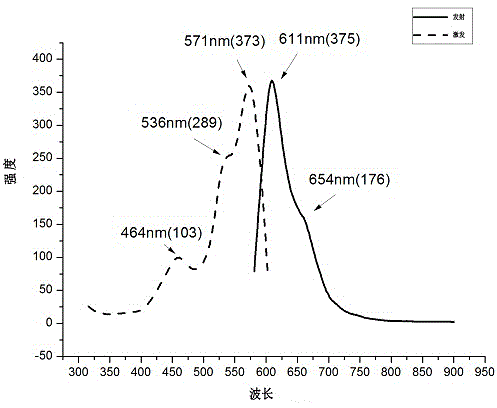
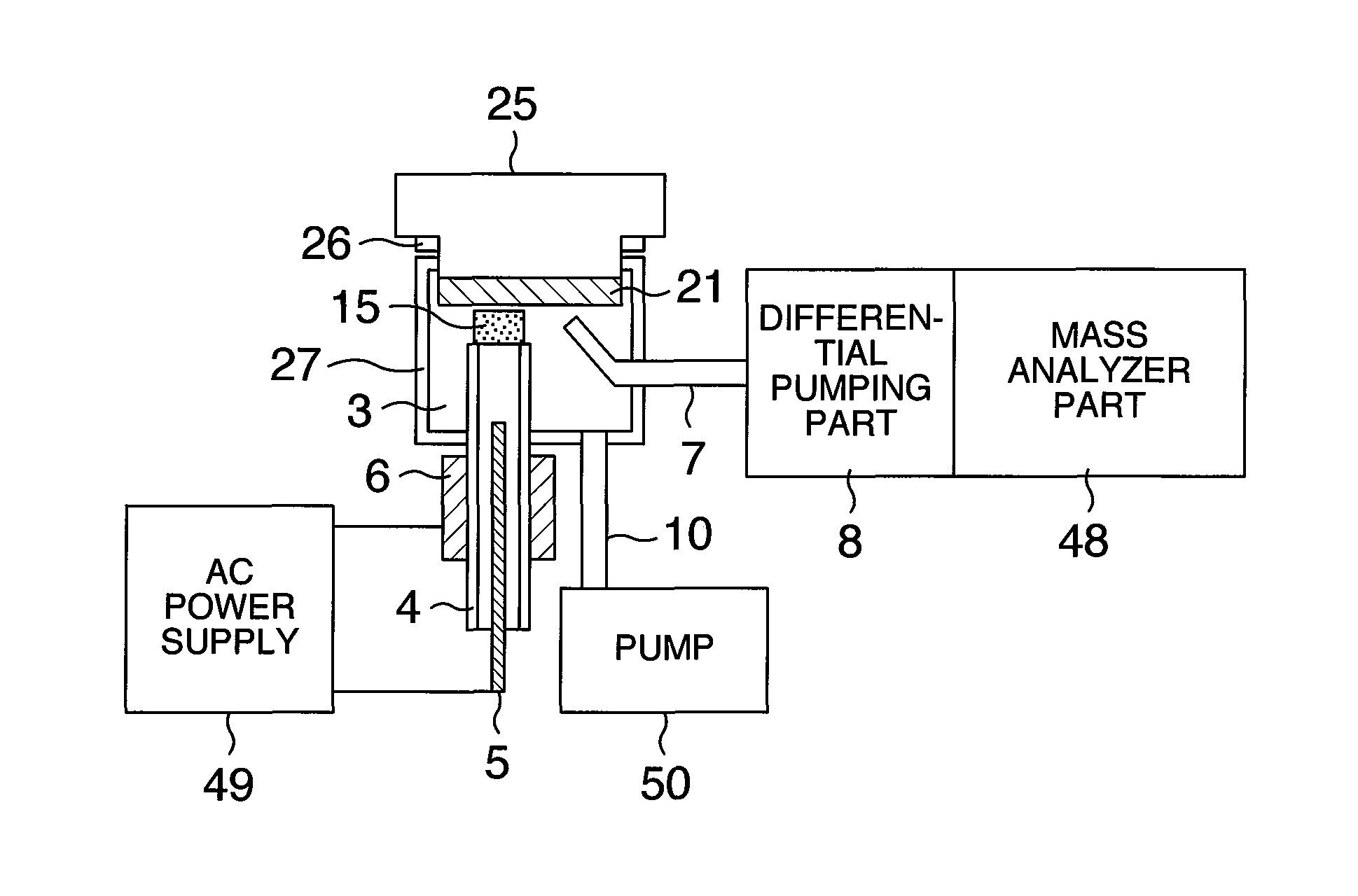
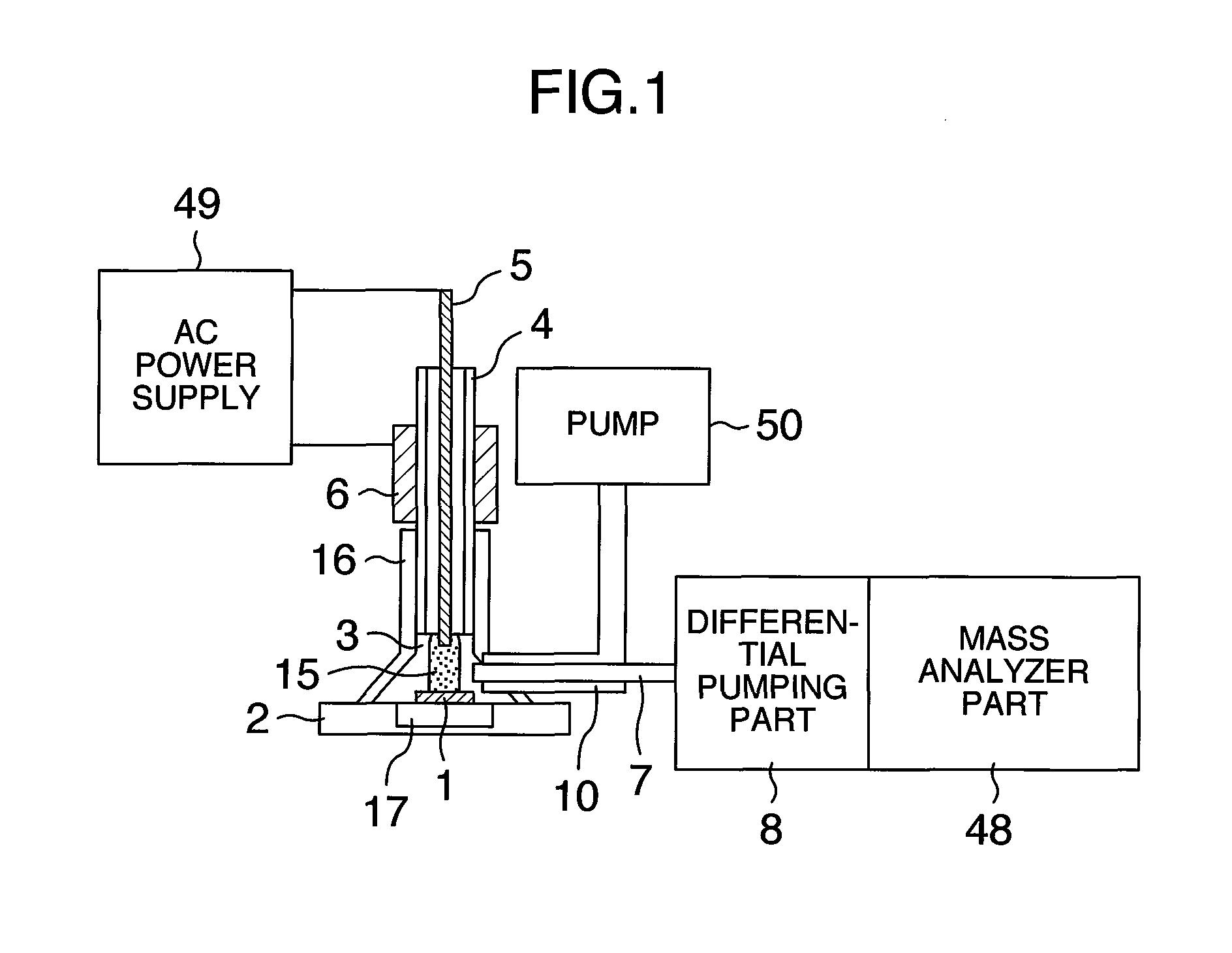
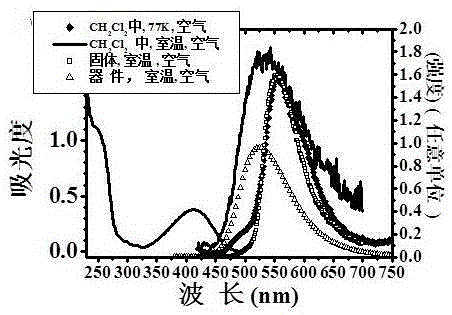
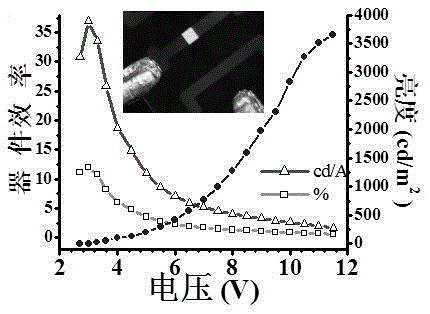
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
36 results about "Excited molecule" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
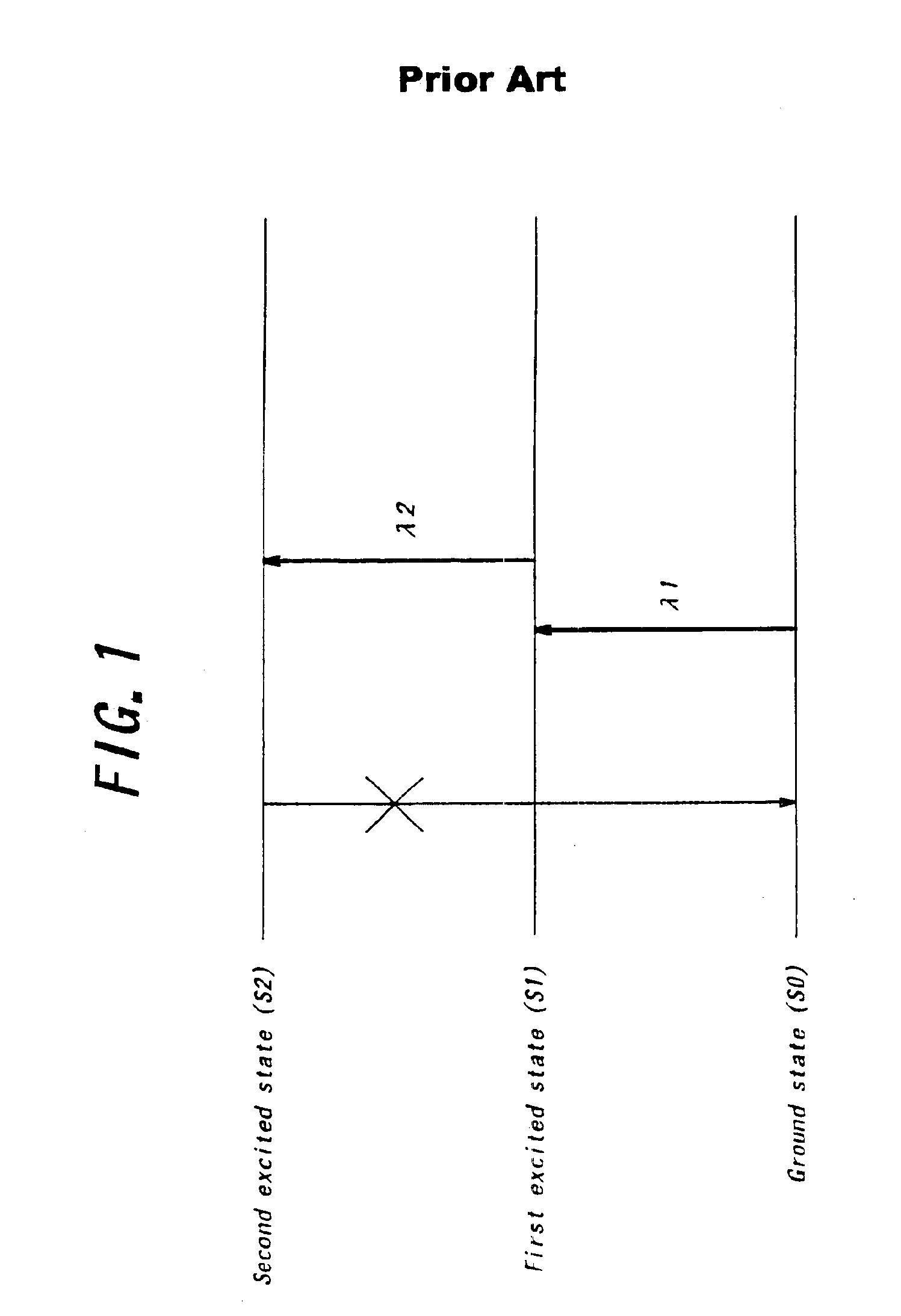
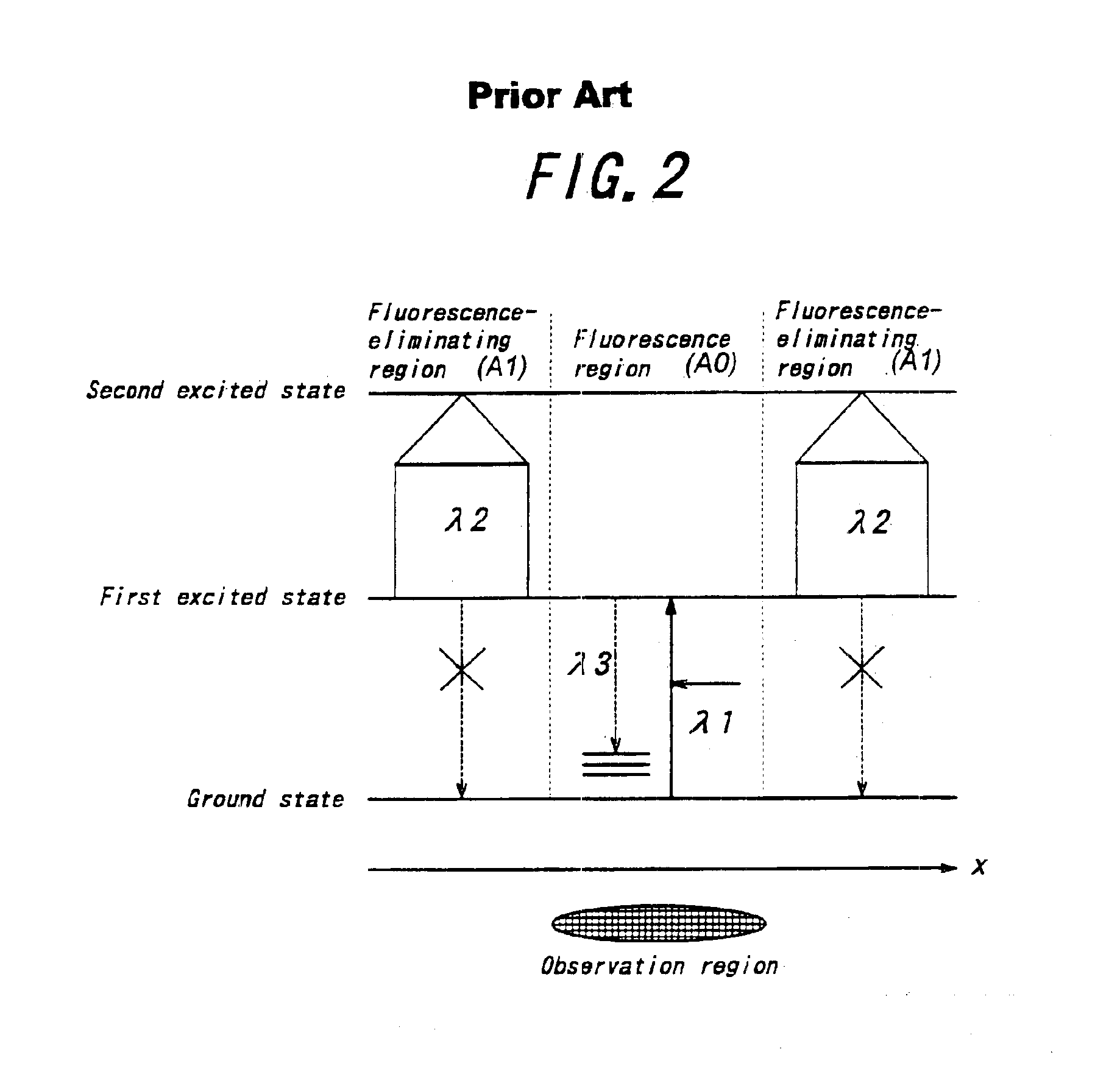
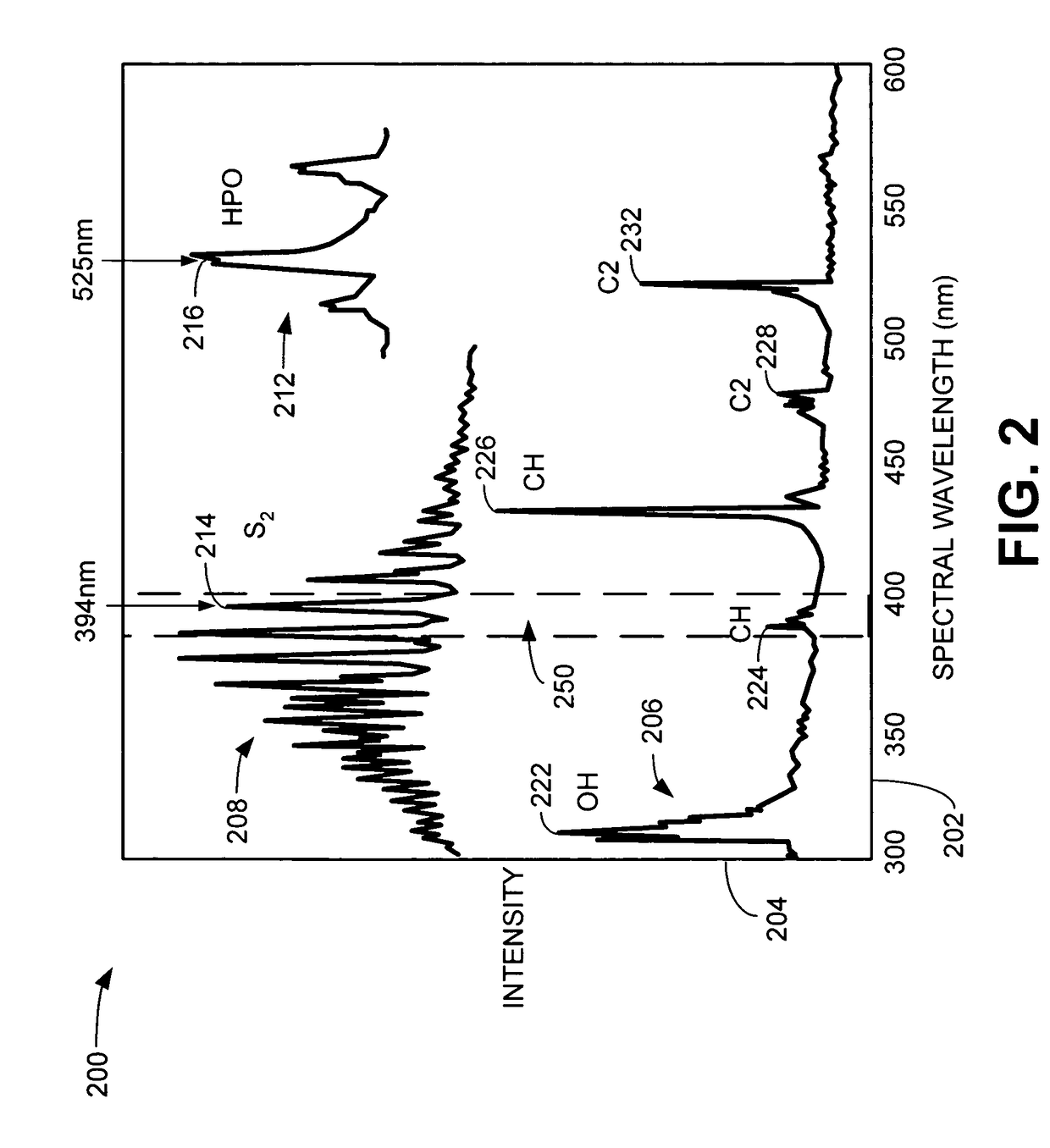
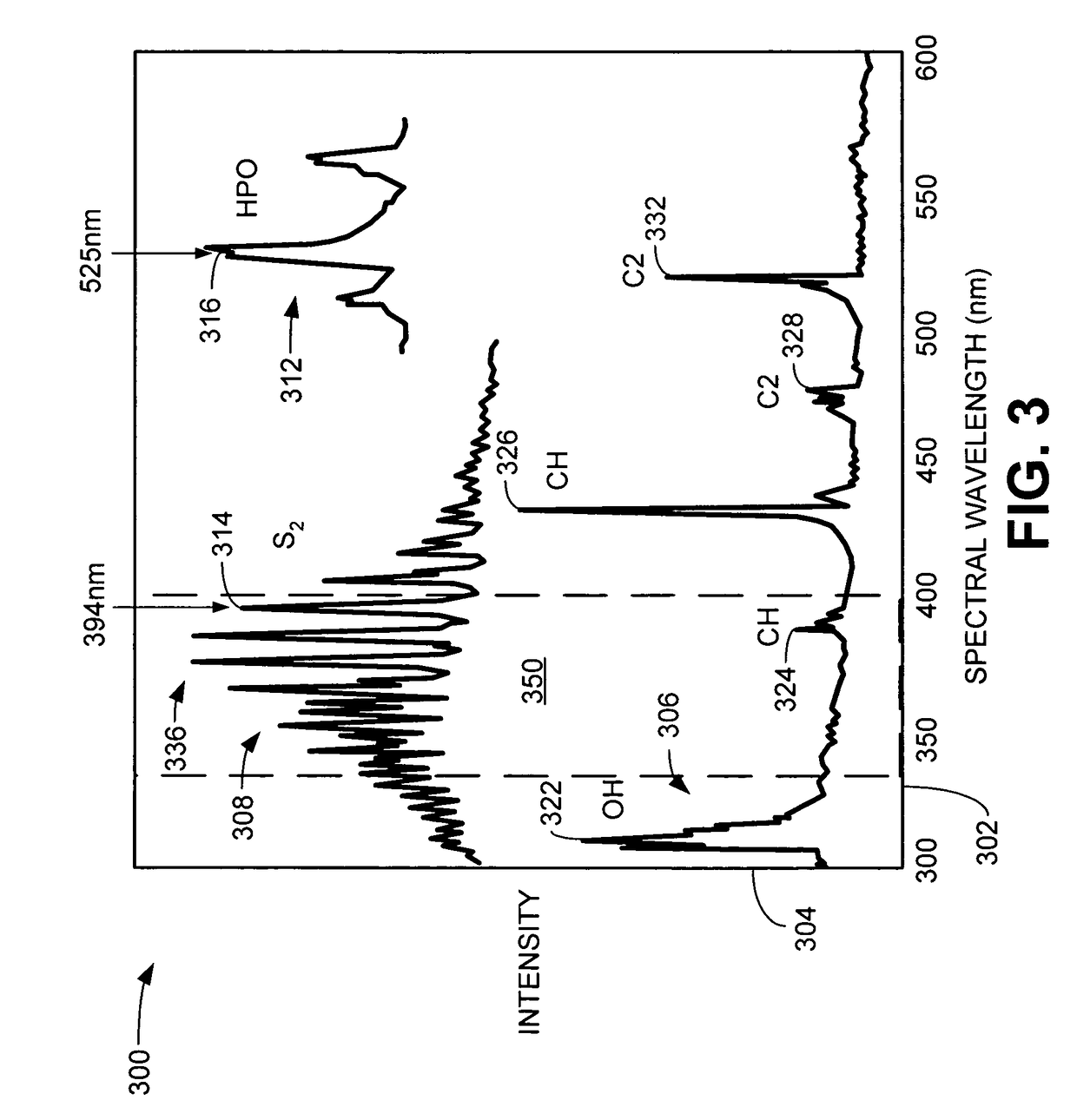
The excited state molecule has extra energy from absorbing a photon of electromagnetic radiation. It can lose the energy in a number of ways. Heat Molecules collide with one another. The excited molecule can transfer its extra energy to one or more molecules. This increases their kinetic energy.
