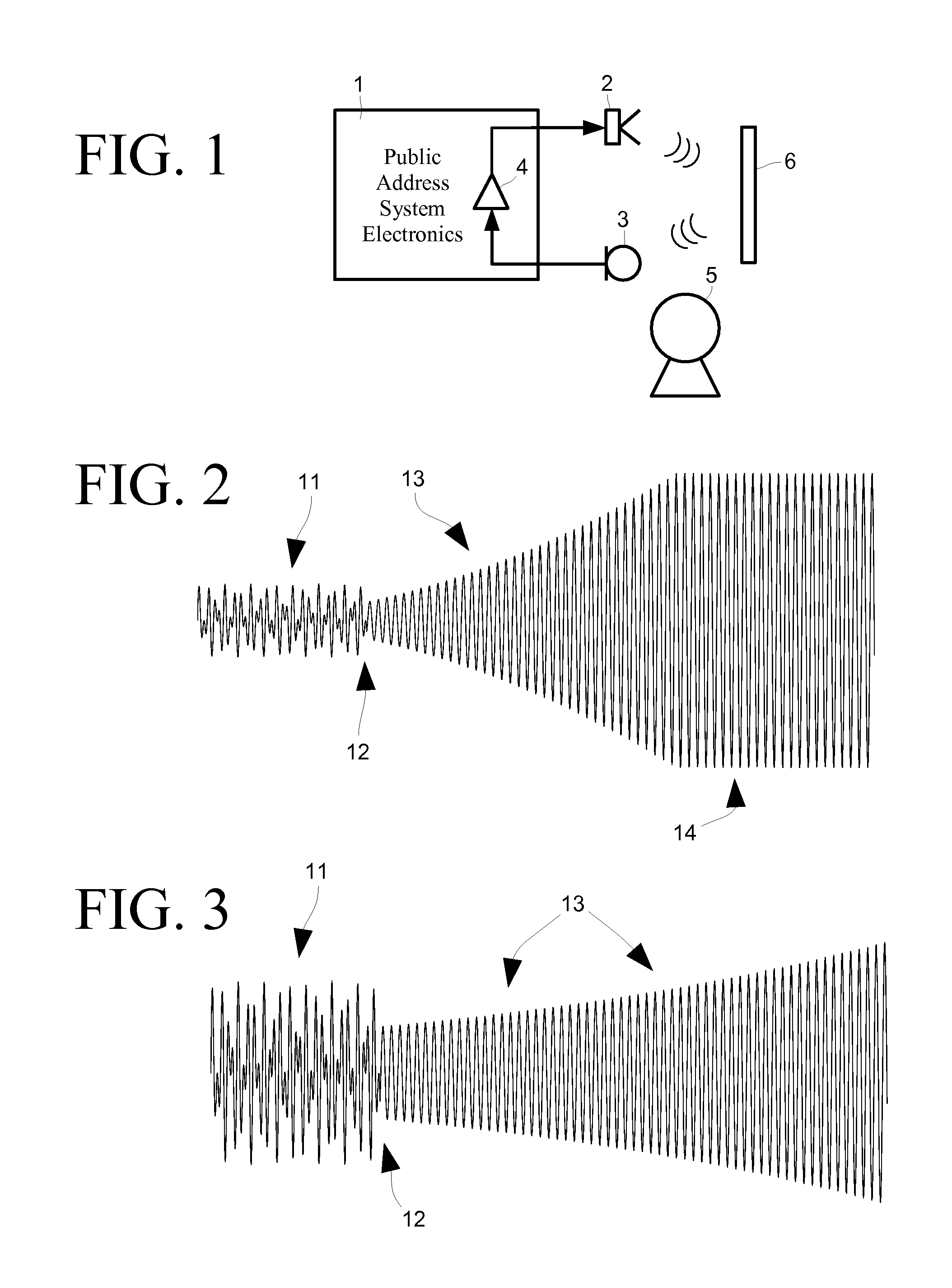
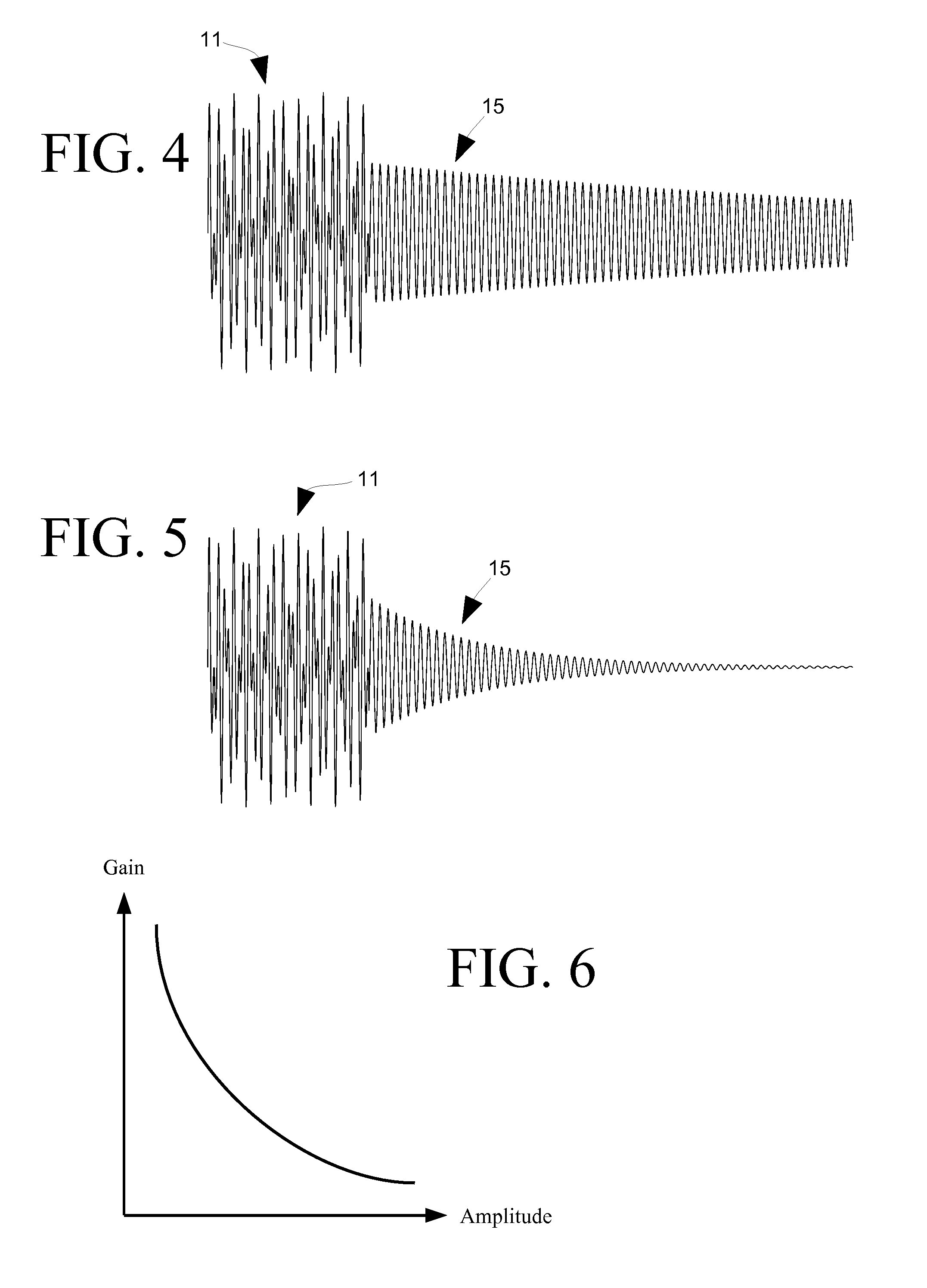
ActiveUS8027486B1Easy to measureHigh resolutionTransducer acoustic reaction preventionTransmission noise suppressionFeedback effectCountermeasure
Disclosed herein are detectors of audio ringing feedback, that is decaying feedback with a gain of less than one, those detectors utilizing a repeated gain measurement that applied to a range of gain values characteristic of ringing-type feedback. Those gain measurements, while in the range, increase a probability measurement of feedback. When the probability of feedback reaches a threshold, a detection of feedback is made and feedback countermeasures, such as the application of a notch filter, may be applied. Optionally, the audio gain around likely frequencies of feedback may be enhanced for a time to increase the resolution of identification of a feedback frequency, which may be identified through an interpolative method. Repeated gain measurements may also identify building-type feedback. A ringing detector may include more than one range of detection, for example for building, strong-ringing and weak-ringing feedback.
Owner:CLEARONCE COMM INC
Apparatus and method for downstream power management in a cable system
InactiveUS7778241B2Power managementData switching by path configurationChannel powerTransmitted power
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Strength-discriminating probabilistic ringing feedback detector
ActiveUS8090118B1Easy to measureHigh resolutionPublic address systemsTransducer acoustic reaction preventionCountermeasureImage resolution
Disclosed herein are detectors of audio ringing feedback, that is decaying feedback with a gain of less than one, those detectors utilizing a repeated gain measurement that applied to a range of gain values characteristic of ringing-type feedback. Those gain measurements, while in the range, increase a probability measurement of feedback. When the probability of feedback reaches a threshold, a detection of feedback is made and feedback countermeasures, such as the application of a notch filter, may be applied. Optionally, the audio gain around likely frequencies of feedback may be enhanced for a time to increase the resolution of identification of a feedback frequency, which may be identified through an interpolative method. Repeated gain measurements may also identify building-type feedback. A ringing detector may include more than one range of detection, for example for building, strong-ringing and weak-ringing feedback.