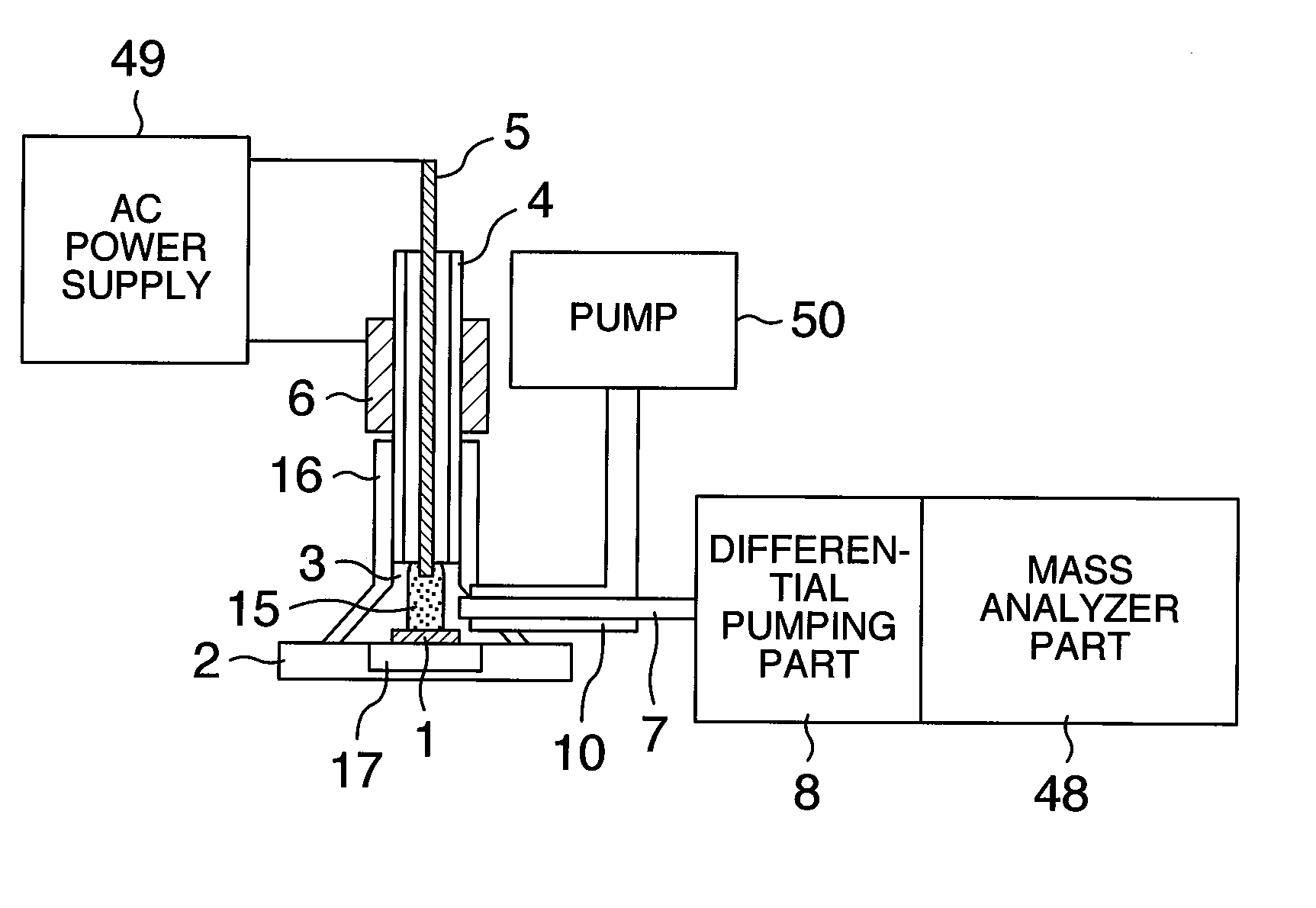
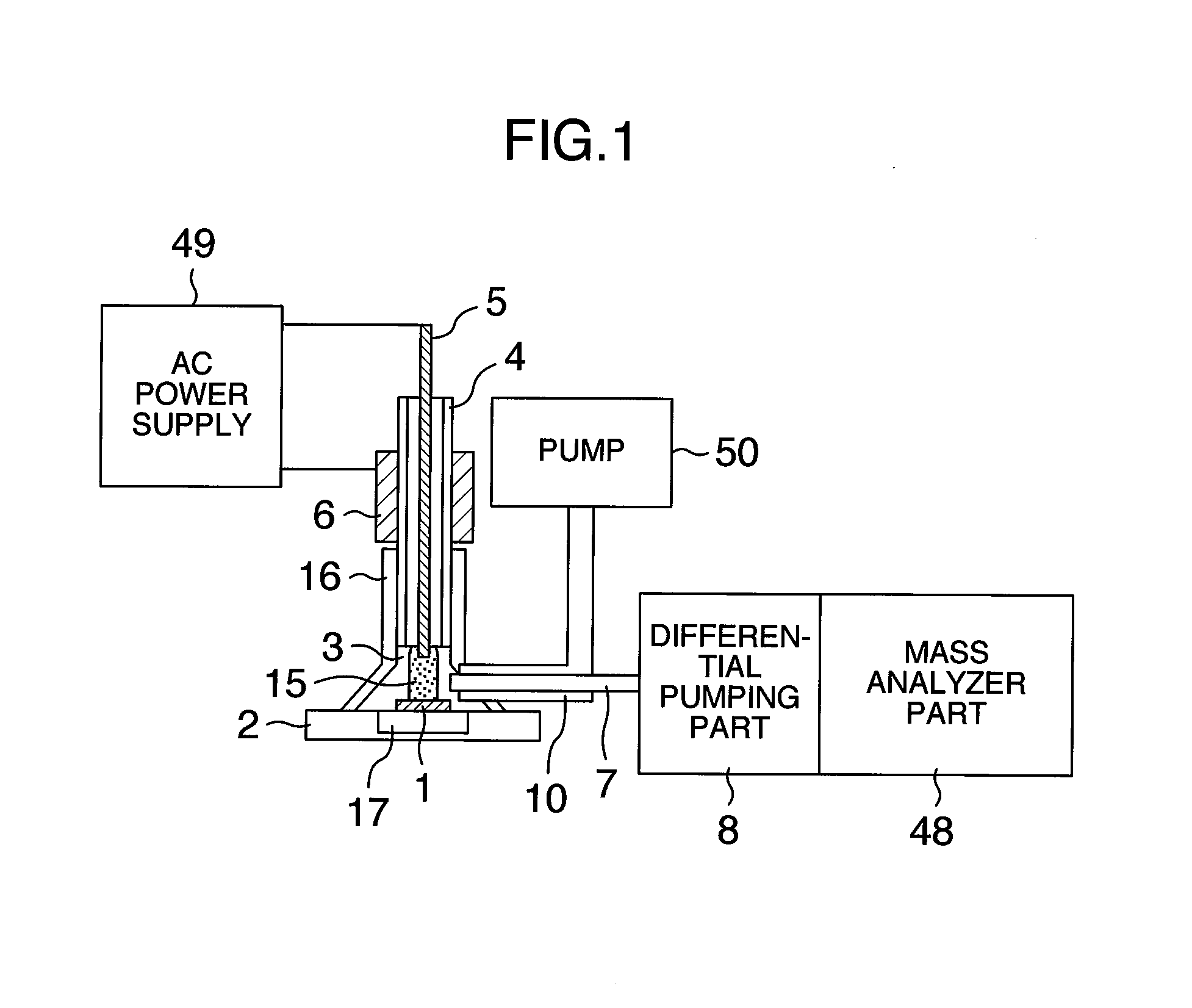
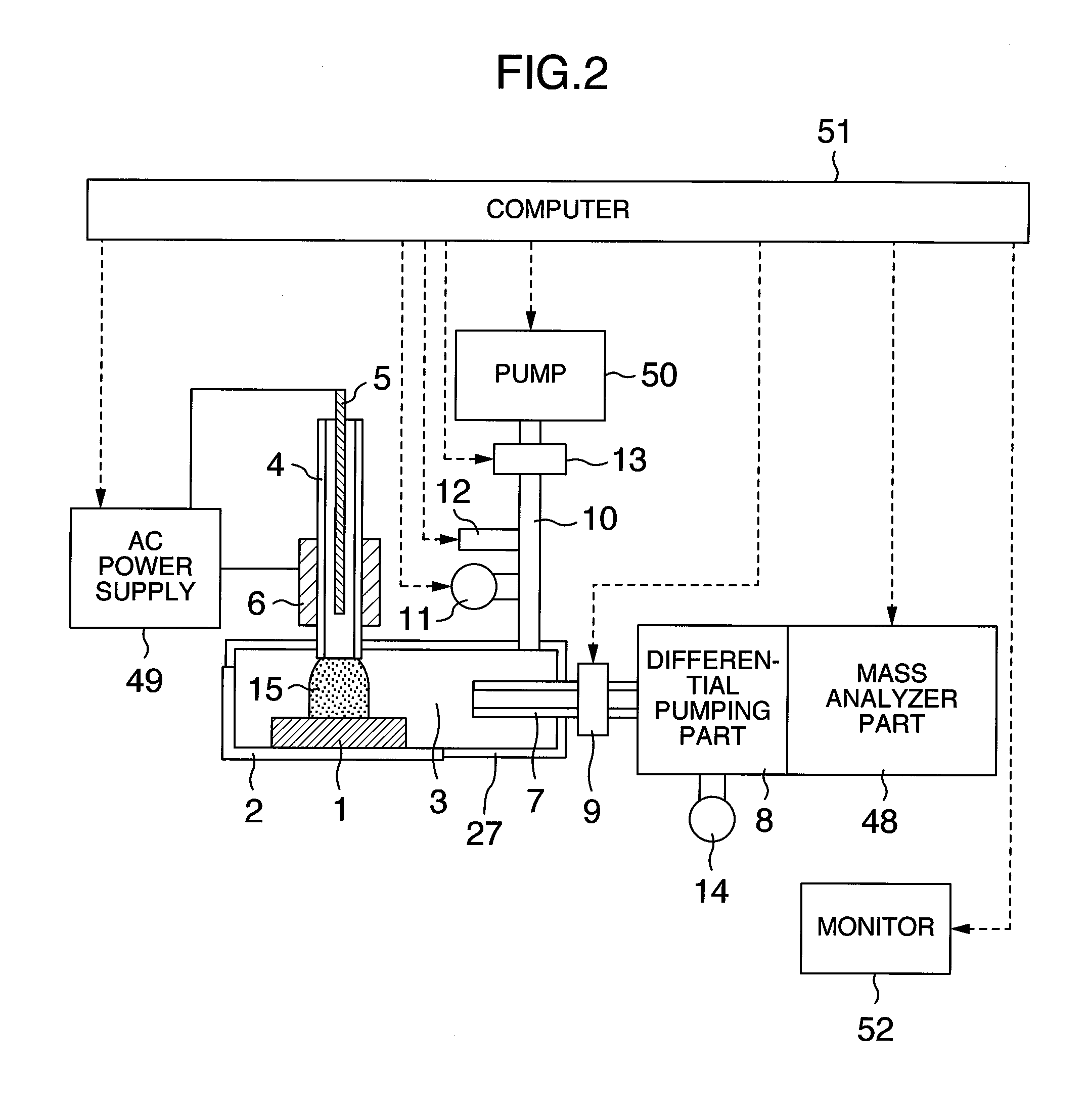
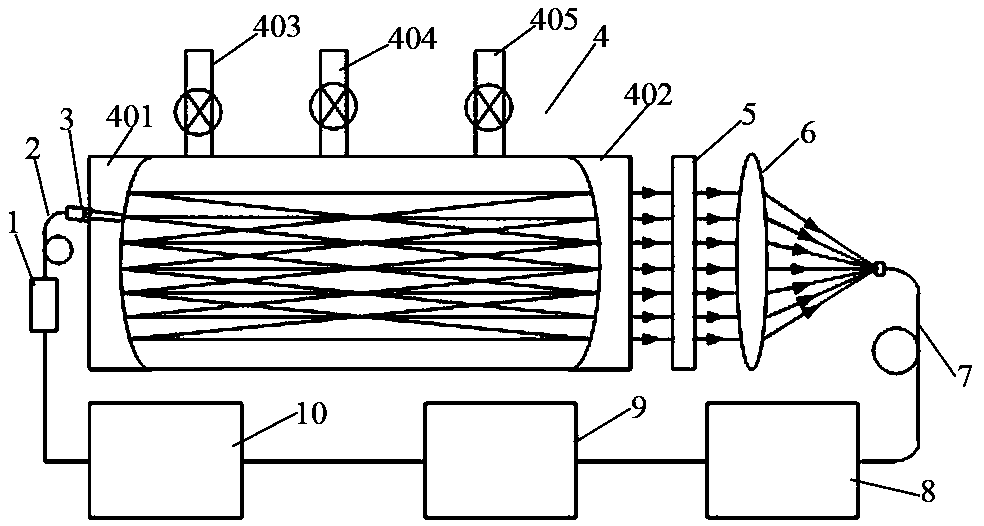
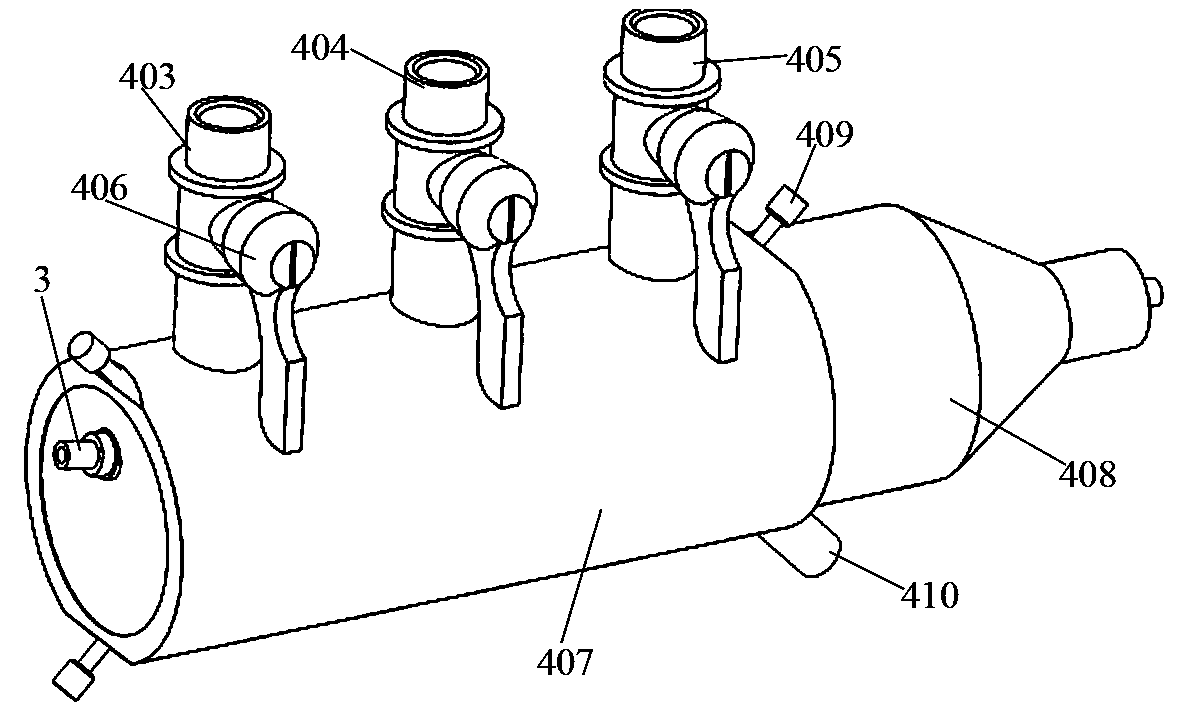
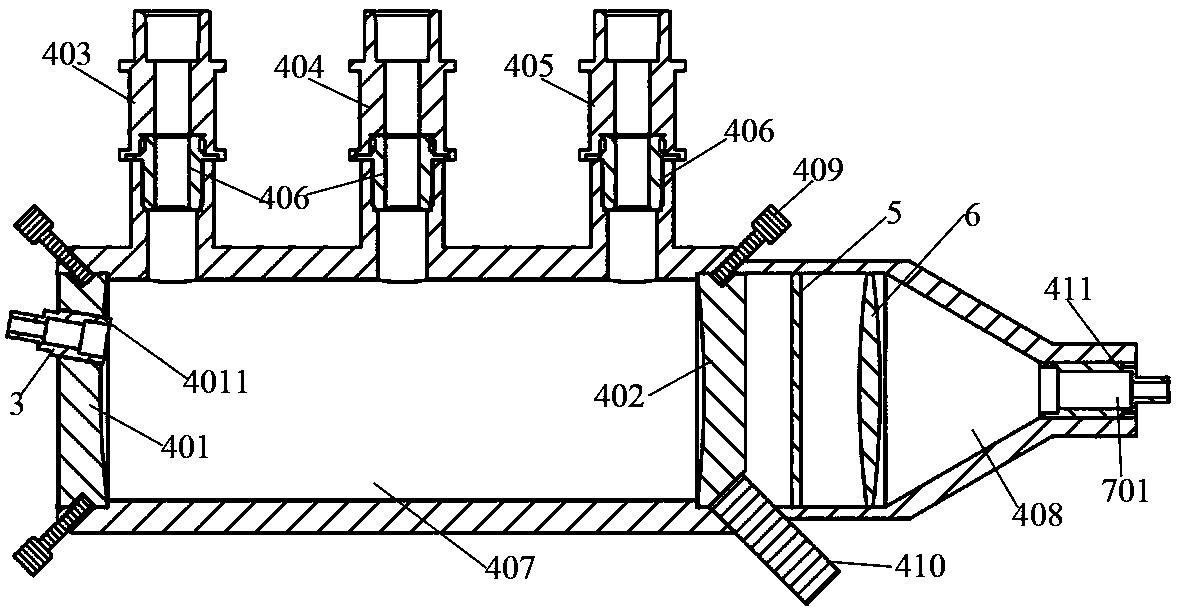
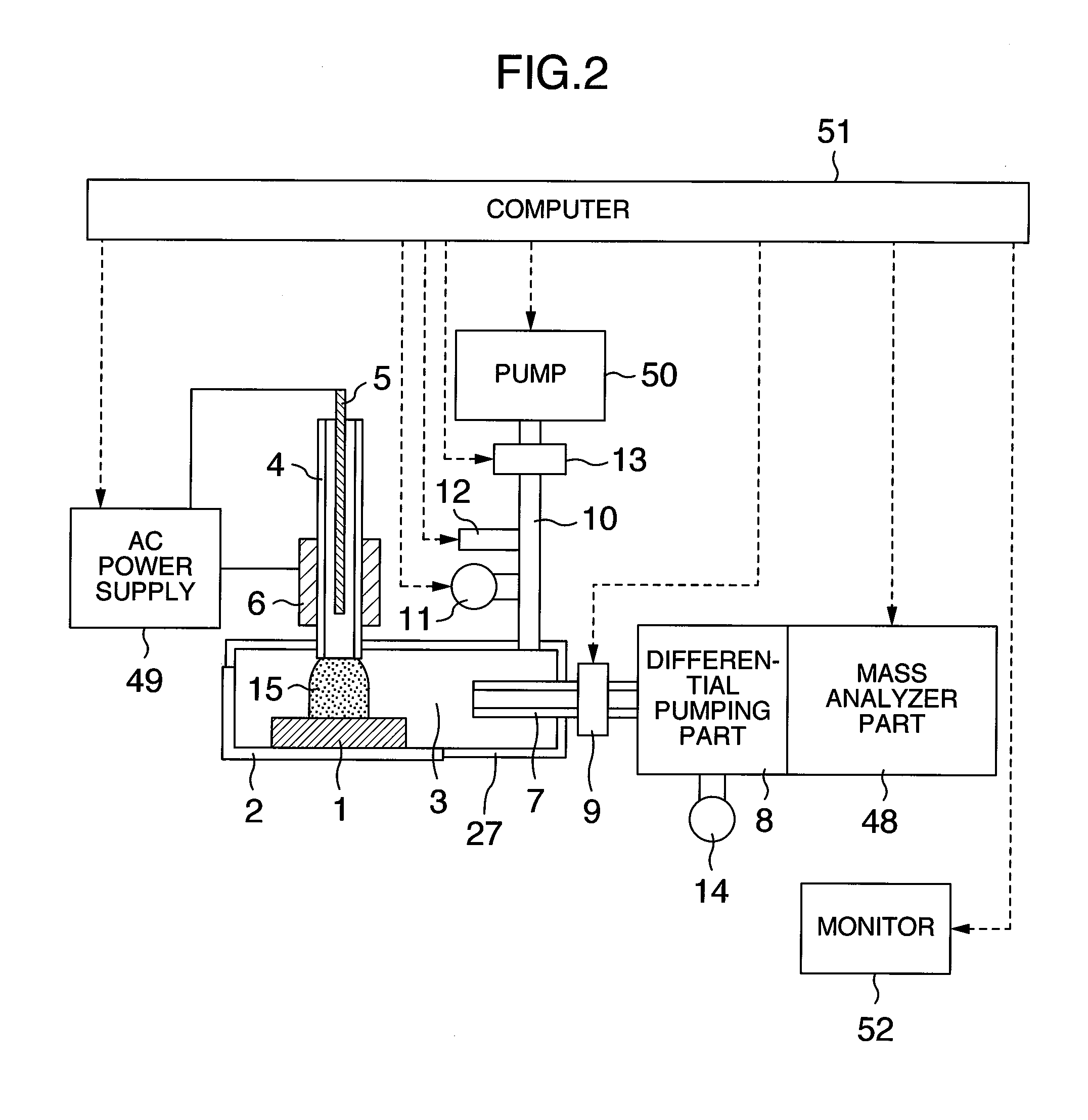
Analyzer, ionization apparatus and analyzing method
ActiveUS20110253889A1Reduce sensitivityReduce loss rateParticle separator tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansExcited moleculeAtmospheric pressure
An analyzer performs dielectric barrier discharge and ionization of a sample by a reaction between the sample and excited molecules or ions generated by the dielectric barrier discharge at a pressure lower than an atmospheric pressure.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
STED-Fluorescent Light Microscopy with Two-Photon Excitation
ActiveUS20100176307A1Improve spatial resolutionPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersFluorescenceImage resolution
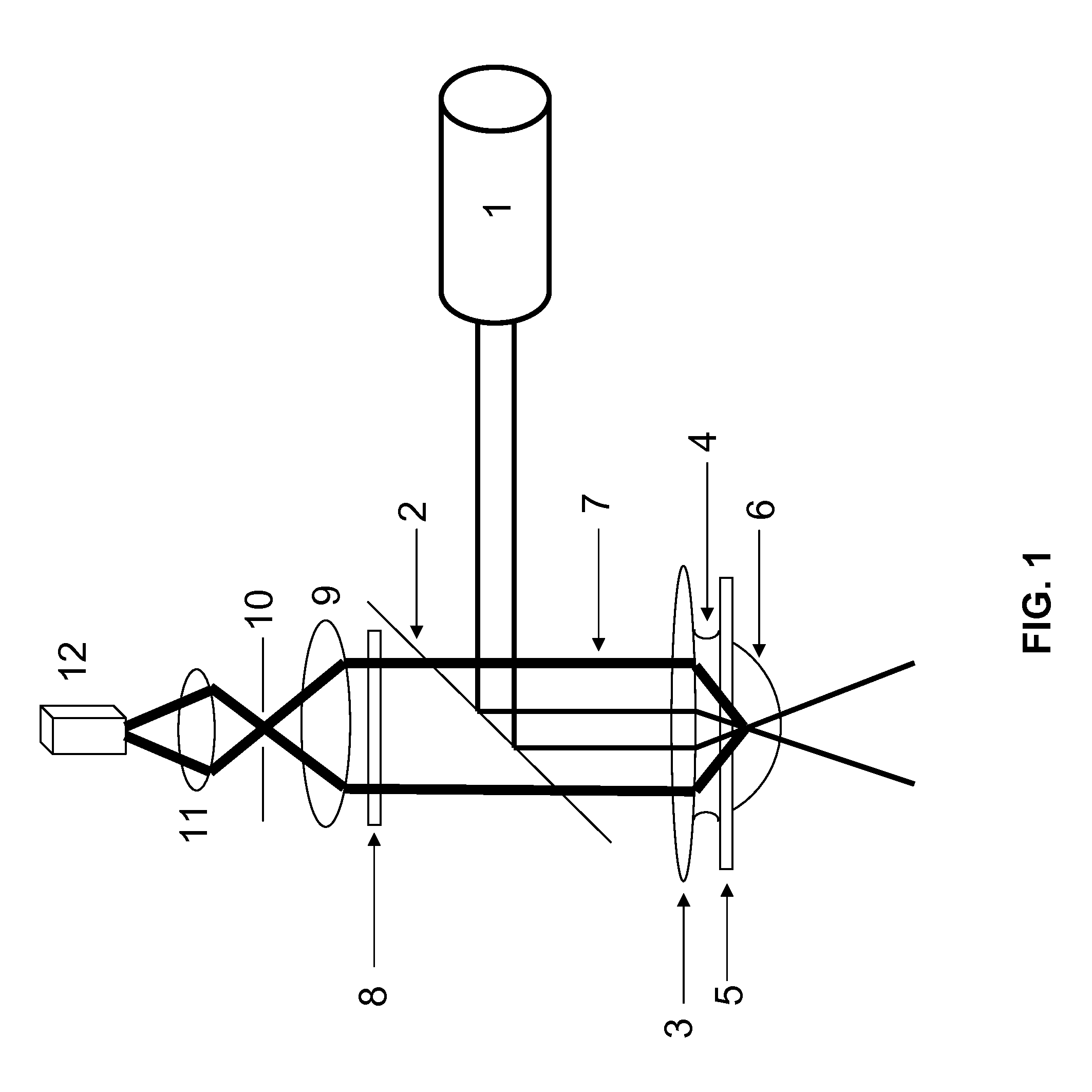
A method of high spatial resolution imaging a structure in a sample comprises: marking the structure with molecules of a fluorescent dye; selecting a first wavelength for excitation light which excites the molecules of the fluorescent dye via a multi photon process for spontaneous emission of fluorescent light; focussing pulses of the excitation light into the sample to excite those molecules of the fluorescent dye present in a focal area of the focussed excitation light; selecting a second wavelength shorter than the first wavelength for de-excitation light which de-excites excited molecules of the fluorescent dye prior to their spontaneous emission; during a plurality of the pulses of the excitation light, continuously directing the de-excitation light onto the sample to de-excite excited molecules of the fluorescent dye, which are located outside an measurement area which is a fraction of the focal area; and recording the fluorescent light spontaneously emitted by the molecules of the fluorescent dye in the sample.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Ultra-fast laser system
ActiveUS8633437B2Accurate and redundant identificationCost effectiveRadiation pyrometryLaser using scattering effectsPulse shaperUltra fast
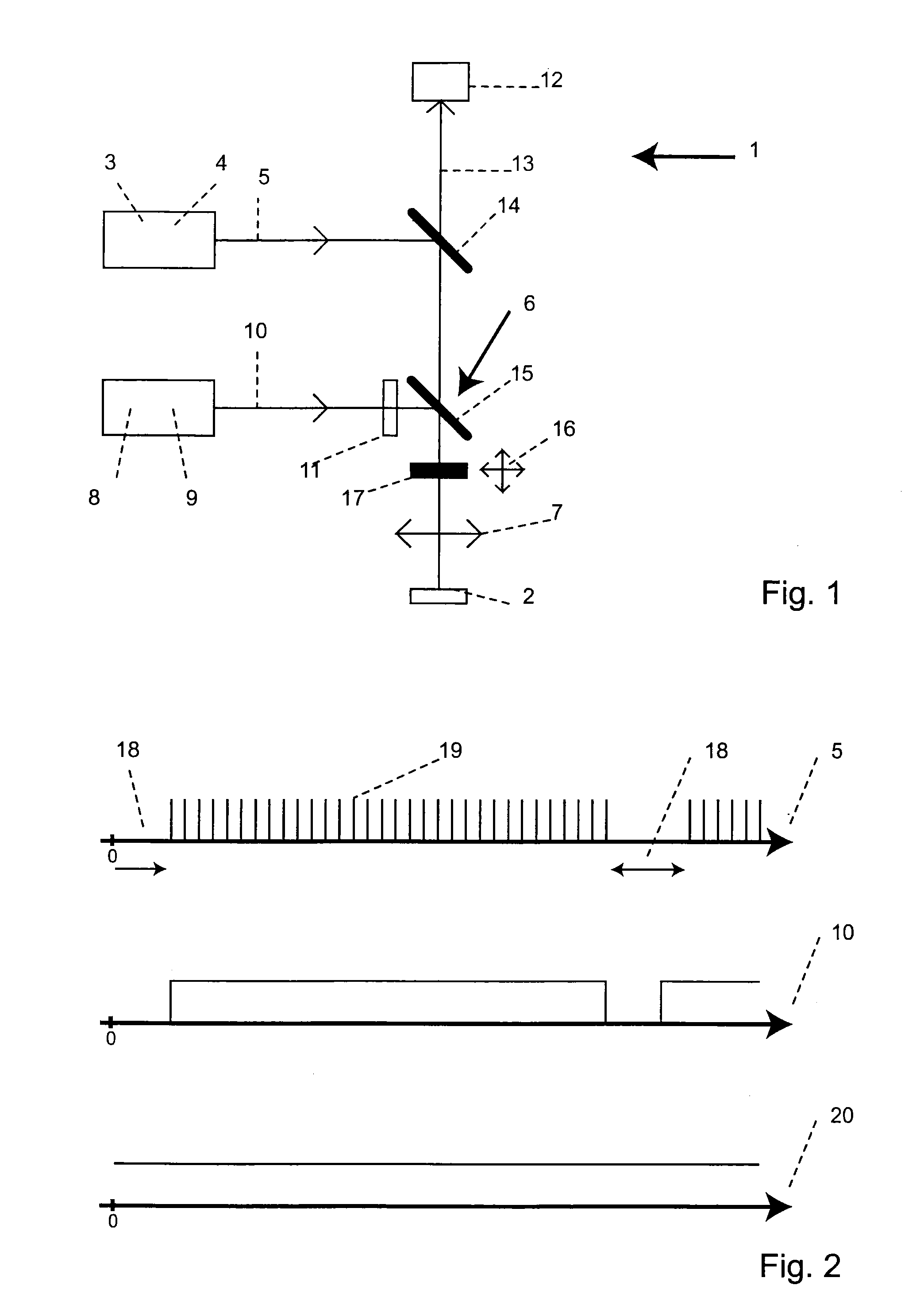
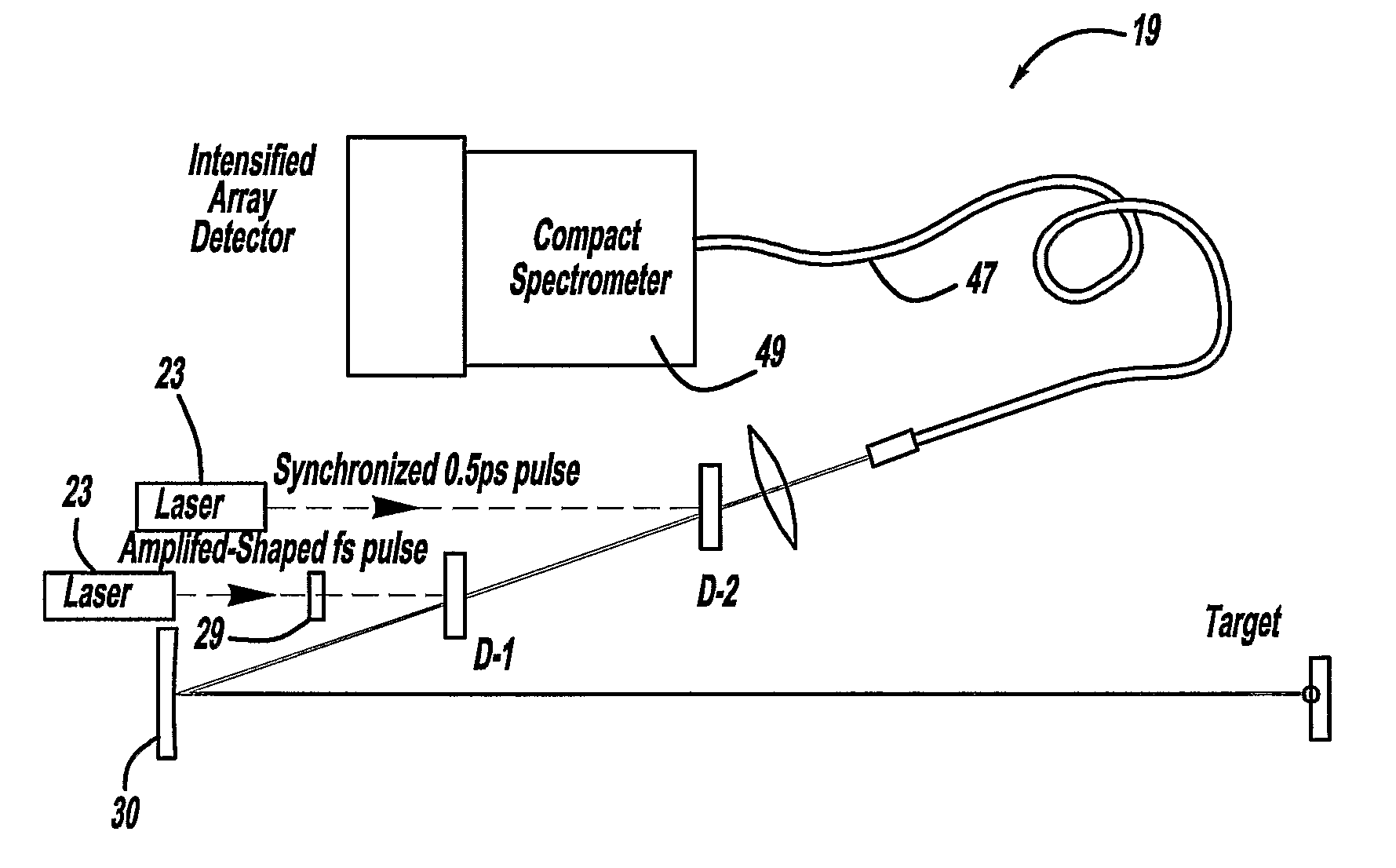
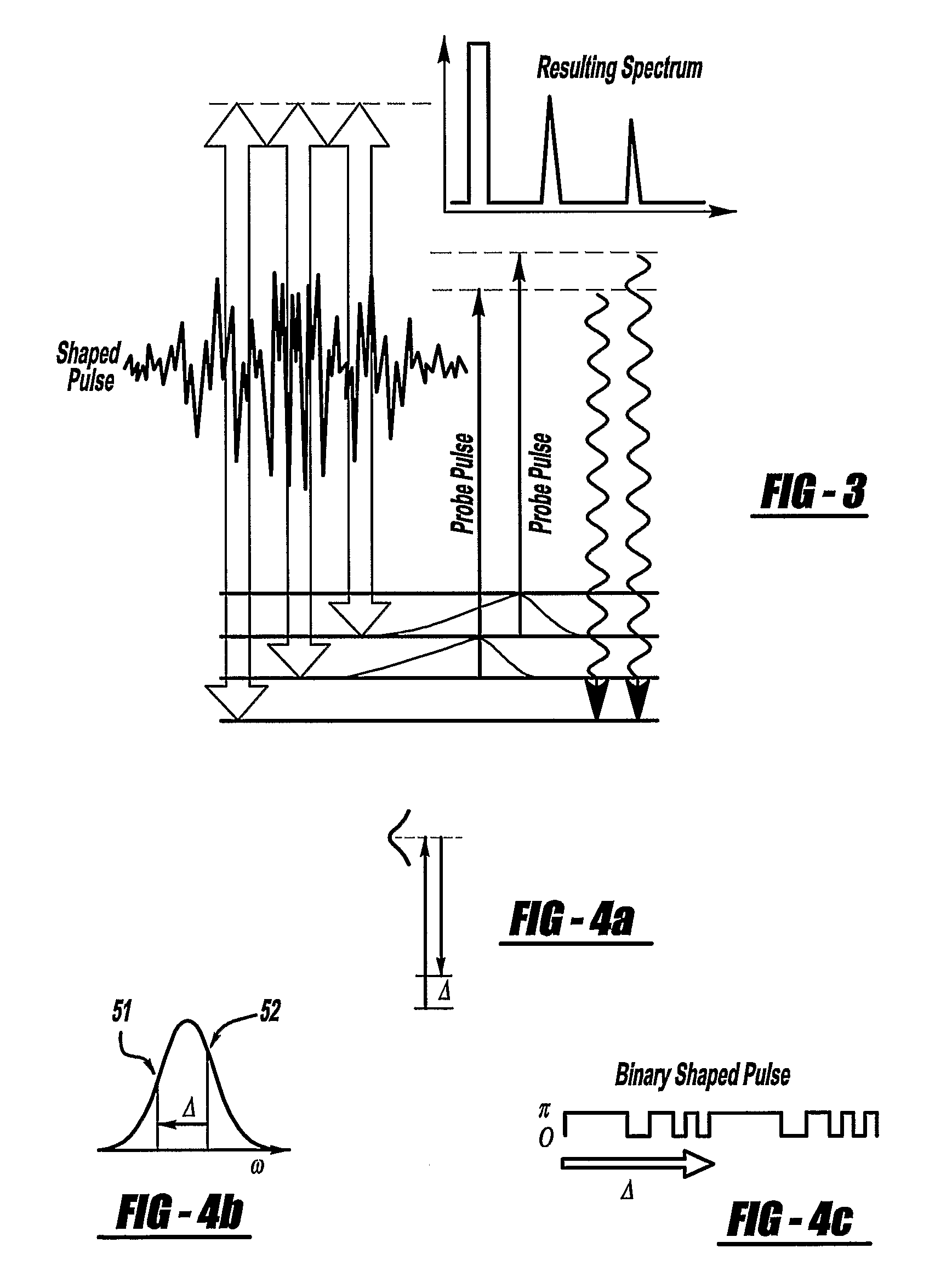
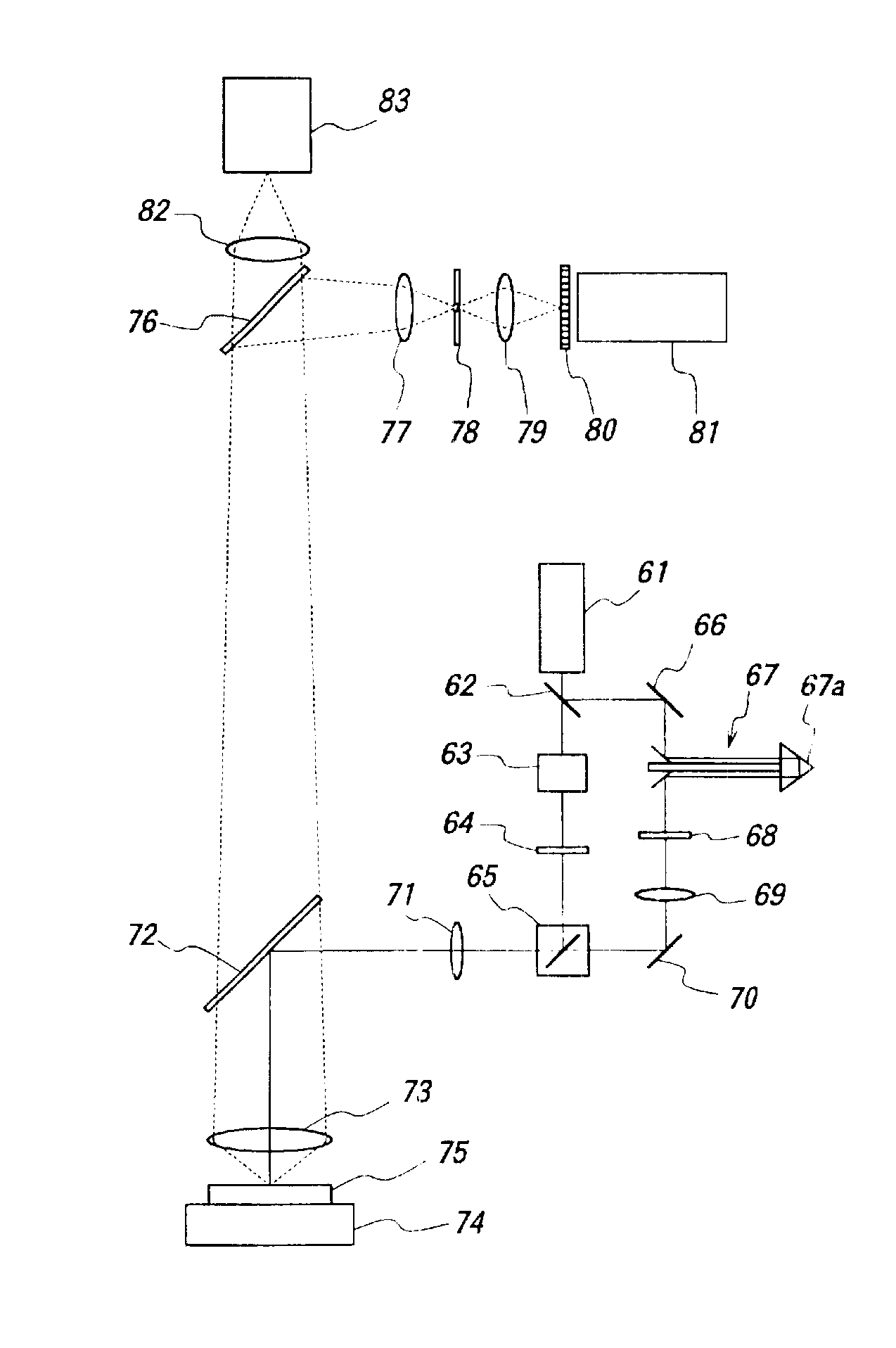
A laser system is provided which selectively excites Raman active vibrations in molecules. In another aspect of the present invention, the system includes a laser, pulse shaper and detection device. A further aspect of the present invention employs a femtosecond laser and binary pulse shaping (BPS). Still another aspect of the present invention uses a laser beam pulse, a pulse shaper and remote sensing.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Super resolution microscope
InactiveUS6859313B2High resolutionHigh sensitivityPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersFluorescenceHigh energy
A microscope includes a first light source to emit a first light to excite a molecule of a sample to a higher energy level vibration state which belongs to a lowest energy level electron state from the ground state, a second light source to emit a second light source to excite the molecule to a higher energy level quantum state from the higher energy vibration state, an optical system to overlap the first light and the second light partially on the sample, and an optical detector to detect a given fluorescence from the irradiated region of the first light and the second light on the sample.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
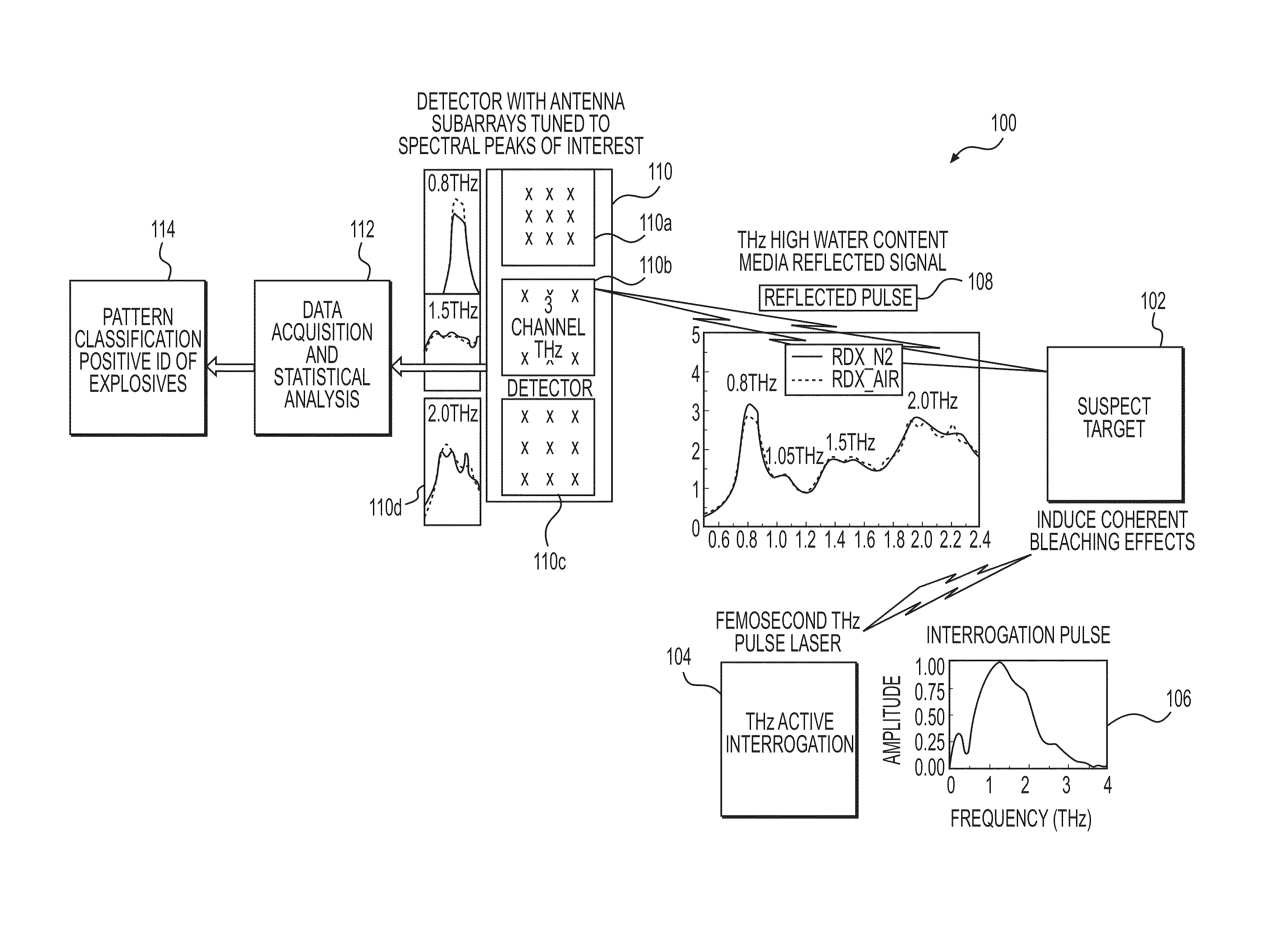
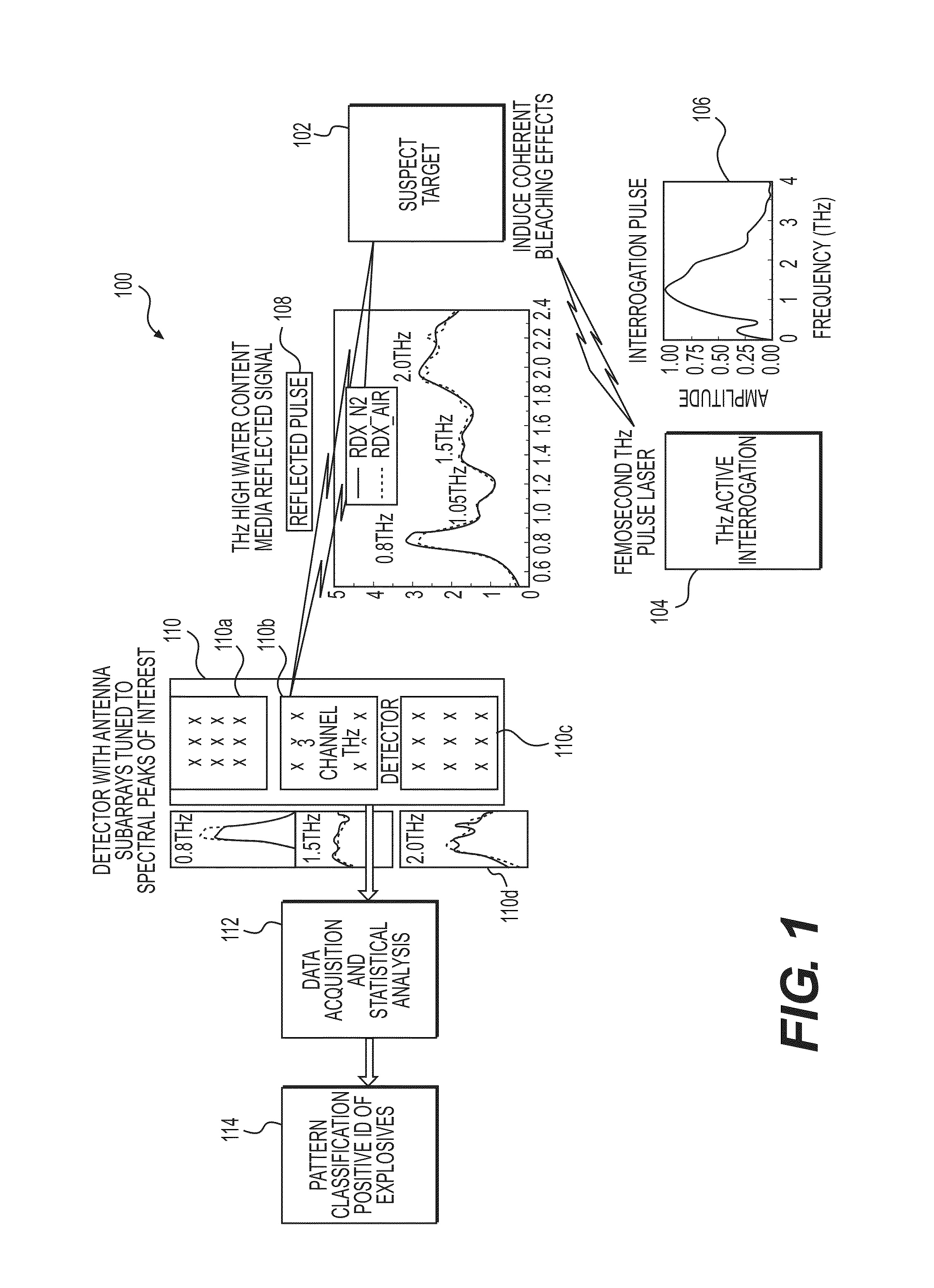
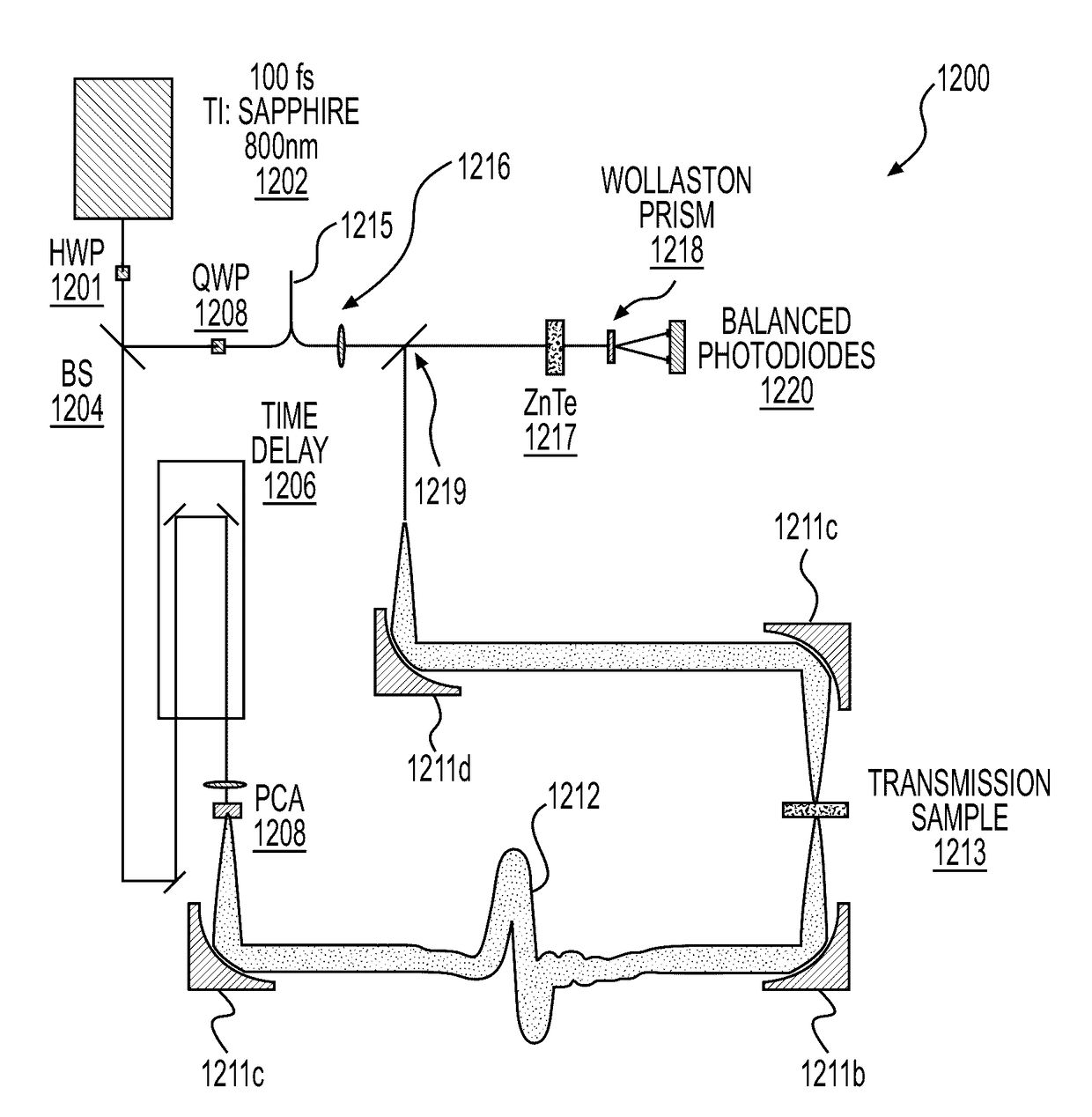
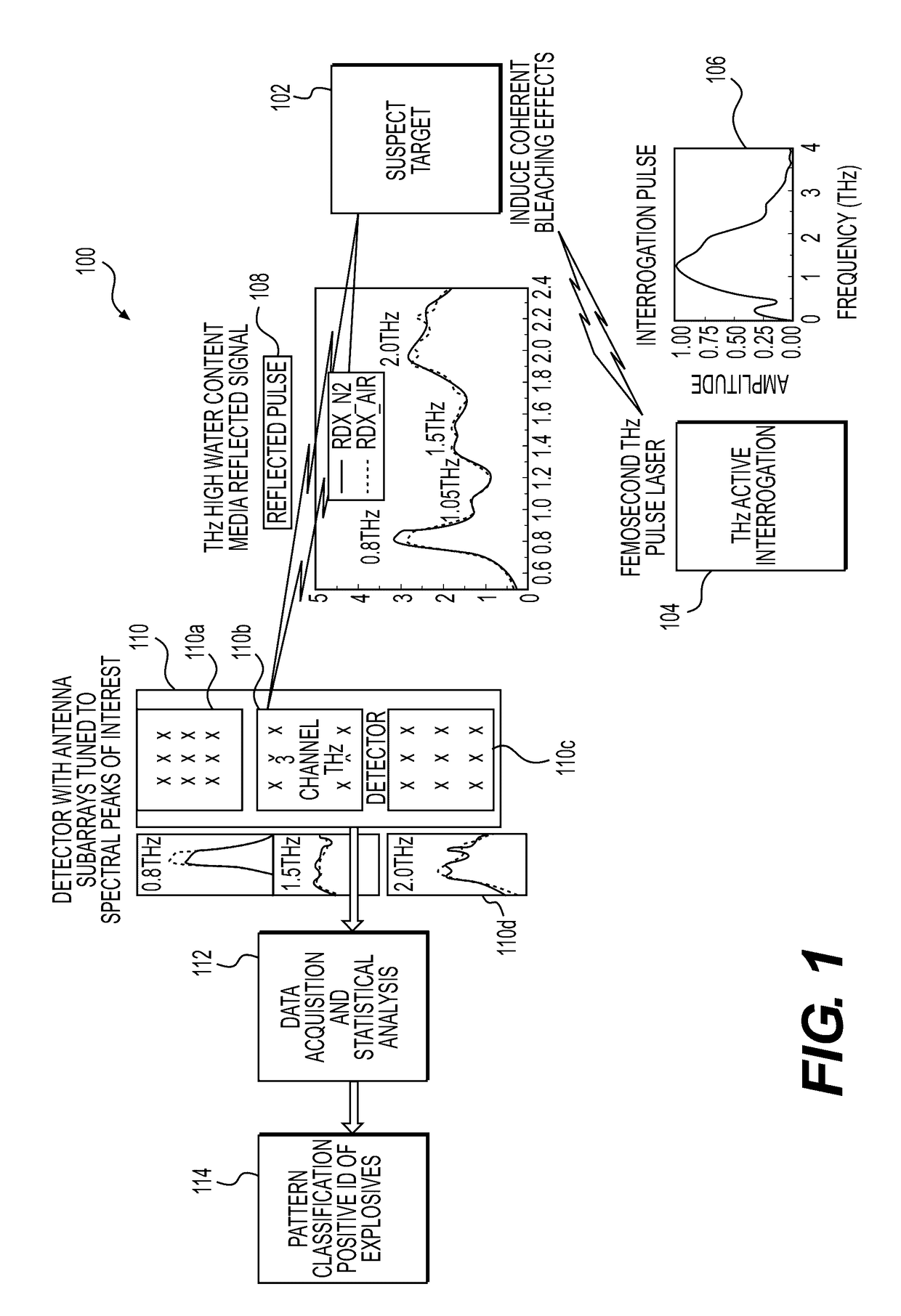
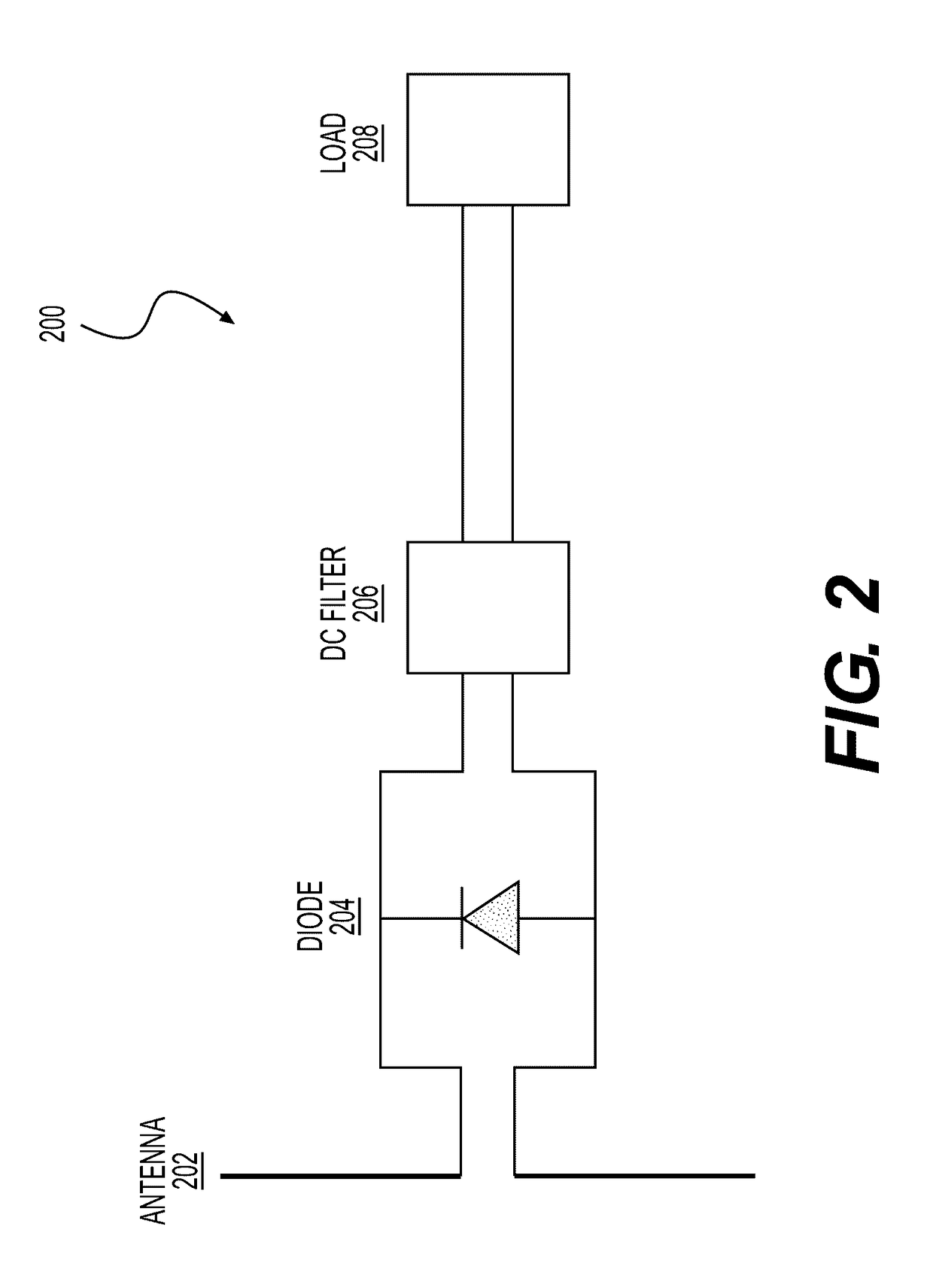
System and Method for Identifying Materials Using a THz Spectral Fingerprint in a Media with High Water Content
InactiveUS20140172374A1Reduce false positiveFalse negativeRadiation pyrometryAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceSpectral emissionStatistical analysis
A material detector includes a pulse generator to generate pulses to excite molecules in the material and a detector to detect a signal generated from excited molecules in the terahertz region. Spectral features in the material are analyzed to identify the material. Detection can be performed using a nanoantenna array structure having antennas tuned to detect the expected spectral emission. The nanoantenna array can include antennas having MIM or MIIM diodes. Signal processing and statistical analysis is use to reduce false positives and false negative in identifying the material.