Owner:CLEARONCE COMM INC
Hearing aid system comprising a matched filter and a measurement method
ActiveUS8442247B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioDeaf aid adaptationStereophonic arrangmentsEngineeringSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
Owner:OTICON
Method of Assembling Turbine, Assembly Work Supporting System, and Control Program
ActiveUS20180307205A1Maintain accuracyShorten the overall cycleProgramme controlGeometric CADSupporting systemEngineering
The invention is directed to maintaining the accuracy in the positional adjustment of a stationary part while shortening a turbine assembly period through the omission of the temporary assembly of a casing. A method of assembling includes gaining measurement data on the configuration of a casing upper half part not fastened to a casing lower half part; gaining measurement data on the configuration of the casing lower half part in an open state in which the casing upper half part and a rotor are removed and in which a stationary part is mounted; comparing measurement data on the configuration of the casing upper half part and the casing lower half part with simulation data on the configuration of the casing upper half part and the casing lower half part previously obtained to select simulation data closest to the measurement data on the configuration of the casing upper half part and the casing lower half part; calculating, based on the selected simulation data, a change amount of the configuration of the casing upper half part and the casing lower half part when the casing upper half part is fastened to the casing lower half part in the open state; and adjusting the installation position of the stationary part inside the casing taking into account the calculated change amount.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POWER LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com