Owner:REDWAVE ENERGY
Gas specie electron-jump chemical energy converter
InactiveUS20050189011A1Thermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesChemical reactionElectrical conductor
An apparatus and method for extracting energy is provided. In one aspect the method includes using chemical reactions to generate vibrationally excited molecules, such as high-quantum-number-vibrationally-excited gas molecules in a region. The vibration energy in the vibrationally excited molecules is converted into hot electrons when the excited molecules contact a conductor. A geometry is provided so that the excited molecules may travel, diffuse or wander into a conductor before loosing a useful fraction of the vibrational energy. Optionally, the generating and the converting process may be thermally separated, at least in part. The short lived hot electrons are converted into longer lived entities such as carriers and potentials in a semiconductor, where the energy is converted into a useful form.
Owner:NEOKISMET L L C
Raman enhanced measurement device and method and off-axis integral cavity structure applied to Raman enhanced measurement
InactiveCN104280338ASimple and accurate judgment of componentsSimple and accurate judgment of concentrationRaman scatteringMeasurement deviceTest sample
The invention relates to the spectral measurement field and discloses a Raman enhanced measurement device. The Raman enhanced measurement device comprises a laser, a collimating system, an off-axis integral cavity, an edge filter, a light receiving lens, a spectrometer and a control system, which are arranged sequentially, wherein the off-axis integral cavity comprises a front plane-concave lens and a rear plane-concave lens, the concave surfaces of the lenses face the cavity, and a tested sample is contained in the cavity; the front plane-concave lens is coated with a total reflection film, a light hole is formed in a place deviated from a central shaft, and the rear plane-concave lens is coated with a laser high-reflection edge filter film. The invention also discloses a Raman enhanced measurement method using the Raman enhanced measurement device and an off-axis integral cavity structure applied to Raman enhanced measurement. The off-axis integral cavity technology is adopted to enable laser to be oscillated back and forth in the cavity for multiple times, the number of excited molecules is greatly increased, the Raman spectrum enhancement is realized, and thus the gas or liquid sample with low molecular concentration also can generate strong Raman spectrum; the composition and the concentration of the tested sample can be simply and accurately judged through analysis of Raman spectrum peaks.
Owner:SHANGHAI BRANCH FUZHOU GAOYI COMM CO LTD
Stimulated emission-based optical detection system
InactiveUS20120112094A1Beam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsPhotometryDistance detectionLight beam
The present invention provides an optical detection system comprising an illumination unit and a detection unit. The illumination unit comprises two laser beams of two different wavelengths. One beam is used to excite targeted molecules in a sample to their excited states. The other beam is used to induce the excited molecules in the sample to generate a stimulated emission signal. The stimulated emission signal can be used for long-distance detection due to its coherent property. Its extraction from the detection unit can be realized by demodulating the second beam's intensity change.
Owner:NATIONAL YANG MING UNIVERSITY
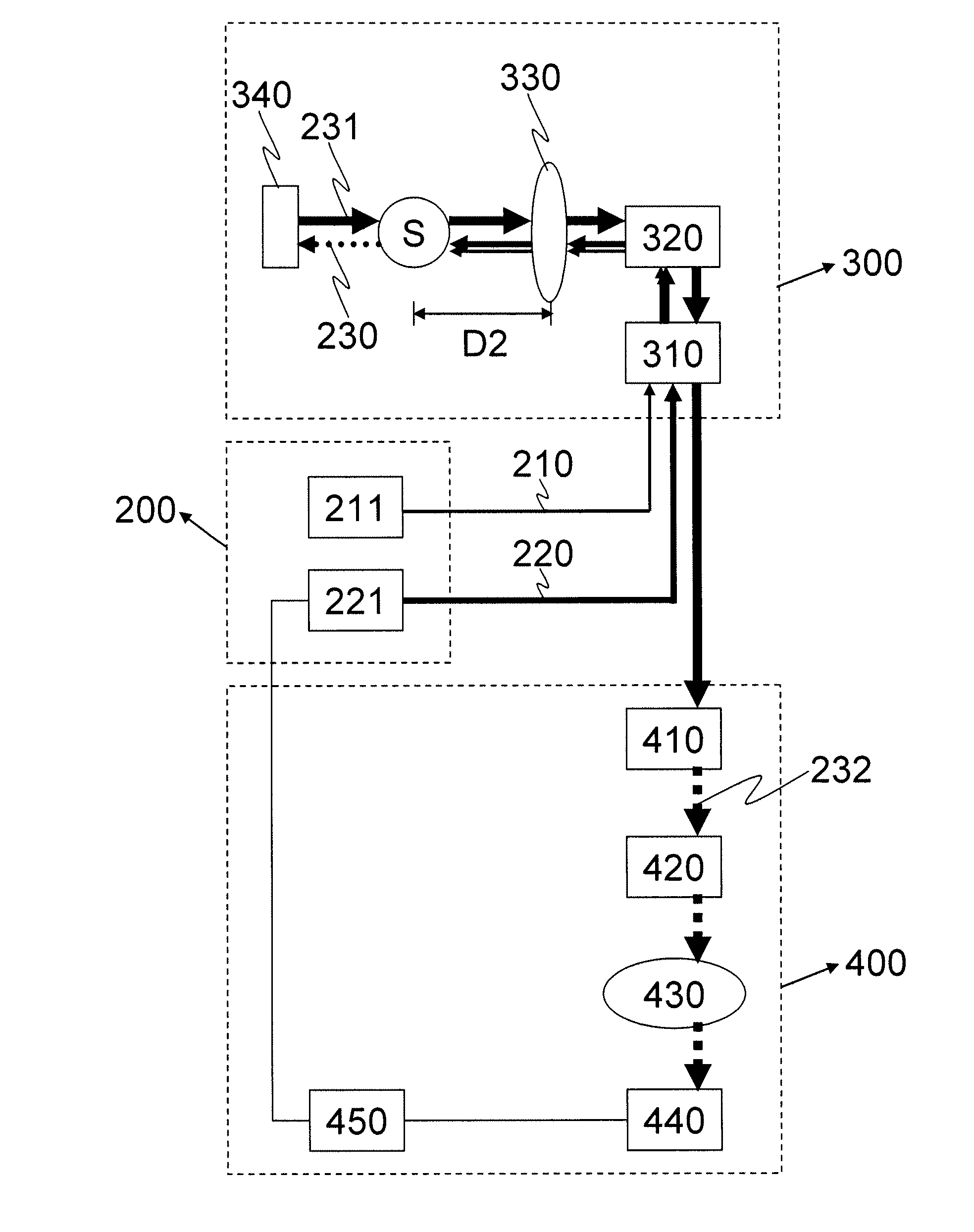
Sample concentration detector with temperature compensation
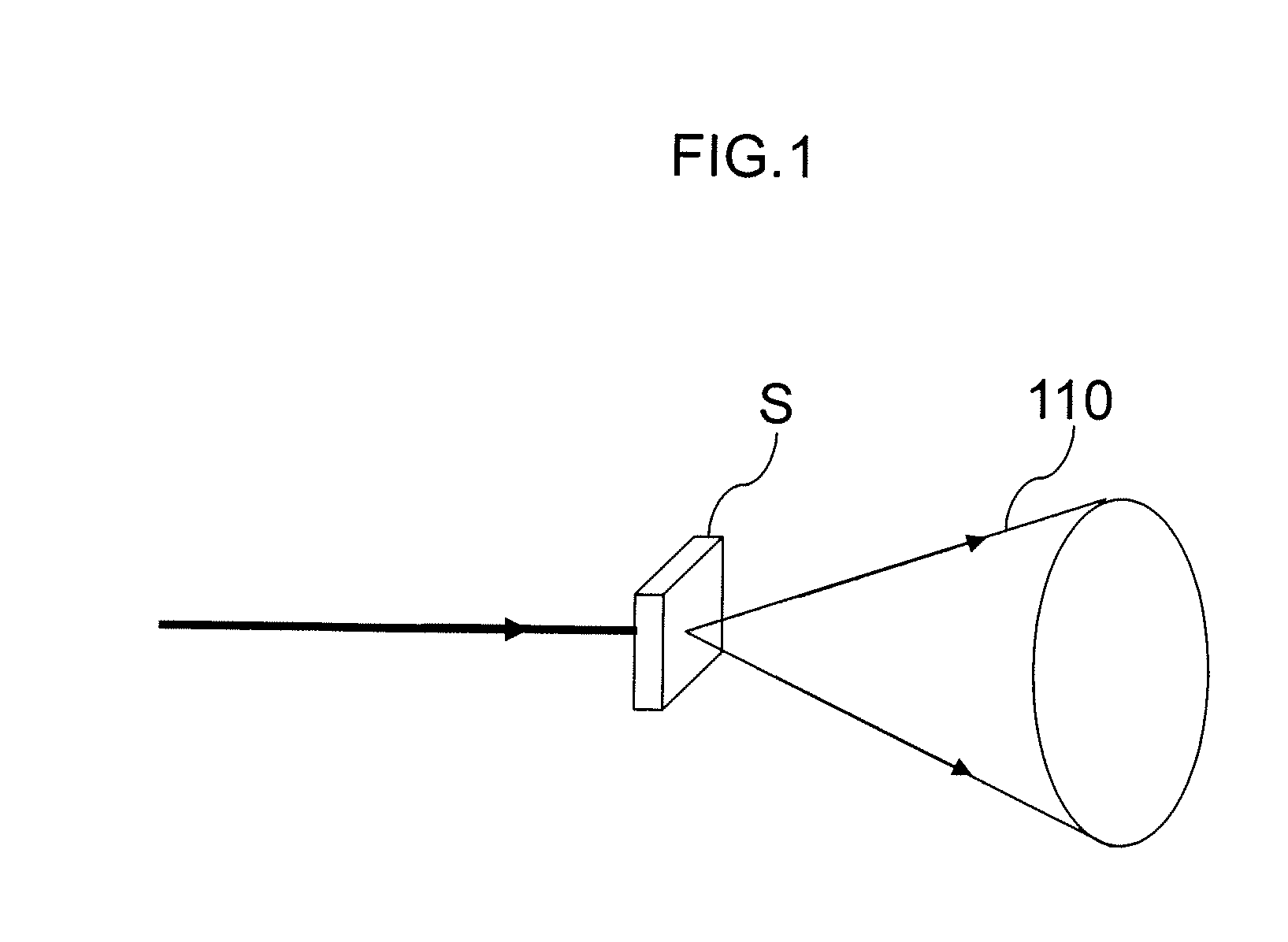
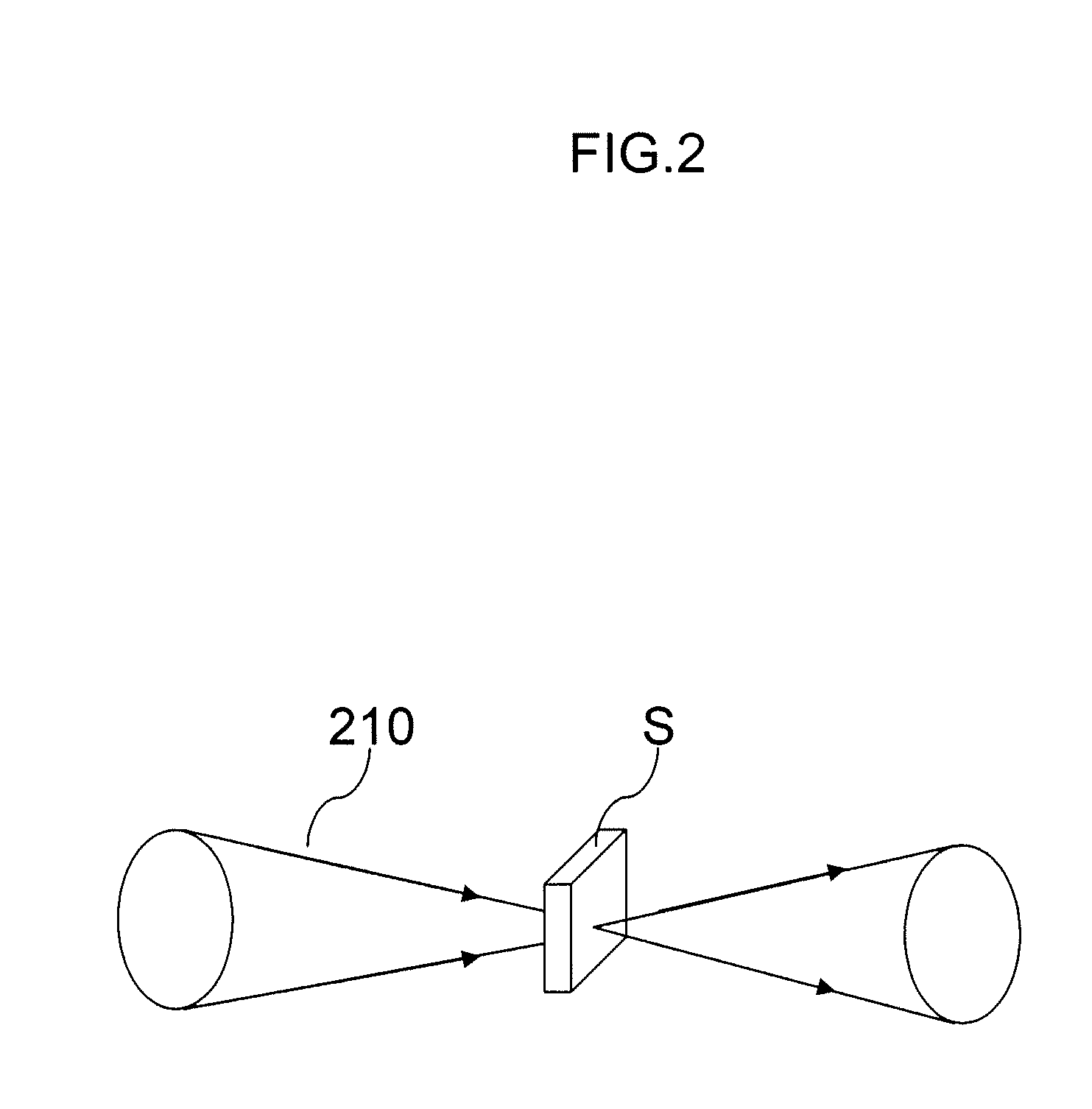
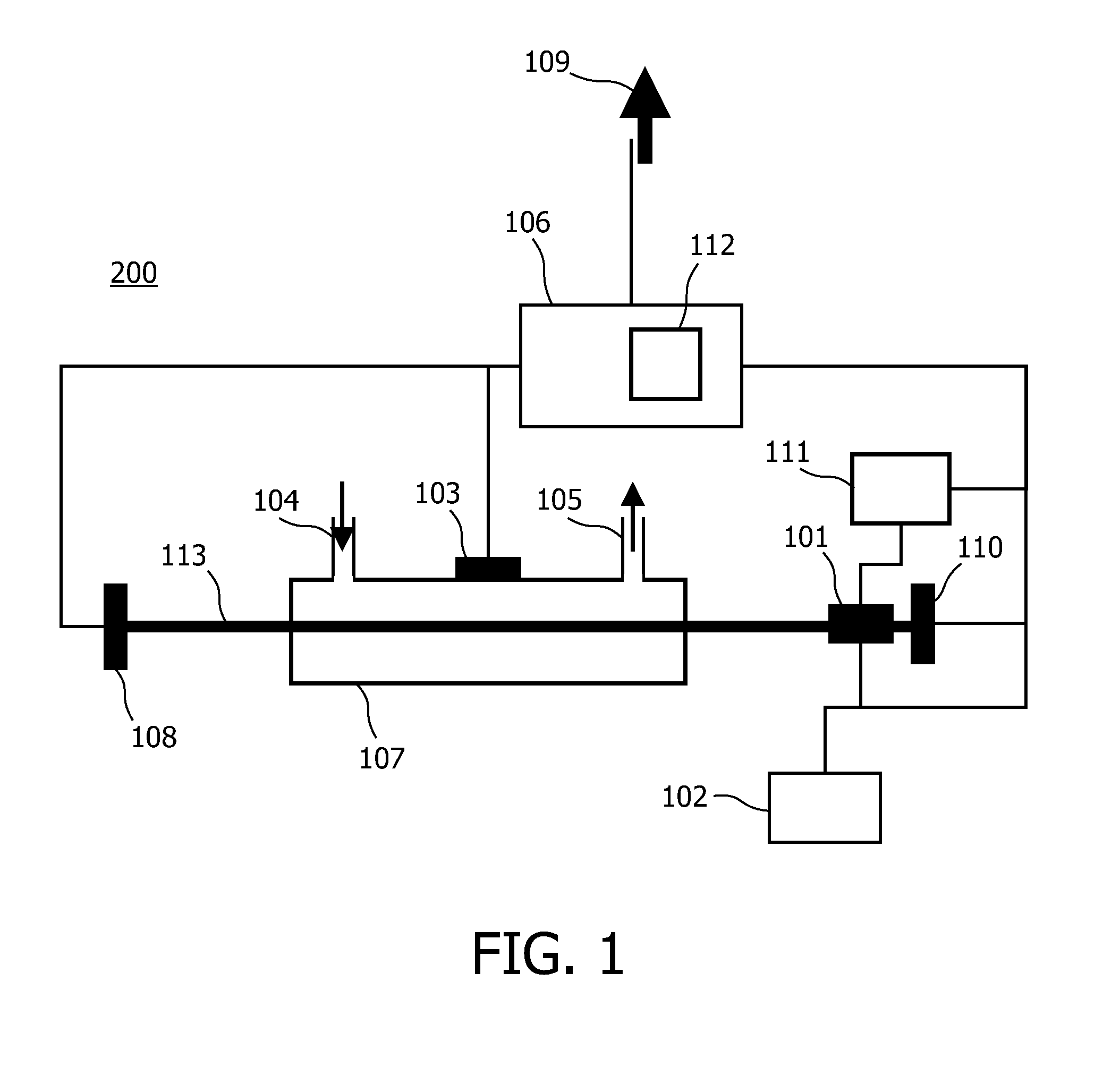
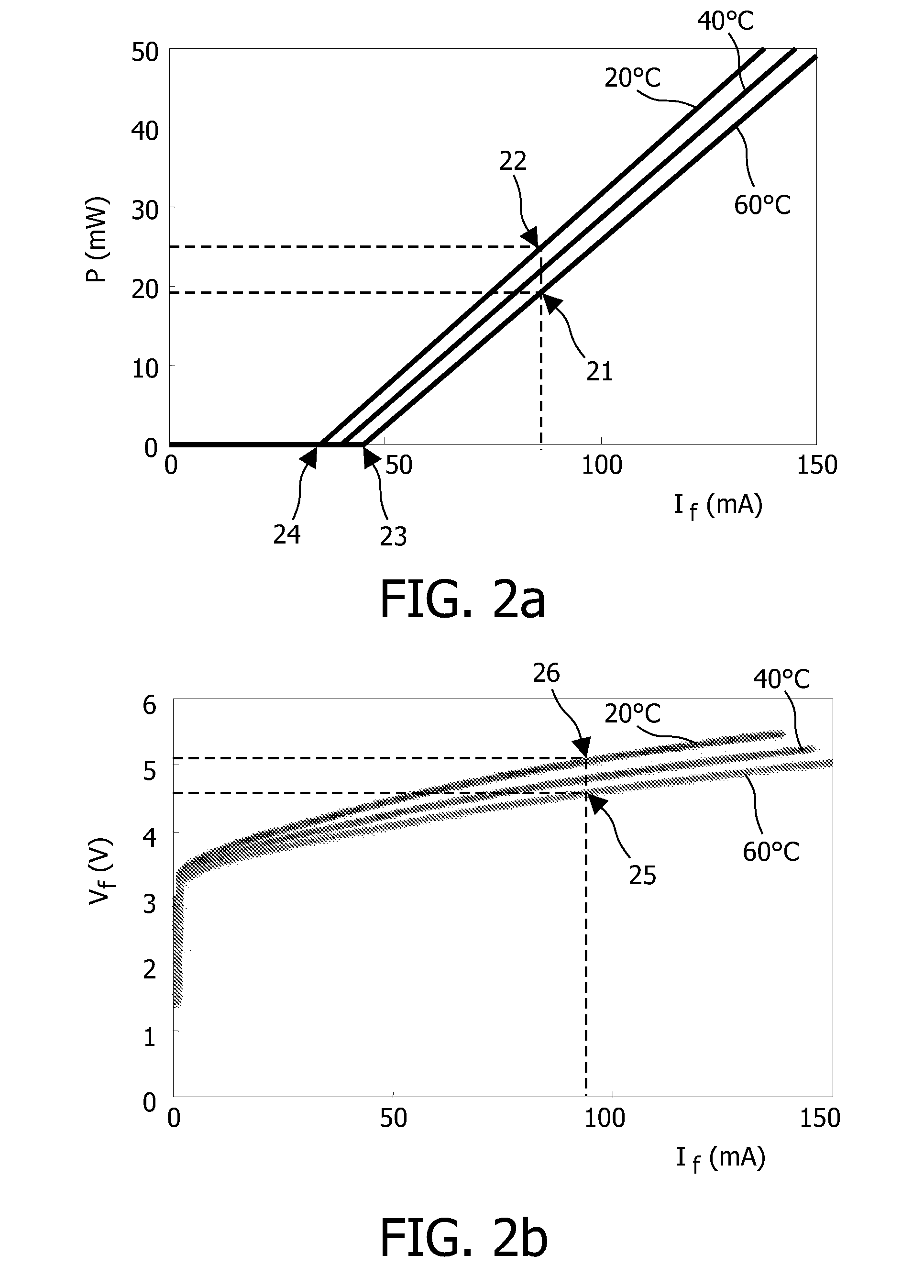
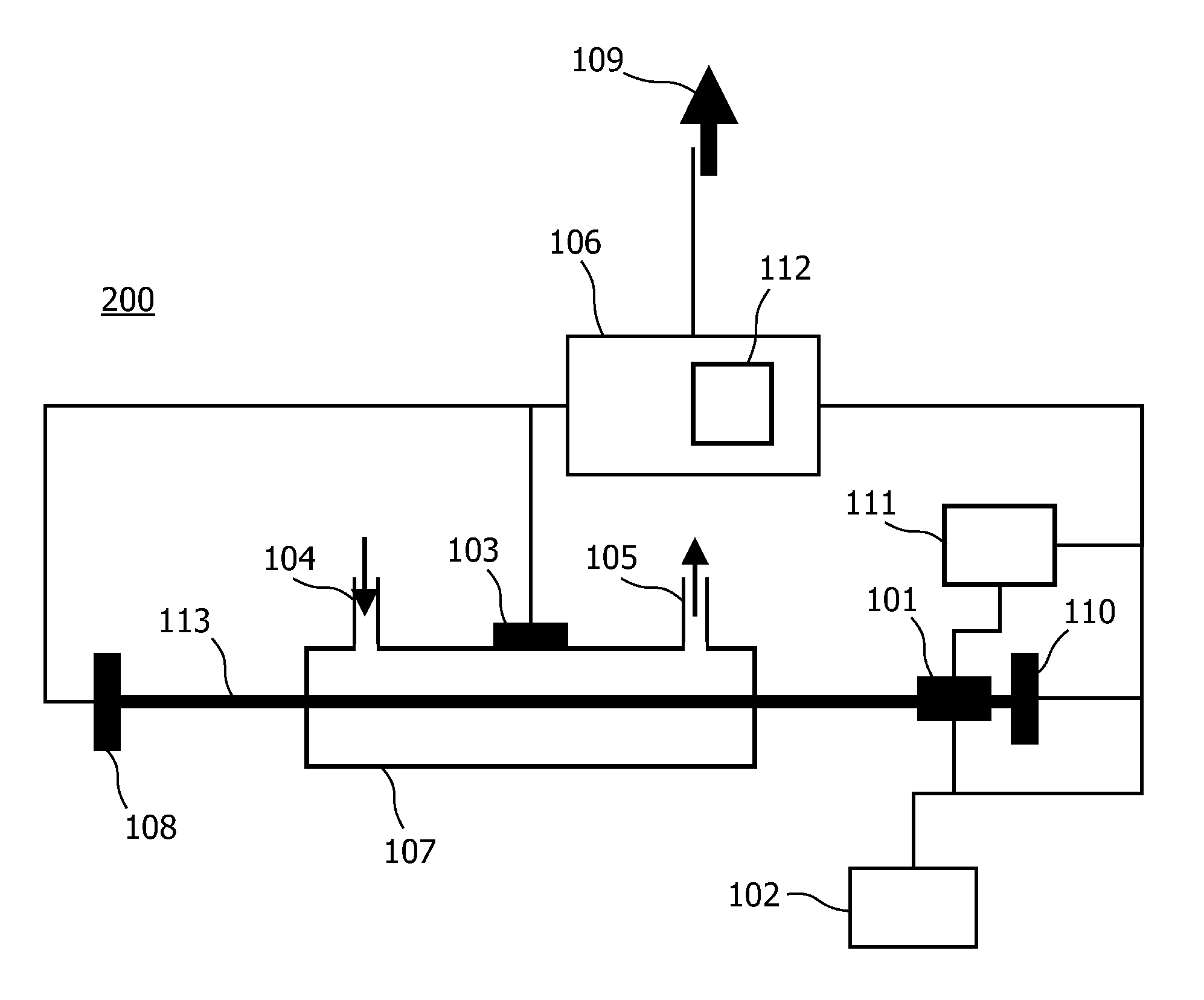
InactiveUS20100007889A1Easy to getImprove powerMaterial analysis by optical meansCalorimeterLight beamExcited molecule
A sample sensor (200) for detecting a concentration of a sample in a sample mixture, the sample sensor (200) comprising a light source (101), a detector element, a processing section (106) and parameter measuring means. The light source (101) produces a light beam (113) for exciting molecules of the sample. The detector element detects an 5 amount of excited molecules of the sample and provides a detector current indicating the amount. The processing section (106) is coupled to the detector element (103) for processing the detector current to generate an output signal (109) representing the concentration. The processing section (106) comprises a temperature compensation module (112) being arranged for compensating for a temperature dependent wavelength shift of the light source (101) 10 based on at least one measured value of a temperature dependent parameter of the light source (101), other than an output wavelength. The parameter measuring means obtain the at least one measured value.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Gas specie electron-jump chemical energy converter
InactiveUS7119272B2Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectElectrical conductorChemical reaction
An apparatus and method for extracting energy is provided. In one aspect the method includes using chemical reactions to generate vibrationally excited molecules, such as high-quantum-number-vibrationally-excited gas molecules in a region. The vibration energy in the vibrationally excited molecules is converted into hot electrons when the excited molecules contact a conductor. A geometry is provided so that the excited molecules may travel, diffuse or wander into a conductor before loosing a useful fraction of the vibrational energy. Optionally, the generating and the converting process may be thermally separated, at least in part. The short lived hot electrons are converted into longer lived entities such as carriers and potentials in a semiconductor, where the energy is converted into a useful form.
Owner:NEOKISMET L L C
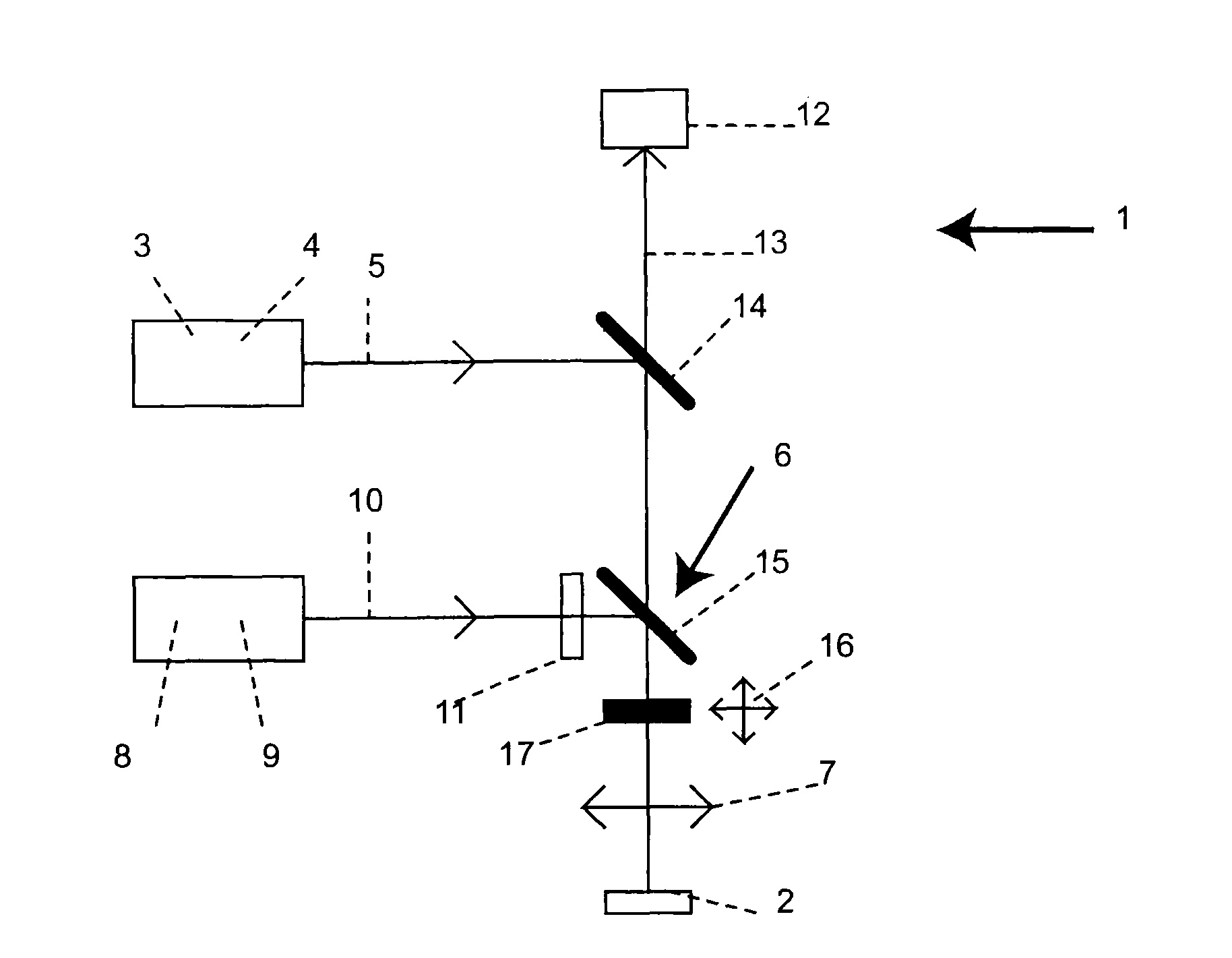
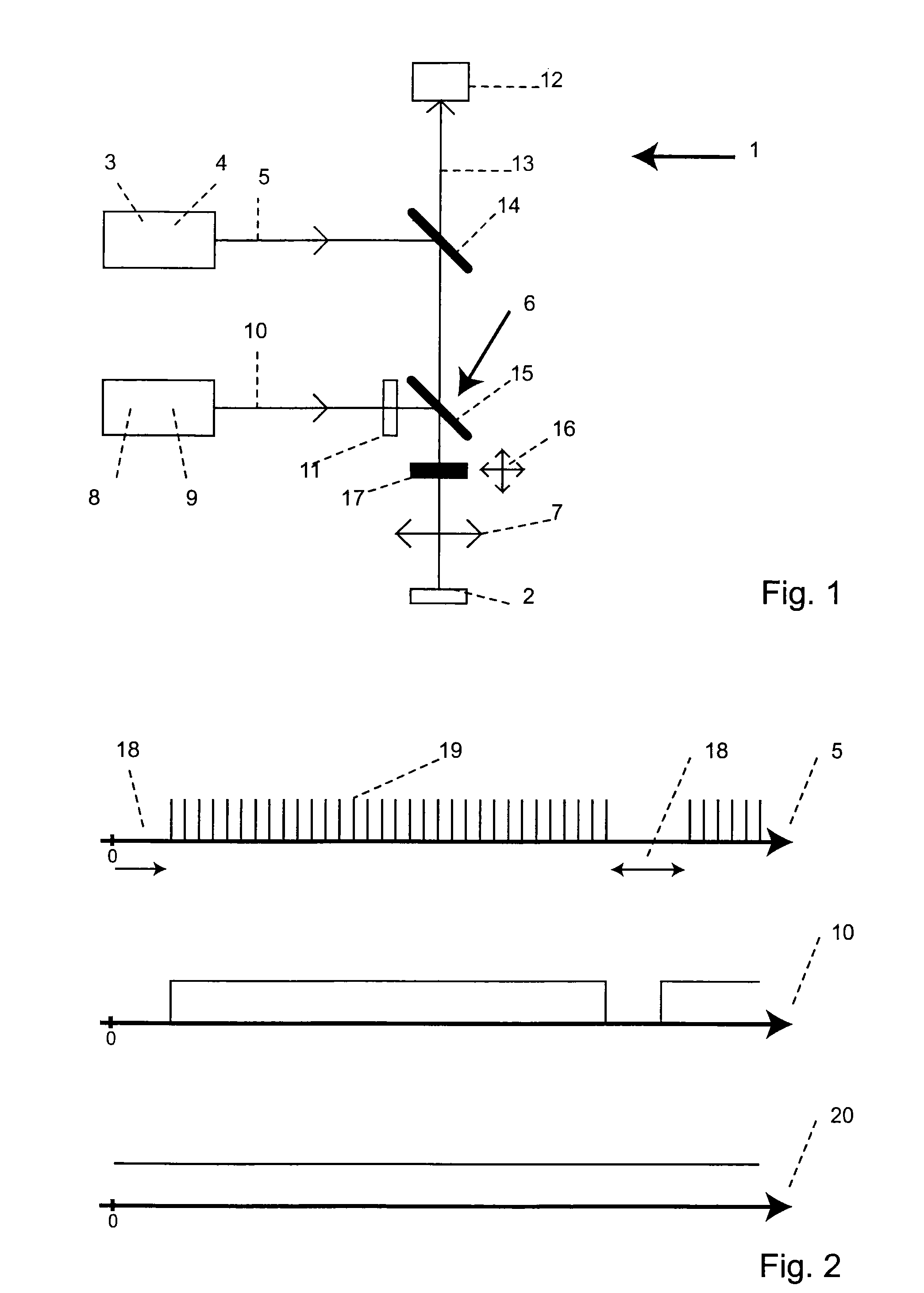
Method of exciting molecules out of a first state into a second states using an optical signal
ActiveUS7224452B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsExcitation beamHigh spatial resolution
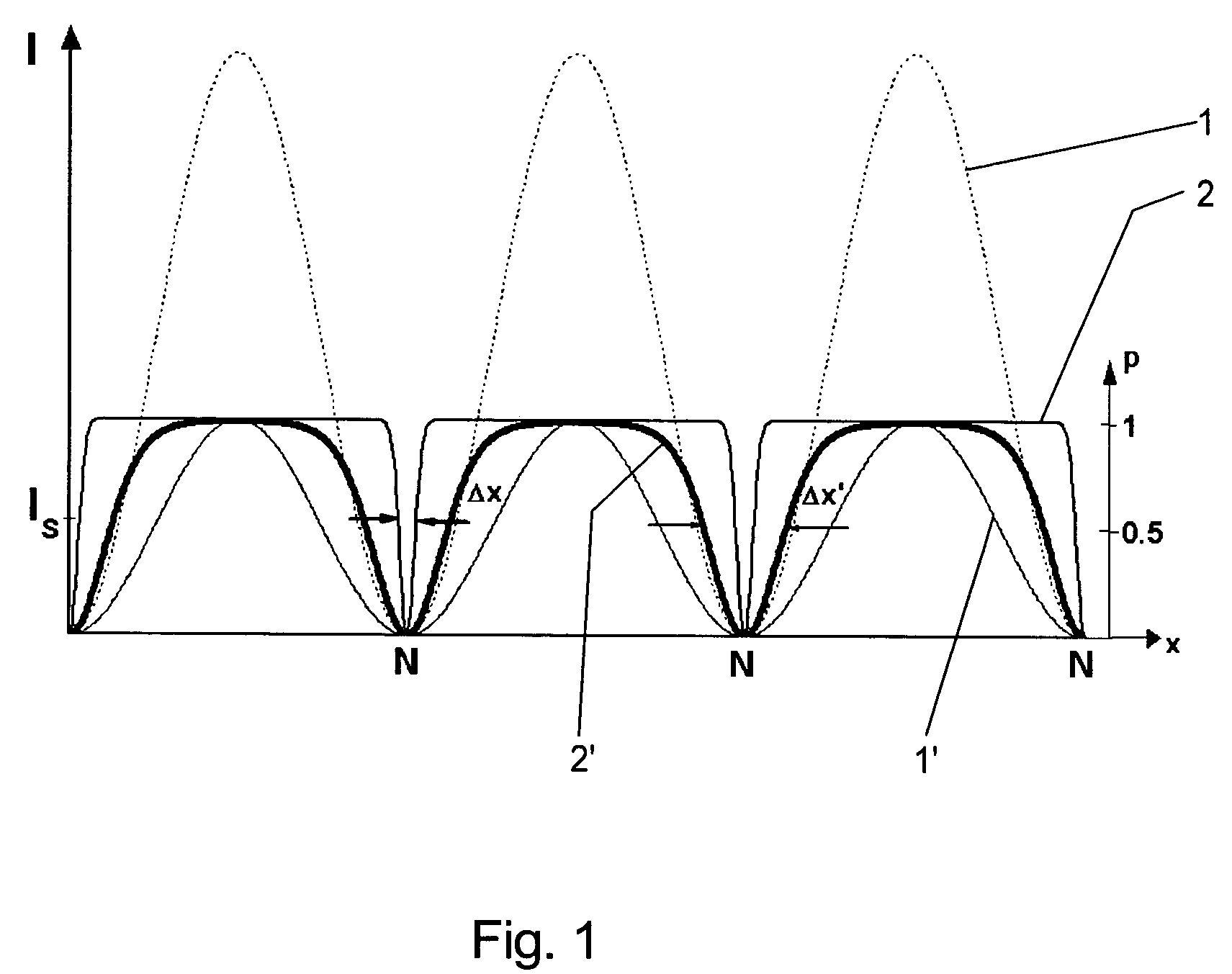
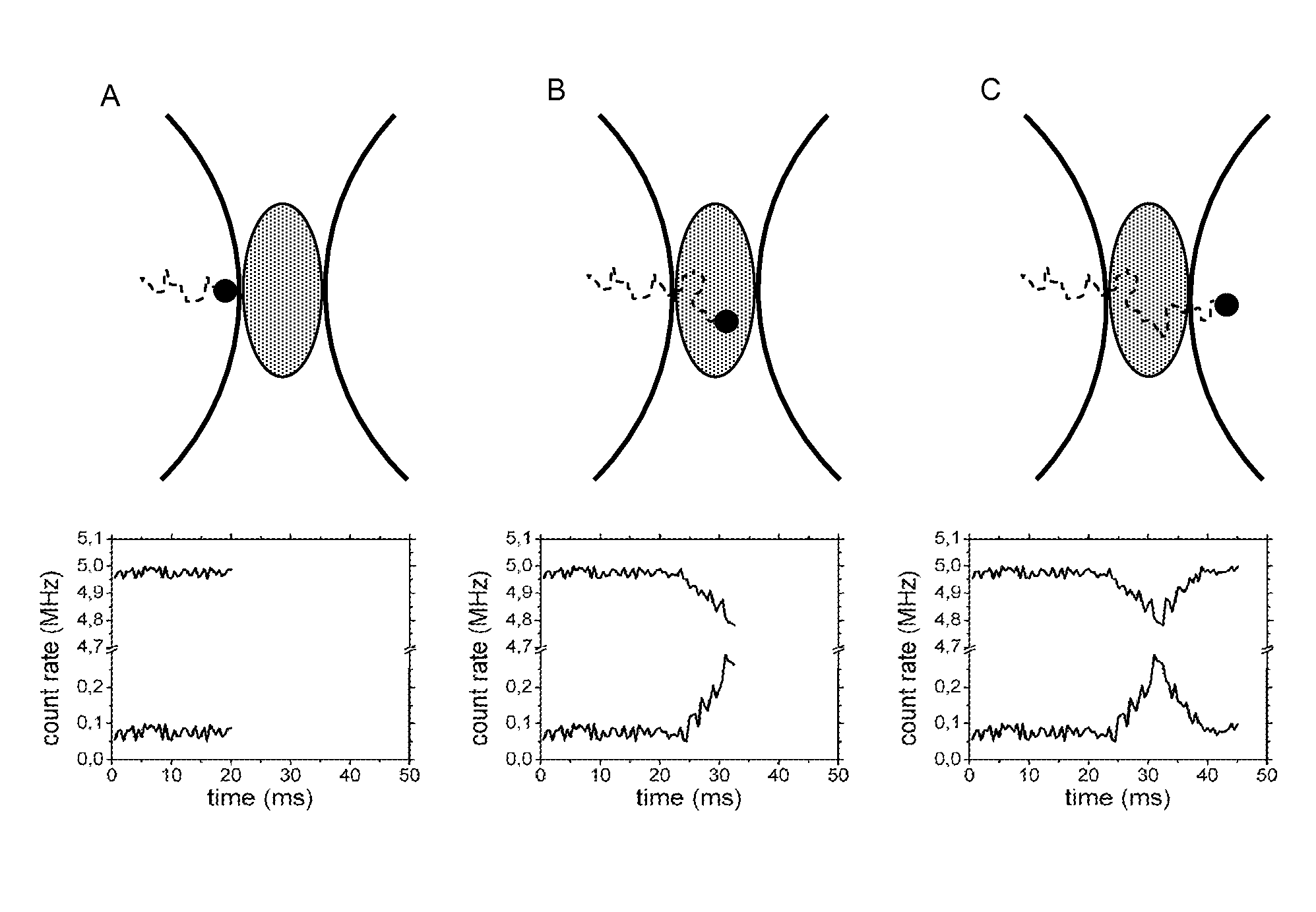
In a fluorescence-microscopic method of examining a sample with high spatial resolution, the sample is first cooled to a temperature of below 5° C.; next the cooled sample is transferred out of a ground state into a fluorescent state within an area captured by a detector using an excitation beam of light; next the cooled sample is subject to de-excitation of excited molecules by stimulated emission in the area captured by the detector, except at desired measuring points, using an de-exciting beam of light, the de-exciting beam of light having a spatial intensity distribution comprising a zero point located at the desired measuring points, and the excited sample being transferred back into its ground state by the de-exciting beam of light; and then fluorescence light spontaneously emitted by the cooled sample is measured with the detector, the detector detecting fluorescence light that is emitted only from the measuring points.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Remote detection of radiation
ActiveUS20120112076A1Material analysis by optical meansX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentLaser transmitterFluorescence
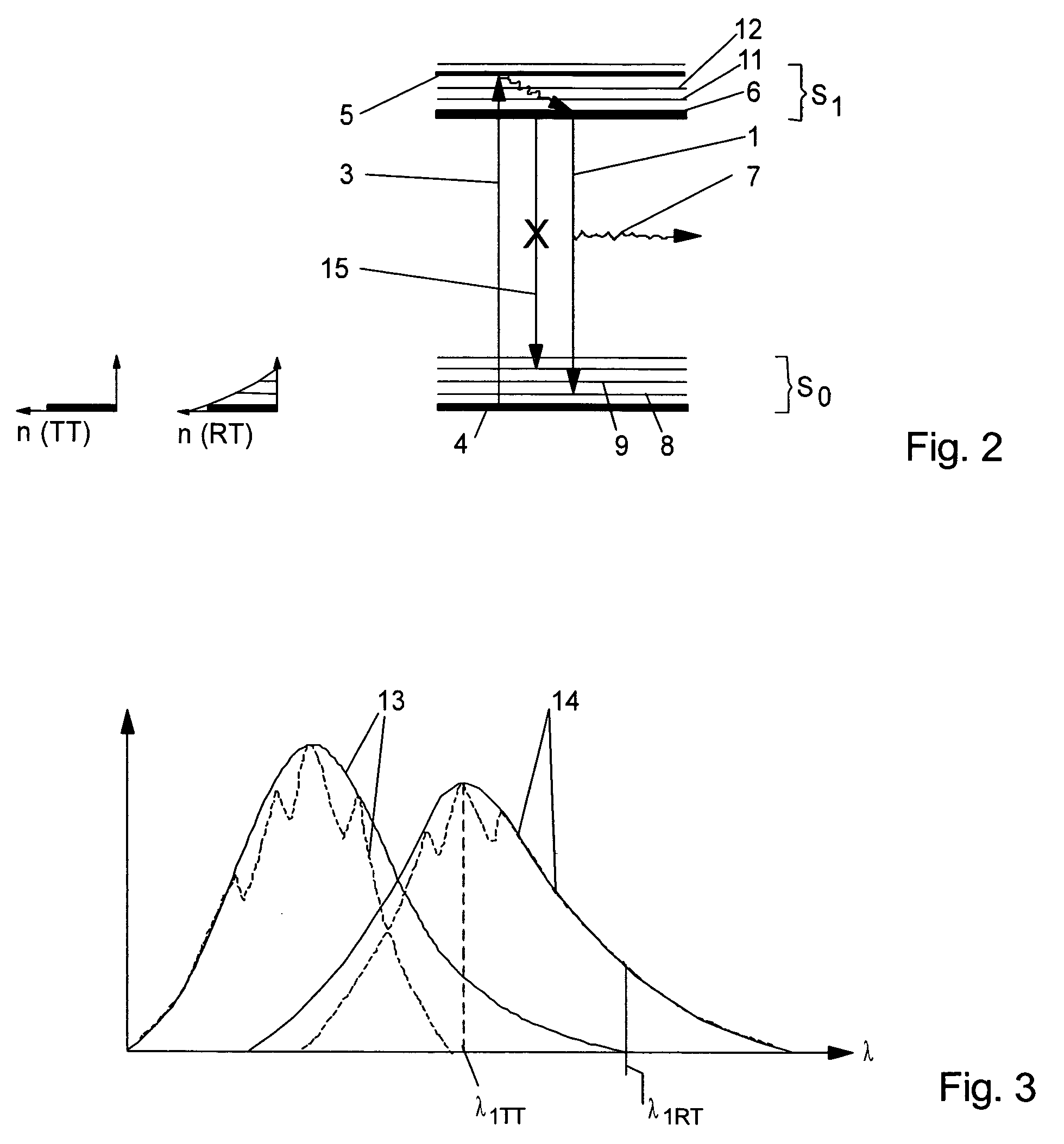
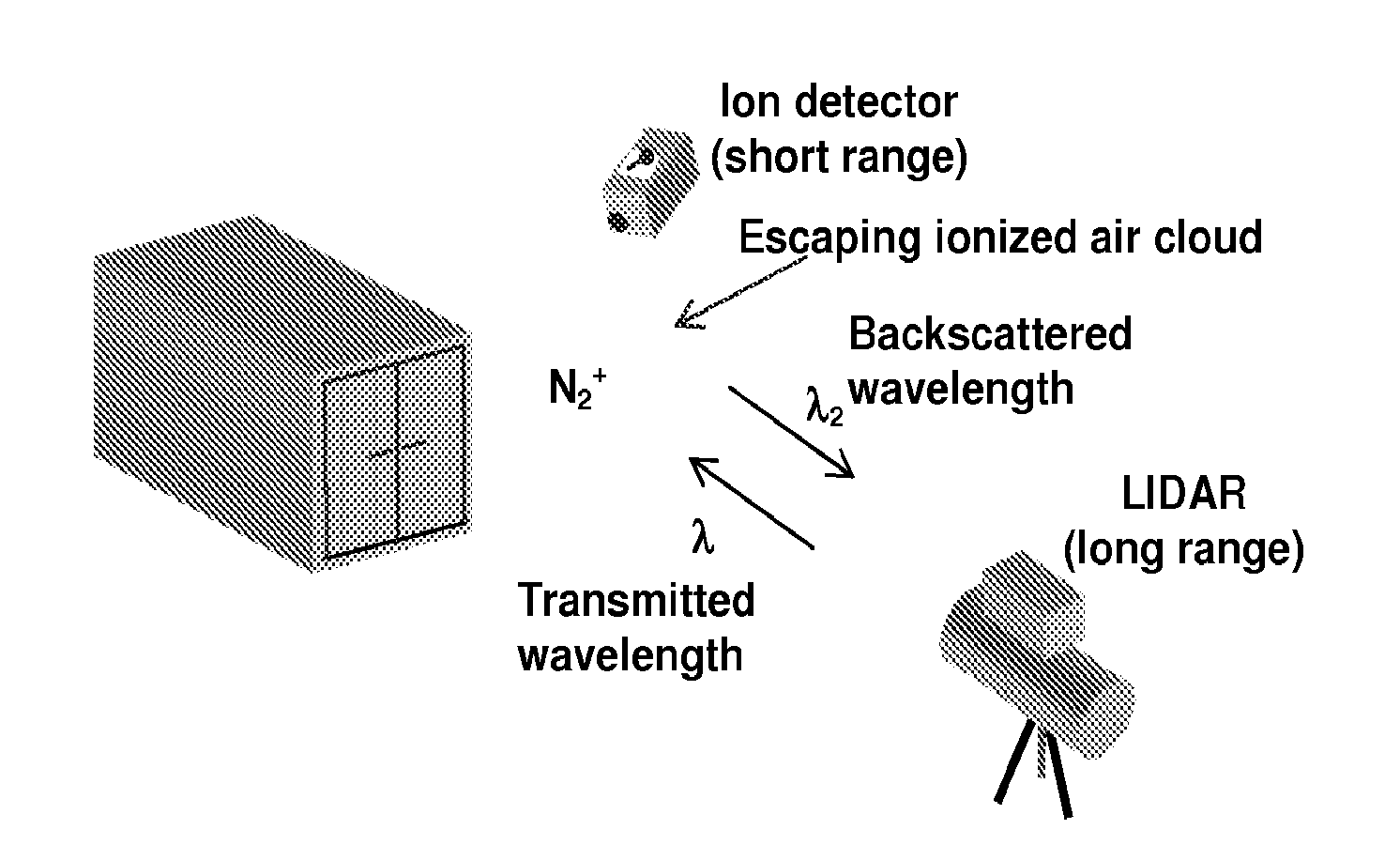
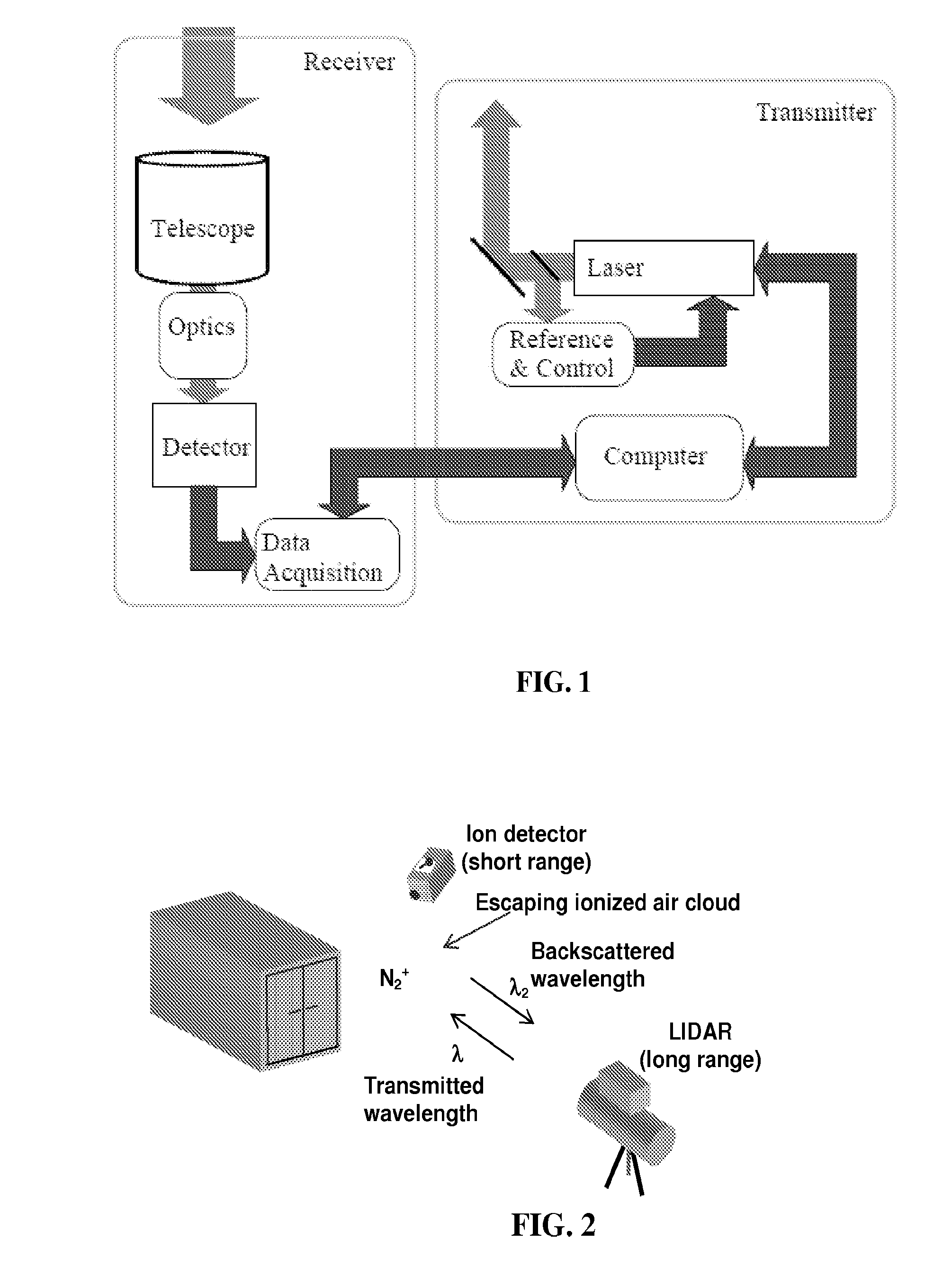
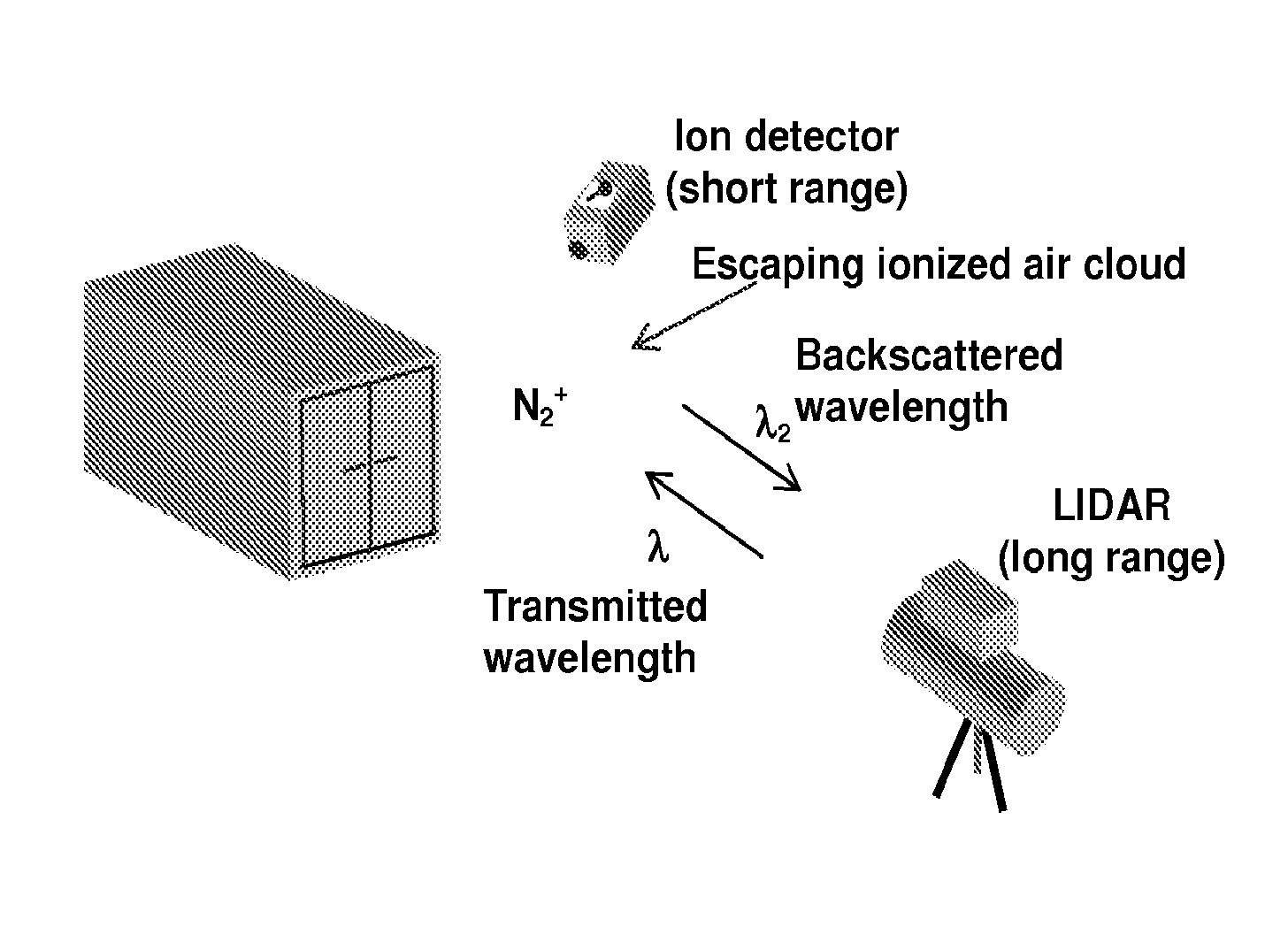
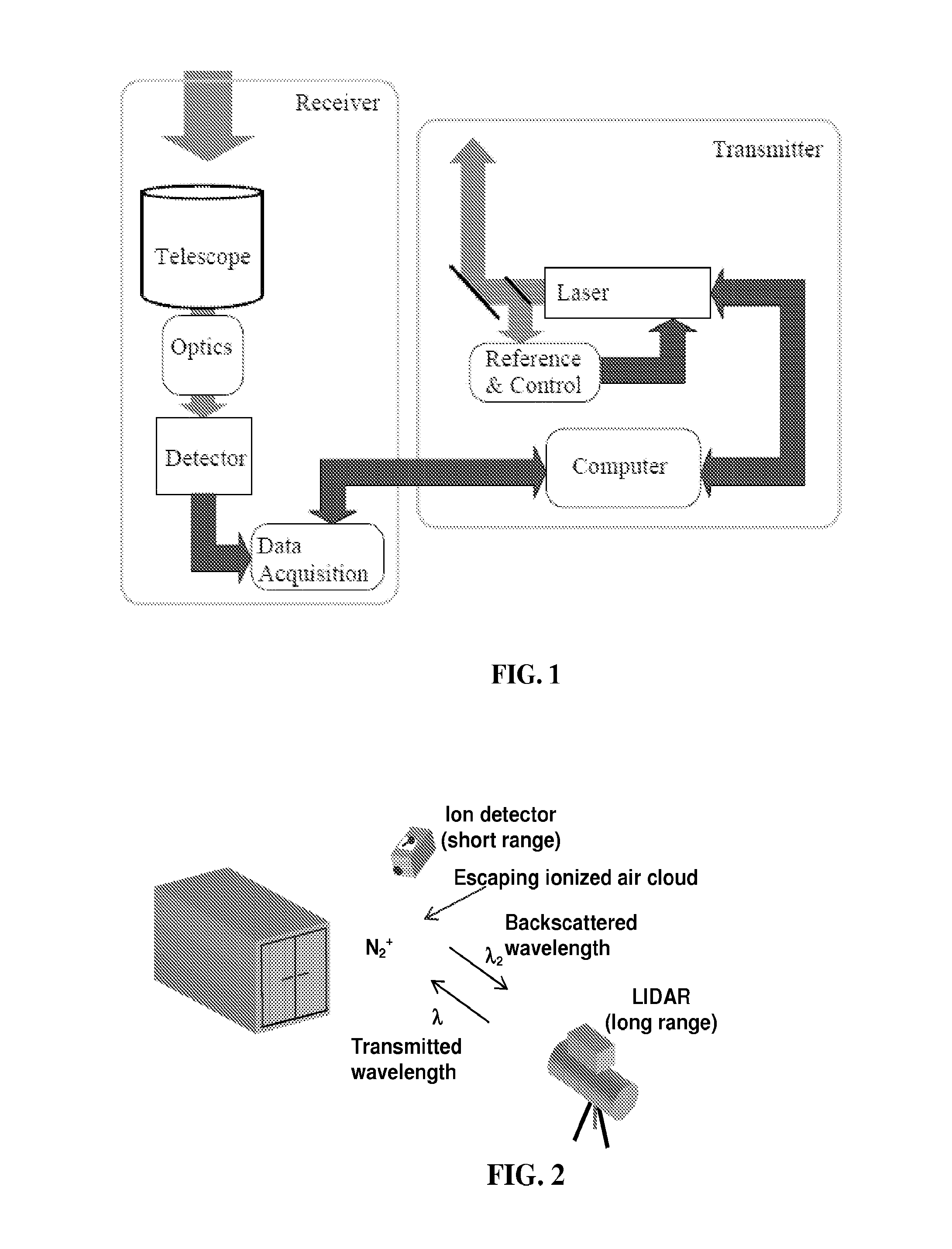
Various embodiments of the present invention provide a method of detecting inaccessible radiation sources by measuring corresponding ions and excited molecules created by radiation, using LIDAR technology. The LIDAR system of the present invention employs a pulsed laser transmitter, a telescope receiver, and associated control and acquisition systems. Light propagates out from the laser transmitted and is directed into the volume surrounding the radioactive source, or the “ion cloud.” The ion cloud absorbs the transmitted light, which induces the non-fluorescing ions to fluoresce. Light from the ion cloud is then backscattered and the telescope receiver subsequently collects the photons from the backscattered light. The intensity of the fluorescence (determined by the photon count) is measured, which provides an indication of the number density of the ionized atoms. Algorithms can then be used to relate the measured ionization rates to the source activity.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Method for online measurement of concentration of OH free radical in flame zone of Class B fire and flame device
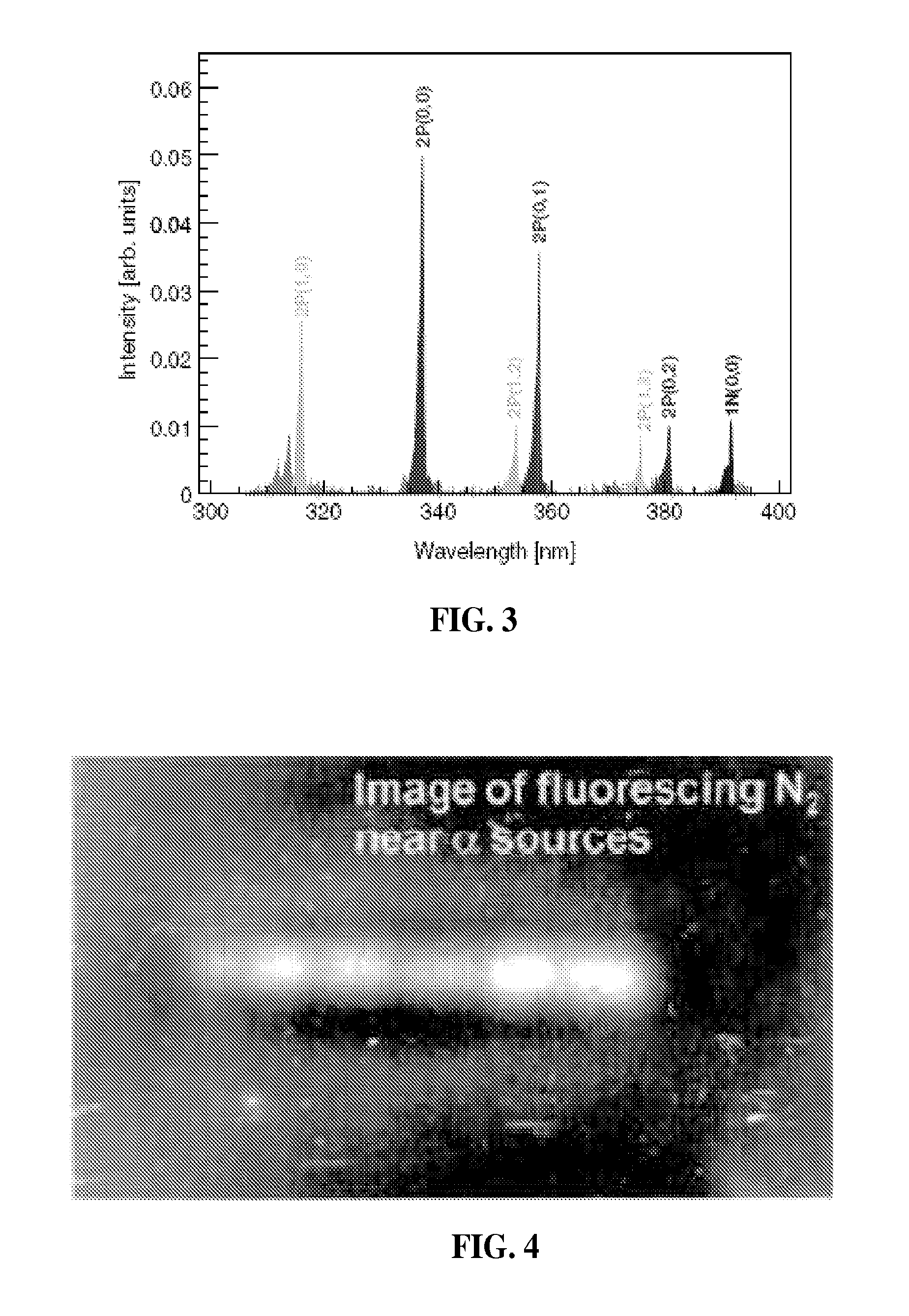
ActiveCN101793827AWide range of environmentsEasy detectionFluorescence/phosphorescenceExcited moleculeLaser intensity
The invention discloses a method for online measurement of concentration of OH free radicals in a flame zone of Class B fire and a flame device. The method adopts the technology of laser-induced fluorescence to make a laser beam with the absorption wavelength of 308nm tuned to OH irradiate OH free radicals in a flame zone, so as to generate resonant transition from a low electronic state to a high electronic state. The excited molecules then self-radiate fluorescent. Under the condition that laser intensity and instrument conditions are maintained unchanged, the total fluorescence intensity is proportional to the concentration of the OH free radicals, thereby obtaining the concentration of the OH free radicals. The device of the invention comprises a pear-shaped funnel (1), a square combustion device (3), an oil cup (5), a mist rising control tube (6), a bracket (7) and a humidifier (8). The invention has the advantages of high measurement accuracy, simple structure and easy implementation.
Owner:SHANGHAI FIRE RES INST OF THE MIN OF PUBLIC SECURITY +1
Inverse-fluorescence correlation spectroscopy
InactiveUS20120050734A1Increase brightnessRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationPhotomultiplierExcited molecule
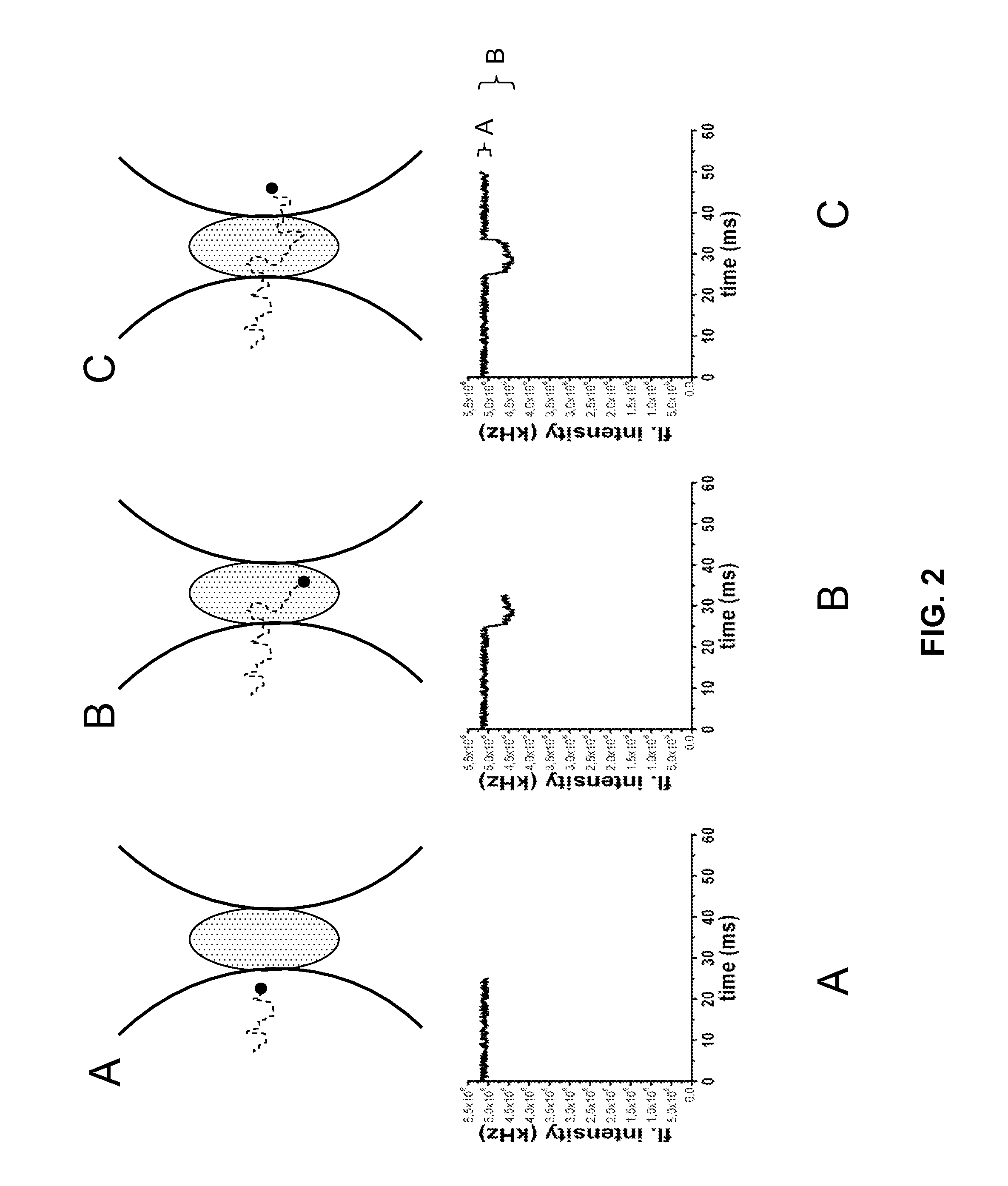
A method is disclosed for analyzing particles or biomolecules in a liquid sample, including: detecting a signal and fluctuations in the signal from a detection volume in the sample; wherein the signal is generated from signal-generating molecules in the medium surrounding the particles or biomolecules and the fluctuations are transient reductions in the signal as the particles or biomolecules transit through the detection volume; and analyzing the detected fluctuations to obtain information about the particles or biomolecules in the liquid sample. At least one example embodiment of the present invention relates to a fluorescence correlation spectroscopy system including a laser, a zero-mode waveguide, guiding device for guiding the laser into the zero-mode waveguide, device for collecting fluorescence emission from excited molecules within the waveguide, a detector for detecting the fluorescence emission and means for autocorrelating the detected fluorescence signal, wherein the detector comprises a photomultiplier tube. Moreover, at least one embodiment relates to the use of a fluorescence correlation spectroscopy system for analyzing molecules of interest in a sample by detecting and analyzing fluctuations in a fluorescence signal that is generated from sample molecules surrounding the molecules of interest, wherein the fluctuations are transient reductions in the detected fluorescence signal.
Owner:WENNMALM STEFAN +1
Fluorine-perylene bisimide molecule internal-energy transferring fluorescence split compound and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104152137AEnhanced charge transferPromote absorptionOrganic chemistryLuminescent compositionsPerylenemonoimideChemical structure
The invention relates to a fluorine-perylene bisimide molecule internal-energy transferring fluorescence split compound and a preparation method thereof. The chemical structure of the fluorescence compound is as shown in the specification, in the formula, R is branched chain alkyl, isooctyl oxy propyl or p-sulfonic acid phenyl of C4-C12. By virtue of SP3 hybridization characteristics of bisphenol fluorine 9-delta-carbon atoms, a D-pi-A system of a spiral structure is constructed, novel D-pi-A structures which are perpendicular to one another are formed, a fluorescence quenching phenomenon caused by planar pi-pi piling is blocked, the excited dipole moment, namely, the charge transferring degree inside excited molecules is improved, the frequency-doubled effect of molecules is improved, and the two-photon absorption property is remarkably improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Analyzer, ionization apparatus and analyzing method
ActiveUS8368013B2Reduce sensitivityReduce loss rateParticle separator tubesIsotope separationExcited moleculeAtmospheric pressure
An analyzer performs dielectric barrier discharge and ionization of a sample by a reaction between the sample and excited molecules or ions generated by the dielectric barrier discharge at a pressure lower than an atmospheric pressure.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
STED-fluorescent light microscopy with two-photon excitation
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
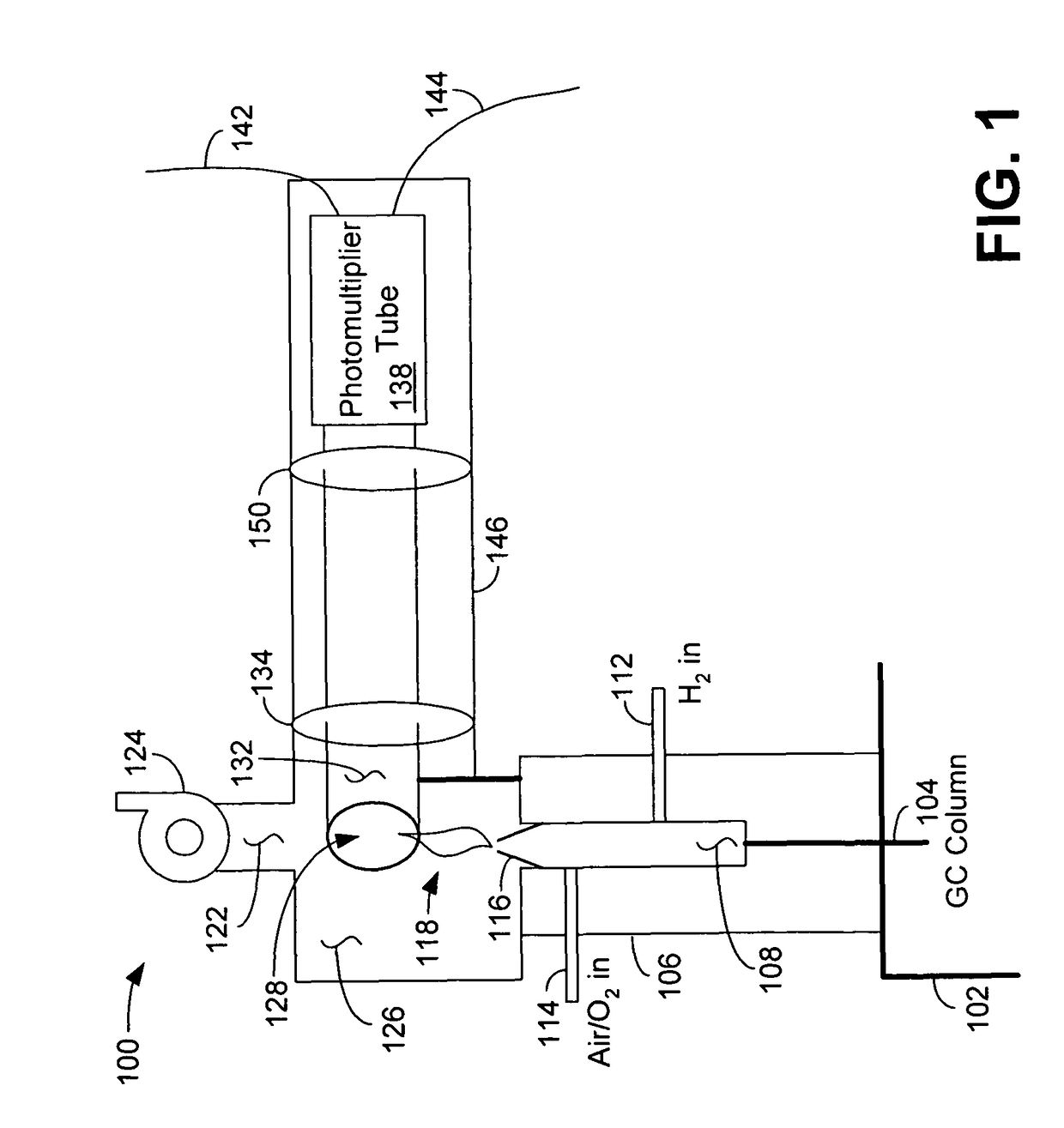
Flame photometric detector having improved sensitivity
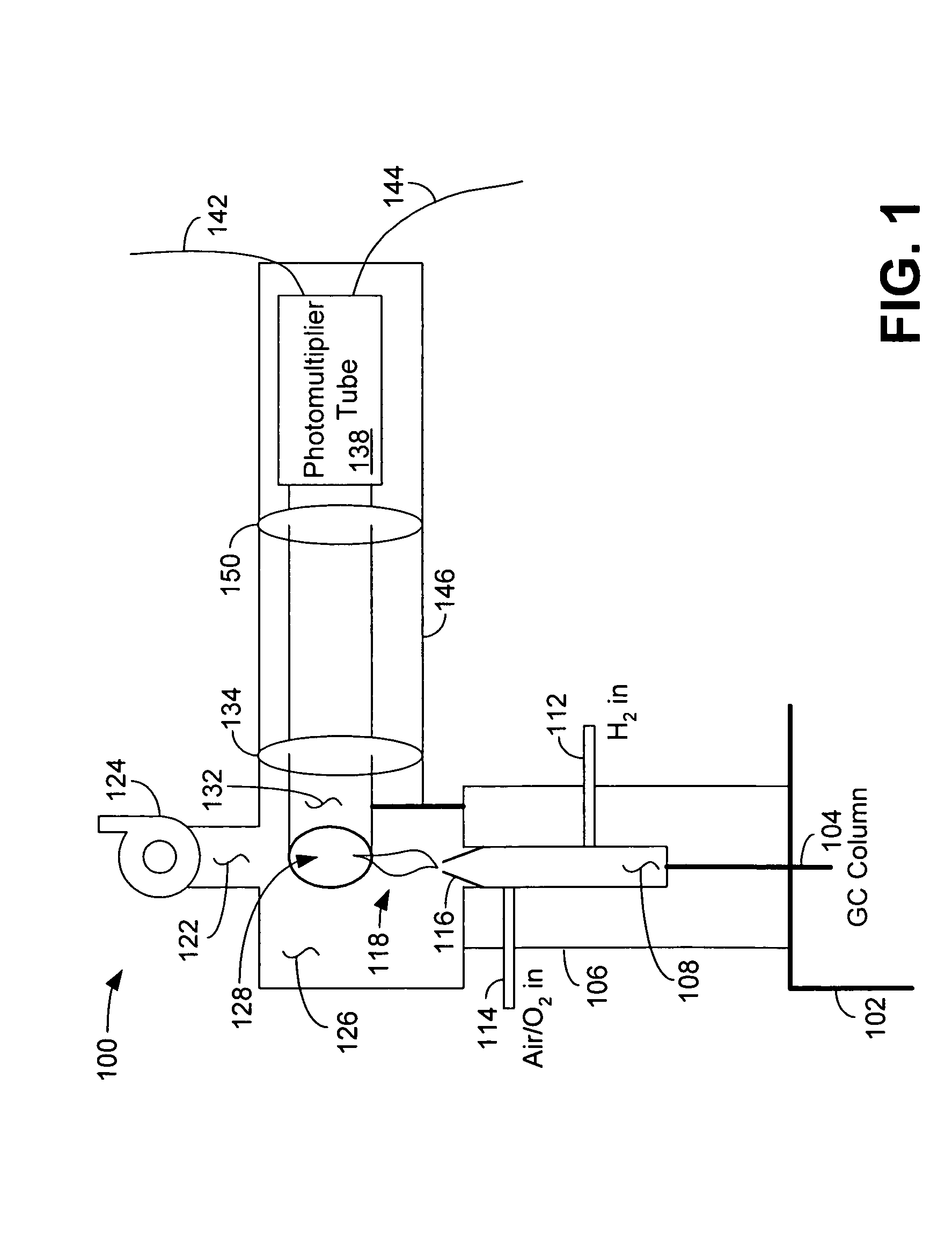
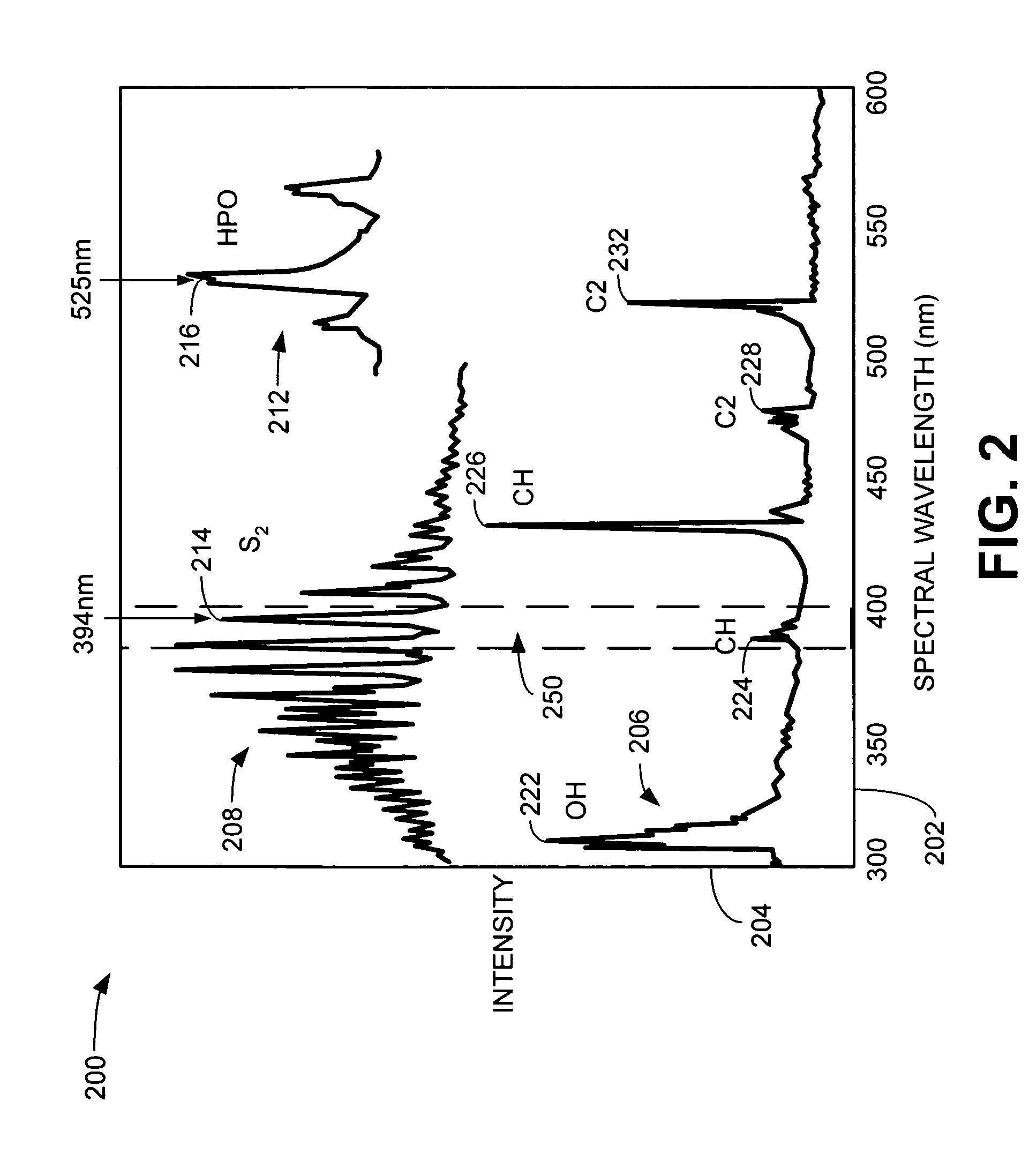
ActiveUS7906071B2Component separationMicrobiological testing/measurementExcited moleculePhotochemistry
A flame photometric detector comprises a burner assembly configured to combust a sample of an effluent, the combusted sample emitting at least one excited molecule, an interchangeable selective optical filter configured to pass a plurality of selected optical wavelengths corresponding to the excited molecule, and a photomultiplier tube configured to quantify the concentration of the excited molecule.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Biosensor device and method for detecting molecules in an analyte
InactiveUS20100047919A1Easy to detectHighly sensitive to various speciesChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceBiological testingAnalyteExcited molecule
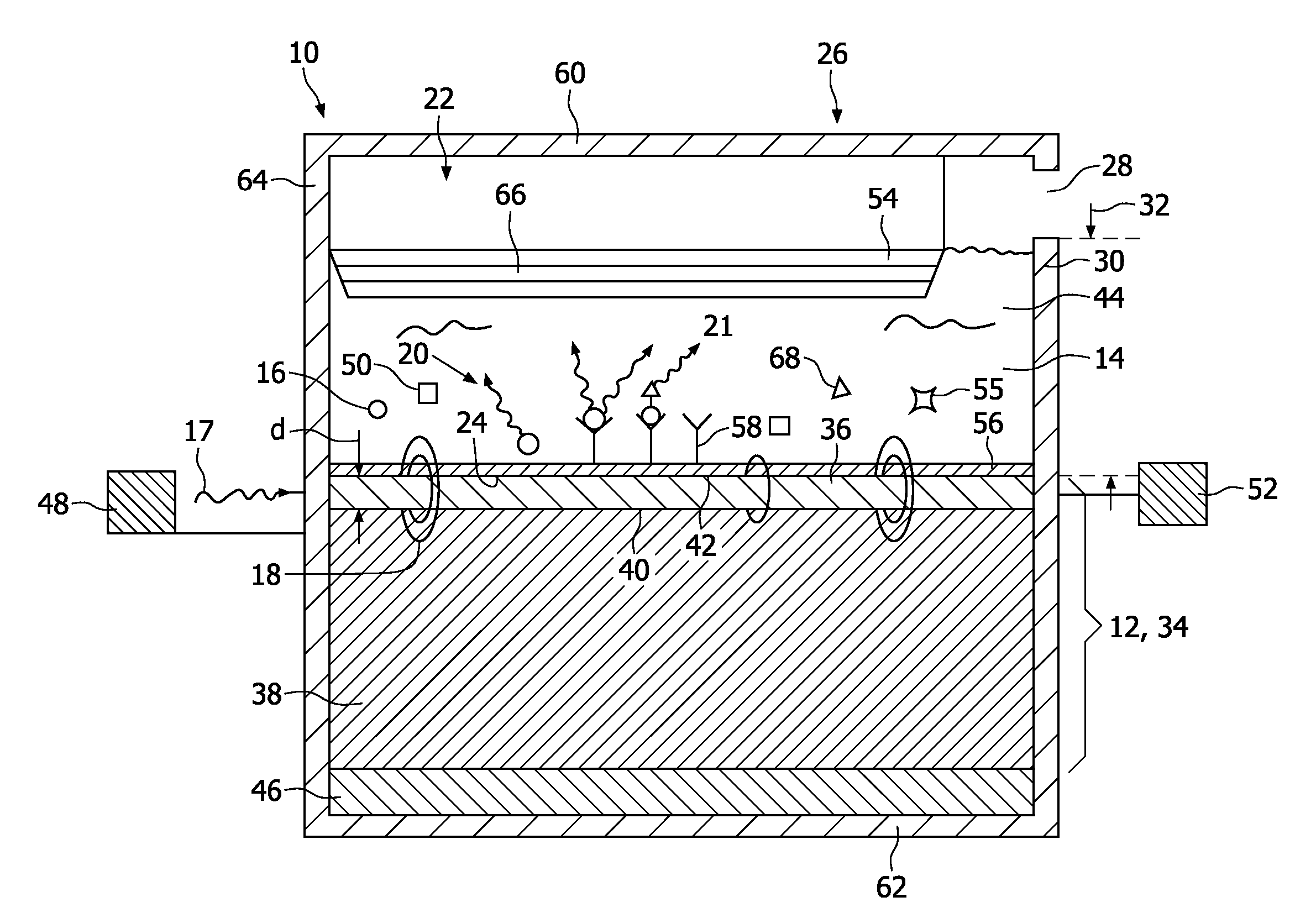
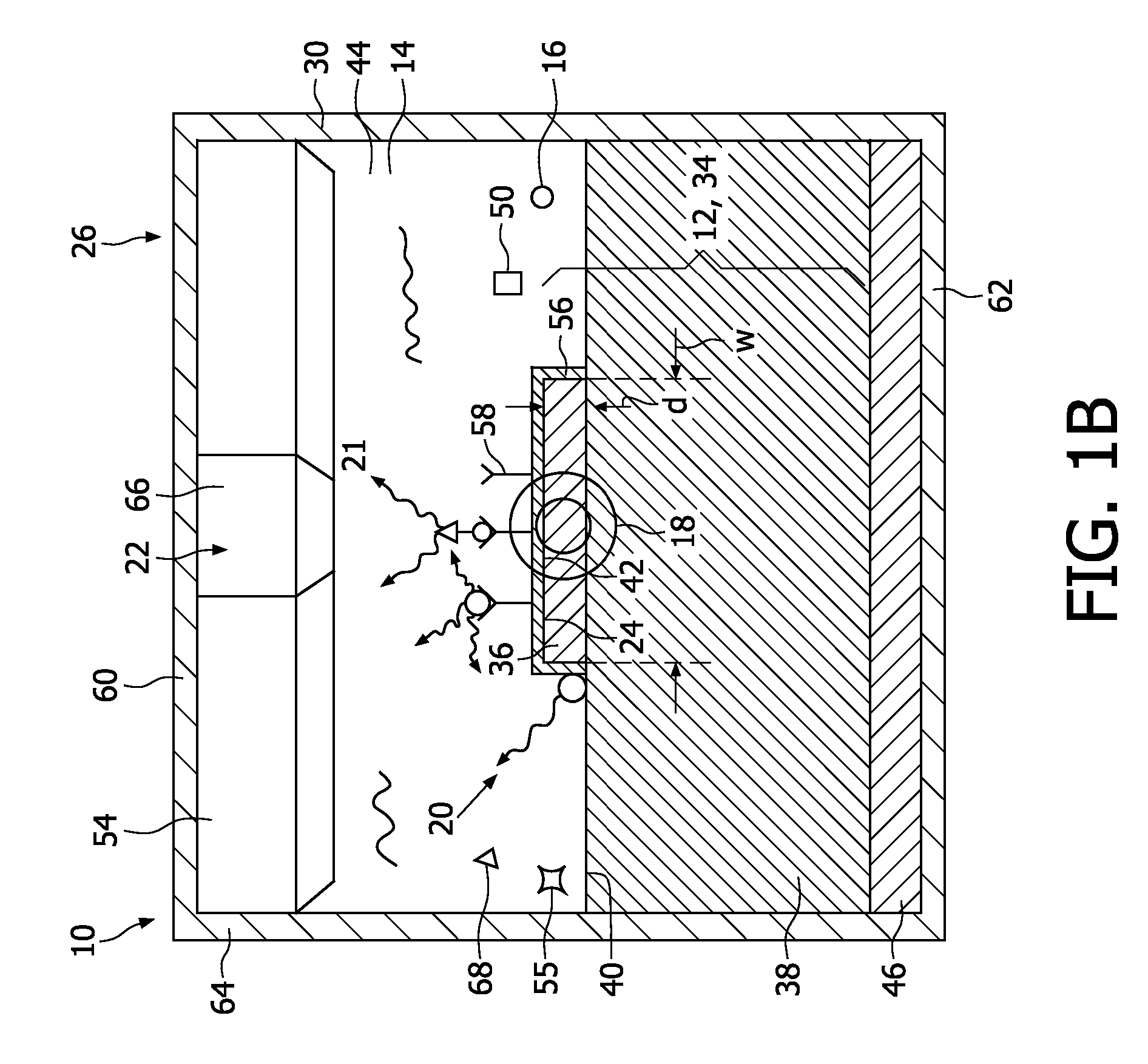
A biosensor device (10) for detecting molecules (16) in an analyte (14) comprises a binding element (12) which can be brought into contact with the analyte (14) for binding the molecules (16) thereto. The binding element (12) is an optical waveguide (34) comprising a strip (36) on a first layer (38). Light (17) can be applied to the strip (36). The biosensor device (10) further comprises an optical detection system (22) for detecting luminescent light (20) emitted by the excited molecules (16).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Remote detection of radiation
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Method of exciting molecules out of a first state into a second states using an optical signal
ActiveUS20070013909A1High strengthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsExcitation beamImage resolution
In a fluorescence-microscopic method of examining a sample with high spatial resolution, the sample is first cooled to a temperature of below 5° C.; next the cooled sample is transferred out of a ground state into a fluorescent state within an area captured by a detector using an excitation beam of light; next the cooled sample is subject to de-excitation of excited molecules by stimulated emission in the area captured by the detector, except at desired measuring points, using an de-exciting beam of light, the de-exciting beam of light having a spatial intensity distribution comprising a zero point located at the desired measuring points, and the excited sample being transferred back into its ground state by the de-exciting beam of light; and then fluorescence light spontaneously emitted by the cooled sample is measured with the detector, the detector detecting fluorescence light that is emitted only from the measuring points.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Sample concentration detector with temperature compensation
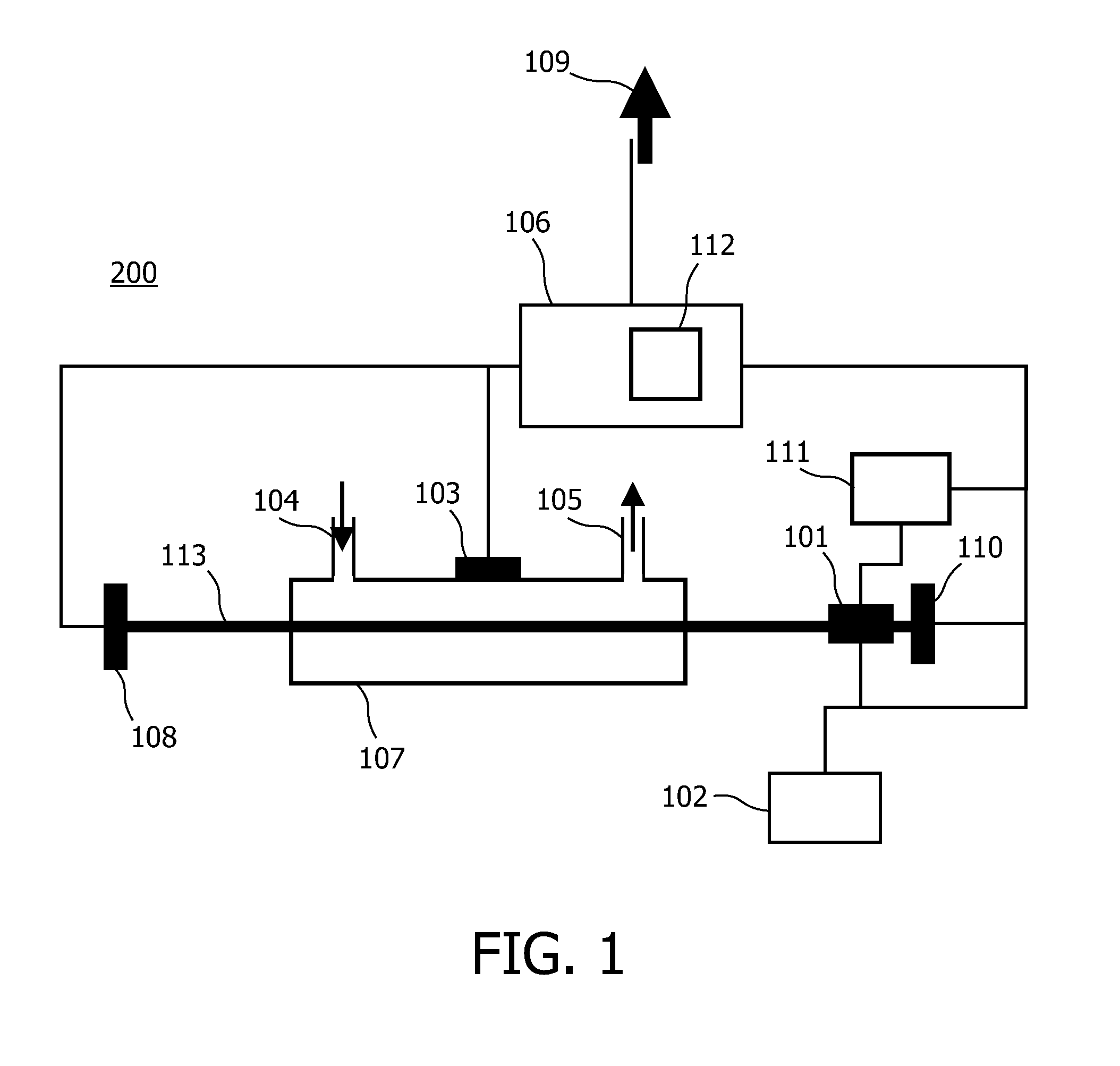
InactiveUS8233150B2Improve powerMeasure directlyMaterial analysis by optical meansCalorimeterLight beamExcited molecule
A sample sensor (200) for detecting a concentration of a sample in a sample mixture, the sample sensor (200) comprising a light source (101), a detector element, a processing section (106) and parameter measuring means. The light source (101) produces a light beam (113) for exciting molecules of the sample. The detector element detects an 5 amount of excited molecules of the sample and provides a detector current indicating the amount. The processing section (106) is coupled to the detector element (103) for processing the detector current to generate an output signal (109) representing the concentration. The processing section (106) comprises a temperature compensation module (112) being arranged for compensating for a temperature dependent wavelength shift of the light source (101) 10 based on at least one measured value of a temperature dependent parameter of the light source (101), other than an output wavelength. The parameter measuring means obtain the at least one measured value.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
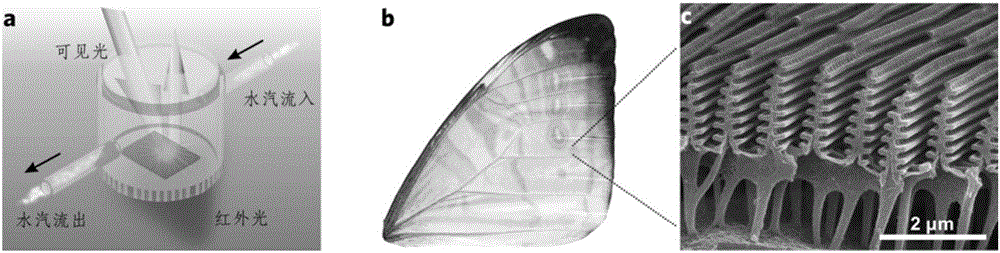
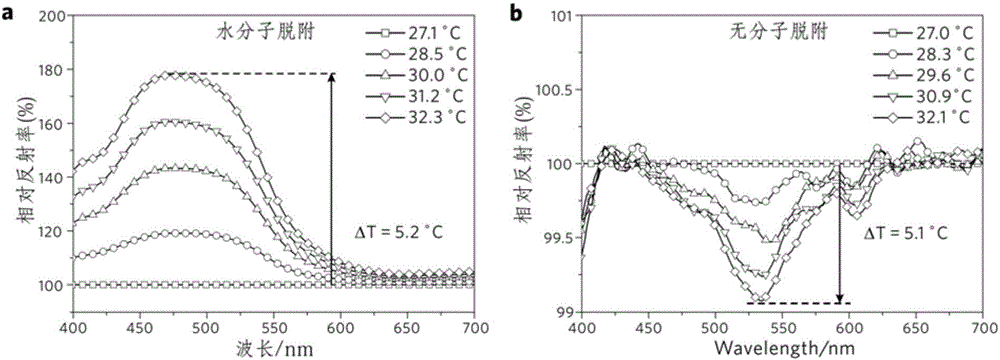
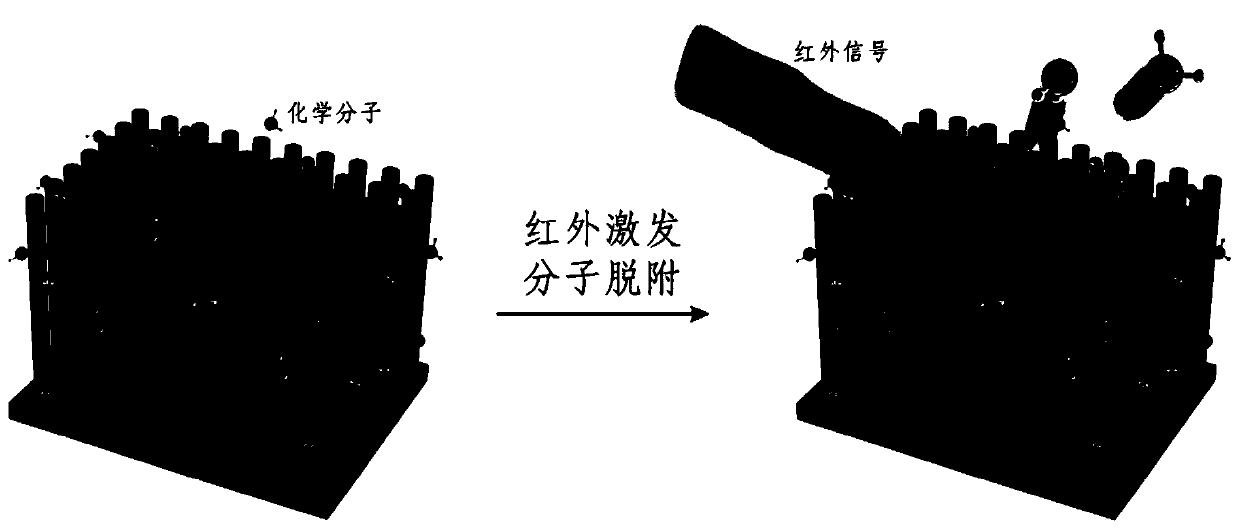
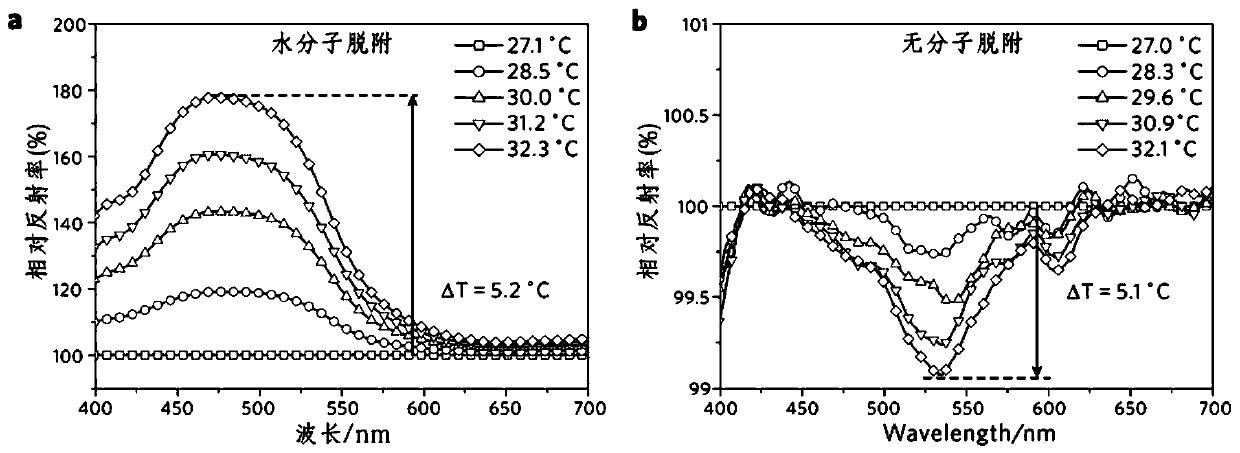
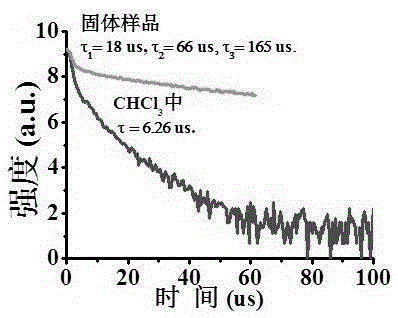
Method for achieving infrared detection by desorption phenomenon of infrared excitation molecules
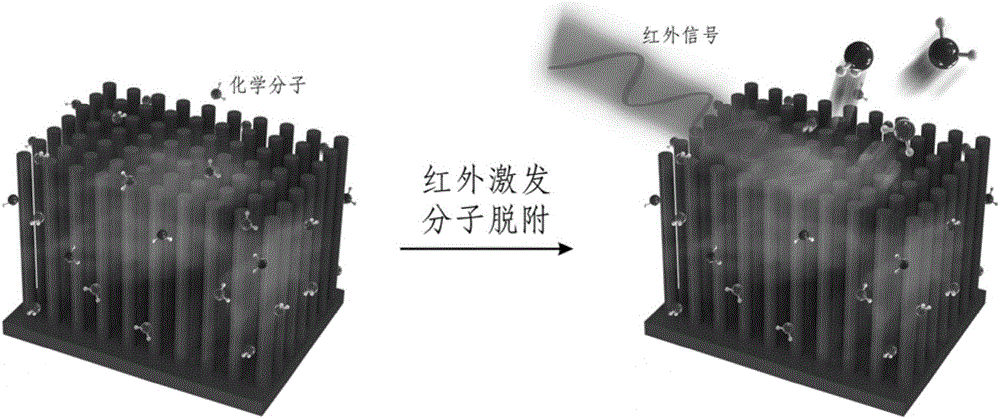
ActiveCN106840415AHigh sensitivityImprove response speedRadiation pyrometryNanotechnologyOptical propertyDesorption
The invention relates to a method for achieving infrared detection by a desorption phenomenon of infrared excitation molecules. The method comprises the following steps that micro-nanometer structure surfaces absorb chemical molecules; infrared signals are added to the micro-nanometer structure surface, and the chemical molecules adsorbed by the micro-nanometer structure surface are desorbed from the micro-nanometer structure surfaces under excitation of the infrared signals; micro-nanometer structures has changes of physical properties due to the molecular desorption, and the changes of the physical properties of the micro-nanometer structures are detected through a device, and therefore detection of the extra infrared signals is achieved. Due to an effect of the extra infrared signals, the chemical molecules adsorbed on the micro-nanometer structure surfaces are desorbed from the micro-nanometer structure surfaces because the chemical molecules absorb the infrared signals to make the temperature rise, the optical property, electrical property, magnetic property and other physical properties of the micro-nanometer structures is caused to change, and therefore the phenomenon is utilized to achieve the detection of the infrared signals. Compared with existing infrared detection technologies, the method for achieving the infrared detection by the desorption phenomenon of the infrared excitation molecules has the advantages that the sensitivity is high and feedback signals are easy to analyze and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Sensor device and method for label-free detection of double strand nucleotides
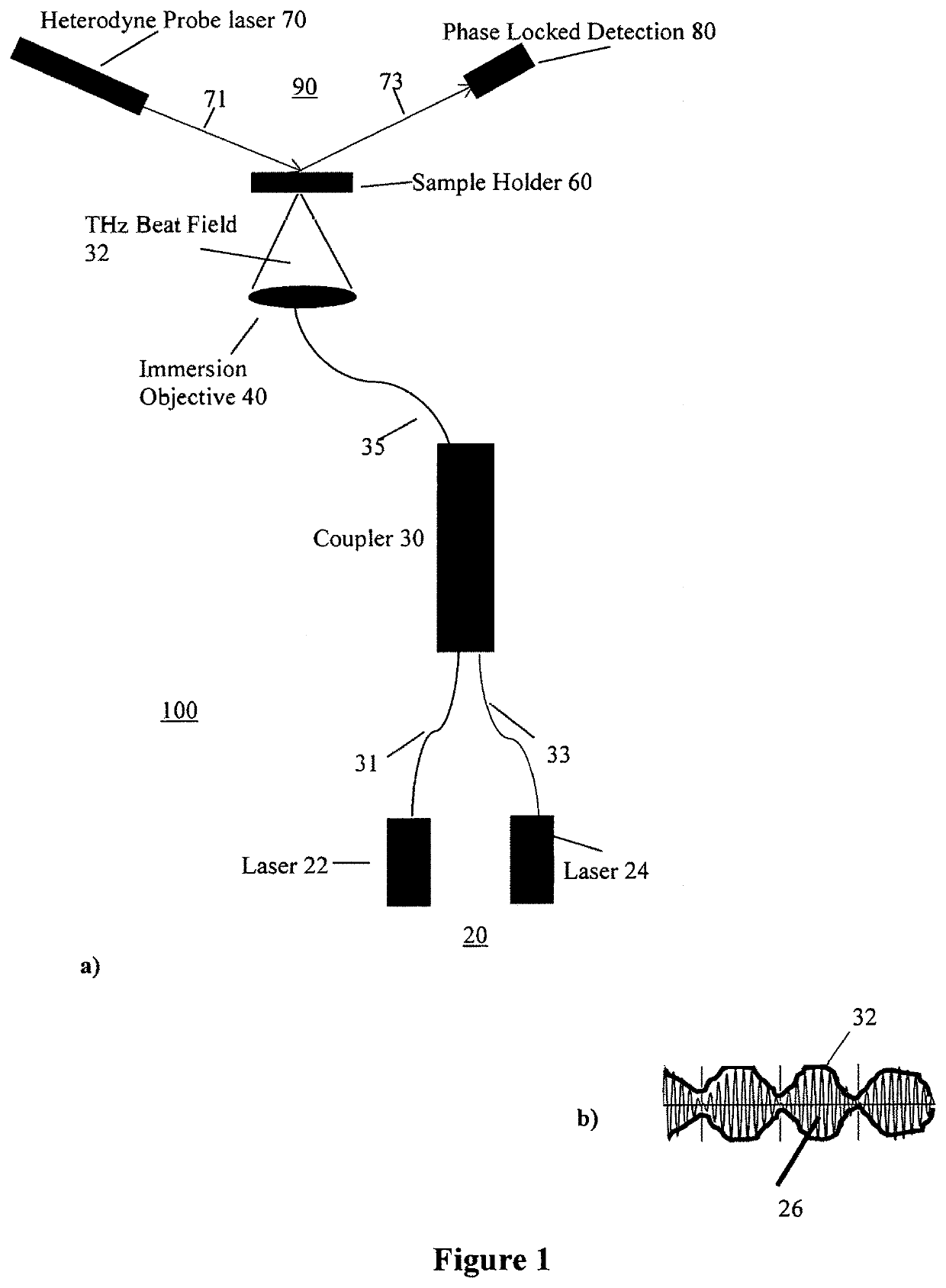
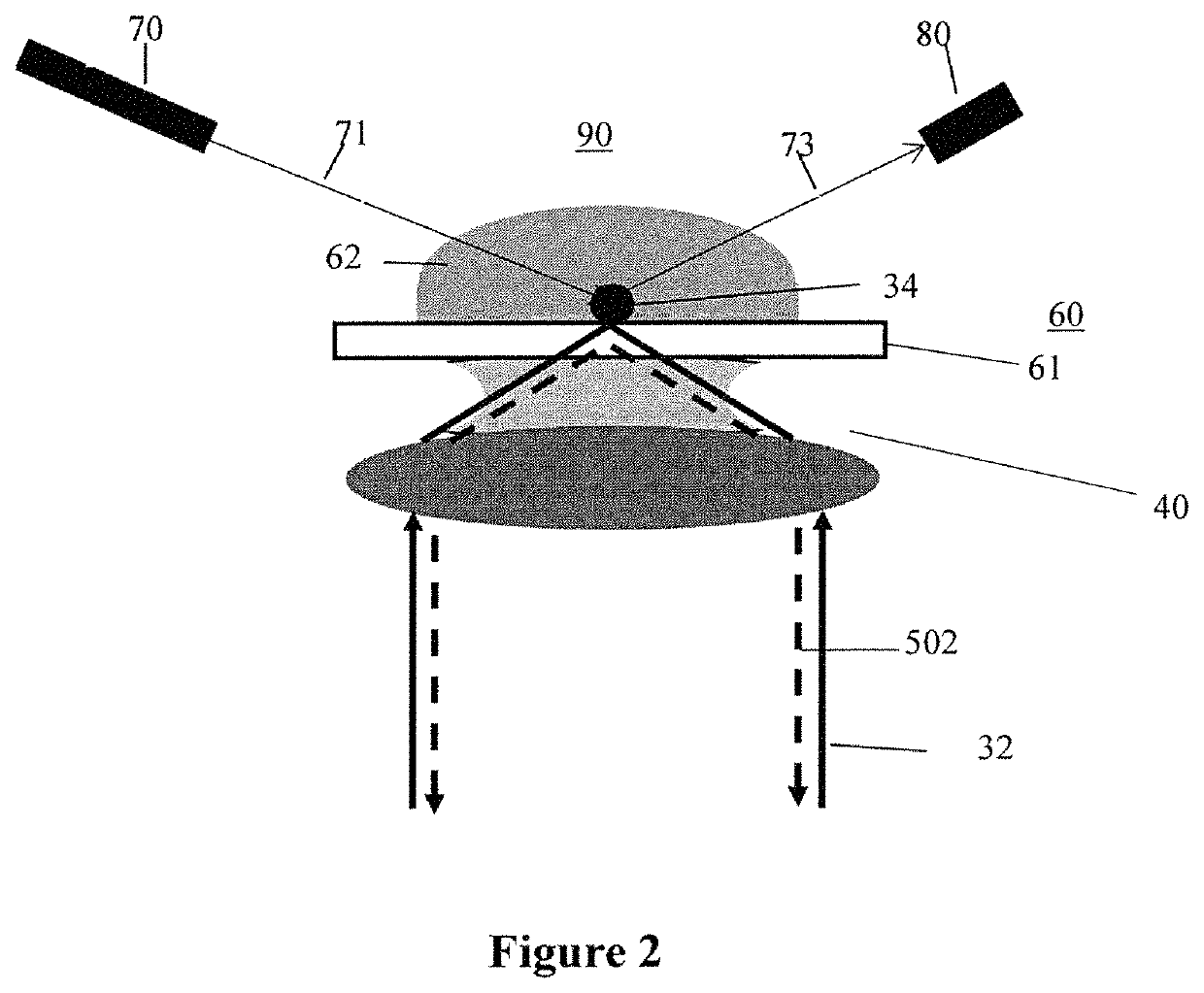
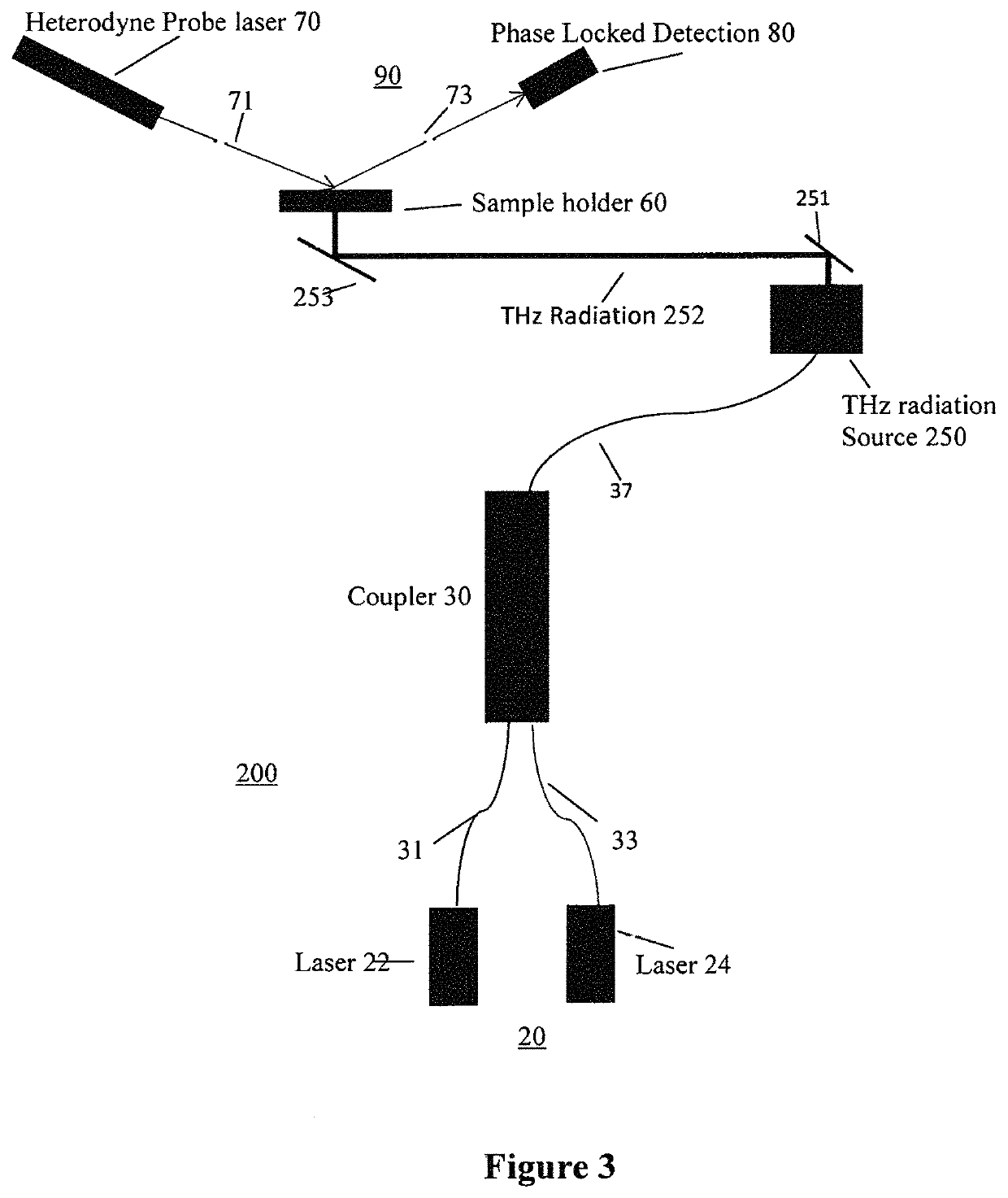
ActiveUS10584372B1Strong specificityIncreased sensitivity & reusabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementPhase-affecting property measurementsHeterodyne interferometerNucleotide
A sensor device which is adapted for detecting target molecules having a target nucleic acid sequence located in nano / micro channels, comprises a THz source for exciting the target molecules and a heterodyne interferometer, having a detection frequency MHz, for probing the excited molecules. The nano-channel array in the sample holder is functionalized with electric field to linearize the target alleles and genes. The linearized molecules are exposed to THz field whereby the different vibrational modes of base pairs are resonantly excited. The excitation of base-breathing mode and base-shifting mode leads to differential induced dipole moments along and perpendicular to the double helix axis. This induced asymmetry in polarizability leads to optical anisotropy. The dipole-dipole interaction between adjacent bases affects polarizability along the helix axis and hence the intrinsic molecular anisotropy is a function of number of base pairs in the strand. The resulting birefringence can be measured using the heterodyne interferometer as a function of changes in the number of base pairs in the strand. Furthermore, a sensing method for detecting birefringence in terms of phase shift of the MHz signal, as a function of target molecule size, is described.
Owner:AIYER ARUN ANANTH
Flame photometric detector having improved sensitivity
ActiveUS20060153734A1Component separationMicrobiological testing/measurementExcited moleculePhotomultiplier
A flame photometric detector comprises a burner assembly configured to combust a sample of an effluent, the combusted sample emitting at least one excited molecule, an interchangeable selective optical filter configured to pass a plurality of selected optical wavelengths corresponding to the excited molecule, and a photomultiplier tube configured to quantify the concentration of the excited molecule.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
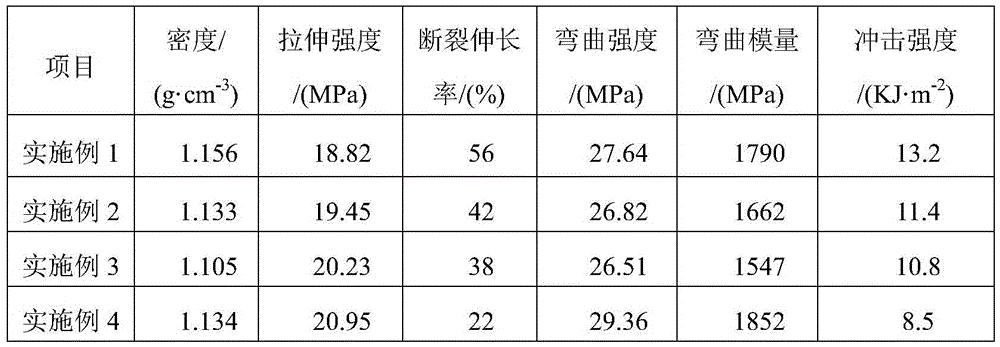
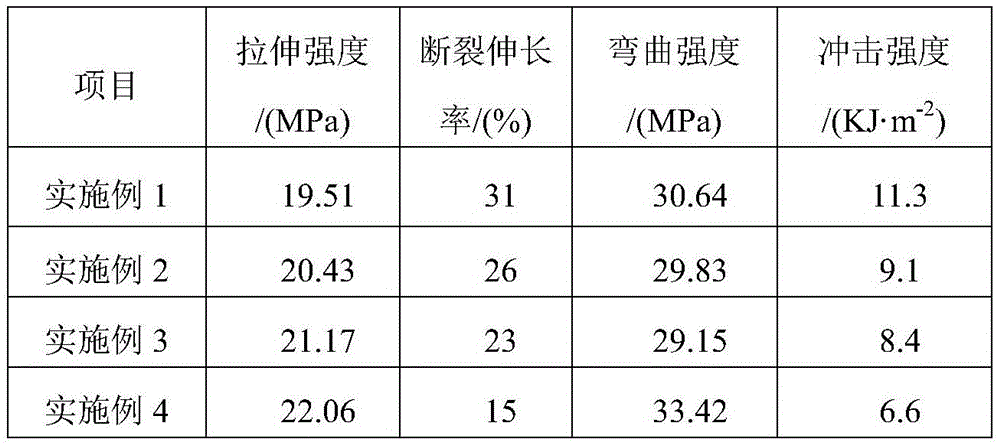
Commercial vehicle reclaimed modified fender material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a commercial vehicle recycled modified fender material and a preparation method thereof. The material is prepared from, by weight, 30%-58% of polypropylene reclaimed materials, 20%-40% of reclaimed toughening agent, 20%-30% of mineral powder, 0.1%-0.5% of antioxidant, 0.1%-0.5% parts of light stabilizer and 0.1%-0.5% of ultraviolet absorbent. According to the commercial vehicle recycled modified fender material and the preparation method thereof, the polypropylene reclaimed materials and waste film materials serve as raw materials for preparation, and the current reuse problem of the waste materials is well solved; meanwhile, the production cost of the fender is saved, the reclaimed materials are subjected to purification, cleaning, drying, homogenization and regeneration, and the stable use performance is achieved. A hindered amine light stabilizer is adopted, a light and oxygen degradation reaction is inhibited through various paths of capturing free radicals, resolving hydroperoxide, delivering excited molecule energy and the like; a benzotriazole ultraviolet absorbent and the hindered amine light stabilizer are used together, the synergistic effect is achieved, and the anti-aging capacity of the material can be improved by 2-4 times.
Owner:CHANGZHOU PLASKING POLYMER TECH
System and method for identifying materials using a THz spectral fingerprint in a media with high water content
InactiveUS9658155B2Easy to detectReduce false positivesAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceMaterial analysis by optical meansSpectral emissionStatistical analysis
A material detector includes a pulse generator to generate pulses to excite molecules in the material and a detector to detect a signal generated from excited molecules in the terahertz region. Spectral features in the material are analyzed to identify the material. Detection can be performed using a nanoantenna array structure having antennas tuned to detect the expected spectral emission. The nanoantenna array can include antennas having MIM or MIIM diodes. Signal processing and statistical analysis is use to reduce false positives and false negative in identifying the material.
Owner:REDWAVE ENERGY
A method for infrared detection by using the desorption phenomenon of infrared excited molecules
ActiveCN106840415BHigh sensitivityImprove response speedRadiation pyrometryNanotechnologyOptical propertyDesorption
The invention relates to a method for achieving infrared detection by a desorption phenomenon of infrared excitation molecules. The method comprises the following steps that micro-nanometer structure surfaces absorb chemical molecules; infrared signals are added to the micro-nanometer structure surface, and the chemical molecules adsorbed by the micro-nanometer structure surface are desorbed from the micro-nanometer structure surfaces under excitation of the infrared signals; micro-nanometer structures has changes of physical properties due to the molecular desorption, and the changes of the physical properties of the micro-nanometer structures are detected through a device, and therefore detection of the extra infrared signals is achieved. Due to an effect of the extra infrared signals, the chemical molecules adsorbed on the micro-nanometer structure surfaces are desorbed from the micro-nanometer structure surfaces because the chemical molecules absorb the infrared signals to make the temperature rise, the optical property, electrical property, magnetic property and other physical properties of the micro-nanometer structures is caused to change, and therefore the phenomenon is utilized to achieve the detection of the infrared signals. Compared with existing infrared detection technologies, the method for achieving the infrared detection by the desorption phenomenon of the infrared excitation molecules has the advantages that the sensitivity is high and feedback signals are easy to analyze and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
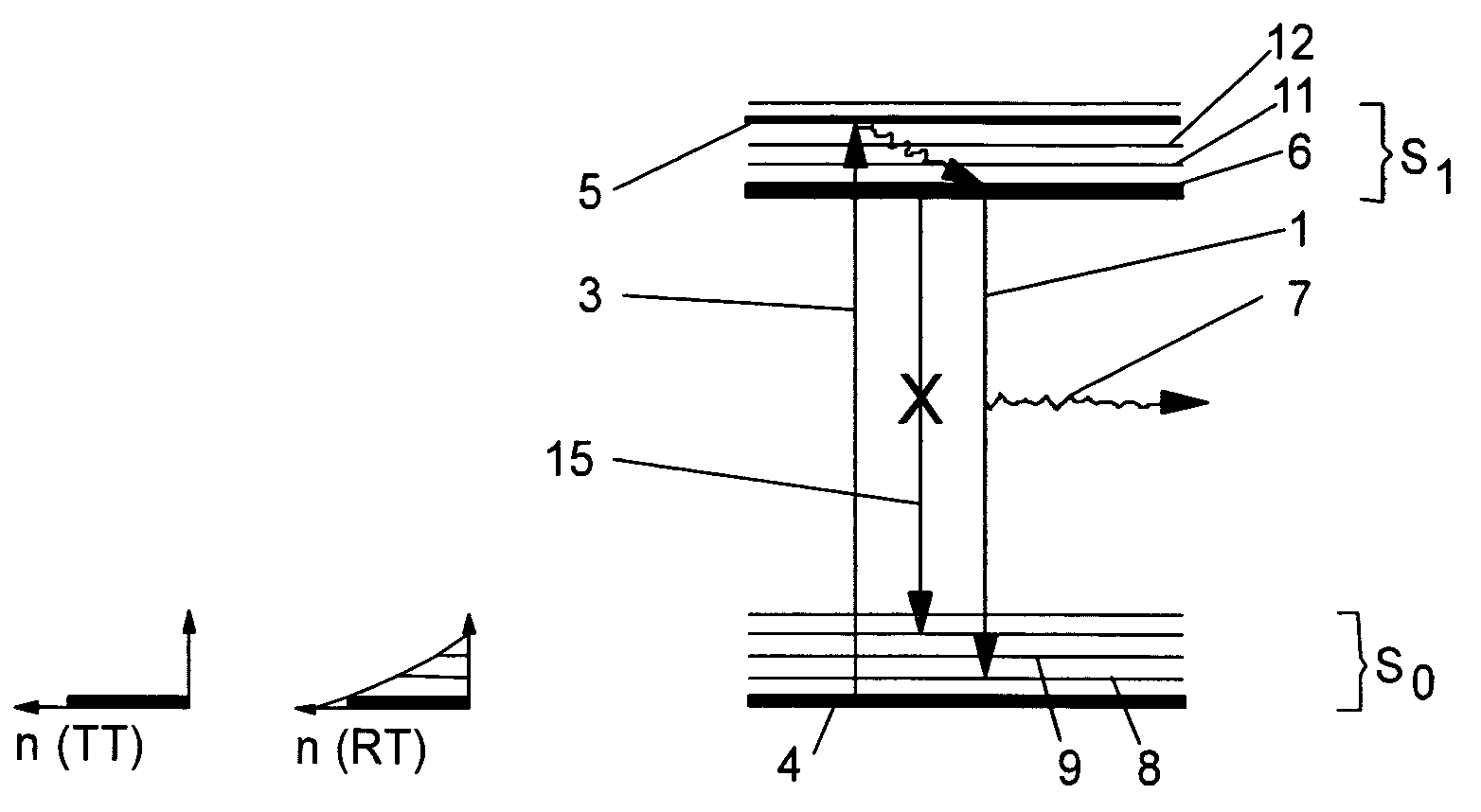
Method for generating phosphorescence in organic compound
The invention relates to a method for generating phosphorescence in an organic compound. The organic compound must have a donor function group and a receptor function group, donor atoms have SP<3> hybrid characteristics, and receptor atoms have SP<2> hybrid characteristics. The donor atoms lose electrons in an SP<3> hybrid state and transfer the electrons in the SP<3> hybrid state to partially positively charged receptor atoms in an SP<2> hybrid state in order to make a molecule be in an excited triplet state, and the excited molecule is resonated to make the receptor atoms become the SP<3> hybrid state from the SP<2> hybrid state in order to make an original donor become a receptor and an original receptor become a donor; and the donor atoms, which are receptor atoms in a ground state, lose the electrons in an SP<3> hybrid state and transfer the electrons in the SP<3> hybrid state to the receptor atoms in the SP<2> hybrid state, and orbit-spin coupling is carried out again to make the molecule return to the ground state in order to generate phosphorescence. An organic phosphorescence generation mechanism is explicated in the invention for the first time, and scientific research personnel can easily synthesize organic molecules in a liquid or solid state and with visible phosphorescence in room temperature air under the guidance of the mechanism.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Nano-cavity laser of molecule-doped thin film layer with electroexcitation
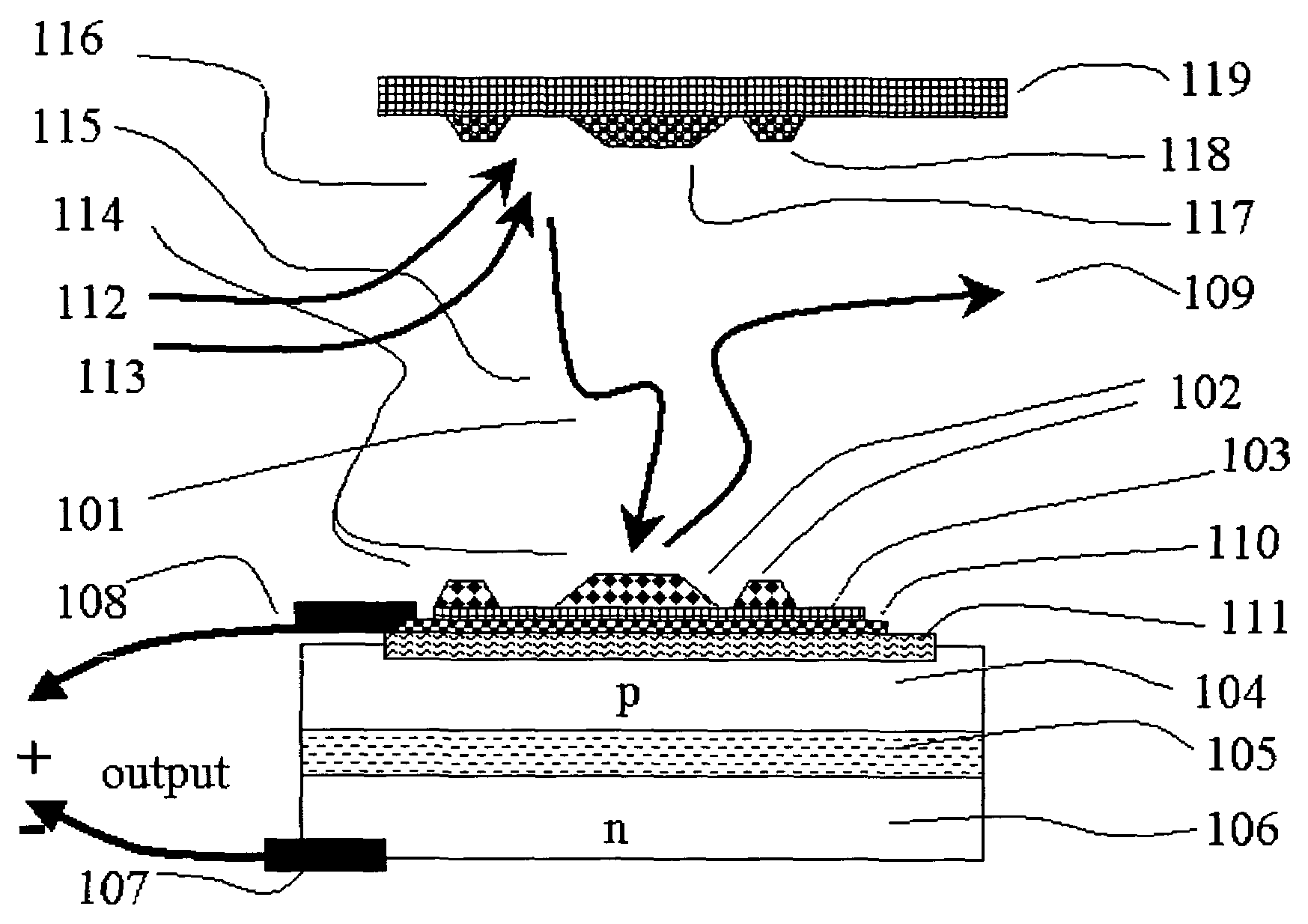
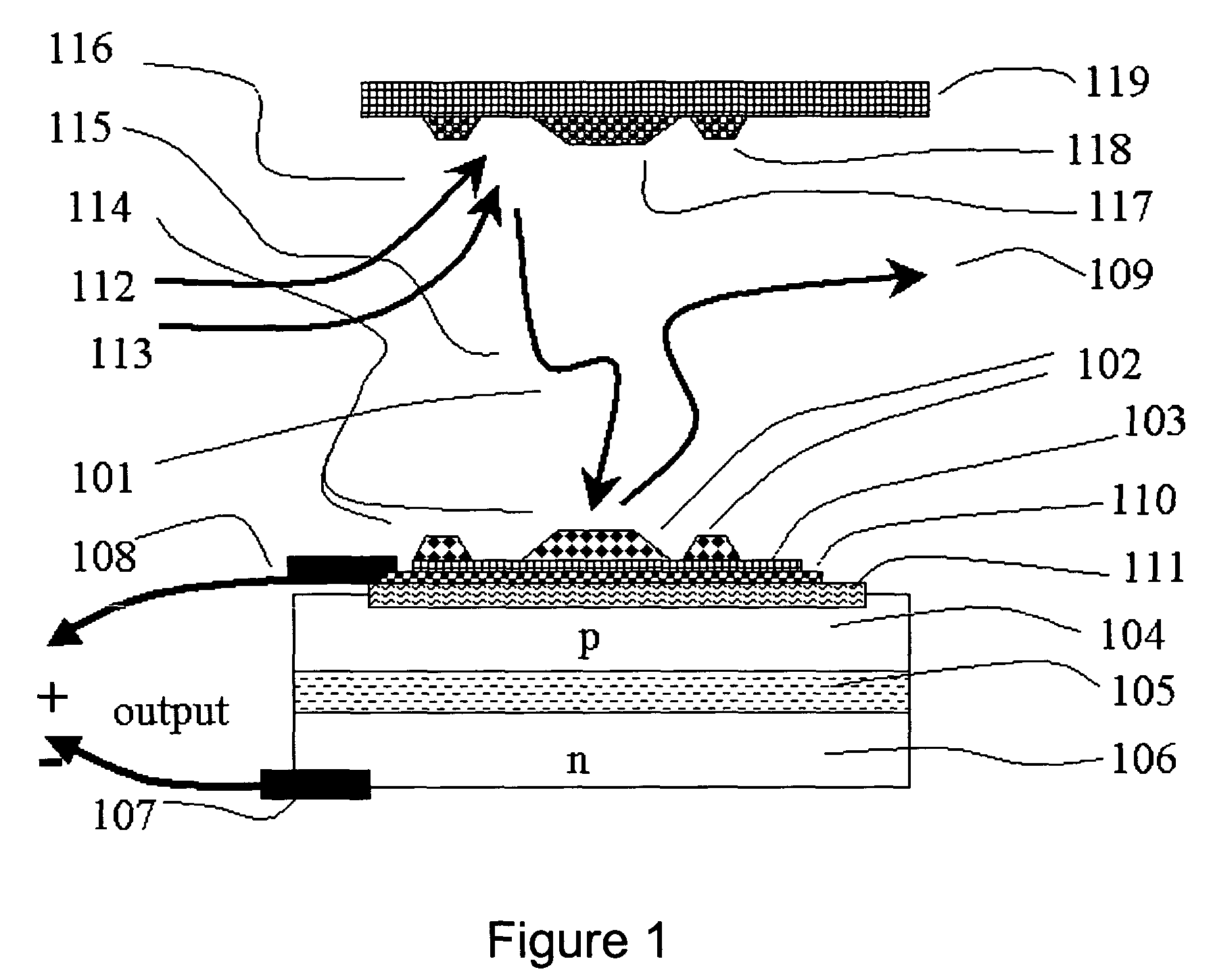
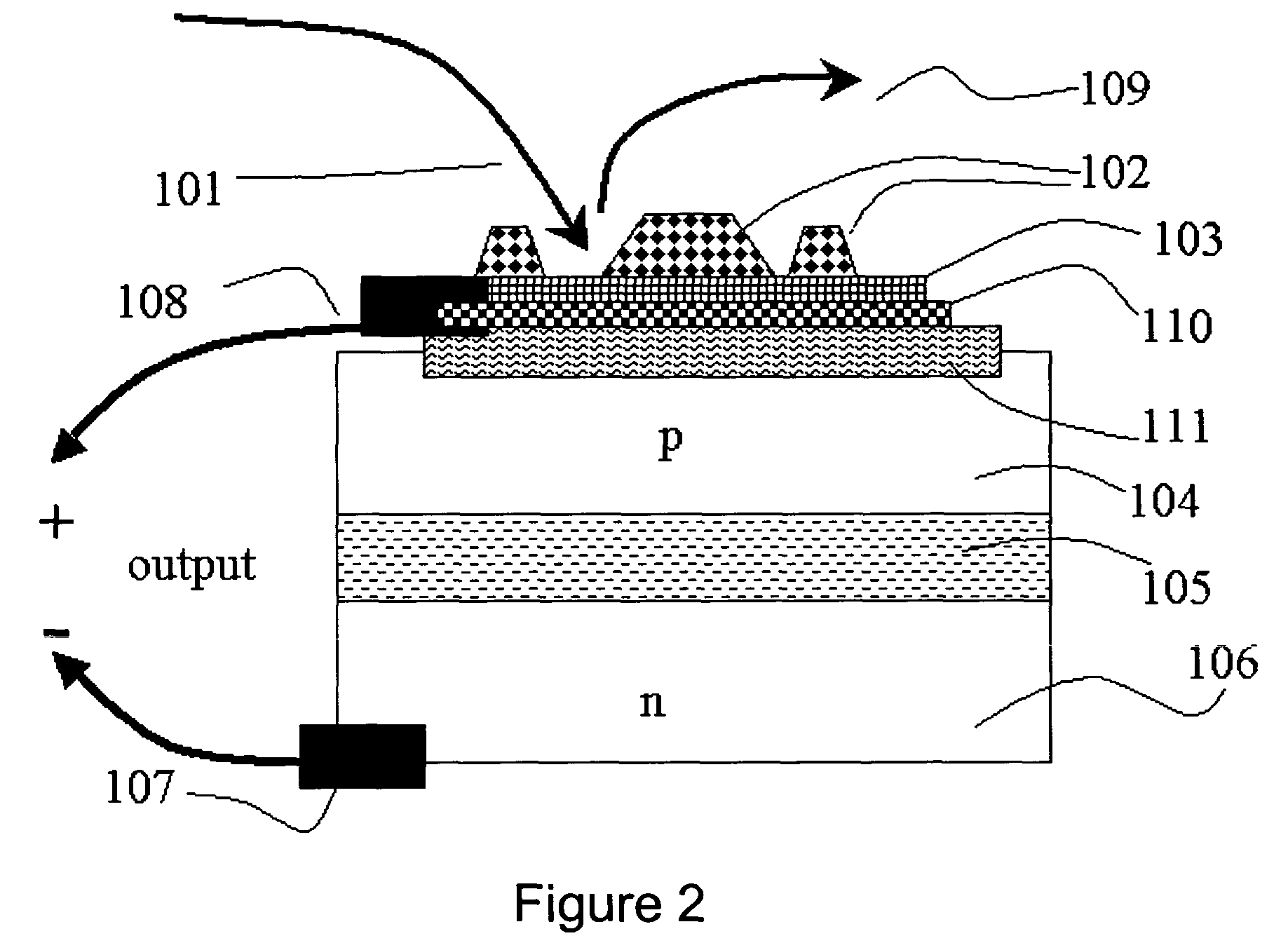
InactiveCN102231471BSimple preparation processImprove performanceExcitation process/apparatusActive medium materialNanowireExcited molecule
The invention, which belongs to the laser field, relates to a nano-cavity laser of a molecule-doped thin film layer with electroexcitation. The laser comprises a p-surface electrode, a substrate, an electroluminescent medium, a molecule-doped thin film layer, an n-surface electrode, and a nanowire structure. The electroluminescent medium, the molecule-doped thin film layer, the n-surface electrode, and the nanowire structure are arranged on the surface of the substrate successively; and the underneath of the substrate is plated with the p-surface electrode. According to the invention, surfaceplasma is provided by a metal electrode; an electric field with strong localization is formed by utilizing a mixing structure of metal, low-dielectric constant thin film layer and electroluminescent medium. Multi-energy-level molecules are doped in an insulating layer; multi-energy-level molecule system is excited to absorb a photon; and transition is formed and another photon is emitted. Direct coupling is carried out on the emitted photon, so that surface plasmon is formed; and the surface plasmon is transmitted and lased along the metal surface of the nanowire. According to the invention, present problems including difficulty in electroexcitation, great difficult in making technology, high cost, and difficulty in promotion are effectively solved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com